
The Project Gutenberg EBook of The Memoirs, Correspondence, And
Miscellanies, From The Papers Of Thomas Jefferson, by Thomas Jefferson
This eBook is for the use of anyone anywhere at no cost and with
almost no restrictions whatsoever. You may copy it, give it away or
re-use it under the terms of the Project Gutenberg License included
with this eBook or online at www.gutenberg.org
Title: The Complete Memoirs, Correspondence, And Miscellanies,
From The Papers of Thomas Jefferson
With A Linked Index to the Project Gutenberg Editions
Author: Thomas Jefferson
Editor: David Widger
Release Date: May 17, 2009 [EBook #28860]
Last Updated: February 2, 2019
Language: English
Character set encoding: UTF-8
*** START OF THIS PROJECT GUTENBERG EBOOK THE PAPERS OF THOMAS JEFFERSON ***
Produced by David Widger


|
| PREFACE. | |
|
MEMOIR. |
|
| APPENDIX | TO THE MEMOIR. |
| [NOTE A.] | Letter to John Saunderson, Esq. |
| [NOTE B.] | Letter to Samuel A. Wells, Esq. |
| [NOTE C] | August, 1774, Instructions to the first Delegation |
| [NOTE D.] | August, 1774., Instructions for the Deputies |
| [NOTE E.] | Monticello, November 1, 1778. [Re: Crimes and Punishment] |
| [NOTE F.] | Coinage for the United States |
| [NOTE G.] | |
| [NOTE H.] | |
|
|
| LETTER I. | TO DR. WILLIAM SMALL, May 7, 1775 |
| LETTER II. | TO JOHN RANDOLPH, August 25,1775 |
| LETTER III. | TO JOHN RANDOLPH, November 29, 1775 |
| LETTER IV. | TO BENJAMIN FRANKLIN, August 13, 1777 |
| LETTER V. | TO PATRICK HENRY, March 27, 1779 |
| LETTER VI. | TO JOHN PAGE, January 22, 1779 |
| LETTER VII. | TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, June 23, 1779 |
| LETTER VIII. | TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, July 17, 1779 |
| LETTER IX. | TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, October 1, 1779 |
| LETTER X. | TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, October 2, 1779 |
| LETTER XI. | TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, Oct. 8, 1779 |
| LETTER XII. | TO COLONEL MATHEWS, October, 1779 |
| LETTER XIII. | TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, November 28, 1779 |
| LETTER XIV. | TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, December 10,1779 |
| LETTER XV. | TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, February 10, 1780 |
| LETTER XVI. | TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, June 11, 1780 |
| LETTER XVII. | TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, July 2, 1780 |
| LETTER XVIII. | TO GENERAL EDWARD STEVENS, August 4, 1780 |
| LETTER XIX. | TO MAJOR GENERAL GATES, August 15, 1780 |
| LETTER XX. | TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, September 8, 1780 |
| LETTER XXI. | TO GENERAL EDWARD STEVENS, September 12,1780 |
| LETTER XXII. | TO GENERAL EDWARD STEVENS, September 15, 1780 |
| LETTER XXIII. | TO MAJOR GENERAL GATES, September 23, 1780 |
| LETTER XXIV. | TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, September 23, 1780 |
| LETTER XXV. | TO HIS EXCELLENCY GENERAL WASHINGTON, September 26,1780 |
| LETTER XXVI. | TO MAJOR GENERAL GATES, October 4, 1780 |
| LETTER XXVII. | TO GENERAL GATES, October 15, 1780 |
| LETTER XXVIII. | TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, October 22, 1780 |
| LETTER XXIX. | TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, October 25,1780 |
| LETTER XXX. | TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, October 26, 1780 |
| LETTER XXXI. | TO GENERAL GATES, October 28, 1780 |
| LETTER XXXII. | TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, November 3,1780 |
| LETTER XXXIII. | TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, November 10, 1780 |
| LETTER XXXIV. | TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, November 26, 1780 |
| LETTER XXXV. | TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, December 15,1780 |
| LETTER XXXVI. | TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, January 10, 1781 |
| LETTER XXXVII. | TO THE PRESIDENT OF CONGRESS, Jan. 15, 1781 |
| LETTER XXXVIII. | TO THE PRESIDENT OF CONGRESS, Jan. 15, 1781 |
| LETTER XXXIX. | TO THE PRESIDENT OF CONGRESS, Jan. 17, 1781 |
| LETTER XL. | TO THE VIRGINIA DELEGATES IN CONGRESS, Jan. 18, 1781 |
| LETTER XLI. | TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, February 8, 1781 |
| LETTER XLII. | TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, February 12, 1781 |
| LETTER XLIII. | TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, February 17, 1781 |
| LETTER XLIV. | TO GENERAL GATES, February 17, 1781 |
| LETTER XLV. | TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, February 26,1781 |
| LETTER XLVI. | TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, March 8, 1781 |
| LETTER XLVII. | TO THE PRESIDENT OF CONGRESS, March 19,1781 |
| LETTER XLVIII. | TO THE PRESIDENT OF CONGRESS, March 21, 1781 |
| LETTER XLIX. | TO THE PRESIDENT OF CONGRESS, March 26,1781 |
| LETTER L. | TO THE PRESIDENT OF CONGRESS, March 28, 1781 |
| LETTER LI. | TO THE PRESIDENT OF CONGRESS, March 31, 1781 |
| LETTER LII. | TO THE PRESIDENT OF CONGRESS, April 7, 1781 |
| LETTER LIII. | TO THE PRESIDENT OF CONGRESS, April 18, 1781 |
| LETTER LIV. | TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, April 23,1781 |
| LETTER LV. | TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, May 9, 1781 |
| LETTER LVI. | TO THE VIRGINIA DELEGATES IN CONGRESS, May 10, 1781 |
| LETTER LVII. | TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, May 28,1781 |
| LETTER, LVIII. | TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, April 16, 1784 |
| LETTER LIX. | TO COLONEL URIAH FORREST, October 20, 1784 |
| LETTER LX. | TO JOHN JAY, May 11, 1785 |
| LETTER LXI. | TO GENERAL CHASTELLUX, June 7,1785 |
| LETTER LXII. | TO JOHN ADAMS, June 15, 1785 |
| LETTER LXIII. | TO THE GOVERNOR OF VIRGINIA, June 16, 1785 |
| LETTER LXIV. | TO COLONEL MONROE, June 17, 1785 |
| LETTER LXV. | TO CHARLES THOMSON, June 21, 1785 |
| LETTER LXVI. | TO WILLIAM CARMICHAEL, June 22, 1785 |
| LETTER LXVII. | TO JOHN ADAMS, June 23, 1785 |
| LETTER LXVIII. | TO COLONEL MONROE, July 5, 1785 |
| LETTER LXIX. | TO MRS. SPROWLE, July 5,1785 |
| LETTER LXX. | TO JOHN ADAMS, July 7, 1785 |
| LETTER LXXI. | TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, July 10, 1785 |
| LETTER LXXII. | TO THE GOVERNOR OF VIRGINIA, July 11, 1785 |
| LETTER LXXIII. | TO THE PRESIDENT OF CONGRESS, July 12, 1785 |
| LETTER LXXIV. | TO THE VIRGINIA DELEGATES IN CONGRESS, July 12,1785 |
| LETTER LXXV. | TO JOHN JAY, July 12,1785 |
| LETTER LXXVI. | TO MONSIEUR BRIET, July 13, 1785 |
| LETTER LXXVII. | TO MESSRS. FRENCH AND NEPHEW, July 13,1785 |
| LETTER LXXVIII. | TO DR. STILES, July 17,1785 |
| LETTER LXXIX. | TO JOHN ADAMS, July 28, 1785 |
| LETTER LXXX. | TO HOGENDORP, July 29, 1785 |
| LETTER LXXXI. | TO MESSRS. N. AND J. VAN STAPHORST, July 30, 1785 |
| LETTER LXXXII. | TO JOHN ADAMS, July 31, 1785 |
| LETTER LXXXIII. | TO M. DE CASTRIES, August 3,1785 |
| LETTER LXXXIV. | TO CAPTAIN JOHN PAUL JONES, August 3,1785 |
| LETTER LXXXV. | TO JOHN ADAMS, August 6, 1785 |
| LETTER LXXXVI. | TO DR. PRICE, August 7,1785 |
| LETTER LXXXVII. | TO JOHN ADAMS, August 10,1785 |
| LETTER LXXXVIII. | TO MRS. SPROWLE, August 10, 1785 |
| LETTER LXXXIX. | TO CAPTAIN JOHN PAUL JONES, August 13, 1785 |
| LETTER XC. | TO MESSRS. BUCHANAN AND HAY, August 13, 1785 |
| LETTER XCI. | TO JOHN JAY, August 14, 1785 |
| LETTER XCII. | TO THE COUNT DE VERGENNES, August 15, 1785 |
| LETTER XCIII. | TO CAPTAIN JOHN PAUL JONES, August 17, 1785 |
| LETTER XCIV. | TO WILLIAM CARMICHAEL, August 18, 1785 |
| LETTER XCV. | TO PETER CARR |
| LETTER XCVI. | TO JOHN PAGE, August 20 1785 |
| LETTER XCVII. | TO JOHN JAY, August 23, 1785 |
| LETTER XCVIII. | TO COLONEL MONROE, August 28, 1735 |
| LETTER XCIX. | TO CAPTAIN JOHN PAUL JONES, August 29,1785 |
| LETTER C. | TO JOHN JAY, August 30,1785 |
| LETTER CI. | TO JAMES MADISON, September 1,1785 |
| LETTER CII. | TO MESSRS. DUMAS AND SHORT, September 1, 1785 |
| LETTER CIII. | TO JOHN ADAMS, September 4, 1785 |
| LETTER CIV. | TO DAVID HARTLEY, September 5, 1785 |
| LETTER CV. | TO BARON GEISMER, September 6, 1785 |
| LETTER CVI. | TO JOHN LANGDON, September 11, 1785 |
| LETTER CVII. | LISTER ASQUITH, September 14, 1785 |
| LETTER CVIII. | TO JOHN ADAMS, September 19, 1785 |
| LETTER CIX. | TO JAMES MADISON, September 20, 1785 |
| LETTER CX. | TO EDMUND RANDOLPH, September 20,1785 |
| LETTER CXI. | TO JOHN ADAMS, September 24, 1785 |
| LETTER CXII. | TO JOHN ADAMS, September 24,1785 |
| LETTER CXIII. | TO F. HOPKINSON, September 25, 1785 |
| LETTER CXIV. | TO LISTER ASQUITH, September 26,1785 |
| LETTER CXV. | TO R. IZARD, September 26,1783 |
| LETTER CXVI. | TO RICHARD O'BRYAN, September 29, 1785 |
| LETTER CXVII. | TO MR. BELLINI, September 30,1785 |
| LETTER CXVIII. | JAMES MADISON, October 2, 1785 |
| LETTER CXIX. | TO DR. FRANKLIN, October 5,1785 |
| LETTER CXX. | TO SAMUEL OSGOOD, October 5, 1785 |
| LETTER CXXI. | TO JOHN JAY, October 6, 1785 |
| LETTER CXXII. | TO ELBRIDGE GERRY, October 11, 1785 |
| LETTER CXXIII. | TO THE COUNT DE VERGENNES, October 11, 1785 |
| LETTER CXXIV. | TO JOHN JAY, October 11,1785 |
| LETTER CXXV. | TO MESSRS. VAN STAPHORST, October 12, 1785 |
| LETTER CXXVI. | TO MONSIEUR DESBORDES, October 12,1785 |
| LETTER CXXVII. | TO HOGENDORP, October 13,1785 |
| LETTER CXXVIII. | TO J. BANNISTER, JUNIOR, October 15,1785 |
| LETTER CXXIX. | TO MR. CARMICHAEL, October 18, 1785 |
| LETTER CXXX. | TO MESSRS. VAN STAPHORSTS, October 25,1785 |
| LETTER CXXXI. | TO WILLIAM CARMICHAEL, November 4, 1785 |
| LETTER CXXXII. | TO RICHARD O'BRYAN, November 4, 1785 |
| LETTER CXXXIII. | TO W. W. SEWARD, November 12,1785 |
| LETTER CXXXIV. | TO THE COUNT DE VERGENNES, November 14,1785 |
| LETTER CXXXV. | TO JOHN ADAMS, November 19, 1785 |
| LETTER CXXXVI. | TO THE COUNT DE VERGENNES, November 20, 1785 |
| LETTER CXXXVII. | TO LISTER ASQUITH, November 23, 1785 |
| LETTER CXXXVIII. | TO JOHN ADAMS, November 27, 1785 |
| LETTER CXXXIX. | TO COLONEL HUMPHREYS, December 4,1785 |
| LETTER CXL. | TO JOHN ADAMS, December 10, 1785 |
| LETTER CXLI. | TO JOHN ADAMS, December 11, 1785 |
| LETTER CXLII. | TO THE COUNT DE VERGENNES, December 21, 1785 |
| LETTER CXLIII. | TO THE GOVERNOR OF GEORGIA, December 22, 1785 |
| LETTER CXLIV. | TO THE GEORGIA DELEGATES IN CONGRESS, Dec. 22, 1785 |
| LETTER CXLV. | TO JOHN ADAMS, December 27, 1785 |
| LETTER CXLVI. | TO JOHN JAY, January 2,1786 |
| LETTER CXLVII. | TO T. HOPKINSON, January 3, 1786 |
| LETTER CXLVIII. | TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, January 4, 1786 |
| LETTER CXLIX. | TO A. CARY, January 7, 1786 |
| LETTER CL. | TO MAJOR GENERAL GREENE, January 12, 1786 |
| LETTER CLI. | TO LISTER ASQUITH, January 13, 1786 |
| RE QUESTIONS | FOR ECONOMIE POLITIQUE ET DIPLOMATIQUE |
| ARTICLE | BY JEFFERSON: 'Etats Unis,' FOR THE Encyclopédie Méthodique |
| LETTER CLII. | TO MR. RITTENHOUSE, January 25,1786 |
| LETTER CLIII. | TO A. STEWART, January 25, 1786 |
| LETTER CLIV. | TO THE COMMISSIONERS OF THE TREASURY, January 26, 1786 |
| LETTER CLV. | TO MESSRS. BUCHANAN AND HAY, January 26, 1786 |
| LETTER CLVI. | TO JOHN ADAMS, February 7, 1786 |
| LETTER CLVII. | TO JAMES MADISON, February 8, 1786 |
| LETTER CLVIII. | TO THE MARQUIS DE LA FAYETTE, February 9, 1786 |
| LETTER CLIX. | TO MONSIEUR HILLIARD d'AUBERTEUIL, Feb. 20, 1786 |
| LETTER CLX. | TO THE COUNT DE VERGENNES, February 28,1786 |
| LETTER CLXI. | TO MONSIEUR DE REYNEVAL, March 8, 1786 |
| LETTER CLXII. | TO JOHN JAY, March 12, 1786 |
| LETTER CLXIII. | TO COLONEL HUMPHREYS, March 14, 1786 |
|
APPENDIX. |
|
| [NOTE A.] | TO THE GOVERNOR OF VIRGINIA. |
| IN COUNCIL, | June 18, 1779 |
| [NOTE B] | IN COUNCIL, September 29, 1779. |
| [NOTE C] | IN COUNCIL, October 8, 1779. |
| [NOTE D.] | FEMALE CONTRIBUTIONS, IN AID OF THE WAR, probably in 1780 |
| [NOTE E.] | FROM LORD CORNWALLIS |
| [NOTE F.] | TO LORD CORNWALLIS |
| LETTER I. | TO RICHARD HENRY LEE, April 22, 1786 |
| LETTER II. | TO CHARLES THOMSON, April 22, 1786 |
| LETTER III. | TO JOHN JAY, April 23, 1786 |
| LETTER IV. | TO JOHN JAY, April 23, 1786 |
| LETTER V. | TO JAMES MADISON, April 25, 1786 |
| LETTER VI. | TO THE COUNT DE VERGENNES, May 3, 1786 |
| LETTER VII. | TO JOHN PAGE, May 4, 1786 |
| LETTER VIII. | TO WILLIAM CARMICHAEL |
| LETTER IX. | TO MR. DUMAS, May 6, 1789 |
| LETTER X. | TO WILLIAM DRAYTON, May 6, 1786 |
| LETTER XI. | TO W. T. FRANKLIN, May 7, 1786 |
| LETTER XII. | TO ELBRIDGE GERRY, May 7, 1786 |
| LETTER XIII. | TO JAMES ROSS, May 8, 1786 |
| LETTER XIV. | TO T. PLEASANTS, May 8,1786 |
| LETTER XV. | TO COLONEL MONROE, May 10,1786 |
| LETTER XVI. | TO JOHN ADAMS, May 11, 1786 |
| LETTER XVII. | TO LISTER ASQUITH, May 22, 1786 |
| LETTER XVIII. | TO JOHN JAY, May 23, 1786 |
| LETTER XIX. | TO MR. CARMICHAEL, June 20, 1786 |
| LETTER XX. | TO MR. LAMBE, June 20,1786 |
| LETTER XXI.. | TO MONSIEUR DE REYNEVAL, June 25, 1786 |
| LETTER XXII. | TO THE PREVOT DES MARCHANDS, September 27, 1786 |
| LETTER XXIII. | TO COLONEL MONROE, July 9, 1786 |
| LETTER XXIV. | TO JOHN ADAMS, July 11, 1786 |
| LETTER XXV. | TO JOHN JAY, August 11, 1786 |
| LETTER XXVI. | TO COLONEL MONROE, August 11, 1786 |
| LETTER XXVII. | TO MR. WYTHE, August 13,1786 |
| LETTER XXVIII. | TO MRS. COSWAY, October 12, 1786 |
| LETTER XXIX. | TO MRS. COSWAY, October 13, 1786 |
| LETTER XXX. | M. LE ROY DE L'ACADEMIE DES SCIENCES, November 13, 1786 |
| LETTER XXXI. | TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, November 14, 1786 |
| LETTER XXXII. | TO JAMES MADISON, December 16, 1786 |
| LETTER XXXIII. | TO CHARLES THOMSON, December 17,1780 |
| LETTER XXXIV. | TO COLONEL MONROE, December 18, 1786 |
| LETTER XXXV. | TO MR. CARMICHAEL, December 26,1786 |
| LETTER XXXVI. | TO MR. VAUGHAN, December 29, 1786 |
| LETTER XXXVII. | TO JOHN JAY, December 31, 1786 |
| LETTER XXXVIII. | TO SAMUEL OSGOOD, January 5, 1787 |
| LETTER XXXIX. | TO JOHN JAY, January 9, 1787 |
| LETTER XL. | TO JOHN ADAMS, January 11, 1787 |
| LETTER XLI. | TO MONSIEUR LE DUC D'HARCOURT, January 14, 1787 |
| LETTER XLII. | TO MONSIEUR DE CREVE-COEUR, January 15,1787 |
| LETTER XLIII. | TO COLONEL EDWARD CARRINGTON, January 16, 1787 |
| LETTER XLIV | TO JAMES MADISON, January 30, 1787 * |
| LETTER XLV. | TO JOHN JAY, February 1, 1787 |
| LETTER XLVI. | TO MRS. BINGHAM, February 7, 1787 |
| LETTER XLVII. | TO GOVERNOR RANDOLPH, February 7, 1787 |
| LETTER XLVIII. | TO JOHN JAY, February 8, 1787 |
| LETTER XLIX. | TO MR. DUMAS, February 9, 1787 |
| LETTER L. | TO JOHN JAY, February 14, 1787 |
| LETTER LI. | TO JOHN JAY, February 23, 1787 |
| LETTER LII. | TO THE MARQUIS DE LA FAYETTE, February 28, 1787 |
| LETTER LIII. | TO MADAME LA COMTESSE DE TESSE, March 20, 1787 |
| LETTER LIV. | TO THE MARQUIS DE LA FAYETTE, April 11, 1787 |
| LETTER LV. | TO WILLIAM SHORT, April 12, 1787 |
| LETTER LVI. | TO JOHN JAY, May 4, 1787 |
| LETTER LVII. | TO M. GUIDE, May 6, 1787 |
| MEMORANDA | TAKEN ON A JOURNEY FROM PARIS IN 1787 |
| LETTER LVIII. | TO WILLIAM CARMICHAEL, June 14, 1787 |
| LETTER LIX. | TO J. BANNISTER, JUNIOR, June 19, 1787 |
| LETTER LX. | TO JAMES MADISON, June 20, 1787* |
| LETTER LXI. | TO JOHN JAY, June 21,1787 |
| LETTER LXII. | TO MADAME DE CORNY, June 30,1787 |
| LETTER LXIII. | TO JOHN ADAMS, July 1, 1787 |
| LETTER LXIV. | TO DAVID HARTLEY, July 2,1787 |
| LETTER LXV. | TO B. VAUGHAN, July 2, 1787 |
| LETTER LXVI. | TO M. L'ABBE MORELLET, July 2, 1787 |
| OBSERVATIONS | ON THE LETTER OF MONSIEUR DE CALONNE |
| LETTER LXVII. | TO T. M. RANDOLPH, JUNIOR, July 6, 1787 |
| LETTER LXVIII. | TO STEPHEN CATHALAN, JUNIOR, July 21,1787 |
| LETTER LXIX. | TO THE DELEGATES OF RHODE ISLAND, July 22,1787 |
| LETTER LXX. | TO THE COUNT DE MONTMORIN, July 23, 1787 |
| LETTER LXXI. | TO MR. SKIPWITH, July 28, 1787 |
| LETTER LXXII. | TO J. W. EPPES, July 28,1787 |
| LETTER LXXIII. | TO A. DONALD, July 28, 1787 |
| LETTER LXXIV. | TO WILLIAM DRAYTON, July 30, 1787 |
| LETTER LXXV. | TO JAMES MADISON, August 2, 1787 |
| LETTER LXXVI. | TO THOMAS BARCLAY, August 3, 1787 |
| LETTER LXXVII. | TO E. CARRINGTON, August 4,1787 |
| LETTER LXXVIII. | TO DR. CURRIE, August 4, 1787 |
| LETTER LXXIX. | TO MR. HAWKINS, August 4, 1787 |
| LETTER LXXX. | TO COLONEL MONROE, August 5, 1787 |
| LETTER LXXXI. | TO JOHN JAY, August 6,1787 |
| LETTER LXXXII. | TO JOHN CHURCHMAN, August 8, 1787 |
| LETTER LXXXIII. | TO MONSIEUR L HOMMANDE, August 9, 1787 |
| LETTER LXXXIV. | TO PETER CARR, August 10, 1787 |
| LETTER LXXXV. | TO DR. GILMER, August 11, 1787 |
| LETTER LXXXVI. | TO JOSEPH JONES, August 14, 1787 |
| LETTER LXXXVII. | TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, August 14, 1787 |
| LETTER LXXXVIII. | TO COLONEL HUMPHREYS, August 14, 1787 |
| LETTER LXXXIX. | TO JOHN JAY, August 15, 1787 |
| LETTER XC. | TO JOHN ADAMS, August 30, 1787 |
| LETTER XCI. | TO MR. WYTHE, September 16,1787 |
| LETTER XCII. | TO JOHN JAY, September 19, 1787 |
| LETTER XCIII. | TO CHARLES THOMSON, September 20, 1787 |
| LETTER XCIV. | TO JOHN JAY, September 22,1787 |
| LETTER XCV. | TO JOHN JAY, September 22, 1787 |
| LETTER XCVI. | TO MR. CARNES, September 22, 1787 |
| LETTER XCVII. | TO JOHN JAY, September 24, 1787 |
| LETTER XCVIII, | TO JOHN ADAMS, September 28, 1787 |
| LETTER XCIX. | TO COLONEL SMITH, September 28,1787 |
| LETTER C. | TO MONSIEUR LE COMTE DE BUFFON, October 3, 1787 |
| LETTER CI. | TO MR. DUMAS, October 4,1787 |
| LETTER CII. | TO JOHN JAY, October 8, 1787 |
| LETTER CIII. | TO JAMES MADISON, October 8, 1787 |
| LETTER CIV. | TO JOHN JAY, October 8, 1787 |
| LETTER CV. | TO MONSIEUR LE COMTE DE MOUSTIER, October 9,1787 |
| LETTER CVI. | TO MADAME DE BREHAN, October 9, 1787 |
| LETTER CVII. | TO MR. DUMAS, October 14, 1787 |
| LETTER CVIII. | TO MADAME DE CORNY, October 18, 1787 |
| LETTER CIX. | TO THE COUNT DE MONTMORIN, October 23, 1787 |
| LETTER CX. | TO JOHN JAY, November 3, 1787 |
| LETTER CXI. | TO JOHN JAY, November 3, 1787 |
| LETTER CXII. | TO THE COUNT DE MONTMORIN, November 6, 1787 |
| LETTER CXIII. | TO JOHN ADAMS, November 13, 1787 |
| LETTER CXIV. | TO COLONEL SMITH, November 13, 1787 |
| LETTER CXV. | TO WILLIAM CARMICHAEL, December 11, 1787 |
| LETTER CXVI. | TO JOHN ADAMS |
| LETTER CXVII. | TO JAMES MADISON, December 20, 1787 |
| LETTER CXVIII. | TO E. CARRINGTON, December 21, 1787 |
| LETTER CXIX. | TO MONSIEUR LIMOZIN, December 22, 1787 |
| LETTER CXX. | TO JOHN JAY, December 31, 1787 |
| LETTER CXXI. | TO MONSIEUR LAMBERT, January 3, 1788 |
| LETTER CXXII. | TO LE COMTE BERNSTORFF, January 21, 1788 |
| LETTER CXXIII. | TO WILLIAM RUTLEDGE, February 2, 1788 |
| LETTER CXXIV. | TO THE COMMISSIONERS OF THE TREASURY, Feb. 7, 1788 |
| LETTER CXXV. | TO DOCTOR PRICE, February 7, 1788 |
| LETTER CXXVI. | TO A. DONALD, February.7, 1788 |
| LETTER CXXVII. | TO M. WARVILLE, February 12, 1888 |
| LETTER CXXVIII. | TO JOHN ADAMS, March 2, 1788 |
| LETTER CXXIX. | TO JOHN JAY, March 16, 1788 |
| LETTER CXXX. | TO MR. DUMAS, March 29, 1788 |
| LETTER CXXXI. | TO THE COMMISSIONERS OF THE TREASURY, March 29, 1788 |
| LETTER CXXXII. | TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, May 2, 1788 |
| LETTER CXXXIII. | TO JAMES MADISON, May 3,1788 |
| LETTER CXXXIV. | TO JOHN JAY, May 4, 1788 |
| LETTER CXXXV. | TO THE COUNT DE MOUSTIER, May 17, 1788 |
| LETTER CXXXVI. | TO JOHN JAY, May 23,1788 |
| LETTER CXXXVII. | TO JOHN BROWN, May 26,1788 |
| LETTER CXXXVIII. | TO WILLIAM CARMICHAEL, May 27, 1788 |
| LETTER CXXXIX. | TO JOHN JAY, May 27, 1788 |
| LETTER CXL.* | TO JAMES MADISON, May 28, 1788 |
| LETTER CXLI. | TO PETER CARU, May 23, 1788 |
| LETTER CXLII. | TO THE COMTE DE BERNSTORFF, June 19, 1788 |
| LETTER CXLIII. | TO THE COUNT DE MONTMORIN, June 20, 1788 |
| LETTER CXLIV. | TO DOCTOR GORDON, July 16, 1788 |
| LETTER CXLV. | TO JAMES MADISON, July 19, 1788 |
| LETTER CXLVI. | TO E. RUTLEDGE, July 18, 1788 |
| LETTER CXLVII. | TO MR. BELLINI, July 25,1788 |
| LETTER CXLVIII. | TO JAMES MADISON, July 31, 1788 |
| LETTER CXLIX. | TO JOHN JAY, August 3, 1788 |
| LETTER CL. | TO COLONEL MONROE, August 9, 1788 |
| LETTER CLI. | TO MONSIEUR DE CREVE-COEUR, August 9, 1788 |
| LETTER CLII. | TO JOHN JAY, August 10, 1788 |
| LETTER CLIII. | TO JOHN JAY, August 11, 1788 |
| LETTER CLIV. | TO WILLIAM CARMICHAEL, August 12, 1788 |
| LETTER CLV. | TO M. CATHALAN, August 13,1788 |
| LETTER CLVI. | TO JOHN JAY, August 20,1788 |
| LETTER CLVII. | TO MR. CUTTING, August 23, 1788 |
| LETTER CLVIII. | TO JOHN JAY, September 3, 1788 |
| LETTER CLIX. | TO THE COMMISSIONERS OF THE TREASURY, Sep. 6, 1788 |
| LETTER CLX. | TO THE COUNT DE MONTMORIN, |
| LETTER CLXI. | TO M. DE REYNEVAL, September 16, 1788 |
| LETTER CLXII. | TO THE MARQUIS DE LA ROUERIE, September 16,1788 |
| LETTER CLXIII. | TO WILLIAM SHORT, September 20, 1788 |
| LETTER CLXIV. | TO JOHN JAY, September 24,1788 |
| LETTER CLXV. | TO M. DE REYNEVAL, October 1, 1788 |
| LETTER CLXVI. | TO MR. CUTTING, October 2, 1788 |
| LETTER CLXVIII. | TO JAMES MADISON, November 18, 1788 |
| LETTER CLXIX. | TO A. DONALD, November 18,1788 |
| LETTER CLXX. | TO JOHN JAY, November 19, 1788 |
| LETTER CLXXI. | TO JOHN JAY, November 29, 1788 |
| LETTER, CLXXII. | TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, December 4, 1788 |
| LETTER CLXXIII. | TO JOHN ADAMS, December 5, 1788 |
| LETTER CLXXIV. | TO MR. SHORT, December 8, 1788 |
| LETTER CLXXV. | TO DOCTOR GILMER, December 16, 1788 |
| LETTER CLXXVI. | TO THOMAS PAINE, December 23,1788 |
| LETTER CLXXVII. | TO JOHN JAY, January 11, 1789 |
| LETTER CLXXVIII. | TO JAMES MADISON, January 12, 1789 |
| LETTER CLXXIX. | TO JOHN JAY, January 14, 1789 |
| LETTER CLXXX. | TO MADAME NECKER, January 24, 1789 |
| LETTER CLXXXI. | TO JOHN JAY, February 1, 1789 |
| LETTER CLXXXII. | TO JOHN JAY, February 4, 1789 |
| LETTER CLXXXIII. | TO WILLIAM SHORT, February 9,1789 |
| LETTER CLXXXIV. | TO M. DE VILLEDEUIL, February 10, 1789 |
| LETTER CLXXXV. | TO MR. CARNES, February 15,1789 |
| LETTER CLXXXVI. | TO DR. BANCROFT, March 2, 1789 |
| LETTER CLXXXVII. | TO M. DE MALESHERBES, March 11, 1789 |
| LETTER CLXXXVIII. | TO JOHN JAY, March 12, 1789 |
| LETTER CLXXXIX. | TO F. HOPKINSON, March 13, 1789 |
| LETTER CXC. | TO MADAME DE BREHAN, March 14, 1789 |
| LETTER CXCI. | TO JAMES MADISON, March 15, 1789 |
| LETTER, CXCII. | TO THOMAS PAINE, March 17,1789 |
| LETTER CXIII. | TO COLONEL HUMPHREYS, March 18, 1789 |
| LETTER CXCIV. | TO DOCTOR WILLARD, March 24, 1789 |
| LETTER CXCV. | TO J. SARSFIELD, April 3, 1789 |
| LETTER CXCVI. | TO THE MARQUIS DE LA FAYETTE, May 6,1789 |
| LETTER CXCVII. | TO WILLIAM CARMICHAEL, May 8, 1789 |
| LETTER CXCVIII. | TO JOHN JAY, May 9, 1789 |
| LETTER CXCIX. | TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, May 10, 1780 |
| LETTER CC. | TO JAMES MADISON, May 11,1789 |
| LETTER CCI. | TO MONSIEUR DE PONTIERE, May 17, 1789 |
| LETTER CCII. | TO MR. VAUGHAN, May 17, 1789 |
| LETTER CCIII. | TO THOMAS PAINE, May 19,1789 |
| LETTER CCIV. | TO MONSIEUR DE ST. ETIENNE, June 3, 1789 |
| LETTER CCV. | TO THE MARQUIS DE LA FAYETTE, June 12, 1789 |
| LETTER CCVI. | TO JOHN JAY, June 17, 1789 |
| LETTER CCVII. | TO JAMES MADISON, June 18, 1789 |
| LETTER CCVIII. | TO JOHN JAY, June 24,1789 |
| LETTER CCIX. | TO JOHN JAY, June 29, 1789 |
| LETTER CCX. | TO THE MARQUIS DE LA FAYETTE, July 6, 1789 |
| LETTER CCXI. | TO THE MARQUIS DE LA FAYETTE, July 7,1789 |
| LETTER CCXII. | TO MR. NECKER, July 8, 1789 |
| LETTER CCXIII. | TO THE COUNT DE MONTMORIN, July 8, 1789 |
| LETTER CCXIV. | TO THE MARQUIS DE LA FAYETTE, July 9, 1789 |
| LETTER CCXV. | TO THE MARQUIS DE LA FAYETTE, July 10, 1789 |
| LETTER CCXVI. | TO THOMAS PAINE, July 11, 1789 |
|
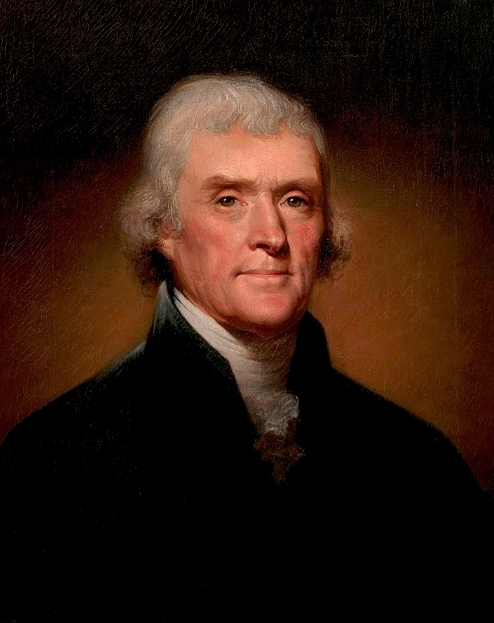
Book Spines, 1829 Set of Jefferson Papers Steel Engraving by Longacre from Painting of G. Stuart |
| LETTER I. | TO JOHN JAY, July 19, 1789 |
| LETTER II. | TO M. L'ABBE ARNOND, July 19, 1789 |
| LETTER III. | TO JOHN JAY, July 23, 1789 |
| LETTER IV. | TO JOHN JAY, July 29, 1789 |
| LETTER V. | TO JOHN JAY, August 5, 1789 |
| LETTER VI. | TO MR. CARMICHAEL, August 9, 1789 |
| LETTER VII. | TO JOHN JAY, August 12, 1789 |
| LETTER VIII. | TO COLONEL GOUVION, August 15,1789 |
| LETTER IX. | TO JOHN JAY, August 27, 1789 |
| LETTER X. | TO JAMES MADISON, August 28,1789 |
| LETTER XI. | TO JAMES MADISON, September 6, 1789 |
| LETTER XII. | TO DR. GEM |
| LETTER XIII. | TO GENERAL KNOX, September 12,1789 |
| LETTER XIV. | TO E. RUTLEDGE, September 18, 1789 |
| LETTER XV. | TO JOHN JAY, September 19, 1789 |
| LETTER XVI. | TO MR. NECKER, September 26,1789 |
| LETTER XVII. | TO JOHN JAY, September 30, 1789 |
| LETTER XVIII. | TO THE PRESIDENT, December 15,1789 |
| LETTER XIX. | TO HENRY LAURENS, ESQUIRE, March 31, 1790 |
| LETTER XX. | TO MR. VANDERKEMP, March 31, 1799 |
| LETTER XXI. | TO GEORGE JOY, March 31, 1790 |
| LETTER XXII. | TO THE COUNT DE MONTMORIN, April 6, 1790 |
| LETTER XXIII. | TO THE COUNT DE MONTMORIN, April 6,1790 |
| LETTER XXIV. | TO WILLIAM SHORT, April 6, 1790 |
| LETTER XXV. | TO THE COUNT DE FLORIDA BLANCA, April 11, 1790 |
| LETTER XXVI. | TO WILLIAM CARMICHAEL, April 11, 1789 |
| LETTER XXVII. | TO MR. GRAND, April 23, 1790 |
| LETTER XXVIII. | TO THE MARQUIS DE LA LUZERNE, April 30,1790 |
| LETTER XXIX. | TO WILLIAM SHORT, April 30, 1790 |
| LETTER XXX. | TO MR. DUMAS, June 23, 1790 |
| LETTER XXXI. | TO MR. DUMAS, July 13,1790 |
| LETTER XXXII | TO WILLIAM SHORT, July 26, 1790 |
| LETTER XXXIII. | TO WILLIAM CARMICHAEL, August 2, 1790 |
| LETTER XXXIV. | TO M. DE PINTO, August 7, 1790 |
| LETTER XXXV. | TO JOSHUA JOHNSON, August 7,1790 |
| LETTER XXXVI. | TO WILLIAM SHORT, August 10,1790 |
| LETTER XXXVII. | TO COLONEL DAVID HUMPHREYS, August 11, 1790 |
| LETTER XXXVIII. | TO GOUVERNEUR MORRIS, August 12, 1790 |
| LETTER XXXIX. | TO GOVERNOR HANCOCK, August 24, 1790 |
| LETTER XL. | TO SYLVANUS BOURNE, August 25, 1790 |
| LETTER XLI. | CIRCULAR TO THE CONSULS, August 26, 1790 |
| LETTER XLII. | TO WILLIAM SHORT, August 26, 1790 |
| LETTER XLIII. | TO M. LA FOREST, August 30, 1790 |
| LETTER XLIV. | TO WILLIAM SHORT, August 31,1790 |
| LETTER XLV. | TO GOUVERNEUR MORRIS, December 17, 1790 |
| LETTER XLVI. | TO JOSHUA JOHNSON, December 17, 1790 |
| LETTER XLVII. | TO JOSHUA JOHNSON, December 23, 1790 |
| LETTER XLVIII. | TO CHARLES HELLSTEDT, February 14,1791 |
| LETTER XLIX. | TO M. DE PINTO, February 21,1791 |
| LETTER L. | TO WILLIAM SHORT, March 8,1791 |
| LETTER LI. | TO THE PRESIDENT OF THE NATIONAL ASSEMBLY, March 8, 1791 |
| LETTER LII. | TO WILLIAM CARMICHAEL, March 12, 1791 |
| LETTER LIII. | TO WILLIAM SHORT, March 12,1791 |
| LETTER LIV. | TO WILLIAM SHORT, March 15, 1791 |
| LETTER LV. | TO WILLIAM CARMICHAEL, March 17,1791 |
| LETTER LVI. | TO WILLIAM SHORT, March 19, 1791 |
| LETTER LVII. | TO MR. OTTO, March 29, 1791 |
| LETTER | FROM THE PRESIDENT, April 4, 1791 |
| LETTER LVIII. | TO COLONEL HUMPHREYS, April 11, 1791 |
| LETTER LIX. | TO WILLIAM CARMICHAEL, April 11,1791 |
| LETTER LX. | TO WILLIAM SHORT, April 25, 1791 |
| LETTER LXI. | TO MR. OTTO, May 7, 1791 |
| LETTER LXII. | TO THE ATTORNEY OF THE DISTRICT OF KENTUCKY, May 7,1791 |
| LETTER LXIII. | TO THOMAS BARCLAY, May 13,1791 |
| LETTER LXIV. | TO FULWAR SKIPWITH, May 13,1791 |
| LETTER LXV. | TO WILLIAM CARMICHAEL, May 16, 1791 |
| LETTER LXVI. | TO COLONEL HUMPHREYS, July 13,1791 |
| LETTER LXVII. | TO M. VAN BERKEL, July 14,1791 |
| LETTER LXVIII. | TO GOUVERNEUR MORRIS, July 26,1791 |
| LETTER LXIX. | TO WILLIAM SHORT, July 28,1791 |
| LETTER LXX. | TO THE PRESIDENT, July 30,1791 |
| LETTER LXXI. | TO GENERAL KNOX, August 10, 1791 |
| LETTER LXXII. | TO THE MINISTER OF FRANCE, August 12, 1791 |
| LETTER LXXIII. | TO SYLVANUS BOURNE, August 14,1791 |
| LETTER LXXIV. | TO WILLIAM SHORT, August 29, 1791 |
| LETTER LXXV. | TO M. LA MOTTE, August 30, 1791 |
| LETTER LXXVI. | TO GOUVERNEUR MORRIS, August 30, 1791 |
| LETTER LXXVII. | TO MONSIEUR DE TERNANT, September 1, 1791 |
| LETTER LXXVIII. | TO T. NEWTON, September 8, 1791 |
| LETTER LXXIX. | TO MR. HAMMOND, October 26,1791 |
| LETTER LXXX. | TO WILLIAM CARMICHAEL, November 6, 1791 |
| LETTER LXXXI. | TO THE PRESIDENT, November 6, 1791 |
| LETTER LXXXII. | TO MAJOR THOMAS PINCKNEY, November 6, 1791 |
| LETTER LXXXIII. | TO THE PRESIDENT, November 7, 1791 |
| LETTER LXXXIV. | TO WILLIAM SHORT, November 24, 1791 |
| LETTER LXXXV. | TO THE ATTORNEY GENERAL, December 5,1791 |
| LETTER LXXXVI. | TO MR. HAMMOND, December 5, 1791 |
| LETTER LXXXVII. | TO MR. HAMMOND, December 12, 1791 |
| LETTER LXXXVIII. | TO MR. HAMMOND, December 13, 1791 |
| LETTER LXXXIX. | TO THE PRESIDENT, December 23, 1791 |
| LETTER XC. | TO THE PRESIDENT, January 4, 1792 |
| LETTER XCI. | TO THOMAS PINCKNEY, January 17, 1792 |
| LETTER XCII. | TO WILLINKS, VAN STAPHORSTS, AND HUBARD, Jan. 23,1792 |
| LETTER XCIII. | TO WILLIAM SHORT, January 23, 1792 |
| LETTER XCIV. | TO GOUVERNEUR MORRIS, January 23, 1792 |
| LETTER XCV. | TO MR. HAMMOND, February 2, 1792 |
| LETTER XCVI. | TO MR. HAMMOND, February 25, 1792 |
| LETTER XCVII. | TO MESSRS. JOHNSON, CARROL, AND STEWART, March 6, 1792 |
| LETTER XCVIII. | TO GOUVERNEUR MORRIS, |
| LETTER XCIX. | TO MESSRS. CARMICHAEL AND SHORT, March 18, 1792 |
| LETTER C. | TO COLONEL PICKERING, March 28, 1792 |
| LETTER CI. | TO MR. HAMMOND, March 31, 1792 |
| LETTER CII. | TO GOVERNOR PINCKNEY, April 1, 1792 |
| LETTER CIII. | TO COLONEL HUMPHREYS, April 9, 1792 |
| LETTER CIV. | TO MR. HAMMOND, April 12, 1792 |
| LETTER CV. | TO MR. HAMMOND, April 13,1792 |
| LETTER CVI. | TO THE PRESIDENT, April 13, 1792 |
| LETTER CVII. | TO MESSRS. CARMICHAEL AND SHORT, April 24, 1792 |
| LETTER CVIII. | TO GOUVERNEUR MORRIS, April 28,1792 |
| LETTER CIX. | CIRCULAR TO THE AMERICAN CONSULS, May 31, 1792 |
| LETTER CX. | TO JOHN PAUL JONES, June 1, 1792 |
| LETTER CXI. | TO MR. PINCKNEY, June 11, 1792 |
| LETTER CXII. | TO THOMAS PINCKNEY, June 11, 1792 |
| LETTER CXIII. | TO MR. PINCKNEY, June 14, 1792 |
| LETTER CXIV. | TO GOUVERNEUR MORRIS, June 16, 1792 |
| LETTER CXV. | TO MR. VAN BERCKEL, July 2,1792 |
| LETTER CXVI. | TO MR. PALESKE, August 19,1792 |
| LETTER CXVII. | TO THE PRESIDENT, August 19, 1792 |
| LETTER CXVIII. | TO M. DE TERNANT, September 27,1792 |
| LETTER CXIX. | TO MR. PINCKNEY, October 12,1792 |
| LETTER CXX. | TO MESSRS. CARMICHAEL AND SHORT, October 14,1792 |
| LETTER CXXI. | TO GOUVERNEUR MORRIS, October 15, 1792 |
| LETTER CXXII. | TO M. DE TERNANT, October 16,1792 |
| LETTER CXXIII. | TO MESSRS. VIAR AND JAUDENES, November 1, 1792 |
| LETTER CXXIV. | TO THE PRESIDENT, November 2,1792 |
| LETTER CXXV. | TO MESSRS. CARMICHAEL AND SHORT, November 3, 1792 |
| LETTER CXXVI. | TO GOUVERNEUR MORRIS, November 7, 1792 |
| LETTER CXXVII. | TO M. DE TERNANT, November 20, 1792 |
| LETTER CXXVIII. | TO MR. RUTHERFORD, December 25, 1792 |
| LETTER CXXIX. | TO THE SPEAKER OF THE HOUSE, January 2, 1793 |
| LETTER CXXX. | CIRCULAR TO THE MINISTERS, February 13, 1793 |
| LETTER CXXXI. | TO MR. HAMMOND, February 16, 1793 |
| LETTER CXXXII. | TO M. DE TERNANT, February 17, 1793 |
| LETTER CXXXIII. | TO M. DE TERNANT, February 20, 1793 |
| LETTER CXXXIV. | TO THE SPEAKER OF THE HOUSE, February 20, 1793 |
| LETTER CXXXV. | TO GOUVERNEUR MORRIS, March 12,1793 |
| LETTER CXXXVI. | TO GOUVERNEUR MORRIS, March 15, 1793 |
| LETTER CXXXVII. | TO MR. PINCKNEY, March 16, 1793 |
| LETTER CXXXVIII. | TO COLONEL HUMPHREYS, March 21, 1793 |
| LETTER CXXXIX. | TO COLONEL HUMPHREYS, March 22, 1793 |
| LETTER CXL.* | TO MESSRS. CARMICHAEL AND SHORT, March 23, 1793 |
| LETTER CXLI. | TO MR. HAMMOND, April 18, 1793 |
| LETTER CXLII. | TO MR. PINCKNEY, April 20, 1793 |
| LETTER CXLIII. | CIRCULAR TO MORRIS, PINCKNEY, AND SHORT, April 26,1793 |
| LETTER CXLIV. | TO M. DE TERNANT, April 27,1793 |
| LETTER CXLV. | TO M. DE TERNANT, May 3,1793 |
| LETTER CXLVI. | TO MR. PINCKNEY, May 7, 1793 |
| LETTER CXLVII. | TO MR. HAMMOND, May 15, 1793 |
| LETTER CXLVIII.* | TO M. DE TERNANT, May 15, 1793 |
| LETTER CXLIX. | TO THE GOVERNOR OF VIRGINIA, May 21,1793 |
| LETTER CL. | TO MR. VAN BERCKEL, May 29,1793 |
| LETTER CLI. | TO MESSRS. CARMICHAEL AND SHORT, May 31, 1793 |
| LETTER CLII. | TO MR. GENET, June 5,1793 |
| LETTER CLIII. | TO MR. HAMMOND, June 5, 1793 |
| LETTER CLIV. | TO GOUVERNEUR MORRIS, June 13, 1793 |
| LETTERS | RE THE LOST MILLION, June 10, 1793 |
| LETTER CLV. | TO GOUVERNEUR MORRIS, June 13, 1793 |
| LETTER CLVI. | TO MR. PINCKNEY, June 14, 1793 |
| LETTER CLVII. | TO MR. GENET, June 17, X |
| LETTER CLVIII. | TO MR. HAMMOND, June 19, 1793 |
| LETTER CLIX. | TO MESSRS. CARMICHAEL AND SHORT, June 30, 1793 |
| LETTER CLX. | TO THE SUPREME COURT OF THE UNITED STATES, July 18,1793 |
| LETTER CLXI. | TO MR. GENET, July 24,1793 |
| LETTER CLXII. | TO MR. GENET, August 7, 1793 |
| LETTER CLXIII. | TO GOUVERNEUR MORRIS, August 16,1793 |
| LETTER CLXIV. | CIRCULAR TO THE MERCHANTS OF THE U.S., August 23, 1793 |
| LETTER CLXV. | TO MR. GORE, September 2, 1793 |
| LETTER CLXVI. | TO MR. HAMMOND, September 5, 1793 |
| LETTER CLXVII. | TO MR. PINCKNEY, September 7,1793 |
| LETTER CLXVIII. | TO MR. HAMMOND, September 9, 1793 |
| LETTER CLXIX. | TO MR. GENET, September 9, 1793 |
| LETTER CLXX. | TO COLONEL HUMPHREYS, September 11, 1793 |
| LETTER CLXXI. | TO MR. GENET, October 3, 1793 |
| LETTER CLXXII. | TO MR. GENET, November 8,1793 |
| LETTER CLXXIII. | TO MR. GENET, November 22, 1793 |
| LETTER CLXXIV. | TO MR. GENET, December 9, 1793 |
| LETTER CLXXV. | TO THE ATTORNEY GENERAL OF THE U.S., December 18, 1793 |
| LETTER CLXXVI. | TO E. RANDOLPH, February 3, 1794 |
| LETTER CLXXVII. | TO JAMES MADISON, April 3, 1794 |
| LETTER CLXXVIII. | TO TENCH COXE, May 1,1794 |
| LETTER CLXXIX. | TO THE PRESIDENT, May 14, 1794 |
| LETTER CLXXX. | TO THE SECRETARY OF STATE, September 7, 1794 |
| LETTER CLXXXI. | TO JAMES MADISON, December 28, 1794 |
| LETTER CLXXXII. | TO M. D'IVERNOIS, February 6,1795 |
| LETTER CLXXXIII. | TO JAMES MADISON, April 27, 1795 |
| LETTER CLXXXIV. | TO WILLIAM B. GILES, April 27, 1795 |
| LETTER CLXXXV. | TO MANN PAGE, August 30, 1795 |
| LETTER CLXXXVI. | TO JAMES MADISON |
| LETTER CLXXXVII. | TO EDWARD RUTLEDGE, November 30, 1795 |
| LETTER CLXXXVIII. | TO WILLIAM B. GILES, December 31, 1795 |
| LETTER CLXXXIX. | TO JAMES MADISON, March 6, 1796 |
| LETTER CXC. | TO WILLIAM B. GILES, March 19,1796. |
| LETTER CXCI. | TO COLONEL MONROE, March 21, 1796 |
| LETTER CXCII. | TO JAMES MADISON, March 27,1796 |
| LETTER CXCIII. | TO JAMES MADISON, April 19, 1796 |
| LETTER CXCIV.* | TO P. MAZZEI, April 24, 1796 |
| LETTER CXCV. | TO COLONEL MONROE, June 12, 1796 |
| LETTER CXCVI. | TO THE PRESIDENT, June 19, 1796 |
| LETTER CXCVII. | TO M. DE LA FAYETTE, June 19, 1796 |
| LETTER CXCVIII. | TO JONATHAN WILLIAMS, July 3,1796 |
| LETTER CXCIX. | TO COLONEL MONROE, July 10, 1796 |
| LETTER CC. | TO JAMES MADISON |
| LETTER CCI. | TO EDWARD RUTLEDGE, December 27, 1796 |
| LETTER CCII. | TO JOHN ADAMS, December 28,1796 |
| LETTER CCIII. | to James Madison, January 1, 1797 |
| LETTER CCIV. | TO MR. VOLNEY, January 8, 1797 |
| LETTER CCV. | TO HENRY TAZEWELL, January 16, 1797 |
| LETTER CCVI. | TO JAMES MADISON, January 16, 1797 |
| LETTER CCVII. | TO JAMES MADISON, January 22, 1797 |
| LETTER CCVIII. | TO JAMES MADISON, January 30, 1797 |
| LETTER CCIX. | TO JAMES SULLIVAN, February 9, 1797 |
| LETTER CCX. | TO ELBRIDGE GERRY, May 13, 1797 |
| LETTER CCXI. | TO GENERAL GATES, May 30,1797 |
| LETTER CCXII. | TO JAMES MADISON, June 1, 1797 |
| LETTER CCXIII. | TO COLONEL BURR, June 17,1797 |
| LETTER CCXIV. | TO ELBRIDGE GERRY, June 21, 1797 |
| LETTER CCXV. | TO EDWARD RUTLEDGE, June 24, 1797 |
| LETTER, CCXVI. | TO JAMES MADISON, August 3, 1797 |
| LETTER CCXVII. | TO COLONEL ARTHUR CAMPBELL, September 1, 1797 |
| LETTER CCXVIII. | TO JAMES MONROE, September 7, 1797 |
| LETTER CCXIX. | TO JAMES MADISON, January 3, 1798 |
| LETTER CCXX. | TO JAMES MADISON, January 25, 1798 |
| LETTER CCXXI. | TO JAMES MADISON, February 8, 1798 |
| LETTER CCXXII. | TO JAMES MADISON, February 15, 1798 |
| LETTER CCXXIII. | TO GENERAL GATES, February 21, 1798 |
| LETTER CCXXIV. | TO JAMES MADISON, February 22, 1798 |
| LETTER CCXXV. | TO JAMES MADISON, March 2, 1798 |
| LETTER CCXXVI. | TO JAMES MADISON, March 15, 1798 |
| LETTER CCXXVII. | TO JAMES MADISON, March 21, 1798 |
| LETTER CCXXVIII. | TO JAMES MADISON, March 29, 1798 |
| LETTER CCXXIX. | TO JAMES MADISON, April 5, 1798 |
| LETTER CCXXX. | TO JAMES MADISON, April 6, 1798 |
| LETTER CCXXXI. | TO JAMES MADISON, April 12, 1798 |
| LETTER CCXXXII. | TO JAMES MADISON, April 26, 1798 |
| LETTER CCXXXIII. | TO JAMES MADISON, May 3, 1798 |
| LETTER CCXXXIV. | TO JAMES LEWIS, JUNIOR, May 9, 1798 |
| LETTER CCXXXV. | TO JAMES MADISON, May 31, 1798 |
| LETTER CCXXXVI. | TO JOHN TAYLOR, June 1, 1798 |
| LETTER CCXXXVII. | TO GENERAL KOSCIUSKO, June 1, 1798 |
| LETTER CCXXXVIII. | TO JAMES MADISON, June 21, 1798 |
| LETTER CCXXXIX. | TO SAMUEL SMITH, August 22, 1798 |
| LETTER CCXL. | TO A. H. ROWAN, September 26, 1798 |
| LETTER CCXLI. | TO STEPHENS THOMPSON MASON, October 11, 1798 |
| LETTER CCXLII. | TO JOHN TAYLOR, November 26, 1798 |
| LETTER CCXLIII. | TO JAMES MADISON, January 3, 1799 |
| LETTER CCXLIV. | TO JAMES MADISON, January 16, 1799 |
| LETTER CCXLV. | TO ELBRIDGE GERRY |
| LETTER CCXLVI. | TO EDMUND PENDLETON, January 29, 1799 |
| LETTER CCXLVII. | TO JAMES MADISON, February 5, 1799 |
| LETTER CCXLVIII. | TO EDMUND PENDLETON, February 14, 1799 |
| LETTER CCXLIX. | TO JAMES MADISON, February 19, 1799 |
| LETTER CCL. | TO GENERAL KOSCIUSKO, February 21, 1799 |
| LETTER CCLI. | TO JAMES MADISON, February 26, 1799 |
| LETTER CCLII. | TO T. LOMAX, March 12, 1799 |
| LETTER CCLIII. | TO EDMUND RANDOLPH, August 18, 1799 |
| LETTER CCLIV. | TO WILSON C. NICHOLAS, September 5, 1799 |
| LETTER CCLV. | TO JAMES MADISON, November 22, 1799 |
| LETTER CCLVI. | TO COLONEL MONROE, January 12, 1800 |
| LETTER CCLVII. | TO SAMUEL ADAMS |
| LETTER CCLVIII. | TO JAMES MADISON, March 4, 1800 |
| LETTER CCLIX. | TO JAMES MADISON, May 12, 1800 |
| LETTER CCLX. | TO GIDEON GRANGER, August 13, 1800 |
| LETTER CCLXI. | TO URIAH M'GREGORY, August 13, 1800 |
| LETTER CCLXII. | TO DOCTOR RUSH, September 23, 1800 |
| LETTER, CCLXIII. | TO ROBERT R. LIVINGSTON, December 14, 1800 |
| LETTER CCLXIV. | TO COLONEL BURR, December 15,1800 |
| LETTER CCLXV. | TO JUDGE BRECKENRIDGE, December 18,1800 |
| LETTER CCLXVI. | TO JAMES MADISON, December 19,1800 |
| LETTER CCLXVII. | TO JAMES MADISON, December 26, 1800 |
| LETTER CCLXVIII. | TO COLONEL BURR, February 1, 1801 |
| LETTER CCLXIX. | TO GOVERNOR M'KEAN, February 2, 1801 |
| LETTER CCLXX. | TO TENCH COXE, February 11,1801 |
| LETTER CCLXXI. | TO JAMES MONROE, February 15, 1801 |
| LETTER CCLXXII. | TO JAMES MADISON, February 18,1801 |
| LETTER CCLXXIII. | TO JOHN DICKINSON, March 6, 1801 |
| LETTER CCLXXIV. | TO COLONEL MONROE, March 7, 1801 |
| LETTER CCLXXV. | TO GOVERNOR M'KEAN, March 9, 1801 |
| LETTER CCLXXVI. | TO JOEL BARLOW, March 14, 1801 |
| LETTER CCLXXVII. | TO THOMAS PAINE, March 18, 1801 |
| LETTER CCLXXVIII. | TO M. DE REYNEVAL, March 20, 1801 |
| LETTER CCLXXIX. | TO DOCTOR JOSEPH PRIESTLEY, March 21, 1801 |
| LETTER CCLXXX. | TO MOSES ROBINSON, March 23,1801 |
| LETTER CCLXXXI. | TO WILLIAM B. GILES, March 23, 1801 |
| LETTER CCLXXXII. | TO SAMUEL ADAMS, March 29, 1801 |
| LETTER CCLXXXIII. | TO ELBRIDGE GERRY, March 29, 1801 |
| LETTER CCLXXXIV. | TO GIDEON GRANGER, May 3, 1801 |
| LETTER CCLXXXV. | TO NATHANIEL MACON, May 14, 1801 |
| LETTER CCLXXXVI. | TO LEVI LINCOLN, July 11, 1801 |
| LETTER CCLXXXVII. | TO GOVERNOR MONROE, July 11, 1801 |
| LETTER CCLXXXVIII. | TO A COMMITTEE OF MERCHANTS, July 12, 1801 |
| LETTER CCLXXXIX. | TO LEVI LINCOLN, August 26, 1801 |
| LETTER CCXC. | TO ROBERT R. LIVINGSTON, September 9, 1801 |
| LETTER CCXCI. | TO WILLIAM SHORT, October 3, 1801 |
| LETTER CCXCII. | TO THE HEADS OF THE DEPARTMENTS, November 6, 1801 |
| LETTER CCXCIII. | TO JOHN DICKINSON, December 19, 1801 |
| LETTER CCXCIV. | TO ALBERT GALLATIN, April 1,1802 |
| LETTER CCXCV. | TO GENERAL KOSCIUSKO, April 2,1802 |
| LETTER CCXCVI. | TO ROBERT R. LIVINGSTON, April 18, 1802 |
| LETTER CCXCVII. | TO GOVERNOR MONROE, July 15, 1802 |
| LETTER CCXCVIII. | TO GOVERNOR MONROE, July 17, 1802 |
| LETTER CCXCIX. | TO ROBERT R. LIVINGSTON, October 10, 1802 |
| LETTER CCC. | TO ALBERT GALLATIN, October 13, 1802 |
| LETTER CCCI. | TO LEVI LINCOLN, October 25, 1802 |
| LETTER CCCII. | TO GOVERNOR MONROE, January 13,1803 |
| LETTER CCCIII. | TO M. DUPONT, February 1, 1803 |
| LETTER CCCIV. | TO DOCTOR BENJAMIN RUSH, April 21, 1803 |
| LETTER CCCV. | TO GENERAL GATES, July 11, 1803 |
| LETTER CCCVI. | TO MR. BRECKENRIDGE, August 12, 1803 |
|
Book Spines, 1829 Set of Jefferson Papers Steel Engraving by Longacre from Painting of G. Stuart |
| LETTER I. | TO LEVI LINCOLN, August 30, 1803 |
| LETTER II. | TO WILSON C NICHOLAS, September 7, 1803 |
| LETTER III. | TO DOCTOR BENJAMIN RUSH, October 4, 1803 |
| LETTER IV. | TO M. DUPONT DE NEMOURS, November 1, 1803 |
| LETTER V. | TO ROBERT R. LIVINGSTON, November 4,1803 |
| LETTER VI. | TO DAVID WILLIAMS, November 14, 1803 |
| LETTER VII. | TO JOHN RANDOLH, December 1, 1803 |
| LETTER VIII. | TO MR. GALLATIN, December 13, 1803 |
| LETTER IX. | TO DOCTOR PRIESTLEY, January 29, 1804 |
| LETTER X. | TO ELBRIDGE GERRY, March 3, 1804 |
| LETTER XI. | TO GIDEON GRANGER, April 16, 1804 |
| LETTER XII. | TO MRS. ADAMS, June 13,1804 |
| LETTER XIII. | TO GOVERNOR PAGE, June 25, 1804 |
| LETTER, XIV. | TO P. MAZZEI, July 18, 1804 |
| LETTER XV. | TO MRS. ADAMS, July 22, 1804 |
| LETTER XVI. | TO JAMES MADISON, August 15, 1804 |
| LETTER XVII. | TO GOVERNOR CLAIBORNE, August 30, 1804 |
| LETTER XVIII. | TO MRS. ADAMS, September 11, 1804 |
| LETTER XIX. | TO MR. NICHOLSON, January 29, 1805 |
| LETTER XX. | TO MR. VOLNEY, February 8, 1805 |
| LETTER XXI. | TO JUDGE TYLER, March 29, 1805 |
| LETTER XXII. | TO DOCTOR LOGAN, May 11, 1805 |
| LETTER XXIII. | TO JUDGE SULLIVAN, May 21, 1805 |
| LETTER XXIV. | TO THOMAS PAINE, June 5, 1805 |
| LETTER XXV. | TO DOCTORS ROGERS AND SLAUGHTER, March 2, 1806 |
| LETTER XXVI. | TO MR. DUANE, March 22, 1806 |
| LETTER XXVII. | TO WILSON C. NICHOLAS, March 24,1806 |
| LETTER XXVIII. | TO WILSON C. NICHOLAS, April 13, 1806 |
| LETTER XXIX. | TO MR. HARRIS, April 18, 1806 |
| LETTER XXX. | TO THE EMPEROR OF RUSSIA |
| LETTER XXXI. | TO COLONEL MONROE, May 4, 1806 |
| LETTER XXXII. | TO GENERAL SMITH, May 4,1806 |
| LETTER XXXIII. | TO MR DIGGES, July 1, 1806 |
| LETTER XXXIV. | TO MR. BIDWELL, July 5, 1806 |
| LETTER XXXV. | TO MR. BOWDOIN, July 10, 1806 |
| LETTER XXXVI. | TO W. A. BURWELL, September 17, 1806 |
| LETTER XXXVII. | TO ALBERT GALLATIN, October 12, 1806 |
| LETTER XXXVIII. | TO JOHN DICKINSON, January 13, 1807 |
| LETTER XXXIX, | TO WILSON C. NICHOLAS, February 28,1807 |
| LETTER XL. | TO JAMES MONROE, March 21, 1807 |
| LETTER XLI. | M. LE COMTE DIODATI, March 29, 1807 |
| LETTER XLII. | TO MR. BOWDOIN, April 2, 1807 |
| LETTER XLIII. | TO WILLIAM B. GILES, April 20, 1807 |
| LETTER XLIV. | TO GEORGE HAY, June 2, 1807 |
| LETTER XLV. | TO ALBERT GALLATIN, June 3, 1807 |
| LETTER XLVI. | TO GEORGE HAY, June 5, 1807 |
| LETTER XLVII. | TO DOCTOR HORATIO TURPIN, June 10, 1807 |
| LETTER XLVIII. | TO JOHN NORVELL, June 11, 1807 |
| LETTER XLIX. | TO WILLIAM SHORT, June 12, 1807 |
| LETTER L. | TO GEORGE HAY, June 12, 1807 |
| LETTER LI. | TO GEORGE HAY, June 17, 1807 |
| LETTER LII. | TO GEORGE HAY, June 19,1807 |
| LETTER LIII. | TO GOVERNOR SULLIVAN, June 19, 1807 |
| LETTER LIV. | TO GEORGE HAY, June 20, 1807 |
| LETTER LV. | TO DOCTOR WISTAR, June 21, 1807 |
| LETTER LVI. | TO MR. BOWDOIN, July 10, 1807 |
| LETTER LVII. | TO THE MARQUIS DE LA FAYETTE, July 14, 1807 |
| LETTER LVIII. | TO JOHN PAGE, July 17, 1807 |
| LETTER LIX. | TO WILLIAM DUANE, July 20, 1807 |
| LETTER LX. | TO GEORGE HAY, August 20, 1807 |
| LETTER LXI. | TO GEORGE HAY, September 4, 1807 |
| LETTER LXII. | TO GEORGE HAY, September 7, 1807 |
| LETTER LXIII. | TO THE REV. MR. MILLAR, January 23, 1808 |
| LETTER LXIV. | TO COLONEL MONROE, February 18, 1808 |
| LETTER LXV. | TO COLONEL MONROE, March 10, 1808 |
| LETTER LXVI. | TO RICHARD M. JOHNSON, March 10, 1808 |
| LETTER LXVII. | TO LEVI LINCOLN, March 23, 1808 |
| LETTER LXVIII. | TO CHARLES PINCKNEY, March 30, 1808 |
| LETTER LXIX. | TO DOCTOR LEIB, June 23, 1808 |
| LETTER LXX. | TO ROBERT L. LIVINGSTON, October 15, 1808 |
| LETTER LXXI. | TO DOCTOR JAMES BROWN, October 27, 1808 |
| LETTER LXXII. | TO LIEUTENANT GOVERNOR LINCOLN, November 13, 1808 |
| LETTER LXXIII. | TO THOMAS JEFFERSON RANDOLPH, November 24, 1808 |
| LETTER LXXIV. | TO DOCTOR EUSTIS, January 14, 1809 |
| LETTER LXXV. | TO COLONEL MONROE, January 28, 1809 |
| LETTER LXXVI. | TO THOMAS MANN RANDOLPH, February 7, 1809 |
| LETTER LXXVII. | TO JOHN HOLLINS, February 19, 1809 |
| LETTER LXXVIII. | TO M. DUPONT DE NEMOURS, March 2, 1809 |
| LETTER LXXIX. | TO THE PRESIDENT, March 17, 1809 |
| LETTER LXXX. | TO THE INHABITANTS OF ALBEMARLE COUNTY, April 3, 1809 |
| LETTER LXXXI. | TO WILSON C. NICHOLAS, June 13, 1809 |
| LETTER LXXXII. | TO THE PRESIDENT, August 17, 1809 |
| LETTER LXXXIII. | TO DOCTOR BARTON, September 21, 1809 |
| LETTER LXXXIV. | TO DON VALENTINE DE FORONDA, October 4, 1809 |
| LETTER LXXXV. | TO ALBERT GALLATIN, October 11, 1809 |
| LETTER LXXXVI. | TO CÆSAR A. RODNEY, February 10, 1810 |
| LETTER LXXXVII.* | TO SAMUEL KERCHEVAL, February 19,1810 |
| LETTER LXXXVIII. | TO GENERAL KOSCIUSKO, February 26, 1810 |
| LETTER LXXXIX. | TO DOCTOR JONES, March 5, 1810 |
| LETTER XC. | TO GOVERNOR LANGDON, March 5, 1810 |
| LETTER XCI. | TO GENERAL DEARBORN, July 16,1810 |
| LETTER XCII. | TO J. B. COLVIN, September 20, 1810 |
| LETTER XCIII. | TO MR. LAW, January 15, 1811 |
| LETTER XCIV. | TO DOCTOR BENJAMIN RUSH, January 16, 1811 |
| LETTER XCV. | TO M. DESTUTT TRACY, January 26, 1811 |
| LETTER XCVI. | TO COLONEL MONROE, May 5, 1811 |
| LETTER XCVII. | TO GENERAL DEARBORN, August 14, 1811 |
| LETTER XCVIII. | TO DOCTOR BENJAMIN RUSH |
| LETTER XCIX. | TO JOHN ADAMS, January 21, 1812 |
| LETTER C. | TO JOHN ADAMS, April 20, 1812 |
| LETTER CI. | TO JAMES MAURY, April 25, 1812 |
| LETTER CII. | TO THE PRESIDENT, May 30, 1812 |
| LETTER CIII. | TO ELBRIDGE GERRY, June 11, 1812 |
| LETTER CIV. | TO JUDGE TYLER, June 17,1812 |
| LETTER CV. | TO COLONEL WILLIAM DUANE, October 1, 1812 |
| LETTER CVI. | TO MR. MELISH, January 13, 1813 |
| LETTER CVII. | TO MADAME DE STAEL-HOLSTEIN, May 24, 1818 |
| LETTER CVIII. | TO JOHN ADAMS, May 27, 1813 |
| LETTER CIX. | TO JOHN ADAMS, June 15, 1813 |
| LETTER CX. | TO JOHN W. EPPES, June 24, 1813 |
| LETTER CXI. | TO JOHN ADAMS, June 21, 1813 |
| LETTER CXII. | TO JOHN ADAMS, August 22, 1813 |
| LETTER CXIII. | TO JOHN W. EPPES, November 6, 1813 |
| LETTER CXIV. | TO JOHN ADAMS, October 13, 1813 |
| LETTER CXV. | TO JOHN ADAMS, October 28, 1813 |
| LETTER CXVI. | TO THOMAS LIEPER, January 1, 1814 |
| LETTER CXVII. | TO DOCTOR WALTER JONES, January 2,1814 |
| LETTER CXVIII. | TO JOSEPH C. CABELL, January 31, 1814 |
| LETTER CXIX. | TO JOHN ADAMS, July 5, 1814 |
| LETTER CXX. | TO COLONEL MONROE, January 1, 1815 |
| LETTER CXXI. | TO THE MARQUIS DE LA FAYETTE, February 14, 1815 |
| LETTER CXXII.* | TO MR. WENDOVER, March 13, 1815 |
| LETTER CXXIII. | TO CÆSAR A. RODNEY, March 16, 1815 |
| LETTER CXXIV. | TO GENERAL DEARBORN, March 17, 1815 |
| LETTER CXXV. | TO THE PRESIDENT, March 23,1815 |
| LETTER CXXVI. | TO JOHN ADAMS, June 10,1815 |
| LETTER CXXVII. | TO MR. LEIPER, June 12, 1815 |
| LETTER CXXVIII. | TO JOHN ADAMS, August 10,1815 |
| LETTER CXXIX. | TO DABNEY CARR, January 19, 1816 |
| LETTER CXXX. | TO JOHN ADAMS, April 8, 1816 |
| LETTER CXXXI. | TO JOHN TAYLOR, May 28,1816 |
| LETTER CXXXII. | TO FRANCIS W. GILMER, June 7,1816 |
| LETTER CXXXIII.* | TO BENJAMIN AUSTIN, January 9, 1816 |
| LETTER CXXXIV. | TO WILLIAM H. CRAWFORD, June 20, 1816 |
| LETTER CXXXV. | TO SAMUEL KERCHIVAL, July 12, 1816 |
| LETTER CXXXVI. | TO JOHN TAYLOR, July 21, 1816 |
| LETTER CXXXVII. | TO SAMUEL KERCHIVAL, September 5, 1816 |
| LETTER CXXXVIII. | TO JOHN ADAMS, October 14, 1816 |
| LETTER CXXXIX. | TO JOHN ADAMS, TO JOHN ADAMS |
| LETTER CXL. | TO JOHN ADAMS, May 5, 1817 |
| LETTER CXLI. | TO MARQUIS DE LA FAYETTE, May 14, 1817 |
| LETTER CXLII. | TO ALBERT GALLATIN, June 16, 1817 |
| LETTER CXLIII. | TO JOHN ADAMS, May 17, 1818 |
| LETTER CXLIV. | TO JOHN ADAMS, November 13, 1818 |
| LETTER CXLV. | TO ROBERT WALSH, December 4, 1818 |
| LETTER CXLVI. | TO M. DE NEUVILLE, December 13, 1818 |
| LETTER CXLVII. | TO DOCTOR VINE UTLEY, March 21, 1819 |
| LETTER CXLVIII. | TO JOHN ADAMS, July 9, 1819 |
| LETTER CXLIX. | TO JUDGE ROANE, September 6,1819 |
| LETTER CL. | TO JOHN ADAMS, December 10, 1819 |
| LETTER CLI. | TO WILLIAM SHORT, April 13, 1820 |
| LETTER CLII. | TO JOHN HOLMES, April 22, 1820 |
| LETTER CLIII. | TO WILLIAM SHORT, August 4, 1820 |
| LETTER CLIV. | TO JOHN ADAMS, August 15, 1820 |
| LETTER CLV. | TO JOSEPH C. CABELL, November 28, 1820 |
| LETTER CLVI. | TO THOMAS RITCHIE, December, 25, 1820 |
| LETTER CLVII. | TO JOHN ADAMS, January 22, 1821 |
| LETTER CLVIII. | TO JOSEPH C CABELL, January 31, 1821 |
| LETTER CLIX. | TO GENERAL BRECKENRIDGE, February 15, 1821 |
| LETTER CLX. | TO — — — NICHOLAS, December 11,1821 |
| LETTER CLXI. | TO JEDIDIAH MORSE, March 6, 1822 |
| LETTER CLXII. | TO DOCTOR BENJAMIN WATERHOUSE, June 26, 1822 |
| LETTER CLXIII. | TO JOHN ADAMS |
| LETTER CLXIV. | TO WILLIAM T. BARRY, July 2, 1822 |
| LETTER CLXV. | TO DOCTOR WATERHOUSE, July 19, 1822 |
| LETTER CLXVI. | TO JOHN ADAMS |
| LETTER CLXVII. | TO DOCTOR COOPER, November 2, 1822 |
| LETTER CLXVIII. | TO JAMES SMITH, December 8, 1822 |
| LETTER, CLXIX. | TO JOHN ADAMS, February 25, 1823 |
| LETTER CLXX. | TO JOHN ADAMS, April 11, 1823 |
| LETTER CLXXI. | TO THE PRESIDENT, June 11, 1823 |
| LETTER CLXXII. | TO JUDGE JOHNSON, June 12, 1823 |
| LETTER CLXXIII. | TO JAMES MADISON, August 30,1823 |
| LETTER CLXXIV. | TO JOHN ADAMS, September 4, 1823 |
| LETTER CLXXV. | TO JOHN ADAMS, October 12, 1823 |
| LETTER CLXXVI. | TO THE PRESIDENT, October 24,1823 |
| LETTER CLXXVII. | TO THE MARQUIS DE LA FAYETTE, November 4, 1823 |
| LETTER CLXXVIII. | TO JOSEPH C CABELL, February 3, 1824 |
| LETTER CLXXIX. | TO JARED SPARKS, February 4, 1824 |
| LETTER CLXXX. | TO EDWARD LIVINGSTON, April 4, 1824 |
| LETTER CLXXXI. | TO MAJOR JOHN CARTWRIGHT, June 5,1824 |
| LETTER CLXXXII. | TO MARTIN VAN BUREN, June 29, 1824 |
| LETTER CLXXXIII. | TO EDWARD EVERETT, October 15, 1824 |
| LETTER CLXXXIV. | TO JOSEPH C. CABELL, January 11, 1825 |
| LETTER CLXXXV. | TO THOMAS JEFFERSON SMITH, February 21, 1825 |
| LETTER CLXXXVI. | TO JAMES MADISON, December 24, 1825 |
| LETTER CLXXXVII. | TO WILLIAM B. GILES, December 25, 1825 |
| LETTER CLXXXVIII. | TO WILLIAM B. GILES, December 26, 1825 |
| LETTER CLXXXIX. | TO CLAIBORNE W. GOOCH, January 9, 1826 |
| LETTER CXC. | TO [ANONYMOUS], January 21, 1826 |
| LETTER CXCI. | TO JAMES MADISON, February 17,1826 |
| THOUGHTS | ON LOTTERIES. |
| LETTER CXCII. | TO JOHN QUINCY ADAMS, March 30, 1826 |
| LETTER CXCIII. | TO MR. WEIGHTMAN, June 24, 1826 |
| ANA. | EXPLANATION OF VOLUMES IN MARBLED PAPER |
|
Steel Engraving by Longacre from Painting of G. Stuart Titlepage of Volume Three (of Four) Pages With Greek Phrases and Tables: |

| Contents |
| Illustrations |
| Volume II. |
| Volume III. |
| Volume IV. |
| Facsimile of The Declaration of Independence: | Page 1 | Page 2 | Page 3 | Page 4 |



EASTERN DISTRICT OF VIRGINIA, to wit: Be it remembered, that on the seventeenth day of January, in the fifty-third year of the Independence of the United States of America, Thomas Jefferson Randolph, of the said District, hath deposited in this office the title of a book, the right whereof he claims as proprietor, in the words following, to wit: “Memoir, Correspondence, and Miscellanies, from the Papers of Thomas Jefferson. Edited by Thomas Jefferson Randolph.” In conformity to the act of the Congress of the United States, entitled “An act for the encouragement of learning, by securing the copies of maps, charts, and books, to the authors and proprietors of such copies, during the times therein mentioned.” RD. JEFFRIES, Clerk of the Eastern District of Virginia. CAMBRIDGE: E. W. Metcalf & Company.
CONTENTS
PREFACE.
MEMOIR.
APPENDIX TO THE MEMOIR.
[NOTE A.] Letter to John Saunderson, Esq.
[NOTE B.] Letter to Samuel A. Wells, Esq.
[NOTE C] August, 1774, Instructions to the first Delegation
[NOTE D.] August, 1774., Instructions for the Deputies
[NOTE E.] Monticello, November 1, 1778. [Re: Crimes and Punishment]
[NOTE F.] Coinage for the United States
[NOTE G.]
[NOTE H.]
CORRESPONDENCE
LETTER I. TO DR. WILLIAM SMALL, May 7, 1775
LETTER II. TO JOHN RANDOLPH, August 25,1775
LETTER III. TO JOHN RANDOLPH, November 29, 1775
LETTER IV. TO BENJAMIN FRANKLIN, August 13, 1777
LETTER V. TO PATRICK HENRY, March 27, 1779
LETTER VI. TO JOHN PAGE, January 22, 1779
LETTER VII. TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, June 23, 1779
LETTER VIII. TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, July 17, 1779
LETTER IX. TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, October 1, 1779
LETTER X. TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, October 2, 1779
LETTER XI. TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, Oct. 8, 1779
LETTER XII. TO COLONEL MATHEWS, October, 1779
LETTER XIII. TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, November 28, 1779
LETTER XIV. TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, December 10,1779
LETTER XV. TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, February 10, 1780
LETTER XVI. TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, June 11, 1780
LETTER XVII. TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, July 2, 1780
LETTER XVIII. TO GENERAL EDWARD STEVENS, August 4, 1780
LETTER XIX. TO MAJOR GENERAL GATES, August 15, 1780
LETTER XX. TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, September 8, 1780
LETTER XXI. TO GENERAL EDWARD STEVENS, September 12,1780
LETTER XXII. TO GENERAL EDWARD STEVENS, September 15, 1780
LETTER XXIII. TO MAJOR GENERAL GATES, September 23, 1780
LETTER XXIV. TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, September 23, 1780
LETTER XXV. TO HIS EXCELLENCY GENERAL WASHINGTON, September 26,1780
LETTER XXVI. TO MAJOR GENERAL GATES, October 4, 1780
LETTER XXVII. TO GENERAL GATES, October 15, 1780
LETTER XXVIII. TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, October 22, 1780
LETTER XXIX. TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, October 25,1780
LETTER XXX. TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, October 26, 1780
LETTER XXXI. TO GENERAL GATES, October 28, 1780
LETTER XXXII. TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, November 3,1780
LETTER XXXIII. TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, November 10, 1780
LETTER XXXIV. TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, November 26, 1780
LETTER XXXV. TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, December 15,1780
LETTER XXXVI. TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, January 10, 1781
LETTER XXXVII. TO THE PRESIDENT OF CONGRESS, Jan. 15, 1781
LETTER XXXVIII. TO THE PRESIDENT OF CONGRESS, Jan. 15, 1781
LETTER XXXIX. TO THE PRESIDENT OF CONGRESS, Jan. 17, 1781
LETTER XL. TO THE VIRGINIA DELEGATES IN CONGRESS, Jan. 18, 1781
LETTER XLI. TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, February 8, 1781
LETTER XLII. TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, February 12, 1781
LETTER XLIII. TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, February 17, 1781
LETTER XLIV. TO GENERAL GATES, February 17, 1781
LETTER XLV. TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, February 26,1781
LETTER XLVI. TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, March 8, 1781
LETTER XLVII. TO THE PRESIDENT OF CONGRESS, March 19,1781
LETTER XLVIII. TO THE PRESIDENT OF CONGRESS, March 21, 1781
LETTER XLIX. TO THE PRESIDENT OF CONGRESS, March 26,1781
LETTER L. TO THE PRESIDENT OF CONGRESS, March 28, 1781
LETTER LI. TO THE PRESIDENT OF CONGRESS, March 31, 1781
LETTER LII. TO THE PRESIDENT OF CONGRESS, April 7, 1781
LETTER LIII. TO THE PRESIDENT OF CONGRESS, April 18, 1781
LETTER LIV. TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, April 23,1781
LETTER LV. TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, May 9, 1781
LETTER LVI. TO THE VIRGINIA DELEGATES IN CONGRESS, May 10, 1781
LETTER LVII. TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, May 28,1781
LETTER, LVIII. TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, April 16, 1784
LETTER LIX. TO COLONEL URIAH FORREST, October 20, 1784
LETTER LX. TO JOHN JAY, May 11, 1785
LETTER LXI. TO GENERAL CHASTELLUX, June 7,1785
LETTER LXII. TO JOHN ADAMS, June 15, 1785
LETTER LXIII. TO THE GOVERNOR OF VIRGINIA, June 16, 1785
LETTER LXIV. TO COLONEL MONROE, June 17, 1785
LETTER LXV. TO CHARLES THOMSON, June 21, 1785
LETTER LXVI. TO WILLIAM CARMICHAEL, June 22, 1785
LETTER LXVII. TO JOHN ADAMS, June 23, 1785
LETTER LXVIII. TO COLONEL MONROE, July 5, 1785
LETTER LXIX. TO MRS. SPROWLE, July 5,1785
LETTER LXX. TO JOHN ADAMS, July 7, 1785
LETTER LXXI. TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, July 10, 1785
LETTER LXXII. TO THE GOVERNOR OF VIRGINIA, July 11, 1785
LETTER LXXIII. TO THE PRESIDENT OF CONGRESS, July 12, 1785
LETTER LXXIV. TO THE VIRGINIA DELEGATES IN CONGRESS, July 12,1785
LETTER LXXV. TO JOHN JAY, July 12,1785
LETTER LXXVI. TO MONSIEUR BRIET, July 13, 1785
LETTER LXXVII. TO MESSRS. FRENCH AND NEPHEW, July 13,1785
LETTER LXXVIII. TO DR. STILES, July 17,1785
LETTER LXXIX. TO JOHN ADAMS, July 28, 1785
LETTER LXXX. TO HOGENDORP, July 29, 1785
LETTER LXXXI. TO MESSRS. N. AND J. VAN STAPHORST, July 30, 1785
LETTER LXXXII. TO JOHN ADAMS, July 31, 1785
LETTER LXXXIII. TO M. DE CASTRIES, August 3,1785
LETTER LXXXIV. TO CAPTAIN JOHN PAUL JONES, August 3,1785
LETTER LXXXV. TO JOHN ADAMS, August 6, 1785
LETTER LXXXVI. TO DR. PRICE, August 7,1785
LETTER LXXXVII. TO JOHN ADAMS, August 10,1785
LETTER LXXXVIII. TO MRS. SPROWLE, August 10, 1785
LETTER LXXXIX. TO CAPTAIN JOHN PAUL JONES, August 13, 1785
LETTER XC. TO MESSRS. BUCHANAN AND HAY, August 13, 1785
LETTER XCI. TO JOHN JAY, August 14, 1785
LETTER XCII. TO THE COUNT DE VERGENNES, August 15, 1785
LETTER XCIII. TO CAPTAIN JOHN PAUL JONES, August 17, 1785
LETTER XCIV. TO WILLIAM CARMICHAEL, August 18, 1785
LETTER XCV. TO PETER CARR
LETTER XCVI. TO JOHN PAGE, August 20 1785
LETTER XCVII. TO JOHN JAY, August 23, 1785
LETTER XCVIII. TO COLONEL MONROE, August 28, 1735
LETTER XCIX. TO CAPTAIN JOHN PAUL JONES, August 29,1785
LETTER C. TO JOHN JAY, August 30,1785
LETTER CI. TO JAMES MADISON, September 1,1785
LETTER CII. TO MESSRS. DUMAS AND SHORT, September 1, 1785
LETTER CIII. TO JOHN ADAMS, September 4, 1785
LETTER CIV. TO DAVID HARTLEY, September 5, 1785
LETTER CV. TO BARON GEISMER, September 6, 1785
LETTER CVI. TO JOHN LANGDON, September 11, 1785
LETTER CVII. LISTER ASQUITH, September 14, 1785
LETTER CVIII. TO JOHN ADAMS, September 19, 1785
LETTER CIX. TO JAMES MADISON, September 20, 1785
LETTER CX. TO EDMUND RANDOLPH, September 20,1785
LETTER CXI. TO JOHN ADAMS, September 24, 1785
LETTER CXII. TO JOHN ADAMS, September 24,1785
LETTER CXIII. TO F. HOPKINSON, September 25, 1785
LETTER CXIV. TO LISTER ASQUITH, September 26,1785
LETTER CXV. TO R. IZARD, September 26,1783
LETTER CXVI. TO RICHARD O’BRYAN, September 29, 1785
LETTER CXVII. TO MR. BELLINI, September 30,1785
LETTER CXVIII. JAMES MADISON, October 2, 1785
LETTER CXIX. TO DR. FRANKLIN, October 5,1785
LETTER CXX. TO SAMUEL OSGOOD, October 5, 1785
LETTER CXXI. TO JOHN JAY, October 6, 1785
LETTER CXXII. TO ELBRIDGE GERRY, October 11, 1785
LETTER CXXIII. TO THE COUNT DE VERGENNES, October 11, 1785
LETTER CXXIV. TO JOHN JAY, October 11,1785
LETTER CXXV. TO MESSRS. VAN STAPHORST, October 12, 1785
LETTER CXXVI. TO MONSIEUR DESBORDES, October 12,1785
LETTER CXXVII. TO HOGENDORP, October 13,1785
LETTER CXXVIII. TO J. BANNISTER, JUNIOR, October 15,1785
LETTER CXXIX. TO MR. CARMICHAEL, October 18, 1785
LETTER CXXX. TO MESSRS. VAN STAPHORSTS, October 25,1785
LETTER CXXXI. TO WILLIAM CARMICHAEL, November 4, 1785
LETTER CXXXII. TO RICHARD O’BRYAN, November 4, 1785
LETTER CXXXIII. TO W. W. SEWARD, November 12,1785
LETTER CXXXIV. TO THE COUNT DE VERGENNES, November 14,1785
LETTER CXXXV. TO JOHN ADAMS, November 19, 1785
LETTER CXXXVI. TO THE COUNT DE VERGENNES, November 20, 1785
LETTER CXXXVII. TO LISTER ASQUITH, November 23, 1785
LETTER CXXXVIII. TO JOHN ADAMS, November 27, 1785
LETTER CXXXIX. TO COLONEL HUMPHREYS, December 4,1785
LETTER CXL. TO JOHN ADAMS, December 10, 1785
LETTER CXLI. TO JOHN ADAMS, December 11, 1785
LETTER CXLII. TO THE COUNT DE VERGENNES, December 21, 1785
LETTER CXLIII. TO THE GOVERNOR OF GEORGIA, December 22, 1785
LETTER CXLIV. TO THE GEORGIA DELEGATES IN CONGRESS, Dec. 22, 1785
LETTER CXLV. TO JOHN ADAMS, December 27, 1785
LETTER CXLVI. TO JOHN JAY, January 2,1786
LETTER CXLVII. TO T. HOPKINSON, January 3, 1786
LETTER CXLVIII. TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, January 4, 1786
LETTER CXLIX. TO A. CARY, January 7, 1786
LETTER CL. TO MAJOR GENERAL GREENE, January 12, 1786
LETTER CLI. TO LISTER ASQUITH, January 13, 1786
RE QUESTIONS FOR ECONOMIE POLITIQUE ET DIPLOMATIQUE
ARTICLE BY JEFFERSON: ‘Etats Unis,’ FOR THE Encyclopédie Méthodique
LETTER CLII. TO MR. RITTENHOUSE, January 25,1786
LETTER CLIII. TO A. STEWART, January 25, 1786
LETTER CLIV. TO THE COMMISSIONERS OF THE TREASURY, January 26, 1786
LETTER CLV. TO MESSRS. BUCHANAN AND HAY, January 26, 1786
LETTER CLVI. TO JOHN ADAMS, February 7, 1786
LETTER CLVII. TO JAMES MADISON, February 8, 1786
LETTER CLVIII. TO THE MARQUIS DE LA FAYETTE, February 9, 1786
LETTER CLIX. TO MONSIEUR HILLIARD d’AUBERTEUIL, Feb. 20, 1786
LETTER CLX. TO THE COUNT DE VERGENNES, February 28,1786
LETTER CLXI. TO MONSIEUR DE REYNEVAL, March 8, 1786
LETTER CLXII. TO JOHN JAY, March 12, 1786
LETTER CLXIII. TO COLONEL HUMPHREYS, March 14, 1786
APPENDIX.
[NOTE A.] TO THE GOVERNOR OF VIRGINIA.
IN COUNCIL, June 18, 1779
[NOTE B] IN COUNCIL, September 29, 1779.
[NOTE C] IN COUNCIL, October 8, 1779.
[NOTE D.] FEMALE CONTRIBUTIONS, IN AID OF THE WAR, probably in 1780
[NOTE E.] FROM LORD CORNWALLIS
[NOTE F.] TO LORD CORNWALLIS
List of Illustrations
Book Spines, 1829 Set of Jefferson Papers
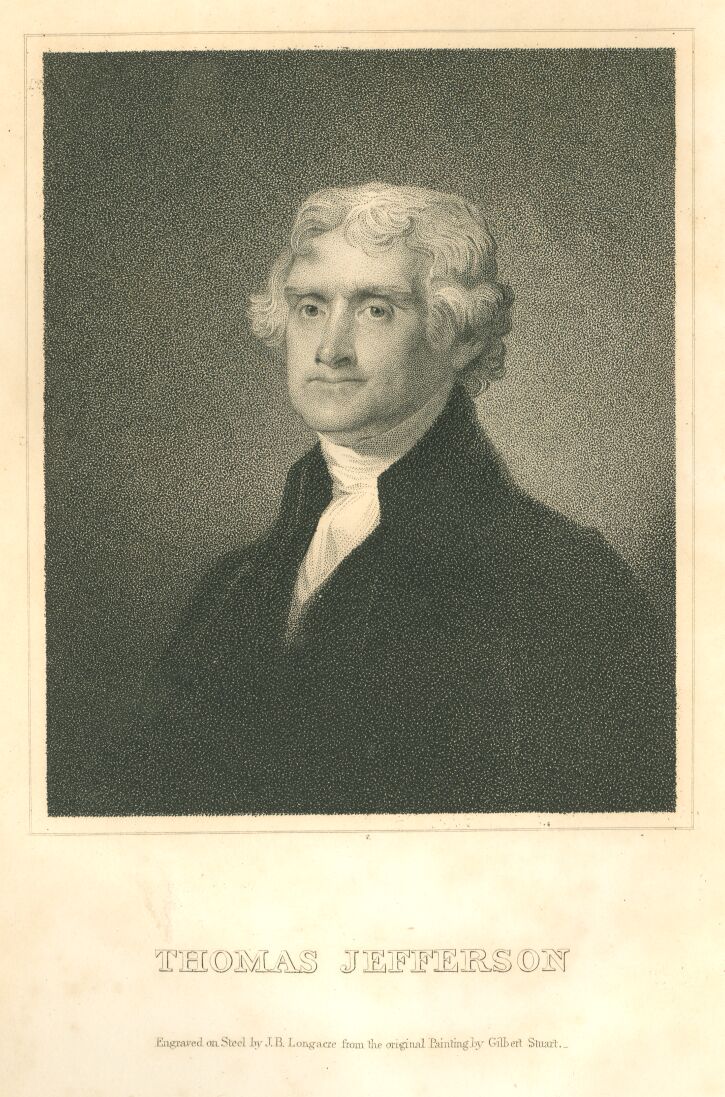
Steel Engraving by Longacre from Painting of G. Stuart
Titlepage of Volume One (of Four)
Page One of Jefferson’s Memoir, Page001
Draft of Declaration Of Independence, Page016
Draft of Declaration Of Independence, Page017
Draft of Declaration Of Independence, Page018
Draft of Declaration Of Independence, Page019
Draft of Declaration Of Independence, Page020
Draft of Declaration Of Independence, Page021
Facsimile of Declaration in Jefferson’s Handwriting—p1
Facsimile of Declaration in Jefferson’s Handwriting—p2
Facsimile of Declaration in Jefferson’s Handwriting—p3
Facsimile of Declaration in Jefferson’s Handwriting—p4
Financial Projection, American Embassy Paris, Page068
Acts of King George and Parliament, Page107
Bill for Proportioning Crimes and Punishments, Page120
Bill for Proportioning Crimes and Punishments, Page121
Bill for Proportioning Crimes and Punishments, Page122
Bill for Proportioning Crimes and Punishments, Page123
Bill for Proportioning Crimes and Punishments, Page124
Bill for Proportioning Crimes and Punishments, Page125
Bill for Proportioning Crimes and Punishments, Page126
Bill for Proportioning Crimes and Punishments, Page127
Bill for Proportioning Crimes and Punishments, Page128
Bill for Proportioning Crimes and Punishments, Page129
Bill for Proportioning Crimes and Punishments, Page130
Bill for Proportioning Crimes and Punishments, Page131
Bill for Proportioning Crimes and Punishments, Page132
Bill for Proportioning Crimes and Punishments, Page133
Sir Isaac Newton’s Assay, Page137
Projected Coin Weights, Page138
Suggested Packet Project, Page251
The Plexi-chronometer, Page391
The opinion universally entertained of the extraordinary abilities of Thomas Jefferson, and the signal evidence given by his country, of a profound sense of his patriotic services, and of veneration for his memory, have induced the Editor, who is both his Executor and the Legatee of his Manuscript Papers, to believe that an extensive publication from them would be particularly acceptable to the American people.
The Memoir, contained in the first volume, commences with circumstantial notices of his earliest life; and is continued to his arrival in New York, in March, 1790, when he entered on the duties of the Department of State, of which he had been just appointed Secretary.
From the aspect of the Memoir, it may be presumed that parts of it, at least, had been written for his own and his family’s use only; and in a style without the finish of his revising pen. There is, however, no part of it, minute and personal as it may be, which the Reader would wish to have been passed over by the Editor; whilst not a few parts of that description will, by some, be regarded with a particular interest.
The contents of the Memoir, succeeding the biographical pages, may be designated as follows:
I. General facts and anecdotes relating to the origin and early stages of the contest with Great Britain.
II. Historical circumstances relating to the Confederation of the States.
III. Facts and anecdotes, local and general, preliminary to the Declaration of Independence.
IV. An exact account of the circumstances attending that memorable act, in its preparation and its progress through Congress; with a copy from the original draught, in the hand-writing of the Author; and a parallel column, in the same hand, showing the alterations made in the draught by Congress.
The Memoir will be considered not a little enriched by the Debates in Congress, on the great question of Independence, as they were taken down by Mr. Jefferson at the time, and which, though in a compressed form, present the substance of what passed on that memorable occasion. This portion of the work derives peculiar value from its perfect authenticity, being all in the hand-writing of that distinguished member of the body; from the certainty that this is the first disclosure to the world of those Debates; and from the probability, or rather certainty, that a like knowledge of them is not to be expected from any other source. The same remarks are applicable to the Debates in the same Congress, preserved in the same manner, on two of the original Articles of Confederation. The first is the Article fixing the rate of assessing the quotas of supply to the common Treasury: the second is the Article which declares, “that in determining questions, each Colony shall have one vote.” The Debates on both are not only interesting in themselves, but curious, also, in relation to like discussions of the same subjects on subsequent occasions.
V. Views of the connections and transactions of the United States with foreign nations, at different periods; particularly, a narrative, with many details, personal and political, of the causes and early course of the French Revolution, as exhibited to the observation of the Author, during his diplomatic residence at Paris. The narrative, with the intermingled reflections on the character and consequences of that Revolution, fills a considerable space in the Memoir, and forms a very important part of it.
VI. Within the body of the Memoir, or referred to as an appendix, are other papers which were thought well entitled to the place they occupy. Among them, are, 1. A paper drawn up in the year 1774, as “Instructions to our Delegates in Congress.” Though heretofore in print, it will be new to most readers; and will be regarded by all, as the most ample and precise enumeration of British violations that had then appeared, or, perhaps, that has since been presented in a form at once so compact and so complete. 2. A Penal Code, being part of a Revised Code of Laws, prepared by appointment of the Legislature of Virginia, in 1776, with reference to the Republican form of Government, and to the principles of humanity congenial therewith, and with the improving spirit of the age. Annexed to the several articles, are explanatory and other remarks of the Author, worthy of being preserved by the aid of the press. 3. A historical and critical review of the repeal of the laws establishing the Church in Virginia; which was followed by the “Act for establishing religious freedom.” This act, it is well known, was always held by Mr. Jefferson to be one of his best efforts in the cause of liberty, to which he was devoted: and it is certainly the strongest legal barrier that could be erected against a connection between Church and State, so fatal in its tendency to the purity of both. 4. An elaborate paper concerning a Money Unit, prepared in the year 1784, and which laid the foundation of the system adopted by Congress, for a coinage and money of account. For other particulars, not here noted, the Reader is referred to the volume itself.
The termination of the Memoir, at the date mentioned, by the Author, may be explained by the laborious tasks assumed or not declined by him, on his return to private life; which, with his great age, did not permit him to reduce his materials into a state proper to be embodied in such a work.
The other volumes contain, I. Letters from 1775, to his death, addressed to a very great variety of individuals; and comprising a range of information, and, in many instances, regular essays, on subjects of History, Politics, Science, Morals, and Religion. The letters to him are omitted, except in a very few instances, where it was supposed their publication would be generally acceptable, from the important character of the communication, or the general interest in the views of the writer; or where the whole or a part of a letter had been filed for the better understanding of the answer.
In these cases, such letters are inserted in the body of the work, or in an appendix, as their importance, and connection with the subject discussed by the author, rendered advisable. And where inferences from the tenor of the answer, might in any way affect the correspondent, his name does not appear in the copy filed. The historical parts of the letters, and the entire publication, have the rare value of coming from one of the chief actors himself, and of being written, not for the public eye, but in the freedom and confidence of private friendship.
II. Notes of conversations, whilst Secretary of State, with President Washington, and others high in office; and memoranda of Cabinet Councils, committed to paper on the spot, and filed; the whole, with the explanatory and miscellaneous additions, showing the views and tendencies of parties, from the year 1789 to 1800.
Appended to the publication, is a ‘Facsimile’ of the rough draught of the Declaration of Independence, in which will be seen the erasures, interlineations, and additions of Dr. Franklin and Mr. Adams, two of the appointed Committee, in the handwriting of each.
The Editor, though he cannot be insensible to the genius, the learning, the philosophic inspiration, the generous devotion to virtue, and the love of country, displayed in the writings now committed to the press, is restrained, not less by his incompetency, than by his relation to the Author, from dwelling on themes which belong to an eloquence that can do justice to the names of illustrious benefactors to their country and to their fellow men.
Albemarle, Va., January, 1829.

January 6, 1821. At the age of 77, I begin to make some memoranda, and state some recollections of dates and facts concerning myself, for my own more ready reference, and for the information of my family.
The tradition in my father’s family was, that their ancestor came to this country from Wales, and from near the mountain of Snowden, the highest in Great Britain. I noted once a case from Wales, in the law reports, where a person of our name was either plaintiff or defendant; and one of the same name was secretary to the Virginia Company. These are the only instances in which I have met with the name in that country. I have found it in our early records; but the first particular information I have of any ancestor was of my grandfather, who lived at the place in Chesterfield called Ozborne’s, and owned the lands afterwards the glebe of the parish. He had three sons; Thomas who died young, Field who settled on the waters of Roanoke and left numerous descendants, and Peter, my father, who settled on the lands I still own, called Shadwell, adjoining my present residence. He was born February 29, 1707-8, and intermarried 1739, with Jane Randolph, of the age of 19, daughter of Isham Randolph, one of the seven sons of that name and family settled at Dungeoness in Goochland. They trace their pedigree far back in England and Scotland, to which let every one ascribe the faith and merit he chooses.
My father’s education had been quite neglected; but being of a strong mind, sound judgment, and eager after information, he read much and improved himself, insomuch that he was chosen, with Joshua Fry, professor of Mathematics in William and Mary college, to continue the boundary line between Virginia and North Carolina, which had been begun by Colonel Byrd; and was afterwards employed with the same Mr. Fry, to make the first map of Virginia which had ever been made, that of Captain Smith being merely a conjectural sketch. They possessed excellent materials for so much of the country as is below the Blue Ridge; little being then known beyond that Ridge. He was the third or fourth settler, about the year 1737, of the part of the country in which I live. He died August 17th, 1757, leaving my mother a widow, who lived till 1776, with six daughters and two sons, myself the elder. To my younger brother he left his estate on James river, called Snowden, after the supposed birth-place of the family: to myself, the lands on which I was born and live. He placed me at the English school at five years of age; and at the Latin at nine, where I continued until his death. My teacher, Mr. Douglas, a clergyman from Scotland, with the rudiments of the Latin and Greek languages, taught me the French; and on the death of my father, I went to the Reverend Mr. Maury, a correct classical scholar, with whom I continued two years; and then, to wit, in the spring of 1760, went to William and Mary college, where I continued two years. It was my great good fortune, and what probably fixed the destinies of my life, that Dr. William Small of Scotland was then professor of Mathematics, a man profound in most of the useful branches of science, with a happy talent of communication, correct and gentlemanly manners, and an enlarged and liberal mind. He, most happily for me, became soon attached to me, and made me his daily companion when not engaged in the school; and from his conversation I got my first views of the expansion of science, and of the system of things in which we are placed. Fortunately, the philosophical chair became vacant soon after my arrival at college, and he was appointed to fill it per interim: and he was the first who ever gave, in that college, regular lectures in Ethics, Rhetoric, and Belles lettres. He returned to Europe in 1762, having previously filled up the measure of his goodness to me, by procuring for me, from his most intimate friend George Wythe, a reception as a student of Law, under his direction, and introduced me to the acquaintance and familiar table of Govenor Fauquier, the ablest man who had ever filled that office. With him, and at his table, Dr. Small and Mr. Wythe, his amici omnium horarum, and myself, formed a partie quarrée, and to the habitual conversations on these occasions I owed much instruction. Mr. Wythe continued to be my faithful and beloved Mentor in youth, and my most affectionate friend through life. In 1767, he led me into the practice of the law at the bar of the General Court, at which I continued until the Revolution shut up the courts of justice.*
* For a sketch of the life and character of Mr. Wythe, see
my letter of August 31, 1820, to Mr. John Saunderson. [See
Appendix, note A.]
In 1769, I became a member of the legislature by the choice of the county in which I live, and so continued until it was closed by the Revolution. I made one effort in that body for the permission of the emancipation of slaves, which was rejected: and indeed, during the regal government, nothing liberal could expect success. Our minds were circumscribed within narrow limits, by an habitual belief that it was our duty to be subordinate to the mother country in all matters of government, to direct all our labors in subservience to her interests, and even to observe a bigoted intolerance for all religions but hers. The difficulties with our representatives were of habit and despair, not of reflection and conviction. Experience soon proved that they could bring their minds to rights, on the first summons of their attention. But the King’s Council, which acted as another house of legislature, held their places at will, and were in most humble obedience to that will: the Governor too, who had a negative on our laws, held by the same tenure, and with still greater devotedness to it: and, last of all, the Royal negative closed the last door to every hope of melioration.
On the 1st of January, 1772, I was married to Martha Skelton, widow of Bathurst Skelton, and daughter of John Wayles, then twenty-three years old. Mr. Wayles was a lawyer of much practice, to which he was introduced more by his great industry, punctuality and practical readiness, than by eminence in the science of his profession. He was a most agreeable companion, full of pleasantry and good humor, and welcomed in every society. He acquired a handsome fortune, and died in May, 1773, leaving three daughters: the portion which came on that event to Mrs. Jefferson, after the debts should be paid, which were very considerable, was about equal to my own patrimony, and consequently doubled the ease of our circumstances.
When the famous Resolutions of 1765, against the Stamp-act, were proposed, I was yet a student of law in Williamsburg. I attended the debate, however, at the door of the lobby of the House of Burgesses, and heard the splendid display of Mr. Henry’s talents as a popular orator. They were great indeed; such as I have never heard from any other man. He appeared to me, to speak as Homer wrote. Mr. Johnson, a lawyer, and member from the Northern Neck, seconded the resolutions, and by him the learning and logic of the case were chiefly maintained. My recollections of these transactions may be seen page 60 of the “Life of Patrick Henry,” by Wirt, to whom I furnished them.
In May, 1769, a meeting of the General Assembly was called by the Governor, Lord Botetourt. I had then become a member; and to that meeting became known the joint resolutions and address of the Lords and Commons of 1768-9, on the proceedings in Massachusetts. Counter-resolutions, and an address to the King by the House of Burgesses, were agreed to with little opposition, and a spirit manifestly displayed itself of considering the cause of Massachusetts as a common one. The Governor dissolved us: but we met the next day in the Apollo* of the Raleigh tavern, formed ourselves into a voluntary convention, drew up articles of association against the use of any merchandise imported from Great Britain, signed and recommended them to the people, repaired to our several counties, and were re-elected without any other exception than of the very few who had declined assent to our proceedings.
* The name of a public room in the Raleigh.
Nothing of particular excitement occurring for a considerable time, our countrymen seemed to fall into a state of insensibility to our situation; the duty on tea, not yet repealed, and the declaratory act of a right in the British Parliament, to bind us by their laws in all cases whatsoever, still suspended over us. But a court of inquiry held in Rhode Island in 1762, with a power to send persons to England to be tried for offences committed here, was considered, at our session of the spring of 1773, as demanding attention. Not thinking our old and leading members up to the point of forwardness and zeal which the times required, Mr. Henry, Richard Henry Lee, Francis L. Lee, Mr. Carr, and myself agreed to meet in the evening, in a private room of the Raleigh, to consult on the state of things. There may have been a member or two more whom I do not recollect. We were all sensible that the most urgent of all measures was that of coming to an understanding with all the other colonies, to consider the British claims as a common cause to all, and to produce a unity of action: and for this purpose that a committee of correspondence in each colony would be the best instrument for intercommunication: and that their first measure would probably be, to propose a meeting of deputies from every colony, at some central place, who should be charged with the direction of the measures which should be taken by all. We therefore drew up the resolutions which may be seen in Wirt, page 87. The consulting members proposed to me to move them, but I urged that it should be done by Mr. Carr, my friend and brother-in-law, then a new member, to whom I wished an opportunity should be given of making known to the house his great worth and talents. It was so agreed; he moved them, they were agreed to nem. con. and a committee of correspondence appointed, of whom Peyton Randolph, the speaker, was chairman.
The Governor (then Lord Dunmore) dissolved us, but the committee met the next day, prepared a circular letter to the speakers, of the other colonies, inclosing to each a copy of the resolutions, and left it in charge with their chairman to forward them by expresses.
The origination of these committees of correspondence between the colonies, has been since claimed for Massachusetts, and Marshall * has given in to this error, although the very note of his appendix to which he refers, shows that their establishment was confined to their own towns. This matter will be seen clearly stated in a letter of Samuel Adams Wells to me of April 2nd, 1819, and my answer of May 12th. I was corrected by the letter of Mr. Wells in the information I had given Mr. Wirt, as stated in his note, page 87, that the messengers of Massachusetts and Virginia crossed each other on the way, bearing similar propositions; for Mr. Wells shows that Massachusetts did not adopt the measure, but on the receipt of our proposition, delivered at their next session. Their message, therefore, which passed ours, must have related to something else, for I well remember Peyton Randolph’s informing me of the crossing of our messengers. **
* Life of Washington, vol. ii. p. 151.
** See Appendix, note B.
The next event which excited our sympathies for Massachusetts, was the Boston port bill, by which that port was to be shut up on the 1st of June, 1774. This arrived while we were in session in the spring of that year. The lead in the House, on these subjects, being no longer left to the old members, Mr. Henry, R. H. Lee, Fr. L. Lee, three or four other members, whom I do not recollect, and myself, agreeing that we must boldly take an unequivocal stand in the line with Massachusetts, determined to meet and consult on the proper measures, in the council chamber, for the benefit of the library in that room. We were under conviction of the necessity of arousing our people from the lethargy into which they had fallen, as to passing events; and thought that the appointment of a day of general fasting and prayer, would be most likely to call up and alarm their attention. No example of such a solemnity had existed since the days of our distress in the war of ‘55, since which a new generation had grown up. With the help, therefore, of Rushworth, whom we rummaged over for the revolutionary precedents and forms of the Puritans of that day, preserved by him, we cooked up a resolution, somewhat modernizing their phrases, for appointing the 1st day of June, on which the port bill was to commence, for a day of fasting, humiliation, and prayer, to implore Heaven to avert from us the evils of civil war, to inspire us with firmness in support of our rights, and to turn the hearts of the King and Parliament to moderation and justice. To give greater emphasis to our proposition, we agreed to wait the next morning on Mr. Nicholas, whose grave and religious character was more in unison with the tone of our resolution, and to solicit him to move it. We accordingly went to him in the morning. He moved it the same day; the 1st of June was proposed; and it passed without opposition. The Governor dissolved us, as usual. We retired to the Apollo, as before, agreed to an association, and instructed the committee of correspondence to propose to the corresponding committees of the other colonies, to appoint deputies to meet in Congress at such place, annually, as should be convenient, to direct, from time to time, the measures required by the general interest: and we declared that an attack on any one colony should be considered as an attack on the whole. This was in May. We further recommended to the several counties to elect deputies to meet at Williamsburg, the 1st of August ensuing, to consider the state of the colony, and particularly to appoint delegates to a general Congress, should that measure be acceded to by the committees of correspondence generally. It was acceded to; Philadelphia was appointed for the place, and the 5th of September for the time of meeting. We returned home, and in our several counties invited the clergy to meet assemblies of the people on the 1st of June, to perform the ceremonies of the day, and to address to them discourses suited to the occasion. The people met generally, with anxiety and alarm in their countenances, and the effect of the day, through the whole colony, was like a shock of electricity, arousing every man and placing him erect and solidly on his centre. They chose, universally, delegates for the convention. Being elected one for my own county, I prepared a draught of instructions to be given to the delegates whom we should send to the Congress, which I meant to propose at our meeting. [See Appendix, note C.] In this I took the ground that, from the beginning, I had thought the only one orthodox or tenable, which was, that the relation between Great Britain and these colonies was exactly the same as that of England and Scotland, after the accession of James and until the union, and the same as her present relations with Hanover, having the same executive chief, but no other necessary political connection; and that our emigration from England to this country gave her no more rights over us, than the emigrations of the Danes and Saxons gave to the present authorities of the mother country, over England. In this doctrine, however, I had never been able to get any one to agree with me but Mr. Wythe. He concurred in it from the first dawn of the question, What was the political relation between us and England? Our other patriots, Randolph, the Lees, Nicholas, Pendleton, stopped at the half-way house of John Dickinson, who admitted that England had a right to regulate our commerce, and to lay duties on it for the purposes of regulation, but not of raising revenue. But for this ground there was no foundation in compact, in any acknowledged principles of colonization, nor in reason: expatriation being a natural right, and acted on as such, by all nations, in all ages. I set out for Williamsburg some days before that appointed for the meeting, but taken ill of a dysentery on the road, and was unable to proceed, I sent on, therefore, to Williamsburg two copies of my draught, the one under cover to Peyton Randolph, who I knew would be in the of the convention, the other to Patrick Henry. Whether Mr. Henry disapproved the ground taken, or was too lazy to read it (for he was the laziest man in reading I ever knew) I never learned: but he communicated it to nobody. Peyton Randolph informed the convention he had received such a paper from a member, prevented by sickness from offering it in his place, and he laid it on the table for perusal. It was read generally by the members, approved by many, though thought too bold for the present state of things; but they printed it in pamphlet form, under the title of ‘A Summary View of the Rights of British America.’ It found its way to England, was taken up by the opposition, interpolated a little by Mr. Burke so as to make it answer opposition purposes, and in that form ran rapidly through several editions. This information I had from Parson Hurt, who happened at the time to be in London, whither he had gone to receive clerical orders; and I was informed afterwards by Peyton Randolph, that it had procured me the honor of having my name inserted in a long list of proscriptions, enrolled in a bill of attainder commenced in one of the Houses of Parliament, but suppressed in embryo by the hasty step of events, which warned them to be a little cautious. Montague, agent of the House of Burgesses in England, made extracts from the bill, copied the names, and sent them to Peyton Randolph. The names I think were about twenty, which he repeated to me, but I recollect those only of Hancock, the two Adamses, Peyton Randolph himself, Patrick Henry, and myself.* The convention met on the 1st of August, renewed their association, appointed delegates to the Congress, gave them instructions very temperately and properly expressed, both as to style and matter; ** and they repaired to Philadelphia at the time appointed. The splendid proceedings of that Congress, at their first session, belong to general history, are known to every one, and need not therefore be noted here. They terminated their session on the 26th of October, to meet again on the 10th of May ensuing. The convention, at their ensuing session of March ‘75, approved of the proceedings of Congress, thanked their delegates, and reappointed the same persons to represent the colony at the meeting to be held in May: and foreseeing the probability that Peyton Randolph, their president, and speaker also of the House of Burgesses, might be called off, they added me, in that event, to the delegation.
* See Girardin’s History of Virginia, Appendix No. 12. note.
** See Appendix, note D.
Mr. Randolph was according to expectation obliged the chair of Congress, to attend the General Assembly summoned by Lord Dunmore, to meet on the 1st day of June,1775. Lord North’s conciliatory propositions, as they were called received by the Governor, and furnished the subject for which this assembly was convened. Mr. Randolph accordingly attended, and the tenor of these propositions being generally known, as having been addressed to all the governors, he was anxious that the answer of our Assembly, likely to be the first, should harmonise with what he knew to be the sentiments and wishes of the body he had recently left. He feared that Mr. Nicholas, whose mind was not yet up to the mark of the times, would undertake the answer, and therefore pressed me to prepare it. I did so, and, with his aid, carried it through the House, with long and doubtful scruples from Mr. Nicholas and James Mercer, and a dash of cold water on it here and there, enfeebling it somewhat, but finally with unanimity, or a vote approaching it. This being passed, I repaired immediately to Philadelphia, and conveyed to Congress the first notice they had of it. It was entirely approved there. I took my seat with them on the 21st of June. On the 24th, a committee which had been appointed to prepare a declaration of the causes of taking up arms, brought in their report (drawn, I believe, by J. Rutledge) which, not being liked, the House recommitted it, on the 26th, and added Mr. Dickinson and myself to the committee. On the rising of the House, the committee having not yet met, I happened to find myself near Governor W. Livingston, and proposed to him to draw the paper. He excused himself and proposed that I should draw it. On my pressing him with urgency, ‘We are as yet but new acquaintances, sir,’ said he, ‘why are you so earnest for my doing it?’ ‘Because,’ said I, ‘I have been informed that you drew the Address to the people of Great Britain, a production, certainly, of the finest pen in America.’ ‘On that,’ says he, ‘perhaps, sir, you may not have been correctly informed.’ I had received the information in Virginia from Colonel Harrison on his return from that Congress. Lee, Livingston, and Jay had been the committee for the draught. The first, prepared by Lee, had been disapproved and recommitted. The second was drawn by Jay, but being presented by Governor Livingston, had led Colonel Harrison into the error. The next morning, walking in the hall of Congress, many members being assembled, but the House formed, I observed Mr. Jay speaking to R. H. Lee, and leading him by the button of his coat to me. ‘I understand, sir,’ said he to me, ‘that this gentleman informed you, that Governor Livingston drew the Address to the people of Great Britain.’ I assured him at once that I had not received that information from Mr. Lee and that not a word had ever passed on the subject between Mr. Lee and myself; and after some explanations the subject was dropped. These gentlemen had had some sparrings in debate before, and continued ever very hostile to each other.
I prepared a draught of the declaration committed to us. It was too strong for Mr. Dickinson. He still retained the hope of reconciliation with the mother country, and was unwilling it should be lessened by offensive statements. He was so honest a man, and so able a one, that he was greatly indulged even by those who could not feel his scruples. We therefore requested him to take the paper, and put it into a form he could approve. He did so, preparing an entire new statement, and preserving of the former only the last four paragraphs and half of the preceding one. We approved and reported it to Congress, who accepted it. Congress gave a signal proof of their indulgence to Mr. Dickinson, and of their great desire not to go too fast for any respectable part of our body, in permitting him to draw their second petition to the King according to his own ideas, and passing it with scarcely any amendment. The disgust against its humility was general; and Mr. Dickinson’s delight at its passage was the only circumstance which reconciled them to it. The vote being passed, although further observation on it was out of order, he could not refrain from rising and expressing his satisfaction, and concluded by saying, ‘There is but one word, Mr. President, in the paper which I disapprove, and that is the word Congress;’ on which Ben Harrison rose and said, ‘There is but one word in the paper, Mr. President, of which I approve, and that is the word Congress?’
On the 22nd of July, Dr. Franklin, Mr. Adams, R. H. Lee, and myself were appointed a committee to consider and report on Lord North’s conciliatory resolution. The answer of the Virginia Assembly on that subject having been approved, I was requested by the committee to prepare this report, which will account for the similarity of feature in the two instruments.
On the 15th of May, 1776, the convention of Virginia instructed their delegates in Congress, to propose to that body to declare the colonies independent of Great Britain, and appointed a committee to prepare a declaration of rights and plan of government.
Here, in the original manuscript, commence the ‘two
preceding sheets’ referred to by Mr. Jefferson, page 21, as
containing ‘notes’ taken by him ‘whilst these things were
going on.’ They are easily distinguished from the body of
the MS. in which they were inserted by him, being of a paper
very different in size, quality, and color, from that on
which the latter is written:
In Congress, Friday, June 7, 1776. The delegates from Virginia moved, in obedience to instructions from their constituents, that the Congress should declare that these United Colonies and of right ought to be, free and independent states, that they are absolved from all allegiance to the British crown, and that all political connection between them and the state of Great Britain is and ought to be, totally dissolved; that measures should be immediately taken for procuring the assistance of foreign powers and a confederation be formed to bind the colonial more closely together.
The House being obliged to attend at that time to some other business, the proposition was referred to the next day, when the members were ordered to attend punctually at ten o’clock.
Saturday, June 8. They proceeded to take it into consideration, and referred it to a committee of the whole, into which they immediately resolved themselves, and passed that day and Monday the 10th in debating on the subject.
It was argued by Wilson, Robert R. Livingston, E. Rutledge, Dickinson, and others—
That, though they were friends to the measures themselves, and saw the impossibility that we should ever again be united with Great Britain, yet they were against adopting them at this time:
That the conduct we had formerly observed was wise and proper now, of deferring to take any capital step till the voice of the people drove us into it:
That they were our power, and without them our declarations could not be carried into effect:
That the people of the middle colonies (Maryland, Delaware, Pennsylvania, the Jerseys, and New York) were not yet ripe for bidding adieu to British connection, but that they were fast ripening, and, in a short time, would join in the general voice of America:
That the resolution, entered into by this House on the 15th of May, for suppressing the exercise of all powers derived from the crown, had shown, by the ferment into which it had thrown these middle colonies, that they had not yet accommodated their minds to a separation from the mother country:
That some of them had expressly forbidden their delegates to consent to such a declaration, and others had given no instructions, and consequently no powers to give such consent:
That if the delegates of any particular colony had no power to declare such colony independent, certain they were, the others could not declare it for them; the colonies being as yet perfectly independent of each other:
That the assembly of Pennsylvania was now sitting above stairs, their convention would sit within a few days, the convention of New York was now sitting, and those of the Jerseys and Delaware counties would meet on the Monday following, and it was probable these bodies would take up the question of Independence, and would declare to their delegates the voice of their state:
That if such a declaration should now be agreed to, these delegates must retire, and possibly their colonies might secede from the Union:
That such a secession would weaken us more than could be compensated by any foreign alliance:
That in the event of such a division, foreign powers would either refuse to join themselves to our fortunes, or, having us so much in their power as that desperate declaration would place us, they would insist on terms proportionably more hard and prejudicial:
That we had little reason to expect an alliance with those to whom alone, as yet, we had cast our eyes:
That France and Spain had reason to be jealous of that rising power, which would one day certainly strip them of all their American possessions:
That it was more likely they should form a connection with the British Court, who, if they should find themselves unable otherwise to extricate themselves from their difficulties, would agree to a partition of our territories, restoring Canada to France, and the Floridas to Spain, to accomplish for themselves a recovery of these colonies:
That it would not be long before we should receive certain information of the disposition of the French court, from the agent whom we had sent to Paris for that purpose:
That if this disposition should be favorable, by waiting the event of the present campaign, which we all hoped would be successful, we should have reason to expect an alliance on better terms:
That this would in fact work no delay of any effectual aid from such ally, as, from the advance of the season and distance of our situation, it was impossible we could receive any assistance during this campaign:
That it was prudent to fix among ourselves the terms on which we would form alliance, before we declared we would form one at all events:
And that if these were agreed on, and our Declaration of Independence ready by the time our Ambassador should be prepared to sail, it would be as well, as to go into that Declaration at this day.
On the other side, it was urged by J. Adams, Lee, Wythe and others, that no gentleman had argued against the policy or the right of separation from Britain, nor had supposed it possible we should ever renew our connection; that they had only opposed its being now declared:
That the question was not whether, by a Declaration of Independence, we should make ourselves what we are not; but whether we should declare a fact which already exists:
That, as to the people or parliament of England, we had always been independent of them, their restraints on our trade deriving efficacy from our acquiescence only, and not from any rights they possessed of imposing them, and that so far, our connection had been federal only, and was now dissolved by the commencement of hostilities:
That, as to the King, we had been bound to him by allegiance, but that this bond was now dissolved by his assent to the late act of parliament, by which he declares us out of his protection, and by his levying war on us, a fact which had long ago proved us out of his protection; it being a certain position in law, that allegiance and protection are reciprocal, the one ceasing when the other is withdrawn:
That James the II. never declared the people of England out of his protection, yet his actions proved it and the parliament declared it:
No delegates then can be denied, or ever want, a power of declaring an existent truth:
That the delegates from the Delaware counties having declared their constituents ready to join, there are only two colonies, Pennsylvania and Maryland, whose delegates are absolutely tied up, and that these had, by their instructions, only reserved a right of confirming or rejecting the measure:
That the instructions from Pennsylvania might be accounted for from the times in which they were drawn, near a twelvemonth ago, since which the face of affairs has totally changed:
That within that time, it had become apparent that Britain was determined to accept nothing less than a carte-blanche, and that the King’s answer to the Lord Mayor, Aldermen, and Common Council of London, which had come to hand four days ago, must have satisfied every one of this point:
That the people wait for us to lead the way:
That they are in favor of the measure, though the instructions given by some of their representatives are not:
That the voice of the representatives is not always consonant with the voice of the people, and that this is remarkably the case in these middle colonies:
That the effect of the resolution of the 15th of May has proved this, which, raising the murmurs of some in the colonies of Pennsylvania and Maryland, called forth the opposing voice of the freer part of the people, and proved them to be the majority even in these colonies:
That the backwardness of these two colonies might be ascribed, partly to the influence of proprietary power and connections, and partly, to their having not yet been attacked by the enemy:
That these causes were not likely to be soon removed, as there seemed no probability that the enemy would make either of these the seat of this summer’s war:
That it would be vain to wait either weeks or months for perfect unanimity, since it was impossible that all men should ever become of one sentiment on any question:
That the conduct of some colonies, from the beginning of this contest, had given reason to suspect it was their settled policy to keep in the rear of the confederacy, that their particular prospect might be better, even in the worst event:
That, therefore, it was necessary for those colonies who had thrown themselves forward and hazarded all from the beginning, to come forward now also, and put all again to their own hazard:
That the history of the Dutch revolution, of whom three states only confederated at first, proved that a secession of some colonies would not be so dangerous as some apprehended:
That a declaration of Independence alone could render it consistent with European delicacy, for European powers to treat with us, or even to receive an Ambassador from us:
That till this, they would not receive our vessels into their ports, nor acknowledge the adjudications of our courts of admiralty to be legitimate, in cases of capture of British vessels:
That though France and Spain may be jealous of our rising power, they must think it will be much more formidable with the addition of Great Britain; and will therefore see it their interest to prevent a coalition; but should they refuse, we shall be but where we are; whereas without trying, we shall never know whether they will aid us or not:
That the present campaign may be unsuccessful, and therefore we had better propose an alliance while our affairs wear a hopeful aspect:
That to wait the event of this campaign will certainly work delay, because, during this summer, France may assist us effectually, by cutting off those supplies of provisions from England and Ireland, on which the enemy’s armies here are to depend; or by setting in motion the great power they have collected in the West Indies, and calling our enemy to the defence of the possessions they have there:
That it would be idle to lose time in settling the terms of alliance, till we had first determined we would enter into alliance:
That it is necessary to lose no time in opening a trade for our people, who will want clothes, and will want money too, for the payment of taxes:
And that the only misfortune is, that we did not enter into alliance with France six months sooner, as, besides opening her ports for the vent of our last year’s produce, she might have marched an army into Germany, and prevented the petty princes there, from selling their unhappy subjects to subdue us.
It appearing in the course of these debates, that the colonies of New York, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, Delaware, Maryland, and South Carolina were not yet matured for falling from the parent stem, but that they were fast advancing to that state, it was thought most prudent to wait awhile for them, and to postpone the final decision to July 1st: but, that this might occasion as little delay as possible, a committee was appointed to prepare a Declaration of Independence. The committee were John Adams, Dr. Franklin, Roger Sherman, Robert R. Livingston, and myself. Committees were also appointed, at the same time, to prepare a plan of confederation for the colonies, and to state the terms proper to be proposed for foreign alliance. The committee for drawing the Declaration of Independence, desired me to do it. It was accordingly done, and being approved by them, I reported it to the House on Friday, the 28th of June, when it was read and ordered to lie on the table. On Monday, the 1st of July, the House resolved itself into a committee of the whole, and resumed the consideration of the original motion made by the delegates of Virginia, which, being again debated through the day, was carried in the affirmative by the votes of New Hampshire, Connecticut, Massachusetts, Rhode Island, New Jersey, Maryland, Virginia, North Carolina, and Georgia. South Carolina and Pennsylvania voted against it. Delaware had but two members present, and they were divided. The delegates from New York declared they were for it themselves, and were assured their constituents were for it; but that their instructions having been drawn near a twelvemonth before, when reconciliation was still the general object, they were enjoined by them to do nothing which should impede that object. They therefore thought themselves not justifiable in voting on either side, and asked leave to withdraw from the question; which was given them. The committee rose and reported their resolution to the House. Mr. Edward Rutledge, of South Carolina, then requested the determination might be put off to the next day, as he believed his colleagues, though they disapproved of the resolution, would then join in it for the sake of unanimity. The ultimate question, whether the House would agree to the resolution of the committee, was accordingly postponed to the next day, when it was again moved, and South Carolina concurred in voting for it. In the mean time, a third member had come post from the Delaware counties, and turned the vote of that colony in favor of the resolution. Members of a different sentiment attending that morning from Pennsylvania also, her vote was changed, so that the whole twelve colonies, who were authorized to vote at all, gave their voices for it; and, within a few days, [July 9.] the convention of New York approved of it, and thus supplied the void occasioned by the withdrawing of her delegates from the vote.
Congress proceeded the same day to consider the Declaration of Independence, which had been reported and laid on the table the Friday preceding, and on Monday referred to a committee of the whole. The pusillanimous idea that we had friends in England worth keeping terms with, still haunted the minds of many. For this reason, those passages which conveyed censures on the people of England were struck out, lest they should give them offence. The clause too, reprobating the enslaving the inhabitants of Africa, was struck out in complaisance to South Carolina and Georgia, who had never attempted to restrain the importation of slaves, and who, on the contrary, still wished to continue it. Our northern brethren also, I believe, felt a little tender under those censures; for though their people had very few slaves themselves, yet they had been pretty considerable carriers of them to others. The debates having taken up the greater parts of the 2nd, 3rd, and 4th days of July, were, on the evening of the last, closed; the Declaration was reported by the committee, agreed to by the House, and signed by every member present, except Mr. Dickinson. As the sentiments of men are known, not only by what they receive, but what they reject also, I will state the form of the Declaration as originally reported. The parts struck out by Congress shall be distinguished by a black line drawn under them; * and those inserted by them shall be placed in the margin, or in a concurrent column.






* In this publication, the parts struck out are printed in
Italics and inclosed in brackets—and those inserted are
inclosed in parenthesis.
A DECLARATION BY THE REPRESENTATIVES OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA, IN GENERAL CONGRESS ASSEMBLED.
When, in the course of human events, it becomes necessary for one people to dissolve the political bands which have connected them with another, and to assume among the powers of the earth the separate and equal station to which the laws of nature and of nature’s God entitle them, a decent respect to the opinions of mankind requires that they should declare the causes which impel them to the separation.
We hold these truths to be self evident: that all men are created equal; that they are endowed by their creator with [inherent and] (certain) inalienable rights; that among these are life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness; that to secure these rights, governments are instituted among men, deriving their just powers from the consent of the governed; that whenever any form of government becomes destructive of these ends, it is the right of the people to alter or abolish it, and to institute new government, laying its foundation on such principles, and organizing its powers in such form, as to them shall seem most likely to effect their safety and happiness. Prudence, indeed, will dictate that governments long established should not be changed for light and transient causes; and accordingly all experience hath shown that mankind are more disposed to suffer while evils are sufferable, than to right themselves by abolishing the forms to which they are accustomed. But when a long train of abuses and usurpations [begun at a distinguished period and] pursuing invariably the same object, evinces a design to reduce them under absolute despotism, it is their right, it is their duty to throw off such government, and to provide new guards for their future security. Such has been the patient sufferance of these colonies; and such is now the necessity which constrains them to [expunge] (alter) their former systems of government. The history of the present king of Great Britain is a history of [unremitting] (repeated) injuries and usurpations, [among which appears no solitary act to contradict the uniform tenor of the rest, but all have] (all having) in direct object the establishment of an absolute tyranny over these states. To prove this, let facts be submitted to a candid world [for the truth of which we pledge a faith yet unsullied by falsehood.]
He has refused his assent to laws the most wholesome and necessary for the public good.
He has forbidden his governors to pass laws of immediate and pressing importance, unless suspended in their operation till his assent should be obtained; and, when so suspended, he has utterly neglected to attend to them.
He has refused to pass other laws for the accommodation of large districts of people, unless those people would relinquish the right of representation in the legislature, a right inestimable to them, and formidable to tyrants only.
He has called together legislative bodies at places unusual, uncomfortable, and distant from the depository of their public records, for the sole purpose of fatiguing them into compliance with his measures.
He has dissolved representative houses repeatedly [and continually] for opposing with manly firmness his invasions on the rights of the people.
He has refused for a long time after such dissolutions to cause others to be elected, whereby the legislative powers, incapable of annihilation, have returned to the people at large for their exercise, the state remaining, in the mean time, exposed to all the dangers of invasion from without and convulsions within.
He has endeavored to prevent the population of these states; for that purpose obstructing the laws for naturalization of foreigners, refusing to pass others to encourage their migrations hither, and raising the conditions of new appropriations of lands.
He has [suffered] (obstructed) the administration of justice [totally to cease in some of these states] (by) refusing his assent to laws for establishing judiciary powers.
He has made [our] judges dependant on his will alone for the tenure of their offices, and the amount and payment of their salaries.
He has erected a multitude of new offices, [by a self-assumed power] and sent hither swarms of new officers to harass our people and eat out their substance.
He has kept among us in times of peace standing armies [and ships of war] without the consent of our legislatures.
He has affected to render the military independent of, and superior to, the civil power.
He has combined with others to subject us to a jurisdiction foreign to our constitutions and unacknowledged by our laws, giving his assent to their acts of pretended legislation for quartering large bodies of armed troops among us; for protecting them by a mock trial from punishment for any murders which they should commit on the inhabitants of these states; for cutting off our trade with all parts of the world; for imposing taxes on us without our consent; for depriving us [ ] in many cases of the benefits of trial by jury; for transporting us beyond seas to be tried for pretended offences; for abolishing the free system of English laws in a neighboring province, establishing therein an arbitrary government, and enlarging its boundaries, so as to render it at once an example and fit instrument for introducing the same absolute rule into these [states] (colonies); for taking away our charters, abolishing our most valuable laws, and altering fundamentally the forms of our governments; for suspending our own legislatures, and declaring themselves invested with power to legislate for us in all cases whatsoever.
He has abdicated government here [withdrawing his governors, and declaring us out of his allegiance and protection.] (by declaring us out of his protection and waging war against us.)
He has plundered our seas, ravaged our coasts, burnt our towns, and destroyed the lives of our people.
He is at this time transporting large armies of foreign mercenaries to complete the works of death, desolation, and tyranny already begun with circumstances of cruelty and perfidy [ ] (scarcely paralleled in the most barbarous ages and totally) unworthy the head of a civilized nation.
He has constrained our fellow citizens taken captive on the high seas to bear arms against their country, to become the executioners of their friends and brethren, or to fall themselves by their hands.
He has [ ] (excited domestic insurrections amoungst us and has) endeavored to bring on the inhabitants of our frontiers the merciless Indian savages, whose known rule of warfare is an undistinguished destruction of all ages, sexes, and conditions [of existence.]
[He has incited treasonable insurrections of our fellow citizens, with the allurements of forfeiture and confiscation of our property.
He has waged cruel war against human nature itself, violating its most sacred rights of life and, liberty in the persons of a distant people who never offended him, captivating and carrying them into slavery in another hemisphere, or to incur miserable death in their transportation thither. This piratical warfare, the opprobrium of INFIDEL powers, is the warfare of the CHRISTIAN king of Great Britain. Determined to keep open a market where men should be bought and sold, he has prostituted his negative for suppressing every legislative attempt to prohibit or to restrain this execrable commerce. And that this assemblage of horrors might want no fact of distinguished die, he is now exciting those very people to rise in arms among us, and to purchase that liberty of which he has deprived them, by murdering the people on whom he also obtruded them: thus paying off former crimes committed against the liberties of one people with crimes which he urges them to commit against the lives of another.]
In every stage of these oppressions we have petitioned for redress in the most humble terms: our repeated petitions have been answered only by repeated injuries.
A prince whose character is thus marked by every act which may define a tyrant is unfit to be the ruler of a [ ] (free) people [who mean to be free. Future ages will scarcely believe that the hardiness of one man adventured, within the short compass of twelve years only, to lay a foundation so broad and so undisguised for tyranny over a people fostered and fixed in principles of freedom.]
Nor have we been wanting in attentions to our British brethren. We have warned them from time to time of attempts by their legislature to extend [a] (an unwarrantable) jurisdiction over [these our states] (us). We have reminded them of the circumstances of our emigration and settlement here, [no one of which could warrant so strange a pretension: that these were effected at the expense of our own blood and treasure, unassisted by the wealth or the strength of Great Britain: that in constituting indeed our several forms of government, we had adopted one common king, thereby laying a foundation for perpetual league and amity with them: but that submission to their parliament was no part of our constitution, nor ever in idea, if history may be credited: and,] we [ ] (have) appealed to their native justice and magnanimity [as well as to] (and we have conjured them by) the ties of our common kindred to disavow these usurpations which [were likely to] (would inevitably) interrupt our connection and correspondence. They too have been deaf to the voice of justice and of consanguinity, [and when occasions have been given them, by the regular course of their laws, of removing from their councils the disturbers of our harmony, they have, by their free election, re-established, them in power. At this very time too, they are permitting their chief magistrate to send over not only soldiers of our common blood, but Scotch and foreign mercenaries to invade and destroy us. These facts have given the last stab to agonizing affection, and manly spirit bids us to renounce for ever these unfeeling brethren. We must endeavor to forget our former love for them, and hold them as we hold the rest of mankind, enemies in war, in peace friends. We might have been a free and a great people together; but a communication of grandeur and of freedom, it seems, is below their dignity. Be it so, since they will have it. The road to happiness and to glory is open to us too. We will tread it apart from them, and] (We must therefore) acquiesce in the necessity which denounces our [eternal] separation [ ]! (and hold them as we hold the rest of mankind, enemies in war, in peace friends.)
[We therefore the representatives of the United States of America in General Congress assembled, do in the name, and by the authority of the good people of these states reject and renounce all allegiance and subjection to the kings of Great Britain and all others who may hereafter claim by, through, or under them; we utterly dissolve all political connection which may heretofore have subsisted between us and, the people or parliament of Great Britain: and finally we do assert and declare these colonies to be free and independent states, and that as free and independent states, they have full power to levy war, conclude peace, contract alliances, establish commerce, and to do all other acts and things which independent states may of right do.
And for the support of this declaration, we mutually pledge to each other our lives, our fortunes, and our sacred honor.]
(We therefore the representatives of the United States of America in General Congress assembled, appealing to the supreme judge of the world for the rectitude of our intentions, do in the name, and by the authority of the good people of these colonies, solemnly publish and declare, that these united colonies are, and of right ought to be, free and independent states; that they are absolved from all allegiance to the British crown, and that all political connection between them and the state of Great Britain is, and ought to be, totally dissolved; and that as free and independent states, they have full power to levy war, conclude peace, contract alliances, establish commerce, and to do all other acts and things which independent states may of right do.
And for the support of this declaration, with a firm reliance on the protection of divine providence, we mutually pledge to each other our lives, our fortunes, and our sacred honor.)
The declaration thus signed on the 4th, on paper, was engrossed on parchment, and signed again on the 2nd of August.
[* Some erroneous statements of the proceedings on the Declaration of Independence having got before the public in latter times, Mr. Samuel A. Wells asked explanations of me, which are given in my letter to him of May 12, ‘19, before and now again referred to. (See Appendix, note B.) I took notes in my place while these things were going on, and at their close wrote them out in form and with correctness, and from 1 to 7 of the two preceding sheets, are the originals then written; as the two following are of the earlier debates on the Confederation, which I took in like manner.]
* The above note of the author is on a slip of paper, pasted
in at the end of the Declaration. Here is also sewed into
the MS. a slip of newspaper containing, under the head
‘Declaration of Independence,’ a letter from Thomas Mc’Kean
to Messrs. William M’Corkle & Son, dated ‘Philadelphia,
June 16 1817.’ This letter is to be found in the Port Folio,
Sept. 1817, p. 249.
[The following four images are from engravings taken from the Jefferson’s draft of the Declaration of Independence in his handwriting with some ammendations and changes in the handrwriting of Benjamin Franklin and John Adams--Click on any of these to enlarge the image to full-size.]




On Friday, July 12, the committee appointed to draw the articles of Confederation reported them, and on the 22nd, the House resolved themselves into a committee to take them into consideration. On the 30th and 31st of that month, and 1st of the ensuing, those articles were debated which determined the proportion, or quota, of money which each state should furnish to the common treasury, and the manner of voting in Congress. The first of these articles was expressed in the original draught in these words. ‘Art. XI. All charges of war and all other expenses that shall be incurred for the common defence, or general welfare, and allowed by the United States assembled, shall be defrayed out of a common treasury, which shall be supplied by the several colonies in proportion to the number of inhabitants of every age, sex, and quality, except Indians not paying taxes, in each colony, a true account-of which, distinguishing the white inhabitants, shall be triennially taken and transmitted to the Assembly of the United States.’
Mr. Chase moved that the quotas should be fixed, not by the number of inhabitants of every condition, but by that of the ‘white inhabitants.’ He admitted that taxation should be always in proportion to property; that this was, in theory, the true rule; but that, from a variety of difficulties, it was a rule which could never be adopted in practice. The value of the property in every state, could never be estimated justly and equally. Some other measures for the wealth of the state must therefore be devised, some standard referred to, which would be more simple. He considered the number of inhabitants as a tolerably good criterion of property, and that this might always be obtained. He therefore thought it the best mode which we could adopt, with one exception only: he observed that negroes are property, and as such, cannot be distinguished from the lands or personalities held in those states where there are few slaves; that the surplus of profit which a Northern farmer is able to lay by, he invests in cattle, horses, &c. whereas a Southern farmer lays out the same surplus in slaves. There is no more reason therefore for taxing the Southern states on the farmer’s head, and on his slave’s head, than the Northern ones on their farmers’ heads and the heads of their cattle: that the method proposed would, therefore, tax the Southern states according to their numbers and their wealth conjunctly, while the Northern would be taxed on numbers only; that negroes, in fact, should not be considered as members of the state, more than cattle, and that they have no more interest in it.
Mr. John Adams observed, that the numbers of people were taken by this article, as an index of the wealth of the state, and not as subjects of taxation; that, as to this matter, it was of no consequence by what name you called your people, whether by that of freemen or of slaves; that in some countries the laboring poor were called freemen, in others they were called slaves; but that the difference as to the state was imaginary only. What matters it whether a landlord employing ten laborers on his farm, give them annually as much money as will buy them the necessaries of life, or gives them those necessaries at short hand? The ten laborers add as much wealth annually to the state, increase its exports as much, in the one case as the other. Certainly five hundred freemen produce no more profits, no greater surplus for the payment of taxes, than five hundred slaves. Therefore the state in which are the laborers called freemen, should be taxed no more than that in which are those called slaves. Suppose, by an extraordinary operation of nature or of law, one half the laborers of a state could in the course of one night be transformed into slaves; would the state be made the poorer or the less able to pay taxes? That the condition of the laboring poor in most countries, that of the fishermen particularly of the Northern states, is as abject as that of slaves. It is the number of laborers which produces the surplus for taxation, and numbers, therefore, indiscriminately, are the fair index of wealth; that it is the use of the word ‘property’ here, and its application to some of the people of the state, which produces the fallacy. How does the Southern farmer procure slaves? Either by importation or by purchase from his neighbor. If he imports a slave, he adds one to the number of laborers in his country, and proportionably to its profits and abilities to pay-taxes; if he buys from his neighbor, it is only a transfer of a laborer from one farm to another, which does not change the annual produce of the state, and therefore should not change its tax: that if a Northern farmer works ten laborers on his farm, he can, it is true, invest the surplus of ten men’s labor in cattle; but so may the Southern farmer, working ten slaves; that a state of one hundred thousand freemen can maintain no more cattle, than one of one hundred thousand slaves. Therefore, they have no more of that kind of property; that a slave may, indeed, from the custom of speech, be more properly called the wealth of his master, than the free laborer might be called the wealth of his employer: but as to the state, both were equally its wealth, and should therefore equally add to the quota of its tax.
Mr. Harrison proposed, as a compromise, that two slaves should be counted as one freeman. He affirmed that slaves did not do as much work as freemen, and doubted if two effected more than one; that this was proved by the price of labor; the hire of a laborer in the Southern colonies being from £8 to £12, while in the Northern it was generally £24.
Mr. Wilson said, that if this amendment should take place, the Southern colonies would have all the benefit of slaves, whilst the Northern ones would bear the burthen: that slaves increase the profits of a state, which the Southern states mean to take to themselves; that they also increase the burthen of defence, which would of course fall so much the heavier on the Northern: that slaves occupy the places of freemen and eat their food. Dismiss your slaves, and freemen will take their places. It is our duty to lay every discouragement on the importation of slaves; but this amendment would give the jus trium liberorum to him who would import slaves: that other kinds of property were pretty equally distributed through all the colonies: there were as many cattle, horses, and sheep, in the North as the South, and South as the North; but not so as to slaves: that experience has shown that those colonies have, been always able to pay most, which have the most inhabitants, whether they be black or white: and the practice of the Southern colonies has always been to make every farmer pay poll taxes upon all his laborers, whether they be black or white. He acknowledges indeed, that freemen work the most; but they consume the most also. They do not produce a greater surplus for taxation. The slave is neither fed nor clothed so expensively as a freeman. Again, white women are exempted from labor generally, but negro women are not. In this then the Southern states have an advantage as the article now stands. It has sometimes been said that slavery is necessary, because the commodities they raise would be too dear for market if cultivated by freemen: but now it is said that the labor of the slave is the dearest.
Mr. Payne urged the original resolution of Congress, to proportion the quotas of the states to the number of souls.
Dr. Witherspoon was of opinion, that the value of lands and houses was the best estimate of the wealth of a nation, and that it was practicable to obtain such a valuation. This is the true barometer of wealth. The one now proposed is imperfect in itself, and unequal between the states. It has been objected that negroes eat the food of freemen, and therefore should be taxed; horses also eat the food of freemen; therefore they also should be taxed. It has been said too, that in carrying slaves into the estimate of the taxes the state is to pay, we do no more than those states themselves do, who always take slaves into the estimate of the taxes the individual is to pay. But the cases are not parallel. In the Southern colonies slaves pervade the whole colony; but they do not pervade the whole continent. That as to the original resolution of Congress, to proportion the quotas according to the souls, it was temporary only, and related to the monies heretofore emitted; whereas we are now entering into a new compact, and therefore stand on original ground.
August 1. The question being put, the amendment proposed was rejected by the votes of New Hampshire, Massachusetts, Rhode Island, Connecticut, New York, New Jersey, and Pennsylvania, against those of Delaware, Maryland, Virginia, North and South Carolina. Georgia was divided.
The other article was in these words. ‘Art. XVII. In determining questions, each colony shall have one vote.’
July 30, 31, August 1. Present forty-one members. Mr. Chase observed that this article was the most likely to divide us, of any one proposed in the draught then under consideration: that the larger colonies had threatened they would not confederate at all, if their weight in Congress should not be equal to the numbers of people they added to the confederacy; while the smaller ones declared against a union, if they did not retain an equal vote for the protection of their rights. That it was of the utmost consequence to bring the parties together, as, should we sever from each other, either no foreign power will ally with us at all, or the different states will form different alliances, and thus increase the horrors of those scenes of civil war and bloodshed, which in such a state of separation and independence, would render us a miserable people. That our importance, our interests, our peace required that we should confederate, and that mutual sacrifices should be made to effect a compromise of this difficult question. He was of opinion, the smaller colonies would lose their rights, if they were not in some instances allowed an equal vote; and, therefore, that a discrimination should take place among the questions which would come before Congress. That the smaller states should be secured in all questions concerning life or liberty, and the greater ones, in all respecting property. He therefore proposed, that in votes relating to money, the voice of each colony should be proportioned to the number of its inhabitants.
Dr. Franklin thought, that the votes should be so proportioned in all cases. He took notice that the Delaware counties had bound up their delegates to disagree to this article. He thought it a very extraordinary language to be held by any state, that they would not confederate with us, unless we would let them dispose of our money. Certainly, if we vote equally, we ought to pay equally; but the smaller states will hardly purchase the privilege at this price. That had he lived in a state where the representation, originally equal, had become unequal by time and accident, he might have submitted rather than disturb government: but that we should be very wrong to set out in this practice, when it is in our power to establish what is right. That at the time of the Union between England and Scotland, the latter had made the objection which the smaller states now do; but experience had proved that no unfairness had ever been shown them: that their advocates had prognosticated that it would again happen, as in times of old, that the whale would swallow Jonas, but he thought the prediction reversed in event, and that Jonas had swallowed the whale; for the Scotch had in fact got possession of the government, and gave laws to the English. He reprobated the original agreement of Congress to vote by colonies, and, therefore, was for their voting, in all cases, according to the number of taxables.
Dr. Witherspoon opposed every alteration of the article. All men admit that a confederacy is necessary. Should the idea get abroad that there is likely to be no union among us, it will damp the minds of the people, diminish the glory of our struggle, and lessen its importance; because it will open to our view future prospects of war and dissension among ourselves. If an equal vote be refused, the smaller states will become vassals to the larger; and all experience has shown that the vassals and subjects of free states are the most enslaved. He instanced the Helots of Sparta, and the provinces of Rome. He observed that foreign powers, discovering this blemish, would make it a handle for disengaging the smaller states from so unequal a confederacy. That the colonies should in fact be considered as individuals; and that, as such, in all disputes, they should have an equal vote; that they are now collected as individuals making a bargain with each other, and, of course, had a right to vote as individuals. That in the East India Company they voted by persons, and not by their proportion of stock. That the Belgic confederacy voted by provinces. That in questions of war the smaller states were as much interested as the larger, and therefore, should vote equally; and indeed, that the larger states were more likely to bring war on the confederacy, in proportion as their frontier was more extensive. He admitted that equality of representation was an excellent principle, but then it must be of things which are co-ordinate; that is of things similar, and of the same nature: that nothing relating to individuals could ever come before Congress; nothing but what would respect colonies. He distinguished between an incorporating and a federal union. The union of England was an incorporating one; yet Scotland had suffered by that union; for that its inhabitants were drawn from it by the hopes of places and employments; nor was it an instance of equality of representation; because, while Scotland was allowed nearly a thirteenth of representation, they were to pay only one fortieth of the land tax. He expressed his hopes, that in the present enlightened state of men’s minds, we might expect a lasting confederacy, if it was founded on fair principles.
John Adams advocated the voting in proportion to numbers. He said, that we stand here as the representatives of the people; that in some states the people are many, in others they are few; that therefore their vote here should be proportioned to the numbers from whom it comes. Reason, justice, and equity never had weight enough on the face of the earth, to govern the councils of men. It is interest alone which does it, and it is interest alone which can be trusted; that therefore the interests, within doors, should be the mathematical representatives of the interests without doors; that the individuality of the colonies is a mere sound. Does the individuality of a colony increase its wealth or numbers? If it does, pay equally. If it does not add weight in the scale of the confederacy, it cannot add to their rights, nor weigh in argument. A. has £50, B. £500, C. £1000, in partnership. Is it just they should equally dispose of the monies of the partnership? It has been said, we are independent individuals, making a bargain together. The question is not, what we are now, but what we ought to be, when our bargain shall be made. The confederacy is to make us one individual only; it is to form us, like separate parcels of metal, into one common mass. We shall no longer retain our separate individuality, but become a single individual as to all questions submitted to the confederacy. Therefore all those reasons, which prove the justice and expediency of equal representation in other assemblies, hold good here. It has been objected, that a proportional vote will endanger the smaller states. We answer, that an equal vote will endanger the larger. Virginia, Pennsylvania, and Massachusetts, are the three greater colonies. Consider their distance, their difference of produce, of interests, and of manners, and it is apparent they can never have an interest or inclination to combine for the oppression of the smaller; that the smaller will naturally divide on all questions with the larger. Rhode Island, from its relation, similarity, and intercourse, will generally pursue the same objects with Massachusetts; Jersey, Delaware, and Maryland, with Pennsylvania.
Dr. Rush took notice, that the decay of the liberties of the Dutch republic proceeded from three causes. 1. The perfect unanimity requisite on all occasions. 2. Their obligation to consult their constituents. 3. Their voting by provinces. This last destroyed the equality of representation, and the liberties of Great Britain also are sinking from the same defect. That a part of our rights is deposited in the hands of our legislatures. There, it was admitted, there should be an equality of representation. Another part of our rights is deposited in the hands of Congress; why is it not equally necessary, there should be an equal representation there? Were it possible to collect the whole body of the people together, they would determine the questions submitted to them by their majority. Why should not the same majority decide, when voting here, by their representatives? The larger colonies are so providentially divided in situation, as to render every fear of their combining visionary. Their interests are different, and their circumstances dissimilar. It is more probable they will become rivals, and leave it in the power of the smaller states to give preponderance to any scale they please. The voting by the number of free inhabitants, will have one excellent effect, that of inducing the colonies to discourage slavery, and to encourage the increase of their free inhabitants.
Mr. Hopkins observed, there were four larger, four smaller, and four middle-sized colonies. That the four largest would contain more than half the inhabitants of the confederating states, and therefore would govern the others as they should please. That history affords no instance of such a thing as equal representation. The Germanic body votes by states. The Helvetic body does the same; and so does the Belgic confederacy. That too little is known of the ancient confederations, to say what was their practice.
Mr. Wilson thought, that taxation should be in proportion to wealth, but that representation should accord with the number of freemen. That government is a collection or result of the wills of all: that if any government could speak the will of all, it would be perfect; and that, so far as it departs from this, it becomes imperfect. It has been said, that Congress is a representation of states, not of individuals. I say, that the objects of its care are all the individuals of the states. It is strange, that annexing the name of ‘State’ to ten thousand men, should give them an equal right with forty thousand. This must be the effect of magic, not of reason. As to those matters which are referred to Congress, we are not so many states; we are one large state. We lay aside our individuality, whenever we come here. The Germanic body is a burlesque on government: and their practice on any point, is a sufficient authority and proof that it is wrong. The greatest imperfection in the constitution of the Belgic confederacy is their voting by provinces. The interest of the whole is constantly sacrificed to that of the small, states. The history of the war in the reign of Queen Anne, sufficiently proves this. It is asked, shall nine colonies put it into the power of four, to govern them as they please? I invert the question, and ask, shall two millions of people put it into the power of one million, to govern them as they please? It is pretended, too, that the smaller colonies will be in danger from the greater. Speak in honest language and say, the minority will be in danger from the majority. And is there an assembly on earth, where this danger may not be equally pretended? The truth is, that our proceedings will then be consentaneous with the interests of the majority, and so they ought to be. The probability is much greater, that the larger states will disagree, than that they will combine. I defy the wit of man to invent a possible case, or to suggest any one thing on earth, which shall be for the interests of Virginia, Pennsylvania, and Massachusetts, and which will not also be for the interest of the other states.*
* Here terminate the author’s notes of the ‘earlier debates
on the confederation,’ and recommences the MS. begun by him
in 1821.
These articles, reported July 12, ‘76, were debated from day to day, and time to time, for two years, were ratified July 9, ‘78, by ten states, by New-Jersey on the 26th of November of the same year, and by Delaware on the 23rd of February following. Maryland alone held off two years more, acceding to them March 1, ‘81, and thus closing the obligation.
Our delegation had been renewed for the ensuing year, commencing August 11; but the new government was now organized, a meeting of the legislature was to be held in October, and I had been elected a member by my county. I knew that our legislation, under the regal government, had many very vicious points which urgently required reformation, and I thought I could be of more use in forwarding that work. I therefore retired from my seat in Congress on the 2nd of September, resigned it, and took my place in the legislature of my state, on the 7th of October.
On the 11th, I moved for leave to bring in a bill for the establishment of courts of justice, the organization of which was of importance. I drew the bill; it was approved by the committee, reported and passed, after going through its due course.
On the 12th, I obtained leave to bring in a bill declaring tenants in tail to hold their lands in fee simple. In the earlier times of the colony, when lands were to be obtained for little or nothing, some provident individuals procured large grants; and, desirous of founding great families for themselves, settled them on their descendants in fee tail. The transmission of this property from generation to generation, in the same name, raised up a distinct set of families, who, being privileged by law in the perpetuation of their wealth, were thus formed into a Patrician order, distinguished by the splendor and luxury of their establishments. From this order, too, the king habitually selected his Counsellors of state; the hope of which distinction devoted the whole corps to the interests and will of the crown. To annul this privilege, and instead of an aristocracy of wealth, of more harm and danger, than benefit, to society, to make an opening for the aristocracy of virtue and talent, which nature has wisely provided for the direction of the interests of society, and scattered with equal hand through all its conditions, was deemed essential to a well ordered republic. To effect it, no violence was necessary, no deprivation of natural right, but rather an enlargement of it by a repeal of the law. For this would authorize the present holder to divide the property among his children equally, as his affections were divided; and would place them, by natural generation, on the level of their fellow citizens. But this repeal was strongly opposed by Mr. Pendleton, who was zealously attached to ancient establishments; and who, taken all in all, was the ablest man in debate I have ever met with. He had not indeed the poetical fancy of Mr. Henry, his sublime imagination, his lofty and overwhelming diction; but he was cool, smooth, and persuasive; his language flowing, chaste, and embellished; his conceptions quick, acute, and full of resource; never vanquished; for if he lost the main battle, he returned upon you, and regained so much of it as to make it a drawn one, by dexterous manoeuvres, skirmishes in detail, and the recovery of small advantages which, little singly, were important all together. You never knew when you were clear of him, but were harassed by his perseverance, until the patience was worn down of all who had less of it than himself. Add to this, that he was one of the most virtuous and benevolent of men, the kindest friend, the most amiable and pleasant of companions, which ensured a favorable reception to whatever came from him. Finding that the general principle of entails could not be maintained, he took his stand on an amendment which he proposed, instead of an absolute abolition, to permit the tenant in tail to convey in fee simple, if he chose it: and he was within a few votes of saving so much of the old law. But the bill passed finally for entire abolition.
In that one of the bills for organizing our judiciary system, which proposed a court of Chancery, I had provided for a trial by jury of all matters of fact, in that as well as in the courts of law. He defeated it by the introduction of four words only, ‘if either party choose?’ The consequence has been, that as no suitor will say to his judge, ‘Sir, I distrust you, give me a jury,’ juries are rarely, I might say perhaps never, seen in that court, but when called for by the Chancellor of his own accord.
The first establishment in Virginia, which became permanent, was made in 1607. I have found no mention of negroes in the colony until about 1650. The first brought here as slaves were by a Dutch ship; after which the English commenced the trade, and continued it until the revolutionary war. That suspended, ipso facto, their further importation for the present, and the business of the war pressing constantly on the legislature, this subject was not acted on finally until the year ‘78, when I brought in a bill to prevent their further importation. This passed without opposition, and stopped the increase of the evil by importation, leaving to future efforts its final eradication.
The first settlers of this colony were Englishmen, loyal subjects to their king and church; and the grant to Sir Walter Raleigh contained an express proviso, that their laws should not be against the true Christian faith, now professed in the church of England.’ As soon as the state of the colony admitted, it was divided into parishes, in each of which was established a minister of the Anglican church, endowed with a fixed salary, in tobacco, a glebe house and land, with the other necessary appendages. To meet these expenses, all the inhabitants of the parishes were assessed, whether they were or not members of the established church. Towards Quakers, who came here, they were most cruelly intolerant, driving them from the colony by the severest penalties. In process of time, however, other sectarisms were introduced, chiefly of the Presbyterian family; and the established clergy, secure for life in their glebes and salaries, adding to these, generally, the emoluments of a classical school, found employment enough in their farms and school-rooms, for the rest of the week, and devoted Sunday only to the edification of their flock, by service, and a sermon at their parish church. Their other pastoral functions were little attended to. Against this inactivity, the zeal and industry of sectarian preachers had an open and undisputed field; and by the time of the revolution, a majority of the inhabitants had become dissenters from the established church, but were still obliged to pay contributions to support the pastors of the minority. This unrighteous compulsion, to maintain teachers of what they deemed religious errors, was grievously felt during the regal government, and without a hope of relief. But the first republican legislature, which met in ‘76, was crowded with petitions to abolish, this spiritual tyranny. These brought on the severest contests in which I have ever been engaged. Our great opponents were Mr. Pendleton and Robert Carter Nicholas; honest men, but zealous churchmen. The petitions were referred to the committee of the whole House on the state of the country; and, after desperate contests in that committee, almost daily, from the 11th of October to the 5th of December, we prevailed so far only, as to repeal the laws, which rendered criminal the maintenance of any religious opinions, the forbearance of repairing to church, or the exercise of any mode of worship: and further, to exempt dissenters from contributions to the support of the established church; and to suspend, only until the next session, levies on the members of the church for the salaries of their own incumbents. For although the majority of our citizens were dissenters, as has been observed, a majority of the legislature were churchmen. Among these, however, were some reasonable and liberal men, who enabled us, on some points, to obtain feeble majorities. But our opponents carried, in the general resolutions of the committee of November 19, a declaration, that religious assemblies ought to be regulated, and that provision ought to be made for continuing the succession of the clergy, and superintending their conduct. And in the bill now passed, was inserted an express reservation of the question, Whether a general assessment should not be established by law, on every one, to the support of the pastor of his choice; or whether all should be left to voluntary contributions: and on this question, debated at every session from ‘76 to ‘79 (some of our dissenting allies, having now secured their particular object, going over to the advocates of a general assessment), we could only obtain a suspension from session to session until ‘79, when the question against a general assessment was finally carried, and the establishment of the Anglican church entirely put down. In justice to the two honest but zealous opponents, who have been named, I must add, that although, from their natural temperaments, they were more disposed generally to acquiesce in things as they are, than to risk innovations; yet, whenever the public will had once decided, none were more faithful or exact in their obedience to it.
The seat of our government had been originally fixed in the peninsula of Jamestown, the first settlement of the colonists; and had been afterwards removed a few miles inland to Williamsburg. But this was at a time when our settlements had not extended beyond the tide waters. Now they had crossed the Allegany; and the centre of population was very far removed from what it had been. Yet Williamsburg was still the depository of our archives, the habitual residence of the Governor, and many other of the public functionaries, the established place for the sessions of the legislature, and the magazine of our military stores: and its situation was so exposed, that it might be taken at any time in war, and, at this time particularly, an enemy might in the night run up either of the rivers, between which it lies, land a force above, and take possession of the place, without the possibility of saving either persons or things. I had proposed its removal so early as October, ‘76; but it did not prevail until the session of May, ‘79.
Early in the session of May, ‘79, I prepared, and obtained leave to bring in a bill, declaring who should be deemed citizens, asserting the natural right of expatriation, and prescribing the mode of exercising it. This, when I withdrew from the house on the 1st of June following, I left in the hands of George Mason, and it was passed on the 26th of that month.
In giving this account of the laws, of which I was myself the mover and draughtsman, I by no means mean to claim to myself the merit of obtaining their passage. I had many occasional and strenuous coadjutors in debate, and one, most steadfast, able, and zealous; who was himself a host. This was George Mason, a man of the first order of wisdom among those who acted on the theatre of the revolution, of expansive mind, profound judgment, cogent in argument, learned in the lore of our former constitution, and earnest for the republican change, on democratic principles. His elocution was neither flowing nor smooth; but his language was strong, his manner most impressive, and strengthened by a dash of biting cynicism, when provocation made it seasonable.
Mr. Wythe, while speaker in the two sessions of 1777, between his return from Congress and his appointment to the Chancery, was an able and constant associate in whatever was before a committee of the whole. His pure integrity, judgment, and reasoning powers gave him great weight. Of him, see more in some notes inclosed in my letter of August 31, 1821, to Mr. John Saunderson. [See Appendix, note A.]
Mr. Madison came into the House in 1776, a new member, and young; which circumstances, concurring with his extreme modesty, prevented his venturing himself in debate before his removal to the Council of State, in November, ‘77. From thence he went to Congress, then consisting of few members. Trained in these successive schools, he acquired a habit of self-possession, which placed at ready command the rich resources of his luminous and discriminating mind, and of his extensive information, and rendered him the first of every assembly afterwards, of which he became a member. Never wandering from his subject into vain declamation, but pursuing it closely, in language pure, classical, and copious, soothing always the feelings of his adversaries by civilities and softness of expression, he rose to the eminent station which he held in the great National Convention of 1787; and in that of Virginia, which followed, he sustained the new constitution in all its parts, bearing off the palm against the logic of George Mason, and the fervid declamation of Mr. Henry. With these consummate powers, was united a pure and spotless virtue, which no calumny has ever attempted to sully. Of the powers and polish of his pen, and of the wisdom of his administration in the highest office of the nation, I need say nothing. They have spoken, and will for ever speak for themselves.
So far we were proceeding in the details of reformation only; selecting points of legislation, prominent in character and principle, urgent, and indicative of the strength of the general pulse of reformation. When I left Congress in ‘76, it was in the persuasion, that our whole code must be reviewed, adapted to our republican form of government, and, now that we had no negatives of Councils, Governors, and Kings to restrain us from doing right, that it should be corrected, in all its parts, with a single eye to reason, and the good of those for whose government it was framed. Early, therefore, in the session of ‘76, to which I returned, I moved and presented a bill for the revision of the laws; which was passed on the 24th of October, and on the 5th of November, Mr. Pendleton, Mr. Wythe, George Mason, Thomas L. Lee, and myself, were appointed a committee to execute the work. We agreed to meet at Fredericksburg to settle the plan of operation, and to distribute the work. We met there accordingly, on the 13th of January, 1777. The first question was, whether we should propose to abolish the whole existing system of laws, and prepare a new and complete Institute, or preserve the general system, and only modify it to the present state of things. Mr. Pendleton, contrary to his usual disposition in favor of ancient things, was for the former proposition, in which he was joined by Mr. Lee. To this it was objected, that to abrogate our whole system would be a bold measure, and probably far beyond the views of the legislature; that they had been in the practice of revising, from time to time, the laws of the colony, omitting the expired, the repealed, and the obsolete, amending only those retained, and probably meant we should now do the same, only including the British statutes as well as our own: that to compose a new Institute, like those of Justinian and Bracton, or that of Blackstone, which was the model proposed by Mr. Pendleton, would be an arduous undertaking, of vast research, of great consideration and judgment; and when reduced to a text, every word of that text, from the imperfection of human language, and its incompetence to express distinctly every shade of idea, would become a subject of question and chicanery, until settled by repeated adjudications; that this would involve us for ages in litigation, and render property uncertain, until, like the statutes of old, every word had been tried and settled by numerous decisions, and by new volumes of reports and commentaries; and that no one of us, probably, would undertake such a work, which, to be systematical, must be the work of one hand. This last was the opinion of Mr. Wythe, Mr. Mason, and myself. When we proceeded to the distribution of the work, Mr. Mason excused himself, as, being no lawyer, he felt himself unqualified for the work, and he resigned soon after. Mr. Lee excused himself on the same ground, and died indeed in a short time. The other two gentlemen, therefore, and myself, divided the work among us. The common law and statutes to the 4 James I. (when our separate legislature was established) were assigned to me; the British statutes, from that period to the present day, to Mr. Wythe; and the Virginia laws to Mr. Pendleton. As the law of Descents, and the Criminal law, fell of course within my portion, I wished the committee to settle the leading principles of these, as a guide for me in framing them; and, with respect to the first, I proposed to abolish the law of primogeniture, and to make real estate descendible in parcenery to the next of kin, as personal property is, by the statute of distribution. Mr. Pendleton wished to preserve the right of primogeniture; but seeing at once that that could not prevail, he proposed we should adopt the Hebrew principle, and give a double portion to the elder son. I observed, that if the elder son could eat twice as much, or do double work, it might be a natural evidence of his right to a double portion; but being on a par, in his powers and wants, with his brothers and sisters, he should be on a par also in the partition of the patrimony; and such was the decision of the other members.
On the subject of the Criminal law, all were agreed, that the punishment of death should be abolished, except for treason and murder; and that, for other felonies, should be substituted hard labor in the public works, and, in some cases, the Lex talionis. How this last revolting principle came to obtain our approbation, I do not remember. There remained, indeed, in our laws, a vestige of it in a single case of a slave; it was the English law, in the time of the Anglo-Saxons, copied probably from the Hebrew law of an ‘eye for an eye, a tooth for a tooth,’ and it was the law of several ancient people; but the modern mind had left it far in the rear of its advances. These points, however, being settled, we repaired to our respective homes for the preparation of the work.
In the execution of my part, I thought it material not to vary the diction of the ancient statutes by modernizing it, nor to give rise to new questions by new expressions. The text of these statutes had been so fully explained and defined, by numerous adjudications, as scarcely ever now to produce a question in our courts. I thought it would be useful, also, in all new draughts, to reform the style of the later British statutes, and of our own acts of Assembly; which, from their verbosity, their endless tautologies, their involutions of case within case, and parenthesis within parenthesis, and their multiplied efforts at certainty, by saids and afore-saids, by ors and by ands, to make them more plain, are really rendered more perplexed and incomprehensible, not only to common readers, but to the lawyers themselves. We were employed in this work from that time to February, 1779, when we met at Williamsburg; that is to say, Mr. Pendleton, Mr. Wythe, and myself; and meeting day by day, we examined critically our several parts, sentence by sentence, scrutinizing and amending, until we had agreed on the whole. We then returned home, had fair copies made of our several parts, which were reported to the General Assembly, June 18, 1779, by Mr. Wythe and myself, Mr. Pendleton’s residence being distant, and he having authorized us by letter to declare his approbation. We had, in this work, brought so much of the Common law as it was thought necessary to alter, all the British statutes from Magna Charta to the present day, and all the laws of Virginia, from the establishment of our legislature in the 4th Jac. I. to the present time, which we thought should be retained, within the compass of one hundred and twenty-six bills, making a printed folio of ninety pages only. Some bills were taken out, occasionally, from time to time, and passed; but the main body of the work was not entered on by the legislature, until after the general peace, in 1785, when, by the unwearied exertions of Mr. Madison, in opposition to the endless quibbles, chicaneries, perversions, vexations, and delays of lawyers and demi-lawyers, most of the bills were passed by the legislature, with little alteration.
The bill for establishing religious freedom, the principles of which had, to a certain degree, been enacted before, I had drawn in all the latitude of reason and right. It still met with opposition; but, with some mutilations in the preamble, it was finally passed; and a singular proposition proved, that its protection of opinion was meant to be universal. Where the preamble declares that coercion is a departure from the plan of the holy author of our religion, an amendment was proposed, by inserting the words ‘Jesus Christ,’ so that it should read, ‘a departure from the plan of Jesus Christ, the holy author of our religion;’ the insertion was rejected by a great majority, in proof that they meant to comprehend, within the mantle of its protection, the Jew and the Gentile, the Christian and Mahometan, the Hindoo, and Infidel of every denomination.
Beccaria, and other writers on crimes and punishments, had satisfied the reasonable world of the unrightfulness and inefficacy of the punishment of crimes by death; and hard labor on roads, canals, and other public works, had been suggested as a proper substitute. The Revisors had adopted these opinions; but the general idea of our country had not yet advanced to that point. The bill, therefore, for proportioning crimes and punishments, was lost in the House of Delegates by a majority of a single vote. I learned afterwards, that the substitute of hard labor in public, was tried (I believe it was in Pennsylvania) without success. Exhibited as a public spectacle, with shaved heads, and mean clothing, working on the high roads, produced in the criminals such a prostration of character, such an abandonment of self-respect, as, instead of reforming, plunged them into the most desperate and hardened depravity of morals and character. To pursue the subject of this law.—I was written to in 1785 (being then in Paris) by Directors appointed to superintend the building of a Capitol in Richmond, to advise them as to a plan, and to add to it one of a Prison. Thinking it a favorable opportunity of introducing into the state an example of architecture, in the classic style of antiquity, and the Maison Quarrée of Nismes, an ancient Roman temple, being considered as the most perfect model existing of what may be called Cubic architecture, I applied to M. Clerissault, who had published drawings of the antiquities of Nismes, to have me a model of the building made in stucco, only changing the order from Corinthian to Ionic, on account of the difficulty of the Corinthian capitals. I yielded, with reluctance, to the taste of Clerissault, in his preference of the modern capital of Scamozzi to the more noble capital of antiquity. This was executed by the artist whom Choiseul Gouffier had carried with him to Constantinople, and employed, while Ambassador there, in making those beautiful models of the remains of Grecian architecture, which are to be seen at Paris. To adapt the exterior to our use, I drew a plan for the interior, with the apartments necessary for legislative, executive, and judiciary purposes; and accommodated in their size and distribution to the form and dimensions of the building. These were forwarded to the Directors, in 1786, and were carried into execution, with some variations, not for the better, the most important of which, however, admit of future correction. With respect to the plan of a Prison, requested at the same time, I had heard of a benevolent society, in England, which had been indulged by the government, in an experiment of the effect of labor, in solitary confinement, on some of their criminals; which experiment had succeeded beyond expectation. The same idea had been suggested in France, and an Architect of Lyons had proposed a plan of a well contrived edifice, on the principle of solitary confinement. I procured a copy, and as it was too large for our purposes, I drew one on a scale less extensive, but susceptible of additions as they should be wanting. This I sent to the Directors, instead of a plan of a common prison, in the hope that it would suggest the idea of labor in solitary confinement, instead of that on the public works, which we had adopted in our Revised Code. Its principle, accordingly, but not its exact form, was adopted by Latrobe in carrying the plan into execution, by the erection of what is now called the Penitentiary, built under his direction. In the mean while, the public opinion was ripening, by time, by reflection, and by the example of Pennsylvania, where labor on the highways had been tried, without approbation, from 1786 to ‘89, and had been followed by their Penitentiary system on the principle of confinement and labor, which was proceeding auspiciously. In 1796, our legislature resumed the subject, and passed the law for amending the Penal laws of the commonwealth. They adopted solitary, instead of public, labor, established a gradation in the duration of the confinement, approximated the style of the law more to the modern usage, and, instead of the settled distinctions of murder and manslaughter, preserved in my bill, they introduced the new terms of murder in the first and second degree. Whether these have produced more or fewer questions of definition, I am not sufficiently informed of our judiciary transactions, to say. I will here, however, insert the text of my bill, with the notes I made in the course of my researches into the subject. [See Appendix, Note E.]
The acts of Assembly concerning the College of William and Mary, were properly within Mr. Pendleton’s portion of the work; but these related chiefly to its revenue, while its constitution, organization, and scope of science, were derived from its charter. We thought that on this subject, a systematical plan of general education should be proposed, and I was requested to undertake it. I accordingly prepared three bills for the Revisal, proposing three distinct grades of education, reaching all classes. 1st. Elementary schools, for all children generally, rich and poor. 2nd. Colleges, for a middle degree of instruction, calculated for the common purposes of life, and such as would be desirable for all who were in easy circumstances. And, 3rd., an ultimate grade for teaching the sciences generally, and in their highest degree. The first bill proposed to lay off every county into Hundreds, or Wards, of a proper size and population for a school, in which reading, writing, and common arithmetic should be taught; and that the whole state should be divided into twenty-four districts, in each of which should be a school for classical learning, grammar, geography, and the higher branches of numerical arithmetic. The second bill proposed to amend the constitution of William and Mary college, to enlarge its sphere of science, and to make it in fact a University. The third was for the establishment of a library. These bills were not acted on until the same year, ‘96, and then only so much of the first as provided for elementary schools. The College of William and Mary was an establishment purely of the Church of England; the Visitors were required to be all of that Church; the Professors to subscribe its Thirty-nine Articles; its Students to learn its Catechism; and one of its fundamental objects was declared to be, to raise up Ministers for that Church. The religious jealousies, therefore, of all the dissenters, took alarm lest this might give an ascendancy to the Anglican sect, and refused acting on that bill. Its local eccentricity, too, and unhealthy autumnal climate, lessened the general inclination towards it. And in the Elementary bill, they inserted a provision which completely defeated it; for they left it to the court of each county to determine for itself, when this act should be carried into execution, within their county. One provision of the bill was, that the expenses of these schools should be borne by the inhabitants of the county, every one in proportion to his general tax rate. This would throw on wealth the education of the poor; and the justices, being generally of the more wealthy class, were unwilling to incur that burthen, and I believe it was not suffered to commence in a single county. I shall recur again to this subject, towards the close of my story, if I should have life and resolution enough to reach that term; for I am already tired of talking about myself.
The bill on the subject of slaves, was a mere digest of the existing laws respecting them, without any intimation of a plan for a future and general emancipation. It was thought better that this should be kept back, and attempted only by way of amendment, whenever the bill should be brought on. The principles of the amendment, however, were agreed on, that is to say, the freedom of all born after a certain day, and deportation at a proper age. But it was found that the public mind would not yet bear the proposition, nor will it bear it even at this day. Yet the day is not distant when it must bear and adopt it, or worse will follow. Nothing is more certainly written in the book of fate, than that these people are to be free; nor is it less certain that the two races, equally free, cannot live in the same government. Nature, habit, opinion, have drawn indelible lines of distinction between them. It is still in our power to direct the process of emancipation and deportation, peaceably, and in such slow degree, as that the evil will wear off insensibly, and their place be, pari passu, filled up by free white laborers. If, on the contrary, it is left to force itself on, human nature must shudder at the prospect held up. We should in vain look for an example in the Spanish deportation or deletion of the Moors. This precedent would fall far short of our case.
I considered four of these bills, passed or reported, as forming a system by which every fibre would be eradicated of ancient or future aristocracy; and a foundation laid for a government truly republican. The repeal of the laws of entail would prevent the accumulation and perpetuation of wealth, in select families, and preserve the soil of the country from being daily more and more absorbed in mortmain. The abolition of primogeniture, and equal partition of inheritances, removed the feudal and unnatural distinctions which made one member of every family rich, and all the rest poor, substituting equal partition, the best of all Agrarian laws. The restoration of the rights of conscience relieved the people from taxation for the support of a religion not theirs; for the establishment was truly of the religion of the rich, the dissenting sects being entirely composed of the less wealthy people; and these, by the bill for a general education, would be qualified to understand their rights, to maintain them, and to exercise with intelligence their parts in self-government: and all this would be effected, without the violation of a single natural right of any one individual citizen. To these, too, might be added, as a further security, the introduction of the trial by jury into the Chancery courts, which have already ingulphed, and continue to ingulph, so great a proportion of the jurisdiction over our property.
On the 1st of June, 1779, I was appointed Governor of the Commonwealth, and retired from the legislature. Being elected, also, one of the Visitors of William and Mary college, a self-electing body, I effected, during my residence in Williamsburg that year, a change in the organization of that institution, by abolishing the Grammar school, and the two professorships of Divinity and Oriental languages, and substituting a professorship of Law and Police, one of Anatomy, Medicine, and Chemistry, and one of Modern Languages; and the charter confining us to six professorships, We added the Law of Nature and Nations, and the Fine Arts, to the duties of the Moral professor, and Natural History to those of the professor of Mathematics and Natural Philosophy.
Being now, as it were, identified with the Commonwealth itself, to write my own history, during the two years of my administration, would be to write the public history of that portion of the revolution within this state. This has been done by others, and particularly by Mr. Girardin, who wrote his Continuation of Burke’s History of Virginia, while at Milton in this neighborhood, had free access to all my papers while composing it, and has given as faithful an account as I could myself. For this portion, therefore, of my own life, I refer altogether to his history. From a belief that, under the pressure of the invasion under which we were then laboring, the public would have more confidence in a military chief, and that the military commander, being invested with the civil power also, both might be wielded with more energy, promptitude, and effect for the defence of the state, I resigned the administration at the end of my second year, and General Nelson was appointed to succeed me.
Soon after my leaving Congress, in September, ‘76, to wit, on the last day of that month, I had been appointed, with Dr. Franklin, to go to France, as a Commissioner to negotiate treaties of alliance and commerce with that government. Silas Deane, then in France, acting as agent for procuring military stores,* was joined with us in commission. But such was the state of my family that I could not leave it, nor could I expose it to the dangers of the sea, and of capture by the British ships, then covering the ocean. I saw, too, that the laboring oar was really at home, where much was to be done, of the most permanent interest, in new-modelling our governments, and much to defend our fanes and fire-sides from the desolations of an invading enemy, pressing on our country in every point. I declined, therefore, and Dr. Lee was appointed in my place. On the 15th of June, 1781, I had been appointed, with Mr. Adams, Dr. Franklin, Mr. Jay, and Mr. Laurens, a Minister Plenipotentiary for negotiating peace, then expected to be effected through the mediation of the Empress of Russia. The same reasons obliged me still to decline; and the negotiation was in fact never entered on. But, in the autumn of the next year, 1782, Congress receiving assurances that a general peace would be concluded in the winter and spring, they renewed my appointment on the 13th of November of that year. I had, two months before that, lost the cherished companion of my life, in whose affections, unabated on both sides, I had lived the last ten years in unchequered happiness. With the public interests, the state of my mind concurred in recommending the change of scene proposed; and I accepted the appointment, and left Monticello on the 19th of December, 1782, for Philadelphia, where I arrived on the 27th. The Minister of France, Luzerne, offered me a passage in the Romulus frigate, which I accepted; but she was then lying a few miles below Baltimore, blocked up in the ice. I remained, therefore, a month in Philadelphia, looking over the papers in the office of State, in order to possess myself of the general state of our foreign relations, and then went to Baltimore, to await the liberation of the frigate from the ice. After waiting there nearly a month, we received information that a Provisional treaty of peace had been signed by our Commissioners on the 3rd of September, 1782, to become absolute, on the conclusion of peace between France and Great Britain. Considering my proceeding to Europe as now of no utility to the public, I returned immediately to Philadelphia, to take the orders of Congress, and was excused by them from further proceeding. I therefore returned home, where I arrived on the 15th of May, 1783.
* His ostensible character was to be that of a merchant, his
real one that of agent for military supplies, and also for
sounding the dispositions of the government of France, and
seeing how far they would favor us, either secretly or
openly. His appointment had been by the Committee of Foreign
Correspondence, March, 1776.
On the 6th of the following month, I was appointed by the legislature a delegate to Congress, the appointment to take place on the 1st of November ensuing, when that of the existing delegation would expire. I accordingly left home on the 16th of October, arrived at Trenton, where Congress was sitting, on the 3rd of November, and took my seat on the 4th, on which day Congress adjourned, to meet at Annapolis on the 26th.
Congress had now become a very small body, and the members very remiss in their attendance on its duties, insomuch that a majority of the states, necessary by the Confederation to constitute a House, even for minor business, did not assemble until the 13th of December.
They, as early as January 7, 1782, had turned their attention to the monies current in the several states, and had directed the Financier, Robert Morris, to report to them a table of rates, at which the foreign coins should be received at the treasury. That officer, or rather his assistant, Gouverneur Morris, answered them on the 15th, in an able and elaborate statement of the denominations of money current in the several states, and of the comparative value of the foreign coins chiefly in circulation with us, He went into the consideration of the necessity of establishing a standard of value with us, and of the adoption of a money unit. He proposed for that unit, such a fraction of pure silver as would be a common measure of the penny of every state, without leaving a fraction. This common divisor he found to be 1/1440 of a dollar, or 1/1600 the crown sterling. The value of a dollar was, therefore, to be expressed by 1440 units, and of a crown by 1600; each unit containing a quarter of a grain of fine silver. Congress turning again their attention to this subject the following year, the Financier, by a letter of April 30,1783, further explained and urged the unit he had proposed: but nothing more was done on it until the ensuing year, when it was again taken up, and referred to a committee, of which I was a member. The general views of the Financier were sound, and the principle was ingenious, on which he proposed to found his unit; but it was too minute for ordinary use, too laborious for computation, either by the head or in figures. The price of a loaf of bread, 1/20 of a dollar, would be 72 units. A pound of butter, 1/5 of a dollar, 288 units. A horse, or bullock, of eighty dollars’ value, would require a notation of six figures, to wit, 115,200, and the public debt, suppose of eighty millions, would require twelve figures, to wit, 115,200,000,000 units. Such a system of money-arithmetic would be entirely unmanageable for the common purposes of society. I proposed, therefore, instead of this, to adopt the Dollar as our unit of account and payment, and that its divisions and subdivisions should be in the decimal ratio. I wrote some Notes on the subject, which I submitted to the consideration of the Financier. I received his answer and adherence to his general system, only agreeing to take for his unit one hundred of those he first proposed, so that a Dollar should be 14 40/100 and a crown 16 units. I replied to this, and printed my Notes and Reply on a flying sheet, which I put into the hands of the members of Congress for consideration, and the Committee agreed to report on my principle. This was adopted the ensuing year, and is the system which now prevails. I insert, here, the Notes and Reply, as showing the different views on which the adoption of our money system hung. [See Appendix, note F.]The divisions into dismes, cents, and mills is now so well understood, that it would be easy of introduction into the kindred branches of weights and measures. I use, when I travel, an Odometer of Clarke’s invention, which divides the mile into cents, and I find every one comprehends a distance readily, when stated to him in miles and cents; so he would in feet and cents, pounds and cents, &c.
The remissness of Congress, and their permanent session began to be a subject of uneasiness; and even some of the legislatures had recommended to them intermissions, and periodical sessions. As the Confederation had made no provision for a visible head of the government, during vacations of Congress, and such a one was necessary to superintend the executive business, to receive and communicate with foreign ministers and nations, and to assemble Congress on sudden and extraordinary emergencies, I proposed, early in April, the appointment of a committee, to be called the ‘Committee of the States,’ to consist of a member from each state, who should remain in session during the recess of Congress: that the functions of Congress should be divided into executive and legislative, the latter to be reserved, and the former, by a general resolution, to be delegated to that Committee. This proposition was afterwards agreed to; a Committee appointed who entered on duty on the subsequent adjournment of Congress, quarrelled very soon, split into two parties, abandoned their post, and left the government without any visible head, until the next meeting of Congress. We have since seen the same thing take place, in the Directory of France; and I believe it will for ever take place in any Executive consisting of a plurality. Our plan, best, I believe, combines wisdom and practicability, by providing a plurality of Counsellors, but a single Arbiter for ultimate decision. I was in France when we heard of this schism and separation of our Committee, and, speaking with Dr. Franklin of this singular disposition of men to quarrel, and divide into parties, he gave his sentiments, as usual, by way of Apologue. He mentioned the Eddystone light-house, in the British channel, as being built on a rock, in the mid-channel, totally inaccessible in winter, from the boisterous character of that sea, in that season; that, therefore, for the two keepers employed to keep up the lights, all provisions for the winter were necessarily carried to them in autumn, as they could never be visited again till the return of the milder season; that, on the first practicable day in the spring, a boat put off to them with fresh supplies. The boatmen met at the door one of the keepers, and accosted him with a ‘How goes it, friend?’ ‘Very well.’ ‘How is your companion?’ ‘I do not know.’ ‘Don’t know? Is not he here?’ ‘I can’t tell.’ ‘Have not you seen him to-day?’ ‘No.’ ‘When did you see him?’ ‘Not since last fall.’ ‘You have killed him?’ ‘Not I, indeed.’ They were about to lay hold of him, as having certainly murdered his companion; but he desired them to go up stairs and examine for themselves. They went up, and there found the other keeper. They had quarrelled, it seems, soon after being left there, had divided into two parties, assigned the cares below to one, and those above to the other, and had never spoken to, or seen, one another since.
But to return to our Congress at Annapolis. The definitive treaty of peace which had been signed at Paris on the 3rd of September, 1783, and received here, could not be ratified without a House of nine states. On the 23rd of December, therefore, we addressed letters to the several Governors, stating the receipt of the definitive treaty; that seven states only were in attendance, while nine were necessary to its ratification; and urging them to press on their delegates the necessity of their immediate attendance. And on the 26th, to save time, I moved that the Agent of Marine (Robert Morris) should be instructed to have ready a vessel at this place, at New York, and at some Eastern port, to carry over the ratification of the treaty when agreed to. It met the general sense of the House, but was opposed by Dr. Lee, on the ground of expense, which it would authorize the Agent to incur for us; and, he said, it would be better to ratify at once, and send on the ratification. Some members had before suggested, that seven states were competent to the ratification. My motion was therefore postponed, and another brought forward by Mr. Read, of South Carolina, for an immediate ratification. This was debated the 26th and 27th. Read, Lee, Williamson, and Jeremiah Chase urged that ratification was a mere matter of form; that the treaty was conclusive from the moment it was signed by the ministers; that, although the Confederation requires the assent of nine states to enter into a treaty, yet, that its conclusion could not be called the entrance into it; that supposing nine states requisite, it would be in the power of five states to keep us always at war; that nine states had virtually authorized the ratification, having ratified the provisional treaty, and instructed their ministers to agree to a definitive one in the same terms, and the present one was, in fact, substantially, and almost verbatim, the same; that there now remain but sixty-seven days for the ratification, for its passage across the Atlantic, and its exchange; that there was no hope of our soon having nine states present in fact, that this was the ultimate point of time to which we could venture to wait; that if the ratification was not in Paris by the time stipulated, the treaty would become void; that if ratified by seven states, it would go under our seal, without its being known to Great Britain that only seven had concurred; that it was a question of which they had no right to take cognizance, and we were only answerable for it to our constituents; that it was like the ratification which Great Britain had received from the Dutch, by the negotiations of Sir William Temple.
On the contrary, it was argued by Monroe, Gerry, Howel, Ellery, and myself, that by the modern usage of Europe, the ratification was considered as the act which gave validity to a treaty, until which, it was not obligatory.* That the commission to the ministers, reserved the ratification to Congress; that the treaty itself stipulated, that it should be ratified; that it became a second question, who were competent to the ratification? That the Confederation expressly required nine states to enter into any treaty; that, by this, that instrument must have intended, that the assent of nine states should be necessary, as well to the completion as to the commencement of the treaty, its object having been to guard the rights of the Union in all those important cases, where nine states are called for; that by the contrary construction, seven states, containing less than one third of our whole citizens, might rivet on us a treaty, commenced indeed under commission and instructions from nine states, but formed by the minister in express contradiction to such instructions, and in direct sacrifice of the interests of so great a majority; that the definitive treaty was admitted not to be a verbal copy of the provisional one, and whether the departures from it were of substance, or not, was a question on which nine states alone were competent to decide; that the circumstances of the ratification of the provisional articles by nine states, the instructions to our ministers to form a definitive one by them, and their actual agreement in substance, do not render us competent to ratify in the present instance; if these circumstances are in themselves a ratification, nothing further is requisite than to give attested copies of them, in exchange for the British ratification; if they are not, we remain where we were, without a ratification by nine states, and incompetent ourselves to ratify; that it was but four days since the seven states, now present, unanimously concurred in a resolution to be forwarded to the Governors of the absent states, in which they stated, as a cause for urging on their delegates, that nine states were necessary to ratify the treaty; that in the case of the Dutch ratification, Great Britain had courted it, and therefore was glad to accept it as it was; that they knew our Constitution, and would object to a ratification by seven; that, if that circumstance was kept back, it would be known hereafter, and would give them ground to deny the validity of a ratification, into which they should have been surprised and cheated, and it would be a dishonorable prostitution of our seal; that there is a hope of nine states; that if the treaty would become null, if not ratified in time, it would not be saved by an imperfect ratification; but that, in fact, it would not be null, and would be placed on better ground, going in unexceptionable form, though a few days too late, and rested on the small importance of this circumstance, and the physical impossibilities which had prevented a punctual compliance in point of time; that this would be approved by all nations, and by Great Britain herself, if not determined to renew the war, and if so determined, she would never want excuses, were this out of the way. Mr. Read gave notice, he should call for the yeas and nays; whereon those in opposition, prepared a resolution, expressing pointedly the reasons of their dissent from his motion. It appearing, however, that his proposition could not be carried, it was thought better to make no entry at all. Massachusetts alone would have been for it; Rhode Island, Pennsylvania, and Virginia against it, Delaware, Maryland, and North Carolina, would have been divided.
Our body was little numerous, but very contentious. Day after day was wasted on the most unimportant questions. A member, one of those afflicted with the morbid rage of debate, of an ardent mind, prompt imagination, and copious flow of words, who heard with impatience any logic which was not his own, sitting near me on some occasion of a trifling but wordy debate, asked me how I could sit in silence, hearing so much false reasoning, which a word should refute? I observed to him, that to refute indeed was easy, but to silence impossible; that in measures brought forward by myself, I took the laboring oar, as was incumbent on me; but that in general, I was willing to listen; that if every sound argument or objection was used by some one or other of the numerous debaters, it was enough; if not, I thought it sufficient to suggest the omission, without going into a repetition of what had been already said by others: that this was a waste and abuse of the time and patience of the House, which could not be justified. And I believe, that if the members of deliberate bodies were to observe this course generally, they would do in a day, what takes them a week; and it is really more questionable, than may at first be thought, whether Bonaparte’s dumb legislature, which said nothing, and did much, may not be preferable to one which talks much, and does nothing. I served with General Washington in the legislature of Virginia, before the revolution, and, during it, with Dr. Franklin in Congress. I never heard either of them speak ten minutes at a time, nor to any but the main point, which was to decide the question. They laid their shoulders to the great points, knowing that the little ones would follow of themselves. If the present Congress errs in too much talking, how can it be otherwise, in a body to which the people send one hundred and fifty lawyers, whose trade it is, to question every thing, yield nothing, and talk by the hour? That one hundred and fifty lawyers should do business together, ought not to be expected. But to return again to our subject.
Those, who thought seven states competent to the ratification, being very restless under the loss of their motion, I proposed, on the third of January, to meet them on middle ground, and therefore moved a resolution, which premised, that there were but seven states present, who were unanimous for the ratification, but that they differed in opinion on the question of competency; that those however in the negative, were unwilling, that any powers which it might be supposed they possessed, should remain unexercised for the restoration of peace, provided it could be done, saving their good faith, and without importing any opinion of Congress, that seven states were competent, and resolving that the treaty be ratified so far as they had power; that it should be transmitted to our ministers, with instructions to keep it uncommunicated; to endeavor to obtain three months longer for exchange of ratifications; that they should be informed, that so soon as nine states shall be present, a ratification by nine shall be sent them: if this should get to them before the ultimate point of time for exchange, they were to use it, and not the other; if not, they were to offer the act of the seven states in exchange, informing them the treaty had come to hand while Congress was not in session, that but seven states were as yet assembled, and these had unanimously concurred in the ratification. This was debated on the third and fourth; and on the fifth, a vessel being to sail for England, from this port, (Annapolis), the House directed the President to write to our ministers accordingly.
January 14. Delegates from Connecticut having attended yesterday, and another from South Carolina coming in this day, the treaty was ratified without a dissenting voice; and three instruments of ratification were ordered to be made out, one of which was sent by Colonel Harmer, another by Colonel Franks, and the third transmitted to the Agent of Marine, to be forwarded by any good opportunity.
Congress soon took up the consideration of their foreign relations. They deemed it necessary to get their commerce placed, with every nation, on a footing as favorable as that of other nations; and for this purpose, to propose to each a distinct treaty of commerce. This act too would amount to an acknowledgment, by each, of our independence, and of our reception into the fraternity of nations; which, although as possessing our station of right, and, in fact, we would not condescend to ask, we were not unwilling to furnish opportunities for receiving their friendly salutations and welcome. With France, the United Netherlands, and Sweden, we had already treaties of commerce; but commissions were given for those countries also, should any amendments be thought necessary. The other states to which treaties were to be proposed, were England, Hamburg, Saxony, Prussia, Denmark, Russia, Austria, Venice, Rome, Naples, Tuscany, Sardinia, Genoa, Spain, Portugal, the Porte, Algiers, Tripoli, Tunis, and Morocco.
On the 7th of May, Congress resolved that a Minister Plenipotentiary should be appointed, in addition to Mr. Adams and Dr. Franklin, for negotiating treaties of commerce with foreign nations, and I was elected to that duty. I accordingly left Annapolis on the 11th, took with me my eldest daughter; then at Philadelphia (the two others being too young for the voyage), and proceeded to Boston, in quest of a passage. While passing through the different states, I made a point of informing myself of the state of the commerce of each, went on to New Hampshire with the same view, and returned to Boston. Thence I sailed on the 5th of July, in the Ceres, a merchant ship of Mr. Nathaniel Tracy, bound to Cowes. He was himself a passenger, and, after a pleasant voyage of nineteen days, from land to land, we arrived at Cowes on the 26th. I was detained there a few days by the indisposition of my daughter. On the 30th we embarked for Havre, arrived there on the 31st, left it on the 3rd of August, and arrived at Paris on the 6th. I called immediately on Dr. Franklin, at Passy, communicated to him our charge, and we wrote to Mr. Adams, then at the Hague, to join us at Paris.
Before I had left America, that is to say, in the year 1781, 1 had received a letter from M. de Marbois, of the French legation in Philadelphia, informing me, he had been instructed by his government to obtain such statistical accounts of the different states of our Union, as might be useful for their information; and addressing to me a number of queries relative to the state of Virginia. I had always made it a practice, whenever an opportunity occurred of obtaining any information of our country, which might be of use to me in any station, public or private, to commit it to writing. These memoranda were on loose papers, bundled up without order, and difficult of recurrence, when I had occasion for a particular one. I thought this a good occasion to embody their substance, which I did in the order of Mr. Marbois’ queries, so as to answer his wish, and to arrange them for my own use. Some friends, to whom they were occasionally communicated, wished for copies; but their volume rendering this too laborious by hand, I proposed to get a few printed for their gratification. I was asked such a price however, as exceeded the importance of the object. On my arrival at Paris, I found it could be done for a fourth of what I had been asked here. I therefore corrected and enlarged them, and had two hundred copies printed, under the title of ‘Notes on Virginia.’ I gave a very few copies to some particular friends in Europe, and sent the rest to my friends in America. An European copy, by the death of the owner, got into the hands of a bookseller, who engaged its translation, and when ready for the press, communicated his intentions and manuscript to me, suggesting that I should correct it, without asking any other permission for the publication. I never had seen so wretched an attempt at translation. Interverted, abridged, mutilated, and often reversing the sense of the original, I found it a blotch of errors from beginning to end. I corrected some of the most material, and, in that form, it was printed in French. A London bookseller, on seeing the translation, requested me to permit him to print the English original. I thought it best to do so, to let the world see that it was not really so bad as the French translation had made it appear. And this is the true history of that publication.
Mr. Adams soon joined us at Paris, and our first employment was to prepare a general form, to be proposed to such nations as were disposed to treat with us. During the negotiations for peace with the British Commissioner, David Hartley, our Commissioners had proposed, on the suggestion of Dr. Franklin, to insert an article, exempting from capture by the public or private armed ships, of either belligerent, when at war, all merchant vessels and their cargoes, employed merely in carrying on the commerce between nations. It was refused by England, and unwisely, in my opinion. For, in the case of a war with us, their superior commerce places infinitely more at hazard on the ocean, than ours; and, as hawks abound in proportion to game, so our privateers would swarm, in proportion to the wealth exposed to their prize, while theirs would be few, for want of subjects of capture. We inserted this article in our form, with a provision against the molestation of fishermen, husbandmen, citizens unarmed, and following their occupations in unfortified places, for the humane treatment of prisoners of war, the abolition of contraband of war, which exposes merchant vessels to such vexatious and ruinous detentions and abuses; and for the principle of free bottoms, free goods.
In a conference with the Count de Vergennes, it was thought better to leave to legislative regulation, on both sides, such modifications of our commercial intercourse, as would voluntarily flow from amicable dispositions. Without urging, we sounded the ministers of the several European nations, at the court of Versailles, on their dispositions towards mutual commerce, and the expediency of encouraging it by the protection of a treaty. Old Frederic, of Prussia, met us cordially, and without hesitation, and appointing the Baron de Thulemeyer, his minister at the Hague, to negotiate with us, we communicated to him our Projet, which, with little alteration by the King, was soon concluded. Denmark and Tuscany entered also into negotiations with us. Other powers appearing indifferent, we did not think it proper to press them. They seemed, in fact, to know little about us, but as rebels, who had been successful in throwing off the yoke of the mother country. They were ignorant of our commerce, which had been always monopolized by England, and of the exchange of articles it might offer advantageously to both parties. They were inclined, therefore, to stand aloof, until they could see better what relations might be usefully instituted with us. The negotiations, therefore, begun with Denmark and Tuscany, we protracted designedly, until our powers had expired; and abstained from making new propositions to others having no colonies; because our commerce being an exchange of raw for wrought materials, is a competent price for admission into the colonies of those possessing them; but were we to give it, without price, to others, all would claim it, without price, on the ordinary ground of gentis amicissimæ.
Mr. Adams, being appointed Minister Plenipotentiary of the United States to London, left us in June, and in July, 1785, Dr. Franklin returned to America, and I was appointed his successor at Paris. In February, 1786, Mr. Adams wrote to me, pressingly, to join him in London immediately, as he thought he discovered there some symptoms of better disposition towards us. Colonel Smith, his secretary of legation, was the bearer of his urgencies for my immediate attendance. I, accordingly, left Paris on the 1st of March, and, on my arrival in London, we agreed on a very summary form of treaty, proposing an exchange of citizenship for our citizens, our ships, and our productions generally, except as to office. On my presentation, as usual, to the King and Queen, at their levees, it was impossible for any thing to be more ungracious, than their notice of Mr. Adams and myself. I saw, at once, that the ulcerations of mind in that quarter left nothing to be expected on the subject of my attendance; and, on the first conference with the Marquis of Caermarthen, the Minister for foreign affairs, the distance and disinclination which he betrayed in his conversation, the vagueness and evasions of his answers to us, confirmed me in the belief of their aversion to have any thing to do with us. We delivered him, however, our Projet, Mr. Adams not despairing as much as I did of its effect. We afterwards, by one or more, notes, requested his appointment of an interview and conference, which, without directly declining, he evaded, by pretence of other pressing occupations for the moment. After staying there seven weeks, till within a few days of the expiration of our commission, I informed the minister, by note, that my duties at Paris required my return to that place, and that I should, with pleasure, be the bearer of any commands to his Ambassador there. He answered, that he had none, and, wishing me a pleasant journey, I left London the 26th, and arrived at Paris the 30th of April.
While in London, we entered into negotiations with the Chevalier Pinto, Ambassador of Portugal, at that place. The only article of difficulty between us was, a stipulation that our bread-stuff should be received in Portugal, in the form of flour as well as of grain. He approved of it himself, but observed that several nobles, of great influence at their court, were the owners of windmills in the neighborhood of Lisbon, which depended much for their profits on manufacturing our wheat, and that this stipulation would endanger the whole treaty. He signed it, however, and its fate was what he had candidly portended.
My duties, at Paris, were confined to a few objects; the receipt of our whale-oils, salted fish, and salted meats, on favorable terms; the admission of our rice on equal terms with that of Piedmont, Egypt, and the Levant; a mitigation of the monopolies of our tobacco by the farmers-general, and a free admission of our productions into their islands, were the principal commercial objects which required attention; and on these occasions, I was powerfully aided by all the influence and the energies of the Marquis de la Fayette, who proved himself equally zealous for the friendship and welfare of both nations; and, in justice, I must also say, that I found the government entirely disposed to befriend us on all occasions, and to yield us every indulgence, not absolutely injurious to themselves. The Count de Vergennes had the reputation with the diplomatic corps, of being wary and slippery in his diplomatic intercourse; and so he might be, with those whom he knew to be slippery, and double-faced themselves. As he saw that I had no indirect views, practised no subtleties, meddled in no intrigues, pursued no concealed object, I found him as frank, as honorable, as easy of access to reason, as any man with whom I had ever done business; and I must say the same for his successor, Montmorin, one of the most honest and worthy of human beings.
Our commerce, in the Mediterranean, was placed under early alarm, by the capture of two of our vessels and crews by the Barbary cruisers. I was very unwilling that we should acquiesce in the European humiliation, of paying a tribute to those lawless pirates, and endeavored to form an association of the powers subject to habitual depredations from them. I accordingly prepared, and proposed to their Ministers at Paris, for consultation with their governments, articles of a special confederation, in the following form.
‘Proposals for concerted operation among the powers at war with the piratical States of Barbary.
‘1. It is proposed, that the several powers at war with the piratical States of Barbary, or any two or more of them who shall be willing, shall enter into a convention to carry on their operations against those States, in concert, beginning with the Algerines.
‘2. This convention shall remain open to any other power, who shall, at any future time, wish to accede to it; the parties reserving the right to prescribe the conditions of such accession, according to the circumstances existing at the time it shall be proposed.
‘3. The object of the convention shall be to compel the piratical States to perpetual peace, without price, and to guaranty that peace to each other.
‘4. The operations for obtaining this peace shall be constant cruises on their coast, with a naval force now to be agreed on. It is not proposed, that this force shall be so considerable, as to be inconvenient to any party. It is believed, that half a dozen frigates, with as many tenders or xebecs, one half of which shall be in cruise, while the other half is at rest, will suffice.
‘5. The force agreed to be necessary, shall be furnished by the parties, in certain quotas, now to be fixed; it being expected, that each will be willing to contribute, in such proportion as circumstances may render reasonable.
‘6. As miscarriages often proceed from the want of harmony among officers of different nations, the parties shall now consider and decide, whether it will not be better to contribute their quotas in money, to be employed in fitting out and keeping on duty a single fleet of the force agreed on.
‘7. The difficulties and delays, too, which will attend the management of these operations, if conducted by the parties themselves separately, distant as their courts may be from one another, and incapable of meeting in consultation, suggest a question, whether it will not be better for them to give full powers, for that purpose, to their Ambassadors, or other Ministers resident at some one court of Europe, who shall form a Committee, or Council, for carrying this convention into effect; wherein, the vote of each member shall be computed in proportion to the quota of his sovereign, and the majority so computed, shall prevail in all questions within the view of this convention. The court of Versailles is proposed, on account of its neighborhood to the Mediterranean, and because all those powers are represented there, who are likely to become parties to this convention.
‘8. To save to that Council the embarrassment of personal solicitations for office, and to assure the parties, that their contributions will be applied solely to the object for which they are destined, there shall be no establishment of officers for the said Council, such as Commissioners, Secretaries, or any other kind, with either salaries or perquisites, nor any other lucrative appointments, but such whose functions are to be exercised on board the said vessels.
‘9. Should war arise between any two of the parties to this convention, it shall not extend to this enterprise, nor interrupt it; but as to this, they shall be reputed at peace.
‘10. When Algiers shall be reduced to peace, the other piratical States, if they refuse to discontinue their piracies, shall become the objects of this convention, either successively or together, as shall seem best.
‘11. Where this convention would interfere with treaties actually existing between any of the parties and the said States of Barbary, the treaty shall prevail, and such party shall be allowed to withdraw from the operations against that state.’
Spain had just concluded a treaty with Algiers, at the expense of three millions of dollars, and did not like to relinquish the benefit of that, until the other party should fail in their observance of it. Portugal, Naples, the Two Sicilies, Venice, Malta, Denmark, and Sweden were favorably disposed to such an association; but their representatives at Paris expressed apprehensions that France would interfere, and, either openly or secretly, support the Barbary powers; and they required, that I should ascertain the dispositions of the Count de Vergennes on the subject. I had before taken occasion to inform him of what we were proposing, and, therefore, did not think it proper to insinuate any doubt of the fair conduct of his government; but stating our propositions, I mentioned the apprehensions entertained by us that England would interfere in behalf of those piratical governments. ‘She dares not do it,’ said he. I pressed it no further. The other Agents were satisfied with this indication of his sentiments, and nothing was now wanting to bring it into direct and formal consideration, but the assent of our government, and their authority to make the formal proposition. I communicated to them the favorable prospect of protecting our commerce from the Barbary depredations, and for such a continuance of time, as, by an exclusion of them from the sea, to change their habits and characters, from a predatory to an agricultural people: towards which, however, it was expected they would contribute a frigate, and its expenses, to be in constant cruise. But they were in no condition to make any such engagement. Their recommendatory powers for obtaining contributions, were so openly neglected by the several states, that they declined an engagement, which they were conscious they could not fulfil with punctuality; and so it fell through.
[In the original MS., the paragraph ending with ‘fell
through,’ terminates page 81; between this page and the
next, there is stitched in a leaf of old writing,
constituting a memorandum, whereof note G, in the Appendix,
is a copy.]
In 1786, while at Paris, I became acquainted with John Ledyard, of Connecticut, a man of genius, of some science, and of fearless courage and enterprise. He had accompanied Captain Cook in his voyage to the Pacific, had distinguished himself on several occasions by an unrivalled intrepidity, and published an account of that voyage, with details unfavorable to Cook’s deportment towards the savages, and lessening our regrets at his fate; Ledyard had come to Paris, in the hope of forming a company to engage in the fur-trade of the Western coast of America. He was disappointed in this, and being out of business, and of a roaming, restless character, I suggested to him the enterprise of exploring the Western part of our continent, by passing through St. Petersburg to Kamtschatka, and procuring a passage thence in some of the Russian vessels to Nootka sound, whence he might make his way across the continent to the United States; and I undertook to have the permission of the Empress of Russia solicited. He eagerly embraced the proposition, and M. de Semoulin, the Russian Ambassador, and more particularly Baron Grimm, the special correspondent of the Empress, solicited her permission for him to pass through her dominions, to the Western coast of America. And here I must correct a material error, which I have committed in another place, to the prejudice of the Empress. In writing some notes of the life of Captain Lewis, prefixed to his ‘Expedition to the Pacific,’ I stated, that the Empress gave the permission asked, and afterwards retracted it. This idea, after a lapse of twenty-six years, had so insinuated itself into my mind, that I committed it to paper, without the least suspicion of error. Yet I find, on returning to my letters of that date, that the Empress refused permission at once, considering the enterprise as entirely chimerical. But Ledyard would not relinquish it, persuading himself, that, by proceeding to St. Petersburg, he could satisfy the Empress of its practicability, and obtain her permission. He went accordingly, but she was absent on a visit to some distant part of her dominions, and he pursued his course to within two hundred miles of Kamtschatka, where he was overtaken by an arrest from the Empress, brought back to Poland, and there dismissed. I must, therefore, in justice, acquit the Empress of ever having for a moment countenanced, even by the indulgence of an innocent passage through her territories, this interesting enterprise.
The pecuniary distresses of France produced this year a measure, of which there had been no example for near two centuries; and the consequences of which, good and evil, are not yet calculable. For its remote causes, we must go a little back.
Celebrated writers of France and England had already sketched good principles on the subject of government: yet the American Revolution seems first to have awakened the thinking part of the French nation in general from the sleep of despotism in which they were sunk. The officers, too, who had been to America, were mostly young men, less shackled by habit and prejudice, and more ready to assent to the suggestions of common sense, and feeling of common rights, than others. They came back with new ideas and impressions. The press, notwithstanding its shackles, began to disseminate them; conversation assumed new freedoms; politics became the theme of all societies, male and female, and a very extensive and zealous party was formed, which acquired the appellation of the Patriotic party, who, sensible of the abusive government under which they lived, sighed for occasions for reforming it. This party comprehended all the honesty of the kingdom, sufficiently at leisure to think, the men of letters, the easy Bourgeois, the young nobility, partly from reflection, partly from mode; for these sentiments became matter of mode, and, as such, united most of the young women to the party. Happily for the nation, it happened, at the same moment, that the dissipations of the queen and court, the abuses of the pension-list, and dilapidations in the administration of every branch of the finances, had exhausted the treasures and credit of the nation, insomuch, that its most necessary functions were paralyzed. To reform these abuses would have overset the Minister; to impose new taxes by the authority of the king, was known to be impossible, from the determined opposition of the Parliament to their enregistry. No resource remained, then, but to appeal to the nation. He advised, therefore, the call of an Assembly of the most distinguished characters of the nation, in the hope, that, by promises of various and valuable improvements in the organization and regimen of the government, they would be induced to authorize new taxes, to control the opposition of the Parliament, and to raise the annual revenue to the level of expenditures. An Assembly of Notables, therefore, about one hundred and fifty in number, named by the King, convened on the 22nd of February. The Minister (Calonne) stated to them, that the annual excess of expenses beyond the revenue, when Louis XVI. came to the throne, was thirty-seven millions of livres; that four hundred and forty millions had been borrowed to re-establish the navy; that the American war had cost them fourteen hundred and forty millions (two hundred and fifty-six millions of dollars), and that the interest of these sums, with other increased expenses, had added forty millions more to the annual deficit. (But a subsequent and more candid estimate made it fifty-six millions.) He proffered them an universal redress of grievances, laid open those grievances fully, pointed out sound remedies, and, covering his canvass with objects of this magnitude, the deficit dwindled to a little accessory, scarcely attracting attention. The persons chosen, were the most able and independent characters in the kingdom, and their support, if it could be obtained, would be enough for him. They improved the occasion for redressing their grievances, and agreed that the public wants should be relieved; but went into an examination of the causes of them. It was supposed that Calonne was conscious that his accounts could not bear examination; and it was said, and believed, that he asked of the King, to send four members to the Bastile, of whom the Marquis de la Fayette was one, to banish twenty others, and two of his Ministers. The King found it shorter to banish him. His successor went on in full concert with the Assembly. The result was an augmentation of the revenue, a promise of economies in its expenditure, of an annual settlement of the public accounts before a council, which the Comptroller, having been heretofore obliged to settle only with the King in person, of course never settled at all; an acknowledgment that the King could not lay a new tax, a reformation of the Criminal laws, abolition of torture, suppression of corvees, reformation of the gabelles, removal of the interior custom-houses, free commerce of grain, internal and external, and the establishment of Provincial Assemblies; which, altogether, constituted a great mass of improvement in the condition of the nation. The establishment of the Provincial Assemblies was, in itself, a fundamental improvement. They would be, of the choice of the people, one third renewed every year, in those provinces where there are no states, that is to say, over about three fourths of the kingdom. They would be partly an Executive themselves, and partly an Executive Council to the Intendant, to whom the executive power, in his province, had been heretofore entirely delegated. Chosen by the people, they would soften the execution of hard laws, and, having a right of representation to the King, they would censure bad laws, suggest good ones, expose abuses, and their representations, when united, would command respect. To the other advantages, might be added the precedent itself of calling the Assemblée des Notables, which would perhaps grow into habit. The hope was, that the improvements thus promised would be carried into effect; that they would be maintained during the present reign, and that that would be long enough for them to take some root in the constitution, so that they might come to be considered as a part of that, and be protected by time, and the attachment of the nation.
The Count de Vergennes had died a few days before the meeting of the Assembly, and the Count de Montmorin had been named Minister of foreign affairs, in his place. Villedeuil succeeded Calonne, as Comptroller General, and Lomenie de Brienne, Archbishop of Toulouse, afterwards of Sens, and ultimately Cardinal Lomenie, was named Minister principal, with whom the other Ministers were to transact the business of their departments, heretofore done with the King in person; and the Duke de Nivernois, and M. de Malesherbes, were called to the Council. On the nomination of the Minister principal, the Marshals de Segur and de Castries retired from the departments of War and Marine, unwilling to act subordinately, or to share the blame of proceedings taken out of their direction. They were succeeded by the Count de Brienne, brother of the Prime Minister, and the Marquis de la Luzerne, brother to him who had been Minister in the United States.
A dislocated wrist, unsuccessfully set, occasioned advice from my surgeon, to try the mineral waters of Aix, in Provence, as a corroborant. I left Paris for that place therefore, on the 28th of February, and proceeded up the Seine, through Champagne and Burgundy, and down the Rhone through the Beaujolais by Lyons, Avignon, Nismes, to Aix; where, finding on trial no benefit from the waters, I concluded to visit the rice country of Piedmont, to see if any thing might be learned there, to benefit the rivalship of our Carolina rice with that, and thence to make a tour of the seaport towns of France, along its Southern and Western coast, to inform myself, if any thing could be done to favor our commerce with them. From Aix, therefore, I took my route by Marseilles, Toulon, Hieres, Nice, across the Col de Tende, by Coni, Turin, Vercelli, Novara, Milan, Pavia, Novi, Genoa. Thence, returning along the coast by Savona. Noli, Albenga, Oneglia, Monaco, Nice, Antibes, Frejus, Aix, Marseilles, Avignon, Nismes, Montpellier, Frontignan, Sette, Agde, and along the canal of Languedoc, by Beziers, Narbonne, Carcassonne, Castelnaudari, through the Souterrain of St. Feriol, and back by Castelnaudari, to Toulouse; thence to Montauban, and down the Garonne by Langon to Bordeaux. Thence to Rochefort, la Rochelle, Nantes, L’Orient; then back by Rennes to Nantes, and up the Loire by Angers, Tours, Amboise, Blois, to Orleans, thence direct to Paris, where I arrived on the 10th of June. Soon after my return from this journey, to wit, about the latter part of July, I received my younger daughter, Maria, from Virginia, by the way of London, the youngest having died some time before.
The treasonable perfidy of the Prince of Orange, Stadtholder and Captain General of the United Netherlands, in the war which England waged against them, for entering into a treaty of commerce with the United States, is known to all. As their Executive officer, charged with the conduct of the war, he contrived to baffle all the measures of the States General, to dislocate all their military plans, and played false into the hands of England against his own country, on every possible occasion, confident in her protection, and in that of the King of Prussia, brother to his Princess. The States General, indignant at this patricidal conduct, applied to France for aid, according to the stipulations of the treaty, concluded with her in ‘85. It was assured to them readily, and in cordial terms, in a letter from the Count de Vergennes, to the Marquis de Verac, Ambassador of France at the Hague, of which the following is an extract.
‘Extrait de la dépêche de Monsieur le Comte de Vergennes à Monsieur le Marquis de Verac, Ambassadeurde France à la Haye, du ler Mars, 1786.
‘Le Roi concourrera, autant qu’il sera en son pouvoir, au succès de la chose, et vous inviterez, de sa part, les Patriotes de lui communiquer leurs vues, leurs plans, et leurs envies. Vous les assurerez, que le roi prend un interêt véritable à leurs personnes cornme à leur cause, et qu’ils peuvent compter sur sa protection. Us doivent y compter d’autant plus, Monsieur, que nous ne dissimulons pas, que si Monsieur le Stadtholder reprend son ancienne influence, le système Anglois ne tardera pas de prévaloir, et que notre alliance deviendroit un être de raison. Les Patriotes sentiront facilement, que cette position seroit incompatible avec la dignité, comme avec la considération de sa Majesté. Mais dans le cas, Monsieur, ou les chefs des Patriotes auroient à craindre une scission, ils auroient le temps suffisant peur ramener ceux de leurs amis, que les Anglomanes ont égarés, et préparer les choses, de maniere que la question de nouveau mise en délibération, soit decidée selon leurs desirs. Dans cette hypothèse, le roi vous autorise à agir de concert avec eux, de suivre la direction qu’ils jugeront devoir vous donner, et d’employer tous les moyens pour augmenter le nombre des partisans de la bonne cause. Il me reste, Monsieur, de vous parler de la sureté personelle des Patriotes. Vous les assurerez, que dans tout état de cause, le roi les prend sous sa protection immédiate, et vous ferez connoître, partout où vous le jugerez nécessaire, que sa Majesté regarderoit comme une offense personelle, tout ce qu’on entreprenderoit contre leur liberté. Il est á presumer que ce langage, tenu avec énergie, en imposera á l’audace des Anglomanes, et que Monsieur le Prince de Nassau croira courir quelque risque en provoquant le ressentiment de sa Majesté.’ *
[*Extract from the despatch of the Count de Vergennes, to
the Marquis de Verac, Ambassador from France, at the Hague,
dated March 1, 1788.
‘The King will give his aid, as far as may be in his power,
towards the success of the affair, and you will, on his
part, invite the Patriots to communicate to him their views,
their plans, and their discontents. You may assure them,
that the King takes a real interest in themselves, as well
as their cause, and that they may rely upon his protection.
On this they may place the greater dependence, as we do not
conceal, that if the Stadtholder resumes his former
influence, the English system will soon prevail, and our
alliance become a mere affair of the imagination. The
Patriots will readily feel, that this position would be
incompatible both with the dignity and consideration of his
Majesty. But in case the chief of the Patriots should have
to fear a division, they would have time sufficient to
reclaim those whom the Anglomaniacs had misled, and to
prepare matters in such a manner, that the question when
again agitated, might be decided according to their wishes.
In such a hypothetical case, the King authorizes you to act
in concert with them, to pursue the direction which they may
think proper to give you, and to employ every means to
augment the number of the partisans of the good cause. It
remains for me to speak of the personal security of the
Patriots. You may assure them, that under every
circumstance, the King will take them under his immediate
protection, and you will make known wherever you may judge
necessary, that his Majesty will regard, as a personal
offence, every undertaking against their libeity. It is to
be presumed that this language, energetically maintained,
may have some effect on the audacity of the Anglomaniacs,
and that the Prince de Nassau will feel that he runs some
risk in provoking the resentment of his Majesty.‘]
This letter was communicated by the Patriots to me, when at Amsterdam, in 1788, and a copy sent by me to Mr. Jay, in my letter to him of March 16, 1788.
The object of the Patriots was, to establish a representative and republican government. The majority of the States General were with them, but the majority of the populace of the towns was with the Prince of Orange; and that populace was played off with great effect by the triumvirate of * * * Harris, the English Ambassador, afterwards Lord Malmesbury, the Prince of Orange, a stupid man, and the Princess, as much a man as either of her colleagues, in audaciousness, in enterprise, and in the thirst of domination. By these, the mobs of the Hague were excited against the members of the States General; their persons were insulted, and endangered in the streets; the sanctuary of their houses was violated; and the Prince, whose function and duty it was to repress and punish these violations of order, took no steps for that purpose. The States General, for their own protection, were therefore obliged to place their militia under the command of a Committee. The Prince filled the courts of London and Berlin with complaints at this usurpation of his prerogatives, and, forgetting that he was but the first servant of a Republic, marched his regular troops against the city of Utrecht, where the States were in session. They were repulsed by the militia. His interests now became marshaled with those of the public enemy, and against his own country. The States, therefore, exercising their rights of sovereignty, deprived him of all his powers. The great Frederic had died in August, ‘86. He had never intended to break with France in support of the Prince of Orange. During the illness of which he died, he had, through the Duke of Brunswick, declared to the Marquis de la Fayette, who was then at Berlin, that he meant not to support the English interest in Holland: that he might assure the government of France, his only wish was, that some honorable place in the Constitution should be reserved for the Stadtholder and his children, and that he would take no part in the quarrel, unless an entire abolition of the Stadtholderate should be attempted. But his place was now occupied by Frederic William, his great nephew, a man of little understanding, much caprice, and very inconsiderate: and the Princess, his sister, although her husband was in arms against the legitimate authorities of the country, attempting to go to Amsterdam, for the purpose of exciting the mobs of that place, and being refused permission to pass a military post on the way, he put the Duke of Brunswick at the head of twenty thousand men, and made demonstrations of marching on Holland. The King of France hereupon declared, by his Chargé des Affaires in Holland, that if the Prussian troops continued to menace Holland with an invasion, his Majesty, in quality of Ally, was determined to succor that province. In answer to this, Eden gave official information to Count Montmorin, that England must consider as at an end, its convention with France relative to giving notice of its naval armaments, and that she was arming generally. War being now imminent, Eden, since Lord Aukland, questioned me on the effect of our treaty with France, in the case of a war, and what might be our dispositions. I told him frankly, and without hesitation, that our dispositions would be neutral, and that I thought it would be the interest of both these powers that we should be so; because, it would relieve both from all anxiety as to feeding their West India islands; that, England, too, by suffering us to remain so, would avoid a heavy land war on our Continent, which might very much cripple her proceedings elsewhere; that our treaty, indeed, obliged us to receive into our ports the armed vessels of France, with their prizes, and to refuse admission to the prizes made on her by her enemies: that there was a clause, also, by which we guaranteed to France her American possessions, which might perhaps force us into the war, if these were attacked. ‘Then it will be war,’ said he, ‘for they will assuredly be attacked.’ Liston, at Madrid, about the same time, made the same enquiries of Carmichael. The government of France then declared a determination to form a camp of observation at Givet, commenced arming her marine, and named the Bailli de Suffrein their Generalissimo on the Ocean. She secretly engaged, also, in negotiations with Russia, Austria, and Spain, to form a quadruple alliance. The Duke of Brunswick having advanced to the confines of Holland, sent some of his officers to Givet, to reconnoitre the state of things there, and report them to him. He said afterwards, that ‘if there, had been only a few tents at that place, he should not have advanced further, for that the king would not, merely for the interest of his sister, engage in a war with France.’ But, finding that there was not a single company there, he boldly entered the country, took their towns as fast as he presented himself before them, and advanced on Utrecht. The States had appointed the Rhingrave of Salm their Commander in chief; a Prince without talents, without courage, and without principle. He might have held out in Utrecht, for a considerable time, but he surrendered the place without firing a gun, literally ran away and hid himself, so that for months it was not known what was become of him. Amsterdam was then attacked, and capitulated. In the mean time, the negotiations for the quadruple alliance were proceeding favorably; but the secrecy with which they were attempted to be conducted, was penetrated by Fraser, Chargé des Affaires of England at St. Petersburg, who instantly notified his court, and gave the alarm to Prussia. The King saw at once what would be his situation, between the jaws of France, Austria, and Russia. In great dismay, he besought the court of London not to abandon him, sent Alvensleben to Paris to explain and soothe; and England, through the Duke of Dorset and Eden, renewed her conferences for accommodation. The Archbishop, who shuddered at the idea of war, and preferred a peaceful surrender of right, to an armed vindication of it, received them with open arms, entered into cordial conferences, and a declaration, and counter-declaration, were cooked up at Versailles, and sent to London for approbation. They were approved there, reached Paris at one o’clock of the 27th, and were signed that night at Versailles. It was said and believed at Paris, that M. de Montrnorin, literally ‘pleuroit cotnrae un enfant,’ when obliged to sign this counter-declaration; so distressed was he by the dishonor of sacrificing the Patriots, after assurances so solemn of protection, and absolute encouragement to proceed. The Prince of Orange was reinstated in all his powers, now become regal. A great emigration of the Patriots took place; all were deprived of office, many exiled, and their property confiscated. They were received in France, and subsisted, for some time, on her bounty. Thus fell Holland, by the treachery of her Chief, from her honorable independence, to become a province of England; and so, also, her Stadtholder, from the high station of the first citizen of a free Republic, to be the servile Viceroy of a foreign Sovereign. And this was effected by a mere scene of bullying and demonstration; not one of the parties, France, England, or Prussia, having ever really meant to encounter actual war for the interest of the Prince of Orange. But it had all the effect of a real and decisive war.
Our first essay, in America, to establish a federative government had fallen, on trial, very short of its object. During the war of Independence, while the pressure of an external enemy hooped us together, and their enterprises kept us necessarily on the alert, the spirit of the people, excited by danger, was a supplement to the Confederation, and urged them to zealous exertions, whether claimed by that instrument or not; but, when peace and safety were restored, and every man became engaged in useful and profitable occupation, less attention was paid to the calls of Congress. The fundamental defect of the Confederation was, that Congress was not authorized to act immediately on the people, and by its own officers. Their power was only requisitory, and these requisitions were addressed to the several Legislatures, to be by them carried into execution, without other coercion than the moral principle of duty. This allowed, in fact, a negative to every legislature, on every measure proposed by Congress; a negative so frequently exercised in practice, as to benumb the action of the Federal government, and to render it inefficient in its general objects, and more especially in pecuniary and foreign concerns. The want, too, of a separation of the Legislative, Executive, and Judiciary functions, worked disadvantageously in practice. Yet this state of things afforded a happy augury of the future march of our Confederacy, when it was seen that the good sense and good dispositions of the people, as soon as they perceived the incompetence of their first compact, instead of leaving its correction to insurrection and civil war, agreed, with one voice, to elect deputies to a general Convention, who should peaceably meet and agree on such a Constitution as ‘would ensure peace, justice, liberty, the common defence, and general welfare.’
This Convention met at Philadelphia on the 25th of May, ‘87. It sat with closed doors, and kept all its proceedings secret, until its dissolution on the 17th of September, when the results of its labors were published all together. I received a copy, early in November, and read and contemplated its provisions with great satisfaction. As not a member of the Convention, however, nor probably a single citizen of the Union, had approved it in all its parts, so I, too, found articles which I thought objectionable. The absence of express declarations ensuring freedom of religion, freedom of the press, freedom of the person under the uninterrupted protection of the habeas corpus and trial by jury in civil, as well as in criminal cases, excited my jealousy; and the re-eligibility of the President for life, I quite disapproved. I expressed freely, in letters to my friends, and most particularly to Mr. Madison and General Washington, my approbations and objections. How the good should be secured, and the ill brought to rights, was the difficulty. To refer it back to a new Convention, might endanger the loss of the whole. My first idea was, that the nine states first acting, should accept it unconditionally, and thus secure what in it was good, and that the four last should accept on the previous condition, that certain amendments should be agreed to; but a better course was devised, of accepting the whole, and trusting that the good sense and honest intentions of our citizens would make the alterations which should be deemed necessary. Accordingly, all accepted, six without objection, and seven with recommendations of specified amendments. Those respecting the press, religion, and juries, with several others, of great value, were accordingly made; but the habeas corpus was left to the discretion of Congress, and the amendment against the re-eligibility of the President was not proposed. My fears of that feature were founded on the importance of the office, on the fierce contentions it might excite among ourselves, if continuable for life, and the dangers of interference, either with money or arms, by foreign nations, to whom the choice of an American President might become interesting. Examples of this abounded in history; in the case of the Roman Emperors, for instance; of the Popes, while of any significance; of the German Emperors; the Kings of Poland, and the Deys of Barbary. I had observed, too, in the feudal history, and in the recent instance, particularly, of the Stadtholder of Holland, how easily offices, or tenures for life, slide into inheritances. My wish, therefore, was that the President should be elected for seven years, and be ineligible afterwards. This term I thought sufficient to enable him, with the concurrence of the Legislature, to carry though and establish any system of improvement he should propose for the general good. But the practice adopted, I think, is better, allowing his continuance for eight years, with a liability to be dropped at half way of the term, making that a period of probation. That his continuance should be restrained to seven years, was the opinion of the Convention at an earlier stage of its session, when it voted that term, by a majority of eight against two, and by a simple majority, that he should be ineligible a second time. This opinion was confirmed by the House so late as July 26, referred to the Committee of detail, reported favorably by them, and changed to the present form by final vote, on the last day, but one only, of their session. Of this change, three states expressed their disapprobation; New York, by recommending an amendment, that the President should not be eligible a third time, and Virginia and North Carolina, that he should not be capable of serving more than eight, in any term of sixteen years; and although this amendment has not been made in form, yet practice seems to have established it. The example of four Presidents, voluntarily retiring at the end of their eighth year, and the progress of public opinion, that the principle is salutary, have given it in practice the force of precedent and usage; insomuch, that should a President consent to be a candidate for a third election, I trust he would be rejected, on this demonstration of ambitious views.
But there was another amendment, of which none of us thought at the time, and in the omission of which, lurks the germ that is to destroy this happy combination of National powers, in the general government, for matters of National concern, and independent powers in the States, for what concerns the States severally. In England, it was a great point gained at the Revolution, that the commissions of the Judges, which had hitherto been during pleasure, should thenceforth be made during good behavior. A Judiciary, dependant on the will of the King, had proved itself the most oppressive of all tools in the hands of that magistrate. Nothing, then, could be more salutary, than a change there, to the tenure of good behavior; and the question of good behavior, left to the vote of a simple majority in the two Houses of Parliament. Before the Revolution, we were all good English Whigs, cordial in their free principles, and in their jealousies of their Executive magistrate. These jealousies are very apparent, in all our state Constitutions; and, in the General government in this instance, we have gone even beyond the English caution, by requiring a vote of two thirds, in one of the Houses, for removing a Judge; a vote so impossible, where * any defence is made, before men of ordinary prejudices and passions, that our Judges are effectually independent of the nation. But this ought not to be. I would not, indeed, make them dependant on the Executive authority, as they formerly were in England; but I deem it indispensable to the continuance of this government, that they should be submitted to some practical and impartial control; and that this, to be impartial, must be compounded of a mixture of State and Federal authorities. It is not enough, that honest men are appointed Judges. All know the influence of interest on the mind of man, and how unconsciously his judgment is warped by that influence. To this bias add that of the esprit de corps, of their peculiar maxim and creed, that ‘it is the office of a good Judge to enlarge his jurisdiction,’ and the absence of responsibility; and how can we expect impartial decision between the General government, of which they are themselves so eminent a part, and an individual state, from which they have nothing to hope or fear? We have seen, too, that, contrary to all correct example, they are in the habit of going out of the question before them, to throw an anchor ahead, and grapple further hold for future advances of power. They are then, in fact, the corps of sappers and miners, steadily working to undermine the independent rights of the states, and to consolidate all power in the hands of that government, in which they have so important a freehold estate. But it is not by the consolidation, or concentration of powers, but by their distribution, that good government is effected. Were not this great country already divided into states, that division must be made, that each might do for itself what concerns itself directly, and what it can so much better do than a distant authority. Every state again is divided into counties, each to take care of what lies within its local bounds; each county again into townships or wards, to manage minuter details; and every ward into farms, to be governed each by its individual proprietor. Were we directed from Washington when to sow, and when to reap, we should soon want bread. It is by this partition of cares, descending in gradation from general to particular, that the mass of human affairs may be best managed, for the good and prosperity of all. I repeat, that I do not charge the judges with wilful and ill-intentioned error; but honest error must be arrested, where its toleration leads to public ruin. As, for the safety of society, we commit honest maniacs to Bedlam, so judges should be withdrawn from their bench, whose erroneous biases are leading us to dissolution. It may, indeed, injure them in fame or in fortune; but it saves the Republic, which is the first and supreme law.
* In the impeachment of Judge Pickering, of New Hampshire, a
habitual and maniac drunkard, no defence was made. Had there
been, the party vote of more than one third of the Senate
would have acquitted him.
Among the debilities of the government of the Confederation, no one was more distinguished or more distressing, than the utter impossibility of obtaining, from the States, the monies necessary for the payment of debts, or even for the ordinary expenses of the government. Some contributed a little, some less, and some nothing; and the last, furnished at length an excuse for the first, to do nothing also. Mr. Adams, while residing at the Hague, had a general authority to borrow what sums might be requisite, for ordinary and necessary expenses. Interest on the public debt, and the maintenance of the diplomatic establishment in Europe, had been habitually provided in this way. He was now elected Vice-President of the United States, was soon to return to America, and had referred our bankers to me for future counsel, on our affairs in their hands. But I had no powers, no instructions, no means, and no familiarity with the subject. It had always been exclusively under his management, except as to occasional and partial deposites in the hands of Mr. Grand, banker in Paris, for special and local purposes. These last had been exhausted for some time, and I had fervently pressed the Treasury board to replenish this particular deposite, as Mr. Grand now refused to make further advances. They answered candidly, that no funds could be obtained until the new government should get into action, and have time to make its arrangements. Mr. Adams had received his appointment to the court of London, while engaged at Paris, with Dr. Franklin and myself, in the negotiations under our joint commissions. He had repaired thence to London, without returning to the Hague, to take leave of that government. He thought it necessary, however, to do so now, before he should leave Europe, and accordingly went there. I learned his departure from London, by a letter from Mrs. Adams, received on the very day on which he would arrive at the Hague. A consultation with him, and some provision for the future, was indispensable, while we could yet avail ourselves of his powers; for when they would be gone, we should be without resource. I was daily dunned by a Company who had formerly made a small loan to the United States, the principal of which was now become due; and our bankers in Amsterdam had notified me, that the interest on our general debt would be expected in June; that if we failed to pay it, it would be deemed an act of bankruptcy, and would effectually destroy the credit of the Upited States, and all future prospects of obtaining money there; that the loan they had been authorized to open, of which a third only was filled, had now ceased to get forward, and rendered desperate that hope of resource. I saw that there was not a moment to lose, and set out for the Hague on the 2nd morning after receiving the information of Mr. Adams’s journey. I went the direct road by Louvres, Senlis, Roye, Pont St. Maxence, Bois le Due, Gournay, Peronne, Cambray, Bouchain, Valenciennes, Mons, Bruxelles, Malines, Antwerp, Mordick, and Rotterdam, to the Hague, where I happily found Mr. Adams. He concurred with me at once in opinion, that something must be done, and that we ought to risk ourselves on doing it without instructions, to save the credit of the United States. We foresaw, that before the new government could be adopted, assembled, establish its financial system, get the money into the Treasury, and place it in Europe, considerable time would elapse; that, therefore, we had better provide at once for the years ‘88, ‘89, and ‘90, in order to place our government at its ease, and our credit in security, during that trying interval. We set out, therefore, by the way of Leyden, for Amsterdam, where we arrived on the 10th, I had prepared an estimate, showing, that

