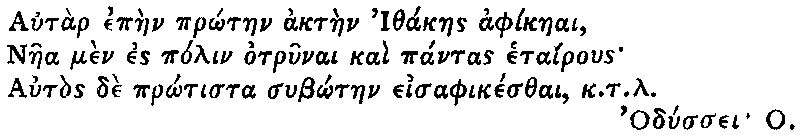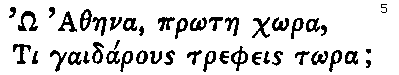The Project Gutenberg EBook of The Works Of Lord Byron, Letters and
Journals, Vol. 1, by Lord Byron
This eBook is for the use of anyone anywhere in the United States and most
other parts of the world at no cost and with almost no restrictions
whatsoever. You may copy it, give it away or re-use it under the terms of
the Project Gutenberg License included with this eBook or online at
www.gutenberg.org. If you are not located in the United States, you'll have
to check the laws of the country where you are located before using this ebook.
Title: The Works Of Lord Byron, Letters and Journals, Vol. 1
Author: Lord Byron
Editor: Roland E. Prothero
Posting Date: February 22, 2015 [EBook #8901]
Release Date: September, 2005
First Posted: August 22, 2003
Language: English
Character set encoding: ISO-8859-1
*** START OF THIS PROJECT GUTENBERG EBOOK BYRON, LETTERS AND JOURNALS, VOL 1 ***
Produced by Distributed Proofreaders
Byron's Letter and Journals
Volume 1
Part of Byron's Works
a New, Revised and Enlarged Edition,
with Illustrations.
This volume edited by
Rowland E. Prothero
1898
Table of Contents
Two great collections of Byron's letters have been already printed. In
Moore's Life, which appeared in 1830, 561 were given. These, in
FitzGreene Halleck's American edition of Byron's Works, published
in 1847, were increased to 635. The first volume of a third collection,
edited by Mr. W. E. Henley, appeared early in 1897. A comparison of the
number of letters contained in these three collections down to August
22, 1811, shows that Moore prints 61, Halleck 78, and Mr. Henley 88. In
other words, the edition of 1897, which was the most complete so far as
it goes, added 27 letters to that of 1830, and 10 to that of 1847. But
it should be remembered that by far the greater part of the material
added by Halleck and Mr. Henley was seen and rejected by Moore.
The present edition, down to August 22, 1811, prints 168 letters, or an
addition of 107 to Moore, 90 to Halleck, and 80 to Mr. Henley. Of this
additional matter considerably more than two-thirds was inaccessible to
Moore in 1830.
In preparing this volume for the press, use has been also made of a mass
of material, bearing more or less directly on Byron's life, which was
accumulated by the grandfather and father of Mr. Murray. The notes thus
contain, it is believed, many details of biographical interest, which
are now for the first time published.
It is necessary to make these comparisons, in order to define the
position which this edition claims to hold with regard to its
predecessors. On the other hand, no one can regret more sincerely than
myself — no one has more cause to regret — the circumstances which placed
this wealth of new material in my hands rather than in those of the true
poet and brilliant critic, who, to enthusiasm for Byron, and wide
acquaintance with the literature and social life of the day, adds the
rarer gift of giving life and significance to bygone events or trivial
details by unconsciously interesting his readers in his own living
personality.
Byron's letters appeal on three special grounds to all lovers of English
literature. They offer the most suggestive commentary on his poetry;
they give the truest portrait of the man; they possess, at their best,
in their ease, freshness, and racy vigour, a very high literary value.
The present volume, which covers the period from 1798 to August, 1811,
includes the letters written Lord Byron from his eleventh to his
twenty-third year. They therefore illustrate the composition of his
youthful poetry, of English Bards, and Scotch Reviewers, and of
the first two cantos of Childe Harold. They carry his history
down to the eve of that morning in March, 1812, when he awoke and found
himself famous — in a degree and to an extent which to the present
generation seem almost incomprehensible.
If the letters were selected for their literary value alone, it is
probable that very few of those contained in the present volume would
find a place in a collection formed on this principle. But biographical
interest also demands consideration, and, in the case of Byron, this
claim is peculiarly strong. He has for years suffered much from the
suppression of the material on which a just estimate of his life may be
formed. It is difficult not to regret the destruction of the
Memoirs, in which he himself intended his history to be told.
Their loss cannot be replaced; but their best substitute is found in his
letters. Through them a truer conception of Byron can be formed than any
impression which is derived from Dallas, Leigh Hunt, Medwin, or even
Moore. It therefore seems only fair to Byron, that they should be
allowed, as far as possible, to interpret his career. For other reasons
also it appears to me too late, or too soon, to publish only those
letters which possess a high literary value. The real motive of such a
selection would probably be misread, and thus further misconceptions of
Byron's character would be encouraged.
With one exception, therefore, the whole of the available material has
been published. The exception consists of some of the business letters
written by Byron to his solicitor. Enough of these have been printed to
indicate the pecuniary difficulties which undoubtedly influenced his
life and character; but it was not considered necessary to publish the
whole series. Men of genius ask money from their lawyers in the same
language, and with the same arguments, as the most ordinary persons.
The picture which the letters give of Byron, is, it is believed, unique
in its completeness, while the portrait has the additional value of
being painted by his own hand. Byron's career lends itself only too
easily to that method of treatment, which dashes off a likeness by
vigorous strokes with a full brush, seizing with false emphasis on some
salient feature, and revelling in striking contrasts of light and shade.
But the style here adopted by the unconscious artist is rather that in
which Richardson the novelist painted his pathetic picture of Clarissa
Harlowe. With slow, laborious touches, with delicate gradations of
colour, sometimes with almost tedious minuteness and iteration, the
gradual growth of a strangely composite character is presented,
surrounded by the influences which controlled or moulded its
development, and traced through all the varieties of its rapidly
changing moods. Written, as Byron wrote, with habitual exaggeration, and
on the impulse of the moment, his letters correct one another, and, from
this point of view, every letter contained in the volume adds something
to the truth and completeness of the portrait.
Round the central figure of Byron are grouped his relations and friends,
and two of the most interesting features in the volume are the strength
of his family affections, and the width, if not the depth, of his
capacity for friendship. His father died when the child was only three
years old. But a bundle of his letters, written from Valenciennes to his
sister, Mrs. Leigh, in 1790-91, still exists, to attest, with startling
plainness of speech, the strength of the tendencies which John Byron
transmitted to his son. The following extract contains the father's only
allusion to the boy:-
"Valenciennes, Feb. 16, 1791.
Have you never received any letters from me by way of Bologne? I have
sent two. For God's sake send me some, as I have a great deal to pay.
With regard to Mrs. Byron, I am glad she writes to you. She is very
amiable at a distance; but I defy you and all the Apostles to live
with her two months, for, if any body could live with her, it was me.
Mais jeu de Mains, jeu de Vilains. For my son, I am happy to
hear he is well; but for his walking, 'tis impossible, as he is
club-footed.
Between his mother and himself, in spite of frequent and violent
collisions, there existed a real affection, while the warmth of his love
for his half-sister Augusta, who had much of her brother's power of
winning affection, lost nothing in its permanence from the rarity of
their personal intercourse. Outside the family circle, the volume
introduces the only two men among his contemporaries who remained his
lifelong friends. In his affection for Lord Clare, whom he very rarely
saw after leaving school, there was a tinge of romance, and in him Byron
seems to have personified the best memories of an idealized Harrow. In
Hobhouse he found at once the truest and the most intimate of his
friends, a man whom he both liked and respected, and to whose opinion
and judgment he repeatedly deferred. On Hobhouse's side, the sentiment
which induced him, eminently sensible and practical as he was, to
treasure the nosegay which Byron had given him, long after it was
withered, shows how attractive must have been the personality of the
donor.
Without the Dictionary of National Biography, the labour of
preparing the letters for the press would be trebled. Both in the facts
which it supplies, and in the sources of information which it suggests,
it is an invaluable aid.
In conclusion, I desire to express my special obligations to Lord
Lovelace and Mr. Richard Edgcumbe, who have read the greater part of the
proofs, and to both of whom I am indebted for several useful
suggestions.
R. E. Prothero.
March, 1898.
Contents
1788—1805
Catherine Gordon of Gight (1765-1811), afterwards Mrs. Byron, and mother
of the poet, was descended on the paternal side from Sir William Gordon
of Gight, the third son, by Annabella Stewart, daughter of James I of
Scotland, of George, second Earl of Huntly, Chancellor of Scotland
(1498-1502), and Lord-Lieutenant of the North from 1491 to his death in
1507. The owners of Gight, now a ruin, once a feudal stronghold, were a
hot-headed, hasty-handed race, sufficiently notable to be commemorated
by Thomas the Rhymer, and to leave their mark in the traditions of
Aberdeenshire. In the seventh generation from Sir William Gordon, the
property passed to an heiress, Mary Gordon. By her marriage with
Alexander Davidson of Newton, who assumed the name of Gordon, she had a
son Alexander, Mrs. Byron's grandfather, who married Margaret Duff of
Craigston, a cousin of the first Earl of Fife. Their eldest son, George,
the fifth of the Gordons of Gight who bore that name, married Catherine
Innes of Rosieburn, and by her became the father of Catherine Gordon,
born in 1765, afterwards Mrs. Byron. Both her parents dying early,
Catherine Gordon was brought up at Banff by her grandmother, commonly
called Lady Gight, a penurious, illiterate woman, who, however, was
careful that her granddaughter was better educated than herself. Thus,
for the second time, Gight, which, with other property, was worth
between £23,000 and £24,000, passed to an heiress.
Miss Catherine Gordon had her full share of feminine vanity. At the age
of thirty-five she was a stout, dumpy, coarse-looking woman, awkward in
her movements, provincial in her accent and manner. But as her son was
vain of his personal appearance, and especially of his hands, neck, and
ears, so she, when other charms had vanished, clung to her pride in her
arms and hands. She exhausted the patience of Stewartson the artist, who
in 1806, after forty sittings, painted her portrait, by her anxiety to
have a particular turn in her elbow exhibited in the most pleasing
light. Of her ancestry she was, to use her son's expression, as "proud
as Lucifer," looked down upon the Byron family, and regarded the Duke of
Gordon as an inferior member of her clan. In later life, at any rate,
her temper was ungovernable; her language, when excited, unrestrained;
her love of gossip insatiable. Capricious in her moods, she flew from
one extreme to the other, passing, for the slightest cause, from
passionate affection to equally passionate resentment. How far these
defects were produced, as they certainly were aggravated, by her
husband's ill treatment and her hard struggle with poverty, it is
impossible to say. She had many good qualities. She bore her ruin, as
her letters show, with good sense, dignity, and composure. She lived on
a miserable pittance without running into debt; she pinched herself in
order to give her son a liberal supply of money; she was warm-hearted
and generous to those in distress. She adored her scamp of a husband,
and, in her own way, was a devoted mother. In politics she affected
democratic opinions, took in the Morning Chronicle_ and paid for it,
as is shown by a bill sent in after her death, at the rate of £4 17s.
6d. for the half-year — no small deduction from her narrow income. She
was fond of books, subscribed to the Southwell Book Club, copied
passages which struck her in the course of her reading, collected all
the criticisms on her son's poetry, made shrewd remarks upon them
herself (Moore's Journal and Correspondence, vol. v. p. 295), and
corresponded with her friends on literary subjects.
In 1785 Miss Catherine Gordon was at Bath, where, it may be mentioned,
her father had, some years before, committed suicide. There she met, and
there, on May 13, 1785, in the parish church of St. Michael, as the
register shows, she married Captain John Byron.
Captain John Byron (1755-91), born at Plymouth, was the eldest son of
Admiral the Hon. John Byron (1723-86) — known in the Royal Navy as "Hardy
Byron" or "Foul-weather Jack" — by his marriage (1748) with Sophia
Trevanion of Carhais, in Cornwall. The admiral, next brother to William,
fifth Lord Byron, was a distinguished naval officer, whose Narrative
of his shipwreck in the Wager was published in 1768, and whose Voyage
round the World in the Dolphin was described by "an officer in the
said ship" in 1767. His eldest son, John Byron, educated at Westminster
and a French Military Academy, entered the Guards and served in America.
A gambler, a spendthrift, a profligate scamp, disowned by his father, he
in 1778 ran away with, and in 1779 married, Lady Carmarthen, wife of
Francis, afterwards fifth Duke of Leeds, née Lady Amelia d'Arcy, only
child and heiress of the last Earl of Holderness, and Baroness Conyers
in her own right.
Captain Byron and his wife lived in Paris, where were born to them a son
and a daughter, both of whom died in infancy, and Augusta, born 1783,
the poet's half-sister, who subsequently married her first cousin,
Colonel George Leigh. In 1784 Lady Conyers died, and Captain Byron
returned to England, a widower, over head and ears in debt, and in
search of an heiress.
It was a rhyme in Aberdeenshire —
"When the heron leaves the tree,
The laird of Gight shall landless be."
Tradition has it that, at the marriage of Catherine Gordon with "mad
Jack Byron," the heronry at Gight passed over to Kelly or Haddo, the
property of the Earl of Aberdeen. "The land itself will not be long in
following," said his lordship, and so it proved. For a few months Mrs.
Byron Gordon — for her husband assumed the name, and by this title her
Scottish friends always addressed her — lived at Gight. But the ready
money, the outlying lands, the rights of fishery, the timber, failed to
liquidate Captain Byron's debts, and in 1786 Gight itself was sold to
Lord Aberdeen for £17,850. Mrs. Byron Gordon found herself, at the end
of eighteen months, stripped of her property, and reduced to the income
derived from £4200, subject to an annuity payable to her grandmother.
She bore the reverse with a composure which shows her to have been a
woman of no ordinary courage. Her letters on the subject are sensible,
not ill-expressed, and, considering the circumstances in which they were
written, give a favourable impression of her character.
The wreck of their fortunes compelled Mrs. Byron Gordon and her husband
to retire to France. At the beginning of 1788 she had returned to
London, and on January 22, 1788, at 16, Holles Street (since numbered
24, and now destroyed), in the back drawing-room of the first floor,
gave birth to her only child, George Gordon, afterwards sixth Lord
Byron. Hanson gives the names of the nurse, Mrs. Mills, the man-midwife,
Mr. Combe, the doctor, Dr. Denman, who attended Mrs. Byron at her
confinement. Dallas was, therefore, mistaken in his supposition that the
poet was born at Dover. The child was baptized in London on February 29,
1788, as is proved by the register of the parish of Marylebone.
Shortly after the birth of her son, Mrs. Byron settled in Aberdeen,
where she lived for upwards of eight years. During her stay there, in
the summer of 1791, her husband died at Valenciennes. In the year 1794,
by the death of his cousin William John Byron (1772-94) from a wound
received at the siege of Calvi, in Corsica, her son became the heir to
his great-uncle, the "wicked Lord Byron" (William, fifth Lord Byron,
1722-98), and a solicitor named Hanson was appointed to protect the
boy's interests. From Aberdeen Mrs. Byron kept up a correspondence with
her sister-in-law, Frances Leigh (née Byron), wife of General Charles
Leigh, to whom, in a letter, dated March 27, 1791, she speaks of her son
as "very well, and really a charming boy." Writing again to Mrs. Leigh,
December 8, 1794, she says,
"I think myself much obliged to you for
being so interested for George; you may be sure I would do anything I
could for my son, but I really don't see what can be done for him in
that case. You say you are afraid Lord B. will dispose of the estates
that are left, if he can; if he has it in his power, nobody can prevent
him from selling them; if he has not, no one will buy them from him. You
know Lord Byron. Do you think he will do anything for George, or be at
any expense to give him a proper education; or, if he wish to do it, is
his present fortune such a one that he could spare anything out of it?
You know how poor I am, not that I mean to ask him to do anything for
him, that is to say, to be of any expense on his account."
If any
application was made to the boy's great-uncle, it was unsuccessful. On
May 19, 1798, Lord Byron died, and Hanson informed Mrs. Byron that her
son had succeeded to the title and estates. At the end of the summer of
that year, the little Lord Byron, with his mother and the nurse May
Gray, reached Newstead, and, within a few weeks from their arrival, his
first letter was written. His letters to his mother, it may be observed,
are always addressed to "the Honourable Mrs. Byron," a title to which
she had no claim.
Contents
cross-reference: return to Footnote 1 of Letter 72
1. to Mrs. Parker1
Newstead Abbey, Nov. 8th, 1798.
Dear Madam, — My Mamma being unable to write herself desires I will let
you know that the potatoes are now ready and you are welcome to them
whenever you please.
She begs you will ask Mrs. Parkyns if she would wish the poney to go
round by Nottingham or to go home the nearest way as it is now quite
well but too small to carry me.
I have sent a young Rabbit which I beg Miss Frances will accept off
and which I promised to send before. My Mamma desires her best
compliments to you all in which I join.
I am, Dear Aunt, yours sincerely,
Byron.
I hope you will excuse all blunders as it is the first
letter I ever wrote.
Footnote 1: This letter, the first that Byron wrote, was written when he
was ten years and ten months old. It is preserved in the Library
of Trinity College, Cambridge, and a facsimile is given by Elze, in
his Life of Lord Byron.
It is apparently addressed to his aunt, Mrs. Parker. Charlotte
Augusta Byron, daughter of Admiral the Hon. John Byron, married
Christopher Parker (1761-1804), Vice-Admiral 1804, the son of
Admiral of the Fleet Sir Peter Parker, Bart. (1721-1811). Her
son, who, on the death of his grandfather, succeeded to the baronetcy
as Sir Peter Parker, second Bart. (1786-1814), commanded H.M.S.
Menelaus, and was killed in an attack on a body of American
militia encamped near Baltimore. (See Byron's Elegy on the
Death of Sir Peter Parker, and his letter to Moore, October 7, 1814.) Her daughter Margaret, one of Byron's early loves, inspired,
as he says, his "first dash into poetry" (see Poems, vol. i, p. 5,
note 1).
return to footnote mark
List of Letters
Nottingham, 13 March, 1799.
Dear Mama, — I am very glad to hear you are well. I am so myself, thank
God; upon my word I did not expect so long a Letter from you; however
I will answer it as well as I can. Mrs. Parkyns and the rest are well
and are much obliged to you for the present. Mr. Rogers1 could
attend me every night at a separate hour from the Miss Parkynses, and
I am astonished you do not acquiesce in this Scheme which would keep
me in Mind of what I have almost entirely forgot. I recommend this to
you because, if some plan of this kind is not adopted, I shall be
called, or rather branded with the name of a dunce, which you know I
could never bear. I beg you will consider this plan seriously and I
will lend it all the assistance in my power. I shall be very glad to
see the Letter you talk of, and I have time just to say I hope every
body is well at Newstead,
And remain, your affectionate Son,
Byron.
P.S. — Pray let me know when you are to send in the Horses to go to
Newstead. May2 desires her Duty and I also expect an answer by the
miller.
Footnote 1: Dummer Rogers, "Teacher of French, English, Latin, and
"Mathematicks," was, according to Notes and Queries (4th series,
vol. iii. p. 561), an American loyalist, pensioned by the English
Government. He lived at Hen Cross, Nottingham, when Byron
was staying in that city, partly with Mrs. Parkyns, partly at Mr.
Gill's, in St. James's Lane, to be attended by a man named Lavender,
"trussmaker to the general hospital," who had some local reputation
for the treatment of misshapen limbs. Lavender, in 1814 (Nottingham Directory for 1814), appears as a "surgeon." Rogers, who read
parts of Virgil and Cicero with Byron, represents him as, for his age,
a fair scholar. He was often, during his lessons, in violent pain, from the position in which his foot was kept; and Rogers one day
said to him, "It makes me uncomfortable, my Lord, to see you
sitting there in such pain as I know you must be suffering." "Never
mind, Mr. Rogers," answered the boy; "you shall not see any signs
of it in me." Many years after, when in the neighbourhood of
Nottingham, Byron sent a kind message to his old instructor, bidding
the bearer tell him that he could still recite twenty verses of
Virgil which he had read with Rogers when suffering torture all
the time.
return to footnote mark
cross-reference: return to footnote of Letter 4
Footnote 2:
Byron's nurse, who had accompanied him from Aberdeen (see
p. 10, note 1).
return
List of Letters
3 — to John Hanson1
Sir, — I am not a little disappointed at your Stay, for this last week I
expected you every hour; but, however, I beg it as a favour that you
will come up soon from Newstead as the Holidays commence in three weeks
Time. I congratulate you on Capt. Hanson's2 being appointed commander
of The Brazen Sloop of War, and I congratulate myself on Lord
Portsmouth's3 Marriage, hoping his Lady, when he and I meet next,
will keep him in a little better order. The manner I knew that Capt.
Hanson was appointed Commander of the Ship before mentioned was this. I
saw it in the public Paper, and now, since you are going to Newstead, I
beg if you meet Gray4 send her a packing as fast as possible, and
give my Compliments to Mrs. Hanson and to all my comrades of the
Battalions in and out upon different Stations,
And remain, your little friend,
Byron.
I forgot to tell you how I was. I am at present very well and my foot
goes but indifferently; I cannot perceive any alteration.
Footnote 1: John Hanson, of 6, Chancery Lane, a well-known London
solicitor, was introduced to the Byron family by an Aberdeenshire friend
of Mrs. Byron, Mr. Farquhar, a member of Parliament, and a civilian
practising in Doctors' Commons. The acquaintance began in January, 1788,
with Byron's birth, for the midwife and the nurse were recommended by
Mrs. Hanson. Six years later, Hanson was employed by Mrs.
Byron to watch the interests of her son, who in 1794 had become
heir-presumptive to his great-uncle. It was Hanson who, in the summer of
1798, communicated the news of the death of Lord Byron to Mrs. Byron,
and with his wife received her and her son at Newstead. From that time
till the close of the minority, Hanson was intimately associated with
Byron, both as a man of business and a friend. He selected Dr. Glennie's
school for the boy, persuaded Lord Carlisle to become his guardian,
introduced the ward to Lord Carlisle, and entered him at Harrow. It was
at his house in Earl's Court that Byron, for five years, spent a
considerable part of his successive holidays. There he made acquaintance
with Hanson's children — his sons Charles, Hargreaves (his contemporary
at Harrow), and Newton, and his daughter, Mary Anne, who subsequently
(March 7, 1814) married the Earl of Portsmouth, Byron giving her away.
This letter was written by Byron a few weeks after he had gone to school
at Dr. Glennie's, in Lordship Lane, Dulwich. He remained there from
August, 1799, to April, 1801.
In a letter to Mrs. Byron, dated September 1, 1799, Hanson describes Dr.
Glennie's "Academy," where he had shortly before left the boy:—
"I left my entertaining companion with Mr. Glennie last Thursday week,
and I have since learnt from him that he is very comfortable and likes
the situation. His schoolfellows are very fine youths, and their
deportment does very great credit to their Preceptor. I succeeded in
getting Lord Byron a separate room, and I am persuaded the greatest
attention will be paid to him. Mr. Glennie is a Scotchman, has
travelled a great deal, and seems every way qualified for his present
situation."
return to footnote mark
Footnote 2: Captain James Hanson, R.N., was the brother of John Hanson
to whom the letter is written. Byron was born with a caul, prized by
sailors as a preservative from drowning. The caul was sold by Mrs.
Mills, the nurse who attended Mrs. Byron in January, 1788, to Captain
Hanson. In January, 1800, Captain Hanson, in command of H.M.S.
Brazen, had captured a French vessel, which he sent to Portsmouth
with a prize crew. On the 26th of the month, while shorthanded, he was
caught in a storm off Newhaven. The Brazen foundered, and Captain
Hanson with all his men, except one, were drowned.
return
Footnote 3: In the late autumn of 1799 Lord Portsmouth was staying with
the Hansons before his marriage (November 23, 1799) with Miss Norton,
sister of Lord Grantley. In rough play he pinched Byron's ear; the boy
picked up a conch shell which was lying on the ground, and hurled it at
Lord Portsmouth's head, missing it by a hair's breadth, and smashing the
glass behind. In vain Mrs. Hanson tried to make the peace by saying that
Byron did not mean the missile for Lord Portsmouth. "But I did
mean it!" he reiterated; "I will teach a fool of an earl to pinch
another noble's ear."
return
Footnote 4: The following extract from a letter written by Hanson to
Mrs. Byron (September 1, 1799) places the character of Byron's nurse in
a different light to that which is given in Moore's Life:—
"I assure you, Madam, I should not have taken the liberty to have
interfered in your domestic Arrangements, had I not thought it
absolutely necessary to apprize you of the proceedings of your
Servant, Mrs. Gray; her conduct towards your son while at Nottingham
was shocking, and I was persuaded you needed but a hint of it to
dismiss her. Mrs. Parkyns, when I saw her, said something to me about
her; but when I found from dispassionate persons at Nottingham, it was
the general Topic of conversation, it would have ill become me to have
remained silent.
My honourable little companion, tho' disposed to retain his feelings,
could not refrain, from the harsh usage he had received at her hands,
from complaining to me, and such is his dread of the Woman that I
really believe he would forego the satisfaction of seeing you if he
thought he was to meet her again. He told me that she was perpetually
beating him, and that his bones sometimes ached from it; that she
brought all sorts of Company of the very lowest Description into his
apartments; that she was out late at nights, and he was frequently
left to put himself to bed; that she would take the Chaise-boys into
the Chaise with her, and stopped at every little Ale-house to drink
with them. But, Madam, this is not all; she has even — traduced
yourself.
I entertain a very great affection for Lord Byron, and I trust I shall
not be considered solely in my professional character, but as his
Friend. I introduced him to my Friends, Lord Grantley and his Brother
General Norton, who were vastly taken with him, as indeed are every
one. And I should be mortified in the highest degree to see the
honourable feelings of my little fellow exposed to insult by the
inordinate Indiscretions of any Servant. He has Ability and a
quickness of Conception, and a correct Discrimination that is seldom
seen in a youth, and he is a fit associate of men, and choice indeed
must be the Company that is selected for him."
return
cross-reference: return to footnote of Letter 2
List of Letters
Harrow-on-the-Hill, Sunday, May 1st, 1803.
My Dear Mother, — I received your Letter the other day. And am happy to
hear you are well. I hope you will find Newstead in as favorable a state
as you can wish. I wish you would write to Sheldrake to tell him to make
haste with my shoes1.
I am sorry to say that Mr. Henry Drury2 has behaved himself to me in
a manner I neither can nor will bear. He has seized now an
opportunity of showing his resentment towards me. To day in church I was
talking to a Boy who was sitting next me; that perhaps was not right,
but hear what followed. After Church he spoke not a word to me, but he
took this Boy to his pupil room, where he abused me in a most violent
manner, called me blackguard, said he would and could have me
expelled from the School, and bade me thank his Charity that
prevented him; this was the Message he sent me, to which I shall
return no answer, but submit my case to you and those you may think
fit to consult. Is this fit usage for any body? had I stole or
behaved in the most abominable way to him, his language could not have
been more outrageous. What must the boys think of me to hear such a
Message ordered to be delivered to me by a Master? Better let him take
away my life than ruin my Character. My Conscience acquits me of ever
meriting expulsion at this School; I have been idle and I certainly
ought not to talk in church, but I have never done a mean action at this
School to him or any one. If I had done anything so heinous, why
should he allow me to stay at the School? Why should he himself be so
criminal as to overlook faults which merit the appellation of a
blackguard? If he had had it in his power to have me expelled, he
would long ago have done it; as it is, he has done worse. If I am
treated in this Manner, I will not stay at this School. I write you that
I will not as yet appeal to Dr. Drury; his Son's influence is more than
mine and justice would be refused me. Remember I told you, when I
left you at Bath, that he would seize every means and opportunity of
revenge, not for leaving him so much as the mortification he suffered,
because I begged you to let me leave him. If I had been the Blackguard
he talks of, why did he not of his own accord refuse to keep me as his
pupil? You know Dr. Drury's first letter, in it were these Words: "My
son and Lord Byron have had some Disagreements; but I hope that his
future behaviour will render a change of Tutors unnecessary." Last Term
I was here but a short time, and though he endeavoured, he could find
nothing to abuse me in. Among other things I forgot to tell you he said
he had a great mind to expel the Boy for speaking to me, and that if he
ever again spoke to me he would expel him. Let him explain his meaning;
he abused me, but he neither did nor can mention anything bad of me,
further than what every boy else in the School has done. I fear him not;
but let him explain his meaning; 'tis all I ask. I beg you will write to
Dr. Drury to let him know what I have said. He has behaved to me, as
also Mr. Evans, very kindly. If you do not take notice of this, I will
leave the School myself; but I am sure you will not see me ill
treated; better that I should suffer anything than this. I believe
you will be tired by this time of reading my letter, but, if you love
me, you will now show it. Pray write me immediately. I shall ever
remain, Your affectionate Son, Byron.
P.S. — Hargreaves Hanson desires his love to you and hopes you are very
well. I am not in want of any Money so will not ask you for any. God
bless, bless you.
Footnote 1: Byron appears to have suffered from what would now be
described as infantile paralysis, which affected the inner muscles
of the right leg and foot, and rendered him permanently lame.
Before leaving London for Aberdeen, Mrs. Byron consulted John
Hunter, who, in correspondence with Dr. Livingstone of Aberdeen,
advised her as to the treatment of her son. Writing, May 31, 1791,
to Mrs. Leigh, she says, "George's foot turns inward, and it is the
right foot; he walks quite on the side of his foot." In 1798 the
child was placed under the care of Lavender (see p. 7, note 1) at
Nottingham, doubtless on the recommendation of his aunt. In July,
1799, he was taken to London, in order to consult Dr. Baillie.
From July, 1799, till the end of 1802, he was attended by Baillie
in consultation with Dr. Laurie of 2, Bartholomew's Close. Special
appliances were made for the boy, under their superintendence,
by a scientific bootmaker named Sheldrake, in the Strand. In
The Lancet for 1827-8 (vol. ii. p. 779) Mr. T. Sheldrake describes
"Lord Byron's case," giving an illustration of the foot. His
account does not tally, in some respects, with that taken from contemporary
letters, and his sketch represents the left not the right leg.
But the nature and extent of Byron's lameness have been the subject
of a curious variety of opinion. Lady Blessington, Moore, Gait,
the Contessa Albrizzi, never knew which foot was deformed. Jackson,
the boxer, thought it was the left foot. Trelawney says that
it proceeded from a contraction of the back sinews, and that the
right foot was most distorted. The lasts from which his shoes
were made by Swift, the Southwell bootmaker, are preserved in
the Nottingham Museum, and in both the foot is perfect in shape.
The last pair of shoes modelled on them were made May 7, 1807.
Mrs. Leigh Hunt says that the left foot was shrunken, but was not a club-foot. Stendhal says the right foot. Thorwaldsen indicates the left foot. Dr. James Millingen, who inspected the feet after the poet's death, says that there was a malformation of the left foot and leg, and that he was born club-footed. Two surgical boots are in the possession of Mr. Murray, made for Byron as a child; both are for the right foot, ankle, and leg, and, assuming that they were made to fit the foot, they are too long and thin for a club-foot. Both at Dulwich and at Harrow, Byron was frequently seen by Laurie, whom Mrs. Byron paid, as she once complained in a letter to Laurie, "at the rate of £150 a year." It is difficult to see what more could have been done for the boy, and the explanation of the failure to effect a cure is probably to be found in the following extracts from two of Laurie's letters to Mrs. Byron. The first is dated December 7, 1801:—
"Agreeable to your desire, I waited on Lord Byron at Harrow, and I
think it proper to inform you that I found his foot in a much worse
state than when I last saw it, — the shoe entirely wet through and the
brace round his ancle quite loose. I much fear his extreme inattention
will counteract every exertion on my part to make him better. I have
only to add that with proper care and bandaging, his foot may still be
greatly recovered; but any delay further than the present vacation
would render it folly to undertake it."
The second letter is dated October 2, 1802. In it Laurie complains
that the boy had spent several days in London without seeing him, and
adds —
"I cannot help lamenting he has so little sense of the Benefit he has
already received as to be so apparently neglectful."
return to footnote mark
Footnote 2: For Henry Drury (afterwards an intimate friend of Byron)
and his father, the Head-master of Harrow, see p. 41, note 2.
When Byron went to Harrow, in April, 1801, he was placed in Henry
Drury's house. But in January, 1803, he refused to go back to school
unless he was removed from Drury's care. He was in consequence placed at
Evans's house. Dr. Drury, writing to explain the new arrangement, says,
in a letter to Hanson, dated February 4, 1803 —
"The reason why Lord Byron wishes for this change arises from the
repeated complaints of Mr. Henry Drury respecting his Inattention to
Business, and his propensity to make others laugh and disregard their
Employments as much as himself. On this subject I have had many very
serious conversations with him, and though Mr. H. D. had repeatedly
requested me to withdraw him from his Tuition, yet, relying on my own
remonstrances and arguments to rectify his Error, and on his own
reflection to confirm him in what is right, I was unwilling to accede
to my son's wishes. Lord Byron has now made the request himself; I am
glad it has been made, as he thereby imposes on himself an additional
responsibility, and encourages me to hope that by this change he
intends to lay aside all that negligence and those Childish Practices
which were the cause of former complaints."
Fresh troubles soon arose, as Byron's letter indicates. Hanson forwarded
the boy's complaint to Dr. Drury, from whom he received the following
answer, dated May 15, 1803:-
"The Perusal of the inclosed has allowed me to inquire into the whole
Matter, and to relieve your young friend's Mind from any uneasy
impression it might have sustained from a hasty word I fairly confess.
I am sorry it was ever uttered; but certainly it was never intended to
make so deep a wound as his letter intimates.
"I may truly say, without any parade of words, that I am deeply
interested in Lord Byron's welfare. He possesses, as his letter
proves, a mind that feels, and that can discriminate reasonably on
points in which it conceives itself injured. When I look forward to
the Possibility of the exercise of his Talents hereafter, and his
supplying the Deficiencies of fortune by the exertion of his abilities
and by application, I feel particularly hurt to see him idle, and
negligent, and apparently indifferent to the great object to be
pursued. This event, and the conversations which have passed between
us relative to it, will probably awaken in his mind a greater degree
of emulation, and make him studious of acquiring Distinction among his
Schoolfellows, as well as of securing to himself the affectionate
regard of his Instructors."
return
cross-reference: return to Footnote 1 of Letter 85
List of Letters
Harrow-on-the-Hill, June 23rd, 6th, 8th, 30th, 1803.
My dear Mother, — I am much obliged to you for the Money you sent me. I
have already wrote to you several times about writing to Sheldrake: I
wish you would write to him, or Mr. Hanson to call on him, to tell him
to make an Instrument for my leg immediately, as I want one, rather. I
have been placed in a higher form in this School to day, and Dr. Drury
and I go on very well; write soon, my Dear Mother.
I remain, your affectionate Son,
Byron.
List of Letters
6 — to his Mother1
Southwell, [Sept. 1803].
My Dear Mother, — I have sent Mealey2 to day to you, before William
came, but now I shall write myself. I promise you, upon my honour, I
will come over tomorrow in the Afternoon. I was not wishing to resist
your Commands, and really seriously intended coming over tomorrow,
ever since I received your last Letter; you know as well as I do that it
is not your Company I dislike, but the place you reside in. I know it is
time to go to Harrow. It will make me unhappy; but I will obey. I
only desire, entreat, this one day, and on my honour I will be over
tomorrow in the evening or afternoon. I am sorry you disapprove my
Companions, who, however, are the first this County affords, and my
equals in most respects; but I will be permitted to chuse for myself. I
shall never interfere in your's and I desire you will not molest me in
mine. If you grant me this favour, and allow me this one day unmolested,
you will eternally oblige your
Unhappy Son,
Byron.
I shall attempt to offer no excuse as you do not desire one. I only
entreat you as a Governor, not as a Mother, to allow me this one day.
Those that I most love live in this County; therefore in the name of
Mercy I entreat this one day to take leave, and then I will join you
again at Southwell to prepare to go to a place where — I will write no
more; it would only incense you. Adieu. Tomorrow I come.
Footnote 1: This letter is endorsed by Hanson, "Lord Byron to his
mother, "1803." In September, 1803, at the end of the summer holidays,
Byron did not return to Harrow. Dr. Drury asked the reason, received no
reply, and, on October 4, applied to Hanson for an explanation. Hanson's
inquiry drew from Mrs. Byron, on October 30, the following answer, with
which was enclosed the above letter from Byron:—
"You may well be surprized, and so may Dr. Drury, that Byron is not
returned to Harrow. But the Truth is, I cannot get him to return to
school, though I have done all in my power for six weeks past. He has
no indisposition that I know of, but love, desperate love, the worst
of all maladies in my opinion. In short, the Boy is distractedly in
love with Miss Chaworth, and he has not been with me three weeks all
the time he has been in this county, but spent all his time at
Annesley.
If my son was of a proper age and the lady disengaged, it is the
last of all connexions that I would wish to take place; it has given
me much uneasiness. To prevent all trouble in future, I am determined
he shall not come here again till Easter; therefore I beg you will
find some proper situation for him at the next Holydays. I don't care
what I pay. I wish Dr. Drury would keep him.
I shall go over to Newstead to-morrow and make a last effort to get
him to Town."
The effort, if made, failed. On November 7, 1803, Mrs. Byron wrote
again:—
"Byron is really so unhappy that I have agreed, much against my
inclination, to let him remain in this County till after the next
Holydays."
It was not till January, 1804, that Byron returned to Harrow.
Miss Mary Anne Chaworth, the object of Byron's passion, was then living
with her mother, Mrs. Clarke, at Annesley, near Newstead (see Poems,
vol. i. p. 189, and note 1). The grand-niece of the Mr. Chaworth who
was killed in a duel by William, fifth Lord Byron, on January 26, 1765
(Annual Register, 1765, pp. 208-212; and State Trials, vol. xix. pp.
1178-1236), and the heiress of Annesley, she married, in August, 1805,
John Musters, by whom she had a daughter, born in 1806. (See "Well! thou
art happy!" Poems, vol. i. p. 277; see also, for other allusions to
Mrs. Chaworth Musters, ibid., pp. 210, 239, 282, 285; and "The Dream"
of July, 1816.) In Byron's memorandum-book, he describes a visit which
he paid to Matlock with Miss Chaworth's mother, her stepfather Mr.
Clarke, some friends,
"and my M. A. C. Alas! why do I say MY? Our
union would have healed feuds in which blood had been shed by our
fathers, — it would have joined lands broad and rich, it would have
joined at least one heart, and two persons not ill matched in years
(she is two years my elder) and — and — and — what has been the
result?"
(Life, p. 27).
Mrs. Musters, after an unhappy married life, died in February, 1832, at
Wiverton Hall, near Nottingham.
The connection between the families of Chaworth and Byron came through
the marriage of William, third Lord Byron (died 1695), with Elizabeth
Chaworth (died 1683), daughter of George Chaworth, created (1627)
Viscount Chaworth of Armagh (Thoroton's Nottinghamshire, vol. i. p.
198).
return to footnote mark
Footnote 2: Owen Mealey, the steward at Newstead.
return
List of Letters
7 — to the Hon. Augusta Byron1
[At 63, Portland Place, London.]
Burgage Manor, [Thursday], March 22d, 1804.
Although, My ever Dear Augusta, I have hitherto appeared remiss in
replying to your kind and affectionate letters; yet I hope you will not
attribute my neglect to a want of affection, but rather to a shyness
naturally inherent in my Disposition. I will now endeavour as amply as
lies in my power to repay your kindness, and for the Future I hope you
will consider me not only as a Brother but as your warmest and most
affectionate Friend, and if ever Circumstances should require it your
protector. Recollect, My Dearest Sister, that you are the nearest
relation I have in the world both by the ties of Blood and
affection. If there is anything in which I can serve you, you have
only to mention it; Trust to your Brother, and be assured he will never
betray your confidence. When You see my Cousin and future Brother George
Leigh2, tell him that I already consider him as my Friend, for
whoever is beloved by you, my amiable Sister, will always be equally
Dear to me.
I arrived here today at 2 o'clock after a fatiguing Journey, I found my
Mother perfectly well. She desires to be kindly remembered to you; as
she is just now Gone out to an assembly, I have taken the first
opportunity to write to you, I hope she will not return immediately; for
if she was to take it into her head to peruse my epistle, there is one
part of it which would produce from her a panegyric on a friend of
yours, not at all agreeable to me, and I fancy, not particularly
delightful to you. If you see Lord Sidney Osborne3 I beg you will
remember me to him; I fancy he has almost forgot me by this time, for it
is rather more than a year Since I had the pleasure of Seeing him. — Also
remember me to poor old Murray4; tell him we will see that something
is to be done for him, for while I live he shall never be abandoned In
his old Age. Write to me Soon, my Dear Augusta, And do not forget to
love me, In the meantime, I remain, more than words can express, your
ever sincere, affectionate
Brother and Friend,
Byron.
P.S. Do not forget to knit the purse you promised me, Adieu my beloved
Sister.
Footnote 1: The Hon. Augusta Byron, Byron's half-sister (January,
1783—November, 1851), was the daughter of Captain John Byron by his
first wife, Amelia d'Arcy (died 1784), only child of the last Earl of
Holderness, Baroness Conyers in her own right, the divorced wife of
Francis, Marquis of Carmarthen, subsequently fifth Duke of Leeds. After
the return of Captain and Mrs. Byron to London early in 1788, she was
brought up by her grandmother, the Countess of Holderness. When the
latter died, Augusta Byron divided her time between her half-sister,
Lady Mary Osborne, who married, July 16, 1801, Lord Pelham, subsequently
(1805) Earl of Chichester; her half-brother George, who succeeded his
father as sixth Duke of Leeds in 1799; her cousin, the Earl of Carlisle;
and General and Mrs. Harcourt. From their houses her letters during the
period 1803-7 are written. In 1807 she married her first cousin, Colonel
George Leigh of the Tenth Dragoons, the son of General Charles Leigh, by
Frances, daughter of Admiral the Hon. John Byron. By her husband, who
was a friend of the Prince Regent and well known in society, she was the
mother of seven children. Their home was at Newmarket, till, in April,
1818, they were granted apartments in Flag Court, St. James's Palace,
where she died in November, 1851.
Augusta Byron seems scarcely to have seen her brother between his
infancy and 1802. Lady Holderness and Mrs. Byron were not on friendly
terms, and it was not till the former's death that any intimacy was
renewed between the brother and sister. Writing on October 18, 1801, to
Augusta Byron, Mrs. Byron says, in allusion to the death of Lady
Holderness,
"As I wish to bury what is past in oblivion, I shall
avoid all reflections on a person now no more; my opinion of yourself I
have suspended for some years; the time is now arrived when I shall form
a very decided one. I take up my pen now, however, to condole
with you on the melancholy event that has happened, to offer you every
consolation in my power, to assure you of the inalterable regard and
friendship of myself and son. We will be extremely happy if ever we can be of any service to you, now or at any future period.
I take it upon me to answer for him; although he knows so little of you,
he often mentions you to me in the most affectionate manner, indeed the
goodness of his heart and amiable disposition is such that your being
his sister, had he never seen you, would be a sufficient claim upon him
and ensure you every attention in his power to bestow.
Ah, Augusta, need I assure you that you will ever be dear to me as the
Daughter of the man I tenderly loved, as the sister of my beloved, my
darling Boy, and I take God to witness you once was dear to me on
your own account, and may be so again. I still recollect with a
degree of horror the many sleepless nights, and days of agony, I
have passed by your bedside drowned in tears, while you lay insensible
and at the gates of death. Your recovery certainly was wonderful, and
thank God I did my duty. These days you cannot remember, but I never
will forget them ... Your brother is at Harrow School, and, if you wish
to see him, I have now no desire to keep you asunder."
From 1802 till Byron's death, Augusta took in him the interest of an
elder sister. Writing to Hanson (June 17, 1804), she says —
"Pray write me a line and mention all you hear of my dear Brother: he
was a most delightful correspondent while he remained in
Nottinghamshire: but I can't obtain a single line from Harrow. I was
much struck with his general improvement; it was beyond the
expectations raised by what you had told me, and his letters gave me
the most excellent opinion of both his Head and Heart."
In this tone the letters are continued (see extracts p. 39; p. 45,
note 1; and p. 97, note 1).
From the end of 1805, with some interruptions, and less regularity, the
correspondence between brother and sister was maintained to the end of
Byron's life. To Augusta, then Mrs. Leigh, Byron sent a presentation
copy of Childe Harold, with the inscription:
"To Augusta, my dearest sister, and my best friend, who has ever loved
me much better than I deserved, this volume is presented by her
father's son and most affectionate brother."
She was the god-mother of Byron's daughter Augusta Ada, born December
10, 1815. In January, 1816, when Lady Byron was still with her husband,
she writes of and to Mrs. Leigh:
"In this at least, I am 'truth itself,' when I say that, whatever
the situation may be, there is no one whose society is dearer to me,
or can contribute more to my happiness."
Lady Byron left Byron on January 15, 1816. Writing to Mrs. Leigh from
Kirby Mallory, she speaks of her as her "best comforter," notices her
absolute unselfishness, and says that Augusta's presence in Byron's
house in Piccadilly is her "great comfort" (Lady Byron's letters to Mrs.
Leigh, January 16 and January 23, 1816, quoted in the Quarterly Review
for October, 1869, p. 414). Through Mrs. Leigh passed many
communications between Byron and Lady Byron after the separation. To
her, Byron, in 1816 and 1817, wrote the two sets of "Stanzas to
Augusta," the "Epistle to Augusta," and the Journal of his journey
through the Alps, "which contains all the germs of Manfred (letter to
Murray, August, 1817). She was in his thoughts on the Rhine, and in the
third canto of Childe Harold:—
"But one thing want these banks of Rhine,
Thy gentle hand to clasp in mine."
To her he was writing a letter at Missolonghi (February 23, 1824), which
he did not live to finish, "My dearest Augusta, I received a few days
ago your and Lady Byron's report of Ada's health." He carried with him
everywhere the pocket Bible which she had given him. "I have a Bible,"
he told Dr. Kennedy (Conversations), "which my sister gave me, who is
an excellent woman, and I read it very often." His last articulate words
were "My sister — my child."
Several volumes of Mrs. Leigh's commonplace books are in existence,
filled with extracts mostly on religious topics. She was, wrote the late
Earl Stanhope, in a letter quoted in the Quarterly Review (October,
1869, p. 421), "very fond" of talking about Byron.
"She was," he continues, "extremely unprepossessing in her person and
appearance — more like a nun than anything, and never can have had the
least pretension to beauty. I thought her shy and sensitive to a fault
in her mind and character."
Frances, Lady Shelley, who died in January, 1873, and was intimately
acquainted with Byron and his contemporaries, speaks of her as a "Dowdy-Goody."
"I have seen," she writesA , "a great deal of Mrs. Leigh
(Augusta), having passed some days with her and Colonel Leigh, for my
husband's shooting near Newmarket, when Lord Byron was in the house,
and, as she told me, was writing The Corsair, to my great
astonishment, for it was a wretched small house, full of her
ill-trained children, who were always running up and down stairs, and
going into 'uncle's' bedroom, where he remained all the morning."
Sub-Footnote A: see Quarterly Review, October, 1869, p.
421, quoting from a letter signed E. M. U., which appeared in the
Times for September II, 1869
return to letter
cross-reference: return to Footnote 5 of Letter 141
Footnote 2: See preceding note.
Footnote 3: Francis, fifth Duke of Leeds, married, October 14, 1788, as
his second wife, Miss Catherine Anguish, by whom he had two
children: the eldest, a son, Sydney Godolphin Osborne, was born
December 16, 1789.
return
Footnote 4: Joe Murray had been for many years in the employment of
William, fifth Lord Byron. At his master's death, in 1798, he was
taken into the service of the Duke of Leeds.
"I saw poor Joseph Murray the other night," writes Augusta
Byron to Hanson (June 17, 1804), "who wishes me particularly to
apply to Col. Leigh, to get him into some City Charity which the
Prince of Wales is at the head of.
I cannot understand what he means, nor can any body else, and
therefore, as he said he was advised by you, I think it better to
apply to you on the subject. I'm sure Col. Leigh would be happy
to oblige him; but in general he dislikes asking favours of the
Prince, and this present moment is a bad one to chuse for the
purpose, as H.R.H. is so much taken up with public affairs. I
am very anxious about poor Joseph, and would almost do anything
to serve him. I fear he is too old and infirm to go to service
again."
Three years later (March 19, 1807), Augusta Byron writes again
to Hanson:—
"I have just had a pitiful note from poor old Murray, telling me of
his dismissal from the Duchess of Leeds; but he says he does not leave
her till June. I therefore hope something may in the mean time be done
for him. He requests me to write word of it to my Brother. I shall
certainly comply with his wishes, and send two lines on that subject
to Southwell, where I conclude he is."
Byron made Murray an allowance of £20 a year (see Letter 83), took him,
as soon as he could, into his service, and was careful, as he promises,
to provide that he should not be "abandoned in his old age." His
affection for Murray is marked by the postscript to the letter to Mrs.
Byron of June 22, 1809 (see also Life, pp. 74, 121); as also by his
draft will of 1811, in which he leaves Murray £50 a year for life.
return
cross-reference: return to Footnote 1 of Letter 83
List of Letters
[63, Portland Place, London.]
Southwell, March 26th, 1804.
I received your affectionate letter, my ever Dear Sister, yesterday and
I now hasten to comply with your injunction by answering it as soon as
possible. Not, my Dear Girl, that it can be in the least irksome to me
to write to you, on the Contrary it will always prove my Greatest
pleasure, but I am sorry that I am afraid my correspondence will not
prove the most entertaining, for I have nothing that I can relate to
you, except my affection for you, which I can never sufficiently
express, therefore I should tire you, before I had half satisfied
myself. Ah, How unhappy I have hitherto been in being so long separated
from so amiable a Sister! but fortune has now sufficiently atoned by
discovering to me a relation whom I love, a Friend in whom I can
confide. In both these lights, my Dear Augusta, I shall ever look upon
you, and I hope you will never find your Brother unworthy of your
affection and Friendship.
I am as you may imagine a little dull here; not being on terms of
intimacy with Lord Grey1 I avoid Newstead, and my resources of
amusement are Books, and writing to my Augusta, which, wherever I am,
will always constitute my Greatest pleasure. I am not reconciled to Lord
Grey, and I never will. He was once my Greatest Friend, my reasons
for ceasing that Friendship are such as I cannot explain, not even to
you, my Dear Sister, (although were they to be made known to any body,
you would be the first) but they will ever remain hidden in my own
breast.
They are Good ones, however, for although I am violent I am not
capricious in my attachments. My mother disapproves of my
quarrelling with him, but if she knew the cause (which she never will
know) She would reproach me no more. He Has forfeited all title to my
esteem, but I hold him in too much contempt ever to hate him. My
mother desires to be kindly remembered to you. I shall soon be in town
to resume my studies at Harrow; I will certainly call upon you in my way
up. Present my respects to Mrs. Harcourt2; I am Glad to hear that I
am in her Good Graces for I shall always esteem her on account of her
behaviour to you, my Dear Girl. Pray tell me If you see Lord S. Osborne,
and how he is; what little I know of him I like very much and If we were
better acquainted I doubt not I should like him still better. Do not
forget to tell me how Murray is. As to your Future prospects, my Dear
Girl, may they be happy! I am sure you deserve Happiness and if you
do not meet with it I shall begin to think it is "a bad world we live
in." Write to me soon. I am impatient to hear from you. God bless you,
My amiable Augusta, I remain,
Your ever affectionate Brother and Friend,
Byron.
Footnote 1: Henry, third Earl of Sussex, died in 1799, when the earldom
lapsed. He was, however, succeeded in the ancient barony of Grey de
Ruthyn by his daughter's son, Henry Edward, twentieth Baron Grey de
Ruthyn (1780-1810), to whom Newstead was let.
"I am glad," writes Mrs. Byron to Hanson, March 10, 1803, "that
Newstead is well let. I cannot find Lord Grey de Ruthin's Title in the
Peerage of England, Ireland, or Scotland. I suppose he is a new
Peer."
Lord Grey de Ruthyn married, in 1809, Anna Maria, daughter of William
Kelham, of Ryton-upon-Dunsmore, Warwick. (See postscript to Byron's Letter to his
mother, August 11, 1809.) The lease of Newstead terminated in April,
1808.
return to footnote mark
cross-reference: return to footnote of Letter 15
cross-reference: return to Footnote 7 of Letter 128
Footnote 2: Probably the wife of General the Hon. William Harcourt
(1742-1830), who distinguished himself in the War of American
Independence, succeeded his only brother in 1809 as third (and last)
Earl Harcourt, was created a field-marshal in 1821, and died in 1830. He
married, in 1778, Mary, daughter of the Rev. William Danby, and widow of
Thomas Lockhart. She died in 1833.
return
List of Letters
[At General Harcourt's, St. Leonard's Hill, Windsor, Berkshire.]
Burgage Manor, April 2d, 1804.
I received your present, my beloved Augusta, which was very acceptable,
not that it will be of any use as a token of remembrance, No, my
affection for you will never permit me to forget you.
I am afraid, my Dear Girl, that you will be absent when I am in town. I
cannot exactly say when I return to Harrow, but however it will be in a
very short time. I hope you were entertained by Sir Wm. Fawcet's funeral
on Saturday1. Though I should imagine such spectacles rather
calculated to excite Gloomy ideas. But I believe your motive was not
quite of so mournful a cast.
You tell me that you are tired of London. I am rather surprised to hear
that, for I thought the Gaieties of the Metropolis were particularly
pleasing to young ladies. For my part I detest it; the smoke and the
noise feel particularly unpleasant; but however it is preferable to this
horrid place, where I am oppressed with ennui, and have no amusement
of any kind, except the conversation of my mother, which is sometimes
very edifying, but not always very agreeable. There are very few
books of any kind that are either instructive or amusing, no society but
old parsons and old Maids; — I shoot a Good deal; but, thank God, I have
not so far lost my reason as to make shooting my only amusement. There
are indeed some of my neighbours whose only pleasures consist in field
sports, but in other respects they are only one degree removed from the
brute creation.
These however I endeavour not to imitate, but I sincerely wish for the
company of a few friends about my own age to soften the austerity of the
scene. I am an absolute Hermit; in a short time my Gravity which is
increased by my solitude will qualify me for an Archbishoprick; I really
begin to think that I should become a mitre amazingly well. You tell me
to write to you when I have nothing better to do; I am sure writing to
you, my Dear Sister, must ever form my Greatest pleasure, but especially
so, at this time. Your letters and those of one of my Harrow friends
form my only resources for driving away dull care. For Godsake write
me a letter as long as may fill twenty sheets of paper, recollect it
is my only pleasure, if you won't Give me twenty sheets, at least send
me as long an epistle as you can and as soon as possible; there will be
time for me to receive one more Letter at Southwell, and as soon as I
Get to Harrow I will write to you. Excuse my not writing more, my Dear
Augusta, for I am sure you will be sufficiently tired of reading this
complaining narrative. God bless you, my beloved Sister. Adieu.
I remain your sincere and affectionate
Friend and Brother,
Byron.
Remember me kindly to Mrs. Harcourt.
Footnote 1: General the Right Hon. Sir William Fawcett, K.B. (1728-1804), Colonel of the 3rd Dragoon Guards, Adjutant-General (1778-1797), and Governor of Chelsea Hospital (1796-1804), died at his
house in Great George Street, Westminster, March 22, 1804. He
had served during the rebellion of 1745, and distinguished himself
during the Seven Years' War, where he was aide-de-camp first to
General Elliot, and afterwards to the Marquis of Granby. An
excellent linguist, he translated from the French, Reveries: or
Memoirs upon the Art of War, by Field-Marshal Count Saxe (1757);
and from the German, Regulations for the Prussian Cavalry (1757),
Regulations for the Prussian Infantry, and The Prussian Tacticks
(1759). His military and diplomatic services were commemorated
by a magnificent funeral on Saturday, March 31, 1804. The body
was carried through the streets from Westminster to the chapel of
Chelsea Hospital, the Prince Regent, the Duke of Clarence, and
the Duke of Kent following the hearse, and eight general officers
acting as pall-bearers.
return to footnote mark
List of Letters
[At General Harcourt's, St. Leonard's Hill, Windsor, Berkshire.]
Burgage Manor, April 9th, 1804.
A thousand thanks, my dear and Beloved Augusta, for your affectionate
Letter, and so ready compliance with the request of a peevish and
fretful Brother; it acted as a cordial on my drooping spirits and for a
while dispelled the Gloom which envelopes me in this uncomfortable
place. You see what power your letters have over me, so I hope you will
be liberal in your epistolary consolation.
You will address your next letter to Harrow as I set out from Southwell
on Wednesday, and am sorry that I cannot contrive to be with you, as I
must resume my studies at Harrow directly. If I speak in public at all,
it will not be till the latter end of June or the beginning of July. You
are right in your conjecture for I feel not a little nervous in the
anticipation of my Debut1 as an orator. By the bye, I do not
dislike Harrow. I find ways and means to amuse myself very
pleasantly there; the friend, whose correspondence I find so amusing,
is an old sporting companion of mine, whose recitals of Shooting and
Hunting expeditions are amusing to me as having often been his companion
in them, and I hope to be so still oftener.
My mother Gives a party to night at which the principal Southwell
Belles will be present, with one of which, although I don't as yet know
whom I shall so far honour, having never seen them, I intend to fall
violently in love; it will serve as an amusement pour passer le temps
and it will at least have the charm of novelty to recommend it, then you
know in the course of a few weeks I shall be quite au désespoir, shoot
myself and Go out of the world with éclat, and my History will furnish
materials for a pretty little Romance which shall be entitled and
denominated the loves of Lord B. and the cruel and Inconstant Sigismunda
Cunegunda Bridgetina, etc., etc., Princess of Terra Incognita.
Don't you think that I have a very good Knack for novel writing? I
have Just this minute been called away from writing to you by two
Gentlemen who have given me an invitation to go over to Screveton, a
village a few miles off, and spend a few days; but however I shall not
accept it, so you will continue to address your letters to Harrow as
usual. Write to me as soon as possible and give me a long letter.
Remember me to Mrs. Harcourt and all who enquire after me. Continue to
love me and believe me,
Your truly affectionate Brother and Friend,
Byron.
P.S. — My Mother's love to you, Adieu.
Footnote 1: Mrs. Byron, writing to Hanson, July 24, 1804, says,
"I was informed by a Gentleman yesterday that he had been at Harrow
and heard him speaking, and that he acquitted himself uncommonly
well."
Byron's name occurs in three of the Harrow speech-bills — July 5, 1804;
June 6, 1805; and July 4, 1805. The three bills are printed below:—
| Harrow School Public Speeches |
|
1. July 5, 1804. |
| Erskine, Maj. |
Cæsar |
ex Sallustio |
| Sinclair |
Cato |
ex Sallustio |
| Long |
C. Canuleius ad Pleb. |
ex Livia |
| Molloy, Sr. |
The Country Box |
Lloyd |
| Lord Byron |
Latinus |
Ex Virgilio |
| Leeke |
Drances |
Ex Virgilio |
| Peel, Sr. |
Turnus |
Ex Virgilio |
| Chaplin |
Henry V to his soldiers |
Shakespear |
| Clayton |
Micispa ad Jugurtham |
ex Sullustia |
| Rowley |
Germanicus moriens |
ex Tacito |
| Grenside, Sr. |
General Wolfe to his soldiers |
Enfield |
| Morant, Sr. |
Dido |
Ex Virgilio |
| Mr.Calthorpe, Sr. |
In Catilinam |
Ex Cicerone |
| Lloyd, Sr. |
The Ghost |
Shakespear |
| Mr. Powys |
Tiresias |
Ex Horatio |
| Sir Thomas Acland |
The Boil'd Pig |
Wesley |
| Leveson Gower |
Ad Antonium |
Ex Cicerone |
| Drury, Max |
Earl of Strafford |
Hume |
2. June 6, 1805.
There were no Speeches for May, 1805. Dr. Butler came to Harrow this
year, after the Easter Holiday. — G.B.A
| Daveton |
Canulcius |
Ex Livio |
| Farrer, Sr. |
Medea |
Ex Ovidio |
| Long |
Caractacus |
Mason |
| Rogers |
Manlius |
Ex Sallustio |
| Molloy |
Micipsa |
Ex Sallustio |
| Lord Byron |
Zanga |
Young |
| Drury, Sr. |
Memmius |
Ex Sallustio |
| Hoare |
Ajax |
Ex Ovidio |
| East |
Ulysses |
Ex Ovidio |
| Leeke |
The Passions: an Ode |
Collins |
| Calvert, Sr. |
Galgacus |
Ex Tacito |
| Bazett |
Catilina ad Consp. |
Ex Sallustio |
| Franks, Sr. |
Antony |
Shakespeare |
| Wildman, Maj. |
Sat. ix, Lib. i |
Ex Horatio |
| Lloyd, Sr. |
The Bard: an Ode |
Gray |
3. July 4, 1805.
| Lyon |
Piso ad Milites |
Ex Tacito |
| East |
Cato |
Addison |
| Saumerez |
Drances |
Ex Virgilio, Æn. xi |
| Annesley |
Turnus |
Ex Virgilio, Æn. xi |
| Calvert |
Lord Strafford's Defence |
Hume |
| Erskine, Sr. |
Achilles |
Ex Homero, Il. xvi |
| Bazett |
York |
Shakespeare |
| Harrington |
Camillus |
Ex Livio. |
| Leeke |
Ode to the Passions |
Collins |
| Sneyd |
Electra |
Ex Sophocle |
| Long |
Satan's Soliloquy |
Milton, P.L., b. iv |
| Gibson |
Brutus |
Ex Lucano |
| Drury, Sr. |
Cato |
Ex Lucano |
| Lord Byron |
Lear |
Shakespeare |
| Hoare |
Otho ad Milites |
Ex Livio |
| Wildman |
Caractacus |
Mason |
| Franks |
Wolsey |
Shakespeare |
Of Byron's oratorical powers, Dr. Drury, Head-master of Harrow, formed a
high opinion.
"The upper part of the school," he writes (see Life, p. 20), composed
declamations, which, after a revisal by the tutors, were submitted to
the master. To him the authors repeated them, that they might be
improved in manner and action, before their public delivery. I certainly
was much pleased with Lord Byron's attitude, gesture, and delivery, as
well as with his composition. All who spoke on that day adhered, as
usual, to the letter of their composition, as, in the earlier part of
his delivery, did Lord Byron; but, to my surprise, he suddenly diverged
from the written composition, with a boldness and rapidity sufficient to
alarm me, lest he should fail in memory as to the conclusion. There was
no failure; he came round to the close of his composition without
discovering any impediment and irregularity on the whole. I questioned
him why he had altered his declamation. He declared he had made no
alteration, and did not know, in speaking, that he had deviated from it
one letter. I believed him; and, from a knowledge of his temperament, am
convinced that, fully impressed with the sense and substance of the
subject, he was hurried on to expressions and colourings more striking
than what his pen had expressed."
"My qualities," says Byron, in one of his note-books (quoted by Moore,
Life, p. 20), "were much more oratorical and martial than poetical;
and Dr. Drury, my grand patron (our head-master), had a great notion
that I should turn out an orator, from my fluency, my turbulence, my
voice, my copiousness of declamation, and my action. I remember that
my first declamation astonished him into some unwonted (for he was
economical of such) and sudden compliments before the declaimers at
our first rehearsal."
For his subjects Byron chose passages expressive of vehement passion,
such as Lear's address to the storm, or the speech of Zanga over the
body of Alonzo, from Young's tragedy The Revenge. Zanga's character
and speech are famous in history from their application to Benjamin
Franklin, in Wedderburn's speech before the Privy Council (January,
1774) on the Whately Letters (Stanhope's History of England, vol. v.
p. 327, ed. 1853):—
"I forg'd the letter, and dispos'd the picture,
I hated, I despis'd, and I destroy."
Sub-Footnote A: Note, in Dr. G. Butler's writing, in the bound volume of
Speech-Bills presented by him to the Harrow School Library.
return to footnote
return to letter
cross-reference: return to Footnote of Letter 28
cross-reference: return to Footnote 1 of Letter 31
cross-reference: return to Footnote 1 of Letter 97
List of Letters
Burgage Manor, August 18th, 1804.
My Dearest Augusta, — I seize this interval of my amiable mother's
absence this afternoon, again to inform you, or rather to desire to be
informed by you, of what is going on. For my own part I can send nothing
to amuse you, excepting a repetition of my complaints against my
tormentor, whose diabolical disposition (pardon me for staining my
paper with so harsh a word) seems to increase with age, and to acquire
new force with Time. The more I see of her the more my dislike augments;
nor can I so entirely conquer the appearance of it, as to prevent her
from perceiving my opinion; this, so far from calming the Gale, blows it
into a hurricane, which threatens to destroy everything, till
exhausted by its own violence, it is lulled into a sullen torpor, which,
after a short period, is again roused into fresh and revived phrenzy, to
me most terrible, and to every other Spectator astonishing. She then
declares that she plainly sees I hate her, that I am leagued with her
bitter enemies, viz. Yourself, L'd C[arlisle] and Mr. H[anson], and, as
I never Dissemble or contradict her, we are all honoured with a
multiplicity of epithets, too numerous, and some of them too gross,
to be repeated. In this society, and in this amusing and instructive
manner, have I dragged out a weary fortnight, and am condemned to pass
another or three weeks as happily as the former. No captive Negro, or
Prisoner of war, ever looked forward to their emancipation, and return
to Liberty with more Joy, and with more lingering expectation, than I do
to my escape from this maternal bondage, and this accursed place, which
is the region of dullness itself, and more stupid than the banks of
Lethe, though it possesses contrary qualities to the river of oblivion,
as the detested scenes I now witness, make me regret the happier ones
already passed, and wish their restoration.
Such Augusta is the happy life I now lead, such my amusements. I
wander about hating everything I behold, and if I remained here a few
months longer, I should become, what with envy, spleen and all
uncharitableness, a complete misanthrope, but notwithstanding this,
Believe me, Dearest Augusta, ever yours, etc., etc.,
Byron.
List of Letters
12 — To Elizabeth Bridget Pigot1
Burgage Manor, August 29, 1804.
I received the arms, my dear Miss Pigot, and am very much obliged to you
for the trouble you have taken. It is impossible I should have any fault
to find with them. The sight of the drawings gives me great pleasure for
a double reason, — in the first place, they will ornament my books, in
the next, they convince me that you have not entirely forgot me. I
am, however, sorry you do not return sooner — you have already been gone
an age. I perhaps may have taken my departure for London before
you come back; but, however, I will hope not. Do not overlook my
watch-riband and purse, as I wish to carry them with me. Your note was
given me by Harry2, at the play, whither I attended Miss Leacroft3, and Dr. S — — ; and now I have sat down to answer it before I go to
bed. If I am at Southwell when you return, — and I sincerely hope you
will soon, for I very much regret your absence, — I shall be happy to
hear you sing my favourite, "The Maid of Lodi."4 My mother, together
with myself, desires to be affectionately remembered to Mrs. Pigot, and,
believe me, my dear Miss Pigot, I remain, your affectionate friend,
Byron.
P.S. — If you think proper to send me any answer to this, I shall be
extremely happy to receive it. Adieu.
P.S.2d. — As you say you are a novice in the art of knitting, I hope it
don't give you too much trouble. Go on slowly, but surely. Once
more, adieu.
Footnote 1: Elizabeth Bridget Pigot lived with her mother and two brothers
on Southwell Green, in a house opposite Burgage Manor. Miss
Pigot thus describes her first meeting with Byron (Life, p. 32):—
"The first time I was introduced to him was at a party at his
mother's, when he was so shy that she was forced to send for him three
times before she could persuade him to come into the drawing-room, to
play with the young people at a round game. He was then a fat, bashful
boy, with his hair combed straight over his forehead, and extremely
like a miniature picture that his mother had painted by M. de
Chambruland. The next morning Mrs. Byron brought him to call at our
house, when he still continued shy and formal in his manner. The
conversation turned upon Cheltenham, where we had been staying, the
amusements there, the plays, etc.; and I mentioned that I had seen the
character of Gabriel Lackbrain very well performed. His mother getting
up to go, he accompanied her, making a formal bow, and I, in allusion
to the play, said, 'Good-by, Gaby.' His countenance lighted up, his
handsome mouth displayed a broad grin, all his shyness vanished, never
to return, and, upon his mother's saying, 'Come, Byron, are you
ready?' — no, she might go by herself, he would stay and talk a little
longer; and from that moment he used to come in and go out at all
hours, as it pleased him, and in our house considered himself
perfectly at home."
The character of "Gabriel Lackbrain," mentioned above, occurs in Life,
a comedy by F. Reynolds. It was at Byron's suggestion that Moore, when
preparing the Life, applied to Miss Pigot for letters. On January 22,
1828, he was taken to call on her and her mother by the Rev. John
Becher.
"Their reception of me most cordial and flattering; made me sit in the
chair which Byron used to sit in, and remarked, as a singularity, that
this was the poor fellow's birthday; he would to-day have been forty.
On parting with Mrs. Pigot, a fine, intelligent old lady, who has been
bedridden for years, she kissed my hand most affectionately, and said
that, much as she had always admired me as a poet, it was as the
friend of Byron she valued and loved me ... Her affection, indeed, to
his memory is unbounded, and she seems unwilling to allow that he had
a single fault ... Miss Pigot in the evening, with his letters, which
interested me exceedingly; some written when he was quite a boy, and
the bad spelling and scrambling handwriting delightful; spelling,
indeed, was a very late accomplishment with him"
(Diary of Thomas Moore, vol. v. p. 249). (See "To Eliza," Poems,
vol. i. pp.47-49; see also the lines "To M. S. G.," Poems, vol. i. pp.
79, 80; see for the lines which Byron wrote in her copy of Burns,
Poems, vol. i. pp. 233, 234.)
Miss Pigot died at Southwell in 1866, her brother John (see letter of
August 9, 1806, p. 100, note 3) in 1871. Her brother Henry, whom Byron
used to call his grandson, died October 28, 1830, a captain in the 23rd
Native Infantry in the service of the East India Company.
[cross-reference: return to Footnote 2 of Letter 12]
The following undated note (1810) from Mrs. Pigot to Mrs. Byron
illustrates the enthusiastic interest with which the Pigots followed
Byron's career:—
"Indeed, my dear Mrs. Byron, you have given me a very great treat in
sending me English Bards to look at; you know how very highly I
thought of the first edition, and this is certainly much improved;
indeed, I do not think anybody but Lord Byron could (in these our
days) have produced such a work, for it has all the fire of ancient
genius. I have always been accustomed to tell you my thoughts most
sincerely, and I cannot say that I like that addition to the part
where Bowles is mentioned; it wants that brilliant spirit which
almost invariably accompanies Lord B.'s writings. Maurice, too, and
his granite weight of leaves, is in truth a heavy comparison. But I
turn with pleasure from these specks in the sun to notice 'Vice and
folly, Greville and Argyle;' it is most admirable: the same pen
may equal, but I think it is not in the power of human abilities to
exceed it. As to Lord Carlisle, I think he well deserves the Note
Lord B. has put in; I am very much pleased with it, and the little
word Amen at the end, gives a point indescribably good. The whole
of the conclusion is excellent, and the Postscript I think must
entertain everybody except Jeffrey. I hope the poor Bear is well; I
wish you could make him understand that he is immortalized, for, if
four-leg'd Bears have any vanity, it would certainly delight him.
Walter Scott, too (I really do not mean to call him a Bear), will be
highly gratified: the compliment to him is very elegant: in short, I
look upon it as a most highly finished work, and Lord Byron has
certainly taken the Palm from all our Poets ... A good account of
yourself I assure you will always give the most sincere pleasure to my
dear Mrs. Byron's very affectionate friend, Margt. Pigot. Elizabeth
begs her compts."
return to footnote mark
cross-reference: return to Footnote 1 of Letter 52
Footnote 2: Henry Pigot. (See p. 33 [above], note 1.)
return
Footnote 3: Miss Julia Leacroft, daughter of a neighbour, Mr. John
Leacroft. (See lines "To Lesbia," Poems, vol. i. pp. 41-43.) The
private theatricals in September, 1806 (see p. 117, note 3), were
held at Mr. Leacroft's house. Later, Captain Leacroft expostulated with
Byron on his attentions to his sister, and, according to Moore,
threatened to call him out. Byron was ready to meet him; but afterwards,
on consulting Becher, resolved never to go near the house
again. — Prose and Verse of Thomas Moore, edited by Richard Herne
Shepherd (London, 1878), p. 420. (But see Letters 62, 63, 64.)
return
cross-reference: return to Footnote 1 of Letter 62
Footnote 4: By Dibdin, set to music by Shield. (See Moore's
Life, p. 33.) Byron's love for simple ballad music lasted
throughout his life. As a boy at Harrow, he was famous for the vigour
with which he sang "This Bottle's the Sun of our Table" at Mother
Barnard's. He liked the Welsh air "Mary Anne," sung by Miss Chaworth;
the songs in The Duenna; "When Time who steals our Years away,"
which he sang with Miss Pigot; or "Robin Adair," in which he was
accompanied by Miss Hanson on her harp.
"It is very odd," he said to
Miss Pigot, "I sing much better to your playing than to any one else's."
"That is," she answered, "because I play to your singing."
Moore
(Journal and Correspondence, vol. v. pp. 295, 296), speaking of
"Byron's chanting method of repeating poetry," says that "it is the men
who have the worst ears for music that sing out poetry in this
manner, having no nice perception of the difference there ought to be
between animated reading and chant." Rogers (Table-Talk,
etc., pp. 224, 225) expresses the same opinion, when he says, "I can
discover from a poet's versification whether or not he has an ear for
music. To instance poets of the present day:— from Bowles's and Moore's,
I should know that they had fine ears for music; from Southey's,
Wordsworth's, and Byron's, that they had no ears for it."
return
List of Letters
[Castle Howard, Malton, Yorkshire.]
Harrow-on-the-Hill, October 25th, 1804.
My dear Augusta, — In compliance with your wishes, as well as gratitude
for your affectionate letter, I proceed as soon as possible to answer
it; I am glad to hear that any body gives a good account of me;
but from the quarter you mention, I should imagine it was exaggerated.
That you are unhappy, my dear Sister, makes me so also; were it in my
power to relieve your sorrows you would soon recover your spirits; as it
is, I sympathize better than you yourself expect. But really, after all
(pardon me my dear Sister), I feel a little inclined to laugh at you,
for love, in my humble opinion, is utter nonsense, a mere jargon of
compliments, romance, and deceit; now, for my part, had I fifty
mistresses, I should in the course of a fortnight, forget them all, and,
if by any chance I ever recollected one, should laugh at it as a dream,
and bless my stars, for delivering me from the hands of the little
mischievous Blind God. Can't you drive this Cousin1 of ours out of
your pretty little head (for as to hearts I think they are out of
the question), or if you are so far gone, why don't you give old
L'Harpagon2 (I mean the General) the slip, and take a trip to
Scotland, you are now pretty near the Borders. Be sure to Remember me to
my formal Guardy Lord Carlisle3, whose magisterial presence I have not
been into for some years, nor have I any ambition to attain so great an
honour. As to your favourite Lady Gertrude, I don't remember her; pray,
is she handsome? I dare say she is, for although they are a
disagreeable, formal, stiff Generation, yet they have by no means
plain persons, I remember Lady Cawdor was a sweet, pretty woman;
pray, does your sentimental Gertrude resemble her? I have heard that the
duchess of Rutland was handsome also, but we will say nothing about her
temper, as I hate Scandal.
Adieu, my pretty Sister, forgive my levity, write soon, and God bless
you.
I remain, your very affectionate Brother,
Byron.
P.S. — I left my mother at Southwell, some time since, in a monstrous pet
with you for not writing. I am sorry to say the old lady and myself
don't agree like lambs in a meadow, but I believe it is all my own
fault, I am rather too fidgety, which my precise mama objects to, we
differ, then argue, and to my shame be it spoken fall out a little,
however after a storm comes a calm; what's become of our aunt the
amiable antiquated Sophia4? is she yet in the land of the living, or
does she sing psalms with the Blessed in the other world. Adieu.
I am happy enough and Comfortable here. My friends are not numerous, but
select; among them I rank as the principal Lord Delawarr5, who is very
amiable and my particular friend; do you know the family at all? Lady
Delawarr is frequently in town, perhaps you may have seen her; if she
resembles her son she is the most amiable woman in Europe. I have plenty
of acquaintances, but I reckon them as mere Blanks. Adieu, my dear
Augusta.
Footnote 1: Colonel George Leigh.
return to footnote mark
Footnote 2: General Leigh, father of the colonel. Both Harpagon and
Cléante (L'Avare) wish to marry Mariane; but the miser prefers
his casket to the lady, who therefore marries Cléante.
return
Footnote 3: Frederick Howard, fifth Earl of Carlisle (1748-1825), was,
on his mother's side, connected with the Byron family. The Hon. Isabella
Byron (1721-1795), daughter of the fourth Lord Byron, married, in 1742,
Henry, fourth Earl of Carlisle. She subsequently, after the death of
Lord Carlisle (1758), married, as her second husband, Sir William
Musgrave. She was a woman of considerable ability, and apparently, in
later life, of eccentric habits — a "recluse in pride and rags." She was
the reputed writer of some published poetry, and of Maxims addressed
to Young Ladies. Some of these maxims might have been of use to her
grand-nephew: "Habituate yourself to that way of life most agreeable to
the person to whom you are united; be content in retirement, or with
society, in town, or country." Her Answer to Mrs. Greville's ode
on Indifference has more of the neck-or-nothing temper of the
Byrons:—
"Is that your wish, to lose all sense
In dull lethargic ease,
And wrapt in cold indifference,
But half be pleased or please?
...
It never shall be my desire
To bear a heart unmov'd,
To feel by halves the gen'rous fire,
Or be but half belov'd.
Let me drink deep the dang'rous cup,
In hopes the prize to gain,
Nor tamely give the pleasure up
For fear to share the pain.
Give me, whatever I possess,
To know and feel it all;
When youth and love no more can bless,
Let death obey my call."
Lady Carlisle's son, Frederick, who was educated at Eton and Cambridge,
succeeded his father as fifth Earl of Carlisle, in 1758, when he was ten
years old. After leaving Cambridge, he started on a continental tour
with two Eton friends — Lord FitzWilliam and Charles James Fox. A lively
letter-writer, his correspondence with his friend George Selwyn, while
in Italy, shows him to have been a young man of wit, feeling, and taste.
It is curious to notice that, at Rome, he singles out, like his cousin
in Childe Harold or Manfred, as the most striking objects, the
general aspect of the "marbled "wilderness," the moonlight view of the
amphitheatre, the Laocoon, the Belvedere Apollo, and the group of Niobe
and her daughters. One other taste he shared with Byron — he was a lover
of dogs, and "Rover" was his constant companion abroad.
Lord Carlisle returned to England in 1769. Like Fox, he was a prodigious
dandy. They "once travelled from Paris to Lyons for the express purpose
of buying waistcoats; and during the whole journey they talked of
nothing else" (Table-Talk of Samuel Rogers, pp. 73, 74). Already well
known in London society, Carlisle was a close friend of George Selwyn, a
familiar figure at White's and Brookes's, an inveterate gambler, an
adorer of Lady Sarah Bunbury, who, as Lady Sarah Lennox, had won the
heart of George III. The flirtation provoked from Lord Holland an
adaptation of Lydia, dic per omnes:—
"Sally, Sally, don't deny,
But, for God's sake, tell me why
You have flirted so, to spoil
That once lively youth, Carlisle?
He used to mount while it was dark;
Now he lies in bed till noon,
And, you not meeting in the park,
Thinks that he gets up too soon," etc.
In 1770 Lord Carlisle married Lady Margaret Leveson Gower, a beautiful
and charming woman. "Everybody," writes Lord Holland to George Selwyn
(May 2, 1770), "says it is impossible not to admire Lady Carlisle." But
matrimony did not at once steady his character. For the next few
years — though in 1773 he published a volume of Poems — his pursuits
were mainly those of a young man of fashion, and he impoverished himself
at the gaming-table. From 1777 onwards, however, his life took a more
serious turn. In that year he became Treasurer of the Household, and was
sworn a member of the Privy Council. In 1778 he was the chief of the
three commissioners sent out by Lord North to negotiate with the United
States. There he declined a challenge from Lafayette, provoked by
reflections on the French court and nation, which he had issued with his
fellow-commissioners in their political capacity. In 1779 he was
nominated Lord-Lieutenant of Yorkshire, and First Lord of Trade and
Plantations. He was Lord-Lieutenant of Ireland from 1780 to 1782, and
held the post of Lord Privy Seal in the Duke of Portland's
administration of 1783. Till the outbreak of the French Revolutionary
wars, he was an opponent of Pitt; but after 1792 he consistently
supported the Government.
Carlisle was a collector of pictures, statuary, and works of art. He was
also a writer of verse, tragedies, and pamphlets; but, in literature,
his admirable letters are his best claim to be remembered. One of his
two tragedies, The Father's Revenge (1783), was praised by
Walpole, and received the guarded approval of Dr. Johnson. His published
poetry consisted of an ode on the death of Gray, verses on that of Lord
Nelson, "Lines for the Monument of a favourite Spaniel," an address to
Sir Joshua Reynolds, and translations from Dante. The first two poems
provoked Richard Tickell to write the Wreath of Fashion (1780).
"The following lines," says Tickell, in his "Advertisement," were
"occasioned by the Author's having lately studied, with infinite
attention, several fashionable productions in the Sentimental
stile.... For example, A Noble Author has lately published his works,
which consist of three compositions: one an Ode upon the
death of Mr. Gray; the two others upon the death of his Lordship's
Spaniel."
"Here, placid Carlisle breathes his gentle line,
Or haply, gen'rous Hare, re-echoes thine.
Soft flows the lay: as when, with tears, He paid
The last sad honours to his — — — Spaniel's shade!
And lo! he grasps the badge of wit, a wand;
He waves it thrice and Storer is at hand."
