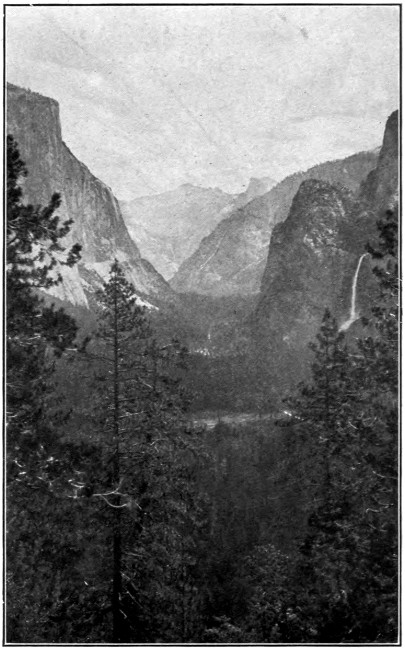

The Yosemite Valley
This eBook is for the use of anyone anywhere in the United States and most other parts of the world at no cost and with almost no restrictions whatsoever. You may copy it, give it away or re-use it under the terms of the Project Gutenberg License included with this eBook or online at www.gutenberg.org. If you are not located in the United States, you'll have to check the laws of the country where you are located before using this ebook.
Title: Seeing the West
Suggestions for the Westbound Traveller
Author: K. E. M. (Kate Ethel Mary) Dumbell
Release Date: May 20, 2018 [eBook #57190]
Language: English
Character set encoding: UTF-8
***START OF THE PROJECT GUTENBERG EBOOK SEEING THE WEST***
| Note: | Images of the original pages are available through Internet Archive. See https://archive.org/details/seeingwestsugges00dumbuoft |

The Yosemite Valley
Seeing the West
Suggestions for the
Westbound Traveller
By
K. E. M. Dumbell
Frontispiece
COPYRIGHT, 1920, BY
DOUBLEDAY, PAGE & COMPANY
ALL RIGHTS RESERVED, INCLUDING THAT OF TRANSLATION
INTO FOREIGN LANGUAGES, INCLUDING THE SCANDINAVIAN
COPYRIGHT, 1914, BY JAMES POTT & COMPANY
“I knew it would call, or soon or late, a it calls the whirring wings,
It’s the olden lure, it’s the golden lure, it’s the lure of the timeless things.”
R. W. Service.
The author begs to acknowledge, with thanks, the courtesy of the publishers and others named below for their kindness in granting her permission to use the extracts from their publications incorporated in this book:
The Century Company,
Messrs. Barse & Hopkins,
The American Forestry Association,
The U. S. Department of the Interior,
The Western Guidebook Company,
Mr. George Perkins Merrill,
The Western chambers of commerce, and the various railroads.
The extracts from Mr. John Muir and Mr. J. G. Percival are published by permission of, and by special arrangement with, Messrs. Houghton Mifflin Company, publishers of their works.
To Mr. Robert Sterling Yard, Executive Secretary of the National Parks Association, especial thanks are extended for his interest and assistance and the permission to quote freely from his most valuable book, “The Book of National Parks.”
To you who have travelled in our great American West this book may serve not only as a reminder of what you saw, but also as a lure to draw you back to the glorious regions which, perhaps, you were obliged to neglect before. One, two, or three trips would fall far short of showing you all your country has to offer, unless you were fortunate enough to make the period of each visit cover many months.
The average American citizen has only a hazy knowledge of what he possesses in his national playgrounds. The area alone is stupendous. We have set aside, for our pleasure and amusement, nearly ELEVEN THOUSAND SQUARE MILES of national parks.
It is your privilege to become a member of the National Parks Association if you so wish; through this interesting channel you can learn in detail the particular charms of each park.
If these playgrounds are ever connected by automobile highways, as we hope they will be some day, there will be in this country a region for sightseeing tours as the world has not yet dreamed of.
We have thought serious thoughts, and done serious things, for some time past; now the reaction has set in and play we must and will.
In one park alone, within easy reach, close to Denver, “The Gateway to the Rockies,” you may find 51 mountains having an altitude of more than 10,000 feet, mountain streams, mountain lakes, big game, etc., etc., indefinitely. Then go on to Mount Rainier National Park in Washington, or Glacier Park in Montana, where await you sights that fairly stagger even those who think they are familiar with mountain scenery, glaciers, etc.
When weary of ascents, or seeking other sights, where, in what part of the world, can you find anything to compare with the Grand Canyon of Arizona? Here your descent is one mile! No foreign picture gallery can give you such pictures as you will get here, for it has not been given to man to depict such things; Kipling’s “ten-league canvas with brushes of comets’ hair” would be necessary!
Pass a night on the floor of this canyon, and choose the time of full moon for it; you have never had such an experience, nor could you have elsewhere. If you are fortunate enough to have unlimited time, do not leave El Tovar until you have seen one superb storm, it will stretch your very soul. This place draws so tremendously upon the emotions that after it you will want—what? I can tell you what, the perfect peace of the Yosemite Valley, for quiet, intimate beauty, ahead of any spot on this continent. Here enter a camp and rest, and roam up and down the valley floor at your will. Do not leave without climbing one of the trails, or rather letting a horse or mule climb it with you on his back At Glacier Point and you will know full well why I urge you to make the trip.
For the student who would know more of his country, the West is an open book, waiting only for him to turn the pages.
For the automobilist, Paradise awaits you! For the aviator, landings are being prepared; the one which I saw at Crater Lake in the summer of 1919 will enable you to reach an extinct volcano of incomparable beauty. For you who have never been in our wondrous West, may this book help you to decide to spend what has been saved for your next trip there, where you get 100 per cent. value for your money!
As my object is to give, in the shortest space possible, suggestions for the westbound traveller, the matter is arranged in five parts.
K. E. M. D.
New London, N. H., July 1, 1920.
PART ONE
Denver, the capital of Colorado, “The Gateway To The Rockies,” is situated on the South Platte River and is only a few miles east of the Rocky Mountains. The city has developed tremendously along civic lines of recent years and there are many public buildings which are well worth visiting, but as my rule will be throughout this book to omit any descriptions of cities, I must begin here. One can always procure maps of our cities and information regarding them from the Civic Centres, so here we will consider Denver as the best starting place from which to make countless charming trips.
Boulder is 29 miles northwest of Denver; this is a fine drive; the trip to Georgetown and the famous “Loop” is also well worth while.
If one has time for an all-day trip, “Corona” is satisfying; situated, as it is, on the crest of the main range, it is quite a tremendous climb; this is said to be the highest point reached by a standard-gauge railroad in the United States. The station is decidedly crude and there was sad disorder to pass through in 1919, but having overlooked that, the view fully repaid one.
The drive through Bear Creek Canyon, via Lookout Mountain, is magnificent.
There are countless trips to be made all round the city of Denver. If one only has a few hours here the view from the top of the Equitable Building is perhaps the most satisfactory, and the beautiful city parks may be visited.
In a wonderful unbroken line stand the great mountains, the view extending from Long’s Peak on the north to Pike’s Peak on the south. Almost any of these mountains may be ascended nowadays, some parties starting from Denver, others from Estes Park.
The Denver and Rio Grande Railway makes a delightful tour called “Around the Circle,” a four-day trip, stopping overnight at Durango, Silverton, and Ouray. On this trip the traveller passes through four beautiful canyons, over three or four mountain passes, winding back and forth over 1,000 miles of the Rocky Mountains. The ticket is good for 60 days, so that the stops may be made to suit any one.
This beautiful park lies 7,500 feet above sea level, and can be reached in five hours from Denver by the Union Pacific Railway or automobile.
In the park are splendid hotels, where the traveller is made welcome, and from which fine tours are made through such scenery as only our great West can boast, mountains, valleys, lakes, and rivers; the views include many peaks of the Rocky Mountains—Long’s, 14,270 feet; Ypsilon, 13,500 feet; Hague, 13,832 feet. Mountain climbing to the heart’s content, hunting, fishing, and all the quieter sports may also be enjoyed here.
The trails take us in two hours from flower-strewn meadows to glaciers.
Leaving Estes Park, which forms the eastern gateway to the Rocky Mountain Park, we enter one of the finest sections of this magnificent range.
The park embraces a most interesting part of the Continental Divide. For the mountain climber this is a veritable Paradise, for there seem to be peaks of every size and trails leading in every direction. For those who like the more easy method, the automobile roads are excellent. The drive through Big Thompson Canyon is one to rejoice the heart of the most blasé. The area of the park is 398 square miles. “There are 51 mountains with summits more than 10,000 feet high, also unnumbered canyons, about 200 lakes, waterfalls, glaciers, native forests, and endless numbers of beautiful wild flowers.” The richness of this park is inconceivable. One is tempted to go into endless detailed descriptions, but it must not be.
Many weeks may be spent here making different trips every day. There is every kind of accommodation, from the simplest camp to the most comfortable hotel, and all of this only 70 miles from Denver.
The big game in the park is increasing all the time, Rocky Mountain sheep, elk, deer, etc., and there are one hundred varieties of wild bird life.
“Entry to the park by any route is dramatic. If the visitor comes the all-motor way through Ward he picks up the range at Arapaho Peak, and follows it closely for miles. If he comes by any of the rail routes, his motor stage emerges from the foothills upon a sudden spectacle of magnificence—the snowy range, its highest summit crowned with cloud, looming upon the horizon across the peaceful plateau. By any route the appearance of the range begins a panorama of ever-changing beauty and inspiration, whose progress will outlive many a summer’s stay.
“Wherever one lives, however one lives, in this broad tableland, he is under the spell of the range. The call of the mountains is ever present. Riding, walking, motoring, fishing, golfing, sitting under the trees with a book, continually he lifts his eyes to their calm heights. Unconsciously he throws them the first morning glance. Instinctively he gazes long upon their gleaming moon-lit summits before turning in at night. In time they possess his spirit. They calm him, exalt him, ennoble him. Unconsciously he comes to know them in all their myriad moods. Cold and stern before sunrise, brilliant and vivid in mid-morning, soft and restful toward evening, gorgeously coloured at sunset, angry, at times terrifying, in storm, their fascination never weakens, their beauty changes but does not lessen.”
New roads and wonderful trails are being built on all sides here, and there is every variety of mountain scenery, large and small canyons with glacial lakes; broad, rolling plains, and mountain climbing, from the most simple to the wildest, steepest that heart could desire. Some of the smaller trips are those leading to Fern and Odessa lakes, to Bear Lake at the outlet of the Tyndall Gorge, to Loch Vale, Sky Pond, and the Lake of Glass, etc., etc., until one may reach Longs Peak’s western precipice. “These spots are each a day’s round trip from convenient overnight hotels, which deserve all the fame which will be theirs when the people come to know them, for as yet only a few hundreds a summer, of Rocky Mountain’s hundred thousand guests, take the trouble to visit them.”
Those planning to stay any length of time in this park will find “The Book of The National Parks,”1 from which I should like to quote a great deal more, their best guide.
Colorado Springs, to the south of Denver, with its sparkling, life-giving air, is situated upon an elevated plateau from whence may be had a superb view of Pike’s Peak, 14,100 feet.
This peak is probably the best known of the Rocky Mountains. It lies about six miles west of Colorado Springs. It is ascended by a cog-wheel railway, “The Manitou and Pike’s Peak Railway,” in about one and one half hours, or by bridle path in six hours; there is also a most excellent automobile road, and powerful cars with good drivers make the round trip in six hours. On the summit there is a small inn, where a light luncheon and a cup of coffee can be had. The ascent is made during the summer months only, there being too much snow in winter. The view is unusually extensive, and the fascination of being in such a world of snow is not soon forgotten.
The Cheyenne Mountain Road may well be considered one of Colorado Springs’ most beautiful trips. Passing around the base of Cheyenne Mountain one glorious view after another appears. The road rises pretty steadily and grows decidedly more narrow, so narrow that only those with steady heads can really enjoy it. This drive takes us all the way to Seven Lakes, a distance of about 22 miles, and by continuing some five miles farther we come to Cripple Creek. From Colorado Springs the trip to the Cheyenne Canyons may be made. See especially the South Canyon which can be reached by electric car. There is a small admission fee (50 cents), but it is well worth it; there are beautiful walks here. An easy climb takes one to the rim.
Seven Falls and the South Cheyenne Canyon are reached in about an hour’s drive from Colorado Springs or Manitou, the return trip being made through Bear Creek Canyon and over the famous High Drive. About three hours should be allowed for the round trip, which is very well worth while.
On this trip may be seen the last resting place of Helen Hunt Jackson, who, according to her own request, lies at the head of Seven Falls.
Leave your car and stand between Hercules Pillars, where miles of massive granite walls tower above you; a more impressive, picturesque spot is hard to find. I was distressed here, as I am in many of the beautiful places of our country, by the thoughtless scattering of chewing-gum papers, candy boxes, etc. Why, when we are really learning to love the great out-of-doors, should this awful disorder continue? Where are the Boy and Girl Scouts? Why are they not enforcing the law of order, at least by example?
The Cripple Creek trip is made in a day, either by train or automobile. Here one is enabled to visit one of the world’s most famous gold mines.
The great charm of staying in Manitou is that you are within walking distance of so many interesting sights, then, too, you are right among the wonderful Springs. You can have the waters fresh from the source as many times a day as you wish. Manitou is a fascinating little town, situated in the foothills about Pike’s Peak and just at the head of the old Ute Pass. It is six miles from Colorado Springs, and for those who wish quiet, may be found more attractive as a stopping place, than the more prosperous city.
The Garden of the Gods is only a short walk from Manitou, and is a most charming place in which to pass the sunset hour; where better could one beat this time than beneath the Cathedral Spires? This is quite the most impressive spot in this unique garden.
“This monument, which is near Grand Junction, Colorado, is similar to the Garden of the Gods, and is said by some to be more picturesque.
“It contains fine examples of erosion, particularly of lofty monoliths; these latter are found in several tributary canyons, some of them of very great size, one being more than 400 feet high.”
The trip up Mount Manitou is made by incline. It would seem hardly worth while to ascend so comparatively small a mountain so near the famous Pike’s Peak; but this is not so; the view from the top of Manitou is particularly pleasing, and the tramps on the top are very lovely. If I had been obliged to miss either ascent I know now that I would rather it had been Pike’s Peak.
This cave is only a short walk from Manitou, about two miles, through the lovely Williams Canyon, and following the Temple Drive. It is, perhaps, rather too severe a climb for those who are not used to this exercise, but the trip is easily made by automobile. The cave is most unusually interesting, it is three quarters of a mile deep, and is composed of sixteen large rooms and long, winding passages on three levels. The stalactites and stalagmites are most fascinating in their formation, and a brilliant electrical illumination shows off to perfection all of this truly remarkable place. The cave alone would repay one for the trip to Manitou.
I went to see these dwellings the first time with rather scornful feelings, having read and always understood that they were entirely artificial; but I was so impressed by their natural appearance and solidity that I made inquiries in Manitou, and was fortunate enough to meet, and hear at first hand, the entire story of the bringing of this dwelling from the Mesa Verde by the gentleman who moved it, brick by brick and stone by stone. He assured me that the greatest care had been used in resetting every atom exactly as it was found, in a cliff as nearly like the original as possible. Hence, this dwelling may be taken as a good example of the ancient cliff dwellings by those who are not fortunate enough to see the original dwellings at the Mesa Verde.
The capital of the state of Utah is situated in a large valley surrounded by mountains, chiefly the Wahsatch range. This city was founded by the Mormons in 1847 before the “Territory of Utah” was organized.
The Tabernacle was built in 1864-67, a large, unusual, oval-shaped building, 250 feet long, 150 feet wide and 70 feet high; it is said to seat 12,000 people. It is open to visitors. The Tabernacle was built in its present form in 1893, and is reported to have cost more than $4,000,000; this building is not open to visitors.
From Prospect Hill an excellent view of the city may be had, and a more extensive view of the surrounding country from Ensign Peak.
Some 5 miles from Salt Lake City is the Great Salt Lake, 80 miles long and 30 miles wide; it varies greatly in depth.
Beautiful mountainous islands rise out of the lake and the whole body of water is picturesque to a degree. The tints of the water at sunset are exquisite, and the floating spars, so often seen here, heavily encrusted with salt crystals, add greatly to the dazzling effects of the rays of light.
The trip across the lake by rail is one of the interesting experiences in going to the Far West via Salt Lake City.
Ogden lies 30 miles north of Salt Lake City; it is a railroad centre. For those who may be delayed here it may be well to know that the Ogden River Canyon is a beautiful spot. It can be reached by automobile or by street car.
At Canyon City, situated at the mouth of the canyon of the Arkansas, if you happen to have taken the “Denver and Rio Grande Scenic Railway” for this section of your trip, you leave the Pullman car and take your seat in a flat, uncovered observation car (during the summer months) and so pass through this superb gorge. The next ten miles takes you through a bit of scenery worth going anywhere to see. There is a fine piece of engineering here. The train seems in spots to cling to the sides of the gorge, and it is here that we cross the famous Hanging Bridge, the waters of the Arkansas dashing madly past. Strangers who have never been in this part of the world before may possibly be misled into thinking they are seeing the Grand Canyon while passing through here; but this canyon of the Arkansas must not be confounded with the canyon of the Colorado River, which is known all over the world as “The Grand Canyon.” It is a sad pity that the word GRAND has been used in connection with these lesser canyons. It is a misnomer, and I know that many people have been misled by it.
Of all the ruins of prehistoric peoples in our great Southwest, these are the largest, best preserved, and most picturesquely situated, hence Congress has set aside as a National Park this large area of 48,966 acres under the above title.
This mesa, or high tableland, is cut by many canyons, and in these canyon walls are found most of the cliff dwellings of this truly remarkable region. Much has been done here to make it possible for the traveller to reach and explore, for himself, these dwellings of the ancients.
The best approach is from Mancos, Colorado; from here to the ruins is only 10 miles (as the crow flies) and some 30 miles by auto road on account of the various canyons to be traversed; a trip more full of interest would be hard to find in any country.
The trip from Mancos to Spruce Tree Camp is made in about three hours, and here we are taken care of for the night.
The park was established to protect the wonderful cliff dwellings of the Mancos Canyons, which are said to be among the most important remains of this mysterious race. There is one dwelling here in excellent preservation, others in varying stages of demolition. The age of these ruins is supposed to be from 500 to 1,000 years. To those who are especially interested in this region and who desire further information, I recommend Mr. T. H. Chapin’s “The Land of the Cliff Dwellers.”
“The principle and most accessible ruins are the Spruce Tree House, Cliff Palace, Balcony House, and Tunnel House. Spruce Tree House is located in the head of Spruce Tree Canyon, a branch of Navajo Canyon. It originally contained about 130 rooms, built of dressed stone laid in adobe mortar, with the outside tiers chinked with chips of rocks and broken pottery.
“Cliff Palace is located about two miles east of Spruce Tree House, in a left branch of Cliff Canyon, and consists of a group of houses with ruins of 164 rooms, including 20 round kivas, or ceremonial rooms, and a tapering, loopholed tower forming a crescent of about 100 yards from horn to horn, which is reputed to be one of the most famous works of prehistoric man in existence.
“Balcony House, a mile east of Cliff Palace, in Ruin Canyon, contains about 25 rooms, some of which are in almost perfect condition.
