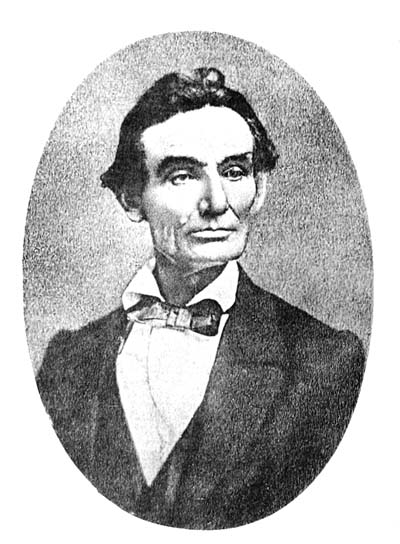




MAY 29, 1856

NEW YORK
PRINTED FOR THE COMMITTEE
1897
Copyright, 1896, by Sarah A. Whitney
THE DE VINNE PRESS
THE REPUBLICAN CLUB
Of the City of New York
| President. | |
| ARTHUR L. MERRIAM. | |
| First Vice-President. | Second Vice-President. |
| ELLIS H. ROBERTS. | W. M. K. OLCOTT. |
| Third Vice-President. | |
| LOUIS STERN. | |
| Recording Secretary. | Corresponding Secretary. |
| JOHN A. DUTTON. | JAMES L. WANDLING. |
| Treasurer. | |
| J. EDGAR LEAYCRAFT. | |

LINCOLN DINNER COMMITTEE
For 1897
| ELIHU ROOT, Chairman. | |
| MORTIMER C. ADDOMS. | JOHN R. TRESIDDER. |
| Treasurer. | Secretary. |
| EDMUND WETMORE. | J. CLARKE THOMAS. |
| WILLIAM C. ROBERTS. | CORNELIUS N. BLISS. |
| Ex Officio. | |
THE lost speech of Abraham Lincoln was delivered at the first Republican State Convention of Illinois, at Bloomington, on the 29th of May, 1856. The excitement caused among the audience by the speech was so great that the reporters forgot to take their notes, and for many years it was generally supposed that no record of the speech had been preserved. It appears, however, that Mr. H. C. Whitney, then a young lawyer of Illinois, did take notes of the speech, which he preserved; and after a lapse of forty years they were transcribed and were published in “McClure’s Magazine” for September, 1896, together with a letter from Mr. Joseph Medill, of the “Chicago Tribune,” who was present at the Convention and confirms the accuracy of Mr. Whitney’s report.
By the kind consent of Mr. Whitney, and through the courtesy of Mr. S. S. McClure, the speech is now reproduced by the Republican Club of the City of New York as a souvenir of Lincoln for its Annual Dinner on the 12th of February, 1897.
MR. Chairman and Gentlemen: I was over at—[Cries of “Platform!” “Take the platform!”] I say, that while I was at Danville Court, some of our friends of anti-Nebraska got together in Springfield and elected me as one delegate to represent old Sangamon with them in this convention, and I am here certainly as a sympathizer in this movement and by virtue of that meeting and selection. But we can hardly be called delegates strictly, inasmuch as, properly speaking, we represent[10] nobody but ourselves. I think it altogether fair to say that we have no anti-Nebraska party in Sangamon, although there is a good deal of anti-Nebraska feeling there; but I say for myself, and I think I may speak also for my colleagues, that we who are here fully approve of the platform and of all that has been done [A voice: “Yes!”]; and even if we are not regularly delegates, it will be right for me to answer your call to speak. I suppose we truly stand for the public sentiment of Sangamon on the great question of the repeal, although we do not yet represent many numbers who have taken a distinct position on the question.
We are in a trying time—it ranges above mere party—and this movement to call a halt and turn our steps backward needs all the help and good counsels it can get; for unless popular opinion makes itself very strongly felt, and a change is made in our present course, blood will flow[11] on account of Nebraska, and brother’s hand will be raised against brother! [The last sentence was uttered in such an earnest, impressive, if not indeed tragic, manner as to make a cold chill creep over me. Others gave a similar experience.]
I have listened with great interest to the earnest appeal made to Illinois men by the gentleman from Lawrence [James S. Emery] who has just addressed us so eloquently and forcibly. I was deeply moved by his statement of the wrongs done to free-State men out there. I think it just to say that all true men North should sympathize with them, and ought to be willing to do any possible and needful thing to right their wrongs. But we must not promise what we ought not, lest we be called on to perform what we cannot; we must be calm and moderate, and consider the whole difficulty, and determine what is possible and just. We must not be led by excitement and passion to do that which our sober judgments would not approve in[12] our cooler moments. We have higher aims; we will have more serious business than to dally with temporary measures.
We are here to stand firmly for a principle—to stand firmly for a right. We know that great political and moral wrongs are done, and outrages committed, and we denounce those wrongs and outrages, although we cannot, at present, do much more. But we desire to reach out beyond those personal outrages and establish a rule that will apply to all, and so prevent any future outrages.