Florins.
There would be necessary for the year ‘88—531,937-10 ‘89—538,540 ‘90—473,540 —————————— Total, 1,544,017-10
Florins.
To meet this, the bankers had in hand, 79,268-2-8 and the unsold bonds would yield, 542,800
622,068-2-8
Leaving a deficit of 921,949-7-4
We proposed then to borrow a million, yielding 920,000
Which would leave a small deficiency of 1,949-7-4
Mr. Adams accordingly executed 1000 bonds, for 1000 florins each, and deposited them in the hands of our bankers, with instructions, however, not to issue them until Congress should ratify the measure. This done, he returned to London, and I set out for Paris; and, as nothing urgent forbade it, I determined to return along the banks of the Rhine, to Strasburg, and thence strike off to Paris. I accordingly left Amsterdam on the 30th of March, and proceeded by Utrecht, Nimegnen, Cleves, Duysberg, Dusseldorf, Cologne, Bonne, Coblentz, Nassau, Hocheim, Frankfort, and made an excursion to Hanau, then to Mayence, and another excursion to Rudesheim, and Johansberg; then by Oppenheim, Worms, and Manheim, making an excursion to Heidelberg, then by Spire, Carlsruhe, Rastadt, and Kelh, to Sfrasburg, where I arrived April the 16th, and proceeded again on the 18th, by Phalsbourg, Fenestrange, Dieuze, Moyenvie, Nancy, Toul, Ligny, Barleduc, St. Diziers, Vitry, Chalons sur Marne, Epernay, Chateau Thierri, Meaux, to Paris, where I arrived on the 23d of April: and I had the satisfaction to reflect, that by this journey, our credit was secured, the new government was placed at ease for two years to come, and that, as well as myself, relieved from the torment of incessant duns, whose just complaints could not be silenced by any means within our power.
A Consular Convention had been agreed on in ‘84, between Dr. Franklin and the French government, containing several articles, so entirely inconsistent with the laws of the several states, and the general spirit of our citizens, that Congress withheld their ratification, and sent it back to me, with instructions to get those articles expunged, or modified, so as to render them compatible with our laws. The Minister unwillingly released us from these concessions, which, indeed, authorized the exercise of powers very offensive in a free state. After much discussion, the Convention was reformed in a considerable degree, and was signed by the Count Montmorin and myself, on the 14th of November, ‘88; not indeed, such as I would have wished; but such as could be obtained with good humor and friendship.
On my return from Holland, I found Paris as I had left it, still in high fermentation. Had the Archbishop, on the close of the Assembly of Notables, immediately carried into operation the measures contemplated, it was believed they would all have been registered by the Parliament; but he was slow, presented his edicts, one after another, and at considerable intervals, which gave time for the feelings excited by the proceedings of the Notables to cool off, new claims to be advanced, and a pressure to arise for a fixed constitution, not subject to changes at the will of the King. Nor should we wonder at this pressure, when we consider the monstrous abuses of power under which this people were ground to powder; when we pass in review the weight of their taxes, and the inequality of their distribution; the oppressions of the tythes, the failles, the corvees, the gabelles, the farms and the barriers; the shackles on commerce by monopolies; on industry by guilds and corporations; on the freedom of conscience, of thought, and of speech; on the freedom of the press by the censure; and of the person by lettres de cachet; the cruelty of the criminal code generally; the atrocities of the rack; the venality of Judges, and their partialities to the rich; the monopoly of military honors by the noblesse; the enormous expenses of the Queen, the Princes, and the Court; the prodigalities of pensions; and the riches, luxury, indolence, and immorality of the Clergy. Surely under such a mass of misrule and oppression, a people might justly press for thorough reformation, and might even dismount their roughshod riders, and leave them to walk, on their own legs. The edicts, relative to the corvees and free circulation of grain, were first presented to the Parliament and registered; but those for the impot territorial, and stamp tax, offered some time after, were refused by the Parliament, which proposed a call of the States General, as alone competent to their authorization. Their refusal produced a bed of justice, and their exile to Troyes. The Advocates, however, refusing to attend them, a suspension in the administration of justice took place. The Parliament held out for awhile, but the ennui of their exile and absence from Paris, began at length to be felt, and some dispositions for compromise to appear. On their consent, therefore, to prolong some of the former taxes, they were recalled from exile. The King met them in session, November 19, ‘87, promised to call the States General in the year ‘92, and a majority expressed their assent to register an edict for successive and annual loans from 1788 to ‘92; but a protest being entered by the Duke of Orleans, and this encouraging others in a disposition to retract, the King ordered peremptorily the registry of the edict, and left the assembly abruptly. The Parliament immediately protested, that the votes for the enregistry had not been legally taken, and that they gave no sanction to the loans proposed. This was enough to discredit and defeat them. Hereupon issued another edict, for the establishment of a cour plenière and the suspension of all the Parliaments in the kingdom. This being opposed, as might be expected, by reclamations from all the Parliaments and Provinces, the King gave way, and by an edict of July 5th, ‘88, renounced his cour plenière, and promised the States General for the first of May, of the ensuing year: and the Archbishop, finding the times beyond his faculties, accepted the promise of a Cardinal’s hat, was removed (September ‘88) from the Ministry, and Mr. Necker was called to the department of finance. The innocent rejoicings of the people of Paris on this change, provoked the interference of an officer of the city guards, whose order for their dispersion not being obeyed, he charged them with fixed bayonets, killed two or three, and wounded many. This dispersed them for the moment, but they collected the next day in great numbers, burnt ten or twelve guardhouses, killed two or three of the guards, and lost six or eight more of their own number. The city was hereupon put under martial law, and after a while the tumult subsided. The effect of this change of ministers, and the promise of the States General at an early day tranquillized the nation. But two great questions now occurred. 1st. What proportion shall the number of deputies of the Tiers Etat bear to those of the Nobles and Clergy? And, 2nd. Shall they sit in the same or in distinct apartments? Mr. Necker, desirous of avoiding himself these knotty questions, proposed a second call of the same Notables, and that their advice should be asked on the subject. They met, November 9, ‘88, and, by five bureaux against one, they recommended the forms of the States General of 1614; wherein the Houses were separate, and voted by orders, not by persons. But the whole nation declaring at once against this, and that the Tiers Etat should be, in numbers, equal to both the other orders, and the Parliament deciding for the same proportion, it was determined so to be, by a declaration of December 27th, ‘88. A Report of Mr. Necker, to the King, of about the same date, contained other very important concessions. 1. That the King could neither lay a new tax, nor prolong an old one. 2. It expressed a readiness to agree on the periodical meeting of the States. 3. To consult on the necessary restriction on lettres de cachet; and 4. How far the press might be made free. 5. It admits that the States are to appropriate the public money; and 6. That Ministers shall be responsible for public expenditures. And these concessions came from the very heart of the King. He had not a wish but for the good of the nation; and for that object, no personal sacrifice would ever have cost him a moment’s regret; but his mind was weakness itself, his constitution timid, his judgment null, and without sufficient firmness even to stand by the faith of his word. His Queen, too, haughty and bearing no contradiction, had an absolute ascendancy over him; and around her were rallied the King’s brother D’Artois, the court generally, and the aristocratic part of his Ministers, particularly Breteuil, Broglio, Vauguyon, Foulon, Luzerne, men whose principles of government were those of the age of Louis XIV. Against this host, the good counsels of Necker, Montmorin, St. Priest, although in unison with the wishes of the King himself, were of little avail. The resolutions of the morning, formed under their advice, would be reversed in the evening, by the influence of the Queen and court. But the hand of Heaven weighed heavily indeed on the machinations of this junto; producing collateral incidents, not arising out of the case, yet powerfully co-exciting the nation to force a regeneration of its government, and overwhelming, with accumulated difficulties, this liberticide resistance. For, while laboring under the want of money for even ordinary purposes, in a government which required a million of livres a day, and driven to the last ditch by the universal call for liberty, there came on a winter of such severe cold, as was without example in the memory of man, or in the written records of history. The Mercury was at times 50° below the freezing point of Farenheit, and 22° below that of Reaumur. All out-door labor was suspended, and the poor, without the wages of labor, were, of course, without either bread or fuel. The government found its necessities aggravated by that of procuring immense quantities of firewood, and of keeping great fires at all the cross streets, around which the people gathered in crowds, to avoid perishing with cold. Bread, too, was to be bought, and distributed daily, gratis, until a relaxation of the season should enable the people to work: and the slender stock of bread-stuff had for some time threatened famine, and had raised that article to an enormous price. So great, indeed, was the scarcity of bread, that, from the highest to the lowest citizen, the bakers were permitted to deal but a scanty allowance per head, even to those who paid for it; and, in cards of invitation to dine in the richest houses, the guest was notified to bring his own bread. To eke out the existence of the people, every person who had the means, was called on for a weekly subscription, which the Cures collected, and employed in providing messes for the nourishment of the poor, and vied with each other in devising such economical compositions of food, as would subsist the greatest number with the smallest means. This want of bread had been foreseen for some time past, and M. de Montmorin had desired me to notify it in America, and that, in addition to the market price, a premium should be given on what should be brought from the United States. Notice was accordingly given, and produced considerable supplies. Subsequent information made the importations from America, during the months of March, April, and May, into the Atlantic ports of France, amount to about twenty-one thousand barrels of flour, besides what went to other ports, and in other months; while our supplies to their West Indian islands relieved them also from that drain. This distress for bread continued till July.
Hitherto no acts of popular violence had been produced by the struggle for political reformation. Little riots, on ordinary incidents, had taken place at other times, in different parts of the kingdom, in which some lives, perhaps a dozen or twenty, had been lost; but in the month of April, a more serious one occurred in Paris, unconnected, indeed, with the Revolutionary principle, but making part of the history of the day. The Fauxbourg St. Antoine, is a quarter of the city inhabited entirely by the class of day-laborers and journeymen in every line. A rumor was spread among them, that a great paper-manufacturer, of the name of Reveillon, had proposed, on some occasion, that their wages should be lowered to fifteen sous a day. Inflamed at once into rage, and without inquiring into its truth, they flew to his house in vast numbers, destroyed every thing in it, and in his magazines and work-shops, without secreting, however, a pin’s worth to themselves, and were continuing this work of devastation, when the regular troops were called in. Admonitions being disregarded, they were of necessity fired on, and a regular action ensued, in which about one hundred of them were killed, before the rest would disperse. There had rarely passed a year without such a riot, in some part or other of the kingdom; and this is distinguished only as cotemporary with the Revolution, although not produced by it.
The States General were opened on the 5th of May, ‘89, by speeches from the King, the Garde des Sceaux, Lamoignon, and Mr. Necker. The last was thought to trip too lightly over the constitutional reformations which were expected. His notices of them in this speech, were not as full as in his previous Rapport au Roi. This was observed, to his disadvantage: but much allowance should have been made for the situation in which he was placed, between his own counsels and those of the ministers and party of the court. Overruled in his own opinions, compelled to deliver, and to gloss over those of his opponents, and even to keep their secrets, he could not come forward in his own attitude.
The composition of the Assembly, although equivalent, on the whole, to what had been expected, was something different in its elements. It had been supposed, that a superior education would carry into the scale of the Commons, a respectable portion of the Noblesse. It did so as to those of Paris, of its vicinity, and of the other considerable cities, whose greater intercourse with enlightened society had liberalized their minds, and prepared them to advance up to the measure of the times. But the Noblesse of the country, which constituted two thirds of that body, were far in their rear. Residing constantly on their patrimonial feuds, and familiarized, by daily habit, with Seigneurial powers and practices, they had not yet learned to suspect their inconsistence with reason and right. They were willing to submit to equality of taxation, but not to descend from their rank and prerogatives to be incorporated in session with the Tiers Etat. Among the Clergy, on the other hand, it had been apprehended that the higher orders of the Hierarchy, by their wealth and connections, would have carried the elections generally; but it turned out, that in most cases, the lower clergy had obtained the popular majorities. These consisted of the Cureés sons of the peasantry, who had been employed to do all the drudgery of parochial services for ten, twenty, or thirty louis a year; while their superiors were consuming their princely revenues in palaces of luxury and indolence. The objects for which this body was convened, being of the first order of importance, I felt it very interesting to understand the views of the parties of which it was composed, and especially the ideas prevalent, as to the organization contemplated for their government. I went, therefore, daily from Paris to Versailles, and attended their debates, generally till the hour of adjournment. Those of the Noblesse were impassioned and tempestuous. They had some able men on both sides, actuated by equal zeal. The debates of the Commons were temperate, rational, and inflexibly firm. As preliminary to all other business, the awful questions came on: Shall the States sit in one, or in distinct apartments? And shall they vote by heads or houses? The opposition was soon found to consist of the Episcopal order among the clergy, and two thirds of the Noblesse; while the Tiers Etat were, to a man, united and determined. After various propositions of compromise had failed, the Commons undertook to cut the Gordian knot. The Abbe Sieyes, the most logical head of the nation, (author of the pamphlet ‘Qu’est ce que le Tiers Etat?’ which had electrified that country, as Paine’s ‘Common Sense’ did us,) after an impressive speech on the 10th of June, moved that a last invitation should be sent to the Nobles and Clergy, to attend in the hall of the States, collectively or individually, for the verification of powers, to which the Commons would proceed immediately, either in their presence or absence. This verification being finished, a motion was made, on the 15th, that they should constitute themselves a National Assembly; which was decided on the 17th, by a majority of four fifths. During the debates on this question, about twenty of the Curés had joined them, and a proposition was made, in the chamber of the Clergy, that their whole body should join. This was rejected, at first, by a small majority only; but, being afterwards somewhat modified, it was decided affirmatively, by a majority of eleven. While this was under debate, and unknown to the court, to wit, on the 19th, a council was held in the afternoon, at Marly, wherein it was proposed that the King should interpose, by a declaration of his sentiments, in a séance royale. A form of declaration was proposed by Necker, which, while it censured, in general, the preceedings, both of the Nobles and Commons, announced the King’s views, such as substantially to coincide with the Commons. It was agreed to in Council, the séance was fixed for the 22nd, the meetings of the States were till then to be suspended, and every thing, in the mean time, kept secret. The members, the next morning (the 20th) repairing to their house, as usual, found the doors shut and guarded, a proclamation posted up for a séance, royale on the 22nd, and a suspension of their meetings in the mean, time. Concluding that their dissolution was now to take place, they repaired to a building called the Jeu de paume (or Tennis court), and there bound themselves by oath to each other, never to separate, of their own accord, till they had settled a constitution for the nation, on a solid basis, and, if separated by force, that they would reassemble in some other place. The next day they met in the church of St. Louis, and were joined by a majority of the clergy. The heads of the aristocracy saw that all was lost without some bold exertion. The King was still at Marly. Nobody was permitted to approach him but their friends. He was assailed by falsehoods in all shapes. He was made to believe that the Commons were about to absolve the army from their oath of fidelity to him, and to raise their pay. The court party were now all rage and desperation. They procured a committee to be held, consisting of the King and his Ministers, to which Monsieur and the Count d’Artois should be admitted. At this committee, the latter attacked Mr. Necker personally, arraigned his declaration, and proposed one which some of his prompters had put into his hands. Mr. Necker was browbeaten and intimidated, and the King shaken. He determined that the two plans should be deliberated on the next day, and the séance royale put off a day longer. This encouraged a fiercer attack on Mr. Necker the next day. His draught of a declaration was entirely broken up, and that of the Count d’Artois inserted into it. Himself and Montmorin offered their resignation, which was refused; the Count d’Artois saying to Mr. Necker, ‘No, sir, you must be kept as the hostage; we hold you responsible for all the ill which shall happen.’ This change of plan was immediately whispered without doors. The Noblesse were in triumph; the people in consternation. I was quite alarmed at this state of things. The soldiery had not yet indicated which side they should take, and that which they should support would be sure to prevail. I considered a successful reformation of government in France as insuring a general reformation through Europe, and the resurrection to a new life of their people, now ground to dust by the abuses of the governing powers. I was much acquainted with the leading patriots of the Assembly. Being from a country which had successfully passed through a similar reformation, they were disposed to my acquaintance, and had some confidence in me. I urged, most strenuously, an immediate compromise; to secure what the government was now ready to yield, and trust to future occasions for what might still be wanting. It was well understood that the King would grant, at this time, 1. Freedom of the person by habeas corpus. 2. Freedom of conscience: 3. Freedom of the press: 4. Trial by jury: 5. A representative legislature: 6. Annual meetings: 7. The origination of laws: 8. The exclusive right of taxation and appropriation: and 9. The responsibility of ministers: and with the exercise of these powers they could obtain, in future, whatever might be further necessary to improve and preserve their constitution. They thought otherwise, however, and events have proved their lamentable error. For, after thirty years of war, foreign and domestic, the loss of millions of lives, the prostration of private happiness, and the foreign subjugation of their own country for a time, they have obtained no more, nor even that securely. They were unconscious of (for who could foresee?) the melancholy sequel of their well-meant perseverance; that their physical force would be usurped by a first tyrant to trample on the independence, and even the existence, of other nations: that this would afford a fatal example for the atrocious conspiracy of kings against their people; would generate their unholy and homicide alliance to make common cause among themselves, and to crush, by the power of the whole, the efforts of any part, to moderate their abuses and oppressions. When the King passed, the next day, through the lane formed from the Chateau to the Hotel des Etats, there was a dead silence. He was about an hour in the House, delivering his speech and declaration. On his coming out, a feeble cry of Vive le Roy was raised by some children, but the people remained silent and sullen. In the close of his speech, he had ordered that the members should follow him, and resume their deliberations the next day. The Noblesse followed him, and so did the clergy, except about thirty, who, with the Tiers, remained in the room, and entered into deliberation. They protested against what the King had done, adhered to all their former proceedings, and resolved the inviolability of their own persons. An officer came to order them out of the room in the King’s name. ‘Tell those who sent you,’ said Mirabeau, ‘that we shall not move hence but at our own will, or the point of the bayonet.’ In the afternoon, the people, uneasy, began to assemble in great numbers in the courts and vicinities of the palace. This produced alarm. The Queen sent for Mr. Necker. He was conducted, amidst the shouts and acclamations of the multitude, who filled all the apartments of the palace. He was a few minutes only with the Queen, and what passed between them did not transpire. The King went out to ride. He passed through the crowd to his carriage, and into it, without being in the least noticed. As Mr. Necker followed him, universal acclamations were raised of ‘Vive Monsieur Necker, vive le sauveur de la France opprimée.’ He was conducted back to his house, with the same demonstrations of affection and anxiety. About two hundred deputies of the Tiers, catching the enthusiasm of the moment, went to his house, and extorted from him a promise that he would not resign. On the 25th, forty-eight of the Nobles joined the Tiers, and among them the Duke of Orleans. There were then with them one hundred and sixty-four members of the clergy, although the minority of that body still sat apart, and called themselves the Chamber of the Clergy. On the 26th, the Archbishop of Paris joined the Tiers, as did some others of the clergy and of the Noblesse.
These proceedings had thrown the people into violent ferment. It gained the soldiery, first of the French guards, extended to those of every other denomination, except the Swiss, and even to the body guards of the King. They began to quit their barracks, to assemble in squads, to declare they would defend the life of the King, but would not be the murderers of their fellow-citizens. They called themselves the soldiers of the nation, and left now no doubt on which side they would be, in case of a rupture. Similar accounts came in from the troops in other parts of the kingdom, giving good reason to believe they would side with their fathers and brothers, rather than with their officers. The operation of this medicine at Versailles, was as sudden as it was powerful. The alarm there was so complete, that in the afternoon of the 27th, the King wrote with his own hand letters to the Presidents of the Clergy and Nobles, engaging them immediately to join the Tiers. These two bodies were debating, and hesitating, when notes from the Count d’Artois decided their compliance. They went in a body, and took their seats with the Tiers, and thus rendered the union of the orders in one chamber complete.
The Assembly now entered on the business of their mission, and first proceeded to arrange the order in which they would take up the heads of their constitution, as follows:
First, and as preliminary to the whole, a general declaration of the rights of man. Then, specifically, the principles of the monarchy; rights of the nation; rights of the king; rights of the citizens; organization and rights of the National Assembly; forms necessary for the enactment of laws; organization and functions of the Provincial and Municipal Assemblies; duties and limits of the Judiciary power; functions and duties of the Military power.
A declaration of the rights of man, as the preliminary of their work, was accordingly prepared and proposed by the Marquis de la Fayette.
But the quiet of their march was soon disturbed by information that troops, and particularly the foreign troops, were advancing on Paris from various quarters. The King had probably been advised to this on the pretext of preserving peace in Paris. But his advisers were believed to have other things in contemplation. The Marshal de Broglio was appointed to their command, a highflying aristocrat, cool and capable of every thing. Some of the French guards were soon arrested, under other pretexts, but really on account of their dispositions in favor of the national cause. The people of Paris forced their prison, liberated them, and sent a deputation to the Assembly to solicit a pardon. The Assembly recommended peace and order to the people of Paris, the prisoners to the King, and asked from him the removal of the troops. His answer was negative and dry, saying they might remove themselves, if they pleased, to Noyon or Soissons. In the mean time, these troops, to the number of twenty or thirty thousand, had arrived, and were posted in and between Paris and Versailles. The bridges and passes were guarded. At three o’clock in the afternoon of the 11th of July, the Count de la Luzerne was sent to notify Mr. Necker of his dismission, and to enjoin him to retire instantly, without saying a word of it to any body. He went home, dined, and proposed to his wife a visit to a friend, but went in fact to his country-house at St. Ouen, and at midnight set out for Brussels. This was not known till the next day (the 12th), when the whole ministry was changed, except Villedeuil, of the domestic department, and Barenton, Garde des Sceaux. The changes were as follows.
The Baron de Breteuil, President of the Council of Finance; de la Galasiere, Comptroller General, in the room of Mr. Necker; the Marshal de Broglio, Minister of War, and Foulon under him, in the room of Puy-Segur; the Duke de la Vauguyon, Minister of Foreign Affairs, instead of the Count de Montmorin; de la Porte, Minister of Marine, in place of the Count de la Luzerne; St. Priest was also removed from the Council. Lucerne and Puy Segur had been strongly of the aristocratic party in the Council but they were not considered as equal to the work now to be done. The King was now completely in the hands of men, the principal among whom had been noted through their lives for the Turkish despotism of their characters, and who were associated around the King as proper instruments for what was to be executed. The news of this change began to be known at Paris about one or two o’clock. In the afternoon, a body of about one hundred German cavalry were advanced, and drawn up in the Place Louis XV., and about two hundred Swiss posted at a little distance in their rear. This drew people to the spot, who thus accidentally found themselves in front of the troops, merely at first as spectators; but, as their numbers increased, their indignation rose. They retired a few steps, and posted themselves on and behind large piles of stones, large and small, collected in that place for a bridge, which was to be built adjacent to it. In this position, happening to be in my carriage on a visit, I passed through the lane they had formed, without interruption. But the moment after I had passed, the people attacked the cavalry with stones. They charged, but the advantageous position of the people, and the showers of stones, obliged the horse to retire, and quit the field altogether, leaving one of their number on the ground, and the Swiss in their rear, not moving to their aid. This was the signal for universal insurrection, and this body of cavalry, to avoid being massacred, retired towards Versailles. The people now armed themselves with such weapons as they could find in armorers’ shops, and private houses, and with bludgeons; and were roaming all night, through all parts of the city, without any decided object. The next day (the 13th), the Assembly pressed on the king to send away the troops, to permit the Bourgeoisie of Paris, to arm for the preservation of order in the city, and offered to send a deputation from their body to tranquillize them: but their propositions were refused. A committee of magistrates and electors of the city were appointed by those bodies, to take upon them its government. The people, now openly joined by the French guards, forced the prison of St. Lazare, released all the prisoners, and took a great store of corn, which they carried to the corn market. Here they got some arms, and the French guards began to form and train; them. The city-committee determined to raise forty-eight thousand Bourgeois, or rather to restrain their numbers to forty-eight thousand. On the 14th, they sent one of their members (Monsieur de Corny) to the Hotel des Invalides, to ask arms for their Garde Bourgeoise. He was followed by, and he found there, a great collection of people. The Governor of the Invalids came out, and represented the impossibility of his delivering arms, without the orders of those from whom he received them. De Corny advised the people then to retire, and retired himself; but the people took possession of the arms, it was remarkable, that not only the Invalids themselves made no opposition, but that a body of five thousand foreign troops, within four hundred yards, never stirred. M. de Corny, and five others, were then sent to ask arms of M. de Launay, Governor of the Bastile. They found a great collection of people already before the place, and they immediately planted a flag of truce, which was answered by a like flag hoisted on the parapet. The deputation prevailed on the people to fall back a little, advanced themselves to make their demand of the Governor, and in that instant, a discharge from the Bastile killed four persons, of those nearest to the deputies. The deputies retired. I happened to be at the house of M. de Corny, when he returned to it, and received from him a narrative of these transactions. On the retirement of the deputies, the people rushed forward, and almost in an instant, were in possession of a fortification, of infinite strength, defended by one hundred men, which in other times, had stood several regular sieges, and had never been taken. How they forced their entrance has never been explained. They took all the arms, discharged the prisoners, and such of the garrison as were not killed in the first moment of fury; carried the Governor and Lieutenant Governor to the Place de Greve (the place of public execution), cut off their heads, and sent them through the city, in triumph, to the Palais Royal. About the same instant, a treacherous correspondence having been discovered in M. de Flesselles, Prévôt des Marchands, they seized him in the Hotel de Ville, where he was in the execution of his office, and cut off his head. These events, carried imperfectly to Versailles, were the subject of two successive deputations from the Assembly to the King, to both of which he gave dry and hard answers; for nobody had as yet been permitted to inform him, truly and fully, of what had passed at Paris. But at night, the Duke de Liancourt forced his way into the King’s bed-chamber, and obliged him to hear a full and animated detail of the disasters of the day in Paris. He went to bed fearfully impressed. The decapitation of De Launay worked powerfully, through the night, on the whole Aristocratical party; insomuch, that in the morning, those of the greatest influence on the Count d’Artois, represented to him the absolute necessity, that the King should give up every thing to the Assembly. This according with the dispositions of the King, he went about eleven o’clock, accompanied only by his brothers, to the Assembly, and there read to them a speech, in which he asked their interposition to re-establish order. Although couched in terms of some caution, yet the manner in which it was delivered made it evident, that it was meant as a surrender at discretion. He returned to the Chateau afoot, accompanied by the Assembly. They sent off a deputation to quiet Paris, at the head of which was the Marquis de la Fayette, who had, the same morning, been named Commandant en Chef of the Milice Bourgeoise; and Monsieur Bailly, former President of the States General, was called for as Prévôt des Marchands. The demolition of the Bastile was now ordered and begun. A body of the Swiss guards, of the regiment of Ventimille, and the city horse-guards joined the people. The alarm at Versailles increased. The foreign troops were ordered off instantly. Every Minister resigned. The King confirmed Bailly as Prévôt des Marchands, wrote to Mr. Necker, to recall him, sent his letter open to the Assembly, to be forwarded by them, and invited them to go with him to Paris the next day, to satisfy the city of his dispositions; and that night, and the next morning, the Count d’Artois, and M. de Montesson, a deputy connected with him, Madame de Polignac, Madame de Guiche, and the Count de Vaudreuil, favorites of the Queen, the Abbe de Vermont her confessor, the Prince of Conde. and Duke of Bourbon fled. The King came to Paris, leaving the Queen in consternation for his return. Omitting the less important figures of the procession, the King’s carriage was in the centre; on each side of it, the Assembly, in two ranks afoot; at their head the Marquis de la Fayette, as commander-in-chief, on horse-back, and Bourgeois guards before and behind. About sixty thousand citizens, of all forms and conditions, armed with the conquests of the Bastile and Invalids, as far as they would go, the rest with pistols, swords, pikes, pruning hooks, scythes, &c. lined all the streets through which the procession passed, and with the crowds of people in the streets, doors, and windows, saluted them everywhere with the cries of ‘Vive la Nation,’ but not a single ‘Vive le Roi’ was heard. The King stopped at the Hotel de Ville. There M. Bailly presented, and put into his hat, the popular cockade, and addressed him. The King being unprepared, and unable to answer, Bailly went to him, gathered from him some scraps of sentences, and made out an answer, which he delivered to the audience, as from the King. On their return, the popular cries were ‘Vive le Roi et la Nation.’ He was conducted by a garde Bourgeoise, to his palace at Versailles, and thus concluded such an ‘amende honorable,’ as no sovereign ever made, and no people ever received.
And here, again, was lost another precious occasion of sparing to France the crimes and cruelties through which she has since passed, and to Europe, and finally America, the evils which flowed on them also from this mortal source. The King was now become a passive machine in the hands of the National Assembly, and had he been left to himself, he would have willingly acquiesced in whatever they should devise as best for the nation. A wise constitution would have been formed, hereditary in his line, himself placed at its head, with powers so large, as to enable him to do all the good of his station, and so limited, as to restrain him from its abuse. This he would have faithfully administered, and more than this, I do not believe, he ever wished. But he had a Queen of absolute sway over his weak mind and timid virtue, and of a character the reverse of his in all points. This angel, as gaudily painted in the rhapsodies of Burke, with some smartness of fancy, but no sound sense, was proud, disdainful of restraint, indignant at all obstacles to her will, eager in the pursuit of pleasure, and firm enough to hold to her desires, or perish in their wreck. Her inordinate gambling and dissipations, with those of the Count d’Artois, and others of her clique, had been a sensible item in the exhaustion of the treasury, which called into action the reforming hand of the nation; and her opposition to it, her inflexible perverseness, and dauntless spirit, led herself to the Guillotine, drew the King on with her, and plunged the world into crimes and calamities which will for ever stain the pages of modern history. I have ever believed, that had there been no Queen, there would have been no revolution. No force would have been provoked, nor exercised. The King would have gone hand in hand with the wisdom of his sounder counsellors, who, guided by the increased lights of the age, wished only, with the same pace, to advance the principles of their social constitution. The deed which closed the mortal course of these sovereigns, I shall neither approve nor condemn. I am not prepared to say, that the first magistrate of a nation cannot commit treason against his country, or is unamenable to its punishment: nor yet, that where there is no written law, no regulated tribunal, there is not a law in our hearts, and a power in our hands, given for righteous employment in maintaining right, and redressing wrong. Of those who judged the King, many thought him wilfully criminal; many, that his existence would keep the nation in perpetual conflict with the horde of Kings, who would war against a regeneration which might come home to themselves, and that it were better that one should die than all. I should not have voted with this portion of the legislature. I should have shut up the Queen in a convent, putting harm out of her power, and placed the King in his station, investing him with limited powers, which, I verily believe, he would have honestly exercised, according to the measure of his understanding. In this way, no void would have been created, courting the usurpation of a military adventurer, nor occasion given for those enormities which demoralized the nations of the world, and destroyed, and is yet to destroy, millions and millions of its inhabitants. There are three epochs in history, signalized by the total extinction of national morality. The first was of the successors of Alexander, not omitting himself: the next, the successors of the first Cæsar: the third, our own age. This was begun by the partition of Poland, followed by that of the treaty of Pilnitz; next the conflagration of Copenhagen; then the enormities of Bonaparte, partitioning the earth at his will, and devastating it with fire and sword; now the conspiracy of Kings, the successors of Bonaparte, blasphemously calling themselves ‘The Holy Alliance,’ and treading in the footsteps of their incarcerated leader; not yet, indeed, usurping the government of other nations, avowedly and in detail, but controlling by their armies the forms in which they will permit them to be governed; and reserving, in petto, the order and extent of the usurpations further meditated. But I will return from a digression, anticipated, too, in time, into which I have been led by reflection on the criminal passions which refused to the world a favorable occasion of saving it from the afflictions it has since suffered.
Mr. Necker had reached Basle before he was overtaken by the letter of the King, inviting him back to resume the office he had recently left. He returned immediately, and all the other ministers having resigned, a new administration was named, to wit: St. Priest and Montmorin were restored; the Archbishop of Bordeaux was appointed Garde des Sceaux; La Tour du Pin, Minister of War; La Luzerne, Minister of Marine. This last was believed to have been effected by the friendship of Montmorin; for although differing in politics, they continued firm in friendship, and Luzerne, although not an able man, was thought an honest one. And the Prince of Bauvau was taken into the Council.
Seven Princes of the blood royal, six ex-ministers, and many of the high Noblesse, having fled, and the present ministers, except Luzerne, being all of the popular party, all the functionaries of government moved, for the present, in perfect harmony.
In the evening of August the 4th, and on the motion of the Viscount de Noailles, brother-in-law of La Fayette, the Assembly abolished all titles of rank, all the abusive privileges of feudalism, the tythes and casuals of the clergy, all provincial privileges, and, in fine, the feudal regimen generally. To the suppression of tythes, the Abbe Sieyes was vehemently opposed; but his learned and logical arguments were unheeded, and his estimation lessened by a contrast of his egoism (for he was beneficed on them) with the generous abandonment of rights by the other members of the Assembly. Many days were employed in putting into the form of laws the numerous demolitions of ancient abuses; which done, they proceeded to the preliminary work of a declaration of rights. There being much concord of sentiment on the elements of this instrument, it was liberally framed, and passed with a very general approbation. They then appointed a committee for the ‘reduction of a projet’ of a constitution, at the head of which was the Archbishop of Bordeaux. I received from him, as chairman of the committee, a letter of July the 20th, requesting me to attend and assist at their deliberations; but I excused myself, on the obvious considerations, that my mission was to the King as Chief Magistrate of the nation, that my duties were limited to the concerns of my own country, and forbade me to intermeddle with the internal transactions of that in which I had been received under a specific character only. Their plan of a constitution was discussed in sections, and so reported from time to time, as agreed to by the committee. The first respected the general frame of the government; and that this should be formed into three departments, executive, legislative, and judiciary, was generally agreed. But when they proceeded to subordinate developments, many and various shades of opinion came into conflict, and schism, strongly marked, broke the Patriots into fragments of very discordant principles. The first question, Whether there should be a King? met with no open opposition; and it was readily agreed, that the government of France should be monarchical and hereditary. Shall the King have a negative on the laws? Shall that negative be absolute, or suspensive only? Shall there be two Chambers of Legislation, or one only? If two, shall one of them be hereditary? or for life? or for a fixed term? and named by the King? or elected by the people? These questions found strong differences of opinion, and produced repulsive combinations among the Patriots. The aristocracy was cemented by a common principle of preserving the ancient regime or whatever should be nearest to it. Making this their polar star, they moved in phalanx, gave preponderance on every question to the minorities of the Patriots, and always to those who advocated the least change. The features of the new constitution were thus assuming a fearful aspect, and great alarm was produced among the honest Patriots by these dissensions in their ranks. In this uneasy state of things, I received one day a note from the Marquis de la Fayette, informing me, that he should bring a party of six or eight friends, to ask a dinner of me the next day. I assured him of their welcome. When they arrived, they were La Fayette himself, Duport, Barnave, Alexander la Meth, Blacon, Mounier, Maubourg, and Dagout. These were leading Patriots, of honest but differing opinions, sensible of the necessity of effecting a coalition by mutual sacrifices, knowing each other, and not afraid, therefore, to unbosom themselves mutually. This last was a material principle in the selection. With this view, the Marquis had invited the conference, and had fixed the time and place inadvertently, as to the embarrassment under which it might place me. The cloth being removed, and wine set on the table, after the American manner, the Marquis introduced the objects of the conference, by summarily reminding them of the state of things in the Assembly, the course which the principles of the constitution were taking, and the inevitable result, unless checked by more concord among the Patriots themselves. He observed, that although he also had his opinion, he was ready to sacrifice it to that of his brethren of the same cause; but that a common opinion must now be formed, or the aristocracy would carry every thing, and that, whatever they should now agree on, he, at the head of the national force, would maintain. The discussions began at the hour of four, and were continued till ten o’clock in the evening; during which time I was a silent witness to a coolness and candor of argument unusual in the conflicts of political opinion; to a logical reasoning, and chaste eloquence, disfigured by no gaudy tinsel of rhetoric or declamation, and truly worthy of being placed in parallel with the finest dialogues of antiquity, as handed to us by Xenophon, by Plato, and Cicero. The result was, that the King should have a suspensive veto on the laws, that the legislature should be composed of a single body only, and that to be chosen by the people. This Concordat decided the fate of the constitution. The Patriots all rallied to the principles thus settled, carried every question agreeably to them, and reduced the aristocracy to insignificance and impotence. But duties of exculpation were now incumbent on me. I waited on Count Montmorin the next morning, and explained to him, with truth and candor, how it happened that my house had been made the scene of conferences of such a character. He told me he already knew every thing which had passed, that so far from taking umbrage at the use made of my house on that occasion, he earnestly wished I would habitually assist at such conferences, being sure I should be useful in moderating the warmer spirits, and promoting a wholesome and practicable reformation only. I told him I knew too well the duties I owed to the King, to the nation, and to my own country, to take any part in councils concerning their internal government, and that I should persevere, with care, in the character of a neutral and passive spectator, with wishes only, and very sincere ones, that those measures might prevail which would be for the greatest good of the nation. I have no doubt, indeed, that this conference was previously known and approved by this honest minister, who was in confidence and communication with the Patriots, and wished for a reasonable reform of the constitution.
Here I discontinue my relation of the French Revolution. The minuteness with which I have so far given its details, is disproportioned to the general scale of my narrative. But I have thought it justified by the interest which the whole world must take in this Revolution. As yet, we are but in the first chapter of its history. The appeal to the rights of man, which had been made in the United States, was taken up by France, first of the European nations. From her the spirit has spread over those of the South. The tyrants of the North have allied indeed against it; but it is irresistible. Their opposition will only multiply its millions of human victims; their own satellites will catch it, and the condition of man through the civilized world, will be finally and greatly meliorated. This is a wonderful instance of great events from small causes. So inscrutable is the arrangement of causes and consequences in this world, that a two-penny duty on tea, unjustly imposed in a sequestered part of it, changes the condition of all its inhabitants. I have been more minute in relating the early transactions of this regeneration, because I was in circumstances peculiarly favorable for a knowledge of the truth. Possessing the confidence and intimacy of the leading Patriots, and more than all, of the Marquis Fayette, their head and Atlas, who had no secrets from me, I learned with correctness the views and proceedings of that party; while my intercourse with the diplomatic missionaries of Europe at Paris, all of them with the court, and eager in prying into its councils and proceedings, gave me a knowledge of these also. My information was always, and immediately committed to writing, in letters to Mr. Jay, and often to my friends, and a recurrence to these letters now insures me against errors of memory. These opportunities of information ceased at this period, with my retirement from this interesting scene of action. I had been more than a year soliciting leave to go home, with a view to place my daughters in the society and care of their friends, and to return for a short time to my station at Paris. But the metamorphosis through which our government was then passing from its chrysalid to its organic form, suspended its action in a great degree; and it was not till the last of August that I received the permission I had asked. And here I cannot leave this great and good country, without expressing my sense of its pre-eminence of character among the nations of the earth. A more benevolent people I have never known, nor greater warmth and devotedness in their select friendships. Their kindness and accommodation to strangers is unparalleled, and the hospitality of Paris is beyond any thing I had conceived to be practicable in a large city. Their eminence, too, in science, the communicative dispositions of their scientific men, the politeness of the general manners, the ease and vivacity of their conversation, give a charm to their society, to be found nowhere else. In a comparison of this with other countries, we have the proof of primacy, which was given to Themistocles after the battle of Salamis. Every general voted to himself the first reward of valor, and the second to Themistocles. So, ask the traveled inhabitant of any nation, In what country on earth would you rather live?—Certainly, in my own, where are all my friends, my relations, and the earliest and sweetest affections and recollections of my life. Which would be your second choice? France.
On the 26th of September, I left Paris for Havre, where I was detained by contrary winds, until the 8th of October. On that day, and the 9th, I crossed over to Cowes, where I had engaged the Clermont, Capt. Colley, to touch for me. She did so; but here again we were detained by contrary winds, until the 22nd, when we embarked, and landed at Norfolk on the 23rd of November. On my way home, I passed some days at Eppington, in Chesterfield, the residence of my friend and connection, Mr. Eppes; and, while there, I received a letter from the President, General Washington, by express, covering an appointment to be Secretary of State. [See Appendix, note H.] I received it with real regret. My wish had been to return to Paris, where I had left my household establishment, as if there myself, and to see the end of the Revolution, which, I then thought, would be certainly and happily closed in less than a year. I then meant to return home, to withdraw from political life, into which I had been impressed by the circumstances of the times, to sink into the bosom of my family and friends, and devote myself to studies more congenial to my mind. In my answer of December 15th, I expressed these dispositions candidly to the President, and my preference of a return to Paris; but assured him, that if it was believed I could be more useful in the administration of the government, I would sacrifice my own inclinations without hesitation, and repair to that destination: this I left to his decision. I arrived at Monticello on the 23rd of December, where I received a second letter from the President, expressing his continued wish, that I should take my station there, but leaving me still at liberty to continue in my former office, if I could not reconcile myself to that now proposed. This silenced my reluctance, and I accepted the new appointment.
In the interval of my stay at home, my eldest daughter had been happily married to the eldest son of the Tuckahoe branch of Randolphs, a young gentleman of genius, science, and honorable mind, who afterwards filled a dignified station in the General Government, and the most dignified in his own State. I left Monticello on the 1st of March, 1790, for New York. At Philadelphia I called on the venerable and beloved Franklin. He was then on the bed of sickness from which he never rose. My recent return from a country in which he had left so many friends, and the perilous convulsions to which they had been exposed, revived all his anxieties to know what part they had taken, what had been their course, and what their fate. He went over all in succession, with a rapidity and animation, almost too much for his strength. When all his inquiries were satisfied, and a pause took place, I told him I had learned with much pleasure that, since his return to America, he had been occupied in preparing for the world, the history of his own life. ‘I cannot say much of that,’ said he; ‘but I will give you a sample of what I shall leave:’ and he directed his little grandson (William Bache) who was standing by the bedside, to hand him a paper from the table, to which he pointed. He did so; and the Doctor putting it into my hands, desired me to take it, and read it at my leisure. It was about a quire of folio paper, written in a large and running hand, very like his own. I looked into it slightly, then shut it, and said I would accept his permission to read it, and would carefully return it. He said, ‘No, keep it.’ Not certain of his meaning, I again looked into it, folded it for my pocket, and said again, I would certainly return it. ‘No,’ said he, ‘keep it.’ I put it into my pocket, and shortly after, took leave of him. He died on the 17th of the ensuing month of April; and as I understood that he had bequeathed all his papers to his grandson, William Temple Franklin, I immediately wrote to Mr. Franklin, to inform him I possessed this paper, which I should consider as his property, and would deliver to his order. He came on immediately to New York, called on me for it, and I delivered it to him. As he put it into his pocket, he said carelessly, he had either the original, or another copy of it, I do not recollect which. This last expression struck my attention forcibly, and for the first time suggested to me the thought, that Dr. Franklin had meant it as a confidential deposite in my hands, and that I had done wrong in parting from it. I have not yet seen the collection he published of Dr. Franklin’s works, and therefore know not if this is among them. I have been told it is not. It contained a narrative of the negotiations between Dr. Franklin and the British Ministry, when he was endeavoring to prevent the contest of arms which followed. The negotiation was brought about by the intervention of Lord Howe and his sister, who, I believe, was called Lady Howe, but I may misremember her title. Lord Howe seems to have been friendly to America, and exceedingly anxious to prevent a rupture. His intimacy with Dr. Franklin, and his position with the Ministry, induced him to undertake a mediation between them; in which his sister seemed to have been associated. They carried from one to the other, backwards and forwards, the several propositions and answers which passed, and seconded with their own intercessions, the importance of mutual sacrifices, to preserve the peace and connection of the two countries. I remember that Lord North’s answers were dry, unyielding, in the spirit of unconditional submission, and betrayed an absolute indifference to the occurrence of a rupture; and he said to the mediators distinctly, at last, that ‘a rebellion was not to be deprecated on the part of Great Britain; that the confiscations it would produce, would provide for many of their friends.’ This expression was reported by the mediators to Dr. Franklin, and indicated so cool and calculated a purpose in the Ministry, as to render compromise hopeless, and the negotiation was discontinued. If this is not among the papers published, we ask, what has become of it? I delivered it with my own hands, into those of Temple Franklin. It certainly established views so atrocious in the British government, that its suppression would, to them, be worth a great price. But could the grandson of Dr. Franklin be, in such degree, an accomplice in the parricide of the memory of his immortal grandfather? The suspension, for more than twenty years, of the general publication, bequeathed and confided to him, produced for a while hard suspicions against him: and if, at last, all are not published, a part of these suspicions may remain with some.
I arrived at New York on the 21st of March, where Congress was in session.
Sir,
Monticello, August 31, 1820.
Your letter of the 19th was received in due time, and I wish it were in my power to furnish you more fully, than in the enclosed paper, with materials for the biography of George Wythe; but I possess none in writing, am very distant from the place of his birth and early life, and know not a single person in that quarter from whom inquiry could be made, with the expectation of collecting any thing material. Add to this, that feeble health disables me, almost, from writing; and, entirely, from the labor of going into difficult research. I became acquainted with Mr. Wythe when he was about thirty-five years of age. He directed my studies in the law, led me into business, and continued, until death, my most affectionate friend. A close intimacy with him, during that period of forty odd years, the most important of his life, enables me to state its leading facts, which, being of my own knowledge, I vouch their truth. Of what precedes that period, I speak from hearsay only, in which there may be error, but of little account, as the character of the facts will themselves manifest. In the epoch of his birth I may err a little, stating that from the recollection of a particular incident, the date of which, within a year or two, I do not distinctly remember. These scanty outlines, you will be able, I hope, to fill up from other information, and they may serve you, sometimes, as landmarks to distinguish truth from error, in what you hear from others. The exalted virtue of the man will also be a polar star to guide you in all matters which may touch that element of his character. But on that you will receive imputation from no man; for, as far as I know, he never had an enemy. Little as I am able to contribute to the just reputation of this excellent man, it is the act of my life most gratifying to my heart: and leaves me only to regret that a waning memory can do no more.
Of Mr. Hancock I can say nothing, having known him only in the chair of Congress. Having myself been the youngest man but one in that body, the disparity of age prevented any particular intimacy. But of him there can be no difficulty in obtaining full information in the North.
I salute you, Sir, with sentiments of great respect.
Th: Jefferson.
Notes for the Biography of George Wythe.
George Wythe was born about the year 1727 or 1728, of a respectable family in the county of Elizabeth City, on the shores of the Chesapeake. He inherited, from his father, a fortune sufficient for independence and ease. He had not the benefit of a regular education in the schools, but acquired a good one of himself, and without assistance; insomuch, as to become the best Latin and Greek scholar in the state. It is said, that while reading the Greek Testament, his mother held an English one, to aid him in rendering the Greek text conformably with that. He also acquired, by his own reading, a good knowledge of Mathematics, and of Natural and Moral Philosophy. He engaged in the study of the law under the direction of a Mr. Lewis, of that profession, and went early to the bar of the General Court, then occupied by men of great ability, learning, and dignity in their profession. He soon became eminent among them, and, in process of time, the first at the bar, taking into consideration his superior learning, correct elocution, and logical style of reasoning; for in pleading he never indulged himself with an useless or declamatory thought or word; and became as distinguished by correctness and purity of conduct in his profession, as he was by his industry and fidelity to those who employed him. He was early elected to the House of Representatives, then called the House of Burgesses, and continued in it until the Revolution. On the first dawn of that, instead of higgling on half-way principles, as others did who feared to follow their reason, he took his stand on the solid ground, that the only link of political union between us and Great Britain, was the identity of our Executive; that that nation and its Parliament had no more authority over us, than we had over them, and that we were co-ordinate nations with Great Britain and Hanover.
In 1774, he was a member of a Committee of the House of Burgesses, appointed to prepare a Petition to the King, a Memorial to the House of Lords, and a Remonstrance to the House of Commons, on the subject of the proposed Stamp Act. He was made draughtsman of the last, and, following his own principles, he so far overwent the timid hesitations of his colleagues, that his draught was subjected by them to material modifications; and, when the famous Resolutions of Mr. Henry, in 1775, were proposed, it was not on any difference of principle that they were opposed by Wythe. Randolph, Pendleton, Nicholas, Bland, and other worthies, who had long been the habitual leaders of the House; but because those papers of the preceding session had already expressed the same sentiments and assertions of right, and that an answer to them was yet to be expected.
In August, 1775, he was appointed a member of Congress, and in 1776, signed the Declaration of Independence, of which he had, in debate, been an eminent supporter. And subsequently, in the same year, he was appointed by the Legislature of Virginia, one of a committee to revise the laws of the state, as well of British, as of Colonial enactment, and to prepare bills for re-enacting them, with such alterations as the change in the form and principles of the government, and other circumstances, required: and of this work, he executed the period commencing with the revolution in England, and ending with the establishment of the new government here; excepting the Acts for regulating descents, for religious freedom, and for proportioning crimes and punishments. In 1777, he was chosen speaker of the House of Delegates, being of distinguished learning in parliamentary law and proceedings; and towards the end of the same year, he was appointed one of the three Chancellors, to whom that department of the Judiciary was confided, on the first organization of the new government. On a subsequent change of the form of that court, he was appointed sole Chancellor, in which office he continued to act until his death, which happened in June, 1806, about the seventy-eighth or seventy-ninth year of his age.
Mr. Wythe had been twice married; first, I believe, to a daughter of Mr. Lewis, with whom he had studied law, and afterwards, to a Miss Taliaferro, of a wealthy and respectable family in the neighborhood of Williamsburg; by neither of whom did he leave issue.
No man ever left behind him a character more venerated than George Wythe. His virtue was of the purest tint; his integrity inflexible, and his justice exact; of warm patriotism, and, devoted as he was to liberty, and the natural and equal rights of man, he might truly be called the Cato of his country, without the avarice of the Roman; for a more disinterested person never lived. Temperance and regularity in all his habits, gave him general good health, and his unaffected modesty and suavity of manners endeared him to every one. He was of easy elocution, his language chaste, methodical in the arrangement of his matter, learned and logical in the use of it, and of great urbanity in debate; not quick of apprehension, but, with a little time, profound in penetration, and sound in conclusion. In his philosophy he was firm, and neither troubling, nor perhaps trusting, any one with his religious creed, he left the world to the conclusion, that that religion must be good which could produce a life of exemplary virtue.
His stature was of the middle size, well formed and proportioned, and the features of his face were manly, comely, and engaging. Such was George Wythe, the honor of his own, and the model of future times.
Sir,
Monticello, May 12, 1829.
An absence, of sometime, at an occasional and distant residence, must apologize for the delay in acknowledging the receipt of your favor of April 12th; and candor obliges me to add, that it has been somewhat extended by an aversion to writing, as well as to calls on my memory for facts so much obliterated from it by time, as to lessen my own confidence in the traces which seem to remain. One of the enquiries in your letter, however, may be answered without an appeal to the memory. It is that respecting the question, Whether committees of correspondence originated in Virginia, or Massachusetts? on which you suppose me to have claimed it for Virginia; but certainly I have never made such a claim. The idea, I suppose, has been taken up from what is said in Wirt’s history of Mr. Henry, page 87, and from an inexact attention to its precise terms. It is there said, ‘This House [of Burgesses, of Virginia] had the merit of originating that powerful engine of resistance, corresponding committees between the legislatures of the different colonies.’ That the fact, as here expressed, is true, your letter bears witness, when it says, that the resolutions of Virginia, for this purpose, were transmitted to the speakers of the different assemblies, and by that of Massachusetts was laid, at the next session, before that body, who appointed a committee for the specified object: adding, ‘Thus, in Massachusetts, there were two committees of correspondence, one chosen by the people, the other appointed by the House of Assembly; in the former, Massachusetts preceded Virginia; in the latter, Virginia preceded Massachusetts.’ To the origination of committees for the interior correspondence between the counties and towns of a state, I know of no claim on the part of Virginia; and certainly none was ever made by myself. I perceive, however, one error, into which memory had led me. Our committee for national correspondence was appointed in March, ‘73, and I well remember, that going to Williamsburg in the month of June following, Peyton Randolph, our chairman, told me that messengers bearing despatches between the two states had crossed each other by the way, that of Virginia carrying our propositions for a committee of national correspondence, and that of Massachusetts, bringing, as my memory suggested, a similar proposition. But here I must have misremembered; and the resolutions brought us from Massachusetts were probably those you mention of the town-meeting of Boston, on the motion of Mr. Samuel Adams, appointing a committee ‘to state the rights of the colonists, and of that province in particular, and the infringements of them; to communicate them to the several towns, as the sense of the town of Boston, and to request, of each town, a free, communication of its sentiments on this subject.’ I suppose, therefore, that these resolutions were not received, as you think, while the House of Burgesses was in session in March, 1773, but a few days after we rose, and were probably what was sent by the messenger, who crossed ours by the way. They may, however, have been still different. I must, therefore, have been mistaken in supposing, and stating to Mr. Wirt, that the proposition of a committee for national correspondence was nearly simultaneous in Virginia and Massachusetts.
A similar misapprehension of another passage in Mr. Wirt’s book, for which I am also quoted, has produced a similar reclamation on the part of Massachusetts, by some of her most distinguished and estimable citizens. I had been applied to by Mr. Wirt, for such facts respecting Mr. Henry, as my intimacy with him and participation in the transactions of the day, might have placed within my knowledge. I accordingly committed them to paper; and Virginia being the theatre of his action, was the only subject within my contemplation. While speaking of him, of the resolutions and measures here, in which he had the acknowledged lead, I used the expression that ‘Mr. Henry certainly gave the first impulse to the ball of revolution.’ [Wirt, page 41.] The expression is indeed general, and in all its extension would comprehend all the sister states; but indulgent construction would restrain it, as was really meant, to the subject matter under contemplation, which was Virginia alone; according to the rule of the lawyers, and a fair canon of general criticism, that every expression should be construed secundum subjectam materiam. Where the first attack was made, there must have been of course, the first act of resistance, and that was in Massachusetts. Our first overt act of war, was Mr. Henry’s embodying a force of militia from several counties, regularly armed and organized, marching them in military array, and making reprisal on the King’s treasury at the seat of government, for the public powder taken away by his Governor. This was on the last days of April, 1775. Your formal battle of Lexington was ten or twelve days before that, and greatly overshadowed in importance, as it preceded in time, our little affray, which merely amounted to a levying of arms against the King; and very possibly, you had had military affrays before the regular battle of Lexington.
These explanations will, I hope, assure you, Sir, that so far as either facts or opinions have been truly quoted from me, they have never been meant to intercept the just fame of Massachusetts, for the promptitude and perseverance of her early resistance. We willingly cede to her the laud of having been (although not exclusively) ‘the cradle of sound principles,’ and, if some of us believe she has deflected from them in her course, we retain full confidence in her ultimate return to them.
I will now proceed to your quotation from Mr. Galloway’s statement of what passed in Congress, on their Declaration of Independence; in which statement there is not one word of truth, and where bearing some resemblance to truth, it is an entire perversion of it. I do not charge this on Mr. Galloway himself; his desertion having taken place long before these measures, he doubtless received his information from some of the loyal friends whom he left behind him. But as yourself, as well as others, appear embarrassed by inconsistent accounts of the proceedings on that memorable occasion, and as those who have endeavored to restore the truth, have themselves committed some errors, I will give you some extracts from a written document on that subject; for the truth of which, I pledge myself to heaven and earth; having, while the question of Independence was under consideration before Congress, taken written notes, in my seat, of what was passing, and reduced them to form on the final conclusion. I have now before me that paper, from which the following are extracts. ‘Friday, June 7th, 1776. The delegates from Virginia moved, in obedience to instructions from their constituents, that the Congress should declare that these United Colonies are, and of right ought to be, free and independent states; that they are absolved from all allegiance to the British crown, and that all political connection between them and the state of Great Britain is, and ought to be, totally dissolved; that measures should be immediately taken for procuring the assistance of foreign powers, and a Confederation be formed to bind the colonies more closely together. The House being obliged to attend at that time to some other business, the proposition was referred to the next day, when the members were ordered to attend punctually at ten o’clock. Saturday, June 8th. They proceeded to take it into consideration, and referred it to a committee of the whole, into which they immediately resolved themselves, and passed that day and Monday, the 10th, in debating on the subject.
‘It appearing, in the course of these debates, that the colonies of New York, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, Delware, Maryland, and South Carolina, were not yet matured for falling from the parent stem, but that they were fast advancing to that state, it was thought most prudent to wait a while for them, and to postpone the final decision to July 1st. But, that this might occasion as little delay as possible, a Committee was appointed to prepare a Declaration of Independence. The Committee were John Adams, Dr. Franklin, Roger Sherman, Robert R. Livingston, and myself. This was reported to the House on Friday the 28th of June, when it was read and ordered to lie on the table. On Monday, the 1st of July, the House resolved itself into a Committee of the whole, and resumed the consideration of the original motion made by the delegates of Virginia, which, being again debated through the day, was carried in the affirmative by the votes of New Hampshire, Connecticut, Massachusetts, Rhode Island, New Jersey, Maryland, Virginia, North Carolina, and Georgia. South Carolina and Pennsylvania voted against it. Delaware had but two members present, and they were divided. The delegates from New York declared they were for it themselves, and were assured their constituents were for it; but that their instructions having been drawn near a twelvemonth before, when reconciliation was still the general object, they were enjoined by them, to do nothing which should impede that object. They, therefore, thought themselves not justifiable in voting on either side, and asked leave to withdraw from the question, which was given them. The Committee rose, and reported their resolution to the House. Mr. Rutledge, of South Carolina, then requested the determination might be put off to the next day, as he believed his colleagues, though they disapproved of the resolution, would then join in it for the sake of unanimity. The ultimate question, whether the House would agree to the resolution of the Committee, was accordingly postponed to the next day, when it was again moved, and South Carolina concurred in voting for it. In the mean time, a third member had come post from the Delaware counties, and turned the vote of that colony in favor of the resolution. Members of a different sentiment attending that morning from Pennsylvania also, her vote was changed; so that the whole twelve colonies, who were authorized to vote at all, gave their votes for it; and within a few days [July 9th] the convention of New York approved of it, and thus supplied the void occasioned by the withdrawing of their delegates from the vote.’ [Be careful to observe, that this vacillation and vote were on the original motion of the 7th of June, by the Virginia delegates, that Congress should declare the colonies independent.] ‘Congress proceeded, the same day, to consider the Declaration of Independence, which had been reported and laid on the table the Friday preceding, and on Monday referred to a Committee of the whole. The pusillanimous idea, that we had friends in England worth keeping terms with, still haunted the minds of many. For this reason, those passages which conveyed censures on the people of England were struck out, lest they should give them offence. The debates having taken up the greater parts of the second, third, and fourth days of July, were, in the evening of the last, closed: the Declaration was reported by the Committee, agreed to by the House, and signed by every member present except Mr. Dickinson.’ So far my notes.
Governor M’Kean, in his letter to M’Corkle of July 16th, 1817, has thrown some lights on the transactions of that day: but, trusting to his memory chiefly, at an age when our memories are not to be trusted, he has confounded two questions, and ascribed proceedings to one which belonged to the other. These two questions were, 1st, the Virginia motion of June the 7th, to declare Independence; and 2nd, the actual Declaration, its matter and form. Thus he states the question on the Declaration itself, as decided on the 1st of July; but it was the Virginia motion which was voted on that day in committee of the whole; South Carolina, as well as Pennsylvania, then voting against it. But the ultimate decision in the House, on the report of the Committee, being, by request, postponed to the next morning, all the states voted for it, except New York, whose vote was delayed for the reason before stated. It was not till the 2nd of July, that the Declaration itself was taken up; nor till the 4th, that it was decided, and it was signed by every member present, except Mr. Dickinson.
The subsequent signatures of members who were not then present, and some of them not yet in office, is easily explained, if we observe who they were; to wit, that they were of New York and Pennsylvania. New York did not sign till the 15th, because it was not till the 9th, (five days after the general signature,) that their Convention authorized them to do so. The Convention of Pennsylvania, learning that it had been signed by a majority only of their delegates, named a new delegation on the 20th, leaving out Mr. Dickinson, who had refused to sign, Willing and Humphreys, who had withdrawn, reappointing the three members who had signed, Morris, who had not been present, and five new ones, to wit, Rush, Clymer, Smith, Taylor, and Ross: and Morris and the five new members were permitted to sign, because it manifested the assent of their full delegation, and the express will of their Convention, which might have been doubted on the former signature of a minority only. Why the signature of Thornton, of New Hampshire, was permitted so late as the 4th of November, I cannot now say; but undoubtedly for some particular reason, which we should find to have been good, had it been expressed. These were the only post-signers, and you see, sir, that there were solid reasons for receiving those of New York and Pennsylvania, and that this circumstance in no wise affects the faith of this Declaratory Charter of our rights, and of the rights of man.
With a view to correct errors of fact before they become inveterate by repetition, I have stated what I find essentially material in my papers, but with that brevity which the labor of writing constrains me to use.
On the four particular articles of inquiry in your letter, respecting your grandfather, the venerable Samuel Adams, neither memory nor memorandums enable me to give any information. I can say that he was truly a great man, wise in council, fertile in resources, immovable in his purposes, and had, I think, a greater share than any other member, in advising and directing our measures in the Northern war. As a speaker, he could not be compared with his living colleague and namesake, whose deep conceptions, nervous style, and undaunted firmness, made him truly our bulwark in debate. But Mr. Samuel Adams, although not of fluent elocution, was so rigorously logical, so clear in his views, abundant in good sense, and master always of his subject, that he commanded the most profound attention whenever he rose in an assembly, by which the froth of declamation was heard with the most sovereign contempt. I sincerely rejoice that the record of his worth is to be undertaken by one so much disposed as you will be, to hand him down fairly to that posterity, for whose liberty and happiness he was so zealous a laborer.
With sentiments of sincere veneration for his memory, accept yourself this tribute to it, with the assurances of my great respect.
Th: Jefferson.
P. S. August 6th, 1822. Since the date of this letter, to wit, this day, August 6, ‘22, I have received the new publication of the Secret Journals of Congress, wherein is stated a resolution of July 19th, 1776, that the Declaration passed on the 4th, be fairly engrossed on parchment, and when engrossed, be signed by every member; and another of August 2nd, that being engrossed and compared at the table, it was signed by the members; that is to say, the copy engrossed on parchment (for durability) was signed by the members, after being compared at the table with the original one signed on paper, as before stated. I add this P. S. to the copy of my letter to Mr. Wells, to prevent confounding the signature of the original with that of the copy engrossed on parchment.
On the Instructions given to the first Delegation of Virginia to Congress, in August, 1774.
The Legislature of Virginia happened to be in session in Williamsburg, when news was received of the passage, by the British Parliament, of the Boston Port Bill, which was to take effect on the first day of June then ensuing. The House of Burgesses, thereupon, passed a resolution, recommending to their fellow-citizens that that day should be set apart for fasting and prayer to the Supreme Being, imploring him to avert the calamities then threatening us, and to give us one heart and one mind to oppose every invasion of our liberties. The next day, May the 20th, 1774, the Governor dissolved us. We immediately repaired to a room in the Raleigh tavern, about one hundred paces distant from the Capitol, formed ourselves into a meeting, Peyton Randolph in the chair, and came to resolutions, declaring, that an attack on one colony to enforce arbitrary acts, ought to be considered as an attack on all, and to be opposed by the united wisdom of all. We, therefore, appointed a Committee of Correspondence, to address letters to the Speakers of the several Houses of Representatives of the colonies, proposing the appointment of deputies from each, to meet annually in a general Congress, to deliberate on their common interests, and on the measures to be pursued in common. The members then separated to their several homes, except those of the Committee, who met the next day, prepared letters according to instructions, and despatched them by messengers express, to their several destinations. It had been agreed, also by the meeting, that the Burgesses, who should be elected under the writs then issuing, should be requested to meet in Convention on a certain day in August, to learn the result of these letters, and to appoint delegates to a Congress, should that measure be approved by the other colonies. At the election, the people re-elected every man of the former Assembly, as a proof of their approbation of what they had done. Before I left home to attend the Convention, I prepared what I thought might be given, in instruction, to the Delegates who should be appointed to attend the General Congress proposed. They were drawn in haste, with a number of blanks, with some uncertainties and inaccuracies of historical facts, which I neglected at the moment, knowing they could be readily corrected at the meeting. I set out on my journey, but was taken sick on the road, and was unable to proceed. I therefore sent on, by express, two copies, one under cover to Patrick Henry, the other to Peyton Randolph, who I knew would be in the chair of the Convention. Of the former no more was ever heard or known. Mr. Henry probably thought it too bold, as a first measure, as the majority of the members did. On the other copy being laid on the table of the Convention, by Peyton Randolph, as the proposition of a member who was prevented from attendance by sickness on the road, tamer sentiments were preferred, and, I believe, wisely preferred; the leap I proposed being too long, as yet, for the mass of our citizens. The distance between these, and the instructions actually adopted, is of some curiosity, however, as it shows the inequality of pace with which we moved, and the prudence required to keep front and rear together. My creed had been formed on unsheathing the sword at Lexington. They printed the paper, however, and gave it the title of ‘A Summary View of the Rights of British America.’ In this form it got to London, where the opposition took it up, shaped it to opposition views, and, in that form, it ran rapidly through several editions.
Mr. Marshall, in his history of General Washington, chapter 3, speaking of this proposition for Committees of correspondence and for a General Congress, says, ‘this measure had already been proposed in town meeting in Boston,’ and some pages before he had said, that ‘at a session of the General Court of Massachusetts, in September, 1770, that Court, in pursuance of a favorite idea of uniting all the colonies in one system of measures, elected a Committee of correspondence, to communicate with such Committees as might be appointed by the other colonies.’ This is an error. The Committees of correspondence, elected by Massachusetts, were expressly for a correspondence among the several towns of that province only. Besides the text of their proceedings, his own note X, proves this. The first proposition for a general correspondence between the several states, and for a General Congress, was made by our meeting of May, 1774. Botta, copying Marshall, has repeated his error, and so it will be handed on from copyist to copyist, ad infinitum. Here follow my proposition, and the more prudent one which was adopted.
‘Resolved, That it be an instruction to the said deputies, when assembled in General Congress, with the deputies from the other states of British America, to propose to the said Congress that an humble and dutiful address be presented to his Majesty, begging leave to lay before him, as Chief Magistrate of the British empire, the united complaints of his Majesty’s subjects in America; complaints which are excited by many unwarrantable encroachments and usurpations, attempted to be made by the legislature of one part of the empire upon the rights which God and the laws have given equally and independently to all. To represent to his Majesty that, these, his States, have often individually made humble application to his imperial throne, to obtain, through its intervention, some redress of their injured rights; to none of which was ever even an answer condescended. Humbly to hope that this, their joint address, penned in the language of truth, and divested of those expressions of servility which would persuade his Majesty that we are asking favors, and not rights, shall obtain from his Majesty a more respectful acceptance; and this his Majesty will think we have reason to expect, when he reflects that he is no more than the chief officer of the people, appointed by the laws, and circumscribed with definite powers, to assist in working the great machine of government, erected for their use, and, consequently, subject to their superintendence; and in order that these, our rights, as well as the invasions of them, may be laid more fully before his Majesty, to take a view of them from the origin and first settlement of these countries.
‘To remind him that our ancestors, before their emigration to America, were the free inhabitants of the British dominions in Europe, and possessed a right, which nature has given to all men, of departing from the country in which chance, not choice, has placed them, of going in quest of new habitations, and of there establishing new societies, under such laws and regulations, as to them shall seem most likely to promote public happiness. That their Saxon ancestors had, under this universal law, in like manner left their native wilds and woods in the North of Europe, had possessed themselves of the island of Britain, then less charged with inhabitants, and had established there that system of laws which has so long been the glory and protection of that country. Nor was ever any claim of superiority or dependence asserted over them, by that mother country from which they had migrated: and were such a claim made, it is believed his Majesty’s subjects in Great Britain have too firm a feeling of the rights derived to them from their ancestors, to bow down the sovereignty of their state before such visionary pretensions. And it is thought that no circumstance has occurred to distinguish, materially, the British from the Saxon emigration. America was conquered, and her settlements made and firmly established, at the expense of individuals, and not of the British public. Their own blood was spilt in acquiring lands for their settlement, their own fortunes expended in making that settlement effectual. For themselves they fought, for themselves they conquered, and for themselves alone they have right to hold. No shilling was ever issued from the public treasures of his Majesty, or his ancestors, for their assistance, till of very late times, after the colonies had become established on a firm and permanent fooling. That then, indeed, having become valuable to Great Britain for her commercial purposes, his Parliament was pleased to lend them assistance, against an enemy who would fain have drawn to herself the benefits of their commerce, to the great aggrandizement of herself, and danger of Great Britain. Such assistance, and in such circumstances, they had often before given to Portugal and other allied states, with whom they carry on a commercial intercourse. Yet these states never supposed, that by calling in her aid, they thereby submitted themselves to her sovereignty. Had such terms been proposed, they would have rejected them with disdain, and trusted for better to the moderation of their enemies, or to a vigorous exertion of their own force. We do not, however, mean to underrate those aids, which, to us, were doubtless valuable, on whatever principles granted: but we would show that they cannot give a title to that authority which the British Parliament would arrogate over us; and that they may amply be repaid, by our giving to the inhabitants of Great Britain such exclusive privileges in trade as may be advantageous to them, and, at the same time, not too restrictive to ourselves. That settlement having been thus effected in the wilds of America, the emigrants thought proper to adopt that system of laws, under which they had hitherto lived in the mother country, and to continue their union with her, by submitting themselves to the same common sovereign, who was thereby made the central link, connecting the several parts of the empire thus newly multiplied.
‘But that not long were they permitted, however far they thought themselves removed from the hand of oppression, to hold undisturbed, the rights thus acquired at the hazard of their lives and loss of their fortunes. A family of Princes was then on the British throne, whose treasonable crimes against their people brought on them, afterwards, the exertion of those sacred and sovereign rights of punishment, reserved in the hands of the people for cases of extreme necessity, and judged by the constitution unsafe to be delegated to any other judicature. While every day brought forth some new and unjustifiable exertion of power over their subjects on that side the water, it, was not to be expected that those here, much less able at that time to oppose the designs of despotism, should be exempted from injury. Accordingly, this country, which had been acquired by the lives, the labors, and fortunes of individual adventurers, was by these Princes, at several times, parted out and distributed among the favorites and followers of their fortunes; and, by an assumed right of the crown alone, were erected into distinct and independent governments; a measure, which, it is believed, his Majesty’s prudence and understanding would prevent him from imitating at this day; as no exercise of such power, of dividing and dismembering a country, has ever occurred in his Majesty’s realm of England, though now of very ancient standing; nor could it be justified or acquiesced under there, or in any other part of his Majesty’s empire.
‘That the exercise of a free trade with all parts of the world, possessed by the American colonists, as of natural right, and which no law of their own had taken away or abridged, was next the object of unjust encroachment. Some of the colonies having thought proper to continue the administration of their government in the name and under the authority of his Majesty, King Charles the First, whom, notwithstanding his late deposition by the Commonwealth of England, they continued in the sovereignty of their State, the Parliament, for the Commonwealth, took the same in high offence, and assumed upon themselves the power of prohibiting their trade with all other parts of the world, except the Island of Great Britain. This arbitrary act, however, they soon recalled, and by solemn treaty entered into on the 12th day of March, 1651, between the said Commonwealth by their Commissioners, and the colony of Virginia by their House of Burgesses, it was expressly stipulated by the eighth article of the said treaty, that they should have “free trade as the people of England do enjoy to all places and with all nations, according to the laws of that Commonwealth.” But that, upon the restoration of his Majesty, King Charles the Second, their rights of free commerce fell once more a victim to arbitrary power: and by several acts of his reign, as well as of some of his successors, the trade of the colonies was laid under such restrictions, as show what hopes they might form from the justice of a British Parliament, were its uncontrolled power admitted over these States.*
*12. C.2. c. 18. 15. C.2. c.11. 25. C.2. c.7. 7. 8. W. M.
c.22. 11. W.34. Anne. 6. C.2. c.13.
History has informed us, that bodies of men, as well as individuals, are susceptible of the spirit of tyranny. A view of these acts of Parliament for regulation, as it has been affectedly called, of the American trade, if all other evidences were removed out of the case, would undeniably evince the truth of this observation. Besides the duties they impose on our articles of export and import, they prohibit our going to any markets northward of Cape Finisterra, in the kingdom of Spain, for the sale of commodities which Great Britian will not take from us, and for the purchase of others, with which she cannot supply us; and that, for no other than the arbitrary purpose of purchasing for themselves, by a sacrifice of our rights and interests, certain privileges in their commerce with an allied state, who, in confidence that their exclusive trade with America will be continued, while the principles and power of the British Parliament be the same, have indulged themselves in every exorbitance which their avarice could dictate, or our necessities extort; have raised their commodities called for in America, to the double and treble of what they sold for, before such exclusive privileges were given them, and of what better commodities of the same kind would cost us elsewhere; and, at the same time, give us much less for what we carry thither, than might be had at more convenient ports. That these acts prohibit us from carrying, in quest of other purchasers, the surplus of our tobaccos, remaining after the consumption of Great Britain is supplied: so that we must leave them with the British merchant, for whatever he will please to allow us, to be by him re-shipped to foreign markets, where he will reap the benefits of making sale of them for full value. That, to heighten still the idea of Parliamentary justice, and to show with what moderation they are like to exercise power, where themselves are to feel no part of its weight, we take leave to mention to his Majesty certain other acts of the British Parliament, by which they would prohibit us from manufacturing, for our own use, the articles we raise on our own lands, with our own labor. By an act passed in the fifth year of the reign of his late Majesty, King George the Second, an American subject is forbidden to make a hat for himself, of the fur which he has taken, perhaps on his own soil; an instance of despotism, to which no parallel can be produced in the most arbitrary ages of British history. By one other act, passed in the twenty-third year of the same reign, the iron which we make, we are forbidden to manufacture; and, heavy as that article is, and necessary in every branch of husbandry, besides commission and insurance, we are to pay freight for it to Great Britain, and freight for it back again, for the purpose of supporting, not men, but machines, in the island of Great Britain. In the same spirit of equal and impartial legislation, is to be viewed the act of Parliament, passed in the fifth year of the same reign, by which American lands are made subject to the demands of British creditors, while their own lands were still continued unanswerable for their debts; from which one of these conclusions must necessarily follow, either that justice is not the same thing in America as in Britain, or else that the British Parliament pay less regard to it here than there. But, that we do not point out to his Majesty the injustice of these acts, with intent to rest on that principle the cause of their nullity; but to show that experience confirms the propriety of those political principles, which exempt us from the jurisdiction of the British Parliament. The true ground on which we declare these acts void, is, that the British Parliament has no right to exercise authority over us.
‘That these exercises of usurped power have not been confined to instances alone, in which themselves were interested; but they have also intermeddled with the regulation of the internal affairs of the colonies. The act of the 9th of Anne for establishing a post-office in America seems to have had little connection with British convenience, except that of accommodating his Majesty’s ministers and favorites with the sale of a lucrative and easy office.
‘That thus have we hastened through the reigns which preceded his Majesty’s, during which the violations of our rights were less alarming, because repeated at more distant intervals, than that rapid and bold succession of injuries, which is likely to distinguish the present from all other periods of American story. Scarcely have our minds been able to emerge from the astonishment, into which one stroke of Parliamentary thunder has involved us, before another more heavy and more alarming is fallen on us. Single acts of tyranny may be ascribed to the accidental opinion of a day; but a series of oppressions, begun at a distinguished period, and pursued unalterably through every change of ministers, too plainly prove a deliberate, systematical plan of reducing us to slavery.

‘That the act passed in the fourth year of his Majesty’s reign, entitled “an act [ Act for granting certain duties.]
‘One other act passed in the fifth year of his reign, entitled “an act [Stamp Act.]
‘One other act passed in the sixth year of his reign, entitled “an act [Act declaring the right of Parliament over the colonies.]
‘And one other act passed in the seventh year of his reign, entitled an act [ Act for granting duties on paper, tea, &c.
‘Form that connected chain of parliamentary usurpation, which has already been the subject of frequent applications to his Majesty, and the Houses of Lords and Commons of Great Britain; and, no answers having yet been condescended to any of these, we shall not trouble his Majesty with a repetition of the matters they contained.
‘But that one other act passed in the same seventh year of his reign, having been a peculiar attempt, must ever require peculiar mention. It is entitled “an act [Act suspending Legislature of New York.]
‘One free and independent legislature hereby takes upon itself to suspend the powers of another, free and independent as itself. Thus exhibiting a phenomenon unknown in nature, the creator and creature of its own power. Not only the principles of common sense, but the common feelings of human nature must be surrendered up, before his Majesty’s subjects here can be persuaded to believe, that they hold their political existence at the will of a British Parliament. Shall these governments be dissolved, their property annihilated, and their people reduced to a state of nature, at the imperious breath of a body of men whom they never saw, in whom they never confided, and over whom they have no powers of punishment or removal, let their crimes against the American public be ever so great? Can any one reason be assigned, why one hundred and sixty thousand electors in the island of Great Britain should give law to four millions in the states of America, every individual of whom is equal to every individual of them in virtue, in understanding, and in bodily strength? Were this to be admitted, instead of being a free people, as we have hitherto supposed, and mean to continue ourselves, we should suddenly be found the slaves, not of one, but of one hundred and sixty thousand tyrants; distinguished, too, from all others, by this singular circumstance, that they are removed from the reach of fear, the only restraining motive which may hold the hand of a tyrant.
‘That, by “an act to discontinue in such manner, and for such time as are therein mentioned, the landing and discharging, lading or shipping of goods, wares, and merchandise, at the town and within the harbor of Boston, in the province of Massachusetts Bay, in North America,” [14 G.3.] which was passed at the last session of the British Parliament, a large and populous town, whose trade was their sole subsistence, was deprived of that trade, and involved in utter ruin. Let us for a while, suppose the question of right suspended, in order to examine this act on principles of justice. An act of Parliament had been passed, imposing duties on teas, to be paid in America, against which act the Americans had protested, as inauthoritative. The East India Company, who till that time had never sent a pound of tea to America on their own account, step forth on that occasion, the asserters of Parliamentary right, and send hither many ship-loads of that obnoxious commodity. The masters of their several vessels, however, on their arrival in America, wisely attended to admonition, and returned with their cargoes. In the province of New England alone, the remonstrances of the people were disregarded, and a compliance, after being many days waited for, was flatly refused. Whether in this, the master of the vessel was governed by his obstinacy, or his instructions, let those who know, say. There are extraordinary situations which require extraordinary interposition. An exasperated people, who feel that they possess power, are not easily restrained within limits strictly regular. A number of them assembled in the town of Boston, threw the tea into the ocean, and dispersed without doing any other act of violence. If in this they did wrong, they were known, and were amenable to the laws of the land; against which, it could not be objected that they had ever, in any instance, been obstructed or diverted from their regular course, in favor of popular offenders. They should, therefore, not have been distrusted on this occasion. But that ill-fated colony had formerly been bold in their enmities against the House of Stuart, and were now devoted to ruin, by that unseen hand which governs the momentous affairs of this great empire. On the partial representations of a few worthless ministerial dependants, whose constant office it has been to keep that government embroiled, and who, by their treacheries, hope to obtain the dignity of British knighthood, without calling for a party accused, without asking a proof, without attempting a distinction between the guilty and the innocent, the whole of that ancient and wealthy town, is in a moment reduced from opulence to beggary. Men who had spent their lives in extending the British commerce, who had invested in that place, the wealth their honest endeavors had merited, found themselves and their families, thrown at once on the world, for subsistence by its charities. Not the hundredth part of the inhabitants of that town had been concerned in the act complained of; many of them were in Great Britain, and in other parts beyond sea; yet all were involved in one indiscriminate ruin, by a new executive power, unheard of till then, that of a British Parliament. A property of the value of many millions of money was sacrificed to revenge, not to repay, the loss of a few thousands. This is administering justice with a heavy hand indeed! And when is this tempest to be arrested in its course? Two wharves are to be opened again when his Majesty shall think proper: the residue which lined the extensive shores of the bay of Boston, are for ever interdicted the exercise of commerce. This little exception seems to have been thrown in for no other purpose, than that of setting a precedent for investing his Majesty with legislative powers. If the pulse of his people shall beat calmly under this experiment, another and another will be tried, till the measure of despotism be filled up. It would be an insult on common sense, to pretend that this exception was made in order to restore its commerce to that great town. The trade which cannot be received at two wharves alone, must of necessity be transferred to some other place; to which it will soon be followed by that of the two wharves. Considered in this light, it would be an insolent and cruel mockery at the annihilation of the town of Boston. By the act for the suppression of riots and tumults in the town of Boston, [14 G.3.] passed also in the last session of Parliament, a murder committed there, is, if the Governor pleases, to be tried in the court of King’s Bench, in the island of Great Britain, by a jury of Middlesex. The witnesses, too, on receipt of such a sum as the Governor shall think it reasonable for them to expend, are to enter into recognisance to appear at the trial. This is, in other words, taxing them to the amount of their recognisance; and that amount may be whatever a Governor pleases. For who does his Majesty think can be prevailed on to cross the Atlantic, for the sole purpose of bearing evidence to a fact? His expenses are to be borne, indeed, as they shall be estimated by a Governor; but who are to feed the wife and children whom he leaves behind, and who have had no other subsistence but his daily labor? Those epidemical disorders, too, so terrible in a foreign climate, is the cure of them to be estimated among the articles of expense, and their danger to be warded off by the almighty power of a Parliament? And the wretched criminal, if he happen to have offended on the American side, stripped of his privilege of trial by peers of his vicinage, removed from the place where alone full evidence could be obtained, without money, without counsel, without friends, without exculpatory proof, is tried before Judges predetermined to condemn. The cowards who would suffer a countryman to be torn from the bowelss of their society, in order to be thus offered a sacrifice to Parliamentary tyranny, would merit that everlasting infamy now fixed on the authors of the act! A clause, for a similar purpose, had been introduced into an act passed in the twelfth year of his Majesty’s reign, entitled, “an act for the better securing and preserving his Majesty’s dock-yards, magazines, ships, ammunition, and stores;” against which, as meriting the same censures, the several colonies have already protested.
‘That these are the acts of power, assumed by a body of men foreign to our constitutions, and unacknowledged by our laws; against which we do, on behalf of the inhabitants of British America, enter this our solemn and determined protest. And we do earnestly entreat his Majesty, as yet the only mediatory power between the several states of the British empire, to recommend to his Parliament of Great Britain, the total revocation of these acts, which, however nugatory they be, may yet prove the cause of further discontents and jealousies among us.
‘That we next proceed to consider the conduct of his Majesty, as holding the Executive powers of the laws of these states, and mark out his deviations from the line of duty. By the constitution of Great Britain, as well as of the several American States, his Majesty possesses the power of refusing to pass into a law, any bill which has already passed the other two branches of the legislature. His Majesty, however, and his ancestors, conscious of the impropriety of opposing their single opinion to the united wisdom of two Houses of Parliament, while their proceedings were unbiased by interested principles, for several ages past, have modestly declined the exercise of this power, in that part of his empire called Great Britain. But, by change of circumstances, other principles than those of justice simply, have obtained an influence on their determinations. The addition of new states to the British empire, has produced an addition of new, and sometimes, opposite interests. It is now, therefore, the great office of his Majesty, to resume the exercise of his negative power, and to prevent the passage of laws by any one legislature of the empire, which might bear injuriously on the rights and interests of another. Yet this will not excuse the wanton exercise of this power, which we have seen his Majesty practise on the laws of the American legislatures. For the most trifling reasons, and sometimes for no conceivable reason at all, his Majesty has rejected laws of the most salutary tendency. The abolition of domestic slavery is the great object of desire in those colonies, where it was, unhappily, introduced in their infant state. But previous to the enfranchisement of the slaves we have, it is necessary to exclude all further importations from Africa. Yet our repeated attempts to effect this, by prohibitions, and by imposing duties which might amount to a prohibition, have been hitherto defeated by his Majesty’s negative: thus preferring the immediate advantages of a few British corsairs to the lasting interests of the American States, and to the rights of human nature, deeply wounded by this infamous practice. Nay, the single interposition of an interested individual against a law, was scarcely ever known to fail of success, though in the opposite scale were placed the interests of a whole country. That this is so shameful an abuse of a power, trusted with his Majesty for other purposes, as if, not reformed, would call for some legal restrictions.
‘With equal inattention to the necessities of his people here, has his Majesty permitted our laws to lie neglected in England for years, neither confirming them by his assent, nor annulling them by his negative: so that such of them as have no suspending clause, we hold on the most precarious of all tenures, his Majesty’s will; and such of them as suspend themselves till his Majesty’s assent be obtained, we have feared might be called into existence at some future and distant period, when time and change of circumstances shall have rendered them destructive to his people here. And, to render this grievance still more oppressive, his Majesty, by his instructions, has laid his Governors under such restrictions, that they can pass no law of any moment, unless it have such suspending clause: so that, however immediate may be the call for legislative interposition, the law cannot be executed till it has twice crossed the Atlantic, by which time the evil may have spent its whole force.
‘But in what terms reconcilable to Majesty, and,at the same time to truth, shall we speak of a late instruction to his Majesty’s Governor of the colony of Virginia, by which he is forbidden to assent to any law for the division of a county, unless the new county will consent to have no representative in Assembly? That colony has as yet affixed no boundary to the westward. Their Western counties, therefore, are of indefinite extent. Some of them are actually seated many hundred miles from their Eastern limits. Is it possible, then that his Majesty can have bestowed a single thought on the situation of those people, who, in order to obtain justice for injuries, however great or small, must, by the laws of that colony, attend their county court at such a distance, with all their witnesses, monthly, till their litigation be determined? Or does his Majesty seriously wish, and publish it to the world, that his subjects should give up the glorious right of representation, with all the benefits derived from that, and submit themselves to be absolute slaves of his sovereign will? Or is it rather meant to confine the legislative body to their present numbers, that they may be the cheaper bargain, whenever they shall become worth a purchase?
‘One of the articles of impeachment against Tresilian and the other Judges of Westminster Hall, in the reign of Richard the Second, for which they suffered death, as traitors to their country, was, that they had advised the King that he might dissolve his Parliament at any time: and succeeding Kings have adopted the opinion of these unjust Judges. Since the establishment, however, of the British constitution, at the glorious Revolution, on its free and ancient principles, neither his Majesty nor his ancestors have exercised such a power of dissolution in the island of Great Britain;* and, when his Majesty was petitioned by the united voice of his people there to dissolve the present Parliament, who had become obnoxious to them, his Ministers were heard to declare, in open Parliament, that his Majesty possessed no such power by the constitution. But how different their language, and his practice, here! To declare, as their duty required, the known rights of their country, to oppose the usurpation of every foreign judicature, to disregard the imperious mandates of a Minister or Governor, have been the avowed causes of dissolving Houses of Representatives in America. But if such powers be really vested in his Majesty, can he suppose they are there placed to awe the members from such purposes as these? When the representative body have lost the confidence of their constituents, when they have notoriously made sale of their most valuable rights, when they have assumed to themselves powers which the people never put into their hands, then, indeed, their continuing in office becomes dangerous to the state, and calls for an exercise of the power of dissolution. Such being the causes for which the representative body should, and should not, be dissolved, will it not appear strange, to an unbiassed observer, that that of Great Britain was not dissolved, while those of the colonies have repeatedly incurred that sentence?
* On further inquiry, I find two instances of dissolutions
before the Parliament would, of itself, have been at an end:
viz. the Parliament called to meet August 24, 1698, was
dissolved by King William, December 19, 1700, and a new one
called, to meet February 6, 1701, which was also dissolved
November 11, 1701, and a new one met December 30, 1701.
But your Majesty or your Governors have carried this power beyond every limit known or provided for by the laws. After dissolving one House of Representatives, they have refused to call another, so that, for a great length of time, the legislature provided by the laws has been out of existence. From the nature of things, every society must at all times possess within itself the sovereign powers of legislation. The feelings of human nature revolt against the supposition of a state so situated, as that it may not, in any emergency, provide against dangers which perhaps threaten immediate ruin. While those bodies are in existence to whom the people have delegated the powers of legislation, they alone possess, and may exercise, those powers. But when they are dissolved, by the lopping off one or more of their branches, the power reverts to the people, who may use it to unlimited extent, either assembling together in person, sending deputies, or in any other way they may think proper. We forbear to trace consequences further; the dangers are conspicuous with which this practice is replete.
‘That we shall, at this time also, take notice of an error in the nature of our land-holdings, which crept in at a very early period of our settlement. The introduction of the feudal tenures into the kingdom of England, though ancient, is well enough understood to set this matter in a proper light. In the earlier ages of the Saxon settlement, feudal holdings were certainly altogether unknown, and very few, if any, had been introduced at the time of the Norman conquest. Our Saxon ancestors held their lands, as they did their personal property, in absolute dominion, disencumbered with any superior, answering nearly to the nature of those possessions which the Feudalists term Allodial. William the Norman first introduced that system generally. The lands which had belonged to those who fell in the battle of Hastings, and in the subsequent insurrections of his reign, formed a considerable proportion of the lands of the whole kingdom. These he granted out, subject to feudal duties, as did he also those of a great number of his new subjects, who, by persuasions or threats, were induced to surrender them for that purpose. But still much was left in the hands of his Saxon subjects, held of no superior, and not subject to feudal conditions. These, therefore, by express laws, enacted to render uniform the system of military defence, were made liable to the same military duties as if they had been feuds: and the Norman lawyers soon found means to saddle them, also, with all the other feudal burthens. But still they had not been surrendered to the King, they were not derived from his grant, and therefore they were not holden of him. A general principle, indeed, was introduced, that “all lands in England were held either mediately or immediately of the Crown:” but this was borrowed from those holdings which were truly feudal, and only applied to others for the purposes of illustration. Feudal holdings were, therefore, but exceptions out of the Saxon laws of possession, under which all lands were held in absolute right. These, therefore, still form the basis or groundwork of the common law, to prevail wheresoever the exceptions have not taken place. America was not conquered by William the Norman, nor its lands surrendered to him or any of his successors. Possessions there are, undoubtedly, of the Allodial nature. Our ancestors, however, who migrated hither, were laborers, not lawyers. The fictitious principle, that all lands belong originally to the King, they were early persuaded to believe real, and accordingly took grants of their own lands from the Crown. And while the Crown continued to grant for small sums and on reasonable rents, there was no inducement to arrest the error, and lay it open to public view. But his Majesty has lately taken on him to advance the terms of purchase and of holding to the double of what they were; by which means the acquisition of lands being rendered difficult, the population of our country is likely to be checked. It is time, therefore, for us to lay this matter before his Majesty, and to declare that he has no right to grant lands of himself. From the nature and purpose of civil institutions, all the lands within the limits which any particular society has circumscribed around itself, are assumed by that society, and subject to their allotment; this may be done by themselves assembled collectively, or by their legislature, to whom they may have delegated sovereign authority: and, if they are allotted in neither of these ways, each individual of the society may appropriate to himself such lands as he finds vacant, and occupancy will give him title.
‘That, in order to enforce the arbitrary measures before complained of, his Majesty has, from time to time, sent among us large bodies of armed forces, not made up of the people here, nor raised by the authority of our laws. Did his Majesty possess such a right as this, it might swallow up all our other rights whenever he should think proper. But his Majesty has no right to land a single armed man on our shores; and those whom he sends here are liable to our laws for the suppression and punishment of riots, routs, and unlawful assemblies, or are hostile bodies invading us in defiance of law. When, in the course of the late war, it became expedient that a body of Hanoverian troops should be brought over for the defence of Great Britain, his Majesty’s grandfather, our late sovereign, did not pretend to introduce them under any authority he possessed. Such a measure would have given just alarm to his subjects of Great Britain, whose liberties would not be safe if armed men of another country, and of another spirit, might be brought into the realm at any time, without the consent, of their legislature. He, therefore, applied to Parliament, who passed an act for that purpose, limiting the number to be brought in, and the time they were to continue. In like manner is his Majesty restrained in every part of the empire. He possesses indeed the executive power of the laws in every state; but they are the laws of the particular state, which he is to administer within that state, and not those of any one within the limits of another. Every state must judge for itself, the number of armed men which they may safely trust among them, of whom they are to consist, and under what restrictions they are to be laid. To render these proceedings still more criminal against our laws, instead of subjecting the military to the civil power, his Majesty has expressly made the civil subordinate to the military. But can his Majesty thus put down all law under his feet? Can he erect a power superior to that which erected himself? He has done it indeed by force; but let him remember that force cannot give right.
‘That these are our grievances, which we have thus laid before his Majesty, with that freedom of language and sentiment which becomes a free people, claiming their rights as derived from the laws of nature, and not as the gift of their Chief Magistrate. Let those flatter, who fear: it is not an American art. To give praise where it is not due, might be well from the venal, but would ill beseem those who are asserting the rights of human nature. They know, and will, therefore, say, that Kings are the servants, not the proprietors of the people. Open your breast, Sire, to liberal and expanded thought. Let not the name of George the Third be a blot on the page of history. You are surrounded by British counsellors, but remember that they are parties. You have no ministers for American affairs, because you have none taken from among us, nor amenable to the laws on which they are to give you advice. It behoves you, therefore, to think and to act for yourself and your people. The great principles of right and wrong are legible to every reader: to pursue them, requires not the aid of many counsellors. The whole art of government consists in the art of being honest. Only aim to do your duty, and mankind will give you credit where you fail. No longer persevere in sacrificing the rights of one part of the empire, to the inordinate desires of another: but deal out to all, equal and impartial right. Let no act be passed by any one legislature, which may infringe on the rights and liberties of another. This is the important post in which fortune has placed you, holding the balance of a great, if a well poised empire. This, Sire, is the advice of your great American council, on the observance of which may, perhaps, depend your felicity and future fame, and the preservation of that harmony which alone can continue, both to Great Britain and America, the reciprocal advantages of their connection. It is neither our wish nor our interest to separate from her. We are willing, on our part, to sacrifice every thing which reason can ask, to the restoration of that tranquillity for which all must wish. On their part, let them be ready to establish union on a generous plan. Let them name their terms, but let them be just. Accept of every commercial preference it is in our power to give, for such things as we can raise for their use, or they make for ours. But let them not think to exclude us from going to other markets, to dispose of those commodities which they cannot use, nor to supply those wants which they cannot supply. Still less, let it be proposed, that our properties, within our own territories, shall be taxed or regulated by any power on earth, but our own. The God who gave us life, gave us liberty at the same time: the hand of force may destroy, but cannot disjoin them. This, Sire, is our last, our determined resolution. And that you will be pleased to interpose, with that efficacy which your earnest endeavors may insure, to procure redress of these our great grievances, to quiet the minds of your subjects in British America against any apprehensions of future encroachment, to establish fraternal love and harmony through the whole empire, and that that may continue to the latest ages of time, is the fervent prayer of all British America,’
Instructions for the Deputies appointed to meet in General Congress on the Part of this Colony.
The unhappy disputes between Great Britain and her American colonies, which began about the third year of the reign of his present Majesty, and since, continually increasing, have proceeded to lengths so dangerous and alarming, as to excite just apprehensions in the minds of his Majesty’s faithful subjects of this colony, that they are in danger of being deprived of their natural, ancient, constitutional, and chartered rights, have compelled them to take the same into their most serious consideration; and, being deprived of their usual and accustomed mode of making known their grievances, have appointed us their representatives, to consider what is proper to be done in this dangerous crisis of American affairs. It being our opinion that the united wisdom of North America should be collected in a general congress of all the colonies, we have appointed the Honorable Peyton Randolph, Richard Henry Lee, George Washington, Patrick Henry, Richard Bland, Benjamin Harrison, and Edmund Pendleton, Esquires, deputies to represent this colony in the said Congress, to be held at Philadelphia, on the first Monday in September next.
And that they may be the better informed of our sentiments, touching the conduct we wish them to observe on this important occasion, we desire that they will express, in the first place, our faith and true allegiance to his Majesty, King George the Third, our lawful and rightful sovereign; and that we are determined, with our lives and fortunes, to support him in the legal exercise of all his just rights and prerogatives. And, however misrepresented, we sincerely approve of a constitutional connection with Great Britain, and wish, most ardently, a return of that intercourse of affection and commercial connection, that formerly united both countries, which can only be effected by a removal of those causes of discontent, which have of late unhappily divided us.
It cannot admit of a doubt, but that British subjects in America are entitled to the same rights and privileges, as their fellow subjects possess in Britain; and therefore, that the power assumed by the British Parliament, to bind America by their statutes, in all cases whatsoever, is unconstitutional, and the source of these unhappy differences.
The end of government would be defeated by the British Parliament exercising a power over the lives, the property, and the liberty of American subjects; who are not, and, from their local circumstances, cannot be, there represented. Of this nature, we consider the several acts of Parliament, for raising a revenue in America, for extending the jurisdiction of the courts of Admiralty, for seizing American subjects, and transporting them to Britain, to be tried for crimes committed in America, and the several late oppressive acts respecting the town of Boston and Province of the Massachusetts Bay.
The original constitution of the American colonies possessing their assemblies with the sole right of directing their internal polity, it is absolutely destructive of the end of their institution, that their legislatures should be suspended, or prevented, by hasty dissolutions, from exercising their legislative powers.
Wanting the protection of Britain, we have long acquiesced in their acts of navigation, restrictive of our commerce, which we consider as an ample recompense for such protection; but as those acts derive their efficacy from that foundation alone, we have reason to expect they will be restrained, so as to produce the reasonable purposes of Britain, and not injurious to us.
To obtain redress of these grievances, without which the people of America can neither be safe, free, nor happy, they are willing to undergo the great inconvenience that will be derived to them, from stopping all imports whatsoever, from Great Britain, after the first day of November next, and also to cease exporting any commodity whatsoever, to the same place, after the tenth day of August, 1775. The earnest desire we have to make as quick and full payment as possible of our debts to Great Britain, and to avoid the heavy injury that would arise to this country from an earlier adoption of the non-exportation plan, after the people have already applied so much of their labor to the perfecting of the present crop, by which means they have been prevented from pursuing other methods of clothing and supporting their families, have rendered it necessary to restrain you in this article of non-exportation; but it is our desire, that you cordially co-operate with our sister colonies in General Congress, in such other just and proper methods as they, or the majority, shall deem necessary for the accomplishment of these valuable ends.
The proclamation issued by General Gage, in the government of the Province of the Massachusetts Bay, declaring it treason for the inhabitants of that province to assemble themselves to consider of their grievances, and form associations for their common conduct on the occasion, and requiring the civil magistrates and officers to apprehend all such persons, to be tried for their supposed offences, is the most alarming process that ever appeared in a British government; that the said General Gage hath, thereby, assumed, and taken upon himself, powers denied by the constitution to our legal sovereign; that he, not having condescended to disclose by what authority he exercises such extensive and unheard-of powers, we are at a loss to determine, whether he intends to justify himself as the representative of the King, or as the Commander in Chief of his Majesty’s forces in America. If he considers himself as acting in the character of his Majesty’s representative, we would remind him that the statute 25 Edward the Third has expressed and defined all treasonable offences, and that the legislature of Great Britain hath declared, that no offence shall be construed to be treason, but such as is pointed out by that statute, and that this was done to take out of the hands of tyrannical Kings, and of weak and wicked Ministers, that deadly weapon, which constructive treason had furnished them with, and which had drawn the blood of the best and honestest men in the kingdom; and that the King of Great Britain hath no right by his proclamation to subject his people to imprisonment, pains, and penalties.
That if the said General Gage conceives he is empowered to act in this manner, as the Commander in Chief of his Majesty’s forces in America, this odious and illegal proclamation must be considered as a plain and full declaration, that this despotic Viceroy will be bound by no law, nor regard the constitutional rights of his Majesty’s subjects, whenever they interfere with the plan he has formed for oppressing the good people of the Massachusetts Bay; and, therefore, that the executing, or attempting to execute, such proclamation, will justify resistance and reprisal.
Dear Sir,
I have got through the bill ‘for proportioning crimes and punishments in cases heretofore capital,’ and now enclose it to you with a request that you will be so good, as scrupulously to examine and correct it, that it may be presented to our committee, with as few defects as possible. In its style, I have aimed at accuracy, brevity, and simplicity, preserving, however, the very words of the established law, wherever their meaning had been sanctioned by judicial decisions, or rendered technical by usage. The same matter, if couched in the modern statutory language, with all its tautologies, redundancies, and circumlocutions, would have spread itself over many pages, and been unintelligible to those whom it most concerns. Indeed, I wished to exhibit a sample of reformation in the barbarous style, into which modern statutes have degenerated from their ancient simplicity. And I must pray you to be as watchful over what I have not said, as what is said; for the omissions of this bill have all their positive meaning. I have thought it better to drop, in silence, the laws we mean to discontinue, and let them be swept away by the general negative words of this, than to detail them in clauses of express repeal. By the side of the text I have written the note? I made, as I went along, for the benefit of my own memory. They may serve to draw your attention to questions, to which the expressions or the omissions of the text may give rise. The extracts from the Anglo-Saxon laws, the sources of the Common law, I wrote in their original, for my own satisfaction;* but I have added Latin, or liberal English translations. From the time of Canute to that of the Magna Charta, you know, the text of our statutes is preserved to us in Latin only, and some old French.
* In this publication, the original Saxon words are given,
but, owing to the want of Saxon letter, they are printed in
common type.
I have strictly observed the scale of punishments settled by the Committee, without being entirely satisfied with it. The Lex talionis, although a restitution of the Common law, to the simplicity of which we have generally found it so advantageous to return, will be revolting to the humanized feelings of modern times. An eye for an eye, and a hand for a hand, will exhibit spectacles in execution, whose moral effect would be questionable; and even the membrum pro membro of Bracton, or the punishment of the offending member, although long authorized by our law, for the same offence in a slave, has, you know, been not long since repealed, in conformity with public sentiment. This needs reconsideration.
I have heard little of the proceedings of the Assembly, and do not expect to be with you till about the close of the month. In the mean time, present me respectfully to Mrs. Wythe, and accept assurances of the affectionate esteem and respect of, Dear Sir, Your friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
George Wythe, Esq.














Bill for proportioning Crimes and Punishments, in Cases heretofore Capital.
Whereas, it frequently happens that wicked and dissolute men, resigning themselves to the dominion of inordinate passions, commit violations on the lives, liberties, and property of others, and, the secure enjoyment of these having principally induced men to enter into society, government would be defective in its principal purpose, were it not to restrain such criminal acts, by inflicting due punishments on those who perpetrate them; but it appears, at the same time, equally deducible from the purposes of society, that a member thereof, committing an inferior injury, does not wholly forfeit the protection of his fellow-citizens, but, after suffering a punishment in proportion to his offence, is entitled to their protection from all greater pain, so that it becomes a duty in the legislature to arrange, in a proper scale, the crimes which it may be necessary for them to repress, and to adjust thereto a corresponding gradation of punishments.
And whereas, the reformation of offenders, though an object worthy the attention of the laws, is not effected at all by capital punishments, which exterminate, instead of reforming, and should be the last melancholy resource against those whose existence is become inconsistent with the safety of their fellow-citizens, which also weaken the State, by cutting off so many who, if reformed, might be restored sound members to society, who, even under a course of correction, might be rendered useful in various labors for the public, and would be living and long continued spectacles to deter others from committing the like offences.
And forasmuch as the experience of all ages and countries hath shown, that cruel and sanguinary laws defeat their own purpose, by engaging the benevolence of mankind to withhold prosecutions, to smother testimony, or to listen to it with bias, when, if the punishment were only proportioned to the injury, men would feel it their inclination, as well as their duty, to see the laws observed.
For rendering crimes and punishments, therefore, more proportionate to each other.
Be it enacted by the General Assembly, that no crime shall be henceforth punished by deprivation of life or limb,* except those hereinafter ordained to be so punished.
* This takes away the punishment of cutting off the hand of
a person striking another, or drawing his sword in one of
the superior courts of justice. Stamf. P. C. 38; 33 H. 8. c.
12. In an earlier stage of the Common law, it was death.
‘Gif hwa gefeohte on Cyninges huse sy he scyldig ealles his
yrfes, and sy on Cyninges dome hwsether he lif age de nage:
si quis in regis domo pugnet, perdat omnem suam
ha; reditatem, et in regis sit arbitrio, possideat vitarn an
non possideat.‘ LI. Inae. 6. &c.
*If a man do levy war** against the Commonwealth [in the same], or be adherent to the enemies of the Commonwealth [within the same],*** giving to them aid or comfort in the Commonwealth, or elsewhere, and thereof be convicted of open deed, by the evidence of two sufficient witnesses, or his own voluntary confession, the said cases, and no others,**** shall be adjudged treasons which extend to the Commonwealth, and the person so convicted shall suffer death by hanging,***** and shall forfeit his lands and goods to the Commonwealth.
* 25 E 3. st. 5. c. 2; 7 W. 3. c. 3, § 2.
** Though the crime of an accomplice in treason is not here
described yet Lord Coke says, the partaking and maintaining
a treason herein described makes him a principal in that
treason. It being a rule that in treason all are principals.
3 inst. 138; 2 Inst. 590; H. 6. c. 5.
*** These words in the English statute narrow its operation.
A man adhering to the enemies of the Commonwealth, in a
foreign country, would certainly not be guilty of treason
with us, if these words be retained. The convictions of
treason of that kind in England, have been under that branch
of the statute which makes the compassing the king’s death
treason. Foster, 196, 197. But as we omit that branch, we
must by other means reach this flagrant case.
**** The stat. 25 E. 3. directs all other cases of treason
to await the opinion of Parliament. This has the effect of
negative words, excluding all other treasons. As we drop
that part of the statute, we must, by negative words,
prevent an inundation of common law treasons. I strike out
the word ‘it,’ therefore, and insert ‘the said cases and no
others.’ Quaere, how far those negative words may affect the
case of accomplices above mentioned? Though if their case
was within the statute, so as that it needed not await the
opinion of Parliament, it should seem to be also within our
act, so as not to be ousted by the negative words.
If any person commit petty treason, or a husband murder his wife, a parent his child,* or a child his parent, he shall suffer death by hanging, and his body be delivered to anatomists to be dissected.
* By the stat. 21.Tac. 1. c. 27. and Act Ass. 1710, c. 12.
concealment by the mother of the death of a bastard child is
made murder. In justification of this, it is said, that
shame is a feeling which operates so strongly on the mind,
as frequently to induce the mother of such a child to murder
it, in order to conceal her disgrace. The act of
concealment, therefore, proves she was influenced by shame,
and that influence produces a presumption that she murdered
the child. The effect of this law, then, is, to make what,
in its nature, is only presumptive evidence of a murder,
conclusive of that fact. To this I answer, 1. So many
children die before, or soon after birth, that to presume
all those murdered who are found dead, is a presumption
which will lead us oftener wrong than right, and
consequently would shed more blood than it would save. 2. If
the child were born dead, the mother would naturally choose
rather to conceal it, in hopes of still keeping a good
character in the neighborhood. So that the act of
concealment is far from proving the guilt of murder on the
mother. 3. If shame be a powerful affection of the mind, is
not parental love also? Is it not the strongest affection
known? Is it not greater than even that of self-
preservation? While we draw presumptions from shame, one
affection of the mind, against the life of the prisoner,
should we not give some weight to presumptions from parental
love, an affection at least as strong in favor of life? If
concealment of the fact is a presumptive evidence of murder,
so strong as to overbalance all other evidence that may
possibly be produced to take away the presumption, why not
trust the force of this incontestable presumption to the
jury, who are, in a regular course, to hear presumptive, as
well as positive testimony? If the presumption, arising from
the act of concealment, may be destroyed by proof positive
or circumstantial to the contrary, why should the
legislature preclude that contrary proof? Objection. The
crime is difficult to prove, being usually committed in
secret. Answer. But circumstantial proof will do; for
example, marks of violence, the behavior, countenance, &c.
of the prisoner, &c. And if conclusive proof be difficult to
be obtained, shall we therefore fasten irremovably upon
equivocal proof? Can we change the nature of what is
contestable, and make it incontestable? Can we make that
conclusive which God and nature have made inconclusive?
Solon made no law against, parricide, supposing it
impossible any one could be guilty of it; and the Persians,
from the same opinion, adjudged all who killed their reputed
parents to be bastards: and although parental, be yet
stronger than filial affection, we admit saticide proved on
the most equivocal testimony, whilst they rejected all proof
of an act, certainly not more repugnant to nature, as of a
thing impossible, improvable. See Beccaria, § 31.
Whosoever committeth murder by poisoning, shall suffer death by poison.
Whosoever committeth murder by way of duel, shall suffer death by hanging; and if he were the challenger, his body, after death, shall be gibbeted.* He who removeth it from the gibbet, shall be guilty of a misdemeanor; and the officer shall see that it be replaced.
* 25 G. 2. c. 37.
Whosoever shall commit murder in any other way, shall suffer death by hanging.
And in all cases of petty treason and murder, one half of the lands and goods of the offender shall be forfeited to the next of kin to the person killed, and the other half descend and go to his own representatives. Save only, where one shall slay the challenger in a duel,* in which case, no part of his lands or goods shall be forfeited to the kindred of the party slain, but, instead thereof, a moiety shall go to the Commonwealth.
* Quære, if the estates of both parties in a duel should not
be forfeited? The deceased is equally guilty with a suicide.
The same evidence* shall suffice, and order and course** of trial be observed in cases of petty treason, as in those of other*** murders.
* Quære, if these words may not be omitted? By the Common
law, one witness in treason was sufficient. Foster, 233.
Plowd. 8. a. Mirror, c. 3. § 34. Waterhouse on Fortesc de
Laud. 252. Carth. 144 per Holt. But Lord Coke, contra, 3
Inst 26. The stat. 1 E. 6. c 12. &5E.6. c. 11. first
required two witnesses in treason. The clause against high
treason supra, does the same as to high treason; but it
seems if 1st and 5th E. 6. are dropped, petty treason will
be tried and proved, as at Common law, by one witness. But
quære, Lord Coke being contra, whose opinion it is ever
dangerous to neglect.
** These words are intended to take away the peremptory
challenge of thirty-five jurors. The same words being used 1
& 2 Ph. k. M. c. 10. are deemed to have restored the
peremptory challenge in high treason; and consequently are
sufficient to take it away. Foster, 237.
*** Petty treason is considered in law only as an aggravated
murder. Foster, 107,323. A pardon of all murders, pardons
petty treason. 1 Hale P. C. 378. See 2 H. P. C. 340, 342. It
is also included in the word ‘felony,’ so that a pardon of
all felonies, pardons petty treason.
Whosoever shall be guilty of manslaughter,* shall, for the first offence, be condemned to hard labor** for seven years, in the public works, shall forfeit one half of his lands and goods to the next of kin to the person slain; the other half to be sequestered during such term, in the hands and to the use of the Commonwealth, allowing a reasonable part of the profits for the support of his family. The second offence shall be deemed murder.
* Manslaughter is punishable at law, by burning in the hand,
and forfeiture of chattels.
** It is best, in this act, to lay down principles only, in
order that it may not for ever be undergoing change: and, to
carry into effect the minuter parts of it; frame a bill ‘for
the employment and government of felons, or male-factors,
condemned to labor for the Commonwealth,’ which may serve as
an Appendix to this, and in which all the particulars
requisite may be directed: and as experience will, from time
to time, be pointing out amendments, these may be made
without touching this fundamental act. See More’s Utopia pa.
50, for some good hints. Fugitives might, in such a bill, be
obliged to work two days for every one they absent
themselves.
And where persons, meaning to commit a trespass* only, or larceny, or other unlawful deed, and doing an act from which involuntary homicide hath ensued, have heretofore been adjudged guilty of manslaughter, or of murder, by transferring such their unlawful intention to an act much more penal than they could have in probable contemplation; no such case shall hereafter be deemed manslaughter, unless manslaughter was intended, nor murder, unless murder was intended.
* The shooting at a wild fowl, and killing a man, is
homicide by misadventure. Shooting at a pullet, without any
design to take it away, is manslaughter; and with a design
to take it away, is murder. 6 Sta. tr. 222. To shoot at the
poultry of another, and thereby set fire to his house, is
arson, in the opinion of some. Dalt. c. 116 1 Hale’s P. C.
569, contra.
In other cases of homicide, the law will not add to the miseries of the party, by punishments or forfeitures.*
* Beccaria, § 32. Suicide. Homicides are, 1. Justifiable. 2.
Excusable. 3. Felonious. For the last, punishments have been
already provided. The first are held to be totally without
guilt, or rather commendable. The second are, in some cases,
not quite unblamable. These should subject the party to
marks of contrition; viz. the killing of a man in defence of
property; so also in defence of one’s person, which is a
species of excusable homicide; because, although cases may
happen where these also are commendable, yet most frequently
they are done on too slight appearance of danger; as in
return for a blow, kick, fillip, &c; or on a person’s
getting into a house, not anirno furandi, but perhaps
veneris causa, &c. Bracton says, ‘Si quis furem noctupnum
occiderit, ita demum impune foret, si parcere ei sine
periculo suo non potuit; si autem potuit, aliter erit.’
‘Item erit si quis hamsokne qua; dicitur invasio domus
contra pacem domini regis in domo sua se defenderit, et
invasor occisus fuerit; impersecutus et inultus ramanebit,
si ille quem invasit aliter se defendere non potuit; dicitur
enim quod non est dignus habere pacem qui non vult observare
earn.’ L.3. c.23. § 3. ‘Qui latronetn Occident, non tenetur,
nocturnum vel diurnnm, si aliter periculum evadere non
possit; tenetur ta-men, si possit. Item non tenetur si per
inforlunium, et non anitno et voluntate occidendi, nee
dolus, nec culpa ejus inveniatur.’ L.3. c.36. § 1. The stat.
24 H. 8. c. 5 is therefore merely declaratory of the Common
law. See on the general subject, Puffend. 2. 5. § 10, 11,
12, 16, 17. Excusable homicides are by misadventure, or in
self-defence. It is the opinion of some lawyers, that the
Common law punished these with death, and that the statute
of Marlbridge, c. 26. and Gloucester, c. 9. first took away
this by giving them title to a pardon, as matter of right,
and a writ of restitution of their goods. See 2 Inst, 148.
315; 3 Inst. 55. Bracton, L. 3. c. 4. § 2. Fleta L, 1. c.
23. § 14, 15; 21 E. 3. 23. But it is believed never to have
been capital. 1 H. P. C. 425; 1 Hawk. 75; Foster, 282; 4 Bl.
188. It seems doubtful also, whether at Common law, the
party forfeited all his chattels in this case, or only paid
a weregild. Foster, ubi supra, doubts, and thinks it of no
consequence, as the statute of Gloucester entitles the party
to Royal grace, which goes as well to forfeiture as life. To
me, there seems no reason for calling these excusable
homicides, and the killing a man in defence of property, a
justifiable homicide. The latter is less guiltless than
misadventure or self defence.
Suicide is by law punishable by forfeiture of chattels. This
bill exempts it from forfeiture. The suicide injures the
state less than he who leaves it with his effects. If the
latter then be not punished, the former should not. As to
the example, we need not fear its influence. Men are too
much attached to life, to exhibit frequent instances of
depriving themselves of it. At any rate, the quasi-
punishment of confiscation will not prevent it. For if one
be found who can calmly determine to renounce life, who is
so weary of his existence here, as rather to make experiment
of what is beyond the grave, can we suppose him, in such a
state of mind, susceptible of influence from the losses to
his family by confiscation? That men in general, too,
disapprove of this severity, is apparent from the constant
practice of juries finding the suicide in a state of
insanity; because they have no other way of saving the
forfeiture. Let it then be done away.
Whenever sentence of death shall have been pronounced against any person for treason or murder, execution shall be done on the next day but one after such sentence, unless it be Sunday, and then on the Monday following.*
* Beccaria, § 19; 25 G. 2. c. 37.
Whosoever shall be guilty of Rape,* Polygamy,** or Sodomy,*** with man or woman, shall be punished, if a man, by castration,**** if a woman, by cutting through the cartilage of her nose, a hole of one half inch in diameter at the least.
* 13 E. 1. c. 34. Forcible abduction of a woman having
substance, is felony by 3 H. 7, c 2; 3. Inst. 61; 4 Bl. 208.
If goods be taken, it will be felony as to them, without
this statute: and as to the abduction of the woman, quære if
not better to leave that, and also kidnapping, 4 Bl. 219. to
the Common law remedies, viz. fine, imprisonment, and
pillory, Raym. 474; 2 Show. 221; Skin. 47; Comb. 10. the
writs of Homine replegiando, Capias in Withernam, Habeas
corpus, and the action of trespass? Rape was felony at the
Common law. 3 Inst. 60 but see 2 Inst. 181. Further—for its
definition see 2 Inst. 180. Bracton L.3. 28. § 1. says, the
punishment of rape is ‘amissio membrorum, ut sit membrumpro
membra, quia virgo, cum corrumpitur, membrum amittit, et
ideo corruptor puniatur in eo in quo deliquit; oculos igitur
amittat propter aspectum decoris quo virginem concupivit;
amittat et testiculos qui calorem stupri induxerunt. Olim
quidem corruptores virginitatis et castitatis suspendebantur
et eorum fautores, &c. Modernis tamen temporibus aliter
observatur,’ &.c. And Fleta, ‘Solet justiciarius pro
quolibet mahemio ad amissionem testiculorum vel oculorum
convictum coudemnare, sed non sine errore, eo quod id
judicium nisi in corruptione virginum lantum competebat; nam
pro virginitatis corruptione solebant abscidi et merito
judicari, ut sic pro membro quod abstulit, membrum per quod
deliquit amitteret, viz. lesticulos, qui calorem stupri
induxerunt,’ &c. Fleta. L. 1. c. 40. § 4. ‘Gif theow man
theowne to nydhffimed genyde, gabete mid his eowende: Si
servus servam ad sfuprum coegerit, compenset hoc virga sua
virili. Si quis pnellam,’ &c. Ll.Æliridi. 25. ‘Hi purgst
femme per forze forfait ad les membres.’ LI. Gul. Conq. 19.
** 1 Jac. 1. c. 11. Polygamy was not penal till the statute
of 1 Jac. The law contented itself with the nullity of the
act. 4 Bl. 163. 3 Inst. 88.
*** 25. H. 8. c. 6. Buggery is twofold. 1. With mankind, 2.
with beasts. Buggery is the genus, of which Sodomy and
Bestiality are the species. 12 Co. 37. says, In Dyer, 304. a
man was indicted, and found guilty of a rape on a girl of
seven years old. The court doubted of the rape of so tender
a girl; but if she had been nine years old, it would have
been otherwise.’ 14 Eliz. Therefore the statute 18 Eliz. c.
6, says, ‘For plain declaration of law, be it enacted, that
if any person shall unlawfully and carnally know and abuse
any woman child, under the age of ten years, &c. he shall
suffer as a felon, without allowance of clergy.’ Lord Hale,
however, 1 P. C. 630. thinks it rape independent of that
statute, to know carnally a girl under twelve, the age of
consent. Yet, 4 Bl. 212. seems to neglect this opinion; and
as it was founded on the words of 3 E. 1. c. 13. and this is
with us omitted, the offence of carnally knowing a girl
under twelve, or ten years of age, will not be distinguished
from that of any other. Co. 37. says ‘note that Sodomy is
with mankind.’ But Finch’s L. B. 3. c. 24. ‘Sodomitry is a
carnal copulation against nature, to wit, of man or woman in
the same sex, or of either of them with beasts.’ 12 Co 36.
says, ‘It appears by the ancient authorities of the law
that this was felony.’ Yet the 25 H. 8. declares it felony,
as if supposed not to be so. Britton, c, 9. says, that
Sodomites are to be burnt. F. N. B. 269. b. Fleta, L 1. c.
37. says, ‘Pecorantes et Sodomise in terra, vivi
confodiantur.’ The Mirror makes it treason. Bestiality can
never make any progress; it cannot therefore be injurious to
society in any great degree, which is the true measure of
criminality in foro cirili, and will ever be properly and
severely punished, by universal derision. It may, therefore,
be omitted. It was anciently punished with death, as it has
been latterly. LI Ælfrid. 31. and 25 H. 8. c. 6. see
Beccaria, § 31. Montesq.
****Bracton, Fleta, &c.
But no one shall be punished for Polygamy, who shall have married after probable information of the death of his or her husband or wife, or after his or her husband or wife hath absented him or herself, so that no notice of his or her being alive hath reached such person for seven years together, or hath suffered the punishments before prescribed for rape, polygamy, or sodomy.
Whosoever, on purpose, and of malice forethought, shall maim* another, or shall disfigure him by cutting out or disabling the tongue, slitting or cutting off a nose, lip, or ear, branding, or otherwise, shall be maimed, or disfigured in like** sort: or if that cannot be for want of the same part, then as nearly as may be, in some other part of at least equal value and estimation, in the opinion of a jury, and moreover, shall forfeit one half of his lands and goods to the sufferer.
* 22 &l 23 Car. 2, c. 1. Maiming was felony at the Common
law. Britton, c 95. Mehemiurn autem dici poterit, ubi
aliquis in aliqua. parte sui corporis la sionern acceperit,
per quam affectus sit inutilis ad pugnandum: ut sirnanus
ampuletur, vel pes, octilus privetur, vel scerda de osse
capitis lavetnr, vel si quis dentes praer. isores amiserit,
vel castratus fuerit, et talis pro mahemiato poterit
adjudicari.’ Flela, L. 1. c. 40. ‘Et volons que nul maheme
nesoit tenus forsque de membre toilet dount home est plus
feble a combatre, sicome, del oyl, on de la mayn, ou del
pie, on de la tete debruse, ou de les dentz devant.’
Britton, c. 25. For further definitions, see Braclon, L. 3.
c. 24 § 3. 4. Finch, L. B. 3. c. 12; Co. L. 126. a b 288. a;
3 Bl. 121; 4 Bl 205; Stamf. P C. L. 1. c. 41. I do not find
any of these definitions confine the offence to wilful and
malicious perpetrations of it. 22&23 Car. 2. c. 1, called
the Coventry act, has the words ‘on purpose and of malice
forethought.’ or does the Common law-prescribe the same
punishment for disfiguring, as for maiming.
** The punishment was by retaliation. ‘Et come ascun appele
serra de tele felonie atteint et attende jugement, si soit
le jugement tiel que il perde autriel membre come il avera
toilet al pleintyre. El sy la pleynte soit faite de femme
que avera toilet a home ses membres, en tiei cas perdra la
femmela une meyn par jugement, come le membre dount ele
avera trespasse.’ Britton, c 25. Flela, B 1. c. 40; LI.
Ælfr. 19. 40.
Whosoever shall counterfeit* any coin, current by law within this Commonwealth, or any paper bills issued in the nature of money, or of certificates of loan on the credit of this Commonwealth, or of all or any of the United States of America, or any Inspectors’ notes for tobacco, or shall pass any such counterfeited coin, paper, bills, or notes, knowing them to be counterfeit; or, for the sake of lucre shall diminish,** case, or wash any such coin, shall be condemned to hard labor six years in the public works, and shall forfeit all his lands and goods to the Commonwealth.
* 25E.3. st 5. c. 2; 5 El c. 11; 18 El. c. 1; 8 and 9 W. 3.
c. 26; 15. and 16 G 2. c. 28; 7 Ann. q. 25. By the laws of
Æthelstan and Canute, this was punished by cutting off the
hand. ‘Gifse mynetereful wurthe sleaman tha hand of, the he
that fil mid worthe and sette iippon tha rnynet smithlhan.’
In English characters and words ‘if the minler foul
[Criminal] wert, slay the hand off, that he the foul [crime]
with wrought, and set upon the mint-smithery.’ LI,iEthelst.
14. ‘And selhe ofer this false wyrce, tholige thaera handa
the he thaet false mid worhte.’ ‘Et si quis prater hanc,
falsam fecerit, perdat manum quacum falsam confecit.’ LI.
Cnuti, 8. It had been death by the LI. Æihelredi, sub fine.
By those of H. 1. ‘Si quis cum falso deuario inventus
fueril—fiat justitia mea, saltern de dextro pugno et de
testiculis.’ Anno 1108. ‘Opera prelium vero est audire quam
severus rex fuerit in pravos. Monetarios enim fere omnes
totius Angliee fecit ementulari, et manus dextras abscindi,
quia monetam furtive corruperant.’ Wilkins ib. et anno 1125.
When the Common law became settled, it appears to have been
punishable by death. ‘Est aliud genus crirninis quod sub
nomine falsi continetur, et tangit coronam domini regis, et
nlfimum indncit supplicium, sicut de illis qui falsam
fabricant monetasn, et qui de re non reproba, faciunt
reprobam; sicut sunt retonsores deriarinruno’ Bract. L. 3. c
3. § 2. Fleta, L. 1. c. 22 § 4 Lord Hale thinks it was
deemed petty treason at common law. 1 H. P. C. 220, 224. The
bringing in false money with intent to merchandise, and make
payment of it is treason, by 25 E. 3. But the best proof of
the intention, is the act of passing it, and why not leave
room for repentance here, as in other cases of felonies
intended? I H P. C. 229.
** Clipping, filing, rounding, impairing, scaling,
lightening, (the words in the statutes) are included in
‘diminishing;’ gilding, in the word ‘casing;’ coloring in
the word ‘washing;’ and falsifying or marking, is
counterfeiting.’
Whosoever committeth Arson,* shall be condemned to hard labor five years in the public works, and shall make good the loss of the sufferers threefold.**
*43 El. c. 13. confined to four counties. 22 ^ 23 Car. 2. c.
7; 9 G. 1. c. 22, 9 G. 3. c. 29.
** Arson was a felony at Common law—3 Inst. 66; punished by
a fine, Ll. Æthelst. 6. But LI. Cnuti, 61. make it a ‘scetus
inexpiable.’ ‘Hus brec and baernet and open thyfth and
asbereniorth and hlaford swice after woruld laga is
boileds.’ Word for word, ‘House break and burnt, and open
theft, and manifest murdher, and lord-treachery, after
world’s law is bootless.’ Bracton says, it was punished by
death. ‘Si quis turbida seditione iricendium fecerit
nequiter et in felonia, vel ob inimicitias, vel praedandi
causa, capital puniatur pcena vel sententia.’ Bract. L. 3.
c. 27. He defines it as commissible by burning ‘cedes alien
as.’ Ib. Britton, c. 9. ‘Ausi soitenquis de ceux que
felonise-ment en temps de pees eient a litre blees ou autre
messons ars, et ceux que ser-rount de ceo alteyniz, soient
ars issint que eux soient punys par mesme cele chose dount
ils pecherent.’ Fleia, L. I. c. 37. is a copy of Bracton.
The Mirror, c. 1. § 8. says, ‘Ardours sont que ardent cilie,
ville, maison home, maison beast, ou auters chatelx, de lour
felonie en temps de pace pour haine ou vengeance.’ Again, c.
2. § II., pointing oul the words of the appellor ‘jeo dise
que Sebright, &c. entiel meas. on ou hiens mist de feu.’
Coke, 3 Inst. 67. says, ‘The ancient authors extended this
felony further than houses, viz. to stacks of corn, waynes
or carts of coal, wood, or other goods.’ He defines it as
commissibie, not only on the inset houses, parcel of the
mansion-house, but the outset also, as barn, stable, cow-
house, sheep-house, dairy-house, mill-house, and the like,
parcel of the mansion house.’ But ‘burning of a barn, being
no parcel of a mansion-house, is no felony,’ unless there be
corn or hay within it. Ib. The 22 k. 23 Car. 2. and 9 G. 1.
are the principal statutes against arson. They extend the
offence beyond the Common law.
If any person shall, within this Commonwealth, or, being a citizen thereof, shall without the same, wilfully destroy,* or run** away with any sea-vessel, or goods laden on board thereof, or plunder or pilfer any wreck, he shall be condemned to hard labor five years in the public works, and shall make good the loss of the sufferers threefold.
* Ann. st. 2. c. 9. 12 Ann. c. 18. 4 G. 1. c. 12. 26 G. 2.
c. 19.
** 11 h 12 W.3. c.7.
Whosoever committeth Robbery,* shall be condemned to hard labor four years in the public works, and shall make double reparation to the persons injured.
* Robbery was a felony at Common law. 3 Inst. 68. ‘Scelus
inexpiable,’ by the LI. Cnuti. 61. [See before in Arson.] It
was punished with death. Briit c. 15, ‘De robbours et de
larouns et de semblables mesfesours, soitaussi
ententivernent enquis—et tauntost soient ceux robbours
juges a la morl.’ Fleta says, ‘Si quis conviclus fuerit de
bonis viri robbatis vel asportatis ad sectam regis judicium
capitale subibit.’ L. 1. c. 39. See also Bract. L. 3. c. 32
§ I.
Whatsoever act, if committed on any mansion-house, would be deemed Burglary,* shall be Burglary, if committed on any other house; and he who is guilty of Burglary, shall be condemned to hard labor four years in the public works, and shall make double reparation to the persons injured.
* Burglary was felony at the Common law. 3 Inst. 63 It was
not distinguished by ancient authors, except the Mirror,
from simple House-breaking, ib. 65. Burglary and House-
breaking were called ‘Hamsockne.’ ‘Diximus etiam de pacis
violatione et de immunitatibus domus, si quis hoc in
posterum fecetit ut perdat ornne quod habet, et sit in regis
arbitro utrum vitam habeat.’ ‘Eac we quasdon be mundbryce
and be ham socnum,sethe hit ofer this do tha:t he dolie
enlles thces the age, and sy on Cyninges Jome hwsether be
life age: and we quoth of mound-breach, and of home-seeking
he who it after this do, that he dole all that he owe
[owns], and is in kings doom whether he life owes [owns].’
LI. Eadmundi, c. 6 and see LI. Cnuti. 61. ‘bus btec,’ in
notesion Arson, ante. A Burglar was also called a Burgessor.
‘Et soit enquis de Burgessours et sunt tenus Burgessours
trestous ceux que felonisement en temps de pees debrusornt
esglises ou auter mesons, ou murs ou portes de nos cytes, ou
de nos Burghes.’ Britt. c. 10. ‘Burglaria est nocturna
diruptio habitaculi alicujus, vel ecclesise, etiam murorum,
portarurnve civitatis aut burgi, ad feloniam aliquam
perpetrandam. Noclanter dico, recentiores se-cutus; veteres
enim hoc non adjungunt.’ Spelm. Gloss, verb. Burglaria. It
was punished with death. Ib. citn. from the office of a
Coroner. It may be committed in the outset houses, as well
as inset, 3 Inst. 65. though not under the same roof or
contiguous, provided they be within the Curtilage or Home-
stall. 4 BI. 225. As by the Common law all felonies were
clergiable, the stat. 23 H. 8. c. 1; 5 E. 6. c. 9. and 18
El. c. 7. first distinguished tfiem, by taking the clerical
privilege of impunity from the principals, and 3 & 4 W. M.
c. 9. from accessories before the fact. No statute defines
what Burglary is. The 12 Ann. c. 7. decides the doubt
whether, where breaking is subsequent to entry, it is
Burglary. Bacon’s Elements had affirmed, and T. H. P. C.
554. had denied it. Our bill must distinguish them by
different degrees of punishment.
Whatsoever act, if committed in the night time, shall constitute the crime of Burglary, shall, if committed in the day, be deemed House-breaking;* and whosoever is guilty thereof, shall be condemned to hard labor three years in the public works, and shall make reparation to the persons injured.
* At the Common law, the offence of House-breaking was not
distinguished from Burglary, and neither of them from any
other larceny. The statutes at first took away clergy from
Burglary, which made a leading distinction between the two
offences. Later statutes, however, have taken clergy from so
many cases of House-breaking, as nearly to bring the
offences together again. These are 23 H. 8. c. 1; 1 E. 6. c.
12; 5 k 6 E. 6. c. 9; 3 & 4 W. M. c. 9; 39 El. c. 15; 10&11
W. 3. c.23; 12 Ann. c. 7. See Burr. 428; 4 Bl. 240. The
circumstances, which in these statutes characterize the
offence, seem to have been occasional and unsystematical.
The houses on which Burglary may be committed, and the
circumstances which constitute that crime, being
ascertained, it will be better to define House-breoking by
the same subjects and circumstances, and let the crimes be
distinguished only by the hour at which they are committed,
and the degree of punishment.
Whosoever shall be guilty of Horse-stealing,* shall be condemned to hard labor three years in the public works, and shall make reparation to the person injured.
* The offence of Horse-stealing seems properly
distinguishable from other larcenies, here, where these
animals generally run at large, the temptation being so
great and frequent, and the facility of commission so
remarkable. See 1 E. 6. c. 12; 23 E. 6. c. 33; 31 El. c. 12.
Grand Larceny* shall be where the goods stolen are of the value of five dollars; and whosoever shall be guilty thereof, shall be forthwith put in the pillory for one half hour, shall be condemned to hard labor** two years in the public works, and shall make reparation to the person injured.
* The distinction between grand and petty larceny is very
ancient. At first 8d. was the sum which constituted grand
larceny. LI. Ælhelst. c. 1. ‘Ne parcatur ulli furi, qui
furtum manutenens captus sit, supra 12 annos nafo, et supra
8 denarios.’ Afterwards, in the same king’s reign, it was
raised to 12d. ‘Non parcaturalicui furi ultra 12 denarios,
et ultra 12 annos nato—ut occide-mus ilium et capiamus omne
quod possidet, et inprimis sumamus rei furto ablatse pretium
ab hserede, ac dividatur postea reliquum in duas partes, una
pars uxori, si munda, et facinoris conscia non sit; et
residuum in duo, dimi-dium capiat rex, dimidium societas.’
LI. Æthelst. Wilkins, p. 65. VOL. I. 17
** LI. Inse, c. 7. ‘Si quis furetur ita ut uxor ejus et
infans ipsius nesciani, solvat 60. solidos pcenae loco. Si
autem furetur testantibus omuibus haere-dibus suis, abeant
omnes in servilutem.’ Ina was King of the West Saxons, and
began to reign A. C. 688. After the union of the Heptarchy,
i. e. temp. Æthelst. inter 924 and 940, we find it
punishable with death as above. So it was inter 1017 and
1035, i. e. temp. Cnuti. LI. Cnuti 61. cited in notes on
Arson. In the time of William the Conqueror, it seems lo
have been made punishable by fine only. LI. Gul. Cohq. apud
Wilk. p. 218. 220. This commutation, however, was taken away
by LI. H. 1. anno 1108. ‘Si quis in furto vel latro-cinio
deprehensus fuisset, suspenderetur: sublata wirgildorum, id
est, pecu-niarse redemptions lege.’ Larceny is the felonious
taking and carrying away of the personal goods of another.
1. As to the taking, the 3 & 4 VV. M. c. 9. § 5, is not
additional to the Common law, but declaratory of it; because
where only the care or use, and not the possession, of
things is delivered, to take them was larceny at the Common
law. The 33 H. 6. c. 1 and 21 11. 8. c. 7., indeed., have
added to the Common law by making it larceny in a servant to
convert things of his master’s. But quære, if they should be
imitated more than as to other breaches of trust in general.
2. As to the subject of larceny, 4 G. 2. c.32; 6 G. 3. c. 36
48; 43 El. c. 7; 15 Car. 2. c. 2; 23 G. 2 c. 26; 31 G. 2. c.
35; 9 G. 3. c. 41; 25 G. 2. c. 10. have extended larceny to
things of various sorts, either real, or fixed to the
realty. But the enumeration is unsystematical, and in this
country, where the produce of the earth is so spontaneous as
to have rendered things of this kind scarcely a breach of
civility or good manners in the eyes of the people, quære,
if it would not too much enlarge the field of Criminal law?
The same may be questioned of 9 G. J. c. 22; 13 Car. 2. c.
10; 10 G. 2. c. 32; 5 G. 3. c. 14; 22 h 23 Car. 2. c. 25; 37
E. 3. c. 19. making it felony to steal animals ferte
natures.
Petty Larceny shall be, where the goods stolen are of less value than five dollars; and whosoever shall be guilty thereof, shall be forthwith put in the pillory for a quarter of an hour, shall be condemned to hard labor one year in the public works, and shall make reparation to the person injured.
Robbery* or larceny of bonds, bills obligatory, bills of exchange, or
promissory notes for the payment of money or tobacco, lottery tickets,
paper bills issued in the nature of money, or of certificates of loan on
the credit of this Commonwealth, or of all or any of the United States
of America, or Inspectors’ notes for tobacco, shall be punished in the
same manner as robbery,or larceny of the money or tobacco due on or
represented by such papers.* 2 G. 2. c. 25 §3; 7 G 3. c. 50.
Buyers* and receivers of goods taken by way of robbery or larceny, knowing them to have been so taken, shall be deemed accessaries to such robbery or larceny after the fact.
* 3 &. 4 W. & M. c. 9. § 4; 5 Ann. c. 31. § 5; 4 G. 1. c.
11. § 1.
Prison breakers,* also, shall be deemed accessaries after the fact, to traitors or felons whom they enlarge from prison.**
* 1 E. 2.
** Breach of prison at the Common law was capital, without
regard to the crime for which the party was committed. ‘Cum
pro criminis qualitate in carcerem recepti fuerint,
conspiraverint (ut ruptis vinculis aut fracto carcere)
evadant, atnplius (quam causa pro qua recepti sunt exposuit)
puniendi sunt, videlicet ultimo supplicio, quamvis ex eo
crimine innocentes inveniantur, propter quod inducti sunt in
carcerem et imparcati.’ Bracton L. 3, c. 9. § 4. Britt. c.
11. Fleta, L. 1. c. 26. § 4. Yet in the Y. B. Hill. 1 H. 7.
2. Hussey says, that, by the opinion of Billing and Choke,
and all the Justices, it was a felony in strangers only, but
not in the prisoner himself. S. C. Fitz. Abr. Co-ron. 48.
They are principal felons, not accessaries, ib. Whether it
was felony in the prisoner at Common law, is doubted. Stam.
P. C. 30. b. The Mirror c. 5. § 1. says, ‘Abusion est a
tener escape de prisoner, ou de bruserie del gaole pur peche
mortal 1, car eel usage nest garrant per nul ley, ne in nul
part est use forsque in cest realme, et en France, ems
[mais] est leu garrantie de ceo faire per la ley de nature’
2 Inst. 589. The stat. 1 E. 2, ‘de fragentibus priso-nam,’
‘restrained the judgment of life and limb for prison-
breaking, to cases where the offence of the prisoner
required such judgment.’
It is not only vain but wicked, in a legislator to frame
laws in opposition to the laws of nature, and to arm them
with the terrors of death. This is truly creating crimes in
order to punish them. The law of nature impels every one to
escape from confinement; it should not, therefore, be
subjected to punishment. Let the legislator restrain his
criminal by walls, not by parchment. As to strangers
breaking prison to enlarge an offender, they should, and may
be fairly considered as accessaries after the fact. This
bill saying nothing of the prisoner releasing himself by
breach of jail, he will have the benefit of the first
section of the bill, which repeals the judgment of life and
death at the Common law.
All attempts to delude the people, or to abuse their understanding by exercise of the pretended arts of witchcraft, conjuration, enchantment, or sorcery, or by pretended prophecies, shall be punished by ducking and whipping, at the discretion of a jury, not, exceeding fifteen stripes.*
* ‘Gifwiecan owwe wigleras mansworan, owwe morthwyrhtan owwe
fule afylede eebere horcwenan ahwhar on lande wurthan
agytene, thonne fyrsie man of earde, and claensie lha.
theode, owwe on earde forfare hi mid ealle, buton hi
geswican and the deoper gebetan:’ ‘if witches, or weirds,
man-swearers, or murther-wroughters, or foul, defiled, open
whore-queens, ay—where in the land were gotten, then force
them off earth, and cleanse the nation, or in earth forth-
fare them withal, buton they beseech, and deeply better.’
LI. Ed. et Guthr. c. 11. ‘Saga; mulieres barbara
factitantes sacrificia, aut pestiferi, si cui mortem
intulerint, neque id inficiari poterint, capitis pcena
esto.’ LI. Aethelst. c. 6. apud Lambard. LI. Aelfr. 30. LI.
Cnuti. c. 4. ‘Mesmo eel jugement (d’etrears) eyent
sorcers, et sorceresses,’ &c. ut supra. Fleta tit et ubi
supra. 3 Inst. 44. Trial of witches before Hale, in 1664.
The statutes 33 H. 8. c. 8. 5. El. c. 16 and 1. Jac. 1. c.
12. seem to be only in confirmation of the Common law. 9 G.
2. c. 25. punishes them with pillory and a year’s
imprisonment 3 E. 6 c 15. 5 El. c. 15. punish fond,
fantastical, and false prophecies, by fine and imprisonment.
If the principal offenders be fled,* or secreted from justice, in any case not touching life or member, the accessaries may, notwithstanding, be prosecuted as if their principal were convicted.**
* 1 Ann. c. 9. § 2.
**As every treason includes within it a misprision of
treason, so every felony includes a misprision, or
misdemeanor. 1 Hale P. C. 652. 75S. ‘Licet fuerit felonia,
tamen in eo continetur misprisio.’ 2 R. 3.10. Both principal
and accessary, therefore, may be proceeded against in any
case, either for felony, or misprision, at the Common law.
Capital cases not being mentioned here, accessaries to them
will of course be triable for misprisions, if the offender
flies.
If any offender stand mute of obstinacy,* or challenge preremp-torily more of the jurors than by law he may, being first warned of the consequence thereof, the court shall proceed as if he had confessed the charge,**
* 3E. I.e. 12.
** Whether the judgment of penance lay at Common law. See 2
Inst. 178.2. H. P. C. 321. 4 Bl. 322. It was given on
standing mute: but on challenging more than the legal
number, whether that sentence, or sentence of death is to be
given, seems doubtful. 2 H. P. C. 316. Quære, whether it
would not be better to consider the supernumerary challenge
as merely void, and to proceed in the trial. Quære too, in
case of silence.
Pardon and privilege of clergy shall henceforth be abolished, that none may be induced to injure through hope of impunity. But if the verdict be against the defendant, and the court, before whom the offence is heard and determined, shall doubt that it may be untrue for defect of testimony, or other cause, they may direct a new trial to be had.*
* ‘Cum Clericus sic de crimine convictus degradetur, non
sequitur aliapoe-na pro uno delicto, vel pluribus ante
degradationem perpetratis. Satis enim sufficit ei pro pcena
degradatio, quse est magna capitis diminutio, nisi forte
convictus fuerit de apostatia, quia hinc primo degradetur,
et postea per manum laicalem comburetur, secundum quod
accidit in concilio Oxoni celebrato a bonas memoriae S.
Cantuaren. Archiepiscopo de quodam diacono, qui seapos-
tatavit pro quadam Judaea; qui cum esset per episcopum
degradatus, statim fuit igni traditus per manum laicalem.’
Bract. L. 3. c. 9. § 2. ‘Et mesme eel jugement (i. e. qui
ils soient ars) eye n’t sorcers et sorceresses, et sodomites
et mescreauntz apertement atteyntz.’ Britt. c. 9.
‘Christiani autem Apostatae, sortilegii, et hujusmodi
detractari debent et comburi.’ Fleta, L. 1. c. 37. § 2. see
3 Inst. 39; 12 Rep. 92; 1 H. P. C. 393. The extent of the
clerical privilege at the Common law, 1. As to the crimes,
seems very obscure and uncertain. It extended to no case
where the judgment was not of life or limb. Note in 2. H. P.
C. 326. This, therefore, excluded it in trespass, petty
larceny, or killing se defendendo. In high treason against
the person of the King, it seems not to have been allowed.
Note 1 H. P. C. 185. Treasons, therefore, not against the
King’s person immediately, petty treasons and felonies, seem
to have been the cases where it was allowed; and even of
those, not for insidiatio viarum, depopulatio agrorum, or
combustio domorum. The statute de Clero, 25 E. 3. st. 3. c.
4. settled the law on this head. 2. As to the persons, it
extended to all clerks, always, and toties quoiies. 2 H. P.
C. 374. To nuns also. Fitz. Abr. Coron. 461. 22 E. 3. The
clerical habit and tonsure were considered as evidence of
the person being clerical. 26 Assiz. 19 & 20 E. 2. Fitz.
Coron. 233. By the 9 E. 4. 28. b. 34 H. 6. 49. a. b. simple
reading became the evidence. This extended impunity to a
great number of laymen, and toties quoties. The stat. 4 H.
7. c. 13. directed that real clerks should upon a second
arraignment, produce their orders, and all others to be
burnt in the hand with M. or T. on the first allowance of
clergy, and not to be admitted to it a second time. A
heretic, Jew, or Turk, (as being incapable of orders) could
not have clergy. H Co. Rep. 29. b. But a Greek, or other
alien, reading in a book of his own country, might. Bro.
Clergie. 20. So a blind man, if he could speak Latin. Ib.
21. qu, 11. Rep. 29. b. The orders entitling the party were
bishops, priests, deacons, and sub-deacons, the inferior
being reckoned Clerici in minoribus. 2 H. P. C. 373. Quære,
however, if this distinction is not founded on the stat. 23.
H. 8. c. 1; 25. H. 8. c. 32. By merely dropping all the
statutes, it should seem that none but clerks would be
entitled to this privilege, and that they would, toties
quoties.
No attainder shall work corruption of blood in any case.
In all cases of forfeiture, the widow’s dower shall be saved to her, during her title thereto; after which it shall be disposed of as if no such saving had been.
The aid of Counsel,* and examination of their witnesses on oath, shall be allowed to defendants in criminal prosecutions.
* 1 Ann. c. 9.
Slaves guilty of any offence* punishable in others by labor in the public works, shall be transported to such parts in the West Indies, South America, or Africa, as the Governor shall direct, there to be continued in slavery.
* Manslaghter, counterfeiting, arson, asportation of
vessels, robbery, burglary, house-breaking, horse-stealing,
larceny.
On the Establishment of a Money Unit, and of a Coinage for the United States.
In fixing the Unit of Money, these circumstances are of principal importance.
I. That it be of convenient size to be applied as a measure to the common money transactions of life.
II. That its parts and multiplies be in an easy proportion to each other, so as to facilitate the money arithmetic;
III. That the Unit and its parts, or divisions, be so nearly of the value of some of the known coins, as that they may be of easy adoption for the people.
The Spanish Dollar seems to fulfil all these conditions.
I. Taking into our view all money transactions, great and small, I question if a common measure of more convenient size than the Dollar could be proposed. The value of 100, 1000, 10,000 dollars is well estimated by the mind; so is that of the tenth or the hundredth of a dollar. Few transactions are above or below these limits. The expediency of attending to the size of the Money Unit will be evident to any one who will consider how inconvenient it would be to a manufacturer or merchant, if instead of the yard for measuring cloth, either the inch or the mile had been made the Unit of Measure.
II. The most easy ratio of multiplication and division is that by ten. Every one knows the facility of Decimal Arithmetic. Every one remembers, that, when learning Money-Arithmetic, he used to be puzzled with adding the farthings, taking out the fours and carrying them on; adding the pence, taking out the twelves and carrying them on; adding the shillings, taking out the twenties and carrying them on; but when he came to the pounds, where he had only tens to carry forward, it was easy and free from error. The bulk of mankind are school-boys through life. These little perplexities are always great to them. And even mathematical heads feel the relief of an easier, substituted for a more difficult process. Foreigners, too, who trade or travel among us, will find a great facility in understanding our coins and accounts from this ratio of subdivision. Those who have had occasion to convert the Livres, sols, and deniers of the French; the Gilders, stivers, and frenings of the Dutch; the Pounds, shillings, pence, and farthings of these several States, into each other, can judge how much they would have been aided, had their several subdivisions been in a decimal ratio. Certainly, in all cases, where we are free to choose between easy and difficult modes of operation, it is most rational to choose the easy. The Financier, therefore, in his report, well proposes that our Coins should be in decimal proportions to one another. If we adopt the Dollar for our Unit, we should strike four coins, one of gold, two of silver, and one of copper, viz.
1. A golden piece, equal in value to ten dollars:
2. The Unit or Dollar itself, of silver:
3. The tenth of a Dollar, of silver also:
4. The hundreth of a Dollar, of copper.
Compare the arithmetical operations, on the same sum of money expressed in this form, and expressed in the pound sterling and its divisions.
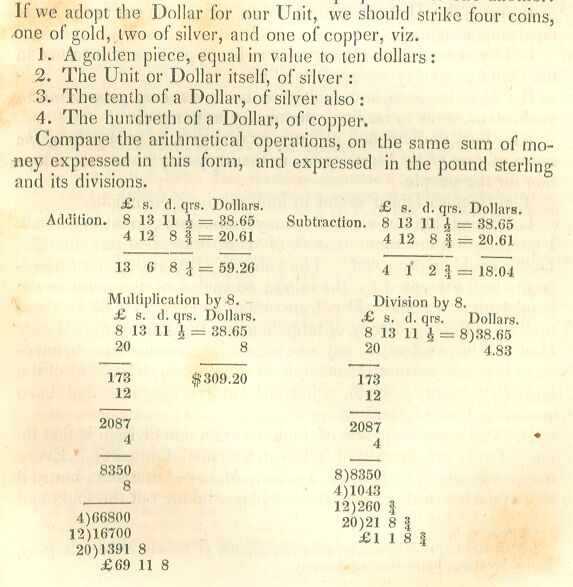
A bare inspection of the above operations, will evince the labor which is occasioned by subdividing the Unit into 20ths, 240ths, and 960ths, as the English do, and as we have done; and the ease of subdivision in a decimal ratio. The same difference arises in making payment. An Englishman, to pay £8 13s. 11d. 1/2qrs. must find, by calculation, what combination of the coins of his country will pay this sum; but an American, having the same sum to pay, thus expressed $38.65, will know, by inspection only, that three golden pieces, eight units or dollars, six tenths, and five coppers, pay it precisely.
III. The third condition required is, that the Unit, its multiples, and subdivisions, coincide in value with some of the known coins so nearly, that the people may, by a quick reference in the mind, estimate their value. If this be not attended to, they will be very long in adopting the innovation, if ever they adopt it. Let us examine, in this point of view, each of the four coins proposed.
1. The golden piece will be 1/5 more than a half joe and 1/15 more than a double guinea. It will be readily estimated, then, by reference to either of them; but more readily and accurately as equal to ten dollars.
2. The Unit, or Dollar, is a known coin, and the most familiar of all to the minds of the people. It is already adopted from South to North; has identified our currency, and therefore happily offers itself as a Unit already introduced. Our public debt, our requisitions, and their apportionments, have given it actual and long possession of the place of Unit. The course of our commerce, too, will bring us more of this than of any other foreign coin, and therefore renders it more worthy of attention. I know of no Unit which can be proposed in competition with the Dollar, but the Pound. But what is the Pound? 1547 grains of fine silver in Georgia; 1289 grains in Virginia, Connecticut, Rhode Island, Massachusetts, and New Hampshire; 1031 grains in Maryland, Delaware, Pennsylvania, and New Jersey; 966 grains in North Carolina and New York. Which of these shall we adopt? To which State give that pre-eminence of which all are so jealous? And on which impose the difficulties of a new estimate of their corn, their cattle, and other commodities? Or shall we hang the pound sterling, as a common badge, about all their necks? This contains 1718 grains of pure silver. It is difficult to familiarize a new coin to the people; it is more difficult to familiarize them to a new coin with an old name. Happily, the Dollar is familiar to them all, and is already as much referred to for a measure of value, as their respective provincial pounds.
3. The tenth will be precisely the Spanish bit, or half pistereen. This is a coin perfectly familiar to us all. When we shall make a new coin, then, equal in value to this, it will be of ready estimate with the people.
4. The hundredth, or copper, will differ little from the copper of the four Eastern States, which is 1/108 of a dollar; still less from the penny of New York and North Carolina, which is 1/96 of a dollar; and somewhat more from the penny or copper of Jersey, Pennsylvania, Delaware, and Maryland, which is 1/90 of a dollar. It will be about the medium between the old and the new coppers of these States, and will therefore soon be substituted for them both. In Virginia, coppers have never been in use. It will be as easy, therefore, to introduce them there of one value as of another. The copper coin proposed, will be nearly equal to three fourths of their penny, which is the same with the penny lawful of the Eastern States.
A great deal of small change is useful in a State, and tends to reduce the price of small articles. Perhaps it would not be amiss to coin three, more pieces of silver, one of the value of five tenths, or half a dollar, one of the value of two tenths, which would be equal to the Spanish pistereen, and one of the value of five coppers, which would be equal to the Spanish half-bit. We should then have five silver coins, viz.
1. The Unit or Dollar:
2. The half dollar or five tenths:
3. The double tenth, equal to 2/10, or one fifth of a dollar, or to the pistereen:
4. The tenth, equal to a Spanish bit:
5. The five copper piece, equal to 5/100 or one twentieth of a dollar, or the half-bit.
The plan reported by the Financier is worthy of his sound judgment. It admits, however, of objection, in the size of the Unit. He proposes that this shall be the 1440th part of a dollar; so that it will require 1440 of his units to make the one before proposed. He was led to adopt this by a mathematical attention to our old currencies, all of which this Unit will measure without leaving a fraction. But as our object is to get rid of those currencies, the advantage derived from this coincidence will soon be past, whereas the inconveniences of this Unit will for ever remain, if they do not altogether prevent its introduction. It is defective in two of the three requisites of a Money Unit. 1. It is inconvenient in its application to the ordinary money transactions. 10,000 dollars will require eight figures to express them, to wit, 14,400,000 units. A horse or bullock of eighty dollars’ value, will require a notation of six figures, to wit, 115,200 units. As a money of account, this will be laborious, even when facilitated by the aid of decimal arithmetic: as a common measure of the value of property, it will be too minute to be comprehended by the people. The French are subjected to very laborious calculations, the Livre being their ordinary money of account, and this but between 1/5 and 1/6 of a dollar; but what will be our labors, should our money of account be 1/1440 of a dollar only? 2. It is neither equal, nor near to any of the known coins in value.
If we determine that a Dollar shall be our Unit, we must then say with precision what a Dollar is. This coin, struck at different times, of different weights and fineness, is of different values. Sir Isaac Newton’s assay and representation to the Lords of the Treasury, in 1717, of those which he examined, make their values as follows:

The Seville piece of eight . . . . 387 grains of pure silver
The Mexico piece of eight . . . . 385 1/2 ”
The Pillar piece of eight . . . . 385 3/4 ”
The new Seville piece of eight . . 308 7/10 ”
The Financier states the old Dollar as containing 376 grains of fine silver, and the new 365 grains. If the Dollars circulating among us be of every date equally, we should examine the quantity of pure metal in each, and from them form an average for our Unit. This is a work proper to be committed to mathematicians as well as merchants, and which should be decided on actual and accurate experiment.
The quantum of alloy is also to be decided. Some is necessary, to prevent the coin from wearing too fast; too much, fills our pockets with copper, instead of silver. The silver coin assayed by Sir Isaac Newton, varied from 1 1/2 to 76 pennyweights alloy, in the pound troy of mixed metal. The British standard has 18 dwt.; the Spanish coins assayed by Sir Isaac Newton, have from 18 to 19 1/2 dwt.; the new French crown has in fact 19 1/2, though by edict it should have 20 dwt., that is 1/12.
The taste of our countrymen will require, that their furniture plate should be as good as the British standard. Taste cannot be controlled by law. Let it then give the law, in a point which is indifferent to a certain degree. Let the Legislatures fix the alloy of furniture plate at 18 dwt., the British standard, and Congress that of their coin at one ounce in the pound, the French standard. This proportion has been found convenient for the alloy of gold coin, and it will simplify the system of our mint to alloy both metals in the same degree. The coin too, being the least pure, will be the less easily melted into plate. These reasons are light, indeed, and, of course, will only weigh, if no heavier ones can be opposed to them.
The proportion between the values of gold and silver is a mercantile problem altogether. It would be inaccurate to fix it by the popular exchanges of a half Joe for eight dollars, a Louis for four French crowns, or five Louis for twenty-three dollars. The first of these, would be to adopt the Spanish proportion between gold and silver; the second, the French; the third, a mere popular barter, wherein convenience is consulted more than accuracy. The legal proportion in Spain is 16 for 1; in England, 15 1/2 for 1; in France, 15 for 1. The Spaniards and English are found, in experience, to retain an over proportion of gold coins, and to lose their silver. The French have a greater proportion of silver. The difference at market has been on the decrease. The Financier states it at present, as at 141/2 for one. Just principles will lead us to disregard legal proportions altogether; to inquire into the market price of gold, in the several countries with which we shall principally be connected in commerce, and to take an average from them. Perhaps we might, with safety, lean to a proportion somewhat above par for gold, considering our neighborhood and commerce with the sources of the coins, and the tendency which the high price of gold in Spain has, to draw thither all that of their mines, leaving silver principally for our and other markets. It is not impossible that 15 for 1, may be found an eligible proportion. I state it, however, as a conjecture only.
As to the alloy for gold coin, the British is an ounce in the pound; the French, Spanish, and Portuguese differ from that, only from a quarter of a grain, to a grain and a half. I should, therefore, prefer the British, merely because its fraction stands in a more simple form, and facilitates the calculations into which it enters.
Should the Unit be fixed at 365 grains of pure silver, gold at 15 for 1, and the alloy of both be one twelfth, the weights of the coins will be as follows:

The quantity of fine silver which shall constitute the Unit, being-settled, and the proportion of the value of gold, to that of silver; a table should be formed from the assay before suggested, classing the several foreign coins according to their fineness, declaring the worth of a pennyweight or grain in each class, and that they shall be lawful tenders at those rates, if not clipped or otherwise diminished; and where diminished, offering their value for them at the mint, deducting the expense of re-coinage. Here the Legislatures should co-operate with Congress, in providing that no money be received or paid at their treasuries, or by any of their officers, or any bank, but on actual weight; in making it criminal, in a high degree, to diminish their own coins, and, in some smaller degree, to offer them in payment when diminished.
That this subject may be properly prepared and in readiness for Congress to take up at their meeting in November, something must now be done. The present session drawing to a close, they probably would not choose to enter far into this undertaking themselves. The Committee of the States, however, during the recess, will have time to digest it thoroughly, if Congress will fix some general principles for their government. Suppose they be instructed,—
To appoint proper persons to assay and examine, with the utmost accuracy practicable, the Spanish milled dollars of different dates in circulation with us.
To assay and examine, in like manner, the fineness of all the other coins which may be found in circulation within these states.
To report to the Committee the result of these assays, by them to be laid before Congress.
To appoint, also, proper persons to inquire what are the proportions between the values of fine gold and fine silver, at the markets of the several countries with which we are, or probably may be, connected in commerce; and what would be a proper proportion here, having regard to the average of their values at those markets, and to other circumstances, and to report the same to the Committee, by them to be laid before Congress.
To prepare an Ordinance for establishing the Unit of Money within these States; for subdividing it; and for striking coins of gold, silver, and copper, on the following principles.
That the Money Unit of these States shall be equal in value to a Spanish milled dollar containing so much fine silver as the assay, before directed, shall show to be contained, on an average, in dollars of the several dates in circulation with us.
That this Unit shall be divided into tenths and hundredths; that there shall be a coin of silver of the value of a Unit; one other of the same metal, of the value of one tenth of a Unit; one other of copper, of the value of the hundredth of a Unit.
That there shall be a coin of gold of the value of ten units, according to the report before directed, and the judgment of the Committee thereon.
That the alloy of the said coins of gold and silver shall be equal in weight to one eleventh part of the fine metal.
That there be proper devices for these coins.
That measures be proposed for preventing their diminution, and also their currency, and that of any others, when diminished.
That the several foreign coins be described and classed in the said Ordinance, the fineness of each class stated, and its value by weight estimated in Units and decimal parts of Units.
And that the said draught of an Ordinance be reported to Congress at their next meeting, for their consideration and determination.
Supplementary Explanations.
The preceding notes having been submitted to the consideration of the Financier, he favored me with his opinion and observations on them, which render necessary the following supplementary explanations.
I observed in the preceding notes, that the true proportion of value between gold and silver was a mercantile problem altogether, and that, perhaps, fifteen for one, might be found an eligible proportion. The Financier is so good as to inform me, that this would be higher than the market would justify. Confident of his better information on this subject, I recede from that idea.*
* In a Newspaper, which frequently gives good details in political economy, I find, under the Hamburg head, that the present market price of Gold and Silver is, in England, 15.5 for 1: in Russia, 15: in Holland, 14.75: in Savoy, 14.96: in Fiance, 14.42: in Spain, 14.3: in Germany, 14.155: the average of which is 14.615 or 14 1/2. I would still incline to give a little more than the market price for gold, because of its superior convenience in transportation.
He also informs me, that the several coins in circulation among us, have already been assayed with accuracy, and the result published in a work on that subject. The assay of Sir Isaac Newton had superseded, in my mind, the necessity of this operation as to the older coins, which were the subject of his examination. This later work, with equal reason, may be considered as saving the same trouble as to the latter coins.
So far, then, I accede to the opinions of the Financier. On the other hand, he seems to concur with me, in thinking his smallest fractional division too minute for a Unit, and, therefore, proposes to transfer that denomination to his largest silver coin, containing 1000 of the units first proposed, and worth about 4s. 2d. lawful, or 25/36 of a dollar. The only question then remaining between us is, whether the Dollar, or this coin, be best for the Unit. We both agree that the ease of adoption with the people, is the thing to be aimed at.
1. As to the Dollar, events have overtaken and superseded the question. It is no longer a doubt whether the people can adopt it with ease; they have adopted it, and will have to be turned out of that, into another track of calculation, if another Unit be assumed. They have now two Units, which they use with equal facility, viz. the Pound of their respective state, and the Dollar. The first of these is peculiar to each state; the second, happily, common to all. In each state, the people have an easy rule for converting the pound of their state into dollars, or dollars into pounds; and this is enough for them, without knowing how this may be done in every state of the Union. Such of them as live near enough the borders of their state to have dealings with their neighbors, learn also the rule of their neighbors: Thus, in Virginia and the Eastern States, where the dollar is 6s. or 3/10 of a pound, to turn pounds into dollars, they multiply by 10, and divide by 3. To turn dollars into pounds, they multiply by 3, and divide by 10. Those in Virginia who live near to Carolina, where the dollar is 8s. or 4/10 of a pound, learn the operation of that state, which is a multiplication by 4, and division by 10, et e converso. Those who live near Maryland, where the dollar is 7s. 6d. or 3/8 of a pound, multiply by 3, and divide by 8, et e converso. All these operations are easy, and have been found by experience, not too much for the arithmetic of the people, when they have occasion to convert their old Unit into dollars, or the reverse.
2. As to the Unit of the Financier; in the States where the dollar is 3/10 of a pound, this Unit will be 5/24. Its conversion into the pound then, will be by a multiplication by 5, and a division by 24. In the States where the dollar is 3/8 of a pound, this Unit will be 25/96 of a pound, and the operation must be to multiply by 25, and divide by 96, et e converso. Where the dollar is 4/10 of a pound, this Unit will be 5/18. The simplicity of the fraction, and of course the facility of conversion and reconversion, is therefore against this Unit, and in favor of the dollar, in every instance. The only advantage it has over the dollar, is, that it will in every case express our farthing without a remainder; whereas, though the dollar and its decimals will do this in many cases, it will not in all. But, even in these, by extending your notation one figure farther, to wit, to thousands, you approximate a perfect accuracy within less than the two thousandth part of a dollar; an atom in money which every one would neglect. Against this single inconvenience, the other advantages of the dollar are more than sufficient to preponderate. This Unit will present to the people a new coin, and whether they endeavor to estimate its value by comparing it with a Pound, or with a Dollar, the Units they now possess, they will find the fraction very compound, and of course less accommodated to their comprehension and habits than the dollar. Indeed the probability is, that they could never be led to compute in it generally.
The Financier supposes that the 1/100 of a dollar is not sufficiently small, where the poor are purchasers or vendors. If it is not, make a smaller coin. But I suspect that it is small enough. Let us examine facts, in countries where we are acquainted with them. In Virginia, where our towns are few, small, and of course their demand for necessaries very limited, we have never yet been able to introduce a copper coin at all. The smallest coin which any body will receive there, is the half-bit, or 1/20 of a dollar. In those states where the towns are larger and more populous, a more habitual barter for small wants, has called for a copper coin of 1/90 or 1/96 or 1/108 of a dollar. In England, where the towns are many and pouplous, and where ages of experience have matured the conveniences of intercourse, they have found that some wants may be supplied for a farthing, or 1/208 of a dollar, and they have accommodated a coin to this want. This business is evidently progressive. In Virginia we are far behind. In some other states, they are farther advanced, to wit, to the appreciation of 1/90, 1/96 or 1/108 of a dollar. To this most advanced state, then, I accommodated my smartest coin in the decimal arrangement, as a money of payment, corresponding with the money of account. I have no doubt the time will come when a smaller coin will be called for. When that comes, let it be made. It will probably be the half of the copper I propose, that is to say 5/1000 or.005 of a dollar, this being very nearly the farthing of England. But it will be time enough to make it, when the people shall be ready to receive it.
My proposition then, is, that our notation of money shall be decimal, descending ad libitum of the person noting; that the Unit of this notation shall be a Dollar; that coins shall be accommodated to it from ten dollars to the hundredth of a dollar; and that, to set this on foot, the resolutions be adopted which were proposed in the notes, only substituting an inquiry into the fineness of the coins in lieu of an assay of them.
I have sometimes asked myself, whether my country is the better for my having lived at all. I do not know that it is. I have been the instrument of doing the following things; but they would have been done by others; some of them, perhaps, a little better.
The Rivanna had never been used for navigation; scarcely an empty canoe had ever passed down it. Soon after I came of age I examined its obstructions, set on foot a subscription for removing them, got an act of Assembly passed, and the thing effected, so as to be used completely and fully for carrying down all our produce.
The Declaration of Independence.
I proposed the demolition of the Church establishment, and the freedom of religion. It could only be done by degrees; to wit, the act of 1776, c. 2. exempted dissenters from contributions to the Church, and left the Church clergy to be supported by voluntary contributions of their own sect; was continued from year to year, and made perpetual 1779, c. 36. I prepared the act for religious freedom in 1777, as part of the revisal, which was not reported to the Assembly till 1779, and that particular law not passed till 1785, and then by the efforts of Mr. Madison.
The act putting an end to entails.
The act prohibiting the importation of slaves.
The act concerning citizens, and establishing the natural right of man to expatriate himself at will.
The act changing the course of descents, and giving the inheritance to all the children, &c. equally, I drew as part of the revisal.
The act for apportioning crimes and punishments, part of the same work, I drew. When proposed to the Legislature by Mr. Madison, in 1785, it failed by a single vote. G. K. Taylor afterwards, in 1796, proposed the same subject; avoiding the adoption of any part of the diction of mine, the text of which had been studiously drawn in the technical terms of the law, so as to give no occasion for new questions by new expressions. When I drew mine, public labor was thought the best punishment to be substituted for death. But, while I was in France, I heard of a society in England who had successfully introduced solitary confinement, and saw the drawing of a prison at Lyons, in France, formed on the idea of solitary confinement. And, being applied to by the Governor of Virginia for the plan of a Capitol and Prison, I sent him the Lyons plan, accompanying it with a drawing on a smaller scale, better adapted to our use. This was in June, 1786. Mr. Taylor very judiciously adopted this idea, (which had now been acted on in Philadelphia, probably from the English model,) and substituted labor in confinement, to the public labor proposed by the Committee of revisal; which themselves would have done, had they been to act on the subject again. The public mind was ripe for this in 1796, when Mr. Taylor proposed it, and ripened chiefly by the experiment in Philadelphia; whereas, in 1785, when it had been proposed to our Assembly, they were not quite ripe for it.
In 1789 and 1790, I had a great number of olive plants, of the best kind, sent from Marseilles to Charleston, for South Carolina and Georgia. They were planted, and are flourishing; and, though not yet multiplied, they will be the germ of that cultivation in those States.
In 1790, I got a cask of heavy upland rice, from the river Denbigh, in Africa, about lat. 9° 30’ North, which I sent to Charleston, in hopes it might supersede the culture of the wet rice, which renders South Carolina and Georgia so pestilential through the summer. It was divided, and a part sent to Georgia. I know not whether it has been attended to in South Carolina; but it has spread in the upper parts of Georgia, so as to have become almost general, and is highly prized. Perhaps it may answer in Tennessee and Kentucky. The greatest service which can be rendered any country is, to add an useful plant to its culture; especially a bread grain; next in value to bread is oil.
Whether the Act for the more general diffusion of knowledge will ever be carried into complete effect, I know not. It was received, by the legislature, with great enthusiasm at first; and a small effort was made in 1796, by the act to establish public schools, to carry a part of it into effect, viz. that for the establishment of free English schools; but the option given to the courts has defeated the intention of the Act.*
* It appears, from a blank space at the bottom of this
paper, that a continuation had been intended. Indeed, from
the loose manner in which the above notes are written, it
may be inferred that they were originally intended as
memoranda only, to be used in some more permanent form.
Sir,
New York, October 13, 1789.
In the selection of characters to fill the important offices of Government in the United States, I was naturally led to contemplate the talents and dispositions which I knew you to possess and entertain for the service of your country; and without being able to consult your inclination, or to derive any knowledge of your intentions from your letters, either to myself or to any other of your friends, I was determined, as well by motives of private regard, as a conviction of public propriety, to nominate you for the Department of State, which, under its present organization, involves many of the most interesting objects of the Executive authority.
But grateful as your acceptance of this commission would be to me, I am, at the same time, desirous to accommodate your wishes, and I have, therefore, forborne to nominate your successor at the court of Versailles until I should be informed of your determination.
Being on the eve of a journey through the Eastern States, with a view to observe the situation of the country, and in a hope of perfectly re-establishing my health, which a series of indispositions has much impaired, I have deemed it proper to make this communication of your appointment, in order that you might lose no time, should it be your wish to visit Virginia during the recess of Congress, which will probably be the most convenient season, both as it may respect your private concerns, and the public service.
Unwilling, as I am, to interfere in the direction of your choice of assistants, I shall only take the liberty of observing to you, that, from warm recommendations which I have received in behalf of Roger Alden, Esq., Assistant Secretary to the late Congress, I have placed all the papers thereunto belonging under his care. Those papers which more properly appertain to the office of Foreign Affairs, are under the superintendence of Mr. Jay, who has been so obliging as to continue his good offices, and they are in the immediate charge of Mr. Remsen.
With sentiments of very great esteem and regard, I have the honor to be, Sir,
Your most obedient servant,
George Washington.
The Honorable Thomas Jefferson.
I take the occasion to acknowledge the receipt of your several favors of the 4th and 5th of December of the last, and 10th of May of the present year, and to thank you for the communications therein. G. W.
New York, November 30, 1789.
Dear Sir,
You will perceive by the inclosed letter (which was left for you at the office of Foreign Affairs when I made a journey to the Eastern States), the motives, on which I acted with regard to yourself, and the occasion of my explaining them at that early period.
Having now reason to hope, from Mr. Trumbull’s report, that you will be arrived at Norfolk before this time (on which event I would most cordially congratulate you), and having a safe conveyance by Mr. Griffin, I forward your commission to Virginia; with a request to be made acquainted with your sentiments as soon as you shall find it convenient to communicate them to me. With sentiments of very great esteem and regard,
I am, dear Sir,
Your most obedient, humble servant,
George Washington.
The Honorable Thomas Jefferson.
TO DR. WILLIAM SMALL.
May 7, 1775.
Dear Sir,
Within this week we have received the unhappy news of an action of considerable magnitude, between the King’s troops and our brethren of Boston, in which, it is said, five hundred of the former, with the Earl of Percy, are slain. That such an action has occurred, is undoubted, though perhaps the circumstances may not have reached us with truth. This accident has cut off our last hope of reconciliation, and a phrenzy of revenge seems to have seized all ranks of people. It is a lamentable circumstance, that the only mediatory power, acknowledged by both parties, instead of leading to a reconciliation his divided people, should pursue the incendiary purpose of still blowing up the flames, as we find him constantly doing, in every speech and public declaration. This may, perhaps, be intended to intimidate into acquiescence, but the effect has been most unfortunately otherwise. A little knowledge of human nature, and attention to its ordinary workings, might have foreseen that the spirits of the people here were in a state, in which they were more likely to be provoked, than frightened, by haughty deportment. And to fill up the measure of irritation, a proscription of individuals has been substituted in the room of just trial. Can it be believed, that a grateful people will suffer those to be consigned to execution, whose sole crime has been the developing and asserting their rights? Had the Parliament possessed the power of reflection, they would have avoided a measure as impotent, as it was inflammatory. When I saw Lord Chatham’s bill, I entertained high hope that a reconciliation could have been brought about. The difference between his terms, and those offered by our Congress, might have been accommodated, if entered on, by both parties, with a disposition to accommodate. But the dignity of Parliament, it seems, can brook no opposition to its power. Strange, that a set of men, who have made sale of their virtue to the minister, should yet talk of retaining dignity. But I am getting into politics, though I sat down only to ask your acceptance of the wine: and express my constant wishes for your happiness.
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN RANDOLPH, ESQ.,
Monticello,
August 25,1775.
Dear Sir,
I am sorry the situation of our country should render it not eligible to you to remain longer in it. I hope the returning wisdom of Great Britain will, ere long, put an end to this unnatural contest. There may be people to whose tempers and dispositions contention is pleasing, and who, therefore, wish a continuance of confusion; but to me it is of all states but one, the most horrid: My first wish is a restoration of our just rights; my second, a return of the happy period, when, consistently with duty, I may withdraw myself totally from the public stage, and pass the rest of my days in domestic ease and tranquillity, banishing every desire of ever hearing what passes in the world. Perhaps, (for the latter adds considerably to the warmth of the former wish,) looking with fondness towards a reconciliation with Great Britain, I cannot help hoping you may be able to contribute towards expediting this good work. I think it must be evident to yourself, that the Ministry have been deceived by their officers on this side of the water, who (for what purpose, I cannot tell) have constantly represented the American opposition as that of a small faction, in which the body of the people took little part. This, you can inform them, of your own knowledge, is untrue. They have taken it into their heads, too, that we are cowards, and shall surrender at discretion to an armed force. The past and future operations of the war must confirm or undeceive them on that head. I wish they were thoroughly and minutely acquainted with every circumstance relative to America, as it exists in truth. I am persuaded, this would go far towards disposing them to reconciliation. Even those in Parliament who are called friends to America, seem to know nothing of our real determinations. I observe, they pronounced in the last Parliament, that the Congress of 1774 did not mean to insist rigorously on the terms they held out, but kept something in reserve, to give up: and, in fact, that they would give up every thing but the article of taxation. Now, the truth is far from this, as I can affirm, and put my honor to the assertion. Their continuance in this error may perhaps produce very ill consequences. The Congress stated the lowest terms they thought possible to be accepted, in order to convince the world they were not unreasonable. They gave up the monopoly and regulation of trade, and all acts of Parliament prior to 1764, leaving to British generosity to render these, at some future time, as easy to America as the interest of Britain would admit. But this was before blood was spilt. I cannot affirm, but have reason to think, these terms would not now be accepted. I wish no false sense of honor, no ignorance of our real intentions, no vain hope that partial concessions of right will be accepted, may induce the Ministry to trifle with accommodation, till it shall be out of their power ever to accommodate. If, indeed, Great Britain, disjoined from her colonies, be a match for the most potent nations of Europe, with the colonies thrown into their scale, they may go on securely. But if they are not assured of this, it would be certainly unwise, by trying the event of another campaign, to risk our accepting a foreign aid, which perhaps may not be obtainable but on condition of everlasting avulsion from Great Britain. This would be thought a hard condition to those who still wish for reunion with their parent country. I am sincerely one of those, and would rather be in dependence on Great Britain, properly limited, than on any nation upon earth, or than on no nation. But I am one of those, too, who, rather than submit to the rights of legislating for us, assumed by the British Parliament, and which late experience has shown they will so cruelly exercise, would lend my hand to sink the whole island in the ocean.
If undeceiving the Minister, as to matters of fact, may change his disposition, it will perhaps be in your power, by assisting to do this, to render service to the whole empire at the most critical time, certainly, that it has ever seen. Whether Britain shall continue the head of the greatest empire on earth, or shall return to her original station in the political scale of Europe, depends perhaps on the resolutions of the succeeding winter. God send they may be wise and salutary for us all. I shall be glad to hear from you as often as you may be disposed to think of things here. You may be at liberty, I expect; to communicate some things, consistently with your honor and the duties you will owe to a protecting nation. Such a communication among individuals may be mutually beneficial to the contending parties. On this or any future occasion, if I affirm to you any facts, your knowledge of me will enable you to decide on their credibility; if I hazard opinions on the dispositions of men or other speculative points, you can only know they are my opinions. My best wishes for your felicity attend you wherever you go; and believe me to be, assuredly,
Your friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN RANDOLPH, ESQ..
Philadelphia,
November 29, 1775.
Dear Sir,
I am to give you the melancholy intelligence of the death of our most worthy Speaker, which happened here on the 22nd of the last month. He was struck with an apoplexy, and expired within five hours.
I have it in my power to acquaint you that the success of our arms has corresponded with the justness of our cause. Chambly and St. Johns were taken some weeks ago, and in them the whole regular army in Canada, except about forty or fifty men. This day certain intelligence has reached us that our General, Montgomery, is received into Montreal: and we expect every hour to be informed that Quebec has opened its arms to Colonel Arnold, who, with eleven hundred men, was sent from Boston up the Kennebec, and down the Chaudiere river to that place. He expected to be there early this month. Montreal acceded to us on the 13th, and Carleton set out, with the shattered remains of his little army, for Quebec, where we hope he will be taken up by Arnold. In a short time, we have reason to hope, the delegates of Canada will join us in Congress, and complete the American union as far as we wish to have it completed. We hear that one of the British transports has arrived at Boston; the rest are beating off the coast, in very bad weather. You will have heard, before this reaches you, that Lord Dunmore has commenced hostilities in Virginia. That people bore with every thing, till he attempted to burn the town of Hampton. They opposed and repelled him, with considerable loss on his side, and none on ours. It has raised our countrymen into a perfect phrenzy. It is an immense misfortune to the whole empire to have a King of such a disposition at such a time. We are told, and every thing proves it true, that he is the bitterest enemy we have. His Minister is able, and that satisfies me that ignorance, or wickedness, somewhere, controls him. In an earlier part of this contest, our petitions told him, that from our King there was but one appeal. The admonition was despised, and that appeal forced on us. To undo his empire, he has but one truth more to learn; that, after colonies have drawn the sword, there is but one step more they can take. That step is now pressed upon us by the measures adopted, as if they were afraid we would not take it. Believe me, dear Sir, there is not in the British empire a man who more cordially loves a union with Great Britain than I do. But, by the God that made me, I will cease to exist before I yield to a connection on such terms as the British Parliament propose; and in this, I think I speak the sentiments of America. We want neither inducement nor power to declare and assert a separation. It is will alone which is wanting, and that is growing apace under the fostering hand of our King. One bloody campaign will probably decide everlastingly our future course; I am sorry to find a bloody campaign is decided on. If our winds and waters should not combine to rescue their shores from slavery, and General Howe’s reinforcement should arrive in safety, we have hopes he will be inspirited to come out of Boston and take another drubbing: and we must drub him soundly before the sceptred tyrant will know we are not mere brutes, to crouch under his hand, and kiss the rod with which he deigns to scourge us.
Yours, &c.
Th: Jefferson.
TO DR. BENJAMIN FRANKLIN, PARIS.
Virginia,
August 13, 1777.
Honorable Sir,
I forbear to write you news, as the time of Mr. Shore’s departure being uncertain, it might be old before you receive it, and he can, in person, possess you of all we have. With respect to the State of Virginia in particular, the people seem to have laid aside the monarchical, and taken up the republican government, with as much ease as would have attended their throwing off an old and putting on a new suit of clothes. Not a single throe has attended this important transformation. A half dozen aristocratical gentlemen, agonizing under the loss of pre-eminence, have sometimes ventured their sarcasms on our political metamorphosis. They have been thought fitter objects of pity than of punishment. We are at present in the complete and quiet exercise of well organized government, save only that our courts of justice do not open till the fall. I think nothing can bring the security of our continent and its cause into danger, if we can support the credit of our paper. To do that, I apprehend one of two steps must be taken. Either to procure free trade by alliance with some naval power able to protect it; or, if we find there is no prospect of that, to shut our ports totally to all the world, and turn our colonies into manufactories. The former would be most eligible, because most conformable to the habits and wishes of our people. Were the British Court to return to their senses in time to seize the little advantage which still remains within their reach from this quarter, I judge that, on acknowledging our absolute independence and sovereignty, a commercial treaty beneficial to them, and perhaps even a league of mutual offence and defence, might, not seeing the expense or consequences of such a measure, be approved by our people, if nothing in the mean time, done on your part, should prevent it. But they will continue to grasp at their desperate sovereignty, till every benefit short of that is for ever out of their reach. I wish my domestic situation had rendered it possible for me to join you in the very honorable charge confided to you. Residence in a polite Court, society of literati of the first order, a just cause and an approving God, will add length to a life for which all men pray, and none more than
Your most obedient
and humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO HIS EXCELLENCY PATRICK HENRY.
Albemarle,
March 27, 1779.
Sir,
A report prevailing here, that in consequence of some powers from Congress, the Governor and Council have it in contemplation to remove the Convention troops, [The troops under Burgoyne, captured at Saratoga.] either wholly or in part, from their present situation, I take the liberty of troubling you with some observations on that subject. The reputation and interest of our country, in general, may be affected by such a measure; it would, therefore, hardly be deemed an indecent liberty, in the most private citizen, to offer his thoughts to the consideration of the Executive. The locality of my situation, particularly, in the neighborhood of the present barracks, and the public relation in which I stand to the people among whom they are situated, together with a confidence, which a personal knowledge of the members of the Executive gives me, that they Will be glad of information from any quarter, on a subject interesting to the public, induce me to hope that they will acquit me of impropriety in the present representation.
By an article in the Convention of Saratoga, it is stipulated, on the part of the United States, that the officers shall not be separated from their men. I suppose the term officers, includes general as well as regimental officers. As there are general officers who command all the troops, no part of them can be separated from these officers without a violation of the article: they cannot, of course, be separated from one another, unless the same general officer could be in different places at the same time. It is true, the article adds the words, ‘as far as circumstances will admit.’ This was a necessary qualification; because, in no place in America, I suppose, could there have been found quarters for both officers and men together; those for the officers to be according to their rank. So far, then, as the circumstances of the place where they should be quartered, should render a separation necessary, in order to procure quarters for the officers, according to their rank, the article admits that separation. And these are the circumstances which must have been under the contemplation of the parties; both of whom, and all the world beside (who are ultimate judges in the case), would still understand that they were to be as near in the environs of the camp, as convenient quarters could be procured; and not that the qualification of the article destroyed the article itself and laid it wholly at our discretion. Congress, indeed, have admitted of this separation; but are they so far lords of right and wrong as that our consciences may be quiet with their dispensation? Or is the case amended by saying they leave it optional in the Governor and Council to separate the troops or not? At the same time that it exculpates not them, it is drawing the Governor and Council into a participation in the breach of faith. If indeed it is only proposed, that a separation of the troops shall be referred to the consent of their officers; that is a very different matter. Having carefully avoided conversation with them on public subjects, I cannot say, of my own knowledge, how they would relish such a proposition. I have heard from others, that they will choose to undergo any thing together, rather than to be separated, and that they will remonstrate against it in the strongest terms. The Executive, therefore, if voluntary agents in this measure, must be drawn into a paper war with them, the more disagreeable, as it seems that faith and reason will be on the other side. As an American, I cannot help feeling a thorough mortification, that our Congress should have permitted an infraction of our public honor; as a citizen of Virginia, I cannot help hoping and confiding, that our supreme Executive, whose acts will be considered as the acts of the Commonwealth, estimate that honor too highly to make its infraction their own act. I may be permitted to hope, then, that if any removal takes place, it will be a general one: and, as it is said to be left to the Governor and Council to determine on this, I am satisfied, that, suppressing every other consideration, and weighing the matter dispassionately, they will determine upon this sole question, Is it for the benefit of those for whom they act, that, the Convention troops should be removed from among them? Under the head of interest, these circumstances, viz. the expense of building barracks, said to have been £25,000, and of removing the troops backwards and forwards, amounting to I know not how much, are not to be pre-termitted, merely because they are Continental expenses; for we are a part of the Continent; we must pay a shilling of every dollar wasted. But the sums of money, which, by these troops, or on their account, are brought into, and expended in this State, are a great and local advantage. This can require no proof. If, at the conclusion of the war, for instance, our share of the Continental debt should be twenty millions of dollars, or say that we are called on to furnish an annual quota of two millions four hundred thousand dollars, to Congress, to be raised by tax, it is obvious that we should raise these given sums with greater or less ease, in proportion to the greater or less quantity of money found in circulation among us. I expect that our circulating money is, by the presence of these troops, at the rate of $30,000 a week, at the least. I have heard, indeed, that an objection arises to their being kept within this state, from the information of the commissary that they cannot be subsisted here. In attending to the information of that officer, it should be borne in mind that the county of King William and its vicinities are one thing, the territory of Virginia another. If the troops could be fed upon long letters, I believe the gentleman at the head of that department in this country would be the best commissary upon earth. But till I see him determined to act, not to write; to sacrifice his domestic ease to the duties of his appointment, and apply to the resources of this country, wheresoever they are to be had, I must entertain a different opinion of him. I am mistaken, if, for the animal sub-sistence of the troops hitherto, we are not principally indebted to the genius and exertions of Hawkins, during the very short time he lived after his appointment to that department, by your board. His eye immediately pervaded the whole state; it was reduced at once to a regular machine, to a system, and the whole put into movement and animation by the fiat of a comprehensive mind. If the Commonwealth of Virginia cannot furnish these troops with bread, I would ask of the commissariat, which of the thirteen is now become the grain colony? If we are in danger of famine from the addition of four thousand mouths, what is become of that surplus of bread, the exportation of which used to feed the West Indies and Eastern States, and fill the colony with hard money? When I urge the sufficiency of this State, however, to subsist these troops, I beg to be understood, as having in contemplation the quantity of provisions necessary for their real use, and not as calculating what is to be lost by the wanton waste, mismanagement, and carelessness of those employed about it. If magazines of beef and pork are suffered to rot by slovenly butchering, or for want of timely provision and sale; if quantities of flour are exposed by the commissaries entrusted with the keeping it, to pillage and destruction; and if, when laid up in the Continental stores, it is still to be embezzled and sold, the land of Egypt itself would be insufficient for their supply, and their removal would be necessary, not to a more plentiful country, but to more able and honest commissaries. Perhaps, the magnitude of this question, and its relation to the whole state, may render it worth while to await, the opinion of the National Council, which is now to meet within a few weeks. There is no danger of distress in the mean time, as the commissaries affirm they have a great sufficiency of provisions for some time to come. Should the measure of removing them into another State be adopted, and carried into execution, before the meeting of Assembly, no disapprobation of theirs will bring them back, because they will then be in the power of others, who will hardly give them up.
Want of information as to what may be the precise measure proposed by the Governor and Council, obliges me to shift my ground, and take up the subject in every possible form. Perhaps they have not thought to remove the troops out of this State altogether, but to some other part of it. Here, the objections arising from the expenses of removal, and of building new barracks, recur. As to animal food, it may be driven to one part of the country as easily as to another: that circumstance, therefore, may be thrown out of the question. As to bread, I suppose they will require about forty or forty-five thousand bushels of grain a year. The place to which it is to be brought to them, is about the centre of the State. Besides that the country round about is fertile, all the grain made in the counties adjacent to any kind of navigation, may be brought by water to within twelve miles of the spot. For these twelve miles, wagons must be employed; I suppose half a dozen will be a plenty. Perhaps this part of the expense might have been saved, had the barracks been built on the water; but it is not sufficient to justify their being abandoned now they are built. Wagonage, indeed, seems to the commissariat, an article not worth economizing. The most wanton and studied circuity of transportation has been practised: to mention only one act, they have bought quantities of flour for these troops in Cumberland, have ordered it to be wagoned down to Manchester, and wagoned thence up to the barracks. This fact happened to fall within my own knowledge. I doubt not there are many more such, in order either to produce their total removal, or to run up the expenses of the present situation, and satisfy Congress that the nearer they are brought to the commissary’s own bed, the cheaper they will be subsisted. The grain made in the Western counties may be brought partly in wagons, as conveniently to this as to any other place; perhaps more so, on account of its vicinity to one of the best passes through the Blue Ridge; and partly by water, as it is near to James river, to the navigation of which, ten counties are adjacent above the falls. When I said that the grain might be brought hither from all the counties of the State, adjacent to navigation, I did not mean to say it would be proper to bring it from all. On the contrary, I think the commissary should be instructed, after the next harvest, not to send one bushel of grain to the barracks from below the falls of the rivers, or from the northern counties. The counties on tide water are accessible to the calls for our own army. Their supplies ought, therefore, to be husbanded for them. The counties in the northwestern parts of the State are not only within reach for our own grand army, but peculiarly necessary for the support of Macintosh’s army; or for the support of any other northwestern expedition, which the uncertain conduct of the Indians should render necessary; insomuch that if the supplies of that quarter should be misapplied to any other purpose, it would destroy in embryo every exertion, either for particular or general safety there. The counties above tide water, in the middle and southern and western parts of the country, are not accessible to calls for either of those purposes, but at such an expense of transportation as the article would not bear. Here, then, is a great field, whose supplies of bread cannot be carried to our army, or, rather, which will raise no supplies of bread, because there is no body to eat them. Was it not, then, wise in Congress to remove to that field four thousand idle mouths, who must otherwise have interfered with the pasture of our own troops? And, if they are removed to any other part of the country, will it not defeat this wise purpose? The mills on the waters of James river, above the falls, open to canoe navigation, are very many. Some of them are of great note, as manufacturers. The barracks are surrounded by mills. There are five or six round about Charlottesville. Any two or three of the whole might, in the course of the winter, manufacture flour sufficient for the year. To say the worst, then, of this situation, it is but twelve miles wrong. The safe custody of these troops is another circumstance worthy consideration. Equally removed from the access of an eastern or western enemy; central to the whole State, so that, should they attempt an irruption in any direction, they must pass through a great extent of hostile country; in a neighborhood thickly inhabited by a robust and hardy people, zealous in the American cause, acquainted with the use of arms, and the defiles and passes by which they must issue: it would seem, that in this point of view, no place could have been better chosen.
Their health is also of importance. I would not endeavor to show that their lives are valuable to us, because it would suppose a possibility, that humanity was kicked out of doors in America, and interest only attended to. The barracks occupy the top and brow of a very high hill, (you have been untruly told they were in a bottom.) They are free from fog, have four springs which seem to be plentiful, one within twenty yards of the piquet, two within fifty yards, and another within two hundred and fifty, and they propose to sink wells within the piquet. Of four thousand people, it should be expected, according to the ordinary calculations, that one should die every day. Yet, in the space of near three months, there have been but four deaths among them; two infants under three weeks old, and two others by apoplexy. The officers tell me, the troops were never before so healthy since they were embodied.
But is an enemy so execrable, that, though in captivity, his wishes and comforts are to be disregarded and even crossed? I think not. It is for the benefit of mankind to mitigate the horrors of war as much as possible. The practice, therefore, of modern nations, of treating captive enemies with politeness and generosity, is not only delightful in contemplation, but really interesting to all the world, friends, foes, and neutrals. Let us apply this: the officers, after considerable hardships, have all procured quarters comfortable and satisfactory to them. In order to do this, they were obliged, in many instances, to hire houses for a year certain, and at such exorbitant rents, as were sufficient to tempt independent owners to go out of them, and shift as they could. These houses, in most cases, were much out of repair. They have repaired them at a considerable expense. One of the general officers has taken a place for two years, advanced the rent for the whole time, and been obliged, moreover, to erect additional buildings for the accommodation of part of his family, for which there was not room in the house rented. Independent of the brick work, for the carpentry of these additional buildings, I know he is to pay fifteen hundred dollars. The same gentleman, to my knowledge, has-paid to one person, three thousand six hundred, and seventy dollars, for different articles to fix himself commodiously. They have generally laid in their stocks of grain and other provisions, for it is well known that officers do not live on their rations. They have purchased cows, sheep, &c, set in to farming, prepared their gardens, and have a prospect of comfort and quiet before them. To turn to the soldiers: the environs of the barracks are delightful, the ground cleared, laid off in hundreds of gardens, each enclosed in its separate paling; these well prepared, and exhibiting, a fine appearance. General Riedesel, alone, laid out upwards of two hundred pounds in garden seeds, for the German troops only. Judge what an extent of ground these seeds would cover. There is little doubt that their own gardens will furnish them a great abundance of vegetables through the year. Their poultry, pigeons, and other preparations of that kind, present to the mind the idea of a company of farmers, rather than a camp of soldiers. In addition to the barracks built for them by the public, and now very comfortable, they have built great numbers for themselves, in such messes as fancied each other: and the whole corps, both officers and men, seem now, happy and satisfied with their situation. Having thus found the art of rendering captivity itself comfortable, and carried it into execution, at their own great expense and labor, their spirit sustained by the prospect of gratifications rising before their eyes, does not every sentiment of humanity revolt against the proposition of stripping them of all this, and removing them into new situations, where from the advanced season of the year, no preparations can be made for carrying themselves comfortably through the heats of summer; and when it is known that the necessary advances for the conveniences already provided, have exhausted their funds and left them unable to make the like exertions anew. Again; review this matter as it may regard appearances. A body of troops, after staying a twelvemonth at Boston, are ordered to take a march of seven hundred miles to Virginia, where, it is said, they may be plentifully subsisted. As soon as they are there, they are ordered on some other march, because, in Virginia, it is said, they cannot be subsisted. Indifferent nations will charge this either to ignorance, or to whim and caprice; the parties interested, to cruelty. They now view the proposition in that light, and it is said, there is a general and firm persuasion among them, that they were marched from Boston with no other purpose than to harass and destroy them with eternal marches. Perseverance in object, though not by the most direct way, is often more laudable than perpetual changes, as often as the object shifts light. A character of steadiness in our councils is worth more than the subsistence of four thousand people.
There could not have been a more unlucky concurrence of circumstances than when these troops first came. The barracks were unfinished for want of laborers, the spell of weather the worst ever known within the memory of man, no stores of bread laid in, the roads, by the weather and number of wagons, soon rendered impassable: not only the troops themselves were greatly disappointed, but the people in the neighborhood were alarmed at the consequences which a total failure of provisions might produce. In this worst state of things, their situation was seen by many and disseminated through the country, so as to occasion a general dissatisfaction, which even seized the minds of reasonable men, who, if not infected with the contagion, must have foreseen that the prospect must brighten, and that great advantages to the people must necessarily arise. It has, accordingly, so happened. The planters, being more generally sellers than buyers, have felt the benefit of their presence in the most vital part about them, their purses, and are now sensible of its source. I have too good an opinion of their love of order, to believe that a removal of these troops would produce any irregular proofs of their disapprobation, but I am well assured it would be extremely odious to them.
To conclude. The separation of these troops would be a breach of public faith; therefore suppose it impossible. If they are removed to another State, it is the fault of the commissaries; if they are removed to any other part of the State, it is the fault of the commissaries; and in both cases, the public interest and public security suffer, the comfortable and plentiful subsistence of our own army is lessened, the health of the troops neglected, their wishes crossed, and their comforts torn from them, the character of whim and caprice, or, what is worse, of cruelty, fixed on us as a nation, and, to crown the whole, our own people disgusted with such a proceeding.
I have thus taken the liberty of representing to you the facts and the reasons, which seem to militate against the separation or removal of these troops. I am sensible, however, that the same subject may appear to different persons in very different lights. What I have urged as reasons, may, to sounder minds, be apparent fallacies. I hope they will appear, at least, so plausible, as to excuse the interposition of
your Excellency’s
most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN PAGE.
Williamsburg,
January 22, 1779.
Dear Page,
I received your letter by Mr. Jamieson. It had given me much pain, that the zeal of our respective friends should ever have placed you and me in the situation of competitors. I was comforted, however, with the reflection, that it was their competition, not ours, and that the difference of the numbers which decided between us, was too insignificant to give you a pain, or me a pleasure, had our dispositions towards each other been such as to admit those sensations. I know you too well to need an apology for any thing you do, and hope you will for ever be assured of this; and as to the constructions of the world, they would only have added one to the many sins for which they are to go to the devil. As this is the first, I hope it will be the last, instance of ceremony between us. A desire to see my family, which is in Charles City, carries me thither to-morrow, and I shall not return till Monday. Be pleased to present my compliments to Mrs. Page, and add this to the assurances I have ever given you, that I am, dear Page,
your affectionate friend,
Th: Jefferson.
TO HIS EXCELLENCY GENERAL WASHINGTON.
Williamsburg,
June 23, 1779.
Sir,
I have the pleasure to enclose you the particulars of Colonel Clarke’s success against St. Vincennes, as stated in his letter but lately received; the messenger, with his first letter, having been killed. I fear it will be impossible for Colonel Clarke to be so strengthened, as to enable him to do what he desires. Indeed, the express who brought this letter, gives us reason to fear, St. Vincennes is in danger from a large body of Indians, collected to attack it, and said, when he came from Kaskaskias, to be within thirty leagues of the place. I also enclose you a letter from Colonel Shelby, stating the effect of his success against the seceding Cherokees and Chuccamogga. The damage done them, was killing half a dozen, burning eleven towns, twenty thousand bushels of corn, collected probably to forward the expeditions which were to have been planned at the council which was to meet Governor Hamilton at the mouth of Tennessee, and taking as many goods as sold for twenty-five thousand pounds. I hope these two blows coming together, and the depriving them of their head, will, in some measure, effect the quiet of our frontiers this summer. We have intelligence, also, that Colonel Bowman, from Kentucky, is in the midst of the Shawnee country, with three hundred men, and hope to hear a good account of him. The enclosed order being in its nature important, and generally interesting, I think it proper to transmit it to you, with the reasons supporting it.* It will add much to our satisfaction, to know it meets your approbation.
I have the honor to be, with every sentiment of private respect and public gratitude,
Sir, your most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
P. S. The distance of our northern and western counties from the scene of southern service, and the necessity of strengthening our western quarter, have induced the Council to direct the new levies from the counties of Yohogania, Ohio, Monongalia, Frederick, Hampshire, Berkeley, Rockingham, and Greenbrier, amounting to somewhat less than three hundred men, to enter into the ninth regiment at Pittsburg. The aid they may give there, will be so immediate and important, and what they could do to the southward, would be so late, as, I hope, will apologize for their interference. T. J.
* For the letter of Colonel Clarke, and the order referred
to, see Appendix A.
TO HIS EXCELLENCY GENERAL WASHINGTON
Williamsburg,
July 17, 1779.
Sir,
I some time ago enclosed to you a printed copy of an order of Council, by which Governor Hamilton was to be confined in irons, in close jail, which has occasioned a letter from General Phillips, of which the enclosed is a copy. The General seems to think that a prisoner on capitulation cannot be put in close confinement, though his capitulation should not have provided against it. My idea was, that all persons taken in war, were to be deemed prisoners of war. That those who surrender on capitulation (or convention) are prisoners of war also, subject to the same treatment with those who surrender at discretion, except only so far as the terms of their capitulation or convention shall have guarded them. In the capitulation of Governor Hamilton (a copy of which I enclose), no stipulation is made as to the treatment of himself, or those taken with him. The Governor, indeed, when he signs, adds a flourish of reasons inducing him to capitulate, one of which is the generosity of his enemy. Generosity, on a large and comprehensive scale, seems to dictate the making a signal example of this gentleman; but waving that, these are only the private motives inducing him to surrender, and do not enter into the contract of Colonel Clarke. I have the highest idea of those contracts which take place between nation and nation, at war, and would be the last on earth to do any thing in violation of them. I can find nothing in those books usually recurred to as testimonials of the laws and usages of nature and nations, which convicts the opinions I have above expressed of error. Yet there may be such an usage as General Phillips seems to suppose, though not taken notice of by these writers. I am obliged to trouble your Excellency on this occasion, by asking of you information on this point. There is no other person, whose decision will so authoritatively decide this doubt in the public mind, and none with which I am disposed so implicitly to comply. If you shall be of opinion that the bare existence of a capitulation, in the case of Governor Hamilton, privileges him from confinement, though there be no article to that effect in the capitulation, justice shall most assuredly be done him. The importance of this point, in a public view, and my own anxiety under a charge of violation of national faith by the Executive of this Commonwealth, will, I hope, apologize for my adding this to the many troubles with which I know you to be burdened. I have the honor to be, with the most profound respect, your Excellency’s most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
P. S. I have just received a letter from Colonel Bland, containing information of numerous desertions from the Convention troops, not less than four hundred in the last fortnight. He thinks he has reason to believe it is with the connivance of some of their officers. Some of these have been retaken, all of them going northwardly. They had provided themselves with forged passports, and with certificates of having taken the oath of fidelity to the State; some of them forged, others really given by weak magistrates. I give this information to your Excellency, as perhaps it may be in your power to have such of them intercepted as shall be passing through Pennsylvania and Jersey.
Your letter enclosing the opinion of the board of war in the case of Allison and Lee, has come safe to hand, after a long passage. It shall be answered by next post. T. J.
TO HIS EXCELLENCY GENERAL WASHINGTON.
Williamsburg,
October 1, 1779.
Sir,
On receipt of your letter of August 6th, during my absence, the Council had the irons taken off the prisoners of war. When your advice was asked, we meant it should decide with us; and upon my return to Williamsburg, the matter was taken up and the enclosed advice given. [See Appendix, note B.] A parole was formed, of which the enclosed is a copy, and tendered to the prisoners. They objected to that part of it which restrained them from saying any thing to the prejudice of the United States, and insisted on ‘freedom of speech.’ They were, in consequence, remanded to their confinement in the jail, which must be considered as a voluntary one, until they can determine with themselves to be inoffensive in word as well as deed. A flag sails hence to-morrow to New York, to negotiate the exchange of some prisoners. By her I have written to General Phillips on this subject, and enclosed to him copies of the within; intending it as an answer to a letter I received from him on the subject of Governor Hamilton.
I have the honor to be, Sir,
your most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO HIS EXCELLENCY GENERAL WASHINGTON.
Williamsburg,
October 2, 1779.
Sir,
Just as the letter accompanying this was going off, Colonel Mathews arrived on parole from New York, by the way of headquarters, bringing your Excellency’s letter on this subject, with that of the British commissary of prisoners. The subject is of great importance, and I must, therefore, reserve myself to answer after further consideration. Were I to speak from present impressions, I should say it was happy for Governor Hamilton that a final determination of his fate was formed before this new information. As the enemy have released Captain Willing from his irons, the Executive of this State will be induced perhaps not to alter their former opinion. But it is impossible they can be serious in attempting to bully us in this manner. We have too many of their subjects in our power, and too much iron to clothe them with, and, I will add, too much resolution to avail ourselves of both, to fear their pretended retaliation. However, I will do myself the honor of forwarding to your Excellency the ultimate result of Council on this subject.
In consequence of the information in the letter from the British commissary of prisoners, that no officers of the Virginia line should be exchanged till Governor Hamilton’s affair should be settled, we have stopped our flag, which was just hoisting anchor with a load of privates for New York. I must, therefore, ask the favor of your Excellency to forward the enclosed by flag, when an opportunity offers, as I suppose General Phillips will be in New York before it reaches you.
I have the honor to be, Sir, with the greatest esteem,
your most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO HIS EXCELLENCY GENERAL WASHINGTON.
In Council, Oct. 8, 1779.
Sir,
In mine of the second of the present month, written in the instant of Colonel Mathews’ delivery of your letter, I informed you what had been done on the subject of Governor Hamilton and his companions previous to that moment. I now enclose you an advice of Council, [See Appendix, note C.] in consequence of the letter you were pleased to enclose me, from the British commissary of prisoners, with one from Lord Rawdon; also a copy of my letter to Colonel Mathews, enclosing, also, the papers therein named. The advice of Council to allow the enlargement of prisoners, on their giving a proper parole, has not been recalled, nor will be, I suppose, unless something on the part of the enemy should render it necessary. I rather expect, however, that they will see it their interest to discontinue this kind of conduct. I am afraid I shall hereafter, perhaps be obliged to give your Excellency some trouble in aiding me to obtain information of the future usage of our prisoners. I shall give immediate orders for having in readiness every engine which the enemy have contrived for the destruction of our unhappy citizens, captivated by them. The presentiment of these operations is shocking beyond expression. I pray Heaven to avert them: but nothing in this world will do it, but a proper conduct in the enemy. In every event, I shall resign myself to the hard necessity under which I shall act.
I have the honor to be, with great regard and esteem,
your Excellency’s
most obedient and
most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO COLONEL MATHEWS.
In Council, October, 1779.
Sir,
The proceedings respecting Governor Hamilton and his companions, previous to your arrival here, you are acquainted with. For your more precise information, I enclose you the advice of Council, of June the 16th, of that of August the 28th, another of September the 19th, on the parole tendered them the 1st instant, and Governor Hamilton’s letter of the same day, stating his objections, in which he persevered: from that time his confinement has become a voluntary one. You delivered us your letters the next day, when, the post being just setting out, much business prevented the Council from taking them into consideration. They have this day attended to them, and found their resolution expressed in the enclosed advice bearing date this day. It gives us great pain that any of our countrymen should be cut off from the society of their friends and tenderest connections, while it seems as if it was in our power, to administer relief. But we trust to their good sense for discerning, and their spirit for bearing up against the fallacy of this appearance. Governor Hamilton and his companions were imprisoned and ironed, 1st. In retaliation for cruel treatment of our captive citizens by the enemy in general. 2nd. For the barbarous species of warfare which himself and his savage allies carried on in our western frontier. 3d. For particular acts of barbarity, of which he himself was personally guilty, to some of our citizens in his power. Any one of these charges was sufficient to justify the measures we took. Of the truth of the first, yourselves are witnesses. Your situation, indeed, seems to have been better since you were sent to New York; but reflect on what you suffered before that, and knew others of our countrymen to suffer, and what you know is now suffered by that more unhappy part of them, who are still confined on board the prison-ships of the enemy. Proofs of the second charge, we have under Hamilton’s own hand: and of the third, as sacred assurances as human testimony is capable of giving. Humane conduct on our part, was found to produce no effect; the contrary, therefore, was to be tried. If it produces a proper lenity to our citizens in captivity, it will have the effect we meant; if it does not, we shall return a severity as terrible as universal. If the causes of our rigor against Hamilton were founded in truth, that rigor was just, and would not give right to the enemy to commence any new hostilities on their part: and all such new severities are to be considered, not as retaliation, but as original and unprovoked. If those causes were, not founded in truth, they should have denied them. If, declining the tribunal of truth and reason, they choose to pervert this into a contest of cruelty and destruction, we will contend with them in that line, and measure out misery to those in our power, in that multiplied proportion which the advantage of superior numbers enables us to do. We shall think it our particular duty, after the information we gather from the papers which have been laid before us, to pay very constant attention to your situation, and that of your fellow prisoners. We hope that the prudence of the enemy will be your protection from injury; and we are assured that your regard for the honor of your country would not permit you to wish we should suffer ourselves to be bullied into an acquiescence, under every insult and cruelty they may choose to practise, and a fear to retaliate, lest you should be made to experience additional sufferings. Their officers and soldiers in our hands are pledges for your safety: we are determined to use them as such. Iron will be retaliated by iron, but a great multiplication on distinguished objects; prison-ships by prison-ships, and like for like in general. I do not mean by this to cover any officer who has acted, or shall act, improperly. They say Captain Willing was guilty of great cruelties at the Natchez; if so, they do right in punishing him. I would use any powers I have, for the punishment of any officer of our own, who should be guilty of excesses unjustifiable under the usages of civilized nations. However, I do not find myself obliged to believe the charge against Captain Willing to be true, on the affirmation of the British commissary, because, in the next breath, he affirms no cruelties have as yet been inflicted on him. Captain Willing has been in irons.
I beg you to be assured, there is nothing consistent with the honor of your country, which we shall not, at all times, be ready to do for the relief of yourself and companions in captivity. We know, that ardent spirit and hatred for tyranny, which brought you into your present situation, will enable you to bear up against it with the firmness, which has distinguished you as a soldier, and to look forward with pleasure to the day, when events shall take place, against which the wounded spirits of your enemies will find no comfort, even from reflections on the most refined of the cruelties with which they have glutted themselves.
I am, with great respect,
your most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO HIS EXCELLENCY GENERAL WASHINGTON.
Willlamsburg, November 28, 1779.
Sir,
Your Excellency’s letter on the discriminations which have been heretofore made, between the troops raised within this state, and considered as part of our quota, and those not so considered, was delivered me four days ago. I immediately laid it before the Assembly, who thereupon came to the resolution I now do myself the honor of enclosing you. The resolution of Congress, of March 15th, 1779, which you were so kind as to enclose, was never known in this state till a few weeks ago, when we received printed copies of the Journals of Congress. It would be a great satisfaction to us, to receive an exact return of all the men we have in Continental service, who come within the description of the resolution, together with our state troops in Continental service. Colonel Cabell was so kind as to send me a return of the Continental regiments, commanded by Lord Sterling, of the first and second Virginia State regiments, and of Colonel Gist’s regiment. Besides these are the following, viz. Colonel Harrison’s regiment of artillery, Colonel Bayler’s horse, Colonel Eland’s horse, General Scott’s new levies, part of which are gone to Carolina, and part are here, Colonel Gibson’s regiment stationed on the Ohio, Heath and Ohara’s independent companies at the same stations. Colonel Taylor’s regiment of guards to the Convention troops: of these, we have a return. There may, possibly, be others not occurring to me. A return of all these would enable us to see what proportion of the Continental army is contributed by us. We have, at present, very pressing calls to send additional numbers of men to the southward. No inclination is wanting in either the Legislature or Executive, to aid them or strengthen you: but we find it very difficult to procure men. I herewith transmit to your Excellency some recruiting commissions, to be put into such hands as you may think proper, for re-enlisting such of our soldiery as are not already engaged for the war. The Act of Assembly authorizing these instructions, requires that the men enlisted should be reviewed and received by an officer to be appointed for that purpose; a caution, less necessary in the case of men now actually in Service, therefore, doubtless able-bodied, than in the raising new recruits. The direction, however, goes to all cases, and, therefore, we must trouble your Excellency with the appointment of one or more officers of review. Mr. Moss, our agent, receives orders, which accompany this, to pay the bounty money and recruiting money, and to deliver the clothing. We have, however, certain reason to fear he has not any great sum of money on hand; and it is absolutely out of our power, at this time, to supply him, or to say, with certainty, when we shall be able to do it. He is instructed to note his acceptances under the draughts, and to assure payment as soon as we shall have it in our power to furnish him, as the only substitute for money. Your Excellency’s directions to the officer of review, will probably procure us the satisfaction of being informed, from time to time, how many men shall be re-enlisted.
By Colonel Mathews I informed your Excellency fully of the situation of Governor Hamilton and his companions. Lamothe and Dejean have given their paroles, and are at Hanover Court-House: Hamilton, Hay, and others, are still obstinate; therefore, still in close confinement, though their irons have never been on, since your second letter on the subject. I wrote full information of this matter to General Phillips also, from whom I had received letters on the subject. I cannot, in reason, believe that the enemy, on receiving this information either from yourself or General Phillips, will venture to impose any new cruelties on our officers in captivity with them. Yet their conduct, hitherto, has been most successfully prognosticated by reversing the conclusions of right reason. It is, therefore, my duty, as well as it was my promise to the Virginia captives, to take measures for discovering any change which may be made in their situation. For this purpose, I must apply for your Excellency’s interposition. I doubt not but you have an established mode of knowing, at all times, through your commissary of prisoners, the precise state of those in the power of the enemy. I must, therefore, pray you to put into motion any such means you have, for obtaining knowledge of the situation of Virginia officers in captivity. If you should think proper, as I could wish, to take upon yourself to retaliate any new sufferings which may be imposed on them, it will be more likely to have-due weight, and to restore the unhappy on both sides, to that benevolent treatment for which all should wish.
I have the honor to be, &c. &c.
Th: Jefferson.
TO HIS EXCELLENCY GENERAL WASHINGTON.
Williamsburg, December 10,1779.
Sir,
I take the liberty of putting under cover to your Excellency some letters to Generals Phillips and Reidesel, uninformed whether they are gone into New York or not, and knowing that you can best forward them in either case.
I also trouble you with a letter from the master of the flag in this State, to the British commissary of prisoners in New York, trusting it will thus be more certainly conveyed than if sent to Mr. Adams. It is my wish the British commissary should return his answer through your Excellency, or your commissary of prisoners, and that they should not propose, under this pretext, to send another flag, as the mission of the present flag is not unattended with circumstances of suspicion; and a certain information of the situation of ourselves and our allies here, might influence the measures of the enemy.
Perhaps your commissary of prisoners can effect the former method of answer.
I enclose to you part of an Act of Assembly ascertaining the quantity of land, which shall be allowed to the officers and soldiers at the close of the war, and providing means of keeping that country vacant which has been allotted for them.
I am advised to ask your Excellency’s attention to the case of Colonel Bland, late commander of the barracks in Albemarle. When that gentleman was appointed to that command, he attended the Executive here and informed them he must either decline it, or be supported in such a way as would keep up that respect which was essential to his command; without, at the same time, ruining his private fortune.
The Executive were sensible he would be exposed to great and unavoidable expense: they observed, his command would be in a department separate from any other, and that he actually relieved a Major General from the same service. They did not think themselves authorized to say what should be done in this case, but undertook to represent the matter to Congress, and, in the mean time, gave it as their opinion that he ought to be allowed a decent table. On this, he undertook the office, and in the course of it incurred expenses which seemed to have been unavoidable, unless he would have lived in such a way as is hardly reconcileable to the spirit of an officer, or the reputation of those in whose service he is. Governor Henry wrote on the subject to Congress; Colonel Bland did the same; but we learn they have concluded the allowance to be unprecedented, and inadmissible in the case of an officer of his rank. The commissaries, on this, have called on Colonel Bland for reimbursement. A sale of his estate was about to take place, when we undertook to recommend to them to suspend their demand, till we could ask the favor of you to advocate this matter so far with Congress, as you may think it right; otherwise the ruin of a very worthy officer must inevitably follow. I have the honor to be, with the greatest respect and esteem,
your Excellency’s
most obedient servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO HIS EXCELLENCY GENERAL WASHINGTON.
Williamsburg, February 10, 1780.
Sir,
It is possible you may have heard, that in the course of last summer an expedition was meditated, by our Colonel Clarke, against Detroit: that he had proceeded so far as to rendezvous a considerable body of Indians, I believe four or five thousand, at St. Vincennes; but, being disappointed in the number of whites he expected, and not choosing to rely principally on the Indians, he was obliged to decline it. We have a tolerable prospect of reinforcing him this spring, to the number which he thinks sufficient for the enterprise. We have informed him of this, and left him to decide between this object, and that of giving vigorous chastisement to those tribes of Indians, whose eternal hostilities have proved them incapable of living on friendly terms with us. It is our opinion, his inclination will lead him to determine on the former. The reason of my laying before your Excellency this matter, is, that it has been intimated to me that Colonel Broadhead is meditating a similar expedition. I wished, therefore, to make you acquainted with what we had in contemplation. The enterprising and energetic genius of Clarke is not altogether unknown to you. You also know (what I am a stranger to) the abilities of Broadhead, and the particular force with which you will be able to arm him for such an expedition. We wish the most hopeful means should be used for removing so uneasy a thorn from our side. As yourself, alone, are acquainted with all the circumstances necessary for well informed decision, I am to ask the favor of your Excellency, if you should think Broadhead’s undertaking it most likely to produce success, that you will be so kind as to intimate to us to divert Clarke to the other object, which is also important to this State. It will, of course, have weight with you in forming your determination, that our prospect of strengthening Clarke’s hands, sufficiently, is not absolutely certain. It may be necessary, perhaps, to inform you, that these two officers cannot act together, which excludes the hopes of ensuring success by a joint expedition.
I have the honor to be, with the most sincere esteem,
your Excellency’s most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO HIS EXCELLENCY GENERAL WASHINGTON.
Richmond, June 11, 1780.
Sir,
Major Galvan, as recommended by your Excellency, was despatched to his station without delay, and has been furnished with every thing he desired, as far as we were able. The line of expresses formed between us is such, as will communicate intelligence from one to the other in twenty-three hours. I have forwarded to him information of our disasters in the South, as they have come to me.
Our intelligence from the southward is most lamentably defective. Though Charleston has been in the hands of the enemy a month, we hear nothing of their movements which can be relied on. Rumors are, that they are penetrating northward. To remedy this defect, I shall immediately establish a line of expresses from hence to the neighborhood of their army, and send thither a sensible, judicious person, to give us information of their movements. This intelligence will, I hope, be conveyed to us at the rate of one hundred and twenty miles in the twenty-four hours. They set out to their stations to-morrow. I wish it were possible, that a like speedy line of communication could be formed from hence to your Excellency’s head-quarters. Perfect and speedy information of what is passing in the South, might put it in your power, perhaps, to frame your measures by theirs. There is really nothing to oppose the progress of the enemy northward, but the cautious principles of the military art. North Carolina is without arms. We do not abound. Those we have, are freely imparted to them; but such is the state of their resources, that they have not been able to move a single musket from this State to theirs. All the wagons we can collect, have been furnished to the Marquis de Kalb, and are assembled for the march of twenty-five hundred men, under General Stevens, of Culpeper, who will move on the 19th instant. I have written to Congress to hasten supplies of arms and military stores for the southern states, and particularly to aid us with cartridge paper and boxes, the want of which articles, small as they are, renders our stores useless. The want of money cramps every effort. This will be supplied by the most unpalatable of all substitutes, force. Your Excellency will readily conceive, that after the loss of one arm, our eyes are turned towards the other, and that we comfort ourselves, if any aids can be furnished by you, without defeating the operations more beneficial to the general union, they will be furnished. At the same time, I am happy to find that the wishes of the people go no further, as far as I have an opportunity of learning their sentiments. Could arms be furnished, I think this State and North Carolina would embody from ten to fifteen thousand militia immediately, and more if necessary.
I hope, ere long, to be able to give you a more certain statement of the enemy’s as well as our situation, which I shall not fail to do. I enclose you a letter from Major Galvan, being the second I have forwarded to you.
With sentiments of the most perfect esteem and respect,
I have the honor to be
your Excellency’s
most obedient, humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO HIS EXCELLENCY GENERAL WASHINGTON.
Richmond, July 2, 1780.
Sir,
I have received from the Committee of Congress, at headquarters, three letters calling for aids of men and provisions. I beg leave to refer you to my letter to them, of this date, on those subjects. I thought it necessary, however, to suggest to you the preparing an arrangement of officers for the men; for, though they are to supply our battalions, yet, as our whole line officers, almost, are in captivity, I suppose some temporary provision must be made. We cheerfully transfer to you every power which the Executive might exercise on this occasion. As it is possible you may cast your eye on the unemployed officers now within the State, I write to General Muhlenburg, to send you a return of them. I think the men will be rendezvoused within the present month. The bill, indeed, for raising them is not actually passed, but it is in its last stage, and no opposition to any essential parts of it. I will take care to notify you of its passage.
I have, with great pain, perceived your situation; and, the more so, as being situated between two fires, a division of sentiment has arisen, both in Congress and here, as to which the resources of this country should be sent. The removal of General Clinton to the northward, must, of course, have great influence on the determination of this question; and I have no doubt but considerable aids may be drawn hence for your army, unless a larger one should be embodied in the South, than the force of the enemy there seems to call for. I have the honor to be, with every sentiment of respect and esteem,
your Excellency’s
most obedient, humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
[See Appendix, Note D.]
TO GENERAL EDWARD STEVENS.
Richmond, August 4, 1780.
Sir,
Your several favors of July the 16th, 21st, and 22nd, are now before me. Our smiths are engaged in making five hundred axes and some tomahawks for General Gates. About one hundred of these will go by the wagons now taking in their loads. As these are for the army in general, no doubt but you will participate of them. A chest of medicine was made up for you in Williamsburg, and by a strange kind of forgetfulness, the vessel ordered to bring that, left it and brought the rest of the shop. It is sent for again, and I am not without hopes will be here in time to go by the present wagons. They will carry some ammunition and the axes, and will make up their load with spirits. Tents, I fear, cannot be got in this country; we have, however, sent out powers to all the trading towns here, to take it wherever they can find it. I write to General Gates, to try whether the duck in North Carolina cannot be procured by the Executive of that State on Continental account; for, surely, the whole army, as well our militia as the rest, is Continental. The arms you have to spare may be delivered to General Gates’s order, taking and furnishing us with proper vouchers. We shall endeavor to send our drafts armed. I cannot conceive how the arms before sent could have got into so very bad order; they certainly went from hence in good condition. You wish to know how far the property of this State in your hands is meant to be subject to the orders of the commander in chief. Arms and military stores we mean to be perfectly subject to him. The provisions going from this country will be for the whole army. If we can get any tents, they must be appropriated to the use of our own troops. Medicine, sick stores, spirits, and such things, we expect shall be on the same footing as with the northern army. There, you know, each State furnishes its own troops with these articles, and, of course, has an exclusive right to what is furnished. The money put into your hands, was meant as a particular resource for any extra wants of our own troops, yet in case of great distress, you would probably not see the others suffer without communicating part of it for their use. We debit Congress with this whole sum. There can be nothing but what is right in your paying Major Mazaret’s troops out of it. I wish the plan you have adopted for securing a return of the arms from the militia, may answer. I apprehend any man, who has a good gun on his shoulder, would agree to keep it, and have the worth of it deducted out of his pay, more especially when the receipt of the pay is at some distance. What would you think of notifying to them, further, that a proper certificate that they are discharged, and have returned their arms, will be required before any pay is issued to them. A roll, kept and forwarded, of those so discharged, and who have delivered up their arms, would supply accidental losses of their certificates. We are endeavoring to get bayonet belts made. The State quarter-master affirms the cartouch boxes sent from this place, (nine hundred and fifty-nine in number,) were all in good condition. I therefore suppose the three hundred you received in such very bad order, must have gone from the continental quarter-master at Petersburg, or, perhaps, have been pillaged, on the road, of their flaps, to mend shoes, &c. I must still press the return of as many wagons as possible. All you will send, shall be loaded with spirits or something else for the army. By their next return, we shall have a good deal of bacon collected. The enclosed is a copy of what was reported to me, as heretofore sent by the wagons.
I am. Sir, with the greatest esteem,
your most obedient, humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MAJOR GENERAL GATES.
Richmond, August 15, 1780.
Sir,
Your favor of August 3rd is just now put into my hand. Those formerly received have been duly answered, and my replies will, no doubt, have reached you before this date. My last letter to you was by Colonel Drayton.
I spoke fully with you on the difficulty of procuring wagons here, when I had the pleasure of seeing you, and for that reason pressed the sending back as many as possible. One brigade of twelve has since returned, and is again on its way with medicine, military stores, and spirit. Any others which come, and as fast as they come, shall be returned to you with spirit and bacon. I have ever been informed, that the very plentiful harvests of North Carolina would render the transportation of flour from this State, as unnecessary as it would be tedious, and that, in this point of view, the wagons should carry hence only the articles before mentioned, which are equally wanting with you. Finding that no great number of wagons is likely to return to us, we will immediately order as many more to be bought and sent on, as we possibly can. But to prevent too great expectations, I must again repeat, that I fear no great number can be got. I do assure you, however, that neither attention nor expense shall be spared, to forward to you every support for which we can obtain means of transportation. You have, probably, received our order on Colonel Lewis to deliver you any of the beeves he may have purchased.
Tents, I fear, it is in vain to expect, because there is not in this country stuff to make them. We have agents and commissioners in constant pursuit of stuff, but hitherto researches have been fruitless. Your order to Colonel Carrington shall be immediately communicated. A hundred copies of the proclamation shall also be immediately printed and forwarded to you. General Muhlenburg is come to this place, which he will now make his headquarters. I think he will be able to set into motion, within a very few days, five hundred regulars, who are now equipped for their march, except some blankets still wanting, but I hope nearly procured and ready to be delivered.
I sincerely congratulate you on your successful advances on the enemy, and wish to do every thing to second your enterprises, which the situation of this country, and the means and powers put into my hands, enable me to do.
I am, Sir, with sincere respect and esteem,
your most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO HIS EXCELLENCY GENERAL WASHINGTON.
Richmond, September 8, 1780.
Sir,
As I know the anxieties you must have felt, since the late misfortune to the South, and our latter accounts have not been quite so unfavorable as the first, I take the liberty of enclosing you a statement of this unlucky affair, taken from letters from General Gates, General Stevens, and Governor Nash, and, as to some circumstances, from an officer who was in the action.* Another army is collecting; this amounted, on the 23rd ultimo, to between four and five thousand men, consisting of about five hundred Maryland regulars, a few of Hamilton’s artillery, and Porterfield’s corps, Armand’s legion, such of the Virginia militia as had been reclaimed, and about three thousand North Carolina militia, newly embodied. We are told they will increase these to eight thousand. Our new recruits will rendezvous in this State between the 10th and 25th instant. We are calling out two thousand militia, who, I think, however, will not be got to Hillsborough till the 25th of October. About three hundred and fifty regulars marched from Chesterfield a week ago. Fifty march to-morrow, and there will be one hundred or one hundred and fifty more from that post, when they can be cleared of the hospital. This is as good a view as I can give you of the force we are endeavoring to collect; but they are unarmed. Almost the whole small arms seem to have been lost in the late rout. There are here, on their way southwardly, three thousand stand of arms, sent by Congress, and we have still a few in our magazine. I have written pressingly, as the subject well deserves, to Congress, to send immediate supplies, and to think of forming a magazine here, that in case of another disaster, we may not be left without all means of opposition.
[* The circumstances of the defeat of General Gates’s army,
near Camden in August, 1780, being of historical notoriety,
this statement is omitted.]
I enclosed to your Excellency, some time ago, a resolution of the Assembly, instructing us to send a quantity of tobacco to New York for the relief of our officers there, and asking the favor of you to obtain permission. Having received no answer, I fear my letter or your answer has miscarried. I therefore take the liberty of repeating my application to you.
I have the honor to be, with the most profound respect,
your Excellency’s most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO GENERAL EDWARD STEVENS.
Richmond, September 12,1780.
Sir,
Your letters of August 27th and 30th are now before me. The subsequent desertions of your militia have taken away the necessity of answering the question, how they shall be armed. On the contrary, as there must now be a surplus of arms, I am in hopes you will endeavor to reserve them, as we have not here a sufficient number by fifteen hundred or two thousand, for the men who will march hence, if they march in numbers equal to our expectations. I have sent expresses into all the counties from which those militia went, requiring the county lieutenants to exert themselves in taking them; and such is the detestation with which they have been received, that I have heard from many counties they were going back of themselves. You will of course, hold courts martial on them, and make them soldiers for eight months. If you will be so good as to inform me, from time to time, how many you have, we may, perhaps, get the supernumerary officers in the State, to take command of them. By the same opportunities, I desired notice to be given to the friends of the few remaining with you, that they had lost their clothes and blankets, and recommended, that they should avail themselves of any good opportunity to send them supplies.
We approve of your accommodating the hospital with medicines, and the Maryland troops with spirits. They really deserve the whole, and I wish we had means of transportation for much greater quantities, which we have on hand and cannot convey. This article we could furnish plentifully to you and them. What is to be done for wagons, I do not know. We have not now one shilling in the treasury to purchase them. We have ordered an active quarter-master to go to the westward, and endeavor to purchase on credit, or impress a hundred wagons and teams. But I really see no prospect of sending you additional supplies, till the same wagons return from you, which we sent on with the last. I informed you in my last letter, we had ordered two thousand militia more, to rendezvous at Hillsborough on the 25th of October. You will judge yourself, whether in the mean time you can be more useful by remaining where you are, with the few militia left and coming in, or by returning home, where, besides again accommodating yourself after your losses, you may also aid us in getting those men into motion, and in pointing out such things as are within our power, and may be useful to the service. And you will act accordingly. I am with great friendship and esteem, dear Sir,
your most obedient, humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO GENERAL EDWARD STEVENS.
Richmond, September 15, 1780.
Sir,
I beg leave to trouble you with a private letter, on a little matter of my own, having no acquaintance at camp, with whom I can take that, liberty. Among the wagons impressed, for the use of your militia, were two of mine. One of these, I know is safe, having been on its way from hence to Hillsborough, at the time of the late engagement. The other, I have reason to believe, was on the field. A wagon-master, who says he was near it, informs me the brigade quarter-master cut out one of my best horses, and made his escape on him, and that he saw my wagoner loosening his own horse to come off, but the enemy’s horse were then coming up, and he knows nothing further. He was a negro man, named Phill, lame in one arm and leg. If you will do me the favor to inquire what is become of him, what horses are saved, and to send them to me, I shall be much obliged to you. The horses were not public property, as they were only impressed and not sold. Perhaps your certificate of what is lost, may be necessary for me. The wagon-master told me, that the public money was in my wagon, a circumstance, which, perhaps, may aid your inquiries. After apologizing for the trouble, I beg leave to assure you, that I am, with great sincerity,
your friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MAJOR GENERAL GATES.
Richmond, September 23, 1780.
Sir,
I have empowered Colonel Carrington to have twelve boats, scows, or batteaux, built at Taylor’s Ferry, and to draw on me for the cost. I recommended the constructing them so as to answer the transportation of provisions along that river, as a change of position of the two armies may render them unnecessary at Taylor’s Ferry, and I am thoroughly persuaded, that, unless we can find out some channel of transportation by water, no supplies of bread, of any consequence can be sent you from this State for a long time to come. The want of wagons is a bar insuperable, at least in any reasonable time. I have given orders to have Fry and Jefferson’s map, and Henry’s map of Virginia, sought for and purchased. As soon as they can be got, I will forward them. I have also written to General Washington on the subject of wintering the French fleet in the Chesapeake. Our new levies rendezvous in large numbers. As General Washington had constituted them in eight battalions, and allotted none to Colonel Harrison, we think to deliver him about four hundred drafts of another kind, who are to serve eighteen months also. Unless Congress furnish small arms, we cannot arm more than half the men who will go from this State. The prize you mention of tents and blankets is very fortunate. It is absolutely out of our power to get these articles, to any amount, in this country, nor have we clothing for our new levies. They must, therefore, go to you clothed as militia, till we can procure and send on supplies. They will be as warm in their present clothing at Hillsborough, as at Chesterfield Court House.
We have an agent collecting all the beeves which can be got from the counties round about Portsmouth, to send off to you.
They have there also plentiful crops of corn growing. We have instructed him to try whether means of conveying it down into the Sounds, and up some of the rivers of North Carolina, or by land to Meherrin river, and thence down Chowan, and up Roanoke, cannot be rendered practicable.
I am, with every sentiment of esteem and respect,
your most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
P.S. I enclose a certificate, acknowledging satisfaction for the money furnished Colonel Kosciusko. T. J.
TO HIS EXCELLENCY GENERAL WASHINGTON.
Richmond, September 23, 1780.
Sir,
I yesterday forwarded to you a letter from Colonel Wood, informing you of his situation. That post has, for some time past, been pretty regularly supplied, and I hope will continue to be for some time to come. A person whose punctuality can be relied on, offers to contract for victualling it. If we can agree on terms, and the Assembly will strengthen our hands sufficiently, we think to adopt that method, as the only one to be relied on with certainty. I have heard it hinted that Colonel Wood thinks of quitting that post. I should be exceedingly sorry, indeed, were he to do it. He has given to those under his charge, the most perfect satisfaction, and, at the same time, used all the cautions which the nature of his charge has required. It is principally owing to his prudence and good temper that the late difficulties have been passed over, almost without a murmur. Any influence which your Excellency shall think proper to me, for retaining him in his present situation, will promote the public good, and have a great tendency to keep up a desirable harmony with the officers of that corps. Our new recruits are rendezvousing very generally. Colonel Harrison was uneasy at having none of them assigned to his corps of artillery, who have very much distinguished themselves in the late unfortunate action, and are reduced almost to nothing. We happened to have about four hundred drafts, raised in the last year, and never called out and sent on duty by their county lieutenants, whom we have collected and are collecting. We think to deliver these to Colonel Harrison: they are to serve eighteen months from the time of rendezvous. The numbers of regulars and militia ordered from this State into the southern service, are about seven thousand. I trust we may count that fifty-five hundred will actually proceed: but we have arms for three thousand only. If, therefore, we do not speedily receive a supply from Congress, we must countermand a proper number of these troops. Besides this supply, there should certainly be a magazine laid in here, to provide against a general loss as well as daily waste. When we deliver out those now in our magazine, we shall have sent seven thousand stand of our own into the southern service, in the course of this summer. We are still more destitute of clothing, tents, and wagons for our troops. The southern army suffers for provisions, which we could plentifully supply, were it possible to find means of transportation. Despairing of this, we directed very considerable quantities, collected on the navigable waters, to be sent northwardly by the quarter-master. This he is now doing; slowly, however. Unapprized what may be proposed by our allies to be done with their fleet in the course of the ensuing winter, I would beg leave to intimate to you, that if it should appear to them eligible that it should winter in the Chesapeake, they can be well supplied with provisions, taking their necessary measures in due time. The waters communicating with that bay furnish easy, and (in that case) safe transportation, and their money will call forth what is denied to ours.
I am, with all possible esteem and respect, your Excellency’s
most obedient and humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
Richmond, September 26,1780.
Sir,
The enclosed copy of a letter from Lord Cornwallis [See Appendix, note E.] to Colonel Balfour, was sent me by Governor Rutledge: lest you should not have seen it, I do myself the pleasure of transmitting it, with a letter from General Harrington to General Gates giving information of some late movements of the enemy.
I was honored yesterday with your favor of the 5th instant, on the subject of prisoners, and particularly Lieutenant Governor Hamilton. You are not unapprized of the influence of this officer with the Indians, his activity and embittered zeal against us. You also, perhaps, know how precarious is our tenure of the Illinois country, and how critical is the situation of the new counties on the Ohio. These circumstances determined us to detain Governor Hamilton and Major Hay within our power, when we delivered up the other prisoners. On a late representation from the people of Kentucky, by a person sent here from that country, and expressions of what they had reason to apprehend from these two prisoners, in the event of their liberation, we assured them they would not be parted with, though we were giving up our other prisoners. Lieutenant Colonel Dabusson, aid to Baron de Kalb, lately came here on his parole, with an offer from Lord Rawdon, to exchange him for Hamilton. Colonel Towles is now here with a like proposition for himself, from General Phillips, very strongly urged by the General. These, and other overtures, do not lessen our opinion of the importance of retaining him; and they have been, and will be, uniformly rejected. Should the settlement, indeed, of a cartel become impracticable, without the consent of the States to submit their separate prisoners to its obligation, we will give up these two prisoners, as we would any thing, rather than be an obstacle to a general good. But no other circumstance would, I believe, extract them from us. These two gentlemen, with a Lieutenant Colonel Elligood, are the only separate prisoners we have retained, and the last, only on his own request, and not because we set any store by him. There is, indeed, a Lieutenant Governor Rocheblawe of Kaskaskia, who has broken his parole and gone to New York, whom we must shortly trouble your Excellency to demand for us, as soon as we can forward to you the proper documents. Since the forty prisoners sent to Winchester, as mentioned in my letter of the 9th ultimo, about one hundred and fifty more have been sent thither, some of them taken by us at sea, others sent on by General Gates.
The exposed and weak state of our western settlements, and the danger to which they are subject from the northern Indians, acting under the influence of the British post at Detroit, render it necessary for us to keep from five to eight hundred men on duty for their defence. This is a great and perpetual expense. Could that post be reduced and retained, it would cover all the States to the southeast of it. We have long meditated the attempt under the direction of Colonel Clarke, but the expense would be so great, that whenever we have wished to take it up, this circumstance has obliged us to decline it. Two different estimates make it amount to two millions of pounds, present money. We could furnish the men, provisions, and every necessary, except powder, had we the money, or could the demand from us be so far supplied from other quarters, as to leave it in our power to apply such a sum to that purpose; and, when once done, it would save annual expenditures to a great amount. When I speak of furnishing the men, I mean they should be militia; such being the popularity of Colonel Clarke, and the confidence of the western people in him, that he could raise the requisite number at any time. We, therefore, beg leave to refer this matter to yourself, to determine whether such an enterprise would not be for the general good, and if you think it would, to authorize it at the general expense. This is become the more reasonable, if, as I understand, the ratification of the Confederation has been rested on our cession of a part of our western claim; a cession which (speaking my private opinion) I verily believe will be agreed to, if the quantity demanded is not unreasonably great. Should this proposition be approved of, it should be immediately made known to us, as the season is now coming on, at which some of the preparations must be made. The time of execution, I think, should be at the time of the breaking up of the ice in the Wabash, and before the lakes open. The interval, I am told, is considerable.
I have the honor to be, &c.
your most obedient and humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MAJOR GENERAL GATES.
Richmond, October 4, 1780.
Sir,
My letter of September 23rd answered your favors received before that date, and the present serves to acknowledge the receipt of those of September 24th and 27th. I retain in mind, and recur, almost daily, to your requisitions of August; we have, as yet, no prospect of more than one hundred tents. Flour is ordered to be manufactured, as soon as the season will render it safe; out of which, I trust, we can furnish not only your requisition of August, but that of Congress of September 11th. The corn you desire, we could furnish when the new crops come in, fully, if water transportation can be found; if not, we shall be able only to send you what lies convenient to the southern boundary, in which neighborhood the crops have been much abridged by a flood in Roanoke. We have no rice. Rum and other spirits, we can furnish to a greater amount than you require, as soon as our wagons are in readiness, and shall be glad to commute into that article some others which we have not, particularly sugar, coffee, and salt. The vinegar is provided. Colonel Finnie promised to furnish to Colonel Muter, a list of the shades, hoes, &c. which could be furnished from the Continental stores. This list has never yet come to hand. It is believed the Continental stores here will fall little short of your requisition, except in the article of axes, which our shops are proceeding on. Your information of September 24th, as to the quality of the axes, has been notified to the workmen, and will, I hope, have a proper effect on those made hereafter. Application has been made to the courts, to have the bridges put in a proper state, which they have promised to do. We are endeavoring again to collect wagons. About twenty are nearly finished at this place. We employed, about three weeks ago, agents to purchase, in the western counties, a hundred wagons and teams. Till these can be got, it will be impossible to furnish any thing from this place. I am exceedingly pleased to hear of your regulation for stopping our wagons at Roanoke. This will put it in our power to repair and replace them, to calculate their returns, provide loads, and will be a great encouragement to increase their number, if possible, as their departure hence will no longer produce the idea of a final adieu to them.
Colonel Senf arrived here the evening before the last. He was employed yesterday and to-day, in copying some actual and accurate surveys, which we had had made of the country round about Portsmouth, as far as Cape Henry to the eastward, Nansemond river to the westward, the Dismal Swamp to the southward, and northwardly, the line of country from Portsmouth by Hampton and York to Williamsburg, and including the vicinities of these three last posts. This will leave him nothing to do, but to take drawings of particular places, and the soundings of such waters as he thinks material. He will proceed on this business to-morrow, with a letter to General Nelson, and powers to call for the attendance of a proper vessel.
I suppose that your drafts in favor of the quarter-master, if attended with sixty days’ grace, may be complied with to a certain amount. We will certainly use our best endeavors to answer them. I have only to desire that they may be made payable to the quarter-master alone, and not to the bearer. This is to prevent the mortification of seeing an unapprized individual taken in by an assignment of them, as if they were ready money. Your letter to Colonel Finnie will go to Williamsburg immediately. Those to Congress, with a copy of the papers enclosed to me, went yesterday by express. I will take order as to the bacon you mention. I fear there is little of it, and that not capable of being long kept. You are surely not uninformed, that Congress required the greater part of this article to be sent northward, which has been done. I hope, by this time, you receive supplies of beeves from our commissary, Mr. Eaton, who was sent three weeks or a month ago, to exhaust of that article the counties below, and in the neighborhood of Portsmouth; and from thence, was to proceed to other counties, in order, as they stood exposed to an enemy.
The arrival of the French West India fleet (which, though not authentically communicated, seems supported by so many concurring accounts from individuals, as to leave scarcely room for doubt,) will, I hope, prevent the enemy from carrying into effect the embarkation they had certainly intended from New York, though they are strengthened by the arrival of Admiral Rodney, at that place, with twelve sail of the line and four frigates, as announced by General Washington to Congress, on the 19th ultimo. The accounts of the additional French fleet are varied from sixteen to nineteen ships of the line, besides frigates. The number of the latter has never been mentioned. The extracts of letters, which you will see in our paper of this day, are from General Washington, President Huntington, and our Delegates in Congress to me. That from Bladensburg is from a particular acquaintance of mine, whose credit cannot be doubted. The distress we are experiencing from want of leather to make shoes, is great. I am sure you have thought of preventing it in future, by the appointment of a commissary of hides, or some other good regulation for saving and tanning the hides, which the consumption of your army will afford.
I have the honor to be, with all possible esteem and respect, Sir,
your most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO GENERAL GATES.
Richmond, October 15, 1780.
Sir,
I am rendered not a little anxious by the paragraph of yours of the 7th instant, wherein you say, ‘It is near a month since I received any letter from your Excellency; indeed, the receipt of most that I have written to you, remains unacknowledged.’ You ought, within that time, to have received my letter of September the 3rd, written immediately on my return to this place, after a fortnight’s absence; that of September the 11th, acknowledging the receipt of yours which covered drafts for money; that of September the 23rd, on the subject of batteaux at Taylor’s Ferry, wagons, maps of Virginia, wintering the French fleet in the Chesapeake, our new levies, and provisions from our lower counties; and that of October the 4th, in answer to yours of September the 24th and 27th. I begin to apprehend treachery in some part of our chain of expresses, and beg the favor of you, in your next, to mention whether any, and which of these letters have come to hand. This acknowledges the receipt of yours of September the 28th, and October the 3rd, 5th, and 7th. The first of these was delivered four or five days ago by Captain Drew. He will be permitted to return as you desire, as we would fulfil your wishes in every point in our power, as well as indulge the ardor of a good officer. Our militia from the western counties are now on their march to join you. They are fond of the kind of service in which Colonel Morgan is generally engaged, and are made very happy by being informed you intend to put them under him. Such as pass by this place, take muskets in their hands. Those from the,southern counties, beyond the Blue Ridge, were advised to carry their rifles. For those who carry neither rifles nor muskets, as well as for our eighteen months men, we shall send on arms as soon as wagons can be procured. In the mean time, I had hoped that there were arms for those who should first arrive at Hillsborough, as by General Steven’s return, dated at his departure thence, there were somewhere between five and eight hundred muskets (I speak from memory, not having present access to the return) belonging to this State, either in the hands of the few militia who were there, or stored. Captain Fauntleroy, of the cavalry, gives me hopes he shall immediately forward a very considerable supply of accoutrements, for White’s and Washington’s cavalry. He told me yesterday he had received one hundred and thirteen horses for that service, from us. Besides these, he had rejected sixty odd, after we had purchased them, at £3000 apiece. Nelson’s two troops were returned to me, deficient only twelve horses, since which, ten have been sent to him by Lieutenant Armstead. I am not a little disappointed, therefore, in the number of cavalry fit for duty, as mentioned in the letter you enclosed me. Your request (as stated in your letter of the 7th) that we will send no men into the field, or even to your camp, that are not well furnished with shoes, blankets, and every necessary for immediate service, would amount to a stoppage of every man; as we have it not in our power to furnish them with real necessaries completely. I hope they will be all shod. What proportion will have blankets I cannot say: we purchase every one which can be found out; and now I begin to have a prospect of furnishing about half of them with tents, as soon as they can be made and forwarded. As to provisions, our agent, Eaton, of whom I before wrote, informs me in a letter of the 5th instant, he shall immediately get supplies of beef into motion, and shall send some corn by a circuitous navigation. But till we receive our wagons from the western country, I cannot hope to aid you in bread. I expect daily to see wagons coming in to us. The militia were ordered to rendezvous at Hillsborough, expecting they would thence be ordered by you into service. I send you herewith a copy of Henry’s map of Virginia. It is a mere cento of blunders. It may serve to give you a general idea of the courses of rivers, and positions of counties. We are endeavoring to get you a copy of Fry and Jefferson’s; but they are now very scarce. I also enclose you some newspapers, in which you will find a detail of Arnold’s apostacy and villany.
I am, with all sentiments of sincere respect and esteem, Sir,
your most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
P. S. Just as I was closing my letter, yours of the 9th instant was put into my hands. I enclose by this express, a power to Mr. Lambe, quarter-master, to impress, for a month, ten wagons from each of the counties of Brunswick, Mecklenburg, Lunenburg, Charlotte, and Halifax, and direct him to take your orders, whether they shall go first to you, or come here. If the latter, we can load them with arms and spirits. Before their month is out, I hope the hundred wagons from the westward will have come in. We will otherwise provide a relief for these. I am perfectly astonished at your not having yet received my letters before mentioned. I send you a copy of that of the 4th of October, as being most material. I learn, from one of General Muhlenburg’s family, that five wagons have set out from hence, with three hundred stand of arms, &c. However, the General writes to you himself. T.J.
TO HIS EXCELLENCY GENERAL WASHINGTON.
Richmond, October 22, 1780.
Sir,
I have this morning received certain information of the arrival of a hostile fleet in our bay, of about sixty sail. The debarkation of some light-horse, in the neighborhood of Portsmouth, seems to indicate that as the first scene of action. We are endeavoring to collect as large a body to oppose them as we can arm: this will be lamentably inadequate, if the enemy be in any force. It is mortifying to suppose that a people, able and zealous to contend with their enemy, should be reduced to fold their arms for want of the means of defence. Yet no resources, that we know of, ensure us against this event. It has become necessary to divert to this new object, a considerable part of the aids we had destined for General Gates. We are still, however, sensible of the necessity of supporting him, and have left that part of our country nearest him uncalled on, at present, that they may reinforce him as soon as arms can be received. We have called to the command of our forces, Generals Weeden and Muhlenburg, of the line, and Nelson and Stevens of the militia. You will be pleased to make to these such additions as you may think proper. As to the aids of men, I ask for none, knowing that if the late detachment of the enemy shall have left it safe for you to spare aids of that kind, you will not await my application. Of the troops we shall raise, there is not a single man who ever saw the face of an enemy. Whether the Convention troops will be removed or not, is yet undetermined. This must depend on the force of the enemy, and the aspect of their movements.
I have the honor to be
your Excellency’s most obedient,
humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO HIS EXCELLENCY GENERAL WASHINGTON.
Richmond, October 25,1780.
Sir,
I take the liberty of enclosing to you letters from Governor Hamilton, for New York. On some representations received by Colonel Towles, that an indulgence to Governor Hamilton and his companions to go to New York, on parole, would produce the happiest,effect on the situation of our officers in Long Island, we have given him, Major Hay, and some of the same party at Winchester, leave to go there on parole. The two former go by water, the latter by land.
By this express I hand on, from General Gates to Congress, intelligence of the capture of Augusta, in Georgia, with considerable quantities of goods; and information, which carries a fair appearance, of the taking of Georgetown, in South Carolina, by a party of ours, and that an army of six thousand French and Spaniards had landed at Sunbury. This is the more credible, as Cornwallis retreated from Charlotte on the 12th instant, with great marks of precipitation. Since my last to you, informing you of an enemy’s fleet, they have landed eight hundred men in the neighborhood of Portsmouth, and some more on the bay side of Princess Anne. One thousand infantry landed at New-ports-news, on the morning of the 23rd, and immediately took possession of Hampton. The horse were proceeding up the road. Such a corps as Major Lee’s would be of infinite service to us. Next to a naval force, horse seems to be the most capable of protecting a country so intersected by waters.
I am, with the most sincere esteem,
your Excellency’s most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO HIS EXCELLENCY GENERAL WASHINGTON.
Richmond, October 26, 1780.
Sir,
The Executive of this State think it expedient, under our present circumstances, that the prisoners of war under the Convention of Saratoga, be removed from their present situation. It will be impossible, as long as they remain with us, to prevent the hostile army from being reinforced by numerous desertions from this corps; and this expectation may be one among the probable causes of this movement of the enemy. Should, moreover, a rescue of them be attempted, the extensive disaffection which has of late been discovered, and the almost total want of arms in the hands of our good people, render the success of such an enterprise by no means desperate. The fear of this, and the dangerous convulsions to which such an attempt would expose us, divert the attention of a very considerable part of our militia, from an opposition to an invading enemy. An order has been, therefore, this day issued to Colonel Wood, to take immediate measures for their removal; and every aid has been and will be given him, for transporting, guarding, and subsisting them on the road, which our powers can accomplish. Notice hereof is sent to his Excellency Governor Lee, on whose part, I doubt not, necessary preparations will be made.
I have the honor to be, with the greatest esteem and respect,
your Excellency’s most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO GENERAL GATES.
Richmond, October 28, 1780.
Sir,
Your letters of the 14th, 20th, and 21st have come to hand, and your despatches to Congress have been regularly forwarded. I shall attend to the caveat against Mr. Ochiltree’s bill. Your letter to Colonel Senf remains still in my hands, as it did not come till the enemy had taken possession of the ground, on which I knew him to have been, and I have since no certain information where a letter might surely find him. My proposition as to your bills in favor of the quarter-master, referred to yours of September 27th. I have notified to the Continental quarter-master, your advance of nine hundred dollars to Cooper. As yet, we have received no wagons. I wish Mr. Lambe may have supplied you. Should those from the western quarter not come in, we will authorize him or some other, to procure a relief, in time, for those first impressed. We are upon the eve of a new arrangement as to our commissary’s and quarter-master’s departments, as the want of money, introducing its substitute, force, requires the establishment of a different kind of system.
Since my first information to you of the arrival of an enemy, they have landed about eight hundred men near Portsmouth, some on the bay side of Princess Anne, one thousand at Hampton, and still retained considerable part on board their ships. Those at Hampton, after committing horrid depredations, have again retired to their ships, which, on the evening of the 26th, were strung along the Road from New-ports-news, to the mouth of Nansemond, which seems to indicate an intention of coming up James river. Our information is, that they have from four to five thousand men, commanded by General Leslie, and that they have come under convoy of one forty-gun ship, and some frigates (how many, has never been said), commanded by Commodore Rodney. Would it not be worth while to send out a swift boat from some of the inlets of Carolina, to notify the French Admiral that his enemies are in a net, if he has leisure to close the mouth of it? Generals Muhlenburg and Nelson are assembling a force to be ready for them, and General Weeden has come to this place, where he is at present employed in some arrangements. We have ordered the removal of the Saratoga prisoners, that we may have our hands clear for these new guests.
I have the honor to be, with the most perfect esteem and respect, Sir,
your most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO HIS EXCELLENCY GENERAL WASHINGTON.
Richmond, November 3,1780.
Sir,
Since I had the honor of writing to your Excellency, on the 25th ultimo, the enemy have withdrawn their forces from the north side of James river, and have taken post at Portsmouth, which, we learn, they are fortifying. Their highest post is Suffolk, where there is a very narrow and defensible pass between Nansemond river and the Dismal Swamp, which covers the country below, from being entered by us. More accurate information of their force, than we at first had, gives us reason to suppose them to be from twenty-five hundred to three thousand strong, of which, between sixty and seventy are cavalry. They are commanded by General Leslie, and were convoyed by the Romulus, of forty guns, the Blonde, of thirty-two guns, the Delight sloop, of sixteen, a twenty-gun ship of John Goodwick’s, and two row-galleys, commanded by Commodore Grayton. We are not assured, as yet, that they have landed their whole force. Indeed, they give out themselves, that after drawing the force of this State to Suffolk, they mean, to go to Baltimore. Their movements had induced me to think they came with an expectation of meeting with Lord Cornwallis in this country, that his precipitate retreat has left them without a concerted object, and that they were waiting further orders. Information of this morning says, that being informed of Lord Cornwallis’s retreat, and a public paper having been procured by them, wherein were printed the several despatches which brought this intelligence from General Gates, they unladed a vessel and sent, her off to Charleston immediately. The fate of this army of theirs hangs on a very slender naval force, indeed.
The want of barracks at Fort Frederick, as represented by Colonel Wood, the difficulty of getting wagons sufficient to move the whole Convention troops, and the state of uneasiness in which the regiment of guards is, have induced me to think it would be better to move these troops in two divisions; and as the whole danger of desertion to the enemy, and correspondence with the disaffected in our southern counties, is from the British only (for from the Germans we have no apprehensions on either head), we have advised Colonel Wood to move on the British in the first division, and to leave the Germans in their present situation, to form a second division, when barracks may be erected at Fort Frederick. By these means, the British may march immediately under the guard of Colonel Crochet’s battalion, while Colonel Taylor’s regiment of guards remains with the Germans. I cannot suppose this will be deemed such a separation as is provided against by the Convention, nor that their officers will wish to have the whole troops crowded into barracks, probably not sufficient for half of them. Should they, however, insist on their being kept together, I suppose it would be the opinion that the second division should follow the first as soon as possible, and that their being exposed, in that case, to a want of covering, would be justly imputable to themselves only. The delay of the second division will lessen the distress for provisions, which may, perhaps, take place on their first going to the new post, before matters are properly arranged.
I have the honor to be, with great esteem and respect,
your Excellency’s most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO HIS EXCELLENCY GENERAL WASHINGTON.
Richmond, November 10, 1780.
Sir,
I enclose your Excellency a copy of an intercepted letter from Major General Leslie to Lord Cornwallis. [See Appendix, note F.] It was taken from a person endeavoring to pass through the country from Portsmouth towards Carolina. When apprehended, and a proposal made to search him, he readily consented to be searched, but, at the same time, was observed to put his hand into his pocket and carry something towards his mouth, as if it were a quid of tobacco: it was examined, and found to be a letter, of which the enclosed is a copy, written on silk paper, rolled up in gold-beater’s skin, and nicely tied at each end, so as not to be larger than a goose quill. As this is the first authentic disclosure of their purpose in coming here, and may serve to found, with somewhat more of certainty, conjectures respecting their future movements, while their disappointment in not meeting with Lord Cornwallis may occasion new plans at New York, I thought it worthy of communication to your Excellency.
Some deserters were taken yesterday, said to be of the British Convention troops, who had found means to get to the enemy at Portsmouth, and were seventy or eighty miles on their way back to the barracks, when they were taken. They were passing under the guise of deserters from Portsmouth.
I have the honor to be, with the greatest esteem and respect,
your Exellency’s most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO HIS EXCELLENCY GENERAL WASHINGTON.
Richmond, November 26, 1780.
Sir,
I have been honored with your Excellency’s letter of the 8th instant. Having found it impracticable to move, suddenly, the whole Convention troops, British and German, and it being represented that there could not, immediately, be covering provided for them all at Fort Frederick, we concluded to march off the British first, from whom was the principal danger of desertion, and to permit the Germans, who show little disposition to join the enemy, to remain in their present quarters till something further be done. The British, accordingly, marched the 20th instant. They cross the Blue Ridge at Rock Fish gap, and proceed along that valley. I am to apprize your Excellency, that the officers of every rank, both British and German, but particularly the former, have purchased within this State some of the finest horses in it. You will be pleased to determine, whether it be proper that they carry them within their lines. I believe the Convention of Saratoga entitles them to keep the horses they then had. But I presume none of the line below the rank of field-officers, had a horse. Considering the British will be now at Fort Frederick, and the Germans in Albemarle, Alexandria seems to be the most central point to which there is navigation. Would it not, therefore, be better that the flag-vessel, solicited by General Phillips, should go to that place? It is about equally distant from the two posts. The roads to Albemarle are good. I know not how those are which lead to Fort Frederick. Your letter referring me to General Green, for the mode of constructing light, portable boats, unfortunately did not come to hand till he had left us. We had before determined to have something done in that way, and as they are still unexecuted, we should be greatly obliged by any draughts or hints, which could be given by any person within the reach of your Excellency.
I received advice, that on the 22nd instant, the enemy’s fleet got all under way, and were standing toward the Capes: as it still remained undecided, whether they would leave the bay, or turn up it, I waited the next stage of information, that you might so far be enabled to judge of their destination. This I hourly expected, but it did not come till this evening, when I am informed they all got out to sea in the night of the 22nd. What course they steered afterwards, is not known. I must do their General and Commander the justice to say, that in every case to which their attention and influence could reach, as far as I have been well-informed, their conduct was such as does them the greatest honor. In the few instances of wanton and unnecessary devastation, they punished the aggressors.
I have the honor to be,
your Excellency’s
most obedient, humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO HIS EXCELLENCY GENERAL WASHINGTON.
Richmond, December 15,1780.
Sir,
I had the honor of writing to your Excellency on the subject of an expedition contemplated by this State, against the British post at Detroit, and of receiving your answer of October the 10th. Since the date of my letter, the face of things has so far changed, as to leave it no longer optional in us to attempt or decline the expedition, but compels us to decide in the affirmative, and to begin our preparations immediately. The army the enemy at present have in the South, the reinforcements still expected there, and their determination to direct their future exertions to that quarter, are not unknown to you. The regular force proposed on our part to counteract those exertions, is such, either from the real or supposed inability of this State, as by no means to allow a hope that it may be effectual. It is, therefore, to be expected that the scene of war will either be within our country, or very nearly advanced to it; and that our principal dependence is to be on militia, for which reason it becomes incumbent to keep as great a proportion of our people as possible, free to act in that quarter. In the mean time, a combination is forming in the westward, which, if not diverted, will call thither a principal and most valuable part of our militia. From intelligence received, we have reason to expect that a confederacy of British and Indians, to the amount of two thousand men, is formed for the purpose of spreading destruction and dismay through the whole extent of our frontier, in the ensuing spring. Should this take place, we shall certainly lose in the South all aids of militia beyond the Blue Ridge, besides the inhabitants who must fall a sacrifice in the course of the savage irruptions.
There seems to be but one method of preventing this, which is to give the western enemy employment in their own country. The regular force Colonel Clarke already has, with a proper draft from the militia beyond the Allegany, and that of three or four of our most northern counties, will be adequate to the reduction of Fort Detroit, in the opinion of Colonel Clarke; and he assigns the most probable reasons for that opinion. We have, therefore, determined to undertake it, and commit it to his direction. Whether the expense of the enterprise shall be defrayed by the Continent or State, we will leave to be decided hereafter by Congress, in whose justice we can confide as to the determination. In the mean time, we only ask the loan of such necessaries as, being already at Fort Pitt, will save time and an immense expense of transportation. These articles shall either be identically or specifically returned; should we prove successful, it is not improbable they may be where Congress would choose to keep them. I am, therefore, to solicit your Excellency’s order to the commandant at Fort Pitt, for the articles contained on the annexed list, which shall not be called for until every thing is in readiness; after which, there can be no danger of their being wanted for the post at which they are: indeed, there are few of the articles essential for the defence of the post.
I hope your Excellency will think yourself justified in lending us this aid without awaiting the effect of an application elsewhere, as such a delay would render the undertaking abortive, by postponing it to the breaking up of the ice in the lake. Independent of the favorable effects which a successful enterprise against Detroit must produce to the United States in general, by keeping in quiet the frontier of the northern ones, and leaving our western militia at liberty to aid those of the South, we think the like friendly offices performed by us to the Sates, whenever desired, and almost to the absolute exhausture of our own magazines, give well founded hopes that we may be accommodated on this occasion. The supplies of military stores which have been furnished by us to Fort Pitt itself, to the northern army, and, most of all, to the southern, are not altogether unknown to you. I am the more urgent for an immediate order, because Colonel Clarke awaits here your Excellency’s answer by the express, though his presence in the western country to make preparations for the expedition is so very necessary, if you enable him to undertake it. To the above, I must add a request to you to send for us to Pittsburg, persons proper to work the mortars, &c, as Colonel Clarke has none such, nor is there one in this State. They shall be in the pay of this State from the time they leave you. Any money necessary for their journey, shall be repaid at Pittsburg, without fail, by the first of March.
At the desire of the General Assembly, I take the liberty of transmitting to you the enclosed resolution; and have the honor to be, with the most perfect esteem and regard,
your Excellency’s most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO HIS EXCELLENCY GENERAL WASHINGTON.
Richmond, January 10, 1781.
Sir,
It may seem odd, considering the important events which have taken place in this State within the course of ten days, that I should not have transmitted an account of them to your Excellency; but such has been their extraordinary rapidity, and such the unremitted attention they have required from all concerned in government, that I do not recollect the portion of time which I could have taken to commit them to paper.
On the 31st of December, a letter from a private gentleman to General Nelson came to my hands, notifying, that in the morning of the preceding day, twenty-seven sail of vessels had entered the Capes; and from the tenor of the letter, we had reason to expect, within a few hours, further intelligence; whether they were friends or foes, their force, and other circumstances. We immediately despatched General Nelson to the lower country, with powers to call on the militia in that quarter, or act otherwise as exigencies should require; but waited further intelligence, before we would call for militia from the middle or upper country. No further intelligence came till the 2nd instant, when the former was confirmed; it was ascertained they had advanced up James river to Wanasqueak bay. All arrangements were immediately taken for calling in a sufficient body of militia for opposition. In the night of the 3rd, we received advice that they were at anchor opposite Jamestown; we then supposed Williamsburg to be their object. The wind, however, which had hitherto been unfavorable, shifted fair, and the tide being also in their favor, they ascended the river to Kennons’ that evening, and, with the next tide, came up to Westover, having, on their way, taken possession of some works we had at Hood’s, by which two or three of their vessels received some damage, but which were of necessity abandoned by the small garrison of fifty men placed there, on the enemy’s landing to invest the works. Intelligence of their having quitted the station at Jamestown, from which we supposed they meant to land for Williamsburg, and of their having got in the evening to Kennon’s, reached us the next morning at five o’clock, and was the first indication of their meaning to penetrate towards this place or Petersburg. As the order for drawing miliatia here had been given but two days, no opposition was in readiness. Every effort was therefore necessary, to withdraw the arms and other military stores, records, &c. from this place. Every effort was, accordingly, exerted to convey them to the foundery five miles, and to a laboratory six miles, above this place, till about sunset of that day, when we learned the enemy had come to an anchor at Westover that morning. We then knew that this, and not Petersburg was their object, and began to carry across the river every thing remaining here, and to remove what had been transported to the foundery and laboratory to Westham, the nearest crossing, seven miles above this place, which operation was continued till they had approached very near. They marched from Westover, at two o’clock in the afternoon of the 4th, and entered Richmond at one o’clock in the afternoon of the 5th. A regiment of infantry and about thirty horse continued on, without halting, to the foundery. They burnt that, the boring mill, the magazine, and two other houses, and proceeded to Westharn; but nothing being in their power there, they retired to Richmond. The next morning they burned some buildings of public and private property, with what stores remained in them, destroyed a great quantity of private stores, and about twelve o’clock, retired towards Westover, where they encamped within the Neck, the next day.
The loss sustained is not yet accurately known. As far as I have been able to discover, it consisted, at this place, of about three hundred muskets, some soldiers’ clothing to a small amount, some quarter-master’s stores, of which one hundred and twenty sides of leather was the principal article, part of the artificers’ tools, and three wagons. Besides which, five brass four-pounders, which we had sunk in the river, were discovered to them, raised and carried off. At the foundery, we lost the greater part of the papers belonging to the Auditor’s office, and of the books and papers of the Council office. About five or six tons of powder, as we conjecture, was thrown into the canal, of which there will be a considerable saving by re-manufacturing it. The roof of the foundery was burned, but the stacks of chimneys and furnaces not at all injured. The boring mill was consumed. Within less than forty-eight hours from the time of their landing, and nineteen from our knowing their destination, they had penetrated thirty-three miles, done the whole injury, and retired. Their numbers, from the best intelligence I have had, are about fifteen hundred infantry, and as to their cavalry, accounts vary from fifty to one hundred and twenty; and the whole commanded by the parricide Arnold. Our militia, dispersed over a large tract of country, can be called in but slowly. On the day the enemy advanced to this place, two hundred only were embodied. They were of this town and its neighborhood, and were too few to do any thing. At this time, they are assembled in pretty considerable numbers on the south side of James river, but are not yet brought to a point. On the north side are two or three small bodies, amounting in the whole to about nine hundred men. The enemy were, at four o’clock yesterday evening, still remaining in their encampment at Westover and Berkeley Neck. In the mean while, Baron Steuben, a zealous friend, has descended from the dignity of his proper command, to direct our smallest movements. His vigilance has in a great measure supplied the want of force in preventing the enemy from crossing the river, which might have been very fatal. He has been assiduously employed in preparing equipments for the militia, as they should assemble, in pointing them to a proper object, and in other offices of a good commander. Should they loiter a little longer, and he be able to have a sufficient force, I still flatter myself they will not escape with total impunity. To what place they will point their next exertions, we cannot even conjecture. The whole country on the tide waters and some distance from them, is equally open to similar insult.
I have the honor to be, with every sentiment of respect,
your Excellency’s most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO HIS EXCELLENCY THE PRESIDENT OF CONGRESS.
Richmond, January 15,1781.
Sir,
As the dangers which threaten our western frontiers, the ensuing spring, render it necessary that we should send thither Colonel Crocket’s battalion, at present on guard at Fredericktown, but raised for the western service, I thought it necessary to give your Excellency previous information thereof, that other forces may be provided in time to succeed to their duties. Captain Read’s troop of horse, if necessary, may be continued a while longer on guard.
I have the honor to be, with the greatest respect,
your Excellency’s most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO HIS EXCELLENCY THE PRESIDENT OF CONGRESS.
Sir,
Richmond, January 15, 1781.
I received some time ago from Major Forsyth, and afterwards from you, a requisition to furnish one half the supplies of provision for the Convention troops, removed into Maryland. I should sooner have done myself the honor of writing to you on this subject, but that I hoped to have laid it before you more fully than could be done in writing, by a gentleman who was to pass on other public business to Philadelphia. The late events in this State having retarded his setting out, I think it my duty no longer to postpone explanation on this head.
You cannot be unapprized of the powerful armies of our enemy, at this time in this and the southern States, and that their future plan is to push their successes in the same quarter, by still larger reinforcements. The forces to be opposed to these must be proportionably great, and these forces must be fed. By whom are they to be fed? Georgia and South Carolina are annihilated, at least, as to us. By the requisition to us to send provisions into Maryland, it is to be supposed that none are to come to the southern army, from any State north of this; for it would seem inconsistent, that while we should be sending north, Maryland, and other states beyond that, should be sending their provisions south. Upon North Carolina, then, already exhausted by the ravages of two armies, and on this State, are to depend for subsistence those bodies of men, who are to oppose the greater part of the enemy’s force in the United States, the subsistence of the German, and of half the British Conventioners. To take a view of this matter on the Continental requisitions of November the 4th, 1780, for specific quotas of provisions, it is observable that North Carolina and Virginia are to furnish 10,475,740 pounds of animal food, and 13,529 barrels of flour, while the States north of these will yield 25,293,810 pounds of animal food, and 106,471 barrels of flour.
If the greater part of the British armies be employed in the South, it is to be supposed that the greater part of the American force will be sent there to oppose them. But should this be the case, while the distribution of the provisions is so very unequal, would it be proper to render it still more so, by withdrawing a part of our contributions to the support of posts northward of us? It would certainly be a great convenience to us, to deliver a portion of our specifics at Fredericktown, rather than in Carolina: but I leave it to you to judge, whether this would be consistent with the general good or safety. Instead of sending aids of any kind to the northward, it seems but too certain that unless very timely and substantial assistance be received from thence, our enemies are yet far short of the ultimate term of their successes. I beg leave, therefore, to refer to you, whether the specifics of Maryland, as far as shall be necessary, had not better be applied to the support of the posts within it, for which its quota is much more than sufficient, or, were it otherwise, whether those of the States north of Maryland had not better be called on, than to detract any thing from the resources of the southern opposition, already much too small for the encounter to which it is left. I am far from wishing to count or measure our contributions by the requisitions of Congress. Were they ever so much beyond these. I should readily strain them in aid of any one of our sister States. But while they are so short of those calls to which they must be pointed in the first instance, it would be great misapplication to divert them to any other purpose: and I am persuaded you will think me perfectly within the line of duty, when I ask a revisal of this requisition.
I have the honor to be, with the greatest respect, Sir,
your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO HIS EXCELLENCY THE PRESIDENT OF CONGRESS.
Richmond, January 17, 1781.
Sir,
I do myself the honor of transmitting to your Excellency a resolution of the General Assembly of this Commonwealth, entered into in consequence of the resolution of Congress of September the 6th, 1780, on the subject of the Confederation. I shall be rendered very happy if the other States of the Union, equally impressed with the necessity of that important convention, shall be willing to sacrifice equally to its completion. This single event, could it take place shortly, would overweigh every success which the enemy have hitherto obtained, and render desperate the hopes to which those successes have given birth.
I have the honor to be, with the most real esteem and respect,
your Excellency’s most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO THE VIRGINIA DELEGATES IN CONGRESS.
Richmond, January 18, 1781.
Gentlemen,
I enclose you a Resolution of Assembly, directing your conduct as to the navigation of the Mississippi.
The loss of powder lately sustained by us (about five tons), together with the quantities sent on to the southward, have reduced our stock very low indeed. We lent to Congress, in the course of the last year (previous to our issues for the southern army), about ten tons of powder. I shall be obliged to you to procure an order from the board of war, for any quantity from five to ten tons, to be sent us immediately from Philadelphia or Baltimore, and to inquire into and hasten, from time to time, the execution of it. The stock of cartridge-paper is nearly exhausted. I do not know whether Captain Irish, or what other officer, should apply for this. It is essential that a good stock should be forwarded, and without a moment’s delay. If there be a rock on which we are to split, it is the want of muskets, bayonets, and cartouch-boxes.
The occurrences, since my last to the President, are not of any magnitude. Three little rencounters have happened with the enemy. In the first, General Smallwood led on a party of two or three hundred militia, and obliged some armed vessels of the enemy to retire from a prize they had taken at Broadway’s, and renewing his attack the next day with a four-pounder or two (for on the first day he had only muskets), he obliged some of their vessels to fall down from City Point to their main fleet at Westover. The enemy’s loss is not known; ours was four men wounded. One of the evenings, during their encampment at Westover and Berkeley, their light-horse surprised a party of about one hundred or one hundred and fifty militia at Charles City Court House, killed and wounded four, and took, as has been generally said, about seven or eight. On Baron Steuben’s approach towards Hood’s, they embarked at Westover; the wind, which, till then, had set directly up the river from the time of their leaving Jamestown, shifted in the moment to the opposite point. Baron Steuben had not reached Hood’s by eight or ten miles, when they arrived there. They landed their whole army in the night, Arnold attending in person. Colonel Clarke (of Kaskaskias) had been sent on with two hundred and forty men by Baron Steuben, and having properly disposed of them in ambuscade, gave them a deliberate fire, which killed seventeen on the spot, and wounded thirteen. They returned it in confusion, by which we had three or four wounded, and our party being so small and without bayonets, were obliged to retire on the enemy’s charging with bayonets. They fell down to Cobham, whence they carried all the tobacco there (about sixty hogsheads); and the last intelligence was, that on the 16th they were standing for New-ports-news. Baron Steuben is of opinion, they are proceeding to fix a post in some of the lower counties. Later information has given no reason to believe their force more considerable than we at first supposed. I think, since the arrival of the three transports which had been separated in a storm, they may be considered as about two thousand strong. Their naval force, according to the best intelligence, is the Charon, of forty-four guns, Commodore Symmonds, the Amphitrite, Iris, Thames, and Charlestown frigates, the Forvey, of twenty guns, two sloops of war, a privateer ship, and two brigs. We have about thirty-seven hundred militia embodied, but at present they are divided into three distant encampments: one under General Weeden, at Fredericksburg, for the protection of the important works there; another under General Nelson, at and near Williamsburg; and a third under Baron Steuben, at Cabin Point. As soon as the enemy fix themselves, these will be brought to a point.
I have the honor to be, with very great respect, gentlemen,
your most obedient servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO HIS EXCELLENCY GENERAL WASHINGTON.
Richmond, February 8, 1781.
Sir,
I have just received intelligence, which, though from a private hand, I believe is to be relied on, that a fleet of the enemy’s ships have entered Cape Fear river, that eight of them had got over the bar, and many others were lying off; and that it was supposed to be a reinforcement to Lord Cornwallis, under the command of General Prevost. This account, which had come through another channel, is confirmed by a letter from General Parsons at Halifax, to the gentleman who forwards it to me. I thought it of sufficient importance to be communicated to your Excellency by the stationed expresses. The fatal want of arms puts it out of our power to bring a greater force into the field, than will barely suffice to restrain the adventures of the pitiful body of men they have at Portsmouth. Should any more be added to them, this country will be perfectly open to them, by land as well as water.
I have the honor to be, with all possible respect,
Your Excellency’s most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO HIS EXCELLENCY GENERAL WASHINGTON.
Richmond, February 12, 1781.
Sir,
The enclosed extract from a letter from Governor Nash, which I received this day, being a confirmation of the intelligence I transmitted in a former letter, I take the liberty of transmitting it to your Excellency. I am informed, through a private channel, on which I have considerable reliance, that the enemy had landed five hundred troops under the command of a Major Craig, who were joined by a number of disaffected; that they had penetrated forty miles; that their aim appeared to be the magazine at Kingston, from which place they were about twenty miles distant.
Baron Steuben transmits to your Excellency a letter from General Greene, by which you will learn the events which have taken place in that quarter since the defeat of Colonel Tarleton, by General Morgan. These events speak best for themselves, and no doubt will suggest what is necessary to be done to prevent the successive losses of State after State, to which the want of arms, and of a regular soldiery, seem more especially to expose those in the South.
I have the honor to be, with every sentiment of respect, your Excellency’s most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO HIS EXCELLENCY GENERAL WASHINGTON.
Richmond, February 17, 1781.
Sir,
By a letter from General Greene, dated Guilford Court House, February 10th, we are informed that Lord Cornwallis had burned his own wagons in order to enable himself to move with greater facility, and had pressed immediately on. The prisoners taken at the Cow-pens, were happily saved by the accidental rise of a water-course, which gave so much time as to withdraw them from the reach of the enemy. Lord Cornwallis had advanced to the vicinities of the Moravian towns, and was still moving on rapidly. His object was supposed to be to compel General Greene to an action, which, under the difference of force they had, would probably be ruinous to the latter. General Greene meant to retire by the way of Boyd’s Ferry, on the Roanoke. As yet he had lost little or no stores or baggage, but they were far from being safe. In the instant of receiving this intelligence, we ordered a reinforcement of militia to him, from the most convenient counties in which there was a hope of finding any arms. Some great event must arise from the present situation of things, which, for a long time, will determine the condition of southern affairs.
Arnold lies close in his quarters. Two days ago, I received information of the arrival of a sixty-four gun ship and two frigates in our bay, being part of the fleet of our good ally at Rhode Island. Could they get at the British fleet here, they are sufficient to destroy them; but these being drawn up into Elizabeth river, into which the sixty-four cannot enter, I apprehend they could do nothing more than block up the river. This, indeed, would reduce the enemy, as we could cut off their supplies by land; but the operation being tedious, would probably be too dangerous for the auxiliary force. Not having yet had any particular information of the designs of the French Commander, I cannot pretend to say what measures this aid will lead to.
Our proposition to the Cherokee Chiefs, to visit Congress, for the purpose of preventing or delaying a rupture with that nation, was too late. Their distresses had too much ripened their alienation from us, and the storm had gathered to a head, when Major Martin got back. It was determined to carry the war into their country, rather than await it in ours, and thus disagreeably circumstanced, the issue has been successful.
The militia’ of this State and North Corolina penetrated into their country, burned almost every town they had, amounting to about one thousand houses in the whole, destroyed fifty thousand bushels of grain, killed twenty-nine, and took seventeen prisoners. The latter are mostly women and children.
I have the honor to be, &c. your Excellency’s
most obedient, humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
P.S. Since writing the above, I have received information which, though not authentic, deserves attention: that Lord Cornwallis had got to Boyd’s Ferry on the 14th. I am issuing orders, in consequence, to other counties, to embody and march all the men they can arm. In this fatal situation, without arms, there will be no safety for the Convention troops but in their removal, which I shall accordingly order. The prisoners of the Cowpens were at New London (Bedford Court House) on the 14th. T. J.
TO GENERAL GATES.
Richmond, February 17, 1781.
Dear General,
The situation of affairs here and in Carolina is such as must shortly turn up important events, one way orihe other. By letter from General Greene, dated Guilford Court House, February the 10th, I learn that Lord Cornwallis, rendered furious by the affair of the Cowpens and the surprise of Georgetown, had burned his own wagons, to enable himself to move with facility, had pressed on to the vicinity of the Moravian towns, and was still advancing: The prisoners taken at the Cowpens were saved by a hair’s-breadth accident, and Greene was retreating. His force, two thousand regulars, and no militia; Cornwallis, three thousand. General Davidson was killed in a skirmish. Arnold lies still at Portsmouth with fifteen hundred men. A French sixty-four gun ship and two frigates, of thirty-six each, arrived in our bay three days ago. They would suffice to destroy the British shipping here (a forty, four frigates, and a twenty), could they get at them. But these are withdrawn up Elizabeth river, which the sixty-four cannot enter. We have ordered about seven hundred riflemen from Washington, Montgomery, and Bedford, and five hundred common militia from Pittsylvania and Henry, to reinforce General Greene; and five hundred new levies will march from Chesterfield Court House in a few days. I have no doubt, however, that the southwestern counties will have turned out in greater numbers before our orders reach them.
I have been knocking at the door of Congress for aids of all kinds, but especially of arms, ever since the middle of summer. The speaker, Harrison, is gone to be heard on that subject. Justice, indeed, requires that we should be aided powerfully. Yet if they would repay us the arms we have lent them, we should give the enemy trouble, though abandoned to ourselves.
After repeated applications, I have obtained a warrant for your advance money, £18,000, which I have put into the hands of Mr. McAlister, to receive the money from the Treasurer, and carry it to you.
I am, with very sincere esteem,
Dear Sir, your friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO HIS EXCELLENCY GENERAL WASHINGTON.
Richmond, February 26,1781.
Sir,
I gave you information in my last letter, that General Greene had crossed the Dan, at Boyd’s Ferry, and that Lord Cornwallis had arrived at the opposite shore. Large reinforcements of militia having embodied both in front and rear of the enemy, he is retreating with as much rapidity as he advanced; his route is towards Hillsborough. General Greene re-crossed the Dan on the 21st, in pursuit of him. I have the pleasure to inform you, that the spirit of opposition was as universal, as could have been wished for. There was no restraint on the numbers that embodied, but the want of arms.
The British at Portsmouth lie close in their lines. The French squadron keep them in by water, and since their arrival, as they put it out of the power of the enemy to cut off our retreat by sending up Nansemond river, our force has been moved down close to their lines.
I have the honor to be, with the greatest respect,
your most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO HIS EXCELLENCY GENERAL WASHINGTON.
Richmond, March 8, 1781.
Sir,
I had the pleasure of receiving a letter from General Greene, dated High-rock Ford, February 29th (probably March the 1st), who informs me, that, on the night of the 24th, Colonel M’Call surprised a subaltern’s guard at Hart’s Mill, killed eight, and wounded and took nine prisoners, and that on the 25th, General Pickens and Lieutenant Colonel Lee routed a body of near three hundred tories, on the Haw river, who were in arms to join the British army, killed upwards of one hundred, and wounded most of the rest; which had a very happy effect on the disaffected in that country.
By a letter from Major Magill, an officer of this State, whom I had sent to General Greene’s head-quarters, for the purpose of giving us regular intelligence, dated Guilford County, March 2nd, I am informed that Lord Cornwallis, on his retreat, erected the British standard at Hillsborough; that numbers of disaffected, under the command of Colonel Piles, were resorting to it, when they were intercepted by General Pickens and Lieutenant Colonel Lee, as mentioned by General Greene; and that their commanding officer was among the slain: that Lord Cornwallis, after destroying every thing he could, moved down the Haw river from Hillsborough: that General Greene was within six miles of him: that our superiority in the goodness, though not in the number of our cavalry, prevented the enemy from moving with rapidity, or foraging. Having been particular in desiring Major Magill to inform me what corps of militia, from this State, joined General Greene, he accordingly mentioned, that seven hundred under General Stevens, and four hundred from Botetourt, had actually joined him; that Colonel Campbell was to join, him that day with six hundred, and that Colonel Lynch, with three hundred from Bedford, was shortly expected: the last three numbers being riflemen. Besides these mentioned by Major Magill, General Lawson must, before this, have crossed Roanoke with a body of militia, the number of which has not been stated to me. Report makes them a thousand, but I suppose the number to be exaggerated. Four hundred of our new levies left Chesterfield Court House on the 25th of February, and probably would cross the Roanoke about the 1st or 2nd of March.
I was honored with your Excellency’s letter of February the 21st, within seven days after its date. We have, accordingly, been making every preparation on our part, which we are able to make. The militia proposed to co-operate, will be upwards of four thousand from this State, and one thousand or twelve hundred from Carolina, said to be under General Gregory. The enemy are, at this time, in a great measure blockaded by land, there being a force on the east side of Elizabeth river. They suffer for provisions, as they are afraid to venture far, lest the French squadron should be in the neighborhood, and come upon them. Were it possible to block up the river, a little time would suffice to reduce them by want and desertions, and would be more sure in its event than an attempt by storm. I shall be very happy to have it in my power to hand you a favorable account of these two armies in the South.
I have the honor to be, with the greatest esteem and respect,
your Excellency’s most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO HIS EXCELLENCY THE PRESIDENT OF CONGRESS.
Richmond, March 19,1781;
Sir,
I have the honor of enclosing to your Excellency a copy of a letter from General Greene, with some other intelligence received, not doubting your anxiety to know the movements in the South.
I find we have deceived ourselves not a little, by counting on the whole numbers of the militia which have been in motion, as if they had all remained with General Greene, when, in fact, they seem only to have visited and quitted him.
The Marquis Fayette arrived at New York on the 15th. His troops still remained at the head of the bay, till the appearance of some force which should render their passage down safe.
I have the honor to be, with sentiments of the highest esteem and respect, your Excellency’s
most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO HIS EXCELLENCY THE PRESIDENT OF CONGRESS.
Richmond, March 21, 1781.
Sir,
The enclosed letter will inform you of the arrival of a British fleet in Chesapeake bay.
The extreme negligence of our stationed expresses is no doubt the cause why, as yet, no authentic account has reached us of a general action, which happened on the 15th instant, about a mile and a half from Guilford Court House, between General Greene and Lord Cornwallis. Captain Singleton, an intelligent officer of Harrison’s artillery, who was in the action, has this moment arrived here, and gives the general information that both parties were prepared and desirous for action; the enemy were supposed about twenty-five hundred strong, our army about four thousand. That after a very warm and general engagement, of about an hour and a half, we retreated about a mile and a half from the field, in good order, having, as he supposed, between two and three hundred killed and wounded, the enemy between five and seven hundred killed and wounded: that we lost four pieces of artillery: that the militia, as well as regulars, behaved exceedingly well: that General Greene, he believes, would have renewed the action the next day, had it not proved rainy, and would renew it as soon as possible, as he supposes: that the whole of his troops, both regulars and militia, were in high spirits and wishing a second engagement: that the loss has fallen pretty equally on the militia and regulars: that General Stevens received a ball through the thigh.
Major Anderson, of Maryland, was killed, and Captain Barrett, of Washington’s cavalry; Captain Fauntleroy, of the same cavalry, was shot through the thigh, and left in the field.
Captain Singleton, having left the camp the day after the battle, does, not speak from particular returns, none such having been then made. I must inform your Excellency from him, till more regular applications can reach you, that they are in extreme want of lead, cartridge-paper, and thread. I think it improper, however it might urge an instantaneous supply, to repeat to you his statement of the extent of their stock of these articles. In a former letter, I mentioned to you the failure of the vein of our lead mines, which has left the army here in a state of equal distress and danger.
I have the honor to be, with very high respect and esteem,
your Excellency’s most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
P. S. Look-out boats have been ordered from the sea-board of the eastern shore, to apprise the Commander of the French fleet, on its approach, of the British being in the Chesapeake. T. J.
TO HIS EXCELLENCY THE PRESIDENT OF CONGRESS.
In Council, Richmond, March 26,1781.
Sir,
The appointment of commissioner to the war-office of this State having lately become vacant, the Executive are desirous to place Colonel William Davies, of the Virginia Continentals, in that office. This gentleman, however, declines undertaking it, unless his rank in the army, half pay for life and allowance for depreciation of pay, can be reserved to him; observing with justice, that these emoluments, distant as they are, are important to a person who has spent the most valuable part of his youth in the service of his country. As this indulgence rests in the power of Congress alone, I am induced to request it of them on behalf of the State, to whom it is very interesting that the office be properly filled, and I may say, on behalf of the Continent also, to whom the same circumstance is interesting, in proportion to its reliance upon this State for supplies to the southern war. We should not have given Congress the trouble of this application, had we found it easy to call any other to the office, who was likely to answer our wishes in the exercise of it.
I have the honor to be, with sentiments of the highest respect,
your Excellency’s most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO HIS EXCELLENCY THE PRESIDENT OF CONGRESS.
Richmond, March 28, 1781.
Sir,
I forward to your Excellency, under cover with this, copies of letters received from Major General Greene and Baron Steuben, which will give you the latest account of the situation of things with us and in North Carolina.
I observe a late resolve of Congress, for furnishing a number of arms to the southern states; and I lately wrote you on the subject of ammunition and cartridge-paper. How much of this State, the enemy thus reinforced, may think proper to possess themselves of, must depend on their own moderation and caution, till these supplies arrive. We had hoped to receive, by the French squadron under Monsieur Destouches, eleven hundred stand of arms, which we had at Rhode Island, but were disappointed. The necessity of hurrying forward the troops intended for the southern operations will be doubtless apparent from this letter.
I have the honor to be, with the greatest respect,
your Excellency’s most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO HIS EXCELLENCY THE PRESIDENT OF CONGRESS.
Richmond, March 31, 1781.
Sir,
The letters and papers accompanying this, will inform your Excellency of the arrival of a British flag vessel with clothing, refreshments, money, &c. for their prisoners under the Convention of Saratoga. The gentlemen conducting them have, on supposition that the prisoners, or a part of them, still remained in this State, applied to me by letters, copies of which I transmit your Excellency, for leave to allow water transportation as far as possible, and then, for themselves to attend them to the post where they are to be issued. These indulgencies were usually granted them here, but the prisoners being removed, it becomes necessary to transmit the application to Congress for their direction. In the mean time the flag will wait in James river.
Our intelligence from General Greene’s camp as late as the 24th, is, that Lord Cornwallis’s march of the day before had decided his route to Cross creek.
The amount of the reinforcements to the enemy, arrived at Portsmouth, is not yet known with certainty. Accounts differ from fifteen hundred to much larger numbers. We are informed they have a considerable number of horse. The affliction of the people for want of arms is great; that of ammunition is not yet known to them. An apprehension is added, that, the enterprise on Portsmouth being laid aside, the troops under the Marquis Fayette will not come on. An enemy three thousand strong, not a regular in the State, nor arms to put in the hands of the militia, are, indeed, discouraging circumstances.
I have the honor to be, with sentiments of the highest respect,
your Excellency’s most obedient
and most humble servant
Th: Jefferson.
TO HIS EXCELLENCY THE PRESIDENT OF CONGRESS.
Richmond, April 7, 1781.
Sir,
Hearing that our arms from Rhode Island have arrived at Philadelphia, I have begged the favor of our Delegates to send them on in wagons immediately, and, for the conveyance of my letter, have taken the liberty of setting the Continental line of expresses in motion, which I hope our distress for arms will justify, though the errand be not purely Continental.
I have nothing from General Greene later than the 27th of March; our accounts from Portsmouth vary the reinforcements which came under General Phillips, from twenty-five hundred to three thousand. Arnold’s strength before, was, I think, reduced to eleven hundred. They have made no movement yet. Their preparation of boats is considerable; whether they mean to go southwardly or up the river, no leading circumstance has yet decided.
I have the honor to be, with the highest respect,
your Excellency’s most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson,
TO HIS EXCELLENCY THE PRESIDENT OF CONGRESS.
In Council, April 18, 1781.
Sir,
I was honored, yesterday, with your Excellency’s favor enclosing the resolutions of Congress of the 8th instant, for removing stores and provisions from the counties of Accomack and Northampton. We have there no military stores, except a few muskets in the hands of the militia. There are some collections of forage and provisions belonging to the Continent, and some to the State, and the country there, generally, furnishes an abundance of forage. But such is the present condition of Chesapeake bay, that we cannot even get an advice-boat across it, with any certainty, much less adventure on transportation. Should, however, any interval happen, in which these articles may be withdrawn, we shall certainly avail ourselves of it, and bring thence whatever we can.
If I have been rightly informed, the horses there are by no means such, as that the enemy could apply them to the purposes of cavalry. Some, large enough for the draught, may, perhaps, be found, but of these not many.
I have the honor to be, with the greatest respect,
your Excellency’s most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO HIS EXCELLENCY GENERAL WASHINGTON
Richmond, April 23,1781.
Sir,
On the 18th instant, the enemy came from Portsmouth up James river, in considerable force, though their numbers are not yet precisely known to us. They landed at Burwell’s Ferry, below Williamsburg, and also a short distance above the mouth of Chickahominy. This latter circumstance obliged Colonel Innis, who commanded a body of militia, stationed on that side the river to cover the country from depredation, to retire upwards, lest he should be placed between their two bodies. One of these entered Williamsburg on the 20th, and the other proceeded to a ship-yard we had on Chickahominy. What injury they did there, I am not yet informed. I take for granted, they have burned an unfinished twenty-gun ship we had there. Such of the stores belonging to the yard as were moveable, had been carried some miles higher up the river. Two small galleys also retired up the river. Whether by this, either the stores or galleys were saved, is yet unknown. I am just informed from a private hand, that they left Williamsburg early yesterday morning. If this sudden departure was not in consequence of some circumstance of alarm unknown to us, their expedition to Williamsburg has been unaccountable. There were no public stores at that place, but those which were necessary for the daily subsistence of the men there. Where they mean to descend next, the event alone can determine. Besides harassing our militia with this kind of war, the taking them from their farms at the interesting season of planting their corn, will have an unfortunate effect on the crop of the ensuing year.
I have heard nothing certain of General Greene since the 6th instant, except that his head-quarters were on Little river on the 11th.
I have the honor to be, with the highest respect and esteem,
your Excellency’s most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO HIS EXCELLENCY GENERAL WASHINGTON.
Richmond, May 9, 1781.
Sir,
Since the last letter which I had the honor of addressing to your Excellency, the military movements in this State, except a very late one, have scarcely merited communication.
The enemy, after leaving Williamsburg, came directly up James river and landed at City Point, being the point of land on the southern side of the confluence of Appomatox and James rivers. They marched up to Petersburg, where they were received by Baron Steuben with a body of militia somewhat under one thousand, who, though the enemy were two thousand and three hundred strong, disputed the ground very handsomely, two hours, during which time the enemy gained only one mile, and that by inches. Our troops were then ordered to retire over a bridge, which they did in perfectly good order. Our loss was between sixty and seventy, killed, wounded, and taken. The enemy’s is unknown, but it must be equal to ours; for their own honor they must confess this, as they broke twice and run like sheep, till supported by fresh troops. An inferiority in number obliged our force to withdraw about twelve miles upwards, till more militia should be assembled. The enemy burned all the tobacco in the warehouses at Petersburg, and its, neighborhood. They afterwards proceeded to Osborne’s, where they did the same, and also destroyed the residue of the public armed vessels, and several of private property, and then came to Manchester, which is on the hill opposite this place.
By this time, Major General Marquis Fayette, having been advised of our danger, had, by forced marches, got here with his detachment of Continental troops; and reinforcements of militia having also come in, the enemy finding we were able to meet them on equal footing, thought proper to burn the warehouses and tobacco at Manchester, and retire to Warwick, where they did the same. Ill armed and untried militia, who never before saw the face of an enemy, have, at times, during the course of this war, given occasions of exultation to our enemies; but they afforded us, while at Warwick, a little satisfaction in the same way. Six or eight hundred of their picked men of light-infantry, with General Arnold at their head, having crossed the river from Warwick, fled from a patrole of sixteen horse, every man into his boat as he could, some pushing north, some south, as their fears drove them. Their whole force then proceeded to the Hundred, being the point of land within the confluence of the two rivers, embarked, and fell down the river. Their foremost vessels had got below Burwell’s Ferry on the 6th instant, when on the arrival of a boat from Portsmouth, and a signal given, the whole crowded sail up the river again with a fair wind and tide, and came to anchor at Brandon; there six days’ provision was dealt out to every man; they landed, and had orders to march an hour before day the next morning. We have not yet heard which way they went, or whether they have gone; but having, about the same time, received authentic information that Lord Cornwallis had, on the 1st instant, advanced from Wilmington half way to Halifax, we have no doubt, putting all circumstances together, that these two armies are forming a junction.
We are strengthening our hands with militia, as far as arms, either public or private, can be collected, but cannot arm a force which may face the combined armies of the enemy. It will, therefore, be of very great importance that General Wayne’s forces be pressed on with the utmost despatch. Arms and a naval force, however, are what must ultimately save us. This movement of our enemies we consider as most perilous in its consequences.
Our latest advices from General Greene were of the 26th ult., when he was lying before Camden, the works and garrison of which were much stronger than he had expected to find them.
I have the honor to be, with great respect,
your Excellency’s most obedient, humble servant,
Th: Jefferson,
TO THE VIRGINIA DELEGATES IN CONGRESS.
In Council, May 10, 1781.
Gentlemen,
A small affair has taken place between the British commanding officer in this state, General Phillips, and the Executive, of which, as he may endeavor to get rid of it through the medium of Congress, I think it necessary previously to apprise you.
General Scott obtained permission from the Commandant at Charleston, for vessels with necessary supplies to go from hence to them, but instead of sending the original, sent only a copy of the permission taken by his brigade-major. I applied to General Phillips to supply this omission by furnishing a passport for the vessel. Having just before taken great offence at a threat of retaliation in the treatment of prisoners, he enclosed his answer to my letter under this address, ‘To Thomas Jefferson Esq., American Governor of Virginia.’ I paused on receiving the letter, and for some time would not open it; however, when the miserable condition of our brethren in Charleston occurred to me, I could not determine that they should be left without the necessaries of life, while a punctilio should be discussing between the British General and myself; and knowing that I had an opportunity of returning the compliment to Mr. Phillips in a case perfectly corresponding, I opened the letter.
Very shortly after, I received, as I expected, the permission of the board of war, for the British flag-vessel, then in Hampton Roads with clothing and refreshments, to proceed to Alexandria. I enclosed and addressed it, ‘To William Phillips Esq., commanding the British forces in the Commonwealth of Virginia.’ Personally knowing Phillips to be the proudest man of the proudest nation on earth, I well know he will not open this letter; but having occasion at the same time to write to Captain Gerlach, the flag-master, I informed him that the Convention troops in this state should perish-for want of necessaries, before any should be carried to them through this state, till General Phillips either swallowed this pill of retaliation, or made an apology for his rudeness. And in this, should the matter come ultimately to Congress, we hope for their support.
He has the less right to insist on the expedition of his flag, because his letter, instead of enclosing a passport to expedite ours, contained only an evasion of the application, by saying he had referred it to Sir Henry Clinton, and in the mean time, he has come up the river, and taken the vessel with her loading, which we had chartered and prepared to send to Charleston, and which wanted nothing but the passport to enable her to depart.
I would further observe to you, that this gentleman’s letters to the Baron Steuben first, and afterwards to the Marquis Fayette, have been in a style so intolerably insolent and haughty, that both these gentlemen have, been obliged to inform him, that if he thinks proper to address them again in the same spirit, all intercourse shall be discontinued.
I am, with great respect and esteem,
Gentlemen, your most obedient servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO HIS EXCELLENCY GENERAL WASHINGTON.
Charlottesville, May 28,1781.
Sir,
I make no doubt you will have heard, before this shall have the honor of being presented to your Excellency, of the junction of Lord Cornwallis with the force at Petersburg under Arnold, who had succeeded to the command on the death of Major General Phillips. I am now advised that they have evacuated Petersburg, joined at Westover a reinforcement of two thousand men just arrived from New York, crossed James river, and on the 26th instant were three miles advanced on their way towards Richmond; at which place Major General the Marquis Fayette lay with three thousand men, regulars and militia: these being the whole number we could arm, until the arrival of the eleven hundred arms from Rhode Island, which are, about this time, at the place where our public stores are deposited, The whole force of the enemy within this State, from the best intelligence I have been able to get, is, I think, about seven thousand men, infantry and cavalry, including also the small garrison left at Portsmouth. A number of privateers, which are constantly ravaging the shores of our rivers, prevent us from receiving any aid from the counties lying on navigable waters: and powerful operations meditated against our western frontier, by a joint force of British and Indian savages, have, as your Excellency before knew, obliged us to embody between two and three thousand men in that quarter. Your Excellency will judge from this state of things, and from what you know of our country, what it may probably suffer during the present campaign. Should the enemy be able to produce no opportunity of annihilating the Marquis’s army, a small proportion of their force may yet restrain his movements effectually, while the greater part are employed, in detachment, to waste an unarmed country, and lead the minds of the people to acquiescence under those events, which they see no human power prepared to ward off. We are too far removed from the other scenes of war to say, whether the main force of the enemy be within this state. But I suppose they cannot any where spare so great an army for the operations of the field. Were it possible for this circumstance to justify in your Excellency a determination to lend us your personal aid, it is evident from the universal voice, that the presence of their beloved countryman, whose talents have so long been successfully employed in establishing the freedom of kindred States, to whose person they have still flattered themselves they retained some right, and have ever looked up, as their dernier resort in distress, would restore full confidence of salvation to our citizens, and would render them equal to whatever is not impossible. I cannot undertake to foresee and obviate the difficulties which lie in the way of such a resolution. The whole subject is before you, of which I see only detached parts: and your judgment will be formed on a view of the whole. Should the danger of this State, and its consequence to the Union, be such, as to render it best for the whole that you should repair to its assistance, the difficulty would then be, how to keep men out of the field. I have undertaken to hint this matter to your Excellency, not only on my own sense of its importance to us, but at the solicitations of many members of weight in our legislature, which has not yet assembled to speak their own desires.
A few days will bring to me that relief which the constitution has prepared for those oppressed with the labors of my office, and a long declared resolution of relinquishing it to abler hands, has prepared my way for retirement to a private station: still, as an individual, I should feel the comfortable effects of your presence, and have (what I thought could not have been) an additional motive for that gratitude, esteem, and respect, with which
I have the honor to be,
your Excellency’s most obedient, humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
[An interval of near three years here occurs in the
Author’s correspondence, during which he preserved only
memoranda of the contents of the letters written by him.]
TO GENERAL WASHINGTON.
Annapolis, April 16, 1784.
Dear Sir,
I received your favor of April the 8th, by Colonel Harrison, The subject of it is interesting, and, so far as you have stood connected with it, has been matter of anxiety to me; because, whatever may be the ultimate fate of the institution of the Cincinnati, as, in its course, it draws to it some degree of disapprobation, I have wished to see you standing on ground separated from it, and that the character which will be handed to future ages at the head of our Revolution, may, in no instance, be compromitted in subordinate altercations. The subject has been at the point of my pen in every letter I have written to you, but has been still restrained by the reflection that you had among your friends more able counsellors, and, in yourself, one abler than them all. Your letter has now rendered a duty what was before a desire, and I cannot better merit your confidence than by a full and free communication of facts and sentiments, as far as they have come within my observation. When the army was about to be disbanded, and the officers to take final leave, perhaps never again to meet, it was natural for men who had accompanied each other through so many scenes of hardship, of difficulty and danger, who, in a variety of instances, must have been rendered mutually dear by those aids and good offices, to which their situations had given occasion, it was natural, I say, for these to seize with fondness any proposition which promised to bring them together again, at certain and regular periods. And this, I take for granted, was the origin and object of this institution: and I have no suspicion that they foresaw, much less intended, those mischiefs which exist perhaps in the forebodings of politicians only. I doubt, however, whether in its execution, it would be found to answer the wishes of those who framed it, and to foster those friendships it was intended to preserve. The members would be brought together at their annual assemblies no longer to encounter a common enemy, but to encounter one another in debate and sentiment. For something, I suppose, is to be done at these meetings, and, however unimportant, it will suffice to produce difference of opinion, contradiction, and irritation. The way to make friends quarrel is to put them in disputation under the public eye. An experience of near twenty years has taught me, that few friendships stand this test, and that public assemblies where every one is free to act and speak, are the most powerful looseners of the bands of private friendship. I think, therefore, that this institution would fail in its principal object, the perpetuation of the personal friendships contracted through the war.
The objections of those who are opposed to the institution shall be briefly sketched. You will readily fill them up. They urge that it is against the Confederation—against the letter of some of our constitutions—against the spirit of all of them;—that the foundation on which all these are built, is the natural equality of man, the denial of every pre-eminence but that annexed to legal office, and, particularly, the denial of a pre-eminence by birth; that however, in their present dispositions, citizens might decline accepting honorary instalments[sp.]into the order; but a time, may come, when a change of dispositions would render these flattering, when a well directed distribution of them might draw into the order all the men of talents, of office, and wealth, and in this case, would probably procure an ingraftment into the government; that in this, they will be supported by their foreign members, and the wishes and influence of foreign courts; that experience has shown that the hereditary branches of modern governments are the patrons of privilege and prerogative, and not of the natural rights of the people, whose oppressors they generally are: that besides these evils, which are remote, others may take place more immediately; that a distinction is kept up between the civil and military, which it is for the happiness of both to obliterate; that when the members assemble the, will be proposing to do something, and what that something may be, will depend on actual circumstances; that being an organized body, under habits of subordination, the first obstruction to enterprise will be already surmounted; that the moderation and virtue of a single character have probably prevented this Revolution from being closed as most others have been, by a subversion of that liberty it was intended to establish; that he is not immortal, and his successor, or some of his successors, may be led by false calculation into a less certain road to glory.
What are the sentiments of Congress on this subject, and what line they will pursue, can only be stated, conjecturally. Congress as a body, if left to themselves, will in my opinion say nothing on the subject. They may, however, be forced into a declaration by instructions from some of the States, or by other incidents. Their sentiments, if forced from them, will be unfriendly to the institution. If permitted to pursue their own path, they will check it by side-blows whenever it comes in their way, and in competitions for office, on equal or nearly equal ground, will give silent preferences to those who are not of the fraternity. My reasons for thinking this are, 1. The grounds on which they lately declined the foreign order proposed to be conferred on some of our citizens. 2. The fourth of the fundamental articles of constitution for the new States. I enclose you the report; it has been considered by Congress, recommitted and reformed by a committee, according to sentiments expressed on other parts of it, but the principle referred to, having not been controverted at all, stands in this as in the original report; it is not yet confirmed by Congress. 3. Private conversations on this subject with the members. Since the receipt of your letter I have taken occasion to extend these; not, indeed, to the military members, because, being of the order, delicacy forbade it, but to the others pretty generally; and, among these, I have as yet found but one who is not opposed to the institution, and that with an anguish of mind, though covered under a guarded silence which I have not seen produced by any circumstance before. I arrived at Philadelphia before the separation of the last Congress, and saw there and at Princeton some of its members not now in delegation. Burke’s piece happened to come out at that time, which occasioned this institution to be the subject of conversation. I found the same impressions made on them which their successors have received. I hear from other quarters that it is disagreeable, generally, to such citizens as have attended to it, and, therefore, will probably be so to all, when any circumstance shall present it to the notice of all.
This, Sir, is as faithful an account of sentiments and facts as I am able to give you. You know the extent of the circle within which my observations are at present circumscribed, and can estimate how far, as forming a part of the general opinion, it may merit notice, or ought to influence your particular conduct.
It now remains to pay obedience to that part of your letter, which requests sentiments on the most eligible measures to be pursued by the society, at their next meeting. I must be far from pretending to be a judge of what would, in fact, be the most, eligible measures for the society. I can only give you the opinions of those with whom I have conversed, and who, as I have before observed, are unfriendly to it. They lead to these conclusions. 1. If the society proceed according to its institution, it will be better to make no applications to Congress on that subject, or any other, in their associated character. 2. If they should propose to modify it, so as to render it unobjectionable, I think it would not be effected without such a modification as would amount almost to annihilation: for such would it be to part with its inheritability, its organization, and its assemblies. 3. If they shall be disposed to discontinue the whole, it would remain with them to determine whether they would choose it to be done by their own act only, or by a reference of the matter to Congress, which would infallibly produce a recommendation of total discontinuance.
You will be sensible, Sir, that these communications are without reserve. I supposed such to be your wish, and mean them but as materials, with such others as you may collect, for your better judgment to work on. I consider the whole matter as between ourselves alone, having determined to take no active part in this or any thing else, which may lead to altercation, or disturb that quiet and tranquillity of mind, to which I consign the remaining portion of my life. I have been thrown back by events, on a stage where I had never more thought to appear. It is but for a time, however, and as a day-laborer, free to withdraw, or be withdrawn at will. While I remain, I shall pursue in silence the path of right, but in every situation, public or private, I shall be gratified by all occasions of rendering you service, and of convincing you there is no one, to whom your reputation and happiness are dearer than to, Sir,
your most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO COLONEL URIAH FORREST.
Paris, Cul-de-Sac Tetebout,
October 20, 1784.
Sir,
I received yesterday your favor of the 8th instant, and this morning went to Auteuil and Passy, to consult with Mr. Adams and Dr. Franklin on the subject of it. We conferred together, and think it is a case in which we could not interpose (were there as yet cause for interposition) without express instructions from Congress. It is, however, our private opinion, which we give as individuals, only, that Mr. McLanahan, while in England, is subject to the laws of England; that, therefore, he must employ counsel, and be guided in his defence by their advice. The law of nations and the treaty of peace, as making a part of the law of the land, will undoubtedly be under the consideration of the judges who pronounce on Mr. McLanahan’s case; and we are willing to hope that, in their knowledge and integrity, he will find certain resources against injustice, and a reparation of all injury to which he may have been groundlessly exposed. A final and palpable failure on their part, which we have no reason to apprehend, might make the case proper for the consideration of Congress.
I have the honor to be, with sentiments of great respect and esteem, for Mr. McLanahan, as well as yourself.
Sir, your most obedient, humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN JAY.
Paris, May 11, 1785.
Sir,
I was honored on the 2nd instant with the receipt of your favor of March the 15th, enclosing the resolution of Congress of the 10th of the same month, appointing me their Minister Plenipotentiary at this court, and also of your second letter of March 22nd, covering the commission and letter of credence for that appointment. I beg permission through you, Sir, to testify to Congress my gratitude for this new mark of their favor, and my assurances of endeavoring to merit it by a faithful attention to the discharge of the duties annexed to it. Fervent zeal is all which I can be sure of carrying into their service; and where I fail through a want of those powers which nature and circumstances deny me, I shall rely on their indulgence, and much also on that candor with which your Goodness will present my proceedings to their eye. The kind terms in which you are pleased to notify this honor to me, require mv sincere thanks. I beg you to accept them, and to be assured of the perfect esteem, with which I have the honor to be, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO GENERAL CHASTELLUX.
Paris, June 7,1785.
Dear Sir,
I have been honored with the receipt of your letter of the 2nd instant, and am to thank you, as I do sincerely, for the partiality with which you receive the copy of the Notes on my country. As I can answer for the facts therein reported on my own observation, and have admitted none on the report of others, which were not supported by evidence sufficient to command my own assent, I am not afraid that you should make any extracts you please for the Journal de Physique, which come within their plan of publication. The strictures on slavery and on the constitution of Virginia, are not of that kind, and they are the parts which I do not wish to have made public, at least, till I know whether their publication would do most harm or good. It is possible, that in my own country, these strictures might produce an irritation, which would indispose the people towards the two great objects I have in view, that is, the emancipation of their slaves, and the settlement of their constitution on a firmer and more permanent basis. If I learn from thence, that they will not produce that effect, I have printed and reserved just copies enough to be able to give one to every young man at the College. It is to them I look, to the rising generation, and not to the one now in power, for these great reformations. The other copy, delivered at your hotel, was for Monsieur de Buffon. I meant to ask the favor of you to have it sent to him, as I was ignorant how to do it. I have one also for Monsieur Daubenton, but being utterly unknown to him, I cannot take the liberty of presenting it, till I can do it through some common acquaintance.
I will beg leave to say here a few words on the general question of the degeneracy of animals in America. 1. As to the degeneracy of the man of Europe transplanted to America, it is no part of Monsieur de Buffon’s system. He goes, indeed, within one step of it, but he stops there. The Abbe Raynal alone has taken that step. Your knowledge of America enables you to judge this question; to say, whether the lower class of people in America, are less informed, and less susceptible of information, than the lower class in Europe: and whether those in America who have received such an education as that country can give, are less improved by it than Europeans of the same degree of education. 2. As to the aboriginal man of America, I know of no respectable evidence on which the opinion of his inferiority of genius has been founded, but that of Don Ulloa. As to Robertson, he never was in America; he relates nothing on his own knowledge; he is a compiler only of the relations of others, and a mere translator of the opinions of Monsieur de Buffon. I should as soon, therefore, add the translators of Robertson to the witnesses of this fact, as himself. Paw, the beginner of this charge, was a compiler from the works of others; and of the most unlucky description; for he seems to have read the writings of travellers, only to collect and republish their lies. It is really remarkable, that in three volumes 12mo, of small print, it is scarcely possible to find one truth, and yet, that the author should be able to produce authority for every fact he states, as he says he can. Don Ulloa’s testimony is of the most respectable. He wrote of what he saw, but he saw the Indian of South America only, and that, after he had passed through ten generations of slavery. It is very unfair, from this sample, to judge of the natural genius of this race of men; and after supposing that Don Ulloa had not sufficiently calculated the allowance which should be made for this circumstance, we do him no injury in considering the picture he draws of the present Indians of South America, as no picture of what their ancestors were, three hundred years ago. It is in North America we are to seek their original character. And I am safe in affirming that the proofs of genius given by the Indians of North America, place them on a level with whites in the same uncultivated state. The North of Europe furnishes subjects enough for comparison with them, and for a proof of their equality. I have seen some thousands myself, and conversed much with them, and have found in them a masculine, sound understanding. I have had much information from men who had lived among them, and whose veracity and good sense were so far known to me, as to establish a reliance on their information. They have all agreed in bearing witness in favor of the genius of this a people. As to their bodily strength, their manners rendering it disgraceful to labor, those muscles employed in labor will be weaker with them, than with the European laborer; but those which are exerted in the chase, and those faculties which are employed in the tracing an enemy or a wild beast, in contriving ambuscades for him, and in carrying them through their execution, are much stronger than with us, because they are more exercised. I believe the Indian, then, to be, in body and mind, equal to the white man. I have supposed the black man, in his present state, might not be so; but it would be hazardous to affirm, that, equally cultivated for a few generations, he would not become so. 3. As to the inferiority of the other animals of America, without more facts, I can add nothing to what I have said in my Notes.
As to the theory of Monsieur de Buffon, that heat is friendly, and moisture adverse to the production of large animals, I am lately furnished with a fact by Dr. Franklin, which proves the air of London and of Paris to be more humid than that of Philadelphia, and so creates a suspicion that the opinion of the superior humidity of America, may, perhaps, have been too hastily adopted. And supposing that fact admitted, I think the physical reasonings urged to show, that in a moist country animals must be small, and that in a hot one they must be large, are not built on the basis of experiment. These questions, however, cannot be decided ultimately, at this day. More facts must be collected, and more time flow off, before the world will be ripe for decision. In the mean time, doubt is wisdom.
I have been fully sensible of the anxieties of your situation, and that your attentions were wholly consecrated, where alone they were wholly due, to the succor of friendship and worth. However much I prize your society, I wait with patience the moment when I can have it without taking what is due to another. In the mean time, I am solaced with the hope of possessing your friendship, and that it is not ungrateful to you to receive the assurances of that with which I have the honor to be, Dear Sir,
your most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN ADAMS.
Passy, June 15, 1785.
Sir,
Among the instructions given to the ministers of the United States for treating with foreign powers, was one of the 11th of May, 1784, relative to an individual of the name of John Baptist Picquet. It contains an acknowledgement, on the part of Congress, of his merits and sufferings by friendly services rendered to great numbers of American seamen carried prisoners into Lisbon, and refers to us the delivering him these acknowledgements in honorable terms, and the making him such gratification, as may indemnify his losses, and properly reward his zeal. This person is now is Paris, and asks whatever return is intended for him. Being in immediate want of money, he has been furnished with ten guineas. He expressed, desires of some appointment either for himself or son at Lisbon, but has been told that none such are in our gift, and that nothing more could be done for him in that line, than to mention to Congress that his services will merit their recollection, if they should make any appointment there analogous to his talents. He says his expenses in the relief of our prisoners have been upwards of fifty moidores. Supposing that, as he is poor, a pecuniary gratification will be most useful to him, we propose, in addition to what he has received, to give him a hundred and fifty guineas, or perhaps four thousand livres, and to write a joint letter to him expressing the sense Congress entertain of his services. We pray you to give us your sentiments on this subject by return of the first post, as he is waiting here, and we wish the aid of your counsels therein.
We are to acknowledge the receipt of your letter of June 3rd, informing us of your reception at the court of London.
I am, with sentiments of great respect and esteem, Dear Sir,
your friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO THE GOVERNOR OF VIRGINIA.
Paris,
June 16, 1785.
Sir,
I had the honor of receiving, the day before yesterday, the resolution of Council, of March the 10th, and your letter of March the 30th, and shall, with great pleasure, unite my endeavors with those of the Marquis de la Fayette and Mr. Barclay, for the purpose of procuring the arms desired. Nothing can be more wise than this determination to arm our people, as it is impossible to say when our neighbors may think proper to give them exercise. I suppose that the establishing a manufacture of arms, to go hand in hand with the purchase of them from hence, is at present opposed by good reasons. This alone would make us independent for an article essential to our preservation; and workmen could probably be either got here, or drawn from England, to be embarked hence.
In a letter of January the 12th, to Governor Harrison, I informed him of the necessity that the statuary should see General Washington; that we should accordingly send him over unless the Executive disapproved of it, in which case I prayed to receive their pleasure. Mr. Houdon being new re-established in his health, and no countermand received, I hope this measure met the approbation of the Executive: Mr. Houdon will therefore go over with Dr. Franklin, some time in the next month.
I have the honor of enclosing you the substance of propositions which have been made from London to the Farmers General of this country, to furnish them with the tobacco of Virginia and Maryland, which propositions were procured for me by the Marquis de la Fayette. I take the liberty of troubling you with them, on a supposition that it may be possible to have this article furnished from those two States to this country, immediately, without its passing through the entrepot of London, and the returns for it being made, of course, in London merchandise. Twenty thousand hogsheads of tobacco a year, delivered here in exchange for the produce and manufactures of this country, many of which are as good, some better, and most of them cheaper than in England, would establish a rivalship for our commerce, which would have happy effects in all the three countries. Whether this end will be best effected by giving out these propositions to our merchants, and exciting them to become candidates with the Farmers General for this contract, or by any other means, your Excellency will best judge on the spot.
I have the honor to be, with sentiments of due respect, your Excellency’s most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
P.S. I have written on the last subject to the Governor of Maryland also.
TO COLONEL MONROE.
Paris, June 17, 1785.
Dear Sir,
I received three days ago your favor of April the 12th. You therein speak of a former letter to me, but it has not come to hand, nor any other of later date than the 14th of December. My last to you was of the 11th of May, by Mr. Adams, who went in the packet of that month. These conveyances are now becoming deranged. We have had expectations of their coming to Havre, which would infinitely facilitate the communication between Paris and Congress; but their deliberations on the subject seem to be taking another turn. They complain of the expense, and that their commerce with us is too small to justify it. They therefore talk of sending a packet every six weeks only. The present one, therefore, which should have sailed about this time, will not sail till the 1st of July. However, the whole matter is as yet undecided. I have hopes that when Mr. St. John arrives from New York, he will get them replaced on their monthly system. By the bye, what is the meaning of a very angry resolution of Congress on his subject? I have it not by me, and therefore cannot cite it by date, but you will remember it, and oblige me by explaining its foundation. This will be handed you by Mr. Otto, who comes to America as Charge, des Affaires, in the room of Mr. Marbois, promoted to the Intendancy of Hispaniola, which office is next to that of Governor. He becomes the head of the civil, as the Governor is of the military department.
I am much pleased with Otto’s appointment; he is good-humored, affectionate to America, will see things in a friendly light when they admit of it, in a rational one always, and will not pique himself on writing every trifling circumstance of irritation to his court. I wish you to be acquainted with him, as a friendly intercourse between individuals who do business together, produces a mutual spirit of accommodation useful to both parties. It is very much our interest to keep up the affection of this country for us, which is considerable. A court has no affections; but those of the people whom they govern, influence their decisions even in the most arbitrary governments.
The negotiations between the Emperor and Dutch are spun out to an amazing length. At present there is no apprehension but that they will terminate in peace. This court seems to press it with ardor, and the Dutch are averse, considering the terms cruel and unjust, as they evidently are. The present delays, therefore, are imputed to their coldness and to their forms. In the mean time, the Turk is delaying the demarcation of limits between him and the Emperor, is making the most vigorous preparations for war, and has composed his ministry of warlike characters, deemed personally hostile, to the Emperor. Thus time seems to be spinning out, both by the Dutch and Turks, and time is wanting for France. Every year’s delay is a great thing for her. It is not impossible, therefore, but that she may secretly encourage the delays of the Dutch, and hasten the preparations of the Porte, while she is recovering vigor herself also, in order to be able to present such a combination to the Emperor as may dictate to him to be quiet. But the designs of these courts are unsearchable. It is our interest to pray that this country may have no continental war, till our peace with England is perfectly settled. The. merchants of this country continue as loud and furious as ever against the Arrêt of August, 1784, permitting our commerce with their islands to a certain degree. Many of them have actually abandoned their trade. The ministry are disposed to be firm; but there is a point at which they will give way: that is, if the clamors should become such as to endanger their places. It is evident that nothing can be done by us, at this time, if we may hope it hereafter. I like your removal to New York, and hope Congress will continue there, and never execute the idea of building their Federal town. Before it could be finished, a change of members in Congress, or the admission of new States, would remove them some where else. It is evident that when a sufficient number of the western states come in, they will remove it to Georgetown. In the mean time, it is our interest that it should remain where it is, and give no new pretensions to any other place. I am also much pleased with the proposition to the States to invest Congress with the regulation of their trade, reserving its revenue to the States. I think it a happy idea, removing the only objection which could have been justly made to the proposition. The time too is the present, before the admission of the western States. I am very differently affected towards the new plan of opening our land office, by dividing the lands among the States, and selling them at vendue. It separates still more the interests of the States, which ought to be made joint in every possible instance, in order to cultivate the idea of our being one nation, and to multiply the instances in which the people should look up to Congress as their head. And when the States get their portions they will either fool them away, or make a job of it to serve individuals. Proofs of both these practices have been furnished, and by either of them that invaluable fund is lost, which ought to pay our public debt. To sell them at vendue, is to give them to the bidders of the day, be they many or few. It is ripping up the hen which lays golden eggs. If sold in lots at a fixed price, as first proposed, the best lots will be sold first; as these become occupied, it gives a value to the interjacent ones, and raises them, though of inferior quality, to the price of the first. I send you by Mr. Otto, a copy of my book. Be so good as to apologize to Mr. Thomson for my not sending him one by this conveyance. I could not burthen Mr. Otto with more, on so long a road as that from here to L’Orient. I will send him one by a Mr. Williams, who will go ere long. I have taken measures to prevent its publication. My reason is, that I fear the terms in which I speak of slavery, and of our constitution, may produce an irritation which will revolt the minds of our countrymen against reformation in these two articles, and thus do more harm than good. I have asked of Mr. Madison to sound this matter as far as he can, and if he thinks it will not produce that effect, I have then copies enough printed to give one to each of the young men at the College, and to my friends in the country.
I am sorry to see a possibility of * * being put into the Treasury. He has no talents for the office, and what he has, will be employed in rummaging old accounts to involve you in eternal war with * *, and he will, in a short time, introduce such dissensions into the commission, as to break it up. If he goes on the other appointment to Kaskaskia, he will produce a revolt of that settlement from the United States. I thank you for your attention to my outfit. For the articles of household furniture, clothes, and a carriage, I have already paid twenty-eight thousand livres, and have still more to pay. For the greatest part of this, I have been obliged to anticipate my salary, from which, however, I shall never be able to repay it. I find, that by a rigid economy, bordering however on meanness, I can save perhaps, five hundred livres a month, at least in the summer. The residue goes for expenses so much of course and of necessity, that I cannot avoid them without abandoning all respect to my public character. Yet I will pray you to touch this string, which I know to be a tender one with Congress, with the utmost delicacy. I had rather be ruined in my fortune, than in their esteem. If they allow me half a year’s salary as an outfit, I can get through my debts in time. If they raise the salary to what it was, or even pay our house rent and taxes, I can live with more decency. I trust that Mr. Adams’s house at the Hague, and Dr. Franklin’s at Passy,—the rent of which has been always allowed him, will give just expectations of the same allowance to me. Mr. Jay, however, did not charge it, but he lived economically and laid up money.
I will take the liberty of hazarding to you some thoughts on the policy of entering into treaties with the European nations, and the nature of them. I am not wedded to these ideas, and, therefore, shall relinquish them cheerfully when Congress shall adopt others, and zealously endeavor to carry theirs into effect. First, as to the policy of making treaties. Congress, by the Confederation, have no original and inherent power over the commerce of the States. But by the 9th article, they are authorized to enter into treaties of commerce. The moment these treaties are concluded, the jurisdiction of Congress over the commerce of the States, springs into existence, and that of the particular States is superseded so far as the articles of the treaty may have taken up the subject. There are two restrictions only, on the exercise of the power of treaty by Congress. 1st. That they shall not, by such treaty, restrain the legislatures of the States from imposing such duties on foreigners, as their own people are subject to: nor 2ndly, from prohibiting the exportation or importation of any particular species of goods. Leaving these two points free, Congress may, by treaty, establish any system of commerce they please; but, as I before observed, it is by treaty alone they can do it. Though they may exercise their other powers by resolution or ordinance, those over commerce can only be exercised by forming a treaty, and this, probably, by an accidental wording of our Confederation. If, therefore, it is better for the States that Congress should regulate their commerce, it is proper that they should form treaties with all nations with whom we may possibly trade. You see that my primary object in the formation of treaties, is to take the commerce of the States out of the hands of the States, and to place it under the superintendence of Congress, so far as the imperfect provisions of our constitution will admit, and until the States shall, by new compact, make them more perfect. I would say then to every nation on earth, by treaty, your people shall trade freely with us, and ours with you, paying no more than the most favored nation in order to put an end to the right of individual States, acting by fits and starts, to interrupt our commerce or to embroil us with any nation. As to the terms of these treaties, the question becomes more difficult. I will mention three different plans. 1. That no duties shall be laid by either party on the productions of the other. 2. That each may be permitted to equalize their duties to those laid by the other. 3. That each shall pay in the ports of the other, such duties only as the most favored nations pay.
1. Were the nations of Europe as free and unembarrassed of established systems as we are, I do verily believe they would concur with us in the first plan. But it is impossible. These establishments are fixed upon them; they are interwoven with the body of their laws and the organization of their government, and they make a great part of their revenue; they cannot then get rid of them.
2. The plan of equal imposts presents difficulties insurmountable. For how are the equal imposts to be effected? Is it by laying in the ports of A, an equal per cent, on the goods of B, with that which B has laid in his ports on the goods of A? But how are we to find what is that per cent.? For this is not the usual form of imposts. They generally pay by the-ton, by the measure, by the weight, and not by the value. Besides, if A sends a million’s worth of goods to B, and takes back but the half of that, and each pays the same per cent., it is evident that A pays the double of what he recovers in the same way from B: this would be our case with Spain. Shall we endeavor to effect equality, then, by saying A may levy so much on the sum of B’s importations into his ports, as B does on the sum of A’s importations into the ports of B.? But how find out that sum? Will either party lay open their custom-house books candidly to evince this sum? Does either keep their books so exactly as to be able to do it? This proposition was started in Congress when our instructions were formed, as you may remember, and the impossibility of executing it occasioned it to be disapproved. Besides, who should have a right of deciding when the imposts were equal. A would say to B, My imposts do not raise so much as yours; I raise them therefore. B would then say, You have made them greater than mine, I will raise mine; and thus a kind of auction would be carried on between them, and a mutual irritation, which would end in any thing, sooner than equality and right.
3. I confess then to you, that I see no alternative left but that which Congress adopted, of each party placing the other on the footing of the most favored nation. If the nations of Europe, from their actual establishments, are not at liberty to say to America, that she shall trade in their ports duty free, they may say she may trade there paying no higher duties than the most favored nation; and this is valuable in many of these countries, where a very great difference is made between different nations. There is no difficulty in the execution of this contract, because there is not a merchant who does not know, or may not know, the duty paid by every nation on every article. This stipulation leaves each party at liberty to regulate their own commerce by general rules, while it secures the other from partial and oppressive discriminations. The difficulty which arises in our case is with the nations having American territory. Access to the West Indies is indispensably necessary to us. Yet how to gain it when it is the established system of these nations to exclude all foreigners from their colonies? The only chance seems to be this: our commerce to the mother countries is valuable to them. We must indeavor, then, to make this the price of an admission into their West Indies, and to those who refuse the admission, we must refuse our commerce, or load theirs by odious discriminations in our ports. We have this circumstance in our favor too, that what one grants us in their islands, the others will not find it worth their while to refuse. The misfortune is, that with this country we gave this price for their aid in the war, and we have now nothing more to offer. She being withdrawn from the competition, leaves Great Britain much more at liberty to hold out against us. This is the difficult part of the business of treaty, and I own it does not hold out the most flattering prospects.
I wish you would consider this subject, and write me your thoughts on it. Mr. Gerry wrote me on the same subject. Will you give me leave to impose on you the trouble of communicating this to him? It is long, and will save me much labor in copying. I hope he will be so indulgent as to consider it as an answer to that part of his letter, and will give me his further thoughts on it. Shall I send you so much of the Encyclopédie as is already published, or reserve it here till you come? It is about forty volumes which is probably about half the work. Give yourself no uneasiness about the money; perhaps I may find it convenient to ask you to pay trifles occasionally for me in America. I sincerely wish you may find it convenient to come here; the pleasure of the trip will be less than you expect, but the utility greater. It will make you adore your own country, its soil, its climate, its equality, liberty, laws, people, and manners. My God! how little do my countrymen know what precious blessings they are in possession of, and which no other people on earth enjoy. I confess I had no idea of it myself. While we shall see multiplied instances of Europeans going to live in America, I will venture to say no man now living, will ever see an instance of an American removing to settle in Europe, and continuing there. Come then and see the proofs of this, and on your return add your testimony to that of every thinking American, in order to satisfy our countrymen how much it is their interest to preserve, uninfected by contagion, those peculiarities in their governments and manners, to which they are indebted for those blessings. Adieu, my dear friend; present me affectionately to your colleagues. If any of them think me worth writing to, they may be assured that in the epistolary account I will keep the debit side against them. Once more, adieu.
Yours affectionately,
Th: Jefferson.
P.S. June 19. Since writing the above we have received the following account: Monsieur Pilatre de Roziere, who had been waiting for some months at Boulogne for a fair wind to cross the channel, at length took his ascent with a companion. The wind changed after a while, and brought him back on the French coast. Being at a height of about six thousand feet, some accident happened to his balloon of inflammable air; it burst, they fell from that height, and were crushed to atoms. There was a montgolfier combined with the balloon of inflammable air. It is suspected the heat of the montgolfier rarefied too much the inflammable air of the other, and occasioned it to burst. The montgolfier came down in good order.
TO CHARLES THOMSON.
Paris, June 21, 1785.
Dear Sir,
Your favor of March the 6th has come duly to hand. You therein acknowledge the receipt of mine of November the 11th; at that time you could not have received my last, of February the 8th. At present there is so little new in politics, literature, or the arts, that I write rather to prove to you my desire of nourishing your correspondence than of being able to give you any thing interesting at this time. The political world is almost lulled to sleep by the lethargic state of the Dutch negotiation, which will probably end in peace. Nor does this court profess to apprehend, that the Emperor will involve this hemisphere in war by his schemes on Bavaria and Turkey. The arts, instead of advancing, have lately received a check, which will probably render stationary for a while, that branch of them which had promised to elevate us to the skies. Pilatre de Roziere, who had first ventured into that region, has fallen a sacrifice to it. In an attempt to pass from Boulogne over to England, a change in the wind having brought him back on the coast of France, some accident happened to his balloon of inflammable air, which occasioned it to burst, and that of rarefied air combined with it being then unequal to the weight, they fell to the earth from a height, which the first reports made six thousand feet, but later ones have reduced to sixteen hundred. Pilatre de Roziere was dead when a peasant, distant one hundred yards only, run to him; but Romain, his companion, lived about ten minutes, though speechless, and without his senses. In literature there is nothing new. For I do not consider as having added any thing to that field, my own Notes, of which I have had a few copies printed. I will send you a copy by the first safe conveyance. Having troubled Mr. Otto with one for Colonel Monroe, I could not charge him with one for you. Pray ask the favor of Colonel Monroe, in page 5, line 17, to strike out the words ‘above the mouth of Appamatox,’ which make nonsense of the passage; and I forgot to correct it before I had enclosed and sent off the copy to him. I am desirous of preventing the reprinting this, should any book-merchant think it worth it, till I hear from my friends, whether the terms in which I have spoken of slavery and the constitution of our State, will not, by producing an irritation, retard that reformation which I wish, instead of promoting it. Dr. Franklin proposes to sail for America about the first or second week of July. He does not yet know, however, by what conveyance he can go. Unable to travel by land, he must descend the Seine in a boat to Havre. He has sent to England to get some vessel bound for Philadelphia, to touch at Havre for him. But he receives information that this cannot be done. He has been on the lookout ever since he received his permission to return; but, as yet, no possible means of getting a passage have offered, and I fear it is very uncertain when any will offer. I am with very great esteem, Dear Sir,
your friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO WILLIAM CARMICHAEL.
Paris, June 22, 1785.
Sir,
Your letter of April the 4th came to my hands on the 16th of that month, and was acknowledged by mine of May the 3rd. That which you did me the honor to write me on the 5th of April, never came to hand until the 19th of May, upwards of a month after the one of the day before. I have hopes of sending the present by a Mr. Jarvis, who went from hence to Holland some time ago. About this date, I suppose him to be at Brussels, and that from thence he will inform me, whether, in his way to Madrid, he will pass by this place. If he does, this shall be accompanied by a cipher for our future use; if he does not, I must still await a safe opportunity. Mr. Jarvis is a citizen of the United States from New-York, a gentleman of intelligence, in the mercantile line, from whom you will be able to get considerable information of American affairs. I think he left America in January. He informed us that Congress were about to appoint a Mr. Lambe, of Connecticut, their consul to Morocco, and to send him to their ministers, commissioned to treat with the Barbary powers, for instructions. Since that, Mr. Jay enclosed to Mr. Adams, in London, a resolution of Congress deciding definitively on amicable treaties with the Barbary States, in the usual way, and informing him that he had sent a letter and instructions to us, by Mr. Lambe. Though it is near three weeks since we received a communication of this from Mr. Adams, yet we hear nothing further of Mr. Lambe. Our powers of treating with the Barbary States are full, but in the amount of the expense we are limited. I believe you may safely assure them, that they will soon receive propositions from us, if you find such an assurance necessary to keep them quiet. Turning at this instant to your letter dated April 5th, and considering it attentively, I am persuaded it must have been written on the 5th of May: of this little mistake I ought to have been sooner sensible. Our latest letters from America are of the middle of April, and are extremely barren of news. Congress had not yet proposed a time for their recess, though it was thought a recess would take place. Mr. Morris had retired, and the treasury was actually administered by commissioners. Their land-office was not yet opened. The settlements at Kaskaskia, within the territory ceded to them by Virginia, had prayed the establishment of a regular government, and they were about sending a commissioner to them. General Knox was appointed their secretary of the war-office. These, I think, are the only facts we have learned which are worth communicating to you. The inhabitants of Canada have sent a sensible petition to their King, praying the establishment of an Assembly, the benefits of the habeas corpus laws, and other privileges of British subjects. The establishment of an Assembly is denied, but most of their other desires granted. We are now in hourly expectation of the arrival of the packet which should have sailed from New York in May. Perhaps that may bring us matter which may furnish the subject of a more interesting letter.
In the mean time, I have the honor to be, with the highest respect, Sir,
your most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
P.S. July 14. I have thus long waited, day after day, hoping to hear from Mr. Jarvis, that I might send a cipher with this: but now give up the hope. No news yet of Mr. Lambe. The packet has arrived, but brings no intelligence, except that it is doubtful whether Congress will adjourn this summer. The Assembly of Pennsylvania propose to suppress their bank on principles of policy. T.J.
TO JOHN ADAMS.
Paris, June 23, 1785.
Dear Sir,
My last to you was of the 2nd instant, since which I have received yours of the 3rd and 7th. I informed you in mine of the substance of our letter to Baron Thulemeyer: last night came to hand his acknowledgment of the receipt of it. He accedes to the method proposed for signing, and has forwarded our despatch to the King. I enclose you a copy of our letter to Mr. Jay, to go by the packet of this month. It contains a statement of our proceedings since the preceding letter, which you had signed with us. This statement contains nothing but what you had concurred with us in; and, as Dr. Franklin expects to go early in July to America, it is probable that the future letters must be written by you and myself. I shall therefore take care that you be furnished with copies of every thing which comes to hand on the joint business.
What is become of this Mr. Lambe? I am uneasy at the delay of that business, since we know the ultimate decision of Congress. Dr. Franklin, having a copy of the Corps Diplomatique, has promised to prepare a draught of a treaty to be offered to the Barbary States: as soon as he has done so, we will send it to you for your corrections. We think it will be best to have it in readiness against the arrival of Mr. Lambe, on the supposition that he may be addressed to the joint ministers for instructions.
I asked the favor of you in my last, to choose two of the best London papers for me; one of each party. The Duke of Dorset has given me leave to have them put under his address, and sent to the office from which his despatches come. I think he called it Cleveland office, or Cleveland lane, or by some such name; however, I suppose it can easily be known there. Will Mr. Stockdale undertake to have these papers sent regularly, or is this out of the line of his business? Pray order me also any really good pamphlets that come out from time to time, which he will charge to me.
I am, with great esteem, dear Sir,
your friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO COLONEL MONROE.
Paris, July 5, 1785.
Dear Sir,
I wrote you, by Mr. Adams, May the 11th, and by Mr. Otto, June the 17th. The latter acknowledged the receipt of yours of April the 12th, which is the only one come to hand of later date than December the 14th. Little has occurred since my last. Peace seems to show herself under a more decided form. The Emperor is now on a journey to Italy, and the two Dutch Plenipotentiaries have set out for Vienna; there to make an apology for their State having dared to fire a gun in defence of her invaded rights: this is insisted on as a preliminary condition. The Emperor seems to prefer the glory of terror to that of justice; and, to satisfy this tinsel passion, plants a dagger in the heart of every Dutchman which no time will extract. I inquired lately of a gentleman who lived long at Constantinople, in a public character, and enjoyed the confidence of that government, insomuch, as to become well acquainted with its spirit and its powers, what he thought might be the issue of the present affair between the Emperor and the Porte. He thinks the latter will not push matters to a war; and, if they do, they must fail under it. They have lost their warlike spirit, and their troops cannot be induced to adopt the European arms. We have no news yet of Mr. Lambe; of course our Barbary proceedings are still at a stand.*
[* The remainder of this letter is in cipher, to which there is no key in the Editor’s possession.]
Yours affectionately,
Th: Jefferson
TO MRS. SPROWLE.
Paris, July 5,1785.
Madam,
Your letter of the 21st of June, has come safely to hand. That which you had done me the honor of writing before, has not yet been received. It having gone by Dr. Witherspoon to America, which I had left before his return to it, the delay is easily accounted for.
I wish you may be rightly informed that the property of Mr. Sprowle is yet unsold. It was advertised so long ago, as to found a presumption that the sale has taken place. In any event, you may safely go to Virginia. It is in the London newspapers only, that exist those mobs and riots, which are fabricated to deter strangers from going to America. Your person will be sacredly safe, and free from insult. You can best judge from the character and qualities of your son, whether he may be an useful co-adjutor to you there. I suppose him to have taken side with the British, before our Declaration of Independence; and, if this was the case, I respect the candor of the measure, though I do not its wisdom. A right to take the side which every man’s conscience approves in a civil contest, is too precious a right, and too favorable to the preservation of liberty, not to be protected by all its well informed friends. The Assembly of Virginia have given sanction to this right in several of their laws, discriminating honorably those who took side against us before the Declaration of Independence, from those who remained among us, and strove to injure us by their treacheries. I sincerely wish that you, and every other to whom this distinction applies favorably, may find, in the Assembly of Virginia, the good effects of that justice and generosity, which have dictated to them this discrimination. It is a sentiment which will gain strength in their breasts, in proportion as they can forget the savage cruelties committed on them, and will, I hope, in the end, reduce them to restore the property itself, wherever it is unsold, and the price received for it, where it has been actually sold.
I am, Madam,
your very humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN ADAMS.
Paris, July 7, 1785.
Dear Sir,
This will accompany a joint letter enclosing the draft of a treaty? and my private letter of June 23rd, which has waited so long for a private conveyance. We daily expect from the Baron Thulemeyer the French column for our treaty with his sovereign. In the mean while, two copies are preparing with the English column, which Dr. Franklin wishes to sign before his departure, which will be within four or five days. The French, when received, will be inserted in the blank columns of each copy. As the measure of signing at separate times and places is new, we think it necessary to omit no other circumstance of ceremony which can be observed. That of sending it by a person of confidence, and invested with a character relative to the object, who shall attest our signature, yours in London, and Baron Thulemeyer’s at the Hague, and who shall make the actual exchanges, we think will contribute to supply the departure from the original form, in other instances. For this reason, we have agreed to send Mr. Short on this business, to make him a secretary pro hac vice, and to join Mr. Dumas for the operations of exchange, &c. As Dr. Franklin will have left us before Mr. Short’s mission will commence, and I have never been concerned in the ceremonials of a treaty, I will thank you for your immediate information as to the papers he should be furnished with from hence. He will repair first to you in London, thence to the Hague, and then return to Paris.
What has become of Mr. Lambe? Supposing he was to call on the commissioners for instructions, and thinking it best these should be in readiness, Dr. Franklin undertook to consult well the Barbary treaties with other nations, and to prepare a sketch which we should have sent for your correction. He tells me he has consulted those treaties, and made references to the articles proper for us, which, however, he will not have time to put into form, but will leave them with me to reduce. As soon as I see them, you shall hear from me. A late conversation with an English gentleman here, makes me believe, what I did not believe before; that his nation thinks seriously that Congress have no power to form a treaty of commerce. As the explanations of this matter, which you and I may separately give, may be handed to their minister, it would be well that they should agree. For this reason, as well as for the hope of your showing me wherein I am wrong, and confirming me where I am right, I will give you my creed on the subject. It is contained in these four principles. By the Confederation, Congress have no power given them, in the first instance, over the commerce of the States. But they have a power given them of entering into treaties of commerce, and these treaties may cover the whole field of commerce, with two restrictions only. 1. That the States may impose equal duties on foreigners as natives: and 2. That they may prohibit the exportation or importation of any species of goods whatsoever. When they shall have entered into such treaty, the superintendence of it results to them; all the operations of commerce, which are protected by its stipulations, come under their jurisdiction, and the power of the States to thwart them by their separate acts, ceases. If Great Britain asks, then, why she should enter into treaty with us? why not carry on her commerce without treaty? I answer; because till a treaty is made, no consul of hers can be received (his functions being called into existence by a convention only, and the States having abandoned the right of separate agreements and treaties); no protection to her commerce can be given by Congress; no cover to it from those checks and discouragements, with which the States will oppress it, acting separately, and by fits and starts. That they will act so till a treaty is made, Great Britain has had several proofs; and I am convinced those proofs will become general. It is then to put her commerce with us on systematical ground, and under safe cover, that it behoves Great Britain to enter into treaty. And I own to you, that my wish to enter into treaties with the other powers of Europe, arises more from a desire of bringing all our commerce under the jurisdiction of Congress, than from any other views. Because, according to my idea, the commerce of the United States with those countries not under treaty with us, is under the jurisdiction of each State separately; but that of the countries which have treated with us, is under the jurisdiction of Congress, with the two fundamental restraints only, which I have before noted.
I shall be happy to receive your corrections of these ideas, as I have found, in the course of our joint services, that I think right when I think with you.
I am, with sincere affection, Dear Sir,
your friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
P.S. Monsieur Houdon has agreed to go to America to take the figure of General Washington. In the case of his death, between his departure from Paris and his return to it, we may lose twenty thousand livres. I ask the favor of you to inquire what it will cost to ensure that sum on his life, in London, and to give me as early an answer as possible, that I may order the ensurance, if I think the terms easy enough. He is, I believe, between thirty and thirty-five years of age, healthy enough, and will be absent about six months. T.J.
TO GENERAL WASHINGTON.
Paris, July 10, 1785.
Dear Sir,
Mr. Houdon would much sooner have had the honor of attending you, but for a spell of sickness, which long induced us to despair of his recovery, and from which he is but recently recovered. He comes now, for the purpose of lending the aid of his art to transmit you to posterity. He is without rivalship in it, being employed from all parts of Europe in whatever is capital. He has had a difficulty to withdraw himself from an order of the Empress of Russia; a difficulty, however, that arose from a desire to show her respect, but which never gave him a moment’s hesitation about his present voyage, which he considers as promising the brightest chapter of his history. I have spoken of him as an artist only; but I can assure you also, that, as a man, he is disinterested, generous, candid, and panting after glory: in every circumstance meriting your good opinion. He will have need to see you much while he shall have the honor of being with you; which you can the more freely admit, as his eminence and merit give him admission into genteel societies here. He will need an interpreter. I suppose you could procure some person from Alexandria, who might be agreeable to yourself, to perform this office. He brings with him one or two subordinate workmen, who of course will associate with their own class only.
On receiving the favor of your letter of February the 25th, I communicated the plan for clearing the Potomac, with the act of Assembly, and an explanation of its probable advantages, to Mr. Grand, whose acquaintance and connection with the monied men here, enabled him best to try its success. He has done so; but to no end. I enclose you his letter. I am pleased to hear in the mean time, that the subscriptions are likely to be filled up at home. This is infinitely better, and will render the proceedings of the company much more harmonious. I place an immense importance to my own country, on this channel of connection with the new western States. I shall continue uneasy till I know that Virginia has assumed her ultimate boundary to the westward. The late example of the State of Franklin separating from North Carolina, increases my anxieties for Virginia.
The confidence you are so good as to place in me, on the subject of the interest lately given you by Virginia in the Potomac company, is very flattering to me. But it is distressing also, inasmuch as, to deserve it, it obliges me to give my whole opinion. My wishes to see you made perfectly easy, by receiving, those just returns of gratitude from our country to which you are entitled, would induce me to be contented with saying, what is a certain truth, that the world would be pleased with seeing them heaped on you, and would consider your receiving them as no derogation from your reputation. But I must own that the declining them will add to that reputation, as it will show that your motives have been pure and without any alloy. This testimony, however, is not wanting either to those who know you, or who do not. I must therefore repeat, that I think the receiving them will not, in the least, lessen the respect of the world, if from any circumstances they would be convenient to you. The candor of my communication will find its justification, I know, with you.
A tolerable certainty of peace leaves little interesting in the way of intelligence. Holland and the emperor will be quiet. If any thing is brewing, it is between the latter and the Porte. Nothing in prospect as yet from England. We shall bring them, however, to a decision, now that Mr. Adams is received there. I wish much to hear that the canal through the Dismal Swamp is resumed.
I have the honor to be, with the highest respect and esteem,
Dear Sir, your most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO THE GOVERNOR OF VIRGINIA.
Paris, July 11, 1785.
Sir,
Mr. Houdon’s long and desperate illness has retarded, till now, his departure for Virginia. We had hoped, from our first conversations with him, that it would be easy to make our terms, and that the cost of the statue and expense of sending him, would be but about a thousand guineas. But when we came to settle this precisely, he thought himself obliged to ask vastly more insomuch, that, at one moment, we thought our treaty at an end. But unwilling to commit such a work to an inferior hand, we made nim an ultimate proposition on our part. He was as much mortified at the prospect of not being the executor of such a work, as we were, not to have it done by such a hand. He therefore acceded to our terms; though we are satisfied he will be a considerable loser. We were led to insist on them, because, in a former letter to the Governor, I had given the hope we entertained of bringing the whole within one thousand guineas. The terms are twenty-five thousand livres, or one thousand English guineas (the English guinea being worth twenty-five livres) for the statue and pedestal. Besides this, we pay his expenses going and returning, which we expect will be between four and five thousand livres: and if he dies on the voyage, we pay his family ten thousand livres. This latter proposition was disagreeable to us; but he has a father, mother, and sisters, who have no resource but in his labor: and he is himself one of the best men in the world. He therefore made it a sine qua non, without which all would have been off. We have reconciled it to ourselves, by determining to get insurance on his life made in London, which we expect can be done for five per cent.; so that it becomes an additional sum of five hundred livres. I have written to Mr. Adams to know, for what per cent, the insurance can be had. I enclose you, for a more particular detail, a copy of the agreement. Dr. Franklin, being on his departure, did not become a party to the instrument, though it has been concluded with his approbation. He was disposed to give two hundred and fifty guineas more, which would have split the difference between the actual terms and Mr Houdon’s demand. I wish the State, at the conclusion of the work, may agree to give him this much more; because I am persuaded he will be a loser, which I am sure their generosity would not wish. But I have not given him the smallest expectation of it, choosing the proposition should come from the State, which will be more honorable. You will perceive by the agreement, that I pay him immediately 8333 1/3 livres, which is to be employed in getting the marble in Italy, its transportation, he. The package and transportation of his stucco to make the moulds, will be about five hundred livres. I shall furnish him with money for his expenses in France, and I have authorized Dr. Franklin, when he arrives in Philadelphia, to draw on me for money for his other expenses, going, staying, and returning. These drafts will have been made probably, and will be on their way to me, before you receive this, and with the payments made here, will amount to about five thousand livres more than the amount of the bill remitted me. Another third, of 8333 1/3 livres, will become due at the end of the ensuing year.
Dr. Franklin leaves Passy this morning. As he travels in a litter, Mr. Houdon will follow him some days hence, and will embark with him for Philadelphia. I am in hopes he need not stay in America more than a month.
I have the honor to be, with due respect,
your Excellency’s most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.