His contemporaries seem to have thought that his poetry, weak though it
was, was indebted to his Eton friends, "the Hare with many friends," and
Antony Storer. The latter's name is linked with that of Carlisle in
another satire, Pandolfo Attonito:—
"Fall'n though I am, I ne'er shall mourn,
Like the dark Peer on Storer's urn,"
where a note refers to "Antony Storer, formerly Member for Morpeth
(as some persons near Carlisle and Castle Howard may possibly
recollect), a gentleman well known in the circles of fashion and
polite literature." Carlisle's name occurs in many of the satires of the
day on literary subjects. The Shade of Pope (ii. 191, 192) says —
"Carlisle is lost with Gillies in surprize,
As Lysias charms soft Jersey's classic eyes;"
and in the Pursuits of Literature (Dialogue ii. line 234), a note to
the line —
"While lyric Carlisle purrs o'er love transformed,"
again associates his name with that of Lady Jersey.
In 1799 Lord Carlisle was persuaded by Hanson to become Byron's
guardian, in order to facilitate legal proceedings for the recovery of
the Rochdale property, illegally sold by William, fifth Lord Byron. He
was introduced to his ward by Hanson, who took the boy to Grosvenor Place, to see his guardian and consult Dr. Baillie in July,
1799. He seemed anxious to befriend the boy; but Byron was eager, as
Hanson notes, to leave the house. When Mrs. Byron, in 1800, was anxious
to remove her son from Dr. Glennie's care, Carlisle exercised his
authority, and forbade the schoolmaster to give him up to his mother. He
probably, on this occasion, experienced Mrs. Byron's temper, for Augusta
Byron, writing to Hanson (November 18, 1804), says that he dreaded
"having any concern whatever with Mrs. Byron." Byron does not seem to
have met his guardian again till January, 1805, when Augusta Byron
writes to Hanson:
"I hear from Lady Gertrude Howard that Lord Carlisle
was very much pleased with my brother, and I am sure, from what
he said to me at Castle Howard, is disposed to show him all the kindness
and attention in his power. I know you are so partial to Byron and so
much interested in all that concerns him, that you will rejoice almost
as much as I do that his acquaintance with Lord C. is renewed. In the
mean time it is a great comfort for me to think that he has spent his
Holydays so comfortably and so much to his wishes. You will easily
believe that he is a very great favourite of mine, and I may add
the more I see and hear of him, the more I must love and esteem
him."
It may be doubted whether Carlisle ever saw the dedication of Hours
of Idleness. Augusta Byron, in a letter to Hanson of February 7,
1807, says,
"I return you my Brother's poems with many Thanks. Mrs. B.
has had the attention to send me 2 copies. I like some of them very
much: but you will laugh when I tell you I have never had courage to
shew them to Lord Carlisle for fear of his disapproving others."
The
years 1806-7, spent at Southwell, as his sister says, "in idleness and
ill humour with the whole World," were not the most creditable of
Byron's life, and Carlisle's efforts to make him return to Cambridge
failed. It is, moreover, certain that in 1809 Carlisle was ill; it is
also probable that at a time when the scandal of Mary Anne Clarke and
the Duke of York threatened to come before the House of Lords, he was
unwilling to connect himself in public with a cousin of whom he knew no
good, and of whose political views he was ignorant. These causes may
have combined to produce the coldly formal letter, in which he told
Byron the course of procedure to be adopted in taking his seat in the
House of Lords, and ignored the young man's wish that his cousin and
guardian should introduce him. (For Byron's attack upon Carlisle, and
his subsequent admission of having done him "some wrong," see English
Bards, and Scotch Reviewers, lines 723-740; and Childe
Harold, Canto III. stanzas xxix., xxx.)
It is possible that the "paralytic puling" may have been suggested by
the "placid purring" of previous satirists. In March, 1814, his sister
Augusta was trying hard to persuade Byron, as he notes in his Diary,
"to
make it up with Carlisle. I have refused every body else, but I
can't deny her anything, though I had as leif 'drink up Eisel — eat a
crocodile.'"
Lord Carlisle had three daughters: the eldest, Lady Caroline Isabella
Howard, married, in 1789, John, first Lord Cawdor, and died in 1848; the
second, Lady Elizabeth, married, in 1799, John Henry, fifth Duke of
Rutland, and died in 1825; the third, Lady Gertrude, married, in 1806,
William Sloane Stanley, of Paultons, Hants, and died in 1870.
return
cross-reference: return to Footnote 1 of Letter 7
cross-reference: return to Footnote 2 of Letter 110
Footnote 4: No "Aunt Sophia" appears in the pedigree; but his
grandmother was Sophia Trevanion, who married, in 1748, the Hon. John
Byron, afterwards Admiral Byron. Mrs. Byron knew Dr. Johnson well, and
she and Miss Burney were the only two friends who, as Mrs. Piozzi (then
Mrs. Thrale) thought, might regret her departure from Streatham in 1782
(Life and Writings of Mrs. Piozzi, vol. i. p. 171). "Mrs. Byron, who
really loves me," says Mrs. Piozzi (ibid., p. 125), "was disgusted at
Miss Burney's carriage to me." In August, 1820, Mrs. Piozzi writes to a
Miss Willoughby, to tell her
"what wonders Lord Byron is come home to
do, for I see his arrival in the paper. His grandmother was my intimate
friend, a Cornish lady, Sophia Trevanion, wife to the Admiral, pour ses
péchés, and we called her Mrs. Biron always, after the French
fashion"
(Life and Writings, etc., vol. ii. pp. 456, 457)' Mrs. Byron
died at Bath in 1790.
return
Footnote 5: Lady Delawarr, widow of John Richard, fourth Earl Delawarr,
whom she married in 1783, died in 1826. Her only son, George
John, fifth earl, succeeded his father in 1795. He went from Harrow
to Brasenose College, Oxford; married, in 1813, Lady Elizabeth
Sackville; was Lord Chamberlain 1858-9; and died in 1869. He
was the "Euryalus" of "Childish Recollections" (see Poems,
vol. i. p. 100; and lines "To George, Earl of Delawarr," ibid.,
p. 126).
return
cross-reference: return to Footnote 2 of Letter 65
cross-reference: return to Footnote 1 of Letter 93
List of Letters
Friday, November 2d, 1804.
This morning, my dear Augusta, I received your affectionate letter, and
it reached me at a time when I wanted consolation, not however of your
kind for I am not yet old enough or Goose enough to be in love; no, my
sorrows are of a different nature, though more calculated to provoke
risibility than excite compassion. You must know, Sister of mine, that I
am the most unlucky wight in Harrow, perhaps in Christendom, and am no
sooner out of one scrape than into another. And to day, this very
morning, I had a thundering Jobation from our Good Doctor1, which
deranged my nervous system, for at least five minutes. But
notwithstanding He and I now and then disagree, yet upon the whole we
are very good friends, for there is so much of the Gentleman, so much
mildness, and nothing of pedantry in his character, that I cannot help
liking him, and will remember his instructions with gratitude as long as
I live. He leaves Harrow soon, apropos, so do I. This quitting
will be a considerable loss to the school. He is the best master we ever
had, and at the same time respected and feared; greatly will he be
regretted by all who know him. You tell me you don't know my friend L'd
Delawarr; he is considerably younger than me, but the most good
tempered, amiable, clever fellow in the universe. To all which he adds
the quality (a good one in the eyes of women) of being remarkably
handsome, almost too much so for a boy. He is at present very low in the
school, not owing to his want of ability, but to his years. I am nearly
at the top of it; by the rules of our Seminary he is under my power, but
he is too goodnatured ever to offend me, and I like him too well ever to
exert my authority over him. If ever you should meet, and chance to know
him, take notice of him on my account.
You say that you shall write to the Dowager Soon; her address is at
Southwell, that I need hardly inform you. Now, Augusta, I am
going to tell you a secret, perhaps I shall appear undutiful to you,
but, believe me, my affection for you is founded on a more firm basis.
My mother has lately behaved to me in such an eccentric manner, that so
far from feeling the affection of a Son, it is with difficulty I can
restrain my dislike. Not that I can complain of want of liberality; no,
She always supplies me with as much money as I can spend, and more than
most boys hope for or desire. But with all this she is so hasty, so
impatient, that I dread the approach of the holidays, more than most
boys do their return from them. In former days she spoilt me; now she is
altered to the contrary; for the most trifling thing, she upbraids me in
a most outrageous manner, and all our disputes have been lately
heightened by my one with that object of my cordial, deliberate
detestation, Lord Grey de Ruthyn. She wishes me to explain my reasons
for disliking him, which I will never do; would I do it to any one, be
assured you, my dear Augusta, would be the first who would know them.
She also insists on my being reconciled to him, and once she let drop
such an odd expression that I was half inclined to believe the dowager
was in love with him. But I hope not, for he is the most disagreeable
person (in my opinion) that exists. He called once during my last
vacation; she threatened, stormed, begged me to make it up, "he himself
loved me, and wished it;" but my reason was so excellent — that neither
had effect, nor would I speak or stay in the same room, till he took his
departure. No doubt this appears odd; but was my reason known, which it
never will be if I can help it, I should be justified in my conduct. Now
if I am to be tormented with her and him in this style, I cannot submit
to it. You, Augusta, are the only relation I have who treats me as a
friend; if you too desert me, I have nobody I can love but Delawarr. If
it was not for his sake, Harrow would be a desert, and I should dislike
staying at it. You desire me to burn your epistles; indeed I cannot do
that, but I will take care that They shall be invisible. If you burn any
of mine, I shall be monstrous angry; take care of them till we
meet.
Delawarr2 and myself are in a manner connected, for one of our
forefathers in Charles the 1st's time married into their family.
Hartington3, whom you enquire after, is on very good terms with me,
nothing more, he is of a soft milky disposition, and of a happy apathy
of temper which defies the softer emotions, and is insensible of ill
treatment; so much for him. Don't betray me to the Dowager. I should
like to know your Lady Gertrude, as you and her are so great Friends.
Adieu, my Sister, write. From
[Signature, etc., cut out.]
Footnote 1: The Rev. Joseph Drury, D.D. (1750-1834), educated at
Westminster and Trinity College, Cambridge, was appointed an
Assistant-master at Harrow before he was one and twenty. He was
Head-master from 1784 to 1805. In that year he retired, and till his
death in 1834 lived at Cockwood, in Devonshire, where he devoted
himself to farming. The following statement by Dr. Drury illustrates
Byron's respect for his Head-master (Life, p. 20):—
"After my retreat from Harrow, I received from him two very
affectionate letters. In my occasional visits subsequently to London,
when he had fascinated the public with his productions, I demanded of
him, why, as in duty bound, he had sent none to me? 'Because,'
said he, 'you are the only man I never wish to read them;' but in a
few moments, he added, 'What do you think of the Corsair?'"
Dr. Drury married Louisa Heath, sister of the Rev. Benjamin Heath, his
predecessor in the Head-mastership. They had four children, all of whom
have some connection with Byron's life.
- Henry Joseph Drury
(1778-1841), educated at Eton and King's College, Cambridge (Fellow),
Assistant-master at Harrow School, married (December 20, 1808) Ann
Caroline Tayler, and had a numerous family. Mrs. Drury's sister married
the Rev. F. Hodgson (see page 195, note 1).
- Benjamin Heath
Drury (1782-1835), educated at Eton and King's College, Cambridge
(Fellow), Assistant-master at Eton.
- Charles Drury (1788-1869),
educated at Harrow and Queen's College, Oxford (Fellow).
- Louisa
Heath Drury (1787-1873) married John Herman Merivale.
Dr. Drury's brother, Mark Drury, the Lower Master at Harrow, was the
candidate whom Byron supported for the Head-mastership.
return to footnote mark
cross-reference: return to Footnote 2 of Letter 4
cross-reference: return to Footnote 1 of Letter 85
cross-reference: return to Footnote 2 of Letter 102
cross-reference: return to Footnote 1 of Letter 108
Footnote 2: Thomas, third Lord Delawarr, Captain-general of all the
Colonies planted or to be planted in Virginia, died in 1618. His fourth
daughter, Cecilie, widow of Sir Francis Bindlose, married Sir John
Byron, created Lord Byron by Charles I. His fifth daughter, Lucy,
married Sir Robert Byron, brother to Lord Byron. But the first Lord
Byron left no heirs, and the title descended to his brother, Richard
Byron, from whom the poet was descended.
return
Footnote 3: William Spencer, Marquis of Hartington
(1790-1858), succeeded his father as sixth Duke of Devonshire in 1811,
and died unmarried. His sister, Georgiana Dorothy, married, in 1801,
Lord Carlisle's eldest son.
return
List of Letters
Harrow, Saturday, 11th Novr, 1804.
I thought, my dear Augusta1, that your opinion of my meek mamma
would coincide with mine; Her temper is so variable, and, when inflamed,
so furious, that I dread our meeting; not but I dare say, that I am
troublesome enough, but I always endeavour to be as dutiful as possible.
She is so very strenuous, and so tormenting in her entreaties and
commands, with regard to my reconciliation, with that detestable Lord G.2 that I suppose she has a penchant for his Lordship; but I am
confident that he does not return it, for he rather dislikes her than
otherwise, at least as far as I can judge. But she has an excellent
opinion of her personal attractions, sinks her age a good six years,
avers that when I was born she was only eighteen, when you, my dear
Sister, know as well as I know that she was of age when she married my
father, and that I was not born for three years afterwards. But vanity
is the weakness of your sex, — and these are mere foibles that I
have related to you, and, provided she never molested me, I should look
upon them as follies very excusable in a woman.
But I am now coming to
what must shock you, as much as it does me, when she has occasion to
lecture me (not very seldom you will think no doubt) she does not do it
in a manner that commands respect, and in an impressive style. No! did
she do that, I should amend my faults with pleasure, and dread to offend
a kind though just mother. But she flies into a fit of phrenzy, upbraids
me as if I was the most undutiful wretch in existence, rakes up the
ashes of my father, abuses him, says I shall be a true Byrrone,
which is the worst epithet she can invent. Am I to call this woman
mother? Because by nature's law she has authority over me, am I to be
trampled upon in this manner? am I to be goaded with insult, loaded with
obloquy, and suffer my feelings to be outraged on the most trivial
occasions? I owe her respect as a Son, But I renounce her as a Friend.
What an example does she shew me! I hope in God I shall never follow it.
I have not told you all, nor can I; I respect you as a female, nor,
although I ought to confide in you as a Sister, will I shock you with
the repetition of Scenes, which you may judge of by the Sample I have
given you, and which to all but you are buried in oblivion. Would they
were so in my mind! I am afraid they never will. And can I, my dear
Sister, look up to this mother, with that respect, that affection I
ought? Am I to be eternally subjected to her caprice? I hope not — ;
indeed a few short years will emancipate me from the Shackles I now
wear, and then perhaps she will govern her passion better than at
present.
You mistake me, if you think I dislike Lord Carlisle; I respect
him, and might like him did I know him better. For him too my mother has
an antipathy, why I know not. I am afraid he could be but of little use
to me, in separating me from her, which she would oppose with all her
might; but I dare say he would assist me if he could, so I take the will
for the Deed, and am obliged to him in exactly the same manner as if he
succeeded in his efforts.
I am in great hopes, that at Christmas I shall
be with Mr. Hanson during the vacation, I shall do all I can to avoid a
visit to my mother wherever she is. It is the first duty of a parent, to
impress precepts of obedience in their children, but her method is so
violent, so capricious, that the patience of Job, the versatility of a
member of the House of Commons could not support it. I revere Dr. Drury
much more than I do her, yet he is never violent, never outrageous: I
dread offending him, not however through fear, but the respect I bear
him makes me unhappy when I am under his displeasure. My mother's
precepts, never convey instruction, never fix upon my mind; to be sure
they are calculated, to inculcate obedience, so are chains, and
tortures, but though they may restrain for a time, the mind revolts from
such treatment. Not that Mrs. Byron ever injures my sacred
person. I am rather too old for that, but her words are of that rough
texture, which offend more than personal ill usage. "A talkative woman
is like an Adder's tongue," so says one of the prophets, but which I
can't tell, and very likely you don't wish to know, but he was a true
one whoever he was.
The postage of your letters, My dear Augusta, don't fall upon me; but if
they did, it would make no difference, for I am Generally in cash, and
should think the trifle I paid for your epistles the best laid out I
ever spent in my life. Write Soon. Remember me to Lord Carlisle, and,
believe me, I ever am
Your affectionate Brother and Friend,
Byrone.
Footnote 1: In consequence of this letter, Augusta Byron wrote as
follows to Hanson, and Byron spent the Christmas holidays of 1804 with
his solicitor:—
"Castle Howard, Nov. 18, 1804.
"My Dear Sir, — I am afraid you will think I presume almost too much
upon the kind permission you have so often given me of applying to you
about my Brother's concerns. The reason that induces me now to do so
is his having lately written me several Letters containing the most
extraordinary accounts of his Mother's conduct towards him and
complaints of the uncomfortable Situation he is in during the Holidays
when with her. All this you will easily imagine has more vexed than
surprized me. I am quite unhappy about him, and wish I could in any
way remedy the grievances he confides to me. I wished, as the most
likely means of doing this, to mention the subject to Lord Carlisle,
who has always expressed the greatest interest about Byron and also
shewn me the greatest Kindness. Finding that he did not object to
it, I yesterday had some conversation with Lord C. on the subject, and
it is partly by his advice and wishes that I trouble you with this
Letter. He authorized me to tell you that, if you would allow my
Brother to spend the next vacation with you (which he seems
strongly to wish), that it would put it into his power to see more
of him and shew him more attention than he has hitherto, being
withheld from doing so from the dread of having any concern whatever
with Mrs. Byron.
I need hardly add that it is almost my first wish that this should be
accomplished. I am sure you are of my opinion that it is now of the
greatest consequence to Byron to secure the friendship of Lord C., the
only relation he has who possesses the Will and power to be of use
to him. I think the Letters he writes me quite perfect and he does
not express one sentiment or idea I should wish different; he tells me
he is soon to leave Harrow, but does not say where he is to go. I
conclude to Oxford or Cambridge. Pray be so good as to write me a
few lines on this subject.
I trust entirely to the interest and friendship you have ever so
kindly expressed for my Brother, for my Forgiveness. Of course you
will not mention to Mrs. B. having heard from me, as she would only
accuse me of wishing to estrange her Son from her, which would be very
far from being the case further than his Happiness and comfort are
concerned in it. My opinion is that as they cannot agree, they had
better be separated, for such eternal Scenes of wrangling are enough
to spoil the very best temper and Disposition in the universe. I shall
hope to hear from you soon, my dear sir, and remain, Most sincerely
yours, Augusta Byron."
return to footnote mark
cross-reference: return to Footnote 1 of Letter 7
Footnote 2: Lord Grey de Ruthyn. (See p. 23, note 1.)
return
List of Letters
[Castle Howard, Malton, Yorkshire.]
Harrow-on-the-Hill, Novr., Saturday, 17th, 1804.
I am glad to hear, My dear Sister, that you like Castle Howard so well,
I have no doubt what you say is true and that Lord C. is much more
amiable than he has been represented to me. Never having been much with
him and always hearing him reviled, it was hardly possible I should have
conceived a very great friendship for his L'dship. My mother, you
inform me, commends my amiable disposition and good
understanding; if she does this to you, it is a great deal more than
I ever hear myself, for the one or the other is always found fault with,
and I am told to copy the excellent pattern which I see before me
in herself. You have got an invitation too, you may accept it if
you please, but if you value your own comfort, and like a pleasant
situation, I advise you to avoid Southwell. — I thank you, My dear
Augusta, for your readiness to assist me, and will in some manner avail
myself of it; I do not however wish to be separated from her
entirely, but not to be so much with her as I hitherto have been, for I
do believe she likes me; she manifests that in many instances,
particularly with regard to money, which I never want, and have as much
as I desire. But her conduct is so strange, her caprices so impossible
to be complied with, her passions so outrageous, that the evil quite
overbalances her agreeable qualities. Amongst other things I
forgot to mention a most ungovernable appetite for Scandal, which
she never can govern, and employs most of her time abroad, in displaying
the faults, and censuring the foibles, of her acquaintance; therefore I
do not wonder, that my precious Aunt, comes in for her share of
encomiums; This however is nothing to what happens when my conduct
admits of animadversion; "then comes the tug of war." My whole family
from the conquest are upbraided! myself abused, and I am told that what
little accomplishments I possess either in mind or body are derived from
her and her alone.
When I leave Harrow I know not; that depends on her nod; I like it very
well. The master Dr. Drury, is the most amiable clergyman I ever
knew; he unites the Gentleman with the Scholar, without affectation or
pedantry, what little I have learnt I owe to him alone, nor is it his
fault that it was not more. I shall always remember his instructions
with Gratitude, and cherish a hope that it may one day be in my power to
repay the numerous obligations, I am under; to him or some of his
family.
Our holidays come on in about a fortnight. I however have not mentioned
that to my mother, nor do I intend it; but if I can, I shall contrive to
evade going to Southwell. Depend upon it I will not approach her for
some time to come if It is in my power to avoid it, but she must not
know, that it is my wish to be absent. I hope you will excuse my sending
so short a letter, but the Bell has just rung to summon us together.
Write Soon, and believe me, Ever your affectionate Brother, Byron.
I am afraid you will have some difficulty in decyphering my epistles,
but that I know you will excuse. Adieu. Remember me to Lord
Carlisle.
List of Letters
[Castle Howard, Malton, Yorkshire.]
Harrow-on-the-Hill, Novr. 21st,
1804.
My Dearest Augusta, — This morning I received your by no means unwelcome
epistle, and thinking it demands an immediate answer, once more take up
my pen to employ it in your service. There is no necessity for my mother
to know anything of my intentions, till the time approaches; and when it
does come, Mr. H. has only to write her a note saying, that, as I could
not accept the invitation he gave me last holidays, he imagined I might
do it now; to this she surely can make no objections; but, if she
entertained the slightest idea of my making any complaint of her very
lenient treatment, the scene that would ensue beggars all power
of description. You may have some little idea of it, from what I have
told you, and what you yourself know.
I wrote to you the other day; but you make no mention of receiving my
letter in yours of the 18th inst. It is however of little importance,
containing merely a recapitulation of circumstances which I have before
detailed at full length.
To Lord Carlisle make my warmest acknowledgements. I feel more
gratitude, than my feelings can well express; I am truly obliged to him
for his endeavours, and am perfectly satisfied with your explanation of
his reserve, though I was hitherto afraid it might proceed from personal
dislike. I have some idea that I leave Harrow these holidays. The Dr.,
whose character I gave you in my last, leaves the mastership at Easter.
Who his successor may be I know not, but he will not be a better I am
confident. You inform me that you intend to visit my mother, then you
will have an opportunity of seeing what I have described, and hearing a
great deal of Scandal. She does not trouble me much with
epistolary communications; when I do receive them, they are very
concise, and much to the purpose. However I will do her the justice to
say that she behaves, or rather means, well, and is in some respects
very kind, though her manners are not the most conciliating. She
likewise expresses a great deal of affection for you, but disapproves
your marriage, wishes to know my opinion of it, and complains that you
are negligent and do not write to her or care about her. How far her
opinion of your love for her is well grounded, you best know. I again
request you will return my sincere thanks to Lord Carlisle, and for the
future I shall consider him as more my friend than I have hitherto been
taught to think. I have more reasons than one, to wish to avoid going to
Notts, for there I should be obliged to associate with Lord G. whom I
detest, his manners being unlike those of a Gentleman, and the
information to be derived from him but little except about shooting,
which I do not intend to devote my life to. Besides, I have a particular
reason for not liking him. Pray write to me soon. Adieu, my Dear
Augusta.
I remain, your affectionate Brother, Byron.
List of Letters
18 — to John Hanson1
Saturday, Dec. 1st, 1804.
My Dear Sir, — Our vacation commences on the 5th of this Month, when I
propose to myself the pleasure of spending the Holidays at your House,
if it is not too great an Inconvenience. I tell you fairly, that at
Southwell I should have nothing in the World to do, but play at cards
and listen to the edifying Conversation of old Maids, two things which
do not at all suit my inclinations. In my Mother's last Letter I find
that my poney and pointers are not yet procured, and that Lord Grey is
still at Newstead. The former I should be very dull at such a place as
Southwell without; the latter is still more disagreeable to be with. I
presume he goes on in the old way, — quarrelling with the farmers, and
stretching his judicial powers (he being now in the commission) to the
utmost, becoming a torment to himself, and a pest to all around him. — I
am glad you approve of my Gun, feeling myself happy, that it has been
tried by so distinguished a Sportsman.
I hope your Campaigns against the Partridges and the rest of the
feathered Tribe have been attended with no serious
Consequences — trifling accidents such as the top of a few fingers
and a Thumb, you Gentlemen of the city being used to, of
course occasion no interruption to your field sports.
Your Accommodation I have no doubt I shall be perfectly satisfied with,
only do exterminate that vile Generation of Bugs which
nearly ate me up the last Time I sojourned at your House. After
undergoing the Purgatory of Harrow board and Lodging for
three Months I shall not be particular or exorbitant in my
demands.
Pray give my best Compliments to Mrs. Hanson and the now
quilldriving Hargreaves2. Till I see you, I remain, Yours,
etc., Byron.
Footnote 1: Byron spent the Christmas holidays of 1804-5 with the
Hansons. He gave Hanson to understand that it was his wish to leave the
school, and that Dr. Drury agreed with him in the decision. Hanson,
after consulting Lord Carlisle, wrote to Drury, urging that Byron was
too young to leave the school. Drury's reply, dated December 29, 1804,
gave a different colour to the matter.
"Your letter," he writes, "supposes that Lord Byron was desirous to
leave school, and that I acquiesced in his Wish: but I must do him the
Justice to observe that the wish originated with me. During his
last residence at Harrow his conduct gave me much trouble and
uneasiness; and as two of his Associates were to leave me at
Christmas, I certainly suggested to him my wish that he might
be placed under the care of some private Tutor previously to his
admission to either of the Universities. This I did no less with a
view to the forming of his mind and manners, than to my own comfort;
and I am fully convinced that if such a situation can be procured for
his Lordship, it will be much more advantageous for him than a longer
residence at school, where his animal spirits and want of judgment may
induce him to do wrong, whilst his age and person must prevent his
Instructors from treating him in some respects as a schoolboy. If we
part now, we may entertain affectionate dispositions towards each
other, and his Lordship will have left the school with credit; as my
dissatisfactions were expressed to him only privately, and in such a
manner as not to affect his public situation in the school."
Finally, however, Dr. Drury, yielding to the appeal of Lord Carlisle and
Hanson, allowed the boy to return to Harrow, and Byron remained at the
school till July, 1805, the last three months being passed under the
rule of Dr. Butler.
return to footnote mark
Footnote 2: Hargreaves Hanson, second son of John Hanson, had just left
Harrow, and was articled as a pupil in his father's business. He died in
1811, at the age of 23.
return
cross-reference: return to Footnote 2 of Letter 161
List of Letters
6, Chancery Lane, Wednesday, 30th Jany., 1805.
I have delayed writing to you so long, My dearest Augusta, from
ignorance of your residence, not knowing whether you graced
Castle Howard, or Kireton with your presence. The instant Mr.
H[anson] informed me where you was, I prepared to address you, and you
have but just forestalled my intention. And now, I scarcely know what to
begin with; I have so many things, to tell you. I wish to God, that we
were together, for It is impossible that I can confine all I have got to
say in an epistle, without I was to follow your example, and fill eleven
pages, as I was informed, by my proficiency in the art of
magic, that you sometimes send that number to Lady
Gertrude.
To begin with an article of grand importance; I on Saturday dined
with Lord Carlisle, and on further acquaintance I like them all very
much. Amongst other circumstances, I heard of your boldness as a
Rider, especially one anecdote about your horse carrying you into
the stable perforce. I should have admired amazingly to have seen
your progress, provided you met with no accident. I hope you recollect
the circumstance, and know what I allude to; else, you may think that I
am soaring into the Regions of Romance. I wish you to
corroborate my account in your next, and inform me whether my
information was correct.
I think your friend Lady G. is a sweet girl. If your taste in love, is
as good as it is in friendship, I shall think you a very discerning
little Gentlewoman. His Lordship too improves upon further
acquaintance, Her Ladyship I always liked, but of the Junior part of the
family Frederick1 is my favourite. I believe with regard to my future
destination, that I return to Harrow until June, and then I'm off for
the university. Could I have found Room there, I was to have gone
immediately.
I have contrived to pass the holidays with Mr. and Mrs. Hanson, to whom
I am greatly obliged for their hospitality. You are now within a days
journey of my amiable Mama. If you wish your spirits raised, or
rather roused, I would recommend you to pass a week or two with her.
However I daresay she would behave very well to you, for you do not
know her disposition so well as I do. I return you, my dear Girl, a
thousand thanks for hinting to Mr. H. and Lord C. my uncomfortable
situation, I shall always remember it with gratitude, as a most
essential service. I rather think that, if you were any time with my
mother, she would bore you about your marriage which she disapproves
of, as much for the sake of finding fault as any thing, for that is her
favourite amusement. At any rate she would be very inquisitive, for she
was always tormenting me about it, and, if you told her any thing, she
might very possibly divulge it; I therefore advise you, when you see
her to say nothing, or as little, about it, as you can help. If you
make haste, you can answer this well written epistle by return of
post, for I wish again to hear from you immediately; you need not fill
eleven pages, nine will be sufficient; but whether it contains nine
pages or nine lines, it will always be most welcome, my beloved Sister,
to Your affectionate Brother and Friend, Byron.
Footnote 1: The Hon. Frederick Howard, third son of Lord Carlisle, the
"young, gallant Howard" of Childe Harold (Canto III. stanzas xxix.,
xxx.; see Byron's note), was killed at Waterloo. "The best of his race,"
says Byron, in a letter to Moore, July 7, 1815.
return to footnote mark
cross-reference: return to Footnote 2 of Letter 166
List of Letters
[London], Thursday, 4th April, 1805.
My Dearest Augusta, — You certainly have excellent reasons for complaint
against my want of punctuality in our correspondence; but, as it does
not proceed from want of affection, but an idle disposition, you will, I
hope, accept my excuses. I am afraid, however, that when I shall take up
my pen, you will not be greatly edified or amused, especially at
present, since, I sit down in very bad spirits, out of humour with
myself, and all the world, except you. I left Harrow yesterday, and am
now at Mr. Hanson's till Sunday morning, when I depart for
Nottinghamshire, to pay a visit to my mother, with whom I shall remain
for a week or two, when I return to town, and from thence to Harrow,
until July, when I take my departure for the university, but which I am
as yet undecided. Mr. H. Recommends Cambridge; Ld. Carlisle allows me to
chuse for myself, and I must own I prefer Oxford. But, I am not
violently bent upon it, and whichever is determined upon will meet with
my concurrence. — This is the outline of my plans for the next 6 months.
I am Glad that you are Going to pay his Lordship a visit, as I shall
have an opportunity of seeing you on my return to town, a pleasure,
which, as I have been long debarred of it, will be doubly felt after so
long a separation. My visit to the Dowager does not promise me all the
happiness I could wish; however, it must be gone through, as it is some
time since I have seen her. It shall be as short as possible. I shall
expect to find a letter from you, when I come down, as I wish to know
when you go to town, and how long you remain there. If you stay till The
middle of next month, you may have an opportunity of hearing me speak,
as the first day of our Harrow orations occurs in May. My friend
Delawarr1, (as you observed) danced with the little Princess, nor did
I in the least envy him the honour. I presume you have heard That Dr.
Drury leaves Harrow this Easter, and That, as a memorial of our
Gratitude for his long services, The scholars presented him with plate
to the amount of 330 Guineas.
I hope you will excuse this Hypocondriac epistle, as I never was in
such low spirits in my life. Adieu, my Dearest Sister, and believe me,
Your ever affectionate though negligent Brother, Byron.
Footnote 1: On February 25,1805, their Majesties gave a magnificent
"house-warming" at Windsor Castle.
"The expenditure," says the Gentleman's Magazine for 1805 (part
i. pp. 262-264), "cannot have cost less than £50,000. The floor of the
ball-room, instead of being chalked, was painted with most fanciful
and appropriate devices by an eminent artist." The "little Princess"
Charlotte of Wales, we are told, left the Castle at half-past nine.
return to footnote mark
List of Letters
Burgage Manor, Southwell, Notts, 15 April, 1805.
Dear Hargreaves, — As I have been unable to return to Town with your
father, I must request, that you will take care of my Books, and a
parcel which I expect from my Taylor's, and, as I understand you are
going to pay Farleigh a visit, I would be obliged to you to leave them
under the care of one of the Clerks, or a Servant, who may inform me
where to find them. I shall be in Town on Wednesday the 24th at
furthest, when I shall not hope to see you, or wish it; not but what I
should be glad of your entertaining and loquacious Society, but as I
think you will be more amused at Farleigh, it would be selfish in me to
wish that you should forego the pleasures of contemplating pigs,
poultry, pork, pease, and potatoes together, with other Rural
Delights, for my Company. Much pleasure may you find in your excursion
and I dare say, when you have exchanged pleadings for ploughshares
and fleecing clients for feeding flocks, you will be in no hurry to
resume your Law Functions.
Remember me to your Father and Mother and the Juniors, and if you should
find it convenient to dispatch a note in answer to this epistle, it will
afford great pleasure to
Yours very sincerely and affectionately,
Byron.
P.S. — It is hardly necessary to inform you that I am heartily tired of
Southwell, for I am at this minute experiencing those delights which I
have recapitulated to you and which are more entertaining to be
talked of at a distance than enjoyed at Home. I allude to the
Eloquence of a near relation of mine, which is as remarkable as your
taciturnity.
List of Letters
Burgage Manor, April 20, 1805.
Dear Hargreaves, — Dr. Butler1, our new Master, has thought proper to
postpone our Meeting till the 8th of May, which obliges me to delay my
return to Town for one week, so that instead of Wednesday the 24th I
shall not arrive in London till the 1st of May, on which Day (If I live)
I shall certainly be in town, where I hope to have the pleasure of
seeing you. I shall remain with you only a week, as we are all to return
to the very day, on account of the prolongation of our Holidays.
However, if you shall previous to that period take a jaunt into Hants,
I beg you will leave my valuables, etc., etc., in the care of one of
the Gentlemen of your office, as that Razor faced Villain, James,
might perhaps take the Liberty of walking off with a suit. I have heard
several times from Tattersall2 and it is very probable we may see him
on my return. I beg you will excuse this short epistle as my time is at
present rather taken up, and Believe Me,
Yours very sincerely,
Byron.
Footnote 1: The Rev. George Butler (1774-1853), who was Senior Wrangler
(1794), succeeded Dr. Drury as Head-master of Harrow School in April,
1805. He was then Fellow, tutor, and classical lecturer at Sydney Sussex
College, Cambridge. From affection to Dr. Drury, Byron supported the
candidature of his brother, Mark Drury, and avenged himself on Butler
for the defeat of his candidate by the lines on "Pomposus" (see Poems,
vol. i. pp. 16, 17, "On a Change of Masters," etc.; and pp. 84-106,
"Childish Recollections"). At a later period he became reconciled to
Butler, who knew the Continent well, was an excellent linguist, and gave
him valuable advice for his foreign tour in 1809-11. Butler resigned the
Head-mastership of Harrow in April, 1824, and retired to a country
living. In 1842 he was appointed to the Deanery of Peterborough, where
he died in 1853.]
return to footnote mark
cross-reference: return to Footnote 2 of Letter 67
cross-reference: return to Footnote 2 of Letter 85
Footnote 2: John Cecil Tattersall entered Harrow in May, 1801. He was
the "Davus" of "Childish Recollections" (Poems, vol. i. pp. 97, 98,
and notes). He went from Harrow to Christ Church, Oxford, took
orders, and died December 8, 1812.
return
cross-reference: return to Footnote 3 of Letter 85
List of Letters
[The Earl of Carlisle's, Grosvenor Place, London.]
Burgage Manor, April
23d, 1805.
My Dearest Augusta, — I presume by this time, that you are safely arrived
at the Earl's, at least I hope so; nor shall I feel myself perfectly
easy, till I have the pleasure of hearing from yourself of your safety.
I myself shall set out for town this day (Tuesday) week, and intend
waiting upon you on Thursday at farthest; in the mean time I must
console myself as well as I can; and I am sure, no unhappy mortal ever
required much more consolation than I do at present. You as well as
myself know the sweet and amiable temper of a certain personage to
whom I am nearly related; of course, the pleasure I have enjoyed
during my vacation, (although it has been greater than I expected) yet
has not been so superabundant as to make me wish to stay a day longer
than I can avoid. However, notwithstanding the dullness of the place,
and certain unpleasant things that occur In a family not a hundred
miles distant from Southwell, I contrived to pass my time in peace, till
to day, when unhappily, In a most inadvertent manner, I said that
Southwell was not peculiarly to my taste; but however, I merely
expressed this in common conversation, without speaking disrespectfully
of the sweet town; (which, between you and I, I wish was swallowed up
by an earthquake, provided my Eloquent mother was not in it). No
sooner had the unlucky sentence, which I believe was prompted by my evil
Genius, escaped my lips, than I was treated with an Oration in the
ancient style, which I have often so pathetically described to you,
unequalled by any thing of modern or antique date; nay the
Philippics against Lord Melville1 were nothing to it; one would
really Imagine, to have heard the Good Lady, that I was a most
treasonable culprit, but thank St. Peter, after undergoing this
Purgatory for the last hour, it is at length blown over, and I have
sat down under these pleasing impressions to address you, so that I am
afraid my epistle will not be the most entertaining. I assure you upon
my honour, jesting apart, I have never been so scurrilously, and
violently abused by any person, as by that woman, whom I think I am to
call mother, by that being who gave me birth, to whom I ought to look up
with veneration and respect, but whom I am sorry I cannot love or
admire. Within one little hour, I have not only heard myself, but have
heard my whole family, by the father's side, stigmatized in terms
that the blackest malevolence would perhaps shrink from, and that too
in words you would be shocked to hear. Such, Augusta, such is my mother;
my mother! I disclaim her from this time, and although I cannot help
treating her with respect, I cannot reverence, as I ought to do, that
parent who by her outrageous conduct forfeits all title to filial
affection. To you, Augusta, I must look up, as my nearest relation, to
you I must confide what I cannot mention to others, and I am sure you
will pity me; but I entreat you to keep this a secret, nor expose that
unhappy failing of this woman, which I must bear with patience. I would
be very sorry to have it discovered, as I have only one week more, for
the present. In the mean time you may write to me with the greatest
safety, as she would not open any of my letters, even from you. I
entreat then that you will favour me with an answer to this. I hope
however to have the pleasure of seeing you on the day appointed, but If
you could contrive any way that I may avoid being asked to dinner by L'd
C. I would be obliged to you, as I hate strangers. Adieu, my Beloved
Sister,
I remain ever yours,
Byron.
Footnote 1: Henry Dundas (1742-1811), created Viscount Melville in
1802, Lord Advocate (1775-83), made himself useful to Lord North's
Government as a shrewd, hard-working man of business, a ready
speaker — in broad Scotch, and a consummate election agent. For twenty
years he was the right-hand man of Pitt —
"Too proud from pilfered greatness to descend,
Too humble not to call Dundas his friend."
Not only was he Pitt's political colleague, but in private life his boon
companion. A well-known epigram commemorates in a dialogue their
convivial habits —
Pitt. "I cannot see the Speaker, Hal; can you?"
Dundas. "Not see the Speaker, Billy? I see two."
Melville, for a long series of years, held important political posts. He
was Treasurer of the Navy (1782-1800); member of the Board of Control
for India (1784-1802) and President (1790-1802); Home Secretary
(1791-94); Secretary of War (1794-1801); First Lord of the Admiralty
(1804-5). In 1802 a Commission had been appointed to examine into the
accounts of the naval department for the past twenty years, and, in
consequence of their tenth report, a series of resolutions were moved in
the House of Commons (April, 1805) against Melville. The voting was
even — 216 for and 216 against; the resolutions were carried by the
casting vote of Speaker Abbott.
"Pitt was overcome; his friend was
ruined. At the sound of the Speaker's voice, the Prime Minister crushed
his hat over his brows to hide the tears that poured over his cheeks: he
pushed in haste out of the House. Some of his opponents, I am ashamed to
say, thrust themselves near, 'to see how Billy took it.'"
(Mark Boyd's
Reminiscences of Fifty Years, p. 404.) Melville, who was heard at the
bar of the House of Commons in his own defence, was impeached before the
House of Lords (June 26, 1805) of high crimes and misdemeanours. At the
close of the proceedings, which began in Westminster Hall on April 29,
1806, Melville was acquitted on all the charges. Whitbread took the
leading part in the impeachment. See All the Talents: a Satirical
Poem, by Polypus (E. S. Barrett) —
"Rough as his porter, bitter as his barm,
He sacrificed his fame to M — lv — lle's harm."
Dialogue ii.
return to footnote mark
List of Letters
[The Earl of Carlisle's, Grosvenor Place, London.]
Burgage Manor,
Southwell, Friday, April 25th, 1805.
My dearest Augusta, — Thank God, I believe I shall be in town on
Wednesday next, and at last relieved from those agreeable amusements,
I described to you in my last. I return you and Lady G. many thanks for
your benediction, nor do I doubt its efficacy as it is bestowed by
two such Angelic beings; but as I am afraid my profane blessing
would but expedite your road to Purgatory, instead of Salvation, you
must be content with my best wishes in return, since the unhallowed
adjurations of a mere mortal would be of no effect. You say, you are
sick of the Installation1; and that L'd C. was not present; I however
saw his name in the Morning Post, as one of the Knights Companions. I
indeed expected that you would have been present at the Ceremony.
I have seen this young Roscius2 several times at the hazard of my
life, from the affectionate squeezes of the surrounding crowd. I think
him tolerable in some characters, but by no means equal to the
ridiculous praises showered upon him by John Bull.
I am afraid that my stay in town ceases after the 10th. I should not
continue it so long, as we meet on the 8th at Harrow, But, I remain on
purpose to hear our Sapient and noble Legislators of Both Houses
debate on the Catholic Question3, as I have no doubt there will be
many nonsensical, and some Clever things said on the occasion. I am
extremely glad that you sport an audience Chamber for the Benefit of
your modest visitors, amongst whom I have the honour to reckon
myself: I shall certainly be most happy again to see you,
notwithstanding my wise and Good mother (who is at this minute
thundering against Somebody or other below in the Dining Room), has
interdicted my visiting at his Lordship's house, with the threat of
her malediction, in case of disobedience, as she says he has behaved
very ill to her; the truth of this I much doubt, nor should the orders
of all the mothers (especially such mothers) in the world, prevent me
from seeing my Beloved Sister after so long an Absence. I beg you will
forgive this well written epistle, for I write in a great Hurry, and,
believe me, with the greatest impatience again to behold you, your
Attached Brother and [Friend,
Byron].
P.S. — By the bye Lady G. ought not to complain of your writing a
decent long letter to me, since I remember your 11 Pages to her, at
which I did not make the least complaint, but submitted like a meek
Lamb to the innovation of my privileges, for nobody ought to have had
so long an epistle but my most excellent Self.
Footnote 1: On St. George's Day, April 23, 1805, seven Knights were
installed at Windsor as Knights of the Garter, each in turn being
invested with the surcoat, girdle, and sword. The new Knights were the
Dukes of Rutland and Beaufort; the Marquis of Abercorn; the Earls of
Chesterfield, Pembroke, and Winchilsea; and, by proxy, the Earl of
Hardwicke.
Lady Louisa Strangways, writing to her sister, Lady Harriet Frampton, on
April 24, 1805 (Journal of Mary Frampton, p. 129), says,
"I was full
dressed for seventeen hours yesterday, and sat in one spot for seven,
which is enough to tire any one who enjoyed what was going on, which I
did not. I saw them walk to St. George's Chapel, which was the best
part, as it did not last long ... Their dresses were very magnificent.
The Knights, before they were installed, were in white and silver, like
the old pictures of Henry VIII., and afterwards they had a purple mantle
put on. They had immense plumes of ostrich feathers, with a heron's
feather in the middle."
return to footnote mark
Footnote 2: William Henry West Betty (1791-1874), the "Young Roscius,"
made his first appearance on the stage at Belfast, in 1803, in the part
of "Osman," in Hill's Zara; and on December 1, 1804, at Covent Garden,
as "Selim" disguised as "Achmet," in Browne's Barbarossa. In the
winter season of 1804-5, when he appeared at Covent Garden and Drury
Lane, such crowds collected to see him, that the military were called
out to preserve order. Leslie (Autobiographical Recollections, vol. i
p. 218) speaks of him as a boy "of handsome features and graceful
manners, with a charming voice." Fox, who saw him in Hamlet, said,
"This is finer than Garrick" (Table-Talk of Samuel Rogers, p. 88).
Northcote (Conversations, p. 23) spoke of his acting as "a beautiful
effusion of natural sensibility; and then that graceful play of the
limbs in youth gave such an advantage over every one about him."
"Young
Roscius's premature powers," writes Mrs. Piozzi, February 21, 1805,
"attract universal attention, and I suppose that if less than an angel
had told his parents that a bulletin of that child's health should be
necessary to quiet the anxiety of a metropolis for his safety, they
would not have believed the prediction"
(Life and Writings of Mrs.
Piozzi, vol. ii. p. 263). In society he was the universal topic of
conversation, and he commanded a salary of £50 a night, at a time when
John Kemble was paid £37 16s. a week (Life of Frederick Reynolds,
vol. ii. p. 364).
"When," writes Mrs. Byron of her son to Hanson (December 8, 1804), "he
goes to see the Young Roscius, I hope he will take care of himself in
the crowd, and not go alone."
Betty lost his attractiveness with the growth of his beard. Byron's
opinion of the merits of the youthful prodigy became that of the general
public; but not till the actor had made a large fortune. He retired from
the stage in 1824.
return
Footnote 3: On March 25, 1805, petitions were presented by Lord
Grenville in the House of Lords, and Fox in the House of Commons,
calling the attention of the country to the claims of the Roman
Catholics, and praying their relief from their disabilities, civil,
naval, and military. On Friday, May 10, Lord Grenville moved, in the
Upper House, for a committee of the whole House to consider the
petition. At six o'clock on the morning of Tuesday, May 14, the motion
was negatived by a division of 178 against 49. On Monday, May 13, Fox,
in the Lower House, made a similar motion, which was negatived, at five
o'clock on the morning of Wednesday, May 15, by a division of 336
against 126. Byron, on April 21, 1812, in the second of his three
Parliamentary speeches, supported the relief of the Roman Catholics.
return
List of Letters
Harrow-on-the-Hill, 11 May, 1805.
Dear Sir, — As you promised to cash my Draft on the Day that I left your
house, and as you was only prevented by the Bankers being shut up, I
will be very much obliged to you to give the ready to this old
Girl, Mother Barnard1, who will either present herself or send a
Messenger, as she demurs on its being not payable till the 25th of June.
Believe me, Sir, by doing this you will greatly oblige
Yours very truly,
Byron.
Footnote 1: Mother Barnard was the keeper of the "tuck-shop" at Harrow.
return to footnote mark
List of Letters
[The Earl of Carlisle's, Grosvenor Place, London.]
[Harrow, Wednesday,
June 5, 1805.]
My Dearest Augusta, — At last you have a decent specimen of the
dowager's talents for epistles in the furioso style. You are now
freed from the shackles of her correspondence, and when I revisit
her, I shall be bored with long stories of your ingratitude,
etc., etc. She is as I have before declared certainly mad (to say she
was in her senses, would be condemning her as a Criminal), her conduct
is a happy compound of derangement and Folly. I had the other day
an epistle from her; not a word was mentioned about you, but I had some
of the usual compliments on my own account. I am now about to
answer her letter, though I shall scarcely have patience, to treat her
with civility, far less with affection, that was almost over before, and
this has given the finishing stroke to filial, which now gives
way to fraternal duty. Believe me, dearest Augusta, not ten
thousand such mothers, or indeed any mothers, Could induce me to
give you up. — No, No, as the dowager says in that rare epistle which
now lies before me, "the time has been, but that is past long since,"
and nothing now can influence your pretty sort of a brother
(bad as he is) to forget that he is your Brother. Our first Speech day
will be over ere this reaches you, but against the 2d you shall have
timely notice. — I am glad to hear your illness is not of a Serious
nature; young Ladies ought not to throw themselves in to the fidgets
about a trifling delay of 9 or 10 years; age brings experience and when
you in the flower of youth, between 40 and 50, shall then marry, you
will no doubt say that I am a wise man, and that the later one makes
one's self miserable with the matrimonial clog, the better. Adieu, my
dearest Augusta, I bestow my patriarchal blessing on you and Lady G.
and remain,
[Signature cut out.]
List of Letters
Harrow-on-the-Hill, 27 June, 1805.
Dear Sir, — I will be in Town on Saturday Morning, but it is absolutely
necessary for me to return to Harrow on Tuesday or Wednesday, as
Thursday is our 2d Speechday and Butler says he cannot dispense with my
Presence on that Day. I thank you for your Compliment in the Beginning
of your Letter, and with the Hope of seeing you and Hargreaves well on
Saturday,
I remain, yours, etc., etc.,
Byron.
List of Letters
[Address cut out], Tuesday, July 2d, 1805.
My dearest Augusta, — I am just returned from Cambridge, where I have
been to enter myself at Trinity College. — Thursday is our Speechday at
Harrow, and as I forgot to remind you of its approach, previous to our
first declamation1, I have given you timely notice this time. If you
intend doing me the honour of attending, I would recommend you not to
come without a Gentleman, as I shall be too much engaged all the morning
to take care of you, and I should not imagine you would admire
stalking about by yourself. You had better be there by 12 o'clock as
we begin at 1, and I should like to procure you a good place; Harrow is
11 miles from town, it will just make a comfortable mornings drive for
you. I don't know how you are to come, but for Godsake bring as few
women with you as possible. I would wish you to Write me an answer
immediately, that I may know on Thursday morning, whether you will drive
over or not, and I will arrange my other engagements accordingly. I
beg, Madam, you may make your appearance in one of his Lordships
most dashing carriages, as our Harrow etiquette, admits of nothing
but the most superb vehicles, on our Grand Festivals. In the mean
time, believe me, dearest Augusta,
Your affectionate Brother,
Byron.
Footnote 1: Mrs. Byron, writing to Hanson (June 25, 1805), says, "The
"fame of Byron's oratory has reached Southwell" (see page 27, note 1).
return to footnote mark
List of Letters
Harrow, 8 July, 1805.
My dear Sir, — I have just received a Letter from my Mother, in which she
talks of coming to Town about the commencement of our Holidays. If she
does, it will be impossible for me to call on my Sister, previous to
my leaving it, and at the same time I cannot conceive what the Deuce she
can want at this season in London. I have written to tell her that my
Holidays commence on the 6th of August, but however, July the 1st is the
proper day. — I beg that if you cannot find some means to keep her in the
Country that you at least will connive at this deception which I can
palliate, and then I shall be down in the country before she knows where
I am. My reasons for this are, that I do not wish to be detained in
Town so uncomfortably as I know I shall be if I remain with her; that I
do wish to see my Sister; and in the next place she can just as well
come to Town after my return to Notts, as I don't desire to be dragged
about according to her caprice, and there are some other causes I think
unnecessary to be now mentioned. If you will only contrive by settling
this business (if it is in your power), or if that is impossible, not
mention anything about the day our Holidays commence, of which you can
be easily supposed not to be informed. If, I repeat, you can by any
means prevent this Mother from executing her purposes, believe me, you
will greatly oblige
Yours truly,
Byron.
List of Letters
30 — To Charles O. Gordon1
Burgage Manor, Southwell, Notts, August 4, 1805.
Although I am greatly afraid, my Dearest Gordon, that you will not
receive this epistle till you return from Abergeldie, (as your letter
stated that you would be at Ledbury on Thursday next) yet, that is not
my fault, for I have not deferred answering yours a moment, and, as I
have just now concluded my Journey, my first, and, I trust you will
believe me when I say, most pleasing occupation will be to write to you.
We have played the Eton and were most confoundedly beat2; however it
was some comfort to me that I got 11 notches the 1st Innings and 7 the
2nd, which was more than any of our side except Brockman & Ipswich could
contrive to hit. After the match we dined together, and were extremely
friendly, not a single discordant word was uttered by either party. To
be sure, we were most of us rather drunk and went together to the
Haymarket Theatre, where we kicked up a row, As you may suppose, when so
many Harrovians & Etonians met at one place; I was one of seven in a
single hackney, 4 Eton and 3 Harrow, and then we all got into the same
box, and the consequence was that such a devil of a noise arose that
none of our neighbours could hear a word of the drama, at which, not
being highly delighted, they began to quarrel with us, and we nearly
came to a battle royal. How I got home after the play God knows. I
hardly recollect, as my brain was so much confused by the heat, the row,
and the wine I drank, that I could not remember in the morning how I
found my way to bed.
The rain was so incessant in the evening that we could hardly get our
Jarveys, which was the cause of so many being stowed into one. I saw
young Twilt, your brother, with Malet, and saw also an old schoolfellow
of mine whom I had not beheld for six years, but he was not the one whom
you were so good as to enquire after for me, and for which I return you
my sincere thanks. I set off last night at eight o'clock to my mother's,
and am just arrived this afternoon, and have not delayed a second in
thanking you for so soon fulfilling my request that you would correspond
with me. My address at Cambridge will be Trinity College, but I shall
not go there till the 20th of October. You may continue to direct your
letters here, when I go to Hampshire which will not be till you have
returned to Harrow. I will send my address previous to my departure from
my mother's. I agree with you in the hope that we shall continue our
correspondence for a long time. I trust, my dearest friend, that it will
only be interrupted by our being some time or other in the same place or
under the same roof, as, when I have finished my Classical Labour, and
my minority is expired, I shall expect you to be a frequent visitor to
Newstead Abbey, my seat in this county which is about 12 miles from my
mother's house where I now am. There I can show you plenty of hunting,
shooting and fishing, and be assured no one ever will be more welcome
guest than yourself — nor is there any one whose correspondence can give
me more pleasure, or whose friendship yield me greater delight than
yours, sweet, dearest Charles, believe me, will always be the sentiments
of
Yours most affectionately,
Byron.
Footnote 1: This and Letter 33 are written to Byron's Harrow friend,
Charles Gordon, one of his "juniors and favourites," whom he "spoilt by
indulgence." Gordon, who was the son of David Gordon of Abergeldie, died
in 1829.
return to footnote mark
Footnote 2: Byron's reputation as a cricketer rests on this match
between Eton and Harrow. It was played on the old cricket ground in
Dorset Square, August 2, 1805, and ended in a victory for Eton by an
innings and two runs. The score is thus given by Lillywhite, in his
Cricket Scores and Biographies of Celebrated Cricketers from 1745 to
1826 (vol. i. pp. 319, 320) —
| HARROW |
|
First Innings |
|
Second Innings |
|
| Lord Ipswich |
b. Carter |
10 |
b. Heaton |
21 |
| T. Farrer, Esq. |
b. Carter |
7 |
c. Bradley |
3 |
| T. Drury, Esq. |
b. Carter |
0 |
st. Heaton |
6 |
| —— Bolton, Esq. |
run out |
2 |
b. Heaton |
0 |
| C. Lloyd, Esq. |
b. Carter |
0 |
b. Carter |
0 |
| A. Shakespeare, Esq. |
st. Heaton |
8 |
run out |
5 |
| Lord Byron |
c Barnard |
7 |
b. Carter |
2 |
| Hon. T. Erskine |
b. Carter |
4 |
b. Heaton |
8 |
| W. Brockman, Esq. |
b. Heaton |
9 |
b. Heaton |
10 |
| E. Stanley, Esq. |
not out |
3 |
c. Canning |
7 |
| —— Asheton, Esq. |
b. Carter |
3 |
not out |
0 |
|
Byes |
2 |
Byes |
3 |
| Totals |
|
55 |
|
65 |
|
|
|
|
|
| ETON |
| —— Heaton, Esq. |
b. Lloyd |
0 |
| —— Slingsby, Esq. |
b. Shakespeare |
29 |
| —— Carter, Esq. |
b. Shakespeare |
3 |
| —— Farhill, Esq. |
c. Lloyd |
6 |
| —— Canning, Esq. |
c. Farrer |
12 |
| —— Camplin, Esq. |
b. Ipswich |
42 |
| —— Bradley, Esq. |
b. Lloyd |
16 |
| —— Barnard, Esq. |
b. Shakespeare |
0 |
| —— Barnard, Esq. |
not out |
3 |
| —— Kaye, Esq. |
b. Byron |
7 |
| —— Dover, esq. |
c. Bolton |
4 |
|
Byes |
0 |
| Total |
|
122 |
At this match Lord Stratford de Redcliffe remembers seeing a
"moody-looking boy" dismissed for a small score. The boy was Byron. But
the moment is not favourable to expression of countenance.
return
List of Letters
[Castle Howard, Malton, Yorkshire.]
Burgage Manor, August 6th, 1805.
Well, my dearest Augusta, here I am, once more situated at my mother's
house, which together with its inmate is as agreeable as ever. I am
at this moment vis à vis and Téte à téte with that amiable personage,
who is, whilst I am writing, pouring forth complaints against your
ingratitude, giving me many oblique hints that I ought not to
correspond with you, and concluding with an interdiction that if you
ever after the expiration of my minority are invited to my residence,
she will no longer condescend to grace it with her Imperial
presence. You may figure to yourself, for your amusement, my solemn
countenance on the occasion, and the meek Lamblike demeanour of her
Ladyship, which, contrasted with my Saintlike visage, forms a
striking family painting, whilst in the back ground, the portraits of
my Great Grandfather and Grandmother, suspended in their frames, seem to
look with an eye of pity on their unfortunate descendant, whose
worth and accomplishments deserve a milder fate.
I am to remain in
this Garden of Eden one month, I do not indeed reside at Cambridge
till October, but I set out for Hampshire in September where I shall be
on a visit till the commencement of the term. In the mean time, Augusta,
your sympathetic correspondence must be some alleviation to my
sorrows, which however are too ludicrous for me to regard them very
seriously; but they are really more uncomfortable than amusing.
I
presume you were rather surprised not to see my consequential name in
the papers1 amongst the orators of our 2nd speech day, but
unfortunately some wit who had formerly been at Harrow, suppressed the
merits of Long2, Farrer3 and myself, who were always supposed to
take the Lead in Harrow eloquence, and by way of a hoax thought
proper to insert a panegyric on those speakers who were really and truly
allowed to have rather disgraced than distinguished themselves, of
course for the wit of the thing, the best were left out and the
worst inserted, which accounts for the Gothic omission of my
superior talents. Perhaps it was done with a view to weaken our
vanity, which might be too much raised by the flattering paragraphs
bestowed on our performance the 1st speechday; be that as it may, we
were omitted in the account of the 2nd, to the astonishment of all
Harrow. These are disappointments we great men are liable
to, and we must learn to bear them with philosophy, especially when they
arise from attempts at wit. I was indeed very ill at that time, and
after I had finished my speech was so overcome by the exertion that I
was obliged to quit the room. I had caught cold by sleeping in damp
sheets which was the cause of my indisposition. However I am now
perfectly recovered, and live in hopes of being emancipated from the
slavery of Burgage manor. But Believe me, Dearest Augusta, whether well
or ill,
I always am your affect. Brother,
Byron.
Footnote 1: See page 27, note 1.
return to footnote mark
Footnote 2: Edward Noel Long, son of E. B. Long of Hampton Lodge,
Surrey, the "Cleon" of "Childish Recollections" (Poems, vol. i. pp.
101, 102), entered Harrow in April, 1801. He went with Byron to Trinity
College, Cambridge, and till the end of the summer of 1806 was his most
intimate friend.
"We were," says Byron, in his Diary (Life, p. 31),
"rival swimmers, fond of riding, reading, and of conviviality. Our
evenings we passed in music (he was musical, and played on more than one
instrument — flute and violoncello), in which I was audience; and I think
that our chief beverage was soda-water. In the day we rode, bathed, and
lounged, reading occasionally. I remember our buying, with vast
alacrity, Moore's new quarto (in 1806), and reading it together in the
evenings. ... His friendship, and a violent though pure passion — which
held me at the same period — were the then romance of the most romantic
period of my life."
Long was Byron's companion at Littlehampton in
August, 1806. In 1807 he entered the Guards, served with distinction in
the expedition to Copenhagen, and was drowned early in 1809, "on his
passage to Lisbon with his regiment in the St. George transport, which
was run foul of in the night by another transport" (Life, p. 31. See
also Byron's lines "To Edward Noel Long, Esq.," Poems, vol. i. pp.
184-188).
return
cross-reference: return to Footnote 4 of Letter 84
Footnote 3: Thomas Farrer entered Harrow in April, 1801. He played in
Byron's XI against Eton, on the ground in Dorset Square, on August 2,
1805.
return
List of Letters
Contents
1805-1808.
[Castle Howard, Malton, Yorkshire.] Burgage Manor, August 10th, 1805.
I have at last succeeded, my dearest Augusta, in pacifying the dowager,
and mollifying that piece of flint which the good Lady denominates
her heart. She now has condescended to send you her love, although
with many comments on the occasion, and many compliments to herself. But
to me she still continues to be a torment, and I doubt not would
continue so till the end of my life. However this is the last time she
ever will have an opportunity, as, when I go to college, I shall employ
my vacations either in town; or during the summer I intend making a tour
through the Highlands, and to Visit the Hebrides with a party of my
friends, whom I have engaged for the purpose. This my old preceptor
Drury recommended as the most improving way of employing my Summer
Vacation, and I have now an additional reason for following his advice,
as I by that means will avoid the society of this woman, whose
detestable temper destroys every Idea of domestic comfort. It is a happy
thing that she is my mother and not my wife, so that I can rid myself of
her when I please, and indeed, if she goes on in the style that she has
done for this last week that I have been with her, I shall quit her
before the month I was to drag out in her company, is expired, and place
myself any where, rather than remain with such a vixen. As I am to have
a very handsome allowance1, which does not deprive her of a sixpence,
since there is an addition made from my fortune by the Chancellor for
the purpose, I shall be perfectly independent of her, and, as she has
long since trampled upon, and harrowed up every affectionate tie, It is
my serious determination never again to visit, or be upon any friendly
terms with her. This I owe to myself, and to my own comfort, as well as
Justice to the memory of my nearest relations, who have been most
shamefully libelled by this female Tisiphom, a name which your
Ladyship will recollect to have belonged to one of the Furies.
You need not take the precaution of writing in so enigmatical a style in
your next, as, bad as the woman is, she would not dare to open any
letter addressed to me from you. Whenever you can find time to write,
believe me, your epistles will be productive of the greatest pleasure,
to your
Affectionate Brother,
Byron.
Footnote 1: During Byron's schooldays, Mrs. Byron received £500 a year
from the Court of Chancery for his education. When he went to Cambridge,
she gave up this allowance to her son, and the expenditure of a certain
sum was sanctioned by Chancery for furniture, clothes, plate, etc. At
the same time, Mrs. Byron applied for an allowance of £200 a year, but
in 1807 the allowance had not been granted. Her pension, it may be
added, most irregularly paid at all times, was reduced to £200 a year.
Writing to Hanson (September 23, 1805), she says,
"I give up the five
hundred a year to my son, and you will supply him with money
accordingly. The two hundred a year addition I shall reserve for myself;
nor can I do with less, as my house will always be a home for my son
whenever he chooses to come to it."
return to footnote mark
cross-reference: return to Footnote 2 of Letter 38
List of Letters
Burgage Manor, August 14, 1805.
Believe me, my dearest Charles, no letter from you can ever be
unentertaining or dull, at least to me; on the contrary they will always
be productive of the highest pleasure as often as you think proper to
gratify me by your correspondence. My answer to your first was addressed
to Ledbury; and I fear you will not receive it till you return from your
tour, which I hope may answer your expectation in every respect; I
recollect some years ago passing near Abergeldie on an excursion through
the Highlands, it was at that time a most beautiful place.
I suppose you will soon have a view of the eternal snows that summit the
top of Lachin y Gair, which towers so magnificently above the rest of
our Northern Alps. I still remember with pleasure the admiration which
filled my mind, when I first beheld it, and further on the dark frowning
mountains which rise near Invercauld, together with the romantic rocks
that overshadow Mar Lodge, a seat of Lord Fife's, and the cataract of
the Dee, which dashes down the declivity with impetuous violence in the
grounds adjoining to the House. All these I presume you will soon see,
so that it is unnecessary for me to expatiate on the subject. I
sincerely wish that every happiness may attend you in your progress. I
have given you an account of our match in my epistle to Herefordshire.
We unfortunately lost it. I got 11 notches the first innings and 7 the
2nd, making 18 in all, which was more runs than any of our side (except
Ipswich) could make. Brockman also scored 18. We were very convivial
in the evening1.
Footnote 1: Here the letter, which is printed from a copy made by the
Rev. W. Harness (see page 177, note 1), comes to an end.
return to footnote mark
cross-reference: return to Footnote 1 of Letter 30
List of Letters
My Dear Hargreaves, — You may depend upon my Observance of your father's
Invitation to Farleigh1 in September, where I hope we shall be the
cause of much destruction to the feathered Tribe and great Amusement to
ourselves. The Lancashire Trial2 comes on very soon, and Mr. Hanson
will come down by Nottingham; perhaps, I may then have a chance of
seeing him; at all events, I shall probably accompany him on his way
back; as I hope his Health is by this time perfectly reestablished, and
will not require a journey to Harrowgate. I shall not as you justly
conjecture have any occasion for my Chapeau de Bras, as there is
nobody in the Neighbourhood who would be worth the trouble of wearing
it, when I went to their parties. I am uncommonly dull at this place, as
you may easily imagine, nor do I think I shall have much Amusement till
the commencement of the shooting season. I shall expect (when you next
write) an account of your military preparations, to repel the Invader of
our Isle whenever he makes the attempt. — You will doubtless acquire
great Glory on the occasion, and in expectation of hearing of your
Warlike Exploits,
I remain, yours very truly,
Byron.
Footnote 1: Hanson had property at Farleigh, near Basingstoke.
return to footnote mark
Footnote 2: The Rochdale property of the Byron family had been
illegally sold by William, fifth Lord Byron. Proceedings were taken to
recover the property; but fresh points arose at every stage, and
eventually Byron, unable to wait longer, sold Newstead.
return
cross-reference: return to Footnote 1 of Letter 57
List of Letters
Burgage Manor.
My Dear Hargeaves, — I would be obliged to you, if you would write to
your father, and enquire — what time it will be most convenient for him
to receive my visit, and I will come to Town immediately to the time
appointed and accompany you to the Rural Shades and Fertile
Fields of Hants. You must excuse the laconic Style of my Epistle as
this place is damned dull and I have nothing to relate, but believe me,
Yours truly,
Byron.
List of Letters
Trinity Coll., October 25, 1805.
Dear Hargreaves, — I presume your father has by this time informed you of
our safe Arrival here1. I can as yet hardly form an Opinion in favour,
or against the College, but as soon as I am settled you shall have an
account. I wish you to pack up carefully — & send immediately the
remainder of my books, and also my Stocks which were left in
Chancery Lane. Mon Chapeau de Bras take care of till Winter
extends his Icy Reign and I shall visit the Metropolis. Tell your father
that I am getting in the furniture he spoke of, but shall defer papering
and painting till the Recess. The sooner you execute my commands the
better. Beware of Mr. Terry,
And believe me, yours faithfully,
Byron.
The Bills for Furniture I shall send to Mr. H., your worthy papa,
according to his particular Desire. The Cambridge Coach sets off from
the White Horse, Fetter Lane.
Footnote 1: Byron entered Trinity on July 1, 1805; but he did not go
into residence till the following October. His tutors were the Rev.
Thomas Jones (1756-1807), who was Senior Tutor from 1787 till his death
in 1807, and the Rev. George Frederick Tavell (B.A., 1792; M.A., 1795),
to whom Byron alludes in Hints from Horace, lines 228-230:—
"Unlucky Tavell! doom'd to daily cares
By pugilistic pupils, and by bears!"
return
cross-reference: return to Footnote 8 of Letter 87
List of Letters
Trinity Coll., Oct. 26, 1805.
Dear Sir, — I will be obliged to you to order me down 4 Dozen of
Wine — Port, Sherry, Claret, and Madeira, one dozen of each. I have got
part of my furniture in, and begin to admire a College life. Yesterday
my appearance in the Hall in my State Robes was Superb, but
uncomfortable to my Diffidence. You may order the Saddle, etc., etc.,
for "Oateater" as soon as you please and I will pay for them.
I remain, Sir, yours truly,
Byron.
P.S. — Give Hargreaves a hint to be expeditious in his sending my
Valuables which I begin to want. Your Cook had the Impudence to charge
my Servant 15 Shillings for 5 Days provision which I think is
exorbitant; but I hear that in Town it is but reasonable. Pray is it
the custom to allow your Servants 3/6 per Diem, in London? I will thank
you for Information on the Subject.
List of Letters
[Castle Howard, near Malton, Yorkshire.]
Trin. Coll. [Wednesday], Novr. 6th, 1805.
My dear Augusta, — As might be supposed I like a College Life extremely,
especially as I have escaped the Trammels or rather Fetters of my
domestic Tyrant Mrs. Byron, who continued to plague me during my visit
in July and September. I am now most pleasantly situated in
Superexcellent Rooms, flanked on one side by my Tutor, on the other by
an old Fellow, both of whom are rather checks upon my vivacity. I am
allowed 500 a year, a Servant and Horse, so Feel as independent as a
German Prince who coins his own Cash, or a Cherokee Chief who coins no
Cash at all, but enjoys what is more precious, Liberty. I talk in
raptures of that Goddess because my amiable Mama was so despotic. I am
afraid the Specimens I have lately given her of my Spirit, and
determination to submit to no more unreasonable demands, (or the insults
which follow a refusal to obey her implicitly whether right or wrong,)
have given high offence, as I had a most fiery Letter from the Court
at Southwell on Tuesday, because I would not turn off my Servant,
(whom I had not the least reason to distrust, and who had an excellent
Character from his last Master) at her suggestion, from some caprice she
had taken into her head1. I sent back to the Epistle, which was
couched in elegant terms, a severe answer, which so nettled her
Ladyship, that after reading it, she returned it in a Cover without
deigning a Syllable in return.
The Letter and my answer you shall behold when you next see me, that you
may judge of the Comparative merits of Each. I shall let her go on in
the Heroics, till she cools, without taking the least notice. Her
Behaviour to me for the last two Years neither merits my respect, nor
deserves my affection. I am comfortable here, and having one of the best
allowances in College, go on Gaily, but not extravagantly. I need
scarcely inform you that I am not the least obliged to Mrs. B. for it,
as it comes off my property, and She refused to fit out a single thing
for me from her own pocket2; my Furniture is paid for, & she has
moreover a handsome addition made to her own income, which I do not in
the least regret, as I would wish her to be happy, but by no means to
live with me in person. The sweets of her society I have already drunk
to the last dregs, I hope we shall meet on more affectionate Terms, or
meet no more.
But why do I say meet? her temper precludes every idea of happiness,
and therefore in future I shall avoid her hospitable mansion, though
she has the folly to suppose She is to be mistress of my house when I
come of age3. I must apologize to you for the dullness? of this
letter, but to tell you the truth the effects of last nights Claret
have not gone out of my head, as I supped with a large party. I
suppose that Fool Hanson in his vulgar Idiom, by the word Jolly did
not mean Fat, but High Spirits, for so far from increasing I have lost
one pound in a fortnight as I find by being regularly weighed.
Adieu, Dearest Augusta.
[Signature cut out.]
Footnote 1: The servant, Byron's valet Frank, was accused of obtaining
money on false pretences from a Nottingham tradesman, and Mrs.
Byron informed her son of the charge. Frank was afterwards transported.
(See letter to Lord Clare, February 6, 1807; and letter to
Hanson, April 19, 1807.)
return to footnote mark
cross-reference: return to Footnote 3 of Letter 65
Footnote 2: See page 76, note 1.
return
Footnote 3: Words in grey were cut out of the text with the seal.
return
List of Letters
Dear Hargreaves, — Return my Thanks to your father for the
Expedition he has used in filling my Cellar.
He deserves commendation for the Attention he paid to my Request.
The Time of "Oateater's" Journey approaches; I presume he means to
repair his Neglect by Punctuality in this Respect. However, no
Trinity Ale will be forthcoming, till I have broached the
promised Falernum.
College improves in every thing but Learning.
Nobody here seems to look into an Author, ancient or modern, if they can
avoid it. The Muses, poor Devils, are totally neglected, except by a few
Musty old Sophs and Fellows, who, however agreeable they
may be to Minerva, are perfect Antidotes to the Graces.
Even I (great as is my inclination for Knowledge) am carried away
by the Tide, having only supped at Home twice since I saw your father,
and have more engagements on my Hands for a week to come. Still my Tutor
and I go on extremely well and for the first three weeks of my life I
have not involved myself in any Scrape of Consequence.
I have News for
you which I bear with Christian Resignation and without any
violent Transports of Grief. My Mother (whose diabolical
Temper you well know) has taken it into her Sagacious Head to
quarrel with me her dutiful Son. She has such a Devil of a
Disposition, that she cannot be quiet, though there are fourscore miles
between us, which I wish were lengthened to 400. The Cause too frivolous
to require taking up your time to read or mine to write. At last in
answer to a Furious Epistle I returned a Sarcastick
Answer, which so incensed the Amiable Dowager that my Letter was
sent back without her deigning a Line in the cover. When I next see you,
you shall behold her Letter and my Answer, which will amuse you as they
both contain fiery Philippics. I must request you will write
immediately, that I may be informed when my Servant shall convey
"Oateater" from London; the 20th was the appointed; but I wish to hear
further from your father. I hope all the family are in a convalescent
State. I shall see you at Christmas (if I live) as I propose passing the
Vacation, which is only a Month, in London.
Believe me, Mr. Terry, your's Truly,
Byron.
List of Letters
Trin. Coll. Cambridge, Novr. 23, 1805.
Dear Sir, — Your Advice was good but I have not determined whether I
shall follow it; this Place is the Devil or at least his principal
residence. They call it the University, but any other Appellation would
have suited it much better, for Study is the last pursuit of the
Society; the Master1 eats, drinks, and sleeps, the Fellows2 Drink, dispute and pun; the Employment of the Under graduates you will
probably conjecture without my description. I sit down to write with a
Head confused with Dissipation which, tho' I hate, I cannot avoid.
I have only supped at Home 3 times since my Arrival, and my table is
constantly covered with invitations, after all I am the most steady
Man in College, nor have I got into many Scrapes, and none of
consequence. Whenever you appoint a day my Servant shall come up for
"Oateater," and as the Time of paying my Bills now approaches, the
remaining £50 will be very agreeable. You need not make any deduction
as I shall want most of it; I will settle with you for the Saddle and
Accoutrements next quarter. The Upholsterer's Bill will not be sent in
yet as my rooms are to be papered and painted at Xmas when I will
procure them. No Furniture has been got except what was absolutely
necessary including some Decanters and Wine Glasses.
Your Cook certainly deceived you, as I know my Servant was in Town 5
days, and she stated 4. I have yet had no reason to distrust him, but we
will examine the affair when I come to Town when I intend lodging at
Mrs. Massingbird's. My Mother and I have quarrelled, which I bear with
the patience of a Philosopher; custom reconciles me to everything.
In the Hope that Mrs. H. and the Battalion are in good Health.
I remain, Sir, etc., etc.,
Byron.
Footnote 1: William Lort Mansel (1753-1820), Master of Trinity
(1798-1820), Bishop of Bristol (1808-1820), was the chief wit of
Cambridge in his day, and the author of many neat epigrams. "I wish,"
said Rogers (Table-Talk, etc., p. 60), "somebody would collect all the
Epigrams written by Dr. Mansel; they are remarkably neat and clever."
Beloe, in The Sexagenarian (vol. i. p. 98), speaks of Mansel as "a
young man remarkable for his personal confidence, for his wit and
humour, and, above all, for his gallantries." Apparently, on the same
somewhat unreliable authority, he was, as Master, a severe
disciplinarian, and extremely tenacious of his dignity (i. p. 99).
return to footnote mark
cross-reference: return to Footnote 3 of Letter 51
cross-reference: return to Footnote 1 of Letter 58
Footnote 2: Byron probably refers to Richard Porson (1759-1808),
Professor of Greek (1792-1808). The son of the parish clerk of Bacton
and Earl Ruston, in Norfolk, Porson was entered, by the kindness of
friends, on the foundation of Eton College (1774-1778). At Trinity,
Cambridge, he became a Scholar in 1780, and a Fellow (1782-1792). In
1792, as he could not conscientiously take orders, he vacated his
Fellowship, but was elected Professor of Greek. When Byron was at
Cambridge, Porson's health and powers were failing. Silent and reserved,
except in the society of his friends, a sloven in his person, he had
probably taken to drink as a cure for sleeplessness. In a note to the
Pursuits of Literature (Dialogue iv. lines 508-516),
"What," asks the author, J. T. Mathias, himself a Fellow of Trinity,
"is mere genius without a regulated life! To show the deformity of
vice to the rising hopes of the country, the policy of ancient Sparta
exhibited an inebriated slave."
Yet Porson's fine love of truth and genius for textual criticism make
him one of the greatest, if not the greatest, name in British
scholarship. Porson married, in 1795, Mrs. Lunan, sister of Mr. Perry,
the editor of the Morning Chronicle, for which he frequently wrote. In
the Shade of Alexander Pope, Mathias again attacks him as "Dogmatic
Bardolph in his nuptial noose." Porson's wife died shortly after their
marriage. His controversial method was merciless. Of his Letters to
Archdeacon Travis, Green (Lover of Literature, p. 213) says that
"he
dandles Travis as a tyger would a fawn: and appears only to reserve him
alive, for a time, that he may gratify his appetite for sport, before he
consigns his feeble prey, by a rougher squeeze, to destruction."
return
List of Letters
Trinity College, Cambridge, Novr. 30, 1805.
Sir, — After the contents of your Epistle, you will probably be less
surprized at my answer, than I have been at many points of yours1;
never was I more astonished than at the perusal, for I confess I
expected very different treatment. Your indirect charge of Dissipation
does not affect me, nor do I fear the strictest inquiry into my conduct;
neither here nor at Harrow have I disgraced myself, the "Metropolis"
and the "Cloisters" are alike unconscious of my Debauchery, and on the
plains of merry Sherwood I have experienced Misery alone; in July I
visited them for the last time.
Mrs. Byron and myself are now totally separated, injured by her, I
sought refuge with Strangers, too late I see my error, for how was
kindness to be expected from others, when denied by a parent? In
you, Sir, I imagined I had found an Instructor; for your advice I thank
you; the Hospitality of yourself and Mrs. H. on many occasions I shall
always gratefully remember, for I am not of opinion that even present
Injustice can cancel past obligations.
Before I proceed, it will be necessary to say a few words concerning
Mrs. Byron; you hinted a probability of her appearance at Trinity; the
instant I hear of her arrival I quit Cambridge, though Rustication or
Expulsion be the consequence. Many a weary week of torment have I
passed with her, nor have I forgot the insulting Epithets with which
myself, my Sister, my father and my Family have been repeatedly
reviled.
To return to you, Sir, though I feel obliged by your Hospitality, etc.,
etc., in the present instance I have been completely deceived. When I
came down to College, and even previous to that period I stipulated that
not only my Furniture, but even my Gowns and Books, should be paid for
that I might set out free from Debt. Now with all the Sang Froid of
your profession you tell me, that not only I shall not be permitted to
repair my rooms (which was at first agreed to) but that I shall not even
be indemnified for my present expence. In one word, hear my
determination. I will never pay for them out of my allowance, and the
Disgrace will not attach to me but to those by whom I have been
deceived. Still, Sir, not even the Shadow of dishonour shall reflect on
my Name, for I will see that the Bills are discharged; whether by you
or not is to me indifferent, so that the men I employ are not the
victims of my Imprudence or your Duplicity. I have ordered nothing
extravagant; every man in College is allowed to fit up his rooms; mine
are secured to me during my residence which will probably be some time,
and in rendering them decent I am more praiseworthy than culpable. The
Money I requested was but a secondary consideration; as a Lawyer you
were not obliged to advance it till due; as a Friend the request might
have been complied with. When it is required at Xmas I shall expect the
demand will be answered. In the course of my letter I perhaps have
expressed more asperity than I intended, it is my nature to feel warmly,
nor shall any consideration of interest or Fear ever deter me from
giving vent to my Sentiments, when injured, whether by a Sovereign or a
Subject.
I remain, etc., etc.,
Byron.
Footnote 1: The quarrel arose from Byron misunderstanding a letter from
Hanson on the subject of the allowance made by the Court of Chancery for
his furniture.
return to footnote mark
List of Letters
Trin. Coll. Cambridge, Dec. 4, 1805.
Sir, — In charging you with downright Duplicity I wronged you, nor do I
hesitate to atone for an Injury which I feel I have committed, or add to
my Fault by the Vindication of an expression dictated by Resentment, an
expression which deserves Censure, and demands the apology I now
offer; for I think that Disposition indeed mean which adds Obstinacy
to Insult, by attempting the Palliation of unmerited Invective from the
mistaken principle of disdaining the Avowal of even self convicted
Error. In regard to the other Declarations my Sentiments remain
unaltered; the event will shew whether my Prediction is false. I know
Mrs. Byron too well to imagine that she would part with a Sous, and if
by some Miracle she was prevailed upon, the Details of her
Generosity in allowing me part of my own property would be
continually thundered in my ears, or launched in the Lightening of
her letters, so that I had rather encounter the Evils of Embarrassment
than lie under an obligation to one who would continually reproach me
with her Benevolence, as if her Charity had been extended to a
Stranger to the Detriment of her own Fortune. My opinion is perhaps
harsh for a Son, but it is justified by experience, it is confirmed by
Facts, it was generated by oppression, it has been nourished by
Injury. To you, Sir, I attach no Blame. I am too much indebted to your
kindness to retain my anger for a length of Time, that Kindness which,
by a forcible contrast, has taught me to spurn the Ties of Blood
unless strengthened by proper and gentle Treatment. I declare upon my
honor that the Horror of entering Mrs. Byron's House has of late years
been so implanted in my Soul, that I dreaded the approach of the
Vacations as the Harbingers of Misery. My letters to my Sister,
written during my residence at Southwell, would prove my Assertion. With
my kind remembrances to Mrs. H. and Hargreaves,
I remain, Sir, yours truly,
Byron.
List of Letters
Trin. Coll. Cambridge, Dec. 13, 1805.