“Tunnel House, about two miles south of Spruce Tree House, contains about 20 rooms and two kivas connected by an elaborate system of underground passages, and a burial ground of 5,000 square feet. In each of these villages is an elaborate system of fortification, with, in some cases, walls two to three feet thick and 20 feet high, watchtowers 30 feet high, and blockhouses pierced with small loopholes for arrows....”
I should advise any traveller planning to visit any of the Southwest Indian Reservations to go well armed with literature. The U. S. Government circulars, from which the above is quoted, may be had from the Department of the Interior, and the Santa Fé Railroad provides excellent literature.
“With the creation of the Zion National Park in 1919 there entered into our National Park system a reservation as remarkable, as brilliantly beautiful, and as highly differentiated from all others as any of the distinguished group. It contains a hundred and twenty square miles of painted terrace country of southern Utah, surrounding from its source a shallow river whose carved and fretted and monumented canyon lies between sandstone walls which rise two thousand feet in gorgeous mottled reds, surmounted by a thousand feet in marble-white.
“This Park makes two principal appeals, that to the universal delight in extraordinary beauty of colour and form, and that to the intelligence of the student of earth’s history.... To the best of my knowledge, there is no place in the world where one may see so easily so much of the record of the earth’s history.
“This canyon winding like a snake, abounding in enormous peaks and domes and glowing like a Roman sash, is one of the most striking spectacles which America has to offer.”2
The canyon is some 60 miles north of the Grand Canyon; it is reached by rail from Salt Lake City or Los Angeles; leaving the main line at Lund, the last 100 miles is made by auto-stage.
“The natural bridges for whose preservation this National Monument in San Juan County, Utah, was created are understood to be the largest examples of their kind, the greatest of the three having a height of 222 feet and a thickness of 65 feet at the top of the arch. The arch is 28 feet wide, the span 261 feet and the height of the span 157 feet.
“The three bridges are within a five-mile area and constitute an imposing spectacle. In this region are two fine cavern springs as well as other interesting and scientifically valuable natural curiosities.”
Just south of the Uinta Mountains and 18 miles east of the town of Vernal, in the northeastern section of Utah, lies this area (80 acres) which has been set aside, as a national monument, under the above title, on account of its remarkable fossil deposits of extinct reptiles of great size. Remains of many enormous animals, which once inhabited what is now our southwest, have been unearthed in a state of fine preservation. These include complete and perfect skeletons of large Dinosaurs.
Near here may be visited the Uinta Indian Reservation.
PART TWO
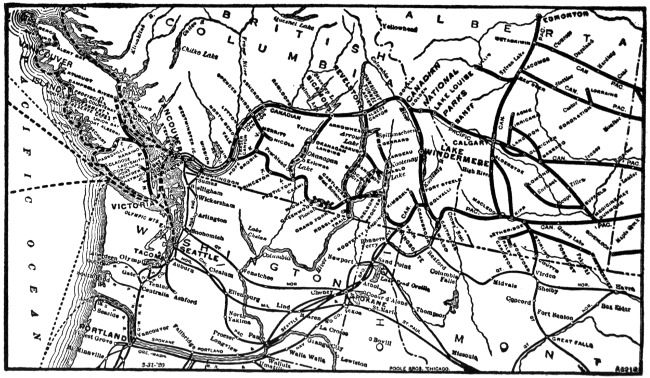
In writing of the Northern Rockies we must leave our own territory long enough to say a few words of the superb section of this great range, which is known as the “Canadian Rockies,” where for 500 miles, east and west, the Canadian Pacific trains pass through incomparable scenery. One stands amazed at the feats of engineering which have been carried through all along these lines. One great mountain after another looms up before us, their bald heads seeming to pierce the very sky, while the snow lies many feet deep on their sides. The Selkirks defy description! The train glides through one wonderful pass after another.
The traveller should arrange to stop at Banff, the gateway to the Canadian Rockies. The railroad has a fine hotel there from which may be made many splendid excursions in the vicinity, all are easily accessible by motor, carriage, horseback, or on donkeys. The lake, about nine miles off, known as “Lake Minnewanka,” sixteen miles long, makes a delightful excursion; this lake, whose waters are very deep, is walled in by tremendous cliffs; steam launches make the round trip.
Continuing westward from here, we come, in about two hours, to Laggan, the station for Lake Louise. Leaving the train and taking an incline car we soon find ourselves part way up one of these splendid mountains, where this indescribable gem, Lake Louise, suddenly bursts upon our sight. There is hardly a finer spot than this in Switzerland; the lake, 5,645 feet above sea level, lies in a hollow at the base of three great mountains, and at the far end, in the most dramatic setting, is the superb Victoria Glacier, facing directly the Château Lake Louise, where we immediately try to procure rooms looking out upon this lovely view. As soon as you are settled, start out and walk round the lake, 3 or 4 miles. This gives you an intimate, friendly feeling which will almost undoubtedly be succeeded by a feeling of awe as the majestic splendour of the place grows upon you.
From here a most interesting set of mountain trips may be made by either road or bridle path; the latter is of course the better, as one can go farther and climb higher. I cannot go into detail, but the hotel gives full information, provides horses, guides, etc. Do not fail to see Mirror Lake (altitude 6,550 feet) or Lake Agnes (altitude 6,820 feet), truly a lake in the clouds, and encircled by majestic peaks. The beauty of this region cannot be exaggerated.
The “Valley of the Ten Peaks” is unique, and this is a trip all can make, a 10-mile drive over good roads. I shall attempt no description of this valley, one must see it. Leaving Lake Louise and Laggan, we pass through Field, where another stop may be made, and various interesting excursions taken.
Glacier, near the summit of the inexpressibly beautiful Selkirk Range, ought not to be passed by; here again comfortable accommodations have been arranged. Mount Sir Donald, pointed out as we pass, rises to a height of more than a mile from the railroad.
At Sicamous there is also a temptation to stop and explore, for we are nearing the end of the five hundred miles of the Rocky Mountains through which we pass. Beyond Ashcroft we enter the canyon of the Thompson, through Agassiz and Mission Junction, and about 50 miles farther on we reach Vancouver. I attempt no description of this interesting city for the reason given above, adequate information and local maps can always be had in every metropolis.
A suggestion for a camping trip, to be taken from Lake Louise, has just come to me. I insert it for those who may wish to plan such a trip.
“Lake Louise, Alberta, is the point from which you start on this little-used and superb trail, with saddle and pack horses and the guides who will cook the meals, wrangle the horses, and steer you safely over any or all difficulties, bad trails, steep cliffs, and treacherous glaciers. You take with you all your provisions, tents, and whatever you may need for the trip.
“Along the Bow River you wend your way, vast snow-topped mountains on every side, and the trail winding now over steep shale slopes, with the panorama of sparkling glaciers, rushing rivers, and deep canyons; again, plunging into a pine forest where the ground is covered with delicate pink twin flowers and white anemones; riding all day and sleeping out under the blue sky where, if you are fortunate, the Northern Lights flash in flames of red and gold. Here one wants to linger indefinitely.
“Passing Pyramid Peak, with its almost insurmountable overhanging cliffs, Mount Murchison, calm and majestic, at last you reach the Saskatchewan River. The horses plunge up to their withers in icy water which rushes by foaming around the knees of the rider, but the other side is reached in safety. Sometimes your camping ground is by an old wigwam of the Stoney Indians, littered with grotesque, carved wooden animals and people, made by the children, with here and there a discarded moccasin or broken knife; again you may find an Indian ‘sweat-bath’ made of saplings bent in a half circle; the Indians cover this framework with blankets and pour water over red-hot stones which are placed at one end, making a regular Turkish bath. Usually, however, the trail is unmarred by signs of man; in many places great trees have fallen across the path and have to be cut away before you can ride on.
“Mount Athabaska and Mount Wilcox loom before you, or perhaps you turn to the north, into the Brazeau country, where the mountain sheep roam in great flocks. But ever you follow the sparkling rivers, now passing deep blue-green lakes nestling among the rocks and now crossing high, treeless passes, or barren, boulder-strewn hillsides, and always surrounded by the mountains with their ever-changing colours, now gray and sombre, now red, amber, and purple as they catch the glow of the sinking sun.
“The solitude and stillness are broken only by the thunder of a distant avalanche, or murmur of a near-by stream, the glorious scenery and the wildness of it all catching and holding you with a fascination that cannot be cast off.”1
The main features of interest to the average American traveller in this Northern Rocky Mountain region are, of course, Glacier National Park and the Yellowstone National Park.
Glacier Park is situated in the northwest of Montana. The reservation comprises 915,000 acres and contains 260 lakes and 60 glaciers, varying from five square miles to a few acres in area.
Here as in all the other great national parks of our western country, camps have been provided, and every kind of accommodation, from this to elaborate hotels, is to be had there.
It is quite impossible to attempt a description of all these parks without a very long list of new adjectives, for Nature has been more than generous in dowering this part of the world with wonderful scenery. See lakes McDonald, St. Mary, McDuff, and Iceberg Lake; this last is almost surrounded by great towering cliffs, many of them rising to an elevation of 2,000 feet, in the crevices of which lie large glaciers. Even in the short space of time which the average tourist gives this spot, he is frequently rewarded by hearing and seeing some great fragment break from its parent glacier and crash into the water, where, in the form of small icebergs, they are always seen floating; hence the name of the lake.
Blackfeet Glacier is the largest and by far the most impressive in the park; none but hardy mountain climbers should attempt the ascent.
The park is reached by the Great Northern Railroad, from either Belton or Glacier Park. “Stop-overs” are allowed on any transcontinental ticket, and one, two, or three day tours will be arranged as requested.
There is a fine hotel at Glacier Park Station and from here automobile roads lead in to the “Many-Glacier” Hotel and the chalet-like groups of camping places.
But I do not wish to give the impression that Glacier Park is a place to be visited en route; far from it; it is a place to go to for weeks or months, a place for the invalid to rest in, for the student of Nature to revel in, or for the most vigorous young people to tramp in. By far the most attractive way to see the park is on foot and is becoming more and more popular. Walking tours can be arranged at a very small cost, the party either taking its own outfit, or using the chalets scattered through the park for their benefit.
Full information on this park can be obtained from the Great Northern R. R. or the Department of the Interior.
“The Devil’s Tower is one of the most conspicuous features in the Black Hill region of Wyoming. It rises with extreme abruptness from the rough Wyoming levels just back of the Black Hills. It is on the bank of the Belle Fourche River. This extraordinary tower emerges from a rounded forested hill of sedimentary rock which rises six hundred feet above the plain; from the top of that the tower rises six hundred feet still higher. It is visible for a hundred miles or more in every direction. The visitor approaching by automobile sees it hours away, and its growth upon the horizon as he approaches is the least of his memorable experience....
“The Devil’s Tower can be likened to nothing but itself. It is the core of a volcanic formation which doubtless once had a considerably larger circumference. At its base lies an immense talus of broken columns which the loosening frosts and the winter gales are constantly increasing; the process has been going on for untold thousands of years, during which the softer rock of the surrounding plains has been eroded to its present level.”2
The Bitter Root Valley, at the foot of which Missoula lies, is one of the rich and beautiful western valleys and is interesting historically. Lewis and Clark traversed the valley in 1805-06 and some of their great hardships were encountered in crossing the Bitter Root Mountains. The point where their trail turned into the range is about 12 miles above Missoula.
At Stevensville, about 28 miles up this valley, Father De Smet established his first mission to the Salish, or Flathead, Indians, in 1841. The old church, St. Mary’s, still stands and is used at intervals. The Indians were removed from here many years ago.
The valley has a great reputation for its fruits and vegetables.
At Ravalli, on the Flathead Reservation, the Government has established a bison preserve of about 18,000 acres, with a herd of from one to two hundred of these fine creatures. This reservation is reached by the Northern Pacific Railroad from Arlee, Montana, and a drive of four or five miles.
From here westward to Pend d’Oreille we follow the Clark fork of the Columbia River. Lake Pend d’Oreille, Idaho, is one of the crystal gems of the west; it is 55 miles long and from 2 to 15 miles wide. These sparkling waters fill what was a deep mountain canyon. Soundings have been made to the depth of 4,000 feet without finding bottom. Exquisitely wooded mountains rise from the water’s edge, forming a wonderful setting.
Lake Coeur d’Alene, the source of the Spokane River, is another lovely spot in Idaho. Here there are some fine summer homes.
Through wild and rugged scenery we reach Spokane, and beyond cross the beautiful Columbia River and enter the Yakima Valley, another perfection of irrigation.
Crossing a spur of the Rocky Mountains just west of Livingston, where Lewis and Clark crossed in 1806, we pass through Galatin Valley, a famous barley-raising region; here are more than 100 miles of irrigating canals. At Bozeman the Montana State Agriculture College is located.
Near the great mining city of Butte is the Lewis and Clark Cavern, presented to the United States, as a national monument, by the Northern Pacific Railway. These huge, beautiful caves attract many visitors. Near Butte are also the Pipestone Hot Springs and Boulder Hot Springs.
Spokane, which used to be a trading post, is now a prosperous city.
Fort Wright, one of the military posts of the United States Government, is on the outskirts of the city on the bank of the Spokane River. Crossing the Cascade Range and passing down through the Green River Canyon, we reach Seattle or Tacoma, at the extreme south of Puget Sound.
On the way to the Yellowstone National Park by way of the Wyoming entrance, at Cody, and three miles east of the great Shoshone Dam, a limestone cave has been set apart under the above title.
The way in is rough and precipitous, and after entering the cave a descent by rope is necessary to reach the chambers, which are of unusual beauty and extend for more than a mile through galleries, some of which are heavily encrusted with crystals.
The Yellowstone National Park is situated in the extreme northwest corner of Wyoming, extending a few miles into Montana on the north and into Idaho and Montana on the west. The reservation, set apart by act of Congress in 1872, is 5,500 square miles.
From Salt Lake City or Ogden this park is reached by the Denver Rio Grande Railway or the Union Pacific in about 12 hours, but this trip, like so many others, can be arranged for you by whatever line you take.
The Northern Pacific Railway offers a splendidly arranged tour to and through the park by way of Livingston, the Gate of the Mountains, and the Upper Yellowstone River to Gardiner, the original entrance to the park, and only five miles from Mammoth Hot Springs, the official headquarters of the park.
The Yellowstone Park season is from June 15th to September 15th. It is not necessary to suggest what shall be seen here, for the trips are all arranged for one, and none should leave without making the complete tour. This park is unlike any other; it is unique in many ways. It contains geysers, mud volcanoes, mineral springs, and the most gloriously coloured pools. The Yellowstone Canyon can be compared with no other; here we have a riot of colour, said by many to rival the colours of the Grand Canyon, really so entirely different as to make comparison impossible. The walls of the Yellowstone Canyon are divided by a space of many miles at the top, which narrows down to three quarters of a mile at the base, where the foaming waters dash between them, and here the fragments of all the lost rainbows seem to have been collected.
There are many fine mountain peaks, the finest being Mount Washburn, which has an elevation of 10,346 feet, named for General Washburn, the head of the Washburn-Doane exploration party, who first climbed it in 1870. From here one gets the only view of the park as a whole. I have never forgotten a remark which I heard John Muir make about this spot; he said: “When you go to the Yellowstone Park do not leave it under any consideration until you have been taken up Mount Washburn, and when you reach the top of the mountain refuse to come down until you have passed a night on the summit; never mind about sleep; remember that there will come a time when you will take a long enough sleep to make up for all you can ever lose; this will be a sublime experience.”
Words cannot tell of the impressiveness of the geysers. One may sit comfortably on the veranda of Old Faithful Inn and watch one eruption after another, repeated endlessly. But with every change of light, early morning, noontide, at sunset, or by moonlight, they are seen with new interest, and on the moonless nights the visitors are called to see some of these great spouts with the rays of a powerful searchlight upon them.
Old Faithful, which is described as the most perfect illustration of geyseric phenomena and whose curious fascination and real beauty cannot be described, plays every 85 minutes to a height of 125 to 150 feet, the eruptions lasting about five minutes.
The Giant Geyser, generally conceded to be the finest in the park, throws its great volume of water to a height of 250 feet, playing irregularly about three times a month and lasting about 90 minutes.
The Castle Geyser, so named for its beautifully formed crater, plays only once every 26 or 27 hours, but lasts from 25 minutes to three quarters of an hour. This is truly an awe-inspiring sight.
The Riverside Geyser is among the favourites. Standing on the right bank of the Firehole River, it throws its spray into the air in a beautiful, graceful arch across the waters of the river, playing every 7 hours and lasting about seven minutes, and almost invariably displaying wonderful rainbow colours.
There is a plateau a quarter of a mile in extent, covered with hot pools, each of the most marvellously brilliant colours—reds, greens, yellows, etc.—perhaps the most beautiful of all being the one known as Morning-Glory Pool, so named from its curious shape resembling this well-known flower.
This park is a famous animal preserve. Elk deer, buffalo and bear thrive here. The bears cause great entertainment, coming down near some of the hotels to feed upon whatever may be offered them; having been protected so long, they have no fear.
Of all of our national parks the Yellowstone is the largest. It is also the highest and coolest. We are told that frosts occur there every month of the year. Mr. Muir says of it: “The air is electric and full of ozone; healing, reviving, exhilarating, kept pure by frost and fire, while the scenery is wild enough to awaken the dead.
“It is a glorious place to grow in and rest in. Camping on the shores of the lakes in the warm openings of the woods, golden with sunflowers, on the banks of the streams, by the snowy waterfalls, beside the exciting wonders or away from them in the scallops of the mountain walls sheltered from every wind, on smooth, silky lawns enamelled with gentians, up in the fountain hollows of the ancient glaciers between the peaks, where cool pools and brooks and gardens of precious plants charmingly embowered are never wanting....
“Again and again amid the calmest, stillest scenery you will be brought to a standstill, hushed and awe-stricken before phenomena wholly new to you. Boiling springs and huge, deep pools of purest green and azure water, thousands of them are splashing and heaving in these high, cool mountains as if a fierce fire were burning beneath each one of them; and a hundred geysers, white torrents of boiling water and steam, like inverted waterfalls, are ever and anon rushing up out of the hot, black underworld.
“Some of these ponderous geyser columns are as large as sequoias—5 to 60 feet in diameter, 150 to 300 feet high—and are sustained at this great height with tremendous energy for a few minutes, or perhaps nearly an hour, standing rigid and erect, hissing, throbbing, booming, as if thunderstorms were raging beneath their roots.... No frost cools them, snow never covers them ... winter and summer they welcome alike ... faithfully rising and sinking in fairy, rhythmic dance night and day, in all sorts of weather, at varying periods of minutes, hours, or weeks.... The largest and one of the most beautiful of the springs is the Prismatic, which the guide will be sure to show you. With a circumference of three hundred yards, it is more like a lake than a spring. The water is pure deep, blue in the centre, fading to green on the edges, and its basin and the slightly terraced pavement about it are astonishingly bright and varied in colour. This one of the Yellowstone fountains is of itself object enough for a trip across the continent....
“Near the Prismatic Spring is the great Excelsior Geyser, which is said to throw a column of boiling water 60 to 70 feet in diameter to a height of from 50 to 300 feet at irregular periods....”
But I could quote this great nature lover indefinitely. He is absolutely fascinating on any of these subjects. See for yourself “Our National Parks,” by John Muir, and if you are going west, as he would have you go, quietly, with time to draw near to nature, to read and to think, take a copy of his book with you.
