
Project Gutenberg's Harper's Young People, May 18, 1880, by Various
This eBook is for the use of anyone anywhere at no cost and with
almost no restrictions whatsoever. You may copy it, give it away or
re-use it under the terms of the Project Gutenberg License included
with this eBook or online at www.gutenberg.org
Title: Harper's Young People, May 18, 1880
An Illustrated Weekly
Author: Various
Release Date: May 20, 2009 [EBook #28895]
Language: English
Character set encoding: ISO-8859-1
*** START OF THIS PROJECT GUTENBERG EBOOK HARPER'S YOUNG PEOPLE, MAY 18, 1880 ***
Produced by Annie McGuire

| Vol. I.—No. 29. | Published by HARPER & BROTHERS, New York. | Price Four Cents. |
| Tuesday, May 18, 1880. | Copyright, 1880, by Harper & Brothers. | $1.50 per Year, in Advance. |
They found the city one blaze of lanterns, banners, and many-colored fire-works. All the ships in the harbor were gay with brilliant bunting, and the air echoed with the boom of cannon and the snapping of firecrackers, in honor of the Chinese New-Year. In fact, it was quite a Fourth-of-July celebration; and at night there began such a burst of sky-rockets and fire-balloons that the whole town seemed to be in flames.
Early next morning the Arizona opened her ports to receive cargo; and Frank, being told off to assist, saw for the first time one of the most picturesque sights in the world—a gang of coolies at work. On the other side of the "entering port," beside which he was posted, stood a Parsee merchant, whose long white robe, dark face, and high black cap made him look very much like a cigar wrapped in paper. Along the quivering line of sunlight that streamed through the port came filing, like figures in a magic lantern, an endless procession of tall, sinewy, fierce-looking Malays, and yellow, narrow-eyed, doll-faced Chinamen, carrying blocks of tin, rice sacks, opium chests, or pepper bags, and all moving in time to a dismal tune, suggestive of a dog shut out on a cold night.
Each man shouted his name in passing, and the merchant then handed Frank a short piece of cane. These canes were the "tally sticks," their different colors indicating the nature of the articles counted. At every tenth entry the Parsee cried, "Tally," and Austin, reckoning the sticks in his hand, and finding them correct, answered, "Tally."
Our hero soon found that these were not the only sticks employed. A rice sack burst suddenly, and all the coolies stopped their work to pick it up to the last grain, it being thought far too sacred to be wasted. They were not quite brisk enough about it, however, to please the worthy merchant, who, seizing a stout bamboo, with a shrill yell of "Bree! bree!" (hurry up) laid about him as if he were beating a carpet, till the hold echoed again.
"You take 'tick too; give 'em whack-whack," cried he, offering Austin another bamboo. "Dey no work proper widout 'tick; dat 'courage 'em."
"Hum!" thought Frank; "I don't think it would encourage me much."
The remedy seemed to answer, however, for the coolies at once quickened their movements, grinning as if the whole thing was a capital joke. But it was not long before Frank had to exercise his stick upon a fellow whom he caught in the act of dropping a package overboard, to be fished up and rifled later on—a common trick with the natives, who are most expert thieves. What with all this, and what with the constant counting, he found it very tiring work, and was not sorry when the gang "knocked off," and he went to hand in his accounts to the Captain.
"Very good, my boy; you've done capitally for a first trial. After this I'll rate you as supercargo, and give you a state-room on the officers' deck."
This was promotion indeed, and our hero, tired as he was, "turned in" with a light heart.
Next morning the work began again. Bags, boxes, chests, crowded so fast upon each other that Frank and the Parsee were soon forced to shift to one of the six huge barges that lay alongside, piled high with spices, pepper, and bundles of rattan. Two native servants stood by to fan them, while two others shielded them from the burning sun with huge umbrellas; and this group, together with the long file of black or yellow skinned figures below, pouring into the ship with their burdens like a stream of ants, and still chanting their strange, monotonous song, made a very curious picture.
About two o'clock (the sailors' dinner hour) the gang had a short rest, which the Malays employed in squatting about in groups, and chewing betel-nut. A piece of the nut was folded between two green leaves, and munched vigorously, the result being to cover their mouths with a red froth, which, as Frank thought, made them all look as if they had just had two or three teeth out.
After night-fall the work went on by lamp-light, and a very picturesque sight it was. Tired as they were, the men worked with a will, and by midnight the last package was stowed, the last receipt signed, and the Arizona all ready to sail the next day.
After his hard day's work, Frank slept like a top; but he was aroused soon after sunrise by a knock at his door, and in came a venerable old native in a long white robe, crimson girdle, and hat exactly like a stove-pipe, minus the rim. Shutting the door as carefully as if he were about to confess a murder, he opened a small silk bag, and flashed upon Frank's astonished eyes a perfect heap of precious stones of all sorts and sizes; then holding up the fingers of both hands several times in succession, he uttered the one word "Rupees."[1]
But the price, though low, was far beyond Austin's means. He shook his head, and the old gentleman bowed himself out as politely as if Frank had purchased his entire stock. Five minutes later came a second tap, and another native entered, with a basket of delicious fruits, answering our hero's "How much?" by pointing to a pair of worn-out shoes, and saying, "Can do." Before Austin could recover from his amazement at the idea of a country where men preferred old shoes to hard dollars, the fruit merchant had made his "salam" (bow), and departed with his prize.
He was hardly gone, when a third trader turned up, with a splendid collection of shells and coral, and the same scene was repeated. This time the "Can do" referred to some ragged old flannel shirts and pants that hung on the wall, in exchange for which the dealer handed over the entire contents of his basket. Frank, more puzzled than ever, went to old Herrick for an explanation.
"Well, lad," said the veteran, "these natyve fellers, d'ye see, are divided into so many 'castes,' one above t'other, like men and officers aboard ship, and the lower castes have got to pay toll to the higher 'uns. Now the high-caste crowd are too great swells to touch a furriner's clothes or shoes, though they'll touch his money fast enough; so them two chaps'll be able to keep all you gave 'em, whereas if you'd paid 'em in dollars, they'd ha' had to go halves with the 'upper crust.'"
May brings so many wild flowers that the mere names would easily fill all the space I can have.
But the young flower-hunter must get an idea of some of the flowers sure to appear in May, and those who will notice the habits of plants will soon discover where these fair friends dwell, and will learn which selects the valley, which the hill-side, finding that as a general thing they may be looked for with the certainty of being found in their favorite haunts.
Botanical authorities have arranged all known plants[Pg 395] in families, and each plant belongs to some floral family, the members of which possess certain qualities in common, making it suitable to class them together; for instance, all the buttercups, anemones, clematis, hepaticas, larkspur, columbine, and many others, belong to the Crowfoot family—a large family, all possessing a colorless but acrid juice, which is, in some of them, a narcotic poison, as hellebore, aconite, larkspur, and monk's-hood. Others are quite harmless, as the marsh-marigold, so well known as cowslips, or the "greens" of early spring. Others have a delicate beauty, as the anemones, hepaticas, and others.
Another family, the Poppy family, takes in all the poppies, the bloodroot, celandine, and others. These have a milky or colored juice, often used medicinally, and from one species of poppy opium is made.
The Crucifers, or Mustard family, have cross-shaped flowers, and abound in a pungent, biting juice, with which we are familiar; and thus we could go on enumerating the distinctive qualities of one hundred and thirty families.
In every month are to be found some peculiarly rare and interesting plants, and May can show a fair array. In cold bogs and swamps of New England the genial airs awaken many a blossom that seems too lovely for such dismal surroundings. But bogs and swamps and wet pastures are well worth exploring, and are justly dear to the botanical heart; for here, springing from a bed of soft black mud, may be seen the pink Arethusa, fair as a rose leaf, the rare Calypso, the singular trilliums, the graceful adder's-tongue, and several species of the remarkable Cypripediums, or lady's-slipper. The beautiful spring orchis, the only orchis blossoming early, of most delicate white and purple tints, flourishes in damp, rich woods, and the Cornus, or dogwood, lights up the shady nooks with level sheets of bloom.
Violets, more than twenty varieties, come on in April, May, and June; but I can specify but one—a charming species of pansy-like beauty, found at Farmington, Connecticut, with the two upper petals of the finest violet tint, and of velvet softness. In moist woodlands in Western Connecticut the staphylea, or bladder-nut, attracts attention by its drooping racemes of white flowers, and later in the season the rich brown seed-vessels are as handsome as the flowers in the spring. All around on the rocky road-side banks and in dry fields the airy wild columbine and pretty corydalis blossoms nod in every breeze, and the ravines on the hills are fringed with the softest frills of exquisite leaves and odd flowers of the Dutchman's-breeches and squirrel-corn, whitish and pinkish, and with the scent of hyacinths.
One other must not be forgotten, though so well known as hardly needing to be named. Who has not searched in dim New England woods, under solemn pines, for the sweet, shy, waxen clusters of this dearest of all the flowery train, hiding under old rusty leaves, but betraying itself by that indescribably delicious fragrance which perfumes the wood paths? Surely all the young hands have been filled with the pilgrim's-flower, the epigæa, the trailing arbutus, the beloved May-flower of olden and of modern time.