Dear Sir, — I return you my Thanks for the remaining £50 which came in
extremely apropos, and on my visit to Town about the 19th will give
you a regular receipt. In your Extenuation of Mrs. Byron's Conduct you
use as a plea, that, by her being my Mother, greater allowance ought
to be made for those little Traits in her Disposition, so much more
energetic than elegant. I am afraid, (however good your intention)
that you have added to rather than diminished my Dislike, for
independent of the moral Obligations she is under to protect, cherish,
and instruct her offspring, what can be expected of that Man's heart
and understanding who has continually (from Childhood to Maturity)
beheld so pernicious an Example? His nearest relation is the first
person he is taught to revere as his Guide and Instructor; the
perversion of Temper before him leads to a corruption of his own, and
when that is depraved, vice quickly becomes habitual, and, though timely
Severity may sometimes be necessary & justifiable, surely a peevish
harassing System of Torment is by no means commendable, & when that is
interrupted by ridiculous Indulgence, the only purpose answered is to
soften the feelings for a moment which are soon after to be doubly
wounded by the recal of accustomed Harshness. I will now give this
disagreeable Subject to the Winds. I conclude by observing that I am
the more confirmed in my opinion of the Futility of Natural Ties, unless
supported not only by Attachment but affectionate and prudent
Behaviour.
Tell Mrs. H. that the predicted alteration in my Manners and Habits has
not taken place. I am still the Schoolboy and as great a Rattle as
ever, and between ourselves College is not the place to improve either
Morals or Income.
I am, Sir, yours truly,
Byron.
List of Letters
[Castle Howard, near Malton, Yorkshire.]
16, Piccadilly, [Thursday], Decr. 26th, 1805.
My dearest Augusta, — By the Date of my Letter you will perceive that I
have taken up my Residence in the metropolis, where I presume we shall
behold you in the latter end of January. I sincerely hope you will make
your appearance at that Time, as I have some subjects to discuss with
you, which I do not wish to communicate in my Epistle.
The Dowager has thought proper to solicit a reconciliation which in some
measure I have agreed to; still there is a coolness which I do not feel
inclined to thaw, as terms of Civility are the only resource against
her impertinent and unjust proceedings with which you are already
acquainted.
Town is not very full and the weather has been so unpropitious that I
have not been able to make use of my Horses above twice since my
arrival. I hope your everlasting negotiation with the Father of your
Intended is near a conclusion in some manner; if you do not hurry a
little, you will be verging into the "Vale of Years," and, though you
may be blest with Sons and daughters, you will never live to see your
Grandchildren.
When convenient, favour me with an Answer and believe me,
[Signature cut out.]
List of Letters
[Castle Howard, neat Malton, Yorkshire.] 16, Piccadilly, Friday,
Decr. 27th, 1805.
My Dear Augusta, — You will doubtless be surprised to see a second
epistle so close upon the arrival of the first, (especially as it is not
my custom) but the Business I mentioned rather mysteriously in my last
compels me again to proceed. But before I disclose it, I must require
the most inviolable Secrecy, for if ever I find that it has transpired,
all confidence, all Friendship between us has concluded. I do not mean
this exordium as a threat to induce you to comply with my request but
merely (whether you accede or not) to keep it a Secret. And although
your compliance would essentially oblige me, yet, believe me, my esteem
will not be diminished by your Refusal; nor shall I suffer a complaint
to escape. The Affair is briefly thus; like all other young men just let
loose, and especially one as I am, freed from the worse than bondage of
my maternal home, I have been extravagant, and consequently am in want
of Money. You will probably now imagine that I am going to apply to you
for some. No, if you would offer me thousands, I declare solemnly that I
would without hesitation refuse, nor would I accept them were I in
danger of Starvation. All I expect or wish is, that you will be joint
Security with me for a few Hundreds a person (one of the money lending
tribe) has offered to advance in case I can bring forward any collateral
guarantee that he will not be a loser, the reason of this requisition is
my being a Minor, and might refuse to discharge a debt contracted in my
non-age. If I live till the period of my minority expires, you cannot
doubt my paying, as I have property to the amount of 100 times the sum I
am about to raise; if, as I think rather probable, a pistol or a Fever
cuts short the thread of my existence, you will receive half the Dross
saved since I was ten years old, and can be no great loser by
discharging a debt of 7 or £800 from as many thousands. It is far from
my Breast to exact any promise from you that would be detrimental, or
tend to lower me in your opinion. If you suppose this leads to either of
those consequences, forgive my impertinence and bury it in oblivion. I
have many Friends, most of them in the same predicament with myself; to
those who are not, I am too proud to apply, for I hate obligation; my
Relations you know I detest; who then is there that I can address on
the subject but yourself? to you therefore I appeal, and if I am
disappointed, at least let me not be tormented by the advice of
Guardians, and let silence rule your Resolution. I know you will think
me foolish, if not criminal; but tell me so yourself, and do not
rehearse my failings to others, no, not even to that proud Grandee the
Earl, who, whatever his qualities may be, is certainly not amiable, and
that Chattering puppy Hanson would make still less allowance for the
foibles of a Boy. I am now trying the experiment, whether a woman can
retain a secret; let me not be deceived. If you have the least doubt of
my integrity, or that you run too great a Risk, do not hesitate in your
refusal. Adieu. I expect an answer with impatience, believe me, whether
you accede or not,
[Signature cut out.]
P.S. — I apologize for the numerous errors probably enveloped in this
cover; the temper of my mind at present, and the hurry I have written
in, must plead for pardon. Adieu.
List of Letters
[Castle Howard, near Malton, Yorkshire.]
16, Piccadilly, Tuesday, January 7th, 1805.
[In another hand] — 6.
My dearest Augusta, — Your efforts to reanimate my sinking spirits will,
I am afraid, fail in their effect, for my melancholy proceeds from a
very different cause to that which you assign, as, my nerves were always
of the strongest texture. — I will not however pretend to say I possess
that Gaieté de Coeur which formerly distinguished me, but as the
diminution of it arises from what you could not alleviate, and might
possibly be painful, you will excuse the Disclosure. Suffice it to know,
that it cannot spring from Indisposition, as my Health was never more
firmly established than now, nor from the subject on which I lately
wrote, as that is in a promising Train, and even were it otherwise, the
Failure would not lead to Despair. You know me too well to think it is
Love; & I have had no quarrel or dissention with Friend or enemy, you
may therefore be easy, since no unpleasant consequence will be produced
from the present Sombre cast of my Temper. I fear the Business will not
be concluded before your arrival in Town, when we will settle it
together, as by the 20th these sordid Bloodsuckers who have agreed to
furnish the Sum, will have drawn up the Bond. Believe me, my dearest
Sister, it never entered in to my head, that you either could or would
propose to anticipate my application to others, by a Present
from? yourself; I and I only will be injured by my own
extravagance, nor would I have wished you to take the least concern, had
any other means been open for extrication. As it is, I hope you will
excuse my Impertinence, or if you feel an inclination to retreat, do not
let affection for me counterbalance prudence.
[Signature cut out.]
List of Letters
16, Piccadilly, Febry. 26, 1806.
Dear Mother, — Notwithstanding your sage and economical advice I have
paid my Harrow Debts, as I can better afford to wait for the Money
than the poor Devils who were my creditors. I have also discharged my
college Bills amounting to £231, — £75 of which I shall trouble Hanson to
repay, being for Furniture, and as my allowance is £500 per annum, I do
not chuse to lose the overplus as it makes only £125 per Quarter. I
happen to have a few hundreds in ready Cash by me1, so I have paid the
accounts; but I find it inconvenient to remain at College, not for the
expence, as I could live on my allowance (only I am naturally
extravagant); however the mode of going on does not suit my
constitution. Improvement at an English University to a Man of Rank is,
you know, impossible, and the very Idea ridiculous. Now I sincerely
desire to finish my Education and, having been sometime at Cambridge,
the Credit of the University is as much attached to my Name, as if I had
pursued my Studies there for a Century; but, believe me, it is nothing
more than a Name, which is already acquired. I can now leave it with
Honour, as I have paid everything, & wish to pass a couple of years
abroad, where I am certain of employing my time to far more advantage
and at much less expence, than at our English Seminaries. 'Tis true I
cannot enter France; but Germany and the Courts of Berlin, Vienna &
Petersburg are still open, I shall lay the Plan before Hanson & Lord C.
I presume you will all agree, and if you do not, I will, if possible,
get away without your Consent, though I should admire it more in the
regular manner & with a Tutor of your furnishing. This is my project, at
present I wish you to be silent to Hanson about it. Let me have your
Answer. I intend remaining in Town a Month longer, when perhaps I shall
bring my Horses and myself down to your residence in that execrable
Kennel. I hope you have engaged a Man Servant, else it will be
impossible for me to visit you, since my Servant must attend chiefly to
his horses; at the same Time you must cut an indifferent Figure with
only maids in your habitation.
I remain, your's,
Byron.
Footnote 1:
"The Bills," writes Mrs. Byron to Hanson (January 11, 1806), "are
coming in thick upon me to double the amount I expected; he went and
ordered just what he pleased here, at Nottingham, and in London.
However, it is of no use to say anything about it, and I beg you will
take no notice. I am determined to have everything clear within the
year, if possible."
Again she writes (March 1, 1806):
"I beg you will not mention to my son, having heard from me, but try
to get out of him his reason for wishing to leave England, and where
he got the money. I much fear he has fallen into bad hands, not only
in regard to Money Matters, but in other respects. My idea is that he
has inveigled himself with some woman that he wishes to get rid of and
finds it difficult. But whatever it is, he must be got out of it."
Again (March 4, 1806):
"That Boy will be the death of me, and drive me mad! I never will
consent to his going Abroad. Where can he get Hundreds? Has he got
into the hands of Moneylenders? He has no feeling, no Heart. This I
have long known; he has behaved as ill as possible to me for years
back. This bitter Truth I can no longer conceal: it is wrung from me
by heart-rending agony. I am well rewarded. I came to
Nottinghamshire to please him, and now he hates it. He knows that I am
doing everything in my power to pay his Debts, and he writes to me
about hiring servants!"
Once more (April 24, 1806):
"Lord Byron has given £31 10s. to Pitt's statue. He has also bought a
Carriage, which he says was intended for me, which I refused to
accept of, being in hopes it would stop his having one."
return to footnote mark
List of Letters
16, Piccadilly, March 3, 1806.
Sir, — I called at your House in Chancery Lane yesterday Evening, as I
expected you would have been in Town, but was disappointed. If
convenient, I should be glad to see you on Wednesday Morning about one
o'Clock, as I wish for your advice on some Business. On Saturday one of
my Horses threw me; I was stunned for a short time, but soon recovered
and suffered no material Injury; the accident happened on the Harrow
Road. I have paid Jones's Bill amounting to £231.4.5 of which I expect
to be reimbursed £75 for Furniture. I have got his Bankers' receipt and
the account ready for your Inspection. I now owe nothing at Cambridge;
but shall not return this Term1, as I have been extremely
unwell, and at the same time can stay where I am at much less
Expence and equal Improvement. I wish to consult you on several
Subjects and expect you will pay me a visit on Wednesday; in the mean
time,
I remain, yours, etc., Byron.
Footnote 1: Lectures began on February 5, 1806, as is stated on the
College bills, sent in by Mr. Jones, the Senior Tutor of Trinity. But
Byron preferred to remain in London. Augusta Byron writes to Hanson
(March 7, 1806) — —
"I trouble you again in consequence of some conversation I had last
night with Lord Carlisle about my Brother. He expressed himself to me
as kindly on that subject as on all others, and though he says it may
not be productive of any good, and that he may be only able to join
his lamentations with yours, he should like to talk to you and try
if anything can be done. I was much surprized and vexed to see my
Brother a week ago at the Play, as I think he ought to be employing
his time more profitably at Cambridge."
return to footnote mark
cross-reference: return to Footnote 1 of Letter 7
List of Letters
Sir, — As in all probability you will not make your appearance tomorrow I
must disclose by Letter the Business I intended to have discussed at our
interview. — We know each other sufficiently to render Apology
unnecessary. I shall therefore without further Prelude proceed to the
Subject in Question. You are not ignorant, that I have lately lived at
considerable Expence, to support which my allotted Income by the
sapient Court of Chancery is inadequate. — I confess I have
borrowed a trifling sum and now wish to raise £500 to discharge some
Debts I have contracted; my approaching Quarter will bring me £200 due
from my Allowance, and if you can procure me the other £300 at a
moderate Interest, it will save 100 per cent I must pay my Israelite
for the same purpose. — You see by this I have an excellent Idea of
Œconomy even in my Extravagance by being willing to pay as little Money
as possible, for the Cash must be disbursed somewhere or somehow,
and if you decline (as in prudence I tell you fairly you ought), the
Tribe of Levi will be my dernier resort. However I thought proper
to make this Experiment with very slender hopes of success indeed, since
Recourse to the Law is at best a desperate effort. I have now laid
open my affairs to you without Disguise and Stated the Facts as they
appear, declining all Comments, or the use of any Sophistry to palliate
my application, or urge my request. All I desire is a speedy Answer,
whether successful or not.
Believe me, yours truly, Byron.
List of Letters
16, Piccadilly, 25th March, 1806.
Sir, — Your last Letter, as I expected, contained much advice, but no
Money. I could have excused the former unaccompanied by the latter,
since any one thinks himself capable of giving that, but very few chuse
to own themselves competent to the other. I do not now write to urge a
2nd Request, one Denial is sufficient. I only require what is my right.
This is Lady Day. £125 is due for my last Quarter, and £75 for my
expenditure in Furniture at Cambridge and I will thank you to remit.
The Court of Chancery may perhaps put in Force your Threat. I have
always understood it formed a Sanction for legal plunderers to protract
the Decision of Justice from year to year, till weary of spoil it at
length condescended to give Sentence, but I never yet understood even
its unhallowed Hands preyed upon the Orphan it was bound to protect. Be
it so, only let me have your answer.
I remain, etc., etc., Byron.
List of Letters
51 — To Henry Angelo1
Trinity College, Cambridge, May 16, 1806.
Sir, — You cannot be more indignant, at the insolent and unmerited
conduct of Mr. Mortlock2, than those who authorised you to request
his permission. However we do not yet despair of gaining our point, and
every effort shall be made to remove the obstacles, which at present
prevent the execution of our project. I yesterday waited on the Master
of this College3, who, having a personal dispute with the Mayor,
declined interfering, but recommended an application to the Vice
Chancellor, whose authority is paramount in the University. I shall
communicate this to Lord Altamount4, and we will endeavour to bend the
obstinacy of the upstart magistrate, who seems to be equally deficient
in justice and common civility. On my arrival in town, which will take
place in a few days, you will see me at Albany Buildings, when we will
discuss the subject further. Present my remembrance to the Messrs.
Angelo, junior, and believe me, we will yet humble this impertinent
bourgeois.
I remain, Sir, your obedient servant,
Byron.
Footnote 1: Henry Angelo, the famous fencing-master, was at the head of
his profession for nearly forty years. His position was recognized at
least as early as 1787, when he published The School of Fencing, and
fenced, with the Chevalier de St. George and other celebrities, before
the Prince of Wales at Carlton House. In 1806 he was travelling down
every other week to Cambridge, as he states in his Pic Nic (1837), to
visit his pupils. He had made Byron's acquaintance at Harrow by teaching
him to fence, and in later years had many bouts with him with the foils,
single-sticks, and Highland broadsword. His Reminiscences (1830),
together with his Pic Nic, contain numerous anecdotes of Byron, to
whom he seems to have been sincerely attached. In 1806 he had several
rooms in London for the use of his pupils. One of these was at 13, Bond
Street, which he shared with Gentleman Jackson, the pugilist and
ex-champion. In Cruikshank's picture of the room (Pierce Egan's Life in
London, p. 254), two fencers have unmasked and stopped their bout to
see Jackson spar with Corinthian Tom. Angelo contributed an article on
fencing to Sir John Sinclair's Code of Health and Longevity, vol. ii.
p. 163.
Angelo, who retired from London in 1821, and lived near Bath, was in
1806 at the height of his reputation. An old Etonian (1767), he knew
every one in London; had dined at the same table with the Prince of
Wales, acted with Lord Barrymore, sung comic songs with Dibdin, punned
with Bannister and Colman, fished at Benham on the invitation of the
Margravine of Anspach, played the flute to Lady Melfort's accompaniment
on the piano, and claimed his share of the table-talk at the Keep Line
Club. Nearly every celebrity of the day, from Lord Sidmouth and Lord
Liverpool to Kean and Macready, was his pupil.
return to footnote mark
cross-reference: return to Footnote 1 of Letter 98
Footnote 2: Mr. Mortlock, the Mayor of Cambridge, is thus mentioned in
a letter from S. T. Coleridge to Southey, dated September 26, 1794: "All
last night I was obliged to listen to the damned chatter of "Mortlock,
our mayor, a fellow that would certainly be a pantisocrat were his head
and heart as highly illuminated as his face. In the tropical latitude
of this fellow's nose was I obliged to fry" (Letters of S. T.
Coleridge (1895), vol. i. p. 87).
return
Footnote 3: William Lort Mansel, Master of Trinity, and Bishop of
Bristol. (See page 84, note 1.)
return
Footnote 4: Howe Peter Browne, Lord Altamont (1788-1845), of Jesus
College, succeeded his father in 1809 as second Marquis of Sligo. Byron
spent some time with him at Athens in 1810. Lord Sligo's letter on the
origin of the Giaour is quoted by Moore (Life, p. 178). (See also
page 289, note 1.)
return
cross-reference: return to Footnote 3 of Letter 144
List of Letters
52 — To John M. B. Pigot1
16, Piccadilly, August 9, 1806.
My Dear Pigot, — Many thanks for your amusing narrative of the last
proceedings of my amiable Alecto, who now begins to feel the effects of
her folly. I have just received a penitential epistle, to which,
apprehensive of pursuit, I have despatched a moderate answer, with a
kind of promise to return in a fortnight; — this, however (entre
nous), I never mean to fulfil. Her soft warblings must have delighted
her auditors, her higher notes being particularly musical, and on a calm
moonlight evening would be heard to great advantage. Had I been present
as a spectator, nothing would have pleased me more; but to have come
forward as one of the dramatis personae — St. Dominic defend me from
such a scene! Seriously, your mother has laid me under great
obligations, and you, with the rest of your family, merit my warmest
thanks for your kind connivance at my escape from "Mrs. Byron
furiosa."
Oh! for the pen of Ariosto to rehearse, in epic, the scolding of that
momentous eve, — or rather, let me invoke the shade of Dante to inspire
me, for none but the author of the Inferno could properly preside over
such an attempt. But, perhaps, where the pen might fail, the pencil
would succeed. What a group! — Mrs. B. the principal figure; you cramming
your ears with cotton, as the only antidote to total deafness; Mrs. — —
in vain endeavouring to mitigate the wrath of the lioness robbed of her
whelp; and last, though not least, Elizabeth and Wousky, — wonderful to
relate! — both deprived of their parts of speech, and bringing up the
rear in mute astonishment. How did S. B. receive the intelligence? How
many puns did he utter on so facetious an event? In your next inform
me on this point, and what excuse you made to A. You are probably, by
this time, tired of deciphering this hieroglyphical letter; — like Tony
Lumpkin, you will pronounce mine to be "a damned up and down hand." All
Southwell, without doubt, is involved in amazement. Apropos, how does
my blue-eyed nun, the fair ——? Is she "robed in sable garb of woe?"
Here I remain at least a week or ten days; previous to my departure you
shall receive my address, but what it will be I have not determined. My
lodgings must be kept secret from Mrs. B. You may present my compliments
to her, and say any attempt to pursue me will fail, as I have taken
measures to retreat immediately to Portsmouth, on the first intimation
of her removal from Southwell. You may add, I have proceeded to a
friend's house in the country, there to remain a fortnight.
I have now blotted (I must not say written) a complete double letter,
and in return shall expect a monstrous budget. Without doubt, the
dames of Southwell reprobate the pernicious example I have shown, and
tremble lest their babes should disobey their mandates, and quit, in
dudgeon, their mammas on any grievance. Adieu. When you begin your next,
drop the "lordship," and put "Byron" in its place.
Believe me yours, etc.,
Byron.
Footnote 1: J. M. B. Pigot, eldest brother of Miss E. B. Pigot (see
Letter of August 29, 1804, page 32, note 1). To him Byron addressed
his "Reply" (Poems, vol. i. pp. 53-56) and verses "To the Sighing
Strephon" (Ibid., pp. 63-66). In 1805-6 Pigot was studying medicine at
Edinburgh, and in his vacations saw much of Byron. He died at
Ruddington, Notts., November 26, 1871, aged 86. It would appear that
Byron had, with the connivance of the Pigots, escaped to London, after a
quarrel with his mother; but the caution to keep his lodgings secret
gives a theatrical air to the letter, as the rooms, kept by Mrs.
Massingberd, were originally taken by Mrs. Byron, and often occupied by
her, and she was at the time corresponding with Hanson about her son's
debt to Mrs. Massingberd, who seems to have been both landlady and
money-lender to Byron.
return to footnote mark
cross-reference: return to Footnote 1 of Letter 12
List of Letters
London, August 10, 1806.
My Dear Bridget, — As I have already troubled your brother with more than
he will find pleasure in deciphering, you are the next to whom I shall
assign the employment of perusing this second epistle. You will perceive
from my first, that no idea of Mrs. B.'s arrival had disturbed me at the
time it was written; not so the present, since the appearance of a
note from the illustrious cause of my sudden decampment has driven
the "natural ruby from my cheeks," and completely blanched my woebegone
countenance. This gunpowder intimation of her arrival (confound her
activity!) breathes less of terror and dismay than you will probably
imagine, from the volcanic temperament of her ladyship; and concludes
with the comfortable assurance of present motion being prevented by
the fatigue of her journey, for which my blessings are due to the
rough roads and restive quadrupeds of his Majesty's highways. As I have
not the smallest inclination to be chased round the country, I shall
e'en make a merit of necessity; and since, like Macbeth, "they've tied
me to the stake, I cannot fly," I shall imitate that valorous tyrant,
and bear-like fight the "course," all escape being precluded. I can now
engage with less disadvantage, having drawn the enemy from her
intrenchments, though, like the prototype to whom I have compared
myself, with an excellent chance of being knocked on the head. However,
"lay on Macduff", and "damned be he who first cries, Hold, enough."
I shall remain in town for, at least, a week, and expect to hear from
you before its expiration. I presume the printer has brought you the
offspring of my poetic mania1. Remember in the first line to read
"loud the winds whistle," instead of "round," which that blockhead
Ridge had inserted by mistake, and makes nonsense of the whole stanza.
Addio! — Now to encounter my Hydra.
Yours ever.
Footnote 1: Byron's first volume of verse was now in the press. The
line to which he alludes is the first line of the poem, "On Leaving
Newstead Abbey" (Poems, vol. i. pp. 1-4). It now runs —
"Through thy battlements, Newstead, the hollow winds whistle."
(For the bibliography of his early poems, see Poems, vol. i.,
Bibliographical Note; and vol. vi., Appendix.) The first collection
(Fugitive Pieces, printed by S. and J. Ridge, Newark, 4to, 1806) was
destroyed, with the exception of two copies, by the advice of the Rev.
J. T. Becher (see page 182, note 1). The second collection (Poems on
Various Occasions, printed by S. and J. Ridge, Newark, 12mo, 1807) was
published anonymously. It is to this edition that Letters 60, 61, 65,
67, 68, 69, 70, refer.
In the summer of 1807, Poems on Various Occasions was superseded by
the third collection, called Hours of Idleness (printed by S. and J.
Ridge, Newark, 12mo, 1807), published with the author's name. To this
edition Letters 76 and 78 refer. Hours of Idleness was reviewed by
Lord Brougham (Notes from a Diary, by Sir M. E. Grant Duff, vol. ii.
p. 189) in the Edinburgh Review for January, 1808.
The fourth and final collection, entitled Poems Original and
Translated (printed by S. and J. Ridge, Newark, 12mo, 1808), was
dedicated to the Earl of Carlisle.
return to footnote mark
cross-reference: return to Footnote 1 of Letter 61
cross-reference: return to Footnote 1 of Letter 76
List of Letters
London, Sunday, midnight, August 10, 1806.
Dear Pigot, — This astonishing packet will, doubtless, amaze you; but
having an idle hour this evening, I wrote the enclosed stanzas1, which
I request you will deliver to Ridge, to be printed separate from my
other compositions, as you will perceive them to be improper for the
perusal of ladies; of course, none of the females of your family must
see them. I offer 1000 apologies for the trouble I have given you in
this and other instances.
Yours truly.
Footnote 1: These are probably some silly lines "To Mary," written in
the erotic style of Moore's early verse. To the same Mary, of whom
nothing is known, are addressed the lines "To Mary, on receiving her
Picture" (Poems, vol. i. pp. 32, 33).
return to footnote mark
List of Letters
Piccadilly, August 16, 1806.
I cannot exactly say with Caesar, "Veni, vidi, vici:" however, the most
important part of his laconic account of success applies to my present
situation; for, though Mrs. Byron took the trouble of "coming," and
"seeing," yet your humble servant proved the victor. After an
obstinate engagement of some hours, in which we suffered considerable
damage, from the quickness of the enemy's fire, they at length retired
in confusion, leaving behind the artillery, field equipage, and some
prisoners: their defeat is decisive for the present campaign. To speak
more intelligibly, Mrs. B. returns immediately, but I proceed, with all
my laurels, to Worthing, on the Sussex coast; to which place you will
address (to be left at the post office) your next epistle. By the
enclosure of a second gingle of rhyme, you will probably conceive my
muse to be vastly prolific; her inserted production was brought forth
a few years ago, and found by accident on Thursday among some old
papers. I have recopied it, and, adding the proper date, request that it
may be printed with the rest of the family. I thought your sentiments on
the last bantling would coincide with mine, but it was impossible to
give it any other garb, being founded on facts. My stay at Worthing
will not exceed three weeks, and you may possibly behold me again at
Southwell the middle of September.
Will you desire Ridge to suspend the printing of my poems till he hears
further from me, as I have determined to give them a new form entirely?
This prohibition does not extend to the two last pieces I have sent with
my letters to you. You will excuse the dull vanity of this epistle, as
my brain is a chaos of absurd images, and full of business,
preparations, and projects.
I shall expect an answer with impatience; — believe me, there is nothing
at this moment could give me greater delight than your letter.
List of Letters
London, August 18, 1806.
I am just on the point of setting off for Worthing, and write merely to
request you will send that idle scoundrel Charles with my horses
immediately; tell him I am excessively provoked he has not made his
appearance before, or written to inform me of the cause of his delay,
particularly as I supplied him with money for his journey. On no
pretext is he to postpone his march one day longer; and if, in
obedience to the caprices of Mrs. B. (who, I presume, is again spreading
desolation through her little monarchy), he thinks proper to disregard
my positive orders, I shall not, in future, consider him as my servant.
He must bring the surgeon's bill with him, which I will discharge
immediately on receiving it. Nor can I conceive the reason of his not
acquainting Frank with the state of my unfortunate quadrupeds. Dear
Pigot, forgive this petulant effusion, and attribute it to the idle
conduct of that precious rascal, who, instead of obeying my
injunctions, is sauntering through the streets of that political
Pandemonium, Nottingham. Present my remembrance to your family and the
Leacrofts, and believe me, etc.
P.S. — I delegate to you the unpleasant task of despatching him on his
journey — Mrs. B.'s orders to the contrary are not to be attended to: he
is to proceed first to London, and then to Worthing, without delay.
Every thing I have left must be sent to London. My Poetics you will
pack up for the same place, and not even reserve a copy for yourself
and sister, as I am about to give them an entire new form: when they
are complete, you shall have the first fruits. Mrs. B. on no account
is to see or touch them. Adieu.
List of Letters
Little Hampton, August 26, 1806.
I this morning received your epistle, which I was obliged to send for to
Worthing, whence I have removed to this place, on the same coast, about
eight miles distant from the former. You will probably not be displeased
with this letter, when it informs you that I am £30,000 richer than I
was at our parting, having just received intelligence from my lawyer
that a cause has been gained at Lancaster assizes1, which will be
worth that sum by the time I come of age. Mrs. B. is, doubtless,
acquainted of this acquisition, though not apprised of its exact
value, of which she had better be ignorant; for her behaviour under
any sudden piece of favourable intelligence, is, if possible, more
ridiculous than her detestable conduct on the most trifling
circumstances of an unpleasant nature. You may give my compliments to
her, and say that her detaining my servant's things shall only lengthen
my absence: for unless they are immediately despatched to 16,
Piccadilly, together with those which have been so long delayed,
belonging to myself, she shall never again behold my radiant
countenance illuminating her gloomy mansion. If they are sent, I may
probably appear in less than two years from the date of my present
epistle.
Metrical compliment is an ample reward for my strains: you are one of
the few votaries of Apollo who unite the sciences over which that deity
presides. I wish you to send my poems to my lodgings in London
immediately, as I have several alterations and some additions to make;
every copy must be sent, as I am about to amend them, and you shall
soon behold them in all their glory. I hope you have kept them from that
upas tree, that antidote to the arts, Mrs. B. Entre nous, — you may
expect to see me soon. Adieu.
Yours ever.
Footnote 1: Byron was disappointed in his expectations. Fresh legal
difficulties arose, and Newstead had to be sold before they were settled
(see page 78, note 2).
return to footnote mark
List of Letters
58 — To Elizabeth Bridget Pigot1
My Dear Bridget, — I have only just dismounted from my Pegasus, which
has prevented me from descending to plain prose in an epistle of
greater length to your fair self. You regretted, in a former letter,
that my poems were not more extensive; I now for your satisfaction
announce that I have nearly doubled them, partly by the discovery of
some I conceived to be lost, and partly by some new productions. We
shall meet on Wednesday next; till then, believe me,
Yours affectionately,
Byron.
P.S. — Your brother John is seized with a poetic mania, and is now
rhyming away at the rate of three lines per hour — so much for
inspiration! Adieu!
Footnote 1: This letter was written about September, 1806, from
Harrogate, where Byron had gone with John Pigot. It forms the conclusion
of a longer letter, written by Pigot to his sister, from which Moore
quotes (Life, p. 37) the following passage:—
"Harrowgate is still extremely full; Wednesday (to-day) is our
ball-night, and I meditate going into the room for an hour, although I
am by no means fond of strange faces. Lord B., you know, is even more
shy than myself; but for an hour this evening I will shake it off ...
How do our theatricals proceed? Lord Byron can say all his part, and
I most of mine. He certainly acts it inimitably. Lord B. is now
poetising, and, since he has been here, has written some very pretty
verses ['To a Beautiful Quaker,' see Poems, vol. i. pp. 38-41]. He
is very good in trying to amuse me as much as possible, but it is not
in my nature to be happy without either female society or study ...
There are many pleasant rides about here, which I have taken in
company with Bo'swain, who, with Brighton, is universally admired.
You must read this to Mrs. B., as it is a little Tony Lumpkinish.
Lord B. desires some space left: therefore, with respect to all the
comedians elect, believe me," etc., etc.
(For the theatricals to which Mr. Pigot alludes, see page 117, note
3.) Brighton, it may be added, was one of Byron's horses; the other was
called Sultan. Bo'swain was the dog to which Byron addressed the
well-known epitaph (see Poems, vol. i. pp. 280, 281, and note 1).
Moore also quotes Pigot's recollections of the visit to Harrogate
(Life, pp. 37, 38).
"We, I remember, went in Lord Byron's own carriage, with post-horses;
and he sent his groom with two saddle-horses, and a beautifully
formed, very ferocious, bull-mastiff, called Nelson, to meet us there.
Boatswain went by the side of his valet Frank on the box, with us.
"The bull-dog, Nelson, always wore a muzzle, and was occasionally sent
for into our private room, when the muzzle was taken off, much to my
annoyance, and he and his master amused themselves with throwing the
room into disorder. There was always a jealous feud between this
Nelson and Boatswain; and whenever he latter came into the room while
the former was there, they instantly seized each other; and then,
Byron, myself, Frank, and all the waiters that could be found, were
vigorously engaged in parting them, — which was in general only
effected by thrusting poker and tongs into the mouths of each. But,
one day, Nelson unfortunately escaped out of the room without his
muzzle, and going into the stable-yard fastened upon the throat of a
horse from which he could not be disengaged. The stable-boys ran in
alarm to find Frank, who taking one of his Lord's Wogdon's pistols,
always kept loaded in his room, shot poor Nelson through the head, to
the great regret of Byron.
"We were at the Crown Inn, at Low Harrowgate. We always dined in the
public room, but retired very soon after dinner to our private one;
for Byron was no more a friend to drinking than myself. We lived
retired, and made few acquaintance; for he was naturally shy, very
shy; which people who did not know him mistook for pride. While at
Harrowgate he accidentally met with Professor Hailstone from
Cambridge, and appeared much delighted to see him. The professor was
at Upper Harrowgate: we called upon him one evening to take him to the
theatre, I think, — and Lord Byron sent his carriage for him, another
time, to a ball at the Granby. This desire to show attention to one of
the professors of his college is a proof that, though he might choose
to satirise the mode of education in the university, and to abuse the
antiquated regulations and restrictions to which undergraduates are
subjected, he had yet a due discrimination in his respect for the
individuals who belonged to it. I have always, indeed, heard him speak
in high terms of praise of Hailstone, as well as of his master, Bishop
Mansel, of Trinity College, and of others whose names I have now
forgotten.
"Few people understood Byron; but I know that he had naturally a kind
and feeling heart, and that there was not a single spark of malice in
his composition."
Professor Hailstone was Woodwardian Professor of Geology (1788-1818).
(For Bishop Mansel, see page 84, note 1.)
return to footnote mark
List of Letters
59 — To John Hanson1
Southwell, Dec. 7th, 1806.
Sir, — A Letter to Mrs. Byron has just arrived which states, from what
"you have heard of the Tenor of my Letters," you will not put up with
Insult. I presume this means (for I will not be positive on what is
rather ambiguously expressed) that some offence to you has been conveyed
in the above mentioned Epistles. If you will peruse the papers in
question, you will discover that the person insulted is not
yourself, or any one of your "Connections." On Mr. B.'s apology, I
have expressed my opinion in a Letter to your Son, if any
Misrepresentation has taken place, it must be those "Connections" to
whom I am to pay such Deference, & whose conduct to me has deserved such
ample respect. I must now beg leave to observe in turn, that I am
by no means disposed to bear Insult, &, be the consequences what they
may, I will always declare, in plain and explicit Terms, my Grievance,
nor will I overlook the slightest Mark of disrespect, & silently brood
over affronts from a mean and interested dread of Injury to my person or
property. The former I have Strength and resolution to protect; the
latter is too trifling by its Loss to occasion a moments Uneasiness.
Though not conversant with the methodical & dilatory arrangements of Law
or Business, I know enough of Justice to direct my conduct by the
principles of Equity, nor can I reconcile the "Insolence of office" to
her regulations or forget in an Instant a poignant Affront.
But enough of this Dispute. You will perceive my Sentiments on the
Subject, in my correspondence with Mr. B. and Mr. H. Junior. In future
to prevent a repetition and altercation I shall advise; but as, even
then, some Demur may take place, I wish to be informed, if the equitable
Court of Chancery, whose paternal care of their Ward can never be
sufficiently commended, have determined, in the great Flow of parental
Affection, to withhold their beneficent Support, till I return to "Alma Mater" (i. e.) Cambridge. Your Information on this point will oblige,
as a College life is neither conducive to my Improvement, nor suitable
to my Inclination. As to the reverse of the Rochdale Trial, I received
the News of Success without confidence or exultation; I now sustain the
Loss without repining. My Expectations from Law were never very
sanguine.
I remain, yr very obedt. sert.,
Byron.
Footnote 1: Hanson's partner, Birch, the "Mr. B." of the letter, seems to have irritated Byron by withholding the income allotted
to him by the Court of Chancery for his education at Cambridge. The
attempt to compel his return to Trinity by cutting off the supplies,
failed. He did not appear again at Cambridge till the summer term of
1807.
return to footnote mark
List of Letters
Dorant's Hotel, Albemarle Street, Jany. 12, 1807.
Mr. Ridge, — I understand from some of my friends, that several of the
papers are in the habit of publishing extracts from my volume,
particularly the Morning Herald. I cannot say for my own part I have
observed this, but I am assured it is so. The thing is of no consequence
to me, except that I dislike it. But it is to you, and as publisher you
should put a stop to it. The Morning Herald is the paper; of course
you cannot address any other, as I am sure I have seen nothing of the
kind in mine. You will act upon this as you think proper, and proceed
with the 2d. Edition as you please. I am in no hurry, and I still think
you were premature in undertaking it.
Etc., etc.,
Byron.
P.S. — Present a copy of the Antijacobin therein to Mrs. Byron.
List of Letters
Southwell, Jan. 13, 1807.
I ought to begin with sundry apologies, for my own negligence, but the
variety of my avocations in prose and verse must plead my excuse.
With this epistle you will receive a volume of all my Juvenilia,
published since your departure: it is of considerably greater size than
the copy in your possession, which I beg you will destroy, as the
present is much more complete. That unlucky poem to my poor Mary1
has been the cause of some animadversion from ladies in years. I have
not printed it in this collection, in consequence of my being pronounced
a most profligate sinner, in short, a "young Moore,"2 by — — — ,
your — — friend. I believe, in general, they have been favourably
received, and surely the age of their author will preclude severe
criticism. The adventures of my life from sixteen to nineteen, and the
dissipation into which I have been thrown in London, have given a
voluptuous tint to my ideas; but the occasions which called forth my
muse could hardly admit any other colouring. This volume is vastly
correct and miraculously chaste. Apropos, talking of love, ...
...
If you can find leisure to answer this farrago of unconnected nonsense,
you need not doubt what gratification will accrue from your reply to
yours ever, etc.
Footnote 1: See page 104, note 2.
return to footnote mark
Footnote 2: Thomas Moore (1779-1852) had already published Anacreon
(1800), The Poetical Works of the late Thomas Little (1801), and
Odes, Epistles, and other Poems (1806). In all, especially in the
second, the poetry was of an erotic character.
"So heartily," said
Rogers (Table-Talk, etc., pp. 281, 282), "has Moore repented of having
published Little's Poems, that I have seen him shed tears — tears of
deep contrition — when we were talking of them. Young ladies read his
Lalla Rookh without being aware (I presume) of the grossness of The
Veiled Prophet. These lines by Mr. Sneyd are amusing enough —
"'Lalla Rookh
Is a naughty book
By Tommy Moore,
Who has written four,
Each warmer
Than the former.
So the most recent
Is the least decent.'"
return
List of Letters
62 — To Captain John Leacroft1
January 31, 1807.
Sir, — Upon serious reflection on the conversation we last night held, I
am concerned to say, that the only effectual method to crash the
animadversions of officious malevolence, is by my declining all future
intercourse with those whom my acquaintance has unintentionally injured.
At the same time I must observe that I do not form this resolution from
any resentment at your representation, which was temperate and
gentlemanly, but from a thorough conviction that the desirable end can
be attained by no other line of conduct.
I beg leave to return my thanks to Mr. & Mrs. Leacroft, for the
attention and hospitality I have always experienced, of which I shall
ever retain a grateful remembrance.
So much to them; with your permission, I must add a few words for
myself. You will be sensible, that a coolness between families, hitherto
remarkable for their intimacy, cannot remain unobserved in a town, whose
inhabitants are notorious for officious curiosity; that the causes for
our separation will be mis-represented I have little doubt; if,
therefore, I discover that such misrepresentation does take place, I
shall call upon you, to unite with myself in making a serious example of
those men, be they who they may, that dare to cast an aspersion on
the character I am sacrificing my own comfort to protect.
If, on the other hand, they imagine, that my conduct is the consequence
of intimidation, from my conference with you, I must require a further
explanation of what passed between us on the subject, as, however
careful I am of your Sister's honour, I am equally tenacious of my own.
I do not wish this to be misconstrued into any desire to quarrel; it is
what I shall endeavour to avoid; but, as a young man very lately entered
into the world, I feel compelled to state, that I can permit no
suspicion to be attached to my name with impunity.
I have the honour to remain,
Your very obedient Servant,
Byron.
Footnote 1: This and the two following letters refer to a quarrel
between Byron and the Leacroft family, which arose from his attentions
to Miss Julia Leacroft. Moore's statement, that Captain Leacroft, the
lady's brother (see page 34, note 2), sent a challenge to Byron, who
was at first inclined to accept it, is inaccurate. But it is possible
that Byron was acting on the advice of the Rev. J. T. Becher, when he
decided, in order to prevent misunderstanding, to break off his
acquaintance with the Leacrofts absolutely.
return to footnote mark
cross-reference: return to Footnote 3 of Letter 12
List of Letters
February 4th, 1807.
Sir, — I have just received your note, which conveys all that can be said
on the subject. I can easily conceive your feelings must have been
irritated in the course of the affair. I am sorry that I have been the
unintentional cause of so disagreeable a business. The line of conduct,
however painful to myself, which I have adopted, is the only effectual
method to prevent the remarks of a meddling world. I therefore again
take my leave for the last time. I repeat, that, though the intercourse,
from which I have derived so many hours of happiness, is for ever
interrupted, the remembrance can never be effaced from the bosom of
Your very obedient Servant,
Byron.
cross-reference: return to Footnote 3 of Letter 12
List of Letters
February 4th, 1807.
Sir, — I am concerned to be obliged again to trouble you, as I had hoped
that our conversations had terminated amicably. Your good Father, it
seems, has desired otherwise; he has just sent a most agreeable
epistle, in which I am honoured with the appellations of
unfeeling and ungrateful. But as the consequences of all this
must ultimately fall on you and myself, I merely write this to apprise
you that the dispute is not of my seeking, and that, if we must cut each
other's throats to please our relations, you will do me the justice to
say it is from no personal animosity between us, or from any
insult on my part, that such disagreeable events (for I am not so
much enamoured of quarrels as to call them pleasant) have arisen.
I remain, your's, etc.,
Byron.
cross-reference: return to Footnote 3 of Letter 12
List of Letters
65 — To the Earl of Clare1
Southwell, Notts, February 6, 1807.
My Dearest Clare, — Were I to make all the apologies necessary to atone
for my late negligence, you would justly say you had received a petition
instead of a letter, as it would be filled with prayers for forgiveness;
but instead of this, I will acknowledge my sins at once, and I trust
to your friendship and generosity rather than to my own excuses. Though
my health is not perfectly re-established, I am out of all danger, and
have recovered every thing but my spirits, which are subject to
depression. You will be astonished to hear I have lately written to
Delawarr2, for the purpose of explaining (as far as possible without
involving some old friends of mine in the business) the cause of my
behaviour to him during my last residence at Harrow (nearly two years
ago), which you will recollect was rather "en cavalier." Since that
period, I have discovered he was treated with injustice both by those
who misrepresented his conduct, and by me in consequence of their
suggestions. I have therefore made all the reparation in my power, by
apologizing for my mistake, though with very faint hopes of success;
indeed I never expected any answer, but desired one for form's sake;
that has not yet arrived, and most probably never will. However, I
have eased my own conscience by the atonement, which is humiliating
enough to one of my disposition; yet I could not have slept satisfied
with the reflection of having, even unintentionally, injured any
individual. I have done all that could be done to repair the injury, and
there the affair must end. Whether we renew our intimacy or not is of
very trivial consequence.
My time has lately been much occupied with very different pursuits. I
have been transporting a servant3, who cheated me, — rather a
disagreeable event; — performing in private theatricals4; — publishing
a volume of poems (at the request of my friends, for their perusal);
— making love, — and taking physic. The two last amusements have not had
the best effect in the world; for my attentions have been divided
amongst so many fair damsels, and the drugs I swallow are of such
variety in their composition, that between Venus and Æsculapius I am
harassed to death. However, I have still leisure to devote some hours to
the recollections of past, regretted friendships, and in the interval to
take the advantage of the moment, to assure you how much I am, and ever
will be, my dearest Clare,
Your truly attached and sincere
Byron.
Footnote 1: John Fitzgibbon (1792-1851), son of the first Earl of
Clare, by his wife Anne Whaley, succeeded his father as second Earl in
January, 1802. A schoolfellow of Byron's at Harrow, he was the "Lycus"
of "Childish Recollections," and one of his dearest friends. Clare,
after leaving Harrow, went to a private tutor, the Rev. Mr. Smith, at
Woodnesborough, near Sandwich. There he formed so close a friendship
with Lord John Russell as to provoke Byron's jealousy (Life, p.
21). Clare was at Christ Church, Oxford (B.A. 1812); Byron at Trinity,
Cambridge. They rarely met after leaving Harrow. Their meeting on the
road between Imola and Bologna in 1821,
"annihilated for a moment," says Byron (see Life, p. 540;
Detached Thoughts, November 5, 1821), "all the years between
the present time and the days of Harrow. We were but five minutes
together, and on the public road; but I hardly recollect an hour of my
existence which could be weighed against them. Of all I have ever
known, he has always been the least altered in everything from the
excellent qualities and kind affections which attached me to him so
strongly at school. I should hardly have thought it possible for
society (or the world, as it is called) to leave a being with so
little of the leaven of bad passions. I do not speak from personal
experience only, but from all I have ever heard of him from others,
during absence and distance."
Lord Clare was Governor of Bombay from 1830 to 1834.
return to footnote mark
Footnote 2: See page 41, note 1.
return
Footnote 3: See page 81, note 1.
return
cross-reference: return to Footnote 1 of Letter 38
Footnote 4: In the theatricals, which took place at Southwell in the
autumn of 1806, Byron was the chief mover. A letter received by Mr.
Pigot, quoted by Moore (Life, p. 38), shows how eagerly his return
from Harrogate was expected:—
"Tell Lord Byron that, if any accident should retard his return, his
mother desires he will write to her, as she shall be miserable if he
does not arrive the day he fixes. Mr. W. B. has written a card to Mrs.
H. to offer for the character of 'Henry Woodville,' — Mr. and Mrs.
— — not approving of their son's taking a part in the play: but I
believe he will persist in it. Mr. G. W. says, that sooner than the
party should be disappointed, he will take any
part, — sing — dance — in short, do any thing to oblige. Till Lord Byron
returns, nothing can be done; and positively he must not be later than
Tuesday or Wednesday."
A full account of the theatricals is given in a manuscript written by
Miss Bristoe, one of the performers. Two plays were represented,
- Cumberland's Wheel of Fortune and
- Allingham's Weathercock.
The following were the respective casts:—
| 1. |
|
| Penruddock |
Lord Byron |
| Sir David Daw |
Mr. C. Becher |
| Woodville |
Captain Lightfoot |
| Sydenham |
Mr. Pigot |
| Henry Woodville |
Mr. H. Houson |
| Mrs. Woodville |
Miss Bristoe |
| Emily Tempest |
Miss J. Leacroft |
| Dame Dunckley |
Miss Leacroft |
| Weazel |
Mr. G. Wylde |
| Jenkins |
Mr. G. Heathcote
|
| 2. |
|
| Tristram Fickle |
Lord Byron |
| Old Fickle |
Mr. Pigot |
| Briefwit |
Captain Lightfoot |
| Sneer |
Mr. R. Leacroft |
| Variella |
Miss Bristoe |
| Ready |
Miss Leacroft |
| Gardener |
Mr. C. Becher |
| Barber |
Mr. G. Wylde |
Between the two plays, a member of the Southwell choir sang "The Death
of Abercrombie." The brave General, attended by two aides-de-camp, all
three in the costume of the Southwell volunteers, appeared on the stage,
and the General, sinking into the outstretched arms of his two friends,
warbled out his dying words in a style which convulsed Byron with
laughter.
The play itself nearly came to an untimely conclusion. Captain Lightfoot
screwed his failing courage to the sticking point by several glasses of
wine, with the result that, being a very abstemious man, he became
tipsy. But "restoratives were administered," and he went through his
part with credit. Byron, who was the star of the company, repeatedly
brought down the house by his acting.
(For Byron's Prologue to The Wheel of Fortune, see Poems, vol. i.
pp. 45, 46.) Moore's account of the epilogue, written by the Rev. J. T.
Becher, and spoken by Byron, is erroneous. Only one word gave any
opportunity for mimicry. It occurs in the lines —
"Tempest becalmed forgets his blust'ring rage,
He calls Dame Dunckley 'sister' off the stage."
In pronouncing the word "sister," Byron "took off exactly the voice and
manner of Mr. R. Leacroft."
return
cross-reference: return to Footnote 3 of Letter 12
cross-reference: return to Footnote 1 of Letter 58
List of Letters
Southwell, Feb. 8, 1807.
Dear Madam, — Having understood from Mrs. Byron that Mr. Hanson is in a
very indifferent State of Health, I have taken the Liberty of addressing
you on the Subject.
Though the Governor & I have lately not been on the best of
Terms, yet I should be extremely sorry to learn he was in Danger, and
I trust he and I will live to have many more Squabbles in this
world, before we finally make peace in the next. If therefore you can
favor me with any salutary Intelligence of the aforesaid Gentleman,
believe me, nothing will be more acceptable to
Yours very truly,
Byron.
P.S. — Remember me to all the family now in Garrison, particularly my
old Friend Harriet.
List of Letters
67 — To William Bankes1
Southwell, March 6, 1807.
Dear Bankes, — Your critique is valuable for many reasons: in the first
place, it is the only one in which flattery has borne so slight a part;
in the next, I am cloyed with insipid compliments. I have a better
opinion of your judgment and ability than your feelings. Accept my
most sincere thanks for your kind decision, not less welcome, because
totally unexpected. With regard to a more exact estimate, I need not
remind you how few of the best poems, in our language, will stand the
test of minute or verbal criticism: it can, therefore, hardly be
expected the effusions of a boy (and most of these pieces have been
produced at an early period) can derive much merit either from the
subject or composition. Many of them were written under great depression
of spirits, and during severe indisposition:— hence the gloomy turn of
the ideas. We coincide in opinion that the "poësies érotiques" are the
most exceptionable; they were, however, grateful to the deities, on
whose altars they were offered — more I seek not.
The portrait of Pomposus2 was drawn at Harrow, after a long
sitting; this accounts for the resemblance, or rather the caricatura.
He is your friend, he never was mine — for both our sakes I shall be
silent on this head. The collegiate rhymes3 are not personal — one
of the notes may appear so, but could not be omitted. I have little
doubt they will be deservedly abused — a just punishment for my unfilial
treatment of so excellent an Alma Mater. I sent you no copy, lest we
should be placed in the situation of Gil Blas and the Archbishop of
Grenada4; though running some hazard from the experiment, I wished
your verdict to be unbiassed. Had my "Libellus" been presented
previous to your letter, it would have appeared a species of bribe to
purchase compliment. I feel no hesitation in saying, I was more anxious
to hear your critique, however severe, than the praises of the
million. On the same day I was honoured with the encomiums of
Mackenzie, the celebrated author of the Man of Feeling5
Whether his approbation or yours elated me most, I cannot
decide.
You will receive my Juvenilia, — at least all yet published. I
have a large volume in manuscript, which may in part appear hereafter;
at present I have neither time nor inclination to prepare it for the
press. In the spring I shall return to Trinity, to dismantle my rooms,
and bid you a final adieu. The Cam will not be much increased by
my tears on the occasion. Your further remarks, however
caustic or bitter, to a palate vitiated with the sweets of
adulation, will be of service. Johnson has shown us that no
poetry is perfect; but to correct mine would be an Herculean labour.
In fact I never looked beyond the moment of composition, and published
merely at the request of my friends. Notwithstanding so much has been
said concerning the "Genus irritabile vatum," we shall never quarrel on
the subject — poetic fame is by no means the "acme" of my wishes. — Adieu.
Yours ever,
Byron.
Footnote 1: William John Bankes, of Kingston Lacy, Dorsetshire, was
Byron's friend, possibly at Harrow, though his name does not occur in
the school lists, certainly at Trinity College, Cambridge (B.A. 1808).
He represented Truro from 1810 to 1812, when he left England on his
Eastern travels. At Philæ he discovered an obelisk, the geometrical
elevation and inscriptions of which he published in 1820. In Mesopotamia
he encountered John Silk Buckingham, whom he afterwards charged with
making use of his notes in his Travels, a statement, found to be
libellous, which (October 19, 1826) cost Bankes £400 in damages. He also
travelled with Giovanni Finati, a native of Ferrara, who, under the
assumed name of Mahomet, made the campaigns against the Wahabees for the
recovery of Mecca and Medina. Finati's Italian Narrative was
translated by Bankes, to whom it is dedicated by his "attached and
faithful servant Hadjee Mahomet," and published in 1830. In 1822 Bankes
was elected M.P. for Cambridge University, but lost his seat to Sir J.
Copley in 1826. At a bye-election in 1827, he was again unsuccessful.
His candidature gave occasion to Macaulay's squib, which appeared in the
Times for May 14, 1827, A Country Clergyman's Trip to Cambridge.
"A letter — and free — bring it here:
I have no correspondent who franks.
No! Yes! Can it be? Why, my dear,
'Tis our glorious, our Protestant Bankes.
'Dear Sir as I know your desire
That the Church should receive due protection,
I humbly presume to require
Your aid at the Cambridge election,'"etc., etc.
Bankes subsequently represented Marlborough (1829-1832) and Dorsetshire
(1833-1834). He was Byron's "collegiate pastor, and master and patron,"
"ruled the roast" at Trinity, "or, rather, the roasting, and was
father of all mischief" (Byron to Murray, October 12, 1820). "William
Bankes," Byron told Lady Blessington (Conversations, p. 172), "is
another of my early friends. He is very clever, very original, and has
a fund of information: he is also very good-natured, but he is not much
of a flatterer." Bankes died at Venice in 1855.
return to footnote mark
cross-reference: return to Footnote 3 of Letter 84
Footnote 2: Dr. Butler, Head-master of Harrow. (See page 58, note
1.)
return
Footnote 3: "Thoughts suggested by a College Examination" (Poems,
vol. i. pp. 28-31); and "Granta, A Medley" (Poems, vol. i. pp. 56-62).
return
Footnote 4: Alluding to Gil Blas, bk. vii. chap, iv., where Gil Blas
ventures to criticize the Archbishop's work, and is dismissed for his
candour.
"Adieu, monsieur Gil Blas; Je vous souhaite toutes sortes de
prosperités, avec un peu plus de goût."
return
cross-reference: return to Footnote 2 of Letter 158
Footnote 5: The praise was worth having. Henry Mackenzie (1745-1831)
was not only the author of the lackadaisical Man of Feeling, but
in real life a shrewd, hard-headed man. As a novelist, he wrote The
Man of Feeling (1771), The Man of Honour (1773), and Julia
de Roubigne (1777). As a playwright, he produced four plays, none of
which succeeded. As an essayist, he contributed to the Mirror
(1779-80) and the Lounger (1785-86). As a political writer, he
supported Pitt, and was rewarded by the comptrollership of taxes. An
original member of the Royal Society of Edinburgh, many of his papers
appear in its Transactions. In Edinburgh society he was "the life
of the company," a connecting link on the literary side between David
Hume, Walter Scott, and Lord Cockburn, and in all matters of sport a
fund of anecdotes and reminiscences.
return
List of Letters
68 — To William Bankes1
For my own part, I have suffered severely in the decease of my two
greatest friends, the only beings I ever loved (females excepted); I am
therefore a solitary animal, miserable enough, and so perfectly a
citizen of the world, that whether I pass my days in Great Britain or
Kamschatka, is to me a matter of perfect indifference. I cannot evince
greater respect for your alteration than by immediately adopting
it — this shall be done in the next edition. I am sorry your remarks are
not more frequent, as I am certain they would be equally beneficial.
Since my last, I have received two critical opinions from Edinburgh,
both too flattering for me to detail. One is from Lord Woodhouselee2,
at the head of the Scotch literati, and a most voluminous writer (his
last work is a Life of Lord Kaimes); the other from Mackenzie, who
sent his decision a second time, more at length. I am not personally
acquainted with either of these gentlemen, nor ever requested their
sentiments on the subject: their praise is voluntary, and transmitted
through the medium of a friend, at whose house they read the
productions.
Contrary to my former intention, I am now preparing a volume for the
public at large: my amatory pieces will be exchanged, and others
substituted in their place. The whole will be considerably enlarged, and
appear the latter end of May. This is a hazardous experiment; but want
of better employment, the encouragement I have met with, and my own
vanity, induce me to stand the test, though not without sundry
palpitations. The book will circulate fast enough in this country from
mere curiosity; what I prin — — ...
[letter incomplete]
Footnote 1: This fragment refers, like the previous letter, to Byron's
volume of verse, Poems on Various Occasions.
return to footnote mark
Footnote 2: Alexander Fraser Tytler, Lord Woodhouselee, one of the
Senators of the College of Justice in Scotland, and a friend of Robert
Burns. Besides the Memoirs of the Life and Writings of the Hon. Henry
Home of Kames (1807), he published Elements of General History
(1801), Essay on the Principles of Translation, etc. He died in 1813.
His Universal History, in six vols., appeared in 1834.
return
List of Letters
69 — To — — Falkner1
Sir, — The volume of little pieces which accompanies this, would have
been presented before, had I not been apprehensive that Miss Falkner's
indisposition might render some trifles unwelcome. There are some errors
of the printer which I have not had time to correct in the collection:
you have it thus, with "all its imperfections on its head," a heavy
weight, when joined with the faults of its author. Such Juvenilia, as
they can claim no great degree of approbation, I may venture to hope,
will also escape the severity of uncalled for, though perhaps not
undeserved, criticism.
They were written on many and various occasions, and are now published
merely for the perusal of a friendly circle. Believe me, sir, if they
afford the slightest amusement to yourself and the rest of my social
readers, I shall have gathered all the bays I ever wish to adorn the
head of yours very truly,
Byron.
Footnote 1: Mrs. Byron's landlord at Burgage Manor.
return to footnote mark
List of Letters
[Farleigh House, Basingstoke, Hants.]
Southwell, April 2nd, 1807.
Dear Sir, — Before I proceed in Reply to the other parts of your Epistle,
allow me to congratulate you on the Accession of Dignity and
profit, which will doubtless accrue, from your official appointment.
You was fortunate in obtaining Possession at so critical a period; your
Patrons "exeunt omnes."1 I trust they will soon supersede the
Cyphers, their successors. The Reestablishment of your Health is another
happy event, and, though secondary in my Statement, is by no means
so in my Wishes. As to our Feuds, they are purely official, the
natural consequence of our relative Situations, but as little connected
with personal animosity, as the Florid Declamations of
parliamentary Demagogues. I return you my thanks for your favorable
opinion of my muse; I have lately been honoured with many very
flattering literary critiques, from men of high Reputation in the
Sciences, particularly Lord Woodhouselee and Henry Mackenzie, both
Scots and of great Eminence as Authors themselves. I have received
also some most favorable Testimonies from Cambridge. This you will
marvel at, as indeed I did myself. Encouraged by these and several
other Encomiums, I am about to publish a Volume at large; this will be
very different from the present; the amatory effusions, not to be
wondered at from the dissipated Life I have led, will be cut out, and
others substituted. I coincide with you in opinion that the Poet
yields to the orator; but as nothing can be done in the latter
capacity till the Expiration of my Minority, the former occupies my
present attention, and both ancients and moderns have declared that
the two pursuits are so nearly similar as to require in a great measure
the same Talents, and he who excels in the one, would on application
succeed in the other. Lyttleton, Glover, and Young (who was a celebrated
Preacher and a Bard) are instances of the kind. Sheridan & Fox also;
these are great Names. I may imitate, I can never equal them.
You speak of the Charms of Southwell; the Place I abhor. The Fact
is I remain here because I can appear no where else, being completely
done up. Wine and Women have dished your humble Servant, not a
Sou to be had; all over; condemned to exist (I cannot say live) at
this Crater of Dullness till my Lease of Infancy expires. To
appear at Cambridge is impossible; no money even to pay my College
expences. You will be surprized to hear I am grown very thin; however
it is the Fact, so much so, that the people here think I am going. I
have lost 18 LB in my weight, that is one Stone & 4 pounds since
January, this was ascertained last Wednesday, on account of a Bet with
an acquaintance. However don't be alarmed; I have taken every means to
accomplish the end, by violent exercise and Fasting, as I found myself
too plump. I shall continue my Exertions, having no other amusement; I
wear seven Waistcoats and a great Coat, run, and play at cricket in
this Dress, till quite exhausted by excessive perspiration, use the Hip
Bath daily; eat only a quarter of a pound of Butcher's Meat in 24 hours,
no Suppers or Breakfast, only one Meal a Day; drink no malt liquor, but
a little Wine, and take Physic occasionally. By these means my Ribs
display Skin of no great Thickness, & my Clothes have been taken in
nearly half a yard. Do you believe me now?
Adieu. Remembrance to Spouse and the Acorns.
Yours ever,
Byron.
Footnote 1: In March, 1807, George III demanded from the Coalition
Ministry a written pledge that they would propose no further concessions
to the Roman Catholics. They refused to give it, and the Tories, with
the Duke of Portland as their nominal head, were recalled to the
Government.
return to footnote mark
List of Letters
Southwell, April, 1807.
My Dear Pigot, — Allow me to congratulate you on the success of your
first examination — "Courage, mon ami." The title of Doctor will do
wonders with the damsels. I shall most probably be in Essex or London
when you arrive at this damned place, where I am detained by the
publication of my rhymes.
Adieu. — Believe me,
Yours very truly,
Byron.
P.S. — Since we met, I have reduced myself by violent exercise, much
physic, and hot bathing, from 14 stone 6 lb. to 12 stone 7 lb. In all
I have lost 27 pounds1. Bravo! — what say you?
Footnote 1: The following extract is taken from a ledger in the
possession of Messrs. Merry, of St. James's Street, S.W.:—
| 1806 |
January 4 |
Lord Byron |
(boots, no hat) |
13 st. |
12 lbs. |
| 1807 |
July 8 |
Lord Byron |
(shoes) |
10 st. |
13 lbs. |
| 1807 |
July 23 |
Lord Byron |
(shoes) |
11 st. |
0 lbs. |
| 1807 |
August 13 |
Lord Byron |
(shoes) |
10 st. |
11 1/2 lbs. |
| 1808 |
May 27 |
Lord Byron |
(shoes) |
11 st. |
1 lb. |
| 1809 |
June 10 |
Lord Byron |
(shoes) |
11 st. |
5 3/4 lbs. |
| 1811 |
July 15 |
Lord Byron |
(shoes) |
9 st. |
11 1/2 lbs. |
return to footnote mark
cross-reference: return to Footnote 3 of Letter 144
List of Letters
[6, Chancery Lane, Temple Bar, London.]
Southwell, 19 April, 1807.
Sir, — My last was an Epistle "entre nous;" this is a Letter of
Business, Of course the formalities of official communication must
be attended to. From lying under pecuniary difficulties, I shall draw
for the Quarter due the 25th June, in a short Time. You will recollect I
was to receive £100 for the Expence of Furniture, etc., at Cambridge. I
placed in your possession accounts to amount and then I have received
£70, for which I believe you have my Receipt. This extra £25 or £30
(though the Bills are long ago discharged from my own purse) I should
not have troubled you for, had not my present Situation rendered even
that Trifle of some Consequence. I have therefore to request that my
Draft for £150, instead of £125 the simple Quarter, may be honoured, but
think it necessary to apprize you previous to its appearance, and indeed
to request an early Answer, as I had one Draft returned by Mistake from
your House, some Months past. I have no Inclination to be placed in a
similar Dilemma.
I lent Mrs. B. £60 last year; of this I have never received a Sou and
in all probability never shall. I do not mention the circumstance as any
Reproach on that worthy and lamblike Dame1, but merely to show you
how affairs stand. 'Tis true myself and two Servants lodge in the House,
but my Horses, etc., and their expences are defrayed by your humble
Sert. I quit Cambridge in July, and shall have considerable payments to
make at that period; for this purpose I must sell my Steeds. I paid
Jones in January £150, £38 to my Stable Keeper, £21 to my wine Merchant,
£20 to a Lawyer for the prosecution of a Scoundrel, a late Servant. In
short I have done all I can, but am now completely done up.
Your answer will oblige
Yours, etc., etc.,
Byron.
Footnote 1: Mrs. Byron, on the other hand, tells a different story.
"Lord Byron," she writes to Hanson (March 19, 1807), "has now been with
me seven months, with two Men Servants, for which I have never received
one farthing, as he requires the five hundred a year for himself.
Therefore it is impossible I can keep him and them out of my small
income of four hundred a year, — two in Scotland [Mrs. Gordon of Gight
(see Chapter I p. 4) was dead], and the pension is now reduced to two
hundred a year. But if the "Court allows the additional two hundred, I
shall be perfectly satisfied.
"I do not know what to say about Byron's returning to Cambridge. When he
was there, I believe he did nothing but drink, gamble, and spend money."
A month later (April 29, 1807), she consults Hanson about raising £1000
by a loan from Mrs. Parkyns on her security. "Byron from their last
letter gave up all hopes of getting the money, and behaved very well on
the occasion, and proposed selling his Horses and plans of Œconomy that
I much fear will be laid aside if the Money is procured. My only motive
for wishing it was to keep him clear of the Jews; but at present he does
not seem at all disposed to have anything to do with them, even if he is
disappointed in this resource. I wish to act for the best: but God knows
what is for the best."
Eventually money was provided on Mrs. Byron's security (see Letters of
March 6 and April 26, 1809), and he resided at Trinity for a few days at
the end of the May term, 1807.
return to footnote mark
cross-reference: return to Footnote 1 of Letter 38
List of Letters
June 11, 1807.
Dear Queen Bess, — Savage ought to be immortal: — though not a
thorough-bred bull-dog, he is the finest puppy I ever saw, and
will answer much better; in his great and manifold kindness he has
already bitten my fingers, and disturbed the gravity of old
Boatswain, who is grievously discomposed. I wish to be informed what
he costs, his expenses, etc., etc., that I may indemnify Mr.
G — — . My thanks are all I can give for the trouble he has taken,
make a long speech, and conclude it with 1 2 3 4 5 6 71. I am out
of practice, so deputize you as a legate, — ambassador would not do
in a matter concerning the Pope, which I presume this must, as the
whole turns upon a Bull.
Yours,
Byron.
P.S. — I write in bed.
Footnote 1: He here alludes to an odd fancy or trick of his
own; — whenever he was at a loss for something to say, he used always to
gabble over "1 2 3 4 5 6 7" (Moore).
return to footnote mark
List of Letters
Cambridge, June 30, 1807.
"Better late than never, Pal,"1 is a saying of which you know the
origin, and as it is applicable on the present occasion, you will excuse
its conspicuous place in the front of my epistle. I am almost
superannuated here. My old friends (with the exception of a very few)
all departed, and I am preparing to follow them, but remain till Monday
to be present at three Oratorios, two Concerts, a Fair, and a
Ball. I find I am not only thinner but taller by an inch since my
last visit. I was obliged to tell every body my name, nobody having
the least recollection of my visage, or person. Even the hero of my
Cornelian2 (who is now sitting vis-à-vis reading a volume of my
Poetics) passed me in Trinity walks without recognising me in the
least, and was thunderstruck at the alteration which had taken place in
my countenance, etc., etc. Some say I look better, others worse, but
all agree I am thinner, — more I do not require. I have lost two pounds
in my weight since I left your cursed, detestable, and abhorred
abode of scandal, where, excepting yourself and John Becher3, I care
not if the whole race were consigned to the Pit of Acheron, which I
would visit in person rather than contaminate my sandals with the
polluted dust of Southwell. Seriously, unless obliged by the
emptiness of my purse to revisit Mrs. B., you will see me no more.
On Monday I depart for London. I quit Cambridge with little regret,
because our set are vanished, and my musical protégé before
mentioned has left the choir, and is stationed in a mercantile house of
considerable eminence in the metropolis. You may have heard me observe
he is exactly to an hour two years younger than myself. I found him
grown considerably, and as you will suppose, very glad to see his former
Patron. He is nearly my height, very thin, very fair complexion,
dark eyes, and light locks. My opinion of his mind you already know; — I
hope I shall never have occasion to change it. Every body here conceives
me to be an invalid. The University at present is very gay from the
fètes of divers kinds. I supped out last night, but eat (or ate)
nothing, sipped a bottle of claret, went to bed at two, and rose at
eight. I have commenced early rising, and find it agrees with me. The
Masters and the Fellows all very polite, but look a little askance
— don't much admire lampoons4 — truth always disagreeable.
Write, and tell me how the inhabitants of your Menagerie go on, and
if my publication goes off well: do the quadrupeds growl? Apropos,
my bull-dog is deceased — "Flesh both of cur and man is grass." Address
your answer to Cambridge. If I am gone, it will be forwarded. Sad news
just arrived — Russians beat5 — a bad set, eat nothing but oil,
consequently must melt before a hard fire. I get awkward in my
academic habiliments for want of practice. Got up in a window to hear
the oratorio at St. Mary's, popped down in the middle of the Messiah,
tore a woeful rent in the back of my best black silk gown, and damaged
an egregious pair of breeches. Mem. — never tumble from a church window
during service. Adieu, dear — — ! do not remember me to any body:— to
forget and be forgotten by the people of Southwell is all I aspire to.
Footnote 1: The allusion is to the farce Better Late than Never
(attributed to Miles Peter Andrews, but really, according to Reynolds
(Life, vol. ii. pp. 79, 80), by himself, Topham, and Andrews), in
which Pallet, an artist, is a prominent character. It was played at
Drury Lane for the first time October 17, 1790, with Kemble as "Saville"
and Mrs. Jordan as "Augusta."
return to footnote mark
Footnote 2: "The hero of my Cornelian" was a Cambridge chorister named Edleston, whose life, as
Harness has recorded in a MS. note, Byron saved from drowning. This
began their acquaintance. (See Byron's lines on "The Cornelian,"
Poems, vol. i. 66-67.) Edleston died of consumption in May, 1811.
Byron, writing to Mrs. Pigot, gives the following account of his death:—
"Cambridge, Oct. 28, 1811.
Dear Madam, — I am about to write to you on a silly subject, and yet I
cannot well do otherwise. You may remember a cornelian, which some
years ago I consigned to Miss Pigot, indeed gave to her, and now I
am going to make the most selfish and rude of requests. The person who
gave it to me, when I was very young, is dead, and though a long
time has elapsed since we met, as it was the only memorial I possessed
of that person (in whom I was very much interested), it has acquired a
value by this event I could have wished it never to have borne in my
eyes. If, therefore, Miss Pigot should have preserved it, I must,
under these circumstances, beg her to excuse my requesting it to be
transmitted to me at No. 8, St. James's Street, London, and I will
replace it by something she may remember me by equally well. As she
was always so kind as to feel interested in the fate of him that
formed the subject of our conversation, you may tell her that the
giver of that cornelian died in May last of a consumption, at the age
of twenty-one, making the sixth, within four months, of friends and
relatives that I have lost between May and the end of August.
"Believe me, dear Madam, yours very sincerely,
"Byron.
"P.S. — I go to London to-morrow."
The cornelian heart was, of course, returned, and Lord Byron, at the
same time, reminded that he had left it with Miss Pigot as a deposit,
not a gift (Moore).
return
cross-reference: return to Footnote 2 of Letter 161
Footnote 3: See page 182, note 1.
return
Footnote 4: See "Thoughts suggested by a College Examination" (Poems,
vol. i. pp. 28-31), also "Granta: a Medley" (Poems, vol. i. pp.
56-62).
return
Footnote 5: The Battle of Friedland, June 15, 1807. This is almost the
first allusion that Byron makes to the war.
return
List of Letters
Trin. Coll. Camb. July 5, 1807.
Since my last letter I have determined to reside another year at
Granta, as my rooms, etc., etc., are finished in great style, several
old friends come up again, and many new acquaintances made; consequently
my inclination leads me forward, and I shall return to college in
October if still alive. My life here has been one continued routine of
dissipation — out at different places every day, engaged to more dinners,
etc., etc., than my stay would permit me to fulfil. At this moment I
write with a bottle of claret in my head and tears in my eyes; for
I have just parted with my "Cornelian" who spent the evening with me.
As it was our last interview, I postponed my engagement to devote the
hours of the Sabbath to friendship:— Edleston and I have separated for
the present, and my mind is a chaos of hope and sorrow. To-morrow I set
out for London: you will address your answer to "Gordon's Hotel,
Albemarle Street," where I sojourn during my visit to the metropolis.
I rejoice to hear you are interested in my protégé; he has been my
almost constant associate since October, 1805, when I entered Trinity
College. His voice first attracted my attention, his countenance
fixed it, and his manners attached me to him for ever. He departs for
a mercantile house in town in October, and we shall probably not
meet till the expiration of my minority, when I shall leave to his
decision either entering as a partner through my interest, or residing
with me altogether. Of course he would in his present frame of mind
prefer the latter, but he may alter his opinion previous to that
period; — however, he shall have his choice. I certainly love him more
than any human being, and neither time nor distance have had the least
effect on my (in general) changeable disposition. In short, we shall,
put Lady E. Butler and Miss Ponsonby1 to the blush, Pylades and Orestes out of countenance, and want nothing but a catastrophe like Nisus and Euryalus, to give Jonathan and David the "go by." He
certainly is perhaps more attached to me than even I am in return.
During the whole of my residence at Cambridge we met every day, summer
and winter, without passing one tiresome moment, and separated each
time with increasing reluctance. I hope you will one day see us
together. He is the only being I esteem, though I like many.
The Marquis of Tavistock2 was down the other day; I supped with him
at his tutor's — entirely a Whig party. The opposition muster strong here
now, and Lord Hartington, the Duke of Leinster, etc., etc., are to join
us in October, so every thing will be splendid. The music is all
over at present. Met with another "accidency" — upset a butter-boat in
the lap of a lady — look'd very blue — spectators grinned — "curse
'em!" Apropos, sorry to say, been drunk every day, and not quite
sober yet — however, touch no meat, nothing but fish, soup, and
vegetables, consequently it does me no harm — sad dogs all the Cantabs.
Mem. — we mean to reform next January. This place is a monotony of
endless variety — like it — hate Southwell. Has Ridge sold well? or do
the ancients demur? What ladies have bought?
Saw a girl at St. Mary's the image of Anne — — 3, thought it was
her — all in the wrong — the lady stared, so did I — I blushed, so did not the lady, — sad thing — wish women had more modesty. Talking of
women, puts me in mind of my terrier Fanny — how is she? Got a headache,
must go to bed, up early in the morning to travel. My protégé
breakfasts with me; parting spoils my appetite — excepting from
Southwell. Mem. I hate Southwell.
Yours, etc.
Footnote 1: Lady Eleanor Butler (c. 1745-1829), sister of the
seventeenth Earl of Ormonde, and Sarah Ponsonby (circ. 1755-1831),
cousin of the Earl of Bessborough, were the two "Ladies of the Vale," or
"Ladies of Llangollen." About the year 1779 they settled in a cottage at
Plasnewydd, in the Vale of Llangollen, where they lived, with their
maidservant, Mary Caryll, for upwards of half a century. They are
buried, with their servant, in the churchyard of Plasnewydd, under a
triangular pyramid. Though they had withdrawn from the world, they
watched its proceedings with the keenest interest.
"If," writes Mrs. Piozzi, from Brynbella, July 9, 1796, "Mr. Bunbury's
Little Gray Man is printed, do send it hither; the ladies at
Llangollen are dying for it. They like those old Scandinavian tales
and the imitations of them exceedingly; and tell me about the prince
and princess of this loyal country, one province of which alone had
disgraced itself"
(Life and Writings of Mrs. Piozzi, vol. ii. p. 234). Nor did they
despise the theatre. Charles Mathews (Memoirs, vol. iii. pp. 150,
151), writing from Oswestry, September 4, 1820, says,
"The dear inseparable inimitables, Lady Butler and Miss Ponsonby, were
in the boxes here on Friday. They came twelve miles from Llangollen,
and returned, as they never sleep from home. Oh, such curiosities! I
was nearly convulsed.... As they are seated, there is not one point to
distinguish them from men; the dressing and powdering of the hair;
their well-starched neckcloths; the upper part of their habits, which
they always wear, even at a dinner-party, made precisely like men's
coats; and regular black beaver men's hats. They looked exactly like
two respectable superannuated old clergymen.... I was highly
flattered, as they never were in the theatre before."
Among the many people who visited them in their retreat, and have left
descriptions of them, are Madame de Genlis, De Quincey, Prince
Pückler-Muskau. Their friendships were sung by Sotheby and Anne Seward,
and their cottage was depicted by Pennant.
"It is very singular," writes
John Murray, August 24, 1829, to his son (Memoir of John Murray, vol.
ii. p. 304),
"that the ladies, intending to retire from the world, absolutely
brought all the world to visit them, for after a few years of
seclusion their strange story was the universal subject of
conversation, and there has been no person of rank, talent, and
importance in any way who did not procure introductions to them."
return to footnote mark
Footnote 2: Lord Tavistock's experience at Cambridge resembled that of
Byron. He had received only a "pretended education," and the Duke of
Bedford had come to the conclusion that "nothing was learned at English
Universities." "Tavistock left Cambridge in May," Lord J. Russell notes
in his Diary for 1808, "having been there in supposition two years"
(Walpole's Life of Lord John Russell, vol. i. pp. 44 and 35).
return
Footnote 3: Probably Miss Anne Houson, daughter of the Rev. Henry
Houson of Southwell. She married the Rev. Luke Jackson, died December
25, 1821, and is buried at Hucknall Torkard. (For verses addressed to
her, see Poems, vol. i. pp. 70-2, 244-45, 246-47, 251-52, 253.)
return
List of Letters
Gordon's Hotel, July 13, 1807.
You write most excellent epistles — a fig for other correspondents, with
their nonsensical apologies for "knowing nought about it" — you send me
a delightful budget. I am here in a perpetual vortex of dissipation
(very pleasant for all that), and, strange to tell, I get thinner, being
now below eleven stone considerably. Stay in town a month, perhaps six
weeks, trip into Essex, and then, as a favour, irradiate Southwell for
three days with the light of my countenance; but nothing shall ever make
me reside there again. I positively return to Cambridge in October; we
are to be uncommonly gay, or in truth I should cut the University. An
extraordinary circumstance occurred to me at Cambridge; a girl so very
like — — made her appearance, that nothing but the most minute
inspection could have undeceived me. I wish I had asked if she had
ever been at H — —
What the devil would Ridge have? is not fifty in a fortnight, before the
advertisements, a sufficient sale1? I hear many of the London
booksellers have them, and Crosby2 has sent copies to the principal
watering places. Are they liked or not in Southwell?
...
I wish
Boatswain had swallowed Damon! How is Bran? by the immortal gods, Bran
ought to be a Count of the Holy Roman Empire.
The intelligence of London cannot be interesting to you, who have
rusticated all your life — the annals of routs riots, balls and
boxing-matches, cards and crim. cons., parliamentary discussion,
political details, masquerades, mechanics, Argyle Street Institution and
aquatic races, love and lotteries, Brookes's and Buonaparte,
opera-singers and oratorios, wine, women, wax-work, and weathercocks,
can't accord with your insulated ideas of decorum and other silly
expressions not inserted in our vocabulary.
Oh! Southwell, Southwell, how I rejoice to have left thee, and how I
curse the heavy hours I dragged along, for so many months, among the
Mohawks who inhabit your kraals! — However, one thing I do not regret,
which is having pared off a sufficient quantity of flesh to enable me
to slip into "an eel-skin," and vie with the slim beaux of modern
times; though I am sorry to say, it seems to be the mode amongst
gentlemen to grow fat, and I am told I am at least fourteen pound
below the fashion. However, I decrease instead of enlarging, which is
extraordinary, as violent exercise in London is impracticable; but I
attribute the phenomenon to our evening squeezes at public and
private parties. I heard from Ridge this morning (the 14th, my letter
was begun yesterday): he says the poems go on as well as can be wished;
the seventy-five sent to town are circulated, and a demand for fifty
more complied with, the day he dated his epistle, though the
advertisements are not yet half published. Adieu.
P.S. — Lord Carlisle, on receiving my poems, sent, before he opened the
book, a tolerably handsome letter3:— I have not heard from him since.
His opinions I neither know nor care about: if he is the least insolent,
I shall enrol him with Butler and the other worthies. He is in
Yorkshire, poor man! and very ill! He said he had not had time to read
the contents, but thought it necessary to acknowledge the receipt of the
volume immediately. Perhaps the Earl "bears no brother near the
throne" — if so, I will make his sceptre totter in his
hands. — Adieu!
Footnote 1: : This is probably the third collection of early verse,
Hours of Idleness, the first collection published with Byron's name
(see page 104, note 1).
return to footnote mark
Footnote 2: B. Crosby & Co., of Stationers' Court, were the London
agents of Ridge, the Newark bookseller. Crosby was also the publisher of
a magazine called Monthly Literary Recreations, in which (July, 1807)
appeared a highly laudatory notice of Hours of Idleness, and Byron's
review of Wordsworth's Poems (2 vols. 1807. See Appendix I), and his
"Stanzas to Jessy" (see Poems, vol. i. pp. 234-236). These lines were
enclosed with the following letter, addressed to "Mr. Crosby,
Stationers' Court:" —
"July 21, 1807.
Sir, — I have sent according to my promise some Stanzas for
Literary Recreations. The insertion I leave to the option of the
Editors. They have never appeared before. I should wish to
know whether they are admitted or not, and when the work will
appear, as I am desirous of a copy.
Etc., etc.,
Byron.
P.S. — Send your answer when convenient."
return
cross-reference: return to Footnote 1 of Letter 78
Footnote 3:
"My Dear Lord, — Your letter of yesterday found me an invalid, and
unable to do justice to your poems by a dilligent [sic] perusal of
them. In the meantime I take the first occasion to thank you for
sending them to me, and to express a sincere satisfaction in finding
you employ your leisure in such occupations. Be not disconcerted if
the reception of your works should not be that you may have a right to
look for from the public. Persevere, whatever that reception may be,
and tho' the Public maybe found very fastidious, ... you will stand
better with the world than others who only pursue their studies in
Bond St. or at Tatershall's.
Believe me to be, yours most sincerely,
Carlisle.
July 8th, 1807."
return
List of Letters
July 20th, 1807.
