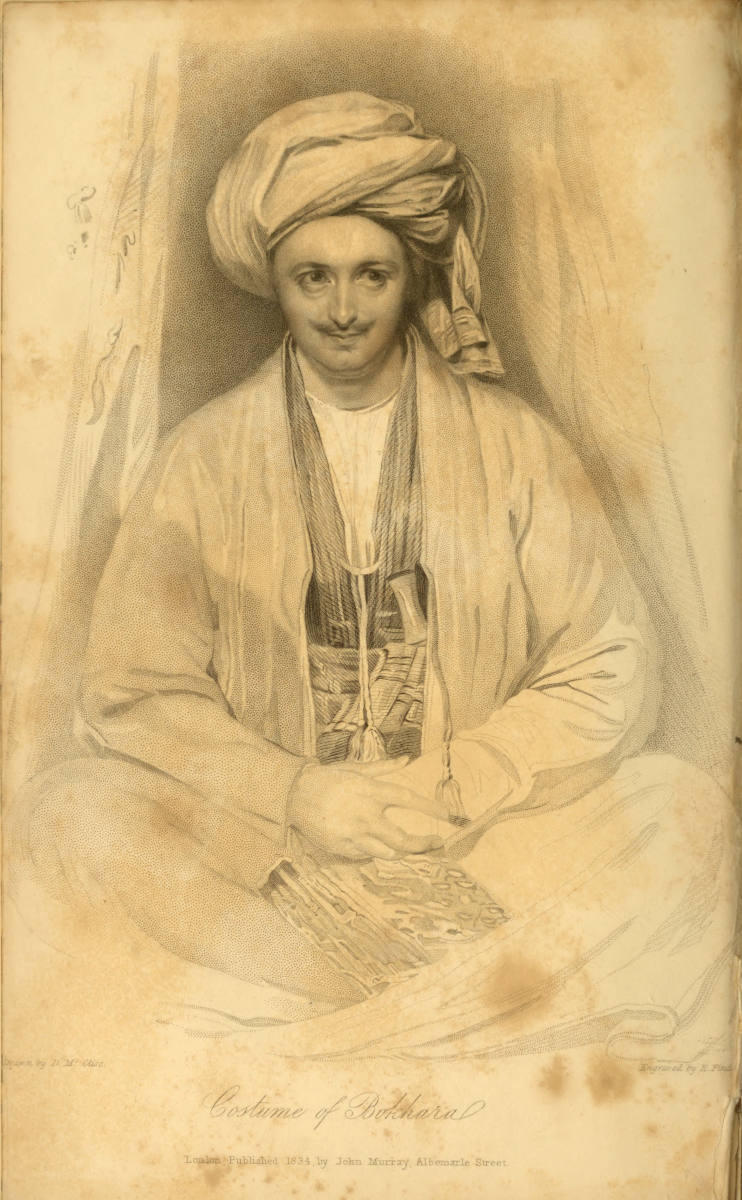

Drawn by D. Mc. Clise. Engraved by E. Find.
Costume of Bokhara
London, Published 1834, by John Murray, Albemarle Street.
Project Gutenberg's Travels into Bokhara (Volume 1 of 3), by Alexander Burnes
This eBook is for the use of anyone anywhere in the United States and
most other parts of the world at no cost and with almost no restrictions
whatsoever. You may copy it, give it away or re-use it under the terms
of the Project Gutenberg License included with this eBook or online at
www.gutenberg.org. If you are not located in the United States, you'll
have to check the laws of the country where you are located before using
this ebook.
Title: Travels into Bokhara (Volume 1 of 3)
Being the Account of A Journey from India to Cabool, Tartary, and Persia
Author: Alexander Burnes
Release Date: October 11, 2018 [EBook #58074]
Language: English
Character set encoding: UTF-8
*** START OF THIS PROJECT GUTENBERG EBOOK TRAVELS INTO BOKHARA (VOLUME ***
Produced by Henry Flower and the Online Distributed
Proofreading Team at http://www.pgdp.net (This file was
produced from images generously made available by The
Internet Archive/Canadian Libraries)
In the html edition of this eBook, the image on p. 183 is linked to a higher-resolution version of the illustration.
&c. &c.
VOL. I.
London:
Printed by A. Spottiswoode,
New-Street-Square.

Drawn by D. Mc. Clise. Engraved by E. Find.
Costume of Bokhara
London, Published 1834, by John Murray, Albemarle Street.
TRAVELS
INTO
BOKHARA;
BEING THE ACCOUNT OF
A JOURNEY FROM INDIA TO CABOOL, TARTARY,
AND PERSIA;
ALSO, NARRATIVE OF
A VOYAGE ON THE INDUS,
FROM THE SEA TO LAHORE,
WITH PRESENTS FROM THE KING OF GREAT BRITAIN;
PERFORMED UNDER THE ORDERS OF THE SUPREME GOVERNMENT
OF INDIA, IN THE YEARS 1831, 1832, AND 1833.
BY
LIEUT. ALEXR BURNES, F.R.S.
OF THE EAST INDIA COMPANY’S SERVICE;
AST POLITICAL RESIDENT IN CUTCH, AND LATE ON A MISSION TO
THE COURT of LAHORE.
IN THREE VOLUMES.
VOL. I.
LONDON:
JOHN MURRAY, ALBEMARLE STREET.
MDCCCXXXIV.
THESE
TRAVELS INTO BOKHARA
ARE INSCRIBED
TO THE RIGHT HONOURABLE
LORD WILLIAM CAVENDISH BENTINCK, G.C.B.
GOVERNOR-GENERAL OF INDIA,
&c. &c. &c.
UNDER WHOSE AUSPICES
THEY WERE UNDERTAKEN AND PERFORMED,
BY
HIS LORDSHIP’S MOST OBEDIENT,
FAITHFUL SERVANT,
ALEXR BURNES.
The following volumes contain the Narrative of my Voyage on the Indus, and subsequent Journey into Bokhara. I have thrown the Journey into the first two volumes, from its interest being, perhaps, greater than that of the Voyage; and since the two subjects, though parts of a whole, are distinct from each other.
| VOL. I. | |
| Plate I. | Costume of Bokhara, to face the title-page. |
| II. | Colossal Idols at Bameean, to face page 183. |
| (This is a double plate, and must be folded.) | |
| VOL. II. | |
| III. | Bactrian and other Coins, to face page 455. |
| IV. | Bactrian and other Coins, to face page 455. |
| VOL. III. | |
| V. | View of Hydrabad on the Indus, to face title-page. |
| VI. | Natives of Cutch, to face page 9. |
| VII. | Natives of Sinde, to face page 87. |
| VIII. | View of Sindree, to face page 309. |
N.B. Mr. John Arrowsmith’s Map, constructed expressly for this work, is sold separately by all booksellers, price, in sheets 7s., in cover 7s. 6d., and in case 10s.
On my return to Europe, I gave my original manuscript surveys, protractions, and the whole of the observations which I had made during a period of nine years, while employed in different surveys throughout Asia, together with such other authentic documents as I had collected, to Mr. John Arrowsmith.[1] He has embodied these in a large and comprehensive map, to illustrate this work; combining, at the same time, the latest and best information on the various countries within the limits of the map. The task has been most laborious; but the accuracy with which it has been performed will, I am sure, entitle him to the high approbation of the public: since this map throws a new light on the geography of this portion of the globe. It is due to Mr. Arrowsmith to state, that this map has been engraved at his own expense, and is now published, in the most public-spirited manner, at his own risk.
London, June, 1834.
In the year 1831, I was deputed in a political capacity to the Court of Lahore, charged with a letter from the King of England, and a present of some horses, to the ruler of that country. The principal object of my journey was to trace the course of the Indus; which had only been crossed at particular points by former travellers, and had never been surveyed but between Tatta and Hydrabad. My success in this undertaking, which was attended with many difficulties, and the sight of so many tribes hitherto little known, gave fresh strength to a desire that I had always felt to see new countries, and visit the conquests of Alexander. As the first European of modern times who had navigated the Indus, I now found myself stimulated to extend my journey beyond that[x] river—the scene of romantic achievements which I had read of in early youth with the most intense interest.
The design received the most liberal encouragement from the Governor-general of India, Lord William Bentinck, whom I joined at Simla, in the Himalaya Mountains, after the termination of my mission to Lahore. His Lordship was of opinion that a knowledge of the general condition of the countries through which I was to travel, would be useful to the British Government, independent of other advantages which might be expected from such a journey.
The hazardous nature of the expedition, and the mode in which it could be best accomplished, required consideration. It would have been objectionable, and highly imprudent, to have entered the countries lying between India and Europe, as I had voyaged on the Indus, an accredited agent; and I was directed to appear (which I myself had suggested) as a private individual.
I was furnished with passports as a Captain in the British army returning to Europe, drawn out in French, English, and Persian; and in such terms as would satisfy the people of my real character; and show, at the same time, that Government was interested in my good treatment.
Every other arrangement regarding the journey was left to myself; and I received the sanction of the Governor-general to associate with me Ensign John Leckie—a young officer of the most buoyant disposition, who had been the companion of my voyage up the Indus. On the eve of departure, my fellow-traveller was recalled by the Government of Bombay. Believing that his place might be well supplied by a medical gentleman, which I thought would facilitate our progress through such countries, I prevailed on Mr. James Gerard, a Surgeon of the Bengal army, to accompany me. That gentleman had passed most of his life in India, in traversing the Himalaya regions; and possessed an ardent desire for travel. I was also attended by a native Surveyor, Mahommed Ali, a public servant, who had been educated in[xii] the Engineer Institution of Bombay, under Captain G. Jervis, of the Engineers; and who had entitled himself to my utmost confidence by faithful and devoted conduct on many trying occasions during the voyage to Lahore.[2] I also took a Hindoo lad, of Cashmere family, named Mohun Lal, who had been educated at the English Institution at Delhi, as he would assist me in my Persian correspondence; the forms of which amount to a science in the East. His youth and his creed would, I believed, free me from all danger of his entering into intrigues with the people; and both he and the Surveyor proved themselves to be zealous and trustworthy men, devoted to our interests. Being natives, they could detach[xiii] themselves from us; and, by reducing our retinue, maintain our character for poverty, which I ever considered our best safeguard. We discharged the whole of our Indian servants but one individual, Ghoolam Hoosn, who demands my lasting gratitude for the hardships which he underwent on my account, and who is yet my faithful servant.
From the time I resolved to traverse the countries that lie between India and the Caspian, I determined to retain the character of a European, accommodating myself in dress, habits, and customs, to those with whom I should mingle. The sequel has proved that the design had much to recommend it, though the character involved us in some difficulties. I adopted the resolution, however, in an utter hopelessness of supporting the disguise of a native; and from having observed that no European traveller has ever journeyed in such countries without suspicion, and seldom without discovery. From long intercourse with Asiatics, I had acquired some insight into their character, and possessed at the same time a fair colloquial knowledge of the Persian language, the lingua franca of the people I[xiv] should meet. I did not, then, hesitate to appear among them in their own garb, and avow myself a foreigner. By all the accounts which I collected, it did not appear to me that there was any just cause for apprehending personal injury or danger; but I received little consolation from my friends in India, who referred to the fate of our predecessors, poor Moorcroft and his party, as our inevitable lot. I trust, however, that the happy termination of this journey will give a more favourable impression of the Asiatic character, and stimulate others (which I shall consider a high reward) to view and visit these lands.
Such is a brief detail of the circumstances which led me into these countries; the manner in which I have performed my task must be decided by the public. I have to solicit much indulgence, in the perusal of my book; I have had no assistance in its composition, and my career in the East has been one of constant employment. I am, however, deeply indebted to the Hon. Mountstuart Elphinstone, the late Governor of Bombay, for his advice in preparing for the press; and by which I have not failed to profit. If[xv] I had to congratulate myself on having reached my native shores in safety, I consider my good fortune great indeed, to have met a gentleman so eminently qualified to give me counsel. The aversion to display, for which Mr. Elphinstone is so distinguished, alone prevents my enlarging on this subject.
From Mr. James Bailie Fraser, the well-known author of the Kuzzilbash, and my esteemed friend and brother officer, Lieut. G. L. Jacob, of the Bombay army, I have received some judicious hints. To Mr. Horace Hayman Wilson, Sanscrit Professor in the University of Oxford, and Mr. James Prinsep, Secretary of the Asiatic Society of Bengal, my acknowledgments are due for illustrating my collection of coins: the notes of these gentlemen will speak for themselves.
To Captain R. M. Grindlay, author of a series of Views of Western India, I am indebted for most of the illustrations, which do ample credit to his talents and pencil. To my brother, Dr. David Burnes, who has assisted me in the laborious task of correcting the press, I offer my best thanks; which, I think, completes the whole of my obligations.
I have now only to express an anxious hope, that my fellow traveller, Dr. Gerard, who has not yet reached India, may soon be restored to his friends, to share in the approbation which has been bestowed, I fear too liberally, upon myself.
ALEXR BURNES.
London, June, 1834.
| CHAPTER I. | |
| LAHORE. | |
| Page | |
| [xviii]Departure from Delhi.—Communication from Runjeet Sing.—Himalaya.—Villages on the Sutlege: People.—Banks of the Sutlege.—Physical Phenomena of Rivers.—Altars of Alexander.—Enter the Punjab.—Our Welcome chanted.—Civilities at Hurree.—Seik Fanatics.—Manja; country so called.—Antient Canals.—Town of Puttee.—Stud of Horses at Puttee.—An Acali, or Fanatic.—A Seik Chief and his Castle.—Famous Road of Juhangeer.—Enter Lahore.—Visit the Maharaja.—Earthquake at Lahore.—Join Runjeet Sing in the Field.—Description of his Camp.—Runjeet Sing marching.—Conversations of Runjeet Sing.—Superb Cashmere Tents.—A Visit from the Physician-general.—Runjeet Sing sporting.—Conversations of Runjeet Sing.—Return to Lahore.—Festival of the Busunt, or Spring.—Entertainment by the Maharaja.—Preparations for our Journey.—Kindness of Messrs. Allard and Court.—Audience of Leave.—Mons. Court’s Instructions | 1-38 |
| CHAP. II. | |
| ACROSS THE PUNJAB TO THE INDUS. | |
| Quit Lahore.—Reduction of Baggage.—Arrangements.—Garden described.—Himalaya.—Reach the Chenab or Acesines.—Soil and Wells.—Sugar.—A Seik Chief.—Seiks: Peculiarities of the Tribe.—Cross the Chenab.—Diseases: Opinions regarding them.—Cross the Jelum, or Hydaspes.—Arrival at Pind Dadun Khan.—Antiquities.—Salt Mines of Pind Dadun Khan.—Position of the Salt Range.—Formation, &c.—Mines, Strata, Temperature.—Manner of working the Salt.—Its Quality.—Supply of the Mineral.—Banks of the Hydaspes.—Villages.—Scene of Porus’s Battle.—Extensive Ruins.—Speculations.—Nicæ and Bucephalia.—Porus’s Army compared with Runjeet Sing’s.—Floating Islands.—Costume of the Ladies.—Arrival at Rotas.—Fortress.—Nature and Formation of Rocks.—Tope of Manikyala.—Coins and Antiques.—Manikyala identified with Taxilla.—Rawil Pindee.—Marks of quitting India.—Hurdwar Pilgrims: Reflections on seeing them.—Seik Priest.—Pass of Margulla.—Tope of Belur.—Garden of Hoosn Abdall.—See the Indus.—Encamp on the Indus.—Ford it.—Story of a Soldier.—Attok.—Phenomenon at Attok.—Washing Gold | 39-80 |
| CHAP. III. | |
| PESHAWUR. | |
| [xix]Entrance into the Country of the Afghans.—Precautionary Arrangements.—Farewell Letter to Runjeet Sing.—Salt Monopoly.—Fields of Battle.—Entrance into Peshawur.—Afghan Entertainment.—Visitors.—Ride out with the Chief.—His Character.—Afghan manner of spending Friday.—Horrible Spectacle.—Brother of the Chief.—Arrangements for our Advance.—The Chief and his Court.—Visitors.—Juvenile Intelligence.—Rambles in Peshawur.—Quail fighting.—Hawking.—Moollah Nujeeb.—A Saint.—Disadvantages of giving Medicine.—Antiquities.—Conclusions regarding the “Topes.”—Preparations for Departure.—Maître d’Hôtel of the Chief | 81-111 |
| CHAP. IV. | |
| JOURNEY TO CABOOL. | |
| Departure from Peshawur.—Khyberees.—Passage of the Cabool River.—Caravan.—Scene in the Cabool River.—Mountains.—Formation of the Hills.—Interview with a Momund Chief.—Civility of a Khyberee.—Incident.—Pestilential Wind.—Antiquities.—Julalabad.—Snowy Mountains.—Bala-bagh.—Treatment by the People.—Gundamuk.—Cold Countries.—Neemla.—Manner of keeping Horses.—Jugduluk.—Post-houses of the Emperors.—Wandering Ghiljees.—Pastoral Scenes.—Ispahan.—Story of Futtih Khan.—Pass of Luta-bund.—Arrival in Cabool.—Our Conductor, Mahommed Shureeff | 112-132 |
| CHAP. V. | |
| CABOOL. | |
| [xx]Arrival of Mr. Wolff.—Nawab Jubbar Khan.—Introduction to the Chief of Cabool.—Conversations.—Tomb of the Emperor Baber.—Prospect.—Intercourse with the People.—Cabool; its Bazars.—Traditions.—Coins.—Armenians.—Entertainment.—Gardens of Cabool.—Fruits and Wines.—Bala Hissar, or Prison.—Difference in Asiatic and European Manners.—Eed, or Festival.—Tomb of Timour Shah.—Alchymy and Minerals.—Freemasonry.—Jewish Origin of the Afghans; Opinions regarding it.—Party.—The Kaffirs, a singular People.—Preparations.—Shikarpooree Merchants.—Money Arrangements.—Civilisation by Commerce | 133-170 |
| CHAP. VI. | |
| JOURNEY OVER THE HINDOO KOOSH, OR SNOWY MOUNTAINS. | |
| Quit Cabool.—Cafila-bashee.—Contraband Korans.—Julraiz.—Valley of the Cabool River.—Fish Preserve.—Ghuzni.—Pass of Oonna.—Effects of Snow.—Family of Huzaras.—Goître.—Ali Illahi.—Yezdan Buksh Huzara.—Pass of Hajeeguk and Kaloo.—Mountain Scenery.—Bameean excavated City.—Idols of Bameean.—Geographical Errors.—Leave Afghanistan.—Uzbek Chief of Syghan.—Feelings on entering Tartary.—Pass of Dundan Shikun.—Ruhmut oollah Khan.—Uzbek Pity.—Mahommedan Law.—Companions.—Asiatic Opinions of Europe.—Pass of Kara Koottul.—Adventures.—Life of a Traveller.—Modes of Salutation.—Tremendous Defiles.—Poisonous Plant.—Heibuk reptiles.—Houses.—People.—Khooloom and Plains of Tartary | 171-206 |
| CHAP. VII. | |
| SERIOUS DIFFICULTIES.—JOURNEY TO KOONDOOZ. | |
| [xxi]Difficulties at Khooloom.—Sketch of Moorcroft’s disasters.—Departure for Koondooz.—Favourable Opportunity for escape.—Night Adventure.—My Account of myself.—Imbecility of our Conductor.—Visiters, manner of Tea-drinking.—Traditions of Alexander the Great.—Interview with the Chief of Koondooz.—Incidents illustrative of Uzbek Character.—Koondooz; its Chief.—Departure from Koondooz.—Quit Khooloom.—Avaricious Conduct of our Conductor.—Dangers of the Road to Balkh.—Mirage.—Muzar.—Tomb of Mr. Trebeck.—Arrival at Balkh.—Intelligence of the Cafila-bashee | 207-236 |
| CHAP. VIII. | |
| BALKH, AND JOURNEY TO BOKHARA. | |
| Description of Balkh.—Climate.—Coins found at Balkh.—Cafila-bashee.—Grave of Mr. Moorcroft.—Quit Balkh.—Ancient Bactriana.—Correctness of Quintus Curtius.—Desert of the Toorkmuns.—Reach the Oxus.—Singular manner of crossing it.—The Caravan.—Kiz Kooduk.—A Khwaju.—Literature.—Amazons of Lakay.—Kirkinjuk.—A Slave.—Knotty Points.—Snowy Mountains.—Kurshee.—Sickness of our Party.—Alarms of a Traveller.—Letter to the Minister of Bokhara.—Kurshee.—Market at Karsan.—Uzbeks.—Abdoolla Khan; his Munificence.—Acquaintances.—Fatigues.—Reflections.—Arrival in Bokhara | 237-266 |
| CHAP. IX. | |
| BOKHARA. | |
| [xxii]Change of Dress.—Visit the Minister.—Suspicions regarding us.—Description of the Registan, or great Bazar of Bokhara.—Employments in the Bazar.—Society at Bokhara.—Slave Bazar at Bokhara.—Offenders against Mahommedanism.—Hindoos.—A Wanderer.—An Indian Sepoy.—A pretty Fair One.—Costume.—Baths of Bokhara.—Interview with the Minister.—The King.—Life of a King.—Russian Slaves.—Acquaintances at Bokhara | 267-299 |
| CHAP. X. | |
| BOKHARA. | |
| The City of Bokhara.—Historical Sketch of it.—Colleges of Bokhara.—Rigour of Mahommedanism.—Literature of Central Asia.—Interview with the Vizier.—Samarcand.—Tomb of Bhawa Deen.—An Ancient City, Coins, &c.—An Uzbek Family.—Bokhara on Friday.—Arrangements.—Farewell Visit to the Vizier.—Departure | 300-329 |
| CHAP. XI. | |
| DETENTION IN THE KINGDOM OF BOKHARA. | |
| Detention of the Caravan.—Assemblage of Merchants.—Country between Bokhara and the Oxus.—Intercourse with the Toorkmuns.—A Toorkmun Acquaintance.—Ersaree Toorkmuns.—Slavery in Toorkistan.—Fellow-travellers.—Music.—Our own Party.—Ruins of Bykund.—Alexander’s Marches.—Reply from the Khan of Orgunje.—Uzbek Customs.—Preparations for Departure.—Receive Letters from India.—Reflections | 330-356 |
In the end of December, 1831, I had the honour to obtain the final sanction of the Governor-general of India to proceed to Central Asia. I received my passports from his lordship at Delhi on the 23d of that month, and proceeded by express to Lodiana on the frontiers, where I had the pleasure of meeting my fellow-traveller Mr. James Gerard, of the Bengal army. We here experienced many acts of kindness and assistance from Capt. C. M. Wade, the political agent, whose good offices I have to acknowledge with gratitude. The society of this, the most remote station of British India, also evinced an interest in our welfare which was truly gratifying. We took leave of it at a convivial party given for the occasion on the 2d of January, and on the following day bade a long farewell to such scenes, and plunged into the solitude of an Indian desert.[2] We took the route that leads along the left bank of the Sutlege, till that river is joined by the Beas or Hyphasis.
Before crossing the boundaries of India it was both prudent and necessary to receive the permission of Maharaja Runjeet Sing, the ruler of the Punjab. It was suggested to me that a private application was in every respect preferable to an official letter from government, since the most favourable reception which I had already experienced from his highness left no doubt of his ready compliance. I consequently addressed his highness, and solicited the indulgence of again entering his territories. I gave him a brief outline of the objects which I had in view, and congratulated myself on having to traverse at the outset the territories of so friendly an ally. In the true style of oriental hyperbole, I assured his highness that “when I had again the pleasure of seeing him it would add to my happiness, because it would afford me an opportunity of renewing my terms of friendship with a prince whose exalted virtues filled me with recollections of perpetual delight!” In the course of three days we were joined by a small escort of cavalry sent to welcome us, and their commandant brought a most friendly reply from the Maharaja, expressive of his pleasure at our approach. It was also intimated to us that we should receive[3] presents of money and gifts as we advanced; but, as it would better suit our character to pass without these attentions, I civilly declined them. Reports would precede us, and doubtless in an exaggerated enough shape, which made it desirable to shun all pomp and show, and the more so since we had really no right to them.
As we descended the banks of the Sutlege, we gradually lost sight of the Hemilaya mountains. For the first twenty miles they could be seen in great grandeur, clothed in snow from base to summit, without an inferior ridge to hide their majesty. They were about 150 miles distant, and not so peaked in their outline as the same range of mountains to the eastward. The hoary aspect of this stupendous chain formed a striking contrast with the pleasing verdure of the plains of the Punjab. In the morning these, indeed, were covered with hoar frost, but it disappeared under the first rays of the sun, and left, in this alternation of heat and cold, a hard green sward, which is not often seen in tropical countries.
On the banks of the river we passed innumerable villages, the houses of which were terrace-roofed, and formed of sun-dried brick on a wooden frame-work. They had a clean and comfortable look, and the peasantry appeared well clad and happy. They consist of Juts, both Hindoo and[4] Mahommedan, and a few Seiks. People. All the Mahommedans have been converted from Hindooism; and it is a curious fact, that the Moslems predominate on the southern bank, where, from the vicinity to the Hindoo world, one would have expected to find those of that persuasion. In the upper parts of the Sutlege, near Lodiana, the inhabitants are exclusively agricultural; but, after that river has been joined by the Beas or Hyphasis, the habits of the people are predatory. There they are known under the various denominations of Dogur, Julmairee, Salairee, &c. and by the general designation of Raat, and live in a perpetual state of opposition to one another. In the cultivated parts this country has the appearance of an extensive meadow. It is entirely free from underwood, and some of the wheat fields extend for miles without a hedge. The grain is raised without irrigation, though the water is but twenty-six feet from the surface. There are no trees except in the vicinity of the villages; and such is the scarcity of fuel, that cow dung is universally used in its stead. This is dried and stacked. The fire formed of it throws out a most powerful heat, which leaves the people no cause to regret the want of other fuel. The country below that stripe which fringes the river is known by the name of Malwa. It has a dry climate and soil, and produces gram and barley,[5] with bajree[3] and mut, which are exported to the Punjab.
After a journey of fifty miles from Lodiana, we encamped at Huree, on the banks of the Hyphasis, below the confluence of that river and the Sutlege. In all our maps this junction takes place some fifty miles lower down, which appears to have been only correct at a remote period. These united rivers form a beautiful stream, which is never fordable; and, at this season, was 275 yards wide. The actual channel exceeded a mile and a half; and the high bank lay on the northern shore; the water was running at the rate of two miles and a quarter an hour, and was at this season perfectly clear, and free from the foul, muddy appearance of a river that is swollen by the water of the mountains. The depth did not exceed twelve feet since the river had retired to its summer bed, and the melting snow had ceased to feed it. Both rivers stood at a temperature of 57°, which was 6° below that of the atmosphere. Physical phenomena of rivers. The people informed us, that about fifty years ago the Sutlege had been hemmed in among the mountains, by a hill falling in upon its bed. After an obstruction for some weeks, it vomited forth its imprisoned stream with great destruction. A similar case occurred about eight years ago, in the Ravee or[6] river of Lahore. It did little injury, and the terror of the inhabitants was excited only by the black earthy colour of the water which forced itself over the obstructing mound. The Sutlege has altered its course at no distant period, and swept away some of the villages on its banks. These are of a clayey, crumbling nature, easily undermined by the current. Near the existing point of union between the rivers, we passed the dry bed of the old Sutlege, which is said to have once joined the Hyphasis at Feerozpoor. The space between this and the present channel, from twelve to fifteen miles across, is entirely destitute of trees, and covered by a rich mould, the deposit of the river.
In a country subject to such changes, how are we to look for an identity between the topography of modern and ancient days? Yet we were now in the vicinity of the altars of Alexander; and if we sought for these ancient relics of the “Macedonian madman” without success, we sought not without industry and enthusiasm. When the army of Alexander mutinied on the banks of the Hyphasis, he crossed that river, and raised twelve colossal altars, to indicate the limit and glory of his expedition. Major Rennell has placed the site of these monuments between the Beas and Sutlege; but that eminent geographer is not here supported by the text of Alexander’s[7] historians. They do not even mention the Sutlege; and their allusions to a desert that lay beyond the Hyphasis can only be identified with the country beyond that river, and below its junction with the Sutlege, where that desert is still to be found. Nor is it probable that Alexander would erect the trophies of his conquest, where a small and fordable river yet separated him from India. We wandered about for a few days, and extended our researches on every side. We crossed the Sutlege, and found, at the point of its junction with the Beas, a brick ruin, of small dimensions, called Andreesa, which sounded like Greek, but the building was of a Mahommedan age. We then embarked on the Hyphasis, and passed the confluence of the two streams, where the waters meet each other gently, and glide smoothly along. Both rivers have an equal breadth of 200 yards, but the Sutlege discharges a greater volume of water. It was with faint hopes of success that we prosecuted our enquiries after these remnants of antiquity, since the inhabitants did not remember to have even seen an European. It is an approximation, nevertheless, to discovery, to ascertain where these altars are not; and if any traces of them be hereafter found, they probably lie lower down, and on the left bank of the united stream of the Beas and Sutlege, there called the Garra. I should[8] here mention that, on our way from Lodiana, and about twenty miles from that cantonment, we heard of the ruins of Tiharu, on the southern bank of the Sutlege, which had been washed into the river within the last thirty years. Kiln-burnt bricks of large dimensions and peculiar shape are yet found on this site, which may have been an ancient ruin. If the altars stood here, my surmises are erroneous.
On the 11th we crossed by the ferry boats at Huree Ka Puttun, and landed in the Punjab at the village of that name. There are twenty-three boats at this ferry; and it is protected by a party of 400 horse, whom the ruler of the Punjab has stationed here to prevent the fanatics of the Seik creed from passing into the British territories. Our welcome chanted. As we entered the village, we were met by a crowd of females and children, who approached to chant our welcome. They are the poorer peasantry, and, of course, actuated by the hope of reward; but the custom has something pleasing in it. The boys of the village had also assembled to gratify their curiosity; while we approached, they were silent, and looked with attention: when we had passed, all was bustle and uproar, running and falling, jumping and laughing, till the head man and his troopers called the urchins to order.
We had no sooner set foot on the Punjab than[9] a sirdar, or chief, of the name of Sham Sing, appeared by order of his master. He presented me with a bow, according to the custom of the Seiks, and two bags of money; which latter I declined, being amply satisfied at the readiness with which we had received permission to enter the country. I wished also to dispense with this personage and his cavalcade; but it was impossible, since he had been deputed from Lahore to escort us, and the road was described as not altogether safe for a small party. It was well we did not separate ourselves from the chief, as we afterwards passed a village on fire, and in possession of the Seik fanatics, to whom I have before alluded. Seik fanatics. We met a body of 500 horse, with two field-pieces, proceeding to chastise these “wrong-headed and short-sighted” men, as they are styled in the language of the Punjab cabinet.
On the following morning we commenced our march across the “Doab[4],” between the Beas and Ravee (Hydraotes), which has the name of Manja. It is the highest portion of the Punjab east of the Hydaspes; a fact which is established by the eastern bank of the one river as well as the western one of the other being both elevated. The left bank of the Ravee is about forty feet high, and so is the right bank of the Beas. The wells are also much deeper than south of the[10] Sutlege; here they exceed sixty feet, there they are not twenty-six. The soil is a hard, indurated clay, sometimes gravelly, producing thorny shrubs and brambles, called by the natives jund, khureel[5], and babool.[6] Cultivation depends upon the rain, and irrigation is by no means general. Herds of neelgaee roam over it. Ancient canals. In former years the Mogul emperors, seeing the comparative sterility of this tract, fertilised it by canals from the Ravee, which connected that river with the Beas. The remains of one of them may be yet traced at the town of Puttee, running down at right angles upon the Beas, though it has been choked up for the last 150 years. The district of Manja is celebrated for the bravery of its soldiers, and the breed of its horses, which would always entitle it to the patronage of a sovereign.
The first town we entered was Puttee, which contains about 5000 people, and, with the adjoining town of Sooltanpoor, was built in the reign of Akbar. The houses are constructed of bricks, and the streets are even laid with them. Some workmen, digging a well in this neighbourhood, lately hit upon a former well, on which was a Hindoo inscription. It set forth that it had been built by one Agurtuta, of whom tradition gives no account. The district of Puttee[11] held, at one time, a supremacy over 1360 villages, and yielded a revenue of nine lacks of rupees, when fertilised by its canal.
At Puttee we visited one of the royal studs of Runjeet Sing. We found about sixty brood mares, chiefly of the Dunnee breed, from beyond the Hydaspes, where the country is of the same description as Manja, dry and elevated. May not this aridity, as resembling the soil of Arabia, where the horse attains such perfection, have something to do with its excellence? These animals are exclusively fed on barley, and a kind of creeping grass called “doob,” which is considered most nutritive. The horses at this stud were lately attacked with an epidemic disease, of which a Mahommedan, who resides in a neighbouring sanctuary, is believed to have cured them. Though a Mahommedan, the Seiks have in gratitude repaired and beautified his temple, which is now a conspicuous white building, that glitters in the sun. The Seik people are most tolerant in their religion; and I have remarked in India generally much more of this virtue than the people receive credit for. It may be superstition which excites this general respect of all religions, but, be the feeling grounded on what it may, it is a sound and wholesome one. The Mahommedans have, no doubt, been overbearing in their conquests (and what conquerors have[12] not been overbearing); but, as they settled among the people, their prejudices disappeared, to the mutual benefit of themselves and their subjects.
On the 13th we received a message from the Acali who had set fire to the village a few days previous, and whose acts of fanaticism had called for the interference of the court. This outlaw, by name Nehna Sing, wished to visit us, and I felt equal anxiety to hear from so notorious a character some history of himself and his adventures. These fanatics of the Seik creed acknowledge no superior, and the ruler of the country can only moderate their frenzy by intrigues and bribery. They go about every where with naked swords, and lavish their abuse without ceremony on the nobles, as well as the peaceable subjects; nor are they always so harmless, since they have, on several occasions, even attempted the life of Runjeet Sing. An interview with such a person excited considerable anxiety on the part of our conductors, who strongly dissuaded me from it, and, at length, completely frustrated our wishes by informing the Acali that he must come unattended. This he declined, and we were obliged to forego the pleasure of seeing a man who had dared Runjeet Sing himself, within a few miles of his capital. We were obliged to rest satisfied with a hearsay account of this Seik bigot, nor could I discover[13] any difference in the shades of fanaticism here and in other countries. These Acalis or Nihungs are not numerous, but commit the grossest outrages, and shield themselves under their religious character. They evince no greater hostility to those of another creed than to a Seik, and would appear to be at war with mankind. Their fanaticism borders on insanity. The creed of the Seiks is well known: it has been ably described by Sir John Malcolm. Like their neighbours, the Mahommedans, they have forgotten much of its primitive form, and found their distinction from other sects on a few ritual observances. A Seik will tell you that tobacco is the most debasing of stimulants, since the founder of their sect, Gooroo Govind Sing, proved it by exhibiting the contamination in the interior of a tobacco pipe, as a type of its corruption in the human body! A Seik once told me that tobacco and flies were the greatest of ills in this degenerate age.
About half way across the “Doab” we reached Pidana, the seat of one of the principal chiefs of the Punjab, Sirdar Juwala Sing, who had been sent from Lahore to entertain us at his family mansion. He met us about a mile out, and delivered a letter with a bow and a bag of money. The chief had robed himself in a rich dress of brocade, and his retainers were arrayed[14] in tunics of yellow, which is the favourite colour of the Seiks. Juwala Sing has the reputation of a brave soldier, and possesses a suavity of manner and address which appear to great advantage in a fine soldier-looking person about six feet high. It was twilight as he led us through his fort and under his baronial castle to our camp, which gave a favourable idea of the residence of a Seik chief. The castle stood in the centre, surrounded by a village, peopled by his retainers, the whole being enclosed by a mud wall and outer ditch. Within this space is to be found a bazar, extensive stables, and, in the present instance, these were built on a plan of great regularity. In the tranquillity which has followed the conquest of this country, most of the chiefs have turned their minds to improving their places of residence; and their habitations have at a distance a most imposing and respectable appearance, though inferior to the fortified dwellings of the Rajpoot chiefs in Marwar. They are always built in a military style, of a quadrangular shape, with lofty walls and turrets. Our worthy host made us such welcome guests, that we remained with him for two days. From the top of his castle we had a commanding view of the surrounding country, which is very rich, from its vicinity to the two capitals of the country, Lahore and Umritsir; yet the soil is unproductive.
In our progress to Lahore, we entered the great road of Juhangeer, which was once shaded with trees, and studded with minarets and caravanserais. It conducted the traveller
and has been celebrated in Lalla Rookh, in the royal procession to Cashmeer. In the lapse of time the trees have disappeared; but many minarets and superb caravanserais yet mark the munificence of the Mogul emperors. The road itself is yet a broad and beaten way; nor was it possible to tread upon it without participating in the excitement which the author of Lalla Rookh has raised, and I may almost say gratified.
On the morning of the 17th we entered the imperial city of Lahore, which has once rivalled Delhi. We wound among its ruins; and, when yet three miles distant, were met by Monsieur Allard, and two natives of rank sent to welcome us. The Chevalier came in his carriage drawn by four mules, into which the Dr. and myself stepped, and drove to his hospitable mansion, where we alighted and took up our quarters. After the ceremony of receiving various friendly and formal messages from Runjeet, the native part of the deputation withdrew, leaving a profusion of the fruits of Cashmeer and Cabool as an earnest of the condescension of their master.[16] In the evening, a purse of 1100 rupees was sent to us by the Maharaja; nor was it possible to refuse the money without giving offence.
We next morning paid our respects to the Maharaja, who received us with marked affability in a garden about two miles from the city. We found him in great spirits, and continued with him for about two hours. His conversation ranged from points of the utmost importance to mere trifles: he expressed much satisfaction at an interview which he had lately had, for the first time, with the Governor-general; and said, that he might now reduce the pay of his troops, after having seen so efficient an army as the Indian with so little pay. His highness was much interested in shell practice; and conducted us to the front of his garden, to show the success which had attended his exertions. They are unacquainted with the mode of fusing iron in this country, and the shells are constructed of brass. Monsieur Court, one of his French officers, exhibited these to him on the day of our arrival, and was presented with a purse of 5000 rupees, jewels, and other gifts. Runjeet made the most particular enquiries regarding our journey; and, since it was no part of my object to develope the entire plans we had in view, we informed his highness that we were proceeding towards our native country. He requested me to take a com[17]plimentary letter to the King of England; which I declined, on the excuse of its endangering my safety in the intermediate territories. I then presented a handsome brace of pistols, that drew forth his Highness’s commendation, and which he said he would keep for my sake. The Dr. produced a spy-glass as the token of his homage. Runjeet received us, surrounded by troops: four regiments of infantry could be seen at parade from his audience tent. We passed through a street formed by his infantry and cavalry, and were honoured by a salute. On taking leave, he requested that we would continue as long as possible at his court, since he wished to show us some tiger hunting, and give an entertainment in his palace,—honours which we duly appreciated. We meanwhile returned to enjoy the friendly society of M. Allard and his brother officers. I shall make no further mention of Lahore, since it is described in my first visit to the court, and was now no longer a scene of curious novelty.
Near midnight on the 22d, we were much alarmed by an earthquake, which continued for about ten seconds with great violence. The house in which we were lodged, though a substantial dwelling of brick and mortar, shook with great violence. The atmosphere had indicated nothing unusual; the barometer underwent no[18] variation either before or after it; and the thermometer stood so low as 37°, and fell four degrees under the freezing point before sun-rise. In July last, it had risen to 102°. I was informed that earthquakes are of frequent occurrence at Lahore, particularly during winter. In Cashmeer they are still more common; and appear to be more usual on approaching the mountains. The lofty minarets of Lahore afford the most convincing proof that there can have been no very violent commotion of nature since they were built,—nearly two hundred years ago. The shock on the present occasion appeared to run from south-east to north-west; and it was singular to discover, after crossing Hindoo Koosh, that this was also the exact direction of its course. In the valley of Badukhshan, and the whole upper course of the Oxus, the greater portion of the villages had been overthrown, which had buried some thousands of people in their ruins. The shock had occurred there at the same time, and, as far as I could judge, at the same hour, since they mentioned the midnight horrors of the sad event.
A week after our arrival we received the promised invitation to join his Highness in the sports of the field. He himself had quitted the capital, and sent a friendly letter, along with four elephants to convey us and our baggage. We[19] immediately mounted, and took the route by the banks of the Ravee, in which direction the court had proceeded. On our way, we passed an hour in the celebrated garden of “Shalimar,” which was now more beautiful than ever. Though it was winter, the trees were loaded with oranges. We halted for the night, near the village of Lakodur, famous in history as the spot at which Nadir Shah crossed the river and captured Lahore. The stream has forsaken its former channel, which is now dry and cultivated. The hordes of the destroying Nadir have been in like manner long withdrawn, and given place to the industrious and reformed inhabitants of this country. On the following morning we entered the royal camp, which was about twenty miles from the city. On the road we passed crowds of soldiers, porters and messengers bearing fruits and rarities. Description of his camp. Since leaving Lahore, it was evident that we were approaching a hive of men. About a mile distant we were welcomed by a Rajah and his train, who met us on elephants, and conducted us to the camp, pitched close on the banks of the river. The scene, as we approached, was magnificent. A large pavilion of red cloth, surrounded by extensive walls of the same materials, marked the encampment of Runjeet, while his troops and chiefs were cantoned in picturesque groups around. The suite of tents which had been[20] pitched for our accommodation was most elegant. They were made of scarlet and yellow cloth, and the ground was covered with the carpets of Cashmeer, and pieces of French satin. It was with some reluctance that I set foot upon such valuable materials. In each tent was a camp bed, with curtains of yellow silk, and coverlets of the same description. Such costly splendour was ill suited to men who had so little prospect even of comfort; but I must say that it was exhilarating at the moment. One of the officers of the court welcomed us in the name of his Highness; and in the evening we were joined by Captain Wade and Dr. Murray, who had been sent on a political mission to the court of Lahore.
On the morning of the 27th, we marched with the Maharaja; and fording the Ravee, proceeded inland. The order of the march was very picturesque, and the retinue in every respect that of a soldier king. His horses were led in front of him, but the journey was performed on elephants. Two of these stupendous animals bore houdas of gold, in one of which his Highness sat. Six or seven others followed with his courtiers and favourites. A small body of cavalry, and a field piece, formed his escort; and the carriage, which he had received from the Governor-general, drawn by four horses, completed the procession.
Runjeet was very talkative during the march, and detained us in conversation for about an hour after it had terminated. He spoke of the good fortune of Ameer Khan, in receiving so large a grant of land from the Indian Government without military service; and commented on his rise from so low an origin, to such an elevation. He need not have gone farther than himself for a remarkable instance of the caprice of fortune. Runjeet said that a disciplined army did not suit the manners of an Eastern prince, for it could not be regularly paid, and complained, consequently, of its duties: he wished to know if our troops ever clamoured for pay, and expressed some surprise to learn that such behaviour was viewed as mutinous. A conversation could not, of course, conclude without his favourite topic of wine; and, as he first sat down, he remarked that the site of his tent was an agreeable one for a drinking party, since it commanded a fine view of the surrounding country. He enquired of the doctors, whether wine was best before or after food; and laughed heartily at an answer from myself, when I recommended both. During this conversation, a peasant rushed in upon our party, calling loudly for justice: he was stopped by the guards, and gagged; but Runjeet called out in a stern voice,—“Strike him not!” An officer of high rank was sent to[22] hear his complaint; but I fear that, if received opinions be true, justice is here an equally expensive article as in other Asiatic governments.
On taking leave of his Highness, we proceeded to our tents, which were a distinct suite from that we had yesterday occupied. They were made of Cashmeer shawls, and about fourteen feet square. Two of these were connected by tent walls of the same superb materials; while the intervening space was shaded by a lofty screen, supported on four massy poles, adorned with silver. The shawls of one tent were red; of the other, white. In each of them stood a camp bed, with curtains of Cashmeer shawls, which gave one an impression of a fairy abode more than an encampment in the jungles of the Punjab.
Among our visiters in the camp, I must not omit to mention the sage Uzeezodeen, the physician and secretary of Runjeet Sing, who, according to Eastern notions, is a very learned person, deeply versed in theology, metaphysics, and physics, which he professes to have acquired from the Greek authors. He displayed his acquirements in many long discourses, from which I have extracted the following, as a specimen of what sometimes passes for wisdom in the East. The world possesses three different atoms, all excellent, and all of which enter into the ‘noblest[23] work of God,’ man.—Neither the gem nor the precious metals can multiply or increase their size or number; in their beauty we find their excellence. In the vegetable kingdom, we see the trees and plants, sucking moisture from the earth and moulding it to their nature, increase in size and glory. In the animal kingdom, we see the beasts of the field cropping those plants which afford them nourishment, and avoiding these which are noxious. We see them propagating the species without the institutions of society. In man alone have we every excellence: he possesses the beauty and ornament of the gem; understands and wields the properties of the vegetable kingdom; and, to the instinct of the animal creation, he adds reason and looks to futurity. As the learned physician said, “he chooses his wife considerately, nor herds in flocks like the other animals of the creation.”
But we had come to hunt, not to philosophise; and next day accompanied the Maharaja on a sporting expedition at noon. He rode a favourite bay horse, covered with an elegant saddle-cloth of the richest embroidery, ornamented, in its border, by almost every beast and bird which the sportsman calls his own. Runjeet was dressed in a tunic of green shawls, lined with fur; his dagger was studded with the richest brilliants; and a light metal shield, the gift of the ex-King[24] of Cabool, completed his equipment. A train of elephants followed him; and a pack of dogs, of motley breed, natives of Sinde, Bokhara, Iran, and his own dominions, led the van. His falconers supported their noble birds on their fists. They fluttered at his side, and shook the bells suspended from their feet. A company of infantry in extended order, with two or three hundred horsemen, swept the ground; and we followed the foresters with their rude halberds, who soon disturbed the game. We were to encounter hogs instead of tigers. The swords of the Seiks glittered in the sun; and in the course of half an hour eight monsters had bitten the dust, and many more were entrapped by snares. Most of the animals had been slain by the horsemen with their swords; a few had been first wounded by the matchlock. The sport might not be duly appreciated by a European sportsman, since the hogs had but a small chance of escape; yet I am sure the excitement of the field was great. The scene took place in a plain covered with high grass, in the open patches of which we could see from our elephants the brilliant display with great advantage. The bright coloured dresses of the courtiers had a striking effect. Runjeet himself viewed each hog as it fell, and keenly turned to the scenes of passing slaughter; in the course of an hour[25] and a half we returned to our tents, and saw each of the successful sportsmen rewarded. The live hogs were then brought, tied by one leg to a stake, and baited with dogs. The sport is a cruel one, and does not afford any great amusement; the courage and fire of the animals are renewed by dashing water over them. After witnessing it for a short time, an order was given to set all the live hogs at liberty, as Runjeet said that they might praise his humanity; and the infuriated animals scampered through the crowded encampment, to the great delight of the assembled multitude.
After the bustle had passed, we continued for some time with the Maharaja, who gave us an animated account of his exploits beyond the Indus. He described the bravery of a Nihung, or Seik fanatic, who had perished on that occasion. He had fought on foot and received a wound, which he dressed, and returned to the field on horseback. He received a second wound; but, not discomfited, seated himself on an elephant; and was at last shot through the lungs. “He was a brave man,” continued he, “but a great villain; and had he not fallen on that day, I must have imprisoned him for life: he wished to cross the frontier and set fire to some of the British cantonments.” The particular battle to which his Highness now alluded was fought at[26] Noushero, near Peshawur, and was the most glorious victory which he gained after passing the Indus in a heroic manner, without a ford. It was quite delightful to hear Runjeet speak of his charges, his squares, his battles, and his success; and his only eye brightened with the description. “You will pass the field of battle,” added he, “and you must reconnoitre it well. I shall give you letters to the neighbouring chiefs and the marauding Khyberees, who will describe the ground, and ensure your protection and honourable treatment.” The favour was well meant; and I felt it the more, as it was unsolicited, though the letters proved useless.
We continued in the enjoyment of his society till the end of the month, when we returned to Lahore, with the same pomp and pageantry that we had witnessed in the field. On the way we had some sport with the hawks, which is an amusement that can be enjoyed even by those who are no sportsmen. A hundred cannon announced the arrival of Runjeet Sing in his capital; and we again took up our abode with our worthy friend Monsieur Allard.
On the 6th of February, the festival of the “Busunt,” which simply means the Spring, was celebrated with great splendour. Runjeet invited us on the occasion; and we accompanied him on elephants to witness the demonstration[27] of joy with which returning spring is here hailed, as in other countries. The troops of the Punjab were drawn out, forming a street of about two miles long, which it took upwards of thirty-five minutes to traverse. The army consisted entirely of regular troops—cavalry, infantry, and artillery; and the whole corps was uniformly dressed in yellow, which is the gala costume of this Carnival. The Maharaja passed down the line, and received the salute of his forces. Our road lay entirely through the ruins of old Lahore, over irregular ground, which gave the line a waving appearance that greatly heightened the beauty of the scene. At the end of this magnificent array stood the royal tents, lined with yellow silk. Among them was a canopy, valued at a lac of rupees, covered with pearls, and having a border of precious stones. Nothing can be imagined more grand. At one end Runjeet took his seat, and heard the Grinth, or sacred volume of the Seiks, for about ten minutes. He made a present to the priest; and the holy book was borne away wrapped in ten different covers, the outside one of which, in honour of the day, was of yellow velvet. Flowers and fruits were then placed before his Highness; and every kind of shrub or tree that produced a yellow flower must have been shorn of its beauties on this day. I could[28] discover no reason for the selection of so plain a colour, but the arbitrary will of a ruler. After this came the nobles and commandants of his troops, dressed in yellow, to make their offerings in money. Two sons of the fallen Kings of Cabool, Shah Zuman and Shah Eyoob, then entered, and conversed for some time. The Nawab of Mooltan, clad also in yellow, and accompanied by five of his sons, followed to pay his homage, and was most kindly received. This is the same individual who was so much frightened at the Cabool mission, now a subservient vassal of Runjeet Sing. His name is Surufraz Khan. The agents from Bhawulpoor and Sinde approached in their turn, and were closely questioned about a subject of great political importance at the present time,—the opening of the Indus. One could ill discover, from the sycophancy of these persons, that they were the representatives of those who so cordially hated the Maharaja. With these ceremonies the dancing girls were introduced; and as they share the favour of his Highness, they partook most bounteously of the pile of money now lying before him. He appeared almost to divide it among them. They were desired to chant the amorous songs of the festival; also an ode on wine. Runjeet then introduced the bottle, and insisted on our drinking a stirrup-cup, with which we parted.