In the Middle States many plants are found which New England does not furnish. New Jersey is famed for woodland treasures; not only Orange Mountains, but the pine-barrens, show many a charming blossom, and the dweller at the West finds on the flower-tinted prairies a profusion which the Eastern fields can not approach. On the hills of Pennsylvania may be seen the brilliant flame-colored azalea and the North American papaw—a relative of the tropical custard-apple—and the pink blossoms of the Judas-tree, and several varieties of larkspur, and in low thickets are found the white adder's-tongue and the dwarf white trillium. At the West, the interesting anemone called Easter or Pasque flower, from its blossoming near Easter; and another beautiful Western flower is the American cowslip, called also the shooting-star, which is found in Pennsylvania as well as on Western prairies. The following is a list of some of the flowers of May, with the localities in which they are most abundant:
| COMMON NAME. | COLOR. | LOCALITY, ETC. |
| Adder's-tongue | Bluish-white | Thickets, banks; N. Y., Pa., West. |
| Adder's-tongue | Light yellow | Low copses and fields; New England. |
| American cowslip | Pink, white, violet | Rich woods; Pa., Western prairies. |
| Arbutus, May-flower. | Pink, white | Rocky banks, under pines; New Eng. |
| Arethusa | Bright rose | Cold bogs; Maine, N. J., South. |
| Azalea | Flame-colored | Pennsylvania mountains, and South. |
| Azure larkspur | Uplands; Pa. and West. | |
| Barberry | Yellow | Open fields, dry banks; New England. |
| Bellwort | Pale yellow | Damp woods; New England, West. |
| Bladder-nut | White | Western Conn.; woods. Rare. |
| Blue cohosh | Deep, rich woods; West. | |
| Bulbous buttercup. | Bright yellow | Pastures, meadows; New England and elsewhere. |
| Calypso | Purple, pink, yellow | Swamps, bogs; Northern New England. Rare. |
| Chickweed | White | Fields, door-yards; everywhere. |
| Columbine | Scarlet, yellow | Dry, sunny, rocky banks. Common. |
| Common buttercup | Golden yellow | Hills, fields. Common everywhere. |
| Dandelion | Bright yellow | Fields, road-sides; everywhere. |
| Dark purple clematis | Rich soil; Middle States, Southwest. | |
| Dwarf trillium | White | Shaded woods; West. Rare. |
| Easter flower | Pale purple | Western prairies. |
| Flowering dogwood | White | Rocky, open woods; Middle States. |
| Fly honeysuckle | Greenish-yellow | Rocky woods; Mass., Pa. |
| Gay wings | Rose purple | Light soil; New England and South. |
| Golden corydalis | Rocky banks; Vt., Pa. Rare. | |
| Gold-thread | White | Bogs; throughout the States. |
| Green hellebore | Green | Damp places; Long Island. Rare. |
| Ivory plum | Bright white | Cold bogs; Maine woods. Rare. |
| Jack-in-pulpit | Stripes of green and white | Rich woods; North and South. |
| Jersey tea, red-root | White | Woods and groves; N. J. and South. |
| Judas-tree, redbud | Purplish-red | Rich woods; N. Y., Pa., and South. |
| Lady's-slipper | Greenish-white | Bogs and swamps; N. Y., Pa. Rare. |
| Large climbing clematis | Light purple | Rocky New England hills. Rare. |
| Meadow-rue | Yellowish | Fields and woods; Northward. |
| Mountain heath | Drooping purple | Rocky hills; White Mountains, Vt. |
| Mountain holly | White | Damp, cold woods; North and West. |
| Mount. honeysuckle | Yellowish | Mountain woods and bogs; Mass., West. |
| N. American papaw | Lurid purple | Banks of streams; Pa. and South. |
| Pepper-root | White | Rich woods; Middle States. Rare. |
| Puccoon | Yellow | Shady woods; N. Y. and West. |
| Red bane-berry | Rocky woods. Common Northward. | |
| Red sandwort | Sandy fields; sea-coast. Common. | |
| Rheumatism-root | White | Low woods; Middle States, West. |
| Rhodora | Rose-color | Damp, cold New England woods. |
| Scarlet corydalis | Dry woods and fields; Northeast and West. Common. | |
| Sea sandwort | White | Atlantic coast, N. J. to Labrador. |
| Small buttercup | White | Under water; Maine to Texas. |
| Small honeysuckle | Dull purple | Rocky banks; Northward. |
| Spring beauty | Pink with deeper lines | Sheltered fields; Middle States. |
| Spring orchis | White, purple | Rich woods; New Eng., West, South. |
| Squirrel-corn | White, purplish | Rocky woods; Canada to Ky. Common. |
| Star flower | White | Damp, shady New England woods. |
| Straw lily | Straw-color | Cold swamps; Me. to Pa. Common. |
| Sweet viburnum | White | Cold swamps; New England woods. |
| Trillium | Dull purple | Rich woods; Northward. Common. |
| Tulip-tree | Yellow, green | Southern New England, Middle States, West. |
| Umbrella-leaf | White | Wet pastures; West and South. |
| Violets (many) | Blue, white, yellow | Fields, meadows, hills; Me. to Fla. |
| Wayfaring-tree | White | Cold swamps; New England woods. |
| White bane-berry | Rich soil; North and West. | |
| Wild pink | Red, with white spots | Sandy plains; N. J., West, and South. |
| Wild hyacinth | Pale blue | River-banks, moist prairies; West. |
| Withe-rod | White | Cold swamps; New England woods. |
| Wood-rush | Straw-color and brown | Dry fields and woods. Common. |
| Wild strawberry | White | Fields, meadows; Maine to Texas. |
| Yellowish clematis | River-banks; Pa., N. Y. Rare. | |
| Yellow-root | Dark purple | River-banks; N. Y., Pa., and West. |
Little Ruth looked at her dolly one day,
Said: "Dolly, they wish me to give you away;
They say you are old, and I know it's quite true;
But, dolly, dear dolly, I can't part from you.
"Your color has faded, your nose is quite gone,
Yet I love you as well as the day you were born;
You've great cracks on your face, and scarcely a hair,
Yet, dolly, my dear, to me you are fair.
"Though you're hurt, darling dolly, too often, I fear,
But you are so brave that you won't shed a tear;
And although you've one arm, one leg, and no nose,
You're dearer to me because of your woes.
"But what was the hardest and cruelest sting
Was that father once called you a horrid old thing:
He said, 'What a battered and wretched old fright!
Do take her away, pray, out of my sight.'
"And, dolly, he said that a new doll he'd buy;
To find me a nice one he really would try;
She should have two legs, and more than one arm:
I am sure that papa did not mean any harm.
"Pray what would they all say if I asked mamma
To go out and buy me a nice new papa,
Because father dear is old, bald, and gray?
I should like very much to hear what he'd say."
 WASHINGTON AT THE AGE OF FIFTY.
WASHINGTON AT THE AGE OF FIFTY.The private life of Washington was very simple. He was very fond of farming, and studied it carefully, as he seems to have studied everything that he took in hand. Some of his letters to Arthur Young, a great English traveller, who was also a writer on farming, are very interesting. In reading them it is easy to forget the General and the public man, and to think only of the painstaking planter, eager to know what was the best way to plant his various crops, or to plough his different fields. He liked shade trees greatly, and had a great many kinds of them at Mount Vernon, set out under his own direction, and some of them with his own hand. Some of my readers may yet see them on the pleasant sloping banks of the Potomac, below the city of Washington. Even among the cares of the camp and the battle-field Washington found time nearly every week to write minute directions to his superintendent, who had charge of his farm, telling him just what work to do each day, and how to do it. When he got back to his home, he took up the task of seeing to things himself with the greatest enjoyment. Every morning after breakfast he mounted his horse and rode about his ample fields, and he seldom let anything prevent his doing so—neither bad weather, nor the claims of visitors, of whom he had a host, nor anything else. He laid out his time on an exact system. Each morning he arose before sunrise to write letters and to read, and on his return from his ride over his estate he again went to his study, and staid there attending to business until three o'clock in the afternoon. At three he dined, and gave the rest of the day and evening to his family and his guests. At ten he went to bed.
But he was not to enjoy this happy, peaceful life very long. His countrymen needed him as much in peace as in war, and soon called him again to public life. After the American States had cut loose from Great Britain, they found that their common affairs did not get on very well. They had borrowed a good deal of money to carry on the war, and the only way to pay it was by each State giving its part. But the people of the various States were jealous of each other, and quarrelled over the amount they ought to pay. There was danger that the States would divide from each other, and then be much less able to defend themselves against foreign governments. Washington dreaded such a thing. He believed that the only means by which the States could keep the freedom they had won was by uniting closely. He wished to see a national government formed, with power to raise money by equal taxes, to pay the common debts, and to make war if need be. He wrote on this subject to many of his friends, who agreed with him.
After a while, by general consent, each State chose some of its ablest men to come together at Philadelphia and[Pg 397] make a plan for a national government which should take charge of all public affairs not belonging to any one State by itself. This was done, and a plan was formed in the year 1787, and adopted by the people of all the States. This was called the Constitution of the United States. It set up a government of three parts. First, there was Congress, made up of men chosen, in one way or another, by the people. Congress was to make the laws. Second, there was the President, chosen by the people, who was to see that the laws were carried out and obeyed. The President was to be aided by a large number of officers of various kinds, whom he was to choose, with the consent of a part of Congress called the Senate. Finally, there were the Judges, who were to decide any disputes that might come up about the meaning of the laws. The Judges were also chosen by the President, with the help and consent of the Senate.
Of course the one man in the government who had more to do with it than any other was the President. As soon as it was seen that the new Constitution would be taken by the people, every one turned to General Washington as sure to make the best President. He had shown himself so wise and true in war, how could he be otherwise in peace? People knew that he would try to do his whole duty, and serve the country at any cost to himself. It was the same feeling the boys in school had had forty years before, when they chose him to be their captain, and left all their quarrels to him to settle. So Washington was elected President, and though he disliked to leave his tranquil home, his fields, and his trees and his horses, he felt that it was his duty to do so, and promptly accepted the office.
He was all by himself in as pretty a patch of sunny green meadow-land as you could wish to see, yet he had plenty of company. To say nothing of the birds chattering on the fence, the tall thick grass was as full of hopping, fluttering, and creeping things as a wheat beard is of grain. These tiny little creatures seemed to find life so pleasant and comfortable, and the glisten and "swish" of John Goodnow's scythe so very odd and amusing, that they kept only a little out of his way as he mowed, and when he stopped to whet his scythe they flocked around and settled on his boot-legs, on the brim of his hat, and even in the creases of his shirt sleeves, to see how he did it.
John Goodnow was just sixteen. He was a manly boy, strong, straight, and good-looking. He had plenty of spirit and energy, and liked what he was doing well enough; but he had some ideas in his head which made him think he could do something else much—very much—better.
John's father did not happen to think about John as John thought about himself. This very often happens between parents and their children. Your parents are older and wiser than you, but then you boys and girls often think a great deal more, and with more good sense, than you get credit for. When your parents do not think as you do about what you are to be and do in life, it is hard to tell which is wisest, and there is no sure rule to help you out; but I will tell you one little thing that I think it will be good for you to remember; it is very much in your own power to decide for yourself, to get your own way by giving it up, as John did.
"I wish father could see this as I do," John thought.
He had put the whetstone in his pocket, and was once more leaning to the scythe.
"Of course I can be a farmer, and of course farmers are as necessary as Presidents; and a farmer can be a President, and eat potatoes and corn in the White House, instead of hoeing and hilling them in the field. But I want to be a lawyer, and that settles it for me. I just wish it would do as much for father. He did look queer when I told him I didn't believe a lawyer that was always hankerin' after a farm would amount to much in lawyerin'. Mother said, 'Do let the boy have his way; it's his life he's got to live, you know, not yours.'
"She's so sensible, and just the best mother in the world. I made up my mind, when she said that, that if I did get my way, I'd just like to be the one to fix Uncle Si. Stingy old fellow! I'd make him pay mother what he owes her. Guess he knows it, an' that's why he looks at me so sour, and tells father to 'keep him at the plough; he'll never come to nuthin' moonin' over them lyin' lawyer books.'"
John smiled, with a bright, mischievous look, as if he had already won the case against his uncle.
Then he whistled till he came to the end of the swath. He liked the sweet, fresh smell that rose from the cut grass.
"I know farming is good, useful work," he thought, "and pleasant, when any one likes it; but I want to do what I can do best, and I'm sure it's law. When things happen, I want to know how they happen, and who was wrong, and how to fix things so that they'll happen right. It just makes me tingle all over when I can get hold of a case, and read up all about it, and I can talk it over with, mother. She's smarter'n a steel-trap, and might have been a lawyer herself. But I can't show off to father at all. He shuts right down on me so—almost makes me[Pg 398] think I don't know anything, after all. He's a real good father, though, and I hate to disappoint him."
John set his lips, and his young face looked troubled. He cut the swath very neatly to the edge of the brook as he went along.
"I told him I'd say no more about it now," John went on thinking, as he looked at the pretty rippling stream, which kept up such a merry little song over its round pebbles, "and I promised him I'd stick to the farm for this year, and do my best to like it, and so I will. Mother said, 'It isn't because he doesn't like you to be a lawyer; it's because he thinks you aren't old enough to judge, and he thinks good farming is the best and noblest work in the world, and that you can't help liking it if you try. But he won't stand in your way a moment, my boy, when he sees that you know your own mind. You just yield to him first, and he'll yield to you last.'"
 NOON-TIME IN THE MEADOW.
NOON-TIME IN THE MEADOW.
It was nearing noon, and the sun was hot. John lifted his hat just enough to wipe his forehead; then resting the scythe upon the bank, he leaned against its curving handle. He looked well as he stood there, like a boy who would one day be a man of purpose, and will to carry out his purpose. He was tired, just tired enough to make rest sweet. He looked across the little hollow at the foot of the meadow toward his home. He was very hungry, and glad to see a little girl coming down the path through the hollow with a pail in her hand. "Thank goodness! there's Kitty coming with the lunch. I'm hungry enough to eat a crow, feathers and all. I know just what's in that pail—ham sandwich, a big slice of brown-bread, bottle of milk or sweetened water, and some of mother's apple-pie, with a slice of cheese. Hurry up!" he shouted aloud, in a strong, pleasant voice—"hurry up, Kitty dear; I'm as hungry as a cat."
When the end of the year came, Mr. Goodnow did not wait for John to speak. On New-Year's Eve, just before bed-time, he laid down his paper, crossed the room, put his hand on John's shoulder, and, as if only an hour instead of seven months had passed since he had last spoken of what he wished John to be, he said, "Well, my boy, speak out: will ye be farmer or lawyer?"