Sir, — Your proposal to make Mrs. Byron my Treasurer is very kind,
but does not meet with my approbation. Mrs. Byron has already made more
free with my funds than suits my convenience & I do not
chuse to expose her to the Danger of Temptation.
Things will therefore stand as they are; the remedy would be worse than
the Disease.
I wish you would order your Drafts payable to me and not Mrs. B. This is
worse than Hannibal Higgins1; who the Devil could suppose that any
Body would have mistaken him for a real personage? & what earthly
consequence could it be whether the Blank in the Draft was filled up
with Wilkins, Tomkyns, Simkins, Wiggins, Spriggins, Jiggins, or
Higgins? If I had put in James Johnson you would not have
demurred, & why object to Hannibal Higgins? particularly after his
respectable Endorsements. As to Business, I make no pretensions
to a Knowledge of any thing but a Greek Grammer or a Racing Calendar;
but if the Quintessence of information on that head consists in
unnecessary & unpleasant delays, explanations, rebuffs, retorts,
repartees, & recriminations, the House of H. & B. stands pre-eminent in
the profession, as from the Bottom of his Soul testifies
Yours, etc., etc.,
Byron.
P.S — Will you dine with me on Sunday Tête a Tête at six o'clock? I
should be happy to see you before, but my Engagements will not permit
me, as on Wednesday I go to the House. I shall have Hargreaves & his
Brother on some day after you; I don't like to annoy Children with the
formal Faces of legal papas.
Footnote 1: The point of the allusion is that Byron had endorsed one of
Hanson's drafts with the name of "Hannibal Higgins," and had
been solemnly warned of the consequences of so tampering with the
dignity of the law.
return to footnote mark
List of Letters
August 2, 1807.
London begins to disgorge its contents — town is empty — consequently I
can scribble at leisure, as occupations are less numerous. In a
fortnight I shall depart to fulfil a country engagement; but expect two
epistles from you previous to that period. Ridge does not proceed
rapidly in Notts — very possible. In town things wear a more promising
aspect, and a man whose works are praised by reviewers, admired by
duchesses, and sold by every bookseller of the metropolis, does not
dedicate much consideration to rustic readers. I have now a review
before me, entitled Literary Recreations1 where my hardship is
applauded far beyond my deserts. I know nothing of the critic, but think
him a very discerning gentleman, and myself a devilish clever
fellow. His critique pleases me particularly, because it is of great
length, and a proper quantum of censure is administered, just to give an
agreeable relish to the praise. You know I hate insipid, unqualified,
common-place compliment. If you would wish to see it, order the 13th
Number of Literary Recreations for the last month. I assure you I have
not the most distant idea of the writer of the article — it is printed in
a periodical publication — and though I have written a paper (a review of
Wordsworth), which appears in the same work, I am ignorant of every
other person concerned in it — even the editor, whose name I have not
heard. My cousin, Lord Alexander Gordon, who resided in the same hotel,
told me his mother, her Grace of Gordon2, requested he would
introduce my Poetical Lordship to her Highness, as she had bought my
volume, admired it exceedingly, in common with the rest of the
fashionable world, and wished to claim her relationship with the author.
I was unluckily engaged on an excursion for some days afterwards; and,
as the Duchess was on the eve of departing for Scotland, I have
postponed my introduction till the winter, when I shall favour the lady,
whose taste I shall not dispute, with my most sublime and edifying
conversation. She is now in the Highlands, and Alexander took his
departure, a few days ago, for the same blessed seat of "dark rolling
winds."
Crosby, my London publisher, has disposed of his second importation, and
has sent to Ridge for a third — at least so he says. In every
bookseller's window I see my own name, and say nothing,
but enjoy my fame in secret. My last reviewer kindly requests me to
alter my determination of writing no more: and "A Friend to the Cause
of Literature" begs I will gratify the public with some
new work "at no very distant period." Who would not be a bard? — that is
to say, if all critics would be so polite. However, the others will pay
me off, I doubt not, for this gentle encouragement. If so, have
at 'em? By the by, I have written at my intervals of leisure, after two
in the morning, 380 lines in blank verse, of Bosworth Field. I have
luckily got Hutton's account3. I shall extend the poem to eight or ten
books, and shall have finished it in a year. Whether it will be
published or not must depend on circumstances. So much for
egotism! My laurels have turned my brain, but the
cooling acids of forthcoming criticism will probably restore me
to modesty.
Southwell is a damned place — I have done with it — at least in all
probability; excepting yourself, I esteem no one within its precincts.
You were my only rational companion; and in plain truth, I had
more respect for you than the whole bevy, with whose foibles I
amused myself in compliance with their prevailing propensities. You gave
yourself more trouble with me and my manuscripts than a thousand
dolls would have done.
Believe me, I have not forgotten your good nature in this circle
of sin, and one day I trust I shall be able to evince my
gratitude. Adieu.
Yours, etc.
P.S. — Remember me to Dr. P.
Footnote 1: See page 137, note 2.
return to footnote mark
Footnote 2: The Duchess of Gordon (1748-1812), née Jean Maxwell of
Monreith, daughter of Sir W. Maxwell, Bart., married in 1767 the Duke of
Gordon. The most successful matchmaker of the age, she married three of
her daughters to three dukes — Manchester, Richmond, and Bedford. A
fourth daughter was Lady Mandalina Sinclair, afterwards, by a second
marriage, Lady Mandalina Palmer. A fifth was married to Lord Cornwallis
(see the extraordinary story told in the Recollections of Samuel
Rogers, pp. 145-146). According to Wraxall (Posthumous Memoirs, vol.
ii. p. 319), she schemed to secure Pitt for her daughter Lady Charlotte,
and Eugène Beauharnais for Lady Georgiana, afterwards Duchess of
Bedford. Cyrus Redding (Memoirs of William Beckford, vol. ii. pp.
337-339) describes her attack upon the owner of Fonthill, where she
stayed upwards of a week, magnificently entertained, without once seeing
the wary master of the house.
She was also the social leader of the Tories, and her house in Pall
Mall, rented from the Duke of Buckingham, was the meeting-place of the
party. Malcontents accused her of using her power tyrannically:—
"Not Gordon's broad and brawny Grace,
The last new Woman in the Place
With more contempt could blast."
Pandolfo Attonito.
(1800).
Lord Alexander Gordon died in 1808.
return
Footnote 3: William Hutton (1723-1815), a Birmingham bookseller, who
took to literature and became a voluminous writer of poems, and of
topographical works which still have their value. In his Trip to
Redcar and Coatham (Preface, p. vi.) he says,
"I took up my pen
at the advanced age of fifty-six ... I drove the quill thirty
years, during which time I wrote and published thirty books."
The Battle of Bosworth Field was published in 1788. A new
edition, with additions by John Nichols, appeared in 1813. Byron's
poem was never published.
return
List of Letters
London, August 11, 1807.
On Sunday next I set off for the Highlands1. A friend of mine
accompanies me in my carriage to Edinburgh. There we shall leave it, and
proceed in a tandem (a species of open carriage) though the
western passes to Inverary, where we shall purchase shelties, to
enable us to view places inaccessible to vehicular conveyances.
On the coast we shall hire a vessel, and visit the most remarkable of
the Hebrides; and, if we have time and favourable weather, mean to sail
as far as Iceland, only 300 miles from the northern extremity of
Caledonia, to peep at Hecla. This last intention you will keep a
secret, as my nice mamma would imagine I was on a Voyage of
Discovery, and raised the accustomed maternal warwhoop.
Last week I swam in the Thames from Lambeth through the two bridges,
Westminster and Blackfriars, a distance, including the different turns
and tracks made on the way, of three miles2! You see I am in
excellent training in case of a squall at sea. I mean to collect
all the Erse traditions, poems, etc., etc., and translate, or expand the
subject to fill a volume, which may appear next spring under the
denomination of "The Highland Harp" or some title equally
picturesque. Of Bosworth Field, one book is finished, another
just began. It will be a work of three or four years, and most probably
never conclude. What would you say to some stanzas on Mount
Hecla? they would be written at least with fire. How is the
immortal Bran? and the Phoenix of canine quadrupeds, Boatswain? I have
lately purchased a thorough-bred bull-dog, worthy to be the coadjutor of
the aforesaid celestials — his name is Smut!
"Bear it, ye breezes,
on your balmy wings."
Write to me before I set off, I conjure you, by the fifth rib of your
grandfather. Ridge goes on well with the books — I thought that worthy
had not done much in the country. In town they have been very
successful; Carpenter (Moore's publisher) told me a few days ago they
sold all their's immediately, and had several enquiries made since,
which, from the books being gone, they could not supply. The Duke of
York, the Marchioness of Headfort, the Duchess of Gordon, etc., etc.,
were among the purchasers; and Crosby says the circulation will be still
more extensive in the winter, the summer season being very bad for a
sale, as most people are absent from London. However, they have gone off
extremely well altogether. I shall pass very near you on my journey
through Newark, but cannot approach. Don't tell this to Mrs. B, who
supposes I travel a different road. If you have a letter, order it to be
left at Ridge's shop, where I shall call, or the post-office, Newark,
about six or eight in the evening. If your brother would ride over, I
should be devilish glad to see him — he can return the same night, or sup
with us and go home the next morning — the Kingston Arms is my inn.
Adieu.
Yours ever,
Byron.
Footnote 1: This projected trip to the Highlands, mentioned in his
letter to Augusta Byron of August 30, 1805, seems to have become a joke
among Byron's friends. Moore quotes (Life, p. 56) a letter
written by Miss Pigot to her brother:
"How can you ask if Lord B. is going to visit the Highlands in the
summer? Why, don't you know that he never knows his own mind
for ten minutes together? I tell him he is as fickle as the winds, and
as uncertain as the waves."
return to footnote mark
Footnote 2:
"The first time I saw Lord Byron," says Leigh Hunt (Lord Byron and
his Contemporaries, p. 1), "he was rehearsing the part of Leander,
under the auspices of Mr. Jackson the prize-fighter. It was in the
river Thames, before he went to Greece. I had been bathing, and was
standing on the floating machine adjusting my clothes, when I noticed
a respectable-looking manly person who was eyeing something at a
distance. This was Mr. Jackson waiting for his pupil. The latter was
swimming with somebody for a wager."
On this occasion, however, Hunt only saw "his Lordship's head bob up and
down in the water, like a "buoy."
return
List of Letters
Dorant's Hotel, October 19th, 1807.
Dear Hanson, — I will thank you to disburse the quarter due as soon as
possible, for I am at this moment contemplating with woeful visage, one
solitary Guinea, two bad sixpences and a shilling, being
all the cash at present in possession of
Yours very truly,
Byron.
List of Letters
Trinity College, Cambridge, October 26, 1807.
My Dear Elizabeth, — Fatigued with sitting up till four in the morning
for the last two days at hazard, I take up my pen to inquire how your
highness and the rest of my female acquaintance at the seat of
archiepiscopal grandeur go on. I know I deserve a scolding for my
negligence in not writing more frequently; but racing up and down the
country for these last three months, how was it possible to fulfil the
duties of a correspondent? Fixed at last for six weeks, I write, as
thin as ever (not having gained an ounce since my reduction), and
rather in better humour; — but, after all, Southwell was a detestable
residence. Thank St. Dominica, I have done with it: I have been twice
within eight miles of it, but could not prevail on myself to
suffocate in its heavy atmosphere. This place is wretched
enough — a villainous chaos of din and drunkenness, nothing but hazard
and burgundy, hunting, mathematics, and Newmarket, riot and racing. Yet
it is a paradise compared with the eternal dulness of Southwell. Oh! the
misery of doing nothing but make love, enemies, and
verses.
Next January (but this is entre nous only, and pray let it be so,
or my maternal persecutor will be throwing her tomahawk at any of my
curious projects,) I am going to sea for four or five months,
with my cousin Captain Bettesworth1, who commands the Tartar,
the finest frigate in the navy. I have seen most scenes, and wish to
look at a naval life. We are going probably to the Mediterranean, or to
the West Indies, or — to the devil; and if there is a possibility of
taking me to the latter, Bettesworth will do it; for he has received
four and twenty wounds in different places, and at this moment possesses
a letter from the late Lord Nelson, stating Bettesworth as the only
officer in the navy who had more wounds than himself.
I have got a new friend, the finest in the world, a tame bear2.
When I brought him here, they asked me what I meant to do with him, and
my reply was, "he should sit for a fellowship." Sherard will
explain the meaning of the sentence, if it is ambiguous. This answer
delighted them not. We have several parties here, and this evening a
large assortment of jockeys, gamblers, boxers, authors, parsons, and
poets, sup with me, — a precious mixture, but they go on well together;
and for me, I am a spice of every thing except a jockey; by the
bye, I was dismounted again the other day.
Thank your brother in my name for his treatise. I have written 214 pages
of a novel — one poem of 380 lines3, to be published (without my name)
in a few weeks, with notes, — 560 lines of Bosworth Field, and 250 lines
of another poem in rhyme, besides half a dozen smaller pieces. The poem
to be published is a Satire. Apropos, I have been praised to the
skies in the Critical Review4, and abused greatly in another
publication5. So much the better, they tell me, for the sale of the
book: it keeps up controversy, and prevents it being forgotten. Besides,
the first men of all ages have had their share, nor do the humblest
escape; — so I bear it like a philosopher. It is odd two opposite
critiques came out on the same day, and out of five pages of abuse, my
censor only quotes two lines from different poems, in support of his
opinion. Now, the proper way to cut up, is to quote long passages, and
make them appear absurd, because simple allegation is no proof. On the
other hand, there are seven pages of praise, and more than my modesty will allow said on the subject. Adieu.
P.S. — Write, write, write!!!
Footnote 1: George Edmund Byron Bettesworth (1780-1808), as lieutenant
of the Centaur, was wounded (1804) in the capture of the
Curieux. In command of the latter vessel he captured the Dame Ernouf (1805), and was again wounded. He was made a post-captain in
the latter year, when he brought home despatches from Nelson at Antigua,
announcing Villeneuve's return to Europe. He was killed off Bergen in
1808, while in command of the Tartar. Captain Bettesworth, whose
father assumed the name of Bettesworth in addition to that of Trevanion,
married, in 1807, Lady Alethea Grey, daughter of Earl Grey. Through his
grandmother, Sophia Trevanion, Byron was Captain Bettesworth's cousin.
return to footnote mark
Footnote 2: See Poems, vol. i. p. 406.
return
Footnote 3: This poem, printed in book form, but not published, under
the title of British Bards, is the foundation of English
Bards, and Scotch Reviewers. The MS. is in the possession of Mr.
Murray.
return
Footnote 4: For September, 1807. In noticing the Elegy on Newstead
Abbey, the writer says, "We could not but hail, with something of
prophetic rapture, the hope conveyed in the closing stanza:—
"'Haply thy sun, emerging, yet may shine,
Thee to irradiate with meridian ray.'"
return
Footnote 5: The first number of The Satirist: A Monthly Meteor
(October, 1807).
return
List of Letters
Trinity College, Cambridge, November 20, 1807.
Sir, — I am happy to hear every thing goes on so well, and I presume you
will soon commence, though I am still of opinion the first Edition had
better be entirely sold, before you risk the printing of a second. As
Curly recommends fine wove Foolscap, let it be used, and I will order a
design in London for a plate, my own portrait would perhaps be best, but
as that would take up so long a time in completing we will substitute
probably a view of Harrow1, or Newstead in its stead.
You will omit the poems mentioned below:
Stanzas on a view of Harrow.
To a Quaker.
The First Kiss of Love.
College Examinations.
Lines to the Rev. J. T. Becher.
To be inserted, not exactly in the place, but in different parts of the
volume, I will send you five poems never yet published. Two of tolerable
length, at least much longer than any of the above, which are ordered to
be omitted.
Mention in your answer when you would like to receive the manuscripts
that they may be sent. By the bye, I must have the proofs of the
Manuscripts sent to Cambridge as they occur; the proofs from the printed
copy you can manage with care, if Mr. Becher will assist you. Attend to
the list of Errata, that we may not have a Second Edition
of them also.
The Preface we have done with, perhaps I may send an Advertisement, a
dedication shall be forthcoming in due Season.
You will send a proof of the first Sheet for Inspection, and soon too,
for I am about to set out for London next week. If I remain there any
time, I shall apprize you where to send the Manuscript Proofs.
Do you think the others will be sold before the next are ready, what
says Curly? remember I have advised you not to risk it a second time,
and it is not too late to retract. However, you must abide by your own
discretion:
Etc., etc.,
Byron.
P.S. — You will print from the Copy I sent you with the alterations, pray
attend to these, and be careful of mistakes. In my last I gave you
directions concerning the Title page and Mottoes.
Footnote 1: A view of Harrow was given.
return to footnote mark
List of Letters
Trin. Coll., Cambridge, Dec. 2nd, 1807.
My Dear Sir, — I hope to take my New Years Day dinner with you en
famille. Tell Hargreaves I will bring his Blackstones, and shall
have no objection to see my Daniel's Field Sports, if they have
not escaped his recollection. — I certainly wish the expiration of my
minority as much as you do, though for a reason more nearly affecting my
magisterial person at this moment, namely, the want of twenty pounds,
for no spendthrift peer, or unlucky poet, was ever less indebted to
Cash than George Gordon is at present, or is more likely to
continue in the same predicament. — My present quarter due on the 25th
was drawn long ago, and I must be obliged to you for the loan of twenty
on my next, to be deducted when the whole becomes tangible, that is,
probably, some months after it is exhausted. Reserve Murray's
quarter1, of course, and I shall have just £100 to receive at
Easter, but if the risk of my demand is too great, inform me, that I may
if possible convert my Title into cash, though I am afraid twenty pounds
will be too much to ask as Times go, if I were an Earl ... but a Barony
must fetch ten, perhaps fifteen, and that is something when we have not
as many pence. Your answer will oblige
Yours very truly,
Byron.
P.S. — Remember me to Mrs. H. in particular, and the family in general.
Footnote 1: Joe Murray. (See page 21, note 3.)
return to footnote mark
cross-reference: return to Footnote 4 of Letter 7
List of Letters
84 — To John Murray1
Ravenna, 9bre 19, 1820.
What you said of the late Charles Skinner Matthews2 has set me to my
recollections; but I have not been able to turn up any thing which would
do for the purposed Memoir of his brother, — even if he had previously
done enough during his life to sanction the introduction of anecdotes so
merely personal. He was, however, a very extraordinary man, and would
have been a great one. No one ever succeeded in a more surpassing degree
than he did as far as he went. He was indolent, too; but whenever he
stripped, he overthrew all antagonists. His conquests will be found
registered at Cambridge, particularly his Downing one, which was
hotly and highly contested, and yet easily won. Hobhouse was his
most intimate friend, and can tell you more of him than any man. William
Bankes3 also a great deal. I myself recollect more of his oddities
than of his academical qualities, for we lived most together at a very
idle period of my life. When I went up to Trinity, in 1805, at
the age of seventeen and a half, I was miserable and untoward to a
degree. I was wretched at leaving Harrow, to which I had become attached
during the two last years of my stay there; wretched at going to
Cambridge instead of Oxford (there were no rooms vacant at
Christchurch); wretched from some private domestic circumstances of
different kinds, and consequently about as unsocial as a wolf taken from
the troop. So that, although I knew Matthews, and met him often then at Bankes's, (who was my collegiate pastor, and master, and patron,) and
at Rhode's, Milnes's, Price's, Dick's, Macnamara's, Farrell's, Gally
Knight's, and others of that set of contemporaries, yet I was neither
intimate with him nor with any one else, except my old schoolfellow
Edward Long4 (with whom I used to pass the day in riding and
swimming), and William Bankes, who was good-naturedly tolerant of my
ferocities.
It was not till 1807, after I had been upwards of a year away from
Cambridge, to which I had returned again to reside for my degree, that
I became one of Matthews's familiars, by means of Hobhouse5, who,
after hating me for two years, because I wore a white hat, and a grey coat, and rode a grey horse (as he says himself), took me into
his good graces because I had written some poetry. I had always lived a
good deal, and got drunk occasionally, in their company — but now we
became really friends in a morning. Matthews, however, was not at this
period resident in College. I met him chiefly in London, and at
uncertain periods at Cambridge. Hobhouse, in the mean time, did great
things: he founded the Cambridge "Whig Club" (which he seems to have
forgotten), and the "Amicable Society," which was dissolved in
consequence of the members constantly quarrelling, and made himself very
popular with "us youth," and no less formidable to all tutors,
professors, and heads of Colleges. William Bankes was gone; while he
stayed, he ruled the roast — or rather the roasting — and was father of
all mischiefs.
Matthews and I, meeting in London, and elsewhere, became great cronies.
He was not good tempered — nor am I — but with a little tact his temper
was manageable, and I thought him so superior a man, that I was willing
to sacrifice something to his humours, which were often, at the same
time, amusing and provoking. What became of his papers (and he
certainly had many), at the time of his death, was never known. I
mention this by the way, fearing to skip it over, and as he
wrote remarkably well, both in Latin and English. We went down to
Newstead together6, where I had got a famous cellar, and
Monks' dresses from a masquerade warehouse. We were a company of
some seven or eight, with an occasional neighbour or so for visiters,
and used to sit up late in our friars' dresses, drinking burgundy,
claret, champagne, and what not, out of the skull-cup, and all
sorts of glasses, and buffooning all round the house, in our conventual
garments7. Matthews always denominated me "the Abbot," and never
called me by any other name in his good humours, to the day of his
death. The harmony of these our symposia was somewhat interrupted, a few
days after our assembling, by Matthews's threatening to throw Hobhouse
out of a window, in consequence of I know not what commerce of
jokes ending in this epigram. Hobhouse came to me and said, that "his
respect and regard for me as host would not permit him to call out any
of my guests, and that he should go to town next morning." He did. It
was in vain that I represented to him that the window was not high, and
that the turf under it was particularly soft. Away he went.
Matthews and myself had travelled down from London together, talking all
the way incessantly upon one single topic. When we got to Loughborough,
I know not what chasm had made us diverge for a moment to some other
subject, at which he was indignant. "Come," said he, "don't let us break
through — let us go on as we began, to our journey's end;" and so he
continued, and was as entertaining as ever to the very end. He had
previously occupied, during my year's absence from Cambridge, my rooms
in Trinity, with the furniture; and Jones8, the tutor, in his odd way,
had said, on putting him in,
"Mr. Matthews, I recommend to your
attention not to damage any of the moveables, for Lord Byron, Sir, is a
young man of tumultuous passions."
Matthews was delighted with
this; and whenever anybody came to visit him, begged them to handle the
very door with caution; and used to repeat Jones's admonition in his
tone and manner. There was a large mirror in the room, on which he
remarked, "that he thought his friends were grown uncommonly assiduous
in coming to see him, but he soon discovered that they only came
to see themselves." Jones's phrase of "tumultuous
passions" and the whole scene, had put him into such good humour,
that I verily believe that I owed to it a portion of his good graces.
When at Newstead, somebody by accident rubbed against one of his white
silk stockings, one day before dinner; of course the gentleman
apologised.
"Sir," answered Matthews, "it may be all very well for you,
who have a great many silk stockings, to dirty other people's; but to
me, who have only this one pair, which I have put on in honour of
the Abbot here, no apology can compensate for such carelessness;
besides, the expense of washing."
He had the same sort of droll sardonic
way about every thing. A wild Irishman, named Farrell, one evening began
to say something at a large supper at Cambridge, Matthews roared out
"Silence!" and then, pointing to Farrell, cried out, in the words of the
oracle, "Orson is endowed with reason." You may easily suppose that
Orson lost what reason he had acquired, on hearing this compliment. When
Hobhouse published his volume of poems, the Miscellany (which Matthews
would call the "Miss-sell-any"), all that could be drawn from him was,
that the preface was "extremely like Walsh." Hobhouse thought this at
first a compliment; but we never could make out what it was9, for all
we know of Walsh is his Ode to King William10, and Pope's epithet of
"knowing Walsh."11 When the Newstead party broke up for London,
Hobhouse and Matthews, who were the greatest friends possible, agreed,
for a whim, to walk together to town. They quarrelled by the way, and
actually walked the latter half of the journey, occasionally passing and
repassing, without speaking. When Matthews had got to Highgate, he had
spent all his money but three-pence halfpenny, and determined to spend
that also in a pint of beer, which I believe he was drinking before a
public-house, as Hobhouse passed him (still without speaking) for the
last time on their route. They were reconciled in London again.
One of Matthews's passions was "the fancy;" and he sparred uncommonly
well. But he always got beaten in rows, or combats with the bare fist.
In swimming, too, he swam well; but with effort and labour, and too
high out of the water; so that Scrope Davies12 and myself, of whom he
was therein somewhat emulous, always told him that he would be drowned
if ever he came to a difficult pass in the water. He was so; but surely
Scrope and myself would have been most heartily glad that
"the Dean had lived,
And our prediction proved a lie."
His head was uncommonly handsome, very like what Pope's was in his
youth.
His voice, and laugh, and features, are strongly resembled by his
brother Henry's, if Henry be he of King's College. His passion for
boxing was so great, that he actually wanted me to match him with
Dogherty13 (whom I had backed and made the match for against Tom
Belcher14), and I saw them spar together at my own lodgings with the
gloves on. As he was bent upon it, I would have backed Dogherty to
please him, but the match went off. It was of course to have been a
private fight, in a private room.
On one occasion, being too late to go home and dress, he was equipped by
a friend (Mr. Baillie, I believe,) in a magnificently fashionable and
somewhat exaggerated shirt and neckcloth. He proceeded to the Opera, and
took his station in Fop's Alley. During the interval between the opera
and the ballet, an acquaintance took his station by him and saluted him:
"Come round," said Matthews, "come round."
"Why should I come round?"
said the other; "you have only to turn your head — I am close by
you."
"That is exactly what I cannot do," said Matthews; "don't you see
the state I am in?"
pointing to his buckram shirt collar and inflexible
cravat, — and there he stood with his head always in the same
perpendicular position during the whole spectacle.
One evening, after dining together, as we were going to the Opera, I
happened to have a spare Opera ticket (as subscriber to a box), and
presented it to Matthews.
"Now, sir," said he to Hobhouse afterwards,
"this I call courteous in the Abbot — another man would never have
thought that I might do better with half a guinea than throw it to a
door-keeper; — but here is a man not only asks me to dinner, but gives me
a ticket for the theatre."
These were only his oddities, for no man was
more liberal, or more honourable in all his doings and dealings, than
Matthews. He gave Hobhouse and me, before we set out for Constantinople,
a most splendid entertainment, to which we did ample justice. One of his
fancies was dining at all sorts of out-of-the-way places. Somebody
popped upon him in I know not what coffee-house in the Strand — and what
do you think was the attraction? Why, that he paid a shilling (I think)
to dine with his hat on. This he called his "hat house," and used to
boast of the comfort of being covered at meal times.
When Sir Henry Smith15 was expelled from Cambridge for a row with a
tradesman named "Hiron," Matthews solaced himself with shouting under
Hiron's windows every evening,
"Ah me! what perils do environ
The man who meddles with hot Hiron."
He was also of that band of profane scoffers who, under the auspices of
— — , used to rouse Lort Mansel (late Bishop of Bristol) from his
slumbers in the lodge of Trinity; and when he appeared at the window
foaming with wrath, and crying out, "I know you, gentlemen, I know you!"
were wont to reply, "We beseech thee to hear us, good Lort!" — "Good Lort
deliver us!" (Lort was his Christian name.) As he was very free in his
speculations upon all kinds of subjects, although by no means either
dissolute or intemperate in his conduct, and as I was no less
independent, our conversation and correspondence used to alarm our
friend Hobhouse to a considerable degree.
You must be almost tired of my packets, which will have cost a mint of
postage.
Salute Gifford and all my friends.
Yours, etc.
Footnote 1: This letter, though written twelve years later, belongs to the
Cambridge period of Byron's life. It is therefore introduced here.
(For John Murray, see note to letter to R. C. Dallas of August
21, 1811.)
return to footnote mark
Footnote 2: Charles Skinner Matthews was known at Eton as Matthews
major, his minor being his brother Henry, the author of
The Diary of an Invalid, afterwards a Judge in the Supreme Court
of Ceylon, who died in 1828. They were the sons of John Matthews of
Belmont, Herefordshire, M.P. for that county (1802-6). C. S. Matthews
became a Scholar of Trinity, Cambridge; Ninth Wrangler in 1805; First
Members' Prizeman in 1807; Fellow of Downing in 1808. He was drowned in
the Cam in August, 1811. He at the time contemplated standing as Member
for the University of Cambridge. For a description of the accident, see
letter from Henry Drury to Francis Hodgson (Life of the Rev. Francis
Hodgson, vol. i. pp. 182-185). In the note to Childe Harold,
Canto I. stanza xci., Byron speaks of Matthews:
"I should have ventured a verse to the memory of the late Charles
Skinner Matthews, Fellow of Downing College, Cambridge, were he not
too much above all praise of mine. His powers of mind, shown in the
attainment of greater honours, against the ablest candidates, than
those of any graduate on record at Cambridge, have sufficiently
established his fame on the spot where it was acquired; while his
softer qualities live in the recollection of friends who loved him too
well to envy his superiority."
return
cross-reference: return to Footnote 1 of Letter 161
Footnote 3: See page 120, note 1.
return
Footnote 4: See page 73, note 2.
return
Footnote 5: See page 163, note 1.
return
Footnote 6: Of this visit to Newstead, Matthews wrote the following account
to his sister:—
"London, May 22, 1809.
My Dear — — , — I must begin with giving you a few particulars of the
singular place which I have lately quitted.
Newstead Abbey is situate 136 miles from London, — four on this side
Mansfield. It is so fine a piece of antiquity, that I should think
there must be a description, and, perhaps, a picture of it in Grose.
The ancestors of its present owner came into possession of it at the
time of the dissolution of the monasteries, — but the building itself
is of a much earlier date. Though sadly fallen to decay, it is still
completely an abbey, and most part of it is still standing in the
same state as when it was first built. There are two tiers of
cloisters, with a variety of cells and rooms about them, which, though
not inhabited, nor in an inhabitable state, might easily be made so;
and many of the original rooms, amongst which is a fine stone hall,
are still in use. Of the abbey church only one end remains; and the
old kitchen, with a long range of apartments, is reduced to a heap of
rubbish. Leading from the abbey to the modern part of the habitation
is a noble room, seventy feet in length, and twenty-three in breadth;
but every part of the house displays neglect and decay, save those
which the present Lord has lately fitted up.
The house and gardens are entirely surrounded by a wall with
battlements. In front is a large lake, bordered here and there with
castellated buildings, the chief of which stands on an eminence at the
further extremity of it. Fancy all this surrounded with bleak and
barren hills, with scarce a tree to be seen for miles, except a
solitary clump or two, and you will have some idea of Newstead. For
the late Lord, being at enmity with his son, to whom the estate was
secured by entail, resolved, out of spite to the same, that the estate
should descend to him in as miserable a plight as he could possibly
reduce it to; for which cause, he took no care of the mansion, and
fell to lopping of every tree he could lay his hands on, so furiously,
that he reduced immense tracts of woodland country to the desolate
state I have just described. However, his son died before him, so that
all his rage was thrown away.
So much for the place, concerning which I have thrown together these
few particulars, meaning my account to be, like the place itself,
without any order or connection. But if the place itself appear rather
strange to you, the ways of the inhabitants will not appear much less
so. Ascend, then, with me the hall steps, that I may introduce you to
my Lord and his visitants. But have a care how you proceed; be mindful
to go there in broad daylight, and with your eyes about you. For,
should you make any blunder, — should you go to the right of the hall
steps, you are laid hold of by a bear; and should you go to the left,
your case is still worse, for you run full against a wolf! — Nor, when
you have attained the door, is your danger over; for the hall being
decayed, and therefore standing in need of repair, a bevy of inmates
are very probably banging at one end of it with their pistols; so that
if you enter without giving loud notice of your approach, you have
only escaped the wolf and the bear to expire by the pistol-shots of
the merry monks of Newstead.
Our party consisted of Lord Byron and four others, and was, now and
then, increased by the presence of a neighbouring parson. As for our
way of living, the order of the day was generally this:— for
breakfast we had no set hour, but each suited his own convenience,
— everything remaining on the table till the whole party had done;
though had one wished to breakfast at the early hour of ten, one would
have been rather lucky to find any of the servants up. Our average
hour of rising was one. I, who generally got up between eleven and
twelve, was always, — even when an invalid, — the first of the party,
and was esteemed a prodigy of early rising. It was frequently past two
before the breakfast party broke up. Then, for the amusements of the
morning, there was reading, fencing, single-stick, or shuttle-cock, in
the great room; practising with pistols in the hall;
walking — riding — cricket — sailing on the lake, playing with the bear,
or teasing the wolf. Between seven and eight we dined; and our evening
lasted from that time till one, two, or three in the morning. The
evening diversions may be easily conceived.
I must not omit the custom of handing round, after dinner, on the
removal of the cloth, a human skull filled with burgundy. After
revelling on choice viands, and the finest wines of France, we
adjourned to tea, where we amused ourselves with reading, or improving
conversation, — each, according to his fancy, — and, after sandwiches,
etc., retired to rest. A set of monkish dresses, which had been
provided, with all the proper apparatus of crosses, beads, tonsures,
etc., often gave a variety to our appearance, and to our pursuits.
"You may easily imagine how chagrined I was at being ill nearly the
first half of the time I was there. But I was led into a very
different reflection from that of Dr. Swift, who left Pope's house
without ceremony, and afterwards informed him, by letter, that it was
impossible for two sick friends to live together; for I found my
shivering and invalid frame so perpetually annoyed by the thoughtless
and tumultuous health of every one about me, that I heartily wished
every soul in the house to be as ill as myself.
"The journey back I performed on foot, together with another of the
guests. We walked about twenty-five miles a day; but were a week on
the road, from being detained by the rain. So here I close my account
of an expedition which has somewhat extended my knowledge of this
country. And where do you think I am going next? To
Constantinople! — at least, such an excursion has been proposed to me.
Lord B. and another friend of mine are going thither next month, and
have asked me to join the party; but it seems to be but a wild scheme,
and requires twice thinking upon.
"Addio, my dear I., yours very affectionately, C. S. MATTHEWS."
return
Footnote 7: A joke, related by Hobhouse, reminds us of the youth of the
party. In the Long Gallery at Newstead was placed a stone coffin,
from which, as he passed down the Gallery at night, he heard a
groan proceeding. On going nearer, a cowled figure rose from the
coffin and blew out the candle. It was Matthews.
return
Footnote 8: The Rev. Thomas Jones. (See page 79, note 1.)
return
Footnote 9: The only thing remarkable about Walsh's preface is that
Dr. Johnson praises it as "very judicious," but is, at the same time,
silent respecting the poems to which it is prefixed (Moore).
return
Footnote 10: No "Ode" under this title is to be found in Walsh's Poems.
Byron had, no doubt, in mind The Golden Age Restored — a composition in
which, says Dr. Johnson, "there was something of humour, while the facts
were recent; but it now strikes no longer."
return
Footnote 11:
" — — Granville the polite,
And knowing Walsh, would tell me I could write."
"About fifteen," says Pope, "I got acquainted with Mr. Walsh. He used to
encourage me much, and tell me, that there was one way left of
excelling: for though we had several great poets, we never had any one
great poet that was correct; and he desired me to make that my study and
aim"
(Spence's Anecdotes, edit. 1820, p. 280).
return
Footnote 12: See page 165, note 2.
return
Footnote 13: Dan Dogherty, Irish champion (1806-11), came into notice as
a pugilist in 1806. He was beaten by Belcher in April, 1808, near
the Rubbing House on Epsom Downs, and again on the Curragh
of Kildare, in 1813, in thirty-five minutes, after twenty-six rounds.
return
Footnote 14: Tom Belcher (1783-1854), younger brother of Jem Belcher
the champion, fought and won his first fight in London, in 1804,
against Warr. The fight took place in Tothill Fields, Westminster.
Twice beaten by Dutch Sam (Elias Samuel), in 1806 and 1807, he
never held the championship, which a man of his height (5 ft. 9 ins.)
and weight (10 st. 12 lbs.) could scarcely hope to win. But he
repeatedly established the superiority of art over strength, and was
one of the most popular and respectable pugilists of the day. Under his management the Castle Tavern at Holborn, in which he succeeded
Gregson (page 207, note l), was the head-quarters of pugilism.
return
Footnote 15: Sir Henry Smyth, Baronet, of Trinity Hall, A.M. 1805, was
found between eleven and twelve at night, on May 11, 1805, "inciting to a
disturbance" at the shop of a Mrs. Thrower on Market Hill. Other members
of the University seem to have been equally guilty. The sentence of the
Vice-Chancellor and Heads was "that he be suspended from his degree and
banished from the University." The others were admonished only; so it
was clearly considered that Smyth was the ring-leader.
return
cross-reference: return to Footnote 1 of Letter 86
List of Letters
85 — To Henry Drury1
Dorant's Hotel, Jan. 13, 1808.
My Dear Sir, — Though the stupidity of my servants, or the porter of the
house, in not showing you up stairs (where I should have joined you
directly), prevented me the pleasure of seeing you yesterday, I hoped to
meet you at some public place in the evening. However, my stars decreed
otherwise, as they generally do, when I have any favour to request of
them. I think you would have been surprised at my figure, for, since our
last meeting, I am reduced four stone in weight. I then weighed fourteen
stone seven pound, and now only ten stone and a half. I have disposed
of my superfluities by means of hard exercise and abstinence.
Should your Harrow engagements allow you to visit town between this and
February, I shall be most happy to see you in Albemarle Street. If I am
not so fortunate, I shall endeavour to join you for an afternoon at
Harrow, though, I fear, your cellar will by no means contribute to my
cure. As for my worthy preceptor, Dr. B.2, our encounter would by no
means prevent the mutual endearments he and I were wont to lavish on
each other. We have only spoken once since my departure from Harrow in
1805, and then he politely told Tatersall3 I was not a proper
associate for his pupils. This was long before my strictures in verse;
but, in plain prose, had I been some years older, I should have held
my tongue on his perfections. But, being laid on my back, when that
schoolboy thing was written — or rather dictated — expecting to rise no
more, my physician having taken his sixteenth fee, and I his
prescription, I could not quit this earth without leaving a memento of
my constant attachment to Butler in gratitude for his manifold good
offices.
I meant to have been down in July; but thinking my appearance,
immediately after the publication, would be construed into an insult, I
directed my steps elsewhere. Besides, I heard that some of the boys had
got hold of my Libellus, contrary to my wishes certainly, for I never
transmitted a single copy till October, when I gave one to a boy, since
gone, after repeated importunities. You will, I trust, pardon this
egotism. As you had touched on the subject I thought some explanation
necessary. Defence I shall not attempt, Hic murus aheneus esto, nil
conscire sibi — and "so on" (as Lord Baltimore4 said on his trial for
a rape) — I have been so long at Trinity as to forget the conclusion of
the line; but though I cannot finish my quotation, I will my letter, and
entreat you to believe me, gratefully and affectionately, etc.
P.S. — I will not lay a tax on your time by requiring an answer, lest you
say, as Butler said to Tatersall (when I had written his reverence an
impudent epistle on the expression before mentioned), viz. "that I
wanted to draw him into a correspondence."
Footnote 1: See page 12, note 1 ; and page 41, note 2.
return to footnote mark
Footnote 2: Dr. Butler, Head-master of Harrow (see page 58, note 1).
return
Footnote 3: See page 59, note 1.
return
Footnote 4: Francis Calvert, seventh Lord Baltimore (1731-1771), was
charged with decoying a young milliner, named Sarah Woodcock, to his
house, and with rape. On February 12, 1768, he was committed for trial
at the Spring assizes, was tried at Kingston, March 26, 1768, and
acquitted. The story is the subject of a romance, Injured Innocence; or
the Rape of Sarah Woodcock; A Tale, by S. J., Esq., of Magdalen
College, Oxford. New York (no date).
"I thank God," Lord Baltimore is
reported to have said, "that I have had firmness and resolution to meet
my accusers face to face, and provoke an enquiry into my conduct, Hic
murus aheneus esto, nil conscire sibi"
(Ann. Register for 1768, p.
234). His body lay in state at Exeter Change, previous to its interment
at Epsom (Leigh Hunt's The Town, edit. 1893, p. 191).
return
List of Letters
86 — To John Cam Hobhouse1
Newstead Abbey, Notts, January 16, 1808.
My Dear Hobhouse, — I do not know how the dens-descended Davies2
came to mention his having received a copy of my epistle to you, but I
addressed him and you on the same evening, and being much incensed at
the account I had received from Wallace, I communicated the contents to
the Birdmore, though without any of that malice wherewith you charge me.
I shall leave my card at Batts, and hope to see you in your progress to
the North.
I have lately discovered Scrope's genealogy to be ennobled by a
collateral tie with the Beardmore, Chirurgeon and Dentist to Royalty,
and that the town of Southwell contains cousins of Scrope's, who
disowned them (I grieve to speak it) on visiting that city in my
society.
How I found this out I will disclose, the first time "we three meet
again." But why did he conceal his lineage? "Ah, my dear H., it was
cruel, it was insulting, it was unnecessary."
I have (notwithstanding your kind invitation to Wallace) been alone
since the 8th of December; nothing of moment has occurred since our
anniversary row. I shall be in London on the 19th; there are to be oxen
roasted and sheep boiled on the 22nd, with ale and uproar for the
mobility; a feast is also providing for the tenantry. For my own part, I
shall know as little of the matter as a corpse of the funeral solemnized
in its honour.
A letter addressed to Reddish's will find me. I still intend publishing
the Bards, but I have altered a good deal of the "Body of the Book,"
added and interpolated, with some excisions; your lines still stand3,
and in all there will appear 624 lines.
I should like much to see your Essay upon Entrails: is there any
honorary token of silver gilt? any cups, or pounds sterling attached to
the prize, besides glory? I expect to see you with a medal suspended
from your button-hole, like a Croix de St. Louis.
Fletcher's father is deceased, and has left his son tway cottages, value
ten pounds per annum. I know not how it is, but Fletch., though only the
third brother, conceives himself entitled to all the estates of the
defunct, and I have recommended him to a lawyer, who, I fear, will
triumph in the spoils of this ancient family. A Birthday Ode has been
addressed to me by a country schoolmaster, in which I am likened to the
Sun, or Sol, as he classically saith; the people of Newstead are
compared to Laplanders. I am said to be a Baron, and a Byron, the truth
of which is indisputable. Feronia is again to reign (she must have some
woods to govern first), but it is altogether a very pleasant
performance, and the author is as superior to Pye, as George Gordon to
George Guelph. To be sure some of the lines are too short, but then, to
make amends, the Alexandrines have from fifteen to seventeen syllables,
so we may call them Alexandrines the great.
I shall be glad to hear from you, and beg you to believe me,
Yours very truly,
Byron.
Footnote 1: John Cam Hobhouse (1786-1869), created in 1851 Baron
Broughton de Gyfford, was the eldest son of Mr. Benjamin Hobhouse,
created a baronet in 1812, and M.P. (from 1797 to 1818) successively for
Bletchingley, Grampound, and Hindon. From a school at Bristol, John Cam
Hobhouse was sent to Westminster, and thence to Trinity, Cambridge,
where he won (1808) the Hulsean Prize for an essay on "Sacrifices," and
made acquaintance with Byron, as related in Letter 84. In 1809 he
published a poetical miscellany, consisting of sixty-five pieces, under
the title of Imitations and Translations from the Ancient and Modern
Classics, together with original Poems never before published (London,
1809, 8vo). (For Byron's nine contributions, see Poems, vol. i.,
Bibliographical Note.) In 1809-10 he was Byron's travelling companion
abroad (see A Journey through Albania, etc. London, 1813, 4to).
In 1813 he travelled with Douglas Kinnaird in Sweden, Germany, Austria,
and Italy; in 1814 he was at Paris with the allied armies; and in April,
1815, was there again till the second Napoleonic war broke out,
returning to witness the second restoration of the Bourbons (see his
Letters — written by an Englishman resident in Paris, etc. Anon.,
London, 1816, 2 vols., 8vo). During 1814 he was much with Byron in
London. He notes going with him to Drury Lane, and being introduced with
him to Kean (May 19); dining with him at Lord Tavistock's (June 4);
dining with him at Douglas Kinnaird's, to meet Kean (December 14). He
was Byron's best man at his marriage at Seaham (January 2, 1815), and it
was to him that the bride said, "If I am not happy, it will be my own
fault." He was the last person who shook hands with Byron on Dover pier,
when the latter left England in 1816. Later in the same year he was with
him at the Villa Diodati, on the Lake of Geneva, and travelled with him
to Venice. To him Byron dedicated The Siege of Corinth, In the next
year he was again with Byron in the Villa La Mira on the banks of the
Brenta, and at Venice, where he prepared the commentary on the fourth
canto of Childe Harold, which Byron dedicated to him. Part of the
notes were published separately (Historical Illustrations, etc. London, 1818, 8vo). In 1818 Hobhouse stood for Westminster, but was
defeated by George Lamb, the representative of the official Whigs. He
was an original member of "The Rota Club," afterwards known as
"Harrington's," to which Michael Bruce, Douglas Kinnaird, Scrope Davies,
and others belonged, and which Byron, writing from Italy, expressed a
wish to join. He had now embarked on political life. His pamphlet, A
Defence of the People (1819), was followed in the same year by A
Trifling Mistake, which was declared by the House of Commons to be a
breach of privilege. In consequence, he was committed to Newgate. The
death of George III., and the dissolution of Parliament, set him free.
He contested Westminster, won the seat with Sir Francis Burdett as his
colleague, and represented it for thirteen years. He took the part of
Queen Caroline against the Government. At the Queen's funeral (August 7,
1821) he attended the procession which escorted her body (August 13)
from Brandenburg House to Harwich, and saw the coffin placed upon the
vessel.
His political career was long, independent, useful, and distinguished,
and he specially associated himself with such questions as the
shortening of the hours for infant labour, the opening up of
metropolitan vestries, and the subject of parliamentary reform. In 1832
he was made a Privy Councillor, and became Secretary at War in Lord
Grey's Ministry. This post, finding himself unable to effect essential
reforms at the War Office, he exchanged for that of Secretary for
Ireland (1833); but he resigned both his office and his seat a few weeks
later, being opposed to the Government on a question of taxation. In
1834 he joined Lord Melbourne's Government as First Commissioner of
Woods and Forests, with a seat in the Cabinet. In Lord Melbourne's
second administration, and again in Lord J. Russell's Government of
1846, he was President of the Board of Control. On his retirement from
public life, in 1852, he received high recognition of his official
services from the Queen, who conferred on him the Grand Cross of the
Bath and a peerage. Hobhouse was present at Her Majesty's first Council,
and is said to have originated the phrase, "Her Majesty's Opposition."
In 1822 he travelled in Italy (see Italy: Remarks made in Several
Visits from the Year 1816 to 1834, London, 1859, 2 vols., 8vo). There,
on September 20, at Pisa, he for the last time saw Byron, whose parting
words were, "Hobhouse, you should never have come, or you should never
go." In July, 1824, when Byron's body was brought home, he boarded the
Florida in Sandgate Creek, and took charge of the funeral ceremonies
from Westminster Stairs to the interment at Hucknall Torkard. He
prepared an article for the Quarterly Review, exposing the absurdities
of Medwin's Conversations and of Dallas's Recollections; but, owing
to difficulties with Southey, it was not published. It was the substance
of this article which afterwards appeared in the Westminster Review in
1825. In 1830 he wrote, but, by Lord Holland's advice, withheld, a
refutation of the charges made against the dead poet as to his
separation from Lady Byron. He has, however, left on record that it was
not fear which induced Byron to agree to the separation, but that, on
the contrary, he was ready to "go into court."
The staunchest of Byron's friends, Hobhouse was also the most sensible
and candid. As such Byron valued him. Talking to Lady Blessington at
Genoa, in 1823, he said (Conversations, p. 93) that Hobhouse was
"the
most impartial, or perhaps," added he, "unpartial, of my friends; he
always told me my faults, but I must do him the justice to add, that he
told them to me, and not to others."
On another occasion he said (p.
172),
"If friendship, as most people imagine, consists in telling one
truth — unvarnished, unadorned truth — he is indeed a friend: yet, hang
it, I must be candid, and say I have had many other, and more agreeable,
proofs of Hobhouse's friendship than the truths he always told me; but
the fact is, I wanted him to sugar them over a little with flattery, as
nurses do the physic given to children; and he never would, and
therefore I have never felt quite content with him, though, au fond, I
respect him the more for his candour, while I respect myself very much
less for my weakness in disliking it."
return to footnote mark
cross-reference: return to Footnote 5 of Letter 84
cross-reference: return to Footnote 1 of Letter 120
Footnote 2: Scrope Berdmore Davies (1783-1852), born at Horsley, in
Gloucestershire, was educated at Eton, and King's College, Cambridge,
where he was admitted a Scholar in July, 1802, and a Fellow in July,
1805. In 1803 he was awarded by the Provost of Eton the Belham
Scholarship, given to those Scholars of King's who had behaved well at
Eton, and held it till 1816. A witty companion, with "a dry caustic
manner, and an irresistible stammer" (Life of Rev, F. Hodgson, vol. i
p. 204), Davies was, during the Regency and afterwards, a popular member
of fashionable society. A daring gambler and shrewd calculator, he at
one time won heavily at the gaming-tables. On June 10, 1814, as he told
Hobhouse, he won £6065 at Watier's Club at Macao. Captain Cronow, in his
Reminiscences (ed. 1860, vol. i. pp. 93-96), sketches him among
"Golden Ball" Hughes, "King" Allen, and other dandies. But luck turned
against him, and he retired, poverty-stricken and almost dependent upon
his Fellowship, to Paris, where he died, May 23, 1852. It was supposed
he had for many years occupied himself with writing his recollections of
his friends. But the notes, if they were ever written, have disappeared.
Byron, who hated obligations, as he himself says, counted Davies as a
friend, though not on the same plane as Hobhouse. He borrowed from
Davies £4800 before he left England in 1809, repaid him in 1814, and
dedicated to him his Parisina. In his MS. Journal (Life, pp. 129,
130) he says,
"One of the cleverest men I ever knew, in conversation,
was Scrope Berdmore Davies. Hobhouse is also very good in that line,
though it is of less consequence to a man who has other ways of showing
his talents than in company. Scrope was always ready, and often
witty — Hobhouse was witty, but not always so ready, being more
diffident."
Byron appointed him one of the executors of his will of 1811. In his Journal for March 28, 1814 (Life, p. 234), occurs this entry:
"Yesterday, dined tête à tête at the Cocoa with Scrope Davies — sat from
six till midnight — drank between us one bottle of champagne and six of
claret, neither of which wines ever affect me. Offered to take Scrope
home in my carriage; but he was tipsy and pious, and I was obliged to
leave him on his knees praying to I know not what purpose or pagod. No
headach, nor sickness, that night, nor to-day. Got up, if anything,
earlier than usual — sparred with Jackson ad sudorem, and have been
much better in health than for many days. I have heard nothing more from
Scrope."
Scrope Davies visited Byron at the Villa Diodati, in 1816, and brought
back with him Childe Harold, canto iii. On his return he gave evidence
in the case of Byron v. Johnson, before the Lord Chancellor, November
28, 1816, when an injunction was obtained to restrain Johnson from
publishing a volume containing Lord Byron's Childe Harold's Pilgrimage
to the Holy Land, and other works, which he professed to have bought
from Byron for £500.
According to Gronow (Reminiscences, vol. i. p. 153, 154), Scrope
Davies, asked to give his private opinion of Byron, said that he
considered him
"very agreeable and clever, but vain, overbearing,
suspicious, and jealous. Byron hated Palmerston, but liked Peel, and
thought that the whole world ought to be constantly employed in admiring
his poetry and himself."
return
cross-reference: return to Footnote 12 of Letter 83
cross-reference: return to Footnote 3 of Letter 140
Footnote 3: For Hobhouse's lines on Bowles, see English Bards, etc.,
line 384, and note.
return
List of Letters
87 — To Robert Charles Dallas1
Dorant's Hotel, Albemarle Street, Jan. 20, 1808.
Sir, — Your letter was not received till this morning, I presume from
being addressed to me in Notts., where I have not resided since last
June; and as the date is the 6th, you will excuse the delay of my
answer.
If the little volume you mention has given pleasure to the author of Percival and Aubrey, I am sufficiently repaid by his praise. Though
our periodical censors have been uncommonly lenient, I confess a tribute
from a man of acknowledged genius is still more flattering. But I am
afraid I should forfeit all claim to candour, if I did not decline such
praise as I do not deserve; and this is, I am sorry to say, the case in
the present instance.
My compositions speak for themselves, and must stand or fall by their
own worth or demerit: thus far I feel highly gratified by your
favourable opinion. But my pretensions to virtue are unluckily so few,
that though I should be happy to merit, I cannot accept, your applause
in that respect. One passage in your letter struck me forcibly: you
mention the two Lords Lyttleton2 in the manner they respectively
deserve, and will be surprised to hear the person who is now addressing
you has been frequently compared to the latter. I know I am injuring
myself in your esteem by this avowal, but the circumstance was so
remarkable from your observation, that I cannot help relating the fact.
The events of my short life have been of so singular a nature, that,
though the pride commonly called honour has, and I trust ever will,
prevent me from disgracing my name by a mean or cowardly action, I have
been already held up as the votary of licentiousness, and the disciple
of infidelity. How far justice may have dictated this accusation, I
cannot pretend to say; but, like the gentleman to whom my religious
friends, in the warmth of their charity, have already devoted me, I am
made worse than I really am. However, to quit myself (the worst theme I
could pitch upon), and return to my poems, I cannot sufficiently express
my thanks, and I hope I shall some day have an opportunity of rendering
them in person. A second edition is now in the press, with some
additions and considerable omissions; you will allow me to present you
with a copy. The Critical3, Monthly4, and Anti-Jacobin5
Reviews have been very indulgent; but the Eclectic6 has pronounced
a furious Philippic, not against the book but the author, where you
will find all I have mentioned asserted by a reverend divine who wrote
the critique.
Your name and connection with our family have been long known to me, and
I hope your person will be not less so: you will find me an excellent
compound of a "Brainless" and a "Stanhope."7 I am afraid you will
hardly be able to read this, for my hand is almost as bad as my
character; but you will find me, as legibly as possible,
Your obliged and obedient servant,
Byron.
Footnote 1: Robert Charles Dallas (1754-1842), born in Jamaica and
educated in Scotland, read law at the Inner Temple. About 1775 he
returned to Jamaica to look after his property and take up a lucrative
appointment. Three years later he returned to England, married, and took
his wife back with him to the West Indies. His wife's health compelled
him to return to Europe, and he lived for some time in France. At the
outbreak of the Revolution he emigrated to America; but finally settled
down to literary work in England. His first publication (1797) was
Miscellaneous Writings consisting of Poems; Lucretia, a Tragedy; and
Moral Essays, with a Vocabulary of the Passions. He translated a number
of French books bearing on the French Revolution, by Bertrand de
Moleville, Mallet du Pan, Hue, and Joseph Weber; also a work on
Volcanoes by the Abbé Ordinaire, and an historical novel by Madame de
Genlis, The Siege of Rochelle. He wrote a number of novels, among them
Percival, or Nature Vindicated (1801); Aubrey: a Novel (1804); The
Morlands; Tales illustrative of the Simple and Surprising (1805); The
Knights; Tales illustrative of the Marvellous (1808). Later (1819 and
1823) he published two volumes of poems. He says (preface to Percival,
p. ix.) that his object is "to improve the heart, as well as to please
the fancy, and to be the auxiliary of the Divine and the Moralist." He
is one of the writers, others being "Gleaner" Pratt and Lord Carlisle,
"whose writings" (Memoirs of the Life and Writings of Percival
Stockdale, 1809, vol. i. Preface, p. xvi.) "dart through the general
fog of our literary dulness." Stockdale further says of him that he was
"a man of a most affectionate and virtuous mind. He has had the moral
honour, in several novels, to exert his talents, which were worthy of
their glorious cause, in the service of good conduct and religion."
Dallas's sister, Henrietta Charlotte, married George Anson Byron, the
son of Admiral the Hon. John Byron, and was therefore Byron's aunt by
marriage. On the score of this connection, Dallas introduced himself to
Byron by complimenting him, in a letter dated January 6, 1808, on his
Hours of Idleness. A well-meaning, self-satisfied, dull, industrious
man, he gave Byron excellent moral advice, to which the latter responded
as the fanfaron de ses vices, evidently with great amusement to
himself. English Bards, and Scotch Reviewers was brought out under
Dallas's auspices, as well as Childe Harold and The Corsair, the
profits of which Byron made over to him. Dallas distrusted his own
literary judgment in the matter of Byron's verse, and consulted Walter
Wright, the author of Horæ Ioniæ, about the prospects of Childe
Harold.
"I have told him," said Wright, "that I have no doubt this will
succeed. Lord Byron had offered him before some translations from
Horace, which I told him would never sell, and he did not take them"
(Diary of H. Crabb Robinson, vol. i. pp. 29, 30).
The connection between Dallas and Byron practically ended in 1814. The
publication of Dallas's Recollections of the Life of Lord Byron from
the Year 1808 to the end of 1814 was stopped by a decree obtained by
Byron's executors, in the Court of Chancery, August 23, 1824. But the
book was published by the writer's son, the Rev. A. R. C. Dallas.
return to footnote mark
cross-reference: return to Footnote 3 of Letter 148
Footnote 2: Byron refers to the following passage in Dallas's letter of
January 6, 1808:
"A spirit that brings to my mind another noble author, who was not
only a fine poet, orator, and historian, but one of the closest
reasoners we have on the truth of that religion, of which forgiveness
is a prominent principle: the great and the good Lord Lyttelton, whose
fame will never die. His son, to whom he had transmitted genius but
not virtue, sparkled for a moment, and went out like a falling star,
and with him the title became extinct. He was the victim of inordinate
passions, and he will be heard of in this world only by those who read
the English Peerage"
(Correspondence of Lord Byron, p. 20, the suppressed edition).
Dallas was, of course, aware that Byron's predecessor in the title,
William, fifth Lord Byron, was known as the "wicked Lord Byron." George,
first Lord Lyttelton (1709-1773), to whom Pope refers (Imitations of
Horace, bk. i. Ep. i. 1. 30) as
"Still true to virtue, and as warm as true,"
was a voluminous writer in prose and verse, but owed his political
importance to his family connection with Chatham, Temple, and George
Grenville. Horace Walpole calls him a "wise moppet" (Letters, vol. ii.
p. 28, ed. Cunningham), and repeatedly sneers at his dulness. His son
Thomas, second Lord Lyttelton (1744-1779), the "wicked Lord Lyttelton,"
appears in W. Combe's Diaboliad as the
"Peer of words,
Well known, — and honour'd in the House of Lords, —
Whose Eloquence all Parallel defies!"
who claims the throne of Hell as the worst of living men. His Poems by
a Young Nobleman lately deceased (published in 1780, after his death)
may have helped Dallas in his allusion. He was the hero and the victim
of the famous ghost story which Dr. Johnson was "willing to believe."
return
Footnote 3: The Critical Review (3rd series, vol. xii. pp. 47-53)
specially praises lines "On Leaving Newstead Abbey" and "Childish
Recollections."
return
Footnote 4: In Monthly Literary Recreations (July, 1807, pp. 67-71),
"Childish Recollections" and "The Tear" are particularly commended.
"As
friends to the cause of literature, we have thought proper not to
disguise our opinion of his powers, that we might alter his
determination, and lead him once more to the Castalian fount."
return
Footnote 5: The Anti-Jacobin Review (December, 1807, pp. 407, 408)
says that the poems
"exhibit strong proofs of genius, accompanied by a
lively but chastened imagination, a classical taste, and a benevolent
heart."
return
Footnote 6: The Eclectic Review (vol. iii. part ii. pp. 989-993)
begins its review thus:
"The notice we take of this publication regards
the author rather than the book; the book is a collection of juvenile
pieces, some of very moderate merit, and others of very questionable
morality; but the author is a nobleman!"
return
Footnote 7: Characters in the novel called Percival.
return
List of Letters
Dorant's, January 21, 1808.
Sir, — Whenever leisure and inclination permit me the pleasure of a
visit, I shall feel truly gratified in a personal acquaintance with one
whose mind has been long known to me in his writings.
You are so far correct in your conjecture, that I am a member of the
University of Cambridge, where I shall take my degree of A.M. this term;
but were reasoning, eloquence, or virtue, the objects of my search,
Granta is not their metropolis, nor is the place of her situation an "El
Dorado," far less an Utopia. The intellects of her children are as
stagnant as her Cam, and their pursuits limited to the church — not of
Christ, but of the nearest benefice.
As to my reading, I believe I may aver, without hyperbole, it has been
tolerably extensive in the historical department; so that few nations
exist, or have existed, with whose records I am not in some degree
acquainted, from Herodotus down to Gibbon. Of the classics, I know about
as much as most school-boys after a discipline of thirteen years; of the
law of the land as much as enables me to keep "within the statute" — to
use the poacher's vocabulary. I did study the "Spirit of Laws"1 and
the Law of Nations; but when I saw the latter violated every month, I
gave up my attempts at so useless an accomplishment:— of geography, I
have seen more land on maps than I should wish to traverse on foot; — of
mathematics, enough to give me the headach without clearing the part
affected; — of philosophy, astronomy, and metaphysics, more than I can
comprehend; and of common sense so little, that I mean to leave a
Byronian prize at each of our "Almæ Matres" for the first
discovery, — though I rather fear that of the longitude will precede it.
I once thought myself a philosopher, and talked nonsense with great
decorum: I defied pain, and preached up equanimity. For some time this
did very well, for no one was in pain for me but my friends, and none
lost their patience but my hearers. At last, a fall from my horse
convinced me bodily suffering was an evil; and the worst of an argument
overset my maxims and my temper at the same moment: so I quitted Zeno
for Aristippus, and conceive that pleasure constitutes the  .
.
In morality, I prefer Confucius to the Ten Commandments, and Socrates to
St. Paul (though the two latter agree in their opinion of marriage). In
religion, I favour the Catholic emancipation, but do not acknowledge the
Pope; and I have refused to take the sacrament, because I do not think
eating bread or drinking wine from the hand of an earthly vicar will
make me an inheritor of heaven. I hold virtue, in general, or the
virtues severally, to be only in the disposition, each a feeling, not
a principle. I believe truth the prime attribute of the Deity, and death
an eternal sleep, at least of the body. You have here a brief compendium
of the sentiments of the wicked George, Lord Byron; and, till I get a
new suit, you will perceive I am badly cloathed.
I remain yours, etc.,
Byron.
Footnote 1: In Byron's "List of historical writers whose works I have
perused in different languages" (Life, pp. 46, 47), occurs the name of
Montesquieu. It is to his Esprit des Lois that Byron refers.
return to footnote mark
List of Letters
Dorant's, January 25th, 1808.
Sir, — The picture I have drawn of my finances is unfortunately a true
one, and I find the colours may be heightened but not improved by
time. — I have inclosed the receipt, and return my thanks for the loan,
which shall be repaid the first opportunity. In the concluding part of
my last I gave my reasons for not troubling you with my society at
present, but when I can either communicate or receive pleasure, I shall
not be long absent.
Yrs., etc.,
Byron.
P.S. — I have received a letter from Whitehead, of course you know the
contents, and must act as you think proper.
List of Letters
Dorant's, January 25th, 1808.
Dear Sir, — Some time ago I gave Mitchell the sadler [sic] a letter for
you, requesting his bill might be paid from the Balance of the Quarter
you obliged me by advancing. If he has received this you will further
oblige me by paying what remains, I believe somewhere about five pounds,
if so much.
You will confer a favour upon me by the loan of twenty. I will endeavour
to repay it next week, as I have immediate occasion for that sum, and I
should not require it of you could I obtain it elsewhere.
I am now in my one and twentieth year, and cannot command as many
pounds. To Cambridge I cannot go without paying my bills, and at present
I could as soon compass the National Debt; in London I must not remain,
nor shall I, when I can procure a trifle to take me out of it. Home I
have none; and if there was a possibility of getting out of the Country,
I would gladly avail myself of it. But even that is denied me, my Debts
amount to three thousand, three hundred to Jews, eight hundred to Mrs.
B. of Nottingham, to coachmaker and other tradesmen a thousand more, and
these must be much increased, before they are lessened.
Such is the prospect before me, which is by no means brightened by
ill-health. I would have called on you, but I have neither spirits to
enliven myself or others, or inclination to bring a gloomy face to spoil
a group of happy ones. I remain,
Your obliged and obedt. sert.,
Byron.
P.S. — Your answer to the former part will oblige, as I shall be reduced
to a most unpleasant dilemma if it does not arrive.
List of Letters
91 — To James De Bathe1
Dorant's Hotel, February 2d, 1808.
My Dear De Bathe, — Last Night I saw your Father and Brother, the former
I have not the pleasure of knowing, but the latter informed me you came to Town on Saturday and returned yesterday.
I have received a pressing Invitation from Henry Drury to pay him a
visit; in his Letter he mentions a very old Friend of yours, who told
him he would join my party, if I could inform him on what day I meant to
go over. This Friend you will readily conclude to be a Lord B.; but
not the one who now addresses you. Shall I bring him to you? and insure
a welcome for myself which perhaps might not otherwise be the case. This
will not be for a Fortnight to come. I am waiting for Long, who is now
at Chatham, when he arrives we shall probably drive down and dine with
Drury.
I confess Harrow has lost most of its charms for me. I do not know if
Delawarr is still there; but, with the exception of yourself and the
Earl, I shall find myself among Strangers. Long has a Brother at
Butler's, and all his predilections remain in full force; mine are
weakened, if not destroyed, and though I can safely say, I never knew a
Friend out of Harrow, I question whether I have one left in it. You
leave Harrow in July; may I ask what is your future Destination?
In January 1809 I shall be twenty one & in the Spring of the same year
proceed abroad, not on the usual Tour, but a route of a more extensive
Description. What say you? are you disposed for a view of the
Peloponnesus and a voyage through the Archipelago? I am merely in jest
with regard to you, but very serious with regard to my own Intention
which is fixed on the Pilgrimage, unless some political view or
accident induce me to postpone it. Adieu! if you have Leisure, I shall
be as happy to hear from you, as I would have been to have seen you.
Believe me,
Yours very truly,
Byron.
Footnote 1: Sir James Wynne De Bathe (1792-1828) succeeded his father
as second baronet, February 22, 1808.
"Clare, Dorset, Charles Gordon, De
Bathe, Claridge, and John Wingfield, were my juniors and favourites,
whom I spoilt by indulgence"
(Life, p. 21). De Bathe's name does not
appear in the Harrow School lists. A Captain De Bathe interested himself
in the case of Medora Leigh in 1843 (see Charles Mackay's Medora
Leigh, pp. 92, 93, and elsewhere in the volume).
return to footnote mark
List of Letters
92 — To William Harness1
Dorant's Hotel, Albemarle Street, Feb. II, 1808.
My Dear Harness, — As I had no opportunity of returning my verbal thanks,
I trust you will accept my written acknowledgments for the compliment
you were pleased to pay some production of my unlucky muse last
November, — I am induced to do this not less from the pleasure I feel in
the praise of an old schoolfellow, than from justice to you, for I had
heard the story with some slight variations. Indeed, when we met this
morning, Wingfield2 had not undeceived me; but he will tell you that
I displayed no resentment in mentioning what I had heard, though I was
not sorry to discover the truth. Perhaps you hardly recollect, some
years ago, a short, though, for the time, a warm friendship between us.
Why it was not of longer duration I know not. I have still a gift of
yours in my possession, that must always prevent me from forgetting it.
I also remember being favoured with the perusal of many of your
compositions, and several other circumstances very pleasant in their
day, which I will not force upon your memory, but entreat you to believe
me, with much regret at their short continuance, and a hope they are not
irrevocable,
Yours very sincerely, etc.,
Byron.
Footnote 1: William Harness (1790-1869), son of Dr. J. Harness, Commissioner
of the Transport Board, was educated at Harrow and Christ's
College, Cambridge. Ordained in 1812, he was, from 1823 to 1826,
Curate at Hampstead.
"I could quiz you heartily," writes Mrs. Franklin to Miss Mitford
(September 6, 1824), "for having told me in three successive letters
of Mr. Harness's chapel at Hampstead. I understand he now lives a very
retired life"
(The Friendships of Mary Russell Mitford, vol. i. p. 61). From 1826 to
1844 he was Incumbent of Regent Square Chapel; Minister of Brompton
Chapel (1844-47); Perpetual Curate (1849-69) of All Saints',
Knightsbridge, which he built from subscriptions raised by himself. He
is described by Crabb Robinson (Diary, vol. iii. p. 212) as
"a clergyman with Oxford propensities, and a worshipper of the heathen
Muses as well as of the Christian Graces;"
and again (iii. 326), as
"a man of taste, of High Church principles and liberal in spirit."
Miss Mitford (The Friendships of Mary Russell Mitford, vol. ii. p.
289) writes that
"he has neither Catholic nor Puseyite tendencies, — only it is a large and liberal mind like Bishop Stanley's, believing good
men and good Christians may exist among Papists, and will be as safe
there as if they were Protestants."
Again (vol. ii. p. 295) she says of him:
"Besides his varied accomplishments, and his admirable goodness and
kindness, he has all sorts of amusing peculiarities. With a temper
never known to fail, an indulgence the largest, a tenderness as of a
woman, he has the habit of talking like a cynic! and with more
learning, ancient and modern, and a wider grasp of literature than
almost any one I know, professes to read nothing and care for nothing
but 'Shakespeare and the Bible.' He is the finest reader of both that
I ever heard. His preaching, which has been so much admired, is too
rapid, but his reading the prayers is perfection. The best parish
priest in London, and the truest Christian."
Miss Mitford's praise may be exaggerated; but she had known Harness for
a lifetime.
Harness edited Shakespeare (1825, 8 vols.), as well as Massinger
(1830) and Ford (1831); wrote for the Quarterly and Blackwood; and
published a number of sermons, including The Wrath of Cain, A Boyle
Lecture (1822). He wrote The Life of Mary Russell Mitford (1870), in
collaboration with the Rev. A. G. L'Estrange, whose Life of the Rev. W.
Harness is the chief authority for his career.
His friendship with Byron began at Harrow (Life, pp. 23, 24), where
Byron, who was older than Harness, took pity upon his lameness and
weakness, and protected him from the bullies of the school. At a later
period they became estranged, as is shown by the following letter from
Byron to Harness (Life, pp. 24, 25):—
"We both seem perfectly to recollect, with a mixture of pleasure and
regret, the hours we once passed together, and I assure you, most
sincerely, they are numbered among the happiest of my brief chronicle
of enjoyment. I am now getting into years, that is to say, I was
twenty a month ago, and another year will send me into the world to
run my career of folly with the rest. I was then just fourteen, — you
were almost the first of my Harrow friends, certainly the first in
my esteem, if not in date; but an absence from Harrow for some time,
shortly after, and new connections on your side, and the difference in
our conduct (an advantage decidedly in your favour) from that
turbulent and riotous disposition of mine, which impelled me into
every species of mischief, — all these circumstances combined to
destroy an intimacy, which affection urged me to continue, and memory
compels me to regret. But there is not a circumstance attending that
period, hardly a sentence we exchanged, which is not impressed on my
mind at this moment. I need not say more, — this assurance alone must
convince you, had I considered them as trivial, they would have been
less indelible. How well I recollect the perusal of your 'first
flights'! There is another circumstance you do not know; — the first
lines I ever attempted at Harrow were addressed to you. You were to
have seen them; but Sinclair had the copy in his possession when we
went home; — and, on our return, we were strangers. They were
destroyed, and certainly no great loss; but you will perceive from
this circumstance my opinions at an age when we cannot be hypocrites.
I have dwelt longer on this theme than I intended, and I shall now
conclude with what I ought to have begun. We were once friends, — nay,
we have always been so, for our separation was the effect of chance,
not of dissension. I do not know how far our destinations in life may
throw us together, but if opportunity and inclination allow you to
waste a thought on such a hare-brained being as myself, you will find
me at least sincere, and not so bigoted to my faults as to involve
others in the consequences. Will you sometimes write to me? I do not
ask it often; and, if we meet, let us be what we should be, and what
we were."
The following is Harness's own account of the circumstances in which
Letter 92 was written:—
"A coolness afterwards arose, which Byron alludes to in the first of
the accompanying letters, and we never spoke during the last year of
his remaining at school, nor till after the publication of his Hours
of Idleness. Lord Byron was then at Cambridge; I, in one of the upper
forms, at Harrow. In an English theme I happened to quote from the
volume, and mention it with praise. It was reported to Byron that I
had, on the contrary, spoken slightingly of his work and of himself,
for the purpose of conciliating the favour of Dr. Butler, the master,
who had been severely satirised in one of the poems. Wingfield, who
was afterwards Lord Powerscourt, a mutual friend of Byron and myself,
disabused him of the error into which he had been led, and this was
the occasion of the first letter of the collection. Our intimacy was
renewed, and continued from that time till his going abroad. Whatever
faults Lord Byron might have had towards others, to myself he was
always uniformly affectionate. I have many slights and neglects
towards him to reproach myself with; but I cannot call to mind a
single instance of caprice or unkindness, in the whole course of our
friendship, to allege against him."
In December, 1811, Harness paid Byron a visit at Newstead, the only
other guest being Francis Hodgson, who, like Harness, was not then
ordained. He thus describes the visit (Life of the Rev. Francis
Hodgson, vol. i. pp. 219-221}:—
"When Byron returned, with the MS. of the first two cantos of Childe
Harold in his portmanteau, I paid him a visit at Newstead. It was
winter — dark, dreary weather — the snow upon the ground; and a
straggling, gloomy, depressive, partially inhabited place the Abbey
was. Those rooms, however, which had been fitted up for residence were
so comfortably appointed, glowing with crimson hangings, and cheerful
with capacious fires, that one soon lost the melancholy feeling of
being domiciled in the wing of an extensive ruin. Many tales are
related or fabled of the orgies which, in the poet's early youth, had
made clamorous these ancient halls of the Byrons. I can only say that
nothing in the shape of riot or excess occurred when I was there. The
only other visitor was Dr. Hodgson, the translator of Juvenal, and
nothing could be more quiet and regular than the course of our days.
Byron was retouching, as the sheets passed through the press, the
stanzas of Childe Harold. Hodgson was at work in getting out the
ensuing number of the Monthly Review, of which he was principal
editor. I was reading for my degree. When we met, our general talk was
of poets and poetry — of who could or who could not write; but it
occasionally rose into very serious discussions on religion. Byron,
from his early education in Scotland, had been taught to identify the
principles of Christianity with the extreme dogmas of Calvinism. His
mind had thus imbibed a most miserable prejudice, which appeared to be
the only obstacle to his hearty acceptance of the Gospel. Of this
error we were most anxious to disabuse him. The chief weight of the
argument rested with Hodgson, who was older, a good deal, than myself.
I cannot even now — at a distance of more than fifty years — recall
those conversations without a deep feeling of admiration for the
judicious zeal and affectionate earnestness (often speaking with tears
in his eyes) which Dr. Hodgson evinced in his advocacy of the truth.
The only difference, except perhaps in the subjects talked about,
between our life at Newstead Abbey and that of the great families
around us, was the hours we kept. It was, as I have said, winter, and
the days were cold; and, as nothing tempted us to rise early, we got
up late. This flung the routine of the day rather backward, and we did
not go early to bed. My visit to Newstead lasted about three weeks,
when I returned to Cambridge to take my degree."
To Harness Byron intended to dedicate Childe Harold, but feared to do
so, "lest it should injure him in his profession."
return to footnote mark
cross-reference: return to Footnote 1 of Letter 33
cross-reference: return to Footnote 1 of Letter 102
Footnote 2: Three Wingfields, sons of Lord Powerscourt, entered Harrow
in February, 1801. The Hon. Richard Wingfield succeeded his father as
fifth Viscount Powerscourt in 1809, and died in 1823. Edward became a
clergyman and died of cholera in 1825; John, Byron's friend, the
"Alonzo" of "Childish Recollections" entered the Coldstream Guards, and
died of fever at Coimbra, May 14, 1811.
"Of all human beings, I was
perhaps at one time most attached to poor Wingfield, who died at
Coimbra, 1811, before I returned to England"
(Life, p. 21). To his
memory Byron wrote the lines in Childe Harold, Canto I stanza xci.
return
cross-reference: return to Footnote 2 of Letter 161
List of Letters
[Mr. Ridge, Newark.]
Dorant's Hotel, February 21st, 1808.
Mr. Ridge, — Something has occurred which will make considerable
alteration in my new volume. You must go back and cut out the whole poem of Childish Recollections1. Of course you will be surprized
at this, and perhaps displeased, but it must be done. I cannot help
its detaining you a month longer, but there will be enough in the
volume without it, and as I am now reconciled to Dr. Butler I cannot
allow my satire to appear against him, nor can I alter that part
relating to him without spoiling the whole. You will therefore omit the
whole poem. Send me an immediate answer to this letter but obey the
directions. It is better that my reputation should suffer as a poet by
the omission than as a man of honour by the insertion.
Etc., etc.,
Byron.
Footnote 1: For "Childish Recollections," see Poems, vol.i. p.101. A
previous letter, written to Ridge from Dorant's Hotel, January 9, 1808,
illustrates the rapidity with which Byron's moods changed. In this case,
the lines on "Euryalus" (Lord Delawarr: see page 41, note 1) were to
be omitted:—
"Mr. Ridge, — In Childish Recollections omit the whole character of
Euryalus, and insert instead the lines to Florio as a part of the
poem, and send me a proof in due course.
"Etc. etc.,
"Byron.
"P.S. — The first line of the passage to be omitted begins 'Shall fair
Euryalus,' etc., and ends at 'Toil for more;' omit the whole."
return to footnote mark
List of Letters
Contents
1808-1809
94 — To the Rev. John Becher1
Dorant's Hotel, Feb. 26, 1808.
My Dear Becher, — Now for Apollo. I am happy that you still retain your
predilection, and that the public allow me some share of praise. I am
of so much importance that a most violent attack is preparing for me
in the next number of the Edinburgh Review2. This I had from the
authority of a friend who has seen the proof and manuscript of the
critique. You know the system of the Edinburgh gentlemen is universal
attack. They praise none; and neither the public nor the author
expects praise from them. It is, however, something to be noticed, as
they profess to pass judgment only on works requiring the public
attention. You will see this when it comes out; — it is, I understand,
of the most unmerciful description; but I am aware of it, and hope
you will not be hurt by its severity.
Tell Mrs. Byron not to be out of humour with them, and to prepare her
mind for the greatest hostility on their part. It will do no injury
whatever, and I trust her mind will not be ruffled. They defeat their
object by indiscriminate abuse, and they never praise except the
partisans of Lord Holland and Co3. It is nothing to be abused when
Southey, Moore, Lauderdale, Strangford, and Payne Knight, share the
same fate4.
I am sorry — but "Childish Recollections" must be suppressed during
this edition. I have altered, at your suggestion, the obnoxious
allusions in the sixth stanza of my last ode.
And now, my dear Becher, I must return my best acknowledgments for the
interest you have taken in me and my poetical bantlings, and I shall
ever be proud to show how much I esteem the advice and the
adviser.
Believe me, most truly, etc.
Footnote 1: The Rev. John Thomas Becher (1770-1848), educated at
Westminster and Christ Church, Oxford, was appointed Vicar of Rumpton,
Notts., and Midsomer Norton, 1801; Prebendary of Southwell in 1818; and
chairman of Newark Quarter Sessions in 1816. In all matters relating to
the condition of the poor he made himself an acknowledged authority. He
was the originator of a house of correction, a Friendly Society, and a
workhouse at Southwell. He was one of the "supervisors" appointed to
organize the Milbank Penitentiary, which was opened in June, 1816. On
Friendly Societies he published three works (1824, 1825, and 1826), in
which, inter alia, he sought to prove that labourers, paying sixpence
a week from the time they were twenty, could secure not only sick-pay,
but an annuity of five shillings a week at the age of sixty-five. His
Anti-Pauper System (1828) pointed to indoor relief as the true cure to
pauperism. It was by Becher's advice that Byron destroyed his Fugitive
Pieces. No one who has read the silly verses which Becher condemned,
can doubt that the counsel was wise (see Byron's Lines to Becher,
Poems, vol. i. pp. 112-114, 114-116, 247- 251). The following are the
lines in which Becher expostulated with Byron on the mischievous
tendency of his verses:—
"Say, Byron! why compel me to deplore
Talents designed for choice poetic lore,
Deigning to varnish scenes, that shun the day,
With guilty lustre, and with amorous lay?
Forbear to taint the Virgin's spotless mind,
In Power though mighty, be in Mercy kind,
Bid the chaste Muse diffuse her hallowed light,
So shall thy Page enkindle pure delight,
Enhance thy native worth, and proudly twine,
With Britain's Honors, those that are divine."
return to footnote mark
Footnote 2: See, for the Review itself, Appendix II.
"As an author,"
writes Byron to Hobhouse, February 27, 1808, "I am cut to atoms by the
E — — - Review; it is just out, and has completely demolished my
little fabric of fame. This is rather scurvy treatment for a Whig
Review; but politics and poetry are different things, and I am no adept
in either. I therefore submit in silence."
Among the less sentimental
effects of this Review upon Byron's mind, he used to mention that, on
the day he read it, he drank three bottles of claret to his own share
after dinner; that nothing, however, relieved him till he had given vent
to his indignation in rhyme, and that "after the first twenty lines, he
felt himself considerably better" (Moore, Life, p. 69).
"I was sitting with Charles Lamb," H. Crabb Robinson told De Morgan,
"when Wordsworth came in, with fume in his countenance and the
Edinburgh Review in his hand.
'I have no patience with these
Reviewers,' he said; 'here is a young man, a lord, and a minor, it
appears, who publishes a little volume of poetry; and these fellows
attack him, as if no one may write poetry unless he lives in a garret.
The young man will do something, if he goes on.'
When I became
acquainted with Lady Byron, I told her this story, and she said,
'Ah!
if Byron had known that, he would never have attacked Wordsworth. He
once went out to dinner where Wordsworth was to be; when he came home,
I said,
"Well, how did the young poet get on with the old one?"
"To
tell you the truth," said he, "I had but one feeling from the
beginning of the visit to the end — reverence!"'"