We have seen to-day that every shade of popular opinion is represented here, with Freedom, or rather Free-Soil, as the basis. We have come together as in some sort representatives of popular opinion against the extension of slavery into territory now free in fact as well as by law, and the pledged word of the statesmen of the nation who are now no more. We come—we are here assembled together—to protest as well as we can against a great[13] wrong, and to take measures, as well as we now can, to make that wrong right; to place the nation, as far as it may be possible now, as it was before the repeal of the Missouri Compromise; and the plain way to do this is to restore the Compromise, and to demand and determine that Kansas shall be free! [Immense applause.] While we affirm, and reaffirm, if necessary, our devotion to the principles of the Declaration of Independence, let our practical work here be limited to the above. We know that there is not a perfect agreement of sentiment here on the public questions which might be rightfully considered in this convention, and that the indignation which we all must feel cannot be helped; but all of us must give up something for the good of the cause. There is one desire which is uppermost in the mind, one wish common to us all—to which no dissent will be made; and I counsel you earnestly to bury all resentment, to sink all personal feeling, make all things work to[14] a common purpose in which we are united and agreed about, and which all present will agree is absolutely necessary—which must be done by any rightful mode if there be such: Slavery must be kept out of Kansas! [Applause.] The test—the pinch—is right there. If we lose Kansas to freedom, an example will be set which will prove fatal to freedom in the end. We, therefore, in the language of the Bible, must “lay the axe to the root of the tree.” Temporizing will not do longer; now is the time for decision—for firm, persistent, resolute action. [Applause.]
The Nebraska bill, or rather Nebraska law, is not one of wholesome legislation, but was and is an act of legislative usurpation, whose result, if not indeed intention, is to make slavery national; and unless headed off in some effective way, we are in a fair way to see this land of boasted freedom converted into a land of slavery in fact. [Sensation.] Just open your two eyes, and see if this be not so.[15] I need do no more than state, to command universal approval, that almost the entire North, as well as a large following in the border States, is radically opposed to the planting of slavery in free territory. Probably in a popular vote throughout the nation nine-tenths of the voters in the free States, and at least one-half in the border States, if they could express their sentiments freely, would vote NO on such an issue; and it is safe to say that two-thirds of the votes of the entire nation would be opposed to it. And yet, in spite of this overbalancing of sentiment in this free country, we are in a fair way to see Kansas present itself for admission as a slave State. Indeed, it is a felony, by the local law of Kansas, to deny that slavery exists there even now. By every principle of law, a negro in Kansas is free; yet the bogus legislature makes it an infamous crime to tell him that he is free![1]
[16]The party lash and the fear of ridicule will overawe justice and liberty; for it is a singular fact, but none the less a fact, and well known by the most common experience, that men will do things under the terror of the party lash that they would not on any account or for any consideration do otherwise; while men who will march up to the mouth of a loaded cannon without shrinking will run from the terrible name of “Abolitionist,” even when pronounced by a worthless creature whom they, with good reason, despise. For instance—to press this point a little—Judge Douglas introduced his anti-Nebraska[17] bill in January; and we had an extra session of our legislature in the succeeding February, in which were seventy-five Democrats; and at a party caucus, fully attended, there were just three votes, out of the whole seventy-five, for the measure. But in a few days orders came on from Washington, commanding them to approve the measure; the party lash was applied, and it was brought up again in caucus, and passed by a large majority. The masses were against it, but party necessity carried it; and it was passed through the lower house of Congress against the will of the people, for the same reason. Here is where the greatest danger lies—that, while we profess to be a government of law and reason, law will give way to violence on demand of this awful and crushing power. Like the great Juggernaut—I think that is the name—the great idol, it crushes everything that comes in its way, and makes a—or as I read once, in a black-letter law[18] book, “a slave is a human being who is legally not a person but a thing.” And if the safeguards to liberty are broken down, as is now attempted, when they have made things of all the free negroes, how long, think you, before they will begin to make things of poor white men? [Applause.] Be not deceived. Revolutions do not go backward. The founder of the Democratic party declared that all men were created equal. His successor in the leadership has written the word “white” before men, making it read “all white men are created equal.” Pray, will or may not the Know-nothings, if they should get in power, add the word “protestant,” making it read “all protestant white men”?
Meanwhile the hapless negro is the fruitful subject of reprisals in other quarters. John Pettit, whom Tom Benton paid his respects to, you will recollect, calls the immortal Declaration “a self-evident lie”; while at the birthplace of freedom—in the shadow of Bunker Hill and of[19] the “cradle of liberty,” at the home of the Adamses and Warren and Otis—Choate, from our side of the house, dares to fritter away the birthday promise of liberty by proclaiming the Declaration to be “a string of glittering generalities”; and the Southern Whigs, working hand in hand with pro-slavery Democrats, are making Choate’s theories practical. Thomas Jefferson, a slaveholder, mindful of the moral element in slavery, solemnly declared that he “trembled for his country when he remembered that God is just”; while Judge Douglas, with an insignificant wave of the hand, “don’t care whether slavery is voted up or voted down.” Now, if slavery is right, or even negative, he has a right to treat it in this trifling manner. But if it is a moral and political wrong, as all Christendom considers it to be, how can he answer to God for this attempt to spread and fortify it? [Applause.]
