
This eBook is for the use of anyone anywhere in the United States and most other parts of the world at no cost and with almost no restrictions whatsoever. You may copy it, give it away or re-use it under the terms of the Project Gutenberg License included with this eBook or online at www.gutenberg.org. If you are not located in the United States, you'll have to check the laws of the country where you are located before using this ebook.
Title: The Story of Our Flag
Colonial and National, with Historical Sketch of the Quakeress Betsy Ross
Author: Addie Guthrie Weaver
Release Date: June 16, 2016 [eBook #52354]
Language: English
Character set encoding: UTF-8
***START OF THE PROJECT GUTENBERG EBOOK THE STORY OF OUR FLAG***
| Note: | Images of the original pages are available through Internet Archive. See https://archive.org/details/storyofourflagco00weav |


For some years the Author has been interested in the history of our First Flag and its fair maker, Betsy Ross, and fortunately, through a family relationship with one of the descendants, became familiar with much of the family history.
It seemed that so beautiful and estimable a lady, and one who played so important a part in those stirring events of our early history should be better known and appreciated by her sisters of to-day.
Fitting, it seems, that while man in defending our Flag has accomplished his greatest achievements, and won undying fame, woman first fashioned into “a thing of beauty” the symbol of that patriotic devotion.
To Mr. George Canby of Philadelphia, and Mrs. Sophia Campion Guthrie of Washington, D. C., grandson and great granddaughter, respectively, of Betsy Ross, the author is indebted for family history that has inspired this work, and to them and other descendants, this book is affectionately dedicated by

The history of our flag from its inception, in fact, the inception itself, has been a source of much argument and great diversity of opinion. Many theories and mystifications have gone forth, mingled with a few facts, giving just enough color of truth to make them seem plausible. It is for the purpose of clearing away the veil of doubt that hangs around the origin of the Stars and Stripes that this book has been written.
The Continental Congress in 1775 was very much disturbed over the embarrassing situation of the colonies, and after Washington was appointed Commander-in-Chief of the Army, it showed its independence by appointing a committee composed of Benjamin Franklin, Benjamin Harrison and Mr. Lynch to create a colonial flag that would be national in its tendency. They finally decided on one with thirteen bars, alternate red and white, the “King’s Colors” with the crosses of St. Andrew and St. George in a field of blue. The cross of St. Andrew then, as now, was of white, while the cross of St. George was of red. The colonies still acknowledged the sovereignty of England—as this flag attested—but united against her tyranny. This was known as the “flag of our union”—that is, the union of the colonies, and was not created until after the committee had been to the camp at Cambridge and consulted with Washington. It was probably made either at the camp at Cambridge or in Boston, as it was unfurled by Washington under the Charter Oak on January 2, 1776. It received thirteen cheers and a salute of thirteen guns.
It is not known whether Samuel Adams, the “Father of Liberty,” was consulted in regard to this flag, but it is a well known fact that he was looking forward, even then, to the independence of the colonies, while Washington, Franklin and the others still looked for justice,—tardy though it might be,—from England.
Two days later, on the 4th of January, 1776, Washington received the King’s speech, and as it happened to come so near to the time of the adoption of the new flag, with the English crosses of St. Andrew and St. George, many of the regulars thought it meant submission, and the English seemed for the time to so understand it; but our army showed great indignation over the King’s speech to parliament, and burned all of the copies.
In a letter of General Washington to Joseph Reed, written January 4, he says: “We are at length favored with the sight of his majesty’s most gracious speech, breathing sentiments of tenderness and compassion for his deluded American subjects. The speech I send you (a volume of them were sent out by the Boston gentry) was farcical enough and gave great joy to them without knowing or intending it, for on that day (the 2nd) which gave being to our new army, but before the proclamation came to hand, we hoisted the Union flag, in compliment to the United Colonies, but behold it was received at Boston as a token of the deep impression the speech had made upon us and as a signal of submission. By this time I presume they begin to think it strange that we have not made a formal surrender of our lines.”
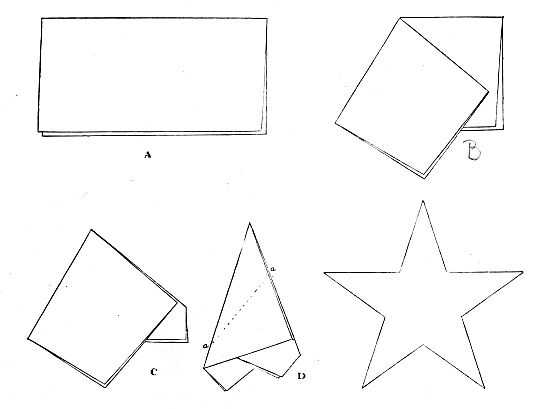
At this time the number and kinds of flags that were in use on land and sea, were only limited to the ingenuity of the state and military officials. This was very embarrassing. On May 20, 1776, Washington was requested to appear before Congress on important secret military business. Major-General Putnam, according to Washington’s letters, was left in command at New York during his absence. It was in the latter part of May, 1776, that Washington, accompanied by Colonel George Ross, a member[9] of his staff, and by the Honorable Robert Morris, the great financier of the revolution, called upon Mrs. Betsy Ross, a niece of Colonel Ross. She was a young and beautiful widow, only twenty-four years of age, and known to be expert at needle work. They called to engage her services in preparing our first starry flag. She lived in a little house in Arch street, Philadelphia, which stands to-day unchanged, with the exception of one large window, which has been placed in the front. It was here, in this house, that Washington unfolded a paper on which had been rudely sketched a plan of a flag of thirteen stripes, with a blue field dotted with thirteen stars. They talked over the plan of this flag in detail, and Mrs. Ross noticed that the stars which were sketched were six-pointed, and suggested that they should[10] have five points. Washington admitted that she was correct, but he preferred a star that would not be an exact copy of that on his coat of arms, and he also thought that a six-pointed star would be easier to cut. Mrs. Ross liked the five-pointed star, and to show that they were easily cut she deftly folded a piece of paper and with one clip of her scissors unfolded a perfect star with five points. (See illustration showing the way Betsy Ross folded the paper giving the five-pointed star which has ever since graced our country’s banner. A, first fold of a square piece of paper; B, second; C, third, and D, fourth fold. The dotted line AA is the clip of the scissors.)
There is no record that Congress took any action on the national colors at this session,—but this first flag was made by Betsy Ross at this time, and in this way, and we find in Washington’s letter of May 28, 1776, to General Putnam at New York, positive instructions “to the several colonels to hurry to get their colors done.” In the orderly book, May 31, 1776, are these words: “General Washington has written to General Putnam desiring him in the most pressing terms, to give positive orders to all the colonels to have colors immediately completed for their respective regiments.” The proof is positive that the committee approved the finished flag of Betsy Ross, and she was instructed to procure all the bunting possible in Philadelphia and make flags for the use of congress, Colonel Ross furnishing the money.
It is easily understood how on account of the meager resources of Congress and the unsettled condition of affairs generally, together with the fact that legislative action was extremely slow and tedious, that Colonel Ross should expedite matters by defraying the expense of this first order for our national colors. There is little, if any, doubt but that Washington on December 24th, Christmas Eve, in 1776, carried the starry flag in making that perilous trip through ice and snow across the Delaware, leading his sturdy, but poorly equipped troops. How inspiring to[11] look back to that night when the Massachusetts fishermen so skilfully managed the boats that the whole army was safely landed and in line of march at four o’clock on Christmas morning. The story of how they plodded on through ice and snow, surprising and defeating the Hessians and capturing a thousand men and their ammunition and equipments, is well known. This was the battle of Trenton, which changed the whole aspect of the war, even causing Lord Cornwallis to disembark and again start in pursuit of Washington, whose cause he had so lately declared lost. It is fitting here to speak of that friend of Washington, Robert Morris, one of the committee that originated our national colors, the great patriot who after the battle of Trenton went from house to house, soliciting money from his friends to clothe and feed this glorious army, which had fought so well.
Congress was very slow to act, and did not seem able to command even the meager resources of the different colonies. It lacked the centralized government which gives it such strength to-day. Considering the grave questions affecting the life and liberty of the people, it is not strange that the flag or any definite action regarding it, was not given prompt consideration. To indicate how slow Congress was to act in regard to the flag, we have only to refer to the Congressional records, which show that the resolution for its adoption was dated over one year after it was actually created, by the committee of which Washington was chief; that is on June 14, 1777. However, a month previous to this, Congress sent Betsy Ross an order on the treasury for £14, 12s. 2d., for flags for the fleet in the Delaware River, and she soon received an order to make all the government flags. The first flag was made of English bunting, exactly the same as those of to-day, excepting that our bunting now is of home manufacture.
There seems to be no question but that these colors, the stars and stripes, were unofficially adopted immediately after the[12] completion of the first flag, the latter part of May, 1776, and that they went into general use at once, so far as it was practicable under the conditions then existing. Washington had the first flag created at this time. It was satisfactory, and he immediately instructed General Putnam to have the colonels prepare their colors—the colors that had just been approved, and which we know to be our flag of to-day.
The first reference we have of an English description of our flag is at the surrender of General Burgoyne, October 17, 1777, when one of the officers said: “The stars of the new flag represent a constellation of states.”
Mr. George Canby, an estimable gentleman of the old school, and a grandson of Betsy Ross, has been tireless and indefatigable in his researches on the subject of our flag, and he claims, as did his brother, Mr. William J. Canby, before him, that the first flag with stars and stripes went into immediate use after its inception in the latter part of May, 1776.
The Declaration of Independence was passed by Congress on July 4, 1776, and some authorities, of whom Admiral Preble is the best, seem to infer that the Cambridge flag, with its English crosses, which was unfurled by Washington under the Charter Oak, was still carried by our armies until Congress took action in 1777. That Washington or Congress would sanction the carrying of this flag after the Declaration of Independence seems absurd, and it is certainly against all proof, as well as against the records of the family whose ancestor made the first flag.
Peak’s portrait of Washington at the battle of Trenton, December 26 and 27, 1776, shows the Union Jack with the thirteen stars in the field of blue. Admiral Preble says, this is “only presumptive proof” that the stars were at that time in use on our flag, but Titian R. Peale, son of the painter, says: “I visited the Smithsonian Institute to see the portrait of Washington painted by my father after the battle of Trenton. The flag represented[13] has a blue field with white stars arranged in a circle. I don’t know that I ever heard my father speak of that flag, but the trophies at Washington’s feet I know he painted from the flags then captured, and which were left with him for the purpose.” He further says: “He was always very particular in the matters of historic record in his pictures.”