Mr. Muir used his pen as a great artist uses his brush, his descriptions are the most exquisite of pictures.
“The Fossil Forests of the Yellowstone National Park cover an extensive area in the northern portion of the park, being especially abundant along the west side of Lamar River for about 20 miles above its junction with the Yellowstone. Here the land rises rather abruptly to a height of approximately 2,000 feet above the valley floor. It is known as Specimen Ridge, and forms an approach to Amethyst Mountain. There is also a small fossil forest containing a number of standing trunks near Tower Falls, and near the eastern border of the park along Lamar River in the vicinity of Cache, Calfee, and Miller creeks, there are many more or less isolated trunks and stumps of fossil trees, but so far as known none of these is equal in interest to the fossil forest on the slopes of Specimen Ridge.”
The fossil forests are easily reached over the wagon roads from the Mammoth Hot Springs, or from the Wylie Camp at Tower Falls.
Those who really wish to see these petrified trees must make a special point of it, or else they may be told, as I was, that the two small stumps seen in passing are all that are there.
In addition to a large redwood stump which stands 12 feet high, there are two trunks which stand 25 feet high and are two feet in diameter; another, three feet in diameter and 30 feet high, etc.
In addition to these standing trees many trunks lie prone upon the ground.
Ten species of trees have been found in the fossil forests of this park as well as some 150 fossil plants.
For further information on this, or any other of the national parks or monuments, apply to “The Department of the Interior,” Washington, D. C.
The Jackson Lake region is reached by automobile, from Old Faithful Inn, at which place arrangements can be made for the trip.
The lake lies just north of the very beautiful Teton Range, across the southern boundary of the park and about 70 miles from Old Faithful; this trip makes a most delightfully worth-while addition to a visit to the Yellowstone Park; the drive down is very fine, following the Yellowstone Lake for a time, crossing the Continental Divide, with views of the Absoroka Range to the east, where we see such great peaks as Mount Langford with an altitude of 10,600 feet; Mount Shurz, 10,600 feet; Colton Peak, 10,500 feet, and Table Mountain, 10,800 feet, standing, snow clad, in the distance.
From Lewis Lake to the border of the park the drive follows the Snake River, and shortly after leaving the park the river is crossed and Jackson Lake comes clearly into view; the road leads down the east side of the lake to Moran and here there is a small hotel where we are taken care of.
There are lovely wild excursions to be made in every direction. Bold peaks, unsealed by man, and glacial canyons. The great ragged peaks of the Teton Range show every variety of shape and size: Grand Teton, 13,747 feet, and Moran, 12,100 feet, are the finest, standing as they do only about five or six miles apart, each with a lovely lake nestled at its base; what a superb gateway they may some day make for a southern entrance to the Yellowstone Park if, as is now hoped, this region, including the two mountains and the two lakes, is to be added to the Yellowstone Park area.
Mount Moran stands majestically, directly across the lake from Moran, where the lake is about nine miles wide; the view of this exceptionally beautiful mountain across the clear, deep-blue water, is one not easy to forget. To nature lovers, trampers, and climbers I commend this region.
Jackson Lake has been connected with the great system of trails which runs all through the Yellowstone Park. The traveller taking this route will follow the east side of the Yellowstone Lake to the extreme south end, then the river of the same name, until, after crossing the river, the trail follows the Atlantic Creek to the Divide, over the Divide, and down, following the Pacific Creek to Moran.
PART THREE
There where the livid tundras keep their tryst with the tranquil snows;
There where the silences are spawned, and the light of hell-fire flows
Into the bowl of the midnight sky, violet, amber, and rose.
There where the rapids churn and roar, and the ice-floes bellowing run;
Where the tortured, twisted rivers of blood rush to the setting sun.
—Robert W. Service.
One might spend weeks taking the trips on Puget Sound alone, for this is one of the most beautiful bits of salt water to be found anywhere. The mountains seem to rise right out of the water and are wooded to the water’s edge.
The area of Puget Sound is about 2,000 square miles and its irregular shore-line is said to be 8,600 miles long.
Beautiful views of Mt. Rainier and Mt. Baker are had as one sails up the sound, and to the west lie the Olympics.
To speak of the various trips here would require too much space, for they are as numerous by land as by sea, and the beautiful roads invite one to motor endlessly.
For 60 miles or more east and west across the Olympian Peninsula, in the northwestern corner of Washington, between Puget Sound and the Pacific Ocean, stretch the Olympian Mountains.
Mount Olympus, 8,100 feet in altitude, rises majestically between the Strait of Juan de Fuca and the Pacific Ocean. The peninsula is wild, though there is a road connecting the water-front towns. Access to the mountain is by arduous trail.
This area was set aside as a national monument to preserve the Olympic elk, a species peculiar to the region.
From Vancouver, British Columbia, to Skagway, Alaska, is one thousand miles.
This is a most fascinating steamer trip, which may also be made from either Seattle or San Francisco. Winding between islands and the mainland, passing glaciers with the summer sun shining overhead, the steamers stop at various places, and the interesting Totem Pole People (the Alaskan Indians), may be interviewed.
Captain Stretch, whose many years of connection as an engineer with mining and railroad enterprises in the West and Alaska render him an authority, says: “Alaska is a country unique in its geographical situation, unique in its climate, and unique in its physical beauties. Cape Barrow, its northernmost cape, is warmer than any point in the world as far north of the equator; and its southern shores bordering the North Pacific Ocean are likewise warmer than any point in the world in similar latitudes during the winter months as the result of the beneficent influence of the Japan current. Norway alone can approach it in these respects, but in Norway the mountain backbone runs parallel to the coastline, and its rivers are insignificant streams, and there is no room for extensive valleys; while in Alaska the immense quadrangle is divided into three zones by lofty mountains ... which leave between them broad plains, through which such streams as the Kuskokwin, with 600, and the Yukon, with 2,000 miles of navigable waters, open up its vast interior. Norway and Sweden are the Mecca and Medina of the European tourist in search of the picturesque and sublime, and the latter country takes its annual toll of American pilgrims on similar sights intent; but Alaska can discount anything which these countries can boast. Its mountains overtop Mont Blanc, the Jungfrau, or the Matterhorn; its glaciers dwarf the Mer de Glace....
“At the Childs Glacier you may loll at ease by the river bank on a carpet of flowers while the glacier splits with a noise like a cannon shot or the staccato reports of small arms, and watch avalanche after avalanche start 300 feet above, driving the water in mighty waves up the general slope below you as they take the final plunge and float away in the narrow river. When the mist has drifted by, the dead-white face of the ice disappears. The new dress glistens with the brilliancy of diamonds, and the deeper recesses of the façade gleam blue as a summer sky unflecked by clouds.
“The charm of the glaciers is never-ending.... The peace and silence of the rock-bound fiords, clad in green, with the snowy peaks of far-off mountains gleaming through the tree tops on the skyline, suggest the delights of Lotus land; picture after picture more beautiful than anything that the Hudson can show, or either Norway or the Rhine can boast.... There are sunsets such as no painter could ever put on canvas, veritable vortices of flame, as though the world was on fire.... Even the sun is loath to leave the scene which his warmth has endowed with life, and forsakes it for only a few minutes at midnight.
“Along the Alaskan Peninsula the tourist may witness in safety the tremendous pent-up energy of the internal fires; islands raised from the bottom of the ocean one year, only to be engulfed the next, as at Bogoslop....”
Here may be seen: “The crowning peaks of a mountain range which, dividing to the east, culminate in Mount McKinley, 20,4641 feet high, north of Cook Inlet; and Mounts St. Elias and Fairweather and their cold virginal sisters, grim guardians of the northern shores of the Pacific. These stupendous mountain masses (a mile taller than Switzerland’s champion), their feet buried under a glacier which lines the coast for more than a hundred miles, are even more impressive than the loftiest of the world’s famous peaks, either in the Himalayas or the Andes; for while these rise from lofty interior plateaus, the sweep of St. Elias is from ocean to sky, with nothing to break the foreground.... The scenic beauties of Alaska, whether they be of earth or water or of sky, are varied enough to bring enthusiasm to the lips of the most blasé traveller.”2
This reservation lies about one mile from the steamboat landing at Sitka, Alaska.
Here was located the village of a warlike tribe, the Kik-Siti Indians. A celebrated witch-tree of the natives and sixteen totem poles, several of which are examples of the best work of the tribes, stand along the beach.
In 1917 Congress set aside as a national park 2,200 square miles in this region; as in so many other cases, the reason was to protect the big game, as well as the magnificent territory.
“Mount McKinley rises 20,300 feet above tidewater and 17,000 feet above the eyes of the beholder standing on the plateau at its base. Its enormous bulk is shrouded in perpetual snow two thirds down from its summit, and the foothills and broad plains upon its north and west are populated with mountain sheep and caribou in unprecedented numbers.
“In 1915 the Government began the railroad from Seward to Fairbanks. Its course lies from Cook Inlet up the Susitna River to the headwaters of the Nenana River, where it crosses the range. This will make access to the region easy and comfortable.
“Here lies a rugged highland area far greater in extent than all of Switzerland, a virgin field for explorers and mountaineers.
“But it must be remembered that this is not Switzerland, with its hotels, railways, trained guides, and well-worn paths. It will appeal only to him who prefers to strike out for himself, who can break his own trail through trackless wilds, and will take the chances of life and limb so dear to the heart of the true explorer. He who would master unattained summits, explore unknown rivers, or traverse untrodden glaciers in a region whose scenic beauties are hardly equalled, has not to seek them in South America or Central America, for generations will pass before the possibilities of the Alaskan Range are exhausted.”3
In 1902 Congress set aside as a national park this area of 159,360 acres. The lake lies on the summit of the Cascade Range, in Oregon, some 65 miles north of the California border. There are two ways to reach the park, from Medford or Ashland on the west, and from Klamath Falls on the south.
From Medford the trip, 80 miles, is made by private automobile or by auto-stage; many interesting features are pointed out en route. The road leads through the Rogue River Valley, beside mountain torrents, and through Oregon’s majestic forests.
Going in via Klamath Falls, we leave the main line at Weed, and break the journey at Klamath, where, as at Medford, there is a comfortable hotel. From Klamath, starting in the early morning, either by private conveyance or auto-stage, the road runs through the Modoc Valley following the shore of Klamath Lake; if preferred, the first part of the trip, from end to end of the lake, some 40 miles, may be made by boat. The lake is an interesting body of water and is the home of great flocks of pelican. At the north end of the lake the automobile must be taken for the remainder of the trip. This region is full of the historic lore of the Modoc Indians.
Entering the park thus, by the south gate, and driving up beside the Anna Creek Canyon, there are very striking features to be seen; the remarkable walls of the canyon are unlike anything else, they have the appearance of lying in folds, and take the forms of spires and pinnacles of every variety.
If you are in a hired automobile, insist upon being driven slowly; if time is no object, you will probably walk while this canyon is in view.
Well within the park we become conscious of the rise in elevation, and about three miles before reaching the rim of the crater the real pull begins. The rim elevation is 6,239 feet.
Crater Lake is the only lake of its variety in the United States. As the name implies, the lake lies in the crater of an extinct volcano. It has been called: “The Sea of Silence.”
It is well that I am limited to a short space on each place mentioned in this book, for it is a great temptation to write pages of enthusiastic accounts of Crater Lake. I can conceive of nothing more interesting or more beautiful in nature. The colour is indescribable. The water lies 1,000 feet below the rim of the crater, and is 2,000 feet deep.
An excellent trail leads down to the water’s edge and the descent may be made either on horseback or on foot; the walk is absolutely easy. There are launches and rowboats on the lake, which tempt one to explore this most unusual and exquisite body of water from end to end, or side to side; the lake is about five miles in diameter. Places to be visited are Wizard Island, the Phantom Ship, and the various caves in the walls of the crater, walls which lift their towering heads from 1,456 feet to 8,156 feet into the clear, glistening, deep-blue sky.
Guests are accommodated in the park in tents, or at the hotel, which though not completed is in use. The hotel stands on the rim and the front windows command a superb view.
The trip around the rim is not to be compared with anything else that I know; it is a unique experience; it is as impossible to write of it as it is to speak of it; one could give no adequate idea of it. Go and see it for yourself.
The distant views on all sides are superb, as are the wooded valleys of the park.
Plenty of time should be allowed here; for the real nature lover, there is mountain climbing to the heart’s content, and for those who are less strong, the never-ending changes of light and shadow, with all the glory which colour can give.
Seattle is one of the largest and most energetic cities of the Northwest, most beautifully situated on Puget Sound, girded by the Cascade and Olympic Mountains.
The city is built on seven hills and is the proud possessor of one of the finest of harbours, a triple harbour one might almost say, for the great salt harbour proper is connected by canal to Lake Union and again to the great Lake Washington, some twenty miles long, thus giving an inland fresh-water harbour of great value.
Seattle’s tallest building, to the tower of which one gladly mounts for the superb views, is only surpassed by the tall buildings of New York City. Seattle maintains thirty-four picturesque parks and connects them by splendid highways. Scenically, as in many other ways, this city ranks very high.
Tacoma is an industrial seaport, beautifully situated on Puget Sound, of which it commands a fine view. Here one sees the Cascade Mountains, and has one of the finest views possible of that truly noble mountain, Rainier, that is, if the traveller has chosen the right time of the year. I have sat and waited day after day in mid-summer just to get a glimpse of any mountain, and failed, but a return trip in the spring fully repaid me.
Point Defiance Park should be visited, and the Ferry Museum, which contains an interesting collection of Indian baskets, domestic utensils, canoes, and implements of hunting and war.
This park is situated in western Washington, about 55 miles from Seattle and 42 miles from Tacoma. When the atmosphere is clear the mountain can be seen more than a hundred miles away; it has an altitude of 14,408 feet and one of the largest glacial systems in the world radiating from any single peak.
An excellent automobile highway has been built from Seattle and Tacoma to the park, and trips are made daily, in good cars. The southern part of the park is reached by rail to Ashford, on the Tacoma Eastern R. R. (Chicago, Milwaukee and St. Paul Railroad), thence via automobile stage to Longmire Springs, in the park. The northern part of the park is reached by rail to Fairfax, on the Northern Pacific Railroad, and by trails from there in; or from Enumclaw R. R. Station and from there by automobile.
By far the finest entrance is the southern or Nisqually River entrance via Longmire Springs and the great Nisqually Glacier. The fine Government road running through the park winds back and forth, beside the lovely Nisqually River, through fine forests, up the heavily wooded mountainside, past stretches of brilliant wild flowers, stopping for one superb view after another, until the great Nisqually Glacier is seen close by; here we reach the end of the old motor road; from here the trip had to be made by stage or on horseback a few years ago, the highway ending where the eternal snows began, but to-day the splendid motor road goes all the way to Paradise Valley. The traveller who has been fortunate enough to take this trip will never forget it. The climb is a steep one, 1,557 feet from Nisqually Glacier to Paradise Valley; the road is a one-way road only, all cars leaving must pass out before the entering cars are admitted.
The Narada Falls are visited on the way up the mountain, then comes Inspiration Point, where a wonderful view of the Tatoosh Range is had; the road zigzags back and forth, each view of the noble Rainier more lovely than the last, until we arrive at Paradise Valley and Paradise Inn, where we are well cared for, be our stay a day, a week, or a month. From here the mountain towers above us, 8,700 feet, looking as enormous as it did from below.
The season of tourist travel is confined largely to June, July, August, September, and the first part of October, although parties of tourists enter the park for snowshoeing and winter sports. The ideal time is early in August, when the wild flowers are at their best; I have seen the valley at this time, with a quivering cover of red, white, and blue; the exquisite deer-tooth lily, the blue lupin, and the flaming red of the Indian paint brush. I am told that there are 300 varieties of wild flowers in this park.
The summit of the mountain is accessible from Paradise Valley, and from St. Elmo Pass, on the northern side. The difficulty of the ascent depends largely upon the condition of the snow fields, which varies from year to year. It is dangerous and should not be attempted unless the party is accompanied by an official guide.
Campers are made welcome and are provided with all sorts of conveniences, from the simplest canvas tent to the fine electrically lighted and heated tents. Those who wish the full camping experience may buy groceries at the pavilion and do their own cooking over open fires. While at the same time those who wish the regular hotel comforts can have them at the inn. Guides, horses, and outfits are furnished by the Rainier National Park Company to those desiring to take long or short trail outings. In recent years the trails have been extended and new trails are opened each season; we are told that they now extend over 150 miles.
The western part of the United States is so full of wonderful mountain peaks that the desire to climb one or more is sure to be one of the results of a western trip.
There are many important rules to be observed before undertaking one of these ascents. Firstly, those who intend visiting any of the national parks should be careful to go well supplied with warm clothing, including warm sleeping apparel. Proper boots are essential; they should be made of good heavy material and have thick, strong soles. Skirts cannot be worn in real mountain climbing, either bloomers or knicker-bockers are necessary. The latter garment one sees so many of the women campers wearing that they are not at all conspicuous. It is a great convenience to have with you a shoulder strap with which to fasten on the extra jacket or sweater necessary for use on the crest; arrange to have nothing in the hands but the stout walking stick which is indispensable.
Under no consideration should any party start out to climb any of the great mountains without the aid of a registered guide. The trails may easily be lost, especially so as they lead frequently over snow fields where the footprints melting from day to day make a full and accurate knowledge absolutely essential. Again, there are important rules as to hours of starting and arriving, in order to avoid being overtaken by dark, or in case of being overtaken by one of the many sudden, blinding snowstorms; also a knowledge of how fast or how slowly one should climb, what food and drink should be taken, etc., etc., is necessary. Real mountain climbing is not in any way like an ordinary tramp, in fact, as we are told of something else: It is not by any to be entered into unadvisedly or lightly, but reverently, discreetly, advisedly, and soberly.
Where it is a possible thing, those who contemplate climbing a real mountain should spend several days in the higher altitudes of the mountain regions, climbing about the foothills and becoming accustomed to the rarefied atmosphere. Strong stimulants, tea and coffee, should not be taken, and no heavy, fried food eaten while preparing to climb.
To those who wish further information on this subject, again I suggest that they write to the Department of the Interior, or to the National Parks Association, either of which places will send full detailed information.
In the Cascade Range, in north-central Washington, lies a remarkably beautiful and, at present, little-known lake. This exquisite body of water, some 50 miles long and about one and a half miles wide, nestles in an ancient glacial cirque basin 1,075 feet above sea level, with peaks one mile high surrounding it. Little has been said of this region heretofore because of its inaccessibility, but to-day it is easily reached by the Great Northern R. R.
From Wenatchee a train trip of a little more than one hour beside the lovely Columbia River takes you to Chelan Station, and from there an auto-stage takes you the last four miles to the foot of the lake.
Hotels have been built at both the upper and lower end of the lake, where you will be taken good care of. But the thing to do here is to take one of the camping trips and see the magnificence of the surrounding country; the Field Hotel at the head of the lake arranges these trips, providing all the necessities for a very reasonable price.
Boats of all varieties are to be had on the lake; only those who cannot spare the time to see the lake in the more leisurely way should use the motor launches, for this beautiful, green, river-like lake should not be hurried over; if you are on it for sunset you will not be satisfied until you have had a glorious sunrise the same way.
I am told that the fishing, in the many streams which empty into the lake, is unusually fine.