But no man, and Judge Douglas no more than any other, can maintain a negative,[20] or merely neutral, position on this question; and, accordingly, he avows that the Union was made by white men and for white men and their descendants. As matter of fact, the first branch of the proposition is historically true; the government was made by white men, and they were and are the superior race. This I admit. But the corner-stone of the government, so to speak, was the declaration that “all men are created equal,” and all entitled to “life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness.” [Applause.]
And not only so, but the framers of the Constitution were particular to keep out of that instrument the word “slave,” the reason being that slavery would ultimately come to an end, and they did not wish to have any reminder that in this free country human beings were ever prostituted to slavery. [Applause.] Nor is it any argument that we are superior and the negro inferior—that he has but one talent while we have ten. Let the negro[21] possess the little he has in independence; if he has but one talent, he should be permitted to keep the little he has. [Applause.] But slavery will endure no test of reason or logic; and yet its advocates, like Douglas, use a sort of bastard logic, or noisy assumption, it might better be termed, like the above, in order to prepare the mind for the gradual, but none the less certain, encroachments of the Moloch of slavery upon the fair domain of freedom. But however much you may argue upon it, or smother it in soft phrases, slavery can only be maintained by force—by violence. The repeal of the Missouri Compromise was by violence. It was a violation of both law and the sacred obligations of honor, to overthrow and trample underfoot a solemn compromise, obtained by the fearful loss to freedom of one of the fairest of our Western domains. Congress violated the will and confidence of its constituents in voting for the bill; and while public sentiment, as shown by the[22] elections of 1854, demanded the restoration of this compromise, Congress violated its trust by refusing, simply because it had the force of numbers to hold on to it. And murderous violence is being used now, in order to force slavery on to Kansas; for it cannot be done in any other way. [Sensation.]
The necessary result was to establish the rule of violence—force, instead of the rule of law and reason; to perpetuate and spread slavery, and, in time, to make it general. We see it at both ends of the line. In Washington, on the very spot where the outrage was started, the fearless Sumner is beaten to insensibility, and is now slowly dying; while senators who claim to be gentlemen and Christians stood by, countenancing the act, and even applauding it afterward in their places in the Senate. Even Douglas, our man, saw it all and was within helping distance, yet let the murderous blows fall unopposed. Then, at the other end of the line, at the[23] very time Sumner was being murdered, Lawrence was being destroyed for the crime of Freedom. It was the most prominent stronghold of liberty in Kansas, and must give way to the all-dominating power of slavery. Only two days ago, Judge Trumbull found it necessary to propose a bill in the Senate to prevent a general civil war and to restore peace in Kansas.
We live in the midst of alarms; anxiety beclouds the future; we expect some new disaster with each newspaper we read. Are we in a healthful political state? Are not the tendencies plain? Do not the signs of the times point plainly the way in which we are going? [Sensation.]
In the early days of the Constitution slavery was recognized, by South and North alike, as an evil, and the division of sentiment about it was not controlled by geographical lines or considerations of climate, but by moral and philanthropic views. Petitions for the abolition of slavery[24] were presented to the very first Congress by Virginia and Massachusetts alike. To show the harmony which prevailed, I will state that a fugitive slave law was passed in 1793, with no dissenting voice in the Senate, and but seven dissenting votes in the House. It was, however, a wise law, moderate, and, under the Constitution, a just one. Twenty-five years later, a more stringent law was proposed and defeated; and thirty-five years after that, the present law, drafted by Mason of Virginia, was passed by Northern votes. I am not, just now, complaining of this law, but I am trying to show how the current sets; for the proposed law of 1817 was far less offensive than the present one. In 1774 the Continental Congress pledged itself, without a dissenting vote, to wholly discontinue the slave trade, and to neither purchase nor import any slave; and less than three months before the passage of the Declaration of Independence, the same Congress which adopted[25] that Declaration unanimously resolved “that no slave be imported into any of the thirteen United Colonies.” [Great applause.]