This Preble admits in his book, but evidently thought that the artist, Peale, took the flag as it was then (1779), and not the flag of 1776, which the writer claims was identically the same. Through persistent research many facts have come to light that would doubtless have changed the opinion of the late Admiral Preble—facts that were unknown to him.
On Saturday, June 14, 1777, Congress finally officially adopted the flag of our Union and independence, to-wit:
Resolved, “That the flag of the thirteen United States be thirteen stripes, alternate red and white; that the Union be thirteen stars, white in the blue field, representing a new constellation.”
There is not the slightest record in any of the mss. journals in the library of Congress, or in the original files or in the drafts in motions made in the continental Congress of any previous legislative action for the establishment of a national flag for the United States of America, whose independence was declared nearly a year previous. Even after the official adoption of the flag it was not thoroughly brought before the people for many months. All of this adds to the proof that Congress was simply adopting and legalizing a flag that was in general use. That there was no recorded discussion in Congress regarding the adoption of our flag, was perfectly natural, because the star spangled banner came in with our independence, and at this time (June 14, 1777) was simply being officially acknowledged.
There is some diversity of opinion as to how the red, white and blue arranged in the stars and stripes came to be thought of as our flag.
The flag of the Netherlands, which is of red, white and blue stripes, had been familiar to the pilgrims while they lived in Holland, and its three stripes of red, white and blue were doubtless not forgotten. But it seems most probable that the coat of arms of the Washington family furnished more than a suggestion. The coat of arms of his ancestors, that had been adopted by him, comprised the red, white and blue and the stars; and was familiar to all who were associated with Washington. He it was who brought the pencil drawing, when, with the others, he called upon Mrs. Ross to have a suitable flag made, and as we find no mention in history, records or diaries as to who made the drawing, it seems conclusive that he himself designed and drew the plan from his own coat of arms, which was entirely different from England’s colors which had become necessarily distasteful.
It seems fitting in this place to write a little history in regard to the Washington coat of arms, the earliest mention of which was by Lawrence Washington, worshipful mayor of Northampton, England, in 1532. In 1540 he placed it upon the porch of his manor house, and on the tomb of Ann, his wife, in 1564. At the old church at Brighton, England, the tombs of Washington’s ancestors are marked by memorial plates of brass bearing the arms of the family, which consisted of a shield that bore the stars and stripes. The Archeological Society of England, the highest authority on ancient churches and heraldic matters, states that from the red and white bars, and stars of this shield, and the raven issuant from its crest (borne later by General Washington), the framers of the constitution took their idea of the flag.
When General Washington’s great-grandfather, Sir John Washington, came to this country in 1657, the family shield was brought with him. Sir John settled in Virginia, and established the American line of Washingtons. George Washington afterwards had it emblazoned upon the panels of his carriages, on his watch seals, book marks, and his dishes also bore the same emblem.

The accompanying plate shows the form and colors of the Coat of Arms of the Washington family, back as early as 1300.
The name first appeared as De Wessynton; then Weshyngton, and, finally, Washington.
How appropriately our own beautiful shield of the United States comes in here, and why not? was he not the “Father of Our Country”? and what more natural than that he should have left the imprint of his life and characteristics in symbol?
The central figure is a fac-simile of his book plate.
After the admission of Vermont and Kentucky into the Union, Congress passed an act in 1794, increasing both the stars and stripes from thirteen to fifteen, to take effect May, 1795. It was as follows:
“An act making alterations in the flag of the United States. Be it enacted, etc., That from and after the first day of May, one thousand, seven hundred and ninety-five, the flag of the United States be fifteen stripes, alternate red and white, and that the union be fifteen stars, white in a blue field.
“Approved January 13, 1794.”
This flag was used for several years. It flew at the mastheads of our gallant ships and was carried by our little army in the war with England in 1812. A few years later Tennessee, Ohio, Louisiana and Indiana, now won to civilization by hardy pioneers, clamored for admittance into the Union. When they were finally admitted as states, another change in the flag became necessary. The sturdy young republic was advancing by leaps and bounds in civilization and wealth; its hardy sons pushing further west and south constantly, reclaiming from wild savages, to the uses of their own race, greater and larger areas, which were bound to be erected into states and take their places in the family of the original thirteen. It became manifest that legislation was necessary, permanently defining the national flag, and providing for such changes as the future development of the country would require. Congress rose to the occasion. A committee, with Hon. Peter Wendover of New York as chairman, was appointed to frame a law, and with very little delay the committee reported a measure fulfilling every requirement then existing, and providing for all the future. The measure was passed by congress and went on the statute books as the law establishing the flag as our great-grandfathers of that day knew it, and as we know it to-day. The law has never been changed, and here it is:
“An act to establish the flag of the United States.
“Section 1. Be it enacted, etc., That from and after the fourth day of July next, the flag of the United States be thirteen horizontal stripes, alternate red and white; that the Union have twenty stars, white in the blue field.
“Sec. 2. And be it further enacted, That on the admission of every new state into the Union, one star be added to the union of the flag, and that such addition shall take effect on the fourth of July next succeeding such admission. Approved April 4, 1818.”
The thirteen stripes will always represent the number of the “old thirteen” whose patriotism and love of justice brought about the independence of America. The stars that come into the blue sky of the flag will mark or indicate the increase of the states since the adoption of the Constitution. It is interesting to note that under the stars and stripes Washington, in 1793, laid the corner stone of the capitol of the United States, first having personally selected the site of the building. It is also interesting to know that Washington did not live to see the capitol completed, but died before the seat of government was moved to Washington in 1800. The main capitol building was not completed till 1811. It is also a matter of historical interest that the president’s home, now called the White House, was completed during the life of Washington, and it is an authenticated fact that he and his wife inspected the house in all its parts only a few days before his death. The president’s house was practically destroyed by the British in 1814; the walls alone remained intact, but the stone was so discolored that when the building was reconstructed, it had to be painted, and from this came the name of the “White House.”
The large picture of Washington, by Stewart, which is now in the east room, at the time of the bombardment by the British, was taken out of its frame by Mrs. Dolly Madison, wife of the president, and sent to a secure place across the river.
This flag of forty-five stars, this flag of our country, is our inspiration. It kindles in our hearts patriotic feelings, it carries our thoughts and our minds forward in the cause of liberty and right. On sea and on land, wherever the star spangled banner waves, it thrills the heart of every true American with pride. It recalls the memories of battles bravely fought. It recalls the victories of Trenton and Princeton, it recalls the victories of Gettysburg and Appomattox. We see the flag as first carried by Paul Jones across the sea; we see the flag as carried by Commodore Perry on Lake Erie; we see the flag as carried by Farragut at New Orleans; we see Admiral Dewey through smoke and fire hoisting the flag in the Philippines. This same flag was carried to victory by Admirals Sampson and Schley in Cuba. This flag recalls the many battles bravely fought and grandly won. It symbolizes the principles of human progress and human liberty. The stars represent the unity and harmony of our states. They are the constellation of our country. Their luster reflects to every nation of the world. The flag of 1776, the old thirteen, has grown to be one of the great flags of the earth. Its stars reach from ocean to ocean. We see it leading the armies of Washington and Greene, of Grant and Sherman and Sheridan, and of Miles, Shafter and Merritt.
This is the flag of the “dawn’s early light” that was immortalized by Francis Scott Key—“The Star Spangled Banner.”
General Grant once said, “No one is great enough to write his name on the flag.”
A century under the stars and stripes has been the greatest century of progress in the history of the world. No other nation that has ever existed has carried forward such a banner. Its colors were taken from various sources and brought into one harmonious combination, and it “waves over a country which unites all nationalities and all races, and in the end brings about a homogeneous population, representing the highest type of[19] civilization.” It is not strange that this flag of Washington, of Hamilton, of Adams, of Jefferson; this flag of Jackson, of Webster, of Clay, this flag of Lincoln, of Grant and of McKinley should exert such world-wide influence. It holds a unique place in the nations of the world. It has spread knowledge and faith and hope among all classes. It means liberty with justice. Its international influence places it in the first rank. It twines itself among the flags of other nations, not for destruction or war, but for friendship and progress in the cause of humanity. In the councils of peace; in the conquests of war; in everything that pertains to government, in everything that pertains to the advancement of humanity, it calls forth the admiration of mankind. Under its influence the arts and sciences have been fostered, commerce has expanded and education has been made universal. It waves for the right and the harbors of the globe will salute this banner as a harbinger of progress and peace.
The youngest nation has the oldest flag.
It is of historical interest that our flag is older than the present flag of Great Britain, which was adopted in 1801, and it is nine years older than the flag of Spain, which was adopted in 1785. The French tricolor was decreed in 1794; then comes the flag of Portugal in 1830; then the Italian tricolor in 1848; then the flags of the old empires of China and Japan, and of the empire of Germany, which represents the sovereignty of fourteen distinct states established in 1870.
Prior to the Revolution, and indeed during the evolution of a nation through the crucible of war, separate and distinct flags were popular with the colonists. Nearly every colony had at least one. They were not abandoned until it became apparent the colonies were never again to be colonies, but to form a nation with one flag, one set of institutions and laws, a fact which inspired the visit of Washington to Betsy Ross as told in the foregoing papers. Many of the colonial flags were interesting.
The two upper flags of this group represent those used at Bunker Hill July 18, 1775, and bore these inscriptions: On one side, “An Appeal to Heaven,” and on the other, “Qui Transtulit Sustinet”—He who transported will sustain.
These were beautiful flags, and research shows that both colors were used.
Trumbull gives the red in his celebrated painting in the capitol at Washington, and other authentic accounts show that the blue flag was carried also—the color being the only difference in the two.
The pine tree flag which was a favorite with the officers of the American privateers, had a white field with a green pine tree in the middle and bore the motto, “An appeal to heaven.”
This flag was officially endorsed by the Massachusetts council, which in April, 1776, passed a series of resolutions providing for the regulation of the sea service, among which was the following:
Resolved, That the uniform of the officers be green and white, and that they furnish themselves accordingly, and that the colors be a white flag with a green pine tree and the inscription, “An appeal to heaven.”—Harper’s Round Table.