TO THE PRESIDENT OF CONGRESS.
(Private.) Paris, July 12, 1785.
Dear Sir,
I was honored, two days ago, with yours of May the 16th, and thank you for the intelligence it contained, much of which was new to me. It was the only letter I received by this packet, except one from Mr. Hopkinson, on philosophical subjects. I generally write about a dozen by every packet, and receive sometimes one, sometimes two, and sometimes ne’er a one. You are right in supposing all letters opened which come either through the French or English channel, unless trusted to a passenger. Yours had evidently been opened, and I think I never received one through the post office which had not been. It is generally discoverable by the smokiness of the wax, and faintness of the re-impression. Once they sent me a letter open, having forgotten to re-seal it. I should be happy to hear that Congress thought of establishing packets of their own between New York and Havre; to send a packet from each port once in two months. The business might possibly be done by two packets, as will be seen by the following scheme, wherein we will call the two packets A and B.
January, A sails from New York, B from Havre. February. March. B sails from New York, A from Havre. April. May. A sails from New York, B from Havre. June. July. B sails from New York, A from Havre. August. September. A sails from New York, B from Havre. October. November. B sails from New York, A from Havre. December.
I am persuaded that government would gladly arrange this method with us, and send their packets in the intermediate months, as they are tired of the expense. We should then have a safe conveyance every two months, and one for common matters every month. A courier would pass between this and Havre in twenty-four hours. Could not the surplus of the post office revenue be applied to this? This establishment would look like the commencement of a little navy; the only kind of force we ought to possess. You mention that Congress is on the subject of requisition. No subject is more interesting to the honor of the States. It is an opinion which prevails much in Europe, that our government wants authority to draw money from the States, and that the States want faith to pay their debts. I shall wish much to hear how far the requisitions on the States are productive of actual cash. Mr. Grand informed me, the other day, that the commissioners were dissatisfied with his having paid to this country but two hundred thousand livres, of the four hundred thousand for which Mr. Adams drew on Holland; reserving the residue to replace his advances and furnish current expenses. They observed that these last objects might have been effected by the residue of the money in Holland, which was lying dead. Mr. Grand’s observation to me was, that Mr. Adams did not like to draw for these purposes, that he himself had no authority, and that the commissioners had not accompanied their complaints with any draft on that fund; so that the debt still remains unpaid, while the money is lying dead in Holland. He did not desire me to mention this circumstance; but should you see the commissioners, it might not be amiss to communicate it to them, that they may take any measures they please, if they think it proper to do any thing in it. I am anxious to hear what is done with the States of Vermont and Franklin. I think that the former is the only innovation on the system of April 23rd, 1784, which ought ever possibly to be admitted. If Congress are not firm on that head, our several States will crumble to atoms by the spirit of establishing every little canton into a separate State. I hope Virginia will concur in that plan as to her territory south of the Ohio; and not leave to the western country to withdraw themselves by force, and become our worst enemies instead of our best friends.
I have the honor to be, with sentiments of great respect,
your Excellency’s most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO THE VIRGINIA DELEGATES IN CONGRESS.
Paris, July 12,1785.
Gentlemen,
In consequence of the orders of the legislative and executive bodies of Virginia, I have engaged Monsieur Houdon to make the statue of General Washington. For this purpose it is necessary for him to see the General. He therefore goes with Doctor Franklin, and will have the honor of delivering you this himself. As his journey is at the expense of the State, according to our contract, I will pray you to favor him with your patronage and counsels, and to protect him as much as possible, from those impositions to which strangers are but too much exposed. I have advised him to proceed in the stages to the General’s. I have also agreed, if he can see Generals Greene and Gates, whose busts he has a desire to execute, that he may make a moderate deviation for this purpose, after he has done with General Washington.
But the most important object with him, is to be employed to make General Washington’s equestrian statue for Congress. Nothing but the expectation of this, could have engaged him to have undertaken this voyage; as the pedestrian statue for Virginia will not make it worth the business he loses by absenting himself. I was therefore obliged to assure him of my recommendations for this greater work. Having acted in this for the State, you will, I hope, think yourselves in some measure bound to patronize and urge his being employed by Congress. I would not have done this myself, nor asked you to do it, did I not see that it would be better for Congress to put this business into his hands, than into those of any other person living, for these reasons: 1. He is, without rivalship, the first statuary of this age; as a proof of which, he receives orders from every other country for things intended to be capital. 2. He will have seen General Washington, have taken his measures in every part, and, of course, whatever he does of him will have the merit of being original, from which other workmen can only furnish copies. 3. He is in possession of the house, the furnaces, and all the apparatus provided for making the statue of Louis XV. If any other workman be employed, this will all have to be provided anew, and of course, to be added to the price of the statue; for no man can ever expect to make two equestrian statues. The addition which this would be to the price, will much exceed the expectation of any person who has not seen that apparatus. In truth it is immense. As to the price of the work, it will be much greater than Congress is probably aware of. I have inquired somewhat into this circumstance, and find the prices of those made for two centuries past, have been from one hundred and twenty thousand guineas, down to sixteen thousand guineas, according to the size. And as far as I have seen, the smaller they are, the more agreeable. The smallest yet made, is infinitely above the size of life, and they all appear outrees and monstrous. That of Louis XV., is probably the best in the world, and it is the smallest here. Yet it is impossible to find a point of view, from which it does not appear a monster, unless you go so far as to lose sight of the features, and finer lineaments of the face and body. A statue is not made like a mountain, to be seen at a great distance. To perceive those minuter circumstances which constitute its beauty, you must be near it, and, in that case, it should be so little above the size of the life, as to appear actually of that size, from your point of view. I should not, therefore, fear to propose, that the one intended by Congress should be considerably smaller than any of those to be seen here; as I think it will be more beautiful, and also cheaper. I have troubled you with these observations, as they have been suggested to me from an actual sight of works of this kind, and I supposed they might assist you in making up your minds on this subject. In making a contract with Monsieur Houdon it would not be proper to advance money, but as his disbursements and labor advance. As it is a work of many years, this will render the expense insensible. The pedestrian statue of marble, is to take three years; the equestrian, of course, would take much more. Therefore the sooner it is begun, the better.
I am, with sentiments of the highest respect, Gentlemen,
your most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN JAY.
Paris, July 12,1785.
Sir,
My last letter to you was dated the 17th of June. The present serves to cover some papers put into my hands by Captain Paul Jones. They respect an ancient matter, which is shortly this.
While Captain Jones was hovering on the coast of England, in the year 1779, a British pilot, John Jackson by name, came on board him, supposing him to be British. Captain Jones found it convenient to detain him as a pilot, and, in the action with the Serapis, which ensued, this man lost his arm. It is thought that this gives him a just claim to the same allowance with others, who have met with the like misfortune in the service of the United States. Congress alone being competent to this application, it is my duty to present the case to their consideration; which I beg leave to do through you.
Dr. Franklin will be able to give you so perfect a state of all transactions relative to his particular office in France, as well as to the subjects included in our general commission, that it is unnecessary for me to enter on them. His departure, with the separate situation of Mr. Adams and myself, will render it difficult to communicate to you the future proceedings of the commission, as regularly as they have been heretofore. We shall do it, however, with all the punctuality practicable, either separately or jointly, as circumstances may require and admit.
I have the honor to be, with sentiments of the highest respect, Sir,
your most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
Paris, July 13, 1785.
Sir,
I am glad to hear that the Council have ordered restitution of the merchandise seized at L’Orient, contrary to the freedom of the place. When a court of justice has taken cognizance of a complaint, and has given restitution of the principal subject, if it refuses some of the accessories, we are to presume that some circumstance of evidence appeared to them, unknown to us, and which rendered its refusal just and proper. So, in the present case, if any circumstances in the conduct of the owner, or relative to the merchandise itself, gave probable grounds of suspicion that they were not entitled to the freedom of the port, damages for the detention might be properly denied. Respect for the integrity of courts of justice, and especially of so high a one as that of the King’s Council, obliges us to presume that circumstances arose which justified this part of their order. It is only in cases where justice is palpably denied, that one nation, or its ministers, are authorized to complain of the courts of another. I hope you will see, therefore, that an application from me as to the damages for detention, would be improper.
I have the honor to be, Sir,
your most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MESSRS. FRENCH AND NEPHEW.
Paris, July 13,1785.
Gentlemen,
I had the honor of receiving your letter of June the 21st, enclosing one from Mr. Alexander of June the 17th, and a copy of his application to Monsieur de Calonne. I am very sensible that no trade can be on a more desperate footing than that of tobacco, in this country; and that our merchants must abandon the French markets, if they are not permitted to sell the productions they bring, on such terms as will enable them to purchase reasonable returns in the manufactures of France. I know but one remedy to the evil; that of allowing a free vent: and I should be very happy in being instrumental to the obtaining this. But while the purchase of tobacco is monopolized by a company, and they pay for that monopoly a heavy price to the government, they doubtless are at liberty to fix such places and terms of purchase, as may enable them to make good their engagements with government. I see no more reason for obliging them to give a greater price for tobacco than they think they can afford, than to do the same between two individuals treating for a horse, a house, or any thing else. Could this be effected by applications to the minister, it would only be a palliative which would retard the ultimate cure, so much to be wished for and aimed at by every friend to this country, as well as to America.
I have the honor to be, Gentlemen,
your most obedient, humble servant,
Th: Jefferson
Sir,
Paris, July 17,1785.
I have long deferred doing myself the honor of writing to you, wishing for an opportunity to accompany my letter with a copy of the Bibliothèque Physico-oeconomique, a book published here lately in four small volumes, and which gives an account of all the improvements in the arts which have been made for some years past. I flatter myself you will find in it many things agreeable and useful. I accompany it with the volumes of the Connoissance des Terns for the years 1781, 1784, 1785, 1786, 1787. But why, you will ask, do I send you old almanacs, which are proverbially useless? Because, in these publications have appeared, from time to time, some of the most precious things in astronomy. I have searched out those particular volumes which might be valuable to you on this account. That of 1781 contains De la Caillie’s catalogue of fixed stars reduced to the commencement of that year, and a table of the aberrations and nutations of the principal stars. 1784 contains the same catalogue with the nébuleuses of Messier. 1785 contains the famous catalogue of Flamsteed, with the positions of the stars reduced to the beginning of the year 1784, and which supersedes the use of that immense book. 1786 gives you Euler’s lunar tables corrected; and 1787, the tables for the planet Herschel. The two last needed not an apology, as not being within the description of old almanacs. It is fixed on grounds which scarcely admit a doubt, that the planet Herschel was seen by Mayer in the year 1756, and was considered by him as one of the zodiacal stars, and, as such, arranged in his catalogue, being the 964th which he describes. This 964th of Mayer has been since missing, and the calculations for the planet Herschel show that, it should have been, at the time of Mayer’s observation, where he places his 964th star. The volume of 1787 gives you Mayer’s catalogue of the zodiacal stars. The researches of the natural philosophers of Europe seem mostly in the field of chemistry, and here, principally, on the subjects of air and fire. The analysis of these two subjects presents to us very new ideas. When speaking of the Bibliothèque Physico-oeconomique, T should have observed, that since its publication, a man in this city has invented a method of moving a vessel on the water, by a machine worked within the vessel. I went to see it. He did not know himself the principle of his own invention. It is a screw with a very broad, thin worm, or rather it is a thin plate with its edge applied spirally round an axis. This being turned, operates on the air, as a screw does, and may be literally said to screw the vessel along: the thinness of the medium, and its want of resistance, occasion a loss of much of the force. The screw, I think, would be more effectual, if placed below the surface of the water. I very much suspect that a countrymen of ours, Mr. Bushnel of Connecticut, is entitled to the merit of a prior discovery of this use of the screw. I remember to have heard of his submarine navigation during the war, and, from what Colonel Humphreys now tells me, I conjecture that the screw was the power he used. He joined to this a machine for exploding under water at a given moment. If it were not too great a liberty for a stranger to take, I would ask from him a narration of his actual experiments, with or without a communication of his principle, as he should choose. If he thought proper to communicate it, I would engage never to disclose it, unless I could find an opportunity of doing it for his benefit. I thank you for your information as to the greatest bones found on the Hudson river. I suspect that they must have been of the same animal with those found on the Ohio: and if so, they could not have belonged to any human figure, because they are accompanied with tusks of the size, form, and substance of those of the elephant. I have seen a part of the ivory, which was very good. The animal itself must have been much larger than an elephant. Mrs. Adams gives me an account of a flower found in Connecticut, which vegetates when suspended in the air. She brought one to Europe. What can be this flower? It would be a curious present to this continent.
The accommodation likely to take place between the Dutch and the Emperor, leaves us without that unfortunate resource for news, which wars give us. The Emperor has certainly had in view the Bavarian exchange of which you have heard; but so formidable an opposition presented itself, that he has thought proper to disavow it. The Turks show a disposition to go to war with him; but if this country can prevail on them to remain in peace, they will do so. It has been thought that the two Imperial courts have a plan of expelling the Turks from Europe. It is really a pity, so charming a country should remain in the hands of a people, whose religion forbids the admission of science and the arts among them. We should wish success to the object of the two empires, if they meant to leave the country in possession of the Greek inhabitants. We might then expect, once more, to see the language of Homer and Demosthenes a living language. For I am persuaded the modern Greek would easily get back to its classical models. But this is not intended. They only propose to put the Greeks under other masters; to substitute one set of barbarians for another.
Colonel Humphreys having satisfied you that all attempts would be fruitless here, to obtain money or other advantages for your college, I need add nothing on that head. It is a method of supporting colleges of which they have no idea, though they practise it for the support of their lazy monkish institutions.
I have the honor to be, with the highest respect and esteem, Sir,
your most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
Paris, July 28, 1785.
Dear Sir,
Your favors of Jury the 16th and 18th came to hand the same day on which I had received Baron Thulemeyer’s, enclosing the ultimate draught for the treaty. As this draught, which was in French, was to be copied into the two instruments which Dr. Franklin had signed, it is finished this day only. Mr. Short sets out immediately. I have put into his hands a letter of instructions how to conduct himself, which I have signed, leaving a space above for your signature. The two treaties I have signed at the left hand, Dr. Franklin having informed me that the signatures are read backwards. Besides the instructions to Mr. Short, I signed also a letter to. Mr. Dumas, associating him with Mr. Short. These two letters I made out as nearly conformably as I could, to your ideas expressed in your letter of the 18th. If any thing more be necessary, be so good as to make a separate instruction for them, signed by yourself, to which I will accede. I have not directed Mr. Dumas’s letter. I have heretofore directed to him as ‘Agent for the United States at the Hague,’ that being the description under which the journals of Congress speak of him. In his last letter to me, is a paragraph, from which I conclude that the address I have used is not agreeable, and perhaps may be wrong. Will you be so good as to address the letter to him, and to inform me how to address him hereafter. Mr. Short carries also the other papers necessary. His equipment for his journey requiring expenses which cannot come into the account of ordinary expenses, such as clothes, &,c. what allowance should be made him? I have supposed somewhere between a guinea a day, and one thousand dollars a year, which I believe is the salary of a private secretary. This I mean as over and above his travelling expenses. Be so good as to say, and I will give him an order on his return. The danger of robbery has induced me to furnish him with only money enough to carry him to London. You will be so good as to procure him enough to carry him to the Hague and back to Paris. The confederation of the King of Prussia with some members of the Germanic body, for the preservation of their constitution, is, I think, beyond a doubt. The Emperor has certainly complained of it in formal communications at several courts. By what can be collected from diplomatic conversation here, I also conclude it tolerably certain, that the Elector of Hanover has been invited to accede to the confederation, and has done or is doing so. You will have better circumstances however, on the spot, to form a just judgment. Our matters with the first of these powers being now in conclusion, I wish it was so with the Elector of Hanover. I conclude, from the general expressions in your letter, that little may be expected. Mr. Short furnishing so safe a conveyance that the trouble of the cipher may me dispensed with, I will thank you for such details of what has passed, as may not be too troublesome to you.
The difficulties of getting books into Paris, delayed for some time my receipt of the Corps Diplomatique left by Dr. Franklin. Since that, we have been engaged with expediting Mr. Short. A huge packet also, brought by Mr. Mazzei, has added to the causes which have as yet prevented me from examining Dr. Franklin’s notes on the Barbary treaty. It shall be one of my first occupations. Still the possibility is too obvious that we may run counter to the instructions of Congress, of which Mr. Lambe is said to be the bearer. There is a great impatience in America for these treaties. I am much distressed between this impatience and the known will of Congress, on the one hand, and the uncertainty of the details committed to this tardy servant.
The Duke of Dorset sets out for London to-morrow. He says he shall be absent two months. There is some whisper that he will not return, and that, Lord Carmarthen wishes to come here. I am sorry to lose so honest a man as the Duke. I take the liberty to ask an answer about the insurance of Houdon’s life.
Congress is not likely to adjourn this summer. They have passed an ordinance for selling their lands. I have not received it.
What would you think of the enclosed draught to be proposed to the courts of London and Versailles? I would add Madrid and Lisbon, but that they are still more desperate than the others. I know it goes beyond our powers; and beyond the powers of Congress too; but it is so evidently for the good of all the States, that I should not be afraid to risk myself on it, if you are of the same opinion. Consider it, if you please, and give me your thoughts on it by Mr. Short: but I do not communicate it to him, nor any other mortal living but yourself.
Be pleased to present me in the most friendly terms to the ladies, and believe me to be, with great esteem,
Dear Sir, your friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO HOGENDORP.
Paris, July 29, 1785.
Dear Sir,
By an American gentleman who went to the Hague, about a month ago, I sent you a copy of my Notes on Virginia. Having since that received some copies of the revisal of our laws, of which you had desired one, I now send it to you. I congratulate you sincerely on the prospect of your country’s being freed from the menace of war, which, however just, is always expensive and calamitous, and sometimes unsuccessful.
Congress, having made a very considerable purchase of land from the Indians, have established a land office, and settled the mode of selling the lands. Their plan is judicious. I apprehend some inconveniences in some parts of it; but if such should be found to exist, they will amend them. They receive in payment their own certificates, at par with actual money. We have a proof the last year, that the failure of the States to bring money into the treasury, has proceeded, not from any unwillingness, but from the distresses of their situation. Heretofore, Massachusetts and Pennsylvania had brought in the most money, and Virginia was among the least. The last year, Virgjnia has paid in more than all the rest together. The reason is, that she is at liberty to avail herself of her natural resources and has free markets for them; whereas the others which, while they were sure of a sale for their commodities, brought more into the treasury; now, that that sale is, by circumstances, rendered more precarious, they bring in but little.
The impost is not yet granted. Rhode Island and New York hold off. Congress have it in contemplation to propose to the States, that the direction of all their commerce shall be committed to Congress, reserving to the States, respectively, the revenue which shall be laid on it. The operations of our good friends, the English, are calculated as precisely to bring the States into this measure as if we directed them ourselves, and as they were, through the whole war, to produce that union which was so necessary for us. I doubt whether Congress will adjourn this summer.
Should you be at the Hague, I will beg leave to make known to you bearer hereof, M, William Short. He of Virginia, has come to stay some time with me at Paris being among my most particular friends. Though young, his talents and merit are such as to have placed him in the Council of State of Virginia; an office which he relinquished to make a visit to Europe.
I have the honor to be, with very high esteem, Dear Sir,
your most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
Paris, July 30, 1785.
Gentlemen,
I received yesterday your favor of the 25th. Supposing that the funds, which are the object of your inquiry, are those which constitute what we call our domestic debt, it is my opinion that they are absolutely secure: I have no doubt at all but that they will be paid, with their interest at six per cent. But I cannot say that they are as secure and solid as the funds which constitute our foreign debt: because no man in America ever entertained a doubt that our foreign debt is to be paid fully; but some people in America have seriously contended, that the certificates and other evidences of our domestic debt, ought to be redeemed only at what they have cost the holder; for I must observe to you, that these certificates of domestic debt, having as yet no provision for the payment of principal or interest, and the original holders being mostly needy, have been sold at a very great discount. When I left America (July, 1784,) they sold in different States at from 15s. to 2s. 6d. in the pound; and any amount of them might, then have been purchased. Hence some thought that full justice would be done, if the public paid the purchasers of them what they actually paid for them, and interest on that. But this is very far from being a general opinion; a very great majority being firmly decided that they shall be paid fully. Were I the holder of any of them, I should not have the least fear of their full payment. There is also a difference between different species of certificates; some of them being receivable in taxes, others having the benefit of particular assurances, &c. Again, some of these certificates are for paper-money debts. A deception here must be guarded against. Congress ordered all such to be re-settled by the depreciation tables, and a new certificate to be given in exchange for them, expressing their value in real money. But all have not yet been re-settled. In short, this is a science in which few in America are expert, and no person in a foreign country can be so. Foreigners should therefore be sure that they are well advised, before they meddle with them, or they may suffer. If you will reflect with what degree of success persons actually in America could speculate in the European funds, which rise and fall daily, you may judge how far those in Europe may do it in the American funds, which are more variable from a variety of causes.
I am not at all acquainted with Mr. Daniel Parker, farther than having once seen him in Philadelphia. He is of Massachusetts, I believe, and I am of Virginia. His circumstances are utterly unknown to me. I think there are few men in America, if there is a single one, who could command a hundred thousand pounds’ sterling worth of these notes, at their real value. At their nominal amount, this might be done perhaps with twenty-five thousand pounds sterling, if the market price of them be as low as when I left America. I am with very great respect, Gentlemen,
your most obedient, humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN ADAMS.
Paris, July 31, 1785.
Dear Sir,
I was honored yesterday with yours of the 24th instant. When the first article of our instructions of May 7th, 1784, was under debate in Congress, it was proposed that neither party should make the other pay, in their ports, greater duties, than they paid in the ports of the other. One objection to this was, its impracticability; another, that it would put it out of our power to lay such duties on alien importation as might encourage importation by natives. Some members, much attached to English policy, thought such a distinction should actually be established. Some thought the power to do it should be reserved, in case any peculiar circumstances should call for it, though under the present, or perhaps, any probable circumstances, they did not think it would be good policy ever to exercise it. The footing gentis amicissimæ was therefore adopted, as you see in the instruction. As far as my inquiries enable me to judge, France and Holland make no distinction of duties between aliens and natives. I also rather believe that the other states of Europe make none, England excepted, to whom this policy, as that of her navigation act, seems peculiar. The question then is, should we disarm ourselves of the power to make this distinction against all nations, in order to purchase an exemption from the alien duties in England only; for if we put her importations on the footing of native, all other nations with whom we treat will have a right to claim the same. I think we should, because against other nations, who make no distinction in their ports between us and their own subjects, we ought not to make a distinction in ours. And if the English will agree, in like manner, to make none, we should, with equal reason, abandon the right as against them. I think all the world would gain, by setting commerce at perfect liberty. I remember that when we were digesting the general form of our treaty, this proposition to put foreigners and natives on the same footing, was considered: and we were all three, Dr. Franklin as well as you and myself, in favor of it. We finally, however, did not admit it, partly from the objection you mention, but more still on account of our instructions. But though the English proclamation had appeared in America at the time of framing these instructions, I think its effect, as to alien duties, had not yet been experienced, and therefore was not attended to. If it had been noted in the debate, I am sure that the annihilation of our whole trade would have been thought too great a price to pay for the reservation of a barren power, which a majority of the members did not propose ever to exercise, though they were willing to retain it. Stipulating for equal rights to foreigners and natives, we obtain more in foreign ports than our instructions required, and we only part with, in our own ports, a power, of which sound policy would probably for ever forbid the exercise. Add to this, that our treaty will be for a very short term, and if any evil be experienced under it, a reformation will soon be in our power. I am, therefore, for putting this among our original propositions to the court of London.
If it should prove an insuperable obstacle with them, or if it should stand in the way of a greater advantage, we can but abandon it in the course of the negotiation.
In my copy of the cipher, on the alphabetical side, numbers are wanting from ‘Denmark’ to ‘disc’ inclusive, and from ‘gone’ to ‘governor’ inclusive. I suppose them to have been omitted in copying; will you be so good as to send them to me from yours, by the first safe conveyance.
With compliments to the ladies and to Colonel Smith,
I am, dear Sir,
your friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.*
[* The original of this letter was in cipher. But annexed to the copy in cipher, is the above literal copy by the author.]
TO M. DE CASTRIES.
Paris, August 3,1785.
Sir,
The enclosed copy of a letter from Captain John Paul Jones, on the subject on which your Excellency did me the honor to write me, on the day of July, will inform you that there is still occasion to be troublesome to you. A Mr. Puchilburg, a merchant of L’Orient, who seems to have kept himself unknown till money was to be received, now presents powers to receive it, signed by the American officers and crews: and this produces a hesitation in the person to whom your order was directed. Congress, however, having substituted Captain Jones, as agent, to solicit and receive this money, he having given them security to forward it, when received, to their treasury, to be thence distributed to the claimants, and having at a considerable expense of time, trouble, and money, attended it to a conclusion, are circumstances of weight, against which Mr. Puchilburg seems to have nothing to oppose, but a nomination by individuals of the crew, under which he has declined to act, and permitted the business to be done by another without contradiction from him. Against him, too, it is urged that he fomented the sedition which took place among them, that he obtained this nomination from them while their minds were under ferment; and that he has given no security for the faithful payment of the money to those entitled to it.
I will add to these, one more circumstance which appears to render it impossible that he should execute this trust. It is now several years since the right to this money arose. The persons in whom it originally vested, were probably from different States in America. Many of them must be now dead; and their rights passed on to their representatives. But who are their representatives? The laws of some States prefer one degree of relations, those of others prefer another, there being no uniformity among the States on this point. Mr. Puchilberg, therefore, should know which of the parties are dead; in what order the laws of their respective States call their relations to the succession; and, in every case, which of those orders are actually in existence, and entitled to the share of the deceased. With the Atlantic ocean between the principals and their substitute, your Excellency will perceive what an inexhaustible source of difficulties, of chicanery, and delay, this might furnish to a person who should find an interest in keeping this money, as long as possible, in his own hands. Whereas, if it be lodged in the treasury of Congress, they, by an easy reference to the tribunals of the different States, can have every one’s portion immediately rendered to himself, if living; and if dead, to such of his relations as the laws of his particular State prefer, and as shall be found actually living. I the rather urge this course, as I foresee that it will relieve your Excellency from numberless appeals which these people will continually be making from the decisions of Mr. Puchilberg; appeals likely to perpetuate that trouble of which you have already had too much, and to which I am sorry to be obliged to add, by asking a peremptory order for the execution of what you were before pleased to decide, on this subject.
I have the honor to be, with sentiments of the most perfect respect,
your Excellency’s most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO CAPTAIN JOHN PAUL JONES.
Paris, August 3,1785.
Sir,
I received yesterday your favor of the 29th, and have written on the subject of it to the Maréchal de Castries this morning. You shall have an answer as soon as I receive one. Will you be so good as to make an inquiry into all the circumstances relative to Peyrouse’s expedition, which seem to ascertain his destination. Particularly what number of men, and of what conditions and vocations, had he on board? What animals, their species and number? What trees, plants, or seeds? What utensils? What merchandise or other necessaries? This inquiry should be made with as little appearance of interest in it as possible. Should you not be able to get satisfactory information without going to Brest, and it be inconvenient for you to go there, I will have the expenses, this shall occasion you, paid. Commit all the circumstances to writing, and bring them when you come yourself, or send them by a safe hand.
I am, with much respect, Sir,
your most obedient, humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN ADAMS.
Paris, August 6, 1785.
Dear Sir,
I now enclose you a draught of a treaty for the Barbary States, together with the notes Dr. Franklin left me. I have retained a press copy of this draught, so that by referring to any article, line, and word, in it, you can propose amendments and send them by the post, without any body’s being able to make much of the main subject. I shall be glad to receive any alterations you may think necessary, as soon as convenient, that this matter may be in readiness. I enclose also a letter containing intelligence from Algiers. I know not how far it is to be relied on. My anxiety is extreme indeed, as to these treaties. We know that Congress have decided ultimately to treat. We know how far they will go. But unfortunately we know also, that a particular person has been charged with instructions for us, these five months, who neither comes nor writes to us. What are we to do? It is my opinion that if Mr. Lambe does not come in either of the packets (English or French) now expected, we ought to proceed. I therefore propose to you this term, as the end of our expectations of him, and that if he does not come, we send some other person. Dr. Bancroft or Captain Jones occurs to me as the fittest. If we consider the present object only, I think the former would be the most proper: but if we look forward to the very probable event of war with those pirates, an important object would be obtained by Captain Jones’s becoming acquainted with their ports, force, tactics, &c. Let me know your opinion on this. I have never mentioned it to either, but I suppose either might be induced to go. Present me affectionately to the ladies and Colonel Smith, and be assured of the sincerity with which I am,
Dear Sir, your friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO DR. PRICE.
Paris, August 7,1785.
Sir,
Your favor of July the 2nd came duly to hand. The concern you therein express as to the effect of your pamphlet in America, induces me to trouble you with some observations on that subject. From my acquaintance with that country, I think I am able to judge, with some degree of certainty, of the manner in which it will have been received. Southward of the Chesapeake it will find but few readers concurring with it in sentiment, on the subject of slavery. From the mouth to the head of the Chesapeake, the bulk of the people will approve it in theory, and it will find a respectable minority ready to adopt it in practice; a minority, which, for weight and worth of character, preponderates against the greater number, who have not the courage to divest their families of a property, which, however, keeps their consciences unquiet. Northward of the Chesapeake, you may find here and there an opponent to your doctrine, as you may find here and there a robber and murderer; but in no greater number. In that part of America, there being but few slaves, they can easily disencumber themselves of them; and emancipation is put into such a train, that in a few years there will be no slaves northward of Maryland. In Maryland, I do not find such a disposition to begin the redress of this enormity, as in Virginia. This is the next State to which we may turn our eyes for the interesting spectacle of justice, in conflict with avarice and oppression: a conflict wherein the sacred side is gaining daily recruits, from the influx into office of young men grown and growing up. These have sucked in the principles of liberty, as it were, with their mothers’ milk; and it is to them I look with anxiety to turn the fate of this question. Be not therefore discouraged. What you have written will do a great deal of good: and could you still trouble yourself with our welfare, no man is more able to give aid to the laboring side. The College of William and Mary in Williamsburg, since the re-modelling of its plan, is the place where are collected together all the young men of Virginia, under preparation for public life. They are there under the direction (most of them) of a Mr. Wythe, one of the most virtuous of characters, and whose sentiments on the subject of slavery are unequivocal. I am satisfied, if you could resolve to address an exhortation to those young men, with all that eloquence of which you are master, that its influence on the future decision of this important question would be great, perhaps decisive. Thus you see, that, so far from thinking you have cause to repent of what you have done, I wish you to do more, and wish it on an assurance of its effect. The information I have received from America, of the reception of your pamphlet in the different States, agrees with the expectations I had formed.
Our country is getting into a ferment against yours, or rather has caught it from yours. God knows how this will end; but assuredly in one extreme or the other. There can be no medium between those who have loved so much. I think the decision is in your power as yet, but will not be so long.
I pray you to be assured of the sincerity of the esteem and respect, with which I have the honor to be, Sir,
your most obedient,
humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN ADAMS.
Paris, August 10,1785.
Dear Sir,
Your favor of the 4th instant came to hand yesterday. I now enclose you the two Arrêts against the importation of foreign manufactures into this kingdom. The cause of the balance against this country in favor of England, as well as its amount, is not agreed on. No doubt, the rage for English manufactures must be a principal cause. The speculators in exchange say, also, that those of the circumjacent countries, who have a balance in their favor against France, remit that balance to England from France. If so, it is possible that the English may count this balance twice: that is, in summing their exports to one of these States, and their imports from it, they count the difference once in their favor; then a second time, when they sum the remittances of cash they receive from France. There has been no Arrêt relative to our commerce, since that of August, 1784. And all the late advices from the French West Indies are, that they have now in their ports always three times as many vessels as there ever were before, and that the increase is principally from our States. I have now no further fears of that Arrêts standing its ground. When it shall become firm, I do not think its extension desperate. But whether the placing it on the firm basis of treaty be practicable, is a very different question. As far as it is possible to judge from appearances, I conjecture that Crawford will do nothing. I infer this from some things in his conversation, and from an expression of the Count de Vergennes, in a conversation with me yesterday. I pressed upon him the importance of opening their ports freely to us, in the moment of the oppressions of the English regulations against us, and perhaps of the suspension of their commerce. He admitted it; but said we had free ingress with our productions. I enumerated them to him, and showed him on what footing they were, and how they might be improved. We are to have further conversations on the subject. I am afraid the voyage to Fontainebleau will interrupt them. From the inquiries I have made, I find I cannot get a very small and indifferent house there, for the season, (that is, for a month) for less than one hundred or one hundred and fifty guineas. This is nearly the whole salary for the time, and would leave nothing to eat. I therefore cannot accompany the court thither, but I will endeavor to go there occasionally from Paris.
They tell me it is the most favorable scene for business with the Count de Vergennes, because he is then more abstracted from the domestic applications. Count d’Aranda is not yet returned from the waters of Vichy. As soon as he returns, I will apply to him in the case of Mr. Watson. I will pray you to insure Houdon’s life from the 27th of last month till his return to Paris. As he was to stay in America a month or two, he will probably be about six months absent; but the three per cent, for the voyage being once paid, I suppose they will insure his life by the month, whether his absence be longer or shorter. The sum to be insured is fifteen thousand livres tournois. If it be not necessary to pay the money immediately, there is a prospect of exchange becoming more favorable. But whenever it is necessary, be so good as to procure it by selling a draft on Mr. Grand, which I will take care shall be honored. With compliments to the ladies,
I am, dear Sir, your friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MRS. SPROWLE.
Paris, August 10, 1785.
Madam,
In your letter of June the 21st, you asked my opinion whether yourself or your son might venture to go to Virginia, to claim your possessions there? I had the honor of writing you, on the 5th of July, that you might safely go there; that your person would be sacredly safe, and free from insult. I expressed my hopes, too, that the Assembly of Virginia would, in the end, adopt the just and useful measure of restoring property unsold, and the price of that actually sold. In yours of July the 30th, you entreat my influence with the Assembly for retribution, and that, if I think your personal presence in Virginia would facilitate that end, you were willing and ready to go. This seems to propose to me to take on myself the solicitation of your cause, and that you will go, if I think your personal presence will be auxiliary to my applications. I feel myself obliged to inform you frankly, that it is improper for me to solicit your case with the Assembly of Virginia. The application can only go with propriety from yourself, or the minister of your court to America, whenever there shall be one. If you think the sentiments expressed in my former letter will serve you, you are free to exhibit it to members individually; but I wish the letter not to be offered to the Assembly as a body, or referred to in any petition or memorial to them.
I am, with much respect, Madam,
your most obedient, humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO CAPTAIN JOHN PAUL JONES.
Paris, August 13, 1785.
Sir,
Supposing you may be anxious to hear from hence, though there should be nothing interesting to communicate, I write by Mr. Cairnes merely to inform you, that I have, as yet, received no answer from the Marechal de Castries. I am in daily expectation of one. Should it not be received soon, I shall urge it again, which I wish to avoid however, if possible; because I think it better to await with patience a favorable decision, than by becoming importunate, to produce unfavorable dispositions, and, perhaps, a final determination of the same complexion. Should my occupations prevent my writing awhile, be assured that it will only be as long as I have nothing to communicate, and that as soon as I receive any answer, it shall be forwarded to you.
I am, with much esteem, Sir,
your most obedient, humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MESSRS. BUCHANAN AND HAY.
Paris, August 13, 1785.
Gentlemen,
Your favor of March the 20th came to hand the 14th of June, and the next day I wrote to you, acknowledging the receipt, and apprizing you, that between that date and the 1st of August, it would be impossible to procure, and get to your hands, the drafts you desired. I did hope, indeed, to have had them prepared before this, but it will yet be some time before they will be in readiness. I flatter myself, however, they will give you satisfaction when you receive them, and that you will think the object will not have lost by the delay. It was a considerable time before I could find an architect whose taste had been formed on a study of the ancient models of his art: the style of architecture in this capital being far from chaste. I at length heard of one, to whom I immediately addressed myself, and who perfectly fulfils my wishes. He has studied twenty years in Rome, and has given proofs of his skill and taste, by a publication of some antiquities of this country. You intimate that you should be willing to have a workman sent to you to superintend the execution of this work. Were I to send one on this errand from hence, he would consider himself as the superintendant of the Directors themselves, and probably, of the government of the State also. I will give you my ideas on this subject. The columns of the building, and the external architraves of the doors and windows, should be of stone. Whether these are made here or there, you will need one good stone-cutter; and one will be enough; because, under his direction, negroes, who never saw a tool, will be able to prepare the work for him to finish. I will therefore send you such a one, in time to begin work in the spring. All the internal cornices, and other ornaments not exposed to the weather, will be much handsomer, cheaper, and more durable in plaister, than in wood. I will therefore employ a good workman in this way, and send him to you. But he will have no employment till the house is covered; of course he need not be sent till next summer. I will take him on wages so long before hand, as that he may draw all the ornaments in detail, under the eye of the architect, which he will have to execute when he comes to you. It will be the cheapest way of getting them drawn, and the most certain of putting him in possession of his precise duty. Plaister will not answer for your external cornice, and stone will be too dear. You will probably find yourselves obliged to be contented with wood. For this, therefore, and for your window sashes, doors, frames, wainscoting, &c. you will need a capital house-joiner; and a capital one he ought to be, capable of directing all the circumstances in the construction of the walls, which the execution of the plan will require. Such a workman cannot be got here. Nothing can be worse done than the house-joinery of Paris. Besides that his speaking the language perfectly would be essential, I think this character must be got from England. There are no workmen in wood, in Europe, comparable to those of England. I submit to you, therefore, the following proposition: to wit, I will get a correspondent in England to engage a workman of this kind. I will direct him to come here, which will cost five guineas. We will make proof of his execution. He shall also make, under the eye of the architect, all the drawings for the building, which he is to execute himself: and if we find him sober and capable, he shall be forwarded to you. I expect that in the article of the drawings, and the cheapness of passage from France, you will save the expense of his coming here. But as to this workman, I shall do nothing unless I receive your commands. With respect to your stone work, it may be got much cheaper here than in England. The stone of Paris is very white and beautiful; but it always remains soft, and suffers from the weather. The cliffs of the Seine, from hence to Havre, are all of stone. I am not yet informed whether it is all liable to the same objections. At Lyons, and all along the Rhone, is a stone as beautiful as that of Paris, soft when it comes out of the quarry, but very soon becoming hard in the open air, and very durable. I doubt, however, whether the commerce between Virginia and Marseilles would afford opportunities of conveyance sufficient. It remains to be inquired, what addition to the original cost would be made by the short land carriage from Lyons to the Loire, and the water transportation down that to Bordeaux;, and also, whether a stone of the same quality may not be found on the Loire. In this, and all other matters relative to your charge, you may command my services freely.
Having heard high commendations of a plan of a prison, drawn by an architect at Lyons, I sent there for it. The architect furnished me with it. It is certainly the best plan I ever saw. It unites, in the most perfect manner, the objects of security and health, and has, moreover, the advantage, valuable to us, of being capable of being adjusted to any number of prisoners, small or great, and admitting an execution from time to time, as it may be convenient. The plan is under preparation as for forty prisoners. Will you have any occasion for slate? It may be got very good and ready prepared at Havre; and a workman or more might be sent on easy terms. Perhaps the quarry at Tuckahoe would leave you no other want than that of a workman.
I shall be glad to receive your sentiments on the several matters herein mentioned, that I may know how far you approve of them, as I shall with pleasure pursue strictly whatever you desire. I have the honor to be, with great respect and esteem, Gentlemen,
your most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN JAY.
Paris, August 14, 1785.
Sir,
I was honored, on the 22nd ultimo, with the receipt of your letter of June the 15th; and delivered the letter therein enclosed, from the President of Congress to the King. I took an opportunity of asking the Count de Vergennes, whether the Chevalier Luzerne proposed to return to America. He answered me that he did; and that he was here, for a time only, to arrange his private affairs. Of course, this stopped my proceeding further in compliance with the hint in your letter. I knew that the Chevalier Luzerne still retained the character of minister to Congress, which occasioned my premising the question I did. But, notwithstanding the answer, which indeed was the only one the Count de Vergennes could give me, I believe it is not expected that the Chevalier will return to America: that he is waiting an appointment here, to some of their embassies, or some other promotion, and in the mean time, as a favor, is permitted to retain his former character. Knowing the esteem borne him in America, I did not suppose it would be wished, that I should add any thing which might occasion an injury to him; and the rather, as I presumed that, at this time, there did not exist the same reason for wishing the arrival of a minister in America, which perhaps existed there at the date of your letter. Count Adhemar is just arrived from London, on account of a paralytic disease with which he has been struck. It does not seem improbable, that his place will be supplied, and perhaps by the Chevalier de la Luzerne.
A French vessel has lately refused the salute to a British armed vessel in the channel. The Chargé des Affaires of Great Britain at this court (their ambassador having gone to London a few days ago) made this the subject of a conference with the Count de Vergennes, on Tuesday last. He told me that the Count explained the transaction as the act of the individual master of the French vessel, not founded in any public orders. His earnestness, and his endeavors to find terms sufficiently soft to express the Count’s explanation, had no tendency to lessen any doubts I might have entertained on this subject. I think it possible the refusal may have been by order: nor can I believe that Great Britain is in a condition to resent it, if it was so. In this case, we shall see it repeated by France and her example will then be soon followed by other nations. The news-writers bring together this circumstance with the departure of the French ambassador from London, and the English ambassador from Paris, the manoeuvring of the French fleet just off the channel, the collecting some English vessels of war in the channel, the failure of a commercial treaty between the two countries, and a severe Arrêt here against English manufacturers, as foreboding war. It is possible that the fleet of manoeuvre, the refusal of the salute, and the English fleet of observation, may have a connexion with one another. But I am persuaded the other facts are totally independent of these, and of one another, and are accidentally brought together in point of time. Neither nation is in a condition to go to war: Great Britain, indeed, the least so of the two. The latter power, or rather its monarch, as Elector of Hanover, has lately confederated with the King of Prussia and others of the Germanic body, evidently in opposition to the Emperor’s designs on Bavaria. An alliance, too, between the Empress of Russia and the Republic of Venice, seems to have had him in view, as he had meditated some exchange of territory with that republic. This desertion of the powers heretofore thought friendly to him, seems to leave no issue for his ambition, but on the side of Turkey. His demarkation with that country is still unsettled. His difference with the Dutch is certainly agreed. The articles are not yet made public; perhaps not quite adjusted. Upon the whole, we may count on another year’s peace in Europe, and that our friends will not, within that time, be brought into any embarrassments, which might encourage Great Britain to be difficult in settling the points still unsettled between us.
You have, doubtless, seen in the papers, that this court was sending two vessels into the south sea, under the conduct of a Captain Peyrouse. They give out, that the object is merely for the improvement of our knowledge of the geography of that part of the globe. And certain it is, that they carry men of eminence in different branches of science. Their loading, however, as detailed in conversations, and some other circumstances, appeared to me to indicate some other design: perhaps that of colonizing on the western coast of America; or, it may be, only to establish one or more factories there, for the fur-trade. Perhaps we may be little interested in either of these objects. But we are interested in another, that is, to know whether they are perfectly weaned from the desire of possessing continental colonies in America. Events might arise, which would render it very desirable for Congress to be satisfied they have no such wish. If they would desire a colony on the western side of America, I should not be quite satisfied that they would refuse one which should offer itself on the eastern side. Captain Paul Jones being at L’Orient, within a day’s journey of Brest, where Captain Peyrouse’s vessels lay, I desired him, if he could not satisfy himself at L’Orient of the nature of this equipment, to go to Brest for that purpose: conducting himself so as to excite no suspicion that we attended at all to this expedition. His discretion can be relied on, and his expenses for so short a journey will be a trifling price for satisfaction on this point. I hope, therefore, that my undertaking that the expenses of his journey shall be reimbursed him, will not be disapproved.
A gentleman lately arrived from New York tells me, he thinks it will be satisfactory to Congress, to be informed of the effect produced here by the insult of Longchamps on Monsieur de Marbois. Soon after my arrival in France last summer, it was the matter of a conversation between the Count de Vergennes and myself. I explained to him the effect of the judgment against Longchamps. He did not say that it was satisfactory, but neither did he say a word from which I could collect that it was not so. The conversation was not official, because foreign to the character in which I then was. He has never mentioned a word on the subject to me since, and it was not for me to introduce it at any time. I have never once heard it mentioned in conversation, by any person of this country, and have no reason to suppose that there remains any uneasiness on the subject. I have indeed been told, that they had sent orders to make a formal demand of Longchamps from Congress, and had immediately countermanded these orders. You know whether this be true. If it be, I should suspect the first orders to have been surprised from them by some exaggeration, and that the latter was a correction of their error, in the moment of further reflection. Upon the whole, there certainly appears to me no reason to urge the State, in which the fact happened, to any violation of their laws, nor to set a precedent which might hereafter be used in cases more interesting to us than the late one.
In a late conversation with the Count de Vergennes, he asked me if the condition of our finances was improving. He did not make an application of the question to the arrearages of their interest, though perhaps he meant that I should apply it. I told him the impost still found obstacles, and explained to him the effects which I hoped from our land office. Your letter of the 15th of April did not come to hand till the 27th ultimo. I enclose a letter from Mr. Dumas to the President of Congress, and accompany the present with the Leyden Gazette and Gazette of France, from the date last sent you to the present time. I have the honor to be, with high esteem, Sir,
your most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO THE COUNT DE VERGENNES.
Paris, August 15, 1785.
Sir,
In the conversation which I had the honor of having with your Excellency, a few days ago, on the importance of placing, at this time, the commerce between France and America on the best footing possible, among other objects of this commerce, that of tobacco was mentioned, as susceptible of greater encouragement and advantage to the two nations. Always distrusting what I say in a language I speak so imperfectly, I will beg your permission to state, in English, the substance of what I had then the honor to observe, adding some more particular details for your consideration.
I find the consumption of tobacco in France estimated at from fifteen to thirty millions of pounds. The most probable estimate, however, places it at twenty-four millions.
This costing eight sous the pound, delivered in
a port of France, amounts to...............9,600,000 livres.
Allow six sous a pound, as the average cost of the
different manufactures.....................7,200,000
The revenue which the King derives from this, is
something less than.......................30,000,000
Which would make the cost of the whole... 46,800,000
But it is sold to the consumers at an average of
three livres the pound....................72,000,000
There remain then for the expenses
of collection............................ 25,200,000 livres.
This is within a sixth as much as the King receives, and so gives nearly one half for collecting the other. It would be presumption in me, a stranger, to suppose my numbers perfectly accurate. I have taken them from the best and most disinterested authorities I could find. Your Excellency will know how far they are wrong; and should you find them considerably wrong, yet I am persuaded you will find, after strictly correcting them, that the collection of this branch of the revenue still absorbs too much.
My apology for making these remarks will, I hope, be found in my wishes to improve the commerce between the two nations, and the interest which my own country will derive from this improvement. The monopoly of the purchase of tobacco in France, discourages both the French and American merchant from bringing it here, and from taking in exchange the manufactures and productions of France. It is contrary to the spirit of trade, and to the dispositions of merchants, to carry a commodity to any market where but one person is allowed to buy it, and where, of course, that person fixes its price, which the seller must receive, or reexport his commodity, at the loss of his voyage thither. Experience accordingly shows, that they carry it to other markets, and that they take in exchange the merchandise of the place where they deliver it. I am misinformed, if France has not been furnished from a neighboring nation with considerable quantities of tobacco, since the peace, and been obliged to pay there in coin, what might have been paid here in manufactures, had the French and American merchants bought the tobacco originally here. I suppose, too, that the purchases made by the Farmers General, in America, are paid for chiefly in coin, which coin is also remitted directly hence to England, and makes an important part of the balance supposed to be in favor of that nation against this. Should the Farmers General, by themselves, or by the company to whom they may commit the procuring these tobaccos from America, require, for the satisfaction of government on this head, the exportation of a proportion of merchandise in exchange for them, it would be an unpromising expedient. It would only commit the exports, as well as imports, between France and America, to a monopoly, which, being secure against rivals in the sale of the merchandise of France, would not be likely to sell at such moderate prices as might encourage its consumption there, and enable it to bear a competition with similar articles from other countries. I am persuaded this exportation of coin may be prevented, and that of commodities effected, by leaving both operations to the French and American merchants, instead of the Farmers General. They will import a sufficient quantity of tobacco, if they are allowed a perfect freedom in the sale; and they will receive in payment, wines, oils, brandies, and manufactures, instead of coin; forcing each other, by their competition, to bring tobaccos of the best quality; to give to the French manufacturer the full worth of his merchandise; and to sell to the American consumer at the lowest price they can afford; thus encouraging him to use, in preference, the merchandise of this country.
It is not necessary that this exchange should be favored by any loss of revenue to the King. I do not mean to urge any thing which shall injure either his Majesty or his people. On the contrary, the measure I have the honor of proposing, will increase his revenue, while it places both the seller and buyer on a better footing. It is not for me to say, what system of collection may be best adapted to the organization of this government; nor whether any useful hints may be taken from the practice of that country, which has heretofore been the principal entrepot for this commodity. Their system is simple and little expensive. The importer there, pays the whole duty to the King: and as this would be inconvenient for him to do before he has sold his tobacco, he is permitted, on arrival, to deposite it in the King’s warehouse, under the locks of the King’s officer. As soon as he has sold it, he goes with the purchaser to the warehouse; the money is there divided between the King and him, to each his proportion, and the purchaser takes out the tobacco. The payment of the King’s duty is thus ensured in ready money. What is the expense of its collection, I cannot say; but it certainly need not exceed six livres a hogshead of one thousand pounds. That government levies a higher duty on tobacco than is levied here. Yet so tempting and so valuable is the perfect liberty of sale, that the merchant carries it there and finds his account in doing so.
If, by a simplification of the collection of the King’s duty on tobacco, the cost of that collection can be reduced even to five per cent., or a million and a half, instead of twenty-five millions; the price to the consumer will be reduced from three to two livres the pound. For thus I calculate.
The cost, manufacture, and revenue, on twenty-four million pounds
of tobacco being (as before stated)................46,800,000 livres.
Five per cent, on thirty millions of livres,
expenses of collection .............................1,500,000
Give what the consumers would pay, being
about two livres a pound...........................48,300,000
But they pay at present three livres a pound...... 72,000,000
The difference is..................................23,700,000
The price being thus reduced one third, would be brought within the reach of a new and numerous circle of the people, who cannot, at present, afford themselves this luxury. The consumption, then, would probably increase, and perhaps in the same if not a greater proportion, with the reduction of the price; that is to say, from twenty-four to thirty-sis millions of pounds: and the King, continuing to receive twenty-five sous on the pound, as at present, would receive forty-fire instead of thirty millions of livres, while his subjects would pay but two livres for an object which has heretofore cost them three. Or if, in event, the consumption were not to be increased, he would levy only forty-eight millions on his people, where seventy-two millions are now levied, and would leave twenty-four millions in their pockets, either to remain there, or to be levied in some other form, should the state of revenue require it. It will enable his subjects, also, to dispose of between nine and ten millions’ worth of their produce and manufactures, instead of sending nearly that sum annually, in coin, to enrich a neighboring nation.
I have heard two objections made to the suppression of this monopoly. 1. That it might increase the importation of tobacco in contraband. 2. That it would lessen the abilities of the Farmers General to make occasional loans of money to the public treasury. These objections will surely be better answered by those who are better acquainted than I am with the details and circumstances of the country. With respect to the first, however, I may observe, that contraband does not increase on lessening the temptations to it. It is now encouraged, by those who engage in it being able to sell for sixty sous what cost but fourteen, leaving a gain of forty-six sous. When the price shall be reduced from sixty to forty sous, the gain will be but twenty-six, that is to say, a little more than one half of what it is at present. It does not seem a natural consequence, then, that contraband should be increased by reducing its gain nearly one half. As to the second objection, if we suppose (for elucidation and without presuming to fix) the proportion of the farm on tobacco, at one eighth of the whole mass farmed, the abilities of the Farmers General to lend will be reduced one eighth, that is, they can hereafter lend only seven millions, where heretofore they have lent eight. It is to be considered, then, whether this eighth (or other proportion, whatever it be) is worth the annual sacrifice of twenty-four millions, or if a much smaller sacrifice to other monied men, will not produce the same loans of money in the ordinary way.
While the advantages of an increase of revenue to the crown, a diminution of impost on the people, and a payment in merchandise instead of money, are conjectured as likely to result to France from a suppression of the monopoly on tobacco, we have also reason to hope some advantages on our part; and this hope alone could justify my entering into the present details. I do not expect this advantage will be by an augmentation of price. The other markets of Europe have too much influence on this article, to admit any sensible augmentation of price to take place. But the advantage I principally expect, is an increase of consumption. This will give us a vent for so much more, and, of consequence, find employment for so many more cultivators of the earth: and in whatever proportion it increases this production for us, in the same proportion will it procure additional vent for the merchandise of France, and employment for the hands which produce it. I expect too, that by bringing our merchants here, they would procure a number of commodities in exchange, better in kind, and cheaper in price. It is with sincerity I add, that warm feelings are indulged in my breast by the further hope, that it would bind the two nations still closer in friendship, by binding them in interest. In truth, no two countries are better calculated for the exchanges of commerce. France wants rice, tobacco, potash, furs, and ship timber. We want wines, brandies, oils, and manufactures. There is an affection, too, between the two people, which disposes them to favor one another. They do not come together, then, to make the exchange in their own ports, it shows there is some substantial obstruction in the way. We have had the benefit of too many proofs of his Majesty’s friendly disposition towards the United States, and know too well his affectionate care of his own subjects, to doubt his willingness to remove these obstructions, if they can be unequivocally pointed out. It is for his wisdom to decide, whether the monopoly, which is the subject of this letter, be deservedly classed with the principal of these. It is a great comfort to me too, that in presenting this to the mind of his Majesty, your Excellency will correct my ideas where an insufficient knowledge of facts may have led me into error; and that while the interests of the King and of his people are the first object of your attention, an additional one will be presented by those dispositions towards us, which have heretofore so often befriended our nation.
I avail myself of this occasion to repeat the assurance of that high respect and esteem, with which I have the honor to be
your Excellency’s most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO CAPTAIN JOHN PAUL JONES.
Sir,
Paris, August 17, 1785.
Mine of the 13th informed you that I had written to the M. de Castries on the subject of Puchilberg’s interference. Yesterday I received his answer dated the 12th. In that, he says that he is informed by the Ordonnateur, that he has not been able to get an authentic roll of the crew of the Alliance, and that, in the probable case of there having been some French subjects among them, it will be just that you should give security to repay their portions. I wrote to him this morning, that as you have obliged yourself to transmit the money to the treasury of the United States, it does not seem just to require you to be answerable for money which will be no longer within your power; that the repayment of such portions will be incumbent on Congress; that I will immediately solicit their orders to have all such claims paid by their banker here: and that should any be presented before I receive their orders, I will undertake to direct the banker of the United States to pay them, that there may be no delay. I trust that this will remove the difficulty, and that it is the last which will be offered. The ultimate answer shall be communicated the moment I receive it. Having pledged myself for the claims which may be offered, before I receive the orders of Congress, it is necessary to arm myself with the proper checks. Can you give me a roll of the crew, pointing out the French subjects? If not, can you recollect personally the French subjects, and name them to me, and the sums they are entitled to? it there were none such, yet the roll will be material, because I have no doubt that Puchilberg will excite claims upon me, either true or false,
I am, with much respect, Sir,
your most obedient, humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO WILLIAM CARMICHAEL.
Pads, August 18, 1785.
Dear Sir,
My last to you was of June the 22nd, with a postscript of July the 14th. Yours of June the 27th came to hand the 23rd of July, and that of July the 28th came to hand the 10th instant. The papers enclosed in the last shall be communicated to Mr. Adams. I see with extreme satisfaction and gratitude, the friendly interposition of the court of Spain with the Emperor of Morocco, on the subject of the brig Betsy, and I am persuaded it will produce the happiest effects in America. Those who are entrusted with the public affairs there, are sufficiently sensible how essentially it is for our interest to cultivate peace with Spain, and they will be pleased to see a corresponding disposition in that court. The late good office of emancipating a number of our countrymen from slavery is peculiarly calculated to produce a sensation among our people, and to dispose them to relish and adopt the pacific and friendly views of their leaders towards Spain. We hear nothing yet of Mr. Lambe. I have therefore lately proposed to Mr. Adams, that if he does not come in the French or English packet of this month, we will wait no longer. If he accedes to the proposition, you will be sure of hearing of, and perhaps of seeing, some agent proceeding on that business. The immense sum said to have been proposed, on the part of Spain, to Algiers, leaves us little hope of satisfying their avarice. It may happen then, that the interests of Spain and America may call for a concert of proceedings against that State. The dispositions of the Emperor of Morocco give us better hopes there. May not the affairs of the Musquito coast, and our western ports, produce another instance of a common interest? Indeed, I meet this correspondence of interest in so many quarters, that I look with anxiety to the issue of Mr. Gardoqui’s mission; hoping it will be a removal of the only difficulty at present subsisting between the two nations, or which is likely to arise.
Congress are not likely to adjourn this summer. They have purchased the Indian right of soil to about fifty millions of acres of land, between the Ohio and lakes, and expected to make another purchase of an equal quantity. They have, in consequence, passed an ordinance for disposing of their lands, and I think a very judicious one. They propose to sell them at auction for not less than a dollar an acre, receiving their own certificates of debt as money. I am of opinion all the certificates of our domestic debt will immediately be exchanged for land, Our foreign debt, in that case, will soon be discharged. New York and Rhode Island still refuse the impost. A general disposition is taking place to commit the whole management of our commerce to Congress. This has been much promoted by the interested policy of England, which, it was apparent, could not be counter-worked by the States separately. In the mean time, the other great towns are acceding to the proceedings of Boston for annihilating, in a great measure, their commercial connections with Great Britain. I will send the cipher by a gentleman who goes from here to Madrid about a month hence. It shall be a copy of the one I gave Mr. Adams. The letter of Don Gomez has been delivered at the hotel of the Portuguese ambassador, who is, however, in the country. I am with much respect, Dear Sir,
your most obedient, humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO PETER CARR.
Paris, August 19, 1785.
Dear Peter,
I received, by Mr. Mazzei, your letter of April the 20th. I am much mortified to hear that you have lost so much time; and that when you arrived in Williamsburg, you were not at all advanced from what you were when you left Monticello. Time now begins to be precious to you. Every day you lose, will retard a day your entrance on that public stage whereon you may begin to be useful to yourself. However, the way to repair the loss is to improve the future time. I trust, that with your dispositions, even the acquisition of science is a pleasing employment. I can assure you, that the possession of it is, what (next to an honest heart) will above all things render you dear to your friends, and give you fame and promotion in your own country. When your mind shall be well improved with science, nothing will be necessary to place you in the highest points of view, but to pursue the interests of your country, the interests of your friends and your own interests also, with the purest integrity, the most chaste honor. The defect of these virtues can never be made up by all the other acquirements of body and mind. Make these then your first object. Give up money, give up fame, give up science, give the earth itself and all it contains, rather than do an immoral act. And never suppose, that in any possible situation, or under any circumstances, it is best for you to do a dishonorable thing, however slightly so it may appear to you. Whenever you are to do a thing, though it can never be known but to yourself, ask yourself how you would act were all the world looking at you, and act accordingly. Encourage all your virtuous dispositions, and exercise them whenever an opportunity arises; being assured that they will gain strength by exercise, as a limb of the body does, and that exercise will make them habitual. From the practice of the purest virtue, you may be assured you will derive the most sublime comforts in every moment of life, and in the moment of death. If ever you find yourself environed with difficulties and perplexing circumstances, out of which you are at a loss how to extricate yourself, do what is right, and be assured that that will extricate you the best out of the worst situations. Though you cannot see, when you take one step, what will be the next, yet follow truth, justice, and plain dealing, and never fear their leading you out of the labyrinth, in the easiest manner possible. The knot which you thought a Gordian one, will untie itself before you. Nothing is so mistaken as the supposition, that a person is to extricate himself from a difficulty by intrigue, by chicanery, by dissimulation, by trimming, by an untruth, by an injustice. This increases the difficulties ten fold; and those who pursue these methods, get themselves so involved at length, that they can turn no way but their infamy becomes more exposed. It is of great importance to set a resolution, not to be shaken, never to tell an untruth. There is no vice so mean, so pitiful, so contemptible; and he who permits himself to tell a lie once, finds it much easier to do it a second and third time, till a length it becomes habitual; he tells lies without attending to it, and truths without the world’s believing him. This falsehood of the tongue leads to that of the heart, and in time depraves all its good dispositions.
An honest heart being the first blessing, a knowing head is the second. It is time for you now to begin to be choice in your reading; to begin to pursue a regular course in it; and not to suffer yourself to be turned to the right or left by reading any thing out of that course. 1 have long ago digested a plan for you, suited to the circumstances in which you will be placed. This I will detail to you, from time to time, as you advance. For the present, I advise you to begin a course of ancient history, reading every thing in the original and not in translations. First read Goldsmith’s History of Greece. This will give you a digested view of that field. Then take up ancient history in the detail, reading the following books in the following order: Herodotus, Thucydides, Xenophontis Hellenica, Xenophontis Anabasis, Arrian, Quintus Curtius, Diodorus Siculus, Justin. This shall form the first stage of your historical reading, and is all I need mention to you now. The next, will be of Roman history.* From that we will come down to modern history. In Greek and Latin poetry, you have read or will read at school, Virgil, Terence, Horace, Anacreon, Theocritus, Homer, Euripides, Sophocles. Read also Milton’s Paradise Lost, Shakspeare, Ossian, Pope’s and Swift’s works, in order to form your style in your own language. In morality, read Epictetus, Xenophontis Memorabilia, Plato’s Socratic dialogues, Cicero’s philosophies, Antoninus, and Seneca.
* Livy, Sullust, Cæsar, Cicero’s Epistles, Suetonius,
Tacitus, Gibbon.
In order to assure a certain progress in this reading, consider what hours you have free from the school and the exercises of the school. Give about two of them every day to exercise; for health must not be sacrificed to learning. A strong body makes the mind strong. As to the species of exercise, I advise the gun. While this gives a moderate exercise to the body, it gives boldness, enterprise, and independence to the mind. Games played with the ball, and others of that nature, are too violent for the body, and stamp no character on the mind. Let your gun therefore be the constant companion of your walks. Never think of taking a book with you. The object of walking is to relax the mind. You should therefore not permit yourself even to think while you walk; but divert your attention by the objects surrounding you. Walking is the best possible exercise. Habituate yourself to walk very far. The Europeans value themselves on having subdued the horse to the uses of man; but I doubt whether we have not lost more than we have gained, by the use of this animal. No one has occasioned so much the degeneracy of the human body. An Indian goes on foot nearly as far in a day, for a long journey, as an enfeebled white does on his horse; and he will tire the best horses. There is no habit you will value so much as that of walking far without fatigue. I would advise you to take your,exercise in the afternoon: not because it is the best time for exercise, for certainly it is not; but because it is the best time to spare from your studies; and habit will soon reconcile it to health, and render it nearly as useful as if you gave to that the more precious hours of the day. A little walk of half an hour in the morning, when you first rise, is advisable also. It shakes off sleep, and produces other good effects in the animal economy. Rise at a fixed and an early hour, and go to bed at a fixed and early hour also. Sitting up late at night is injurious to the health, and not useful to the mind. Having ascribed proper hours to exercise, divide what remain (I mean of your vacant hours) into three portions. Give the principal to History, the other two, which should be shorter, to Philosophy and Poetry. Write to me once every month or two, and let me know the progress you make. Tell me in what manner you employ every hour in the day. The plan I have proposed for you is adapted to your present situation only. When that is changed, I shall propose a corresponding change of plan. I have ordered the following books to be sent you from London, to the care of Mr. Madison. Herodotus, Thucydides, Xenophon’s Hellenics, Anabasis, and Memorabilia, Cicero’s works, Baretti’s Spanish and English Dictionary, Martin’s Philosophical Grammar, and Martin’s Philosophia Britannica. I will send you the following from hence. Bezout’s Mathematics, De la Lande’s Astronomy, Muschenbroeck’s Physics, Quintus Curtius, Justin, a Spanish Grammar, and some Spanish books, You will observe that Martin, Bezout, De la Lande, and Muschenbroeck are not in the preceding plan. They are not to be opened till you go to the University. You are now, I expect, learning French. You must push this; because the books which will be put into your hands when you advance into Mathematics, Natural Philosophy, Natural History, &c. will be mostly French, these sciences being better treated by the French than the English writers. Our future connection with Spain renders that the most necessary of the modern languages, after the French. When you become a public man, you may have occasion for it, and the circumstance of your possessing that language may give you a preference over other candidates. I have nothing further to add for the present, but husband well your time, cherish your instructors, strive to make every body your friend; and be assured that nothing will be so pleasing, as your success, to, Dear Peter,
Your’s affectionately,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN PAGE.
Paris, August 20 1785.
Dear Page,
I received your friendly letter of April the 28th, by Mr. Mazzei, on the 22nd of July. That of the month before, by Monsieur La Croix, has not come to hand. This correspondence is grateful to some of my warmest feelings, as the friendships of my youth are those which adhere closest to me, and in which I most confide. My principal happiness is now in the retrospect of life.
I thank you for your notes of your operations on the Pennsylvania boundary. I am in hopes that from yourself, Madison, Rittenhouse, or Hutchings, I shall receive a chart of the line as actually run. It will be a great present to me. I think Hutchings promised to send it to me. I have been much pleased to hear you had it in contemplation, to endeavor to establish Rittenhouse in our college. This would be an immense acquisition, and would draw youth to it from every part of the continent. You will do much more honor to our society, on reviving it, by placing him at its head, than so useless a member as I should be. I have been so long diverted from this my favorite line, and that, too, without acquiring an attachment to my adopted one, that I am become a mongrel, of no decided order, unowned by any, and incapable of serving any. I should feel myself out of my true place too, to stand before McLurg. But why withdraw yourself? You have more zeal, more application, and more constant attention to the subjects proper to the society, and can, therefore, serve them best.
The affair of the Emperor and Dutch is settled, though not signed. The particulars have not yet transpired. That of the Bavarian exchange is dropped, and his views on Venice defeated. The alliance of Russia with Venice, to prevent his designs in that quarter, and that of the Hanoverian Elector with the King of Prussia and other members of the Germanic body, to prevent his acquisition of Bavaria, leave him in a solitary situation. In truth, he has lost much reputation by his late manoeuvres. He is a restless, ambitious character, aiming at every thing, persevering in nothing, taking up designs without calculating the force which will be opposed to him, and dropping them on the appearance of firm opposition. He has some just views and much activity. The only quarter in which the peace of Europe seems at present capable of being disturbed, is on that of the Porte. It is believed that the Emperor and Empress have schemes in contemplation for driving the Turks out of Europe. Were this with a view to re-establish the native Greeks in the sovereignty of their own country, I could wish them success, and to see driven from that delightful country, a set of barbarians, with whom an opposition to all science is an article of religion. The modern Greek is not yet so far departed from its ancient model, but that we might still hope to see the language of Homer and Demosthenes flow with purity from the lips of a free and ingenious people. But these powers have in object to divide the country between themselves. This is only to substitute one set of barbarians for another, breaking, at the same time, the balance among the European powers. You have been told with truth, that the Emperor of Morocco has shown a disposition to enter into treaty with us: but not truly, that Congress has not attended to his advances, and thereby disgusted him. It is long since they took measures to meet his advances. But some unlucky incidents have delayed their effect. His dispositions continue good. As a proof of this, he has lately released freely, and clothed well, the crew of an American brig he took last winter; the only vessel ever taken from us by any of the States of Barbary. But what is the English of these good dispositions? Plainly this; he is ready to receive us into the number of his tributaries. What will be the amount of tribute, remains yet to be known, but it probably will not be as small as you may have conjectured. It will surely be more than a free people ought to pay to a power owning only four or five frigates, under twenty-two guns: he has not a port into which a larger vessel can enter. The Algerines possess fifteen or twenty frigates, from that size up to fifty guns. Disinclination on their part has lately broken off a treaty between Spain and them, whereon they were to have received a million of dollars, besides great presents in naval stores. What sum they intend we shall pay, I cannot say. Then follow Tunis and Tripoli. You will probably find the tribute to all these powers make such a proportion of the federal taxes, as that every man will feel them sensibly, when he pays those taxes. The question is whether their peace or war will be cheapest. But it is a question which should be addressed to our honor, as well as our avarice. Nor does it respect us as to these pirates only, but as to the nations of Europe. If we wish our commerce to be free and uninsuked, we must let these nations see that we have an energy which at present they disbelieve. The low opinion they entertain of our powers, cannot fail to involve us soon in a naval war.
I shall send you with this, if I can., and if not, then by the first good conveyance, the Connoissance des Tems for the years 1786 and 1787, being all as yet published. You will find in these the tables for the planet Herschel, as far as the observations, hitherto made, admit them to be calculated. You will see, also, that Herschel was only the first astronomer who discovered it to be a planet, and not the first who saw it. Mayer saw it in the year 1756, and placed it in the catalogue of his zodiacal stars, supposing it to be such. A Prussian astronomer, in the year 1781, observed that the 964th star of Mayer’s catalogue was missing: and the calculations now prove that at the time Mayer saw his 964th star, the planet Herschel should have been precisely in the place where he noted that star. I shall send you also a little publication here, called the Bibliothèque Physico-oeconomique. It will communicate all the improvements and new discoveries in the arts and sciences, made in Europe for some years past. I shall be happy to hear from you often. Details, political and literary, and even of the small history of our country, are the most pleasing communications possible. Present me affectionately to Mrs. Page, and to your family, in the members of which, though unknown to me, I feel an interest on account of their parents. Believe me to be with warm esteem, dear Page, your sincere friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN JAY.
(Private.) Paris, August 23, 1785.
Dear Sir,
I shall sometimes ask your permission to write you letters, not official, but private. The present is of this kind, and is occasioned by the question proposed in yours of June the 14th; ‘Whether it would be useful to us, to carry all our own productions, or none?’
Were we perfectly free to decide this question, I should reason as follows. We have now lands enough to employ an infinite number of people in their cultivation. Cultivators of the earth are the most valuable citizens. They are the most vigorous, the most independent, the most virtuous, and they are tied to their country, and wedded to its liberty and interests, by the most lasting bonds. As long, therefore, as they can find employment in this line, I would not convert them into mariners, artisans, or any thing else. But our citizens will find employment in this line, till their numbers, and of course their productions, become too great for the demand, both internal and foreign. This is not the case as yet, and probably will not be for a considerable time. As soon as it is, the surplus of hands must be turned to something else. I should then, perhaps, wish to turn them to the sea in preference to manufactures; because, comparing the characters of the two classes, I find the former the most valuable citizens. I consider the class of artificers as the panders of vice, and the instruments by which the liberties of a country are generally overturned. However, we are not free to decide this question on principles of theory only. Our people are decided in the opinion, that it is necessary for us to take a share in the occupation of the ocean, and their established habits induce them to require that the sea be kept open to them, and that that line of policy be pursued, which will render the use of that element to them as great as possible. I think it a duty in those entrusted with the administration of their affairs, to conform themselves to the decided choice of their constituents: and that therefore, we should, in every instance, preserve an equality of right to them in the transportation of commodities, in the right of fishing, and in the other uses of the sea.
But what will be the consequence? Frequent wars without a doubt. Their property will be violated on the sea and in foreign ports, their persons will be insulted, imprisoned, &c. for pretended debts, contracts, crimes, contraband, &c. &c. These insults must be resented, even if we had no feelings, yet to prevent their eternal repetition; or, in other words, our commerce on the ocean and in other countries must be paid for by frequent war. The justest dispositions possible in ourselves will not secure us against it. It would be necessary that all other nations were just also. Justice indeed, on our part, will save us from those wars which would have been produced by a contrary disposition. But how can we prevent those produced by the wrongs of other nations? By putting ourselves in a condition to punish them. Weakness provokes insult and injury, while a condition to punish, often prevents them. This reasoning leads to the necessity of some naval force; that being the only weapon with which we can reach an enemy. I think it to our interest to punish the first insult: because an insult unpunished is the parent of many others. We are not, at this moment, in a condition to do it, but we should put ourselves into it, as soon as possible. If a war with England should take place, it seems to me that the first thing necessary, would be a resolution to abandon the carrying trade, because we cannot protect it. Foreign nations must, in that case, be invited to bring us what we want, and to take our productions in their own bottoms. This alone could prevent the loss of those productions to us, and the acquisition of them to our enemy. Our seamen might be employed in depredations on their trade. But how dreadfully we shall suffer on our coasts, if we have no force on the water, former experience has taught us. Indeed, I look forward with horror to the very possible case of war with an European power, and think there is no protection against them, but from the possession of some force on the sea. Our vicinity to their West India possessions, and to the fisheries, is a bridle which a small naval force, on our part, would hold in the mouths of the most powerful of these countries. I hope our land office will rid us of our debts, and that our first attention then will be, to the beginning a naval force, of some sort. This alone can countenance our people as carriers on the water, and I suppose them to be determined to continue such.
I wrote you two public letters on the 14th instant, since which I have received yours of July the 13th. I shall always be pleased to receive from you, in a private way, such communications as you might not choose to put into a public letter.
I have the honor to be, with very sincere esteem, Dear Sir,
your most obedient, humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
Paris, August 28, 1735.
Dear Sir,
I wrote you on the 5th of July by Mr. Franklin, and on the 12th of the same month by Monsieur Houdon. Since that date, yours of June the 16th, by Mr. Mazzei, has been received. Every thing looks like peace here. The settlement between the Emperor and Dutch is not yet published, but it is believed to be agreed on. Nothing is done, as yet, between him and the Porte. He is much wounded by the confederation of several of the Germanic body, at the head of which is the King of Prussia, and to which the King of England, as Elector of Hanover, is believed to accede. The object is to preserve the constitution of that empire. It shows that these princes entertain serious jealousies of the ambition of the Emperor, and this will very much endanger the election of his nephew as King of the Romans. A late Arrêt of this court against the admission of British manufactures produces a great sensation in England. I wish it may produce a disposition there to receive our commerce in all their dominions, on advantageous terms. This is the only balm which can heal the wounds that it has received. It is but too true, that that country furnished markets for three fourths of the exports of the eight northernmost states. A truth not proper to be spoken of, but which should influence our proceedings with them.
The July French packet having arrived without bringing any news of Mr. Lambe, if the English one of the same month be also arrived, without news of him, I expect Mr. Adams will concur with me in sending some other person to treat with the Barbary States. Mr. Barclay is willing to go, and I have proposed him to Mr. Adams, but have not yet received his answer. The peace expected between Spain and Algiers will probably not take place. It is said the former was to have given a million of dollars. Would it not be prudent to send a minister to Portugal? Our commerce with that country is very important; perhaps more so than with any other country in Europe. It is possible too, that they might permit our whaling vessels to refresh in Brazil, or give some other indulgences in America. The lethargic character of their ambassador here, gives a very unhopeful aspect to a treaty on this ground. I lately spoke with him on the subject, and he has promised to interest himself in obtaining an answer from his court.
I have waited to see what was the pleasure of Congress, as to the secretaryship of my office here; that is, to see whether they proposed to appoint a secretary of legation, or leave me to appoint a private secretary. Colonel Humphreys’ occupation in the despatches and records of the matters which relate to the general commissions, does not afford him leisure to aid me in my office, were I entitled to ask that aid. In the mean time, the long papers which often accompany the communications between the ministers here and myself, and the other business of the office, absolutely require a scribe. I shall, therefore, on Mr. Short’s return from the Hague, appoint him my private secretary, ‘til congress shall think proper to signify their pleasure. The salary allowed Mr. Franklin, in the same office, was one thousand dollars a year. I shall presume that Mr Short may draw the same allowance from the funds of the United States here. As soon as I shall have made this appointment, I shall give official notice of it to Mr. Jay, that Congress may, if they disapprove it, say so.
I am much pleased with your land ordinance, and think it improved from the first, in the most material circumstances. I had mistaken the object of the division of the lands among the States. I am sanguine in my expectations of lessening our debts by this fund, and have expressed my expectations to the minister and others here. I see by the public papers, you have adopted the dollar as your money unit. In the arrangement of coins, I proposed, I ought to have inserted a gold coin of five dollars, which, being within two shillings of the value of a guinea, would be very convenient.
The English papers are so incessantly repeating their lies, about the tumults, the anarchy, the bankruptcies, and distresses of America, that these ideas prevail very generally in Europe. At a large table where I dined the other day, a gentleman from Switzerland expressed his apprehensions for the fate of Dr. Franklin, as he said he had been informed, that he would be received with stones by the people, who were generally dissatisfied with the Revolution, and incensed against all those who had assisted in bringing it about. I told him his apprehensions were just, and that the people of America would probably salute Dr. Franklin with the same stones they had thrown at the Marquis Fayette. The reception of the Doctor is an object of very general attention, and will weigh in Europe, as an evidence of the satisfaction or dissatisfaction of America with their Revolution. As you are to be in Williamsburg early in November, this is the last letter I shall write you till about that time.
I am, with very sincere esteem, dear Sir,
your friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO CAPTAIN JOHN PAUL JONES.
Paris, August 29,1785.
Sir,
I received this moment a letter from the Marechal de Castries, of which the enclosed is a copy. Having engaged to him to solicit orders for the payment of any part of this money due to French subjects to be made here, and moreover engaged that, in the mean time, I will order payment, should any such claimants offer themselves; I pray you to furnish me with all the evidence you can, as to what French subjects may be entitled to any part of the monies you will receive, and to how much, each of them; and also to advise me by what means I can obtain a certain roll of all such claimants.
I am, Sir, with great esteem,
your most obedient, humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
Paris, August 30,1785.
Sir,
I had the honor of writing to you on the 14th instant, by a Mr. Cannon of Connecticut, who was to sail in the packet. Since that date yours of July the 13th has come to hand. The times for the sailing of the packets being somewhat deranged, I avail myself of a conveyance for the present, by the Mr. Fitzhugbs of Virginia, who expect to land at Philadelphia.
I enclose you a correspondence which has taken place between the Marechal de Castries, minister of the Marine, and myself. It is on the subject of the prize-money, due to the officers and crew of the Alliance, for prizes taken in Europe, under the command of Captain Jones. That officer has been here, under the direction of Congress, near two years, soliciting the liquidation and payment of that money. Infinite delays had retarded the liquidation till the month of June. It was expected, when the liquidation was announced to be completed, that the money was to be received. The M. de Castries doubted the authority of Captain Jones to receive it, and wrote to me for information. I wrote him a letter dated July the 10th, which seemed to clear away that difficulty. Another arose. A Mr. Puchilberg presented powers to receive the money. I wrote then the letter of August the 3rd, and received that of the M. de Castries, of August the 12th, acknowledging he was satisfied as to this difficulty, but announcing another; to wit, that possibly some French subjects might have been on board the Alliance, and therefore, that Captain Jones ought to give security for the repayment of their portions. Captain Jones had before told me there was not a Frenchman on board that vessel, but the captain. I inquired of Mr. Barclay.. He told me he was satisfied there was not one. Here, then, was a mere possibility, a shadow of right, opposed to a certain, to a substantial one, which existed in the mass of the crew, and which was likely to be delayed; for it was not to be expected that Captain Jones could, in a strange country, find the security required. These difficulties I suppose to have been conjured up, one after another, by Mr. Puchilberg, who wanted to get hold of the money. I saw but one way to cut short these everlasting delays, which were ruining the officer soliciting the payment of the money, and keeping our seamen out of what they had hardly fought for, years ago. This was, to undertake to ask an order from Congress, for the payment of any French claimants by their banker in Paris; and, in the mean time, to undertake to order such payment, should any such claimant prove his title, before the pleasure of Congress should be made known to me. I consulted with Mr. Barclay, who seemed satisfied I might venture this undertaking, because no such claim could be presented. I therefore wrote the letter of August the 17th, and received that of August the 26th, finally closing this tedious business. Should what I have done, not meet the approbation of Congress, I would pray their immediate sense, because it is not probable that the whole of this money will be paid so hastily, but that their orders may arrive in time to stop a sufficiency for any French claimants who may possibly exist. The following paragraph of a letter from Captain Jones, dated L’Orient, August the 25th, 1785, further satisfies me, that my undertaking amounted to nothing in fact. He says, ‘It is impossible that any legal demands should be made on you for French subjects, in consequence of your engagement to the Marechal. The Alliance was manned in America, and I never heard of any person’s having served on board that frigate, who had been born in France, except the captain, who, as I was informed, had, in America, abjured the church of Rome, and been naturalized.’ Should Congress approve what I have done, I will then ask their resolution for the payment, by their banker here, of any such claims as may be properly authenticated, and will moreover pray of you an authentic roll of the crew of the Alliance, with the sums to be allowed to each person; on the subject of which roll, Captain Jones, in the letter above mentioned, says, ‘I carried a set of the rolls with me to America, and before I embarked in the French fleet at Boston, I put them into the hands of Mr. Secretary Livingston, and they were sealed up among the papers of his office, when I left America.’ I think it possible that Mr. Puchilberg may excite claims. Should any name be offered which shall not be found on the roll, it will be a sufficient disproof of the pretension. Should it be found on the roll, it will remain to prove the identity of person, and to inquire if payment may not have been made in America. I conjecture from the journals of Congress of June the 2nd, that Landais, who, I believe, was the captain, may be in America. As his portion of prize-money may be considerable, I hope it will be settled in America, where only it can be known whether any advances have been made him.
The person at the head of the post office here, says, he proposed to Dr. Franklin a convention to facilitate the passage of letters through their office and ours, and that he delivered a draught of the convention proposed, that it might be sent to Congress. I think it possible he may be mistaken in this, as, on my mentioning it to Dr. Franklin, he did not recollect any such draught having been put into his hands. An answer, however, is expected by them. I mention it, that Congress may decide whether they will make any convention on the subject, and on what principle. The one proposed here was, that for letters passing hence into America, the French postage should be collected by our post-officers, and paid every six months, and for letters coming from America here, the American postage should be collected by the post-officers here, and paid to us in like manner. A second plan, however, presents itself; that is, to suppose the sums to be thus collected, on each side, will be equal, or so nearly equal, that the balance will not pay for the trouble of keeping accounts, and for the little bickerings that the settlement of accounts and demands of the balances may occasion: and therefore, to make an exchange of postage. This would better secure our harmony; but I do not know that it would be agreed to here. If not, the other might then be agreed to.
I have waited hitherto, supposing that Congress might, possibly, appoint a secretary to the legation here, or signify their pleasure that I should appoint a private secretary, to aid me in my office. The communications between the ministers and myself requiring often that many and long papers should be copied, and that in a shorter time than could be done by myself, were I otherwise unoccupied, other correspondences and proceedings, of all which copies must be retained, and still more the necessity of having some confidential person, who, in case of any accident to myself, might be authorized to take possession of the instructions, letters, and other papers of the office, have rendered it absolutely necessary for me to appoint a private secretary. Colonel Humphreys finds full occupation, and often more than he can do, in writing and recording the despatches and proceedings of the general commissions. I shall, therefore, appoint Mr. Short, on his return from the Hague, with an express condition, that the appointment shall cease whenever Congress shall think proper to make any other arrangement. He will, of course, expect the allowance heretofore made to the private secretaries of the ministers, which, I believe, has been a thousand dollars a year.
An improvement is made here in the construction of muskets, which it may be interesting to Congress to know, should they at any time propose to procure any. It consists in the making every part of them so exactly alike, that what belongs to any one, may be used for every other musket in the magazine. The government here has examined and approved the method, and is establishing a large manufactory for the purpose of putting it into execution. As yet, the inventor has only completed the lock of the musket, on this plan. He will proceed immediately to have the barrel, stock, and other parts, executed in the same way. Supposing it might be useful to the United States, I went to the workman. He presented me the parts of fifty locks taken to pieces, and arranged in compartments. I put several together myself, taking pieces at hazard as they came to hand, and they fitted in the most perfect manner. The advantages of this, when arms need repair, are evident. He effects it by tools of his own contrivance, which, at the same time, abridge the work, so that he thinks he shall be able to furnish the musket two livres cheaper than the common price. But it will be two or three years before he will be able to furnish any quantity. I mention it now, as it may have an influence on the plan for furnishing our magazines with this arm.
Every thing in Europe remains as when I wrote you last. The peace between Spain and Algiers has the appearance of being broken off. The French packet having arrived without Mr. Lambe, or any news of him, I await Mr. Adams’s acceding to the proposition mentioned in my last. I send you the Gazettes of Leyden and France to this date, and have the honor to be, with the highest respect and esteem, Sir,
your most obedient, humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JAMES MADISON.
Paris, September 1,1785.
Dear Sir,
My last to you by Monsieur de Doradour, was dated May the 11th. Since that, I have received yours of January the 22nd with six copies of the revisal, and that of April the 27th by Mr. Mazzei.
All is quiet here. The Emperor and Dutch have certainly agreed, though they have not published their agreement. Most of his schemes in Germany must be postponed, if they are not prevented by the confederacy of many of the Germanic body, at the head of which is the King of Prussia, and to which the Elector of Hanover is supposed to have acceded. The object of the league is to preserve the members of the empire in their present state. I doubt whether the jealousy entertained of this prince, and which is so fully evidenced by this league, may not defeat the election of his nephew to be King of the Romans, and thus produce an instance of breaking the lineal succession. Nothing is as yet done between him and the Turks. If any thing is produced in that quarter, it will not be for this year. The court of Madrid has obtained the delivery of the crew of the brig Betsey, taken by the Emperor of Morocco. The Emperor had treated them kindly, new-clothed them, and delivered them to the Spanish minister, who sent them to Cadiz. This is the only American vessel ever taken by the Barbary States. The Emperor continues to give proofs of his desire to be in friendship with us, or, in other words, of receiving us into the number of his tributaries. Nothing further need be feared from him. I wish the Algerines may be as easily dealt with. I fancy the peace expected between them and Spain is not likely to take place. I am well informed that the late proceedings in America have produced a wonderful sensation in England in our favor. I mean the disposition, which seems to be becoming general, to invest Congress with the regulation of our commerce, and, in the mean time, the measures taken to defeat the avidity of the British government, grasping at our carrying business. I can add with truth, that it was not till these symptoms appeared in America, that I have been able to discover the smallest token of respect towards the United States, in any part of Europe. There was an enthusiasm towards us, all over Europe, at the moment of the peace. The torrent of lies published unremittingly, in every day’s London paper, first made an impression, and produce a coolness. The republication of these lies in most of the papers of Europe (done probably by authority of the governments to discourage emigrations) carried them home to the belief of every mind. They supposed every thing in America was anarchy, tumult, and civil war. The reception of the Marquis Fayette gave a check to these ideas. The late proceedings seem to be producing a decisive vibration in our favor. I think it possible that England may ply before them. It is a nation which nothing but views of interest can govern. If they produce us good there, they will here also. The defeat of the Irish propositions is also in our favor.
I have at length made up the purchase of books for you, as far as it can be done at present. The objects which I have not yet been able to get, I shall continue to seek for. Those purchased, are packed this morning in two trunks, and you have the catalogue and prices herein inclosed. The future charges of transportation shall be carried into the next bill. The amount of the present is 1154 livres, 13 sous, which, reckoning the French crown of six livres at six shillings and eight pence, Virginia money, is £64. 3s., which sum you will be so good as to keep in your hands, to be used occasionally in the education of my nephews, when the regular resources disappoint you. To the same use I would pray you to apply twenty-five guineas, which I have lent the two Mr. Fitz-hughs of Marmion, and which I have desired them to repay into your hands. You will of course deduct the price of the revisals, and of any other articles you may have been so kind as to pay for me. Greek and Roman authors are dearer here, than, I believe, any where in the world. Nobody here reads them; wherefore they are not reprinted. Don Ulloa, in the original, is not to be found. The collection of tracts on the economies of different nations, we cannot find; nor Amelot’s Travels into China. I shall send these two trunks of books to Havre, there to wait a conveyance to America; for as to the fixing the packets there, it is as uncertain as ever. The other articles you mention, shall be procured as far as they can be. Knowing that some of them would be better got in London, I commissioned Mr. Short, who was going there, to get them. He has not yet returned. They will be of such a nature as that I can get some gentleman who may be going to America, to take them in his portmanteau. Le Maire being now able to stand on his own legs, there will be no necessity for your advancing him the money I desired, if it is not already done. I am anxious to hear from you on the subject of my Notes on Virginia. I have been obliged to give so many of them here, that I fear their getting published. I have received an application from the Directors of the public buildings, to procure them a plan for their capitol. I shall send them one taken from the best morsel of ancient architecture now remaining. It has obtained the approbation of fifteen or sixteen centuries, and is, therefore, preferable to any design which might be newly contrived. It will give more room, be more convenient, and cost less, than the plan they sent me. Pray encourage them to wait for it, and to execute it. It will be superior in beauty to any thing in America, and not inferior to any thing in the world. It is very simple. Have you a copying press? If you have not, you should get one. Mine (exclusive of paper, which costs a guinea a ream) has cost me about fourteen guineas. I would give ten times that sum, to have had it from the date of the stamp act. I hope you will be so good as to continue your communications, both of the great and small kind, which are equally useful to me. Be assured of the sincerity with which I am, Dear Sir,
your friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MESSRS. DUMAS AND SHORT.
Paris, September 1, 1785.
Gentlemen,
I have been duly honored with the receipt of your separate letters of August 23rd, and should sooner have returned an answer, but that as you had written also to Mr. Adams, I thought it possible I might receive his sentiments on the subject, in time for the post. Not thinking it proper to lose the occasion of the post, I have concluded to communicate to you my separate sentiments, which you will of course pay attention to, only so far as they may concur with what you shall receive from Mr. Adams.
On a review of our letters to the Baron de Thulemeyer, I do not find that we had proposed that the treaty should be in two columns, the one English, and the other what he should think proper. We certainly intended to have proposed it. We had agreed together that it should be an article of system with us, and the omission of it, in this instance, has been accidental. My own opinion, therefore, is, that to avoid the appearance of urging new propositions when every thing appeared to be arranged, we should agree to consider the French column as the original, if the Baron de Thulemeyer thinks himself bound to insist on it: but if the practice of his court will admit of the execution in the two languages, each to be considered as equally original, it would be very pleasing to me, as it will accommodate it to our views, relieve us from the embarrassment of this precedent, which may be urged against us on other occasions, and be more agreeable to our country, where the French language is spoken by very few. This method will be also attended with the advantage, that if any expression in any part of the treaty is equivocal in the one language, its true sense will be known by the corresponding passage in the other.
The errors of the copyist, in the French column, you will correct of course.
I have the honor to be, with very high esteem, Gentlemen,
your most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN ADAMS.
Paris, September 4, 1785.
Dear Sir,
On receipt of your favors of August the 18th and 23rd, I conferred with Mr. Barclay on the measures necessary to be taken to set our treaty with the piratical States into motion, through his agency. Supposing that we should begin with the Emperor of Morocco, a letter to the Emperor and instructions to Mr. Barclay, seemed necessary. I have therefore sketched such outlines for these, as appear to me to be proper. You will be so good as to detract, add to, or alter them as you please, to return such as you approve under your signature, to which I will add mine. A person understanding English, French, and Italian, and at the same time meriting confidence, was not to be met with here. Colonel Franks, understanding the two first languages perfectly, and a little Spanish instead of Italian, occurred to Mr. Barclay as the fittest person he could employ for a secretary. We think his allowance (exclusive of his travelling expenses and his board, which will be paid by Mr. Barclay in common with his own) should be between one hundred and one hundred and fifty guineas a year. Fix it where you please, between these limits. What is said in the instructions to Mr. Barclay, as to his own allowance, was proposed by himself. My idea as to the partition of the whole sum to which we are limited (eighty thousand dollars), was, that one half of it should be kept in reserve for the Algerines. They certainly possess more than half the whole power of the piratical States. I thought then, that Morocco might claim the half of the remainder, that is to say, one fourth of the whole. For this reason, in the instructions, I propose twenty thousand dollars as the limit of the expenses of the Morocco treaty. Be so good as to think of it, and make it what you please. I should be more disposed to enlarge than abridge it, on account of their neighborhood to our Atlantic trade. I did not think that these papers should be trusted through the post office, and therefore, as Colonel Franks is engaged in the business, he comes with them. Passing by the diligence, the whole expense will not exceed twelve or fourteen guineas. I suppose we are bound to avail ourselves of the co-operation of France. I will join you, therefore, in any letter you think proper to write to the Count de Vergennes. Would you think it expedient to write to Mr. Carmichael, to interest the interposition of the Spanish court? I will join you in any thing of this kind you will originate. In short, be so good as to supply whatever you may think necessary. With respect to the money, Mr. Jay’s information to you was, that it was to be drawn from Holland. It will rest therefore with you, to avail Mr. Barclay of that fund, either by your draft, or by a letter of credit to the bankers in his favor, to the necessary amount. I imagine the Dutch consul at Morocco may be rendered an useful character, in the remittances of money to Mr. Barclay, while at Morocco.
You were apprised, by a letter from Mr. Short, of the delay which had arisen in the execution of the treaty with Prussia. I wrote a separate letter, of which I enclose you a copy, hoping it would meet one from you, and set them again into motion.
I have the honor to be, with the highest respect, Dear Sir,
your most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
[The following are the sketches of the letter to the Emperor of Morocco, and of the instructions to Mr. Barclay, referred to in the preceding letter.]
HEADS FOR A LETTER TO THE EMPEROR OF MOROCCO.
That the United States of America, heretofore connected in government with Great Britain, had found it necessary for their happiness to separate from her, and to assume an independent station.
That, consisting of a number of separate States, they had confederated together, and placed the sovereignty of the whole, in matters relating to foreign nations, in a body consisting of delegates from every State, and called the Congress of the United States.
That Great Britain had solemnly confirmed their separation and acknowledged their independence.
That after the conclusion of the peace, which terminated the war in which they had been engaged for the establishment of their independence, the first attentions of Congress were necessarily engrossed by the re-establishment of order and regular government.
That they had, as soon as possible, turned their attention to foreign nations, and, desirous of entering into amity and commerce with them, had been pleased to appoint us, with Dr. Benjamin Franklin, to execute such treaties for this purpose, as should be agreed on by such nations, with us, or any two of us.
That Dr. Franklin having found it, necessary to return to America, the execution of these several commissions had devolved on us. That being placed as Ministers Plenipotentiary for the United States at the courts of England and France; this circumstance, with the commissions with which we are charged for entering into treaties with various other nations, puts it out of our power to attend at the other courts in person, and obliges us to negotiate by the intervention of confidential persons.
That, respecting the friendly dispositions shown by his Majesty, the Emperor of Morocco, towards the United States, and indulging the desire of forming a connection with a sovereign, so renowned for his power, his wisdom, and his justice, we had embraced the first moment possible, of assuring him of these the sentiments of our country and of ourselves, and of expressing to him our wishes to enter into a connection of friendship and commerce with him. That for this purpose, we had commissioned the bearer hereof, Thomas Barclay, a person in the highest confidence of the Congress of the United States, and as such, having been several years, and still being, their consul general with our great and good friend and ally, the King of France, to arrange with his Majesty the Emperor, those conditions which it might be advantageous for both nations to adopt, for the regulation of their commerce, and their mutual conduct towards each other.
That we deliver to him a copy of the full powers with which we are invested, to conclude a treaty with his Majesty, which copy he is instructed to present to his Majesty.
That though by these, we are not authorized to delegate to him the power of ultimately signing the treaty, yet such is our reliance on his wisdom, his integrity, and his attention to the instructions with which he is charged, that we assure his Majesty, the conditions which he shall arrange and send to us, shall be returned with our signature, in order to receive that of the person whom his Majesty shall commission for the same purpose.
HEADS OF INSTRUCTION TO MR. BARCLAY.
Congress having been pleased to invest us with full powers for entering into a treaty of amity and alliance with the Emperor of Morocco, and it being impracticable for us to attend his court in person, and equally impracticable, on account of our separate stations, to receive a minister from him, we have concluded to effect our object by the intervention of a confidential person. We concur in wishing to avail the United States of your talents in the execution of this business, and therefore furnish you with a letter to the Emperor of Morocco, to give due credit to your transactions with him.
We advise you to proceed by the way of Madrid, where you will have opportunities of deriving many lights from Mr. Carmichael, through whom many communications with the court of Morocco have already passed.
From thence you will proceed, by such route as you shall think best, to the court of the Emperor.
You will present to him our letter, with the copy of our full powers, with which you are furnished, at such time or times, and in such manner, as you shall find best.
You will proceed to negotiate with his minister the terms of a treaty of amity and commerce, as nearly conformed as possible to the draught we give you. Where alterations, which, in your opinion, shall not be of great importance, shall be urged by the other party, you are at liberty to agree to them. Where they shall be of great importance, and such as you think should be rejected, you will reject them: but where they are of great importance, and you think they may be accepted, you will ask time to take our advice, and will advise with us accordingly, by letter or by courier, as you shall think best. When the articles shall all be agreed, you will send them to us by some proper person, for our signature.
The whole expense of this treaty, including as well the expenses of all persons employed about it, as the presents to the Emperor and his servants, must not exceed twenty thousand dollars: and we urge you to use your best endeavors, to bring it as much below that sum as you possibly can. As custom may have rendered some presents necessary in the beginning or progress of this business, and before it is concluded, or even in a way to be concluded, we authorize you to conform to the custom, confiding in your discretion to hazard as little as possible, before a certainty of the event. We trust to you also to procure the best information, as to what persons, and in what form, these presents should be made, and to make them accordingly.
The difference between the customs of that and other courts, the difficulty of obtaining knowledge of those customs, but on the spot, and our great confidence in your discretion, induce us to leave to that, all other circumstances relative to the object of your mission. It will be necessary for you to take a secretary, well skilled in the French language, to aid you in your business, and to take charge of your papers in case of any accident to yourself. We think you may allow him ¦————-guineas a year, besides his expenses for travelling and subsistence. We engage to furnish your own expenses, according to the respectability of the character with which you are invested, but as to the allowance for your trouble, we wish to leave it to Congress. We annex hereto sundry heads of inquiry which we wish you to make, and to give us thereon the best information you shall be able to obtain. We desire you to correspond with us by every opportunity which you think should be trusted, giving us, from time to time, an account of your proceedings and prospects.
HEADS OF INQUIRY FOR MR. BARCLAY, AS TO MOROCCO.
1. Commerce. What are the articles of their export and import? What duties are levied by them on exports and imports? Do all nations pay the same, or what nations are favored, and how far? Are they their own carriers, or who carries for them? Do they trade themselves to other countries, or are they merely passive?
2. Ports. What are their principal ports? What depth of water in them? What works of defence protect these ports?
3. Naval force. How many armed vessels have they? Of what kind and force? What is the constitution of their naval force? What resources for increasing their navy? What number of seamen? Their cruising grounds, and seasons of cruising?
4. Prisoners. What is their condition and treatment? At what price are they ordinarily redeemed, and how?
Do they pay respect to the treaties they make?
Land forces. Their numbers, constitution, and respectability?
Revenues. Their amount.
Coins. What coins pass there, and at what rates?
TO DAVID HARTLEY.
Paris, September 5, 1785.
Dear Sir,
Your favor of April the 15th happened to be put into my hands at the same time with a large parcel of letters from America, which contained a variety of intelligence. It was then put where I usually place my unanswered letters; and I, from time to time, put off acknowledging the receipt of it, till I should be able to furnish you American intelligence worth communicating. A favorable opportunity, by a courier, of writing to you occurring this morning, what has been my astonishment and chagrin on reading your letter again, to find there was a case in it which required an immediate answer, but which, by the variety of matters, which happened to be presented to my mind, at the same time, had utterly escaped my recollection. I pray you to be assured, that nothing but this slip of memory would have prevented my immediate answer, and no other circumstance would have prevented its making such an impression on my mind, as that it could not have escaped. I hope you will therefore obliterate the imputation of want of respect, which, under actual appearances, must have arisen in your mind, but which would refer to an untrue cause the occasion of my silence. I am not sufficiently acquainted with the proceedings of the New York Assembly, to say, with certainty, in what predicament the lands of Mr. Upton may stand. But on conferring with Colonel Humphreys, who, being from the neighboring State, was more in the way of knowing what passed in New York, he thinks that the descriptions in their confiscation laws were such, as not to include a case of this nature. The first thing to be done by Mr. Upton is, to state his case to some intelligent lawyer of the country, that he may know with certainty whether they be confiscated, or not; and if not confiscated, to know what measures are necessary for completing and securing his grant. But if confiscated, there is then no other tribunal of redress but their General Assembly. If he is unacquainted there, I would advise him to apply to Colonel Hamilton, who was aid to General Washington, and is now very eminent at the bar, and much to be relied on. Your letter in his favor to Mr. Jay will also procure him the benefit of his counsel.
With respect to America, I will rather give you a general view of its situation, than merely relate recent events. The impost is still unpassed by the two States of New York and Rhode Island: for the manner in which the latter has passed it does not appear to me to answer the principal object, of establishing a fund, which, by being subject to Congress alone, may give such credit to the certificates of public debt, as will make them negotiable. This matter, then, is still suspended.
Congress have lately purchased the Indian right to nearly the whole of the land lying in the new State, bounded by lake Erie, Pennsylvania, and the Ohio. The northwestern corner alone is reserved to the Delawares and Wyandots. I expect a purchase is also concluded with other tribes, for a considerable proportion of the State next to this, on the north side of the Ohio. They have passed an ordinance establishing a land-office, considerably improved, I think, on the plan, of which I had the honor of giving you a copy. The lands are to be offered for sale to the highest bidder. For this purpose, portions of them are to be proposed in each State, that each may have the means of purchase carried equally to their doors, and that the purchasers may be a proper mixture of the citizens from all the different States. But such lots as cannot be sold for a dollar an acre, are not to be parted with. They will receive as money the certificates of public debt. I flatter myself that this arrangement will very soon absorb the whole of these certificates, and thus rid us of our domestic debt, which is four fifths of our whole debt. Our foreign debt will be then a bagatelle.
I think it probable that Vermont will be made independent, as I am told the State of New York is likely to agree to it. Maine will probably in time be also permitted to separate from Massachusetts. As yet, they only begin to think of it. Whenever the people of Kentucky shall have agreed among themselves, my friends write me word, that Virginia will consent to their separation. They will constitute the new State on the south side of Ohio, joining Virginia. North Corolina, by an act of their Assembly, ceded to Congress all their lands westward of the Allegany. The people inhabiting that territory thereon declared themselves independent, called their State by the name of Franklin, and solicited Congress to be received into the Union. But before Congress met, North Carolina (for what reasons I could never learn) resumed their session. The people, however, persist; Congress recommend to the State to desist from their opposition, and I have no doubt they will do it. It will, therefore, result from the act of Congress laying off the western country into new States, that these States will come into the Union in the manner therein provided, and without any disputes as to their boundaries.
I am told that some hostile transaction by our people at the Natchez, against the Spaniards, has taken place. If it be a fact, Congress will certainly not protect them, but leave them to be chastised by the Spaniards, saving the right to the territory. A Spanish minister being now with Congress, and both parties interested in keeping the peace, I think, if such an event has happened, it will be easily arranged.
I told you when here, of the propositions made by Congress to the States, to be authorized to make certain regulations in their commerce; and, that from the disposition to strengthen the hands of Congress, which was then growing fast, I thought they would consent to it. Most of them did so, and I suppose all of them would have done it, if they have not actually done it, but that events proved a much more extensive power would be requisite. Congress have, therefore, desired to be invested with the whole regulation of their trade, and for ever; and to prevent all temptations to abuse the power, and all fears of it, they propose that whatever monies shall be levied on commerce, either for the purpose of revenue, or by way of forfeitures or penalty, shall go directly into the coffers of the State wherein it is levied, without being touched by Congress. From the present temper of the States, and the conviction which your country has carried home to their minds, that there is no other method of defeating the greedy attempts of other countries to trade with them on unequal terms, I think they will add an article for this purpose to their Confederation. But the present powers of Congress over the commerce of the States, under the Confederation, seem not at all understood by your ministry. They say that body has no power to enter into a treaty of commerce; why then make one? This is a mistake. By the sixth article of the Confederation, the States renounce, individually, all power to make any treaty, of whatever nature, with a foreign nation. By the ninth article, they give the power of making treaties wholly to Congress with two reservations only. 1. That no treaty of commerce shall be made, which shall restrain the legislatures from making foreigners pay the same imposts with their own people: nor 2. from prohibiting the exportation or importation of any species of merchandise, which they might think proper. Were any treaty to be made which should violate either of these two reservations, it would be so far void. In the treaties, therefore, made with France, Holland, &c. this has been cautiously avoided. But are these treaties of no advantage to these nations? Besides the advantages expressly given by them, there results another, of great value. The commerce of those nations with the United States is thereby under the protection of Congress, and no particular State, acting by fits and starts, can harass the trade of France, Holland, &c. by such measures as several of them have practised against England, by loading her merchandise with partial imposts, refusing admittance to it altogether, excluding her merchants, &c. &c. For you will observe, that though, by the second reservation before mentioned, they can prohibit the importation of any species of merchandise, as, for instance, though they may prohibit the importation of wines in general, yet they cannot prohibit that of French wines in particular. Another advantage is, that the nations having treaties with Congress, can and do provide in such treaties for the admission of their consuls, a kind of officer very necessary for the regulation and protection of commerce. You know that a consul is the creature of treaty. No nation, without an agreement, can place an officer in another country, with any powers or jurisdiction whatever. But as the States have renounced the separate power of making treaties with foreign nations, they cannot separately receive a consul: and as Congress have, by the Confederation, no immediate jurisdiction over commerce, as they have only a power of bringing that jurisdiction into existence by entering into a treaty, till such treaty be entered into, Congress themselves cannot receive a consul. Till a treaty then, there exists no power in any part of our government, federal or particular, to admit a consul among us: and if it be true, as the papers say, that you have lately sent one over, he cannot be admitted by any power in existence to an exercise of any function. Nothing less than a new article, to be agreed to by all the States, would enable Congress, or the particular States, to receive him. You must not be surprised then, if he be not received.
I think I have by this time tired you with American politics, and will therefore only add assurances of the sincere regard and esteem, with which I have the honor to be, Dear Sir,
your most obedient, humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO BARON GEISMER.
Paris, September 6, 1785.
Dear Sir,
Your letter of March the 28th, which I received about a month after its date, gave me a very real pleasure, as it assured me of an existence which I valued, and of which I had been led to doubt. You are now too distant from America, to be much interested in what passes there. From the London gazettes, and the papers copying them, you are led to suppose that all there is anarchy, discontent, and civil war. Nothing, however, is less true. There are not on the face of the earth, more tranquil governments than ours, nor a happier and more contented people. Their commerce has not as yet found the channels, which their new relations with the world will offer to best advantage, and the old ones remain as yet unopened by new conventions. This occasions a stagnation in the sale of their produce, the only truth among all the circumstances published about them. Their hatred against Great Britain, having lately received from that nation new cause and new aliment, has taken a new spring. Among the individuals of your acquaintance, nothing remarkable has happened. No revolution in the happiness of any of them has taken place, except that of the loss of their only child to Mr. and Mrs. Walker, who, however, left them a grandchild for their solace, and that of your humble servant, who remains with no other family than two daughters, the elder here (who was of your acquaintance), the younger in Virginia, but expected here the next summer. The character in which I am here, at present, confines me to this place, and will confine me as long as I continue in Europe. How long this will be, I cannot tell. I am now of an age which does not easily accommodate itself to new manners and new modes of living: and I am savage enough to prefer the woods, the wilds, and the independence of Monticello, to all the brilliant pleasures of this gay capital. I shall, therefore, rejoin myself to my native country, with new attachments, and with exaggerated esteem for its advantages; for though there is less wealth there, there is more freedom, more ease, and less misery. I should like it better, however, if it could tempt you once more to visit it: but that is not to be expected. Be this as it may, and whether fortune means to allow or deny me the pleasure of ever seeing you again, be assured that the worth which gave birth to my attachment, and which still animates it, will continue to keep it up while we both live, and that it is with sincerity I subscribe myself, Dear Sir,
your friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN LANGDON.
Paris, September 11, 1785.
Dear Sir,
Your Captain Yeaton being here, furnishes me an opportunity of paying the tribute of my congratulations on your appointment to the government of your State, which I do sincerely. He gives me the grateful intelligence of your health, and that of Mrs. Langdon. Anxious to promote your service, and believing he could do it by getting himself naturalized here, and authorized to command your vessel he came from Havre to Paris. But on making the best inquiries I could, it seemed that the time requisite to go through with this business, would be much more than he could spare. He therefore declined it. I wish it were in my power to give you a hope that our commerce, either with this country, or its islands, was likely to be put on better footing. But if it be altered at all, it will probably be for the worse. The regulations respecting their commerce are by no means sufficiently stable to be relied on.
Europe is in quiet, and likely to remain so. The affairs of the Emperor and Dutch are as good as settled, and no other cloud portends any immediate storm. You have heard much of American vessels taken by the Barbary pirates. The Emperor of Morocco took one last winter (the brig Betsey of Philadelphia); he did not however reduce the crew to slavery, nor confiscate the vessel or cargo. He has lately delivered up the crew on the solicitation of the Spanish court. No other has ever been taken by them. There are, indeed, rumors of one having been lately taken by the Algerines. The fact is possible, as there is nothing to hinder their taking them, but it is not as yet confirmed. I have little doubt that we shall be able to place our commerce on a popular footing with the Barbary States this summer, and thus not only render our navigation to Portugal and Spain safe, but open the Mediterranean as formerly. In spite of treaties, England is still our enemy. Her hatred is deep-rooted and cordial, and nothing is wanting with her but the power, to wipe us and the land we live on out of existence. Her interest, however, is her ruling passion! and the late American measures have struck at that so vitally, and with an energy, too, of which she had thought us quite incapable, that a possibility seems to open of forming some arrangement with her. When they shall see decidedly, that, without it we shall suppress their commerce with us, they will be agitated by their avarice on the one hand, and their hatred and their fear of us on the other. The result of this conflict of dirty passions is yet to be awaited. The body of the people of this country love us cordially. But ministers and merchants love nobody. The merchants here are endeavoring to exclude, us from their islands. The ministers will be governed in it by political motives, and will do it, or not do it, as these shall appear to dictate, without love or hatred to any body. It were to be wished that they were able to combine better the various circumstances, which prove, beyond a doubt, that all the advantages of their colonies result, in the end, to the mother country. I pray you to present me in the most friendly terms to Mrs. Langdon, and be assured of the esteem with which I am
your Excellency’s most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson
TO LISTER ASQUITH.
Paris, September 14, 1785.
Sir,
Several of your letters have been received, and we have been occupied in endeavors to have you discharged: but these have been ineffectual. If our information be right, you are mistaken in supposing you are already condemned. The Farmers General tell us, you are to be tried at Brest, and this trial may perhaps be a month hence. From that court you may appeal to the Parliament of Rennes, and from that to the King in Council. They say, that from the depositions sent to them, there can be no doubt you came to smuggle, and that in that case, the judgment of the law is a forfeiture of the vessel and cargo, a fine of a thousand livres on each of you, and six years’ condemnation to the galleys. These several appeals will be attended with considerable expense. They offer to discharge your persons and vessel (but not the cargo) on your paying two thousand livres, and the costs already incurred; which are three or four hundred more. You will therefore choose, whether to go through the trial, or to compromise, and you are the best judge, what may be the evidence for or against you. In either case, I shall render you all the service I can. I will add, that if you are disposed to have the matter tried, I am of opinion, that, if found against you, there will be no danger of their sending you to the galleys; so that you may decide what course you will take, without any bias from that fear. If you choose to compromise, I will endeavor to have it done for you, on the best terms we can. I fear they will abate little from the two thousand livres, because Captain Deville, whom you sent here, fixed the matter by offering that sum, and has done you more harm than good. I shall be glad if you will desire your lawyer to make out a state of your case, (which he may do in French,) and send it to me. Write me also yourself a plain and full narration of your voyage, and the circumstances which have brought so small a vessel, with so small a cargo, from America into France. As far as we yet know them, they are not in your favor. Inform me who you are, and what papers you have on board. But do not state to me a single fact which is not true: for if I am led by your information to advance any thing which they shall prove to be untrue, I will abandon your case from that moment: whereas, sending me a true statement, I will make the best of it I can. Mr. Barclay, the American consul, will be here some few days yet. He will be, as he has already been, of much service to you, if the information I ask both from yourself and your lawyer, can come before his departure. I repeat my assurances of doing whatever I can for you, and am, Sir,
your very humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN ADAMS.
Paris, September 19, 1785.
Dear Sir,
Lambe has arrived. He brings new full powers to us from Congress, to appoint persons to negotiate with the Barbary States; but we are to sign the treaties. Lambe has not even a recommendation from them to us, but it seems clear that he would be approved by them. I told him of Mr. Barclay’s appointment to Morocco, and proposed Algiers to him. He agrees. A small alteration in the form of our despatches will be necessary, and, of course, another courier shall be despatched to you on the return of Colonel Franks, for your pleasure herein.
I am, with great esteem,
your friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.*
[* The original of the above was in cipher; though, as in
the case of most of the Author’s letters in cipher, he
prepared and preserved a literal copy of it.]
TO JAMES MADISON.
Paris, September 20, 1785.
Dear Sir,
By Mr. Fitzhugh, you will receive my letter of the first instant. He is still here, and gives me an opportunity of again addressing you much sooner than I should have done, but for the discovery of a great piece of inattention. In that letter I send you a detail of the cost of your books, and desire you to keep the amount in your hands, as if I had forgot that a part of it was in fact your own, as being a balance of what I had remained in your debt. I really did not attend to it in the moment of writing, and when it occurred to me, I revised my memorandum book from the time of our being in Philadelphia together, and stated our account from the beginning, lest I should forget or mistake any part of it. I enclose you this statement. You will always be so good as to let me know, from time to time, your advances for me. Correct with freedom all my proceedings for you, as, in what I do, I have no other desire than that of doing exactly what will be most pleasing to you.
I received this summer a letter from Messrs. Buchanan and Hay, as Directors of the public buildings desiring I would have drawn for them plans of sundry buildings, and, in the first place, of a capital. They fixed; for their receiving this plan, a day which Was within about six weeks of that on which their letter came to my hand. I engaged an architect of capital abilities in this business. Much time was requisite, after the external form was agreed on, to make the internal distribution convenient for the three branches of government. This time was much lengthened by my avocations to other objects, which I had no right to neglect. The plan however Was settled. The gentlemen had sent me one which they had thought of. The one agreed on here is more convenient, more beautiful, gives more room, and will not cost more than two thirds of what that would. We took for our model what is called the Maison Quarrée (Nismes), one of the most beautiful, if not the most beautiful and precious morsel of architecture left us by antiquity. It was built by Caius and Lucius Cæsar, and repaired by Louis XIV., and has the suffrage of all the judges of architecture who have seen it, as yielding to no one of the beautiful monuments of Greece, Rome, Palmyra, and Balbec, which late travellers have communicated to us. It is very simple, but it is noble beyond expression, and would have done honor to our country, as presenting to travellers a specimen of taste in our infancy, promising much for our maturer age. I have been much mortified with information, which I received two days ago from Virginia, that the first brick of the Capitol would be laid within a few days. But surely, the delay of this piece of a summer would have been repaired by the savings in the plan preparing here, were we to value its other superiorities as nothing. But how is a taste in this beautiful art to be formed in our countrymen, unless we avail ourselves of every occasion when public buildings are to be erected, of presenting to them models for their study and imitation? Pray try if you can effect the slopping of this work. I have written also to E. R. on the subject. The loss will be only of the laying the bricks already laid, or a part of them. The bricks themselves will do again for the interior walls, and one side wall and one end wall may remain, as they will answer equally well for our plan. This loss is not to be weighed against the saving of money which will arise, against the comfort of laying out the public money for something honorable, the satisfaction of seeing an object and proof of national good taste, and the regret and mortification of erecting a monument of our barbarism, which will be loaded with execrations as long as it shall endure. The plans are in good forwardness, and I hope will be ready within three or four weeks. They could not be stopped now, but on paying their whole price, which will be considerable. If the undertakers are afraid to undo what they have done, encourage them to it by a recommendation from the Assembly. You see I am an enthusiast on the subject of the arts. But it is an enthusiasm of which I am not ashamed, as its object is to improve the taste of my countrymen, to increase their reputation, to reconcile to them the respect of the world, and procure them its praise.
I shall send off your books, in two trunks, to Havre, within two or three days, to the care of Mr. Limozin, American agent there. I will advise you, as soon as I know by what vessel he forwards them. Adieu.
Yours affectionately,
Th: Jefferson.
TO EDMUND RANDOLPH.
Paris, September 20,1785.
Dear Sir,
Being in your debt for ten volumes of Buffon, I have endeavored to find something that would be agreeable to you to receive, in return. I therefore send you, by way of Havre, a dictionary of law, natural and municipal, in thirteen volumes 4to, called Le Code de l’Humanité. It is published by Felice, but written by him and several other authors of established reputation. It is an excellent work. I do not mean to say, that it answers fully to its title. That would have required fifty times the volume. It wants many articles which the title would induce us to seek in it. But the articles which it contains are well written. It is better than the voluminous Dictionnaire Diplomatique, and better also than the same branch of the Encyclopédie Méthodigue. There has been nothing published here, since I came, of extraordinary merit. The Encyclopédie Méthodique, which is coming out from time to time, must be excepted from this. It is to be had at two guineas less than the subscription price. I shall be happy to send you any thing in this way which you may desire. French books are to be bought here for two thirds of what they can in England. English and Greek and Latin authors cost from twenty-five to fifty per cent, more here than in England.
I received, some time ago, a letter from Messrs. Hay and Buchanan, as Directors of the public buildings, desiring I would have plans drawn for our public buildings, and in the first place for the capitol. I did not receive their letter till within about six weeks of the time they had fixed on for receiving the drawings. Nevertheless, I engaged an excellent architect to comply with their desire. It has taken much time to accommodate the external adopted, to the internal arrangement necessary for the three branches of government. However, it is effected on a plan, which, with a great deal of beauty and convenience within, unites an external form on the most perfect model of antiquity now existing. This is the Maison Quarrée of Nismes, built by Caius and Lucius Cæsar, and repaired by Louis XIV., which, in the opinion of all who have seen it, yields, in beauty, to no piece of architecture on earth. The gentlemen enclosed me a plan of which they had thought. The one preparing here will be more convenient, give more room, and cost but two thirds of that: and as a piece of architecture, doing honor to our country, will leave nothing to be desired. The plans will be ready soon. But, two days ago, I received a letter from Virginia, informing me the first brick of the capitol would be laid within a few days. This mortifies my extremely. The delay of this summer would have been amply repaid by the superiority and economy of the plan preparing here. Is it impossible to stop the work where it is? You will gain money by losing what is done, and general approbation, instead of occasioning a regret, which will endure as long as your building does. How is a taste for a chaste and good style of building to be formed in our countrymen, unless we seize all occasions which the erection of public buildings offers, of presenting to them models for their imitation? Do, my dear Sir, exert your influence to stay the further progress of the work, till you can receive these plans. You will only lose the price of laying what bricks are already laid, and of taking part of them asunder. They will do again for the inner walls. A plan for a prison will be sent at the same time.
Mazzei is here, and in pressing distress for money. I have helped him as far as I have been able, but particular circumstances put it out of my power to do more. He is looking with anxiety to the arrival of every vessel, in hopes of relief through your means. If he does not receive it soon, it is difficult to foresee his fate.
The quiet which Europe enjoys at present, leaves nothing to communicate to you in the political way. The Emperor and Dutch still differ about the quantum of money to be paid by the latter; they know not for what. Perhaps their internal convulsions will hasten them to a decision. France is improving her navy, as if she were already in a naval war: yet I see no immediate prospect of her having occasion for it. England is not likely to offer war to any nation, unless, perhaps, to ours. This would cost us our whole shipping: but in every other respect, we might flatter ourselves with success. But the most successful war seldom pays for its losses. I shall be glad to hear from you when convenient, and am, with much esteem, Dear Sir,
your friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN ADAMS.
Paris, September 24, 1785.
Dear Sir,
I have received your favor of the 18th, enclosing your compliments on your presentation. The sentiments you therein expressed, were such as were entertained in America till the commercial proclamation, and such as would again return, were a rational conduct to be adopted by Great Britain. I think, therefore, you by no means compromitted yourself or our country, nor expressed more than it would be our interest to encourage, if they were disposed to meet us. I am pleased, however, to see the answer of the King. It bears the marks of suddenness and surprise, and as he seems not to have had time for reflection, we may suppose he was obliged to find his answer in the real sentiments of his heart if that heart has any sentiment. I have no doubt however that it contains the real creed of an Englishman, and that the word which he has let escape is the true word of the enigma. ‘The moment I see such sentiments as yours prevail, and a disposition to give this country the preference, I will,’ &c. All this I steadfastly believe. But the condition is impossible. Our interest calls for a perfect equality in our conduct towards these two nations; but no preferences any where. If, however, circumstances should ever oblige us to show a preference, a respect for our character, if we had no better motive, would decide to which it should be given.
My letters from members of Congress render it doubtful, whether they would not rather that full time should be given for the present disposition of America to mature itself, and to produce a permanent improvement in the federal constitution, rather than, by removing the incentive, to prevent the improvement. It is certain that our commerce is in agonies at present, and that these would be relieved by opening the British ports in the West Indies. It remains to consider, whether a temporary continuance under these sufferings would be paid for, by the amendment it is likely to produce. However, I believe there is no fear that Great Britain will puzzle us, by leaving it in our choice to hasten or delay a treaty.
Is insurance made on Houdon’s life? I am uneasy about it, lest we should hear of any accident. As yet there is no reason to doubt their safe passage. If the insurance is not made, I will pray you to have it done immediately.
As I have not received any London newspapers as yet, I am obliged to ask you what is done as to them, lest the delay should proceed from some obstacle to be removed.
There is a Mr. Thompson at Dover, who has proposed to me a method of getting them post-free: but I have declined resorting to it, till I should know in what train the matter is at present.
I have the honor to be, with the most perfect esteem, Dear Sir,
your friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
Paris, September 24,1785.
Dear Sir,
My letter of September the 19th, written the morning after Mr. Lambe’s arrival here, will inform you of that circumstance. I transmit you herewith, copies of the papers he brought to us on the subject of the Barbary treaties. You will see by them, that Congress have adopted the very plan which we were proposing to pursue. It will now go on with less danger of objection from the other parties. The receipt of these new papers, therefore, has rendered necessary no change, in matter of substance, in the despatches we had prepared. But they render some formal changes necessary. For instance, in our letter of credence for Mr. Barclay to the Emperor of Morocco, it becomes improper to enter into those explanations which seemed proper when that letter was drawn; because Congress in their letter enter into those explanations. In the letter to the Count de Vergennes, it became proper to mention the new full powers received from Congress, and which, in some measure, accord with the idea communicated by him to us, from the Marechal de Castries. These and other formal alterations, which appeared necessary to me, I have made, leaving so much of the original draughts, approved and amended by you, as were not inconsistent with these alterations. I have therefore had these prepared fair, to save you the trouble of copying; yet, wherever you choose to make alterations, you will be so good as to make them; taking, in that case, the trouble of having new fair copies made out.
You will perceive by Mr. Jay’s letter, that Congress had not thought proper to give Mr. Lambe any appointment. I imagine they apprehended it might interfere with measures actually taken by us. Notwithstanding the perfect freedom which they are pleased to leave to us, on this subject, I cannot feel myself clear of that bias, which a presumption of their pleasure gives, and ought to give. I presume that Mr. Lambe met their approbation, because of the recommendations he carried from the Governor and State of Connecticut, because of his actual knowledge of the country and people of the States of Barbary, because of the detention of these letters from March to July, which, considering their pressing-nature, would otherwise have been sent by other Americans, who, in the mean time, have come from New York to Paris; and because, too, of the information we received by Mr. Jarvis. These reasons are not strong enough to set aside our appointment of Mr. Barclay to Morocco: that I think should go on, as no man could be sent who would enjoy more the confidence of Congress. But they are strong enough to induce me to propose to you the appointment of Lambe to Algiers. He has followed for many years the Barbary trade, and seems intimately acquainted with those States. I have not seen enough of him to judge of his abilities. He seems not deficient, as far as I can see, and the footing on which he comes, must furnish a presumption for what we do not see. We must say the same as to his integrity; we must rely for this on the recommendations he brings, as it is impossible for us to judge of this for ourselves. Yet it will be our duty to use such reasonable cautions as are in our power. Two occur to me. 1. To give him a clerk capable of assisting and attending to his proceedings, and who, in case he thought any thing was going amiss, might give us information. 2. Not to give him a credit on Van Staphorst and Willinck, but let his drafts be made on yourself, which, with the knowledge you will have of his proceedings, will enable you to check them, if you are sensible of any abuse intended. This will give you trouble; but as I have never found you declining trouble, when it is necessary, I venture to propose it. I hope it will not expose you to inconvenience, as by instructing Lambe to insert in his drafts a proper usance, you can, in the mean time, raise the money for them by drawing on Holland. I must inform you that Mr. Barclay wishes to be put on the same footing with Mr. Lambe, as to this article, and therefore I return you your letter of credit on Van Staphorst &, Co. As to the first article, there is great difficulty. There is nobody at Paris fit for the undertaking, who would be likely to accept it. I mean there is no American, for I should be anxious to place a native in the trust. Perhaps you can send us one from London. There is a Mr. Randall there, from New York, whom Mr. Barclay thinks might be relied on very firmly for integrity and capacity. He is there for his health; perhaps you can persuade him to go to Algiers in pursuit of it. If you cannot, I really know not what will be done. It is impossible to propose to Bancroft to go in a secondary capacity. Mr. Barclay and myself have thought of Cairnes, at L’Ori-ent, as a dernier ressort. But it is uncertain, or rather improbable, that he will undertake it. You will be pleased in the first place, to consider of my proposition to send Lambe to Algiers; and in the next, all the circumstances before detailed, as consequences of that.
The enclosed letter from Richard O’Bryan furnishes powerful motives for commencing, by some means or other, the treaty with Algiers, more immediately than would be done, if left on Mr. Barclay. You will perceive by that, that two of our vessels, with their crews and cargoes, have been carried captive into that port. What is to be done as to those poor people? I am for hazarding the supplementary instruction to Lambe, which accompanies these papers. Alter it, or reject it, as you please. You ask what I think of claiming the Dutch interposition. I doubt the fidelity of any interposition too much to desire it sincerely. Our letters to this court, heretofore, seemed to oblige us to communicate with them on the subject. If you think the Dutch would take amiss our not applying to them, I will join you in the application. Otherwise, the fewer who are apprized of our proceedings, the better. To communicate them to the States of Holland, is to communicate them to the whole world.
Mr. Short returned last night, and brought the Prussian treaty, duly executed in English and French. We may send it to Congress by the Mr. Fitzhughs going from hence. Will you draw and sign a short letter for that purpose? I send you a copy of a letter received from the Marquis Fayette. In the present unsettled state of American commerce, I had as lieve avoid all further treaties, except with American powers. If Count Merci, therefore, does not propose the subject to me, I shall not to him, nor do more than decency requires, if he does propose it. I am, with great esteem, Dear Sir,
your most obedient, humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO F. HOPKINSON.
Paris, September 25, 1785.
Dear Sir,
My last to you was of the 6th of July. Since that, I have received yours of July the 23rd. I do not altogether despair of making something of your method of quilling, though, as yet, the prospect is not favorable. I applaud much your perseverance in improving this instrument, and benefiting mankind almost in spite of their teeth. I mentioned to Piccini the improvement with which I am entrusted. He plays on the piano-forte, and therefore did not feel himself personally interested. I hope some better opportunity will yet fall in my way of doing it justice. I had almost decided, on his advice, to get a piano-forte for my daughter; but your last letter may pause me, till I see its effect.
Arts and arms are alike asleep for the moment. Ballooning indeed goes on. There are two artists in the neighborhood of Paris, who seem to be advancing towards the desideratum in this business. They are able to rise and fall at will, without expending their gas, and to deflect forty-five degrees from the course of the wind.
I desired you in my last to send the newspapers, notwithstanding the expense. I had then no idea of it. Some late instances have made me perfectly acquainted with it. I have therefore been obliged to adopt the following plan. To have my newspapers, from the different States, enclosed to the office for Foreign Affairs, and to desire Mr. Jay to pack the whole in a box, and send it by the packet as merchandise, directed to the American consul at L’Orient, who will forward it to me by the periodical wagons. In this way they will only cost me livres where they now cost me guineas, I must pray you, just before the departure of every French packet, to send my papers on hand to Mr. Jay, in this way. I do not know whether I am subject to American postage or not, in general; but I think newspapers never are. I have sometimes thought of sending a copy of my Notes to the Philosophical Society, as a tribute due to them: but this would seem as if I considered them as worth something, which I am conscious they are not. I will not ask you for your advice on this occasion, because it is one of those on which no man is authorized to ask a sincere opinion. I shall therefore refer it to further thoughts.
I am, with very sincere esteem, Dear Sir,
your friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO LISTER ASQUITH.
Paris, September 26,1785.
Sir,
I have received your letter of September the 19th, with your log-book and other papers. I now wait for the letter from your lawyer, as, till I know the real nature and state of your process, it is impossible for me to judge what can be done for you here. As soon as I receive them, you shall hear from me. In the mean time, I supposed it would be a comfort to you to know that your papers had come safe to hand, and that I shall be attentive to do whatever circumstances will admit.
I am, Sir, your very humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO R. IZARD.
Paris, September 26,1783.
Dear Sir,
I received, a few days ago, your favor of the 10th of June, and am to thank you for the trouble you have given yourself, to procure me information on the subject of the commerce of your State. I pray you, also, to take the trouble of expressing my acknowledgments to the Governor and Chamber of Commerce, as well as to Mr. Hall, for the very precise details on this subject, with which they have been pleased to honor me. Your letter of last January, of which you make mention, never came to my hands. Of course, the papers now received are the first and only ones which have come safe. The infidelities of the post-offices, both of England and France, are not unknown to you. The former are the most rascally, because they retain one’s letters, not choosing to take the trouble of copying them. The latter, when they have taken copies, are so civil as to send the originals, re-sealed clumsily with a composition, on which they had previously taken the impression of the seal. England shows no dispositions to enter into friendly connections with us. On the contrary, her detention of our posts, seems to be the speck which is to produce a storm. I judge that a war with America would be a popular war in England. Perhaps the situation of Ireland may deter the ministry from hastening it on. Peace is at length made between the Emperor and Dutch. The terms are not published, but it is said he gets ten millions of florins, the navigation of the Scheldt not quite to Antwerp, and two forts. However, this is not to be absolutely relied on. The league formed by the King of Prussia against the Emperor is a most formidable obstacle to his ambitious designs. It certainly has defeated his views on Bavaria, and will render doubtful the election of his nephew to be King of the Romans. Matters are not yet settled between him and the Turk. In truth, he undertakes too much. At home he has made some good regulations.
Your present pursuit being (the wisest of all) agriculture, I am not in a situation to be useful to it. You know that France is not the country most celebrated for this art. I went the other day to see a plough which was to be worked by a windlass, without horses or oxen. It was a poor affair. With a very troublesome apparatus, applicable only to a dead level, four men could do the work of two horses. There seems a possibility that the great desideratum in the use of the balloon may be obtained. There are two persons at Javel (opposite to Auteuil) who are pushing this matter. They are able to rise and fall at will, without expending their gas, and they can deflect forty-five degrees from the course of the wind.
I took the liberty of asking you to order me a Charleston newspaper. The expense of French postage is so enormous that I have been obliged to desire that my newspapers, from the different States, may be sent to the office for Foreign Affairs at New York; and I have requested of Mr. Jay to have them always packed in a box, and sent by the French packets as merchandise to the care of the American consul at L’Orient, who will send them on by the periodical wagons. Will you permit me to add this to the trouble I have before given you, of ordering the printer to send them under cover to Mr. Jay, by such opportunities by water, as occur from time to time. This request must go to the acts of your Assembly also. I shall be on the watch to send you any thing that may appear here on the subjects of agriculture or the arts, which may be worth your perusal, I sincerely congratulate Mrs. Izard and yourself on the double accession to your family by marriage and a new birth. My daughter values much your remembrance of her, and prays to have her respects presented to the ladies and yourself. In this I join her, and shall embrace with pleasure every opportunity of assuring you of the sincere esteem, with which I have the honor to be, Dear Sir, your most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO RICHARD O’BRYAN.
Paris, September 29, 1785.
Sir,
I have received your letter, and shall exert myself for you. Be assured of hearing from me soon: but say nothing to any body, except what may be necessary to comfort your companions. I add no more, because the fate of this letter is uncertain. I am, Sir,
your very humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MR. BELLINI.
Paris, September 30,1785.
Dear Sir,
Your estimable favor, covering a letter to Mr. Mazzei, came to hand on the 26th instant. The letter to Mr. Mazzei was put into his hands in the same moment, as he happened to be present. I leave to him to convey to you all his complaints, as it will be more agreeable to me to express to you the satisfaction I received, on being informed of your perfect health. Though I could not receive the same pleasing news of Mrs. Bellini, yet the philosophy, with which I am told she bears the loss of health, is a testimony the more, how much she deserved the esteem I bear her. Behold me at length on the vaunted scene of Europe! It is not necessary for your information, that I should enter into details concerning it. But you are, perhaps, curious to know how this new scene has struck a savage of the mountains of America. Not advantageously, I assure you. I find the general fate of humanity here most deplorable. The truth of Voltaire’s observation offers itself perpetually, that every man here must be either the hammer or the anvil. It is a true picture of that country to which they say we shall pass hereafter, and where we are to see God and his angels in splendor, and crowds of the damned trampled under their feet. While the great mass of the people are thus suffering under physical and moral oppression, I have endeavored to examine more nearly the condition of the great, to appreciate the true value of the circumstances in their situation which dazzle the bulk of spectators, and, especially, to compare it with that degree of happiness which is enjoyed in America by every class of people. Intrigues of love occupy the younger, and those of ambition the elder part of the great. Conjugal love having no existence among them, domestic happiness, of which that is the basis, is utterly unknown. In lieu of this, are substituted pursuits which nourish and invigorate all our bad passions, and which offer only moments of ecstacy, amidst days and months of restlessness and torment. Much, very much inferior, this, to the tranquil, permanent felicity, with which domestic society in America blesses most of its inhabitants; leaving them to follow steadily those pursuits which health and reason approve, and rendering truly delicious the intervals of those pursuits.
In science, the mass of the people is two centuries behind ours; their literati, half a dozen years before us. Books, really good, acquire just reputation in that time, and so become known to us, and communicate to us all their advances in knowledge. Is not this delay compensated, by our being placed out of the reach of that swarm of nonsensical publications, which issues daily from a thousand presses, and perishes almost in issuing? With respect to what are termed polite manners, without sacrificing too much the sincerity of language, I would wish my countrymen to adopt just so much of European politeness, as to be ready to make all those little sacrifices of self, which really render European manners amiable, and relieve society from the disagreeable scenes to which rudeness often subjects it. Here, it seems that a man might pass a life without encountering a single rudeness. In the pleasures of the table they are far before us, because with good taste they unite temperance. They do not terminate the most sociable meals by transforming themselves into brutes. I have never yet seen a man drunk in France, even among the lowest of the people. Were I to proceed to tell you how much I enjoy their architecture, sculpture, painting, music, I should want words. It is in these arts they shine. The last of them, particularly, is an enjoyment, the deprivation of which with us cannot be calculated. I am almost ready to say, it is the only thing which from my heart I envy them, and which, in spite of all the authority of the Decalogue, I do covet. But I am running on in an estimate of things infinitely better known to you than to me, and which will only serve to convince you, that I have brought with me all the prejudices of country, habit, and age. But whatever I may allow to be charged to me as prejudice, in every other instance, I have one sentiment at least founded on reality: it is that of the perfect esteem which your merit and that of Mrs. Bellini have produced, and which will for ever enable me to assure you of the sincere regard with which I am, Dear Sir,
your friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
JAMES MADISON, of William and Mary College.
Paris, October 2, 1785.
Dear Sir,
I have duly received your favor of April the 10th, by Mr. Mazzei. You therein speak of a new method of raising water by steam, which you suppose will come into general use. I know of no new method of that kind, and suppose (as you say that the account you have received of it is very imperfect) that some person has represented to you, as new, a fire-engine erected at Paris, and which supplies the greater part of the town with water. But this is nothing more than the fire-engine you have seen described in the books of hydraulics, and particularly in the Dictionary of Arts and Sciences, published in 8vo, by Owen, the idea of which was first taken from Papin’s Digester. It would have been better called the steam-engine. The force of the steam of water, you know, is immense. In this-engine it is made to exert itself towards the working of pumps. That of Paris is, I believe, the largest known, raising four hundred thousand cubic feet (French) of water, in twenty-four hours; or rather I should have said, those of Paris, for there are two under one roof, each raising that quantity.
The Abbe Rochon not living at Paris, I have not had an opportunity of seeing him, and of asking him the questions you desire, relative to the crystal of which I wrote you. I shall avail myself of the earliest opportunity I can, of doing it. I shall cheerfully execute your commands as to the Encyclopédie, when I receive them. The price will be only thirty guineas. About half the work is out. The volumes of your Buffon, which are spoiled, can be replaced here.
I expect that this letter will be carried by the Mr. Fitzhughs, in a ship from Havre to Portsmouth. I have therefore sent to Havre some books, which I expected would be acceptable to you. These are the Bibliothèque Physico-oeconomique, which will give you most of the late improvements in the arts; the Connoissance des Terns for 1786 and 1787, which is as late as they are published; and some pieces on air and fire, wherein you will find all the discoveries hitherto made on these subjects. These books are made into a packet, with your address on them, and are put into a trunk wherein is a small packet for Mr. Wythe, another for Mr. Page, and a parcel of books, without direction, for Peter Carr. I have taken the liberty of directing the trunk to you, as the surest means of its getting safe. I pay the freight of it here, so that there will be no new demands, but for the transportation from the ship’s side to Williamsburg, which I will pray you to pay; and as much the greatest part is for my nephew, I will take care to repay it to you.
In the last volume of the Connoissance des Terns, you will find the tables for the planet Herschel. It is a curious circumstance, that this planet was seen thirty years ago by Mayer, and supposed by him to be a fixed star. He accordingly determined a place for it, in his catalogue of the zodiacal stars, making it the 964th of that catalogue. Bode, of Berlin, observed in 1781, that this star was missing. Subsequent calculations of the motion of the planet Herschel show, that it must have been, at the time of Mayer’s observation, where he had placed his 964th star.
Herschel has pushed his discoveries of double stars, now, to upwards of nine hundred, being twice the number of those communicated in the Philosophical Transactions. You have probably seen, that a Mr. Pigott had discovered periodical variations of light in the star Algol. He has observed the same in the n of Antinous, and makes the period of variation seven days, four hours, and thirty minutes, the duration of the increase sixty-three hours, and of the decrease thirty-six hours. What are we to conclude from this? That there are suns which have their orbits of revolution too? But this would suppose a wonderful harmony in their planets, and present a new scene, where the attracting powers should be without, and not within the orbit. The motion of our sun would be a miniature of this. But this must be left to you astronomers.
I went some time ago to see a machine, which offers something new. A man had applied to a light boat, a very large screw, the thread of which was a thin plate, two feet broad, applied by its edge spirally round a small axis. It somewhat resembled a bottle-brush, if you will suppose the hairs of the bottle-brush joining together, and forming a spiral plane. This, turned on its axis in the air, carried the vessel across the Seine. It is, in fact, a screw which takes hold of the air and draws itself along by it: losing, indeed, much of its effort by the yielding nature of the body it lays hold of, to pull itself on by. I think it may be applied in the water with much greater effect, and to very useful purposes Perhaps it may be used also for the balloon.
It is impossible but you must have heard long ago of the machine for copying letters at a single stroke, as we had received it in America before I left there. I have written a long letter to my nephew, in whose education I feel myself extremely interested. I shall rely much on your friendship for conducting him in the plan I mark out for him, and for guarding him against those shoals, on which youth sometimes shipwreck. I trouble you to present to Mr. Wythe my affectionate remembrance of him, and am with very great esteem, Dear Sir,
your friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO DR. FRANKLIN.
Paris, October 5,1785.
Dear Sir,
A vessel sailing from Havre to Philadelphia, furnishes the Messrs. Fitzhughs with a passage to that place. To them, therefore, I confide a number of letters and packets which I have received for you from sundry quarters, and which, I doubt not, they will deliver safe. Among these is one from M. Du Plessis. On receipt of your letter, in answer to the one I had written you, on the subject of his memorial, I sent to M. La Motte, M. Chaumont, and wherever else I thought there was a probability of finding out Du Plessis’ address. But all in vain. I meant to examine his memoir, as you desired, and to have it copied. Lately, he came and brought it with him, copied by himself. He desired me to read it, and enclose it to you, which I have done.
We have no public news worth communicating to you, but the signing of preliminaries between the Emperor and Dutch. The question is, then, with whom the Emperor will pick the next quarrel. Our treaty with Prussia goes by this conveyance. But it is not to be spoken of till a convenient time is allowed for exchanging ratifications.
Science offers nothing new since your departure, nor any new publication worth your notice. All your friends here are well. Those in England have carried you captive to Algiers. They have published a letter, as if written by Truxen, the 20th of August, from Algiers, stating the circumstances of the capture, and that you bore your slavery to admiration. I happened to receive a letter from Algiers, dated August the 24th, informing me that two vessels were then there, taken from us, and naming the vessels and captains. This was a satisfactory proof to us, that you were not there. The fact being so, we would have gladly dispensed with the proof, as the situation of our countrymen there was described as very distressing.
Were I to mention all those who make inquiries after you, there would be no end to my letter. I cannot, however, pass over those of the good old Countess d’Hoditot, with whom I dined on Saturday, at Sanois. They were very affectionate. I hope you have had a good passage. Your essay in crossing the channel gave us great hopes you would experience little inconvenience on the rest of the voyage. My wishes place you in the bosom of your friends, in good health, and with a well grounded prospect of preserving it long, for your own sake, for theirs, and that of the world.
I am, with the sincerest attachment and respect, Dear Sir,
your most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO SAMUEL OSGOOD.
Paris, October 5, 1785.
Dear Sir,
It was with very sincere pleasure I heard of your appointment to the board of treasury, as well from the hope that it might not be disagreeable to yourself, as from the confidence that your administration would be wise. I heartily wish the States may, by their contributions, enable you to re-establish a credit, which cannot be lower than at present, to exist at all. This is partly owing to their real deficiencies, and partly to the lies propagated by the London papers, which are probably paid for by the minister, to reconcile the people to the loss of us. Unluckily, it indisposes them, at the same time, to form rational connections with us. Should this produce the amendment of our federal constitution, of which your papers give us hopes, we shall receive a permanent indemnification for a temporary loss.
All things here promise an arrangement between the Emperor and Dutch. Their ministers have signed preliminary articles, some of which, however, leave room for further cavil. The Dutch pay ten millions of florins, yield some forts and territory, and the navigation of the Scheldt to Saftingen. Till our treaty with England be fully executed, it is desirable to us, that all the world should be in peace. That done, their wars would do us little harm.
I find myself under difficulties here, which I will take the liberty of explaining to you as a friend. Mr. Carmichael lately drew a bill on Mr. Grand for four thousand livres, I suppose for his salary. Mr. Grand said, he was not used to accept drafts but by the desire of Dr. Franklin, and rested it on me to say, whether this bill should be paid or not. I thought it improper, that the credit of so confidential a person, as Mr. Carmichael, should be affected by a refusal, and therefore advised payment. Mr. Dumas has drawn on me for twenty-seven hundred livres, his half year’s salary, informing me he always drew on Dr. Franklin. I shall advise the payment. I have had loan-office bills, drawn on the commissioners of the United States, presented to me. My answer has been, ‘These are very old bills. Had they been presented while those gentlemen were in Europe, they would have been paid. You have kept them up till Dr. Franklin, the last of them, has returned to America; you must therefore send them there, and they will be paid. I am not the drawee described in the bill.’ It is impossible for me to meddle with these bills. The gentlemen who had been familiar with them, from the beginning, who kept books of them, and knew well the form of these books, often paid bills twice. But how can I interfere with them, who have not a scrip of a pen on their subject, who never saw a book relating to them, and who, if I had the books, should much oftener be bewildered in the labyrinth, than the gentlemen who have kept them? I think it, therefore, most advisable, that what bills remain out, should be sent back to America for payment, and therefore advise Mr. Barclay to return thither all the books and papers relative to them. There, is the proper and ultimate deposite of all records of this nature. All these articles are very foreign to my talents, and foreign also, as I conceive, to the nature of my duties. Dr. Franklin was obliged to meddle with them, from the circumstances which existed. But, these having ceased, I suppose it practicable for your board to direct the administration of your monies here, in every circumstance. It is only necessary for me to draw my own allowances, and to order payment for services done by others, by my direction, and within the immediate line of my office; such as paying couriers, postage, and other extraordinary services, which must rest on my discretion, and at my risk, if disapproved by Congress. I will thank you for your advice on this subject, and if you think a resolution of your board necessary, I will pray you to send me such a one, and that it may relieve me from all concerns with the money of the United States, other than those I have just spoken of. I do not mean by this to testify a disposition to render no service but what is rigorously within my duty. I am the farthest in the world from this; it is a question I shall never ask myself; nothing making me more happy than to render any service in my power of whatever description. But I wish only to be excused from intermeddling in business, in which I have no skill, and should do more harm than good.
Congress were pleased to order me an advance of two quarters’ salary. At that time, I supposed that I might refund it, or spare so much from my expenses, by the time the third quarter became due. Probably, they might expect the same. But it has been impossible. The expense of my outfit, though I have taken it up on a scale as small as could be admitted, has been very far beyond what I had conceived. I have, therefore, not only been unable to refund the advance ordered, but been obliged to go beyond it. I wished to have avoided so much, as was occasioned by the purchase of furniture. But those who hire furniture, asked me forty per cent, a year for the use of it. It was better to buy, therefore; and this article, clothes, carriage, &c. have amounted to considerably more than the advance ordered. Perhaps it may be thought reasonable to allow me an outfit. The usage of every other nation has established this, and reason really pleads for it. I do not wish to make a shilling; but only my expenses to be defrayed, and in a moderate style. On the most moderate, which the reputation or interest of those I serve would admit, it will take me several years to liquidate the advances for my outfit. I mention this, to enable you to understand the necessities which have obliged me to call for more money than was probably expected, and, understanding them, to explain them to others. Being perfectly disposed to conform myself decisively to what shall be thought proper, you cannot oblige me more, than by communicating to me your sentiments hereon, which I shall receive as those of a friend, and govern myself accordingly.
I am, with the most perfect esteem, Dear Sir,
your friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN JAY.
Paris, October 6, 1785.
Sir,
My letter of August the 30th acknowledged the receipt of yours of July the 13th. Since that, I have received your letter of August the 13th, enclosing a correspondence between the Marquis de la Fayette and Monsieur de Calonne, and another of the same date, enclosing the papers in Fortin’s case. I immediately wrote to M. Limozin, at Havre, desiring he would send me a state of the case, and inform me what were the difficulties which suspended its decision. He has promised me, by letter, to do this as soon as possible, and I shall not fail in attention to it.
The Emperor and Dutch have signed preliminaries, which are now made public. You will see them in the papers which accompany this. They still leave a good deal to discussion. However, it is probable they will end in peace. The party in Holland, possessed actually of the sovereignty, wish for peace, that they may push their designs on the Stadtholderate. This country wishes for peace, because her finances need arrangement. The Bavarian exchange has produced to public view that jealousy and. rancor between the courts of Vienna and Berlin, which existed before, though it was smothered. This will appear by the declarations of the two courts. The demarcation between the Emperor and Turk does not advance. Still, however, I suppose neither of those two germs of war likely to open soon. I consider the conduct of France as the best evidence of this. If she had apprehended a war from either of those quarters, she would not have been so anxious to leave the Emperor one enemy the less, by placing him at peace with the Dutch. While she is exerting all her powers to preserve peace by land, and making no preparation which indicates a fear of its being disturbed in that quarter, she is pushing her naval preparations, with a spirit unexampled in time of peace. By the opening of the next spring, she will have eighty ships, of seventy-four guns and upwards, ready for sea at a moment’s warning; and the further constructions proposed, will probably, within two years, raise the number to an hundred. New regulations have been made, too, for perfecting the classification of her seamen; an institution, which, dividing all the seamen of the nation into classes, subjects them to tours of duty by rotation and enables government, at all times, to man their ships. Their works for rendering Cherbourg a harbor for their vessels of war, and Dunkirk, for frigates and privateers, leave now little doubt of success. It is impossible that these preparations can have in view any other nation than the English. Of course, they show a greater diffidence of their peace with them, than with any other power.
I mentioned to you, in my letter of August the 14th, that I had desired Captain John Paul Jones to inquire into the circumstances of Peyrouse’s expedition. I have now the honor of enclosing you copies of my letter to him, and of his answer. He refuses to accept of any indemnification for his expenses, which is an additional proof of his disinterested spirit, and of his devotion to the service of America. The circumstances are obvious, which indicate an intention to settle factories, and not colonies, at least, for the present. However, nothing shows for what place they are destined. The conjectures are divided between New Holland, and the northwest coast of America.
According to what I mentioned in my letter of August the 30th, I have appointed Mr. Short my secretary here. I enclose to you copies of my letters to him and Mr. Grand, which will show to Congress that he stands altogether at their pleasure. I mention this circumstance, that if what I have done meets with their disapprobation, they may have the goodness to signify it immediately, as I should otherwise conclude that they do not disapprove it. I shall be ready to conform myself to what would be most agreeable to them.
This will be accompanied by the gazettes of France and Ley-den, to the present date.
I have the honor to be, with sentiments of the highest esteem and respect, Sir,
your most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO ELBRIDGE GERRY.
Paris, October 11, 1785.
Dear Sir,
I received, last night, the letter signed by yourself and the other gentlemen, delegates of Massachusetts and Virginia, recommending Mr. Sayre for the Barbary negotiations. As that was the first moment of its suggestion to me, you will perceive by my letter of this day, to Mr Jay, that the business was already established in other hands, as your letter came at the same time with the papers actually signed by Mr. Adams, for Messrs. Barclay and Lambe, according to arrangements previously taken between us. I should, with great satisfaction, have acceded to the recommendation in the letter: not indeed as to Morocco, because, no better man than Mr. Barclay could have been substituted; but as to Algiers, Mr. Lambe being less known to me. However, I hope well of him, and rely considerably on the aid he will receive from his secretary, Mr. Randall, who bears a very good character. I suppose Mr. Adams entitled to the same just apology, as matters were settled otherwise, before he probably received your letter. I pray you to communicate this to the other gentlemen of your and our delegation as my justification.
The peace made between the Emperor and Dutch, leaves Europe quiet for this campaign. As yet, we do not know where the storm, dissipated for the moment, will gather again. Probably over Bavaria or Turkey. But this will be for another year.
When our instructions were made out, they were conceived on a general scale, and supposed that all the European nations would be disposed to form commercial connections with us. It is evident, however, that a very different degree of importance was annexed to these different states. Spain, Portugal, England, and France, were most important. Holland, Sweden, Denmark, in a middling degree. The others, still less so. Spain treats in another line. Portugal is disposed to do the same. England will not treat at all; nor will France, probably, add to her former treaty. Failing in the execution of these our capital objects, it has appeared to me, that the pushing the treaties with the lesser powers, might do us more harm than good, by hampering the measures the States may find it necessary to take, for securing those commercial interests, by separate measures, which is refused to be done here, in concert. I have understood through various channels, that the members of Congress wished a change in our instructions. I have, in my letter to Mr. Jay, of this date, mentioned the present situation and aspect of these treaties, for their information.
My letter of the 6th instant to Mr. Jay, having communicated what little there is new here, I have only to add assurances of the sincere esteem, with which I have the honor to be, Dear Sir,
your friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO THE COUNT DE VERGENNES.
Paris, October 11, 1785.
Sir,
I have the honor of enclosing to your Excellency, a report of the voyage of an American ship, the first which has gone to China. The circumstance which induces Congress to direct this communication, is the very friendly conduct of the consul of his Majesty at Macao, and of the commanders and other officers of the French vessels in those seas. It has been with singular satisfaction, that Congress have seen these added to the many other proofs of the cordiality of this nation towards our citizens. It is the more pleasing, when it appears in the officers of government, because it is then viewed as an emanation of the spirit of the government. It would be an additional gratification to Congress, in this particular instance, should any occasion arise of notifying those officers, that their conduct has been justly represented to your Excellency, on the part of the United States, and has met your approbation. Nothing will be wanting, on our part, to foster corresponding dispositions in our citizens, and we hope that proofs of their actual existence have appeared, and will appear, whenever, occasion shall offer. A sincere affection between the two people, is the broadest basis on which their peace can be built.
It will always be among the most pleasing functions of my office, to be made the channel of communicating the friendly sentiments of the two governments. It is additionally so, as it gives me an opportunity of assuring your Excellency of the high respect and esteem, with which I have the honor to be,
your Excellency’s most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN JAY.
Paris, October 11,1785.
Sir,
In my letter of August the 14th, I had the honor of expressing to you the uneasiness I felt at the delay of the instructions on the subject of the Barbary treaties, of which Mr.. Lambe was the bearer, and of informing you that I had proposed to Mr. Adams, that if he did not arrive either in the French or English packets, then expected, we should send some person to negotiate these treaties. As he did not arrive in those packets, and I found Mr. Barclay was willing to undertake the negotiations, I wrote to Mr. Adams (who had concurred in the proposition made him), informing him that Mr. Barclay would go, and proposing papers for our immediate signature. The day before the return of the courier, Mr. Lambe arrived with our instructions, the letters of credence, he enclosed in yours of March the 11th, 1785. Just about the same time, came to hand the letter No. 1, informing me, that two American vessels were actually taken and carried into Algiers, and leaving no further doubt that that power was exercising hostilities against us in the Atlantic. The conduct of the Emperor of Morocco had been such, as forbade us to postpone his treaty to that with Algiers. But the commencement of hostilities by the latter, and their known activity, pressed the necessity of immediate propositions to them. It was therefore thought best, while Mr. Barclay should be proceeding with the Emperor of Morocco, that some other agent should go to Algiers. We had few subjects to choose out of. Mr. Lambe’s knowledge of the country, of its inhabitants, of their manner of transacting business, the recommendations from his State to Congress, of his fitness for this employment, and other information founding a presumption that he would be approved, occasioned our concluding to send him to Algiers. The giving him proper authorities, and new ones to Mr. Barclay conformable to our own new powers, was the subject of a new courier between Mr. Adams and myself. He returned last night, and I have the honor of enclosing you copies of all the papers we furnish those gentlemen with; which will possess Congress fully of our proceedings herein. They are numbered from two to ten inclusive. The supplementary instruction to Mr. Lambe, No. 5, must rest for justification on the emergency of the case. The motives which led to it, must be found in the feelings of the human heart, in a partiality for those sufferers who are of our own country, and in the obligations of every government to yield protection to their citizens, as the consideration for their obedience. It will be a comfort to know, that Congress does not disapprove this step.
Considering the treaty with Portugal among the most interesting to the United States, I some time ago, took occasion at Versailles, to ask of the Portuguese ambassador, if he had yet received from his court an answer to our letter. He told me he had not, but that he would make it the subject of another letter. Two days ago, his secrétaire d’ambassade called on me, with a letter from his minister to the ambassador, in which was the following paragraph, as he translated it to me; and I committed it to writing from his mouth. ‘Your Excellency has communicated to us the substance of your conversation with the American minister. That power ought to have been already persuaded, by the manner in which its vessels have been received here; and consequently that his Majesty would have much satisfaction in maintaining perfect harmony and good understanding with the same United States. But it would be proper to begin with the reciprocal nomination, on both sides, of persons, who, at least with the character of agents, might reciprocally inform their constituents, of what might conduce to a knowledge of the interests of the two nations, without prejudice to either. This first step appears necessary to lead to the proposed object.’
By this, it would seem, that this power is more disposed to pursue a track of negotiation, similar to that which Spain has done. I consider this answer as definitive of all further measures, under our commission to Portugal. That to Spain was superseded by proceedings in another line. That to Prussia is concluded by actual treaty; to Tuscany will probably be so; and perhaps to Denmark: and these, I believe, will be the sum of the effects of our commissions for making treaties of alliance. England shows no disposition to treat. France, should her ministers be able to keep the ground of the Arrêt of August, 1784, against the clamors of her merchants, and should they be disposed, hereafter, to give us more, very probably will not bind herself to it by treaty, but keep her regulations dependent on her own will. Sweden will establish a free port at St. Bartholomew’s, which, perhaps, will render any new engagement, on our part, unnecessary. Holland is so immovable in her system of colony administration, that, as propositions to her, on that subject, would be desperate, they had better not be made. You will perceive by the letter No. 11, from the Marquis de la Fayette, that there is a possibility of an overture from the Emperor. A hint from the charge des affaires of Naples, lately, has induced me to suppose something of the same kind from thence. But the advanced period of our commissions now offers good cause for avoiding to begin, what probably cannot be terminated during their continuance; and with respect to these two, and all other powers not before mentioned, I doubt whether the advantages to be derived from treaties with them, will countervail the additional embarrassments they may impose on the States, when they shall proceed to make those commercial arrangements necessary to counteract the designs of the British cabinet. I repeat it, therefore, that the conclusion of the treaty with Prussia, and the probability of others with Denmark, Tuscany and the Barbary States, may be expected to wind up the proceedings of the general commissions. I think that, in possible events, it may be advantageous to us, by treaties with Prussia, Denmark, and Tuscany, to have secured ports in the Northern and Mediterranean seas. I have the honor to be, with sentiments of the highest respect and esteem,
Sir, your most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MESSRS. VAN STAPHORST.
Paris, October 12, 1785.
Gentlemen,
The receipt of your favor, of September the 19th, should not have been so long unacknowledged, but that I have been peculiarly and very closely engaged ever since it came to hand.
With respect to the expediency of the arrangement you propose to make with Mr. Parker, I must observe to you, that it would be altogether out of my province to give an official opinion, for your direction. These transactions appertain altogether to the commissioners of the treasury, to whom you have very properly written on the occasion. I shall always be willing, however, to apprize you of any facts I may be acquainted with, and which might enable you to proceed with more certainty; and even to give my private opinion, where I am acquainted with the subject, leaving you the most perfect liberty to give it what weight you may think proper. In the present case, I cannot give even a private opinion, because I am not told what are precisely the securities offered by Mr. Parker. So various are the securities of the United States, that unless they are precisely described by their dates, consideration, and other material circumstances, no man on earth can say what they are worth. One fact, however, is certain, that all debts of any considerable amount contracted by the United States, while their paper money existed, are subject to a deduction, and not payable at any fixed period. I think I may venture to say, also, that there are no debts of the United States, ‘on the same footing with the money loaned by Holland,’ except those due to the Kings of France and Spain. However, I hope you will soon receive the answer of the commissioners, which alone can decide authoritatively what can be done.
Congress have thought proper to entrust to Mr. Adams and myself a certain business, which may eventually call for great advances of money: perhaps four hundred thousand livres or upwards. They have authorized us to draw for this on their funds in Holland. The separate situation of Mr. Adams and myself rendering joint drafts inconvenient, we have agreed that they shall be made by him alone. You will be pleased, therefore, to give the same credit to these bills, drawn by him, as if they were also subscribed by me.
I have the honor to be, with high respect, Gentlemen,
your most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MONSIEUR DESBORDES.
Paris, October 12,1785.
Sir,
There are, in the prison of St. Pol de Léon, six or seven citizens of the United States of America, charged with having attempted a contraband of tobacco, but, as they say themselves, forced into that port by stress of weather. I believe that they are innocent. Their situation is described to me to be as deplorable, as should be that of men found guilty of the worst of crimes. They are in close jail, allowed three sous a day only, and unable to speak a word of the language of the country. I hope their distress, which it is my duty to relieve, and the recommendation of Mr. Barclay to address myself to you, will apologize for the liberty I take, of asking you to advise them what to do for their defence, to engage some good lawyer for them, and to pass to them the pecuniary reliefs necessary. I write to Mr. Lister Asquith, the owner of the vessel, that he may draw bills on me, from time to time, for a livre a day for every person of them, and for what may be necessary to engage a lawyer for him. I will pray the favor of you to furnish him money for his bills drawn on me for these purposes, which I will pay on sight. You will judge if he should go beyond this allowance, and be so good as to reject the surplus. I must desire his lawyer to send me immediately a state of their case, and let me know in what court their process is, and when it is likely to be decided. I hope the circumstances of the case will excuse the freedom I take; and I have the honor to be, with great respect, Sir,
your most obedient, humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO HOGENDORP.
Paris, October 13,1785.
Dear Sir,
Having been much engaged lately, I have been unable sooner to acknowledge the receipt of your favor of September the 8th. What you are pleased to say on the subject of my Notes, is more than they deserve. The condition in which you first saw them, would prove to you how hastily they had been originally written; as you may remember the numerous insertions I had made in them, from time to time, when I could find a moment for turning to them from other occupations. I have never yet seen Monsieur de Buffon. He has been in the country all the summer. I sent him a copy of the book, and have only heard his sentiments on one particular of it, that of the identity of the mammoth and elephant. As to this, he retains his opinion that they are the same. If you had formed any considerable expectations from our revised code of laws, you will be much disappointed. It contains not more than three or four laws which could strike the attention of a foreigner. Had it been a digest of all our laws, it would not have been comprehensible or instructive, but to a native. But it is still less so, as it digests only the British statutes and our own acts of Assembly, which are but a supplementary part of our law. The great basis of it is anterior to the date of the Magna Charta, which is the oldest statute extant. The only merit of this work is, that it may remove from our book-shelves about twenty folio volumes of statutes, retaining all the parts of them, which either their own merit or the established system of laws required.
You ask me what are those operations of the British nation, which are likely to befriend us, and how they will produce this effect? The British government, as you may naturally suppose, have it much at heart to reconcile their nation to the loss of America. This is essential to the repose, perhaps even to the safety of the King and his ministers. The most effectual engines for this purpose are the public papers. You know well, that that government always kept a kind of standing army of news-writers, who, without any regard to truth, or to what should be like truth, invented, and put into the papers, whatever might serve the ministers. This suffices with the mass of the people, who have no means of distinguishing the false from the true paragraphs of a newspaper. When forced to acknowledge our independence, they were forced to redouble their efforts to keep the nation quiet. Instead of a few of the papers, formerly engaged, they now engaged every one. No paper, therefore, comes out without a dose of paragraphs against America. These are calculated for a secondary purpose also, that of preventing the emigrations of their people to America. They dwell very much on American bankruptcies. To explain these, would require a long detail; but would show you that nine tenths of these bankruptcies are truly English bankruptcies, in no wise chargeable on America. However, they have produced effects the most desirable of all others for us. They have destroyed our credit, and thus checked our disposition to luxury; and, forcing our merchants to buy no more than they have ready money to pay for, they force them to go to those markets where that ready money will buy most. Thus you see, they check our luxury, they force us to connect ourselves with all the world, and they prevent foreign emigrations to our country, all of which I consider as advantageous to us. They are doing us another good turn. They attempt, without disguise, to possess themselves of the carriage of our produce, and to prohibit our own vessels from participating of it. This has raised a general indignation in America. The States see, however, that their constitutions have provided no means of counteracting it. They are therefore beginning to vest Congress with the absolute power of regulating their commerce, only reserving all revenue arising from it, to the State in which it is levied. This will consolidate our federal building very much, and for this we shall be indebted to the British.
You ask what I think on the expediency of encouraging our States to be commercial? Were I to indulge my own theory, I should wish them to practise neither commerce nor navigation, but to stand, with respect to Europe, precisely on the footing of China. We should thus avoid wars, and all our citizens would be husbandmen. Whenever, indeed, our numbers should so increase, as that our produce would overstock the markets of those nations who should come to seek it, the farmers must either employ the surplus of their time in manufactures, or the surplus of our hands must be employed in manufactures, or in navigation. But that day would, I think, be distant, and we should long keep our workmen in Europe, while Europe should be drawing rough materials, and even subsistence, from America. But this is theory only, and a theory which the servants of America are not at liberty to follow. Our people have a decided taste for navigation and commerce. They take this from their mother country; and their servants are in duty bound to calculate all their measures on this datum: we wish to do it by throwing open all the doors of commerce, and knocking off its shackles. But as this cannot be done for others, unless they will do it for us, and there is no great probability that Europe will do this, I suppose we shall be obliged to adopt a system which may shackle them in our ports, as they do us in theirs. With respect to the sale of our lands, that cannot begin till a considerable portion shall have been surveyed. They cannot begin to survey till the fall of the leaf of this year, nor to sell probably till the ensuing spring. So that it will be yet a twelvemonth, before we shall be able to judge of the efficacy of our land-office, to sink our national debt. It is made a fundamental, that the proceeds shall be solely and sacredly applied as a sinking fund, to discharge the capital only of the debt.
It is true that the tobaccos of Virginia go almost entirely to England. The reason is, the people of that State owe a great debt there, which they are paying as fast as they can. I think I have now answered your several queries, and shall be happy to receive your reflections on the same subjects, and at all times to hear of your welfare, and to give you assurances of the esteem, with which I have the honor to be, Dear Sir,
your most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO J. BANNISTER, JUNIOR.
Paris, October 15,1785.
Dear Sir,
I should sooner have answered the paragraph in your letter, of September the 19th, respecting the best seminary for the education of youth, in Europe, but that it was necessary for me to make inquiries on the subject. The result of these has been, to consider the competition as resting between Geneva and Rome. They are equally cheap, and probably are equal in the course of education pursued. The advantage of Geneva is, that students acquire there the habit of speaking French. The advantages of Rome are, the acquiring a local knowledge of a spot so classical and so celebrated; the acquiring the true pronunciation of the Latin language; a just taste in the fine arts, more particularly those of painting, sculpture, architecture, and music; a familiarity with those objects and processes of agriculture, which experience has shown best adapted to a climate like ours; and lastly, the advantage of a fine climate for health. It is probable, too, that by being boarded in a French family, the habit of speaking that language may be obtained. I do not count on any advantage to be derived in Geneva from a familiar acquaintance with the principles of that government. The late revolution has rendered it a tyrannical aristocracy, more likely to give ill, than good ideas to an American. I think the balance in favor of Rome. Pisa is sometimes spoken of, as a place of education. But it does not offer the first and third of the advantages of Rome. But why send an American youth to Europe for education? What are the objects of an useful American education? Classical knowledge, modern languages, chiefly French, Spanish, and Italian; Mathematics, Natural Philosophy, Natural History, Civil History, and Ethics. In Natural Philosophy, I mean to include Chemistry and Agriculture, and in Natural History, to include Botany, as well as the other branches of those departments. It is true, that the habit of speaking the modern languages cannot be so well acquired in America; but every other article can be as well acquired at William and Mary College, as at any place in Europe. When college education is done with, and a young man is to prepare himself for public life, he must cast his eyes (for America) either on Law or Physic. For the former, where can he apply so advantageously as to Mr. Wythe? For the latter, he must come to Europe: the medical class of students, therefore, is the only one which need come to Europe. Let us view the disadvantages of sending a youth to Europe. To enumerate them all, would require a volume. I will select a few. If he goes to England, he learns drinking, horse-racing, and boxing. These are the peculiarities of English education. The following circumstances are common to education in that, and the other countries of Europe. He acquires a fondness for European luxury,and dissipation, and a contempt for the simplicity of his own country; he is fascinated with the privileges of the European aristocrats, and sees, with abhorrence, the lovely equality which the poor enjoy with the rich in his own country; he contracts a partiality for aristocracy or monarchy; he forms foreign friendships which will never be useful to him, and loses the season of life for forming in his own country those friendships, which, of all others, are the most faithful and permanent; he is led by the strongest of all the human passions into a spirit for female intrigue, destructive of his own and others’ happiness, or a passion for whores, destructive of his health, and in both cases, learns to consider fidelity to the marriage bed as an ungentlemanly practice, and inconsistent with happiness; he recollects the voluptuary dress and arts of the European women, and pities and despises the chaste affections and simplicity of those of his own country; he retains, through life, a fond recollection, and a hankering after those places, which were the scenes of his first pleasures and of his first connections; he returns to his own country a foreigner, unacquainted with the practices of domestic economy necessary to preserve him from ruin, speaking and writing his native tongue as a foreigner, and therefore unqualified to obtain those distinctions, which eloquence of the pen and tongue ensures in a free country; for, I would observe to you, that what is called style in writing or speaking, is formed very early in life, while the imagination is warm, and impressions are permanent. I am of opinion, that there never was an instance of a man’s writing or speaking his native tongue with elegance, who passed from fifteen to twenty years of age out of the country where it was spoken. Thus, no instance exists of a person’s writing two languages perfectly. That will always appear to be his native language, which was most familiar to him in his youth. It appears to me then, that an American coming to Europe for education, loses in his knowledge, in his morals, in his health, in his habits, and in his happiness. I had entertained only doubts on this head, before I came to Europe: what I see and hear, since I came here, proves more than I had even suspected. Cast your eye over America: who are the men of most learning, of most eloquence, most beloved by their countrymen, and most trusted and promoted by them? They are those who have been educated among them, and whose manners, morals, and habits, are perfectly homogeneous with those of the country.
Did you expect by so short a question, to draw such a sermon on yourself? I daresay you did not. But the consequences of foreign education are alarming to me, as an American. I sin, therefore, through zeal, whenever I enter on the subject. You are sufficiently American to pardon me for it. Let me hear of your health, and be assured of the esteem with which I am, Dear Sir,
your friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MR. CARMICHAEL.
Paris, October 18, 1785.
Dear Sir,
Your favor of the 29th of September came safely to hand: the constant expectation of the departure of the persons whom I formerly gave you reason to expect, has prevented my writing, as it has done yours. They will probably leave this in a week, but their route will be circuitous and attended with delays. Between the middle and last of November, they may be with you. By them, you will receive a cipher, by which you may communicate with Mr. Adams and myself. I should have sent it by Baron Dreyer, the Danish minister; but I then expected our own conveyance would have been quicker. Having mentioned this gentleman, give me leave to recommend him to your acquaintance. He is plain, sensible, and open: he speaks English well, and had he been to remain here, I should have cultivated his acquaintance much. Be so good as to present me very respectfully to him.
This being to go by post, I shall only add the few articles of general American news, by the last packet. Dr. Franklin arrived in good health at Philadelphia, the 15th ult., and was received amidst the acclamations of an immense crowd. No late event has produced greater demonstrations of joy. It is doubted whether Congress will adjourn this summer; but they are so thin, they do not undertake important business. Our western posts are in statu quo.
I have the honor to be, with great esteem, Dear Sir,
your friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MESSRS. VAN STAPHORSTS.
Paris, October 25,1785.
Gentlemen,
I received yesterday your favor of the 20th instant. In order to give you the information you desire, on the subject of the liquidated debts of the United States, and the comparative footing on which they stand, I must observe to you, that the first and great division of our federal debt, is, into 1. foreign; and 2. domestic. The foreign debt comprehends, 1. the loan from the government of Spain; 2. the loans from the government of France, and from the Farmers General; 3. the loans negotiated in Holland, by order of Congress. This branch of our debt stands absolutely singular: no man in the United States having ever supposed that Congress, or their legislatures, can, in any wise, modify or alter it. They justly view the United States as the one party, and the lenders as the other, and that the consent of both would be requisite, were any modification to be proposed. But with respect to the domestic debt, they consider Congress as representing both the borrowers and lenders, and that the modifications which have taken place in this, have been necessary to do justice between the two parties, and that they flowed properly from Congress as their mutual umpire. The domestic debt comprehends 1. the army debt; 2. the loan-office debt; 3. the liquidated debt; and 4. the unliquidated debt. The first term includes debts to the officers and soldiers for pay, bounty, and subsistence. The second term means monies put into the loan-office of the United States. The third comprehends all debts contracted by quarter-masters, commissioners, and others duly authorized to procure supplies for the army, and which have been liquidated (that is, settled) by commissioners appointed under the resolution of Congress, of June the 12th, 1780, or by the officer who made the contract. The fourth comprehends the whole mass of debts, described in the preceding article, which have not yet been liquidated. These are in a course of liquidation, and are passing over daily into the third class. The debts of this third class, that is, the liquidated debt, is the object of your inquiry. No time is fixed for the payment of it, no fund as yet determined, nor any firm provision for the interest in the mean time. The consequence is, that the certificates of these debts sell greatly below par. When I left America, they could be bought for from two shillings and sixpence to fifteen shillings, in the pound: this difference proceeding from the circumstance of some STates having provided for paying the interest on those due in their own State, which others had not. Hence, an opinion had arisen with some, and propositions had even been made in the legislatures, for paying off the principal of these debts with what they had cost the holder, and interest on that. This opinion is far from being general, and I think will not prevail. But it is among possible events.
I have been thus particular, that you might be able to judge, not only in the present case, but also in others, should any attempts be made to speculate in your city, on these papers. It is a business, in which foreigners will be in great danger of being duped. It is a science which bids defiance to the powers of reason. To understand it, a man must not only be on the spot, and be perfectly possessed of all the circumstances relative to every species of these papers, but he must have that dexterity which the habit of buying and selling them alone gives. The brokers of these certificates are few in number, and any other person venturing to deal with them, engages in a very unequal contest.
i have the honor to be, with the highest respect, gentlemen,
your most obedient humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO WILLIAM CARMICHAEL.
Paris, November 4, 1785.
Dear Sir,
I had the honor of writing you on the 18th of October, and again on the 25th of the same month. Both letters, being to pass through the post-offices, were confined to particular subjects. The first of them acknowledged the receipt of yours of September the 29th.
At length a confidential opportunity arrives for conveying to you a cipher; it will be handed you by the bearer, Mr, Lambe. Copies of it are in the hands of Mr. Adams, at London, Mr. Barclay, who is proceeding to Morocco, and Mr. Lambe, who is proceeding to Algiers. This enables us to keep up such correspondences with each other, as maybe requisite. Congress, in the spring of 1784, gave powers to Mr. Adams, Dr. Franklin, and myself, to treat with the Barbary States. But they gave us no money for them, and the other duties assigned us rendered it impossible for us to proceed thither in person. These things having been represented to them, they assigned to us a certain sum of money, and gave us powers to delegate agents to treat with those States, and to form preliminary articles, but confining to us the signing of them in a definitive form. They did not restrain us in the appointment of the agents; but the orders of Congress were brought to us by Mr. Lambe, they had waited for him four months, and the recommendations he brought, pointed him out, in our opinion, as a person who would meet the approbation of Congress. We therefore appointed him to negotiate with the Algerines. His manners and appearance are not promising. But he is a sensible man, and seems to possess some talents which may be proper in a matter of bargain. We have joined with him, as secretary, a Mr. Randall, from New York, in whose prudence we hope he will find considerable aid. They now proceed to Madrid, merely with the view of seeing you, as we are assured they will receive from you lights which may be useful to them. I hear that D’Expilly and the Algerine ministers have gone from Madrid. Letters from Algiers, of August the 24th, inform me, that we had two vessels and their crews in captivity there, at that time. I have never had reason to believe certainly, that any others had been captured. Should Mr. Lambe have occasion to draw bills, while in Spain, on Mr. Adams, you may safely assure the purchasers that they will be paid.
An important matter detains Mr. Barclay some days longer, and his journey to Madrid will be circuitous. Perhaps he may arrive there a month later than Lambe. It would be well if the Emperor of Morocco could, in the mean time, know that such a person is on the road. Perhaps you may have an opportunity of notifying this to him officially, by asking from him passports for Mr. Barclay and his suite. This would be effecting too[sp.] good purposes at once, if you can find an opportunity.
Your letter of September the 2d did not get to my hands till these arrangements were all taken between Mr. Adams and myself, and the persons appointed. That gave me the first hint that you would have acted in this business. I mean no flattery when I assure you, that no person would have better answered my wishes. At the same time, I doubt whether Mr. Adams and myself should have thought ourselves justifiable in withdrawing a servant of the United States from a post equally important with those, which prevented our acting personally in the same business. I am sure, that, remaining where you are, you will be able to forward much the business, and that you will do it with the zeal you have hitherto manifested on every occasion.
Your intercourse with America being less frequent than ours, from this place, I will state to you, generally, such new occurrences there, as may be interesting; some of which, perhaps, you will not have been informed of. It was doubtful, at the date of my last letters, whether Congress would adjourn this summer. They were too thin, however, to undertake important business. They had begun arrangements for the establishment of a mint. The Dollar was decided on as the money unit of America. I believe, they proposed to have gold, silver, and copper coins, descending and ascending decimally; viz. a gold coin of ten dollars, a silver coin of one tenth of a dollar (equal to a Spanish bit), and a copper, of one hundredth of a dollar. These parts of the plan, however, were not ultimately decided on. They have adopted the late improvement in the British post-office, of sending their mails by the stages. I am told, this is done from New Hampshire to Georgia, and from New York to Albany. Their treasury is administered by a board, of which Mr. Walter Livingston, Mr. Osgood, and Dr. Arthur Lee, are members. Governor Rutledge who had been appointed minister to the Hague, on the refusal of Governor Livingston, declines coming. We are uncertain whether the States will generally come into the proposition of investing. Congress with the regulation of their commerce. Massachusetts has passed an act, the first object of which seemed to be, to retaliate on the British commercial measures, but in the close of it, they impose double duties on all goods imported in bottoms not wholly owned by citizens of our States. New Hampshire has followed the example. This is much complained of here, and will probably draw retaliating measures from the States of Europe, if generally adopted in America, or not corrected by the States which have adopted it. It must be our endeavor to keep them quiet on this side the water, under the hope that our countrymen will correct this step; as I trust they will do. It is no ways akin to their general system. I am trying here to get contracts for the supplying the cities of France with whale-oil, by the Boston merchants. It would be the greatest relief possible to that State, whose commerce is in agonies, in consequence of being subjected to alien duties on their oil in Great Britain, which has been heretofore their only market. Can any thing be done, in this way, in Spain? Or do they there light their streets in the night?
A fracas, which has lately happened in Boston, becoming a serious matter, I will give you the details of it, as transmitted to Mr. Adams in depositions. A Captain Stanhope, commanding the frigate Mercury, was sent with a convoy of vessels from Nova Scotia to Boston, to get a supply of provisions for that colony. It had happened, that two persons living near Boston, of the names of Dunbar and Lowthorp, had been taken prisoners during the war, and transferred from one vessel to another, till they were placed on board Stanhope’s ship. He treated them most cruelly, whipping them frequently, in order to make them do duty against their country, as sailors, on board his ship. The ship going to Antigua to refit, he put all his prisoners into jail, first giving Dunbar twenty-four lashes. Peace took place, and the prisoners got home under the general liberation. These men were quietly pursuing their occupations at home, when they heard that Stanhope was in Boston. Their indignation was kindled. They immediately went there, and meeting Stanhope walking in the mall, Dunbar stepped up to him, and asked him if he recollected him, and the whipping him on board his ship. Having no weapon in his hand, he struck at Stanhope with his fist. Stanhope stepped back, and drew his sword. The people interposed, and guarded him to the door of a Mr. Morton, to which he retreated. There Dunbar again attempted to seize him; but the high-sheriff had by this time arrived, who interposed and protected him. The assailants withdrew, and here ended all appearance of force. But Captain Stanhope thought proper to write to the Governor, which brought on the correspondence published in the papers of Europe. Lest you should not have seen it, I enclose it, as cut from a London paper; though not perfectly exact, it is substantially so. You will doubtless judge, that Governor Bowdoin referred him properly to the laws for redress, as he was obliged to do, and as would have been done in England, in a like case. Had he applied to the courts, the question would have been whether they would have punished Dunbar. This must be answered now by conjecture only; and, to form that conjecture, every man must ask himself, whether he would not have done as Dunbar did; and whether the people should not have permitted him to return to Stanhope the twenty-four lashes. This affair has been stated in the London papers, without mixing with it one circumstance of truth.
In your letter of the 27th of June, you were so good as to tell me that you should shortly send off some of the books I had taken the liberty to ask you to get for me, and that your correspondent at Bayonne would give me notice of their arrival there. Not having heard from him, I mention it to you, lest they should be stopped any where.
I am, with great respect, Dear Sir,
your most obedient, humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO RICHARD O’BRYAN.
Paris, November 4, 1785.
Sir,
I wrote you a short letter on the 29th of September, acknowledging the receipt of yours of August the 24th, from Algiers, and promising that you should hear further from me soon. Mr. Adams, the American minister at London, and myself, have agreed to authorize the bearer hereof, Mr. Lambe, to treat for your redemption, and that of your companions taken in American vessels, and, if it can be obtained for sums within our power, we shall have the money paid. But in this we act without instruction from Congress, and are therefore obliged to take the precaution of requiring, that you bind your owners for yourself and crew, and the other captain, in like manner, his owners for himself and crew, and that each person separately make himself answerable for his own redemption, in case Congress requires it. I suppose Congress will not require it: but we have no authority to decide that, but must leave it to their own decision; which renders necessary the precautions I have mentioned, in order to justify ourselves for undertaking to redeem you without orders. Mr. Lambe is instructed to make no bargain without your approbation, and that of the other prisoners, each for himself. We also direct him to relieve your present necessities. I sincerely wish you a speedy deliverance from your distresses, and a happy return to your family.
I am, Sir, your most obedient, humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO W. W. SEWARD.
Paris, November 12,1785.
Sir,
I received the honor of your letter, of the 25th ult., written by desire of the associated company of Irish merchants, in London, and return you thanks for the kind congratulations you express therein. The freedom of commerce between Ireland and America is undoubtedly very interesting to both countries. If fair play be given to the natural advantages of Ireland, she must come in for a distinguished share of that commerce. She is entitled to it, from the excellence of some of her manufactures, the cheapness of most of them, their correspondence with the American taste, a sameness of language, laws, and manners, a reciprocal affection between the people, and the singular circumstance of her being the nearest European land to the United States. I am not, at present, so well acquainted with the trammels of Irish commerce, as to know what they are, particularly, which obstruct the intercourse between Ireland and America; nor, therefore, what can be the object of a fleet stationed in the western ocean, to intercept that intercourse. Experience, however, has taught us to infer that the fact is probable, because it is impolitic. On the supposition that this interruption will take place, you suggest Ostend as a convenient entrepot for the commerce between America and Ireland. Here, too, I find myself, on account of the same ignorance of your commercial regulations, at a loss to say why this is preferable to L’Orient, which, you know, is a free port and in great latitude, which is nearer to both parties, and accessible by a less dangerous navigation. I make no doubt, however, that the reasons of the preference are good. You find by this essay, that I am not likely to be a very instructive correspondent: you shall find me, however, zealous in whatever may concern the interests of the two countries. The system into which the United States wished to go, was that of freeing commerce from every shackle. A contrary conduct in Great Britain will occasion, them to adopt the contrary system, at least as to that island. I am sure they would be glad, if it should be, found practicable, to make that discrimination between Great Britain and Ireland, which their commercial principles, and their affection for the latter, would dictate.
I have the honor to be, with the highest respect for yourself and the company for whom you write, Sir,
your most obedient
and most humble servant,
Tm: Jefferson.
TO THE COUNT DE VERGENNES.
Paris, November 14,1785.
Sir,
I take the liberty of troubling your Excellency on behalf of six citizens of the United States, who have been for some time confined in the prison of St. Pol de Léon, and of referring for particulars to the enclosed state of their case. Some of the material facts therein mentioned, are founded on the bill of sale for the vessel, her clearance from Baltimore, and her log-book. The originals of the two last, and a copy of the first, are in my hands. I have, also, letters from a merchant in Liverpool to Asquith, which render it really probable that his vessel was bound to Liverpool. The other circumstances depend on their affirmation, but I must say that in these facts they have been uniform and steady. I have thus long avoided troubling your Excellency with this case, in hopes it would receive its decision in the ordinary course of law, and I relied, that that would indemnify the sufferers, if they had been used unjustly: but though they have been in close confinement now near three months, it has yet no appearance of approaching to decision. In the mean time, the cold of the winter is coming on, and to men in their situation, may produce events which would render all indemnification too late. I must, therefore, pray the assistance of your Excellency, for the liberation of their persons, if the established order of things may possibly admit of it. As to their property and their personal sufferings hitherto, I have full confidence that the laws have provided some tribunal where justice will be done them. I enclose the opinion of an advocate, forwarded to me by a gentleman whom I had desired to obtain, from some judicious person of that faculty, a state of their case. This may perhaps give a better idea than I can, of the situation of their cause. His inquiries have led him to believe they are innocent men, but that they must lose their vessel under the edict, which forbids those under thirty tons to approach the coast. Admitting their innocence, as he does, I should suppose them not the objects on whom such an edict was meant to operate. The essential papers, which he says they re-demanded from him, and did not return, were sent to me, at my desire. I am, with sentiments of the highest respect, your Excellency’s most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
The case of Lister Asquith, owner of the schooner William and Catharine, William M’Neil, captain, William Thomson, William Neily, Robert Anderson, mariners, and William Fowler, passenger.
Lister Asquith, citizen of the State of Maryland, having a lawsuit depending in England which required his presence, as involving in its issue nearly his whole fortune, determined to go thither in a small schooner of his own, that he might, at the same time, take with him an adventure of tobacco and flour to Liverpool, where he had commercial connections. This schooner he purchased as of fifty-nine and a quarter tons, as appears by his bill of sale, but she had been registered by her owner at twenty-one tons, in order to evade the double duties in England, to which American vessels are now subject. He cleared out from Baltimore for Liverpool, the 11th of June, 1785, with eight hogsheads of tobacco and sixty barrels of flour, but ran aground at Smith’s point, sprung a leak, and was obliged to return to Baltimore to refit. Having stopped his leak, he took his cargo on board again, and his health being infirm, he engaged Captain William M’Neil* to go with him, and on the 20th of June sailed for Norfolk in Virginia, and, on the 22nd, came to in Hampton road, at the mouth of the river on which Norfolk is. Learning here, that tobacco would be better than flour for the English market, he landed fifty barrels of his flour and one hogshead of tobacco, which he found to be bad, meaning to take, instead thereof, nine hogsheads of tobacco more. But the same night it began to blow very hard, with much rain. The 23d, the storm became more heavy; they let go both their anchors, but were driven, notwithstanding, from their anchorage, forced to put to sea and to go before the wind. The occurrences of their voyage will be best detailed by short extracts from the log-book.
* This was the officer, who, on the evacuation of Fort
Mifflin, after the British had passed the chevaux-de-frise
on the Delaware, was left with fifteen men to destroy the
works, which he did, and brought off his men successfully.
He had, before that, been commander of the Rattlesnake sloop
of war, and had much annoyed the British trade; Being bred a
seaman, he has returned to that vocation.
June 24. The weather becomes worse. One of the fore shrouds and the foremast, carried away.
June 25. Shifted their ballast, which threw them on their beam ends, and shipped a very heavy sea. Held a consultation; the result of which was, that seeing they were now driven so far to sea, and the weather continuing still very bad, it was better to steer for Liverpool, their port of destination, though they had not their cargo on board, and no other clearance but that which they took from Baltimore.
June 29. The first observation they had been able to take N.lat. 38° 13’.
June 30. Winds begin to be light, but the sea still very heavy.
July 5. Light winds and a smooth sea for the first time, in lat. 43° 12’.
July 9. Spoke a French brig, Comte D’Artois, Captain Mieaux, from St. Maloes, in distress for provisions. Relieved her with three barrels of flour.
Aug. 6. Thick weather and strong wind. Made the Land’s End of England.
Aug. 7. Unable to fetch the land, therefore bore off for Scilly, and came to with both anchors. Drove, notwithstanding, and obliged to get up the anchors, and put to sea, running southwardly.
Aug. 8. Made the land of France, but did not know what part.
Here the log-book ends. At this time they had on board but ten gallons of water, four or five barrels of bread, two or three pounds of candles, no firewood. Their sails unfit to be trusted to any longer, and all their materials for mending them exhausted by the constant repairs which the violence of the weather had called for. They therefore took a pilot aboard, who carried them into Pont Duval; but being informed by the captain of a vessel there, that the schooner was too sharp built (as the American vessels mostly are) to lie in that port, they put out immediately, and the next morning the pilot brought them to anchor in the road of the Isle de Bas. Asquith went immediately to Roscaff, protested at the admiralty the true state of his case, and reported his vessel and cargo at the custom-house. In making the report of his vessel, he stated her as of twenty-one tons, according to his register. The officer informed him that if she was no larger, she would be confiscated by an edict, which forbids all vessels, under thirty tons, to approach the coast. He told the officer what was the real truth as to his register and his bill of sale, and was permitted to report her according to the latter. He paid the usual fees of ten livres and seven sols, and obtained a clearance. Notwithstanding this, he was soon visited by other persons, whom he supposes to have been commis of the Fermes, who seized his vessel, carried her to the pier, and confined the crew to the vessel and half the pier, putting centinels over them. They brought a guager, who measured only her hold and part of her steerage, allowing nothing for the cockpit, cabin, forecastle, and above one half of the steerage, which is almost half the vessel, and thus made her contents (if that had been of any importance) much below the truth. The tobacco was weighed, and found to be six thousand four hundred and eighty-seven pounds,* which was sent on the 18th to Landivisiau, and on the 19th, they were committed to close prison at St. Pol de Léon, where they have been confined ever since. They had, when they first landed, some money, of which they were soon disembarrassed by different persons, who, in various forms, undertook to serve them. Unable to speak or understand a word of the language of the country, friendless, and left without money, they have languished three months in a loathsome jail, without any other sustenance, a great part of the time, than what could be procured for three sous a day, which have been furnished them to prevent their perishing.
* A hogshead of tobacco weighs generally about one thousand
pounds, English, equal to nine hundred and seventeen pounds
French. The seven hogsheads he sailed with, would therefore
weigh, according to this estimate, six thousand four hundred
and twenty-three pounds. They actually weighed more on the
first essay. When afterwards weighed at Landivisiau, they
had lost eighty-four pounds on being carried into a drier
air. Perhaps, too, a difference of weights may have entered
into this apparent loss.
They have been made to understand that a criminal process is going on against them under two heads. 1. As having sold tobacco in contraband; and 2., as having entered a port of France in a vessel of less than thirty tons’ burthen. In support of the first charge, they understand that the circumstance is relied on, of their having been seen off the coast by the employés des Fermes, one or two days. They acknowledge they may have been so seen while beating off Pont Duval, till they could get a pilot, while entering that port, and again going round from thence to the road of the Isle de Bas. The reasons for this have been explained. They further add, that all the time they were at Pont Duval they had a King’s officer on board, from whom, as well as from their pilot, and the captain, by whose advise they left that port for the Isle de Bas, information can be obtained by their accusers (who are not imprisoned) of the true motives for that measure. It is said to be urged also, that there was found in their vessel some loose tobacco in a blanket, which excites a suspicion that they had been selling tobacco. When they were stowing their loading, they broke a hogshead, as is always necessary, and is always done, to fill up the stowage, and to consolidate and keep the whole mass firm and in place. The loose tobacco which had come out of the broken hogshead, they re-packed in bags: but in the course of the distress of their disastrous voyage, they had employed these bags, as they had done every thing else of the same nature, in mending their sails. The condition of their sails when they came into port will prove this, and they were seen by witnesses enough, to whom their accusers, being at their liberty, can have access. Besides, the sale of a part of their tobacco is a fact, which, had it taken place, might have been proved; but they deny that it has been proved, or ever can be proved by true men, because it never existed. And they hope the justice of this country does not permit strangers, seeking in her ports an asylum from death, to be thrown into jail and continued there indefinitely, on the possibility of a fact, without any proof. More especially when, as in the present case, a demonstration to the contrary is furnished by their clearance, which shows they never had more than eight hogsheads of tobacco on board, of which one had been put ashore at Hampton in Virginia, as has been before related, and the seven others remained when they first entered port. If they had been smugglers of tobacco, the opposite coast offered a much fairer field, because the gain there is as great; because they understand the language and laws of the country, they know its harbors and coasts, and have connections in them. These circumstances are so important to smugglers, that it is believed no instance has ever occurred of the contraband tobacco, attempted on this side the channel, by a crew wholly American. Be this as it may, they are not of that description of men.
As to the second charge, that they have entered a port of France in a vessel of less than thirty tons’ burthen, they, in the first place, observe, that they saw the guager measure the vessel, and affirm that his method of measuring could render little more than half her true contents: but they say, further, that were she below the size of thirty tons, and, when entering the port, had they known of the alternative of either forfeiting their vessel and cargo, or of perishing at sea; they must still have entered the port: the loss of their vessel and cargo being the lesser evil. But the character of the lawgiver assures them, that the intention of his laws are perverted, when misapplied to persons, who, under their circumstances, take refuge in his ports. They have no occasion to recur from his clemency to his justice, by claiming the benefit of that article in the treaty which binds the two nations together, and which assures to the fugitives of either from the dangers of the sea, a hospitable reception and necessary aids in the ports of the other, and that, without measuring the size of their vessel.
Upon the whole, they protest themselves to have been as innocent as they have been unfortunate. Instead of relief in a friendly port, they have seen their misfortunes aggravated by the conduct of officers, who, in their greediness for gain, can see in no circumstance any thing but proofs of guilt. They have already long suffered and are still suffering whatever scanty sustenance, an inclement season, and close confinement can offer most distressing to men who have been used to neither, and who have wives and children at home participating of their distresses; they are utterly ignorant of the laws and language of the country, where they are suffering; they are deprived of that property which would have enabled them to procure counsel to place their injuries in a true light; they are distant from the stations of those who are appointed by their country to patronize their rights; they are not at liberty to go to them, nor able to have communication through any other than the uncertain medium of the posts; and they see themselves already ruined by the losses and delays they have been made to incur, and by the failure of the original object of their voyage. They throw themselves, therefore, on the patronage of the government, and pray that its energy may be interposed in aid of their poverty and ignorance, to restore them to their liberty, and to extend to them that retribution which the laws of every country mean to extend to those who suffer unjustly.
TO JOHN ADAMS.
Paris, November 19, 1785.
Dear Sir,
I wrote to you on the 11th of October, by Mr. Preston, and again on the 18th of the same month, by post. Since that, yours of September the 25th, by Mr. Boylston, of October the 24th, November the 1st, and November the 4th, have come safe to hand. I will take up their several subjects in order. Boylston’s object was, first, to dispose of a cargo of spermaceti oil, which he brought to Havre. A secondary one, was to obtain a contract for future supplies. I carried him to the Marquis de la Fayette. As to his first object, we are in hopes of getting the duties taken off, which will enable him to sell his cargo. This has led to discussions with the ministers, which give us a hope that we may get the duties taken off in perpetuum. This done, a most abundant market for our oil will be opened by this country, and one which will be absolutely dependant on us; for they have little expectation themselves of establishing a successful whale-fishery. It is possible they may only take the duties off of those oils, which shall be the produce of associated companies of French and American merchants. But as yet, nothing certain can be said.
I thank you for the trouble you have taken to obtain insurance on Houdon’s life. I place the thirty-two pounds and eleven shillings to your credit, and not being able, as yet, to determine precisely how our accounts stand, I send a sum by Colonel Smith, which may draw the scales towards a balance.
The determination of the British cabinet to make no equal treaty with us, confirms me in the opinion expressed in your letter of October the 24th, that the United States must pass a navigation act against Great Britain, and load her manufactures with duties, so as to give a preference to those of other countries: and I hope our Assemblies will wait no longer, but transfer such a power to Congress, at the sessions of this fall. I suppose, however, it will only be against Great Britain, and I think it will be right not to involve other nations in the consequences of her injustice. I take for granted, that the commercial system wished for by Congress, was such a one, as should leave commerce on the freest footing possible. This was the plan on which we prepared our general draught for treating with all nations. Of those with whom we were to treat, I ever considered England, France, Spain, and Portugal as capitally important; the first two, on account of their American possessions, the last, for their European as well as American. Spain is treating in America, and probably will give an advantageous treaty. Portugal shows dispositions to do the same. France does not treat. It is likely enough she will choose to keep the staff in her own hands. But, in the mean time, she gives us an access to her West Indies, which, though not all we wish, is yet extremely valuable to us: this access, indeed, is much affected by the late Arrêts of the 18th and 25th of September, which I enclose to you. I consider these as a reprisal for the navigation acts of Massachusetts and New Hampshire. The minister has complained to me, officially, of these acts, as a departure from the reciprocity stipulated for by the treaty. I have assured him that his complaints shall be communicated to Congress, and in the mean time, observed that the example of discriminating between foreigners and natives had been set by the Arrêt of August, 1784, and still more remarkably by those of September the 18th and 25th, which, in effect, are a prohibition of our fish in their islands. However, it is better for us, that both sides should revise what they have done. I am in hopes this country did not mean these as permanent regulations. Mr. Bingham, lately from Holland, tells me that the Dutch are much dissatisfied with these acts. In fact, I expect the European nations, in general, will rise up against an attempt of this kind, and wage a general commercial war against us. They can do well without all our commodities except tobacco, and we cannot find, elsewhere, markets for them. The selfishness of England alone will not justify our hazarding a contest of this kind against all Europe. Spain, Portugal, and France, have not yet shut their doors against us: it will be time enough, when they do, to take up the commercial hatchet. I hope, therefore, those States will repeal their navigation clauses, except as against Great Britain and other nations not treating with us.
I have made the inquiries you desire, as to American ship-timber for this country. You know they sent some person (whose name was not told us) to America, to examine the quality of our masts, spars, &c. I think this was young Chaumont’s business. They have, besides this, instructed the officer who superintends their supplies of masts, spars, foe., to procure good quantities from our northern States; but I think they have made no contract: on the contrary, that they await the trials projected, but with a determination to look to us for considerable supplies, if they find our timber answer. They have on the carpet a contract for live-oak from the southern States.
You ask why the Virginia merchants do not learn to sort their own tobaccos? They can sort them as well as any other merchants whatever. Nothing is better known than the quality of every hogshead of tobacco, from the place of its growth. They know, too, the particular qualities required in every market. They do not send their tobaccos, therefore, to London to be sorted, but to pay their debts: and though they could send them to other markets and remit the money to London, yet they find it necessary to give their English merchant the benefit of the consignment of the tobacco (which is enormously gainful), in order to induce him to continue his indulgence for the balance due.
Is it impossible to persuade our countrymen to make peace with the Nova Scotians? I am persuaded nothing is wanting but advances on our part; and that it is in our power to draw off the greatest proportion of that settlement, and thus to free ourselves from rivals who may become of consequence. We are, at present, co-operating with Great Britain, whose policy it is to give aliment to that bitter enmity between her States and ours, which may secure her against their ever joining us. But would not the existence of a cordial friendship between us and them, be the best bridle we could possibly put into the mouth of England?
With respect to the Danish business, you will observe that the instructions of Congress, article 3, of October the 29th, 1783, put it entirely into the hands of the Ministers Plenipotentiary of the United States of America at the court of Versailles, empower to to negotiate a peace, or to any one or more of them. At that time, I did not come under this description. I had received the permission of Congress to decline coming, in the spring preceding that date. On the first day of November, 1783, that is to say, two days after the date of the instructions to the commissioners, Congress recommended John Paul Jones to the Minister Plenipotentiary of the United States, at Versailles, as agent, to solicit, under his direction, the payment of all prizes taken in Europe under his command. But the object under their view, at that time, was assuredly the money due from the court of Versailles, for the prizes taken in the expedition by the Bon-homme Richard, the Alliance, &c. In this business, I have aided him effectually, having obtained a definitive order for paying the money to him, and a considerable proportion being actually paid him. But they could not mean by their resolution of November the 1st, to take from the commissioners, powers which they had given them two days before. If there could remain a doubt that this whole power has resulted to you, it would be cleared up by the instructions of May the 7th, 1784, article 9, which declare, ‘that these instructions be considered as supplementary to those of October the 29th, 1783, and not as revoking, except where they contradict them;’ which shows that they considered the instructions of October the 29th, 1783, as still in full force. I do not give you the trouble of this discussion, to save myself the trouble of the negotiation. I should have no objections to this part: but it is to avoid the impropriety of meddling in a matter wherein I am unauthorized to act, and where any thing I should pretend to conclude with the court of Denmark, might have the appearance of a deception on them. Should it be in my power to render any service in it, I shall do it with cheerfulness; but I repeat, that I think you are the only person authorized.
I received, a few days ago, the Nuova Minuta of Tuscany, which Colonel Humphreys will deliver you. I have been so engaged that I have not been able to go over it with any attention. I observe, in general, that the order of the articles is entirely deranged, and their diction almost totally changed. When you shall have examined it, if you will be so good as to send me your observations by post, in cipher, I will communicate with you in the same way, and try to mature this matter.
The deaths of the Dukes of Orleans and Praslin, will probably reach you through the channel of the public papers, before this letter does. Your friends the Abbes are well, and always speak of you with affection. Colonel Humphreys comes to pass some time in London. My curiosity would render a short trip thither agreeable to me also, but I see no probability of taking it. I will trouble you with my respects to Dr. Price. Those to Mrs. Adams, I witness in a letter to herself.
I am, with very great esteem, Dear Sir,
your most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO THE COUNT DE VERGENNES.
Paris, November 20, 1785.
Sir,
I found here, on my return from Fontainebleau, the letter of October the 30th, which your Excellency did me the honor there of informing me had been addressed to me at this place; and I shall avail myself of the first occasion of transmitting it to Congress, who will receive, with great pleasure; these new assurances of the friendly sentiments, which his Majesty is pleased to continue towards the United States.
I am equally persuaded they will pay the most serious attention to that part of your Excellency’s letter, which mentions the information you have received of certain acts or regulations of navigation and commerce, passed in some of the United States, which are injurious to the commerce of France. In the mean time, I wish to remove the unfavorable impressions which those acts seem to have made, as if they were a departure from the reciprocity of conduct, stipulated for by the treaty of February the 6th, 1776. The effect of that treaty is, to place each party with the other, always on the footing of the most favored nation. But those who framed the acts, probably did not consider the treaty as restraining either from discriminating between foreigners and natives. Yet this is the sole effect of these acts. The same opinion, as to the meaning of the treaty, seems to have been entertained by this government, both before and since the date of these acts. For the Arrêt of the King’s Council, of August the 30th, 1784, furnished an example of such a discrimination between foreigners and natives, importing salted fish into his Majesty’s dominions in the West Indies; by laying a duty on that imported, by foreigners, and giving out the same, in bounty, to native importers. This opinion shows itself more remarkably in the late Arrêts of the 18th and 25th of September, which, increasing to excess the duty on foreign importations of fish into the West Indies, giving the double, in bounty, on those of natives, and thereby rendering it impossible for the former to sell in competition with the latter, have, in effect, prohibited the importation of that article by the citizens of the United States.
Both nations, perhaps, may come into the opinion, that their friendship and their interests may be better cemented, by approaching the condition of their citizens, reciprocally, to that of natives, as a better ground of intercourse than that of the most favored nation. I shall rest with hopes of being authorized, in due time, to inform your Excellency that nothing will be wanting, on our part, to evince a disposition to concur in revising whatever regulations may, on either side, bear hard on the commerce of the other nation. In the mean time I have the honor to assure you of the profound respect and esteem, with which
I have the honor to be,
your Excellency’s
most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO LISTER ASQUITH.
Paris, November 23, 1785.
Sir,
I have received your letter of the 14th instant. It was not till the 8th of this month, that I could obtain information from any quarter, of the particular court in which your prosecution was instituted, and the ground on which it was founded. I then received it through the hands of Monsieur Desbordes, at Brest. I have sent to the Count de Vergennes a statement of your case, of which the enclosed is a copy. I wish you would read it over, and if there be any fact stated in it, which is wrong, let me know it, that I may have it corrected. I at the same time wrote him an urgent letter in your behalf. I have daily expected an answer, which has occasioned my deferring writing to you. The moment I receive one, you may be assured of my communicating it to you. My hopes are, that I may obtain from the King a discharge of the persons of all of you: but, probably, your vessel and cargo must go through a process. I have sincerely sympathized with your misfortunes, and have taken every step in my power to get into the right line for obtaining relief. If it will add any comfort to your situation and that of your companions, to be assured that I never lose sight of your sufferings, and leave nothing undone to extricate you, you have that assurance. I am, Sir,
your very humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN ADAMS.
Paris, November 27, 1785.
Dear Sir,
Your favor of the 5th came to hand yesterday, and Colonel Smith and Colonel Humphreys (by whom you will receive one of the 19th from me) being to set out to-morrow, I hasten to answer it. I sincerely rejoice that Portugal is stepping forward in the business of treaty, and that there is a probability that we may at length do something under our commissions, which may produce a solid benefit to our constituents. I as much rejoice, that it is not to be negotiated through the medium of the torpid, uninformed machine, at first made use of. I conjecture, from your relation of the conference with the Chevalier de Pinto, that he is well informed and sensible. So much the better. It is one of those cases, where the better the interests of the two parties are understood, the broader will be the basis on which they will connect them.
To the very judicious observations on the subjects of the conference, which were made by you, I have little to add.
Flour. It may be observed, that we can sell them the flour ready manufactured, for much less than the wheat of which it is made. In carrying to them wheat, we carry also the bran, which does not pay its own freight. In attempting to save and transport wheat to them, much is lost by the weavil, and much spoiled by heat in the hold of the vessel. This loss must be laid on the wheat which gets safe to market, where it is paid for by the consumer. Now, this is much more than the cost of manufacturing it with us, which would prevent that loss. I suppose the cost of manufacturing does not exceed seven per cent, on the value. But the loss by the weavil, and other damage on ship-board, amount to much more. Let them buy of us as much wheat as will make a hundred weight of flour. They will find that they have paid more for the wheat, than we should have asked for the flour, besides having lost the labor of their mills in grinding it. The obliging us, therefore, to carry it to them in the form of wheat, is a useless loss to both parties.
Iron. They will get none from us. We cannot make it in competition with Sweden, or any other nation of Europe, where labor is so much cheaper.
Wines. The strength of the wines of Portugal will give them always an almost exclusive possession of a country, where the summers are so hot as in America. The present demand will be very great, if they will enable us to pay for them; but if they consider the extent and rapid population of the United States, they must see that the time is not distant, when they will not be able to make enough for us, and that it is of great importance to avail themselves of the prejudices already established in favor of their wines, and to continue them, by facilitating the purchase. Let them do this, and they need not care for the decline of their use in England. They will be independent of that country.
Salt. I do not know where the northern States supplied themselves with salt, but the southern ones took great quantities from Portugal.
Cotton and Wool. The southern States will take manufactures, of both: the northern, will take both the manufactures and raw materials.
East India goods of every kind. Philadelphia and New York have begun a trade to the East Indies. Perhaps Boston may follow their example. But their importations will be sold only to the country adjacent to them. For a long time to come, the States south of the Delaware, will not engage in a direct commerce with the East Indies. They neither have nor will have ships or seamen for their other commerce: nor will they buy East India goods of the northern States. Experience shows that the States never bought foreign goods of one another. The reasons are, that they would, in so doing, pay double freight and charges; and again, that they would have to pay mostly in cash, what they could obtain for commodities in Europe. I know that the American merchants have looked, with some anxiety, to the arrangements to be taken with Portugual, in expectation that they could, through her, get their East India articles on better and more convenient terms; and I am of opinion, Portugal will come in for a good share of this traffic with the southern States, if they facilitate our payments.
Coffee. Can they not furnish us with this article from Brazil?
Sugar. The Brazil sugars are esteemed, with us, more than any other.
Chocolate. This article, when ready made, as also the cocoa, becomes so soon rancid, and the difficulties of getting it fresh, have been so great in America, that its use has spread but little. The way to increase its consumption would be, to permit it to be brought to us immediately from the country of its growth. By getting it good in quality, and cheap in price, the superiority of the article, both for health and nourishment, will soon give it the same preference over tea and coffee in America, which it has in Spain, where they can get it by a single voyage, and, of course, while it is sweet. The use of the sugars, coffee, and cotton of Brazil, would also be much extended by a similar indulgence.
Ginger and spices from the Brazils, if they had the advantage of a direct transportation, might take place of the same articles from the East Indies.
Ginseng. We can furnish them with enough to supply their whole demand for the East Indies.
They should be prepared to expect, that in the beginning of this commerce, more money will be taken by us than after a while. The reasons are, that our heavy debt to Great Britain must be paid, before we shall be masters of our own returns; and again, that habits of using particular things are produced only by time and practice.
That as little time as possible may be lost in this negotiation, I will communicate to you at once, my sentiments as to the alterations in the draught sent them, which will probably be proposed by them, or which ought to be proposed by us, noting only those articles.
Article 3. They will probably restrain us to their dominions in Europe. We must expressly include the Azores, Madeiras, and Cape de Verde Islands, some of which are deemed to be in Africa. We should also contend for an access to their possessions in America, according to the gradation in the 2nd article of our instructions, of May the 7th, 1784. But if we can obtain it in no one of these forms, I am of opinion we should give it up.
Article 4. This should be put into the form we gave it, in the draught sent you by Dr. Franklin and myself, for Great Britain. I think we had not reformed this article, when we sent our draught to Portugal. You know, the Confederation renders the reformation absolutely necessary; a circumstance which had escaped us at first.
Article 9. Add, from the British draught, the clause about wrecks.
Article 13. The passage ‘nevertheless,’ &c. to run as in the British draught.
Article 18. After the word ‘accident,’ insert ‘or wanting supplies of provisions or other refreshments.’ And again, instead of ‘take refuge,’ insert ‘come,’ and after ‘of the other,’ insert ‘in any part of the world.’ The object of this is to obtain leave for our whaling vessels to refit and refresh on the coast of the Brazils; an object of immense importance to that class of our vessels. We must acquiesce under such modifications as they may think necessary for regulating this indulgence, in hopes to lessen them in time, and to get a pied a terre in that country.
Article 19. Can we get this extended to the Brazils? It would be precious in case of war with Spain.
Article 23. Between ‘places’ and ‘whose,’ insert ‘and in general, all others,’ as in the British draught.
Article 24. For ‘necessaries,’ substitute ‘comforts.’
Article 25. Add ‘but if any such consuls shall exercise commerce,’ &c. as in the British draught.
We should give to Congress as early notice as possible, of the re-institution of this negotiation; because, in a letter by a gentleman who sailed from Havre, the 10th instant, I communicated to them the answer of the Portuguese minister, through the ambassador here, which I sent to you. They may, in consequence, be making other arrangements, which might do injury. The little time which now remains, of the continuance of our commissions, should also be used with the Chevalier de Pinto, to hasten the movements of his court.
But all these preparations for trade with Portugal will fail in their effect, unless the depredations of the Algerines can be prevented. I am far from confiding in the measures taken for this purpose. Very possibly war must be recurred to. Portugal is at war with them. Suppose the Chevalier de Pinto was to be sounded on the subject of an union of force, and even a stipulation for contributing each a certain force, to be kept in constant cruise. Such a league once begun, other nations would drop into it, one by one. If he should seem to approve it, it might then be suggested to Congress, who, if they should be forced to try the measure of war, would doubtless be glad of such an ally. As the Portuguese negotiation should be hastened, I suppose our communications must often be trusted to the post, availing ourselves of the cover of our cipher.
I am, with sincere esteem, Dear Sir,
your friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO COLONEL HUMPHREYS.
Paris, December 4,1785.
Dear Sir,
I enclose you a letter from Gatteaux, observing that there will be an anachronism, if, in making a medal to commemorate the victory of Saratoga, he puts on General Gates the insignia of the Cincinnati, which did not exist at that date. I wrote him, in answer, that I thought so too, but that you had the direction of the business; that you were now in London; that I would write to you, and probably should have an answer within a fortnight; and that, in the mean time, he could be employed on other parts of the die. I supposed you might not have observed on the print of General Gates, the insignia of the Cincinnati, or did not mean that that particular should be copied. Another reason against it strikes me. Congress have studiously avoided giving to the public their sense of this institution. Should medals be prepared, to be presented from them to certain officers, and bearing on them the insignia of the order, as the presenting them would involve an approbation of the institution, a previous question would be forced on them, whether they would present these medals. I am of opinion it would be very disagreeable to them to be placed under the necessity of making this declaration. Be so good as to let me know your wishes on this subject by the first post.
Mr. Short has been sick ever since you left us. Nothing new has occurred here, since your departure. I imagine you have American news. If so, pray give us some. Present me affectionately to Mr. Adams and the ladies, and to Colonel Smith; and be assured of the esteem with which I am, Dear Sir,
your friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN ADAMS,
Paris, December 10, 1785.
Dear Sir,
On the arrival of Mr. Boylston, I carried him to the Marquis de la Fayette, who received from him communications of his object. This was to get a remission of the duties on his cargo of oil, and he was willing to propose a future contract. I suggested however to the Marquis, when we were alone, that instead of wasting our efforts on individual applications, we had better take up the subject on general ground, and whatever could be obtained, let it be common to all. He concurred with me. As the jealousy of office between ministers does not permit me to apply immediately to the one in whose department this was, the Marquis’s agency was used. The result was to put us on the footing of the Hanseatic towns, as to whale-oil, and to reduce the duties to eleven livres and five sols for five hundred and twenty pounds French, which is very nearly two livres on the English hundred weight, or about a guinea and a half the ton. But the oil must be brought in American or French ships, and the indulgence is limited to one year. However, as to this, I expressed to Count de Vergennes my hopes that it would be continued; and should a doubt arise, I should propose, at the proper time, to claim it under the treaty on the footing gentis amicissimæ. After all, I believe Mr. Boylston has failed of selling to Sangrain, and from what I learn, through a little too much hastiness of temper. Perhaps they may yet come together, or he may sell to somebody else.
When the general matter was thus arranged, a Mr. Barrett arrived here from Boston, with letters of recommendation from Governor Bowdoin, Gushing, and others. His errand was to get the whale business here put on a general bottom, instead of the particular one which had been settled, you know, the last year, for a special company. We told him what was done. He thinks it will answer, and proposes to settle at L’Orient for conducting the sales of the oil and the returns. I hope, therefore, that this matter is tolerably well fixed, as far as the consumption of this country goes. I know not as yet to what amount that is; but shall endeavor to find out how much they consume, and how much they furnish themselves. I propose to Mr. Barrett, that he should induce either his State, or individuals, to send a sufficient number of boxes of the spermaceti candle to give one to every leading house in Paris; I mean to those who lead the ton: and at the same time to deposite a quantity for sale here, and advertise them in the petites affiches. I have written to Mr. Carmichael to know on what footing the use and introduction of the whale-oil is there, or can be placed.
I have the honor to be, with very sincere esteem, Dear Sir,
your most obedient, humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN ADAMS.
Paris, December 11, 1785.
Dear Sir,
Baron Polnitz not going off till to-day enables me to add some information which I received from Mr. Barclay this morning. You know the immense amount of Beaumarchais’ accounts with the United States, and that Mr. Barclay was authorized to settle them. Beaumarchais had pertinaciously insisted on settling them with Congress. Probably he received from them a denial: for just as Mr. Barclay was about to set out on the journey we destined him, Beaumarchais tendered him a settlement. It was thought best not to refuse this, and that it would produce a very short delay. However, it becomes long, and Mr. Barclay thinks it will occupy him all this month. The importance of the account, and a belief that nobody can settle it so well as Mr. Barclay, who is intimately acquainted with most of the articles, induce me to think we must yield to this delay. Be so good as to give me your opinion on this subject.
I have the honor to be, with very great esteem, Dear Sir,
your most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO THE COUNT DE VERGENNES.
Paris, December 21, 1785.
Sir,
I have received this moment a letter, of which I have the honor to enclose your Excellency a copy. It is on the case of Asquith and others, citizens of the United States, in whose behalf I had taken the liberty of asking your interference. I understand by this letter, that they have been condemned to lose their vessel and cargo, and to pay six thousand livres and the costs of the prosecution before the 25th instant, or to go to the galleys. This payment being palpably impossible to men in their situation, and the execution of the judgment pressing, I am obliged to trouble your Excellency again, by praying, if the government can admit any mitigation of their sentence, it may be extended to them in time to save their persons from its effect.
I have the honor to be, with very great respect, your Excellency’s most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO THE GOVERNOR OF GEORGIA.
Paris, December 22, 1785.
Sir,
The death of the late General Oglethorpe, who had considerable possessions in Georgia, has given rise, as we understand, to questions whether these possessions have become the property of the State, or have been transferred by his will to his widow, or descended on the nearest heir capable in law of taking them. In the latter case, the Chevalier de Mezieres, a subject of France, stands foremost, as being made capable of the inheritance by the treaty between this country and the United States. Under the regal government, it was the practice with us, when lands passed to the crown by escheat or forfeiture, to grant them to such relation of the party as stood on the fairest ground. This was even a chartered right in some of the States. The practice has been continued among them, as deeming that the late Revolution should in no instance abridge the rights of the people. Should this have been the practice in the State of Georgia, or should they in any instance think proper to admit it, I am persuaded none will arise in which it will be more expedient to do it, than in the present, and that no person’s expectations should be fairer than those of the Chevalier de Mezieres. He is the nephew of General Oglethorpe, he is of singular personal merit, an officer of rank, of high connections, and patronized by the ministers. His case has drawn their attention, and seems to be considered as protected by the treaty of alliance, and as presenting a trial of our regard to that. Should these lands be considered as having passed to the State, I take the liberty of recommending him to the legislature of Georgia, as worthy of their generosity, and as presenting an opportunity of proving the favorable dispositions which exist throughout America towards the subjects of this country, and an opportunity too, which will probably be known and noted here.
In the several views, therefore, of personal merit, justice, generosity and policy, I presume to recommend the Chevalier de Mezieres, and his interests, to the notice and patronage of your Excellency, whom the choice of your country has sufficiently marked as possessing the dispositions, while it has at the same time given you the power, to befriend just claims. The Chevalier de Mezieres will pass over to Georgia in the ensuing spring; but should he find an opportunity, he will probably forward this letter sooner. I have the honor to be, with sentiments of the most profound respect,
your Excellency’s most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
Paris, December 22, 1785.
Gentlemen,
By my despatch to Mr. Jay which accompanies this, you will perceive that the claims of the Chevalier de Mezieres, nephew to the late General Oglethorpe, to his possessions within your State, have attracted the attention of the ministry here; and that considering them as protected by their treaty with us, they have viewed as derogatory of that, the doubts which have been expressed on the subject. I have thought it best to present to them those claims in the least favorable point of view, to lessen as much as possible the ill effects of a disappointment: but I think it my duty to ask your notice and patronage of this case, as one whose decision will have an effect on the general interests of the Union.
The Chevalier de Mezieres is nephew to General Oglethorpe; he is a person of great estimation, powerfully related and protected. His interests are espoused by those whom it is our interest to gratify. I will take the liberty, therefore, of soliciting your recommendations of him to the generosity of your legislature, and to the patronage and good offices of your friends, whose efforts, though in a private case, will do a public good. The pecuniary advantages of confiscation, in this instance, cannot compensate its ill effects. It is difficult to make foreigners understand those legal distinctions between the effects of forfeiture of escheat, and of conveyance, on which the professors of the law might build their opinions in this case. They can see only the outlines of the case; to wit, the death of a possessor of lands lying within the United States, leaving an heir in France, and the State claiming those lands in opposition to the heir. An individual thinking himself injured makes more noise than a State. Perhaps too, in every case which either party to a treaty thinks to be within its provisions, it is better not to weigh the syllables and letters of the treaty, but to show that gratitude and affection render that appeal unnecessary. I take the freedom, therefore, of submitting to your wisdom the motives which present themselves in favor of a grant to the Chevalier de Mezieres, and the expediency of urging them on your State as far as you may think proper.
I have the honor to be, with sentiments of the highest respect, Gentlemen,
your most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN ADAMS.
Paris, December 27, 1785.
Dear Sir,
Your favors of the 13th and 20th were put into my hands today. This will be delivered to you by Mr. Dalrymple, secretary to the legation of Mr. Crawford. I do not know whether you were acquainted with him here. He is a young man of learning and candor, and exhibits a phenomenon I never before met with, that is, a republican born on the north side of the Tweed.
You have been consulted in the case of the Chevalier de Mezieres, nephew to General Oglethorpe, and are understood to have given an opinion derogatory of our treaty with France. I was also consulted, and understood in the same way. I was of opinion the Chevalier had no right to the estate, and as he had determined the treaty gave him a right, I suppose he made the inference for me, that the treaty was of no weight. The Count de Vergennes mentioned it to me in such a manner, that I found it was necessary to explain the case to him, and show him that the treaty had nothing to do with it. I enclose you a copy of the explanation I delivered him.
Mr. Boylston sold his cargo to an agent of Monsieur Sangrain. He got for it fifty-five livres the hundred weight. I do not think that his being joined to a company here would contribute to its success. His capital is not wanting. Le Conteux has agreed that the merchants of Boston, sending whale-oil here, may draw-on him for a certain proportion of money, only giving such a time in their drafts, as will admit the actual arrival of the oil into a port of France for his security. Upon these drafts, Mr. Barrett is satisfied they will be able to raise money to make their purchases in America. The duty is seven livres and ten sols on the barrel of five hundred and twenty pounds French, and ten sous on every livre, which raises it to eleven livres and five sols, the sum I mentioned to you. France uses between five and six millions of pounds’ weight French, which is between three and four thousand tons English. Their own fisheries do not furnish one million, and there is no probability of their improving. Sangrain purchases himself upwards of a million. He tells me our oil is better than the Dutch or English, because we make it fresh; whereas they cut up the whale, and bring it home to be made, so that it is by that time entered into fermentation. Mr. Barrett says, that fifty livres the hundred weight will pay the prime cost and duties, and leave a profit of sixteen per cent, to the merchant. I hope that England will, within a year or two, be obliged to come here to buy whale-oil for her lamps.
I like as little as you do, to have the gift of appointments. I hope Congress will not transfer the appointment of their consuls to their ministers. But if they do, Portugal is more naturally under the superintendence of the minister at Madrid, and still more naturally under that of the minister at Lisbon, where it is clear they ought to have one. If all my hopes fail, the letters of Governor Bowdoin and Gushing, in favor of young Mr. Warren, and your more detailed testimony in his behalf, are not likely to be opposed by evidence of equal weight, in favor of any other. I think with you, too, that it is for the public interest to encourage sacrifices and services, by rewarding them, and that they should weigh to a certain point, in the decision between candidates.
I am sorry for the illness of the Chevalier Pinto. I think that treaty important: and the moment to urge it, is that of a treaty between France and England.
Lambe, who left this place the 6th of November, was at Madrid the 10th of this month. Since his departure, Mr. Barclay has discovered that no copies of the full powers were furnished to himself, nor of course to Lambe. Colonel Franks has prepared copies, which I will endeavor to get, to send by this conveyance for your attestation: which you will be so good as to send back by the first safe conveyance, and I will forward them. Mr. Barclay and Colonel Franks being at this moment at St. Germain, I am not sure of getting the papers in time to go by Mr. Dalrymple. In that case, I will send them by Mr. Bingham.
Be so good as to present me affectionately to Mrs. and Miss Adams, to Colonels Smith and Humphreys, and accept assurances of the esteem with which I am, Dear Sir,
your friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN JAY.
Sir,
Paris, January 2,1786
Several conferences and letters having passed between the Count de Vergennes and myself, on the subject of the commerce of this country with the United States, I think them sufficiently interesting to be communicated to Congress. They are stated in the form of a report, and are herein enclosed. The length of this despatch, perhaps, needs apology. Yet I have not been able to abridge it, without omitting circumstances which I thought Congress would rather choose to know. Some of the objects of these conferences present but small hopes for the present, but they seem to admit a possibility of success at some future moment.
I am, Sir, your most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
[The following is an extract from the report referred to in
the preceding letter, embracing every thing interesting
therein, not communicated to the reader in the previous
correspondence.]
The next levee day at Versailles, I meant to bring again under the view of the Count de Vergennes, the whole subject of our commerce with France; but the number of audiences of ambassadors and other ministers, which take place, of course, before mine, and which seldom, indeed, leave me an opportunity of audience at all, prevented me that day. I was only able to ask of the Count de Vergennes, as a particular favor, that he would permit me to wait on him some day that week. He did so, and I went to Versailles the Friday following, (the 9th of December.) M. de Reyneval was with the Count. Our conversation began with the usual topic; that the trade of the United States had not yet learned the way to France, but continued to centre in England, though no longer obliged by law to go there. I observed, that the real cause of this was to be found in the difference of the commercial arrangements in the two countries; that merchants would not, and could not, trade but where there was to be some gain; that the commerce between two countries could not be kept up, but by an exchange of commodities; that, if an American merchant was forced to carry his produce to London, it could not be expected he would make a voyage from thence to France, with the money, to lay it out here; and, in like manner, that if he could bring his commodities with advantage to this country, he would not make another voyage to England, with the money, to lay it out there, but would take in exchange the merchandise of this country. The Count de Vergennes agreed to this, and particularly, that where there was no exchange of merchandise, there could be no durable commerce; and that it was natural for merchants to take their returns in the port where they sold their cargo. I desired his permission then, to take a summary view of the productions of the United States, that we might see which of them could be brought here to advantage.
1. Rice. France gets from the Mediterranean a rice not so good indeed, but cheaper than ours. He said that they bought of our rice, but that they got from Egypt, also, rice of a very fine quality. I observed that such was the actual state of their commerce in that article, that they take little from us. 2. Indigo. They make a plenty in their own colonies. He observed that they did, and that they thought it better than ours. 3. Flour, fish, and provisions of all sorts, they produce for themselves. That these articles might, therefore, be considered as not existing, for commerce, between the United States and the kingdom of France.
I proceeded to those capable of becoming objects of exchange between the two nations. 1. Peltry and furs. Our posts being in the hands of the English, we are cut off from that article. I am not sure even, whether we are not obliged to buy of them, for our own use. When these posts are given up, if ever they are, we shall be able to furnish France with skins and furs, to the amount of two millions of livres, in exchange for her merchandise: but, at present, these articles are to be counted as nothing. 2. Potash. An experiment is making whether this can be brought here. We hope it may, but at present it stands for nothing. He observed that it was much wanted in France, and he thought it would succeed. 3. Naval stores. Trials are also making on these, as subjects of commerce with France. They are heavy, and the voyage long. The result, therefore, is doubtful. At present, they are as nothing in our commerce with this country. 4. Whale-oil: I told him I had great hopes, that the late diminution of duty would enable us to bring this article with advantage, to France: that a merchant was just arrived (Mr. Barrett), who proposed to settle at L’Orient, for the purpose of selling the cargoes of this article, and choosing the returns. That he had informed me, that in the first year, it would be necessary to take one third in money, and the remainder only in merchandise; because the fishermen require, indispensably, some money. But he thought that after the first year, the merchandise of the preceding year would always produce money for the ensuing one, and that the whole amount would continue to be taken annually afterwards, in merchandise. I added, that though the diminution of duty was expressed to be but for one year, yet I hoped they would find their advantage in renewing and continuing it: for that if they intended really to admit it for one year only, the fishermen would not find it worth while to rebuild their vessels and to prepare themselves for the business. The Count expressed satisfaction on the view of commercial exchange held up by this article. He made no answer as to the continuance of it; and I did not choose to tell him, at that time, that we should claim its continuance under their treaty with the Hanseatic towns, which fixes this duty for them, and our own treaty, which gives us the rights of the most favored nation. 5. Tobacco. I recalled to the memory of the Count de Vergennes the letter I had written to him on this article; and the object of the present conversation being, how to facilitate the exchange of commerciable articles between the two countries, I pressed that of tobacco in this point of view; observed that France, at present, paid us two millions of livres for this article; that for such portions of it as were bought in London, they sent the money directly there, and for what they bought in the United States, the money was still remitted to London, by bills of exchange: whereas, if thy would permit our merchants to sell this article freely, they would bring it here, and take the returns on the spot, in merchandise, not money. The Count observed, that my proposition contained what was doubtless useful, but that the King received on this article, at present, a revenue of twenty-eight millions, which was so considerable, as to render them fearful of tampering with it; that the collection of this revenue by way of Farm, was of very ancient date, and that it was always hazardous to alter arrangements of long standing, and of such infinite combinations with the fiscal system. I answered, that the simplicity of the mode of collection proposed for this article, withdrew it from all fear of deranging other parts of their system; that I supposed they would confine the importation to some of their principal ports, probably not more than five or six; that a single collector in each of these, was the only new officer requisite; that he could get rich himself on six livres a hogshead, and would receive the whole revenue, and pay it into the treasury, at short hand. M. de Reyneval entered particularly into this part of the conversation, and explained to the Count, more in detail, the advantages and simplicity of it, and concluded by observing to me, that it sometimes happened that useful propositions, though not practicable at one time, might become so at another. I told him that that consideration had induced me to press the matter when I did, because I had understood the renewal of the Farm was then on the carpet, and that it was the precise moment, when I supposed that this portion might be detached from the mass of the Farms. I asked the Count de Vergennes whether, if the renewal of the Farm was pressing, this article might not be separated, merely in suspense, till government should have time to satisfy themselves on the expediency of renewing it. He said no promise could be made.
In the course of this conversation, he had mentioned the liberty we enjoyed of carrying our fish to the French islands. I repeated to him what I had hinted in my letter of November the 20th, 1785, that I considered as a prohibition, the laying such duties on our fish, and giving such premiums on theirs, as made a difference between their and our fishermen of fifteen livres the quintal, in an article which sold for but fifteen livres. He said it would not have that effect, for two reasons. 1. That their fishermen could not furnish supplies sufficient for their islands, and, of course, the inhabitants must, of necessity, buy our fish. 2. That from the constancy of our fishery, and the short season during which theirs continued, and also from the economy and management of ours, compared with the expense of theirs, we had always been able to sell our fish, in their islands, at twenty-five livres the quintal, while they were obliged to ask thirty-six livres. (I suppose he meant the livre of the French islands.) That thus, the duty and premium had been a necessary operation on their side, to place the sale of their fish on a level with ours, and, that without this, theirs could not bear the competition.
I have here brought together the substance of what was said on the preceding subjects, not pretending to give it verbatim, which my memory does not enable me to do. I have, probably, omitted many things which were spoken, but have mentioned nothing which was not. I was interrupted, at times, with collateral matters. One of these was important. The Count de Vergennes complained, and with a good deal of stress, that they did not find a sufficient dependence on arrangements taken with us. This was the third time, too, he had done it; first, in a conversation at Fontainebleau, when he first complained to me of the navigation acts of Massachusetts and New Hampshire; secondly, in his letter of October the 30th, 1785, on the same subject; and now, in the present conversation, wherein he added, as another instance, the case of the Chevalier de Mezieres, heir of General Oglethorpe, who, notwithstanding that the 11th article of the treaty provides, that the subjects or citizens of either party shall succeed, ab intestato, to the lands of their ancestors, within the dominions of the other, had been informed from Mr. Adams, and by me also, that his right of succession to the General’s estate in Georgia was doubtful. He observed too, that the administration of justice with us was tardy, insomuch, that their merchants, when they had money due to them within our States, considered it as desperate; and, that our commercial regulations, in general, were disgusting to them. These ideas were new, serious, and delicate. I decided, therefore, not to enter into them at that moment, and the rather, as we were speaking in French, in which language I did not choose to hazard myself. I withdrew from the objections of the tardiness of justice with us, and the disagreeableness of our commercial regulations, by a general observation, that I was not sensible they were well founded. With respect to the case of the Chevalier de Mezieres, I was obliged to enter into some explanations. They related chiefly to the legal operation of our Declaration of Independence, to the undecided question whether our citizens and British subjects were thereby made aliens to one another, to the general laws as to conveyances of land to aliens, and the doubt, whether an act of the Assembly of Georgia might not have been passed, to confiscate General Oglethorpe’s property, which would of course prevent its devolution on any heir. M. Reyneval observed, that in this case, it became a mere question of fact, whether a confiscation of these lands had taken place before the death of General Oglethorpe, which fact might be easily known by, inquiries in Georgia, where the possessions lay. I thought it very material, that the opinion of this court should be set to rights on these points. On my return, therefore, I wrote the following observations on them, which, the next time I went to Versailles (not having an opportunity of speaking to the Count de Vergennes), I put into the hands of M. Reyneval, praying him to read them, and to ask the favor of the Count to do the same.
Explanations on some of the subjects of the conversation, which I had the honor of having with his Excellency, the Count de Vergennes, when I was last at Versailles.
The principal design of that conversation was, to discuss, those articles of commerce which the United States could spare, which are wanted in France, and, if received there on a convenient footing, would be exchanged for the productions of France. But in the course of the conversation, some circumstances were incidentally mentioned by the Count de Vergennes, which induced me to suppose he had received impressions, neither favorable to us, nor derived from perfect information.
The case of the Chevalier de Mezieres was supposed to furnish an instance of our disregard to treatises; and the event of that case was inferred from opinions supposed to have been given by Mr. Adams and myself. This is ascribing a weight to our opinions, to which they are not entitled. They will have no influence on the decision of the case. The judges in our courts would not suffer them to be read. Their guide is the law of the land, of which law its treaties make a part. Indeed, I know not what opinion Mr. Adams may have given on the case. And, if any be imputed to him derogatory of our regard to the treaty with France, I think his opinion has been misunderstood. With respect to myself, the doubts which I expressed to the Chevalier de Mezieres, as to the success of his claims, were not founded on any question whether the treaty between France and the United States would be observed. On the contrary, I venture to pronounce that it will be religiously observed, if his case comes under it. But I doubted whether it would come under the treaty. The case, as I understand it, is this. General Oglethorpe, a British subject, had lands in Georgia. He died since the peace, having devised these lands to his wife. His heirs are the Chevalier de Mezieres, son of his eldest sister, and the Marquis de Bellegarde, son of his younger sister. This case gives rise to legal questions, some of which have not yet been decided, either in England or America, the laws of which countries are nearly the same.
1. It is a question under the laws of those countries, whether persons born before their separation, and once completely invested, in both, with the character of natural subjects, can ever become aliens in either? There are respectable opinions on both sides. If the negative be right, then General Oglethorpe having never become an alien, and having devised his lands to his wife, who, on this supposition, also, was not an alien, the devise has transferred the lands to her, and there is nothing left for the treaty to operate on.
2. If the affirmative opinion be right, and the inhabitants of Great Britain and America, born before the Revolution, are become aliens to each other, it follows by the laws of both, that the lands which either possessed, within the jurisdiction of the other, became the property of the State in which they are. But a question arises, whether the transfer of the property took place on the Declaration of Independence, or not till an office, or an act of Assembly, had declared the transfer. If the property passed to the State on the Declaration of Independence, then it did not remain in General Oglethorpe, and, of course, at the time of his death, he having nothing, there was nothing to pass to his heirs, and so nothing for the treaty to operate on.
3. If the property does not pass till declared by an office found by jury, or an act passed by the Assembly, the question then is, whether an office had been found, or an act of Assembly been passed for that purpose, before the peace. If there was, the lands had passed to the State during his life, and nothing being left in him, there is nothing for his heirs to claim under the treaty.
4. If the property had not been transferred to the State, before the peace, either by the Declaration of Independence, or an office or an act of Assembly, then it remained in General Oglethorpe at the epoch of the peace and it will be insisted, no doubt, that, by the sixth article of the treaty of peace between the United States and Great Britain, which forbids future confiscations, General Oglethorpe acquired a capacity of holding and of conveying his lands. He has conveyed them to his wife. But, she being an alien, it will be decided by the laws of the land, whether she took them for her own use, or for the use of the State. For it is a general principle of our law, that conveyances to aliens pass the lands to the State; and it may be urged, that though, by the treaty of peace, General Oglethorpe could convey, yet that treaty did not mean to give him a greater privilege of conveyance, than natives hold, to wit, a privilege of transferring the property to persons incapable, by law, of taking it. However, this would be a question between the State of Georgia and the widow of General Oglethorpe, in the decision of which the Chevalier de Mezieres is not interested, because, whether she takes the land by the will, for her own use, or for that of the State, it is equally prevented from descending to him: there is neither a conveyance to him, nor a succession ab intestato devolving on him, which are the cases provided for by our treaty with France. To sum up the matter in a few words; if the lands had passed to the State before the epoch of peace, the heirs of General Oglethorpe cannot say they have descended on them, and if they remained in the General at that epoch, the treaty saving them to him, he could convey them away from his heirs, and he has conveyed them to his widow, either for her own use, or for that of the State.
Seeing no event, in which, according to the facts stated to me, the treaty could be applied to this case, or could give any right, whatever, to the heirs of General Oglethorpe, I advised the Chevalier de Mezieres not to urge his pretensions on the footing of right, nor under the treaty, but to petition the Assembly of Georgia for a grant of these lands. If, in the question between the State and the widow of General Oglethorpe, it should be decided that they were the property of the State, I expected from their generosity, and the friendly dispositions in America towards the subjects of France, that they would be favorable to the Chevalier de Mezieres. There is nothing in the preceding observations, which would not have applied against the heir of General Ogiethorpe, had he been a native citizen of Georgia, as it now applies against him, being a subject of France. The treaty has placed the subjects of France on a footing with natives, as to conveyances and descent of property. There was no occasion for the assemblies to pass laws on this subject; the treaty being a law, as I conceive, superior to those of particular Assemblies, and repealing them where they stand in the way of its operations.
The supposition that the treaty was disregarded on our part, in the instance of the acts of Assembly of Massachusetts and New Hampshire, which made a distinction between natives and foreigners, as to the duties to be paid on commerce, was taken notice of in the letter of November the 20th, which I had the honor of addressing to the Count de Vergennes. And while I express my hopes, that, on a revision of these subjects, nothing will be found in them derogatory from either the letter or spirit of our treaty, I will add assurances that the United States will not be behind hand, in going beyond both, when occasions shall ever offer of manifesting their sincere attachment to this country.
I will pass on to the observation, that our commercial regulations are difficult and repugnant to the French merchants. To detail these regulations minutely, as they exist in every State, would be beyond my information. A general view of them, however, will suffice because the States differ little in their several regulations. On the arrival of a ship in America, her cargo must be reported at the proper office. The duties on it are to be paid. These are commonly from two and a half to five per cent, on its value. On many articles, the value of which is tolerably uniform, the precise sum is fixed by law. A tariff of these is presented to the importer, and he can see what he has to pay, as well as the officer. For other articles, the duty is such a per cent, on their value. That value is either shown by the invoice, or by the oath of the importer. This operation being once over, and it is a very short one, the goods are considered as entered, and may then pass through the whole thirteen States, without their being ever more subject to a question, unless they be re-shipped. Exportation is still more simple: because, as we prohibit the exportation of nothing, and very rarely lay a duty on any article of export, the State is little interested in examining outward bound vessels. The captain asks a clearance for his own purposes. As to the operations of internal commerce, such as matters of exchange, of buying, selling, bartering, &c, our laws are the same as the English. If they have been altered in any instance, it has been to render them more simple. Lastly, as to the tardiness of the administration of justice with us, it would be equally tedious and impracticable for me to give a precise account of it in every State. But I think it probable, that it is much on the same footing through all the States, and that an account of it in any one of them, may found a general presumption of it in the others. Being best acquainted with its administration in Virginia, I shall confine myself to that. Before the Revolution, a judgment could not be obtained under eight years, in the supreme court, where the suit was in the department of the common law, which department embraces about nine tenths of the subjects of legal contestation. In that of the chancery, from twelve to twenty years were requisite. This did not proceed from any vice in the laws, but from the indolence of the judges appointed by the King: and these judges holding their offices during his will only, he could have reformed the evil at any time. This reformation was among the first works of the legislature, after our independence. A judgment can now be obtained in the supreme court, in one year, at the common law, and in about three years, in the chancery. But more particularly to protect the commerce of France, which at that moment was considerable with us, a law was passed, giving all suits wherein a foreigner was a party, a privilege to be tried immediately, on the return of his process, without waiting till those of natives, which stand before them, shall have been decided on. Out of this act, however, the British stand excluded by a subsequent one. This, with its causes, must be explained. The British army, after ravaging the State of Virginia, had sent off a very great number of slaves to New York. By the seventh article of the treaty of peace, they stipulated not to carry away any of these. Notwithstanding this, it was known, when they were evacuating New York, that they were carrying away the slaves. General Washington made an official demand of Sir Guy Carleton, that he should cease to send them away. He answered, that these people had come to them under promise of the King’s protection, and that that promise should be fulfilled, in preference to the stipulation in the treaty. The State of Virginia, to which nearly the whole of these slaves belonged, passed a law to forbid the recovery of debts due to British subjects. They declared, at the same time, they would repeal the law, if Congress were of opinion they ought to do it. But, desirous that their citizens should be discharging their debts, they afterwards permitted British creditors to prosecute their suits, and to receive their debts in seven equal and annual payments; relying that the demand for the slaves would either be admitted or denied, in time to lay their hands on some of the latter payments for reimbursement. The immensity of this debt was another reason for forbidding such a mass of property to be offered for sale under execution at once, as, from the small quantity of circulating money, it must have sold for little or nothing, whereby the creditor would have failed to receive his money, and the debtor would have lost his whole estate, without being discharged of his debt. This is the history of the delay of justice in that country, in the case of British creditors. As to all others, its administration is as speedy as justice itself will admit. I presume it is equally so in all the other States, and can add, that it is administered in them all with a purity and integrity, of which few countries afford an example.
I cannot take leave, altogether, of the subjects of this conversation, without recalling the attention of the Count de Vergennes to what had been its principal drift. This was to endeavor to bring about a direct exchange between France and the United States, (without the intervention of a third nation) of those productions, with which each could furnish the other. We can furnish to France (because we have heretofore furnished to England) of whale-oil and spermaceti, of furs and peltry, of ships and naval stores, and of potash, to the amount of fifteen millions of livres; and the quantities will admit of increase. Of our tobacco, France consumes the value of ten millions more. Twenty-five millions of livres, then, mark the extent of that commerce of exchange, which is, at present, practicable between us. We want, in return, productions and manufactures, not money. If the duties on our produce are light, and the sale free, we shall undoubtedly bring it here, and lay out the proceeds on the spot, in the productions and manufactures which we want. The merchants of France will, on their part, become active in the same business. We shall no more think, when we shall have sold our produce here, of making an useless voyage to another country, to lay out the money, than we think, at present, when we have sold it elsewhere, of coming here to lay out the money. The conclusion is, that there are commodities which form a basis of exchange, to the extent of a million of guineas annually: it is for the wisdom of those in power, to contrive that the exchange shall be made.
Having put this paper into the hands of Monsieur Reyneval, we entered into conversation again, on the subject of the Farms, which were now understood to be approaching to a conclusion. He told me, that he was decidedly of opinion, that the interest of the State required the Farm of tobacco to be discontinued, and that he had, accordingly, given every aid to my proposition, which lay within his sphere: that the Count de Vergennes was very clearly of the same opinion, and had supported it strongly with reasons of his own, when he transmitted it to the Comptroller General; but that the Comptroller, in the discussions of this subject which had taken place, besides the objections which the Count de Vergennes had repeated to me, and which are before mentioned, had added, that the contract with the Farmers General was now so far advanced, that the article of tobacco could not be withdrawn from it, without unraveling the whole transaction. Having understood, that, in this contract, there was always reserved to the crown, a right to discontinue it at any moment, making just reimbursements to the Farmers, I asked M. Reyneval, if the contract should be concluded in its present form, whether it might still be practicable to have it discontinued, as to the article of tobacco, at some future moment. He said it might be possible.
Upon the whole, the true obstacle to this proposition has penetrated, in various ways, through the veil which covers it. The influence of the Farmers General has been heretofore found sufficient to shake a minister in his office. Monsieur de Calonne’s continuance or dismission has been thought, for some time, to be on a poise. Were he to shift this great weight, therefore, out of his own scale into that of his adversaries, it would decide their preponderance. The joint interests of France and America would be an insufficient counterpoise in his favor.
It will be observed, that these efforts to improve the commerce of the United States have been confined to that branch only, which respects France itself, and that nothing passed on the subject of our commerce with the West Indies, except an incidental conversation as to our fish. The reason of this was no want of a due sense of its importance. Of that I am thoroughly sensible. But efforts in favor of this branch would, at present, be desperate. To nations with which we have not yet treated, and who have possessions in America, we may offer a free vent of their manufactures in the United States, for a full, or a modified admittance into those possessions. But to France, we are obliged to give that freedom for a different compensation; to wit, for her aid in effecting our independence. It is difficult, therefore, to say what we have now to offer her, for an admission into her West Indies. Doubtless it has its price. But the question is, what this would be, and whether worth our while to give it. Were we to propose to give to each other’s citizens all the rights of natives, they would, of course, count what they should gain by this enlargement of right, and examine whether it would be worth to them, as much as their monopoly of their West India commerce. If not, that commercial freedom which we wish to preserve, and which, indeed, is so valuable, leaves us little else to offer. An expression in my letter to the Count de Vergennes, of November the 20th, wherein I hinted, that both nations might, perhaps, come into the opinion, that the condition of natives might be a better ground of intercourse for their citizens, than that of the most favored nation, was intended to furnish an opportunity to the minister, of parleying on that subject, if he was so disposed, and to myself, of seeing whereabouts they would begin, that I might communicate it to Congress, and leave them to judge of the expediency of pursuing the subject. But no overtures have followed; for I have no right to consider, as coming from the minister, certain questions which were, very soon after, proposed to me by an individual. It sufficiently accounts for these questions, that that individual had written a memorial on the subject, for the consideration of the minister, and might wish to know what we would be willing to do. The idea that I should answer such questions to him, is equally unaccountable, whether we suppose them originating with himself, or coming from the minister. In fact, I must suppose them to be his own; and I transmit them, only that Congress my see what one Frenchman, at least, thinks on the subject. If we can obtain from Great Britain reasonable conditions of commerce (which, in my idea, must for ever include an admission into her islands), the freest ground between these two nations would seem to be the best. But if we can obtain no equal terms from her, perhaps Congress might think it prudent, as Holland has done, to connect us unequivocally with France. Holland has purchased the protection of France. The price she pays is, aid in time of war. It is interesting for us to purchase a free commerce with the French islands. But whether it is best to pay for it, by aids in war, or by privileges in commerce; or not to purchase it at all, is the question.
TO T. HOPKINSON.
Paris, January 3, 1786.
Dear Sir,
I wrote you last on the 25th of September. Since that I have received yours of October the 25th, enclosing a duplicate of the last invented tongue for the harpsichord. The letter enclosing another of them, and accompanied by newspapers, which you mention in that of October the 25th, has never come to hand. I will embrace the first opportunity of sending you the crayons. Perhaps they may come with this, which I think to deliver to Mr. Bingham, who leaves us on Saturday, for London. If, on consulting him, I find the conveyance from London uncertain, you shall receive them by a Mr. Barrett, who goes from hence for New York, next month. You have not authorized me to try to avail you of the new tongue. Indeed, the ill success of my endeavors with the last does not promise much with this. However, I shall try. Houdon only stopped a moment, to deliver me your letter, so that I have not yet had an opportunity of asking his opinion of the improvement. I am glad you are pleased with his work. He is among the foremost, or, perhaps, the foremost artist in the world.
Turning to your Encyclopédie, Arts et Metiers, tome 3, part 1, page 393, you will find mentioned an instrument, invented by a Monsieur Renaudin, for determining the true time of the musical movements, largo, adagio, &c. I went to see it. He showed me his first invention; the price of the machine was twenty-five guineas: then his second, which he had been able to make for about half that sum. Both of these had a mainspring and a balance-wheel, for their mover and regulator. The strokes are made by a small hammer. He then showed me his last, which is moved by a weight and regulated by a pendulum, and which cost only-two guineas and a half. It presents, in front, a dial-plate like that of a clock, on which are arranged, in a circle, the words largo, adagio, andante, allegro, presto. The circle is moreover divided into fifty-two equal degrees. Largo is at 1, adagio at 11, andante at 22, allegro at 36, and presto at 46. Turning the index to any one of these, the pendulum (which is a string, with a ball hanging to it) shortens or lengthens, so that one of its vibrations gives you a crochet for that movement. This instrument has been examined by the academy of music here, who were so well satisfied of its utility, that they have ordered all music which shall be printed here, in future, to have the movements numbered in correspondence with this plexi-chronometer. I need not tell you that the numbers between two movements, as between 22 and 36, give the quicker or slower degrees of the movements, such as the quick andante, or moderate allegro. The instrument is useful, but still it may be greatly simplified. I got him to make me one, and having fixed a pendulum vibrating seconds, I tried by that the vibrations of his pendulum, according to the several movements. I find the pendulum regulated to Largo