On the second day of July, 1776, the draft of a Declaration of Independence was reported to Congress by the committee, and in it the slave trade was characterized as “an execrable commerce,” as “a piratical warfare,” as the “opprobrium of infidel powers,” and as “a cruel war against human nature.” [Applause.] All agreed on this except South Carolina and Georgia, and in order to preserve harmony, and from the necessity of the case, these expressions were omitted. Indeed, abolition societies existed as far south as Virginia; and it is a well-known fact that Washington, Jefferson, Madison, Lee, Henry, Mason, and Pendleton were qualified abolitionists, and much more radical on that subject than we of the Whig and Democratic parties claim to be to-day. On March 1, 1784, Virginia ceded to the confederation all its lands lying northwest[26] of the Ohio River. Jefferson, Chase of Maryland, and Howell of Rhode Island, as a committee on that and territory thereafter to be ceded, reported that no slavery should exist after the year 1800. Had this report been adopted, not only the Northwest, but Kentucky, Tennessee, Alabama, and Mississippi also would have been free; but it required the assent of nine States to ratify it. North Carolina was divided, and thus its vote was lost; and Delaware, Georgia, and New Jersey refused to vote. In point of fact, as it was, it was assented to by six States. Three years later, on a square vote to exclude slavery from the Northwest, only one vote, and that from New York, was against it. And yet, thirty-seven years later, five thousand citizens of Illinois out of a voting mass of less than twelve thousand, deliberately, after a long and heated contest, voted to introduce slavery in Illinois; and, to-day, a large party in the free State of Illinois are willing to vote to[27] fasten the shackles of slavery on the fair domain of Kansas, notwithstanding it received the dowry of freedom long before its birth as a political community. I repeat, therefore, the question: Is it not plain in what direction we are tending? [Sensation.] In the colonial time, Mason, Pendleton, and Jefferson were as hostile to slavery in Virginia as Otis, Ames, and the Adamses were in Massachusetts; and Virginia made as earnest an effort to get rid of it as old Massachusetts did. But circumstances were against them, and they failed; but not that the good will of its leading men was lacking. Yet within less than fifty years Virginia changed its tune, and made negro-breeding for the cotton and sugar States one of its leading industries. [Laughter and applause.]
In the Constitutional Convention, George Mason of Virginia made a more violent abolition speech than my friends Lovejoy or Codding would desire to make here to-day—a speech which could not[28] be safely repeated anywhere on Southern soil in this enlightened year. But while there were some differences of opinion on this subject even then, discussion was allowed; but as you see by the Kansas slave code, which, as you know, is the Missouri slave code merely ferried across the river, it is a felony to even express an opinion hostile to that foul blot in the land of Washington and the Declaration of Independence. [Sensation.]
In Kentucky—my State—in 1849, on a test vote, the mighty influence of Henry Clay and many other good men there could not get a symptom of expression in favor of gradual emancipation on a plain issue of marching toward the light of civilization with Ohio and Illinois; but the State of Boone and Hardin and Henry Clay, with a nigger under each arm, took the black trail toward the deadly swamps of barbarism. Is there—can there be—any doubt about this thing? And is there any doubt that we must all lay aside our[29] prejudices and march, shoulder to shoulder, in the great army of Freedom? [Applause.]
Every Fourth of July our young orators all proclaim this to be “the land of the free and the home of the brave!” Well, now, when you orators get that off next year, and maybe this very year, how would you like some old grizzled farmer to get up in the grove and deny it? [Laughter.] How would you like that? But suppose Kansas comes in as a slave State, and all the “border ruffians” have barbecues about it, and free-State men come trailing back to the dishonored North, like whipped dogs with their tails between their legs, it is—ain’t it?—evident that this is no more the “land of the free”; and if we let it go so, we won’t dare to say “home of the brave” out loud. [Sensation and confusion.]
Can any man doubt that, even in spite of the people’s will, slavery will triumph through violence, unless that will be made[30] manifest and enforced? Even Governor Reeder claimed at the outset that the contest in Kansas was to be fair, but he got his eyes open at last; and I believe that, as a result of this moral and physical violence, Kansas will soon apply for admission as a slave State. And yet we can’t mistake that the people don’t want it so, and that it is a land which is free both by natural and political law. No law, is free law! Such is the understanding of all Christendom. In the Somerset case, decided nearly a century ago, the great Lord Mansfield held that slavery was of such a nature that it must take its rise in positive (as distinguished from natural) law; and that in no country or age could it be traced back to any other source. Will some one please tell me where is the positive law that establishes slavery in Kansas? [A voice: “The bogus laws.”] Aye, the bogus laws! And, on the same principle, a gang of Missouri horse-thieves could come into Illinois and declare horse-stealing[31] to be legal [laughter], and it would be just as legal as slavery is in Kansas. But by express statute, in the land of Washington and Jefferson, we may soon be brought face to face with the discreditable fact of showing to the world by our acts that we prefer slavery to freedom—darkness to light! [Sensation.]