John rose quickly, and looked at his father. "I will be a lawyer, if I can," said he. "But, father, I do wish you could like it;" and his voice trembled a little.
"I do like it—I like it very much," said Mr. Goodnow, quickly; "for if ye can do so well as ye have done at a work ye don't take to, I'm sure ye'll prove a master-hand at what yer heart's so sot on. Ye've helped me in my way, and I'll help ye in yourn. Ye shall have the best schoolin' in law that money can buy, and ye've shown ye'll do the rest yourself. Happy New-Year, my boy!" Mr. Goodnow held out his hand, and John took it with a grip that made his father wince and smile at the same time.
Then John went to his mother, who, of course, knew all about it, and was as happy, yes, happier, than her boy over the happiness which he had earned so well. When he went to his own room, he was so busy thinking, that it was some time before he looked up; but when he did he started, and shouted "Jerusalem!" as if the word had been a bullet and he the gun. On the wall over the table were three pictures which had not been there before. One was of Charles Sumner, one of Rufus Choate, and one of Abraham Lincoln. On the table beneath was this note in his mother's hand:
"I want you, my own good boy, to learn what you attempt to know as thoroughly, and do what you believe to be right as fearlessly, as Charles Sumner did. Rufus Choate had the great power to so move men's minds that they were like something melted which he could shape as he chose. If you can be as brave, tender, and good as Abraham Lincoln was, I shall wish with all my heart that you may have power like Rufus Choate's and opportunity like Charles Sumner's. You mustn't fret about father. He's as pleased and satisfied as we are. You won him just as I told you you would, by yielding. It is more than a month since he brought home the books you will find on your table. They are for your first term in the law-school. Now good-night, and a happy New-Year from your loving
"Mother."
Under the books on the table lay a flat package which his mother did not know about, as Mr. Goodnow had slyly placed it there the last thing before John went up to bed. John untied it, and found a fine picture of Horace Greeley, and this note from his father:
"You needn't be afraid of putting Horace Greeley along of them chaps your mother has given you. He can stand it if they can; and they'll make a good beginning of your picter-gallery. I've heard tell of lawyers getting to be editors, too, afore now. If you should ever run a paper, what you know about farming won't hurt it none."
Many years have passed away since John talked with himself as he mowed the home meadow on that pleasant summer morning. If I should tell you the real name of John Goodnow, you would know at once how well his good mother's wish had been granted in the noble career of her well-known son. And there isn't a father in the land prouder of his son than Farmer Goodnow of his son, Judge ——.
"What am I a-stoppin' for? Why, this 'ere's the eend of the road. It's as fur as I can git, even with one hoss and a buckboard."
It looked like it, for the wood road had been getting dreadfully scrubby for a mile or so.
"Wade, was it like this when you and your father and the rest were here before?"
"A good deal like it. How far are we from Pot Lake now, Mr. Jones?"
The queer-looking old teamster was busily unfastening several small packages from the broad "buckboard" of his rude wagon, but he looked gruffly up to say, "'Baout a mile 'n' a half."
"It's all of that, Sid, but it's of no use to grumble. We've got to foot it the rest of the way. It's a plain enough path."
"Foot it! And lug all that?"
"Guess you'll be glad there ain't any more of it afore ye git thar."
Mr. Jones was right, for they were both of them glad already, considering how warm a day it was.
Neither of the boys was much over sixteen, but Wade Norton looked the older of the two, although his companion was fully as tall and strong. Standing together, they made a good "specimen pair" of vigorous, bright-eyed, self-reliant youngsters.
In three minutes more Mr. Jones and his pony and his buckboard were out of sight among the trees, and Sid and Wade were left to their own resources.
It was seven miles due south, and a good deal longer by the road, to the nearest clearing, and all to the north of them was wilderness—woods, lakes, and mountains.
"Now, Wade, how'll we divide the load? There's a heap of it."
"Guess we won't divide it. I'll show you—here's the hatchet."
"Go ahead. I'm a greenhorn yet. What are you going to do?"
Wade was too busy to answer, but he quickly had a pair of very slender ash saplings hacked down, trimmed clean, and laid side by side about two feet apart. To these he tied a couple of cross-sticks, six feet from each other. Then he spread his blanket on the ground, laid the frame[Pg 399] in the middle, folded the blanket across, and pinned it firmly.
"Looks like a litter," said Sid.
"That's what it is. Put the tin box of hard-tack in the middle. It's the heaviest thing we've got; weighs ten pounds. Now the bacon; that only weighs five. Now the other things. The guns ain't loaded; lay 'em along the sides. And the fishing-rods. Now we're ready."
One boy in front between the poles, and one behind, and it was a pleasant surprise to Sid to find how easy it worked. Still, it was a dreadfully long and warm mile and a half over that rough forest path before they came out on the slope that led down to the blue waters of Pot Lake.
"It's just beautiful," said Sid, as they set down their load for a rest and a look.
"Hist! Let me get my gun."
A cartridge was slipped in like a flash; and then there came another flash, and a report.
"Thought you said it was unsportsmanlike to kill a partridge sitting?"
"So it is, my boy; but it's a question of dinner. Our breakfast was an early one. Look at 'em, will you?"
Sid was looking, and there was a very strong suggestion of dinner in that pair of barely full-grown young birds. Fat, plump, the very thing for a boy whose breakfast had been eaten early. There was a sort of natural "open" on that side of the little lake, and Wade led the way straight to it.
"Just as I expected. The old shanty's knocked all to pieces. The boards and the nails are there, though. They may be good for something."
"What next? Shall I unpack?"
"Hold up, Sid. Yes, there's the spring. Down yonder; that's where we'll pitch our tent."
"Needn't do that, yet awhile."
"First thing always. We're not in camp till the tent's up."
"Go ahead. Don't you wish you had the tent poles here now?"
"Not if I had 'em to carry besides the other things. We can cut all we want."
As they talked they walked, and they were now standing by the spring, on the slope, not more than a hundred yards from the shore.
"There's the place for the tent."
"Isn't one spot as good as another?" asked Sid.
"You don't want to sleep slanting, do you? That isn't all, either. That little hump of ground in front of it's a tiptop fire-place."
"Don't look much like one."
"You'll see. Come on and let's cut some tent poles."
Two five-foot sticks, each with a "crotch" at the upper end, were soon set in the ground about six feet apart, and a ridge pole laid across them.
"You haven't set 'em deep enough," said Sid. "They'd go over too easy."
"No they won't. The strength of a tent is in the canvas and pegs, not in the poles," said Wade.
He was unrolling the great square piece of strong but light "cotton duck," and in a moment more it was flapping over the poles.
"Stretch it well, and peg it strong. That tent won't blow down."
"Can't stand up in it."
"That isn't what it's for. In with the supplies. The sun's as bad as rain would be, for part of 'em, spite of the tin boxes."
"Nothing extra—not even butter."
"Butter? There's one roll of it, but the bacon's the butter for us. Now for the butcher-knives. We must ditch our tent."
"What for?"
"To drain away the water, if it rains. We must cut a V."
The apex of the V was cut pretty deeply on the slope above the tent, and the arms were cut around it till they led out below.
"Water doesn't run up hill," said Sid. "We're drained. What next?"
"Fire."
"A day like this? Are you going to cook right away? I'd rather try the lake for some fish."
"Of course we will. But it takes an hour for an open fire to be fit to cook by. Got to have plenty of coals and ashes."
Fuel was plentiful enough, and a rousing fire was speedily blazing on the little hump of ground, a rod in front of the tent.
"Not near enough to set anything on fire. If that hump hadn't been there, we'd have made one."
As it was, he had levelled it on top a little, and the surface so made was barely two feet across.
Sid was a little curious about such a fire-place, but decided to wait and see what his friend meant.
Wade's father was an old army officer, and had taken his boy with him on more than one "camping-out" excursion, while Sid was taking his very first lesson.
"That'll do. Now for some fish. You go ahead, while I pluck the partridges."
"Guess not. I can do that as well as you can. Give me one of 'em."
It was easy work to strip the tender game and hang it in the tent, but the boys were thoroughly tired of mere "going into camp" by the time they started for the lake.
"Hullo, Sid! If there isn't the old dug-out floating yet!"
"That thing out there by the snag? We can't get at her."
"Can't we? Can't you swim as far as that? I can."
"Swim? Oh yes, of course we can. Shall you go now?"
"Why, no; not till we get in fish enough for dinner."
"That's it. We're Indians. Got to fish, hunt, or starve—or live on hard-tack and bacon."
Pot Lake was a great place for trout, and both of the boys knew how to handle a rod.
"No three-inchers; none of your speckled minnows," shouted Sid, as he landed a half-pound beauty.
"Here comes a bigger one. Oh, but isn't this fun?"
"Better fun than going into camp."
"Or tramping through the woods with a load. But don't you begin to feel hungry?"
"Begin? Well, you may say begin if you want to. Seems to me I began a little while after breakfast," replied Sid.
They had caught more fish than any two boys could eat; but Sid's first remark on reaching the tent with them was, "I do hate cleaning fish."
"Clean fish? Out here in the woods? While we're Indians? You wait till I find a bass-wood tree."
There were plenty of lindens, or bass-woods, in that vicinity, and the broad flat leaves were as good as brown paper to wrap up a trout in, fold over fold.
The fire had now burned long enough to supply Wade with a heap of hot ashes, which he raked out on one edge of it. All the little coals were carefully poked aside, the leaf-covered trout were put down and smothered an inch deep in their ashy bed, and then a pile of glowing cinders was raked over them.
"They'll cook, Sid. You go to the lake for a kettle of water, while I get out the frying-pan and the coffee-pot."
"Frying-pan! We won't need any bacon with all those fish and the partridges."
"We'll only broil one bird, but we must have some hard-tack. I'll show you."
Sid went for the water, but when he got back Wade was[Pg 400] putting the frying-pan on a bed of coals, with a couple of thin slices of bacon in it.
 CAMP LIFE.—Drawn by Charles Graham.
CAMP LIFE.—Drawn by Charles Graham.
"They look lonely," said Sid.
"They'll have company enough. This coffee smells first rate."
"No milk, Wade, and nothing to settle it with."
"I thought I'd surprise you, Sid. I've brought some little cans of condensed milk."
"Why not a big can?"
"Spoils after it's opened, just like other milk."
"Next thing to having a cow. But, oh, won't the coffee be muddy!"
"I guess not. There, the bacon's beginning to fry."
Half a dozen ship biscuit, hard as dinner plates, were dipped for a moment in the water, and quickly transferred to the frying-pan.
It was wonderful how puffed up and soft they became, and what a fine flavor of bacon improved their taste when it came time to eat them.
Wade was at his coffee-pot before that, however.
Two heaping table-spoonfuls of the ground coffee were first poured into one of the tin cups, which were all the "table crockery" in that camp, and just covered with cold water.
That had been done before the bacon was put on, and now the coffee-pot full of water was sitting on a bed of coals and beginning to steam.
"She's boiling," shouted Sid.
In went the contents of the tin cup, and on went the cover.
"Let her boil awhile."
"The hard-tack's a-swelling."
"The fish must be done, too. Now for settling."
The cover of the coffee-pot was lifted, and half a cupful of cold water was suddenly dashed in, and then the pot was lifted from the coals to the grass.
"Let her stand a bit. Now for the fish. Have your tin plate ready."
"Ain't they splendid?"
So they were, when they were dug out from the ashes, their leafy coats removed; and Sid discovered that by a careful use of his fork and fingers all the parts of the fish that he did not want seemed to come away together. A little salt and pepper improved both them and the hard-tack, and the coffee poured out beautifully clear and strong.
Just as he and Sid were getting ready to begin their meal, however, Wade took one of the partridges and spread him flat on the forks of a long crooked branch he had cut.
"That'll hold him just high enough above the coals."
"Yes, but you stuck him right into the heat, first thing."