Our departure from Lahore was stayed by the entertainment which his Highness had resolved on giving us in his palace of the Sumun Boorj. We met in a garden, and proceeded with him to the appointed place, which was superbly illuminated with waxen tapers on the occasion. Bottles filled with different coloured water were placed near the lights, and increased the splendour. We were first conducted to the great hall, the ancient seat of the Mogul Emperors, which is about seventy feet long, and opened to the front by an arched colonnade of marble. The ceiling and walls are entirely inlaid with mirrors, or gilded; and on this occasion presented a scene of great magnificence. There are many parts of this place, which, like that of Delhi, evidently owe much of their architectural beauty to the genius of an European artist. We withdrew from the great hall to a small apartment, the bed-room of the Maharaja, where it was intended that the festivities of the evening should take place. Captain Wade and Dr. Murray were likewise present; and we sat round his Highness on silver chairs. In one end of the room stood a camp bedstead, which merits a description. Its frame-work, posts, and legs were entirely covered with gold, and the canopy was one massy sheet of the same precious metal. It[30] stood on footstools raised about ten inches from the ground, and which were also of gold. The curtains were of Cashmeer shawls. Near it stood a round chair of gold; and in one of the upper rooms of the palace we saw the counterpart of these costly ornaments. The candles that lighted up the apartment were held in branch sticks of gold. The little room in which we sat was superbly gilded; and the side which was next the court was closed by a screen of yellow silk. Here we enjoyed the society of our royal entertainer, who freely circulated the wine, filled our glasses himself, and gave every encouragement by his own example. Runjeet drinks by the weight, and his usual dose does not exceed that of eight pice[7]; but on this occasion he had quaffed the measure of eighteen. His favourite beverage is a spirit distilled from the grapes of Cabool, which is very fiery, and stronger than brandy. In his cups he became very amusing, and mentioned many incidents of his private life. He had quelled two mutinies among his troops; three of his chiefs had, at different times, fallen by his side; and he had once challenged his adversary to settle the dispute by single combat. The battles of his Highness infected the dancing ladies whom he[31] had introduced, in a later period of the evening, according to his custom. He gave them spirits; and they tore and fought with each other, much to his amusement, and to the pain of the poor creatures, who lost some ponderous ornaments from their ears and noses in the scuffle. Supper was introduced, and consisted of different kinds of meats, richly cooked, and which in contrast to the surrounding magnificence, were handed up in leaves sewed into the shape of cups. They contained hare, partridge, pork, and all sorts of game, &c., of which Runjeet partook freely, and handed to us. There were also a variety of confections and ices: but it is easier to describe these matters of fact than the scene in which they took place. We broke up long past midnight.
During these gay and festive scenes, we were not forgetful of the difficulties which awaited us; and availed ourselves of the experience of Messrs. Allard and Court, who had travelled overland from Persia through a part of the countries we were now about to traverse. These gentlemen seemed to vie with each other in every act of kindness. Kindness of Messrs. Allard and Court. They furnished us with various letters to their acquaintances in Afghanistan, and gave us many hints to guide our conduct. Monsieur Court, indeed, drew up a précis of them,[32] the result of his own experience, which I annex[8], since it conveys, at the same time, most valuable information to a traveller, and gives me an opportunity of expressing my gratitude both to him and M. Allard, and the reasons on which I found it. These gentlemen did not disguise from me the many apprehensions which they entertained for our safety; but our visit to Lahore had not been made to discuss the chances of our success, but only in prosecution of the journey.
On the evening of the 10th of February, we took our leave of Maharajah Runjeet Sing on the parade-ground, where he again exhibited to us, with apparent pride, the progress which his troops had made in throwing shells. On this occasion he asked for my opinions on opening the Indus; and remarked, that, as that river and its five great tributaries passed through his territories, he ought to derive greater advantages than the British government. He spoke of the scheme as might have been expected from a man of his enlightened views; but said that he did not relish the idea of vessels navigating all parts of his territories. He fears collision with the British government. His Highness then proceeded to dictate letters in our behalf to the chiefs of Peshawur and Cabool, as well as several[33] other personages beyond the Indus. He also issued orders to all the chiefs and agents between his capital and the frontier; and stretching his hand from the elephant, gave each of us a hearty shake, and said farewell. He particularly requested me to write to him frequently, and give an account of the countries I traversed, with their politics and customs, and never forget him in whatever region I might be placed. Nor did we forget his request when far from his territories. We received letters from Runjeet Sing himself in the deserts of Tartary and in Bokhara. I never quitted the presence of a native of Asia with such impressions as I left this man: without education, and without a guide, he conducts all the affairs of his kingdom with surpassing energy and vigour, and yet he wields his power with a moderation quite unprecedented in an Eastern prince.
“A Monsieur Burnes, par son Ami, M. Court.
“Le proverbe Français dit, ‘Si tu veux vivre en paix en voyageant, fais en sorte de hurler comme les loups avec qui tu te trouves:’ c’est-à-dire, Conforme toi en tout aux mœurs et cou[34]tumes des habitans des contrées que tu parcours. C’est là la base de vos instructions.
“Commencez d’abord par vous dépouiller de tout ce qui pourrait faire connaître que vous êtes Européen; car si l’on vient à savoir que vous êtes tel, on va se figurer que vous emportez avec vous toutes les mines de Pérou. Par là vous vous attirez sur les bras une nuée d’ennemis, vu que les peuplades barbares que vous allez traverser n’en veulent qu’à l’argent, et non à la personne. Evitez donc de produire le moindre objet qui puisse tenter leur cupidité. Songez que souvent je les ai entendus se glorifier, comme d’un acte héroïque, d’avoir fait assassiner telle et telle personne, pour lui enlever un objet qu’ils avaient convoité.
“Evitez autant que possible les occasions qui pourraient donner atteinte à votre honneur. Si des cas imprévus surviennent, n’y répondez jamais avec emportement; car répondre à l’insolence Asiatique c’est ajouter de la matière combustible à un feu qui brûle déjà. Si vous vous voyez forcé d’y répondre, il faut alors leur présenter des raisons solides accompagnées d’expressions obligeantes et courageuses.
“Ayez pour maxime qu’il ne faut pas faire d’amitié particulière avec les Orientaux, vu qu’ils sont incapables d’attachement sincère. Vivez bien avec tous, mais ne vous attachez à aucun.[35] Par ce moyen il vous en coûtera moins. Sachez qu’ils n’ont ni la bonne foi, ni la franchise, ni la loyauté qui nous caractérisent. Ils sont doux, flatteurs, caressans, il est vrai; mais sous ces formes séduisantes ils cachent presque toujours de sinistres desseins. La perfidie, la trahison, le parjure n’ont rien qui leur paraisse répréhensible. A leurs yeux le droit n’est rien, la force fait tout. N’allez pas vous imaginer que ce que vous appelez bonté, douceur, complaisance, puisse vous être utile. Ils ne savent nullement apprécier de telles qualités. Comme Européen, ne craignez pas de faire usage de la flatterie. Etant d’usage parmi eux, vous ne sauriez trop l’employer; elle peut même vous être avantageuse.
“En quittant Lahore, dites adieu à Bacchus, pour ne le revoir que dans la belle Europe. C’est là un sacrifice essentiel à faire. Il vous évitera bien des querelles que pourraient vous susciter les Mahométans. Soyez modeste dans vos dépenses: moins vous en ferez, moins vous tenterez la cupidité des Orientaux. Evitez surtout de donner le moindre cadeau; car si vous faites tant que de régaler quelqu’un, vous vous trouverez bientôt assiégé par une infinité d’autres, qui ne désempareront que quand vous les aurez satisfaits. Paraissez en public le moins qu’il vous sera possible. Evitez toute sorte de conversation, surtout celles qui traitent de théologie,[36] point sur lequel les Mahométans aiment à tomber avec un Européen. Donnez leur toujours raison lorsque vous vous verrez forcé de donner votre avis. Que vos mémoires soient écrits en secret, autrement vous donneriez lieu à des soupçons qui pourraient vous être préjudiciables.
“En prenant des renseignemens, faites le avec adresse et prudence; n’ayez jamais l’air d’insister à les avoir. Si le pays offre des curiosités, visitez les comme pour passer le tems: si elles sont écartées, n’y allez jamais qu’en bonne compagnie.
“Ne vous mettez en route qu’avec des caravanes sûres, et ayez surtout l’attention de ne jamais vous en écarter. Ayez de petites attentions pour le caravanseraskier, car c’est toujours de lui que dépend l’heureux succès des voyageurs. En vous attirant son amitié, il pourra vous donner des renseignemens que vous pourrez désirer, et par là vous éviterez de vous adresser à des personnes étrangères. Que votre campement soit toujours à ses côtés; mais, nonobstant cela, que l’un de vous ait sans cesse l’œil au guet.
“Soyez toujours armé jusqu’aux dents pour en imposer. Evitez les gens qui font les empressés pour vous servir, car ce sont là ordinairement des marauds qui en veulent à votre bourse. Avant votre départ, tâchez de faire connaître[37] que vous partez sans argent, et que ce qu’il vous en faut vous l’avez pris en lettres de change. Faites en sorte d’avoir toujours la moitié de votre argent sur vous, et bien caché. Dans les endroits où vous craindrez d’être visité, cachez le d’avance pour qu’il ne soit pas vu. Songez que j’ai été plus d’une fois visité, et que cela pourrait fort bien vous arriver; trouvez donc de bonnes cachettes pour l’argent.
“Lorsqu’il s’agira de payer la traite foraine, soldez la sans difficulté, à moins que les exigeances du douanier ne soient trop fortes. Sachez que ce sont là des coquins qui peuvent vous susciter plus d’une querelle.
“Quoique voyageant dans des contrées livrées au plus affreux despotisme, vous ne pourrez vous empêcher d’admirer la grande familiarité qui existe du petit au grand, ainsi ne soyez nullement étonné si vous vous voyez par fois accosté par des vauriens qui vous arracheront des mains le kalion pour en tirer de la fumée. N’ayez donc aucun air hautain avec qui que ce soit; l’air de fakhir est celui qui vous convient le plus.
“Le Nevab Dgiabar Khan peut vous aplanir toutes les difficultés que vous pourrez rencontrer de Caboul à Bokhara; tâchez donc de lui plaire: c’est d’ailleurs le plus parfait honnête homme que j’ai rencontré en Asie. Quant à votre projet de traverser la Khiva pour vous rendre sur les[38] bords de la mer Caspienne, je le trouve impraticable: je désire, cependant, que vous puissiez le surmonter. Dans le cas contraire, repliez vous sur Hérat ou Méched, mais alors ne vous mettez en route qu’avec une nombreuse caravane bien armée, car le pays que vous devez traverser est infesté de Turcomans, qui ravagent impunément toutes ces contrées. D’ailleurs, l’expérience que vous acquerrez en traversant ces contrées vous fournira des lumières propres à vous guider mieux que ne le feroient mes instructions.
“Que Dieu vous fasse arriver à bon port!”
After taking an affectionate farewell of Messrs. Allard and Court, we quitted Lahore in the forenoon of the 11th of February, and alighted at the tomb of Juhangeer, a splendid mausoleum across the Ravee. Without any depression of spirits, or diminution of zeal, I felt no small degree of solitude at being separated from our hospitable friends; and I now look back on the few weeks which I passed at Lahore as some of the happiest days of my life. Nor was there much in our first night’s lodging to cheer us—the wreck of a royal cemetery, which the manes of a king had once rendered sacred, but lately converted into a barrack for a brigade of infantry, who had further contributed to its desolate appearance. We put up for the night in one of the garden houses which surround it, and listened to the puerile stories of the people, who assured us that the body of the emperor, like the fabled tale of that of Mohammed, was suspended by loadstones. One has only to enter a chamber underneath to see it resting on the ground.
It now became necessary to divest ourselves almost of every thing which belonged to us, and discontinue many habits and practices which had become a second nature: but the success of our enterprise depended upon these sacrifices. We threw away all our European clothes, and adopted, without reserve, the costume of the Asiatic. We exchanged our tight dress for the flowing robe of the Afghans, girt on swords, and “kummur-bunds” (sashes); and with our heads shaved, and groaning under ponderous turbans, we strutted about slipshod; and had now to uncover the feet instead of the head. We gave away our tents, beds, and boxes, and broke our tables and chairs. A hut, or the ground, we knew, must be our shelter, and a coarse carpet or mat our bed. A blanket, or “kummul,” served to cover the native saddle, and to sleep under during night; and the greater portion of my now limited wardrobe found a place in the “koorjeen,” or saddle-bags, which were thrown across the horse’s quarter. A single mule for each of us carried the whole of our baggage, with my books and instruments; and a servant likewise found a seat upon the animal. A pony carried the surveyor, Mohammed Ali; and the Hindoo lad had the same allowance. These arrangements took some time and consideration; and we burned, gave away, and destroyed whole[41] mule-loads of baggage—a propitiatory offering, as I called it, to those immortal demons the Khyberees, who have plundered the traveller, from time immemorial, across the Indus. Every one seemed sensible of the imperious necessity of the sacrifice, since we valued our lives more than our property. Of what use would it have been to have adopted the costume and customs of the country, and to be yet burdened with the useless paraphernalia of civilisation? It is, nevertheless, a curious feeling to be sitting cross-legged, and to pen a journal on one’s knees. Custom soon habituated us to these changes; and we did not do the less justice to our meals because we discarded wine and spirits in every shape, and ate with our fingers from copper dishes without knives and forks.
Half-way across to the Chenab, we halted in a garden at Kote, the residence of one of Runjeet Sing’s colonels. It was an agreeable halting-place. It was not 100 yards square, but well stored with fruit-trees and flowers: most of the former were now in blossom, and an enumeration of them would give a favourable idea of this climate. They consisted of the peach, apricot, greengage, fig, pomegranate, quince, orange sweet and bitter, lime, lemon, guava, grape, mango, jamboo, bair, date, cardamom, almond, and the apple; with seven or eight other kinds,[42] of which I can only give the native names,—the gooler, sohaujna, goolcheen, umltass, bell, bussoora. The walks of the garden were lined with beautiful cypresses and weeping willows; and in the flower-beds were the narcissus, and rose-bushes of the “sidburg,” or an hundred leaves. Most of the trees and flowers are indigenous, but many had been introduced from Cashmeer; and a native of that valley was the gardener. The proprietor of this pleasant spot was absent: his villa was in disorder, and much neglected, since he is suffering from the avarice of his ruler. His son, a sharp boy of nine years old, paid us a visit, and repeated some lines of a Persian poet which he was reading at school. Little fellow, he is growing up to witness scenes of blood, at all events of alteration, in this land!
At a distance of about twenty miles from the river, we again sighted the towering Hemilaya, which burst forth in all their glory. They were the mountains over Bimbur, on the road to Cashmeer, where Bernier had deplored his sufferings from the heat, now over-topped with snow. It is impossible to look on these mountains without feelings of delight; for they afford a relief to the eye after the monotony of the vast plains of the Punjab. Judging from the heights which have been determined more to[43] the eastward, they cannot be lower than 16,000 feet. It is difficult to estimate their distance, since the map gives no correct notion of the range. Making every allowance, the loftiest of them could not be nearer than 160 miles, and subtended an angle of 51 minutes. There was scarcely a single peak, or feature, in any way remarkable throughout the range. May not this regular lineation indicate a trap or limestone formation?
We reached the banks of the Chenab, or Acesines, at Ramnuggur, a small town, the favourite resort of Runjeet Sing, and where he has often mustered his troops when proceeding on his campaigns beyond the Indus. It stands on a spacious plain for the exercise of his troops. The name of the place has been altered from Russool to Ramnuggur since the Mahommedan supremacy has been overthrown. The one name signifies the city of the prophet, the other the city of a god; nor is it remarkable that the name of the Deity should prevail.
The “Doab,” between the Ravee and Chenab, is a little better cultivated, and more fertile, than that which we had passed. Its soil is sandy, and in its centre the wells are but twenty-five feet deep. Their temperature averaged about 70° of Fahrenheit. In the morning, vapour or clouds of smoke ascended from them, till the[44] atmosphere was sufficiently heated to hide it. At this season the climate is cold and bleak, frequently rainy, and always cloudy. The wind generally blows from the north. Sugar. The sugar-cane thrives here; and they were now expressing its juice, which is extracted by placing two wooden rollers horizontally on the top of each other, and setting them in motion by a pair of oxen. They turn a wheel which acts on two lesser ones, placed vertically at right angles to it, and these communicate with the wooden rollers. While I examined one of these machines, the head man of the village explained it; and then made me a present of some “goor,” or coarse sugar, the first-fruits of the season. He was an ignorant Jut: his son accompanied him. When I enquired into the knowledge of the boy, and advised his being sent to school, he replied, that education was useless to a cultivator of the soil. The same opinion, I am sorry to say, prevails in higher quarters; for Runjeet and his son are equally unlettered, and they object to the education of the grandson, who is otherwise a promising boy.
At Ramnuggur we had a visit from a venerable Seik chief, of eighty-two, who had fought in the wars under the grandfather of Runjeet Sing. His beard was silvered by age; but he was a hale old man, and appeared in an[45] entire suit of white clothes, which in this country mark the old school as distinctly as the queue and Spencer of England. The garrulity of years had overtaken him; yet he gave us a lively account of his early career, and the increasing power of the Seik nation. “It had been predicted,” he said, “in their Grinth, or Bible, that wherever there was a horse or a spear, there would be chiefs and soldiers in the land. Every day serves to verify the prediction,” continued he; “since the number of converts to the Seik creed increases, and now averages about 5000 yearly.” When political aggrandisement follows the religious supremacy of a sect, it requires little prediction or foresight to know that that sect will increase. With the Patan invasion the Hindoo became a Mahommedan; and with the Seik power both he and the Hindoo have become Seiks, or Sings. The genuine Sing, or Khalsa, knows no occupation but war and agriculture; and he more affects the one than the other. The follower of Baba Nanuk is a merchant. The Seiks are doubtless the most rising people in modern India. Our venerable acquaintance spoke of the degeneracy of the land; but the vigorous government and tone of the people do not countenance his opinions.
There is a curious subject for speculation in the appearance of the Seik people, and their general resemblance to each other. As a tribe they were unknown 400 years ago; and the features of the whole nation are now as distinct from those of their neighbours as the Indian and the Chinese. With an extreme regularity of physiognomy, and an elongation of the countenance, they may be readily distinguished from the other tribes. That any nation possessing peculiar customs should have a common manner and character, is easily understood; but that, in such a short period of time, some hundred thousand people should exhibit as strong a national likeness as is to be seen among the children of Israel, is, to say the least of it, remarkable.
We crossed the Chenab, or Acesines, by the usual ferry, which is about three miles from the village. It was three hundred yards wide, and had a depth of nine feet for two thirds of the channel. Its banks are low on either side, and speedily inundated in the hot and rainy seasons. We are informed that Alexander the Great had to move his camp precipitately from the Acesines, which Arrian describes to be a rapid river. During the rains it is so, but the current did not now exceed one mile and a half an hour; and it is passable by a ford. The temperature of this[47] river was 53°, and lower than the three other rivers of the Punjab which we had already crossed—the Sutlege, Beas, and Ravee.
We halted at a mosque on the right bank of the river, but our quarters must not be mistaken for a St. Sophia. These buildings consist of mud walls, over which a terrace roof is formed by wooden rafters, also covered with mud. The “faithful” are luxurious enough to have a fireplace inside, to heat the water used in their ablutions. Our violations of a place so holy was, in some degree, compensated by the liberal distribution of our medicines. Some noxious wind, as the people had it, had lately blown over this country, which, with the arrival of such a personage as a Firingee (European) physician, made every person sick. As in other countries, the ladies had the most numerous catalogue of complaints; and if the doctor did not actually cure, I believe he worked on their imaginations, which is of some consequence. The people are much afflicted with a disease called “Noozlu,” (literally defluxion,) which I thought meant cold. They describe it as a running at the nostrils, which wastes the brain and stamina of the body, and ends fatally. It is attributed to the salt used in the country, which is procured from the salt range. There is much eye disease in the Punjab, which may be caused by the[48] nitrous particles on the banks of its different rivers. Ask a native for an explanation of it, or any other complaint, and he will tell you that it, and all other inflictions, are the punishment of offences committed by ourselves, or in the former state of our being. In the doctrine of metempsychosis, they have, at all events, found a future state of punishments, and, as optimists, I hope, rewards.
A journey of forty-five miles brought us to the banks of the Jelum, or the famous Hydaspes of the Greeks. It winds its way through an alluvial plain, at the base of a low rocky range of hills. We embarked upon this fine river, and sailed down with the stream for a distance of five miles. On the voyage we disturbed several crocodiles from the different islands, which are more numerous than in the other Punjab rivers. The same fact is mentioned by Arrian, who speaks of the Hydaspes as a “muddy and rapid” river, with a current of three or four miles an hour, which is correct. It had rained on the day preceding our arrival; the stream was discoloured, and the water bubbled in eddies at various places. The Jelum is a smaller river than the Chenab, but at this season their breadth is similar. On disembarking, we crossed a rich and beautiful sheet of verdure that stretches to the town of Pind[49] Dadun Khan, where we halted. Historical association and natural beauties united to please as we trod the routes of Hyphestion and Craterus, and sailed on the stream which had wafted the fleet of Alexander. In our progress from the Chenab, we had been travelling in the domain which that conqueror had added to the kingdom of Porus after the battle of the Hydaspes. In Arrian’s description I see the existing population:—“The inhabitants are strong built and large limbed, and taller in stature than all the rest of the Asiatics.” Nothing, however, can be more miserable than the country between the Acesines and Hydaspes,—a sterile waste of underwood, the abode of shepherds, scantily supplied with water, which is sixty-five feet below the surface. At one of the few villages in this tract, we halted at the well of a vestal virgin, who had dug it, and founded a mosque from feelings of charity. Such people are called “pak damun,” which literally means pure garment. They marry themselves to the Koran. The Mohammedans of our party visited the lady, and we repaired her well by fixing new pots for drawing the water.
At Pind Dadun Khan we were met and welcomed by the authorities on the banks of the river. They presented us with a purse of 500 rupees, and some jars of sweetmeats. Pind[50] Dadun Khan is the capital of a small district, and has a population of about 6000 souls. It consists of three small towns situated close to each other, and about four miles from the river. Its houses are like others in the Punjab; but their frameworks are made of cedar (deodar), which is floated down with the inundations of the river from the Hemilaya. The durability and fragrance of this wood recommend it for building of every description. We saw a cedar-tree lying on the banks of the Hydaspes, with a circumference of thirteen feet. On this river the Macedonians constructed the fleet by which they navigated the Indus; and it is a remarkable fact, that in none of the other Punjab rivers are such trees floated down, nor do there exist any where else such facilities for the construction of vessels.
Pind Dadun Khan lies within five miles of the salt range, which stretches from the Indus to the Hydaspes, and in which numerous mines are dug for the extraction of that mineral. We halted a day to examine these curious excavations, and which I shall now describe. We found about 100 persons at work in one of the mines, who were as much surprised to see us, as we were to behold the bright and beautiful crystals of red salt which formed the walls of the cave. We converted our visit into a day of rejoicing, by a liberal distribution of some of the money which was every where[51] heaped upon us, nor could it be better bestowed, for the poor creatures presented to us a spectacle of misery. Mothers with their infants, children, and old men, were alike employed in bringing the salt to the surface, and their cadaverous looks and stifled breathing excited the utmost compassion. We gave them a rupee each, the value of which could be justly appreciated, since they could only earn it after extracting 2000 pounds of salt.
In the high lands of Cabool, between the city of that name and Peshawur, a range of hills springing from the roots of the White Mountain (Sufeed Koh) crosses the Indus at Karabagh, and terminates on the right bank of the Jelum, or Hydaspes of the ancients. This range formerly figured in our maps under the name of Jood, after it had passed the river; but it has been more appropriately denominated the “Salt Range,” from the extensive deposits of rock-salt which it contains. An account of that part of it near Karabagh, where the Indus, in its course southward, cuts this range, and lays open its mineral treasures, will be found in Mr. Elphinstone’s work.[9] In the neighbourhood of Pind Dadun Khan, a town about 100 miles N. W. of Lahore, the salt mines which supply the northern provinces of India with that neces[52]sary of life are excavated in the same range. The following particulars pretend not to rank as a scientific account of these mines, my only object being to convey that information which a journey to so unfrequented a part of the Punjab has enabled me to collect.
The salt range forms the southern boundary of a table land, between the Indus and Hydaspes, which rises about 800 feet from the plains of the Punjab. The hills attain an actual height of 1200 feet from the valley of the Jelum, which gives them an elevation of about 2000 feet from the sea. They exceed five miles in breadth. The formation is sandstone, occurring in vertical strata, with pebbles or round stones imbedded in various parts of it. Vegetation is scanty; and the bold and bare precipices, some of which rise at once from the plain, present a frightful aspect of desolation. Hot springs are found in various places. Alum, antimony, and sulphur also occur; but a red clay, which is chiefly seen in the valleys, is a sure indication of a salt deposit, and is to be found at intervals throughout this range. The supply of the mineral is now drawn from Pind Dadun Khan, whence it can be conveyed with facility both up and down a navigable river.
At the village of Keora, five miles from Pind Dadun Khan, we examined one of the principal mines. It was situated near the outside of the[53] range, in a valley, which was cut by a rivulet of salt water. It opened into the hill through the red clayey formation above mentioned, at a distance of about 200 feet from the base. We were conducted by a narrow gallery, sufficient to admit of one person passing another, for about 350 yards, of which fifty may be taken as actual descent. Here we entered a cavern of irregular dimensions, and about 100 feet high, excavated entirely in salt. The mineral is deposited in strata of the utmost regularity, occurring, like the external rock, in vertical layers. Some of them, however, subtend an angle of from twenty to thirty degrees, and have the same appearance as bricks that have been placed upon one another. None of the layers exceed a foot and a half in thickness, and each is distinctly separated from its neighbour by a deposit of argillaceous earth about an eighth of an inch thick, which lies like mortar between the strata. Some of the salt occurs in hexagonal crystals, but oftener in masses: the whole of it is tinged with red, varying from the slightest shade to the deepest hue; when pounded, the salt is white. The temperature of the cavern exceeded that of the open air by twenty degrees, where the thermometer stood at sixty-four (in February). The natives state that these mines are much colder in the hot season; but this only shows that they undergo little or[54] no alteration, while the heat outside alters with the season. There was no moist feeling, which one might have expected in a salt mine.
There were upwards of 100 persons, men, women, and children, at work in the mine; and their little dim burning lamps on the sides of the cavern and its recesses shone with reflected lustre from the ruby crystals of the rock. The cavity has been excavated from the roof downwards. The salt is hard and brittle, so that it splinters when struck with the sledge-hammer and pickaxe. The rock is never blasted with gunpowder, from fear of the roof falling in; and accidents of this kind sometimes happen in the present simple mode of excavation. The mines are not worked for two months during the rains, for the same reason. The miners live in villages among the hills. They have a most unhealthy complexion, but do not appear to be subject to any particular disease. They receive a rupee for every twenty maunds of salt brought to the surface, a task which may be performed by a man, his wife and child, in two days. In those mines where the mineral is near the surface, it is hewn into blocks of four maunds, two of which load a camel, but it is usually broken in small pieces. This salt holds a high reputation throughout India, with native practitioners, from its medical virtues. It is not pure, having a con[55]siderable mixture of some substance (probably magnesia), which renders it unfit for curing meat. The natives of the Punjab ascribe the prevalence of “noozlu” to its effects.
As the salt range contains a supply which is inexhaustible, the mines yield any quantity that may be desired. Two thousand five hundred maunds of Lahore (one of which is equal to 100 lbs. English) are extracted daily, which gives about 800,000 maunds annually. A few years since the salt was sold at the mine for a half, and even a quarter, of a rupee per maund; but its price has been now raised to two rupees per maund, exclusive of duties. It is closely monopolised by the Punjab government; and Runjeet Sing hopes to derive an annual revenue of sixteen lacs of rupees, with two and a half more for the duties. A lac and a half of rupees, however, is expended in working the mineral. The profits amount to about 1100 per cent., though the salt is sold for one third the price of that of Bengal, which averages five rupees per maund of 80 lbs.[10] The Punjab salt is exported by the Jelum to Mooltan and Bhawulpoor, where it meets that of the Sambre lake. It finds its way to the banks of the Jumna and Cashmeer, but it is not exported westward of the[56] Indus. Runjeet Sing has prohibited the manufacture of salt in all parts of his dominions; yet it is very questionable if he will permanently derive so large a revenue from it as he now receives. The farmer of the monopoly, a cruel and tyrannical man, is now mercilessly oppressing the people to extract it. The natives do not know the period at which these mines were first worked; but it must have been at an early date, since the mineral is laid open by the Indus. They were used by the emperors of Hindostan; but the enquiring Baber does not mention them in his commentaries.
We marched up the right bank of the Jelum to Julalpoor for about thirty miles by a tract of rich land and great fertility. The husbandmen were mowing down the green wheat for the use of their cattle. The salt range runs parallel with the river, and presents a perfect contrast of desolation to its fertile valley; for it has no vegetation. Villages. Many villages, however, are perched upon the outer hills, which rise over one another in a picturesque manner. Nor are they more remarkable for their romantic situation than their comfort. We halted at one of them, which was neat and well kept, and lodged in a room which was about sixteen feet long, and half that breadth. It had cupboards and shelves, while the magazines for grain, which are formed[57] of earth, answered the purposes of tables. The whole buildings, both inside and out, are plastered with a grey-coloured earth, which gives them a cleanly appearance; and since these villages stand on the declivity of the hills, the rain washes down all that is disagreeable with it. In return for the hospitality which gave us this house, Dr. Gerard had the good fortune to save the life of a poor woman who was dying of inflammation, and whom he bled copiously.
It has been conjectured that Julalpoor is the scene of Alexander’s battle with Porus, when he crossed the stream by a stratagem, and defeated that prince. There is much to favour the opinion; for, in the words of Quintus Curtius, we have “islands in the stream, projecting banks, and waters dilated.” Yet the mention “of sunken rocks” seems to point higher up the river, near the village of Jelum. The high roads from the Indus pass this river at two places, at Julalpoor and Jelum; but the latter is the great road from Tartary, and appears to have been the one followed by Alexander. The rocky nature of its banks and bed here assists us in identifying the localities of the route, since the course of the river is not liable to fluctuation. At Jelum the river is also divided into five or six channels, and fordable at all times, except in the monsoon.
About fifteen miles below Jelum, and about a[58] thousand yards from the Hydaspes, near the modern village of Darapoor, we hit upon some extensive ruins called Oodeenuggur, which seems to have been a city that extended for three or four miles. Speculations. The traditions of the people are vague and unsatisfactory, for they referred us to the deluge, and the time of the prophet Noah. Many copper coins are found, but those which were brought to me bore Arabic inscriptions. A slab, with an inscription in that language, which had been lately dug up, was also shown to us; and I learn from M. Court that he found a fluted pillar near this site with a capital very like the Corinthian order. It, however, had a Hindoo figure on it. At present there are no buildings standing; but the ground is strewed with broken pieces of kiln-burnt bricks and pottery, the latter of a superior description. On the opposite side of the Hydaspes to Darapoor stands a mound said to be coeval with Oodeenuggur, where the village of Moong is built, at which I procured two Sanscrit coins. There are likewise some extensive ruins beyond Moong, near Huria Badshahpoor. Nicæ and Bucephalia. I do not conceive it improbable that Oodeenuggur may represent the site of Nicæ, and that the mounds and ruins on the western bank mark the position of Bucephalia. We are told that these cities were built so close to the[59] river, that Alexander had to repair them on his return from the Punjab campaign, since they stood within the influence of the inundation. It is to be observed that towns which have an advantageous locality are seldom deserted; and if so, that others rise near them, which will account for the Arabic coins found in the neighbourhood. Alexander is said to have pitched his camp at a distance of 150 stadia from the river, on a plain; and there is an extensive champaign tract behind this very site.
In our search for the remnants of Alexander’s cities, we are led into reflections on the state of the country in those days; and it is curious to compare them with our own times. We are informed that Porus, with whom Alexander fought on the banks of this river, maintained a force of 30,000 infantry and 4000 cavalry, with 200 elephants and 300 war chariots; and that he had subdued all his neighbours. Now, if we change the war chariots into guns, we have precisely the regular force of Runjeet Sing, the modern Porus, who has likewise overwhelmed all his neighbours. The same country will generally produce the same number of troops, if its population be not reduced by adventitious circumstances.
We quitted the banks of the Jelum, and entered the country of Potewar, inhabited by a[60] tribe of people called Gukers, famed for their beauty, and claiming a Rajpoot origin. The credulity of these people is as great as in other parts of India. A grave and respectable man assured me that he had seen a lake, called Ruwaesir, in the hill district of Mundee, on the Sutlege, which had three small islets floating upon it. These are a place of Hindoo pilgrimage; and my informant assured me that they approach to receive the votaries who embark upon them, and are floated out with their offerings! It is obvious that there must be some delusion or deception, which is practised with no small dexterity, as the place retains its character. A native told me that he had heard it was an artificial heap of soil placed over reeds; but he had not visited the spot, and seemed to proffer his information from hearing my doubts as strongly expressed as I felt them. In the valley of Cashmeer there are moveable beds of melons, which in some degree, may be considered in the light of islands. The ingenious people of that valley spread a thick mat on the surface of their lake, and sprinkle it over with soil: it soon acquires a consistency, from the grass growing upon it. On the following year they sow melons and cucumbers, and reap the harvest from a boat; and thus turn to account the very surface of the lake in their rich country. The melon islands[61] of Cashmeer may have supplied a hint to the Hindoo priests of Mundee.
Our approach to the Mohammedan countries became evident daily, and showed itself in nothing more than the costume of the women, many of whom we now met veiled. One girl whom we saw on the road had a canopy of red cloth erected over her on horseback, which had a ludicrous appearance. It seemed to be a framework of wood, but as the cloth concealed every thing as well as the countenance of the fair lady, I did not discover the contrivance. The costume of the unveiled portion of the sex had likewise undergone a change; and they wore wide blue trowsers, tightly tied at the ankle, which taper down, and have a graceful appearance. A web of cloth sixty yards long is sometimes used in a single pair, for one fold falls upon the other.
On the 1st of March we reached the celebrated fort of Rotas, considered to be one of the great bulwarks between Tartary and India. As we wound through the dismal defiles, and might be ruminating on the various expeditions which had traversed this very road, the fort burst upon our view like the scene of a magic lantern. It had been hidden from us by towering precipices. We approached its ponderous walls by a straggling path which time had chiselled in the rock, and soon reached its lofty gateway. The black[62] hoary aspect of the fort, and the arid sterility of the surrounding rocks, inspired us with no favourable idea of the neighbourhood, which has been the resort of many a desperate band. We had omitted to provide ourselves with Runjeet Sing’s order for admission into this fortress; but we proceeded to the gateway, as a matter of course, and after a parley the doors were thrown open. The official permission arrived from Lahore on the following day.
We soon found ourselves among friends, and listened to the tales of the veterans without any fear of witnessing the scenes of their ancestors. The Afghan officers of the Mogul empire under the Emperor Humaioon dethroned that monarch, and fortified themselves in Rotas, in the year 1531. Shere Shah was its founder. Twelve years, and some millions of rupees, are said to have been wasted in its construction; yet it was betrayed, and fell. Humaioon returned from his wanderings with the auxiliaries of Iran, and recovered the kingdom of his forefathers. He commanded that the fort of Rotas should be levelled; but so massy are its walls, and so strong is the whole edifice, that his Ameers and Oomrahs ventured to ask his majesty, whether he came to recover his throne or destroy a single fort, since the one undertaking would require as much energy as the other. Humaioon contented[63] himself with levelling a palace and a gateway as the monument of his conquest, and prudently marched to Delhi. We examined its walls and outworks, its gateways and bastions: and the people pointed out to us the orifices for pouring oil on the besiegers. We viewed with admiration the elaborate loopholes for the matchlock, the deep wells cut in the live rock, and the bomb-proof magazines of the fortification. From one of the towers we had a commanding view of the plain, in which we could distinguish a spacious caravansary, the work of the generous and tolerant Akbar. He here eclipsed his father Humaioon as much as he did in all the acts of his protracted reign. The son raised an edifice to shelter the weary traveller in his pilgrimage; the parent, full of wrath, wasted a greater sum in the demolition of a palace. These caravansaries have been erected at every stage as far west as the Indus; and the traveller cannot pass them without a pleasurable feeling at the enlightened design of their founder. The Emperor Akbar was a philanthropist.
From Rotas we entered into a mountainous and rugged country of great strength, and our road lay in ravines. The chaos of rocks, their vertical strata, terminating in needles from decomposition, the round pebbles that lay imbedded in the sandstone, and the wild scenery,[64] made this an interesting neighbourhood. Humboldt mentions somewhere, that deposits of rock-salt and mineral springs manifest some connection with volcanoes; and among these hills we had both. One may almost convince himself of the upheavings of nature, from a glance at the rock. Though generally vertical, it may be observed in some places to descend upon the ravines, as if the one half of the hill had been suddenly raised, or the other as suddenly depressed. Water is abundant in the ravines, and is also found in wells at a depth of thirty-five feet. To our right we could see the spot at which the Jelum or Hydaspes issues from the mountains. It is called Damgully. There is no route into the valley of Cashmeer by this river; and the most frequented one lies by Meerpoor and Poonch, about twelve miles to the eastward. Near the point where the Jelum enters the plain, there is an isolated rock about sixty feet high, called Raoka, which may be ascended by steps. A Mohammedan saint resides on it. In searching for an obelisk called Rawjee, mentioned by Mr. Elphinstone, we heard of Raoka; but since it only appeared to be a detached portion of rock, we did not visit it.
On the 6th of March we reached the village of Manikyala, at which there is a singular “tope”[65] or mound of masonry. It has been described by Mr. Elphinstone, who gives a correct drawing of it; and tells us, that “it was, indeed, as like Grecian architecture as any building which Europeans, in remote parts of the country, could now construct by the hands of unpractised native builders.”[11] It has been lately opened by M. Ventura, a general in Runjeet Sing’s service. We are much indebted to that gentleman, since his labours were conducted at considerable expense and trouble. Coins and antiques. Through the kindness of my friend M. Allard, I had an opportunity of looking at the reliques which that officer found. A brief description of them has been published in the Researches of the Asiatic Society of Bengal; but I may here observe that they consist of three cylindrical boxes of gold, pewter (or some mixed metal), and iron, which were found cased within one another, and placed in a chamber cut in a large block of stone at the foundation of the pile. The gold box is about three inches long and an inch and a half in diameter, filled with a black dirty substance like mud, half liquid, and mixed up with small pieces of glass or amber; which would suggest an opinion of its once being cased in a glass that had been fractured and shivered. Among[66] this substance, two coins or medals were found: the smaller one is of gold, and about the size of a sixpence, having a human figure, and the four-pronged instrument which marks all the Manikyala coins; the other has two lines of rude character, probably Hindee, on one side, and no writing or symbol on the reverse. Many other coins and reliques were found during the opening of the tope; and the people informed me that some human bones had been disinterred. On my arrival at Manikyala, I had an opportunity of appreciating the valuable services of M. Ventura, by a personal inspection of the “tope,” which his persevering labour has now laid open. That gentleman had first endeavoured to enter the building from below, but failed on account of the great solidity of the structure. Further observation had discovered to him that there was a shaft or well (if I can use the expression) descending into the building from the top; and here M. Ventura dug with success. He first cleared the well, which reaches half way down, and is flagged at the bottom with large blocks of stone. He then completed his work by tearing up these enormous blocks till he reached the foundation, where he was rewarded by finding the cylinders which I have described, as well as a variety of coins, which have been forwarded to Paris, but are yet undeciphered.
In a place of such celebrity I did not expect to find my search for coins and antiques rewarded beyond the most sanguine expectations, since none are mentioned to have been seen by the gentlemen of the Cabool mission. I procured two antiques and seventy copper coins. The value of the latter is much heightened by their corresponding with those found in the interior of the tope by M. Ventura. One of the antiques is a ruby or red crystal, cut in the shape of a head, with a frightful countenance and very long ears; while the other is an oval cornelian, with the figure of a female holding out a flower, and gracefully dressed in a mantle. The execution is superior.[12] I shall notice these coins hereafter, having presented some of them to the Asiatic Society of Bengal, and received the most ample return from Mr. James Prinsep, its able secretary, in various notes regarding them.
I was much struck with the position of Manikyala, for it stands on a spacious plain, and the “tope” is to be distinguished at a distance of sixteen miles. Various surmises have been thrown out regarding this site, but I do not hesitate to fix upon it as Taxilla, since Arrian expressly tells us that “that was the most[68] populous city between the Indus and Hydaspes;” which is the exact position of Manikyala. M. Ventura decides on it as Bucephalia, from a derivation that interprets Manikyala to mean the city of the horse; but this is not founded on history, as Bucephalia stood on the banks of the Hydaspes, and, I believe, I have already described its true position.
I shall describe the “tope” of Belur, which we afterwards visited, before I give any conclusion regarding these buildings.
We reached Rawil Pindee on the 7th, and alighted at the house which the ex-King of Cabool built in his exile. It was a miserable hovel. The town of Rawil Pindee is agreeable; and we were pleased to find the mountains covered with snow, and but twelve miles distant. Some specimens of crystalised sulphur, in its native state, were brought to me from these hills; and there is a town among them called Porewala, which led me to think that it might have some relation to the renowned Porus of the Hydaspes.
We were now fast leaving Hindoostan and its customs behind us. The dandelion had become a common weed. At Manikyala, we halted next door to a bakery, where the whole bread of the village is cooked. How much more sensible is this custom, than that every[69] family should prepare it separately, as in India, and live in perpetual terror of defilement from one another. We were glad to be considered customers of the village oven. On our road we met a numerous body of Afghans, and also Hindoo pilgrims, crowding from beyond the Indus to the great religious fair of Hurdwar: they looked more like Mohammedans than the followers of Brahma. The festival occurs every twelve years, and distance serves to increase the devotion of the pilgrim. The sight of these people from beyond the Indus gave rise to many curious sensations. We wore their dress, and they knew us not; we received their salutations as countrymen, and could not participate in their feelings. Some of them would ask, as we passed, whether we were going to Cabool or Candahar; and from their looks and questions, I found many a secret and doubtful thrill pass across me. This I found to arise from the novelty of our situation, for it soon wore off after we mingled familiarly with the people; and, in course of time, I gave and returned the usual salutations with all the indifference of a practised traveller.
At Rawil Pindee we had a visit from the government officers, among whom was a Seik priest, or Bedee, who had taken the singular vow, never to repeat three or four words without the name[70] of “Vishnu,” one of the Gods of the Hindoo Trinity. His conversation was, therefore, most remarkable; for, on all subjects, and in all answers, he so interlarded the words “Vishnu, Vishnu,” that I could not suppress a smile. This personage presented us with a purse of 200 rupees; but it appeared to come from Vishnu, and not from the Maharaja Runjeet Sing.
About fifteen miles from Rawil Pindee, we passed the defile of Margulla, and descried with joy the mountains beyond the Indus. This is a narrow pass over the low hills, and paved with blocks of stone for 150 yards. A Persian inscription, let into the rock, commemorates the fame of the civilised Emperor who cut the road. The defiles continue for about a mile; when a bridge across a rivulet conducts the traveller to the next caravansary. A bridge, a caravansary, and a road cut through a hill, and within a distance of two miles, bespeak a different rule from that of the Punjab in modern times. We continued our march to Osman, about twenty miles from Rawil Pindee. It stands on a plain, at the mouth of a valley, close to the base of the outlying hills. Its meadows are watered by the most beautiful and crystal rivulets, that flow from the mountains. Some of them are conducted by artificial means through the village, and turn little water mills that grind flour. Up the valley[71] stands the fort of Khanpoor, with some beautiful gardens; and over it snow-clad mountains rear their peaks. The fields of this fruitful valley lie neglected, from the exorbitant assessment of the person who farms it. The peasants have no hope of redress but by such an expedient; and this entire suspension of the labours of the husbandmen may open the understanding of the misguided governor.
TOPE OF BELUR.
We visited Osman, which is about four miles from the King’s road, at the base of the lower Hemilaya, to examine a mound or “tope,” like that of Manikyala, which stands on the nook of a range of hills near the ruined village of Belur,[72] about a mile beyond Osman. The construction of the building, as depicted in the annexed sketch, gives it to the same era as that of Manikyala. Neither of the buildings are perfect; and the one now delineated differs from the other in the greater length of the shaft. It is fifty feet high, or about two thirds of the height of Manikyala. It has also been opened, and the square aperture formed of cut stone has descended into the building. The small pilasters are likewise to be recognised, but the mouldings are more numerous, and the general outline of the building somewhat different. The “tope” of Belur is a conspicuous object, from its elevated situation, but I could not gather a tradition regarding it from the numerous population. Like one in search of the philosopher’s stone, I was led from place to place, and now learned that there were two buildings similar to these “topes,” beyond the Indus, between Peshawur and Cabool. We also discovered the ruins of another tope, three miles eastward of Rawil Pindee. The few coins which I found at the tope of Belur were of the same type as those already described. Seeing that both the structures of Manikyala and Belur are pierced by a shaft that descends into the building, I incline to a belief, that in these “topes” we have the tombs of a race of princes who once reigned in Upper India, and that they[73] are either the sepulchres of the Bactrian kings, or their Indo-Scythic successors, mentioned in the Periplus of the second Arrian. The rudeness of the coins would point to the latter age, or second century of the Christian era.
From the beautiful rivulets of Osman we passed down the valley, and, after a march of seven miles, found ourselves in the garden of Hoosn Abdall,—a spot which attracted the munificent Emperors of Hindoostan. It is situated between two bare and lofty hills, whose brown and naked tops do not contribute much to its beauty; still it must be an enchanting place in the hot months. The garden houses are now mouldering to decay, and weeds hide the flowers and roses; yet the peach and apricot trees glowed with blossom, the vines clung to their branches, and the limpid water gushed in torrents from the rock. Some hundred springs rise in the limit of this small garden, and, after washing its beds, pay their tribute to a brook which passes on to the Indus. They form pools, which are stored with fish, that may be seen darting about in the clear water. The spring had commenced when we visited this delightful place. As we passed it, our view opened upon the valley of Drumtour, that leads to Cashmeer; and the range of hills at Puklee, covered with snow, were to be traced in chain with more lofty mountains beyond them. The[74] fertile plain of Chuch and Huzara also lay before us.
We came in sight of the Indus, at a distance of fifteen miles. It could be traced from its exit through the lower hills to the fort of Attok, by the vapour which hung over it like smoke. As the water of the Indus is much colder than the atmosphere, it may account for this phenomenon. We encamped at Huzroo, which is a mart between Peshawur and Lahore. The people were now quite changed; they were Afghans, and spoke Pooshtoo. I was struck with their manly mien, and sat down with delight on a felt, with an Afghan, who civilly invited me to converse with him. I did not regret to exchange the cringing servility of the Indians for the more free and independent manners of Cabool. An itinerant goldsmith, who had heard of our intended journey to Bokhara, came and chatted with us. He had travelled there, and even in Russia; and showed us a copper copec which he had brought with him on his return. He spoke of the equity and justice of the people among whom we were to travel, which made this rambling jeweller a welcome visiter. He was a Hindoo.
On the morning of the 14th of March, we had the pleasure of encamping on the banks of the Indus, with the troops of Runjeet Sing, now on the frontier, under Sirdar Huree Sing. That[75] chief came to meet us with all the forms of eastern pomp, and conducted us to a comfortable suite of tents which he had prepared for us. On our march to the river, we passed the field of battle where the Afghans made their last stand, now some twenty years ago, on the eastern side of the Indus. They were commanded by the Vizier Futteh Khan, who fled, panic struck, though not defeated. A horde, as numerous as that of Xerxes or Timour, might encamp on this spacious plain, which is an entire sheet of cultivation. It was covered with rounded stones, (many of which were granite,)—an unerring proof of the agency of water. We visited our host, the commandant, who welcomed us with his troops and officers in array, and gave us the cordial reception of friends. Our conversation turned on the warlike deeds of Runjeet, and his passing the Indus both with and without a ford. We grew interested in the subject, and soon made up our minds to, at least, make the attempt of fording this great river.