The striped Continental flag opposite the pine tree flag was of red and white stripes without a field.
The device of a rattlesnake was popular among the colonists, and its origin as an American emblem is a curious feature in our national history.
It has been stated, that its use grew out of a humorous suggestion made by a writer in Franklin’s paper—the Pennsylvania Gazette—that, in return for the wrongs which England was forcing upon the colonists, a cargo of rattlesnakes should be sent to the mother country and “distributed in St. James’ Park, Spring Garden and other places of pleasure.”
Colonel Gadsden, one of the marine committee, presented to Congress, on the 8th of February, 1776, “an elegant standard, such as is to be used by the commander-in-chief of the American navy; being a yellow flag with a representation of a rattlesnake coiled for attack.”
There is probably no more interesting revolutionary flag than this. The Washington Life Guard was organized in 1776, soon after the siege of Boston, while the American army was encamped near New York.
It was said to have been in the museum at Alexandria, Va., which was burned soon after the war of the rebellion, and nearly everything lost. It was of white silk with the design painted on it.
The uniform of the guard was as follows: blue coat with white facings, white waistcoat and breeches, with blue half gaiters, a cocked hat and white plume.
These were the colors selected by Franklin, Harrison and Lynch, and unfurled by Washington under the Charter Oak, January 2, 1776, and hereafter described.
The flag of the Richmond Rifles follows with the one used at Moultrie.
The latter was of blue with white crescent in the dexter corner and was used by Colonel Moultrie, September 13, 1775, when he received orders from the Council of Safety for taking Fort Johnson on James Island, South Carolina.
In the early years of the Revolution, a number of emblems were in use which became famous. The standard on the southeast bastion of Fort Sullivan (or Moultrie, as it was afterward named), on June 28, 1776, by Colonel Moultrie, was a blue flag with a white crescent in the upper left hand corner, and the word “Liberty” in white letters emblazoned upon it.
This was the flag that fell outside the fort and was secured by Sergeant Jasper, who leaped the parapet, walked the whole length of the fort, seized the flag, fastened it to a sponge staff and in sight of the whole British fleet and in the midst of a perfect hail of bullets planted it firmly upon the bastion. The next day Governor Rutledge visited the fort and rewarded him by giving him his sword.
Then comes the flag of White Plains, October 28, 1776, with little historical importance.
The flag made by Betsy Ross, under the direction of General Washington, Robert Morris, and Colonel George Ross, consisted of thirteen bars, alternate red and white, with a circle of thirteen stars in the field of blue.

The Moravian sisters of Bethlehem, Pennsylvania, gave to Count Pulaski’s corps, which he had previously organized at Baltimore and which was called “Pulaski’s Legion,” a beautiful crimson silk banner, embroidered in yellow silk and sent it with their blessing. Pulaski was at this time suffering from a wound, and was on a visit to Lafayette, whose headquarters were at Bethlehem. Count Pulaski was a Polish patriot, born March 4, 1747. After having bravely fought for Poland with his father and brothers until the Polish cause became hopeless, he came to America, arriving in Philadelphia in 1777. He entered the army as a volunteer, but performing such brave service at Brandywine, he was promoted to the command of cavalry with rank of brigadier-general. In 1778 Congress gave him leave to raise a body of men under his own command. Longfellow has most beautifully described the presentation of the flag in verse. Pulaski bore this flag to victory through many battles until he fell mortally wounded at Savannah, October 14, 1779. The banner was saved by his first lieutenant, who received fourteen wounds, and delivered it to Captain Bentalon, who on retiring from the army, took it home to Baltimore. It was carried in the procession which welcomed Lafayette in 1824, and was then deposited in the Peale Museum. In 1844 Mr. Edmund Peale presented it to the Historical Society of Maryland, where it is now preserved in a glass case. These are interesting historical facts.
Flag of red and blue bars with serpent stretched across and words, “Don’t Tread on Me.”
Another flag of white, with blue bands top and bottom and a pine tree in center, with the inscriptions: Liberty Tree and An Appeal to Heaven.
Another use of the rattlesnake was upon a ground of thirteen horizontal bars alternate red and white, the snake extending diagonally across the stripes, and the lower white stripes bearing the motto—“Don’t Tread on Me.” The snake was always represented as having thirteen rattles, and the number thirteen seems constantly to have been kept in mind. Thus, thirteen vessels are ordered to be built; thirteen stripes are placed on the flag; in one design thirteen arrows are grasped in a mailed hand; and in a later one thirteen arrows are in the talons of an eagle.
One of the favorite flags also was of white with a pine tree in the center. The words at the top were “An Appeal to God,” and underneath the snake were the words, “Don’t Tread on Me.” Several of the companies of minute men adopted a similar flag, giving the name of their company with the motto “Liberty or Death.” This flag is familiar to the public as the annual celebrations bring out descriptions of it in the press.
Within the last few years special flags have been designed for the President, the Secretary of the Navy and Secretary of War. The President’s flag is a very beautiful blue banner, in the center of which is a spread eagle bearing the United States shield on its breast, with the thirteen stars in a half circle overhead. It is flown at the main mast-head of naval vessels while the President remains on board, and on being hoisted it is the signal for the firing of the President’s salute.
The colonial music was mostly borrowed and adapted to the occasion. The Pilgrims had more important duties to perform and in those years of stirring events no one was in a mood to write music.
The first song to be used was that old and familiar one, “Yankee Doodle.” It made a powerful rallying cry in calling to arms against England. It is so old that it is impossible to decide just where the term came from.
It has been traced back to Greece—“Iankhe Doule,” meaning “Rejoice, O Slave,” and to the Chinese—“Yong Kee,” meaning “Flag of the Ocean.” It is said the Persians called Americans “Yanki Doon’iah,” “Inhabitants of the New World.” The Indians too, come in for their share of the credit of originating the term, as the Cherokee word “Eankke,” which means “coward” and “slave,” was often bestowed upon the inhabitants of New England.
At the time of the uprising against Charles the First, Oliver Cromwell rode into Oxford, on an insignificant little horse, wearing a single plume in a knot called a “macaroni.” The song was sung derisively by the cavaliers at that time. The tune is said to have come from Spain or France, there being several versions of the words.
It came into play when our ancestors flocked into Ticonderoga in answer to the call of Abercrombie. At that early day no one refused, but all answered the call and came equipped as best they could, but hardly any two alike, and to the trained English regulars must have presented a ridiculous appearance. Dr. Shamburg changed the words of the old satire to fit the new occasion. But in less than a year it was turned by the Yankees against the English in the form of a rallying cry and possessed new meaning.
History had emphasized it, and with the accompaniment of the shrill pipe and half worn drum calling the simple cottagers together, it must have aroused all their noble and sturdy patriotism.
Who that has viewed that stirring picture in the Corcoran Art Gallery at Washington, “Yankee Doodle,” could fail to catch the inspiration of the scene. The old man with his thin grey locks, but head erect and face glowing with enthusiasm as he keeps time to the old tune, followed by the small boy with his drum. One scarcely knows whether humor or pathos predominates: but certain we are that all alike stepped to its chords; it found an answering echo in each heart and led them on to glory.
Rev. Samuel Francis Smith was born in Boston October 21, 1808, and graduated in the class of ’29 from Harvard University. He enjoyed the honor of having for his classmate Oliver Wendell Holmes, in whose beautiful poem, entitled “The Boys,” the name of the author of “America” is affectionately mentioned.
“America” was written in 1832, the tune being the old one of “God Save the Queen,” and first rendered on the 4th of July of the same year by the children of Park St. Church, Boston.
Peace follows where it finds the Old Thirteen, the nucleus around which the other stars have gathered in their glory.


The Home Magazine contains the following beautiful suggestion regarding the placing of the stars on the flag:
Number 1 is the field of our first stars and stripes made by Betsy Ross.
Number 2 represents that field of flag of 1814 which inspired the “Star Spangled Banner.”
Number 3 the field of 1818 designed by Capt. S. C. Reid.
Number 4, field of our present flag.
Although there is no law saying who shall arrange the stars on our flag, or how they shall be arranged, it is customary for the changes to be made in the war department when new states have been admitted to the Union.

The incongruous variations in figures A, B, C, which are reproductions of unions taken from new flags, made by different manufacturers, would not exist if there was a law fixing the arrangement of the stars.
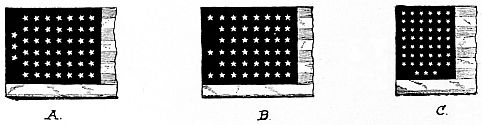
[33]It is believed by many that the stars on our flag should be arranged into a permanent and symmetrical form, fixed by law, instead of the present changeable and uncertain form, which is subject in a great measure, to the caprice or convenience of the flag maker. It is not generally known that among the many flags in use in our country to-day, there is an utter lack of uniformity in the arrangement of the stars.
In the selection of a form, three different things should be considered—its historical significance, symmetry, and adaptability. The stars should be so arranged that it will not be necessary to make any noticeable change when new ones are added. The stars should always remain equal in size, representing the equality of the states.

In the form which is submitted, No. 8, with the group of thirteen stars in the center, representing the thirteen original states, they are arranged in exactly the same form as they appear on the great seal of the United States. The circle containing twenty-three stars, represents the states which were admitted to the Union up to the close of the civil war. These two features are symbolic of the two great events in the nation’s history—the one which brought our flag into existence, and the other which made its life permanent by welding the sisterhood of states into a perfect and indestructible union. The circle is also symbolic of unity, peace, and preservation.
The outside circle of nine stars, represents the states which have been added to the Union since the civil war. New stars can be added to this circle without changing the symmetry of the arrangement, as will be seen by reference to the illustration. As this circle will always remain an open one, there will always be room for one more star, and it is thus significant of progression.
One great advantage in this form is, that it is suggestive of a constellation, and thus carries out, as far as practicable, the idea of the framers of the resolution of 1777 in establishing the flag.
John F. Earhart is the author of the above description of the different forms of flags.
The historians who have searched the archives of ancient and medieval times tell us that this has been a symbol of liberty since the Phrygians made the conquest of the eastern part of Asia Minor.