"Always. That shuts up his outside coat, so he won't lose all his juice in broiling. Cook him slow, now. I've put a little salt and pepper on him, and a piece of butter as big as a chestnut. He'll do."
"We can't eat all we're cooking."
"Take our time to it."
So they did, and Wade went so far as to clean a small trout, and show Sid how to fry him.
"Always break up a little hard-tack fine as you can, and sprinkle it on the bottom of the frying-pan as soon as your bacon fat begins to smoke. Then your fish won't stick, unless your pan's too hot. You must look out for that."
Dinner was over at last, and then the boys went to the edge of the woods for a couple of strong forked stakes and a cross-stick to hang their kettle on.
"What are you setting the crotches so far from the fire for?" asked Sid.
"So they won't burn down. Besides, when you don't want your kettle on the fire, you can just slide it along; needn't take it off every time."
"Look, Wade—the sky isn't as clear as it was."
"That's so. May have rain. We must cut our bedding and lay in our wood-pile."
Plenty of small hemlock boughs were heaped on the bottom of the[Pg 401] tent to spread their blankets on; and Sid almost rebelled at the amount of dry wood Wade insisted on piling up.
"May rain all day to-morrow, Sid. We must catch a lot of fish to-night."
"What are all these great slabs of bark for? Kindling?"
"I'll show you. It's mean work starting an open fire with wet wood."
The first day in camp was clearly a day of hard work; but the fish seemed to bite better than ever as the sun went down, and the boys had each a capital "string" before supper-time.
The old dug-out canoe was swam after, and brought to the shore.
"We can use it, Sid. It was a tottlish thing to get into, till father nailed a keel-board on the bottom of it. We'll bail it out to-morrow. I'm too tired for that sort of fun now."
"So am I. Let's go for supper. Let me make the coffee this time."
"All right. But don't put any more wood on the fire. I'll broil some fish instead of frying them. Clean 'em, and split 'em down along the backbone inside, and they'll lie flat. Spread 'em on a forked stick, so they won't touch the coals and ashes. Season 'em just a little."
Sid decided afterward that there was very little to be said against broiled trout.
They were both of them tired enough to go to bed early, but it was hardly eight o'clock when the rain-drops began to patter on the tent cover.
"We must keep our fire, Sid," said Wade.
He was raking' it from the top of the "hump" as he spoke, and putting down there several solid pieces of dry wood. These he covered with the live coals and burning fragments, and these again with ashes; and then he made over all a sort of conical "wigwam" of his slabs of bark, putting flat stones against them at the bottom, so they would not easily blow away.
"Couldn't do that with too big a fire. Always make a camp fire as small as possible, so my father told me. That'll keep, if it rains ever so hard."
"It's going to do that. Will our fish be safe?"
"Hanging in the water by the canoe? Of course they will. Who'll steal 'em? They'll be fresh, too, in the morning. We can't live on fish, though. I can show you twenty ways of cooking birds."
They had crept into the tent now, and the rain was pelting harder and harder.
"Glad the tent's well ditched," said Wade. "We'll be as dry as two bones."
"Oh, but isn't it fun! But I tell you what, Wade Norton, I feel as if I wanted to sleep about twenty-four hours."
The French are a very merry nation, and for their fête or festival days have many jolly games to amuse both the children and older people. In one of these a weighted string is hung up at one end of a tent, and the children, starting from the other end, try to cut it with a pair of scissors. This would be easy enough, were it not that each player is blindfolded by a great hollow head with a grinning, ugly face, something like the comic masks we see in the shop windows. There are no holes for the eyes, and the head rests down on the shoulders of the player, like a great extinguisher, making her look like the caricatures in which little bodies are represented with big heads. The player turns around several times before starting, and having no idea of the proper direction, sometimes walks toward the sides, and snips the scissors in the faces of the spectators. A drummer marches toward the string, making a loud noise with his drum, but the sound oftener confuses than guides. If the player really succeeds in cutting the string, a present is awarded as a prize.
The same play-ground also serves at night as a dancing hall, for the French are very fond of dancing. Here[Pg 402] is a little poem about French fêtes, which perhaps some of your grandparents will remember, as it was written about sixty years ago.
"Come with the fiddle, and play us a tune or two;
Lasses and lads, bring your dancing-shoes.
Here on the green is the light of the moon for you—
None but the lazy or lame can refuse.
Jig it with tweedledum,
Let frolic wheedle 'em,
Making Anxiety laugh as she views.
"Come, little Annette, with tresses all curling bright,
Sporting and frisking like lambkin or kid,
Foot it so sprightly, and dance it all down aright—
Never for languor shall Annette be chid.
Right hand and left again,
Round about set amain,
Jokingly, laughingly, just as you're bid.
"See, there is Lubin and Javotte already there—
Hark! 'tis the fife and the jerked tambourine—
Mother and granddad sitting all steady there,
Smiling and nodding, enjoying the scene.
They will delighted be,
While all benighted we
Dance in the moonlight that checkers the green.
"Farewell to misery, poverty, sorrowing;
While we've a fiddle we gayly will dance;
Supper we've none, nor can we go borrowing;
Dance and forget is the fashion of France.
Long live gay jollity!
'Tis a good quality—
Caper all, sing all, and laugh all, and prance."
As most of the young people love dogs, and many of them own one or more of these faithful pets, they will, perhaps, be glad of a few hints as to their proper care and treatment.
Dogs are subject to accidents, and swellings or tumors of various kinds on different parts of the body; and in such cases, if you do not know just what to do, it is better to consult some good authority, such as the editor of a first-class sporting paper, than to try experiments which may or may not be for the good of your favorite. In order that you may be able to describe minutely and accurately the part of the animal's body where the trouble seems to be, the diagram showing the "points" of a dog is given:
Nearly all dogs enjoy an occasional washing, and if they do not get it, their skin is apt to become foul, and vermin may collect, which will prove very troublesome and difficult to remove. When the dog is to be washed, get two large buckets full of soft water, a rough towel, and a cake of Spratt's soap, for which you may be obliged to send to a dog-fancier. The water in one bucket should be lukewarm, and that in the other cold. Tie the dog in the yard or on the grass under a tree, and begin by pouring a little of the warm water on his shoulder, at the same time rubbing on the soap. Keep on in this way until every inch of the dog's body is covered with a lather, washing the head last, and taking care not to let the soapy water get into either his eyes or ears.
After the dog is thus thoroughly covered with lather, wash it off with clean warm water, at the same time gently squeezing the hide and rubbing downward. When the soap is all rinsed off, dash a few dipperfuls of cold water over the dog, and rub his jacket briskly with the rough towel. Then untie him and let him have a good run, after which, and when his coat is nearly dry, is the time to give him a thorough combing and grooming, carefully unravelling every bit of tangle or "mat" you may find in his feather. (The long hair of a dog is called his "feather," not feathers.)
In order that a dog may be kept in good health, his kennel requires frequent attention. Not only should the bedding be always sweet and dry, but the place should be occasionally scrubbed with soap and boiling water, and left to become thoroughly dry in the sun before it is again occupied.
If your dog has a collar—and every well-behaved dog deserves a pretty collar to wear when he goes out for a walk—be sure and take it off as soon as he comes in. Remember, also, that while the outside of the collar must be kept clean and bright in order to look well, it is very important for the good of the dog that the inside should be kept clean as well, and not allowed to become foul.
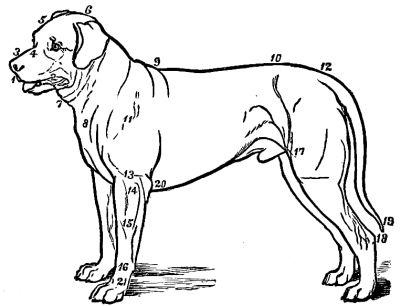 POINTS OF A DOG.
POINTS OF A DOG.Very strange dishes came upon the board at our New-Year's dinner at the hotel in Tokio. A preliminary pipe of mild tobacco was handed around. The tobacco was too mild an affair altogether to take the edge off one's appetite, if intended for that purpose. The first course consisted of sweetmeats, served upon lacquered plates. The whole meal was of a Frenchified character. Balls of golden, scarlet, and green jellies were among the things in this dish; rice, flour, and sugar made up the constituents of the other parts of it. Saki (rice spirit) and the ever-present tea were then served round. The second course consisted of soup, into which were shredded hard-boiled eggs. This was served in bowls, but without spoons. I had, however, my purchased spoon, fork, and knife always with me, and so escaped trouble. Then came a very strange dish: it was a collop cut from a living fish wriggling on the sideboard. The Japs are a great fish-eating folk, and this raw fish-eating is quite common. The steak cut for Bruce from the living ox, told of in his Abyssinian travels, occurred to one's memory. The live tidbit is supposed to be eaten with the Japanese "Soy"—a sauce that makes everything palatable—but I let my portion of it pass. It is not possible to comply with all Japanese fashions at once. Time is necessary to the acquirement of taste. Cooked fish was next served, and that in great variety, including shell-fish. A sort of lime or small lemon was used as the flavoring to this dish. Then came boiled beans, with ginger roots, and some fried fish and horse-radish. To follow that came boiled fish and clams, the latter cut up, and served with pears. Rice in tea-cups followed, and then a salad, and the dishes were ended. The hot saki and tea cups were sent round after each course. The health of our landlord was proposed in Japanese, and drunk in saki. He then rose to reply. I thought that he would never have done bowing before he began to speak. He appeared to speak very well, and easily.[Pg 403]
Of the four little housekeepers, Patty, the eldest, who was fifteen, was chief. Johnny came next. He was housekeeper number two. And then there was Katie, who was eleven, and Nan, nine. Their mother had died two years before, and when the housekeeper left, about a year afterward, Patty, in all the dignity of her fourteen years, decided to dispense with help in future, and that they could do the work among themselves. Mr. Harvey was absorbed in his business, and never greatly disturbed by any irregularities in his household, provided the children were generally peaceable and happy.
So Patty's decision was allowed to stand. Housekeeping had seemed a very easy thing to her, as she had seen her mother go about quietly doing one thing after another, without hurry or confusion. But she found doing the same things herself to be another thing. Oh, the trouble they had with the cooking! The same fire that would not bake the biscuits burned the steak to a crisp. After repeated efforts and experiments, however, bread, steak, and potatoes that could be eaten appeared on the table.
Then they decided to try some cake. Patty, and Johnny, who was always ready to help, knit their brows and puzzled their brains over the recipes. Johnny volunteered to read the directions from the cook-book, while Patty measured and mixed the ingredients.
He read, "'Four eggs, two cups sugar—'"
"Stop, Johnny—don't read so fast. I wonder if the eggs ought to be beaten?"
"Course they ought to; sh'd think any goose'd know that," said Johnny, contemptuously.
"I don't believe they ought to be; the recipe doesn't say anything about beating." So the eggs were broken in with the sugar, and they were stirred together. Then the butter—a liberal quantity—and milk and flour. "'Two tea-spoons cream-tartar; flavor to taste,'" read Johnny.
At length the cake was in the oven, and they watched and waited for it to rise. But it never rose. The fire was made quick; then it was allowed to burn slower; still the cake was an inch below the top of the pan. More than an hour passed, then Patty took it from the oven. What could be the trouble? It was as heavy as lead. Johnny read the recipe over again carefully. "'One tea-spoonful soda'—that's the trouble, Pat; we forgot the soda."
Katie was the most unfortunate of the housekeepers. If she trimmed the lamps, she was sure to spill the oil; if she cooked the dinner, in spite of her wisest precautions it was sure to be burned. And Johnny used laughingly to warn her against looking at stakes, or nails, or twigs, as a rent in her dress was sure to be the result.
Then there was Nan. She did so hate dish-washing! Sometimes, if in the very midst of hot water and rattling crockery, she saw her girl friends outside at play, away she would go, not thinking again of her unfinished task until returning, perhaps half an hour afterward, she would find the towels wet and the water cold in the pan.