It is, I believe, a principle in law that when one party to a contract violates it so grossly as to chiefly destroy the object for which it is made, the other party may rescind it. I will ask Browning if that ain’t good law. [Voices: “Yes!”] Well, now if that be right, I go for rescinding the whole, entire Missouri Compromise and thus turning Missouri into a free State; and I should like to know the difference—should like for any one to point out the difference—between our making a free State of Missouri and their making a slave State of Kansas. [Great applause.] There ain’t one bit of difference, except that our way would be a great mercy to humanity.[32] But I have never said—and the Whig party has never said—and those who oppose the Nebraska bill do not as a body say, that they have any intention of interfering with slavery in the slave States. Our platform says just the contrary. We allow slavery to exist in the slave States,—not because slavery is right or good, but from the necessities of our Union. We grant a fugitive slave law because it is so “nominated in the bond”; because our fathers so stipulated—had to—and we are bound to carry out this agreement. But they did not agree to introduce slavery in regions where it did not previously exist. On the contrary, they said by their example and teachings that they did not deem it expedient—did not consider it right—to do so; and it is wise and right to do just as they did about it [Voices: “Good!”], and that is what we propose—not to interfere with slavery where it exists (we have never tried to do it), and to give them a reasonable and efficient[33] fugitive slave law. [A voice: “No!”] I say YES! [Applause.] It was part of the bargain, and I’m for living up to it; but I go no further; I’m not bound to do more, and I won’t agree any further. [Great applause.]
We, here in Illinois, should feel especially proud of the provision of the Missouri Compromise excluding slavery from what is now Kansas; for an Illinois man, Jesse B. Thomas, was its father. Henry Clay, who is credited with the authorship of the Compromise in general terms, did not even vote for that provision, but only advocated the ultimate admission by a second compromise; and Thomas was, beyond all controversy, the real author of the “slavery restriction” branch of the Compromise. To show the generosity of the Northern members toward the Southern side: on a test vote to exclude slavery from Missouri, ninety voted not to exclude, and eighty-seven to exclude, every vote from the slave States being ranged[34] with the former and fourteen votes from the free States, of whom seven were from New England alone; while on a vote to exclude slavery from what is now Kansas, the vote was one hundred and thirty-four for, to forty-two against. The scheme, as a whole, was, of course, a Southern triumph. It is idle to contend otherwise, as is now being done by the Nebraskaites; it was so shown by the votes and quite as emphatically by the expressions of representative men. Mr. Lowndes of South Carolina was never known to commit a political mistake; his was the great judgment of that section; and he declared that this measure “would restore tranquillity to the country—a result demanded by every consideration of discretion, of moderation, of wisdom, and of virtue.” When the measure came before President Monroe for his approval, he put to each member of his cabinet this question: “Has Congress the constitutional power to prohibit slavery in a Territory?” And John[35] C. Calhoun and William H. Crawford from the South, equally with John Quincy Adams, Benjamin Rush, and Smith Thompson from the North, alike answered, “Yes!” without qualification or equivocation; and this measure, of so great consequence to the South, was passed; and Missouri was, by means of it, finally enabled to knock at the door of the Republic for an open passage to its brood of slaves. And, in spite of this, Freedom’s share is about to be taken by violence—by the force of misrepresentative votes, not called for by the popular will. What name can I, in common decency, give to this wicked transaction? [Sensation.]
But even then the contest was not over; for when the Missouri constitution came before Congress for its approval, it forbade any free negro or mulatto from entering the State. In short, our Illinois “black laws” were hidden away in their constitution [Laughter], and the controversy was thus revived. Then it was that Mr. Clay’s[36] talents shone out conspicuously, and the controversy that shook the Union to its foundation was finally settled to the satisfaction of the conservative parties on both sides of the line, though not to the extremists on either, and Missouri was admitted by the small majority of six in the lower House. How great a majority, do you think, would have been given had Kansas also been secured for slavery? [A voice: “A majority the other way.”] “A majority the other way,” is answered. Do you think it would have been safe for a Northern man to have confronted his constituents after having voted to consign both Missouri and Kansas to hopeless slavery? And yet this man Douglas, who misrepresents his constituents and who has exerted his highest talents in that direction, will be carried in triumph through the State and hailed with honor while applauding that act. [Three groans for “Dug!”] And this shows whither we are tending. This thing of slavery is[37] more powerful than its supporters—even than the high priests that minister at its altar. It debauches even our greatest men. It gathers strength, like a rolling snowball, by its own infamy. Monstrous crimes are committed in its name by persons collectively which they would not dare to commit as individuals. Its aggressions and encroachments almost surpass belief. In a despotism, one might not wonder to see slavery advance steadily and remorselessly into new dominions; but is it not wonderful, is it not even alarming, to see its steady advance in a land dedicated to the proposition that “all men are created equal”? [Sensation.]