After the conquest they stamped it on their coins, and to distinguish themselves from the primitive peoples they used the liberty cap as a head dress. The Romans used a small red cap called a “pileus,” which they placed on the head of a slave in making him free, and when Caesar was murdered a Phrygian cap was carried through the streets of Rome proclaiming the liberty of the people. The liberty cap of the English is blue with a white border.
It remained for the United States to adopt the British cap, adding to it the crescent of thirteen stars. Generals Lee and Schuyler, with the Philadelphia Light Horse troop, adopted it in 1775. This is the famous troop that escorted Washington to New York.
It is most familiar to us as seen on our coins, on which it was first used after the Revolution as a symbol of freedom.
Edward Everett Hale, in one of his impressive orations, says: “The starry banner speaks for itself; its mute eloquence needs no aid to interpret its significance. Fidelity to the Union blazes from its stars; allegiance to the government beneath which we live is wrapped in its folds.”
The Stars and Stripes was officially first unfolded over Ft. Schuyler, a military port in New York state, now the city of Rome, Oneida county. It was first saluted on the sea by a foreign power, when floating from the masthead of the Ranger, Capt. Paul Jones commanding, at Quiberon Bay, France, February 14, 1778. The salute was given by Admiral La Motte, representing the French government.
The first vessel over which the Union flag floated was the ship Ranger, built at Portsmouth, New Hampshire, whose gallant commander was the famous Paul Jones.
Its first trip around the world was on the ship Columbia, which left Boston September 30, 1787, commanded by Captains Kendrick and Gray. It was three years then in circling the globe. To-day it waves in every clime, on every sea.
It is pleasing to note how Franklin, when minister to France, secured the ship Doria from the French and gave to Paul Jones the command, who immediately renamed the old ship “Bon homme Richard,” in honor of Franklin.
The term Old Glory is said to have been originated by an old sailor—Stephen Driver.
While upon the seas he performed an act of bravery for which he was rewarded by the gift of an American flag, whereupon he pledged its givers to always defend it faithfully.
At the outbreak of the civil war he was living in Nashville, Tenn.
In order to keep the flag safely he concealed it in a bed-quilt under which he slept. To the enemies of the Union he declared that Old Glory would yet float from the staff of the Tennessee state house, and sure enough when Nashville fell into the hands of Gen. Buell he secured the flag from its hiding place and hoisted it to a more fitting position on the state house—thus his nick-name for it became popular.
He said, “Swear anew and teach the oath to our children, that with God’s help the American Republic shall stand unmoved though all the powers of piracy and European jealousy should combine to overthrow it. That we shall have in the future as we have had in the past, one country, one constitution, one destiny; and that when we shall have passed from earth, and the acts of to-day shall be matters of history, and the dark power which sought our overthrow shall have been overthrown, our sons may gather strength from our example in every contest with despotism that time may have in store to try their virtue, and that they may rally under the Stars and Stripes with our old time war cry,
This term originated at the time of our war with England in 1812. Provisions were purchased at Troy, N. Y., and the agent was Elbert Anderson, the work being superintended by Ebenezer and Samuel Wilson, the packages being marked E. A. U. S. Samuel Wilson was known all over as Uncle Sam and he was often joked about his amount of provisions, then the newspapers took it up and the term Uncle Sam came into general use and is typical of our increasing national prosperity.[37] Quite recently a portrait of an actual personage whose features are identical with those made familiar by caricatures of Uncle Sam, was found in possession of a family near Toledo, Ohio. The portrait was painted about 1818, but nothing is known of the shrewd, kindly old man represented. His face was undoubtedly the origin of the accepted caricature.
Jonathan Trumbull, governor of Connecticut, was a warm friend of General Washington, who had great confidence in his judgment.
When in need of ammunition and the question arose as to where they could get the necessary means for defense Washington said: “We will consult Brother Jonathan.”
After that whenever they needed help the expression became a common one and naturally came to mean the United States Government.
Our bald headed eagle, so called because the feathers on the top of the head are white, was named the Washington eagle by Audubon. Like Washington it was brave and fearless, and as his name and greatness is known the world over, so the greatest of birds can soar to the heights beyond all others.
In 1785 it became the emblem of the United States.
It is used on the tips of flag staffs, on coins, on the United States seals, and on the shield of liberty.
It is not generally known that the tassels which are pendent customarily from the upper part of banners and standards, and the fringe which surrounds them are relics of the practice of observing sacred emblems. They originated in pagan devices and the garments of priests and were consecrated to specific forms of worship.
Sacred history is full of instances of the consecration of tassels and peculiar fringes to special sacerdotal uses. Blue was early the emblem of purity and innocence and that fact accounts for the predominance of that color in the ecclesiastical badges of these early times. When the use of the tassels passed into profane customs, they were used as ornaments for national standards and for royal girdles, and it was not infrequent that they were first blessed by the priests. It has followed naturally that this use has continued up to the present time, although now it is retained probably because of the artistic effect of the swinging pendants.
The flag in the White House which formerly hung in the center of the largest window in the east room, has a unique history.
It is woven of silk in one piece without a seam. There are gold stars in the field and among them are seen the words in French, “Popular subscription to the Republic of the United States, offered in memory of Abraham Lincoln. Lyons, 1865.”
As the colonies had their flags of different kinds so the states one by one adopted special flags and nearly all the states of the Union now have a state flag or regimental color. In some states this emblem is established by law, in other states by the[39] military department or the governor. There are a few states in which this special flag is covered with particular devices chosen by the caprice of the donor or the officials by whom the flag was authorized, but in all these cases, the state arms form a part of the emblazonment. There is a general feeling, however, that these special states flags should have no legal recognition, and that the only flag to be thus recognized should be the Stars and Stripes.
It is interesting to know how and why the little white flag which is always looked upon with breathless interest in the emergencies that call it forth, first came to be used.
When carried by the lone soldier on horse or on foot between the armies it has a significance that is always respected, and on the sea the hoisting of this flag at the ship’s mast or the carrying of the flag of white by boat to the enemy stops the firing of the guns. The custom originated in the church in the tenth or eleventh century.
Curiously enough while it is the only flag that is to-day used by all nations of the earth alike, no regularly made flag of truce is found in the flag lockers of nations. It is improvised when the emergency arises for its use. In the late war with Spain, such flags of truce as were used were made of blankets, sheets, table cloths. It is a flag that commands the enemy’s respect. An account of the origin of the flag of truce lately published, is as follows:
“La peace et la treve de Dieu” (The peace and the truce of God) was an agreement between the turbulent barons and the church, as severe injury and loss was most frequently the result of the private warfares which constantly raged.
To protect itself, but more especially to preserve justice and moral order, the church established a system which has exercised a beneficent influence down to this day.[40]
The agreement stipulated a cessation of hostilities on certain festivities and saint’s days, and from Saturday to Monday. The barons and warrior class pledged during the time of war to extend full protection to women, pilgrims, priests, monks, travelers, merchants and agriculturists; to abstain from the destruction or injury of farm implements, the burning of crops, and the killing of live stock of the peasants. Penalties in violation of this agreement comprised money fines, bafflings, banishment, and excommunication.
Originating in the south of France this system was soon adopted through the whole of France, Italy, Spain, Germany, and England, and in 1095 Pope Urban II. proclaimed its universal extension throughout Christendom.
In time the Crown assumed this protective power, and the phrase was changed to “La paix et la treve du Roi,” or “The peace and truce of the king.” The republics recognized the time-honored institution, and the simple unfolding of a white cloth will instantly cause a cessation of hostilities. The adoption of a white emblem appears to be lost in tradition, as authorities do not reveal it. Doubtless it is similar, or may have arisen through a belief in the white Samite which shielded the Holy Grail from the gaze of unbelievers. Emblematic of purity, associated with the mythical knights of the Round Table, and used in the Crusades, it is probable that this sacred truce flag may have originated from the Samite of the Holy Grail.
At the present time, if presented during an engagement firing is not required to cease; nor, if the bearer be killed or wounded, is there ground for complaint. The truce emblem can be retained if admitted, during an engagement. Penalties are incurred if the truce emblem be wrongfully used, the severest being the ignominious death of a spy.
The following was written at the tomb of Washington in 1833 by Dr. Andrew Reed, English philanthropist:
| Valiant without Ambition. |
Discreet without Fear. |
Confident without Presumption. |

Elizabeth Griscom, a daughter of Samuel and Rebecka (James) Griscom of Philadelphia, was born January 1, 1752. They were “Friends” and the young Elizabeth grew into a most charming, bright and beautiful girl of prepossessing manners and plain and quiet tastes.
Her father was a noted builder and assisted in the erection of the state house, now Independence Hall. His house, shop and a very large garden were on Arch street, between 3d and 4th streets.
Elizabeth, or Betsy, as she was fondly called, was the seventh daughter. Her birthday was the first day under the new Gregorian calendar.
It was frequently said by the family that “she was born the first day of the month, the first day of the year, the first day of the new style.” She was well trained by her mother, became very expert with her needle and was very fond of embroidery.
Among her many admirers was John Ross, son of Æneas Ross, assistant rector of Christ Episcopal Church. The young man was a nephew of the Hon. George Ross, delegate to Congress, one of the signers of the Declaration of Independence.
In December, 1773, at the age of twenty-one years, Elizabeth married John Ross, an estimable young man. He was an Episcopalian, and in consequence of her marrying out of meeting, she was disowned by the Friends.
The first husband of Betsy Ross was of distinguished ancestry. The Hon. George Ross, of New Castle, Delaware, had by his first wife, two sons: John, who died May 5th, 1776; and Rev. Æneas, born Sept. 9th. 1716, who was father of John Ross (husband of Betsy Ross).
By his second wife he had Hon. George Ross, signer of Declaration of Independence, born 1730, died 1780; also one daughter, Gertrude, who married George Read, also a signer of the Declaration of Independence; also a son, Jacob, a physician.
The Hon. George Ross was a noted lawyer, and a resident of Lancaster. He was a brave soldier and a man of ability.
John Ross was an apprentice with a man named Webster, an upholsterer on Chestnut street. It was with him that John and afterwards Betsy, learned the trade before they “ran off” to be married.