We mounted one of the chief’s elephants, and, accompanied by himself and 200 horsemen, passed a few miles down the river to the village of Khyrakhuel, about five miles above Attok. The stream was here divided into three branches, and in the two first gushed with amazing violence. I did not like the appearance[76] of the torrent; and, though I said nothing, would have willingly turned back; but how could that be, when I had been the foremost to propose it? The chief rallied his escort round him, threw a piece of silver money into the river, according to custom, and dashed into it. We followed, and the whole of our party reached in safety. While on the island, and preparing to enter the principal branch, a melancholy accident occurred to some stragglers who attempted to follow us. They were seven in number; and, instead of crossing at the exact point where we had effected the passage, they passed a few yards lower down, with the water but knee deep, yet very rapid. The whole seven were unhorsed in a moment, and swept into the stream. The ferrymen ran to their assistance, and extricated them all but one poor fellow and two horses, whom we could see struggle, and at last sink. The others were rescued with great difficulty, and two of them were all but dead. We were shocked at the catastrophe, and proposed to return, but the chief would not listen to it. He gave a laugh, and said, “What know ye, that these fellows (we thought they had all gone) may be kings in another world; and what is the use of a Seik if he cannot pass the Attok?” (Indus). The principal branch, however, was still in our front; and I only[77] agreed to cross if the horsemen were left behind. “Leave my guard,” cried the chief, “impossible!” but we did leave it, and safely passed the ford. The footing was slippery, and the current shot with great rapidity: the colour of the water was blue, and it was exceedingly cold, which makes it trying to both man and beast. The elephants pressed up against the stream, and roared as we advanced. The excitement of such an undertaking is great, and would have been exhilarating, had not our joy been dimmed by such a calamity. This ford has often been used by the Seiks, but the passage has involved many serious accidents.
A tale of a desperate soldier was here related to me, as having occurred at Lahore. He was a native of Hindoostan, and had murdered the adjutant of the regiment in which he was serving, in Runjeet’s army. An example was called for in the support of discipline; but Runjeet Sing has never shed blood since he attained his throne, and refused to put him to death, though urged to it by the French officers. The hands of the culprit were ordered to be amputated on the parade ground, before the troops, and were chopped off by an axe; the hemorrhage was arrested by immersing the stump in burning oil. The hands were nailed on a board, as a warning to the army, and the unfortunate man was dis[78]missed with ignominy. A comrade conducted him to a ruined mosque, where he passed the night, but his spirit forbade him to survive his disgrace, and he resolved on committing suicide. Next day he threw himself into the river (Ravee): his resolution was shaken, and instead of drowning himself, he crossed the river, swimming with his handless stumps!
We now proceeded to the fortress of Attok, which stands on a black slaty ridge, at the verge of the Indus, the “forbidden river” of the Hindoos. It was, indeed, a forbidden one to us, for the garrison had mutinied, ejected their officers, and seized upon the ferry-boats. Their arrears of pay were not forthcoming, and they had taken this means of informing Runjeet of their grievances. It was in vain that we produced the most peremptory orders, to receive us inside the walls, and show us the curiosities of the place; they replied, that our complaints would now be heard, since the Maharaja will know of their ill treatment towards us. Since they evinced no further contumacy, we halted outside, in a dilapidated mosque, and were not molested. It was useless to parley with irritated men, and I thought we were fortunate in prevailing on them, after a detention of two days, to give us a boat, in which we were ferried across the grand boundary of India, on the afternoon of the 17th[79] of March. The water was azure blue, and the current exceeded six miles an hour. We passed in four minutes. About 200 yards above Attok, and before the Indus is joined by the Cabool river, it gushes over a rapid with amazing fury. Its breadth does not here exceed 120 yards; the water is much ruffled, and dashes like the waves and spray of the ocean. It hisses and rolls with a loud noise, and exceeds the rate of ten miles in the hour. A boat cannot live in this tempestuous torrent; but after the Cabool river has joined it, the Indus passes in a tranquil stream, about 260 yards wide and 35 fathoms deep, under the walls of Attok. This fortress is a place of no strength: it has a population of about 2000 souls.
Before crossing the Indus, we observed a singular phenomenon at the fork of the Indus and Cabool river, where an ignis fatuus shows itself every evening. Two, three, and even four bright lights, are visible at a time, and continue to shine throughout the night, ranging within a few yards of each other. The natives could not account for them, and their continuance during the rainy season is the most inexplicable part of the phenomenon, in their estimation. They tell you, that the valiant Man Sing, a Rajpoot, who carried his war of revenge against the Mahommedans across the Indus, fought a[80] battle in this spot; and that the lights now seen are the spirits of the departed. I should not have credited the constancy of this will-o’-the-wisp, had I not seen it. It may arise from the reflection of the water on the rock, smoothed by the current: but then it only shows itself on a particular spot, and the whole bank is smoothed. It may also be an exhalation of some gas from a fissure in the rock, but its position prevented our examining it.
We found the fishermen on the Indus and Cabool river washing the sand for gold. The operation is performed with most profit after the swell has subsided. The sand is passed through a sieve, and the larger particles that remain are mixed with quicksilver, to which the metal adheres. Some of the minor rivers, such as the Swan and Hurroo, yield more gold than the Indus; and as their sources are not remote, it would show that the ores lie on the southern side of the Hemilaya.
It required some arrangement to commence our advance into the country of the Afghans; for they and the Seiks entertain the most deep-rooted animosity towards each other. At Attok, a friendly letter was sent to us by the chief of Peshawur, expressive of his good wishes. I, therefore, addressed that personage, Sooltan Mahommed Khan, informing him of our intentions, and soliciting his protection. I likewise sent a letter of introduction from Runjeet to the chief of Acora; but so inconstant is power in these countries, that that person had been ejected during the few weeks we had been travelling from Lahore: but the usurper opened the communication, and kindly despatched a party to meet us. The subjects of Runjeet Sing escorted us to their frontier, which is three miles beyond the Indus; here we met the Afghans. Neither party would approach, and we drew up at a distance of about 300 yards from each other. The Seiks gave us their “wagroojee futtih,” synonymous[82] with our three cheers, and we advanced, and delivered ourselves to the Mahommedans; who said, Wus-sulam alaikoom! “Peace be unto you!” We trod our way to Acora, with our new people, the Khuttuks, a lawless race, and alighted at that village, which is nearly deserted, from the constant inroads of the Seiks. The chief immediately waited upon us, and expressed his dissatisfaction at our having purchased some articles from the bazar, since it was a reflection on his hospitality. I begged his pardon, and placed the mistake on my ignorance of the Afghan customs, adding, that I would not forget, as I advanced, the hospitality of the Khuttuks of Acora. The chief took his leave, charging us, before his departure, to consider ourselves as secure as eggs under a hen; a homely enough simile, the truth of which we had no reason to doubt. Yet it was at this place that poor Moorcroft and his party encountered some serious difficulties, and were obliged to fight their way. We here received a second letter from the chief of Peshawur, which was most satisfactory, since it contained a friendly reply without his having received any of the letters of introduction which we possessed. It intimated that a person was approaching to conduct us.
We had now quitted the territories of Hin[83]doostan, and entered on a land where covetousness of a neighbour’s goods is the ruling passion; we therefore marched with our baggage. Our few servants were also divided into regular watches for the night. We had two Afghans, two Indians, and two natives of Cashmeer. A Cashmeerian paired with an Indian, and the trustworthy with the most lazy; while we ourselves were to superintend the posting of the sentries. Our people laughed heartily at this military disposition; but it was ever after enforced in all our travels. We ourselves were now living as natives, and had ceased to repine at the hardness of the ground and the miserable hovels in which we sometimes halted. I had also disposed of my own valuables in what then appeared to me a masterly manner: a letter of credit for five thousand rupees was fastened to my left arm, in the way that the Asiatics wear amulets. My polyglot passport was fixed to my right arm, and a bag of ducats was tied round my waist. I also distributed a part of my ready money to each of the servants, and so perfect was the check that had been established over them, that we never lost a single ducat in all our journey, and found most faithful servants in men who might have ruined and betrayed us. We trusted them, and they rewarded our[84] confidence. One man, Ghoolam Hoosun, a native of Surat, followed me throughout the whole journey, cooked our food, and never uttered a complaint at the performance of such duties, foreign as they were to his engagements. He is now with me in England.
Our conductor, on the part of Runjeet Sing left us at Acora. Choonee Lal, for that was his name, was a quiet inoffensive Brahmin, who did not seem at ease across the Indus. Salt monopoly. I gave him a farewell letter to his master; and, since his Highness had written for my sentiments regarding the salt-mines of the Punjab, and the best means of profiting by them, I gave him a long account of salt monopolies, telling him, that it was better to levy high duties upon salt than grain. I told him, also, in as many words, that the salt-range was as valuable a portion of his territory as the valley of Cashmeer; but I do not believe that his Highness stood in need of much explanation, as the measures which we had seen at the mines practically proved.
On our road to Acora, we passed a field of battle, at the small village of Sydoo, where 8000 Seiks had defended themselves against an enraged population of 150,000 Mahommedans. Bood Sing, their commander, threw up a small breast-work of loose stones, and extricated him[85]self from his dilemma, so as to secure the praise even of his enemies. We now saw the place, and the bleaching bones of the horses, which had fallen on the occasion. On the next march we passed the more celebrated field of Noushero, to which our attention had been directed by Runjeet Sing himself. He here encountered the Afghans for the last time; but their chief, Azeem Khan, was separated from the greater part of his army by the river of Cabool. The Seiks defeated the divisions on the opposite side, mainly through the personal courage of Runjeet Sing, who carried a hillock with his guards, from which his other troops had three times retreated. Azeem Khan, of Cabool, fled without encountering the successful army, which had partly crossed the river to oppose him. It is believed, that he feared the capture of his treasure, which would have fallen into Runjeet’s power if he had advanced; but it is also said, that he was terrified by the shouts of the Seiks on the night of their victory. He attributed their exclamations to the fresh arrival of troops: for they have a custom of shouting on such occasions. We have already compared this potentate with Porus; and the similar stratagem by which Alexander defeated that prince will also be remembered. As the Greeks had terrified his predecessor on the Hydaspes, the[86] Seiks now frightened the Afghans by their shouts and pæons.
As we traversed the plain to Peshawar, I felt elevated and happy. Thyme and violets perfumed the air, and the green sod and clover put us in mind of a distant country. The violet has the name of “gool i pueghumbur,” or the rose of the Prophet, par excellence, I suppose, from its fragrance. At Peerpaee, which is a march from Peshawur, we were joined by six horsemen, whom the chief sent to escort us. We saddled at sunrise, though it rained heavily, and accompanied the party to the city, sorely trying the patience of the horsemen, by declining to halt half way, that they might give timely information of our approach. We pushed on till near the city; when their persuasion could be no longer resisted. “The chief sent us only to welcome you, and has ordered his son to meet you outside the city,” said their commander, “and we are now within a few hundred yards of his house.” We halted, and in a few minutes the son of the chief made his appearance, attended by an elephant and a body of horse. He was his eldest son, a handsome boy, about twelve years old, and dressed in a blue tunic, with a Cashmeer shawl as a turban. We dismounted on the high road and embraced; when the youth[87] immediately conducted us to the presence of his father. Never were people received with more kindness: he met us in person at the door-way, and led us inside of an apartment, studded with mirror glass and daubed over with paint in exceedingly bad taste. His house, his country, his property, his all, were ours; he was the ally of the British government, and he had shown it by his kindness to Mr. Moorcroft, which he considered as a treaty of friendship. We were not the persons who wished to infringe its articles. Sooltan Mahommed Khan is about thirty-five years old, of rather tall stature, and dark complexion. He was dressed in a pelisse, lined with fur, and ornamented over the shoulders with the down of the peacock, which had a richer look than the furniture that surrounded him. We were glad to withdraw and change our wet clothes, and were conducted to the seraglio of Sooltan Mahommed Khan, which he had prepared, I need not add, emptied, for our reception. This was, indeed, a kind of welcome we had not anticipated.
An hour had not passed before we were visited by Peer Mahommed Khan, the younger brother of the chief, a jolly and agreeable person. The chief himself followed in the course of the evening; and a sumptuous dinner succeeded, of which we all partook. The meat[88] was delicious, and so was the cookery. I need not add, that we ate with our hands; but we soon ceased to wonder at a nobleman tearing a lamb in pieces and selecting the choice bits, which he held out for our acceptance. A long roll of leavened bread was spread in front of each of us as a plate; and, since its size diminished as the meat disappeared, it did its part well. Pilaos and stews, sweets and sours, filled the trays; but the bonne bouche of the day was a lamb, that had never tasted aught but milk. A bitter orange had been squeezed over it, and made it very savoury. Four trays of sweetmeats followed, with fruit; and the repast concluded with sherbet, mixed with snow, the sight of which delighted us as much as our new friends. A watch of night was spent before we broke up; and after the chief had repeated in a whisper his devotion to our nation and anxiety for our welfare, he bade us good night. I had almost lost the use of my legs from the irksome position of constraint in which I had so long sat. If we had been prepared to like the manners of this people, there was much to confirm it on this evening.
On the following day we were introduced to the remainder of the family. There are two brothers besides the chief, and a host of sons and relations. The most remarkable person of the[89] family was a son of Futtih Khan, the Vizier of Shah Mahmood, who had been so basely and cruelly murdered. The lad is about fourteen years of age, and the solitary descendant of his ill-fated father. The sons of the Meer Waeez and Mookhtar o-doula, whose parents had dethroned Shah Shooja, were among the party, and the day passed most agreeably. The people were sociable and well-informed, free from prejudice on points of religion, and many of them were well versed in Asiatic history. They were always cheerful, and frequently noisy in their good-humour. During the conversation many of them rose up, and prayed in the room when the stated hours arrived. As we got better acquainted in Peshawur, our circle of acquaintance was widely extended, and visitors would drop in at all hours, and more particularly if they found us alone. The Afghans never sit by themselves, and always made some apology if they found any of us solitary, though it would have been sometimes agreeable to continue so. In the afternoon the chief invited us to accompany him and his brothers to see the environs of Peshawur. The doctor stayed away, but I rode with them. Of the town of Peshawur I shall say nothing, since the graphic and accurate descriptions of Mr. Elphinstone require no addition. Such, indeed, is the nature of[90] the information contained in his valuable work, that I shall always avoid the ground on which he trod, and, in Afghanistan, confine myself to incidents and adventures of a personal nature. I say this in my own defence. I had accompanied the chief on a day most favourable to a stranger, the “nouroz,” or new year (the 21st of March), which is celebrated by the people. The greater part of the community were gathered in gardens, and paraded about with nosegays and bunches of peach-blossom. We entered the garden of Ali Murdan Khan, and seated ourselves on the top of the garden-house, and looked down upon the assembled multitude. The trees were covered with blossom, and nothing could be more beautiful than the surrounding scene. The chief and his brothers took great pains to point out the neighbouring hills to me, explaining by whom they were inhabited, with every other particular which they thought might interest. They also informed me, that the nobleman who had prepared this garden possessed the philosopher’s stone (the “sung-i-fars”), since there was no other way of accounting for his great riches. They added, that he threw it into the Indus; which at least eases them of the dilemma as to his heir.
We soon got accustomed to our new mode of life, and, as we made it a rule never on any[91] occasion to write during the day or in public, had leisure to receive every person who came to see us. In a short time we became acquainted with the whole society of Peshawur, and, during the thirty days we remained there, had an uninterrupted series of visiting and feasting. Nothing, however, more contributed to our comfort and happiness than the kindness of our worthy host. Sooltan Mahommed Khan was not the illiterate Afghan whom I expected to find, but an educated well-bred gentleman, whose open and affable manner made a lasting impression upon me. As we were sitting down to dinner, he would frequently slip in, quite unattended, and pass the evening with us. He would sometimes be followed by various trays of dishes, which he had had cooked in his harem, and believed might be palatable to us. He is a person more remarkable for his urbanity than his wisdom; but he transacts all his own business: he is a brave soldier; his seraglio has about thirty inmates, and he has already had a family of sixty children. He could not tell the exact number of survivors when I asked him!
On the Friday after our arrival we accompanied the chief and his family to some flower-gardens, where we spent the greater part of the day in conversation. The chief himself sat[92] under one tree, and we ranged ourselves beneath another. Iced sherbet and confections were brought to us, and we heard much of the munificence of Mr. Elphinstone from Moollah Nujeeb, an elderly man, who had accompanied him to Calcutta. In the afternoon we returned to the King’s garden, which is a most spacious one, and sat down on the ground with Sooltan Mahommed Khan and his family, to partake of sugar-cane cut into small pieces. Four of the chief’s sons accompanied us; and it was delightful to see the affectionate notice which he took of his children, none of whom were five years old. Each of them sat on horseback in front of one of his suite, and held the reins in a masterly manner: for the Dooranees are taught to ride from infancy. We then followed the chief to his family burying-ground, where his two elder brothers, Atta and Yar Mahommed Khan, who fell in battle, lie interred. The whole branches of the family were present, and offered up their afternoon prayers in a mosque, close to the grave. The sight was an impressive one, and the more so, since the sons of the deceased brothers were among the party. The day finished with a visit to a holy man named Shekh Iwuz: and such is the usual manner of spending a Friday among the Dooranee nobles of Peshawur. The chief’s retinue consisted of his[93] relations and servants: he had no guards, and, at first starting, was only accompanied by ourselves and two horsemen. There is a simplicity and freedom about these people greatly to be admired; and, whatever the rule may be, I can vouch for petitioners having an ear, at least, given to their complaints. Every one seems on an equality with the chief, and the meanest servant addresses him without ceremony. He himself seems quite free from every sort of pride or affectation, and is only to be distinguished in the crowd by his dress, in which he is fond of richness and ornament.
In one of our rides about Peshawur with the chief, we had a specimen of justice and Mahommedan retribution. As we passed the suburbs of the city we discovered a crowd of people, and, on a nearer approach, saw the mangled bodies of a man and woman, the former not quite dead, lying on a dung-hill. The crowd instantly surrounded the chief and our party, and one person stepped forward and represented, in a trembling attitude, to Sooltan Mahommed Khan, that he had discovered his wife in an act of infidelity, and had put both parties to death; he held the bloody sword in his hands, and described how he had committed the deed. His wife was pregnant, and already the mother of three children. The chief asked[94] a few questions, which did not occupy him three minutes; he then said, in a loud voice, “You have acted the part of a good Mahommedan, and performed a justifiable act.” He then moved on, and the crowd cried out “Bravo!” (“Afreen!”) The man was immediately set at liberty. We stood by the chief during the investigation; and, when it finished, he turned to me, and carefully explained the law. “Guilt,” added he, “committed on a Friday, is sure to be discovered;” for that happened to be the day on which it occurred. There is nothing new in these facts; but, as an European, I felt my blood run chill as I looked on the mangled bodies, and heard the husband justifying the murder of her who had borne him three children: nor was the summary justice of the chief, who happened to be passing, the least remarkable part of the dismal scene. It seems that the exposure of the bodies on a dung-hill is believed to expiate in some degree the sins of the culprit, by the example it holds out to the community; they are afterwards interred in the same spot.
We were invited, shortly after our arrival at Peshawur, to pass a day with the chief’s brother, Peer Mahommed Khan. He received us in a garden, under a bower of fruit-trees, loaded with blossom. Carpets were spread, and the boughs shaken before we sat down, which[95] covered them with the variegated leaves of the apricot and peach. The fragrance and beauty were equally delightful. The party consisted of about fifty persons, all of whom partook of the entertainment, which was on a substantial and large scale. There were performers in attendance, who chanted odes in Pooshtoo and Persian. The conversation was general, and related chiefly to their own expeditions. The children of the chief and his brothers were again present: they rioted among the confectionery, and four of them had a pitched battle with the blossom of the trees, which they threw at each other like snow. I do not remember to have seen any place more delightful than Peshawur at this season: the climate, garden, and landscape, delight the senses, and to all we had been so fortunate as to add the hospitality of the people. I had brought no presents to conciliate these men, and I therefore would receive none at their hands; but, on the present occasion, our host produced a small horse, of a hill breed, and insisted on my accepting it. “Mr. Moorcroft,” said he, “accepted one of these same horses, which availed him in his difficulties; and I cannot, therefore, receive a refusal, since you are entering such dangerous countries.” The horse was forcibly sent to my house. The sequel will[96] show the strange providence which is sometimes to be traced in the acts of man.
But our residence at the house of the chief was not without inconvenience, and it required some consideration to devise a plan for our extrication with credit. The chief was at enmity with his brother of Cabool, and wished to persuade us to pass through that city by stealth, and without seeing him. He offered, indeed, to send a Persian gentleman as our conductor beyond Afghanistan; and, had I believed the arrangement practicable, I would have rejoiced: but it was obviously difficult to pass through the city of Cabool and the country of its chief without his knowledge; and a discovery of such an attempt might bring down upon us the wrath of a man from whom we had nothing to fear by openly avowing ourselves as British officers. I was resolved, therefore, to trust the chief of Cabool as I had trusted his brother of Peshawur, so soon as I could persuade Sooltan Mahommed Khan that our intercourse there should never diminish the regard which we felt for him personally! A few days afterwards, he consented to our writing to Cabool, and notifying our approach to Nuwab, Jabbar Khan, the brother of the governor, whom I addressed under a new seal, cut after the manner of the[97] country, and bearing the name of “Sikunder Burnes.” Sooltan Mahommed Khan now confined himself to advice, and such good offices as would conduct us in safety beyond his dominions. He requested that we might still further change our dress, which we did, and left it as the best sign of our poverty. The outer garment which I wore cost me a rupee and a half, ready made, in the bazaar. We also resolved to conceal our character as Europeans from the common people, though we should frankly avow to every chief, and indeed every individual with whom we might come into contact, our true character. But our compliance with this counsel subjected us to the strongest importunities to avoid Toorkistan, and pass by the route of Candahar, into Persia. Nothing could save us from the ferocious and man-selling Uzbeks; the country, the people, everything was bad. They judged of the calamities of Moorcroft and his associates, and I listened in silence. The chief thought that he had so far worked upon us to abandon the design, that he prepared various letters for Candahar, and a particular introduction to his brother, who is chief of that place.
Shortly after our arrival in Peshawur, Sooltan Mahommed Khan illuminated his palace, and invited us to an entertainment, given, as he[98] assured us, on our account. His mansion was only separated from ours by a single wall, and he came in person to conduct us in the afternoon. The ladies had been spending the day in these apartments, but the “krook”[13] was given before we entered, and a solitary eunuch, who looked more like an old woman, only now remained. In the evening the party assembled, which did not exceed fifteen persons, the most distinguished in Peshawur: we sat in the hall, which was brilliantly lighted: behind it there was a large fountain in the interior of the house, shaded by a cupola about fifty feet high, and on the sides of it were different rooms, that overlooked the water. The reflection from the dome, which was painted, had a pleasing effect. About eight o’clock we sat down to dinner, which commenced with sweetmeats and confections, that had been prepared in the harem. They were far superior to anything seen in India; the dinner succeeded, and the time passed very agreeably. The chief and his courtiers talked of their wars and revolutions, and I answered their numerous queries regarding our own country. The assembly were ever ready to draw comparisons between anything stated, and the records of Asiatic history,[99] referring familiarly to Timour, Baber and Aurungzebe, and exhibiting at the same time much general knowledge. I gave them accounts of steam-engines, galvanic batteries, balloons, and electrifying machines, which appeared to give universal satisfaction. If they disbelieved, they did not express their scepticism. Many of the courtiers of course flattered the chief as they commented on his remarks, but their style of address was by no means cringing, and the mild affability of Sooltan Mohammed Khan himself quite delighted me. He spoke without reserve of Runjeet Sing, and sighed for some change that might release him from the disgrace of having his son a hostage at Lahore. The subject of the Russians was introduced, and a Persian in the party declared that his country was quite independent of Russia. The chief, with much good humour, remarked, that their independence was something like his own with the Seiks, unable to resist, and glad to compromise.
Among our visitors, none came more frequently than the sons of the chief and his brothers; and none were more welcome, for they displayed an intelligence and address which surprised me. Nearly the whole of them were suffering from intermittent fever, that was soon cured by a few doses of quinine, of which we[100] had a large supply. The knowledge exhibited by these little fellows induced me on one occasion to note their conversation. There were four of them present, and none had attained his twelfth year. I interrogated them, as they sat round me, on the good qualities of Cabool, giving to each two answers; they were as follows: 1. the salubrity of the climate; 2. the flavour of the fruit; 3. the beauty of the people; 4. the handsome bazaar; 5. the citadel of the Bala Hissar; 6. the justice of the ruler; 7. the pomegranates without seed; and, 8. its incomparable “ruwash,” or rhubarb. Four answers to its bad qualities gave the following information: 1. Food is expensive; 2. the houses cannot be kept in repair without constantly removing the snow from the roof; and the floods of the river dirty the streets; and, 4. the immorality of the fair sex, which last is a proverb, given in a couplet. It does not appear to me that boys in Europe show such precocity, and it is no doubt here attributable to their earlier introduction into the society of grown up people. When a boy has arrived at his twelfth year, a separate establishment is maintained on his account, and, long before that time of life, he is prohibited from frequenting his mother’s apartments but on certain occasions. Khoju Mahommed, the eldest son of the chief of Peshawur, whom I have already mentioned, came one[101] day to invite me to dinner, and I expressed some surprise to hear that he had a house of his own. What! replied the youth, would you have me imbibe the disposition of a woman, when I am the son of a Doorannee? I occasionally accompanied these scions to the gardens of Peshawur, and found them good associates, as no person ever thought of disturbing us. I remember of hearing from one of them, a tale of his father’s wars and untimely end in battle two years before, and how he took the bloody head of his parent in his arms, when brought from the field without its trunk.
These rambles in Peshawur were not always undertaken in such company, for I used latterly to go unattended even by a capchee or doorkeeper of the chief, who used to accompany us on our first arrival. I visited the Bala Hissar, in which Shah Shooja had received so gorgeously the Cabool mission of 1809. It is now a heap of ruins, having been burned by the Seiks in one of their expeditions to this country. I also went to the large caravansary, where that amusing and talented traveller Mr. Forster describes with such humour the covetous Moollah, who wished to steal his clothes. Circumstances were strangely changed since his days, now some fifty years ago; he considered his journey and dangers at an end on reaching Cabool, where[102] we looked for their commencement. Passing a gate of the city, I observed it studded with horse shoes, which are as superstitious emblems in this country as in remote Scotland. A farrier had no customers: a saint to whom he applied recommended his nailing a pair of horse shoes to a gate of the city: he afterwards prospered, and the farriers of Peshawur have since propitiated the same saint by the same expedient, in which they place implicit reliance.
One of our most welcome visitors in Peshawur was a seal engraver, a native of the city, who had travelled over the greater part of Asia and Eastern Europe, though he had not yet attained his thirtieth year. In early life he had conceived the strongest passion to visit foreign countries, and with the avowed, but by no means the only, motive of making a pilgrimage to Mecca, quitted his house without the knowledge of his family, and proceeded by the Indus to Arabia. He had performed the haj, and then visited Egypt, Syria, Constantinople, Greece, and the islands of the Archipelago, supporting himself during the journey by engraving the names of the faithful, which appears to be a profitable sort of occupation. With his wealth he enjoyed the new scenes of the Levant, and united himself to other wanderers, from one of whom he had happily escaped a base attempt to poison. After an absence of five or six years, he returned to his[103] family, who had long looked upon him as lost. His father took the earliest opportunity of settling him in life, to check his roaming propensities, so that he now lived quietly in Peshawur. He appeared quite delighted to visit us, and talk of the Nile and the pyramids, Istambool and its golden horn, the accounts of which he could get few of his countrymen to believe. He looked back upon his peregrinations with great delight, and sighed that his being the father of a family prevented his joining us. This disposition to wander is a curious trait on the part of the Afghans, for they are great lovers of their country. A Mahommedan, however, is at home everywhere his creed is professed, for there is a sort of fellowship in that religion, like free-masonry, which binds its members together; among them there are no distinctions of grade or rank, which so strongly mark the society of other sects and countries.
We arrived at the season of the quails, when every one who could escape from his other vocations was engaged in hawking, netting, or fighting these courageous little birds. Every Tuesday morning the chief had a meeting in his court yard, to encourage the sport. He used to send for us to witness it; it is by no means destitute of amusement, whether we regard the men or the birds; for chief, servant, and subject[104] were here on an equality, the quails being the heroes, not the men. They are carried about in bags, and enticed to fight with each other for grain, which is sprinkled between them. When the quail once runs he is worthless, and immediately slain, but they seldom make a precipitate retreat. Nothing can exceed the passion of the Afghans for this kind of sport; almost every boy in the street may be seen with a quail in his hand, and crowds assemble in all parts of the city to witness their game battles.
Seeing the interest which we took in these scenes, the chief invited us to accompany him on a hawking party, about five miles from Peshawur; but we were unsuccessful, and killed nothing. We went in search of water-fowl, and a party that preceded us had disturbed the ducks. We had, however, an Afghan pic-nic, and an insight into national manners. We sat down under a slight awning, and the servants produced eight or ten young lambs, which had been slain on the occasion. The chief called for a knife, cut up one of them, spitted the pieces on a ramrod drawn from one of his attendant’s match-locks, and handed it to be roasted. He remarked to me that meat so dressed had a better flavour than if cooked by regular servants, and that if we were really in the field he would hold one end of the ramrod and give the other to some[105] one else till the meat was ready, which would make the entertainment thoroughly Doorannee. I liked this unaffected simplicity. There were about thirty in the party to partake of the déjeuné and not a morsel of it was left, so keen were our appetites, and so good our fare; but the Afghans are enormous eaters.
As the time of our departure drew near, we had nothing but a continued succession of feasting. We dined with all the chiefs and many of their sons, with priests and Meerzas. Among the most pleasant of our parties was one given by Moollah Nujeeb, a worthy man who had made an enterprising journey into the Kaffir country at the instigation of Mr. Elphinstone, and for which he enjoys and merits a pension. He gave us good counsel, and showed much interest in our behalf; but strongly dissuaded us from entertaining a holy person as our guide, on which I had resolved.[14] The Uzbeks are described to be much under the influence of their priests and Syuds, and I thought that the company of one of them might avail us on an occasion of difficulty, since Moorcroft had entirely trusted to one of them, who is now in Peshawur.[106] Moollah Nujeeb assured me, on the other hand, that such a person could never extricate us from any difficulties, and would publish our approach every where; and he further insinuated, that many of the disasters which had befallen the unfortunate Moorcroft were to be attributed to one of these worthies. Such advice from one who was a priest himself deserved notice, and I afterwards ascertained the justness of the Moollah’s views.
It was however necessary to conciliate the holy man to whom I have alluded, and I visited him. His name was Fuzil Huq, and he boasts a horde of disciples towards Bokhara, nearly as numerous as the inhabitants. My introduction to him was curious, for Monsieur Court had desired his secretary to write to another holy man of Peshawur, whose name he had forgotten. In his difficulties he applied to me, and knowing the influence of Fuzil Huq, I mentioned him at random: the letter was written; I delivered it, and the saint was gratified at its receipt from a quarter where he had no acquaintance. He received me with kindness, and tendered his services most freely, offering letters of introduction to all the influential persons in Tartary. He had heard that I was of Armenian descent, though in the English employ, nor did I deem it necessary to open his eyes on the subject.[107] I thanked him for his kindness with all the meekness and humility of a poor traveller, and he proceeded to give his advice with a considerable degree of kindness. Your safety, he said, will depend on your laying aside the name of European, at all events of Englishman; for the natives of those countries believe the English to be political intriguers, and to possess boundless wealth. Common sense and reflection suggested a similar conduct, but the performance was more difficult. The saint prepared his epistles, which he sent to us; they were addressed to the king of Bokhara and the chiefs on the Oxus, five in number, who owned him as their spiritual guide. We were described as “poor blind travellers,” who are entitled to protection from all members of the faithful. They abounded in extracts from the Koran, with other moral aphorisms enlisted for the occasion on our behalf. The saint, however, made a request that we should not produce these letters unless an absolute necessity compelled us; but I looked upon them as very valuable documents. I did not quit this man’s house without envying him of the influence over such tribes, which he owes to his descent from a respected parent, of whom he inherited a large patrimony. I had many misgivings about him, for he is not without suspicion of having increased Moorcroft’s troubles; and it is certain that the[108] family of one of his disciples was enriched by the wealth of that ill-fated traveller. He however possesses documents which lead me to acquit him of every thing, yet I would rather avoid than court the man, and rather please than displease him.
Among other items of advice we were strongly recommended to desist from giving medicines to the people, for it had already rallied round the doctor some hundreds of patients, and would sound the tocsin of our approach as we advanced. I had thought that the medical character would have been our passport, and to adventurers I do not doubt its advantage, but our only object being to pass through in safety, it became a subject of great doubt if it should be maintained at all; besides the continued applications of the people, which left us no time to ourselves, many surmises were made as to the riches and treasures we possessed, that enabled us gratuitously to distribute medicines. It was therefore resolved to withdraw from the field by the earliest opportunity, and a plan which I had thought from the beginning as likely to aid us considerably in our enterprise, was at once abandoned. The bleeding of the people would alone have furnished employment to a medical man, for the Afghans let blood annually at the vernal equinox till they reach their fortieth year. The people were[109] also labouring under a tertian fever, which increased the number of patients.
The only antiquity which we discovered near Peshawur was a “tope,” or mound, about five miles distant, on the road to Cabool, and evidently of the same era as those of Manikyala and Belur. It is in a very decayed state, and the remains would not suggest any idea of the design, had we not seen those in the Punjab. It was nearly a hundred feet high, but the stone with which it had been faced had fallen down or been removed. We procured no coins at it, and the natives could not give any tradition farther than it was a “tope.” We also heard of another building similar to this in the Khyber pass about eighteen miles distant, which we could not visit, from the unsettled state of the country where it is situated. It is in a perfect state of preservation, and both loftier and larger than that of Manikyala. I also heard of eight or ten towers of a like description towards the country of the Kaffirs in Swat and Boonere. It seems very probable that these buildings are the cemeteries of kings, since they are all built with a chamber in the midst of the pile. They may, however, be Boodhist buildings.
A month had now elapsed since we arrived at Peshawur, and the rapid approach of the hot weather admonished us that we need not much longer fear the snows of Cabool and Hindoo Koosh. The thermometer, which had stood in[110] mid-day at 60° on our arrival, now rose to 87°; the mulberries had ripened, and the snow had entirely disappeared from the hither range; yet the winter had been very severe; and during our stay at Peshawur hail-stones fell which were fully as large as a musket ball. All was therefore bustle for our departure; and our movements were accelerated by the arrival of a letter from Cabool, which begged us to advance without delay. Yet it was no easy matter to bring the chief to pronounce our leave, which was fixed for the 19th of April, after much procrastination.
Among the inmates of Sooltan Mahommed Khan’s house, it would be unpardonable to omit the mention of his “Maître d’hôtel,” Sutar Khan, a native of Cashmeer, a stout good-humoured man, who so long regaled us with his pillaos and other savoury dishes. During the whole of our stay we were entertained by the chief; and this person, who was a merry-hearted good soul, with all the polish of his countrymen, sought to gratify us in every way. Though he did not figure in any high capacity, yet his sister was married to the chief, and his influence was considerable. He was a tall portly man, with large black eyes, which I shall ever remember, for they followed with delight every morsel of his master’s which he saw us eat. His appearance showed that he liked the good things of this life, and his[111] disposition made him anxious to share them with others. Such was Sutar Khan, the Cashmeeree butler; he pressed us for some recipes to improve the gastronomic art, but we had no cook to tutor him.
On the 19th of April we took our leave of Sooltan Mahommed Khan, and Peshawur. Nothing could have surpassed the kindness of this nobleman, and now that we were leaving him he consigned us to a Persian, one of his own officers, who was sent to Cabool on our account: he then produced a letter to his brother at Candahar, as also to several persons in Cabool; likewise six blank sheets bearing his seal, which he begged we would fill up to any person of his acquaintance whom we believed could avail us. Such treatment, as may be imagined, called for our gratitude; but it was with difficulty that I could prevail on the chief to take a pair of pistols of small value. I gave his son a musical box, and he regretted my doing so. As we left his house he saw us mount, and wished us every success and prosperity; and would have accompanied us for some distance, had we not objected. Several of the good people about him, with whom we had become acquainted, came with us for the first[113] march, and among these were Gholam Kadir, and Meer Alum, two sons of a Cazee, at Lodiana, to whose good offices we were indebted on many occasions while at Peshawur.
There are five different roads to Cabool; but we chose that which leads by the river, since the pass of Khyber is unsafe from the lawless habits of the people; and we therefore crossed the beautiful plain of Peshawur to Muchnee. At the city we had become intimate with one of the hill chiefs, who urged us to take the Khyber route; but no one trusts a Khyberee, and it was not deemed prudent. Nadir Shah paid a sum of money to secure his passage through the defile in that country, which is about eighteen miles in length, and very strong. I should have liked much to see these people in their native state; but our acquaintance, though a chief, was not to be depended on. He was a tall, bony, gaunt-looking man, like the rest of his tribe, much addicted to spirits; and, when speaking of his country, he called it “Yaghistan,” or the land of the rebels. I accompanied this person to an orchard near Peshawur, where he wished us to join in a drinking party; but we considered him and his associates savage enough without intoxication.
We crossed the river of Cabool above Muchnee on a raft, which was supported on[114] inflated skins, and but a frail and unsafe mode of transport. The river is only 250 yards wide, but runs with such rapidity, that we were carried more than a mile down before gaining the opposite bank. The horses and baggage ponies swam across. Muchnee is a straggling village, at the gorge of the valley where the Cabool river enters the plain. Below that place it divides into three branches in its course towards the Indus. It is usual to navigate this river on rafts; but there are likewise a few boats, and the pilgrims proceeding to Mecca often embark at Acora, and pass down the Indus in them to the sea. Merchandise is never sent by this route; but it is important to know there is a water channel of communication from near Cabool to the ocean.
On the 23d we had adjusted all matters for our advance, by conciliating the Momunds, a plundering tribe, somewhat less ferocious than their neighbours of Khyber, through whose country we were to pass. They demanded half a rupee of every Mahommedan, and double the sum of a Hindoo; but much less satisfied them, though they quarrelled about its distribution. We commenced our march, by scrambling over hills and rocks, and were soon satisfied of the influence of our friends, as we met some individual passengers, attended by mere chil[115]dren, whose tribe was a sufficient protection for them. Scene in the Cabool river. After a fatiguing march over mountain passes we found ourselves on the Cabool river, which was to be crossed a second time. We had now a full insight into our mode of travelling, and the treatment which we were to expect. We never moved but in a body; and when we got to the banks of the river under a scorching sun, had no means of crossing it till our friends the Momunds could be again appeased. We laid ourselves down in the shade of some rocks, which had fallen from precipices that rose in grandeur over us to the height of about 2000 feet, and before us the Cabool river rushed with great rapidity in its course onwards. Its breadth did not exceed 120 yards. Towards afternoon, our highlanders produced eight or ten skins, and we commenced crossing; but it was night before we had all passed, and we then set fire to the grass of the mountains to illuminate our neighbourhood and ensure safety to the frail raft. The passage of the river was tedious and difficult: in some places the rapidity of the stream, formed into eddies, wheeled us round, and we had the agreeable satisfaction of being told that, if we went some way down, there was a whirlpool, and, if once enclosed in its circle, we might revolve in hunger and giddiness for a day. This inconvenience we all escaped, though[116] some of the passengers were carried far down the river, and we ourselves had various revolutions in the smaller eddies. There was no village or people on either side of the river, and we spread our carpets on the ground, and heartily enjoyed a cool night after the day’s fatigue. The noise of the stream soon lulled most of us to sleep, and towards midnight nothing was to be heard but the voices of the mountaineers, who had perched themselves on a rock that projected over our camp, and watched till daylight. A truly cut-throat band they appeared, and it was amusing to observe the studied respect which all of us paid them. Their chief, a ragged ruffian without a turban, was mounted on a horse: his praises were sung, and presents were given him; but we had no sooner left the country, than every one abused those whom we had been caressing. The spirit of the party might be discovered by one old man, who drove his horse into a wheat-field, on the verge of the Momund country, calling out, “Eat away, my good animal; the Momund scoundrels have ate much of my wealth in their time.”
After an exposure of about eight hours to a powerful sun, on the following morning we reached Duka by a rocky and difficult road, and pushed on, in the afternoon, to Huzarnow, a journey of upwards of twenty miles. On reach[117]ing Duka, we had surmounted the chief part of our difficulties on the road to Cabool. The view from the top of a mountain pass, before we descended into the valley of the Cabool river, was very magnificent. We could see the town of Julalabad, forty miles distant, and the river winding its way in a snaky course through the plain, and dividing it into innumerably fertile islands as it passed. The Sufued Koh, or white mountain, reared its crest on one side, and the towering hill of Noorgil or Kooner on the other; here the Afghans believe the ark of Noah to have rested after the deluge, and this Mount Ararat of Afghanistan, from its great height, is certainly worthy of the distinction: it is covered with perpetual snow. There is an isolated rock not far from this place, called Näogee, in Bajour, which answers, in my mind, to Arrian’s description of the celebrated rock of Aornus, which indubitably lay in that neighbourhood. Rock of Aornus. It is said to be inaccessible, but by one road, to be strong and lofty, and large enough to produce grain for the garrison, having likewise an abundant supply of water, which is literally an account of Aornus. It is also within twenty miles of Bajour; and we are informed that the citizens of Bazaria (supposed to be Bajour) fled to Aornus for safety in the night. I have not seen the hill of Näogee.
At Muchnee, the hills are sandstone: on the tops of the passes there are veins of quartz. In the bed of the Cabool river the rocks are granite; and over the village of Duka the formation is mica, which occurs in vertical strata. A sweet aromatic smell was exhaled from the grass and plants. One shrub looked very like broom; another resembled the flower-de-luce, and supplies the people with mats to build their huts as well as sandals for their feet, to which they are fixed by a string of the same material. Our thirst and fatigue were much relieved by a plant of the sorrel kind, which we found most grateful, and gathered and ate as we climbed over the hills. The pasture is here favourable to cattle, and the mutton used in Peshawur owes its flavour to it.
Before leaving Duka we had a visit from the chief of the Momunds, Sadut Khan, of Lalpoor, a handsome man of about thirty, with a good-humoured countenance. We sat under a mulberry tree, on a cot or bed, for half an hour; he pressed us much to cross the river, and become his guests for a few days, when he would entertain and amuse us with his hawks, some of which were carried by his attendants. We declined his civilities on the excuse of our journey. I afterwards learned that this smiling Momund had raised himself to the chiefship of[119] his clan, by murdering two young nephews with their mother.
At Huzarnow we met a Khyberee, with whom we had some acquaintance in the Punjab, where he had served as an hirkaru, or messenger, to Runjeet Sing. Immediately he heard of our arrival he made his appearance, and, catching me by the feet, and then by the beard, intimated, in the little Persian he could speak, that we were his guests, and must occupy his house in the village; which we gladly accepted. He was a most uncouth looking being, with a low brow and sunken eyes: he had two sons, neither of whom he had seen for fourteen years, till within a few days of our arrival. He had, nevertheless, twice carried expresses to Cabool; and though he had passed his native village and home, he had never stopped to make an enquiry. He had now returned for good to his country.
After a fatiguing march of twelve hours on the saddle, three of which were spent in waiting for stragglers, we reached Julalabad on the morning of the 26th. As we passed Soorkhdewar, where the caravans are sometimes plundered, our conductor, the Persian, whether to show his courage or the disordered state of his imaginations, fancied himself attacked by robbers. He fired his carbine, and, by the time those in the rear came up, had completed a long story of his[120] own daring bravery; how he had punished one of the robbers with the but end of his piece, and the danger which he had undergone from his antagonist’s ball, that had whistled past his ear! His followers applauded his bravery, and I added my share of praise. It appeared singular that the Persian alone should have seen the highwaymen: but the whole matter was explained by a quiet remark from a member of the caravan; that the gentleman wished to give proof of his courage now that we were beyond danger.
Our route from Huzarnow to Julalabad lay through a wide stony waste, a part of which is known by the name of the “dusht,” or plain of Buttecote, and famed for the pestilential wind or “simoom” that prevails here in the hot season, though the mountains on both sides are covered with perpetual snow. The natives of this country describe the simoom as generally fatal. Travellers, who have recovered, say, that it attacks them like a cold wind, which makes them senseless. Water poured with great violence into the mouth sometimes recovers the patient; and a fire kindled near him has a good effect. Sugar and the dried plums of Bokhara are also given with advantage. Horses and animals are subject to the simoom as well as man; and the flesh of those who fall victims to it is said to become so soft and putrid, that the limbs separate from each other,[121] and the hair may be pulled out with the least force. This pestilential wind is unknown in the highlands of Cabool, and principally confined to the plain of Butteecote now described. It is as malignant in its effects during night as in the day; and in summer no one ever thinks of travelling while the sun is above the horizon. In a party of thirty or forty individuals, one only may be attacked: nor are those who escape sensible of any change in the atmosphere. It may be simply the effects of heat on a certain state of the body.
We were not travelling in the season of hot and pestilential winds; but on this march we encountered one of these storms of wind and dust which are common in countries near the tropic. In the present instance, it was attended with a singular phenomenon: clouds of dust approached each other from opposite sides of the compass, and, when they met, took quite a different direction. It is, perhaps, to be accounted for by the eddy of the wind in a low plain, about twelve or fifteen miles broad, with lofty mountains on either side. Julalabad, we found, had been deluged with rain, which we had entirely escaped.
In a hill north of the Cabool river and the village of Bussoul, we observed some extensive excavations in the rock, which are ascribed to the[122] days of the Kaffirs, or infidels. These caves were hewn out in groups, the entrance to each being separated, and about the size of a common doorway. They may have formed so many villages, since it appears to have been common throughout Asia to dwell in such excavated places; as we learn in the account of the Troglodites given by different historians. I do not suppose that we can draw an inference as to the people from the existence of this practice in different countries, since it would occur to most uncivilised nations, that a cave in a rock was a more safe residence, in a troubled society, than a hut on the plain. Near Julalabad there are seven round towers; but they differ in construction from the “topes” which I have described. They are said to be ancient, and very large copper coins are found near them. In the country of Lughman, between Julalabad and the mountains, the people point out the tomb of Metur Lam, or Lamech, the father of Noah. Some refer the place to the age of the Kaffirs; but the good Mahommedans are satisfied to believe it the grave of a prophet, and that there are only three others on the earth.
We halted for a couple of days at Julalabad, which is one of the filthiest places I have seen in the East. It is a small town, with a bazar of fifty shops, and a population of about 2000 people;[123] but its number increases tenfold in the cold season, as the people flock to it from the surrounding hills. Julalabad is the residence of a chief of the Barukzye family; who has a revenue of about seven lacs of rupees a year. The Cabool river passes a quarter of a mile north of the town, and is about 150 yards wide: it is not fordable. Snowy mountains. There are mountains of snow to the north and south of Julalabad, that run parallel with one another. The southern range is called Sufued Koh, but more frequently Rajgul. It decreases in size as it runs eastward, and loses its snow before reaching Duka. In the higher parts the snow never melts; which would give an elevation of about 15,000 feet in this latitude. To the north of Julalabad lies the famous Noorgil, before mentioned, about thirty miles distant; and to the north-west the lofty peaks of Hindoo Koosh begin to show themselves.
We left the river of Cabool, and passed up a valley to Bala-bagh, and could now distinguish the rich gardens that lie under the snowy hills, and produce the famous pomegranates without seed, that are exported to India. We halted in a vineyard. The vines of this country are not cut or pruned, but allowed to ascend the highest trees, and were growing, at Bala-bagh, on lilyoaks, about eighty feet from the ground. The grapes so produced are inferior to those reared on a frame-work. It rained at Bala-bagh[124] and our quarters were more romantic than comfortable; which led us, at dusk, to seek for shelter in the mosque. Treatment by the people. The people seemed too busy in the exercise of religious and worldly matters to mind us, and as yet we had not experienced the slightest incivility from any person in the country: though we strolled about everywhere. They do not appear to have the smallest prejudice against a Christian; and I had never heard from their lips the name of dog or infidel, which figures so prominently in the works of many travellers. “Every country has its customs,” is a proverb among them; and the Afghan Mahommedans seem to pay a respect to Christians which they deny to their Hindoo fellow-citizens. Us they call “people of the book;” while they consider them benighted and without a prophet.
At Gundamuk we reached the boundary of the hot and cold countries. It is said to snow on one side of the rivulet, and to rain on the other. Vegetable life assumes a new form; the wheat, which was being cut at Julalabad, was only three inches above ground at Gundamuk. The distance does not exceed twenty-five miles. In the fields we discovered the white daisies among the clover; and the mountains, which were but ten miles distant, were covered with forests of pine, that commenced about a thousand feet below the limit of the snow; we required[125] additional clothing in the keen air. Travellers are subject to a variety of little troubles, which amuse or try the temper, according to the disposition of the moment. A cat possessed itself of my dinner this evening, as I was about to swallow it; yet I satisfied the cravings of a hungry appetite with bread and water; which, I may add, was ate in a filthy stable: but we were fortunate in getting such accommodation. I beg to add my encomia on the bread of this country, which they leaven and bake much to the palate.
About three miles from Gundamuk we passed the garden of Neemla, celebrated for the field of battle in which Shah Shooja-ool Moolk lost his crown, in the year 1809. The garden is situated in a highly cultivated valley surrounded by barren hills. It is a beautiful spot; the trees have all been pruned to, or attained, the same height, and shade beneath their bows a variety of flowers; among which the narcissus grows most luxuriantly. The spot, though ornamented by art, is ill chosen for a battle; and the fortune of war was here strangely capricious. Shooja lost his throne and his vizier, sustaining a defeat from an army ten times inferior to his own. Never dreading such a result, he had brought his jewels and his wealth along with him; which he was happy to relinquish for his life. Futteh Khan, the vizier of Mahmood, who succeeded in gaining the day[126] for his master, seated him on one of the state elephants, which had been prepared for the king, and took this mode to proclaim his victory. Shooja fled to the Khyber country, and has since failed in all his attempts to regain his kingdom.
Nothing strikes a stranger in this country more than the manner of keeping their horses, which differs so much from India. They never remove the saddle during the day; which they believe gives the horse a better rest at night. They never walk a horse up and down, but either mount him, or make him go round in a circle till he is cool. They give no grain, at this season, feeding them on green barley, which has not eared. They picket eight or ten horses to two ropes, which they fix in line parallel to one another. They always tie a knot on the tail. They keep the hind quarters of the horse covered at all times by a very neat felt, fringed with silk, which is held on by the crupper. They use the Uzbek saddle, which resembles that of our own huzars, and which I found agreeable enough, and always used. The riders tie their whip to the wrist. The Afghans take great care of their horses, but do not pamper them with spices, as in India, and always have them in excellent condition.