(Diary, iii. 488.)
return
cross-reference: return to Footnote 1 of Letter 53
cross-reference: return to Footnote 3 of Letter 74
Footnote 3: That is to say, the Edinburgh Review praised only
Whigs. Henry Richard Vassall Fox, third Lord Holland (1773-1840), the
"nephew of Fox, and friend of Grey," married, in 1797, Elizabeth
Vassall, the divorced wife of Sir Godfrey Webster. He held the office of
Lord Privy Seal in the Ministry of All the Talents (October, 1806, to
March, 1807). During the long exclusion of the Whigs from office
(1807-32), when there seemed as little chance of a Whig Administration
as of "a thaw in Nova Zembla," Holland, in the House of Lords, supported
Catholic Emancipation, advocated the emancipation of slaves, opposed the
detention of Napoleon as a prisoner of war, and moved the abolition of
capital punishment for minor offences. From November, 1830, to his
death, with brief intervals, he was Chancellor of the Duchy of
Lancaster, in the administrations of Lord Grey and of Lord Melbourne.
Outside the House he kept the party together by his great social gifts.
An admirable talker, raconteur, and mimic, with a wit's relish
for wit, the charm of his good temper was irresistible.
"In my whole experience of our race," said Lord Brougham, "I never saw
such a temper, nor anything that at all resembled it"
(Statesmen of the
Time of George III., ed. 1843, 3rd series, p. 341). Greville speaks of
"his imperturbable temper, unflagging vivacity and spirit, his
inexhaustible fund of anecdote, extensive information, sprightly wit"
(Memoirs, iii. 446). Leslie, in his Autobiographical Recollections
(vol. i. p. 100), adds the tribute that
"he was, without any exception, the very best-tempered man I have ever
known."
Lord John Russell (preface to vol. vi. of the Life of Thomas
Moore) says that
"he won without seeming to court, instructed without seeming to teach,
and he amused without labouring to be witty."
George Ticknor (Life,
vol. i. p. 264)
"never met a man who so disarms opposition in discussion, as I have
often seen him, without yielding an iota, merely by the unpretending
simplicity and sincerity of his manner."
Sydney Smith (Memoir of the Rev. Sydney Smith, chap. x. p. 187)
considered that his
"career was one great, incessant, and unrewarded effort to resist
oppression, promote justice, and restrain the abuse of power. He had
an invincible hatred of tyranny and oppression, and the most ardent
love of public happiness and attachment to public rights."
A lover of art, a scholar, a linguist, he wrote memoirs, satires, and
verses, collected materials for a life of his uncle, Charles James Fox,
and translated both from the Spanish and Italian. His Account of the
Life and Writings of Lope Felix de Vega Carpio (1806) was reviewed
favourably by the Edinburgh Review for October, 1806. Byron attacked
him in English Bards, and Scotch Reviewers (lines 540-559, and
notes), on the supposition that Lord Holland had instigated the
article in the Edinburgh Review on Hours of Idleness (January,
1808). In 1812, learning his mistake, and hearing from Rogers that Lord
and Lady Holland desired the satire to be withdrawn, he gave orders that
the whole impression should be burned (see Introduction to English
Sards, and Scotch Reviewers, Poems, vol. i. p. 294). In his Journal
(November 17, 1813) he writes,
"I have had a most kind letter from Lord Holland on The Bride of
Abydos, which he likes, and so does Lady H. This is very good-natured
in both, from whom I do not deserve any quarter. Yet I did think at
the time, that my cause of enmity proceeded from Holland House, and am
glad I was wrong, and wish I had not been in such a hurry with that
confounded Satire, of which I would suppress even the memory; but
people, now they can't get it, make a fuss, I verily believe out of
contradiction."
return
Footnote 4: In the early numbers of the Edinburgh Review reviews were
published of Southey's Thalaba and Madoc; of Moore's Odes of
Anacreon and Poems; of Lord Lauderdale's Inquiry into the
Nature and Origin of Public Wealth; of Lord Strangford's Translations
from Camoëns; of Payne Knight's Principles of Taste.
return
List of Letters
Dorant's, March 28, 1808.
I have lately received a copy of the new edition from Ridge, and it is
high time for me to return my best thanks to you for the trouble you
have taken in the superintendence. This I do most sincerely, and only
regret that Ridge has not seconded you as I could wish, — at least, in
the bindings, paper, etc., of the copy he sent to me. Perhaps those for
the public may be more respectable in such articles.
You have seen the Edinburgh Review, of course. I regret that Mrs.
Byron is so much annoyed. For my own part, these "paper bullets of the
brain" have only taught me to stand fire; and, as I have been lucky
enough upon the whole, my repose and appetite are not discomposed.
Pratt1, the gleaner, author, poet, etc., etc., addressed a long
rhyming epistle to me on the subject, by way of consolation; but it was
not well done, so I do not send it, though the name of the man might
make it go down. The E. Rs. have not performed their task well; at least
the literati tell me this; and I think I could write a more
sarcastic critique on myself than any yet published. For
instance, instead of the remark, — ill-natured enough, but not
keen, — about Macpherson, I (quoad reviewers) could have said,
"Alas,
this imitation only proves the assertion of Dr. Johnson, that many men,
women, and children, could write such poetry as Ossian's."2
I am thin and in exercise. During the spring or summer I trust we
shall meet. I hear Lord Ruthyn leaves Newstead in April. As soon as he
quits it for ever, I wish much you would take a ride over, survey the
mansion, and give me your candid opinion on the most advisable mode of
proceeding with regard to the house. Entre nous, I am
cursedly dipped; my debts, every thing inclusive, will be nine or
ten thousand before I am twenty-one. But I have reason to think my
property will turn out better than general expectation may conceive. Of
Newstead I have little hope or care; but Hanson, my agent, intimated my
Lancashire property was worth three Newsteads. I believe we have it
hollow; though the defendants are protracting the surrender, if
possible, till after my majority, for the purpose of forming some
arrangement with me, thinking I shall probably prefer a sum in hand to a
reversion. Newstead I may sell; — perhaps I will not, — though of
that more anon. I will come down in May or June.
Yours most truly, etc.
Footnote 1: Samuel Jackson Pratt (1749-1814), actor, itinerant lecturer,
poet of the Cruscan school, tragedian, and novelist, published a
large number of volumes. His Gleanings in England, Holland,
Wales, and Westphalia attained some reputation. His Sympathy,
a Poem (1788) passed through several editions. His stage-name, as
well as his nom de plume, was Courtney Melmoth. He was the
discoverer and patron of the cobbler-poet, Blacket (see also English
Bards, and Scotch Reviewers, line 319, note 2).
return to footnote mark
cross-reference: return to Footnote 1 of Letter 154
Footnote 2: "Dr. Johnson's reply to the friend who asked him if any man
living could have written such a book, is well known: 'Yes, sir;
many men, many women, and many children.' I inquired of him
myself if this story was authentic, and he said it was" (Mrs. Piozzi,
Johnsoniana, p. 84). — [Moore.]
return
List of Letters
[Six Mile Bottom, Newmarket, Cambridge.]
Dorant's, [Tuesday], April 26th, 1808.
My dear Augusta, — I regret being compelled to trouble you again, but it
is necessary I should request you will inform Col. Leigh, if the P's
consent is not obtained in a few days, it will be of little service to
Mr. Wallace, who is ordered to join the 17th in ten days, the Regiment
is stationed in the East Indies, and, as he has already served there
nine years, he is unwilling to return. I shall feel particularly obliged
by Col. Leigh's interference, as I think from his influence the Prince's
consent might be obtained. I am not much in the habit of asking favours,
or pressing exertion, but, on this occasion, my wish to save Wallace
must plead my excuse.
I have been introduced to Julia Byron1 by Trevannion at the Opera;
she is pretty, but I do not admire her; there is too much Byron in her
countenance, I hear she is clever, a very great defect in a woman, who
becomes conceited in course; altogether I have not much inclination to
improve the acquaintance.
I have seen my old friend George1, who will prove the best of the
family, and will one day be Lord B. I do not much care how soon.
Pray name my nephew after his uncle; it must be a nephew, (I won't
have a niece,) I will make him my heir, for I shall never marry,
unless I am ruined, and then his inheritance would not be great.
George will have the title and his laurels; my property, (if any is
left in five years time,) I can leave to whom I please, and your son
shall be the legatee. Adieu.
Yours ever,
Byron.
Footnote 1: George Anson Byron, R.N. (1758-1793), second son of Admiral
the Hon. John Byron, by his wife Sophia Trevanion, and brother of
Byron's father, married Henrietta Charlotte Dallas, by whom he had a
son, George, who was at this time in the Royal Navy, and in 1824
succeeded as seventh Lord Byron; and a daughter, Julia Byron, who
married, in 1817, the Rev. Robert Heath. Of his cousin George, Byron
writes in his Journal for November 30, 1813 (Life, p. 209):
"I like
George much more than most people like their heirs. He is a fine fellow,
and every inch a sailor."
Again on December 1, 1813, he says,
"I hope he
will be an admiral, and, perhaps, Lord Byron into the bargain. If he
would but marry, I would engage never to marry myself, or cut him out of
the heirship."
George Anson Byron and his wife both died in 1793.
return to footnote mark
List of Letters
Newstead Abbey, Notts., Sept. 14, 1808.
My dear Becher, — I am much obliged to you for your inquiries, and shall
profit by them accordingly. I am going to get up a play here; the hall
will constitute a most admirable theatre. I have settled the dram.
pers., and can do without ladies, as I have some young friends who will
make tolerable substitutes for females, and we only want three male
characters, beside Mr. Hobhouse and myself, for the play we have fixed
on, which will be the Revenge1. Pray direct Nicholson the carpenter
to come over to me immediately, and inform me what day you will dine and
pass the night here.
Believe me, etc.
Footnote 1: Young's tragedy (1721), from which one of Byron's Harrow
speeches in the character of "Zanga" was taken (see page 27, note 1).
return to footnote mark
List of Letters
98 — To John Jackson1
N. A., Notts., September 18, 1808.
Dear Jack, — I wish you would inform me what has been done by Jekyll, at
No. 40, Sloane Square, concerning the pony I returned as unsound.
I have also to request you will call on Louch at Brompton, and inquire
what the devil he meant by sending such an insolent letter to me at
Brighton; and at the same time tell him I by no means can comply with
the charge he has made for things pretended to be damaged.
Ambrose behaved most scandalously about the pony. You may tell Jekyll if
he does not refund the money, I shall put the affair into my lawyer's
hands. Five and twenty guineas is a sound price for a pony, and by God,
if it costs me five hundred pounds, I will make an example of Mr.
Jekyll, and that immediately, unless the cash is returned.
Believe me, dear Jack, etc.
Footnote 1: John Jackson (1769-1845), better known as "Gentleman"
Jackson, was champion of England from 1795 to 1803. His three fights
were against Fewterel (1788), George Ingleston (1789), and Mendoza
(1795). In his fight at Ingatestone with "George the Brewer," he slipped
on the wet stage, and, falling, dislocated his ankle and broke his leg.
His fight with Mendoza at Hornchurch, Essex, was decided in nine rounds.
At the end of the third round "the odds rose two to one on Mendoza." In
the fifth, Jackson "seized hold of his opponent by the hair, and served
him out in that defenceless state till he fell to the ground." The fight
was practically over, and the odds at once turned in favour of Jackson,
who thenceforward had matters all his own way. Even if Mendoza had worn
a wig, he probably would have succumbed to Jackson, who was a more
powerful man with a longer reach, and as scientific, though not so
ornamental, a boxer. In 1803 Jackson retired from the ring.
"I can see him now" (Pugilistica, vol. i. 98), "as I saw him in '84,
walking down Holborn Hill towards Smithfield. He had on a scarlet coat
worked in gold at the button-holes, ruffles, and frill of fine lace, a
small white stock, no collar (they were not then invented), a looped
hat with a broad black band, buff knee-breeches, and long silk
strings, striped white silk stockings, pumps, and paste buckles; his
waistcoat was pale blue satin, sprigged with white. It was impossible
to look on his fine ample chest, his noble shoulders, his waist, (if
anything too small,) his large, but not too large hips, ... his limbs,
his balustrade calf and beautifully turned, but not over delicate
ankle, his firm foot, and peculiarly small hand, without thinking that
nature had sent him on earth as a model. On he went at a good five
miles and a half an hour, the envy of all men, and the admiration of
all women."
His rooms at 13, Bond Street, became the head-quarters of the Pugilistic
Club, with whose initials, P.C., the ropes and stakes at prize-rings
were marked (see page 99, note 1; and Pierce Egan's Life in London,
pp. 252-254). From 1803 to 1824, when he retired from the profession, he
was, as Pierce Egan says of him (p. 254), unrivalled as "a teacher of
the Art of self-defence." His character stood high. "From the highest
to the lowest person in the Sporting World, his decision is law."
"This gentleman," says Moore, in a note to Tom Crib's Memorial to
Congress (p. 13), "as he well deserves to be called, from the
correctness of his conduct and the peculiar urbanity of his manners,
forms that useful link between the amateurs and the professors of
pugilism, which, when broken, it will be difficult, if not wholly
impossible, to replace."
He was Byron's guest at Cambridge, Newstead, and Brighton; received from
him many letters; and is described by him, in a note to Don Juan
(Canto XI. stanza xix.), as "my old friend and corporeal pastor and
master." Jackson's monument in Brompton Cemetery, a couchant lion and a
mourning athlete, was subscribed for "by several noblemen and gentlemen,
to record their admiration of one whose excellence of heart and
incorruptible worth endeared him to all who knew him."
return to footnote mark
List of Letters
N. A., Notts., October 4, 1808.
You will make as good a bargain as possible with this Master Jekyll, if
he is not a gentleman. If he is a gentleman, inform me, for I shall
take very different steps. If he is not, you must get what you can of
the money, for I have too much business on hand at present to commence
an action. Besides, Ambrose is the man who ought to refund, — but I have
done with him. You can settle with L. out of the balance, and dispose of
the bidets, etc., as you best can.
I should be very glad to see you here; but the house is filled with
workmen, and undergoing a thorough repair. I hope, however, to be more
fortunate before many months have elapsed.
If you see Bold Webster1, remember me to him, and tell him I have to
regret Sydney, who has perished, I fear, in my rabbit warren, for we
have seen nothing of him for the last fortnight. Adieu2.
Believe me, etc.
Footnote 1: Sir Godfrey Vassal Webster (1788-1836).
return to footnote mark
Footnote 2: A third letter to Jackson, written from Newstead, December
12, 1808, runs as follows:—
"My Dear Jack, — You will get the greyhound from the owner at any
price, and as many more of the same breed (male or female) as you can
collect.
"Tell D'Egville his dress shall be returned — I am obliged to him for
the pattern. I am sorry you should have so much trouble, but I was not
aware of the difficulty of procuring the animals in question. I
shall have finished part of my mansion in a few weeks, and, if you can
pay me a visit at Christmas, I shall be very glad to see you.
Believe me, etc."
In a bill, for 1808, sent in to Byron by Messrs. Finn and Johnson,
tailors, of Nottingham, appears the following item: "Masquerade Jackett
with belt and rich Turban, £11:9:6." This is probably the dress made
from d'Egville's pattern.
James d'Egville learned dancing from Gaetano Vestris, well known at the
Court of Frederick the Great, and from Gardel, the Court teacher of
Marie Antoinette. He, his brother Louis, and his sister Madame Michau,
were the most famous teachers of the day in England. The real name of
the family was Hervey; that of d'Egville was assumed for professional
purposes. James d'Egville enjoyed a great reputation, both as an actor
and a dancer, in Paris and London. He was Acting-Manager and Director of
the King's Theatre (October, 1807, to January, 1808), but was dismissed,
owing to a disagreement between the managers, in the course of which he
was accused of French proclivities and republican principles (see
Waters's Opera-Glass, pp. 133-145). A man of taste and cultivation, he
produced some musical extravaganzas and ballets; e. g. Don Quichotte ou
les Noces de Gamache, L'Elèvement d'Adonis, The Rape of Dejanira, etc.
A coloured print, in the possession of his great-nephew, Mr. Louis
d'Egville, represents him, with Deshayes, in one of his most successful
appearances, the ballet-pantomime of Achille et Deidamie. He was an
enthusiastic sportsman.
return
List of Letters
Newstead Abbey, Notts, October 7, 1808.
Dear Madam, — I have no beds for the Hansons or any body else at present.
The Hansons sleep at Mansfield. I do not know that I resemble Jean
Jacques Rousseau1. I have no ambition to be like so illustrious a
madman — but this I know, that I shall live in my own manner, and as
much alone as possible. When my rooms are ready I shall be glad to see
you: at present it would be improper, and uncomfortable to both parties.
You can hardly object to my rendering my mansion habitable,
notwithstanding my departure for Persia in March (or May at farthest),
since you will be tenant till my return; and in case of
any accident (for I have already arranged my will to be drawn up the
moment I am twenty-one), I have taken care you shall have the house and
manor for life, besides a sufficient income. So you see my
improvements are not entirely selfish. As I have a friend here, we will
go to the Infirmary Ball on the 12th; we will drink tea with Mrs. Byron2 at eight o'clock, and expect to see you at the ball. If that lady
will allow us a couple of rooms to dress in, we shall be highly obliged:
— if we are at the ball by ten or eleven, it will be time enough, and we
shall return to Newstead about three or four. Adieu.
Believe me, yours very truly,
Byron.
Footnote 1: In Byron's Detached Thoughts, quoted by Moore (Life, p.
72), he thus refers to the comparison with Rousseau:—
"My mother, before I was twenty, would have it that I was like
Rousseau, and Madame de Stael used to say so too in 1813, and the
Edinburgh Review has something of the sort in its critique on the
fourth canto of Childe Harold. I can't see any point of
resemblance:— he wrote prose, I verse: he was of the people; I of the
aristocracy: he was a philosopher; I am none: he published his first
work at forty; I mine at eighteen: his first essay brought him
universal applause; mine the contrary: he married his housekeeper; I
could not keep house with my wife: he thought all the world in a plot
against him; my little world seems to think me in a plot against it,
if I may judge by their abuse in print and coterie: he liked botany; I
like flowers, herbs, and trees, but know nothing of their pedigrees:
he wrote music; I limit my knowledge of it to what I catch by
ear — I never could learn any thing by study, not even a
language — it was all by rote and ear, and memory: he had a
bad memory; I had, at least, an excellent one (ask
Hodgson the poet — a good judge, for he has an astonishing one): he
wrote with hesitation and care; I with rapidity, and rarely with
pains: he could never ride, nor swim, nor 'was cunning of
fence;' I am an excellent swimmer, a decent, though not at all
a dashing, rider, (having staved in a rib at eighteen, in the course
of scampering,) and was sufficient of fence, particularly of the
Highland broadsword, — not a bad boxer, when I could keep my temper,
which was difficult, but which I strove to do ever since I knocked
down Mr. Purling, and put his knee-pan out (with the gloves on), in
Angelo's and Jackson's rooms in 1806, during the sparring, — and I was,
besides, a very fair cricketer, — one of the Harrow eleven, when we
played against Eton in 1805. Besides, Rousseau's way of life, his
country, his manners, his whole character, were so very different,
that I am at a loss to conceive how such a comparison could have
arisen, as it has done three several times, and all in rather a
remarkable manner. I forgot to say that he was also
short-sighted, and that hitherto my eyes have been the contrary, to
such a degree that, in the largest theatre of Bologna, I distinguished
and read some busts and inscriptions, painted near the stage, from a
box so distant and so darkly lighted, that none of the company
(composed of young and very bright-eyed people, some of them in the
same box,) could make out a letter, and thought it was a trick, though
I had never been in that theatre before.
"Altogether, I think myself justified in thinking the comparison not
well founded. I don't say this out of pique, for Rousseau was a great
man; and the thing, if true, were flattering enough; — but I have no
idea of being pleased with the chimera."
return to footnote mark
Footnote 2: The Hon. Mrs. George Byron, née Frances Levett,
Byron's great-aunt, widow of the Hon. George Byron, fourth brother of
William, fifth Lord Byron.
return
List of Letters
Newstead Abbey, November 2, 1808.
Dear Mother, — If you please, we will forget the things you mention. I
have no desire to remember them. When my rooms are finished, I shall be
happy to see you; as I tell but the truth, you will not suspect me of
evasion. I am furnishing the house more for you than myself, and I shall
establish you in it before I sail for India, which I expect to do in
March, if nothing particularly obstructive occurs. I am now fitting up
the green drawing-room; the red for a bed-room, and the rooms
over as sleeping-rooms. They will be soon completed; — at least I hope
so.
I wish you would inquire of Major Watson (who is an old Indian) what
things will be necessary to provide for my voyage. I have already
procured a friend to write to the Arabic Professor at Cambridge1, for
some information I am anxious to procure. I can easily get letters from
government to the ambassadors, consuls, etc., and also to the governors
at Calcutta and Madras. I shall place my property and my will in the
hands of trustees till my return, and I mean to appoint you one. From
Hanson I have heard nothing — when I do, you shall have the particulars.
After all, you must own my project is not a bad one. If I do not travel
now, I never shall, and all men should one day or other. I have at
present no connections to keep me at home; no wife, or unprovided
sisters, brothers, etc. I shall take care of you, and when I return I
may possibly become a politician. A few years' knowledge of other
countries than our own will not incapacitate me for that part. If we see
no nation but our own, we do not give mankind a fair chance; — it is from
experience, not books, we ought to judge of them. There is nothing
like inspection, and trusting to our own senses.
Yours, etc.
Footnote 1: The Rev. John Palmer, Fellow of St. John's, Adam's
Professor of Arabic (1804-19).
return to footnote mark
List of Letters
102 — To Francis Hodgson1
Newstead Abbey, Notts., Nov. 3, 1808.
My Dear Hodgson, — I expected to have heard ere this the event of your
interview with the mysterious Mr. Haynes, my volunteer correspondent;
however, as I had no business to trouble you with the adjustment of my
concerns with that illustrious stranger, I have no right to complain of
your silence.
You have of course seen Drury2, in all the pleasing palpitations of
anticipated wedlock. Well! he has still something to look forward to,
and his present extacies are certainly enviable. "Peace be with him and
with his spirit," and his flesh also, at least just now ...
Hobhouse and your humble are still here. Hobhouse hunts, etc., and I do
nothing; we dined the other day with a neighbouring Esquire (not Collet
of Staines), and regretted your absence, as the Bouquet of Staines was
scarcely to be compared to our last "feast of reason." You know,
laughing is the sign of a rational animal; so says Dr. Smollett. I think
so, too, but unluckily my spirits don't always keep pace with my
opinions. I had not so much scope for risibility the other day as I
could have wished, for I was seated near a woman, to whom, when a boy, I
was as much attached as boys generally are, and more than a man should
be3. I knew this before I went, and was determined to be valiant, and
converse with sang froid; but instead I forgot my valour and my
nonchalance, and never opened my lips even to laugh, far less to speak,
and the lady was almost as absurd as myself, which made both the object
of more observation than if we had conducted ourselves with easy
indifference. You will think all this great nonsense; if you had seen
it, you would have thought it still more ridiculous. What fools we are!
We cry for a plaything, which, like children, we are never satisfied
with till we break open, though like them we cannot get rid of it by
putting it in the fire.
I have tried for Gifford's Epistle to Pindar4, and the bookseller
says the copies were cut up for waste paper; if you can procure
me a copy I shall be much obliged. Adieu!
Believe me, my dear Sir, yours ever sincerely,
Byron.
Footnote 1: Francis Hodgson (1781-1852), educated at Eton (1794-99)
and at King's College, Cambridge, Scholar (1799), Fellow (1802),
hesitated between literature and the bar as his profession. For
three years he was a private tutor, for one (1806) a master at Eton.
In 1807 he became a resident tutor at King's. It was not till 1812
that he decided to take orders. Two years later he married Miss
Tayler, a sister of Mrs. Henry Drury, and took a country curacy.
In 1816 he was given the Eton living of Bakewell, in Derbyshire,
became Archdeacon of Derby in 1836, and in 1840 Provost of Eton.
At Eton he died December 29, 1852.
Hodgson's literary facility was extraordinary. He rhymed with an ease which almost rivals that of Byron, and from 1807 to 1818
he poured out quantities of verse, English and Latin, original and
translated, besides writing articles for the Quarterly, the Monthly,
and the Critical Reviews. He published his Translation of Juvenal
in 1807, in which he was assisted by Drury and Merivale; Lady
Jane Grey, a Tale; and other Poems (1809); Sir Edgar, a Tale
(1810); Leaves of Laurel (1812); Charlemagne, an Epic Poem
(1815), translated from the original of Lucien Bonaparte, Prince of
Canino, by S. Butler and Francis Hodgson; The Friends, a Poem
in Four Books; Mythology for Versification (1831); A Charge, as
Archdeacon of Derby (1837); Sermons (1846); and other works.
His acquaintance with Byron began in 1807, when Byron was
meditating British Bards, and Hodgson, provoked by a review of
his Juvenal in the Edinburgh Review, was composing his Gentle
Alterative prepared for the Reviewers, which appears on pp. 56, 57
of Lady Jane Grey. There are some curious points of resemblance
between the two poems, though Hodgson's lines can hardly be
compared for force and sting to English Bards, and Scotch Reviewers.
Like Byron (see English Bards, etc., line 513, note 7), he makes
merry over the blunder of the Edinburgh reviewer, who, in an
article on Payne Knight's Principles of Taste, severely criticized
some Greek lines which he attributed to Knight, but which, in fact,
were by Pindar:—
"And when he frown'd on Kn — 's erroneous Greek,
Bad him in Pindar's page that error seek."
Like Byron also, he attributes the blunder to Hallam, and speaks
of "Hallam's baffled art." The article was written by Lord
Holland's physician, Dr. Allen, who, according to Sydney Smith,
had "the creed of a philosopher and the legs of a clergyman."
Like Byron also (see English Bards, etc., line 820), he appeals to
Gifford, who was an old family friend, to return to the fray:—
"Oh! for that voice, whose cadence loud and strong
Drove Delia Crusca from the field of song —
And with a force that guiltier fools should feel,
Rack'd a vain butterfly on Satire's wheel."
In a note appended to the words in his satire — "Like clowns detest
nobility" — he refers to the Edinburgh's treatment of Byron's verse.
The link thus established between Byron and Hodgson grew
stronger for the next few years. Hodgson suppressed Moore's
challenge to the author of English Bards; was Byron's guest at
Newstead (see page 179, in note); pleaded with him on the subject
of religion; translated his lines, "I would I were a careless child,"
into Latin verse (Lady Jane Grey, p. 94); addressed him in poetry,
as, for instance, in the "Lines to a Friend going abroad" (Sir
Edgar, p. 173). Byron, on his side, seems to have been sincerely attached to Hodgson, to whom he left, by his first will (1811),
one-third
of his personal goods, and in 1813 gave £1000 to enable him
to marry. Hodgson corresponded with Mrs. Leigh and with Miss
Milbanke, afterwards Lady Byron, endeavoured to heal the breach
between husband and wife, and was one of the mourners at Hucknall
Torkard Church.
In Haydon's Table-Talk (vol. ii pp. 367-8) is recorded a conversation
with Hobhouse on the subject of Hodgson. Haydon's account
of Hobhouse's words is confused; but he definitely asserts that
Hodgson's life was dissipated, and insinuates that he perverted
Byron's character. Part of the explanation is probably this: Hodgson's
friend, the Rev. Robert Bland, kept a mistress, described as a
woman of great personal and mental attraction. He asked Hodgson,
during his absence on the Continent, to visit the lady and send
him frequent news of her. Hodgson did so, with the result that,
at Bland's return, the lady refused to see him. When Byron came
back from his Eastern tour, he received a frantic letter from Bland,
telling him that Hodgson had stolen her love. To this Byron refers
in his letter to Harness, December 15, 1811, and probably told an
embellished story to Hobhouse. But Hodgson himself warmly
repudiated the charge; and there is no reason to think that his
version of the affair is not the truth.
return to footnote mark
cross-reference: return to Footnote 1 of Letter 14
cross-reference: return to Footnote 2 of Letter 137
Footnote 2: The Rev. Henry Drury married, December 20, 1808, Ann
Caroline, daughter of Archdale Wilson Tayler, of Boreham Wood,
Herts. Their five sons were all educated at Harrow: Henry,
Archdeacon of Wilts and editor of Arundines Cami (1841); Byron,
Vice-Admiral R.N.; Benjamin Heath, Vice-President of Caius
College, Cambridge; Heber, Colonel in the Madras Army; Charles
Curtis, General of the Bengal Staff Corps (see also page 41,
note 2).
return
Footnote 3: Mrs. Chaworth Musters (see Byron's lines, "Well! thou art
happy," Poems, vol. i. pp. 277-279).
return
Footnote 4: William Gifford (1756-1826), a self-taught scholar, first a
ploughboy, then boy on board a Brixham coaster, afterwards shoemaker's
apprentice, was sent by friends to Exeter College, Oxford
(1779-81). In the Baviad (1794) and the Mæviad (1795) he
attacked many of the smaller writers of the day, who were either
silly, like the Delia Cruscan school, or discreditable, like Williams,
who wrote as "Anthony Pasquin." In his Epistle to Peter Pindar
(1800) he succeeds in laying bare the true character of John Wolcot.
As editor of the Anti-Jacobin, or Weekly Examiner (November, 1797,
to July, 1798), he supported the political views of Canning and his
friends. As editor of the Quarterly Review, from its foundation
(February, 1809) to his resignation in September, 1824, he did
yeoman's service to sound literature by his good sense and adherence
to the best models. It was a period when all criticism was narrow,
and, to some degree, warped by political prejudice. In these
respects, Gifford's work may not have risen above — it certainly did
not fall below — the highest standard of contemporary criticism.
His editions of Massinger (1805), which superseded that of Monck
Mason and Davies (1765), of Ben Jonson (1816), of Ford (1827), are valuable. To his translation of Juvenal (1802) is prefixed his
autobiography. His translation of Persius appeared in 1821. To
Gifford, Byron usually paid the utmost deference.
"Any suggestion
of yours, even if it were conveyed," he writes to him, in 1813,
"in the less tender text of the Baviad, or a Monk Mason note to
Massinger, would be obeyed."
See also his letter (September 7,
1811), in which he calls Gifford his "Magnus Apollo," and values
his praise above the gems of Samarcand.
"He was," says Sir
Walter Scott (Diary, January 18, 1827), "a little man, dumpled
up together, and so ill-made as to seem almost deformed, but
with a singular expression of talent in his countenance."
Byron
was attracted to Gifford, partly by his devotion to the classical
models of literature, partly by the outspoken frankness of his literary
criticism, partly also, perhaps, by his physical deformity.
return
List of Letters
Newstead Abbey, Notts., November 18th, 1808.
Dear Sir, — I am truly glad to hear your health is reinstated. As for my
affairs I am sure you will do your best, and, though I should be glad to
get rid of my Lancashire property for an equivalent in money, I shall
not take any steps of that nature without good advice and mature
consideration.
I am (as I have already told you) going abroad in the spring; for this I
have many reasons. In the first place, I wish to study India and Asiatic
policy and manners. I am young, tolerably vigorous, abstemious in my way
of living; I have no pleasure in fashionable dissipation, and I am
determined to take a wider field than is customary with travellers. If I
return, my judgment will be more mature, and I shall still be young
enough for politics. With regard to expence, travelling through the East
is rather inconvenient than expensive: it is not like the tour of
Europe, you undergo hardship, but incur little hazard of spending money.
If I live here I must have my house in town, a separate house for Mrs.
Byron; I must keep horses, etc., etc. When I go abroad I place Mrs.
Byron at Newstead (there is one great expence saved), I have no horses
to keep. A voyage to India will take me six months, and if I had a dozen
attendants cannot cost me five hundred pounds; and you will agree with
me that a like term of months in England would lead me into four times
that expenditure. I have written to Government for letters and
permission of the Company, so you see I am serious.
You honour my debts; they amount to perhaps twelve thousand pounds, and
I shall require perhaps three or four thousand at setting out, with
credit on a Bengal agent. This you must manage for me. If my resources
are not adequate to the supply I must sell, but not
Newstead. I will at least transmit that to the next Lord. My debts
must be paid, if possible, in February. I shall leave my affairs to the
care of trustees, of whom, with your acquiescence, I shall
name you one, Mr. Parker another, and two more, on whom I am not
yet determined.
Pray let me hear from you soon. Remember me to Mrs. Hanson, whom I hope
to see on her return. Present my best respects to the young lady, and
believe me, etc.,
Byron.
List of Letters
Newstead Abbey, Notts., Nov. 27, 1808.
My Dear Sir, — Boatswain1 is to be buried in a vault waiting for
myself. I have also written an epitaph, which I would send, were it not
for two reasons: one is, that it is too long for a letter; and the
other, that I hope you will some day read it on the spot where it will
be engraved.
You discomfort me with the intelligence of the real orthodoxy of the
Arch-fiend's name2, but alas! it must stand with me at present; if
ever I have an opportunity of correcting, I shall liken him to Geoffrey
of Monmouth, a noted liar in his way, and perhaps a more correct
prototype than the Carnifex of James II.
I do not think the composition of your poem "a sufficing reason" for not
keeping your promise of a Christmas visit. Why not come? I will never
disturb you in your moments of inspiration; and if you wish to collect
any materials for the scenery?3, Hardwicke (where Mary was confined
for several years) is not eight miles distant, and, independent of the
interest you must take in it as her vindicator, is a most beautiful and
venerable object of curiosity. I shall take it very ill if you do not
come; my mansion is improving in comfort, and, when you require
solitude, I shall have an apartment devoted to the purpose of receiving
your poetical reveries.
I have heard from our Drury; he says little of the Row, which I regret:
indeed I would have sacrificed much to have contributed in any way (as a
schoolboy) to its consummation; but Butler survives, and thirteen boys
have been expelled in vain. Davies is not here, but Hobhouse hunts as
usual, and your humble servant "drags at each remove a lengthened
chain." I have heard from his Grace of Portland4 on the subject of my
expedition: he talks of difficulties; by the gods! if he throws any in
my way I will next session ring such a peal in his ears,
That he shall wish the fiery Dane
Had rather been his guest again5.
You do not tell me if Gifford is really my commentator: it is too good
to be true, for I know nothing would gratify my vanity so much as the
reality; even the idea is too precious to part with.
I shall expect you here; let me have no more excuses. Hobhouse desires
his best remembrance. We are now lingering over our evening potations. I
have extended my letter further than I ought, and beg you will excuse
it; on the opposite page I send you some stanzas6 I wrote off on
being questioned by a former flame as to my motives for quitting this
country. You are the first reader. Hobhouse hates everything of the
kind, therefore I do not show them to him. Adieu!
Believe me, yours very sincerely,
Byron.
Footnote 1: Boatswain, the Newfoundland dog, died November 18, 1808.
(For Byron's inscriptions in prose and verse, see Poems, vol. i p.
280.)
return to footnote mark
Footnote 2: Byron at first thought that Jeffrey, the editor of the Edinburgh Review, spelt his name in the same way as the Judge Jeffreys
of the Bloody Assizes. He probably writes "orthodoxy" for "orthography"
as a joke. (See the lines quoted from British Bards in notes to English. Bards, etc., line 439, note 2.)
return
Footnote 3: It is stated that Hodgson was writing a poem on Mary Queen
of Scots (Life of Rev. Francis Hodgson, vol. i p. 107). No such poem
was apparently ever published. In Hodgson's Lady Jane Grey, Queen Mary
of England plays a part; hence, possibly, the mistake.
return
Footnote 4: Byron asked the Duke of Portland to procure him "permission
from the E. I. Directors to pass through their settlements." The duke
replied, in effect, that Byron trespassed on his time and patience. So
Byron at least took his answer (see English Bards, and Scotch
Reviewers, line 1016 and note 2).
return
Footnote 5: Marmion, Canto II. stanza xxxi.
return
Footnote 6: See stanzas "To a Lady on being asked my Reason for
Quitting England in the Spring" (Poems, vol. i. p. 282).
return
List of Letters
[Ld. Chichester's, Stratton Street, London.]
Newstead Abbey, Notts., [Wednesday], Novr. 30th, 1808.
My Dearest Augusta, — I return you my best thanks for making me an uncle,
and forgive the sex this time; but the next must be a nephew. You
will be happy to hear my Lancashire property is likely to prove
extremely valuable; indeed my pecuniary affairs are altogether far
superior to my expectations or any other person's. If I would
sell, my income would probably be six thousand per annum; but I
will not part at least with Newstead, or indeed with the other, which is
of a nature to increase in value yearly. I am living here alone,
which suits my inclinations better than society of any kind. Mrs. Byron
I have shaken off for two years, and I shall not resume her yoke in
future, I am afraid my disposition will suffer in your estimation; but I
never can forgive that woman, or breathe in comfort under the same roof.
I am a very unlucky fellow, for I think I had naturally not a bad heart;
but it has been so bent, twisted, and trampled on, that it has now
become as hard as a Highlander's heelpiece.
I do not know that much alteration has taken place in my person, except
that I am grown much thinner, and somewhat taller! I saw Col. Leigh at
Brighton in July, where I should have been glad to have seen you; I only
know your husband by sight, though I am acquainted with many of the
Tenth. Indeed my relations are those whom I know the least, and in most
instances, I am not very anxious to improve the acquaintance. I hope you
are quite recovered, I shall be in town in January to take my seat, and
will call, if convenient; let me hear from you before.
[Signature cut off, and over the page is, in Mrs. Leigh's writing, this
endorsement: "Sent to Miss Alderson to go to Germany, May 29th, 1843."]
List of Letters
[Ld. Chichester's, Stratton Street, London.]
Newstead Abbey, Notts., Decr. 14th, 1808.
My Dearest Augusta, — When I stated in my last, that my intercourse with
the world had hardened my heart, I did not mean from any matrimonial
disappointment, no, I have been guilty of many absurdities, but I hope
in God I shall always escape that worst of evils, Marriage. I have no
doubt there are exceptions, and of course include you amongst them, but
you will recollect, that "exceptions only prove the Rule."
I live here much in my own manner, that is, alone, for I could
not bear the company of my best friend, above a month; there is such a
sameness in mankind upon the whole, and they grow so much more
disgusting every day, that, were it not for a portion of Ambition, and a
conviction that in times like the present we ought to perform our
respective duties, I should live here all my life, in unvaried Solitude.
I have been visited by all our Nobility and Gentry; but I return no
visits. Joseph Murray is at the head of my household, poor honest
fellow! I should be a great Brute, if I had not provided for him in the
manner most congenial to his own feelings, and to mine. I have several
horses, and a considerable establishment, but I am not addicted to
hunting or shooting. I hate all field sports, though a few years since I
was a tolerable adept in the polite arts of Foxhunting, Hawking,
Boxing, etc., etc. My Library is rather extensive, (and as you perhaps
know) I am a mighty Scribbler; I flatter myself I have made some
improvements in Newstead, and, as I am independent, I am happy, as far
as any person unfortunate enough to be born into this world, can be said
to be so.
I shall be glad to hear from you when convenient, and beg you to believe
me,
Very sincerely yours,
Byron.
List of Letters
Newstead Abbey, Notts., Dec. 17, 1808.
My Dear Sir, — I regret the contents of your letter as I think we shall
be thrown on our backs from the delay. I do not know if our best method
would not be to compromise if possible, as you know the state of my
affairs will not be much bettered by a protracted and possibly
unsuccessful litigation. However, I am and have been so much in the dark
during the whole transaction that I am not a competent judge of the most
expedient measures. I suppose it will end in my marrying a Golden
Dolly1 or blowing my brains out; it does not much matter which,
the remedies are nearly alike. I shall be glad to hear from you further
on the business. I suppose now it will be still more difficult to come
to any terms. Have you seen Mrs. Massingberd, and have you arranged my
Israelitish accounts? Pray remember me to Mrs. Hanson, to Harriet, and
all the family, female and male.
Believe me also, yours very sincerely,
Byron.
Footnote 1: Mrs. Byron also advised his marriage with an heiress. The
following passage is taken from her letter to Hanson, January 30, 1809:—
"I was sorry I could not see you here. Byron told me he intended to
put his servants on Board Wages at Newstead. I was very sorry to hear
of the great expence the Newstead fête would put him to. I can
see nothing but the Road to Ruin in all this, which grieves me to the
heart and makes me still worse than I would otherwise be (unless,
indeed, Coal Mines turn to Gold Mines), or that he mends his fortune
in the old and usual way by marrying a Woman with two or three hundred
thousand pounds. I have no doubt of his being a great speaker and a
celebrated public character, and all that; but that won't add to
his fortune, but bring on more expenses on him, and there is nothing
to be had in this country to make a man rich in his line of life."
In another letter to Hanson, dated March 4, 1809, she returns to the
same subject:—
"I have had a very dismal letter from my son, informing me that he is
ruined. He wishes to borrow my money. This I shall be very ready to
oblige him in, on such security as you approve. As it is my all,
this is very necessary, and I am sure he would not wish to have it on
any other terms. It cannot be paid up, however, under six months'
notice. I wish he would take the debt of a thousand pounds, that I
have been security for, on himself, and pay about eighty pounds he
owes here.
I wish to God he would exert himself and retrieve his affairs. He
must marry a Woman of fortune this spring; love matches is all
nonsense. Let him make use of the Talents God has given him. He is an
English Peer, and has all the privileges of that situation. What is
this about proving his grandfather's marriage? I thought it had been
in Lancashire. If it was not, it surely easily can be proved. Is
nothing going forward concerning the Rochdale Property? I am sure, if
I was Lord Byron, I would sell no estates to pay Jews; I only would
pay what was lawful. Pray answer the note immediately, and answer all
my questions concerning lending the money, the Rochdale property, and
why B. don't or can't take his seat, which is very hard, and very
provoking.
I am, Dear Sir, yours sincerely,
C. G. Byron."
List of Letters
Newstead Abbey, Notts., Dec. 17, 1808.
My Dear Hodgson, — I have just received your letter, and one from B.
Drury1, which I would send, were it not too bulky to despatch within
a sheet of paper; but I must impart the contents and consign the answer
to your care. In the first place, I cannot address the answer to him,
because the epistle is without date or direction; and in the next, the
contents are so singular that I can scarce believe my optics, "which are
made the fools of the other senses, or else worth all the rest."
A few weeks ago, I wrote to our friend Harry Drury of facetious memory,
to request he would prevail on his brother at Eton to receive the son of
a citizen in London well known unto me as a pupil; the family having
been particularly polite during the short time I was with them, induced
me to this application. "Now mark what follows," as somebody or Southey
sublimely saith: on this day, the 17th December, arrives an epistle
signed B. Drury, containing not the smallest reference to tuition or
intuition, but a petition for Robert Gregson2, of pugilistic
notoriety, now in bondage for certain paltry pounds sterling, and liable
to take up his everlasting abode in Banco Regis. Had this letter been
from any of my lay acquaintance, or, in short, from anyone but
the gentleman whose signature it bears, I should have marvelled not. If
Drury is serious, I congratulate pugilism on the acquisition of such a
patron, and shall be happy to advance any sum necessary for the
liberation of the captive Gregson; but I certainly hope to be certified
from you or some reputable housekeeper of the fact, before I write to
Drury on the subject. When I say the fact, I mean of the
letter being written by Drury, not having any doubt as to
the authenticity of the statement. The letter is now before me, and I
keep it for your perusal. When I hear from you I shall address my answer
to him, under your care; for as it is now the vacation at Eton,
and the letter is without time or place, I cannot venture
to consign my sentiments on so momentous a concern to
chance.
To you, my dear Hodgson, I have not much to say. If you can make it
convenient or pleasant to trust yourself here, be assured it will be
both to me.
Footnote 1: Benjamin Heath Drury (1782-1835), second son of the
Headmaster of Harrow (see page 41, note 2), was a Fellow of King's
College, Cambridge, and Assistant-master at Eton. Gronow
(Reminiscences, vol. i. pp. 209 and 233} says that Drury was
"passionately devoted to theatricals," and, with his friend Knapp,
frequently drove up to London after school-hours to sup with Edmund Kean
and Arnold at Drury Lane or the Hummums in Covent Garden. On one
occasion they took with them Lord Eldon's son, then a school-boy at
Eton. After supper the party were "run in" by the watchmen, and bailed
out at Bow Street by the Lord Chancellor's secretary.
return to footnote mark
Footnote 2: Bob Gregson (1778-1824), the big-boned, burly landlord of
the Castle, Holborn, known as "Bob's Chop-house," was a familiar figure
in the sporting world. When captain of the Liverpool and Wigan Packet,
he established his reputation in Lancashire as a fighter. He stood 6
feet 1-1/2 inches in height, and weighed 15 stone 6 pounds. But, in
spite of the eulogies of Pierce Egan — a low-caste Irishman, who was
first a compositor, then a comedian, and afterwards a newspaper reporter
(see Grantley Berkeley's My Life and Recollections, vol. i pp. 107,
108) — Gregson had no science, and depended only on his strength,
courage, and endurance. He was beaten by Gully at Six Mile Bottom in
1807, and again in 1808 at Markyate Street; also by Tom Cribb at Moulsey
Hurst in 1808 (Pugilistica, vol. i pp. 237-241). Failing as landlord
of the Castle, he set up a school of boxing at Dublin, where he
afterwards kept "the Punch House," in Moor Street. He died at Liverpool
in 1824. According to Egan (Boxiana, vol. i. pp. 357, 358),
Gregson "united Pugilism with Poetry." On this claim he adopted the
letters "P.P." after his name. Egan gives some of his doggerel among
"Prime Chaunts for the Fancy" (Ibid., p. 358). Moore, in Tom
Crib's Memorial to Congress, attributes to him his "Lines to Miss
Grace Maddox" (pp. 75-77); "Ya-Hip, my Hearties!" (pp. 80-83); and "The
Annual Pill" (pp. 84-86).
return
cross-reference: return to Footnote 14 of Letter 84
List of Letters
Newstead Abbey, Jan. 15th, 1809.
My Dear Sir, — I am much obliged by your kind invitation, but I wish you,
if possible, to be here on the 22nd1. Your presence will be of great
service, everything is prepared for your reception exactly as if I
remained, and I think Hargreaves will be gratified by the appearance of
the place, and the humours of the day. I shall on the first opportunity
pay my respects to your family, and though I will not trespass on your
hospitality on the 22nd, my obligation is not less for your agreeable
offer, which on any other occasion would be immediately accepted, but I
wish you much to be present at the festivities, and I hope you will add
Charles to the party. Consider, as the Courtier says in the tragedy of
Tom Thumb2 —
"This is a day; your Majesties may boast of it,
And since it never can come o'er, 'tis fit you make the most of it."
I shall take my seat as soon as circumstances will admit. I have not yet
chosen my side in politics, nor shall I hastily commit myself with
professions, or pledge my support to any men or measures, but though I
shall not run headlong into opposition, I will studiously avoid a
connection with ministry. I cannot say that my opinion is strongly in
favour of either party3; on the one side we have the late underlings
of Pitt, possessing all his ill fortune, without his talents; this may
render their failure more excusable, but will not diminish the public
contempt; on the other, we have the ill-assorted fragments of a worn-out
minority; Mr. Windham with his coat twice turned, and my Lord
Grenville who perhaps has more sense than he can make good use of;
between the two and the shuttlecock of both, a Sidmouth, and the general
football Sir F. Burdett, kicked at by all, and owned by none.
I shall stand aloof, speak what I think, but not often, nor too soon. I
will preserve my independence, if possible, but if involved with a
party, I will take care not to be the last or least in the ranks. As
to patriotism, the word is obsolete, perhaps improperly, so, for all
men in the Country are patriots, knowing that their own existence must
stand or fall with the Constitution, yet everybody thinks he could alter
it for the better, and govern a people, who are in fact easily governed,
but always claim the privilege of grumbling. So much for Politics, of
which I at present know little and care less; bye and bye, I shall use
the senatorial privilege of talking, and indeed in such times, and in
such a crew, it must be difficult to hold one's tongue.
Believe me, etc.,
Byron.
Footnote 1: Byron's coming of age was celebrated at Newstead on January
22, 1809.
return to footnote mark
Footnote 2: See O'Hara's acting version of Fielding's Tom Thumb the
Great, act i. sc. I —
"Doodle. A Day we never saw before;
A Day of fun and drollery.
Noodle. That you may say,
Their Majesties may boast of it;
And since it never can come more,
'Tis fit they make the most of it."
return
Footnote 3: Lord Grenville (1759-1834) became First Lord of the
Treasury; Lord Sidmouth, Lord Privy Seal; and William Windham, Secretary
for War, in February, 1806. They, with Fox and his friends, formed the
administration of "All the Talents," which in March, 1807, fell over the
Roman Catholic question. They were succeeded by the Duke of Portland's
Ministry, which included the "late underlings of Pitt," — Perceval,
Canning, Dundas, etc. "Weathercock" Windham, in the Ministry of "All the
Talents," was responsible for the conduct of a war which, as leader of
the so-called "New Opposition," he had vigorously opposed. Sir Francis
Burdett's zeal for Parliamentary Reform involved him in hostility to
both Whigs and Tories, who had combined to exclude him from Parliament
after his election for Middlesex (1802-6). In 1807 he had been elected
for Westminster.
return
List of Letters
Reddish's Hotel, Jan. 25, 1809.
My Dear Sir, — My only reason for not adopting your lines is because they
are your lines1. You will recollect that Lady Wortley Montague said
to Pope: "No touching, for the good will be given to you, and the bad
attributed to me." I am determined it shall be all my own, except such
alterations as may be absolutely required; but I am much obliged by the
trouble you have taken, and your good opinion.
The couplet on Lord C.2 may be scratched out and the following
inserted:
Roscommon! Sheffield! with your spirits fled,
No future laurels deck a noble head.
Nor e'en a hackney'd Muse will deign to smile
On minor Byron, nor mature Carlisle.
This will answer the purpose of concealment. Now for some couplets on
Mr. Crabbe3, which you may place after "Gifford, Sotheby, M'Niel:"
There be who say, in these enlightened days,
That splendid lies are all the Poet's praise;
That strained invention, ever on the wing,
Alone impels the modern Bard to sing.
'Tis true that all who rhyme, nay, all who write,
Shrink from that fatal word to genius, trite:
Yet Truth will sometimes lend her noblest fires,
And decorate the verse herself inspires.
This fact in Virtue's name let Crabbe attest;
Though Nature's sternest painter, yet the best.
I am sorry to differ with you with regard to the title4, but I mean
to retain it with this addition: The British [the word "British" is
struck through] English Bards and Scotch Reviewers; and if we call it a
Satire, it will obviate the objection, as the Bards also were Welch.
Your title is too humorous; — and as I know a little of — — , I wish not
to embroil myself with him, though I do not commend his treatment
of — — . I shall be glad to hear from you or see you, and beg you to
believe me,
Yours very sincerely,
Byron.
Footnote 1: Dallas (January 24, 1809) takes "the liberty of sending you
some two dozen lines," etc.
return to footnote mark
Footnote 2: The couplet on Lord Carlisle, as it stood in British Bards,
was —
"On one alone Apollo deigns to smile,
And crowns a new Roscommon in Carlisle."
(See English Bards, etc., lines 723, et seqq.; see also line 927,
note 2. For Lord Carlisle, see page 36, note 2.)
return
Footnote 3: For "Gifford, Sotheby, Macneil," see English Bards, etc.,
line 818, and notes. Dallas had written (January 24, 1809),
"I am
sorry you have not found a place among the genuine sons of Apollo for
Crabbe, who, in spite of something bordering on servility in his
dedication, may surely rank with some you have admitted to his temple"
(see English Bards, etc., lines 849-858).
return
Footnote 4: Dallas suggested as a title, The Parish Poor of
Parnassus.
return
List of Letters
February 7, 1809.
My Dear Sir, — Suppose we have this couplet —
Though sweet the sound, disdain a borrow'd tone,
Resign Achaia's lyre, and strike your own1:
or,
Though soft the echo, scorn a borrow'd tone,
Resign Achaia's lyre, and strike your own.
So much for your admonition; but my note of notes, my
solitary pun2, must not be given up — no, rather
"Let mightiest of all the beasts of chace
That roam in woody Caledon"
come against me; my annotation must stand.
We shall never sell a thousand; then why print so many? Did you receive
my yesterday's note? I am troubling you, but I am apprehensive some of
the lines are omitted by your young amanuensis, to whom, however, I am
infinitely obliged.
Believe me, yours very truly,
Byron.
Footnote 1: Dallas (February 6, 1809) objected to the rhyme in the
couplet:—
"Translation's servile work at length disown,
And quit Achaia's Muse to court your own."
(For the corrected couplet, see English Bards, etc., lines 889, 890.)
return to footnote mark
Footnote 2: See English Bards, etc., line 1016, note 2.
return
List of Letters
February 11, 1809.
I wish you to call, if possible, as I have some alterations
to suggest as to the part about Brougham1.
B.
Footnote 1: See ibid., line 524, note 2.
return to footnote mark
List of Letters
February 12, 1809.
Excuse the trouble, but I have added two lines which
are necessary to complete the poetical character of Lord
Carlisle1.
..........in his age
His scenes alone had damn'd our singing stage;
But Managers for once cried, "hold, enough!"
Nor drugg'd their audience with the tragic stuff!
Yours, etc.,
B.
Footnote 1: See ibid., lines 733-736. Another letter, written
February 15, 1809, runs as follows:—
"I wish you much to call on me, about One, not later, if convenient,
as I have some thirty or forty lines for addition.
Believe me, etc.,
B."
return to footnote mark
List of Letters
February 16, 1809.
Ecce iterum Crispinus! — I send you some lines to be
placed after "Gifford, Sotheby, M'Niel."1 Pray call tomorrow
any time before two, and
Believe me, etc.,
B.
P.S. — Print soon, or I shall overflow with more rhyme.
Footnote 1: See English Bards, etc., lines 819-830.
return to footnote mark
List of Letters
February 19, 1809.
I enclose some lines to be inserted, the first six after "Lords too
are bards," etc., or rather immediately following the line:
"Ah! who would take their titles with their rhymes."
The four next will wind up the panegyric on Lord Carlisle, and come
after "tragic stuff."1
Yours truly.
In these our times with daily wonders big,
A letter'd Peer is like a letter'd Pig:
Both know their alphabet, but who from thence
Infers that Peers or Pigs have manly sense?
Still less that such should woo the graceful Nine?
Parnassus was not made for Lords and Swine.
Roscommon, Sheffield, etc., etc.
...
... tragic stuff.
Yet at their judgment let his Lordship laugh,
And case his volumes in congenial calf:
Yes, doff that covering where morocco shines,
"And hang a calf-skin on those recreant" lines.
Footnote 1: See ibid., lines 736-740.
return to footnote mark
List of Letters
February 22, 1809.
A cut at the opera. — Ecce signum! from last night's
observation, and inuendos against the Society for the
Suppression of Vice1. The lines will come well in after
the couplets concerning Naldi and Catalani2!
Yours truly,
Byron.
Footnote 1: See English Bards, etc., lines 618-631, note 1, for the
"cut at the opera." The piece which provoked the outburst was I
Villegiatori Rezzani, at the King's Theatre, February 21, 1809.
Guiseppe Naldi (1770-1820) made his début in London, at the King's
Theatre, in April, 1806. (For further details, see English Bards,
etc., line 613, note 2.) Angelica Catalani, born at Sinigaglia, in
1779, or, according to some authorities, 1785, came out at Venice, in an
opera by Nasolini. She sang in many capitals of Europe, married at
Lisbon a French officer named Vallabrègue, and came to London in
October, 1806. The salary paid her was a cause of the O. P. riots at
Covent Garden in 1809, when one of the cries was, "No foreigners! No
Catalani!" A series of caricatures, one set by Isaac Cruikshank, and
several medals, commemorate the riots. Madame Catalani died at Paris in
1849.
return to footnote mark
Footnote 2: See English Bards, etc., lines 632-637.
return
List of Letters
8, St. James's Street, March 6, 1809.
Dear Mother, — My last letter was written under great depression of
spirits from poor Falkland's death1, who has left without a shilling
four children and his wife. I have been endeavouring to assist them,
which, God knows, I cannot do as I could wish, for my own embarrassments
and the many claims upon me from other quarters.
What you say is all very true: come what may, Newstead and I stand
or fall together. I have now lived on the spot, I have fixed my heart
upon it, and no pressure, present or future, shall induce me to barter
the last vestige of our inheritance. I have that pride within me which
will enable me to support difficulties. I can endure privations; but
could I obtain in exchange for Newstead Abbey the first fortune in the
country, I would reject the proposition. Set your mind at ease on that
score; Mr. Hanson talks like a man of business on the subject, — I feel
like a man of honour, and I will not sell Newstead.
I shall get my seat2 on the return of the affidavits from Carhais, in
Cornwall, and will do something in the House soon: I must dash, or it is
all over. My Satire must be kept secret for a month; after that you
may say what you please on the subject. Lord Carlisle has used me
infamously, and refused to state any particulars of my family to the
Chancellor. I have lashed him in my rhymes, and perhaps his lordship
may regret not being more conciliatory. They tell me it will have a
sale; I hope so, for the bookseller has behaved well, as far as
publishing well goes.
Believe me, etc.
P.S. — You shall have a mortgage on one of the farms3.
Footnote 1: Captain Charles John Cary, R.N., succeeded his brother
Thomas in 1796 as ninth Lord Falkland. He married, in 1803, Miss Anton,
the daughter of a West India merchant. He had been recently dismissed
from his ship "on account of some irregularities arising from too free a
circulation of the bottle." But he had received a promise of being
reinstated, and, in high spirits at the prospect, dined one evening in
March, 1809, at Stevens's Coffeehouse, in Bond Street. There he applied
to Mr. Powell an offensive nickname. "He lost his life for a joke, and
one too he did not make himself" (Medwin, Conversations, ed. 1825, p.
66). A challenge resulted. The parties met on Goldar's Green, and
Falkland, mortally wounded, died two days later in Powell's house in
Devonshire Place, on March 7, 1809. (Annual Register, vol. li. pp.
449, 450.) For a more detailed account, see Gentleman's Magazine for
March, 1809. Both accounts give March 7 as the date of Falkland's death.
A posthumous child was born to Lady Falkland. Byron stood godfather, and
gave £500 at the christening.
return to footnote mark
Footnote 2: Byron took his seat in the House of Lords, March 13, 1809.
The delay was caused by the difficulty of proving the marriage of
Admiral the Hon. John Byron with Miss Sophia Trevanion in the private
chapel of Carhais. Probably Carlisle neither possessed nor withheld any
information.
return
Footnote 3: Byron had borrowed £1000 for his return to Cambridge in
1807: £200 from Messrs. Wylde and Co., bankers, of Southwell; and the
remainder from the Misses Parkyns, and his great-aunt, the Hon. Mrs.
George Byron. For this debt his mother made herself liable. No mortgage
was given (see page 221, note 2).
return
cross-reference: return to Footnote 1 of Letter 72
List of Letters
8, St. James's Street, March 18, 1809.
There was no necessity for your excuses: if you have time and
inclination to write, "for what we receive, the Lord make us
thankful," — if I do not hear from you, I console myself with the idea
that you are much more agreeably employed.
I send down to you by this post a certain Satire lately published, and
in return for the three and sixpence expenditure upon it, only beg that
if you should guess the author, you will keep his name secret; at least
for the present. London is full of the Duke's business1. The Commons
have been at it these last three nights, and are not yet come to a
decision. I do not know if the affair will be brought before our House,
unless in the shape of an impeachment. If it makes its appearance in a
debatable form, I believe I shall be tempted to say something on the
subject. — I am glad to hear you like Cambridge: firstly, because, to
know that you are happy is pleasant to one who wishes you all possible
sublunary enjoyment; and, secondly, I admire the morality of the
sentiment. Alma Mater was to me injusta noverca; and the old beldam
only gave me my M.A. degree because she could not avoid it2. — You
know what a farce a noble Cantab. must perform.
I am going abroad, if possible, in the spring, and before I depart I am
collecting the pictures of my most intimate school-fellows; I have
already a few, and shall want yours, or my cabinet will be incomplete. I
have employed one of the first miniature painters3 of the day to take
them, of course, at my own expense, as I never allow my acquaintance to
incur the least expenditure to gratify a whim of mine. To mention this
may seem indelicate; but when I tell you a friend of ours first refused
to sit, under the idea that he was to disburse on the occasion, you will
see that it is necessary to state these preliminaries to prevent the
recurrence of any similar mistake. I shall see you in time, and will
carry you to the limner. It will be a tax on your patience for a
week; but pray excuse it, as it is possible the resemblance may be the
sole trace I shall be able to preserve of our past friendship and
acquaintance. Just now it seems foolish enough; but in a few years, when
some of us are dead, and others are separated by inevitable
circumstances, it will be a kind of satisfaction to retain in these
images of the living the idea of our former selves, and, to contemplate,
in the resemblances of the dead, all that remains of judgment, feeling,
and a host of passions. But all this will be dull enough for you, and so
good night; and, to end my chapter, or rather my homily,
Believe me, my dear H., yours most affectionately,
Footnote 1: This was the inquiry into the charges made by Colonel
Gwyllym Wardle, M.P. for Okehampton (1807-12), against the Duke of York
and his mistress, Mary Ann Clarke. The inquiry began January 27, 1809,
and ended March 20, 1809, with the duke's resignation, the Commons
having previously (March 17) acquitted him of "personal connivance and
corruption."
The case has passed into literature. Wardle, the valorous Dowler, and
Lowten, Mr. Perker's clerk, had all figured in the trial before they
played their parts in Pickwick. Wardle, who was a colonel of the Welsh
Fusiliers ("Wynne's Lambs") had fought at Vinegar Hill. After losing his
seat, he took a farm between Tunbridge Wells and Rochester, from which
he fled to escape his creditors, and died at Florence, November 30,
1834, aged seventy-two.
return to footnote mark
Footnote 2: Byron took his M.A. degree, July 4, 1808. In another letter
to Harness, dated February, 1809, he says,
"I do not know how you and
Alma Mater agree. I was but an untoward child myself, and I believe the
good lady and her brat were equally rejoiced when I was weaned, and if I
obtained her benediction at parting, it was, at best, equivocal."
return
Footnote 3: George Sanders (1774-1846) painted miniatures, made
watercolour copies of continental master-pieces, and afterwards became a
portrait-painter in oils. He painted several portraits of Byron, two of
which have been often engraved.
return
List of Letters
Twelve o'clock, Friday night.
My Dear Bankes, — I have just received your note; believe me I regret
most sincerely that I was not fortunate enough to see it before, as I
need not repeat to you that your conversation for half an hour would
have been much more agreeable to me than gambling1 or drinking, or
any other fashionable mode of passing an evening abroad or at home. — I
really am very sorry that I went out previous to the arrival of your
despatch: in future pray let me hear from you before six, and whatever
my engagements may be, I will always postpone them. — Believe me, with
that deference which I have always from my childhood paid to your
talents, and with somewhat a better opinion of your heart than I
have hitherto entertained,
Yours ever, etc.
Footnote 1:
"I learn with delight," writes Hobhouse from Cambridge, May 12, 1808,
"from Scrope Davies, that you have totally given up dice. To be sure
you must give it up; for you to be seen every night in the very vilest
company in town — could anything be more shocking, anything more unfit?
I speak feelingly on this occasion, non ignara mali miseris,
&c. I know of nothing that should bribe me to be present once more
at such horrible scenes. Perhaps 'tis as well that we are both
acquainted with the extent of the evil, that we may be the more
earnest in abstaining from it. You shall henceforth be Diis
animosus hostis."
Moore quotes (Life, p. 86) the following extract from Byron's
Journal:—
"I have a notion that gamblers are as happy as many people, being
always excited. Women, wine, fame, the table, — even ambition,
sate now and then; but every turn of the card and cast of the
dice keeps the gamester alive: besides, one can game ten times longer
than one can do any thing else. I was very fond of it when young, that
is to say, of hazard, for I hate all card games, — even faro.
When macco (or whatever they spell it) was introduced, I gave up the
whole thing, for I loved and missed the rattle and dash
of the box and dice, and the glorious uncertainty, not only of good
luck or bad luck, but of any luck at all, as one had sometimes
to throw often to decide at all. I have thrown as many as
fourteen mains running, and carried off all the cash upon the table
occasionally; but I had no coolness, or judgment, or calculation. It
was the delight of the thing that pleased me. Upon the whole, I left
off in time, without being much a winner or loser. Since
one-and-twenty years of age I played but little, and then never above
a hundred, or two, or three."
return to footnote mark
List of Letters
April 25, 1809.
Dear Sir, — I am just arrived at Batt's Hotel, Jermyn Street, St.
James's, from Newstead, and shall be very glad to see you when
convenient or agreeable. Hobhouse is on his way up to town, full of
printing resolution1, and proof against criticism. — Believe me, with
great sincerity,
Yours truly,
Byron.
Footnote 1: See page 163, note 1. Hobhouse's miscellany was
published in 1809, under the title of Imitations and Translations
from the Antient and Modern Classics: Together with Original Poems never
before published.
return to footnote mark
List of Letters
Batt's Hotel, Jermyn Street, April 26th, 1809.
Dear Sir, — I wish to know before I make my final effort elsewhere, if
you can or cannot assist me in raising a sum of money on fair and
equitable terms and immediately1. I called twice this morning, and
beg you will favour me with an answer when convenient. I hope all your
family are well. I should like to see them together before my departure.
The Court of Chancery it seems will not pay the money, of which indeed I
do not know the precise amount; the Duke of Portland will not pay his
debt, and with the Rochdale property nothing is done. — My debts are
daily increasing, and it is with difficulty I can command a shilling. As
soon as possible I shall get quit of this country, but I wish to do
justice to my creditors (though I do not like their importunity), and
particularly to my securities, for their annuities must be paid off
soon, or the interest will swallow up everything. Come what may, in
every shape and in any shape, I can meet ruin, but I will never sell
Newstead; the Abbey and I shall stand or fall together, and, were my
head as grey and defenceless as the Arch of the Priory, I would abide by
this resolution. The whole of my wishes are summed up in this; procure
me, either of my own or borrowed of others, three thousand pounds, and
place two in Hammersley's hands for letters of credit at Constantinople;
if possible sell Rochdale in my absence, pay off these annuities and my
debts, and with the little that remains do as you will, but allow me to
depart from this cursed country, and I promise to turn Mussulman, rather
than return to it. Believe me to be,
Yours truly, Byron.
P.S. — Is my will finished? I should like to sign it while I have
anything to leave.
Footnote 1: Money was obtained, partly by means of a life insurance
effected with the Provident Institution. The medical report, signed by
Benjamin Hutchinson, F.R.C.S., London, states that Hutchinson had
attended Byron for the last four or five years; that he was, when last
seen by Hutchinson, in very good health; that he never was afflicted
with any serious malady; that he was sober and temperate; that he
"sometimes used much exercise, and at others was of a studious and
sedentary turn;" and thus concludes: "I do believe that he possesses an
unimpaired, healthy constitution, and I am not aware of any circumstance
which may be considered as tending to shorten his life."
Mrs. Byron (April 9, 1809) begs Hanson to see that Byron gave some
security for the thousand pounds for which she was bound. She adds:
"There is some Trades People at Nottingham that will be completely
ruined if he does not pay them, which I would not have happen for the
whole world." No security seems to have been given, and the tradesmen
remained unpaid. Mrs. Byron's death was doubtless accelerated by anxiety
from these causes.
return to footnote mark
cross-reference: return to Footnote 3 of Letter 117
cross-reference: return to Footnote 1 of Letter 22
List of Letters
122 — To the Rev. R. Lowe1
8, St. James Street, May 15, 1809.
My Dear Sir, — I have just been informed that a report is circulating in
Notts of an intention on my part to sell Newstead, which is rather
unfortunate, as I have just tied the property up in such a manner as to
prevent the practicability, even if my inclination led me to dispose of
it. But as such a report may render my tenants uncomfortable, I will
feel very much obliged if you will be good enough to contradict the
rumour, should it come to your ears, on my authority. I rather
conjecture it has arisen from the sale of some copyholds of mine in
Norfolk2. I sail for Gibraltar in June, and thence to Malta when, of
course, you shall have the promised detail. I saw your friend Thornhill
last night, who spoke of you as a friend ought to do. Excuse this
trouble, and believe me to be, with great sincerity,
Yours affectionately, Byron.
Footnote 1: The Rev. Robert Lowe was some years older than Byron, and
had known him intimately at Southwell in his early youth. Miss Pigot was
a cousin of Mr. Lowe, as was also the Rev. J. T. Becher of Southwell.
Mrs. Chaworth Musters, who contributed this letter to The Life and
Letters of Viscount Sherbrooke (vol. i. p. 46), adds that her
grandfather was, naturally, excessively annoyed at having been made the
mouthpiece of an untruth, and that the coolness which arose in
consequence lasted up to the end of Byron's life. There can, however, be
no doubt that Byron made the statement in all sincerity.
return to footnote mark
Footnote 2: At Wymondham.
return
List of Letters
Contents
1809-1811
Falmouth, June 22, 1809.
Dear Mother, — I am about to sail in a few days; probably before this
reaches you. Fletcher begged so hard, that I have continued him in my
service. If he does not behave well abroad, I will send him back in a
transport. I have a German servant (who has been with Mr.
Wilbraham in Persia before, and was strongly recommended to me by Dr.
Butler, of Harrow), Robert and William1; they constitute my whole
suite. I have letters in plenty:— you shall hear from me at the
different ports I touch upon; but you must not be alarmed if my letters
miscarry. The Continent is in a fine state — an insurrection has broken
out at Paris, and the Austrians are beating Buonaparte — the Tyrolese
have risen.
There is a picture of me in oil, to be sent down to Newstead soon2.
— I wish the Miss Pigots had something better to do than carry my
miniatures to Nottingham to copy. Now they have done it, you may ask
them to copy the others, which are greater favourites than my own. As to
money matters, I am ruined — at least till Rochdale is sold; and if that
does not turn out well, I shall enter into the Austrian or Russian
service — perhaps the Turkish, if I like their manners. The world is all
before me, and I leave England without regret, and without a wish to
revisit any thing it contains, except yourself, and your present
residence.
Believe me, yours ever sincerely.
P.S. — Pray tell Mr. Rushton his son is well, and doing well; so is
Murray3, indeed better than I ever saw him; he will be back in about
a month. I ought to add the leaving Murray to my few regrets, as his age
perhaps will prevent my seeing him again. Robert I take with me; I like
him, because, like myself, he seems a friendless animal.
Footnote 1: Robert Rushton and William Fletcher, the "little page" and
"staunch yeoman" of Childe Harold's "Good Night," Canto I. stanza xiii.
return to footnote mark
Footnote 2: By George Sanders.
return
Footnote 3: "Joe" Murray was sent back from Gibraltar, and with him
returned the homesick Robert Rushton.
return
cross-reference: return to Footnote 4 of Letter 7
List of Letters
Falmouth, June 28, 1809.
My Dear Drury, — We sail to-morrow in the Lisbon packet, having been
detained till now by the lack of wind, and other necessaries. These
being at last procured, by this time tomorrow evening we shall be
embarked on the vide vorld of vaters, vor all the vorld like Robinson
Crusoe. The Malta vessel not sailing for some weeks, we have determined
to go by way of Lisbon, and, as my servants term it, to see "that there
"Portingale" — thence to Cadiz and Gibraltar, and so on our old
route to Malta and Constantinople, if so be that Captain Kidd, our
gallant, or rather gallows, commander, understands plain sailing and
Mercator, and takes us on a voyage all according to the chart.
Will you tell Dr. Butler that I have taken the treasure of a servant,
Friese, the native of Prussia Proper, into my service from his
recommendation? He has been all among the Worshippers of Fire in Persia,
and has seen Persepolis and all that.
Hobhouse has made woundy preparations for a book on his return; 100
pens, two gallons of Japan Ink, and several volumes of best blank, is no
bad provision for a discerning public. I have laid down my pen, but have
promised to contribute a chapter on the state of morals, and a further
treatise on the same to be intituled "..., Simplified,... or Proved
to be Praiseworthy from Ancient Authors and Modern Practice."
Hobhouse further hopes to indemnify himself in Turkey for a life of
exemplary chastity at home. Pray buy his Missellingany, as the
Printer's Devil calls it. I suppose it is in print by this time.
Providence has interposed in our favour with a fair wind to carry us out
of its reach, or he would have hired a Faqui to translate it into the
Turcoman lingo.
"The cock is crowing,
I must be going,
And can no more."
Ghost of Gaffer Thumb1.
Adieu. — Believe me, etc., etc.
Footnote 1: In Fielding's burlesque tragedy, The Tragedy of Tragedies;
or the Life and Death of Tom Thumb the Great(1730), occur the
lines —
"Arthur, beware; I must this moment hence,
Not frighted by your voice, but by the cock's."
The burlesque was altered by Kane O'Hara, and published as performed at
the Theatre Royal, Haymarket, in 1805. In this prompt-book version (act
i) appear the lines quoted by Byron.
"Ghost. Grizzle's Rebellion,
What need I tell you on?
Or by a red cow
Tom Thumb devoured?
(cock crows)
Hark the cock crowing!
I must be going:
I can no more {vanishes}."
return to footnote mark
cross-reference: return to Footnote 7 of Letter 149
List of Letters
Falmouth, June 25, 1809.
My Dear Hodgson, — Before this reaches you, Hobhouse, two officers'
wives, three children, two waiting-maids, ditto subalterns for the
troops, three Portuguese esquires and domestics, in all nineteen souls,
will have sailed in the Lisbon packet, with the noble Captain Kidd, a
gallant commander as ever smuggled an anker of right Nantz.
We are going to Lisbon first, because the Malta packet has sailed, d'ye
see? — from Lisbon to Gibraltar, Malta, Constantinople, and "all that,"
as Orator Henley said, when he put the Church, and "all that," in
danger1.
This town of Falmouth, as you will partly conjecture, is no great ways
from the sea. It is defended on the sea-side by tway castles, St. Maws
and Pendennis, extremely well calculated for annoying every body except
an enemy. St. Maws is garrisoned by an able-bodied person of fourscore,
a widower. He has the whole command and sole management of six most
unmanageable pieces of ordnance, admirably adapted for the destruction
of Pendennis, a like tower of strength on the opposite side of the
Channel. We have seen St. Maws, but Pendennis they will not let us
behold, save at a distance, because Hobhouse and I are suspected of
having already taken St. Maws by a coup de main.
The town contains many Quakers and salt fish — the oysters have a taste
of copper, owing to the soil of a mining country — the women (blessed be
the Corporation therefor!) are flogged at the cart's tail when they pick
and steal, as happened to one of the fair sex yesterday noon. She was
pertinacious in her behaviour, and damned the mayor.
This is all I know of Falmouth. Nothing occurred of note in our way
down, except that on Hartford Bridge we changed horses at an inn, where
the great — —, Beckford2, sojourned for the night. We tried in
vain to see the martyr of prejudice, but could not. What we thought
singular, though you perhaps will not, was that Ld Courtney3
travelled the same night on the same road, only one stage behind
him.
Hodgson, remember me to the Drury, and remember me to yourself when
drunk. I am not worth a sober thought. Look to my satire at Cawthorn's,
Cockspur Street, and look to the Miscellany of the Hobhouse. It
has pleased Providence to interfere in behalf of a suffering public by
giving him a sprained wrist, so that he cannot write, and there is a
cessation of ink-shed.
I don't know when I can write again, because it depends on that
experienced navigator, Captain Kidd, and the "stormy winds that (don't)
blow" at this season. I leave England without regret — I shall return to
it without pleasure. I am like Adam, the first convict sentenced to
transportation, but I have no Eve, and have eaten no apple but what was
sour as a crab; — and thus ends my first chapter. Adieu4.
Yours, etc.
Footnote 1: Henley, in one of his publications entitled Oratory
Transactions, engaged
"to execute singly what would sprain a dozen of modern doctors of the
tribe of Issachar — to write, read, and study twelve hours a day, and
yet appear as untouched by the yoke as if he never wore it — to teach
in one year what schools or universities teach in five;" and he
furthermore pledged himself to persevere in his bold scheme until he
had "put the church, — and all that — , in danger."
(Moore).
return to footnote mark
Footnote 2: William Beckford (1760-1844), son of Chatham's friend who
was twice Lord Mayor of London, at the age of eleven succeeded it is
said, to a million of ready money and a hundred thousand a year. Before
he was seventeen he wrote his Biographical Memoirs of Extraordinary
Painters, designed as a satire on the Vies des Peintres
Flamands, (Memoirs of William Beckford, by Cyrus Redding,
vol. i. p. 96.) His travels (1777-82) in Switzerland, the Low Countries,
and Italy are described in his Dreams, Waking Thoughts, and
Incidents, in a series of letters from various parts of Europe,
published anonymously in 1783, and reprinted, with additions and
omissions, in 1834 and 1840. In the previous year he had written
Vathek in French, in "three days and two nights," without, as he
says, taking off his clothes; "the severe application made me very ill." This statement, if made by Beckford, as Redding implies, is
untrue. Evidence exists to prove that Vathek was a careful and
elaborate composition. The book was published with his name in 1787; but
a translation, made and printed without his leave, had already (1784)
appeared, and was often mistaken for the original. In 1783 he married
Lady Margaret Gordon, with whom he lived in Switzerland till her death
in 1786. One of his two daughters — he had no son — became Mrs. Orde, the
other the Duchess of Hamilton. From 1787 to 1791, and again from 1794 to
1796, he visited Portugal and Spain, and to this period belong his
Sketches of Spain and Portugal (1834), and his Recollections
of an Excursion to the Monasteries of Alobaca and Batalha
(1835). Between his two visits to Portugal, on the last of which he
occupied the retreat at Cintra celebrated by Byron (Childe
Harold, Canto I. stanzas xviii.-xxii.), he saw the destruction of
the Bastille, bought Gibbon's library at Lausanne (in 1796), and,
shutting himself up in it "for six weeks, from early in the morning
until night, only now and then taking "a ride," read himself "nearly
blind" (Cyrus Redding's "Recollections of the Author of Vathek," New
Monthly Magazine, vol. lxxi. p. 307). He also wrote two burlesque
novels, to ridicule, it is said, those written by his sister, Mrs.
Henry: Azemia; a Descriptive and Sentimental Novel. By Jacquetta
Agneta Mariana Jenks of Bellgrove Priory in Wales (1796); and
Modern Novel- Writing, or the Elegant Enthusiast. By the Rt. Hon.
Lady Harriet Marlow(1797). He represented Wells from 1784 to 1790,
and Hindon from 1806 to 1820; but took no part in political life. He was
now settled at Fonthill (1796-1822), absorbed in collecting books,
pictures, and engravings, laying out the grounds, indulging his
architectural extravagances, and shutting himself and his palace out
from the world by a gigantic wall. When Rogers visited him at Fonthill,
and arrived at the gate, he was told that neither his servant nor his
horses could be admitted, but that Mr. Beckford's attendants and horses
would be at his service (Recollections of the Table-Talk of Samuel
Rogers, p. 217). Beckford had been taught music by Mozart, and
Rogers says (ibid.) that "in the evening Beckford would amuse us
by reading one of his unpublished works; or he would extemporize on the
pianoforte, producing the most novel and charming melodies."
In 1822 his gigantic fortune had dwindled; he was in embarrassed
circumstances; Fonthill and most of its contents were sold, and Beckford
settled in Lansdowne Terrace, Bath, where he still collected books and
works of art, laid out the grounds, and built the tower on Lansdowne
Hill, which are now the property of the city. At Bath he died in 1844.
Vathek is a masterpiece, which, as an Eastern tale, is unrivalled
in European literature.
"For correctness of costume," says Byron, in one
of his diaries, "beauty of description, and power of imagination, it far
surpasses all European imitations; and bears such marks of originality,
that those who have visited the East will find some difficulty in
believing it to be a translation. As an Eastern tale, even
Rasselas must bow before it: his 'Happy Valley' will not bear a
comparison with the Hall of Eblis."
Beckford's letters are, in their
way, equally masterpieces, and, like Vathek, have the appearance
of being struck off without labour. Reprinted, as their writer says
(Preface to the edition of 1840), because "some justly admired
Authors... condescended to glean a few stray thoughts from these
letters," they suggest, in some respects, comparison with Byron's own
work. There is the same prodigality of power, the same simple nervous
style, the same vein of melancholy, the same cynical contempt for
mankind. In both writers there is a passionate feeling for the grander
aspects of nature, though Beckford was also thrilled, as Byron was not,
by the beauties of art. In both there are similar inconsistencies and
incongruities of temperament, and the same vein of reckless
self-indulgence appears to run by the side of nobler enthusiasms. In
both there is a taste for Oriental magnificence, which, in Beckford, was
to some degree corrected by his artistic perceptions. Both, finally,
described not so much the objects they saw, as the impression which
those objects produced on themselves, and thus steeped their pictures,
clear and vivid though they are, in an atmosphere of their own
personality.
return
Footnote 3: William, third Viscount Courtenay, died unmarried in 1835,
and with him the viscountcy became extinct. In 1831 he proved before
Parliament his title to the earldom of Devon, which passed at his death
to a cousin, William, tenth Earl of Devon (1777- 1859).
return
Footnote 4: In this letter the following verses were enclosed:—
"Falmouth Roads, June 30, 1809.
"Huzza! Hodgson, we are going,
Our embargo's off at last;
Favourable breezes blowing
Bend the canvass o'er the mast.
From aloft the signal's streaming,
Hark! the farewell gun is fired,
Women screeching, tars blaspheming,
Tell us that our time's expired.
Here's a rascal
Come to task all,
Prying from the Custom-house;
Trunks unpacking,
Cases cracking,
Not a corner for a mouse
'Scapes unsearch'd amid the racket,
Ere we sail on board the Packet.
Now our boatmen quit their mooring,
And all hands must ply the oar;
Baggage from the quay is lowering,
We're impatient — push from shore.
'Have a care! that case holds liquor —
Stop the boat — I'm sick — oh Lord!'
'Sick, ma'am, damme, you'll be sicker
Ere you've been an hour on board.'
Thus are screaming
Men and women,
Gemmen, ladies, servants, Jacks;
Here entangling,
All are wrangling,
Stuck together close as wax.-
Such the general noise and racket,
Ere we reach the Lisbon Packet.