Those who consider going to Lake Chelan should write to the Great Northern R. R. for their excellent literature on the subject, also read Walter Prichard Eaton’s “Green Trails and Upland Pastures,” from which I should like to quote several pages if space were unlimited.
“In the heart of the vast lava plains which occupy a large part of the States of Washington, Idaho, and Oregon, lies the Grand Coulee, a natural feature of grandeur and wild beauty which is well worthy of a place among the wonder sights of America, but which is practically unknown and unvisited at present....
“The Grand Coulee is a dry gorge or canyon, cut by the Columbia River, when it was diverted from its course ages ago in the glacial period....
“It extends nearly 100 miles across a part of the so-called ‘Big Bend’ region of the Columbia River....
“This enormous dry canyon, with its numerous beautiful lakes and its site of a great prehistoric waterfall, which was as high as the Victoria Falls of the Zambesi River in Africa and of much greater extent, may be visited by tourists travelling over the Northern Pacific Railway, by leaving the main line at Spokane and travelling over the branch line 125 miles to Coulee City, a small town situated on the level floor of the Upper Coulee, just at the point to get most of the interesting views of this curious region.”
Here guests can get comfortable accommodations, and from here make the various trips by automobile, carriage, horseback, or on foot. One should see, first, the site of the ancient cataract, with its 400- to 440-foot wall, which separates the Upper from the Lower Coulee. About four miles further on one comes to the brink of the western margin, and following a short distance a wonderful panorama is disclosed, hummocks and hollows, lakes and pools, some of clear and some of strongly saline water.
The basalt rock of the cliffs turns a rusty brown under the effects of the weather, and is frequently covered with orange or greenish-yellow lichens in great patches, so that the cliffs are a glorious riot of colour.
The eastern branch of the Lower Coulee is in many respects the most interesting and beautiful, because it is comparatively narrow, and a large part of it is occupied by a long lake bordered by vertical cliffs; this is called Deep Lake. A charming walk of about two miles takes one to this part.
A visit to this region is a unique experience.
The Columbia River is the great river of the Far West, it is especially interesting historically; the mere name, to those of us in the East, recalls the old cry of “54°-40´ or fight,” the slogan of the Democratic Convention of 1844, which elected James K. Polk President of the United States, when this motto was inscribed upon its banner. The story of the “Oregon Claims” makes interesting reading indeed, and history has shown us how the matter was settled without “fight.” This beautiful river means much to the Northwest to-day.
Taking the famous Columbia River Highway from Portland and going westward, the traveller finds himself shortly in Astoria, at the mouth of the Columbia River, and so on to the Pacific Ocean.
There are many trips to the beach from Portland; at Astoria the great water craft attract attention; here the river is five miles wide and there are fine fisheries. Across the river from Astoria and extending from Columbia to Willapa Harbour is a peninsula known as North Beach. This is a popular summer resort, with a superb beach, an unbroken stretch of sand 26 miles long and from 200 to 400 feet wide, according to the tides.
Any amount of exploring may be done on the coast of Oregon, which is wild, rugged, and wooded in places almost to the water’s edge.
Various trips on, or beside, the Willamette River, which flows into the Columbia 12 miles below Portland, can be made from this city.
The Columbia River trip is made by steamer daily, leaving Portland in the early morning. (Hours for departing and returning on such trips are not given, as they change from time to time, and are easily obtained in the office of any of the hotels.)
The steamers go all the way up to the Dalles, through most unusual scenery. The snow-crowned tops of the great mountains of the Cascade Range, with their glaciers and dashing mountain streams, greet the eye from time to time, while here and there magnificent cataracts lend excitement; add to this the unending mystery of the deep, dark canyons and gorges, and what more can one ask for a river trip?
The Pillars of Hercules are twin monuments of great height, one rising almost from the water’s edge and the other separated by a distance of but a few feet. Castle Rock, which, we are told, was a lookout station for the Indians, rises 1,146 feet above the river. This rock was not scaled by white men until 1901.
The waters of the Multnomah Falls have a sheer drop of 700 feet into a great rock basin. These are the finest falls on the Columbia River. The spray-filled air gives out beautiful rainbow colours.
Oneonta Gorge, a little farther up the river, is like a great garden in the spring of the year; it leads back into the hills for about a mile, and is carpeted with exquisite wild flowers and ferns.
We are told that at the Cascades, 45 miles east of Portland, a natural bridge once spanned the river, the ruins of which now lie in the river bed, obstructing the flow and impeding navigation. The story as told by Balch in his “Bridge of the Gods” is as follows: “The red men tell how Mount Hood and Mount Adams, situated on opposite sides of the river, engaged in controversy, leading to a quarrel, and they resolved to engage in combat. Advancing to a common centre, they met on the bridge. Their combined weight was too much for the structure and it crumbled beneath its load. The conflict was thus avoided, and the peaks returned to their respective places.”
A canal has been constructed through these rapids, permitting steamers to pass.
Probably few visitors to Portland fail to take this justly famous drive; certainly none should fail to take it. Here has been built a magnificent boulevard reaching from Portland to the Pacific on the west and extending to Central Oregon on the east, following the bank of the lovely Columbia River. “The Road of Falling Waters” it has been called, on account of the many magnificent waterfalls passed en route; of these “The Multnomah Falls” are the most famous. In scenic grandeur it recalls the Alps, the Rhine, and southern Italy, with all the wild bigness of the Rockies. It is a wonderful bit of engineering, in some places the road being cut through the living rock; again fine concrete bridges span gorges and narrow valleys; to the south may be seen that most picturesque of mountains, Mount Hood, and to the north, kingly Mount Rainier, Mount Adams, and Mount St. Helens. Driving eastward one passes over 60 miles of towering cliffs and sparkling waterfalls.
The highway at Crown Point is 700 feet above the river and gives the traveller a superb view; from here on it drops gradually until Bonneville is reached, where those who wish may visit the great fish hatchery; then on through the tunnel at Mitchell’s Point to the sunken forests of the Colorado, where I am told that giant trees are seen beneath the waters, finally reaching the beautiful Hood River Valley.
Portland is a city of peculiar charm; built upon rolling ground, between the Cascade Mountains and the ocean, with its two exceptionally beautiful rivers, it is provided with unusually fine scenery. The Rose Festival, held each year in June, has attracted great attention, Portland is called “The Rose City,” and it justifies its name, for verily, to see the city at this time is like finding a metropolis hidden in a fairy garden.
Back of the city, or rather to the west, rises Council Crest, which commands a splendid view of the city, the rivers, and (when it is not foggy) the surrounding country. Travellers who cannot arrange to stay in Portland may get a lasting impression of its charm by stopping over a few hours and motoring, or going by trolley, to this spot.
Council Crest is merely a pleasure park, but there is an observatory there from which may be had an excellent view of the fine snow-clad mountains of the Cascade Range. I have seen from here on a clear day, Mount Rainier, Mount St. Helens, Mount Adams, Mount Jefferson, and Mount Hood. These white monarchs stand far enough apart to be utterly unspoiled; each is entirely different in outline from the others, and the lights and shadows and cloud effects from here cannot be excelled.
Mount Hood, 11,225 feet, is reached by automobile from Portland. It is a 55 mile drive through the most lovely forested country, such cedar trees as one does not often see, wonderful firs draped in long moss, stumps of old trees long since dead, with a heavy growth of young green shoots sprouting from them such as one sees in California. The last time I was in Portland I had waited a week for a clear day to make this trip; as the clear day did not come, I made it in a drizzling mist, hoping all day that the clouds would lift just long enough to let us see the mountain, even if only the top; it did not clear all day, but still that drive stands out in my memory as one of the loveliest I ever took; the mist in the forest, a dewdrop on every cedar tip and fern frond, the waving to and fro of the glistening boughs, and the stillness and mystery of everything, made it an unforgettable occasion. There is a Government camp on the south slope and the return trip can be made in a day. For those with time to stay, “Cloud Cap Inn,” on the north side, may be better. There are a number of trips from the inn to points of interest, but the climb to the summit is the most popular. This is said to be the easiest peak in the west to climb. Guides are necessary here, as for the other mountains.
In the far southwestern corner of Oregon, on a slope of the Coast Range, there is a group of limestone caves which were set aside as a national monument, by Presidential Proclamation, under the above title.
There are two entrances to the caves, one above and one below. The stalagmites and stalactites are unusually fine. The vaults and passages are long, and there is one chamber 25 feet across, the ceiling of which is said to be 200 feet high. For the traveller in this region a trip to the caves will prove most interesting.
PART FOUR
Note—For convenience this state is here divided into four sections as follows:
Northern California
San Francisco and Environs
Central California
Southern California
Without doubt, the point of greatest interest in the extreme north of California is Mount Shasta, which rises just at the juncture of the Sierra Nevada and the Cascade Ranges, near the head of the Sacramento Valley.
Mount Shasta is a huge extinct volcano, 14,380 feet high; it is most accessible from Sissons, from whence the trip may be made by automobile (12 miles) to the summit. Taking Sissons for headquarters, there are innumerable trips to be made, on foot, horseback, or by motor. Soda Springs, Castle Lake, the McCloud River, etc. Mr. Muir says of the trip to the summit: “During the bright days of midsummer the ascent of Shasta is only a long, safe saunter without fright or nerve strain, or even serious fatigue, to those in sound health. Setting out from Sissons on horseback, accompanied by a guide leading a pack animal with provisions, blankets, and other necessaries, you follow a trail that leads up to the edge of the timber line, where you camp for the night, eight or ten miles from the hotel, at an elevation of about 10,000 feet. The next day, rising early, you may push on to the summit and return to Sissons.... The view from the top in clear weather extends to an immense distance in every direction....”
The same writer highly recommends the trip round the base of Shasta, about one hundred miles; after reading his “Steep Trails” one feels very sure that no one could know more about this Shasta country than Mr. Muir for he seems to have walked over every inch of it.
The railroad track runs close to the Soda Springs, in fact so near that one must leave the car to see the Springs. Travelling either north or south from here the views of the mountain are exceptionally beautiful, for Shasta is one of the picturesque, single-peak mountains; rising in solitary grandeur from a low, lava plain, it is thought by many to be California’s most beautiful mountain; snow-clad and supreme it stands here; it has been called the Pole-star of the landscape.
To the south of Shasta County lies a beautiful and little-known region—the Feather River Canyon, which has been opened up by the Western Pacific R. R.
We are told that the rivers and streams fairly teem with bass and trout; I give the suggestion for what it may be worth, as I know no one who has fished these waters.
The northern section of California has one great attraction: it is far less crowded than the southern sections; here real exploring may still be indulged in.
In the year 1914 Mount Lassen, after 200 years of quiet, burst forth with a series of eruptions covering a period of 19 months.
Mount Lassen has an altitude of 10,437 feet; unlike the more familiar examples of volcanic mountains, Vesuvius and Fujiyama, Lassen has not one large peak, but four distinct summits, any of which may be ascended. The view from the top is one of wonder. Seventy miles away gleams Mount Shasta; across a line of cones and craters 150 miles long sparkles the diamond crown of Mount Pitt. Westward and southward a vast ocean of ridges falls lower and lower into the Sacramento Valley.
“In 1906, in order to conserve the best examples of recent volcanism, Lassen Peak and Cinder Cone, in the same region, were set aside as national monuments, but in 1916, after the great eruptions of Mount Lassen, a reservation of 124 square miles in this region, including both peaks, was made a national park.
“It is believed by scientists that the volcano will now remain quiet; this will in all likelihood become a point of great interest to the American traveller, being the only volcano which has been in eruption in the national boundaries. Many tourists have already visited it. The park, though undeveloped as yet, has other charms, such as forests, lakes, and fine streams, but the volcano will remain the chief interest for some time to come.”1
Hot Springs Valley and the geyser country extend some 50 miles east of Mount Lassen, as far as Mountain Meadows, and in this stretch there are more than 200 geysers. This region is well named “The Devil’s Kitchen,” or, as above, “The Devil’s Half Acre.” “Boiling Lake, two miles from the geysers, is a pool of hot water 600 feet long and 300 feet wide, lying between two streams of lava and with banks 100 feet high,” from which there seems to be but one small outlet.
Going west by the Southern Pacific Railway we go so near the beautiful Lake Tahoe that those who can will do well to stop at Truckee, and taking the train of the Lake Tahoe Railway and Transportation Company, follow this lovely mountain stream, the Truckee, up to the lake (15 miles). You will be made most welcome and have every comfort at the Tahoe Tavern.
This place is mentioned on page 105 where its accessibility by automobile from Sacramento is given, the state road thus reaching the lake at its southern end and taking the visitors to Al-Tahoe, another fine hotel from which the various trips may equally well be made. Small cottages, with private baths, also open-air sleeping cabins, can be rented by the day, week, or month.
Fine automobile roads lead in the various directions and there are numerous trips to be made. Tamarack Lake makes a nice day’s jaunt, taking a picnic luncheon. Cascade Lake and Eagle Falls can be reached either by water or by automobile. Fallen Leaf Lake makes another lovely drive. Horseback trips are plentiful, and the boating is most lovely.
For the fisherman, I am told that one June day here will bring him back year after year.
Lake Tahoe lies 6,225 feet above sea level, it is 23 miles long and 13 miles wide. Its beauty cannot well be exaggerated. It is as lovely as Italy’s Lake Como, and while the mountains rise round Como to a height of 7,000 feet, these great peaks of the Sierra Nevadas have an elevation of 11,120 feet.
It is quite impossible to do justice to the Tahoe region in short space. There are scores of lakes, linked like a chain, and lying all round Tahoe.
To the aviator this section must look like a glorious breastplate: Tahoe the great central stone with the myriads of smaller lakes round it and the hundreds of glistening, winding rivers making the platinum setting, the whole lying lightly upon the breast of mother earth.
There are numbers of hotels, boarding-houses, and camps in this lake region, but do not let this make you think that it is spoiled by crowding, there are not yet as many houses as there are lakes.
Sacramento, the capital of California, is situated on the east bank of the Sacramento River. The city is finely laid out, with wide, handsome streets. The most important building, which attracts the eye before the traveller reaches the city, is the State Capitol, with a beautiful dome, which recalls that of the National Capitol. The surrounding country is interesting. From Sacramento down to the mouth of the river the banks are like one great garden. Here we get our first view of the beautifully kept olive groves, the soft gray-green of the foliage reminding one of Italy.
From here many charming trips can be made, Sacramento being one of the railway centres for the interior of California. Electric lines also run from here in almost every direction. The trip from this city to San Francisco by boat is well worth while. There is a line of steamers which makes the round trip from San Francisco several times a week.
About 30 miles south of Sacramento lies Lodi, one of the largest grape-growing centres of the state, and from here, by the Valley Spring branch of the Southern Pacific Railroad, may be reached the Calaveras Big Trees and the mining district made familiar to many through Mark Twain’s “Jumping Frog of Calaveras” and Bret Harte’s “Bellringer of Angels.” These writers both lived in the small town of Angels, Calaveras County.
The Calaveras Grove of Big Trees is the farthest north of any of the Big Tree groves, and was the first of these forests discovered. Here may be seen some of the finest specimens of this woodland monarch. There are about 100 trees ranging from 300 to 375 feet in height and from 70 to 90 feet in circumference. From here one may drive to the most important of all the groves in point of number, South, or Stanislaus, Grove, where the trees are not nearly as large, but where there are said to be more than 1,000 of them. In both of these groves, as in the well-known Mariposa Groves, one sees traces of the great damage done by fire. The trees are now carefully guarded, and it is to be hoped that fires from carelessness may never happen again. The average American citizen is becoming more and more awakened to the value of the great nature wonders and their preservation each year, and yet how recent is the tragedy of the Hetch Hetchy Valley.
At Murphys, in the Calaveras district, there is quite a remarkable cave, discovered by the miners in 1850, where there are some curious formations and stalactites.
A wonderful trip by motor from Sacramento is made via the State Road, or what is locally known as “The Wishbone Route.” The drive covers 275 miles, going from Sacramento to Donner Lake and Truckee, then 15 miles along the beautiful Truckee River to Al-Tahoe, that most enticing place mentioned on page 100. On the return trip the drive follows the lake shore for about 25 miles, coming back to the State Road and through Placerville to Sacramento.
The usual entrances to the Yosemite Valley are via Fresno and Merced. The best time to visit this park is perhaps April or May, while the falls are still full. From Merced to El Portal (the gate), the Yosemite Valley Railway runs some 70 miles along the banks of the Merced River, for which trip the right-hand side of the train is best (right as one stands facing the engine); the view is better from this side. The train crosses and recrosses this gaily-romping river, and the valley view changes continually, the walls becoming quite high in places and the river foaming rapids.
Reaching El Portal in the late afternoon, one climbs up the winding footpath through a picturesque tangle of brush to the Hotel Del Portal, where all the necessary comforts are provided. After passing the night in this delightful spot, one is taken early the next morning into the valley proper, by a road which follows the winding course of the Merced River, and from which giant granite walls reach up toward the sky on either side.
Arriving at El Capitan, the great rock 7,630 feet high which stands, as it were, at the inner gate of this Paradise, we learn that this granite mountain exhibits to view 400 acres of bare rock! Yet this is only one of many. The Yosemite Valley is 7 miles long and three quarters of a mile wide. It lies 4,060 feet above sea level and is enclosed by walls rising from 3,000 to 4,000 feet above the floor of the valley. Many are the delightful trips which may be taken here. They are all carefully organized and conducted by guides who know and love the place.
Before passing El Capitan we are attracted by the exquisite Bridal Veil Falls on the opposite side, higher than the highest fall in Switzerland. On the same side as El Capitan and beyond, we see the Three Brothers; one of these peaks is accessible by trail; from the summit (3,700 feet) there is one of the finest views of the valley. Next come the Cathedral Spires, and on the south side Sentinel Rock and Sentinel Dome. North and South Dome are most curious and especially interesting. There are trails leading to nearly all of these individual crests now.
Of all the falls, the one called, like the valley, Yosemite, is the finest. It is the highest known fall of its volume. The waters dash down one half mile. The fall is in three sections, but appears all one at a distance. In the early spring, when the volume is greatest, the booming of the waters is deafening and the force with which it strikes the ground shakes windows one mile away.
From Yosemite Point, the crest above the falls, the view is magnificent, but for the full effect of this fall one should walk to the foot and look up; the sensation received will not soon be forgotten.
The flora and fauna are enchanting. There are scores of varieties of wild flowers, shrubs, ferns, etc. To those interested in the botany of the valley, “Yosemite Flora,” issued by the Department of Botany, University of California, will be of great value.
Camping in the Yosemite is more popular than life in the hotels, the camps are provided with all the necessary comforts. Full particulars can be had by writing to the Sentinel Hotel, Camp Curry, Camp Lost Arrow, or Camp Awahnee.