And it must be confessed that sometimes even Patty herself would drop her broom, and at the same time her dignity, and join the children, as eager as any of them, forgetful of the dinner hour and the uncooked dinner.
But the sewing—making the clothes—was the worst. Patty was so proud that she would not ask help from anybody—no, not if she ruined her eyes, and worked her fingers to the bone. Garments were picked to pieces, stitch by stitch, to learn how they were made. Dresses were puzzled over, and pulled this way and that; a little cut off here and a piece sewed on there to make them fit.
But now was coming the tug of war. In a week would be the examination at the grammar school to which Nan went, and she had not a thing fit to wear.
Patty wondered what she should do. She consulted her father.
"Why, buy her a dress," he said.
"But I can not buy one all made."
"Make her one, then," and he laid a crisp bill on the table.
So Patty was left to manage as best she might. Taking Nan with her, she went first to the shoe store, where she selected a pair of the daintiest, nicest-fitting boots; then to the dry-goods store, where she bought a number of yards of some sort of twilled goods of a lovely shade of blue. With these, a lace bib, and a large blue bow for her hair, Patty thought Nan would look very pretty.
Purchasing the material had been quite easy; but now came the cutting and making of the dress. The dresses of other girls were studied, fashion plates consulted by all the little housekeepers, and at last a style was decided upon. Then there was a laying on of patterns, and cutting, and basting, and ripping out, and sewing together, till at last the dress was completed. It is true that it was a little too long on the shoulder, and a little too short under the arm, and a little too scant in the skirt. But it was pretty, and the effect was good.
At length the day before examination came, and everything was ready. The lace had been basted into the sleeves, and the dress, French kid boots, bow, and collar were laid away in the best chamber.
But just before dark a lady living in another part of the city sent for Patty to come and spend the night with her, as she was alone. How could she go? There was Nan to be dressed in the morning. But then she could not disappoint her kind friend; so, after giving Katie and Nan many directions for the morning, she left them, promising to meet them at the school-house.
The next morning Johnny got the breakfast, and Nan and Katie cleared away the dishes. Then they went up stairs to dress. Nan had just finished her hair, having pinned on the blue bow, and was surveying its effect in the glass, when the sound of music on the street, just in front of the house, attracted her attention. She rushed to the window. There was a chariot painted in gay colors, and men in scarlet and gold uniforms, and such music! The new dress was forgotten, and she flew down stairs and out of the door. With a troop of children she followed the gaudy chariot and gayly caparisoned horses from street to street.
At length, before she realized how far she had gone, she found herself before the school-house door, and the clock was striking nine. There was no time to go back. She thought of the new dress. No matter; she had on the blue bow.
Patty had gone directly to the school-house, instead of first going home, and was awaiting Nan's appearance.
The bell rang for the second class to come down; and though trying to be calm and dignified, Patty could not help leaning eagerly forward, as the girls came trooping into the recitation-room. She wanted to see how Nan looked in the new blue dress and neat boots.
One by one the girls pushed forward and took their seats, until at last— Could that be Nan? Poor Patty's cheeks burned with mortification as she saw her pressing eagerly forward among the rest, her freckled face beaming with satisfaction. Instead of the beautiful blue dress, she had on a faded calico, considerably outgrown, and her coarse every-day boots with copper tips, half laced up, and much the worse for wear. But, in striking contrast, the blue bow was perched proudly on the top of her head. Then she had forgotten her pocket-handkerchief, and poor Patty was anything but soothed by the snuffs that she gave from time to time.
But when the recitations were heard Nan's dress was forgotten. Her answers were prompt, correct, and distinct; and Patty's feelings were somewhat soothed by the[Pg 404] looks and words of praise that passed from one to another of the examining committee, as Nan, still fresh and unwearied, answered the last question correctly.
Then came the awarding of prizes. The silence of expectancy reigned in the school-room, unbroken, save by the whispered consultation of teachers and examiners. At last the principal called the second class forward to the recitation seats.
As the girls passed down the aisles, another great wave of mortification swept over poor Patty, as Nan, in striking contrast to the other girls, in their pretty dresses, still careless and eager, pressed forward among the rest. When the girls reached their places, and all had become quiet, one of the committee rose and said: "You have all done well. I am pleased with the interest which you seem to manifest in your school and studies, and with the industry and application shown by your ready responses. But for prompt, correct, and distinct answers, which her teachers tell me have been uniform throughout the term, I award to Miss Nannie Harvey the first prize." And as Nan, bright and unconscious as ever, stepped forward to receive it, an almost audible smile passed round the room, mingled with a murmur of applause.
But after this, as they trudged home together, Patty was almost as forgetful as Nan of the shabby dress and thick half-worn shoes.
Listen! No; you can not hear them;
Never do they make a sound,
All these thousand sweet blue flowers
Starting up from out the ground.
Scattered are they up the hill-side,
Hidden in the woodland nooks,
Sprinkled over sunny meadows,
Nestled close by sparkling brooks.
Where, I wonder, have they sprung from?
Do they live in worlds below?
Have they slept the livelong winter
Underneath the soft white snow?
Ah! if only they had voices,
What strange stories they might tell
Of the land where winsome fairies
With the flowers love to dwell!
Oh, you dainty wee blue flowers!
Brightest roses June may bring,
But they can not match your sweetness,
Gentle messengers of spring.
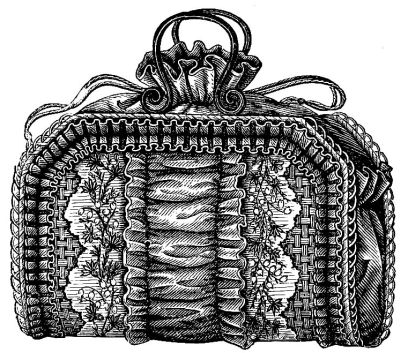 Fig. 1.—EMBROIDERED WORK-BAG.
Fig. 1.—EMBROIDERED WORK-BAG.
This pretty work-bag has a foundation of splints, wicker-work, Manila braid, or whatever material of the kind may be found most convenient, fourteen inches and seven-eighths long and ten inches and a half wide, which is sloped off on the corners, and trimmed with two strips of embroidery, separated by a bias strip of blue satin, which is turned down on the edges an inch wide on the wrong side, and gathered so as to form a puff. The embroidered strips are worked on a foundation of white cloth as shown by Fig. 2. For the corn-flowers use blue silk, and work them in chain stitch. The calyxes are worked in satin stitch with moss green silk, and the lilies-of-the-valley with white silk. The stems and sprays are worked in tent and herring-bone stitch with green silk in several shades. For the ends cut of blue satin two pieces each six inches and a half wide and seven inches and a quarter high, fold down the upper edge an inch and a quarter wide on the wrong side, and gather it twice. Having sloped off the lower corners of these parts, pleat them, and join them with the foundation. For the bag cut of blue satin one piece twenty-four inches wide and ten inches and a half high, sew it up on the sides, and fold down the upper edge two inches and a half wide on the wrong side, for a shirr, through which blue silk cord is run, and sew it to the upper edge of the foundation on the wrong side. The work-bag is trimmed on the outside with a ruche of blue satin ribbon seven-eighths of an inch wide. Light gray instead of white cloth forms a pretty and more serviceable foundation for the embroidered strips. Little girls who do not know how to embroider may make a very handsome work-bag from this pattern by using ribbon brocaded in bright colors, or a double row of ruching around the edge in the place of the embroidery. Bamboo handle.
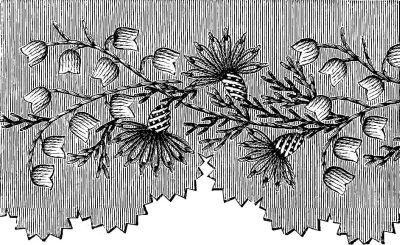 Fig. 2.—BORDER FOR WORK-BAG.
Fig. 2.—BORDER FOR WORK-BAG.

I am the lad in the cadet gray—
Rat-a-tat, rat-a-tat, rat-tat, hey!
My buttons are bright, my jacket is tight,
My step is a soldier's, quick and light;
I'm ready to dance, I'm ready to fight—
Hurrah! hurrah! for the boy in gray.
I am the lad in the cadet gray—
Rat-a-tat, rat-a-tat, rat-tat, hey!
The bugle wakes me at dawn of day;
I'm out at drill in the morning gray,
Prompt and trig, not a hair astray—
Hurrah! hurrah! for the boy in gray.
I am the lad in the cadet gray—
Rat-a-tat, rat-a-tat, rat-tat, hey!
My hardest tasks are cheerfully done;
I'm under orders from sun to sun;
You should see me handle sword and gun—
Hurrah! hurrah! for the boy in gray.
I am the lad in the cadet gray—
Rat-a-tat, rat-a-tat, rat-tat, hey!
At "four-o'clocks," and at dress parade,
My chevrons, buttons, and fancy braid
Win smiles from many a lovely maid
For the handsome lad in cadet gray.
For the lad in gray the drum is rolled—
Rat-a-tat, rat-a-tat, quick and bold;
And when the days of drilling are through,
This is the thing that I shall do:
Doff cadet gray for the army blue—
The army blue with its stars of gold.
Braver and freer a thousandfold—
Rat-a-tat, rat-a-tat, true and bold.
Pistols and sword in my silken sash,
After my country's foes I'll dash,
Where muskets rattle and sabres clash—
Hurrah! for the army blue and gold.
Hurrah! for the lad so brave and true,
In cadet gray or in army blue.
On his heart he wears his country's name,
And his hand will keep her spotless fame;
In gray or blue he is just the same—
Hurrah! for the lad in gray or blue.

The following communication is from a member of an old and well-known publishing firm in this city:
New York, April 28, 1880.
Messrs. Harper & Brothers:
Gentlemen,—When you announced your intention of making a paper for the young, I must own I felt a little sorry. I had always believed, and believe still, that Harper's Monthly was the best magazine in the English language, and Harper's Weekly the best of all illustrated papers; but it is so hard to make a periodical for the young—the number of people capable of editing such a periodical being extremely small—I felt it must be a failure, and so for a good while I gave it very little attention. I have a boy of seven, and another of five—bright boys, of course—and I have read every line (almost) of three late consecutive numbers of Harper's Young People; and I must say, if these are specimens—and I have no doubt they are—it is as complete a success in its own way as the Magazine and the Weekly. I am not sure whether the boys or their papa were most interested. The only fault I see in it is that it increases the difficulty of getting the children off early to bed.
I congratulate you on having a paper that will do as much good as any paper or periodical published in the world.
Grahamville, Florida.
I live on the Oklawaha River. The Silver Spring is six miles from this place. We live at the edge of the hummock, and see many kinds of birds and flowers. A little bird has built its nest in one of our hen's nests. I have one brother. His name is Philip. I will be seven years old in May. We cut down a palmetto-tree yesterday. The cabbage, which is the tender part at the end of the tree, is good to eat. The bud I brought home, and am curing it to braid for a hat. It makes a pretty hat that looks like straw. Some people here use the palmetto leaves for fans or brooms. They are very large, and have long stems. The small leaves make nice fly-brushes.
E. Pearl L.
Brazoria, Texas.
We take Young People, and like it very much. I read the papers until I know them almost by heart, and I thought it would be nice to write a letter for the Post-office Box. I am a little boy nine years old, and I live on the Brazos River, in Texas. I and my little brother have never been to school, but papa and mamma teach us at home. We have beautiful redbirds, bluebirds, and woodpeckers here, and a pair of mocking-birds have built their nest in a rose-bush near our window. We have two pet chickens, named Poll and Nelly, that have never been with a hen since they were hatched. When I call, "Cluck! cluck!" they come running to me, but they are afraid of a hen. Every night they cry to be put to bed.
Walter H. S.
Refugio, Texas.