We continued our march to Jugduluk, and passed the Soorkh road, or red river, by a bridge with a variety of other small streams, which pour[127] the melted snow of the Sufued Koh into that rivulet. The waters of all of them were reddish: hence the name. The country is barren and miserable. Jugduluk is a wretched place, with a few caves for a village. There is a proverb which describes its misery: “When the wood of Jugduluk begins to burn, you melt gold:” for there is no wood at hand in the bleak hills. We halted under a grove of trees, which is memorable as the spot where Shah Zuman, one of the kings of Cabool was blinded.
On our way we could distinguish that the road had once been made, and also the remains of the post-houses, which had been constructed every five or six miles by the Mogul emperors, to keep up a communication between Delhi and Cabool. They may even be traced across the mountains to Balkh; for both Humaioon and Aurungzebe, in their youth, were governors of that country. What an opinion does this inspire of the grandeur of the Mogul empire! We have a system of communication between the most distant provinces as perfect as the posts of the Cæsars.
On our way to Cabool we met thousands of sheep tended by the wandering Ghiljees, a tribe of Afghans; who now that the snow was off the ground, were driving their flocks towards Hindoo Koosh, where they pass the summer. Nothing could be more pastoral. Pastoral scenes. The grown-[128]up people followed the sheep as they browsed on the margin of the hills, and the boys and girls came up about a mile or two in rear, in charge of the young lambs. An old goat or sheep encouraged them to advance, and the young people assisted with switches of grass, and such ejaculations as they could raise. Some of the children were so young, that they could hardly walk; but the delight of the sport enticed them on. On the margin of the road we passed many encampments, where they were either moving or packing up. The Afghans have a low black, or rather, brown tent. The women did every thing for their lazy husbands, loaded the camels and drove them on: they are indeed swarthy dames, not very remarkable for beauty, with all their Arcadian life. They are well clad, and shod with broad iron nails fixed to their soles. The children were uncommonly healthy and chubby; and it is said that these wandering people do not marry till they reach their twentieth year.
After passing the Soorkh road, we reached Ispahan, a village that marks another of Shooja’s defeats, but before he gained the throne. Story of Futteh Khan. A story is told of the vizier Futteh Khan, who was afraid of being supplanted on this field of battle by the Dooranee nobleman who aspired to the office of vizier. This individual, whose name was Meer Alum, had, on a former occasion,[129] insulted Futteh Khan, and even knocked out one of his front teeth. The injury had to all appearance been forgiven, for he had since married a sister of the Vizier; but the alliance had only been formed that Futteh Khan might easier accomplish his base intentions. The night before the battle he seized upon his brother-in-law and put him to death. A heap of stones, here called a “toda,” marks the scene of the murder. The Vizier’s sister threw herself at her brother’s feet, and asked why he had murdered her husband? “What!” said he, “have you more regard for your husband, than your brother’s honour. Look at my broken teeth; and know that the insult is now avenged. If you are in grief at the loss of a husband, I’ll marry you to a mule driver.” This incident is not a bad illustration of the boisterous manners and feelings of the Afghans. A saying among them bids one fear the more, when an apparent reconcilement has taken place by an intermarriage.
By midnight on the 30th we reached the pass of Luta-bund, from the top of which the city of Cabool first becomes visible, at a distance of twenty-five miles. The pass is about six miles long, and the road runs over loose round stones. We lay down at a spring called Koke Chushma, or the Partridge Fountain, and slept without shelter through a bitterly cold night. Our con[130]ductor’s hawks died from its effects, to his great grief. Luta means a shred or patch; and this pass is so called, from travellers leaving some shred of their clothes on the bushes in the pass. In the winter the snow blocks up this road.
We rose with the morning star, and prosecuted our journey to Cabool, which we did not reach till the afternoon. The approach to this celebrated city is any thing but imposing, nor was it till I found myself under the shade of its fine bazar, that I believed myself in the capital of an empire. On our road we passed the village of Bootkhak, where Mahmood of Ghuzni, on his return from India, is said to have interred the rich Hindoo idol which he brought from the famous Somnat. At Cabool, we proceeded straight to the house of the Nawab Jubbar Khan, the brother of the governor, who gave us a cordial welcome, and sent to the bazar for a dinner, which I enjoyed. Not so my unfortunate companion, whose health forsook him immediately after crossing the Indus; his strength was now completely undermined. A doubt arose as to the examination of our baggage at the Custom-house; but I judged it more prudent to exhibit our poverty than allow the good people to form designs against our supposed wealth. We were not, however, prepared for the search;[131] and my sextant and books, with the doctor’s few bottles and paraphernalia, were laid out in state for the inspection of the citizens. They did them no harm, but set us down without doubt as conjurors, after a display of such unintelligible apparatus.
Our worthy conductor, after he had safely delivered us into the hands of the Nawab, took his leave to enjoy his native city, which he had not seen for eight years. Mahommed Shureef was what might be termed a good fellow. Though but a young man, he had been a merchant, and realised a fortune, which he now enjoyed in hunting and hawking, with “a cup of good sack.” He was corpulent and dropsical, but might be seen every morning with his hawks and pointer at his heels. He kept his revels more secretly. I never saw a boy more delighted than was this person as we entered Cabool; had it been Elysium, he could not have said more in its praise. He had been a most companionable traveller, and added the address of a Persian to the warmth and good feeling of an Afghan. An incident occurred on our entering Cabool, which would have delighted other men than him. A beggar had found out who he was, and within half a mile of the city gate began to call down every blessing on his head, and welcomed him by name to his[132] home, in a strain of great adulation. “Give the poor man some money,” said Mahommed Shureef to his servant, with a significant nod of his head; and it would have been a difficult matter to determine whether the merchant or the beggar seemed most delighted. Our conductor then bid us adieu, with a recommendation that we should trust anybody but those who volunteered their services; as he did not give his countrymen the credit for a high standard of morality. He exacted a promise that we should dine with him, and I thanked him for his advice and attentions.
We had not been many hours in Cabool before we heard of the misfortunes of Mr. Wolff, the missionary of the Jews, who was now detained at a neighbouring village, and lost no time in despatching assistance to him. He joined us the following day, and gave a long and singular account of his escape from death and slavery. This gentleman, it appears, had issued forth, like another Benjamin of Tudela, to enquire after the Israelites, and entered Tartary as a Jew, which is the best travelling character in a Mahommedan country. Mr. Wolff, however, is a convert to Christianity, and he published his creed to the wreck of the Hebrew people. He also gave himself out as being in search of the lost tribes; yet he made but few enquiries among the Afghans of Cabool, though they declare themselves to be their descendants. The narration of Mr. Wolff’s adventures excited our sympathy and compassion; and, if we could not coincide in many of his speculations regarding the termination of the world, we made the reverend gentleman most welcome, and found[134] him an addition to our society in Cabool. He had been in Bokhara, but had not ventured to preach in that centre of Islam. His after misfortunes had originated from his denominating himself a Hajee, which implies a Mahommedan pilgrim, and for which he had been plundered and beaten.
We had previously heard of the amiable character of our host, Nawab Jubbar Khan; and even found him, on personal acquaintance, to be quite a patriarch. He heals every difference among his many and turbulent brothers: himself the eldest of his family, he has no ambitious views, though he once held the government of Cashmeer, and other provinces of the Dooranee empire. His brother, the present chief of Cabool, has requited many services by confiscating his estate; but he speaks not of his ingratitude. He tells you that God has given him abundance for his wants, and to reward those who serve him; that there are few pleasures equal to being able to give to those around, and to enjoy this world without being obliged to govern. I discovered, during my stay at Cabool, that the Nawab assumes no false character, but expresses himself, as he feels, with sincerity. Never was a man more modest, and more beloved: he will permit but a single attendant to follow him; and the people on the high and[135] by ways stop to bless him; the politicians assail him at home to enter into intrigues, and yet he possesses the respect of the whole community, and has, at the present moment, a greater moral influence than any of the Barukzye family in Afghanistan. His manners are remarkably mild and pleasing; and from his dress one would not imagine him to be an influential member of a warlike family. It is delightful to be in his society, to witness his acts, and hear his conversation. He is particularly partial to Europeans, and makes every one of them his guest who enters Cabool. All the French officers in the Punjab lived with him, and keep up a friendly intercourse. Such is the patriarch of Cabool; he is now about fifty years of age; and such the master of the house in which we were so fortunate as to dwell.
Our first object, after arrival, was to be introduced to the chief of Cabool, Sidar Dost Mahommed Khan. The Nawab intimated our wishes, and we were very politely invited to dine with the governor on the evening of the 4th of May. Dr. Gerard was unable to attend from sickness; but Mr. Wolff and myself were conducted, in the evening, to the Bala Hissar, or Palace of the Kings, where the governor received us most courteously. He rose on our entrance, saluted in the Persian fashion, and[136] then desired us to be seated on a velvet carpet near himself. He assured us that we were welcome to his country; and, though he had seen few of us, he respected our nation and character. To this I replied as civilly as I could, praising the equity of his government, and the protection which he extended to the traveller and the merchant. When we sat down, we found our party consist of six or eight native gentlemen, and three sons of the chief. We occupied a small but neat apartment, which had no other furniture than the carpet. The conversation of the evening was varied, and embraced such a number of topics, that I find it difficult to detail them; such was the knowledge, intelligence, and curiosity that the chief displayed. He was anxious to know the state of Europe, the number of kings, the terms on which they lived with one another; and, since it appeared that their territories were adjacent, how they existed without destroying each other. I named the different nations, sketched out their relative power, and informed him, that our advancement in civilisation did no more exempt us from war and quarrels than his own country; that we viewed each other’s acts with jealousy, and endeavoured to maintain a balance of power, to prevent one king from overturning another. Of this, however, there were, I added,[137] various instances in European history; and the chief himself had heard of Napoleon. He next requested me to inform him of the revenues of England; how they were collected; how the laws were enacted; and what were the productions of the soil. He perfectly comprehended our constitution from a brief explanation; and said there was nothing wonderful in our universal success, since the only revenue which we drew from the people was to defray the debts and expenses of the state. “Your wealth, then,” added he, “must come from India.” I assured him that the revenues of that country were spent in it; that the sole benefits derived from its possession consisted in its being an outlet to our commerce; and that the only wealth sent to the mother country consisted of a few hundred thousand pounds, and the fortunes taken away by the servants of the government. I never met an Asiatic who credited this fact before. Dost Mahommed Khan observed, that “this satisfactorily accounts for the subjection of India. You have left much of its wealth to the native princes; you have not had to encounter their despair, and you are just in your courts.” He enquired into the state of the Mahommedan principalities in India, and as to the exact power of Runjeet Sing, for sparing whose country he gave us no credit. He wished to know if we had any designs upon[138] Cabool. He had heard from some Russian merchants of the manner of recruiting the armies by conscription in that country, and wished to know if it were general in Europe. He had also heard of their foundling hospitals, and required an explanation of their utility and advantage. He begged I would inform him about China; if its people were warlike, and if their country could be invaded from India; if its soil were productive, and its climate salubrious; and why the inhabitants differed so much from those of other countries. The mention of Chinese manufactures led to a notice of those in England; he enquired about our machinery and steam engines, and then expressed his wonder at the cheapness of our goods. He asked about the curiosities which I had seen, and which of the cities in Hindostan I had most admired. I replied, Delhi. He then questioned me if I had seen the rhinoceros, and if the Indian animals differed from those of Cabool. He had heard of our music, and was desirous of knowing if it surpassed that of Cabool. From these matters he turned to those which concerned myself; asked why I had left India, and the reasons for changing my dress. I informed him that I had a great desire to see foreign countries, and I now purposed travelling towards Europe by Bokhara; and that I had changed my dress to prevent my being[139] pointed at in this land; but that I had no desire to conceal from him and the chiefs of every country I entered, that I was an Englishman, and that my entire adoption of the habits of the people had added to my comfort. The chief replied in very kind terms, applauded the design, and the propriety of changing our dress.
Dost Mahommed Khan then turned to Mr. Wolff for an explanation of his history; and, as he was aware of the gentleman’s vocations, he had assembled among the party several Mahommedan doctors, who were prepared to dispute on points of religion. Since I stood as Mr. Wolff’s interpreter, I might proceed to make mention of the various arguments which were adduced on either side; but I do not anticipate what the reverend gentleman will, no doubt, give to the world. As is usual on such subjects, the one party failed to convince the other; and, but for the admirable tact of the chief himself, the consequence might have been disagreeable. The Mahommedans seemed to think that they had gained the day, and even referred it for my decision; but I excused myself from the difficult task, on the grounds of being no moollah (priest). As these reverend doctors, however, appeared to found their creed upon reason, I thought the opportunity too favourable to let them escape, if the argument I intended to use did not boast[140] of being original. I asked them to state their time of prayers; and, among others, they named before sunrise, and after sunset. “Such are the hours,” said I, “rigidly enjoined by the Koran?”—“Yes,” replied the priest; “and every one is an infidel who neglects them.” These premises being given, I begged the doctor to inform me how these prayers could be performed in the Arctic circle, where the sun neither rose nor set for five or six months in the year. The divine had not before heard the argument: he stammered out various confused sentences; and at last asserted that prayers were not required in those countries, where it was sufficient to repeat the “Culuma,” or creed of the Mahommedans. I immediately required the divine to name the chapter of the Koran on which he founded his doctrine, since I did not remember to have seen it in the book. He could not, for the Koran does not contain it. A sharp dispute now arose among the Afghans; nor was the subject renewed, but changed to more intelligible matters. Before we withdrew, the chief made a very friendly tender to assist us in our journey, and offered us letters to the chiefs on the Oxus, and the King of Bokhara. He also requested that we should frequently visit him while in Cabool, as he liked to hear of other countries, and would make us welcome. We left him at midnight, quite charmed with our[141] reception, and the accomplished address and manners of Dost Mahommed Khan.
I lost no time in making excursions near Cabool, and chose the earliest opportunity to visit the tomb of the Emperor Baber, which is about a mile from the city, and situated in the sweetest spot of the neighbourhood. The good Nawab was my conductor in the pilgrimage. I have a profound respect for the memory of Baber, which had been increased by a late perusal of his most interesting Commentaries. He had directed his body to be interred in this place, to him the choicest in his wide dominions. These are his own words regarding Cabool:—“The climate is extremely delightful, and there is no such place in the known world.”—“Drink wine in the citadel of Cabool, and send round the cup without stopping: for it is at once a mountain, a sea, a town, and a desert.”[15]
The grave is marked by two erect slabs of white marble, and, as is usual, the last words of the inscription give the date of the Emperor’s death. The device in the present instance seems to me happy: “When in heaven, Roozvan asked the date of his death. I told him that heaven is the eternal abode of Baber Badshah.” He died[142] in the year 1530. Near the Emperor, many of his wives and children have been interred; and the garden, which is small, has been once surrounded by a wall of marble. A running and clear stream yet waters the fragrant flowers of this cemetery, which is the great holiday resort of the people of Cabool. In front of the grave, there is a small but chaste mosque of marble; and an inscription upon it sets forth that it was built in the year 1640, by order of the Emperor Shah Jehan, after defeating Mahommed Nuzur Khan in Balkh, and Budukhshan, “that poor Mahommedans might here offer up their prayers.” It is pleasing to see the tomb of so great a man as Baber honoured by his posterity.
There is a noble prospect from the hill which overlooks Baber’s tomb, and a summer-house has been erected upon it by Shah Zuman, from which it may be admired. The Nawab and myself climbed up to it, and seated ourselves. If my reader can imagine a plain, about twenty miles in circumference, laid out with gardens and fields in pleasing irregularity, intersected by three rivulets, which wind through it by a serpentine course, and wash innumerable little forts and villages, he will have before him one of the meadows of Cabool. To the north lie the hills of Pughman, covered half way down with snow, and separated from the eye by a[143] sheet of the richest verdure. On the other side, the mountains, which are bleak and rocky, mark the hunting preserves of the kings; and the gardens of this city, so celebrated for fruit, lie beneath, the water being conducted to them with great ingenuity. I do not wonder at the hearts of the people being captivated with the landscape, and of Baber’s admiration; for, in his own words, “its verdure and flowers render Cabool, in spring, a heaven.”
Our intercourse with the people was on a much better footing at Cabool than in Peshawur, for we were no longer in the house of a chief, and not troubled by too many visiters. The Nawab occupied one side of a large mansion, and left the other part to us. He, however, rallied round him many good sort of people, with whom we became acquainted; he brought them over in person, and we passed to and fro between each other’s apartments during the whole day. The habits which we had adopted, now gave us many advantages in our communications with the people. We sat along with them on the same carpet, ate with them, and freely mingled in their society. their character. The Afghans are a sober, simple, steady people. They always interrogated me closely regarding Europe, the nations of which they divide into twelve “koollahs,” or crowns, literally hats. It was delightful to[144] see the curiosity of even the oldest men. The greatest evil of Mahommedanism consists in its keeping those who profess it within a certain circle of civilisation. Their manners do not appear ever to alter. They have learning, but it is of another age, and any thing like philosophy in their history is unknown. The language of the Afghans is Persian, but it is not the smooth and elegant tongue of Iran. Pooshtoo is the dialect of the common people, but some of the higher classes cannot even speak it. The Afghans are a nation of children; in their quarrels they fight, and become friends without any ceremony. They cannot conceal their feelings from one another, and a person with any discrimination may at all times pierce their designs. If they themselves are to be believed, their ruling vice is envy, which besets even the nearest and dearest relations. No people are more incapable of managing an intrigue. I was particularly struck with their idleness; they seem to sit, listlessly for the whole day, staring at each other; how they live it would be difficult to discover, yet they dress well, and are healthy and happy. I imbibed a very favourable impression of their national character.
Cabool is a most bustling and populous city. Such is the noise in the afternoon, that in the[145] streets one cannot make an attendant hear. The great bazar, or “Chouchut,” is an elegant arcade, nearly 600 feet long, and about 30 broad: it is divided into four equal parts. Its roof is painted; and over the shops are the houses of some of the citizens. The plan is judicious; but it has been left unfinished; and the fountains and cisterns, that formed a part of it, lie neglected. Still there are few such bazars in the East; and one wonders at the silks, cloths, and goods, which are arrayed under its piazzas. In the evening it presents a very interesting sight: each shop is lighted up by a lamp suspended in front, which gives the city an appearance of being illuminated. The number of shops for the sale of dried fruits is remarkable, and their arrangement tasteful. In May, one may purchase the grapes, pears, apples, quinces, and even the melons of the by-gone season, then ten months old. There are poulterers’ shops, at which snipes, ducks, partridges, and plovers, with other game, may be purchased. The shops of the shoemakers and hardware retailers are also arranged with singular neatness. Every trade has its separate bazar, and all of them seem busy. There are booksellers and venders of paper, much of which is Russian, and of a blue colour. The month of May is the season of the “falodeh,”[146] which is a white jelly strained from wheat, and drunk with sherbet and snow. The people are very fond of it, and the shop-keepers in all parts of the town seem constantly at work with their customers. A pillar of snow stands on one side of them, and a fountain plays near it, which gives these places a cool and clean appearance. Around the bakers’ shops crowds of people may be seen, waiting for their bread. I observed that they baked it by plastering it to the sides of the oven. Cabool is famed for its kabobs, or cooked meats, which are in great request: few cook at home. “Rhuwash” was the dainty of the May season in Cabool. It is merely blanched rhubarb, which is reared under a careful protection from the sun, and grows up rankly under the hills in the neighbourhood. Its flavour is delicious. “Shabash rhuwash! Bravo rhuwash!” is the cry in the streets; and every one buys it. In the most crowded parts of the city there are story-tellers amusing the idlers, or dervises proclaiming the glories and deeds of the Prophets. If a baker makes his appearance before these worthies, they demand a cake in the name of some prophet; and, to judge by the number who follow their occupation, it must be a profitable one. There are no wheeled carriages in Cabool: the streets are not very narrow; they are kept in a good state[147] during dry weather, and are intersected by small covered aqueducts of clean water, which is a great convenience to the people. We passed along them without observation, and even without an attendant. To me, the appearance of the people was more novel than the bazars. They sauntered about, dressed in sheep-skin cloaks, and seemed huge from the quantity of clothes they wore. All the children have chubby red cheeks, which I at first took for an artificial colour, till I found it to be the gay bloom of youth. The older people seem to lose it. Cabool is a compactly built city, but its houses have no pretension to elegance. They are constructed of sun-dried bricks and wood, and few of them are more than two stories high. It is thickly peopled, and has a population of about sixty thousand souls. The river of Cabool passes through the city; and tradition says that it has three times carried it away, or inundated it. In rain, there is not a dirtier place than Cabool.
It is in the mouth of every one, that Cabool is a very ancient city; they call it 6000 years old. It formed once, with Ghuzni, the tributary cities of Bameean. Strange has been the reverse of circumstances;—Ghuzni, under Mahmood, in the eleventh century, became a great capital; and Cabool is now the metropolis both[148] over it and Bameean. It is said that Cabool was formerly named Zabool, from a kaffir, or infidel king, who founded it; hence the name of Zaboolistan. Some authors have stated, that the remains of the tomb of Cabool, or Cain, the son of Adam, are pointed out in the city; but the people have no such traditions. It is, however, a popular belief, that when the devil was cast out of heaven, he fell in Cabool. In Cabool itself there are not exactly traditions of Alexander, but both Herat and Lahore are said to have been founded by slaves of that conqueror, whom they call a prophet. Their names were Heri (the old name of Herat) and Lahore. Candahar is said to be an older city than either of these. Coins. While at Cabool, I made every attempt to procure coins, but without success, excepting a Cufic coin of Bokhara, which was 843 years old. Among the rarities brought to the Cabool mint, I heard of a coin of the shape and size of a sparrow’s egg,—a whimsical model. Triangular and square coins are common: the latter belong to the age of Acbar.
In the number of our visiters was an Armenian, of the name of Simon Mugurditch, commonly called Sooliman, who gave us a sad account of the dispersion of his tribe. There are but twenty-one persons now remaining, from a colony of some hundreds introduced by Nadir[149] and Ahmed Shah from Joolfa and Meshid in Persia. By inscriptions in their burying-ground, it would appear that some Armenian merchants had settled in Cabool even before that period. During the Dooranee monarchy, they held offices under the government, and were respected, till the time of Timour Shah’s death. In the disputes about the succession, they have gradually withdrawn their families to other countries; and the present chief of Cabool, with the best intentions, has put a finishing blow to the Armenian colony, by a strict prohibition of wine and spirits. He has also forbidden dice, with every description of incontinence, and likewise threatened to grill some of the bakers in their ovens for light weights. After a life by no means temperate, this chief has renounced wine, and, under the severest penalties, commands that his subjects should be equally abstemious. The Armenians and Jews of Cabool have, therefore, fled to other lands, as they had no means of support but in distilling spirits and wine. There are but three Jewish families in Cabool, the wreck of a hundred which it could last year boast. If Dost Mohammed Khan can succeed in suppressing drunkenness by the sacrifice of a few foreign inhabitants, he is not to be blamed; since forty bottles of wine or ten[150] of brandy might be purchased from them for a single rupee. As the chief in person shows so good an example to his people, we shall not criticise his motives, nor comment with severity on the inconsistency of a reformed drunkard. Cabool seems to have been always famed for its revels.
The Armenians clung to us as if we had been an addition to their colony, and we breakfasted with Simon Mugurditch and his family, where we met all the members of it. The little children came running out to meet us, kissed our hands, and then placed their foreheads upon them. They are a very handsome people. We saw their church—a small building, which could never have contained a hundred people. Our host Simon gave us a very comfortable entertainment, and laid it out on a cloth covered with sentences of the Koran. “It was an Afghan cloth,” said he, “and Christians are not injured by these sentences, nor eat a less hearty meal.” The Armenians have adopted all the customs and manners of Mahommedans, and take off both shoes and turbans on entering their church. They are a harmless inoffensive people, but fond of money.
Since our departure, we had been travelling in a perpetual spring. The trees were blossoming as we left Lahore, in February; and[151] we found them full blown in March, at Peshawur. We had now the same joyous state of the season in Cabool, and arrived at an opportune time to see it. This state of the spring will give a good idea of the relative height of the different places, and of the progress of their seasons. Cabool is more than 6000 feet above the level of the sea. I passed some delightful days in its beautiful gardens. One evening I visited a very fine one, in company with the Nawab, about six miles from the city. They are well kept and laid out; the fruit trees are planted at regular distances; and most of the gardens rise with the acclivity of the ground in plateaus, or shelves, over one another. The ground was covered with the fallen blossom, which had drifted into the corners, like so much snow. The Nawab and myself seated ourselves under a pear-tree of Samarcand, the most celebrated kind in the country, and admired the prospect. Great was the variety and number of fruit trees. There were peaches, plums, apricots, pears, apples, quinces, cherries, walnuts, mulberries, pomegranates, and vines, all growing in one garden. There were also nightingales, blackbirds, thrushes, and doves, to raise their notes, and chattering magpies, on almost every tree, which were not without their attraction, as reminding me of England. I was highly pleased[152] with the nightingale; and, on our return home, the Nawab sent me one in a cage, which sang throughout the night. It is called the “Boolbool i huzar dastan,” or, the nightingale of a thousand tales; and it really seemed to imitate the song of every bird. The cage was surrounded by cloth; and it became so noisy a companion, that I was obliged to send it away before I could sleep. This bird is a native of Budukhshan. The finest garden about Cabool is that called the King’s garden, laid out by Timour Shah, which lies north of the town, and is about half a mile square. The road which leads to it is about three miles long, and formed the royal race-ground. There is a spacious octagon summer-house in the centre, with walks that run up from each of its sides, shaded with fruit trees, having a very pretty effect. A marble seat in front shows where the kings of Cabool sat in their prosperity, among
The people are passionately fond of sauntering about these gardens, and may be seen flocking to them every evening. The climate of Cabool is most genial. At mid-day the sun is hotter than in England; but the nights and[153] evenings are cool, and only in August do the people find it necessary to sleep on their balconies. There is no rainy season, but constant showers fall as in England. The snow lasts for five months in winter. During May, the thermometer stood at 64° in the hottest time of the day; and there was generally a wind from the north, cooled by the snow that covers the mountains. It must usually blow from that quarter, since all the trees of Cabool bend to the south.
Cabool is particularly celebrated for its fruit, which is exported in great abundance to India. Its vines are so plentiful, that the grapes are given, for three months of the year, to cattle. There are ten different kinds of these: the best grow on frame-works; for those which are allowed to creep on the ground are inferior. They are pruned in the beginning of May. The wine of Cabool has a flavour not unlike Madeira; and it cannot be doubted, that a very superior description might be produced in this country with a little care. The people of Cabool convert the grape into more uses than in most other countries. They use its juice in roasting meat; and, during meals, have grape powder as a pickle. This is procured by pounding the grapes before they get ripe, after drying them. It looks like Cayenne pepper, and has a pleasant[154] acid taste. They also dry many of them as raisins, and use much grape syrup. A pound of grapes sells for a halfpenny. I have already mentioned the “rhuwash,” or rhubarb of Cabool: it grows spontaneously under the snowy hills of Pughman; and Cabool has a great celebrity from producing it. The natives believe it exceedingly wholesome, and use it both raw, and cooked as vegetables. They tell an anecdote of some Indian doctors, who practised for a short time at Cabool, and waited for the fruit season, when the people would probably be unhealthy. Seeing this rhubarb in May and June, these members of the faculty abruptly left the country, pronouncing it a specific for the catalogue of Cabool diseases. This, at all events, proves it to be considered a healthy article of food. When the rhubarb is brought to market, the stalks are about a foot long, and the leaves are just budding. They are red; the stalk is white: when it first appears above ground, it has a sweet taste like milk, and will not bear carriage. As it grows older, it gets strong, stones being piled round to protect it from the sun. The root of the plant is not used as medicine. There are no date trees in Cabool, though they are to be found both east and west of it—at Candahar and Peshawur. There the people are ignorant of the art of ex[155]tracting an intoxicating juice from them, as in India. Peshawur is celebrated for its pears; Ghuzni for its plums, which are sold in India under the name of the plum of Bokhara; Candahar for its figs, and Cabool for its mulberries; but almost every description, particularly stone fruits, thrive in Cabool. Fruit is more plentiful than bread, and is considered one of the necessaries of human life. There are no less than fourteen different ways of preserving the apricot of Cabool: it is dried with and without the stone; the kernel is sometimes left, or an almond is substituted in its stead; it is also formed into cakes, and folded up like paper. It is the most delicious of the dried fruits.
Among the public buildings in Cabool, the Bala Hissar, or citadel, claims the first importance; but not from its strength. Cabool is enclosed to the south and west by high rocky hills; and at the eastern extremity of these the Bala Hissar is situated, which commands the city. It stands on a neck of land, and may have an elevation of about 150 feet from the meadows of the surrounding country. There is another fort under it, also called the Bala Hissar, which is occupied by the governor and his guards. The citadel is uninhabited by the present chief; but his brother built a palace in it called the “Koollah i Firingee,” or the Europeans’ Hat, which is the highest build[156]ing. Dost Mahommed Khan captured the Bala Hissar, by blowing up one of its towers: it is a poor, irregular, and dilapidated fortification, and could never withstand an escalade. The upper fort is small, but that below contains about five thousand people. The King’s palace stands in it. The Bala Hissar was built by different princes of the house of Timour, from Baber downwards. Aurungzebe prepared extensive vaults under it, to deposit his treasure; and which may yet be seen. While it formed the palace of the kings of Cabool, it was also the prison of the younger branches of the royal family, in which they were confined for life. They tell a story, that, when set free from their prison, after murdering their keeper, they looked with astonishment at seeing water flow—so close had been the confinement in their walled abode. It is difficult to say, whether these unfortunate men were not happier than in their present state, which is that of abject poverty. Many of the sons of Timour Shah came in absolute hunger to solicit alms from us. I advised them to make a petition to the chief for some permanent relief, but they said that they had no mercy to expect from the Barukzye family, now in power, who thirsted after their blood.
Near the Bala Hissar, and separated from it and every part of the city, the Persians, or Kuz[157]zilbashes, as they are called, reside. They are Toorks, and principally of the tribe of Juwansheer, who were fixed in this country by Nadir Shah. Under the kings of Cabool they served as body-guards, and were a powerful engine of the state. They yet retain their language, and are attached to the present chief, whose mother is of their tribe. I had an opportunity of seeing these people to advantage; being invited to a party given by our conductor from Peshawur, the jolly Naib Mahommed Shureef. I met the whole of the principal men, and their chief, Sheereen Khan. The entertainment was more Persian than Afghan. Among them, I could discover a new people, and new mode of thinking; for they have retained some of the wit that marks their countrymen. As the evening was drawing to a close, the chief called on a person to display his powers, not in a tale, but in depicting the peculiarities of the neighbouring nations. He began with the Afghans; and, after an amusing enough exordium, which excepted the Dooranees or chiefs, (who, he said, were not like other Afghans,) he described the entry of some twenty or thirty nations into paradise. When the turn of the Afghans came, he went on blasphemously to relate, that their horrid language was unintelligible, and that, as the prophet had pronounced it to be the dialect[158] of hell, there was no place in heaven for those who spoke it. The fellow had humour, and brought in some Afghan phrases, much to the amusement of the company. He then attacked the Uzbeks for their peculiar way of making tea, and their uncouth manners. He now levelled his batteries against the whining, cheating and deceitful Cashmeerian; and these people must be belied indeed, if they be not masters in vice.[16] All parties, however, admit their talents and ingenuity, which is a considerable counterbalance. The natives of Herat, and their peculiar dialect, exercised the powers of this loquacious Meerza: he imitated the roguery of their custom-house; and allowed himself, as the officer on duty, to be bribed out of his due, by accepting some wine, which he pretended was not for himself.
The difference between Eastern manners, and those of Europe, is nowhere more discernible than in their manner of saying good things. An European enjoys an anecdote; but he would be very much surprised to be called on in a company to tell one for its amusement. In the[159] East, there are professional anecdote makers; in the West, we are content with a bon-mot as it flows in the course of conversation. Both may be traced to the government: for, in the East, though there is much familiarity, there is little social intercourse; and, in Europe, good manners teach us to consider every one at the same board on an equality.
During our stay, the “Eed” occurred, which is the festival kept in commemoration of Abraham’s intention to sacrifice his son Isaac. It was observed with every demonstration of respect: the shops were shut; and the chief proceeded to prayer at an appointed place, with a great concourse of persons. In the afternoon, every one was to be seen flocking to the gardens; nor could I resist the impulse, and followed the crowd. In Cabool, you no sooner leave the bazar, than you find yourself on the banks of the river, which are beautifully shaded by trees of mulberry, willow, and poplar. Almost all the roads round the city lead by the verge of aqueducts or running water. They are crossed by bridges; and the large river has three or four of these edifices; but they cannot boast of architectural beauty. The finest gardens of Cabool lie north of the city; and they, again, are far surpassed by those beyond, in the district of Istalif, under the first snow-clad mountains,[160] towards Hindoo Koosh. Their site is to be seen from Cabool. Tomb of Timour Shah. I was conducted to the tomb of Timour Shah, which stands outside the city, and is a brick building of an octagon shape, rising to the height of 50 feet. The interior of it is about 40 feet square, and the architecture resembles that of Delhi. The building is unfinished. A lamp was formerly lighted on this sepulchre; but the sense of this king’s favours, like that of many others, has faded. Timour Shah made Cabool his capital, and here is his tomb. His father is interred at Candahar, which is the native country of the Dooranees.
I moved about every where during the day, and had the pleasure of many sociable evenings with our host the Nawab, whom I found, like many of his countrymen, in search of the philosopher’s stone. Such an opportunity as our arrival seemed to promise him a rich harvest. I soon undeceived him, and laughed at the crucibles and recipes, which he produced. I explained to him, that chemistry had succeeded alchymy, as astronomy had followed astrology; but as I had to detail the exact nature of these sciences, my asseverations of being no alchymist had little effect. He therefore applied himself to the doctor, from whom he requested recipes for the manufacture of calomel and quinine[161] plasters and liniments; which it was no easy matter to furnish. He could not credit that the arts of giving and manufacturing medicines were distinct; and set us down as very ignorant or very obstinate. He would not receive the prepared medicines, as they would be of no use to him after we had left. We found this feeling generally prevalent; and woe be to the doctor in these parts who gives medicines which he cannot make. We kept the Nawab in good humour, though we would not believe that he could convert iron into silver. We heard from him the position of many metallic veins in the country. He produced among other curiosities some asbestos, here called cotton-stone (sung i poomba), found near Julalabad. The good man declared that he must have some of our knowledge in return for what he told so freely. Freemasonry. I informed him that I belonged to a sect called Freemasons, and gave some account of the craft, into which he requested to be admitted without delay. But, as the number of brethren must be equal to that of the Pleiades, we put it off to a convenient opportunity. He confidently believed that he had at last got scent of magic in its purest dye; and had it been in my power, I would have willingly initiated him. He made me promise to send some flower-seeds of our country, which he[162] wished to see in Cabool; and I faithfully forwarded them. I cut the plates out of Mr. Elphinstone’s History of Cabool, and presented them to the Nawab at a large party; and not only is the costume exact, but in some of the figures, to their great delight, they discovered likenesses. Pictures are forbidden among the Soonee Mahommedans; but in the present instance they proved very acceptable. Among the Nawab’s friends we met a man 114 years old, who had served with Nadir Shah. He had been upwards of eighty years in Cabool, and seen the Dooranee dynasty founded and pass away. This venerable person walked up stairs to our rooms.
From the crowd of people we constantly met at the house of our host, I was resolved on gathering some information on the much disputed point of the Afghans being Jews. They brought me all their histories, but I had no time to examine them, and wished for oral information. The Afghans call themselves, “Bin i Israeel,” or children of Israel; but consider the term of “Yahoodee,” or Jew, to be one of reproach. Their traditions. They say that Nebuchadnezzar, after the overthrow of the temple of Jerusalem, transplanted them to the town of Ghore, near Bameean; and that they are called Afghans, from their chief Afghana, who was a son of the uncle of Asof[163] (the vizier of Solomon), who was the son of Berkia. The genealogy of this person is traced from a collateral branch, on account of the obscurity of his own parent, which is by no means uncommon in the East. They say that they lived as Jews, till Khaleed (called by the title of Caliph) summoned them, in the first century of Mahommedanism, to assist in the wars with the Infidels. For their services on that occasion, Kyse, their leader, got the title of Abdoolrusheed, which means the Son of the mighty. He was also told to consider himself the “butan” (an Arabic word), or mast of his tribe, on which its prosperity would hinge, and by which the vessel of their state was to be governed. Since that time, the Afghans are sometimes called Putan, by which name they are familiarly known in India. I never before heard this explanation of the term. After the campaign with Khaleed, the Afghans returned to their native country, and were governed by a king of the line of Kyanee, or Cyrus, till the eleventh century, when they were subdued by Mahmood of Ghuzni. A race of kings sprung from Ghore, subverted the house of Ghuzni, and conquered India. As is well known, this dynasty was divided, at the death of its founder, into the divisions east and west of the Indus; a state of things which[164] lasted till the posterity of Timourlane reduced both to a new yoke.
Having precisely stated the traditions and history of the Afghans, I can see no good reason for discrediting them, though there be some anachronisms, and the dates do not exactly correspond with those of the Old Testament. In the histories of Greece and Rome we find similar corruptions, as well as in the later works of the Arab and Mahommedan writers. The Afghans look like Jews; they say they are descended from Jews; and the younger brother marries the widow of the elder, according to the law of Moses. The Afghans entertain strong prejudices against the Jewish nation; which would at least show that they had no desire to claim, without a just cause, a descent from them. Since some of the tribes of Israel came to the East, why should we not admit that the Afghans are their descendants, converted to Mahommedanism? I am aware that I am differing from a high authority[17]; but I trust that I have made it appear on reasonable grounds.
As the chief desired, I passed another evening with him; and the doctor, being convalescent, accompanied me; Mr. Wolff had[165] proceeded on his journey to India. Dost Mahommed Khan pleased us as much as ever; he kept us till long past midnight, and gave us a full insight into the political affairs of his country, and the unfortunate differences that exist between him and his brothers. Politics. He expressed hopes of being able to restore the monarchy, evinced a cordial hatred towards Runjeet Sing, and seemed anxious to know if the British Government would accept his services as an auxiliary to root him out; but I replied, that he was our friend. He then promised me the command of his army, if I would remain with him; an offer which he afterwards repeated. “Twelve thousand horse and twenty guns shall be at your disposal.” When he found that I could not accept the honour, he requested me to send some friend to be his generalissimo. The Kaffirs a singular people. On this occasion, we had some highly interesting conversation regarding the Kaffirs, who live in the hills north of Peshawur and Cabool, and are supposed to descend from Alexander. The chief, on the former occasion, had produced a young Kaffir boy, one of his slaves, about ten years old, who had been captured for two years. His complexion, hair, and features were quite European; his eyes were of a bluish colour. We made him repeat various words of his language, some of which[166] were Indian. The Kaffirs live in a most barbarous state, eating bears and monkeys. There is a tribe of them called “Neemchu Moossulman,” or half Mahommedans, who occupy the frontier villages between them and the Afghans, and transact the little trade that exists among them. It is curious to find a people so entirely distinct from the other inhabitants, and unfortunately every thing that regards them rests in obscurity. I have hereafter stated the particulars which I collected regarding the Kaffirs, whom I take to be the aborigines of Afghanistan, and in no wise connected with the reputed descendants of Alexander the Great, as has been stated by some authors.
We had passed nearly three weeks in Cabool; which appeared as a few days. It was now necessary to prepare for our journey, which seemed no easy matter. No caravan was yet ready; and it was even doubtful if the roads were passable, as snow had fallen during the month. It occurred to me that our best plan would be to hire a Cafila-bashee, or one of the conductors of the great caravans, as one of our own servants; and we might thus proceed at once, without the delay attendant upon a caravan, and, I hoped, with equal safety. The Nawab did not altogether relish the plan, nor our precipitate departure. He would have[167] willingly kept us for months. We, however, entertained one Hyat, a sturdy but hale old man, who had grown grey in crossing the Hindoo Koosh. When the Nawab found our determination to depart, he urged his relative, the Ameen ool Moolk, a nobleman of the late Shah Mahmood, who carries on commercial transactions with Bokhara and Russia, to despatch one of his trusty persons with us. It was therefore determined that a brother of his Nazir, or steward, named Doulut, a respectable Afghan, also styled the Nazir, should proceed with us. He had business in Bokhara, and was even going on to Russia: our movements expedited his departure. Every thing looked well, and we were furnished by the Nawab’s kindness with letters to the Afghans in Bokhara. The most influential of these was Budr-oo-deen. His agent in Cabool, who brought me the letters, was resolved on being rewarded for doing so by an enjoyment of our society. His name was Khodadad, and he was a Moollah. He stopped and dined with us; but declared, that whatever might be our wisdom as a nation, we had no correct ideas of good living. He did not like our English fare, which was cooked with water, he said, and only fit for an invalid. Khodadad was a very intelligent man, who had travelled in India and Tartary, and was well[168] read in Asiatic lore. He had also studied Euclid, whom his countryman, he said, nicknamed “Uql doozd,” or wisdom-stealer, from the confusion which he had produced in men’s heads. He was not fond of mathematics, and wished to know our motive for studying them: he had not heard that it improved the reasoning faculties; and only considered the persons versed in Euclid, as deeper read than others. The chief also prepared his letters; but there is little communication between the Afghans and Uzbeks, and we found them of no service; that for the King of Bokhara was lost or stolen. One of Dost Mahommed Khan’s court, however, the governor of Bameean, Hajee Kauker, furnished us with letters, which were of real use, as will afterwards appear. This man, though serving under the chief of Cabool, is more friendly to his brother of Peshawur, by whom we were introduced to him. I held my intercourse with him secret, and he tendered the services of fifty horsemen, which it was prudent to decline.
Before our departure from Cabool, I made the acquaintance of many of the Hindoo or Shikarpooree merchants. The whole trade of Central Asia is in the hands of these people, who have houses of agency from Astracan and Meshid to Calcutta. They are a plodding race, who take[169] no share in any other matters than their own, and secure protection from the Government by lending it money. They have a peculiar cast of countenance, with a very high nose: they dress very dirtily. Few of them are permitted to wear turbans. They never bring their families from their country, which is Upper Sinde, and are constantly passing to and from it; which keeps up a national spirit among them. In Cabool, there are eight great houses of agency belonging to these people, who are quite separate from the other Hindoo inhabitants. Of them, there are about three hundred families. I met one of these Shikarpooree merchants on the Island of Kisham, in the Gulf of Persia; and were Hindoos tolerated in that country, I feel satisfied that they would spread all over Persia, and even Turkey.
With such an extensive agency distributed in the parts of Asia which we were now about to traverse, it was not, as may be supposed, a very difficult task to adjust our money matters, and arrange for our receiving a supply of that necessary article, even at the distance we should shortly find ourselves from India. Our expenses were small, and golden ducats were carefully sewed up in our belts and turbans, and sometimes even transferred to our slippers; though, as we had to leave them at the door of every house, I did not always approve[170] of such stowage. I had a letter of credit in my possession for the sum of five thousand rupees, payable from the public treasuries of Lodiana or Delhi; and the Cabool merchants did not hesitate to accept it. They expressed their readiness either to discharge it on the spot with gold, or give bills on Russia at St. Macaire (Nijnei Novgorod), Astracan, or at Bokhara, which I had no reason to question: I took orders on the latter city. The merchants enjoined the strictest secrecy; and their anxiety was not surpassed by that of our own to appear poor; for the possession of so much gold would have ill tallied with the coarse and tattered garments which we now wore. Great proofs of the civilisation by commerce. But what a gratifying proof have we here of the high character of our nation, to find the bills of those who almost appeared as beggars cashed, without hesitation, in a foreign and far distant capital. Above all, how much is our wonder excited to find the ramifications of commerce extending uninterruptedly over such vast and remote regions, differing as they do from each other in language, religion, manners, and laws.
If we had quitted Peshawur with the good wishes of the chief, we were now accompanied by those of his brother, the Nawab. On the 18th of May, which happened on a Friday, we quitted Cabool after noontide prayers, according to the usual custom of travellers, that we might not offend the prejudices of the people, who also consider that hour auspicious. We thought we had parted from the good Nawab at the door of his house, where he gave us his blessing; but before leaving the city, he once more joined us, and rode out for two or three miles. I do not think I ever took leave of an Asiatic with more regret than I left this worthy man. He seemed to live for every one but himself. He entertained us with great hospitality during our stay; and had, day by day, urged us to take any other road than that of Toorkistan, prognosticating every evil to us. He now took leave of us with much feeling; nor was it possible to suppress a tear as we said adieu. Though his[172] brother, the chief, had not caressed us as he of Peshawur, he had yet shown great politeness and attention, of which we expressed ourselves most sensible before taking our departure.
We halted for the night at a small village called Killa-i-Kazee, and, at our first outset, experienced the influence and utility of our Cafila-bashee. He cleared out a house for us, by bribing a Moollah to leave it; and we found the quarters very snug, for it was piercingly cold. Our friend Hyat was a good-humoured man, and we made the reasonable bargain with him, that he was to be rewarded according to his merits, of which we were to be the judges. We committed ourselves to him as a bale of goods, and desired him to march as he thought best. I gave him my few books and instruments, which he passed off as part of the property of the Jewish families who had left Cabool in the preceding year. Prudence dictated our proceeding very quietly in this part of our journey; and we were now designated “Meerza,” or secretary, a common appellation in these countries, and which we ever after retained. The Dr. allowed his title to slumber: but it was soon apparent that we should have been helpless without our conductor; for, on the following morning, a fellow possessing some little authority seized my horse’s bridle, and demanded a sight of the contents[173] of my saddle-bags. I was proceeding with all promptness to display my poverty, when a word from the Cafila-bashee terminated the investigation. We were not here recognised as Europeans by any one, which certainly gave a pleasing liberty to our actions. Contraband Korans. Among the contraband goods, for which the officers of the Custom-house were desired to search, was the singular article of Korans; for it appeared that the traders had exported so many of these good books beyond Hindoo Koosh, that the “Faithful” in Afghanistan were likely to be robbed of the whole of them. The suppression of the trade was a highly popular act on the part of the chief of Cabool; since they are very expensive works, written with great pains and labour, and most valuable.
We left the road which leads to Candahar on our left, and proceeded up the valley of the Cabool river to its source at Sirchushma. Our first halting place was Julraiz, which is so called from two Persian words that signify running water; and near the village there were two beautifully clear brooks, the banks of which were shaded by trees. It is these running rivulets that make this country so enchanting, in spite of its bleak rocks. Valley of the Cabool river. The valley was not above a mile in breadth, and most industriously cultivated; the water being in some[174] places conducted for a hundred feet up hill. In the lower lands, the rice fields rose most picturesquely in gradation above each other, and hills on either side were topped with snow. The thermometer stood at 60°.
At Sirchushma, which literally means the fountain-head, we visited two natural ponds, the sources of the river of Cabool, replenished by springs, and formed into preserves for fish, which are kept with great care. It is a place of pilgrimage sacred to Ali, who is said to have visited it,—a “pious lie,” which is not supported by any authority, since the son-in-law of Mahommed never saw Cabool, though his reputed deeds in this neighbourhood be both numerous and wonderful. We fed the fish with bread, which disappeared in a moment, torn from our hands by some thousands of them: they are molested by no one, since it is believed that a curse rests on the head of an intruder.
Before entering the valley of the river, we left the famous Ghuzni to the south: it is only sixty miles from Cabool. This ancient capital is now a dependency on that city, and a place of small note: it contains the tomb of the great Mahmood, its founder. There is a more honourable monument to his memory in a magnificent dam, constructed at a great expense, and the only one of seven now remaining.[175] It is worthy of remark, that the ruler of the Punjab, in a negociation which he lately carried on with the ex-King of Cabool, Shooja ool Moolk, stipulated, as one of the conditions of his restoration to the throne of his ancestors, that he should deliver up the sandal-wood gates at the shrine of the Emperor Mahmood,—being the same which were brought from Somnat, in India, when that destroyer smote the idol, and the precious stones fell from his body. Upwards of eight hundred years have elapsed since the spoliation, but the Hindoo still remembers it, though these doors have so long adorned the tomb of the Sultan Mahmood. Baber expresses his wonder that so great a monarch should have ever made Ghuzni his capital; but the natives will tell you that the cold renders it inaccessible for some months in the year, which gave him greater confidence while desolating Hindostan and the land of the infidels.
We wound up the valley, which became gradually narrower till we reached a level tract on the mountains,—the pass of Oonna,—the ascent to which is guarded by three small forts. Before reaching the summit, we first encountered the snow, with which I was too happy to claim acquaintance after a separation of a dozen winters; though there were no companions with whom I could renew the frolics of youth. It snowed[176] as we crossed the pass, which is about 11,000 feet high; and at length we found ourselves, with pleasure, at a small village, free from the chilling wind which blew all day. We had already made considerable progress in our mountain journey: the rivers now ran in opposite directions; and our advance had brought us into the cold country of the Huzaras, where the peasants were only ploughing and sowing, while we had seen the harvest home at Peshawur, and the grain in ear at Cabool.
We continued our mountain journey by the base of the lofty and ever-snow-clad mountain of Koh i Baba, which is a remarkable ridge, having three peaks that rise to the height of about 18,000 feet. On the evening of the 21st of May, we reached the bottom of the pass of Hajeeguk, half dead with fatigue, and nearly blind from the reflection of the snow. For about ten miles we had travelled in the bed of a rivulet, that was knee deep, formed by melting snow, which we crossed more than twenty times. We then entered the region of the snow, which still lay deep on the ground: by noon it became so soft that our horses sunk into it, threw their burdens and riders, and in several places were, with the utmost difficulty, extricated. That part of the ground which was free from snow had become saturated with the melted water, and a quagmire;[177] so that we alternately waded through mud and snow. The heat was oppressive,—I imagine from reflection; I had quite lost the use of my eyes, and the skin peeled from my nose, before we reached a little fort under the pass, at which we alighted in the evening with a Huzara family.