Before leaving the valley the Lower Drive must surely be taken by those who have not had time to take the trip on foot. The valley is so small that the floor can be pretty thoroughly explored (as far as mere sight-seeing goes) in a single drive, and it is most pleasing to carry away with us a picture of this green spot, starred over with the lovely wild flowers; it is like an oasis in a desert. The trip up the trail on the morrow, leading over the bare, brown face of rocky cliffs, will have amid the white of the everlasting snows and the sparkling of the sunlight in the various falls, only the occasional appearing and disappearing of this emerald valley threaded by the silver stream of the Merced to give it colour. The climb to Glacier Point is made cross-saddle only, and the traveller who has gone out unprepared can rent a skirt by making known her want when she engages her horse or mule. But before starting on this trip which is to take the traveller out of the valley, I must mention the drive to the lovely Tenaya Canyon and Mirror Lake. This is usually taken in the early morning, in time to see the sunrise, and fully does it repay one; those planning to take the Glacier Point Trail usually start this way and from here pass Cathedral Rocks, Clouds’ Rest, etc., to where the horses are waiting for the start. Glacier Point is 7,297 feet above sea level, and between 3,000 and 4,000 feet above the valley. The trail winds up the east end of the valley, past the foot of the beautiful Vernal Falls, and up, up, over the top, past the splendid Nevada Falls and again over the top, zigzagging back and forth, on every turn new views greeting the sight. Liberty Cap and Mount Star King, as seen from the point on this trail known as Panorama View, 4,000 feet above the valley, are more impressive than words can tell.
At Glacier Point we find a comfortable hotel, with a veranda which makes one want to stay indefinitely, so wonderful is the view seen from it, with the valley, the falls, and ridge after ridge of the snow-clad Sierras. From here there are fine walks and many fine views to be had.
From Glacier Point the trip to Wawona is made; the drive leads through beautiful woods, via Wawona to the Mariposa Grove of Big Trees, where the stage passes through the living gateways that have been cut through several of these monsters. So much has been written and said of the Big Trees that I can add nothing. I think they are the most impressive sight, except perhaps one or two spots in the Far East, to be found in the world to-day, and while these fine old monuments of Europe are the dead ruins of a dead people, these great trees are the living monuments of a world that was old before Europe was born.
The Hetch-Hetchy Valley is now being dammed below Kolana Rock, to supply water to the city of San Francisco. Many persons will recall the efforts which were made by public-spirited citizens to prevent this, and many are still mourning the loss of this beautiful canyon as a playground, but Robert Sterling Yard tells us, for our comfort, that in prehistoric times the valley was once a great lake, and that the remains of Nature’s dam are not far from the site of the dam which man is building to-day. He adds that, with care, this restoration may not work out so inappropriately as once we feared.
To the north of the Hetch-Hetchy Valley is the Tuolumne Canyon, famous for its waterfalls, through which the Tuolumne River flows to the lovely meadows of the same name. These meadows in the springtime are like stretches of marvellous stained glass, or a freshly laid brilliant mosaic, embedded in a surface of jade, there is such a riot of colours from the wild flowers growing here. The river winding its way through the meadows descends in a torrent to the Hetch-Hetchy Valley almost 5,000 feet below.
“This park is the gateway to one of the grandest scenic areas in this or any other land.
“Of the 1,156,000 sequoias, young and old, which form these groves, 12,000 exceed 10 feet in diameter, ‘General Sherman,’ the largest known tree, being 36.5 feet in diameter and 279.9 ft. in height. Its exact age cannot be determined without counting the rings, but it is probably in excess of 3,500 years. There are many thousand trees in this park which were growing thriftily when Christ was born, hundreds which were flourishing while Babylon was in its prime, several which antedate the pyramids on the Egyptian Desert.
“Well outside the park boundaries and overlooking it from the east, the amazing craggy Sierras give birth in glacial chambers to two noble rivers, the Kings River and the Kern. The canyons of these rivers are practically matchless for the wild quality of their beauty and the majesty of their setting.
“Unlike many areas of extreme rocky character, this is not especially difficult to travel, it curiously adapts itself to trails. It is an ideal land for the camper, but one must go well equipped. There must be good guides, good horses, and plenty of warm clothing.”2
“The Sierra reaches its mightiest climax a few miles east of the present Sequoia National Park, in Mount Whitney, the highest mountain in the United States. Its altitude is 14,501 feet. The journey to Whitney’s summit is a progress of inspiration and climax.
“From Visalia automobiles carry one under the very shadow of the Big Trees. Over the park boundaries, into the magic of the mountains; up to the headwaters of the Kaweah; across the splendours of the great Western Divide; into the Kern Valley, then up winding passes, skirting precipices, edging glaciers to the top.”3
Mount Whitney lies some 90 miles south of the Yosemite Valley. It is in this region that Congress is considering setting apart another large area, 1,600 square miles, to be known as “Roosevelt National Park,” which will embrace both the General Grant and the Sequoia National Park.
The General Grant Park is only 4 square miles in area. It was created to protect what is believed to be the second largest tree in the world, “General Grant,” with a diameter of 35 feet and a height of 264 feet.
Were it not for a narrow strip of land which is privately owned, and which separates this park from the Sequoia National Park, they would be one.
The section of California lying east and south of the above chain of parks, the Yosemite, the General Grant, and the Sequoia, were it in any other state than California, so full of scenic attractions, would be the show place of the entire region, but so far, to the average American traveller, it is almost unknown. This great Valley, so rich in beautiful rivers, lakes, and canyons, is the proposed site of the Roosevelt National Park.
In shape it is a long oval, lying north and south, bounded on the east by the Sierras, with such great peaks as Mount Humphreys, 13,972 feet; Mount Darwin, 13,841 feet; Mount Winchell, 13,749 feet; Split Mountain, 14,051 feet; Striped Mountain, 13,160 feet; Mount Buxton, 13,118 feet; Junction Peak, 13,902 feet; Mount Tyndall, 14,025 feet; Mount Whitney, 14,501 feet; and Mount Langley, 14,042 feet. It is difficult to picture such a wall, nine great mountains all connected by jagged peaks of almost equal height. In this valley are rivers of inconceivable beauty, such as the Kings River, the Kern River, and the Kaweah, each of which has carved superb canyons and, forming lesser rivers with their forks, has again carved lesser canyons with them.
The Kings River, rising in the Sierras and flowing southward, crosses the valley from east to west almost at its centre, sending tributaries in all directions. The Kings River Canyon was called by Mr. Muir a second Yosemite; one should have that great naturalist’s gift of expression to describe this region. The walls of the Kings River Canyon are not as precipitous as those of the Yosemite and there are not the great falls, but the floor of the canyon is wider and it is more extensive, and the mountains are higher.
The Kings River has many branches, such as the Roaring River, Arrow Creek, Woods Creek, Bubbs Creek, Boulder Creek, etc., etc., streams to gladden the heart of any fisherman, and bordered by such meadows as only mountain streams can produce.
The main river consists of three forks and it is hard to say which is the most lovely. The canyon of the middle fork, “The Tehipite,” is not as easily reached as is the south, but, judging by what Mr. Yard says of it, it is worth going through a good deal to see it. This enthusiastic nature lover, author of “The Book of National Parks,” says: “Time will not dim my memory of Tehipite Dome, the august valley and the leaping, singing river which it overlooks. Well short of the Yosemite in the kind of beauty that plunges the observer into silence, the Tehipite Valley far excels it in bigness, power, and majesty.
“Lookout Point on the north rim, a couple of miles south of the Dome, gave us our first sensation. Three thousand feet above the river, it offered by far the grandest valley view I have looked upon, for the rim view into Yosemite by comparison is not so grand, as it is beautiful.”
The Tehipite Dome, the same writer tells us, compares favourably with El Capitan in height and prominence, and it occupies a similar position at the valley’s western gate.
To the south fork of the Kings River the traveller is taken to Sanger by the Southern Pacific Railroad, and from there automobiles run daily.
An electric line runs from Visalia to Lemon Cove and there again one is met by automobiles and driven to Juanita Meadows, where camping accommodations have been arranged and from whence innumerable trails may be taken. If you have gone via Hume and stopped in the camp overnight, you may leave by pack train early the next morning and make the trip eastward, beside the river, to Horse Corral, where you camp again, and the third day, from Lookout Point, the descent is made to the canyon. Passing down a three-mile zigzag trail you make a drop of more than three thousand feet, while one beautiful view after another opens out before you. At Cedar Creek the floor is reached and the river crossed, then comes the six-mile ride up the canyon to Camp Kaweah, a most beautiful trip. At this camp you may stop a day, a week, or indefinitely. There are numberless lovely spots to be visited, the rivers come tumbling down the gorges in cascades, or in filmy, lace-like falls, and five or six miles farther on lies the picturesque Paradise Valley. The trail to Bubbs Creek is one of the finest, leading eastward and giving the view of the great Sierras. A chain of glacial lakes lies below the trail and back of them the Kearsarge Pinnacles, University Peak, etc. Look at your map of California and see what a marvellous region this is. It may be reached in various ways, either by the “John Muir Trail” from the north, or across the Kearsarge Pass, down to Independence and Lone Pine; or again by going back to Horse Corral, camping there and leaving the next day for Alta Meadows, across to Mineral King, over Franklin Pass, and so down into the Kern Canyon.
The Kearsarge Pass is one of the highest of all the Sierra passes, 12,056 feet. It is literally on the sharp edge of the mountain range, so narrow that we are told the horse strides it, standing on both sides of the range at once; here may be seen the contrasting sides of this wonderful range, the long, green slope of the west, and the steep, bare, rocky descent of the east.
This great region (Roosevelt Park as we hope it is to be), 1,600 square miles, will include both the General Grant and the Sequoia National Parks; a trail leads from here to the Yosemite, California’s memorial to Mr. Muir; nothing could have been more appropriate, as the trail was the one way by which Mr. Muir felt a man could know this part of the world, either afoot, or on horse or mule back. The southwestern area is beautified by the Kaweah River and its five forks, and rising between the Kaweah and the Kern rivers is the Western Divide. The Kern Valley is said by some to exceed the Kings River Valley in beauty.
The southern portion of the whole great interior basin of California is commonly known as the San Joaquin Valley. It comprises the San Joaquin, the Tulare, and the Kern valleys. Its greatest length is 260 miles and its width from 30 to 40 miles.
The Coast Range on the west of the valley has an average height of 1,700 feet, and the base averages 65 miles in width. The Sierra Nevada Range on the east rises, as we have seen, to a much greater height. Between these two ranges lies as well as the San Joaquin, the Sacramento Valley. The ranges are connected in the southern part of the state at Tehachipi, and in the northern at Mount Shasta. The length of the combined valleys is about 450 miles and the width is 55 miles. The Coast Range is composed of a multitude of ridges, and is intersected by numerous long, narrow, fertile valleys, Los Angeles, Salinas, Santa Clara, Sonoma, etc., etc.
One must understand a little of the topography of San Francisco to appreciate its unusual advantages. The city is built upon a peninsula, which juts northward from the mainland, bounded on the south by San Mateo, on the east by the San Francisco Bay, and on the west by the Pacific Ocean.
Sausalito is situated upon a peninsula jutting southward from the mainland to the north, and bounded on the east and west as San Francisco is. The opening between these two points, one mile wide, is the Golden Gate, the world-famous entrance to the beautiful San Francisco Bay. Those entering by steamer get the best view of this great gateway. The bay is 50 miles long and five to ten miles wide, and provides San Francisco with one of the finest harbours in the world.
The bay is magnificently fortified. Points Lobos and Bonita are the two points reaching out into the Pacific Ocean, the former at the outer point of the crescent, which forms Bonita Cove to the north, and the latter at the outer point of the crescent, which forms South Bay to the south. These peninsulas extend like great arms into the Pacific Ocean, forming the outer bay. At the inner ends are Point Diablo and Fort Point, both fortified and impressive looking. Those who are unable to see the bay from the water should not fail to take the Presidio Drive, the drive to the U. S. Military Reservation, where the most wonderful view may be had far out over the ocean.
The islands which lie in San Francisco Bay and are the most noticeable from this city are known as Alcatras, Angel, and Yerba Buena Islands. They are the property of the United States Government.
On Alcatras is the U. S. Military Prison. A permit is necessary to visit the island; permission may also be had to visit Angel Island, where there is a recruiting station, Fort McDowell. On Yerba Buena, known as Goat Island, there is a Government Naval Training School.
The U. S. Military Reservation, known as The Presidio, comprises 1,500 acres, and lies along the bay for four or five miles. This stretch is strongly fortified. Here may be seen Fort Winfield Scott, Fort McDowell, Fort Baker, Fort Miley, and Fort Barry.
The Golden Gate Park, of more than 1,000 acres, may be reached by almost any of the trolley lines; laid out on sand hills and reclaimed ground, with one end fronting on the Pacific Ocean, it is beautifully planted with many unusual trees and plants, shrubs and flowers, and has some 20 miles of the finest driveways. Points of special interest are many: The Japanese Tea Garden, which really looks like a bit of old Japan. Here two dainty little Japanese ladies serve tea. Admission to the garden is free, but of course one pays a small sum for the tea and rice cakes. A military band plays in the park on Sundays and holiday afternoons. There are some good statues in the grounds: “The Wine Press” by Thomas S. Clarke, near the front of the museum, is unusually fine. In the Memorial Museum there is an especially good collection of Japanese ivories, Indian basketry, and ceramics. The Academy of Sciences Museum has very fine groups of animals and birds of the Pacific Coast. The Fern Glen must not be overlooked; here may be seen, growing in the open, lovely specimens of the tree fern.
On a small hill near Stone Lake stands Prayer-book Cross, erected by Mr. George William Childs, of Philadelphia, in commemoration of the first English church service held on this continent in 1579.
Ocean Beach is a favourite resort, sea bathing goes on here the year round, but by strong and expert swimmers only, the currents being dangerous. From the beach or the terrace in front of the Cliff House the famous Seal Rocks are easily seen. Here one is at times fortunate enough to he able to watch the antics of scores of sea lions.
A little north of this are the Sutro Baths and Sutro Gardens. The picturesque Dutch windmills in the Golden Gate Park were presented by a private citizen; they furnish water for the lakes etc., in the park. There are several very pretty artificial lakes.
Of animals, there are about what the usual park has, buffalo, deer, elk, etc.
The great Exposition which in 1915 celebrated the opening of the Panama Canal and which has now become a part of the history of San Francisco, was held upon the site now known as the Marina. This site comprised a tract of approximately 625 acres, with almost three miles of waterfront. So much has been written of the beauty of the buildings, the grounds, the statuary, etc., that it need not be repeated here; those who saw it will not forget it and those who were less fortunate will never know just what they missed. Through the efforts of the San Francisco Arts Association the Fine Arts building has been saved for a time; the state of California has taken over the California building for a normal school. The Exposition Preservation League has plans for a fine boulevard which is to extend from Fort Mason to the Presidio, connecting with the present boulevard in the Presidio.
From San Francisco the trip to Mount Tamalpais must be made, crossing the bay to Sausalito and from there taking the electric car to Mill Valley, where one passes some charming homes. From here the ascent is made (about eight miles) by what we are told is the “crookedest” railroad in the world. Superb views are had during this climb, one moment looking out across the blue waters of the bay, and the next piercing the black depths of the forest, only to turn again to the sparkling sunshine in another moment. The view from the summit fully repays one for the trip, the Pacific Ocean stretching as far as the eye can reach on the one side, with the ships coming and going, and the San Francisco Bay, with its fascinating shore lines, on the other side.
From a station part way up Mount Tamalpais a branch line runs to Muir Woods, one of the most beautiful bits of redwood forest to be seen anywhere. I cannot worthily describe it, one must see it. Possibly the greatest charm of the place lies in the fact that these trees rise tall and erect above what to us in the East would be in itself a fine forest of oak, beech, maple, etc., the rich, variegated foliage of the deciduous trees making a most charming contrast to the deep, dark green of the redwood. The trees grow in circular clusters, which are explained by the theory that the present trees are all off-shoots from giant trees which had stood there at some time past. What giants they must have been! These circles are from 30 to 60 feet in diameter, the trees themselves are about 10 feet in diameter.
An exquisite stream flows through the woods and there is a fine driveway, but to enjoy it to the full one should walk through. It is said that the redwood does not thrive where the salt fog does not reach it; here the soft, misty veil, which floats over and filters into the woods from time to time, is another of its charms.
It is to Mr. William Kent, one of California’s most worthy citizens, that we owe this National Monument. He bought it, paying $80,000 for it, that it might not be destroyed, and presented it to the United States; having discovered an old law enabling the United States to accept gifts of “American Antiquities,” this collection was presented and accepted as such. The wish of the people was to call the woods, Kent Woods, but the modest donor insisted that it be named for Mr. John Muir, and so it is that it appears upon the map to-day as Muir Woods.
Another delightful short trip from San Francisco is to cross the bay to Belvedere. This little mountain of a peninsula rises up out of the water in the most picturesque way, and is one of the loveliest spots anywhere in this region. Beautiful homes, built up and down the sides of the hills, each with a garden more alluring than the last, makes the whole seem a veritable Eden. The planting goes down to the water’s edge—a riot of colour, making the whole seem one great garden, entwined about and laced together by the exquisite green tendrils of the soft mosses. Here are trees of all sorts, and it seemed to me birds of all sorts. A merry, happy, singing little spot.
Mount Diablo is the peak which can be seen in the distance due east from San Francisco; it rises 3,850 feet above sea level. A good automobile road leads to the summit, and makes a favourite week-end drive. The view from the summit is particularly fine, because it is so extensive. On a clear day a nickel-plated monument is visible, through a telescope, on the summit of Mount Shasta, 193 miles to the north, while to the south one sees as far as Mount Whitney, over the great Sacramento and San Joaquin valleys.
Sonoma, some 40 miles north of San Francisco, reached by ferry and railway, is interesting as being one of the chief centres of the famous vine-growing district. In this region is Santa Rosa, the home of Luther Burbank, where he has large experimental gardens. Extensive work is also done on his farm eight miles west of Santa Rosa, near Sebastopol, called the Gold Ridge Proving Grounds. The farm is, I believe, open to visitors. While at Santa Rosa it is interesting to see the church which is built of the wood of one redwood tree.
Oakland, five miles from San Francisco, is reached by ferry, and from there we go to Berkeley, the seat of the University of California. There are several entrances to the university grounds, and visitors are admitted by any of them. The university is delightfully situated on the lower slopes of the Berkeley Hills. The site comprises about 530 acres of land, which rises gradually from 200 feet above sea level to 1,300 feet. The university is well endowed, tuition is free to residents of California. There is to be in time a very fine collection of buildings, many of which have already been put up. The chief sight-seeing features of the university are the Greek Theatre, which seats 10,000 people, and the Campanile. There are in these grounds wonderful old oaks said to be thousands of years old; extremes in the tree family meet when one compares these bent, gnarled gray oaks with the tall, straight dignity of the eucalyptus trees growing round the theatre. There are several statues in the grounds, but one in bronze, by Douglas Tilden, who is deaf and dumb, which is known as the Football Player, is especially virile.
A fine automobile road leads from San Francisco through San Mateo and Palo Alto, to the Leland Stanford University, California’s other great centre of learning, which, it is well known, was built by Mr. and Mrs. Leland Stanford as a memorial to their only child.
The driveway, of about one mile from the entrance to the main buildings, is charmingly planted with palms; the grounds are beautifully kept, and the cactus garden is most interesting. The group of buildings is probably as fine as any in this country. The architecture is an adaptation of the old Spanish Mission architecture, with long colonnades, graceful arches, and picturesque red tile roofing. The inner quadrangle consists of twelve one-story buildings and the Memorial Church, connected by a continuous open arcade. The decorations of the church are very ornate; they were terribly damaged by the earthquake in 1906, but are now entirely restored.