I want to tell you about some minnows I had. I got them out of a mud hole, and put them in a large candy jar in some fresh rain-water. I kept them about two months. I fed them on flies and bread-crumbs, and when I dropped their food in the water, they would swim to the surface as fast as they could and swallow it. I put some shells and a calla lily in the jar, and the little fish would dart around after each other, and hide behind the shells. They were very amusing.
Lula B.
Flint, Michigan.
I had Young People for a Christmas present, and I like it very much. I have a puppy. I call him Champion, after that brave dog in the story I read in Young People No. 20. He is two months old, and my papa thinks he will be big enough next winter to draw me on my sled.
Josie A. U.
Duncansby, Mississippi.
I am a little girl ten years old, and I have a brother eight. I live in the country, two miles from the Mississippi River, where there is nothing to see but big fields of cotton and corn. Papa is a planter. I wait patiently every week for Young People. I was born in Louisiana, but my grandpa was born in New York State. I have never been to school. I am taught at home.
Callie R. H.
Windsor, Connecticut.
I send you the names of all the flowers I have found in the month of April. I bring them in from the fields, and mamma tells me the names, and I write them down in a book. I think I can find more flowers in May, as I live too far north to find many in April. Here is the list: Round-lobed hepatica (Hepatica triloba), trailing arbutus (Epigœa repens), yellow adder-tongue violets (Erythronium americanum), bloodroot (Sanguinaria canadensis), cinque-foil (Potentilla canadensis), sweet white violet (Viola blanda), common blue violets (Viola cucullata), wood-anemone (Anemone nemorosa), rue-anemone (Thalictrum anemonoides), wild strawberry (Fragaria vesca), shepherd's-purse (Capsella bursa), leather-leaf (Cassandra calyculata), dandelion (Taraxacum dens-leonis), bluets (Oldenlandia cerulia).
Harry H. M.
Fair Haven, Vermont.
I have watched the reports of willow "pussies" coming out in different parts of the country with a good deal of interest, and I thought I would write and tell you that on April 25, when riding to church, I saw some cowslips in bloom. I think that is doing pretty well for our New England spring. My little brother and I found two handfuls of arbutus to-day, but it has been in bloom for some time. We have a black and white shepherd dog. He can climb an apple-tree that leans a little to one side a good deal quicker than my little brother, who is eight years old.
Sadie H.
Moortown, California.
I am a little boy nine years old. I was born in the Sierra Nevada Mountains. It storms fearfully here. Last winter was an awful hard one—the coldest ever known. It has been snowing here to-day (April 13), although the wild flowers are just in bloom. I have a pet fox and a squirrel. They are very tame.
Danie R.
Marlborough-on-Hudson, New York.
I am seven years old. I live in Brooklyn, but I am visiting my grandpa and grandma now. I have a little uncle not much older than myself. We play archery sometimes, and we like to hunt eggs for grandma. There are two cats here—a big yellow one we call Solomon, because he looks so wise; and another real pretty one we call Harriet, because Harriet gave it to us. We have lots of fun here—swinging, playing croquet, riding, and rolling in the hammocks.
May T.
Lawrence, Kansas.
I am twelve years old. Papa takes Young People for my brother and me, and we like it very much. I have two pets—a cat and a canary. I let my canary out of its cage almost every day. If I do not, it seems to think itself very badly treated. Violets were in blossom here about the 1st of April.
Antoinette R.
Princess Anne County, Virginia.
I am a little boy. My sister takes your paper, and we take so much pleasure in reading it that I thought I would like to write to you. We live on the sea-shore, and have seines hauled for fish. Sometimes we catch sword-fish, sharks, and saw-fish. The other day we caught a sea-spider. It was like a common spider, but larger, and had a hard shell like a crab. Its fore-feet were something like a crab's claws.
R. D. G.
Erie, Pennsylvania.
I live on the shore of Presque Isle Bay, where "Mad" Anthony Wayne was buried. There is a monument erected over his grave. They are now rebuilding the old block-house, which was burned a few years ago. The flag-ship Lawrence, which Perry commanded when he gained the victory over the British on Lake Erie, used to lie buried in our bay, but in 1876 some enterprising young man raised it out of the water, and took it to the Centennial. I think we have the nicest place in the United States for rowing, fishing, camping out, and having lots of fun. I am eight years old.
Mamie H.
I like to read the letters in Young People, and I thought I would tell you about a wild-cat. On the evening of April 28, about five o'clock, I had just finished my music lesson, when I saw a large crowd standing near our house. I ran out, and I heard some one saying, "It is a wild-cat." I thought at first it was a prairie-wolf. It was two feet in height, and two feet and a half long. It had a cat's head, but its claws were as big as a dog's. It was dead, and a boy had a string round its neck. It came into the city from the country in a load of trees; and when the men took the trees out of the car, it sprang out, and jumped over our fence into our yard. It ran through the yard and back again, when a gentleman shot it. The boy dragged it away, and I did not see it any more. We live in the heart of the city of Chicago. I would like to exchange pressed flowers with "Wee Tot," and will send her some pressed jasmine.
Annie D. Mullally,
285 West Sixteenth Street, Chicago, Illinois.
I would like to exchange pressed flowers or shells, or any pretty curiosity, with readers of Young People in other localities, but especially in the Southern and far Western States and Territories. I liked the letters from Gertrude Balch and Charles W. S. very much, and wish they would write again. I tried to make a tombola, and succeeded admirably. Do you know who was the inventor of the 15-13-14 puzzle?
Laura Bingham, Lansing, Michigan.
The famous puzzle is said to have been invented by a poor deaf and dumb man living in a small country town in New England, but we can not substantiate the statement.
I have been in the woods to a picnic to-day, and have been reading the letters in Young People's Post-office Box this evening. I have no pets, as most little girls. I had a redbird, but it died. I would like to exchange pressed leaves with little girls in other localities.
Mary Wright,
Elk City, Kansas.
If "Genevieve," of California, will send me her address, I will press her some flowers that grow here, and send them to her. I live in a little village not far from Chicago.
Annie De Pfuhl,
Humboldt Park, Cook County, Illinois.
In Harper's Young People No. 22 "Genevieve," of California, asks some little girl to press some specimens of Eastern flowers, and exchange with her. I will be happy to do so.
Carrie Hard,
Pittsford, Monroe County, New York.
St. Johnsbury, Vermont.
My little sister takes Young People, and I read it, and like it very much. I have tried Nellie H.'s rule for candy, and it is splendid. I go to school, and have a good teacher. I had two pet rabbits last summer. I am nine years old.
Katy L. H.
I am a constant reader of the charming little paper, Young People, and think it is a splendid journal for boys and girls. I like "A Boy's First Voyage" very much indeed. In answer to one of the correspondents, I would say that I have a cabinet of curiosities, and have a good many queer specimens, such as idols, gourds from Brazil made by the natives, and other things. I also collect birds' eggs and coins. I would like to exchange with any correspondents who collect eggs, if they have any specimens to spare.
I. Quackenboss,
306 Carleton Avenue, Brooklyn, New York.
I am a little girl nine years old. I live in the country, where there are lots of pretty wild flowers, and I would like very much to exchange pressed flowers with "Genevieve," of Galt, California, if she will send me her address.
Aggie Meyer,
Georgetown, D. C.
If "Wee Tot" Brainard will wait until summer, I will be very glad to exchange some of our pressed flowers for hers, and I will send her a nice bouquet.
Julia R. Walker,
Frostburg, Allegany County, Maryland.
I have been making a collection of birds' eggs, iron ores, and stones, and if any one would like to exchange eggs or minerals with me, I will be very glad to do so.
Samuel P. Higgins,
Phillipsburg, New Jersey.
Eddie A. L.—Africa is not an island, but a continent. It is much larger than Australia, which has always been known as a continent, as it contains a greater area than the largest island. The only real distinction between a continent and an island is the difference of size.
Little Falls, New York.
I would like to ask Bertie Brown and M. R. L. if the Indians in their vicinity make dolls. I have two very curious ones made by the Nez Percés in the guard-house at Fort Vancouver, Washington Territory. On the heads of the squaws are long braids of real hair. Will you please tell me what a guard-house is, and also why barbers' signs are painted in stripes?
Susie C. B.
The guard-house is that portion of a fort where prisoners are confined and kept under guard.—In former times the barber's craft was dignified with the title of a profession, being conjoined with the art of surgery. In France, the barber-surgeons were separated from the hair-dressers, and incorporated as a distinct body in the reign of Louis the Fourteenth. In England, barbers first received incorporation from Edward the Fourth in 1461. In the reign of Henry the Eighth they were united with the Company of Surgeons, it being enacted that the barbers should confine themselves to the minor operations of blood-letting and drawing teeth. In 1745, barbers and surgeons were separated in England into distinct corporations. The barber's sign consisted in ancient times, as now, of a striped pole, from which a basin was formerly suspended. The fillet round the pole indicated the ribbon used for bandaging the arm in bleeding and the basin the vessel to receive the blood.
F. Haynes.—Many thanks for your kindness and trouble in copying the poem. You have done it very neatly. It is, however, much too long to be printed in Young People.
W. Atkinson.—A water-mark is any device stamped in the substance of a sheet of paper[Pg 407] while it is in a damp or pulpy condition. The practice dates back to the early part of the sixteenth century, and came into vogue soon after the invention of printing. The mark is produced by pressure as the paper passes over a wire-gauze net, or under a roller, in its progress from the vat, the raised lines of the design making the paper thinner at the points of contact.
Louie B.—We shall soon begin the publication of "The Story of the American Navy," by Benson J. Lossing.
B. H. Smith.—Your idea of our "Wiggle" is entirely original, and very good. We are very sorry it arrived too late to be engraved among other answers.
[Two cities are hidden in each sentence.]
1. I oft have looked at royal apparel, but a regal vest on the Prince was the finest I have seen. 2. If you went with a carriage, how did you make that rent on your dress? 3. The mob I led so well I made keep in very good order. 4. I know I am not wanted, but I came, for I am a constable. 5. Is a lemon good with salt on it?
F. B.
My first is in mist, but not in fog.
My second is in cat, but not in dog.
My third is in cart, but not in wagon.
My fourth is in beast, but not in dragon.
My fifth is in wheat, but not in corn.
My sixth is in birth, but not in born.
My seventh is in hurt, but not in sting.
My whole was an ancient Scottish king.
K. K.
First, a musical instrument. Second, a boy's name. Third, darkness. Fourth, solitary. Fifth, titles.
Florence.
I am composed of 20 letters.
My 8, 5. 4, 20 is very small.
My 13, 3, 11 is found in every farm-yard.
My 14, 10, 6, 1 is a coin.
My 16, 5, 11, 7 is a number.
My 18, 19, 6 is a vase.
My 12, 15, 9, 17, 2 give a great deal of pain and
trouble, and yet no one likes to part with them.
My whole has witnessed many remarkable events.
Eddie.
[The two following geographical puzzles are sent by Sadie in answer to Maud T. K.'s request in Post-office Box No. 24.]
A symbol of one of the points of the compass. A river in Switzerland. A country in Europe. A tributary of the Mississippi River. A symbol of one of the points of the compass.
A city in China. One of the United States. A city in China. A town in New York State. One of the grand divisions of land. An island in the Grecian Archipelago. Answer—Two cities in Europe.
Robert Bruce.
Remember me.
Robin Redbreast.
| P | I | N | E | |||
| N | E | A | R | |||
| T | R | O | T | |||
| L | E | O | N |
1. Approbation. 2. Sweetheart. 3. Instruction. 4. Operator. 5. Gasometer. 6. Congratulate.
Algebra.
Aunt Flora, a Broken Rhyme, on page 360:
Scold, cold, old.
Scant, cant, ant.
Charm, harm, arm.
Stone, tone, one.
Favors are acknowledged from George A. W., Harry Starr K., Mary L. Hannam, Leslie Ray, Jamie C. Edgerton, Ruth Marshall, Horace Barlow, J. R. Gleason, Oliver Arden, Bertha Thompson, C. R. F., Grace W. Watson, Willie Dorrance, Jessie E. Watt, Cloyd D. Brown.