We had here an opportunity of seeing the Huzaras in their native state among the mountains; and were received by an old lady, in a miserable flat-roofed house, partly below ground, with two or three openings in the roof, as windows. She was taking care of her grandchild, and bade us welcome, by the lordly name of “Agha.” I called her “Mother;” and the old dame chatted about her house and family matters. We were taken for Persians; and, since the Huzaras are of the same creed as that nation, were honoured guests. Our mendicant garb could lead to no discovery that we were Europeans. The old woman assured us that the snow prevented them from stirring out of their houses for six months in the year (for it never rains), and that they sowed the barley in June, and reaped it in September. These people have no money, and are almost ignorant of its value. We got every thing from them by barter, and had no occasion to show them gold, by which Englishmen are so soon found out in every country. A traveller among them can only purchase[178] the necessaries of life by giving a few yards of coarse cloth, a little tobacco, pepper, or sugar, which are here appreciated far above their value. The Huzaras are a simple-hearted people, and differ much from the Afghan tribes. In physiognomy, they more resemble Chinese, with their square faces and small eyes. They are Tartars by descent, and one of their tribes is now called Tatar Huzaras. There is a current belief that they bestow their wives on their guests, which is certainly erroneous. The women have great influence, and go unveiled: they are handsome, and not very chaste; which has perhaps given rise to the scandal among their Soonee neighbours, who detest them as heretics. Were their country not strong, they would soon be extirpated; for they have enemies in every direction. The good matron, who gave us an asylum from the snow and frost, tendered also her advice for my eyes, which she said had been burned by the snow. She recommended the use of antimony, which I applied with the pencil, much to the improvement of my appearance, as she informed me; but I can more surely add, to my relief and comfort when I again encountered the snow.
I observed that these mountaineers, though some of them were living at elevations of 10,000 feet, were altogether free from that unseemly[179] disease, the goître, which I had observed in the same range—the Himalaya, eastward of the Indus, even below 4000 feet. Perhaps bronchocele is a disease confined to the lesser altitudes; an opinion held by members of the faculty of the first eminence on the Continent, as I find from a paper in the Transactions of the Medical Society of Calcutta, by Dr. M. J. Bramley, of the Bengal army. That gentleman, however, in his treatise on the disease, which is founded on personal experience during a residence in the mountainous regions of Nipal, adduces facts that would lead to a contrary conclusion regarding its locality, which he states to be more general on the crest of a high mountain than in the valley of Nipal.
One would have imagined, that, in these elevated and dreary regions, the inhabitants would be engaged with other subjects than abstruse points of theology. A moollah, or priest, however, had lately appeared among them to proclaim some novel doctrines; and, among others, that Ali was the Deity, and greater than Mahommed himself. He had found some hundred followers, whom this fanatic had impressed with such an opinion of his power, that they believed he could raise the dead, and pass through fire without injury. One of the Huzara chiefs, who was shocked at the blasphemy of this false prophet,[180] had preached a crusade against him for misleading the faithful; and many of the people accompanied him to assist in reclaiming the deluded to Islam. They informed us that this sect was styled “Ali Illahi,” and had adopted many odious customs; among others, that of the community of women: they also held bacchanalian orgies in the dark, from which they were named “Chiragh Koosh,” or lamp-killers, in allusion to the darkness which concealed their iniquities. Such a sect, I am assured, is not at all novel, since the Mogots of Cabool have long since professed some of its tenets, and still secretly practise them. It is also known in several parts of Persia and Turkey; but the march of intellect had not hitherto extended it to the gelid regions of Hindoo Koosh.
The crusade of the Huzaras proved a fortunate circumstance for us, as the chieftain of 12,000 families, and of these passes, by name Yezdan Bukhsh, was absent upon it; and he is a person who acknowledges but a doubtful allegiance to Cabool. By the kindness of Hajee Khan Kauker, we were introduced to him; but the report of his character did not lead us to hope for more than common civility, if we even received that. We escaped, however, in the religious turmoil, after waiting for an hour at the door of the fort, and each of us paying a rupee[181] as tax to his deputy, since we were not Mahommedans. Our letter might, perhaps, have prevailed on the Huzaras to let us pass at this cheap rate; but it was long before they adjusted the demand with the Cafila-bashee, who gave me many a significant glance during the treaty. The doctor and myself sought no closer connection than a look at these mountaineers; but, as it appeared, we were altogether unworthy of their notice.
After a night’s rest, and the friendly advice of the Huzara matron, we commenced the ascent of the pass of Hajeeguk, which was about 1000 feet above us, and 12,400 feet from the sea. We took our departure early in the morning of the 22d of May; the frozen snow bore our horses, and we reached the summit before the sun’s influence had softened it. The thermometer fell 4 degrees below the freezing point; the cold was very oppressive, though we were clad in skins with the fur inside. I often blessed the good Nawab of Cabool, who had forced a pelisse of otter skin upon me, that proved most useful. The passage was not achieved without adventure, for there was no road to guide us through the snow; and the surveyor, Mahommed Ali, along with his horse, went rolling down a declivity, one after the other, for about thirty yards. This exhibition in front, served to guide[182] the rear to a better path; but it was impossible to resist laughing at the Jack and Jill expedition of the poor surveyor and his horse; he, a round figure wrapped up in fur, and far outstripping his long-shanked animal, which made deeper indentations in the snow. We were now about to commence the ascent of the pass of Kaloo, which is still 1000 feet higher than that of Hajeeguk; but our progress was again arrested by snow. We doubled it, by passing round its shoulder, and took a side path through a valley, watered by a tributary of the Oxus, which led us to Bameean.
Nothing could be more grand than the scenery which we met in this valley. Frightful precipices hung over us; and many a fragment beneath informed us of their instability. For about a mile it was impossible to proceed on horseback, and we advanced on foot, with a gulf beneath us. The dell presented a beautiful section of the mountains to the eye of the geologist[18]; and, though a by-path, appeared to have been fortified in former years, as innumerable ruins testified. Some of these were pointed out as the remnants of the post-houses of the Mogul emperors; but by far the greater number were assigned to the age of Zohak, an ancient king of[183] Persia. One castle in particular, at the northern termination of the valley, and commanding the gorge, had been constructed with great labour on the summit of a precipice, and was ingeniously supplied with water. It would be useless to record all the fables of the people regarding these buildings.
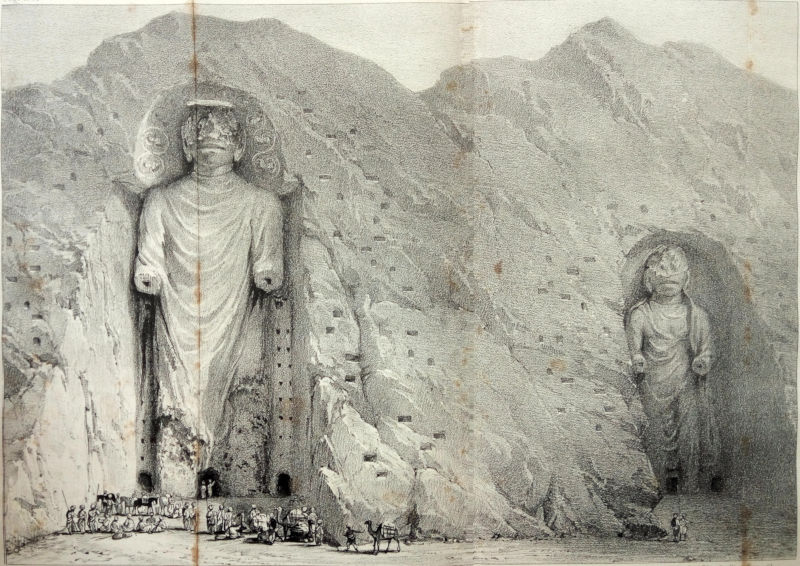

Page 183. Pl. II. Vol. 1.
THE COLOSSAL IDOLS AT BAMEEAN.
On Stone by L. Haghe for Burnes’ Travels into Bokhara
Day & Haghe Lithrs to the King, Gate St.
J. Murray Albemarle St. 1834.
Bameean is celebrated for its colossal idols and innumerable excavations, which are to be seen in all parts of the valley, for about eight miles, and still form the residence of the greater part of the population. They are called “Soomuch” by the people. A detached hill in the middle of the valley is quite honeycombed by them, and brings to our recollection the Troglodites of Alexander’s historians. It is called the city of Ghoolghoola, and consists of a continued succession of caves in every direction, which are said to have been the work of a king named Julal. The hills at Bameean are formed of indurated clay and pebbles, which renders their excavation a matter of little difficulty; but the great extent to which it has been carried, excites attention. Caves are dug on both sides of the valley, but the greater number lie on the northern face, where we found the idols: altogether they form an immense city. Labourers are frequently hired to dig in them; and their trouble is rewarded by rings, relics, coins, &c. They gene[184]rally bear Cufic inscriptions, and are of a later date than the age of Mahommed. These excavated caves, or houses, have no pretensions to architectural ornament, being no more than squared holes in the hill. Some of them are finished in the shape of a dome, and have a carved frieze below the point, from which the cupola springs. The inhabitants tell many remarkable tales of the caves of Bameean; one in particular—that a mother had lost her child among them, and recovered it after a lapse of twelve years! The tale need not be believed; but it will convey an idea of the extent of the works. There are excavations on all sides of the idols; and below the larger one, half a regiment might find quarters. Bameean is subject to Cabool: it would appear to be a place of high antiquity; and is, perhaps, the city which Alexander founded at the base of Paropamisus, before entering Bactria. The country, indeed, from Cabool to Balkh, is yet styled “Bakhtur Zumeen,” or Bakhtur country. The name of Bameean is said to be derived from its elevation,—“bam” signifying balcony, and the affix “eean” country. It may be so called from the caves rising one over another in the rock.
There are no relics of Asiatic antiquity which have roused the curiosity of the learned more than the gigantic idols of Bameean. It is[185] fortunately in my power to present a drawing of these images. They consist of two figures, a male and a female; the one named Silsal, the other Shahmama. The figures are cut in alto relievo on the face of the hill, and represent two colossal images. The male is the larger of the two, and about 120 feet high. It occupies a front of 70 feet; and the niche in which it is excavated, extends about that depth into the hill. This idol is mutilated; both legs having been fractured by cannon; and the countenance above the mouth is destroyed. The lips are very large; the ears long and pendent; and there appears to have been a tiara on the head. The figure is covered by a mantle, which hangs over it in all parts, and has been formed of a kind of plaster; the image having been studded with wooden pins in various places, to assist in fixing it. The figure itself is without symmetry, nor is there much elegance in the drapery. The hands, which held out the mantle, have been both broken. The female figure is more perfect than the male, and has been dressed in the same manner. It is cut in the same hill, at a distance of 200 yards, and is about half the size. It was not to be discovered whether the smaller idol was a brother or son of the Colossus, but from the information of the natives. The sketch which is attached will convey better notions of these idols than a more[186] elaborate description. The square and arched apertures which appear in the plate represent the entrance of the different caves or excavations; and through these there is a road which leads to the summit of both the images. In the lower caves, the caravans to and from Cabool generally halt; and the upper ones are used as granaries by the community.
I have now to note the most remarkable curiosity in the idols of Bameean. The niches of both have been at one time plastered, and ornamented with paintings of human figures, which have now disappeared from all parts but that immediately over the heads of the idols. Here the colours are as vivid, and the paintings as distinct, as in the Egyptian tombs. There is little variety in the design of these figures; which represent the bust of a woman, with a knob of hair on the head, and a plaid thrown half over the chest; the whole surrounded by a halo, and the head again by another halo. In one part, I could trace a groupe of three female figures following each other. The execution of the work was indifferent, and not superior to the pictures which the Chinese make in imitation of an European artist.
The traditions of the people regarding the idols of Bameean are vague and unsatisfactory. It is stated, that they were excavated about the Christian era, by a tribe of Kaffirs (infidels), to[187] represent a king, named Silsal, and his wife, who ruled in a distant country, and was worshipped for his greatness. The Hindoos assert that they were excavated by the Pandoos, and that they are mentioned in the great epic poem of the Mahaburat. Certain it is, that the Hindoos, on passing these idols, at this day, hold up their hands in adoration: they do not make offerings; and the custom may have fallen into disuse since the rise of Islam. I am aware that a conjecture attributes these images to the Boodhists; and the long ears of the great figure render the surmise probable. I did not trace any resemblance to the colossal figures in the caves of Salsette, near Bombay; but the shape of the head is not unlike that of the great trifaced idol of Elephanta. At Manikyala, in the Punjab, near the celebrated “tope,” I found a glass or cornelian antique, which exactly resembles this head. In the paintings over the idols I observed a close resemblance to the images of the Jain temples in Western India, on Mount Aboo, Girnar, and Politana in Kattywar. I judge the figures to be female; but they are very rude; though the colours in which they are sketched are bright and beautiful. There is nothing in the images of Bameean to evince any great advancement in the arts, or what the most common people might not have easily executed. They cannot,[188] certainly, be referred to the Greek invasion; nor are they mentioned by any of the historians of Alexander’s expedition. I find, in the history of Timourlane, that both the idols and excavations of Bameean are described by Sherif o deen, his historian. The idols are there stated to be so high that none of the archers could strike the head. They are called Lat and Munat; two celebrated idols which are mentioned in the Koran: the writer also alludes to the road which led up to their summit from the interior of the hill. There are no inscriptions at Bameean to guide us in their history; and the whole of the later traditions are so mixed up with Ali, the son-in-law of Mahommed, who, we well know, never came into this part of Asia, that they are most unsatisfactory. It is by no means improbable that we owe the idols of Bameean to the caprice of some person of rank, who resided in this cave-digging neighbourhood, and sought for an immortality in the colossal images which we have now described.
After a day’s delay at Bameean, where we could not boast of much hospitality—since we procured a house with difficulty, and were obliged to quit several that we entered—we set out for Syghan, a distance of thirty miles. At the pass of Akrobat, which we crossed half way, we left the dominions of modern Cabool, and entered[189] Toorkistan, which is denominated Tartary (more properly Tatary) by Europeans. Following the geography of our maps, I had expected to find the great snowy mountains beyond us; but we now looked upon them in range behind. The “Koh i Baba” is the great continuation of Hindoo Koosh. In our front we had yet to cross a wide belt of mountains, but they were almost free from snow, and much lower than those which we had traversed. Leave Afghanistan. We were conducted to the pass of Akrobat by twenty horsemen, which a letter of introduction to the governor of Bameean from Hajee Khan of Cabool had procured as a protection from the Dih Zungee Huzaras, who plunder these roads. The escort was mounted on fine Toorkmun horses, and accompanied by some native greyhounds—a fleet sort of dog, with long shaggy hair on the legs and body. The party took their leave on the pass, where we bade farewell to them and the kingdom of Cabool.
At Syghan we found ourselves in the territory of Mahommed Ali Beg, an Uzbek, who is alternately subject to Cabool and Koondooz, as the chiefs of these states respectively rise in power. He satisfies the chief of Cabool with a few horses, and his Koondooz lord with a few men, captured in forays by his sons and officers, who are occasionally sent out for the purpose. Such is the difference between the taste of his northern and southern[190] neighbours. The captives are Huzaras, on whom the Uzbeks nominally wage war for their Shiah creed, that they may be converted to Soonees and good Mahommedans. A friend lately remonstrated with this chief for his gross infringement of the laws of the Prophet, in the practice of man-stealing. He admitted the crime; but as God did not forbid him in his sleep, and his conscience was easy, he said that he did not see why he should desist from so profitable a traffic! I should have liked an opportunity to administer a sleeping draught to this conscience-satisfied Uzbek. He is nowise famed for justice, or protection of the traveller; a caravan of Jews passed his town last year, on route to Bokhara, he detained some of their women, and defended the outrage, by replying to every remonstrance, that their progeny would become Mahommedan, and justify the act. So this wretch steals men, and violates the honour of a traveller’s wife, because he believes it acceptable conduct before his God, and in consonance with the principles of his creed! Intercourse with him. Our Cafila-bashee waited on this person, to report our arrival; and told him, it seems, that we were poor Armenians. He jested with him, and said we might be Europeans; but our conductor appealed to a letter of introduction from Cabool, in which we had not been so denominated. A nankeen pelisse, with eight or nine[191] rupees (the usual tax on a caravan), satisfied this man-selling Uzbek, and we passed a comfortable night in a very nicely carpeted “mihman khana,” or public-house of guests, which is situated at the verge of the village; the chief himself sending us a leg of venison, as we were known to his friends in Cabool. We were already in a different country; the mosques were spread with felts, which indicated greater attention to matters of religion, and they were also much better buildings. We were instructed not to sleep with our feet towards Mecca; which would be evincing our contempt for that holy place; and I ever after observed the bearings of the compass in-doors, as attentively as I had hitherto done outside. I also cut the central portion of the hair of my mustachoes; since the neglect of such a custom would point me out as a Shiah, and consequently an infidel. We made all these arrangements in Syghan; which is a pretty place, with fine gardens, though situated in a dreary valley, destitute of all vegetation beyond its precincts. When we left it next morning, a man came about 500 yards from the village to give us the “fatha” or blessing, as is usual in this country; and we departed, and stroked down our beards with gravity at the honour.
Seeing this rigid adherence to the laws of Mahommed, and the constant recurrence to the[192] practice of the Koran in every act of life, I was not disposed to augur favourably for our comfort, or the reliance which we could place upon the people with whom we were now to mingle. I thought of the expeditions of Prince Beckevitch, and our own unfortunate predecessors, poor Moorcroft and his party. The fate of the Russian Count and his little army is well known; they were betrayed, and barbarously massacred. The lot of Moorcroft was equally melancholy; since he and his associates perished of fever, and not without suspicions of some more violent death. I shall have occasion to speak of them hereafter. We could not, however, but persuade ourselves, that a more encouraging field lay before us. We had not appeared, as the Russian, to search for gold, nor to found a settlement; and we had none of the wealth of the English traveller, which, I do not hesitate to say, proved his ruin. We appeared even without presents to the chiefs; for it was better to be thought mean, than to risk our heads by exciting the cupidity of avaricious men. It may be imagined that our feelings at this moment were not of an agreeable nature; but fuller experience dissipated many of our fears. The notions of our conductor even were singular. Shortly after leaving Cabool, I took up a stone by the road side, to examine its formation; and the Cafila-bashee, who[193] observed me, asked me with anxiety, “Have you found it?”—“What?”—“gold.” I threw away the stone, and became more cautious in my future observations.
From Syghan we crossed the pass of “Dundan Shikun,” or the Tooth-breaker, which is aptly named from its steepness and difficulty. We here found the assafœtida plant in exuberance, which our fellow travellers ate with great relish. This plant, I believe, is the silphium of Alexander’s historians; for the sheep cropped it most greedily, and the people consider it a nutritious food. We now descended into a narrow valley, with a beautiful orchard of apricots, that extended for some miles beyond the village of Kamurd. The rocks rose on either side to a height of 3000 feet, frequently precipitous; nor was the dell any where more than 300 yards wide. We could not see the stars, to take an observation at night: the whole scene was most imposing.
At Kamurd we passed the seat of another petty chief, Ruhmut oollah Khan, a Tajik deeply addicted to wine. He had been without a supply for ten days, and gave vent to such ejaculations and regrets as amused our party for the remainder of the march. Heaven and earth were the same to him, he said, without his dose; and he produced a flagon, with an earnest re[194]quest that the Cafila-bashee would replenish it at Khoolloom, and send it to him by the first opportunity. A coarse loongee, coupled with a promise of the wine, satisfied this chief; for he also claims a tax on the traveller, though he is but a tributary of Koondooz. His power is limited, and it is curious to observe how he keeps on terms with his master, Mahommed Moorad Beg. Unable to make “chupaos,” or forays, and capture human beings, like his neighbour of Syghan, he, last year, deliberately seized the whole of the inhabitants of one of his villages, and despatched them, men, women, and children, as slaves, to Koondooz. Uzbek pity. He was rewarded by three additional villages for his allegiance and services; yet we here hired a son of this man to escort us on our travels; and it was well we did so.
The chief of Kamurd, in a quarrel which he had some years since with one of his neighbours, unfortunately lost his wife, who was captured. She was immediately transferred to his rival’s seraglio, and in time bore him a numerous family. After a lapse of years, circumstances restored her to her husband; but the propriety of receiving her into his family was referred to the Mahommedan doctors. As the woman had been carried off without her consent, it was decided that she should be taken back, with all her family.[195] It is common among the Toorks to marry the wives of their enemies captured in battle; but the custom is barbarous, and appears to contradict the nice principles of delicacy regarding women, which are professed by all Mahommedans.
I have hitherto forgotten to mention, that our companion the Nazir was accompanied by a person named Mahommed Hoosein, an amusing character, who had travelled into Russia, and often entertained us with an account of that country, and the metropolis of the Czars. It appeared to him, and several other Asiatics whom I afterwards met, a very close approximation, in wine and women, to the paradise of their blessed Prophet. Asiatic opinions of Europe. A Mahommedan, who is transported from a country where females are so much secluded, would at all times be struck with the great change in an European country; but in Russia, where the moral tone of society appears, from every account, to be rather loose, their amazement is great indeed. The foundling hospitals and their inmates are a subject of perpetual remark; and however much the Arabian prophet may have condemned the use of intoxicating fluids, I could discover, from those who I have visited Russia, that the temptations of the gin and punch shops had not been resisted. Many[196] of the Asiatics, too, become gamblers; and commerce has imported cards into the holy city of Bokhara. The pack consists of thirty-six cards, and the games are strictly Russian. In describing the feelings of an Asiatic on the subject of Europe, there must be much sameness; but it is at all times most interesting to listen to their tales. Particulars which quite escape us, and a multiplicity of trifles, are noticed with great gravity. Nothing is so wonderful to an Asiatic as the European notions of military discipline and drill, which he considers to be a description of torture and despotism. I had to answer reiterated and endless questions on the utility of making a man look always one way, march off always with one foot, and hold his hands in certain positions on a parade ground. As they had not heard of the great Frederick, I could not refer them to his high name for an example; but I pointed to India and Persia as sure proofs of the advantage of disciplined over undisciplined valour. The Asiatics, however, have a far higher opinion of European wisdom than valour; and truly, since the age of physical strength has ceased, wisdom is bravery.
On the 26th of May, we crossed the last pass of the Indian Caucasus,—the Kara Koottul, or Black Pass,—but had yet a journey of ninety-five miles before we cleared the mountains. We de[197]scended at the village of Dooab into the bed of the river of Khooloom, and followed it to that place among terrific precipices, which at night obscured all the stars but those of the zenith. Adventures. On this pass we had an adventure, which illustrates the manners of the people among whom we were travelling, and might have proved serious. Our Cafila-bashee had intimated to us that we had reached a dangerous neighbourhood, and consequently hired an escort, headed, as I have stated, by the son of Rhumut oollah Khan. In ascending the pass, we met a large caravan of horses, en route to Cabool; and, on reaching the top, descried a party of robbers advancing over a ridge of hills, and from the direction of Hindoo Koosh. The cry of “Allaman, Allaman!” which here means a robber, soon spread; and we drew up with our escort to meet, and, if possible, fight the party. The robbers observed our motions, and were now joined by some other men, who had lain in ambush, which increased their party to about thirty. Each of us sent on a couple of horsemen, who drew up at a distance of a hundred yards, and parleyed. The robbers were Tatar Huzaras, commanded by a notorious free-booter named Dilawur, who had come in search of the horse caravan. On discovering that it had passed, and that we were in such good company as the son of the chief of Kamurd, they gave[198] up all intentions of attack, and we pushed on without delay; immediately we had cleared the pass, they occupied it; but the whole of their booty consisted of two laden camels of the caravan, which had loitered behind. These they seized in our view, as well as their drivers, who would now become slaves for life; and had we not hired our escort, we should have perhaps shared a similar fate, and found ourselves next day tending herds and flocks among the mountains. The party was well mounted, and composed of desperate men: disappointed of their prey, they attacked the village of Dooab at night, where we first intended to halt. We had luckily pushed on three miles further, and bivouacked in the bed of a torrent in safety. The incidents of our escape furnished some room for reflection; and we had to thank the Cafila-bashee for his prudence, which had cleared us of the danger. The old gentleman stroked down his beard, blessed the lucky day, and thanked God for preserving his good name and person from such scoundrels.
The life we now passed was far more agreeable than a detail of its circumstances would lead one to believe, with our dangers and fatigues. We mounted at daylight, and generally travelled without intermission till two or three in the afternoon. Our day’s progress averaged about twenty[199] miles; but the people have no standard of measure; and miles, coses, and fursukhs, were equally unknown, for they always reckon by the day’s journey. We often breakfasted on the saddle, on dry bread and cheese; slept always on the ground, and in the open air; and after the day’s march, sat down cross-legged, till night and sleep overtook us. Our own party was every thing that could be wished, for the Nazir and his amusing fellow-traveller were very obliging: we ourselves only amounted to eight persons; three of them were natives of the country, and two others were instructed to pretend that they were quite distinct from us; though one of them noted the few bearings of the compass, which I myself could not conveniently take without leading to discovery. We were quite happy in such scenes, and at the novelty of every thing; and it was also delightful to recognise some old friends among the weeds and shrubs. The hawthorn and sweet brier grew on the verge of the river; and the rank hemlock, that sprung up under their shade, now appeared beautiful from the associations which it awakened. Our society, too, was amusing; and I took every favourable occasion of mingling with the travellers whom we met by the way, and at the halting places.
I found nothing more puzzling than the different modes of salutation among the Afghans,[200] with which time only can familiarise a foreigner. When you join a party, you must put your right hand on your heart, and say “Peace be unto you!” (Salam Alaikoom.) You are then told you are welcome; and when you depart, you repeat the ceremony, and are again told you are welcome. On the road a traveller salutes you with “May you not be fatigued!” (Mandu nu bashee;) to which you reply, “May you live long!” (Zindu bashee.) If acquainted, the salutations become more numerous. Are you strong? are you well? are you free from misfortunes? &c. &c.: to all of which, you must answer, “Thanks be to God!” (Shookur.) On parting, your friend will tell you that your journey is not a tedious one, and consign you to God’s keeping (bu uman i Khooda). If invited to dinner, you must reply to the civility, “May your house be peopled!” (Khana i to abad;) and if you be complimented on any occasion, you must answer that “I am not worthy of you; it is your greatness.” Every person, high and low, you must address by the title of Khan or Agha, to gain his good graces. If he is a moollah or priest, you must call him Akhoond or teacher, if a moollah’s son, Akhoondzada. A secretary is called Meerza; which is, however, a cognomen for all nondescript characters, in which class we were numbered. Intimate acquaintances call each[201] other “lalu” or brother. The Afghans must have learned all this ceremony from the Persians, for there is not a more unsophisticated race of people in Asia. It was quite entertaining to hear the various salutations which were addressed to our Cafila-bashee: every person on the road seemed to know him; and, as we passed along, he used to teach us lessons of good breeding, which I took every occasion, as his apt scholar, to display.
We continued our descent by Khoorrum and Sarbagh to Heibuk, which is but a march within the mountains; and gradually exchanged our elevated barren rocks for more hospitable lands. Our road led us through most tremendous defiles, which rose over us to a height of from 2000 to 3000 feet, and overhung the pathway, while eagles and hawks whirled in giddy circles over us: among them we distinguished the black eagle, which is a noble bird. Near Heibuk, the defile becomes so narrow, that it is called the “Dura i Zindan,” or Valley of the Dungeon; and so high are the rocks, that the sun is excluded from some parts of it at mid-day. Poisonous plant. There is a poisonous plant found here, which is fatal even to a mule or a horse: it grows something like a lily; and the flower, which is about four inches long, hangs over and presents a long seed nodule. Both it and the flower resemble the richest crimson velvet. It is called “zuhr boota” by[202] the natives, which merely explains its poisonous qualities. I brought a specimen of this plant to Calcutta, and am informed by Dr. Wallich, the intelligent and scientific superintendent of the Honourable Company’s botanic garden, that it is of the Arum species. We now found vast flocks browsing on the aromatic pastures of the mountains, and we passed extensive orchards of fruit trees. Herds of deer might be seen bounding on the summit of the rocks; and in the valleys, the soil was every where turned up by wild hogs, which are here found in great numbers. The people also became more numerous as we approached the plains of Tartary, and at Heibuk we had to encounter another Uzbek chief named Baba Beg, a petty tyrant of some notoriety.
As we approached his town, a traveller informed us that the chief was anticipating the arrival of the Firingees (Europeans), whose approach had been announced for some time past. This person is a son of Khilich Ali Beg, who once ruled in Khooloom with great moderation; but the child has not imitated the example of his parent. He poisoned a brother at a feast, and seized upon his father’s wealth before his life was extinct. He had greatly augmented the difficulties of Mr. Moorcroft’s party; and was known to be by no means favourable to Eu[203]ropeans. His subjects had driven him from his native town of Khooloom for his tyranny, and he now only possessed the district of Heibuk. We saw his castle about four in the afternoon, and approached with reluctance; but our arrangements were conducted with address, and here also we escaped in safety. On our arrival, our small caravan alighted outside Heibuk, and we lay down on the ground as fatigued travellers, covering ourselves with a coarse horse blanket till it was night. In the evening, the chief came in person to visit our Cabool friend the Nazir, to whom he offered every service; nor did he appear to be at all aware of our presence. Baba Beg, on this occasion, made an offer to send the party, under an escort of his own, direct to Balkh, avoiding Khooloom,—an arrangement, which I heard with pleasure, and, as it will soon appear, that might have saved us a world of anxiety. Our fellow-travellers, however, declined the proffered kindness, and vaunted so much of their influence at Khooloom, that we had no dread in approaching a place where we were ultimately ensnared. While this Uzbek chief was visiting the Nazir, we were eating a mutton chop by the fireside within a few yards, and near enough to see him and hear his conversation. He was an ill-looking man, of debauched habits. He was under[204] some obligation to our fellow-travellers; and we and our animals fared well on the flesh and barley which he sent for their entertainment. Our character was never suspected; and so beautiful a starlight night was it, that I did not let this, the first opportunity, pass without observing our latitude north of Hindoo Koosh. We set out in the morning before the sun had risen, and congratulated ourselves at having passed with such success a man who would have certainly injured us.
Heibuk is a thriving village, with a castle of sun-dried brick, built on a commanding hillock. For the first time among the mountains, the valley opens, and presents a sheet of gardens and most luxuriant verdure. The climate also undergoes a great change; and we find the fig tree, which does not grow in Cabool, or higher up the mountains. The elevation of Heibuk is about 4000 feet. The soil is rich, and the vegetation rank. We had expected to be rid of those troublesome companions of a tropical climate, snakes and scorpions; but here they were more numerous than in India, and we disturbed numbers of them on the road. One of our servants was stung by a scorpion; and as there is a popular belief that the pain ceases if the reptile be killed, it was put to death accordingly. Houses. The construction of the houses at[205] Heibuk arrested our attention: they have domes instead of terraces, with a hole in the roof as a chimney; so that a village has the appearance of a cluster of large brown beehives. The inhabitants adopt this style of building, as wood is scarce. People. The people, who were now as different as their houses, wore conical skull-caps, instead of turbans, and almost every one we met, whether traveller or villager, appeared in long brown boots. The ladies seemed to select the gayest colours for their dresses; and I could now distinguish some very handsome faces, for the Mahommedan ladies do not pay scrupulous attention to being veiled in the villages. They were much fairer than their husbands, with nothing ungainly in their appearance, though they were Tartars. I could now, indeed, understand the praises of the Orientals in the beauty of these Toorkee girls.
On the 30th of May we made our last march among the mountains, and debouched into the plains of Tartary at Khooloom, or Tash Koorghan, where we had a noble view of the country north of us, sloping down to the Oxus. We left the last hills about two miles from the town, rising at once in an abrupt and imposing manner; the road passing through them by a narrow defile, which might easily be defended. Khooloom contains about ten thousand inhabit[206]ants, and is the frontier town of Moorad Beg of Koondooz, a powerful chief, who has reduced all the countries north of Hindoo Koosh to his yoke. We alighted at one of the caravansarais, where we were scarcely noticed. A caravansary is too well known to require much description:—it is a square, enclosed by walls, under which are so many rooms or cells for accommodation. The merchandise and cattle stand in the area. Each party has his chamber, and is strictly private; since it is contrary to custom for one person to disturb another. All are travellers, and many are fatigued. If society were every where on as good a footing as in a caravansary, the world would be spared the evils of calumny. We here rested after our arduous and fatiguing journey over rocks and mountains; and were, indeed, refreshed by the change. Since leaving Cabool, we had slept in our clothes, and could seldom or ever change them. We had halted among mud, waded through rivers, tumbled among snow, and for the last few days been sunned by heat. These are but the petty inconveniences of a traveller; which sink into insignificance, when compared with the pleasure of seeing new men and countries, strange manners and customs, and being able to temper the prejudices of one’s country, by observing those of other nations.
We had entered Khooloom, with an intention of setting out next day on our journey to Balkh; placing implicit reliance on the assertion of our friends, that we had nothing to apprehend in doing so. Judge, then, of our surprise, when we learned that the officers of the custom-house had despatched a messenger to the chief of Koondooz, to report our arrival, and request his instructions as to our disposal. We were, meanwhile, desired to await the answer. Our companion, the Nazir, was much chagrined at the detention; but it was now useless to upbraid him for having ever brought us to Khooloom. He assured us that it was a mere temporary inconvenience; and likewise despatched a letter to the minister at Koondooz, requesting that we might not be detained, since his business in Russia could not be transacted without us. The minister was a friend of the Nazir’s family; and since we had plunged ourselves into difficulties, matters seemed at least to look favourable for our safe conduct through them. I could not[208] but regret, that I had ever allowed myself to be seduced by the advice of any one; and would, even at this late period, have endeavoured to escape to Balkh, had not the Cafila-bashee, and every one, pronounced it headstrong and impracticable. At one time, indeed, about midnight, the Cafila-bashee acceded to our proposals for escaping to Balkh in the course of the next night, and even said the first verse of the Koran as his oath and blessing. I did not, however, understand the plan was to be kept secret from the Nazir, to whom I revealed it next day, to the great dissatisfaction and dismay of the Cafila-bashee, who was visited with a due share of his wrath. “Wait,” said the Nazir to us, “for a reply from Koondooz, and we cannot doubt its favourable nature.” We did wait; and at midnight, on the 1st of June, received a summons to repair to Koondooz with all despatch; while the minister, in reply to our conductor’s letter, begged he would not allow himself to be detained on our account, but proceed on his journey to Bokhara! Our surprise may be better imagined than described. It was now too late to make our escape, for we were watched in the caravansary, and the officers would not even allow my horse to be taken into the town and shod. It might have been accomplished on our first arrival, but then it was deemed[209] injudicious, and it only remained, therefore, for us to face the difficulties of our situation in a prompt and becoming manner. I urged an immediate departure for Koondooz, leaving Dr. Gerard, and all the party, except two Afghans, at Khooloom. I was now resolved on personating the character of an Armenian, and believed that despatch would avail me and allay suspicion. I had letters from the saint at Peshawur, which would bear me out, as I thought, in the new character, since we were there denominated Armenians; but my fellow-travellers assured me that the very possession of such documents would prove our real condition, and I destroyed them all, as well as the letters of the Cabool chief, which were alike objectionable. I divested myself, indeed, of all my Persian correspondence, and tore up among the rest many of Runjeet Sing’s epistles, which were now in my eyes less acceptable than I thought they would ever prove. During these arrangements, I discovered that the Nazir had no relish for a journey to Koondooz, and seemed disposed to stay behind, almost frantic with despair; but shame is a great promoter of exertion, and I begged he would accompany me, to which he agreed.
The better to understand the critical situation in which we were now placed, I shall give a[210] brief sketch of the disasters which befell Mr. Moorcroft in this part of the country, in the year 1824, from the very personage who now summoned us to Koondooz. On that traveller crossing the mountains, he proceeded to wait on the chief, and having made him some presents suitable to his rank, returned to Khooloom. He had no sooner arrived there, than he received a message from the chief, saying, that some of his soldiers had been wounded, and requesting that he would hasten his return, and bring along with him his medical instruments, and Mr. Guthrie, an Indo-Briton, who had accompanied Mr. Moorcroft, as a surgeon. Mr. Moorcroft’s own abilities in that capacity were also known, for he had already given proofs of his great skill to these people. He set out for Koondooz without suspicion, but found, on his arrival there, that his surgical services were not wanted, and it was merely a plan to ensnare him. The chief ordered him to send for all his party and baggage, which he did; and, after a month’s delay, he only succeeded in liberating himself, by complying with the most extravagant demands of Moorad Beg. By one means or another, he possessed himself of cash to the value of 23,000 rupees, before Mr. Moorcroft was permitted to depart; and it would have been well had the matter here terminated,[211] but the cupidity of the chief had been excited. It is also said, that he entertained some dread of Moorcroft’s designs, from the arms and two small field-pieces, which he carried with him for purposes of protection. The party prepared to quit Khooloom for Bokhara, but, on the very eve of departure, were surrounded by 400 horsemen, and again summoned to Koondooz. It was not now concealed, that the chief was resolved on seizing the whole of the property, and putting the party to death. Mr. Moorcroft took the only course which could have ever extricated his party and himself. In the disguise of a native he fled at night, and after a surprising journey, at length reached Talighan, a town beyond Koondooz, where a holy man lived, who was reputed to possess much influence over the conscience of Moorad Beg. He threw himself at the feet of this saint, seized the hem of his garment, and sued for his protection. “Rise up,” said he, “it is granted; fear nothing.” This good man immediately sent a messenger to Koondooz, to summon the chief, who appeared in person with the answer. At his peril, he could not now touch a hair of the traveller’s head; Moorad Beg obeyed, and the holy man declined to receive the smallest reward for his services. After Mr. Moorcroft’s flight, the Uzbeks[212] marched his fellow-traveller, Mr. George Trebeck, with all the party and property, to Koondooz. Their anxiety was not allayed till their arrival at that place, when they heard of the success of Moorcroft, his safety, and their own. After these disasters, Moorcroft pursued his journey into Bokhara, but unfortunately died on his return, in the following year, at Andkhooee, about eighty miles from Balkh. His fellow-traveller, Mr. Trebeck, was unable to force his way beyond Mazar, in the neighbourhood of that city, since the chief of Koondooz was resolved on way-laying the party on its return, and the only safe road to Cabool led by Khooloom, where they had already encountered such difficulties. He lingered about Balkh for four or five months, and died of fever, from which he had been suffering during the whole of that time. The Indo-Briton, Mr. Guthrie, was previously cut off by the same disease to which most of their followers also fell victims. Thus terminated their unfortunate expedition into Tartary.
On the evening of the 2d of June, I set out on my journey to Koondooz, which lies higher up the valley of the Oxus, having previously prevailed on the custom-house officer, who was a Hindoo, to accompany me. I did not leave Khooloom under very encouraging circum[213]stances, having just discovered that a Hindoo of Peshawur had kindly apprised the authorities of many of our acts, circumstances, and condition, since leaving Hindoostan; adding, indeed, numerous exaggerations to the narration, in which we were set forth as wealthy individuals, whose bills had even affected the money market. When beyond the town, we found our caravan to consist of eight or ten tea merchants, of Budukhshan and Yarkund, who had disposed of their property, and were returning to their country. In our own party there was the Nazir, Cafila bashee, and myself, with the Hindoo, whose name was Chumundass, who came unattended. I discovered that this latter person had a pretty correct knowledge of our affairs, but I did not assist to fill up the thread of his discourse, and boldly denominated myself an Hindoostan Armenian. The name of Englishman, which had carried us in safety in all other places, was here replete with danger; since it not only conveyed notions of great wealth, but a belief that that can be renewed from the inferior metals. I had, however, discovered that the Hindoo was a good man, for his easy manner in searching our baggage at the caravansary, after our first arrival, left a favourable impression on my mind; and he himself declared to the Nazir, that it was no fault of his[214] that we were dragged to Koondooz, since he was but a custom-house officer, and obliged to report our arrival. It was evident to me, that an impression might be made on such a person by persuasion and gold, and from his very presence with us, I construed that money might be his god. He and I soon fell into conversation, and I found him to be a native of Mooltan, who had long resided in these countries. I spoke much of India, and its people and customs; told him that I had seen his native town, using as much eloquence as I was possessed of to praise its people, and every thing connected with it. It would have been difficult to discover, from the varied topics of our conversation, that the time was one of most anxious suspense. I ran over the gods of the Hindoo catalogue as far as I remembered, and produced almost a fever of delight in my associate, who had long ceased to hear them named in aught but terms of deep reproach. It was now time to turn my persuasion to account, and as we talked in the language of India, our conversation was conducted in a dialect foreign to most of our party, and unheeded by them. I pointed out, in plain terms, to the Hindoo, our forlorn and hopeless condition, when in the power of a person like the chief of Koondooz; and I put it to himself, if our baggage did not testify[215] our poverty. I then showed him, that as I belonged to India, I might one day serve him in that country, and finally offered to give him a reward in money, and conjured him by all his Pantheon to aid us in our difficulties. Favourable opportunity for escape. When about twelve miles from Khooloom, we alighted at a village called Ungaruk, to feed our horses, and it now occurred to me that a truly favourable opportunity to make an escape presented itself. There was no guard or escort to attend us, and the honest Hindoo was far from Khooloom, and without the means of giving an alarm, whilst the most moderate speed would carry us beyond Moorad Beg’s frontier, and even to the city of Balkh before morning. This feasible plan, however, could not evidently be put into execution, since Dr. Gerard would be left at Khooloom, and his safety more than ever endangered; and it could only now be regretted, that the scheme had not sooner presented itself. The tone of the Hindoo had, however, reconciled me in a great degree to my situation, and we again prosecuted our midnight journey and renewed our conversation. Before the sun had risen, I was satisfied that if more honourable motives had not opened this man’s heart, the baser metals had, and I almost then believed, that we should triumph over our misfortunes. A new dilemma, however, now overtook us.
We journeyed till within an hour of dawn by a dreary road, over two low passes, among hills, not enlivened by a single tree, nor blessed with a drop of fresh water for forty-five miles. In this dismal waste, our attention was roused by some lighted matches in front, that appeared to cross our path, and which we could not but conclude were robbers, since this country is infested by banditti. One of the tea merchants busied himself in tearing up rags, rubbing them with gunpowder, and lighting them, literally as demonstrations of our force; and, judging by the number of lights that appeared from the opposite party, they must have done the same, which might have been amusing enough had we not construed them into real matchlocks. We had but one piece, and five or six swords, and could have made but a sorry resistance; but generalship may be shown with a small as well as a large band, and the tea merchant, who seemed accustomed to such scenes, called on us to dismount, and prepare for the attack. I will not conceal my feelings at this moment, which were those of vexation and irritability, at so many succeeding disasters. At length we approached within speaking distance, and one forward youth in our party challenged in Persian, but he was instantly silenced by an elderly man, who spoke out in Turkish. The[217] Persian, being the language of commerce, would at once betray our character, and it was proper that we should at least appear as soldiers. The other party gave no reply, but veered off towards Khooloom, and we ourselves took the road of Koondooz, mutually glad, I suppose, to be rid of each other. At the town we discovered that we had drawn up against peaceable travellers, who must have been as glad as us to escape. About eleven in the forenoon we reached the first fields, and alighted in an orchard of apricots, about twelve miles distant from Koondooz, and stole a few hours’ rest after the night’s journey. I found myself near a hedge of honeysuckles, a bush that delighted me, and which I had never before seen in the east. We reached Koondooz at night-fall, after performing a journey of more than seventy miles.
We were received on our arrival at the house of Atmaram, the minister, or as he is styled the Dewan Begee, of Moorad Beg, and sat in his doorway till he came out. I shall long remember the silent look which passed between him and the Nazir. The reception augured well, for the minister conducted us to his house of guests, and fine beds were brought for our use, but he said nothing on the subject which most interested us, and we were left to think about our own affairs. I was now to personate[218] the character of a very poor traveller, and as it behoved me to act as such, I looked demure, took up my seat in a corner, fared with the servants, and treated the Nazir, my master, with great respect; and evinced, on every occasion, as much humility as possible. It was prudent, however, that when questioned, we should all tell the same story, and in a quiet hour, before going to sleep, I gave out my character as follows. That I was an Armenian from Lucknow, Sikunder Alaverdi, by profession a watchmaker, and that, on reaching Cabool, I had procured intelligence from Bokhara regarding my relatives in that country, which led me to take a journey to it, and that I was the more induced to do so from the protection I should receive from the Nazir, to whose brother in Cabool I was, in some manner, a servant. We discarded the subject of my accompanying the Nazir to Russia, as it might lead to unpleasant enquiries. I then went on to state, that Dr. Gerard was a relative of my own, and that he was left sick at Khooloom, and thus brought within a short space as much evasion as my ingenuity could invent. All our party agreed, that it would be most advisable to take the name of an Armenian, and entirely discard that of European; but the Cafila bashee wished to know how far it was proper to deal in such[219] wholesale lies, which had excited his merriment. I replied in the words of Sady,
“An untruth that preserves peace is better than truth that stirs up troubles.” He shook his head in approbation of the moralist’s wisdom, and I afterwards found him the most forward in the party to enlarge on my pretended narrative and circumstances. It was agreed that we should first tell the consistent tale to the Hindoo of the custom-house, and then adopt it generally; and the Nazir promised in the course of to-morrow to unfold it to the minister.
The 4th of June slipped away without any adjustment of our concerns, and the Nazir now evinced an imbecility and weakness of intellect, which there was no tolerating. At one moment he was whining out to the visiters a sorrowful detail of our disasters, half in tears; at another time he was sitting erect, with all the pride and self-sufficiency of a man of consequence. In the afternoon he retired to a garden, and returned with a train of followers, as if he had been a grandee instead of a prisoner; nor had he even visited the minister during the day, and our affairs were no further advanced at night than in the morning. As soon as it was dark, I took an[220] opportunity of pointing out to my friend the great impropriety of his conduct, for which I encountered a good share of his indignation. I told him that his grief and his pride were equally ill-timed and impolitic; that every hour added to the danger of our situation; and, if he acted rightly, he would immediately seek an interview with the minister, and endeavour either to convince or deceive him. You are in the house of a Hindoo, I added, and you may effect any thing by throwing yourself upon him, and sitting in “dhurna,” that is, without food, till your request is granted. Your course, continued I, is now the reverse, as you appear to prefer parading in his gardens, and devouring the savoury viands he sends us. The earnestness with which I enforced these views produced a good effect, and the Nazir sent a messenger to the minister to say, that if he were the friend of his family, he would not detain him in this manner, for he had not come as a dog, to eat his bread, but as an acquaintance, to solicit a favour. I rejoiced at the decision which he was now displaying, and called out in accents of delight from my corner of the apartment, but the Nazir here requested me to conduct myself with greater discretion, and remain more peaceable. I deserved the rebuke, and was thus glad to compromise matters between us. When the[221] minister received the message, he called the Nazir to him, and a long explanation ensued regarding our affairs, which, as far as I could gather, had left him bewildered as to their reality. It now appeared, however, that we were to have his good offices, for it was settled that we should set out early next morning to the country seat of the chief, where we should see that personage. The Nazir, as being a man of consequence, was instructed not to appear empty handed, and the minister with great kindness returned a shawl, which he had presented to him on his arrival, and desired him to give it and another to the chief of Koondooz.
During the day I had seen a good deal of the people, for there were many visiters, and though most of them courted the great man, a few found their way to me in the corner. Nothing is done in this country without tea, which is handed round at all times and hours, and gives a social character to conversation, which is very agreeable. Manner of tea-drinking. The Uzbeks drink their tea with salt instead of sugar, and sometimes mix it with fat; it is then called “keimuk chah.” After each person has had one or two large cups, a smaller one is handed round, made in the usual manner, without milk. The leaves of the pot are then divided among the party, and chewed like tobacco. Many of the strangers evinced[222] an interest in the affairs of Cabool; some spoke of Runjeet Sing, and a few of the English in India. Most of them were merchants, who trade between this and China. They spoke much of their intercourse with that singular nation, and praised the equity and justice that characterised their commercial transactions. These merchants were Tajiks, and natives of Budukhshan, a country on which we now bordered. Traditions of Alexander the Great. I heard from these people a variety of particulars regarding the reputed descendants of Alexander the Great, which are yet said to exist in this neighbourhood, and the valley of the Oxus, as well as the countries near the head of the Indus. The subject had occupied much of my attention, and a tea merchant of our small caravan had amused me on the road from Khooloom, with the received lineage of these Macedonians. He was a priest, and believed Alexander the Great to be a prophet, which, in his eyes, satisfactorily accounted for the uninterrupted progeny of Greeks, since no human being could injure so holy a race. In Koondooz, I heard the traditions, which I have stated at length in the next volume.