Journeying southward from here we come to Santa Clara, where there is an old mission. From there to San José (Ho-sai) one gets interesting glimpses of the famous prune-growing district in the lovely, fertile Santa Clara Valley where they claim to have the largest fruit-packing house in the world. San José, a little farther south, is one of the old historic towns; from here there are a number of trips to be made, the most important being to Mount Hamilton, to see the Lick Observatory; stages leave San José daily, the trip is very lovely and full of interest. For those who can spare the time, Saturday is the day to go up, as that night visitors are allowed to use the telescope. There is a little inn not far from the observatory where the traveller is taken care of. This observatory was built and endowed by a Californian, James Lick, whose body is buried under the great telescope. The observatory now belongs to the University of California, and possesses the second most powerful refracting telescope in existence.
Santa Cruz is delightfully situated at the north end of the Monterey Bay. All of these places can be reached nowadays by automobile as well as by the Southern Pacific Coast Line; there are many companies that run excursions down the coast, using large, comfortable cars and arranging for a certain amount of small baggage; at any of the hotels this information is given. Of course the automobile is the ideal mode of travel these days, but it is especially so in the West, where there is something to see on all sides, and up and down the coast, from Vancouver to San Diego.
Going to the California State Redwood Park, we leave the main line at Felton and take a branch road to Boulder Creek, where the stage line starts; this is a reservation of 7,000 acres, and as beautiful a bit of woodland as one could ask to see, covered with trees larger than those of the Muir Woods. Here, as elsewhere, camps are provided, and the traveller is made most comfortable for a day, a week, or a month, as he chooses.
Monterey is situated at the extreme south of this lovely Monterey Bay; this is one of the most interesting spots in the state historically, and is full of old landmarks. It was the capital of California until 1849. Perhaps the most interesting of the old buildings is the Spanish Customs House. The first opera house of the state is pointed out, and we are told that Jenny Lind sang there. The house in which Robert Louis Stevenson lived is pointed out, etc., etc.
“Forty miles east of Monterey, in a spur of the low Coast Range, is a region which erosion has carved into many fantastic shapes. Because of its crowded, pointed rocks, it has been set apart as a national monument, under the above title, though it has long been known as Vancouver’s Pinnacles because the great explorer visited it while his ships lay at anchor in Monterey Bay, and afterward described it in his ‘Voyages and Discoveries.’
“Two deep gorges, bordered by fantastic walls 600 to 1,000 feet high, and a broad semi-circular, flower-grown amphitheatre, constitute the central feature.”4
The best approach is from Gilroy, which lies between San José and Monterey.
The Hotel Del Monte, at Del Monte, is one of the most famous on the Pacific Coast; the hotel and its gardens are among the show places of this region. This is perhaps the best known point from which to take the famous 17-mile drive, a drive which though still called by the old name has been extended to many times that length, and is a very beautiful beach drive, one not to be missed by those who are in this region.
At Pacific Grove there are lovely beaches, and here, as at Santa Catalina Island, the glass-bottomed boats are enjoyed, from which we seem to peep into Fairyland; as we gaze down through the clear salt water those charming lines of Percival’s come to us:
Deep in the wave is a coral grove,
Where the purple mullet and goldfish rove,
Where the sea-flower spreads its leaves of blue,
That never are wet with falling dew,
But in bright and changeful beauty shine
Far down in the green and glassy brine.
At Carmel-by-the-Sea an artists’ settlement, just a short drive from Monterey, there is an unusually beautiful beach, the sand is of dazzling whiteness; here there are two hotels, and those who like a quiet, restful place will revel in this spot. The old mission here is of exceptional interest, being the burial place of Padre Junipero Serra, the first of the Franciscan Monks who entered California, and established the first of their missions for the Indians in 1769.
Continuing southward we come to Paso Robles Hot Springs, which rank among the best of the many well-known hot sulphur springs. These baths are wonderful, curatively as well as architecturally. The Indians are said to have brought their sick here from all the surrounding country. Splendid cures from the mud baths at this place have been reported. The swimming pool is an unusually fine one. This is a great place for rest, fine air, lovely walks and drives. Through the park one might wander indefinitely; the place takes its name from the old oaks Paso Robles, or Pass of the Oaks.
Again farther south, the stop must be made at San Luis Obispo, where there is another old mission.
Travelling south, by either train or automobile, when one runs into the lovely Santa Barbara country, there is a feeling of satisfaction. The coast faces due south and the mountains rising back of the valley protect it from the cold winds. For more than a hundred miles the sea is in full view.
Before reaching Santa Barbara the Santa Ynez Mountains are crossed; from the crest of this range there is a fine view of the four islands which bound the Santa Barbara Channel. The roads are of the best, the air is like champagne, the sun is sure to be bright, and altogether this is a most satisfying drive.
Ventura is the town for the Mission San Buenaventura, very picturesque and in pretty good preservation. At Carpinteria we are shown what we are told is the largest grapevine in the world, not as old as the famous vine at Hampton Court, England, but much larger. Here also, in a beautiful spot near the beach, the home of the author, Stewart Edward White, is pointed out.
Santa Barbara, that lovely place called by many the Mentone of our country, is particularly happily situated. Nestled at the foot of the Santa Ynez Mountains, it is entirely protected by them from the north and west winds, and here the blue waters of the Pacific Ocean, the lovely coast and wonderful sunshine, flowers, and ocean bathing may be enjoyed just as on the Riviera these joys of the Mediterranean are to be found. This is one of the most charming resorts in all this resort-filled state. At Santa Barbara there is another very fine old mission. There are numerous trips to be made in this region. The beautiful Cliff Drive; the San Marco Pass; the Santa Ynez Valley, etc., etc. The sea trips to the islands should also be made. Santa Cruz and Santa Rosa are most interesting, and here may be found fine specimens of the Abalone shells.
Beverly Hills is a delightful suburb, where there is a fine modern hotel, Beverly Hills Hotel, and where every comfort may be had. This place stands up in such a way that one seems to get more than the ordinary share of bracing salt air; the Pacific Electric Line runs between here and Los Angeles. A little farther on, by the same line, Santa Monica is reached; this is a popular resort, with various places of amusement, built on a bluff overlooking the ocean from which there is a view of the long, white, sandy beach, which leads on to Ocean Park, a popular resort on the order of Atlantic City, N. J.
San Pedro, the fine Los Angeles port, some 20 miles from the centre of the city and reached by the Pacific Electric, or any one of the various railroads of that region, is the starting place for Santa Catalina Island. Comfortable steamers make the trip in about two hours. It may be as smooth a crossing as any one could desire, but again I have seen it very rough. It is a beautiful sail almost due south; one is strongly reminded of the Mediterranean Sea here, with the deep blue of the water and the mountainous island rising right from the sea. The first view of Santa Catalina rejoices the soul, especially if one chances to approach it through one of the soft white mists which at times hang over these waters. This was the case on the day of my first trip there—the mist lifting and rolling away, while we were still some miles off—the full splendour of the noonday sun bringing out the island as we stood in the bow of the approaching ship. “Santa Catalina is in reality a range of mountains 23 miles long and sufficiently rugged in its upper reaches to win the devotion of the most venturesome. The highest peak, Orizaba, has an elevation of 2,700 feet. For genuine excitement the visitor will choose a trip to the crags to hunt the wild goats. Horses, guides, rifles, and other necessaries are obtainable on the island.”5
This is a spot which would satisfy any one, from the hunter out for adventure, to the frailest invalid, with a desire only for a warm, sunny, peaceful spot in which to rest and grow strong.
The land slopes gently down to the water’s edge. The landward side of the island, being shaped like a great crescent, presents to the gaze of the approaching visitor a lovely green amphitheatre in the centre of which stands the Hotel Metropole (there are countless hotels, boarding-houses, and camps), to the left the Open Air Theatre, where the band plays each evening. There is an incline road, which takes to the top of the mountain those who do not care to climb. Trails lead off on every side. The Aquarium, though only a small beginning, has some rare specimens. The glass-bottomed boats are a never-ending source of delight, the small ones can be rented for very little, and one sits spellbound, gazing down into the marine gardens, watching the exquisitely coloured fish as they pass silently to and fro, brilliant blue in the sunshine, dark in the shadow, while the glint of the goldfish now here, now there, never ceases.
“And life, in rare and beautiful forms,
Is sporting amid those bowers of stone,
And is safe, where the wrathful spirit of storms
Has made the top of the wave his own.”6
The seaweed is so heavy in places that it suggests a forest under water, trees with leaves of every shape, bearing various fruits and berries. In the evening the favourite thing seems to be the small steamer, which puts out with a searchlight, to attract the flying fish; they respond very readily, rising and following the path of light, looking like fairy forms with their transparent silver wings.
Los Angeles, the metropolis of southern California, lies about 15 miles inland. It is a fine, prosperous city, of almost unprecedentedly rapid growth.
Los Angeles County is one of the great fruit-growing centres, the valleys being fairly covered with vineyards; orange, lemon, and olive groves also abound here.
The residences, in and about the city, are famous for their beautiful gardens. The parks are fine and well kept, and the public play grounds are the most fascinating I have ever seen. There is an interesting ostrich farm, opposite Eastlake Park, where these birds of all ages may be seen. There are trips to be made on all sides, but here, as elsewhere, the hotels provide all sorts of circulars, telling in detail of the surrounding country. In California one can hardly take the wrong turn, for there is something worth seeing in every direction.
Pasadena, about ten miles northeast of Los Angeles, lies in the lovely, fertile valley of San Gabriel, where thousands of tourists come annually to the Floral Parade and Rose Tournament. More beautiful homes can be seen here than in any other one place in California. The city is charmingly planted. Its avenues, the finest of which is Marengo Avenue, with its exquisite pepper trees on either side, presents a picture hard to equal. Many of the sunken gardens belonging to private residences we were allowed to visit; we found them all they had ever been said to be.
To the north of Pasadena is Mount Lowe. This trip is made from Los Angeles by electric, and takes about two hours. The car stops at Pasadena for passengers from there, then very soon begins to run upgrade and into the Rubio Canyon, where we leave the electric and take a cable car up to Echo Mountain, 3,500 feet above sea level, where a really superb view lies spread before us on all sides. From Echo a car runs to Alpine Tavern, quite an exciting bit of the trip, following in places the very edge of the precipice. The tavern, they tell us, is 5,000 feet above sea level; from here there are several delightful trails, all ending in superb views, extending many miles in every direction.
Mount Wilson is a little to the southeast of Mount Lowe, and makes another interesting excursion. Like Mount Lowe, it is reached by electric, which takes one almost to the top. The last bit can be made on foot. Here again are fine views, and on the summit we find the Carnegie Solar Observatory, with the largest solar reflecting telescopes in the world. Those wishing to remain overnight can do so; there is a small hotel.
About two hours out of Los Angeles, situated in the centre of one of the most famous orange-growing regions, is the city of Riverside, one of the most attractive of the many charming places which surround Los Angeles.
The Mission Inn is worth going a long way to see, it is an exceptionally fine bit of the always-pleasing Spanish-Mission architecture; the central court, or patio, has unusual charm, with its very beautiful planting; there is a famous old orange tree here.
The city is built in the Santa Ana Valley, from which the hills roll up on all sides. By driving or walking to the summit of one of these hills an extensive view of the valley may be had. On one of the drives we come upon a tablet set into a boulder, upon which may be read the following words written by that dear nature lover whom all the West loves to quote:
“Climb the mountains and get their good tidings. Nature’s peace will flow into you as sunshine flows into the trees. The winds will blow their own freshness into you and the storms their energy, while cares will drop off like autumn leaves.”
San Diego is the most southern port on the west coast of the United States, it was one of the earliest settlements on this coast.
The city has a very good harbour, which is as interesting to the tourist as it is commercially, for there are many good trips to be made by water here; the kelp beds are especially interesting.
The climate of San Diego is famous; it is said to be equally delightful the year round, and much is being done to make the city attractive. Six thousand acres have been set aside as parkland; the finest is Balboa Park, where the beautiful buildings erected for the Panama-California Exposition, 1915, still stand.
Coronado Beach, with its great Hotel Del Coronado, is one of the most famous of year-round resorts. The beach, some 15 miles long, lies on the peninsula which forms the outer arm of the San Diego Bay, and is a very beautiful stretch. The hotel, like the Del Monte at Monterey, is set in a tropical garden; the flower beds, great sheets of colour, are an endless delight to the Easterner; here may be enjoyed every luxury of modern life with all the ease and freedom of the tropics.
In the old town one may see the Estudillo House, made famous by Helen Hunt Jackson as the place where Ramona was married. This is a very picturesque spot, the courtyard especially so, and in the garden the old oven still stands.
Point Loma, a small peninsula which juts into the ocean at the most northern point of San Diego Bay, should be visited; fine views can be had from the point, and interesting caves, on the ocean side, are visited en route. “The Theosophical Institute of Universal Brotherhood” is on this peninsula. Here, under the leadership of Katharine Tingley, this society has established itself and its model school. The colony is open to tourists. The architecture is unusual.
The Great American Desert was almost better known a generation ago than it is to-day. Then the hardy Argonauts traversed that fearful waste on foot with their dawdling ox trains, and hundreds of them left their bones to bleach in that thirsty land. The survivors of these deadly journeys had a very definite idea of what that desert was, but now that we can cross it in a day in Pullman cars, its real and still-existing horrors are largely forgotten.
“The first scientific exploration of this deadly area was Lieutenant Wheeler’s United States survey in the early fifties; and he was the first to give scientific assurance that we have here a desert as absolute as the Sahara. It is full of strange, burnt, ragged mountain ranges, with deceptive, sloping, broad valleys between. There are countless extinct volcanoes upon it and hundreds of square miles of black, bristling lava flows. The summer heat is inconceivable, often reaching 136 degrees in the shade; even in winter the mid-day heat is sometimes insufferable, while at night ice frequently forms on the water tanks.
“There are oases in the desert, chief of which are the narrow valleys of the Mojave River and the lower Colorado. It is a strange thing to see these soft green ribbons athwart the molten landscape.
“The Arabian simoon is not deadlier than the sandstorm of the Colorado Desert (as the lower half is generally called). Man or beast caught in one of these sand-laden tempests has little chance of escape.
“In the southern portions of the desert are many strange freaks of vegetable life—huge cacti 60 feet tall and as large around as a barrel, with singular arms, which make them look like giant candelabra; smaller but equally fantastic varieties of cactus, from the tall, lithe Ocalilla, or whipstock cactus, down to the tiny knob smaller than a china cup. There are countless more modest flowers, too, and in the rainy season thousands of square miles are carpeted with a floral carpet, which makes it hard for the traveller to believe that he is really gazing upon a desert.
“This American Sahara is more than 1,500 miles long from north to south and nearly half as wide. The most fatally famous part is Death Valley, in California.”7
The Colorado Desert is best known to many of us through George Wharton James’ fascinating book called: “The Wonders of the Colorado Desert”; according to this writer there is here a wealth of pleasure awaiting those who care to enter into the silent places of nature.
Probably the most attractive, as well as the most convenient, points from which to make the trip into the real desert are Riverside and Redlands, passing through Nature’s magnificent gateway, which lies between the San Jacinto and San Bernardino Ranges. The most satisfactory way to make this trip is on horseback, with camping outfit. Such trips are not for those who are dependent upon modern hotel comforts.
Mr. James says: “In the desert the soul of man finds itself as nowhere else on earth. On every hand are strange, wonderful, beautiful things. No hall of necromancers can equal the desert in its marvels and revelations. Wonder follows wonder in quick succession, etc.”
The Encyclopedia Britannica says:
“The Jesuit Missionaries entered California in 1697 and established their first mission at Loreto, continuing to spread these missions until 1767, when they were expelled from the country by order of Charles III of Spain and all their property was turned over to the Franciscan Monks, who later moved north to upper California.... Mexico’s becoming independent of Spain in 1822 was the death-blow to the establishment of the Franciscans, which finally broke up in 1840 after they had founded twenty-one missions.”
Many of these old buildings have been restored and are in a fine state of preservation to-day; they have had a distinct effect upon the architecture of California. The picturesque Spanish lines are particularly suitable to this climate, where the open courts and the beautiful arcades have a perpetual background of blue sky, with the clear, sparkling atmosphere of California. It is impossible in a very limited space to give a description of each mission, and there are various books to be had on the subject—“In and Out of the Old Missions of California,” by George Wharton James; “The Missions of California and the Old Southwest,” by Jesse S. Hildrup, etc. A delightful trip is made by motor, visiting each in turn; they are, mentioning them in order from the most southern up, as they follow the coastline, San Diego, San Luis Rey, San Juan Capistrano, San Gabriel, Los Angeles, San Buenaventura, Santa Barbara, Santa Ynez, La Purisima Concepcion, San Luis Obispo, San Miguel, San Antonio, Mission Soledad, San Carlos, San Juan Bautista, Santa Cruz, Santa Clara, San José, Mission Dolores, San Rafael Archangel, Mission San Francisco Solano.
These missions were built a day’s walk apart in order that the travellers on foot could always find shelter at the end of a day’s tramp. In Los Angeles there is given each year a mission play commemorating this period in the history of California. An ambulatory surrounding the playhouse shows models of all the missions in their order; a visit to this place and witnessing a performance of the play will do much toward impressing upon the tourist the early settlement of this part of the west coast.
PART FIVE
I’ve stood in some mighty-mouthed hollow
That’s plum-full of hush to the brim;
I’ve watched the big, husky sun wallow
In crimson and gold, and grow dim,
Till the moon set the pearly peaks gleaming,
And the stars tumbled out, neck and crop;
And I’ve thought that I surely was dreaming,
With the peace o’ the world piled on top.
—SERVICE
The Grand Canyon of the Colorado is the world’s most famous gorge, in which Mr. Lummis says: “All the world’s famous gorges could be lost forever.”
Charles Dudley Warner said of this spot: “Human experience has no prototype of this region, and the imagination has never conceived of its forms and colours.... The scene is one to strike dumb with awe, or to unstring the nerves.... All that we could comprehend was a vast confusion of amphitheatres and strange architectural forms resplendent with colour.... Streaks of solid hues 1,000 feet in width, yellows mingled with white and gray, orange, dull red, brown, blue, carmine, and green all blending in the sunlight into one transcendent effusion of splendour.”
Here is truly one of the most marvellous nature wonders of the world, and comparatively few of us have seen it. It is stupendous! It is incomprehensible!
The canyon lies chiefly in Arizona, though Utah, Nevada, and California touch each a corner. It is nearly 300 miles long and in places 6,600 feet deep; the width at the top is from 8 to 20 miles. The river lying below is in places 300 feet wide, and is 2,400 feet above sea level; yet looking down from the rim it seems the smallest stream, the merest thread.
The Santa Fé trains run twice a day to the canyon.1 There is a fine, big hotel, the El Tovar, with every modern comfort, built on a site 7,000 feet above sea level and quite near the rim, commanding such a view as can hardly be equalled in the world.
Mr. C. A. Higgins in his “The Titan of Chasms,” says: “Stolid indeed is he who can front the awful scene and view its unearthly splendour of colour and form without quaking knee or tremulous breath. An inferno swathed in soft, celestial fires; a whole chaotic under-world, just emptied of primeval floods and waiting for a new creative word; eluding all sense of perspective or dimension, outstretching the faculty of measurement, overlapping the confines of definite apprehension; a boding, terrible thing, unflinchingly real, yet spectral as a dream.... A labyrinth of huge architectural forms, endlessly varied in design, fretted with ornamental devices, festooned with lace-like webs formed of talus from the upper cliffs and painted with every colour known to the palette in pure, transparent tones of marvellous delicacy.