Now we've reach'd her, lo! the captain,
Gallant Kidd, commands the crew;
Passengers their berths are clapt in,
Some to grumble, some to spew.
'Hey day! call you that a cabin?
Why 'tis hardly three feet square;
Not enough to stow Queen Mab in —
Who the deuce can harbour there?'
'Who, sir? plenty —
Nobles twenty —
Did at once my vessel fill' —
'Did they? Jesus,
How you squeeze us!
Would to God they did so still:
Then I'd 'scape the heat and racket,
Of the good ship, Lisbon Packet.'
Fletcher! Murray! Bob! where are you?
Stretch'd along the deck like logs —
Bear a hand, you jolly tar you!
Here's a rope's end for the dogs.
Hobhouse muttering fearful curses,
As the hatchway down he rolls;
Now his breakfast, now his verses,
Vomits forth — and damns our souls.
'Here's a stanza
On Braganza —
Help!' — 'A couplet?' — 'No, a cup
Of warm water.' —
'What's the matter?'
'Zounds! my liver's coming up;
I shall not survive the racket
Of this brutal Lisbon Packet.'
Now at length we're off for Turkey,
Lord knows when we shall come back!
Breezes foul and tempests murky
May unship us in a crack.
But, since life at most a jest is,
As philosophers allow,
Still to laugh by far the best is,
Then laugh on — as I do now.
Laugh at all things,
Great and small things,
Sick or well, at sea or shore;
While we're quaffing,
Let's have laughing —
Who the devil cares for more? —
Some good wine! and who would lack it,
Ev'n on board the Lisbon Packet?
"Byron."
return
List of Letters
Lisbon, July 16, 1809.
Thus far have we pursued our route, and seen all sorts of marvellous
sights, palaces, convents, etc.; — which, being to be heard in my friend
Hobhouse's forthcoming Book of Travels, I shall not anticipate by
smuggling any account whatsoever to you in a private and clandestine
manner. I must just observe, that the village of Cintra in Estremadura
is the most beautiful, perhaps, in the world.
I am very happy here, because I loves oranges, and talks bad Latin to
the monks, who understand it, as it is like their own, — and I goes into
society (with my pocket-pistols), and I swims in the Tagus all across at
once, and I rides on an ass or a mule, and swears Portuguese, and have
got a diarrhoea and bites from the mosquitoes. But what of that? Comfort
must not be expected by folks that go a pleasuring.
When the Portuguese are pertinacious, I say Carracho! — the great
oath of the grandees, that very well supplies the place of
"Damme," — and, when dissatisfied with my neighbour, I pronounce him
Ambra di merdo. With these two phrases, and a third, Avra
louro, which signifieth "Get an ass," I am universally understood to
be a person of degree and a master of languages. How merrily we lives
that travellers be! — if we had food and raiment. But, in sober sadness,
any thing is better than England, and I am infinitely amused with my
pilgrimage as far as it has gone.
To-morrow we start to ride post near 400 miles as far as Gibraltar,
where we embark for Melita and Byzantium. A letter to Malta will find
me, or to be forwarded, if I am absent. Pray embrace the Drury and
Dwyer, and all the Ephesians you encounter. I am writing with Butler's
donative pencil, which makes my bad hand worse. Excuse illegibility.
Hodgson! send me the news, and the deaths and defeats and capital crimes
and the misfortunes of one's friends; and let us hear of literary
matters, and the controversies and the criticisms. All this will be
pleasant — Suave mari magno, etc. Talking of that, I have been
sea-sick, and sick of the sea. Adieu.
Yours faithfully, etc.
List of Letters
Gibraltar, August 6, 1809.
I have just arrived at this place after a journey through Portugal, and
a part of Spain, of nearly 500 miles. We left Lisbon and travelled on
horseback to Seville and Cadiz, and thence in the Hyperion
frigate to Gibraltar. The horses are excellent — we rode seventy miles a
day. Eggs and wine, and hard beds, are all the accommodation we found,
and, in such torrid weather, quite enough. My health is better than in
England.
Seville is a fine town, and the Sierra Morena, part of which we crossed,
a very sufficient mountain; but damn description, it is always
disgusting. Cadiz, sweet Cadiz1! — it is the first spot in the
creation. The beauty of its streets and mansions is only excelled by the
loveliness of its inhabitants. For, with all national prejudice, I must
confess the women of Cadiz are as far superior to the English women in
beauty as the Spaniards are inferior to the English in every quality
that dignifies the name of man. Just as I began to know the principal
persons of the city, I was obliged to sail.
You will not expect a long letter after my riding so far "on hollow
pampered jades of Asia." Talking of Asia puts me in mind of Africa,
which is within five miles of my present residence. I am going over
before I go on to Constantinople.
Cadiz is a complete Cythera. Many of the grandees who have left Madrid
during the troubles reside there, and I do believe it is the prettiest
and cleanest town in Europe. London is filthy in the comparison. The
Spanish women are all alike, their education the same. The wife of a
duke is, in information, as the wife of a peasant, — the wife of peasant,
in manner, equal to a duchess. Certainly they are fascinating; but their
minds have only one idea, and the business of their lives is intrigue.
I have seen Sir John Carr2 at Seville and Cadiz, and, like Swift's
barber, have been down on my knees to beg he would not put me into black
and white3. Pray remember me4. to the Drurys and the Davies, and all of
that stamp who are yet extant. Send me a letter and news to Malta. My
next epistle shall be from Mount Caucasus or Mount Sion. I shall return
to Spain before I see England, for I am enamoured of the country. Adieu,
and believe me, etc.
Footnote 1: In Childe Harold (Canto I., after stanza lxxxiv.),
instead of the song "To Inez," Byron originally wrote the song beginning
"Oh never talk again to me
Of northern climes and British ladies,
It has not been your lot to see,
Like me, the lovely girl of Cadiz."
return to footnote mark
Footnote 2: Sir John Carr (1772-1832), a native of Devonshire, and a
barrister of the Middle Temple, was knighted by the Duke of Bedford as
Viceroy of Ireland about 1807. He published The Fury of Discord, a
Poem (1803); The Sea-side Hero, a Drama in 3 Acts (1804); and
Poems(1809). But he is best known by his travels, which gained
him the nickname of "Jaunting Carr," and considerable profit. The
Stranger in France (1803) was bought by Johnson for £100. A
Northern Summer, or Travels round the Baltic, etc.(1805), The
Stranger in Ireland (1806), and A Tour through Holland(1807),
were bought for £500, £700, and £600 respectively by Sir Richard
Phillips, who, but for the ridicule cast upon Carr by Edward Dubois (in
My Pocket Book; or Hints for a Ryhte Merrie and Conceited Tour in
Quarto, to be called "The Stranger in Ireland in 1805," by a Knight
Errant), would have given £600 for his Caledonian Sketches
(1808). In spite, however, of this proof of damages, the jury found, in
Carr's action against Messrs. Hood and Sharpe, the publishers of My
Pocket Book, that the criticism was fair and justifiable (1808).
Carr published, in 1811, his Descriptive Travels in the Southern and
Eastern Parts of Spain, without mentioning Byron's name. Byron
concluded his MS. of Childe Harold, Canto I. with three stanzas
on "Green Erin's Knight and Europe's Wandering Star" (see, for the
lines, Childe Harold, at the end of Canto I.). In letter vii. of
Intercepted Letters; or the Twopenny Post-bag, by Thomas Brown
the Younger (1813), occur the following lines:—
"Since the Chevalier C — rr took to marrying lately,
The Trade is in want of a Traveller greatly —
No job, Sir, more easy — your Country once plann'd,
A month aboard ship and a fortnight on land
Puts your Quarto of Travels, Sir, clean out of hand."
return
Footnote 3:
"Once stopping at an inn at Dundalk, the Dean was so much amused with
a prating barber, that rather than be alone he invited him to dinner.
The fellow was rejoiced at this unexpected honour, and being dressed
out in his best apparel came to the inn, first inquiring of the groom
what the clergyman's name was who had so kindly invited him. 'What the
vengeance!' said the servant,' don't you know Dean Swift?' At which
the barber turned pale, and, running into the house, fell upon his
knees and intreated the Dean 'not to put him into print; for that he
was a poor barber, had a large family to maintain, and if his
reverence put him into black and white he should lose all his
customers.' Swift laughed heartily at the poor fellow's simplicity,
bade him sit down and eat his dinner in peace, for he assured him he
would neither put him nor his wife in print."
Sheridan's Life of Swift. — (Moore).
return
Footnote 4:
"This sort of passage," says the Rev. Francis Hodgson, in a
note on his copy of this letter, "constantly occurs in his
correspondence. Nor was his interest confined to mere remembrances and
inquiries after health. Were it possible to state all he has done
for numerous friends, he would appear amiable indeed. For myself, I am
bound to acknowledge, in the fullest and warmest manner, his most
generous and well-timed aid; and, were my poor friend Bland alive, he
would as gladly bear the like testimony; — though I have most reason, of
all men, to do so "
(Moore).
return
List of Letters
Gibraltar, August 11th, 1809.
Dear Mother,-I have been so much occupied since my departure from
England, that till I could address you at length I have forborne writing
altogether. As I have now passed through Portugal, and a considerable
part of Spain, and have leisure at this place, I shall endeavour to give
you a short detail of my movements.
We sailed from Falmouth on the 2nd of July, reached Lisbon after a very
favourable passage of four days and a half, and took up our abode in
that city. It has been often described without being worthy of
description; for, except the view from the Tagus, which is beautiful,
and some fine churches and convents, it contains little but filthy
streets, and more filthy inhabitants. To make amends for this, the
village of Cintra, about fifteen miles from the capital, is, perhaps in
every respect, the most delightful in Europe; it contains beauties of
every description, natural and artificial. Palaces and gardens rising in
the midst of rocks, cataracts, and precipices; convents on stupendous
heights — a distant view of the sea and the Tagus; and, besides (though
that is a secondary consideration), is remarkable as the scene of Sir
Hew Dalrymple's Convention1. It unites in itself all the wildness of
the western highlands, with the verdure of the south of France. Near
this place, about ten miles to the right, is the palace of Mafra, the
boast of Portugal, as it might be of any other country, in point of
magnificence without elegance. There is a convent annexed; the monks,
who possess large revenues, are courteous enough, and understand Latin,
so that we had a long conversation: they have a large library, and asked
me if the English had any books in their country?
I sent my baggage, and part of the servants, by sea to Gibraltar, and
travelled on horseback from Aldea Galbega (the first stage from Lisbon,
which is only accessible by water) to Seville (one of the most famous
cities in Spain), where the Government called the Junta is now held. The
distance to Seville is nearly four hundred miles, and to Cadiz almost
ninety farther towards the coast. I had orders from the governments, and
every possible accommodation on the road, as an English nobleman, in an
English uniform, is a very respectable personage in Spain at present.
The horses are remarkably good, and the roads (I assure you upon my
honour, for you will hardly believe it) very far superior to the best
English roads, without the smallest toll or turnpike. You will suppose
this when I rode post to Seville, in four days, through this parching
country in the midst of summer, without fatigue or annoyance.
Seville is a beautiful town; though the streets are narrow, they are
clean. We lodged in the house of two Spanish unmarried ladies, who
possess six houses in Seville, and gave me a curious specimen of
Spanish manners. They are women of character, and the eldest a fine
woman, the youngest pretty, but not so good a figure as Donna Josepha.
The freedom of manner, which is general here, astonished me not a
little; and in the course of further observation, I find that reserve is
not the characteristic of the Spanish belles, who are, in general, very
handsome, with large black eyes, and very fine forms. The eldest
honoured your unworthy son with very particular attention,
embracing him with great tenderness at parting (I was there but three
days), after cutting off a lock of his hair, and presenting him with one
of her own, about three feet in length, which I send, and beg you will
retain till my return. Her last words were, Adios, tu hermoso! me
gusto mucho — "Adieu, you pretty fellow! you please me much." She
offered me a share of her apartment, which my virtue induced me
to decline; she laughed, and said I had some English amante
(lover), and added that she was going to be married to an officer in the
Spanish army.
I left Seville, and rode on to Cadiz, through a beautiful country. At
Xeres, where the sherry we drink is made, I met a great
merchant — a Mr. Gordon of Scotland — who was extremely polite, and
favoured me with the inspection of his vaults and cellars, so that I
quaffed at the fountain head.
Cadiz, sweet Cadiz, is the most delightful town I ever beheld, very
different from our English cities in every respect except cleanliness
(and it is as clean as London), but still beautiful, and full of the
finest women in Spain, the Cadiz belles being the Lancashire witches of
their land. Just as I was introduced and began to like the grandees, I
was forced to leave it for this cursed place; but before I return to
England I will visit it again. The night before I left it, I sat in the
box at the opera with Admiral Cordova's family2; he is the commander
whom Lord St. Vincent defeated in 1797, and has an aged wife and a fine
daughter, Sennorita Cordova. The girl is very pretty, in the Spanish
style; in my opinion, by no means inferior to the English in charms, and
certainly superior in fascination. Long black hair, dark languishing
eyes, clear olive complexions, and forms more graceful in motion
than can be conceived by an Englishman used to the drowsy, listless air
of his countrywomen, added to the most becoming dress, and, at the same
time, the most decent in the world, render a Spanish beauty
irresistible.
I beg leave to observe that intrigue here is the business of life; when
a woman marries she throws off all restraint, but I believe their
conduct is chaste enough before. If you make a proposal, which in
England will bring a box on the ear from the meekest of virgins, to a
Spanish girl, she thanks you for the honour you intend her, and replies,
"Wait till I am married, and I shall be too happy." This is literally
and strictly true.
Miss Cordova and her little brother understood a little French, and,
after regretting my ignorance of the Spanish, she proposed to become my
preceptress in that language. I could only reply by a low bow, and
express my regret that I quitted Cadiz too soon to permit me to make the
progress which would doubtless attend my studies under so charming a
directress. I was standing at the back of the box, which resembles our
Opera boxes, (the theatre is large and finely decorated, the music
admirable,) in the manner which Englishmen generally adopt, for fear of
incommoding the ladies in front, when this fair Spaniard dispossessed an
old woman (an aunt or a duenna) of her chair, and commanded me to be
seated next herself, at a tolerable distance from her mamma. At the
close of the performance I withdrew, and was lounging with a party of
men in the passage, when, en passant, the lady turned round and called
me, and I had the honour of attending her to the admiral's mansion. I
have an invitation on my return to Cadiz, which I shall accept if I
repass through the country on my return from Asia3.
I have met Sir John Carr, Knight Errant, at Seville and Cadiz. He is a
pleasant man. I like the Spaniards much. You have heard of the battle
near Madrid4, and in England they would call it a victory — a pretty
victory! Two hundred officers and five thousand men killed, all English,
and the French in as great force as ever. I should have joined the army,
but we have no time to lose before we get up the Mediterranean and
Archipelago. I am going over to Africa tomorrow; it is only six miles
from this fortress. My next stage is Cagliari in Sardinia, where I shall
be presented to His Majesty. I have a most superb uniform as a court
dress, indispensable in travelling.
August 13. — I have not yet been to Africa — the wind is contrary — but I
dined yesterday at Algesiras, with Lady Westmorland5, where I met
General Castanos, the celebrated Spanish leader in the late and present
war. To-day I dine with him. He has offered me letters to Tetuan in
Barbary, for the principal Moors, and I am to have the house for a few
days of one of the great men, which was intended for Lady W., whose
health will not permit her to cross the Straits.
August 15. — I could not dine with Castanos6 yesterday, but this
afternoon I had that honour. He is pleasant and, for aught I know to the
contrary, clever. I cannot go to Barbary. The Malta packet sails
to-morrow, and myself in it. Admiral Purvis, with whom I dined at Cadiz,
gave me a passage in a frigate to Gibraltar, but we have no ship of war
destined for Malta at present. The packets sail fast, and have good
accommodation. You shall hear from me on our route.
Joe Murray delivers this; I have sent him and the boy back. Pray show
the lad kindness, as he is my great favourite; I would have taken him
on. And say this to his father, who may otherwise think he has behaved
ill. I hope this will find you well. Believe me,
Yours ever sincerely,
Byron.
P.S. — So Lord G — — 7 is married to a rustic. Well done! If I wed, I
will bring home a Sultana, with half a dozen cities for a dowry, and
reconcile you to an Ottoman daughter-in-law, with a bushel of pearls not
larger than ostrich eggs, or smaller than walnuts.
Footnote 1: Sir Hew Whitefoord Dalrymple (1750-1830) took command of
the British forces in the Peninsular War, August 22, 1808, and signed
the Convention of Cintra (August 31), by which Junot, whom Sir Arthur
Wellesley had defeated at Vimeira, evacuated Portugal, and surrendered
Elvas and Lisbon. The Convention was approved by a court of general
officers ordered to sit at Chelsea Hospital; but Dalrymple never again
obtained a command.
The so-called Convention of Cintra was signed at the palace of the
Marquis de Marialva, thirty miles distant.
return to footnote mark
Footnote 2: Admiral Cordova commanded the Spanish Fleet, defeated,
February 14, 1797, off Cape St. Vincent, by Sir John Jervis, afterwards
Earl St. Vincent.
return
Footnote 3: To these adventures in his hasty passage through Spain
Byron briefly alludes in the early part of his Memoranda.
"For some time," he said, "I went on prosperously both as a linguist
and a lover, till at length the lady took a fancy to a ring which I
wore, and set her heart on my giving it to her, as a pledge of my
sincerity. This, however, could not be:— any thing but the ring, I
declared, was at her service, and much more than its value, — but the
ring itself I had made a vow never to give away." The young Spaniard
grew angry as the contention went on, and it was not long before the
lover became angry also; till, at length, the affair ended by their
separating. "Soon after this," said he, "I sailed for Malta, and there
parted with both my heart and ring."
(Life, p.93). He also alludes to the incident in Don Juan, Canto II,
stanza clxiv.-
"'Tis pleasing to be school'd in a strange tongue
By female lips and eyes — that is, I mean,
When both the teacher and the taught are young,
As was the case, at least, where I have been,"
etc.
return
Footnote 4: The battle of Talavera, July 27 and 28, 1809, in which Sir
Arthur Wellesley defeated Marshal Victor. In Cuesta's despatch to the
Spanish Government, dated Seville, August 7, the British loss is
mentioned as 260 officers and 5000 men.
return
Footnote 5: Lady Westmorland, nee Jane Saunders, daughter of Dr. R.
H. Saunders, married, in 1800, as his second wife, John, tenth Earl of
Westmorland (1759-1841). At her house Lady Caroline Lamb refused to be
introduced to Byron (Life of Lord Melbourne, vol. i. p.103).
return
Footnote 6: General Francisco de Castanos, Duke of Baylen (1758-1852)
defeated General Dupont at Baylen in 1808, and distinguished himself at
Vittoria in 1813. He was guardian to Queen Isabella in 1843.
return
Footnote 7: Lord Grey de Ruthyn. (See page 23, note 1.)
return
cross-reference: return to Footnote 1 of Letter 8
List of Letters
Gibraltar, August 15, 1809.
Mr. Rushton, — I have sent Robert home with Mr. Murray, because the
country which I am about to travel through is in a state which renders
it unsafe, particularly for one so young. I allow you to deduct
five-and-twenty pounds a year for his education for three years,
provided I do not return before that time, and I desire he may be
considered as in my service. Let every care be taken of him, and let him
be sent to school. In case of my death I have provided enough in my will
to render him independent. He has behaved extremely well, and has
travelled a great deal for the time of his absence. Deduct the expense
of his education from your rent.
Byron.
List of Letters
Malta, September 15, 1809.
Dear Mother, — Though I have a very short time to spare, being to sail
immediately for Greece, I cannot avoid taking an opportunity of telling
you that I am well. I have been in Malta1 a short time, and have
found the inhabitants hospitable and pleasant.
This letter is committed to the charge of a very extraordinary woman,
whom you have doubtless heard of, Mrs. Spencer Smith, of whose escape
the Marquis de Salvo published a narrative a few years ago2. She has
since been shipwrecked, and her life has been from its commencement so
fertile in remarkable incidents, that in a romance they would appear
improbable. She was born at Constantinople, where her father, Baron
Herbert, was Austrian Ambassador; married unhappily, yet has never been
impeached in point of character; excited the vengeance of Buonaparte by
a part in some conspiracy; several times risked her life; and is not yet
twenty-five. She is here on her way to England, to join her husband,
being obliged to leave Trieste, where she was paying a visit to her
mother, by the approach of the French, and embarks soon in a ship of
war. Since my arrival here, I have had scarcely any other companion. I
have found her very pretty, very accomplished, and extremely eccentric.
Buonaparte is even now so incensed against her, that her life would be
in some danger if she were taken prisoner a second time.
You have seen Murray and Robert by this time, and received my letter.
Little has happened since that date. I have touched at Cagliari in
Sardinia, and at Girgenti in Sicily, and embark to-morrow for Patras,
from whence I proceed to Yanina, where Ali Pacha holds his court. So I
shall soon be among the Mussulmans. Adieu. Believe me, with sincerity,
yours ever,
Byron.
Footnote 1: At Gibraltar, John Galt, who was travelling for his health,
met Byron, whom he did not know by sight, but by whose appearance he was
attracted.
"His dress indicated a Londoner of some fashion, partly by its
neatness and simplicity, with just so much of a peculiarity of style
as served to show that, although he belonged to the order of
metropolitan beaux, he was not altogether a common one ... His
physiognomy was prepossessing and intelligent, but ever and anon his
brows lowered and gathered — a habit, as I then thought, with a degree
of affectation in it, probably first assumed for picturesque effect
and energetic expression, but which I afterwards discovered was
undoubtedly the scowl of some unpleasant reminiscence; it was
certainly disagreeable, forbidding, but still the general cast of his
features was impressed with elegance and character."
Afterwards Galt was a fellow-passenger on board the packet from
Gibraltar to Malta.
"In the little bustle and process of embarking their luggage, his
Lordship affected, as it seemed to me, more aristocracy than befitted
his years, or the occasion; and then I thought of his singular scowl,
and suspected him of pride and irascibility. The impression that
evening was not agreeable, but it was interesting; and that forehead
mark, the frown, was calculated to awaken curiosity, and beget
conjectures ... Byron held himself aloof, and sat on the rail, leaning
on the mizzen shrouds, inhaling, as it were, poetical sympathy from
the gloomy rock, then dark and stern in the twilight. There was, in
all about him that evening, much waywardness. He spoke petulantly to
Fletcher, his valet, and was evidently ill at ease with himself, and
fretful towards others. I thought he would turn out an unsatisfactory
shipmate; yet there was something redeeming in the tones of his voice,
and when, some time after having indulged his sullen meditation he
again addressed Fletcher; so that, instead of finding him ill-natured,
I was soon convinced he was only capricious."
On the voyage,
"about the third day, Byron relented from his rapt mood, as if he felt
it was out of place, and became playful, and disposed to contribute
his fair proportion to the general endeavour to while away the
tediousness of the dull voyage."
But yet throughout the whole passage,
"if," says Galt, "my remembrance is not treacherous, he only spent one
evening in the cabin with us — the evening before we came to anchor at
Cagliari; for, when the lights were placed, he made himself a man
forbid, took his station on the railing, between the pegs on which the
sheets are belayed and the shrouds, and there, for hours, sat in
silence, enamoured, it may be, of the moon. All these peculiarities,
with his caprices, and something inexplicable in the cast of his
metaphysics, while they served to awaken interest, contributed little
to conciliate esteem. He was often strangely rapt — it may have been
from his genius; and, had its grandeur and darkness been then
divulged, susceptible of explanation; but, at the time, it threw, as
it were, around him the sackcloth of penitence. Sitting amid the
shrouds and rattlings, in the tranquillity of the moonlight, churning
an inarticulate melody, he seemed almost apparitional, suggesting dim
reminiscences of him who shot the albatross"
(Galt's Life of Byron, pp. 57-61).
return
cross-reference: return to Footnote 5 of Letter 149
Footnote 2: Byron's "new Calypso." Mrs. Spencer Smith (born about 1785)
was the daughter of Baron Herbert, Austrian Ambassador at
Constantinople, wife of Spencer Smith, the British Minister at
Stuttgart, and sister-in-law of Sir Sidney Smith, the hero of Acre. In
1805 she was staying, for her health, at the baths of Valdagno, near
Vicenza, when the Napoleonic wars overspread Northern Italy, and she
took refuge with her sister, the Countess Attems, at Venice. In 1806
General Lauriston took over the government of the city in the name of
Napoleon, and M. de La Garde was appointed Prefect of the Police. A few
days after their arrival, on April 18, Mrs. Smith was arrested, and,
guarded by gendarmes, conveyed towards the Italian frontier, to be
confined, as La Garde told a Sicilian nobleman, the Marquis de Salvo, at
Valenciennes. Mrs. Smith's beauty and impending fate deeply impressed
the marquis, who determined to rescue her. The prisoner and her guard
had reached Brescia, and were lodged at the Albergo delle due Torre,
The opportunity seemed favourable. Once across the Guarda Lake, and in
the passes of Tyrol, it would be easy to reach Styria. The marquis made
his arrangements — hired two boats, one for the fugitives, the other for
their post-chaise and horses; procured for Mrs. Smith a boy's dress, as
a disguise; made a ladder long enough to reach her window in the inn,
and succeeded in making known his plan to the prisoner. The escape was
effected; but all along the road the danger continued, for their way lay
through a country which was practically French territory. It was not
till they reached Gratz, and Mrs. Smith was under the roof of her
sister, the Countess Strassoldo, that she was safe. The story is told in
detail by the Marquis de Salvo, in his Travels in the Year 1806 from
Italy to England (1807), and by the Duchesse d'Abrantes (Mémoires,
vol. xv. pp. 1-74).
To Mrs. Spencer Smith are addressed the "Lines to Florence," the
"Stanzas composed during a Thunderstorm" (near Zitza, in October, 1809),
and stanzas xxx.-xxxii. of the second canto of Childe Harold. The
Duchesse d'Abrantés (Mémoires, vol. xv. pp. 4, 5) thus describes her:
"Une jeune femme, dont la délicate et elégante tournure, la peau
blanche et diaphane, les cheveux blonds, les mouvemens onduleux, toute
une tournure impossible à décrire autrement qu'en disant qu'elle était
de toutes les créatures la plus gracieuse, lui donnaient l'aspect
d'une de ces apparitions amenées par un rêve heureux... il y avail de
la Sylphide en elle. Sa vue excessivement basse n'etait qu'un charme
de plus."
Moore (Life, p. 95) thinks that Byron was less in love with Mrs.
Smith than with his recollection of her. According to Gait (Life of
Byron, p. 66),
"he affected a passion for her, but it was only Platonic. She,
however, beguiled him of his valuable yellow diamond ring."
return
cross-reference: return to Footnote 2 of Letter 137
List of Letters
Prevesa, November 12, 1809.
My Dear Mother, — I have now been some time in Turkey: this place is on
the coast, but I have traversed the interior of the province of Albania
on a visit to the Pacha. I left Malta in the Spider, a brig of war, on
the 21st of September, and arrived in eight days at Prevesa. I thence
have been about 150 miles, as far as Tepaleen, his Highness's country
palace, where I stayed three days. The name of the Pacha is Ali1
and he is considered a man of the first abilities: he governs the whole
of Albania (the ancient Illyricum), Epirus, and part of Macedonia. His
son, Vely Pacha2, to whom he has given me letters, governs the Morea,
and has great influence in Egypt; in short, he is one of the most
powerful men in the Ottoman empire. When I reached Yanina, the capital,
after a journey of three days over the mountains, through a country of
the most picturesque beauty, I found that Ali Pacha was with his army in
Illyricum, besieging Ibrahim Pacha in the castle of Berat. He had heard
that an Englishman of rank was in his dominions, and had left orders in
Yanina with the commandant to provide a house, and supply me with every
kind of necessary gratis; and, though I have been allowed to make
presents to the slaves, etc., I have not been permitted to pay for a
single article of household consumption.
I rode out on the vizier's horses, and saw the palaces of himself and
grandsons: they are splendid, but too much ornamented with silk and
gold. I then went over the mountains through Zitza3, a village with a
Greek monastery (where I slept on my return), in the most beautiful
situation (always excepting Cintra, in Portugal) I ever beheld. In nine
days I reached Tepaleen. Our journey was much prolonged by the torrents
that had fallen from the mountains, and intersected the roads. I shall
never forget the singular scene on entering Tepaleen at five in the
afternoon, as the sun was going down. It brought to my mind (with some
change of dress, however) Scott's description of Branksome Castle in
his Lay, and the feudal system4. The Albanians, in their dresses,
(the most magnificent in the world, consisting of a long white kilt,
gold-worked cloak, crimson velvet gold-laced jacket and waistcoat,
silver-mounted pistols and daggers,) the Tartars with their high caps,
the Turks in their vast pelisses and turbans, the soldiers and black
slaves with the horses, the former in groups in an immense large open
gallery in front of the palace, the latter placed in a kind of cloister
below it, two hundred steeds ready caparisoned to move in a moment,
couriers entering or passing out with the despatches, the kettle-drums
beating, boys calling the hour from the minaret of the mosque,
altogether, with the singular appearance of the building itself, formed
a new and delightful spectacle to a stranger. I was conducted to a very
handsome apartment, and my health inquired after by the vizier's
secretary, à-la-mode Turque!
The next day I was introduced to Ali Pacha. I was dressed in a full suit
of staff uniform, with a very magnificent sabre, etc. The vizier
received me in a large room paved with marble; a fountain was playing in
the centre; the apartment was surrounded by scarlet ottomans. He
received me standing, a wonderful compliment from a Mussulman, and made
me sit down on his right hand. I have a Greek interpreter for general
use, but a physician of Ali's named Femlario, who understands Latin,
acted for me on this occasion. His first question was, why, at so early
an age, I left my country? — (the Turks have no idea of travelling for
amusement). He then said, the English minister, Captain Leake5, had
told him I was of a great family, and desired his respects to my mother;
which I now, in the name of Ali Pacha, present to you. He said he was
certain I was a man of birth, because I had small ears, curling hair,
and little white hands, and expressed himself pleased with my appearance
and garb. He told me to consider him as a father whilst I was in Turkey,
and said he looked on me as his son. Indeed, he treated me like a child,
sending me almonds and sugared sherbet, fruit and sweetmeats, twenty
times a day. He begged me to visit him often, and at night, when he was
at leisure. I then, after coffee and pipes, retired for the first time.
I saw him thrice afterwards. It is singular that the Turks, who have no
hereditary dignities, and few great families, except the Sultans, pay so
much respect to birth; for I found my pedigree more regarded than my
title.
To-day I saw the remains of the town of Actium6, near which Antony
lost the world, in a small bay, where two frigates could hardly
manoeuvre: a broken wall is the sole remnant. On another part of the
gulf stand the ruins of Nicopolis, built by Augustus in honour of his
victory. Last night I was at a Greek marriage; but this and a thousand
things more I have neither time nor space to describe.
His highness is sixty years old, very fat, and not tall, but with a fine
face, light blue eyes, and a white beard; his manner is very kind, and
at the same time he possesses that dignity which I find universal
amongst the Turks. He has the appearance of anything but his real
character, for he is a remorseless tyrant, guilty of the most horrible
cruelties, very brave, and so good a general that they call him the
Mahometan Buonaparte. Napoleon has twice offered to make him King of
Epirus, but he prefers the English interest, and abhors the French, as
he himself told me. He is of so much consequence, that he is much
courted by both, the Albanians being the most warlike subjects of the
Sultan, though Ali is only nominally dependent on the Porte; he has been
a mighty warrior, but is as barbarous as he is successful, roasting
rebels, etc., etc. Buonaparte sent him a snuff-box with his picture. He
said the snuff-box was very well, but the picture he could excuse, as he
neither liked it nor the original. His ideas of judging of a man's birth
from ears, hands, etc., were curious enough. To me he was, indeed, a
father, giving me letters, guards, and every possible accommodation. Our
next conversations were of war and travelling, politics and England. He
called my Albanian soldier, who attends me, and told him to protect me
at all hazard; his name is Viseillie, and, like all the Albanians, he is
brave, rigidly honest, and faithful; but they are cruel, though not
treacherous, and have several vices but no meannesses. They are,
perhaps, the most beautiful race, in point of countenance, in the world;
their women are sometimes handsome also, but they are treated like
slaves, beaten, and, in short, complete beasts of burden; they plough,
dig, and sow. I found them carrying wood, and actually repairing the
highways. The men are all soldiers, and war and the chase their sole
occupations. The women are the labourers, which after all is no great
hardship in so delightful a climate. Yesterday, the 11th of November, I
bathed in the sea; to-day is so hot that I am writing in a shady room of
the English consul's, with three doors wide open, no fire, or even
fireplace, in the house, except for culinary purposes.
I am going to-morrow, with a guard of fifty men, to Patras in the Morea,
and thence to Athens, where I shall winter7. Two days ago I was
nearly lost in a Turkish ship of war, owing to the ignorance of the
captain and crew, though the storm was not violent. Fletcher yelled
after his wife, the Greeks called on all the saints, the Mussulmans on
Alla; the captain burst into tears and ran below deck, telling us to
call on God; the sails were split, the main-yard shivered, the wind
blowing fresh, the night setting in, and all our chance was to make
Corfu, which is in possession of the French, or (as Fletcher
pathetically termed it) "a watery grave." I did what I could to console
Fletcher, but finding him incorrigible, wrapped myself up in my Albanian
capote (an immense cloak), and lay down on deck to wait the worst. I
have learnt to philosophise in my travels; and if I had not, complaint
was useless. Luckily the wind abated, and only drove us on the coast of
Suli, on the main land, where we landed, and proceeded, by the help of
the natives, to Prevesa again; but I shall not trust Turkish sailors in
future, though the Pacha had ordered one of his own galliots to take me
to Patras. I am therefore going as far as Missolonghi by land, and there
have only to cross a small gulf to get to Patras.
Fletcher's next epistle will be full of marvels. We were one night lost
for nine hours in the mountains in a thunder-storm, and since nearly
wrecked. In both cases Fletcher was sorely bewildered, from
apprehensions of famine and banditti in the first, and drowning in the
second instance. His eyes were a little hurt by the lightning, or crying
(I don't know which), but are now recovered. When you write, address to
me at Mr. Strané's, English consul, Patras, Morea.
I could tell you I know not how many incidents that I think would amuse
you, but they crowd on my mind as much as they would swell my paper, and
I can neither arrange them in the one, nor put them down on the other,
except in the greatest confusion. I like the Albanians much; they are
not all Turks; some tribes are Christians. But their religion makes
little difference in their manner or conduct. They are esteemed the best
troops in the Turkish service. I lived on my route, two days at once,
and three days again, in a barrack at Salora, and never found soldiers
so tolerable, though I have been in the garrisons of Gibraltar and
Malta, and seen Spanish, French, Sicilian, and British troops in
abundance. I have had nothing stolen, and was always welcome to their
provision and milk. Not a week ago an Albanian chief, (every village has
its chief, who is called Primate,) after helping us out of the Turkish
galley in her distress, feeding us, and lodging my suite, consisting of
Fletcher, a Greek, two Athenians, a Greek priest, and my companion, Mr.
Hobhouse, refused any compensation but a written paper stating that I
was well received; and when I pressed him to accept a few sequins, "No,"
he replied; "I wish you to love me, not to pay me." These are his words.
It is astonishing how far money goes in this country. While I was in the
capital I had nothing to pay by the vizier's order; but since, though I
have generally had sixteen horses, and generally six or seven men, the
expense has not been half as much as staying only three weeks in
Malta, though Sir A. Ball8, the governor, gave me a house for
nothing, and I had only one servant. By the by, I expect Hanson to
remit regularly; for I am not about to stay in this province for ever.
Let him write to me at Mr. Strané's, English consul, Patras. The fact
is, the fertility of the plains is wonderful, and specie is scarce,
which makes this remarkable cheapness. I am going to Athens, to study
modern Greek, which differs much from the ancient, though radically
similar. I have no desire to return to England, nor shall I, unless
compelled by absolute want, and Hanson's neglect; but I shall not enter
into Asia for a year or two, as I have much to see in Greece, and I may
perhaps cross into Africa, at least the Egyptian part. Fletcher, like
all Englishmen, is very much dissatisfied, though a little reconciled to
the Turks by a present of eighty piastres from the vizier, which, if you
consider every thing, and the value of specie here, is nearly worth ten
guineas English. He has suffered nothing but from cold, heat, and
vermin, which those who lie in cottages and cross mountains in a cold
country must undergo, and of which I have equally partaken with himself;
but he is not valiant, and is afraid of robbers and tempests. I have no
one to be remembered to in England, and wish to hear nothing from it,
but that you are well, and a letter or two on business from Hanson, whom
you may tell to write. I will write when I can, and beg you to believe
me,
Your affectionate son,
Byron.
P.S. — I have some very "magnifiques" Albanian dresses, the only
expensive articles in this country. They cost fifty guineas each, and
have so much gold, they would cost in England two hundred. I have been
introduced to Hussein Bey9, and Mahmout Pacha9, both little boys,
grandchildren of Ali, at Yanina; they are totally unlike our lads, have
painted complexions like rouged dowagers, large black eyes, and features
perfectly regular. They are the prettiest little animals I ever saw, and
are broken into the court ceremonies already. The Turkish salute is a
slight inclination of the head, with the hand on the heart; intimates
always kiss. Mahmout is ten years old, and hopes to see me again; we are
friends without understanding each other, like many other folks, though
from a different cause. He has given me a letter to his father in the
Morea, to whom I have also letters from Ali Pacha.
Footnote 1: Ali Pasha (1741-1822) was born in Albania, at Tepeleni, a
town 75 miles north of Janina, of which his father was governor. This
"Mahometan Buonaparte," or "Rob Roy of Albania," made himself the
supreme ruler of Epirus and Albania, acquired a predominance over the
Agas of Thessaly, and pushed his troops to the frontiers of ancient
Attica (see Raumer's Historisches Taschenbuch, pp. 87-175). A
merciless and unscrupulous tyrant, he was also a fine soldier and a born
administrator. Intriguing now with the Porte, now with Buonaparte, now
with the English, using the rival despots of the country against each
other, hand in glove with the brigands while commanding the police for
their suppression, he extended his power by using conflicting interests
to aggrandize himself. The Venetian possessions on the eastern shores of
the Adriatic, which had passed in 1797 to France, by the treaty of Campo
Formio, were wrested from the French by Ali, who defeated General La
Salsette (1798) in the plains of Nicopolis, and, with the exception of
Parga, seized and held the principal towns in the name of the Sultan.
Byron speaks of his "aged venerable face" in Childe Harold (Canto II.
stanza lxii.; see also stanza xlvii.), and of the delicacy of his hand
in Don Juan (Canto IV. stanza xlv.), and finds in his treatment of
"Giaffir, Pacha of Argyro Castro or Scutari (I am not sure which)," the
material for stanzas xiv., xv. of Canto II. of The Bride of Abydos.
Hobhouse (Journey through Albania, edit. 1854, vol. i pp. 96, 97)
describes Ali as
"a short man, about five feet five inches in height,
and very fat, though not particularly corpulent. He had a very pleasing
face, fair and round, with blue quick eyes, not at all settled into a
Turkish gravity. His beard was long and white, and such a one as any
other Turk would have been proud of; though he, who was more taken up
with his guests than himself, did not continue looking at it, nor
smelling and stroking it, as is usually the custom of his country-men,
to fill up the pauses of conversation."
Dr. (afterwards Sir Henry) Holland, in his Travels in the Ionian Isles,
Albania, Thessaly, and Greece in 1812-13, pp. 125, 126 (1815), gives an
account of his first interview with Ali:
"Were I to attempt a
description of Ali, I should speak of his face as large and full; the
forehead remarkably broad and open, and traced by many deep
furrows; the eye penetrating, yet not expressive of ferocity; the nose
handsome and well formed; the mouth and lower part of the face
concealed, except when speaking, by his mustachios and the long beard
which flows over his breast. His complexion is somewhat lighter than
that usual among the Turks, and his general appearance does not indicate
more than his actual age ... The neck is short and thick, the figure
corpulent and unwieldy; his stature I had afterwards the means of
ascertaining to be about five feet nine inches. The general character
and expression of the countenance are unquestionably fine, and the
forehead especially is a striking and majestic feature. Much of the
talent of the man may be inferred from his exterior; the moral
qualities, however, may not equally be determined in this way; and to
the casual observation of the stranger I can conceive from my own
experience, that nothing may appear but what is open, placid, and
alluring. Opportunities were afterwards afforded me of looking beneath
this exterior of expression; it is the fire of a stove burning fiercely
under a smooth and polished surface.... The inquiries he made respecting
our journey to Joannina, gave us the opportunity of complimenting him on
the excellent police of his dominions, and the attention he has paid to
his roads. I mentioned to him generally Lord Byron's poetical
description of Albania, the interest it had excited in England, and Mr.
Hobhouse's intended publication of his travels in the same country. He
seemed pleased with these circumstances, and stated his recollection of
Lord Byron."
Dr. Holland brought back to England a letter to Byron from
Ali (see Letter to Moore, September 8, 1813).
A further account of Ali, together with a portrait, will be found in
Hughes's Travels in Sicily, etc. (pp. 446-449). He again (1813) "asked
with much apparent interest respecting Lord Byron." At the close of the
Napoleonic struggle, the interest of this country was excited by the
resistance of Parga to his arms, especially as, during the late war, the
Pargiotes had received the protection of Great Britain. After the fall
of Parga (1819), Ali's power roused the jealousy of the Sultan, and it
was partly in consequence of his open defiance of the Porte, that
insurrections broke out in Wallachia, and that Ypsilanti proclaimed
himself the liberator of Greece. The Turkish troops, under Kurchid
Pasha, gradually overpowered Ali, and, at the end of 1821, shut him up
in his citadel of Janina. In the following January he surrendered, and
was at first treated with respect. But on February 5, 1822, Ali was
informed that the Sultan demanded his head. His answer was to fire his
pistol at the messenger. In the fray that followed he was killed.
Another and better account (Walsh's Narrative of a Journey from
Constantinople to England, p. 62) says that he was stabbed in the back
as he was bowing to the departing messenger, who had solemnly assured
him of the Sultan's pardon and favour. His head was cut off, sent to
Constantinople, and fixed on the grand gate of the Seraglio, with the
sentence of death by its side. Recently fresh interest has been aroused
in Ali by the publication of Mr. Bain's translation of Maurus Jókai's
semi-historical novel Janicsárok végnapjai, under the title of The
Lion of Janina (1897).
return to footnote mark
Footnote 2: Veli Pasha was the son of Ali by a daughter of Coul Pasha,
the governor of Berat, in whose army Ali had served as a young man. He
was married (1798) to a daughter of Ibrahim Pasha, who had succeeded
Coul Pasha in the pashalik of Berat. The war with Ibrahim, to which
Byron alludes, ended in his defeat, and the transference of his pashalik
to Ali. Veli, at this time Vizier of the Morea, resided at Tripolizza,
when he was visited by Galt, who describes him as sitting
"on a crimson
velvet cushion, wrapped in a superb pelisse; on his head was a vast
turban, in his belt a dagger encrusted with jewels, and on the little
finger of his right hand he wore a solitaire which was said to have cost
two thousand five hundred pounds sterling. In his left hand he held a
string of small coral beads, a comboloio which he twisted backwards and
forwards during the greater part of the visit." "In his manners," says
Galt, "I found him free and urbane, with a considerable tincture of
humour and drollery"
(Life of Byron, p. 83). Hobhouse (Journey through
Albania, etc., vol. i. p. 193) says,
"The Vizier, for he is a Pasha of
three tails, is a lively young man; and besides the Albanian, Greek, and
Turkish languages, speaks Italian — an accomplishment not possessed, I
should think, by any other man of his high rank in Turkey. It is
reported that he, as well as his father, is preparing, in case of the
overthrow of the Ottoman power, to establish an independent
sovereignty."
Veli, in his father's struggle with the Sultan, betrayed
Prevesa to the Turks. He was executed in 1822, and is buried at the
Silivria Gate of Constantinople.
return
cross-reference: return to Footnote 1 of Letter 146
Footnote 3: For "monastic Zitza," see Childe Harold, Canto II. stanza
xlviii., and Byron's note.
return
Footnote 4: See Lay of the Last Minstrel, canto i.
return
Footnote 5: William Martin Leake (1777-1860) received his commission as
second lieutenant in the artillery in 1794, became a captain in 1799,
major in 1809, and lieutenant-colonel in 1813. His professional life, up
to 1815, was spent abroad, chiefly at Constantinople, in Egypt, or in
various parts of European Turkey. In 1808 he had been sent by the
British Government with stores of artillery, ammunition, and Congreve
rockets, to Ali, Pasha of Albania, and he remained at Preveza, or
Janina, as the representative of Great Britain, till 1810. During his
travels he collected the vases, gems, bronzes, marbles, and coins now
placed in the British Museum, and in the Fitzwilliam Museum at
Cambridge. At the same time, he accumulated the materials which, during
his literary life (1815-59), he embodied in numerous books. Of these the
more important are — The Topography of Athens (1821); Journal of a
Tour in Asia Minor (1824); An Historical Outline of the Greek
Revolution (1825); Travels in the Morea (1830); Travels in Northern
Greece (1835); Numismata Hellenica (1854-59). As a diplomatist he was
remarkably successful; but his reputation mainly rests on his
topographical works. With his antiquarian labours Byron would have had
little sympathy; but Leake was also a warm-hearted advocate of the
Christian population of Greece against their Turkish rulers.
return
Footnote 6: The battle of Actium (B.C. 31) was fought at the entrance
of the Gulf of Arta, and Nicopolis, the city of victory, the
Palaio-Kastro of the modern Greek, was founded by Augustus on an
isthmus connecting Prevesa with the mainland to commemorate his triumph.
Leake (Travels in Northern Greece, vol. i. p. 175) identifies Actium
with Punda ( , "the head of a promontory") on the headland
opposite Prevesa (see Childe Harold, Canto II. stanza xlv.).
, "the head of a promontory") on the headland
opposite Prevesa (see Childe Harold, Canto II. stanza xlv.).
return
Footnote 7: "Upon Parnassus going to the fountain of Delphi (Castri) in
1809," writes Byron, in his Diary for 1821 (Life, pp. 99, 100),
"I
saw a flight of twelve eagles (H. says they were vultures — at least in
conversation), and I seized the omen. On the day before I composed the
lines to Parnassus (in Childe Harold), and, on beholding the birds,
had a hope that Apollo had accepted my homage. I have at least had the
name and fame of a poet during the poetical part of life (from twenty to
thirty); — whether it will last is another matter."
(For the lines to
Parnassus, see Childe Harold, Canto I. stanzas lx.-lxii.) To this
journey belongs another incident, recorded by Byron.
"The last bird I
ever fired at was an eaglet, on the shore of the Gulf of Lepanto, near
Vostizza. It was only wounded, and I tried to save it, — the eye was so
bright. But it pined, and died in a few days; and I never did since, and
never will, attempt the death of another bird."
return
Footnote 8: Rear-Admiral Sir Alexander John Ball (1757-1809), who
belonged to a Gloucestershire family, entered the navy, inspired by
Robinson Crusoe. A lieutenant in 1778, he distinguished himself with
Rodney in 1782 (post-captain, 1783; rear-admiral, 1805), and at the
battle of the Nile, when he commanded the Alexander. Nelson had no
liking for Ball until the latter saved the dismasted Vanguard from
going on shore by taking her in tow. Henceforward they were friends, and
Nelson spoke of him as one of his "three right arms." By his skill in
blockading Valetta (1798-1800), Ball was the hero of the siege of Malta,
and (June 6, 1801) was created a baronet for his services, and received
the Order of Merit from Ferdinand IV of Naples. When Byron met him,
Ball was "His Majesty's Civil Commissioner for the Island of Malta and
its Dependencies, and Minister Plenipotentiary to the Order of St.
John." S.T. Coleridge, who was with him as secretary from May, 1804, to
October, 1805, wrote enthusiastically of him in his letters, and in The
Friend (3rd edit., vol. i. essay i., and vol. iii. pp. 226-301). But
his picture of the admiral would have been more definite had he
remembered the spirit of the remark (quoted in The Friend) which Ball
once made to him:
"The distinction is just, and, now I understand you,
abundantly obvious; but hardly worth the trouble of your inventing a
puzzle of words to make it appear otherwise."
return
Footnote 9: Hussein Bey, then a boy of ten years old, son of Mouctar
Pasha, the eldest son of Ali, in after years (1820-22) remained faithful
to his grandfather, when his father, uncles, and cousin had gone over to
the Sultan, and held Tepeleni for Ali in his last struggle against the
Turks. Mahomet Pasha, son of Veli Pasha, second son of Ali, though only
twelve years old, was already in possession of a pashalik. In Ali's
contest with Turkey, he betrayed Parga to the Sultan, and persuaded his
father to surrender Prevesa. He was, however, rewarded for his treachery
by execution, and is among the five members of his family who lie buried
at the Silivria Gate at Constantinople (Walsh's Narrative, p. 67).
return
List of Letters
Smyrna, March 19, 1810.
Dear Mother, — I cannot write you a long letter; but as I know you will
not be sorry to receive any intelligence of my movements, pray accept
what I can give. I have traversed the greatest part of Greece, besides
Epirus, etc., etc., resided ten weeks at Athens, and am now on the
Asiatic side on my way to Constantinople. I have just returned from
viewing the ruins of Ephesus, a day's journey from Smyrna1. I presume
you have received a long letter I wrote from Albania, with an account of
my reception by the Pacha of the Province.
When I arrive at Constantinople, I shall determine whether to proceed
into Persia or return, which latter I do not wish, if I can avoid it.
But I have no intelligence from Mr. Hanson, and but one letter from
yourself. I shall stand in need of remittances whether I proceed or
return. I have written to him repeatedly, that he may not plead
ignorance of my situation for neglect. I can give you no account of any
thing, for I have not time or opportunity, the frigate sailing
immediately. Indeed the further I go the more my laziness increases, and
my aversion to letter-writing becomes more confirmed. I have written to
no one but to yourself and Mr. Hanson, and these are communications of
business and duty rather than of inclination.
Fletcher is very much disgusted with his fatigues, though he has
undergone nothing that I have not shared. He is a poor creature; indeed
English servants are detestable travellers. I have, besides him, two
Albanian soldiers and a Greek interpreter; all excellent in their way.
Greece, particularly in the vicinity of Athens, is
delightful; — cloudless skies and lovely landscapes. But I must reserve
all account of my adventures till we meet. I keep no journal, but my
friend Hobhouse scribbles incessantly. Pray take care of Murray and
Robert, and tell the boy it is the most fortunate thing for him that he
did not accompany me to Turkey. Consider this as merely a notice of my
safety, and believe me,
Yours, etc., etc.,
Byron.
Footnote 1: It was at Smyrna that the two first cantos of Childe
Harold were completed. To his original MS. of the poem is prefixed the
following memorandum:—
"Byron, Ioannina in Albania.
Begun October 31st, 1809;
Concluded Canto 2d, Smyrna,
March 28th, 1810.
— Byron."
return to footnote mark
List of Letters
Smyrna, April 9, 1810.
Dear Mother, — I know you will be glad to hear from me: I wish I could
say I am equally delighted to write. However, there is no great loss in
my scribbles, except to the portmanteau-makers, who, I suppose, will get
all by and by.
Nobody but yourself asks me about my creed, — what I am, am not, etc.,
etc. If I were to begin explaining, God knows where I should leave
off; so we will say no more about that, if you please.
I am no "good soul," and not an atheist, but an English gentleman, I
hope, who loves his mother, mankind, and his country. I have not time to
write more at present, and beg you to believe me,
Ever yours, etc.,
Byron.
P.S.-Are the Miss — — anxiously expecting my arrival and contributions
to their gossip and rhymes, which are about as bad as they can be?
B.
List of Letters
Smyrna, April 10, 1810.
Dear Mother, — To-morrow, or this evening, I sail for Constantinople in
the Salsette frigate, of thirty-six guns. She returns to England with
our ambassador1, whom she is going up on purpose to receive. I have
written to you short letters from Athens, Smyrna, and a long one from
Albania. I have not yet mustered courage for a second large epistle, and
you must not be angry, since I take all opportunities of apprizing you
of my safety; but even that is an effort, writing is so irksome.
I have been traversing Greece, and Epirus, Illyria, etc., etc., and you
see by my date, have got into Asia. I have made but one excursion lately
to the ruins of Ephesus. Malta is the rendez-vous of my letters, so
address to that island. Mr. Hanson has not written, though I wished to
hear of the Norfolk sale2, the Lancashire law-suit, etc., etc., I am
anxiously expecting fresh remittances. I believe you will like
Nottinghamshire, at least my share of it3. Pray accept my good wishes
in lieu of a long letter, and believe me,
Yours sincerely and affectionately,
Byron.
Footnote 1: Robert (afterwards the Right Hon. Sir Robert) Adair (1763-1855), son of Sergeant-Surgeon Adair and Lady Caroline Keppel, described
by an Austrian aristocrat as "le fils du plus grand Seigneur d'Angleterre," was educated at Westminster and the University of
Gottingen. At the latter place Adair, always, as his kinsman Lord
Albemarle said of him, "an enthusiastic admirer of the fair sex"
(Recollections, vol. i. p. 229), fell in love with his tutor's
daughter. He did not, however, marry "Sweet Matilda Pottingen," but
Angélique Gabrielle, daughter of the Marquis d'Hazincourt. He is
supposed to have contributed to the Rolliad; and the "Dedication to
Sir Lloyd Kenyon," "Margaret Nicholson" (Political Eclogues, p. 207),
and the "Song of Scrutina" (Probationary Odes, p. 285), have been
attributed to him. He, however, denied (Moore's Journal and
Correspondence, vol. ii. p. 304) that he wrote any part of the
Rolliad. A Whig, and an intimate friend and follower of Fox, he was in
1791 at St. Petersburg, where the Tories believed that he had been sent
by his chief on "half a mission" to intrigue with Russia against Pitt.
The charge was published by Dr. Pretyman, Bishop of Winchester, in his
Life of Pitt (1821), who may have wished to pay off old scores, and to
retaliate on one of the reputed authors of the Rolliad for the
"Pretymaniana," and was answered in Two Letters from Mr. Adair to the
Bishop of Winchester. It is to this accusation that Ellis and Frere, in
the Anti-Jacobin, refer in "A Bit of an Ode to Mr. Fox" (Poetry of
the Anti-Jacobin, edit. 1854, pp. 71-73):—
"I mount, I mount into the sky,
Sweet bird, to Petersburg I'll fly,
Or, if you bid, to Paris.
Fresh missions of the Fox and Goose
Successful Treaties may produce,
Though Pitt in all miscarries."
Sir James Mackintosh, speaking of the story, told Moore (Journals and
Correspondence, vol. iv. p. 267) that a private letter from Adair,
reporting his conversations with a high official in St. Petersburg, fell
into the hands of the British Government; that some members of the
Council were desirous of taking proceedings upon it; but that Lord
Grenville and Pitt threatened to resign, if any use was made of such a
document so obtained. (See also the "Translation of a Letter from
Bawba-Dara-Adul-Phoola," etc. — i. e. "Bob Adair, a dull fool" — in the
Anti-Jacobin, p. 208.) Adair was in 1806 sent by Fox as Ambassador to
Vienna, and in 1809 was appointed by Canning Ambassador Extraordinary at
Constantinople, where, with Stratford Canning as his secretary, he
negotiated the Treaty of the Dardanelles. For his services, on his
return in 1810, he was made a K.C.B. He was subsequently (1831-35)
employed on a mission to the Low Countries, when war appeared imminent
between William, Prince of Orange and King Leopold. He was afterwards
sworn a member of the Privy Council, and received a pension. George
Ticknor (Life, vol. i. p. 269), who met him at Woburn in 1819, speaks
of his great conversational charms, and Moore (Journals and
Correspondence, vol. vii. p. 216) describes him, in 1838, as a man
"from whom one gets, now and then, an agreeable whiff of the days of
Fox, Tickell, and Sheridan." Many years after Fox's death, Adair was at
a fête at Chiswick House. "'In which room,' he asked of Samuel Rogers,
'did Fox expire?' 'In this very room,' I replied. Immediately, Adair
burst into tears with a vehemence of grief such as I hardly ever saw
exhibited by a man" (Recollections of the Table-Talk of Samuel Rogers,
p. 97).
return to footnote mark
cross-reference: return to Footnote 4 of Letter 137
Footnote 2: The sale of Wymondham and other property in Norfolk, which
had come to him through his great-uncle.
return
Footnote 3: Probably an allusion to his mother leaving Burgage Manor
and taking up her residence at Newstead.
return
List of Letters
Salsette Frigate, off the Dardanelles, April 17, 1810.
Dear Madam, — I write at anchor (on our way to Constantinople) off the
Troad, which I traversed ten days ago. All the remains of Troy are the
tombs of her destroyers, amongst which I saw that of Antilochus from my
cabin window. These are large mounds of earth, like the barrows of the
Danes in your island. There are several monuments, about twelve miles
distant, of the Alexandrian Troas, which I also examined, but by no
means to be compared with the remnants of Athens and Ephesus. This will
be sent in a ship of war, bound with despatches for Malta. In a few days
we shall be at Constantinople, barring accidents. I have also written
from Smyrna, and shall, from time to time, transmit short accounts of my
movements, but I feel totally unequal to long letters.
Believe me, yours very sincerely,
Byron.
P.S. — No accounts from Hanson!!! Do not complain of short letters; I
write to nobody but yourself and Mr. H.
List of Letters
Salsette frigate, May 3, 1810.
My Dear Drury, — When I left England, nearly a year ago, you requested me
to write to you — I will do so. I have crossed Portugal, traversed the
south of Spain, visited Sardinia, Sicily, Malta, and thence passed into
Turkey, where I am still wandering. I first landed in Albania, the
ancient Epirus, where we penetrated as far as Mount Tomarit — excellently
treated by the chief Ali Pacha, — and, after journeying through Illyria,
Chaonia, etc., crossed the Gulf of Actium, with a guard of fifty
Albanians, and passed the Achelous in our route through Acarnania and
Ætolia. We stopped a short time in the Morea, crossed the Gulf of
Lepanto, and landed at the foot of Parnassus; — saw all that Delphi
retains, and so on to Thebes and Athens, at which last we remained ten
weeks.
His Majesty's ship, Pylades, brought us to Smyrna; but not before we
had topographised Attica, including, of course, Marathon and the Sunian
promontory. From Smyrna to the Troad (which we visited when at anchor,
for a fortnight, off the tomb of Antilochus) was our next stage; and now
we are in the Dardanelles, waiting for a wind to proceed to
Constantinople.
This morning I swam from Sestos to Abydos1. The immediate
distance is not above a mile, but the current renders it hazardous; — so
much so that I doubt whether Leander's conjugal affection must not have
been a little chilled in his passage to Paradise. I attempted it a week
ago, and failed, — owing to the north wind, and the wonderful rapidity of
the tide, — though I have been from my childhood a strong swimmer. But,
this morning being calmer, I succeeded, and crossed the "broad
Hellespont" in an hour and ten minutes.
Well, my dear sir, I have left my home, and seen part of Africa and
Asia, and a tolerable portion of Europe. I have been with generals and
admirals, princes and pashas, governors and ungovernables, — but I have
not time or paper to expatiate. I wish to let you know that I live with
a friendly remembrance of you, and a hope to meet you again; and if I do
this as shortly as possible, attribute it to any thing but
forgetfulness.
Greece, ancient and modern, you know too well to require description.
Albania, indeed, I have seen more of than any Englishman (except a Mr.
Leake), for it is a country rarely visited, from the savage character of
the natives, though abounding in more natural beauties than the
classical regions of Greece, — which, however, are still eminently
beautiful, particularly Delphi and Cape Colonna in Attica. Yet these are
nothing to parts of Illyria and Epirus, where places without a name, and
rivers not laid down in maps, may, one day, when more known, be justly
esteemed superior subjects, for the pencil and the pen, to the dry ditch
of the Ilissus and the bogs of Boeotia.
The Troad is a fine field for conjecture and snipe-shooting, and a good
sportsman and an ingenious scholar may exercise their feet and faculties
to great advantage upon the spot; — or, if they prefer riding, lose their
way (as I did) in a cursed quagmire of the Scamander, who wriggles about
as if the Dardan virgins still offered their wonted tribute. The only
vestige of Troy, or her destroyers, are the barrows supposed to contain
the carcasses of Achilles, Antilochus, Ajax, etc.; — but Mount Ida is
still in high feather, though the shepherds are now-a-days not much like
Ganymede. But why should I say more of these things? are they not
written in the Boke of Gell2? and has not Hobhouse got a journal?
I keep none, as I have renounced scribbling.
I see not much difference between ourselves and the Turks, save that we
have — — and they have none — that they have long dresses, and we short,
and that we talk much, and they little. They are sensible people. Ali
Pacha told me he was sure I was a man of rank, because I had small
ears and hands, and curling hair. By the by, I speak the Romaic, or
modern Greek, tolerably. It does not differ from the ancient dialects so
much as you would conceive; but the pronunciation is diametrically
opposite. Of verse, except in rhyme, they have no idea.
I like the Greeks, who are plausible rascals, — with all the Turkish
vices, without their courage. However, some are brave, and all are
beautiful, very much resembling the busts of Alcibiades; — the women not
quite so handsome. I can swear in Turkish; but, except one horrible
oath, and "pimp," and "bread," and "water," I have got no great
vocabulary in that language. They are extremely polite to strangers of
any rank, properly protected; and as I have two servants and two
soldiers, we get on with great éclat. We have been occasionally in
danger of thieves, and once of shipwreck, — but always escaped.
Of Spain I sent some account to our Hodgson, but have subsequently
written to no one, save notes to relations and lawyers, to keep them out
of my premises. I mean to give up all connection, on my return, with
many of my best friends — as I supposed them — and to snarl all my life.
But I hope to have one good-humoured laugh with you, and to embrace
Dwyer, and pledge Hodgson, before I commence cynicism.
Tell Dr. Butler I am now writing with the gold pen he gave me before I
left England, which is the reason my scrawl is more unintelligible than
usual. I have been at Athens, and seen plenty of these reeds for
scribbling, some of which he refused to bestow upon me, because
topographic Gell had brought them from Attica. But I will not
describe, — no — you must be satisfied with simple detail till my return,
and then we will unfold the floodgates of colloquy. I am in a thirty-six
gun frigate, going up to fetch Bob Adair from Constantinople, who will
have the honour to carry this letter.
And so Hobhouse's boke is out3, with some sentimental sing-song of
my own to fill up, — and how does it take, eh? and where the devil is the
second edition of my Satire, with additions? and my name on the title
page? and more lines tagged to the end, with a new exordium and what
not, hot from my anvil before I cleared the Channel? The Mediterranean
and the Atlantic roll between me and criticism; and the thunders of the
Hyperborean Review are deafened by the roar of the Hellespont.
Remember me to Claridge4, if not translated to college, and present
to Hodgson assurances of my high consideration. Now, you will ask, what
shall I do next? and I answer, I do not know. I may return in a few
months, but I have intents and projects after visiting Constantinople.
Hobhouse, however, will probably be back in September.
On the 2d of July we have left Albion one year — oblitus meorum
obliviscendus et illis. I was sick of my own country, and not much
prepossessed in favour of any other; but I "drag on my chain" without
"lengthening it at each remove."5 I am like the Jolly Miller, caring
for nobody, and not cared for6. All countries are much the same in my
eyes. I smoke, and stare at mountains, and twirl my mustachios very
independently. I miss no comforts, and the musquitoes that rack the
morbid frame of H. have, luckily for me, little effect on mine, because
I live more temperately.
I omitted Ephesus in my catalogue, which I visited during my sojourn at
Smyrna; but the Temple has almost perished, and St. Paul need not
trouble himself to epistolise the present brood of Ephesians, who have
converted a large church built entirely of marble into a mosque, and I
don't know that the edifice looks the worse for it.
My paper is full, and my ink ebbing — good afternoon! If you address to
me at Malta, the letter will be forwarded wherever I may be. H. greets
you; he pines for his poetry, — at least, some tidings of it. I almost
forgot to tell you that I am dying for love of three Greek girls at
Athens, sisters. I lived in the same house. Teresa, Mariana, and
Katinka7, are the names of these divinities, — all of them under
fifteen.
Your 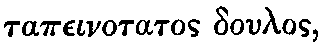 Byron.
Byron.
Footnote 1: Byron made two attempts to swim across the Hellespont from
Abydos to Sestos. The first, April 16, failed; the second, May 3, in
warmer weather, succeeded.
"Byron was one hour and ten minutes in the water; his companion, Mr.
Ekenhead, five minutes less ... My fellow-traveller had before made a
more perilous, but less celebrated, passage; for I recollect that,
when we were in Portugal, he swam from Old Lisbon to Belem Castle,
and, having to contend with a tide and counter-current, the wind
blowing freshly, was but little less than two hours in crossing the
river"
(Hobhouse, Travels in Albania, etc., vol. ii. p. 195). In Hobhouse's
journal, Byron made the following note:
"The whole distance E. and myself swam was more than four miles — the
current very strong and cold — some large fish near us when half
across — we were not fatigued, but a little chilled — did it with little
difficulty. — May 26, 1810. Byron."
Of his feat Byron was always proud. See the "Lines Written after
Swimming from Sestos to Abydos" ("by the by, from Abydos to Sestos would
have been more correct"), and Don Juan, Canto II. stanza cv.:—
"A better swimmer you could scarce see ever;
He could, perhaps, have pass'd the Hellespont,
As once (a feat on which ourselves we prided)
Leander, Mr. Ekenhead, and I did."
In a note to the "Lines Written after Swimming from Sestos to Abydos," Byron writes,
"Chevalier says that a young Jew swam the same distance for his
mistress; and Oliver mentions its having been done by a Neapolitan;
but our consul, Tarragona, remembered neither of these circumstances,
and tried to dissuade us from the attempt. A number of the
Salsette's crew were known to have accomplished a greater distance;
and the only thing that surprised me was that, as doubts had been
entertained of the truth of Leander's story, no traveller had ever
endeavoured to ascertain its practicability."
Lieutenant Ekenhead, of the Marines, was afterwards killed by a fall
from the fortifications of Malta.
return to footnote mark
Footnote 2: Sir William Gell (1777-1836) published the Topography of
Troy (1804); Geography and Antiquities of Ithaca (1807); the
Itinerary of Greece (1810); and many other subsequent works. (For
Byron's review of Ithaca and Greece, in the Monthly Review for
August, 1811, see Appendix III.) In the MS. of English Bards, and
Scotch Reviewers (line 1034) he called him "coxcomb Gell;" but, having
made his personal acquaintance before the Satire was printed, he changed
the epithet to "classic." After seeing the country himself, he again
altered the epithet —
"Of Dardan tours let Dilettanti tell,
I leave topography to rapid Gell."
To these lines is appended the following note:
"'Rapid,' indeed! He topographised and typographised King Priam's
dominions in three days! I called him 'classic' before I saw the
Troad, but since have learned better than to tack to his name what
don't belong to it."
To this passage Byron, in 1816, added the further expression of his
opinion, that "Gell's survey was hasty and superficial." One of two
suppressed stanzas in Childe Harold (Canto II. stanza xiii.) refers to
Gell and his works:—
"Or will the gentle Dilettanti crew
Now delegate the task to digging Gell?
That mighty limner of a bird's-eye view,
How like to Nature let his volumes tell;
Who can with him the folio's limits swell
With all the Author saw, or said he saw?
Who can topographise or delve so well?
No boaster he, nor impudent and raw,
His pencil, pen, and shade, alike without a flaw."
return
Footnote 3: Imitations and Translations from the Ancient and Modern
Classics, etc. (London, 1809, 8vo). Of the sixty-five pieces, nine were
by Byron (see Poems, vol. i, Bibliographical note; and vol. vi,
Bibliographical note). The second and enlarged edition of English
Bards, and Scotch Reviewers, with Byron's name attached, appeared in
October, 1809.
return
Footnote 4: Two boys of this name, sons of J. Claridge, of Sevenoaks,
entered Harrow School in April, 1805. George became a. solicitor, and
died at Sevenoaks in 1841; John (afterwards Sir John) went to Christ
Church, Oxford, became a barrister, and died in 1868. John Claridge
seems to have been one of Byron's "juniors and favourites," whom he
"spoilt by indulgence."
return
Footnote 5:
"Still to my brother turns with ceaseless pain,
And drags at each remove a lengthening chain."
Goldsmith's Traveller, lines 9, 10.
return
Footnote 6: The allusion is to the familiar lines inserted by Isaac
Bickerstaffe in Love in a Village (1762), act i. sc. 3 —
"There was a jolly miller once,
Liv'd on the river Dee;
He work'd and sung from morn till night;
No lark more blithe than he.
"And this the burden of his song,
For ever us'd to be —
I care for nobody, not I,
If no one cares for me."
return
Footnote 7:
"During our stay at Athens," writes Hobhouse (Travels in Albania,
etc., vol. i. pp. 242, 243), "we occupied two houses separated from
each other only by a single wall, through which we opened a doorway.
One of them belongs to a Greek lady, whose name is Theodora Macri, the
daughter of the late English Vice-Consul, and who has to show many
letters of recommendation left in her hands by several English
travellers. Her lodgings consisted of a sitting-room and two bedrooms,
opening into a court-yard where there were five or six lemon-trees,
from which, during our residence in the place, was plucked the fruit
that seasoned the pilaf and other national dishes served up at our
frugal table."
The beauty of the Greek women is transient. Hughes (Travels
in Sicily, etc., vol. i. p. 254, published in 1820) speaks of the three
daughters of Madame Macri as "the belles of Athens." Of Theresa,
the eldest, he says that "her countenance was extremely interesting,
and her eye retained much of its wonted brilliancy; but the roses
had already deserted the cheek, and we observed the remains only
of that loveliness which elicited such strains from an impassioned
poet." Walsh, in his Narrative of a Resident in Constantinople
(vol. i p. 122), speaks of Theresa Macri, the "Maid of Athens,"
whom he saw in 1821, as "still very elegant in her person, and
gentle and ladylike in her manners," but adds that "she has
lost all pretensions to beauty, and has a countenance singularly
marked by hopeless sadness." On the other hand, Williams, in
his Travels in Italy, etc. (vol. ii. pp. 290, 291), speaks, in 1820,
with an artist's enthusiasm, of the beauty of the three daughters of
Theodora Macri. He quotes from the "Visitors' Book," to which
Hobhouse alludes, four lines written by Byron in answer to an
anonymous versifier —
"This modest bard, like many a bard unknown,
Rhymes on our names, but wisely hides his own;
But yet, whoe'er he be, to say no worse,
His name would bring more credit than his verse."
Theresa and Mariana Macri were dark; Katinka was fair. The latter name
Byron uses as that of the fair Georgian in Don Juan (Canto VI. stanza
xli.).
"It was," says Moore, "if I recollect right, in making love to one of
these girls that he had recourse to an act of courtship often
practised in that country; — namely, giving himself a wound across the
breast with his dagger. The young Athenian, by his own account, looked
on very coolly during the operation, considering it a fit tribute to
her beauty, but in no degree moved to gratitude."
Theresa, sometimes called Thyrza, Macri married an Englishman named
Black, employed in H.M.'s Consular service at Missolonghi. She survived
her husband, and fell into great poverty. Finlay, the historian of
Greece, made an appeal on her behalf, which obtained the support of the
leading members of Athenian society, including M. Charilaus Tricoupi,
for some time Prime Minister at Athens, the son of Spiridion
Tricoupi — Byron's intimate friend. In the New York Times for October
22, 1875, Mr. Anthony Martelaus, United States Consular Agent at Athens,
describes Mrs. Black, whom he visited in August, 1875, as "a tall old
lady, with features inspiring reverence, and showing that at a time past
she was a beautiful woman." Theresa Black died October 15, 1875, aged 80
years. (See letters to the Times, October 25 and October 27, 1875, by
Richard Edgcumbe and Neocles Mussabini respectively.)
return
List of Letters
Salsette frigate, in the Dardanelles, off Abydos, May 5, 1810.
I am on my way to Constantinople, after a tour through Greece, Epirus,
etc., and part of Asia Minor, some particulars of which I have just
communicated to our friend and host, H. Drury. With these, then, I shall
not trouble you; but as you will perhaps be pleased to hear that I am
well, etc., I take the opportunity of our ambassador's return to forward
the few lines I have time to despatch. We have undergone some
inconveniences, and incurred partial perils, but no events worthy of
communication, unless you will deem it one that two days ago I swam from
Sestos to Abydos. This, with a few alarms from robbers, and some danger
of shipwreck in a Turkish galliot six months ago, a visit to a Pacha, a
passion for a married woman at Malta1, a challenge to an officer, an
attachment to three Greek girls at Athens, with a great deal of
buffoonery and fine prospects, form all that has distinguished my
progress since my departure from Spain.
Hobhouse rhymes and journalises; I stare and do nothing — unless smoking
can be deemed an active amusement. The Turks take too much care of their
women to permit them to be scrutinised; but I have lived a good deal
with the Greeks, whose modern dialect I can converse in enough for my
purposes. With the Turks I have also some male acquaintances — female
society is out of the question. I have been very well treated by the
Pachas and Governors, and have no complaint to make of any kind.
Hobhouse will one day inform you of all our adventures — were I to
attempt the recital, neither my paper nor your patience would hold
out during the operation.
Nobody, save yourself, has written to me since I left England; but
indeed I did not request it. I except my relations, who write quite as
often as I wish. Of Hobhouse's volume I know nothing, except that it is
out; and of my second edition I do not even know that, and certainly
do not, at this distance, interest myself in the matter. I hope you and
Bland2 roll down the stream of sale with rapidity.
Of my return I cannot positively speak, but think it probable Hobhouse
will precede me in that respect. We have been very nearly one year
abroad. I should wish to gaze away another, at least, in these evergreen
climates; but I fear business, law business, the worst of employments,
will recall me previous to that period, if not very quickly. If so, you
shall have due notice.
I hope you will find me an altered personage, — I do not mean in body,
but in manner, for I begin to find out that nothing but virtue will do
in this damned world. I am tolerably sick of vice, which I have tried in
its agreeable varieties, and mean, on my return, to cut all my dissolute
acquaintance, leave off wine and carnal company, and betake myself to
politics and decorum. I am very serious and cynical, and a good deal
disposed to moralise; but fortunately for you the coming homily is cut
off by default of pen and defection of paper.
Good morrow! If you write, address to me at Malta, whence your letters
will be forwarded. You need not remember me to any body, but believe me,
Yours with all faith,
Byron.
Constantinople, May 15, 1810.
P.S. — My dear H., — The date of my postscript "will prate to you of my
whereabouts." We anchored between the Seven Towers and the Seraglio on
the 13th, and yesterday settled ashore3. The ambassador4 is laid
up; but the secretary5 does the honours of the palace, and we have a
general invitation to his palace. In a short time he has his leave of
audience, and we accompany him in our uniforms to the Sultan, etc., and
in a few days I am to visit the Captain Pacha with the commander of our
frigate6. I have seen enough of their Pashas already; but I wish to
have a view of the Sultan, the last of the Ottoman race.
Of Constantinople you have Gibbon's description, very correct as far as
I have seen. The mosques I shall have a firman to visit. I shall most
probably (Deo volente), after a full inspection of Stamboul, bend
my course homewards; but this is uncertain. I have seen the most
interesting parts, particularly Albania, where few Franks have ever
been, and all the most celebrated ruins of Greece and Ionia.
Of England I know nothing, hear nothing, and can find no person better
informed on the subject than myself. I this moment drink your health in
a bumper of hock; Hobhouse fills and empties to the same; do you and
Drury pledge us in a pint of any liquid you please — vinegar will bear
the nearest resemblance to that which I have just swallowed to your
name; but when we meet again the draught shall be mended and the wine
also.
Yours ever,
B.
Footnote 1: Mrs. Spencer Smith (see page 244, note i).
"In the mean time," writes Galt, who was at Malta with him, "besides
his "Platonic dalliance with Mrs. Spencer Smith, Byron had involved
himself in a quarrel with an officer; but it was satisfactorily
settled"
(Life of Byron, p. 67).
return to footnote mark
Footnote 2: The Rev. Robert Bland (1780-1825), the son of a well-known
London doctor, educated at Harrow and Pembroke College, Cambridge, was
an assistant-master at Harrow when Byron was a schoolboy. There he
became one of a "social club or circle," to which belonged J. Herman
Merivale, Hodgson, Henry Drury, Denman (afterwards Lord Chief Justice),
Charles Pepys (afterwards Lord Chancellor), Launcelot Shadwell
(afterwards Vice-Chancellor), Walford (afterwards Solicitor to the
Customs), and Paley, a son of the archdeacon. A good singer, an amusing
companion, and a clever, impulsive, eccentric creature, he was nicknamed
by his friends "Don Hyperbolo" for his humorous extravagances. Some of
his letters, together with a sketch of his life, are given in the Life
of the Rev. Francis Hodgson, vol. i pp. 226-250. In the Monthly
Magazine for March, 1805, he and Merivale began to publish a series of
translations from the Greek minor poets and epigrammatists, which were
afterwards collected, with additions by Denman, Hodgson, Drury, and
others, and published (1806) under the title of Translations, chiefly
from the Greek Anthology, with Tales and Miscellaneous Poems. Bland and
Merivale (1779-1844) are addressed by Byron (English Bards, and Scotch
Reviewers, lines 881-890) as "associate bards," and adjured to "resign
Achaia's lyre, and strike your own." The two friends also collaborated
in the Collections from the Greek Anthology (1813), and A Collection
of the most Beautiful Poems of the Minor Poets of Greece (1813). Bland
also published two volumes of original verse: Edwy and Elgiva (1808),
and The Four Slaves of Cythera, a Poetical Romance (1809). Several
generations of schoolboys have learned to write Latin verse from his
Elements of Latin Hexameters and Pentameters. A lover of France, and
of the French nation and of French acting, he spoke the language like a
native, travelled in disguise over the countries occupied by Napoleon's
armies, and (1813) published, in collaboration with Miss Plumptre, a
translation of the Memoirs of Baron Grimm and Diderot. He was
appointed Chaplain at Amsterdam, whence he returned in 1811. (For the
circumstances of his quarrel with Hodgson, see page 195, note 1.) He
was successively Curate of Prittlewell and Kenilworth. At the latter
place, where he eked out a scanty income by taking pupils, he died in
1825 from breaking a blood-vessel.
return
Footnote 3: Byron and Hobhouse landed on May 14, and rode to their inn.
"This," says Hobhouse (Travels in Albania, etc., vol. ii pp. 216,
217), "was situated at the corner of the main street of Pera, here
four ways meet, all of which were not less mean and dirty than the
lanes of Wapping. The hotel, however (kept by a Mons. Marchand), was a
very comfortable mansion, containing many chambers handsomely
furnished, and a large billiard-room, which is the resort of all the
idle young men of the place. Our dinners there were better served, and
composed of meats more to the English taste, than we had seen at any
tavern since our departure from Falmouth; and the butter of Belgrade
(perfectly fresh, though not of a proper consistency) was a delicacy
to which we had long been unaccustomed. The best London porter, and
nearly every species of wine, except port, were also to be procured in
any quantity. To this eulogy cannot be added the material
recommendation of cheapness."
return
Footnote 4: Robert Adair. (See page 260, note 1.)
return
Footnote 5: Stratford Canning, afterwards Lord Stratford de Redcliffe.
return
Footnote 6: Captain Bathurst, and the officers of the Salsette,
anxious to see the arsenal and the Turkish fleet, paid a visit with
Byron to Ali, the Capudan-Pasha, or Lord High Admiral.
"He was," writes
Hobhouse (Travels in Albania, etc., vol. ii. p. 279), "in his kiosk of
audience at Divan-Hane, a splendid chamber, surrounded by his
attendants, and, contrary to custom, received us sitting. He is reported
to be a ferocious character, and certainly had the appearance of being
so."
return
List of Letters
Constantinople, May 18, 1810.
Dear Madam, — I arrived here in an English frigate from Smyrna a few days
ago, without any events worth mentioning, except landing to view the
plains of Troy, and afterwards, when we were at anchor in the
Dardanelles, swimming from Sestos to Abydos, in imitation of
Monsieur Leander, whose story you, no doubt, know too well for me to add
anything on the subject except that I crossed the Hellespont without so
good a motive for the undertaking. As I am just going to visit the
Captain-Pacha, you will excuse the brevity of my letter. When Mr. Adair
takes leave I am to see the Sultan and the mosques, etc.
Believe me, yours ever,
Byron.
List of Letters
Constantinople, May 24, 1810.
Dear Mother, — I wrote to you very shortly the other day on my arrival
here, and, as another opportunity avails, take up my pen again, that the
frequency of my letters may atone for their brevity. Pray did you ever
receive a picture of me in oil by Sanders in Vigo Lane, London? (a
noted limner); if not, write for it immediately; it was paid for, except
the frame (if frame there be), before I left England. I believe I
mentioned to you in my last that my only notable exploit lately has been
swimming from Sestos to Abydos in humble imitation of Leander, of
amorous memory; though I had no Hero to receive me on the other shore
of the Hellespont.
Of Constantinople you have of course read fifty descriptions by sundry
travellers, which are in general so correct that I have nothing to add
on the subject. When our ambassador takes his leave I shall accompany
him to see the Sultan, and afterwards probably return to Greece. I have
heard nothing of Mr. H — — , but one remittance without any letter from
that legal gentleman. If you have occasion for any pecuniary supply,
pray use my funds as far as they go, without reserve; and lest there
should not be enough, in my next to Mr. H — — I will direct him to
advance any sum you want, leaving at your discretion how much, in the
present state of my affairs, you may think proper to require.
I have already seen the most interesting part of Turkey in Europe and
Asia Minor, but shall not proceed further till I hear from England. In
the mean time I shall expect occasional supplies, according to
circumstances, and shall pass my summer amongst my friends the Greeks of
the Morea. You will direct to Malta, where my letters are forwarded.
And believe me, with great sincerity, yours ever,
Byron.
P.S. — Fletcher is well. Pray take care of my boy Robert and the old man
Murray. It is fortunate they returned; neither the youth of the one nor
the age of the other would have suited the changes of climate and
fatigue of travelling.
List of Letters
Constantinople, June 17, 1810.