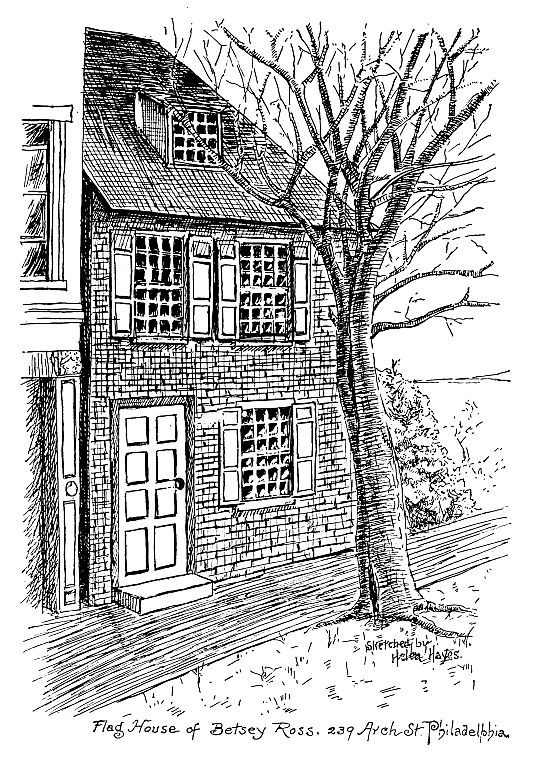
They then set up business for themselves, first on Chestnut street and afterwards moved to the little house on Arch street, which was a simple building when first occupied by them. It was built some time after 1752, notwithstanding romantic stories to the contrary. The first room was utilized as a shop; the store front not having been added until about 1858.
It was in this house that the flag was made later on.
In 1775 John Ross was injured while guarding military stores on the wharf, from the effects of which he died at this house in January, 1776. He was buried in Christ Churchyard, 5th and Arch streets. He left no children.
Mrs. Ross continued the upholstery business and the manufacture of flags.
Betsy Ross married for her second husband, at Old Swedes Church, Philadelphia, Captain Joseph Ashburn, June 15, 1777, and to them were born two daughters:
Jillah, born September 15th, 1779. Died young.
Eliza, born February 25th, 1781. Who married Capt. Isaack Silliman, May 29th, 1799. After Capt. Silliman’s death in the army, his wife Eliza lived with her mother, Betsy Ross, until her death in 1836.
To them were born four children:
Joseph Ashburn; Emilia; Jane; Willys.
Emilia left one daughter, Mrs. Mary Sidney Garrett, a widow and childless. She is the only living descendant of the second marriage.
Joseph Ashburn was taken prisoner by the British on the sea, and with the other soldiers was taken to England where he died in Mill Prison, March 3d, 1782. The prisoners were all given an opportunity to enter the British service, and on their refusal were thrown into prison. John Claypoole, a comrade, and also a prisoner of war, nursed and cared for Ashburn until he died. He brought home to his widow, on his release, the diary of Ashburn, together with messages to his wife, with whom he fell in love and afterward married.
John Claypoole, son of William and Elizabeth Claypoole, of Philadelphia, was married to Elizabeth Ashburn (Betsy Ross) the 8th of May, 1783, at Christ Church. His ancestor was James Claypoole, who came to America as the friend of William Penn; and from whom all the Claypooles mentioned are descended. He was a brother of Sir John Claypoole, who married Elizabeth, daughter of Oliver Cromwell.
The children of John and Elizabeth Claypoole were: Clarissa Sidney, born April 3, 1785, 9 a. m.; Susanna, born November 15, 1786, 4 p. m.; Rachel, born February 1, 1789, 7 p. m.; Jane, born November 13, 1793, 7 p. m.; Harriet, born December 20, 1795, 5 a. m., died October 8, 1796.
There is an old Bible over a hundred years old, which has a record of all these births and those of the Ashburn daughters; and of the deaths in the handwriting of John Claypoole. It was “The legacy of Sarah Hallowell to her niece, Elizabeth Claypoole,” that is, Betsy Ross.
John Claypoole was wounded in the battle of Germantown which, with imprisonment and the hardships of war, so impaired his health that he never regained it. So it may be truthfully said that the lives of her three husbands were sacrificed to their[46] country, and her experience in these very important events in her life is certainly heroic. John Claypoole died August 3, 1817.
Betsy Ross attended Christ Church, Philadelphia, with her first husband and after his death continued in attendance until the Free Quaker Society was organized in 1793. The pew in which she sat was quite near one occupied by Gen. Washington, and is marked by a brass plate bearing these words:
“In this pew worshipped Betsey Ross, who made the first flag.”
All Friends who took part in the Revolution were disowned by “The Society of Friends.” After the war, they organized a society of “Free Quakers” often called “Fighting Quakers.”
As the time went by, nearly all were taken back into the original “Society of Friends,” but Clarissa Wilson and John Price Wetherell, of Philadelphia, were the last of the Free Quakers. They used to attend the little meeting house at 5th and Arch streets until there were just the two of them. In the fall of 1830 they decided it was unwise to have the little meeting house heated for them, so after that Clarissa Wilson attended the Orange street meeting house, but was never again received into the original society. She did not wish to be. She died a Free Quaker. Betsy Ross, her mother, lived to be 84 years old and died in 1836. The following are from the original autographs of Betsy Ross and her husband:
| Clarissa Sidney (Wilson) | Elizabeth Griscom | twins | married | James Campion | ||
| Sophia | “ | Charles Hildebrandt | ||||
| Aquila Bolton | married | Sarah Ghriskey | ||||
| Clarissa Sidney | “ | James Hanna | ||||
| Susan | “ | Abram Sellers | ||||
| Rachel | “ | Jacob Wilson Albright | ||||
| Susanna (Satterthwaite) | James, | bachelor | ||||
| Edwin | married | Martha Hallowell | ||||
| Abel | “ | Mary Burton | ||||
| Sidney | “ | Cyrus Kinsey | ||||
| Mary | not married | |||||
| Susan | married | David Newport | This couple still living in 1898 at Willow Grove, Philadelphia. | |||
| Rachel (1st, Edward Jones; 2nd, John Fletcher) | Margaretta | married | —— Elliot | |||
| Mary | “ | Arthur Wigert | ||||
| Daniel | not married; died at 21 yrs. of age | |||||
| Jane (Canby) | Catharine | married | Lloyd Balderston | |||
| Elizabeth | unmarried | |||||
| Charles | married | Susanna Kirk | ||||
| John | “ | Elizabeth Boustead | ||||
| William | “ | Louise Prescott | ||||
| Caleb | “ | Mary Preswick | ||||
| George | “ | Matilda Goodwin | ||||
| Jane | “ | Abel Hopkins | Nephew of Johns Hopkins | |||
| Mary | “ | Robert Culin | ||||
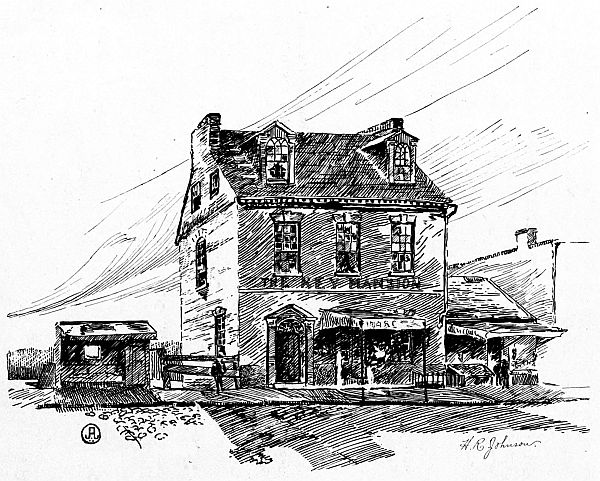

The old Key mansion is one of the historic places that still remains on the banks of the Potomac in Georgetown, to remind us that here lived Francis Scott Key, the author of the national hymn “The Star Spangled Banner.” In unveiling to him the monument which had been erected at Fredericksburg, Maryland, during the past summer (1898), the Hon. Murat Halsted paid an eloquent tribute to this poet, who crystallized the best thought of the American people in giving to them “The Star Spangled Banner.” “O’er the land of the free and the home of the brave,” this flag still waves. Freedom to-day has a broader meaning than in the days of 1814. Slavery has been abolished and freedom has spread her wings o’er all the land. The history of the writing of this beautiful song can be told in a few words. It was an inspiration. The British had captured a friend of Francis Scott Key, Dr. Beans, and when Key heard of it, he called upon President Madison, who furnished him with a vessel to go to the British Admiral Cockburn’s ship, to endeavor to secure his release. General Ross, of the British army, agreed to release him, but insisted upon Key’s remaining on the admiral’s ship until after the bombardment of Fort McHenry, which was then taking place. Key was intensely anxious and in the early morning, he looked across to the fort and saw that “the flag was still there.” It is said that he then wrote a sketch of the “Star Spangled Banner” on the back of a letter. The burning of the capitol and of the White House a few days previous by them are well known matters of history. A few days after, the British fleet sailed for Baltimore, where they were gallantly repulsed with the loss of their commander, General Ross. The fleet in passing Mount Vernon, lowered their flags out of respect to the memory of the immortal Washington, whose remains are here entombed.
Key was born in Frederick county, Maryland, August 1, 1779. He graduated at St. John’s College, Annapolis, Maryland.

This beautiful song, which is set to the tune of “John Brown,” was written by Julia Ward Howe in 1861 just after her escape from a rebel raid when witnessing, with friends, a review of troops near Washington. In her dreams she was inspired by the beautiful thoughts and she immediately arose, and hastily noted them down.
It is considered one of the grandest battle hymns of the Republic and has been a favorite with several of our presidents.
This beautiful poem was written during the late war with Spain, and is inserted here, as entwined among the lines there is a sentiment that appeals to the hearts of the whole people.
This historic old flag, also known as the Paul Jones Flag, composed of thirteen bars and but twelve stars, was unfurled by him and borne on the Bon Homme Richard September 23, 1776, during the action with the British frigate, the “Serapis,” and is probably the first flag bearing the stars and stripes ever hoisted over an American vessel of war, and also the first ever saluted by a foreign naval power.
This flag has been in the family of Mrs. H. R. P. Stafford, of Cottage City, Martha’s Vineyard, since 1784, and bequeathed by her to the National Museum at Washington.
But it must be remembered that Washington adopted the flag made by Betsy Ross five months previous to this.