Every one, therefore, may make a chronometer adapted to his instrument.
For a harpsichord, the following occurs to me:
In the wall of your chamber, over the instrument, drive five little brads, as, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, in the following manner. Take a string with a bob to it, of such length, as, that hung on No. 1, it shall vibrate fifty-two times in a minute. Then proceed by trial to drive No. 2, at such a distance, that drawing the loop of the string to that, the part remaining between 1 and the bob, shall vibrate sixty times in a minute. Fix the third for seventy vibrations, &c.; the cord always hanging over No. 1, as the centre of vibration. A person playing on the violin may fix this on his music-stand. A pendulum thrown into vibration will continue in motion long enough to give you the time of your piece. I have been thus particular, on the supposition that you would fix one of these simple things for yourself.
You have heard often of the metal called platina, to be found only in South America. It is insusceptible of rust, as gold and silver are, none of the acids affecting it, excepting the aqua regia. It also admits of as perfect a polish as the metal hitherto used for the specula of telescopes. These two properties had suggested to the Spaniards the substitution of it for that use. But the mines being closed up by the government, it is difficult to get the metal. The experiment has been lately tried here by the Abbe Rochon (whom I formerly mentioned to Mr. Rittenhouse, as having discovered that lenses of certain natural crystals have two different and uncombined magnifying powers), and he thinks the polish as high as that of the metal heretofore used, and that it will never be injured by the air, a touch of the finger, &c. I examined it in a dull day, which did not admit a fair judgment of the strength of its reflection.
Good qualities are sometimes misfortunes. I will prove it from your own experience. You are punctual; and almost the only one of my correspondents on whom I can firmly rely, for the execution of commissions which combine a little trouble with more attention. I am very sorry however that I have three commissions to charge you with, which will give you more than a little trouble. Two of them are for Monsieur de Buffon. Many, many years ago, Cadwallader Golden wrote a very small pamphlet on the subjects of attraction and impulsion, a copy of which he sent to Monsieur de Buffon. He was so charmed with it, that he put it into the hands of a friend to translate, who lost it. It has ever since weighed on his mind, and he has made repeated trials to have it found in England. But in vain. He applied to me. I am in hopes, if you will write a line to the booksellers of Philadelphia to rummage their shops, that some of them may find it. Or, perhaps, some of the careful old people of Pennsylvania or New Jersey may have preserved a copy. In the King’s cabinet of Natural History, of which Monsieur de Buffon has the superintendence, I observed that they had neither our grouse nor our pheasant. These, I know, may be bought in the market of Philadelphia, on any day while they are in season. Pray buy the male and female of each, and employ some apothecary’s boys to prepare them, and pack them. Methods may be seen in the preliminary discourse to the first volume of Birds, in the Encyclopédie, or in the Natural History of Buffon, where he describes the King’s cabinet. And this done, you will be so good as to send them to me. The third commission is more distant. It is to precure me two or three hundred paccan nuts from the western country. I expect they can always be got at Pittsburgh and am in hopes, that by yourself or your friends, some attentive person there may be engaged to send them to you. They should come as fresh as possible, and come best, I believe, in a box of sand. Of this, Barham could best advise you. I imagine vessels are always coming from Philadelphia to France. If there be a choice of ports, Havre would be the best. I must beg you to direct them to the care of the American consul or agent at the port, to be sent by the Diligence or Fourgon. A thousand apologies would not suffice for this trouble, if I meant to pay you in apologies only. But I sincerely ask, and will punctually execute, the appointment of your chargé des affaires in Europe generally. From the smallest to the highest commission, I will execute with zeal and punctually, in buying, or doing any thing you wish, on this side the water. And you may judge from the preceding specimen, that I shall not be behind hand in the trouble I shall impose on you. Make a note of all the expenses attending my commissions, and favor me with it every now and then, and I will replace them. My daughter is well, and retains an affectionate remembrance of her ancient patroness, your mother, as well as of your lady and family. She joins me in wishing to them, and to Mr. and Mrs. Rittenhouse and family, every happiness. Accept, yourself, assurances of the esteem with which I am, Dear Sir,
your friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
P.S. What is become of the Lunarium for the King?
TO GENERAL WASHINGTON.
Paris, January 4, 1786.
Dear Sir,
I have been honored with your letter of September the 26th, which was delivered me by Mr. Houdon, who is safely returned. He has brought with him the mould of the face only, having left the other parts of his work with his workmen to come by some other conveyance. Doctor Franklin, who was joined with me in the superintendence of this just monument, having left us before what is called the costume of the statue was decided on, I cannot so well satisfy myself, and I am persuaded I should not so well satisfy the world, as by consulting your own wish or inclination as to this article. Permit me, therefore, to ask you whether there is any particular dress, or any particular attitude, which you would rather wish to be adopted. I shall take a singular pleasure in having your own idea executed, if you will be so good as to make it known to me.
I thank you for the trouble you have taken in answering my inquiries on the subject of Bushnel’s machine. Colonel Humphreys could only give me a general idea of it from the effects proposed, rather than the means contrived to produce them.
I sincerely rejoice that three such works as the opening the Potomac and James rivers, and a canal from the Dismal Swamp are likely to be carried through. There is still a fourth, however, which I had the honor I believe of mentioning to you in a letter of March the 15th, 1784, from Annapolis. It is the cutting a canal which shall unite the heads of the Cayahoga and Beaver Creek. The utility of this, and even the necessity of it, if we mean to aim at the trade of the lakes, will be palpable to you. The only question is its practicability. The best information I could get as to this was from General Hand, who described the country as champain, and these waters as heading in lagoons, which would be easily united. Maryland and Pennsylvania are both interested to concur with us in this work. The institutions you propose to establish by the shares in the Potomac and James river companies, given you by the Assembly, and the particular objects of those institutions, are most worthy. It occurs to me, however, that if the bill ‘for the more general diffusion of knowledge,’ which is in the revisal, should be passed, it would supersede the use and obscure the existence of the charity schools you have thought of. I suppose in fact, that that bill or some other like it will be passed. I never saw one received with more enthusiasm than that was in the year 1778, by the House of Delegates, who ordered it to be printed. And it seemed afterwards, that nothing but the extreme distress of our resources prevented its being carried into execution even during the war. It is an axiom in my mind, that our liberty can never be safe but in the hands of the people themselves, and that too of the people with a certain degree of instruction. This it is the business of the State to effect, and on a general plan. Should you see a probability of this, however, you can never be at a loss for worthy objects of this donation. Even the remitting that proportion of the toll on all articles transported, would present itself under many favorable considerations, and it would in effect be to make the State do in a certain proportion what they ought to have done wholly: for I think they should clear all the rivers, and lay them open and free to all. However, you are infinitely the best judge, how the most good may be effected with these shares.
All is quiet here. There are indeed two specks in the horizon: the exchange of Bavaria, and the demarcation between the Emperor and Turks. We may add as a third, the interference by the King of Prussia in the domestic disputes of the Dutch. Great Britain, it is said, begins to look towards us with a little more good humor. But how true this may be, I cannot say with certainty. We are trying to render her commerce as little necessary to us as possible, by finding other markets for our produce. A most favorable reduction of duties on whale-oil has taken place here, which will give us a vent for that article, paying a duty of a guinea and a half a ton only.
I have the honor to be, with the highest esteem and respect, Dear Sir,
your most obedient and
most humble servant,
Tm: Jefferson.
Paris, January 7, 1786.
Dear Sir,
The very few of my countrymen who happen to be punctual, will find their punctuality a misfortune to them. Of this I shall give you a proof by the present application, which I should not make to you, if I did not know you to be superior to the torpidity of our climate. In my conversations with the Count de Buffon on the subjects of Natural History, I find him absolutely unacquainted with our elk and our deer. He has hitherto believed that our deer never had horns more than a foot long; and has, therefore, classed them with the roe-buck, which I am sure you know them to be different from. I have examined some of the red deer of this country at the distance of about sixty yards, and I find no other difference between them and ours, than a shade or two in the color. Will you take the trouble to procure for me the largest pair of buck’s horns you can, and a large skin of each color, that is to say, a red and a blue? If it were possible to take these from a buck just killed, to leave all the bones of the head in the skin with the horns on, to leave the bones of the legs in the skin also, and the hoofs to it, so that having only made an incision all along the belly and neck to take the animal out at, we could by sewing up that incision and stuffing the skin, present the true size and form of the animal, it would be a most precious present. Our deer have been often sent to England and Scotland. Do you know (with certainty) whether they have ever bred with the red deer of those countries? With respect to the elk, I despair of your being able to get for me any thing but the horns of it. David Ross I know has a pair; perhaps he would give them to us. It is useless to ask for the skin and skeleton, because I think it is not in your power to get them, otherwise they would be most desirable. A gentleman, fellow-passenger with me from Boston to England, promised to send to you in my name some hares, rabbits, pheasants, and partridges, by the return of the ship which was to go to Virginia, and the captain promised to take great care of them. My friend procured the animals, and the ship changing her destination, he kept them, in hopes of finding some other conveyance, till they all perished. I do not despair, however, of finding some opportunity still of sending a colony of useful animals. I am making a collection of vines for wine, and for the table; also of some trees, such as the cork-oak, &c. &c.
Every thing is absolutely quiet in Europe. There is not, therefore, a word of news to communicate. I pray you to present me affectionately to your family and that of Tuckahoe. Whatever expense is necessary for procuring me the articles above-mentioned, I will instantly replace, either in cash, or in any thing you may wish from hence.
I am with very sincere esteem, Dear Sir,
your most obedient, humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MAJOR GENERAL GREENE.
Paris, January 12, 1786.
Dear Sir,
Your favor of June the 1st did not come to hand till the 3rd of September. I immediately made inquiries on the subject of the frigate you had authorized your relation to sell to this government, and I found that he had long before that sold her to government, and sold her very well, as I understood. I noted the price on the back of your letter, which I have since unfortunately mislaid, so that I cannot at this moment state to you the price. But the transaction is of so long standing that you cannot fail to have received advice of it. I should without delay have given you this information, but that I hoped to be able to accompany it with information as to the live-oak, which was another object of your letter. This matter, though it has been constantly pressed by Mr. St. John, and also by the Marquis de la Fayette, since his return from Berlin, has been spun to a great length, and at last they have only decided to send to you for samples of the wood. Letters on this subject from the Marquis de la Fayette accompany this.
Every thing in Europe is quiet, and promises quiet for at least a year to come. We do not find it easy to make commercial arrangements in Europe. There is a want of confidence in us. This country has lately reduced the duties on American whale-oil to about a guinea and a half the ton, and I think they will take the greatest part of what we can furnish. I hope, therefore, that this branch of our commerce will resume its activity. Portugal shows a disposition to court our trade; but this has for some time been discouraged by the hostilities of the piratical states of Barbary. The Emperor of Morocco, who had taken one of our vessels, immediately consented to suspend hostilities and ultimately gave up the vessel, cargo, and crew. I think we shall be able to settle matters with him. But I am not sanguine as to the Algerines. They have taken two of our vessels, and I fear will ask such a tribute for a forbearance of their piracies as the United States would be unwilling to pay. When this idea comes across my mind, my faculties are absolutely suspended between indignation and impatience. I think whatever sums we are obliged to pay for freedom of navigation in the European seas, should be levied on the European commerce with us by a separate impost, that these powers may see that they protect these enormities for their own loss. I have the honor to be, with sentiments of the most perfect esteem and respect, Dear Sir,
your most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO LISTER ASQUITH.
Paris, January 13, 1786.
Sir,
I have duly received your letter of the 2nd instant. The delays, which have attended your enlargement, have been much beyond my expectation. The reason I have not written to you for some time, has been the constant expectation of receiving an order for your discharge. I have not received it however. I went to Versailles three days ago, and made fresh applications on the subject. I received assurances which give me reason to hope that the order for your discharge will soon be made out. Be assured it shall not be delayed a moment after it comes to my hands, and that I shall omit no opportunity of hastening it. In the mean time, I think you may comfort yourself and companions with the certainty of receiving it ere long.
I am, Sir, your most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
[The following were answers by Mr. Jefferson to questions
addressed to him by Monsieur de Meusnier, author of that
part of the Encylopédie Méthodique, entitled Economie
Politique et Diplomatique.]
1. What has led Congress to determine that the concurrence of seven votes is requisite in questions, which by the Confederation are submitted to the decision of a majority of the United States in Congress assembled?
The ninth article of Confederation, section sixth, evidently establishes three orders of questions in Congress. 1. The greater ones which relate to making peace or war, alliances, coinage, requisitions for money, raising military force, or appointing its commander-in-chief. 2. The lesser ones which comprehend all other matters submitted by the Confederation to the federal head. 3. The single question of adjourning from day to day. This gradation of questions is distinctly characterized by the article.
In proportion to the magnitude of these questions, a greater concurrence of the voices composing the Union was thought necessary. Three degrees of concurrence, well distinguished by substantial circumstances, offered themselves to notice. 1. A concurrence of a majority of the people of the Union. It was thought that this would be insured by requiring the voices of nine States; because according to the loose estimates which had then been made of the inhabitants, and the proportion of them which were free, it was believed, that even the nine smallest would include a majority of the free citizens of the Union. The voices, therefore, of nine States were required in the greater questions. 2. A concurrence of the majority of the States. Seven constitute that majority. This number, therefore, was required in the lesser questions. 3. A concurrence of the majority of Congress, that is to say, of the States actually present in it. As there is no Congress when there are not seven States present, this concurrence could never be of less than four States. But these might happen to be the four smallest, which would not include one ninth part of the free citizens of the Union. This kind of majority, therefore, was entrusted with nothing but the power of adjourning themselves from day to day.
Here then are three kinds of majorities. 1. Of the people. 2. Of the States. 3. Of the Congress. Each of which is entrusted to a certain length.
Though the paragraph in question be clumsily expressed, yet it strictly announces its own intentions. It defines with precision, the greater questions, for which nine votes shall be requisite. In the lesser questions, it then requires a majority of the United States in Congress assembled: a term which will apply either to the number seven, as being a majority of the States, or to the number four, as being a majority of Congress. Which of the two kinds of majority was meant. Clearly that which would leave a still smaller kind for the decision of the question of adjournment. The contrary construction would be absurd.
This paragraph, therefore, should be understood as if it had been expressed in the following terms. ‘The United States in Congress assembled, shall never engage in war, &c. but with the consent of nine States: nor determine any other question, but with the consent of a majority of the whole States, except the question of adjournment from day to day, which may be determined by a majority of the States actually present in Congress.’
2. How far is it permitted to bring on the reconsideration of a question which Congress has once determined?
The first Congress which met being composed mostly of persons who had been members of the legislatures of their respective States, it was natural for them to adopt those rules in their proceedings, to which they had been accustomed in their legislative houses; and the more so, as these happened to be nearly the same, as having been copied from the same original, those of the British parliament. One of those rules of proceeding was, that ‘a question once determined cannot be proposed a second time in the same session.’ Congress, during their first session in the autumn of 1774, observed this rule strictly. But before their meeting in the spring of the following year, the war had broken out. They found themselves at the head of that war, in an executive as well as legislative capacity. They found that a rule, wise and necessary for a legislative body, did not suit an executive one, which, being governed by events, must change their purposes as those change. Besides, their session was then to become of equal duration with the war; and a rule, which should render their legislation immutable during all that period, could not be submitted to. They, therefore, renounced it in practice, and have ever since continued to reconsider their questions freely. The only restraint, as yet provided against the abuse of this permission to reconsider, is, that when a question has been decided, it cannot be proposed for reconsideration, but by some one who voted in favor of the former decision, and declares that he has since changed his opinion. I do not recollect accurately enough, whether it be necessary that his vote should have decided that of his State, and the vote of his State have decided that of Congress.
Perhaps it might have been better, when they were forming the federal constitution, to have assimilated it as much as possible to the particular constitutions of the States. All of these have distributed the legislative, executive, and judiciary powers into different departments. In the federal constitution the judiciary powers are separated from the others; but the legislative and executive are both exercised by Congress. A means of amending this defect has been thought of. Congress having a power to establish what committees of their own body they please, and to arrange among them the distribution of their business, they might, on the first day of their annual meeting, appoint an executive committee consisting of a member from each State, and refer to them all executive business which should occur during their session; confining themselves to what is of a legislative nature, that is to say, to the heads described in the ninth article, as of the competence of nine States only, and to such other questions as should lead to the establishment of general rules. The journal of this committee of the preceding day might be read the next morning in Congress, and considered as approved, unless a vote was demanded on a particular article, and that article changed. The sessions of Congress would then be short, and when they separated, the Confederation authorizes the appointment of a committee of the States which would naturally succeed to the business of the executive committee. The legislative business would be better done, because the attention of the members would not be interrupted by the details of execution; and the executive business would be better done, because business of this nature is better adapted to small than great bodies. A monarchical head should confide the execution of its will to departments, consisting each of a plurality of hands, who would warp that will as much as possible towards wisdom and moderation, the two qualities it generally wants. But a republican head, founding its decrees originally in these two qualities, should commit them to a single hand for execution, giving them thereby a promptitude which republican proceedings generally want. Congress could not, indeed, confide their executive business to a smaller number than a committee consisting of a member from each State. This is necessary to insure the confidence of the Union. But it would be gaining a great deal to reduce the executive head to thirteen, and to relieve themselves of those details. This, however, has as yet been the subject of private conversations only.
3. A succinct account of paper money, in America?
Previous to the late revolution, most of the States were in the habit, whenever they had occasion for more money than could be raised immediately, by taxes, to issue paper notes or bills, in the name of the State, wherein they promised to pay to the bearer the sum named in the note or bill. In some of the States, no time of payment was fixed, nor tax laid to enable payment. In these, the bills depreciated. But others of the States named in the bill the day when it should be paid, laid taxes to bring in money enough for that purpose, and paid the bills punctually, on or before the day named. In these States, paper money was in as high estimation as gold and silver. On the commencement of the late Revolution, Congress had no money. The external commerce of the States being suppressed, the farmer could not sell his produce, and, of course, could not pay a tax. Congress had no resource then, but in paper money. Not being able to lay a tax for its redemption, they could only promise that taxes should be laid for that purpose, so as to redeem the bills by a certain day. They did not foresee the long continuance of the war, the almost total suppression of their exports, and other events, which rendered the performance of their engagement impossible. The paper money continued, for a twelvemonth, equal to gold and silver. But the quantities which they were obliged to emit, for the purposes of the war, exceeded what had been the usual quantity of the circulating medium. It began, therefore, to become cheaper, or, as we expressed it, it depreciated, as gold and silver would have done, had they been thrown into circulation in equal quantities. But not having, like them, an intrinsic value, its depreciation was more rapid, and greater, than could ever have happened with them. In two years, it had fallen to two dollars of paper money for one of silver; in three years, to four for one; in nine months more, it fell to ten for one; and in the six months following, that is to say, by September, 1779, it had fallen to twenty for one.
Congress, alarmed at the consequences which were to be apprehended, should they lose this resource altogether, thought it necessary to make a vigorous effort to stop its further depreciation. They, therefore, determined, in the first place, that their emissions should not exceed two hundred millions of dollars, to which term they were then nearly arrived: and, though they knew that twenty dollars of what they were then issuing, would buy no more for their army than one silver dollar would buy, yet they thought it would be worth while to submit to the sacrifices of nineteen out of twenty dollars, if they could thereby stop further depreciation. They, therefore, published an address to their constituents, in which they renewed their original declarations, that this paper money should be redeemed at dollar for dollar. They proved the ability of the States to do this, and that their liberty would be cheaply bought at that price. The declaration was ineffectual. No man received the money at a better rate; on the contrary, in six months more, that is, by March, 1780, it had fallen to forty for one. Congress then tried an experiment of a different kind. Considering their former offers to redeem this money, at par, as relinquished by the general refusal to take it, but in progressive depreciation, they required the whole to be brought in, declared it should be redeemed at its present value, of forty for one, and that they would give to the holders new bills, reduced in their denomination to the sum of gold or silver, which was actually to be paid for them. This would reduce the nominal sum of the mass in circulation, to the present worth of that mass, which was five millions; a sum not too great for the circulation of the States, and which, they therefore hoped, would not depreciate further, as they continued firm in their purpose of emitting no more. This effort was as unavailing as the former. Very little of the money was brought in. It continued to circulate and to depreciate, till the end of 1780, when it had fallen to seventy-five for one, and the money circulated from the French army, being, by that time, sensible in all the States north of the Potomac, the paper ceased its circulation altogether, in those States. In Virginia and North Carolina, it continued a year longer, within which time it fell to one thousand for one, and then expired, as it had done in the other States, without a single groan. Not a murmur was heard, on this occasion, among the people. On the contrary, universal congratulations took place, on their seeing this gigantic mass, whose dissolution had threatened convulsions which should shake their infant confederacy to its centre, quietly interred in its grave. Foreigners, indeed, who do not, like the natives, feel indulgence for its memory, as of a being which has vindicated their liberties, and fallen in the moment of victory, have been loud, and still are loud in their complaints. A few of them have reason; but the most noisy are not the best of them. They are persons who have become bankrupt, by unskilful attempts at commerce with America. That they may have some pretext to offer to their creditors, they have bought up great masses of this dead money in America, where it is to be had at five thousand for one, and they show the certificates of their paper possessions, as if they had all died in their hands, and had been the cause of their bankruptcy. Justice will be done to all, by paying to all persons what this money actually cost them, with an interest of six per cent, from the time they received it. If difficulties present themselves in the ascertaining the epoch of the receipt, it has been thought better that the State should lose, by admitting easy proofs, than that individuals, and especially foreigners, should, by being held to such as would be difficult, perhaps impossible.
4. Virginia certainly owed two millions, sterling, to Great Britain, at the conclusion of the war. Some have conjectured the debt as high as three millions. I think that state owed near as much as all the rest put together. This is to be ascribed to peculiarities in the tobacco trade. The advantages made by the British merchants, on the tobaccos consigned to them, were so enormous, that they spared no means of increasing those consignments. A powerful engine for this purpose, was the giving good prices and credit to the planter, till they got him more immersed in debt than he could pay, without selling his lands or slaves. They then reduced the prices given for his tobacco, so that let his shipments be ever so great, and his demand of necessaries ever so economical, they never permitted him to clear off his debt. These debts had become hereditary from father to son, for many generations, so that the planters were a species of property, annexed to certain mercantile houses in London.
5. The members of Congress are differently paid by different States. Some are on fixed allowances, from four to eight dollars a day. Others have their expenses paid, and a surplus for their time. This surplus is of two, three, or four dollars a day.
6. I do not believe there has ever been a moment, when a single whig, in any one State, would not have shuddered at the very idea of a separation of their State from the confederacy. The tories would, at all times, have been glad to see the confederacy dissolved, even by particles at a time, in hopes of their attaching themselves again to Great Britain.
7. The 11th article of Confederation admits Canada to accede to the Confederation, at its own will, but adds, ‘no other colony shall be admitted to the same, unless such admission be agreed to by nine States.’ When the plan of April, 1784, for establishing new States, was on the carpet, the committee who framed the report of that plan, had inserted this clause, ‘provided nine States agree to such admission, according to the reservation of the 11th of the articles of Confederation.’ It was objected, 1. That the words of the Confederation, ‘no other colony,’ could refer only to the residuary possessions of Great Britain, as the two Floridas, Nova Scotia, &c. not being already parts of the Union; that the law for ‘admitting’ a new member into the Union, could not be applied to a territory which was already in the Union, as making part of a State which was a member of it. 2. That it would be improper to allow ‘nine’ States to receive a new member, because the same reasons which rendered that number proper now, would render a greater one proper, when the number composing the Union should be increased. They therefore struck out this paragraph, and inserted a proviso, that, ‘the consent of so many States, in Congress, shall be first obtained, as may, at the time, be competent;’ thus leaving the question, whether the 11th article applies to the admission of new States, to be decided when that admission shall be asked. See the Journal of Congress of April 20, 1784. Another doubt was started in this debate; viz. whether the agreement of the nine Stales, required by the Confederation, was to be made by their legislatures, or by their delegates in Congress. The expression adopted, viz. ‘so many States, in Congress, is first obtained,’ show what was their sense of this matter. If it be agreed, that the 11th article of the Confederation is not to be applied to the admission of these new States, then it is contended that their admission comes within the 13th article, which forbids ‘any alteration, unless agreed to in a Congress of the United States, and afterwards confirmed by the legislatures of every State.’ The independence of the new States of Kentucky and Franklin, will soon bring on the ultimate decision of all these questions.
8. Particular instances, whereby the General Assembly of Virginia have shown, that they considered the ordinance called their constitution, as every other ordinance, or act of the legislature, subject to be altered by the legislature for the time being.
1. The convention which formed that constitution, declared themselves to be the House of Delegates, during the term for which they were originally elected, and, in the autumn of the year, met the Senate, elected under the new constitution, and did legislative business with them. At this time, there were malefactors in the public jail, and there was, as yet, no court established for their trial. They passed a law, appointing certain members by name, who were then members of the Executive Council, to be a court for the trial of these malefactors, though the constitution had said, in express words, that no person should exercise the powers of more than one of the three departments, legislative, executive, and judiciary, at the same time. This proves, that the very men who had made that constitution, understood that it would be alterable by the General Assembly. This court was only for that occasion. When the next General Assembly met, after the election of the ensuing year, there was a new set of malefactors in the jail, and no court to try them. This Assembly passed a similar law to the former, appointing certain members of the Executive Council to be an occasional court for this particular case. Not having the journals of Assembly by me, I am unable to say whether this measure was repealed afterwards. However, they are instances of executive and judiciary powers exercised by the same persons, under the authority of a law, made in contradiction to the constitution.
2. There was a process depending in the ordinary courts of justice, between two individuals of the name of Robinson and Fauntleroy, who were relations, of different descriptions, to one Robinson, a British subject, lately dead. Each party claimed a right to inherit the lands of the decedent, according to the laws. Their right should, by the constitution, have been decided by the judiciary courts; and it was actually depending before them. One of the parties petitioned the Assembly, (I think it was in the year 1782,) who passed a law deciding the right in his favor. In the following year, a Frenchman, master of a vessel, entered into port without complying with the laws established in such cases, whereby he incurred the forfeitures of the law to any person who would sue for them. An individual instituted a legal process to recover these forfeitures, according to the law of the land. The Frenchman petitioned the Assembly, who passed a law deciding the question of forfeiture in his favor. These acts are occasional repeals of that part of the constitution, which forbids the same persons to exercise legislative and judiciary powers, at the same time.
3. The Assembly is in the habitual exercise, during their sessions, of directing the Executive what to do. There are few pages of their journals, which do not furnish proofs of this, and, consequently, instances of the legislative and executive powers exercised by the same persons, at the same time. These things prove, that it has been the uninterrupted opinion of every Assembly, from that which passed the ordinance called the constitution, down to the present day, that their, acts may control that ordinance, and, of course, that the State of Virginia has no fixed constitution at all.
[The succeeding observations were made by Mr. Jefferson on
an article entitled ‘Etats Unis,’ prepared for the
Encyclopédie Méthodique, and submitted to him before its
publication.]
Page 8. The malefactors sent to America were not sufficient in number to merit enumeration, as one class out of three, which peopled America. It was at a late period of their history, that this practice began. I have no book by me, which enables me to point out the date of its commencement. But I do not think the whole number sent would amount to two thousand, and being principally men, eaten up with disease, they married seldom and propagated little. I do not suppose that themselves and their descendants are, at present, four thousand, which is little more than one thousandth part of the whole inhabitants.
Indented servants formed a considerable supply. These were poor Europeans, who went to America to settle themselves. If they could pay their passage, it was well. If not, they must find means of paying it. They were at liberty, therefore, to make an agreement with any person they chose, to serve him such a length of time as they agreed on, upon condition that he would repay, to the master of the vessel, the expenses of their passage. If, being foreigners, unable to speak the language, they did not know how to make a bargain for themselves, the captain of the vessel contracted for them, with such persons as he could. This contract was by deed indented, which occasioned them to be called indented servants. Sometimes they were called redemptioners, because, by their agreement with the master of the vessel, they could redeem themselves from his power by paying their passage; which they frequently effected, by hiring themselves on their arrival, as is before mentioned. In some States, I know that these people had a right of marrying themselves, without their master’s leave, and I did suppose they had that right every where. I did not know, that, in any of the States, they demanded so much as a week for every day’s absence, without leave. I suspect this must have been at a very early period, while the governments were in the hands of the first emigrants, who, being mostly laborers, were narrow-minded and severe. I know that in Virginia, the laws allowed their servitude to be protracted only two days for every one they were absent without leave. So mild was this kind of servitude, that it was very frequent for foreigners, who carried to America money enough, not only to pay their passage, but to buy themselves a farm, to indent themselves to a master for three years, for a certain sum of money, with a view to learn the husbandry of the country. I will here make a general observation. So desirous are the poor of Europe to get to America, where they may better their condition, that, being unable to pay their passage, they will agree to serve two or three years on their arrival there, rather than not go. During the time of that service, they are better fed, better clothed, and have lighter labor, than while in Europe. Continuing to work for hire, a few years longer, they buy a farm, marry, and enjoy all the sweets of a domestic society of their own. The American governments are censured for permitting this species of servitude, which lays the foundation of the happiness of these people. But what should these governments do? Pay the passage of all those who choose to go into their country? They are not able; nor, were they able, do they think the purchase worth the price. Should they exclude these people from their shores? Those who know their situations in Europe and America, would not say, that this is the alternative which humanity dictates. It is said these people are deceived by those who carry them over. But this is done in Europe. How can the American governments prevent it? Should they punish the deceiver? It seems more incumbent on the European government, where the act is done, and where a public injury is sustained from it. However, it is only in Europe that this deception is heard of. The individuals are generally satisfied in America, with their adventure, and very few of them wish not to have made it. I must add, that the Congress have nothing to do with this matter. It belongs to the legislatures of the several States.
Page 26. ‘Une puissance, en effet,’ &c. The account of the settlement of the colonies, which precedes this paragraph, shows that that settlement was not made by public authority, or at the public expense of England; but by the exertions, and at the expense, of individuals. Hence it happened, that their constitutions were not formed systematically, but according to the circumstances which happened to exist in each. Hence, too, the principles of the political connection between the old and new countries were never settled. That it would have been advantageous to have settled them, is certain; and, particularly, to have provided a body which should decide, in the last resort, all cases wherein both parties were interested. But it is not certain that that right would have been given, or ought to have been given, to the Parliament; much less, that it resulted to the Parliament, without having been given to it expressly. Why was it necessary, that there should have been a body to decide in the last resort? Because, it would have been for the good of both parties. But this reason shows, it ought not to have been the Parliament, since that would have exercised it for the good of one party only.
Page 105. As to the change of the 8th article of Confederation, for quotaing requisitions of money on the States.
By a report of the secretary of Congress, dated January the 4th, 1786, eight States had then acceded to the proposition; to wit, Massachusetts, Connecticut, New York, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, Maryland, Virginia, and North Carolina.
Congress, on the 18th of April, 1783, recommended to the States to invest them with a power, for twenty-five years, to levy an impost of five per cent, on all articles imported from abroad. New Hampshire, Massachusetts, Connecticut, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, Delaware, Virginia, North Carolina, and South Carolina, had complied with this, before the 4th of January, 1786. Maryland had passed an act for the same purpose; but, by a mistake in referring to the date of the recommendation of Congress, the act failed of its effect. This was therefore to be rectified. Since the 4th of January, the public papers tell us, that Rhode Island has complied fully with this recommendation. It remains still for New York and Georgia to do it. The exportations of America, which are tolerably well known, are the best measure for estimating the importations. These are probably worth about twenty millions of dollars annually. Of course, this impost will pay the interest of a debt to that amount. If confined to the foreign debt, it will pay the whole interest of that, and sink half a million of the capital annually. The expenses of collecting this impost, will probably be six per cent, on its amount, this being the usual expense of collection in the United States. This will be sixty thousand dollars.
On the 30th of April, 1784, Congress recommended to the States, to invest them with a power, for fifteen years, to exclude from their ports the vessels of all nations, not having a treaty of commerce with them; and to pass, as to all nations, an act on the principles of the British navigation act. Not that they were disposed to carry these powers into execution, with such as would meet them in fair and equal arrangements of commerce; but that they might be able to do it against those who should not. On the 4th of January, 1786, New Hampshire, Massachusetts, Rhode Island, Connecticut, New York, Pennsylvania, Maryland, Virginia, and North Carolina, had done it: It remained for New Jersey, Delaware, South Carolina, and Georgia to do the same.
in the mean time, the general idea has advanced before the demands of Congress, and several States have passed acts, for vesting Congress with the whole regulation of their commerce, reserving the revenue arising from these regulations, to the disposal of the State in which it is levied. The States which, according to the public papers, have passed such acts, are New Hampshire, Massachusetts, Rhode Island, New Jersey, Delaware, and Virginia: but the Assembly of Virginia, apprehensive that this disjointed method of proceeding may fail in its effect, or be much retarded, passed a resolution on the 21st of January, 1786, appointing commissioners to meet others from the other States, whom they invite into the same measure, to digest the form of an act for investing Congress with, such powers over their commerce, as shall be thought expedient, which act is to be reported to their several Assemblies for their adoption. This was the state of the several propositions relative to the impost and regulation of commerce at the date of our latest advices from America.
Page 125. The General Assembly of Virginia, at their session in 1785, passed an act, declaring that the district called Kentucky shall be a separate and independent State on these conditions. 1. That the people of that district shall consent to it. 2. That Congress shall consent to it, and shall receive them into the federal Union. 3. That they shall take on themselves a proportionable part of the public debt of Virginia. 4. That they shall confirm all titles to lands within their district made by the State of Virginia before their separation.
Page 139. It was in 1783, and not in 1781, that Congress quitted Philadelphia.
Page 140, ‘Le Congrès qui se trouvoit a la portée des rebelles fut effrayé.’ I was not present on this occasion, but, I have had relations of the transaction from several who were. The conduct of Congress was marked with indignation and firmness. They received no propositions from the mutineers. They came to the resolutions which may be seen in the journals of June the 21st, 1783, then adjourned regularly and went through the body of the mutineers to their respective lodgings. The measures taken by Dickinson, the President of Pennsylvania, for punishing this insult, not being satisfactory to Congress, they assembled nine days after at Princeton, in Jersey. The people of Pennsylvania sent petitions, declaring their indignation at what had passed, their devotion to the federal head, and their dispositions to protect it, and praying them to return; the legislature as soon as assembled did the same thing; the Executive, whose irresolution had been so exceptionable, made apologies. But Congress were now removed; and to the opinion that this example was proper, other causes were now added sufficient to prevent their return to Philadelphia.
Page 155, I. 2. Omit ‘La dette actuelle,’ &c.
And also, ‘Les details,’ &c. &c. to the end of the paragraph, ‘celles des Etats Unis’ page 156. The reason is, that these passages seem to suppose that the several sums emitted by Congress at different times, amounting nominally to two hundred millions of dollars, had been actually worth that at the time of emission, and of course, that the soldiers and others had received that sum from Congress. But nothing is further from the truth. The soldier, victualler, or other persons who received forty dollars for a service at the close of the year 1779, received, in fact, no more than he who received one dollar for the same service in the year 1775, or 1776; because in those years the paper money was at par with silver; whereas, by the close of 1779, forty paper dollars were worth but one of silver, and would buy no more of the necessaries of life. To know what the monies emitted by Congress were worth to the people at the time they received them, we will state the date and amount of every several emission, the depreciation of paper money at the time, and the real worth of the emission in silver or gold.
[Illustration: Depreciation of Money 1775-1779, page411]
[* The sum actually voted was 50,000,400, but part of it was
for exchange of old bills, without saying how much. It is
presumed that these exchanges absorbed 25,552,780, because
the remainder 24,447,620, with all the other emissions
preceding September 2nd, 1779, will amount to 159,948,880,
the sum which Congress declared to be then in circulation.]
Thus it appears that the two hundred millions of dollars, emitted by Congress, were worth to those who received them, but about thirty-six millions of silver dollars. If we estimate at the same value the like sum of two hundred millions, supposed to have been emitted by the States, and reckon the Federal debt, foreign and domestic, at about forty-three millions, and the State debts at about twenty-five millions, it will form an amount of one hundred and forty millions of dollars, or seven hundred and thirty-five millions of livres Tournois, the total sum which the war has cost the inhabitants of the United States. It continued eight years, from the battle of Lexington to the cessation of hostilities in America. The annual expense then was about seventeen millions and five hundred thousand dollars, while that of our enemies was a greater number of guineas.
It will be asked, how will the two masses of Continental and of State money have cost the people of the United States seventy-two millions of dollars, when they are to be redeemed now with about six millions? I answer, that the difference, being sixty-six millions, has been lost on the paper bills separately by the successive holders of them. Every one through whose hands a bill passed lost on that bill what it lost in value, during the time it was in his hands. This was a real tax on him; and in this way, the people of the United States actually contributed those sixty-six millions of dollars during the war, and by a mode of taxation the most oppressive of all, because the most unequal of all.
Page 166; bottom line. Leave out ‘Et c’est une autre économie,’ &c. The reason of this is, that in 1784, purchases of lands were to be made of the Indians, which were accordingly made. But in 1785 they did not propose to make any purchase. The money desired in 1785, five thousand dollars, was probably to pay agents residing among the Indians, or balances of the purchases of 1784. These purchases will not be made every year; but only at distant intervals, as our settlements are extended: and it may be regarded as certain, that not a foot of land will ever be taken from the Indians without their own consent. The sacredness of their rights is felt by all thinking persons in America, as much as in Europe.
Page 170. Virginia was quotaed the highest of any State in the Union. But during the war several States appear to have paid more, because they were free from the enemy, whilst Virginia was cruelly ravaged. The requisition of 1784 was so quotaed on the several States, as to bring up their arrearages; so that, when they should have paid the sums then demanded, all would be on an equal footing. It is necessary to give a further explanation of this requisition. The requisitions of one million and two hundred thousand dollars, of eight millions, and two millions, had been made during the war, as an experiment to see whether in that situation the States could furnish the necessary supplies. It was found they could not. The money was thereupon obtained by loans in Europe: and Congress meant by their requisition of 1784, to abandon the requisitions of one million and two hundred thousand dollars, and of two millions, and also one half of the eight millions. But as all the States almost had made some payments in part of that requisition, they were obliged to retain such a proportion of it as would enable them to call for equal contributions from all the others.
Page 170. I cannot say how it has happened, that the debt of Connecticut is greater than that of Virginia. The latter is the richest in productions, and, perhaps, made greater exertions to pay for her supplies in the course of the war.
Page 172. ‘Les Americains levant après une banqueroute, &c. The objections made to the United States being here condensed together in a short compass, perhaps it would not be improper to condense the answers in as small a compass in some such form as follows. That is, after the words ‘aucun espoir,’ add, ‘But to these charges it may be justly answered, that those are no bankrupts who acknowledge the sacredness of their debts in their just and real amount, who are able within a reasonable time to pay them, and who are actually proceeding in that payment; that they furnish, in fact, the supplies necessary for the support of their government; that their officers and soldiers are satisfied, as the interest of their debt is paid regularly, and the principal is in a course of payment; that the question, whether they fought ill should be asked of those who met them at Bunker’s Hill, Bennington, Stillwater, King’s Mountain, the Cowpens, Guilford, and the Eutaw. And that the charges of ingratitude, madness, infidelity, and corruption, are easily made by those to whom falsehoods cost nothing; but that no instances in support of them have been produced or can be produced.’
Page 182. ‘Les officiers et les soldats ont été payés,’ &c. The balances due to the officers and soldiers have been ascertained, and a certificate of the sum given to each; on these the interest is regularly paid; and every occasion is seized of paying the principal by receiving these certificates as money whenever public property is sold, till a more regular and effectual method can be taken for paying the whole.
Page 191. ‘Quoique la loi dont nous parlons, ne s’observe plus en Angleterre.’ ‘An alien born may purchase lands or other estates, but not for his own use; for the King is thereupon entitled to them.’ ‘Yet an alien may acquire a property in goods, money, and other personal estate, or may hire a house for his habitation. For this is necessary for the advancement of trade.’ ‘Also, an alien may bring an action concerning personal property, and may make a will and dispose of his personal estate.’ When I mention these rights of an alien, I must be understood of alien friends only, or such whose countries are in peace with ours; for alien enemies have no rights, no privileges, unless by the King’s special favor during the time of war.‘Blackstone, B.1. c.10. page 372. ‘An alien friend may have personal actions, but not real; an alien enemy shall have neither real, personal, nor mixed actions. The reason why an alien friend is allowed to maintain a personal action is, because he would otherwise be incapacitated to merchandise, which may be as much to our prejudice as his.’ Cunningham’s Law Diet, title, Aliens. The above is the clear law of England, practised from the earliest ages to this day, and never denied. The passage quoted by M. de Meusnier from Black-stone, c.26. is from his chapter ‘Of title to things personal by occupancy.’ The word ‘personal’ shows that nothing in this chapter relates to lands which are real estate; and therefore, this passage does not contradict the one before quoted from the same author (1.B. c.10.), which says, that the lands of an alien belong to the King. The words, ‘of title by occupancy,’ show, that it does not relate to debts, which being a moral existence only, cannot be the subject of occupancy. Blackstone, in this passage (B.2. c.26.), speaks only of personal goods of an alien, which another may find and seize as prime occupant.
Page 193. ‘Le remboursement presentera des difficultés des sommes considérables,’ &c. There is no difficulty nor doubt on this subject. Every one is sensible how this is to be ultimately settled. Neither the British creditor, nor the State, will be permitted to lose by these payments. The debtor will be credited for what he paid, according to what it was really worth at the time he paid it, and he must pay the balance. Nor does he lose by this; for if a man who owed one thousand dollars to a British merchant, paid eight hundred paper dollars into the treasury, when the depreciation was at eight for one, it is clear he paid but one hundred real dollars, and must now pay nine hundred. It is probable he received those eight hundred dollars for one hundred bushels of wheat, which were never worth more than one hundred silver dollars. He is credited, therefore, the full worth of his wheat. The equivoque is in the use of the word ‘dollar.’
Page 226. ‘Qu’on abolisse les privilèges du clergé.’ This privilege, originally allowed to the clergy, is now extended to every man, and even to women. It is a right of exemption from capital punishment for the first offence in most cases. It is then a pardon by the law. In other cases, the Executive gives the pardon. But when laws are made as mild as they should be, both those pardons are absurd. The principle of Beccaria is sound. Let the legislators be merciful, but the executors of the law inexorable. As the term ‘privilèges du clergé’ may be misunderstood by foreigners, perhaps it will be better to strike it out here and substitute the word ‘pardon.’
Page 239. ‘Les commissaires veulent,’ &c. Manslaughter is the killing a man with design, but in a sudden gust of passion, and where the killer has not had time to cool. The first offence is not punished capitally, but the second is. This is the law of England and of all the American States; and is not a new proposition. Those laws have supposed that a man, whose passions have so much dominion over him, as to lead him to repeated acts of murder, is unsafe to society: that it is better he should be put to death by the law, than others more innocent than himself on the movements of his impetuous passions.
Ibid. ‘Mal-aisé d’indiquer la nuance précise,’ &c. In forming a scale of crimes and punishments, two considerations have principal weight. 1. The atrocity of the crime. 2. The peculiar circumstances of a country, which furnish greater temptations to commit it, or greater facilities for escaping detection, The punishment must be heavier to counterbalance this. Were the first the only consideration, all nations would form the same scale. But as the circumstances of a country have influence on the punishment, and no two countries exist precisely under the same circumstances, no two countries will form the same scale of crimes and punishments. For example; in America the inhabitants let their horses go at large in the uninclosed lands which are so extensive as to maintain them altogether. It is easy, therefore, to steal them and easy to escape. Therefore the laws are obliged to oppose these temptations with a heavier degree of punishment. For this reason the stealing of a horse in America is punished more severely, than stealing the same value in any other form. In Europe where horses are confined so securely, that it is impossible to steal them, that species of theft need not be punished more severely than any other. In some countries of Europe, stealing fruit from trees in punished capitally. The reason is, that it being impossible to lock fruit trees up in coffers, as we do our money, it is impossible to oppose physical bars to this species of theft. Moral ones are therefore opposed by the laws. This to an unreflecting American appears the most enormous of all the abuses of power; because he has been used to see fruits hanging in such quantities, that if not taken by men they would rot: he has been used to consider them therefore as of no value, and as not furnishing materials for the commission of a crime. This must serve as an apology for the arrangement of crimes and punishments in the scale under our consideration. A different one would be formed here; and still different ones in Italy, Turkey, China, &c.
Page 240. ‘Les officiers Americains,’ &c. to page 264, ‘qui le méritoient.’ I would propose to new-model this section in the following manner, 1. Give a succinct history of the origin and establishment of the Cincinnati. 2. Examine whether in its present form it threatens any dangers to the State. 3. Propose the most practicable method of preventing them.
Having been in America during the period in which this institution was formed, and being then in a situation which gave me opportunities of seeing it in all its stages, I may venture to give M. de Meusnier materials for the first branch of the preceding distribution of the subject. The second and third he will best execute himself. I should write its history in the following form. When on the close of that war which established the independence of America, its army was about to be disbanded, the officers, who, during the course of it, had gone through the most trying scenes together, who by mutual aids and good offices had become dear to one another, felt with great oppression of mind the approach of that moment which was to separate them, never perhaps to meet again. They were from different States, and from distant parts of the same State. Hazard alone could therefore give them but rare and partial occasions of seeing each other. They were of course to abandon altogether the hope of ever meeting again, or to devise some occasion which might bring them together. And why not come together on purpose at stated times? Would not the trouble of such a journey be greatly overpaid by the pleasure of seeing each other again, by the sweetest of all consolations, the talking over the scenes of difficulty and of endearment they had gone through? This too would enable them to know who of them should succeed in the world, who should be unsuccessful, and to open the purses of all to every laboring brother. This idea was too soothing not to be cherished in conversation. It was improved into that of a regular association, with an organized administration, with periodical meetings, general and particular, fixed contributions for those who should be in distress, and a badge by which not only those who had not had occasion to become personally known should be able to recognise one another, but which should be worn by their descendants, to perpetuate among them the friendships which had bound their ancestors together.
General Washington was, at that moment, oppressed with the operation of disbanding an army which was not paid, and the difficulty of this operation was increased, by some two or three States having expressed sentiments, which did not indicate a sufficient attention to their payment. He was sometimes present, when his officers were fashioning, in their conversations, their newly proposed society. He saw the innocence of its origin, and foresaw no effects less innocent. He was, at that time, writing his valedictory letter to the States, which has been so deservedly applauded by the world. Far from thinking it a moment to multiply the causes of irritation, by thwarting a proposition which had absolutely no other basis but that of benevolence and friendship, he was rather satisfied to find himself aided in his difficulties by this new incident, which occupied, and, at the same time, soothed the minds of the officers. He thought, too, that this institution would be one instrument the more, for strengthening the federal bond, and for promoting federal ideas. The institution was formed. They incorporated into it the officers of the French army and navy, by whose sides they had fought, and with whose aid they had finally prevailed, extending it to such grades, as they were told might be permitted to enter into it. They sent an officer to France, to make the proposition to them, and to procure the badges which they had devised for their order. The moment of disbanding the army having come, before they could have a full meeting to appoint their President, the General was prayed to act in that office till their first general meeting, which was to be held at Philadelphia, in the month of May following.
The laws of the society were published. Men who read them in their closers, unwarmed by those sentiments of friendship which had produced them, inattentive to those pains which an approaching separation had excited in the minds of the instituters, politicians, who see in every thing only the dangers with which it threatens civil society, in fine, the laboring people, who, shielded by equal laws, had never seen any difference between man and man, but had read of terrible oppressions, which people of their description experience in other countries, from those who are distinguished by titles and badges, began to be alarmed at this new institution. A remarkable silence, however, was observed. Their solicitudes were long confined within the circles of private conversation. At length, however, a Mr. Burke, Chief Justice of South Carolina, broke that silence. He wrote against the new institution, foreboding its dangers, very imperfectly indeed, because he had nothing but his imagination to aid him. An American could do no more; for to detail the real evils of aristocracy, they must be seen in Europe. Burke’s fears were thought exaggerations in America; while in Europe, it is known that even Mirabeau has but faintly sketched the curses of hereditary aristocracy, as they are experienced here, and as they would have followed in America, had this institution remained. The epigraph of Burke’s pamphlet, was ‘Blow ye the trumpet in Zion.’ Its effect corresponded with its epigraph. This institution became, first, the subject of general conversation. Next, it was made the subject of deliberation in the legislative Assemblies of some of the States. The Governor of South Carolina censured it, in an address to the Assembly of that State. The Assemblies of Massachusetts, Rhode Island, and Pennsylvania condemned its principles. No circumstance, indeed, brought the consideration of it expressly before Congress; yet it had sunk deep into their minds. An offer having been made to them, on the part of the Polish order of Divine Providence, to receive some of their distinguished citizens into that order, they made that an occasion to declare, that these distinctions were contrary to the principles of their Confederation.
The uneasiness excited by this institution had very early caught the notice of General Washington. Still recollecting all the purity of the motives which gave it birth, he became sensible that it might produce political evils, which the warmth of those motives had masked. Add to this, that it was disapproved by the mass of citizens of the Union. This, alone, was reason strong enough, in a country where the will of the majority is the law, and ought to be the law. He saw that the objects of the institution were too light to be opposed to considerations as serious as these; and that it was become necessary to annihilate it absolutely. On this, therefore, he was decided. The first annual meeting at Philadelphia was now at hand; he went to that, determined to exert all his influence for its suppression. He proposed it to his fellow officers, and urged it with all his powers. It met an opposition which was observed to cloud his face with an anxiety, that the most distressful scenes of the war had scarcely ever produced. It was canvassed for several days, and, at length, it was no more a doubt, what would be its ultimate fate. The order was on the point of receiving its annihilation, by the vote of a great majority of its members. In this moment, their envoy arrived from France, charged with letters from the French officers, accepting with cordiality the proposed badges of union, with solicitations from others to be received into the order, and with notice that their respectable Sovereign had been pleased to recognise it, and to permit his officers to wear its badges. The prospect was now changed. The question assumed a new form. After the offer made by them, and accepted by their friends, in what words could they clothe a proposition to retract it, which would not cover themselves with the reproaches of levity and ingratitude? which would not appear an insult to those whom they loved? Federal principles, popular discontent, were considerations, whose weight was known and felt by themselves. But would foreigners know and feel them equally? Would they so far acknowledge their cogency, as to permit, without any indignation, the eagle and ribbon to be torn from their breasts, by the very hands which had placed them there? The idea revolted the whole society. They found it necessary, then, to preserve so much of their institution as might continue to support this foreign branch, while they should prune off every other, which would give offence to their fellow citizens: thus sacrificing, on each hand, to their friends and to their country.
The society was to retain its existence, its name, its meetings, and its charitable funds: but these last were to be deposited with their respective legislatures. The order was to be no longer hereditary; a reformation, which had been pressed even from this side the Atlantic; it was to be communicated to no new members; the general meetings, instead of annual, were to be triennial only. The eagle and ribbon, indeed, were retained, because they were worn, and they wished them to be worn, by their friends who were in a country where they would not be objects of offence; but themselves never wore them. They laid them up in their bureaus, with the medals of American Independence, with those of the trophies they had taken, and the battles they had won. But through all the United States, no officer is seen to offend the public eye with the display of this badge. These changes have tranquillized the American States. Their citizens feel too much interest in the reputation of their officers, and value too much whatever may serve to recall to the memory of their allies, the moments wherein they formed but one people, not to do justice to the circumstance which prevented a total annihilation of the order. Though they are obliged by a prudent foresight, to keep out every thing from among themselves, which might pretend to divide them into orders, and to degrade one description of men below another, yet they hear with pleasure, that their allies, whom circumstances have already placed under these distinctions, are willing to consider it as one, to have aided them in the establishment of their liberties, and to wear a badge which may recall them to their remembrance; and it would be an extreme affliction to them, if the domestic reformation which has been found necessary, if the censures of individual writers, or if any other circumstance, should discourage the wearing of their badge, or lessen its reputation.
This short but true, history of the order of the Cincinnati, taken from the mouths of persons on the spot, who were privy to its origin and progress, and who know its present state, is the best apology which can be made for an institution, which appeared to be, and was really, so heterogeneous to the governments in which it was erected.
It should be further considered, that, in America, no other distinction between man and man had ever been known, but that of persons in office, exercising powers by authority of the laws, and private individuals. Among these last, the poorest laborer stood on equal ground with the wealthiest millionary, and generally, on a more favored one, whenever their rights seemed to jar. It has been seen that a shoemaker, or other artisan, removed by the voice of his country from his work-bench, into a chair of office, has instantly commanded all the respect and obedience, which the laws ascribe to his office. But of distinctions by birth or badge, they had no more idea than they had of the mode of existence in the moon or planets. They had heard only that there were such, and knew that they must be wrong. A due horror of the evils which flow from these distinctions, could be excited in Europe only, where the dignity of man is lost in arbitrary distinctions, where the human species is classed into several stages of degradation, where the many are crouched under the weight of the few, and where the order established can present to the contemplation of a thinking being, no other picture, than that of God Almighty and his angels, trampling under foot the host of the damned. No wonder, then, that the institution of the Cincinnati should be innocently conceived by one order of American citizens, should raise in the other orders, only a slow, temperate, and rational opposition, and should be viewed in Europe as a detestable parricide.
The second and third branches of this subject, nobody can better execute than M. de Meusnier. Perhaps it may be curious to him to see how they strike an American mind at present. He shall, therefore, have the ideas of one, who was an enemy to the institution from the first moment of its conception, but who was always sensible, that the officers neither foresaw nor intended the injury they were doing to their country.
As to the question, then, whether any evil can proceed from the institution, as it stands at present, I am of opinion there may. 1. From the meetings. These will keep the officers formed into a body; will continue a distinction between the civil and military, which, it would be for the good of the whole to obliterate, as soon as possible; and military assemblies will not only keep alive the jealousies and fears of the civil government, but give ground for these fears and jealousies. For when men meet together, they will make business, if they have none; they will collate their grievances, some real, some imaginary, all highly painted; they will communicate to each other the sparks of discontent; and these may engender a flame, which will consume their particular, as well as the general happiness. 2. The charitable part of the institution is still more likely to do mischief, as it perpetuates the dangers apprehended in the preceding clause. For here is a fund provided, of permanent existence. To whom will it belong? To the descendants of American officers, of a certain description. These descendants, then, will form a body, having a sufficient interest to keep up an attention to their description, to continue meetings, and perhaps, in some moment, when the political eye shall be slumbering, or the firmness of their fellow citizens relaxed, to replace the insignia of the order, and revive all its pretensions. What good can the officers propose, which may weigh against these possible evils? The securing their descendants against want? Why afraid to trust them to the same fertile soil, and the same genial climate, which will secure from want the descendants of their other fellow citizens? Are they afraid they will be reduced to labor the earth for their sustenance? They will be rendered thereby both more honest and happy. An industrious farmer occupies a more dignified place in the scale of beings, whether moral or political, than a lazy lounger, valuing himself on his family, too proud to work, and drawing out a miserable existence, by eating on that surplus of other men’s labor, which is the sacred fund of the helpless poor. A pitiful annuity will only prevent them from exerting that industry and those talents, which would soon lead them to better fortune.
How are these evils to be prevented? 1. At their first general meeting, let them distribute the funds on hand to the existing objects of their destination, and discontinue all further contributions. 2. Let them declare, at the same time, that their meetings, general and particular, shall thenceforth cease. 3. Let them melt up their eagles, and add the mass to the distributable fund, that their descendants may have no temptation to hang them in their button-holes.
These reflections are not proposed as worthy the notice of M. de Meusnier. He will be so good as to treat the subject in his own way, and no body has a better. I will only pray him to avail us of his forcible manner, to evince that there is evil to be apprehended, even from the ashes of this institution, and to exhort the society in America to make their reformation complete; bearing in mind, that we must keep the passions of men on our side, even when we are persuading them to do what they ought to do.
Page 268. ‘Et en effet la population,’ &c. Page 270. ‘Plus de confiance.’
To this, we answer, that no such census of the numbers was ever given out by Congress, nor ever presented to them: and further, that Congress never have, at any time, declared by their vote, the number of inhabitants in their respective States. On the 22nd of June, 1775, they first resolved to emit paper money. The sum resolved on was two millions of dollars. They declared, then, that the twelve confederate colonies (for Georgia had not yet joined them) should be pledged for the redemption of these bills. To ascertain in what proportion each State should be bound, the members from each were desired to say, as nearly as they could, what was the number of the inhabitants of their respective States. They were very much unprepared for such a declaration. They guessed, however, as well as they could. The following are the numbers, as they conjectured them, and the consequent apportionment of the two millions of dollars.

Georgia, having not yet acceded to the measures of the other States, was not quotaed; but her numbers were generally estimated at about thirty thousand, and so would have made the whole, two million four hundred and forty-eight thousand persons, of every condition. But it is to be observed, that though Congress made this census the basis of their apportionment, yet they did not even give it a place on their journals; much less, publish it to the world with their sanction. The way it got abroad was this. As the members declared from their seats the number of inhabitants which they conjectured to be in their State, the secretary of Congress wrote them on a piece of paper, calculated the portion of two millions of dollars, to be paid by each, and entered the sum only in the journals. The members, however, for their own satisfaction, and the information of their States, took copies of this enumeration, and sent them to their States. From thence, they got into the public papers: and when the English news-writers found it answer their purpose to compare this with the enumeration of 1783, as their principle is ‘to lie boldly, that they may not be suspected of lying,’ they made it amount to three millions one hundred and thirty-seven thousand eight hundred and nine, and ascribed its publication to Congress itself.
in April, 1785, Congress being to call on the States to raise a million and a half of dollars annually, for twenty-five years, it was necessary to apportion this among them. The States had never furnished them with their exact numbers. It was agreed, too, that in this apportionment, five slaves should be counted as three freemen only. The preparation of this business was in the hands of a committee; they applied to the members for the best information they could give them, of the numbers of their States. Some of the States had taken pains to discover their numbers. Others had done nothing in that way, and, of course, were now where they were in 1775, when their members were first called on to declare their numbers. Under these circumstances, and on the principle of counting three fifths only of the slaves, the committee apportioned the money among the States, and reported their work to Congress. In this, they had assessed South Carolina as having one hundred and seventy thousand inhabitants. The delegates for that State, however, prevailed on Congress to assess them on the footing of one hundred and fifty thousand only, in consideration of the state of total devastation, in which the enemy had left their country. The difference was then laid on the other States, and the following was the result.

Still, however, Congress refused to give the enumeration the sanction of a place on their journals, because it was not formed on such evidence, as a strict attention to accuracy and truth required. They used it from necessity, because they could get no better rule, and they entered on their journals only the apportionment of money. The members, however, as before, took copies of the enumeration, which was the ground work of the apportionment, sent them to their States, and thus, this second enumeration got into the public papers, and was, by the English, ascribed to Congress, as their declaration of their present numbers. To get at the real numbers which this enumeration supposes, we must add twenty thousand to the number, on which South Carolina was quotaed; we must consider, that seven hundred thousand slaves are counted but as four hundred and twenty thousand persons, and add, on that account, two hundred and eighty thousand. This will give us a total of two millions six hundred and thirty-nine thousand three hundred inhabitants, of every condition, in the thirteen States; being two hundred and twenty-one thousand three hundred more, than the enumeration of 1775, instead of seven hundred and ninety-eight thousand five hundred and nine less, which the English papers asserted to be the diminution of numbers, in the United States, according to the confession of Congress themselves.
Page 272.‘Comportera, peut être, une population de 30,000,000.’ The territory of the United States contains about a million of square miles, English. There is, in them, a greater proportion of fertile lands, than in the British dominions in Europe. Suppose the territory of the United States, then, to attain an equal degree of population, with the British European dominions; they will have an hundred millions of inhabitants. Let us extend our views to what may be the population of the two continents of North and South America, supposing them divided at the narrowest part of the isthmus of Panama. Between this line and that of 50° of north latitude, the northern continent contains about five millions of square miles, and south of this line of division, the southern continent contains about seven millions of square miles. I do not pass the 50th degree of northern latitude in my reckoning, because we must draw a line somewhere, and considering the soil and climate beyond that, I would only avail my calculation of it, as a make-weight, to make good what the colder regions, within that line, may be supposed to fall short in their future population. Here are twelve millions of square miles, then, which, at the rate of population before assumed, will nourish twelve hundred millions of inhabitants, a number greater than the present population of the whole globe is supposed to amount to. If those who propose medals for the resolution of questions, about which nobody makes any question, those who have invited discussion on the pretended problem, Whether the discovery of America was for the good of mankind? if they, I say, would have viewed it only as doubling the numbers of mankind, and, of course, the quantum of existence and happiness, they might have saved the money and the reputation which their proposition has cost them. The present population of the inhabited parts of the United States is of about ten to the square mile; and experience has shown us, that wherever we reach that, the inhabitants become uneasy, as too much compressed, and go off, in great numbers, to search for vacant country. Within forty years, their whole territory will be peopled at that rate. We may fix that, then, as the term, beyond which the people of those States will not be restrained within their present limits; we may fix that population, too, as the limit which they will not exceed, till the whole of those two continents are filled up to that mark; that is to say, till they shall contain one hundred and twenty millions of inhabitants. The soil of the country, on the western side of the Mississippi, its climate, and its vicinity to the United States, point it out as the first which will receive population from that nest. The present occupiers will just have force enough to repress and restrain the emigrations, to a certain degree of consistence. We have seen, lately, a single person go, and decide on a settlement in Kentucky, many hundred miles from any white inhabitant, remove thither with his family and a few neighbors, and though perpetually harassed by the Indians, that settlement in the course of ten years has acquired thirty thousand inhabitants; its numbers are increasing while we are writing, and the State, of which it formerly made a part, has offered it independence.
Page 280, line five. ‘Huit des onze Etats,’ &c. Say, ‘there were ten States present; six voted unanimously for it, three against it, and one was divided: and seven votes being requisite to decide the proposition affirmatively, it was lost. The voice of a single individual of the State which was divided, or of one of those which were of the negative, would have prevented this abominable crime from spreading itself over the new country. Thus we see the fate of millions unborn, hanging on the tongue of one man, and Heaven was silent in that awful moment! But it is to be hoped it will not always be silent, and that the friends to the rights of human nature will, in the end, prevail.
On the 16th of March, 1785, it was moved in Congress, that the same proposition should be referred to a committee, and it was referred by the votes of eight States against three. We do not hear that any thing further is yet done on it.’
Page 286. ‘L’autorité du Congrès étoit nécessaire.’ The substance of the passage alluded to, in the journal of Congress, May the 26th, 1784, is, ‘That the authority of Congress to make requisitions of troops, during peace, is questioned; that such an authority would be dangerous, combined with the acknowledged one of emitting or of borrowing money; and that a few troops only, being wanted, to guard magazines and garrison the frontier posts, it would be more proper, at present, to recommend than to require.’
Mr. Jefferson presents his compliments to M. de Meusnier, and sends him copies of the thirteenth, twenty-third, and twenty-fourth articles of the treaty between the King of Prussia and the United States.
If M. de Meusnier proposes to mention the facts of cruelty, of which he and Mr Jefferson spoke yesterday, the twenty-fourth article will introduce them properly, because they produced a sense of the necessity of that article. These facts are, 1. The death of upwards of eleven thousand American prisoners, in one prison-ship (the Jersey), and in the space of three years. 2. General Howe’s permitting our prisoners, taken at the battle of Germantown, and placed under a guard, in the yard of the State-house of Philadelphia, to be so long without any food furnished them, that many perished with hunger. Where the bodies lay, it was seen that they had eaten all the grass around them, within their reach, after they had lost the power of rising or moving from their place. 3. The second fact was the act of a commanding officer: the first, of several commanding officers, and, for so long a time, as must suppose the approbation of government. But the following was the act of government itself. During the periods that our affairs seemed unfavorable, and theirs successful, that is to say, after the evacuation of New York, and again after the taking of Charleston, in South Carolina, they regularly sent our prisoners, taken on the seas and carried to England, to the East Indies. This is so certain, that in the month of November or December, 1785, Mr. Adams having officially demanded a delivery of the American prisoners sent to the East Indies, Lord Caermarthen answered, officially, ‘that orders were immediately issued for their discharge.’ M. de Meusnier is at liberty to quote this fact. 4. A fact, to be ascribed not only to the government, but to the parliament, who passed an act for that purpose, in the beginning of the war, was the obliging our prisoners, taken at sea, to join them, and fight against their countrymen. This they effected by starving and whipping them. The insult on Captain Stanhope, which happened at Boston last year, was a consequence of this. Two persons, Dunbar and Lowthorp, whom Stanhope had treated in this manner (having particularly inflicted twenty-four lashes on Dunbar), meeting him at Boston, attempted to beat him. But the people interposed, and saved him. The fact is referred to in that paragraph of the Declaration of Independence, which says, ‘He has constrained our fellow citizens, taken captive on the high seas, to bear arms against their country, to become the executioners of their friends and brethren, or to fall themselves by their hands.’ This was the most afflicting to our prisoners, of all the cruelties exercised on them. The others affected the body only, but this the mind; they were haunted by the horror of having, perhaps, themselves shot the ball by which a father or a brother fell. Some of them had constancy enough to hold out against half-allowance of food and repeated whippings. These were generally sent to England, and from thence to the East Indies. One of them escaped from the East Indies, and got back to Paris, where he gave an account of his sufferings to Mr. Adams, who happened to be then at Paris.
M. de Meusnier, where he mentions that the slave-law has been passed in Virginia, without the clause of emancipation, is pleased to mention, that neither Mr. Wythe nor Mr. Jefferson was present, to make the proposition they had meditated; from which, people, who do not give themselves the trouble to reflect or inquire, might conclude, hastily, that their absence was the cause why the proposition was not made; and, of course, that there were not, in the Assembly, persons of virtue and firmness enough to propose the clause for emancipation. This supposition would not be true. There were persons there, who wanted neither the virtue to propose, nor talents to enforce the proposition, had they seen that the disposition of the legislature was ripe for it. These worthy characters would feel themselves wounded, degraded, and discouraged by this idea. Mr. Jefferson would therefore be obliged to M. de Meusnier to mention it in some such manner as this. ‘Of the two commissioners, who had concerted the amendatory clause for the gradual emancipation of slaves, Mr. Wythe could not be present, he being a member of the judiciary department, and Mr. Jefferson was absent on the legation to France. But there were not wanting in that Assembly, men of virtue enough to propose, and talents to vindicate this clause. But they saw, that the moment of doing it with success, was not yet arrived, and that an unsuccessful effort, as too often happens, would only rivet still closer the chains of bondage, and retard the moment of delivery to this oppressed description of men. What a stupendous, what an incomprehensible machine is man! who can endure toil, famine, stripes, imprisonment, and death itself, in vindication of his own liberty, and, the next moment, be deaf to all those motives whose power supported him through his trial, and inflict on his fellow men a bondage, one hour of which is fraught with more misery, than ages of that which he rose in rebellion to oppose! But we must await, with patience, the workings of an overruling Providence, and hope that that is preparing the deliverance of these our suffering brethren. When the measure of their tears shall be full, when their groans shall have involved heaven itself in darkness, doubtless, a God of justice will awaken to their distress, and by diffusing light and liberality among their oppressors, or, at length, by his exterminating thunder, manifest his attention to the things of this world, and that they are not left to the guidance of a blind fatality.’
[The following are the articles of the treaty with Prussia,
referred to in the preceding observations.]
Article 13. And in the same case, of one of the contracting parties being engaged in war with any other power, to prevent all the difficulties and misunderstandings, that usually arise respecting the merchandise heretofore called contraband, such as arms, ammunition, and military stores of every kind, no such articles, carried in the vessels, or by the subjects or citizens of one of the parties, to the enemies of the other, shall be deemed contraband, so as to induce confiscation or condemnation, and a loss of property to individuals. Nevertheless, it shall be lawful to stop such vessels and articles, and to detain them for such length of time, as the captors may think necessary to prevent the inconvenience or damage that might ensue from their proceeding, paying, however, a reasonable compensation for the loss such arrest shall occasion to the proprietors: and it shall further be allowed to use, in the service of the captors, the whole or any part of the military stores so detained, paying the owners the full value of the same, to be ascertained by the current price at the place of its destination. But in the case supposed, of a vessel stopped for articles heretofore deemed contraband, if the master of the vessel stopped will deliver out the goods supposed to be of contraband nature, he shall be admitted to do it, and the vessel shall not, in that case be carried into any port, nor further detained, but shall be allowed to proceed on her voyage.
Article 23. If war should arise between the two contracting parties, the merchants of either country, then residing in the other, shall be allowed to remain nine months to collect their debts, and settle their affairs, and may depart freely, carrying off all their effects, without molestation or hindrance: and all women and children, scholars of every faculty, cultivators of the earth, artisans, manufacturers, and fishermen, unarmed, and inhabiting unfortified towns, villages, or places, and, in general, all others whose occupations are for the common subsistence and benefit of mankind, shall be allowed to continue their respective employments, and shall not be molested in their persons, nor shall their houses be burned or otherwise destroyed, nor their fields wasted by the armed force of the enemy, into whose power, by the events of war, they may happen to fall: but if any thing is necessary to be taken from them, for the use of such armed force, the same shall be paid for at a reasonable price. And all merchant and trading vessels, employed in exchanging the products of different places, and thereby rendering the necessaries, conveniences, and comforts of human life more easy to be obtained, and more general, shall be allowed to pass free and unmolested. And neither of the contracting parties shall grant or issue any commission to any private armed vessels, empowering them to take or destroy such trading vessels, or interrupt such commerce.
Article 24. And to prevent the destruction of prisoners of war, by sending them into distant and inclement countries, or by crowding them into close and noxious places, the two contracting parties solemnly pledge themselves to each other and the world, that they will not adopt any such practice: that neither will send the prisoners whom they may take from the other, into the East Indies or any other parts of Asia or Africa: but that they shall be placed in some part of their dominions in Europe or America, in wholesome situations; that they shall not be confined in dungeons, prison-ships, nor prisons, nor be put into irons, nor bound, nor otherwise restrained in the use of their limbs. That the officers shall be enlarged, on their paroles, within convenient districts, and have comfortable quarters, and the common men be disposed in cantonments, open and extensive enough for air and exercise, and lodged in barracks as roomy and good, as are provided by the party, in whose power they are, for their own troops; that the officers shall be daily furnished by the party, in whose power they are, with as many rations, and of the same articles and quality, as are allowed by them, either in kind or by commutation, to officers of equal rank in their own army; and all others shall be daily furnished by them, with such rations as they allow to a common soldier in their own service; the value whereof shall be paid by the other party, on a mutual adjustment of accounts for the subsistence of prisoners, at the close of the war: and the said accounts shall not be mingled with, or set off against any others, nor the balances due on them, be withheld as a satisfaction or reprisal for any other article, or for any other cause, real or pretended, whatever. That each party shall be allowed to keep a commissary of prisoners, of their own appointment, with every separate cantonment of prisoners in possession of the other, which commissary shall see the prisoners as often as he pleases, shall be allowed to receive and distribute whatever comforts may be sent to them by their friends, and shall be free to make his reports, in open letters, to those who employ him. But if any officer shall break his parole, or any other prisoner shall escape from the limits of his cantonment, after they shall have been designated to him, such individual officer, or other prisoner, shall forfeit so much of the benefit of this article, as provides for his enlargement on parole or cantonment. And it is declared, that neither the pretence that war dissolves all treaties, nor any other whatever, shall be considered as annulling or suspending this, or the next preceding article, but, on the contrary, that the state of war is precisely that for which they are provided, and during which, they are to be as sacredly observed, as the most acknowledged articles in the law of nature and nations.
TO MR. RITTENHOUSE.
Paris, January 25,1786.
Dear Sir,
Your favor of September the 28th came to hand a few days ago. I thank you for the details on the subject of the southern and western lines. There remains thereon, one article, however, which I will still beg you to inform me of; viz. how far is the western boundary beyond the meridian of Pittsburg? This information is necessary, to enable me to trace that boundary in my map. I shall be much gratified, also, with a communication of your observations on the curiosities of the western country. It will not be difficult to induce me to give up the theory of the growth of shells, without their being the nidus of animals. It is only an idea, and not an opinion with me. In the Notes, with which I troubled you, I had observed that there were three opinions as to the origin of these shells. 1. That they have been deposited even in the highest mountains, by an universal deluge. 2. That they, with all the calcareous stones and earths, are animal remains. 3. That they grow or shoot as crystals do. I find that I could swallow the last opinion, sooner than either of the others; but I have not yet swallowed it. Another opinion might have been added, that some throe of nature has forced up parts which had been the bed of the ocean. But have we any better proof of such an effort of nature, than of her shooting a lapidific juice into the form of a shell? No such convulsion has taken place in our time, nor within the annals of history: nor is the distance greater, between the shooting of the lapidific juice into the form of a crystal or a diamond, which we see, and into the form of a shell, which we do not see, than between the forcing volcanic matter a little above the surface, where it is in fusion, which we see, and the forcing the bed of the sea fifteen thousand feet above the ordinary surface of the earth, which we do not see. It is not possible to believe any of these hypotheses; and if we lean towards any of them, it should be only till some other is produced, more analogous to the known operations of nature. In a letter to Mr. Hopkinson, I mentioned to him that the Abbe Rochon, who discovered the double refracting power in some of the natural crystals, had lately made a telescope with the metal called platina, which, while it is as susceptible of as perfect a polish as the metal heretofore used for the specula of telescopes, is insusceptible of rust, as gold and silver are. There is a person here, who has hit on a new method of engraving. He gives you an ink of his composition. Write on copper plates, any thing of which you would wish to take several copies, and, in an hour, the plate will be ready to strike them off; so of plans, engravings, &c. This art will be amusing to individuals, if he should make it known. I send you herewith, the Nautical Almanacs for 1786, 1787, 1788, 1789, 1790, which are as late as they are published. You ask, how you may reimburse the expense of these trifles? I answer, by accepting them; as the procuring you a gratification, is a higher one to me than money. We have had nothing curious published lately. I do not know whether you are fond of chemical reading. There are some things in this science worth reading. I will send them to you, if you wish it. My daughter is well, and joins me in respects to Mrs. Rittenhouse and the young ladies. After asking when we are to have the Lunarium, I will close with assurances of the sincere regard and esteem, with which I am, Dear Sir, your most obedient,
humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO A. STEWART.
Paris, January 25, 1786.
Dear Sir,
I have received your favor of the 17th of October, which, though you mention it as the third you have written me, is the first that has come to hand. I sincerely thank you for the communications it contains. Nothing is so grateful to me, at this distance, as details, both great and small, of what is passing in my own country. Of the latter, we receive little here, because they either escape my correspondents, or are thought unworthy of notice. This, however, is a very mistaken opinion, as every one may observe, by recollecting, that when he has been long absent from his neighborhood, the small news of that is the most pleasing, and occupies his first attention, either when he meets with a person from thence, or returns thither himself. I still hope, therefore, that the letter, in which you have been so good as to give me the minute occurrences in the neighborhood of Monticello, may yet come to hand, and I venture to rely on the many proofs of friendship I have received from you for a continuance of your favors. This will be the more meritorious, as I have nothing to give you in exchange.
The quiet of Europe at this moment furnishes little which can attract your notice. Nor will that quiet be soon disturbed, at least for the current year. Perhaps it hangs on the life of the King of Prussia, and that hangs by a very slender thread. American reputation in Europe is not such as to be flattering to its citizens. Two circumstances are particularly objected to us; the nonpayment of our debts, and the want of energy in our government. These discourage a connection with us. I own it to be my opinion, that good will arise from the destruction of our credit. I see nothing else which can restrain our disposition to luxury, and to the change of those manners, which alone can preserve republican government. As it is impossible to prevent credit, the best way would be to cure its ill effects by giving an instantaneous recovery to the creditor. This would be reducing purchases on credit to purchases for ready money. A man would then see a prison painted on every thing he wished, but had not ready money to pay for.
I fear from an expression in your letter, that the people of Kentucky think of separating, not only from Virginia (in which they are right), but also from the confederacy. I own, I should think this a most calamitous event, and such a one as every good citizen should set himself against. Our present federal limits are not too large for good government, nor will the increase of votes in Congress produce any ill effect. On the contrary, it will drown the little divisions at present existing there. Our confederacy must be viewed as the nest from which all America, North and South, is to be peopled. We should take care, too, not to think it for the interest of that great continent to press too soon on the Spaniards. Those countries cannot be in better hands. My fear is, that they are too feeble to hold them till our population can be sufficiently advanced to gain it from them piece by piece. The navigation of the Mississippi we must have. This is all we are, as yet, ready to receive. I have made acquaintance with a very sensible, candid gentleman here, who was in South America during the revolt which took place there while our Revolution was going on. He says, that those disturbances (of which we scarcely heard any thing) cost, on both sides, an hundred thousand lives.
I have made a particular acquaintance here with Monsieur de Buffon, and have a great desire to give him the best idea I can of our elk. Perhaps your situation may enable you to aid me in this. You could not oblige me more, than by sending me the horns, skeleton, and skin of an elk, were it possible to procure them. The most desirable form of receiving them would be to have the skin slit from the under jaw along the belly to the tail, and down the thighs to the knee, to take the animal out, leaving the legs and hoofs, the bones of the head, and the horns attached to the skin. By sewing-up the belly, &c. and stuffing the skin, it would present the form of the animal. However, as an opportunity of doing this is scarcely to be expected, I shall be glad to receive them detached, packed in a box and sent to Richmond, to the care of Dr. Currie. Every thing of this kind is precious here. And to prevent my adding to your trouble, I must close my letter with assurances of the esteem and attachment, with which I am, Dear Sir,
your friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO THE COMMISSIONERS OF THE TREASURY.
Paris, January 26, 1786.
Gentlemen,
I have been duly honored by the receipt of your letter of December the 6th, and am to thank you for the communications it contained on the state of our funds and expectations here. Your idea, that these communications, occasionally, may be useful to the United States, is certainly just, as I am frequently obliged to explain our prospects of paying interest, &c. which I should better do with fuller information. If you would be so good as to instruct Mr. Grand, always to furnish me with a duplicate of those cash accounts which he furnishes to you, from time to time, and if you would be so good as to direct your secretary to send me copies of such letters, as you transmit to Mr. Grand, advising him of the remittances he may expect, from time to time. I should, thereby, be always informed of the sum of money on hand here, and the probable expectations of supply. Dr. Franklin, during his residence here, having been authorized to borrow large sums of money, the disposal of that money seemed naturally to rest with him. It was Mr. Grand’s practice, therefore, never to pay money, but on his warrant. On his departure, Mr. Grand sent all money drafts to me, to authorize their payment. I informed him, that this was in nowise within my province; that I was unqualified to direct him in it, and that were I to presume to meddle, it would be no additional sanction to him. He refused, however, to pay a shilling without my order. I have been obliged, therefore, to a nugatory interference, merely to prevent the affairs of the United States from standing still. I need not represent to you the impropriety of my continuing to direct Mr. Grand, longer than till we can receive your orders, the mischief which might ensue from the uncertainty in which this would place you, as to the extent to which you might venture to draw on your funds here, and the little necessity there is for my interference. Whenever you order a sum of money into Mr. Grand’s hands, nothing will be more natural than your instructing him how to apply it, so as that he shall observe your instructions alone. Among these, you would doubtless judge it necessary to give him one standing instruction, to answer my drafts for such sums, as my office authorizes me to call for. These would be salary, couriers, postage, and such other articles as circumstances will require, which cannot be previously defined. These will never be so considerable as to endanger the honor of your drafts. I shall certainly exercise in them the greatest caution, and stand responsible to Congress.
Mr. Grand conceives that he has suffered in your opinion, by an application of two hundred thousand livres, during the last year, differently from what the office of finance had instructed him. This was a consequence of his being thought subject to direction here, and it is but justice to relieve him from blame on that account, and to show that it ought to fall, if any where, on Dr. Franklin, Mr. Adams, and myself. The case was thus. The monies here were exhausted, Mr. Grand was in advance about fifty thousand livres, and the diplomatic establishments in France, Spain, and Holland, subsisting on his bounties, which they were subject to see stopped every moment, and feared a protest on every bill. Other current expenses, too, were depending on advances from him, and though these were small in their amount, they sometimes involved great consequences. In this situation, he received four hundred thousand livres, to be paid to this government for one year’s interest. We thought the honor of the United States would suffer less by suspending half the payment to this government, replacing Mr. Grand’s advances, and providing a fund for current expenses. We advised him so to do. I still think it was for the best, and I believe my colleagues have continued to see the matter in the same point of view. We may have been biassed by feelings excited by our own distressing situation. But certainly, as to Mr. Grand, no blame belongs to him. We explained this matter in a letter to Congress, at the time, and justice requires this explanation to you, as I conjecture that the former one has not come to your knowledge.
The two hundred thousand livres retained, as before mentioned, have been applied to the purposes described, to the payment of a year’s interest to the French officers (which is about forty-two thousand livres), and other current expenses, which, doubtless, Mr. Grand has explained to you. About a week ago, there remained in his hands but about twelve thousand livres. In this situation, the demands of the French officers for a second year’s interest were presented. But Mr. Grand observed there were neither money nor orders for them. The payment of these gentlemen, the last year, had the happiest effect imaginable; it procured so many advocates for the credit and honor of the United States, who were heard, in all companies. It corrected the idea that we were unwilling to pay our debts. I fear that our present failure towards them will give new birth to new imputations, and a relapse of credit. Under this fear I have written to Mr. Adams, to know whether he can have this money supplied from the funds in Holland; though I have little hope from that quarter, because he had before informed me, that those funds would be exhausted by the spring of the present year, and I doubt, too, whether he would venture to order these payments, without authority from you. I have thought it my duty to state these matters to you.
I have had the honor of enclosing to Mr. Jay, Commodore Jones’s receipts for one hundred and eighty-one thousand and thirty-nine livres, one sol and ten deniers, prize-money, which (after deducting his own proportion) he is to remit to you, for the officers and soldiers who were under his command. I take the liberty of suggesting, whether the expense and risk of double remittances might not be saved, by ordering it into the hands of Mr. Grand immediately, for the purposes of the treasury in Europe, while you could make provision at home for the officers and soldiers, whose demands will come in so slowly, as to leave you the use of a great proportion of this money for a considerable time, and some of it for ever. We could then, immediately, quiet the French officers.
I have the honor to be, with the most perfect respect and esteem, Gentlemen,
your most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MESSRS. BUCHANAN AND HAY.
Paris, January 26, 1786.
Gentlemen,
I had the honor of writing to you on the receipt of your orders to procure draughts for the public buildings, and again on the 13th of August. In the execution of these orders, two methods of proceeding presented themselves to my mind. The one was, to leave to some architect to draw an external according to his fancy, in which way, experience shows, that about once in a thousand times a pleasing form is hit upon; the other was, to take some model already devised, and approved by the general suffrage of the world. I had no hesitation in deciding that the latter was best, nor after the decision, was there any doubt what model to take, There is at Nismes, in the south of France, a building, called the Maison Quarrée, erected in the time of the Cæsars, and which is allowed, without contradiction, to be the most perfect and precious remain of antiquity in existence. Its superiority over any thing at Rome, in Greece, at Balbec, or Palmyra, is allowed on all hands; and this single object has placed Nismes in the general tour of travellers. Having not yet had leisure to visit it, I could only judge of it from drawings, and from the relation of numbers who had been to see it. I determined, therefore, to adopt this model, and to have all its proportions justly observed. As it was impossible for a foreign artist to know what number and sizes of apartments would suit the different corps of our government, nor how they should be connected with one another, I undertook to form that arrangement, and this being done, I committed them to an architect (Monsieur Clerissauk), who had studied this art twenty years in Rome, who had particularly studied and measured the Maison Quarrée of Nismes, and had published a book containing most excellent plans, descriptions, and observations on it. He was too well acquainted with the merit of that building, to find himself restrained by my injunctions not to depart from his model. In one instance, only, he persuaded me to admit of this. That was, to make the portico two columns deep only, instead of three, as the original is. His reason was, that this latter depth would too much darken the apartments. Economy might be added, as a second reason. I consented to it, to satisfy him, and the plans are so drawn. I knew that it would still be easy to execute the building with a depth of three columns, and it is what I would certainly recommend. We know that the Maison Quarrée has pleased, universally, for near two thousand years. By leaving out a column, the proportions will be changed, and perhaps the effect may be injured more than is expected. What is good, is often spoiled by trying to make it better.
The present is the first opportunity which has occurred of sending the plans. You will, accordingly, receive herewith the ground plan, the elevation of the front, and the elevation of the side. The architect having been much busied, and knowing that this was all which would be necessary in the beginning, has not yet finished the sections of the building. They must go by some future occasion, as well as the models of the front and side, which are making in plaster of Paris. These were absolutely necessary for the guide of workmen, not very expert in their art. It will add considerably to the expense, and I would not have incurred it, but that I was sensible of its necessity. The price of the model will be fifteen guineas. 1 shall know, in a few days, the cost of the drawings, which probably will be the triple of the model: however, this is but conjecture. I will make it as small as possible, pay it, and render you an account in my next letter. You will find, on examination, that the body of this building covers an area but two fifths of that which is proposed and begun; of course, it will take but about one half the bricks; and, of course, this circumstance will enlist all the workmen, and people of the art, against the plan. Again, the building begun is to have four porticoes; this but one. It is true that this will be deeper than those were probably proposed, but even if it be made three columns deep, it will not take half the number of columns. The beauty of this is insured by experience, and by the suffrage of the whole world: the beauty of that is problematical, as is every drawing, however well it looks on paper, till it be actually executed: and though I suppose there is more room in the plan begun, than in that now sent, yet there is enough in this for all the three branches of government, and more than enough is not wanted. This contains sixteen rooms; to wit, four on the first floor, for the General Court, Delegates, lobby, and conference. Eight on the second floor, for the Executive, the Senate, and six rooms for committees and juries: and over four of these smaller rooms of the second floor, are four mezzininos or entresols, serving as offices for the clerks of the Executive, the Senate, the Delegates, and the Court in actual session. It will be an objection, that the work is begun on the other plan. But the whole of this need not be taken to pieces, and of what shall be taken to pieces, the bricks will do for inner work. Mortar never becomes so hard and adhesive to the bricks, in a few months, but that it may be easily chipped off. And upon the whole, the plan now sent will save a great proportion of the expense.
Hitherto, I have spoken of the capital only. The plans for the prison, also, accompany this. They will explain themselves. I send, also, the plan of the prison proposed at Lyons, which was sent me by the architect, and to which we are indebted for the fundamental idea of ours. You will see, that of a great thing a very small one is made. Perhaps you may find it convenient to build, at first, only two sides, forming an L; but of this, you are the best judges. It has been suggested to me, that fine gravel, mixed in the mortar, prevents the prisoners from cutting themselves out, as that will destroy their tools. In my letter of August the 13th, I mentioned that I could send workmen from hence. As I am in hopes of receiving your orders precisely, in answer to that letter, I shall defer actually engaging any, till I receive them. In like manner, I shall defer having plans drawn for a Governor’s house, &c, till further orders; only assuring you, that the receiving and executing these orders, will always give me a very great pleasure, and the more, should I find that what I have done meets your approbation.
I have the honor to be, with sentiments of the most perfect esteem, Gentlemen,
your most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN ADAMS.
Paris, February 7, 1786.
Dear Sir,
I am honored with yours of January the 19th. Mine of January the 12th, had not, I suppose, at that time got to your hands, as the receipt of it is unacknowledged. I shall be anxious till I receive your answer to it.
I was perfectly satisfied before I received your letter, that your opinion had been misunderstood or misrepresented in the case of the Chevalier de Mezieres. Your letter, however, will enable me to say so with authority. It is proper it should be known, that you had not given the opinion imputed to you, though, as to the main question, it is become useless; Monsieur de Reyneval having assured me, that what I had written on that subject had perfectly satisfied the Count de Vergennes and himself, that this case could never come under the treaty. To evince, still further, the impropriety of taking up subjects gravely, on such imperfect information as this court had, I have this moment received a copy of an act of the Georgia Assembly, placing the subjects of France, as to real estates, on the footing of natural citizens, and expressly recognising the treaty. Would you think any thing could be added, after this, to put this question still further out of doors? A gentleman of Georgia assured me, General Oglethorpe did not own a foot of land in the State. I do not know whether there has been any American determination on the question, whether American citizens and British subjects, born before the Revolution, can be aliens to one another. I know there is an opinion of Lord Coke’s, in Colvin’s case, that if England and Scotland should, in a course of descent, pass to separate Kings, those born under the same sovereign during the union, would remain natural subjects and not aliens. Common sense urges some considerations against this. Natural subjects owe allegiance; but we owe none. Aliens are the subjects of a foreign power; we are subjects of a foreign power. The King, by the treaty, acknowledges our independence; how then can we remain natural subjects? The King’s power is, by the constitution, competent to the making peace, war, and treaties. He had, therefore, authority to relinquish our allegiance by treaty. But if an act of parliament had been necessary, the parliament passed an act to confirm the treaty. So that it appears to me, that in this question, fictions of law alone are opposed to sound sense.
I am in hopes Congress will send a minister to Lisbon. I know no country, with which we are likely to cultivate a more useful commerce. I have pressed this in my private letters.
It is difficult to learn any thing certain here, about the French and English treaty. Yet, in general, little is expected to be done between them. I am glad to hear that the Delegates of Virginia had made the vote relative to English commerce, though they afterwards repealed it. I hope they will come to again. When my last letters came away, they were engaged in passing the revisal of their laws, with some small alterations. The bearer of this, Mr. Lyons, is a sensible, worthy young physician, son of one of our judges, and on his return to Virginia. Remember me with affection to Mrs. and Miss Adams, Colonels Smith and Humphreys, and be assured of the esteem with which I am, Dear Sir,
your friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
Paris, February 8, 1786.
Dear Sir,
My last letters were of the 1st and 20th of September, and the 28th of October. Yours, unacknowledged, are of August the 20th, October the 3rd, and November the 15th. I take this, the first safe opportunity, of enclosing to you the bills of lading for your books, and two others for your namesake of Williamsburg, and for the attorney, which I will pray you to forward. I thank you for the communication of the remonstrance against the assessment. Mazzei, who is now in Holland, promised me to have it published in the Leyden gazette. It will do us great honor. I wish it may be as much approved by our Assembly, as by the wisest part of Europe. I have heard, with great pleasure, that our Assembly have come to the resolution, of giving the regulation of their commerce to the federal head. I will venture to assert, that there is not one of its opposers, who, placed on this ground, would not see the wisdom of this measure. The politics of Europe render it indispensably necessary, that, with respect to every thing external, we be one nation only, firmly hooped together. Interior government is what each State should keep to itself. If it were seen in Europe, that all our States could be brought to concur in what the Virginia Assembly has done, it would produce a total revolution in their opinion of us, and respect for us. And it should ever be held in mind, that insult and war are the consequences of a want of respectability in the national character. As long as the States exercise, separately, those acts of power which respect foreign nations, so long will there continue to be irregularities committed by some one or other of them, which will constantly keep us on an ill footing with foreign nations.
I thank you for your information as to my Notes. The copies I have remaining shall be sent over, to be given to some of my friends and to select subjects in the College. I have been unfortunate here with this trifle. I gave out a few copies only, and to confidential persons, writing in every copy a restraint against its publication. Among others, I gave a copy to a Mr. Williams: he died. I immediately took every precaution I could to recover this copy. But, by some means or other, a bookseller had got hold of it. He employed a hireling translator, and is about publishing it in the most injurious form possible. I am now at a loss what to do as to England. Every thing, good or bad, is thought worth publishing there; and I apprehend a translation back from the French, and a publication there. I rather believe it will be most eligible to let the original come out in that country: but am not yet decided.
I have purchased little for you in the book way since I sent the catalogue of my former purchases. I wish, first, to have your answer to that, and your information, what parts of these purchases went out of your plan. You can easily say, Buy more of this kind, less of that, &c. My wish is to conform myself to yours. I can get for you the original Paris edition of the Encyclopédie, in thirty-five volumes, folio, for six hundred and twenty livres; a good edition, in thirty-nine volumes, 4to, for three hundred and eighty livres; and a good one, in thirty-nine volumes, 8vo, for two hundred and eighty livres. The new one will be superior in far the greater number of articles; but not in all. And the possession of the ancient one has, moreover, the advantage of supplying present use. I have bought one for myself, but wait your orders as to you. I remember your purchase of a watch in Philadelphia. If it should not have proved good, you can probably sell it. In that case, I can get for you here, one made as perfect as human art can make it, for about twenty-four louis. I have had such a one made, by the best and most faithful hand in Paris. It has a second hand, but no repeating, no day of the month, nor other useless thing to impede and injure the movements which are necessary. For twelve louis more, you can have in the same cover, but on the back, and absolutely unconnected with the movements of the watch, a pedometer, which shall render you an exact account of the distances you walk. Your pleasure hereon shall be awaited.
Houdon has returned. He called on me, the other day, to remonstrate against the inscription proposed for General Washington’s statue. He says it is too long to be put on the pedestal. I told him, I was not at liberty to permit any alteration, but I would represent his objection to a friend, who could judge of its validity, and whether a change could be authorized. This has been the subject of conversations here, and various devices and inscriptions have been suggested. The one which has appeared best to me, may be translated as follows: ‘Behold, Reader, the form of George Washington. For his worth, ask History; that will tell it, when this stone shall have yielded to the decays of time. His country erects this monument.’ Houdon makes it.‘This for one side. On the second, represent the evacuation of Boston, with the motto, ‘Hostibus primum fugatis.’ On the third, the capture of the Hessians, with ‘Hostibus iterum devictis.’ On the fourth, the surrender of York, with ‘Hostibus ultimum debellatis.’ This is seizing the three most brilliant actions of his military life. By giving out, here, a wish of receiving mottos for this statue, we might have thousands offered, from which still better might be chosen. The artist made the same objection, of length, to the inscription for the bust of the Marquis de la Fayette. An alteration of that might come in time still, if an alteration was wished. However, I am not certain that it is desirable in either case. The State of Georgia has given twenty thousand acres of land, to the Count d’Estaing. This gift is considered here as very honorable to him, and it has gratified him much. I am persuaded, that a gift of lands by the State of Virginia to the Marquis de la Fayette, would give a good opinion here of our character, and would reflect honor on the Marquis. Nor am I sure that the day will not come, when it might be an useful asylum to him. The time of life at which he visited America was too well adapted to receive good and lasting impressions, to permit him ever to accommodate himself to the principles of monarchical government; and it will need all his own prudence, and that of his friends, to make this country a safe residence for him. How glorious, how comfortable in reflection, will it be, to have prepared a refuge for him in case of a reverse. In the mean time, he could settle it with tenants from the freest part of this country, Bretaigne. I have never suggested the smallest idea of this kind to him: because the execution of it should convey the first notice. If the State has not a right to give him lands with their own officers, they could buy up, at cheap prices, the shares of others. I am not certain, however, whether, in the public or private opinion, a similar gift to Count Rochambeau could be dispensed with. If the State could give to both, it would be better: but, in any event, I think they should to the Marquis. Count Rochambeau, too, has really deserved more attention than he has received. Why not set up his bust, that of Gates, Greene, Franklin, in your new capitol? A propos of the capital. Do, my dear friend, exert yourself to get the plan begun on set aside, and that adopted, which was drawn here. It was taken from a model which has been the admiration of sixteen centuries; which has been the object of as many pilgrimages as the tomb of Mahomet; which will give unrivalled honor to our State, and furnish a model whereon to form the taste of our young men. It will cost much less too, than the one begun; because it does not cover one half of the area. Ask, if you please, a sight of my letter of January the 26th, to Messrs. Buchanan and Hay, which will spare me the repeating its substance here.
Every thing is quiet in Europe. I recollect but one new invention in the arts which is worth mentioning. It is a mixture of the arts of engraving and printing, rendering both cheaper. Write or draw any thing on a plate of brass, with the ink of the inventor, and, in half an hour, he gives you engraved copies of it, so perfectly like the original, that they could not be suspected to be copies. His types for printing a whole page, are all in one solid piece. An author, therefore, only prints a few copies of his work, from time to time, as they are called for. This saves the loss of printing more copies than may possibly be sold, and prevents an edition from being ever exhausted.
I am, with a lively esteem, Dear Sir,
your sincere friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO THE MARQUIS DE LA FAYETTE.
Paris, February 9, 1786.
Dear Sir,
The Mr. John Ledyard, who proposes to undertake the journey through the northern parts of Asia and America, is a citizen of Connecticut, one of the United States of America. He accompanied Captain Cook in his last voyage to the northwestern parts of America, and rendered himself useful to that officer, on some occasions, by a spirit of enterprise which has distinguished his whole life. He has genius, and education better than the common, and a talent for useful and interesting observation. I believe him to be an honest man, and a man of truth. To all this, he adds just as much singularity of character, and of that particular kind too, as was necessary to make him undertake the journey he proposes. Should he get safe through it, I think he will give an interesting account of what he shall have seen.
I have the honor to be, with sentiments of sincere esteem and respect, Dear Sir,
your most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MONSIEUR HILLIARD d’AUBERTEUIL.
Paris, February 20, 1786.
Sir,
I have been honored with your letter, and the books which accompanied it, for which I return you my hearty thanks. America cannot but be flattered with the choice of the subject, on which you are at present employing your pen. The memory of the American Revolution will be immortal, and will immortalize those who record it. The reward is encouraging, and will justify all those pains, which a rigorous investigation of facts will render necessary. Many important facts, which preceded the commencement of hostilities, took place in England. These may mostly be obtained from good publications in that country. Some took place in this country. They will be probably hidden from the present age. But America is the field where the greatest mass of important events were transacted, and where, alone, they can now be collected. I therefore much applaud your idea of going to that country, for the verification of the facts you mean to record. Every man there can tell you more than any man here, who has not been there: and the very ground itself will give you new insight into some of the most interesting transactions. If I can be of service to you, in promoting your object there, I offer myself freely to your use. I shall be flattered by the honor of your visit here, at any time. I am seldom from home before noon; but if any later hour should suit you better, I will take care to be at home, at any hour and day, you will be pleased to indicate.
I have the honor to be, with great respect, Sir,
your most obedient, humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO THE COUNT DE VERGENNES.
Paris, February 28,1786.
Sir,
Circumstances of public duty calling me suddenly to London, I take the liberty of mentioning it to your Excellency, and of asking a few minutes’ audience of you, at as early a day and hour as will be convenient to you, and that you will be so good as to indicate them to me. I would wish to leave Paris about Friday or Saturday, and suppose that my stay in London will be of about three weeks. I shall be happy to be the bearer of any commands your Excellency may have for that place, and will faithfully execute them. I cannot omit mentioning, how pleasing it would be to me to be enabled, before my departure, to convey to the American prisoners at St. Pol de Léon such mitigation of their fate, as may be thought admissible.
I have the honor to be, with sentiments of the highest respect and esteem, your Excellency’s
most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MONSIEUR DE REYNEVAL.
Paris, March 8, 1786.
Sir,
His Excellency, Count de Vergennes, having been pleased to say that he would give orders at Calais, for the admission of certain articles which I wish to bring with me from England, I have thought it best to give a description of them, before my departure. They will be as follows:
1. A set of table furniture, consisting of China, silver, and plated ware, distributed into three or four boxes or canteens, for the convenience of removing them.
2. A box containing small tools for wooden and iron work, for my own amusement.
3. A box, probably, of books.
4. I expect to bring with me a riding horse, saddle, &c.
The mathematical instruments will probably be so light that I may bring them in my carriage, in which case, I presume they will pass with my baggage, under the authority of the passport for my person. If these orders can be made out in time, I would willingly be the bearer of them myself.
I have the honor to be, with sentiments of the most perfect esteem and respect, Sir, ,
your most obedient servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN JAY.
London, March 12, 1786.
Sir.
The date of a letter from London will doubtless be as unexpected to you as it was unforeseen by myself, a few days ago. On the 27th of the last month, Colonel Smith arrived in Paris, with a letter from Mr. Adams, informing me that there was at this place a minister from Tripoli, having general powers to enter into treaties on behalf of his State, and with whom it was possible we might do something, under our commission to that power: and that he gave reason to believe, he could also make arrangements with us, for Tunis. He further added, that the minister of Portugal here had received ultimate instructions from his court, and that, probably, that treaty might be concluded in the space of three weeks, were we all on the spot together. He, therefore, pressed me to come over immediately. The first of these objects had some weight on my mind, because, as we had sent no person to Tripoli or Tunis, I thought if we could meet a minister from them on this ground, our arrangements would be settled much sooner, and at less expense. But what principally decided me, was, the desire of bringing matters to a conclusion with Portugal, before the term of our commissions should expire, or any new turn in the negotiations of France and England should abate their willingness to fix a connection with us. A third motive had also its weight. I hoped that my attendance here, and the necessity of shortening it, might be made use of to force a decisive answer from this court. I therefore concluded to comply with Mr. Adams’s request. I went immediately to Versailles, and apprized the Count de Vergennes, that circumstances of public duty called me hither for three or four weeks, arranged with him some matters, and set out with Colonel Smith for this place, where we arrived last night, which was as early as the excessive rigor of the weather admitted. I saw Mr. Adams immediately, and again to-day. He informs me, that the minister of Portugal was taken ill five or six days ago, has been very much so, but is now somewhat better. It would be very mortifying, indeed, should this accident, with the shortness of the term to which I limit my stay here, defeat what was the principal object of my journey, and that, without which, I should hardly have undertaken it. With respect to this country, I had no doubt but that every consideration had been urged by Mr. Adams, which was proper to be urged. Nothing remains undone in this way. But we shall avail ourselves of my journey here, as if made on purpose, just before the expiration of our commission, to form our report to Congress on the execution of that commission, which report, they may be given to know, cannot be formed without decisive information of the ultimate determination of their court. There is no doubt what that determination will be: but it will be useful to have it; as it may put an end to all further expectations on our side the water, and show that the time is come for doing whatever is to be done by us, for counteracting the unjust and greedy designs of this country. We shall have the honor, before I leave this place, to inform you of the result of the several matters which have brought me to it.
A day or two before my departure from Paris, I received your letter of January———. The question therein proposed, How far France considers herself as bound to insist on the delivery of the posts, would infallibly produce another, How far we consider ourselves as guarantees of their American possessions, and bound to enter into any future war, in which these may be attacked? The words of the treaty of alliance seem to be without ambiguity on either head, yet, I should be afraid to commit Congress, by answering without authority. I will endeavor, on my return, to sound the opinion of the minister, if possible, without exposing myself to the other question. Should any thing forcible be meditated on these posts, it would possibly be thought prudent, previously to ask the good offices of France, to obtain their delivery. In this case, they would probably say, we must first execute the treaty, on our part, by repealing all acts which have contravened it. Now this measure, if there be any candor in the court of London, would suffice to obtain a delivery of the posts from them, without the mediation of any third power. However, if this mediation should be finally needed, I see no reason to doubt our obtaining it, and still less to question its omnipotent influence on the British court.
I have the honor to be, with the highest respect and esteem, Sir, your most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO COLONEL HUMPHREYS.
London, March 14, 1786.
Dear Sir,
I have been honoured with your letter, in which you mention to me your intention of returning to America in the April packet. It is with sincere concern that I meet this event, as it deprives me not only of your aid in the office in which we have been joined, but also of your society, which has been to me a source of the greatest satisfaction. I think myself bound to return you my thanks for it, and, at the same time, to bear testimony, that in the discharge of the office of Secretary of Legation to the several commissions, you have fulfilled all its duties with readiness, propriety, and fidelity. I sincerely wish, that on your return, our country may avail itself of your talents in the public service, and that you may be willing so to employ them. You carry with you my wishes for your prosperity, and a desire of being instrumental to it: and I hope, that in every situation in which we may be placed, you will freely command and count on my services. I will beg to be favored with your letters, whenever it is convenient. You have seen our want of intelligence here, and well know the nature of that which will be useful or agreeable. I fear I shall have little interesting to give you in return; but such news as my situation affords, you shall be sure to receive. I pray you to be the bearer of the enclosed letter to Mr. Jay, to accept my wishes for a favorable passage, a happy meeting with your friends, and for every future felicity which this life can afford, being with the greatest esteem, Dear Sir,
your sincere friend
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
Kaskaskias, Illinois, April 29,1779.
Dear Sir,
A few days ago, I received certain intelligence of William Morris, my express to you, being killed near the falls of Ohio, news truly disagreeable to me, as I fear many of my letters will fall into the hands of the enemy, at Detroit, although some of them, as I learn, were found in the woods torn in pieces. I do not doubt but before the receipt of this, you will have heard of my late success against Governor Hamilton, at post St. Vincenne. That gentleman, with a body of men, possessed himself of that post on the 15th of December last, repaired the fortifications for a repository, and in the spring, meant to attack this place, which he made no doubt of carrying; where he was to be joined by two hundred Indians from Michilimackinac, and five hundred Cherokees, Chickasaws, and other nations. With this body, he was to penetrate up the Ohio to Fort Pitt, sweeping Kentucky on his way, having light brass cannon for the purpose, joined on his march by all the Indians that could be got to him. He made no doubt, that he could force all West Augusta. This expedition was ordered by the commander in chief of Canada. Destruction seemed to hover over us from every quarter; detached parties of the enemy were in the neighborhood every day, but afraid to attack. I ordered Major Bowman to evacuate the fort at the Cohas, and join me immediately, which he did. Having not received a scrape of a pen from you, for near twelve months, I could see but little probability of keeping possession of the country, as my number of men was too small to stand a siege, and my situation too remote to call for assistance. I made all the preparations I possibly could for the attack, and was necessitated to set fire to some of the houses in town, to clear them out of the way. But in the height of the hurry, a Spanish merchant, who had been at St. Vincenne, arrived, and gave the following intelligence: that Mr. Hamilton had weakened himself, by sending his Indians against the frontiers, and to block up the Ohio; that he had not more than eighty men in garrison, three pieces of cannon, and some swivels mounted; and that he intended to attack this place, as soon as the winter opened, and made no doubt of clearing the western waters by the fall. My situation and circumstances induced me to fall on the resolution of attacking him, before he could collect his Indians again. I was sensible the resolution was as desperate as my situation, but I saw no other probability of securing the country. I immediately despatched a small galley, which I had fitted up, mounting two four-pounders and four swivels, with a company of men and necessary stores on board, with orders to force her way, if possible, and station herself a few miles below the enemy, suffer nothing to pass her, and wait for further orders. In the mean time, I marched across the country with one hundred and thirty men, being all I could raise, after leaving this place garrisoned by the militia. The inhabitants of the country behaved exceedingly well, numbers of young men turned out on the expedition, and every other one embodied to guard the different towns. I marched the 7th of February. Although so small a body, it took me sixteen days on the route. The inclemency of the season, high waters, &c. seemed to threaten the loss of the expedition. When within three leagues of the enemy, in a direct line, it took us five days to cross the drowned lands of the Wabash river, having to wade often upwards of two leagues, to our breast in water. Had not the weather been warm, we must have perished. But on the evening of the 23rd, we got on dry land, in sight of the enemy; and at seven o’clock, made the attack, before they knew any thing of us. The town immediately surrendered with joy, and assisted in the siege. There was a continual fire on both sides, for eighteen hours. I had no expectation of gaining the fort until the arrival of my artillery. The moon setting about one o’clock, I had an entrenchment thrown up within rifle-shot of their strongest battery, and poured such showers of well directed balls into their ports, that we silenced two pieces of cannon in fifteen minutes, without getting a man hurt.
Governor Hamilton and myself had, on the following day, several conferences, but did not agree until the evening, when he agreed to surrender the garrison (seventy-nine in number) prisoners of war, with considerable stores. I got only one man wounded; not being able to lose many, I made them secure themselves well. Seven were badly wounded in the fort, through ports. In the height of this action, an Indian party that had been to war, and taken two prisoners, came in, not knowing of us. Hearing of them, I despatched a party to give them battle in the commons, and got nine of them, with the two prisoners, who proved to be Frenchmen. Hearing of a convoy of goods from Detroit, I sent a party of sixty men, in armed boats well mounted with swivels, to meet them, before they could receive any intelligence. They met the convoy forty leagues up the river, and made a prize of the whole, taking forty prisoners, and about ten thousand pounds’ worth of goods and provisions; also the mail from Canada to Governor Hamilton, containing, however, no news of importance. But what crowned the general joy, was the arrival of William Morris, my express to you, with your letters, which gave general satisfaction. The soldiery, being made sensible of the gratitude of their country for their services, were so much elated, that they would have attempted the reduction of Detroit, had I ordered them. Having more prisoners than I knew what to do with, I was obliged to discharge a greater part of them on parole. Mr. Hamilton, his principal officers, and a few soldiers, I have sent to Kentucky, under convoy of Captain Williams, in order to be conducted to you. After despatching Morris with letters to you, treating with the neighboring Indians, &c, I returned to this place, leaving a sufficient garrison at St. Vincenne.
During my absence, Captain Robert George, who now commands the company formerly commanded by Captain Willing, had returned from New Orleans, which greatly added to our strength. It gave great satisfaction to the inhabitants, when acquainted with the protection which was given them, the alliance with France, &c. I am impatient for the arrival of Colonel Montgomery, but have heard nothing of him lately. By your instructions to me, I find you put no confidence in General M’Intosh’s taking Detroit, as you encourage me to attempt it, if possible. It has been twice in my power. Had I been able to raise only five hundred men when I first arrived in the country, or when I was at St. Vincenne, could I have secured my prisoners, and only have had three hundred good men, I should have attempted it, and since learn there could have been no doubt of success, as by some gentlemen, lately from that post, we are informed that the town and country kept three days in feasting and diversions on hearing of my success against Mr. Hamilton, and were so certain of my embracing the fair opportunity of possessing myself of that post, that the merchants and others provided many necessaries for us on our arrival; the garrison, consisting of only eighty men, not daring to stop their diversions. They are now completing a new fort, and I fear too strong for any force I shall ever be able to raise in this country. We are proud to hear Congress intends putting their forces on the frontiers, under your direction. A small army from Pittsburg, conducted with spirit, may easily take Detroit, and put an end to the Indian war. Those Indians who are active against us, are the Six Nations, part of the Shawnese, the Meamonies, and about half the Chesaweys, Ottawas, Jowaas, and Pottawatimas nations, bordering on the lakes. Those nations, who have treated with me, have behaved since very well, to wit, the Peankishaws, Kiccapoos, Orcaottenans of the Wabash river, the Kaskias, Perrians, Mechigamies, Foxes, Sacks, Opays, Illinois, and Poues, nations of the Mississippi and Illinois rivers. Part of the Chesaweys have also treated, and are peaceable. I continually keep agents among them, to watch their motions and keep them peaceably inclined. Many of the Cherokees, Chickasaws, and their confederates, are, I fear, ill disposed. It would be well if Colonel Montgomery should give them a dressing, as he comes down the Tennessee. There can be no peace expected from many nations, while the English are at Detroit. I strongly suspect they will turn their arms against the Illinois, as they will be encouraged. I shall always be on my guard, watching every opportunity to take the advantage of the enemy, and, if I am ever able to muster six or seven hundred men, I shall give them a shorter distance to come and fight me, than at this place.
There is one circumstance very distressing, that of our money’s being discredited, to all intents and purposes, by the great number of traders who come here in my absence, each outbidding the other, giving prices unknown in this country by five hundred per cent., by which the people conceived it to be of no value, and both French and Spaniards refused to take a farthing of it. Provision is three times the price it was two months past, and to be got by no other means than my own bonds, goods, or force. Several merchants are now advancing considerable sums of their own property, rather than the service should suffer, by which I am sensible they must lose greatly, unless some method is taken to raise the credit of our coin, or a fund be sent to Orleans, for the payment of the expenses of this place, which should at once reduce the price of every species of provision; money being of little service to them, unless it would pass at the ports they trade at. I mentioned to you, my drawing some bills on Mr. Pollock in New Orleans, as I had no money with me. He would accept the bills, but had not money to pay them off, though the sums were trifling; so that we have little credit to expect from that quarter. I shall take every step I possibly can, for laying up a sufficient quantity of provisions, and hope you will immediately send me an express with your instructions. Public expenses in this country have hitherto been very low, and may still continue so, if a correspondence is fixed at New Orleans for payment of expenses in this country, or gold and silver sent. I am glad to hear of Colonel Todd’s appointment. I think government has taken the only step they could have done, to make this country flourish, and be of service to them. No other regulation would have suited the people. The last account I had of Colonel Rogers, was his being in New Orleans, with six of his men. The rest he left at the Spanish Ozack, above the Natches. I shall immediately send him some provisions, as I learn he is in great want. I doubt he will not be able to get his goods up the river except in Spanish bottoms. One regiment would be able to clear the Mississippi, and to do great damage to the British interest in Florida, and by properly conducting themselves might perhaps gain the affection of the people, so as to raise a sufficient force to give a shock to Pensacola. Our alliance with France has entirely devoted this people to our interest. I have sent several copies of the articles to Detroit, and do not doubt but they will produce the desired effect. Your instructions, I shall pay implicit regard to, and hope to conduct myself in such a manner as to do honor to my country.
I am, with the greatest respect,
your humble servant,
G. R. Clarke.
P. S. I understand there is a considerable quantity of cannon ball at Pittsburg. We are much in want of four and six pound ball. I hope you will immediately order some down.
The board proceeded to the consideration of the letters of Colonel Clarke, and other papers relating to Henry Hamilton, Esq. who has acted for some years past as Lieutenant Governor of the settlement at and about Detroit, and commandant of the British garrison there, under Sir Guy Carleton, as Governor in chief; Philip Dejean, justice of the peace for Detroit, and William Lamothe, captain of volunteers, prisoners of war, taken in the county of Illinois.
They find, that Governor Hamilton has executed the task of inciting the Indians to perpetrate their accustomed cruelties on the citizens of the United States, without distinction of age, sex, or condition, with an eagerness and avidity which evince, that the general nature of his charge harmonized with his particular disposition. They should have been satisfied, from the other testimony adduced, that these enormities were committed by savages acting under his commission, but the number of proclamations, which, at different times, were left in houses, the inhabitants of which were killed or carried away by the Indians, one of which proclamations is in possession of the board, under the hand and seal of Governor Hamilton, puts this fact beyond a doubt. At the time of his captivity, it appears, he had sent considerable bodies of Indians against the frontier settlements of these States, and had actually appointed a great council of Indians, to meet him at Tennessee, to concert the operations of this present campaign. They find that his treatment of our citizens and soldiers, taken and carried within the limits of his command, has been cruel and inhuman; that in the case of John Dodge, a citizen of these States, which has been particularly stated to this board, he loaded him with irons, threw him into a dungeon, without bedding, without straw, without fire, in the dead of winter and severe climate of Detroit; that, in that state, he wasted him with incessant expectations of death: that when the rigors of his situation had brought him so low, that death seemed likely to withdraw him from their power, he was taken out and somewhat attended to, until a little mended, and before he had recovered ability to walk, was again returned to his dungeon, in which a hole was cut, seven inches square only for the admission of air, and the same load of irons again put on him: that appearing, a second time, in imminent danger of being lost to them, he was again taken from his dungeon, in which he had lain from January till June, with the intermission of a few weeks only, before mentioned. That Governor Hamilton gave standing rewards for scalps, but offered none for prisoners, which induced the Indians, after making their captives carry their baggage into the neighborhood of the fort, there to put them to death, and carry in their scalps to the Governor, who welcomed their return and success by a discharge of cannon. That when a prisoner, brought alive, and destined to death by the Indians, the fire already kindled, and himself bound to the stake, was dexterously withdrawn, and secreted from them by the humanity of a fellow prisoner, a large reward was offered for the discovery of the victim, which having tempted a servant to betray his concealment, the present prisoner Dejean, being sent with a party of soldiers, surrounded the house, took and threw into jail the unhappy victim and his deliverer, where the former soon expired under the perpetual assurances of Dejean, that he was to be again restored into the hands of the savages, and the latter when enlarged, was bitterly reprimanded by Governor Hamilton.
It appears to them, that the prisoner Dejean was, on all occasions, the willing and cordial instrument of Governor Hamilton, acting both as judge and keeper of the jails, and instigating and urging him, by malicious insinuations and untruths, to increase, rather than relax his severities, heightening the cruelty of his orders by his manner of executing them, offering at one time a reward to one man to be hangman for another, threatening his life on refusal, and taking from his prisoners the little property their opportunities enabled them to acquire.
It appears, that the prisoner Lamothe, was a captain of the volunteer scalping parties of Indians and whites, who went, from time to time, under general orders to spare neither men, women, nor children. From this detail of circumstances, which arose in a few cases only, coming accidentally to the knowledge of the board, they think themselves authorized by fair deduction, to presume what would be the horrid history of the sufferings of the many, who have expired under their miseries (which, therefore, will remain for ever untold), or who have escaped from them, and are yet too remote and too much dispersed, to bring together their well founded accusations against the prisoners.
They have seen that the conduct of the British officers, civil and military, has in the whole course of this war, been savage, and unprecedented among civilized nations; that our officers taken by them, have been confined in crowded jails, loathsome dungeons, and prison-ships, loaded with irons, supplied often with no food, generally with too little for the sustenance of nature, and that little sometimes unsound and unwholesome, whereby such numbers have perished, that captivity and death have with them been almost synonymous; that they have been transported beyond seas, where their fate is out of the reach of our inquiry, have been compelled to take arms against their country, and, by a refinement in cruelty, to become murderers of their own brethren.
Their prisoners with us have, on the other hand, been treated with humanity and moderation; they have been fed, on all occasions, with wholesome and plentiful food, suffered to go at large within extensive tracts of country, treated with liberal hospitality, permitted to live in the families of our citizens, to labor for themselves, to acquire and enjoy profits, and finally to participate of the principal benefits of society, privileged from all burdens.
Reviewing this contrast, which cannot be denied by our enemies themselves, in a single point, and which has now been kept up during four years of unremitting war, a term long enough to produce well-founded despair that our moderation may ever lead them to the practice of humanity; called on by that justice we owe to those who are fighting the battles of our country, to deal out, at length, miseries to their enemies, measure for measure, and to distress the feelings of mankind by exhibiting to them spectacles of severe retaliation, where we had long and vainly endeavored to introduce an emulation in kindness; happily possessed, by the fortune of war, of some of those very individuals who, having distinguished themselves personally in this line of cruel conduct, are fit subjects to begin on, with the work of retaliation; this board has resolved to advise the Governor, that the said Henry Hamilton, Philip Dejean and William Lamothe, prisoners of war, be put into irons, confined in the dungeon of the public jail, debarred the use of pen, ink, and paper, and excluded all converse, except with their keeper. And the Governor orders accordingly.
Arch. Blair, C. C.
The board having been, at no time, unmindful of the circumstances attending the confinement of Lieutenant Governor Hamilton, Captain Lamothe, and Philip Dejean, which the personal cruelties of those men, as well as the general conduct of the enemy, had constrained them to advise: wishing, and willing to expect, that their sufferings may lead them to the practice of humanity, should any future turn of fortune, in their favor, submit to their discretion the fate of their fellow creatures; that it may prove an admonition to others, meditating like cruelties, not to rely for impunity in any circumstances of distance or present security; and that it may induce the enemy to reflect, what must be the painful consequences, should a continuation of the same conduct on their part impel us again to severities, while such multiplied subjects of retaliation are within our power: sensible that no impression can be made on the event of the war, by wreaking vengeance on miserable captives; that the great cause which has animated the two nations against each other, is not to be decided by unmanly cruelties on wretches, who have bowed their necks to the power of the victor, but by the exercise of honorable valor in the field: earnestly hoping that the enemy, viewing the subject in the same light, will be content to abide the event of that mode of decision, and spare us the pain of a second departure from kindness to our captives: confident that commiseration to our prisoners is the only possible motive, to which can be candidly ascribed, in the present actual circumstances of the war, the advice we are now about to give; the board does advise the Governor to send Lieutenant Governor Hamilton, Captain Lamothe, and Philip Dejean, to Hanover court house, there to remain at large, within certain reasonable limits, taking their parole in the usual manner. The Governor orders accordingly.
Arch. Blair, C. C.
Ordered, that Major John Hay be sent, also, under parole to the same place.
Arch. Blair, C. C.
The Governor is advised to take proper and effectual measures for knowing, from time to time, the situation and treatment of our prisoners by the enemy, and to extend to theirs, with us a like treatment, in every circumstance; and, also, to order to a proper station, the prison-ship fitted up on recommendation from Congress from the reception and confinement of such prisoners of war, as shall be sent to it.
Arch. Blair, C. C.
[After letter XVII. in the MS. is inserted the following
memorandum.]
Female Contributions, in aid of the War, probably in 1780.
Mrs. Sarah Gary, of Scotchtown, a watch-chain, cost £7 sterling.
Mrs.——— Ambler, five gold rings.
Mrs. Rebecca Ambler, three gold rings.
Mrs.————— Nicholas, a diamond drop.
Mrs. Griffin, of Dover, ten half joes.
Mrs. Gilmer, five guineas.
Mrs. Anne Ramsay (for Fairfax), one half joe, three guineas, three pistereens, one bit.
Do. for do. paper money, bundle No. 1, twenty thousand dollars, No. 2, twenty-seven thousand dollars, No. 3, fifteen thousand dollars, No. 4, thirteen thousand five hundred and eighteen dollars and one third.
Mrs. Lewis (for Albemarle), £1559 8s. paper money,
Mrs. Weldon, £39 18s. new, instead of £1600, old paper money,
Mrs. Blackburn (for Prince William), seven thousand five hundred and six dollars, paper money.
Mrs. Randolph, the younger, of Chatsworth, eight hundred dollars.
Mrs. Fitzhugh and others, £558.
Lord Cornwallis’s Letter to Lieutenant Colonel Nisbet Balfour, Commander at Ninety Six.
I have the happiness to inform you, that on Wednesday the 16th instant, I totally defeated General Gates’s army. One thousand were killed and wounded, about eight hundred taken prisoners. We are in possession of eight pieces of brass cannon, all they had in the field, all their ammunition wagons, a great number of arms, and one hundred and thirty baggage wagons: in short, there never was a more complete victory. I have written to Lieutenant Colonel Turnbull, whom I sent to join Major Johnson on Little river, to push on after General Sumpter to the Wax-haws, whose detachment is the only collected force of rebels in all this country. Colonel Tarleton is in pursuit of Sumpter. Our loss is about three hundred killed and wounded, chiefly of the thirty-third regiment and volunteers, of Ireland. I have given orders that all the inhabitants of this province, who have subscribed and taken part in this revolt, should be punished with the greatest rigor; also, that those who will not turn out, may be imprisoned, and their whole property taken from them, and destroyed. I have also ordered that satisfaction should be made for their estates, to those who have been injured and oppressed by them. I have ordered, in the most positive manner, that every militia man who has borne arms with us and afterwards joined the enemy, shall be immediately hanged. I desire you will take the most rigorous measure to punish the rebels in the district in which you command, and that you will obey, in the strictest manner, the directions I have given in this letter, relative to the inhabitants of this country.
Cornwallis.
August, 1780.
TO LORD CORNWALLIS.
Portsmouth, Virginia, November 4, 1780.
My Lord,
I have been here near a week, establishing a post. I wrote to you to Charleston, and by another messenger, by land. I cannot hear, for a certainty, where you are: I wait your orders. The bearer is to be handsomely rewarded, if he brings me any note or mark from your Lordship.
A. L.