Early on the morning of the 5th, we set out on our journey to Moorad Beg. We found him at the village of Khanu-abad, which is about[223] fifteen miles distant, and situated on the brow of the hills above the fens of Koondooz, enlivened by a rivulet, which runs briskly past a fort, shaded by trees of the richest verdure. We crossed this stream by a bridge, and found ourselves at the gate of a small, but neatly fortified dwelling, in which the chief was now holding his court. There were about five hundred saddled horses standing at it, and the cavaliers came and returned in great numbers. All of them were booted, and wore long knives, stuck into the girdle for swords, some of which were richly mounted with gold. We sat down under the wall, and had ample time to survey the passing scene, and admire the martial air and pomp of these warlike Uzbeks. None of the chiefs had more than a single attendant, and there was great simplicity in the whole arrangements. A Hindoo belonging to the minister went inside to announce our arrival, and, in the mean time, I rehearsed my tale, and drew on a pair of boots as well for the uniformity as to hide my provokingly white ankles. My face had long been burned into an Asiatic hue, and from it I feared no detection. The custom-house officer stood by, and I had taken care to have him previously schooled in all the particulars above related. We were summoned, after about an hour’s delay, and passed into the first gateway. We here[224] found an area, in which stood the attendants and horses of the chief. Six or eight “yessawuls” or doorkeepers then announced our approach, as we entered the inner building. The Nazir headed the party, and marching up to the chief kissed his hand, and presented his shawls. The Hindoo of the custom-house followed, with two loaves of Russian white sugar, which he gave as his offering; and, in my humble capacity, I brought up the rear, and advanced to make my obeisance, sending forth a loud “sulam alaikoom,” and placing my hands between those of the chief, kissed them according to custom, and exclaimed “tukseer,” the usual mode of expressing inferiority. The Uzbek gave a growl of approbation, and rolling on one side, said, “Ay, ay, he understands the sulam.” The “yessawul” then gave a signal for my retreat, and I stood at the portal with my hands crossed among the lower domestics. Moorad Beg was seated on a tiger skin, and stretched out his legs covered with huge boots, in contempt of all eastern rules of decorum. He sat at the door, for, contrary to the custom of all Asiatic courts, an Uzbek there takes up his position, and his visiters pass into the interior of the apartment. The chief was a man of tall stature, with harsh Tartar features; his eyes were small to deformity, his forehead broad and frowning, and he[225] wanted the beard which adorns the countenance in most oriental nations. He proceeded to converse with the Nazir; and put several questions regarding Cabool, and then on his own affairs, during which he spoke of our poverty and situation. Then came the Hindoo of the Custom-house with my tale. “Your slave,” said he, “has examined the baggage of the two Armenians, and found them to be poor travellers. It is in every person’s mouth that they are Europeans (Firingees), and it would have placed me under your displeasure had I let them depart; I have, therefore, brought one of them to know your orders.” The moment was critical; and the chief gave me a look, and said in Turkish,—“Are you certain he is an Armenian?” A second assurance carried conviction, and he issued an order for our safe conduct beyond the frontier. I stood by, and saw his secretary prepare and seal the paper; and I could have embraced him when he pronounced it finished.
It was now necessary to retreat with caution, and evince as little of the joy which we felt as possible. The chief had not considered me even worthy of a question; and my garb, torn and threadbare, could give him no clue to my condition. His attendants and chiefs, however, asked me many questions; and his son, a youth[226] with the unpromising name of Atalik, sent for me to know the tenets of the Armenians—if they said prayers, believed in Mahommed, and would eat with the “Faithful.” I replied, that we were “people of the book,” and had our prophets; but to the home question of our credence in Mahommed, I said, that the New Testament had been written before that personage (on whom be peace) had appeared on earth. The lad turned to the Hindoos who were present, and said, Why this poor man is better than you. I then narrated my story to the prince with more confidence, and kissed the young chief’s hand for the honour he had done in listening to it.
We were soon outside the fortification, and across the bridge; but the heat of the sun was oppressive, and we alighted at a garden to pass a few hours. The Hindoos got us refreshment; and, yet enacting the part of a poor man, I had a portion of the Nazir’s pillao sent to me, and ate heartily by myself. In the afternoon we returned to Koondooz; and the good Hindoo of the Custom-house told me by the way, that the Uzbeks were bad people, and did not deserve truth. “Whoever you be, therefore, you are now safe.” I did most sincerely rejoice at the success of the journey; for if the chief had suspected our true character for a moment, we[227] should have been deprived of all our money, subjected to great vexation, and, perhaps, been confined for months in the unhealthy climate of Koondooz. We must, at all events, have abandoned every hope of prosecuting our journey; and our assumed poverty would have soon availed us little; since there were not wanting persons who had a shrewd guess at our concerns. The whole affair exhibits a simplicity on the part of the Uzbeks which is hardly to be credited; but no people are more simple. The veteran Cafila-bashee, who accompanied me, was taken for my fellow-traveller, Dr. Gerard, though a grave, grey bearded, demure Moslem; and the whole court of Moorad Beg were left in ignorance of what many of the Hindoo community knew as well as ourselves,—that we were Europeans.
At Koondooz we alighted in our old quarters, at the house of the minister. The town is situated in a valley, surrounded on all sides by hills, except the north, where the Oxus flows at a distance of about forty miles. It is watered by two rivers, which join north of the town. The climate is so insalubrious, that there is a proverb among the people, which runs as follows:—“If you wish to die, go to Koondooz.” The greater part of the valley is so marshy, that the roads are constructed on piles of wood, and[228] run through the rankest weeds; yet wheat and barley are produced, as also rice, in the places which are not entirely inundated. The heat is described as intolerable, yet snow lies for three months in the year. Koondooz has at one time been a large town, but its population does not now exceed 1500 souls; and no person makes it a residence, who can live in any other place, though it be yet the market-town of the neighbourhood. The chief never visits it but in winter. It has a fort, surrounded by a ditch, which is a place of strength: the walls are constructed of sun-dried brick; and such is the heat, that they crumble under the sun’s rays, and require constant repair. The great mountains of Hindoo Koosh lie in sight, south of Koondooz, covered with snow: the neighbouring hills are low, creeping ridges, covered with grass and flowers, but destitute of trees or brushwood. A little further up the valley the climate becomes much more genial; and the people speak in raptures of the groves and rivulets, the fruits and flowers, of Budukhshan. Its chief. The ruler of Koondooz, Mahommed Moorad Beg, is an Uzbek of the tribe of Kudghun, who has but lately risen into power. He is now encroaching in every direction, and possesses all the valley of the Oxus; and very lately had sovereignty over Balkh. He yet stamps his[229] coin with the general appellation of that capital, the “Mother of Cities.” He is quite independent, and now rules all the countries immediately north of Hindoo Koosh.
We could not quit Koondooz without the formal sanction of the minister; and waited for his pleasure till three in the afternoon. He then sent a khillut, or dress of honour, to the Nazir; and a tunic, with some other articles of dress, to me and the Cafila-bashee; for we could not, it seems, leave the house of guests of so great a person without some mark of his favour. I, however, discovered that the Nazir, now that he had recovered from his fright, was resolved on profiting to the utmost by the minister’s bounty; and had set on foot a negotiation, by means of one of his servants, to get as large a present as possible. I was horrified at such conduct, as it might again involve us in difficulty; but the mean fellow succeeded, and we were all covered in dresses of honour, as I have stated. He, indeed, got a horse in addition. It is necessary to mention, that the minister was contemplating a journey to Cabool, where he hoped for some good offices from the Nazir’s family. I, who was but a spectator of events, enjoyed the display of character which they brought forth. We dressed ourselves in our new robes, and saddled at three P.M.; nor[230] did we halt till we reached Khooloom on the following morning,—a distance of more than seventy miles,—worn out with fatigue, after being seated on one horse for twenty hours. It is singular, that I rode the very same animal that had been given to me by the brother of the Peshawur chief; and which, it will be remembered, he had forced upon me, as it might serve me in my difficulties among the Uzbeks; a horse of the same breed having formerly availed Mr. Moorcroft when he escaped to Talighan. How singular the coincidence! how much more singular the gift! It was with heartfelt satisfaction that I again found myself with Dr. Gerard and our own party, and witnessed the universal joy. I could detail to them my adventures at Koondooz, but could not relieve myself by sleep from the fatigue which I had undergone. I have found that, after a certain period, the frame is beyond sleep, which only returns to refresh and recruit the system after the body has been rubbed and rested, and the stomach refreshed by tea, the most cheering beverage to the way-worn traveller. Among the Uzbeks, we frequently lived upon it.
Khooloom is a much more pleasant place than Koondooz, and has many beautiful gardens, and fine fruit. Its apricots, cherries, and mulberries[231] were now ripe; but it was not prudent to incur further risks, with such an example as that of poor Moorcroft before us, and we prepared for a start on the following morning. We showed the order of Moorad Beg to the Wallee, or governor, and he appointed the prescribed escort to attend us. Avaricious conduct of our conductor. During night, I transferred a portion of my gold to the Hindoo of the custom house, for his eminent services; and, to elude discovery, paid it through the hands of the Nazir: but my astonishment may be conceived, when I discovered in the morning, that, out of twenty gold pieces, he had pocketed fifteen, and put off the Hindoo with five! It was no time for explanation, and, after ascertaining the correctness of the fact, I paid it a second time, and left Khooloom in the company of our avaricious friend the Nazir. This honest person made us stop by the way, to give him an opportunity of reading a chapter of the Koran, with which he always travelled; suspending it in a bag from the pommel of his saddle, and pulling it forth at stated hours. Dr. Gerard and myself preceded our people, who followed with a caravan, and reached Muzar in the afternoon of the 8th, a distance of thirty miles beyond Khooloom.
The country between these places is barren and dreary; and the road leads over a low pass,[232] called Abdoo, which is the resort of robbers from every quarter; since the whole of the neighbouring chiefs plunder on it. Our escort of Uzbeks reconnoitred the pass, from which Muzar is visible about fifteen miles off, and then left us to journey by ourselves. These men were speaking of the spoil which they themselves had captured a few days before, and I cannot say that I regretted their departure. The ruins of aqueducts and houses prove that this country has been at one time peopled; but it is now destitute of water, and, consequently, of inhabitants. Mirage. On our route we saw a very magnificent mirage on our right hand,—a snaky line of vapour, as large as the Oxus itself, and which had all the appearance of that river. It mocked our parched tongues; for we had expended the contents of the leathern bottles we always carried, long before we reached the village.
Muzar contains about 500 houses, and is within the limits of the canal of Balkh. It can muster about 1000 horse, and is independent of that city and Khooloom. It belongs to a priest, or Mootuwullee, who superintends the worship at a shrine of great sanctity, which is here dedicated to Ali. Muzar means a tomb; and that of this place consists of two lofty cupolas, built by Sultan Ali Meerza of Herat, about 350[233] years ago. I visited the shrine, went round it as a pilgrim, and gave my mite in that character. If I could not believe the legends of this pretended sanctuary, and join in the devotions of the people, I could offer up thanks in my own way for our late escape. The congregation at evening prayers was numerous; and the priests sat at the door of the shrine, and divided the proceeds of the day, copper by copper, among certain families, who are entitled to it by hereditary right. A priest came up, and asked me why I did not pray with the rest. I told him I was not a Mahommedan; yet they did not object to my entering the shrine; though I ought not to have risked a trial. There was no object of curiosity to be seen that differs from similar Mahommedan buildings. In the evening, it is illuminated by lights from brass chandeliers.
Muzar is the place where Mr. Trebeck, the last of Moorcroft’s unfortunate party, expired. One of our companions, a Hajee, attended him on his death-bed, and conducted us to the spot in which he is laid; which is in a small burying-ground, westward of the town, under a mulberry tree, that was now shedding its fruit upon it. This young man has left a most favourable impression of his good qualities throughout the country which we passed; and I could not but feel for his melancholy fate. After burying[234] his two European fellow-travellers, he sunk, at an early age, after four months’ suffering, in a far distant country, without a friend, without assistance, and without consolation. The whole of his property was either embezzled by a priest who accompanied the party, or confiscated by the holy men of this sanctuary, who yet retain it: it consisted of some valuable horses, camp equipage, money, and a few printed books. All the manuscripts of Moorcroft have been fortunately recovered; and, in justice to an amiable man, who devoted his life to a passion for travel and research, they ought, long ere this, to have been published. The money did not fall into the hands of the people of Muzar: it may be traced, but I cannot say found.
On the morning of the 9th of June, we entered the ancient city of Balkh, which is in the dominions of the King of Bokhara; and wound among its extensive ruins for nearly three miles before reaching a caravansary in the inhabited corner of this once proud “Mother of Cities” (Amo ool Bulad). On the way we were met by two police officers, Toorkmans, who searched us for our money, that they might tax it. I told them at once that we had twenty gold tillas[19] each; and they demanded one in twenty, according to[235] their law, since we were not Mahommedans. We complied, and took a sealed receipt; but they returned in the evening, and demanded as much more, since we avowed ourselves as Europeans, and were not subject to a Mahommedan ruler. I discovered that their position was legal, and paid the sum; but I had a greater store of gold than that about my own person. The people gave us no molestation; and our baggage and books were freely submitted to the eye and astonishment of the police. We should, of course, have concealed them, had it been in our power. One of the most satisfactory feelings we experienced on our arrival at Balkh, was the sure relief from the hands of our enemy at Koondooz, and, I may now add, from the tricks of our conductor, the Nazir; for he had lately adopted so unworthy a line of conduct, that we resolved no longer to place reliance upon him. As we were now in the territories of a king, we could tell him our opinions; though it had, perhaps, been more prudent to keep them to ourselves. Intelligence of the Cafila-bashee. If experience had proved the Nazir unworthy of our confidence, Hyat, the Cafila-bashee, had fully established himself in our good graces by his sensible and faithful conduct. He deprecated the meanness of the Nazir, and evinced more detestation of it than ourselves. Hyat was a man of no small penetration; and I[236] was a little staggered at a conversation which passed between us as we approached Balkh, when discussing the motives which had led to our undertaking such a journey. I stated that Bokhara lay on the road to Europe: but Hyat rejoined, that the Firingees sought for information on all countries, and that the untimely death of Mr. Moorcroft had withheld any correct knowledge of Toorkistan; and we had, probably, been despatched in a quiet way to procure it, as much of that gentleman’s misfortunes were to be referred to the mode in which he had travelled. I smiled at the shrewd guess of the man, and gave an ironical shout of “Barikilla!” (Bravo!), and praised his sagacity: but Hyat and I had become good friends; and we had not only nothing to fear, but much to hope from his kind offices.
We continued at Balkh for three days, to examine the remains of this once proud city. Its ruins extend for a circuit of about twenty miles, but present no symptoms of magnificence; they consist of fallen mosques and decayed tombs, which have been built of sun-dried brick; nor are any of these ruins of an age prior to Mahommedanism, though Balkh boasts an antiquity beyond most other cities in the globe. By the Asiatics it is named the “Mother of Cities,” and said to have been built by Kyamoors, the founder of the Persian monarchy. After the conquest of Alexander the Great, it flourished under the name of Bactria, with a dynasty of Grecian kings. In the third century of the Christian era, “Artaxerxes had his authority solemnly acknowledged in a great assembly held at Balkh, in Khorasan.”[20] It continued subject to the Persian empire, and the residence of the Archimagus, or head of the Magi, till the[238] followers of Zoroaster were overthrown by the inroads of the caliphs. Its inhabitants were butchered in cold blood by Jenghis Khan; and under the house of Timour it became a province of the Mogul empire. It formed the government of Aurungzebe in his youth; and was at last invaded by the great Nadir. On the establishment of the Dooranee monarchy, after his death, it fell into the hands of the Afghans, and within the last eight years has been seized by the King of Bokhara, whose deputy now governs it. Its present population does not amount to 2000 souls; who are chiefly natives of Cabool, and the remnant of the Kara noukur, a description of militia established here by the Afghans. There are also a few Arabs. The Koondooz chief has marched off a great portion of its population, and constantly threatens the city; which has driven the inhabitants to the neighbouring villages. In its wide area, the city appears to have enclosed innumerable gardens; which increased its size without adding to its population: and from the frail materials of which its buildings are constructed, the foundations being only brick, I doubt if Balkh ever were a substantial city. There are three large colleges of a handsome structure, now in a state of decay, with their cells empty. A mud wall surrounds a portion of the town; but it must be of a[239] late age, since it excludes the ruins on every side for about two miles. The citadel, or ark, on the northern side has been more solidly constructed; yet it is a place of no strength. There is a stone of white marble in it, which is yet pointed out as the throne of Kai Kaoos, or Cyrus. Balkh stands on a plain, about six miles from the hills, and not upon them, as is erroneously represented. There are many inequalities in the surrounding fields, which may arise from ruins and rubbish. The city itself, like Babylon, has become a perfect mine of bricks for the surrounding country. These are of an oblong shape, rather square. Most of the old gardens are now neglected and overgrown with weeds; the aqueducts are dried up; but there are clumps of trees in many directions. The people have a great veneration for the city; believing it was one of the earliest peopled portions of the earth, and that the re-occupation of it will be one of the signs of the approaching end of the world. The fruit of Balkh is most luscious; particularly the apricots, which are nearly as large as apples. They are almost below value; for 2000 of them were to be purchased for a rupee; and, with iced water, they are indeed luxuries, though dangerous ones. Snow is brought in quantities from the mountains south[240] of Balkh, about twenty miles distant, and sold for a trifle throughout the year.
The clime of Balkh is very insalubrious, but it is not disagreeable. In June, the thermometer did not rise above 80°, and the next month is the hottest in the year. The wheat ripens in that month, which makes the harvest fifty days later than Peshawur. Its unhealthiness is ascribed to the water, which is so mixed up with earth and clay as to look like a puddle after rain. The soil is of a greyish colour, like pipe-clay, and very rich; when wet, it is slimy. The crops are good; the wheat stalks grow as high as in England, and do not present the stunted stubble of India. In Balkh, the water has been distributed, with great labour, by aqueducts from a river. Of these there are said to be no less than eighteen; but many are not now discoverable. They frequently overflow, and leave marshes, which are rapidly dried up under the sun’s rays. This seems to account for the diseases of the place. All old cities and ruins are, perhaps, more or less unhealthy. It is not probable, however, that so many kings and princes would have patronised a site which was always unfavourable to the health of man; and Balkh itself is not situated in a country naturally marshy, but on a gentle slope which sinks towards the Oxus,[241] about 1800 feet above the level of the sea. All the water of its river is lost long before reaching that stream.
At Balkh, I used every endeavour to collect ancient coins, which could not fail to be valuable in such classic ground. They brought me several copper ones, similar to those I found at Manikyala in the Punjab, representing a full-length figure, holding a censer or pot in his right hand, and dressed in a high cap; which, I believe, determines the whole series of them to be Persian. It is well known that India formed one of the satrapies of Darius; and we read of a connexion between it and Persia in ancient times, which will perhaps clear up the history of these coins. The execution is rude; and as they differ from one another, it would appear they are rather medals than coins. I have, in the succeeding volume, given accurate engravings of these relics. Those who feel interested in the subject will find that some of a like description have been found in India and mentioned in the Transactions of the Asiatic Society of Bengal. Among the coins which I examined at Balkh, there were many Cufic and Arabic, and a whole series of those of the emperors of Hindostan. One gold piece of Shah Jehan spoke well for the execution of his age. It is remarkable, that, in the countries north of Hindoo[242] Koosh, the current coinage of the present time is that of the emperors of Delhi who ruled prior to the age of Nadir.
On the 12th of June, the caravan arrived from Khooloom with our people, and we prepared to accompany it in its onward journey to Bokhara. For three days we had been living with our friend the Cafila-bashee, who managed to get rice and meat for us from the bazar; but we made a bungling matter of our cookery. This was but a minor inconvenience, and not without a hope of remedy. It was now necessary, however, to give our Cafila-bashee leave to return to Cabool; since an Afghan would be of little use among the Uzbeks. I was, indeed, sorry to part with Hyat, as he had a temper and disposition admirably fitted for managing the people, and had friends every where who esteemed and respected him. I feared we should miss the man who used to get us food and lodging, when procurable, and tell lies by wholesale regarding our character when necessary. We made him presents in return for his good offices;—their value far surpassed his expectations; so that he was more than happy. I gave him a note of hand expressive of our sense of his services; and he ran about in every direction to assist in our setting out, took the Cafila-bashee of the new caravan aside, and pointed out to[243] him how much it would be his interest to serve us: he waited till the caravan departed; and seeing us in our panniers, (the new mode of travelling on camels,) he bade us farewell, consigned us to God, and left us to plod our way. As an instance of this man’s honesty, I may mention, that on his return to Cabool he found a knife, which we had left in a caravansary; this he despatched by a trusty man who was coming to Bokhara, along with a letter expressive of his remembrance of us, and thanks for our kindness.
The caravan assembled outside the city, and near to another melancholy spot, the grave of poor Moorcroft, which we were conducted to see. Mr. Guthrie lies by his side. It was a bright moonlight night, but we had some difficulty in finding the spot. At last, under a mud wall which had been purposely thrown over, our eyes were directed to it. The bigoted people of Balkh refused permission to the travellers being interred in their burial ground; and only sanctioned it near the city, upon condition of its being concealed, lest any Mahommedan might mistake it for a tomb of one of the true believers, and offer up a blessing as he passed it. It was impossible to view such a scene at the dead of night, without many melancholy reflections. A whole party buried within twelve miles of each other, held out small encourage[244]ment to us, who were pursuing the same track, and led on by nearly similar motives. It was fortunate that the living experienced no such contempt as the dead, for we received no slight from any one, though our creed and our nation were not concealed. The corpse of Moorcroft was brought from Andkhooee, where he perished, at a distance from his party. He was attended by a few followers, all of whom were plundered by the people. If he died a natural death, I do not think he sunk without exciting suspicions; he was unaccompanied by any of his European associates or confidential servants, and brought back lifeless on a camel, after a short absence of eight days; the health of Mr. Trebeck did not admit of his examining the body.
We left Balkh at midnight, with a small caravan of twenty camels; and now exchanged our horses for these useful animals. Two panniers, called “kujawas,” are thrown across each camel: the Dr. weighed against an Afghan; and I was balanced by my Hindoostanee servant. At first, this sort of conveyance was most inconvenient; for the panniers were but four feet long and two and a half wide, and it required some suppleness and ingenuity to stow away a body of five feet nine inches in such a space, tumbled in like a bale of goods. Custom soon reconciled us to the jolting of the camels and the smallness of[245] the conveyance; and it was a great counterbalance to discover that we could read and even note without observation.
A march of thirty miles brought us to the limits of the water of Balkh, through a rich country every where intersected by canals. Such is their effect on the temperature, that the thermometer fell below 52° in the morning; though more than two thirds of the land lay waste. Our camels revelled on a thorny shrub called “chooch” or “zooz” by the natives. The language of the most graphic writer could not delineate this country with greater exactness than Quintus Curtius has done, and I marked the following passage on the spot:—“The face of Bactriana is contrastingly diversified: in many places, luxuriant trees and vines yield fruit of fine growth and flavour; numerous springs (canals?) irrigate a rich soil. The more generous land is sowed with corn; other fields afford pasturage. Further, great part of the country is deformed by tracts of barren sand, in which a mournful absence of vegetation refuses nourishment to man. When the winds blow from the Indian Ocean, the floating dust is swept into masses. The cultivated portion of the country is crowded with inhabitants, and well stocked with horses. Bactra, the capital, is situated under Mount[246] Paropamisus. The river Bactrus, which washes its walls, gives name to the city and province.”[21] The trees, fruit, and corn of Balkh have a great celebrity; its horses are equally well known. Though it has no springs, and a river does not now pass its walls, yet the country is intersected by the canals of one that flows from the neighbouring mountains, the water of which is artificially divided before reaching the town.
On the 14th of June we entered the desert, and travelled all night on our way to the Oxus. We left the great high road from Balkh to Kilef, the usual ferry, from a fear of robbers, and journeyed westward. At daylight we halted, and had an insight of what we were to expect in the deserts of Tartary. The mountains of Hindoo Koosh had entirely disappeared below the horizon, and a wide plain like an ocean of sand surrounded us on all sides. Here and there were a few round huts, or, as they are called, “khirgahs,” the abode of the erratic Toorkmuns. The inhabitants were few in number; at first sight, they present a fierce and terrible aspect to a stranger. We alighted near one of their settlements; and they strutted about dressed in huge black sheepskin caps, but did[247] not molest us; and I have here only to introduce our new acquaintances, since we shall have ample opportunities to speak of them hereafter. We pitched our camp in their desert, and found a scanty supply of water that had trickled down thus far from the canals of Balkh. We had now no tent, nor shelter of any kind, but a coarse single blanket, which we used to stretch across two sets of panniers. Even this flimsy covering sheltered us from the sun’s rays; and at night we had it removed, and slept in the open air. Our food now consisted of bread and tea; for the Toorkmuns often object to dispose of their sheep, since it injures their estate; and we could only look on their countless flocks with a desire to possess a single lamb, which often could not be gratified. Europeans, who are so much accustomed to animal food, are sensible of the change to a diet of bread; but we found it tolerably nutritive, and had much refreshment from the tea, which we drank with it at all hours. I found that abstinence from wine and spirits proved rather salutary than otherwise; and I doubt if we could have undergone the vicissitudes of climate, had we used such stimulants.
It appeared that we had not altogether escaped the tracks of plunderers by our diversion from[248] the main road, and we therefore hired a guard of Toorkmuns to escort us to the Oxus, now only a march distant. We saddled at sunset; and after a journey of fifteen hours, and a distance of thirty miles, found ourselves on the banks of that great river, which I gazed on with feelings of pure delight. It now ran before us in all the grandeur of solitude, as a reward for the toil and anxiety which we had experienced in approaching it. It might not have been prudent to commit ourselves to a guard of Toorkmuns in such a desert; but they conducted us in safety, and made few or no enquiries about us. They spoke nothing but Turkish. They rode good horses, and were armed with a sword and long spear. They were not encumbered with shields and powder-horns, like other Asiatics; and a few only had matchlocks. They beguiled the time by singing together in a language that is harsh but sonorous. They appeared to be the very beau idéal of light dragoons; and their caps gave to the whole of them a becoming uniformity. They never use more than a single rein, which sets off their horses to advantage. Some of the Toorkmun chiefs, I afterwards observed, had rosettes and loose pieces of leather ornamented with gold and silver, which fell behind the ear of the animal, giving his head a showy and becoming appear[249]ance. Till within a mile and a half of the river, we had traversed a peculiarly inhospitable and unpromising country, quite destitute of water; and its stunted herbage either protruded from mounds of loose drifting sand, or made its appearance through sheets of hard clay. I shall long remember our dreary advance on the Oxus, and the wild society in which it was made.
We halted on the banks of the river, near the small village of Khoju Salu. The vicinity of the Oxus is intersected by aqueducts for nearly two miles, but by no means industriously cultivated; it was a better sign of a more tranquil country, to see each peasant’s house standing at a distance from that of his neighbour, and in the midst of his own fields. We were detained for two days on the banks of the river, till it came to our turn of the ferry-boat; which transferred our caravan, on the 17th, to the northern bank, or the country of Toorkistan, more commonly known to Europeans by the name of Tartary. The river was upwards of 800 yards wide, and about 20 feet deep. Its waters were loaded with clay, and the current passed on at the rate of about three miles and a half an hour. This river is called Jihoon and Amoo by the Asiatics.
The mode in which we passed the Oxus was singular, and, I believe, quite peculiar to this part of the country. We were drawn by a[250] pair of horses, who were yoked to the boat, on each bow, by a rope fixed to the hair of the mane. The bridle is then put on as if the horse were to be mounted; the boat is pushed into the stream, and, without any other assistance than the horses, is ferried directly across the most rapid channel. A man on board holds the reins of each horse, and allows them to play loosely in the mouth, urging him to swim; and, thus guided, he advances without difficulty. There is not an oar to aid in impelling the boat; and the only assistance from those on board consists in manœuvring a rude rounded pole at the stern, to prevent the vessel from wheeling in the current, and to give both horses clear water to swim. They sometimes use four horses; and in that case, two are fixed at the stern. These horses require no preparatory training, since they indiscriminately yoke all that cross the river. One of the boats was dragged over by the aid of two of our jaded ponies; and the vessel which attempted to follow us without them, was carried so far down the stream as to detain us a whole day on the banks, till it could be brought up to the camp of our caravan. By this ingenious mode, we crossed a river nearly half a mile wide, and running at the rate of three miles and a half an hour, in fifteen minutes of actual sailing; but there was some detention from[251] having to thread our way among the sand banks that separated the branches. I see nothing to prevent the general adoption of this expeditious mode of passing a river, and it would be an invaluable improvement below the Ghats of India. I had never before seen the horse converted to such a use; and in my travels through India, I had always considered that noble animal as a great incumbrance in crossing a river.
After our passage of the Oxus, we commenced our journey towards Bokhara, and halted at Shorkudduk, where there were no inhabitants, and about fifteen or twenty brackish wells. The water was clear, but bitter and ill tasted. Our manner of journeying now became more agreeable. We started about five or six P.M., and travelled till eight or nine next morning. The stages exceeded twenty-five miles; but camels cannot march for a continuance beyond that distance, on account of heat. At night, they move steadily forward at the rate of two miles an hour, and are urged on by a pair of tingling bells hung from the breast or ears of the favourite, that precedes each “quittar” or string. The sound is enlivening and cheerful; and when their jingle ceases by a halt of the caravan, the silence which succeeds, in the midst of an uninhabited waste, is truly[252] striking. At the setting and rising of the sun, the caravan halts to admit of the performance of prayers; and the sonorous sound of “Ullaho Akbar” summons all “true believers” to the presence of God. They stroke down their beards, and, with their eyes turned towards Mecca, perform the genuflexions prescribed by their creed. We sat and looked at the solemnity, without suffering either taunts or abuse; and experienced a toleration that would have done credit to the most civilised country of Europe. In the society of a caravan, there is much good fellowship, and many valuable lessons for a selfish man. It levels all distinctions between master and servant; and where both share every thing, it is impossible to be singular. Our servants now ate from the same dishes as ourselves. An Asiatic will never take a piece of bread, without offering a portion of it to those near him. The Indian Mahommedans were surprised at their brethren in the faith, who gave us a share of their food, and freely partook of our own.
We next reached Kiz Kooduk, or the Maiden’s Well, as the words signify in Turkish. I blessed the young lady who had dug it; for we had suffered much from the want of water, and now found a beautiful well in the midst of some hundred others, all of which, as well as the springs we met on[253] the road, were salt. It is said to have been dug by a virgin. Yesterday we had no water; to-day we had no wood; and it was only by collecting the dung of the camels that we could boil the water for our tea. Who could have imagined that we were approaching those paradises of the East, Samarcand and Bokhara. We had been travelling among low waving hills, or rather ridges, destitute of trees or wood; covered with a dry kind of grass, growing on a soil that was hard and gravelly. The wells were about eighteen feet deep. At different intervals on the road, we saw robats or caravansaries, which have been constructed with large covered cisterns, called “surdabas,” or water coolers, to collect the rain water in behalf of the travellers. The whole of these were now empty. The climate was dry and variable; and the thermometer, which stood at 103° in the day, fell to 60° at night, which was cool and delightful. In this country, a steady wind generally blows from the north. Our day broke at twenty minutes after three, and we had a long and refreshing twilight, which compensated in some degree for the scorching heat of the sun.
One of the tea merchants of the caravan paid us frequent visits at our halting ground, and we soon became intimate with him. He was a Khwaju, as the followers of the first caliphs are[254] called, and was both a priest and a merchant. He appeared pleased with our society; and we drank tea together on the banks of the Oxus. We told him our true story. From our intercourse with this Khwaju, I gained some insight into the state of literature among the Uzbeks. I gave him the perusal of a small Persian work, the “Memoirs of King Shooja of Cabool,” which I had received from that unfortunate monarch. The book was written by the King himself; and gives a detail of his life and adventures, in a simple style, free from extracts of the Koran, metaphors, and other extravagancies of Oriental authors. It also dispenses with any mention of those miracles which never fail to be wrought in favour of our Eastern despot, according to the accounts of historians. The work, in fact, was what would be called by us an interesting detail of events. The Khwaju returned it to me a few days after, saying, that it was a dry production, not enlivened by the fear of God, or a remembrance of the Prophet, but entirely occupied with matters of a personal nature. Since that was the object of the book, he could not have given it higher praise. The Khwaju is not the only person who has found such faults in similar works, for a Right Reverend Divine[22], who furnished us with so[255] admirable and interesting a journal of his travels in India, has been blamed by some for its worldliness. Since literature among the Mahommedans is exclusively confined to the moollahs, we should be the less surprised at their finding fault with a work that had not a due sprinkling of the literature of their order.
Near the country we now entered, there is a tribe of Uzbeks, called Lakay, who are celebrated for their plundering propensities. A saying among them curses every one who dies in his bed, since a true Lakay should lay down his life in a foray or “chupao.” I was told that the females sometimes accompany their husbands on these marauding expeditions; but it is stated, with greater probability, that the young ladies plunder the caravans which pass near their home. This tribe lives near Hissar, which is a romantic neighbourhood; since, besides the Amazons of Lakay, three or four neighbouring tribes claim a descent from Alexander the Great.
Our next march, to a place called Kirkinjuk, brought us to a settlement of the Toorkmuns, and the country changed from hillocks to mounds of bare sand. The well water was now double the depth, or about thirty-six feet from the surface. The flocks of the Toorkmuns cropped the scanty grass around us; and horses, camels, and sheep roamed about loose, as in a[256] state of nature. A slave. A shepherd who tended these flocks lingered long near our encampment. He was an unfortunate Persian, who had been captured about eight years before near Meshid, along with 300 other persons, and now sighed for his liberty, that he might visit the famous shrine of Imam Ruza in his own holy city. His name had been Mahommed; it was changed to Doulut, or the Rich—a singular cognomen for a poor wretch who tended sheep in a desert under a scorching sun. He gave us a favourable account of his treatment by his master, who intended to purchase a wife for him; but he had no hope of his liberty. The poor man prowled all day about our caravan, and expressed many a wish to accompany it; he had, however, been purchased for thirty pieces of gold, and if he had no riches of his own, he yet formed a part of those of his owner.
I overheard a controversy among some of the merchants regarding Christians, whether they were or were not infidels (Kaffirs), and, as may be imagined, was not a little anxious to hear the decision. One person, who was a priest, maintained that they could not be infidels, since they were people of the book. When it was asserted that they did not believe in Mahommed, the subject became more complicated. I learned, from their conversation, that a[257] universal belief prevails among the Mahommedans of the overthrow of their creed by Christians. Christ, they say, lives, but Mahommed is dead; yet their deductions are curious, since Jesus is to descend from the fourth heaven, and the whole world will be Mahommedanised! A singular instance of blasphemy was related by this party. “A native of Budukhshan blackened his face, and sallied forth into the highway, telling all the passengers that as he had prayed to God without any good effect for eight years, he now appeared to disgrace the Creator in the eyes of his creatures.” Fanatical madman!
In the afternoon of the 20th, as we approached the town of Kurshee, we descried at sunset, far to the eastward of us, a stupendous range of mountains covered with snow. As this was in the middle of summer, their elevation must be greater than is assigned to any range north of Hindoo Koosh. They were at a distance of perhaps 150 miles, and we could distinguish them but faintly on the following morning, and never saw them again. At daylight we came to the öasis of Kurshee, a cheering scene, after having marched from the Oxus, a distance of eighty-five miles, without seeing a tree. On nearing this town, we entered a flat and champaign country, which was entirely[258] desolate, till within the limits of the river: tortoises, lizards, and ants, appeared to be its only inhabitants. As a welcome to this first Tartar town, one of our friends in the caravan sent us, as a delicacy, two bowls of “keimuk chah,” or tea, on which the fat floated so profusely that I took it for soup; but it was really tea mixed with salt and fat, and is the morning beverage of the Uzbeks. Custom never reconciled me to this tea, but our Afghan fellow-travellers spoke of it in loud strains of praise; nor did the manner in which our gift speedily disappeared, when handed over to them, at all belie their taste.
We had looked forward to our arrival at an inhabited place with much delight, after our marches in the desert; but we here experienced that misfortune to which travellers are more liable than other people, sickness. Some of us had been complaining for a few days previously, and immediately on our arrival, I was prostrated by a severe attack of intermittent fever; the surveyor was seized at the same time; and, on the following day, the doctor and two others of our party were ill. The merchants and people of the caravan likewise suffered, and we came to the conclusion that we must have caught the disease at Balkh, or on the banks of the Oxus. The terror of the Balkh fever had vanished, and we had not feared the seeds of[259] disease. We adopted the usual treatment of India, taking emetics and medicine; and, in my own case, I followed them up with quinine, which had the most happy effect. In three days my teeth ceased to chatter, and my body to burn; but the doctor, who persisted in treating himself with calomel secundum artem, was not so fortunate, and he did not shake off the disease till long after we had left the country. One of our fellow-travellers, a merchant of Budukhshan, who had endeared himself to us, died on his reaching Bokhara. Our chances of life were far less than his: he offered up sacrifices, and refused quinine. Our stay at Kurshee was prolonged for three or four days, during which we lived in a garden under some trees, and without other shelter. It was a miserable hospital; but we quenched our parching thirst, under a thermometer at 108°, with sherbet of cherries, cooled by ice, which we here found in great plenty.
In the midst of our indisposition, we were disturbed by some vexatious rumours regarding ourselves. We were informed that the king had heard of our approach, and not only had prohibited our entering the city of Bokhara, but objected to our prosecuting the journey. This tale was further exaggerated by the mention of certain yessawuls or officers of the court having been[260] sent to seize us, which we credited the more readily, since these persons paid us no less than three visits for the examination of our baggage, which in nowise contributed to our repose. We had become pretty well accustomed to rumours of every kind, for an European who travels in eastern countries must expect many alarms. Letter to the minister of Bokhara. I resolved to take immediate steps to counteract any bad impression towards us, and forthwith addressed the minister of Bokhara, and despatched Sooliman, an Afghan, one of our own people, with the letter. I approached the minister with all the forms of eastern etiquette and eloquence; and, as we were in a bigoted country, denominated him “the Tower of Islam; the Gem of the Faith, the Star of Religion, the Dispenser of Justice, Pillar of the State,” &c. &c. I went on to inform him particularly of our circumstances, and of our having passed in safety through the dominions of other princes, and stated the delight which we now felt at being in the neighbourhood of Bokhara, “the citadel of Islam.” I concluded by telling him that in all countries we had considered ourselves as the subjects of the ruler, and that we now approached the capital of the Commander of the Faithful (so the King of Bokhara is called), whose protection of the merchant and the traveller is known in the[261] utmost corners of the East. I had, on former occasions, found the advantage of being the first to convey information of our own approach, nor did I doubt a good result from this communication. We were not deceived, and before reaching the city, discovered that a lying Persian in our caravan had given currency to these rumours, which were altogether destitute of foundation. The minister sent back our servant to meet us, and say, that we should be welcome in Bokhara.
Our halt at Kurshee gave us some opportunity of seeing the place. It is a straggling town, a mile long, with a considerable bazar, and about 10,000 inhabitants. The houses are flat roofed, but mean. A mud fort, surrounded by a wet ditch, forms a respectable defence on the south-west side of the town. A river, which rises from Shuhur Subz, about fifty miles distant, and famous as the birthplace of Timour, passes north of Kurshee, and enables its inhabitants to form innumerable gardens, which are shaded by trees groaning under fruit, and some lofty poplars. These trees have a tall and noble aspect; and their leaves, when rustling in the wind, assume a white silvery appearance, though actually green, which has a curious and pleasing effect on the landscape. Never were the blessings of water more apparent than in this spot,[262] which must otherwise have been a barren waste. On the banks of the rivulet and its branches, every thing is verdant and beautiful; away from them, all is sandy and sterile. Kurshee is the largest place in the kingdom of Bokhara, next to the capital. Its öasis is about twenty-two miles broad, but the river expends itself in the surrounding fields.
We marched from Kurshee to Karsan, sixteen miles distant, which is a thriving village, situated on the extremity of this öasis. We arrived on the market-day, for in the towns of Toorkistan they hold their bazars on stated days, as in Europe. We met many people proceeding to the throng, but not a single individual on foot—all were equestrians. A stranger is amused at seeing a horse literally converted into a family conveyance, and a man jogging along with his wife behind him. The ladies are of course veiled, like most females in this country: they prefer blue cloths to white, as in Cabool, and Uzbeks are sombre-looking figures. Uzbeks. We now found ourselves among the Uzbeks, a grave, broad-faced, peaceable people, with a Tartar expression of countenance. They are fair, and some of them are handsome; but the great bulk of the people, the men at least, are without personal beauty. I was struck with the great number of old looking men among them. We had now[263] left the Toorkmun tribes, who do not here extend much beyond the Oxus.
In our second march from Kurshee, we halted at Kuroul-tuppa, where there is a caravansary built by Abdoolla, a king of Bokhara, who reigned in the sixteenth century. It put me in mind of Hindostan and its monarchs. We also passed three large reservoirs (surdabas), which were made by order of this philanthropic prince. They had been erected at great expense in a flat and desert country, and the rain water that falls is conducted to them by ditches often from a great distance. The king Abdoolla had made a pilgrimage to Mecca, but imbibed an impression that it had not proved acceptable in the sight of God. In the hope of propitiating divine favour, he set about the construction of caravansarais and cisterns in all parts of his dominions, acts more beneficial to mankind, and therefore more acceptable, I venture to believe, than pilgrimages to shrines or tombs.
At Kurshee, we were joined by some other travellers, among whom was a Moollah from Bokhara, who introduced himself to me: the people of this country possess great affability of manner, and make agreeable companions. The priest and I rode together on our last march to the city, being the only persons on horseback. He gave me an account of the college to which[264] he belonged in Bokhara, and requested me to visit it, which I did not fail to do. My other friend, the Khwaju, at length changed conveyances with the priest, and entertained me for half the night, by repeating and explaining odes and lines of poetry, more to my amusement than edification, for they were all about nightingales and love. It is curious to find so much said on this passion, in a country where there is really so little of it. It does not appear to strike the people themselves; though some of their verses breathe a spirit which one might think would discover it to them, thus:
“I fell in love with an infidel girl, destitute of religion. This is love, what has it to do with religion?” Yet, after this, they marry without seeing each other, or knowing further than that they are of different sexes; nor is this all: a merchant, in a foreign land, marries for the time he is to continue in it, and dismisses the lady when he returns to his native country; when both of them seek for other alliances.
Our journey from the Oxus to Bokhara had been of a most fatiguing and trying nature. In Cabool, we had been chilled by cold, and were now almost burned up with heat. Our mode of[265] travelling, too, had been extremely irksome, for camels only advance at half the pace of a horse, and we spent double the time on the march, which increased the fatigue. The only horse which accompanied us was so completely knocked up that he fell down in several places before entering Bokhara. We also travelled at night, and the rest which one gets on a camel is broken and disturbed. Our water had often been bad, and our food chiefly consisted of hard biscuit. All these inconveniences were, however, drawing to a close; and, before we had reached the gates of Bokhara, they had given rise to reflections of a more pleasing nature. At the outset of our journey we used to look forward with some anxiety to the treatment we might experience in that city; and, indeed, in many of the then remote places which we had already passed. As we advanced, these apprehensions had subsided, and we now looked back with surprise at the vast expanse of country which we had traversed in safety. Bokhara, which had once sounded as so distant from us, was now at hand, and the success which had hitherto attended our endeavours gave us every hope of bringing the journey to a happy termination. Arrival in Bokhara. With these feelings, we found ourselves at the gates of this eastern capital, an hour after sunrise, on the 27th of June; but[266] there was nothing striking in the approach to Bokhara. Though the country is rich, it is flat, and the trees hide the walls and mosques till close upon it. We entered with the caravan, and alighted in a retired quarter of the city, where our messenger had hired a house.
Our first care on entering Bokhara was to change our garb, and conform to the usages prescribed by the laws of the country. A petition to the minister might, perhaps, have relieved us from the necessity, but the measure was in consonance with our own principle, and we did not delay a moment in adopting it. Our turbans were exchanged for shabby sheep-skin caps, with the fur inside; and our “kummurbunds” (girdles) were thrown aside for a rude piece of rope or tape. The outer garment of the country was discontinued, as well as our stockings; since these are the emblems of distinction in the holy city of Bokhara between an infidel and a true believer. We knew also that none but a Mahommedan might ride within the walls of the city, and had an inward feeling which told us to be satisfied if we were permitted, at such trifling sacrifices, to continue our abode in the capital. A couplet[23], which describes Samarcand as the[268] paradise of the world, also names Bokhara as the strength of religion and of Islam; and, impious and powerless as we were, we could have no desire to try experiments among those who seemed, outwardly at least, such bigots. The dress which I have described is nowhere enjoined by the Koran; nor did it obtain in these countries for two centuries after the prophet, when the prejudice of some of the caliphs discovered that the “Faithful” should be distinguished from those who were not Mahommedans.
On entering the city, the authorities did not even search us; but in the afternoon, an officer summoned us to the presence of the minister. My fellow-traveller was still labouring under fever, and could not accompany me; I therefore proceeded alone to the ark or palace, where the minister lived along with the king. I was lost in amazement at the novel scene before me, since we had to walk for about two miles through the streets of Bokhara, before reaching the citadel. I was immediately introduced to the minister, or as he is styled the Koosh Begee, or Lord of all the Begs, an elderly man, of great influence, who was sitting in a small room that had a private courtyard in front of it. He desired me to be seated outside on the pavement, yet evinced both a kind and considerate[269] manner, which set my mind at ease. The hardness of my seat, and the distance from the minister, did not overpower me with grief, since his son, who came in during the interview, was even seated farther off than myself. I presented a silver watch and a Cashmeer dress, which I had brought for the purpose; but he declined to receive any thing, saying, that he was but the slave of the king. He then interrogated me for about two hours as to my own affairs, and the objects which had brought me to a country so remote as Bokhara. I told our usual tale of being in progress towards our native country, and produced my passport, from the Governor-General of India, which the minister read with peculiar attention. I then added, that Bokhara was a country of such celebrity among Eastern nations, that I had been chiefly induced to visit Toorkistan for the purpose of seeing it. “But what is your profession?” said the minister. I replied, that I was an officer of the Indian army. “But tell me,” said he, “something about your knowledge,” and he here made various observations on the customs and politics of Europe, but particularly of Russia, on which he was well informed. In reply to some enquiries regarding our baggage, I considered it prudent to acquaint him, that I had a sextant, since I concluded that we should be searched, and it was[270] better to make a merit of necessity. I informed him, therefore, that I liked to observe the stars and the other heavenly bodies, since it was a most attractive study. On hearing this, the Vizier’s attention was roused, and he begged, with some earnestness, and in a subdued tone of voice, that I would inform him of a favourable conjunction of the planets and the price of grain which it indicated in the ensuing year. I told him, that our astronomical knowledge did not lead to such information; at which he expressed himself disappointed. On the whole, however, he appeared to be satisfied of our character, and assured me of his protection. While in Bokhara, he said that he must prohibit our using pen and ink, since it might lead to our conduct being misrepresented to the king, and prove injurious. He also stated, that the route to the Caspian Sea, by way of Khiva, had been closed for the last year; and that if we intended to enter Russia, we must either pursue the northern route from Bokhara, or cross the Toorkmun desert, below Orgunje, to Astrabad on the Caspian.
Two days after this interview, I was again summoned by the Vizier, and found him surrounded by a great number of respectable persons, to whom he appeared desirous of exhibiting me. I was questioned in such a way as to make[271] me believe that our character was not altogether free from suspicion; but the Vizier said jocularly, “I suppose you have been writing about Bokhara.” Since I had in the first instance given so true a tale, I had here no apprehensions of contradiction, and freely told the party that I had come to see the world and the wonders of Bokhara, and that, by the Vizier’s favour, I had been already perambulating the city, and seen the gardens outside its walls. The minister was the only person who appeared pleased with my candour, and said, that he would be always happy to see me in the evening. He enquired if I had any curiosity to exhibit to him either of India or my own country; but I regretted my inability to meet his wishes. On my return home, it struck me that the all-curious Vizier might be gratified by the sight of a patent compass, with its glasses, screws, and reflectors; but it also occurred that he might regard my possession of this complicated piece of mechanism in a light which would not be favourable. I, however, sallied forth with the instrument in my pocket, and soon found myself again in his presence. I told him, that I believed I had a curiosity which would gratify him, and produced the compass, which was quite new and of very beautiful workmanship. I described its utility,[272] and pointed out its beauty, till the Vizier seemed quite to have forgotten “that he was but a slave of the king, and could receive nothing;” indeed, he was proceeding to bargain for its price, when I interrupted him by an assurance, that I had brought it from Hindostan to present to him, since I had heard of his zeal in the cause of religion, and it would enable him to point to the holy Mecca and rectify the “kiblu” of the grand mosque, which he was now building in Bokhara. I could therefore receive no return, since we were already rewarded above all price by his protection. The Koosh Begee packed up the compass with all the haste and anxiety of a child, and said that he would take it direct to his majesty, and describe the wonderful ingenuity of our nation. Thus fell one of my compasses. It was a fine instrument by Schmalcalder, but I had a duplicate, and I think it will be admitted that it was not sacrificed without an ample return. Had we been in Bokhara in disguise, and personating some assumed character, our feelings would have been very different from what they now were. Like owls, we should only have appeared at night; but, after this incident, we stalked abroad in the noontide sun, and visited all parts of the city.