In the little city of Shawneetown which is next in age to Kaskaskia, and consequently the second oldest town in the State, there reposes a relic of rare value, a genuine flag of Colonial days. It was found in the attic of the “Posey” building and is supposed to have been placed there by General Posey, who served under Washington in the Revolutionary war. The flag is now owned by Mr. Robinson, an eminent scientist, who for a life-time has taken pains to collect and preserve many valuable things for Illinois’ posterity to see, especially rare Indian curios excavated from in and around Shawneetown, which site was once the pottery of the Shawanee Indians.
The old flag is in rather a good state of preservation although faded and marred. Its thirteen stars are arranged similar to those on “Paul Jones’ flag”—in bars, but not horizontal. The[59] rows of stars are placed diagonally and consist of one, three, five, three and one, which leaves a star in each corner and five forming the center diagonal. Illinois’ “Old Thirteen” has been framed and covered with glass to preserve it from the ravages of Time and to save it for the eyes of the children of coming generations.
This song sometimes goes by the title of The Red, White and Blue. It was written and composed by David T. Shaw in 1843; later on, however, it was rearranged by Thomas à Becket, Esq., an Englishman.
This was written by Hon. Joseph Hopkinson, of Philadelphia, at the request of a young friend—a theatrical singer whose appeal was for a patriotic song suitable for the times. England and France were quarreling and this country was necessarily a good deal agitated.
It was set to the music called The President’s March, which was composed by Philip Roth, a German, for Gen. Washington’s inauguration in the City Hall in New York. A great many people were for standing by our ally, France, but Gen. Washington insisted on strict neutrality; thus the song was requited to voice this sentiment. It appealed at once to both parties and charmed every one who heard it—was sung night after night, audiences joining in the chorus.
Washington took the oath of office as first President of the United States on the steps of Federal Hall in Wall street, New York city, April 30, 1789, and for a short time the seat of government was here before being changed to Philadelphia.
The history of how Alexander Hamilton, the great Secretary of the Treasury under Washington, made the trade with Jefferson whereby the present site of the capital was selected is interesting, as showing that Hamilton, while constructing a powerful centralized government with skill and ability, as even Jefferson’s biographer admits, cared little about the location of the capital itself. The Southern States wanted it on the Potomac; the Middle and Eastern States wished it to be further north. Hamilton wanted the government to assume the State debts, brought about by the war. Jefferson and his party were opposed to it. Hamilton finally secured the support of Jefferson and his friends in Congress in support of the assumption, while he delivered to the Jefferson party the location of the capital at Washington. In after years this was a source of great discomfort to Jefferson, he claiming to have been duped by Hamilton.
In 1800 Napoleon forced Spain to cede Louisiana back to France, after thirty-seven years of ownership. The idea of LaSalle, who had looked forward to establishing here a new France, was long since forgotten, but Napoleon, now in the zenith of his power, formed the brilliant plan of colonizing this great country from the Mississippi to the Rockies and from the Gulf to the British possessions in the North, thereby hemming in[64] the United States. Napoleon tried to subdue the Island of San Domingo, with the idea of using it as an outside base of supplies, but his troops were terribly slaughtered by the natives, and the army that he intended to send to Louisiana never came. About this time Napoleon was busy looking after England, and as after events proved needed all of his troops at home. He succeeded, however, in creating great alarm in America. The settlers west of the Alleghenies were especially disturbed. The Mississippi was practically closed for navigation, as the Spaniards, who held possession of New Orleans, would not allow them to bring their products down the river and reship, as had long been the custom.
President Jefferson appointed James Monroe and Livingston, then our minister at Paris, to call on Napoleon, and, if possible, purchase West Florida and New Orleans, the amount to be paid not to exceed $3,000,000.
Napoleon was very much in need of money to conduct his war against England, and his disastrous attempt to subdue the natives of San Domingo probably made him decide to offer the whole of Louisiana, which he did for $15,000,000. This great purchase was consummated by Monroe in 1803. This was the greatest act of Jefferson’s administration, but the people bitterly opposed it, claiming that we had no use for the additional territory. Napoleon said that in selling Louisiana to the United States “he had placed a thorn where England would some day feel it.” The acquisition of Louisiana more than doubled the area of the United States, which was 827,844 square miles, increasing it to 1,999,775 square miles. It constitutes about ten of our largest States to-day.
This State, with all its old traditions, has seen many vicissitudes. It belonged to Spain from 1565 until 1763, nearly two hundred years, when Great Britain traded Cuba for it. In 1781, the British were expelled by Spain and that country again assumed possession of Florida. In a very few years the inability which Spain has ever shown to properly govern her Colonial possessions was manifest. A war broke out between the Spaniards and the Seminole Indians of Florida and soon the whole State was in a condition of virtual anarchy. Emboldened by their successes in warfare, the Indians molested the frontier of Georgia. The Government of the United States then took an action which constituted a precedent for its action in invading Cuba in the late war with Spain. It despatched a military force into Florida under command of General Andrew Jackson. He virtually took possession of Florida and speedily restored order. His conduct excited much debate in Congress and in the Cabinet, a strong anti-expansion sentiment developing. The matter was finally settled by purchasing Florida from Spain for $5,000,000. This was done in 1819. Emigration poured into the territory from the States further north and soon the value of Florida as an acquisition to the country became evident and the anti-expansion sentiment died away. In 1845 Florida was admitted into the Union as a State. In 1861 it seceded with other Southern States and returned again to the Union in 1868.
It may be pertinent right here to say that when the United States buys or comes into possession of a tract of land it becomes the property of the country and is called a Territory, and under the Constitution it is so treated, without representation in Congress until such time as it is admitted into the Union and becomes one of the United States.
This great Territory comprising 370,472 square miles originally belonged to Mexico. In 1820 Moses Austin, a native of Connecticut, obtained a grant of land and threw it open to settlement by people from the United States, mostly the Southern States. In a few years more than 20,000 had settled there and the strong Anglo-Saxon spirit of liberty began to rebel against the oppressive Mexican rule. In a few years this feeling burst into an open revolt. Texans met and declared their independence and formed a Republic and placed an army in the field under Gen. Sam. Houston. He met the Mexicans under Gen. Santa Anna at San Jacinto in 1836 and gained a complete victory, thus achieving the independence of Texas. Next year Texas applied for admission into the Union but no action was taken by Congress for several years. Meantime in the north a strong sentiment had developed against the institution of slavery. The subject was vigorously agitated in the pulpit, in literature and in public. The Southern people, perceiving the strength of the opposition to their favorite institution, determined in self defense to acquire more territory for the sake of the strength additional votes would give them, and so in 1844 the proposal to admit Texas came up in Congress in earnest.
No concealment of the underlying purpose was made by the Southern Congressmen who led the movement. A bitter struggle followed but the annexationists prevailed and in 1845 the “Lone Star State,” as Texas had been called, was added to the Union. The South welcomed the new comer with great demonstrations, but the greetings of the North were not cordial, for in that section it was clearly understood that a great extension was given to slave territory.
The vast territory included in these two Territories was acquired mostly from Mexico in 1848 as one of the terms of the treaty of peace between the United States and that country made after the war of 1846-47. The war with Mexico was brought about by the refusal of the Mexican Government to concede the claims of Texas to land between the Rio Grande and the Nueces Rivers. The actual rights in the case were somewhat obscure, but war was eagerly undertaken by the Southern people, who believed that a further extension of slave territory would be the ultimate result. The North was less enthusiastic, for this reason, but sent a quota of troops into the field before whose valor, directed by commanding officers who later became prominent in the great war of the Rebellion, the Mexican armies were defeated. The United States paid Mexico $15,000,000 for the territory ceded under the treaty and in addition paid $3,500,000 in settlement of the claims of private individuals. The boundary line remained in dispute for five years more, until 1853, when James Gadsden negotiated a treaty with Mexico settling all questions. Under its terms the United States gained the Mesilla Valley, forming the southern part of what is now New Mexico and Arizona, and comprising 20,000,000 acres. The United States paid Mexico $10,000,000 for this land which was afterwards known as the Gadsden purchase and is so marked on the larger maps issued by the Interior Department at Washington. Including the territory acquired by the Mexican war, the State of Texas and that included in the Gadsden purchase, the whole area is sufficient to make one hundred and seventy States the size of Connecticut.
This great State was ceded to us by Mexico, being part of that country before the war. In 1848 gold was discovered by Capt. Sutter in a river near Sacramento. On examination gold was found to occur in abundance. News of the wonderful discovery drew an immense emigration into California from all parts of the world, the majority of those traveling across the plains by the way of the Isthmus of Panama being, of course, from the United States. The people who poured into the golden State lost no time in applying for admission into the Union. In 1849, one year after Sutter’s discovery, the State presented itself at the door of Congress. In 1850 California was admitted. The celerity of the operation was due to the fact the North recognized, that California would offset to an extent the growth of slave territory actually made by the admission of Texas and threatened in Arizona and New Mexico, areas peculiarly adapted by climate and other conditions to the institution of slavery.
Oregon, Washington and Idaho were part of what was called the great Oregon country. They were acquired under an agreement with Great Britain in 1846. The United States claimed the territory up to the parallel of 54° 49′, but a compromise was made and the 49th parallel accepted as the dividing line between the United States and the British possessions. The country north of the line is now known as British Columbia.
Alaska, whose area is equal to about 120 States the size of Connecticut, became the property of the United States in 1867 by purchase from Russia. The sum paid for it was $7,000,000. The purchase, negotiated by Secretary of State Seward, was denounced by many as an extravagant use of public funds because Alaska appeared to be practically worthless. The Government,[69] however, unheeding the kind of criticism paid $200,000 in addition to the first price named to extinguish the rights of various commercial companies and thus acquired a clear title. It was soon found the supposed ice bound land was full of wealth in fisheries and lumber, the income from seal fisheries alone amounting in one year to $2,500,000. Alaska’s wealth in gold was, however, not suspected until recent years and not demonstrated until the summer of 1896, when the now famous treasure ship arrived in San Francisco having on board over $600,000 in gold, the property of 50 prospectors who had washed it out of the bars of the creeks emptying into the Yukon river. Alaska, the “ice bound, inhospitable desert of the north,” as it was designated in 1868, was a Mecca for the world for the next few months and thousands braved the dangers of Chilkoot pass to search for the yellow metal, and at this time it is estimated over 50,000 people are in that part of the Territory which two years ago was practically uninhabited.