It yields nothing itself; it keeps all it has, and gets all it can besides. It really came dangerously near securing Illinois in 1824; it did get Missouri in 1821. The first proposition was to admit what is now Arkansas and Missouri as one slave State. But the territory was divided, and Arkansas came in, without serious question, as a[38] slave State; and afterwards Missouri, not as a sort of equality, free, but also as a slave State. Then we had Florida and Texas; and now Kansas is about to be forced into the dismal procession. [Sensation.] And so it is wherever you look. We have not forgotten—it is but six years since—how dangerously near California came to being a slave State. Texas is a slave State, and four other slave States may be carved from its vast domain. And yet, in the year 1829, slavery was abolished throughout that vast region by a royal decree of the then sovereign of Mexico. Will you please tell me by what right slavery exists in Texas to-day? By the same right as, and no higher or greater than, slavery is seeking dominion in Kansas: by political force—peaceful, if that will suffice; by the torch (as in Kansas) and the bludgeon (as in the Senate chamber), if required. And so history repeats itself; and even as slavery has kept its course by craft, intimidation, and violence in the past, so it will[39] persist, in my judgment, until met and dominated by the will of a people bent on its restriction.
We have, this very afternoon, heard bitter denunciations of Brooks in Washington, and Titus, Stringfellow, Atchison, Jones, and Shannon in Kansas—the battle-ground of slavery. I certainly am not going to advocate or shield them; but they and their acts are but the necessary outcome of the Nebraska law. We should reserve our highest censure for the authors of the mischief, and not for the catspaws which they use. I believe it was Shakespeare who said, “Where the offence lies, there let the axe fall”; and, in my opinion, this man Douglas and the Northern men in Congress who advocate “Nebraska” are more guilty than a thousand Joneses and Stringfellows, with all their murderous practices, can be. [Applause.]
We have made a good beginning here to-day. As our Methodist friends would say, “I feel it is good to be here.” While[40] extremists may find some fault with the moderation of our platform, they should recollect that “the battle is not always to the strong, nor the race to the swift.” In grave emergencies, moderation is generally safer than radicalism; and as this struggle is likely to be long and earnest, we must not, by our action, repel any who are in sympathy with us in the main, but rather win all that we can to our standard. We must not belittle nor overlook the facts of our condition—that we are new and comparatively weak, while our enemies are entrenched and relatively strong. They have the administration and the political power; and, right or wrong, at present they have the numbers. Our friends who urge an appeal to arms with so much force and eloquence, should recollect that the government is arrayed against us, and that the numbers are now arrayed against us as well; or, to state it nearer to the truth, they are not yet expressly and affirmatively for us; and we should repel friends rather[41] than gain them by anything savoring of revolutionary methods. As it now stands, we must appeal to the sober sense and patriotism of the people. We will make converts day by day; we will grow strong by calmness and moderation; we will grow strong by the violence and injustice of our adversaries. And, unless truth be a mockery and justice a hollow lie, we will be in the majority after a while, and then the revolution which we will accomplish will be none the less radical from being the result of pacific measures. The battle of freedom is to be fought out on principle. Slavery is a violation of the eternal right. We have temporized with it from the necessities of our condition; but as sure as God reigns and school children read that black foul lie can never be consecrated into God’s hallowed truth! [Immense applause lasting some time.] One of our greatest difficulties is, that men who know that slavery is a detestable crime and ruinous to[42] the nation, are compelled, by our peculiar condition and other circumstances, to advocate it concretely, though damning it in the raw. Henry Clay was a brilliant example of this tendency; others of our purest statesmen are compelled to do so; and thus slavery secures actual support from those who detest it at heart. Yet Henry Clay perfected and forced through the Compromise which secured to slavery a great State as well as a political advantage; not that he hated slavery less, but that he loved the whole Union more. As long as slavery profited by his great Compromise, the hosts of pro-slavery could not sufficiently cover him with praise; but now that this Compromise stands in their way—
They have slaughtered one of his most cherished measures, and his ghost would arise to rebuke them. [Great applause.]
[43]Two years ago, at Springfield, Judge Douglas avowed that Illinois came into the Union as a slave State, and that slavery was weeded out by the operation of his great, patent, everlasting principle of “popular sovereignty.” [Laughter.] Well, now, that argument must be answered, for it has a little grain of truth at the bottom. I do not mean that it is true in essence, as he would have us believe. It could not be essentially true if the ordinance of ’87 was valid. But, in point of fact, there were some degraded beings called slaves in Kaskaskia and the other French settlements when our first State constitution was adopted; that is a fact, and I don’t deny it. Slaves were brought here as early as 1720, and were kept here in spite of the ordinance of 1787 against it. But slavery did not thrive here. On the contrary, under the influence of the ordinance, the number decreased fifty-one from 1810 to 1820; while under the influence of squatter sovereignty, right across the river[44] in Missouri, they increased seven thousand two hundred and eleven in the same time; and slavery finally faded out in Illinois, under the influence of the law of freedom, while it grew stronger and stronger in Missouri, under the law or practice of “popular sovereignty.” In point of fact, there were but one hundred and seventeen slaves in Illinois one year after its admission, or one to every four hundred and seventy of its population;[2] or, to state it in another way, if Illinois was a slave State in 1820, so were New York and New Jersey much greater slave States from having had greater numbers, slavery having been established there in very early times. But there is this vital difference between all these States and the judge’s Kansas experiment: that they sought to disestablish slavery which had been already established, while the judge seeks, so far[45] as he can, to disestablish freedom, which had been established there by the Missouri Compromise. [Voices: “Good!”]