“A canyon, truly, but not after the accepted type. An intricate system of canyons, rather.... Only by descending into the canyon may one arrive at anything like comprehension of its proportions, and the descent cannot be too urgently recommended to every visitor who is sufficiently robust to bear a reasonable amount of fatigue.”
There are several paths down the southern wall of the canyon, and the trip is safely made on horseback. A word of advice here in regard to clothing may be of use. It is absolutely necessary to have good, warm clothing with one, for the night, which is spent on the floor; but for the descent a light shade hat is advisable; the heat of the afternoon sun can be very oppressive.
Mr. William Winter said of the Grand Canyon: “It is a pageant of ghastly desolation and yet of frightful vitality, such as neither Dante nor Milton in their most sublime conceptions ever even approached.... Your heart is moved with feeling that is far too deep for words. Hour after hour you would sit, entranced, at the edge of this mighty subterranean spectacle, lost in the wonder and glory of it, forgetful of self, and conscious only of the Divine Spirit.”
“If the falls of Niagara were installed in the Grand Canyon between your visits—and you knew it by the newspapers—next time you stood on that dizzy rimrock you would probably need good field-glasses and much patience before you could locate that cataract which in its place looks pretty big. If Mount Washington were plucked up bodily by the roots—not from where you see it, but from sea level—and carefully set down in the Grand Canyon, you probably would not notice it next morning, unless its dull colours distinguished it in that innumerable congress of larger and painted giants.
“All this, which is literally true, is a mere trifle of what might be said in trying to fix a standard of comparison for the Grand Canyon. But I fancy there is no standard adjustable to the human mind. You may compare all you will—eloquently and from wide experience—and at last all similes fail. The Grand Canyon is just the Grand Canyon, and that is all you can say. I never have seen any one who was prepared for it. I never have seen any one who could grasp it in a week’s hard exploration; nor any one, except some rare Philistine, who could even think he had grasped it. I have seen people rave over it; better people struck dumb with it; even strong men who wept over it; but I have never yet seen the man or woman who expected it.”2
Last, but by no means least, let me quote a few words from an article published in the Century Magazine by Mr. John Muir:
“It seems a gigantic statement for even Nature to make, all in one stone word. Wildness so Godful, cosmic, primeval, bestows a new sense of earth’s beauty and size.... But the colours, the living, rejoicing colours, chanting, morning and evening, in chorus to heaven. Whose brush or pencil, however lovingly inspired, can give us these? In the supreme flaming glory of sunset the whole canyon is transfigured, as if all the life and light of centuries of sunshine stored up in the rocks was now being poured forth as from one glorious fountain, flooding both earth and sky.”
It is a happy thing to be able to quote such men as the above, for I am among the number of those who were struck dumb by the sight of this place. I can find no words which would give any idea of the impression made upon me by the canyon, I can only advise those planning a western trip to see it, without fail, either going or returning; the time of the year does not matter, the El Tovar is open to you the year round.
Among the interesting trips in this region is that to the Painted Desert, of which one hears little, probably because it is a difficult trip; still it is perfectly possible for any ordinarily hardy traveller. Five to seven days should be allowed for the journey which is made on horse- or mule-back. The descent to the floor of the canyon is a rough ride and very fatiguing, but by no means dangerous. The trail leads down canyon after canyon, dropping lower and lower, for it must be remembered that the Painted Desert lies 200 feet below sea level, while the rim of the canyon from which we start is 7,000 feet above sea level. One can readily imagine the change in temperature in such a descent (mentioned elsewhere); the mercury stands at times at 115°; however, those who care to put up with the hardships are likely to feel themselves fully repaid.
An experienced guide is necessary, especially on account of the quicksands which must be avoided in crossing the Little Colorado River. The colours of the sand, the mountains, and the sky are indescribable; they are so brilliant as to seem absolutely unreal, while beyond in the distance is seen, in all its dazzling whiteness of snow-capped peaks, the lovely San Francisco range, a fitting background for this mad riot of colour.
“The Fossil Forest of Arizona, one of the most remarkable features of a state noted for its scenic wonders, is situated a few miles south of Adamana, a station on the Santa Fé Railroad in Apache County.... Only within a few years have accommodations and transportation facilities been such as to tempt more than a very small proportion of the tourists and travellers to ‘stop off’ on their through tickets to the Grand Canyon and Pacific Coast. Since the setting aside of the area as a national monument, and the appointment of a superintendent, the way has become easy, and the constantly increasing number of visitors has made the preparation of some form of scientific account of the Forest almost a necessity.”
This Mr. George Perkins Merrill follows with a careful geological account of the forest, which can be had by those who wish to go carefully into the matter.
Here, as in the Great Petrified Forest in the Arabian Desert, so called to distinguish it from the one near Cairo, known as the Petrified Forest, the trees are fallen and lie prone upon the ground, glittering fragments of carnelian and jasper all about them. There are not even standing stumps here, as in the Great Petrified Forest of the Arabian Desert and the Yellowstone Forests where superb specimens still may be seen.
There are within the reservation four forests, but the first is the one most generally visited. This first is about six miles from Adamana; it is easily reached in an hour and a half. The second forest is two and one half miles south of the first, the trip taking about half an hour each way. The third forest covers a greater area than the others, it is 13 miles southwest of Adamana and 18 miles southeast of Holbrook. The third forest, known as the Rainbow Forest, is the principal one; it is often called Chalcedony Park. The ground here seems strewn with jewels, and one has the feeling of being in an enchanted spot; the colours are most brilliant; chalcedony, opals, and agates are found here.
One of the most interesting features of this region is the Natural Bridge, consisting of a great petrified trunk of jasper and agate lying across a canyon 60 feet wide and 20 feet deep, and forming a foot-bridge over which any one may easily pass.
“Here we begin to realize that this is an old country rather than a new. Americans are prone to talk about the ‘Settlement Period,’ of Bradford and Brewster, of Captain John Smith and Henry Hudson. But it is well to remember that nearly a century before the Half Moon sailed up the Hudson or the Mayflower dropped her anchor in Massachusetts Bay, the mailed warriors of Cabeza de Vaca and Coronado had discovered the terraced cities of Zuni, where men were clothed in cotton and wool of their own weaving, lived in stone houses, and cultivated the soil.”
At Albuquerque we find ourselves in a half-American and half-Mexican city. It is a junction point of the Santa Fé and the metropolis of New Mexico. Many travellers stop here for a day or two, to break their journey.
The Alvarado, a Harvey hotel, has a fine collection of Indian relics and products and here one is likely to see the Navajo and Hopi weavers, potters, silversmiths, and basketmakers at work.
“Santa Fé lies at the base of a mountain range nearly 2,000 feet higher than Albuquerque, a few miles off the main line of travel, on a branch line. Lamy is the main line junction point, where one changes cars to reach Santa Fé. When first visited by the Spanish, about 1540 (a century before Boston was settled), the town was a populous Indian pueblo. You may read its varied history in the guide books and study its priceless records in the old territorial ‘Palace.’ The Casa Viejo, or old house, where Coronado is said to have lodged in 1540, and the church of San Miguel, which was sacked in 1680, are not distinguishable from their surroundings by any air of superior age. All is old, a bit of desiccated Granada of the 16th century.”
“There are many ways of getting into the Hopi country, but there are three commonly used routes, each of which has certain advantages. At the starting-point of each one of them conveyances may easily be secured for the trip. The three points are the stations of Holbrook, Winslow, and Canyon Diablo, all along the line of the Santa Fé. The Hopi country stretches out north of these three stations; the distance is about the same from each. Holbrook possesses one advantage over the other two routes: the town is situated on the Hopi side of the Little Colorado River; consequently, the question as to whether the river is fordable need not be considered.
“The distance from Holbrook to Wolpi, the easternmost of the Hopi villages, is about 80 miles. This trip, with camping outfit, usually requires about three days.
“Winslow, a much larger town than Holbrook, is a division point on the Santa Fé, and has several hotels and livery stables. Of the latter the writer is able to recommend, from much personal experience, that kept by Mr. Creswell. The route from Winslow to Oraibi, the westernmost village, is not quite 80 miles.
“Canyon Diablo has neither hotel nor livery stable. Mr. Volz, the Indian trader at this point, will, with advance notice, furnish the necessities. Should there be ladies in the party, and should it be possible to secure Mr. Volz’s personal services for the journey, this route offers certain advantages not to be found by either of the other two, and the cost is about the same.
“Whether our journey be made in winter or summer, spring or autumn, we are sure to intrude upon (for they are not to be considered in any sense as ‘shows’) one or more of the great ceremonials, usually an invocation for rain, a propitiation of the gods of the winds for bountiful harvests, or a general thanksgiving for protection, with the brilliant public pageant at the close. But smile not at the curious sand altars, with the ‘tiponi’ or palladium of the fraternity, the childlike ‘bahos’ and ‘nakwakwosi,’ or prayer-sticks and offerings, nor let the ears or eyes be offended by the chanting of the songs to the gods of sun, of winds and of rain, or the ceremonial dances of the priests, for they are serious affairs to the native participants.”3
“It is in these strange, cliff-perched little cities that one of the most astounding barbaric dances in the world is held. Africa has no savages whose mystic performances are more wonderful than the Hopi snake dance.
“The snake is an object of great respect among all uncivilized peoples, and the deadlier his power, the deeper the reverence for him. The Hopi often protect in their houses an esteemed and harmless serpent—about five or six feet long—as a mouse trap; and these quiet mousers keep down the little pests much more effectively than a cat, for they can follow shee-id-deh to the ultimate comer of his hole.”
Up to a generation ago every pueblo protected at least one rattlesnake, but now the Hopi Indian alone continues the custom. Once a year the remarkable ceremony of the snake dance is still performed, and Mr. Lummis, from whom the above is quoted, tells us that after the dance is over he has seen a hillock of rattlesnakes a foot high and four feet across.
“The dancers leap about this squirming pile while sacred corn meal is sprinkled, then thrust each an arm into the mass, grasp a number of snakes, and go running at top speed to the four points of the compass, and thus the unharmed snakes are released.”
To the north and east of the Hopi Reservation is the Navajo Reservation, also accessible by the Santa Fé Railroad. These Indians, unlike their neighbours, will not even touch a snake. Mr. Lummis tells a most interesting story of his having had a Navajo Indian make for him a silver bracelet in the form of a snake. So extreme are their prejudices that this silversmith was almost beaten to death by his fellows, and the bracelet, together with his hut, were destroyed.
The Navajo reveres the bear as the Hopi does the snake. They even go so far as to make prayers and sacrifices to him. They are the most wonderful of jugglers. Dr. Washington Matthews, who was the foremost student of Navajo customs, said officially: “I have seen many fire scenes on the stage, many acts of fire-eating and fire-handling by civilized jugglers, but nothing comparable to this.”
The Navajo blanket is known all over this country; these Indians and the Hopi are especially famous for their weaving. But it is not to-day what it used to be; the blanket to-day is made to sell, not to wear.
The Navajo Reservation is now a national monument, and protects three extensive prehistoric pueblos, or cliff dwellings, in a good state of preservation.
In the Navajo Indian Reservation may be seen the Rainbow Bridge National Monument. The bridge is 309 feet above the water, and its span is 279 feet. Among the natural bridges of the world this one is said to be unique, having not only a symmetrical arch below but presenting also a curved surface above, thus having the appearance of a rainbow. An unusual trip may be made from here to the Natural Bridge National Monument, a distance of 160 miles.
“The most extensive and wonderful cave communities in the world are in the great Cochiti upland, some 50 miles northwest of Santa Fé, New Mexico. The journey is a very laborious one, but by no means dangerous; and if you can get a good guide, you are apt to remember it as the most interesting expedition of your life.
“In the superbly picturesque canyon of the Rito de los Frigoles is the largest of all the villages of caves, deserted for more than 400 years. Outside its unnumbered cave rooms were more rooms yet, of masonry of ‘bricks’ cut from the same cliff.
“A few miles farther up the Rio Grande, not down in a canyon, but on the top of a great plateau, nearly 2,000 feet above the river, are two huge castle-like buttes of chalky tufa, each some 200 feet high. They stand one on each side of the Santa Clara Canyon, and are known to the Indians, respectively, as the Puye and the Shu-fin-ne. They are the most easily accessible of the large cave villages of North America, not being more than 10 miles from the little railroad town of Espanola, on the Rio Grande, some 30 miles by rail from Santa Fé.
“In this same wild region are the only great stone idols (or, to speak more properly, fetiches) in the United States—the mountain lions of Cochiti. They are life size and carved from the solid bedrock on the top of two huge mesas. To this day the Indians of Cochiti, before a hunt, go to one of these almost inaccessible spots, anoint the great stone head, and dance by night, a wild dance, which no white man has seen or ever will see.”4
Acoma is 13 miles south of the Santa Fé Railway in the western part of New Mexico. It is reached from Laguna, which is in itself another most interesting place; it is the most recent of all the pueblos, having been founded in 1699.
“Of all the 19 pueblos of New Mexico, Acoma is by far the most wonderful. Indeed, it is probably the most remarkable city in the whole world. Perched upon the level summit of a great ‘box’ of rock whose perpendicular sides are nearly 400 feet high, and reached by some of the dizziest paths ever trodden by human feet, the prehistoric town looks far across the wilderness. Its quaint terraced houses of gray adobe, its huge church—hardly less wonderful than the pyramids of Egypt as a monument of patient toil—its great reservoir in the solid rock, its superb scenery, its romantic history and the strange customs of its 600 people, all are rife with interest to the few Americans who visit the isolated city. Neither history nor tradition tells us when Acoma was founded. The pueblo was once situated on the top of the Mesa Encantada (Enchanted Tableland), which rises 700 feet, near the mesa now occupied.
“The present Acoma was an old town when the first European—Coronado, the famous Spanish explorer—saw it in 1540. With that its authentic history begins—a strange, weird history, in scattered fragments....
“Acoma is a labyrinth of wonders of which no person alive knows all; the longest visit never wears out its glamour. One feels as among scenes and beings more than human, all of whose rocks are genii and whose people swart conjurors. It is spendthrift of beauty.... It is the noblest specimen of fantastic beauty on the continent.”
Laguna lies some 20 miles northeast of Acoma. Mr. Lummis, from whom the above is quoted, tells a most interesting story of a law-suit carried on between these two cities over the picture of a saint. The story is told in “Some Strange Corners of Our Country.” Not only does the writer know these strange corners, but he has a wonderful way of making his readers see them.
The Apache reservations are in Arizona and New Mexico. There is one, about 100 miles from El Paso, on the border of Texas and New Mexico, but perhaps the most accessible for tourists is the San Carlos Agency of the White Mountain Reservation, reached by stage from Holbrook, a distance of about 96 miles.
There are no Apache ruins, for this tribe lived in tepees made of twigs, and not in pueblos or permanent houses.
Basketmaking is the principal industry among the women.
“This mountain in northeastern New Mexico is a volcanic cinder cone of recent origin, six miles southwest of Folsom. It is the finest specimen of a group of craters. Capulin has an altitude of 8,000 feet and rises 1,500 feet above the surrounding plain. It is almost a perfect cone. It is easily reached by either rail or automobile.”
Eighteen miles west of Santa Fé, N. M., in a beautiful valley with high surrounding walls some six miles long, and about one half mile wide, with an entrance narrow enough to admit but two persons abreast, may be seen the home of a people who lived in caves. This is a region full of interest; there is here a large area which has been suggested for a national park, to be called: “The Cliff Cities National Park”; it is reached by automobile from Santa Fé.
Zuni is also reached by the Santa Fé R. R. from Gallup. This is said to be the largest of all the pueblos. At Zuni, Mr. Frank Hamilton Cushing passed many years of his life, as a member of the tribe. This famous ethnologist probably learned more of the real Indian, because more closely associated with him, than any other white man has done; he is the authority on this particular tribe.
Conveyances can be had at Gallup for the trip to Zuni, which is generally made in a day. The pueblo lies in a level plain on the southern bank of the Zuni River; it may be seen at quite a distance, owing to the irregularity in the height of the houses, some of which are five stories, and the irregular lay of the ground upon which they are built.
To the traveller who has been to Acoma, Zuni may be disappointing, or rather the approach to Zuni, Acoma being built upon a great rock mesa; but why compare such different spots? Each has its own charm. The ladders which are seen upon all sides at Zuni add greatly to its picturesque appearance; they have been well described as: “A wilderness of masts.”
Pottery is the great industry of the Zuni, in which art they excel; not only are the jars, bowls, etc., beautifully shaped, but the decorative designs, mostly semi-geometric, and the combining of the reds, browns, and black is wonderfully artistic.
A great many religious rites exist in Zuni, some such celebration taking place every month, many in the open air, so that it is possible that the tourist may chance upon one of these at almost any time. There is a famous Zuni dance held in November each year, which may be witnessed by all. There are many shrines in this vicinity where visitors are allowed, the most important of which is the one on Thunder Mountain, quite a climb, but worthy the effort; here the Zuni still make their offerings of prayer-sticks, etc., to the gods to whom this shrine is dedicated.
From Zuni the trip into the Painted Desert may be made.
In western central New Mexico there is an enormous sandstone rock, rising some 200 feet out of a plain, which, having a small spring of water at its base, seems to have made it a valuable camping place for the Spanish explorers.
This rock contains some 21 Spanish inscriptions, the earliest of which is dated February 18, 1526; the most interesting is probably that of Juan de Onate, the founder of the city of Santa Fé in 1606.
“Eighty miles southwest of Albuquerque, in the hollow of towering desert ranges, lies the arid country which Indian tradition calls the Accursed Lakes. Here at the points of a large triangle sprawl the ruins of three once flourishing pueblo cities, Abo, Cuaray, and Tabirá. When the Spaniards came these cities were at the flood-tide of prosperity.”5 At Tabirá was built one of the important early Spanish missions. The towns were discovered in 1581. The reservation preserves this interesting mission ruin in Central New Mexico.
Phoenix, the capital of Arizona, is the starting point for several places of interest, the chief, perhaps, being the Roosevelt Dam.
This very picturesque and splendid dam is built in a narrow canyon about 80 miles from Phoenix; it holds in a fine natural basin a great wealth of water. The lake fills a valley 28 miles long, and in the hillsides surrounding the water there are remains of cliff and cave dwellings; here ancient and modern masonry meet. These dwellings are known as the “Tonto National Monument.”
For the traveller the most interesting feature in this region is the Apache Trail. An auto-stage leaves Phoenix daily for what is known as the Globe-Miami district, 120 miles away. The trail leads through the Salt River Valley, the Apache Gap (said to be the scene of a battle between the 7th Cavalry and the Apaches in 1886), to No Man’s Land, and Summit, altitude 3,470 feet. On the descent are unusual panoramic views of castellated cliffs and deep mountain gorges, with the usual magic desert colouring.
The trail leads past the Roosevelt Dam and lake with fine views all the way to Globe, the home of the Old Dominion Copper Co., and Miami, of the Inspiration Copper Co., both mining towns.