My usual resort in the evening was the[273] Registan of Bokhara, which is the name given to a spacious area in the city, near the palace, which opens upon it. On two other sides there are massive buildings, colleges of the learned, and on the fourth side is a fountain, filled with water, and shaded by lofty trees, where idlers and newsmongers assemble round the wares of Asia and Europe, which are here exposed for sale. A stranger has only to seat himself on a bench of the Registan, to know the Uzbeks and the people of Bokhara. He may here converse with the natives of Persia, Turkey, Russia, Tartary, China, India, and Cabool. He will meet with Toorkmuns, Calmuks, and Kuzzaks[24], from the surrounding deserts, as well as the natives of more favoured lands. He may contrast the polished manners of the subjects of the “Great King” with the ruder habits of a roaming Tartar. He may see the Uzbeks from all the states of Mawur-ool nuhr, and speculate from their physiognomy on the changes which time and place effect among any race of men. The Uzbek of Bokhara is hardly to be recognised as a Toork or Tartar from his intermixture of Persian blood. Those from the neighbouring country of Kokan are less changed; and the natives of Orgunje, the ancient Kharasm, have yet a harshness of feature peculiar[274] to themselves. They may be distinguished from all others by dark sheep-skin caps, called “tilpak,” about a foot high. A red beard, grey eyes, and fair skin will now and then arrest the notice of a stranger, and his attention will have been fixed on a poor Russian, who has lost his country and his liberty, and here drags out a miserable life of slavery. A native of China may be seen here and there in the same forlorn predicament, shorn of his long cue of hair, with his crown under a turban, since both he and the Russian act the part of Mahommedans. Then follows a Hindoo, in a garb foreign to himself and his country. A small square cap and a string, instead of a girdle, distinguishes him from the Mahommedans, and, as the Moslems themselves tell you, prevents their profaning the prescribed salutations of their language by using them to an idolater. Without these distinctions, the native of India is to be recognized by his demure look, and the studious manner in which he avoids all communication with the crowd. He herds only with a few individuals, similarly circumstanced with himself. The Jew is as marked a being as the Hindoo: he wears a somewhat different dress, and a conical cap. No mark, however, is so distinguishing as the well known features of the Hebrew people. In Bokhara they are a race[275] remarkably handsome, and I saw more than one Rebecca in my peregrinations. Their features are set off by ringlets of beautiful hair hanging over their cheeks and neck. There are about 4000 Jews in Bokhara, emigrants from Meshid, in Persia, who are chiefly employed in dying cloth. They receive the same treatment as the Hindoos. A stray Armenian, in a still different dress, represents this wandering nation; but there are few of them in Bokhara. With these exceptions, the stranger beholds in the bazars a portly, fair, and well dressed mass of people, the Mahommedans of Toorkistan. A large white turban and a “chogha,” or pelisse, of some dark colour, over three or four others of the same description, is the general costume; but the Registan leads to the palace, and the Uzbeks delight to appear before their king in a mottled garment of silk, called “udrus,” made of the brightest colours, and which would be intolerable to any but an Uzbek. Some of the higher persons are clothed in brocade, and one may distinguish the gradations of the chiefs, since those in favour ride into the citadel, and the others dismount at the gate. Almost every individual who visits the king is attended by his slave; and though this class of people are for the most part Persians or their descendants, they have a peculiar appearance. It is said,[276] indeed, that three fourths of the people of Bokhara are of slave extraction; for of the captives brought from Persia into Toorkistan few are permitted to return, and, by all accounts, there are many who have no inclination to do so. A great portion of the people of Bokhara appear on horseback; but, whether mounted or on foot, they are dressed in boots, and the pedestrians strut on high and small heels, in which it was difficult for me to walk or even stand. They are about an inch and a half high, and the pinnacle is not one third the diameter. This is the national dress of the Uzbeks. Some men of rank have a shoe over the boot, which is taken off on entering a room. I must not forget the ladies in my enumeration of the inhabitants. They generally appear on horseback, riding as the men; a few walk, and all are veiled with a black hair-cloth. The difficulty of seeing through it makes the fair ones stare at every one as in a masquerade. Here, however, no one must speak to them; and if any of the king’s harem pass, you are admonished to look in another direction, and get a blow on the head if you neglect the advice. So holy are the fair ones of the “holy Bokhara.”
My reader may now, perhaps, form some idea of the appearance of the inhabitants of[277] Bokhara. From morn to night the crowd which assembles raises a humming noise, and one is stunned at the moving mass of human beings. In the middle of the area the fruits of the season are sold under the shade of a square piece of mat, supported by a single pole. One wonders at the never-ending employment of the fruiterers in dealing out their grapes, melons, apricots, apples, peaches, pears, and plums to a continued succession of purchasers. It is with difficulty that a passage can be forced through the streets, and it is only done at the momentary risk of being rode over by some one on a horse or donkey. These latter animals are exceedingly fine, and amble along at a quick pace with their riders and burdens. Carts of a light construction are also driving up and down, since the streets are not too narrow to admit of wheeled carriages. In every part of the bazar there are people making tea, which is done in large European urns, instead of teapots, and kept hot by a metal tube. The love of the Bokharees for tea is, I believe, without parallel, for they drink it at all times and places, and in half a dozen ways: with and without sugar, with and without milk, with grease, with salt, &c. Next to the venders of this hot beverage one may purchase “rahut i jan,” or the delight of life,—grape jelly or syrup, mixed up with[278] chopped ice. This abundance of ice is one of the greatest luxuries in Bokhara, and it may be had till the cold weather makes it unnecessary. It is pitted in winter, and sold at a price within the reach of the poorest people. No one ever thinks of drinking water in Bokhara without icing it, and a beggar may be seen purchasing it as he proclaims his poverty and entreats the bounty of the passenger. It is a refreshing sight to see the huge masses of it, with the thermometer at 90°, coloured, scraped, and piled into heaps like snow. It would be endless to describe the whole body of traders; suffice it to say, that almost every thing may be purchased in the Registan: the jewellery and cutlery of Europe, (coarse enough, however,) the tea of China, the sugar of India, the spices of Manilla, &c. &c. One may also add to his lore both Toorkee and Persian at the book-stalls, where the learned, or would-be-so, pore over the tattered pages. As one withdraws in the evening from this bustling crowd to the more retired parts of the city, he winds his way through arched bazars, now empty, and passes mosques, surmounted by handsome cupolas, and adorned by all the simple ornaments which are admitted by Mahommedans. After the bazar hours, these are crowded for evening prayers. At the doors of the colleges, which generally face the[279] mosques, one may see the students lounging after the labours of the day; not, however, so gay or so young as the tyros of an European university, but many of them grave and demure old men, with more hypocrisy, but by no means less vice, than the youths in other quarters of the world. With the twilight this busy scene closes, the king’s drum beats, it is re-echoed by others in every part of the city, and, at a certain hour, no one is permitted to move out without a lantern. From these arrangements the police of the city is excellent, and in every street large bales of cloth are left on the stalls at night with perfect safety. All is silence until morning, when the bustle again commences in the Registan. The day is ushered in with the same guzzling and tea-drinking, and hundreds of boys and donkeys laden with milk hasten to the busy throng. The milk is sold in small bowls, over which the cream floats: a lad will bring twenty or thirty of these to market in shelves, supported and suspended by a stick over his shoulder. Whatever number may be brought speedily disappear among the tea-drinking population of this great city.
Soon after our arrival, I paid a visit to our late travelling companions, the tea-merchants, who had taken up their abode in a caravansary,[280] and were busy in unpacking, praising, and selling their tea. They sent to the bazar for ice and apricots, which we sat down and enjoyed together. One of the purchasers took me for a tea-merchant, from the society I was in, and asked for my investment. His request afforded both the merchants and myself some amusement; but they did not undeceive the person as to my mercantile character, and we continued to converse together. He spoke of the news of the day, the late conquests of the king at Shuhr Sabz, and of the threats of the Persians to attack Bokhara, all without ever suspecting me to be aught but an Asiatic. In return, we had visits from these merchants, and many other persons, who came to gratify curiosity at our expense. We were not permitted to write, and it was an agreeable manner of passing time, since they were very communicative. The Uzbeks are a simple people, with whom one gets most readily acquainted, though they speak in a curious tone of voice, as if they despised or were angry with you. They never saluted us by any of the forms among Mahommedans; but appeared to have another set of expressions, the most common of which are, “May your wealth increase” (doulut zyada), or (oomr duraz) “May your life be long.” They, nevertheless, always said the “fatha,”[281] or prayer, from the Koran, stretching out their hands and stroking down their beards, in which we joined, before they sat down with us. Many of our visiters betrayed suspicions of our character; but still evinced no unwillingness to converse on all points, from the politics of their king to the state of their markets. Simple people! they believe a spy must measure their forts and walls; they have no idea of the value of conversation. With such ready returns on the part of our guests, it was not irksome for me to explain the usages of Europe; but let me advise a traveller to lay in a good stock of that kind of knowledge before he ventures to journey in Eastern countries. One must have a smattering of trade, arts, science, religion, medicine, and, in fact, of every thing; and any answer is better than a negative, since ignorance, real or pretended, is construed into wilful concealment.
I took an early opportunity of seeing the slave-bazar of Bokhara, which is held every Saturday morning. The Uzbeks manage all their affairs by means of slaves, who are chiefly brought from Persia by the Toorkmuns. Here these poor wretches are exposed for sale, and occupy thirty or forty stalls, where they are examined like cattle, only with this difference, that they are able to give an account of them[282]selves vivâ voce. On the morning I visited the bazar, there were only six unfortunate beings, and I witnessed the manner in which they are disposed of. They are first interrogated regarding their parentage and capture, and if they are Mahommedans, that is, Soonees. The question is put in that form, for the Uzbeks do not consider a Shiah to be a true believer; with them, as with the primitive Christians, a sectary is more odious than an unbeliever. After the intended purchaser is satisfied of the slave being an infidel (kaffir), he examines his body, particularly noting if he be free from leprosy, so common in Toorkistan, and then proceeds to bargain for his price. Three of the Persian boys were for sale at thirty tillas of gold apiece[25]; and it was surprising to see how contented the poor fellows sat under their lot. I heard one of them telling how he had been seized south of Meshid, while tending his flocks. Another, who overheard a conversation among the by-standers, regarding the scarcity of slaves that season, stated, that a great number had been taken. His companion said with some feeling, “You and I only think so, because of our own misfortune; but these people must know better.” There was one unfortunate girl, who had been long in service, and was now exposed[283] for sale by her master, because of his poverty. I felt certain that many a tear had been shed in the court where I surveyed the scene; but I was assured from every quarter that slaves are kindly treated; and the circumstance of so many of them continuing in the country after they have been manumitted, seems to establish this fact. The bazars of Bokhara are chiefly supplied from Orgunje. Russian and Chinese are also sold, but rarely. The feelings of an European revolt at this most odious traffic; but the Uzbeks entertain no such notions, and believe that they are conferring a benefit on a Persian when they purchase him, and see that he renounces his heretical opinions.
From the slave-market I passed on that morning to the great bazar, and the very first sight which fell under my notice was the offenders against Mahommedanism of the preceding Friday. They consisted of four individuals, who had been caught asleep at prayer time, and a youth, who had been smoking in public. They were all tied to each other, and the person who had been found using tobacco led the way, holding the hookah, or pipe, in his hand. The officer of police followed with a thick thong, and chastised them as he went, calling aloud, “Ye followers of Islam, behold the punishment of those who violate the law!”[284] Never, however, was there such a series of contradiction and absurdity as in the practice and theory of religion in Bokhara. You may openly purchase tobacco and all the most approved apparatus for inhaling it; yet if seen smoking in public you are straightway dragged before the Cazee, punished by stripes, or paraded on a donkey, with a blackened face, as a warning to others. If a person is caught flying pigeons on a Friday, he is sent forth with the dead bird round his neck, seated on a camel. If seen in the streets at the time of prayers, and convicted of such habitual neglect, fines and imprisonment follow; yet there are bands of the most abominable wretches, who frequent the streets at evening for purposes as contrary to the Koran as to nature. Every thing, indeed, presents a tissue of contrarieties; and none were more apparent to me than the punishment of the culprits who were marching, with all the pomp of publicity, past the very gateway of the court where human beings were levelled with the brutes of the earth, no doubt against the laws of humanity, but as certainly against the laws of Mahommed.
The Hindoos of Bokhara courted our society, for that people seem to look upon the English as their natural superiors. They visited us in every country we passed, and would never[285] speak any other language than Hindoostanee, which was a bond of union between us and them. In this country they appeared to enjoy a sufficient degree of toleration to enable them to live happily. An enumeration of their restrictions might make them appear a persecuted race. They are not permitted to build temples, nor set up idols, nor walk in procession: they do not ride within the walls of the city, and must wear a peculiar dress. They pay the “jizyu,” or poll-tax, which varies from four to eight rupees a year; but this they only render in common with others, not Mahommedans. They must never abuse or ill-use a Mahommedan. When the king passes their quarter of the city, they must draw up, and wish him health and prosperity; when on horseback outside the city, they must dismount if they meet his majesty or the Cazee. They are not permitted to purchase female slaves, as an infidel would defile a believer; nor do any of them bring their families beyond the Oxus. For these sacrifices the Hindoos in Bokhara live unmolested, and, in all trials and suits, have equal justice with the Mahommedans. I could hear of no forcible instance of conversion to Islam, though three or four individuals had changed their creed in as many years. The deportment of these people is most sober and[286] orderly;—one would imagine that the tribe had renounced laughter, if he judged by the gravity of their countenances. They themselves, however, speak highly of their privileges, and are satisfied at the celerity with which they can realise money, though it be at the sacrifice of their prejudices. There are about 300 Hindoos in Bokhara, living in a caravansary of their own. They are chiefly natives of Shikarpoor in Sinde, and their number has of late years rather increased. The Uzbeks, and, indeed, all the Mahommedans, find themselves vanquished by the industry of these people, who will stake the largest sums of money for the smallest gain.
Among the Hindoos we had a singular visiter in a deserter from the Indian army at Bombay. He had set out on a pilgrimage to all the shrines of the Hindoo world, and was then proceeding to the fire temples on the shores of the Caspian! I knew many of the officers of the regiment (the 24th N. I.) to which he had belonged, and felt pleased at hearing names which were familiar to me in this remote city. I listened with interest to the man’s detail of his adventures and travels, nor was he deterred by any fear that I would lodge information against him, and secure his apprehension. I looked upon him as a[287] brother in arms, and he amused me with many a tale of my friend Moorad Beg of Koondooz, whom he had followed in his campaigns, and served as a bombardier. This man, when he first showed himself, was disguised in the dress of a pilgrim; but the carriage of a soldier is not to be mistaken, even if met at Bokhara.
The house in which we lived was exceedingly small, and overlooked on every side, but we could not regret it, since it presented an opportunity of seeing a Toorkee beauty, a handsome young lady, who promenaded one of the surrounding balconies, and wished to think she was not seen. A pretended flight was not even neglected by this fair one, whose curiosity often prompted her to steal a glance at the Firingees. Since we had a fair exchange, she was any thing but an intruder, though unfortunately too distant for us to indulge “in the sweet music of speech.” Costume. The ladies of Bokhara stain their teeth quite black; they braid their hair, and allow it to hang in tresses down their shoulders. Their dress differs little from the men: they wear the same pelisses, only that the two sleeves, instead of being used as such, are tucked together and tied behind. In the house even they dress in huge hessian boots made of velvet, and highly ornamented. What a strange taste[288] for those who are for ever concealed, to choose to be thus booted as if prepared for a journey. On the head they wear large white turbans, but a veil covers the face, and many a lovely countenance is born to blush unseen. The exhibition of beauty, in which so much of a woman’s time is spent in more favoured countries, is here unknown. A man may shoot his neighbour if he sees him on a balcony, at any but a stated hour. Assassination follows suspicion; for the laws of the Koran, regarding the sex, are most strictly enforced. If jealousy is a passion which is rarely known among them, it is replaced by a more debasing vice.[26]
In my travels through Cabool, I had often enjoyed the luxuries of the bath, according to the custom of the Orientals. I now had the same pleasure in Bokhara; but it was only admissible in certain buildings, since the priests had asserted, that the water of certain baths would change into blood if polluted by a woman or an infidel. A bath is too well known to require description, but the operation is most singular. You are laid out at full length, rubbed with a hair brush, scrubbed, buffeted, and kicked; but it is all very refreshing. The baths[289] of Bokhara are most spacious. Many small vaulted chambers surround a great circular hall with a cupola, and are heated to different temperatures. In the daytime the light is admitted from coloured glasses over the large dome; in the night, a single lamp beneath suffices for all the cells. That portion of the circle towards Mecca is appropriated as a mosque, where the luxurious Mahommedan may offer up his orisons while he is enjoying one of the promised blessings of his prophet’s paradise. There are eighteen baths in Bokhara; a few are of very large dimensions, but the generality of them bring in an annual income of 150 tillas (1000 rupees). This is a fact which may serve to number the inhabitants. Each individual pays to the keeper of the bath ten pieces of brass money, of which there are 135 in a rupee. About 100 people may, therefore, bathe for a tilla; and 150 tillas will give 15,000 people to each bath. Eighteen baths will give a total of 270,000 who enjoy the luxury yearly. But the baths are only used for half the year, during the cold months; and the poorer people are never able to afford them.
I did not omit to pay my respects to the minister while I rambled about the city, and Dr. Gerard, in the course of ten days, was sufficiently recovered to accompany me. The Vizier[290] was equally inquisitive with the Nuwab at Cabool regarding the preparation of medicines and plasters, of which he wished the doctor to inform him. We had, however, got into a more civilised region on our approach to Europe, since the Vizier had received quinine and other medicines from Constantinople. We sat with the minister while he was transacting business, and saw him levying duties on the merchants, who are most liberally treated in this country. The webs of cloth are produced, and every fortieth piece is taken in place of duties; which gives the merchant his profit, without distressing him for ready money. A Mahommedan, indeed, has only to take the name of the prophet, stroke down his beard, and declare himself poor, to be relieved from all duties. One man said that he had got witnesses to prove his being in debt, and would produce them. The minister replied, “Give us your oath, we want no witnesses.” He gave it; every one called out “God is great!” and said the “fatha;” on which the goods were returned without an iota of charge. With every disposition to judge favourably of the Asiatics,—and my opinions regarding them improved as I knew them better,—I have not found them free from falsehood. I fear, therefore, that many a false oath is taken among them. No people could be more liberal en[291]couragers of commerce than the rulers of Bokhara. During the reign of the last monarch, the duties on goods were never paid till they were sold, as in the bonding system of a British custom-house. The Vizier, on this occasion, conversed at great length on subjects of commerce relating to Bokhara and Britain, and expressed much anxiety to increase the communication between the countries, requesting that I myself would return, as a trading ambassador, to Bokhara, and not forget to bring a good pair of spectacles for his use. Our intercourse was now established on a footing which promised well: I took occasion, therefore, to express a wish to the Vizier of paying our duty to the king. I had touched on a delicate point; for it appeared that the minister had feared our being charged with some proposals to his majesty, which we concealed from himself. “I am as good as the Ameer,” said he (so the king is called); “and if you have no matters of business to transact with the king, what have travellers to do with courts?” I told him of our curiosity on these points, but he did not choose that we should have the honour, and that was sufficient for abandoning the suit.
I was nevertheless resolved to have a sight of royalty; and, at midday on the following Friday, repaired to the great Mosque, a building of[292] Timourlane, and saw his majesty and his court passing from prayers. The king appeared to be under thirty years of age, and has not a prepossessing countenance: his eyes are small, his visage gaunt and pale. He was plainly dressed in a silken robe of “udrus,” with a white turban. He sometimes wears an aigrette of feathers ornamented with diamonds. The Koran was carried in front of him; and he was preceded and followed by two golden mace bearers, who exclaimed in Turkish, “Pray to God that the Commander of the Faithful may act justly!” His suite did not exceed a hundred people; most of them were dressed in robes of Russian brocade, and wore gold ornamented swords—I should call them knives—the mark of distinction in this country. His present majesty has more state than any of his predecessors; but he may consider it necessary to affect humility in a temple, and in returning from a religious ceremony. The people drew up by the wayside as he passed, and with a stroke of their beards wished his majesty peace; I did the same. The character of this king, Buhadoor Khan, stands high among his countrymen: at his elevation to the throne he gave away all his own wealth. He is strict in his religious observances, but less bigoted than his father, Meer Hyder. He acts according to the Koran[293] in all cases; and it is pretended that he even lives on the capitation tax which is levied from the Jews and Hindoos. The revenues of the country are said to be spent in maintaining Moollahs and Mosques; but this young king is ambitious and warlike, and I believe it to be more probable that he uses his treasures to maintain his troops and increase his power.
The life of this king is less enviable than that of most private men. The water which he drinks is brought in skins from the river, under the charge and seal of two officers. It is opened by the Vizier, first tasted by his people and then by himself, when it is once more sealed and despatched to the king. The daily meals of his majesty undergo a like scrutiny; the minister eats, he gives to those around him, they wait the lapse of an hour to judge of their effect, when they are locked up in a box and despatched. His majesty has one key and his minister another. Fruit, sweetmeats, and every eatable undergo the same examination, and we shall hardly suppose the good king of the Uzbeks ever enjoys a hot meal or a fresh cooked dinner. Poison is common, and the rise of his majesty himself to the throne on which he now sits, is not without strong suspicions of a free distribution of such draughts. A native on one occasion presented me with[294] some figs, one of which I took and ate, to show him that I appreciated the gift. The individual cautioned me against such indiscretion in future: “since,” said he, “you should always present some of the gift in the first instance to the giver; and, if he eats, you may with safety follow his example.”
I expressed a wish soon after reaching Bokhara to see some of the unfortunate Russians who have been sold into this country. One evening a stout and manly-looking person fell at my feet, and kissed them. He was a Russian of the name of Gregory Pulakoff, who had been kidnapped when asleep at a Russian outpost, about twenty-five years ago. He was the son of a soldier, and now followed the trade of a carpenter. I made him sit down with us, and give an account of his woes and condition: it was our dinner-time, and the poor carpenter helped us to eat our pilao. Though but ten years of age when captured, he yet retained his native language, and the most ardent wish to return to his country. He paid seven tillas a year to his master, who allowed him to practise his trade and keep all he might earn beyond that sum. He had a wife and child, also slaves. “I am well treated by master,” said he; “I go where I choose; I associate with the people, and play the part of a Mahommedan; I appear[295] happy, but my heart burns for my native land, where I would serve in the most despotic army with gladness. Could I but see it again, I would willingly die. I tell you my feelings, but I smother them from the Uzbeks. I am yet a Christian (here the poor fellow crossed himself after the manner of the Greek church), and I live among a people who detest, with the utmost cordiality, every individual of that creed. It is only for my own peace that I call myself a Mahommedan.” The poor fellow had acquired all the habits and manners of an Uzbek, nor should I have been able to distinguish him, but for his blue eyes, red beard, and fair skin. He enquired with much earnestness if there were any hopes of him and his comrades being released; but I could give him no further solace than the floating rumours which I had heard of the Emperor’s intention to suppress the traffic by an army. He told me that the last embassy to Bokhara under M. Negri had failed to effect that desired end, but that the sale of Russians had ceased in Bokhara for the last ten years. There were not 130 natives of Russia in the kingdom; but in Khiva their number increased as before. The whole of those in Bokhara would have been released by the ambassador, had not some religious discussion arisen on the propriety of allowing Christians, who had be[296]come Mahommedans, to relapse into their idolatry! The Moollahs had seen the figures in the Greek Church, and no argument will reverse, what they state to be the evidence of their senses, that the Russians worship idols. There is generally some difference of opinion on all points, and that of the Russians and Bokharees on the subject of slavery was much at variance. The Mahommedans are not sensible of any offence in enslaving the Russians, since they state that Russia herself exhibits the example of a whole country of slaves, particularly in the despotic government of her soldiery. “If we purchase Russians,” say they, “the Russians buy the Kuzzaks on our frontier, who are Mahommedans, and they tamper with these people by threats, bribery, and hopes, to make them forsake their creed, and become idolaters. Look, on the other hand, at the Russians in Bokhara, at their life, liberty, and comfort, and compare it with the black bread and unrelenting tyranny which they experience in their native country.” Last, not least, they referred to their cruel banishment to Siberia (as they called it Sibere), which they spoke of with shuddering horror, and stated that it had on some occasions driven Russians voluntarily to betake themselves to Bokhara. We shall not attempt to decide between the parties; but it is a melan[297]choly reflection on the liberties of Russia, that they admit of a comparison with the institutions of a Tartar kingdom, whose pity, it is proverbially said, is only upon a par with the tyranny of the Afghan.
With Russians, Hindoos, and Uzbeks, our circle of acquaintance at Bokhara soon increased, and most of the Afghan and Cabool merchants sought our society, and we could not but feel gratified at the favourable opinion entertained by them of the British in India. One of them, Sirwur Khan, a Lohanee merchant of great opulence, to whom we were never introduced, offered us any money we might require, and did it in a manner that left no doubt of his sincerity. Another individual, Shere Mahommed, a native of Cabool afforded me useful assistance in my enquiries regarding the commerce of Central Asia. We were constantly assailed by Afghans, and even Uzbeks, to give notes of hand, certifying our acquaintance with them; for they believe the hand-writing to be a bond of union with Englishmen; and that the possession of it would secure them an honourable reception in India. We complied with the wishes of those who deserved our confidence. Among our other friends was a Cashmeer merchant, Ahmedjooee, a clever and talkative fellow, who wished me much to assist him in[298] the preparation of a kind of cochineal, which is found, but, I believe, cannot be prepared, in Bokhara. There was also an old man, named Hajee Meeruk, who had seen the world from Canton to Constantinople; and secretly brought some old and valuable Bactrian coins and rarities, which are acceptable to Europeans. The most intimate, perhaps, of all our acquaintance was our landlord, an Uzbek merchant, named Mukhsoom, who traded to Yarkund. He paid us a daily visit, and generally brought some of his friends along with him. I shall mention an incident regarding this person which is creditable to him. He was most communicative, and gave us much useful information: as our intimacy increased, I interrogated him closely on the revenues and resources of Bokhara, on its extent and power, and once opened a small map of the country in his presence. He replied to all my enquiries; and then, begging I would shut up the map, beseeched me never again to produce such a paper in Bokhara, since there were innumerable spies about the king, and it might be productive of very serious consequences. He still continued his visits and his information with the same freedom as before. On our first arrival in the city, the keeper of the caravansary refused us quarters, because we had no character, that is, we were neither[299] merchants nor ambassadors; but this man kindly hired out his house to us. He had been attacked by his neighbours, terrified by his friends, and he himself at first trembled at the risk which he had incurred. The keeper of the caravansary now hid his head in shame; and the landlord shared our intimacy, his neighbours sought his favour to be brought to us, and our society was more courted than was agreeable.
Tradition assigns the foundation of the city of Bokhara to the age of Sikunder Zoolkurnuen, or Alexander the Great, and the geography of the country favours the belief of its having been a city in the earliest ages. A fertile soil, watered by a rivulet, and surrounded by a desert, was like a haven to the mariner. Bokhara lies embosomed among gardens and trees, and cannot be seen from a distance; it is a delightful place, and has a salubrious climate; but I cannot concur with the Arabian geographers, who describe it as the paradise of the world. Ferdoosy, the great Persian poet, says “that when the king saw Mawuroolnuhr, he saw a world of cities.” Compared with Arabia and the arid plains of Persia, this may be true, but some of the banks of the Indian rivers have a like richness, beauty, and fertility. The circumference of Bokhara exceeds eight English miles; its shape is triangular, and it is surrounded by a wall of earth, about twenty feet high, which is pierced by twelve gates. According to the custom of the[301] east, these are named from the cities and places to which they lead. Few great buildings are to be seen from the exterior, but when the traveller passes its gates he winds his way among lofty and arched bazars of brick, and sees each trade in its separate quarter of the city; here the chintz sellers, there the shoemakers; one arcade filled with silks, another with cloth. Every where he meets with ponderous and massy buildings, colleges, mosques, and lofty minarets. About twenty caravansarais contain the merchants of different nations, and about one hundred ponds and fountains, constructed of squared stone, furnish its numerous population with water. The city is intersected by canals, shaded by mulberry trees, which bring water from the river of Samarcand, and there is a belief among the people, which deserves to be mentioned, that the loftiest minaret, which is about 150 feet high, rises to the level of that famous capital of Timour. Bokhara is very indifferently supplied with water, the river is about six miles distant, and the canal is only once opened in fifteen days. In summer the inhabitants are sometimes deprived of good water for months, and when we were in Bokhara the canals had been dry for sixty days; the snow had not melted in the high lands of Samarcand, and the scanty supply of the river[302] had been wasted before reaching Bokhara. The distribution of this necessary of life becomes therefore an object of no mean importance, and an officer of government is specially charged with that duty. After all, the water is bad, and said to be the cause of guinea worm, a disease frightfully prevalent in Bokhara, which the natives will tell you originates from the water; and they add, that these worms are the same that infested the body of the prophet Job! Bokhara has a population of 150,000 souls; for there is scarcely a garden or burying-ground within the city walls. With the exception of its public buildings, most of its houses are small, and of a single story; yet there are many superior dwellings in this city. We saw some of them neatly painted with stuccoed walls; others had Gothic arches, set off with gilding and lapis lazuli, and the apartments were both elegant and comfortable. The common houses are built of sun-dried bricks on a framework of wood, and are all flat roofed. A house in an eastern city commands no prospect, for it is surrounded with high walls on every side. The greatest of the public buildings is a mosque, which occupies a square of 300 feet, and has a dome that rises to about a third of that height. It is covered with enamelled tiles of an azure blue colour, and has a costly appearance. It is a place of some an[303]tiquity, since its cupola, which once was shaken by an earthquake, was repaired by the renowned Timour. Attached to this mosque is a lofty minaret, raised in the 542d year of the Hejira. It is built of bricks, which have been distributed in most ingenious patterns. Criminals are thrown from this tower; and no one but the chief priest may ever ascend it, (and that only on Friday, to summon the people to prayers,) lest he might overlook the women’s apartments of the houses in the city. The handsomest building of Bokhara is a college of the King Abdoolla. The sentences of the Koran, which are written over a lofty arch, under which is the entrance, exceed the size of two feet, and are delineated on the same beautiful enamel. Most of the domes of the city are thus adorned, and their tops are covered by nests of the “luglug,” a kind of crane, and a bird of passage that frequents this country, and is considered lucky by the people.
Bokhara would not appear to have been a large city in ancient times. Its remoteness from all other parts of the Mahommedan world has given it a celebrity, and besides it was one of the earliest conquests of the caliphs. It may be readily imagined, that the numerous offspring of the first Commanders of the Faithful would seek for distinction in its distant and luxuriant[304] groves. Its name was widely spread by the number of learned and religious men it produced; and the affix of “Shureef,” or holy, was soon added to it by its Mahommedan conquerors. It is considered the sure mark of an infidel to say, that the walls of Bokhara are crooked; but strange to add, the architecture is so defective, that I doubt if there be a perpendicular wall in the city. The priests of the present day assert that, in all other parts of the globe, light descends upon earth; but, on the other hand, that it ascends from the holy Bokhara! Mahommed, on his journey to the lower heaven, is said to have observed this fact, which was explained to him by the angel Gabriel, as the reason for its designation. Besides the palpable absurdity of the tale, I shall only mention that the affix of holy is much more modern than the days of the prophet, since I have seen coins which did not bear it, and were less than 850 years old. Bokhara existed as a city in the days of Kizzil (Alp?) Arslan. It was destroyed by Jengis Khan, and threatened by Hulakoo, his grandson; and we have an anecdote of the negotiations with that destroyer, which, I think, I remember as being told of some other place. The people sent forth a sapient boy, accompanied by a camel and goat. When he appeared before the conqueror, he demanded a reason for[305] selecting such a stripling as their envoy. “If you want a larger being,” said the youth, “here is a camel; if you seek for a beard, here is a goat; but if you desire reason, hear me.” Hulakoo listened to the wisdom of the boy—the city was spared and protected; and he granted permission for their enlarging its fortifications. The present walls were built by Ruheem Khan, in the age of Nadir; and, since the equity of its rulers keeps pace with its increasing extent, Bokhara bids fair to be a greater city in modern than in ancient times.
I now availed myself of the acquaintance which I had made with the Moollah on my road from Kurshee, to visit his college, which was one of the principal buildings of that description in Bokhara, the “Madrussa i Cazee Kulan.” I received the fullest information regarding these institutions from my host and his acquaintance, who produced his tea-pot, and gossiped for a length of time. There are about 366 colleges at Bokhara, great and small, a third of which are large buildings that contain upwards of seventy or eighty students. Many have but twenty, some only ten. The colleges are built in the style of caravansarais; a square building is surrounded by a number of small cells, called “hoojrus,” which are sold, and bear a value of sixteen tillas, though in some it is so high[306] as thirty. A fixed allowance is given to the professor, and each of the resident students; the colleges are well endowed; the whole of the bazars and baths of the city, as well as most of the surrounding fields, have been purchased by different pious individuals for that purpose. It is understood by the law, that the revenues of the country are appropriated to the support of the church; a fourth of the sum is distributed on that account in Bokhara; and the custom-house duties are even shared by the priests. In the colleges people may be found from all the neighbouring countries except Persia; and the students are both young and aged. After seven or eight years’ study, they return to their country with an addition to their knowledge and reputation; but some continue for life in Bokhara. The possession of a cell gives the student a claim to a certain yearly maintenance from the foundation, as well as the revenues of the country. The colleges are shut for half the year by order of the King, to enable their inmates to work in the fields, and gain something additional to their livelihood. What would the fellows of Oxford and Cambridge think of mowing down wheat with the sickle? The season of vacation is called “tateel,” that of study “tuhseel.” The students may marry, but cannot bring their[307] wives to the college. In the season of study, the classes are open from sunrise to sunset; the professor attends constantly; and the scholars dispute in his presence on points of theology, while he guides their debates. One person says, “Prove there is a God!” and about five hundred set arguments are adduced: so is it with other matters. The students are entirely occupied with theology, which has superseded all other points: they are quite ignorant even of the historical annals of their country. A more perfect set of drones were never assembled together; and they are a body of men regardless of their religion in most respects beyond the performance of its prayers; but they have great pretensions, and greater show.
I have already mentioned the rigour of the Mahommedan law, which is enforced in Bokhara. A few additional instances will further illustrate it. About twelve years since, a person who had violated the law proceeded to the palace, and, in the presence of the King, stated his crime, and demanded justice according to the Koran. The singularity of an individual appearing as his own accuser induced the King to direct him to be driven away. The man appeared the following day with the same tale, and was again turned out. He repaired a third time to the palace, repeated his sins, and up[308]braided the King for his remissness in declining to dispense justice, which, as a believer of Mahommed, he intreated, that it might lead to his punishment in this world instead of the next. The Ulema, or congress of divines, was assembled: death was the punishment; and the man himself, who was a Moollah, was prepared for this decision. He was condemned to be stoned till dead. He turned his face to Mecca, and, drawing his garment over his head, repeated the kuluma, (“There is but one God, and Mahommed is his prophet!”) and met his fate. The King was present, and threw the first stone: but he had instructed his officers to permit the deluded man to escape if he made the attempt. When dead the King wept over his corpse, ordered it to be washed and buried, and proceeded in person to the grave, over which he read the funeral service. It is said that he was much affected; and to this day verses commemorate the death of this unfortunate man, whom we must either pronounce a bigot or a madman. An incident similar to the above happened within this very year. A son who had cursed his mother appeared as a suppliant for justice, and his own accuser. The mother solicited his pardon and forgiveness; the son demanded punishment: the Ulema directed his death, and he was executed as a criminal in the streets[309] of Bokhara. A merchant lately imported some pictures from China; which were immediately broken, and their value paid by the government; since it is contrary to the Mahommedan laws to make the likeness of any thing on the earth beneath. On some subjects their notions of justice are singular. An Afghan plundered a caravansarai, and was sentenced to die; but permitted to purchase his blood according to the law if he exiled himself from Bokhara, because he was a foreigner. Before the arrangement had been completed, a second robbery occurred by a party of the same nation: the clergy decreed their death; and since they thought that the punishment of the first offender, together with the others, would present a more salutary and impressive example, they returned the blood-money, cancelled the pardon, and executed all the offenders.
Our European notions will revolt at such arbitrary changes, but it cannot be said that the punishment was unjust; and, if it had an influence on evil doers, it was assuredly not very injudicious. Whatever we may think of these customs and laws, they have raised the condition and promoted the welfare of this country; and there is no place in the whole of Asia where such universal protection is extended to all classes. Those who are not Mahommedans[310] have only to conform to a few established customs to be placed on a level with “believers.” The code of laws is sanguinary, but it is not unjust. When we place the vices of Bokhara in juxtaposition with its laws and justice, we have still much to condemn; but the people are happy, the country is flourishing, trade prospers, and property is protected. This is no small praise under the government of a despot.
There is a prevalent opinion in Europe, that this portion of Asia was at one time the seat of civilisation and literature. We cannot doubt but the Greek monarchs of Bactria preserved, in their newly acquired kingdom, the arts and sciences of their native land. An eminent historian[27] has thrown out a hint, that “he harbours a suspicion of most of the learning of Scythia and India being derived from these Greek monarchs.” With India we have, at present, no concern; but, in central and western Asia, I fail to confirm the opinion of the great historian. In the sixth century, when Alaric and Attila invaded the Roman empire, we find them possessed of no arts or literature. In the eighth century, when overwhelmed by the caliphs, we hear of none. In the tenth century, when the same countries sent forth the Seljukian line of kings, we still find them shepherds, and em[311]bracing the religion of Islam, which the caliphs had now firmly planted. The irruptions of Jengis, in the thirteenth century, present to us a horde of barbarians; nor have we any steps towards improvement in the following age, under the all-destroying Timour. The whole of these inroads were undertaken by barbarians; and it is not till Timour’s death that we find a literature in central Asia. The astronomy of Ulug Beg has immortalised Samarcand; and he might have drawn his science from Bactria: but the Arabs were, in early ages, no mean astronomers; and we may then, with more probability, trace this department of science to that people, who overran the country a thousand years after the Macedonians. In an age later than the house of Timour, we have had an inundation of another tribe, the Uzbeks, from the same region which produced Attila and Jengis; and they, too, have been as barbarous as their predecessors of a thousand summers. It is certain that literature received great encouragement in this country during Timour’s age. In Baber’s days we have a constellation of poets of no mean excellence; for he himself gives us an insight into the spirit of the age by his quotations and his rhymes. It would appear that these native graces continued till a very late period; for the people are poetically inclined. They have now, I fear, taken an[312] eternal farewell of Transoxiana: the reign of the late king, Meer Hyder or Saeed (the pure), introduced an era of bigotry and religious enthusiasm. He took the name of “Ameer-ool Momeneen,” or Commander of the Faithful; and performed the duties of a priest, not of a king: he read prayers over the dead, disputed in the mosques, conducted the service, and taught in the colleges. In the street, he once dismounted from his horse to return the salutation of a Syud or Khwaju; and he passed the whole of his spare time in religious contemplation. His neighbour of Kokun pursued a like conduct: he assumed the title of “Ameer-ool Mooslimeen,” or Commander of the Mussulmans; and, between them, they introduced a new order of things into Toorkistan. The Moollahs of the colleges have since despised all learning but theology, and all studies but the Koran and its commentaries. Bokhara and Kokun may be said to include all Toorkistan, since they are the two most influential of its states. One cannot but regret that the 366 colleges of Bokhara should be now involved in the unprofitable maze of polemical discussion.
After we had been about fifteen days in Bokhara, the Vizier sent for us about mid-day, and kept us till evening: he happened to have some leisure time, and took this means to employ it. We found him in the company of a great[313] many Uzbeks; and it came out that the subjects on which he was to interrogate us were not terrestrial. He wished to know if we believed in God, and our general notions upon religion. I told him that we believed the Deity to be without equal; that he was every where; that he had sent prophets on earth; and that there was a day of judgment, a hell and a heaven. He then entered upon the more tender point of the Son of God, and the prophetic character of Mahommed; but, though he could approve of Christian opinions on neither of these subjects, he took no offence, as I named their prophet with every respect. “Do you worship idols?” continued the Vizier; to which I gave a strong and negative reply, that seemed to excite his wonder. He looked to some of the party, and one of them said that we were practising deceit; for it would be found that we had both idols and crosses hung round our necks. I immediately laid open my breast, and convinced the party of their error; and the Vizier observed, with a smile, “They are not bad people.” The servants were preparing the afternoon tea, when the Vizier took a cup, and said, “You must drink with us; for you are people of the book, better than the Russians, and seem to have pretty correct notions of truth!” We bowed at the distinction; and were ever after honoured with tea on our[314] visits to the minister. Since he had begun with our professions of faith, he was resolved to go through them. He wished to know if we regarded the Armenians as the “peers” or saints of the Christians; but I assured him that we conceded no such supremacy to that primitive sect. He expressed his wonder at our associating with Jews, since they were so wicked a people. The determined opposition of the Israelites in Arabia to Mahommed, seems to have disgraced them in the eyes of his followers. The minister now wished to hear of our treatment of the Hindoo and Mahommedan population of India. I told him that we respected the prejudices of both,—that we alike repaired their mosques and pagodas, and spared peacocks, cows, and monkeys, because it was pleasing to them. “Is it a truth,” said the Koosh Begee, “that these people worship these beasts?” I said that they either did so, or respected them. Ustugh-firrolah,—“God have mercy upon us!”—was his reply. The cunning catechist now asked me if we ate pork; but here it was absolutely necessary to give a qualified answer; so I said we did, but that the poor people mostly used it. “What is its taste?” said he. I saw the cross question. “I have heard it is like beef.” He enquired if I had tried horse-flesh since my arrival in Bokhara: I said that I had, and had found[315] it good and palatable. He then asked if we had visited the famous shrine of Bhawa Deen near Bokhara; and, on expressing a wish to see it, he desired a man to accompany us, and begged we would go quietly. The Koosh Begee now asked what we were taking back to our relatives in Europe after so long an absence; a question worthy of the good man’s heart: but I referred to our distant journey, and the inconvenience of carrying baggage; adding also, that soldiers were never rich. The old gentleman on this rose abruptly from his carpet, and called for a musket, which he put in my hands, and requested me to perform the platoon exercise, which I did. He observed that it differed from the drill of the Russians, of which he knew a little; and began, at the same time, to march with much grimace, across the room. As we stood and enjoyed the scene, the Koosh Begee, who was a tall, broad-shouldered Uzbek, looked at us and exclaimed, “All you Firingees are under-sized people: you could not fight an Uzbek, and you move like sticks.” Here followed a conversation on the advantages of discipline, which these people may be excused for disbelieving, since they have had no good opportunity of judging. The Vizier then communicated to us that a caravan was preparing for the Caspian Sea, as also for Russia, and that he would take steps to secure our protection if we proceeded; all of[316] which, as well as the kindness and great toleration of the man (for an Uzbek) were most gratifying. He expressed some desire to know the state of our finances, and the amount of our daily expenditure; but, little as that was, it was unnecessary to tell the whole sum. Our funds were plentiful, but our agents, who were Hindoos, shuddered at being found out in supplying us. We did not leave the minister till it was dark; and he requested the doctor to visit one of his children, whose disease had baffled physic. He found it rickety, and in a very precarious state; and the Vizier afterwards heard of its probable end without emotion, saying that he had thirteen sons, and many more daughters.
We took an early opportunity of visiting the shrine near Bokhara, which lies some few miles on the road to Samarcand. I thought little of any tomb while journeying in such a direction; but I did not deem it prudent to sue for permission to visit it with our doubtful character. It is only 120 miles from Bokhara; and at Kurshee we had been within two marches of it. We were now obliged to rest satisfied with an account of that ancient city, the existence of which may be traced to the time of Alexander. It was the capital of Timour, and the princes of his house passed their winters at it. “In the whole habitable world,” says Baber, “there are few cities so pleasantly situated as[317] Samarcand.” The city has now declined from its grandeur to a provincial town of 8000, or at most 10,000, inhabitants, and gardens and fields occupy the place of its streets and mosques; but it is still regarded with high veneration by the people. Till a king of Bokhara has annexed it to his rule, he is not viewed as a legitimate sovereign. Its possession becomes the first object on the demise of one ruler and the accession of another. Some of its buildings remain, to proclaim its former glory. Three of its colleges are perfect, and one of these, which formed the observatory of the celebrated Ulug Beg, is most handsome. It is ornamented with bronze, and its bricks are enamelled or painted. I could hear nothing of the famous obelisk which he built, excepting some crude tradition regarding its erection, brick by brick, as the clock struck. There is another college, called Sheredar, of beautiful architecture. The tomb of Timour and his family still remains; and the ashes of the emperor rest beneath a lofty dome, the walls of which are beautifully ornamented with agate (yushm). The situation of Samarcand has been deservedly praised by Asiatics; since it stands near low hills, in a country which is every where else plain and level. We are told, that paper was[318] first manufactured in Samarcand: but how great is the change since that article is now supplied from Russia.
The prohibition to ride did not extend beyond the limits of Bokhara; and our servants had the satisfaction of riding our ponies to the gate, as we walked by their side. When outside the city, we soon reached the tomb of Bhawa Deen Nukhsbund, one of the greatest of saints of Asia, who flourished in the time of Timour. A second pilgrimage to his tomb is said to be equal to visiting Mecca itself. A fair is held near it once a week, and the Bokharees gallop out on donkeys to pay their devotions. The reigning king, before he succeeded to his crown, made a solemn vow to this saint, that if he would vouchsafe his assistance, he would visit the shrine every week, and walk to it from the city on foot so many times annually. His majesty, I believe, keeps his word; since we met his baggage going out where he would pray and rest for the night. There are no buildings at the shrine that require any description, which is a square elevated platform, with a fine mosque and a large college near it. It is circumambulated by every pilgrim, who kisses the inscriptions that set forth its age and date. It is very richly endowed, and the descendants of Bhawa[319] Deen are its protectors. We entered the sacred spot with no other ceremonies than leaving our slippers outside. We were also taken to visit the holy man who had charge of it, and who gave us cinnamon tea, and wished to kill a sheep for our entertainment. He, however, had so many diseases, real or imaginary, that, after a detention of two hours, we were glad to get out of his domain. He was most particular in his enquiries regarding the name of the saint, and if it had travelled into India and Europe. It was but Asiatic politeness to bear testimony to his reputation; for Bhawa Deen is really celebrated throughout the Mahommedan world, and the pilgrims of Bokhara are known at Mecca by his name of Nukhsbundee. I observed that this great shrine, and, indeed, most buildings of a similar nature which I saw in my travels, was marked with the horns of the rams that had been sacrificed at the spot. It is said, that they denote power; and it is, perhaps, to this custom that we owe the title given to Alexander the Great of Zulkurnuen, or two-horned; though we know that he used horns as a son of Jupiter Ammon.
About twenty-five miles north-west of Bokhara, and on the verge of the desert, there lie the ruins of an ancient city, called Khojuoban, and which is assigned by tradition to the age of[320] the caliph Omar. Mahommedans seldom go beyond the era of their Prophet, and this proves nothing. There are many coins to be procured in this neighbourhood; and I am fortunate in possessing several beautiful specimens, which have turned out to be genuine relics of the monarchs of Bactria. They are of silver, and nearly as large as a half-crown piece. A head is stamped on one side, and a figure is seated on the reverse. The execution of the former is very superior; and the expression of features and spirit of the whole do credit even to the age of Greece, to which it may be said they belong. They brought numerous antiques from the same place, representing the figures of men and animals cut out on cornelians and other stones. Some of these bore a writing that differs from any which I have before seen, and resembled Hindee. In my search after such curiosities, I heard of some petrified stones shaped like birds, and about the size of a swallow, found in the hills of Budukhshan. I did not see a specimen, as the owner was absent from Bokhara. I am the more disposed to give credence to the existence of such things, since I have seen innumerable stones of the shape of small turtles or tortoises, which were brought from the higher ranges of the Hemilaya. I could not, however, place the same reliance on their[321] tales of an enchanted and petrified city which was described by the Bokharees as lying on the south-western corner of the Sea of Aral, and between Orgunje and Orenburg. They call it “Barsa-gil-mis;” which, in Toorkee, means, to go and never return; since such is said to be the fate of the curious. In a country which has furnished oriental writers with so many metaphors for paradise, and so much praise, as Transoxiana, we may expect to hear stories which are suited to the Arabian Nights. The natives of Bokhara are also firm believers in magic; but they refer to India as the seat of that science. No one, however, doubts its existence; and I found, according to them, that the art was daily practised in Surat, where the magicians were women, while those of Bengal are men. I passed two years in the city of Surat, and two happy years they were. I had a large native acquaintance, and made many enquiries regarding their customs and popular opinions; but I heard, for the first time, in Bokhara, that its ladies were magicians. I can at least assert that, if they do possess witchery, it consists in their own native graces. Distance, I believe, gives countenance to most of the fables which gain ground in the world. Aboolfuzzul asserted, some 300 years ago, that there were men who could eat out one’s liver in India; and the opinion has since passed[322] current, and is still believed in all the countries of Asia.
Circumstances of a peculiar nature made me acquainted with an Uzbek family of high respectability in Bokhara, and I visited it on a Friday. This family had originally come from the “Dusht-i-Kipchak,” and been settled in the country for 150 years: a member of their body had been twice deputed as an ambassador to Constantinople, for which they enjoyed the high title of Bee. They now traded to Russia, and had been considerable losers by the conflagration of Moscow, which had not, with all its horrors, I believe, been supposed to have carried distress into the centre of Tartary. I was received by these people à la Uzbek, and forced to swallow various cups of tea in the middle of a hot day. The Uzbeks have a most unsocial custom at a party, for the landlord becomes a servant, and hands up every dish in person; nor will he himself touch any thing till every member of the party has finished. They are a kind people, and if bigotry is their predominant failing, it is the fault of education; I never observed them show it by an attack on the feelings of others. One may, however, discover it in every act of life, and the whole tenour of their conversation. We happened to speak of the discoveries of the Russians, who[323] have recently hit upon some veins of gold between their country and Bokhara. One of the party remarked, that the ways of God were unsearchable, which had concealed these treasures from the true believers, and now revealed them, near the very surface of the earth, to the kaffirs, or infidels. I smiled; but it was not said in a way that could possibly give offence, and is the manner of speaking about Europeans among themselves. When I left the party to return home, I was much struck with the solemnity with which Friday is observed in the streets: it is as rigidly kept as a Sunday in Europe, and, perhaps, more so, for the virtuous Diocesan of London found of late much to reprehend in his flock of the metropolis. Not a single shop is permitted to be open till after prayers at one o’clock, and all the inhabitants are to be seen crowding to the mosque, arrayed in their best attire. There is a gravity about the Mahommedans, and something in their dress which gives an imposing cast to a body of them proceeding to the temple of God.