Now, let us harmonize, my friends, and appeal to the moderation and patriotism of the people; to the sober second thought; to the awakened public conscience. The repeal of the sacred Missouri Compromise has installed the weapons of violence: the bludgeon, the incendiary torch, the death-dealing rifle, the bristling cannon—the weapons of kingcraft, of the Inquisition, of ignorance, of barbarism, of oppression. We see its fruits in the dying bed of the heroic Sumner; in the ruins of the “Free State” hotel; in the smoking embers of the “Herald of Freedom”; in the free-State Governor of Kansas chained to a stake on freedom’s soil like a horse-thief, for the crime of freedom. [Applause.] We see it in Christian statesmen, and Christian newspapers, and Christian pulpits applauding the cowardly act of a low bully, WHO CRAWLED UPON HIS VICTIM[46] BEHIND HIS BACK AND DEALT THE DEADLY BLOW. [Sensation and applause.] We note our political demoralization in the catch-words that are coming into such common use; on the one hand, “freedom-shriekers,” and sometimes “freedom-screechers” [Laughter]; and, on the other hand, “border ruffians,” and that fully deserved. And the significance of catch-words cannot pass unheeded, for they constitute a sign of the times. Everything in this world “jibes ” in with everything else, and all the fruits of this Nebraska bill are like the poisoned source from which they come. I will not say that we may not sooner or later be compelled to meet force by force; but the time has not yet come, and if we are true to ourselves, may never come. Do not mistake that the ballot is stronger than the bullet. Therefore let the legions of slavery use bullets; but let us wait patiently till November, and fire ballots at them in return; and by that peaceful policy[47] I believe we shall ultimately win. [Applause.]
It was by that policy that here in Illinois the early fathers fought the good fight, and gained the victory. In 1824 the free men of our State, led by Governor Coles (who was President Madison’s private secretary), determined that those beautiful groves should never reëcho the dirge of one who has no title to himself. By their resolute determination, the winds that sweep across our broad prairies shall never cool the parched brow, nor shall the unfettered streams that bring joy and gladness to our free soil water the tired feet, of a slave; but so long as those heavenly breezes and sparkling streams bless the land, or the groves and their fragrance or their memory remain, the humanity to which they minister SHALL BE FOREVER FREE! [Great applause.] Palmer, Yates, Williams, Browning, and some more in this convention came from Kentucky to Illinois (instead of going to Missouri), not[48] only to better their conditions, but also to get away from slavery. They have said so to me, and it is understood among us Kentuckians that we don’t like it one bit. Now, can we, mindful of the blessings of liberty which the early men of Illinois left to us, refuse a like privilege to the free men who seek to plant Freedom’s banner on our Western outposts? [“No! No!”] Should we not stand by our neighbors who seek to better their conditions in Kansas and Nebraska? [“Yes! Yes!”] Can we as Christian men, and strong and free ourselves, wield the sledge or hold the iron which is to manacle anew an already oppressed race? [“No! No!”] “Woe unto them,” it is written, “that decree unrighteous decrees and that write grievousness which they have prescribed.” Can we afford to sin any more deeply against human liberty? [“No! No!”]
One great trouble in the matter is, that slavery is an insidious and crafty power, and gains equally by open violence of the[49] brutal as well as by sly management of the peaceful. Even after the ordinance of 1787, the settlers in Indiana and Illinois (it was all one government then) tried to get Congress to allow slavery temporarily, and petitions to that end were sent from Kaskaskia, and General Harrison, the Governor, urged it from Vincennes, the capital. If that had succeeded, good-by to liberty here. But John Randolph of Virginia made a vigorous report against it; and although they persevered so well as to get three favorable reports for it, yet the United States Senate, with the aid of some slave States, finally squelched it for good. [Applause.] And that is why this hall is to-day a temple for free men instead of a negro livery-stable. [Great applause and laughter.] Once let slavery get planted in a locality, by ever so weak or doubtful a title, and in ever so small numbers, and it is like the Canada thistle or Bermuda grass—you can’t root it out. You yourself may detest slavery; but your neighbor has[50] five or six slaves, and he is an excellent neighbor, or your son has married his daughter, and they beg you to help save their property, and you vote against your interest and principles to accommodate a neighbor, hoping that your vote will be on the losing side. And others do the same; and in those ways slavery gets a sure foot-hold. And when that is done the whole mighty Union—the force of the Nation is committed to its support. And that very process is working in Kansas to-day. And you must recollect that the slave property is worth a billion of dollars; while free-State men must work for sentiment alone. Then there are “blue lodges”—as they call them—everywhere doing their secret and deadly work.