| Contents |
| Illustrations |
| Volume I. |
| Volume III. |
| Volume IV. |


CONTENTS
LETTER I. TO RICHARD HENRY LEE, April 22, 1786
LETTER II. TO CHARLES THOMSON, April 22, 1786
LETTER III. TO JOHN JAY, April 23, 1786
LETTER IV. TO JOHN JAY, April 23, 1786
LETTER V. TO JAMES MADISON, April 25, 1786
LETTER VI. TO THE COUNT DE VERGENNES, May 3, 1786
LETTER VII. TO JOHN PAGE, May 4, 1786
LETTER VIII. TO WILLIAM CARMICHAEL
LETTER IX. TO MR. DUMAS, May 6, 1789
LETTER X. TO WILLIAM DRAYTON, May 6, 1786
LETTER XI. TO W. T. FRANKLIN, May 7, 1786
LETTER XII. TO ELBRIDGE GERRY, May 7, 1786
LETTER XIII. TO JAMES ROSS, May 8, 1786
LETTER XIV. TO T. PLEASANTS, May 8,1786
LETTER XV. TO COLONEL MONROE, May 10,1786
LETTER XVI. TO JOHN ADAMS, May 11, 1786
LETTER XVII. TO LISTER ASQUITH, May 22, 1786
LETTER XVIII. TO JOHN JAY, May 23, 1786
LETTER XIX. TO MR. CARMICHAEL, June 20, 1786
LETTER XX. TO MR. LAMBE, June 20,1786
LETTER XXI.. TO MONSIEUR DE REYNEVAL, June 25, 1786
LETTER XXII. TO THE PREVOT DES MARCHANDS, September 27, 1786
LETTER XXIII. TO COLONEL MONROE, July 9, 1786
LETTER XXIV. TO JOHN ADAMS, July 11, 1786
LETTER XXV. TO JOHN JAY, August 11, 1786
LETTER XXVI. TO COLONEL MONROE, August 11, 1786
LETTER XXVII. TO MR. WYTHE, August 13,1786
LETTER XXVIII. TO MRS. COSWAY, October 12, 1786
LETTER XXIX. TO MRS. COSWAY, October 13, 1786
LETTER XXX. M. LE ROY DE L’ACADEMIE DES SCIENCES, November 13, 1786
LETTER XXXI. TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, November 14, 1786
LETTER XXXII. TO JAMES MADISON, December 16, 1786
LETTER XXXIII. TO CHARLES THOMSON, December 17,1780
LETTER XXXIV. TO COLONEL MONROE, December 18, 1786
LETTER XXXV. TO MR. CARMICHAEL, December 26,1786
LETTER XXXVI. TO MR. VAUGHAN, December 29, 1786
LETTER XXXVII. TO JOHN JAY, December 31, 1786
LETTER XXXVIII. TO SAMUEL OSGOOD, January 5, 1787
LETTER XXXIX. TO JOHN JAY, January 9, 1787
LETTER XL. TO JOHN ADAMS, January 11, 1787
LETTER XLI. TO MONSIEUR LE DUC D’HARCOURT, January 14, 1787
LETTER XLII. TO MONSIEUR DE CREVE-COEUR, January 15,1787
LETTER XLIII. TO COLONEL EDWARD CARRINGTON, January 16, 1787
LETTER XLIV TO JAMES MADISON, January 30, 1787 *
LETTER XLV. TO JOHN JAY, February 1, 1787
LETTER XLVI. TO MRS. BINGHAM, February 7, 1787
LETTER XLVII. TO GOVERNOR RANDOLPH, February 7, 1787
LETTER XLVIII. TO JOHN JAY, February 8, 1787
LETTER XLIX. TO MR. DUMAS, February 9, 1787
LETTER L. TO JOHN JAY, February 14, 1787
LETTER LI. TO JOHN JAY, February 23, 1787
LETTER LII. TO THE MARQUIS DE LA FAYETTE, February 28, 1787
LETTER LIII. TO MADAME LA COMTESSE DE TESSE, March 20, 1787
LETTER LIV. TO THE MARQUIS DE LA FAYETTE, April 11, 1787
LETTER LV. TO WILLIAM SHORT, April 12, 1787
LETTER LVI. TO JOHN JAY, May 4, 1787
LETTER LVII. TO M. GUIDE, May 6, 1787
MEMORANDA TAKEN ON A JOURNEY FROM PARIS IN 1787
LETTER LVIII. TO WILLIAM CARMICHAEL, June 14, 1787
LETTER LIX. TO J. BANNISTER, JUNIOR, June 19, 1787
LETTER LX. TO JAMES MADISON, June 20, 1787*
LETTER LXI. TO JOHN JAY, June 21,1787
LETTER LXII. TO MADAME DE CORNY, June 30,1787
LETTER LXIII. TO JOHN ADAMS, July 1, 1787
LETTER LXIV. TO DAVID HARTLEY, July 2,1787
LETTER LXV. TO B. VAUGHAN, July 2, 1787
LETTER LXVI. TO M. L’ABBE MORELLET, July 2, 1787
OBSERVATIONS ON THE LETTER OF MONSIEUR DE CALONNE
LETTER LXVII. TO T. M. RANDOLPH, JUNIOR, July 6, 1787
LETTER LXVIII. TO STEPHEN CATHALAN, JUNIOR, July 21,1787
LETTER LXIX. TO THE DELEGATES OF RHODE ISLAND, July 22,1787
LETTER LXX. TO THE COUNT DE MONTMORIN, July 23, 1787
LETTER LXXI. TO MR. SKIPWITH, July 28, 1787
LETTER LXXII. TO J. W. EPPES, July 28,1787
LETTER LXXIII. TO A. DONALD, July 28, 1787
LETTER LXXIV. TO WILLIAM DRAYTON, July 30, 1787
LETTER LXXV. TO JAMES MADISON, August 2, 1787
LETTER LXXVI. TO THOMAS BARCLAY, August 3, 1787
LETTER LXXVII. TO E. CARRINGTON, August 4,1787
LETTER LXXVIII. TO DR. CURRIE, August 4, 1787
LETTER LXXIX. TO MR. HAWKINS, August 4, 1787
LETTER LXXX. TO COLONEL MONROE, August 5, 1787
LETTER LXXXI. TO JOHN JAY, August 6,1787
LETTER LXXXII. TO JOHN CHURCHMAN, August 8, 1787
LETTER LXXXIII. TO MONSIEUR L HOMMANDE, August 9, 1787
LETTER LXXXIV. TO PETER CARR, August 10, 1787
LETTER LXXXV. TO DR. GILMER, August 11, 1787
LETTER LXXXVI. TO JOSEPH JONES, August 14, 1787
LETTER LXXXVII. TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, August 14, 1787
LETTER LXXXVIII. TO COLONEL HUMPHREYS, August 14, 1787
LETTER LXXXIX. TO JOHN JAY, August 15, 1787
LETTER XC. TO JOHN ADAMS, August 30, 1787
LETTER XCI. TO MR. WYTHE, September 16,1787
LETTER XCII. TO JOHN JAY, September 19, 1787
LETTER XCIII. TO CHARLES THOMSON, September 20, 1787
LETTER XCIV. TO JOHN JAY, September 22,1787
LETTER XCV. TO JOHN JAY, September 22, 1787
LETTER XCVI. TO MR. CARNES, September 22, 1787
LETTER XCVII. TO JOHN JAY, September 24, 1787
LETTER XCVIII, TO JOHN ADAMS, September 28, 1787
LETTER XCIX. TO COLONEL SMITH, September 28,1787
LETTER C. TO MONSIEUR LE COMTE DE BUFFON, October 3, 1787
LETTER CI. TO MR. DUMAS, October 4,1787
LETTER CII. TO JOHN JAY, October 8, 1787
LETTER CIII. TO JAMES MADISON, October 8, 1787
LETTER CIV. TO JOHN JAY, October 8, 1787
LETTER CV. TO MONSIEUR LE COMTE DE MOUSTIER, October 9,1787
LETTER CVI. TO MADAME DE BREHAN, October 9, 1787
LETTER CVII. TO MR. DUMAS, October 14, 1787
LETTER CVIII. TO MADAME DE CORNY, October 18, 1787
LETTER CIX. TO THE COUNT DE MONTMORIN, October 23, 1787
LETTER CX. TO JOHN JAY, November 3, 1787
LETTER CXI. TO JOHN JAY, November 3, 1787
LETTER CXII. TO THE COUNT DE MONTMORIN, November 6, 1787
LETTER CXIII. TO JOHN ADAMS, November 13, 1787
LETTER CXIV. TO COLONEL SMITH, November 13, 1787
LETTER CXV. TO WILLIAM CARMICHAEL, December 11, 1787
LETTER CXVI. TO JOHN ADAMS
LETTER CXVII. TO JAMES MADISON, December 20, 1787
LETTER CXVIII. TO E. CARRINGTON, December 21, 1787
LETTER CXIX. TO MONSIEUR LIMOZIN, December 22, 1787
LETTER CXX. TO JOHN JAY, December 31, 1787
LETTER CXXI. TO MONSIEUR LAMBERT, January 3, 1788
LETTER CXXII. TO LE COMTE BERNSTORFF, January 21, 1788
LETTER CXXIII. TO WILLIAM RUTLEDGE, February 2, 1788
LETTER CXXIV. TO THE COMMISSIONERS OF THE TREASURY, Feb. 7, 1788
LETTER CXXV. TO DOCTOR PRICE, February 7, 1788
LETTER CXXVI. TO A. DONALD, February.7, 1788
LETTER CXXVII. TO M. WARVILLE, February 12, 1888
LETTER CXXVIII. TO JOHN ADAMS, March 2, 1788
LETTER CXXIX. TO JOHN JAY, March 16, 1788
LETTER CXXX. TO MR. DUMAS, March 29, 1788
LETTER CXXXI. TO THE COMMISSIONERS OF THE TREASURY, March 29, 1788
LETTER CXXXII. TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, May 2, 1788
LETTER CXXXIII. TO JAMES MADISON, May 3,1788
LETTER CXXXIV. TO JOHN JAY, May 4, 1788
LETTER CXXXV. TO THE COUNT DE MOUSTIER, May 17, 1788
LETTER CXXXVI. TO JOHN JAY, May 23,1788
LETTER CXXXVII. TO JOHN BROWN, May 26,1788
LETTER CXXXVIII. TO WILLIAM CARMICHAEL, May 27, 1788
LETTER CXXXIX. TO JOHN JAY, May 27, 1788
LETTER CXL.* TO JAMES MADISON, May 28, 1788
LETTER CXLI. TO PETER CARU, May 23, 1788
LETTER CXLII. TO THE COMTE DE BERNSTORFF, June 19, 1788
LETTER CXLIII. TO THE COUNT DE MONTMORIN, June 20, 1788
LETTER CXLIV. TO DOCTOR GORDON, July 16, 1788
LETTER CXLV. TO JAMES MADISON, July 19, 1788
LETTER CXLVI. TO E. RUTLEDGE, July 18, 1788
LETTER CXLVII. TO MR. BELLINI, July 25,1788
LETTER CXLVIII. TO JAMES MADISON, July 31, 1788
LETTER CXLIX. TO JOHN JAY, August 3, 1788
LETTER CL. TO COLONEL MONROE, August 9, 1788
LETTER CLI. TO MONSIEUR DE CREVE-COEUR, August 9, 1788
LETTER CLII. TO JOHN JAY, August 10, 1788
LETTER CLIII. TO JOHN JAY, August 11, 1788
LETTER CLIV. TO WILLIAM CARMICHAEL, August 12, 1788
LETTER CLV. TO M. CATHALAN, August 13,1788
LETTER CLVI. TO JOHN JAY, August 20,1788
LETTER CLVII. TO MR. CUTTING, August 23, 1788
LETTER CLVIII. TO JOHN JAY, September 3, 1788
LETTER CLIX. TO THE COMMISSIONERS OF THE TREASURY, Sep. 6, 1788
LETTER CLX. TO THE COUNT DE MONTMORIN,
LETTER CLXI. TO M. DE REYNEVAL, September 16, 1788
LETTER CLXII. TO THE MARQUIS DE LA ROUERIE, September 16,1788
LETTER CLXIII. TO WILLIAM SHORT, September 20, 1788
LETTER CLXIV. TO JOHN JAY, September 24,1788
LETTER CLXV. TO M. DE REYNEVAL, October 1, 1788
LETTER CLXVI. TO MR. CUTTING, October 2, 1788
LETTER CLXVIII. TO JAMES MADISON, November 18, 1788
LETTER CLXIX. TO A. DONALD, November 18,1788
LETTER CLXX. TO JOHN JAY, November 19, 1788
LETTER CLXXI. TO JOHN JAY, November 29, 1788
LETTER, CLXXII. TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, December 4, 1788
LETTER CLXXIII. TO JOHN ADAMS, December 5, 1788
LETTER CLXXIV. TO MR. SHORT, December 8, 1788
LETTER CLXXV. TO DOCTOR GILMER, December 16, 1788
LETTER CLXXVI. TO THOMAS PAINE, December 23,1788
LETTER CLXXVII. TO JOHN JAY, January 11, 1789
LETTER CLXXVIII. TO JAMES MADISON, January 12, 1789
LETTER CLXXIX. TO JOHN JAY, January 14, 1789
LETTER CLXXX. TO MADAME NECKER, January 24, 1789
LETTER CLXXXI. TO JOHN JAY, February 1, 1789
LETTER CLXXXII. TO JOHN JAY, February 4, 1789
LETTER CLXXXIII. TO WILLIAM SHORT, February 9,1789
LETTER CLXXXIV. TO M. DE VILLEDEUIL, February 10, 1789
LETTER CLXXXV. TO MR. CARNES, February 15,1789
LETTER CLXXXVI. TO DR. BANCROFT, March 2, 1789
LETTER CLXXXVII. TO M. DE MALESHERBES, March 11, 1789
LETTER CLXXXVIII. TO JOHN JAY, March 12, 1789
LETTER CLXXXIX. TO F. HOPKINSON, March 13, 1789
LETTER CXC. TO MADAME DE BREHAN, March 14, 1789
LETTER CXCI. TO JAMES MADISON, March 15, 1789
LETTER, CXCII. TO THOMAS PAINE, March 17,1789
LETTER CXIII. TO COLONEL HUMPHREYS, March 18, 1789
LETTER CXCIV. TO DOCTOR WILLARD, March 24, 1789
LETTER CXCV. TO J. SARSFIELD, April 3, 1789
LETTER CXCVI. TO THE MARQUIS DE LA FAYETTE, May 6,1789
LETTER CXCVII. TO WILLIAM CARMICHAEL, May 8, 1789
LETTER CXCVIII. TO JOHN JAY, May 9, 1789
LETTER CXCIX. TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, May 10, 1780
LETTER CC. TO JAMES MADISON, May 11,1789
LETTER CCI. TO MONSIEUR DE PONTIERE, May 17, 1789
LETTER CCII. TO MR. VAUGHAN, May 17, 1789
LETTER CCIII. TO THOMAS PAINE, May 19,1789
LETTER CCIV. TO MONSIEUR DE ST. ETIENNE, June 3, 1789
LETTER CCV. TO THE MARQUIS DE LA FAYETTE, June 12, 1789
LETTER CCVI. TO JOHN JAY, June 17, 1789
LETTER CCVII. TO JAMES MADISON, June 18, 1789
LETTER CCVIII. TO JOHN JAY, June 24,1789
LETTER CCIX. TO JOHN JAY, June 29, 1789
LETTER CCX. TO THE MARQUIS DE LA FAYETTE, July 6, 1789
LETTER CCXI. TO THE MARQUIS DE LA FAYETTE, July 7,1789
LETTER CCXII. TO MR. NECKER, July 8, 1789
LETTER CCXIII. TO THE COUNT DE MONTMORIN, July 8, 1789
LETTER CCXIV. TO THE MARQUIS DE LA FAYETTE, July 9, 1789
LETTER CCXV. TO THE MARQUIS DE LA FAYETTE, July 10, 1789
LETTER CCXVI. TO THOMAS PAINE, July 11, 1789
List of Illustrations
Book Spines, 1829 Set of Jefferson Papers
Steel Engraving by Longacre from Painting of G. Stuart
TO RICHARD HENRY LEE.
London, April 22, 1786.
Dear Sir,
In your letter of October the 29th, you desired me to send you one of the new lamps. I tried at every probable place in Paris, and could not get a tolerable one. I have been glad of it since I came here, as I find them much better made here. I now deliver one, with this letter, into the hands of Mr. Fulwar Skipwith, a merchant from Virginia, settled here, who promises to send it to you, with one for Mr. C. Thomson. Of this be pleased to accept, from me. It is now found, that they may be used with almost any oil.
I expect to leave this place in about three days. Our public letters, joint and separate, will inform you what has been done, and what could not be done here. With respect to a commercial treaty with this country, be assured, that this government not only has it not in contemplation at present to make any, but that they do not conceive that any circumstances will arise, which shall render it expedient for them to have any political connection with us. They think we shall be glad of their commerce on their own terms. There is no party in our favor here, either in power or out of power. Even the opposition concur with the ministry and the nation in this. I can scarcely consider as a party, the Marquis of Lansdowne, and a half dozen characters about him, such as Dr. Price, &c. who are impressed with the utility of a friendly connection with us. The former does not venture this sentiment in parliament, and the latter are not in situations to be heard. The Marquis of Lansdowne spoke to me affectionately of your brother, Doctor Lee, and desired his respects to him, which I beg leave to communicate through you. Were he to come into the ministry (of which there is not the most distant prospect), he must adopt the King’s system, or go out again, as he did before, for daring to depart from it. When we see, that through all the changes of ministry, which have taken place during the present reign, there has never been a change of system with respect to America, we cannot reasonably doubt, that this is the system of the King himself. His obstinacy of character we know; his hostility we have known, and it is embittered by ill success. If ever this nation, during his life, enter into arrangements with us, it must be in consequence of events, of which they do not at present see a possibility. The object of the present ministry is to buoy up the nation with flattering calculations of their present prosperity, and to make them believe they are better without us than with us. This they seriously believe; for what is it men cannot be made to believe? I dined the other day in a company of the ministerial party. A General Clark, a Scotchman and ministerialist, sat next to me. He introduced the subject of American affairs, and in the course of the conversation told me, that were America to petition parliament to be again received on their former footing, the petition would be very generally rejected. He was serious in this, and I think it was the sentiment of the company, and is the sentiment perhaps of the nation. In this they are wise, but for a foolish reason. They think they lost more by suffering us to participate of their commercial privileges, at home and abroad, than they lose by our political severance. The true reason, however, why such an application should be rejected, is, that in a very short time we should oblige them to add another hundred millions to their debt, in unsuccessful attempts to retain the subjection offered to them. They are at present in a frenzy, and will not be recovered from it, till they shall have leaped the precipice they are now so boldly advancing to. Writing from England, I write you nothing but English news. The continent, at present, furnishes nothing interesting. I shall hope the favor of your letters, at times. The proceedings and views of Congress and of the Assemblies, the opinions and dispositions of our people in general, which, in governments like ours, must be the foundation of measures, will always be interesting to me, as will whatever respects your own health and happiness; being with great esteem,
Dear Sir, your most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson
TO CHARLES THOMSON.
London, April 22, 1786.
Dear Sir,
In one of your former letters, you expressed a wish to have one of the newly invented lamps. I find them made here much better than at Paris, and take the liberty of asking your acceptance of one, which will accompany this letter. It is now found, that any tolerable oil may be used in them. The spermaceti oil is best, of the cheap kinds.
I could write you volumes on the improvements which I find made, and making here, in the arts. One deserves particular notice, because it is simple, great, and likely to have extensive consequences. It is the application of steam, as an agent for working grist-mills. I have visited the one lately made here. It was at that time turning eight pair of stones. It consumes one hundred bushels of coal a day. It is proposed to put up thirty pair of stones. I do not know whether the quantity of fuel is to be increased. I hear you are applying the same agent in America to navigate boats, and I have little doubt, but that it will be applied generally to machines, so as to supersede the use of water ponds, and of course to lay open all the streams for navigation. We know, that steam is one of the most powerful engines we can employ; and in America fuel is abundant. I find no new publication here worth sending to you. I shall set out for Paris within three or four days. Our public letters will inform you of our public proceedings here.
I am, with sincere esteem, Dear Sir,
your friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN JAY.
London, April 23, 1786.
Sir,
In my letter of March the 12th, I had the honor of explaining to you the motives which had brought me to this place. A joint letter from Mr. Adams and myself, sent by the last packet, informed you of the result of our conferences with the Tripoline minister. The conferences with the minister of Portugal have, been drawn to a greater length than I expected. However, every thing is now agreed, and the treaty will be ready for signature the day after to-morrow. I shall set out for Paris the same day. With this country nothing is done: and that nothing is intended to be done, on their part, admits not the smallest doubt. The nation is against any change of measures: the ministers are against it; some from principle, others from subserviency: and the King, more than all men, is against it. If we take a retrospect to the beginning of the present reign, we observe, that amidst all the changes of ministry, no change of measures with respect to America ever took place; excepting only at the moment of the peace; and the minister of that moment was immediately removed. Judging of the future by the past, I do not expect a change of disposition during the present reign, which bids fair to be a long one, as the King is healthy and temperate. That he is persevering, we know. If he ever changes his plan, it will be in consequence of events, which, at present, neither himself nor his ministers place among those which are probable. Even the opposition dare not open their lips in favor of a connection with us, so unpopular would be the topic. It is not, that they think our commerce unimportant to them. I find that the merchants here set sufficient value on it. But they are sure of keeping it on their own terms. No better proof can be shown of the security in which the ministers think themselves on this head, than that they have not thought it worth while to give us a conference on the subject, though, on my arrival, we exhibited to them our commission, observed to them that it would expire on the 12th of the next month, and that I had come over on purpose to see if any arrangements could be made before that time. Of two months which then remained, six weeks have elapsed without one scrip of a pen, or one word from a minister, except a vague proposition at an accidental meeting. We availed ourselves even of that, to make another essay to extort some sort of declaration from the court. But their silence is invincible. But of all this, as well as of the proceedings in the negotiation with Portugal, information will be given you by a joint letter from Mr. Adams and myself. The moment is certainly arrived, when, the plan of this court being out of all doubt, Congress and the States may decide what their own measures should be.
The Marquis of Lansdowne spoke of you in very friendly terms, and desired me to present his respects to you, in the first letter I should write. He is thoroughly sensible of the folly of the present measures of this country, as are a few other characters about him. Dr. Price is among these, and is particularly disturbed at the present prospect. He acknowledges, however, that all change is desperate: which weighs the more, as he is intimate with Mr. Pitt. This small band of friends, favorable as it is, does not pretend to say one word in public on our subject.
I have the honor to be, with sentiments of the highest esteem and respect,
Sir, your most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN JAY.
London, April 23, 1786.
Sir,
In another letter of this day, I stated to you what had passed with public characters since my arrival here. Conversations with private individuals, I thought it best not to mingle with the contents of that letter. Yet, as some have taken place, which relate to matters within our instructions, and with persons whose opinions deserve to have some weight, I will take the liberty of stating them. In a conversation with an ancient and respectable merchant of this place, such a view of the true state of the commercial connections of America and Great Britain was presented to him, as induced him to acknowledge they had been mistaken in their opinions, and to ask, that Mr. Adams and myself would permit the chairman of the committee of American merchants to call on us. He observed, that the same person happened to be also chairman of the committee of the whole body of British merchants; and that such was the respect paid to his person and office, that we might consider what came from him, as coming from the committees themselves. He called on us at an appointed hour. He was a Mr. Duncan Campbell, formerly much concerned in the American trade. We entered on the subject of the non-execution of the late treaty of peace, alleged on both sides. We observed, that the refusal to deliver the western posts, and the withdrawing American property, contrary to express stipulation, having preceded what they considered as breaches on our part, were to be considered as the causes of our proceedings. The obstructions thrown by our legislatures in the way of the recovery of their debts, were insisted on by him. We observed to him, that the great amount of the debt from America to Great Britain, and the little circulating coin in the formeer country, rendered an immediate payment impossible; that time was necessary; that we had been authorized to enter into explanatory arrangements on this subject; that we had made overtures for the purpose, which had not been attended to, and that the States had, therefore, been obliged to modify the article for themselves. He acknowledged the impossibility of immediate payment, the propriety of an explanatory convention, and said, that they were disposed to allow a reasonable time. We mentioned the term of five years, including the present; but that judgments might be allowed immediately, only dividing the execution into equal and annual parts, so that the last should be levied by the close of the year 1790. This seemed to be quite agreeable to him, and to be as short a term as would be insisted on by them. Proceeding to the sum to be demanded, we agreed that the principal, with the interest incurring before and after the war, should be paid; but as to that incurring during the war, we differed from him. He urged its justice with respect to themselves, who had laid out of the use of their money during that period. This was his only topic. We opposed to it all those which circumstances, both public and private, gave rise to. He appeared to feel their weight, but said the renunciation of this interest was a bitter pill, and such a one as the merchants here could not swallow. He wished, that no declaration should be made as to this article: but we observed, that if we entered into explanatory declarations of the points unfavorable to us, we should expect, as a consideration for this, corresponding declarations on the parts in our favor. In fact, we supposed his view was to leave this part of the interest to stand on the general expressions of the treaty, that they might avail themselves, in individual cases, of the favorable dispositions of debtors or of juries. We proceeded to the necessity of arrangements of our future commerce, were it only as a means of enabling our country to pay its debts. We suggested, that they had been contracted while certain modes of remittance had existed here, which had been an inducement to us to contract these debts. He said he was not authorized to speak on the subject of the future commerce. He appeared really and feelingly anxious, that arrangements should be stipulated as to the payment of the old debts, said he would proceed in that moment to Lord Caermarthen’s, and discuss the subject with him, and that we might expect to hear from him. He took leave, and we have never since heard from him or any other person on the subject. Congress will judge how far these conversations should influence their future proceedings, or those of the States.
I have the honor to be, with the highest respect and esteem, Sir, your most obedient, humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JAMES MADISON.
London, April 25, 1786.
Dear Sir,
Some of the objects of the joint commission, with which we were honored by Congress, called me to this place about six weeks ago. To-morrow I set out on my return to Paris. With this nation nothing is done; and it is now decided, that they intend to do nothing with us.
I wrote you, in a former letter, on the subject of a Mr. Paradise, who owns an estate in Virginia in right of his wife, and who has a considerable sum due to him in our loan office. Since I came here, I have had opportunities of knowing his extreme personal worth, and his losses by the late war. He is, from principle, a pure republican, while his father was as warm a tory. His attachment to the American cause, and his candid warmth, brought him sometimes into altercations on the subject with his father, and some persons interested in their variance, artfully brought up this subject of conversation whenever they met. It produced a neglect in the father. He had already settled on him a sum of money in the funds: but would do no more, and probably would have undone that, if he could. When remittances from Virginia were forbidden, the profits of the Virginia estate were carried into our loan office. Paradise was then obliged to begin to eat his capital in England: from that, to part with conveniences, and to run in debt. His situation is now distressing; and would be completely relieved, could he receive what is due to him from our State. He is coming over to settle there. His wife and family will follow him. I never ask unjust preferences for any body. But if, by any just means, he can be helped to his money, I own I should be much gratified. The goodness of his heart, his kindness to Americans before, during, and since the war, the purity of his political and moral character, interest me in the events impending over him, and which will infallibly be ruinous, if he fails to receive his money. I ask of you, on his behalf, that in pursuing the path of right, you will become active for him, instead of being merely quiescent, as you might be, were his merit and his misfortunes unknown to you.
I have put into the hands of Mr. Fulwar Skipwith for you, a packet containing some catalogues, which he will forward. I am, with very sincere esteem, Dear Sir,
your friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO THE COUNT DE VERGENNES.
Paris, May 3, 1786.
Sir,
After begging leave to present my respects to your Excellency, on my return to this place, I take the liberty of offering to your attention some papers, which I found on my arrival here, written by sundry merchants of L’Orient and others, some of whom are citizens of the United States, and all of them concerned in the trade between the two countries. This has been carried on by an exchange of the manufactures and produce of this country, for the produce of that, and principally for tobacco, which, though, on its arrival here, confined to a single purchaser, has been received equally from all sellers. In confidence of a continuance of this practice, the merchants of both countries were carrying on their commerce of exchange. A late contract by the Farm has, in a great measure, fixed in a single mercantile house the supplies of tobacco wanted for this country. This arrangement found the established merchants with some tobacco on hand, some on the seas coming to them, and more still due. By the papers now enclosed, it seems, that there are six thousand four hundred and eight hogsheads in the single port of L’Orient. Whether government may interfere, as to articles furnished by the merchants after they had notice of the contract before mentioned, must depend on principles of policy. But those of justice seem to urge, that, for commodities furnished before such notice, they should be so far protected, as that they may wind up, without loss, the transactions in which the new arrangement found them actually engaged. Your Excellency is the best judge, how far it may be consistent with the rules of government, to interfere for their relief, and with you, therefore, I beg leave entirely to rest their interests.
Information lately received, relative to the Barbary States, has suggested, that it might be expedient, and perhaps necessary for us, to pave the way to arrangements with them, by a previous application to the Ottoman Porte. Your Excellency’s intimate acquaintance with this subject would render your advice to us equally valuable and desirable. If you would be pleased to permit me to wait on you, any day or hour which shall be most convenient to yourself, I should be much gratified by a little conversation with you on this subject.
I have the honor to be, with great respect, your Excellency’s most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN PAGE.
Paris, May 4, 1786.
Dear Sir,
Your two favors of March the 15th and August the 23, 1785, by Monsieur de la Croix, came to hand on the 15th of November. His return gives me an opportunity of sending you a copy of the Nautical Almanacs for 1786, 7, 8, 9. There is no late and interesting publication here, or I would send it by the same conveyance. With these almanacs, I pack a copy of some Notes I wrote for Monsieur de Marbois, in the year 1781, of which I had a few printed here. They were written in haste, and for his private inspection. A few friends having asked copies, I found it cheaper to print than to write them. They will offer nothing new to you, not even as an oblation of my friendship for you, which is as old almost as we are ourselves. Mazzei brought me your favor of April the 27th. I thank you much for your communications. Nothing can be more grateful at such a distance. It is unfortunate, that most people think the occurrences passing daily under their eyes, are either known to all the world, or not worth being known. They therefore do not give them place in their letters. I hope you will be so good as to continue your friendly information. The proceedings of our public bodies, the progress of the public mind on interesting questions, the casualties which happen among our private friends, and whatever is interesting to yourself and family, will always be anxiously received by me. There is one circumstance in the work you were concerned in, which has not yet come to my knowledge; to wit, How far westward from Fort Pitt, does the western boundary of Pennsylvania pass, and where does it strike the Ohio? The proposition you mention from Mr. Anderson, on the purchase of tobacco, I would have made use of, but that I have engaged the abuses of the tobacco trade on a more general scale. I confess their redress is by no means certain; but till I see all hope of removing the evil by the roots desperate, I cannot propose to prune its branches.
I returned but three or four days ago, from a two months’ trip to England. I traversed that country much, and own, both town and country fell short of my expectations. Comparing it with this, I found a much greater proportion of barrens, a soil, in other parts, not naturally so good as this, not better cultivated, but better manured, and therefore more productive. This proceeds from the practice of long leases there, and short ones here. The laboring people here, are poorer than in England. They pay about one half their produce in rent; the English, in general, about a third. The gardening, in that country, is the article in which it surpasses all the earth. I mean their pleasure gardening. This, indeed, went far beyond my ideas. The city of London, though handsomer than Paris, is not so handsome as Philadelphia. Their architecture is in the most wretched style I ever saw, not meaning to except America, where it is bad, nor even Virginia, where it is worse than in any other part of America which I have seen. The mechanical arts in London are carried to a wonderful perfection. But of these I need not speak, because, of them my countrymen have unfortunately too many samples before their eyes. I consider the extravagance which has seized them, as a more baneful evil than toryism was during the war. It is the more so, as the example is set by the best and most amiable characters among us. Would a missionary appear, who would make frugality the basis of his religious system, and go through the land, preaching it up as the only road to salvation, I would join his school, though not generally disposed to seek my religion out of the dictates of my own reason, and feelings of my own heart. These things have been more deeply impressed on my mind, by what I have heard and seen in England. That nation hate us, their ministers hate us, and their King, more than all other men. They have the impudence to avow this, though they acknowledge our trade important to them. But they think, we cannot prevent our countrymen from bringing that into their laps. A conviction of this determines them to make no terms of commerce with us. They say, they will pocket our carrying trade as well as their own. Our overtures of commercial arrangements have been treated with a derision, which shows their firm persuasion, that we shall never unite to suppress their commerce, or even to impede it. I think their hostility towards us is much more deeply rooted at present, than during the war. In the arts, the most striking thing I saw there, new, was the application of the principle of the steam-engine to grist-mills. I saw eight pair of stones which are worked by steam, and there are to be set up thirty pair in the same house. A hundred bushels of coal, a day, are consumed at present. I do not know in what proportion the consumption will be increased by the additional gear.
Be so good as to present my respects to Mrs. Page and your family, to W. Lewis, F. Willis, and their families, and to accept yourself assurances of the sincere regard, with which I am, Dear Sir, your affectionate friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO WILLIAM CARMICHAEL.
Paris, May 5, 1786.
Dear Sir,
A visit of two months to England has been the cause of your not hearing from me during that period. Your letters of February the 3rd, to Mr. Adams and myself, and of February the 4th, to me, had come to hand before my departure. While I was in London, Mr. Adams received the letters giving information of Mr. Lambe’s arrival at Algiers. In London, we had conferences with a Tripoline ambassador, now at that court, named Abdrahaman. He asked us thirty thousand guineas for a peace with his court, and as much for Tunis, for which he said he could answer. What we were authorized to offer, being to this, but as a drop to a bucket, our conferences were repeated, only for the purpose of obtaining information. If the demands of Algiers and Morocco should be proportioned to this, according to their superior power, it is easy to foresee that the United States will not buy a peace with money. What principally led me to England was, the information that the Chevalier del Pinto, Portuguese minister at that court, had received full powers to treat with us. I accordingly went there, and, in the course of six weeks, we arranged a commercial treaty between our two countries. His powers were only to negotiate, not to sign. And as I could not wait, Mr. Adams and myself signed, and the Chevalier del Pinto expected daily the arrival of powers to do the same. The footing on which each has placed the other, is that of the most favored nation. We wished much to have had some privileges in their American possessions: but this was not to be effected. The right to import flour into Portugal, though not conceded by the treaty, we are not without hopes of obtaining.
My journey furnished us occasion to renew our overtures to the court of London; which it was the more important to do, as our powers to that court were to expire on the 12th of this month. These overtures were not attended to, and our commission expiring, we made our final report to Congress; and I suppose this the last offer of friendship, which will ever be made on our part. The treaty of peace being unexecuted on either part, in important points, each will now take their own measures for obtaining execution. I think the King, ministers, and nation are more bitterly hostile to us at present, than at any period of the late war. A like disposition on our part, has been rising for some time. In what events these things will end, we cannot foresee. Our countrymen are eager in their passions and enterprise, and not disposed to calculate their interests against these. Our enemies (for such they are, in fact) have for twelve years past, followed but one uniform rule, that of doing exactly the contrary of what reason points out. Having early, during our contest, observed this in the British conduct, I governed myself by it, in all prognostications of their measures; and I can say, with truth, it never failed me but in the circumstance of their making peace with us. I have no letters from America of later date than the new year. Mr. Adams had, to the beginning of February. I am in hopes our letters will give a new spur to the proposition, for investing Congress with the regulation of our commerce.
This will be handed you by a Baron Waltersdorf, a Danish gentleman, whom, if you did not already know, I should take the liberty of recommending to you. You were so kind as to write me, that you would forward me a particular map, which has not come to hand.
I beg you to be assured of the respect and esteem, with which I have the honor to be, Dear Sir,
your most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MR. DUMAS.
Paris, May 6, 1789.
Sir,
Having been absent in England, for some time past, your favors of February the 27th, March the 28th, and April the 11th, have not been acknowledged so soon as they should have been. I am obliged to you, for assisting to make me known to the Rhingrave de Salm and the Marquis de la Coste, whose reputations render an acquaintance with them desirable. I have not yet seen either: but expect that honor from the Rhingrave very soon. Your letters to Mr. Jay and Mr. Van Berkel, received in my absence, will be forwarded by a gentleman who leaves this place for New York, within a few days. I sent the treaty with Prussia by a gentleman who sailed from Havre, the 11th of November. The arrival of that vessel in America is not yet known here. Though the time is not long enough to produce despair, it is sufficiently so to give inquietude lest it should be lost. This would be a cause of much concern to me: I beg the favor of you to mention this circumstance to the Baron de Thulemeyer, as an apology for his not hearing from us. The last advices from America bring us nothing interesting. A principal object of my journey to London was, to enter into commercial arrangements with Portugal. This has been done almost in the precise terms of those of Prussia. The English are still our enemies. The spirit existing there, and rising in America, has a very lowering aspect. To what events it may give birth, I cannot foresee. We are young, and can survive them; but their rotten machine must crush under the trial. The animosities of sovereigns are temporary, and may be allayed: but those which seize the whole body of a people, and of a people, too, who dictate their own measures, produce calamities of long duration. I shall not wonder to see the scenes of ancient Rome and Carthage renewed in our day; and if not pursued to the same issue, it may be, because the republic of modern powers will not permit the extinction of any one of its members. Peace and friendship with all mankind is our wisest policy: and I wish we may be permitted to pursue it. But the temper and folly of our enemies may not leave this in our choice. I am happy in our prospect of friendship with the most estimable powers of Europe, and particularly with those of the confederacy, of which yours is. That your present crisis may have a happy issue, is the prayer and wish of him, who has the honor to be, with great respect and esteem, Sir, your most obedient humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO WILLIAM DRAYTON.
Paris, May 6, 1786.
Sir,
Your favor of November the 23rd came duly to hand. A call to England, soon after its receipt, has prevented my acknowledging it so soon as I should have done. I am very sensible of the honor done me by the South Carolina society for promoting and improving agriculture and other rural concerns, when they were pleased to elect me to be of their body: and I beg leave, through you, Sir, to convey to them my grateful thanks for this favor. They will find in me, indeed, but a very unprofitable servant. At present, particularly, my situation is unfavorable to the desire I feel, of promoting their views. However, I shall certainly avail myself of every occasion, which shall occur of doing so. Perhaps I may render some service, by forwarding to the society such new objects of culture, as may be likely to succeed in the soil and climate of South Carolina. In an infant country, as ours is, these experiments are important. We are probably far from possessing, as yet, all the articles of culture for which nature has fitted our country. To find out these, will require abundance of unsuccessful experiments. But if in a multitude of these, we make one useful acquisition, it repays our trouble. Perhaps it is the peculiar duty of associated bodies, to undertake these experiments. Under this sense of the views of the society, and with so little opportunity of being otherwise useful to them, I shall be attentive to procure for them the seeds of such plants, as they will be so good as to point out to me, or as shall occur to myself as worthy their notice. I send at present, by Mr. McQueen, some seeds of a grass, found very useful in the southern parts of Europe, and particularly, and almost solely, cultivated in Malta. It is called by the names of Sulla, and Spanish St. Foin, and is the Hedysarum coronarium of Linnaeus. It is usually sown early in autumn. I shall receive a supply of fresher seed this fall, which I will also do myself the honor of forwarding to you. I expect, in the same season, from the south of France, some acorns of the cork oak, which I propose for your society, as I am persuaded they will succeed with you. I observed it to grow in England, without shelter; not well indeed; but so as to give hopes that it would do well with you. I shall consider myself as always honored by the commands of the society, whenever they shall find it convenient to make use of me, and beg you to be assured, personally, of the sentiments of respect and esteem, with which I have the honor to be, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO W. T. FRANKLIN.
Paris, May 7, 1786.
Dear Sir,
On my return from a two months’ visit to England, I found here your favor of January the 18th. This contains the latest intelligence I have from America. Your effects not being then arrived, gives me anxiety for them, as I think they went in a vessel, which sailed from Havre the 11th of November. In this vessel, went also the two Mr. Fitzhughs of Virginia, with the Prussian treaty, our papers relative to the Barbary States, with the despatches for Congress, and letters which I had been writing to other persons in America for six weeks preceding their departure. I am obliged to you for the information as to Dr. Franklin’s health, in which I feel a great interest. I concur in opinion with you, that in the present factious division of your State, an angel from heaven could do no good. I have been sorry, therefore, from the beginning, to see such time as Dr. Franklin’s wasted on so hopeless a business. You have formed a just opinion of Monroe. He is a man whose soul might be turned wrong side outwards, without discovering a blemish to the world. I wish with all my heart, Congress may call you into the diplomatic line, as that seems to have attracted your own desires. It is not one in which you can do any thing more, than pass the present hour agreeably, without any prospect to future provision. Perhaps the arrangements with Portugal, by adding to the number of those appointments, may give Congress an opportunity of doing justice to your own, and to Dr. Franklin’s services. If my wishes could aid you, you have them sincerely. My late return to this place scarcely enables me to give you any of its news. I have not yet called on M. La Veillard, or seen any of your acquaintances. The marriage of the ambassador of Sweden with Miss Necker, you have heard of. Houdon is about taking a wife also. His bust of the General has arrived, and meets the approbation of those who know the original. Europe enjoys a perfect calm, at present. Perhaps it may be disturbed by the death of the King of Prussia, which is constantly expected. As yet, we have no information from the Barbary States, which may enable us to prognosticate the success of our endeavors to effect a peace in that quarter. Present me respectfully and affectionately to Dr. Franklin, and accept assurances of the esteem, with which I am, Dear Sir, your friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO ELBRIDGE GERRY.
Paris, May 7, 1786.
Dear Sir,
My last to you was of the 11th of October. Soon after that, your favor of the 12th of September came to hand. My acknowledgment of this is made later than it should have been, by my trip to England. Your long silence I ascribe to a more pleasing cause, that of devoting your spare time to one more capable of filling it with happiness, and to whom, as well as to yourself, I wish all those precious blessings which this change of condition is calculated to give you.
My public letters to Mr. Jay will have apprized you of my journey to England, and of its motives; and the joint letters of Mr. Adams and myself, of its effects. With respect to Portugal, it produced arrangements; with respect to England and Barbary, only information. I am quite at a loss what you will do with England. To leave her in possession of our posts, seems inadmissible; and yet to take them, brings on a state of things, for which we seem not to be in readiness. Perhaps a total suppression of her trade, or an exclusion of her vessels from the carriage of our produce, may have some effect; but I believe not very great. Their passions are too deeply and too universally engaged in opposition to us. The ministry have found means to persuade the nation, that they are richer than they were while we participated of their commercial privileges. We should try to turn our trade into other channels. I am in hopes this country will endeavor to give it more encouragement. But what will you do with the piratical States? Buy a peace at their enormous price; force one; or abandon the carriage into the Mediterranean to other powers? All these measures are disagreeable. The decision rests with you. The Emperor is now pressing a treaty with us. In a commercial view, I doubt whether it is desirable: but in a political one, I believe it is. He is now undoubtedly the second power in Europe, and on the death of the King of Prussia, he becomes the first character. An alliance with him will give us respectability in Europe, which we have occasion for. Besides, he will be at the head of the second grand confederacy of Europe, and may at any time serve us with the powers constituting that. I am pressed on so many hands to recommend Dumas to the patronage of Congress, that I cannot avoid it. Every body speaks well of him, and his zeal in our cause. Any thing done for him will gratify this court, and the patriotic party in Holland, as well as some distinguished individuals. I am induced, from my own feelings, to recommend Colonel Humphreys to your care. He is sensible, prudent, and honest, and may be very firmly relied on, in any office which requires these talents. I pray you to accept assurance of the sincere esteem and respect, with which I am,
Dear Sir, your most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JAMES ROSS.
Paris, May 8, 1786.
Dear Sir,
I have duly received your favor of October the 22nd, and am much gratified by the communications therein made. It has given me details, which do not enter into the views of my ordinary correspondents, and which are very entertaining. I experience great satisfaction at seeing my country proceed to facilitate the intercommunications of its several parts, by opening rivers, canals, and roads. How much more rational is this disposal of public money, than that of waging war.
Before the receipt of your letter, Morris’s contract for sixty thousand hogsheads of tobacco was concluded with the Farmers General. I have been for some time occupied in endeavoring to destroy the root of the evils, which the tobacco trade encounters in this country, by making the ministers sensible, that merchants will not bring a commodity to a market, where but one person is allowed to buy it; and that so long as that single purchaser is obliged to go to foreign markets for it, he must pay for it in coin, and not in commodities. These truths have made their way to the minds of the ministry, insomuch, as to have delayed the execution of the new lease of the Farms, six months. It is renewed, however, for three years, but so as not to render impossible a reformation of this great evil. They are sensible of the evil, but it is so interwoven with their fiscal system, that they find it hazardous to disentangle. The temporary distress, too, of the revenue, they are not prepared to meet. My hopes, therefore, are weak, though not quite desperate. When they become so, it will remain to look about for the best palliative this monopoly can bear. My present idea is, that it will be found in a prohibition to the Farmers General, to purchase tobacco any where but in France. You will perceive by this, that my object is to strengthen the connection between this country and my own in all useful points. I am of opinion, that twenty-three thousand hogsheads of tobacco, the annual consumption of this country, do not exceed the amount of those commodities, which it is more advantageous to us to buy here than in England, or elsewhere; and such a commerce would powerfully reinforce the motives for a friendship from this country towards ours. This friendship we ought to cultivate closely, considering the present dispositions of England towards us.
I am lately returned from a visit to that country. The spirit of hostility to us has always existed in the mind of the King, but it has now extended itself through the whole mass of the people, and the majority in the public councils. In a country, where the voice of the people influences so much the measures of administration, and where it coincides with the private temper of the King, there is no pronouncing on future events. It is true, they have nothing to gain, and much to lose, by a war with us. But interest is not the strongest passion in the human breast. There are difficult points, too, still unsettled between us. They have not withdrawn their armies out of our country, nor given satisfaction for the property they brought off. On our part, we have not paid our debts, and it will take time to pay them. In conferences with some distinguished mercantile characters, I found them sensible of the impossibility of our paying these debts at once, and that an endeavor to force universal and immediate payment, would render debts desperate, which are good in themselves. I think we should not have differed in the term necessary. We differed essentially in the article of interest. For while the principal, and interest preceding and subsequent to the war, seem justly due from us, that which accrued during the war does not. Interest is a compensation for the use of money. Their money, in our hands, was in the form of lands and negroes. Tobacco, the produce of these lands and negroes (or, as I may call it, the interest for them), being almost impossible of conveyance to the markets of consumption, because taken by themselves in its way there, sold during the war at five or six shillings the hundred. This did not pay taxes, and for tools, and other plantation charges. A man who should have attempted to remit to his creditor tobacco, for either principal or interest, must have remitted it three times before one cargo would have arrived safe: and this from the depredations of their own nation, and often of the creditor himself; for some of the merchants entered deeply into the privateering business. The individuals who did not, say they have lost this interest: the debtor replies, that he has not gained it, and that it is a case where, a loss having been incurred, every one tries to shift it from himself. The known bias of the human mind from motives of interest should lessen the confidence of each party in the justice of their reasoning: but it is difficult to say, which of them should make the sacrifice, both of reason and interest. Our conferences were intended as preparatory to some arrangement. It is uncertain how far we should have been able to accommodate our opinions. But the absolute aversion of the government to enter into any arrangement prevented the object from being pursued. Each country is left to do justice to itself and to the other, according to its own ideas as to what is past; and to scramble for the future as well as they can: to regulate their commerce by duties and prohibitions, and perhaps by cannons and mortars; in which event, we must abandon the ocean, where we are weak, leaving to neutral nations the carriage of our commodities; and measure with them on land, where they alone can lose. Farewell, then, all our useful improvements of canals and roads, reformations of laws, and other rational employments. I really doubt, whether there is temper enough, on either side, to prevent this issue of our present hatred. Europe is, at this moment, without the appearance of a cloud. The death of the King of Prussia, daily expected, may raise one. My paper admonishes me, that, after asking a continuance of your favors, it is time for me to conclude with assurances of the esteem with which I am,
Dear Sir, your friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO T. PLEASANTS.
Paris, May 8,1786.
Dear Sir,
At the time of the receipt of your favor of October the 24th, the contract between the Farmers General and Mr. Morris, for tobacco, was concluded, and in a course of execution. There was no room, therefore, to offer the proposals which accompanied your letter. I was, moreover, engaged in endeavors to have the monopoly, in the purchase of this article, in this country, suppressed. My hopes on that subject are not desperate, but neither are they flattering. I consider it as the most effectual means of procuring the full value of our produce, of diverting our demands for manufactures from Great Britain to this country, to a certain amount, and of thus producing some equilibrium in our commerce, which at present lies all in the British scale. It would cement an union with our friends, and lessen the torrent of wealth which we are pouring into the laps of our enemies. For my part, I think that the trade with Great Britain is a ruinous one to ourselves; and that nothing would be an inducement to tolerate it, but a free commerce with their West Indies: and that this being denied to us, we should put a stop to the losing branch. The question is, whether they are right in their prognostications, that we have neither resolution nor union enough for this. Every thing I hear from my own country, fills me with despair as to their recovery from their vassalage to Great Britain. Fashion and folly are plunging them deeper and deeper into distress: and the legislators of the country becoming debtors also, there seems no hope of applying the only possible remedy, that of an immediate judgment and execution. We should try, whether the prodigal might not be restrained from taking on credit the gewgaw held out to him in one hand, by seeing the keys of a prison in the other. Be pleased to present my respects to Mrs. Pleasants, and to be assured of the esteem with which I am,
Dear Sir, your friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO COLONEL MONROE.
Paris, May 10,1786.
Dear Sir,
My last to you was of January the 27th. Since that, I have received yours of January the 19th. Information from other quarters gives me reason to suspect you have in negotiation a very important change in your situation. You will carry into its execution all my wishes for your happiness. I hope it will not detach you from a settlement in your own country. I had even entertained hopes of your settling in my neighborhood: but these were determined by your desiring a plan of a house for Richmond. However reluctantly I relinquish this prospect, I shall not the less readily obey your commands, by sending you a plan. Having been much engaged since my return from England, in answering the letters and despatching other business which had accumulated during my absence, and being still much engaged, perhaps I may not be able to send the plan by this conveyance. If I do not send it now, I will surely by the next conveyance after this. Your Encyclopédie, containing eighteen livraisons, went off last night for Havre, from whence it will go in a vessel bound to New York. It will be under the care of M. la Croix, a passenger, who, if he does not find you in New York, will carry it to Virginia, and send it to Richmond. Another copy, in a separate box, goes for Currie. I pay here all charges to New York. What may occur afterwards, I desire him to ask either of you or Currie, as either will pay for the other; or to draw on me for them.
My letters to Mr. Jay will have informed you of the objects which carried me to England: and that the principal one, the treaty with Portugal, has been accomplished. Though we were unable to procure any special advantages in that, yet we thought it of consequence to insure our trade against those particular checks and discouragements, which it has heretofore met with there. The information as to the Barbary States, which we obtained from Abdrahaman the Tripoline ambassador, was also given to Mr. Jay. If it be right, and the scale of proportion between those nations, which we had settled, be also right, eight times the sum required by Tripoli will be necessary to accomplish a peace with the whole; that is to say, about two hundred and forty thousand guineas. The continuance of this peace will depend on their idea of our power to enforce it, and on the life of the particular Dey, or other head of the government, with whom it is contracted. Congress will, no doubt, weigh these circumstances against the expense and probable success of compelling a peace by arms. Count d’Estaing having communicated to me verbally some information as to an experiment formerly made by this country, I shall get him to put it into writing, and I will forward it to Congress, as it may aid them in their choice of measures. However, which plan is most eligible can only be known to yourselves, who are on the spot, and have under your view all the difficulties of both. There is a third measure, that of abandoning the Mediterranean carriage to other nations.
With respect to England, no arrangements can be taken. The merchants were certainly disposed to have consented to accommodation, as to the article of debts. I was not certain, when I left England, that they would relinquish the interest during the war. A letter received since, from the first character among the American merchants in Scotland, satisfies me they would have relinquished it, to insure the capital and residue of interest. Would to heaven, all the States, therefore, would settle a uniform plan. To open the courts to them, so that they might obtain judgments; to divide the executions into so many equal annual instalments, as that the last might be paid in the year 1790; to have the payments in actual money; and to include the capital, and interest preceding and subsequent to the war, would give satisfaction to the world, and to the merchants in general. Since it is left for each nation to pursue their own measures, in the execution of the late treaty, may not Congress, with propriety, recommend a mode of executing that article respecting the debts, and send it to each State to be passed into law? Whether England gives up the posts or not, these debts must be paid, or our character stained with infamy among all nations, and through all time. As to the satisfaction for slaves carried off, it is a bagatelle, which, if not made good before the last instalment becomes due, may be secured out of that.
I formerly communicated the overtures for a treaty, which had been made by the imperial ambassador. The instructions from Congress being in their favor, and Mr. Adams’s opinion also, I encouraged them. He expected his full powers when I went to England. Yet I did not think, nor did Mr. Adams, that this was of importance enough to weigh against the objects of that journey. He received them soon after my departure, and communicated it to me on my return, asking a copy of our propositions. I gave him one, but observed, our commission had then but a few days to run. He desired I should propose to Congress the giving new powers to go on with this, and said, that, in the mean time, he would arrange with us the plan. In a commercial view, no great good is to be gained by this. But in a political one, it may be expedient. As the treaty would, of course, be in the terms of those of Prussia and Portugal, it will give us but little additional embarrassment, in any commercial regulations we may wish to establish. The exceptions from these, which the other treaties will require, may take in the treaty with the Emperor. I should be glad to communicate some answer, as soon as Congress shall have made up their minds on it. My information to Congress, on the subject of our commercial articles with this country, has only come down to January the 27th. Whether I shall say any thing on it, in my letter to Mr. Jay by this conveyance, depends on its not being too early for an appointment I expect hourly from the Count de Vergennes, to meet him on this and other subjects. My last information was, that the lease was too far advanced to withdraw from it the article of tobacco, but that a clause is inserted in it, empowering the King to discontinue it at any time. A discontinuance is, therefore, the only remaining object, and as even this cannot be effected till the expiration of the old lease, which is about the end of the present year, I have wished only to stir the subject, from time to time, so as to keep it alive. This idea led me into a measure proposed by the Marquis de la Fayette, whose return from Berlin found the matter at that point, to which my former report to Congress had conducted it. I communicated to him what I had been engaged on, what were my prospects, and my purpose of keeping the subject just open. He offered his services with that zeal which commands them on every occasion respecting America. He suggested to me the meeting two or three gentlemen, well acquainted with this business. We met. They urged me to propose to the Count de Vergennes, the appointing a committee to take the matter into consideration. I told them, that decency would not permit me to point out to the Count de Vergennes the mode by which he should conduct a negotiation, but that I would press again the necessity of an arrangement, if, whilst that should be operating on his mind, they would suggest the appointment of a committee. The Marquis offered his services for this purpose. The consequence was the appointment of a committee, and the Marquis as a member of it. I communicated to him my papers. He collected other lights wherever he could, and particularly from the gentlemen with whom we had before concerted, and who had a good acquaintance with the subject. The Marquis became our champion in the committee, and two of its members, who were of the corps of Farmers General, entered the lists on the other side. Each gave in memorials. The lease, indeed, was signed while I was gone to England, but the discussions were, and still are continued in the committee: from which we derive two advantages; 1. that of showing, that the object is not to be relinquished; and 2. that of enlightening government, as to its true interest. The Count de Vergennes is absolutely for it; but it is not in his department. Calonne is his friend, and in this instance his principle seems to be, Amica veritas, sed magis amicus Plato. An additional hope is founded in the expectation of a change of the minister of finance. The present one is under the absolute control of the Farmers General. The committee’s views have been somewhat different from mine. They despair of a suppression of the Farm, and therefore wish to obtain palliatives, which would coincide with the particular good of this country. I think, that so long as the monopoly in the sale is kept up, it is of no consequence to us, how they modify the pill for their own internal relief: but, on the contrary, the worse it remains, the more necessary it will render a reformation. Any palliative would take from us all those arguments and friends, that would be satisfied with accommodation. The Marquis, though differing in opinion from me on this point, has, however, adhered to my principle of absolute liberty or nothing. In this condition is the matter at this moment. Whether I say any thing on the subject to Mr. Jay, will depend on my interview with the Count de Vergennes. I doubt whether that will furnish any thing worth communicating, and whether it will be in time. I therefore state thus much to you, that you may see the matter is not laid aside.
I must beg leave to recommend Colonel Humphreys to your acquaintance and good offices. He is an excellent man, an able one, and in need of some provision. Besides former applications to me in favor of Dumas, the Rhingrave of Salm (the effective minister of the government of Holland, while their two ambassadors here are ostensible), who is conducting secret arrangements for them with this court, presses his interests on us. It is evident the two governments make a point of it. You ask, why they do not provide for him themselves. I am not able to answer the question, but by a conjecture, that Dumas’s particular ambition prefers an appointment from us. I know all the difficulty of this application, which Congress has to encounter. I see the reasons against giving him the primary appointment at that court, and the difficulty of his accommodating himself to a subordinate one. Yet I think something must be done in it, to gratify this court, of which we must be always asking favors. In these countries, personal favors weigh more than public interest. The minister who has asked a gratification for Dumas, has embarked his own feelings and reputation in that demand. I do not think it was discreet, by any means. But this reflection might perhaps aggravate a disappointment. I know not really what you can do: but yet hope something will be done. Adieu, my Dear Sir, and believe me to be
yours affectionately,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN ADAMS.
Paris, May 11, 1786.
Dear Sir,
I do myself the honor of enclosing to you, letters which came to hand last night, from Mr. Lambe, Mr. Carmichael, and Mr. Barclay. By these you will perceive, that our peace is not to be purchased at Algiers but at a price far beyond our powers. What that would be, indeed, Mr. Lambe does not say, nor probably does he know. But as he knew our ultimatum, we are to suppose from his letter, that it would be a price infinitely beyond that. A reference to Congress hereon seems to be necessary. Till that can be obtained, Mr. Lambe must be idle at Algiers, Carthagena, or elsewhere. Would he not be better employed in going to Congress? They would be able to draw from him and Mr. Randall, the information necessary to determine what they will do. And if they determine to negotiate, they can re-appoint the same, or appoint a new negotiator, according to the opinion they shall form on their examination. I suggest this to you as my first thoughts; an ultimate opinion should not be formed till we see Mr. Randall, who may be shortly expected. In the mean time, should an opportunity occur, favor me with your ideas hereon that we may be maturing our opinions. I shall send copies of these three letters to Mr. Jay, by the packet which sails from L’Orient the first of the next month.
I have the honor to be, with great esteem, Dear Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson
TO LISTER ASQUITH.
Paris, May 22, 1786.
Sir,
When I left this place for England, I had no suspicion that any thing more would be necessary on my part for your liberation. Being but lately returned, I could not sooner acknowledge the receipt of your letters of April the 21st and May the 1st. I this day write to M. Desbordes, to pay the charges necessary for your enlargement, to furnish you with a guinea apiece, and to take your draft on Mr. Grand for those sums, and the others which he has furnished you at my request. This being a new case, I am unable to say whether you will be held to repay this money. Congress will decide on that, to whom I shall send a report of the case, and to whom you should apply on your return to America, to know whether you are to repay it or not. During the whole of this long transaction, I have never ceased soliciting your discharge. The evidence furnished by the Farmers to the ministers, impressed them with a belief that you were guilty. However, they obtained a remission of all which the King could remit, which was your condemnation to the galleys, and imprisonment, and the sum in which you were fined. The confiscation belonged to the Farmers, and the expenses of subsistence and of prosecution were theirs also, and so could not be remitted by the King. I wish you to be assured of my sensibility for your sufferings, and of my wishes to have obtained an earlier relief, had it been possible. I shall be glad if you can have an immediate and safe return to your own country, and there find your families well, and make those who may be authorized to decide on your case sensible, that these misfortunes have not been brought on you by any desire of yours, to infringe the laws of the country in which you have suffered. I enclose herewith your log-book and the other papers desired by you, and am, Sir,
your most obedient, humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN JAY.
Sir,
Paris, May 23, 1786.
Letters received both from Madrid and Algiers, while I was in London, having suggested that treaties with the States of Barbary would be much facilitated by a previous one with the Ottoman Porte, it was agreed between Mr. Adams and myself, that on my return, I should consult on this subject the Count de Vergennes, whose long residence at Constantinople rendered him the best judge of its expediency. Various circumstances have put it out of my power to consult him, till to-day. I stated to him the difficulties we were likely to meet with at Algiers; and asked his opinion, what would be the probable expense of a diplomatic mission to Constantinople, and what its effect at Algiers. He said that the expense would be very great, for that presents must be made at that court, and every one would be gaping after them: and that it would not procure us a peace at Algiers one penny the cheaper. He observed, that the Barbary States acknowledged a sort of vassalage to the Porte, and availed themselves of that relation, when any thing was to be gained by it; but that whenever it subjected them to a demand from the Porte, they totally disregarded it: that money was the sole agent at Algiers, except so far as fear could be induced also. He cited the present example of Spain, which, though having a treaty with the Porte would probably be obliged to buy a peace at Algiers, at the expense of upwards of six millions of livres. I told him, we had calculated from the demands and information of the Tripoline ambassador, at London, that to make peace with the four Barbary States would cost us between two and three hundred thousand guineas, if bought with money. The sum did not seem to exceed his expectations. I mentioned to him, that considering the uncertainty of a peace, when bought, perhaps Congress might think it more eligible to establish a cruise of frigates in the Mediterranean, and even to blockade Algiers. He supposed it would require ten vessels, great and small. I observed to him that Monsieur de Massiac had formerly done it with five: he said it was true, but that vessels of relief would be necessary. I hinted to him that I thought the English capable of administering aid to the Algerines. He seemed to think it impossible, on account of the scandal it would bring on. I asked him what had occasioned the blockade by Monsieur de Massiac: he said, an infraction of their treaty by the Algerines.
I had a good deal of conversation with him, also, on the situation of affairs between England and the United States: and particularly, on their refusal to deliver up our posts. I observed to him, that the obstructions thrown in the way of the recovery of their debts, were the effect, and not the cause, as they pretended, of their refusal to deliver up the posts; that the merchants interested in these debts, showed a great disposition to make arrangements with us; that the article of time we could certainly have settled, and probably that of the interest during the war: but that, the minister showing no disposition to have these matters arranged, I thought it a sufficient proof that this was not the true cause of their retaining the posts. He concurred as to the justice of our requiring time for the payment of our debts; said nothing which showed a difference of opinion as to the article of interest, and seemed to believe fully, that their object was to divert the channel of the fur-trade, before they delivered up the posts, and expressed a strong sense of the importance of that commerce to us. I told him I really could not foresee what would be the event of this detention; that the situation of the British funds, and the desire of their minister to begin to reduce the national debt, seemed to indicate that they could not wish a war. He thought so, but that neither were we in a condition to go to war. I told him, I was yet uninformed what Congress proposed to do on this subject, but that we should certainly always count on the good offices of France, and I was sure that the offer of them would suffice to induce Great Britain to do us justice. He said that surely we might always count on the friendship of France. I added, that by the treaty of alliance, she was bound to guaranty our limits to us, as they should be established at the moment of peace. He said they were so, ‘mais qu’il nous etoit nécessaire de les constater.’ I told him there was no question what our boundaries were; that the English themselves admitted they were clear beyond all question. I feared, however, to press this any further, lest a reciprocal question should be put to me, and therefore diverted the conversation to another object. This is a sketch only of a conference which was long. I have endeavored to give the substance, and sometimes the expressions, where they were material. I supposed it would be agreeable to Congress to have it communicated to them, in the present undecided state in which these subjects are. I should add, that an explanation of the transaction of Monsieur de Massiac with the Algerines, before hinted at, will be found in the enclosed letter from the Count d’Estaing to me, wherein he gives also his own opinion. The whole is submitted to Congress, as I conceive it my duty to furnish them with whatever information I can gather, which may throw any light on the subjects depending before them. I have the honor to be, with the most perfect esteem and respect, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MR. CARMICHAEL.
Paris, June 20, 1786.
Dear Sir,
My last to you was of the 5th of May, by Baron Waltersdorff. Since that I have been honored with yours of April the 13th, and May the 16th and 18th. The present covers letters to Mr. Lambe and Mr. Randall, informing them that the demands of Algiers for the ransom of our prisoners and also for peace, are so infinitely beyond our instructions, that we must refer the matter back to Congress, and therefore praying them to come on immediately. I will beg the favor of you to forward these letters. The whole of this business, therefore, is suspended till we receive further orders, except as to Mr. Barclay’s mission. Your bills have been received and honored. The first naming expressly a letter of advice, and none coming, it was refused till the receipt of your letter to me, in which you mentioned that you had drawn two bills. I immediately informed Mr. Grand, who thereupon honored the bill.
I have received no public letters of late date. Through other channels, I have collected some articles of information, which may be acceptable to you.
In a letter of March the 20th, from Dr. Franklin to me, is this passage. ‘As to public affairs, the Congress has not been able to assemble more than seven or eight States during the whole winter, so the treaty with Prussia remains still unratified, though there is no doubt of its being done soon, as a full Congress is expected next month. The disposition to furnish Congress with ample powers augments daily, as people become more enlightened. And I do not remember ever to have seen, during my long life, more signs of public felicity than appear at present, throughout these States; the cultivators of the earth, who make the bulk of our nation, have made good crops, which are paid for at high prices, with ready money; the artisans, too, receive high wages; and the value of all real estates is augmented greatly. Merchants and shopkeepers, indeed, complain that there is not business enough. But this is evidently not owing to the fewness of buyers, but to the too great number of sellers; for the consumption of goods was never greater, as appears by the dress, furniture, and manner of living, of all ranks of the people.’ His health is good, except as to the stone, which does not grow worse. I thank you for your attention to my request about the books, which Mr. Barclay writes me he has forwarded from Cadiz.
I have the honor to be with great respect, Dear Sir, your most obedient, humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MR. LAMBE.
Sir,
Paris, June 20,1786.
Having communicated to Mr. Adams the information received, at different times, from yourself, from Mr. Randall, and Mr. Carmichael, we find that the sum likely to be demanded by Algiers for the ransom of our prisoners, as well as for peace, is so infinitely beyond our powers, and the expectations of Congress, that it has become our duty to refer the whole matter back to them. Whether they will choose to buy a peace, to force one, or to do nothing, will rest in their pleasure. But that they may have all the information possible to guide them in their deliberations, we think it important that you should return to them. No time will be lost by this, and perhaps time maybe gained. It is, therefore, our joint desire, that you repair immediately to New York, for the purpose of giving to Congress all the information on this subject, which your journey has enabled you to acquire. You will consider this request as coming from Mr. Adams as well as myself, as it is by express authority from him, that I join him in it. I am of opinion, it will be better for you to come to Marseilles and by Paris: because there is a possibility that fresh orders to us, from Congress, might render it useful that we, also, should have received from you all possible information on this subject. And perhaps no time may be lost by this, as it might be long before you would set a passage from Alicant to America.
I am, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MONSIEUR DE REYNEVAL.
Paris, June 25, 1786.
Sir,
I have received letters from two citizens of the United States, of the names of Geary and Arnold, informing me, that having for some time past exercised commerce in London, and having failed, they were obliged to leave that country; that they came over to Dunkirk, and from thence to Brest, where, one of them having changed his name, the more effectually to elude the search of his creditors, they were both imprisoned by order of the commandant; whether at the suit of their creditors, or because one of them changed his name, they are uninformed. But they are told, that the commandant has sent information of his proceedings to your office. I have some reason to suppose, their creditors are endeavoring to obtain leave to remove them to England, where their imprisonment would be perpetual. Unable to procure information elsewhere, I take the liberty of asking you, whether you know the cause of their imprisonment, and of soliciting your attention to them, so far as that nothing may take place against them by surprise, and out of the ordinary course of the law.
I have the honor to be, with sentiments of the most perfect esteem and respect, Sir, your most obedient and most humble; servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO THE PREVOT DES MARCHANDS ET ECHEVINS DE PARIS.
Paris, September 27, 1786.
Gentlemen,
The commonwealth of Virginia, in gratitude for the services of Major General the Marquis de la Fayette, have determined to erect his bust in their Capital. Desirous to place a like monument of his worth, and of their sense of it, in the country to which they are indebted for his birth, they have hoped that the city of Paris will consent to become the depository of this second testimony of their gratitude. Being charged by them with the execution of their wishes, I have the honor to solicit of Messieurs le Prevot des Marchands et Echevins, on behalf of the city, their acceptance of a bust of this gallant officer, and that they will be pleased to place it where, doing most honor to him, it will most gratify the feelings of an allied nation.
It is with true pleasure that I obey the call of that commonwealth, to render just homage to a character so great in its first developements, that they would honor the close of any other. Their country covered by a small army against a great one, their exhausted means supplied by his talents, their enemies finally forced to that spot whither their allies and confederates were collecting to receive them, and a war which had spread its miseries into the four quarters of the earth thus reduced to a single point, where one blow should terminate it, and through the whole, an implicit respect paid to the laws of the land; these are facts which would illustrate any character, and which fully justify the warmth of those feelings, of which I have the honor, on this occasion, to be the organ.
It would have been more pleasing to me to have executed this office in person, to have mingled the tribute of private gratitude with that of my country, and, at the same time, to have had an opportunity of presenting to your honorable body, the homage of that profound respect which I have the honor to bear them. But I am withheld from these grateful duties, by the consequences of a fall, which confine me to my room. Mr. Short, therefore, a citizen of the State of Virginia, and heretofore a member of its Council of State, will have the honor of delivering you this letter, together with the resolution of the General Assembly of Virginia. He will have that, also, of presenting the bust at such time and place, as you will be so good as to signify your pleasure to receive it. Through him, I beg to be allowed the honor of presenting those sentiments of profound respect and veneration, with which I am, Gentlemen, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO COLONEL MONROE.
Paris, July 9, 1786.
Dear Sir,
I wrote you last on the 10th of May; since which your favor of May the 11th has come to hand. The political world enjoys great quiet here. The King of Prussia is still living, but like the snuff of a candle, which sometimes seems out, and then blazes up again. Some think that his death will not produce any immediate effect in Europe. His kingdom like a machine, will go on for some time with the winding up he has given it. The King’s visit to Cherbourg has made a great sensation in England and here. It proves to the world, that it is a serious object to this country, and that the King commits himself for the accomplishment of it. Indeed, so many cones have been sunk, that no doubt remains of the practicability of it. It will contain, as is said, eighty ships of the line, be one of the best harbors in the world, and by means of two entrances, on different sides, will admit vessels to come in and go out with every wind. The effect of this, in another war with England, defies calculation. Having no news to communicate, I will recur to the subjects of your letter of May the 11th.
With respect to the new States, were the question to stand simply in this form, How may the ultramontane territory be disposed of, so as to produce the greatest and most immediate benefit to the inhabitants of the maritime States of the Union? the plan would be more plausible, of laying it off into two or three States only. Even on this view, however, there would still be something to be said against it, which might render it at least doubtful. But that is a question, which good faith forbids us to receive into discussion. This requires us to state the question in its just form, How may the territories of the Union be disposed of, so as to produce the greatest degree of happiness to their inhabitants? With respect to the maritime States, little or nothing remains to be done. With respect, then, to the ultramontane States, will their inhabitants be happiest, divided into States of thirty thousand square miles, not quite as large as Pennsylvania, or into States of one hundred and sixty thousand square miles each, that is to say, three times as large as Virginia within the Allegany? They will not only be happier in States of moderate size, but it is the only way in which they can exist as a regular society. Considering the American character in general, that of those people particularly, and the energetic nature of our governments, a State of such extent as one hundred and sixty thousand square miles, would soon crumble into little ones. These are the circumstances, which reduce the Indians to such small societies. They would produce an effect on our people, similar to this. They would not be broken into such small pieces, because they are more habituated to subordination, and value more a government of regular law. But you would surely reverse the nature of things, in making small States on the ocean, and large ones beyond the mountains. If we could, in our consciences, say, that great States beyond the mountains will make the people happiest, we must still ask, whether they will be contented to be laid off into large States. They certainly will not: and if they decide to divide themselves, we are not able to restrain them. They will end by separating from our confederacy, and becoming its enemies. We had better then look forward, and see what will be the probable course of things. This will surely be a division of that country into States, of a small, or, at most, of a moderate size. If we lay them off into such, they will acquiesce; and we shall have the advantage of arranging them, so as to produce the best combinations of interest. What Congress have already done in this matter, is an argument the more, in favor of the revolt of those States against a different arrangement, and of their acquiescence under a continuance of that. Upon this plan, we treat them as fellow-citizens; they will have a just share in their own government; they will love us, and pride themselves in an union with us. Upon the other, we treat them as subjects; we govern them, and not they themselves; they will abhor us as masters, and break off from us in defiance. I confess to you, that I can see no other turn that these two plans would take. But I respect your opinion, and your knowledge of the country, too much, to be over-confident in my own.
I thank you sincerely for your communication, that my not having sooner given notice of the Arrêts relative to fish, gave discontent to some persons. These are the most friendly offices you can do me, because they enable me to justify myself, if I am right, or correct myself, if wrong. If those who thought I might have been remiss, would have written to me on the subject, I should have admired them for their candor, and thanked them for it: for I have no jealousies nor resentments at things of this kind, where I have no reason to believe they have been excited by a hostile spirit; and I suspect no such spirit in a single member of Congress. You know there were two Arrêts; the first of August the 30th, 1784, the second of the 18th and 25th of September, 1785. As to the first, it would be a sufficient justification of myself, to say, that it was in the time of my predecessor, nine months before I came into office, and that there was no more reason for my giving information of it, when I did come into office, than of all the other transactions, which preceded that period. But this would seem to lay a blame on Dr. Franklin for not communicating it, which I am confident he did not deserve. This government affects a secrecy in all its transactions whatsoever, though they be of a nature not to admit a perfect secrecy. Their Arrêts respecting the islands go to those islands, and are unpublished and unknown in France, except in the bureau where they are formed. That of August, 1784, would probably be communicated to the merchants of the seaport towns also. But Paris having no commercial connections with them, if any thing makes its way from a seaport town to Paris, it must be by accident. We have, indeed, agents in these seaports; but they value their offices so little, that they do not trouble themselves to inform us of what is passing there. As a proof that these things do not transpire here, nor are easily got at, recollect that Mr. Adams, Dr. Franklin, and myself were all here on the spot together, from August, 1784, to June, 1785, that is to say, ten months, and yet not one of us knew of the Arrêt of August, 1784. September the 18th and 25th, 1785, the second was passed. And here alone I became responsible. I think it was about six weeks before I got notice of it, that is, in November. On the 20th of that month, writing to Count de Vergennes on another subject, I took occasion to remonstrate to him on that. But from early in November, when the Fitzhughs went to America. I had never a confidential opportunity of writing to Mr. Jay from hence, directly, for several months. In a letter of December the 14th, to Mr. Jay, I mentioned to him the want of an opportunity to write to him confidentially, which obliged me at that moment to write by post via London, and on such things only, as both post-offices were welcome to see. On the 2nd of January, Mr. Bingham setting out for London, I wrote to Mr. Jay, sending him a copy of my letter to Count de Vergennes, and stating something, which had passed in conversation on the same subject. I prayed Mr. Bingham to take charge of the letter, and either to send it by a safe hand, or carry it himself, as circumstances should render most advisable. I believe he kept it, to carry himself. He did not sail from London till about the 12th of March, nor arrive in America till the middle of May. Thus you see, that causes had prevented a letter, which I had written on the 20th of November, from getting to America till the month of May. No wonder, then, if notice of this Arrêt came first to you by the way of the West Indies: and, in general, I am confident, that you will receive notice of the regulations of this country, respecting their islands, by the way of those islands, before you will from hence. Nor can this be remedied, but by a system of bribery, which would end in the corruption of your own ministers, and produce no good adequate to the expense. Be so good as to communicate these circumstances to the persons who you think may have supposed me guilty of remissness on this occasion.
I will turn to a subject more pleasing to both, and give you my sincere congratulations on your marriage. Your own dispositions, and the inherent comforts of that state, will insure you a great addition of happiness. Long may you live to enjoy it, and enjoy it in full measure. The interest I feel in every one connected with you, will justify my presenting my earliest respects to the lady, and of tendering her the homage of my friendship. I shall be happy at all times to be useful to either of you, and to receive your commands. I enclose you the bill of lading of your Encyclopédie. With respect to the remittance for it, of which you make mention, I beg you not to think of it. I know, by experience, that on proceeding to make a settlement in life, a man has need of all his resources; and I should be unhappy, were you to lessen them by an attention to this trifle. Let it lie till you have nothing else to do with your money. Adieu, my Dear Sir, and be assured of the esteem with which I am your friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN ADAMS.
Paris, July 11, 1786.
Dear Sir,
Our instructions relative to the Barbary States having required us to proceed by way of negotiation to obtain their peace, it became our duty to do this to the best of our power. Whatever might be our private opinions, they were to be suppressed, and the line marked out to us was to be followed. It has been so, honestly and zealously. It was, therefore, never material for us to consult together on the best plan of conduct towards these States. I acknowledge I very, early thought it would be best to effect a peace through the medium of war. Though it is a question with which we have nothing to do, yet as you propose some discussion of it, I shall trouble you with my reasons. Of the four positions laid down in your letter of the 3rd instant, I agree to the three first, which are, in substance, that the good offices of our friends cannot procure us a peace, without paying its price, that they cannot materially lessen that price; and that paying it, we can have the peace in spite of the intrigues of our enemies. As to the fourth, that the longer the negotiation is delayed, the larger will be the demand; this will depend on the intermediate captures: if they are many and rich, the price may be raised; if few and poor, it will be lessened. However, if it is decided, that we shall buy a peace, I know no reason for delaying the operation, but should rather think it ought to be hastened: but I should prefer the obtaining it by war.
1. Justice is in favor of this opinion. 2. Honor favors it. 3. It will procure us respect in Europe; and respect is a safeguard to interest. 4. It will arm the federal head with the safest of all the instruments of coercion over its delinquent members, and prevent it from using what would be less safe. I think, that so far you go with me. But in the next steps we shall differ. 5. I think it least expensive. 6. Equally effectual. I ask a fleet of one hundred and fifty guns, the one half of which shall be in constant cruise. This fleet, built, manned, and victualled for six months, will cost four hundred and fifty thousand pounds sterling. Its annual expense will be three hundred pounds sterling a gun, including every thing: this will be forty-five thousand pounds sterling a year. I take British experience for the basis of my calculation: though we know, from our own experience, that we can do in this way for pounds lawful, what costs them pounds sterling. Were we to charge all this to the Algerine war, it would amount to little more than we must pay if we buy peace. But as it is proper and necessary, that we should establish a small marine force (even were we to buy a peace from the Algerines), and as that force, laid up in our dock-yard, would cost us half as much annually as if kept in order for service, we have a right to say, that only twenty-two thousand and five hundred pounds sterling, per annum, should be charged to the Algerine war. 6. It will be as effectual. To all the mismanagements of Spain and Portugal, urged to show that war against those people is ineffectual, I urge a single fact to prove the contrary, where there is any management. About forty years ago, the Algerines having broke their treaty with France, this court sent Monsieur de Massiac, with one large and two small frigates: he blockaded the harbor of Algiers three months, and they subscribed to the terms he proposed. If it be admitted, however, that war, on the fairest prospects, is still exposed to uncertainties, I weigh against this the greater uncertainty of the duration of a peace bought with money, from such a people, from a Dey eighty years old, and by a nation who, on the hypothesis of buying peace, is to have no power on the sea to enforce an observance of it.
So far I have gone on the supposition, that the whole weight of this war would rest on us. But, 1. Naples will join us. The character of their naval minister (Acton), his known sentiments with respect to the peace Spain is officiously trying to make for them, and his dispositions against the Algerines, give the best grounds to believe it. 2. Every principle of reason assures,us, that Portugal will join us. I state this as taking for granted, what all seem to believe, that they will not be at peace with Algiers. I suppose, then, that a convention might be formed between Portugal, Naples, and the United States, by which the burthen of the war might be quotaed on them, according to their respective wealth; and the term of it should be, when Algiers should subscribe to a peace with all three on equal terms. This might be left open for other nations to accede to, and many, if not most of the powers of Europe (except France, England, Holland, and Spain, if her peace be made), would sooner or later enter into the confederacy, for the sake of having their peace with the piratical States guarantied by the whole. I suppose, that, in this case, our proportion of force would not be the half of what I first calculated on.
These are the reasons, which have influenced my judgment on this question. I give them to you, to show you that I am imposed on by a semblance of reason at least; and not with an expectation of their changing your opinion. You have viewed the subject, I am sure, in all its bearings. You have weighed both questions, with all their circumstances. You make the result different from what I do. The same facts impress us differently. This is enough to make me suspect an error in my process of reasoning, though I am not able to detect it. It is of no consequence; as I have nothing to say in the decision, and am ready to proceed heartily on any other plan, which may be adopted, if my agency should be thought useful. With respect to the dispositions of the States, I am utterly uninformed. I cannot help thinking, however, that on a view of all the circumstances, they might be united in either of the plans.
Having written this on the receipt of your letter, without knowing of any opportunity of sending it, I know not when it will go: I add nothing, therefore, on any other subject, but assurances of the sincere esteem and respect, with which I am,
Dear Sir, your friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN JAY.
Paris, August 11, 1786.
Sir,
Since the date of my last, which was of July the 8th, I have been honored with the receipt of yours of June the 16th. I am to thank you, on the part of the minister of Geneva, for the intelligence it contained on the subject of Gallatin, whose relations will be relieved by the receipt of it.
The enclosed intelligence, relative to the instructions of the court of London to Sir Guy Carleton, came to me through the Count de la Touche and Marquis de la Fayette. De la Touche is a director under the Marechal de Castries, minister for the marine department, and possibly receives his intelligence from him, and he from their ambassador at London. Possibly, too, it might be fabricated here. Yet weighing the characters of the ministry of St. James’s and Versailles, I think the former more capable of giving such instructions, than the latter of fabricating them for the small purposes the fabrication could answer.
The Gazette of France, of July the 28th, announces the arrival of Peyrouse at Brazil, that he was to touch at Otaheite, and proceed to California, and still further northwardly. This paper, as you well know, gives out such facts as the court are willing the world should be possessed of. The presumption is, therefore, that they will make an establishment of some sort on the northwest coast of America.
I trouble you with the copy of a letter from Schweighauser and Dobree, on a subject with which I am quite unacquainted. Their letter to Congress of November the 30th, 1780, gives their state of the matter. How far it be true and just, can probably be ascertained from Dr. Franklin, Dr. Lee, and other gentlemen now in America. I shall be glad to be honored with the commands of Congress on this subject. I have inquired into the state of the arms, mentioned in their letter to me. The principal articles were about thirty thousand bayonets, fifty thousand gunlocks, thirty cases of arms, twenty-two cases of sabres, and some other things of little consequence. The quay at Nantes having been overflowed by the river Loire, the greatest part of these arms was under water, and they are now, as I am informed, a solid mass of rust, not worth the expense of throwing them out of the warehouse, much less that of storage. Were not their want of value a sufficient reason against reclaiming the property of these arms, it rests with Congress to decide, whether other reasons are not opposed to this reclamation. They were the property of a sovereign body, they were seized by an individual, taken cognizance of by a court of justice, and refused, or at least not restored by the sovereign, within whose State they had been arrested. These are circumstances which have been mentioned to me. Doctor Franklin, however, will be able to inform Congress, with precision, as to what passed on this subject. If the information I have received be any thing like the truth, the discussion of this matter can only be with the court of Versailles. It would be very delicate, and could have but one of two objects; either to recover the arms, which are not worth receiving, or to satisfy us on the point of honor. Congress will judge how far the latter may be worth pursuing against a particular ally, and under actual circumstances. An instance, too, of acquiescence on our part under a wrong, rather than disturb our friendship by altercations, may have its value in some future case. However, I shall be ready to do in this what Congress shall be pleased to direct.
I enclose the despatches relative to the Barbary negotiation, received since my last. It is painful to me to overwhelm Congress and yourself continually with these voluminous papers. But I have no right to suppress any part of them, and it is one of those cases, where, from a want of well digested information, we must be contented to examine a great deal of rubbish, in order to find a little good matter.
The gazettes of Leyden and France, to the present date, accompany this, which, for want of direct and safe opportunities, I am obliged to send by an American gentleman, by the way of London. The irregularity of the French packets has diverted elsewhere the tide of passengers who used to furnish me occasions of writing to you, without permitting my letters to go through the post-office. So that when the packets go now, I can seldom write by them.
I have the honor to be, with sentiments of the highest esteem and respect, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
[The annexed is a translation of the paper referred to in
the preceding letter, on the subject of the instructions
given to Sir Guy Carleton.]
An extract of English political news, concerning North America, July 14th, 1786.
General Carleton departs in a few days with M. de la Naudiere, a Canadian gentleman. He has made me acquainted with the Indian Colonel Joseph Brandt. It is certain that he departs with the most positive instructions to distress the Americans as much as possible, and to create them enemies on all sides.
Colonel Brandt goes loaded with presents for himself, and for several chiefs of the tribes bordering on Canada. It would be well for the Americans to know in time, that enemies are raised against them, in order to derange their system of government, and to add to the confusion which already exists in it. The new possessions of England will not only gain what America shall lose, but will acquire strength in proportion to the weakening of the United States.
Sooner or later, the new States which are forming will place themselves under the protection of England, which can always communicate with them through Canada; and which, in case of future necessity, can harass the United States on one side, by her shipping, and on the other, by her intrigues. This system has not yet come to maturity, but it is unfolded, and we may rely upon the instructions given to Colonel Brandt.
TO COLONEL MONROE.
Paris, August 11, 1786.
Dear Sir,
I wrote you last on the 9th of July; and since that, have received yours of the 16th of June, with the interesting intelligence it contained. I was entirely in the dark as to the progress of that negotiation, and concur entirely in the views you have taken of it The difficulty on which it hangs, is a sine qua non with us. It would be to deceive them and ourselves, to suppose that an amity can be preserved, while this right is withheld. Such a supposition would argue, not only an ignorance of the people to whom this is most interesting, but an ignorance of the nature of man, or an inattention to it. Those who see but halfway into our true interest, will think that that concurs with the views of the other party. But those who see it in all its extent, will be sensible that our true interest will be best promoted, by making all the just claims of our fellow-citizens, wherever situated, our own, by urging and enforcing them with the weight of our whole influence, and by exercising in this, as in every other instance, a just government in their concerns, and making common cause, even where our separate interest would seem opposed to theirs. No other conduct can attach us together; and on this attachment depends our happiness.
The King of Prussia still lives, and is even said to be better. Europe is very quiet at present. The only germ of dissension which shows itself at present, is in the quarter of Turkey. The Emperor, the Empress, and the Venetians seem all to be picking at the Turks. It is not probable, however, that either of the two first will do any thing to bring on an open rupture, while the King of Prussia lives.
You will perceive by the letters I enclose to Mr. Jay, that Lambe, under the pretext of ill health, declines returning either to Congress, Mr. Adams, or myself. This circumstance makes me fear some malversation. The money appropriated to this object being in Holland, and having been always under the care of Mr. Adams, it was concerted between us that all the drafts should be on him. I know not, therefore, what sums may have been advanced to Lambe; I hope, however, nothing great. I am persuaded that an angel sent on this business, and so much limited in his terms, could have done nothing. But should Congress propose to try the line of negotiation again, I think they will perceive that Lambe is not a proper agent. I have written to Mr. Adams on the subject of a settlement with Lambe. There is little prospect of accommodation between the Algerines, and the Portuguese and Neapolitans. A very valuable capture too, lately made by them on the Empress of Russia, bids fair to draw her on them. The probability is therefore, that these three nations will be at war with them, and the possibility is that could we furnish a couple of frigates, a convention might be formed with those powers, establishing a perpetual cruise on the coast of Algiers, which would bring them to reason. Such a convention being left open to all powers willing to come into it, should have for its object a general peace, to be guarantied to each, by the whole. Were only two or three to begin a confederacy of this kind, I think every power in Europe would soon fall into it, except France, England, and perhaps Spain and Holland. Of these there is only England who would give any real aid to the Algerines. Morocco, you perceive, will be at peace with us. Were the honor and advantage of establishing such a confederacy out of the question, yet the necessity that the United States should have some marine force, and the happiness of this, as the ostensible cause for beginning it, would decide on its propriety. It will be said, there is no money in the treasury. There never will be money in the treasury till the confederacy shows its teeth. The States must see the rod; perhaps it must be felt by some one of them. I am persuaded, all of them would rejoice to see every one obliged to furnish its contributions. It is not the difficulty of furnishing them, which beggars the treasury, but the fear that others will not furnish as much. Every rational citizen must wish to see an effective instrument of coercion, and should fear to see it on any other element than the water. A naval force can never endanger our liberties, nor occasion bloodshed: a land force would do both. It is not in the choice of the States, whether they will pay money to cover their trade against the Algerines. If they obtain a peace by negotiation, they must pay a great sum of money for it; if they do nothing, they must pay a great sum of money, in the form of insurance; and in either way, as great a one as in the way of force, and probably less effectual.
I look forward with anxiety to the approaching moment of your departure from Congress. Besides the interest of the confederacy and of the State, I have a personal interest in it. I know not to whom I may venture confidential communications, after you are gone. I take the liberty of placing here my respects to Mrs. Monroe, and assurances of the sincere esteem with which I am, Dear Sir, your friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MR. WYTHE.
Paris, August 13,1786.
Dear Sir
Your favors of January the 10th and February the 10th, came to hand on the 20th and 23rd of May. I availed myself of the first opportunity which occurred, by a gentleman going to England, of sending to Mr. Joddrel a copy of the Notes on our country! with a line informing him, that it was you who had emboldened me to take that liberty. Madison, no doubt, informed you of the reason why I had sent only a single copy to Virginia. Being assured by him, that they will not do the harm I had apprehended, but on the contrary may do some good, I propose to send thither the copies remaining on hand, which are fewer than I had intended. But of the numerous corrections they need, there are one or two so essential, that I must have them made, by printing a few new leaves, and substituting them for the old. This will be done while they are engraving a map which I have constructed, of the country from Albemarle sound to Lake Erie, and which will be inserted in the book. A bad French translation which is getting out here, will probably oblige me to publish the original more freely; which it did not deserve, nor did I intend. Your wishes, which are laws to me, will justify my destining a copy for you, otherwise, I should as soon have thought of sending you a horn-book; for there is no truth in it which is not familiar to you, and its errors I should hardly have proposed to treat you with.
Immediately on the receipt of your letter, I wrote to a correspondent at Florence to inquire after the family of Tagliaferro, as you desired. I received his answer two days ago, a copy of which I now enclose. The original shall be sent by some other occasion. I will have the copper-plate immediately engraved. This may be ready within a few days, but the probability is, that I shall be long getting an opportunity of sending it to you, as these rarely occur. You do not mention the size of the plate, but presuming it is intended for labels for the inside of books, I shall have it made of a proper size for that. I shall omit the word agisos, according to the license you allow me, because I think the beauty of a motto is to condense much matter in as few words as possible. The word omitted will be supplied by every reader.
The European papers have announced, that the Assembly of Virginia were occupied on the revisal of their code of laws. This, with some other similar intelligence, has contributed much to convince the people of Europe, that what the English papers are constantly publishing of our anarchy, is false; as they are sensible that such a work is that of a people only, who are in perfect tranquillity. Our act for freedom of religion is extremely applauded. The ambassadors and ministers of the several nations of Europe, resident at this court, have asked of me copies of it, to send to their sovereigns, and it is inserted at full length in several books now in the press; among others, in the new Encyclopédie. I think it will produce considerable good even in these countries, where ignorance, superstition, poverty, and oppression of body and mind, in every form, are so firmly settled on the mass of the people, that their redemption from them can never be hoped. If all the sovereigns of Europe were to set themselves to work, to emancipate the minds of their subjects from their present ignorance and prejudices, and that, as zealously as they now endeavor the contrary, a thousand years would not place them on that high ground, on which our common people are now setting out. Ours could not have been so fairly placed under the control of the common sense of the people, had they not been separated from their parent stock, and kept from contamination, either from them, or the other people of the old world, by the intervention of so wide an ocean. To know the worth of this, one must see the want of it here. I think by far the most important bill in our whole code, is that for the diffusion of knowledge among the people. No other sure foundation can be devised for the preservation of freedom and happiness. If any body thinks, that kings, nobles, or priests are good conservators of the public happiness, send him here. It is the best school in the universe to cure him of that folly. He will see here, with his own eyes, that these descriptions of men are an abandoned confederacy against the happiness of the mass of the people. The omnipotence of their effect cannot be better proved, than in this country particularly, where, notwithstanding the finest soil upon earth, the finest climate under heaven, and a people of the most benevolent, the most gay and amiable character of which the human form is susceptible; where such a people, I say, surrounded by so many blessings from nature, are loaded with misery by kings, nobles, and priests, and by them alone. Preach, my dear Sir, a crusade against ignorance; establish and improve the law for educating the common people. Let our countrymen know, that the people alone can protect us against these evils, and that the tax which will be paid for this purpose, is not more than the thousandth part of what will be paid to kings, priests, and nobles, who will rise up among us if we leave the people in ignorance. The people of England, I think, are less oppressed than here. But it needs but half an eye to see, when among them, that the foundation is laid in their dispositions for the establishment of a despotism. Nobility, wealth, and pomp are the objects of their admiration. They are by no means the free-minded people, we suppose them in America. Their learned men, too, are few in number, and are less learned, and infinitely less emancipated from prejudice, than those of this country. An event, too, seems to be preparing, in the order of things, which will probably decide the fate of that country. It is no longer doubtful, that the harbor of Cherbourg will be complete, that it will be a most excellent one, and capacious enough to hold the whole navy of France. Nothing has ever been wanting to enable this country to invade that, but a naval force conveniently stationed to protect the transports. This change of situation must oblige the English to keep up a great standing army, and there is no King, who, with sufficient force, is not always ready to make himself absolute. My paper warns me, it is time to recommend myself to the friendly recollection of Mrs. Wythe, of Colonel Taliaferro and his family, and particularly of Mr. R. T. and to assure you of the affectionate esteem, with which I am,
Dear Sir, your friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
Paris, October 12, 1786.
My Dear Madam,
Having performed the last sad office of handing you into your carriage, at the pavillion de St. Denis, and seen the wheels get actually into motion, I turned on my heel and walked, more dead than alive, to the opposite door, where my own was awaiting me. Mr. Danquerville was missing. He was sought for, found, and dragged down stairs. We were crammed into the carriage, like recruits for the Bastille, and not having soul enough to give orders to the coachman, he presumed Paris our destination, and drove off. After a considerable interval, silence was broke, with a ‘Je suis vraiment affligé du depart de ces bons gens.’ This was a signal for mutual confession of distress. We began immediately to talk of Mr. and Mrs. Cosway, of their goodness, their talents, their amiability; and though we spoke of nothing else, we seemed hardly to have entered into the matter, when the coachman announced the rue St. Denis, and that we were opposite Mr. Danquerville’s. He insisted on descending there, and traversing a short passage to his lodgings. I was carried home. Seated by my fire-side, solitary and sad, the following dialogue took place between my Head and my Heart.
Head. Well, friend, you seem to be in a pretty trim.
Heart. I am indeed the most wretched of all earthly beings. Overwhelmed with grief, every fibre of my frame distended beyond its natural powers to bear, I would willingly meet whatever catastrophe should leave me no more to feel, or to fear.
Head. These are the eternal consequences of your warmth and precipitation. This is one of the scrapes into which you are ever leading us. You confess your follies, indeed; but still you hug and cherish them; and no reformation can be hoped, where there is no repentance.
Heart. Oh, my friend! this is no moment to upbraid my foibles. I am rent into fragments by the force of my grief! If you have any balm, pour it into my wounds; if none, do not harrow them by new torments. Spare me in this awful moment! At any other, I will attend with patience to your admonitions.
Head. On the contrary, I never found that the moment of triumph, with you, was the moment of attention to my admonitions. While suffering under your follies, you may perhaps be made sensible of them; but, the paroxysm over, you fancy it can never return. Harsh, therefore, as the medicine may be, it is my office to administer it. You will be pleased to remember, that when our friend Trumbull used to be telling us of the merits and talents of these good people, I never ceased whispering to you that we had no occasion for new acquaintances; that the greater their merit and talents, the more dangerous their friendship to our tranquillity, because the regret at parting would be greater.
Heart. Accordingly, Sir, this acquaintance was not the consequence of my doings. It was one of your projects, which threw us in the way of it. It was you, remember, and not I, who desired the meeting at Legrand and Motinos. I never trouble myself with domes nor arches. The Halle aux bleds might have rotted down, before I should have gone to see it. But you, forsooth, who are eternally getting us to sleep with your diagrams and crotchets, must go and examine this wonderful piece of architecture; and when you had seen it, oh! it was the most superb thing on earth! What you had seen there was worth all you had yet seen in Paris! I thought so too. But I meant it of the lady and gentleman to whom we had been presented; and not of a parcel of sticks and chips put together in pens. You then, Sir, and not I, have been the cause of the present distress.
Head. It would have been happy for you, if my diagrams and crotchets had gotten you to sleep on that day, as you are pleased to say they eternally do. My visit to Legrand and Motinos, had public utility for its object. A market is to be built in Richmond. What a commodious plan is that of Legrand and Motinos; especially, if we put on it the noble dome of the Halle aux bleds. If such a bridge as they showed us, can be thrown across the Schuylkill, at Philadelphia, the floating bridges taken up, and the navigation of that river opened, what a copious resource will be added of wood and provisions, to warm and feed the poor of that city? While I was occupied with these objects, you were dilating with your new acquaintances, and contriving how to prevent a separation from them. Every soul of you had an engagement for the day. Yet all these were to be sacrificed, that you might dine together. Lying messengers were to be despatched into every quarter of the city, with apologies for your breach of engagement. You, particularly, had the effrontery to send word to the Duchess Danville, that on the moment we were setting out to dine with her, despatches came to hand, which required immediate attention. You wanted me to invent a more ingenious excuse; but I knew you were getting into a scrape, and I would have nothing to do with it. Well; after dinner to St. Cloud, from St. Cloud to Ruggieri’s, from Ruggieri’s to Krumfoltz; and if the day had been as long as a Lapland summer day, you would still have contrived means among you to have filled it.
Heart. Oh! my dear friend, how you have revived me, by recalling to mind the transactions of that day! How well I remember them all, and that when I came home at night, and looked back to the morning, it seemed to have been a month agone. Go on, then, like a kind comforter, and paint to me the day we went to St. Germains. How beautiful was every object! the Port de Reuilly, the hills along the Seine, the rainbows of the machine of Marly, the terras of St. Germains, the chateaux, the gardens, the statues of Marly, the pavillion of Lucienne. Recollect, too, Madrid, Bagatelle, the King’s garden, the Desert. How grand the idea excited by the remains of such a column. The spiral staircase, too, was beautiful. Every moment was filled with something agreeable. The wheels of time moved on with a rapidity, of which those of our carriage gave but a faint idea. And yet, in the evening, when one took a retrospect of the day, what a mass of happiness had we travelled over! Retrace all those scenes to me, my good companion, and I will forgive the unkindness with which you were chiding me. The day we went to St. Germains was a little too warm, I think; was it not?
Head. Thou art the most incorrigible of all the beings that ever sinned! I reminded you of the follies of the first day, intending to deduce from thence some useful lessons for you, but instead of listening to them, you kindle at the recollection, you retrace the whole series with a fondness, which shows you want nothing but the opportunity, to act it over again. I often told you, during its course, that you were imprudently engaging your affections, under circumstances that must cost you a great deal of pain; that the persons, indeed, were of the greatest merit, possessing good sense, good humor, honest hearts, honest manners, and eminence in a lovely art; that the lady had, moreover, qualities and accomplishments belonging to her sex, which might form a chapter apart for her; such as music, modesty, beauty, and that softness of disposition, which is the ornament of her sex, and charm of ours: but that all these considerations would increase the pang of separation, that their stay here was to be short; that you rack our whole system when you are parted from those you love, complaining that such a separation is worse than death, inasmuch as this ends our sufferings, whereas that only begins them; and that the separation would, in this instance, be the more severe, as you, would probably never see them again.
Heart. But they told me, they would come back again the next year.
Head. But in the mean time, see what you surfer: and their return, too, depends on so many circumstances, that, if you had a grain of prudence, you would not count upon it. Upon the whole, it is improbable, and therefore you should abandon the idea of ever seeing them again.
Heart. May Heaven abandon me, if I do!
Head. Very well. Suppose, then, they come back. They are to stay two months, and when these are expired, what is to follow? Perhaps you flatter yourself they may come to America?
Heart. God only knows what is to happen. I see nothing impossible in that supposition: and I see things wonderfully contrived sometimes to make us happy. Where could they find such objects as in America, for the exercise of their enchanting art; especially the lady, who paints landscapes so inimitably? She wants only subjects worthy of immortality, to render her pencil immortal. The Falling Spring, the Cascade of Niagara, the Passage of the Potomac through the Blue Mountains, the Natural Bridge; it is worth a voyage across the Atlantic to see these objects; much more to paint, and make them, and thereby ourselves, known to all ages. And our own dear Monticello; where has nature spread so rich a mantle under the eye?—mountains, forests rocks, rivers. With what majesty do we there ride above the storms! How sublime to look down into the workhouse of nature to see her clouds, hail, snow, rain, thunder, all fabricated at our feet! and the glorious sun when rising as if out of a distant water, lust gilding the tops of the mountains, and giving life to all nature! 1 hope in God, no circumstance may ever make either seek an asylum from grief! With what sincere sympathy I would open every cell of my composition, to receive the effusion of their woes!
I would pour my tears into their wounds; and if a drop of balm could be found on the top of the Cordilleras, or at the remotest sources of the Missouri, I would go thither myself to seek and to bring it. Deeply practised in the school of affliction, the human heart knows no joy which I have not lost, no sorrow of which I have not drank! Fortune can present no grief of unknown form to me! Who, then, can so softly bind up the wound of another, as he who has felt the same wound himself? But Heaven forbid, they should ever know a sorrow! Let us turn over another leaf, for this has distracted me.
Head. Well. Let us put this possibility to trial, then, on another point. When you consider the character which is given of our country by the lying newspapers of London, and their credulous copyers in other countries; when you reflect, that all Europe is made to believe we are a lawless banditti, in a state of absolute anarchy, cutting one another’s throats, and plundering without distinction, how could you expect, that any reasonable creature would venture among us?
Heart. But you and I know, that all this is false: that there is not a country on earth, where there is greater tranquillity; where the laws are milder, or better obeyed; where every one is more attentive to his own business, or meddles less with that of others; where strangers are better received, more hospitably treated, and with a more sacred respect.
Head. True, you and I know this, but your friends do not know it.
Heart. But they are sensible people, who think for themselves. They will ask of impartial foreigners, who have been among us, whether they saw or heard on the spot any instance of anarchy. They will judge, too, that a people occupied, as we are, in opening rivers, digging navigable canals, making roads, building public schools, establishing academies, erecting busts and statues to our great men, protecting religious freedom, abolishing sanguinary punishments, reforming and improving our laws in general; they will judge, I say, for themselves, whether these are not the occupations of a people at their ease; whether this is not better evidence of our true state, than a London newspaper, hired to lie, and from which no truth can ever be extracted, but by reversing every thing it says.
Head. I did not begin this lecture, my friend, with a view to learn from you what America is doing. Let us return, then, to our point. I wish to make you sensible how imprudent it is to place your affections without reserve on objects you must so soon lose, and whose loss, when it comes, must cost you such severe pangs. Remember the last night. You knew your friends were to leave Paris to-day. This was enough to throw you into agonies. All night you tossed us from one side of the bed to the other; no sleep, no rest. The poor Crippled wrist, too, never left one moment in the same position; now up, now down, now here, now there; was it to be wondered at, if its pains returned? The surgeon then was to be called, and to be rated as an ignoramus, because he could not divine the cause of this extraordinary change. In fine, my friend, you must mend your manners. This is not a world to live at random in, as you do. To avoid those eternal distresses, to which you are for ever exposing us, you must learn to look forward before you take a step, which may interest our peace. Every thing in this world is matter of calculation. Advance, then, with caution, the balance in your hand. Put into one scale the pleasures which any object may offer; but put fairly into the other the pains which are to follow, and see which preponderates. The making an acquaintance is not a matter of indifference. When a new one is proposed to you, view it all round. Consider what advantages it presents, and to what inconveniences it may expose you. Do not bite at the bait of pleasure, till you know there is no hook beneath it. The art of life is the art of avoiding pain; and he is the best pilot, who steers clearest of the rocks and shoals with which it is beset. Pleasure is always before us; but misfortune is at our side: while running after that, this arrests us. The most effectual means of being secure against pain, is to retire within ourselves, and to suffice for our own happiness. Those which depend on ourselves, are the only pleasures a wise man will count on; for nothing is ours, which another may deprive us of. Hence the inestimable value of intellectual pleasures. Ever in our power, always leading us to something new, never cloying, we ride serene and sublime above the concerns of this mortal world, contemplating truth and nature, matter and motion, the laws which bind up their existence, and that Eternal Being, who made and bound them up by those laws. Let this be our employ. Leave the bustle and tumult of society to those who have not talents to occupy themselves without them. Friendship is but another name for an alliance with the follies and the misfortunes of others. Our own share of miseries is sufficient: why enter then as volunteers into those of another? Is there so little gall poured into our cup, that we must heed help to drink that of our neighbor? A friend dies, or leaves us: we feel as if a limb was cut off. He is sick: we must watch over him, and participate of his pains. His fortune is shipwrecked: ours must be laid under contribution. He loses a child, a parent, or a partner: we must mourn the loss as if it were our own.
Heart. And what more sublime delight, than to mingle tears with one whom the hand of Heaven hath smitten! to watch over the bed of sickness, and to beguile its tedious and its painful moments! to share our bread with one to whom misfortune has left none! This world abounds indeed with misery: to lighten its burthen, we must divide it with one another. But let us now try the virtue of your mathematical balance, and as you have put into one scale the burthens of friendship, let me put its comforts into the other. When languishing then under disease, how grateful is the solace of our friends! how are we penetrated with their assiduities and attentions! how much are we supported by their encouragements and kind offices! When Heaven has taken from us some object of our love, how sweet is it to have a bosom whereon to recline our heads, and into which we may pour the torrent of our tears! Grief, with such a comfort, is almost a luxury! In a life where we are perpetually exposed to want and accident, yours is a wonderful proposition, to insulate ourselves, to retire from all aid, and to wrap ourselves in the mantle of self-sufficiency! For assuredly nobody will care for him, who cares for nobody. But friendship is precious, not only in the shade, but in the sunshine of life: and thanks to a benevolent arrangement of things, the greater part of life is sunshine. I will recur for proof to the days we have lately passed. On these, indeed, the sun shone brightly! How gay did the face of nature appear! Hills, valleys, chateaux, gardens, rivers, every object wore its liveliest hue! Whence did they borrow it? From the presence of our charming companion. They were pleasing, because she seemed pleased. Alone, the scene would have been dull and insipid: the participation of it with her gave it relish. Let the gloomy monk, sequestered from the world, seek unsocial pleasures in the bottom of his cell! Let the sublimated philosopher grasp visionary happiness, while pursuing phantoms dressed in the garb of truth! Their supreme wisdom is supreme folly: and they mistake for happiness the mere absence of pain. Had they ever felt the solid pleasure of one generous spasm of the heart, they would exchange for it all the frigid speculations of their lives, which you have been vaunting in such elevated terms. Believe me, then, my friend, that that is a miserable arithmetic, which could estimate friendship at nothing, or at less than nothing. Respect for you has induced me to enter into this discussion, and to hear principles uttered, which I detest and abjure. Respect for myself now obliges me to recall you into the proper limits of your office. When nature assigned us the same habitation, she gave us over it a divided empire. To you she allotted the field of science; to me that of morals.
When the circle is to be squared, or the orbit of a comet to be traced; when the arch of greatest strength, or the solid of least resistance is to be investigated, take up the problem; it is yours; nature has given me no cognizance of it. In like manner, in denying to you the feelings of sympathy, of benevolence, of gratitude, of justice, of love, of friendship, she has excluded you from their control. To these she has adapted the mechanism of the heart. Morals were too essential to the happiness of man, to be risked on the uncertain combinations of the head. She laid their foundation, therefore, in sentiment, not in science. That she gave to all, as necessary to all: this to a few only, as sufficing with a few. I know indeed, that you pretend authority to the sovereign control of our conduct, in all its parts: and a respect for your grave saws and maxims, a desire to do what is right, has sometimes induced me to conform to your counsels. A few facts, however, which I can readily recall to your memory, will suffice to prove to you, that nature has not organized you for our moral direction. When the poor wearied soldier, whom we overtook at Chickahominy, with his pack on his back, begged us to let him get up behind our chariot, you began to calculate that the road was full of soldiers, and that if all should be taken up, our horses would fail in their journey. We drove on therefore. But soon becoming sensible you had made me do wrong, that though we cannot relieve all the distressed, we should relieve as many as we can, I turned about to take up the soldier; but he had entered a by-path, and was no more to be found: and from that moment to this, I could never find him out to ask his forgiveness. Again, when the poor woman came to ask a charity in Philadelphia, you whispered, that she looked like a drunkard, and that half a dollar was enough to give her for the ale-house. Those who want the dispositions to give, easily find reasons why they ought not to give. When I sought her out afterwards, and did what I should have done at first, you know, that she employed the money immediately towards placing her child at school. If our country, when pressed with wrongs at the point of the bayonet, had been governed by its heads instead of its’ hearts, where should we have been now? Hanging on a gallows as high as Hainan’s. You began to calculate, and to compare wealth and numbers: we threw up a few pulsations of our blood; we supplied enthusiasm against wealth and numbers; we put our existence to the hazard, when the hazard seemed against us, and we saved our country: justifying, at the same time, the ways of Providence, whose precept is, to do always what is right, and leave the issue to him. In short, my friend, as far as my recollection serves me, I do not know that I ever did a good thing on your suggestion, or a dirty one without it. I do for ever, then, disclaim your interference in my province. Fill paper as you please with triangles and squares: try how many ways you can hang and combine them together. I shall never envy nor control your sublime delights. But leave me to decide when and where friendships are to be contracted. You say I contract them at random. So you said the woman at Philadelphia was a drunkard. I receive none into my esteem, till I know they are worthy of it. Wealth, title, office, are no recommendations to my friendship. On the contrary, great good qualities are requisite to make amends for their having wealth, title, and office. You confess, that, in the present case, I could not have made a worthier choice. You only object, that I was so soon to lose them. We are not immortal ourselves, my friend; how can we expect our enjoyments to be so? We have no rose without its thorn; no pleasure without alloy. It is the law of our existence; and we must acquiesce. It is the condition annexed to all our pleasures, not by us who receive, but by him who gives them. True, this condition is pressing cruelly on me at this moment. I feel more fit for death than life. But when I look back on the pleasures of which it is the consequence, I am conscious they were worth the price I am paying. Notwithstanding your endeavors, too, to damp my hopes, I comfort myself with expectations of their promised return. Hope is sweeter than despair; and they were too good to mean to deceive me. ‘In the summer,’ said the gentleman; but ‘In the spring,’ said the lady; and I should love her for ever, were it only for that! Know, then, my friend, that I have taken these good people into my bosom; that I have lodged them in the warmest cell I could find; that I love them, and will continue to love them through life; that if fortune should dispose them on one side the globe, and me on the other, my affections shall pervade its whole mass to reach them. Knowing then my determination, attempt not to disturb it. If you can at any time furnish matter for their amusement, it will be the office of a good neighbor to do it. I will, in like manner, seize any occasion which may offer, to do the like good turn for you with Condorcet, Rittenhouse, Madison, La Cretelle, or any other of those worthy sons of science, whom you so justly prize.
I thought this a favorable proposition whereon to rest the issue of the dialogue. So I put an end to it by calling for my nightcap. Methinks, I hear you wish to Heaven I had called a little sooner, and so spared you the ennui of such a sermon. I did not interrupt them sooner, because I was in a mood for hearing sermons. You, too, were the subject; and on such a thesis, I never think the theme long; not even if I am to write it, and that slowly and awkwardly, as now, with the left hand. But that you may not be discouraged from a correspondence, which begins so formidably, I will promise you, on my honor, that my future letters shall be of a reasonable length. I will even agree to express but half my esteem for you, for fear of cloying you with too full a dose. But on your part, no curtailing. If your letters are as long as the Bible, they will appear short to me. Only let them be brim full of affection. I shall read them with the dispositions with which Arlequin, in Les Deux Billets, spelt the words ‘Je t’aime,’ and wished that the whole alphabet had entered into their composition.
We have had incessant rains since your departure. These make me fear for your health, as well as that you had an uncomfortable journey. The same cause has prevented me from being able to give you any account of your friends here. This voyage to Fontainebleau will probably send the Count de Moutier and the Marquis de Brehan to America. Danquerville promised to visit me, but has not done it as yet. De la Tude comes sometimes to take family soup with me, and entertains me with anecdotes of his five and thirty years’ imprisonment. How fertile is the mind of man, which can make the Bastille and dungeon of Vincennes yield interesting anecdotes! You know this was for making four verses on Madame de Pompadour. But I think you told me you did not know the verses. They were these.
‘Sans esprit, sans sentiment,
Sans etre belle, ni neuve,
En France on peut avoir le premier amant:
Pompadour en est Tepreuve.’
I have read the memoir of his three escapes. As to myself, my health is good, except my wrist, which mends slowly, and my mind, which mends not at all, but broods constantly over your departure. The lateness of the season obliges me to decline my journey into the south of France. Present me in the most friendly terms to Mr. Cosway, and receive me into your own recollection with a partiality and warmth, proportioned not to my own poor merit, but to the sentiments of sincere affection and esteem, with which I have the honor to be, my Dear Madam,
Your most obedient, humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MRS. COSWAY.
Paris, October 13, 1786.
My Dear Madam,
Just as I had sealed the enclosed, I received a letter of a good length, dated Antwerp, with your name at the bottom. I prepared myself for a feast. I read two or three sentences: looked again at the signature, to see if I had not mistaken it. It was visibly yours. Read a sentence or two more. Diable! Spelt your name distinctly. There was not a letter of it omitted. Began to read again. In fine, after reading a little, and examining the signature alternately, half a dozen times, I found that your name was to four lines only, instead of four pages. I thank you for the four lines, however, because they prove you think of me; little, indeed, but better little than none. To show how much I think of you, I send you the enclosed letter of three sheets of paper, being a history of the evening I parted with you. But how expect you should read a letter of three mortal sheets of paper? I will tell you. Divide it into six doses of half a sheet each, and every day, when the toilette begins, take a dose, that is to say, read half a sheet. By this means, it will have the only merit its length and dulness can aspire to, that of assisting your coiffeuse to procure you six good naps of sleep. I will even allow you twelve days to get through it, holding you rigorously to one condition only, that is, that at whatever hour you receive this, you do not break the seal of the enclosed till the next toilette. Of this injunction I require a sacred execution. I rest it on your friendship, and that in your first letter, you tell me honestly, whether you have honestly performed it. I send you the song I promised. Bring me in return the subject, Jours heureux! Were I a songster, I should sing it all to these words; ‘Dans ces lieux qu’elle tarde à se rendre!’ Learn it, I pray you, and sing it with feeling. My right hand presents its devoirs to you, and sees with great indignation the left supplanting it in a correspondence so much valued. You will know the first moment it can resume its rights. The first exercise of them shall be addressed to you, as you had the first essay of its rival. It will yet, however, be many a day. Present my esteem to Mr. Cosway, and believe me to be yours very affectionately,
Th: Jefferson.
M. LE ROY DE L’ACADEMIE DES SCIENCES.
Paris, November 13, 1786.
Sir,
I received the honor of yours of September the 18th, a day or two after the accident of a dislocated wrist had disabled me from writing. I have waited thus long in constant hope of recovering its use. But finding that this hope walks before me like my shadow, I can no longer oppose the desire and duty of answering your polite and learned letter. I therefore employ my left hand in the office of scribe, which it performs indeed slowly, awkwardly, and badly.
The information given by me to the Marquis de Chastellux, and alluded to in his book and in your letter, was, that the sea breezes which prevail in the lower parts of Virginia, during the summer months, and in the warm parts of-the day, had made a sensible progress into the interior country: that formerly, within the memory of persons living, they extended but little above Williamsburg; that afterwards they became sensible as high as Richmond; and that, at present, they penetrate sometimes as far as the first mountains, which are above an hundred miles further from the sea coast, than Williamsburg is. It is very rare, indeed, that they reach those mountains, and not till the afternoon is considerably advanced. A light northwesterly breeze is, for the most part, felt there, while an easterly or northeasterly wind is blowing strongly in the lower country. How far northward and southward of Virginia, this easterly breeze Takes place, I am not informed. I must, therefore, be understood as speaking of that State only, which extends on the sea coast from 36 1/2 to 38° of latitude.
This is the fact. We know too little of the operations of nature in the physical world, to assign causes with any degree of confidence. Willing always, however, to guess at what we do not know, I have sometimes indulged myself with conjectures on the causes of the phenomena above stated. I will hazard them on paper, for your amusement, premising for their foundation some principles believed to be true.
Air resting on a heated and reflecting surface, becomes warmer, rarer, and lighter: it ascends therefore, and the circumjacent air, which is colder and heavier, flows into its place, becomes warmed and lightened in its turn, ascends, and is succeeded as that which went before. If the heated surface be circular, the air flows to it from every quarter, like the rays of a circle to its centre. If it be a zone of determinate breadth and indefinite length, the air will flow from each side perpendicularly on it. If the currents of air flowing from opposite sides, be of equal force, they will meet in equilibrio, at a line drawn longitudinally through the middle of the zone. If one current be stronger than the other, the stronger one will force back the line of equilibrium, towards the further edge of the zone, or even beyond it: the motion it has acquired causing it to overshoot the zone, as the motion acquired by a pendulum in its descent, causes it to vibrate beyond the point of its lowest descent.
Earth, exposed naked to the sun’s rays, absorbs a good portion of them; but, being an opaque body, those rays penetrate to a small depth only. Its surface, by this accumulation of absorbed rays, becomes considerably heated. The residue of the rays are reflected into the air resting on that surface. This air, then, is warmed, 1. by the direct rays of the sun; 2. by its reflected rays; 3. by contact with the heated surface. A forest receiving the sun’s rays, a part of them enters the intervals between the trees, and their reflection upwards is intercepted by the leaves and boughs. The rest fall on the trees, the leaves of which being generally inclined towards the horizon, reflect the rays downwards. The atmosphere here, then, receives little or no heat by reflection. Again, these leaves having a power of keeping themselves cool by their own transpiration, they impart no heat to the air by contact. Reflection and contact, then, two of the three modes before-mentioned, of communicating heat, are wanting here; and, of course, the air over a country covered by forest must be colder than that over cultivated grounds.
The sea being pellucid, the sun’s rays penetrate it to a considerable depth. Being also fluid, and in perpetual agitation, its parts are constantly mixed together; so that instead of its heat being all accumulated in its surface, as in the case of a solid, opaque body, it is diffused through its whole mass. Its surface, therefore, is comparatively cool, for these reasons; to which may be added that of evaporation. The small degree of reflection which might otherwise take place, is generally prevented by the rippled state of its surface. The air resting on the sea, then, like that resting on a forest, receives little or no heat by reflection or contact; and is therefore colder than that which lies over a cultivated country.
To apply these observations to the phenomena under consideration. The first settlements of Virginia were made along the sea coast, bearing from the south, towards the north, a little eastwardly. These settlements formed a zone, in which, though every point was not cleared of its forest, yet a good proportion was cleared and cultivated. The cultivated earth, as the sun advances above the horizon in the morning, acquires from it an intense heat, which is retained and increased through the warm parts of the day. The air resting on it becomes warm in proportion, and rises. On one side is a country still covered with forest: on the other is the ocean. The colder air from both of these, then rushes towards the heated zone, to supply the place left vacant there by the ascent of its warm air. The breeze from the west is light and feeble; because it traverses a country covered with mountains and forests, which retard its current. That from the east is strong; as passing over the ocean, wherein there is no obstacle to its motion. It is probable, therefore, that this easterly breeze forces itself far into, or perhaps beyond, the zone which produces it. This zone is, by the increase of population, continually widening into the interior country. The line of equilibrium between the easterly and westerly breezes is, therefore, progressive.
Did no foreign causes intervene, the sea breezes would be a little southwardly of the east, that direction being perpendicular to our coast. But within the tropics, there are winds which blow continually and strongly from the east. This current affects the course of the air, even without the tropics. The same cause, too, which produces a strong motion of the air, from east to west, between the tropics, to wit, the sun, exercises its influence without those limits, but more feebly, in proportion as the surface of the globe is there more obliquely presented to its rays. This effect, though not great, is not to be neglected when the sun is in or near our summer solstice, which is the season of these easterly breezes. The northern air, too, flowing towards the equatorial parts, to supply the vacuum made there by the ascent of their heated air, has only the small rotary motion of the polar latitudes from which it comes. Nor does it suddenly acquire the swifter rotation of the parts into which it enters. This gives it the effect of a motion opposed to that of the earth, that is to say, of an easterly one. And all these causes together are known to produce currents of air in the Atlantic, varying from east to northeast, as far as the fortieth degree of latitude. It is this current which presses our sea breeze out of its natural southeasterly direction, to an easterly, and sometimes almost a northeasterly one.
We are led naturally to ask, where the progress of our sea breezes will ultimately be stopped? No confidence can be placed in any answer to this question. If they should ever pass the mountainous country which separates the waters of the ocean from those of the Mississippi, there may be circumstances which might aid their further progress, as far as the Mississippi. That mountainous country commences about two hundred miles from the sea coast, and consists of successive ranges passing from northeast to southwest, and rising the one above the other to the Allegany Ridge, which is the highest of all. From that, lower and lower ridges succeed one another again, till having covered, in the whole, a breadth of two hundred miles from southeast to northwest, they subside into a plain, fertile country, extending four hundred miles to the Mississippi, and probably much further on the other side, towards the heads of the western waters. When this country shall become cultivated, it will, for the reasons before explained, draw to it winds from the east and west. In this case, should the sea breezes pass the intermediate mountains, they will rather be aided than opposed in their further progress to the Mississippi. There are circumstances, however, which render it possible that they may not be able to pass those intermediate mountains. 1. These mountains constitute the highest lands within the United States. The air on them must consequently be very cold and heavy, and have a tendency to flow both to the east and west. 2. Ranging across the current of the sea breezes, they are in themselves, so many successive barriers opposed to their progress. 3. The country they occupy is covered with trees, which assist to weaken and spend the force of the breezes. 4. It will remain so covered; a very small proportion of it being capable of culture. 5. The temperature of its air, then, will never be softened by culture.
Whether in the plain country between the Mississippi and Allegany mountains, easterly or westerly winds prevail at present, I am not informed. I conjecture, however, that they must be westerly: and I think with you, Sir, that if those mountains were to subside into plain country, as their opposition to the westerly winds would then be removed, they would repress more powerfully those from the east, and of course would remove the line of equilibrium nearer to the sea coast for the present.
Having had occasion to mention the course of the tropical winds from east to west, I will add some observations connected with them. They are known to occasion a strong current in the ocean, in the same direction. This current breaks on that wedge of land of which Saint Roque is the point; the southern column of it probably turning off and washing the coast of Brazil. I say probably, because I have never heard the fact, and conjecture it from reason only. The northern column, having its western motion diverted towards the north, and reinforced by the currents of the great rivers Orinoko, Amazons, and Tocantin, has probably been the agent which formed the Gulf of Mexico, cutting the American continent nearly in two, in that part. It re-issues into the ocean at the northern end of the Gulf, and passes by the name of the Gulf Stream, all along the coast of the United States, to its northern extremity. There it turns off eastwardly, having formed by its eddy, at this turn, the Banks of Newfoundland. Through the whole of its course, from the Gulf to the Banks, it retains a very sensible warmth. The Spaniards are, at this time, desirous of trading to their Philippine Islands, by the way of the Cape of Good Hope: but opposed in it by the Dutch, under authority of the treaty of Munster, they are examining the practicability of a common passage through the Straits of Magellan, or round Cape Horn. Were they to make an opening through the Isthmus of Panama, a work much less difficult than some even of the inferior canals of France, however small this opening should be in the beginning, the tropical current entering it with all its force, would soon widen it sufficiently for its own passage, and thus complete in a short time, that work which otherwise will still employ it for ages. Less country, too, would be destroyed by it in this way. These consequences would follow. 1. Vessels from Europe or the western coast of Africa, by entering the tropics, would have a steady wind and tide to carry them through the Atlantic, through America and the Pacific ocean, to every part of the Asiatic coast, and of the eastern coast of Africa: thus performing with speed and safety the tour of the whole globe, to within about twenty-four degrees of longitude, or one fifteenth part of its circumference; the African continent, under the line, occupying about that space. 2. The Gulf of Mexico, now the most dangerous navigation in the world on account of its currents and moveable sands, would become stagnant and safe. 3. The Gulf Stream on the coast of the United States would cease, and with that, those derangements of course and reckoning, which now impede and endanger the intercourse with those States. 4. The fogs on the Banks of Newfoundland,* supposed to be the vapors of the Gulf Stream rendered turbid by cold air, would disappear. 5. Those Banks ceasing to receive supplies of sand, weeds, and warm water, by the Gulf Stream, it might become problematical what effect changes of pasture and temperatures would have on the fisheries. However it is time to relieve you from this long lecture. I wish its subject may have been sufficiently interesting to make amends for its details. These are submitted with entire deference to your better judgment. I will only add to them, by assuring you of the sentiments of perfect esteem and respect, with which I have the honor to be, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
[* This ingenious and probable conjecture, I found in a
letter from Dr. Franklin to yourself, published in the late
volume of the American Philosophical Transactions.]
TO GENERAL WASHINGTON.
Paris, November 14, 1786.
Sir,
The house of Le Coulteux, which for some centuries has been the wealthiest of this place, has it in contemplation to establish a great company for the fur trade. They propose that partners interested one half in the establishment, should be American citizens, born and residing in the United States. Yet if I understood them rightly, they expect that the half of the company which resides here, should make the greatest part, or perhaps the whole of the advances, while those on our side the water should superintend the details. They had, at first, thought of Baltimore as the centre of their American transactions. I have pointed out to them the advantages of Alexandria for this purpose. They have concluded to take information as to Baltimore, Philadelphia, and New York, for a principal deposit, and having no correspondent at Alexandria, have asked me to procure a state of the advantages of that place, as also to get a recommendation of the best merchant there, to be adopted as partner and head of the business there. Skill, punctuality, and integrity are the requisites in such a character. They will decide on their whole information, as to the place for their principal factory. Being unwilling that Alexandria should lose its pretensions, I have undertaken to procure them information as to that place. If they undertake this trade at all, it will be on so great a scale as to decide the current of the Indian-trade to the place they adopt. I have no acquaintance at Alexandria or in its neighborhood; but believing you would feel an interest in the matter, from the same motives which I do, I venture to ask the favor of you to recommend to me a proper merchant for their purpose, and to engage some well informed person to send me a representation of the advantages of Alexandria, as the principal deposit of the fur trade.
The author of the political part of the Encyclopédie Méthodique desired me to examine his article, Etats Unis. I did so. I found it a tissue of errors; for in truth they know nothing about us here. Particularly, however, the article Cincinnati was a mere philippic against that institution: in which it appeared that there was an utter ignorance of facts and motives. I gave him notes on it. He reformed it, as he supposed, and sent it again to me to revise. In this reformed state, Colonel Humphreys saw it.
I found it necessary to write that article for him. Before I gave it to him, I showed it to the Marquis de la Fayette, who made a correction or two. I then sent it to the author. He used the materials, mixing a great deal of his own with them. In a work which is sure of going down to the latest posterity, I thought it material to set facts to rights, as much as possible. The author was well disposed; but could not entirely get the better of his original bias. I send you the article as ultimately published. If you find any material errors in it, and will be so good as to inform me of them, I shall probably have opportunities of setting this author to rights. What has heretofore passed between us on this institution, makes it my duty to mention to you, that I have never heard a person in Europe, learned or unlearned, express his thoughts on this institution, who did not consider it as dishonorable and destructive to our governments; and that every writing which has come out since my arrival here, in which it is mentioned, considers it, even as now reformed, as the germ whose developement is one day to destroy the fabric we have reared. I did not apprehend this, while I had American ideas only. But I confess that what I have seen in Europe, has brought me over to that opinion; and that though the day may be at some distance, beyond the reach of our lives perhaps, yet it will certainly come, when a single fibre left of this institution will produce an hereditary aristocracy, which will change the form of our governments from the best to the worst in the world. To know the mass of evil which flows from this fatal source, a person must be in France; he must see the finest soil, the finest climate, the most compact state, the most benevolent character of people, and every earthly advantage combined, insufficient to prevent this scourge from rendering existence a curse to twenty-four out of twenty-five parts of the inhabitants of this country. With us, the branches of this institution cover all the states. The southern ones, at this time, are aristocratical in their dispositions: and that that spirit should grow and extend itself, is within the natural order of things. I do not flatter myself with the immortality of our governments: but I shall think little also of their longevity, unless this germ of destruction be taken out. When the society themselves shall weigh the possibility of evil, against the impossibility of any good to proceed from this institution, I cannot help hoping they will eradicate it. I know they wish the permanence of our governments, as much as any individuals composing them.
An interruption here, and the departure of the gentleman by whom I send this, oblige me to conclude it with assurances of the sincere respect and esteem, with which I have the honor to be, Dear Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JAMES MADISON.
Paris, December 16, 1786.
Dear Sir,
After a very long silence, I am at length able to write to you. An unlucky dislocation of my right wrist has disabled me from using that hand, three months. I now begin to use it a little, but with great pain; so that this letter must be taken up at such intervals as the state of my hand will permit, and will probably be the work of some days. Though the joint seems to be well set, the swelling does not abate, nor the use of it return. I am now, therefore, on the point of setting out, to the south of France, to try the use of some mineral waters there, by immersion. This journey will be of two or three months.
I enclose you herein a copy of the letter from the minister of finance to me, making several advantageous regulations for our commerce. The obtaining this has occupied us a twelvemonth. I say us, because I find the Marquis de la Fayette so useful an auxiliary, that acknowledgements for his co-operation are always due. There remains still something to do for the articles of rice, turpentine, and ship duties. What can be done for tobacco when the late regulation expires, is very uncertain. The commerce between the United States and this country being put on a good footing, we may afterwards proceed to try if any thing can be done to favor our intercourse with her colonies. Admission into them for our fish and flour, is very desirable: but, unfortunately, both those articles would raise a competition against their own.
I find by the public papers, that your commercial convention failed in point of representation. If it should produce a full meeting in May, and a broader reformation, it will still be well. To make us one nation as to foreign concerns, and keep us distinct in domestic ones, gives the outline of the proper division of powers between the general and particular governments. But to enable the federal head to exercise the powers given it, to best advantage, it should be organized, as the particular ones are, into legislative, executive, and judiciary. The first and last are already separated. The second should be. When last with Congress, I often proposed to members to do this, by making of the committee of the States an executive committee during the recess of Congress, and during its sessions to appoint a committee to receive and despatch all executive business, so that Congress itself should meddle only with what should be legislative. But I question if any Congress (much less all successively) can have self-denial enough to go, through with this distribution. The distribution, then, should be imposed on them. I find Congress have reversed their division of the western States, and proposed to make them fewer and larger. This is reversing the natural order of things. A tractable people may be governed in large bodies: but in proportion as they depart from this character, the extent of their government must be less. We see into what small divisions the Indians are obliged to reduce their societies. This measure, with the disposition to shut up the Mississippi, gives me serious apprehensions of the severance of the eastern and western parts of our confederacy. It might have been made the interest of the western States to remain united with us, by managing their interests honestly, and for their own good. But the moment we sacrifice their interests to our own, they will see it better to govern themselves. The moment they resolve to do this, the point is settled. A forced connection is neither our interest, nor within our power. The Virginia act for religious freedom has been received with infinite approbation in Europe, and propagated with enthusiasm. I do not mean by the governments, but by the individuals who compose them. It has been translated into French and Italian, has been sent to most of the courts of Europe, and has been the best evidence of the falsehood of those reports, which stated us to be in anarchy. It is inserted in the new Encyclopédie, and is appearing in most of the publications respecting America. In fact, it is comfortable to see the standard of reason at length erected, after so many ages, during which the human mind has been held in vassalage by kings, priests, and nobles: and it is honorable for us to have produced the first legislature who had the courage to declare, that the reason of man may be trusted with the formation of his own opinions.
I thank you for your communications in Natural History. The several instances of trees, &c. found far below the surface of the earth, as in the case of Mr. Hay’s well, seem to set the reason of man at defiance.
I am, Dear Sir, with sincere esteem, your friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO CHARLES THOMSON.
Paris, December 17,1780.
Dear Sir,
A dislocation of my right wrist has for three months past disabled me from writing, except with my left hand, which was too slow and awkward to be employed often. I begin to have so much use of my wrist as to be able to write, but it is slowly, and in pain. I take the first moment I can, however, to acknowledge the receipt of your letters of April the 6th, July the 8th and 30th. In one of these, you say you have not been able to learn, whether, in the new mills in London, steam is the immediate mover of the machinery, or raises water to move it. It is the immediate mover. The power of this agent, though long known, is but now beginning to be applied to the various purposes of which it is susceptible. You observe, that Whitehurst supposes it to have been the agent, which bursting the earth, threw it up into mountains and vallies. You ask me what I think of this book. I find in it many interesting facts brought together, and many ingenious commentaries on them. But there are great chasms in his facts, and consequently in his reasoning, These he fills up by suppositions, which may be as reasonably denied as granted. A sceptical reader, therefore, like myself, is left in the lurch. I acknowledge, however, he makes more use of fact, than any other writer on a theory of the earth. But I give one answer to all these theorists. That is as follows. They all suppose the earth a created existence. They must suppose a creator then; and that he possessed power and wisdom to a great degree. As he intended the earth for the habitation of animals and vegetables, is it reasonable to suppose, he made two jobs of his creation, that he first made a chaotic lump, and set it into rotatory motion, and then waited the millions of ages necessary to form itself? That when it had done this, he stepped in a second time, to create the animals and plants which were to inhabit it? As the hand of a creator is to be called in, it may as well be called in at one stage of the process as another. We may as well suppose he created the earth at once, nearly in the state in which we see it, fit for the preservation of the beings he placed on it. But it is said, we have a proof that he did not create it in its present solid form, but in a state of fluidity: because its present shape of an oblate spheroid is precisely that, which a fluid mass revolving on its axis would assume.
I suppose, that the same equilibrium between gravity and centrifugal force, which would determine a fluid mass into the form of an oblate spheroid, would determine the wise creator of that mass, if he made it in a solid state, to give it the same spheroidical form. A revolving fluid will continue to change its shape, till it attains that in which its principles of contrary motion are balanced. For if you suppose them not balanced, it will change its form. Now the same balanced form is necessary for the preservation of a revolving solid. The creator, therefore, of a revolving solid, would make it an oblate spheroid, that figure alone admitting a perfect equilibrium. He would make it in that form, for another reason; that is, to prevent a shifting of the axis of rotation. Had he created the earth perfectly spherical, its axis might have been perpetually shifting, by the influence of the other bodies of the system; and by placing the inhabitants of the earth successively under its poles, it might have been depopulated; whereas, being spheroidical, it has but one axis on which it can revolve in equilibrio. Suppose the axis of the earth to shift forty-five degrees; then cut it into one hundred and eighty slices, making every section in the plane of a circle of latitude, perpendicular to the axis: every one of these slices, except the equatorial one, would be unbalanced, as there would be more matter on one side of its axis than on the other. There could be but one diameter drawn through such a slice, which would divide it into two equal parts. On every other possible diameter, the parts would hang unequal. This would produce an irregularity in the diurnal rotation. We may, therefore, conclude it impossible for the poles of the earth to shift, if it was made spheroidical; and that it would be made spheroidical, though solid, to obtain this end. I use this reasoning only on the supposition, that the earth has had a beginning. I am sure I shall read your conjectures on this subject with great pleasure, though I bespeak beforehand, a right to indulge my natural incredulity and scepticism. The pain in which I write, awakens me here from my reverie, and obliges me to conclude with compliments to Mrs. Thomson, and assurances to yourself of the esteem and affection with which I am sincerely, Dear Sir, your friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
P. S. Since writing the preceding, I have had a conversation on the subject of the steam-mills, with the famous Boulton, to whom those of London belong, and who is here at this time. He compares the effect of steam with that of horses, in the following manner. Six horses, aided with the most advantageous combination of the mechanical powers hitherto tried, will grind six bushels of flour in an hour; at the end of which time they are all in a foam, and must rest. They can work thus six hours in the twenty-four, grinding thirty-six bushels of flour, which is six to each horse, for the twenty-four hours. His steam-mill in London consumes one hundred and twenty bushels of coal in twenty-four hours, turns ten pair of stones, which grind eight bushels of flour an hour each, which is nineteen hundred and twenty bushels in the twenty-four hours. This makes a peck and a half of coal perform exactly as much as a horse in one day can perform.
TO COLONEL MONROE.
Paris, December 18, 1786.
Dear Sir,
Your letters of August the 19th and October the 12th have come duly to hand. My last to you was of the 11th of August. Soon after that date I got my right wrist dislocated, which has till now deprived me of the use of that hand; and even now I can use it but slowly, and with pain. The revisal of the Congressional intelligence contained in your letters, makes me regret the loss of it on your departure. I feel, too, the want of a person there to whose discretion I can trust confidential communications, and on whose friendship I can rely against the unjust designs of malevolence. I have no reason to suppose I have enemies in Congress; yet it is too possible, to be without that fear. Some symptoms make me suspect, that my proceedings to redress the abusive administration of tobacco by the Farmers General have indisposed towards me a powerful person in Philadelphia, who was profiting from that abuse. An expression in the enclosed letter of M. de Calonne, would seem to imply, that I had asked the abolition of Mr. Morris’s contract. I never did. On the contrary, I always observed to them, that it would be unjust to annul that contract. I was led to this, by principles both of justice and interest. Of interest, because that contract would keep up the price of tobacco here to thirty-four, thirty-six, and thirty-eight livres, from which it will fall when it shall no longer have that support. However, I have done what was right, and I will not so far wound my privilege of doing that, without regard to any man’s interest, as to enter into any explanations of this paragraph with him. Yet I esteem him highly, and suppose that hitherto he had esteemed me. You will see by Calonne’s letter, that we are doing what we can to get the trade of the United States put on a good footing. I am now about setting out on a journey to the south of France, one object of which is to try the mineral waters there for the restoration of my hand; but another is, to visit all the seaports where we have trade, and to hunt up all the inconveniences under which it labors, in order to get them rectified. I shall visit, and carefully examine too, the canal of Languedoc. On my return, which will be early in the spring, I shall send you several livraisons of the Encyclopédie, and the plan of your house. I wish to Heaven, you may continue in the disposition to fix it in Albemarle. Short will establish himself there, and perhaps Madison may be tempted to do so. This will be society enough, and it will be the great sweetener of our lives. Without society, and a society to our taste, men are never contented. The one here supposed, we can regulate to our minds, and we may extend our regulations to the sumptuary department, so as to set a good example to a country which needs it, and to preserve our own happiness clear of embarrassment. You wish not to engage in the drudgery of the bar. You have two asylums from that. Either to accept a seat in the Council, or in the judiciary department. The latter, however, would require a little previous drudgery at the bar, to qualify you to discharge your duty with satisfaction to yourself. Neither of these would be inconsistent with a continued residence in Albemarle. It is but twelve hours drive in a sulky from Charlottesville to Richmond, keeping a fresh horse always at the half-way, which would be a small annual expense. I am in hopes, that Mrs. M. will have in her domestic cares occupation and pleasure sufficient to fill her time, and insure her against the tedium vitæ: that she will find, that the distractions of a town, and the waste of life under these, can bear no comparison with the tranquil happiness of domestic life. If her own experience has not yet taught her this truth, she has in its favor the testimony of one, who has gone through the various scenes of business, of bustle, of office, of rambling, and of quiet retirement, and who can assure her, that the latter is the only point upon which the mind can settle at rest. Though not clear of inquietudes, because no earthly situation is so, they are fewer in number, and mixed with more objects of contentment, than in any other mode of life. But I must not philosophize too much with her, lest I give her too serious apprehensions of a friendship I shall impose on her. I am with very great esteem, Dear Sir, your sincere friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MR. CARMICHAEL.
Paris, December 26,1786.
Dear Sir,
A note from me of the 22nd of September apprized you it would be some time before I should be able to answer your letters. I did not then expect it would have been so long.
I enclose herein a resolution of Congress recalling Mr. Lambe, which I will beg the favor of you to have delivered him. I have written to Mr. Adams on the subject of directing him to settle with Mr. Barclay, and attend his answer. In the mean time, I am not without hopes Mr. Barclay has done the business. I send also a note desiring Mr. Lambe to deliver you his cipher: and a copy of a letter from the minister of finance here to me, announcing several regulations in favor of our commerce.
My Notes on Virginia, having been hastily written, need abundance of corrections. Two or three of these are so material, that I am reprinting a few leaves to substitute for the old. As soon as these shall be ready, I will beg your acceptance of a copy. I shall be proud to be permitted to send a copy also to the Count de Campomanes, as a tribute to his science and his virtues. You will find in them, that the Natural Bridge has found an admirer in me also. I should be happy to make with you the tour of the curiosities you will find therein mentioned. That kind of pleasure surpasses much, in my estimation, whatever I find on this side the Atlantic. I sometimes think of building a little hermitage at the Natural Bridge (for it is my property), and of passing there a part of the year at least.
I have received American papers to the 1st of November. Some tumultuous meetings of the people have taken place in the eastern States; i.e. one in Massachusetts, one in Connecticut, and one in New Hampshire. Their principal demand was a respite in the judiciary proceedings. No injury was done, however, in a single instance, to the person or property of any one, nor did the tumult continue twenty-four hours in any one instance. In Massachusetts this was owing to the discretion which the malcontents still preserved; in Connecticut and New Hampshire the body of the people rose in support of government, and obliged the malcontents to go to their homes. In the last mentioned State they seized about forty, who were in jail for trial. It is believed this incident will strengthen our government. Those people are not entirely without excuse. Before the war these States depended on their whale-oil and fish. The former was consumed in England, and much of the latter in the Mediterranean. The heavy duties on American whale-oil, now required in England, exclude it from that market: and the Algerines exclude them from bringing their fish into the Mediterranean. France is opening her ports for their oil, but in the mean while their ancient debts are pressing them, and they have nothing to pay with. The Massachusetts Assembly, too, in their zeal for paying their public debt, had laid a tax too heavy to be paid, in the circumstances of their State. The Indians seem disposed, too, to make war on us. These complicated causes determined Congress to increase their forces to two thousand men. The latter was the sole object avowed, yet the former entered for something into the measure. However, I am satisfied the good sense of the people is the strongest army our governments can ever have, and that it will not fail them. The commercial convention at Annapolis was not full enough to do business. They found, too, their appointments too narrow, being confined to the article of commerce. They have proposed a meeting at Philadelphia in May, and that it may be authorized to propose amendments of whatever is defective in the federal constitution.
When I was in England, I formed a portable copying press, on the principles of the large one they make there, for copying letters. I had a model made there, and it has answered perfectly. A workman here has made several from that model. The itinerant temper of your court will, I think, render one of these useful to you. You must, therefore, do me the favor to accept of one. I have it now in readiness, and shall send it by the way of Bayonne, to the care of Mr. Alexander there, unless Don Miguel de Lardi-zabal can carry it with him.
My hand admonishes me it is time to stop, and that I must defer writing to Mr. Barclay till to-morrow.
I have the honor to be, with sentiments of the highest esteem and respect,
Dear Sir, your most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MR. VAUGHAN.
Paris, December 29, 1786.
Sir,
When I had the honor of seeing you in London, you were so kind as to permit me to trouble you, sometimes with my letters, and particularly on the subject of mathematical or philosophical instruments. Such a correspondence will be too agreeable to me, and at the same time too useful, not to avail myself of your permission. It has been an opinion pretty generally received among philosophers, that the atmosphere of America is more humid than that of Europe. Monsieur de Buffon makes this hypothesis one of the two pillars whereon he builds his system of the degeneracy of animals in America. Having had occasion to controvert this opinion of his, as to the degeneracy of animals there, I expressed a doubt of the fact assumed, that our climates are more moist. I did not know of any experiments, which might authorize a denial of it. Speaking afterwards on the subject with Dr. Franklin, he mentioned to me the observations he had made on a case of magnets, made for him by Mr. Nairne in London. Of these you will see a detail in the second volume of the American Philosophical Transactions, in a letter from Dr. Franklin to Mr. Nairne, wherein he recommends to him to take up the principle therein explained, and endeavor to make an hygrometer, which, taking slowly the temperature of the atmosphere, shall give its mean degree of moisture, and enable us thus to make with more certainty a comparison between the humidities of different climates. May I presume to trouble you with an inquiry of Mr. Nairne, whether he has executed the Doctor’s idea; and if he has, to get him to make for me a couple of the instruments he may have contrived. They should be made of the same piece, and under like circumstances, that sending one to America, I may rely on its indications there, compared with those of the one I shall retain here. Being in want of a set of magnets also, I would be glad if he would at the same time send me a set, the case of which should be made as Dr. Franklin describes his to have been, so that I may repeat his experiment. Colonel Smith will do me the favor to receive these things from Mr. Nairne, and to pay him for them.
I think Mr. Rittenhouse never published an invention of his in this way, which was a very good one. It was of an hygrometer, which, like the common ones, was to give the actual moisture of the air. He has two slips of mahogany about five inches long, three fourths of an inch broad, and one tenth of an inch thick, the one having the grain running lengthwise, and the other crosswise. These are glued together by their faces, so as to form a piece five inches long, three fourths of an inch broad, and one third of an inch thick, which is stuck by its lower end into a little plinth of wood, presenting their edge to the view. The fibres of the wood you know are dilated, but not lengthened by moisture. The slip, therefore, whose grain is lengthwise, becomes a standard, retaining always the same precise length. That which has its grain crosswise, dilates with moisture, and contracts for the want of it. If the right hand piece be the cross-grained one, when the air is very moist, it lengthens, and forces its companion to form a kind of interior annulus of a circle on the left. When the air is dry, it contracts, draws its companion to the right, and becomes itself the interior annulus. In order to show this dilation and contraction, an index is fixed on the upper end of the two slips; a plate of metal or wood is fastened to the front of the plinth, so as to cover the two slips from the eye. A slit, being nearly the portion of a circle, is cut in this plate, so that the shank of the index may play freely through its whole range. On the edge of the slit is a graduation. The objection to this instrument is, that it is not fit for comparative observations, because no two pieces of wood being of the same texture exactly, no two will yield exactly alike to the same agent. However, it is less objectionable on this account, than most of the substances used. Mr. Rittenhouse had a thought of trying ivory: but I do not know whether he executed it. All these substances not only vary from one another at the same time, but from themselves at different times. All of them, however, have some peculiar advantages, and I think this, on the whole, appeared preferable to any other I had ever seen. Not knowing whether you had heard of this instrument, and supposing it would amuse you, I have taken the liberty of detailing it to you.
I beg you to be assured of the sentiments of perfect esteem and respect with which I have the honor to be, Sir, your most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN JAY.
Paris, December 31, 1786
Sir,
I had the honor of addressing you on the 12th of the last month; since which your favor of October the 12th has been received, enclosing a copy of the resolution of Congress for recalling Mr. Lambe. My letter by Mr. Randall informed you, that we had put an end to his powers, and required him to repair to Congress. I lately received a letter from him, dated Alicant, October the 10th, of which I have the honor to enclose you a copy: by which you will perceive, that the circumstance of ill health, either true or false, is urged for his not obeying our call. I shall immediately forward the order of Congress. I am not without fear, that some misapplication of the public money may enter into the causes of his declining to return. The moment that I saw a symptom of this in his conduct, as it was a circumstance which did not admit the delay of consulting Mr. Adams, I wrote to Mr. Carmichael, to stop any monies which he might have in the hands of his banker. I am still unable to judge whether he is guilty of this or not, as by the arrangements with Mr. Adams, who alone had done business with the bankers of the United States, in Holland, Mr. Lambe’s drafts were to be made on him, and I know not what their amount has been. His drafts could not have been negotiated, if made on us both, at places so distant. Perhaps it may be thought, that the appointment of Mr. Lambe was censurable in the moment in which it was made. It is a piece of justice, therefore, which I owe to Mr. Adams, to declare that the proposition went first from me to him. I take the liberty of enclosing you a copy of my letter to Mr. Adams, of September the 24th, 1785, in which that proposition was made. It expresses the motives operating on my mind in that moment, as well as the cautions I thought it necessary to take. To these must be added the difficulty of finding an American in Europe fit for the business, and willing to undertake it. I knew afterwards, that Dr. Bancroft (who is named in the letter) could not, on account of his own affairs, have accepted even a primary appointment. I think it evident, that no appointment could have succeeded without a much greater sum of money.
I am happy to find that Mr. Barclay’s mission has been attended with complete success. For this we are indebted, unquestionably, to the influence and good offices of the court of Madrid. Colonel Franks, the bearer of this, will have the honor to put into your hands the original of the treaty, with other papers accompanying it. It will appear by these, that Mr. Barclay has conducted himself with a degree of intelligence and of good faith which reflects the highest honor on him.
A copy of a letter from Captain O’Bryan to Mr. Carmichael is also herewith enclosed. The information it contains will throw farther light on the affairs of Algiers. His observations on the difficulties which arise from the distance of Mr. Adams and myself from that place, and from one another, and the delays occasioned by this circumstance, are certainly just. If Congress should propose to revive the negotiations, they will judge whether it will not be more expedient to send a person to Algiers, who can be trusted with full powers: and also whether a mission to Constantinople may not be previously necessary. Before I quit this subject, I must correct an error in the letter of Captain O’Bryan. Mr. Lambe was not limited, as he says, to one hundred, but to two hundred dollars apiece for our prisoners. This was the price which had been just paid for a large number of French prisoners, and this was our guide.
I have the honor to be, with the most perfect esteem and respect, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO SAMUEL OSGOOD.
Paris, January 5, 1787.
Dear Sir,
I am desired to forward to you the enclosed queries, and to ask the favor of you to give such an answer to them, as may not give you too much trouble. Those which stand foremost on the paper, can be addressed only to your complaisance; but the last may possibly be interesting to your department, and to the United States. I mean those which suggest the possibility of borrowing money in Europe, the principal of which shall be ultimately payable in land, and in the mean time, a good interest. You know best whether the suggestion can be turned to any profit, and whether it will be worth while to introduce any proposition to Congress thereon. Among the possible shapes into which a matter of this kind may be formed, the following is one. Let us suppose the public lands to be worth a dollar, hard money, the acre. If we should ask of a monied man a loan of one hundred dollars, payable with one hundred acres of land at the end of ten years, and in the mean time, carrying an interest of five per cent., this would be more disadvantageous to the lender than a common loan, payable ultimately in cash. But if we should say, we will deliver you the one hundred acres of land immediately, which is in fact an immediate payment of the principal, and will nevertheless pay your interest of five per cent., for ten years, this offers a superior advantage, and might tempt money-holders. But what should we in fact receive, in this way, for our lands? Thirty-seven dollars and one fourth, being left in Europe, on an interest of five per cent., would pay annually the interest of the one hundred dollars for ten years. There would remain then only sixty-two dollars and three quarters, for the one hundred acres of land; that is to say, about two thirds of its price. Congress can best determine, whether any circumstances in our situation, should induce us to get rid of any of our debts in that way. I beg you to understand, that I have named rates of interest, term of payment and price of land, merely to state the case, and without the least knowledge that a loan could be obtained on these terms. It remains to inform you, from whom this suggestion comes. The person from whom I receive it, is a Monsieur Claviere, connected with the monied men of Amsterdam. He is, on behalf of a company there, actually treating with the Comptroller General here, for the purchase of our debt to this country, at a considerable discount. Whether he has an idea of offering a loan to us, on terms such as I have above spoken of, I know not; nor do I know that he is authorized to make the suggestion he has made. If the thing should be deemed worthy the attention of Congress, they can only consider it as a possibility, and take measures to avail themselves of it, if the possibility turns out in their favor, and not to be disappointed if it does not. Claviere’s proposition not being formal enough for me to make an official communication of it, you will make what use of it you see best.
I am, with very sincere esteem and attachment, Dear Sir, your most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN JAY.
Paris, January 9, 1787.
Sir,
My last, of December the 31st, acknowledged the receipt of yours of October the 12th, as the present does those of October the 3rd, 9th, and 27th, together with the resolution of Congress of October the 16th, on the claim of Schweighaeuser. I will proceed in this business on the return of Mr. Barclay, who being fully acquainted with all the circumstances, will be enabled to give me that information, the want of which might lead me to do wrong on the one side or the other.
Information of the signature of the treaty with Morocco has been long on its passage to you. I will beg leave to recur to dates, that you may see that no part of it has been derived from me. The first notice I had of it, was in a letter from Mr. Barclay, dated, Daralbeyda, August the 11th. I received this on the 13th of September. No secure conveyance offered till the 26th of the same month, being thirteen days after my receipt of it. In my letter of that date, which went by the way of London, I had the honor to enclose you a copy of Mr. Barclay’s letter. The conveyance of the treaty itself is suffering a delay here at present, which all my anxiety cannot prevent. Colonel Franks’ baggage, which came by water from Cadiz to Rouen, has been long and hourly expected. The moment it arrives, he will set out to London, to have duplicates of the treaty signed by Mr. Adams, and from thence he will proceed to New York.
The Chevalier del Pinto, who treated with us on behalf of Portugal, being resident at London, I have presumed that causes of the delay of that treaty had been made known to Mr. Adams, and by him communicated to you. I will write to him by Colonel Franks, in order that you may be answered on that subject.
The publication of the enclosed extract from my letter of May the 27th, 1786, will, I fear, have very mischievous effects. It will tend to draw on the Count de Vergennes the formidable phalanx of the Farms; to prevent his committing himself to me in any conversation which he does not mean for the public papers; to inspire the same diffidence into all other ministers, with whom I might have to transact business; to defeat the little hope, if any hope existed, of getting rid of the Farm on the article of tobacco; and to damp that freedom of, communication which the resolution of Congress of May the 3rd, 1784, was intended to re-establish. Observing by the proceedings of Congress, that they are about to establish a coinage, I think it my duty to inform them, that a Swiss, of the name of Drost, established here, has invented a method of striking the two faces and the edge of a coin, at one stroke. By this, and other simplifications of the process of coinage, he is enabled to coin from twenty-five thousand to thirty thousand pieces a day, with the assistance of only two persons, the pieces of metal being first prepared. I send you by Colonel Franks three coins of gold, silver, and copper, which you will perceive to be perfect medals: and I can assure you, from having seen him coin many, that every piece is as perfect as these. There has certainly never yet been seen any coin, in any country, comparable to this. The best workmen in this way acknowledge that his is like a new art. Coin should always be made in the highest perfection possible, because it is a great guard against the danger of false coinage. This man would be willing to furnish his implements to Congress, and if they please, he will go over and instruct a person to carry on the work: nor do I believe he would ask any thing unreasonable. It would be very desirable, that in the institution of a new coinage, we could set out on so perfect a plan as this, and the more so, as while the work is so exquisitely done, it is done cheaper.
I will certainly do the best I can for the reformation of the consular convention, being persuaded that our States would be very unwilling to conform their laws either to the convention, or to the scheme. But it is too difficult and too delicate, to form sanguine hopes. However, that there may be room to reduce the convention, as much as circumstances will admit, will it not be expedient for Congress to give me powers, in which there shall be no reference to the scheme? The powers sent me, oblige me to produce that scheme, and certainly, the moment it is produced, they will not abate a tittle from it. If they recollect the scheme, and insist on it, we can but conclude it; but if they have forgotten it (which may be), and are willing to reconsider the whole subject, perhaps we may get rid of something the more of it. As the delay is not injurious to us, because the convention, whenever and however made, is to put us in a worse state than we are in now, I shall venture to defer saying a word on the subject, till I can hear from you in answer to this. The full powers may be sufficiently guarded, by private instructions to me, not to go beyond the former scheme. This delay may be well enough ascribed (whenever I shall have received new powers) to a journey, I had before apprized the minister that I should be obliged to take, to some mineral waters in the south of France, to see if by their aid I may recover the use of my right hand, of which a dislocation about four months ago, threatens to deprive me in a great measure. The surgeons have long insisted on this measure. I shall return by Bordeaux, Nantes, and L’Orient, to get the necessary information for finishing our commercial regulations here. Permit me, however, to ask, as immediately as possible, an answer, either affirmative or negative, as Congress shall think best, and to ascribe the delay on which I venture, to my desire to do what is for the best.
I send you a copy of the late marine regulations of this country. There are things in it, which may become interesting to us. Particularly, what relates to the establishment of a marine militia, and their classification.
You will have seen in the public papers, that the King has called an Assembly of the Notables of this country. This has not been done for one hundred and sixty years past. Of course, it calls up all the attention of the people. The objects of this Assembly are not named: several are conjectured. The tolerating the Protestant religion; removing all the internal Custom-houses to the frontier; equalizing the gabelles on salt through the kingdom; the sale of the King’s domains, to raise money; or, finally, the effecting this necessary end by some other means, are talked of. But, in truth, nothing is known about it. This government practises secrecy so systematically, that it never publishes its purposes or its proceedings, sooner or more extensively than necessary. I send you a pamphlet, which, giving an account of the last Assemblée des Notable, may give an idea of what the present will be.
A great desire prevails here of encouraging manufactures. The famous Boulton and Watt, who are at the head of the plated manufactures of Birmingham, the steam mills of London, copying presses and other mechanical works, have been here. It is said, also, that Wedgewood has been here, who is famous for his steel manufactories, and an earthen ware in the antique style; but as to this last person, I am not certain. It cannot, I believe be doubted, but that they came at the request of government, and that they will be induced to establish similar manufactures here.
The transferring hither those manufactures, which contribute so much to draw our commerce to England, will have a great tendency to strengthen our connections with this country, and loosen them with that.
The enfranchising the port of Honfleur at the mouth of the Seine, for multiplying the connections with us, is at present an object. It meets with opposition in the ministry; but I am in hopes it will prevail. If natural causes operate, uninfluenced by accidental circumstances, Bordeaux and Honfleur, or Havre, must ultimately take the greatest part of our commerce. The former, by the Garonne and canal of Languedoc, opens the southern provinces to us; the latter, the northern ones and Paris. Honfleur will be peculiarly advantageous for our rice and whale oil, of which the principal consumption is at Paris. Being free, they can be re-exported when the market here shall happen to be overstocked.
The labors of the ensuing summer will close the eastern half of the harbor of Cherbourg, which will contain and protect forty sail of the line. It has from fifty to thirty-five feet of water next to the cones, shallowing gradually to the shore. Between this and Dunkirk, the navigation of the channel will be rendered much safer in the event of a war with England, and invasions on that country become more practicable.
The gazettes of France and Leyden, to the present date, accompany this.
I have the honor to be, with sentiments of the most perfect respect, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN ADAMS.
Paris, January 11, 1787.
Dear Sir,
Mr. Jay, in his last letter to me, observes they hear nothing further of the treaty with Portugal. I have taken the liberty of telling him that I will write to you on the subject, and that he may expect to hear from you on it, by the present conveyance. The Chevalier del Pinto being at London, I presume he has, or can inform you why it is delayed on their part. I will thank you also for the information he shall give you.
There is here an order of priests called the Mathurins, the object of whose institution is, the begging of alms for the redemption of captives. About eighteen months ago, they redeemed three hundred, which cost them about fifteen hundred livres a piece. They have agents residing in the Barbary States, who are constantly employed in searching and contracting for the captives of their nation, and they redeem at a lower price than any other people can. It occurred to me, that their agency might be engaged for our prisoners at Algiers. I have had interviews with them, and the last night a long one with the General of the order. They offer their services with all the benignity and cordiality possible. The General told me, he could not expect to redeem our prisoners as cheap as their own, but that he would use all the means in his power to do it on the best terms possible, which will be the better, as there shall be the less suspicion that he acts for our public. I told him I would write to you on the subject, and speak to him again. What do you think of employing them, limiting them to a certain price, as three hundred dollars, for instance, or any other sum you think proper? He will write immediately to his instruments there, and in two or three months we can know the event. He will deliver them at Marseilles, Cadiz, or where we please, at our expense. The money remaining of the fund destined to the Barbary business, may, I suppose, be drawn on for this object. Write me your opinion, if you please, on this subject, finally, fully, and immediately, that, if you approve the proposition, I may enter into arrangements with the General before my departure to the waters of Aix, which will be about the beginning of February,
I have the honor to be, with very sincere esteem and respect, Dear Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MONSIEUR LE DUC D’HARCOURT, GOUVERNEUR DU DAUPHIN.
Paris, January 14, 1787.
Sir,
In the conversation with which you were pleased to honor me a few days ago, on the enfranchisement of the port of Honfleur, I took the liberty of observing, that I was not instructed by my constituents to make any proposition on that subject. That it would be agreeable to them, however, I must suppose, because it will offer the following advantages.
1. It is a convenient entrepôt for furnishing us with the manufactures of the northern parts of France, and particularly of Paris, and for receiving and distributing the productions of our country in exchange.
2. Cowes, on the opposite side of the channel, has heretofore been the deposite for a considerable part of our productions, landed in Great Britain in the first instance, but intended for re-exportation. From thence our rice, particularly, has been distributed to France and other parts of Europe. I am not certain, whether our tobaccos were deposited there, or carried to London to be sorted for the different markets. To draw this business from Cowes, no place is so favorably situated as Honfleur.
3. It would be a convenient deposite for our whale-oil, of which, after the supply of Paris, there will be a surplus for re-exportation.
4. Should our fur-trade be recovered out of the hands of the English, it will naturally come to Honfleur, as the out-port of Paris.
5. Salt is an important article in all our return cargoes; because, being carried as ballast, its freight costs nothing. But on account of some regulations, with which I am not well acquainted, it cannot at present be shipped to advantage from any port on the Seine.
6. Our vessels being built sharp, for swift sailing, suffer extremely in most of the western ports of France, in which they are left on dry ground at every ebb of the tide. But at Honfleur, I am told, they can ride in bold water, on a good bottom, and near the shore, at all times.
These facts may, perhaps, throw some light on the question in which, for the good of both countries, you are pleased to interest yourself. I take the liberty, therefore, of barely mentioning them, and with the more pleasure, as it furnishes me an occasion of assuring you of those sentiments of respect and esteem, with which I have the honor to be your most obedient, humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MONSIEUR DE CREVE-COEUR.
Paris, January 15,1787.
Dear Sir,
I see by the Journal of this morning, that they are robbing us of another of our inventions, to give it to the English. The writer, indeed, only admits them to have revived what he thinks was known to the Greeks, that is, the making the circumference of a wheel of one single piece. The farmers in New Jersey were the first who practised it, and they practised it commonly. Dr. Franklin, in one of his trips to London, mentioned this practice to the man now in London, who has the patent for making those wheels. The idea struck him. The Doctor promised to go to his shop, and assist him in trying to make the wheel of one piece. The Jersey farmers do it by cutting a young sapling, and bending it, while green and juicy, into a circle; and leaving it so until it becomes perfectly seasoned. But in London there are no saplings. The difficulty was, then, to give to old wood the pliancy of young. The Doctor and the workman labored together some weeks, and succeeded; and the man obtained a patent for it, which has made his fortune. I was in his shop in London; he told me the whole story himself, and acknowledged not only the origin of the idea, but how much the assistance of Dr. Franklin had contributed to perform the operation on dry wood. He spoke of him with love and gratitude. I think I have had a similar account from Dr. Franklin, but cannot be quite certain. I know, that being in Philadelphia when the first set of patent wheels arrived from London, and were spoken of, by the gentleman (an Englishman) who brought them, as a wonderful discovery, the idea of its being a new discovery was laughed at by the Philadelphians, who, in their Sunday parties across the Delaware, had seen every farmer’s cart mounted on such wheels. The writer in the paper supposes the English workman got his idea from Homer. But it is more likely the Jersey farmer got his idea from thence, because ours are the only farmers who can read Homer; because, too, the Jersey practice is precisely that stated by Homer: the English practice very different. Homer’s words are (comparing a young hero killed by Ajax to a poplar felled by a workman) literally thus: ‘He fell on the ground, like a poplar, which has grown smooth, in the west part of a great meadow; with its branches shooting from its summit. But the chariot-maker, with his sharp axe, has felled it, that he may bend a wheel for a beautiful chariot. It lies drying on the banks of the river.’ Observe the circumstances, which coincide with the Jersey practice. 1. It is a tree growing in a moist place, full of juices, and easily bent. 2. It is cut while green. 3. It is bent into the circumference of a wheel. 4. It is left to dry in that form. You, who write French well and readily, should write a line for the Journal, to reclaim the honor of our farmers. Adieu. Yours affectionately,
Th: Jefferson.
TO COLONEL EDWARD CARRINGTON.
Paris, January 16, 1787.
Dear Sir,
Uncertain whether you might be at New York at the moment of Colonel Franks’ arrival, I have enclosed my private letters for Virginia, under cover to our delegation in general, which, otherwise, I would have taken the liberty to enclose particularly to you, as best acquainted with the situation of the persons to whom they are addressed. Should this find you at New York, I will still ask your attention to them.
In my letter to Mr. Jay, I have mentioned the meeting of the Notables, appointed for the 29th instant. It is now put off to the 7th or 8th of next month. This event, which will hardly excite any attention in America, is deemed here the most important one, which has taken place in their civil line during the present century. Some promise their country great things from it, some nothing. Our friend De la Fayette was placed on the list originally. Afterwards his name disappeared; but finally was reinstated. This shows, that his character here is not considered as an indifferent one; and that it excites agitation. His education in our school has drawn on him a very jealous eye, from a court whose principles are the most absolute despotism. But I hope he has nearly passed his crisis. The King, who is a good man, is favorably disposed towards him; and he is supported by powerful family connections, and by the public good will. He is the youngest man of the Notables, except one, whose office placed him on the list.
The Count de Vergennes has, within these ten days, had a very severe attack of what is deemed an unfixed gout. He has been well enough, however, to do business to-day. But anxieties for him are not yet quieted. He is a great and good minister, and an accident to him might endanger the peace of Europe.
The tumults in America I expected would have produced in Europe an unfavorable opinion of our political state. But it has not. On the contrary, the small effect of these tumults seems to have given more confidence in the firmness of our governments. The interposition of the people themselves on the side of government, has had a great effect on the opinion here. I am persuaded myself, that the good sense of the people will always be found to be the best army. They may be led astray for a moment, but will soon correct themselves. The people are the only censors of their governors; and even their errors will tend to keep these to the true principles of their institution. To punish these errors too severely, would be to suppress the only safeguard of the public liberty. The way to prevent these irregular interpositions of the people, is to give them full information of their affairs through the channel of the public papers, and to contrive that those papers should penetrate the whole mass of the people. The basis of our governments being the opinion of the people, the very first object should be to keep that right; and were it left to me to decide, whether we should have a government without newspapers, or newspapers without a government, I should not hesitate a moment to prefer the latter. But I should mean, that every man should receive those papers, and be capable of reading them. I am convinced that those societies (as the Indians), which live without government, enjoy in their general mass an infinitely greater degree of happiness, than those who live under the European governments. Among the former, public opinion is in the place of law, and restrains morals as powerfully as laws ever did any where. Among the latter, under pretence of governing, they have divided their nations into two classes, wolves and sheep. I do not exaggerate. This is a true picture of Europe. Cherish, therefore, the spirit of our people, and keep alive their attention. Do not be too severe upon their errors, but reclaim them by enlightening them. If once they become inattentive to the public affairs, you, and I, and Congress, and Assemblies, Judges and Governors, shall all become wolves. It seems to be the law of our general nature, in spite of individual exceptions: and experience declares, that man is the only animal which devours his own kind; for I can apply no milder term to the governments of Europe, and to the general prey of the rich on the poor. The want of news has led me into disquisition instead of narration, forgetting you have every day enough of that. I shall be happy to hear from you sometimes, only observing, that whatever passes through the post is read, and that when you write what should be read by myself only, you must be so good as to confide your letter to some passenger, or officer of the packet. I will ask your permission to write to you sometimes, and to assure you of the esteem and respect with which I have the honor to be,
Dear Sir, your most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JAMES MADISON.
Paris, January 30, 1787.
[* The latter part of this letter is in cipher; but appended
to the copy preserved, are explanatory notes, which have
enabled us to publish it entire, except a few words, to
which they afford no key. These are either marked thus * * *,
or the words, which the context seemed to require, inserted
in italics.]
Dear Sir,
My last to you was of the 16th of December; since which I have received yours of November the 25th and December the 4th, which afforded me, as your letters always do, a treat on matters public, individual and economical. I am impatient to learn your sentiments on the late troubles in the Eastern States. So far as I have yet seen, they do not appear to threaten serious consequences. Those States have suffered by the stoppage of the channels of their commerce, which have not yet found other issues. This must render money scarce, and make the people uneasy. This uneasiness has produced acts absolutely unjustifiable: but I hope they will provoke no severities from their governments. A consciousness of those in power, that their administration of the public affairs has been honest, may, perhaps, produce too great a degree of indignation: and those characters wherein fear predominates over hope, may apprehend too much from these instances of irregularity. They may conclude too hastily, that nature has formed man insusceptible of any other government than that of force, a conclusion not founded in truth nor experience. Societies exist under three forms, sufficiently distinguishable. 1. Without government, as among our Indians. 2. Under governments, wherein the will of every one has a just influence; as is the case in England, in a slight degree, and in our States, in a great one. 3. Under governments of force; as is the case in all other monarchies, and in most of the other republics. To have an idea of the curse of existence under these last, they must be seen. It is a government of wolves over sheep. It is a problem, not clear in my mind, that the first condition is not the best. But I believe it to be inconsistent with any great degree of population. The second state has a great deal of good in it. The mass of mankind under that enjoys a precious degree of liberty and happiness. It has its evils too: the principal of which is the turbulence to which it is subject. But weigh this against the oppressions of monarchy, and it becomes nothing. Malo periculosam libertatem quam quietam servitutem. Even this evil is productive of good. It prevents the degeneracy of government, and nourishes a general attention to the public affairs. I hold it, that a little rebellion now and then is a good thing, and as necessary in the political world, as storms in the physical. Unsuccessful rebellions, indeed, generally establish the encroachments on the rights of the people, which have produced them. An observation of this truth should render honest republican governors so mild in their punishment of rebellions, as not to discourage them too much. It is a medicine necessary for the sound health of government.
If these transactions give me no uneasiness, I feel very differently at another piece of intelligence, to wit, the possibility that the navigation of the Mississippi may be abandoned to Spain. I never had any interest westward of the Allegany; and I never will have any. But I have had great opportunities of knowing the character of the people who inhabit that country; and I will venture to say, that the act which abandons the navigation of the Mississippi, is an act of separation between the eastern and western country. It is a relinquishment of five parts out of eight of the territory of the United States; an abandonment of the fairest subject for the payment of our public debts, and the chaining those debts on our own necks, in perpetuum. I have the utmost confidence in the honest intentions of those who concur in this measure; but I lament their want of acquaintance with the character and physical advantages of the people, who, right or wrong, will suppose their interests sacrificed on this occasion to the contrary interests of that part of the confederacy in possession of present power. If they declare themselves a separate people, we are incapable of a single effort to retain them. Our citizens can never be induced, either as militia or as soldiers, to go there to cut the throats of their own brothers and sons, or rather, to be themselves the subjects, instead of the perpetrators, of the parricide. Nor would that country quit the cost of being retained against the will of its inhabitants, could it be done. But it cannot be done. They are able already to rescue the navigation of the Mississippi out of the hands of Spain, and to add New Orleans to their own, territory. They will be joined by the inhabitants of Louisiana. This will bring on a war between them and Spain; and that will produce the question with us, whether it will not be worth our while to become parties with them in the war, in order to re-unite them with us, and thus correct our error. And were I to permit my forebodings to go one step further, I should predict, that the inhabitants of the United States would force their rulers to take the affirmative of that question. I wish I may be mistaken in all these opinions.
We have for some time expected, that the Chevalier de la Luzerne would obtain a promotion in the diplomatic line, by being appointed to some of the courts where this country keeps an ambassador. But none of the vacancies taking place, which had been counted on, I think the present disposition is to require his return to his station in America. He told me himself, lately, that he should return in the spring. I have never pressed this matter on the court, though I knew it to be desirable and desired on our part; because if the compulsion on him to return had been the work of Congress, he would have returned in such ill temper with them, as to disappoint them in the good they expected from it. He would for ever have laid at their door his failure of promotion. I did not press it for another reason, which is, that I have great reason to believe, that the character of the Count de Moutier, who would go, were the Chevalier to be otherwise provided for, would give the most perfect satisfaction in America.
As you have now returned into Congress, it will become of importance, that you should form a just estimate of certain public characters; on which, therefore, I will give you such notes as my knowledge of them has furnished me with. You will compare them with the materials you are otherwise possessed of, and decide on a view of the whole.
You know the opinion I formerly entertained of my friend, Mr. Adams. * * * and the Governor were the first who shook that opinion. I afterwards saw proofs, which convicted him of a degree of vanity, and of a blindness to it, of which no germ appeared in Congress. A seven months’ intimacy with him here and as many weeks in London, have given me opportunities of studying him closely. He is vain, irritable, and a bad calculator of the force and probable effect of the motives which govern men. This is all the ill which can possibly be said of him. He is as disinterested as the Being who made him: he is profound in his views; and accurate in his judgment, except where knowledge of the world is necessary to form a judgment. He is so amiable, that I pronounce you will love him, if ever you become acquainted with him. He would be, as he was, a great man in Congress.
Mr. Carmichael is, I think, very little known in America. I never saw him, and while I was in Congress I formed rather a disadvantageous idea of him. His letters received then showed him vain, and more attentive to ceremony and etiquette, than we suppose men of sense should be. I have now a constant correspondence with him, and find him a little hypochondriac and discontented. He possesses a very good understanding, though not of the first order. I have had great opportunities of searching into his character, and have availed myself of them. Many persons of different nations, coming from Madrid to Paris, all speak of him as in high esteem, and I think it certain that he has more of the Count de Florida Blanca’s friendship, than any diplomatic character at that court. As long as this minister is in office, Carmichael can do more than any other person who could be sent there.
You will see Franks, and doubtless he will be asking some appointment. I wish there may be any one for which he is fit. He is light, indiscreet, active, honest, affectionate. Though Bingham is not in diplomatic office, yet as he wishes to be so, I will mention such circumstances of him, as you might otherwise be deceived in. He will make you believe he was on the most intimate footing with the first characters in Europe, and versed in the secrets of every cabinet. Not a word of this is true. He had a rage for being presented to great men, and had no * * * in the methods by which he could effect it. * * * * *
The Marquis de la Fayette is a most valuable auxiliary to me. His zeal is unbounded, and his weight with those in power, great. His education having been merely military, commerce was an unknown field to him. But his good sense enabling him to comprehend perfectly whatever is explained to him, his agency has been very efficacious. He has a great deal of sound genius, is well remarked by the King, and rising in popularity. He has nothing against him, but the suspicion of republican principles. I think he will one day be of the ministry. His foible is a canine appetite for popularity and fame; but he will get above this. The Count de Vergennes is ill. The possibility of his recovery renders it dangerous for us to express a doubt of it; but he is in danger. He is a great minister in European affairs, but has very imperfect ideas of our institutions, and no confidence in them. His devotion to the principles of pure despotism, renders him unaffectionate to our governments. But his fear of England makes him value us as a make-weight. He is cool, reserved in political conversations, but free and familiar on other subjects, and a very attentive, agreeable person to do business with. It is impossible to have a, clearer, better organized head; but age has chilled his heart,
Nothing should be spared on our part, to attach this country to us. It is the only one on which we can rely for support, under every event. Its inhabitants love us more, I think, than they do any other nation on earth. This is very much the effect of the good dispositions with which the French officers returned. In a former letter, I mentioned to you the dislocation of my wrist. I can make not the least use of it, except for the single article of writing, though it is going on five months since the accident happened. I have great anxieties, lest I should never recover any considerable use of it. I shall, by the advice of my surgeons, set out in a fortnight for the waters of Aix, in Provence. I chose these out of several they proposed to me, because if they fail to be effectual, my journey will not be useless altogether. It will give me an opportunity of examining the canal of Languedoc, and of acquiring knowledge of that species of navigation, which may be useful hereafter: but, more immediately, it will enable me to make the tour of the ports concerned in commerce with us, to examine, on the spot, the defects of the late regulations, respecting our commerce, to learn the further improvements which may be made in it, and, on my return, to get this business finished. I shall be absent between two and three months, unless anything happens to recall me here sooner, which may always be effected in ten days, in whatever part of my route I may be.
In speaking of characters, I omitted those of Reyneval and Hennin, the two eyes of Count de Vergennes. The former is the most important character, because possessing the most of the confidence of the Count. He is rather cunning than wise, his views of things being neither great nor liberal. He governs himself by principles which he has learned by rote, and is fit only for the details of execution. His heart is susceptible of little passions, but not of good ones. He is brother-in-law to M. Gerard, from whom he received disadvantageous impressions of us, which cannot be effaced. He has much duplicity. Hennin is a philosopher, sincere, friendly, liberal, learned, beloved by every body: the other by nobody. I think it a great misfortune that the United States are in the department of the former. As particulars of this kind may be useful to you, in your present situation, I may hereafter continue the chapter. I know it will be safely lodged in your discretion. Feb. 5. Since writing thus far, Franks has returned from England. I learn that Mr. Adams desires to be recalled, and that Smith should be appointed Chargé des Affaires there. It is not for me to decide whether any diplomatic character should be kept at a court, which keeps none with us. You can judge of Smith’s abilities by his letters. They are not of the first order, but they are good. For his honesty, he is like our friend Monroe; turn his soul wrong side outwards, and there is not a speck on it. He has one foible, an excessive inflammability of temper, but he feels it when it comes on, and has resolution enough to suppress it, and to remain silent till it passes over.
I send you, by Colonel Franks, your pocket telescope, walking stick, and chemical box. The two former could not be combined together. The latter could not be had in the form you referred to. Having a great desire to have a portable copying machine, and being satisfied from some experiment, that the principle of the large machine might be applied in a small one, I planned one when in England, and had it made. It answers perfectly. I have since set a workman to making them here, and they are in such demand that he has his hands full. Being assured that you will be pleased to have one, when you shall have tried its convenience, I send you one by Colonel Franks. The machine costs ninety-six livres, the appendages twenty-four livres, and I send you paper and ink for twelve livres; in all, one hundred and thirty-two livres. There is a printed paper of directions: but you must expect to make many essays before you succeed perfectly. A soft brush, like a shaving-brush, is more convenient than the sponge. You can get as much ink and paper as you please, from London. The paper costs a guinea a ream. I am, Dear Sir, with sincere esteem and affection, your most obedient, humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN JAY.
Sir,
Paris, February 1, 1787.
My last letters were of the 31st of December and 9th of January; since which last date, I have been honored with yours of December the 13th and 14th. I shall pay immediate attention to your instructions relative to the South Carolina frigate. I had the honor of informing you of an improvement in the art of coining, made here by one Drost, and of sending you, by Colonel Franks, a specimen of his execution in gold and silver. I expected to have sent also a coin of copper. The enclosed note from Drost will explain the reason why this was not sent. It will let you see also, that he may be employed; as I suppose he is not so certain as he was of being engaged here. Mr. Grand, who knows him, gives me reason to believe he may be engaged reasonably. Congress will decide whether it be worth their attention.
In some of my former letters, I suggested an opportunity of obliging the court, by borrowing as much money in Holland as would pay the debt due here, if such a loan could be obtained; as to which, I was altogether ignorant. To save time, I wrote to Mr. Dumas, to know whether he thought it probable a loan could be obtained, enjoining on him the strictest secrecy, and informing him I was making the inquiry merely of my own motion, and without instruction. I enclose you his answer. He thinks purchasers of the debt could be found, with a sacrifice of a small part of the capital, and a postponement be obtained of some of the first reimbursements. The proposition by him, for an immediate adoption of this measure by me, was probably urged, on his mind by a desire to serve our country, more than a strict attention to my duty, and the magnitude of the object. I hope, on the contrary, that if it should be thought worth a trial, it may be put into the hands of Mr. Adams, who knows the ground, and is known there, and whose former successful negotiations in this line would give better founded hopes of success on this occasion.
I formerly mentioned to you the hopes of preferment, entertained by the Chevalier de la Luzerne. They have been baffled by events; none of the vacancies taking place which had been expected. Had I pressed his being ordered back, I have reason to believe the order would have been given. But he would have gone back in ill humor with Congress, he would have laid for ever at their door the failure of a promotion then viewed as certain; and this might have excited dispositions that would have disappointed us of the good we hoped from his return. The line I have observed with him has been, to make him sensible that nothing was more desired by Congress than his return, but that they would not willingly press it, so as to defeat him of a personal advantage. He sees his prospects fail, and will return in the approaching spring unless something unexpected should turn up in his favor. In this case, the Count de Moutier has the promise of succeeding to him, and if I do not mistake his character, he would give great satisfaction. So that I think you may calculate on seeing one or the other, by midsummer.
It had been suspected that France and England might adopt those concerted regulations of commerce for their West Indies, of which your letter expresses some apprehensions. But the expressions in the 4th, 5th, 7th, 11th, 18th, and other articles of their treaty, which communicate to the English the privileges of the most favored European nation only, has lessened, if not removed those fears. They have clearly reserved a right of favoring, specially, any nation not European; and there is no nation out of Europe, who could so probably have been in their eye at that time, as ours. They are wise. They must see it probable, at least, that any concert with England will be but of short duration; and they could hardly propose to sacrifice for that, a connection with us, which may be perpetual.
We have been for some days, in much inquietude for the Count de Vergennes. He is very seriously ill. Nature seems struggling to decide his disease into a gout. A swelled foot, at present gives us a hope-of this issue. His loss would at all times have been great; but it would be immense during the critical poise of European affairs, existing at this moment. I enclose you a letter from one of the foreign officers, complaining of the non-payment of their interest. It is only one out of many I have received. This is accompanied by a second copy of the Moorish declaration sent me by Mr. Barclay. He went to Alicant to settle with Mr. Lambe; but on his arrival there, found he was gone to Minorca. A copy of his letter will inform you of this circumstance, and of some others relative to Algiers, with his opinion on them. Whatever the States may enable Congress to do for obtaining the peace of that country, it is a separate question whether they will redeem our captives, how, and at what price. If they decide to redeem them, I will beg leave to observe, that it is of great importance that the first redemption be made at as low a price as possible, because it will form the future tariff. If these pirates find that they can have a very great price for Americans, they will abandon proportionably their pursuits against other nations, to direct them towards ours. That the choice of Congress may be enlarged, as to the instruments they may use for effecting the redemption, I think it my duty to inform them, that there is here an order of priests called the Mathurins, the object of whose institution is to beg alms for the redemption of captives. They keep members always in Barbary, searching out the captives of their country, and redeem, I believe, on better terms than any other body, public or private. It occurred to me, that their agency might be obtained for the redemption of our prisoners at Algiers. I obtained conferences with the General, and with some members of the order. The General, with all the benevolence and cordiality possible, undertook to act for us if we should, desire it. He told me that their last considerable redemption was of about three hundred prisoners, who cost them somewhat upwards of fifteen hundred livres apiece. But that they should not be able to redeem ours, as cheap as they do their own; and that it must be absolutely unknown that the public concern themselves in the operation, or the price would be greatly enhanced. The difference of religion was not once mentioned, nor did it appear to me to be thought of. It was a silent reclamation and acknowledgment of fraternity, between two religions of the same family, which historical events of ancient date had rendered more hostile to one another, than to their common adversaries. I informed the General, that I should communicate the good dispositions of his order, to those who alone had the authority to decide whatever related to our captives. Mr. Carmichael informs me, that monies have been advanced for the support of our prisoners at Algiers, which ought to be replaced. I infer from the context of his letter, that these advances have been made by the court of Madrid. I submit the information to Congress.
A treaty of commerce is certainly concluded between France and Russia. The particulars of it are yet secret.
I enclose the gazettes of France and Leyden to this date, and have the honor of assuring you of those sentiments of perfect esteem and respect, with which I am, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MRS. BINGHAM.
Paris, February 7, 1787.
I know, Madam, that the twelve-month is not yet expired; but it will be, nearly, before this will have the honor of being put into your hands. You are then engaged to tell me, truly and honestly, whether you do not find the tranquil pleasures of America, preferable to the empty bustle of Paris. For to what does that bustle tend? At eleven o’clock, it is day, chez madame, the curtains are drawn. Propped on bolsters and pillows, and her head scratched into a little order, the bulletins of the sick are read, and the billets of the well. She writes to some of her acquaintance, and receives the visits of others. If the morning is not very thronged, she is able to get out and hobble round the cage of the Palais Royal; but she must hobble quickly, for the coiffeurs turn is come; and a tremendous turn it is! Happy, if he does not make her arrive when dinner is half over! The torpitude of digestion a little passed, she flutters half an hour through the streets, by way of paying visits, and then to the spectacles. These finished; another half hour is devoted to dodging in and out of the doors of her very sincere friends, and away to supper. After supper, cards and after cards, bed; to rise at noon the next day, and to tread, like a mill-horse, the same trodden circle over again. Thus the days of life are consumed, one by one, without an object beyond the present moment; ever flying from the ennui of that, yet carrying it with us; eternally in pursuit of happiness, which keeps eternally before us. If death or bankruptcy happen to trip us out of the circle, it is matter for the buzz of the evening, and is completely forgotten by the next morning. In America, on the other hand, the society of your husband, the fond cares for the children, the arrangements of the house, the improvements of the grounds, fill every moment with a healthy and an useful activity. Every exertion is encouraging, because to present amusement it joins the promise of some future good. The intervals of leisure are filled by the society of real friends, whose affections are not thinned to cobweb, by being spread over a thousand objects. This is the picture, in the light it is presented to my mind; now let me have it in yours. If we do not concur this year, we shall the next; or if not then, in a year or two more. You see I am determined not to suppose myself mistaken.
To let you see that Paris is not changed in its pursuits, since it was honored with your presence, I send you its monthly history. But this relating only to the embellishments of their persons, I must add, that those of the city go on well also. A new bridge, for example, is begun at the Place Louis Quinze; the old ones are clearing of the rubbish which encumbered them in the form of houses 5 new hospitals erecting; magnificent walls of inclosure, and Custom-houses at their entrances, &c. &c. &c. I know of no interesting change among those whom you honored with your acquaintance, unless Monsieur de Saint James was of that number. His bankruptcy, and taking asylum in the Bastille, have furnished matter of astonishment. His garden, at the Pont de Neuilly, where, on seventeen acres of ground he had laid out fifty thousand louis, will probably sell for somewhat less money. The workmen of Paris are making rapid strides towards English perfection. Would you believe, that in the course of the last two years, they have learned even to surpass their London rivals in some articles? Commission me to have you a phaeton made, and if it is not as much handsomer than a London one, as that is than a fiacre, send it back to me. Shall I fill the box with caps, bonnets, &c.? Not of my own choosing, but I was going to say, of Mademoiselle Bertin’s, forgetting for the moment, that she too is bankrupt. They shall be chosen then by whom you please; or, if you are altogether nonplused by her eclipse, we will call an Assemblées des Notables, to help you out of the difficulty, as is now the fashion. In short, honor me with your, commands of any kind, and they shall be faithfully executed. The packets now established from Havre to New York furnish good opportunities of sending whatever you wish.
I shall end where I began, like a Paris day, reminding you of your engagement to write me a letter of respectable length, an engagement the more precious to me, as it has furnished me the occasion, after presenting my respects to Mr. Bingham, of assuring you of the sincerity of those sentiments of esteem and respect, with which I have the honor to be, Dear Madam, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson,
Paris, February 7, 1787.
I have the honor of enclosing to your Excellency a report of the proceedings on the inauguration of the bust of the Marquis de la Fayette, in this city. This has been attended with a considerable, but a necessary delay. The principle that the King is the sole fountain of honor in this country, opposed a barrier to our desires, which threatened to be insurmountable. No instance of a similar proposition from a foreign power, had occurred in their history. The admitting it in this case, is a singular proof of the King’s friendly dispositions towards the States of America, and of his personal esteem for the character of the Marquis de la Fayette.
I take this, the earliest occasion, of congratulating my country on your excellency’s appointment to the chair of government, and of assuring you, with great sincerity, of those sentiments of perfect esteem and respect, with which I have the honor to be your. Excellency’s most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN JAY.
Paris, February 8, 1787.
Sir,
The packet being to sail the day after to-morrow, I have awaited the last possible moment of writing by her, in hopes I might be able to announce some favorable change in the situation of the Count de Vergennes. But none has occurred, and in the mean time he has become weaker by the continuance of his illness. Though not desperately ill, he is dangerously so. The Comptroller General, M. de Calonne, has been very ill also, but he is getting well. These circumstances have occasioned the postponement of the Assemblée des Notables to the 14th instant, and will probably occasion a further postponement. As I shall set out this day se’nnight for the waters of Aix, you will probably hear the issue of the Count de Vergennes illness through some other channel, before I shall have the honor of addressing you again. I may observe the same as to the final decision for the enfranchisement of Honfleur, which is in a fair way of being speedily concluded. The exertions of Monsieur de Creve-coeur, and particularly his influence with the Duke d’Harcourt, the principal instrument in effecting it, have been of chief consequence in this matter.
I have the honor to be, with the most perfect esteem and respect, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MR. DUMAS.
Paris, February 9, 1787.
Sir,
My last to you was dated December the 25th; since which I have been honored with your several favors of December the 29th, January the 5th, 9th, and 23rd. I thought that your affairs could not be more interesting than they have been for a considerable time. Yet in the present moment they are become more so, by the apparent withdrawing of so considerable a personage in the drama, as the King of Prussia. To increase this interest, another person, whose importance scarcely admits calculation, is in a situation which fills us with alarm. Nature is struggling to relieve him by a decided gout; she has my sincere prayers to aid her, as I am persuaded she has yours. I have letters and papers from America as late as the 15th of December. The government of Massachusetts had imprisoned three of the leaders of their insurgents. The insurgents, being collected to the number of three or four hundred, had sent in their petition to the government, praying another act of pardon for their leaders and themselves, and on this condition offering to go every man home, and conduct himself dutifully afterwards. This is the latest intelligence.
I thank you for your attention to the question I had taken the liberty of proposing to you. I think with you, that it would be advisable to have our debt transferred to individuals of your country. There could and would be no objection to the guarantee remaining as you propose; and a postponement of the first payments of capital would surely be a convenience to us. For though the resources of the United States are great and growing, and their dispositions good, yet their machine is new, and they have not got it to go well. It is the object of their general wish at present, and they are all in movement, to set it in a good train; but their movements are necessarily slow. They will surely effect it in the end, because all have the same end in view; the difficulty being only to get all the thirteen States to agree on the same means. Divesting myself of every partiality, and speaking from that thorough knowledge which I have of the country, their resources, and their principles, I had rather trust money in their hands, than in that of any government on earth; because, though for a while the payments of the interest might be less regular, yet the final reimbursement of the capital would be more sure.
I set out next week for the south of France, to try whether some mineral waters in that quarter, much recommended, will restore the use of my hand. I shall be absent from Paris two or three months; but I take arrangements for the regular receipt of your favors, as if I were here. It will be better, however, for you to put your letters to Mr. Jay under cover to Mr. Short, who remains here, and will forward them.
I have thought it my duty to submit to Congress the proposition about the French debt, and may expect their answer in four months.
I have the honor to be, with sincere esteem and respect, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN JAY.
Paris, February 14, 1787.
Sir,
In the letter of the 8th instant, which I had the honor of writing you, I informed you that the Count de Vergennes was dangerously ill. He died yesterday morning, and the Count de Montmorin is appointed his successor. Your personal knowledge of this gentleman renders it unnecessary for me to say any thing of him.
Mr. Morris, during his office, being authorized to have the medals and swords executed, which had been ordered by Congress, he authorized Colonel Humphreys to take measures here for the execution. Colonel Humphreys did so; and the swords were finished in time for him to carry them. The medals not being finished, he desired me to attend to them. The workman who was to make that of General Greene, brought me yesterday the medal in gold, twenty-three in copper, and the die. Mr. Short, during my absence, will avail himself of the first occasion which shall offer, of forwarding the medals to you. I must beg leave, through you, to ask the pleasure of Congress as to the number they would choose to have struck. Perhaps they might be willing to deposite one of each person in every college of the United States. Perhaps they might choose to give a series of them to each of the crowned heads of Europe, which would be an acceptable present to them. They will be pleased to decide. In the mean time I have sealed up the die, and shall retain it till I am honored with their orders as to this medal, and the others also when they shall be finished.
I have the honor to be, with sentiments of the most perfect esteem and respect,
Sir, your most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN JAY.
Paris, February 23, 1787.
Sir,
The Assemblée des Notables being an event in the history of this country which excites notice, I have supposed it would not be disagreeable to you to learn its immediate objects, though no way connected with our interests. The Assembly met yesterday: the King, in a short but affectionate speech, informed them of his wish to consult with them on the plans he had digested, and on the general good of his people, and his desire to imitate the head of his family, Henry IV., whose memory is so dear to the nation. The Garde des Sceaux then spoke about twenty minutes, chiefly in compliment to the orders present. The Comptroller General, in a speech of about an hour, opened the budget, and enlarged on the several subjects which will be under their deliberation. He explained the situation of the finances at his accession to office, the expenses which their arrangement had rendered necessary, their present state with the improvements made in them, the several plans which had been proposed for their further improvement, a change in the form of some of their taxes, the removal of the interior Custom-houses to the frontiers, and the institution of Provincial Assemblies. The Assembly was then divided into committees, with a prince of the blood at the head of each. In this form they are to discuss separately the subjects which will be submitted to them. Their decision will be reported by two members to the minister, who, on view of the separate decisions of all the committees, will make such changes in his plans, as will best accommodate them to their views, without too much departing from his own, and will then submit them to the vote (but I believe not to the debate) of the General Assembly, which will be convened for this purpose one day in every week, and will vote individually.
The event ©f the Count de Vergennes’death, of which I had the honor to inform you in a letter of the 14th instant, the appointment of the Count Montmorin, and the propriety of my attending at his first audience, which will be on the 27th, have retarded the journey I had proposed a few days.
I shall hope, on my return, to meet here new powers for the consular convention, as, under those I have, it will be impossible to make the changes in the convention, which may be wished for.
I have the honor to be, with sentiments of the most perfect esteem and respect, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO THE MARQUIS DE LA FAYETTE.
Paris, February 28, 1787.
Dear Sir,
I am just now in the moment of my departure. Monsieur de Montmorin having given us audience at Paris yesterday, I missed the opportunity of seeing you once more. I am extremely pleased with his modesty, the simplicity of his manners, and his dispositions towards us. I promise myself a great deal of satisfaction in doing business with him. I hope he will not give ear to any unfriendly suggestions. I flatter myself I shall hear from you sometimes. Send your letters to my hotel as usual, and they will be forwarded to me. I wish you success in your meeting. I should form better hopes of it, if it were divided into two Houses instead of seven. Keeping the good model of your neighboring country before your eyes, you may get on, step by step, towards a good constitution. Though that model is not perfect, yet, as it would unite more suffrages than any new one which could be proposed, it is better to make that the object. If every advance is to be purchased by filling the royal coffers with gold, it will be gold well employed. The King, who means so well, should be encouraged to repeat these Assemblies. You see how we republicans are apt to preach, when we get on politics. Adieu, my dear friend.
Yours affectionately,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MADAME LA COMTESSE DE TESSE.
Nismes, March 20, 1787.
Here I am, Madam, gazing whole hours at the Maison Quarrée, like a lover at his mistress. The stocking-weavers and silk-spinners around it, consider me as a hypochondriac Englishman, about to write with a pistol the last chapter of his history. This is the second time I have been in love since I left Paris. The first was with a Diana at the Chateau de Lay-Epinaye in Beaujolois, a delicious morsel of sculpture, by M. A. Slodtz. This, you will say, was in rule, to fall in love with a female beauty: but with a house! It is out of all precedent. No, Madam, it is not without a precedent, in my own history. While in Paris, I was violently smitten with the Hotel de Salm, and used to go to the Tuileries almost daily to look at it. The loueuse des chaises, inattentive to my passion, never had the complaisance to place a chair there, so that, sitting on the parapet, and twisting my neck round to see the object of my admiration, I generally left it with a torticollis.
From Lyons to Nismes I have been nourished with the remains of Roman grandeur. They have always brought you to my mind, because I know your affection for whatever is Roman and noble. At Vienne I thought of you. But I am glad you were not there; for you would have seen me more angry than I hope you will ever see me. The Praetorian palace, as it is called, comparable, for its fine proportions, to the Maison Quarrée, defaced by the barbarians who have converted it to its present purpose, its beautiful fluted Corinthian columns cut out in part to make space for Gothic windows, and hewed down in the residue to the plane of the building, was enough, you must admit, to disturb my composure. At Orange, too, I thought of you. I was sure you had seen with pleasure the sublime triumphal arch of Marius at the entrance of the city. I went then to the Arena. Would you believe, Madam, that in this eighteenth century, in France, under the reign of Louis XVI., they are at this moment pulling down the circular wall of this superb remain to pave a road? And that too from a hill which is itself an entire mass of stone, just as fit, and more accessible? A former intendant, a M. de Basville, has rendered his memory dear to the traveller and amateur, by the pains he took to preserve and restore these monuments of antiquity. The present one (I do not know who he is) is demolishing the object to make a good road to it. I thought of you again, and I was then in great good humor, at the Pont du Gard, a sublime antiquity, and well preserved. But most of all here, where Roman taste, genius, and magnificence excite ideas analogous to yours at every step. I could no longer oppose the inclination to avail myself of your permission to write to you, a permission given with too much complaisance by you, and used by me with too much indiscretion. Madame de Tott did me the same honor.
But she being only the descendant of some of those puny heroes who boiled their own kettles before the walls of Troy, I shall write to her from a Grecian, rather than a Roman canton: when I shall find myself, for example, among her Phocæan relations at Marseilles.
Loving, as you do, Madam, the precious remains of antiquity, loving architecture, gardening, a warm sun, and a clear sky, I wonder you have never thought of moving Chaville to Nismes. This, as you know, has not always been deemed impracticable; and, therefore, the next time a Surintendant des bailments du roi, after the example of M. Colbert, sends persons to Nismes to move the Maison Quarrée to Paris, that they may not come empty-handed, desire them to bring Chaville with them to replace it. A propos of Paris. I have now been three weeks from there, without knowing any thing of what has passed. I suppose I shall meet it all at Aix, where I have directed my letters to be lodged, poste restante. My journey has given me leisure to reflect on this Assemblée des Notables. Under a good and a young King, as the present, I think good may be made of it. I would have the deputies, then, by all means, so conduct themselves as to encourage him to repeat the calls of this Assembly. Their first step should be to get themselves divided into two chambers instead of seven; the Noblesse and the Commons separately. The second, to persuade the King, instead of choosing the deputies of the Commons himself, to summon those chosen by the people for the Provincial administrations. The third, as the Noblesse is too numerous to be all of the Assemblée, to obtain permission for that body to choose its own deputies. Two Houses, so elected, would contain a mass of wisdom, which would make the people happy, and the King great; would place him in history where no other act can possibly place him. They would thus put themselves in the track of the best guide they can follow, they would soon overtake it, become its guide in turn, and lead to the wholesome modifications wanting in that model, and necessary to constitute a rational government. Should they attempt more than the established habits of the people are ripe for, they must lose all, and retard indefinitely the ultimate object of their aim. These, Madam, are my opinions; but I wish to know yours, which I am sure will be better.
From a correspondent at Nismes you will not expect news. Were I to attempt to give you news, I should tell you stories one thousand years old. I should detail to you the intrigues of the courts of the Cæsars, how they affect us here, the oppressions of their praetors, prefects, &c. I am immersed in antiquities from morning to night. For me the city of Rome is actually existing in all the splendor of its empire. I am filled with alarms for the event of the irruptions daily making on us by the Goths, the Visigoths, Ostrogoths, and Vandals, lest they should re-conquer us to our original barbarism. If I am sometimes induced to look forward to the eighteenth century, it is only when recalled to it by the recollection of your goodness and friendship, and by those sentiments of sincere esteem and respect, with which I have the honor to be,
Madam, your most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO THE MARQUIS DE LA FAYETTE.
Nice, April 11, 1787.
Your head, my dear friend, is full of Notable things; and being better employed, therefore, I do not expect letters from you. I am constantly roving about to see what I have never seen before, and shall never see again. In the great cities, I go to see what travellers think alone worthy of being seen; but I make a job of it, and generally gulp it all down in a day. On the other hand, I am never satiated with rambling through the fields and farms, examining the culture and cultivators with a degree of curiosity, which makes some take me to be a fool, and others to be much wiser than I am. I have been pleased to find among the people a less degree of physical misery than I had expected. They are generally well clothed, and have a plenty of food, not animal indeed, but vegetable, which is as wholesome. Perhaps they are over-worked, the excess of the rent required by the landlord obliging them to too many hours of labor in order to produce that, and wherewith to feed and clothe themselves. The soil of Champagne and Burgundy I have found more universally good than I had expected, and as I could not help making a comparison with England, I found that comparison more unfavorable to the latter than is generally admitted. The soil, the climate, and the productions are superior to those of England, and the husbandry as good, except in one point; that of manure. In England, long leases for twenty-one years, or three lives, to wit, that of the farmer, his wife, and son, renewed by the son as soon as he comes to the possession, for his own life, his wife’s, and eldest child’s, and so on, render the farms there almost hereditary, make it worth the farmer’s while to manure the lands highly, and give the landlord an opportunity of occasionally making his rent keep pace with the improved state of the lands. Here the leases are either during pleasure, or for three, six, or nine years, which does not give the farmer time to repay himself for the expensive operation of well manuring, and therefore, he manures ill, or not at all. I suppose, that could the practice of leasing for three lives be introduced in the whole kingdom, it would, within the term of your life, increase agricultural productions fifty per cent.; or were any one proprietor to do it with his own lands, it would increase his rents fifty per cent, in the course of twenty-five years. But I am told the laws do not permit it. The laws then, in this particular, are unwise and unjust, and ought to give that permission. In the southern provinces, where the soil is poor, the climate hot and dry, and there are few animals, they would learn the art, found so precious in England, of making vegetable manure, and thus improving the provinces in the article in which nature has been least kind to them. Indeed, these provinces afford a singular spectacle. Calculating on the poverty of their soil, and their climate by its latitude only, they should have been the poorest in France. On the contrary, they are the richest, from one fortuitous circumstance. Spurs or ramifications of high mountains, making down from the Alps, and, as it were, reticulating these provinces, give to the vallies the protection of a particular inclosure to each, and the benefit of a general stagnation of the northern winds produced by the whole of them, and thus countervail the advantage of several degrees of latitude. From the first olive fields of Pierrelatte, to the orangeries of Hieres, has been continued rapture to me. I have often wished for you. I think you have not made this journey. It is a pleasure you have to come, and an improvement to be added to the many you have already made. It will be a great comfort to you, to know, from your own inspection, the condition of all the provinces of your own country, and it will be interesting to them at some future day, to be known to you. This is, perhaps, the only moment of your life in which you can acquire that knowledge. And to do it most effectually, you must be absolutely incognito, you must ferret the people out of their hovels as I have done, look into their kettles, eat their bread, loll on their beds under pretence of resting yourself, but in fact to find if they are soft. You will feel a sublime pleasure in the course of this investigation, and a sublimer one hereafter, when you shall be able to apply your knowledge to the softening of their beds, or the throwing a morsel of meat into their kettle of vegetables.
You will not wonder at the subjects of my letter: they are the only ones which have been presented to my mind for some time past; and the waters must always be what are the fountains from which they flow. According to this, indeed, I should have intermixed, from beginning to end, warm expressions of friendship to you. But, according to the ideas of our country, we do not permit ourselves to speak even truths, when they may have the air of flattery. I content myself, therefore, with saying once for all, that I love you, your wife, and children. Tell them so, and adieu.
Yours affectionately,
Th: Jefferson.
TO WILLIAM SHORT.
Nice, April 12, 1787,
Dear Sir,
At Marseilles, they told me I should encounter the rice fields of Piedmont soon after crossing the Alps. Here they tell me there are none nearer than Vercelli and Novara, which is carrying me almost to Milan. I fear that this circumstance will occasion me a greater delay than I had calculated on. However, I am embarked in the project, and shall go through with it. To-morrow, I set out on my passage over the Alps, being to pursue it ninety-three miles to Coni, on mules, as the snows are not yet enough melted to admit carriages to pass. I leave mine here, therefore, proposing to return by water from Genoa. I think it will be three weeks before I get back to Nice. I find this climate quite as delightful as it has been represented. Hieres is the only place in France, which may be compared with it. The climates are equal. In favor of this place, are the circumstances of gay and dissipated society, a handsome city, good accommodations, and some commerce. In favor of Hieres, are environs of delicious and extensive plains, a society more contracted, and therefore more capable of esteem, and the neighborhood of Toulon, Marseilles, and other places, to which excursions may be made. Placing Marseilles in comparison with Hieres, it has extensive society, a good theatre, freedom from military control, and the most animated commerce. But its winter climate is far inferior. I am now in the act of putting my baggage into portable form for my bat-mule; after praying you, therefore, to let my daughter know I am well, and that I shall not be heard of again in three weeks, I take my leave of you for that time, with assurances of the sincere esteem with which I am, Dear Sir, your friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN JAY.
Marseilles, May 4, 1787.
Sir,
I had the honor of receiving at Aix, your letter of February the 9th, and immediately wrote to the Count de Montmorin, explaining the delay of the answer of Congress to the King’s letter, and desired Mr. Short to deliver that answer, with my letter, to Monsieur de Montmorin, which he informs me he has accordingly done.
My absence prevented my noting to you, in the first moment, the revolution which has taken place at Paris, in the department of finance, by the substitution of Monsieur de Fourqueux in the place of Monsieur de Calonne; so that you will have heard of it through other channels, before this will have the honor of reaching you.
Having staid at Aix long enough to prove the inefficacy of the waters, I came on to this place, for the purpose of informing myself here, as I mean to do at the other seaport towns, of whatever may be interesting to our commerce. So far as carried on in our own bottoms, I find it almost nothing; and so it must probably remain, till something can be done with the Algerines. Though severely afflicted with the plague, they have come out within these few days, and showed themselves in force along the coast of Genoa, cannonading a little town and taking several vessels.
Among other objects of inquiry, this was the place to learn something more certain on the subject of rice, as it is a great emporium for that of the Levant, and of Italy. I wished particularly to know, whether it was the use of a different machine for cleaning, which brought European rice to market less broken than ours, as had been represented to me, by those who deal in that article in Paris. I found several persons who had passed through the rice country of Italy, but not one who could explain to me the nature of the machine. But I was given to believe, that I might see it myself immediately on entering Piedmont. As this would require but about three weeks, I determined to go, and ascertain this point; as the chance only of placing our rice above all rivalship in quality, as it is in color, by the introduction of a better machine, if a better existed, seemed to justify the application of that much time to it. I found the rice country to be in truth Lombardy, one hundred miles further than had been represented, and that though called Piedmont rice, not a grain is made in the country of Piedmont. I passed through the rice-fields of the Vercellese and Milanese, about sixty miles, and returned from thence last night, having found that the machine is absolutely the same as ours, and of course, that we need not listen more to that suggestion. It is a difference in the species of grain; of which the government of Turin is so sensible, that, as I was informed, they prohibit the exportation of rough rice, on pain of death. I have taken measures, however, which I think will not fail, for obtaining a quantity of it, and I bought on the spot a small parcel, which I have with me. As further details on this subject to Congress would be misplaced, I propose, on my return to Paris, to communicate them, and send the rice to the society at Charleston for promoting agriculture, supposing that they will be best able to try the experiment of cultivating the rice of this quality, and to communicate the species to the two States of South Carolina and Georgia, if they find it answers. I thought the staple of these two States was entitled to this attention, and that it must be desirable to them, to be able to furnish rice of the two qualities demanded in Europe, especially, as the greater consumption is in the forms for which the Lombardy quality is preferred. The mass of our countrymen being interested in agriculture, I hope I do not err in supposing, that in a time of profound peace, as the present, to enable them to adapt their productions to the market, to point out markets for them, and endeavor to obtain favorable terms of reception, is within the line of my duty.
My journey into this part of the country has procured me information, which I will take the liberty of communicating to Congress. In October last, I received a letter, dated Montpelier, October the 2nd, 1786, announcing to me that the writer was a foreigner, who had a matter of very great consequence to communicate to me, and desired I would indicate the channel through which it might pass safely. I did so.
I received soon after, a letter in the following words, omitting only the formal parts. [A translation of it is here given.]
‘I am a native of Brazil. You are not ignorant of the frightful slavery under which my country groans. This continually becomes more insupportable, since the epoch of your glorious independence; for the cruel Portuguese omit nothing which can render our condition more wretched, from an apprehension that we may follow your example. The conviction, that these usurpers against the laws of nature and humanity only meditate new oppressions, has decided us to follow the guiding light which you have held out to us, to break our chains, to revive our almost expiring liberty, which is nearly overwhelmed by that force, which is the sole foundation of the authority that Europeans exercise over America. But it is necessary that some power should extend assistance to the Brazilians, since Spain would certainly unite herself with Portugal; and in spite of our advantages for defence, we could not make it effectual, or, at least, it would be imprudent to hazard the attempt, without some assurance of success. In this state of affairs, Sir, we can, with propriety, look only to the United States, not only because we are following her example, but, moreover, because nature, in making us inhabitants of the same continent, has in some sort united us in the bonds of a common patriotism. On our part, we are prepared to furnish the necessary supplies of money, and at all times to acknowledge the debt of gratitude due to our benefactors. I have thus, Sir, laid before you a summary of my views. It is in discharge of this commission that I have come to France, since I could not effect it in America without exciting suspicion. It now remains for you to decide whether those views can be accomplished. Should you desire to consult your nation on them, it is in my power to give you all the information you may require.’
As by this time, I had been advised to try the waters of Aix, I wrote to the gentleman my design, and that I would go off my road as far as Nismes, under the pretext of seeing the antiquities of that place, if he would meet me there. He met me, and the following is the sum of the information I received from him. ‘Brazil contains as many inhabitants as Portugal. They are, 1. Portuguese. 2. Native whites. 3. Black and mulatto slaves. 4. Indians, civilized and savage. 1. The Portuguese are few in number, mostly married there, have lost sight of their native country, as well as the prospect of returning to it, and are disposed to become independent. 2. The native whites form the body of their nation. 3. The slaves are as numerous as the free. 4. The civilized Indians have no energy, and the savage would not meddle. There are twenty thousand regular troops. Originally these were Portuguese. But as they died off, they were replaced by natives, so that these compose at present the mass of the troops, and may be counted on by their native country. The officers are partly Portuguese, partly Brazilians: their bravery is not doubted, and they understand the parade, but not the science of their profession. They have no bias for Portugal, but no energy either for any thing. The priests are partly Portuguese, partly Brazilians, and will not interest themselves much. The Noblesse are scarcely known as such. They will, in no manner, be distinguished from the people. The men of letters are those most desirous of a revolution. The people are not much under the influence of their priests, most of them read and write, possess arms, and are in the habit of using them for hunting. The slaves will take the side of their masters. In short, as to the question of revolution, there is but one mind in that Country. But there appears no person capable of conducting a revolution, or willing to venture himself at its head, without the aid of some powerful nation, as the people of their own might fail them. There is no printing press in Brazil. They consider the North American revolution as a precedent for theirs. They look to the United States as most likely to give them honest support, and, from a variety of considerations, have the strongest prejudices in our favor. This informant is a native and inhabitant of Rio Janeiro, the present metropolis, which contains fifty thousand inhabitants, knows well St. Salvador, the former one, and the mines d’or, which are in the centre of the country. These are all for a revolution; and, constituting the body of the nation, the other parts will follow them, The King’s fifth of the mines, yields annually thirteen millions of crusadoes or half dollars. He has the sole right of searching for diamonds and other precious stones, which yield him about half as much. His income from those two resources alone, then, is about ten millions of dollars annually; but the remaining part of the produce of the mines, being twenty-six millions, might be counted on for effecting a revolution. Besides the arms in the hands of the people, there are public magazines. They have abundance of horses, but only a part of their country would admit the service of horses. They would want cannon, ammunition, ships, sailors, soldiers, and officers, for which they are disposed to look to the United States, it being always understood, that every service and furniture will be well paid. Corn costs about twenty livres the one hundred pounds. They have flesh in the greatest abundance, insomuch, that in some parts, they kill beeves for the skin only. The whale fishery is carried on by Brazilians altogether, and not by Portuguese; but in very small vessels, so that the fishermen know nothing of managing a large ship. They would want of us; at all times, shipping, corn, and salt fish. The latter is a great article, and they are at present supplied with it from Portugal. Portugal being without either army or navy, could not attempt an invasion under a twelvemonth. Considering of what it would be composed, it would not be much to be feared, and if it failed, they would probably never attempt a second. Indeed, this source of their wealth being intercepted, they are scarcely capable of a first effort. The thinking part of the nation are so sensible of this, that they consider an early separation inevitable. There is an implacable hatred between the Brazilians and Portuguese; to reconcile which, a former minister adopted the policy of letting the Brazilians into a participation of public offices; but subsequent administrations have reverted to the ancient policy of keeping the administrations in the hands of native Portuguese. There is a mixture of natives, of the old appointments, still remaining in office. If Spain should invade them on their southern extremities, these are so distant from the body of their settlements, that they could not penetrate thence; and Spanish enterprise is not formidable. The mines d’or are among mountains, inaccessible to any army; and Rio Janeiro is considered the strongest port in the world after Gibraltar. In case of a successful revolution, a republican government in a single body would probably be established.’
I took care to impress on him, through the whole of our conversation, that I had neither instructions nor authority to say a word to any body on this subject, and that I could only give him my own ideas, as a single individual: which were, that we were not in a condition at present to meddle nationally in any war; that we wished particularly to cultivate the friendship of Portugal, with whom we have an advantageous commerce. That yet, a successful revolution in Brazil could not be uninteresting to us. That prospects of lucre might possibly draw numbers of individuals to their aid, and purer motives our officers, among whom are many excellent. That our citizens being free to leave their own country individually, without the consent of their governments, are equally free to go to any other.
A little before I received the first letter of the Brazilian, a gentleman informed me there was a Mexican in Paris, who wished to have some conversation with me. He accordingly called on me. The substance of the information I drew from him, was as follows. He is himself a native of Mexico, where his relations are, principally. He left it about seventeen years of age, and seems now to be about thirty-three or thirty-four. He classes and characterizes the inhabitants of that country, as follows. 1. The natives of Old Spain, possessed of most of the offices of government, and firmly attached to it. 2. The clergy, equally attached to the government. 3. The natives of Mexico, generally disposed to revolt, but without instruction, without energy, and much under the dominion of their priests. 4. The slaves, mulatto and black; the former enterprising and intelligent, the latter brave, and of very important weight, into whatever scale they throw themselves; but he thinks they will side with their masters. 5. The conquered Indians, cowardly, not likely to take any side, nor important which they take. 6. The free Indians, brave and formidable, should they interfere, but not likely to do so, as being at a great distance. I asked him the numbers of these several classes, but he could not give them. The first, he thought very inconsiderable; that the second formed the body of the freemen; the third equal to the two first; the fourth, to all the preceding: and as to the fifth, he could form no idea of their proportion. Indeed, it appeared to me, that his conjectures as to the others were on loose grounds. He said he knew from good information, there were three hundred thousand inhabitants in the city of Mexico. I was still more cautious with him than with the Brazilian, mentioning it as my private opinion (unauthorized to say a word on the subject, otherwise), that a successful revolution was still at a distance with them; that I feared they must begin by enlightening and emancipating the minds of their people; that as to us, if Spain should give us advantageous terms of commerce, and remove other difficulties, it was not probable that we should relinquish certain and present advantages, though smaller, for uncertain and future ones, however great. I was led into this caution by observing, that this gentleman was intimate at the Spanish ambassador’s, and that he was then at Paris, employed by Spain to settle her boundaries with France, on the Pyrenees. He had much the air of candor, but that can be borrowed; so that I was not able to decide about him in my own mind.
Led by a unity of subject, and a desire to give Congress as general a view of the disposition of our southern countrymen, as my information enables me, I will add an article which, old and insulated, I did not think important enough to mention at the time I received it. You will remember, Sir, that during the late war, the British papers often gave details of a rebellion in Peru. The character of those papers discredited the information. But the truth was, that the insurrections were so general, that the event was long on the poise. Had Commodore Johnson, then expected on that coast, touched and landed there two thousand men, the dominion of Spain in that country would have been at an end. They only wanted a point of union, which this body would have constituted. Not having this, they acted without concert, and were are length subdued separately. This conflagration was quenched in blood; two hundred thousand souls, on both sides, having perished; but the remaining matter is very capable of combustion. I have this information from a person who was on the spot at the time, and whose good faith, understanding, and means of information leave no doubt of the facts. He observed, however, that the numbers above supposed to have perished were on such conjectures only as he could collect.
I trouble Congress with these details, because, however distant we may be, both in condition and dispositions, from taking an active part in any commotions in that country, nature has placed it too near us to make its movements altogether indifferent to our interests, or to our curiosity.
I hear of another Arrêt of this court, increasing the duties on foreign stock-fish, and the premium on their own imported into their islands; but not having yet seen it, I can say nothing certain on it. I hope the effect of this policy will be defeated by the practice which, I am told, takes place on the Banks of Newfoundland, of putting our fish into the French fishing-boats, and the parties sharing the premium, instead of ours paying the duty.
I am in hopes Mr. Short will be able to send you the medals of General Gates by this packet. I await a general instruction as to these medals. The academies of Europe will be much pleased to receive each a set.
I propose to set out the day after to-morrow for Bordeaux (by the canal of Languedoc), Mantes, L’Orient, and Paris.
I have the honor to be, with sentiments of the most perfect esteem and respect, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO M. GUIDE.
Marseilles, May 6, 1787.
Sir,
A desire of seeing a commerce commenced between the dominions of his Majesty, the King of Sardinia, and the United States of America, and a direct exchange of their respective productions, without passing through a third nation, led me into the conversation which I had the honor of having with you on that subject, and afterwards with Monsieur Tallon at Turin, to whom I promised that I would explain to you, in writing, the substance of what passed between us. The articles of your produce wanted with us are brandies, wines, oil, fruits, and manufactured silks: those with which we can furnish you are indigo, potash, tobacco, flour, salt-fish, furs and peltries, ships and materials for building them. The supply of tobacco, particularly, being in the hands of government solely, appeared to me to offer an article for beginning immediately the experiment of direct commerce. That of the first quality can be had at first hand only from James river in Virginia; those of the second and third from the same place, and from Baltimore in Maryland. The first quality is delivered in the ports of France at thirty-eight livres the quintal, the second at thirty-six livres, the third at thirty-four livres, weight and money of France, by individuals generally. I send you the copy of a large contract, wherein the three qualities are averaged at thirty-six livres. They may be delivered at Nice for those prices. Indeed, it is my opinion, that by making shipments of your own produce to those places, and buying the tobaccos on the spot, they may be had more advantageously. In this case, it would be expedient that merchants of Nice, Turin, and America, should form a joint concern for conducting the business in the two countries. Monsieur Tallon desired me to point out proper persons in America who might be addressed for this purpose. The house of the most extensive reputation, concerned in the tobacco trade, and on the firmest funds, is that of Messrs. Ross and Pleasants at Richmond, in Virginia. If it should be concluded on your part to make any attempt of this kind, and to address yourselves to these gentlemen, or any others, it would be best to write them your ideas, and receive theirs, before you make either purchases or shipments. A more hasty conduct might occasion loss, and retard, instead of encouraging, the establishment of this commerce. I would undertake to write, at the same time, to these or any other merchants whom you should prefer, in order to dispose them favorably, and as disinterestedly as possible, for the encouragement of this essay. I must observe to you, that our vessels are fearful of coming into the Mediterranean on account of the Algerines: and that if you should freight vessels, those of the French will be most advantageous for you, because received into our ports without paying any duties on some of those articles, and lighter than others on all of them. English vessels, on the other hand, are distinguished by paying heavier duties than those of any other nation. Should you desire any further information, or to pass letters with certainty to any mercantile house in America, do me the favor to address yourselves to me at Paris, and I shall do whatever depends on me for this object.
I have the honor to be, with sentiments of high esteem and respect, Sir, your most obedient, humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
Memoranda taken on a Journey from Paris into the Southern Parts of France, and Northern of Italy, in the year 1787.
CHAMPAGNE. March 3. Sens to Vermanton. The face of the country is in large hills, not too steep for the plough, somewhat resembling the Elk hill and Beaver-dam hills of Virginia. The soil is generally a rich mulatto loam, with a mixture of coarse sand, and some loose stone. The plains of the Yonne are of the same color. The plains are in corn, the hills in vineyard, but the wine not good. There are a few apple-trees, but none of any other kind, and no enclosures. No cattle, sheep, or swine; fine mules.
Few chateaux; no farm-houses, all the people being gathered in villages. Are they thus collected by that dogma of their religion, which makes them believe, that to keep the Creator in good humor with his own works, they must mumble a mass every day? Certain it is, that they are less happy and less virtuous in villages, than they would be insulated with their families on the grounds they cultivate. The people are illy clothed. Perhaps they have put on their worst clothes at this moment, as it is raining. But I observe women and children carrying heavy burthens, and laboring with the hoe. This is an unequivocal indication of extreme poverty. Men, in a civilized country, never expose their wives and children to labor above their force and sex, as long as their own labor can protect them from it. I see few beggars. Probably this is the effect of a police.
BURGUNDY. March 4. Lucy-le-Bois. Cussy-les-Forges. Rouvray. Maison-neuve. Vitieaux. La Chaleure. Pont de Panis. Dijon. The hills are higher, and more abrupt. The soil a good red loam and sand, mixed with more or less grit, small stone, and sometimes rock. All in corn. Some forest wood here and there, broom, whins, and holly, and a few enclosures of quick-hedge. Now and then a flock of sheep.
The people are well clothed, but it is Sunday. They have the appearance of being well fed. The Chateau de Sevigny, near Cussy-les-Forges, is a charming situation. Between Maison-neuve and Vitteaux the road leads through an avenue of trees, eight American miles long, in a right line. It is impossible to paint the ennui of this avenue. On the summits of the hills, which border the valley in which Vitteaux is, there is a parapet of rock, twenty, thirty, or forty feet perpendicular, which crowns the hills. The tops are nearly level, and appear to be covered with earth. Very singular. Great masses of rock in the hills between La Chaleure and Pont de Panis, and a conical hill in the approach to the last place.
Dijon. The tavern price of a bottle of the best wine (e. g. of Vaune) is four livres. The best round potatoes here, I ever saw. They have begun a canal thirty feet wide, which is to lead into the Saone at ————-. It is fed by springs. They are not allowed to take any water out of the riviere d’Ouche, which runs through this place, on account of the mills on that river. They talk of making a canal to the Seine, the nearest navigable part of which, at present, is fifteen leagues from hence. They have very light wagons here for the transportation of their wine. They are long and narrow; the fore-wheels as high as the hind. Two pieces of wine are drawn by one horse in one of these wagons. The road in this part of the country is divided into portions of forty or fifty feet by stones, numbered, which mark the task of the laborers.
March 7 and 8. From La Baraque to Chagny. On the left are plains, which extend to the Saone; on the right the ridge of mountains, called the Cote. The plains are of a reddish-brown, rich loam, mixed with much small stone. The Cote has for its basis a solid rock, on which is about a foot of soil and small stone, in equal quantities, the soil red, and of middling quality. The plains are in corn; the Cote in vines. The former have no enclosures, the latter is in small ones, of dry stone wall. There is a good deal of forest. Some small herds of small cattle and sheep. Fine mules, which come from Provence, and cost twenty louis. They break them at two years old, and they last to thirty.
The corn-lands here rent for about fifteen livres the arpent. They are now planting, pruning, and sticking their vines. When a new vineyard is made, they plant the vines in gutters about four feet apart. As the vines advance, they lay them down. They put out new shoots, and fill all the intermediate space, till all trace of order is lost. They have ultimately about one foot square to each vine. They begin to yield good profit at five or six years old, and last one hundred, or one hundred and fifty years. A vigneron at Volnay carried me into his vineyard, which was of about ten arpents. He told me, that some years it produced him sixty pieces of wine, and some not more than three pieces. The latter is the most advantageous produce, because the wine is better in quality, and higher in price, in proportion as less is made; and the expenses, at the same time, diminish in the same proportion. Whereas, when much is made, the expenses are increased, while the quality and price become less. In very plentiful years, they often give one half the wine for casks to contain the other half. The cask for two hundred and fifty bottles costs six livres in scarce years, and ten in plentiful. The feuillette is of one hundred and twenty-five bottles, the piece of two hundred and fifty, and the queue or botte of five hundred. An arpent rents at from twenty to sixty livres. A farmer of ten arpents has about three laborers engaged by the year. He pays four louis to a man, and half as much to a woman, and feeds them. He kills one hog, and salts it, which is all the meat used in the family during the year. Their ordinary food is bread and vegetables. At Pomard and Volnay, I observed them eating good wheat bread; at Meursault, rye. I asked the reason of the difference. They told me, that the white wines fail in quality much oftener than the red, and remain on hand. The farmer, therefore, cannot afford to feed his laborers so well. At Meursault only white wines are made, because there is too much stone for the red. On such slight circumstances depends the condition of man! The wines which have given such celebrity to Burgundy grow only on the Cote, an extent of about five leagues long, and half a league wide. They begin at Chambertin, and go through Vougeau, Romanie, Veaune, Nuits, Beaune, Pomard, Volnay, Meursault, and end at Monrachet. Those of the two last are white; the others red. Chambertin, Vougeau, and Beaune are the strongest, and will bear transportation and keeping. They sell, therefore, on the spot for twelve hundred livres the queue, which is forty-eight sous the bottle. Volnay is the best of the other reds, equal in flavor to Chambertin, &c., but being lighter, will not keep, and therefore sells for not more than three hundred livres the queue, which is twelve sous the bottle. It ripens sooner than they do, and consequently is better for those who wish to broach at a year old. In like manner of the white wines, and for the same reason, Monrachet sells for twelve hundred livres the queue (forty-eight sous the bottle), and Meursault of the best quality, viz. the Goutte d’or, at only one hundred and fifty livres (six sous the bottle). It is remarkable, that the best of each kind, that is, of the red and white, is made at the extremities of the line, to wit, at Chambertin and Monrachet. It is pretended, that the adjoining vineyards produce the same qualities, but that, belonging to obscure individuals, they have not obtained a name, and therefore sell as other wines. The aspect of the Cote is a little south of east. The western side is also covered with vines, and is apparently of the same soil; yet the wines are only of the coarsest kinds. Such, too, are those which are produced in the plains; but there the soil is richer, and less strong. Vougeau is the property of the monks of Citeaux, and produces about two hundred pieces. Monrachet contains about fifty arpents, and produces, one year with another, about one hundred and twenty pieces. It belongs to two proprietors only, Monsieur de Clarmont, who leases to some wine-merchants, and the Marquis de Sarsnet, of Dijon, whose part is farmed to a Monsieur de la Tour, whose family, for many generations, have had the farm. The best wines are carried to Paris by land. The transportation costs thirty-six livres the piece. The more indifferent go by water. Bottles cost four and a half sous each.
March 9. Chalons. Sennecey. Tournus. St. Albin. Macon. On the left are the fine plains of the Saone; on the right high lands, rather waving than hilly, sometimes sloping gently to the plains, sometimes dropping down in precipices, and occasionally broken into beautiful vallies[sp.] by the streams which run into the Saone. The plains are a dark rich loam, in pasture and corn; the heights more or less red or reddish, always gritty, of middling quality only, their sides in vines, and their summits in corn. The vineyards are enclosed with dry stone-walls, and there are some quick-hedges in the corn-grounds. The cattle are few and indifferent. There are some good oxen, however. They draw by the head. Few sheep, and small. A good deal of wood-lands.
I passed three times the canal called Le Charollois, which they are opening from Chalons on the Saone to Dijon on the Loire. It passes near Chagny, and will be twenty-three leagues long. They have worked on it three years, and will finish it in four more. It will reanimate the languishing commerce of Champagne and Burgundy, by furnishing a water transportation for their wines to Nantes, which also will receive new consequence by becoming the emporium of that commerce. At some distance on the right are high mountains, which probably form the separation between the waters of the Saone and Loire. Met a malefactor in the hands of one of the Marichausee; perhaps a dove in the talons of the hawk. The people begin now to be in separate establishments, and not in villages. Houses are mostly covered with tile.
BEAUJOLOIS.[Sp.] Maison Blanche. St. George. Chateau de Laye-Epinaye. The face of the country is like that from Chalons to Macon. The plains are a dark rich loam, the hills a red loam of middling quality, mixed generally with more or less coarse sand and grit, and a great deal of small stone. Very little forest. The vineyards are mostly enclosed with dry stone-wall. A few small cattle and sheep. Here, as in Burgundy, the cattle are all white. This is the richest country I ever beheld. It is about ten or twelve leagues in length, and three, four, or five in breadth; at least that part of it, which is under the eye of a traveller. It extends from the top of a ridge of mountains, running parallel with the Saone, and sloping down to the plains of that river, scarce any where too steep for the plough. The whole is thick set with farm-houses, chateaux, and the bastides of the inhabitants of Lyons. The people live separately, and not in villages. The hill-sides are in vine and corn: the plains in corn and pasture. The lands are farmed either for money, or on half-stocks. The rents of the corn-lands, farmed for money, are about ten or twelve livres the arpent. A farmer takes perhaps about one hundred and fifty arpents, for three, six, or nine years. The first year they are in corn; the second in other small grain, with which he sows red clover. The third is for the clover. The spontaneous pasturage is of greensward, which they call fromenteau. When lands are rented on half-stocks, the cattle, sheep, &c. are furnished by the landlord. They are valued, and must be left of equal value. The increase of these, as well as the produce of the farm is divided equally. These leases are only from year to year. They have a method of mixing beautifully the culture of vines, trees, and corn. Rows of fruit-trees are planted about twenty feet apart. Between the trees, in the row, they plant vines four feet apart, and espalier them. The intervals are sowed alternately in corn, so as to be one year in corn, the next in pasture, the third in corn, the fourth in pasture, &c. One hundred toises of vines in length, yield generally about four pieces of wine. In Dauphine, I am told, they plant vines only at the roots of the trees, and let them cover the whole trees. But this spoils both the wine and the fruit. Their wine, when distilled, yields but one-third its quantity in brandy. The wages of a laboring man here are five louis; of a woman, one half. The women do not work with the hoe: they only weed the vines, the corn, &c, and spin. They speak a patois very difficult to understand. I passed some time at the Chateau de Laye-Epinaye. Monsieur de Laye has a seignory of about fifteen thousand arpents, in pasture, corn, vines, and wood. He has over this, as is usual, a certain jurisdiction, both criminal and civil. But this extends only to the first crude examination, which is before his judges. The subject is referred, for final examination and decision, to the regular judicatures of the country. The Seigneur is keeper of the peace on his domains. He is therefore subject to the expenses of maintaining it. A criminal prosecuted to sentence and execution costs M. de Laye about five thousand livres. This is so burthensome to the Seigneurs, that they are slack in criminal prosecutions. A good effect from a bad cause. Through all Champagne, Burgundy, and the Beaujolois, the husbandry seems good, except that they manure too little. This proceeds from the shortness of their leases. The people of Burgundy and Beaujolois are well clothed, and have the appearance of being well fed. But they experience all the oppressions which result from the nature of the general government, and from that of their particular tenures, and of the seignorial government to which they are subject. What a cruel reflection, that a rich country cannot long be a free one. M. de Laye has a Diana and Endymion, a very superior morsel of sculpture by Michael Angelo Slodtz, done in 1740. The wild gooseberry is in leaf; the wild pear and sweet-briar in bud.
Lyons. There are some feeble remains here of an amphitheatre of two hundred feet diameter, and of an aqueduct in brick. The Pont d’Ainay has nine arches of forty feet from centre to centre. The piers are of six feet. The almond is in bloom.
DAUPHINE. From St. Fond to Mornant. March 15, 16, 17, 18. The Rhone makes extensive plains, which lie chiefly on the eastern side, and are often in two stages. Those of Montelimart are three,or four miles wide, and rather good. Sometimes, as in the neighborhood of Vienne, the hills come in precipices to the river, resembling then very much our Susquehanna and its hill, except that the Susquehanna is ten times as wide as the Rhone. The highlands are often very level. The soil both of hill and plain, where there is soil, is generally tinged, more or less, with red. The hills are sometimes mere masses of rock, sometimes a mixture of loose stone and earth. The plains are always stony, and as often as otherwise covered perfectly with a coat of round stones, of the size of the fist, so as to resemble the remains of inundations, from which all the soil has been carried away. Sometimes they are middling good, sometimes barren. In the neighborhood of Lyons there is more corn than wine. Towards Tains more wine than corn. From thence the plains, where best, are in corn, clover, almonds, mulberries, walnuts: where there is still some earth, they are in corn, almonds, and oaks. The hills are in vines. There is a good deal of forest-wood near Lyons, but not much afterwards. Scarcely any enclosures. There are a few small sheep before we reach Tains; there the’number increases.
Nature never formed a country of more savage aspect, than that on both sides the Rhone. A huge torrent rushes like an arrow between high precipices, often of massive rock, at other times of loose stone, with but little earth. Yet has the hand of man subdued this savage scene, by planting corn where there is a little fertility, trees where there is still less, and vines where there is none. On the whole, it assumes a romantic, picturesque, and pleasing air. The hills on the opposite side of the river, being high, steep, and laid up in terraces, are of a singular appearance. Where the hills are quite in waste, they are covered with broom, whins, box, and some clusters of small pines. The high mountains of Dauphine and Languedoc are now covered with snow. The almond is in general bloom, and the willow putting out its leaf. There were formerly olives at Tain; but a great cold, some years ago, killed them, and they have not been replanted. I am told at Montelimart, that an almond tree yields about three livres profit a year. Supposing them three toises apart, there will be one hundred to the arpent, which gives three hundred livres a year, besides the corn growing on the same ground. A league below Vienne, on the opposite side of the river, is Cote Rotie. It is a string of broken hills, extending a league on the river, from the village of Ampuis to the town of Condrieu. The soil is white, tinged a little, sometimes, with yellow, sometimes with red, stony, poor, and laid up in terraces. Those parts of the hills only, which look to the sun at mid-day, or the earlier hours of the afternoon, produce wines of the first quality. Seven hundred vines, three feet apart, yield a feuillette, which is about two and a half pièces, to the arpent. The best red wine is produced at the upper end, in the neighborhood of Ampuis; the best white, next to Condrieu. They sell of the first quality and last vintage, at one hundred and fifty livres the pièce, equal to twelve sous the bottle. Transportation to Paris is sixty livres, and the bottle four sous; so it may be delivered at Paris in bottles, at twenty sous. When old, it costs ten or eleven louis the pièce. There is a quality which keeps well, bears transportation, and cannot be drunk under four years. Another must be drunk at a year old. They are equal in flavor and price.
The wine called Hermitage, is made on the hills impending over the village of Tain; on one of which is the hermitage which gives name to the hills for about two miles, and to the wine made on them. There are but three of those hills which produce wine of the first quality, and of these, the middle regions only. They are about three hundred feet perpendicular height, three quarters of a mile in length, and have a southern aspect. The soil is scarcely tinged red, consists of small rotten stone, and is, where the best wine is made, without any perceptible mixture of earth. It is in sloping terraces. They use a little dung. An homme de vignes, which consists of seven hundred plants, three feet apart, yields generally about three quarters of a pièce, which is nearly four pièces to the arpent. When new, the pièce is sold at about two hundred and twenty-five livres; when old, at three hundred. It cannot be drunk under four years, and improves fastest in a hot situation. There is so little white made in proportion to the red, that it is difficult to buy it separate. They make the white sell the red. If bought separately, it is from fifteen to sixteen louis the pièce, new, and three livres the bottle, old. To give quality to the red, they mix one eighth of white grapes. Portage to Paris is seventy-two livres the pièce, weighing six hundred pounds. There are but about one thousand pièces of both red and white, of the first quality, made annually. Vineyards are never rented here, nor are laborers in the vineyard hired by the year. They leave buds proportioned to the strength of the vine, sometimes as much as fifteen inches. The last hermit died in 1751.
In the neighborhood of Montelimart, and below that, they plant vines in rows, six, eight, or ten feet apart, and two feet asunder in the row, filling the intervals with corn. Sometimes the vines are in double rows, two feet apart. I saw single asses in ploughs proportioned to their strength. There are few chateaux in this province. The people, too, are mostly gathered into villages. There are, however, some scattering farm-houses. These are made either of mud, or of round stone and mud. They make enclosures also, in both those ways. Day-laborers receive, sixteen or eighteen sous the day, and feed themselves. Those by the year receive, men three louis, women half that, and are fed. They rarely eat meat; a single hog, salted, being the year’s stock for a family. But they have plenty of cheese, eggs, potatoes, and other vegetables, and walnut oil with their salad. It is a trade here, to gather dung along the road for their vines. This proves they have few cattle. I have seen neither hares nor partridges since I left Paris, nor wild fowl on any of the rivers. The roads from Lyons to St. Rambert are neither paved nor gravelled. After that, they are coated with broken flint. The ferry-boats on the Rhone and the Isere, are moved by the stream, and very rapidly. On each side of the river is a moveable stage, one end of which is on an axle and two wheels, which, according to the tide, can be advanced or withdrawn, so as to apply to the gunwale of the boat. The Praetorian Palace at Vienne, is forty-four feet wide, of the Corinthian order, four columns in front, and four in flank. It was begun in the year 400, and finished by Charlemagne.
The sepulchral Pyramid, a little way out of the town, has an order for its basement, the pedestal of which, from point to point of its cap, is twenty-four feet, one inch. At each angle, is a column, engaged one fourth in the wall. The circumference of the three fourths disengaged, is four feet four inches; consequently, the diameter is twenty-three inches. The base of the column indicates it to be Ionic, but the capitals are not formed. The cornice, too, is a bastard Ionic, without modillions or dentils. Between the columns, on each side, is an arch of eight feet, four inches, opening with a pilaster on each side of it. On the top of the basement is a zocle, in the plane of the frieze below. On that is the pyramid, its base in the plane of the collarins of the pilaster below. The pyramid is a little truncated on its top. This monument is inedited.
March 18. Principality of Orange. The plains on the Rhone here, are two or three leagues wide, reddish, good, in corn, clover, almonds, olives. No forests. Here begins the country of olives, there being very few till we enter this principality. They are the only tree which I see planted among vines. Thyme grows wild here on the hills. Asses, very small, sell here for two or three louis. The high hills in Dauphine are covered with snow. The remains of the Roman aqueduct are of brick: a fine pièce of Mosaic, still on its bed, forming the floor of a cellar. Twenty feet of it still visible. They are taking down the circular wall of the Amphitheatre to pave a road.
March 19 to 23. LANGUEDOC. Pont-St.-Esprit. Bagnols. Connaux. Valignitres. Remoulins. St. Gervasy. Vismes. Pont d’Aries. To Remoulins, there is a mixture of hill and dale. Thence to Nismes, hills on the right, on the left, plains extending to the Rhone and the sea. The hills are rocky. Where there is soil, it is reddish and poor. The -plains generally reddish and good, but stony. When you approach the Rhone, going to Arles, the soil becomes a dark gray loam with some sand, and very good. The culture is corn, clover, saintfoin, olives, vines, mulberries, willow, and some almonds. There is no forest. The hills are enclosed in dry stone-wall. Many sheep.
From the summit of the first hill, after leaving Pont-St.-Esprit, there is a beautiful view of the bridge at about two miles’ distance, and a fine landscape of the country both ways. From thence, an excellent road, judiciously conducted, through very romantic scenes. In one part, descending the face of a hill, it is laid out in serpentine, and not zigzag, to ease the descent. In others, it passes through a winding meadow, from fifty to one hundred yards wide, walled, as it were, on both sides, by hills of rock; and at length issues into plain country. The waste hills are covered with thyme, box, and chene-vert. Where the body of the mountains has a surface of soil, the summit has sometimes a crown of rock, as observed in Champagne. At Nismes, the earth is full of lime-stone. The horses are shorn. They are now pruning the olive. A very good tree produces sixty pounds of olives, which yield fifteen pounds of oil: the best quality selling at twelve sous the pound, retail, and ten sous, wholesale. The high hills of Languedoc still covered with snow. The horse-chestnut and mulberry are leafing; apple trees and peas blossoming. The first butterfly I have seen. After the vernal equinox, they are often six or eight months without rain. Many separate farm-houses, numbers of people in rags, and abundance of beggars. The mine of wheat, weighing thirty pounds, costs four livres and ten sous. Wheat bread, three sous the pound. Vin ordinaire, good, and of a strong body, two or three sous the bottle. Oranges, one sous apiece. They are nearly finishing at Nismes a great mill, worked by a steam-engine, which pumps water from a lower into an upper cistern, from whence two overshot wheels are supplied, each of which turns two pair of stones. The upper cistern being once filled with water, it passes through the wheels into the lower one, from whence it is returned to the upper by the pumps. A stream of water of one quarter or one half inch diameter, supplies the waste of evaporation, absorption, fee. This is furnished from a well by a horse. The arches of the Pont-St.-Esprit are of eighty-eight feet. Wild figs, very flourishing, grow out of the joints of the Pont-du-Gard. The fountain of Nismes is so deep, that a stone was thirteen seconds descending from the surface to the bottom.
March 24. From Nismes to Arles. The plains extending from Nismes to the Rhone, in the direction of Aries, are broken in one place by a skirt of low hills. They are red and stony at first, but as you approach the Rhone, they are of a dark gray mould, with a little sand, and very good. They are in corn and clover, vines, olives, almonds, mulberries, and willow. There are some sheep, no wood, no enclosures.
The high hills of Languedoc are covered with snow. At an ancient church, in the suburbs of Aries, are some hundreds of ancient stone coffins, along the road-side. The ground is thence called Les Champs Elysees. In a vault in a church, are some curiously wrought, and in a back yard are many ancient statues, inscriptions, &c. Within the town are a part of two Corinthian columns, and of the pediment with which they were crowned, very rich, having belonged to the ancient capitol of the place.
But the principal monument here, is an amphitheatre, the external portico of which is tolerably complete. How many porticoes there were, cannot be seen; but at one of the principal gates there are still five, measuring, from out to in, seventy-eight feet, ten inches, the vault diminishing inwards. There are sixty-four arches, each of which is, from centre to centre, twenty feet, six inches. Of course, the diameter is of four hundred and thirty-eight feet; or of four hundred and fifty feet, if we suppose the four principal arches a little larger than the rest. The ground floor is supported on innumerable vaults. The first story, externally, has a tall pedestal, like a pilaster, between every two arches; the upper story, a column, the base of which would indicate it Corinthian. Every column is truncated as low as the impost of the arch, but the arches are all entire. The whole of the upper entablature is gone, and of the Attic, if there was one. Not a single seat of the internal is visible. The whole of the inside, and nearly the whole of the outside, is masked by buildings. It is supposed there are one thousand inhabitants within the amphitheatre. The walls are more entire and firm than those of the ampitheatre at Nismes. I suspect its plan and distribution to have been very different from that.
Terrasson. The plains of the Rhone from Arles to this place, are a league or two wide; the mould is of a dark gray, good, in corn and lucerne. Neither wood, nor enclosures. Many sheep.
St. Remy. From Terrasson to St. Remy, is a plain of a league or two wide, bordered by broken hills of massive rock. It is gray and stony, mostly in olives. Some almonds, mulberries, willows, vines, corn, and lucerne. Many sheep. No forest, nor enclosures.
A laboring man’s wages here, are one hundred and fifty livres, a woman’s half, and fed. Two hundred and eighty pounds of wheat sell for forty-two livres. They make no butter here. It costs, when brought, fifteen sous the pound. Oil is ten sous the pound. Tolerably good olive trees yield, one with another, about twenty pounds of oil. An olive tree must be twenty years old before it has paid its own expenses. It lasts for ever. In 1765, it was so cold, that the Rhone was frozen over at Aries for two months. In 1767, there was a cold spell of a week, which killed all the olive trees. From being fine weather, in one hour there was ice hard enough to bear a horse. It killed people on the road. The old roots of the olive trees put out again. Olive grounds sell for twenty-four livres a tree, and lease at twenty-four sous the tree. The trees are fifteen pieds apart. But lucerne is a more profitable culture. An arpent yields one hundred quintals of hay a year, worth three livres the quintal. It is cut four or five times a year. It is sowed in the broadcast, and lasts five or six years. An arpent of ground for corn rents at from thirty to thirty-six livres. Their leases are for six or nine years. They plant willow for fire-wood, and for hoops to their casks. It seldom rains here in summer. There are some chateaux, many separate farm-houses, good, and ornamented in the small way, so as to show that the tenant’s whole time is not occupied in procuring physical necessaries.
March 25. Orgon. Pontroyal. St. Cannat. From Orgon to Pontroyal, after quitting the plains of the Rhone, the country seems still to be a plain, cut into compartments by chains of mountains of massive rock, running through it in various directions. From Pontroyal to St. Cannat, the land lies rather in basins. The soil is very various, gray and clay, gray and stony, red and stony; sometimes good, sometimes middling, often barren. We find some golden willows. Towards Pontroyal, the hills begin to be in vines and afterwards in some pasture of greensward and clover. About Orgon are some enclosures of quick-set, others of conical yews planted close. Towards St. Cannat, they begin to be of stone.
The high mountains are covered with snow. Some separate farm-houses of mud. Near Pontroyal is a canal for watering the country; one branch goes to Terrasson, the other to Arles.
March 25, 26, 27, 28. Aix. The country is waving, in vines, pasture of greensward and clover, much enclosed with stone, and abounding with sheep.
On approaching Aix, the valley which opens from thence towards the mouth of the Rhone and the sea, is rich and beautiful; a perfect grove of olive trees, mixed among which are corn, lucerne, and vines. The waste grounds throw out thyme and lavender. Wheat bread is three sous the pound. Cow’s milk sixteen sous the quart, sheep’s milk six sous, butter of sheep’s milk twenty sous the pound. Oil, of the best quality, is twelve sous the pound, and sixteen sous if it be virgin oil. This is what runs from the olive when put into the press, spontaneously; afterwards they are forced by the press and by hot water. Dung costs ten sous the one hundred pounds. Their fire-wood is chene-vert and willow. The latter is lopped every three years. An ass sells for from one to three louis; the best mules for thirty louis. The best asses will carry two hundred pounds; the best horses three hundred pounds; the best mules six hundred pounds. The temperature of the mineral waters of Aix is 90° of Fahrenheit’s thermometer, at the spout. A mule eats half as much as a horse. The allowance to an ass for the day, is a handful of bran mixed with straw. The price of mutton and beef, about six and a half sous the pound. The beef comes from Auvergne, and is poor and bad. The mutton is small, but of excellent flavor. The wages of a laboring man are one hundred and fifty livres the year, a woman’s sixty to sixty-six livres, and fed. Their bread is half wheat, half rye, made once in three or four weeks, to prevent too great a consumption. In the morning they eat bread with an anchovy, or an onion. Their dinner in the middle of the day is bread, soup, and vegetables. Their supper the same. With their vegetables, they have always oil and vinegar. The oil costs about eight sous the pound. They drink what is called piquette. This is made after the grapes are pressed, by pouring hot water on the pumice. On Sunday they have meat and wine. Their wood for building comes mostly from the Alps, down the Durance and Rhone. A stick of pine, fifty feet long, girting six feet and three inches at one end, and three feet three inches at the other, costs, delivered here, from fifty-four to sixty livres. Sixty pounds of wheat cost seven livres. One of their little asses will travel with his burthen about five or six leagues a day, and day by day; a mule from six to eight leagues.*
* It is twenty American miles from Aix to Marseilles, and
they call it five leagues. Their league, then, is of four
American miles.
March 29. Marseilles. The country is hilly, intersected by chains of hills and mountains of massive rock. The soil is reddish, stony, and indifferent where best. Wherever there is any soil, it is covered with olives. Among these are corn, vines, some lucerne, mulberry, some almonds, and willow. Neither enclosures, nor forest. A very few sheep.
On the road I saw one of those little whirlwinds which we have in Virginia, also some gullied hill-sides. The people are in separate establishments. Ten morning observations of the thermometer, from the 20th to the 31st of March inclusive, made at Nismes, St. Remy, Aix, and Marseilles, give me an average of 52 1/2°, and 46° and 61°, for the greatest and least morning heats. Nine afternoon observations, yield an average of 62 2/3°, and 57° and 66°, the greatest and least. The longest day here, from sunrise to sunset, is fifteen hours and fourteen minutes; the shortest is eight hours and forty-six minutes; the latitude being ————-.
There are no tides in the Mediterranean. It is observed to me, that the olive tree grows nowhere more than thirty leagues distant from that sea. I suppose, however, that both Spain and Portugal furnish proofs to the contrary, and doubt its truth as to Asia, Africa, and America. They are six or eight months at a time, here, without rain. The most delicate figs known in Europe, are those growing about this place, called figues Marseilloises, or les veritables Marseilloises, to distinguish them from others of inferior quality growing here. These keep any length of time. All others exude a sugar in the spring of the year, and become sour. The only process for preserving them, is drying them in the sun, without putting any thing to them whatever. They sell at fifteen sous the pound, while there are others as cheap as five sous the pound. I meet here a small dried grape from Smyrna, without a seed. There are few of the plants growing in this neighborhood. The best grape for drying, known here, is called des Panses. They are very large, with a thick skin and much juice. They are best against a wall of southern aspect, as their abundance of juice requires a great deal of sun to dry it. Pretty good fig trees are about the size of the apricot tree, and yield about twenty pounds of figs when dry, each. But the largest will yield the value of a louis. They are sometimes fifteen inches in diameter. It is said that the Marseilles fig degenerates when transported into any other part of the country. The leaves of the mulberry tree will sell for about three livres, the purchaser gathering them. The caper is a creeping plant. It is killed to the roots every winter. In the spring it puts out branches, which creep to the distance of three feet from the centre. The fruit forms on the stem, as that extends itself, and must be gathered every day, as it forms. This is the work of women. The pistache grows in this neighborhood also, but not very good. They eat them in their milky state. Monsieur de Bergasse has a wine-cellar two hundred and forty pieds long, in which are one hundred and twenty tons, of from fifty to one hundred pièces each. These tons are twelve pieds diameter, the staves four inches thick, the heading two and a half pouces thick. The temperature of his cellar is of 9 1/2° of Reaumur. The best method of packing wine, when bottled, is to lay the bottles on their side, and cover them with sand. The 2d of April, the young figs are formed; the 4th we have Windsor beans. They have had asparagus ever since the middle of March. The 5th, I see strawberries and the Guelder rose in blossom. To preserve the raisin, it is first dipped into ley, and then dried in the sun. The aloe grows in the open ground. I measure a mule, not the largest, five feet and two inches high. Marseilles is in an amphitheatre, at the mouth of the Veaune, surrounded by high mountains of naked rock, distant two or three leagues. The country within that amphitheatre is a mixture of small hills, vallies, and plains. The latter are naturally rich. The hills and vallies are forced into production. Looking from the Chateau de Notre Dame de la Garde, it would seem as if there was a bastide for every arpent. The plain-lands sell for one hundred louis the carterelle, which is less than an acre. The ground of the arsenal in Marseilles sold for from fifteen to forty louis the square verge, being nearly the square yard English. In the fields open to the sea, they are obliged to plant rows of canes, every here and there, to break the force of the wind. Saw at the Chateau Borelli pumps worked by the wind.
April 6. From Marseilles to Aubagne. A valley on the Veaune, bordered on each side by high mountains of massive rock, on which are only some small pines. The interjacent valley is of small hills, vallies, and plains, reddish, gravelly, and originally poor, but fertilized by art, and covered with corn, vines, olives, figs, almonds, mulberries, lucerne, and clover. The river is twelve or fifteen feet wide, one or two feet deep, and rapid.
From Aubagne to Cuges, Beausset, Toulon. The road, quitting the Veaune and its wealthy valley, a little after Aubagne, enters those mountains of rock, and is engaged with them about a dozen miles. Then it passes six or eight miles through a country still very hilly and stony, but laid up in terraces, covered with olives, vines, and corn. It then follows for two or three miles a hollow between two of those high mountains, which has been, found or made by a small stream. The mountains then reclining a little from their perpendicular, and presenting a coat of soil, reddish, and tolerably good, have given place to the little village of Olioules, in the gardens of which are oranges in the open ground. It continues hilly till we enter the plain of Toulon. On different parts of this road there are figs in the open fields. At Cuges is a plain of about three fourths of a mile diameter, surrounded by high mountains of rock. In this the caper is principally cultivated. The soil is mulatto, gravelly, and of middling quality, or rather indifferent. The plants are set in quincunx, about eight feet apart. They have been covered during winter by a hill of earth a foot high. They are now enclosing, pruning, and ploughing them.
Toulon. From Olioules to Toulon the figs are in the open fields. Some of them have stems of fifteen inches diameter. They generally fork near the ground, but sometimes have a single stem of five feet long. They are as large as apricot trees. The olive trees of this day’s journey are about the size of large apple trees. The people are in separate establishments. Toulon is in a valley at the mouth of the Goutier, a little river of the size of the Veaune; surrounded by high mountains of naked rock, leaving some space between them and the sea. This space is hilly, reddish, gravelly, and of middling quality, in olives, vines, corn, almonds, figs, and capers. The capers are planted eight feet apart. A bush yields, one year with another, two pounds, worth twelve sous the pound. Every plant, then, yields twenty-four sous, equal to one shilling sterling. An acre, containing six hundred and seventy-six plants, would yield thirty-three pounds sixteen shillings sterling. The fruit is gathered by women, who can gather about twelve pounds a day. They begin to gather about the last of June, and end about the middle of October. Each plant must be picked every day. These plants grow equally well in the best or worst soil, or even in the walls, where there is no soil. They will last the life of a man, or longer. The heat is so great at Toulon in summer, as to occasion very great cracks in the earth. Where the caper is in a soil that will admit it, they plough it. They have pease here through the winter, sheltering them occasionally; and they have had them ever since the 25th of March, without shelter.