Though I wrote to you so recently, I break in upon you again to
congratulate you on a child being born1, as a letter from Hodgson
apprizes me of that event, in which I rejoice.
I am just come from an expedition through the Bosphorus to the Black Sea
and the Cyanean Symplegades, up which last I scrambled with as great
risk as ever the Argonauts escaped in their hoy. You remember the
beginning of the nurse's dole in the Medea, of which I beg you to take
the following translation, done on the summit:—
"Oh how I wish that an embargo
Had kept in port the good ship Argo!
Who, still unlaunched from Grecian docks,
Had never passed the Azure rocks;
But now I fear her trip will be a
Damned business for my Miss Medea, etc., etc.,"2
as it very nearly was to me; — for, had not this sublime passage been in
my head, I should never have dreamed of ascending the said rocks, and
bruising my carcass in honour of the ancients.
I have now sat on the Cyaneans, swam from Sestos to Abydos (as I
trumpeted in my last), and, after passing through the Morea again, shall
set sail for Santa Maura, and toss myself from the Leucadian
promontory; — surviving which operation, I shall probably join you in
England. Hobhouse, who will deliver this, is bound straight for these
parts; and, as he is bursting with his travels, I shall not anticipate
his narratives, but merely beg you not to believe one word he says, but
reserve your ear for me, if you have any desire to be acquainted with
the truth.
I am bound for Athens once more, and thence to the Morea; but my stay
depends so much on my caprice, that I can say nothing of its probable
duration. I have been out a year already, and may stay another; but I am
quicksilver, and say nothing positively. We are all very much occupied
doing nothing, at present. We have seen every thing but the mosques,
which we are to view with a firman on Tuesday next. But of these and
other sundries let H. relate, with this proviso, that I am to be
referred to for authenticity; and I beg leave to contradict all those
things whereon he lays particular stress. But, if he soars at any time
into wit, I give you leave to applaud, because that is necessarily
stolen from his fellow-pilgrim. Tell Davies3 that Hobhouse has made
excellent use of his best jokes in many of his Majesty's ships of war;
but add, also, that I always took care to restore them to the right
owner; in consequence of which he (Davies) is no less famous by water
than by land, and reigns unrivalled in the cabin as in the "Cocoa Tree."4
And Hodgson has been publishing more poesy — I wish he would send me his
Sir Edgar,5 and Bland's Anthology, to Malta, where they
will be forwarded. In my last, which I hope you received, I gave an
outline of the ground we have covered. If you have not been overtaken by
this despatch, Hobhouse's tongue is at your service. Remember me to
Dwyer, who owes me eleven guineas. Tell him to put them in my banker's
hands at Gibraltar or Constantinople. I believe he paid them once, but
that goes for nothing, as it was an annuity.
I wish you would write. I have heard from Hodgson frequently. Malta is
my post-office. I mean to be with you by next Montem. You remember the
last, — I hope for such another; but after having swam across the "broad
Hellespont," I disdain Datchett6. Good afternoon!
I am yours, very sincerely,
Byron.
Footnote 1: Henry Drury, afterwards Archdeacon of Wilts.
return to footnote mark
Footnote 2: Euripides, Medea, lines 1-7 —

return
Footnote 3: For Scrope Berdmore Davies, see page 165, note 2.
return
Footnote 4: "The Cocoa Tree," now 64, St. James's Street, formerly in
Pall Mall, was, in the reign of Queen Anne, the Tory Chocolate House. It
became a club about 1745, and was then regarded as the headquarters of
the Jacobites. Probably for this reason Gibbon, whose father professed
Jacobite opinions, belonged to it on coming to live in London (see his
journal for November, 1762, and his letter to his stepmother, January
18, 1766: "The Cocoa Tree serves "now and then to take off an idle
hour"). Byron was a member.
return
Footnote 5: Hodgson's Sir Edgar was published in 1810.
return
Footnote 6: Alluding to his having swum across the Thames with Henry
Drury, after the Montem, to see how many times they could make the
passage backwards and forwards without touching land. In this trial
Byron was the conqueror.
return
List of Letters
Constantinople, June 28, 1810.
My dear Mother, — I regret to perceive by your last letter that several
of mine have not arrived, particularly a very long one written in
November last from Albania, where I was on a visit to the Pacha of that
province. Fletcher has also written to his spouse perpetually.
Mr. Hobhouse, who will forward or deliver this, and is on his return to
England, can inform you of our different movements, but I am very
uncertain as to my own return. He will probably be down in Notts, some
time or other; but Fletcher, whom I send back as an incumbrance (English
servants are sad travellers), will supply his place in the interim, and
describe our travels, which have been tolerably extensive.
I have written twice briefly from this capital, from Smyrna, from Athens
and other parts of Greece; from Albania, the Pacha of which province
desired his respects to my mother, and said he was sure I was a man of
high birth because I had small ears, curling hair, and white hands!!! He
was very kind to me, begged me to consider him as a father, and gave me
a guard of forty soldiers through the forests of Acarnania. But of this
and other circumstances I have written to you at large, and yet hope you
will receive my letters.
I remember Mahmout Pacha, the grandson of Ali Pacha, at Yanina, (a
little fellow of ten years of age, with large black eyes, which our
ladies would purchase at any price, and those regular features which
distinguish the Turks,) asked me how I came to travel so young, without
anybody to take care of me. This question was put by the little man with
all the gravity of threescore. I cannot now write copiously; I have only
time to tell you that I have passed many a fatiguing, but never a
tedious moment; and all that I am afraid of is that I shall contract a
gypsy like wandering disposition, which will make home tiresome to me:
this, I am told, is very common with men in the habit of peregrination,
and, indeed, I feel it so. On the 3rd of May I swam from Sestos
to Abydos. You know the story of Leander, but I had no
Hero to receive me at landing.
I also passed a fortnight on the Troad. The tombs of Achilles and
Æsyetes still exist in large barrows, similar to those you have
doubtless seen in the North. The other day I was at Belgrade (a village
in these environs), to see the house built on the same site as Lady Mary
Wortley's1. By-the-by, her ladyship, as far as I can judge, has lied,
but not half so much as any other woman would have done in the same
situation.
I have been in all the principal mosques by the virtue of a firman: this
is a favor rarely permitted to Infidels, but the ambassador's departure
obtained it for us. I have been up the Bosphorus into the Black Sea,
round the walls of the city, and, indeed, I know more of it by sight
than I do of London. I hope to amuse you some winter's evening with the
details, but at present you must excuse me; — I am not able to write long
letters in June. I return to spend my summer in Greece. I write often,
but you must not be alarmed when you do not receive my letters; consider
we have no regular post farther than Malta, where I beg you will in
future send your letters, and not to this city.
Fletcher is a poor creature, and requires comforts that I can dispense
with. He is very sick of his travels, but you must not believe his
account of the country. He sighs for ale, and idleness, and a wife, and
the devil knows what besides. I have not been disappointed or disgusted.
I have lived with the highest and the lowest. I have been for days in a
Pacha's palace, and have passed many a night in a cowhouse, and I find
the people inoffensive and kind. I have also passed some time with the
principal Greeks in the Morea and Livadia, and, though inferior to the
Turks, they are better than the Spaniards, who, in their turn, excel the
Portuguese. Of Constantinople you will find many descriptions in
different travels; but Lady Mary Wortley errs strangely when she says,
"St. Paul's would cut a strange figure by St. Sophia's."2 I have
been in both, surveyed them inside and out attentively. St. Sophia's is
undoubtedly the most interesting from its immense antiquity, and the
circumstance of all the Greek emperors, from Justinian, having been
crowned there, and several murdered at the altar, besides the Turkish
Sultans who attend it regularly. But it is inferior in beauty and size
to some of the mosques, particularly "Soleyman," etc., and not to be
mentioned in the same page with St. Paul's (I speak like a Cockney).
However, I prefer the Gothic cathedral of Seville to St. Paul's, St.
Sophia's, and any religious building I have ever seen.
The walls of the Seraglio are like the walls of Newstead gardens, only
higher, and much in the same order; but the ride by the walls of the
city, on the land side, is beautiful. Imagine four miles of immense
triple battlements, covered with ivy, surmounted with 218 towers, and,
on the other side of the road, Turkish burying-grounds (the loveliest
spots on earth), full of enormous cypresses. I have seen the ruins of
Athens, of Ephesus, and Delphi. I have traversed great part of Turkey,
and many other parts of Europe, and some of Asia; but I never beheld a
work of nature or art which yielded an impression like the prospect on
each side from the Seven Towers to the end of the Golden Horn3.
Now for England. I am glad to hear of the progress of English Bards,
etc. Of course, you observed I have made great additions to the new
edition. Have you received my picture from Sanders, Vigo Lane, London?
It was finished and paid for long before I left England: pray, send for
it. You seem to be a mighty reader of magazines: where do you pick up
all this intelligence, quotations, etc., etc.? Though I was happy to
obtain my seat without the assistance of Lord Carlisle, I had no
measures to keep with a man who declined interfering as my relation on
that occasion, and I have done with him, though I regret distressing
Mrs. Leigh4, poor thing! — I hope she is happy.
It is my opinion that Mr. B — — ought to marry Miss R — — . Our first
duty is not to do evil; but, alas! that is impossible: our next is to
repair it, if in our power. The girl is his equal: if she were his
inferior, a sum of money and provision for the child would be some,
though a poor, compensation: as it is, he should marry her. I will have
no gay deceivers on my estate, and I shall not allow my tenants a
privilege I do not permit myself — that of debauching each other's
daughters. God knows, I have been guilty of many excesses; but, as I
have laid down a resolution to reform, and lately kept it, I expect this
Lothario to follow the example, and begin by restoring this girl to
society, or, by the beard of my father! he shall hear of it. Pray take
some notice of Robert, who will miss his master; poor boy, he was very
unwilling to return. I trust you are well and happy. It will be a
pleasure to hear from you.
Believe me, yours very sincerely,
Byron.
P.S. — How is Joe Murray?
P.S. — I open my letter again to tell you that Fletcher having petitioned
to accompany me into the Morea, I have taken him with me, contrary to
the intention expressed in my letter.
Footnote 1: Lady Mary describes the village of Belgrade in a letter to
Pope, dated June 17, 1717 (Letters, edit. 1893, vol. i. pp. 331-333).
But Walsh (Narrative of a Residence in Constantinople, vol. ii
108, 109), who visited Belgrade in 1821, says that no trace of her
description was then to be seen — no view of the Black Sea, no
houses of the wealthy Christians, no fountains, and no fruit-trees.
"The very tradition" of the house, which had disappeared before
Dallaway visited Belgrade in 1794, had perished.
return to footnote mark
Footnote 2: Lady Mary does not compare St. Paul's with St. Sophia's,
but with the mosque of the Valide,
"the largest of all, built entirely
of marble, the most prodigious, and, I think, the most beautiful
structure I ever saw, be it spoken to the honour of our sex, for it was
founded by the mother of Mahomet IV. Between friends, St. Paul's Church
would make a pitiful figure near it"
(Letters, vol. i. p. 356).
return
Footnote 3: "The European with the Asian shore
Sprinkled with palaces; the ocean stream
Here and there studded with a seventy-four;
Sophia's cupola with golden gleam;
The cypress groves; Olympus high and hoar;
The twelve isles, and the more than I could dream,
Far less describe, present the very view
Which charm'd the charming Mary Montagu."
Don Juan, Canto V stanza 3.
return
Footnote 4: For Mrs. Leigh, née Augusta Byron, see page 18,
note 1.
return
List of Letters
Constantinople, July 1, 1810.
My dear Mother, — I have no wish to forget those who have any claim upon
me, and shall be glad of the good wishes of R — — when he can express
them in person, which it seems will be at some very indefinite date. I
shall perhaps essay a speech or two in the House when I return, but I
am not ambitious of a parliamentary career, which is of all things the
most degrading and unthankful. If I could by my own efforts inculcate
the truth, that a man is not intended for a despot or a machine, but as
an individual of a community, and fit for the society of kings, so long
as he does not trespass on the laws or rebel against just governments, I
might attempt to found a new Utopia; but as matters are at present, in
course you will not expect me to sacrifice my health or self to your or
anyone's ambition.
To quit this new idea for something you will understand better, how are
Miss R's, the W's, and Mr. R's blue bastards? for I suppose he will not
deny their authorship, which was, to say the least, imprudent and
immoral. Poor Miss — — : if he does not marry, and marry her speedily, he
shall be no tenant of mine from the day that I set foot on English
shores.
I am glad you have received my portrait from Sanders. It does not
flatter me, I think, but the subject is a bad one, and I must even do
as Fletcher does over his Greek wines — make a face and hope for better.
What you told me of — — is not true, which I regret for your sake and
your gossip-seeking neighbours, whom present with my good wishes, and
believe me,
Yours, etc.,
Byron.
List of Letters
Constantinople, July 4, 1810.
My Dear Hodgson, — Twice have I written — once in answer to your last, and
a former letter when I arrived here in May. That I may have nothing to
reproach myself with, I will write once more — a very superfluous task,
seeing that Hobhouse is bound for your parts full of talk and
wonderment. My first letter went by an ambassadorial express; my second
by the Black John lugger; my third will be conveyed by Cam, the
miscellanist.
I shall begin by telling you, having only told it you twice before, that
I swam from Sestos to Abydos. I do this that you may be impressed with
proper respect for me, the performer; for I plume myself on this
achievement more than I could possibly do on any kind of glory,
political, poetical, or rhetorical. Having told you this, I will tell
you nothing more, because it would be cruel to curtail Cam's narrative,
which, by-the-by, you must not believe till confirmed by me, the
eye-witness. I promise myself much pleasure from contradicting the
greatest part of it. He has been plaguily pleased by the intelligence
contained in your last to me respecting the reviews of his hymns. I
refreshed him with that paragraph immediately, together with the tidings
of my own third edition, which added to his recreation. But then he has
had a letter from a Lincoln's Inn Bencher, full of praise of his
harpings, and vituperation of the other contributions to his
Missellingany, which that sagacious person is pleased to say must
have been put in as Foils (horresco referens!); furthermore he adds
that Cam "is a genuine pupil of Dryden," concluding with a comparison
rather to the disadvantage of Pope.
I have written to Drury by Hobhouse; a letter is also from me on its way
to England intended for that matrimonial man. Before it is very long, I
hope we shall again be together; the moment I set out for England you
shall have intelligence, that we may meet as soon as possible. Next week
the frigate sails with Adair; I am for Greece, Hobhouse for England. A
year together on the 2nd July since we sailed from Falmouth. I have
known a hundred instances of men setting out in couples, but not one of
a similar return. Aberdeen's1 party split; several voyagers at
present have done the same. I am confident that twelve months of any
given individual is perfect ipecacuanha.
The Russians and Turks are at it2, and the Sultan in person is soon
to head the army. The Captain Pasha cuts off heads every day, and a
Frenchman's ears; the last is a serious affair. By-the-by I like the
Pashas in general. Ali Pasha called me his son, desired his compliments
to my mother, and said he was sure I was a man of birth, because I had
"small ears and curling hair." He is Pasha of Albania six hundred miles
off, where I was in October — a fine portly person. His grandson Mahmout,
a little fellow ten years old, with large black eyes as big as pigeon's
eggs, and all the gravity of sixty, asked me what I did travelling so
young without a Lala (tutor)?
Good night, dear H. I have crammed my paper, and crave your indulgence.
Write to me at Malta. I am, with all sincerity,
Yours affectionately,
Byron.
Footnote 1: George Hamilton Gordon, Earl of Aberdeen (1784-1860),
afterwards Prime Minister (1852-55), succeeded his grandfather as fourth
earl in 1801. Grandson of the purchaser of Mrs. Byron's old home of
Gight, and writer of an article in the Edinburgh Review (July, 1805)
on Gell's Topography of Troy, he has a place in English Bards, and
Scotch Reviewers (lines 508, 509). He also appears as "sullen
Aberdeen," in a suppressed stanza of Childe Harold, Canto II., which
in the MS. follows stanza xiii., among those who
" — — pilfer all the Pilgrim loves to see,
All that yet consecrates the fading scene."
After leaving Harrow, and before entering St. John's College, Cambridge,
he spent two years (1801-3) in Greece. On his return he founded the
Athenian Society, and became President of the Society of Antiquaries
from 1812 to 1846. It may be added that he was Foreign Secretary when
the Porte acknowledged the independence of Greece by the Treaty of
Adrianople (1829).
return to footnote mark
Footnote 2: In this war, the scene of which lay chiefly in Wallachia,
Bosnia, Bulgaria, and Servia, the main episodes were the two battles of
Rustchuk (July 4 and October 14, 1811), the recapture of Silistria by
the Russians, and the Convention of Giurgevo between the contending
forces (October 28, 1811).
return
List of Letters
Athens, July 25, 1810.
Dear Mother, — I have arrived here in four days from Constantinople,
which is considered as singularly quick, particularly for the season of
the year. I left Constantinople with Adair, at whose adieux of leave I
saw Sultan Mahmout1, and obtained a firman to visit the mosques, of
which I gave you a description in my last letter, now voyaging to
England in the Salsette frigate, in which I visited the plains of Troy
and Constantinople. Your northern gentry can have no conception of a
Greek summer; which, however, is a perfect frost compared with Malta and
Gibraltar, where I reposed myself in the shade last year, after a gentle
gallop of four hundred miles, without intermission, through Portugal and
Spain. You see, by my date, that I am at Athens again, a place which I
think I prefer, upon the whole, to any I have seen.
My next movement is to-morrow into the Morea, where I shall probably
remain a month or two, and then return to winter here, if I do not
change my plans, which, however, are very variable, as you may suppose;
but none of them verge to England.
The Marquis of Sligo2, my old fellow-collegian, is here, and wishes
to accompany me into the Morea. We shall go together for that purpose;
but I am woefully sick of travelling companions, after a year's
experience of Mr. Hobhouse, who is on his way to Great Britain. Lord S.
will afterwards pursue his way to the capital; and Lord B., having seen
all the wonders in that quarter, will let you know what he does next, of
which at present he is not quite certain. Malta is my perpetual
post-office, from which my letters are forwarded to all parts of the
habitable globe:— by the bye, I have now been in Asia, Africa, and the
east of Europe, and, indeed, made the most of my time, without hurrying
over the most interesting scenes of the ancient world. Fletcher, after
having been toasted and roasted, and baked, and grilled, and eaten by
all sorts of creeping things, begins to philosophise, is grown a refined
as well as a resigned character, and promises at his return to become an
ornament to his own parish, and a very prominent person in the future
family pedigree of the Fletchers, who I take to be Goths by their
accomplishments, Greeks by their acuteness, and ancient Saxons by their
appetite. He (Fletcher) begs leave to send half-a-dozen sighs to Sally
his spouse, and wonders (though I do not) that his ill-written and worse
spelt letters have never come to hand; as for that matter, there is no
great loss in either of our letters, saving and except that I wish you
to know we are well, and warm enough at this present writing, God knows.
You must not expect long letters at present, for they are written with
the sweat of my brow, I assure you. It is rather singular that Mr.
Hanson has not written a syllable since my departure. Your letters I
have mostly received as well as others; from which I conjecture that the
man of law is either angry or busy.
I trust you like Newstead, and agree with your neighbours; but you know
you are a vixen — is not that a dutiful appellation? Pray, take care
of my books and several boxes of papers in the hands of Joseph; and pray
leave me a few bottles of champagne to drink, for I am very
thirsty; — but I do not insist on the last article, without you like it.
I suppose you have your house full of silly women, prating scandalous
things. Have you ever received my picture in oil from Sanders, London?
It has been paid for these sixteen months: why do you not get it? My
suite, consisting of two Turks, two Greeks, a Lutheran, and the
nondescript, Fletcher, are making so much noise, that I am glad to sign
myself
Yours, etc., etc.,
Byron.
Footnote 1: On July 10, 1810, the British ambassador, Robert Adair, had
his audience of Sultan Mahmoud II, and on the 14th the Salsette set
sail. She touched at the island of Zea to land Byron, who thence made
his way to Athens.
It was in making war against Mahmoud II, the conqueror of Ali Pasha and
the destroyer of the Janissaries, that Byron lost his life. The
following description of the Sultan is given by Hobhouse (Travels in
Albania, etc., vol. ii. pp. 364, 365):—
"The chamber was small and dark, or rather illumined with a gloomy
artificial light, reflected from the ornaments of silver, pearls, and
other white brilliants, with which it is thickly studded on every side
and on the roof. The throne, which is supposed the richest in the
world, is like a four-posted bed, but of a dazzling splendour; the
lower part formed of burnished silver and pearls, and the canopy and
supporters encrusted with jewels. It is in an awkward position, being
in one corner of the room, and close to a fireplace.
"Sultan Mahmoud was placed in the middle of the throne, with his feet
upon the ground, which, notwithstanding the common form of squatting
upon the hams, seems the seat of ceremony. He was dressed in a robe of
yellow satin, with a broad border of the darkest sable; his dagger,
and an ornament on his breast, were covered with diamonds; the front
of his white and blue turban shone with a large treble sprig of
diamonds, which served as a buckle to a high, straight plume of
bird-of-paradise feathers. He, for the most part, kept a hand on each
knee, and neither moved his body nor head, but rolled his eyes from
side to side, without fixing them for an instant upon the ambassador
or any other person present. Occasionally he stroked and turned up his
beard, displaying a milk-white hand glittering with diamond rings. His
eyebrows, eyes, and beard, being of a glossy jet black, did not appear
natural, but added to that indescribable majesty which it would be
difficult for any but an Oriental sovereign to assume; his face was
pale, and regularly formed, except that his nose (contrary to the
usual form of that feature in the Ottoman princes) was slightly turned
up and pointed; his whole physiognomy was mild and benevolent, but
expressive and full of dignity. He appeared of a short and small
stature, and about thirty years old, which is somewhat more than his
actual age."
Byron, at the audience, claimed some precedence in the procession as a
peer. On May 23, 1819, Moore sat at dinner next to Stratford Canning
(afterwards Lord Stratford de Redcliffe), who
"gave a ludicrous account
of Lord Byron's insisting upon taking precedence of the corps
diplomatique in a procession at Constantinople (when Canning was
secretary), and upon Adair's refusing it, limping, with as much swagger
as he could muster, up the hall, cocking a foreign military hat on his
head. He found, however, he was wrong, and wrote a very frank letter
acknowledging it, and offering to take his station anywhere"
(Journals,
etc., of Thomas Moore, vol. ii. p. 313).
An incident of the voyage from Constantinople to Zea is mentioned by
Moore (Life, p. 110). Picking up a Turkish dagger on the deck, Byron
looked at the blade, and then, before replacing it in the sheath, was
overheard to say to himself, "I should like to know how a person feels
after committing a murder." In Firmilian; a Spasmodic Tragedy (scene
ix.) the sentiment is parodied. Firmilian determines to murder his
friend, in order to shriek "delirious at the taste of sin!" He had
already blown up a church full of people; but —
"I must have
A more potential draught of guilt than this
With more of wormwood in it!...
...
Courage, Firmilian! for the hour has come
When thou canst know atrocity indeed,
By smiting him that was thy dearest friend.
And think not that he dies a vulgar death —
'Tis poetry demands the sacrifice!"
And he hurls Haverillo from the summit of the Pillar of St. Simeon
Stylites.
return
Footnote 2: For Lord Sligo, see page 100, note 2. Lord Sligo was at
Athens with a 12-gun brig and a crew of fifty men. At Athens, also, were
Lady Hester Stanhope and Michael Bruce, on their way through European
Turkey. As the party were passing the Piraeus, they saw a man jump from
the mole-head into the sea. Lord Sligo, recognizing the bather as Byron,
called to him to dress and join them. Thus began what Byron, in his
Memoranda, speaks of as "the most delightful acquaintance which I formed
in Greece." From Lord Sligo Moore heard the following stories:—
Weakened and thinned by his illness at Patras, Byron returned to Athens.
There, standing one day before a looking-glass, he said to Lord Sligo,
"How pale I look! I should like, I think, to die of a consumption." "Why
of a consumption?" asked his friend. "Because then," he answered, "the
women would all say, 'See that poor Byron — how interesting he looks in
dying!'"
He often spoke of his mother to Lord Sligo, who thought that his feeling
towards her was little short of aversion. "Some time or "other," he
said, "I will tell you why I feel thus towards her." A few days after,
when they were bathing together in the Gulf of Lepanto, pointing to his
naked leg and foot, he exclaimed,
"Look there! It is to her false delicacy at my birth I owe that
deformity; and yet as long as I can remember, she has never ceased to
taunt and reproach me with it. Even a few days before we parted, for
the last time, on my leaving England, she, in one of her fits of
passion, uttered an imprecation upon me, praying that I might prove as
ill formed in mind as I am in body!"
Relics of ancient art only appealed to Byron's imagination among their
original and natural surroundings. For collections and collectors he had
a contempt which, like everything he thought or felt, was unreservedly
expressed. Lord Sligo wished to spend some money in digging for
antiquities, and Byron offered to act as his agent, and to see the money
honestly applied. "You may safely trust me" he said; "I am no
dilettante. Your connoisseurs are all thieves; but I care too little for
these things ever to steal them."
His system of thinning himself, which he had begun before he left
England, was continued abroad. While at Athens, where he stayed at the
Franciscan Convent, he took a Turkish bath three times a week, his usual
drink being vinegar and water, and his food seldom more than a little
rice. The result was that, when he returned to England, he weighed only
9 stone 11-1/2 lbs. (see page 127, note 1).
Moore's account of the "cordial friendship" between Byron and Lady
Hester Stanhope requires modification. Lady Hester (see page 302, note
I) thus referred in after-life to her meeting with Byron, if her
physician's recollection is to be trusted (Memoirs, by Dr. Meryon,
vol. iii. pp. 218, 219) —
"'I think he was a strange character: his generosity was for a motive,
his avarice for a motive; one time he was mopish, and nobody was to
speak to him; another, he was for being jocular with everybody. Then
he was a sort of Don Quixote, fighting with the police for a woman of
the town; and then he wanted to make himself something great ... At
Athens I saw nothing in him but a well-bred man, like many others;
for, as for poetry, it is easy enough to write verses; and as for the
thoughts, who knows where he got them? ... He had a great deal of vice
in his looks — his eyes set close together, and a contracted brow — so'
(imitating it). 'Oh, Lord! I am sure he was not a liberal man,
whatever else he might be. The only good thing about his looks was
this part' (drawing her hand under the cheek down the front of her
neck), 'and the curl on his forehead.'"
Michael Bruce, with the help of Sir Robert Wilson and Capt. Hutchinson,
assisted Count Lavallette to escape from Paris in January, 1816. For an
account, see Wilson's intercepted letter to Lord Grey (Memoires du
Comte Lavallette, vol. ii. p. 132) and the story of their trial,
conviction, and sentence before the Assize Court of the Department of
the Seine (April 22-24, 1816), given in the Annual Register for 1816,
pp. 329-336.
return
cross-reference: return to Footnote 4 of Letter 51
List of Letters
Athens, July 27, 1810.
Dear Mother, — I write again in case you have not received my letters.
To-day I go into the Morea, which will, I trust, be colder than this
place, where I have tarried in the expectation of obtaining rest. Sligo
has very kindly proposed a union of our forces for the occasion, which
will be perhaps as uncomfortable to him as to myself, judging from
previous experience, which, however, may be explained by my own
irritability and hurry.
At Constantinople I visited the Mosques, plains, and grandees of that
place, which, in my opinion, cannot be compared with Athens and its
neighbourhood; indeed I know of no Turkish scenery to equal this, which
would be civilised and Celtic enough with a little alteration in
situation and inhabitants. An usual custom here, as at Cadiz, is to part
with wives, daughters, etc., for a trifling present of gold or English
arms (which the Greeks set a high value upon). The women are generally
of the middle height, with Turkish eyes, straight hair, and clear olive
complexion, but are not nearly so amorous as the Spanish belles, whom I
have described to you in former letters. I have some feats to boast of
when I return, which is undesired and undesirable — I always except you
from my complaints, and hope you will expect me with the same delight
that I anticipate meeting you. You can have no conception of Lord S.'s
ecstasy when I informed him of my probable movements. The man is well
enough and sensible enough by himself; but the swarm of attendants,
Turks, Greeks, Englishmen that he carries with him, makes his society,
or rather theirs, an intolerable annoyance. If you will read this letter
to — — , you may imagine in what capacity I believe you excel.
Before I left England I promised to give my silver-mounted whip (in your
chamber) to Charles. Present it to him, poor boy, for I should not like
him to suppose me as unfaithful as his amante, who, by the way is no
better than she should be, and no great loss to himself or his family.
Hobhouse is silent, and has, I suppose, not yet returned; indeed, like
myself, he appears to love the world better than England, and the Devil
more than either, who I regret is not present to be informed of this. Do
not fail, if you see him (Hobhouse, I mean), to repeat it, and the
assurance that I am to him, with yourself,
Ever affectionately,
Byron.
List of Letters
Patras, July 30, 1810.
Dear Madam, — In four days from Constantinople, with a favourable wind, I
arrived in the frigate at the island of Teos, from whence I took a boat
to Athens, where I met my friend the Marquis of Sligo, who expressed a
wish to proceed with me as far as Corinth. At Corinth we separated, he
for Tripolitza, I for Patras, where I had some business with the consul,
Mr. Strané, in whose house I now write. He has rendered me every service
in his power since I quitted Malta on my way to Constantinople, whence I
have written to you twice or thrice. In a few days I visit the Pacha1
at Tripolitza, make the tour of the Morea, and return again to Athens,
which at present is my head-quarters. The heat is at present intense. In
England, if it reaches 98° you are all on fire: the other day, in
travelling between Athens and Megara, the thermometer was at 125°!!! Yet
I feel no inconvenience; of course I am much bronzed, but I live
temperately, and never enjoyed better health.
Before I left Constantinople, I saw the Sultan (with Mr. Adair), and the
interior of the mosques, things which rarely happen to travellers. Mr.
Hobhouse is gone to England: I am in no hurry to return, but have no
particular communications for your country, except my surprise at Mr.
Hanson's silence, and my desire that he will remit regularly. I suppose
some arrangement has been made with regard to Wymondham and Rochdale.
Malta is my post-office, or to Mr. Strané, consul-general, Patras,
Morea. You complain of my silence — I have written twenty or thirty times
within the last year: never less than twice a month, and often more. If
my letters do not arrive, you must not conclude that we are eaten, or
that there is war, or a pestilence, or famine: neither must you credit
silly reports, which I dare say you have in Notts., as usual. I am very
well, and neither more nor less happy than I usually am; except that I
am very glad to be once more alone, for I was sick of my companion, —
not that he was a bad one, but because my nature leads me to solitude,
and that every day adds to this disposition. If I chose, here are many
men who would wish to join me — one wants me to go to Egypt, another to
Asia, of which I have seen enough. The greater part of Greece is already
my own, so that I shall only go over my old ground, and look upon my old
seas and mountains, the only acquaintances I ever found improve upon me.
I have a tolerable suite, a Tartar, two Albanians, an interpreter,
besides Fletcher; but in this country these are easily maintained. Adair
received me wonderfully well, and indeed I have no complaints against
any one. Hospitality here is necessary, for inns are not. I have lived
in the houses of Greeks, Turks, Italians, and English — to-day in a
palace, to-morrow in a cow-house; this day with a Pacha, the next with a
shepherd. I shall continue to write briefly, but frequently, and am glad
to hear from you; but you fill your letters with things from the papers,
as if English papers were not found all over the world. I have at this
moment a dozen before me. Pray take care of my books, and believe me, my
dear mother,
Yours very faithfully,
Byron.
Footnote 1: For Veli Pasha, see page 248, note 1.
return to footnote mark
List of Letters
Patras, October 2, 1810.
Dear Madam, — It is now several months since I have received any
communication from you; but at this I am not surprised, nor indeed have
I any complaint to make, since you have written frequently, for which I
thank you; but I very much condemn Mr. Hanson, who has not taken the
smallest notice of my many letters, nor of my request before I left
England, which I sailed from on this very day fifteen months ago. Thus
one year and a quarter have passed away, without my receiving the least
intelligence on the state of my affairs, and they were not in a posture
to admit of neglect; and I do conceive and declare that Mr. Hanson has
acted negligently and culpably in not apprising me of his proceedings; I
will also add uncivilly. His letters, were there any, could not easily
miscarry; the communications with the Levant are slow, but tolerably
secure, at least as far as Malta, and there I left directions which I
know would be observed.
I have written to you several times from Constantinople and Smyrna. You
will perceive by my date I am returned into the Morea1, of which I
have been making the tour, and visiting the Pacha, who gave me a fine
horse, and paid me all possible honours and attention. I have now seen a
good portion of Turkey in Europe, and Asia Minor, and shall remain at
Athens, and in the vicinity, till I hear from England.
I have punctually obeyed your injunctions of writing frequently, but I
shall not pretend to describe countries which have been already amply
treated of. I believe before this time Mr. Hobhouse will have arrived in
England, and he brings letters from me, written at Constantinople. In
these I mention having seen the Sultan and the mosques, and that I swam
from Sestos to Abydos, an exploit of which I take care to boast.
I am here on business at present, but Athens is my head-quarters, where
I am very pleasantly situated in a Franciscan convent. Believe me to be,
with great sincerity, yours very affectionately,
Byron.
P.S. — Fletcher is well, and discontented as usual; his wife don't write,
at least her scrawls have not arrived. You will address to Malta. Pray
have you never received my picture in oil from Sanders, Vigo Lane,
London?
Footnote 1: In a note upon the Advertisement prefixed to his Siege of
Corinth, Byron says,
"I visited all three (Tripolitza, Napoli, and Argos) in 1810-11, and,
in the course of journeying through the country, from my first arrival
in 1809, I crossed the Isthmus eight times in my way from Attica to
the Morea, over the mountains, or in the other direction, when passing
from the Gulf of Athens to that of Lepanto."
return to footnote mark
List of Letters
Patras, Morea, October 3, 1810.
As I have just escaped from a physician and a fever, which confined me
five days to bed, you won't expect much allegrezza in the ensuing
letter. In this place there is an indigenous distemper, which when the
wind blows from the Gulf of Corinth (as it does five months out of six),
attacks great and small, and makes woful work with visiters. Here be
also two physicians, one of whom trusts to his genius (never having
studied) — the other to a campaign of eighteen months against the sick of
Otranto, which he made in his youth with great effect.
When I was seized with my disorder, I protested against both these
assassins; — but what can a helpless, feverish, toast-and-watered poor
wretch do? In spite of my teeth and tongue, the English consul, my
Tartar, Albanians, dragoman, forced a physician upon me, and in three
days vomited and glystered me to the last gasp. In this state I made my
epitaph — take it:—
Youth, Nature, and relenting Jove,
To keep my lamp in strongly strove:
But Romanelli was so stout,
He beat all three — and blew it out.
But Nature and Jove, being piqued at my doubts, did, in fact, at last,
beat Romanelli, and here I am, well but weakly, at your service.
Since I left Constantinople, I have made a tour of the Morea, and
visited Veley Pacha, who paid me great honours, and gave me a pretty
stallion. H. is doubtless in England before even the date of this
letter:— he bears a despatch from me to your bardship. He writes to me
from Malta, and requests my journal, if I keep one. I have none, or he
should have it; but I have replied in a consolatory and exhortatory
epistle, praying him to abate three and sixpence in the price of his
next boke, seeing that half a guinea is a price not to be given for any
thing save an opera ticket.
As for England, it is long since I have heard from it. Every one at all
connected with my concerns is asleep, and you are my only correspondent,
agents excepted. I have really no friends in the world; though all my
old school companions are gone forth into that world, and walk about
there in monstrous disguises, in the garb of guardsmen, lawyers,
parsons, fine gentlemen, and such other masquerade dresses. So, I here
shake hands and cut with all these busy people, none of whom write to
me. Indeed I ask it not; — and here I am, a poor traveller and heathenish
philosopher, who hath perambulated the greatest part of the Levant, and
seen a great quantity of very improvable land and sea, and, after all,
am no better than when I set out — Lord help me!
I have been out fifteen months this very day, and I believe my concerns
will draw me to England soon; but of this I will apprise you regularly
from Malta. On all points Hobhouse will inform you, if you are curious
as to our adventures1. I have seen some old English papers up to the
15th of May. I see the Lady of the Lake2 advertised. Of course it is
in his old ballad style, and pretty. After all, Scott is the best of
them. The end of all scribblement is to amuse, and he certainly succeeds
there. I long to read his new romance.
And how does Sir Edgar? and your friend Bland? I suppose you are
involved in some literary squabble. The only way is to despise all
brothers of the quill. I suppose you won't allow me to be an author, but
I contemn you all, you dogs! — I do.
You don't know Dallas, do you? He had a farce3 ready for the stage
before I left England, and asked me for a prologue, which I promised,
but sailed in such a hurry I never penned a couplet. I am afraid to ask
after his drama, for fear it should be damned — Lord forgive me for using
such a word! but the pit, Sir, you know the pit — they will do those
things in spite of merit. I remember this farce from a curious
circumstance. When Drury Lane4 was burnt to the ground, by which
accident Sheridan and his son lost the few remaining shillings they were
worth, what doth my friend Dallas do? Why, before the fire was out, he
writes a note to Tom Sheridan5, the manager of this combustible
concern, to inquire whether this farce was not converted into fuel with
about two thousand other unactable manuscripts, which of course were in
great peril, if not actually consumed. Now was not this
characteristic? — the ruling passions of Pope are nothing to it. Whilst
the poor distracted manager was bewailing the loss of a building only
worth £300,000., together with some twenty thousand pounds of rags and
tinsel in the tiring rooms, Bluebeard's elephants6, and all that — in
comes a note from a scorching author, requiring at his hands two acts
and odd scenes of a farce!!
Dear H., remind Drury that I am his well-wisher, and let Scrope Davies
be well affected towards me. I look forward to meeting you at Newstead,
and renewing our old champagne evenings with all the glee of
anticipation. I have written by every opportunity, and expect responses
as regular as those of the liturgy, and somewhat longer. As it is
impossible for a man in his senses to hope for happy days, let us at
least look forward to merry ones, which come nearest to the other in
appearance, if not in reality; and in such expectations I remain, etc.
Footnote 1: Hobhouse, writing to Byron from Malta, July 31, 1810, says,
"Mrs. Bruce picked out a pretty picture of a woman in a fashionable
dress in Ackerman's Repository, and observed it was vastly like Lord
Byron. I give you warning of this, for fear you should make another
conquest and return to England without a curl upon your head. Surely
the ladies copy Delilah when they crop their lovers after this fashion.
'Successful youth! why mourn thy ravish'd hair,
Since each lost lock bespeaks a conquer'd fair,
And young and old conspire to make thee bare?'
This makes me think of my poor Miscellany, which is quite dead, if
indeed that can be said to be dead which was never alive; not a soul
knows, or knowing will speak of it." Again, July 15, 1811, he writes:
"The Miscellany is so damned that my friends make it a point of
politeness not to mention it ever to me."
return to footnote mark
Footnote 2: The Lady of the Lake was published in May, 1810.
return
Footnote 3: For Dallas, see page 168, note 1. His farce, entitled,
Not at Home, was acted at the Lyceum, by the Drury Lane Company, in
November, 1809. It was afterwards printed, with a prologue (intended to
have been spoken) written by Walter Rodwell Wright, author of Horæ
Ionicæ.
return
Footnote 4: Drury Lane Theatre, burned down in 1791, and reopened in
1794, was again destroyed by fire on February 24, 1809.
return
Footnote 5: Thomas Sheridan (1775-1817), originally in the army, was at
this time assisting his father, Richard Brinsley Sheridan, as manager of
Drury Lane Theatre. His Bonduca was played at Covent Garden in May,
1808. He married, in 1805, Caroline Henrietta Callender, who was "more
beautiful than anybody but her daughters," afterwards Mrs. Norton, the
Duchess of Somerset, and Lady Dufferin. He died at the Cape of Good Hope
in 1817. "Tom Sheridan and his beautiful wife" were at Gibraltar in
1809, when Byron and Hobhouse landed on the Rock, and, as Galt states
(Life of Byron, p. 58), brought the news to Lady Westmorland of their
arrival. (See English Bards, and Scotch Reviewers, lines 572, 573, and
note 1.)
return
Footnote 6: Bluebeard, or Female Curiosity, by George Colman the
Younger (1762-1836), was being acted at Drury Lane in January, 1809.
"Bluebeard's elephants" were wicker-work constructions. It was at Covent
Garden that the first live elephant was introduced two years later.
Johnstone, the machinist employed at Drury Lane, famous for the
construction of wooden children, wicker-work lions, and paste-board
swans, was present with a friend.
"Among the attractions of this Christmas foolery, a real elephant
was introduced.... The friend, who sat close to Johnstone, jogged his
elbow, whispering, 'This is a bitter bad job for Drury! Why, the
elephant's alive! He'll carry all before him, and beat you hollow.
What do you think on't, eh?' 'Think on't?' said Johnstone, in a tone
of utmost contempt, 'I should be very sorry if I couldn't make a much
better elephant than that, at any time'"
(George Colman the Younger, Random Records, vol. i. pp. 228, 229).
return
List of Letters
Patras, Morea, October 4th, 1810.
My Dear Hobhouse, — I wrote to you two days ago, but the weather and my
friend Strané's conversation being much the same, and my ally Nicola1
in bed with a fever, I think I may as well talk to you, the rather, as
you can't answer me, and excite my wrath with impertinent observations,
at least for three months to come.
I will try not to say the same things I have set down in my other letter
of the 2nd, but I can't promise, as my poor head is still giddy with my
late fever.
I saw the Lady Hesther Stanhope2 at Athens, and do not admire "that
dangerous thing a female wit." She told me (take her own words) that she
had given you a good set-down at Malta, in some disputation about the
Navy; from this, of course, I readily inferred the contrary, or in the
words of an acquaintance of ours, that "you had the best of it."
She evinced a similar disposition to argufy with me, which I avoided
by either laughing or yielding. I despise the sex too much to squabble
with them, and I rather wonder you should allow a woman to draw you into
a contest, in which, however, I am sure you had the advantage, she
abuses you so bitterly.
I have seen too little of the Lady to form any decisive opinion, but I
have discovered nothing different from other she-things, except a great
disregard of received notions in her conversation as well as conduct. I
don't know whether this will recommend her to our sex, but I am sure it
won't to her own. She is going on to Constantinople.
Ali Pacha is in a scrape. Ibrahim Pacha and the Pacha of Scutari have
come down upon him with 20,000 Gegdes and Albanians, retaken Berat, and
threaten Tepaleni. Adam Bey is dead, Vely Pacha was on his way to the
Danube, but has gone off suddenly to Yanina, and all Albania is in an
uproar.
The mountains we crossed last year are the scene of warfare, and there
is nothing but carnage and cutting of throats. In my other letter I
mentioned that Vely had given me a fine horse. On my late visit he
received me with great pomp, standing, conducted me to the door with his
arm round my waist, and a variety of civilities, invited me to meet him
at Larissa and see his army, which I should have accepted, had not this
rupture with Ibrahim taken place. Sultan Mahmout is in a phrenzy because
Vely has not joined the army. We have a report here, that the Russians
have beaten the Turks and taken Muchtar Pacha prisoner, but it is a
Greek Bazaar rumour and not to be believed.
I have now treated you with a dish of Turkish politics. You have by this
time gotten into England, and your ears and mouth are full of "Reform
Burdett, Gale Jones3, minority, last night's division, dissolution of
Parliament, battle in Portugal," and all the cream of forty newspapers.
In my t'other letter, to which I am perpetually obliged to refer, I have
offered some moving topics on the head of your Miscellany, the
neglect of which I attribute to the half guinea annexed as the
indispensable equivalent for the said volume.
Now I do hope, notwithstanding that exorbitant demand, that on your
return you will find it selling, or, what is better, sold, in
consequence of which you will be able to face the public with your new
volume, if that intention still subsists.
My journal, did I keep one, should be yours. As it is I can only offer
my sincere wishes for your success, if you will believe it possible for
a brother scribbler to be sincere on such an occasion.
Will you execute a commission for me? Lord Sligo tells me it was the
intention of Miller4 in Albemarle Street to send by him a letter to
me, which he stated to be of consequence. Now I have no concern with Mr.
M. except a bill which I hope is paid before this time; will you visit
the said M. and if it be a pecuniary matter, refer him to Hanson, and if
not, tell me what he means, or forward his letter.
I have just received an epistle from Galt5, with a Candist poem,
which it seems I am to forward to you. This I would willingly do, but it
is too large for a letter, and too small for a parcel, and besides
appears to be damned nonsense, from all which considerations I will
deliver it in person. It is entitled the "Fair Shepherdess," or rather
"Herdswoman;" if you don't like the translation take the original title
" ." Galt also writes something
not very intelligible about a "Spartan State paper" which by his account
is everything but Laconic. Now the said Sparta having some years ceased
to be a state, what the devil does he mean by a paper? he also adds
mysteriously that the affair not being concluded, he cannot at
present apply for it.
." Galt also writes something
not very intelligible about a "Spartan State paper" which by his account
is everything but Laconic. Now the said Sparta having some years ceased
to be a state, what the devil does he mean by a paper? he also adds
mysteriously that the affair not being concluded, he cannot at
present apply for it.
Now, Hobhouse, are you mad? or is he? Are these documents for Longman &
Co.? Spartan state papers! and Cretan rhymes! indeed these circumstances
super-added to his house at Mycone (whither I am invited) and his Levant
wines, make me suspect his sanity. Athens is at present infested with
English people, but they are moving, Dio bendetto! I am returning
to pass a month or two; I think the spring will see me in England, but
do not let this transpire, nor cease to urge the most dilatory of
mortals, Hanson. I have some idea of purchasing the Island of Ithaca; I
suppose you will add me to the Levant lunatics. I shall be glad to hear
from your Signoria of your welfare, politics, and literature.
Your last letter closes pathetically with a postscript about a nosegay6; I advise you to introduce that into your next sentimental novel. I
am sure I did not suspect you of any fine feelings, and I believe you
were laughing, but you are welcome.
Vale; "I can no more," like Lord Grizzle7.
Yours,
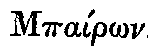
Footnote 1: Nicolo Giraud, from whom Byron was learning Italian.
return to footnote mark
Footnote 2: Hobhouse had written to Byron, speaking of Lady Hester
Stanhope "as the most superior woman, as Bruce says, of all the world."
The daughter of Pitt's favourite sister, Lady Hester (1776-1839) was her
uncle's constant companion (1803-6). In character she resembled her
grandfather far more than her uncle, who owed his cool judgment to the
Grenville blood. Lady Hester inherited the overweening pride,
generosity, courage, and fervent heat of the "Great Commoner," as well
as his indomitable will. Like him, she despised difficulties, and
ignored the word "impossibility." Her romantic ideas were also combined
with keen insight into character, and much practical sagacity. These
were the qualities which made her for many years a power among the wild
tribes of Lebanon, with whom she was in 1810 proceeding to take up her
abode (1813-39).
return
cross-reference: return to Footnote 3 of Letter 144
Footnote 3: Sir Francis Burdett (1770-1844), a lifelong friend of Lady
Hester Stanhope, was afterwards Hobhouse's colleague as M.P. for
Westminster (1820-33). He was committed to the Tower in
1810 for publishing a speech which he delivered in the House of
Commons in defence of John Gale Jones, whom the House (February,
1810) had sent to Newgate for a breach of privilege. Sir Francis
refused to obey the warrant, and told the sergeant-at-arms that he
would not go unless taken by force. His refusal led to riots near his
house (77, Piccadilly), in which the Horse Guards, or "Oxford
Blues" as they were called, gained the name of "Piccadilly
Butchers" (Lord Albemarle's Recollections, vol. i. pp. 317, 318).
return
Footnote 4: See page 319, note 2.
return
Footnote 5: John Galt (1779-1839), the novelist, was at this time
endeavouring to establish a place of business at Mycone, in the Greek
Archipelago. He published in 1812 his Voyages and Travels in the
Years 1809, 1810, 1811. (For his meeting with Byron at Gibraltar,
see page 243, note i.)
return
Footnote 6: Hobhouse's letter to Byron of July 31, 1810, ends with the
following postscript:—
"I kept the half of your little nosegay till it
withered entirely, and even then I could not bear to throw it away. I
can't account for this, nor can you either, I dare say."
return
Footnote 7: Lord Grizzle, in Fielding's Tom Thumb, is the first
peer in the Court of King Arthur, who, jealous of Tom Thumb and in love
with the Princess Huncamunca, turns traitor, and is run through the body
by Tom Thumb. It is the ghost, not Grizzle, who says, "I can no more."
(See page 226, note 1.)
return
List of Letters
Athens, November 14, 1810.
My Dear Hodgson, — This will arrive with an English servant whom I send
homewards with some papers of consequence. I have been journeying in
different parts of Greece for these last four months, and you may expect
me in England somewhere about April, but this is very dubious. Hobhouse
you have doubtless seen; he went home in August to arrange materials for
a tour he talks of publishing. You will find him well and
scribbling — that is, scribbling if well, and well if scribbling.
I suppose you have a score of new works, all of which I hope to see
flourishing, with a hecatomb of reviews. My works are likely to
have a powerful effect with a vengeance, as I hear of divers angry
people, whom it is proper I should shoot at, by way of satisfaction. Be
it so, the same impulse which made "Otho a warrior" will make me one
also. My domestic affairs being moreover considerably deranged, my
appetite for travelling pretty well satiated with my late
peregrinations, my various hopes in this world almost extinct, and not
very brilliant in the next, I trust I shall go through the process with
a creditable sang froid and not disgrace a line of cut-throat
ancestors.
I regret in one of your letters to hear you talk of domestic
embarrassments1, indeed I am at present very well calculated to
sympathise with you on that point. I suppose I must take to
dram-drinking as a succedaneum for philosophy, though as I am
happily not married, I have very little occasion for either just yet.
Talking of marriage puts me in mind of Drury, who I suppose has a dozen
children by this time, all fine fretful brats; I will never forgive
Matrimony for having spoiled such an excellent Bachelor. If anybody
honours my name with an inquiry tell them of "my whereabouts" and write
if you like it. I am living alone in the Franciscan monastery with one
"friar" (a Capuchin of course) and one "frier" (a
bandy-legged Turkish cook), two Albanian savages, a Tartar, and a
Dragoman. My only Englishman departs with this and other letters. The
day before yesterday the Waywode (or Governor of Athens) with the Mufti
of Thebes (a sort of Mussulman Bishop) supped here and made themselves
beastly with raw rum, and the Padré of the convent being as drunk as
we, my Attic feast went off with great éclat. I
have had a present of a stallion from the Pacha of the Morea. I caught a
fever going to Olympia. I was blown ashore on the Island of Salamis, in
my way to Corinth through the Gulf of Ægina. I have kicked an Athenian
postmaster, I have a friendship with the French consul2 and an
Italian painter, and am on good terms with five Teutones and Cimbri,
Danes and Germans2, who are travelling for an Academy. Vale!
Yours, 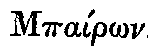 3
3
Footnote 1: Hodgson's father, Rector of Barwick-in-Elmet, Yorkshire,
died in October, 1810, heavily in debt. Francis Hodgson undertook
to satisfy the claims of his father's creditors (Life of the Rev. Francis
Hodgson, vol. i. pp. 147, 148).
return to footnote mark
Footnote 2: M. Fauriel, the French Consul: Lusieri, an Italian artist
employed by Lord Elgin; Nicolo Giraud, from whom Byron learned Italian,
and to whose sister Lusieri proposed; Baron Haller, a Bavarian
savant; and Dr. Bronstett, of Copenhagen, were among his friends
at Athens.
return
Footnote 3: The signature represents "Byron" in modern Greek, Μπ [Greek: Mp] being the correct transliteration of 'B'.
return
List of Letters
Athens, January 14, 1811.
My Dear Madam, — I seize an occasion to write as usual, shortly, but
frequently, as the arrival of letters, where there exists no regular
communication, is, of course, very precarious. I have lately made
several small tours of some hundred or two miles about the Morea,
Attica, etc., as I have finished my grand giro by the Troad,
Constantinople, etc., and am returned down again to Athens. I believe I
have mentioned to you more than once that I swam (in imitation of
Leander, though without his lady) across the Hellespont, from Sestos to
Abydos. Of this, and all other particulars, Fletcher, whom I have sent
home with papers, etc., will apprise you. I cannot find that he is any
loss; being tolerably master of the Italian and modern Greek languages,
which last I am also studying with a master, I can order and discourse
more than enough for a reasonable man. Besides, the perpetual
lamentations after beef and beer, the stupid, bigoted contempt for every
thing foreign, and insurmountable incapacity of acquiring even a few
words of any language, rendered him, like all other English servants, an
incumbrance. I do assure you, the plague of speaking for him, the
comforts he required (more than myself by far), the pilaws (a Turkish
dish of rice and meat) which he could not eat, the wines which he could
not drink, the beds where he could not sleep, and the long list of
calamities, such as stumbling horses, want of tea!!! etc., which
assailed him, would have made a lasting source of laughter to a
spectator, and inconvenience to a master. After all, the man is honest
enough, and, in Christendom, capable enough; but in Turkey, Lord forgive
me! my Albanian soldiers, my Tartars and Jannissary, worked for him and
us too, as my friend Hobhouse can testify.
It is probable I may steer homewards in spring; but to enable me to do
that, I must have remittances. My own funds would have lasted me very
well; but I was obliged to assist a friend, who, I know, will pay me;
but, in the mean time, I am out of pocket. At present, I do not care to
venture a winter's voyage, even if I were otherwise tired of travelling;
but I am so convinced of the advantages of looking at mankind instead of
reading about them, and the bitter effects of staying at home with all
the narrow prejudices of an islander, that I think there should be a law
amongst us, to set our young men abroad, for a term, among the few
allies our wars have left us.
Here I see and have conversed with French, Italians, Germans, Danes,
Greeks, Turks, Americans, etc., etc., etc.; and without losing sight of
my own, I can judge of the countries and manners of others. Where I see
the superiority of England (which, by the by, we are a good deal
mistaken about in many things), I am pleased, and where I find her
inferior, I am at least enlightened. Now, I might have stayed, smoked in
your towns, or fogged in your country, a century, without being sure of
this, and without acquiring any thing more useful or amusing at home. I
keep no journal, nor have I any intention of scribbling my travels. I
have done with authorship, and if, in my last production, I have
convinced the critics or the world I was something more than they took
me for, I am satisfied; nor will I hazard that reputation by a
future effort. It is true I have some others in manuscript, but I leave
them for those who come after me; and, if deemed worth publishing, they
may serve to prolong my memory when I myself shall cease to remember. I
have a famous Bavarian artist taking some views of Athens, etc., etc.,
for me. This will be better than scribbling, a disease I hope myself
cured of. I hope, on my return, to lead a quiet, recluse life, but God
knows and does best for us all; at least, so they say, and I have
nothing to object, as, on the whole, I have no reason to complain of my
lot. I am convinced, however, that men do more harm to themselves than
ever the devil could do to them. I trust this will find you well, and as
happy as we can be; you will, at least, be pleased to hear I am so, and
Yours ever.
List of Letters
Athens, February 28, 1811.
Dear Madam, — As I have received a firman for Egypt, etc., I shall
proceed to that quarter in the spring, and I beg you will state to Mr.
Hanson that it is necessary to [send] further remittances. On the
subject of Newstead, I answer as before, No. If it is necessary
to sell, sell Rochdale. Fletcher will have arrived by this time with my
letters to that purport. I will tell you fairly, I have, in the first
place, no opinion of funded property; if, by any particular
circumstances, I shall be led to adopt such a determination, I will, at
all events, pass my life abroad, as my only tie to England is Newstead,
and, that once gone, neither interest nor inclination lead me northward.
Competence in your country is ample wealth in the East, such is the
difference in the value of money and the abundance of the necessaries of
life; and I feel myself so much a citizen of the world, that the spot
where I can enjoy a delicious climate, and every luxury, at a less
expense than a common college life in England, will always be a country
to me; and such are in fact the shores of the Archipelago. This then is
the alternative — if I preserve Newstead, I return; if I sell it, I stay
away. I have had no letters since yours of June, but I have written
several times, and shall continue, as usual, on the same plan.
Believe me, yours ever, Byron.
P.S. — I shall most likely see you in the course of the summer, but, of
course, at such a distance, I cannot specify any particular month.
List of Letters
Volage frigate, at sea, June 25, 1811.
Dear Mother, — This letter, which will be forwarded on our arrival at
Portsmouth, probably about the 4th of July, is begun about twenty-three
days after our departure from Malta. I have just been two years (to a
day, on the 2d of July) absent from England, and I return to it with
much the same feelings which prevailed on my departure, viz.
indifference; but within that apathy I certainly do not comprise
yourself, as I will prove by every means in my power. You will be good
enough to get my apartments ready at Newstead; but don't disturb
yourself, on any account, particularly mine, nor consider me in any
other light than as a visiter. I must only inform you that for a long
time I have been restricted to an entire vegetable diet, neither fish
nor flesh coming within my regimen; so I expect a powerful stock of
potatoes, greens, and biscuit; I drink no wine. I have two servants,
middle-aged men, and both Greeks. It is my intention to proceed first to
town, to see Mr. Hanson, and thence to Newstead, on my way to Rochdale.
I have only to beg you will not forget my diet, which it is very
necessary for me to observe. I am well in health, as I have generally
been, with the exception of two agues, both of which I quickly got over.
My plans will so much depend on circumstances, that I shall not venture
to lay down an opinion on the subject. My prospects are not very
promising, but I suppose we shall wrestle through life like our
neighbours; indeed, by Hanson's last advices, I have some apprehension
of finding Newstead dismantled by Messrs. Brothers1, etc., and he
seems determined to force me into selling it, but he will be baffled. I
don't suppose I shall be much pestered with visiters; but if I am, you
must receive them, for I am determined to have nobody breaking in upon
my retirement: you know that I never was fond of society, and I am less
so than before. I have brought you a shawl, and a quantity of attar of
roses, but these I must smuggle, if possible. I trust to find my library
in tolerable order.
Fletcher is no doubt arrived. I shall separate the mill from Mr. B — 's
farm, for his son is too gay a deceiver to inherit both, and place
Fletcher in it, who has served me faithfully, and whose wife is a good
woman; besides, it is necessary to sober young Mr. B — , or he will
people the parish with bastards. In a word, if he had seduced a
dairy-maid, he might have found something like an apology; but the girl
is his equal, and in high life or low life reparation is made in such
circumstances. But I shall not interfere further than (like Buonaparte)
by dismembering Mr. B.'s kingdom, and erecting part of it into a
principality for field-marshal Fletcher! I hope you govern my little
empire and its sad load of national debt with a wary hand. To
drop my metaphor, I beg leave to subscribe myself
Yours ever, Byron.
P.S. July 14. — This letter was written to be sent from Portsmouth, but,
on arriving there, the squadron was ordered to the Nore, from whence I
shall forward it. This I have not done before, supposing you might be
alarmed by the interval mentioned in the letter being longer than
expected between our arrival in port and my appearance at Newstead.
Footnote 1: Brothers, an upholsterer of Nottingham, had put in an execution
at Newstead for £1600.
return to footnote mark
List of Letters
Volage Frigate, at sea, June 28, 1811.
After two years' absence (to a day, on the 2d of July, before which we
shall not arrive at Portsmouth), I am retracing my way to England. I
have, as you know, spent the greater part of that period in Turkey,
except two months in Spain and Portugal, which were then accessible. I
have seen every thing most remarkable in Turkey, particularly the Troad,
Greece, Constantinople, and Albania, into which last region very few
have penetrated so high as Hobhouse and myself. I don't know that I have
done anything to distinguish me from other voyagers, unless you will
reckon my swimming from Sestos to Abydos, on May 3d, 1810, a tolerable
feat for a modern.
I am coming back with little prospect of pleasure at home, and with a
body a little shaken by one or two smart fevers, but a spirit I hope yet
unbroken. My affairs, it seems, are considerably involved, and much
business must be done with lawyers, colliers, farmers, and creditors.
Now this, to a man who hates bustle as he hates a bishop, is a serious
concern. But enough of my home department.
I find I have been scolding Cawthorn without a cause, as I found two
parcels with two letters from you on my return to Malta. By these it
appears you have not received a letter from Constantinople, addressed to
Longman's, but it was of no consequence.
My Satire, it seems, is in a fourth edition, a success rather above the
middling run, but not much for a production which, from its topics, must
be temporary, and of course be successful at first, or not at all. At
this period, when I can think and act more coolly, I regret that I have
written it, though I shall probably find it forgotten by all except
those whom it has offended. My friend Hobhouse's Miscellany has
not succeeded; but he himself writes so good-humouredly on the subject,
I don't know whether to laugh or cry with him. He met with your son at
Cadiz, of whom he speaks highly.
Yours and Pratt's1 protégé, Blacket2, the cobbler, is dead,
in spite of his rhymes, and is probably one of the instances where death
has saved a man from damnation. You were the ruin of that poor fellow
amongst you: had it not been for his patrons, he might now have been in
very good plight, shoe- (not verse-) making; but you have made him
immortal with a vengeance. I write this, supposing poetry, patronage,
and strong waters, to have been the death of him. If you are in town in
or about the beginning of July, you will find me at Dorant's, in
Albemarle Street, glad to see you3. I have an imitation of Horace's
Art of Poetry ready for Cawthorn, but don't let that deter you, for I
sha'n't inflict it upon you. You know I never read my rhymes to
visiters. I shall quit town in a few days for Notts., and thence to
Rochdale. I shall send this the moment we arrive in harbour, that is a
week hence.
Yours ever sincerely, Byron.
Footnote 1: For Pratt, see page 186, note 1.
return to footnote mark
Footnote 2: Joseph Blacket (1786-1810) has his place in English
Bards (lines 765, 798) and Hints from Horace (line 734). The
son of a labourer, and himself by trade a cobbler, he wrote verses in
which Pratt saw signs of genius. A volume of his poetry was published in
1809, under the title of Specimens, edited by Pratt. Among those
who befriended him were Elliston the actor, Dallas, and Miss Milbanke,
afterwards Lady Byron (see English Bards, lines 770, and
note 1). His Remains were collected and published by Pratt
in 1811 for the benefit of Blacket's orphan daughter, with a dedication
to "the Duchess of Leeds, Lady Milbanke and family" (see page 337, and
Hints from Horace, line 734, and Byron's note). In the
suppressed edition of Dallas's Correspondence of Lord Byron (pp.
127, 128) occurs the following passage, from which, if Dallas's grammar
is to be trusted, it seems that the famous epitaph on Blacket was not
Byron's composition. Dallas '"was persuaded by Mr. Pratt's warmth to see
some sparkling of genius in the effusions of this young man (Blacket).
It was upon this that Lord Byron and a young friend of his were
sometimes playful in conversation, and in writing to me.
I see,' says
the latter, 'that Blacket the Son of Crispin and Apollo is dead.'
Looking into Boswell's Life of Johnson the other day, I saw, 'We were
talking about the famous Mr. Wordsworth, the poetical Shoemaker.' Now, I
never before heard that there had been a Mr. Wordsworth a Poet, a
Shoemaker, or a famous man; and I dare say you have never heard of him.
Thus it will be with Bloomfield and Blackett — their names two years
after their death will be found neither on the rolls of Curriers' Hall
nor of Parnassus. Who would think that anybody would be such a blockhead
as to sin against an express proverb, Ne sutor ultra crepidam?
'But spare him, ye Critics, his follies are past,
For the Cobler is come, as he ought, to his last.'
Which two lines, with a scratch under last, to show where the joke
lies, I beg that you will prevail on Miss Milbanke to have inserted on
the tomb of her departed Blacket."
It should be added that the
shoemaking poet was not Wordsworth, but Woodhouse.
return
Footnote 3: Dallas called on Byron at Reddish's Hotel, St. James's
Street, July 15, 1811, and received from him the MS. of Hints from
Horace. Byron finished the work March 12, 1811, at the Franciscan
Convent at Athens, where he found a copy of the De Arte Poeticâ.
(Hints from Horace were not, however, published till 1831.) On July 16
Dallas called again, and expressed surprise that Byron had written
nothing else. Byron then produced out of his trunk Childe Harold's
Pilgrimage, saying, "They are not worth troubling you with, but you
shall have them all with you if you like." He was as reluctant to
publish Childe Harold as he was eager to publish Hints from Horace.
return
List of Letters
Volage Frigate, at sea, June 29, 1811.
In a week, with a fair wind, we shall be at Portsmouth, and on the 2d of
July I shall have completed (to a day) two years of peregrination, from
which I am returning with as little emotion as I set out. I think, upon
the whole, I was more grieved at leaving Greece than England, which I am
impatient to see, simply because I am tired of a long voyage.
Indeed, my prospects are not very pleasant. Embarrassed in my private
affairs, indifferent to public, solitary without the wish to be social,
with a body a little enfeebled by a succession of fevers, but a spirit I
trust, yet unbroken, I am returning home without a hope, and almost
without a desire. The first thing I shall have to encounter will be a
lawyer, the next a creditor, then colliers, farmers, surveyors, and all
the agreeable attachments to estates out of repair, and contested
coal-pits. In short, I am sick and sorry, and when I have a little
repaired my irreparable affairs, away I shall march, either to campaign
in Spain, or back again to the East, where I can at least have cloudless
skies and a cessation from impertinence.
I trust to meet, or see you, in town, or at Newstead, whenever you can
make it convenient — I suppose you are in love and in poetry as usual.
That husband, H. Drury, has never written to me, albeit I have sent him
more than one letter; — but I dare say the poor man has a family, and of
course all his cares are confined to his circle.
"For children fresh expenses yet,
And Dicky now for school is fit."
Warton1.
If you see him, tell him I have a letter for him from Tucker, a
regimental chirurgeon and friend of his, who prescribed for me, — — and
is a very worthy man, but too fond of hard words. I should be too late
for a speech-day, or I should probably go down to Harrow. I regretted
very much in Greece having omitted to carry the Anthology with me — I
mean Bland and Merivale's. — What has Sir Edgar done? And the
Imitations and Translations — where are they? I suppose you don't mean
to let the public off so easily, but charge them home with a quarto. For
me, I am "sick of fops, and poesy, and prate," and shall leave the
"whole Castalian state" to Bufo, or any body else2. But you are a
sentimental and sensibilitous person, and will rhyme to the end of the
chapter. Howbeit, I have written some 4000 lines, of one kind or
another, on my travels.
I need not repeat that I shall be happy to see you. I shall be in town
about the 8th, at Dorant's Hotel, in Albemarle Street, and proceed in a
few days to Notts., and thence to Rochdale on business.
I am, here and there, yours, etc.
Footnote 1: Warton's Progress of Discontent, lines 109, 110.
return to footnote mark
Footnote 2:
"But sick of fops, and poetry, and prate,
To Bufo left the whole Castalian state."
Pope, Prologue to the Satires, lines 229, 230.
return
List of Letters
Volage frigate, off Ushant, July 17, 1811.
My Dear Drury, — After two years' absence (on the 2d) and some odd days,
I am approaching your country. The day of our arrival you will see by
the outside date of my letter. At present, we are becalmed comfortably,
close to Brest Harbour; — I have never been so near it since I left Duck
Puddle1. We left Malta thirty-four days ago, and have had a tedious
passage of it. You will either see or hear from or of me, soon after the
receipt of this, as I pass through town to repair my irreparable
affairs; and thence I want to go to Notts. and raise rents, and to
Lanes. and sell collieries, and back to London and pay debts, — for it
seems I shall neither have coals nor comfort till I go down to Rochdale
in person.
I have brought home some marbles for Hobhouse; — for myself, four
ancient Athenian skulls2, dug out of sarcophagi — a phial of Attic
hemlock3 — four live tortoises — a greyhound (died on the
passage) — two live Greek servants, one an Athenian, t'other a Yaniote,
who can speak nothing but Romaic and Italian — and myself, as Moses in
the Vicar of Wakefield says, slily4 and I may say it too, for I
have as little cause to boast of my expedition as he had of his to the
fair.
I wrote to you from the Cyanean Rocks to tell you I had swam from Sestos
to Abydos — have you received my letter? Hobhouse went to England to fish
up his Miscellany, which foundered (so he tells me) in the Gulph of
Lethe. I daresay it capsized with the vile goods of his contributory
friends, for his own share was very portable. However, I hope he will
either weigh up or set sail with a fresh cargo, and a luckier vessel.
Hodgson, I suppose, is four deep by this time. What would he have given
to have seen, like me, the real Parnassus, where I robbed the Bishop
of Chrisso of a book of geography! — but this I only call plagiarism, as
it was done within an hour's ride of Delphi.
Footnote 1: The swimming-bath at Harrow.
return to footnote mark
Footnote 2: Given afterwards to Sir Walter Scott.
return
Footnote 3: At present in the possession of Mr. Murray.
return
Footnote 4:
"'Welcome, welcome, Moses! Well, my boy, what have you brought us from
the fair?'
'I have brought you myself,' cried Moses, with a sly look, and
resting the box on the dresser."
Vicar of Wakefield, ch. xii.
return
List of Letters
Reddish's Hotel, St. James's Street, London, July 23, 1811.
My Dear Madam, — I am only detained by Mr. Hanson to sign some copyhold
papers, and will give you timely notice of my approach. It is with great
reluctance I remain in town1. I shall pay a short visit as we go on
to Lancashire on Rochdale business. I shall attend to your directions,
of course, and am, with great respect, yours ever,
Byron.
P.S. — You will consider Newstead as your house, not mine; and me only as
a visiter.
Footnote 1: On his way to London, Byron paid a visit, at Sittingbourne,
to Hobhouse, who was with his Militia Regiment, and under orders for
Ireland. He also stayed with H. Drury, at Harrow, for two or three days.
return to footnote mark
List of Letters
158 — To William Miller1
Reddish's Hotel, July 30th, 1811.
Sir, — I am perfectly aware of the justice of your remarks, and am
convinced that, if ever the poem is published, the same objections will
be made in much stronger terms. But as it was intended to be a poem on
Ariosto's plan, that is to say on no plan at all, and, as is
usual in similar cases, having a predilection for the worst passages, I
shall retain those parts, though I cannot venture to defend them. Under
these circumstances I regret that you decline the publication, on my own
account, as I think the book would have done better in your hands; the
pecuniary part, you know, I have nothing to do with. But I can perfectly
conceive, and indeed approve your reasons, and assure you my
sensations are not Archiepiscopal2 enough as yet to regard the
rejection of my Homilies.
I am, Sir, your very obed't humble serv't,
Byron.
Footnote 1: William Miller (1769-1844), son of Thomas Miller,
bookseller, of Bungay (see Beloe's Sexagenarian, 2nd edit., vol. ii
pp. 253, 254), served his apprenticeship in Hookham's publishing house.
In 1790 he set up for himself as a bookselling publisher in Bond Street.
From 1804 onwards his place of business was at 50, Albemarle Street. But
in September, 1812, he sold his stock, copyrights, good will, and lease
to John Murray, and retired to a country farm in Hertfordshire. He
declined to publish Childe Harold, on the grounds that it contained
"sceptical stanzas," and attacked Lord Elgin as a plunderer. But on the
latter point, Byron, who was in serious earnest, was not likely to give
way. In Beloe's Sexagenarian (vol. ii pp. 270, 271), Miller is
described as
"the splendid bookseller," who "was enabled to retire to
tranquillity and independence long before the decline of life, or
infirmities of age, rendered it necessary to do so. He was highly
respectable, but could drive a hard bargain with a poor author, as well
as any of his fraternity."
return to footnote mark
cross-reference: return to Footnote 4 of Letter 149
cross-reference: return to Footnote 1 of Letter 167
Footnote 2: Alluding to Gil Blas and the Archbishop of Grenada (see
page 121, note 3).
return
List of Letters
Newport Pagnell, August 2, 1811.
My Dear Doctor, — My poor mother died yesterday! and I am on my way from
town to attend her to the family vault. I heard one day of her
illness, the next of her death1. Thank God her last moments were
most tranquil. I am told she was in little pain, and not aware of her
situation. I now feel the truth of Mr. Gray's observation, "That we can
only have one mother."2 Peace be with her! I have to thank you for
your expressions of regard; and as in six weeks I shall be in Lancashire
on business, I may extend to Liverpool and Chester, — at least I shall
endeavour.
If it will be any satisfaction, I have to inform you that in November
next the Editor of the Scourge3 will be tried for two different
libels on the late Mrs. B. and myself (the decease of Mrs. B. makes no
difference in the proceedings); and as he is guilty, by his very foolish
and unfounded assertion of a breach of privilege, he will be prosecuted
with the utmost rigour.
I inform you of this, as you seem interested in the affair, which is now
in the hands of the Attorney-general.
I shall remain at Newstead the greater part of this month, where I shall
be happy to hear from you, after my two years' absence in the East.
I am, dear Pigot, yours very truly,
Byron.
Footnote 1: On the night after his arrival at Newstead, Mrs. Byron's
maid, passing the room where the body lay, heard a heavy sigh from
within. Entering the room, she found Byron sitting in the dark beside
the bed. When she spoke to him, he burst into tears, and exclaimed,
"Oh, Mrs. By, I had but one friend in the world, and she is gone!"
On the day of the funeral he refused to follow the corpse to the grave,
but watched the procession move away from the door of Newstead; then,
turning to Rushton, bade him bring the gloves, and began his usual
sparring exercise. Only his silence, abstraction, and unusual violence
betrayed to his antagonist, says Moore (Life, p. 128), the state of
his feelings.
return to footnote mark
Footnote 2:
"I had discovered a thing very little known, which is, that in one's
whole life one can never have more than a single mother. You may think
this is obvious, and (what you call) a trite observation. You are a
green gosling! I was at the same age (very near) as wise as you, and
yet I never discovered this (with full evidence and conviction, I
mean) till it was too late. It is thirteen years ago, ... and every
day I live it sinks deeper into my heart."
Gray to Nicholls, Works, vol. i. p. 482.
return
Footnote 3: One of Byron's first acts on returning to England was to
buy a copy of the Scourge, In Ridgway's bill for books supplied from
Piccadilly to Byron on July 24, 1811, is a copy of the Scourge at
2s. 6d. Hewson Clarke (1787-1832) was entered at Emanuel College,
Cambridge, apparently as a sizar, in 1806. Obliged to leave the
University before he had taken his degree, he supported himself in
London by his pen. He wrote two historical works — a continuation of
Hume's History of England (1832), and an Impartial History of the
Naval, etc., Events in Europe from the French Revolution to the Peace
of 1815. It was, however, as a journalist that he came into collision
with Byron. In the Satirist, a monthly magazine, illustrated with
coloured cartoons, three attacks were made on Byron, which he attributed
to Clarke:
- October, 1807 (vol. i pp. 77-81), a review of Hours of Idleness;
- June, 1808 (vol. ii p. 368), verses on "Lord B — n to his Bear. To
the tune of 'Lo chin y gair;'"
- August, 1808 (vol. iii pp. 78-86), a review of Poems Original and
Translated.
Byron's reply was the passage in English Bards, and Scotch Reviewers
(lines 973-980; see also the notes), where Clarke is described as
"A would-be satirist, a hired Buffoon,
A monthly scribbler of some low Lampoon," etc.;
and also the Postscript to the second edition (see Poems, vol. i p.
382). In the Scourge for March, 1811 (vol. i. pp. 191, et seqq.},
appeared an article headed "Lord Byron," in which the alleged libel
occurred.
"We are unacquainted," says the article, "with any act of cowardice
that can be compared with that of keeping a libel ready cut and
dried till some favourable opportunity enable its author to disperse
it without the hazard of personal responsibility, and under
circumstances which deprive the injured party of every means of
reparation ... He confined the knowledge of his lampoon, therefore, to
the circle of his own immediate friends, and left it to be given to
the public as soon as he should have bid adieu to the shores of
Britain. Whether his voyage was in reality no further than to Paris,
in search of the proofs of his own legitimacy, or, as he asserts, to
'Afric's coasts, and Calpe's adverse height', was of little
consequence to Mr. Clarke, who felt that to recriminate during his
absence would be unworthy of his character ... Considering the two
parties not as writers, but as men, Mr. Clarke might confidently
appeal to the knowledge and opinion of the whole university; but a
character like his disdains comparison with that of his noble
calumniator; a temper unruffled by malignant passions, a mind superior
to vicissitude, are gifts for which the pride of doubtful birth, and
the temporary possession of Newstead Abbey are contemptible
equivalents ...
"It may be reasonably asked whether to be a denizen of Berwick-
upon-Tweed be more disgraceful than to be the illegitimate descendant
of a murderer; whether to labour in an honourable profession for the
peace and competence of maturer age be less worthy of praise than to
waste the property of others in vulgar debauchery; whether to be the
offspring of parents whose only crime is their want of title, be not
as honourable as to be the son of a profligate father, and a mother
whose days and nights are spent in the delirium of drunkenness; and,
finally, whether to deserve the kindness of his own college, to obtain
its prizes, and to prepare himself for any examination that might
entitle him to share the highest honours which the university can
bestow, be less indicative of talent and virtue than to be held up to
the derision and contempt of his fellow-students, as a scribbler of
doggerel and a bear-leader; to be hated for malignity of temper and
repulsiveness of manners, and shunned by every man who did not want to
be considered a profligate without wit, and trifling without elegance.
... We ... shall neither expose the infamy of his uncle, the
indiscretions of his mother, nor his personal follies and
embarrassments. But let him not again obtrude himself on our attention
as a moralist, etc."
The Attorney-General, Sir Vicary Gibbs, gave his opinion against legal
proceedings, on the two grounds that a considerable time had elapsed
since the publication, and Byron himself had provoked the attack.
return
List of Letters
Newstead Abbey, August 4th, 1811.
My Dear Sir, — The Earl of Huntley and the Lady Jean Stewart,
daughter of James 1st, of Scotland were the progenitors of Mrs. Byron. I
think it would be as well to be correct in the statement. Every thing is
doing that can be done, plainly yet decently, for the interment.
When you favour me with your company, be kind enough to bring down my
carriage from Messrs. Baxter's & Co., Long Acre. I have written to them,
and beg you will come down in it, as I cannot travel conveniently or
properly without it. I trust that the decease of Mrs. B. will not
interrupt the prosecution of the Editor of the Magazine, less for the
mere punishment of the rascal, than to set the question at rest, which,
with the ignorant & weak-minded, might leave a wrong impression. I will
have no stain on the Memory of my Mother; with a very large portion of
foibles and irritability, she was without a vice (and in these days
that is much). The laws of my country shall do her and me justice in the
first instance; but, if they were deficient, the laws of modern Honour
should decide. Cost what it may, Gold or blood, I will pursue to the
last the cowardly calumniator of an absent man and a defenceless woman.
The effects of the deceased are sealed and untouched. I have sent for
her agent, Mr. Bolton, to ascertain the proper steps and nothing shall
be done precipitately. I understand her jewels and clothes are of
considerable value. I shall write to you again soon, and in the
meantime, with my most particular remembrance to Mrs. Hanson, my regards
to Charles, and my respects to the young ladies, I am, Dear Sir,
Your very sincere and obliged servant,
Byron.
List of Letters
Newstead Abbey, August 7, 1811.
My Dearest Davies, — Some curse hangs over me and mine. My mother lies a
corpse in this house; one of my best friends is drowned in a ditch1.
What can I say, or think, or do? I received a letter from him the day
before yesterday. My dear Scrope, if you can spare a moment, do come
down to me — I want a friend. Matthews's last letter was written on
Friday. — on Saturday he was not. In ability, who was like Matthews?
How did we all shrink before him? You do me but justice in saying, I
would have risked my paltry existence to have preserved his. This very
evening did I mean to write, inviting him, as I invite you, my very dear
friend, to visit me. God forgive — — for his apathy! What will our poor
Hobhouse feel? His letters breathe but of Matthews. Come to me, Scrope,
I am almost desolate — left almost alone in the world2 — I had but you,
and H., and M., and let me enjoy the survivors whilst I can. Poor M., in
his letter of Friday, speaks of his intended contest for Cambridge, and
a speedy journey to London. Write or come, but come if you can, or one
or both.
Yours ever.
Footnote 1: Charles Skinner Matthews (see page 150, note 3).
return to footnote mark
Footnote 2: In 1811 Byron had lost, besides his mother and Matthews
(August), his Harrow friend Wingfield (see page 180, note 1),
Hargreaves Hanson (see page 54, note 1), and Edleston (see page 130,
note 3).
return
List of Letters
Newstead Abbey, Notts., August 12, 1811.
Peace be with the dead! Regret cannot wake them. With a sigh to the
departed, let us resume the dull business of life, in the certainty that
we also shall have our repose. Besides her who gave me being, I have
lost more than one who made that being tolerable. — The best friend of my
friend Hobhouse, Matthews, a man of the first talents, and also not the
worst of my narrow circle, has perished miserably in the muddy waves of
the Cam, always fatal to genius:— my poor school-fellow, Wingfield, at
Coimbra — within a month; and whilst I had heard from all three, but
not seen one. Matthews wrote to me the very day before his death; and
though I feel for his fate, I am still more anxious for Hobhouse, who, I
very much fear, will hardly retain his senses: his letters to me since
the event have been most incoherent1. But let this pass; we shall all
one day pass along with the rest — the world is too full of such things,
and our very sorrow is selfish.
I received a letter from you, which my late occupations prevented me
from duly noticing2. — I hope your friends and family will long hold
together. I shall be glad to hear from you, on business, on commonplace,
or any thing, or nothing — but death — I am already too familiar with the
dead. It is strange that I look on the skulls which stand beside me (I
have always had four in my study) without emotion, but I cannot strip
the features of those I have known of their fleshy covering, even in
idea, without a hideous sensation; but the worms are less
ceremonious. — Surely, the Romans did well when they burned the dead. — I
shall be happy to hear from you, and am,
Yours, etc.
Footnote 1:
"Just," writes Hobhouse to Byron, in an undated letter from Dover, "as
I was preparing to condole with you on your severe misfortune, an
event has taken place, the details of which you will find in the
enclosed letter from S. Davies. I am totally unable to say one word on
the subject. He was my oldest friend, and, though quite unworthy of
his attachment, I believe that I was an object of his regard.
"I now fear that I have not been sufficiently at all times just and
kind to him. Return me this fatal letter, and pray add, if it is but
one line, a few words of your own."