Correct answers to puzzles are received from J. Hartley Merrick, Grace Storey, James C. Smith, Edward L. Hunt, Edith H. Jones, Alice and Mamie Grady, Alexander Maxwell, Charles B. Miller, Robert Davidson, George S. Vail, H. G. B., Marion Norcross, Lula Barlow, A. H. Ellard, George Varker, Beryl Abbott, Julia R. Walker, Ruth Thompson, Rebecca Hedges, Marshall Haywood, George Stevenson, M. Parkinson, Stanley King.
Harper's Young People will be issued every Tuesday, and may be had at the following rates—payable in advance, postage free:
| Single Copies | $0.04 |
| One Subscription, one year | 1.50 |
| Five Subscriptions, one year | 7.00 |
Subscriptions may begin with any Number. When no time is specified, it will be understood that the subscriber desires to commence with the Number issued after the receipt of order.
Remittances should be made by POST-OFFICE MONEY ORDER or DRAFT, to avoid risk of loss.
The extent and character of the circulation of Harper's Young People will render it a first-class medium for advertising. A limited number of approved advertisements will be inserted on two inside pages at 75 cents per line.
Address
HARPER & BROTHERS,
Franklin Square, N. Y.
Our Children's Songs. Illustrated. 8vo, Ornamental Cover, $1.00.
It contains some of the most beautiful thoughts for children that ever found vent in poesy, and beautiful "pictures to match."—Chicago Evening Journal.
The best compilation of songs for the children that we have ever seen.—New Bedford Mercury.
This is a large collection of songs for the nursery, for childhood, for boys and for girls, and sacred songs for all. The range of subjects is a wide one, and the book is handsomely illustrated.—Philadelphia Ledger.
The Child's Book of Nature, for the Use of Families and Schools: intended to aid Mothers and Teachers in Training Children in the Observation of Nature. In Three Parts. Part I. Plants. Part II. Animals. Part III. Air, Water, Heat, Light, &c. By Worthington Hooker, M.D. Illustrated. The Three Parts complete in One Volume, Small 4to, Half Leather, $1.31; or, separately, in Cloth, Part I., 53 cents; Part II., 56 cents; Part III., 56 cents.
A beautiful and useful work. It presents a general survey of the kingdom of nature in a manner adapted to attract the attention of the child, and at the same time to furnish him with accurate and important scientific information. While the work is well suited as a class-book for schools, its fresh and simple style cannot fail to render it a great favorite for family reading.
The Three Parts of this book can be had in separate volumes by those who desire it. This will be advisable when the book is to be used in teaching quite young children, especially in schools.
The Thousand and One Nights; or, The Arabian Nights' Entertainments. Translated and Arranged for Family Reading, with Explanatory Notes, by E. W. Lane. 600 Illustrations by Harvey. 2 vols., 12mo, Cloth, $3.50.
The Life and Surprising Adventures of Robinson Crusoe, of York, Mariner. By Daniel Defoe. With a Biographical Account of Defoe. Illustrated by Adams. Complete Edition. 12mo, Cloth, $1.50.
The Swiss Family Robinson; or, Adventures of a Father and Mother and Four Sons on a Desert Island. Illustrated. 2 vols., 18mo, Cloth, $1.50.
The Swiss Family Robinson—Continued: being a Sequel to the Foregoing. 2 vols., 18mo, Cloth, $1.50.
The History of Sandford and Merton. By Thomas Day. 18mo, Half Bound, 75 cents.
Square 4to, about 300 pages each, beautifully printed on Tinted Paper, embellished with many Illustrations, bound in Cloth, $1.50 per volume.
With Sixty Illustrations by Harrison Weir.
With Eighty Illustrations, from Designs by Steinle, Overbeck, Veit, Schnorr, &c.
Containing One Hundred and Sixty Fables. With Sixty Illustrations by Harrison Weir.
With Sixty-one Illustrations by W. Harvey.
With Sixty-one Illustrations by W. Harvey.
 Fig. 1.
Fig. 1.
A very comical and natural-looking toy spider can be made from very simple material. A cork, a jackknife, three hair-pins, the remains of an old brush or broom, are all the implements necessary. If you have a box of paints, so much the better. In the first place, cut the body of the spider out of a cork, as represented in Fig. 1; then paint it all over with flake-white; when that is perfectly dry, paint it as bright a yellow as you can; and after that, paint black stripes on it with lamp-black or Indian ink. Then get the hairs from an old brush, a few sticks of broom-corn will answer as well, and stick them into the body of the spider, as represented in Figures 1 and 2. Take three hair-pins, bend them into the proper form, run them through the cork, and you have the legs. Now your spider is complete except in two points: you must run a pin in the back to which to tie a thread or string to hold it up by, and two large pins into the place where you have painted the eyes. The bright heads of the pins make the eyes look very natural.
 Fig. 2.
Fig. 2.
I am one, yet it takes many to complete me, though I am intangible. Motion is necessary to make me. I have no motion of my own, being incapable of voluntary action; still, were there not voluntary action on my part, commerce would be at a stand-still. I am necessary to vessels. I am a vessel. I am what vessels take. I am ended every day by some one; and though meant to hold a liquid, still, when there is my full complement, more solid food than liquid is needed to satisfy when I am on myself. If broken, I am useless; yet, when separated, I can be brought together again. I am most agreeable when made at will, am generally an ugly piece of domestic furniture, but need a strong hand to keep up proper discipline.
Treat us kindly, we would probably always be amenable. I don't care how you treat me, provided you don't break me. There is nothing breakable about me, though you can bring me to an end at any moment. Of course I cost money, ordinarily a few pennies. There is a fixed tariff for our employment; contracts must be drawn up; yet I can be made as expensive as one chooses. Sometimes I am undertaken in the cause of science. I am generally in the kitchen, and we certainly need a kitchen and me to provide for our many and daily wants.
The Monkey and the Hawk.—There lives in the south of France a man of wealth whose château, or country place of residence, has around it very tall trees. The cook of the château has a monkey—a pert fellow, who knows ever so many tricks. The monkey often helps the cook to pluck the feathers from fowls. One day the cook gave the monkey two partridges to pluck; and the monkey, seating himself in an open window, went to work. He had picked the feathers from one of the partridges, and placed it on the outer ledge of the window with a satisfied grunt, when, lo! all at once a hawk flew down from one of the tall trees near by, and bore off the plucked bird. Master Monkey was very angry. He shook his fist at the hawk, which took a seat on one of the limbs not far off, and began to eat the partridge with great relish. The owner of the château saw the sport, for he was sitting in a grape arbor, and crept up to watch the end of it. The monkey picked the other partridge, laid it on the ledge in the same place, and hid behind the window-screen on the inside.
The hawk was caught in this trap, for when it flew down after the partridge, out reached the monkey, and caught the thief. In a moment the hawk's neck was wrung, and the monkey soon had the hawk plucked.
Taking the two birds to the cook, the monkey handed them to him, as if to say, "Here are your two partridges, master." The cook thought that one of the birds looked queer, but he served them on the table. The owner of the house shook his head when he saw the dish, and telling the cook of the trick, laughed heartily.
How the Pigeons Help the Doctor.—A celebrated English physician has found a new use for the carrier-pigeon, as a helper in his practice. Describing the operation, he says: "I take out half a dozen birds in a small basket with me on my rounds, and when I have seen my patient, no matter at what distance from home, I write my prescription on a small piece of tissue-paper, and having wound it round the shank of the bird's leg, I gently throw the carrier up into the air. In a few minutes it reaches home, and having been shut up fasting since the previous evening, without much delay it enters the trap cage connected with its loft, where it is at once caught by my assistant, and relieved of its dispatches. The medicine is immediately prepared, and sent off by a messenger, who is thus saved several hours of waiting, and I am enabled to complete my morning round of visits. Should any patient be very ill, and I am desirous of having an early report of him or her next morning, I leave a bird to bring me the tidings."
Aunt Flora's scolding never made you ____,
Her sympathies, though cold, were never ____,
And her old pies were marvels of high ____.'
Poor Flora.
Her homespun dress, though scant, was made with ____,
Her harmless cant would neither cure nor ____,
And, like the busy ant, she knew no ____.
Good Flora.
A nameless charm with face and form did ____;
No harm she did, but graciously would ____
Her arm to guide you safely to your ____.
Kind Flora.
A heart may seem of stone if grief it ____;
Her tone to you was ever like a ____;
One wise was she among the foolish ____.
Wise Flora.
 BREAKERS AHEAD! AH, WHAT A MEETING THAT WILL BE!
BREAKERS AHEAD! AH, WHAT A MEETING THAT WILL BE![1] The rupee is the standard coin of British India, and worth about fifty cents.
End of Project Gutenberg's Harper's Young People, May 18, 1880, by Various
*** END OF THIS PROJECT GUTENBERG EBOOK HARPER'S YOUNG PEOPLE, MAY 18, 1880 ***
***** This file should be named 28895-h.htm or 28895-h.zip *****
This and all associated files of various formats will be found in:
https://www.gutenberg.org/2/8/8/9/28895/
Produced by Annie McGuire
Updated editions will replace the previous one--the old editions
will be renamed.
Creating the works from public domain print editions means that no
one owns a United States copyright in these works, so the Foundation
(and you!) can copy and distribute it in the United States without
permission and without paying copyright royalties. Special rules,
set forth in the General Terms of Use part of this license, apply to
copying and distributing Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works to
protect the PROJECT GUTENBERG-tm concept and trademark. Project
Gutenberg is a registered trademark, and may not be used if you
charge for the eBooks, unless you receive specific permission. If you
do not charge anything for copies of this eBook, complying with the
rules is very easy. You may use this eBook for nearly any purpose
such as creation of derivative works, reports, performances and
research. They may be modified and printed and given away--you may do
practically ANYTHING with public domain eBooks. Redistribution is
subject to the trademark license, especially commercial
redistribution.
*** START: FULL LICENSE ***
THE FULL PROJECT GUTENBERG LICENSE
PLEASE READ THIS BEFORE YOU DISTRIBUTE OR USE THIS WORK
To protect the Project Gutenberg-tm mission of promoting the free
distribution of electronic works, by using or distributing this work
(or any other work associated in any way with the phrase "Project
Gutenberg"), you agree to comply with all the terms of the Full Project
Gutenberg-tm License (available with this file or online at
https://gutenberg.org/license).
Section 1. General Terms of Use and Redistributing Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic works
1.A. By reading or using any part of this Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic work, you indicate that you have read, understand, agree to
and accept all the terms of this license and intellectual property
(trademark/copyright) agreement. If you do not agree to abide by all
the terms of this agreement, you must cease using and return or destroy
all copies of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works in your possession.
If you paid a fee for obtaining a copy of or access to a Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic work and you do not agree to be bound by the
terms of this agreement, you may obtain a refund from the person or
entity to whom you paid the fee as set forth in paragraph 1.E.8.
1.B. "Project Gutenberg" is a registered trademark. It may only be
used on or associated in any way with an electronic work by people who
agree to be bound by the terms of this agreement. There are a few
things that you can do with most Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works
even without complying with the full terms of this agreement. See
paragraph 1.C below. There are a lot of things you can do with Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic works if you follow the terms of this agreement
and help preserve free future access to Project Gutenberg-tm electronic
works. See paragraph 1.E below.
1.C. The Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation ("the Foundation"
or PGLAF), owns a compilation copyright in the collection of Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic works. Nearly all the individual works in the
collection are in the public domain in the United States. If an
individual work is in the public domain in the United States and you are
located in the United States, we do not claim a right to prevent you from
copying, distributing, performing, displaying or creating derivative
works based on the work as long as all references to Project Gutenberg
are removed. Of course, we hope that you will support the Project
Gutenberg-tm mission of promoting free access to electronic works by
freely sharing Project Gutenberg-tm works in compliance with the terms of
this agreement for keeping the Project Gutenberg-tm name associated with
the work. You can easily comply with the terms of this agreement by
keeping this work in the same format with its attached full Project
Gutenberg-tm License when you share it without charge with others.