President Grant in his second inaugural address, March 4, 1873, thus expressed himself: “I do not share in the apprehension held by many as to the danger of governments becoming weakened and destroyed by reason of their extension of territory. Commerce, education and rapid transit of thought and matter by telegraph and steam have changed all this. Rather, I believe that our Great Maker is preparing the world, in his own good way to become one nation, speaking one language, and when armies and navies will no longer be required.”
These great and interesting acquisitions to our territory have not yet entered the blue field of our flag. To a great nation and to a humane people they will look for that protection which[70] has been pledged to them; and if it is decided that these people shall live under our starry flag, no one can look back over its history and doubt the strength and breadth of its folds.
This historic and patriotic order was named after the famous Roman Dictator and Patriot, Cincinnatus, and was founded in May, 1783, on the banks of the Hudson, by the American and French officers who had gathered there at the close of the Revolutionary war.
The resolution adopted at the forming of the society contained these words: “To perpetuate, therefore, as well the remembrance of this vast event as the mutual friendships which have been formed, of common danger, and, in many instances, cemented by the blood of the parties, the officers of the American Army do hereby, in the most solemn manner, associate, constitute and combine themselves into one society of friends to endure as long as they shall endure, or any of their eldest male posterity, and in failure thereof the collateral branches who may be judged worthy of becoming its supporters and defenders.”
Owing to the great distances between the different States, and the fact that at that time the means of transportation were slow and uncertain, it was deemed best to form societies in each of the thirteen States. This was done. One was also organized in France under the patronage of Louis XVI.
The original members included the names of Washington, Greene, Hamilton, Lafayette, Rochambeau, and Paul Jones; in fact, all the historic military and naval characters of the Revolution. Among the honorary members elected for their own lives only were the names of many signers of the Declaration of Independence.
On the pages of the country’s history appears no darker[71] spot than that placed there by the Congress of the United States in its failure to give its soldiers the promised half pay for their services, forcing them to leave their homes and emigrate to the wild lands west of the Alleghenies, which were given to them in lieu of money. On this account several of the orders in the different States went out of existence.
The patriotic societies of the country, the names of which are given here, were all formed for the purpose of perpetuating the memory of events and of the men who in military, naval and civil positions of high trust and responsibility, “kept step to the music of the Union.”
The preservation of historical records and manuscripts and the promoting of fraternal intercourse among their members are the main inspirations of all of these patriotic societies:
Society of Colonial Wars.
Sons of the Revolution.
Society of the Sons of the American Revolution.
Military Order of the Loyal Legion of the United States.
Grand Army of the Republic.
Sons of Veterans U. S. A.
There are three great patriotic societies, organized by the women of America, known as the Daughters of the Revolution, Colonial Dames, and the Mayflower, that may outstrip all other societies in the value and importance of their work.
Commodore Perry carried our flag in 1854 into the harbors of Japan, and the first commercial treaty with that nation was made by and with the United States.
The objects of the American Flag House and Betsy Ross Memorial Association are to purchase and preserve the historic building, situated at No. 239 Arch Street, Philadelphia, Pa., in which the first flag of the United States of America was made by Betsy Ross and subsequently adopted by Congress, June 14th, 1777, and to erect a national memorial in honor of this illustrious woman.
All loyal American hearts will welcome the glad tidings that active steps have been taken to purchase the birthplace of the Star Spangled Banner, and under the auspices of the American Flag House and Betsy Ross Memorial Association shall henceforth be preserved as a lasting tribute to those whose heroism resulted in establishing that freedom which a united people are to-day enjoying.
Appreciating the importance of preserving this relic of the Revolution, a number of patriotic gentlemen of this and other States have taken the matter in hand, thus making the movement national in its scope.
Numerous attempts have been made in the past to remove this historic building to other cities. The present plans provide that it shall remain in Philadelphia, where it rightfully belongs, there to be held in trust for the nation.
It has been left to the option of the American people whether the birthplace of their national emblem shall be permitted to pass into oblivion.
This landmark should be the mecca and shrine of the whole nation. It was associated with one of the most memorable incidents of our early history, and it is most fitting that it should be preserved for future generations.
Like “Independence Hall,” wherein the Declaration of Independence was signed, and Faneuil Hall, the cradle of liberty, it speaks most eloquently of the men and women to whom we owe our freedom.
While we honor the heroes of the past, let us not forget to preserve the mementoes associated with them. Such relics increase in value as they are transmitted from one generation to another and form object lessons in history.
To follow our flag from its birth until to-day would be to write a history which stands absolutely alone, and from the day of its creation[76] to the present time it has never trailed in the dust, being the only exception among the flags of the world. It is not that we have not been called upon to defend it and the underlying principles for which it stands, for to-day as we celebrate the anniversaries of victories on land and sea we cannot but recall, with mingled pride and pleasure, the achievements won under its glorious folds, and when our patriots, inspired by a God-like devotion to flag and country, performed deeds of daring that mark their efforts as the most signal ever accomplished under any flag by any heroes of any nation.
With all these glorious deeds, and others that must necessarily follow, let us as a grateful, patriotic people see to it that the birthplace of our nation’s flag be preserved as a holy shrine.
With the view of making the movement a popular one, arrangements have been made to have all Americans, of every shade of religious and political opinion, affiliate alike, and by their participation to become the preservers of the birthplace of the “Stars and Stripes.”
On these broad principles souvenir certificates of membership in this Association will be issued at a nominal price, and the names of all subscribers placed on the roll of honor.
Any person desiring to see the Old Flag House saved and Betsy Ross honored may become a member of the “American Flag House and Betsy Ross Memorial Association” upon the payment of 10 cents, for which they will receive a beautiful certificate of membership, size 11x14, duly signed by the officers of the Association, and bearing the seal and certificate number. Upon these certificates in the centre is artistically portrayed the room in which Betsy Ross displayed the first Stars and Stripes to the committee appointed by Congress, consisting of General Washington, Robert Morris and Hon. George Ross. On the left is an exterior picture of the Old Flag House as it stands to-day, while on the right is the picture of the grave of Betsy Ross, at Mt. Moriah Cemetery.
These certificates will be mailed to any address upon the receipt of 10c.
A large reproduction, in ten colors, size 22x28 inches, of the original
painting, “Birth of Our Nation’s Flag,” by Charles H. Weisgerber, first
exhibited at the World’s Columbian Exposition, Chicago, 1893, will be
presented as a souvenir to any person forming a club of thirty members,
inclusive. These premium pictures will not be for sale, and when the
objects of the Association are attained the plates will be destroyed: thus[77]
they will become a valuable family heirloom. For upon them will be
engrossed the name of the individual forming the club, as follows:
“Presented to ...................... of ................................
by the American Flag House and Betsy Ross Memorial Association, for
aiding in the preservation of the Birthplace of our Nation’s Flag, and
for the erection of a National Memorial in Honor of Betsy Ross, and
stamped with the seal of the Association.”
The picture referred to above is an exact representation of the room in which the first American Flag was made by Betsy Ross, which was subsequently adopted by Congress, June 14, 1777, and is the only endorsed portrait representation of Betsy Ross by her living descendants.
Address all communications to
Obvious punctuation errors were corrected.
Page 20, “foreging” changed to “foregoing” (foregoing papers)
Page 45, “Claypole” changed to “Claypoole” (John Claypoole, a comrade)
Page 65, “one” changed to “two” (nearly two hundred years)
Page 76, “sixe” changed to “size” (membership, size 11x14)
The book cover was created by the transcriber using images from the text and is placed in the public domain.
***END OF THE PROJECT GUTENBERG EBOOK THE STORY OF OUR FLAG***
******* This file should be named 52354-h.htm or 52354-h.zip *******
This and all associated files of various formats will be found in:
http://www.gutenberg.org/5/2/3/5/52354
Updated editions will replace the previous one--the old editions will be renamed.
Creating the works from print editions not protected by U.S. copyright law means that no one owns a United States copyright in these works, so the Foundation (and you!) can copy and distribute it in the United States without permission and without paying copyright royalties. Special rules, set forth in the General Terms of Use part of this license, apply to copying and distributing Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works to protect the PROJECT GUTENBERG-tm concept and trademark. Project Gutenberg is a registered trademark, and may not be used if you charge for the eBooks, unless you receive specific permission. If you do not charge anything for copies of this eBook, complying with the rules is very easy. You may use this eBook for nearly any purpose such as creation of derivative works, reports, performances and research. They may be modified and printed and given away--you may do practically ANYTHING in the United States with eBooks not protected by U.S. copyright law. Redistribution is subject to the trademark license, especially commercial redistribution.
To protect the Project Gutenberg-tm mission of promoting the free distribution of electronic works, by using or distributing this work (or any other work associated in any way with the phrase "Project Gutenberg"), you agree to comply with all the terms of the Full Project Gutenberg-tm License available with this file or online at www.gutenberg.org/license.
1.A. By reading or using any part of this Project Gutenberg-tm electronic work, you indicate that you have read, understand, agree to and accept all the terms of this license and intellectual property (trademark/copyright) agreement. If you do not agree to abide by all the terms of this agreement, you must cease using and return or destroy all copies of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works in your possession. If you paid a fee for obtaining a copy of or access to a Project Gutenberg-tm electronic work and you do not agree to be bound by the terms of this agreement, you may obtain a refund from the person or entity to whom you paid the fee as set forth in paragraph 1.E.8.
1.B. "Project Gutenberg" is a registered trademark. It may only be used on or associated in any way with an electronic work by people who agree to be bound by the terms of this agreement. There are a few things that you can do with most Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works even without complying with the full terms of this agreement. See paragraph 1.C below. There are a lot of things you can do with Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works if you follow the terms of this agreement and help preserve free future access to Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works. See paragraph 1.E below.
1.C. The Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation ("the Foundation" or PGLAF), owns a compilation copyright in the collection of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works. Nearly all the individual works in the collection are in the public domain in the United States. If an individual work is unprotected by copyright law in the United States and you are located in the United States, we do not claim a right to prevent you from copying, distributing, performing, displaying or creating derivative works based on the work as long as all references to Project Gutenberg are removed. Of course, we hope that you will support the Project Gutenberg-tm mission of promoting free access to electronic works by freely sharing Project Gutenberg-tm works in compliance with the terms of this agreement for keeping the Project Gutenberg-tm name associated with the work. You can easily comply with the terms of this agreement by keeping this work in the same format with its attached full Project Gutenberg-tm License when you share it without charge with others.