A second letter, dated August 8, 1811, is as follows:—
"My Dear Byron, — To-morrow morning we sail for Cork. It is with
difficulty I bring myself to talk of my paltry concerns, but I cannot
refuse giving you such information as may enable me to hear from one
of the friends that I have still left. Pray do give me a line; nothing
is more selfish than sorrow. His great and unrivalled talents were
observable by all, his kindness was known to his friends. You
recollect how affectionately he shook my hand at parting. It was the
last time you ever saw him — did you think it would be the last? But
three days before his death he told me in a letter that he had heard
from you. On Friday he wrote to me again, and on Saturday — alas, alas!
we are not stocks or stones, — every word of our friend Davies' letter
still pierces me to the soul — such a man and such a death! I would
that he had not been so minute in his horrid details. Oh, my dear
Byron, do write to me; I am very, very sick at heart indeed, and,
after various efforts to write upon my own concerns, I still revert to
the same melancholy subject. I wrote to Cawthorn to-day, but knew not
what I said to him; half my incitement to finish that task is for ever
gone. I can neither have his assistance during my labour, his comfort
if I should fail, nor his congratulation if I should succeed. Forgive
me, I do not forget you — but I cannot but remember him.
Ever your obliged and faithful, John C. Hobhouse."
Byron had apparently suggested that Hobhouse should write some brief
record of his friend. Hobhouse replies from Enniscorthy, September 13,
1811:—
"The melancholy subject of your last, in spite of every effort,
perpetually recurs to me. It is indeed a hard science to forget,
though I cannot but think that it is the wisest and indeed the only
remedy for grief. I should be quite incapable every way of doing what
you mention, and I could not even set about such a melancholy task
with spirit or prospect of success. The thing may be better done by a
person less interested than myself in so cruel a catastrophe. Whatever
you say in your book will be well said, and do credit both to your
heart and head; how much would it have gratified him who shall ne'er
hear it!"
return to footnote mark
Footnote 2: Dallas had written on July 29 to protest, on six grounds
which he gives (Correspondence of Lord Byron, pp. 151-153), "against
the sceptical stanzas" of Childe Harold.
return
List of Letters
Newstead Abbey, August 12, 1811.
Sir, — I enclose a rough draught of my intended will which I beg to have
drawn up as soon as possible, in the firmest manner. The alterations are
principally made in consequence of the death of Mrs. Byron. I have only
to request that it may be got ready in a short time, and have the honour
to be,
Your most obedient, humble servant,
Byron.
Newstead Abbey, August 12, 1811.
Directions for the Contents of a Will to be Drawn Up Immediately.
The estate of Newstead to be entailed (subject to certain deductions) on
George Anson Byron, heir-at-law, or whoever may be the heir-at-law on
the death of Lord B. The Rochdale property to be sold in part or the
whole, according to the debts and legacies of the present Lord B.
To Nicolo Giraud of Athens, subject of France, but born in Greece, the
sum of seven thousand pounds sterling, to be paid from the sale of such
parts of Rochdale, Newstead, or elsewhere, as may enable the said Nicolo
Giraud (resident at Athens and Malta in the year 1810) to receive the
above sum on his attaining the age of twenty-one years.
To William Fletcher, Joseph Murray, and Demetrius Zograffo1 (native of
Greece), servants, the sum of fifty pounds pr. ann. each, for their
natural lives. To Wm. Fletcher, the Mill at Newstead, on condition that
he payeth rent, but not subject to the caprice of the landlord. To Rt.
Rushton the sum of fifty pounds per ann. for life, and a further sum of
one thousand pounds on attaining the age of twenty-five years.
To Jn. Hanson, Esq. the sum of two thousand pounds sterling.
The claims of S. B. Davies, Esq. to be satisfied on proving the amount
of the same.
The body of Lord B. to be buried in the vault of the garden of Newstead,
without any ceremony or burial-service whatever, or any inscription,
save his name and age. His dog not to be removed from the said vault.
My library and furniture of every description to my friends Jn. Cam
Hobhouse, Esq., and S. B. Davies, Esq., my executors. In case of their
decease, the Rev. J. Becher, of Southwell, Notts., and R. C. Dallas,
Esq., of Mortlake, Surrey, to be executors2.
The produce of the sale of Wymondham in Norfolk, and the late Mrs. B.'s
Scotch property3, to be appropriated in aid of the payment of debts
and legacies.
This is the last will and testament of me, the Rt. Honble George Gordon,
Lord Byron, Baron Byron of Rochdale, in the county of Lancaster. — I
desire that my body may be buried in the vault of the garden of
Newstead, without any ceremony or burial-service whatever, and that no
inscription, save my name and age, be written on the tomb or tablet; and
it is my will that my faithful dog may not be removed from the said
vault. To the performance of this my particular desire, I rely on the
attention of my executors hereinafter named.
It is submitted to Lord Byron whether this clause relative to the
funeral had not better be omitted. The substance of it can be given in
a letter from his Lordship to the executors, and accompany the will; and
the will may state that the funeral shall be performed in such manner as
his Lordship may by letter direct, and, in default of any such letter,
then at the discretion of his executors4.
It must stand.
B.
I do hereby specifically order and direct that all the claims of the
said S. B. Davies upon me shall be fully paid and satisfied as soon as
conveniently may be after my decease, on his proving by vouchers, or
otherwise, to the satisfaction of my executors hereinafter named5
the amount thereof, and the correctness of the same.
If Mr, Davies has any unsettled claims upon Lord Byron, that
circumstance is a reason for his not being appointed executor; each
executor having an opportunity of paying himself his own debt without
consulting his co-executors.
So much the better — if possible, let him be an executor.
B.
Footnote 1:
"If the papers lie not (which they generally do), Demetrius
Zograffo of Athens is at the head of the Athenian part of the Greek
insurrection. He was my servant in 1809, 1810, 1811, 1812, at different
intervals of those years (for I left him in Greece when I went to
Constantinople), and accompanied me to England in 1811: he returned to
Greece, spring, 1812. He was a clever, but not apparently an
enterprising man; but circumstances make men. His two sons (then
infants) were named Miltiades and Alcibiades: may the omen be
happy!"
Byron's MS. Journal, quoted by Moore, Life, p. 131.
return to footnote mark
Footnote 2: In the clause enumerating the names and places of abode of
the executors, the solicitor had left blanks for the Christian names of
these gentlemen, and Lord Byron, having filled up all but that of
Dallas, writes in the margin, "I forget the Christian name of Dallas
— cut him out."
return
Footnote 3: On the death of Mrs. Byron, the sum of £4200, the remains
of the price of the estate of Gight were paid over to Byron by her
trustee.
return
Footnote 4: The passages printed in italics are suggestions made by the
solicitors.
return
Footnote 5: Over the words printed in grey, Byron drew his pen.
return
List of Letters
Newstead Abbey, August 16, 1811.
Sir, — I have answered the queries on the margin. I wish Mr. Davies's
claims to be most fully allowed, and, further, that he be one of my
executors. I wish the will to be made in a manner to prevent all
discussion, if possible, after my decease; and this I leave to you as a
professional gentleman.
With regard to the few and simple directions for the disposal of my
carcass, I must have them implicitly fulfilled, as they will, at
least, prevent trouble and expense; — and (what would be of little
consequence to me, but may quiet the conscience of the survivors) the
garden is consecrated ground. These directions are copied
verbatim from my former will; the alterations in other parts have arisen
from the death of Mrs. B. I have the honour to be,
Your most obedient, humble servant,
Byron.
List of Letters
Newstead Abbey, August 21st, 1811.
My Dear Sister, — I ought to have answered your letter before, but when
did I ever do any-thing that I ought?
I am losing my relatives & you are adding to the number of yours; but
which is best, God knows; — besides poor Mrs. Byron, I have been
deprived by death of two most particular friends within little more than
a month; but as all observations on such subjects are superfluous and
unavailing, I leave the dead to their rest, and return to the dull
business of life, which however presents nothing very pleasant to me
either in prospect or retrospection.
I hear you have been increasing his Majesty's Subjects, which in these
times of War and tribulation is really patriotic. Notwithstanding
Malthus1 tells us that, were it not for Battle, Murder, and Sudden
death, we should be overstocked, I think we have latterly had a
redundance of these national benefits, and therefore I give you all
credit for your matronly behaviour.
I believe you know that for upwards of two years I have been rambling
round the Archipelago, and am returned just in time to know that I might
as well have staid away for any good I ever have done, or am likely to
do at home, and so, as soon as I have somewhat repaired my
irreparable affairs I shall een go abroad again, for I am
heartily sick of your climate and every thing it rains upon,
always save and except yourself as in duty bound.
I should be glad to see you here (as I think you have never seen the
place) if you could make it convenient. Murray is still like a Rock, and
will probably outlast some six Lords Byron, though in his 75th Autumn. I
took him with me to Portugal & sent him round by sea to Gibraltar whilst
I rode through the Interior of Spain, which was then (1809) accessible.
You say you have much to communicate to me, let us have it by all means,
as I am utterly at a loss to guess; whatever it may be it will meet with
due attention.
Your trusty and well beloved cousin F. Howard2 is married to a Miss
Somebody, I wish him joy on your account, and on his own, though
speaking generally I do not affect that Brood.
By the bye, I shall marry, if I can find any thing inclined to barter
money for rank within six months; after which I shall return to my
friends the Turks.
In the interim I am, Dear Madam,
[Signature cut out.]
Footnote 1: The Rev. T. R. Malthus (1766-1834) published, in 1798, his Essay on the Principle of Population.
return to footnote mark
Footnote 2: The Hon. Frederick Howard (see page 55, note 1) married,
August 6, 1811, Frances Susan Lambton, only daughter of William
Lambton, formerly M.P. for Durham.
return
List of Letters
Newstead, August 21, 1811.
Your letter gives me credit for more acute feelings than I possess; for
though I feel tolerably miserable, yet I am at the same time subject to
a kind of hysterical merriment, or rather laughter without merriment,
which I can neither account for nor conquer, and yet I do not feel
relieved by it; but an indifferent person would think me in excellent
spirits. "We must forget these things," and have recourse to our old
selfish comforts, or rather comfortable selfishness.
I do not think I shall return to London immediately, and shall therefore
accept freely what is offered courteously — your mediation between me
and Murray1. I don't think my name will answer the purpose, and you
must be aware that my plaguy Satire will bring the north and south Grub
Streets down upon the Pilgrimage; — but, nevertheless, if Murray
makes a point of it, and you coincide with him, I will do it daringly;
so let it be entitled "By the author of English Bards and Scotch
Reviewers." My remarks on the Romaic, etc., once intended to accompany
the Hints from Horace, shall go along with the other, as being
indeed more appropriate; also the smaller poems now in my possession,
with a few selected from those published in Hobhouse's
Miscellany. I have found amongst my poor mother's papers all my
letters from the East, and one in particular of some length from
Albania. From this, if necessary, I can work up a note or two on that
subject. As I kept no journal, the letters written on the spot are the
best. But of this anon, when we have definitively arranged.
Has Murray shown the work to any one? He may — but I will have no traps
for applause. Of course there are little things I would wish to alter,
and perhaps the two stanzas of a buffooning cast on London's Sunday are
as well left out. I much wish to avoid identifying Childe Harold's
character with mine, and that, in sooth, is my second objection to my
name appearing in the title-page. When you have made arrangements as to
time, size, type, etc., favour me with a reply. I am giving you an
universe of trouble, which thanks cannot atone for. I made a kind of
prose apology for my scepticism at the head of the MS., which, on
recollection, is so much more like an attack than a defence, that,
haply, it might better be omitted — perpend, pronounce. After all, I fear
Murray will be in a scrape with the orthodox; but I cannot help it,
though I wish him well through it. As for me, "I have supped full of
criticism," and I don't think that the "most dismal treatise" will stir
and rouse my "fell of hair" till "Birnam wood do come to Dunsinane."
I shall continue to write at intervals, and hope you will pay me in
kind. How does Pratt get on, or rather get off, Joe Blackett's
posthumous stock? You killed that poor man amongst you, in spite of your
Ionian friend2 and myself, who would have saved him from Pratt,
poetry, present poverty, and posthumous oblivion. Cruel patronage! to
ruin a man at his calling; but then he is a divine subject for
subscription and biography; and Pratt, who makes the most of his
dedications, has inscribed the volume to no less than five families of
distinction.
I am sorry you don't like Harry White3: with a great deal of cant,
which in him was sincere (indeed it killed him as you killed Joe
Blackett), certes there is poesy and genius. I don't say this on account
of my simile and rhymes; but surely he was beyond all the Bloomfields4 and Blacketts, and their collateral cobblers, whom Lofft5 and
Pratt have or may kidnap from their calling into the service of the
trade. You must excuse my flippancy, for I am writing I know not what,
to escape from myself. Hobhouse is gone to Ireland. Mr. Davies has been
here on his way to Harrowgate.
You did not know Matthews: he was a man of the most astonishing powers,
as he sufficiently proved at Cambridge, by carrying off more prizes and
fellowships, against the ablest candidates, than any other graduate on
record; but a most decided atheist, indeed noxiously so, for he
proclaimed his principles in all societies. I knew him well, and feel a
loss not easily to be supplied to myself — to Hobhouse never. Let me hear
from you, and
Believe me, etc.
Footnote 1: In 1793 John Murray the first (born 1745) died, leaving a
widow, two daughters, and one son, John Murray the second (1778-1843),
then a boy of fifteen. The bookselling and publishing business at 32,
Fleet Street, which the first John Murray had purchased in 1768 from
William Sandby, was for two years carried on by the chief assistant,
Samuel Highley. From 1795, when John Murray the second joined it, it was
conducted as a partnership, under the title of Murray and Highley. But
in 1803 John Murray cancelled the partnership, and started for himself
at 32, Fleet Street. Relieved from a timorous partner, he at once
displayed his shrewdness, energy, and literary enthusiasm. He rapidly
became, as Byron called him, "the 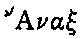 of Publishers," or, as he
was nicknamed, "The Emperor of the West." In February, 1809, he had
launched the Quarterly Review; in March, 1812, he published
Childe Harold; in the following September, he moved to 50,
Albemarle Street, the lease of which, with the stock, good will, and
copyrights, he purchased from William Miller (see page 319, note
2). The remarkable position which the second John Murray created for
himself, has two aspects, one commercial, the other social. He was not
only the publisher, but the friend, of the most distinguished men of the
day; and he was both by reason, partly of his honourable character,
partly of his personal attractiveness. Sir Walter Scott, writing,
October 30, 1828, to Lockhart, speaks of Murray in words which sum up
his character:
of Publishers," or, as he
was nicknamed, "The Emperor of the West." In February, 1809, he had
launched the Quarterly Review; in March, 1812, he published
Childe Harold; in the following September, he moved to 50,
Albemarle Street, the lease of which, with the stock, good will, and
copyrights, he purchased from William Miller (see page 319, note
2). The remarkable position which the second John Murray created for
himself, has two aspects, one commercial, the other social. He was not
only the publisher, but the friend, of the most distinguished men of the
day; and he was both by reason, partly of his honourable character,
partly of his personal attractiveness. Sir Walter Scott, writing,
October 30, 1828, to Lockhart, speaks of Murray in words which sum up
his character:
"By all means do what the Emperor says. He is what
Emperor Nap was not, 'much a gentleman.'"
Murray was the first to
divorce the business of publishing from that of selling books; the first
to see, as he wrote to Sir Walter Scott, October 13, 1825 (A
Publisher and his Friends, vol. ii. p. 199), that
"the business of a
publishing bookseller is not in his shop, or even his connection, but in
his brains."
Quick-tempered and warm-hearted, he was endowed with a
strong sense of humour, and a gift of felicitous expression, which made
him at once an admirable talker and an excellent letter-writer, and
enabled him to hold his own among the noted wits and brilliant men of
letters whom he gathered under his roof. A man of ideas more than a man
of business, of enterprise rather than of calculation, he was always on
the watch for new writers and new openings. But his imagination and
impulsive temperament were checked by his fine taste for sound
literature, and controlled by high principles in matters of trade. Thus
he was saved from those disastrous speculations which involved Scott in
ruin, and might otherwise have appealed with fatal force to his own
sanguine nature. His close relations with Byron, which began in 1811,
and lasted till the poet's death, are set forth in the numerous letters
which follow, and were never embittered even when he refused to continue
the publication of Don Juan. Their names are inseparably
associated in the history of literature. A generous paymaster, he was
also an hospitable host. Round him gathers much of the literary history
of a half-century which includes such names as those of Scott, Byron,
Southey, Coleridge, Hallam, Milman, Mahon, Carlyle, Grote, Benjamin
Disraeli, Sir Robert Peel, Canning, and Mr. Gladstone. His literary
dinners were famous, and his drawing-room was the rallying-place of all
that was witty and agreeable in society. At the same time, he was the
acknowledged head of the publishing trade, unswerving in the rectitude
of his commercial dealings, and in the maintenance of the honourable
traditions of his most distinguished predecessors, as well as sincere in
his enthusiasm for English letters.
return to footnote mark
cross-reference: return to Footnote 1 of Letter 84
Footnote 2: Walter Rodwell Wright, author of Horæ Ionicæ, a Poem
descriptive of the Ionian Islands, and part of the adjacent coast of
Greece, (1809), had been Consul-General of the Seven Islands. On
his return he became Recorder of Bury St. Edmund's. He was
subsequently President of the Court of Appeals in Malta, where he
died in 1826. (See Byron's address to him in English Bards, and
Scotch Reviewers, lines 877-880.)
return
Footnote 3: Henry Kirke White (1785-1806) published Clifton Grove and
other poems in 1803. He died at Cambridge in 1806. His
Remains were published by Southey in 1807. (See English Bards,
and Scotch Reviewers, lines 831-848, and note 2.)
return
Footnote 4: The three brothers, George Bloomfield, a shoemaker, Nathaniel,
a tailor, and Robert, also a shoemaker, were the sons of a
tailor at Honington, in Suffolk, whose wife kept the village school.
(For further details as to George and Nathaniel, see English Bards,
and Scotch Reviewers, lines 765-798, and notes.)
Robert Bloomfield (1766-1823) achieved a success with his
Farmer's Boy (1800), of which thousands of copies were sold in
England, and which was translated into French and Italian. But
however creditable the lines may have been to the author, Byron's
opinion of the merits of the poet was the true one. Bloomfield's
subsequent volumes, of which there were seven, were inferior to The
Farmer's Boy. Good Tidings, or News from the Farm (1804), is perhaps the best known. A collected edition of Bloomfield's Works was published in 1824.
return
cross-reference: return to Footnote 2 of Letter 154
Footnote 5: Capel Lofft (1751-1824), educated at Eton and Cambridge,
was called to the Bar in 1775. Succeeding in 1781 to the family
estates near Bury St. Edmund's, he lived for some years at Troston
Hall. Crabb Robinson (Diary, vol. i. p. 29) describes him, in
1795, as
"a gentleman of good family and estate — an author on an
infinity of subjects; his books were on Law, History, Poetry,
Antiquities, Divinity, and Politics. He was then an acting magistrate,
having abandoned the profession of the Bar. He was one
of the numerous answerers of Burke; and, in spite of a feeble
voice and other disadvantages, was an eloquent speaker."
His
boyish figure, slovenly dress, and involved sentences were well known
on the platforms where he advocated parliamentary reform. On
May 17, 1784, Johnson dined at Mr. Dilly's. Among the guests
was
"Mr. Capel Lofft, who, though a most zealous Whig, has a
mind so full of learning and knowledge, and so much in exercise
in various exertions, and withal so much liberality, that the
stupendous powers of the literary Goliath, though they did not
frighten this little David of popular spirit, could not but excite his
admiration."
Lofft held strong opinions in favour of the French
Revolution, which he admired. He, "Godwin, and Thelwall are
the only three persons I know (except Hazlitt) who grieve at
the late events;" so writes Crabb Robinson, after the battle of
Waterloo (Diary, vol. i. p. 491). He published numerous works
on law and politics, besides four volumes of poetry: The Praises of
Poetry, a Poem (1775); Eudosia, or a Poem on the Universe (1781); The first and second Georgics of Virgil (in blank verse, 1803);
Laura, or an Anthology of Sonnets (1814). He also edited Milton's
Paradise Lost. In November, 1798, Lofft read the manuscript of
The Farmer's Boy, written by Robert Bloomfield in a London
garret, where he worked as a shoemaker. Interested in the poem
and the Suffolk poet, Lofft had it published in 1800, with cuts by
Bewick, and a preface by himself.
return
List of Letters
Newstead Abbey, August 22, 1811.
You may have heard of the sudden death of my mother, and poor Matthews,
which, with that of Wingfield (of which I was not fully aware till just
before I left town, and indeed hardly believed it,) has made a sad chasm
in my connections. Indeed the blows followed each other so rapidly that
I am yet stupid from the shock; and though I do eat, and drink, and
talk, and even laugh, at times, yet I can hardly persuade myself that I
am awake, did not every morning convince me mournfully to the
contrary. — I shall now wave the subject, — the dead are at rest, and none
but the dead can be so.
You will feel for poor Hobhouse, — Matthews was the "god of his
idolatry;" and if intellect could exalt a man above his fellows, no one
could refuse him preeminence. I knew him most intimately, and valued him
proportionably; but I am recurring — so let us talk of life and the
living.
If you should feel a disposition to come here, you will find "beef and a
sea-coal fire," and not ungenerous wine. Whether Otway's two other
requisites for an Englishman or not, I cannot tell, but probably one of
them1. — Let me know when I may expect you, that I may tell you when I
go and when return. I have not yet been to Lancs. Davies has been here,
and has invited me to Cambridge for a week in October, so that,
peradventure, we may encounter glass to glass. His gaiety (death cannot
mar it) has done me service; but, after all, ours was a hollow laughter.
You will write to me? I am solitary, and I never felt solitude irksome
before. Your anxiety about the critique on — — 's book is amusing; as it
was anonymous, certes it was of little consequence: I wish it had
produced a little more confusion, being a lover of literary malice. Are
you doing nothing? writing nothing? printing nothing? why not your
Satire on Methodism? the subject (supposing the public to be blind to
merit) would do wonders. Besides, it would be as well for a destined
deacon to prove his orthodoxy. — It really would give me pleasure to see
you properly appreciated. I say really, as, being an author, my
humanity might be suspected.
Believe me, dear H., yours always.
Footnote 1:
"Give but an Englishman his whore and ease,
Beef and a sea-coal fire, he's yours for ever."
Venice Preserved, act ii. sc. 3.
return to footnote mark
List of Letters
Contents
2 VOLS. 1807.
(From Monthly Literary Recreations for July, 1807.)
The volumes before us are by the author of Lyric Ballads, a collection
which has not undeservedly met with a considerable share of public
applause. The characteristics of Mr. Wordsworth's muse are simple and
flowing, though occasionally inharmonious verse; strong, and sometimes
irresistible appeals to the feelings, with unexceptionable sentiments.
Though the present work may not equal his former efforts, many of the
poems possess a native elegance, natural and unaffected, totally devoid
of the tinsel embellishments and abstract hyperboles of several
contemporary sonneteers. The last sonnet in the first volume, p. 152, is
perhaps the best, without any novelty in the sentiments, which we hope
are common to every Briton at the present crisis; the force and
expression is that of a genuine poet, feeling as he writes —
Another year! another deadly blow!
Another mighty empire overthrown!
And we are left, or shall be left, alone —
The last that dares to struggle with the foe.
'Tis well! — from this day forward we shall know
That in ourselves our safety must be sought,
That by our own right-hands it must be wrought;
That we must stand unprop'd, or be laid low.
O dastard! whom such foretaste doth not cheer!
We shall exult, if they who rule the land
Be men who hold its many blessings dear,
Wise, upright, valiant, not a venal band,
Who are to judge of danger which they fear,
And honour which they do not understand.
The song at the Feast of Brougham Castle, the Seven Sisters, the
Affliction of Margaret — — of — — , possess all the beauties, and few
of the defects, of the writer: the following lines from the last are in
his first style:—
"Ah! little doth the young one dream,
When full of play and childish cares,
What power hath e'en his wildest scream,
Heard by his mother unawares:
He knows it not, he cannot guess:
Years to a mother bring distress,
But do not make her love the less."
The pieces least worthy of the author are those entitled "Moods of my
own Mind." We certainly wish these "Moods" had been less frequent, or
not permitted to occupy a place near works which only make their
deformity more obvious; when Mr. W. ceases to please, it is by
"abandoning" his mind to the most commonplace ideas, at the same time
clothing them in language not simple, but puerile. What will any reader
or auditor, out of the nursery, say to such namby-pamby as "Lines
written at the Foot of Brother's Bridge"?
"The cock is crowing,
The stream is flowing,
The small birds twitter,
The lake doth glitter,
The green field sleeps in the sun;
The oldest and youngest,
Are at work with the strongest;
The cattle are grazing,
Their heads never raising,
There are forty feeding like one.
Like an army defeated,
The snow hath retreated,
And now doth fare ill,
On the top of the bare hill."
"The ploughboy is whooping anon, anon," etc., etc., is in the same
exquisite measure. This appears to us neither more nor less than an
imitation of such minstrelsy as soothed our cries in the cradle, with
the shrill ditty of
"Hey de diddle,
The cat and the fiddle:
The cow jump'd over the moon,
The little dog laugh'd to see such sport,
And the dish ran away with the spoon."
On the whole, however, with the exception of the above, and other
Innocent odes of the same cast, we think these volumes display a genius
worthy of higher pursuits, and regret that Mr. W. confines his muse to
such trifling subjects. We trust his motto will be in future "Paulo
majora canamus." Many, with inferior abilities, have acquired a loftier
seat on Parnassus, merely by attempting strains in which Wordsworth is
more qualified to excel.
Contents
for January, 1808
Hours of Idleness; a Series of Poems, original and translated.
By George Gordon, Lord Byron, a Minor. 8vo,
pp. 200. Newark, 1807.
The poesy of this young lord belongs to the class which neither gods nor
men are said to permit. Indeed, we do not recollect to have seen a
quantity of verse with so few deviations in either direction from that
exact standard. His effusions are spread over a dead flat, and can no
more get above or below the level, than if they were so much stagnant
water. As an extenuation of this offence, the noble author is peculiarly
forward in pleading minority. We have it in the title-page, and on the
very back of the volume; it follows his name like a favourite part of
his style. Much stress is laid upon it in the preface; and the
poems are connected with this general statement of his case, by
particular dates, substantiating the age at which each was written. Now,
the law upon the point of minority we hold to be perfectly clear. It is
a plea available only to the defendant; no plaintiff can offer it as a
supplementary ground of action. Thus, if any suit could be brought
against Lord Byron, for the purpose of compelling him to put into court
a certain quantity of poetry, and if judgment were given against him, it
is highly probable that an exception would be taken, were he to deliver
for poetry the contents of this volume. To this he might plead
minority; but, as he now makes voluntary tender of the article,
he hath no right to sue, on that ground, for the price in good current
praise, should the goods be unmarketable,
This is our view of the law on the point; and, we dare to say, so will
it be ruled. Perhaps, however, in reality, all that he tells us about
his youth is rather with a view to increase our wonder than to soften
our censures. He possibly means to say, "See how a minor can write! This
poem was actually composed by a young man of eighteen, and this by one
of only sixteen!" But, alas! We all remember the poetry of Cowley at
ten, and Pope at twelve; and so far from hearing, with any degree of
surprise, that very poor verses were written by a youth from his leaving
school to his leaving college, inclusive, we really believe this to be
the most common of all occurrences; that it happens in the life of nine
men in ten who are educated in England; and that the tenth man writes
better verse than Lord Byron.
His other plea of privilege our author rather brings forward in order to
waive it. He certainly, however, does allude frequently to his family
and ancestry — sometimes in poetry, sometimes in notes; and, while giving
up his claim on the score of rank, he takes care to remember us of Dr.
Johnson's saying, that when a nobleman appears as an author, his merit
should be handsomely acknowledged. In truth, it is this consideration
only that induces us to give Lord Byron's poems a place in our review,
beside our desire to counsel him, that he do forthwith abandon poetry,
and turn his talents, which are considerable, and his opportunities,
which are great, to better account.
With this view, we must beg leave seriously to assure him, that the mere
rhyming of the final syllable, even when accompanied by the presence of
a certain number of feet, — nay, although (which does not always happen)
those feet should scan regularly, and have been all counted accurately
upon the fingers, — is not the whole art of poetry. We would entreat him
to believe, that a certain portion of liveliness, somewhat of fancy, is
necessary to constitute a poem, and that a poem in the present day, to
be read, must contain at least one thought, either in a little degree
different from the ideas of former writers, or differently expressed. We
put it to his candour, whether there is any thing so deserving the name
of poetry in verses like the following, written in 1806; and whether, if
a youth of eighteen could say any thing so uninteresting to his
ancestors, a youth of nineteen should publish it; —
"Shades of heroes, farewell! your descendant, departing
From the seat of his ancestors, bids you adieu!
Abroad or at home, your remembrance imparting
New courage, he'll think upon glory and you.
"Though a tear dim his eye at this sad separation,
'Tis nature, not fear, that excites his regret;
Far distant he goes, with the same emulation;
The fame of his fathers he ne'er can forget.
"That fame, and that memory, still will he cherish;
He vows that he ne'er will disgrace your renown;
Like you will he live, or like you will he perish;
When decay'd, may he mingle his dust with your own."
Now, we positively do assert, that there is nothing better than these
stanzas in the whole compass of the noble minor's volume.
Lord Byron should also have a care of attempting what the greatest poets
have done before him, for comparisons (as he must have had occasion to
see at his writing-master's) are odious. Gray's Ode on Eton College
should really have kept out the ten hobbling stanzas "On a distant View
of the Village and School of Harrow."
"Where fancy yet joys to retrace the resemblance
Of comrades, in friendship and mischief allied,
How welcome to me your ne'er-fading remembrance,
Which rests in the bosom, though hope is denied."
In like manner, the exquisite lines of Mr. Rogers, "On a Tear,"
might have warned the noble author off those premises, and spared us a
whole dozen such stanzas as the following:—
"Mild Charity's glow, to us mortals below,
Shows the soul from barbarity clear;
Compassion will melt where this virtue is felt,
And its dew is diffused in a Tear.
"The man doom'd to sail with the blast of the gale,
Through billows Atlantic to steer,
As he bends o'er the wave, which may soon be his grave,
The green sparkles bright with a Tear."
And so of instances in which former poets have failed. Thus we do not
think Lord Byron was made for translating, during his nonage, "Adrian's
Address to his Soul," when Pope succeeded so indifferently in the
attempt. If our readers, however, are of another opinion, they may look
at it.
"Ah! gentle, fleeting, wavering sprite,
Friend and associate of this clay!
To what unknown region borne
Wilt thou now wing thy distant flight?
No more with wonted humour gay,
But pallid, cheerless, and forlorn."
However, be this as it may, we fear his translations and imitations are
great favourites with Lord Byron. We have them of all kinds, from
Anacreon to Ossian; and, viewing them as school exercises, they may
pass. Only, why print them after they have had their day and served
their turn? And why call the thing in p. 79 (see p. 380) a translation,
where two words 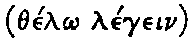 of the original are
expanded into four lines, and the other thing in p. 81 (see
ibid.) where
of the original are
expanded into four lines, and the other thing in p. 81 (see
ibid.) where  is rendered
by means of six hobbling verses? As to his Ossianic poesy, we are not
very good judges, being in truth, so moderately skilled in that species
of composition, that we should, in all probability, be criticizing some
bit of the genuine Macpherson itself, were we to express our opinion of
Lord Byron's rhapsodies. If, then, the following beginning of a "Song of
Bards" is by his lordship, we venture to object to it, as far as we can
comprehend it.
is rendered
by means of six hobbling verses? As to his Ossianic poesy, we are not
very good judges, being in truth, so moderately skilled in that species
of composition, that we should, in all probability, be criticizing some
bit of the genuine Macpherson itself, were we to express our opinion of
Lord Byron's rhapsodies. If, then, the following beginning of a "Song of
Bards" is by his lordship, we venture to object to it, as far as we can
comprehend it.
"What form rises on the roar of clouds? whose dark ghost
gleams on the red stream of tempests? His voice rolls on the thunder;
'tis Orla, the brown chief of Oithona. He was,"
etc. After detaining
this "brown chief" some time, the bards conclude by giving him their
advice to "raise his fair locks;" then to "spread them on the arch of
the rainbow;" and to "smile through the tears of the storm." Of this
kind of thing there are no less than nine pages; and we can so
far venture an opinion in their favour, that they look very like
Macpherson; and we are positive they are pretty nearly as stupid and
tiresome.
It is a sort of privilege of poets to be egotists; but they should "use
it as not abusing it;" and particularly one who piques himself (though
indeed at the ripe age of nineteen) on being "an infant bard," — ("The
artless Helicon I boast is youth") — should either not know, or should
seem not to know, so much about his own ancestry. Besides a poem above
cited, on the family seat of the Byrons, we have another of eleven
pages, on the self-same subject, introduced with an apology, "he
certainly had no intention of inserting it," but really "the particular
request of some friends," etc., etc. It concludes with five stanzas on
himself, "the last and youngest of a noble line." There is a good deal
also about his maternal ancestors, in a poem on Lachin y Gair, a
mountain where he spent part of his youth, and might have learnt that
pibroch is not a bagpipe, any more than duet means a fiddle.
As the author has dedicated so large a part of his volume to immortalise
his employments at school and college, we cannot possibly dismiss it
without presenting the reader with a specimen of these ingenious
effusions. In an ode with a Greek motto, called "Granta," we have the
following magnificent stanzas:—
There, in apartments small and damp,
The candidate for college prizes,
Sits poring by the midnight lamp,
Goes late to bed, yet early rises.
Who reads false quantities in Sele,
Or puzzles o'er the deep triangle,
Deprived of many a wholesome meal,
In barbarous Latin doom'd to wrangle:
Renouncing every pleasing page,
From authors of historic use;
Preferring to the letter'd sage,
The square of the hypothenuse.
Still harmless are these occupations,
That hurt none but the hapless student,
Compared with other recreations,
Which bring together the imprudent."
We are sorry to hear so bad an account of the college psalmody as is
contained in the following Attic stanzas:—
"Our choir would scarcely be excused
Even as a band of raw beginners;
All mercy now must be refused
To such a set of croaking sinners.
If David, when his toils were ended,
Had heard these blockheads sing before him,
To us his psalms had ne'er descended:
In furious mood he would have tore 'em! "
But, whatever judgment may be passed on the poems of this noble minor,
it seems we must take them as we find them, and be content; for they are
the last we shall ever have from him. He is, at best, he says, but an
intruder into the groves of Parnassus: he never lived in a garret, like
thorough-bred poets; and "though he once roved a careless mountaineer
in the Highlands of Scotland," he has not of late enjoyed this
advantage. Moreover, he expects no profit from his publication; and,
whether it succeeds or not, "it is highly improbable, from his situation
and pursuits hereafter," that he should again condescend to become an
author. Therefore, let us take what we get, and be thankful. What right
have we poor devils to be nice? We are well off to have got so much from
a man of this lord's station, who does not live in a garret, but "has
the sway" of Newstead Abbey. Again, we say, let us be thankful; and,
with honest Sancho, bid God bless the giver, nor look the gift horse in
the mouth.
Contents
(From the Monthly Review for August, 1811.)
That laudable curiosity concerning the remains of classical antiquity,
which has of late years increased among our countrymen, is in no
traveller or author more conspicuous than in Mr. Gell. Whatever
difference of opinion may yet exist with regard to the success of the
several disputants in the famous Trojan controversy1, or, indeed,
relating to the present author's merits as an inspector of the Troad, it
must universally be acknowledged that any work, which more forcibly
impresses on our imaginations the scenes of heroic action, and the
subjects of immortal song, possesses claims on the attention of every
scholar.
Of the two works which now demand our report, we conceive the former to
be by far the most interesting to the reader, as the latter is
indisputably the most serviceable to the traveller. Excepting, indeed,
the running commentary which it contains on a number of extracts from
Pausanias and Strabo, it is, as the title imports, a mere itinerary of
Greece, or rather of Argolis only, in its present circumstances. This
being the case, surely it would have answered every purpose of utility
much better by being printed as a pocket road-book of that part of the
Morea; for a quarto is a very unmanageable travelling companion. The
maps2 and drawings, we shall be told, would not permit such an
arrangement; but as to the drawings, they are not in general to be
admired as specimens of the art; and several of them, as we have been
assured by eye-witnesses of the scenes which they describe, do not
compensate for their mediocrity in point of execution, by any
extraordinary fidelity of representation. Others, indeed, are more
faithful, according to our informants. The true reason, however, for
this costly mode of publication is in course to be found in a desire of
gratifying the public passion for large margins, and all the luxury of
typography; and we have before expressed our dissatisfaction with Mr.
Gell's aristocratical mode of communicating a species of knowledge,
which ought to be accessible to a much greater portion of classical
students than can at present acquire it by his means:— but, as such
expostulations are generally useless, we shall be thankful for what we
can obtain, and that in the manner in which Mr. Gell has chosen to
present it.
The former of these volumes, we have observed, is the most attractive in
the closet. It comprehends a very full survey of the far-famed island
which the hero of the Odyssey has immortalized; for we really are
inclined to think that the author has established the identity of the
modern Theaki with the Ithaca of Homer. At all events, if
it be an illusion, it is a very agreeable deception, and is effected by
an ingenious interpretation of the passages in Homer that are supposed
to be descriptive of the scenes which our traveller has visited. We
shall extract some of these adaptations of the ancient picture to the
modern scene, marking the points of resemblance which appear to be
strained and forced, as well as those which are more easy and natural;
but we must first insert some preliminary matter from the opening
chapter. The following passage conveys a sort of general sketch of the
book, which may give our readers a tolerably adequate notion of its
contents:—
"The present work may adduce, by a simple and correct survey of the
island, coincidences in its geography, in its natural productions, and
moral state, before unnoticed. Some will be directly pointed out; the
fancy or ingenuity of the reader may be employed in tracing others;
the mind familiar with the imagery of the Odyssey will
recognise with satisfaction the scenes themselves; and this volume is
offered to the public, not entirely without hopes of vindicating the
poem of Homer from the scepticism of those critics who imagine that
the Odyssey is a mere poetical composition, unsupported by
history, and unconnected with the localities of any particular
situation.
Some have asserted that, in the comparison of places now existing
with the descriptions of Homer, we ought not to expect coincidence in
minute details; yet it seems only by these that the kingdom of
Ulysses, or any other, can be identified, as, if such an idea be
admitted, every small and rocky island in the Ionian Sea, containing a
good port, might, with equal plausibility, assume the appellation of
Ithaca.
The Venetian geographers have in a great degree contributed to raise
those doubts which have existed on the identity of the modern with the
ancient Ithaca, by giving, in their charts, the name of Val di Compare
to the island. That name is, however, totally unknown in the country,
where the isle is invariably called Ithaca by the upper ranks, and
Theaki by the vulgar. The Venetians have equally corrupted the name of
almost every place in Greece; yet, as the natives of Epactos or
Naupactos never heard of Lepanto, those of Zacynthos of Zante, or the
Athenians of Settines, it would be as unfair to rob Ithaca of its
name, on such authority, as it would be to assert that no such island
existed, because no tolerable representation of its form can be found
in the Venetian surveys.
The rare medals of the Island, of which three are represented in the
title-page, might be adduced as a proof that the name of Ithaca was
not lost during the reigns of the Roman emperors. They have the head
of Ulysses, recognised by the pileum, or pointed cap, while the
reverse of one presents the figure of a cock, the emblem of his
vigilance, with the legend 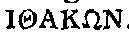 . A few of these medals are
preserved in the cabinets of the curious, and one also, with the cock,
found in the island, is in the possession of Signor Zavo, of Bathi.
The uppermost coin is in the collection of Dr. Hunter; the second is
copied from Newman; and the third is the property of R. P. Knight, Esq.
. A few of these medals are
preserved in the cabinets of the curious, and one also, with the cock,
found in the island, is in the possession of Signor Zavo, of Bathi.
The uppermost coin is in the collection of Dr. Hunter; the second is
copied from Newman; and the third is the property of R. P. Knight, Esq.
"Several inscriptions, which will be hereafter produced, will tend to
the confirmation of the idea that Ithaca was inhabited about the time
when the Romans were masters of Greece; yet there is every reason to
believe that few, if any, of the present proprietors of the soil are
descended from ancestors who had long resided successively in the
island. Even those who lived, at the time of Ulysses, in Ithaca, seem
to have been on the point of emigrating to Argos, and no chief
remained, after the second in descent from that hero, worthy of being
recorded in history. It appears that the isle has been twice colonised
from Cephalonia in modern times, and I was informed that a grant had
been made by the Venetians, entitling each settler in Ithaca to as
much land as his circumstances would enable him to cultivate."
Mr. Gell then proceeds to invalidate the authority of previous writers
on the subject of Ithaca. Sir George Wheeler and M. le Chevalier fall
under his severe animadversion; and, indeed, according to his account,
neither of these gentlemen had visited the island, and the description
of the latter is "absolutely too absurd for refutation." In another
place, he speaks of M. le C. "disgracing a work of such merit by the
introduction of such fabrications;" again, of the inaccuracy of the
author's maps; and, lastly, of his inserting an island at the southern
entry of the channel between Cephalonia and Ithaca, which has no
existence. This observation very nearly approaches to the use of that
monosyllable which Gibbon3, without expressing it, so adroitly applied
to some assertion of his antagonist, Mr. Davies. In truth, our
traveller's words are rather bitter towards his brother tourist; but we
must conclude that their justice warrants their severity.
In the second chapter, the author describes his landing in Ithaca, and
arrival at the rock Korax and the fountain Arethusa, as he designates it
with sufficient positiveness. — This rock, now known by the name of
Korax, or Koraka Petra, he contends to be the same with that which Homer
mentions as contiguous to the habitation of Eumæus, the faithful
swineherd of Ulysses. — We shall take the liberty of adding to our
extracts from Mr. Gell some of the passages in Homer to which he
refers only, conceiving this to be the fairest method of exhibiting
the strength or the weakness of his argument.
"Ulysses," he observes,
"came to the extremity of the isle to visit Eumæus, and that extremity
was the most southern; for Telemachus, coming from Pylos, touched at the
first south-eastern part of Ithaca with the same intention."

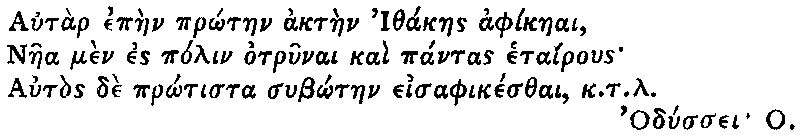
These citations, we think, appear to justify the author in his attempt
to identify the situation of his rock and fountain with the place of
those mentioned by Homer. But let us now follow him in the closer
description of the scene. — After some account of the subjects in the
plate affixed, Mr. Gell remarks:
"It is impossible to visit this
sequestered spot without being struck with the recollection of the Fount
of Arethusa and the rock Korax, which the poet mentions in the same
line, adding, that there the swine ate the sweet4 acorns, and drank
the black water."

"Having passed some time at the fountain, taken a drawing, and made
the necessary observations on the situation of the place, we proceeded
to an examination of the precipice, climbing over the terraces above
the source among shady fig-trees, which, however, did not prevent us
from feeling the powerful effects of the mid-day sun. After a short
but fatiguing ascent, we arrived at the rock, which extends in a vast
perpendicular semicircle, beautifully fringed with trees, facing to
the south-east. Under the crag we found two caves of inconsiderable
extent, the entrance of one of which, not difficult of access, is seen
in the view of the fount. They are still the resort of sheep and
goats, and in one of them are small natural receptacles for the water,
covered by a stalagmatic incrustation.
These caves, being at the extremity of the curve formed by the
precipice, open toward the south, and present us with another
accompaniment of the fount of Arethusa, mentioned by the poet, who
informs us that the swineherd Eumæus left his guests in the house,
whilst he, putting on a thick garment, went to sleep near the herd,
under the hollow of the rock, which sheltered him from the northern
blast. Now we know that the herd fed near the fount; for Minerva tells
Ulysses that he is to go first to Eumæus, whom he should find with
the swine, near the rock Korax and the fount of Arethusa. As the swine
then fed at the fountain, so it is necessary that a cavern should be
found in its vicinity; and this seems to coincide, in distance and
situation, with that of the poem. Near the fount also was the fold or
stathmos of Eumæus; for the goddess informs Ulysses that he should
find his faithful servant at or above the fount.
"Now the hero meets the swineherd close to the fold, which was
consequently very near that source. At the top of the rock, and just
above the spot where the waterfall shoots down the precipice, is at
this day a stagni, or pastoral dwelling, which the herdsmen of Ithaca
still inhabit, on account of the water necessary for their cattle. One
of these people walked on the verge of the precipice at the time of
our visit to the place, and seemed so anxious to know how we had been
conveyed to the spot, that his inquiries reminded us of a question
probably not uncommon in the days of Homer, who more than once
represents the Ithacences demanding of strangers what ship had brought
them to the island, it being evident they could not come on foot. He
told us that there was, on the summit where he stood, a small cistern
of water, and a kalybea, or shepherd's hut. There are also vestiges of
ancient habitations, and the place is now called Amarâthia.
Convenience, as well as safety, seems to have pointed out the lofty
situation of Amarâthia as a fit place for the residence of the
herdsmen of this part of the island from the earliest ages. A small
source of water is a treasure in these climates; and if the
inhabitants of Ithaca now select a rugged and elevated spot, to secure
them from the robbers of the Echinades, it is to be recollected that
the Taphian pirates were not less formidable, even in the days of
Ulysses, and that a residence in a solitary part of the island, far
from the fortress, and close to a celebrated fountain, must at all
times have been dangerous, without some such security as the rocks of
Korax. Indeed, there can be no doubt that the house of Eumæus was on
the top of the precipice; for Ulysses, in order to evince the truth of
his story to the swineherd, desires to be thrown from the summit if
his narration does not prove correct.
Near the bottom of the precipice is a curious natural gallery, about
seven feet high, which is expressed in the plate. It may be fairly
presumed, from the very remarkable coincidence between this place and
the Homeric account, that this was the scene designated by the poet as
the fountain of Arethusa, and the residence of Eumæus; and, perhaps,
it would be impossible to find another spot which bears, at this day,
so strong a resemblance to a poetic description composed at a period
so very remote. There is no other fountain in this part of the island,
nor any rock which bears the slightest resemblance to the Korax of
Homer.
The stathmos of the good Eumæus appears to have been little
different, either in use or construction, from the stagni and kalybea
of the present day. The poet expressly mentions that other herdsmen
drove their flocks into the city at sunset, — a custom which still
prevails throughout Greece during the winter, and that was the season
in which Ulysses visited Eumæus. Yet Homer accounts for this
deviation from the prevailing custom, by observing that he had retired
from the city to avoid the suitors of Penelope. These trifling
occurrences afford a strong presumption that the Ithaca of Homer was
something more than the creature of his own fancy, as some have
supposed it; for though the grand outline of a fable may be easily
imagined, yet the consistent adaptation of minute incidents to a long
and elaborate falsehood is a task of the most arduous and complicated
nature."
After this long extract, by which we have endeavoured to do justice to
Mr. Gell's argument, we cannot allow room for any farther quotations of
such extent; and we must offer a brief and imperfect analysis of the
remainder of the work. In the third chapter the traveller arrives at the
capital, and in the fourth he describes it in an agreeable manner. We
select his account of the mode of celebrating a Christian festival in
the Greek Church:—
"We were present at the celebration of the feast of the Ascension,
when the citizens appeared in their gayest dresses, and saluted each
other in the streets with demonstrations of pleasure. As we sate at
breakfast in the house of Signer Zavo, we were suddenly roused by the
discharge of a gun, succeeded by a tremendous crash of pottery, which
fell on the tiles, steps, and pavements, in every direction. The bells
of the numerous churches commenced a most discordant jingle; colours
were hoisted on every mast in the port, and a general shout of joy
announced some great event. Our host informed us that the feast of the
Ascension was annually commemorated in this manner at Bathi, the
populace exclaiming 
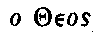 ,
Christ is risen, the true God."
,
Christ is risen, the true God."
In another passage, he continues this account as follows:—
"In the evening of the festival, the inhabitants danced before their
houses; and at one we saw the figure which is said to have been first
used by the youths and virgins of Delos, at the happy return of
Theseus from the expedition of the Cretan Labyrinth. It has now lost
much of that intricacy which was supposed to allude to the windings of
the habitation of the Minotaur,"
etc., etc. This is rather too much for even the inflexible gravity of
our censorial muscles. When the author talks, with all the reality (if
we may use the expression) of a Lemprière, on the stories of the
fabulous ages, we cannot refrain from indulging a momentary smile; nor
can we seriously accompany him in the learned architectural detail by
which he endeavours to give us, from the Odyssey, the ground-plot of
the house of Ulysses, — of which he actually offers a plan in drawing!
"showing how the description of the house of Ulysses in the Odyssey
may be supposed to correspond with the foundations yet visible on the
hill of Aito!" — Oh, Foote! Foote! why are you lost to such inviting
subjects for your ludicrous pencil! — In his account of this celebrated
mansion, Mr. Gell says, one side of the court seems to have been
occupied by the Thalamos, or sleeping apartments of the men, etc., etc.;
and, in confirmation of this hypothesis, he refers to the 10th
Odyssey, line 340. On examining his reference, we read —
where Ulysses records an invitation which he received from Circe to take
a part of her bed. How this illustrates the above conjecture, we are at
a loss to divine: but we suppose that some numerical error has occurred
in the reference, as we have detected a trifling mistake or two of the
same nature.
Mr. G. labours hard to identify the cave of Dexia near Bathi (the
capital of the island), with the grotto of the Nymphs described in the
13th Odyssey. We are disposed to grant that he has succeeded; but we
cannot here enter into the proofs by which he supports his opinion; and
we can only extract one of the concluding sentences of the chapter,
which appears to us candid and judicious:—
"Whatever opinion may be formed as to the identity of the cave of
Dexia with the grotto of the Nymphs, it is fair to state, that Strabo
positively asserts that no such cave as that described by Homer
existed in his time, and that geographer thought it better to assign a
physical change, rather than ignorance in Homer, to account for a
difference which he imagined to exist between the Ithaca of his time
and that of the poet. But Strabo, who was an uncommonly accurate
observer with respect to countries surveyed by himself, appears to
have been wretchedly misled by his informers on many occasions.
"That Strabo had never visited this country is evident, not only from
his inaccurate account of it, but from his citation of Apollodorus and
Scepsius, whose relations are in direct opposition to each other on
the subject of Ithaca, as will be demonstrated on a future
opportunity."
We must, however, observe that "demonstration" is a strong term. — In his
description of the Leucadian Promontory (of which we have a pleasing
representation in the plate), the author remarks that it is "celebrated
for the leap of Sappho, and the death of Artemisia." From this
variety in the expression, a reader would hardly conceive that both the
ladies perished in the same manner; in fact, the sentence is as proper
as it would be to talk of the decapitation of Russell, and the death of
Sidney. The view from this promontory includes the island of Corfu; and
the name suggests to Mr. Gell the following note, which, though rather
irrelevant, is of a curious nature, and we therefore conclude our
citations by transcribing it:—
"It has been generally supposed that Corfu, or Corcyra, was the
Phæacia of Homer; but Sir Henry Englefield thinks the position of
that island inconsistent with the voyage of Ulysses as described in
the Odyssey. That gentleman has also observed a number of such
remarkable coincidences between the courts of Alcinous and Solomon,
that they may be thought curious and interesting. Homer was familiar
with the names of Tyre, Sidon, and Egypt; and, as he lived about the
time of Solomon, it would not have been extraordinary if he had
introduced some account of the magnificence of that prince into his
poem. As Solomon was famous for wisdom, so the name of Alcinous
signifies strength of knowledge; as the gardens of Solomon were
celebrated, so are those of Alcinous (Od. 7. 112); as the
kingdom of Solomon was distinguished by twelve tribes under twelve
princes (1 Kings ch. 4), so that of Alcinous (Od. 8. 390) was
ruled by an equal number: as the throne of Solomon was supported by
lions of gold (1 Kings ch. 10), so that of Alcinous was placed on dogs
of silver and gold (Od. 7. 91); as the fleets of Solomon were
famous, so were those of Alcinous. It is perhaps worthy of remark,
that Neptune sate on the mountains of the SOLYMI, as he returned from
Æthiopia to Ægæ, while he raised the tempest which threw Ulysses on
the coast of Phæacia; and that the Solymi of Pamphylia are very
considerably distant from the route. — The suspicious character, also,
which Nausicaa attributes to her countryman agrees precisely with that
which the Greeks and Romans gave of the Jews."
The seventh chapter contains a description of the Monastery of Kathara,
and several adjacent places. The eighth, among other curiosities, fixes
on an imaginary site for the Farm of Laertes; but this is the agony of
conjecture indeed! — and the ninth chapter mentions another Monastery,
and a rock still called the School of Homer. Some sepulchral
inscriptions of a very simple nature are included. — The tenth and last
chapter brings us round to the Port of Schoenus, near Bathi; after we
have completed, seemingly in a very minute and accurate manner, the tour
of the island.
We can certainly recommend a perusal of this volume to every lover of
classical scene and story. If we may indulge the pleasing belief that
Homer sang of a real kingdom, and that Ulysses governed it, though we
discern many feeble links in Mr. Gell's chain of evidence, we are on the
whole induced to fancy that this is the Ithaca of the bard and of the
monarch. At all events, Mr. Gell has enabled every future traveller to
form a clearer judgment on the question than he could have established
without such a "Vade-mecum to Ithaca," or a "Have with you, to the House
of Ulysses," as the present. With Homer in his pocket, and Gell on his
sumpter-horse or mule, the Odyssean tourist may now make a very
classical and delightful excursion; and we doubt not that the advantages
accruing to the Ithacences, from the increased number of travellers who
will visit them in consequence of Mr. Gell's account of their country,
will induce them to confer on that gentleman any heraldic honours which
they may have to bestow, should he ever look in upon them
again. — Baron Bathi would be a pretty title:—
"Hoc Ithacus velit, et magno mercentur Atridae."
Virgil.
For ourselves, we confess that all our old Grecian feelings would be
alive on approaching the fountain of Melainudros, where, as the
tradition runs, or as the priests relate, Homer was restored to sight.
We now come to the "Grecian Patterson," or "Cary," which Mr. Gell has
begun to publish; and really he has carried the epic rule of concealing
the person of the author to as great a length as either of the
above-mentioned heroes of itinerary writ. We hear nothing of his
"hair-breadth 'scapes" by sea or land; and we do not even know, for the
greater part of his journey through Argolis, whether he relates what he
has seen or what he has heard. From other parts of the book, we find the
former to be the case; but, though there have been tourists and
"strangers" in other countries, who have kindly permitted their readers
to learn rather too much of their sweet selves, yet it is possible to
carry delicacy, or cautious silence, or whatever it may be called, to
the contrary extreme. We think that Mr. Gell has fallen into this error,
so opposite to that of his numerous brethren. It is offensive, indeed,
to be told what a man has eaten for dinner, or how pathetic he was on
certain occasions; but we like to know that there is a being yet living
who describes the scenes to which he introduces us; and that it is not a
mere translation from Strabo or Pausanias which we are reading, or a
commentary on those authors. This reflection leads us to the concluding
remark in Mr. Gell's preface (by much the most interesting part of his
book) to his Itinerary of Greece, in which he thus expresses
himself:—
"The confusion of the modern with the ancient names of places in this
volume is absolutely unavoidable; they are, however, mentioned in such
a manner, that the reader will soon be accustomed to the
indiscriminate use of them. The necessity of applying the ancient
appellations to the different routes, will be evident from the total
ignorance of the public on the subject of the modern names, which,
having never appeared in print, are only known to the few individuals
who have visited the country.
"What could appear less intelligible to the reader, or less useful to
the traveller, than a route from Chione and Zaracca to Kutchukmadi,
from thence by Krabata to Schoenochorio, and by the mills of Peali,
while every one is in some degree acquainted with the names of
Stymphalus, Nemea, Mycenæ, Lyrceia, Lerna, and Tegea?"
Although this may be very true inasmuch as it relates to the reader, yet
to the traveller we must observe, in opposition to Mr. Gell, that
nothing can be less useful than the designation of his route according
to the ancient names. We might as well, and with as much chance of
arriving at the place of our destination, talk to a Hounslow post-boy
about making haste to Augusta, as apply to our Turkish guide in
modern Greece for a direction to Stymphalus, Nemea, Mycenæ, etc., etc.
This is neither more nor less than classical affectation; and it renders
Mr. Gell's book of much more confined use than it would otherwise have
been:— but we have some other and more important remarks to make on his
general directions to Grecian tourists; and we beg leave to assure our
readers that they are derived from travellers who have lately visited
Greece. In the first place, Mr. Cell is absolutely incautious enough to
recommend an interference on the part of English travellers with the
Minister at the Porte, in behalf of the Greeks.
"The folly of such
neglect (page 16, preface), in many instances, where the emancipation of
a district might often be obtained by the present of a snuff-box or a
watch, at Constantinople, and without the smallest danger of exciting
the jealousy of such a court as that of Turkey, will be acknowledged
when we are no longer able to rectify the error."
We have every reason
to believe, on the contrary, that the folly of half a dozen travellers,
taking this advice, might bring us into a war. "Never interfere with any
thing of the kind," is a much sounder and more political suggestion to
all English travellers in Greece.
Mr. Gell apologizes for the introduction of "his panoramic designs," as
he calls them, on the score of the great difficulty of giving any
tolerable idea of the face of a country in writing, and the ease with
which a very accurate knowledge of it may be acquired by maps and
panoramic designs. We are informed that this is not the case with many
of these designs. The small scale of the single map we have already
censured; and we have hinted that some of the drawings are not
remarkable for correct resemblance of their originals. The two nearer
views of the Gate of the Lions at Mycenæ are indeed good likenesses of
their subject, and the first of them is unusually well executed; but the
general view of Mycenæ is not more than tolerable in any respect; and
the prospect of Larissa, etc., is barely equal to the former. The view
from this last place is also indifferent; and we are positively
assured that there are no windows at Nauplia which look like a box of
dominos, — the idea suggested by Mr. Gell's plate. We must not, however,
be too severe on these picturesque bagatelles, which, probably, were
very hasty sketches; and the circumstances of weather, etc., may have
occasioned some difference in the appearance of the same objects to
different spectators. We shall therefore return to Mr. Gell's preface;
endeavouring to set him right in his directions to travellers, where we
think that he is erroneous, and adding what appears to have been
omitted. In his first sentence, he makes an assertion which is by no
means correct. He says, "We are at present as ignorant of Greece, as
of the interior of Africa." Surely not quite so ignorant; or several of
our Grecian Mungo Parks have travelled in vain, and some very
sumptuous works have been published to no purpose! As we proceed, we
find the author observing that "Athens is now the most polished
city of "Greece," when we believe it to be the most barbarous, even to a
proverb —
is a couplet of reproach now applied to this once famous city;
whose inhabitants seem little worthy of the inspiring call which was
addressed to them within these twenty years, by the celebrated Riga:—
Iannina, the capital of Epirus, and the seat of Ali Pacha's government,
is in truth deserving of the honours which Mr. Gell has
improperly bestowed on degraded Athens. As to the correctness of the
remark concerning the fashion of wearing the hair cropped in
Molossia, as Mr. Gell informs us, our authorities cannot depose;
but why will he use the classical term of Eleuthero-Lacones, when that
people are so much better known by their modern name of Mainotes? "The
court of the Pacha of Tripolizza" is said "to realise the splendid
visions of the Arabian Nights." This is true with regard to the
court; but surely the traveller ought to have added that the city
and palace are most miserable, and form an extraordinary contrast to the
splendour of the court. — Mr. Gell mentions gold mines in Greece:
he should have specified their situation, as it certainly is not
universally known. When, also, he remarks that "the first article of
necessity in Greece is a firman, or order from the Sultan,
permitting the traveller to pass unmolested," we are much misinformed if
he be right. On the contrary, we believe this to be almost the only part
of the Turkish dominions in which a firman is not necessary; since the
passport of the Pacha is absolute within his territory (according to Mr.
G.'s own admission), and much more effectual than a firman. —
"Money," he remarks, "is easily procured at Salonica, or Patrass, where
the English have consuls." It is much better procured, we understand,
from the Turkish governors, who never charge discount. The consuls for
the English are not of the most magnanimous order of Greeks, and far
from being so liberal, generally speaking; although there are, in
course, some exceptions, and Strané of Patras has been more honourably
mentioned. — After having observed that "horses seem the best mode of
conveyance in Greece," Mr. Gell proceeds: "Some travellers would prefer
an English saddle; but a saddle of this sort is always objected to by
the owner of the horse, and not without reason," etc. This, we learn,
is far from being the case; and, indeed, for a very simple reason, an
English saddle must seem to be preferable to one of the country, because
it is much lighter. When, too, Mr. Gell calls the postillion
"Menzilgi," he mistakes him for his betters; Serrugees are
postillions; Menzilgis are postmasters. — Our traveller was fortunate
in his Turks, who are hired to walk by the side of the baggage-horses.
They "are certain," he says, "of performing their engagement without
grumbling." We apprehend that this is by no means certain:— but Mr. Gell
is perfectly right in preferring a Turk to a Greek for this purpose; and
in his general recommendation to take a Janissary on the tour: who, we
may add, should be suffered to act as he pleases, since nothing is to be
done by gentle means, or even by offers of money, at the places of
accommodation. A courier, to be sent on before to the place at which the
traveller intends to sleep, is indispensable to comfort; but no tourist
should be misled by the author's advice to suffer the Greeks to gratify
their curiosity, in permitting them to remain for some time about him on
his arrival at an inn. They should be removed as soon as possible; for,
as to the remark that "no stranger would think of intruding when a room
is pre-occupied," our informants were not so well convinced of that
fact.
Though we have made the above exceptions to the accuracy of Mr. Gell's
information, we are most ready to do justice to the general utility of
his directions, and can certainly concede the praise which he is
desirous of obtaining, — namely, "of having facilitated the researches of
future travellers, by affording that local information which it was
before impossible to obtain." This book, indeed, is absolutely necessary
to any person who wishes to explore the Morea advantageously; and we
hope that Mr. Gell will continue his Itinerary over that and over every
other part of Greece. He allows that his volume "is only calculated to
become a book of reference, and not of general entertainment;" but we do
not see any reason against the compatibility of both objects in a survey
of the most celebrated country of the ancient world. To that country, we
trust, the attention not only of our travellers, but of our legislators,
will hereafter be directed. The greatest caution will, indeed, be
required, as we have premised, in touching on so delicate a subject as
the amelioration of the possessions of an ally: but the field for the
exercise of political sagacity is wide and inviting in this portion of
the globe; and Mr. Gell, and all other writers who interest us, however
remotely, in its extraordinary capabilities, deserve well of the
British empire. We shall conclude by an extract from the author's work:
which, even if it fails of exciting that general interest which we hope
most earnestly it may attract towards its important subject, cannot, as
he justly observes, "be entirely uninteresting to the scholar;" since it
is a work "which gives him a faithful description of the remains of
cities, the very existence of which was doubtful, as they perished
before the æra of authentic history." The subjoined quotation is a good
specimen of the author's minuteness of research as a topographer; and we
trust that the credit which must accrue to him from the present
performance will ensure the completion of his Itinerary:—
"The inaccuracies of the maps of Anacharsis are in many respects very
glaring. The situation of Phlius is marked by Strabo as surrounded by
the territories of Sicyon, Argos, Cleonæ, and Stymphalus. Mr. Hawkins
observed, that Phlius, the ruins of which still exist near Agios
Giorgios, lies in a direct line between Cleonæ and Stymphalus, and
another from Sicyon to Argos; so that Strabo was correct in saying
that it lay between those four towns; yet we see Phlius, in the map of
Argolis by M. Barbie du Bocage, placed ten miles to the north of
Stymphalus, contradicting both history and fact. D'Anville is guilty
of the same error.
M. du Bocage places a town named Phlius, and by him Phlionte, on the
point of land which forms the port of Drepano; there are not at
present any ruins there. The maps of D'Anville are generally more
correct than any others where ancient geography is concerned. A
mistake occurs on the subject of Tiryns, and a place named by him
Vathia, but of which nothing can be understood. It is possible that
Vathi, or the profound valley, may be a name sometimes used for the
valley of Barbitsa, and that the place named by D'Anville Claustra may
be the outlet of that valley called Kleisoura, which has a
corresponding signification.
The city of Tiryns is also placed in two different positions, once by
its Greek name, and again as Tirynthus. The mistake between the
islands of Sphæria and Calaura has been noticed in page 135. The
Pontinus, which D'Anville represents as a river, and the Erasinus, are
equally ill placed in his map. There was a place called Creopolis,
somewhere toward Cynouria; but its situation is not easily fixed. The
ports called Bucephalium and Piræus seem to have been nothing more
than little bays in the country between Corinth and Epidaurus. The
town called Athenæ, in Cynouria, by Pausanias, is called Anthena by
Thucydides, book 5. 41.
In general, the map of D'Anville will be found more accurate than
those which have been published since his time; indeed, the mistakes
of that geographer are in general such as could not be avoided without
visiting the country. Two errors of D'Anville may be mentioned, lest
the opportunity of publishing the itinerary of Arcadia should never
occur. The first is, that the rivers Malætas and Mylaon, near
Methydrium, are represented as running toward the south, whereas they
flow northwards to the Ladon; and the second is, that the Aroanius,
which falls into the Erymanthus at Psophis, is represented as flowing
from the lake of Pheneos; a mistake which arises from the ignorance of
the ancients themselves who have written on the subject. The fact is
that the Ladon receives the waters of the lakes of Orchomenos and
Pheneos; but the Aroanius rises at a spot not two hours distant from
Psophis."
In furtherance of our principal object in this critique, we have only to
add a wish that some of our Grecian tourists, among the fresh articles
of information concerning Greece which they have lately imported, would
turn their minds to the language of the country. So strikingly similar
to the ancient Greek is the modern Romaic as a written language, and so
dissimilar in sound, that even a few general rules concerning
pronunciation would be of most extensive use.
Footnote 1: We have it from the best authority that the venerable
leader of the Anti-Homeric sect, Jacob Bryant, several years before his
death, expressed regret for his ungrateful attempt to destroy some of
the most pleasing associations of our youthful studies. One of his last
wishes was — "Trojaque nunc slaves" etc.
return to footnote mark
Footnote 2: Or, rather, map; for we have only one in the volume,
and that is on too small a scale to give more than a general idea of the
relative position of places. The excuse about a larger map not folding
well is trifling; see, for instance, the author's own map of Ithaca.
return
Footnote 3: See his Vindication of the 15th and 16th chapters of the
Decline and Fall, etc.
return
Footnote 4: "Sweet acorns." Does Mr. Gell translate from the Latin?
To avoid similar cause of mistake,  should not be
rendered suavem, but gratam, as Barnes has given it.
should not be
rendered suavem, but gratam, as Barnes has given it.
return
Footnote 5: We write these lines from the recitation of the travellers to
whom we have alluded; but we cannot vouch for the correctness of
the Romaic.
return
Contents
End of Text
End of the Project Gutenberg EBook of The Works Of Lord Byron, Letters and
Journals, Vol. 1, by Lord Byron
*** END OF THIS PROJECT GUTENBERG EBOOK BYRON, LETTERS AND JOURNALS, VOL 1 ***
***** This file should be named 8901-h.htm or 8901-h.zip *****
This and all associated files of various formats will be found in:
http://www.gutenberg.org/8/9/0/8901/
Produced by Distributed Proofreaders
Updated editions will replace the previous one--the old editions will
be renamed.
Creating the works from print editions not protected by U.S. copyright
law means that no one owns a United States copyright in these works,
so the Foundation (and you!) can copy and distribute it in the United
States without permission and without paying copyright
royalties. Special rules, set forth in the General Terms of Use part
of this license, apply to copying and distributing Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic works to protect the PROJECT GUTENBERG-tm
concept and trademark. Project Gutenberg is a registered trademark,
and may not be used if you charge for the eBooks, unless you receive
specific permission. If you do not charge anything for copies of this
eBook, complying with the rules is very easy. You may use this eBook
for nearly any purpose such as creation of derivative works, reports,
performances and research. They may be modified and printed and given
away--you may do practically ANYTHING in the United States with eBooks
not protected by U.S. copyright law. Redistribution is subject to the
trademark license, especially commercial redistribution.
START: FULL LICENSE
THE FULL PROJECT GUTENBERG LICENSE
PLEASE READ THIS BEFORE YOU DISTRIBUTE OR USE THIS WORK
To protect the Project Gutenberg-tm mission of promoting the free
distribution of electronic works, by using or distributing this work
(or any other work associated in any way with the phrase "Project
Gutenberg"), you agree to comply with all the terms of the Full
Project Gutenberg-tm License available with this file or online at
www.gutenberg.org/license.
Section 1. General Terms of Use and Redistributing Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic works
1.A. By reading or using any part of this Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic work, you indicate that you have read, understand, agree to
and accept all the terms of this license and intellectual property
(trademark/copyright) agreement. If you do not agree to abide by all
the terms of this agreement, you must cease using and return or
destroy all copies of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works in your
possession. If you paid a fee for obtaining a copy of or access to a
Project Gutenberg-tm electronic work and you do not agree to be bound
by the terms of this agreement, you may obtain a refund from the
person or entity to whom you paid the fee as set forth in paragraph
1.E.8.
1.B. "Project Gutenberg" is a registered trademark. It may only be
used on or associated in any way with an electronic work by people who
agree to be bound by the terms of this agreement. There are a few
things that you can do with most Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works
even without complying with the full terms of this agreement. See
paragraph 1.C below. There are a lot of things you can do with Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic works if you follow the terms of this
agreement and help preserve free future access to Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic works. See paragraph 1.E below.
1.C. The Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation ("the
Foundation" or PGLAF), owns a compilation copyright in the collection
of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works. Nearly all the individual
works in the collection are in the public domain in the United
States. If an individual work is unprotected by copyright law in the
United States and you are located in the United States, we do not
claim a right to prevent you from copying, distributing, performing,
displaying or creating derivative works based on the work as long as
all references to Project Gutenberg are removed. Of course, we hope
that you will support the Project Gutenberg-tm mission of promoting
free access to electronic works by freely sharing Project Gutenberg-tm
works in compliance with the terms of this agreement for keeping the
Project Gutenberg-tm name associated with the work. You can easily
comply with the terms of this agreement by keeping this work in the
same format with its attached full Project Gutenberg-tm License when
you share it without charge with others.
1.D. The copyright laws of the place where you are located also govern
what you can do with this work. Copyright laws in most countries are
in a constant state of change. If you are outside the United States,
check the laws of your country in addition to the terms of this
agreement before downloading, copying, displaying, performing,
distributing or creating derivative works based on this work or any
other Project Gutenberg-tm work. The Foundation makes no
representations concerning the copyright status of any work in any
country outside the United States.
1.E. Unless you have removed all references to Project Gutenberg:
1.E.1. The following sentence, with active links to, or other
immediate access to, the full Project Gutenberg-tm License must appear
prominently whenever any copy of a Project Gutenberg-tm work (any work
on which the phrase "Project Gutenberg" appears, or with which the
phrase "Project Gutenberg" is associated) is accessed, displayed,
performed, viewed, copied or distributed:
This eBook is for the use of anyone anywhere in the United States and
most other parts of the world at no cost and with almost no
restrictions whatsoever. You may copy it, give it away or re-use it
under the terms of the Project Gutenberg License included with this
eBook or online at www.gutenberg.org. If you are not located in the
United States, you'll have to check the laws of the country where you
are located before using this ebook.
1.E.2. If an individual Project Gutenberg-tm electronic work is
derived from texts not protected by U.S. copyright law (does not
contain a notice indicating that it is posted with permission of the
copyright holder), the work can be copied and distributed to anyone in
the United States without paying any fees or charges. If you are
redistributing or providing access to a work with the phrase "Project
Gutenberg" associated with or appearing on the work, you must comply
either with the requirements of paragraphs 1.E.1 through 1.E.7 or
obtain permission for the use of the work and the Project Gutenberg-tm
trademark as set forth in paragraphs 1.E.8 or 1.E.9.
1.E.3. If an individual Project Gutenberg-tm electronic work is posted
with the permission of the copyright holder, your use and distribution
must comply with both paragraphs 1.E.1 through 1.E.7 and any
additional terms imposed by the copyright holder. Additional terms
will be linked to the Project Gutenberg-tm License for all works
posted with the permission of the copyright holder found at the
beginning of this work.
1.E.4. Do not unlink or detach or remove the full Project Gutenberg-tm
License terms from this work, or any files containing a part of this
work or any other work associated with Project Gutenberg-tm.
1.E.5. Do not copy, display, perform, distribute or redistribute this
electronic work, or any part of this electronic work, without
prominently displaying the sentence set forth in paragraph 1.E.1 with
active links or immediate access to the full terms of the Project
Gutenberg-tm License.
1.E.6. You may convert to and distribute this work in any binary,
compressed, marked up, nonproprietary or proprietary form, including
any word processing or hypertext form. However, if you provide access
to or distribute copies of a Project Gutenberg-tm work in a format
other than "Plain Vanilla ASCII" or other format used in the official
version posted on the official Project Gutenberg-tm web site
(www.gutenberg.org), you must, at no additional cost, fee or expense
to the user, provide a copy, a means of exporting a copy, or a means
of obtaining a copy upon request, of the work in its original "Plain
Vanilla ASCII" or other form. Any alternate format must include the
full Project Gutenberg-tm License as specified in paragraph 1.E.1.
1.E.7. Do not charge a fee for access to, viewing, displaying,
performing, copying or distributing any Project Gutenberg-tm works
unless you comply with paragraph 1.E.8 or 1.E.9.
1.E.8. You may charge a reasonable fee for copies of or providing
access to or distributing Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works
provided that
* You pay a royalty fee of 20% of the gross profits you derive from
the use of Project Gutenberg-tm works calculated using the method
you already use to calculate your applicable taxes. The fee is owed
to the owner of the Project Gutenberg-tm trademark, but he has
agreed to donate royalties under this paragraph to the Project
Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation. Royalty payments must be paid
within 60 days following each date on which you prepare (or are
legally required to prepare) your periodic tax returns. Royalty
payments should be clearly marked as such and sent to the Project
Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation at the address specified in
Section 4, "Information about donations to the Project Gutenberg
Literary Archive Foundation."
* You provide a full refund of any money paid by a user who notifies
you in writing (or by e-mail) within 30 days of receipt that s/he
does not agree to the terms of the full Project Gutenberg-tm
License. You must require such a user to return or destroy all
copies of the works possessed in a physical medium and discontinue
all use of and all access to other copies of Project Gutenberg-tm
works.
* You provide, in accordance with paragraph 1.F.3, a full refund of
any money paid for a work or a replacement copy, if a defect in the
electronic work is discovered and reported to you within 90 days of
receipt of the work.
* You comply with all other terms of this agreement for free
distribution of Project Gutenberg-tm works.
1.E.9. If you wish to charge a fee or distribute a Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic work or group of works on different terms than
are set forth in this agreement, you must obtain permission in writing
from both the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation and The
Project Gutenberg Trademark LLC, the owner of the Project Gutenberg-tm
trademark. Contact the Foundation as set forth in Section 3 below.
1.F.
1.F.1. Project Gutenberg volunteers and employees expend considerable
effort to identify, do copyright research on, transcribe and proofread
works not protected by U.S. copyright law in creating the Project
Gutenberg-tm collection. Despite these efforts, Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic works, and the medium on which they may be stored, may
contain "Defects," such as, but not limited to, incomplete, inaccurate
or corrupt data, transcription errors, a copyright or other
intellectual property infringement, a defective or damaged disk or
other medium, a computer virus, or computer codes that damage or
cannot be read by your equipment.
1.F.2. LIMITED WARRANTY, DISCLAIMER OF DAMAGES - Except for the "Right
of Replacement or Refund" described in paragraph 1.F.3, the Project
Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation, the owner of the Project
Gutenberg-tm trademark, and any other party distributing a Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic work under this agreement, disclaim all
liability to you for damages, costs and expenses, including legal
fees. YOU AGREE THAT YOU HAVE NO REMEDIES FOR NEGLIGENCE, STRICT
LIABILITY, BREACH OF WARRANTY OR BREACH OF CONTRACT EXCEPT THOSE
PROVIDED IN PARAGRAPH 1.F.3. YOU AGREE THAT THE FOUNDATION, THE
TRADEMARK OWNER, AND ANY DISTRIBUTOR UNDER THIS AGREEMENT WILL NOT BE
LIABLE TO YOU FOR ACTUAL, DIRECT, INDIRECT, CONSEQUENTIAL, PUNITIVE OR
INCIDENTAL DAMAGES EVEN IF YOU GIVE NOTICE OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH
DAMAGE.
1.F.3. LIMITED RIGHT OF REPLACEMENT OR REFUND - If you discover a
defect in this electronic work within 90 days of receiving it, you can
receive a refund of the money (if any) you paid for it by sending a
written explanation to the person you received the work from. If you
received the work on a physical medium, you must return the medium
with your written explanation. The person or entity that provided you
with the defective work may elect to provide a replacement copy in
lieu of a refund. If you received the work electronically, the person
or entity providing it to you may choose to give you a second
opportunity to receive the work electronically in lieu of a refund. If
the second copy is also defective, you may demand a refund in writing
without further opportunities to fix the problem.
1.F.4. Except for the limited right of replacement or refund set forth
in paragraph 1.F.3, this work is provided to you 'AS-IS', WITH NO
OTHER WARRANTIES OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT
LIMITED TO WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR ANY PURPOSE.
1.F.5. Some states do not allow disclaimers of certain implied
warranties or the exclusion or limitation of certain types of
damages. If any disclaimer or limitation set forth in this agreement
violates the law of the state applicable to this agreement, the
agreement shall be interpreted to make the maximum disclaimer or
limitation permitted by the applicable state law. The invalidity or
unenforceability of any provision of this agreement shall not void the
remaining provisions.
1.F.6. INDEMNITY - You agree to indemnify and hold the Foundation, the
trademark owner, any agent or employee of the Foundation, anyone
providing copies of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works in
accordance with this agreement, and any volunteers associated with the
production, promotion and distribution of Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic works, harmless from all liability, costs and expenses,
including legal fees, that arise directly or indirectly from any of
the following which you do or cause to occur: (a) distribution of this
or any Project Gutenberg-tm work, (b) alteration, modification, or
additions or deletions to any Project Gutenberg-tm work, and (c) any
Defect you cause.
Section 2. Information about the Mission of Project Gutenberg-tm
Project Gutenberg-tm is synonymous with the free distribution of
electronic works in formats readable by the widest variety of
computers including obsolete, old, middle-aged and new computers. It
exists because of the efforts of hundreds of volunteers and donations
from people in all walks of life.
Volunteers and financial support to provide volunteers with the
assistance they need are critical to reaching Project Gutenberg-tm's
goals and ensuring that the Project Gutenberg-tm collection will
remain freely available for generations to come. In 2001, the Project
Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation was created to provide a secure
and permanent future for Project Gutenberg-tm and future
generations. To learn more about the Project Gutenberg Literary
Archive Foundation and how your efforts and donations can help, see
Sections 3 and 4 and the Foundation information page at
www.gutenberg.org
Section 3. Information about the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation
The Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation is a non profit
501(c)(3) educational corporation organized under the laws of the
state of Mississippi and granted tax exempt status by the Internal
Revenue Service. The Foundation's EIN or federal tax identification
number is 64-6221541. Contributions to the Project Gutenberg Literary
Archive Foundation are tax deductible to the full extent permitted by
U.S. federal laws and your state's laws.
The Foundation's principal office is in Fairbanks, Alaska, with the
mailing address: PO Box 750175, Fairbanks, AK 99775, but its
volunteers and employees are scattered throughout numerous
locations. Its business office is located at 809 North 1500 West, Salt
Lake City, UT 84116, (801) 596-1887. Email contact links and up to
date contact information can be found at the Foundation's web site and
official page at www.gutenberg.org/contact
For additional contact information:
Dr. Gregory B. Newby
Chief Executive and Director
gbnewby@pglaf.org
Section 4. Information about Donations to the Project Gutenberg
Literary Archive Foundation
Project Gutenberg-tm depends upon and cannot survive without wide
spread public support and donations to carry out its mission of
increasing the number of public domain and licensed works that can be
freely distributed in machine readable form accessible by the widest
array of equipment including outdated equipment. Many small donations
($1 to $5,000) are particularly important to maintaining tax exempt
status with the IRS.
The Foundation is committed to complying with the laws regulating
charities and charitable donations in all 50 states of the United
States. Compliance requirements are not uniform and it takes a
considerable effort, much paperwork and many fees to meet and keep up
with these requirements. We do not solicit donations in locations
where we have not received written confirmation of compliance. To SEND
DONATIONS or determine the status of compliance for any particular
state visit www.gutenberg.org/donate
While we cannot and do not solicit contributions from states where we
have not met the solicitation requirements, we know of no prohibition
against accepting unsolicited donations from donors in such states who
approach us with offers to donate.
International donations are gratefully accepted, but we cannot make
any statements concerning tax treatment of donations received from
outside the United States. U.S. laws alone swamp our small staff.
Please check the Project Gutenberg Web pages for current donation
methods and addresses. Donations are accepted in a number of other
ways including checks, online payments and credit card donations. To
donate, please visit: www.gutenberg.org/donate
Section 5. General Information About Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works.
Professor Michael S. Hart was the originator of the Project
Gutenberg-tm concept of a library of electronic works that could be
freely shared with anyone. For forty years, he produced and
distributed Project Gutenberg-tm eBooks with only a loose network of
volunteer support.
Project Gutenberg-tm eBooks are often created from several printed
editions, all of which are confirmed as not protected by copyright in
the U.S. unless a copyright notice is included. Thus, we do not
necessarily keep eBooks in compliance with any particular paper
edition.
Most people start at our Web site which has the main PG search
facility: www.gutenberg.org
This Web site includes information about Project Gutenberg-tm,
including how to make donations to the Project Gutenberg Literary
Archive Foundation, how to help produce our new eBooks, and how to
subscribe to our email newsletter to hear about new eBooks.