April 6. Hieres. This is a plain of two or three miles diameter, bounded by the sea on one side, and mountains of rock on the other. The soil is reddish, gravelly, tolerably good, and well watered. It is in olives, mulberries, vines, figs, corn, and some flax. There are also some cherry trees. From Hieres to the sea, which is two or three miles, is a grove of orange trees, olives, and mulberries. The largest orange tree is of two feet diameter one way, and one foot the other (for the section of all the larger ones would be an oval, not a round), and about twenty feet high. Such a tree will yield about six thousand oranges a year. The garden of M. Fille has fifteen thousand six hundred orange, trees. Some years they yield forty thousand livres, some only ten thousand; but generally about twenty-five thousand. The trees are from eight to ten feet apart. They are blossoming and bearing, all the year, flowers and fruit in every stage at the same time. But the best fruit is that which is gathered in April and May. Hieres is a village of about five thousand inhabitants, at the foot of a mountain, which covers it from the north, and from which extends a plain of two or three miles to the sea-shore. It has no port. Here are palm trees twenty or thirty feet high, but they bear no fruit. There is also a botanical garden kept by the King. Considerable salt-ponds here. Hieres is six miles from the public road. It is built on a narrow spur of the mountain. The streets in every direction are steep, in steps of stairs, and about eight feet wide. No carriage of any kind can enter it. The wealthier inhabitants use chaises à porteurs. But there are few wealthy, the bulk of the inhabitants being laborers of the earth. At a league’s distance in the sea is an island, on which is the Chateau de Géans, belonging to the Marquis de Pontoives: there is a causeway leading to it. The cold of the last November killed the leaves of a great number of the orange-trees, and some of the trees themselves.
From Hieres to Cuers, Pignans, Luc, is mostly a plain, with mountains on each hand at a mile or two distance. The soil is generally reddish, and the latter part very red and good. The growth is olives, figs, vines, mulberries, corn, clover, and lucerne. The olive trees are from three to four feet in diameter. There are hedges of pomegranates, sweet-briar, and broom. A great deal of thyme growing wild. There are some enclosures of stone; some sheep and goats.
April 9. From Luc to Vidavban, Muy, Frejus, the road leads through vallies, and crosses occasionally the mountains which separate them. The vallies are tolerably good, always red and stony, gravelly or gritty. Their produce as before. The mountains are barren.
Lesterelle, Napoule. Eighteen miles of ascent and descent of a very high mountain. Its growth, where capable of any, two-leaved pine, very small, and some chêne vert.
Antibes, Nice. From Napoule the road is generally near the sea, passing over little hills or strings of vallies, the soil stony, and much below mediocrity in its quality. Here and there is a good plain.
There is snow on the high mountains. The first frogs I have heard are of this day (the 9th). At Antibes are oranges in the open ground, but in small enclosures; palm trees also. From thence to the Var are the largest fig trees and olive trees I have seen. The fig trees are eighteen inches in diameter, and six feet stem; the olives sometimes six feet in diameter, and as large heads as the largest low-ground apple trees. This tree was but a shrub where I first fell in with it, and has become larger and larger to this place. The people are mostly in villages. The several provinces, and even cantons, are distinguished by the form of the women’s hats, so that one may know of what canton a woman is by her hat.
Nice. The pine-bur is used here for kindling fires. The people are in separate establishments. With respect to the orange, there seems to be no climate on this side of the Alps sufficiently mild in itself to preserve it without shelter. At Olioules they are between two high mountains; at Hieres covered on the north by a very high mountain; at Antibes and Nice covered by mountains, and also within small, high enclosures. Quære. To trace the true line from east to west, which forms the northern and natural limit of that fruit? Saw an elder tree (sambucus) near Nice, fifteen inches in diameter, and eight feet stem. The wine made in this neighborhood is good, though not of the first quality. There are one thousand mules, loaded with merchandise, which pass every week between Nice and Turin, counting those coming as well as going.
April 13. Scarena. Sospello. There are no orange trees after we leave the environs of Nice. We lose the olive after rising a little above the village of Scarena, on Mount Braus, and find it again on the other side, a little before we get down to Sospello. But wherever there is soil enough it is terraced, and in corn. The waste parts are either in two-leaved pine and thyme, or of absolutely naked rock. Sospello is on a little torrent, called Bevera, which runs into the river Roia, at the mouth of which is Ventimiglia. The olive trees on the mountain are now loaded with fruit; while some at Sospello are in blossom. Fire-wood here and at Scarena costs fifteen sous the quintal.
April 14. Ciandola. Tende. In crossing Mount Brois we lose the olive tree after getting to a certain height, and find it again on the other side at the village of Breglio. Here we come to the river Roia, which, after receiving the branch on which is Sospello, leads to the sea at Ventimiglia. The Roia is about twelve yards wide, and abounds with speckled trout. Were a road made from Breglio, along the side of the Roia to Ventimiglia, it might turn the commerce of Turin to this last place instead of Nice; because it would avoid the mountains of Braus and Brois, leaving only that of Tende; that is to say, it would avoid more than half the difficulties of the passage. Further on, we come to the Chateau di Saorgio, where a scene is presented the most singular and picturesque I ever saw. The castle and village seem hanging to a cloud in front. On the right is a mountain cloven through, to let pass a gurgling stream; on the left, a river, over which is thrown a magnificent bridge. The whole forms a basin, the sides of which are shagged with rocks, olive trees, vines, herds, &c. Near here I saw a tub-wheel without a ream; the trunk descended from the top of the water-fall to the wheel in a direct line, but with the usual inclination. The produce along this passage is most generally olives, except on the heights as before observed; also corn, vines, mulberries, figs, cherries, and walnuts. They have cows, goats, and sheep. In passing on towards Tende, olives fail us ultimately at the village of Fontan, and there the chestnut trees begin in good quantity. Ciandola consists of only two houses, both taverns. Tende is a very inconsiderable village, in which they have not yet the luxury of glass windows: nor in any of the villages on this passage have they yet the fashion of powdering the hair. Common stone and limestone are so abundant, that the apartments of every story are vaulted with stone to save wood.
April 15. Limone. Coni. I see abundance of lime-stone as far as the earth is uncovered with snow; i.e. within half or three quarters of an hour’s walk of the top. The snows descend much lower on the eastern than western side. Wherever there is soil, there is corn quite to the commencement of the snows, and I suppose under them also. The waste parts are in two-leaved pine, lavender, and thyme. From the foot of the mountain to Coni the road follows a branch of the Po, the plains of which begin narrow, and widen at length into a general plain country, bounded on one side by the Alps. They are good, dark-colored, sometimes tinged with red, and in pasture, corn, mulberries, and some almonds. The hill-sides bordering these plains are reddish, and where they admit of it are in corn; but this is seldom. They are mostly in chestnut, and often absolutely barren. The whole of the plains are plentifully watered from the river, as is much of the hill-side. A great deal of golden willow all along the rivers on the whole of this passage through the Alps. The southern parts of France, but still more the passage through the Alps, enable one to form a scale of the tenderer plants, arranging them according to their several powers of resisting cold. Ascending three different mountains, Braus, Brois, and Tende, they disappear one after another: and descending on the other side, they show themselves again one after another. This is their order, from the tenderest to the hardiest. Caper, orange, palm, aloe, olive, pomegranate, walnut, fig, almond. But this must be understood of the plant; for as to the fruit, the order is somewhat different. The caper, for example, is the tenderest plant, yet being so easily protected, it is the most certain in its fruit. The almond, the hardiest plant, loses its fruit the oftenest on account of its forwardness. The palm, hardier than the caper and the orange, never produces perfect fruit in these parts. Coni is a considerable town, and pretty well built. It is walled.
April 16. Centale. Savigliano. Racconigi. Poirino. Turin. The Alps, as far as they are in view from north to south, show the gradation of climate by the line which terminates the snows lying on them. This line begins at their foot northwardly, and rises as they pass on to the south, so as to be half way up their sides on the most southern undulations of the mountain now in view. From the mountains to Turin we see no tree tenderer than the walnut. Of these, as well as of almonds and mulberries, there are a few: somewhat more of vines, but most generally willows and poplars. Corn is sowed with all these. They mix with them also clover and small grass. The country is a general plain; the soil dark, and sometimes, though rarely, reddish. It is rich, and much infested with wild onions. At Racconigi I see the tops and shocks of maize, which prove it is cultivated here: but it can be in small quantities only, because I observe very little ground but what has already something else in it. Here and there are small patches prepared, I suppose, for maize. They have a method of planting the vine, which I have not seen before. At intervals of about eight feet they plant from two to six plants of vine in a cluster At each cluster they fix a forked staff, the plane of the prongs of the fork at a right angle with the row of vines. Athwart these prongs they lash another staff, like a handspike, about eight feet long, horizontally, seven or eight feet from the ground. Of course, it crosses the rows at right angles. The vines are brought from the foot of the fork up to this cross-piece, turned over it, and conducted along over the next, the next, and so on, as far as they will extend, the whole forming an arbor eight feet wide and high and of the whole length of the row, little interrupted by the stems of the vines, which being close around the fork, pass up through hoops, so as to occupy a space only of small diameter. All the buildings in this country are of brick, sometimes covered with plaister, sometimes not. There is a very large and handsome bridge, of seven arches, over the torrent of Sangone. We cross the Po in swinging batteaux. Two are placed side by side, and kept together by a plank-floor, common to both, and lying on the gunwales. The carriage drives on this, without taking out any of the horses. About one hundred and fifty yards up the river is a fixed stake, and a rope tied to it, the other end of which is made fast to one side of the batteaux, so as to throw them oblique to the current. The stream then acting on them, as on an inclined plane, forces them across the current in the portion of a circle, of which the rope is the radius. To support the rope in its whole length, there are two intermediate canoes, about fifty yards apart, in the heads of which are short masts. To the top of these the rope is lashed, the canoes being free otherwise to concur with the general vibration in their smaller arcs of circles. The Po is there about fifty yards wide, and about one hundred in the neighborhood of Turin.
April 17, 18. Turin. The first nightingale I have heard this year is to-day (18th). There is a red wine of Nebiule made in this neighborhood, which is very singular. It is about as sweet as the silky Madeira, as astringent on the palate as Bordeaux, and as brisk as Champagne. It is a pleasing wine. At Moncaglieri, about six miles from Turin, on the right side of the Po, begins a ridge of mountains, which, following the Po by Turin, after some distance, spreads wide, and forms the duchy of Montferrat. The soil is mostly red, and in vines, affording a wine called Montferrat, which is thick and strong.
April 19. Settimo. Chivasso. Ciliano. S. Germano. Vercelli. The country continues plain and rich, the soil black. The culture, corn, pasture, maize, vines, mulberries, walnuts, some willow, and poplar. The maize bears a very small proportion to the small grain. The earth is formed into ridges from three to four feet wide, and the maize sowed in the broad-cast, on the higher parts of the ridge, so as to cover a third or half of the whole surface. It is sowed late in May. This country is plentifully and beautifully watered at present. Much of it is by torrents, which are dry in summer. These torrents make a great deal of waste ground, covering it with sand and stones. These wastes are sometimes planted in trees, sometimes quite unemployed. They make hedges of willows, by setting the plants from one to three feet apart. When they are grown to the height of eight or ten feet, they bend them down, and interlace them one with another. I do not see any of these, however, which are become old. Probably, therefore, they soon die. The women here smite on the anvil, and work with the maul and spade. The people of this country are ill dressed in comparison with those of France, and there are more spots of uncultivated ground. The plough here is made with a single handle, which is a beam twelve feet long, six inches in diameter below, and tapered to about two inches at the upper end. They use goads for the oxen, not whips. The first swallows I have seen are to-day. There is a wine called Gatina, made in the neighborhood of Vercelli, both red and white. The latter resembles Calcavallo. There is also a red wine of Salusola, which is esteemed. It is very light. In the neighborhood of Vercelli begin the rice-fields. The water with which they are watered is very dear. They do not permit rice to be sown within two miles of the cities, on account of the insalubrity. Notwithstanding this, when the water is drawn off the fields, in August, the whole country is subject to agues and fevers. They estimate, that the same measure of ground yields three times as much rice as wheat, and with half the labor. They are now sowing. As soon as sowed, they let on the water two or three inches deep. After six weeks, or two months, they draw it off to weed; then let it on again, and it remains till August, when it is drawn off, about three or four weeks before the grain is ripe. In September they cut it. It is first threshed; then beaten in the mortar to separate the husk; then, by different siftings, it is separated into three qualities. Twelve rupes, equal to three hundred pounds of twelve ounces each, sell for sixteen livres, money of Piedmont, where the livre is exactly the shilling of England. Twelve rupes of maize sell for nine livres. The machine for separating the husk is thus made. In the axis of a water-wheel are a number of arms inserted, which, as they revolve, catches each the cog of a pestle, lifts it to a certain height, and lets it fall again. These pestles are five and a quarter inches square, ten feet long, and at their lower end formed into a truncated cone of three inches diameter, where cut off. The conical part is covered with iron. The pestles are ten and a half inches apart in the clear. They pass through two horizontal beams, which string them, as it were, together, and while the mortises in the beams are so loose, as to let the pestles work vertically, it restrains them to that motion. There is a mortar of wood, twelve or fifteen inches deep, under each pestle, covered with a board, the hole of which is only large enough to let the pestle pass freely. There are two arms in the axis for every pestle, so that the pestle gives two strokes for every revolution of the wheel. Poggio, a muleteer, who passes every week between Vercelli and Genoa, will smuggle a sack of rough rice for me to, Genoa; it being death to export it in that form. They have good cattle, and in good number, mostly cream-colored; and some middle-sized sheep. The streams furnish speckled trout.
April 20. Novara. Buffalora. Sedriano. Milan. From Vercelli to Novara the fields are all in rice, and now mostly under water. The dams separating the several water-plats or ponds, are set in willow. At Novara there are some figs in the gardens in situations well protected. From Novara to the Ticino it is mostly stony and waste, grown up in broom. From Ticino to Milan it is all in corn. Among the corn are willows, principally, a good many mulberries, some walnuts, and here and there an almond. The country still a plain, the soil black and rich, except between Novara and the Ticino, as before mentioned. There is very fine pasture round Vercelli and Novara to the distance of two miles, within which rice is not permitted. We cross the Sisto on the same kind of vibrating or pendulum boat as on the Po. The river is eighty or ninety yards wide; the rope fastened to an island two hundred yards above, and supported by five intermediate canoes. It is about one and a half inches in diameter. On these rivers they use a short oar of twelve feet long, the flat end of which is hooped with iron, shooting out a prong at each corner, so that it may be used occasionally as a setting-pole. There is snow on the Apennines, near Genoa. They have still another method here of planting the vine. Along rows of trees, they lash poles from tree to tree. Between the trees, are set vines, which, passing over the pole, are carried on to the pole of the, next tree, whose vines are in like manner brought to this, and twined together; thus forming the intervals between the rows of trees, alternately, into arbors and open space. They have another method also of making quick-set hedges. Willows are planted from one to two feet apart, and interlaced, so that every one is crossed by three or four others.
April 21, 22. Milan. Figs and pomegranates grow here, unsheltered, as I am told. I saw none, and therefore suppose them rare. They had formerly olives; but a great cold, in 1709, killed them, and they have not been replanted. Among a great many houses painted al fresco, the Casa Roma and Casa Candiani, by Appiani, and Casa Belgioiosa, by Martin, are superior. In the second, is a small cabinet, the ceiling of which is in small hexagons, within which are cameos and heads painted alternately, no two the same. The salon of the Casa-Belgioiosa is superior to any thing 1 have ever seen. The mixture called scagliuola, of which they make their walls and floors, is so like the finest marble, as to be scarcely distinguishable from it. The nights of the 20th and 21st instant, the rice ponds froze half an inch thick. Droughts of two or three months are not uncommon here, in summer. About five years ago, there was such a hail as to kill cats. The Count del Verme tells me of a pendulum odometer for the wheel of a carriage. Leases here are mostly for nine years. Wheat costs a louis d’or the one hundred and forty pounds. A laboring man receives sixty livres, and is fed and lodged. The trade of this country is principally rice, raw silk, and cheese.
April 23. Casino, five miles from Milan. I examined another rice-beater of six pestles. They are eight feet nine inches long. Their ends, instead of being a truncated cone, have nine teeth of iron, bound closely together. Each tooth is a double pyramid, joined at the base. When put together, they stand with the upper ends placed in contact, so as to form them into one great cone, and the lower ends diverging. The upper are socketed into the end of the pestle, and the lower, when a little blunted by use, are not unlike the jaw-teeth of the mammoth, with their studs. They say here, that pestles armed with these teeth, clean the rice faster, and break it less. The mortar, too, is of stone, which is supposed as good as wood, and more durable. One half of these pestles are always up. They rise about twenty-one inches; and each makes thirty-eight strokes in a minute; one hundred pounds of rough rice is put into the six mortars, and beaten somewhat less than a quarter of an hour. It is then taken out, put into a sifter of four feet diameter, suspended horizontally; sifted there; shifted into another of the same size; sifted there; returned to the mortars; beaten a little more than a quarter of an hour; sifted again; and it is finished. The six pestles will clear four thousand pounds in twenty-four hours. The pound here is twenty-eight ounces: the ounce equal to that of Paris. The best rice requires half an hour’s boiling; a more indifferent kind, somewhat less. To sow the rice, they first plough the ground, then level it with a drag-harrow, and let on the water; when the earth has become soft, they smooth it with a shovel under the water, and then sow the rice in the water.
Rozzano. Parmesan cheese. It is supposed this was formerly made at Parma, and took its name thence; but none is made there now. It is made through all the country extending from Milan, for one hundred and fifty miles. The most is made about Lodi. The making of butter being connected with that of making cheese, both must be described together. There are, in the stables I saw, eighty-five cows, fed on hay and grass, not on grain. They are milked twice in twenty-four hours, ten cows yielding at the two milkings a brenta of milk, which is twenty-four of our gallons. The night’s milk is scummed in the morning at daybreak, when the cows are milked again, and the new milk mixed with the old. In three hours, the whole mass is scummed a second time, the milk remaining in a kettle for cheese, and the cream being put into a cylindrical churn, shaped like a grind-stone, eighteen inches radius, and fourteen inches thick. In this churn, there are three staves pointing inwardly, endwise, to break the current of the milk. Through its centre passes an iron axis, with a handle at each end. It is turned, about an hour and an half, by two men, till the butter is produced. Then they pour off the butter-milk, and put in some water which they agitate backwards and forwards about a minute, and pour it off. They take out the butter, press it with their hands into loaves, and stamp it. It has no other washing. Sixteen American gallons of milk yield fifteen pounds of butter, which sell at twenty-four sous the pound.
The milk, which, after being scummed as before, had been put into a copper kettle, receives its due quantity of rennet, and is gently warmed, if the season requires it. In about four hours, it becomes a slip. Then the whey begins to separate. A little, of it is taken out. The curd is then thoroughly broken by a machine like a chocolate-mill. A quarter of an ounce of saffron is put to seven brentas of milk, to give color to the cheese. The kettle is then moved over the hearth, and heated by a quick fire till the curd is hard enough, being broken into small lumps by continued stirring. It is moved off the fire, most of the whey taken out, the curd compressed into a globe by the hand, a linen cloth slipped under it, and it is drawn out in that. A loose hoop is then laid on a bench, and the curd, as wrapped in the linen, is put into the hoop: it is a little pressed by the hand, the hoop drawn tight, and made fast. A board, two inches thick, is laid on it, and a stone on that, of about twenty pounds weight. In an hour, the whey is run off, and the cheese finished. They sprinkle a little salt on it every other day in summer, and every day in winter, for six weeks. Seven brentas of milk make a cheese of fifty pounds, which requires six months to ripen, and is then dried to forty-five pounds. It sells on the spot for eighty-eight livres, the one hundred pounds. There are now one hundred and fifty cheeses in this dairy. They are nineteen inches diameter, and six inches thick. They make a cheese a day, in summer, and two in three days, or one in two days, in winter.
The whey is put back into the kettle, the butter-milk poured into it, and of this, they make a poor cheese for the country people. The whey of this is given to the hogs. Eight men suffice to keep the cows, and to do all the business of this dairy. Mascarponi, a kind of curd, is made by pouring some butter-milk into cream, which is thereby curdled, and is then pressed in a linen cloth.
The ice-houses at Rozzano are dug about fifteen feet deep, and twenty feet diameter, and poles are driven down all round. A conical thatched roof is then put over them, fifteen feet high, and pieces of wood are laid at bottom, to keep the ice out of the water which drips from it, and goes off by a sink. Straw is laid on this wood, and then the house filled with ice, always putting straw between the ice and the walls, and covering ultimately with straw. About a third is lost by melting. Snow gives the most delicate flavor to creams; but ice is the most powerful congealer, and lasts longest. A tuft of trees surrounds these ice-houses.
Round Milan, to the distance of five miles, are corn, pasture, gardens, mulberries, willows, and vines. For, in this state, rice ponds are not permitted within five miles of the cities.
Binasco. Pavia. Near Casino the rice-ponds begin, and continue to within five miles of Pavia, the whole ground being in rice, pasture, and willows. The pasture is in the rice grounds which are resting. In the neighborhood of Pavia, again, are corn, pasture, &c. as round Milan. They gave me green pease at Pavia.
April 24. Voghera. Tortona. Novi. From Pavia to Novi corn, pasture, vines, mulberries, willows; but no rice. The country continues plain, except that the Apennines are approaching on the left. The soil, always good, is dark till we approach Novi, and then red. We cross the Po where it is three hundred yards wide, in a pendulum boat. The rope is fastened on one side of the river, three hundred yards above, and supported by eight intermediate canoes, with little masts in them to give a greater elevation to the rope. We pass in eleven minutes. Women, girls, and boys are working with the hoe, and breaking the clods with mauls.
April 25. Voltaggio. Campo-Marone. Genoa. At Novi, the Apennines begin to rise. Their growth of timber is oak, tall, small, and knotty, and chestnut. We soon lose the walnut, ascending, and find it again, about one fourth of the way down, on the south side. About halfway down, we find figs and vines, which continue fine and in great abundance. The Apennines are mostly covered with soil, and are in corn, pasture, mulberries and figs, in the parts before indicated. About half way from their foot to Genoa, at Campo-Marone, we find again the olive tree. Hence the produce becomes mixed, of all the kinds before mentioned. The method of sowing the Indian corn at Campo-Marone, is as follows. With a hoe shaped like the blade of a trowel, two feet long, and six inches broad at its upper end, pointed below, and a little curved, they make a trench. In that, they drop the grains six inches apart. Then two feet from that, they make another trench, throwing the earth they take out of that on the grain of the last one, with a singular slight and quickness; and so through the whole piece. The last trench is filled with the earth adjoining.
April 26. Genoa. Strawberries at Genoa. Scaffold poles for the upper parts of a wall, as for the third story, rest on the window sills of the story below. Slate is used here for paving, for steps, for stairs (the rise as well as tread), and for fixed Venetian blinds. At the Palazzo Marcello Durazzo, benches with straight legs, and bottoms of cane. At the Palazzo del Prencipe Lomellino, at Sestri, a phaeton with a canopy. At the former, tables folding into one plane. At Nervi they have pease, strawberries, &c. all the year round. The gardens of the Count Durazzo at Nervi, exhibit as rich a mixture of the utile dulci, as I ever saw. All the environs in Genoa are in olives, figs, oranges, mulberries, corn, and garden-stuff. Aloes in many places, but they never flower.
April 28. Noli. The Apennine and Alps appear to me to be one and the same continued ridge of mountains, separating every where the waters of the Adriatic Gulf from those of the Mediterranean. Where it forms an elbow, touching the Mediterranean, as a smaller circle touches a larger, within which it is inscribed, in the manner of a tangent, the name changes from Alps to Apennine. It is the beginning of the Apennine which constitutes the state of Genoa, the mountains there generally falling down in barren, naked precipices into the sea. Wherever there is soil on the lower parts, it is principally in olives and figs, in vines also, mulberries, and corn. Where there are hollows well protected, there are oranges. This is the case at Golfo della Spezia, Sestri, Bugiasco, Nervi, Genoa, Pegli, Savona, Finale, Oneglia (where there are abundance), St. Rerno, Ventimiglia, Mentone, and Monaco. Noli, into which I was obliged to put, by a change of wind, is forty miles from Genoa. There are twelve hundred inhabitants in the village, and many separate houses round about. One of the precipices hanging over the sea, is covered with aloes. But neither here, nor any where else I have been, could I procure satisfactory information that they ever flower. The current of testimony is to the contrary. Noli furnishes many fishermen. Paths penetrate up into the mountains in several directions, about three fourths of a mile; but these are practicable only for asses and mules. I saw no cattle nor sheep in the settlement. The wine they make, is white and indifferent. A curious cruet for oil and vinegar in one piece, I saw here. A bishop resides here, whose revenue is two thousand livres, equal to sixty-six guineas. I heard a nightingale here.
April 29. Albenga. In walking along the shore from Louano to this place, I saw no appearance of shells. The tops of the mountains are covered with snow, while there are olive trees, &c. on the lower parts. I do not remember to have seen assigned any where, the cause of the apparent color of the sea. Its water is generally clear and colorless, if taken up and viewed in a glass. That of the Mediterranean is remarkably so. Yet in the mass, it assumes, by reflection, the color of the sky or atmosphere, black, green, blue, according to the state of the weather. If any person wished to retire from his acquaintance, to live absolutely unknown, and yet in the midst of physical enjoyments, it should be in some of the little villages of this coast, where air, water, and earth concur to offer what each has, most precious. Here are nightingales, beccaficas, ortolans, pheasants, partridges, quails, a superb climate, and the power of changing it from summer to winter at any moment, by ascending the mountains. The earth furnishes wine, oil, figs, oranges, and every production of the garden, in every season. The sea yields lobsters, crabs, oysters, tunny, sardines, anchovies, &c. Ortolans sell, at this time, at thirty sous, equal to one shilling sterling, the dozen. At this season, they must be fattened. Through the whole of my route from Marseilles, I observe they plant a great deal of cane or reed, which is convenient while growing, as a cover from the cold and boisterous winds, and when cut, it serves for espaliers to vines, pease, &c. Through Piedmont, Lombardy, the Milanese, and Genoese, the garden bean is a great article of culture; almost as much so as corn. At Albenga, is a rich plain opening from between two ridges of mountains, triangularly, to the sea, and of several miles extent. Its growth is olives, figs, mulberries, vines, corn, and beans. There is some pasture. A bishop resides here, whose revenue is forty thousand livres. This place is said to be rendered unhealthy in summer, by the river which passes through the valley.
April 30. Oneglia. The wind continuing contrary, I took mules at Albenga for Oneglia. Along this tract are many of the tree called caroubier, being a species of locust. It is the ceratonia siliqua of Linnaeus. Its pods furnish food for horses, and also for the poor, in time of scarcity. It abounds in Naples and Spain. Oneglia and Port Maurice, which are within a mile of each other, are considerable places, and in a rich country. At St. Remo, are abundance of oranges and lemons, and some palm trees.
May 1. Ventimiglia. Mentone. Monaco. Nice. At Bordighera, between Ventimiglia and Mentone, are extensive plantations of palms, on the hill as well as in the plain. They bring fruit, but it does not ripen. Something is made of the midrib which is in great demand at Rome, on the Palm Sunday, and which renders this tree profitable here. From Mentone to Monaco, there is more good land, and extensive groves of oranges and lemons. Orange water sells here at forty sous, equal to sixteen pence sterling, the American quart. The distances on this coast are, from La Spezia, at the eastern end of the territories of Genoa, to Genoa, fifty-five miles, geometrical; to Savona, thirty; Albenga, thirty; Oneglia, twenty; Ventimiglia, twenty-five; Monaco, ten; Nice, ten; in the whole, one hundred and eighty miles. A superb road might be made along the margin of the sea from La Spezai, where the champaign country of Italy opens, to Nice, where the Alps go off northwardly, and the post roads of France begin; and it might even follow the margin of the sea quite to Cette. By this road, travellers would enter Italy without crossing the Alps, and all the little insulated villages of the Genoese would communicate together, and in time, form one continued village along that road.
May 3. Luc, Brignoles. Tourves. Pourcieux. La Galiniere. Long, small mountains, very rocky, the soil reddish, from bad to middling; in olives, grapes, mulberries, vines, and corn. Brignolles is an extensive plain, between two ridges of mountains, and along a water-course which continues to Tourves. Thence to Pourcieux we cross a mountain, low and easy. The country is rocky and poor. To La Galiniere are waving grounds, bounded by mountains of rock at a little distance. There are some enclosures of dry wall from Luc to La Galiniere; also, sheep and hogs. There is snow on the high mountains. I see no plums in the vicinities of Brignoles; which makes me conjecture that the celebrated plum of that name is not derived from this place.
May 8. Orgon. Avignon. Vaucluse. Orgon is on the Durance. From thence, its plain opens till it becomes common with that of the Rhone; so that from Orgon to Avignon is entirely a plain of rich dark loam, which is in willows, mulberries, vines, corn, and pasture. A very few figs. I see no olives in this plain. Probably the cold winds have too much power here. From the Bac de Nova (where we cross the Durance) to Avignon, is about nine American miles; and from the same Bac to Vaucluse, eleven miles. In the valley of Vaucluse, and on the hills impending over it, are olive trees. The stream issuing from the fountain of Vaucluse is about twenty yards wide, four or five feet deep, and of such rapidity that it could not be stemmed by a canoe. They are now mowing hay, and gathering mulberry leaves. The high mountains just back of Vaucluse, are covered with snow. Fine trout in the stream of Vaucluse, and the valley abounds peculiarly with nightingales. The vin blanc de M. de Rochequde of Avignon, resembles dry Lisbon. He sells it, at six years old, for twenty-two sous the bottle, the price of the bottle, &c. included.
Avignon. Remoulins. Some good plains, but generally hills, stony and poor. In olives, mulberries, vines, and corn. Where it is waste the growth is chéne-vert, box, furze, thyme, and rosemary.
May 10. Lismes. Lunel. Hills on the right, plains on the left. The soil reddish, a little stony, and of middling quality. The produce, olives, mulberries, vines, corn, saintfoin. No wood and few enclosures. Lunel is famous for its vin de muscat blanc, thence called Lunel, or vin muscat de Lunel. It is made from the raisin muscat, without fermenting the grain in the hopper. When fermented, it makes a red muscat, taking the tinge from the dissolution of the skin of the grape, which injures the quality. When a red muscat is required, they prefer coloring it with a little Alicant wine. But the white is best. The pièce of two hundred and forty bottles, after being properly drawn off from its lees, and ready for bottling, costs from one hundred and twenty to two hundred livres, the first, quality and last vintage. It cannot be bought old, the demand being sufficient to take it all the first year. There are not more than from fifty to one hundred pièces a year, made of this first quality. A setterie yields about one pièce, and my informer supposes there are about two setteries in an arpent. Portage to Paris, by land, is fifteen livres the quintal. The best récoltes are those of M. Bouquet and M. Tremoulet. The vines are in rows four feet apart, every way.
May 11. Montpelier. Snow on the Cevennes, still visible from here. With respect to the muscat grape, of which the wine is made, there are two kinds, the red and the white. The first has a red skin, but a white juice. If it be fermented in the cuve, the coloring matter which resides in the skin, is imparted to the wine. If not fermented in the cuve, the wine is white. Of the white grape, only a white wine can be made. The species of saintfoin cultivated here by the name of sparsette, is the hedysarum onobrychis. They cultivate a great deal of madder (garance) rubia tinctorum here, which is said to be immensely profitable. Monsieur de Gouan tells me, that the pine, of which they use the burs for fuel, is the pinus sativus, being two-leaved. They use-for an edging to the borders of their gardens, the santolina, which they call garderobe. I find the yellow clover here, in a garden, and the large pigeon succeeding well, confined in a house.
May 12. Frontignan. Some tolerably good plains in olives, vines, corn, saintfoin, and lucerne. A great proportion of the hills are waste. There are some enclosures of stone, and some sheep. The first four years of madder are unproductive; the fifth and sixth yield the whole value of the land. Then it must be renewed. The sparsette is the common or true saintfoin. It lasts about five years: in the best land it is cut twice, in May and September, and yields three thousand pounds of dry hay to the setterie, the first cutting, and five hundred pounds, the second. The setterie is of seventy-five dextres en tout sens, supposed about two arpents. Lucerne is the best of all forage; it is sowed herein the broad-cast, and lasts about twelve or fourteen years. It is cut four times a year, and yields six thousand pounds of dry hay, at the four cuttings, to the setterie. The territory in which the vin muscat de Frontignan is made, is about a league of three thousand toises long, and one fourth of a league broad. The soil is reddish and stony, often as much stone as soil. On the left, it is a plain, on the right hills. There are made about one thousand pièces (of two hundred and fifty bottles each) annually, of which six hundred are of the first quality, made on the coteaux. Of these, Madame Soubeinan makes two hundred, Monsieur Reboulle ninety, Monsieur Lambert, medecin de la faculte de Montpelier, sixty, Monsieur Thomas, notaire, fifty, Monsieur Argilliers fifty, Monsieur Audibert forty; equal to four hundred and ninety; and there are some small proprietors who make small quantities. The first quality is sold, brut, for one hundred and twenty livres the pièce; but it is then thick, and must have a winter and the fouet, to render it potable and brilliant. The fouet is like a chocolate-mill, the handle of iron, the brush of stiff hair. In bottles, this wine costs twenty-four sous, the bottle, &c. included. It is potable the April after it is made, is best that year, and after ten years begins to have a pitchy taste, resembling it to Malaga. It is not permitted to ferment more than half a day, because it would not be so liquorish. The best color, and its natural one, is the amber. By force of whipping, it is made white, but loses flavor. There are but two or three pièces a year of red Muscat made; there being but one vineyard of the red grape, which belongs to a baker called Pascal. This sells in bottles at thirty sous, the bottle included. Rondelle, négociant en vin, Porte St. Bernard, fauxbourg St. Germain, Paris, buys three hundred pieces of the first quality every year. The coteaux yield about half a piece to the setterie, the plains a whole piece. The inferior quality is not at all esteemed. It is bought by the merchants of Cette, as is also the wine of Beziers, and sold by them for Frontignan of the first quality. They sell thirty thousand pièces a year under that name. The town of Frontignan marks its casks with a hot iron: an individual of that place, having two casks emptied, was offered forty livres for the empty cask by a merchant of Cette. The town of Frontignan contains about two thousand inhabitants; it is almost on the level of the ocean. Transportation to Paris is fifteen livres the quintal, and takes fifteen days. The price of packages is about eight livres eight sous the one hundred bottles. A setterie of good vineyard sells for from three hundred and fifty to five hundred livres, and rents for fifty livres. A laboring man hires at one hundred and fifty livres the year, and is fed and lodged; a woman at half as much. Wheat sells at ten livres the settier, which weighs one hundred pounds, poids de table. They make some Indian corn here, which is eaten by the poor. The olives do not extend northward of this into the country above twelve or fifteen leagues. In general, the olive country in Languedoc is about fifteen leagues broad. More of the waste lands between Frontignan and Mirval are capable of culture; but it is a marshy country, very subject to fever and ague, and generally unhealthy. Thence arises, as is said, a want of hands.
Cette. There are in this town about ten thousand inhabitants. Its principal commerce is wine; it furnishes great quantities of grape-pumice for making verdigrise. They have a very growing commerce; but it is kept under by the privileges of Marseilles.
May 13. Agde. On the right of the Etang de Thau are plains of some width, then hills, in olives, vines, mulberry, corn, and pasture. On the left a narrow sand-bar, separating the Etang from the sea, along which it is proposed to make a road from Cette to Agde. In this case, the post would lead from Montpelier by Cette and Agde to Beziers, being leveller, and an hour or an hour and a half nearer. Agde contains six or eight thousand inhabitants.
May 14. Beziers. Rich plains in corn, saintfoin, and pasture; hills at a little distance to the right in olives; the soil both of hill and plain is red going from Agde to Beziers. But at Beziers the country becomes hilly, and is in olives, corn, saintfoin, pasture, some vines, and mulberries.
May 15. Beziers. Argilies. Le Saumal. From Argilies to Saumal are considerable plantations of vines. Those on the red hills, to the right, are said to produce good wine. No wood, no enclosures. There are sheep and good cattle. The Pyrenees are covered with snow. I am told they are so in certain parts all the year. The canal of Languedoc, along which I now travel, is six toises wide at bottom, and ten toises at the surface of the water, which is one toise deep. The barks which navigate it are seventy and eighty feet long, and seventeen or eighteen feet wide. They are drawn by one horse, and worked by two hands, one of which is generally a woman. The locks are mostly kept by women, but the necessary operations are much too laborious for them. The encroachments by the men, on the offices proper for the women, is a great derangement in the order of things. Men are shoemakers, tailors, upholsterers, staymakers, mantua-makers, cooks, housekeepers, house-cleaners, bed-makers, they coiffe the ladies, and bring them to bed: the women, therefore, to live, are obliged to undertake the offices which they abandon. They become porters, carters, reapers, sailors, lock-keepers, smiters on the anvil, cultivators of the earth, &c. Can we wonder, if such of them as have a little beauty, prefer easier courses to get their livelihood, as long as that beauty lasts? Ladies who employ men in the offices which should be reserved for their sex, are they not bawds in effect? For every man whom they thus emply, some girl, whose place he has thus taken, is driven to whoredom. The passage of the eight locks at Beziers, that is, from the opening of the first to the last gate took one hour and thirty-three minutes. The bark in which I go is about thirty-five feet long, drawn by one horse, and goes from two to three geographical miles an hour. The canal yields abundance of carp and eel. I see also small fish, resembling our perch and chub. Some plants of white clover, and some of yellow, on the banks of the canal near Capestan; santolina also, and a great deal of yellow iris. Met a raft of about three hundred and fifty beams, forty feet long, and twelve or thirteen inches in diameter, formed into fourteen rafts, tacked together. The extensive and numerous fields of saintfoin, in general bloom, are beautiful.
May 16. Le Saumal. Marseillette. May 17. Marseilleite. Carcassonne. From Saumal to Carcassonne we have always the river Aube close on our left. This river runs in the valley between the Cevennes and Pyrenees, serving as the common receptacle for both their waters. It is from fifty to one hundred and fifty yards wide, always rapid, rocky, and insusceptible of navigation. The canal passes in the side of hills made by that river, overlooks the river itself, and its plains, and has its prospect ultimately terminated on one side by mountains of rock, overtopped by the Pyrenees, on the other by small mountains, sometimes of rock, sometimes of soil, overtopped by the Cevennes. Marseillette is on a ridge, which separates the river Aube from the Etang de Marseillette. The canal, in its approach to this village, passes the ridge, and rides along the front, overlooking the Etang, and the plains on its border; and having passed the village, re-crosses the ridge, and resumes its general ground in front of the Aube. The land is in corn, saintfoin, pasture, vines, mulberries, willows, and olives.
May 18. Carcassonne. Castelnaudari. Opposite to Carcassonne the canal receives the river Fresquel, about thirty yards wide, which is its substantial supply of water from hence to Beziers. From Beziers to Agde the river Orb furnishes it, and the Eraut, from Agde to the Etang de Thau. By means of the écluse ronde at Agde, the waters of the Eraut can be thrown towards Beziers, to aid those of the Orb, as far as the écluse de Porcaraigne, nine geometrical miles. Where the Fresquel enters the canal, there is, on the opposite side, a waste, to let off the superfluous waters. The horse-way is continued over this waste, by a bridge of stone of eighteen arches. I observe them fishing in the canal, with a skimming net of about fifteen feet diameter, with which they tell me they catch carp. Flax in blossom. Neither strawberries nor peas yet at Carcassonne. The Windsor-bean just come to table. From the écluse de la Lande we see the last olive trees near a metairée, or farm-house-, called La Lande. On a review of what I have seen and heard of this tree, the following seem to be its northern limits. Beginning on the Atlantic, at the Pyrenees, and along them to the meridian of La Lande, or of Carcassonne; up that meridian to the Cevennes, as they begin just there to raise themselves high enough to afford it shelter. Along the Cevennes, to the parallel of forty-five degrees of latitude, and along that parallel (crossing the Rhone near the mouth of the Isere) to the Alps; thence along the Alps and Apennines, to what parallel of latitude I know not. Yet here the tracing of the line becomes the most interesting. For from the Atlantic, so far we see this production the effect of shelter and latitude combined. But where does it venture to launch forth unprotected by shelter, and by the mere force of latitude alone? Where, for instance, does its northern limit cross the Adriatic? I learn, that the olive tree resists cold to eight degrees of Reaumur below the freezing-point, which corresponds to fourteen above zero of Fahrenheit: and that the orange resists to four degrees below freezing of Reaumur, which is twenty-three degrees above zero of Fahrenheit.
May 19. Castelnaudari. St. Feriol. Escamaze. Lampy. Some sheep and cattle; no enclosures. St. Feriol, Escamaze, and Lampy are in the montagnes noires. The country almost entirely waste. Some of it in shrubbery. The voute d’Escamaze is of one hundred and thirty-five yards. Round about Castelnaudari the country is hilly, as it has been constantly from Beziers; it is very rich. Where it is plain, or nearly plain, the soil is black: in general, however, it is hilly and reddish, and in corn. They cultivate a great deal of Indian corn here, which they call millet; it is planted, but not yet up.
May 20. Castelnaudari. Naurouze. Villefranche. Baziege. At Naurouze is the highest ground which the canal had to pass between the two seas. It became necessary, then, to find water still higher to bring it here. The river Fresquel heading by its two principal branches in the montagnes noires, a considerable distance off to the eastward, the springs of the most western one were brought together, and conducted to Naurouze, where its waters are divided, part furnishing the canal towards the ocean, the rest towards the Mediterranean, as far as the écluse de Fresquel, where, as has been before noted, the Lampy branch and the Alzau, under the name of the Fresquel, enter.
May 20. They have found that a lock of six pieds is best; however, eight pieds is well enough. Beyond this, it is bad. Monsieur Pin tells me of a lock of thirty pieds made in Sweden, of which it is impossible to open the gates. They therefore divided it into four locks. The small gates of the locks of this canal have six square pieds of surface. They tried the machinery of the jack for opening them. They were more easily opened, but very subject to be deranged, however strongly made. They returned, therefore, to the original wooden screw, which is excessively slow and laborious. I calculate that five minutes are lost at every basin by this screw, which, on the whole number of basins, is one eighth of the time necessary to navigate the canal: and of course, if a method of lifting the gate at one stroke could be found, it would reduce the passage from eight to seven days, and the freight equally. I suggested to Monsieur Pin and others a quadrantal gate, turning on a pivot, and lifted by a lever like a pump-handle, aided by a windlass and cord, if necessary. He will try it, and inform me of the success. The price of transportation from Cette to Bordeaux, through the canal and Garonne is ——— the quintal: round by the straits of Gibraltar is ———. Two hundred and forty barks, the largest of twenty-two hundred quintals (or say, in general, of one hundred tons), suffice to perform the business of this canal, which is stationary, having neither increased nor diminished for many years. When pressed, they can pass and repass between Toulouse and Beziers in fourteen days; but sixteen is the common period. The canal is navigated ten and a half months of the year: the other month and a half being necessary to lay it dry, cleanse it, and repair the works. This is done in July and August, when there would perhaps be a want of water.
May 21. Baziège. Toulouse. The country continues hilly, but very rich. It is in mulberries, willows, some vines, corn, maize, pasture, beans, flax. A great number of chateaux and good houses in the neighborhood of the canal. The people partly in farm-houses, partly in villages. I suspect that the farm-houses are occupied by the farmers, while the laborers (who are mostly by the day) reside in the villages. Neither strawberries nor pease yet at Baziege or Toulouse. Near the latter are some fields of yellow clover.
At Toulouse the canal ends. It has four communications with the Mediterranean. 1. Through the ponds of Thau, Frontignan, Palavas, Maguelone, and Manjo, the canal de la Radela Aigues-mortes, le canal des Salines de Pecair, and the arm of the Rhone called Bras de Fer, which ends at Fourgues, opposite to Arles, and thence down the Rhone. 2. At Cette, by a canal of a few hundred toises, leading out of the Etang de Thau into the sea. The vessels pass the Etang, though a length of nine thousand toises, with sails. 3. At Agde, by the river Eraut, twenty-five hundred toises. It has but five or six pieds of water at its mouth. It is joined to the canal at the upper part of this communication, by a branch of a canal two hundred and seventy toises long. 4. At Narbonne, by a canal they are now opening, which leads from the great canal near the aqueduct of the river Cesse, twenty-six hundred toises, into the Aude. This new canal will have five lock-basins, of about twelve pieds fall each. Then you are to cross the Aude very obliquely, and descend a branch of it six thousand toises, through four lock-basins to Narbonne, and from Narbonne down the same branch, twelve hundred toises into the Etang de Sigen, across that Etang four thousand toises, issuing at an inlet, called Grau de la Nouvelle, into the Gulf of Lyons. But only vessels of thirty or forty tons can enter this inlet. Of these four communications, that of Cette only leads to a deep sea-port, because the exit is there by a canal, and not a river. Those by the Rhone, Eraut, and Aude, are blocked up by bars at the mouths of those rivers. It is remarkable, that all the rivers running into the Mediterranean are obstructed at their entrance by bars and shallows, which often change their position. This is the case with the Nile, Tiber, the Po, the Lez, le Lyoron, the Orbe, the Gly, the Tech, the Tet, he. Indeed, the formation of these bars seems not confined to the mouths of the rivers, though it takes place at them more certainly. Along almost the whole of the coast, from Marseilles towards the Pyrenees, banks of sand are thrown up parallel with the coast, which have insulated portions of the sea, that is, formed them into etangs, ponds, or sounds, through which here and there narrow and shallow inlets only are preserved by the currents of the rivers. These sounds fill up in time, with the mud and sand deposited in them by the rivers. Thus the Etang de Vendres, navigated formerly by vessels of sixty tons, is now nearly filled up by the mud and sand of the Aude. The Vistre and Vidourle, which formerly emptied themselves into the Gulf of Lyons, are now received by the Etangs de Manjo and Aiguesmortes, that is to say, the part of the Gulf of Lyons, which formerly received, and still receives those rivers, is now cut off from the sea by a bar of sand, which has been thrown up in it, and has formed it into sounds. Other proofs that the land gains there on the sea, are, that the towns of St. Giles and Notre Dame d’Asposts, formerly seaports, are no far from the sea, and that Aiguesmortes, where are still to be seen the iron rings to which vessels were formerly moored, and where St. Louis embarked for Palestine, has now in its vicinities only ponds, which cannot be navigated, and communicates with the sea by an inlet, called Grau du Roy, through which only fishing-barks can pass. It is pretty well established, that all the Delta of Egypt has been formed by the depositions of the Nile, and the alluvions of the sea, and it is probable that that operation is still going on. Has this peculiarity of the Mediterranean any connection with the scantiness of its tides, which, even at the equinoxes, are of two or three feet only? The communication from the western end of the canal to the ocean, is by the river Garonne. This is navigated by flat boats of eight hundred quintals, when the water is well; but when it is scanty, these boats carry only two hundred quintals, till they get to the mouth of the Tarn. It has been proposed to open a canal that far from Toulouse, along the right side of the river.
May 22. Toulouse. 23. Agen. 24. Castres. Bordeaux. The Garonne, and rivers emptying into it, make extensive and rich plains, which are in mulberries, willows, corn, maize, pasture, beans, and flax. The hills are in corn, maize, beans, and a considerable proportion of vines. There seems to be as much maize as corn in this country. Of the latter, there is more rye than wheat. The maize is now up, and about three inches high. It is sowed in rows two feet or two and a half feet apart, and is pretty thick in the row. Doubtless they mean to thin it. There is a great deal of a forage they call farouche. It is a species of red trefoil, with few leaves, a very coarse stalk, and a cylindrical blossom of two inches in length, and three quarters of an inch in diameter, consisting of floscules, exactly as does that of the red clover. It seems to be a coarse food, but very plentiful. They say it is for their oxen. These are very fine, large, and cream-colored. The services of the farm and of transportation are performed chiefly by them. There are a few horses and asses, but no mules. Even in the city of Bordeaux we see scarcely any beasts of draught but oxen. When we cross the Garonne at Langon, we find the plains entirely of sand and gravel, and they continue so to Bordeaux. Where they are capable of any thing, they are in vines, which are in rows, four, five, or six feet apart, and sometimes more. Near Langon is Sauterne, where the best white wines of Bordeaux are made. The waste lands are in fern, furze, shrubbery, and dwarf trees. The farmers live on their farms. At Agen, Castres, Bordeaux, strawberries and pease are now brought to table; so that the country on the canal of Languedoc seems to have later seasons than that east and west of it. What can be the cause? To the eastward, the protection of the Cevennes makes the warm season advance sooner. Does the neighborhood of the Mediterranean co-operate? And does that of the ocean mollify and advance the season to the westward? There are ortolans at Agen, but none at Bordeaux. The buildings on the canal and the Garonne are mostly of brick, the size of the bricks the same with that of the ancient Roman brick, as seen in the remains of their buildings in this country. In those of a circus at Bordeaux, considerable portions of which are standing, I measured the bricks, and found them nineteen or twenty inches long, eleven or twelve inches wide, and from one and a half to two inches thick; their texture as fine, compact, and solid as that of porcelain. The bricks now made, though of the same dimensions, are not so fine. They are burnt in a kind of furnace, and make excellent work. The elm tree shows itself at Bordeaux peculiarly proper for being spread flat for arbors. Many are done in this way on the Quay des Charterons. Strawberries, pease, and cherries at Bordeaux.
May 24, 25, 26, 27, 28. Bordeaux. The cantons in which the most celebrated wines of Bordeaux are made, are Medoc down the river, Grave adjoining the city, and the parishes next above; all on the same side of the river. In the first, is made red wine principally, in the two last, white. In Medoc they plant the vines in cross-rows of three and a half pieds. They keep them so low, that poles extended along the rows one way, horizontally, about fifteen or eighteen inches above the ground, serve to tie the vines to, and leave the cross row open to the plough. In Grave they set the plants in quincunx, i.e. in equilateral triangles of three and a half pieds every side; and they stick a pole of six or eight feet high to every vine, separately. The vine-stock is sometimes three or four feet high. They find these two methods equal in culture, duration, quantity, and quality. The former, however, admits the alternative of tending by hand or with the plough. The grafting of the vine, though a critical operation, is practised with success. When the graft has taken, they bend it into the earth, and let it take root above the scar. They begin to yield an indifferent wine at three years old, but not a good one till twenty-five years, nor after eighty, when they begin to yield less, and worse, and must be renewed. They give three or four workings in the year, each worth seventy or seventy-five livres the journal, which is of eight hundred and forty square ioises, and contains about three thousand plants. They dung a little in Medoc and Grave, because of the poverty of the soil; but very little; as more would affect the wine. The journal yields, communions annis, about three pièces (of two hundred and forty, or two hundred and fifty bottles each). The vineyards of first quality are all worked by their proprietors. Those of the second, rent for three hundred livres the journal: those of third, at two hundred livres. They employ a kind of overseer at four or five hundred livres the year, finding him lodging and drink: but he feeds himself. He superintends and directs, though he is expected to work but little. If the proprietor has a garden, the overseer tends that. They never hire laborers by the year. The day wages for a man are thirty sous, a woman’s fifteen sous, feeding themselves. The women make the bundles of sarment, weed, pull off the snails, tie the vines, and gather the grapes. During the vintage they are paid high, and fed well.
Of Red wines, there are four vineyards of the first quality; viz. 1. Chateau Margau, belonging to the Marquis d’Agincourt, who makes about one hundred and fifty tons, of one thousand bottles each. He has engaged to Jernon, a merchant. 2. La Tour de Segur, en Saint Lambert, belonging to Monsieur Miresmenil, who makes one hundred and twenty-five tons. 3. Hautbrion, belonging two-thirds to M. le Comte de Femelle, who has engaged to Barton, a merchant: the other third to the Comte de Toulouse, at Toulouse. The whole is seventy-five tons. 4. Chateau de la Fite, belonging to the President Pichard, at Bordeaux, who makes one hundred and seventy-five tons. The wines of the three first, are not in perfection till four years old: those of de la Fite, being somewhat lighter, are good at three years; that is, the crop of 1786 is good in the spring of 1789. These growths, of the year 1783, sell now at two thousand livres the ton; those of 1784, on account of the superior quality of that vintage, sell at twenty-four hundred livres; those of 1785, at eighteen hundred livres; those of 1786, at eighteen hundred livres, though they had sold at first for only fifteen hundred livres. Red wines of the second quality, are Rozan, Dabbadie or Lionville, la Rose, Qui-rouen, Durfort; in all eight hundred tons, which sell at one thousand livres, new. The third class, are Galons, Mouton, Gassie, Arboete, Pontette, de Ferme, Candale; in all two thousand tons, at eight or nine hundred livres. After these, they are reckoned common wines, and sell from five hundred livres, down to one hundred and twenty livres, the ton. All red wines decline after a certain age, losing color, flavor, and body. Those of Bordeaux begin to decline at about seven years old.
Of White wines, those made in the canton of Grave, are most esteemed at Bordeaux. The best crops are, 1. Pontac, which formerly belonged to M. de Pontac, but now to M. de Lamont. He makes forty tons, which sell at four hundred livres, new. 2. St. Brise, belonging to M. de Pontac; thirty tons, at three hundred and fifty livres. 3. De Carbonius, belonging to the Benedictine monks, who make fifty tons, and never selling till three or four years old, get eight hundred livres the ton. Those made in the three parishes next above Grave, and more esteemed at Paris, are, 1. Sauterne. The best crop belongs to M. Diquem at Bordeaux, or to M. de Salus, his son-in-law; one hundred and fifty tons, at three hundred livres, new, and six hundred livres, old. The next best crop is M. de Fillotte’s, one hundred tons, sold at the same price. 2. Prignac. The best is the President du Roy’s, at Bordeaux. He makes one hundred and seventy-five tons, which sell at three hundred livres, new, and six hundred livres, old. Those of 1784, for their extraordinary quality, sell at eight hundred livres. 3. Barsac. The best belongs to the President Pichard, who makes one hundred and fifty tons, at two hundred and eighteen livres, new, and six hundred livres, old. Sauterne is the pleasantest; next Prignac, and lastly Barsac: but Barsac is the strongest; next Prignac, and lastly Sauterne; and all stronger than Grave. There are other good crops made in the same parishes of Sauterne, Prignac, and Barsac; but none as good as these. There is a virgin wine, which, though made of a red grape, is of a light rose color, because, being made without pressure, the coloring matter of the skin does not mix with the juice. There are other white wines, from the preceding prices down to seventy-five livres. In general, the white wines keep longest. They will be in perfection till fifteen or twenty years of age. The best vintage now to be bought, is of 1784; both of red and white. There has been no other good year since 1779. The celebrated vineyards before mentioned, are plains, as is generally the canton of Medoc, and that of the Grave. The soil of Hautbrion, particularly, which I examined, is a sand, in which is near as much round gravel or small stone, and very little loam: and this is the general soil of Medoc. That of Pontac, which I examined also, is a little different. It is clayey, with a fourth or fifth of fine rotten stone; and at two feet depth, it becomes all a rotten stone. M. de Lamont tells me, he has a kind of grape without seeds, which I did not formerly suppose to exist; but I saw at Marseilles dried raisins from Smyrna without seeds. I see in his farm at Pontac, some plants of white clover, and a good deal of yellow: also some small peach trees in the open ground. The principal English wine merchants at Bordeaux, are Jernon, Barton, Johnston, Foster, Skinner, Copinger, and M’Cartey: the chief French wine merchants, are Feger, Nerac, Bruneaux Jauge, and Du Verget. Desgrands, a wine-broker, tells me they never mix the wines of first quality: but that they mix the inferior ones to improve them. The smallest wines make the best brandy. They yield about a fifth or sixth.
May 28, 29. From Bordeaux to Blaye, the country near the river is hilly, chiefly in vines, some corn, some pasture: further out, are plains, boggy and waste. The soil, in both cases, clay and grit. Some sheep on the waste. To Etauliers, we have sometimes boggy plains, sometimes waving grounds and sandy, always poor, generally waste, in fern and furze, with some corn however, interspersed. To Mirambeau and St. Genis, it is hilly, poor, and mostly waste. There are some corn and maize however, and better trees than usual. Towards Pons, it becomes a little red, mostly rotten stone. There are vines, corn, and maize, which is up. At Pons we approach the Charente; the country becomes better, a blackish mould mixed with a rotten chalky stone: a great many vines, corn, maize, and farouche. From Lajart to Saintes and Rochefort, the soil is reddish, its foundation a chalky rock, at about a foot depth; in vines, corn, maize, clover, lucerne, and pasture. There are more and better trees than I have seen in all my journey; a great many apple and cherry trees: fine cattle and many sheep.
May 30. From Rochefort to La Rochelle, it is sometimes hilly and red, with a chalky foundation, middling good; in corn, pasture, and some waste: sometimes it is reclaimed marsh, in clover and corn, except the parts accessible to the tide, which are in wild grass. About Rochelle, it is a low plain. Towards Usseau, and halfway to Marans, level highlands, red, mixed with an equal quantity of broken chalk; mostly in vines, some corn, and pasture: then to Marans and halfway to St. Hermine, it is reclaimed marsh, dark, tolerably good, and all in pasture: there we rise to plains a little higher, red, with a chalky foundation, boundless to the eye, and altogether in corn and maize.
May 31. At St. Hermine, the country becomes very hilly, a red clay mixed with chalky stone, generally waste, in furze and broom, with some patches of corn and maize; and so it continues to Chantonay, and St. Fulgent. Through the whole of this road from Bordeaux, are frequent hedge rows, and small patches of forest wood, not good, yet better than I had seen in the preceding part of my journey. Towards Montaigu, the soil mends a little; the cultivated parts in corn and pasture, the uncultivated in broom. It is in very small enclosures of ditch and quickset. On approaching the Loire to Nantes, the country is leveller: the soil from Rochelle to this place may be said to have been sometimes red, but oftener gray, and always on a chalky foundation. The last census, of about 1770, made one hundred and twenty thousand inhabitants at Nantes. They conjecture there are now one hundred and fifty thousand, which equals it to Bordeaux.
June 1,2. The country from Nantes to L’Orient is very hilly and poor, the soil gray; nearly half is waste, in furze and broom, among which is some poor grass. The cultivated parts are in corn, some maize, a good many apple trees; no vines. All is in small enclosures of quick hedge and ditch. There are patches and hedge-rows of forest-wood, not quite deserving the name of timber. The people are mostly in villages; they eat rye-bread, and are ragged. The villages announce a general poverty, as does every other appearance. Women smite on the anvil, and work with the hoe, and cows are yoked to labor. There are great numbers of cattle, insomuch that butter is their staple. Neither asses nor mules: yet it is said that the fine mules I have met with on my journey, are raised in Poictou. There are but few chateaux here. I observe mill-ponds, and hoes with long handles. Have they not, in common with us, derived these from England, of which Bretagne is probably a colony? L’Orient is supposed to contain twenty-five thousand inhabitants. They tell me here, that to make a reasonable profit on potash and pearlash, as bought in America, the former should sell at thirty livres, the latter thirty-six livres, the quintal. Of turpentine they make no use in their vessels. Bayonne furnishes pitch enough; but tar is in demand, and ours sells well. The tower of L’Orient is sixty-five pieds above the level of the sea, one hundred and twenty pieds high, twenty-five pieds in diameter; the stairs four feet radius, and cost thirty thousand livres, besides the materials of the old tower.
June 3, 4, 5. The country and productions from L’Orient to Rennes, and from Rennes to Nantes, are precisely similar to those from Nantes to L’Orient. About Rennes, it is somewhat leveller, perhaps less poor, and almost entirely in pasture. The soil always gray. Some small, separate houses, which seem to be the residence of laborers, or very small farmers; the walls frequently of mud, and the roofs generally covered with slate. Great plantations of walnut, and frequently of pine. Some apple trees and sweet-briar still in bloom, and broom generally so. I have heard no nightingale since the last day of May. There are gates in this country made in such a manner, that the top rail of the gate overshoots backwards the hind post, so as to counterpoise the gate, and prevent its swagging.
Nantes. Vessels of eight feet draught only can come to Nantes. Those which are larger, lie at Painboeuf, ten leagues below Nantes, and five leagues above the mouth of the river. There is a continued navigation from Nantes to Paris, through the Loire, the canal de Briare and the Seine. Carolina rice is preferred to that of Lombardy for the Guinea trade, because it requires less water to boil it.
June 6, 7, 8. Nantes. Ancenis. Angers. Tours. Ascending the Loire from Nantes, the road, as far as Angers, leads over the hills, which are gray, oftener below than above mediocrity, and in corn, pasture, vines, some maize, flax, and hemp. There are no waste lands. About the limits of Bretagne and Anjou, which are between Loriottiere and St. George, the lands change for the better. Here and there, we get views of the plains on the Loire, of some extent, and good appearance, in corn and pasture. After passing Angers, the road is raised out of the reach of inundations, so as at the same time to ward them off from the interior plains. It passes generally along the river side; but sometimes leads through the plains, which, after we pass Angers, become extensive and good, in corn, pasture, some maize, hemp, flax, pease, and beans; many willows, also poplars and walnuts. The flax is near ripe. Sweet-briar in general bloom. Some broom here still, on which the cattle and sheep browse in winter and spring, when they have no other green food; and the hogs eat the blossoms and pods, in spring and summer. This blossom, though disagreeable when smelt in a small quantity, is of delicious fragrance when there is a whole field of it. There are some considerable vineyards in the river plains, just before we reach Les Trois Volets (which is at the one hundred and thirty-sixth milestone), and after that, where the hills on the left come into view, they are mostly in vines. Their soil is clayey and stony, a little reddish, and of southern aspect. The hills on the other side of the river, looking to the north, are not in vines. There is very good wine made on these hills; not equal indeed to the Bordeaux of best quality, but to that of good quality, and like it. It is a great article of exportation from Anjou and Touraine, and probably is sold abroad, under the name of Bordeaux. They are now mowing the first crop of hay. All along both hills of the Loire, is a mass of white stone, not durable, growing black with time, and so soft, that the people cut their houses out of the solid, with all the partitions, chimnies, doors, &c. The hill sides resemble cony burrows, full of inhabitants. The borders of the Loire are almost a continued village. There are many chateaux: many cattle, sheep, and horses; some asses.
Tours is at the one hundred and nineteenth mile-stone. Being desirous of inquiring here into a fact stated by Voltaire, in his Questions Encylopédiques, article Coquilles, relative to the growth of shells unconnected with animal bodies at the Chateau of Monsieur de la Sauvagiere, near Tours, I called on Monsieur Gentil, premier sécrétaire de l’ntendance, to whom the Intendant had written on my behalf, at the request of the Marquis de Chastellux.
I stated to him the fact as advanced by Voltaire, and found he was, of all men, the best to whom I could have addressed myself. He told me he had been in correspondence with Voltaire on that very subject, and was perfectly acquainted with Monsieur de la Sauvagiere, and the Faluniere where the fact is said to have taken place. It is at the Chateau de Grillemont, six leagues from Tours, on the road to Bordeaux, belonging now to Monsieur d’Orcai. He says, that De la Sauvagiere was a man of truth, and might be relied on for whatever facts he stated as of his own observation; but that he was overcharged with imagination, which, in matters of opinion and theory, often led him beyond his facts; that this feature in his character had appeared principally in what he wrote on the antiquities of Touraine; but that as to the fact in question, he believed him. That he himself, indeed, had not watched the same identical shells, as Sauvagiere had done, growing from small to great; but that he had often seen such masses of those shells of all sizes, from a point to a full size, as to carry conviction to his mind that they were in the act of growing; that he had once made a collection of shells for the Emperor’s cabinet, reserving duplicates of them for himself; and that these afforded proofs of the same fact; that he afterwards gave those duplicates to a Monsieur du Verget, a physician of Tours, of great science and candor, who was collecting on a larger scale, and who was perfectly in sentiment with Monsieur de la Sauvagiere, and not only the Faluniere, but many other places about Tours, would convince any unbiassed observer, that shells are a fruit of the earth, spontaneously produced; and he gave me a copy of De la Sauvagiere’s Recueil de Dissertations, presented him by the author, wherein is one Sur la vegetation spontanée des coquilles du Chateau des Places. So far, I repeat from him. What are we to conclude? That we have not materials enough yet, to form any conclusion. The fact stated by Sauvagiere is not against any law of nature, and is therefore possible; but it is so little analogous to her habitual processes, that, if true, it would be extraordinary: that to command our belief, therefore, there should be such a suite of observations, as that their untruth would be more extraordinary than the existence of the fact they affirm. The bark of trees, the skin of fruits and animals, the feathers of birds, receive their growth and nutriment from the internal circulation of a juice through the vessels of the individual they cover. We conclude from analogy, then, that the shells of the testaceous tribe receive also their growth from a like internal circulation. If it be urged, that this does not exclude the possibility of a like shell being produced by the passage of a fluid through the pores of the circumjacent body, whether of earth, stone, or water; I answer, that it is not within the usual economy of nature, to use two processes for one species of production. While I withhold my assent, however, from this hypothesis, I must deny it to every other I have ever seen, by which their authors pretend to account for the origin of shells in high places. Some of these are against the laws of nature, and therefore impossible; and others are built on positions more difficult to assent to, than that of De la Sauvagiere. They all suppose these shells to have covered submarine animals, and have then to answer the question, How came they fifteen thousand feet above the level of the sea? And they answer it, by demanding what cannot be conceded. One, therefore, who had rather have no opinion than a false one, will suppose this question one of those beyond the investigation of human sagacity; or wait till further and fuller observations enable him to decide it.
Chanteloup. I heard a nightingale to-day at Chanteloup. The gardener says it is the male, who alone sings, while the female sits; and that when the young are hatched, he also ceases. In the boudoir at Chanteloup, is an ingenious contrivance to hide the projecting steps of a staircase. Three steps were of necessity to project into the boudoir: they are therefore made triangular steps; and instead of being rested on the floor, as usual, they are made fast at their broad end to the stair door, swinging out and in, with that. When it shuts, it runs them under the other steps; when open it brings them out to their proper place. In the kitchen garden, are three pumps, worked by one horse. The pumps are placed in an equilateral triangle, each side of which is of about thirty-five feet. In the centre is a post, ten or twelve feet high, and one foot in diameter. In the top of this, enters the bent end of a lever, of about twelve or fifteen feet long, with a swingle-tree at the other end. About three feet from the bent end, it receives, on a pin, three horizontal bars of iron, which at their other end lay hold of one corner of a quadrantal crank (like a bell crank) moving in a vertical plane, to the other corner of which is hooked the vertical handle of the pump. The crank turns on its point as a centre, by a pin or pivot passing through it. The horse moving the lever horizontally in a circle, every point of the lever describes a horizontal circle. That which receives the three bars, describes a circle of six feet in diameter. It gives a stroke then of six feet to the handle of each pump, at each revolution.
Blois. Orleans. June 9, 10. At Blois, the road leaves the river, and traverses the hills, which are mostly reddish, sometimes gray, good enough, in vines, corn, saintfoin. From Orleans to the river Juines, at Etampes, it is a continued plain of corn, and saintfoin, tolerably good, sometimes gray, sometimes red. From Etampes to Etrechy, the country is mountainous and rocky, resembling that of Fontainebleau. Quere. If it may not be the same vein?
TO WILLIAM CARMICHAEL.
Paris, June 14, 1787.
Dear Sir,
Having got back to Paris three days ago, I resume immediately the correspondence with which you have been pleased to honor me. I wish I could have begun it with more agreeable information than that furnished me by Mr. Grand, that the funds of the United States here are exhausted, and himself considerably in advance; and by the board of treasury at New York, that they have no immediate prospect of furnishing us supplies. We are thus left to shift for ourselves, without previous warning. As soon as they shall replenish Mr. Grand’s hands, I will give you notice, that you may recommence your usual drafts on him; unless the board should provide a separate fund for you, dependant on yourself alone, which I have strongly and repeatedly pressed on them, in order to remove the indecency of suffering your drafts to pass through any intermediate hand for payment.
My letters from America came down to the 24th of April. The disturbances in the Eastern States were entirely settled. I do not learn that the government had made any examples. Mr. Hancock’s health being re-established, the want of which had occasioned him to resign the government of Massachusetts, he has been re-elected to the exclusion of Governor Bowdoin. New York still refuses to pass the impost in any form, and were she to pass it, Pennsylvania will not uncouple it from the supplementary funds. These two States and Virginia, are the only ones, my letters say, which have paid any thing into the Continental treasury, for a twelvemonth past. I send you a copy of a circular letter from Congress to the several States, insisting on their removing all obstructions to the recovery of British debts. This was hurried, that it might be delivered to the Assembly of New York before they rose. It was delivered, but they did nothing in consequence of it. The convention to be assembled at Philadelphia will be an able one. Ten States were known to have appointed delegates. Maryland was about to appoint; Connecticut was doubtful; and Rhode Island had refused. We are sure, however, of eleven States. South Carolina has prohibited the importation of slaves for three years; which is a step towards a perpetual prohibition. Between six and seven hundred thousand acres of land are actually surveyed into townships, and the sales are to begin immediately. They are not to be sold for less than a dollar the acre, in public certificates. I wrote you from Bordeaux on the subject of Colonel Smith. I was sorry I missed him there, for other reasons as well as from a curiosity to know his errand. The Notables have laid the foundation of much good here: you have seen it detailed in the public papers. The Prince of Wales is likely to recover from his illness, which was very threatening. It is feared, that three powers have combined to lift the Prince of Orange out of his difficulties. Have you yet the cipher of which I formerly wrote to you, or any copy of it?
I am, with sincere esteem, Dear Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO J. BANNISTER, JUNIOR.
Paris, June 19, 1787.
Dear Sir,
I have received your favor of April the 23d, from New York, and am sorry to find you have had a relapse. Time and temperance, however, will cure you; to which add exercise. I hope you have long ago had a happy meeting with your friends, with whom a few hours would be to me an ineffable feast. The face of Europe appears a little turbid, but all will subside. The Empress has endeavored to bully the Turk, who laughed at her, and she is going back. The Emperor’s reformations have occasioned the appearance of insurrection in Flanders, and he, according to character, will probably tread back his steps. A change of system here with respect to the Dutch, is suspected; because the Kings of Prussia and England openly espouse the cause of the Stadtholder, and that of the Patriots is likely to fall. The American acquaintances whom you left here, not being stationary, you will hardly expect news of them. Mrs. Barrett, lately dead, was, I think, known to you. I had a letter from Ledyard lately, dated at St. Petersburg. He had but two shirts, and yet more shirts than shillings. Still he was determined to obtain the palm of being the first circumambulator of the earth. He says, that having no money, they kick him from place to place, and thus he expects to be kicked round the globe. Are you become a great walker? You know I preach up that kind of exercise. Shall I send you a conte-pas? It will cost you a dozen louis, but be a great stimulus to walking, as it will record your steps. I finished my tour a week or ten days ago. I went as far as Turin, Milan, Genoa; and never passed three months and a half more delightfully. I returned through the canal of Languedoc, by Bordeaux, Nantes, L’Orient, and Rennes; then returned to Nantes, and came up the Loire to Orleans. I was alone through the whole, and think one travels more usefully when alone, because he reflects more.
Present me in the most friendly terms to Mrs. Bannister and to your father, and be assured of the sincere esteem of, Dear Sir, your friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JAMES MADISON.
Paris, June 20, 1787.
[* Much of this letter is in cipher: but the notes annexed
to it, have enabled the Editor to decipher and publish it.]
Dear Sir,
I wrote you last on the 30th of January, with a Postscript of February the 5th. Having set out the last day of that month to try the waters of Aix, and been journeying since, till the 10th instant, I have been unable to continue my correspondence with you. In the mean time, I have received your several favors of February the 15th, March the 18th and 19th, and April the 23d. The last arrived here about the 25th of May, while those of March the 18th and 19th, though written, five weeks earlier, arrived three weeks later. I mention this, to show you how uncertain is the conveyance through England.
The idea of separating the executive business of the confederacy from Congress, as the judiciary is already, in some degree, is just and necessary. I had frequently pressed on the members individually, while in Congress, the doing this by a resolution of Congress for appointing an executive committee, to act during the sessions of Congress, as the committee of the States was to act during their vacations. But the referring to this committee all executive business, as it should present itself, would require a more persevering self-denial than I suppose Congress to possess. It will be much better to make that separation by a federal act. The negative proposed to be given them on all the acts of the several legislatures, is now, for the first time, suggested to my mind. Prima facie, I do not like it. It fails in an essential character; that the hole and the patch should be commensurate. But this proposes to mend a small hole, by covering the whole garment. Not more than one out of one hundred State acts, concern the confederacy. This proposition, then, in order to give them one degree of power, which they ought to have, gives them ninety-nine more, which they ought not to have, upon a presumption that they will not exercise the ninety-nine. But upon every act there will be a preliminary question, Does this act concern the confederacy? And was there ever a proposition so plain, as to pass Congress without a debate? Their decisions are almost always wise; they are like pure metal. But you know of how much dross this is the result. Would not an appeal from the State judicature to a federal court, in all cases where the act of Confederation controlled the question, be as effectual a remedy, and exactly commensurate to the defect. A British creditor, for example, sues for his debt in Virginia; the defendant pleads an act of the State, excluding him from their courts; the plaintiff urges the confederation, and the treaty made under that, as controlling the State law; the judges are weak enough to decide according to the views of their legislature. An appeal to a federal court gets all to rights. It will be said, that this court may encroach on the jurisdiction of the State courts. It may. But there will be a power, to wit, Congress, to watch and restrain them. But place the same authority in Congress itself, and there will be no power above them to perform the same office. They will restrain within due bounds a jurisdiction exercised by others, much more rigorously than if exercised by themselves.
I am uneasy at seeing that the sale of our western lands is not yet commenced. That valuable fund for the immediate extinction of our debt will, I fear, be suffered to slip through our fingers. Every day exposes it to events, which no human foresight can guard against. When we consider the temper of the people of that country, derived from the circumstances which surround them, we must suppose their separation possible, at every moment. If they can be retained till their governments become settled and wise, they will remain with us always, and be a precious part of our strength and our virtue. But this affair of the Mississippi, by showing that Congress is capable of hesitating on a question, which proposes a clear sacrifice of the western to the maritime States, will with difficulty be obliterated. The proposition of my going to Madrid, to try to recover there the ground which has been lost at New York, by the concession of the vote of seven States, I should think desperate. With respect to myself, weighing the pleasure of the journey and bare possibility of success in one scale, and the strong probability of failure and the public disappointment directed on me, in the other, the latter preponderates. Add to this, that jealousy might be excited in the breast of a person, who could find occasions of making me uneasy.
The late changes in the ministry here, excite considerable hopes. I think we gain in them all. I am particularly happy at the reentry of Malesherbes into the Council. His knowledge and integrity render his value inappreciable, and the greater to me, because, while he had no views of office, we had established together the most unreserved intimacy. So far, too, I am pleased with Montmorin. His honesty proceeds from the heart as well as the head, and therefore may be more surely counted on. The King loves business, economy, order, and justice, and wishes sincerely the good of his people; but he is irascible, rude, very limited in his understanding, and religious bordering on bigotry. He has no mistress, loves his queen, and is too much governed by her. She is capricious, like her brother, and governed by him; devoted to pleasure and expense; and not remarkable for any other vices or virtues. Unhappily the King shows a propensity for the pleasures of the table. That for drink has increased lately, or at least it has become more known.
For European news in general, I will refer you to my letter to Mr. Jay. Is it not possible, that the occurrences in Holland may excite a desire in many of leaving that country, and transferring their effects out of it, and thus make an opening for shifting into their hands the debts due to this country, to its officers, and Farmers? It would be surely eligible. I believe Dumas, if put on the watch, might alone suffice; but he surely might, if Mr. Adams should go when the moment offers. Dumas has been in the habit of sending his letters open to me, to be forwarded to Mr. Jay. During my absence, they passed through Mr. Short’s hands, who made extracts from them, by which I see he has been recommending himself and me for the money-negotiations in Holland. It might be thought, perhaps, that I have encouraged him in this. Be assured, my Dear Sir, that no such idea ever entered my head. On the contrary, it is a business which would be the most disagreeable to me of all others, and for which I am the most unfit person living. I do not understand bargaining, nor possess the dexterity requisite for the purpose. On the other hand, Mr. Adams, whom I expressly and sincerely recommend, stands already on ground for that business, which I could not gain in years. Pray set me to rights in the minds of those, who may have supposed me privy to this proposition. En passant, I will observe with respect to Mr. Dumas, that the death of the Count de Vergennes places Congress more at their ease, how to dispose of him. Our credit has been ill treated here in public debate, and our debt here deemed apocryphal. We should try to transfer this debt elsewhere, and leave nothing capable of exciting ill thoughts between us. I shall mention in my letter to Mr. Jay, a disagreeable affair which Mr. Barclay has been thrown into, at Bordeaux. An honester man cannot be found, nor a slower, nor more decisive one. His affairs, too, are so embarrassed and desperate, that the public reputation is, every moment, in danger of being compromitted with him. He is perfectly amiable and honest, with all his embarrassments.
By the next packet, I shall be able to send you some books, as also your watch and pedometer. The two last are not yet done. To search for books, and forward them to Havre, will require more time than I had between my return and the departure of this packet. Having been a witness, heretofore, to the divisions in Congress on the subject of their foreign ministers, it would be a weakness in me to suppose none with respect to myself, or to count with any confidence on the renewal of my commission, which expires on the 10th day of March next; and the more so, as instead of requiring the disapprobation of seven States, as formerly, that of one suffices for a recall, when Congress consists of only seven States, two, when of eight, &c. which I suppose to be habitually their numbers at present. Whenever I leave this place, it will be necessary to begin my arrangements six months before my departure; and these, once fairly begun and under way, and my mind set homewards, a change of purpose could hardly take place. If it should be the desire of Congress that I should continue still longer, I could wish to know it, at farthest, by the packet which will sail from New York in September. Because, were I to put off longer the quitting my house, selling my furniture, he, I should not have time left to wind up my affairs; and having once quitted, and sold off my furniture, I could not think of establishing myself here again. I take the liberty of mentioning this matter to you, not with a desire to change the purpose of Congress, but to know it in time. I have never fixed in my mind, the epoch of my return, so far as shall depend on myself, but I never supposed it very distant. Probably I shall not risk a second vote on this subject. Such trifling things may draw on me the displeasure of one or two States, and thus submit me to the disgrace of a recall.
I thank you for the paccan nuts, which accompanied your letter of March. Could you procure me a copy of the bill for proportioning crimes and punishments, in the form in which it was ultimately rejected by the House of Delegates? Young Mr. Bannister desired me to send him regularly the Mercure de France. I will ask leave to do this through you, and that you will adopt such method of forwarding them to him, as will save him from being submitted to postage, which they would not be worth. As a compensation for your trouble, you will be free to keep them till you shall have read them. I am, with sentiments of the most sincere esteem, Dear Sir, your friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN JAY.
Paris, June 21,1787.
Sir,
I had the honor of addressing you in a letter of May the 4th, from Marseilles, which was to have gone by the last packet. Bat it arrived a few hours too late for that conveyance, and has been committed to a private one, passing through England, with a promise that it should go through no post-office.
I was desirous, while at the sea-ports, to obtain a list of the American vessels which have come to them since the peace, in order to estimate their comparative importance to us, as well as the general amount of our commerce with this country, so far as carried on in our own bottoms. At Marseilles, I found there had been thirty-two, since that period; at Cette, not a single one; at Bayonne, one of our free ports, only one. This last fact I learned from other information, not having visited that place; as it would have been a deviation from my route, too considerable for the importance of the object. At Bordeaux, Nantes, and L’Orient, I could not obtain lists in the moment; but am in hopes I shall be able to get them ere long. Though more important to us, they will probably be more imperfect than that of Marseilles. At Nantes, I began with Monsieur Dobrée an arrangement of his claims. I visited the military stores, which have been detained there so long, opened some boxes of each kind, and found the state of their contents much better than had been represented. An exact list of the articles is to be sent me.
The importations into L’Orient of other fish-oils, besides those of the whale, brought to my notice there a defect in the letter of Monsieur de Calonne, of October the 22nd, which letter was formerly communicated to you. In that, whale oil only was named. The other fish-oils, therefore, have continued to pay the old duties. In a conference with Monsieur de Villedeuil, the present Comptroller General, since my return, I proposed the extending the exemption to all fish-oils, according to the letter of the Hanseatic treaty, which had formed the basis of the regulations respecting us. I think this will be agreed to. The delays of office first, then the illness of Monsieur de Colonne, and lastly, his removal and the throng of business occasioned by the Assemblée des Notables, have prevented the reducing the substance of the letter into the form of an Arrêt, as yet though I have continued soliciting it as much as circumstances would bear. I am now promised that it shall be done immediately, and it shall be so far retrospective to the date of the letter, as that all duties paid since that, shall be refunded.
The new accessions of the ministry are valued here. Good is hoped from the Archbishop of Toulouse, who succeeds the Count de Vergennes as Chef du Conseil de finance. Monsieur de Villedeuil, the Comptroller General, has been approved by the public, in the offices he has heretofore exercised. The Duke de Nivernois, called to the Council, is reckoned a good and able man; and Monsieur de Malesherbes, called also to the Council, is unquestionably the first character in the kingdom, for integrity, patriotism, knowledge, and experience in business. There is a fear that the Marechal de Castries is disposed to retire.
The face of things in Europe is a little turbid, at present; but probably all will subside. The Empress of Russia, it is supposed, will not push her pretensions against the Turks to actual war. Weighing the fondness of the Emperor for innovation, against his want of perseverance, it is difficult to calculate what he will do with his discontented subjects in Brabant and Flanders. If those provinces alone were concerned, he would probably give back; but this would induce an opposition to his plan, in all his other dominions. Perhaps he may be able to find a compromise. The cause of the Patriots in Holland is a little clouded at present.
England and Prussia seem disposed to interpose effectually. The former has actually ordered a fleet of six sail of the line, northwardly, under Gore; and the latter threatens to put her troops into motion. The danger of losing such a weight in their scale, as that of Prussia, would occasion this court to prefer conciliation to war. Add to this, the distress of their finances, and perhaps not so warm a zeal in the new ministry for the innovations in Holland. I hardly believe they will think it worth while to purchase the change of constitution proposed there, at the expense of a war. But of these things, you will receive more particular and more certain details from Mr. Dumas, to whom they belong.
Mr. Eden is appointed ambassador from England to Madrid. To the hatred borne us by his court and country, is added a recollection of the circumstances of the unsuccessful embassy to America, of which he made a part. So that I think he will carry to Madrid, dispositions to do us all the ill he can.
The late change in the ministry is very favorable to the prospects of the Chevalier de la Luzerne. The Count de Montmorin, Monsieur de Malesherbes, and Monsieur de Lamoignon, the Garde des Sceaux, are his near relations. Probably something will be done for him, and without delay. The promise of the former administration to the Count de Moutier, to succeed to this vacancy, should it take place, will perhaps be performed by the present one.
Mr. Barclay has probably informed you of his having been arrested in Bordeaux, for a debt contracted in the way of his commerce. He immediately applied to the parliament of that place, who ordered his discharge. This took place after five days’ actual imprisonment. I arrived at Bordeaux a few days after his liberation. As the Procureur General of the King had interested himself to obtain it, with uncommon zeal, and that too on public principles, I thought it my duty to wait on him and return him my thanks. I did the same to the President of the parliament, for the body over which he presided; what would have been an insult in America, being an indispensable duty here. You will see by the enclosed printed paper, on what grounds the Procureur insisted on Mr. Barclay’s liberation. Those on which the parliament ordered it, are not expressed. On my arrival here, I spoke with the minister on the subject. He observed, that the character of Consul is no protection in this country, against process for debt: that as to the character with which Mr. Barclay had been invested at the court of Morocco, it was questionable whether it would be placed on the diplomatic line, as it had not been derived immediately from Congress; that if it were, it would have covered him to Paris only, where he had received his commission, had he proceeded directly thither, but that his long stay at Bordeaux, must be considered as terminating it there. I observed to him, that Mr. Barclay had been arrested almost immediately on his arrival at Bordeaux. But, says he, the arrest was made void by the parliament, and still he has continued there several weeks. True, I replied, but his adversaries declared they would arrest him again, the moment he should be out of the jurisdiction of the parliament of Bordeaux, and have actually engaged the Maréchausée on the road, to do it. This seemed to impress him. He said he could obtain a letter of safe conduct which would protect him to Paris, but that immediately on his arrival here, he would be liable to arrest. I asked him, if such a letter could not be obtained to protect him to Paris, and back to Bordeaux, and even to America? He said, that for that, the consent of the greater part of his creditors would be necessary; and even with this, it was very doubtful whether it could be obtained: still, if I would furnish him with that consent, he would do what should depend on him. I am persuaded he will, and have written to Mr. Barclay to obtain the consent of his creditors. This is the footing on which this matter stands at present. I have stated it thus particularly, that you may know the truth, which will probably be misrepresented in the English papers, to the prejudice of Mr. Barclay. This matter has been a great affliction to him, but no dishonor where its true state is known. Indeed he is incapable of doing any thing not strictly honorable.
In a letter of August the 30th, 1785, I had the honor of mentioning to you what had passed here, on the subject of a convention for the regulation of the two post offices. I now inclose you a letter from the Baron D’Ogny, who is at the head of that department, which shows that he still expects some arrangement. I have heard it said, that M. de Creve-coeur is authorized to treat on this subject. You doubtless know if this be true. The articles may certainly be better adjusted there, than here. This letter from the Baron D’Ogny was in consequence of an application from a servant of mine, during my absence, which would not have been made had I been here. Nor will it be repeated; it being my opinion and practice to pay small sums of money, rather than to ask favors.
I have the honor to inclose you also, copies of a letter and papers from the Marechal de Castries, on the claim of an individual against the State of South Carolina, for services performed on board the Indian; and the petition of another, on a like claim: also copies of letters received from O’Bryan at Algiers, and from Mr. Lambe. A letter of the 26th of May, from Mr. Montgomery, at Alicant, informs me, that by a vessel arrived at Carthagena from Algiers, they learn the death of the Dey of that republic. Yet, as we hear nothing of it through any other channel, it may be doubted. It escaped me at the time of my departure to Aix, to make arrangements for sending you the gazettes regularly, by the packets. The whole are now sent, though a great part of them are so old as to be not worth perusal. Your favor of April the 24th, has been duly received.
I have the honor,to be, with sentiments of the most perfect esteem and respect. Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MADAME DE CORNY.
Paris, June 30,1787.
On my return to Paris, it was among my first attentions to go to the rue Chaussée d’Antin, No. 17, and inquire after my friends whom I had left there. I was told they were in England. And how do you like England, Madam? I know your taste for the works of art gives you little disposition to Anglomania. Their mechanics certainly exceed all others in some lines. But be just to your own nation. They have not patience, it is true, to set rubbing a piece of steel from morning to night, as a lethargic Englishman will do, full charged with porter. But do not their benevolence, their cheerfulness, their amiability, when compared with the growling temper and manners of the people among whom you are, compensate their want of patience? I am in hopes that when the splendor of their shops, which is all that is worth seeing in London, shall have lost the charm of novelty, you will turn a wishful eye to the good people of Paris, and find that you cannot be so happy with any others. The Bois de Boulogne invites you earnestly to come and survey its beautiful verdure, to retire to its umbrage from the heats of the season. I was through it to-day, as I am every day. Every tree charged me with this invitation to you. Passing by la Muette, it wished for you as a mistress. You want a country-house. This is for sale; and in the Bois de Boulogne, which I have always insisted to be most worthy of your preference. Come then, and buy it. If I had had confidence in your speedy return, I should have embarrassed you in earnest with my little daughter. But an impatience to have her with me, after her separation from her friends, added to a respect for your ease, has induced me to send a servant for her.
I tell you no news, because you have correspondents infinitely more au fait of the details at Paris than I am. And I offer you no services, because I hope you will come as soon as the letter could, which should command them. Be assured, however, that nobody is more disposed to render them, nor entertains for you a more sincere and respectful attachment, than him, who, after charging you with his compliments to Monsieur de Corny, has the honor of offering you the homage of those sentiments of distinguished esteem and regard, with which he is, Dear Madam, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN ADAMS.
Paris, July 1, 1787.
Dear Sir,
I returned about three weeks ago from a very useless voyage; useless, I mean, as to the object which first suggested it, that of trying the effect of the mineral waters of Aix, in Provence, on my hand. I tried these, because recommended among six or eight others as equally beneficial, and because they would place me at the beginning of a tour to the seaports of Marseilles, Bordeaux, Nantes, and L’Orient, which I had long meditated, in hopes that a knowledge of the places and persons concerned in our commerce, and the information to be got from them, might enable me sometimes to be useful. I had expected to satisfy myself at Marseilles, of the causes of the difference of quality between the rice of Carolina, and that of Piedmont, which is brought in quantities to Marseilles. Not being able to do it, I made an excursion of three weeks into the rice country beyond the Alps, going through it from Vercelli to Pavia, about sixty miles. I found the difference to be, not in the management, as had been supposed both here and in Carolina, but in the species of rice; and I hope to enable them in Carolina, to begin the cultivation of the Piedmont rice, and carry it on, hand in hand, with their own, that they may supply both qualities which is absolutely necessary at this market. I had before endeavored to lead the depot of rice from Cowes to Honfleur, and hope to get it received there on such terms, as may draw that branch of commerce from England to this country. It is an object of two hundred and fifty thousand guineas a year. While passing through the towns of Turin, Milan, and Genoa, I satisfied myself of the practicability of introducing our whale-oil for their consumption, and suppose it would be equally so in the other great cities of that country. I was sorry that I was not authorized to set the matter on foot. The merchants with whom I chose to ask conferences met me freely, and communicated fully, knowing I was in a public character. I could, however, only prepare a disposition to meet our oil-merchants. On the article of tobacco, I was more in possession of my ground; and put matters into a train for inducing their government to draw their tobaccos directly from the United States, and not, as heretofore, from Great Britain. I am now occupied with the new ministry here, to put the concluding hand to the new regulations for our commerce with this country, announced in the letter of Monsieur de Calonne, which I sent you last fall. I am in hopes, in addition to those, to obtain a suppression of the duties on tar, pitch, and turpentine, and, an extension of the privileges of American whale oil, to their fish oils in general. I find that the quantity of cod-fish oil brought to L’Orient is considerable. This being got off hand (which will be in a few days), the chicaneries and vexations of the Farmers on the article of tobacco, and their elusions of the order of Bernis, call for the next attention. I have reasons to hope good dispositions in the new ministry towards our commerce with this country. Besides endeavoring, on all occasions, to multiply the points of contact and connection with this country, which I consider as our surest mainstay under every event, I have had it much at heart to remove from between us every subject of misunderstanding or irritation. Our debts to the King, to the Officers, and the Farmers, are of this description. The having complied with no part of our engagements in these, draws on us a great deal of censure, and occasioned a language in the Assemblée des Notables, very likely to produce dissatisfaction between us. Dumas being on the spot in Holland, I had asked of him some time ago, in confidence, his opinion of the practicability of transferring these debts from France to Holland, and communicated his answer to Congress, pressing them to get you to go over to Holland, and try to effect this business. Your knowledge of the ground, and former successes, occasioned me to take this liberty without consulting you, because I was sure you would not weigh your personal trouble against public good. I have had no answer from Congress; but hearing of your journey to Holland, have hoped that some money operation had led you there. If it related to the debts of this country, I would ask a communication of what you think yourself at liberty to communicate, as it might change the form of my answers to the eternal applications I receive. The debt to the officers of France, carries an interest of about two thousand guineas, so we may suppose its principal is between thirty and forty thousand. This makes more noise against us, than all our other debts put together.
I send you the Arrêts which begin the reformation here, and some other publications respecting America; together with copies of letters received from O’Bryan and Lambe. It is believed, that a naval armament has been ordered at Brest, in correspondence with that of England. We know, certainly, that orders are given to form a camp in the neighborhood of Brabant, and that Count Rochambeau has the command of it. Its amount I cannot assert. Report says fifteen thousand men. This will derange the plans of economy. I take the liberty of putting under your cover a letter for Mrs. Kinloch, of South Carolina, with a packet, and will trouble you to inquire for her, and have them delivered. The packet is of great consequence, and therefore referred to her care, as she will know the safe opportunities of conveying it. Should you not be able to find her, and can forward the packet to its address, by any very safe conveyance, I will beg you to do it.
I have the honor to be, with sentiments of the most perfect friendship and esteem, Dear Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
Paris, July 2,1787.
Dear Sir,
I received lately your favor of April the 23d, on my return from a journey of three or four months; and am always happy in an occasion of recalling myself to your memory. The most interesting intelligence from America, is that respecting the late insurrection in Massachusetts. The cause of this has not been developed to me to my perfect satisfaction. The most probable is, that those individuals were of the imprudent number of those who have involved themselves in debt beyond their abilities to pay, and that a vigorous effort in that government to compel the payment of private debts, and raise money for public ones, produced the resistance. I believe you may be assured, than an idea or desire of returning to any thing like their ancient government, never entered into their heads. I am not discouraged by this. For thus I calculate. An insurrection in one of thirteen States, in the course of eleven years that they have subsisted, amounts to one in any particular state, in one hundred and forty-three years, say a century and a half. This would not be near as many as have happened in every other government that has ever existed. So that we shall have the difference between a light and a heavy government as clear gain. I have no fear, but that the result of our experiment will be, that men may be trusted to govern themselves without a master. Could the contrary of this be proved, I should conclude, either that there is no God, or that he is a malevolent being. You have heard of the federal convention, now sitting at Philadelphia, for the amendment of the Confederation. Eleven States appointed delegates certainly; it was expected that Connecticut would also appoint, the moment its Assembly met. Rhode Island had refused. I expect they will propose several amendments; that that relative to our commerce will probably be adopted immediately, but that the others must wait to be adopted, one after another, in proportion as the minds of the States ripen for them. Dr. Franklin enjoys good health. I shall always be happy to hear from you, being, with sentiments of very sincere esteem and respect, Dear Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO B. VAUGHAN.
Paris, July 2, 1787.
Dear Sir,
Your favor of February the 16th came to my hands in the moment I was setting out on a tour through the southern parts of France and northern of Italy, from which I am but just now returned. I avail myself of the earliest moment to acknowledge its receipt, and to thank you for the box of magnets which I found here. Though I do not know certainly by or from whom they come, I presume they came by Colonel Smith, who was here in my absence, and from Messrs. Nairne and Blunt, through your good offices. I think your letter of February the 16th flatters me with the expectation of another, with observations on the hygrometers I had proposed. I value what comes from you too much, not to remind you of it. Your favor by Mr. Garnett also came during my absence. I presume he has left Paris, as I can hear nothing of him. I have lost the opportunity, therefore, of seeing his method of resisting friction, as well as of showing, by attentions to him, respect for yourself and your recommendations. Mr. Paine (Common Sense) is here on his way to England. He has brought the model of an iron bridge, with which he supposes a single arch of four hundred feet may be made. It has not yet arrived in Paris. Among other projects, with which we begin to abound in America, is one for finding the longitude by the variation of the magnetic needle. The author supposes two points, one near each pole, through the northern of which pass all the magnetic meridians of the northern hemisphere, and through the southern those of the southern hemisphere. He determines their present position and periodical revolution. It is said his publication is plausible. I have not seen it.
What are you going to do with your naval armament on your side the channel. Perhaps you will ask me, what they are about to do here. A British navy and Prussian army hanging over Holland on one side, a French navy and army hanging over it on the other, looks as if they thought of fighting. Yet I think both parties too wise for that, too laudably intent on economizing, rather than on further embarrassing their finances. May they not propose to have a force on the spot to establish some neutral form of a constitution, which these powers will cook up among themselves, without consulting the parties for whom it is intended? The affair of Geneva shows such combinations possible. Wretched, indeed, is the nation, in whose affairs foreign powers are once permitted to intermeddle. Lord Wycombe is with us at present. His good sense, information, and discretion are much beyond his years, and promise good things for your country.
I beg you to accept assurances of the esteem/and respect, with which I have the honor to be, Dear Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO M. L’ABBE MORELLET.
Paris, July 2, 1787.
I am sorry, my Dear Sir, that your interest should be affected by the ill behavior of Barrois. But when you consider the facts, you will be sensible that I could not have indulged his indolence further, without increasing the injury to a more punctual workman. Stockdale, of London, had asked leave to print my Notes. I agreed to it; and promised he should have the plate of the map as soon as it should be corrected, and the copies struck off for you and myself. He thereupon printed his edition completely in three weeks. The printer, who was to strike off two hundred and fifty maps for me, kept the plate but five days. It was then delivered to Barrois, with notice that it could not be left longer with him, than should suffice to strike off his number. Repeated applications for it, by Mr. Short and my servant, were only answered by repeated promises, and times of delivery fixed, no one of which was performed. When I returned, he had been possessed of the plate upwards of two months. I was astonished and confounded, to be told it had not been sent to Stockdale, and that his edition had been lying dead on his hands three months. I sent to Barrois the very day of my return, to let him know, that justice to Stockdale did not permit me to defer sending him the plate any longer: yet I would wait five days, at the end of which he must deliver me the plate, whether his maps were done or not. I received no answer, but waited ten days. I then sent for the plate. The answer was, he was not at home. I sent again the next day. Answer, he was not at home. I sent the third day. Not at home. I then ordered the messenger to go back, and wait till he should come home. This produced an answer of two lines, qu’il alloit soigner son ouvrier? I wrote him word in return, to deliver the plate instantly. This I think was on a Saturday or Sunday. He told the messenger he would let me have it the Thursday following. I took patience, and sent on the Friday, but telling the messenger, if he refused to deliver it, to inform him I would be plagued no more with sending messages, but apply to the police. He then delivered it, and I sent it off immediately to London. He had kept it three months, of which three weeks were after my return. I think, Sir, you will be satisfied that justice to Stockdale, justice to myself, who had passed my word for sending on the plate, and sensibility to the shuffling conduct of Barrois, permitted me to act no otherwise. But no matter. Let his ill behavior make no odds between you and me. It will affect your interest, and that suffices to determine me to order back the plate, as soon as Stockdale has done with it. He will not require more days, than Barrois months. So that it will be here before you can want it. But it must never go into Barrois’ hands again, nor of any person depending on him, or under his orders. The workman who struck off the two hundred and fifty for me, seems to have been diligent enough. Either he, or any other workman you please of that description, shall have it, to strike what number you wish. I forgot to observe, in its proper place, that when I was in the midst of my difficulties, I did myself the honor of calling on you, as well to have that of asking after your health on my return, as of asking your assistance to obtain the plate. Unluckily you were gone to Versailles; so I was obliged to proceed as well as I could. It is no excuse for Barrois, to say, he could not get his imprimeur to proceed. He should have applied to another. But as to you, it shall be set to rights in the manner I have before stated. Accept my regret that you were in the hands of so underserving a workman, and one who placed me under the necessity of interrupting a work which interested you. Be assured, at the same time, of the sincerity of those sentiments of esteem and respect with which I have the honor to be, Dear Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
[The following observations appear to have been addressed to
the Count de Montmorin, about the 6th of July, 1787.]
Observations on the Letter of Monsieur de Calonne to Monsieur Jefferson, dated, Fontainbleau, October 22, 1786.
A committee was appointed, in the course of the last year, to take a view of the subjects of commerce which might be brought from the United States of America, in exchange for those of France, and to consider what advantages and facilities might be offered to encourage that commerce. The letter of Monsieur de Calonne was founded on their report. It was conclusive as to the articles on which satisfactory information had been then obtained, and reserved, for future consideration, certain others, needing further inquiry. It is proposed now to review those unfinished articles, that they may also be comprehended in the Arrêt, and the regulations on this branch of commerce be rendered complete.
1. The letter promised to diminish the Droits du Roi et d’amirautè, payable by an American vessel entering into a port at France, and to reduce what should remain into a single duty, which shall be regulated by the draught of the vessel, or her number of masts. It is doubted whether it will be expedient to regulate the duty, in either of these ways. If by the draught,of water, it will fall unequally on us as a nation; because we build our vessels sharp-bottomed, for swift sailing, so that they draw more water than those of other nations, of the same burthen. If by the number of masts, it will fall unequally on individuals; because we often see ships of one hundred and eighty tons, and brigs of three hundred and sixty. This, then, would produce an inequality among individuals, of six to one. The present principle is the most just, to regulate by the burthen. It is certainly desirable, that these duties should be reduced to a single one. Their names and numbers perplex and harass the merchant, more than their amount; subject him to imposition, and to the suspicion of it when there is none. An intention of general reformation in this article has been accordingly announced, with augmentation as to foreigners. We are in hopes, that this augmentation is not to respect us; because it is proposed as a measure of reciprocity, whereas, in some of our States, no such duties exist, and in others they are extremely light; because we have been made to hope a diminution, instead of augmentation; and because this distinction cannot draw on France any just claims from other nations; the jura gentis amicissima, conferred by her late treaties, having reference expressly to the nations of Europe only; and those conferred by the more ancient ones not being susceptible of any other interpretation, nor admitting a pretension of reference to a nation which did not then exist, and which has come into existence under circumstances distinguishing its commerce from that of all other nations. Merchandise received from them, takes employment from the poor of France; ours gives it: theirs is brought in, the last stage of manufacture; ours in the first: we bring our tobaccos to be manufactured into snuff, our flax and hemp into linen and cordage, our furs into hats, skins into saddlery, shoes, and clothing; we take nothing till it has received the last hand.
2. Fish-oils. The Hanseatic treaty was the basis, on which the diminution of duty on this article was asked and granted. It is expressly referred to as such, in the letter of Monsieur de Calonne. Instead, however, of the expression, huile et graisse de baleine et d’autres poisons, used in that treaty, the letter uses the terms, ‘huiles de baleine, spermaceti, et tout ce qui est compris sous ces denominations.’ And the Farmers have availed themselves of this variation, to refuse the diminution of duty on the oils of the vache marine, chien de mer, esturgeon, and other fish. It is proposed, therefore, to re-establish in the Arrêt, the expression of the Hanseatic treaty, and to add, from the same treaty, the articles ‘baleine coupée et fanon de baleine.’
The letter states these regulations as finally made by the King. The merchants, on this supposition, entered into speculations. But they found themselves called on for the old duties, not only on other fish-oils, but on the whale-oil. Monsieur de Calonne always promised, that the Arrêt should be retrospective to the date of the letter, so as to refund to them the duties they had thus been obliged to pay. To this, attention is prayed in forming the Arrêt. His majesty having been pleased, as an encouragement to the importation of our fish-oils, to abolish the Droits de fabrication, it is presumed that the purpose announced, of continuing those duties on foreign oils, will not be extended to us.
3. Rice. The duty on this, is only seven and a half deniers the quintal, or about one quarter per cent, on its first cost. While this serves to inform a government of the quantities imported, it cannot discourage that importation. Nothing further, therefore, is necessary on this article.
4. Potasse. This article is of principal utility to France, in her bleacheries of linen, glass-works, and soap-works; and the potash of America, being made of green wood, is known to be the best in the world. All duty on it was, therefore, abolished by the King. But the city of Rouen levies on it a duty of twenty sols the quintal, which is very sensible in its price, brings it dearer to the bleacheries near Paris, to those of Beauvais, Laval, &c. and to the glass-works, and encourages them to give a preference to the potash or soude of other nations. This is a counteraction of the views of the King, expressed in the letter, which it is hoped will be prevented.
5. Turpentine, tar, and pitch were not decided on, on the former occasion. Turpentine (térébenthine) pays ten sols the quintal, and ten sols the livre, making fifteen sols the quintal; which is ten per cent, on its prime cost. Tar (goudron, braigras) pays eight livres the leth of twelve barrels, and ten sols the livre, amounting to twenty sols the barrel; which is twelve and a half per cent, on its prime cost. Pitch (brai sec) pays ten sols the quintal, and ten sols the livre, making fifteen sols the quintal; which is twenty per cent, on its prime cost. Duties of from ten to twenty per cent., on articles of heavy carriage, prevent their importation. They eat up all the profits of the merchant, and often subject him to loss. This has been much the case with respect to turpentine, tar, and pitch, which are principal articles of remittance for the State of North Carolina. It is hoped, that it will coincide with the views of government, in making the present regulations, to suppress the duties on these articles, which, of all others, can bear them least.
TO T. M. RANDOLPH, JUNIOR.
Paris, July 6, 1787.
Dear Sir,
Your favor of April the 14th came here during my absence on a journey through the southern parts of France and northern of Italy, from which I am but lately returned. This cause alone, has prevented your receiving a more early answer to it. I am glad to find, that among the various branches of science presenting themselves to your mind, you have fixed on that of politics as your principal pursuit. Your country will derive from this a more immediate and sensible benefit. She has much for you to do. For though we may say with confidence, that the worst of the American constitutions, is better than the best which ever existed before, in any other country, and that they are wonderfully perfect for a first essay, yet every human essay must have defects. It will remain, therefore, to those now coming on the stage of public affairs, to perfect what has been so well begun by those, going off it. Mathematics, Natural Philosophy, Natural History, Anatomy, Chemistry, Botany, will become amusements for your hours of relaxation, and auxiliaries to your principal studies. Precious and delightful ones they will be. As soon as such a foundation is laid in them, as you may build on as you please, hereafter, I suppose you will proceed to your main objects, Politics, Law, Rhetoric, and History. As to these, the place where you study them is absolutely indifferent. I should except Rhetoric, a very essential member of them, and which I suppose must be taught to advantage where you are. You would do well, therefore, to attend the public exercises in this branch also, and to do it with very particular diligence. This being done, the question arises, where you shall fix yourself for studying Politics, Law, and History. I should not hesitate to decide in favor of France, because you will, at the same time, be learning to speak the language of that country, become absolutely essential under our present circumstances. The best method of doing this, would be to fix yourself in some family where there are women and children, in Passy, Auteuil, or some other of the little towns in reach of Paris. The principal hours of the day you will attend to your studies, and in those of relaxation associate with the family. You will learn to speak better from women and children in three months, than from men in a year. Such a situation, too, will render more easy a due attention to economy of time and money. Having pursued your main studies here about two years, and acquired a facility in speaking French, take a tour of four or five months through this country and Italy, return then to Virginia, and pass a year in Williamsburg, under the care of Mr. Wythe; and you will be ready to enter on the public stage, with superior advantages. I have proposed to you to carry on the study of the law, with that of politics and history. Every political measure will, for ever, have an intimate connection with the laws of the land; and he who knows nothing of these, will always be perplexed, and often foiled by adversaries having the advantage of that knowledge over him. Besides, it is a source of infinite comfort to reflect, that under every change of fortune, we have a resource in ourselves, from which we may be able to derive an honorable subsistence. I would, therefore, propose not only the study, but the practice of the law for some time, to possess yourself of the habit of public speaking. With respect to modern languages, French, as I have before observed, is indispensable. Next to this, the Spanish is most important to an American. Our connection with Spain is already important, and will become daily more so. Besides this, the ancient part of American history is written chiefly in Spanish. To a person who would make a point of reading and speaking French and Spanish, I should doubt the utility of learning Italian. These three languages, being all degeneracies from the Latin, resemble one another so much, that I doubt the probability of keeping in the head a distinct knowledge of them all. I suppose that he who learns them all, will speak a compound of the three, and neither perfectly. The journey which I propose to you, need not be expensive, and would be very useful. With your talents and industry, with science, and that steadfast honesty which eternally pursues right, regardless of consequences, you may promise yourself every thing—but health, without which there is no happiness. An attention to health, then, should take place of every other object. The time necessary to secure this by active exercises, should be devoted to it, in preference to every other pursuit. I know the difficulty with which a studious man tears himself from his studies, at any given moment of the day. But his happiness, and that of his family, depend on it. The most uninformed mind with a healthy body, is happier than the wisest valetudinarian. I need not tell you, that if I can be useful to you in any part of this, or any other plan you shall adopt, you will make me happy by commanding my services.
Will you be so good, Sir, as to return my most respectful thanks for the diploma with which I am honored by the society instituted with you, for the encouragement of the study of Natural History. I am afraid it will never be in my power to contribute any thing to the object of the institution. Circumstances have thrown me into a very different line of life; and not choice, as I am happy to find in your case. In the year 1781, while confined to my room by a fall from my horse, I wrote some Notes, in answer to the inquiries of M. de Marbois, as to the natural and political state of Virginia. They were hasty and undigested: yet as some of these touch slightly on some objects of its natural history, I will take the liberty of asking the society to accept a copy of them. For the same reason, and because too, they touch on the political condition of our country, I will beg leave to present you with a copy, and ask the favor of you to find a conveyance for them, from London to Edinburgh. They are printed by Stockdale, bookseller, Piccadilly, and will be ready in three or four weeks from this time. I will direct him to deliver two copies to your order. Repeating, constantly, the proffer of my services, I shall only add assurances of the esteem and attachment, with which I am, Dear Sir, your friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
Paris, July 21,1787.
Sir,
I received your favor of May the 9th, just as I was stepping into the barge on my departure from Cette; which prevented my answering it from that place. On my arrival here, I thought I would avail myself of the opportunity of paying your balance, to make a little acquaintance with Sir John Lambert. One or two unsuccessful attempts to find him at home, with the intermediate procrastinations well known to men of business, prevented my seeing him till yesterday, and have led me on to this moment, through a perpetual remorse of conscience for not writing to you, and in the constant belief that it would be to morrow and to morrow. At length, I have seen him, paid him the eighty-five livres which you have been so kind as to advance for me, and am actually at my writing table, returning you thanks for this kindness, and to yourself and the family for the thousand others I received at their hands, at Marseilles. My journey, after leaving you, wanted nothing but the company of Madame Cathalan and yourself, to render it perfectly agreeable. I felt the want of it peculiarly on the canal de Languedoc, where, with society, the mode of travelling would have been charming. I was much indebted to M. Minaudier, for a good equipment from Agde, and unceasing attentions to that place; for which I was indebted to your recommendations as well as to his goodness.
I am honored with your father’s letters of June the 30th; and as he does not read English, and I cannot write French, I must beg leave to answer him through you. I thank him for his hints on the subject of tobacco. I am now pressing for arrangements as to that article, to take place on the expiration of Mr. Morris’s contract, and the order of Bernis. What form this business will take, or what will be the nature of the arrangements, or whether there will be any, I am as yet unable to say. I will take care to inform you the moment there is a decision.
The public business with which Mr. Barclay has been charged rendering it necessary for him to repair to Congress, and the interest of his creditors, his family, and himself requiring his return to America, he has departed for that country. I know nothing of Mr. Barclay’s affairs in this country. He has good possessions in America, which, he assured me, were much more than sufficient to satisfy all the demands against him. He went, determined to convert those immediately into money, and to collect the debts due to him there, that he might be enabled to pay his debts. My opinion of his integrity is such, as to leave no doubt in my mind, that he will do every thing in his power to render justice to his creditors; and I know so well his attachment to M. Cathalan, as to be satisfied, that if he makes any difference among his creditors, he will be among the most favored. Mr. Barclay is an honest and honorable man, and is more goaded towards the payment of his debts by his own feelings, than by all the processes of law, which could be set on foot against him.
No arrangements having ever been made as yet, for cases like that of the carpenter of the American ship Sally, I am unable to answer on that subject. I am in hopes, his money will last till he recovers his senses, or till we can receive instructions what to do in that and similar cases.
M. Cathalan wishes a copy of my Notes on Virginia. If you will be so good as to advise me by what channel they will go safely, I will do myself the honor of sending a copy, either of the original or of the translation. Present me affectionately to Mrs. Cathalan, the mother and daughter; tell the latter I feed on the hopes of seeing her one day at Paris. My friendly respects wait also on your father; and on yourself, assurances of the esteem and consideration with which I have the honor to be, Dear Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO THE DELEGATES OF RHODE ISLAND.
Paris, July 22,1787.
Gentlemen,
I was honored, in the month of January last, with a letter from the honorable the Delegates of Rhode Island in Congress, enclosing a letter from the corporation of Rhode Island College to his Most Christian Majesty, and some other papers. I was then in the hurry of a preparation for a journey into the south of France, and therefore unable, at that moment, to make the inquiries which the object of the letter rendered necessary. As soon as I returned, which was in the last month, I turned my attention to that object, which was the establishment of a professorship of the French language in the College, and the obtaining a collection of the best French authors, with the aid of the King. That neither the College nor myself might be compromitted uselessly, I thought it necessary to sound, previously, those who were able to inform me what would be the success of the application. I was assured, so as to leave no doubt, that it would not be complied with; that there had never been an instance of the King’s granting such a demand in a foreign country, and that they would be cautious of setting the precedent: that in this moment, too, they were embarrassed with the difficult operation of putting down all establishments of their own, which could possibly be dispensed with, in order to bring their expenditures down to the level of their receipts. Upon such information I was satisfied, that it was most prudent not to deliver the letter, and spare to both parties the disagreeableness of giving and receiving a denial. The King did give to two colleges in America copies of the works printing in the public press. But were this to be obtained for the College of Rhode Island, it would extend only to a volume or two of Buffon’s works, still to be printed, Manilius’s Astronomicon, and one or two other works in the press, which are of no consequence. I did not think this an object for the College worth being pressed. I beg the favor of you, gentlemen, to assure the corporation, that no endeavors of mine should have been spared, could they have effected their wish: and that they have been faithfully used in making the preliminary inquiries which are necessary, and which ended in an assurance, that nothing could be done. These papers having been transmitted to me through your delegation, will, I hope, be an apology for my availing myself of the same channel for communicating the result.
I have the honor to be, with sentiments of the most perfect esteem and respect, Gentlemen, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
Paris, July 23, 1787.
Sir,
I had the honor, a few days ago, of putting into the hands of your Excellency, some observations on the other articles of American produce, brought into the ports of this country. That of our tobaccos, from the particular form of their administration here, and their importance to the King’s revenues, has been placed on a separate line, and considered separately. I will now ask permission to bring that subject under your consideration.
The mutual extension of their commerce was among the fairest advantages to be derived to France and the United States, from the independence of the latter. An exportation of eighty millions, chiefly in raw materials, is supposed to constitute the present limits of the commerce of the United States with the nations of Europe; limits, however, which extend as their population increases. To draw the best proportion of this into the ports of France, rather than of any other nation, is believed to be the wish and interest of both. Of these eighty millions, thirty are constituted by the single article of tobacco. Could the whole of this be brought into the ports of France, to satisfy its own demands, and the residue to be re-vended to other nations, it would be a powerful link of commercial connection. But we are far from this. Even her own consumption, supposed to be nine millions, under the administration of the monopoly to which it is farmed, enters little, as an article of exchange, into the commerce of the two nations. When this article was first put into Farm, perhaps it did not injure the commercial interests of the kingdom; because nothing but British manufactures were then allowed to be given in return for American tobaccos. The laying the trade open, then, to all the subjects of France, could not have relieved her from a payment in money. Circumstances are changed; yet the old institution remains. The body to which this monopoly was given, was not mercantile. Their object is to simplify, as much as possible, the administration of their affairs. They sell for cash; they purchase, therefore, with cash. Their interest, their principles, and their practice seem opposed to the general interest of the kingdom, which would require, that this capital article should be laid open to a free exchange for the productions of this country. So far does the spirit of simplifying their operations govern this body, that, relinquishing the advantages to be derived from a competition of sellers, they contracted some time ago with a single person (Mr. Morris) for three years’ supplies of American tobacco, to be paid for in cash. They obliged themselves, too, expressly, to employ no other person to purchase in America, during that term. In consequence of this, the mercantile houses of France, concerned in sending her productions to be exchanged for tobacco, cut off for three years from the hope of selling these tobaccos in France, were of necessity to abandon that commerce. In consequence of this, too, a single individual, constituted sole purchaser of so great a proportion of the tobaccos made, had the price in his own power. A great reduction in it took place, and that not only on the quantity he bought, but on the whole quantity made. The loss to the States producing the article, did not go to cheapen it for their friends here. Their price was fixed. What was gained on their consumption, was to enrich the person purchasing it; the rest, the monopolists and merchants of other countries. The effect of this operation was vitally felt by every farmer in America, concerned in the culture of this plant. At the end of the year, he found he had lost a fourth or a third of his revenue; the State, the same proportion of its subjects of exchange with other nations: the manufactures of this country, too, were either not to go there at all, or go through the channel of a new monopoly, which, freed from the control of competition in prices and qualities, was not likely to extend their consumption. It became necessary to relieve the two countries from the fatal effects of this double monopoly. I had the honor of addressing a letter, on the 15th day of August, 1785, to his late Excellency, the Count de Vergennes, upon this subject, a copy of which I do myself the honor herein to enclose. The effectual mode of relief was to lay the commerce open. But the King’s interest was also to be guarded. A committee was appointed to take this matter into consideration; and the result was, an order to the Farmers General, that no such contract should be made again. And to furnish such aliment as might keep that branch of commerce alive, till the expiration of the present contract, they were required to put the merchants in general on a level with Mr. Morris, for the quantity of twelve or fifteen thousand hogsheads a year. That this relief, too, might not be intercepted from the merchants of the two suffering nations, by those of a neighboring one, and that the transportation of so bulky an article might go to nourish their own shipping, no tobaccos were to be counted of this purchase, but those brought in French or American vessels. Of this order, made at Bernis, his Excellency, Count de Vergennes, was pleased to honor me with a communication, by a letter of the 30th of May, 1786; desiring that I would publish it as well in America as to the American merchants in France. I did so; communicating it to Congress at the same time. This order, thus viewed, with the transactions which produced it, will be seen to have been necessary; and its punctual and candid execution has been rendered still more so, by the speculations of the merchants, entered into on the faith of it. Otherwise it would become the instrument of their ruin instead of their relief. A twelvemonth has elapsed some time since; and it is questioned, whether the Farmers General have purchased, within that time, the quantity prescribed, and on the conditions prescribed. It would be impossible for the merchants to prove the negative; it will be easy for the Farmers General to show the affirmative, if it exists. I hope that a branch of commerce of this extent, will be thought interesting enough to both nations to render it the desire of your Excellency to require, as I deem it my duty to ask, a report of the purchases they have made, according to the conditions of the order of Bernis, specifying in that report, 1. The quantities purchased; 2. the prices paid; 3. the dates of the purchase and payment; 4. the flag of the vessel in which imported; 5. her name; 6. her port of delivery; and 7. the name of the seller. The four first articles make part of the conditions required by the order of Bernis; the three last may be necessary for the correction of any errors, which should happen to arise in the report.
But the order of Bernis was never considered but as a temporary relief. The radical evil will still remain. There will be but one purchaser in the kingdom, and the hazard of his refusal will damp every mercantile speculation. It is very much to be desired, that before the expiration of this order, some measure may be devised, which may bring this great article into free commerce between the two nations. Had this been practicable at the time it was put into Farm, that mode of collecting the revenue would probably never have been adopted: now that it has become practicable, it seems reasonable to discontinue this mode, and to substitute some of those practised on other imported articles, on which a revenue is levied, without absolutely suppressing them in commerce. If the revenue can be secured, the interests of a few individuals will hardly be permitted to weigh against those of as many millions, equally subjects of his Majesty, and against those, too, of a nation allied to him by all the ties of treaty, of interest, and of affection. The privileges of the most favored nation have been mutually exchanged by treaty. But the productions of other nations, which do not rival those of France, are suffered to be bought and sold freely within the kingdom. By prohibiting all his Majesty’s subjects from dealing in tobacco, except with a single company, one third of the exports of the United States are rendered uncommerciable here. This production is so peculiarly theirs, that its shackles affect no other nation. A relief from these shackles will form a memorable epoch in the commerce of the two nations. It will establish at once a great basis of exchange serving, like a point of union, to draw to it other members of our commerce. Nature, too, has conveniently assorted our wants and our superfluities to each other. Each nation has exactly to spare the articles which the other wants. We have a surplus of rice, tobacco, furs, peltry, potash, lamp-oils, timber, which France wants; she has a surplus of wines, brandies, esculent oils, fruits, and manufactures of all kinds, which we want. The governments have nothing to do, but not to hinder their merchants from making the exchange. The difference of language, laws, and customs, will be some obstacle for a time; but the interest of the merchants will surmount them. A more serious obstacle is our debt to Great Britain. Yet, since the treaty between this country and that, I should not despair of seeing that debt paid, in part, with the productions of France, if our produce can obtain here a free course of exchange for them. The distant prospect is still more promising. A century’s experience has shown, that we double our numbers every twenty or twenty-five years. No circumstance can be foreseen, at this moment, which will lessen our rate of multiplication for centuries to come. For every article of the productions and manufactures of this country, then, which can be introduced into habit there, the demand will double every twenty or twenty-five years. And to introduce the habit, we have only to let the merchants alone. Whether we may descend, by a single step, from the present state to that of perfect freedom of commerce in this article; whether any, and what, intermediate operation may be necessary to prepare the way to this; what cautions must be observed for the security of his Majesty’s revenue, which we do not wish to impair, will rest with the wisdom of his ministers, whose knowledge of the subject will enable them to devise the best plans, and whose patriotism and justice will dispose them to pursue them. To the friendly dispositions of your Excellency, of which we have had such early and multiplied proofs, I take the liberty of committing this subject, particularly, trusting that some method may be devised of reconciling the collection of his Majesty’s revenues with the interests of the two nations; and have the honor of assuring you of those sincere sentiments of esteem and respect, with which I am your Excellency’s most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MR. SKIPWITH.
Paris, July 28, 1787.
Dear Sir,
A long journey has prevented me from writing to any of my friends for some time past. This was undertaken with a view to benefit a dislocated and ill-set wrist, by the mineral waters of Aix, in Provence. Finding this hope vain, I was led from other views to cross the Alps as far as Turin, Milan, Genoa; to follow the Mediterranean as far as Cette, the canal of Languedoc, the Garonne, &c, to Paris. A most pleasing journey it proved; arts and agriculture offering something new at every step, and often things worth our imitation. But the accounts from our country give me to believe, that we are not in a condition to hope for the imitation of any thing good. All my letters are filled with details of our extravagance. From these accounts, I look back to the time of the war, as a time of happiness and enjoyment, when amidst the privation of many things not essential to happiness, we could not run in debt, because nobody would trust us; when we practised, of necessity, the maxim of buying nothing but what we had money in our pockets to pay for; a maxim, which, of all others, lays the broadest foundation for happiness. I see no remedy to our evils, but an open course of law. Harsh as it may seem, it would relieve the very patients who dread it, by stopping the course of their extravagance, before it renders their affairs entirely desperate. The eternal and bitter strictures on our conduct, which teem in every London paper, and are copied from them into others, fill me with anxiety on this subject. The state of things in Europe is rather threatening at this moment. The innovations of the Emperor in his dominions, have excited a spirit of resistance. His subjects in Brabant and Flanders are arming, and he has put forty-five thousand troops in motion towards that country. I believe they will come to blows. The parties in Holland have already spilt too much blood to be easily stopped. If left to themselves, I apprehend the Stadtholderians will be too strong; and if foreign powers interfere, the weight is still on their side. England and Prussia will be too much for France. As it is certain that neither of these powers wish for war, and that England and France are particularly averse to it, perhaps the matter may end in an armed mediation. If the mediators should not agree, they will draw their negotiations into length, and trust to the chapter of accidents for their final solution. With respect to our country, it stands well with the present ministry here. The non-payment of our debt is against us. We are occupied in procuring favorable terms of reception for our produce.
Adieu, my Dear Sir, and be assured of the sentiments of sincere esteem of your affectionate friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO J. W. EPPES.
Paris, July 28,1787.
Dear Jack,
The letter which you were so kind as to write to me the 22nd of May, 1786, was not delivered to me till the 3rd of May, 1787, when it found me in the neighborhood of Marseilles. Before that time you must have taken your degree, as mentioned in your letter. Those public testimonies which are earned by merit, and not by solicitation, may always be accepted without the imputation of vanity. Of this nature is the degree which your masters proposed to confer on you. I congratulate you sincerely on it. It will be a pleasing event to yourself; it will be the same to your parents and friends, and to none more than myself. Go on deserving applause, and you will be sure to meet with it: and the way to deserve it, is to be good, and to be industrious. I am sure you will be good, and hope you will be industrious. As to your future plan, I am too distant from you, to advise you on sure grounds. In general, I am of opinion that till the age of about sixteen, we are best employed on languages; Latin, Greek, French, and Spanish, or such of them as we can. After this, I think the College of William and Mary the best place to go through courses of Mathematics, Natural Philosophy in its different branches, and Law. Of the languages I have mentioned, I think Greek the least useful. Write me word, from time to time, how you go on. I shall always be glad to assist you with any books you may have occasion for, and you may count with certainty on every service I can ever render you, as well as on the sincere esteem of, Dear Jack, yours affectionately,
Th: Jefferson.
TO A. DONALD.
Paris, July 28, 1787.
Dear Sir,
I received with infinite satisfaction your letter of the 1st of March: it was the first information I had of your being in America. There is no person whom I shall see again with more cordial joy, whenever it shall be my lot to return to my native country; nor any one whose prosperity, in the mean time, will be more interesting to me. I find as I grow older, that I set a higher value on the intimacies of my youth, and am more afflicted by whatever loses one of them to me. Should it be in my power to render any service, in your shipment of tobacco to Havre de Grace, I shall do it with great pleasure. The order of Bernis has, I believe, been evaded by the Farmers General as much as possible. At this moment, I receive information from most of the seaports, that they refuse taking any tobacco, under the pretext, that they have purchased their whole quantity. From Havre I have heard nothing, and believe you will stand a better chance there than any where else. Being one of the ports of manufacture, too, it is entitled to a higher price. I have now desired that the Farmers may make a distinct return of their purchases, which are conformable to the order of Bernis. If they have really bought their quantity, on those terms, we must be satisfied: if they have not, I shall propose their being obliged to make it up instantly. There is a considerable accumulation of tobacco in the ports.
Among many good qualities which my countrymen possess, some of a different character unhappily mix themselves. The most remarkable are indolence, extravagance, and infidelity to their engagements. Cure the two first, and the last would disappear, because it is a consequence of them, and not proceeding from a want of morals. I know of no remedy against indolence and extravagance, but a free course of justice. Every thing else is merely palliative: but unhappily, the evil has gained too generally the mass of the nation, to leave the course of justice unobstructed. The maxim of buying nothing without the money in our pockets to pay for it, would make of our country one of the happiest upon earth. Experience during the war proved this; as I think every man will remember, that under all the privations it obliged him to submit to, during that period, he slept sounder, and awaked happier than he can do now. Desperate of finding relief from a free course of justice, I look forward to the abolition of all credit, as the only other remedy which can take place. I have seen, therefore, with pleasure, the exaggerations of our want of faith, with which the London papers teem. It is, indeed, a strong medicine for sensible minds, but it is a medicine. It will prevent their crediting us abroad, in which case, we cannot be credited at home. I have been much concerned at the losses produced by the fire of Richmond. I hope you have escaped them. It will give me much pleasure to hear from you, as often as you can spare a moment to write. Be assured that nobody entertains for you sentiments of more perfect and sincere esteem than, Dear Sir, your friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO WILLIAM DRAYTON.
Paris, July 30, 1787.
Sir,
Having observed that the consumption of rice in this country, and particularly in this capital, was very great, I thought it my duty to inform myself from what markets they draw their supplies, in what proportion from ours, and whether it might not be practicable to increase that proportion. This city being little concerned in foreign commerce, it is difficult to obtain information on particular branches of it in the detail. I addressed myself to the retailers of rice, and from them received a mixture of truth and error, which I was unable to sift apart in the first moment. Continuing, however, my inquiries, they produced at length this result; that the dealers here, were in the habit of selling two qualities of rice, that of Carolina, with which they were supplied chiefly from England, and that of Piedmont: that the Carolina rice was long, slender, white, and transparent, answers well when prepared with milk, sugar, &ic. but not so well when prepared au gras; that that of Piedmont was shorter, thicker, and less white, but that it presented its form better when dressed au gras, was better tasted, and therefore preferred by good judges for those purposes: that the consumption of rice, in this form, was much the most considerable, but that the superior beauty of the Carolina rice, seducing the eye of those purchasers who are attached to appearances, the demand for it was upon the whole as great as for that of Piedmont. They supposed this difference of quality to proceed from a difference of management; that the Carolina rice was husked with an instrument which broke it more, and that less pains were taken to separate the broken from the unbroken grains; imagining that it was the broken grains which dissolved in oily preparations: that the Carolina rice costs somewhat less than that of Piedmont; but that being obliged to sort the whole grains from the broken, in order to satisfy the taste of their customers, they ask and receive as much for the first quality of Carolina, when sorted, as for the rice of Piedmont; but the second and third qualities, obtained by sorting, are sold much cheaper. The objection to the Carolina rice then, being, that it crumbles in certain forms of preparation, and this supposed to be the effect of a less perfect machine for husking, I flattered myself I should be able to learn what might be the machine of Piedmont, when I should arrive at Marseilles, to which place I was to go in the course of a tour through the seaport towns of this country. At Marseilles, however, they differed as much in the account of the machine, as at Paris they had differed about other circumstances. Some said it was husked between mill-stones, others between rubbers of wood in the form of mill-stones, others of cork. They concurred in one fact, however, that the machine might be seen by me, immediately on crossing the Alps. This would be an affair of three weeks. I crossed them, and went through the rice country from Vercelli to Pavia, about sixty miles. I found the machine to be absolutely the same with that used in Carolina, as well as I could recollect a description which Mr. E. Rutledge had given me of it. It is on the plan of a powder-mill. In some of them, indeed, they arm each pestle with an iron tooth, consisting of nine spikes hooped together, which I do not remember in the description of Mr. Rutledge. I therefore had a tooth made, which I have the honor of forwarding you with this letter; observing, at the same time, that as many of their machines are without teeth as with them, and of course, that the advantage is not very palpable. It seems to follow, then, that the rice of Lombardy (for though called Piedmont rice, it does not grow in that country, but in Lombardy) is of a different species from that of Carolina; different in form, in color, and in quality. We know that in Asia they have several distinct species of this grain. Monsieur Poivre, a former Governor of the Isle of France, in travelling through several countries of Asia, observed with particular attention the objects of their agriculture, and he tells us, that in Cochin-China they cultivate six several kinds of rice, which he describes, three of them requiring water, and three growing on highlands. The rice of Carolina is said to have come from Madagascar, and De Poivre tells us, it is the white rice which is cultivated there. This favors the probability of its being of a different species originally, from that of Piedmont; and time, culture, and climate may have made it still more different. Under this idea, I thought it would be well to furnish you with some of the Piedmont rice, unhusked, but was told it was contrary to the laws to export it in that form. I took such measures as I could, however, to have a quantity brought out, and lest these should fail, I brought, myself, a few pounds. A part of this I have addressed to you by the way of London; a part comes with this letter; and I shall send another parcel by some other conveyance, to prevent the danger of miscarriage. Any one of them arriving safe, may serve to put in seed, should the society think it an object. This seed, too, coming from Vercelli, where the best rice is supposed to grow, is more to be depended on, than what may be sent me hereafter. There is a rice from the Levant, which is considered as of a quality still different, and some think it superior to that of Piedmont. The troubles which have existed in that country for several years back, have intercepted it from the European market, so that it is become almost unknown. I procured a bag of it, however, at Marseilles, and another of the best rice of Lombardy, which are on their way to this place, and when arrived, I will forward you a quantity of each, sufficient to enable you to judge of their qualities when prepared for the table. I have also taken measures to have a quantity of it brought from the Levant, unhusked. If I succeed, it shall be forwarded in like manner. I should think it certainly advantageous to cultivate, in Carolina and Georgia, the two qualities demanded at market; because the progress of culture, with us, may soon get beyond the demand for the white rice; and because, too, there is often a brisk demand for the one quality, when the market is glutted with the other. I should hope there would be no danger of losing the species of white rice, by a confusion with the other. This would be a real misfortune, as I should not hesitate to pronounce the white, upon the whole, the most precious of the two, for us.
The dry rice of Cochin-China has the reputation of being the whitest to the eye, best flavored to the taste, and most productive. It seems then to unite the good qualities of both the others known to us. Could it supplant them, it would be a great happiness, as it would enable us to get rid of those ponds of stagnant water, so fatal to human health and life. But such is the force of habit, and caprice of taste, that we could not be sure beforehand, it would produce this effect. The experiment, however, is worth trying, should it only end in producing a third quality, and increasing the demand. I will endeavor to procure some to be brought from Cochin-China. The event, however, will be uncertain and distant.
I was induced, in the course of my journey through the south of France, to pay very particular attention to the objects of their culture, because the resemblance of their climate to that of the southern parts of the United States authorizes us to presume we may adopt any of their articles of culture, which we would wish for. We should not wish for their wines, though they are good and abundant. The culture of the vine is not desirable in lands capable of producing any thing else. It is a species of gambling, and of desperate gambling too, wherein, whether you make much or nothing, you are equally ruined. The middling crop alone is the saving point, and that the seasons seldom hit. Accordingly, we see much wretchedness among this class of cultivators. Wine, too, is so cheap in these countries, that a laborer with us, employed in the culture of any other article, may exchange it for wine, more and better than he could raise himself. It is a resource for a country, the whole of whose good soil is otherwise employed, and which still has some barren spots, and a surplus of population to employ on them. There the vine is good, because it is something in the place of nothing. It may become a resource to us at a still earlier period: when the increase of population shall increase our productions beyond the demand for them, both at home and abroad. Instead of going on to make an useless surplus of them, we may employ our supernumerary hands on the vine. But that period is not yet arrived.
The almond tree is also so precarious, that none can depend for subsistence on its produce, but persons of capital.
The caper, though a more tender plant, is more certain in its produce, because a mound of earth of the size of a cucumber hill, thrown over the plant in the fall, protects it effectually against the cold of winter. When the danger of frost is over in the spring, they uncover it, and begin its culture. There is a great deal of this in the neighborhood of Toulon. The plants are set about eight feet apart, and yield, one year with another, about two pounds of caper each, worth on the spot six pence sterling the pound. They require little culture, and this may be performed either with the plough or hoe. The principal work is the gathering of the fruit as it forms. Every plant must be picked every other day, from the last of June till the middle of October. But this is the work of women and children. This plant does well in any kind of soil which is dry, or even in walls where there is no soil, and it lasts the life of a man. Toulon would be the proper port to apply for them. I must observe, that the preceding details cannot be relied on with the fullest certainty, because, in the canton where this plant is cultivated, the inhabitants speak no written language, but a medley, which I could understand but very imperfectly.
The fig and mulberry are so well known in America, that nothing need be said of them. Their culture, too, is by women and children, and therefore earnestly to be desired in countries where there are slaves. In these, the women and children are often employed in labors disproportioned to their sex and age. By presenting to the master objects of culture, easier and equally beneficial, all temptation to misemploy them would be removed, and the lot of this tender part of our species be much softened. By varying too the articles of culture, we multiply the chances for making something, and disarm the seasons, in a proportionable degree, of their calamitous effects.
The olive is a tree the least known in America, and yet the most worthy of being known. Of all the gifts of heaven to man, it is next to the most precious, if it be not the most precious. Perhaps it may claim a preference even to bread; because there is such an infinitude of vegetables, which it renders a proper and comfortable nourishment. In passing the Alps at the Col de Tende, where they are mere masses of rock, wherever there happens to be a little soil, there are a number of olive trees, and a village supported by them. Take away these trees, and the same ground, in corn, would not support a single family. A pound of oil, which can be bought for three or four pence sterling, is equivalent to many pounds of flesh, by the quantity of vegetables it will prepare, and render fit and comfortable food. Without this tree, the country of Provence and territory of Genoa, would not support one half, perhaps not one third, their present inhabitants. The nature of the soil is of little consequence, if it be dry. The trees are planted from fifteen to twenty feet apart, and when tolerably good, will yield fifteen or twenty pounds of oil yearly, one with another. There are trees which yield much more. They begin to render good crops at twenty years old, and last till killed by cold, which happens at some time or other, even in their best positions in France. But they put out again from their roots. In Italy, I am told, they have trees of two hundred years old. They afford an easy but constant employment through the year, and require so little nourishment, that if the soil be fit for any other production, it may be cultivated among the olive trees, without injuring them. The northern limits of this tree, are the mountains of the Cevennes, from about the meridian of Carcassonne to the Rhone, and from thence, the Alps and Apennines as far as Genoa, I know, and how much farther I am not informed. The shelter of these mountains may be considered as equivalent to a degree and a half of latitude, at least; because westward of the commencement of the Cevennes, there are no olive trees in 43 1/2° or even 43° of latitude, whereas, we find them now on the Rhone at Pierrelatte, in 44 1/2°, and formerly they were at Tains, above the mouth of the Isere, in 45°, sheltered by the near approach of the Cevennes and Alps, which only leave there a passage for the Rhone. Whether such a shelter exists or not, in the States of South Carolina and Georgia, I know not. But this we may say, either that it exists, or that it is not necessary there; because we know that they produce the orange in open air; and wherever the orange will stand at all, experience shows that the olive will stand well; being a hardier tree. Notwithstanding the great quantities of oil made in France, they have not enough for their own consumption, and therefore import from other countries. This is an article, the consumption of which will always keep pace with its production. Raise it; and it begets its own demand. Little is carried to America, because Europe has it not to spare. We therefore have not learned the use of it. But cover the southern States with it, and every man will become a consumer of oil, within whose reach it can be brought, in point of price. If the memory of those persons is held in great respect in South Carolina, who introduced there the culture of rice, a plant which sows life and death with almost equal hand, what obligations would be due to him who should introduce the olive tree, and set the example of its culture! Were the owner of slaves to view it only as the means of bettering their condition, how much would he better that, by planting one of those trees for every slave he possessed! Having been myself an eye-witness to the blessings which this tree sheds on the poor, I never had my wishes so kindled for the introduction of any article of new culture into our own country. South Carolina and Georgia appear to me to be the States, wherein its success, in favorable positions at least, could not be doubted, and I flattered myself, it would come within the views of the society for agriculture, to begin the experiments which are to prove its practicability. Carcassonne is the place from which the plants may be most certainly and cheaply obtained. They can be sent from thence by water to Bordeaux, where they may be embarked on vessels bound to Charleston. There is too little intercourse between Charleston and Marseilles, to propose this as the port of exportation. I offer my services to the society, for the obtaining and forwarding any number of plants which may be desired.
Before I quit the subject of climates, and the plants adapted to them, I will add, as a matter of curiosity, and of some utility too, that my journey through the southern parts of France, and the territory of Genoa, but still more the crossing of the Alps, enabled me to form a scale of the tenderer plants, and to arrange them according to their different powers of resisting cold. In passing the Alps at the Col de Tende, we cross three very high mountains, successively. In ascending, we lose these plants, one after another, as we rise, and find them again in the contrary order, as we descend on the other side; and this is repeated three times. Their order, proceeding from the tenderest to the hardiest, is as follows. Caper, orange, palm, aloe, olive, pomegranate, walnut, fig, almond. But this must be understood of the plant only; for as to the fruit, the order is somewhat different. The caper, for example, is the tenderest plant; yet, being so easily protected, it is among the most certain in its fruit. The almond, the hardiest plant, loses its fruit the oftenest, on account of its forwardness. The palm, hardier than the caper and orange, never produces perfect fruit here.
I had the honor of sending you, the last year, some seeds of the sulla of Malta, or Spanish saintfoin. Lest they should have miscarried, I now pack with the rice a canister of the same kind of seed, raised by myself. By Colonel Franks, in the month of February last, I sent a parcel of acorns of the cork-oak, which I desired him to ask the favor of the Delegates of South Carolina in Congress, to forward to you.
I have the honor to be, with sentiments of the most perfect esteem and respect, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JAMES MADISON.
Paris, August 2, 1787.
Dear Sir,
My last was of June the 20th. Yours, received since that date, are of May the 15th, and June the 6th. In mine, I acknowledged the receipt of the paccan nuts which came sealed up. I have reason to believe those in the box have arrived at L’Orient. By the Mary, Captain Howland, lately sailed from Havre to New York, I shipped three boxes of books, one marked J. M. for yourself, one marked B. F. for Dr. Franklin, and one marked W. H. for William Hay in Richmond. I have taken the liberty of addressing them all to you, as you will see by the enclosed bill of lading, in hopes you will be so good as to forward the other two. You will have opportunities of calling on the gentlemen for the freight, &c. In yours, you will find the books, noted in the account enclosed herewith. You have now Mably’s works complete, except that on Poland, which I have never been able to get, but shall not cease to search for. Some other volumes are wanting too, to complete your collection of Chronologies. The fourth volume of D’Albon was lost by the bookbinder, and I have not yet been able to get one to replace it. I shall continue to try. The Memoires sur les Droits et Impositions en Europe (cited by Smith) was a scarce and excessively dear book. They are now reprinting it. I think it will be in three or four quartos, of from nine to twelve livres a volume. When it is finished, I shall take a copy for you. Amelot’s Travels into China, I can learn nothing of. I put among the books sent you, two somewhat voluminous, and the object of which will need explanation; these are the Tableau de Paris and L’Espion Anglois. The former is truly a picture of private manners in Paris, but presented on the dark side, and a little darkened moreover. But there is so much truth in its groundwork, that it will be well worth your reading. You will then know Paris (and probably the other large cities of Europe) as well as if you had been there for years. L’Espion Anglois is no caricature. It will give you a just idea of the wheels by which the machine of government is worked here. There are in it, also, many interesting details of the last war, which, in general, may be relied on. It may be considered as the small history of great events. I am in hopes, when you shall have read them, you will not think I have misspent your money for them. My method for making out this assortment was, to revise the list of my own purchases since the invoice of 1785, and to select such as I had found worth your having. Besides this, I have casually met with, and purchased, some few curious and cheap things.
I must trouble you on behalf of a Mr. Thomas Burke, at Loughburke near Loughrea in Ireland, whose brother, James Burke, is supposed to have died, in 1785, on his passage from Jamaica, or St. Eustatius, to New York. His property on board the vessel is understood to have come to the hands of Alderman Groom at New York. The enclosed copy of a letter to him will more fully explain it. A particular friend of mine here, applies to me for information, which I must ask the favor of you to procure, and forward to me.
Writing news to others, much pressed in time, and making this letter one of private business, I did not intend to have said any thing to you on political subjects. But I must press one subject. Mr. Adams informs me he has borrowed money in Holland, which, if confirmed by Congress, will enable them to pay, not only the interest due here to the foreign officers, but the principal. Let me beseech you to reflect on the expediency of transferring this debt to Holland. All our other debts in Europe do not injure our reputation so much as this. These gentlemen have connections both in and out of office, and these again their connections, so that our default on this article is further known, more blamed, and excites worse dispositions against us, than you can conceive. If you think as I do, pray try to procure an order for paying off their capital. Mr. Adams adds, that if any certain tax is provided for the payment of interest, Congress may borrow enough in Holland to pay off their whole debts in France, both public and private, to the crown, to the Farmers, and to Beaumarchais. Surely it will be better to transfer these debts to Holland. So critical is the state of that country, that I imagine the monied men of it, would be glad to place their money in foreign countries, and that Mr. Adams could borrow there for us, without a certain tax for the interest, and saving our faith too, by previous explanations on that subject. This country is really supposed on the eve of a * * * *. Such a spirit has risen within a few weeks, as could not have been believed. They see the great deficit in their revenues, and the hopes of economy lessen daily. The parliament refuse to register any act for a new tax, and require an Assembly of the States. The object of this Assembly is evidently to give law to the King, to fix a constitution, to limit expenses. These views are said to gain upon the nation.*
[ * The parts of this letter marked by asterisks, are in
cipher, and unintelligible.]
A final decision of some sort, should be made on Beaumarchais’ affairs.
I am, with sentiments of the most perfect esteem, Dear Sir, your friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO THOMAS BARCLAY.
Paris, August 3, 1787,
Dear Sir,
I am now to acknowledge the receipt of your several favors of June the 29th, and July the 6th and 8th.
I am of opinion that the affair of Geraud and Roland in Holland, had better be committed to Mr. Dumas in Holland, as lawsuits must always be attended to by some person on the spot. For the same reason, I think that of La Vayse and Puchilberg should be managed by the agent at L’Orient, and Gruel’s by the agent at Nantes. I shall always be ready to assist the agents of L’Orient and Nantes, in any way in my power; but were the details to be left to me, they would languish, necessarily, on account, of my distance from the place, and perhaps suffer too, for want of verbal consultations with the lawyers entrusted with them. You are now with Congress, and can take their orders on the subject. I shall therefore, do nothing in these matters, in reliance that you will put them into such channel as they direct, furnishing the necessary documents and explanations.
With respect to French’s affair, being perfectly satisfied myself, I have not ceased, nor shall I ‘cease, endeavoring to satisfy others, that your conduct has been that of an honest and honorable debtor, and theirs the counterpart of Shylock in the play. I enclose you a letter containing my testimony on your general conduct, which I have written to relieve a debt of justice pressing on my mind, well knowing at the same time, you will not stand in need of it in America. Your conduct is too well known to Congress, your character to all the world, to need any testimonials.
The moment I close my despatches for the packet, which will be the 9th instant, I shall with great pleasure go to pay my respects to Mrs. Barclay at St. Germain, to satisfy her on the subject of your transactions, and to assure her that my resources shall be hers, as long as I have any. A multitude of letters to write, prevents my entering into the field of public news, further than to observe, that it is extremely doubtful whether the affairs of Holland will, or will not produce a war between France, on one side, and England and Prussia, on. the other.
I beg you to accept assurances of the sincere esteem and respect, with which I have the honor to be, Dear Sir, your friend
and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO E. CARRINGTON.
Paris, August 4,1787.
Dear Sir,
Since mine of the 16th of January, I have been honored by your favors of April the 24th and June the 9th. I am happy to find that the States have come so generally into the scheme of the federal convention, from which, I am sure, we shall see wise propositions. I confess, I do not go as far in the reforms thought necessary, as some of my correspondents in America; but if the convention should adopt such propositions, I shall suppose them necessary. My general plan would be, to make the States one as to every thing connected with foreign nations, and several as to every thing purely domestic. But with all the imperfections of our present government, it is, without comparison, the best existing, or that ever did exist. Its greatest defect is the imperfect manner in which matters of commerce have been provided for. It has been so often said, as to be generally believed, that Congress have no power by the Confederation to enforce any thing; for example, contributions of money. It was not necessary to give them that power expressly; they have it by the law of nature. When two parties make a compact, there results to each a power of compelling the other to execute it. Compulsion was never so easy as in our case, where a single frigate would soon levy on the commerce of any State the deficiency of its contributions; nor more safe than in the hands of Congress, which has always shown that it would wait, as it ought to do, to the last extremities, before it would execute any of its powers which are disagreeable. I think it very material, to separate, in the hands of Congress, the executive and legislative powers, as the judiciary already are, in some degree. This, I hope, will be done. The want of it has been the source of more evil, than we have experienced from any other cause. Nothing is so embarrassing nor so mischievous, in a great assembly, as the details of execution. The smallest trifle of that kind, occupies as long as the most important act of legislation, and takes place of every thing else. Let any man recollect, or look over, the files of Congress: he will observe the most important propositions hanging over, from week to week, and month to month, till the occasions have passed them, and the things never done. I have ever viewed the executive details as the greatest cause of evil to us, because they in fact place us as if we had no federal head, by diverting the attention of that head from great to small objects; and should this division of power not be recommended by the convention, it is my opinion, Congress should make it, itself, by establishing an executive committee.
I have the honor to be, with sincere esteem and respect, Dear Sir, your most obedient, humble servant,
Th: Jefferson,
TO DR. CURRIE.
Paris, August 4, 1787.
Dear Sir,
I am favored with your letter of May the 2nd, and most cordially sympathize in your late immense losses. It is a situation in which a man needs the aid of all his wisdom and philosophy. But as it is better to turn from the contemplation of our misfortunes, to the resources we possess for extricating ourselves, you will, of course, have found solace in your vigor of mind, health of body, talents, habits of business, in the consideration that you have time yet to retrieve every thing, and a knowledge that the very activity necessary for this, is a state of greater happiness than the unoccupied one, to which you had a thought of retiring. I wish the bulk of my extravagant countrymen had as good prospects and resources as you. But with many of them, a feebleness of mind makes them afraid to probe the true state of their affairs, and procrastinate the reformation which alone can save something, to those who may yet be saved. How happy a people were we during the war, from the single circumstance that we could not run in debt! This counteracted all the inconveniences we felt, as the present facility of ruining ourselves overweighs all the blessings of peace. I know no condition happier than that of a Virginia farmer might be, conducting himself as he did during the war. His estate supplies a good table, clothes itself and his family with their ordinary apparel, furnishes a small surplus to buy salt, sugar, coffee, and a little finery for his wife and daughters, enables him to receive and to visit his friends, and furnishes him pleasing and healthy occupation. To secure all this, he needs but one act of self-denial, to put off buying any thing till he has the money to pay for it. Mr. Ammonett did not come. He wrote to me, however, and I am making inquiry for the town and family he indicated. As yet, neither can be heard of, and were they to be found, the length of time would probably bar all claims against them. I have seen no object present so many desperate faces. However, if inquiry can lighten our way, that shall not be wanting, and I will write to him as soon as we discover any thing, or despair of discovering. Littlepage has succeeded well in Poland. He has some office, it is said, worth five hundred guineas a year. The box of seeds you were so kind as to forward me, came safe to hand. The arrival of my daughter, in good health, has been a source of immense comfort to me. The injury of which you had heard, was a dislocated wrist, and though it happened eleven months ago, was a simple dislocation, and immediately aided by the best surgeon in Paris, it is neither well, nor ever will be, so as to render me much service. The fingers remain swelled and crooked, the hand withered, and the joint having a very confined motion. You ask me when I shall return. My commission expires next spring, and if not renewed, I shall return then. If renewed, I shall stay somewhat longer: how much, will not depend on me altogether. So far as it does, I cannot fix the epoch of my return, though I always flatter myself it is not very distant. My habits are formed to those of my own country. I am past the time of changing them, and am, therefore, less happy any where else than there.
I shall always be happy to hear from you, being with very sincere esteem, Dear Sir, your friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MR. HAWKINS.
Paris, August 4, 1787.
Dear Sir,
I have to acknowledge the receipt of your favors of March the 8th and June the 9th, and to give you many thanks for the trouble you have taken with the dionæa muscipula. I have not yet heard any thing of them, which makes me fear they have perished by the way. I believe the most effectual means of conveying them hither will be by the seed. I must add my thanks too for the vocabularies. This is an object I mean to pursue, as I am persuaded that the only method of investigating the filiation of the Indian nations, is by that of their languages.
I look up with you to the federal convention, for an amendment of our federal affairs; yet I do not view them in so disadvantageous a light at present, as some do. And above all things, I am astonished at some people’s considering a kingly government as a refuge. Advise such to read the fable of the frogs, who solicited Jupiter for a king. If that does not put them to rights, send them to Europe, to see something of the trappings of monarchy, and I will undertake, that every man shall go back thoroughly cured. If all the evils which can arise among us, from the republican form of our government, from this day to the day of judgment, could be put into a scale against what this country suffers from its monarchical form, in a week, or England, in a month, the latter would preponderate. Consider the contents of the Red Book in England, or the Almanac Royale of France, and say what a people gain by monarchy. No race of kings has ever presented above one man of common, sense, in twenty generations. The best they can do is, to leave things to their ministers; and what are their ministers, but a committee, badly chosen? If the king ever meddles, it is to do harm. Adieu, my Dear Sir, and be assured of the esteem of your friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO COLONEL MONROE.
Paris, August 5, 1787.
Dear Sir,
A journey of between three and four months, into the southern parts of France and northern of Italy, has prevented my writing to you. In the mean time, you have changed your ground, and engaged in different occupations, so that I know not whether the news of this side the water will even amuse you. However, it is all I have for you. The storm which seemed to be raised suddenly in Brabant, will probably blow over. The Emperor, on his return to Vienna, pretended to revoke all the concessions which had been made by his Governors General, to his Brabantine subjects; but he, at the same time, called for deputies from among them to consult with. He will use their agency to draw himself out of the scrape, and all there I think will be quieted. Hostilities go on occasionally in Holland. France espouses the cause of the Patriots, as you know, and England and Prussia that of the Stadtholder. France and England are both unwilling to bring on a war, but a hasty move of the King of Prussia will perplex them. He has thought the stopping his sister sufficient cause for sacrificing a hundred or two thousand of his subjects, and as many Hollanders and French. He has therefore ordered twenty thousand men to march, without consulting England, or even his own ministers. He may thus drag England into a war, and of course this country, against their will. But it is certain they will do every thing they can, to prevent it; and that in this, at least, they agree.
Though such a war might be gainful to us, yet it is much to be deprecated by us at this time. In all probability, France would be unequal to such a war by sea and by land, and it is not our interest or even safe for us, that she should be weakened. The great improvements in their constitution, effected by the Assemblée des Notables, you are apprized of. That of partitioning the country into a number of subordinate governments, under the administration of Provincial Assemblies, chosen by the people, is a capital one. But to the delirium of joy which these improvements gave the nation, a strange reverse of temper has suddenly succeeded. The deficiencies of their revenue were exposed, and they were frightful. Yet there was an appearance of intention to economize and reduce the expenses of government. But expenses are still very, inconsiderately incurred, and all reformation in that point despaired of. The public credit is affected; and such a spirit of discontent has arisen, as has never been seen. The parliament refused to register the edict for a stamp tax, or any other tax, and call for the States General, who alone, they say, can impose a new tax. They speak with a boldness unexampled. The King has called them to Versailles to-morrow, where he will hold a lit de justice and compel them to register the tax. How the chapter will finish, we must wait to see. By a vessel lately sailed from Havre to New York, I have sent you some more livraisons of the Encyclopédie, down to the 22nd inclusive. They were in a box with Dr. Currie’s, and addressed to Mr. Madison, who will forward them to Richmond. I have heard you are in the Assembly. I will beg the favor of you, therefore, to give me, at the close of the session, a history of the most remarkable acts passed, the parties and views of the House, &c. This, with the small news of my country, crops and prices, furnish you abundant matter to treat me, while I have nothing to give you in return, but the history of the follies of nations in their dotage. Present me in respectful and friendly terms to Mrs. Monroe, and be assured of the sincere sentiments of esteem and attachment, with which I am Dear Sir, your friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN JAY.
Paris, August 6,1787.
The last letter I had the honor of addressing you was dated June the 21st. I have now that of enclosing you a letter from the Swedish ambassador, praying that inquiry may be made for a vessel of his nation, piratically carried off, and measures taken relative to the vessel, cargo, and crew. Also a letter from William Russell and others, citizens of America, concerned in trade to the island of Guadaloupe, addressed to the Marechal de Castries, and complaining of the shutting to them the port of Point a Pitre, and receiving them only at Basse-terre. This was enclosed to me by the subscribers, to be delivered to the Marechal de Castries. But the present is not the moment to move in that business: and moreover, I suppose, that whenever parties are within the reach of Congress, they should apply to them, and my instructions come through that channel. Matters, arising within the kingdom of France, to which my commission is limited, and not admitting time to take the orders of Congress, I suppose I may move in originally. I also enclose you the copy of a letter from Mr. Barclay, closing his proceedings in our affairs with Morocco. Before this reaches you, he will have had the honor of presenting himself to you in person. After his departure, the parliament of Bordeaux decided that he was liable to arrest. This was done on a letter from the minister, informing them that Mr. Barclay was invested with no character which privileged him from arrest. His constant character of consul was no protection, and they did not explain whether his character to Morocco was not originally diplomatic, or was expired. Mr. Barclay’s proceedings under this commission being now closed, it would be incumbent on me to declare with respect to them, as well as his consular transactions, my opinion of the judgment, zeal, and disinterestedness with which he has conducted himself; were it not that Congress has been so possessed of those transactions from time to time, as to judge for themselves. I cannot but be uneasy, lest my delay of entering on the subject of the consular convention, may be disapproved. My hope was and is, that more practicable terms might be obtained: in this hope, I do nothing till further orders, observing by an extract from the journals you were pleased to send me, that Congress have referred the matter to your consideration, and conscious that we are not suffering in the mean time, as we have not a single consul in France, since the departure of Mr. Barclay. I mentioned to you in my last, the revival of the hopes of the Chevalier de la Luzerne. I thought it my duty to remind the Count de Montmorin, the other day, of the long absence of their minister from Congress. He told me, the Chevalier de la Luzerne would not be sent back, but that we might rely, that in the month of October a person would be sent, with whom we should be content. He did not name the person, though there is no doubt that it is the Count de Mourtier. It is an appointment, which, according to the opinion I have formed of him, bids as fair to give content, as any one which could be made.
I also mentioned in my last letter, that I had proposed the reducing the substance of Monsieur de Calonne’s letter into the form of an Arrêt, with some alterations, which, on consultation with the merchants at the different ports I visited, I had found to be necessary. I received soon after a letter from the Comptroller General, informing me, that the letter of Monsieur de Calonne was in a course of execution. Of this, I enclose you a copy. I was, in that moment, enclosing to him my general observations on that letter, a copy of which is also enclosed. In these I stated all the alterations I wished to have made. It became expedient soon after, to bring on the article of tobacco; first, to know whether the Farmers had executed the order of Bernis, and also to prepare some arrangements to succeed the expiration of this order. So that I am now pursuing the whole subject of our commerce, 1. to have necessary amendments made in Monsieur de Calonne’s letter; 2. to put it into a more stable form; 3. to have full execution of the order of Bernis; 4. to provide arrangements for the article of tobacco, after that order shall be expired. By the copy of my letter on the two last points, you will perceive that I again press the abolition of the Farm of this article. The conferences on that subject give no hope of effecting that. Some poor palliative is probably all we shall obtain. The Marquis de la Fayette goes hand in hand with me in all these transactions, and is an invaluable auxiliary to me. I hope it will not be imputed either to partiality or affectation, my naming this gentleman so often in my despatches. Were I not to do it, it would be a suppression of truth, and the taking to myself the whole merit where he has the greatest share.
The Emperor, on his return to Vienna, disavowed the concessions of his Governors General to his subjects of Brabant. He at the same time proposed their sending deputies to him, to consult on their affairs. They refused in the first moment; but afterwards nominated deputies; without giving them any power, however, to concede any thing. In the mean time, they are arming and training themselves. Probably the Emperor will avail himself of the aid of these deputies, to tread back his steps. He will be the more prompt to do this, that he may be in readiness to act freely, if he finds occasion, in the new scenes preparing in Holland. What these will be, cannot be foreseen. You well know, that the original party-divisions of that country were into Stadtholderians, Aristocrats, and Democrats. There was a subdivision of the Aristocrats, into violent and moderate, which was important. The violent Aristocrats would have wished to preserve all the powers of government in the hands of the Regents, and that these should remain self-elective: but choosing to receive a modification of these powers from the Stadtholder, rather than from the people, they threw themselves into his scale. The moderate Aristocrats would have consented to a temperate mixture of democracy, and particularly, that the Regents should be elected by the people. They were the declared enemies of the Stadtholder, and acted in concert with the Democrats, forming with them what was called the Patriots. It is the opinion of dispassionate people on the spot, that their views might have been effected. But the democratic party aimed at more. They talked of establishing tribunes of the people, of annual accounts, of depriving the magistrates at the will of the people, &c.; of enforcing all this with the arms in the hands of the corps francs; and in some places, as at Heusden, Sprang, &c. began the execution of these projects. The moderate Aristocrats found it difficult to strain their principles to this pitch. A schism took place between them and the Democrats, and the former have for some time been dropping off from the latter into the scale of the Stadtholder. This is the fatal coalition which governs without obstacle in Zealand, Friesland, and Guelderland, which constitutes the States of Utrecht, at Amersfort, and, with their aid, the plurality in the States General. The States of Holland, Groningen, and Overyssel, vote as yet in the opposition. But the coalition gains ground in the States of Holland, and has been prevalent in the Council of Amsterdam. If its progress be not stopped by a little moderation in the Democrats, it will turn the scale decidedly in favor of the Stadtholder, in the event of their being left to themselves without foreign interference. If foreign powers interfere, their prospect does not brighten. I see no sure friends to the Patriots but France, while Prussia and England are their assured enemies. Nor is it probable, that characters so greedy, so enterprising, as the Emperor and Empress, will be idle during such a struggle. Their views have long shown which side they would take. That France has engaged to interfere, and to support the Patriots, is beyond doubt. This engagement was entered into during the life of the late King of Prussia, whose eye was principally directed on the Emperor, and whose dispositions towards the Prince of Orange would have permitted him to be clipped a little close. But the present King comes in with warmer dispositions towards the Princess his sister. He has shown decidedly, that he will support her, even to the destruction of the balance of Europe, and the disturbance of its peace. The King of England has equally decided to support that house, at the risk of plunging his nation into another war. He supplies the Prince with money at this moment. A particular remittance of one hundred and twenty thousand guineas is known of. But his ministry is divided. Pitt is against the King’s opinion, the Duke of Richmond and the rest of the ministers for it. Or, at least, such is the belief here. Mr. Adams will have informed you more certainly. This division in the English ministry, with the ill condition of their finances for war, produces a disposition even in the King, to try first every pacific measure: and that country and this were laboring jointly to stop the course of hostilities in Holland, to endeavor to effect an accommodation, and were scarcely executing at all the armaments ordered in their ports; when all of a sudden an inflammatory letter, written by the Princess of Orange to the King of Prussia, induces him, without consulting England, without consulting even his own Council, to issue orders by himself to his generals, to march twenty thousand men to revenge the insult supposed to be offered to his sister. With a pride and egotism planted in the heart of every King, he considers her being stopped in the road, as a sufficient cause to sacrifice a hundred or two thousand of his own subjects, and as many of his enemies, and to spread fire, sword, and desolation over the half of Europe. This hasty measure has embarrassed England, undesirous of war, if it can be avoided, yet unwilling to separate from the power who is to render its success probable. Still you may be assured, that that court is going on in concurrence with this, to prevent extremities, if possible; always understood, that if the war cannot be prevented, they will enter into it as parties, and in opposition to one another. This event is, in my opinion, to be deprecated by the friends of France. She never was equal to such a war by land, and such a one by sea; and less so now, than in any moment of the present reign. You remember that the nation was in a delirium of joy on the convocation of the Notables, and on the various reformations agreed on between them and the government. The picture of the distress of their finances was indeed frightful, but the intentions to reduce them to order seemed serious. The constitutional reformations have gone on well, but those of expenses make little progress. Some of the most obviously useless have indeed been lopped off, but the remainder is a heavy mass, difficult to be reduced. Despair has seized every mind, and they have passed from an extreme of joy to one of discontent. The parliament, therefore, oppose the registering any new tax, and insist on an Assembly of the States General. The object of this is to limit expenses, and dictate a constitution. The edict for the stamp tax has been the subject of reiterated orders and refusals to register. At length, the King has summoned the parliament to Versailles to hold a bed of justice, in which he will order them, in person, to register the edict. At the moment of my writing, they are gone to Versailles for this purpose. There will yet remain to them, to protest against the register, as forced, and to issue orders against its execution on pain of death. But as the King would have no peaceable mode of opposition left, it remains to be seen, whether they will push the matter to this extremity. It is evident, I think, that the spirit of this country is advancing towards a revolution in their constitution. There are not wanting persons at the helm, friends to the progress of this spirit. The Provincial Assemblies will be the most probable instrument of effecting it.
Since writing thus far, I have received an intimation, that it will be agreeable not to press our commercial regulations at this moment, the ministry being too much occupied with the difficulties surrounding them, to spare a moment on any subject which will admit of delay. Our business must, therefore, be suspended for a while. To press it out of season, would be to defeat, it. It would be felt as a vital benefit here, could we relieve their finances, by paying what we owe. Congress will judge by Mr. Adams’s letters, how far the transferring all our debts in this country to Holland is practicable. On the replenishing their treasury with our principal and interest, I should not be afraid to ask concessions in favor of our West India trade. It would produce a great change of opinion as to us and our affairs. In the Assemblée des Notables, hard things were said of us. They were induced, however, in committing us to writing, to smother their ideas a little. In their votes, now gone to be printed, our debt is described in these words. The twenty-first article of the account, formed of the interest of the claims of his Majesty on the United States of America, cannot be drawn out for the present, except as a document. The recovery of these claims, as well principal as perhaps even interest, although they appear to rest on the most solid security, may, nevertheless, be long delayed, and should not, consequently, be taken into account in estimating the annual revenue. This article amounts to one million and six hundred thousand livres.’ Above all things, it is desirable to hush the foreign officers by payment. Their wants, the nature of their services, their access to high characters, and connections with them, bespeak the reasons for this. I hear also that Mr. Beaumarchais means to make himself heard, if a memorial which he sends by an agent in the present packet is not attended to, as he thinks it ought to be. He called on me with it, and desired me to recommend his case to a decision, and to note in my despatch, that it was the first time he had spoken to me on the subject. This is true, it being the first time I ever saw him; but my recommendations would be as displaced as unnecessary. I assured him Congress would do in that business what justice should require, and their means enable them. The information sent me by Mr. Montgomery from Alicant, of the death of the Dey of Algiers, was not true. I had expressed my doubt of it in my last, when I communicated it. I send herewith the newspapers to this date, and a remonstrance of the parliament, to show you in what language the King can be addressed at this day. I have received no journal of Congress since the beginning of November last, and will thank you for them, if printed.
I have the honor to be, with sentiments of the most perfect esteem and respect, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
P. S. August 7. The parliament were received yesterday very harshly by the King. He obliged them to register the two edicts for the impôt territorial and stamp tax. When speaking in my letter of the reiterated orders and refusals to register, which passed between the King and parliament, I omitted to insert the King’s answer to a deputation of parliament, which attended him at Versailles. It may serve to show the spirit which exists between them. It was in these words, and these only:—‘Je vous ferai savoir mes intentions. Allez-vous-en. Qu’on ferme la porte.’
TO JOHN CHURCHMAN.
Paris, August 8, 1787.
Sir,
I have duly received your favor of June the 6th, and immediately communicated its contents to a member of the Academy. He told me that they had received the other copy of your memorial, which you mention to have sent through another channel; that your ideas were not conveyed so explicitly, as to enable them to decide finally on their merit, but that they had made an entry in their journals, to preserve to you the claim of the original idea. As far as we can conjecture it here, we imagine you make a table of variations of the needle, for all the different meridians whatever. To apply this table to use in the voyage between America and Europe, suppose the variation to increase a degree in every one hundred and sixty miles. Two difficulties occur; 1. a ready and accurate method of finding the variation of the place; 2. an instrument so perfect, as that (though the degree on it shall represent one hundred and sixty miles) it shall give the parts of the degree so minutely, as to answer the purpose of the navigator. The variation of the needle at Paris, actually, is 21° west. I make no question you have provided against the doubts entertained here, and I shall be happy that our country may have the honor of furnishing the old world, what it has so long sought in vain.
I am with much respect, Sir, your most obedient, humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MONSIEUR L HOMMANDE.
Paris, August 9, 1787.
Sir,
At the time you honored me with your letter of May the 31st, I was not returned from a journey I had taken into Italy. This circumstance, with the mass of business which had accumulated during my absence, must apologize for the delay of my answer. Every discovery, which multiplies the subsistence of man, must be a matter of joy to every friend to humanity. As such, I learn with great satisfaction, that you have found the means of preserving flour more perfectly than has been done hitherto. But I am not authorized to avail my country of it, by making any offer for its communication. Their policy is to leave their citizens free, neither restraining nor aiding them in their pursuits. Though the interposition of government in matters of invention has its use, yet it is in practice so inseparable from abuse, that they think it better not to meddle with it. We are only to hope, therefore, that those governments, who are in the habit of directing all the actions of their subjects by particular law, may be so far sensible of the duty they are under of cultivating useful discoveries, as to reward you amply for yours, which is among the most interesting to humanity.
I have the honor to be, with great consideration and respect, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO PETER CARR.
Paris, August 10, 1787.
Dear Peter,
I have received your two letters of December the 30th and April the 18th, and am very happy to find by them, as well as by letters from Mr. Wythe, that you have been so fortunate as to attract his notice and good will: I am sure you will find this to have been one of the most fortunate events of your life, as I have ever been sensible it was of mine. I enclose you a sketch of the sciences to which I would wish you to apply, in such order as Mr. Wythe shall advise: I mention also the books in them worth your reading, which submit to his correction. Many of these are among your father’s books, which you should have brought to you. As I do not recollect those of them not in his library, you must write to me for them, making out a catalogue of such as you think you shall have occasion for in eighteen months from the date of your letter, and consulting Mr. Wythe on the subject. To this sketch I will add a few particular observations.
1. Italian. I fear the learning this language will confound your French and Spanish. Being all of them degenerated dialects of the Latin, they are apt to mix in conversation. I have never seen a person speaking the three languages, who did not mix them. It is a delightful language, but late events having rendered the Spanish more useful, lay it aside to prosecute that.
2. Spanish. Bestow great attention on this, and endeavor to acquire an accurate knowledge of it. Our future connections with Spain and Spanish America, will render that language a valuable acquisition. The ancient history of a great part of America, too, is written in that language. I send you a dictionary.
3. Moral Philosophy. I think it lost time to attend lectures on this
branch. He who made us would have been a pitiful bungler, if he had made
the rules of our moral conduct a matter of science. For one man of
science, there are thousands who are not. What would have become of them?
Man was destined for society. His morality, therefore, was to be formed to
this object. He was endowed with a sense of right and wrong, merely
relative to this. This sense is as much a part of his nature, as the sense
of hearing, seeing, feeling; it is the true foundation of morality, and
not the
![]() truth, &c, as fanciful writers have
imagined. The moral sense, or conscience, is as much a part of man, as his
leg or arm. It is given to all human beings, in a stronger or weaker
degree, as force of members is given them in a greater or less degree. It
may be strengthened by exercise, as may any particular limb of the body.
This sense is submitted, indeed, in some degree, to the guidance of
reason; but it is a small stock which is required for this: even a less
one than what we call common sense. State a moral case to a ploughman and
a professor. The former will decide it as well, and often better than the
latter, because he has not been led astray by artificial rules. In this
branch, therefore, read good books, because they will encourage, as well
as direct your feelings. The writings of Sterne, particularly, form the
best course of morality that ever was written. Besides these, read the
books mentioned in the enclosed paper: and, above all things, lose no
occasion of exercising your dispositions to be grateful, to be generous,
to be charitable, to be humane, to be true, just, firm, orderly,
courageous, &c. Consider every act of this kind, as an exercise which
will strengthen your moral faculties, and increase your worth.
truth, &c, as fanciful writers have
imagined. The moral sense, or conscience, is as much a part of man, as his
leg or arm. It is given to all human beings, in a stronger or weaker
degree, as force of members is given them in a greater or less degree. It
may be strengthened by exercise, as may any particular limb of the body.
This sense is submitted, indeed, in some degree, to the guidance of
reason; but it is a small stock which is required for this: even a less
one than what we call common sense. State a moral case to a ploughman and
a professor. The former will decide it as well, and often better than the
latter, because he has not been led astray by artificial rules. In this
branch, therefore, read good books, because they will encourage, as well
as direct your feelings. The writings of Sterne, particularly, form the
best course of morality that ever was written. Besides these, read the
books mentioned in the enclosed paper: and, above all things, lose no
occasion of exercising your dispositions to be grateful, to be generous,
to be charitable, to be humane, to be true, just, firm, orderly,
courageous, &c. Consider every act of this kind, as an exercise which
will strengthen your moral faculties, and increase your worth.
4. Religion, Your reason is now mature enough to examine this object. In the first place, divest yourself of all bias in favor of novelty and singularity of opinion. Indulge them in any other subject rather than that of religion. It is too important, and the consequences of error may be too serious. On the other hand, shake off all the fears and servile prejudices, under which weak minds are servilely crouched. Fix reason firmly in her seat, and call to her tribunal every fact, every opinion. Question with boldness even the existence of a God; because, if there be one, he must more approve the homage of reason, than that of blindfolded fear. You will naturally examine, first, the religion of your own country. Read the Bible, then, as you would read Livy or Tacitus. The facts which are within the ordinary course of nature, you will believe on the authority of the writer, as you do those of the same kind in Livy and Tacitus. The testimony of the writer weighs in their favor, in one scale, and their not being against the laws of nature, does not weigh against them. But those facts in the Bible, which contradict the laws of nature, must be examined with more care, and under a variety of faces. Here you must recur to the pretensions of the writer to inspiration from God. Examine upon what evidence his pretensions are founded, and whether that evidence is so strong, as that its falsehood would be more improbable than a change of the laws of nature, in the case he relates. For example, in the book of Joshua we are told the sun stood still several hours. Were we to read that fact in Livy or Tacitus, we should class it with their showers of blood, speaking of statues, beasts, &c. But it is said, that the writer of that book was inspired. Examine, therefore, candidly, what evidence there is of his having been inspired. The pretension is entitled to your inquiry, because millions believe it. On the other hand, you are astronomer enough to know, how contrary it is to the law of nature, that a body revolving on its axis, as the earth does, should have stopped, should not, by that sudden stoppage, have prostrated animals, trees, buildings, and should after a certain time have resumed its revolution, and that without a second general prostration. Is this arrest of the earth’s motion, or the evidence which affirms it, most within the law of probabilities? You will next read the New Testament. It is the history of a personage called Jesus. Keep in your eye the opposite pretensions, 1. of those who say he was begotten by God, born of a virgin, suspended, and reversed the laws of nature at will, and ascended bodily into heaven: and, 2. of those who say he was a man, of illegitimate birth, of a benevolent heart, enthusiastic mind, who set out without pretensions to divinity, ended in believing them, and was punished capitally for sedition, by being gibbeted, according to the Roman law, which punished the first commission of that offence by whipping, and the second by exile or death in furca. See this law in the Digest, Lib. 48, tit. 19, § 28. 3. and Lipsius, Lib. 2. De Cruce, cap. 2. These questions are examined in the books I have mentioned, under the head of Religion, and several others. They will assist you in your inquiries; but keep your reason firmly on the watch in reading them all. Do not be frightened from this inquiry by any fear of its consequences. If it ends in a belief that there is no God, you will find incitements to virtue in the comfort and pleasantness you feel in its exercise, and the love of others which it will procure you. If you find reason to believe there is a God, a consciousness that you are acting under his eye, and that he approves you, will be a vast additional incitement: if that there be a future state, the hope of a happy existence in that, increases the appetite to deserve it: if that Jesus was also a God, you will be comforted by a belief of his aid and love. In fine, I repeat, you must lay aside all prejudice on both sides, and neither believe nor reject any thing, because any other person, or description of persons, have rejected or believed it. Your own reason is the only oracle given you by Heaven, and you are answerable not for the rightness, but uprightness of the decision. I forgot to observe, when speaking of the New Testament, that you should read all the histories of Christ, as well of those whom a council of ecclesiastics have decided for us to be Pseudo-evangelists, as those they named Evangelists. Because these Pseudo-evangelists pretended to inspiration as much as the others, and you are to judge their pretensions by your own reason, and not by the reason of those ecclesiastics. Most of these are lost. There are some, however, still extant, collected by Fabricius, which I will endeavor to get and send you.
5. Travelling. This makes men wiser, but less happy. When men of sober age travel, they gather knowledge, which they may apply usefully for their country; but they are subject ever after to recollections mixed with regret; their affections are weakened by being extended over more objects; and they learn new habits, which cannot be gratified when they return home. Young men who travel are exposed to all these inconveniences in a higher degree, to others still more serious, and do not acquire that wisdom for which a previous foundation is requisite, by repeated and just observations at home. The glare of pomp and pleasure is analogous to the motion of the blood; it absorbs all their affection and attention; they are torn from it as from the only good in this world, and return to their home as to a place of exile and condemnation. Their eyes are for ever turned back to the object they have lost, and its recollection poisons the residue of their lives. Their first and most delicate passions are hackneyed on unworthy objects here, and they carry home the dregs, insufficient to make themselves or any body else happy. Add to this, that a habit of idleness, an inability to apply themselves to business is acquired, and renders them useless to themselves and their country. These observations are founded in experience. There is no place where your pursuit of knowledge will be so little obstructed by foreign objects, as in your own country, nor any wherein the virtues of the heart will be less exposed to be weakened. Be good, be learned, and be industrious, and you will not want the aid of travelling, to render you precious to your country, dear to your friends, happy within yourself. I repeat my advice, to take a great deal of exercise, and on foot. Health is the first requisite after morality. Write to me often, and be assured of the interest I take in your success, as well as the warmth of those sentiments of attachment with which I am, Dear Peter, your affectionate friend,
Th: Jefferson.
TO DR. GILMER.
Paris, August 11, 1787.
Dear Doctor,
Your letter of January the 9th, 1787, came safely to hand in the month of June last. Unluckily you forgot to sign it, and your hand-writing is so Protean, that one cannot be sure it is yours. To increase the causes of incertitude, it was dated Pen-Park, a name which I only know, as the seat of John Harmer. The hand-writing, too, being somewhat in his style, made me ascribe it hastily to him, indorse it with his name, and let it lie in my bundle to be answered at leisure. That moment of leisure arriving, I sat down to answer it to John Harmer, and now, for the first time, discover marks of its being yours, and particularly those expressions of friendship to myself and family, which you have ever been so good as to entertain, and which are to me among the most precious possessions. I wish my sense of this, and my desires of seeing you rich and happy, may not prevent my seeing any difficulty in the case you state of George Harmer’s wills; which, as you state them, are thus.
1. A will, dated December the 26th, 1779, written in his own hand, and devising to his brother the estates he had received from him.
2. Another will, dated June the 25th, 1782, written also in his own hand, devising his estate to trustees, to be conveyed to such of his relations, I. H., I. L., or H. L., as should become capable of acquiring property, or, on failure of that, to be sold, and the money remitted them.
3. A third will, dated September the 12th, 1786, devising all his estate at Marrowbone, and his tracts at Horse-pasture and Poison-field to you; which will is admitted to record, and of course has been duly executed.
You say the learned are divided on these wills. Yet I see no cause of division, as it requires little learning to decide, that ‘the first deed and last will must always prevail.’ I am afraid, therefore, the difficulty may arise on the want of words of inheritance in the devise to you: for you state it as a devise to ‘George Gilmer’ (without adding ‘and to his heirs’) of ‘all the estate called Marrowbone,’ ‘the tract called Horse-pasture,’ and ‘the tract called Poison-field.’ If the question is on this point, and you have copied the words of the will exactly, I suppose you take an estate in fee simple in Marrowbone, and for life only in Horse-pasture and Poison-field; the want of words of inheritance in the two last cases, being supplied as to the first, by the word ‘estate,’ which has been repeatedly decided to be descriptive of the quantum of interest devised, as well as of its locality. I am in hopes, however, you have not copied the words exactly, that there are words of inheritance to all the devises, as the testator certainly knew their necessity, and that the conflict only will be between the different wills, in which case, I see nothing which can be opposed to the last. I shall be very happy to eat at Pen-park some of the good mutton and beef of Marrowbone, Horse-pasture, and Poison-field, with yourself and Mrs. Gilmer, and my good old neighbors. I am as happy no where else, and in no other society, and all my wishes end, where I hope my days will end, at Monticello. Too many scenes of happiness mingle themselves with all the recollections of my native woods and fields, to suffer them to be supplanted in my affection by any other. I consider myself here as a traveller only, and not a resident. My commission expires next spring, and if not renewed, I shall of course return then. If renewed, I shall remain here some time longer. How much, I cannot say; yet my wishes shorten the period. Among the strongest inducements, will be that of your society and Mrs. Gilmer’s, which I am glad to find brought more within reach, by your return to Pen-park. My daughters are importunate to return also. Patsy enjoys good health, and is growing to my stature. Maria arrived here about a month ago, after a favorable voyage, and in perfect health. My own health has been as good as ever, after the first year’s probation. If you knew how agreeable to me are the details of the small news of my neighborhood, your charity would induce you to write frequently. Your letters lodged in the post-office at Richmond (to be forwarded to New York) come with certainty. We are doubtful yet, whether there will be war or not. Present me with warm affection to Mrs. Gilmer, and be assured yourself of the unvarying sentiments of esteem and attachment, with which I am, Dear Doctor, your sincere friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOSEPH JONES.
Paris, August 14, 1787.
Dear Sir,
I have never yet thanked you, but with the heart, for the act of Assembly confirming the agreement with Maryland, the pamphlet, and papers, I received from you a twelvemonth ago. Very soon after their receipt, I got my right wrist dislocated, which prevented me long from writing, and as soon as that was able to bear it, I took a long journey, from which I am but lately returned. I am anxious to hear what our federal convention recommends, and what the States will do in consequence of their recommendation. * * * * With all the defects of our constitution, whether general or particular, the comparison of our governments with those of Europe, is like a comparison of heaven and hell. England, like the earth, may be allowed to take the intermediate station. And yet I hear there are people among you, who think the experience of our governments has already proved, that republican governments will not answer. Send those gentry here, to count the blessings of monarchy. A king’s sister, for instance, stopped in the road, and on a hostile journey, is sufficient cause for him to march immediately twenty thousand men to revenge this insult, when he had shown himself little moved by the matter of right then in question.
From all these broils we are happily free, and that God may keep us long so, and yourself in health and happiness, is the prayer of,
Dear Sir, your most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO GENERAL WASHINGTON.
Paris, August 14, 1787.
Dear Sir,
I was happy to find, by the letter of August the 1st, 1786, which you did me the honor to write to me, that the modern dress for your statue, would meet your approbation. I found it strongly the sentiment of West, Copely, Trumbull, and Brown, in London; after which it would be ridiculous to add, that it was my own. I think a modern in an antique dress, as just an object of ridicule, as a Hercules or Marius with a periwig and chapeau bras.
I remember having written to you, while Congress sat at Annapolis, on the water communication between ours and the western country, and to have mentioned, particularly, the information I had received of the plain face of the country between the sources of Big-beaver and Cayohoga, which made me hope that a canal, of no great expense, might unite the navigation of Lake Erie and the Ohio. You must since have had occasion of getting better information on this subject, and if you have, you would oblige me by a communication of it. I consider this canal, if practicable, as a very important work.
I remain in hopes of great and good effects from the decision of the Assembly over which you are presiding. To make our States one as to all foreign concerns, preserve them several as to all merely domestic, to give to the federal head some peaceable mode of enforcing its just authority, to organize that head into legislative, executive, and judiciary departments, are great desiderata in our federal constitution. Yet with all its defects, and with all those of our particular governments, the inconveniences resulting from them are so light, in comparison with those existing in every other government on earth, that our citizens may certainly be considered as in the happiest political situation which exists.
The Assemblée des Notables has been productive of much good in this country. The reformation of some of the most oppressive laws has taken place, and is taking place. The allotment of the State into subordinate governments, the administration of which is committed to persons chosen by the people, will work in time a very beneficial change in their constitution. The expense of the trappings of monarchy, too, is lightening. Many of the useless officers, high and low, of the King, Queen, and Princes, are struck off. Notwithstanding all this, the discovery of the abominable abuses of public money by the late Comptroller General, some new expenses of the court, not of a piece with the projects of reformation, and the imposition of new taxes, have, in the course of a few weeks, raised a spirit of discontent in this nation, so great and so general, as to threaten serious consequences. The parliaments in general, and particularly that of Paris, put themselves at the head of this effervescence, and direct its object to the calling the States General, who have not been assembled since 1614. The object is to fix a constitution, and to limit expenses. The King has been obliged to hold a bed of justice, to enforce the registering the new taxes: the parliament, on their side, propose to issue a prohibition against their execution. Very possibly this may bring on their exile. The mild and patriotic character of the new ministry is the principal dependence against this extremity.
The turn which the affairs of Europe will take, is not yet decided.
A war, wherein France, Holland, and England should be parties, seems, primâ facie, to promise much advantage to us. But, in the first place, no war can be safe for us, which threatens France with an unfavorable issue. And, in the next, it will probably embark us again into the ocean of speculation, engage us to overtrade ourselves, convert us into sea-rovers, under French and Dutch colors, divert us from agriculture, which is our wisest pursuit, because it will in the end contribute most to real wealth, good morals, and happiness. The wealth acquired by speculation and plunder, is fugacious in its nature, and fills society with the spirit of gambling. The moderate and sure income of husbandry begets permanent improvement, quiet life, and orderly conduct, both public and private. We have no occasion for more commerce than to take off our superfluous produce, and the people complain that some restrictions prevent this; yet the price of articles with us, in general, shows the contrary. Tobacco, indeed, is low, not because we cannot carry it where we please, but because we make more than the consumption requires. Upon the whole, I think peace advantageous to us, necessary for Europe, and desirable for humanity. A few days will decide, probably, whether all these considerations are to give way to the bad passions of Kings, and those who would be Kings.
I have the honor to be, with very sincere esteem and respect, Dear Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
P. S. August 15. The parliament is exiled to Troyes this morning. T. J.
TO COLONEL HUMPHREYS.
Paris, August 14, 1787.
Dear Sir,
I remember when you left us, it was with a promise to supply all the defects of correspondence in our friends, of which we complained, and which you had felt in common with us. Yet I have received but one letter from you, which was dated June the 5th, 1786, and I answered it August the 14th, 1786. Dropping that, however, and beginning a new account, I will observe to you, that wonderful improvements are making here in various lines. In architecture, the wall of circumvallation round Paris, and the palaces by which we are to be let out and in, are nearly completed; four hospitals are to be built instead of the old hôtel-dieu; one of the old bridges has all its houses demolished, and a second nearly so; a new bridge is begun at the Place Louis XV.; the Palais Royal is gutted, a considerable part in the centre of the garden being dug out, and a subterranean circus begun, wherein will be equestrian exhibitions, &c. In society, the habit habille is almost banished, and they begin to go even to great suppers in frock: the court and diplomatic corps, however, must always be excepted. They are too high to be reached by any improvement. They are the last refuge from which etiquette, formality, and folly will be driven. Take away these, and they would be on a level with other people.
[After describing the unsettled state of Europe, as in some
of the preceding letters, the writer proceeds.]
So much for the blessings of having Kings, and magistrates who would be Kings. From these events our young republics may learn useful lessons, never to call on foreign powers to settle their differences, to guard against hereditary magistrates, to prevent their citizens from becoming so established in wealth and power, as to be thought worthy of alliance by marriage with the nieces, sisters, &c. of Kings, and, in short, to besiege the throne of Heaven with eternal prayers, to extirpate from creation this class of human lions, tigers, and mammoths, called Kings; from whom, let him perish who does not say, ‘Good Lord, deliver us;’ and that so we may say, one and all, or perish, is the fervent prayer of him who has the honor to mix with it sincere wishes for your health and happiness, and to be, with real attachment and respect, Dear Sir, your affectionate friend and humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN JAY.
Sir,
Paris, August 15, 1787.
An American gentleman leaving Paris this afternoon, to go by the way of L’Orient to Boston, furnishes me the rare occasion of a conveyance, other than the packet, sure and quick. My letter by the packet informed you of the bed of justice, for enregistering the stamp tax and land tax. The parliament, on their return came to an Arrêtée (a resolution) which, besides protesting against the enregistering, as done by force, laid the foundation for an Arrêt de defence (an act) against the execution of the two new laws. The question on the final Arrêt was adjourned to the day before yesterday. It is believed they did not conclude on this Arrêt, as it has not appeared. However, there was a concourse of about ten thousand people at the parliament house, who, on their adjournment, received them with acclamations of joy, loosened the horses of the most eminent speakers against the tax from their carriages, and drew them home. This morning, the parliament is exiled to Troyes. It is believed to proceed, principally, from the fear of a popular commotion here.
The officer charged by this court, to watch the English squadron, which was under sailing orders, returned about a week ago with information that it had sailed, having shaped its course west-wardly. This is another step towards war. It is the more suspicious, as their minister here denies the fact. Count Adhemar is here from London, by leave from his court. The Duke of Dorset, the British ambassador here, has lately gone to London on leave. Neither of these ambassadors has the confidence of his court, on the point of abilities. The latter merits it for his honesty. The minister of the British court, resident here, remains; but Mr. Eden, their ambassador to Spain, under pretence of taking this in his route, is in truth their fac-totum in the present emergency. Nothing worth noting has occurred since my last, either in the Dutch or Austrian Netherlands.
I have the honor to be, with the most perfect esteem and respect, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN ADAMS.
Paris, August 30, 1787.
Dear Sir,
Since your favor of July the 10th, mine have been of July the 17th, 23rd, and 28th. The last enclosed a bill of exchange from Mr. Grand, on Tessier, for £46. 17s. 10d. sterling, to answer General Sullivan’s bill for that sum. I hope it got safe to hand, though I have been anxious about it, as it went by post, and my letters through that channel sometimes miscarry.
From the separation of the Notables to the present moment, has been perhaps the most interesting interval ever known in this country. The propositions of the government, approved by the Notables, were precious to the nation, and have been in an honest course of execution, some of them being carried into effect, and others preparing. Above all, the establishment of the Provincial Assemblies, some of which have begun their sessions, bid fair to be the instrument for circumscribing the power of the crown, and raising the people into consideration. The election given to them, is what will do this. Though the minister, who proposed these improvements, seems to have meant them as the price of the new supplies, the game has been so played, as to secure the improvements to the nation, without securing the price. The Notables spoke softly on the subject of the additional supplies. But the parliament took them up roundly, refused to register the edicts for the new taxes, till compelled in a bed of justice, and suffered themselves to be transferred to Troyes, rather than withdraw their opposition. It is urged principally against the King, that his revenue is one hundred and thirty millions more than that of his predecessor was, and yet he demands one hundred and twenty millions further. You will see this well explained in the ‘Conference entre un Ministre d’etat et un Conseiller au parliament,’ which I send you with some small pamphlets. In the mean time, all tongues in Paris (and in France as it is said) have been let loose, and never was a license of speaking against the government, exercised in London more freely or more universally. Caricatures, placards, bons-mots, have been indulged in by all ranks of people, and I know of no well attested instance of a single punishment. For some time, mobs of ten, twenty, and thirty thousand people collected daily, surrounded the Parliament house, huzzaed the members, even entered the doors and examined into their conduct, took the horses out of the carriages of those who did well, and drew them home. The government thought it prudent to prevent these, drew some regiments into the neighborhood, multiplied the guards, had the streets constantly patrolled by strong parties, suspended privileged places, forbade all clubs, &c. The mobs have ceased: perhaps this may be partly owing to the absence of Parliament. The Count d’Artois, sent to hold a bed of justice in the Cour des Aides, was hissed and hooted without reserve, by the populace; the carriage of Madame de (I forget the name), in the Queen’s livery, was stopped by the populace, under a belief that it was Madame de Polignac, whom they would have insulted; the Queen, going to the theatre at Versailles with Madame de Polignac, was received with a general hiss. The King, long in the habit of drowning his cares in wine, plunges deeper and deeper. The Queen cries, but sins on. The Count d’Artois is detested, and Monsieur, the general favorite. The Archbishop of Toulouse is made minister principal, a virtuous, patriotic, and able character. The Marechal de Castries retired yesterday, notwithstanding strong solicitations to remain in office. The Marechal de Segur retired at the same time, prompted to it by the court. Their successors are not yet known. Monsieur de St. Priest goes ambassador to Holland, in the room of Verac, transferred to Switzerland, and the Count de Moustier goes to America, in the room of the Chevalier de la Luzerne, who has a promise of the first vacancy. These nominations are not yet made formally, but they are decided on, and the parties are ordered to prepare for their destination.
As it has been long since I have had a confidential conveyance to you, I have brought together the principal facts from the adjournment of the Notables, to the present moment, which, as you will perceive from their nature, required a confidential conveyance. I have done it the rather, because, though you will have heard many of them, and seen them in the public papers, yet, floating in the mass of lies which constitute the atmosphere of London and Paris, you may not have been sure of their truth; and I have mentioned every truth of any consequence, to enable you to stamp as false, the facts pretermitted. I think that in the course of three months, the royal authority has lost, and the rights of the nation gained, as much ground by a revolution of public opinion only, as England gained in all her civil wars under the Stuarts. I rather believe, too, they will retain the ground gained, because it is defended by the young and the middle-aged, in opposition to the old only. The first party increases, and the latter diminishes daily, from the course of nature. You may suppose, that in this situation, war would be unwelcome to France. She will surely avoid it, if not forced into it by the courts of London and Berlin. If forced, it is probable she will change the system of Europe totally, by an alliance with the two empires, to whom nothing would be more desirable. In the event of such a coalition, not only Prussia, but the whole European world must receive from them their laws. But France will probably endeavor to preserve the present system, if it can be done, by sacrificing, to a certain degree, the pretensions of the patriotic party in Holland. But of all these matters, you can judge, in your position, where less secrecy is observed, better than I can.
I have news from America as late as July the 19th. Nothing had transpired from the federal convention. I am sorry they began their deliberations by so abominable a precedent, as that of tying up the tongues of their members. Nothing can justify this example, but the innocence of their intentions, and ignorance of the value of public discussions. I have no doubt that all their other measures will be good and wise. It is really an assembly of demigods. General Washington was of opinion, that they should not separate till October.
I have the honor to be, with every sentiment of friendship and respect, Dear Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MR. WYTHE.
Paris, September 16,1787.
Dear Sir,
I am now to acknowledge the receipt of your favors of December the 13th and 22nd, 1786, and of January, 1787. These should not have been so long unanswered, but that they arrived during my absence on a journey of between three and four months, through the southern parts of France and northern of Italy. In the latter country, my time allowed me to go no further than Turin, Milan, and Genoa: consequently, I scarcely got into classical ground. I took with me some of the writings, in which endeavors have been made to investigate the passage of Annibal over the Alps, and was just able to satisfy myself, from a view of the country, that the descriptions given of his march are not sufficiently particular, to enable us, at this day, even to guess at his track across the Alps. In architecture, painting, sculpture, I found much amusement: but more than all, in their agriculture, many objects of which might be adopted with us to great advantage. I am persuaded, there are many parts of our lower country where the olive tree might be raised, which is assuredly the richest gift of Heaven. I can scarcely except bread. I see this tree supporting thousands among the Alps, where there is not soil enough to make bread for a single family. The caper, too, might be cultivated with us. The fig we do raise. I do not speak of the vine, because it is the parent of misery. Those who cultivate it are always poor, and he who would employ himself with us in the culture of corn, cotton, &c. can procure, in exchange for them, much more wine, and better, than he could raise by its direct culture.
I sent you formerly copies of the documents on the Tagliaferro family, which I had received from Mr. Febroni. I now send the originals. I have procured for you a copy of Polybius, the best edition; but the best edition of Vitruvius which is with the commentaries of Ficinus, is not to be got here. I have sent to Holland for it. In the mean time, the Polybius comes in a box containing books for Peter Carr, and for some of my friends in Williamsburg and its vicinities. I have taken the liberty of addressing the box to you. It goes to New York in the packet-boat which carries this letter, and will be forwarded to you by water, by Mr. Madison. Its freight to New York is paid here. The transportation from thence to Williamsburg, will be demanded of you, and shall stand as the equivalent to the cost of Polybius and Vitruvius, if you please. The difference either way, will not be worth the trouble of raising and transmitting accounts. I send you herewith a state of the contents of the box, and for whom each article is. Among these are some, as you will perceive, of which I ask your acceptance. It is a great comfort to me, that while here, I am able to furnish some amusement to my friends, by sending them such productions of genius, ancient and modern, as might otherwise escape them; and I hope they will permit me to avail myself of the occasion, while it lasts.
This world is going all to war. I hope ours will remain clear of it. It is already declared between the Turks and Russians, and considering the present situation of Holland, it cannot fail to spread itself all over Europe. Perhaps it may not be till next spring, that the other powers will be engaged in it: nor is it as yet clear, how they will arrange themselves. I think it not impossible, that France and the two empires may join against all the rest. The Patriotic party in Holland will be saved by this, and the Turks sacrificed. The only thing which can prevent the union of France and the two empires, is the difficulty of agreeing about the partition of the spoils. Constantinople is the key of Asia. Who shall have it, is the question. I cannot help looking forward to the re-establishment of the Greeks as a people, and the language of Homer becoming again a living language, as among possible events. You have now with you Mr. Paradise, who can tell you how easily the modern may be improved into the ancient Greek.
You ask me in your letter, what ameliorations I think necessary in our federal constitution. It is now too late to answer the question, and it would always have been presumption in me to have done it. Your own ideas, and those of the great characters who were to be concerned with you in these discussions, will give the law, as they ought to do, to us all. My own general idea was, that the States should severally preserve their sovereignty in whatever concerns themselves alone, and that whatever may concern another State, or any foreign nation, should be made a part of the federal sovereignty: that the exercise of the federal sovereignty should be divided among three several bodies, legislative, executive, and judiciary, as the State sovereignties are: and that some peaceable means should be contrived, for the federal head to force compliance on the part of the States. I have reflected on your idea of wooden or ivory diagrams, for the geometrical demonstrations. I should think wood as good as ivory; and that in this case, it might add to the improvement of the young gentlemen, that they should make the figures themselves. Being furnished by a workman with a piece of vineer, no other tool than a penknife and a wooden rule would be necessary. Perhaps pasteboards, or common cards, might be still more convenient. The difficulty is, how to reconcile figures which must have a very sensible breadth, to our ideas of a mathematical line, which, as it has neither breadth nor thickness, will revolt more at these, than at simple lines drawn on paper or slate. If, after reflecting on this proposition, you would prefer having them made here, lay your commands on me, and they shall be executed.
I return you a thousand thanks for your goodness to my nephew. After my debt to you for whatever I am myself, it is increasing it too much, to interest yourself for his future fortune. But I know that to you, a consciousness of doing good is a luxury ineffable. You have enjoyed it already, beyond all human measure, and that you may long live to enjoy it, and to bless your country and friends, is the sincere prayer of him, who is, with every possible sentiment of esteem and respect, Dear Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN JAY.
Sir,
Paris, September 19, 1787.
My last letters to you were of the 6th and 15th of August; since which, I have been honored with yours of July the 24th, acknowledging the receipt of mine of the 14th and 23d of February. I am anxious to hear you have received that also of May the 4th, written from Marseilles. According to the desires of Congress, expressed in their vote confirming the appointments of Francisco Giuseppa and Girolamo Chiappi, their agents in Morocco, I have written letters to these gentlemen, to begin a correspondence with them. To the first, I have enclosed the ratification of the treaty with the Emperor of Morocco, and shall send it either by our agent at Marseilles, who is now here, or by the Count Daranda, who sets out for Madrid in a few days, having relinquished his embassy here. I shall proceed on the redemption of our captives at Algiers, as soon as the commissioners of the treasury shall enable me, by placing the money necessary under my orders. The prisoners redeemed by the religious order of Mathurins, cost about four hundred dollars each, and the General of the order told me, that they had never been able to redeem foreigners on so good terms as their own countrymen. Supposing that their redemption, clothing, feeding, and transportation should amount to five hundred dollars each, there must be, at least, a sum of ten thousand dollars set apart for this purpose. Till this is done, I shall take no other step than the preparatory one, of destroying at Algiers all idea of our intending to redeem the prisoners. This, the General of the Mathurins told me, was indispensably necessary, and that it must not, on any account, transpire, that the public would interest themselves for their redemption. This was rendered the more necessary, by the declaration of the Dey to the Spanish consul, that he should hold him responsible, at the Spanish price, for our prisoners, even for such as should die. Three of them have died of the plague. By authorizing me to redeem at the prices usually paid by the European nations, Congress, I suppose, could not mean the Spanish price, which is not only unusual but unprecedented, and would make our vessels the first object with those pirates. I shall pay no attention, therefore, to the Spanish price, unless further instructed. Hard as it may seem, I should think it necessary, not to let it be known even to the relations of the captives, that we mean to redeem them.
I have the honor to inclose you a paper from the admiralty of Guadaloupe, sent to me as a matter of form, and to be lodged, I suppose, with our marine records. I enclose, also, a copy of a letter from the Count de Florida Blanca to Mr. Carmichael, by which you will perceive, they have referred the settlement of the claim of South Carolina for the use of their frigate, to Mr. Gardoqui, and to the Delegates of South Carolina in Congress.
I had the honor to inform you in my last letter, of the parliament’s being transferred to Troyes. To put an end to the tumults in Paris, some regiments were brought nearer, the patroles were strengthened and multiplied, some mutineers punished by imprisonment: it produced the desired effect. It is confidently believed, however, that the parliament will be immediately recalled, the stamp tax and land tax repealed, and other means devised of accommodating their receipts and expenditures. Those supposed to be in contemplation, are, a rigorous levy of the old tax of the deux vingtiemes, on the rich, who had, in a great measure, withdrawn their property from it, as well as on the poor, on whom it had principally fallen. This will greatly increase the receipts: while they are proceeding on the other hand, to reform their expenses far beyond what they had promised. It is said these reformations will amount to eighty millions. Circumstances render these measures more and more pressing. I mentioned to you in my last letter, that the officer charged by the ministry to watch the motion of the British squadron, had returned with information that it had sailed westwardly. The fact was not true. He had formed his conclusion too hastily, and thus led the ministry into error. The King of Prussia, urged on by England, has pressed more and more the affairs of Holland and lately has given to the States General of Holland four days only to comply with his demand. This measure would, of itself, have rendered it impossible for France to proceed longer in the line of accommodation with Prussia. In the same moment, an event takes place, which seems to render all attempt at accommodation idle. The Turks have declared war against the Russians, and that under circumstances which exclude all prospect of preventing its taking place. The King of Prussia having deserted his ancient friends, there remain only France and Turkey, perhaps Spain also, to oppose the two empires, Prussia and England. By such a piece of Quixotism, France might plunge herself into ruin with the Turks and Dutch, but would save neither. But there is certainly a confederacy secretly in contemplation, of which the public have not yet the smallest suspicion; that is between France and the two empires. I think it sure that Russia has desired this, and that the Emperor, after some hesitation, has acceded. It rests on this country to close. Her indignation against the King of Prussia will be some spur. She will thereby save her party in Holland, and only abandon the Turks to that fate she cannot ward off, and which their precipitation has brought on themselves, by the instigation of the English ambassador at the Porte, and against the remonstrances of the French ambassador. Perhaps this formidable combination, should it take place, may prevent the war of the western powers, as it would seem that neither England nor Prussia would carry their false calculations so far, as, with the aid of the Turks only, to oppose themselves to such a force. In that case, the Patriots of Holland would be peaceably established in the powers of their government, and the war go on against the Turks only, who would probably be driven from Europe. This new arrangement would be a total change of the European system, and a favorable one for our friends. The probability of a general war, in which this country would be engaged on one side, and England on the other, has appeared to me sufficient to justify my writing to our agents in the different ports of France, to put our merchants on their guard, against risking their property in French or English bottoms. The Emperor, instead of treading back his steps in Brabant, as was expected, has pursued the less honorable plan of decoying his subjects thence by false pretences, to let themselves be invested by his troops, and this done, he dictates to them his own terms. Yet it is not certain the matter will end with that.
The Count De Moustier is nominated Minister Plenipotentiary to America; and a frigate is ordered to Cherbourg, to carry him over. He will endeavor to sail by the middle of the next month, but if any delay should make him pass over the whole of October, he will defer his voyage to the spring, being unwilling to undertake a winter passage. Monsieur de St. Priest is sent ambassador to Holland, in the room of Monsieur de Verac, appointed to Switzerland. The Chevalier de Luzerne might, I believe,have gone to Holland, but he preferred a general promise of promotion, and the possibility that it might be to the court of London. His prospects are very fair. His brother, the Count de la Luzerne, (now Governor in the West Indies) is appointed minister of the marine, in the place of Monsieur de Castries, who has resigned. The Archbishop of Toulouse is appointed ministre principal, and his brother Monsieur de Brienne, minister of war, in the place of Monsieur de Segur. The department of the Comptroller has had a very rapid succession of tenants. From Monsieur de Calonne it passed to Monsieur de Forqueux, from him to Villedeuil, and from him to Lambert, who holds it at present, but divided with a Monsieur Cabarrus (whom I believe you knew in Spain), who is named Directeur du tresor royal, the office into which M. Necker came at first. I had the honor to inform you, that before the departure of the Count de Luzerne to his government in the West Indies, I had pressed on him the patronage of our trade with the French islands; that he appeared well disposed, and assured me he would favor us as much as his instructions, and the laws of the colonies, would permit. I am in hopes, these dispositions will be strengthened by his residence in the islands, and that his acquaintance among the people there will be an additional motive to favor them. Probably they will take advantage of his appointment, to press indulgences in commerce with us. The ministry is of a liberal complexion, and well disposed to us. The war may add to the motives for opening their islands to other resources for their subsistence, and for doing what may be agreeable to us. It seems to me at present, then, that the moment of the arrival of the Count de la Luzerne will be the moment for trying to obtain a freer access to their islands. It would be very material to do this, if possible, in a permanent way, that is to say, by treaty. But I know of nothing we have to offer in equivalent. Perhaps the payment of our debt to them might be made use of as some inducement, while they are so distressed for money. Yet the borrowing the money in Holland will be rendered more difficult by the same event, in proportion as it will increase the demand for money by other powers.
The gazettes of Ley den and France, to this date, are enclosed, together with some pamphlets on the internal affairs of this country.
I have the honor to be, with sentiments of the most perfect esteem and respect, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO CHARLES THOMSON.
Paris, September 20, 1787.
Dear Sir,
Your favor of April the 28th did not come to my hands till the 1st instant. Unfortunately, the boxes of plants, which were a day too late to come by the April packet, missed the packet of June the 10th also, and only came by that of July the 25th. They are not yet arrived at Paris, but I expect them daily. I am sensible of your kind attention to them, and that as you were leaving New York, you took the course which bade fair to be the best. That they were forgotten in the hands in which you placed them, was probably owing to much business, and more important. I have desired Mr. Madison to refund to you the money, you were so kind as to advance for me. The delay of your letter will apologize for this delay of the repayment. I thank you also, for the extract of the letter you were so kind as to communicate to me, on the antiquities found in the western country. I wish that the persons who go thither, would make very exact descriptions of what they see of that kind, without forming any theories. The moment a person forms a theory, his imagination sees in every object, only the traits which favor that theory. But it is too early to form theories on those antiquities. We must wait with patience till more facts are collected. I wish your Philosophical Society would collect exact descriptions of the several monuments as yet known, and insert them naked in their Transactions, and continue their attention to those hereafter to be discovered. Patience and observation may enable us, in time, to solve the problem, whether those who formed the scattering monuments in our western country, were colonies sent off from Mexico or the founders of Mexico itself; whether both were the descendants or the progenitors of the Asiatic red men. The Mexican tradition, mentioned by Dr. Robertson, is an evidence, but a feeble one, in favor of the one opinion. The number of languages radically different, is a strong evidence in favor of the contrary one. There is an American by the name of Ledyard, he who was with Captain Cook on his last voyage, and wrote an account of that voyage, who has gone to St. Petersburg; from thence he was to go to Kamtschatka; to cross over thence to the northwest coast of America, and to penetrate through the main continent, to our side of it. He is a person of ingenuity and information. Unfortunately, he has too much imagination. However, if he escapes safely, he will give us new, curious, and useful information. I had a letter from him, dated last March, when he was about to leave St. Petersburg on his way to Kamtschatka.
With respect to the inclination of the strata of rocks, I had observed them between the Blue Ridge and North Mountains in Virginia, to be parallel with the pole of the earth. I observed the same thing in most instances in the Alps, between Cette and Turin: but in returning along the precipices of the Apennines, where they hang over the Mediterranean, their direction was totally different and various: and you mention, that in our western country, they are horizontal. This variety proves they have not been formed by subsidence, as some writers of theories of the earth have pretended; for then they should always have been in circular strata, and concentric. It proves, too, that they have not been formed by the rotation of the earth on its axis, as might have been suspected, had all these strata been parallel with that axis. They may, indeed, have been thrown up by explosions, as Whitehurst supposes, or have been the effect of convulsions. But there can be no proof of the explosion, nor is it probable that convulsions have deformed every spot of the earth. It is now generally agreed that rock grows, and it seems that it grows in layers in every direction, as the branches of trees grow in all directions. Why seek further the solution of this phenomenon? Every thing in nature decays. If it were not reproduced then by growth, there would be a chasm.
I remember you asked me in a former letter, whether the steam-mill in London was turned by the steam immediately, or by the intermediate agency of water raised by the steam. When I was in London, Boulton made a secret of his mill. Therefore, I was permitted to see it only superficially. I saw no water-wheels, and therefore supposed none. I answered you, accordingly, that there were none. But when I was at Nismes, I went to see the steam-mill there, and they showed it to me in all its parts. I saw that their steam raised water, and that this water turned a wheel. I expressed my doubts of the necessity of the inter-agency of water, and that the London mill was without it. But they supposed me mistaken; perhaps I was so: I have had no opportunity since of clearing up the doubt.
I had a letter from Mr. Churchman, but not developing his plan of knowing the longitude, fully. I wrote him what was doubted about it, so far as we could conjecture what it was.
I am with very great and sincere esteem, Dear Sir, your friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN JAY.
Paris, September 22,1787.
Sir,
The letters of which the inclosed are copies, are this moment received, and as there is a possibility that they may reach Havre before the packet sails, I have the honor of enclosing them to you. They contain a promise of reducing the duties on tar, pitch, and turpentine, and that the government will interest itself with the city of Rouen, to reduce the local duty on potash. By this you will perceive, that we are getting on a little in this business, though under their present embarrassments, it is difficult to procure the attention of the ministers to it. The parliament has enregistered the edict for a rigorous levy of the deux vingtièmes. As this was proposed by the King in lieu of the impôt territorial, there is no doubt now, that the latter, with the stamp tax, will be immediately repealed. There can be no better proof of the revolution in the public opinion, as to the powers of the monarch, and of the force, too, of that opinion. Six weeks ago, we saw the King displaying the plenitude of his omnipotence, as hitherto conceived, to enforce these two acts. At this day, he is forced to retract them by the public voice; for as to the opposition of the parliamemt, that body is too little esteemed to produce this effect in any case, where the public do not throw themselves into the same scale.
I have the honor to be, with the most perfect esteem and respect, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
Paris, September 22, 1787.
Sir,
When I had the honor of addressing you this morning, intelligence was handing about, which I did not think well enough authenticated to communicate to you. As it is now ascertained, I avail myself of the chance that another post may yet reach Havre, before the departure of the packet. This will depend on the wind, which has for some days been unfavorable. I must premise that this court, about ten days ago, declared, by their Chargé des Affaires in Holland, that if the Prussian troops continued to menace Holland with an invasion, his Majesty was determined, in quality of ally, to succor that province. An official letter from the Hague, of the 18th instant, assures that the Prussian army entered the territory of Holland on the 15th, that most of the principal towns had submitted, some after firing a gun or two, others without resistance: that the Rhingrave de Salm had evacuated Utrecht, with part of the troops under his command, leaving behind him one hundred and forty-four pieces of cannon, with great warlike stores: that the standard of Orange was hoisted every where: that no other cockade could be worn at the Hague: that the States General were to assemble that night for reinstating the Stadtholder in all his rights. The letter concludes, ‘We have this moment intelligence that Woerden has capitulated; so that Amsterdam remains without defence.’ So far the letter. We know, otherwise, that Monsieur de St. Priest, who had set out on his embassy to the Hague, has stopped at Antwerp, not choosing to proceed further till new orders. This Court has been completely deceived, first by its own great desire to avoid a war, and secondly by calculating that the King of Prussia would have acted on principles of common sense, which would surely have dictated, that a power, lying between the jaws of Russia and Austria, should not separate itself from France, unless, indeed, he had assurances of dispositions in those two powers, which are not supposed to exist. On the contrary, I am persuaded that they ask the alliance of France, whom we suppose to be under hesitations between her reluctance to abandon the Turks, her jealousy of increasing by their spoils the power of the two empires, and her inability to oppose them. If they cannot obtain her alliance, they will surely join themselves to England and Prussia.
Official advices are received, that the first division of the Russian army has passed the Borysthenes into the Polish Ukraine, and is marching towards the frontiers of Turkey. Thus, we may consider the flames of war as completely kindled in two distinct parts of this quarter of the globe, and that though France and England have not yet engaged themselves in it, the probabilities are that they will do it.
I have the honor to be, with the most perfect esteem and respect, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MR. CARNES.
Paris, September 22, 1787.
Sir,
I am honored by your favor of the 17th instant. A war between France and England does not necessarily engage America in it; and I think she will be disposed rather to avail herself of the advantages of a neutral power. By the former usage of nations, the goods of a friend were safe, though taken in an enemy bottom, and those of an enemy were lawful prize, though found in a free bottom. But in our treaties with France, &c. we have established the simpler rule, that a free bottom makes free goods, and an enemy bottom, enemy goods. The same rule has been adopted by the treaty of armed neutrality between Russia, Sweden, Denmark, Holland, and Portugal, and assented to by France and Spain. Contraband goods, however, are always excepted, so that they may still be seized; but the same powers have established that naval stores are not contraband: and this may be considered now as the law of nations. Though England acquiesced under this during the late war, rather than draw on herself the neutral powers, yet she never acceded to the new principle, and her obstinacy on this point is what has prevented the late renewal of her treaty with Russia. On the commencement of a new war, this principle will probably be insisted on by the neutral powers, whom we may suppose to be Sweden, Denmark, Portugal, America, and perhaps Spain. Quere; if England will again acquiesce. Supposing these details might be useful to you, I have taken the liberty of giving them, and of assuring you of the esteem with which I am, Sir, your very humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN JAY.
Paris, September 24, 1787.
Sir,
The times are now so critical, that every day brings something new and important, not known the day before. Observing the wind still unfavorable, I am in hopes the packet may not sail to-morrow, and that this letter may be at Havre in time for that conveyance. Mr. Eden has waited on Count Montmorin to inform him, officially, that England must consider its convention with France, relative to the giving notice of its naval armaments, as at an end, and that they are arming generally. This is considered here as a declaration of war. The Dutch ambassador told me yesterday, that he supposed the Prussian troops probably in possession of the Hague. I asked him if it would interrupt the course of business, commercial or banking, in Amsterdam; and particularly, whether our depot of money there was safe. He said, the people of Amsterdam would be surely so wise as to submit, when they should see that they could not oppose the Stadtholder: therefore he supposed our depot safe, and that there would be no interruption of business. It is the hour of the departure of the post: so I have only time to add assurances of the respect and esteem, with which I have the honor to be, Sir, your most obedient, humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN ADAMS.
Paris, September 28, 1787.
Dear Sir,
I received your favor by Mr. Cutting, and thank you sincerely for the copy of your book. The departure of a packet-boat, which always gives me full employment for some time before, has only permitted me to look into it a little. I judge of it from the first volume, which I thought formed to do a great deal of good. The first principle of a good government, is certainly a distribution of its powers into executive, judiciary, and legislative, and a subdivision of the latter into two or three branches. It is a good step gained, when it is proved that the English constitution, acknowledged to be better than all which have preceded it, is only better, in proportion as it has approached nearer to this distribution of powers. From this, the last step is easy, to show by a comparison of our constitutions with that of England, how much more perfect they are. The article of Confederations is certainly worthy of your pen. It would form a most interesting addition, to show, what has been the nature of the Confederations which have existed hitherto, what were their excellencies, and what their defects.
A comparison of ours with them would be to the advantage of ours, and would increase the veneration of our countrymen for it. It is a misfortune, that they do not sufficiently know the value of their constitutions, and how much happier they are rendered by them, than any other people on earth, by the governments under which they live.
You know all that has happened in the United Netherlands. You know also that our friends, Van Staphorsts, will be among the most likely to become objects of severity, if any severities should be exercised. Is the money in their hands entirely safe? If it is not, I am sure you have already thought of it. Are we to suppose the game already up, and that the Stadtholder is to be reestablished, perhaps erected into a monarch, without the country lifting a finger in opposition to it? If so, it is a lesson the more for us. In fact, what a crowd of lessons do the present miseries of Holland teach us? Never to have an hereditary officer of any sort: never to let a citizen ally himself with kings: never to call in foreign nations to settle domestic differences: never to suppose that any nation will expose itself to war for us, &c. Still I am not without hopes, that a good rod is in soak for Prussia, and that England will feel the end of it. It is known to some, that Russia made propositions to the Emperor and France, for acting in concert; that the Emperor consents, and has disposed four camps of one hundred and eighty thousand men, from the limits of Turkey to those of Prussia. This court hesitates, or rather its Premier hesitates; for the Queen, Montmorin, and Breteuil are for the measure. Should it take place, all may yet come to rights, except for the Turks, who must retire from Europe, and this they must do, were France Quixotic enough to undertake to support them. We, I hope, shall be left free to avail ourselves of the advantages of neutrality: and yet, much I fear, the English, or rather their stupid King, will force us out of it. For thus I reason. By forcing us into the war against them, they will be engaged in an expensive land war, as well as a sea war. Common sense dictates, therefore, that they should let us remain neuter: ergo, they will not let us remain neuter. I never yet found any other general rule for foretelling what they will do, but that of examining what they ought not to do.
I have the honor to be, with my best respects to Mrs. Adams, and sentiments of perfect esteem and regard to yourself, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson
TO COLONEL SMITH.
Paris, September 28,1787.
Dear Sir,
I have duly received your favor by Mr. Cutting. I had before had a transient acquaintance with him, and knew him to be sensible. Your recommendation is always a new merit. I really think, and had taken the liberty some time ago of hinting to Congress, that they would do well to have a diplomatic character at Lisbon. There is no country whose commerce is more interesting to us. I wish Congress would correspond to the wishes of that court, in sending a person there, and to mine, in sending yourself. For I confess, I had rather see you there than at London, because I doubt whether it be honorable for us to keep any body at London, unless they keep some person at New York. Of all nations on earth, they require to be treated with the most hauteur. They require to be kicked into common good manners. You ask, if you shall say any thing to Sullivan about the bill. No. Only that it is paid. I have, within these two or three days, received letters from him explaining the matter. It was really for the skin and bones of the moose, as I had conjectured. It was my fault, that I had not given him a rough idea of the expense I would be willing to incur for them. He had made the acquisition an object of a regular campaign, and that too of a winter one. The troops he employed sallied forth, as he writes me, in the month of March—much snow—a herd attacked—one killed—in the wilderness—a road to cut twenty miles—to be drawn by hand from the frontiers to his house—bones to be cleaned, &c. &c. &c. In fine, he put himself to an infinitude of trouble, more than I meant: he did it cheerfully, and I feel myself really under obligations to him. That the tragedy might not want a proper catastrophe, the box, bones, and all are lost: so that this chapter of Natural History will still remain a blank. But I have written to him not to send me another. I will leave it for my successor to fill up, whenever I shall make my bow here. The purchase for Mrs. Adams shall be made, and sent by Mr. Cutting. I shall always be happy to receive her commands. Petit shall be made happy by her praises of his last purchase for her. I must refer you to Mr. Adams for the news. Those respecting the Dutch you know as well as I. Nor should they be written but with the pen of Jeremiah. Adieu, mon ami! Yours affectionately,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MONSIEUR LE COMTE DE BUFFON.
Paris, October 3, 1787.
Sir,
I had the honor of informing you, some time ago, that I had written to some of my friends in America, desiring they would send me such of the spoils of the moose, caribou, elk, and deer, as might throw light on that class of animals; but more particularly, to send me the complete skeleton, skin, and horns of the moose, in such condition as that the skin might be sewed up and stuffed, on its arrival here. I am happy to be able to present to you at this moment, the bones and skin of a moose, the horns of another individual of the same species, the horns of the caribou, the elk, the deer, the spiked-horned buck, and the roebuck of America. They all come from New Hampshire and Massachusetts, and were received by me yesterday. I give you their popular names, as it rests with yourself to decide their real names. The skin of the moose was dressed with the hair on, but a great deal of it has come off, and the rest is ready to drop off. The horns of the elk are remarkably small. I have certainly seen some of them, which would have weighed five or six times as much. This is the animal which we call elk in the southern parts of America, and of which I have given some description in the Notes on Virginia, of which I had the honor of presenting you a copy. I really doubt, whether the flat-horned elk exists in America: and I think this may be properly classed with the elk, the principal difference being in the horns. I have seen the daim, the cerf, the chevreuil, of Europe. But the animal we call elk, and which may be distinguished as the round-horned elk, is very different from them. I have never seen the brand-hirtz or cerf d’Ardennes, nor the European elk. Could I get a sight of them, I think I should be able to say which of them the American elk resembles most, as I am tolerably well acquainted with that animal. I must observe, also, that the horns of the deer, which accompany these spoils, are not of the fifth or sixth part of the weight of some that I have seen. This individual has been of three years of age, according to our method of judging. I have taken measures, particularly, to be furnished with large horns of our elk and our deer, and therefore beg of you not to consider those now sent, as furnishing a specimen of their ordinary size. I really suspect you will find that the moose, the round-horned elk, and the American deer are species not existing in Europe. The moose is, perhaps, of a new class. I wish these spoils, Sir, may have the merit of adding any thing new to the treasures of nature, which have so fortunately come under your observation, and of which she seems to have given you the key: they will in that case be some gratification to you, which it will always be pleasing to me to have procured; having the honor to be, with sentiments of the most perfect esteem and respect, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MR. DUMAS.
Paris, October 4,1787.
Sir,
I received your favor of the 23rd of September two days ago. That of the 28th and 29th was put in my hands this morning. I immediately waited on the ambassadors, ordinary and extraordinary, of the United Netherlands, and also on the envoy of Prussia, and asked their good offices to have an efficacious protection extended to your person, your family, and your effects, observing, that the United States know no party, but are the friends and allies of the United Netherlands as a nation, and would expect from their friendship, that the person who is charged with their affairs, until the arrival of a minister, should be covered from all insult and injury, which might be offered him by a lawless mob; well assured that their minister, residing with Congress, would on all occasions receive the same. They have been so good as to promise me, each, that he will in his first despatches press this matter on the proper power, and give me reason to hope that it will be efficacious for your safety. I will transmit your letter to Mr. Jay by the Count de Moustier, who sets out within a week for New York, as Minister Plenipotentiary for France, in that country. I sincerely sympathize in your sufferings, and wish that what I have done may effect an end to them; being with much respect and esteem, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN JAY.
Paris, October 8, 1787.
Sir,
I had the honor of writing you on the 19th of September, twice on the 22nd, and again on the 24th. The two first went by the packet, the third by a vessel bound to Philadelphia. I have not yet learned by what occasion the last went. In these several letters, I communicated to you the occurrences of Europe, as far as they were then known. Notwithstanding the advantage which the Emperor seemed to have gained over his subjects of Brabant, by the military arrangements he had been permitted to make under false pretexts, he has not obtained his ends. He certainly wished to enforce his new regulations; but he wished more to be cleared of all domestic difficulties, that he might be free to act in the great scenes which are preparing for the theatre of Europe. He seems, therefore, to have instructed his Governor General of the Netherlands to insist on compliance as far as could be insisted, without producing resistance by arms; but at the same time, to have furnished him with a sufficiently complete recantation, to prevent the effects of insurrection. The Governor pressed; the people were firm; a small act of force was then attempted, which produced a decided resistance, in which the people killed several of the military: the last resource was then used, which was the act of recantation; this produced immediate tranquillity, and every thing there is now finally settled, by the Emperor’s relinquishment of his plans.
My letter of the evening of September the 22nd informed you that the Prussian troops had entered Holland, and that of the 24th, that England had announced to this court that she was arming generally. These two events being simultaneous, proved that the two sovereigns acted in concert. Immediately after, the court of London announced to the other courts of Europe, that if France entered Holland with armed force, she would consider it as an act of hostility, and declare war against her; sending Mr. Grenville here, at the same time, to make what she called a conciliatory proposition. This proposition was received as a new insult, Mr. Grenville very coolly treated, and he has now gone back. It is said, he has carried the ultimatum of France. What it is, particularly, has not transpired; it is only supposed, in general, to be very firm. You will see, in one of the Leyden gazettes, one of the letters written by the ministers of England to the courts of their respective residence, communicating the declaration before mentioned. In the mean time, Holland has been sooner reduced by the Prussian troops, than could have been expected. The abandonment of Utrecht by the Rhingrave of Salm, seems to have thrown the people under a general panic, during which every place submitted, except Amsterdam. That had opened conferences with the Duke of Brunswick; but as late as the 2nd instant, no capitulation was yet concluded. The King of Prussia, on his first move, demanded categorically of the King of Poland, what part he intended to act in the event of war. The latter answered, he should act as events should dictate; and is, in consequence of this species of menace from Prussia, arming himself. He can bring into the field about seventy thousand good cavalry. In the mean time, though nothing transpires publicly of the confederation between France and the two empires, mentioned in my letter of September the 19th, it is not the less sure that it is on the carpet, and will take place. To the circumstances before mentioned, may be added, as further indications of war, the naming as Generalissimo of their marine on the Atlantic, Monsieur de Suffrein, on the Mediterranean, Monsieur Albert de Rioms, the recalling Monsieur de St. Priest, their ambassador, from Antwerp, before he had reached the Hague, and the activity of their armies by sea. On the other hand, the little movement by land would make one suppose they expected to put the King of Prussia into other hands. They too, like the Emperor, are arranging matters at home. The rigorous levy of the deux vingtiemes is enregistered, the stamp act and impot territorial are revoked, the parliament recalled, the nation soothed by these acts, and inspired by the insults of the British court. The part of the Council still leaning towards peace are become unpopular, and perhaps may feel the effects of it. No change in the administration has taken place since my last, unless we may consider as such, Monsieur Cabarrus’s refusal to stand in the lines. Thinking he should be forced to follow, too seriously, plans formed by others, he has declined serving.
Should this war take place, as is quite probable, and should it be as general as it threatens to be, our neutrality must be attended with great advantages. Whether of a nature to improve our morals or our happiness, is another question. But is it sure that Great Britain, by her searches, her seizures, and other measures for harassing us, will permit us to preserve our neutrality? I know it may be argued, that the land-war, which she would superadd to her sea-war, by provoking us to join her enemies, should rationally hold her to her good behavior with us. But since the accession of the present monarch, has it not been passion, and not reason, which, nine times out of ten, has dictated her measures? Has there been a better rule of prognosticating what he would do, than to examine what he ought not to do? When I review his dispositions and review his conduct, I have little hope of his permitting our neutrality. He will find subjects of provocation in various articles of our treaty with France, which will now come into view, in all their consequences, and in consequences very advantageous to the one, and injurious to the other country. I suggest these doubts, on a supposition that our magazines are not prepared for war, and in the opinion that provisions for that event should be thought of.
The enclosed letter from Mr. Dumas came to me open, though directed to you. I immediately waited on the ambassadors, ordinary and extraordinary, of Holland, and the envoy of Prussia, and prayed them to interest themselves to have his person, his family, and his goods protected. They promised me readily to do it, and have written accordingly; I trust it will be with effect. I could not avoid enclosing you the letter from Monsieur Bouebe, though I have satisfied him he is to expect nothing from Congress for his inventions. These are better certified than most of those things are; but if time stamps their worth, time will give them to us. He expects no further answer. The gazettes of Leyden and France to this date accompany this, which will be delivered you by the Count de Moustier, Minister Plenipotentiary from this country.
I have the honor to be, with sentiments of the most perfect esteem and respect, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JAMES MADISON.
Paris, October 8, 1787.
Dear Sir,
The bearer hereof, the Count de Moustier, successor to Monsieur de la Luzerne, would, from his office, need no letter of introduction to you or to any body. Yet I take the liberty of recommending him to you, to shorten those formal approaches, which the same office would otherwise expose him to, in making your acquaintance. He is a great enemy to formality, etiquette, ostentation, and luxury. He goes with the best dispositions to cultivate society, without poisoning it by ill example. He is sensible, disposed to view things favorably, and being well acquainted with the constitution of England, her manners, and language, is the better prepared for his station with us. But I should have performed only the lesser, and least pleasing half of my task, were I not to add my recommendations of Madame de Brehan. She is goodness itself. You must be well acquainted with her. You will find her well disposed to meet your acquaintance, and well worthy of it. The way to please her, is to receive her as an acquaintance of a thousand years’ standing. She speaks little English. You must teach her more, and learn French from her. She hopes, by accompanying Monsieur de Moustier, to improve her health, which is very feeble, and still more, to improve her son in his education, and to remove him to a distance from the seductions of this country. You will wonder to be told, that there are no schools in this country to be compared to ours in the sciences. The husband of Madame de Brehan is an officer, and obliged by the times to remain with the army. Monsieur de Moustier brings your watch. I have worn it two months, and really find it a most incomparable one. It will not want the little re-dressing, which new watches generally do, after going about a year. It costs six hundred livres. To open it in all its parts, press the little pin on the edge with the point of your nail; that opens the crystal; then open the dial-plate in the usual way; then press the stem, at the end within the loop, and it opens the back for winding up or regulating.
De Moustier is remarkably communicative. With adroitness he may be pumped of any thing. His openness is from character, not from affectation. An intimacy with him may, on this account, be politically valuable.
I am, Dear Sir, your affectionate friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN JAY.
(Private.) Paris, October 8, 1787.
Dear Sir,
The Count de Moustier, Minister Plenipotentiary from the court of Versailles to the United States, will have the honor of delivering you this. The connection of your offices will necessarily connect you in acquaintance; but I beg leave to present him to you, on account of his personal as well as his public character. You will find him open, communicative, candid, simple in his manners, and a declared enemy to ostentation and luxury. He goes with a resolution to add no aliment to it by his example, unless he finds that the dispositions of our countrymen require it indispensably. Permit me, at the same time, to solicit your friendly notice, and through you, that also of Mrs. Jay, to Madame la Marquise de Brehan, sister-in-law to Monsieur de Moustier. She accompanies him, in hopes that a change of climate may assist her feeble health, and also, that she may procure a more valuable education for her son, and safer from seduction, in America than in France. I think it impossible to find a better woman, more amiable, more modest, more simple in her manners, dress, and way of thinking. She will deserve the friendship of Mrs. Jay, and the way to obtain hers, is to receive her and treat her without the shadow of etiquette.
The Count d’Aranda leaves us in a day or two. He desired me to recall him to your recollection, and to assure you of his friendship. In a letter which I mean as a private one, I may venture details too minute for a public one, yet not unamusing, or unsatisfactory. I may venture names too, without the danger of their getting into a newspaper. There has long been a division in the Council here, on the question of war and peace. Monsieur de Montmorin and Monsieur de Breteuil have been constantly for war. They are supported in this by the Queen. The King goes for nothing. He hunts one half the day, is drunk the other, and signs whatever he is bid. The Archbishop of Toulouse desires peace. Though brought in by the Queen, he is opposed to her in this capital object, which would produce an alliance with her brother. Whether the Archbishop will yield or not, I know not. But an intrigue is already begun for ousting him from his place, and it is rather probable it will succeed. He is a good and patriotic minister for peace, and very capable in the department of finance. At least he is so in theory. I have heard his talents for execution censured.
Can I be useful here to Mrs. Jay or yourself, in executing any commissions, great or small? I offer you my services with great cordiality. You know whether any of the wines of this country may attract your wishes. In my tour, last spring, I visited the best vineyards of Burgundy, Cote-rotie, Hermitage, Lunelle, Frontignan, and white and red Bordeaux, got acquainted with the proprietors, and can procure for you the best crops from the vigneron himself. Mrs. Jay knows if there is any thing else here, in which I could be useful to her. Command me without ceremony, as it will give me real pleasure to serve you; and be assured of the sincere attachment and friendship, with which I am, Dear Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MONSIEUR LE COMTE DE MOUSTIER.
Paris, October 9,1787.
Mr. Jefferson has the honor of presenting his respects to Monsieur le Comte de Moustier, and of taking leave of him by letter, which he is prevented doing in person, by an unexpected visit to Versailles to-day. He will hope to have the pleasure of sometimes hearing from him, and will take the liberty occasionally, of troubling him with a letter. He considers the Count de Moustier as forming with himself the two end Blinks of that chain which holds the two nations together, and is happy to have observed in him dispositions to strengthen rather than to weaken it. It is a station of importance, as on the cherishing good dispositions and quieting bad ones, will depend in some degree the happiness and prosperity of the two countries. The Count de Moustier will find the affections of the Americans with France, but their habits with England. Chained to that country by circumstances, embracing what they loathe, they realize the fable of the living and the dead bound together. Mr. Jefferson troubles the Count de Moustier with two letters, to gentlemen whom he wishes to recommend to his particular acquaintance, and to that of Madame de Brehan. He bids Monsieur de Moustier a most friendly adieu, and wishes him every thing which may render agreeable his passage across the water, and his residence beyond it.
TO MADAME DE BREHAN.
Paris, October 9, 1787.
Persuaded, Madam, that visits at this moment must be troublesome I beg you to accept my adieus, in this form. Be assured, that no one mingles with them more regret at separating from you. I will ask your permission to inquire of you by letter sometimes, how our country agrees with your health and your expectations, and will hope to hear it from yourself. The imitation of European manners, which you will find in our towns, will, I fear, be little pleasing. I beseech you to practise still your own, which will furnish them a model of what is perfect. Should you be singular, it will be by excellence, and after a while you will see the effect of your example.
Heaven bless you, Madam, and guard you under all circumstances; give you smooth waters, gentle breezes, and clear skies, hushing all its elements into peace, and leading with its own hand the favored bark, till it shall have safely landed its precious charge on the shores of our new world.
Th: Jefferson.
TO MR. DUMAS.
Paris, October 14, 1787.
Sir,
I have duly received your favors of October the 23rd and 26th. With respect to the mission you suggest, in the former, no powers are lodged in the hands of Mr. Adams and myself. Congress commissioned Mr. Adams, Doctor Franklin, and myself, to treat with the Emperor on the subjects of amity and commerce: at the same time, they gave us the commission to Prussia, with which you are acquainted. We proposed treating through the Imperial ambassador here. It was declined on their part, and our powers expired, having been given but for two years. Afterwards, the same ambassador here was instructed to offer to treat with us. I informed him our powers were expired, but that I would write to Congress on the subject. I did so, but have never yet received an answer. Whether this proceeds from a change of opinion in them, or from the multiplicity of their occupations, I am unable to say: but this state of facts will enable you to see that we have no powers, in this instance, to take the measures you had thought of. I sincerely sympathize with you in your sufferings. Though forbidden by my character to meddle in the internal affairs of an allied State, it is the wish of my heart that their troubles may have such an issue, as will secure the greatest degree of happiness to the body of the people: for it is with the mass of the nation we are allied, and not merely with their governors. To inform the minds of the people, and to follow their will, is the chief duty of those placed at their head. What party in your late struggles was most likely to do this, you are more competent to judge than I am. Under every event, that you maybe safe and happy, is the sincere wish of him, who has the honor to be, with sentiments of great esteem, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MADAME DE CORNY.
Paris, October 18, 1787.
I now have the honor, Madam, to send you the Memoire of M. de Calonne. Do not injure yourself by hurrying its perusal. Only, when you shall have read it at your ease, be so good as to send it back, that it may be returned to the Duke of Dorset. You will read it with pleasure. It has carried comfort to my heart, because it must do the same to the King and the nation. Though it does not prove M. de Calonne to be more innocent than his predecessors, it shows him not to have been that exaggerated scoundrel, which the calculations and the clamors of the public have supposed. It shows that the public treasures have not been so inconceivably squandered, as the parliaments of Grenoble, Toulouse, &c. had affirmed. In fine, it shows him less wicked, and France less badly governed, than I had feared. In examining my little collection of books, to see what it could furnish you on the subject of Poland, I find a small piece which may serve as a supplement to the history I had sent you. It contains a mixture of history and politics, which I think you will like—How do you do this morning? I have feared you exerted and exposed yourself too much yesterday. I ask you the question, though I shall not await its answer. The sky is clearing, and I shall away to my hermitage. God bless you, my Dear Madam, now and always. Adieu.
Th: Jefferson.
TO THE COUNT DE MONTMORIN.
Paris, October 23, 1787.
Sir,
I take the liberty of troubling your Excellency on the subject of the Arrêt, which has lately appeared, for prohibiting the importation of whale-oils and spermaceti, the produce of foreign fisheries. This prohibition, being expressed in general terms, seems to exclude the whale-oils of the United States of America, as well as of the nations of Europe. The uniform disposition, however, which his Majesty and his ministers have shown to promote the commerce between France and the United States, by encouraging our productions to come hither, and particularly those of our fisheries, induces me to hope, that these were not within their view, at the passing of this Arrêt. I am led the more into this opinion, when I recollect the assiduity exercised for several months, in the year 1785, by the committee appointed by government to investigate the objects of commerce of the two countries, and to report the encouragements of which it was susceptible; the result of that investigation, which his Majesty’s Comptroller General did me the honor to communicate, in a letter of the 22nd of October, 1786, stating therein the principles which should be established for the future regulation of that commerce, and particularly distinguishing the article of whale-oils by an abatement of the duties on them for the present, and a promise of farther abatement after the year 1790; the thorough re-investigation with which Monsieur de Lambert honored this subject when the letter of 1786 was to be put into the form of an Arrêt; that Arrêt itself, bearing date the 29th of December last, which ultimately confirmed the abatements of duty present and future, and declared that his Majesty reserved to himself to grant other favors to that production, if, on further information, he should find it for the interest of the two nations; and finally, the letter in which Monsieur de Lambert did me the honor to enclose the Arrêt, and to assure me, that the duties which had been levied on our whale-oils, contrary to the intention of the letter of 1786, should be restored. On a review, then, of all these circumstances, I cannot but presume, that it has not been intended to reverse, in a moment, views so maturely digested, and uniformly pursued; and that the general expressions of the Arrêt of September the 28th had within their contemplation the nations of Europe only. This presumption is further strengthened by having observed, that in the treaties of commerce, made since the epoch of our independence, the jura gentis amicissimcæ conceded to other nations, are expressly restrained to those of the ‘most favored European nation’: his Majesty wisely foreseeing that it would be expedient to regulate the commerce of a nation, which brings nothing but raw materials to employ the industry of his subjects, very differently from that of the European nations, who bring mostly what has already passed through all the stages of manufacture.
On these circumstances, I take the liberty of asking information from your Excellency, as to the extent of the late Arrêt: and if I have not been mistaken in supposing it did not mean to abridge that of December the 29th, I would solicit an explanatory Arrêt, to prevent the misconstruction of it, which will otherwise take place. It is much to be desired too, that this explanation could be given as soon as possible, in order that it may be handed out with the Arrêt of September the 28th. Great alarm may otherwise be spread among the merchants, and adventurers in the fisheries, who, confiding in the stability of regulations, which his Majesty’s wisdom had so long and well matured, have embarked their fortunes in speculations in this branch of business.
The importance of the subject to one of the principal members of our Union, induces me to attend with great anxiety the re-assurance from your Excellency, that no change has taken place in his Majesty’s views on this subject; and that his dispositions to multiply, rather than diminish, the combinations of interest between the two people, continue unaltered.
Commerce is slow in changing its channel. That between this country and the United States is as yet but beginning; and this beginning has received some checks. The Arrêt in question would be a considerable one, without the explanation I have the honor to ask. I am persuaded, that a continuation of the dispositions which have been hitherto manifested towards us, will insure effects, political and commercial, of value to both nations.
I have had too many proofs of the friendly interest your Excellency is pleased to take in whatever may strengthen the bands and connect the views of the two countries, to doubt your patronage of the present application; or to pretermit any occasion of repeating assurances of those sentiments of high respect and esteem, with which I have the honor to be
your Excellency’s most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN JAY.
Paris, November 3, 1787.
Sir,
My last letters to you were of the 8th and 27th of October. In the former? I mentioned to you the declaration of this country, that they would interpose with force, if the Prussian troops entered Holland; the entry of those troops into Holland; the declaration of England, that if France did oppose force, they would consider it as an act of war; the naval armaments on both sides; the nomination of the Bailli de Suffrein as Generalissimo on the ocean; and the cold reception of Mr. Grenville here, with his conciliatory propositions, as so many symptoms which seemed to indicate a certain and immediate rupture. It was indeed universally and hourly expected. But the king of Prussia, a little before these last events, got wind of the alliance on the carpet between France and the two empires: he awaked to the situation in which that would place him: he made some application to the court of St. Petersburg, to divert the Empress from the proposed alliance, and supplicated the court of London not to abandon him. That court had also received a hint of the same project; both seemed to suspect, for the first time, that it would be possible for France to abandon the Turks, and that they were likely to get more than they had played for at Constantinople: for they had meant nothing more there, than to divert the Empress and Emperor from the affairs of the west, by employing them in the east, and, at the same time, to embroil them with France as the patroness of the Turks. The court of London engaged not to abandon Prussia: but both of them relaxed a little the tone of their proceedings. The King of Prussia sent a Mr. Alvensleben here, expressly to explain and soothe: the King of England, notwithstanding the cold reception of his propositions by Grenville, renewed conferences here through Eden and the Duke of Dorset. The minister, in the affection of his heart for peace, readily joined in conference, and a declaration and counter-declaration were cooked up at Versailles, and sent to London for approbation. They were approved, arrived here at one o’clock the 27th, were signed that night at Versailles, and on the next day, I had the honor of enclosing them to you, under cover to the Count de Moustier, whom I supposed still at Brest, dating my letter as of the 27th, by mistake for the 28th. Lest, however, these papers should not have got to Brest before the departure of the Count de Moustier, I now enclose you other copies. The English declaration states a notification of this court, in September, by Barthelemy, their minister at London, ‘that they would send succors into Holland,’ as the first cause of England’s arming; desires an explanation of the intentions of this court, as to the affairs of Holland, and proposes to disarm; on condition, however, that the King of France shall not retain any hostile views in any quarter, for what has been done in Holland. This last phrase was to secure Prussia, according to promise. The King of France acknowledges the notification by his minister at London, promises he will do nothing in consequence of it, declares he has no intention to intermeddle with force in the affairs of Holland, and that he will entertain hostile views in no quarter, for what has been done there. He disavows having ever had any intention to interpose with force in the affairs of that republic. This disavowal begins the sentence, which acknowledges he had notified the contrary to the court of London, and it includes no apology to soothe the feelings which may be excited in the breasts of the Patriots of Holland, at hearing the King declare he never did intend to aid them with force, when promises to do this were the basis of those very attempts to better their constitution, which have ended in its ruin, as well as their own.
I have analyzed these declarations, because, being somewhat wrapped up in their expressions, their full import might escape, on a transient reading; and it is necessary it should not escape. It conveys to us the important lesson, that no circumstances of morality, honor, interest, or engagement, are sufficient to authorize a secure reliance on any nation, at all times, and in all positions. A moment of difficulty, or a moment of error, may render for ever useless the most friendly dispositions in the King, in the major part of his ministers, and the whole of his nation. The present pacification is considered by most, as only a short truce. They calculate on the spirit of the nation, and not on the aged hand which guides its movements. It is certain, that from this moment the whole system of Europe changes. Instead of counting together England, Austria, and Russia, as heretofore, against France, Spain, Holland, Prussia, and Turkey, the division will probably be, England, Holland, and Prussia, against France, Austria, Russia, and perhaps Spain. This last power is not sure, because the dispositions of its heir apparent are not sure. But whether the present be truce or peace, it will allow time to mature the conditions of the alliance between France and the two empires, always supposed to be on the carpet. It is thought to be obstructed by the avidity of the Emperor, who would swallow a good part of Turkey, Silesia, Bavaria, and the rights of the Germanic body. To the two or three first articles, France might consent, receiving in gratification a well rounded portion of the Austrian Netherlands, with the islands of Candia, Cyprus, Rhodes, and perhaps Lower Egypt. But all this is in embryo, uncertainly known, and counterworked by the machinations of the courts of London and Berlin. The following solution of the British armaments is supposed in a letter of the 25th ultimo, from Colonel Blachden of Connecticut, now at Dunkirk, to the Marquis de la Fayette. I will cite it in his own words. “A gentleman who left London two days ago, and came to this place to-day, informs me that it is now generally supposed that Mr. Pitt’s great secret, which has puzzled the whole nation so long, and to accomplish which design, the whole force of the nation is armed, is to make a vigorous effort for the recovery of America. When I recollect the delay they have made in delivering the forts in America, and that little more than a year ago, one of the British ministry wrote to the King a letter, in which were these remarkable words, ‘If your Majesty pleases, America may yet be yours;’ add to this, if it were possible for the present ministry in England to effect such a matter, they would secure their places and their power for a long time, and should they fail in the end, they would be certain of holding them during the attempt, which it is in their power to prolong as much as they please, and at all events, they would boast of having endeavored the recovery of what a former ministry had abandoned, it is possible.” A similar surmise has come in a letter from a person in Rotterdam to one at this place. I am satisfied that the King of England believes the mass of our people to be tired of their independence, and desirous of returning under his government; and that the same opinion prevails in the ministry and nation. They have hired their news-writers to repeat this lie in their gazettes so long, that they have become the dupes of it themselves. But there is no occasion to recur to this, in order to account for their arming. A more rational purpose avowed, that purpose executed, and when executed, a solemn agreement to disarm, seem to leave no doubt, that the re-establishment of the Stadtholder was their object. Yet it is possible, that having found that this court will not make war in this moment for any ally, new views may arise, and they may think the moment favorable for executing any purposes they may have, in our quarter. Add to this, that reason is of no aid in calculating their movements. We are, therefore, never safe till our magazines are filled with arms. The present season of truce, or peace, should, in my opinion, be improved without a moment’s respite, to effect this essential object, and no means be omitted, by which money may be obtained for the purpose. I say this, however, with due deference to the opinion of Congress, who are better judges of the necessity and practicability of the measure.
I mentioned to you, in a former letter, the application I had made to the Dutch ambassadors and Prussian envoy, for the protection of Mr. Dumas. The latter soon after received an assurance, that he was put under the protection of the States of Holland; and the Dutch ambassador called on me a few days ago, to inform me, by instruction from his constituents, ‘that the States General had received a written application from Mr. Adams, praying their protection of Dumas: that they had instructed their greffier, Fagel, to assure Mr. Adams, by letter, that he was under the protection of the States of Holland; but to inform him, at the same time, that Mr. Dumas’s conduct, out of the line of his office, had been so extraordinary, that they would expect de l’honnêteté de Mr. Adams, that he would charge some other person with the affairs of the United States, during his absence.’
Your letter, of September the 8th, has been duly received. I shall pay due attention to the instructions relative to the medals, and give any aid I can, in the case of Boss’s vessel. As yet, however, my endeavors to find Monsieur Pauly, avocat au conseil d’état, rue Coquilliere, have been ineffectual. There is no such person living in that street. I found a Monsieur Pauly, avocat au parlement, in another part of the town; he opened the letter, but said it could not mean him. I shall advertise in the public papers. If that fails, there will be no other chance of finding him. Mr. Warnum will do well, therefore, to send some other description by which the person may be found. Indeed some friend of the party interested should be engaged to follow up this business, as it will require constant attention, and probably a much larger sum of money than that named in the bill inclosed in Mr. Warnum’s letter.
I have the honor to enclose you a letter from O’Bryan to me, containing information from Algiers, and one from Mr. Montgomery at Alicant. The purpose of sending you this last, is to show you how much the difficulties of ransom are increased since the Spanish negotiations. The Russian captives have cost about eight thousand livres apiece, on an average. I certainly have no idea that we should give any such sum; and, therefore, if it should be the sense of Congress to give such a price, I would be glad to know it by instruction. My idea is, that we should not ransom but on the footing of the nation which pays least, that it may be as little worth their while to go in pursuit of us, as any nation. This is cruelty to the individuals now in captivity, but kindness to the hundreds that would soon be so, were we to make it worth the while of those pirates to go out of the Streights, in quest of us. As soon as money is provided, I shall put this business into train. I have taken measures to damp, at Algiers, all expectations of our proposing to ransom, at any price. I feel the distress which this must occasion to our countrymen there, and their connections; but the object of it is their ultimate good, by bringing down their holders to such a price as we ought to pay, instead of letting them remain in such expectations as cannot be gratified. The gazettes of France and Leyden accompany this.
I have the honor to be, with sentiments of the most perfect esteem and respect, Sir, your most obedient humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
[The annexed are translations of the declaration and
counter-declaration, referred to in the preceding letter.]
DECLARATION.
The events which have taken place in the republic of the United Provinces appearing no longer to leave any subject of discussion, and still less of dispute, between the two courts, the undersigned are authorized to ask, if it be the intention of his Most Christian Majesty to act in pursuance of the notification given, on the 16th of last month, by the Minister Plenipotentiary of his Most Christian Majesty, which, announcing his purpose of aiding Holland, has occasioned maritime armaments on the part of his Majesty, which armaments have become reciprocal.
If the court of Versailles is disposed to explain itself on this subject, and on the conduct adopted towards the republic, in a manner conformably to the desire, evinced by each party, to preserve a good understanding between the two courts, it being also understood, at the same time, that no hostile view is entertained, in any quarter, in consequence of the past; his Majesty, always eager to manifest his concurrence in the friendly sentiments of his Most Christian Majesty, agrees forthwith that the armaments, and, in general, all preparations for war, shall be mutually discontinued, and that the marines of the two nations shall be placed on the footing of a peace establishment, such as existed on the first of January of the present year.
Signed. Dorset Wm. Eden.
At Versailles, the 27th of October, 1787.
COUNTER-DECLARATION.
It neither being, nor ever having been, the intention of his Majesty to interpose by force in the affairs of the republic of the United Provinces, the communication made to the court of London by M. Barthelemy having had no other object than to announce to that court an intention, the motives of which no longer-exist, especially since the King of Prussia has made known his resolution, his Majesty makes no difficulty in declaring, that he has no wish to act in pursuance of the communication aforesaid, and that he entertains no hostile view in any quarter, relative to what has passed in Holland.
Consequently, his Majesty, desiring to concur in the sentiments of his Britannic Majesty, for the preservation of a good understanding between the two courts, consents with pleasure to the proposition of his Britannic Majesty, that the armaments, and, in general, all preparations for war, shall be mutually discontinued, and that the marines of the two nations shall be replaced upon the footing of the peace establishment, as it existed on the first day of January of the present year.
Signed. Montmorin.
At Versailles, the 27th of October, 1787.
(Private.) Paris, November 3, 1787.
Dear Sir,
I shall take the liberty of confiding sometimes to a private letter, such details of the small history of the court or cabinet, as may be worthy of being known, and yet not proper to be publicly communicated. I doubt whether the administration is yet in a permanent form. The Count de Montmorin and Baron de Breteuil are, I believe, firm enough in their places. It was doubted whether they would wait for the Count de la Luzerne, if the war had taken place: but at present I suppose they will. I wish it also, because M. de Hector, his only competitor, has on some occasions shown little value for the connection with us. Lambert, the Comptroller General, is thought to be very insecure. I should be sorry also to lose him. I have worked several days with him, the Marquis de la Fayette, and Monsieur du Pont (father of the young gentleman gone to America with the Count de Moustier), to reduce into one Arrêt whatever concerned our commerce. I have found him a man of great judgment and application, possessing good general principles on subjects of commerce, and friendly dispositions towards us. He passed the Arrêt in a very favorable form, but it has been opposed in the Council, and will, I fear, suffer some alteration in the article of whale-oil. That of tobacco, which was put into a separate instrument, experiences difficulties also, which do not come from him. M. du Pont has rendered us essential services on these occasions. I wish his son could be so well noticed, as to make a favorable report to his father; he would, I think, be gratified by it, and his good dispositions be strengthened, and rendered further useful to us. Whether I shall be able to send you these regulations by the present packet, will depend on their getting through the Council in time. The Archbishop continues well with his patroness. Her object is, a close connection with her brother. I suppose he convinces her, that peace will furnish the best occasion of cementing that connection.
It may not be uninstructive to give you the origin and nature of his influence with the Queen. When the Duke de Choiseul proposed the marriage of the Dauphin with this lady, he thought it proper to send a person to Vienna, to perfect her in the language. He asked his friend, the Archbishop of Toulouse, to recommend to him a proper person. He recommended a certain Abbe. The Abbe, from his first arrival at Vienna, either tutored by his patron, or prompted by gratitude, impressed on the Queen’s mind the exalted talents and merit of the Archbishop, and continually represented him as the only man fit to be placed at the helm of affairs. On his return to Paris, being retained near the person of the Queen, he kept him constantly in her view. The Archbishop was named of the Assembly des Notables, had occasion enough there to prove his talents, and Count de Vergennes, his great enemy, dying opportunely, the Queen got him into place. He uses the Abbe even yet, for instilling all his notions into her mind. That he has imposing talents and patriotic dispositions, I think is certain. Good judges think him a theorist only, little acquainted with the details of business, and spoiling all his plans by a bungled execution. He may perhaps undergo a severe trial. His best actions are exciting against him a host of enemies, particularly the reduction of the pensions, and reforms in other branches of economy. Some think the other ministers are willing he should stay in, till he has effected this odious, yet necessary work, and that they will then make him the scape-goat of the transaction. The declarations too, which I send you in my public letter, if they should become public, will probably raise an universal cry. It will all fall on him, because Montmorin and Breteuil say, without reserve, that the sacrifice of the Dutch has been against their advice. He will, perhaps, not permit these declarations to appear in this country. They are absolutely unknown: they were communicated to me by the Duke of Dorset, and I believe no other copy has been given here. They will be published doubtless in England, as a proof of their triumph, and may from thence make their way into this country. If the Premier can stem a few months, he may remain long in office, and will never make war if he can help it. If he should be removed, the peace will probably be short. He is solely chargeable with the loss of Holland. True, they could not have raised money by taxes to supply the necessities of war; but could they do it were their finances ever so well arranged? No nation makes war now-a-days, but by the aid of loans: and it is probable, that in a war for the liberties of Holland, all the treasures of that country would have been at their service. They have now lost the cow which furnishes the milk of war. She will be on the side of their enemies, whenever a rupture shall take place: and no arrangement of their finances can countervail this circumstance.