1.D. The copyright laws of the place where you are located also govern what you can do with this work. Copyright laws in most countries are in a constant state of change. If you are outside the United States, check the laws of your country in addition to the terms of this agreement before downloading, copying, displaying, performing, distributing or creating derivative works based on this work or any other Project Gutenberg-tm work. The Foundation makes no representations concerning the copyright status of any work in any country outside the United States.
1.E. Unless you have removed all references to Project Gutenberg:
1.E.1. The following sentence, with active links to, or other immediate access to, the full Project Gutenberg-tm License must appear prominently whenever any copy of a Project Gutenberg-tm work (any work on which the phrase "Project Gutenberg" appears, or with which the phrase "Project Gutenberg" is associated) is accessed, displayed, performed, viewed, copied or distributed:
This eBook is for the use of anyone anywhere in the United States and most other parts of the world at no cost and with almost no restrictions whatsoever. You may copy it, give it away or re-use it under the terms of the Project Gutenberg License included with this eBook or online at www.gutenberg.org. If you are not located in the United States, you'll have to check the laws of the country where you are located before using this ebook.
1.E.2. If an individual Project Gutenberg-tm electronic work is derived from texts not protected by U.S. copyright law (does not contain a notice indicating that it is posted with permission of the copyright holder), the work can be copied and distributed to anyone in the United States without paying any fees or charges. If you are redistributing or providing access to a work with the phrase "Project Gutenberg" associated with or appearing on the work, you must comply either with the requirements of paragraphs 1.E.1 through 1.E.7 or obtain permission for the use of the work and the Project Gutenberg-tm trademark as set forth in paragraphs 1.E.8 or 1.E.9.
1.E.3. If an individual Project Gutenberg-tm electronic work is posted with the permission of the copyright holder, your use and distribution must comply with both paragraphs 1.E.1 through 1.E.7 and any additional terms imposed by the copyright holder. Additional terms will be linked to the Project Gutenberg-tm License for all works posted with the permission of the copyright holder found at the beginning of this work.
1.E.4. Do not unlink or detach or remove the full Project Gutenberg-tm License terms from this work, or any files containing a part of this work or any other work associated with Project Gutenberg-tm.
1.E.5. Do not copy, display, perform, distribute or redistribute this electronic work, or any part of this electronic work, without prominently displaying the sentence set forth in paragraph 1.E.1 with active links or immediate access to the full terms of the Project Gutenberg-tm License.
1.E.6. You may convert to and distribute this work in any binary, compressed, marked up, nonproprietary or proprietary form, including any word processing or hypertext form. However, if you provide access to or distribute copies of a Project Gutenberg-tm work in a format other than "Plain Vanilla ASCII" or other format used in the official version posted on the official Project Gutenberg-tm web site (www.gutenberg.org), you must, at no additional cost, fee or expense to the user, provide a copy, a means of exporting a copy, or a means of obtaining a copy upon request, of the work in its original "Plain Vanilla ASCII" or other form. Any alternate format must include the full Project Gutenberg-tm License as specified in paragraph 1.E.1.
1.E.7. Do not charge a fee for access to, viewing, displaying, performing, copying or distributing any Project Gutenberg-tm works unless you comply with paragraph 1.E.8 or 1.E.9.
1.E.8. You may charge a reasonable fee for copies of or providing access to or distributing Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works provided that
1.E.9. If you wish to charge a fee or distribute a Project Gutenberg-tm electronic work or group of works on different terms than are set forth in this agreement, you must obtain permission in writing from both the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation and The Project Gutenberg Trademark LLC, the owner of the Project Gutenberg-tm trademark. Contact the Foundation as set forth in Section 3 below.
1.F.
1.F.1. Project Gutenberg volunteers and employees expend considerable effort to identify, do copyright research on, transcribe and proofread works not protected by U.S. copyright law in creating the Project Gutenberg-tm collection. Despite these efforts, Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works, and the medium on which they may be stored, may contain "Defects," such as, but not limited to, incomplete, inaccurate or corrupt data, transcription errors, a copyright or other intellectual property infringement, a defective or damaged disk or other medium, a computer virus, or computer codes that damage or cannot be read by your equipment.
1.F.2. LIMITED WARRANTY, DISCLAIMER OF DAMAGES - Except for the "Right of Replacement or Refund" described in paragraph 1.F.3, the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation, the owner of the Project Gutenberg-tm trademark, and any other party distributing a Project Gutenberg-tm electronic work under this agreement, disclaim all liability to you for damages, costs and expenses, including legal fees. YOU AGREE THAT YOU HAVE NO REMEDIES FOR NEGLIGENCE, STRICT LIABILITY, BREACH OF WARRANTY OR BREACH OF CONTRACT EXCEPT THOSE PROVIDED IN PARAGRAPH 1.F.3. YOU AGREE THAT THE FOUNDATION, THE TRADEMARK OWNER, AND ANY DISTRIBUTOR UNDER THIS AGREEMENT WILL NOT BE LIABLE TO YOU FOR ACTUAL, DIRECT, INDIRECT, CONSEQUENTIAL, PUNITIVE OR INCIDENTAL DAMAGES EVEN IF YOU GIVE NOTICE OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
1.F.3. LIMITED RIGHT OF REPLACEMENT OR REFUND - If you discover a defect in this electronic work within 90 days of receiving it, you can receive a refund of the money (if any) you paid for it by sending a written explanation to the person you received the work from. If you received the work on a physical medium, you must return the medium with your written explanation. The person or entity that provided you with the defective work may elect to provide a replacement copy in lieu of a refund. If you received the work electronically, the person or entity providing it to you may choose to give you a second opportunity to receive the work electronically in lieu of a refund. If the second copy is also defective, you may demand a refund in writing without further opportunities to fix the problem.
1.F.4. Except for the limited right of replacement or refund set forth in paragraph 1.F.3, this work is provided to you 'AS-IS', WITH NO OTHER WARRANTIES OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR ANY PURPOSE.
1.F.5. Some states do not allow disclaimers of certain implied warranties or the exclusion or limitation of certain types of damages. If any disclaimer or limitation set forth in this agreement violates the law of the state applicable to this agreement, the agreement shall be interpreted to make the maximum disclaimer or limitation permitted by the applicable state law. The invalidity or unenforceability of any provision of this agreement shall not void the remaining provisions.
1.F.6. INDEMNITY - You agree to indemnify and hold the Foundation, the trademark owner, any agent or employee of the Foundation, anyone providing copies of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works in accordance with this agreement, and any volunteers associated with the production, promotion and distribution of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works, harmless from all liability, costs and expenses, including legal fees, that arise directly or indirectly from any of the following which you do or cause to occur: (a) distribution of this or any Project Gutenberg-tm work, (b) alteration, modification, or additions or deletions to any Project Gutenberg-tm work, and (c) any Defect you cause.
Project Gutenberg-tm is synonymous with the free distribution of electronic works in formats readable by the widest variety of computers including obsolete, old, middle-aged and new computers. It exists because of the efforts of hundreds of volunteers and donations from people in all walks of life.
Volunteers and financial support to provide volunteers with the assistance they need are critical to reaching Project Gutenberg-tm's goals and ensuring that the Project Gutenberg-tm collection will remain freely available for generations to come. In 2001, the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation was created to provide a secure and permanent future for Project Gutenberg-tm and future generations. To learn more about the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation and how your efforts and donations can help, see Sections 3 and 4 and the Foundation information page at www.gutenberg.org.
The Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation is a non profit 501(c)(3) educational corporation organized under the laws of the state of Mississippi and granted tax exempt status by the Internal Revenue Service. The Foundation's EIN or federal tax identification number is 64-6221541. Contributions to the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation are tax deductible to the full extent permitted by U.S. federal laws and your state's laws.
The Foundation's principal office is in Fairbanks, Alaska, with the mailing address: PO Box 750175, Fairbanks, AK 99775, but its volunteers and employees are scattered throughout numerous locations. Its business office is located at 809 North 1500 West, Salt Lake City, UT 84116, (801) 596-1887. Email contact links and up to date contact information can be found at the Foundation's web site and official page at www.gutenberg.org/contact
For additional contact information:
Dr. Gregory B. Newby
Chief Executive and Director
gbnewby@pglaf.org
Project Gutenberg-tm depends upon and cannot survive without wide spread public support and donations to carry out its mission of increasing the number of public domain and licensed works that can be freely distributed in machine readable form accessible by the widest array of equipment including outdated equipment. Many small donations ($1 to $5,000) are particularly important to maintaining tax exempt status with the IRS.
The Foundation is committed to complying with the laws regulating charities and charitable donations in all 50 states of the United States. Compliance requirements are not uniform and it takes a considerable effort, much paperwork and many fees to meet and keep up with these requirements. We do not solicit donations in locations where we have not received written confirmation of compliance. To SEND DONATIONS or determine the status of compliance for any particular state visit www.gutenberg.org/donate.
While we cannot and do not solicit contributions from states where we have not met the solicitation requirements, we know of no prohibition against accepting unsolicited donations from donors in such states who approach us with offers to donate.
International donations are gratefully accepted, but we cannot make any statements concerning tax treatment of donations received from outside the United States. U.S. laws alone swamp our small staff.
Please check the Project Gutenberg Web pages for current donation methods and addresses. Donations are accepted in a number of other ways including checks, online payments and credit card donations. To donate, please visit: www.gutenberg.org/donate
Professor Michael S. Hart was the originator of the Project Gutenberg-tm concept of a library of electronic works that could be freely shared with anyone. For forty years, he produced and distributed Project Gutenberg-tm eBooks with only a loose network of volunteer support.
Project Gutenberg-tm eBooks are often created from several printed editions, all of which are confirmed as not protected by copyright in the U.S. unless a copyright notice is included. Thus, we do not necessarily keep eBooks in compliance with any particular paper edition.
Most people start at our Web site which has the main PG search facility: www.gutenberg.org
This Web site includes information about Project Gutenberg-tm, including how to make donations to the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation, how to help produce our new eBooks, and how to subscribe to our email newsletter to hear about new eBooks.