Tucson is a close rival of Phoenix. This old town still has some of the charm of ancient Mexico. A few miles from Tucson there is one of the finest and best preserved old missions of the Southwest, San Xavier. The outside has been considerably restored and, unfortunately, whitewashed, all but the central portion, which happily is in the original brownish colour. The interior decorations, very ornate, are the originals. The crudely carved wooden lions at the sides of the altar rails date undoubtedly from the founding, supposed to have been 1692.
About nine miles east of Phoenix and 12 miles from the Apache Trail, a small area has been made a national monument on account of its splendid examples of characteristic desert flora. Here are to be seen striking specimens of the giant cactus, Saguaro, which attains a height of 30 to 35 feet and is of a beautiful cylindrical form. Not only this, but many other interesting species of cacti and yucca grow here.
Thirty cliff dwellings cling to the sides of the picturesque Walnut Canyon, eight miles from Flagstaff, Arizona. They are excellently preserved. The largest contains eight rooms. This canyon possesses unusual beauty because of the thickets of locust which fringe the trail down from the ruins. Some of the ruins are only accessible by ladder. Because of its nearness to Flagstaff this group of dwellings is easily visited.
“Montezuma Castle, a remarkable relic of a prehistoric race, is the principal feature of a well-preserved group of cliff dwellings in the northeastern part of Yavapai County, Arizona. Its position and size give it the appearance of an ancient castle. The structure is about 50 feet high by 60 feet wide, built in the form of a crescent. It is five stories high, with walls of masonry and adobe, plastered inside with mud.”
This is one of the most remarkable prehistoric ruins in the country. It is about 70 miles from Tucson, perhaps nearer the border town of Sonora. “A building of large size, evidently this was an important centre of population. The builders were probably Pima Indians. Whatever its origin, the community was already in ruins when the Spaniards found it.”
The first report we have of it is in 1539. The whole is now roofed over for protection.
It is earnestly requested of all travellers, old and young alike, that they shall do their part toward preserving unimpaired the beauty of the spots that they visit, and that instead of disfiguring the landscape by scattering the débris of their lunch-baskets, together with torn papers and broken boxes, all along their route, they shall conscientiously avail themselves of the trash-cans everywhere liberally provided for their use.
The names of a few reference books are herewith appended in order that the traveller who is especially interested in any particular line may be enabled to find some extra information along that line if he so wish.
Doubtless there are countless other books to be had on any of these subjects, but I have tried to name one which will be of service in looking up birds, trees, flowers, pottery, blankets, glaciers, Indian basketry, cliff dwellings, etc., etc.
THE END
A Study of Pueblo Pottery, F. H. Cushing
A Thousand Mile Walk to the Gulf, John Muir
A Tramp Across the Continent, Chas. F. Lummis
Arizona Nights, Stewart Edward White
Arizona and New Mexico, H. H. Bancroft
Beyond the Rockies, C. A. Stoddard
Birds of California, Wheelock
Birds of the Rockies, L. S. Keyser
California and the Southwest, F. W. Martin
California Desert Trails, Joseph, S. Chase
California Missions and Landmarks, Mrs. A. S. C. Forbes
California Tourist’s Guide, Wells Drury
California Wild Flowers, Theodore Payne
Designs on Prehistoric Pottery, J. W. Fewkes
Fifteen Thousand Miles by Stage, C. A. Strahorn
Flora of Middle Western California, Jepson
Flora of the Rocky Mountains and Adjacent Plains, P. A. Rydberg
Flora of the West Coast, C. V. Piper
Forest Trees of the Pacific Slope, G. B. Sudworth
Glaciers of Mount Rainier, I. C. Russell
Glaciers of North America, I. C. Russell
Highways and Byways of the Rocky Mts., C. Johnson
In and About the Grand Canyon of Arizona, G. W. James
In and Out of the Old Missions, G. W. James
In the Heart of the Sierras, J. M. Hutchings
In the Land of the Cliff Dweller and Indians of To-day, T. M. Prudden
Indian Basketry, G. W. James
Indians of the Painted Desert, G. W. James
Indians of the Yosemite Valley, Galen Clark
Indians of To-day, G. B. Grinnell
Journal of a Trip Through the Western Country, Theo. Winthrop
Land of the Cliff Dwellers, F. S. Chapin
Land of Poco Tiempo, C. F. Lummis
Land of To-morrow (Alaska)
Land of Enchantment from Pike’s Peak to the Pacific, Lillian Whiting
Mountains of California, John Muir
Mountaineering and Exploration in the Selkirks, Howard Palmer
My First Summer in the Sierras, John Muir
Native Races, H. H. Bancroft
Navajo and His Blankets, U. S. Hollister
Navajo Weavers, Washington Matthews
Nevada, Colorado, and Wyoming, H. H. Bancroft
Official Manual of Motor Car Camping, A. L. Westgard
On the Great American Plateau, T. M. Prudden
Our National Parks, John Muir
Rambles Overland, A. Gunnison
Rocky Mountain Flowers, Clements & Clements
Romance of the Colorado River, Dillenbaugh
Romantic California, E. C. Peixotto
Silent Places (Alaska), S. Ed. White
Some Strange Corners of Our Country, Chas. F. Lummis
Spell of the Rockies, E. A. Mills
Steep Trails, John Muir
Summer Tour of Southern California, S. W. Long
Tales of a Pathfinder, A. L., Westgard
Ten Thousand Miles with a Dog Sled, Hudson Stuck, D.D.
The Adventures of a Nature Guide, Enos A. Mills
The Arapaho Sun Dance, G. A. Dorsey
The Book of National Parks, Robert Sterling Yard
The Conquest of Mt. McKinley, Belmore Browne
The Cliff Dwellers of the Mesa Verde, Nordenskiold
The Desert, John C. Van Dyke
The Grand Canyon of The Colorado, John C. Van Dyke
The Ice Age in North America, G. F. Wright
The Land of Little Rain, Mary Austin
The Mountain That Was God, John H. Williams
The Mountains of Oregon, W. G. Steel
The Seven Wonders of the New World, J. K. Peck
The Snake Dance of the Moqui, J. G. Bourke
The Spell of the Yukon, Robert W. Service
The Winning of the Far West, McElroy
The Yellowstone National Park Historical and Descriptive, Chittenden
The Yosemite Valley, The Discovery of, L. H. Bunnell
Trees of California, Jepson
Trees of the Northern United States, A. C. Apgar
Two Great Canyons, C. C. Cole
Western Bird Guide, Margaret Armstrong
Western Wild Flowers, Margaret Armstrong
With Canoe and Saddle, Theo. Winthrop
Wonders of the Colorado Desert, G. W. James
Wonders of the Yellowstone, J. Richardson
Zuni Folk Tales, Frank Harvey Cushing
THE COUNTRY LIFE PRESS
GARDEN CITY, N. Y.
***END OF THE PROJECT GUTENBERG EBOOK SEEING THE WEST***
******* This file should be named 57190-h.htm or 57190-h.zip *******
This and all associated files of various formats will be found in:
http://www.gutenberg.org/5/7/1/9/57190
Updated editions will replace the previous one--the old editions will be renamed.
Creating the works from print editions not protected by U.S. copyright law means that no one owns a United States copyright in these works, so the Foundation (and you!) can copy and distribute it in the United States without permission and without paying copyright royalties. Special rules, set forth in the General Terms of Use part of this license, apply to copying and distributing Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works to protect the PROJECT GUTENBERG-tm concept and trademark. Project Gutenberg is a registered trademark, and may not be used if you charge for the eBooks, unless you receive specific permission. If you do not charge anything for copies of this eBook, complying with the rules is very easy. You may use this eBook for nearly any purpose such as creation of derivative works, reports, performances and research. They may be modified and printed and given away--you may do practically ANYTHING in the United States with eBooks not protected by U.S. copyright law. Redistribution is subject to the trademark license, especially commercial redistribution.
To protect the Project Gutenberg-tm mission of promoting the free distribution of electronic works, by using or distributing this work (or any other work associated in any way with the phrase "Project Gutenberg"), you agree to comply with all the terms of the Full Project Gutenberg-tm License available with this file or online at www.gutenberg.org/license.
1.A. By reading or using any part of this Project Gutenberg-tm electronic work, you indicate that you have read, understand, agree to and accept all the terms of this license and intellectual property (trademark/copyright) agreement. If you do not agree to abide by all the terms of this agreement, you must cease using and return or destroy all copies of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works in your possession. If you paid a fee for obtaining a copy of or access to a Project Gutenberg-tm electronic work and you do not agree to be bound by the terms of this agreement, you may obtain a refund from the person or entity to whom you paid the fee as set forth in paragraph 1.E.8.
1.B. "Project Gutenberg" is a registered trademark. It may only be used on or associated in any way with an electronic work by people who agree to be bound by the terms of this agreement. There are a few things that you can do with most Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works even without complying with the full terms of this agreement. See paragraph 1.C below. There are a lot of things you can do with Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works if you follow the terms of this agreement and help preserve free future access to Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works. See paragraph 1.E below.
1.C. The Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation ("the Foundation" or PGLAF), owns a compilation copyright in the collection of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works. Nearly all the individual works in the collection are in the public domain in the United States. If an individual work is unprotected by copyright law in the United States and you are located in the United States, we do not claim a right to prevent you from copying, distributing, performing, displaying or creating derivative works based on the work as long as all references to Project Gutenberg are removed. Of course, we hope that you will support the Project Gutenberg-tm mission of promoting free access to electronic works by freely sharing Project Gutenberg-tm works in compliance with the terms of this agreement for keeping the Project Gutenberg-tm name associated with the work. You can easily comply with the terms of this agreement by keeping this work in the same format with its attached full Project Gutenberg-tm License when you share it without charge with others.
1.D. The copyright laws of the place where you are located also govern what you can do with this work. Copyright laws in most countries are in a constant state of change. If you are outside the United States, check the laws of your country in addition to the terms of this agreement before downloading, copying, displaying, performing, distributing or creating derivative works based on this work or any other Project Gutenberg-tm work. The Foundation makes no representations concerning the copyright status of any work in any country outside the United States.
1.E. Unless you have removed all references to Project Gutenberg:
1.E.1. The following sentence, with active links to, or other immediate access to, the full Project Gutenberg-tm License must appear prominently whenever any copy of a Project Gutenberg-tm work (any work on which the phrase "Project Gutenberg" appears, or with which the phrase "Project Gutenberg" is associated) is accessed, displayed, performed, viewed, copied or distributed:
This eBook is for the use of anyone anywhere in the United States and most other parts of the world at no cost and with almost no restrictions whatsoever. You may copy it, give it away or re-use it under the terms of the Project Gutenberg License included with this eBook or online at www.gutenberg.org. If you are not located in the United States, you'll have to check the laws of the country where you are located before using this ebook.
1.E.2. If an individual Project Gutenberg-tm electronic work is derived from texts not protected by U.S. copyright law (does not contain a notice indicating that it is posted with permission of the copyright holder), the work can be copied and distributed to anyone in the United States without paying any fees or charges. If you are redistributing or providing access to a work with the phrase "Project Gutenberg" associated with or appearing on the work, you must comply either with the requirements of paragraphs 1.E.1 through 1.E.7 or obtain permission for the use of the work and the Project Gutenberg-tm trademark as set forth in paragraphs 1.E.8 or 1.E.9.
1.E.3. If an individual Project Gutenberg-tm electronic work is posted with the permission of the copyright holder, your use and distribution must comply with both paragraphs 1.E.1 through 1.E.7 and any additional terms imposed by the copyright holder. Additional terms will be linked to the Project Gutenberg-tm License for all works posted with the permission of the copyright holder found at the beginning of this work.
1.E.4. Do not unlink or detach or remove the full Project Gutenberg-tm License terms from this work, or any files containing a part of this work or any other work associated with Project Gutenberg-tm.
1.E.5. Do not copy, display, perform, distribute or redistribute this electronic work, or any part of this electronic work, without prominently displaying the sentence set forth in paragraph 1.E.1 with active links or immediate access to the full terms of the Project Gutenberg-tm License.
1.E.6. You may convert to and distribute this work in any binary, compressed, marked up, nonproprietary or proprietary form, including any word processing or hypertext form. However, if you provide access to or distribute copies of a Project Gutenberg-tm work in a format other than "Plain Vanilla ASCII" or other format used in the official version posted on the official Project Gutenberg-tm web site (www.gutenberg.org), you must, at no additional cost, fee or expense to the user, provide a copy, a means of exporting a copy, or a means of obtaining a copy upon request, of the work in its original "Plain Vanilla ASCII" or other form. Any alternate format must include the full Project Gutenberg-tm License as specified in paragraph 1.E.1.
1.E.7. Do not charge a fee for access to, viewing, displaying, performing, copying or distributing any Project Gutenberg-tm works unless you comply with paragraph 1.E.8 or 1.E.9.
1.E.8. You may charge a reasonable fee for copies of or providing access to or distributing Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works provided that
1.E.9. If you wish to charge a fee or distribute a Project Gutenberg-tm electronic work or group of works on different terms than are set forth in this agreement, you must obtain permission in writing from both the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation and The Project Gutenberg Trademark LLC, the owner of the Project Gutenberg-tm trademark. Contact the Foundation as set forth in Section 3 below.
1.F.
1.F.1. Project Gutenberg volunteers and employees expend considerable effort to identify, do copyright research on, transcribe and proofread works not protected by U.S. copyright law in creating the Project Gutenberg-tm collection. Despite these efforts, Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works, and the medium on which they may be stored, may contain "Defects," such as, but not limited to, incomplete, inaccurate or corrupt data, transcription errors, a copyright or other intellectual property infringement, a defective or damaged disk or other medium, a computer virus, or computer codes that damage or cannot be read by your equipment.
1.F.2. LIMITED WARRANTY, DISCLAIMER OF DAMAGES - Except for the "Right of Replacement or Refund" described in paragraph 1.F.3, the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation, the owner of the Project Gutenberg-tm trademark, and any other party distributing a Project Gutenberg-tm electronic work under this agreement, disclaim all liability to you for damages, costs and expenses, including legal fees. YOU AGREE THAT YOU HAVE NO REMEDIES FOR NEGLIGENCE, STRICT LIABILITY, BREACH OF WARRANTY OR BREACH OF CONTRACT EXCEPT THOSE PROVIDED IN PARAGRAPH 1.F.3. YOU AGREE THAT THE FOUNDATION, THE TRADEMARK OWNER, AND ANY DISTRIBUTOR UNDER THIS AGREEMENT WILL NOT BE LIABLE TO YOU FOR ACTUAL, DIRECT, INDIRECT, CONSEQUENTIAL, PUNITIVE OR INCIDENTAL DAMAGES EVEN IF YOU GIVE NOTICE OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
1.F.3. LIMITED RIGHT OF REPLACEMENT OR REFUND - If you discover a defect in this electronic work within 90 days of receiving it, you can receive a refund of the money (if any) you paid for it by sending a written explanation to the person you received the work from. If you received the work on a physical medium, you must return the medium with your written explanation. The person or entity that provided you with the defective work may elect to provide a replacement copy in lieu of a refund. If you received the work electronically, the person or entity providing it to you may choose to give you a second opportunity to receive the work electronically in lieu of a refund. If the second copy is also defective, you may demand a refund in writing without further opportunities to fix the problem.
1.F.4. Except for the limited right of replacement or refund set forth in paragraph 1.F.3, this work is provided to you 'AS-IS', WITH NO OTHER WARRANTIES OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR ANY PURPOSE.
1.F.5. Some states do not allow disclaimers of certain implied warranties or the exclusion or limitation of certain types of damages. If any disclaimer or limitation set forth in this agreement violates the law of the state applicable to this agreement, the agreement shall be interpreted to make the maximum disclaimer or limitation permitted by the applicable state law. The invalidity or unenforceability of any provision of this agreement shall not void the remaining provisions.
1.F.6. INDEMNITY - You agree to indemnify and hold the Foundation, the trademark owner, any agent or employee of the Foundation, anyone providing copies of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works in accordance with this agreement, and any volunteers associated with the production, promotion and distribution of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works, harmless from all liability, costs and expenses, including legal fees, that arise directly or indirectly from any of the following which you do or cause to occur: (a) distribution of this or any Project Gutenberg-tm work, (b) alteration, modification, or additions or deletions to any Project Gutenberg-tm work, and (c) any Defect you cause.
Project Gutenberg-tm is synonymous with the free distribution of electronic works in formats readable by the widest variety of computers including obsolete, old, middle-aged and new computers. It exists because of the efforts of hundreds of volunteers and donations from people in all walks of life.
Volunteers and financial support to provide volunteers with the assistance they need are critical to reaching Project Gutenberg-tm's goals and ensuring that the Project Gutenberg-tm collection will remain freely available for generations to come. In 2001, the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation was created to provide a secure and permanent future for Project Gutenberg-tm and future generations. To learn more about the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation and how your efforts and donations can help, see Sections 3 and 4 and the Foundation information page at www.gutenberg.org.
The Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation is a non profit 501(c)(3) educational corporation organized under the laws of the state of Mississippi and granted tax exempt status by the Internal Revenue Service. The Foundation's EIN or federal tax identification number is 64-6221541. Contributions to the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation are tax deductible to the full extent permitted by U.S. federal laws and your state's laws.
The Foundation's principal office is in Fairbanks, Alaska, with the mailing address: PO Box 750175, Fairbanks, AK 99775, but its volunteers and employees are scattered throughout numerous locations. Its business office is located at 809 North 1500 West, Salt Lake City, UT 84116, (801) 596-1887. Email contact links and up to date contact information can be found at the Foundation's web site and official page at www.gutenberg.org/contact
For additional contact information:
Dr. Gregory B. Newby
Chief Executive and Director
gbnewby@pglaf.org
Project Gutenberg-tm depends upon and cannot survive without wide spread public support and donations to carry out its mission of increasing the number of public domain and licensed works that can be freely distributed in machine readable form accessible by the widest array of equipment including outdated equipment. Many small donations ($1 to $5,000) are particularly important to maintaining tax exempt status with the IRS.
The Foundation is committed to complying with the laws regulating charities and charitable donations in all 50 states of the United States. Compliance requirements are not uniform and it takes a considerable effort, much paperwork and many fees to meet and keep up with these requirements. We do not solicit donations in locations where we have not received written confirmation of compliance. To SEND DONATIONS or determine the status of compliance for any particular state visit www.gutenberg.org/donate.
While we cannot and do not solicit contributions from states where we have not met the solicitation requirements, we know of no prohibition against accepting unsolicited donations from donors in such states who approach us with offers to donate.
International donations are gratefully accepted, but we cannot make any statements concerning tax treatment of donations received from outside the United States. U.S. laws alone swamp our small staff.
Please check the Project Gutenberg Web pages for current donation methods and addresses. Donations are accepted in a number of other ways including checks, online payments and credit card donations. To donate, please visit: www.gutenberg.org/donate
Professor Michael S. Hart was the originator of the Project Gutenberg-tm concept of a library of electronic works that could be freely shared with anyone. For forty years, he produced and distributed Project Gutenberg-tm eBooks with only a loose network of volunteer support.
Project Gutenberg-tm eBooks are often created from several printed editions, all of which are confirmed as not protected by copyright in the U.S. unless a copyright notice is included. Thus, we do not necessarily keep eBooks in compliance with any particular paper edition.
Most people start at our Web site which has the main PG search facility: www.gutenberg.org
This Web site includes information about Project Gutenberg-tm, including how to make donations to the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation, how to help produce our new eBooks, and how to subscribe to our email newsletter to hear about new eBooks.