It is a very strange thing, and not solvable by any moral law that I know of, that if a man loses his horse, the whole country will turn out to help hang the thief; but if a man but a shade or two darker than I am is himself stolen, the[51] same crowd will hang one who aids in restoring him to liberty. Such are the inconsistencies of slavery, where a horse is more sacred than a man; and the essence of squatter or popular sovereignty—I don’t care how you call it—is that if one man chooses to make a slave of another, no third man shall be allowed to object. And if you can do this in free Kansas, and it is allowed to stand, the next thing you will see is ship-loads of negroes from Africa at the wharf at Charleston; for one thing is as truly lawful as the other; and these are the bastard notions we have got to stamp out, else they will stamp us out. [Sensation and applause.]
The Union is undergoing a fearful strain; but it is a stout old ship, and has weathered many a hard blow, and “the stars in their courses,” aye, an invisible power, greater than the puny efforts of men, will fight for us. But we ourselves must not decline the burden of responsibility, nor take counsel of unworthy passions. Whatever duty urges[52] us to do or to omit, must be done or omitted; and the recklessness with which our adversaries break the laws, or counsel their violation, should afford no example for us. Therefore, let us revere the Declaration of Independence; let us continue to obey the Constitution and the laws; let us keep step to the music of the Union. Let us draw a cordon, so to speak, around the slave States, and the hateful institution, like a reptile poisoning itself, will perish by its own infamy. [Applause.]
But we cannot be free men if this is, by our national choice, to be a land of slavery. Those who deny freedom to others deserve it not for themselves; and, under the rule of a just God, cannot long retain it. [Loud applause.]
Did you ever, my friends, seriously reflect upon the speed with which we are tending downwards? Within the memory of men now present the leading statesmen of Virginia could make genuine, red-hot abolitionist speeches in old Virginia; and,[53] as I have said, now even in “free Kansas” it is a crime to declare that it is “free Kansas.” The very sentiments that I and others have just uttered would entitle us, and each of us, to the ignominy and seclusion of a dungeon; and yet I suppose that, like Paul, we were “free born.” But if this thing is allowed to continue, it will be but one step further to impress the same rule in Illinois. [Sensation.]
The conclusion of all is, that we must restore the Missouri Compromise. We must highly resolve that Kansas must be free! [Great applause.] We must reinstate the birthday promise of the Republic; we must reaffirm the Declaration of Independence; we must make good in essence as well as in form Madison’s avowal that “the word slave ought not to appear in the Constitution”; and we must even go further, and decree that only local law, and not that time-honored instrument, shall shelter a slaveholder. We must make this a land of liberty in fact, as it is[54] in name. But in seeking to attain these results—so indispensable if the liberty which is our pride and boast shall endure—we will be loyal to the Constitution and to the “flag of our Union,” and no matter what our grievance—even though Kansas shall come in as a slave State; and no matter what theirs—even if we shall restore the Compromise—we will say to the Southern disunionists, We won’t go out of the Union, and you SHA’N’T!!! [This was the climax; the audience rose to its feet en masse, applauded, stamped, waved handkerchiefs, threw hats in the air, and ran riot for several minutes. The arch-enchanter who wrought this transformation looked, meanwhile, like the personification of political justice.]
But let us, meanwhile, appeal to the sense and patriotism of the people, and not to their prejudices; let us spread the floods of enthusiasm here aroused all over these vast prairies, so suggestive of freedom.[55] Let us commence by electing the gallant soldier [Colonel Bissell] governor, who stood for the honor of our State alike on the plains and amidst the chaparral of Mexico and on the floor of Congress, while he defied the Southern Hotspur; and that will have a greater moral effect than all the border ruffians can accomplish in all their raids on Kansas. There is both a power and a magic in popular opinion. To that let us now appeal; and while, in all probability, no resort to force will be needed, our moderation and forbearance will stand us in good stead when, if ever, we must make an appeal to battle and to the God of hosts!! [Immense applause and a rush for the orator.]
[1] Statutes of Kansas, 1855, Chapter 151, Sec. 12. If any free person, by speaking or by writing, assert or maintain that persons have not the right to hold slaves in this Territory, or shall introduce into this Territory, print, publish, write, circulate ... any book, paper, magazine, pamphlet, or circular containing any denial of the right of persons to hold slaves in this Territory, such person shall be deemed guilty of felony, and punished by imprisonment at hard labor for a term of not less than two years.
Sec. 13. No person who is conscientiously opposed to holding slaves, or who does not admit the right to hold slaves in this Territory, shall sit as a juror on the trial of any prosecution for any violation of any Sections of this Act.
[2] It is singular that Mr. Lincoln, usually so accurate, should have been entirely mistaken in his statistics at this point.—H. C. W.

TRANSCRIBER’S NOTES:
Obvious typographical errors have been corrected.
Inconsistencies in hyphenation have been standardized.
Archaic or alternate spelling has been retained from the original.