A month had nearly elapsed since our arrival in Bokhara, and it was necessary to think of moving on our journey; but the route that we should follow became a subject of serious consideration, from the troubled state of the country. The object which we had in view[324] was, to reach the Caspian, and the higher up we should land on its shores, the better; but there were difficulties on every side. No caravan had passed from Khiva to the Caspian for a year, owing to a blood feud with the Kirgizzes of the steppe. A Bokhara caravan lay at Khiva, and one from Astracan at Mungusluck on the Caspian: neither party could advance till some adjustment was made; which was more hoped for than expected. How much our good fortune predominated, in not accompanying this caravan, will hereafter appear. The direct road, by the territories of Khiva to Astrabad in Persia, was also closed to us; for the Khan of Khiva had taken the field to oppose the Persians, and lay encamped in the desert south of his capital, whither he ordered all the caravans to be conducted. The route by Merve and Meshid was open and more safe; but it appeared advisable for us to pursue the second of these routes, since we should see a portion of the territories of Khiva, and might then effect our passage to the frontiers of Persia, and ultimately reach the Caspian Sea by the desert of the Toorkmuns. All our friends, Hindoo, Armenian, and Afghan, dissuaded us from encountering the Khan of Khiva, who was described as inimical to Europeans; but, since we resolved to run every risk, and follow the route which would lead us upon[325] him, I waited on our patron, the Vizier, and made him acquainted with our intentions. He urged our proceeding by a caravan of two hundred camels that was just starting for Russia, and which would lead us to Troitskai in that country; but this did not suit our plans, as the route had been travelled by the Russian mission, and we had no wish to enter Asiatic Russia, but to reach the Caspian. The Vizier said he would make enquiries regarding the departure of the caravan; and as we desired to follow the route that would lead us to the frontiers of Persia, he would afford us his assistance as far as lay in his power. The caravan only awaited his commands to set out on its journey.
On the 21st of July, we made our farewell visit to the Vizier of Bokhara; and our audience of leave places the character of this good man even in a more favourable light than all his previous kindness. The Koosh Begee is a man of sixty, his eyes sparkle, though his beard is silvered by age; his countenance beams with intelligence, but it is marked with cunning, which is said to be the most striking feature in his character. He showed much curiosity regarding our language; and made me write the English numbers from one to a thousand in the Persian character, as well as the common words which expressed the necessaries of life. He[326] spent about an hour in this lesson, and regretted that he had no better opportunity of acquiring our language: he then made me write his name in English, and, handing it over to Doctor Gerard, requested him to read it. He recurred to the subject of medicine, and was greatly pleased with the lever of an instrument for drawing teeth, which was explained to him. He fixed it on the wood of the door, and wrenched out some pieces of it. He then begged that we would return to Bokhara as “trading ambassadors,” to establish a better understanding and a more extended commerce with the country. He now summoned the Cafila-bashee of the caravan, and a chief of the Toorkmuns, who was to accompany it as a safeguard against his tribe. He wrote down their names, families, habitations, and, looking to them, said, “I consign these Europeans to you. If any accident befall them, your wives and families are in my power, and I will root them from the face of the earth. Never return to Bokhara, but with a letter containing an assurance, under their seal, that you have served them well.” Turning to us, he continued, “You must not produce the ‘firman’ of the king, which I now give you, till you find it necessary. Travel without show, and make no acquaintances; for you are to pass[327] through a dangerous country. When you finish your journey, pray for me, as I am an old man, and your well-wisher.” He then gave each of us a dress, which, though far from valuable, was enhanced by the remark, “Do not go away empty-handed: take this, but conceal it.” I thanked the minister, with every sincerity, in the name of my companion and myself. He rose, and, holding up his hands, gave us the “fatha;” and we left the house of the Koosh Begee. I had not reached home till I was again sent for, and found the Vizier sitting with five or six well-dressed people, who had been evidently talking about us. “Sikunder (as I was always addressed), said the Koosh Begee, I have sent for you to ask if any one has molested you in this city, or taken money from you in my name, and if you leave us contented.” I replied, that we had been treated as honoured guests; that our baggage had not even been opened, nor our property taxed, and that I should ever remember, with the deepest sense of gratitude, the many kindnesses that had been shown to us in the holy Bokhara. The reply closed all our communications with the Vizier; and the detail will speak for itself. I quitted this worthy man with a full heart and with sincere wishes, which I still feel, for the prosperity of this country. I now examined[328] the firman which the Vizier gave us; it was laconic, but still most valuable, and it set forth our introduction to his Majesty, which we had not the good fortune to enjoy. It was in Persian, and may be thus translated:—
“At this time, by the will of God, two persons, Firingees, take their departure for their own country. It is proper that the people at the ferries, as well as the governors of towns and districts throughout the kingdom, should offer no hinderance to them, as they set out for their country after having seen the king, and with his permission.” Then follows the seal of Nussier Oollah, Ameer of Bokhara.
In the afternoon our camels were laden, and ready to take their departure. The last person we saw in our house was the landlord, who came running in the bustle of preparation to bid us farewell. He brought me a handsome and highly wrought scull-cap as a present: nor did I consider it necessary to tell him that a few months more would change my costume, and render his present useless. I gave him a pair of scissors in return; and we parted with the greatest demonstrations of friendship. The camels preceded us; and we ourselves, accompanied by an Uzbek acquaintance, took our last walk through the streets of Bokhara. We[329] were not to be distinguished from the natives of the country, for we had adopted their dress and habits, and trimmed our visages according to their prejudices. I pushed smartly along, and at all times evinced as little curiosity as the command I had over my countenance would admit of. We excited but little notice; though a Jew, to whom our costume most assimilated, would now and then ask when we arrived. I cannot say that I felt much regret at clearing the gates of the city, since we should now be more free from suspicion, and able both to ride and write. We had, indeed, managed to use the pen at night with leaden eyes; but, even then, we did it with fear. We joined the caravan about half a mile beyond the city gate, where we bivouacked for the night in a field.
Three short marches brought us to the home of the Cafila-bashee of our caravan; a small village of twenty houses, called Meerabad, and forty miles from Bokhara, in the district of Karakool. What was our disappointment to discover, on the eve of prosecuting our journey, that the whole of the merchants declined to advance, and had taken alarm at the proceedings of the Khan of Khiva. That personage, in examining the bales of a caravan from Persia, discovered some earth from the holy Kerbela, which had been packed up with the goods, according to custom, as a spell on their safe transit. But the precaution, so much at variance with orthodox Mahommedanism, had a very contrary effect. The greater portion of the goods were plundered; and, as many of our merchants were Persians, at least Shiahs, they resolved to run no risks, and wait either for the withdrawal of the army, or an assurance of protection to their property, under the seal of the Khan. The last alternative seemed the most probable means of terminating our anxiety, and it was discussed in full assemblage.
The whole of the merchants formed a congress at the hut in which we were living; for the Vizier had kindly made mention of us to them. It was a highly amusing sight to see these gentlemen, with whip in hand and booted, discussing the important topic. After some pressing and refusing, one individual was singled out as the scribe of a letter to the officer of the Khan of Khiva, and took his seat in the middle of the assembly. He mended his pen, promised to write in a large hand, and begged that but one of the many would dictate. It took about half an hour to decide the style of address, which was even referred to me; but I told the party that I had no such knowledge, since, in our language, we addressed the highest authorities by a brief title and their name. It was at last decided that the document should be headed as a petition; and, with many disputes, the following was produced:—
“The petition of the merchants to the Yooz Bashee of Merve. We salute you with peace! It has been made known to us that the caravan, which lately passed on its route to Bokhara, has not only been taken, as heretofore, but a duty of 4¼ tillas has been levied on each camel, and the loads of the merchants have been opened in the highway, and some of them destroyed. On hearing this, two caravans, en[332] route to Meshid, have halted from fear, and we now despatch this paper by a Toorkmun to inform you. You will render us a service by giving him a note telling what duties you will levy on us; and if his Highness the Khan of Orgunje (Khan Huzrut) has ordered such things, and will offer hinderance to our passing, after paying such duties as he had been pleased heretofore to accept. When your answer reaches us, we will advance and act accordingly. We, a body of merchants, salute you!”
It will be seen that, in matters of importance, the Asiatics can come to the point, and divest themselves of their usual rhodomontade. When the production was read aloud, there was a general shout of “Barikilla!” (bravo!) and five or six Toorkmuns, who had taken their seats near the door, were then consulted regarding its conveyance. One of them agreed to bring an answer on the eighth day; the distance of the place being 60 fursukhs (240 miles). He was to have three tillas for his trouble. When this second matter was settled, the whole party, holding up their hands, pronounced the blessing, and stroked down their beards. The affairs of nations could not have engaged an assembly more earnestly than this occupied the present party. Such grave faces, such surmises,[333] such whiffing of tobacco, such disputes about the words, such varied opinions about the matter: one advocating a measured tone; another a supplicatory one; and a third for a detail of the outs and ins of the whole matter. An intelligent man, a Moollah, rather far advanced in life, had more sense than the whole body, and the party at last had the good sense to adopt most of his views. Will it be believed, after all this serio-comic scene, these Rothschilds and Barings would not consent to reward the Toorkmun for conveying the letter: they would rather wait for a month than diminish their profits; and it ended in my paying the money. It appeared to me a matter of surprise that any answer should draw them to encounter people whom they unanimously considered tyrannical and barbarous. After the messenger had been despatched, the whole of the principal merchants of the caravan returned to Bokhara, and we were left in an obscure village of Tartary, to consider whether we should continue in our present abode, or return to the capital. We resolved to pursue the first course, and made up our minds to our unlucky detention.
In our journey from Bokhara, we had had some opportunities of adding to our knowledge of the country. Four or five miles from the city, we entered on a tract which was at once the extreme of richness and desolation. To the[334] right, the land was irrigated by the aqueducts of the Kohik; and to our left, the dust and sand blew over a region of dreary solitude. After travelling for a distance of twenty miles, in a W.S.W. direction, we found ourselves on the banks of the river of Samarcand, which the poets have styled “zarafshan,” or gold-scattering; but we must attribute its name to the incomparable blessings bestowed upon its banks, rather than the precious ores which it deposits. This river did not exceed the breadth of fifty yards, and was not fordable. It had much the appearance of a canal; for, a little lower down, its waters are hemmed in by a dam, and distributed with care among the neighbouring fields. The stripe of cultivated land on either bank did not exceed a mile in breadth, and was often less; for the desert pressed closely in upon the river. The number of inhabited places was yet great, and each different settlement was surrounded by a wall of sun-dried brick, as in Cabool; but the houses were neither so neat nor so strong as in that country. At this season (July), every cultivated spot groaned under the gigantic melons of Bokhara; many of which were also being transported in caravans of camels to the city. The soil of the country was varied, but, in the neighbourhood of the river, hard and gravelly. I observed that all the pebbles were sharp and angular, and differed[335] much from those which have been subjected to the influence of water. The direct course which we were pursuing to the Oxus led us away from the Kohik; but, after crossing a belt of sand-hills, about three miles wide, we again descended upon it. Its bed was entirely dry; since the dam of Karakool, which we had passed, prevents the egress of its scanty waters at this season. We found that this river, instead of flowing into the Oxus, forms a rather extensive lake, called “Dengiz[28]” by the Uzbeks, and close to which we were now encamped. The lower parts of the river are badly supplied with water, and it is only in certain seasons that it flows in the district of Karakool. We were now living among the Toorkmuns, who occupy the country between the Oxus and Bokhara. They only differ from the great family to which they belong in residing in permanent houses, and being peaceable subjects of the King of Bokhara. About forty different “robats,” or clusters of their habitations, lay in sight of ours; and we passed nearly a month in their neighbourhood and society without receiving insult or injury, or aught, I believe, but their good wishes. In our unprotected state, this was highly creditable to the natives of Toorkistan.
In Bokhara, ample scope had been afforded to observe the manners and customs of the citizen; in the country, we had now like opportunities of remarking the habits of the peasantry. To these we were made known through the means of the Toorkmun chief, to whom we had been introduced at Bokhara. He and the Cafila-bashee used to appear twice or thrice during the day, bringing with them any new acquaintance they might have fallen in with at the neighbouring markets; and we sat down and enjoyed our tea together at all hours. We thus became acquainted with many of the peculiarities of the Toorkmun tribes; and, latterly, I really began to feel an interest in the affairs and prospects of many of the individuals with whom I had been thus associated. The names of tribes and places, which had at one time appeared as far beyond my means of enquiry, were now within its compass. The Toorkmun chief, who was our master of ceremonies on these occasions, was himself a character: he was accompanying the caravan, to instruct his brethren by the way, and prevent our being plundered; but we soon found that he himself had no definite ideas of meum and tuum; since he had already appropriated to himself three gold tillas, which he had asked of me as part of the hire due to the Cafila-bashee, who was also a Toorkmun. Ernuzzar (for that was the name[337] of our friend) was, however, both an useful and amusing companion. He was a tall bony man, about fifty, with a manly countenance, improved by a handsome beard, that was whitening by years. In early life, he had followed the customs of his tribe, and proceeded on “allaman” (plundering) excursions to the countries of the Huzara and Kuzzil-bash; and some fearful wounds on his head showed the dangerous nature of that service. Ernuzzer had now relinquished the occupations of his youth and the propensities of his race. But though he had transferred his family to Merve, as civilized and reformed Toorkmuns, his aspect and his speech were still those of a warrior. He himself had for years escorted caravans to Persia and the Caspian; and, under such a conductor, we had many opportunities of observing the interesting people of which he was a member. The Cafila-bashee was a less sociable person, and had, besides, much business; but we could not help contrasting his indifference towards us with the kind interest of our old friend Hyat. Notwithstanding the injunctions of the Vizier of Bokhara, the Cafila-bashee left us in our secluded residence, and proceeded with his camels for a supply of salt to the banks of the Oxus: nor had we a single individual except the idle Toorkmun chief who cared about us.
One of the most remarkable of our Toorkmun visitors was a man of mature age and blunt address. His name was Soobhan Verdi Ghilich; which, being interpreted, means “the sword given by God;” and his complexion was as ruddy as that of a Bacchanal, though he declared that he had never indulged in the forbidden juice of the grape. He only spoke Toorkee; and my limited knowledge of that language required an interpreter: but, after a few visits, we almost understood each other, and no visitor was more welcome than Verdi, who described, in animated strains, his attacks on the Kuzzil-bash. “We have a proverb,” said he, “that a Toorkmun on horseback knows neither father nor mother;” and, from a Toorkee couplet, which he quoted with energy, we gather the feelings of his race:—
Verdi was of the tribe of Salore, the noblest of the Toorkmuns; and he used to declare that his race had founded the empire of the Osmanlis in Constantinople. There is nothing improbable in the assertion; and the traditions and belief of a people are always worthy of record. The Toorkmun shook with delight as I made him detail the mode of capturing the Kuzzil-bash, and sighed[339] that his age now prevented him from making war on such infidels. His advancing years had, in a small degree, tempered his prejudices; for he added that, if such things were contrary to the laws of God and the Koran, he did not doubt that the prescribed modicum of fasting and prayer would expiate his sins. Verdi now possessed some flocks of sheep and camels; and, since his years did not permit of his continuing his forays, he had despatched his sons on that service. He would tell me that his camels and his sheep were worth so many slaves, and that he had purchased this horse for three men and a boy, and that one for two girls: for such is the mode of valuing their property. I laughed as the robber detailed the price of his animals, and requested he would tell me my own worth, if I should become a Toorkmun captive: but we were too good people to become slaves, he said; and I did not learn his appreciation of us. “But,” said I to him, “you do not surely sell a Syud, one of the sacred descendants of your holy Prophet (on whom be peace!), if he falls among the list of captives?”—“What,” replied he, “is the holy Koran itself not sold? and why should not I dispose of an infidel Syud, who brings its truth into contempt by his heresy?” These are desperate men; and it is a fortunate circumstance that they are divided among one[340] another, or greater might be the evils which they inflict on their fellow-men. This great family of the human race roams from the shores of the Caspian to Balkh; changing their place of abode as their inclination prompts them.
The tribe we were now living with is known by the name of Ersaree; and for the first time, in a Mahommedan country, we saw the ladies unveiled: but this is a prevalent custom throughout the Toorkmun tribes. In no part of the world have I seen a more rude and healthy race of damsels in form or feature, though they are the countrywomen of the delicate Roxana, the bewitching queen of Alexander. Our Toorkmun chief, Ernuzzur, to dissipate his ennui, fell in love with one of these beauties, and applied to me for a magical spell, which he did not doubt I could give him, to secure the girl’s affections. I laughed at the old man’s love and simplicity. These ladies wore turbans; a becoming dress, the magnitude of which is so increased by their neighbours south of the Oxus, that I must reserve my remarks till I enter on their country. The Ersarees have most of the customs of the Toorkmuns, though their vicinity to Bokhara contributes to their partial civilisation. In our caravan we had five or six Toorkmuns from the south of the Oxus; and if these children of the desert practise the virtues of hospitality[341] at home, they do not forget that it is their due abroad; and the Ersarees had, indeed, reason to complain of the detention of our caravan. Every morning, some one of the party took his sword to the house of a Toorkmun; which passes among these people for the well-known signal that the master must kill a sheep, and that the strangers will assist him to eat it. It is impossible to refuse or evade the notice, and the feast takes place at night. We were not invited to these parties, which were purely Toorkmun; but they would frequently send to us some of the cakes of the entertainment. We had many opportunities to mark the fair treatment which was given to us by these people. They knew that we were Europeans and Christians, and, in speaking of us, they would yet use the term “eshan;” which is the respectful address given to khwajus and holy characters. A Persian, who visits Toorkistan, must join his hands when he prays, and give in to a few other customs, some of which are not very cleanly; and for these practices he has toleration and the protection of the state. A Christian has only to speak of Mahommedanism with respect, and avoid discussions, to secure similar treatment. The Persian, by his creed, is enjoined to follow up such conduct. “If there be seventy Shiahs and one Soonee,” says[342] their law, “the whole party are to veil themselves on account of that individual.” We found ourselves constrained by no such ordinances, but gladly conformed to the customs of the people; since the prejudices of a nation are always entitled to respect.
Though the village in which we were now residing could not boast of more than twenty houses, there were yet eight Persian slaves; and these unfortunate men appear to be distributed in like proportion throughout the country. They are employed as cultivators, and were at this time engaged all day in gathering the crop, though the thermometer was 96° within doors. Three or four of them were in the habit of visiting us, and I took letters from them for their friends in Persia, which were afterwards delivered. Many slaves save a sufficiency to redeem themselves: for the Persian is a sharper being than an Uzbek, and does not fail to profit by his opportunities. At Meerabad, two or three slaves had gathered sums that would liberate them; but though they fully intended to avail themselves of an opportunity to return to Persia, I never heard these people, in my different communications with them, complain of the treatment which they experienced in Toorkistan. It is true, that some of their masters object to their saying their prayers and observing the holidays[343] prescribed by the Koran, since such sanctity would deprive them of a portion of their labour; but they are never beaten, and are clothed and fed as if they belonged to the family, and often treated with great kindness. The practice of enslaving the Persians is said to have been unknown before the invasion of the Uzbeks; and some even say that it has not continued for an hundred years. A few Bokhara priests visited Persia, and heard the three first caliphs publicly reviled in that country; on their return, the synod gave their “futwa,” or command for licensing the sale of all such infidels. Sir John Chardin even tells us that, when a Persian shoots an arrow, he frequently exclaims, “May this go to Omar’s heart.” I myself have heard many similar expressions; and, since the report of the Bokhara priests is true, the Persians have brought their present calamities upon themselves. It is said that one of the Persian princes, in a late communication with the Khan of Orgunje, sent him the four books which Mahommedans hold sacred, the Old and New Testament, the Psalms of David, and the Koran, begging him to point out in which of these holy books the laws of slavery, as practised against the Persians, were to be found. The Khan solved the difficulty by replying, that it was a custom from which he had no in[344]tention of departing; and, as the Persians do not possess power to suppress it, it is likely to continue to the detriment and disgrace of their country. It has been observed, that Mahommedan slavery differs widely from that of the negroes, nor is the remark untrue; but the capture of the inhabitants of Persia, and their forcible exile among strangers, where neither their creed or prejudices are respected, is as odious a violation of human rights and liberties as the African slave-trade.
If the customs and manners of the people among whom we were residing afforded an interesting subject of observation, there were also a few individuals belonging to the caravan who deserve mention, and who, like ourselves, had remained in preference to returning to Bokhara. These people were natives of Merve in the desert, or, rather, descended from the colony of that people, who were forcibly marched to Bokhara by Shah Moorad, about forty years ago, and now form the most industrious portion of the population. They were not men of condition, and amused themselves in a manner purely Oriental, passing most of their leisure hours in telling stories and imitating the state and circumstance of the King of Bokhara. One enacted the part of royalty; another petitioned; a third punished; and they[345] passed one whole day in this manner with an uninterrupted flow of mirth. Boys would have quarrelled before evening; but when that time arrived, these people assembled outside to hear a guitar and some Toorkee songs. The style of performance differed from what I have seen in any country; the singer places himself close in front of the musician, so that their knees touch, and the sound, as it were, is conveyed to him by a living conductor, when he sends forth his notes. The Toorkee is a warlike language, and harmoniously sonorous. The bard, I was told, was singing of love, the theme of every clime.
The condition of our own little party, perhaps, afforded as much ground for curiosity and reflection as the strange people among whom we were living. At dusk in the evening we would draw forth our mats and spread them out, and huddle together, master, and servant, to cook, and eat within the limited circle. In a remote country, and in an obscure village of Tartary, we slept in the open air, lived without an escort, and passed weeks without molestation. Before one has encountered such scenes, the vague and indefinite ideas formed of them give rise to many strange thoughts; but when among them they appeared as nothing. In every place we visited[346] we had been in the power of the people, and one cross-brained fool, of which every country has many, might have destroyed at once all our best laid plans and schemes. We mixed with the people, and our continued collision placed us in constant danger: but yet we had happily escaped it all. A chain of circumstances, fortuitous, indeed, and for which we could not but feel sensibly grateful, with the tranquil state of the countries through which we passed, had been the great cause of our good fortune; for confidence and prudence, though they be the foremost requisites of a traveller, avail not in a country that is torn by factions and rebellion. Experience, also, proved, that some of the plans which had been adopted for the journey were to be regretted, since it was much less difficult to personate the character of an Asiatic than I had ever believed. The people we had seen were not of an inquiring turn; but, if satisfied that such a plan were feasible, I was also convinced that it would have afforded a far less share of enjoyment. We had run few risks from the limited nature of our baggage, though our cooking pots, few as they were, made me sometimes deplore the propensities of our country. We were, indeed, living as Asiatics, and had many a hearty dinner from the “kabobs” of the bazar; but my faithful[347] Hindoostanee, once my head servant, but now my cook and factotum, used, I suppose, to remember the more palatable dinners which he had seen me eat, and get things from the bazar which might betray us. We repeatedly prohibited these luxuries: but even in Bokhara we have had a breakfast of fish, eggs, coffee, preserves, and fruit, though it must not be believed that we always fared so sumptuously. Our party had considerably diminished since I last described it on the Indus; one of the Indians had retraced his steps from Cabool, and the chilling blasts of Hindoo Koosh had frightened the doctor’s servant, who was a native of Cashmere. Otherwise we had to bear the most ample testimony to the patience and perseverance of those we had chosen. Of these the most remarkable was Mohun Lall, the Hindoo lad from Delhi, who exhibited a buoyancy of spirit and interest in the undertaking most rare in an Indian. At my request he kept a minute journal of events; and I venture to believe, if hereafter published, that it will arrest and deserve attention. On his route to Bokhara his tale had run, that he was proceeding to his friends in that country, and, as we had passed that city, he was now joining his relatives at Herat! The native surveyor, poor Mahommed Ali, whose loss I have since had to deplore, gene[348]rally travelled as a pilgrim proceeding to Mecca, holding little or no open communications with us. In our retired stay at Meerabad, and under the azure and serene sky of night, it was impossible to suppress many a reflection, heightened, I believe, by the pleasing nature of the climate and the success which was attending our endeavours.
In the neighbourhood we did not fail to extend our inquiries for antiquities, and were fortunate enough to fall upon the ruins of Bykund; which I find to be one of the most ancient cities of Toorkistan. It lies about twenty miles from Bokhara, and appears to have been once watered by an extensive aqueduct, of which the remains may now be traced. In a manuscript history of the country, called Nursukhee[29], which I purchased at Bokhara, it is described as a city which is older than that capital, and to have been formed of a thousand “robats,” or clusters of villages. It is also said to have had many merchants, who traded to China and on the ocean; though the word which is used, “durya,” may also mean the Oxus. In after-times, or about the 240th year of the Hejira, it is said that, when a native of Bokhara went to Bagdad, he explained himself by saying that he was an inhabitant of Bykund. The history goes on to describe it as a[349] most substantial city, which suffered much from the infidels of the northern countries, who invaded it in the cold season. At length, Arslan Khan built a palace here, and improved its aqueducts; and, during this, a circumstance occurred that bears a resemblance to Hannibal’s passage of the Alps. Bykund, it appears, was built on a hillock, which was so hard as to resist the implements of the artificers. They, therefore, moistened it with vinegar and butter, and in the end it yielded to their perseverance, since they dug a whole fursukh through it; which is a distance of about three and a half English miles. The modern town of Bykund is deserted, and the walls of some of its buildings are the only remnants of its former greatness. Since every thing before the Hejira is fable with the Mahommedans, we must look to other works and languages for a history of Bykund, the seat of Afrasiab and the ancient kings of Toorkistan. I failed in procuring any of its relics; nor could I search with safety.
We, perhaps, have not come to any satisfactory conclusion regarding the ruins of Bykund, and we may not be more successful in elucidating some of the passages of the historians of Alexander; but there are a few facts regarding the river of Bokhara, or the Kohik, which deserve notice. It is always mentioned by the Greeks[350] under the name of Polytimetus, and is thus described by Arrian:—“Though it carries a full stream, it sinks from the sight, and hides its stream in the sand.” Curtius tells us, on the other hand, that “it was received into a cavern, the subterraneous torrent rushing on with a noise indicating its course.” The termination of this river, as given in our maps, is not in accordance with fact, since it is represented as falling into the Oxus; while it really deposits its waters in a lake, as has been before observed.[30] In a great portion of the year the supply is too scanty to force the passage, and it loses itself in sands. I venture, therefore, to observe, that we here verify the text of Arrian, who states it to be lost in the sands; while, on the other hand, we have no contradiction to Curtius, who leads its waters into a cavern or lake,—the modern “Dengiz,” which is about twenty-five miles long. The village in which we were residing stood therefore on classical ground, since we are informed that Alexander, after his detachment had been cut up by Spitamanes, followed him to where the Polytimetus loses itself in the sands of the desert, the scene of that disaster. It required every classical association to dispel the weariness of our protracted stay in this small hamlet. Another passage in Curtius, and of a striking[351] nature, deserves a more particular mention, since I have met with one of similar import in a Persian manuscript, descriptive of Bokhara, which I procured in the country. When Alexander had marched into the district of Bazaria, which is supposed to be the modern Bokhara, or to lie in that direction, the following sentence occurs:—“Of the barbarous splendour prevailing in these parts, there is no stronger mark than the extensive forests, in which are shut up untamed beasts of the grandest kind. A spacious wood, in which numerous unfailing springs give cheerfulness to the scenery, is selected, encompassed with a wall, and interspersed with towers for the reception of the hunters. In one park, it was said, that the game had remained undisturbed during four generations. Alexander, entering it with his whole army, commanded that the beasts throughout it should be roused from their lairs.”—B. 8. C. i. This is the excursion in which Alexander encountered the lion: but the king of the forest does not now inhabit Transoxiana. The Persian paragraph, to which I have alluded, runs thus:—
“This is the account of Shumsabad, which was here built by King Shumsoodeen. He purchased a tract of country half a fursung in extent, and laid it out in gardens, orchards, and houses of surpassing splendour; and he[352] dug canals and aqueducts, and expended a great sum of money; and he called the place Shumsabad. In addition to this he constructed a preserve for animals, and bounded it by walls which were a mile in extent: he brought pigeons and birds of every description, as well as all the domestic animals, and placed them in this preserve; and he likewise introduced the wild beasts of the field,—the wolf, the fox, the hog, the deer, the neelghaee, &c. &c.: and those which were tame he separated from those that were wild; and the latter he enclosed by higher walls, that they might not escape. When King Shumsoodeen died, his brother, whose name was Khizr Khan, succeeded him; and he added to the buildings of Shumsabad, and increased the number of the animals in the preserve which his brother had constructed.” The work from which this extract is taken presents us with some curious information regarding the early condition of the country about Bokhara: it expressly denominates it the Valley of the Sogd, and as having been at one time a hunting thicket. In the amusements of Shumsoodeen, long after the age of the Greeks, we still discover a relish for the “barbarous splendour” which called for the notice of the historians of Alexander.
About midnight, on the 10th of August, when we had almost despaired of the return of our[353] messenger to the Orgunje camp, we were roused from sleep by the shout of “Ullaho Acbar” from five or six Toorkmuns. They accompanied their countryman with the joyful information, that the chief of Orgunje would not offer any obstacles to the advance of our caravan. A dirty scrap of paper from the Yooz-bashee contained the information, the authenticity of which I had no desire to question. Uzbek customs. The solemn shout which awoke us in the dead of night might have at one time excited our alarm; but we now knew that it was nothing more than the blessing, which all Uzbeks and Toorkmuns invariably give to any one they approach. In other Mahommedan countries this is confined to the ceremonies on the death of a relative; but in Toorkistan religion is mingled with every affair of life. If a person visits you, he begins with the “fatha,” or the opening verse of the Koran, happily abridged to an “ullaho!” and a stroke of the beard; if you are to travel, all your friends come and give you the “fatha;” if you take an oath, all the party present say the “fatha;” if you meet an acquaintance, you say the “fatha;” and such good people never, of course, finish a meal without it. One would really believe the Uzbeks to be the most religious people on the face of the earth, uttering as they do the sacred[354] texts of their faith on the most trivial occasions. We seated the Toorkmun and his friends, and heard the news of the Orgunje army, and the prospect of our safe passage among them. We refreshed the messenger with tea and a hookah, which I called for with persevering attention, since no person in Toorkistan must ever exceed a single whiff of the same pipe, which is immediately handed to his neighbour and circulated through the assembly. We settled in our small congress that the Toorkmun had better proceed to Bokhara, and convey the tidings to the merchants of the caravan. He gave us a frightful account of the desert south of the Oxus, and the great difficulties of finding the road, which was now hidden by clouds of sand that were disturbed by the wind. I need not mention his adventures, since we ourselves were about to enter on that inhospitable region. We, however, took his advice, and hired two extra camels, which were to be the bearers of six skins of water, the supply which was deemed necessary to store before we took leave of the Oxus.
Our stay near Karakool had now been prolonged to the middle of August, and were I not more anxious to enter on other matters, I might here give some account of this region of lamb skins, supplying, as it does, the whole of[355] Tartary, China, Persia, and Turkey. The caravan soon collected once more at our quarters; and on the morning of the 16th of August, there appeared about eighty camels to prosecute their journey to the Oxus, all of them laden with the precious skins of the little district of Karakool, where we had passed nearly a month, among Toorkmuns and shepherds, who talked of nothing but fleeces and markets. Receive letters from India. Among the arrivals from Bokhara, we were agreeably surprised and delighted to find a small packet to my address, the contents of which consisted of three newspapers and a most kind letter from my friend M. Allard, at Lahore. The packet had been three months in coming, and afforded us indescribable pleasure, after our long ignorance of what was passing in the world. We had not seen a newspaper since crossing the Indus in the middle of March, and were now indebted to a foreigner for those which we had received. In one of the papers it was curious enough to observe a long paragraph regarding the unfortunate Mr. Moorcroft, who preceded us in these countries. We learned from it, that the world were deeply interested in the lands where we now sojourned, and that the Geographical Society of London had resolved on rescuing the papers of the traveller from oblivion that portion of which they had[356] already published under the superintendence of a high name.[31] With these circumstances before us, and even in the absence of any communications from our own countrymen, we had a pleasing reflection that we should not be forgotten in our wanderings. It was impossible, however, to rid ourselves of all remembrance of the fate of the unfortunate traveller on whose footsteps we had so long trod, placed as it was again in more vivid colours before us, and from a quarter that we least of all expected.
END OF THE FIRST VOLUME.
London:
Printed by A. Spottiswoode,
New-Street-Square.
[1] No. 33. East Street, Red Lion Square.
[2] I have now to deplore, with the sincerest sorrow, the death of this worthy man. His fate was indeed cruel: he passed safely through the deserts and dangers of Tartary, and now moulders at Vellore, where he died of cholera, while accompanying me to Calcutta. A generous Government have not forgotten his merits: his widow has been liberally pensioned, his family has been provided for, and his sons, on their attaining a certain age, will be admitted into the public service. This well-timed bounty has not passed unnoticed by the Indian community. I observe it mentioned in a Bengal newspaper, edited by a native, who calls upon his countrymen on that side of India to emulate such a career, and see that they are not left behind those at Bombay in mental advancement.
[3] Holeus spicatus.
[4] A country between two rivers is so called.
[5] Capparis.
[6] Mimosa Arabica.
[7] A small copper coin.
[8] See the end of the chapter.
[9] Vide Introduction, vol. i. p. 58.
[10] Vide Mr. Ramsay’s evidence before the Committee of the Lords.
[11] Introduction to Elphinstone’s Caubul, page 131.
[12] It is with regret that I record the loss of these antiques, though impressions of them have been preserved.
[13] A Tartar custom and word in clearing the outer apartments of the seraglio.
[14] Among other pieces of advice, he suggested that we should eat onions in all the countries we visited; as it is a popular belief that a foreigner becomes sooner acclimated from the use of that vegetable.
[15] Erskine’s Translation of Baber.
[16] A Persian couplet runs thus:—
which may be translated, that there is not an honest man among the Soonees of Balkh or the Shiahs of Cashmeer.
[17] See Mr. Elphinstone’s Cabool, vol. i. p. 244. et seq.
[18] See Vol. II. book i. c. 7.
[19] A tilla is worth 13s.
[20] Gibbon, c. viii.
[21] Quintus Curtius, lib. vii. cap. 4.
[22] Bishop Heber.
[24] Cossacks.
[25] 200 rupees.—20l.
[26] “Formosum pastor Corydon ardebat Alexin.”—Virg.
[27] Gibbon.
[28] The Turkish word for the sea.
[29] I have given this work to the Oriental Translation Committee of London.
[30] I now find that it is correctly given in the Russian maps.
[31] The Hon. M. Elphinstone.
The following apparent errors have been corrected:
Inconsistent or archaic language has otherwise been kept as printed.
End of the Project Gutenberg EBook of Travels into Bokhara (Volume 1 of 3), by
Alexander Burnes
*** END OF THIS PROJECT GUTENBERG EBOOK TRAVELS INTO BOKHARA (VOLUME ***
***** This file should be named 58074-h.htm or 58074-h.zip *****
This and all associated files of various formats will be found in:
http://www.gutenberg.org/5/8/0/7/58074/
Produced by Henry Flower and the Online Distributed
Proofreading Team at http://www.pgdp.net (This file was
produced from images generously made available by The
Internet Archive/Canadian Libraries)
Updated editions will replace the previous one--the old editions will
be renamed.
Creating the works from print editions not protected by U.S. copyright
law means that no one owns a United States copyright in these works,
so the Foundation (and you!) can copy and distribute it in the United
States without permission and without paying copyright
royalties. Special rules, set forth in the General Terms of Use part
of this license, apply to copying and distributing Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic works to protect the PROJECT GUTENBERG-tm
concept and trademark. Project Gutenberg is a registered trademark,
and may not be used if you charge for the eBooks, unless you receive
specific permission. If you do not charge anything for copies of this
eBook, complying with the rules is very easy. You may use this eBook
for nearly any purpose such as creation of derivative works, reports,
performances and research. They may be modified and printed and given
away--you may do practically ANYTHING in the United States with eBooks
not protected by U.S. copyright law. Redistribution is subject to the
trademark license, especially commercial redistribution.
START: FULL LICENSE
THE FULL PROJECT GUTENBERG LICENSE
PLEASE READ THIS BEFORE YOU DISTRIBUTE OR USE THIS WORK
To protect the Project Gutenberg-tm mission of promoting the free
distribution of electronic works, by using or distributing this work
(or any other work associated in any way with the phrase "Project
Gutenberg"), you agree to comply with all the terms of the Full
Project Gutenberg-tm License available with this file or online at
www.gutenberg.org/license.
Section 1. General Terms of Use and Redistributing Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic works
1.A. By reading or using any part of this Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic work, you indicate that you have read, understand, agree to
and accept all the terms of this license and intellectual property
(trademark/copyright) agreement. If you do not agree to abide by all
the terms of this agreement, you must cease using and return or
destroy all copies of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works in your
possession. If you paid a fee for obtaining a copy of or access to a
Project Gutenberg-tm electronic work and you do not agree to be bound
by the terms of this agreement, you may obtain a refund from the
person or entity to whom you paid the fee as set forth in paragraph
1.E.8.
1.B. "Project Gutenberg" is a registered trademark. It may only be
used on or associated in any way with an electronic work by people who
agree to be bound by the terms of this agreement. There are a few
things that you can do with most Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works
even without complying with the full terms of this agreement. See
paragraph 1.C below. There are a lot of things you can do with Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic works if you follow the terms of this
agreement and help preserve free future access to Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic works. See paragraph 1.E below.
1.C. The Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation ("the
Foundation" or PGLAF), owns a compilation copyright in the collection
of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works. Nearly all the individual
works in the collection are in the public domain in the United
States. If an individual work is unprotected by copyright law in the
United States and you are located in the United States, we do not
claim a right to prevent you from copying, distributing, performing,
displaying or creating derivative works based on the work as long as
all references to Project Gutenberg are removed. Of course, we hope
that you will support the Project Gutenberg-tm mission of promoting
free access to electronic works by freely sharing Project Gutenberg-tm
works in compliance with the terms of this agreement for keeping the
Project Gutenberg-tm name associated with the work. You can easily
comply with the terms of this agreement by keeping this work in the
same format with its attached full Project Gutenberg-tm License when
you share it without charge with others.
1.D. The copyright laws of the place where you are located also govern
what you can do with this work. Copyright laws in most countries are
in a constant state of change. If you are outside the United States,
check the laws of your country in addition to the terms of this
agreement before downloading, copying, displaying, performing,
distributing or creating derivative works based on this work or any
other Project Gutenberg-tm work. The Foundation makes no
representations concerning the copyright status of any work in any
country outside the United States.
1.E. Unless you have removed all references to Project Gutenberg:
1.E.1. The following sentence, with active links to, or other
immediate access to, the full Project Gutenberg-tm License must appear
prominently whenever any copy of a Project Gutenberg-tm work (any work
on which the phrase "Project Gutenberg" appears, or with which the
phrase "Project Gutenberg" is associated) is accessed, displayed,
performed, viewed, copied or distributed:
This eBook is for the use of anyone anywhere in the United States and
most other parts of the world at no cost and with almost no
restrictions whatsoever. You may copy it, give it away or re-use it
under the terms of the Project Gutenberg License included with this
eBook or online at www.gutenberg.org. If you are not located in the
United States, you'll have to check the laws of the country where you
are located before using this ebook.
1.E.2. If an individual Project Gutenberg-tm electronic work is
derived from texts not protected by U.S. copyright law (does not
contain a notice indicating that it is posted with permission of the
copyright holder), the work can be copied and distributed to anyone in
the United States without paying any fees or charges. If you are
redistributing or providing access to a work with the phrase "Project
Gutenberg" associated with or appearing on the work, you must comply
either with the requirements of paragraphs 1.E.1 through 1.E.7 or
obtain permission for the use of the work and the Project Gutenberg-tm
trademark as set forth in paragraphs 1.E.8 or 1.E.9.
1.E.3. If an individual Project Gutenberg-tm electronic work is posted
with the permission of the copyright holder, your use and distribution
must comply with both paragraphs 1.E.1 through 1.E.7 and any
additional terms imposed by the copyright holder. Additional terms
will be linked to the Project Gutenberg-tm License for all works
posted with the permission of the copyright holder found at the
beginning of this work.
1.E.4. Do not unlink or detach or remove the full Project Gutenberg-tm
License terms from this work, or any files containing a part of this
work or any other work associated with Project Gutenberg-tm.
1.E.5. Do not copy, display, perform, distribute or redistribute this
electronic work, or any part of this electronic work, without
prominently displaying the sentence set forth in paragraph 1.E.1 with
active links or immediate access to the full terms of the Project
Gutenberg-tm License.
1.E.6. You may convert to and distribute this work in any binary,
compressed, marked up, nonproprietary or proprietary form, including
any word processing or hypertext form. However, if you provide access
to or distribute copies of a Project Gutenberg-tm work in a format
other than "Plain Vanilla ASCII" or other format used in the official
version posted on the official Project Gutenberg-tm web site
(www.gutenberg.org), you must, at no additional cost, fee or expense
to the user, provide a copy, a means of exporting a copy, or a means
of obtaining a copy upon request, of the work in its original "Plain
Vanilla ASCII" or other form. Any alternate format must include the
full Project Gutenberg-tm License as specified in paragraph 1.E.1.
1.E.7. Do not charge a fee for access to, viewing, displaying,
performing, copying or distributing any Project Gutenberg-tm works
unless you comply with paragraph 1.E.8 or 1.E.9.
1.E.8. You may charge a reasonable fee for copies of or providing
access to or distributing Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works
provided that
* You pay a royalty fee of 20% of the gross profits you derive from
the use of Project Gutenberg-tm works calculated using the method
you already use to calculate your applicable taxes. The fee is owed
to the owner of the Project Gutenberg-tm trademark, but he has
agreed to donate royalties under this paragraph to the Project
Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation. Royalty payments must be paid
within 60 days following each date on which you prepare (or are
legally required to prepare) your periodic tax returns. Royalty
payments should be clearly marked as such and sent to the Project
Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation at the address specified in
Section 4, "Information about donations to the Project Gutenberg
Literary Archive Foundation."
* You provide a full refund of any money paid by a user who notifies
you in writing (or by e-mail) within 30 days of receipt that s/he
does not agree to the terms of the full Project Gutenberg-tm
License. You must require such a user to return or destroy all
copies of the works possessed in a physical medium and discontinue
all use of and all access to other copies of Project Gutenberg-tm
works.
* You provide, in accordance with paragraph 1.F.3, a full refund of
any money paid for a work or a replacement copy, if a defect in the
electronic work is discovered and reported to you within 90 days of
receipt of the work.
* You comply with all other terms of this agreement for free
distribution of Project Gutenberg-tm works.
1.E.9. If you wish to charge a fee or distribute a Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic work or group of works on different terms than
are set forth in this agreement, you must obtain permission in writing
from both the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation and The
Project Gutenberg Trademark LLC, the owner of the Project Gutenberg-tm
trademark. Contact the Foundation as set forth in Section 3 below.
1.F.
1.F.1. Project Gutenberg volunteers and employees expend considerable
effort to identify, do copyright research on, transcribe and proofread
works not protected by U.S. copyright law in creating the Project
Gutenberg-tm collection. Despite these efforts, Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic works, and the medium on which they may be stored, may
contain "Defects," such as, but not limited to, incomplete, inaccurate
or corrupt data, transcription errors, a copyright or other
intellectual property infringement, a defective or damaged disk or
other medium, a computer virus, or computer codes that damage or
cannot be read by your equipment.
1.F.2. LIMITED WARRANTY, DISCLAIMER OF DAMAGES - Except for the "Right
of Replacement or Refund" described in paragraph 1.F.3, the Project
Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation, the owner of the Project
Gutenberg-tm trademark, and any other party distributing a Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic work under this agreement, disclaim all
liability to you for damages, costs and expenses, including legal
fees. YOU AGREE THAT YOU HAVE NO REMEDIES FOR NEGLIGENCE, STRICT
LIABILITY, BREACH OF WARRANTY OR BREACH OF CONTRACT EXCEPT THOSE
PROVIDED IN PARAGRAPH 1.F.3. YOU AGREE THAT THE FOUNDATION, THE
TRADEMARK OWNER, AND ANY DISTRIBUTOR UNDER THIS AGREEMENT WILL NOT BE
LIABLE TO YOU FOR ACTUAL, DIRECT, INDIRECT, CONSEQUENTIAL, PUNITIVE OR
INCIDENTAL DAMAGES EVEN IF YOU GIVE NOTICE OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH
DAMAGE.
1.F.3. LIMITED RIGHT OF REPLACEMENT OR REFUND - If you discover a
defect in this electronic work within 90 days of receiving it, you can
receive a refund of the money (if any) you paid for it by sending a
written explanation to the person you received the work from. If you
received the work on a physical medium, you must return the medium
with your written explanation. The person or entity that provided you
with the defective work may elect to provide a replacement copy in
lieu of a refund. If you received the work electronically, the person
or entity providing it to you may choose to give you a second
opportunity to receive the work electronically in lieu of a refund. If
the second copy is also defective, you may demand a refund in writing
without further opportunities to fix the problem.
1.F.4. Except for the limited right of replacement or refund set forth
in paragraph 1.F.3, this work is provided to you 'AS-IS', WITH NO
OTHER WARRANTIES OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT
LIMITED TO WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR ANY PURPOSE.
1.F.5. Some states do not allow disclaimers of certain implied
warranties or the exclusion or limitation of certain types of
damages. If any disclaimer or limitation set forth in this agreement
violates the law of the state applicable to this agreement, the
agreement shall be interpreted to make the maximum disclaimer or
limitation permitted by the applicable state law. The invalidity or
unenforceability of any provision of this agreement shall not void the
remaining provisions.
1.F.6. INDEMNITY - You agree to indemnify and hold the Foundation, the
trademark owner, any agent or employee of the Foundation, anyone
providing copies of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works in
accordance with this agreement, and any volunteers associated with the
production, promotion and distribution of Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic works, harmless from all liability, costs and expenses,
including legal fees, that arise directly or indirectly from any of
the following which you do or cause to occur: (a) distribution of this
or any Project Gutenberg-tm work, (b) alteration, modification, or
additions or deletions to any Project Gutenberg-tm work, and (c) any
Defect you cause.
Section 2. Information about the Mission of Project Gutenberg-tm
Project Gutenberg-tm is synonymous with the free distribution of
electronic works in formats readable by the widest variety of
computers including obsolete, old, middle-aged and new computers. It
exists because of the efforts of hundreds of volunteers and donations
from people in all walks of life.
Volunteers and financial support to provide volunteers with the
assistance they need are critical to reaching Project Gutenberg-tm's
goals and ensuring that the Project Gutenberg-tm collection will
remain freely available for generations to come. In 2001, the Project
Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation was created to provide a secure
and permanent future for Project Gutenberg-tm and future
generations. To learn more about the Project Gutenberg Literary
Archive Foundation and how your efforts and donations can help, see
Sections 3 and 4 and the Foundation information page at
www.gutenberg.org Section 3. Information about the Project Gutenberg
Literary Archive Foundation
The Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation is a non profit
501(c)(3) educational corporation organized under the laws of the
state of Mississippi and granted tax exempt status by the Internal
Revenue Service. The Foundation's EIN or federal tax identification
number is 64-6221541. Contributions to the Project Gutenberg Literary
Archive Foundation are tax deductible to the full extent permitted by
U.S. federal laws and your state's laws.
The Foundation's principal office is in Fairbanks, Alaska, with the
mailing address: PO Box 750175, Fairbanks, AK 99775, but its
volunteers and employees are scattered throughout numerous
locations. Its business office is located at 809 North 1500 West, Salt
Lake City, UT 84116, (801) 596-1887. Email contact links and up to
date contact information can be found at the Foundation's web site and
official page at www.gutenberg.org/contact
For additional contact information:
Dr. Gregory B. Newby
Chief Executive and Director
gbnewby@pglaf.org
Section 4. Information about Donations to the Project Gutenberg
Literary Archive Foundation
Project Gutenberg-tm depends upon and cannot survive without wide
spread public support and donations to carry out its mission of
increasing the number of public domain and licensed works that can be
freely distributed in machine readable form accessible by the widest
array of equipment including outdated equipment. Many small donations
($1 to $5,000) are particularly important to maintaining tax exempt
status with the IRS.
The Foundation is committed to complying with the laws regulating
charities and charitable donations in all 50 states of the United
States. Compliance requirements are not uniform and it takes a
considerable effort, much paperwork and many fees to meet and keep up
with these requirements. We do not solicit donations in locations
where we have not received written confirmation of compliance. To SEND
DONATIONS or determine the status of compliance for any particular
state visit www.gutenberg.org/donate
While we cannot and do not solicit contributions from states where we
have not met the solicitation requirements, we know of no prohibition
against accepting unsolicited donations from donors in such states who
approach us with offers to donate.
International donations are gratefully accepted, but we cannot make
any statements concerning tax treatment of donations received from
outside the United States. U.S. laws alone swamp our small staff.
Please check the Project Gutenberg Web pages for current donation
methods and addresses. Donations are accepted in a number of other
ways including checks, online payments and credit card donations. To
donate, please visit: www.gutenberg.org/donate
Section 5. General Information About Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works.
Professor Michael S. Hart was the originator of the Project
Gutenberg-tm concept of a library of electronic works that could be
freely shared with anyone. For forty years, he produced and
distributed Project Gutenberg-tm eBooks with only a loose network of
volunteer support.
Project Gutenberg-tm eBooks are often created from several printed
editions, all of which are confirmed as not protected by copyright in
the U.S. unless a copyright notice is included. Thus, we do not
necessarily keep eBooks in compliance with any particular paper
edition.
Most people start at our Web site which has the main PG search
facility: www.gutenberg.org
This Web site includes information about Project Gutenberg-tm,
including how to make donations to the Project Gutenberg Literary
Archive Foundation, how to help produce our new eBooks, and how to
subscribe to our email newsletter to hear about new eBooks.