1.D. The copyright laws of the place where you are located also govern
what you can do with this work. Copyright laws in most countries are in
a constant state of change. If you are outside the United States, check
the laws of your country in addition to the terms of this agreement
before downloading, copying, displaying, performing, distributing or
creating derivative works based on this work or any other Project
Gutenberg-tm work. The Foundation makes no representations concerning
the copyright status of any work in any country outside the United
States.
1.E. Unless you have removed all references to Project Gutenberg:
1.E.1. The following sentence, with active links to, or other immediate
access to, the full Project Gutenberg-tm License must appear prominently
whenever any copy of a Project Gutenberg-tm work (any work on which the
phrase "Project Gutenberg" appears, or with which the phrase "Project
Gutenberg" is associated) is accessed, displayed, performed, viewed,
copied or distributed:
This eBook is for the use of anyone anywhere at no cost and with
almost no restrictions whatsoever. You may copy it, give it away or
re-use it under the terms of the Project Gutenberg License included
with this eBook or online at www.gutenberg.org
1.E.2. If an individual Project Gutenberg-tm electronic work is derived
from the public domain (does not contain a notice indicating that it is
posted with permission of the copyright holder), the work can be copied
and distributed to anyone in the United States without paying any fees
or charges. If you are redistributing or providing access to a work
with the phrase "Project Gutenberg" associated with or appearing on the
work, you must comply either with the requirements of paragraphs 1.E.1
through 1.E.7 or obtain permission for the use of the work and the
Project Gutenberg-tm trademark as set forth in paragraphs 1.E.8 or
1.E.9.
1.E.3. If an individual Project Gutenberg-tm electronic work is posted
with the permission of the copyright holder, your use and distribution
must comply with both paragraphs 1.E.1 through 1.E.7 and any additional
terms imposed by the copyright holder. Additional terms will be linked
to the Project Gutenberg-tm License for all works posted with the
permission of the copyright holder found at the beginning of this work.
1.E.4. Do not unlink or detach or remove the full Project Gutenberg-tm
License terms from this work, or any files containing a part of this
work or any other work associated with Project Gutenberg-tm.
1.E.5. Do not copy, display, perform, distribute or redistribute this
electronic work, or any part of this electronic work, without
prominently displaying the sentence set forth in paragraph 1.E.1 with
active links or immediate access to the full terms of the Project
Gutenberg-tm License.
1.E.6. You may convert to and distribute this work in any binary,
compressed, marked up, nonproprietary or proprietary form, including any
word processing or hypertext form. However, if you provide access to or
distribute copies of a Project Gutenberg-tm work in a format other than
"Plain Vanilla ASCII" or other format used in the official version
posted on the official Project Gutenberg-tm web site (www.gutenberg.org),
you must, at no additional cost, fee or expense to the user, provide a
copy, a means of exporting a copy, or a means of obtaining a copy upon
request, of the work in its original "Plain Vanilla ASCII" or other
form. Any alternate format must include the full Project Gutenberg-tm
License as specified in paragraph 1.E.1.
1.E.7. Do not charge a fee for access to, viewing, displaying,
performing, copying or distributing any Project Gutenberg-tm works
unless you comply with paragraph 1.E.8 or 1.E.9.
1.E.8. You may charge a reasonable fee for copies of or providing
access to or distributing Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works provided
that
- You pay a royalty fee of 20% of the gross profits you derive from
the use of Project Gutenberg-tm works calculated using the method
you already use to calculate your applicable taxes. The fee is
owed to the owner of the Project Gutenberg-tm trademark, but he
has agreed to donate royalties under this paragraph to the
Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation. Royalty payments
must be paid within 60 days following each date on which you
prepare (or are legally required to prepare) your periodic tax
returns. Royalty payments should be clearly marked as such and
sent to the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation at the
address specified in Section 4, "Information about donations to
the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation."
- You provide a full refund of any money paid by a user who notifies
you in writing (or by e-mail) within 30 days of receipt that s/he
does not agree to the terms of the full Project Gutenberg-tm
License. You must require such a user to return or
destroy all copies of the works possessed in a physical medium
and discontinue all use of and all access to other copies of
Project Gutenberg-tm works.
- You provide, in accordance with paragraph 1.F.3, a full refund of any
money paid for a work or a replacement copy, if a defect in the
electronic work is discovered and reported to you within 90 days
of receipt of the work.
- You comply with all other terms of this agreement for free
distribution of Project Gutenberg-tm works.
1.E.9. If you wish to charge a fee or distribute a Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic work or group of works on different terms than are set
forth in this agreement, you must obtain permission in writing from
both the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation and Michael
Hart, the owner of the Project Gutenberg-tm trademark. Contact the
Foundation as set forth in Section 3 below.
1.F.
1.F.1. Project Gutenberg volunteers and employees expend considerable
effort to identify, do copyright research on, transcribe and proofread
public domain works in creating the Project Gutenberg-tm
collection. Despite these efforts, Project Gutenberg-tm electronic
works, and the medium on which they may be stored, may contain
"Defects," such as, but not limited to, incomplete, inaccurate or
corrupt data, transcription errors, a copyright or other intellectual
property infringement, a defective or damaged disk or other medium, a
computer virus, or computer codes that damage or cannot be read by
your equipment.
1.F.2. LIMITED WARRANTY, DISCLAIMER OF DAMAGES - Except for the "Right
of Replacement or Refund" described in paragraph 1.F.3, the Project
Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation, the owner of the Project
Gutenberg-tm trademark, and any other party distributing a Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic work under this agreement, disclaim all
liability to you for damages, costs and expenses, including legal
fees. YOU AGREE THAT YOU HAVE NO REMEDIES FOR NEGLIGENCE, STRICT
LIABILITY, BREACH OF WARRANTY OR BREACH OF CONTRACT EXCEPT THOSE
PROVIDED IN PARAGRAPH F3. YOU AGREE THAT THE FOUNDATION, THE
TRADEMARK OWNER, AND ANY DISTRIBUTOR UNDER THIS AGREEMENT WILL NOT BE
LIABLE TO YOU FOR ACTUAL, DIRECT, INDIRECT, CONSEQUENTIAL, PUNITIVE OR
INCIDENTAL DAMAGES EVEN IF YOU GIVE NOTICE OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH
DAMAGE.
1.F.3. LIMITED RIGHT OF REPLACEMENT OR REFUND - If you discover a
defect in this electronic work within 90 days of receiving it, you can
receive a refund of the money (if any) you paid for it by sending a
written explanation to the person you received the work from. If you
received the work on a physical medium, you must return the medium with
your written explanation. The person or entity that provided you with
the defective work may elect to provide a replacement copy in lieu of a
refund. If you received the work electronically, the person or entity
providing it to you may choose to give you a second opportunity to
receive the work electronically in lieu of a refund. If the second copy
is also defective, you may demand a refund in writing without further
opportunities to fix the problem.
1.F.4. Except for the limited right of replacement or refund set forth
in paragraph 1.F.3, this work is provided to you 'AS-IS' WITH NO OTHER
WARRANTIES OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO
WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTIBILITY OR FITNESS FOR ANY PURPOSE.
1.F.5. Some states do not allow disclaimers of certain implied
warranties or the exclusion or limitation of certain types of damages.
If any disclaimer or limitation set forth in this agreement violates the
law of the state applicable to this agreement, the agreement shall be
interpreted to make the maximum disclaimer or limitation permitted by
the applicable state law. The invalidity or unenforceability of any
provision of this agreement shall not void the remaining provisions.
1.F.6. INDEMNITY - You agree to indemnify and hold the Foundation, the
trademark owner, any agent or employee of the Foundation, anyone
providing copies of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works in accordance
with this agreement, and any volunteers associated with the production,
promotion and distribution of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works,
harmless from all liability, costs and expenses, including legal fees,
that arise directly or indirectly from any of the following which you do
or cause to occur: (a) distribution of this or any Project Gutenberg-tm
work, (b) alteration, modification, or additions or deletions to any
Project Gutenberg-tm work, and (c) any Defect you cause.
Section 2. Information about the Mission of Project Gutenberg-tm
Project Gutenberg-tm is synonymous with the free distribution of
electronic works in formats readable by the widest variety of computers
including obsolete, old, middle-aged and new computers. It exists
because of the efforts of hundreds of volunteers and donations from
people in all walks of life.
Volunteers and financial support to provide volunteers with the
assistance they need are critical to reaching Project Gutenberg-tm's
goals and ensuring that the Project Gutenberg-tm collection will
remain freely available for generations to come. In 2001, the Project
Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation was created to provide a secure
and permanent future for Project Gutenberg-tm and future generations.
To learn more about the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation
and how your efforts and donations can help, see Sections 3 and 4
and the Foundation web page at https://www.pglaf.org.
Section 3. Information about the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive
Foundation
The Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation is a non profit
501(c)(3) educational corporation organized under the laws of the
state of Mississippi and granted tax exempt status by the Internal
Revenue Service. The Foundation's EIN or federal tax identification
number is 64-6221541. Its 501(c)(3) letter is posted at
https://pglaf.org/fundraising. Contributions to the Project Gutenberg
Literary Archive Foundation are tax deductible to the full extent
permitted by U.S. federal laws and your state's laws.
The Foundation's principal office is located at 4557 Melan Dr. S.
Fairbanks, AK, 99712., but its volunteers and employees are scattered
throughout numerous locations. Its business office is located at
809 North 1500 West, Salt Lake City, UT 84116, (801) 596-1887, email
business@pglaf.org. Email contact links and up to date contact
information can be found at the Foundation's web site and official
page at https://pglaf.org
For additional contact information:
Dr. Gregory B. Newby
Chief Executive and Director
gbnewby@pglaf.org
Section 4. Information about Donations to the Project Gutenberg
Literary Archive Foundation
Project Gutenberg-tm depends upon and cannot survive without wide
spread public support and donations to carry out its mission of
increasing the number of public domain and licensed works that can be
freely distributed in machine readable form accessible by the widest
array of equipment including outdated equipment. Many small donations
($1 to $5,000) are particularly important to maintaining tax exempt
status with the IRS.
The Foundation is committed to complying with the laws regulating
charities and charitable donations in all 50 states of the United
States. Compliance requirements are not uniform and it takes a
considerable effort, much paperwork and many fees to meet and keep up
with these requirements. We do not solicit donations in locations
where we have not received written confirmation of compliance. To
SEND DONATIONS or determine the status of compliance for any
particular state visit https://pglaf.org
While we cannot and do not solicit contributions from states where we
have not met the solicitation requirements, we know of no prohibition
against accepting unsolicited donations from donors in such states who
approach us with offers to donate.
International donations are gratefully accepted, but we cannot make
any statements concerning tax treatment of donations received from
outside the United States. U.S. laws alone swamp our small staff.
Please check the Project Gutenberg Web pages for current donation
methods and addresses. Donations are accepted in a number of other
ways including including checks, online payments and credit card
donations. To donate, please visit: https://pglaf.org/donate
Section 5. General Information About Project Gutenberg-tm electronic
works.
Professor Michael S. Hart was the originator of the Project Gutenberg-tm
concept of a library of electronic works that could be freely shared
with anyone. For thirty years, he produced and distributed Project
Gutenberg-tm eBooks with only a loose network of volunteer support.
Project Gutenberg-tm eBooks are often created from several printed
editions, all of which are confirmed as Public Domain in the U.S.
unless a copyright notice is included. Thus, we do not necessarily
keep eBooks in compliance with any particular paper edition.
Most people start at our Web site which has the main PG search facility:
https://www.gutenberg.org
This Web site includes information about Project Gutenberg-tm,
including how to make donations to the Project Gutenberg Literary
Archive Foundation, how to help produce our new eBooks, and how to
subscribe to our email newsletter to hear about new eBooks.