I have no doubt, you permit access to the letters of your foreign ministers, by persons only of the most perfect trust. It is in the European system to bribe the clerks high, in order to obtain copies of interesting papers. I am sure you are equally attentive to the conveyance of your letters to us, as you know that all are opened that pass through any post-office of Europe. Your letters which come by the packet, if put into the mail at New York, or into the post-office at Havre, wear proofs that they have been opened. The passenger to whom they are confided, should be cautioned always to keep them in his own hands, till he can deliver them personally in Paris.
I have the honor to be, with very sincere esteem and respect, Dear Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
Sir,
Paris, November 6, 1787.
I take the liberty of asking your Excellency’s perusal of the enclosed case of an American hostage, confined in the prisons of Dunkirk. His continuance there seems to be useless, and yet endless. Not knowing how far the government can interfere for his relief, as it is a case wherein private property is concerned, I do not presume to ask his liberation absolutely: but I will solicit from your Excellency such measures in his behalf, as the laws and usages of the country may permit.
The Comptroller General having been so good as to explain to me in a conversation, that he wished to know what duties were levied in England on American whale-oil, I have had the honor of informing him by letter, that the ancient duties on that article are seventeen pounds, six shillings, and six pence, sterling, the ton, and that some late additional duties make them amount to about eighteen pounds sterling. That the common whale-oil sells there but for about twenty pounds sterling, the ton, and of course the duty amounts to a prohibition. This duty was originally laid on all foreign fish-oil, with a view to favor the British and American fisheries. When we became independent, and of course foreign to Great Britain, we became subject to the foreign duty. No duty, therefore, which France may think proper to lay on this article, can drive it to the English market. It could only oblige the inhabitants of Nantucket to abandon their fishery. But the poverty of their soil offering them no other resource, they must quit their country, and either establish themselves in Nova Scotia, where, as British fishermen, they may participate of the British premium, in addition to the ordinary price of their whale-oil, or they must accept the conditions which this government offers, for the establishment they have proposed at Dunkirk. Your Excellency will judge, what conditions may counterbalance, in their minds, the circumstances of the vicinity of Nova Scotia, sameness of langague,[sp.] laws, religion, customs, and kindred. Remaining in their native country, to which they are most singularly attached, excluded from commerce with England, taught to look to France as the only country from which they can derive sustenance, they will, in case of war, become useful rovers against its enemies. Their position, their poverty, their courage, their address, and their hatred, will render them formidable scourges on the British commerce. It is to be considered then, on the one hand, that the duty which M. de Calonne had proposed to retain on their oil, may endanger the shifting this useful body of seamen out of our joint scale into that of the British; and also may suppress a considerable subject of exchange for the productions of France: on the other hand, that it may produce an addition to his Majesty’s revenue. What I have thus far said, is on the supposition, that the duty may operate a diminution of the price received by the fishermen. If it act in the contrary direction, and produce an augmentation of price to the consumer, it immediately brings into competition a variety of other oils, vegetable and animal, a good part of which France receives from abroad, and the fisherman, thus losing his market, is compelled equally to change either his calling or country. When M. de Calonne first agreed to reduce the duties to what he has declared, I had great hopes the commodity could bear them, and that it would become a medium of commerce between France and the United States. I must confess, however, that my expectations have not been fulfilled, and that but little has come here as yet. This induces me to fear, that it is so poor an article, that any duty whatever will suppress it. Should this take place, and the spirit of emigration once seize those people, perhaps an abolition of all duty might then come too late to stop, what it would now easily prevent. I fear there is danger in the experiment; and it remains for the wisdom of his Majesty and his ministers to decide, whether the prospect of gain to the revenue, or establishing a national fishery, may compensate this danger. If the government should decide to retain the duty, I shall acquiesce in it cheerfully, and do every thing in my power to encourage my countrymen still to continue their occupation.
The actual session of our several legislatures would render it interesting to forward immediately the regulations proposed on our commerce; and the expiration of the order of Bernis, at the close of this month, endangers a suspension and derangement in the commerce of tobacco, very embarrassing to the merchants of the two countries. Pardon me therefore, Sir, if I appear solicitous to obtain the ultimate decision of his Majesty’s Council on these subjects, and to ask as early a communication of that decision, as shall be convenient.
I have the honor to be, with sentiments of the most profound esteem and respect, your Excellency’s most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN ADAMS.
Paris, November 13, 1787.
Dear Sir,
This will be delivered you by young Mr. Rutledge. Your knowledge of his father will introduce him to your notice. He merits it, moreover, on his own account.
I am now to acknowledge your favors of October the 8th and 26th. That of August the 25th was duly received, nor can I recollect by what accident I was prevented from acknowledging it in mine of September the 28th. It has been the source of my subsistence hitherto, and must continue to be so, till I receive letters on the affairs of money from America. Van Staphorsts and WilBlinks have answered my drafts. Your books for Marquis de la Fayette are received here. I will notify it to him, who is at present with his Provincial Assembly in Auvergne.
Little is said lately of the progress of the negotiations between the courts of Petersburg, Vienna, and Versailles. The distance of the former, and the cautious, unassuming character of its minister here, is one cause of delays: a greater one is, the greediness and instable character of the Emperor. Nor do I think that the Principal here, will be easily induced to lend himself to any connection, which shall threaten a war within a considerable number of years. His own reign will be that of peace only, in all probability; and were any accident to tumble him down, this country would immediately gird on its sword and buckler, and trust to occurrences for supplies of money. The wound their honor has sustained, festers in their hearts; and it may be said with truth, that the Archbishop and a few priests, determined to support his measures, because proud to see their order come again into power, are the only advocates for the line of conduct which has been pursued. It is said, and believed through Paris literally, that the Count de Montmorin ‘pleuroit comme un enfant,’ when obliged to sign the counter-declaration. Considering the phrase as figurative, I believe it expresses the distress of his heart. Indeed, he has made no secret of his individual opinion. In the mean time, the Principal goes on with a firm and patriotic spirit in reforming the cruel abuses of the government, and preparing a new constitution, which will give to this people as much liberty as they are capable of managing. This, I think, will be the glory of his administration, because, though a good theorist in finance, he is thought to execute badly. They are about to open a loan of one hundred millions to supply present wants, and it is said, the preface of the Arrêt will contain a promise of the convocation of the States General during the ensuing year. Twelve or fifteen Provincial Assemblies are already in action, and are going on well: and I think, that, though the nation suffers in reputation, it will gain infinitely in happiness under the present administration. I enclose to Mr. Jay a pamphlet, which I will beg of you to forward. I leave it open for your perusal. When you shall have read it, be so good as to stick a wafer in it. It is not yet published, nor will be for some days. This copy has been ceded to me as a favor.
How do you like our new constitution? I confess there are things in it, which stagger all my dispositions to subscribe to what such an Assembly has proposed. The House of federal representatives will not be adequate to the management of affairs, either foreign or federal. Their President seems a bad edition of a Polish King. He may be elected from four years to four years, for life. Reason and experience prove to us, that a chief magistrate, so continuable, is an office for life. When one or two generations shall have proved, that this is an office for life, it becomes, on every succession, worthy of intrigue, of bribery, of force, and even of foreign interference. It will be of great consequence to France and England, to have America governed by a Galloman or Angloman. Once in office, and possessing the military force of the Union, without the aid or check of a council, he would not be easily dethroned, even if the people could be induced to withdraw their votes from him. I wish that at the end of the four years, they had made him for ever ineligible a second time. Indeed, I think all the good of this new constitution might have been couched in three or four new articles to be added to the good, old, and venerable fabric, which should have been preserved even as a religious relique. Present me and my daughters affectionately to Mrs. Adams. The younger one continues to speak of her warmly. Accept yourself assurances of the sincere esteem and respect, with which I have the honor to be, Dear Sir, your friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO COLONEL SMITH.
Paris, November 13, 1787.
Sir,
I am now to acknowledge the receipt of your favors of October the 4th, 8th, and 26th. In the last, you apologize for your letters of introduction to Americans coming here. It is so far from needing apology on your part, that it calls for thanks on mine. I endeavor to show civilities to all the Americans who come here, and who will give me opportunities of doing it: and it is a matter of comfort to know, from a good quarter, what they are, and how far I may go in my attentions to them.
Can you send me Woodmason’s bills for the two copying presses, for the Marquis de la Fayette and the Marquis de Chastellux? The latter makes one article in a considerable account, of old standing, and which I cannot present for want of this article. I do not know whether it is to yourself or Mr. Adams I am to give my thanks for the copy of the new constitution. I beg leave, through you, to place them where due. It will yet be three weeks before I shall receive them from America. There are very good articles in it; and very bad. I do not know which preponderate. What we have lately read in the history of Holland, in the chapter on the Stadtholder, would have sufficed to set me against a chief magistrate eligible for a long duration, if I had ever been disposed towards one: and what we have always read of the elections of Polish Kings, should have for ever excluded the idea of one continuable for life. Wonderful is the effect of impudent and persevering lying. The British ministry have so long hired their gazetteers to repeat, and model into every form, lies about our being in anarchy, that the world has at length believed them, the English nation has believed them, the ministers themselves have come to believe them, and what is more wonderful, we have believed them ourselves. Yet where does this anarchy exist? Where did it ever exist, except in the single instance of Massachusetts? And can history produce an instance of rebellion so honorably conducted? I say nothing of its motives. They were founded in ignorance, not wickedness. God forbid, we should ever be twenty years without such a rebellion. The people cannot be all, and always, well informed. The part which is wrong will be discontented, in proportion to the importance of the facts they misconceive. If they remain quiet under such misconceptions, it is a lethargy, the forerunner of death to the public liberty. We have had thirteen States independent for eleven years. There has been one rebellion. That comes to one rebellion in a century and a half for each State. What country before ever existed a century and a half without a rebellion? And what country can preserve its liberties, if its rulers are not warned from time to time, that this people preserve the spirit of resistance? Let them take arms. The remedy is to set them right as to facts, pardon, and pacify them. What signify a few lives lost in a century or two? The tree of liberty must be refreshed from time to time with the blood of patriots and tyrants. It is its natural manure. Our convention has been too much impressed by the insurrection of Massachusetts: and on the spur of the moment, they are setting up a kite to keep the hen-yard in order. I hope in God, this article will be rectified before the new constitution is accepted. You ask me, if any thing transpires here on the subject of South America? Not a word. I know that there are combustible materials there, and that they wait the torch only. But this country probably will join the extinguishers. The want of facts worth communicating to you, has occasioned me to give a little loose to dissertation. We must be contented to amuse, when we cannot inform.
Present my respects to Mrs. Smith, and be assured of the sincere esteem of, Dear Sir, your friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO WILLIAM CARMICHAEL.
Paris, December 11, 1787.
Dear Sir,
I am later in acknowledging the receipt of your favors of October the 15th, and November the 5th and 15th, because we have been long expecting a packet, which I hoped would bring communications worth detailing to you; and she arrived only a few days ago, after a very long passage indeed. I am very sorry you have not been able to make out the cipher of my letter of September the 25th, because it contained things which I wished you to know at that time. They have lost now a part of their merit; * but still I wish you could decipher them, as there remains a part, which it might yet be agreeable to you to understand. I have examined the cipher, from which it was written. It as precisely a copy of those given to Messrs. Barclay and Lambe. In order that you may examine whether yours corresponds, I will now translate into cipher, the three first lines of my letter of June the 14th.
This will serve to show, whether your cipher corresponds with mine, as well as my manner of using it. But I shall not use it in future, till I know from you the result of your re-examination of it. I have the honor now, to return you the letter you had been so good as to enclose to me. About the same time of Liston’s conversation with you, similar ones were held with me by Mr. Eden. He particularly questioned me on the effect of our treaty with France, in the case of a war, and what might be our dispositions. I told him without hesitation, that our treaty obliged us to receive the armed vessels of France, with their prizes, into our ports, and to refuse the admission of prizes made on her by her enemies; that there was a clause by which we guarantied to France her American possessions, and which might, perhaps, force us into the war, if these were attacked. ‘Then it will be war,’ said he, ‘for they will assuredly be attacked.’ I added, that our dispositions would be to be neutral, and that I thought it the interest of both those powers that we should be so, because it would relieve both from all anxiety as to the feeding their West India islands, and England would, moreover, avoid a heavy land war on our continent, which would cripple all her proceedings elsewhere. He expected these sentiments from me personally, and he knew them to be analogous to those of our country. We had often before had occasions of knowing each other: his peculiar bitterness towards us had sufficiently appeared, and I had never concealed from him, that I considered the British as our natural enemies, and as the only nation on earth, who wished us ill from the bottom of their souls. And I am satisfied, that were our continent to be swallowed up by the ocean, Great Britain would be in a bonfire from one end to the other. Mr. Adams, as you know, has asked his recall. This has been granted, and Colonel Smith is to return too; Congress having determined to put an end to their commission at that court. I suspect and hope they will make no new appointment.
Our new constitution is powerfully attacked in the American newspapers. The objections are, that its effect would be to form the thirteen States into one; that, proposing to melt all down into one general government, they have fenced the people by no declaration of rights; they have not renounced the power of keeping a standing army; they have not secured the liberty of the press; they have reserved the power of abolishing trials by jury in civil cases; they have proposed that the laws of the federal legislatures shall be paramount the laws and constitutions of the States; they have abandoned rotation in office; and particularly their President may be re-elected from four years to four years, for life, so as to render him a King for life, like a King of Poland; and they have not given him either the check or aid of a council. To these, they add calculations of expense, &c. &.c. to frighten the people. You will perceive that those objections are serious and some of them not without foundation. The constitution, however, has been received with a very general enthusiasm, and as far as can be judged from external demonstrations, the bulk of the people are eager to adopt it. In the eastern States, the printers will print nothing against it, unless the writer subscribes his name. Massachusetts and Connecticut have called conventions in January, to consider of it. In New York, there is a division. The Governor (Clinton) is known to be hostile to it. Jersey, it is thought, will certainly accept it. Pennsylvania is divided; and all the bitterness of her factions has been kindled anew on it. But the party in favor of it is strongest, both in and out of the legislature. This is the party anciently of Morris, Wilson, &c., Delaware will do what Pennsylvania shall do. Maryland is thought favorable to it; yet it is supposed Chase and Paca will oppose it. As to Virginia, two of her Delegates, in the first place, refused to sign it. These were Randolph, the Governor, and George Mason. Besides these, Henry, Harrison, Nelson, and the Lees are against it. General Washington will be for it, but it is not in his character to exert himself much in the case. Madison will be its main pillar; but though an immensely powerful one, it is questionable whether he can bear the weight of such a host. So that the presumption is, that Virginia will reject it. We know nothing of the dispositions of the States south of this. Should it fall through, as is possible, notwithstanding the enthusiasm with which it was received in the first moment, it is probable that Congress will propose, that, the objections which the people shall make to it being once known, another convention shall be assembled, to adopt the improvements generally acceptable, and omit those found disagreeable. In this way, union may be produced under a happy constitution, and one which shall not be too energetic, as are the constitutions of Europe. I give you these details, because, possibly, you may not have received them all. The sale of our western lands is immensely successful. Five millions of acres have been sold at private sale, for a dollar an acre, in certificates; and at the public sales, some of them had sold as high as two dollars and forty cents the acre. The sales had not been begun two months. By these means, taxes, &c. our domestic debt, originally twenty-eight millions of dollars, was reduced, by the 1st day of last October, to twelve millions, and they were then in treaty-for two millions of acres more, at a dollar, private sale. Our domestic debt will thus be soon paid off, and that done, the sales will go on for money, at a cheaper rate, no doubt, for the payment of our foreign debt. The petite guerre, always waged by the Indians, seems not to abate the ardor of purchase or emigration. Kentucky is now counted at sixty thousand. Frankland is also growing fast.
I have been told, that the cutting through the Isthmus of Panama, which the world has so often wished, and supposed practicable, has at times been thought of by the government of Spain, and that they once proceeded so far, as to have a survey and examination made of the ground; but that the result was, either impracticability or too great difficulty. Probably the Count de Campomanes, or Don Ulloa, can give you information on this head. I should be exceedingly pleased to get as minute details as possible on it, and even copies of the survey, report, &c. if they could be obtained at a moderate expense. I take the liberty of asking your assistance in this.
I have the honor to be, with great respect and esteem, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN ADAMS.
Paris, December 12, 1787.
Dear Sir,
In the month of July, I received from Fiseaux & Co. of Amsterdam, a letter notifying me that the principal of their loan to the United States would become due the first day of January. I answered them that I had neither powers nor information on the subject, but would transmit their letter to the board of treasury. I did so, by the packet which sailed from Havre, August the 10th. The earliest answer possible would have been by the packet which arrived at Havre three or four days ago. But by her I do not receive the scrip of a pen from any body. This makes me suppose, that my letters are committed to Paul Jones, who was to sail a week after the departure of the packet; and that possibly, he may be the bearer of orders from the treasury, to repay Fiseaux’ loan, with the money you borrowed. But it is also possible, he may bring no order on the subject. The slowness with which measures are adopted on our side the water, does not permit us to count on punctual answers; but, on the contrary, renders it necessary for us to suppose, in the present case, that no orders will arrive in time, and to consider whether any thing, and what, should be done. As it may be found expedient to transfer all our foreign debts to Holland, by borrowing there, and as it may always be prudent to preserve a good credit in that country, because we may be forced into wars, whether we will or not, I should suppose it very imprudent to suffer our credit to be annihilated, for so small a sum as fifty-one thousand guelders. The injury will be greater too, in proportion to the smallness of the sum; for they will ask, ‘How can a people be trusted for large sums, who break their faith for such small ones?’ You know best what effect it will have on the minds of the money-lenders of that country, should we fail in this payment. You know best also, whether it is practicable and prudent for us, to have this debt paid without orders. I refer the matter, therefore, wholly to your consideration, willing to participate with you in any risk and any responsibility, which may arise. I think it one of those cases, where it is a duty to risk one’s self. You will perceive, by the enclosed, the necessity of an immediate answer, and that, if you think any thing can and should be done, all the necessary authorities from you should accompany your letter. In the mean time, should I receive any orders from the treasury by Paul Jones, I will pursue them, and consider whatever you shall have proposed or done, as non avenue.
I am, with much affection, Dear Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JAMES MADISON.
Paris, December 20, 1787.
Dear Sir,
My last to you was of October the 8th, by the Count de Moustier. Yours of July the 18th, September the 6th, and October the 24th, were successively received, yesterday, the day before, and three or four days before that. I have only had time to read the letters; the printed papers communicated with them, however interesting, being obliged to lie over till I finish my despatches for the packet, which despatches must go from hence the day after to-morrow. I have much to thank you for; first and most for the ciphered paragraph respecting myself. These little informations are very material towards forming my own decisions. I would be glad even to know, when any individual member thinks I have gone wrong in any instance. If I know myself, it would not excite ill blood in me, while it would assist to guide my conduct, perhaps to justify it, and to keep me to my duty, alert. I must thank you too, for the information in Thomas Burke’s case; though you will have found by a subsequent letter, that I have asked of you a further investigation of that matter. It is to gratify the lady who is at the head of the convent wherein my daughters are, and who, by her attachment and attention to them, lays me under great obligations, I shall hope, therefore, still to receive from you the result of all the further inquiries my second letter had asked. The parcel of rice which you informed me had miscarried, accompanied my letter to the Delegates of South Carolina. Mr. Bourgoin was to be the bearer of both, and both were delivered together into the hands of his relation here, who introduced him to me, and who, at a subsequent moment, undertook to convey them to Mr. Bourgoin. This person was an engraver, particularly recommended to Dr. Franklin and Mr. Hopkinson. Perhaps he may have mislaid the little parcel of rice among his baggage. I am much pleased, that the sale of western lands is so successful. I hope they will absorb all the certificates of our domestic debt speedily, in the first place, and that then, offered for cash, they will do the same by our foreign ones.
The season admitting only of operations in the cabinet, and these being in a great measure secret, I have little to fill a letter, I will therefore make up the deficiency, by adding a few words on the constitution proposed by our convention.
I like much the general idea of framing a government, which should go on of itself, peaceably, without needing continual recurrence to the State legislatures. I like the organization of the government into legislative, judiciary, and executive. I like the power given the legislature to levy taxes, and for that reason solely, I approve of the greater House being chosen by the people directly. For though I think a House, so chosen, will be very far inferior to the present Congress, will be very illy qualified to legislate for the Union, for foreign nations, &c.; yet this evil does not weigh against the good of preserving inviolate the fundamental principle, that the people are not to be taxed but by representitives[sp.] chosen immediately by themselves. I am captivated by the compromise of the opposite claims of the great and little States, of the latter to equal, and the former to proportional influence. I am much pleased, too, with the substitution of the method of voting by persons, instead of that of voting by States: and I like the negative given to the Executive, conjointly with a third of either House; though I should have liked it better, had the judiciary been associated for that purpose, or invested separately with a similar power. There are other good things of less moment.
I will now tell you what I do not like. First, the omission of a bill of rights, providing clearly, and without the aid of sophism, for freedom of religion, freedom of the press, protection against standing armies, restriction of monopolies, the eternal and unremitting force of the habeas corpus laws, and trials by jury in all matters of fact triable by the laws of the land, and not by the laws of nations. To say, as Mr. Wilson does, that a bill of rights was not necessary, because all is reserved in the case of the general government which is not given, while in the particular ones, all is given which is not reserved, might do for the audience to which it was addressed: but it is surely a gratis dictum, the reverse of which might just as well be said; and it is opposed by strong inferences from the body of the instrument, as well as from the omission of the clause of our present Confederation, which had made the reservation in express terms. It was hard to conclude, because there has been a want of uniformity among the States as to the cases triable by jury, because some have been so incautious as to dispense with this mode of trial in certain cases, therefore the more prudent States shall be reduced to the same level of calamity. It would have been much more just and wise to have concluded the other way, that as most of the States had preserved with jealousy this sacred palladium of liberty, those who had wandered, should be brought back to it: and to have established general right rather than general wrong. For I consider all the ill as established, which maybe established. I have a right to nothing, which another has a right to take away; and Congress will have a right to take away trials by jury in all civil cases. Let me add, that a bill of rights is what the people are entitled to against every government on earth, general or particular; and what no just government should refuse, or rest on inference.
The second feature I dislike, and strongly dislike, is the abandonment, in every instance, of the principle of rotation in office, and most particularly in the case of the President. Reason and experience tell us, that the first magistrate will always be re-elected if he may be re-elected. He is then an officer for life.
This once observed, it becomes of so much consequence to certain nations, to have a friend or a foe at the head of our affairs, that they will interfere with money and with arms. A Galloman, or an Angloman, will be supported by the nation he befriends. If once elected, and at a second or third election outvoted by one or two votes, he will pretend false votes, foul play, hold possession of the reins of government, be supported by the States voting for him, especially if they be the central ones, lying in a compact body themselves, and separating their opponents; and they will be aided by one nation in Europe, while the majority are aided by another. The election of a President of America, some years hence, will be much more interesting to certain nations of Europe, than ever the election of a King of Poland was. Reflect on all the instances in history, ancient and modern, of elective monarchies, and say, if they do not give foundation for my fears; the Roman Emperors, the Popes while they were of any importance, the German Emperors till they became hereditary in practice, the Kings of Poland, the Deys of the Ottoman dependencies. It may be said, that if elections are to be attended with these disorders, the less frequently they are repeated the better. But experience says, that to free them from disorder, they must be rendered less interesting by a necessity of change. No foreign power, nor domestic party, will waste their blood and money to elect a person, who must go out at the end of a short period. The power of removing every fourth year by the vote of the people, is a power which they will not exercise, and if they were disposed to exercise it, they would not be permitted. The King of Poland is removable every day by the diet. But they never remove him. Nor would Russia, the Emperor, &c. permit them to do it. Smaller objections are, the appeals on matters of fact as well as law; and the binding all persons, legislative, executive, and judiciary, by oath, to maintain that constitution. I do not pretend to decide, what would be the best method of procuring the establishment of the manifold good things in this constitution, and of getting rid of the bad. Whether by adopting it, in hopes of future amendment; or, after it shall have been duly weighed and canvassed by the people, after seeing the parts they generally dislike, and those they generally approve, to say to them, ‘We see now what you wish. You are willing to give to your federal government such and such powers: but you wish, at the same time, to have such and such fundamental rights secured to you, and certain sources of convulsion taken away. Be it so. Send together your deputies again. Let them establish your fundamental rights by a sacrosanct declaration, and let them pass the parts of the constitution you have approved. These will give powers to your federal government sufficient for your happiness.’ This is what might be said, and would probably produce a speedy, more perfect, and more permanent form of government. At all events, I hope you will not be discouraged from making other trials, if the present one should fail. We are never permitted to despair of the commonwealth. I have thus told you freely what I like, and what I dislike, merely as a matter of curiosity; for I know it is not in my power to offer matter of information to your judgment, which has been formed after hearing and weighing every thing which the wisdom of man could offer on these subjects. I own, I am not a friend to a very energetic government. It is always oppressive. It places the governors indeed more at their ease, at the expense of the people. The late rebellion in Massachusetts has given more alarm, than I think it should have done. Calculate that one rebellion in thirteen States in the course of eleven years, is but one for each State in a century and a half. No country should be so long without one. Nor will any degree of power in the hands of government prevent insurrections. In England, where the hand of power is heavier than with us, there are seldom half a dozen years without an insurrection. In France, Where it is still heavier, but less despotic, as Montesquieu supposes, than in some other countries, and where there are always two or three hundred thousand men ready to crush insurrections, there have been three in the course of the three years I have been here, in every one of which greater numbers were engaged than in Massachusetts, and a great deal more blood was spilt. In Turkey, where the sole nod of the despot is death, insurrections are the events of every day. Compare again the ferocious depredations of their insurgents, with the order, the moderation, and the almost self-extinguishment of ours. And say, finally, whether peace is best preserved by giving energy to the government, or information to the people. This last is the most certain and the most legitimate engine of government. Educate and inform the whole mass of the people. Enable them to see that it is their interest to preserve peace and order, and they will preserve them. And it requires no very high degree of education to convince them of this. They are the only sure reliance for the preservation of our liberty. After all, it is my principle that the will of the majority should prevail. If they approve the proposed constitution in all its parts, I shall concur in it cheerfully, in hopes they will amend it, whenever they shall find it works wrong. This reliance cannot deceive us, as long as we remain virtuous; and I think we shall be so, as long as agriculture is our principal object, which will be the case, while there remain vacant lands in any part of America. When we get piled upon one another in large cities, as in Europe, we shall become corrupt as in Europe, and go to eating one another as they do there. I have tired you by this time with disquisitions which you have already heard repeated by others, a thousand and a thousand times; and, therefore, shall only add assurances of the esteem and attachment, with which I have the honor to be, Dear Sir, your affectionate friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
P. S. The instability of our laws is really an immense evil. I think it would be well to provide in our constitutions, that there shall always be a twelvemonth between the engrossing a bill and passing it: that it should then be offered to its passage without changing a word: and that if circumstances should be thought to require a speedier passage, it should take two thirds of both Houses, instead of a bare majority.
TO E. CARRINGTON
Paris, December 21, 1787.
Dear Sir,
I have just received your two favors of October the 23rd and November the 10th. I am much obliged to you for your hints in the Danish business. They are the only information I have on that subject, except the resolution of Congress, and warn me of a rock on which I should most certainly have split. The vote plainly points out an agent, only leaving it to my discretion to substitute another. My judgment concurs with that of Congress as to his fitness. But I shall inquire for the surest banker at Copenhagen to receive the money, not because I should have had any doubts, but because I am informed others have them. Against the failure of a banker, were such an accident, or any similar one to happen, I cannot be held accountable in a case, where I act without particular interest. My principal idea in proposing the transfer of the French debt, was, to obtain on the new loans a much longer day for the reimbursement of the principal, hoping that the resources of the United States could have been equal to the article of interest alone. But I shall endeavor to quiet, as well as I can, those interested. A part of them will probably sell out at any rate: and one great claimant may be expected to make a bitter attack on our honor. I am very much pleased to hear, that our western lands sell so successfully. I turn to this precious resource, as that which will, in every event, liberate us from our domestic debt, and perhaps too from our foreign one: and this, much sooner than I had expected. I do not think any thing could have been done with them in Europe. Individual speculators and sharpers had duped so many with their unlocated land-warrants, that every offer would have been suspected.
As to the new constitution, I find myself nearly a neutral. There is a great mass of good in it, in a very desirable form; but there is also, to me, a bitter pill or two. I have written somewhat lengthily to Mr. Madison on this subject, and will take the liberty to refer you to that part of my letter to him. I will add one question to what I have said there. Would it not have been better to assign to Congress exclusively, the article of imposts for federal purposes, and to have left direct taxation exclusively to the States? I should suppose the former fund sufficient for all probable events, aided by the land office.
The form which the affairs of Europe may assume, is not yet decipherable by those out of the cabinet. The Emperor gives himself, at present, the airs of a mediator. This is necessary to justify a breach with the Porte. He has his eye at the same time on Germany, and particularly on Bavaria, the Elector of which has, for a long time, been hanging over the grave. Probably, France would now consent to the exchange of the Austrian Netherlands, to be created into a kingdom for the Duke de Deux-ponts, against the electorate of Bavaria. This will require a war. The Empress longs for Turkey, and viewing France as her principal obstacle, would gladly negotiate her acquiescence. To spur on this, she is coquetting it with England. The King of Prussia, too, is playing a double game between France and England. But I suppose the former incapable of forgiving him, or of ever reposing confidence in him. Perhaps the spring may unfold to us the final arrangement, which will take place among the powers of this continent.
I often doubt whether I should trouble Congress or my friends with these details of European politics. I know they do not excite that interest in America, of which it is impossible for one to divest himself here. I know too, that it is a maxim with us, and I think it is a wise one, not to entangle ourselves with the affairs of Europe. Still, I think, we should know them. The Turks have practised the same maxim of not meddling in the complicated wrangles of this continent. But they have unwisely chosen to be ignorant of them also, and it is this total ignorance of Europe, its combinations, and its movements, which exposes them to that annihilation possibly about taking place. While there are powers in Europe which fear our views, or have views on us, we should keep an eye on them, their connections, and oppositions, that in a moment of need, we may avail ourselves of their weakness with respect to others as well as ourselves, and calculate their designs and movements, on all the circumstances under which they exist. Though I am persuaded, therefore, that these details are read by many with great indifference, yet I think it my duty to enter into them, and to run the risk of giving too much, rather than too little information.
I have the honor to be, with perfect esteem and respect, Dear Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
P. S. The resolution of Congress, relative to the prize money received here, speaks of that money as paid to me. I hope this matter is properly understood. The treasury board desired me to receive it, and apply it to such and such federal purposes; and they would pay the dividends of the claimants in America. This would save the expense of remittance. I declined, however, receiving the money, and ordered it into the hands of their banker, who paid it away for the purposes to which they had destined it. I should be sorry an idea should get abroad, that I had received the money of those poor fellows, and applied it to other purposes. I shall, in like manner, order the Danish and Barbary money into the hands of bankers, carefully avoiding ever to touch a sou of it, or having any other account to make out than what the banker will furnish. T. J.
TO MONSIEUR LIMOZIN.
Paris, December 22, 1787.
Sir,
I have the honor now to acknowledge the receipt of your favors of the 18th and 19th of November, and two of the 18th of the present month. I did not write to you immediately on the receipt of the two first, because the observation they contained were to be acted on here. I was much obliged to you for them, as I have been frequently before for others, and you will find that I have profited by them in the Arrêt which is to come out for the regulation of our commerce, wherein most of the things are provided for, which you have from time to time recommended. With respect to the article of yellow wax, I think there is a general clause in the Arrêt, which will take it in; but I am not sure of it. If there be not, it is now too late to get any alteration made. You shall receive the Arrêt the moment it is communicated to me.
I have examined the case of Captain Thomas, with all the dispositions possible, to interpose for him. But on mature reflection, I find it is one of those cases wherein my solicitation would be ill received. The government of France, to secure to its subjects the carrying trade between her colonies and the mother country, have made a law, forbidding any foreign vessels to undertake to carry between them. Notwithstanding this, an American vessel has undertaken, and has brought a cargo. For me to ask that this vessel shall be received, would be to ask a repeal of the law, because there is no more reason for receiving her, than there will be for receiving the second, third, &c, which shall act against the same law, nor for receiving an American vessel, more than the vessels of other nations. Captain Thomas has probably engaged in this business, not knowing the law; but ignorance of the law is no excuse, in any country. If it were, the laws would lose their effect, because it can be always pretended. Were I to make this application to the Comptroller General, he might possibly ask me, whether, in a like case, of a French vessel in America acting through ignorance, against law, we would suspend the law as to her? I should be obliged honestly to answer, that with us there is no power which can suspend the law for a moment; and Captain Thomas knows that this answer would be the truth. The Senegal company seems to be as much engaged in it as he is. I should suppose his most probable means of extrication, would be with their assistance, and availing himself of their privileges, and the apparent authority he has received from the officers of government there. I am sorry his case is such a one, as I cannot present to the minister. A jealousy of our taking away their carrying trade, is the principal reason which obstructs our admission into their West India islands. It would not be right for me to strengthen that jealousy.
I have the honor to be, with much esteem, Sir, your most obedient, humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
Paris, December 31, 1787.
Sir,
Since the receipt of the letter of Monsieur de Calonne, of October the 22nd, 1786, I have several times had the honor of mentioning to you, that I was endeavoring to get the substance of that letter reduced into an Arrêt, which, instead of being revocable by a single letter of a Comptroller General, would require an Arrêt to repeal or alter it, and of course must be discussed in full Council, and so give time to prevent it. This has been pressed as much as it could be with prudence. One cause of delay has been the frequent changes of the Comptroller General; as we had always our whole work to begin again, with every new one. Monsieur Lambert’s continuance in office for some months has enabled us, at length, to get through the business; and I have just received from him a letter, and the Arrêt duly authenticated; of which I have the honor to send you a number of printed copies. You will find, that the several alterations and additions are made, which, on my visit, to the seaports, I had found to be necessary, and which my letters of June the 21st and August the 6th particularly mentioned to you. Besides these, we have obtained some new articles of value, for which openings arose in the course of the negotiation. I say we have done it, because the Marquis de la Fayette has gone hand in hand with me through this business, and has been a most invaluable aid. I take the liberty of making some observations on the articles of the Arrêt, severally, for their explanation, as well as for the information of Congress.
Article 1. In the course of our conferences with the Comptroller General, we had prevailed on him to pass this article with a suppression of all duty. When he reported the Arrêt, however, to the Council, this suppression was objected to, and it was insisted to re-establish the duties of seven livres and ten sous, and of ten sous the livre, reserved in the letter of M. de Calonne. The passage of the Arrêt was stopped, and the difficulty communicated to me. I urged every thing I could, in letters and in conferences, to convince them that whale-oil was an article which could bear no duty at all. That if the duty fell on the consumer, he would choose to buy vegetable oils; if on the fisherman, he could no longer live by his calling, remaining in his own country; and that if he quitted his own country, the circumstances of vicinity, sameness of language, laws, religion, and manners, and perhaps the ties of kindred, would draw him to Nova Scotia, in spite of every encouragement which could be given at Dunkirk; and that thus those fishermen would be shifted out of a scale friendly to France, into one always hostile. Nothing, however, could prevail. It hung on this article alone, for two months, during which we risked the total loss of the Arrêt on the stability in office of Monsieur Lambert; for if he had gone out, his successor might be less favorable; and if Monsieur Necker were the successor, we might lose the whole, as he never set any store by us, or the connection with us. About ten days ago, it became universally believed that Monsieur Lambert was to go out immediately. I therefore declined further insisting on the total suppression, and desired the Arrêt might pass, leaving the duties on whale-oil, as Monsieur de Calonne had promised them; but with a reservation, which may countenance our bringing on this matter again, at a more favorable moment.
Article 2. The other fish-oils are placed in a separate article; because, whatever encouragements we may hereafter obtain for whale-oils, they will not be extended to those which their own fisheries produce.
Article 3. A company had silently, and by unfair means, obtained a monopoly for the making and selling spermaceti candles: as soon as we discovered it, we solicited its suppression, which is effected by this clause.
Article 4. The duty of an eighth per cent, is merely to oblige the masters of vessels to enter their cargoes, for the information of government; without inducing them to attempt to smuggle.
Article 6. Tar, pitch, and turpentine of America, coming in competition with the same articles produced in the southwestern parts of France, we could obtain no greater reduction, than two and a half per cent. The duties before were from four to six times that amount.
Article 10. The right of entrepôt, given by this article, is almost the same thing, as the making all their ports, free ports for us. The ships are indeed subject to be visited, and the cargoes must be reported in ports of entrepôt, which need not be done in the free ports. But the communication between the entrepôt and the country is not interrupted by continual search of all persons passing into the country, which has proved so troublesome to the inhabitants of our free ports, as that a considerable proportion of them have wished to give back the privilege of their freedom.
Article 13. This article gives us the privileges and advantages of native subjects, in all their possessions in Asia, and in the scales leading thereto. This expression means, at present, the isles of France and Bourbon, and will include the Cape of Good Hope, should any future event put it into the hands of France. It was with a view to this, that I proposed the expression, because we were then in hourly expectation of a war, and it was suspected that France would take possession of that place. It will, in no case, be considered as including any thing westward of the Cape of Good Hope. I must observe further, on this article, that it will only become valuable, on the suppression of their East India Company; because, as long as their monopoly continues, even native subjects cannot enter their Asiatic ports, for the purposes of commerce. It is considered, however, as certain, that this Company will be immediately suppressed.
The article of tobacco could not be introduced into the Arrêt; because it was necessary to consider the Farmers General as parties to that arrangement. It rests, therefore, of necessity, on the basis of a letter only. You will perceive that this is nothing more than a continuation of the order of Bernis, only leaving the prices unfixed; and like that, it will require a constant and vexatious attention, to have its execution enforced.
The States who have much to carry, and few carriers, will observe, perhaps, that the benefits of these regulations are somewhat narrowed, by confining them to articles brought hither in French or American bottoms. But they will consider, that nothing in these instruments moves from us. The advantages they hold out are all given by this country to us, and the givers will modify their gifts as they please. I suppose it to be a determined principle of this court not to suffer our carrying business, so far as their consumption of our commodities extends, to become a nursery for British seamen. Nor would this, perhaps, be advantageous to us, considering the dispositions of the two nations towards us. The preference which our shipping will obtain on this account, may counterpoise the discouragements it experiences from the aggravated dangers of the Barbary States. Nor is the idea unpleasing, which shows itself in various parts of these papers, of naturalizing American bottoms, and American citizens in France and in its foreign possessions. Once established here, and in their eastern settlements, they may revolt less at the proposition to extend it to those westward. They are not yet, however, at that point; we must be contented to go towards it a step at a time, and trust to future events for hastening our progress.
With respect to the alliance between this and the two imperial courts, nothing certain transpires. We are enabled to conjecture its progress, only from facts which now and then show themselves. The following may be considered as indications of it. 1. The Emperor has made an attempt to surprise Belgrade. The attempt failed, but will serve to plunge him into the war, and to show that he had assumed the character of mediator, only to enable himself to gain some advantage by surprise. 2. The mediation of France is probably at an end, and their abandonment of the Turks agreed on; because they have secretly ordered their officers to quit the Turkish service. This fact is known to but few, and not intended to be known: but I think it certain. 3. To the offer of mediation lately made by England and Prussia, the court of Petersburg answered, that having declined the mediation of a friendly power (France), she could not accept that of two courts, with whose dispositions she had reason to be dissatisfied. 4. The States General are said to have instructed their ambassador here, lately, to ask of M. de Montmorin, whether the inquiry had been made, which they had formerly desired; ‘By what authority the French engineers had been placed in the service of Holland?’ And that he answered, that the inquiry had not been made, nor should be made. Though I do not consider the channel through which I get this fact, as absolutely sure, yet it is so respectable, that I give credit to it myself. 5. The King of Prussia is withdrawing his troops from Holland. Should this alliance show itself it would seem that France, thus strengthened, might dictate the re-establishment of the affairs of Holland, in her own form. For it is not conceivable, that Prussia would dare to move, nor that England would alone undertake such a war, and for such a purpose. She appears, indeed, triumphant at present; but the question is, Who will triumph last?
I enclose you a letter from Mr. Dumas. I received one from him myself, wherein he assures me, that no difficulties shall be produced, by what he had suggested relative to his mission to Brussels. The gazettes of France and Leyden to this date accompany this letter, which, with the several papers put under your cover, I shall send to M. Limozin, our agent at Havre, to be forwarded by the Juno, Captain Jenkins, which sails from that port for New York, on the 3d of January.
I have the honor to be, with sentiments of the most perfect esteem and respect, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MONSIEUR LAMBERT.
Paris, January 3, 1788.
Sir,
I am honored with your Excellency’s letter of the 29th of December, enclosing the Arrêt on the commerce between France and the United States. I availed myself of the occasion of a vessel sailing this day from Havre for New York, to forward it to Congress. They will receive with singular satisfaction, this new testimony of his Majesty’s friendship for the United States, of his dispositions to promote their interest, and to strengthen the bands which connect the two nations.
Permit me, Sir, to return you, personally, my sincere thanks for the great attention you have paid to this subject, for the sacrifices you have kindly made of a time so precious as yours, every moment of which is demanded and is occupied by objects interesting to the happiness of millions; and to proffer you the homage of those sincere sentiments of attachment and respect, with which I have the honor to be, your Excellency’s most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO LE COMTE BERNSTORFF, Minister of Foreign Affairs, Copenhagen.
Paris, January 21, 1788.
Sir,
I am instructed by the United States of America, in Congress assembled, to bring again under the consideration of his Majesty, the King of Denmark, and of his ministers, the case of the three prizes taken from the English during the late war, by an American squadron under the command of Commodore Paul Jones, put into Bergen in distress, there rescued from our possession by orders from the court of Denmark, and delivered back to the English. Dr. Franklin, then Minister Plenipotentiary from the United States at the court of Versailles, had the honor of making applications to the court of Denmark, for a just indemnification to the persons interested, and particularly by a letter of the 22nd of December, 1779, a copy of which I have now the honor of enclosing to your Excellency. In consequence of this, the sum of ten thousand pounds was proposed to him, as an indemnification, through the Baron de Waltersdorff, then at Paris. The departure of both those gentlemen from this place, soon after, occasioned an intermission in the correspondence on this subject. But the United States continue to be very sensibly affected by this delivery of their prizes to Great Britain, and the more so, as no part of their conduct had forfeited their claim to those rights of hospitality, which civilized nations extend to each other. Not only a sense of justice due to the individuals interested in those prizes, but also an earnest desire that no subject of discontent may check the cultivation and progress of that friendship, which they wish may subsist and increase between the two countries, prompt them to remind his Majesty of the transaction in question; and they flatter themselves, that his Majesty will concur with them in thinking, that as restitution of the prizes is not practicable, it is reasonable and just that he should render, and that they should accept, a compensation equivalent to the value of them. And the same principles of justice towards the parties, and of amity to the United States, which influenced the breast of his Majesty to make, through the Baron de Waltersdorff, the proposition of a particular sum, will surely lead him to restore their full value, if that were greater, as is believed, than the sum proposed. In order to obtain, therefore, a final arrangement of this demand, Congress have authorized me to depute a special agent to Copenhagen, to attend the pleasure of his Majesty. No agent could be so adequate to this business, as the Commodore Paul Jones, who commanded the squadron which took the prizes. He will therefore have the honor of delivering this letter to your Excellency, in person; of giving such information as may be material, relative to the whole transaction; of entering into conferences for its final adjustment; and being himself principally interested, not only in his own right, but as the natural patron of those who fought under him, whatever shall be satisfactory to him, will have a great right to that ultimate approbation, which Congress have been pleased to confide to me.
I beg your Excellency to accept the homage of that respect, which your exalted station, talents, and merit impress, as well as those sentiments of esteem and regard, with which I have the honor to be
Your Excellency’s most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO WILLIAM RUTLEDGE.
Paris, February 2, 1788.
Dear Sir,
I should have sooner answered your favor of January the 2nd, but that we have expected for some time, to see you here. I beg you not to think of the trifle I furnished you with, nor to propose to return it, till you shall have that sum more than you know what to do with. And on every other occasion of difficulty, I hope you will make use of me freely. I presume you will now remain at London, to see the trial of Hastings. Without suffering yourself to be imposed on by the pomp in which it will be enveloped, I would recommend to you to consider and decide for yourself these questions. If his offence is to be decided by the law of the land, why is he not tried in that court in which his fellow citizens are tried, that is, the King’s Bench? If he is cited before another court, that he may be judged, not according to the law of the land, but by the discretion of his judges, is he not disfranchised of his most precious right, the benefit of the laws of his country, in common with his fellow citizens? I think you will find, in investigating this subject, that every solid argument is against the extraordinary court, and that every one in its favor is specious only. It is a transfer from a judicature of learning and integrity, to one, the greatness of which is both illiterate and unprincipled. Yet such is the force of prejudice with some, and of the want of reflection in others, that many of our constitutions have copied this absurdity, without suspecting it to be one. I am glad to hear that our new constitution is pretty sure of being accepted by States enough to secure the good it contains, and to meet with such opposition in some others, as to give us hopes it will be accommodated to them, by the amendment of its most glaring faults, particularly the want of a declaration of rights.
The long expected edict for the Protestants at length appears here. Its analysis is this. It is an acknowledgment (hitherto withheld by the laws) that Protestants can beget children, and that they can die, and be offensive unless buried. It does not give them permission to think, to speak, or to worship. It enumerates the humiliations to which they shall remain subject, and the burthens to which they shall continue to be unjustly exposed. What are we to think of the condition of the human mind in a country, where such a wretched thing as this has thrown the State into convulsions, and how must we bless our own situation in a country, the most illiterate peasant of which is a Solon, compared with the authors of this law. There is modesty often, which does itself injury; our countrymen possess this. They do not know their own superiority. You see it; you are young, you have time and talents to correct them. Study the subject while in Europe, in all the instances which will present themselves to you, and profit your countrymen of them, by making them to know and value themselves.
Adieu, my dear Sir, and be assured of the esteem with which I am your friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO THE COMMISSIONERS OF THE TREASURY.
Paris, February 7, 1788.
Gentlemen,
Your favors of November the 10th and 13th, and December the 5th, have been duly received. Commodore Jones left this place for Copenhagen, the 5th instant, to carry into execution the resolution of Congress, of October the 25th. Whatever monies that court shall be willing to allow, shall be remitted to your bankers, either in Amsterdam or Paris, as shall be found most beneficial, allowing previously to be withdrawn Commodore Jones’s proportion, which will be necessary for his subsistence. I desired him to endeavor to prevail on the Danish minister, to have the money paid in Amsterdam or Paris, by their banker in either of those cities, if they have one.
M. Ast (secretary to the consulate) is at L’Orient. Whether he comes up with the papers, or sends them, they shall be received, sealed up, and taken care of. I will only ask the favor of you, that I may never be desired to break the seals, unless very important cause for it should arise.
I have just received from Messrs. Willincks and Van Staphorsts, a letter of January the 31st, in which are these words: ‘The official communication we have of the actual situation and prospect of the finances of the United States, would render such a partial payment as that to Fiseaux’s house of no avail towards the support of the public credit, unless effectual measures shall be adopted, to provide funds for the two hundred and seventy thousand florins, interest, that will be due the first of June next; a single day’s retard in which would ground a prejudice of long duration.’ They informed me, at the same time, that they have made to you the following communication; that Mr. Stanitski, our principal broker, and holder of thirteen hundred and forty thousand dollars, of certificates of our domestic debt, offers to have our loan of a million of guilders (of which six hundred and twenty-two thousand eight hundred and forty are still unfilled) immediately made up, on condition that he may retain thereout one hundred and eighty thousand guilders, being one year’s interest on his certificates, allowing a deduction of ten per cent, from his said interest, as a compensation for his receiving it in Amsterdam instead of America, and not pretending that this shall give him any title to ask any payment of future interest in Europe. They observe, that this will enable them to face the demands of Dutch interest, till the 1st of June, 1789, pay the principal of Fiseaux’ debt, and supply the current expenses of your legation in Europe. On these points, it is for you to decide. I will only take the liberty to observe, that if they shall receive your acceptance of the proposition, some days credit will still be to be given for producing the cash, and that this must be produced fifteen days before it is wanting, because that much previous notice is always given to the creditors, that their money is ready. It is, therefore, but three months from this day, before your answer should be in Amsterdam. It might answer a useful purpose also, could I receive a communication of that answer ten days earlier than they. The same stagnation attending our passage from the old to the new form of government, which stops the feeble channel of money hitherto flowing towards our treasury, has suspended also what foreign credit we had. So that, at this moment, we may consider the progress of our loan as stopped. Though much an enemy to the system of borrowing, yet I feel strongly the necessity of preserving the power to borrow. Without this, we might be overwhelmed by another nation, merely by the force of its credit. However, you can best judge whether the payment of a single year’s interest on Stanitski’s certificates, in Europe, instead of America, may be more injurious to us than the shock of our credit in Amsterdam, which may be produced by a failure to pay our interest.
I have only to offer any services which I can render in this business, either here or by going to Holland, at a moment’s warning, if that should be necessary.
I have the honor to be, with sentiments of the most perfect esteem and respect, Gentlemen, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO DOCTOR PRICE.
Paris, February 7, 1788.
Dear Sir,
It is rendering mutual service to men of virtue and understanding, to make them acquainted with one another. I need no other apology for presenting to your notice the bearer hereof, Mr. Barlow. I know you were among the first who read the “Vision of Columbus,” while yet in manuscript: and think the sentiments I heard you express of that poem, will induce you to be pleased with the acquaintance of their author. He comes to pass a few days only at London, merely to know something of it. As I have little acquaintance there, I cannot do better for him than to ask you to be so good as to make him known to such persons, as his turn and his time might render desirable to him.
I thank you for the volume you were so kind as to send me some time ago. Every thing you write is precious, and this volume is on the most precious of all our concerns. We may well admit morality to be the child of the understanding rather than of the senses, when we observe that it becomes dearer to us as the latter weaken, and as the former grows stronger by time and experience, till the hour arrives in which all other objects lose all their value. That that hour may be distant with you, my friend, and that the intermediate space may be filled with health and happiness, is the sincere prayer of him who is, with sentiments of great respect and friendship, Dear Sir, your most obedient, humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
Paris, February.7, 1788.
Dear Sir,
I received duly your friendly letter of November the 12th. By this time, you will have seen published by Congress, the new regulations obtained from this court, in favor of our commerce. You will observe, that the arrangement relative to tobacco is a continuation of the order of Berni for five years, only leaving the price to be settled between the buyer and seller. You will see too, that all contracts for tobacco are forbidden, till it arrives in France. Of course, your proposition for a contract is precluded.
I fear the prices here will be low, especially if the market be crowded. You should be particularly attentive to the article, which requires that the tobacco should come in French or American bottoms, as this article will, in no instance, be departed from.
I wish with all my soul, that the nine first conventions may accept the new constitution, because this will secure to us the good it contains, which I think great and important. But I equally wish, that the four latest conventions, which ever they be, may refuse to accede to it, till a declaration of rights be annexed. This would probably command the offer of such a declaration, and thus give to the whole fabric, perhaps, as much perfection as any one of that kind ever had. By a declaration of rights, I mean one which shall stipulate freedom of religion, freedom of the press, freedom of commerce against monopolies, trial by juries in all cases, no suspensions of the habeas corpus, no standing armies. These are fetters against doing evil, which no honest government should decline. There is another strong feature in the new constitution, which I as strongly dislike. That is, the perpetual re-eligibility of the President. Of this I expect no amendment at present, because I do not see that any body has objected to it on your side the water. But it will be productive of cruel distress to our country, even in your day and mine. The importance to France and England, to have our government in the hands of a friend or foe, will occasion their interference by money, and even by arms. Our President will be of much more consequence to them than a King of Poland. We must take care, however, that neither this, nor any other objection to the new form, produces a schism in our Union. That would be an incurable evil, because near friends falling out, never re-unite cordially; whereas, all of us going together, we shall be sure to cure the evils of our new constitution, before they do great harm. The box of books I had taken the liberty to address to you, is but just gone from Havre for New York. I do not see, at present, any symptoms strongly indicating war. It is true, that the distrust existing between the two courts of Versailles and London, is so great, that they can scarcely do business together. However, the difficulty and doubt of obtaining money make both afraid to enter into war. The little preparations for war, which we see, are the effect of distrust, rather than of a design to commence hostilities. And in such a state of mind, you know, small things may produce a rupture: so that though peace is rather probable, war is very possible.
Your letter has kindled all the fond recollections of ancient times; recollections much dearer to me than any thing I have known since. There are minds which can be pleased by honors and preferments; but I see nothing in them but envy and enmity. It is only necessary to possess them, to know how little they contribute to happiness, or rather how hostile they are to it. No attachments soothe the mind so much as those contracted in early life; nor do I recollect any societies which have given me more pleasure, than those of which you have partaken with me. 1 had rather be shut up in a very modest cottage, with my books, my family, and a few old friends, dining on simple bacon, and letting the world roll on as it liked, than to occupy the most splendid post, which any human power can give. I shall be glad to hear from you often. Give me the small news as well as the great. Tell Dr. Currie, that I believe I am indebted to him a letter, but that like the mass of our countrymen, I am not, at this moment, able to pay all my debts; the post being to depart in an hour, and the last stroke of a pen I am able to send by it, being that which assures you of the sentiments of esteem and attachment, with which I am, Dear Sir, your affectionate friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
Paris, February 12, 1888.
Sir,
I am very sensible of the honor you propose to me, of becoming a member of the society for the abolition of the slave-trade. You know that nobody wishes more ardently, to see an abolition, not only of the trade, but of the condition of slavery: and certainly nobody will be more willing to encounter every sacrifice for that object. But the influence and information of the friends to this proposition in France will be far above the need of my association. I am here as a public servant, and those whom I serve, having never yet been able to give their voice against the practice, it is decent for me to avoid too public a demonstration of my wishes to see it abolished. Without serving the cause here, it might render me less able to serve it beyond the water. I trust you will be sensible of the prudence of those motives, therefore, which govern my conduct on this occasion, and be assured of my wishes for the success of your undertaking, and the sentiments of esteem and respect, with which I have the honor to be, Sir, your most obedient, humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN ADAMS.
Paris, March 2, 1788.—Sunday.
Dear Sir,
I received this day, a letter from Mrs. Adams, of the 26th ultimo, informing me you would set out on the 29th for the Hague. Our affairs at Amsterdam press on my mind like a mountain. I have no information to go on, but that of Willincks and Van Staphorsts, and according to that, something seems necessary to be done. I am so anxious to confer with you on this subject, and to see you and them together, and get some effectual arrangement made in time, that I determine to meet you at the Hague. I will set out the moment some repairs are made to my carriage: it is promised me at three o’clock to-morrow; but probably they will make it night, and that I may not set out till Tuesday morning. In that case, I shall be at the Hague on Friday night: in the mean time, you will perhaps have made all your bows there. I am sensible how irksome this must be to you, in the moment of your departure. But it is a great interest of the United States, which is at stake, and I am sure you will sacrifice to that your feelings and your interest. I hope to shake you by the hand within twenty-four hours after you receive this; and in the mean time, I am, with much esteem and respect, Dear Sir, your affectionate friend and humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN JAY.
Amsterdam, March 16, 1788.
Sir,
In a letter of the 13th instant, which I had the honor of addressing you from this place, I mentioned in general terms, the object of my journey hither, and that I should enter into more particular details, by the confidential conveyance which would occur through Mr. Adams and Colonel Smith.
The board of treasury had, in the month of December, informed me and our bankers here, that it would be impossible for them to make any remittances to Europe for the then ensuing year, and that they must, therefore, rely altogether on the progress of the late loan. But this, in the mean time, after being about one third filled, had ceased to get forward. The bankers who had been referred to me for advice, by Mr. Adams, stated these circumstances, and pressed their apprehension for the ensuing month of June, when two hundred and seventy thousand florins would be wanting for interest. In fine, they urged an offer of the holders of the former bonds, to take all those remaining on hand, provided they might receive out of them the interest on a part of our domestic debt, of which they had also become the holders. This would have been one hundred and eighty thousand florins. To this proposition, I could not presume any authority to listen. Thus pressed between the danger of failure on one hand, and this proposition on the other, I heard of Mr. Adams being gone to the Hague to take leave. His knowledge of the subject was too valuable to be neglected under the present difficulty, and it was the last moment in which we could be availed of it. I set out immediately, therefore, for the Hague, and we came on to this place together, in order to see what could be done. It was easier to discover, than to remove, the causes which obstructed the progress of the loan. Our affairs here, like those of other nations, are in the hands of particular bankers. These employ particular, and they have their particular circle of money-lenders. These moneylenders, as I have before mentioned, while placing a part of their money in our foreign loans, had at the same time employed another part in a joint speculation, to the amount of eight hundred and forty thousand dollars, in our domestic debt. A year’s interest was becoming due on this, and they wished to avail themselves of our want of money for the foreign interest, to obtain payment of the domestic. Our first object was to convince our bankers, that there was no power on this side the Atlantic which could accede to this proposition, or give it any countenance. They at length, therefore, but with difficulty, receded from this ground, and agreed to enter into conferences with the brokers and lenders, and to use every exertion to clear the loan from the embarrassment in which this speculation had engaged it. What will be the result of these conferences, is not yet known. We have hopes, however, that it is not desperate, because the bankers consented yesterday, to pay off the capital of fifty-one thousand florins, which had become due on the first day of January, and which had not yet been paid. We have gone still further. The treasury board gives no hope of remittances, till the new government can procure them. For that government to be adopted, its legislature assembled, its system of taxation and collection arranged, the money gathered from the people into the treasury, and then remitted to Europe, must extend considerably into the year 1790. To secure our credit then, for the present year only, is but to put off the evil day to the next. What remains of the last loan, when it shall be filled up, will little more than clear us of present demands, as may be seen by the estimate enclosed. We thought it better, therefore, to provide at once for the years 1789 and 1790 also; and thus to place the government at its ease, and her credit in security, during that trying interval. The same estimate will show, that another million of florins will be necessary to effect this. We stated this to our bankers, who concurred in our views, and that to ask the whole sum at once would be better than to make demands from time to time, so small, as that they betray to the money-holders the extreme feebleness of our resources. Mr. Adams, therefore, has executed bonds for another million of florins; which, however, are to remain unissued till Congress shall have ratified the measure that this transaction is something or nothing, at their pleasure. We suppose its expediency so apparent, as to leave little doubt of its ratification. In this case, much time will have been saved by the execution of the bonds at this moment, and the proposition will be presented here under a more favorable appearance, according to the opinion of the bankers. Mr. Adams is under a necessity of setting out to-morrow morning, but I shall stay two or three days longer, to attend to and encourage the efforts of the bankers; though it is yet doubtful whether they will ensure us a safe passage over the month of June. Not having my letters here to turn to, I am unable to say whether the last I wrote, mentioned the declaration of the Emperor that he should take part in the war against the Turks. This declaration appeared a little before, or a little after that letter, I do not recollect which. Some little hostilities have taken place between them. The court of Versailles seems to pursue immoveably its pacific system, and from every appearance in the country from which I write, we must conclude that its tragedy is wound up. The triumph appears complete, and tranquillity perfectly established. The numbers who have emigrated are differently estimated, from twenty to forty thousand. A little before I left Paris, I received a piece of intelligence, which should be communicated, leaving you to lay what stress on it, it may seem to deserve. Its authenticity may be surely relied on. At the time of the late pacification, Spain had about fifteen ships of the line nearly ready for sea. The convention for disarming did not extend to her, nor did she disarm. This gave inquietude to the court of London, and they demanded an explanation. One was given, they say, which is perfectly satisfactory. The Russian minister at Versailles, getting knowledge of this, became suspicious on his part. He recollected that Spain, during the late war, had been opposed to the entrance of a Russian fleet into the Mediterranean, and concluded, if England was not the object of this armament, Russia might be. It is known that that power means to send a fleet of about twenty-four ships into the Mediterranean this summer. He sent to the Count de Montmorin, and expressed his apprehensions. The Count de Montmorin declared, that the object of Spain in that armament was totally different; that he was not sure she would succeed; but that France and Spain were to be considered as one, and that the former would become guarantee for the latter, that she would make no opposition to the Russian fleet. If neither England nor Russia be the object, the question recurs, Who is it for? You know best, if our affairs with Spain are in a situation to give jealousy to either of us. I think it very possible, that the satisfaction of the court of London may have been pretended or premature. It is possible also, that the affairs of Spain in South America may require them to assume a threatening appearance. I give you the facts, however, and you will judge whether they are objects of attention or of mere curiosity.
I have the honor to be, with sentiments of sincere esteem and respect, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
P. S. I enclose herewith an extract of a letter from the Count de Vergennes to the French ambassador at the Hague, which will make a remarkable chapter in the history of the late revolution here. It is not public, nor should be made so by us. Probably those who have been the victims of it, will some day publish it.
TO MR. DUMAS.
Amsterdam, March 29, 1788.
Sir,
I have now to acknowledge the receipt of your favors of the 14th, 18th, and 23rd instant. I would have preferred doing it in person, but the season, and the desire of seeing what I have not yet seen, invite me to take the route of the Rhine. I shall leave this place to-morrow morning, and probably not reach Paris till the latter end of April. In the moment we were to have conferred on the subject of paying the arrears due to you, a letter of the 20th of February, from the board of treasury, was received, forbidding the application of money to any purpose, (except our current claims,) till the June interest should be actually in hand. Being by the letter, tied up from giving an order in your favor, I return you the letter you had written to Mr. Jay, on the supposition that the order for your arrears was given. It has been suggested, however, that if you could receive bonds of the loan, you could make them answer your purpose, and the commissioners say, this would in no wise interfere with the views of the treasury board, nor the provision for the June interest. I have, therefore, recommended to them in writing, to give you bonds to the amount of your balance, if you choose to take them, rather than to wait. I wish this may answer your purpose. I remember that in the conversation which I had the honor of having with you, on the evening I was at the Hague, you said that your enemies had endeavored to have it believed, that Congress would abandon you, and withdraw your appointments. An enemy generally says and believes what he wishes, and your enemies, particularly, are not those who are most in the counsels of Congress, nor the best qualified to tell what Congress will do. From the evidences you have received of their approbation, and from their well known steadiness and justice, you must be assured of a continuance of their favor, were they to continue under the present form. Nor do I see any thing in the new government which threatens us with less firmness. The Senate, who will make and remove their foreign officers, must, from its constitution, be a wise and steady body. Nor would a new government begin its administration by discarding old servants; servants who have put all to the risk, and when the risk was great, to obtain that freedom and security under which themselves will be what they shall be. Upon the whole, my Dear Sir, tranquillize yourself and your family upon this subject. All the evidence, which exists as yet, authorizes you to do this, nor can I foresee any cause of disquiet in future. That none may arise, that yourself and family may enjoy health, happiness, and the continued approbation of those by whom you wish most to be approved, is the sincere wish of him, who has the honor to be, with sentiments of sincere esteem and attachment, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO THE COMMISSIONERS OF THE TREASURY.
Gentlemen,
Amsterdam, March 29, 1788.
I cannot close my letter, without some observations on the transfer of our domestic debt to foreigners. This circumstance, and the failure to pay off Fiseaux’ loan, were the sole causes of the stagnation of our late loan. For otherwise our credit would have stood on more hopeful grounds than heretofore. There was a condition in the last loan, that, the lenders furnishing one third of the money, the remaining two thirds of the bonds should remain eighteen months unsold, and at their option to take or not, and that in the mean time, the same bankers should open no other loan for us. These same lenders became purchasers of our domestic debt, and they were disposed to avail themselves of the power they had thus acquired over us as to our foreign demands, to make us pay the domestic one. Should the present necessities have obliged you to comply with their proposition for the present year, I should be of opinion it ought to be the last instance. If the transfer of these debts to Europe meet with any encouragement from us, we can no more borrow money here, let our necessities be what they will. For who will give ninety-six per cent, for the foreign obligations of the same nation, whose domestic ones can be bought at the same market for fifty-five per cent.; the former, too, bearing an interest of only five per cent., while the latter yields six. If any discouragements can be honestly thrown on this transfer, it would seem advisable, in order to keep the domestic debt at home. It would be a very effectual one, if, instead of the title existing in our treasury books alone, it was made to exist in loose papers, as our loan office debts do. The European holder would then be obliged to risk the title paper of his capital, as well as his interest, in the hands of his agent in America, whenever the interest was to be demanded; whereas, at present, he trusts him with the interest only. This single circumstance would put a total stop to all future sales of domestic debt at this market. Whether this, or any other obstruction, can or should be thrown in the way of these operations, is not for me to decide; but I have thought the subject worthy your consideration.
I have the honor to be, with sentiments of the most perfect esteem and respect, Gentlemen, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO GENERAL WASHINGTON.
Paris, May 2, 1788.
Dear Sir,
I am honored with your Excellency’s letter by the last packet, and thank you for the information it contains on the communication between the Cayahoga and Big Beaver. I have ever considered the opening a canal between those two water courses, as the most important work in that line, which the state of Virginia could undertake. If will infallibly turn through the Potomac all the commerce of Lake Erie, and the country west of that, except what may pass down the Mississippi; and it is important that it be soon done, lest that commerce should, in the mean time, get established in another channel. Having, in the spring of the last year, taken a journey through the southern parts of France, and particularly examined the canal of Languedoc, through its whole course, I take the liberty of sending you the notes I made on the spot, as you may find in them something perhaps, which may be turned to account, some time or other, in the prosecution of the Potomac canal. Being merely a copy from my travelling notes, they are undigested and imperfect, but may still, perhaps, give hints capable of improvement in your mind.
The affairs of Europe are in such a state still, that it is impossible to say what form they will take ultimately. France and Prussia, viewing the Emperor as their most dangerous and common enemy, had heretofore seen their common safety as depending on a strict connection with one another. This had naturally inclined the Emperor to the scale of England, and the Empress also, as having views in common with the Emperor, against the Turks. But these two powers would, at any time, have gladly quitted England, to coalesce with France, as being the power which they met every where, opposed as a barrier to all their schemes of aggrandizement. When, therefore, the present King of Prussia took the eccentric measure of bidding defiance to France, by placing his brother-in-law on the throne of Holland, the two empires immediately seized the occasion of soliciting an alliance with France. The motives for this appeared so plausible, that it was believed the latter would have entered into this alliance, and that thus the whole political system of Europe would have taken a new form. What has prevented this court from coming into it, we know not. The unmeasurable ambition of the Emperor, and his total want of moral principle and honor, are suspected. A great share of Turkey, the recovery of Silesia, the consolidation of his dominions by the Bavarian exchange, the liberties of the Germanic body, all occupy his mind together; and his head is not well enough organized, to pursue so much only of all this, as is practicable. Still it was thought that France might safely have coalesced with these powers, because Russia and herself holding close together, as their interests would naturally dictate, the Emperor could never stir, but with their permission. France seems, however, to have taken the worst of all parties, that is, none at all. She folds her arms, lets the two empires go to work to cut up Turkey as they can, and holds Prussia aloof, neither as a friend nor foe. This is withdrawing her opposition from the two empires, without the benefit of any condition whatever. In the mean time, England has clearly overreached herself. She excited the war between the Russians and Turks, in hopes that France, still supporting the Turks, would be embarrassed with the two empires. She did not foresee the event which has taken place, of France abandoning the Turks, and that which may take place, of her union with the two empires. She allied herself with Holland, but cannot obtain the alliance of Prussia. This latter power would be very glad to close again the breach with France, and therefore, while there remains an opening for this, holds off from England, whose fleets could not enter into Silesia, to protect that from the Emperor. Thus you see, that the old system is unhinged, and no new one hung in its place. Probabilities are rather in favor of a connection between the two empires, France, and Spain. Several symptoms show themselves, of friendly dispositions between Russia and France, unfriendly ones between Russia and England, and such as are barely short of hostility between England and France. But into real hostilities, this country would with difficulty be drawn. Her finances are too deranged, her internal union too much dissolved, to hazard a war. The nation is pressing on fast, to a fixed constitution. Such a revolution in the public opinion has taken place, that the crown already feels its powers bounded, and is obliged, by its measures, to acknowledge limits.
A States-General will be called at some epoch not distant; they will probably establish a civil list, and leave the government to temporary provisions of money, so as to render frequent assemblies of the national representative necessary. How that representative will be organized, is yet uncertain. Among a thousand projects, the best seems to me, that of dividing them into two Houses, of Commons and Nobles; the Commons to be chosen by the Provincial Assemblies, who are chosen themselves by the people, and the Nobles by the body of Noblesse, as in Scotland. But there is no reason to conjecture, that this is the particular scheme which will be preferred.
The war between the Russians and Turks has made an opening for our Commodore Paul Jones. The Empress has invited him into her service. She insures to him the rank of rear-admiral; will give him a separate command, and it is understood, that he is never to be commanded. I think she means to oppose him to the Captain Pacha, on the Black Sea. He is by this time, probably, at St. Petersburg. The circumstances did not permit his awaiting the permission of Congress, because the season was close at hand for opening the campaign. But he has made it a condition, that he shall be free at all times to return to the orders of Congress, whenever they shall please to call for him; and also, that he shall not, in any case be expected to bear arms against France. I believe Congress had it in contemplation to give him the grade of admiral, from the date of his taking the Serapis. Such a measure now, would greatly gratify him, second the efforts of fortune in his favor, and better the opportunities of improving him for our service, whenever the moment shall come in which we may want him.
The danger of our incurring something like a bankruptcy in Holland, which might have been long, and even fatally felt in a moment of crisis, induced me to take advantage of Mr. Adams’s journey to take leave at the Hague, to meet him there, get him to go on to Amsterdam, and try to avert the impending danger. The moment of paying a great sum of annual interest was approaching. There was no money on hand; the board of treasury had notified that they could not remit any; and the progress of the loan, which had been opened there, had absolutely stopped. Our bankers there gave me notice of all this; and that a single day’s failure in the payment of interest, would have the most fatal effect on our credit. I am happy to inform you, we were able to set the loan a going again, and that the evil is at least postponed. Indeed, I am tolerably satisfied, that if the measures we proposed, are ratified by Congress, all European calls for money (except the French debt) are secure enough, till the end of the year 1790; by which time, we calculated that the new government might be able to get money into the treasury. Much conversation with the bankers, brokers, and money-holders, gave me insight into the state of national credit there, which I had never before been able satisfactorily to get. The English credit is the first, because they never open a loan, without laying and appropriating taxes for the payment of the interest, and there has never been an instance of their failing one day, in that payment. The Emperor and Empress have good credit, because they use it little, and have hitherto been very punctual. This country is among the lowest, in point of credit. Ours stands in hope only. They consider us as the surest nation on earth for the repayment of the capital; but as the punctual payment of interest is of absolute necessity in their arrangements, we cannot borrow but with difficulty and disadvantage. The monied men, however, look towards our new government with a great degree of partiality, and even anxiety. If they see that set out on the English plan, the first degree of credit will be transferred to us. A favorable occasion will arise to our new government of asserting this ground to themselves. The transfer of the French debt, public and private, to Amsterdam, is certainly desirable. An act of the new government, therefore, for opening a loan in Holland for the purpose, laying taxes at the same time for paying annually the interest and a part of the principal, will answer the two valuable purposes, of ascertaining the degree of our credit, and of removing those causes of bickering and irritation, which should never be permitted to subsist with a nation, with which it is so much our interest to be on cordial terms as with France. A very small portion of this debt, I mean that part due to the French officers, has done us an injury, of which those in office in America cannot have an idea. The interest is unpaid for the last three years; and these creditors, highly connected, and at the same time needy, have felt and communicated hard thoughts of us. Borrowing, as we have done, three hundred thousand florins a year, to pay our interest in Holland, it would have been worth while to have added twenty thousand more, to suppress those clamors. I am anxious about every thing which may affect our credit. My wish would be, to possess it in the highest degree, but to use it little. Were we without credit, we might be crushed by a nation of much inferior resources, but possessing higher credit. The present system of war renders it necessary to make exertions far beyond the annual resources of the State, and consume in one year the efforts of many. And this system we cannot change. It remains, then, that we cultivate our credit with the utmost attention.
I had intended to have written a word to your Excellency on the subject of the new constitution, but I have already spun out my letter to an immoderate length. I will just observe, therefore, that according to my ideas, there is a great deal of good in it. There are two things, however, which I dislike strongly, 1. The want of a declaration of rights. I am in hopes the opposition in Virginia will remedy this, and produce such a declaration. 2. The perpetual re-eligibility of the President. This, I fear, will make that an office for life, first, and then hereditary. I was much an enemy to monarchies before I came to Europe. I am ten thousand times more so, since I have seen what they are. There is scarcely an evil known in these countries, which may not be traced to their king, as its source, nor a good, which is not derived from the small fibres of republicanism existing among them. I can further say, with safety, there is not a crowned head in Europe, whose talents or merits would entitle him to be elected a vestryman by the people of any parish in America. However, I shall hope, that before there is danger of this change taking place in the office of President, the good sense and free spirit of our countrymen will make the changes necessary to prevent it. Under this hope, I look forward to the general adoption of the new constitution with anxiety, as necessary for us under our present circumstances. I have so much trespassed on your patience already, by the length of this letter, that I will add nothing further, than those assurances of sincere esteem and attachment, with which I have the honor to be, your Excellency’s most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JAMES MADISON.
Paris, May 3,1788.
Dear Sir,
Mine of February the 6th acknowledged the receipt of yours of December the 9th and 20th; since that, those of February the 19th and 20th have come to hand. The present will be delivered you by Mr. Warville, whom you will find truly estimable, and a great enthusiast for liberty. His writings will have shown you this.
For public news, I must refer you to my letters to Mr. Jay. Those I wrote to him from Amsterdam will have informed you of my journey thither. While there, I endeavored to get, as well as I could, into the state of national credit there; for though I am an enemy to the using our credit but under absolute necessity, yet the possessing a good credit I consider as indispensable, in the present system of carrying on war. The existence of a nation having no credit, is always precarious. The credit of England is the best. Their paper sells at par on the exchange of Amsterdam, the moment any of it is offered, and they can command there any sum they please. The reason is, that they never borrow, without establishing taxes for the payment of the interest, and they never yet failed one day in that payment. The Emperor and Empress have good credit enough. They use it little and have been ever punctual. This country cannot borrow at all there; for though they always pay their interest within the year, yet it is often some months behind. It is difficult to assign to our credit its exact station in this scale. They consider us as the most certain nation on earth for the principal; but they see that we borrow of themselves to pay the interest, so that this is only a conversion of their interest into principal. Our paper, for this reason, sells for from four to eight per cent, below par, on the exchange, and our loans are negotiated with the Patriots only. But the whole body of money-dealers, Patriot and Stadtholderian, look forward to our new government with a great degree of partiality and interest. They are disposed to have much confidence in it, and it was the prospect of its establishment, which enabled us to set the loan of last year into motion again. They will attend steadfastly to its first money operations. If these are injudiciously begun, correction, whenever they shall be corrected, will come too late. Our borrowings will always be difficult and disadvantageous. If they begin well, our credit will immediately take the first station. Equal provision for the interest, adding to it a certain prospect for the principal, will give us a preference to all nations, the English not excepted. The first act of the new government should be some operation, whereby they may assume to themselves this station. Their European debts form a proper subject for this. Digest the whole, public and private, Dutch, French, and Spanish, into a table, showing the sum of interest due every year, and the portions of principal payable the same year. Take the most certain branch of revenue, and one which shall suffice to pay the interest, and leave such a surplus as may accomplish all the payments of the capital, as terms somewhat short of those, at which they will become due. Let the surpluses of those years, in which no reimbursement of principal falls, be applied to buy up our paper on the exchange of Amsterdam, and thus anticipate the demands of principal. In this way our paper will be kept up at par; and this alone will enable us to command in four and twenty hours, at any time, on the exchange of Amsterdam, as many millions as that capital can produce. The same act which makes this provision for the existing debts, should go on to open a loan to their whole amount; the produce of that loan to be applied, as fast as received, to the payment of such parts of the existing debts as admit of payment. The rate of interest to be as the government should privately instruct their agent, because it must depend on the effect these measures would have on the exchange. Probably it could be lowered from time to time. Honest and annual publications of the payments made, will inspire confidence, while silence would conceal nothing from those interested to know.
You will perceive by the comte rendu which I send you, that this country now calls seriously for its interest at least. The nonpayment of this, hitherto, has done our credit little injury, because the government here, saying nothing about it, the public have supposed they wished to leave us at our ease as to the payment. It is now seen that they call for it, and they will publish annually the effect of that call. A failure here, therefore, will have the same effect on our credit hereafter, as a failure at Amsterdam. I consider it, then, as of a necessity not to be dispensed with, that these calls be effectually provided for. If it shall be seen, that the general provision before hinted at cannot be in time, then it is the present government which should take on itself to borrow in Amsterdam what may be necessary. The new government should by no means be left by the old to the necessity of borrowing a stiver, before it can tax for its interest. This will be to destroy the credit of the new government in its birth. And I am of opinion, that if the present Congress will add to the loan of a million (which Mr. Adams and myself have proposed this year) what may be necessary for the French calls to the year 1790, the money can be obtained at the usual disadvantage. Though I have not at this moment received such authentic information from our bankers as I may communicate to Congress, yet I know privately from one of them (Mr. Jacob Van Staphorst, who is here), that they had on Hand a fortnight ago four hundred thousand florins, and the sale going on well. So that the June interest, which had been in so critical a predicament, was already secured. If the loan of a million on Mr. Adams’s bonds of this year be ratified by Congress, the applications of the money on hand may go on immediately, according to the statement I sent to Mr. Jay. One article in this I must beg you to press on the treasury board; that is, an immediate order for the payment of the three years’ arrearages to the French officers. They were about holding a meeting to take desperate measures on this subject, when I was called to Holland. I desired them to be quiet till my return, and since my return I have pressed a further tranquillity till July, by which time I have given them reason to hope I may have an answer from the treasury board to my letters of March. Their ill humor can be contained no longer; and as I know no reason why they may not be paid at that time, I shall have nothing to urge in our defence after that.
You remember the report, drawn by Governor Randolph, on the navigation of the Mississippi. When I came to Europe, Mr. Thomson was so kind as to have me a copy of it made out. I lent it to Dr. Franklin, and he mislaid it, so that it could never be found. Could you make interest with him to have me another copy made, and send it to me? By Mr. Warville I send your pedometer. To the loop at the bottom of it you must sew a tape, and at the other end of the tape a small hook (such as we use under the name of hooks and eyes), cut a little hole in the bottom of your left watch-pocket, pass the hook and tape through it, and down between the breeches and drawers, and fix the hook on the edge of your knee-band, an inch from the knee-buckle; then hook the instrument itself by its swivel-hook on the upper edge of the watch-pocket. Your tape being well adjusted in length, your double steps will be exactly counted by the instrument, the shortest hand pointing out the thousands, the flat hand the hundreds, and the long hand the tens and units. Never turn the hands backward; indeed, it is best not to set them to any given place, but to note the number they stand at when you begin to walk. The adjusting the tape to its exact length is a critical business, and will cost you many trials. But once done, it is done for ever. The best way is to have a small buckle fixed on the middle of the tape, by which you can take it up, and let it out at pleasure. When you choose it should cease to count, unhook it from the top of the watch-pocket, and let it fall down to the bottom of the pocket.
I am, with sentiments of the most sincere esteem and attachment, Dear Sir, your affectionate friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN JAY.
Paris, May 4, 1788.
Sir,
I had the honor of addressing you in two letters of the 13th and 16th of March from Amsterdam, and have since received Mr. Ramson’s of February the 20th. I staid at Amsterdam about ten or twelve days after the departure of Mr. Adams, in hopes of seeing the million of the last year filled up. This, however, could not be accomplished on the spot. But the prospect was so good as to have dissipated all fears; and since my return here, I learn (not officially from our bankers, but) through a good channel, that they have received near four hundred thousand florins since the date of the statement I sent you in my letter of March the 16th; and I presume we need not fear the completion of that loan, which will provide for all our purposes of the year 1788, as stated in that paper. I hope, therefore, to receive from the treasury orders in conformity thereto, that I may be able to proceed to the redemption of our captives. A provision for the purposes of the years 1789 and 1790, as stated in the same paper, will depend on the ratification by Congress of Mr. Adams’s bonds of this year for another million of florins. But there arises a new call from this government, for its interest at least. Their silence hitherto has made it be believed in general, that they consented to the nonpayment of our interest to them, in order to accommodate us. You will perceive in the seventy-fifth and seventy-sixth pages of the compte rendu, which I have the honor to send you, that they call for this interest, and will publish whether it be paid or not; and by No. 25, page eighty-one, that they count on its regular receipt for the purposes of the year. These calls, for the first days of January, 1789 and 1790, will amount to about a million and a half of florins more; and if to be raised by loan, it must be for two millions, as well to cover the expenses of the loan, as that loans are not opened for fractions of millions. This publication seems to render a provision for this interest as necessary as for that of Amsterdam.
I had taken measures to have it believed at Algiers, that our government withdrew its attention from our captives there. This was to prepare their captors for the ransoming them at a reasonable price. I find, however, that Captain O’Bryan is apprized that I have received some authority on this subject. He writes me a cruel letter, supposing me the obstacle to their redemption. Their own interest requires that I should leave them to think thus hardly of me. Were the views of government communicated to them, they could not keep their own secret, and such a price would be demanded for them, as Congress, probably, would think ought not to be given, lest it should be the cause of involving thousands of others of their citizens in the same condition. The moment I have money, the business shall be set in motion.
By a letter from Joseph Chiappe, our agent at Mogadore, I am notified of a declaration of the Emperor of Morocco, that if the States General of the United Netherlands do not, before the month of May, send him an ambassador, to let him know whether it is war or peace between them, he will send one to them with five frigates; and that if their dispositions be unfavorable, their frigates shall proceed to America to make prizes on the Dutch, and to sell them there. It seems to depend on the Dutch, therefore, whether the Barbary powers shall learn the way to our coasts, and whether we shall have to decide the question of the legality of selling in our ports vessels taken from them. I informed you, in a former letter, of the declaration made by the court of Spain to that of London, relative to its naval armament, and also of the declaration of the Count de Montmorin to the Russian minister here on the same subject. I have good information, that the court of Spain has itself made a similar and formal declaration to the minister of Russia at Madrid. So that Russia is satisfied she is not the object. I doubt whether the English are equally satisfied as to themselves. The season has hitherto prevented any remarkable operation between the Turks and the two empires. The war, however, will probably go on, and the season now admits of more important events. The Empress has engaged Commodore Paul Jones in her service. He is to have the rank of rear-admiral, with a separate command, and it is understood that he is in no case to be commanded. He will probably be opposed to the Captain Pacha on the Black Sea. He received this invitation at Copenhagen, and as the season for commencing the campaign, was too near to admit time for him to ask and await the permission of Congress, he accepted the offer, only stipulating, that he should be always free to return to the orders of Congress whenever called for, and that he should not be expected to bear arms against France. He conceived, that the experience he should gain would enable him to be more useful to the United States, should they ever have occasion for him. It has been understood, that Congress had had it in contemplation to give him the grade of rear-admiral, from the date of the action of the Serapis, and it is supposed, that such a mark of their approbation would have a favorable influence on his fortune in the north. Copies of the letters which passed between him and the Danish minister are herewith transmitted. I shall immediately represent to Count Bernstorff, that the demand for our prizes can have no connection with a treaty of commerce; that there is no reason why the claims of our seamen should await so distant and uncertain an event; and press the settlement of this claim.
This country still pursues its line of peace. The ministry seem now all united in it; some from a belief of their inability to carry on a war; others from a desire to arrange their internal affairs, and improve their constitution. The differences between the King and parliaments threaten a serious issue. Many symptoms indicate that the government has in contemplation some act of highhanded authority. An extra number of printers have for several days been employed, the apartment wherein they are at work being surrounded by a body of guards, who permit no body either to come out or go in. The commanders of the provinces, civil and military, have been ordered to be at their stations on a certain day of the ensuing week. They are accordingly gone: so that the will of the King is probably to be announced through the whole kingdom on the same day. The parliament of Paris, apprehending that some innovation is to be attempted, which may take from them the opportunity of deciding on it after it shall be made known, came last night to the resolution of which I have the honor to enclose you a manuscript copy. This you will perceive to be, in effect, a declaration of rights. I am obliged to close here the present letter, lest I should miss the opportunity of conveying it by a passenger who is to call for it. Should the delay of the packet admit any continuation of these details, they shall be the subject of another letter, to be forwarded by post. The gazettes of Leyden and France accompany this.
I have the honor to be, with sentiments of the most perfect esteem and respect, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO THE COUNT DE MOUSTIER.
Paris, May 17, 1788.
Dear Sir,
I have at length an opportunity of acknowledging the receipt of your favors of February, and March the 14th, and congratulating you on your resurrection from the dead, among whom you had been confidently entombed by the news-dealers of Paris. I am sorry that your first impressions have been disturbed by matters of etiquette, where surely they should least have been expected to occur. These disputes are the most insusceptible of determination, because they have no foundation in reason. Arbitrary and senseless in their nature, they are arbitrarily decided by every nation for itself. These decisions are meant to prevent disputes, but they produce ten, where they prevent one. It would have been better, therefore, in a new country, to have excluded etiquette altogether; or if it must be admitted in some form or other, to have made it depend on some circumstance founded in nature, such as the age or station of the parties. However, you have got over all this, and I am in hopes have been able to make up a society suited to your own dispositions. Your situation will doubtless be improved by the adoption of the new constitution, which I hope will have taken place before you receive this. I see in this instrument a great deal of good. The consolidation of our government, a just representation, an administration of some permanence, and other features of great value, will be gained by it. There are, indeed, some faults, which revolted me a good deal in the first moment; but we must be contented to travel on towards perfection, step by step. We must be contented with the ground which this constitution will gain for us, and hope that a favorable moment will come for correcting what is amiss in it. I view in the same light the innovations making here. The new organization of the judiciary department is undoubtedly for the better. The reformation of the criminal code is an immense step taken towards good. The composition of the Plenary court is indeed vicious in the extreme; but the basis of that court may be retained, and its composition changed. Make of it a representative of the people, by composing it of members sent from the Provincial Assemblies, and it becomes a valuable member of the constitution. But it is said, the court will not consent to do this: the court, however, has consented to call the States General, who will consider the Plenary court but as a canvass for them to work on. The public mind is manifestly advancing on the abusive prerogatives of their governors, and bearing them down. No force in the government can withstand this, in the long run. Courtiers had rather give up power than pleasures; they will barter, therefore, the usurped prerogatives of the King for the money of the people. This is the agent by which modern nations will recover their rights. I sincerely wish that, in this country, they may be contented with a peaceable and passive opposition. At this moment we are not sure of this; though as yet it is difficult to say what form the opposition will take. It is a comfortable circumstance, that their neighboring enemy is under the administration of a minister disposed to keep the peace. Engage in war who will, may my country long continue your peaceful residence, and merit your good offices with that nation, whose affections it is their duty and interest to cultivate.
Accept these and all other the good wishes of him, who has the honor to be, with sincere esteem and respect, Dear Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN JAY.
Paris, May 23,1788.
Sir,
When I wrote my letter of the 4th instant, I had no reason to doubt that a packet would have sailed on the 10th, according to the established order. The passengers had all, except one, gone down to Havre in this expectation. However, none has sailed, and perhaps none will sail, as I think the suppression of the packets is one of the economies in contemplation. An American merchant, concerned in the commerce of the whale-oil, proposed to government to despatch his ships from Havre and Boston at stated periods, and to take on board the French courier and mail, and the proposition has been well enough received. I avail myself of a merchant vessel going from Havre, to write the present.
In my letter of the 4th, I stated to you the symptoms which indicated that government had some great stroke of authority in contemplation. That night they sent guards to seize Monsieur d’Epremenil and Monsieur Goiskind, two members of parliament, in their houses. They escaped, and took sanctuary in the Palais (or parliament house). The parliament assembled itself extraordinarily, summoned the Dukes and Peers specially, and came to the resolution of the 5th, which they sent to Versailles by deputies, determined not to leave the palace till they received an answer. In the course of that night a battalion of guards surrounded the house. The two members were taken by the officers from among their fellows, and sent off to prison, the one to Lyons, the other (d’Epremenil), the most obnoxious, to an island in the Mediterranean. The parliament then separated. On the 8th, a bed of justice was held at Versailles, wherein were enregistered the six ordinances which had been passed in Council on the 1st of May, and which I now send you. They were in like manner enregistered in beds of justice, on the same day, in nearly all the parliaments of the kingdom. By these ordinances, 1. The criminal law is reformed, by abolishing examination on the sellette, which, like our holding up the hand at the bar, remained a stigma on the party, though innocent; by substituting an oath, instead of torture, on the question préalable, which is used after condemnation, to make the prisoner discover his accomplices; (the torture, abolished in 1780, was on the question préparatoire, previous to judgment, in order to make the prisoner accuse himself;) by allowing counsel to the prisoner for his defence; obliging the judges to specify in their judgments the offence for which he is condemned; and respiting execution a month, except in the case of sedition. This reformation is unquestionably good, and within the ordinary legislative powers of the crown. That it should remain to be made at this day, proves that the monarch is the last person in his kingdom who yields to the progress of philanthropy and civilization. 2. The organization of the whole judiciary department is changed, by the institution of subordinate jurisdictions, the taking from the parliaments the cognizance of all causes of less value than twenty thousand livres, reducing their numbers to about a fourth, and suppressing a number of special courts. Even this would be a great improvement, if it did not imply that the King is the only person in this nation, who has any rights or any power. 3. The right of registering the laws is taken from the parliaments, and transferred to a Plenary court, created by the King. This last is the measure most obnoxious to all persons. Though the members are to be for life, yet a great proportion of them are from descriptions of men always candidates for the royal favor in other lines. As yet, the general consternation has not sufficiently passed over, to say whether the matter will end here. I send you some papers, which indicate symptoms of resistance. These are the resolution of the Noblesse of Brittany, the declaration of the Advocate General of Provence, which is said to express the spirit of that province; and the Arrêté of the Châtelet, which is the hustings-court of the city of Paris. Their refusal to act under the new character assigned them, and the suspension of their principal functions, are very embarrassing. The clamors this will excite, and the disorders it may admit, will be loud, and near to the royal ear and person. The parliamentary fragments permitted to remain, have already some of them refused, and probably all will refuse, to act under that form. The assembly of the clergy which happens to be sitting, have addressed the King to call the States General immediately. Of the Dukes and Peers (thirty-eight in number), nearly half are either minors or superannuated; two thirds of the acting half seem disposed to avoid taking a part; the rest, about eight or nine, have refused, by letters to the King, to act in the new courts. A proposition excited among the Dukes and Peers, to assemble and address the King for a modification of the Plenary court, seems to show that the government would be willing to compromise on that head. It has been prevented by the Dukes and Peers in opposition, because they suppose that no modification to be made by the government will give to that body the form they desire, which is that of a representative of the nation. They foresee that if the government is forced to this, they will call them, as nearly as they can, in the ancient forms; in which case, less good will be to be expected from them. But they hope they may be got to concur in a declaration of rights, at least, so that the nation may be acknowledged to have some fundamental rights, not alterable by their ordinary legislature, and that this may form a ground-work for future improvements. These seem to be the views of the most enlightened and disinterested characters of the opposition. But they may be frustrated by the nation’s making no cry at all, or by a hasty and premature appeal to arms. There is neither head nor body in the nation, to promise a successful opposition to two hundred thousand regular troops. Some think the army could not be depended on by the government; but the breaking men to military discipline, is breaking their spirits to principles of passive obedience. A firm, but quiet opposition, will be the most likely to succeed. Whatever turn this crisis takes, a revolution in their constitution seems inevitable, unless foreign war supervene, to suspend the present contest. And a foreign war they will avoid, if possible, from an inability to get money. The loan of one hundred and twenty millions, of the present year, is filled up by such subscriptions as may be relied on. But that of eighty millions, proposed for the next year, cannot be filled up, in the actual situation of things.
The Austrians have been successful in an attack upon Schabatz, intended as a preliminary to that of Belgrade. In that on Dubitza, another town in the neighborhood of Belgrade, they have been repulsed, and as is suspected, with considerable loss. It is still supposed the Russian fleet will go into the Mediterranean, though it will be much retarded by the refusal of the English government to permit its sailors to engage in the voyage. Sweden and Denmark are arming from eight to twelve ships of the line each. The English and Dutch treaty you will find in the Leyden gazettes of May the 9th and 13th. That between England and Prussia is supposed to be stationary. Monsieur de St. Priest, the ambassador from this court to the Hague, has either gone, or is on the point of going. The Emperor of Morocco has declared war against England. I enclose you his orders in our favor, on that occasion. England sends a squadron to the Mediterranean for the protection of her commerce, and she is reinforcing her possessions in the two Indies. France is expecting the arrival of an embassy from Tippoo Saib, is sending some regiments to the East Indies, and a fleet of evolution into the Atlantic. Seven ships of the line and several frigates, sailed from Cadiz on the 22nd of April, destined to perform evolutions off the Western Islands, as the Spaniards say, but really to their American possessions, as is suspected. Thus the several powers are by little and little, taking the position of war, without an immediate intention of waging it. But that the present ill humor will finally end in war, is doubted by nobody.
In my letter of February the 5th, I had the honor of informing you of the discontent produced by our Arrêt of December the 29th, among the merchants of this country, and of the deputations from the chambers of commerce to the minister, on that subject. The articles attacked, were the privileges on the sale of our ships, and the entrepôt for codfish. The former I knew to be valuable: the latter I supposed not so; because during the whole of the time we have had four free ports in this kingdom, we have never used them for the smuggling of fish. I concluded, therefore, the ports of entrepôt would not be used for that purpose. I saw that the ministers would sacrifice something to quiet the merchants, and was glad to save the valuable article relative to our ships, by abandoning the useless one for our codfish. It was settled, therefore, in our conferences, that an Arrêt should be passed, abridging the former one only as to the entrepot of codfish. I was in Holland when the Arrêt came out; and did not get a copy of it till yesterday. Surprised to find that fish-oil was thereby also excluded from the entrepot, I have been to-day to make some inquiry into the cause; and from what I can learn, I conclude it must have been a mere error in the clerk who formed the Arrêt, and that it escaped attention on its passage. The entrepôt of whale-oil was not objected to by a single deputy at the conferences, and the excluding it is contrary to the spirit of encouragement the ministers have shown a disposition to give. I trust, therefore, I may get it altered on the first occasion which occurs, and I believe one will soon occur. In the mean time, we do not store a single drop for re-exportation, as all which comes here is needed for the consumption of this country; which will alone, according to appearances, become so considerable as to require all we can produce.
By a letter of the 8th instant, from our bankers, I learn that they had disposed of bonds enough to pay our June interest, and to replace the temporary advances made by Mr. Grand, and from a fund placed here by the State of Virginia. I have desired them, accordingly, to replace these monies, which had been lent for the moment only, and in confidence of immediate repayment. They add, that the payment of the June interest and the news from America, will, as they trust, enable them to place the remaining bonds of the last year’s million. I suppose, indeed, that there is no doubt of it, and that none would have been expressed, if those two houses could draw better together than they do. In the mean time, I hope the treasury board will send an order for so much as may be necessary for executing the purposes of Congress, as to our captives at Algiers.
I send you herewith, a Mémoire of Monsieur Caseaux, whose name is familiar on the journals of Congress. He prepared it to be delivered to the King, but I believe he will think better, and not deliver it. The gazettes of France and Leyden accompany this.
I have the honor to be, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
P. S. May 27, 1788. I have kept my letter open to the moment of Mr. Warville’s departure (he being the bearer of it), that I might add any new incidents that should occur. The refusal of the Châtelet and Grande Chambre of Paris to act in the new character assigned them, continues. Many of the grandes bailliages accept, some conditionally, some fully. This will facilitate greatly the measures of government, and may possibly give them a favorable issue. The parliament of Toulouse, considering the edicts as nullities, went on with their business. They have been exiled in consequence. Monsieur de St. Priest left Paris for the Hague, on the 23rd. I mention this fact, because it denotes the acquiescence of this government in the late revolution there. A second division of a Spanish fleet will put to sea soon. Its destination not declared. Sweden is arming to a greater extent than was at first supposed. From twelve so sixteen sail of the line are spoken of, on good grounds, Denmark, for her own security, must arm in proportion to this. T. J.
TO JOHN BROWN.
Paris, May 26,1788.
Dear Sir,
It was with great pleasure I saw your name on the roll of Delegates, but I did not know you had actually come onto New-York, till Mr. Paradise informed me of it. Your removal from Carolina to Kentucky was not an indifferent event to me. I wish to see that country in the hands of people well disposed, who know the value of the connection between that and the maritime States, and who wish to cultivate it. I consider their happiness as bound up together, and that every measure should be taken, which may draw the bands of union tighter. It will be an efficacious one to receive them into Congress, as I perceive they are about to desire to this be added an honest and disinterested conduct in Congress, as to every thing relating to them, we may hope for a perfect harmony. The navigation of the Mississippi was, perhaps, the strongest trial to which the justice of the federal government could be put. If ever they thought wrong about it, I trust they have got to rights. I should think it proper for the western country to defer pushing their right to that navigation to extremity, as long as they can do without it, tolerably; but that the moment it becomes absolutely necessary for them, it will become the duty of the maritime states to push it to every extremity, to which they would their own right of navigating the Chesapeake, the Delaware, the Hudson, or any other water. A time of peace will not be the surest for obtaining this object. Those, therefore, who have influence in the new country, would act wisely, to endeavor to keep things quiet till the western parts of Europe shall be engaged in war. Notwithstanding the aversion of the courts of London and Versailles to war, it is not certain that some incident may not engage them in it. England, France, Spain, Russia, Sweden, and Denmark will all have fleets at sea, or ready to put to sea immediately. Who can answer for the prudence of all their officers? War is their interest. Even their courts are pacific from impotence only, not from disposition. I wish to Heaven that our new government may see the importance of putting themselves immediately into a respectable position. To make provision for the speedy payment of their foreign debts, will be the first operation necessary. This will give them credit. A concomitant one should be, magazines and manufactures of arms. This country is at present in a crisis of very uncertain issue. I am in hopes it will be a favorable one to the rights and happiness of the people; and that this will take place quietly. Small changes in the late regulations will render them wholly good. The campaign opens between the Turks and the two empires, with an aspect rather favorable to the former. The Russians seem not yet thawed from the winter’s torpitude. They have no army yet in motion: and the Emperor has been worsted in two thirds of the small actions, which they have had as yet. He is said to be rather retiring. I do not think, however, that the success of the Turks in the partisan affairs which have taken place, can authorize us to presume, that they will be superior also in great decisions. Their want of discipline and skill in military manoeuvres is of little consequence in small engagements, and of great in larger ones. Their grand army was at Adrianople by the last accounts, and to get from thence to Belgrade will require a month. It will be that time at least then, before we can have any very interesting news from them. In the mean time, the plague rages at Constantinople to a terrible degree. I cannot think but that it would be desirable to all commercial nations, to have that nation and all its dependencies driven from the sea-coast, into the interior parts of Asia and Africa. What a field would, thus be restored to commerce! The finest parts of the old world are now dead, in a great degree, to commerce, to arts, to science, and to society. Greece, Syria, Egypt, and the northern coast of Africa, constituted the whole world almost for the Romans, and to us they are scarcely known, scarcely accessible at all. The present summer will enable us to judge, what turn this contest will take. I am greatly anxious to hear that nine States accept our new constitution. We must be contented to accept of its good, and to cure what is evil in it hereafter. It seems necessary for our happiness at home; I am sure it is so for our respectability abroad. I shall, at all times, be glad to hear from you, from New York, from Kentucky, or whatever region of the earth you inhabit; being with sentiments of very sincere esteem and attachment, Dear Sir, your friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO WILLIAM CARMICHAEL.
Paris, May 27, 1788.
Dear Sir,
Your favors of April the 14th and 29th, and May the 8th, have lately come to hand. That of January the 29th, by M. de Moinedo, had been left here during my absence on a journey to Amsterdam. That gentleman had gone, as I presume, before my return, from my being unable to learn any thing of him.
With respect to the Isthmus of Panama, I am assured by Burgoine (who would not chose to be named, however), that a survey was made, that a canal appeared very practicable, and that the idea was suppressed for political reasons altogether. He has seen and minutely examined the report. This report is to me a vast desideratum, for reasons political and philosophical. I cannot help suspecting the Spanish squadrons to be gone to South America, and that some disturbances have been excited there by the British. The court of Madrid may suppose we would not see this with an unwilling eye. This may be true as to the uninformed part of our people: but those who look into futurity farther than the present moment or age, and who combine well what is, with what is to be, must see that our interests, well understood, and our wishes are, that Spain shall (not for ever, but) very long retain her possessions in that quarter; and that her views and ours must, in a good degree, and for a long time, concur. It is said in our gazettes, that the Spaniards have sunk one of our boats on the Mississippi, and that our people retaliated on one of theirs. But my letters, not mentioning this fact, have made me hope it is not true, in which hope your letter confirms me. There are now one hundred thousand inhabitants in Kentucky. They have accepted the offer of independence, on the terms proposed by Virginia, and they have decided that their independent government shall begin on the first day of the next year. In the mean time, they claim admittance into Congress. Georgia has ceded her western territory to the United States, to take place with the commencement of the new federal government. I do not know the boundaries. There has been some dispute of etiquette with the new French minister, which has disgusted him.
The following is a state of the progress and prospects of the new plan of government.
The conduct of Massachusetts has been noble. She accepted the constitution, but voted that it should stand as a perpetual instruction to her Delegates, to endeavor to obtain such and such reformations; and the minority, though very strong both in numbers and abilities, declared viritim and seriatim, that acknowledging the principle that the majority must give the law, they would now support the new constitution with their tongues, and with their blood, if necessary. I was much pleased with many and essential parts of this instrument, from the beginning. But I thought I saw in it many faults, great and small. What I have read and reflected, has brought me over from several of my objections, of the first moment, and to acquiesce under some others. Two only remain, of essential consideration, to wit, the want of a bill of rights, and the expunging the principle of necessary rotation in the offices of President and Senator. At first, I wished that when nine States should have accepted the constitution, so as to insure us what is good in it, the other four might hold off till the want of the bill of rights at least, might be supplied. But I am now convinced that the plan of Massachusetts is the best, that is, to accept and to amend afterwards. If the States which were to decide after her, should all do the same, it is impossible but they must obtain the essential amendments. It will be more difficult, if we lose this instrument, to recover what is good in it, than to correct what is bad, after we shall have adopted it. It has, therefore, my hearty prayers, and I wait with anxiety for news of the votes of Maryland, South Carolina, and Virginia. There is no doubt that General Washington will accept the presidentship; though he is silent on the subject. He would not be chosen to the Virginia convention. A riot has taken place in New York, which I will state to you from an eye-witness. It has long been a practice with the surgeons of that city, to steal from the grave bodies recently buried. A citizen had lost his wife: he went, the first or second evening after her burial, to pay a visit to her grave.. He found that it had been disturbed, and suspected from what quarter. He found means to be admitted to the anatomical lecture of that day, and on his entering the room, saw the body of his wife, naked and under dissection. He raised the people immediately. The body, in the mean time, was secreted. They entered into and searched the houses of the physicians whom they most suspected, but found nothing. One of them however more guilty or more timid than the rest, took asylum in the prison. The mob considered this an acknowledgment of guilt. They attacked the prison. The Governor ordered militia to protect the culprit, and suppress the mob. The militia, thinking the mob had just provocation, refused to turn out. Hereupon the people of more reflection, thinking it more dangerous that even a guilty person should be punished without the forms of law, than that he should escape, armed themselves, and went to protect the physician. They were received by the mob with a volley of stones, which wounded several of them. They hereupon fired on the mob and killed four. By this time, they received a reinforcement of other citizens of the militia horse, the appearance of which, in the critical moment, dispersed the mob. So ended this chapter of history, which I have detailed to you, because it may be represented as a political riot, when politics had nothing to do with it. Mr. Jay and Baron Steuben were both grievously wounded in the head by stones. The former still kept his bed, and the latter his room, when the packet sailed, which was the 24th of April. I am, with sentiments of great esteem and respect, Dear Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN JAY.
(Private.) Paris, May 27, 1788.
Dear Sir,
The change which is likely to take place in the form of our government, seems to render it proper, that, during the existence of the present government, an article should be mentioned which concerns me personally. Uncertain, however, how far Congress may have decided to do business when so near the close of their administration; less capable than those on the spot of foreseeing the character of the new government; and not fully confiding in my own judgment, where it is so liable to be seduced by feeling, I take the liberty of asking your friendly counsel, and that of my friend Mr. Madison, and of referring the matter to your judgments and discretion.
Mr. Barclay when in Europe was authorized to settle all the European accounts of the United States: he settled those of Dr. Franklin and Mr. Adams, and it was intended between us, that he should settle mine. But as what may be done at any time is often put off to the last, this settlement had been made to give way to others, and that of Beaumarchais being pressed on Mr. Barclay before his departure for Morocco, and having long retarded his departure, it was agreed that my affair should await his return from that mission: you know the circumstances which prevented his return to Paris after that mission was finished. My account is therefore unsettled, but I have no anxiety on any article of it, except one, that is, the outfit. This consists of, 1. clothes; 2. carriage and horses; 3. household furniture. When Congress made their first appointments of ministers to be resident in Europe, I have understood (for I was not then in Congress) that they allowed them all their expenses, and a fixed sum over and above for their time. Among their expenses, was necessarily understood their outfit. Afterwards they thought proper to give them fixed salaries of eleven thousand one hundred and eleven dollars and one ninth a year; and again, by a resolution of May the 6th and 8th, 1784, the ‘salaries’ of their ministers at foreign courts were reduced to nine thousand dollars, to take place on the 1st of August ensuing. On the 7th of May I was appointed, in addition to Mr. Adams and Dr. Franklin, for the negotiation of treaties of commerce; but this appointment being temporary, for two years only, and not as of a resident minister, the article of outfit did not come into question. I asked an advance of six months’ salary, that I might be in cash to meet the first expenses; which was ordered. The year following, I was appointed to succeed Dr. Franklin at this court. This was the first appointment of a minister resident, since the original ones, under which all expenses were to be paid. So much of the ancient regulation, as respected annual expenses, had been altered to a sum certain; so much of it as respected first expenses, or outfit, remained unaltered; and I might therefore expect, that the actual expenses for outfit were to be paid. When I prepared my account for settlement with Mr. Barclay, I began a detail of the articles of clothes, carriage, horses, and household furniture. I found that they were numerous, minute, and incapable, from their nature, of being vouched; and often entered in my memorandum-book under a general head only, so that I could not specify them. I found they would exceed a year’s salary. Supposing, therefore, that, mine being the first case, Congress would make a precedent of it, and prefer a sum fixed for the outfit, as well as the salary, I have charged it in my account at a year’s salary; presuming there can be no question that an outfit is a reasonable charge. It is the usage here (and I suppose at all courts), that a minister resident, shall establish his house in the first instant. If this is to be done out of his salary, he will be a twelvemonth at least without a copper to live on. It is the universal practice, therefore, of all nations, to allow the outfit as a separate article from the salary. I have inquired here into the usual amount of it. I find that, sometimes, the sovereign pays the actual cost. This is particularly the case of the Sardinian ambassador now coming here, who is to provide a service of plate, and every article of furniture, and other matters of first expense, to be paid for by his court. In other instances, they give a service of plate, and a fixed sum for all other articles, which fixed sum is in no case lower than a year’s salary.
I desire no service of plate, having no ambition for splendor. My furniture, carriage, and apparel are all plain, yet they have cost me more than a year’s salary. I suppose that in every country, and in every condition of life, a year’s expense would be found a moderate measure for the furniture of a man’s house. It is not more certain to me, that the sun will rise to-morrow, than that our government must allow the outfit, on their future appointment of foreign ministers; and it would be hard on me, so to stand between the discontinuance of a former rule, and institution of a future one, as to have the benefit of neither. I know, I have so long known the character of our federal head, in its present form, that I have the most unlimited confidence in the justice of its decisions. I think I am so far known to many of the present Congress, as that I may be cleared of all views of making money out of any public employment, or of desiring any thing beyond actual and decent expenses, proportioned to the station in which they have been pleased to place me, and to the respect they would wish to see attached to it. It would seem right, that they should decide the claims of those who have acted under their administration, and their pretermission of any article, might amount to a disallowance of it in the opinion of the new government. It would be painful to me to meet that government with a claim under this kind of cloud, and to pass it in review before their several Houses of legislation, and boards of administration, to whom I shall be unknown; and being for money actually expended, it would be too inconvenient to me to relinquish it in silence. I anxiously ask it, therefore, to be decided on by Congress before they go out of office, if it be not out of the line of proceeding they may have chalked out for themselves. If it be against their inclination to determine it, would it be agreeable to them to refer it to the new government, by some resolution, which should show they have not meant to disallow it, by passing it over? Not knowing the circumstances under which Congress may exist and act at the moment you shall receive this, I am unable to judge what should be done on this subject. It is therefore that I ask the aid of your friendship and that of Mr. Madison, that you will do for me in this regard, what you think it is right should be done, and what it would be right for me to do, were I on the spot, or were I apprized of all existing circumstances. Indeed, were you two to think my claim an improper one, I would wish it to be suppressed, as I have so much confidence in your judgment, that I should suspect my own in any case where it varied from yours, and more especially, in one where it is liable to be warped by feeling. Give me leave, then, to ask your consultation with Mr. Madison on this subject; and to assure you that whatever you are so good as to do herein, will be perfectly approved, and considered as a great obligation conferred on him, who has the honor to be, with sentiments of the most perfect esteem and attachment, Dear Sir, your friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JAMES MADISON.
Paris, May 28, 1788.
Dear Sir,
The enclosed letter for Mr. Jay, being of a private nature. I have thought it better to put it under your cover, lest it might be opened by some of his clerks, in the case of his absence. But I enclose a press copy of it for yourself, as you will perceive the subject of it referred to you, as well as to him. I ask your aid in it so far as you think right, and to have done what you think right. If you will now be so good as to cast your eye over the copy enclosed, what follows the present sentence, will be some details, supplementary to that only, necessary for your information, but not proper for me to state to Mr. Jay.
[* It will be seen that a few words of this letter are in
cipher. It is published, however, as written, because
enough of it is literal to interest the reader, to whom
also a specimen of the cipher, used by the Author, may
not be unacceptable.]
378.227.1247. though appointed a minister resident at the court of 514. he never was 663. in that character. He was continually passing from 1042. to 514. and 514. to 1042., so that he had no occasion to establish a household at either. Accordingly, he staid principally in furnished lodgings. Of all our ministers, he had the least occasion for an outfit, and I suppose spent almost nothing on that article. He was of a disposition, too, to restrain himself within any limits of expense whatever, and it suited his recluse turn, which is, to avoid society. Should he judge of what others should do, by what he did, it would be an improper criterion. He was in Europe as a voyageur only, and it was while the salary was five hundred guineas more than at present.
145.1267.1046.7. he came over, when, instead of outfit and salary, all expenses were paid. Of rigorous honesty, and careless of appearances, he lived for a considerable time as an economical private individual. After he was fixed at 812.141. and the salary at a sum certain, he continued his economical style, till, out of the difference between his expenses and his salary, he could purchase furniture for his house. This was the easier, as the salary was at two thousand five hundred guineas then. He was obliged, too, to be passing between 1042. and 812.141. so as to avoid any regular current of expenses. When he established himself, his pecuniary affairs were under the direction of 964.814.7.101.994., one of the most estimable characters on earth, and the most attentive and honorable economists. Neither had a wish to lay up a copper, but both wished to make both ends meet. I suspected, however, from an expression dropped in conversation, that they were not able to do this, and that a deficit in their accounts appeared in their winding up. If this conjecture be true, it is a proof that the salary, so far from admitting savings, is unequal to a very plain style of life; for such was theirs. I presume Congress will be asked to allow it, and it is evident to me, from what I saw while in 1093. that it ought to be done, as they did not expend a shilling which should have been avoided. Would it be more eligible to set the example of making good a deficit, or to give him an outfit, which will cover it? The impossibility of living on the sum allowed, respectably, was the true cause of his insisting on his recall. 821.267.1292. He came over while all expenses were paid. He rented a house with standing furniture, such as tables, chairs, presses, &c., and bought all other necessaries. The latter were charged in his account; the former was included in the article of house-rent, and paid during the whole time of his stay here; and as the established rate of hire for furniture is from thirty to forty per cent, per annum, the standing furniture must have been paid for three times over, during the eight years he staid here. His salary was two thousand five hundred guineas. When Congress reduced it to less than two thousand, he refused to accede to it, asked his recall, and insisted that whenever they chose to alter the conditions on which he came out, if he did not approve of it, they ought to replace him in America on the old conditions. He lived plain, but as decently as his salary would allow. He saved nothing, but avoided debt. He knew he could not do this on the reduced salary, and therefore asked his recall with decision.
To 935.145. succeeded. He had established a certain style of living. The same was expected from 1214. and there were five hundred guineas a year less to do it on. It has been aimed at, however, as far as was practicable. This rendered it constantly necessary to step neither to the right nor to the left, to incur any expense which could possibly be avoided, and it called for an almost womanly attention to the details of the household, equally perplexing, disgusting, and inconsistent with business. You will be sensible, that, in this situation, no savings could be made for reimbursing the half year’s salary, ordered to be advanced under the former commission, and more than as much again, which was unavoidably so applied, without order, for the purchase of the outfit. The reason of the thing, the usage of all nations, the usage of our own, by paying all expenses of preceding ministers, which gave them the outfit, as far as their circumstances appeared to them to render it necessary, have made me take for granted all along, that it would not be refused to me: nor should I have mentioned it now, but that the administration is passing into other hands, and more complicated forms. It would be disagreeable to me to be presented to them, in the first instance, as a suitor. Men come into business at first with visionary principles. It is practice alone, which can correct and conform them to the actual current of affairs. In the mean time, those to whom their errors were first applied, have been their victims. The government may take up the project of appointing foreign ministers without outfits, and they may ruin two or three individuals, before they find that that article is just as indispensable as the salary. They must then fall into the current of general usage, which has become general, only because experience has established its necessity. Upon the whole, be so good as to reflect on it, and to do, not what your friendship to me, but your opinion of what is right, shall dictate.
Accept, in all cases, assurances of the sincere esteem and respect with which I am, Dear Sir, your friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO PETER CARU.
Paris, May 23, 1788.
Dear Peter,
The preceding letter [* For the letter referred to, see ante, LXXIV.] was written at its date, and I supposed you in possession of it, when your letters of December the 10th, 1787, and March the 18th, 1788, told me otherwise. Still I supposed it on its way to you, when a few days ago, having occasion to look among some papers in the drawer, where my letters are usually put away, till an opportunity of sending them occurs, I found that this letter had slipped among them, so that it had never been forwarded. I am sorry for it, on account of the remarks relative to the Spanish language only. Apply to that with all the assiduity you can. That language and the English covering nearly the whole face of America, they should be well known to every inhabitant, who means to look beyond the limits of his farm. I like well the distribution of your time, mentioned in your letter of March the 18th; and the counsels of Mr. Wythe, so kindly extended to you, leave it necessary for me to add nothing of that kind. Be assiduous in learning, take much exercise for your health, and practise much virtue. Health, learning, and virtue, will insure your happiness; they will give you a quiet conscience, private esteem, and public honor. Beyond these, we want nothing but physical necessaries, and they are easily obtained. My daughters are well, and join me in love to yourself, your mother, brothers, and sisters.
I am, with very sincere esteem, Dear Peter, your affectionate
friend,
Th: Jefferson.
TO THE COMTE DE BERNSTORFF.
Paris, June 19, 1788.
I had the honor of addressing your Excellency, by Admiral Paul Jones, on the 21st of January, on the subject of the prizes taken under his command during the late war, and sent into Bergen. I communicated at the same time a copy of the powers which the Congress of the United States of America had been pleased to confide to me therein, having previously shown the original to the Baron de Blome, Envoy Extraordinary of his Majesty, the King of Denmark, at this court; and I furnished, at the same time, to Admiral Paul Jones, such authority as I was empowered to delegate, for the arrangement of this affair. That officer has transmitted me a copy of your Excellency’s letter to him of the 4th of April, wherein you are pleased to observe, that the want of full powers on his part was an invincible obstacle to the definitive discussion of this claim with him, and to express your dispositions to institute a settlement at this place. Always assured of the justice and honor of the court of Denmark, and encouraged by the particular readiness of your Excellency to settle and remove this difficulty from between the two nations, I take the liberty of recalling your attention to it. The place of negotiation proposed by your Excellency, meets no objection from us, and it removes, at the same time, that which the want of full powers in Admiral Paul Jones had produced in your mind. These full powers Congress have been pleased to honor me with. The arrangement taken between the person to be charged with your full powers and myself, will be final and conclusive. You are pleased to express a willingness to treat at the same time on the subjects of amity and commerce. The powers formerly communicated on our part, were given to Mr. Adams, Doctor Franklin, and myself, for a limited term only. That term has expired, and the other two gentlemen returned to America; so that no person is commissioned at this moment to renew those conferences. I may safely, however, assure your Excellency, that the same friendly dispositions still continue, and the same desire of facilitating and encouraging a commerce between the two nations, which produced the former appointment. But our nation is, at this time, proposing a change in the organization of its government. For this change to be agreed to by all the members of the Union, the new administration chosen and brought into activity, their domestic matters arranged, which will require their first attention, their foreign system afterwards decided on and carried into full execution, will require very considerable length of time. To place under the same delay the private claims which I have the honor to present to your Excellency, would be hard on the persons interested: because these claims have no connection with the system of commercial connection, which may be established between the two nations, nor with the particular form of our administration. The justice due to them is complete, and the present administration as competent to final settlement as any future one will be, should a future change take place. These individuals have already lingered nine years in expectation of their hard and perilous earnings. Time lessens their numbers continually, disperses their representatives, weakens the evidence of their right, and renders more and more impracticable his Majesty’s dispositions to repair the private injury, to which public circumstances constrained him. These considerations, the just and honorable intentions of your Excellency, and the assurances you give us in your letter, that no delay is wished on your part, give me strong hopes that we may speedily obtain that final arrangement, which express instructions render it my duty to urge. I have the honor, therefore, of agreeing with your Excellency, that the settlement of this matter, formerly begun at Paris, shall be continued there; and to ask that you will be pleased to give powers and instructions for this purpose to such persons as you shall think proper, and in such full form as may prevent those delays, to which the distance between Copenhagen and Paris might otherwise expose us.
I have the honor to be, with sentiments of the most profound respect, your Excellency’s most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO THE COUNT DE MONTMORIN.
Paris, June 20, 1788.
Sir,
Having had the honor of mentioning to your Excellency the wish of Congress, that certain changes should be made in the articles for a consular convention, which had been sent to them, I have now that, conformably to the desire you expressed, of giving a general idea of the alterations to be proposed.
The fourth article gives to the consuls the immunities of the law of nations. It has been understood, however, that the laws of France do not admit of this; and that it might be desirable to expunge this article. In this we are ready to concur, as in every other case, where an article might call for changes in the established laws, either inconvenient or disagreeable.
After establishing in favor of consuls, the general immunities of the law of nations, one consequence of which would have been, that they could not have been called upon to give testimony in courts of justice, the fifth article requires, that after the observance of certain formalities, which imply very high respect, they shall make a declaration; but in their own houses [chez eux] as may be pretended, if not justly inferred, from the expressions in the article. But our laws require, indispensably, a personal examination of witnesses in the presence of the parties, of their counsel, the jury, and judges, each of whom has a right to ask of them all questions pertinent to the fact. The first and highest officers of our government are obliged to appear personally to the order of a court, to give evidence. The court takes care that they are treated with respect. It is proposed, therefore, to omit this article for these particular reasons, as well as for the general one, that the fourth being expunged, this, which was but an exception to that, falls of course.
The seventh, eighth, tenth, and fourteenth articles extend their pre-eminences far beyond those, which the laws of nations would have given. These articles require that the declarations made in the presence of consuls, and certified by them, shall be received in evidence in all courts whatever: and, in some instances, give to their certificates a credibility which excludes all other testimony. The cases are rare, in which our laws admit written evidence of facts; and such evidence, when admitted, must have been given in the presence of both parties, and must contain the answers to all the pertinent questions, which they may have desired to ask of the witness: and to no evidence, of whatever nature, written or oral, do our laws give so high credit, as to exclude all counter-proof. These principles are of such ancient foundation in our system of jurisprudence, and are so much valued and venerated by our citizens, that perhaps it would be impossible to execute articles, which should contravene them, nor is it imagined that these stipulations can be so interesting to this country, as to balance the inconvenience and hazard of such an innovation with us. Perhaps it might be found, that the laws of both countries require a modification of this article; as it is inconceivable that the certificate of an American consul in France could be permitted by one of its courts to establish a fact, the falsehood of which should be notorious to the court itself.
The eighth article gives to the consuls of either nation a jurisdiction, in certain cases, over foreigners of any other. On a dispute arising in France, between an American and a Spaniard or an Englishman, it would not be fair to abandon the Spaniard or Englishman to an American consul. On the contrary, the territorial judge, as neutral, would seem to be the most impartial. Probably, therefore, it will be thought convenient for both parties, to correct this stipulation.
A dispute arising between two subjects of France, the one being in France and the other in the United States, the regular tribunals of France would seem entitled to a preference of jurisdiction. Yet the twelfth article gives it to their consul in America; and to the consul of the United States in France, in a like case between their citizens.
The power given by the tenth article, of arresting and sending back a vessel, its captain, and crew, is a very great one indeed, and, in our opinion, more safely lodged with the territorial judge. We would ourselves trust the tribunals of France to decide, when there is just cause for so high-handed an act of authority over the persons and property of so many of our citizens, to all of whom these tribunals will stand in a neutral and impartial relation, rather than any single person whom we may appoint as consul, who will seldom be learned in the laws, and often susceptible of influence from private interest and personal pique. With us, applications for the arrest of vessels, and of their masters, are made to the admiralty courts. These are composed of the most learned and virtuous characters in the several States, and the maritime law, common to all nations, is the rule of their proceedings. The exercise of foreign jurisdiction, within the pale of their own laws, in a very high case, and wherein those laws have made honorable provisions, would be a phenomenon never yet seen in our country, and which would be seen with great jealousy and uneasiness. On the contrary, to leave this power with the territorial judge will inspire confidence and friendship, and be really, at the same time, more secure against abuse. The power of arresting deserted seamen seems necessary for the purposes of navigation and commerce, and will be more attentively and effectually exercised by the consul, than by the territorial judge. To this part of the tenth article, therefore, as well as to that which requires the territorial judge to assist the consul in the exercise of this function, we can accede. But the extension of the like power to passengers, seems not necessary for the purposes either of navigation or commerce. It does not come, therefore, within the functions of the consul, whose institution is for those two objects only, nor within the powers of a commissioner, authorized to treat and conclude a convention, solely for regulating the powers, privileges, and duties of consuls. The arrest and detention of passengers, moreover, would often be in contradiction to our bills of rights, which, being fundamental, cannot be obstructed in their operation by any law or convention whatever.
Consular institutions being entirely new with us, Congress think it wise to make their first convention probationary, and not perpetual. They propose, therefore, a clause for limiting its duration to a certain term of years. If after the experience of a few years, it should be found to answer the purposes intended by it, both parties will have sufficient inducements to renew it, either in its present form, or with such alterations and amendments, as time, experience, and other circumstances may indicate.
The convention, as expressed in the French language, will fully answer our purposes in France, because it will there be understood. But it will not equally answer the purposes of France in America, because it will not there be understood. In very few of the courts, wherein it may be presented, will there be found a single judge or advocate, capable of translating it at all, much less of giving to all its terms, legal and technical, their exact equivalent in the laws and language of that country. Should any translation which Congress would undertake to publish, for the use of our courts, be conceived on any occasion not to render fully the idea of the French original, it might be imputed as an indirect attempt to abridge or extend the terms of a contract, at the will of one party only. At no place are there better helps than here, for establishing an English text equivalent to the French, in all its phrases; no persons can be supposed to know what is meant by these phrases, better than those who form them; and no time more proper to ascertain their meaning in both languages than that at which they are formed. I have, therefore, the honor to propose, that the convention shall be faithfully expressed in English as well as in French, in two columns, side by side, that these columns be declared each of them to be text, and to be equally original and authentic in all courts of justice.
This, Sir, is a general sketch of the alterations, which our laws and our manner of thinking render necessary in this convention, before the faith of our country is engaged for its execution. Some of its articles, in their present form, could not be executed at all, and others would produce embarrassments and ill humor, to which it would not be prudent for our government to commit itself. Inexact execution on the one part, would naturally beget dissatisfaction and complaints on the other; and an instrument intended to strengthen our connection, might thus become the means of loosening it. Fewer articles, better observed, will better promote our common interests. As to ourselves, we do not find the institution of consuls very necessary. Its history commences in times of barbarism, and might well have ended with them. During these, they were, perhaps, useful, and may still be so in countries not yet emerged from that condition. But all civilized nations at this day understand so well the advantages of commerce, that they provide protection and encouragement for merchant strangers and vessels coming among them. So extensive, too, have commercial connections now become, that every mercantile house has correspondents in almost every port. They address their vessels to these correspondents, who are found to take better care of their interests, and to obtain more effectually the protection of the laws of the country for them, than the consul of their nation can. He is generally a foreigner, unpossessed of the little details of knowledge of greatest use to them. He makes national questions of all the difficulties which arise; the correspondent prevents them. We carry on commerce with good success in all parts of the world; yet we have not a consul in a single port, nor a complaint for the want of one, except from the persons who wish to be consuls themselves. Though these considerations may not be strong enough to establish the absolute inutility of consuls, they may make us less anxious to extend their privileges and jurisdictions, so as to render them objects of jealousy and irritation, in the places of their residence. That this government thinks them useful, is sufficient reason for us to give them all the functions and facilities which our circumstances will admit. Instead, therefore, of declining every article which will be useless to us, we accede to every one which will not be inconvenient. Had this nation been alone concerned, our desire to gratify them might have tempted us to press still harder on the laws and opinions of our country. But your Excellency knows, that we stand engaged in treaties with some nations, which will give them occasion to claim whatever privileges we yield to any other. This renders circumspection more necessary. Permit me to add one other observation. The English allow to foreign consuls scarcely any functions within their ports. This proceeds, in a great measure, from the character of their laws, which eye, with peculiar jealousy, every exemption from their control. Ours are the same in their general character, and rendered still more unpliant, by our having thirteen parliaments to relax, instead of one. Upon the whole, I hope your Excellency will see the causes of the delay which this convention has met with, in the difficulties it presents, and our desire to surmount them: and will be sensible that the alterations proposed, are dictated to us by the necessity of our circumstances, and by a caution, which cannot be disapproved, to commit ourselves to no engagements which we foresee we might not be able o fulfil.
These alterations, with some other smaller ones, which may be offered on the sole principle of joint convenience, shall be the subject of more particular explanation, whenever your Excellency shall honor me with a conference thereon. I shall then, also, point out the verbal changes which appear to me necessary, to accommodate the instrument to the views before expressed. In the mean time, I have the honor to be, with sentiments of the most perfect respect and esteem, your Excellency’s most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
Paris, July 16, 1788.
Sir,
In your favor of the 8th instant, you mentioned that you had written to me in February last. This letter never came to hand. That of April the 24th came here during my absence on a journey through Holland and Germany; and my having been obliged to devote the first moments after my return to some very pressing matters, must be my apology for not having been able to write to you till now. As soon as I knew that it would be agreeable to you to have such a disposal of your work for translation, as I had made for Dr. Ramsay, I applied to the same bookseller with propositions on your behalf. He told me, that he had lost so much by that work, that he could hardly think of undertaking another, and, at any rate, not without first seeing and examining it. As he was the only bookseller I could induce to give any thing on the former occasion, I went to no other with my proposal, meaning to ask you to send me immediately as much of the work as is printed. This you can do by the Diligence, which comes three times a week from London to Paris. Furnished with this, I will renew my proposition, and do the best for you I can; though I fear that the ill success of the translation of Dr. Ramsay’s work, and of another work on the subject of America, will permit less to be done for you than I had hoped. I think Dr. Ramsay failed from the inelegance of the translation, and the translator’s having departed entirely from the Doctor’s instructions. I will be obliged to you, to set me down as subscriber for half a dozen copies, and to ask Mr. Trumbull (No. 2, North street, Rathbone Place) to pay you the whole subscription price for me, which he will do on showing him this letter. These copies can be sent by the Diligence. I have not yet received the pictures Mr. Trumbull was to send me, nor consequently that of M. de la Fayette. I will take care of it when it arrives. His title is simply, Le Marquis de la Fayette.
You ask, in your letter of April the 24th, details of my sufferings by Colonel Tarleton. I did not suffer by him. On the contrary, he behaved very genteelly with me. On his approach to Charlottesville, which is within three miles of my house at Monticello, he despatched a troop of his horse, under Captain McLeod, with the double object of taking me prisoner, with the two Speakers of the Senate and Delegates, who then lodged with me, and of remaining there in vidette, my house commanding a view often or twelve miles round about. He gave strict orders to Captain McLeod to suffer nothing to be injured. The troop failed in one of their objects, as we had notice of their coming, so that the two Speakers had gone off about two hours before their arrival at Monticello, and myself, with my family, about five minutes. But Captain McLeod preserved every thing with sacred care, during about eighteen hours that he remained there. Colonel Tarleton was just so long at Charlottesville, being hurried from thence by the news of the rising of the militia, and by a sudden fall of rain which threatened to swell the river and intercept his return. In general he did little injury to the inhabitants on that short and hasty excursion, which was of about sixty miles from their main army, then in Spotsylvania, and ours in Orange. It was early in June, 1781. Lord Cornwallis then proceeded to the Point of Fork, and encamped his army from thence all along the main James River, to a seat of mine called Elk-hill, opposite to Elk Island, and a little below the mouth of the Byrd Creek. (You will see all these places exactly laid down in the map annexed to my Notes on Virginia, printed by Stockdale.) He remained in this position ten days, his own head-quarters being in my house, at that place. I had time to remove most of the effects out of the house. He destroyed all my growing crops of corn and tobacco; he burned all my barns, containing the same articles of the last year, having first taken what corn he wanted; he used, as was to be expected, all my stock of cattle, sheep, and hogs, for the sustenance of his army, and carried off all the horses capable of service; of those too young for service he cut the throats; and he burned all the fences on the plantation so as to leave it an absolute waste. He carried off also about thirty slaves. Had this been to give them freedom, he would have done right: but it was to consign them to inevitable death from the small-pox and putrid fever, then raging in his camp. This I knew afterwards to be the fate of twenty-seven of them. I never had news of the remaining three, but presume they shared the same fate. When I say that Lord Cornwallis did all this, I do not mean that he carried about the torch in his own hands, but that it was all done under his eye; the situation of the house in which he was, commanding a view of every part of the plantation, so that he must have seen every fire. I relate these things on my own knowledge, in a great degree, as I was on the ground soon after he left it. He treated the rest of the neighborhood somewhat in the same style, but not with that spirit of total extermination with which he seemed to rage over my possessions. Wherever he went, the dwelling-houses were plundered of every thing which could be carried off. Lord Cornwallis’s character in England would forbid the belief that he shared in the plunder; but that his table was served with the plate thus pillaged from private houses, can be proved by many hundred eye-witnesses. From an estimate I made at that time, on the best information I could collect, I supposed the State of Virginia lost under Lord Cornwallis’s hands, that year, about thirty thousand slaves; and that of these, about twenty-seven thousand died of the small-pox and camp-fever, and the rest were partly sent to the West Indies, and exchanged for rum, sugar, coffee, and fruit, and partly sent to New York, from whence they went, at the peace, either to Nova Scotia or England. From this last place, I believe they have been lately sent to Africa. History will never relate the horrors committed by the British army, in the southern States of America. They raged in Virginia six months only, from the middle of April to the middle of October, 1781, when they were all taken prisoners; and I give you a faithful specimen of their transactions for ten days of that time, and on one spot only. Ex pede Herculem. I suppose their whole devastations during those six months, amounted to about three millions sterling. The copiousness of this subject has only left me space to assure you of the sentiments of esteem and respect, with which I am, Sir, your most obedient, humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JAMES MADISON, of William and Mary College.
Paris, July 19, 1788.
Dear Sir,
My last letter to you was of the 13th of August last. As you seem willing to accept of the crumbs of science on which we are subsisting here, it is with pleasure I continue to hand them on to you, in proportion as they are dealt out. Herschel’s volcano in the moon you have doubtless heard of, and placed among the other vagaries of a head, which seems not organized for sound induction. The wildness of the theories hitherto proposed by him, on his own discoveries, seems to authorize us to consider his merit as that of a good optician only. You know also, that Doctor Ingenhouse had discovered, as he supposed from experiment, that vegetation might be promoted by occasioning streams of the electrical fluid to pass through a plant, and that other physicians had received and confirmed this theory. He now, however, retracts it, and finds by more decisive experiments, that the electrical fluid can neither forward nor retard vegetation. Uncorrected still of the rage of drawing general conclusions from partial and equivocal observations, he hazards the opinion that light promotes vegetation. I have heretofore supposed from observation, that light affects the color of living bodies, whether vegetable or animal; but that either the one or the other receives nutriment from that fluid, must be permitted to be doubted of, till better confirmed by observation. It is always better to have no ideas, than false ones; to believe nothing, than to believe what is wrong. In my mind, theories are more easily demolished than rebuilt.
An Abbe here, has shaken, if not destroyed, the theory of De Dominis, Descartes and Newton, for explaining the phenomenon of the rainbow. According to that theory, you know, a cone of rays issuing from the sun, and falling on a cloud in the opposite part of the heavens, is reflected back in the form of a smaller cone, the apex of which is the eye of the observer: so that the eye of the observer must be in the axis of both cones, and equally distant from every part of the bow. But he observes, that he has repeatedly seen bows, the one end of which has been very near to him, and the other at a very great distance. I have often seen the same thing myself. I recollect well to have seen the end of a rainbow between myself and a house, or between myself and a bank, not twenty yards distant; and this repeatedly. But I never saw, what he says he has seen, different rainbows at the same time, intersecting each other. I never saw coexistent bows, which were not concentric also. Again, according to the theory, if the sun is in the horizon, the horizon intercepts the lower half of the bow, if above the horizon, that intercepts more than the half, in proportion. So that generally the bow is less than a semicircle, and never more. He says he has seen it more than a semicircle. I have often seen the leg of the bow below my level. My situation at Monticello admits this, because there is a mountain there in the opposite direction of the afternoon’s sun, the valley between which and Monticello is five hundred feet deep. I have seen a leg of a rainbow plunge down on the river running through the valley. But I do not recollect to have remarked at any time, that the bow was more than half a circle. It appears to me, that these facts demolish the Newtonian hypothesis, but they do not support that erected in its stead by the Abbe. He supposes a cloud between the sun and observer, and that through some opening in that cloud, the rays pass, and form an iris on the opposite part of the heavens, just as a ray passing through a hole in the shutter of a darkened room, and falling on a prism there, forms the prismatic colors on the opposite wall. According to this, we might see bows of more than the half circle, as often as of less. A thousand other objections occur to this hypothesis, which need not be suggested to you. The result is, that we are wiser than we were, by having an error the less in our catalogue; but the blank occasioned by it, must remain for some happier hypothesist to fill up.
The dispute about the conversion and reconversion of water and air, is still stoutly kept up. The contradictory experiments of chemists, leave us at liberty to conclude what we please. My conclusion is, that art has not yet invented sufficient aids, to enable such subtle bodies to make a well defined impression on organs as blunt as ours: that it is laudable to encourage investigation, but to hold back conclusion. Speaking one day with Monsieur de Buffon on the present ardor of chemical inquiry, he affected to consider chemistry but as cookery, and to place the toils of the laboratory on a footing with those of the kitchen. I think it, on the contrary, among the most useful of sciences, and big with future discoveries for the utility and safety of the human race. It is yet, indeed, a mere embryon. Its principles are contested; experiments seem contradictory; their subjects are so minute as to escape our senses; and their result too fallacious to satisfy the mind. It is probably an age too soon, to propose the establishment of a system. The attempt, therefore, of Lavoisier to reform the chemical nomenclature, is premature. One single experiment may destroy the whole filiation of his terms, and his string of sulfates, sulfiles, and sulfures may have served no other end, than to have retarded the progress of the science, by a jargon, from the confusion of which, time will be requisite to extricate us. Accordingly, it is not likely to be admitted generally.
You are acquainted with the properties of the composition of nitre, salt of tartar, and sulphur, called pulvis fulminans. Of this, the explosion is produced by heat alone. Monsieur Bertholet, by dissolving silver in the nitrous acid, precipitating it with lime-water, and drying the precipitate on ammoniac, has discovered a powder, which fulminates most powerfully, on coming into contact with any substance whatever. Once made, it cannot be touched. It cannot be put into a bottle, but must remain in the capsula, where dried. The property of the spathic acid, to corrode flinty substances, has been lately applied by a Mr. Puymaurin, to engrave on glass, as artists engrave on copper, with aquafortis.
M. de la Place has discovered, that the secular acceleration and retardation of the moon’s motion, is occasioned by the action of the sun, in proportion as his excentricity changes, or, in other words, as the orbit of the earth increases or diminishes. So that this irregularity is now perfectly calculable.
Having seen announced in a gazette, that some person had found, in a library of Sicily, an Arabic translation of Livy, which was thought to be complete, I got the chargé des affaires of Naples here, to write to Naples to inquire into the fact. He obtained in answer, that an Arabic translation was found, and that it would restore to us seventeen of the books lost, to wit, from the sixtieth to the seventy-seventh, inclusive: that it was in possession of an Abbe Vella, who, as soon as he shall have finished a work he has on hand, will give us an Italian, and perhaps a Latin translation of this Livy. There are persons, however, who doubt the truth of this discovery, founding their doubts on some personal circumstances relating to the person who says he has this translation. I find, nevertheless, that the chargé des affaires believes in the discovery, which makes me hope it may be true.
A countryman of ours, a Mr. Ledyard of Connecticut, set out from hence some time ago for St. Petersburg, to go thence to Kamtschatka, thence to cross over to the western coast of America, and penetrate through the continent, to the other side of it. He had got within a few days’ journey of Kamtschatka, when he was arrested by order of the Empress of Russia, sent back, and turned adrift in Poland. He went to London; engaged under the auspices of a private society, formed there for pushing discoveries into Africa; passed by this place, which he left a few days ago for Marseilles, where he will embark for Alexandria and Grand Cairo; thence explore the Nile to its source; cross the head of the Niger, and descend that to its mouth. He promises me, if he escapes through his journey, he will go to Kentucky, and endeavor to penetrate westwardly to the South Sea.
The death of M. de Buffon you have heard long ago. I do not know whether we shall have anything posthumous of his. As to political news, this country is making its way to a good constitution. The only danger is, they may press so fast as to produce an appeal to arms, which might have an unfavorable issue for them. As yet the appeal is not made. Perhaps the war, which seems to be spreading from nation to nation, may reach them this would insure the calling of the States General, and this, as is supposed, the establishment of a constitution.
I have the honor to be, with sentiments of sincere esteem and respect, Dear Sir, your friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO E. RUTLEDGE.
Paris, July 18, 1788.
Dear Sir,
Messrs. Berard were to have given me particular accounts of the proceeds of the shipments of rice made to them. But they have failed. I fear, from what they mention, that the price has been less advantageous than usual; which is unlucky, as it falls the first essay. If on the whole, however, you get as much as you would have done by a sale on the spot, it should encourage other adventures, because the price at Havre or Rouen is commonly higher, and because I think you may, by trials, find out the way to avail yourselves of the Paris retail price. The Carolina rice, sold at Paris, is separated into three kinds; 1. the whole grains; 2. the broken grains; 3. the small stuff; and sell at ten, eight, and six livres the French pound, retail. The whole grains, which constitute the first quality, are picked out by hand. I would not recommend this operation to be done with you, because labor is dearer there than here. But I mention these prices, to show, that after making a reasonable deduction for sorting, and leaving a reasonable profit to the retailer, there should still remain a great wholesale price. I shall wish to know from you, how much your cargo of rice shipped to Berard netts you, and how much it would have netted in hard money, if you had sold it at home.
You promise, in your letter of October the 23rd, 1787, to give me in your next, at large, the conjectures of your philosopher on the descent of the Creek Indians from the Carthaginians, supposed to have been separated from Hanno’s fleet, during his periplus. I shall be very glad to receive them, and see nothing impossible in his conjecture. I am glad he means to appeal to similarity of language, which I consider as the strongest kind of proof it is possible to adduce. I have somewhere read, that the language of the ancient Carthaginians is still spoken by their descendants, inhabiting the mountainous interior parts of Barbary, to which they were obliged to retire by the conquering Arabs. If so, a vocabulary of their tongue can still be got, and if your friend will get one of the Creek languages, the comparison will decide. He probably may have made progress in this business: but if he wishes any inquiries to be made on this side the Atlantic, I offer him my services cheerfully; my wish being, like his to ascertain the history of the American aborigines.
I congratulate you on the accesion of your State to the new federal constitution. This is the last I have yet heard of, but I expect daily to hear that my own has followed the good example, and suppose it to be already established. Our government wanted bracing. Still we must take care not to run from one extreme to another; not to brace too high. I own, I join those in opinion, who think a bill of rights necessary. I apprehend too, that the total abandonment of the principle of rotation in the offices of President and Senator, will end in abuse. But my confidence is, that there will, for a long time, be virtue and good sense enough in our countrymen, to correct abuses. We can surely boast of having set the world a beautiful example of a government reformed by reason alone, without bloodshed. But the world is too far oppressed to profit by the example. On this side of the Atlantic, the blood of the people has become an inheritance, and those who fatten on it, will not relinquish it easily. The struggle in this country is, as yet, of doubtful issue. It is, in fact, between the monarchy and the parliaments. The nation is no otherwise concerned, but as both parties may be induced to let go some of its abuses, to court the public favor. The danger is, that the people, deceived by a false cry of liberty, may be led to take side with one party, and thus give the other a pretext for crushing them still more. If they can avoid the appeal to arms, the nation will be sure to gain much by this controversy. But if that appeal is made, it will depend entirely on the disposition of the army, whether it issue in liberty or despotism. Those dispositions are not as yet known. In the mean time, there is great probability that the war kindled in the east, will spread from nation to nation, and, in the long run, become general.
I am, with the most sincere esteem and attachment, my dear; Sir, your friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MR. BELLINI.
Paris, July 25,1788.
Dear Sir,
Though I have written to you seldom, you are often the object of my thoughts, and always of my affection. The truth is, that the circumstances with which I am surrounded, offer little worth detailing to you. You are too wise to feel an interest in the squabbles, in which the pride, the dissipations, and the tyranny of kings, keep this hemisphere constantly embroiled. Science, indeed, finds some aliment here, and you are one of her sons. But this I have pretty regularly communicated to Mr. Madison, with whom, I am sure, you participate of it. It is with sincere pleasure I congratulate you on the good fortune of our friend Mazzei, who is appointed here, to correspond with the King of Poland. The particular character given him is not well defined, but the salary is, which is more important. It is eight thousand livres a year, which will enable him to live comfortably, while his duties will find him that occupation, without which he cannot exist. Whilst this appointment places him at his ease, it affords a hope of permanence also. It suspends, if not entirely prevents, the visit he had intended to his native country, and the return to his adoptive one, which the death of his wife had rendered possible. This last event has given him three quarters of the globe elbow-room, which he had ceded to her, on condition she would leave him quiet in the fourth. Their partition of the next world will be more difficult, if it be divided only into two parts, according to the protestant faith. Having seen by a letter you wrote him, that you were in want of a pair of spectacles, I undertook to procure you some, which I packed in a box of books addressed to Mr. Wythe, and of which I beg your acceptance. This box lay forgotten at Havre the whole of the last winter, but was at length shipped, and I trust has come to hand. I packed with the spectacles three or four pair of glasses, adapted to the different periods of life, distinguished from each other by numbers, and easily changed. You see I am looking forward in hope of a long life for you; and that it may be long enough to carry you through the whole succession of glasses, is my sincere prayer. Present me respectfully to Mrs. Bellini, assure her of my affectionate remembrance of her, and my wishes for her health and happiness; and accept yourself very sincere professions of the esteem and attachment with which I am, Dear Sir, your affectionate friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JAMES MADISON.
Paris, July 31, 1788.
Dear Sir,
My last letters to you were of the 3rd and the 25th of May. Yours from Orange, of April the 22nd, came to hand on the 10th instant.
My letter to Mr. Jay containing all the public news that is well authenticated, I will not repeat it here, but add some details in the smaller way, which you may be glad to know. The disgrace of the Marquis de la Fayette, which, at any other period of their history, would have had the worst consequences for him, will, on the contrary, mark him favorably to the nation, at present. During the present administration, he can expect nothing; but perhaps it may serve him with their successors, whenever a change shall take place. No change of the Principal will probably take place, before the meeting of the States General; though a change is to be wished, for his operations do not answer the expectations formed of him. These had been calculated, on his brilliancy in society. He is very feebly aided too. Montmorin is weak, though a most worthy character. He is indolent and inattentive too, in the extreme. Luzerne is considerably inferior in abilities to his brother, whom you know. He is a good man too, but so much out of his element, that he has the air of one huskanoyed. The Garde des Sceaux is considered as the Principal’s bull-dog, braving danger like the animal. His talents do not pass mediocrity. The Archbishop’s brother, and the new minister Villedeuil, and Lambert, have no will of their own. They cannot raise money for the peace establishment the next year, without the States General; much less if there be war; and their administration will probably end with the States General.
Littlepage, who was here as a secret agent for the King of Poland, rather overreached himself. He wanted more money. The King furnished it, more than once. Still he wanted more, and thought to obtain a high bid, by saying he was called for in America, and asking leave to go there. Contrary to his expectation, he received leave; but he went to Warsaw instead of America, and from thence, to join the * * * * I do not know
[* Several paragraphs of this letter are in cipher, A few
words here could not be deciphered.]
these facts certainly, but collect them, by putting several things together. The King then sent an ancient secretary here, in whom he had much confidence, to look out for a correspondent, a mere letter-writer for him. A happy hazard threw Mazzei in his way. He recommended him, and he is appointed. He has no diplomatic character whatever, but is to receive eight thousand livres a year, as an intelligencer. I hope this employment may have some permanence. The danger is, that he will over-act his part.
The Marquis de la Luzerne had been for many years married to his brother’s wife’s sister, secretly. She was ugly and deformed, but sensible, amiable, and rather rich. When he was ambassador to London, with ten thousand guineas a year, the marriage was avowed, and he relinquished his cross of Malta, from which he derived a handsome revenue for life, and which was very open to advancement. Not long ago, she died. His real affection for her, which was great and unfeigned, and perhaps the loss of his order, for so short-lived a satisfaction, has thrown him almost into a state of despondency. He is now here.
I send you a book of Dupont’s, on the subject of the commercial treaty with England. Though its general matter may not be interesting, yet you will pick up, in various parts of it, such excellent principles and observations, as will richly repay the trouble of reading it. I send you, also, two little pamphlets of the Marquis de Condorcet, wherein is the most judicious statement I have seen, of the great questions which agitate this nation at present. The new regulations present a preponderance of good over their evil; but they suppose that the King can model the constitution at will, or, in other words, that his government is a pure despotism. The question then arising is, whether a pure despotism in a single head, or one which is divided among a king, nobles, priesthood, and numerous magistracy, is the least bad. I should be puzzled to decide: but I hope they will have neither, and that they are advancing to a limited, moderate government, in which the people will have a good share.
I sincerely rejoice at the acceptance of our new constitution by nine States. It is a good canvass, on which some strokes only want retouching. What these are, I think are sufficiently manifested by the general voice from north to south, which calls for a bill of rights. It seems pretty generally understood, that this should go to juries, habeas corpus, standing armies, printing, religion, and monopolies. I conceive there may be difficulty in finding general modifications of these, suited to the habits of all the States. But if such cannot be found, then it is better to establish trials by jury, the right of habeas corpus, freedom of the press, and freedom of religion, in all cases, and to abolish standing armies in time of peace, and monopolies in all cases, than not to do it in any. The few cases wherein these things may do evil, cannot be weighed against the multitude, wherein the want of them will do evil. In disputes between a foreigner and a native, a trial by jury may be improper. But if this exception cannot be agreed to, the remedy will be to model the jury, by giving the medietas linguæ, in civil as well as criminal cases. Why suspend the habeas corpus in insurrections and rebellions? The parties who may be arrested, may be charged instantly with a well-defined crime: of course, the judge will remand them. If the public safety requires, that the government should have a man imprisoned on less probable testimony in those than in other emergencies, let him be taken and tried, retaken and retried, while the necessity continues, only giving him redress against the government, for damages. Examine the history of England. See how few of the cases of the suspension of the habeas corpus law have been worthy of that suspension. They have been either real treason, wherein the parties might as well have been charged at once, or sham plots, where it was shameful they should ever have been suspected. Yet for the few cases, wherein the suspension of the habeas corpus has done real good, that operation is now become habitual, and the minds of the nation almost prepared to live under its constant suspension. A declaration, that the federal government will never restrain the presses from printing any thing they please, will not take away the liability of the printers for false facts printed. The declaration, that religious faith shall be unpunished, does not give impunity to criminal acts, dictated by religious error. The saying—there shall be no monopolies, lessens the incitements to ingenuity, which is spurred on by the hope of a monopoly for a limited time, as of fourteen years; but the benefit of even limited monopolies is too doubtful, to be opposed to that of their general suppression. If no check can be found to keep the number of standing troops within safe bounds, while they are tolerated as far as necessary, abandon them altogether, discipline well the militia, and guard the magazines with them. More than magazine guards will be useless, if few, and dangerous, if many. No European nation can ever send against us such a regular army as we need fear, and it is hard, if our militia are not equal to those of Canada or Florida. My idea then, is, that though proper exceptions to these general rules are desirable, and probably practicable, yet if the exceptions cannot be agreed on, the establishment of the rules, in all cases, will do ill in very few. I hope, therefore, a bill of rights will be formed, to guard the people against the federal government, as they are already guarded against their State governments, in most instances. The abandoning the principle of necessary rotation in the Senate, has, I see, been disapproved by many: in the case of the President, by none. I readily, therefore, suppose my opinion wrong, when opposed by the majority, as in the former instance, and the totality, as in the latter. In this, however, I should have done it with more complete satisfaction, had we all judged from the same position.
Solicitations, which cannot be directly refused, oblige me to trouble you often with letters, recommending and introducing to you persons who go from hence to America. I will beg the favor of you to distinguish the letters wherein I appeal to recommendations from other persons, from those which I write on my own knowledge. In the former, it is never my intention to compromit myself or you. In both instances, I must beg you to ascribe the trouble I give you, to circumstances which do not leave me at liberty to decline it.
I am, with very sincere esteem, Dear Sir, your affectionate friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN JAY.
Paris, August 3, 1788.
Sir,
My last letters to you were of the 4th and 23d of May, with a Postscript of the 27th. Since that, I have been honored with yours of April the 24th, May the 16th, and June the 9th.
The most remarkable internal occurrences since my last are these. The Noblesse of Bretagne, who had received with so much warmth the late innovations in the government, assembled, and drew up a memorial to the King, and chose twelve members of their body to come and present it. Among these was the Marquis de la Rouerie (Colonel Armand). The King, considering the Noblesse as having no legal right to assemble, declined receiving the memorial. The deputies, to give greater weight to it, called a meeting of the landed proprietors of Bretagne, resident at Paris, and proposed to them to add their signatures—They did so, to the number of about sixty, of whom the Marquis de la Fayette was one. The twelve deputies, for having called this meeting, were immediately sent to the Bastile where they now are, and the Parisian signers were deprived of such favors as they held of the court. There were only four of them, however, who held any thing of that kind. The Marquis de la Fayette was one of these. They had given him a military command, to be exercised in the south of France, during the months of August and September of the present year. This they took from him; so that he is disgraced, in the ancient language of the court, but in truth, honorably marked in the eyes of the nation. The ministers are so sensible of this, that they have had, separately, private conferences with him, to endeavor, through him, to keep things quiet. From the character of the province of Bretagne, it was much apprehended, for some days, that the imprisonment of their deputies would have produced an insurrection. But it took another turn. The Cours intermédiaire of the province, acknowledged to be a legal body, deputed eighteen members of their body to the King. To these he gave an audience, and the answer, of which I send you a copy. This is hard enough. Yet I am in hopes the appeal to the sword will be avoided, and great modifications in the government be obtained without bloodshed. As yet none has been spilt, according to the best evidence I have been able to obtain, notwithstanding what the foreign newspapers have said to the contrary. The convocation of the States General has now become inevitable. Whenever the time shall be announced certainly, it will keep the nation quiet till they meet. According to present probabilities, this must be in the course of the next summer; but to what movements their meeting and measures may give occasion, cannot be foreseen. Should a foreign war take place, still they must assemble the States General, because they cannot, but by their aid, obtain money to carry it on. Monsieur de Malesherbes will, I believe, retire from the King’s Council. He has been much opposed to the late acts of authority. The Baron de Breteuil has resigned his secretaryship of the domestic department; certainly not for the same reasons, as he is known to have been of opinion, that the King had compromitted too much of his authority. The real reason has probably been, an impatience of acting under a principal minister. His successor is M. de Villedeuil, lately Comptroller General.
The ambassadors of Tippoo Saib have arrived here. If their mission has any other object than that of pomp and ceremony, it is not yet made known. Though this court has not avowed that they are in possession of Trincomale, yet the report is believed, and that possession was taken by General Conway, in consequence of orders given in the moment that they thought a war certain. The dispute with the States General of the United Netherlands, on account of the insult to M. de St. Priest, does not tend as yet towards a settlement. He has obtained leave to go to the waters, and perhaps from thence he may come to Paris, to await events. Sweden has commenced hostilities against Russia, by the taking a little fortress by land. This having been their intention, it is wonderful, that when their fleet lately met three Russian ships of one hundred guns each, they saluted instead of taking them. The Empress has declared war against them in her turn. It is well understood, that Sweden is set on by England, and paid by the Turks. The prospect of Russia has much brightened by some late successes. Their fleet of galleys and gun-boats, twenty-seven in number, having been attacked by fifty-seven Turkish vessels of the same kind, commanded by the Captain Pacha, these were repulsed, with the loss of three vessels. In the action, which was on the 18th of June, Admiral Paul Jones commanded the right wing of the Russians, and the Prince of Nassau the left. On the 26th of the same month, the Turkish principal fleet, that is to say, their ships of the line, frigates, &c, having got themselves near the swash, at the mouth of the Borysthenes, the Prince of Nassau took advantage of their position, attacked them while so engaged in the mud that they could not manoeuvre, burnt six, among which were the admiral’s and vice-admiral’s, took two, and made between three and four thousand prisoners. The first reports gave this success to Admiral Paul Jones; but it is now rendered rather probable that he was not there, as he commands the vessels of war which are said not to have been there. It is supposed, that his presence in the affair of the 18th was accidental. But if this success has been so complete as it is represented, the Black Sea must be tolerably open to the Russians: in which case, we may expect, from what we know of that officer, that he will improve to the greatest advantage the situation of things on that sea. The Captain Pacha’s standard was taken in the last action, and himself obliged to make his escape in a small vessel. Prince Potemkin immediately got under march for Oczakow, to take advantage of the consternation into which that place was thrown.
The Spanish squadron, after cruising off the Western Isles and Cape St. Vincent, has returned into port.
A dispute has arisen between the Papal See and the King of Naples, which may, in its progress, enable us to estimate what degree of influence that See retains at the present day. The kingdom of Naples, at an early period of its history, became feudatory to the See of Rome, and in acknowledgment thereof, has annually paid a hackney to the Pope in Rome, to which place it has always been sent by a splendid embassy. The hackney has been refused by the King this year, and the Pope, giving him three months to return to obedience, threatens, if he does not, to proceed seriously against him.
About three weeks ago a person called on me, and informed me, that Silas Deane had taken him in for a sum of one hundred and twenty guineas, and that being unable to obtain any other satisfaction, he had laid hands on his account book and letter book, and had brought them off to Paris, to offer them first to the United States, if they would repay him his money, and if not, that he should return to London, and offer them to the British minister. I desired him to leave them with me four and twenty hours, that I might judge whether they were worth our notice. He did so. They were two volumes. One contained all his accounts with the United States, from his first coming to Europe to January the 10th, 1781. Presuming that the treasury board was in possession of this account till his arrival in Philadelphia, August, 1778, and that he had never given in the subsequent part, I had that subsequent part copied from the book, and now enclose it, as it may on some occasion or other, perhaps, be useful in the treasury office. The other volume contained all his correspondences from March the 30th to August the 23d, 1777. I had a list of the letters taken by their dates and addresses, which will enable you to form a general idea of the collection. On perusal of many of them, I thought it desirable that they should not come to the hands of the British minister, and from an expression dropped by the possessor of them, I believe he would have fallen to fifty or sixty guineas. I did not think them important enough, however, to justify my purchasing them without authority; though, with authority, I should have done it. Indeed, I would have given that sum to cut out a single sentence, which contained evidence of a fact, not proper to be committed to the hands of enemies. I told him I would state his proposition to you, and await orders. I gave him back the books, and he returned to London without making any promise, that he would await the event of the orders you might think proper to give.
News of the accession of nine States to the new form of federal government has been received here about a week. I have the honor to congratulate you sincerely on this event. Of its effect at home, you are in the best situation to judge. On this side the Atlantic, it is considered as a very wise reformation. In consequence of this, speculations are already begun here, to purchase up our domestic liquidated debt. Indeed, I suspect that orders may have been previously lodged in America to do this, as soon as the new constitution was accepted effectually. If it is thought that this debt should be retained at home, there is not a moment to lose; and I know of no means of retaining it, but those I suggested to the treasury board, in my letter to them of March the 29th. The transfer of these debts to Europe will excessively embarrass, and perhaps totally prevent the borrowing any money in Europe, till these shall be paid off. This is a momentous object, and, in my opinion, should receive instantaneous attention.
The gazettes of France, to the departure of my letter, will accompany it, and those of Leyden to the 22nd of July, at which time their distribution in this country was prohibited. How long the prohibition may continue, I cannot tell. As far as I can judge, it is the only paper in Europe worth reading. Since the suppression of the packet-boats, I have never been able to find a safe conveyance for a letter to you, till the present by Mrs. Barclay. Whenever a confidential person shall be going from hence to London, I shall send my letters for you to the care of Mr. Trumbull, who will look out for safe conveyances. This will render the epochs of my writing very irregular. There is a proposition under consideration, for establishing packet-boats on a more economical plan, from Havre to Boston; but its success is uncertain, and still more, its duration.
I have the honor to be, with sentiments of the most perfect esteem and respect, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO COLONEL MONROE.
Paris, August 9, 1788.
Dear Sir,
Since my last to you, I have to thank your for your favors of July the 27th, 1787, and April the 10th, 1788, and the details they contained; and in return, will give you now the leading circumstances of this continent.
This nation is at present under great internal agitation. The authority of the crown on one part, and that of the parliaments on the other, are fairly at issue. Good men take part with neither, but have raised an opposition, the object of which is to obtain a fixed and temperate constitution. There was a moment when this opposition ran so high, as to endanger an appeal to arms, in which case, perhaps, it would have been crushed. The moderation of government has avoided this, and they are yielding daily one right after another to the nation. They have given them Provincial Assemblies, which will be very perfect representations of the nation, and stand somewhat in the place of our State Assemblies; they have reformed the criminal law; acknowledged the King cannot lay a new tax, without the consent of the States General; and they will call the States General the next year. The object of this body, when met, will be a bill of rights, a civil list, a national assembly meeting at certain epochs, and some other matters of that kind. So that I think it probable this country will, within two or three years, be in the enjoyment of a tolerably free constitution, and that without its having cost them a drop of blood; for none has yet been spilt, though the English papers have set the whole nation to cutting throats.
Be assured of those sentiments of esteem and attachment, with which I am, Dear Sir, your friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MONSIEUR DE CREVE-COEUR.
Paris, August 9, 1788.
Dear Sir,
While our second revolution is just brought to a happy end with you, yours here is but cleverly under way. For some days I was really melancholy with the apprehension, that arms would be appealed to, and the opposition crushed in its first efforts. But things seem now to wear a better aspect. While the opposition keeps at its highest wholesome point, government, unwilling to draw the sword, is not forced to do it. The contest here is exactly what it was in Holland: a contest between the monarchical and aristocratical parts of the government for a monopoly of despotism over the people. The aristocracy in Holland, seeing that their common prey was likely to escape out of their clutches, chose rather to retain its former portion, and therefore coalesced with the single head. The people remained victims. Here, I think, it will take a happier turn. The parliamentary part of the aristocracy is alone firmly united. The Noblesse and Clergy, but especially the former, are divided partly between the parliamentary and the despotic party, and partly united with the real patriots, who are endeavoring to gain for the nation what they can, both from the parliamentary and the single despotism. I think I am not mistaken in believing, that the King and some of his ministers are well affected to this band; and surely, that they will make great cessions to the people, rather than small ones to the parliament. They are, accordingly, yielding daily to the national reclamations, and will probably end in according a well-tempered constitution. They promise the States General for the next year, and I have good information that an Arrêt will appear the day after to-morrow, announcing them for May, 1789. How they will be composed, and what they will do, cannot be foreseen. Their convocation, however, will tranquillize the public mind, in a great degree, till their meeting. There are, however, two intervening difficulties. 1. Justice cannot till then continue completely suspended, as it now is. The parliament will not resume their functions, but in their entire body. The bailliages are afraid to accept of them. What will be done? 2. There are well-founded fears of a bankruptcy before the month of May. In the mean time, the war is spreading from nation to nation. Sweden has commenced hostilities against Russia; Denmark is showing its teeth against Sweden; Prussia against Denmark; and England too deeply engaged in playing the back game, to avoid coming forward, and dragging this country and Spain in with her. But even war will not prevent the assembly of the States General, because it cannot be carried on without them. War, however, is not the most favorable moment for divesting the monarchy of power. On the contrary, it is the moment when the energy of a single hand shows itself in the most seducing form.
A very considerable portion of this country has been desolated by a hail. I considered the newspaper accounts of hailstones of ten pounds weight as exaggerations. But in a conversation with the Duke de la Rochefoucault the other day, he assured me, that though he could not say he had seen such himself, yet he considered the fact as perfectly established. Great contributions, public and private, are making for the sufferers. But they will be like the drop of water from the finger of Lazarus. There is no remedy for the present evil, nor way to prevent future ones, but to bring the people to such a state of ease, as not to be ruined by the loss of a single crop. This hail may be considered as the coup de grace to an expiring victim. In the arts there is nothing new discovered since you left us, which is worth communicating. Mr. Paine’s iron bridge was exhibited here with great approbation. An idea has been encouraged of executing it in three arches at the King’s garden. But it will probably not be done.
I am, with sentiments of perfect esteem and attachment, Dear Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN JAY.
Paris, August 10, 1788.
Sir,
I have waited till the last moment of Mrs. Barclay’s departure, to write you the occurrences since my letter of the 3rd instant. We have received the Swedish account of an engagement between their fleet and the Russian, on the Baltic, wherein they say they took one, and burned another Russian vessel, with the loss of one on their side, and that the victory remained with them. They say, at the same time, that their fleet returned into port, and the Russians kept the sea; we must, therefore, suspend our opinion till we get the Russian version of this engagement. The Swedish manifesto was handed about to-day at Versailles, by the Swedish ambassador, in manuscript. The King complains that Russia has been ever endeavoring to sow divisions in his kingdom, in order to re-establish the ancient constitution; that he has long borne it, through a love of peace, but finds it no longer bearable: that still, however, he will make peace on these conditions; 1. That the Empress punishes her minister for the note he gave in to the court of Stockholm; 2. that she restore Crimea to the Turks; and 3. that she repay to him all the expenses of his armament. The Russian force, in vessels of war on the Black Sea, are five frigates, and three ships of the line; but those of the line are shut up in port, and cannot come out till Oczakow shall be taken. This fleet is commanded by Paul Jones, with the rank of rear-admiral. The Prince of Nassau commands the galleys and gun-boats. It is now ascertained, that the States General will assemble the next year, and probably in the month of May. Tippoo Saib’s ambassadors had their reception to-day at Versailles with unusual pomp. The presence was so numerous, that little could be caught of what they said to the king, and he answered to them: from what little I could hear, nothing more passed than mutual assurances of good will. The name of the Marechal de Richelieu is sufficiently remarkable in history, to justify my mentioning his death, which happened two days ago; he was aged ninety-two years.
I have the honor to be, with sentiments of the most perfect esteem and respect, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN JAY.
Paris, August 11, 1788.
Sir,
In my letter of the last night, written in the moment of Mrs. Barclay’s departure, I had the honor of mentioning to you, that it was now pretty certain that the States General would be assembled in the next year, and probably in the month of May. This morning an Arrêt is published, announcing that their meeting is fixed on the first day of May next, of which I enclose you a copy by post, in hopes it will get to Bordeaux in time for Mrs. Barclay. This Arrêt ought to have a great effect towards tranquillizing the nation. There are still, however, two circumstances which must continue to perplex the administration. The first is, the want of money, occasioned not only by the difficulty of filling up the loan of the next year, but by the withholding the ordinary supplies of taxes, which is said to have taken place in some instances: this gives apprehension of a bankruptcy under some form or other, and has occasioned the stocks to fall, in the most alarming manner. The second circumstance is, that justice, both civil and criminal, continues suspended. The parliament will not resume their functions, but with their whole body, and the greater part of the bailliages declined acting; the present Arrêt announces a perseverance in this plan. I have information from Algiers, of the 5th of June, that the plague is raging there, with great violence; that one of our captives was dead of it, and another ill, so that we have there, in all, now, only fifteen or sixteen; that the captives are more exposed to its ravages, than others; that the great redemptions by the Spaniards, Portuguese, and Neapolitans, and the havoc made by the plague, had now left not more than four hundred slaves in Algiers; so that their redemption was become not only exorbitant, but almost inadmissible; that common sailors were held at four hundred pounds sterling, and that our fifteen or sixteen could probably not be redeemed for less than from twenty-five to thirty thousand dollars. An Algerine cruiser, having twenty-eight captives of Genoa aboard, was lately chased ashore, by two Neapolitan vessels: the crew and captives got safe ashore, and the latter, of course, recovered their freedom. The Algerine crew was well treated, and would be sent back by the French. But the government of Algiers demands of France, sixty thousand sequins, or twenty-seven thousand pounds sterling, for the captives escaped; that is, nearly one thousand pounds each. The greater part of the regency were for an immediate declaration of war against France; but the Dey urged the heavy war the Turks were at present engaged in; that it would be better not to draw another power on them, at present; that they would decline renewing the treaty of one hundred years, which expired two years ago, so as to be free to act hereafter; but, for the present, they ought to accept payment for the captives, as a satisfaction. They accordingly declared to the French consul, that they would put him, and all his countrymen there, into irons, unless the sixty thousand sequins were paid: the consul told them, his instructions were, positively, that they should not be paid. In this situation stood matters between that pettifogging nest of robbers and this great kingdom, which will finish, probably, by crouching under them, and paying the sixty thousand sequins. From the personal characters of the present administration, I should have hoped, under any other situation than the present, they might have ventured to quit the beaten track of politics hitherto pursued, in which the honor of their nation has been calculated at nought, and to join in a league for keeping up a perpetual cruise against these pirates, which, though a slow operation, would be a sure one for destroying all their vessels and seamen, and turning the rest of them to agriculture. But a desire of not bringing upon themselves another difficulty, will probably induce the ministers to do as their predecessors have done.
August 12. The enclosed paper of this morning gives some particulars of the action between the Russians and Swedes, the manifesto of the Empress, and the declaration of the court of Versailles, as to the affair of Trincomale.
I have the honor to be, with sentiments of perfect esteem and respect, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO WILLIAM CARMICHAEL.
Paris, August 12, 1788.
Dear Sir,
Since my last to you, I have been honored with yours of the 18th and 29th of May, and 5th of June. My latest American intelligence is of the 24th of June, when nine certainly, and probably ten States, had accepted the new constitution, and there was no doubt of the eleventh (North Carolina), because there was no opposition there. In New York, two thirds of the State were against it, and certainly if they had been called to the decision, in any other stage of the business, they would have rejected it; but before they put it to the vote, they would certainly have heard that eleven States had joined in it, and they would find it safer to go with those eleven, than put themselves into opposition, with Rhode Island only. Though I am much pleased with this successful issue of the new constitution, yet I am more so, to find that one of its principal defects (the want of a declaration of rights) will pretty certainly be remedied. I suppose this, because I see that both people and conventions, in almost every State, have concurred in demanding it. Another defect, the perpetual re-eligibility of the same President, will probably not be cured, during the life of General Washington. His merit has blinded our countrymen to the danger of making so important an officer re-eligible. I presume there will not be a vote against him, in the United States. It is more doubtful, who will be Vice-President. The age of Dr. Franklin, and the doubt whether he would accept it, are the only circumstances that admit a question, but that he would be the man. After these two characters of first magnitude, there are so many which present themselves equally, on the second line, that we cannot see which of them will be singled out. John Adams, Hancock, Jay, Madison, Rutledge, will be all voted for. Congress has acceded to the prayer of Kentucky to become an independent member of the Union. A committee was occupied in settling the plan of receiving them, and their government is to commence on the 1st day of January next.
You are, I dare say, pleased, as I am, with the promotion of our countryman, Paul Jones. He commanded the right wing, in the first engagement between the Russian and Turkish galleys; his absence from the second, proves his superiority over the Captain Pacha, as he did not choose to bring his ships into the shoals in which the Pacha ventured, and lost those entrusted to him. I consider this officer as the principal hope of our future efforts on the ocean. You will have heard of the action between the Swedes and Russians, on the Baltic; as yet, we have only the Swedish version of it. I apprehend this war must catch from nation to nation, till it becomes general.
With respect to the internal affairs of this country, I hope they will be finally well arranged, and without having cost a drop of blood. Looking on as a by-stander, no otherwise interested, than as entertaining a sincere love for the nation in general, and a wish to see their happiness promoted, keeping myself clear of the particular views and passions of individuals, I applaud extremely the patriotic proceedings of the present ministry. Provincial Assemblies established, the States General called, the right of taxing the nation without their consent abandoned, corvées abolished, torture abolished, the criminal code reformed, are facts which will do eternal honor to their administration, in history. But were I their historian, I should not equally applaud their total abandonment of their foreign affairs. A bolder front in the beginning, would have prevented the first loss, and consequently, all the others. Holland, Prussia, Turkey, and Sweden, lost without the acquisition of a single new ally, are painful reflections for the friends of France. They may, indeed, have in their places the two empires, and perhaps Denmark; in which case, physically speaking, they will stand on as good ground as before, but not on as good moral ground. Perhaps, seeing more of the internal working of the machine, they saw, more than we do, the physical impossibility of having money to carry on a war. Their justification must depend on this, and their atonement, on the internal good they are doing to their country; this makes me completely their friend.
I am, with great esteem and attachment, Dear Sir, you friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO M. CATHALAN.
Paris, August 13,1788.
Sir,
I have to acknowledge the receipt of your two favors, of June, and July the 11th, and to thank you for the political intelligence they contained, which is always interesting to me. I will ask a continuance of them, and especially that you inform me, from time to time, of the movements in the ports of Marseilles and Toulon, which may seem to indicate peace or war. These are the most certain presages possible; and being conveyed to me from all the ports, they will always enable me to judge of the intentions or expectations of the ministry, and to notify you of the result of the intelligence from all the ports, that you may communicate it to the American commerce.
I have the pleasure to inform you, that the new constitution proposed to the United States, has been established by the votes of nine States. It is happy for us to get this operation over before the war kindled in Europe could affect us, as by rendering us more respectable, we shall be more probably permitted, by all parties, to remain neutral.
I take the liberty of putting under your cover a letter for Mr. Bernard, containing some seeds, and another to Giuseppe Chiappe, our consul at Mogadore. I thank you for your settlement of the price of the Observations Météorologiques, and I have repaid the sixty livres to Sir John Lambert, in your name. When the nursery man, whom you have been so good as to employ to prepare the olives and olive plants, to be sent to Charleston, shall be executing that commission, I shall be glad if he will, at the same time, prepare a few plants only, of the following kinds. Figs, the best kind for drying, and the best kind for eating fresh, raisins, the best kind for drying, prugnolles, cork trees, pistaches, capers. I desire only a few plants of each of these, that they may not take too much of the place of the olives, which is our great object, and the sole one we have at heart. If you will be so good as to give the nursery man this order immediately, it will save you the necessity of recurring to my letter, when the season comes.
I have the honor to be, with great and sincere esteem, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN JAY.
Paris, August 20,1788.
Sir,
I had the honor to write to you on the 3rd, 10th, and 11th instant, with a postscript of the 12th; all of which went by Mrs. Barclay. Since that date, we have received an account of a third victory obtained by the Russians over the Turks, on the Black Sea, in which the Prince of Nassau, with his galleys, destroyed two frigates, three smaller vessels, and six galleys. The Turkish power on that sea is represented, by their enemies, as now annihilated. There is reason to believe, however, that this is not literally true, and that aided by the supplies furnished by the English, they are making extraordinary efforts to re-establish their marine. The Russian minister here has shown the official report of Admiral Greigh, on the combat of July the 17th, in which he claims the victory, and urges in proof of it, that he kept the field of battle. This report is said to have been written on it. As this paper, together with the report of the Swedish admiral, is printed in the Leyden gazette of the 15th instant, I enclose it to you. The court of Denmark has declared, it will furnish Russia the aid stipulated in their treaty: and it is not doubted they will go beyond this, and become principals in the war. The next probable moves are, that the King of Prussia will succor Sweden; and Poland, Russia, by land: and a possible consequence is, that England may send a squadron into the Baltic, to restore equilibrium in that sea. In my letter of the 11th, I observed to you, that this country would have two difficulties to struggle with, till the meeting of their States General, and that one of these was the want of money: this has, in fact, overborne all their resources, and the day before yesterday, they published an Arrêt, suspending all reimbursements of capital, and reducing the payments of the principal mass of demands for interest, to twelve sous in the livre; the remaining eight sous to be paid with certificates. I enclose you a newspaper with the Arrêt. In this paper you will see the exchange of yesterday, and I have inserted that of the day before, to show you the fall. The consternation is, as yet, too great to let us judge of the issue. It will probably ripen the public mind to the necessity of a change in their constitution, and to the substituting the collected wisdom of the whole, in place of a single will, by which they have been hitherto governed. It is a remarkable proof of the total incompetency of a single head to govern a nation well, when, with a revenue of six hundred millions, they are led to a declared bankruptcy, and to stop the wheels of government, even in its most essential movements, for want of money.
I send the present letter by a private conveyance to a sea-port, in hopes a conveyance may be found by some merchant vessel.
I have the honor to be, with sentiments of the most perfect esteem and respect, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MR. CUTTING.
Paris, August 23, 1788.
Dear Sir,
I have duly received your favors of the 3rd, 8th, 14th, and 15th instant, and have now the honor of enclosing you a letter of introduction to Doctor Ramsay.
I think a certainty that England and France must enter into the war, was a great inducement to the ministry here to suspend the portion of public payments, which they have lately suspended. By this operation, they secure two hundred and three millions of livres, or eight millions and a half of guineas, in the course of this and the ensuing year, which will be sufficient for the campaign of the first year: for what is to, follow, the States General must provide. The interesting question now is, how the States General shall be composed? There are three opinions. 1. To place the three estates, Clergy, Noblesse, and Commons, in three different Houses. The Clergy would, probably, like this, and some of the Nobility; but it has no partisans out of those orders. 2. To put the Clergy and Noblesse into one House, and the Commons into another. The Noblesse will be generally for this. 3. To put the three orders into one House, and make the Commons the majority of that House. This re-unites the greatest number of partisans, and I suspect it is well patronized in the ministry, who, I am persuaded, are proceeding bona fide, to improve the constitution of their country. As to the opposition which the English expect from the personal character of the King, it proves they do not know what his personal character is. He is the honestest man in his kingdom, and the most regular and economical. He has no foible which will enlist him against the good of his people; and whatever constitution will promote this, he will befriend. But he will not befriend it obstinately: he has given repeated proofs of a readiness to sacrifice his opinion to the wish of the nation. I believe he will consider the opinion of the States General, as the best evidence of what will please and profit the nation, and will conform to it. All the characters at court may not be of this disposition, and from thence may, possibly, arise representations, capable of leading the King astray; but upon a full view of all circumstances, I have sanguine hopes, that such a constitution will be established here, as will regenerate the energy of the nation, cover its friends, and make its enemies tremble. I am, with very great esteem, Dear Sir, your friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN JAY.
Paris, September 3, 1788.
Sir,
By Mrs. Barclay I had the honor of sending you letters of the 3rd, 10th, and 11th of August; since which, I wrote you of the 20th of the same month, by a casual conveyance, as is the present.
In my letter of the 20th, I informed you of the act of public bankruptcy which had taken place here. The effect of this would have been a forced loan of about one hundred and eighty millions of livres, in the course of the present and ensuing year. But it did not yield a sufficient immediate relief. The treasury became literally moneyless, and all purposes depending on this mover came to a stand. The Archbishop was hereupon removed, with Monsieur Lambert, the Comptroller General; and Mr. Necker was called in, as Director General of the finance. To soften the Archbishop’s dismission, a cardinal’s hat is asked for him from Rome, and his nephew promised the succession to the Archbishopric of Sens. The public joy, on this change of administration, was very great indeed. The people of Paris were amusing themselves with trying and burning the Archbishop in effigy, and rejoicing on the appointment of Mr. Necker. The commanding officer of the city-guards undertook to forbid this, and not being obeyed, he charged the mob with fixed bayonets, killed two or three, and wounded many: this stopped their rejoicings for that day; but enraged at being thus obstructed in amusements wherein they had committed no disorder whatever, they collected in great numbers the next day, attacked the guards in various places, burnt ten or twelve guard-houses, killed two or three of the guards, and had about six or eight of their own number killed. The city was hereupon put under martial law, and after a while, the tumult subsided, and peace was restored. The public stocks rose ten per cent, on the day of Mr. Necker’s appointment: he was immediately offered considerable sums of money, and has been able so far to wave the benefit of the act of bankruptcy, as to pay in cash all demands, except the remboursements des capitaux. For these, and for a sure supply of other wants, he will depend on the States General, and will hasten their meetings, as is thought. No other change has yet taken place in the administration. The minister of war, however, must certainly follow his brother, and some think, and all wish, that Monsieur de Lamoignon, the Garde des Sceaux, may go out also. The administration of justice is still suspended. The whole kingdom seems tranquil at this moment.
Abroad, no event worth noting has taken place since my last. The court of Denmark has not declared it will do any thing more, than furnish the stipulated aid to Russia. The King of Prussia has as yet made no move, which may decide whether he will engage in the war, nor has England sent any squadron into the Baltic. As the season for action is considerably passed over, it is become more doubtful, whether any other power will enter the lists till the next campaign; this will give time for stopping the further progress of the war, if they really wish to stop it. Two camps of twenty-five thousand men each are forming in this country on its northern limits. The Prince of Conde has the command of one, and the Duke de Broglio of the other.
I trouble you with the enclosed letter from a Henry Watson, claiming prize monies, as having served under Admiral Paul Jones, which I suppose should go to the treasury, or war-office.
I have the honor to be, with sentiments of the most perfect esteem and respect, Sir, your most obedient and most humble; servant,
Th: Jefferson,
TO THE COMMISSIONERS OF THE TREASURY.
Paris, September 6, 1788.
Gentlemen,
Your favor of July the 3rd came to hand some days ago, and that of July the 22nd in the afternoon of yesterday. Knowing that a Mr. Vannet was to leave Paris this morning to go to Virginia in a vessel bound from Havre to Potomac, I have engaged him to receive the papers which are the subject of those letters, to take care of them from thence to Havre, and on the voyage; and when he shall have arrived in Potomac, instead of going directly to Richmond, as he intended, he will proceed with them himself to New York. I shall pay here all expenses to their delivery at the ship’s side in America, freight included: unless, perhaps, he may find it necessary to put another covering over them, if he should not be able to get them into the cabin; in this case, you will have to reimburse him for that. I engage to him that you shall pay him their transportation from the ship’s side to New York, and his own reasonable expenses from the place of his landing to New York, and back to the place of landing. As he takes that journey for this object only, it would be reasonable that you give him some gratuity for his time and trouble, and I suppose it would be accepted by him; but I have made no agreement for this. The papers are contained in a large box and a trunk. They were sent here by Mr. Ast, during my absence in Holland. When they arrived at the gates of Paris, the officers of the customs opened the trunk, to see whether it contained dutiable articles; but finding only books and papers, they concluded the contents of the box to be of the same nature, and did not open that. You receive it, therefore, as it came from the hands of Mr. Ast. A small trunk, which came as a third package from Mr. Ast, and which has never been opened, I have put into the great trunk, without displacing, or ever having touched a single paper, except as far as was necessary to make room for that. I shall have the whole corded and plumbed by the Custom-house here, not only to prevent their being opened at the Custom-houses on the road, and at the port of exportation, but to prove to you, whether they shall have been opened by any body else after going out of my hands. If the stamped leads are entire, and the cords uncut, when you receive them, you will be sure they have not been opened; they will be wrapt in oil-cloth here to guard them against the damps of the sea; and, as I mentioned before, Mr. Vannet will put them under another covering, if he finds it necessary, at Havre.
At the same time with your last letter, I received from the office of Foreign Affairs the ratification by Congress of the loan of 1788, for another million of guilders. As the necessity of this loan resulted from the estimate made by Mr. Adams and myself, which estimate was laid before Congress, I suppose their ratification of the loan implies that of the estimate. One article of this was for the redemption of our captives at Algiers. Though your letter says nothing on this subject, I am in hopes you have sent orders to the commissioners of the loans at Amsterdam to furnish, as soon as they shall have it, what may be necessary for this pressing call. So also for the foreign officers. If the ratification of the loan has been made by Congress, with a view to fulfil the objects of the estimate, a general order from you to the commissioners of the loans at Amsterdam, to pay the monies from time to time, according to that estimate, or to such other as you shall furnish them with, might save the trouble of particular orders on every single occasion, and the disappointments arising from the delay or miscarriage of such orders: but it is for you to decide on this.
I have the honor to be, with sentiments of the most perfect respect, Gentlemen, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO THE COUNT DE MONTMORIN.
Paris, September 11, 1788.
Sir,
In the course of the last war, the house of Schweighaeuser and Dobree of Nantes, and Puchilberg of L’Orient, presented to Dr. Franklin a demand against the United States of America. He, being acquainted with the circumstances of the demand, and knowing it to be unfounded, refused to pay it. They thereupon procured seizure, by judiciary authority, of certain arms and other military stores which we had purchased in this country, and had deposited for embarkation at Nantes: and these stores have remained in that position ever since. Congress have lately instructed me to put an end to this matter. Unwilling to trouble your Excellency, whenever it can be avoided, I proposed to the parties to have the question decided by arbitrators, to be chosen by us jointly. They have refused it, as you will see by their answers to my letters, copies of both which I have the honor to enclose you. I presume it to be well settled in practice, that the property of one sovereign is not permitted to be seized within the dominions of another; and that this practice is founded not only in mutual respect, but in mutual utility. To what the contrary practice would lead, is evident in the present case, wherein military stores have been stopped, in the course of a war, in which our greatest difficulties proceeded from the want of military stores. In their letter, too, they make a merit of not having seized one of our ships of war, and certainly the principle which admits the seizure of arms, would admit that of a whole fleet, and would often furnish an enemy the easiest means of defeating an expedition. The parties obliging me, then, to have recourse to your Excellency on this occasion, I am under the necessity of asking an order from you for the immediate delivery of the stores and other property of the United States at Nantes, detained by the house of Schweighaeuser and Dobree, and that of Puchilberg, or by either of them, under a pretence of a judicial seizure.
I have the honor to be, with sentiments of the most perfect respect and esteem, your Excellency’s most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO M. DE REYNEVAL.
Sir,
Paris, September 16, 1788.
I have the honor now to enclose you my observations on the alteration proposed in the consular convention. There remain only three articles of those heretofore in question between us, to which I am unable to agree; that is to say, the second, proposing still to retain personal immunities for the consuls, and others attached to their office; the eighth, proposing that the navigation code of each nation shall be established in the territories of the other; and the ninth, insisting that the ship’s roll shall be conclusive evidence that a person belongs to the ship.
There are several new matters introduced into the draught: some of these are agreed to; others cannot be admitted, as being contrary to the same principles which had obliged me to disagree to some of the former articles. The greatest part of the eleventh, and the whole of the twelfth new articles, are in this predicament. They propose, that no person shall be arrested on board a merchant vessel, for any cause, but in presence of the consul; that no such vessel shall be visited, but in his presence; and that when the officers of justice have reason to believe that a criminal has taken refuge on board a vessel of war, the captain’s word shall be conclusive evidence that he is not there.
To the objections which I had the honor of stating in my letter to his Excellency, the Count de Montmorin, I have now that of adding some other observations, of which I request your perusal. I enclose with them a draught, on the basis of the one you were pleased to give me, altered so as to reconcile it to the spirit of our laws.
I have the honor to be, with sentiments of the most perfect esteem and respect, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO THE MARQUIS DE LA ROUERIE.
Paris, September 16,1788.
Sir,
On receiving the first letters which you did me the honor to write to me on the arrears due to you from the United States, I informed you that I had nothing to do in the money department; that the subject of your letters belonged altogether to the treasury board, and to Mr. Grand, their banker here, to the former of whom I forwarded your letters. As I felt an anxiety, however, that the foreign officers should be paid, I took the liberty of pressing the treasury board, from time to time, to exert themselves for that effect; and I availed myself of an opportunity which occurred last spring, of setting on foot measures, which, with their approbation, might furnish the means of effecting this payment. So far my information to you went, and I added a supposition, that the treasury board would probably give orders on the subject, in the course of the month of July. But I made you no promise; it would have been strange if I had; nor does my office, nor any thing I have ever said or done, subject me to the demand of immediate payment, which you are pleased to make on me, nor call on me for any declaration or answer, positive or negative.
Finding that my interference, which was friendly only, and avowed to be inofficial, has given occasion to your letter of yesterday, in a style which I did not expect, and to which I can have no motive for further exposing myself, I must take the liberty of desiring that the correspondence between us on this subject may cease. I presume that the certificate given you points out the person, here or elsewhere, to whom your applications are to be made, and that he will inform you when he receives orders on your subject.
I am, Sir, your humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO WILLIAM SHORT.
Paris, September 20, 1788.
Dear Sir,
The evening of your departure, a letter came by the way of London and New York, addressed to you, and probably from Virginia. I think you wished your American letters to remain here; I shall therefore keep it. The passport now enclosed came the day after your departure; so also did a mass of American letters for me, as low down as August the 10th. I shall give you their substance. The convention of Virginia annexed to their ratification of the new constitution a copy of the State declaration of rights, not by way of condition, but to announce their attachment to them. They added also propositions for specific alterations of the constitution. Among these was one for rendering the President incapable of serving more than eight years, in any term of sixteen. New York has followed the example of Virginia, expressing the substance of her bill of rights (that is, Virginia’s), and proposing amendments: these last differ much from those of Virginia; but they concur as to the President, only proposing that he shall be incapable of being elected more than twice. But I own I should like better than either of these, what Luther Martin tells us was repeatedly voted and adhered to by the federal convention, and only altered about twelve days before their rising, when some members had gone off; to wit, that he should be elected for seven years, and incapable for ever after. But New York has taken another step, which gives uneasiness; she has written a circular letter to all the legislatures, asking their concurrence in an immediate convention for making amendments. No news yet from North Carolina. Electors are to be chosen the first Wednesday in January; the President to be elected the first Wednesday in February; the new legislature to meet the third week in March:—the place is not yet decided on. Philadelphia was first proposed, and had six and a half votes; the half vote was Delaware, one of whose members wanted to take a vote on Wilmington; then Baltimore was proposed and carried, and afterwards rescinded: so that the matter stood open as ever on the 10th of August; but it was allowed the dispute lay only between New York and Philadelphia, and rather thought in favor of the last. The Rhode Island Delegates had retired from Congress. Dr. Franklin was dangerously ill of the gout and stone on the 21st of July. My letters of August the 10th not mentioning him, I hope he was recovered. Warville, &c. were arrived. Congress had referred the decision, as to the independence of Kentucky, to the new government. Brown ascribes this to the jealousy of the northern States, who want Vermont to be received at the same time, in order to preserve a balance of interests in Congress. He was just setting out for Kentucky, disgusted, yet disposed to persuade to an acquiescence, though doubting they would immediately separate from the Union. The principal obstacle to this, he thought, would be the Indian war.
The following is a quotation from a letter from Virginia, dated July the 12th. ‘P———n, though much impaired in health, and in every respect in the decline of life, showed as much zeal to carry the new constitution, as if he had been a young man; perhaps more than he discovered in the commencement of the late revolution,in his opposition to Great Britain. W———e acted as chairman to the committee of the whole, and of course took but little part in the debate; but was for the adoption, relying on subsequent amendments. B———r said nothing, but was for it. The G———r exhibited a curious spectacle to view. Having refused to sign the paper, every body supposed him against it; but he afterwards had written a letter, and having taken a part, which might be called rather vehement than active, he was constantly laboring to show, that his present conduct was consistent with that letter, and that letter with his refusal to sign. M—d—n took the principal share in the debate for it; in which, together with the aid I have already mentioned, he was somewhat assisted by I—nn—s, Lee, M———l, C———n, and G. N———s. M—s—n, H———y, and Gr———n were the principal supporters of the opposition. The discussion, as might be expected, where the parties were so nearly on a balance, was conducted generally with great order, propriety, and respect of either party to the other.’
The assembly of Virginia, hurried to their harvests, would not enter into a discussion of the district bill, but suspended it to the next session. E. Winston is appointed a judge, vice Gabriel Jones, resigned. R. Goode and Andrew Moore, Counsellors, vice B. Starke, dead, and Joseph Egglestone, resigned. It is said Wilson, of Philadelphia, is talked of to succeed Mr. A. in London. Quære?
The dispute about Virgil’s tomb and the laurel, seems to be at length settled, by the testimony of two travellers, given separately, and without a communication with each other. These both say, that attempting to pluck off a branch of the laurel, it followed their hand, being, in fact, nothing more than a plant or bough recently cut, and stuck in the ground for the occasion. The Cicerone acknowledged the roguery, and said they practised it with almost every traveller, to get money. You will, of course, tug well at the laurel which shall be shown you, to see if this be the true solution.
The President Dupaty is dead. Monsieur de Barentin, prémier president de la cour des aides, is appointed Garde des Sceaux. The stocks are rather lower than when you left this. Present me in the most friendly terms to Messrs. Shippen and Rutledge. I rely on your communicating to them the news, and, therefore, on their pardoning me for not repeating it in separate letters to them. You can satisfy them how necessary this economy of my time and labor is. This goes to Geneva poste restante. I shall not write again till you tell me where to write to.
Accept very sincere assurances of the affection, with which I am, Dear Sir, your friend and servant,
Th; Jefferson.
TO JOHN JAY.
Paris, September 24,1788.
Sir,
Understanding that the vessel is not yet sailed from Havre, which is to carry my letters of the 3rd and 5th instant, I am in hopes you will receive the present with them. The Russian accounts of their victories on the Black Sea must have been greatly exaggerated. According to these, the Captain Pacha’s fleet was annihilated; yet themselves have lately brought him on the stage again, with fifteen ships of the line, in order to obtain another victory over him. I believe the truth to be, that he has suffered some checks, of what magnitude it is impossible to say, where one side alone is heard, and that he is still master of that sea. He has relieved Oczakow, which still holds out; Choczim also is still untaken, and the Emperor’s situation is apprehended to be bad. He spun his army into a long cord, to cover several hundred miles of frontier, which put it in the power of the Turks to attack with their whole force wherever they pleased. Laudon, now called to head the imperial army, is endeavoring to collect it; but in the mean time the campaign is drawing to a close, and has been worse than fruitless. The resistance of Russia to Sweden has been successful in every point by sea and land, This, with the interference of Denmark, and the discontent of the Swedish nation; at the breach of their constitution, by the King’s undertaking an offensive war without the consent of the Senate, has obliged him to withdraw his attacks by land, and to express a willingness for peace; one third of his officers have refused to serve. England and Prussia have offered their mediation between Sweden and Russia, in such equivocal terms, as to leave themselves at liberty to say it was an offer, or was not, just as it shall suit them. Denmark is asking the counter-offer of mediation from this court. If England and Prussia make a peace effectually in the north (which it is absolutely in their power to do), it will be a proof they do not intend to enter into the war; if they do not impose a peace, I should suspect they mean to engage themselves; as one can hardly suppose they would let the war go on in its present form, wherein Sweden must be crushed between Russia and Denmark.
The Garde des Sceaux, M. de Lamoignon, was dismissed the 14th instant, and M. de Barentin is appointed in his room. The deputies of Bretagne are released from the Bastile, and M. d’Epermesnil and M. Sabatier recalled from their confinement. The parliament is not yet reinstated; but it is confidently said it will be this week. The stocks continue low, and the treasury under a hard struggle to keep the government in motion. It is believed the meeting of the States General will be as early as January, perhaps December. I have received a duplicate of the ratification of the loan of 1788, by Congress, and a duplicate of a letter of July the 22nd, from the treasury board, on another subject, but none on that of the captives, or foreign officers. I suppose some cause of delay must have intervened between the ratification of Congress, and the consequent orders of the treasury board.
I have the honor to be, with sentiments of the most perfect esteem and respect, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant;
Th: Jefferson,
TO M. DE REYNEVAL.
Paris, October 1, 1788
Sir,
I have now the honor of enclosing to you a copy of the letter of September the 16th, which I had that of writing to his Excellency the Count de Montmorin, with the papers therein referred to, and of soliciting the order I have asked for. The originals were sent at the date before mentioned. Notwithstanding the refusal of the houses of Schweighaeuser and Dobree, and of Puchilberg, to settle their claim against the United States by arbitration, as I proposed to them, the United States will still be ready to do them justice. But those houses must first retire from the only two propositions they have ever made; to wit, either a payment of their demand without discussion, or a discussion before the tribunals of the country. In the mean time, I shall hope an acknowledgment with respect to us, of the principle which holds as to other nations; that our public property here cannot be seized by the territorial judge. It is the more interesting to us, as we shall be more and longer exposed than other nations, to draw arms and military stores from Europe. Our preference of this country has occasioned us to draw them from hence alone, since the peace: and the friendship we have constantly experienced from the government, will, we doubt not, on this and every other occasion, insure to us the protection of what we purchase. I have the honor to be, Sir, your friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
Paris, October 2, 1788.
Dear Sir,
I am now to acknowledge the receipt of your favors of the 16th and 23rd ultimo and to thank you for the intelligence they conveyed. That respecting the case of the interrogatories in Pennsylvania, ought to make noise. So evident a heresy in the common law ought not to be tolerated on the authority of two or three civilians, who happened, unfortunately, to make authority in the courts of England. I hold it essential, in America, to forbid that any English decision which has happened since the accession of Lord Mansfield to the bench, should ever be cited in a court: because, though there have come many good ones from him, yet there is so much sly poison instilled into a great part of them, that it is better to proscribe the whole. Can you inform me what has been done by England on the subject of our wheat and flour? The papers say it is prohibited, even in Hanover. How do their whale-fisheries turn out, this year? I hope a deep wound will be given them in that article soon, and such as will leave us in no danger from their competition.
I am, with very great esteem, Dear Sir, your most obedient, humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
LETTER CLXVII.—TO JOHN JAY, November 14, 1788
TO JOHN JAY.
Paris, November 14, 1788.
Sir,
In my letter of December the 21st, 1787, I had the honor of acknowledging the receipts of your two favors of July the 27th, 1787, which had come to my hands December the 19th, and brought with them my full powers for treating on the subject of the consular convention. Being then much engaged in getting forward the Arrêt which came out the 29th of December, and willing to leave some interval between that act, and the solicitation of a reconsideration of our consular convention, I had declined mentioning it, for some time, and was just about to bring it on the carpet, when it became necessary for me to go to Amsterdam. Immediately after my return, which was about the last of April, I introduced the subject to the Count de Montmorin, and have followed it unremittingly, from that time. The office of Marine, as well as that of Foreign Affairs, being to be consulted in all the stages of the negotiation, has protracted its conclusions till this time: it is at length signed this day, and I have now the honor to enclose the original, for the ratification of Congress. The principal changes effected are the following:
The clauses of the Convention of 1784, clothing consuls with privileges of the law of nations, are struck out, and they are expressly subjected, in their persons and property, to the laws of the land.
That giving the right of sanctuary to their houses, is reduced to a protection of their chancery room and its papers.
Their coercive powers over passengers are taken away; and over those, whom they might have termed deserters of their nation, are restrained to deserted seamen only.
The clause, allowing them to arrest and send back vessels, is struck out, and instead of it, they are allowed to exercise a police over the ships of their nation generally.
So is that, which declared the indelibility of the character of subject, and the explanation and extension of the eleventh article of the treaty of amity.
The innovations in the laws of evidence are done away: and the convention is limited to twelve years’ duration. Convinced that the fewer examples, the better, of either persons or causes unamenable to the laws of the land, I could have wished, still more had been done; but more could not be done, with good humor. The extensions of authority given by the convention of 1784, were so homogeneous with the spirit of this government, that they were prized here. Monsieur de Reyneval has had the principal charge of arranging this instrument with me; and, in justice to him, I must say, I could not have desired more reasonable and friendly dispositions, than he demonstrated through the whole of it.
I enclose herewith the several schemes successively proposed between us, together with the copies of the written observations given in with them, and which served as texts of discussion, in our personal conferences. They may serve as a commentary on any passage which may need it, either now or hereafter, and as a history how any particular passage comes to stand as it does. No. 1. is the convention of 1784. No. 2. is my first scheme. No. 3. theirs in answer to it. No. 4. my next, which brought us so near together, that, in a conference on that, we arranged it in the form in which it has been signed. I add No. 5. the copy of a translation which I have put into their hands, with a request, that if they find any passages in which the sense of the original is not faithfully rendered, they will point them out to me; otherwise, we may consider it as having their approbation. This, and the convention of 1784, (marked No. 1.) are placed side by side, so as to present to the eye, with less trouble, the changes made; and I enclose a number of printed copies of them, for the use of the members, who will have to decide on the ratification. It is desirable that the ratification should be sent here for exchange, as soon as possible.
With respect to the consular appointments, it is a duty on me to add some observations, which my situation here has enabled me to make. I think it was in the spring of 1784, that Congress (harassed by multiplied applications from foreigners, of whom nothing was known but on their own information, or on that of others as unknown as themselves) came to a resolution, that the interest of America would not permit the naming any person not a citizen, to the office of consul, vice-consul, agent, or commissary. This was intended as a general answer to that swarm of foreign pretenders. It appears to me, that it will be best, still to preserve a part of this regulation. Native citizens, on several valuable accounts, are preferable to aliens, and to citizens alien-born. They possess our language, know our laws, customs, and commerce; have, generally, acquaintance in the United States; give better satisfaction; and are more to be relied on, in point of fidelity. Their disadvantages are, an imperfect acquaintance with the language of this country, and an ignorance of the organization of its judicial and executive powers, and consequent awkwardness, whenever application to either of these is necessary, as it frequently is. But it happens, that in some of the principal ports of France, there is not a single American (as in Marseilles, L’Orient, and Havre), in others but one (as in Nantes and Rouen), and in Bordeaux only, are there two or three. Fortunately for the present moment, most of these are worthy of appointments. But we should look forward to future times, when there may happen to be no native citizens in a port, but such as, being bankrupt, have taken asylum in France from their creditors, or young ephemeral adventurers in commerce, without substance or conduct, or other descriptions, which might disgrace the consular office, without protecting our commerce. To avail ourselves of our good native citizens, when we have one in a port, and when there are none, to have yet some person to attend to our affairs, it appears to me advisable to declare, by a standing law, that no person but a native citizen shall be capable of the office of consul, and that the consul’s presence in his port should suspend, for the time, the functions of the vice-consul. This is the rule of 1784, restrained to the office of consul, and to native citizens. The establishing this, by a standing law, will guard against the effect of particular applications, and will shut the door against such applications, which will otherwise be numerous. This done, the office of vice-consul may be given to the best subject in the port, whether citizen or alien, and that of consul, be kept open for any native citizen of superior qualifications, who might come afterwards to establish himself in the port. The functions of the vice-consul would become dormant during the presence of his principal, come into activity again on his departure, and thus spare us and them the painful operation of revoking and reviving their commissions perpetually. Add to this, that during the presence of the consul, the vice-consul would not be merely useless, but would be a valuable counsellor to his principal, new in the office, the language, laws, and customs of the country. Every consul and vice-consul should be restrained in his jurisdiction, to the port for which he is named, and the territory nearer to that than to any other consular or vice-consular port, and no idea be permitted to arise, that the grade of consul gives a right to any authority whatever over a vice-consul, or draws on any dependence.
It is now proper I should give some account of the state of our dispute with Schweighaeuser and Dobree. In the conversation I had with Dobree, at Nantes, he appeared to think so rationally on this subject, that I thought there would be no difficulty in accommodating it with him, and I wished rather to settle it by accommodation, than to apply to the minister. I afterwards had it intimated to him, through the medium of Mr. Carnes, that I had it in idea, to propose a reference to arbitrators. He expressed a cheerful concurrence in it. I thereupon made the proposition to him formally, by letter, mentioning particularly, that we would choose our arbitrators of some neutral nation, and, of preference, from among the Dutch refugees here. I was surprised to receive an answer from him, wherein, after expressing his own readiness to accede to this proposition, he added, that on consulting Mr. Puchilberg, he had declined it; nevertheless, he wished a fuller explanation from me, as to the subjects to be submitted to arbitration. I gave him that explanation, and he answered finally, that Mr. Puchilberg refused all accommodation, and insisted that the matter should be decided by the tribunals of the country. Accommodation being at an end, I wrote to Monsieur de Montmorin, and insisted on the usage of nations, which does not permit the effects of one sovereign, to be seized in the territories of another, and subjected to judiciary decision there. I am promised that the stores shall be delivered; but the necessary formalities will occasion some delay. The King being authorized to call all causes before himself, ours will be evoked from the tribunal where it is, and will be ended by an order to deliver up the stores arrested, leaving it to the justice of Congress, to do afterwards what is right, as to the demand of Schweighaeuser and Dobree. I wish I could receive instructions what to do with the stores, when delivered. The arms had certainly better be sent to America, as they are good, and yet will sell here for little or nothing. The gun-stocks and old iron had better be sold here; but what should be done with the anchors? Being thoroughly persuaded that Congress wish that substantial justice should be done to Schweighaeuser and Dobree, I shall, after the stores are secured, repeat my proposition of arbitration to them. If they then refuse it, I shall return all the papers to America, and consider my powers for settling this matter as at an end.
I have received no answer yet from Denmark on the subject of the prizes; nor do I know whether to ascribe this silence to an intention to evade the demand, or to the multitude of affairs they have had on their hands lately. Patience seems to be prudence, in this case; to indispose them, would do no good, and might do harm. I shall write again soon, if no answer be received in the mean time.
I have the honor to be, with sentiments of the most perfect esteem and respect, Sir, your most obedient and most humble
servant,
Th: Jefferson.
[The following is the translation of the convention referred
to as No. 5. in the preceding letter.]
Convention between his Most Christian Majesty and the United States of America, for the purpose of defining and establishing the Functions and Privileges of their respective Consuls and Vice-Consuls.
His Majesty the Most Christian King, and the United States of America, having, by the twenty-ninth article of the treaty of amity and commerce concluded between them, mutually granted the liberty of having, in their respective States and ports, Consuls, Vice-Consuls, Agents, and Commissaries, and being willing, in consequence thereof, to define and establish, in a reciprocal and permanent manner, the functions and privileges of Consuls and Vice-Consuls, which they have judged it convenient to establish of preference, his M. C. Majesty has nominated the Sieur Count of Montmorin of St. Herent, Marechal of his Camps and Armies, Knight of his Orders and of the Golden Fleece, his Counsellor in all his Councils, Minister and Secretary of State, and of his Commandments and Finances, having the department of foreign affairs, and the United States have nominated Thomas Jefferson, citizen of the United States of America and their Minister Plenipotentiary near the King, who after having communicated to each other their respective full powers, have agreed on what follows:
Article I. The Consuls and Vice-Consuls named by the M. C. K. and the United States, shall be bound to present their commissions according to the forms which shall be established respectively by the M. C. K. within his dominions, and by the Congress within the United States; there shall be delivered to them, without any charges, the Exequatur necessary for the exercise of their functions; and on exhibiting the said Exequatur, the governors, commanders, heads of justice, bodies corporate, tribunals, and other officers having authority in the ports and places of their consulates, shall cause them to enjoy immediately, and without difficulty, the pre-eminences, authority, and privileges, reciprocally granted, without exacting from the said Consuls and Vice-Consuls any fee, under any pretext whatever.
Article II. The Consuls and Vice-Consuls, and persons attached to their functions, that is to say, their chancellors and secretaries, shall enjoy a full and entire immunity for their chancery and the papers which shall be therein contained: they shall be exempt from aU, personal service, from soldiers’ billets, militia, watch, guard, guardianship, trusteeship, as well as from all duties, taxes, impositions, and charges whatsoever, except on the estate real and personal of which they may be the proprietors or possessors, which shall be subject to the taxes imposed on the estates of all other individuals: and in all other instances they shall be subject to the laws of the land, as the natives are.
Those of the said Consuls and Vice-Consuls who shall exercise commerce, shall be respectively subject to all taxes, charges, and impositions established on other merchants.
They shall place over the outward door of their house the arms of their sovereign: but this mark of indication shall not give to the said house any privilege of asylum for any person or property whatsoever.
Article III. The respective Consuls and Vice-Consuls may establish agents in the different ports and places of their departments, where necessity shall require. These agents maybe chosen among the merchants, either national or foreign, and furnished with a commission from one of the said Consuls; they shall confine themselves respectively to the rendering to their respective merchants, navigators, and vessels, all possible service, and to inform the nearest Consul of the wants of the said merchants, navigators, and vessels, without the said agents otherwise participating in the immunities, rights, and privileges attributed to Consuls and Vice-Consuls, and without power, under any pretext whatever, to exact from the said merchants any duty or emolument whatsoever.
Article IV. The Consuls and Vice-Consuls respectively, may establish a chancery, where shall be deposited the consular determinations, acts, and proceedings, as also testaments, obligations, contracts, and other acts done by or between persons of their nation, and effects left by decedents, or saved from shipwreck.
They may, consequently, appoint fit persons to act in the said chancery, qualify and swear them in, commit to them the custody of the seal, and authority to seal commissions, sentences, and other consular acts, and also to discharge the functions of notaries and registers of the consulate.
Article V. The Consuls and Vice-Consuls respectively, shall have the exclusive right of receiving in their chancery, or on board their vessels, the declarations and all other the acts which the captains, masters, crews, passengers, and merchants of their nation may choose to make there, even their testaments and other disposals by last will: and the copies of the said acts, duly authenticated by the said Consuls or Vice-Consuls, under the seal of their consulate, shall receive faith in law, equally as their originals would, in all the tribunals of the dominions of the M. C. King and of the United States.
They shall also have, and exclusively, in case of the absence of the testamentary executor, guardian, or lawful representative, the right to inventory, liquidate, and proceed to the sale of the personal estate left by subjects or citizens of their nation, who shall die within the extent of their consulate; they shall proceed therein with the assistance of two merchants of their said nation, or, for want of them, of any other at their choice, and shall cause to be deposited in their chancery, the effects and papers of the said estates; and no officer, military, judiciary, or of the police of the country, shall disturb them or interfere therein, in any manner whatsoever: but the said Consuls and Vice-Consuls shall not deliver up the said effects, nor the proceeds thereof, to the lawful representatives or to their order, till they shall have caused to be paid all debts which the deceased shall have contracted in the country; for which purpose the creditor shall have a right to attach the said effects in their hands, as they might in those of any other individual whatever, and proceed to obtain sale of them, till payment of what shall be lawfully due to them. When the debts shall not have been contracted by judgment, deed, or note, the signature whereof shall be known, payment shall not be ordered, but on the creditor’s giving sufficient surety resident in the country, to refund the sums he shall have unduly received, principal, interest, and costs; which surety, nevertheless, shall stand duly discharged after the term of one year, in time of peace, and of two, in time of war, if the discharge cannot be formed before the end of this term, against the* representatives who shall present themselves.
And in order that the representatives may not be unjustly kept out of the effects of the deceased, the Consuls and Vice-Consuls shall notify his death in some one of the gazettes published within their consulate, and that they shall retain the said effects in their hands four months, to answer all just demands which shall be presented; and they shall be bound, after this delay, to deliver to the persons succeeding thereto, what shall be more than sufficient for the demands which shall have been formed.
Article VI. The Consuls and Vice-Consuls, respectively, shall receive the declarations, protests, and reports of all captains and masters of their respective nations, on account of average losses sustained at sea; and these captains and masters shall lodge in the chancery of the said Consuls and Vice-Consuls, the acts which they may have made in other ports, on account of the accidents which may have happened to them on their voyage. If a subject of the M. C. K. and a citizen of the United States, or a foreigner, are interested in the said cargo, the average shall be settled by the tribunals of the country, and not by the Consuls or Vice-Consuls; but when only the subjects or citizens of their own nation shall be interested, the respective Consuls or Vice-Consuls shall appoint skilful persons to settle the damages and average.
Article VII. In cases where by tempest, or other accident, French ships or vessels shall be stranded on the coasts of the United States, and ships or vessels of the United States shall be stranded on the coasts of the dominions of the M. C. K.,the Consul or Vice-Consul nearest to the place of shipwreck shall do whatever he may judge proper, as well for the purpose of saving the said ship or vessel, its cargo and appurtenances, as for the storing and the security of the effects and merchandise saved. He may take an inventory of them, without the intermeddling of any officers of the military, of the customs, of justice, or of the police of the country, otherwise than to give to the Consuls, Vice-Consuls, captain, and crew of the vessels shipwrecked or stranded, all the succor and favor which they shall ask of them, either for the expedition and security of the saving and of the effects saved, as to prevent all disturbance.
And in order to prevent all kind of dispute and discussion in the said cases of shipwreck, it is agreed that when there shall be no Consul or Vice-Consul to attend to the saving of the wreck, or that the residence of the said Consul or Vice-Consul (he not being at the place of the wreck) shall be more distant from the said place than that of the competent judge of the country, the latter shall immediately proceed therein, with all the despatch, certainty, and precautions, prescribed by the respective laws; but the said territorial judge shall retire, on the arrival of the Consul or Vice-Consul, and shall deliver over to him the report of his proceedings, the expenses of which the Consul and Vice-Consul shall cause to be reimbursed to him, as well as those of saving the wreck.
The merchandise and effects saved, shall be deposited in the nearest Custom-house, or other place of safety, with the inventory thereof, which shall have been made by the Consul or Vice-Consul, or by the judge who shall have proceeded in their absence, that the said effects and merchandise may be afterwards delivered (after levying therefrom the costs), and without form of process, to the owners, who, being furnished with an order for their delivery, from the nearest Consul or Vice-Consul, shall reclaim them by themselves, or by their order, either for the purpose of re-exporting such merchandise, in which case, they shall-pay no kind of duty of exportation, or for that of selling them in the country, if they be not prohibited there; and in this last case, the said merchandise, if they be damaged, shall be allowed an abatement of entrance duties, proportioned to the damage they have sustained, which shall be ascertained by the affidavits taken at the time the vessel was wrecked or struck.
Article VIII. The Consuls and Vice-Consuls shall exercise police over all the vessels of their respective nations, and shall have on board the said vessels, all power and jurisdiction in civil matters, in all the disputes which may there arise; they shall have an entire inspection over the said vessels, their crew, and the changes and substitutions there to be made. For which purpose they may go on board the said vessels whenever they may judge it necessary: well understood, that the functions hereby allowed shall be confined to the interior of the vessels, and that they shall not take place in any case, which shall have any interference with the police of the ports where the said vessels shall be.
Article IX. The Consuls and Vice-Consuls may cause to be arrested the captains, officers, mariners, sailors, and all other persons, being part of the crews of the vessels of their respective nations, who shall have deserted from the said vessels, in order to send them back, and transport them out of the country. For which purpose, the said Consuls and Vice-Consuls shall address themselves to the courts, judges, and officers competent, and shall demand the said deserters in writing, proving by an exhibition of the registers of the vessel or ship’s roll, that those men were part of the said crews: and on this demand, so proved (saving, however, where the contrary is proved), the delivery shall not be refused¦; and there shall be given all aid and assistance to the said Consuls and Vice-Consuls, for the search, seizure, and arrest of the said deserters, who shall even be detained and kept in the prisons of the country, at their request and expense, until they shall have found an opportunity of sending them back. But if they be not sent back within three months, to be counted from the day of their arrest, they shall be set at liberty, and shall be no more arrested for the same cause.
Article X. In cases where the respective subjects, or citizens, shall have committed any crime, or breach of the peace, they shall be amenable to the judges of the country.
Article XI. When the said offenders shall be a part of the crew of a vessel of their nation, and shall have withdrawn themselves on board the said vessel, they may be there seized and arrested by order of the judges of the country: these shall give notice thereof to the Consul or Vice-Consul, who may repair on board, if he thinks proper: but this notification shall not, in any case, delay execution of the order in question. The persons arrested shall not afterwards be set at liberty, until the Consul or Vice-Consul shall have been notified thereof; and they shall be delivered to him, if he requires it, to be put again onboard of the vessel on which they were arrested, or of others of their nation, and to be sent out of the country.
Article XII. All differences and suits between the subjects of the M. C. K. in the U. S., or between the citizens of the United States within the dominions of the M. C. K. and particularly all disputes relative to the wages and terms of engagement of the crews of the respective vessels, and all differences of whatever nature they be, which may arise between the privates of the said crews, or between any of them and their captains, or between the captains of different vessels of their nation, shall be determined by the respective Consuls and Vice-Consuls, either by a reference to arbitrators, or by a summary judgment, and without costs.
No officer of the country, civil or military, shall interfere therein, or take any part whatever in the matter: and the appeals from the said consular sentences shall be carried before the tribunals of France or of the United States, to whom it may appertain to take cognizance thereof.
Article XIII. The general utility of commerce, having caused to be established within the dominions of the M. C. K. particular tribunals and forms, for expediting the decision of commercial affairs, the merchants of the U. S. shall enjoy the benefit of these establishments; and the Congress of the U. S. will provide in the manner the most conformable to its laws, equivalent advantages in favor of the French merchants, for the prompt despatch and decision of affairs of the same nature.
Article XIV. The subjects of the M. C. K. and citizens of the U. S. who shall prove by legal evidence, that they are of the said nations respectively, shall, in consequence, enjoy an exemption from all personal service in the place of their settlement.
Article XV. If any other nation acquires, by virtue of any convention whatever, a treatment more favorable with respect to the consular pre-eminences, powers, authority, and privileges, the Consuls and Vice-Consuls of the M. C. K. or of the U. S., reciprocally, shall participate therein, agreeably to the terms stipulated by the second, third, and fourth articles of the treaty of amity and commerce, concluded between the M. C. K. and the U. S.
Article XVI. The present convention shall be in full force during the term of twelve years, to be counted from the day of the exchange of ratifications, which shall be given in proper form, and exchanged on both sides, within the space of one year, or sooner, if possible.
In faith whereof, we, Ministers Plenipotentiary, have signed the present convention, and have thereto set the seal of our arms.
Done at Versailles, the 14th of November, one thousand seven hundred and eighty eight.
L. C. De MONTMORIN. L. S.
Signed.
Th: Jefferson. L. S.
TO JAMES MADISON.
Paris, November 18, 1788.
Dear Sir,
My last to you was of the 31st of July; since which, I have received yours of July the 24th, August the 10th, and 23rd. The first part of this long silence in me was occasioned by a knowledge that you were absent from New York; the latter part, by a want of opportunity, which has been longer than usual. Mr. Shippen being just arrived here, and to set out to-morrow for London, I avail myself of that channel of conveyance. Mr. Carrington was so kind as to send me the second volume of the American Philosophical Transactions, the Federalist, and some other interesting pamphlets; and I am to thank you for another copy of the Federalist, and the report of the instructions to the ministers for negotiating peace. The latter unluckily omitted exactly the passage I wanted, which was what related to the navigation of the Mississippi. With respect to the Federalist, the three authors had been named to me. I read it with care, pleasure, and improvement, and was satisfied there was nothing in it by one of those hands, and not a great deal by a second. It does the highest honor to the third, as being, in my opinion, the best commentary on the principles of government, which ever was written. In some parts, it is discoverable that the author means only to say what may be best said in defence of opinions, in which he did not concur. But in general, it establishes firmly the plan of government. I confess, it has rectified me on several points. As to the bill of rights, however, I still think it should be added; and I am glad to see, that three States have at length considered the perpetual re-eligibility of the President, as an article which should be amended. I should deprecate with you, indeed, the meeting of a new convention. I hope they will adopt the mode of amendment by Congress and the Assemblies, in which case, I should not fear any dangerous innovation in the plan. But the minorities are too respectable, not to be entitled to some sacrifice of opinion in the majority; especially, when a great proportion of them would be contented with a bill of rights. Here, things internally, are going on well. The Notables now in session, have, indeed, passed one vote, which augurs ill to the rights of the people; but if they do not obtain now so much as they have a right to, they will in the long run. The misfortune is, that they are not yet ripe for receiving the blessings to which they are entitled. I doubt, for instance, whether the body of the nation, if they could be consulted, would accept of a habeas corpus law, if offered them by the King. If the Etats Generaux, when they assemble, do not aim at too much, they may begin a good constitution. There are three articles which they may easily obtain; 1. their own meeting, periodically; 2. the exclusive right of taxation; 3. the right of registering laws and proposing amendments to them, as exercised now by the parliaments. This last would be readily approved by the court, on account of their hostility against the parliaments, and would lead immediately to the origination of laws: the second has been already solemnly avowed by the King; and it is well understood, there would be no opposition to the first. If they push at much more, all may fail. I shall not enter further into public details, because my letter to Mr. Jay will give them. That contains a request of permission to return to America the next spring, for the summer only. The reasons therein urged, drawn from my private affairs, are very cogent. But there is another, more cogent on my mind, though of a nature not to be explained in a public letter. It is the necessity of attending my daughters, myself, to their own country, and depositing them safely in the hands of those, with whom I can safely leave them. I have deferred this request as long as circumstances would permit, and am in hopes it will meet with no difficulty. I have had too many proofs of your friendship, not to rely on your patronage of it, as, in all probability, nothing can suffer by a short absence. But the immediate permission is what I am anxious about; as by going in April and returning in October, I shall be sure of pleasant and short passages, out and in. I must intreat your attention, my friend, to this matter, and that the answers may be sent me through several channels.
Mr. Liniozin, at Havre, sent you, by mistake, a package belonging to somebody else. I do not know what it contained, but he has written to you on the subject, and prayed me to do the same, he is likely to suffer if it be not returned.
Supposing that the funding their foreign debt will be among the first operations of the new government, I send you two estimates; the one by myself, the other by a gentleman infinitely better acquainted with the subject, showing what fund will suffice to discharge the principal and interest, as it shall become due, aided by occasional loans, which the same fund will repay. I enclose them to you, because collating them together, and with your own ideas, you will be able to advise something better than either; but something must be done. This government will expect, I fancy, a very satisfactory provision for the payment of their debt, from the first session of the new Congress. Perhaps, in this matter, as well as the arrangement of your foreign affairs, I may be able, when on the spot with you, to give some information and suggest some hints, which may render my visit to my native country not altogether useless. I consider as no small advantage, the resuming the tone of mind of my constituents, which is lost by long absence, and can only be recovered by mixing with them; and shall, particularly, hope for much profit and pleasure, by contriving to pass as much time as possible with you. Should you have a trip to Virginia in contemplation, for that year, I hope you will time it so as that we may be there together. I will camp you at Monticello, where, if illy entertained otherwise, you shall not want books. In firm hope of a happy meeting with you in the spring, or early in summer, I conclude, with assurances of the sincere esteem and attachment, with which I am, Dear Sir, your affectionate friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO A. DONALD.
Paris, November 18,1788.
Dear Sir,
Often solicited by persons on this side the water, to inquire for their friends in America, about whose fate they are uncertain, I can only hand on their requests to my friends in America. The enclosed letter from, the Chevalier de Sigougne desires some inquiry after his brother, whom he supposes to have settled at Todd’s Bridge. As this is within your reach, I must refer the request to your humanity, and beg of you, if you can hear of him, you will be so good as to give me an account of him, returning me the enclosed letter at the same time.
The campaign between the Turks and Russians has been tolerably equal. The Austrians have suffered through the whole of it. By the interposition of Prussia and England, peace is likely to be made between Russia, Denmark, and Sweden. This is a proof that England does not mean to engage in the war herself. This country will certainly engage herself in no manner, externally, before the meeting of her States General. This assembly has been so long disused, that the forms of its convocation occasion difficulty. The Notables have been convened to prescribe them, and they are now in session. I am in hopes this will end in giving a good degree of liberty to this country. They enjoy, at present, the most perfect tranquillity within; their stocks, however, continue low, and money difficult to be got for current expenses. It is hoped, that Mr. Necker’s talents and popularity, with the aid of a National Assembly, will extricate them from their difficulties. We have been daily expecting to hear of the death of the King of England: our last news is of the 11th, when he was thought in the utmost danger. This event might produce a great change in the situation of things: it is supposed Mr. Fox would come into place, and he has been generally understood to be disposed for war. Should the King survive, I think the continuance of peace more probable at present, than it has been for some time past. Be so good as to contrive the enclosed letter, by a very safe conveyance. Remember me in the most friendly terms to Dr. Currie, and be assured yourself of the esteem and attachment, with which I am. Dear Sir, your affectionate friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN JAY.
Sir,
Paris, November 19, 1788.
Since my letter of September the 5th, wherein I acknowledged Mr. Remsen’s favor of July the 25th, I have written those of September the 24th, and of the 14th instant. This last will accompany the present, both going by the way of London, for want of a direct opportunity; but they go by a private hand.
No late event worth notice has taken place between the Turks and Austrians. The former continue in the territories of the latter, with all the appearances of superiority. On the side of Russia, the war wears an equal face, except that the Turks are still masters of the Black sea. Oczakow is not yet taken. Denmark furnished to Russia its stipulated quota of troops with so much alacrity, and was making such other warlike preparations, that it was believed they meant to become principals in the war against Sweden. Russia and England hereupon interposed efficaciously. Their ministers appointed to meditate, gave notice to the court of Copenhagen, that they would declare war against them in the name of their two sovereigns, if they did not immediately withdraw their troops from the Swedish territories. The court of London has since said, that their minister (Elliott) went further in this than he was authorized. However, the Danish troops are retiring. Poland is augmenting its army from twenty to an hundred thousand men. Nevertheless, it seems as if England and Prussia meant in earnest to stop the war in that quarter, contented to leave the two empires in the hands of the Turks. France, desired by Sweden to join the courts of London and Berlin in their mediation between Sweden and Russia, has declined it. We may be assured, she will meddle in nothing external before the meeting of the States General. Her temporary annihilation in the political scale of Europe, leaves to England and Prussia the splendid roll, of giving the law without meeting the shadow of opposition. The internal tranquillity of this country is perfect: their stocks, however, continue low, and the difficulty of getting money to face current expenses very great. In the contest between the King and parliament, the latter, fearing the power of the former, passed the convoking the States General. The government found itself obliged by other difficulties, also, to recur to the same expedient. The parliament, after its recall, showed that it was now become apprehensive of the States General, and discovered a determination to cavil at their form, so as to have a right to deny their legality, if that body should undertake to abridge their powers. The court, hereupon, very adroitly determined to call the same Notables, who had been approved by the nation the last year, to decide on the form of convoking the Etats Generaux: thus withdrawing itself from the disputes which the parliament might excite, and committing them with the nation. The Notables are now in session. The government had manifestly discovered a disposition that the Tiers-Etat, or Commons, should have as many representatives in the States General, as the Nobility and Clergy together: but five Bureaux of the Notables have voted by very great majorities, that they should have only an equal number with each of the other orders singly. One bureau, by a majority of a single voice, had agreed to give the Commons the double number of representatives. This is the first symptom of a decided combination between the Nobility and Clergy, and will necessarily throw the people into the scale of the King. It is doubted, whether the States can be called so early as January, though the government, urged by the want of money, is for pressing the convocation. It is still more uncertain what the States will do when they meet: there are three objects which they may attain, probably without opposition from the court; 1. A periodical meeting of the States; 2. their exclusive right of taxation; 3. the right of en-registering laws and proposing amendments to them, as now exercised by the parliaments. This would lead, as it did in England, to the right of originating laws. The parliament would, by the last measure, be reduced to a mere judiciary body, and would probably oppose it. But against the King and nation their opposition could not succeed. If the States stop here, for the present moment, all will probably end well, and they may, in future sessions, obtain a suppression of lettres de cachet, a free press, a civil list, and other valuable mollifications of their government. But it is to be feared, that an impatience to rectify every thing at once, which prevails in some minds, may terrify the court, and lead them to appeal to force, and to depend on that alone.
Before this can reach you, you will probably have heard of an Arrêt, passed the 28th of September, for prohibiting the introduction of foreign whale-oils, without exception. The English had glutted the markets of this country with their oils: it was proposed to exclude them, and an Arrêt was drawn, with an exception for us: in the last stage of the Arrêt, the exception was struck out, without my having any warning, or even suspicion of this. I suspect this stroke came from the Count de la Luzerne, minister of marine; but I cannot affirm it positively. As soon as I was apprized of this, which was several days after it passed (because it was kept secret till published in their seaports), I wrote to the Count de Montmorin a letter, of which the enclosed is a copy, and had conferences on the subject, from time to time, with him and the other ministers. I found them prepossessed by the partial information of their Dunkirk fishermen; and therefore thought it necessary to give them a view of the whole subject in writing, which I did, in the piece, of which I enclose you a printed copy. I therein entered into more details, than the question between us seemed rigorously to require. I was led to them by other objects. The most important was to disgust Mr. Necker, as an economist, against their new fishery, by letting him foresee its expense. The particular manufactures suggested to them, were in consequence of repeated applications from the shippers of rice and tobacco: other details, which do not appear immediately pertinent, were occasioned by circumstances which had arisen in conversation, or an apparent necessity of giving information on the whole matter. At a conference, in the presence of M. Lambert, on the 16th (where I was ably aided by the Marquis de la Fayette, as I have been through the whole business), it was agreed to except us from the prohibition. But they will require rigorous assurance, that the oils coming under our name are really of our fishery. They fear we shall cover the introduction of the English oils from Halifax. The Arrêt for excepting us was communicated to me, but the formalities of proving the oils to be American were not yet inserted. I suppose they will require every vessel to bring a certificate from their Consul or Vice-Consul residing in the State from which it comes. More difficult proofs were sometimes talked of. I supposed I might surely affirm to them, that our government would do whatever it could to prevent this fraud, because it is as much our interest as theirs to keep the market for the French and American oils only. I am told Massachusetts has prohibited the introduction of foreign fish-oils into her ports. This law, if well executed, will be an effectual guard against fraud; and a similar one in the other States, interested in the fishery, would much encourage this government to continue her indulgence to us. Though the Arrêt, then, for the re-admission of our oils is not yet passed, I think I may assure you it will be so in a few days, and of course that this branch of commerce, after so threatening an appearance, will be on a better footing than ever, as enjoying, jointly with the French oil, a monopoly of their markets. The continuance of this will depend on the growth of their fishery. Whenever they become able to supply their own wants, it is very possible they may refuse to take our oils; but I do not believe it possible for them to raise their fishery to that, unless they can continue to draw off our fishermen from us. Their seventeen ships, this year, had one hundred and fifty of our sailors on board. I do not know what number the English have got into their service. You will readily perceive, that there are particulars in these printed observations, which it would not be proper to suffer to become public. They were printed, merely that a copy might be given to each minister, and care has been taken to let them go into no other hands.
I must now trouble Congress with a petition on my own behalf. When I left my own house in October, 1783, it was to attend Congress as a member, and in expectation of returning in five or six months. In the month of May following, however, I was desired to come to Europe, as member of a commission, which was to continue two years only. I came off immediately, without going home to make any other arrangements in my affairs, thinking they would not suffer greatly before I should return to them. Before the close of the two years, Doctor Franklin retiring from his charge here, Congress were pleased to name me to it; so that I have been led on by events to an absence of five years, instead of five months. In the mean time, matters of great moment to others as well as myself, and which can be arranged by nobody but myself, will await no longer. Another motive, of still more powerful co-agency on my mind, is the necessity of carrying my family back to their friends and country. I must, therefore, ask of Congress a leave of short absence. Allowing three months on the sea, going and coming, and two months at my own house, which will suffice for my affairs, I need not be from Paris but between five and six months. I do not foresee any thing which can suffer during my absence. The consular convention is finished, except as to the exchange of ratification, which will be the affair of a day only. The difference with Schweighaeuser and Dobree, relative to our arms, will be finished. That of Denmark, if ever finished, will probably be long spun out. The ransom of the Algerine captives is the only matter likely to be on hand. That cannot be set on foot till the money is raised in Holland, and an order received for its application: probably these will take place, so that I may set it into motion, before my departure; if not, I can still leave it on such a footing, as to be put into motion the moment the money can be paid. And even when the leave of Congress shall be received, I will not make use of it, if there is any thing of consequence which may suffer; but would, postpone my departure till circumstances will admit it. But should these be as I expect they will, it will be vastly desirable to me to receive the permission immediately, so that I may go out as soon as the vernal equinox is over, and be sure of my return in good time and season in the fall. Mr. Short, who had had thoughts of returning to America, will postpone that return till I come back. His talents and character allow me to say, with confidence, that nothing will suffer in his hands. The friendly dispositions of Monsieur de Montmorin would induce him readily to communicate with Mr. Short in his present character; but should any of his applications be necessary to be laid before the Council, they might suffer difficulty: nor could he attend the diplomatic societies, which are the most certain sources of good intelligence. Would Congress think it expedient to remove the difficulties, by naming him secretary of legation, so that he would act of course as chargé des affaires during my absence? It would be just, that the difference between the salary of a secretary and a secretary of legation should cease, as soon as he should cease to be charged with the affairs of the United States; that is to say, on my return: and he would expect that. So that this difference for five or six months would be an affair of about one hundred and seventy guineas only, which would be not more than equal to the additional expense that would be brought on him necessarily by the change of character. I mention these particulars, that Congress may see the end as well as beginning of the proposition, and have only to add, ‘their will be done.’ Leave for me being obtained, I will ask it, Sir, of your friendship, to avail yourself of various occasions to the ports of France and England to convey me immediate notice of it, and relieve me as soon as possible from the anxiety of expectation, and the uncertainty in which I shall be. We have been in daily expectation of hearing of the death of the King of England. Our latest news are of the 11th. He had then been despaired of for three or four days; but as my letter is to pass through England, you will have later accounts of him than that can give you. I send you the newspapers to this date, and have the honor to be, with the greatest esteem and respect, Sir, your most obedient, humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
P. S. The last crop of corn in France has been so short, that they apprehend want. Mr. Necker desires me to make known this scarcity to our merchants, in hopes they would send supplies. I promised him I would. If it could be done without naming him, it would be agreeable to him, and probably advantageous to the adventurers. T. J.
[The annexed are the observations on the subject of admitting our whale-oil in the markets of France, referred to in the preceding letter.]
Whale-oil enters, as a raw material, into several branches of manufacture, as of wool, leather, soap: it is used also in painting, architecture, and navigation. But its great consumption is in lighting houses and cities. For this last purpose, however, it has a powerful competitor in the vegetable oils. These do well in warm, still weather, but they fix with cold, they extinguish easily with the wind, their crop is precarious, depending on the seasons, and to yield the same light, a larger wick must be used, and greater quantity of oil consumed. Estimating all these articles of difference together, those employed in lighting cities find their account in giving about twenty-five per cent, more for whale than for vegetable oils. But higher than this the whale-oil, in its present form, cannot rise; because it then becomes more advantageous to the city lighters to use others. This competition, then, limits its price, higher than which no encouragement can raise it; and it becomes, as it were, a law of its nature. But, at this low price, the whale-fishery is the poorest business into which a merchant or sailor can enter. If the sailor, instead of wages, has a part of what is taken, he finds that this, one year with another, yields him less than he could have got as wages in any other business. It is attended, too, with great risk, singular hardships, and long absence from his family, if the voyage is made solely at the expense of the merchant, he finds that, one year with another, it does not reimburse him his expense. As for example; an English ship of three hundred tons and forty-two hands brings home, communibus annis, after four months’ voyage, twenty-five tons of oil, worth four hundred and thirty-seven pounds ten shillings sterling. But the wages of the officers and seamen will be four hundred pounds; the outfit, then, and the merchants’ profit, must be paid by the government: and it is accordingly on this idea, that the British bounty is calculated. From the poverty of this business, then, it has happened, that the nations who have taken it up have successively abandoned it. The Basques began it: but though the most economical and enterprising of the inhabitants of France, they could not continue it; and it is said, they never employed more than thirty ships a year. The Dutch and Hanse towns succeeded them. The latter gave it up long ago. The English carried it on, in competition with the Dutch, during the last and beginning of the present century: but it was too little profitable for them, in comparison with other branches of commerce open to them.
In the mean time, the inhabitants of the barren island of Nantucket had taken up this fishery, invited to it by the whales presenting themselves on their own shore. To them, therefore, the English relinquished it, continuing to them, as British subjects, the importation of their oils into England, duty free, while foreigners were subject to a duty of eighteen pounds five shillings sterling a ton. The Dutch were enabled to continue it long, because, 1. They are so near the northern fishing grounds, that a vessel begins her fishing very soon after she is out of port. 2. They navigate with more economy than the other nations of Europe. 3. Their seamen are content with lower wages: and, 4. Their merchants, with a lower profit on their capital. Under all these favorable circumstances, however, this branch of business, after long languishing, is at length nearly extinct with them. It is said, they did not send above half a dozen ships in pursuit of the whale this present year. The Nantuckois, then, were the only people who exercised this fishery to any extent at the commencement of the late war. Their country, from its barrenness yielding no subsistence, they were obliged to seek it in the sea which surrounded them. Their economy was more rigorous than that of the Dutch. Their seamen, instead of wages, had a share in what was taken: this induced them to fish with fewer hands, so that each had a greater dividend in the profit; it made them more vigilant in seeking game, bolder in pursuing it, and parsimonious in all their expenses. London was their only market. When, therefore, by the late revolution, they became aliens in Great Britain, they became subject to the alien duty of eighteen pounds five shillings the ton of oil, which being more than equal to the price of the common whale-oil, they are obliged to abandon that fishery. So that this people, who, before the war, had employed upwards of three hundred vessels a year in the whale-fishery (while Great Britain had herself never employed one hundred), have now almost ceased to exercise it. But they still had the seamen, the most important material for this fishery; and they still retained the spirit for fishing: so that, at the re-establishment of peace, they were capable, in a very short time, of reviving their fishery in all its splendor. The British government saw that the moment was critical. They knew that their own share in that fishery was as nothing: that the great mass of fishermen was left with a nation now separated from them: that these fishermen, however, had lost their ancient market; had no other resource within their country to which they could turn and they hoped, therefore, they might, in the present moment of distress, be decoyed over to their establishments, and be added to the mass of their seamen. To effect this, they offered extravagant advantages to all persons who should exercise the whale-fishery from British establishments. But not counting with much confidence on a long connection with their remaining possessions on the continent of America, foreseeing that the Nantuckois would settle in them, preferably, if put on an equal footing with those of Great Britain, and that thus they might have to purchase them a second time, they confined their high offers to settlers in Great Britain. The Nantuckois, left without resource by the loss of their market, began to think of removing to the British dominions; some to Nova Scotia, preferring smaller advantages in the neighborhood of their ancient country and friends; others to Great Britain, postponing country and friends to high premiums. A vessel was already arrived from Halifax to Nantucket, to take off some of those who proposed to remove; two families had gone on board, and others were going, when a letter was received there, which had been written by Monsieur le Marquis de la Fayette, to a gentleman in Boston, and transmitted by him to Nantucket. The purport of the letter was to dissuade their accepting the British proposals, and to assure them that their friends in France would endeavor to do something for them. This instantly suspended their design: not another went on board, and the vessel returned to Halifax with only the two families.
In fact the French government had not been inattentive to the views of the British, nor insensible to the crisis. They saw the danger of permitting five or six thousand of the best seamen existing, to be transferred by a single stroke to the marine strength of their enemy, and to carry over with them an art which they possessed almost exclusively. The counterplan which they set on foot was to tempt the Nantuckois, by high offers, to come and settle in France. This was in the year 1785. The British, however, had in their favor, a sameness of language, religion, laws, habits, and kindred. Nine families only, of thirty-three persons in the whole, came to Dunkirk; so that this project was not likely to prevent their emigration to the English establishments, if nothing else had happened.
France had effectually aided in detaching the United States of America from the force of Great Britain: but as yet they seemed to have indulged only a silent wish to detach them from her commerce. They had done nothing to induce that event. In the same year, 1785, while M. de Calonne was in treaty with the Nantuckois, an estimate of the commerce of the United States was submitted to the Count de Vergennes, and it was shown, that, of three millions of pounds sterling, to which their exports amounted, one third might be brought to France, and exchanged against her productions and manufactures, advantageously for both nations; provided the obstacles of prohibition, monopoly, and duty, were either done away, or moderated as far as circumstances would admit. A committee, which had been appointed to investigate a particular one of these objects, was thereupon instructed to extend its researches to the whole, and see what advantages and facilities the government could offer, for the encouragement of a general commerce with the United States. The committee was composed of persons well skilled in commerce; and after laboring assiduously for several months, they made their report: the result of which was given in the letter of his Majesty’s Comptroller General, of the 22nd of October, 1786, wherein he stated the principles which should be established, for the future regulation of the commerce between France and the United States. It was become tolerably evident, at the date of this letter, that the terms offered to the Nantuckois would not produce their emigration to Dunkirk; and that it would be safest, in every event, to offer some other alternative, which might prevent their acceptance of the British offers. The obvious one was, to open the ports of France to their oils, so that they might still exercise their fishery, remaining in their native country, and find a new market for its produce, instead of that which they had lost. The article of whale-oil was, accordingly, distinguished in the letter of M. de Calonne, by an immediate abatement of duty, and promise of further abatement, after the year 1790. This letter was instantly sent to America, and bid fair to produce there the effect intended, by determining the fishermen to carry on their trade from their own homes, with the advantage only of a free market in France, rather than remove to Great Britain, where a free market and great bounty were offered them. An Arrêt was still to be prepared, to give legal sanction to the letter of M. de Calonne. Monsieur Lambert, with a patience and assiduity almost unexampled, went through all the investigations necessary to assure himself, that the conclusion of the committee had been just. Frequent conferences on this subject were held in his presence; the deputies of the chambers of commerce were heard, and the result was, the Arrêt of December the 29th, 1787, confirming the abatements of duty, present and future, which the letter of October, 1786, had promised, and reserving to his Majesty, to grant still further favors to that production, if, on further information, he should find it for the interest of the two nations.
The English had now begun to deluge the markets of France with their whale-oils; and they were enabled by the great premiums given by their government, to undersell the French fisherman, aided by feebler premiums, and the American, aided by his poverty alone. Nor is it certain, that these speculations were not made at the risk of the British government, to suppress the French and American fishermen in their only market. Some remedy seemed necessary. Perhaps it would not have been a bad one, to subject, by a general law, the merchandise of every nation and of every nature, to pay additional duties in the ports of France, exactly equal to the premiums and drawbacks given on the same merchandise by their own government. This might not only counteract the effect of premiums in the instance of whale-oils, but attack the whole British system of bounties and drawbacks, by the aid of which they make London the centre of commerce for the whole earth. A less general remedy, but an effectual one, was, to prohibit the oils of all European nations: the treaty with England requiring only, that she should be treated as well as the most favored European nation. But the remedy adopted was, to prohibit all oils, without exception.
To know how this remedy will operate, we must consider the quantity of whale-oil which France consumes annually, the quantity she obtains from her own fishery; and, if she obtains less than she consumes, we are to consider what will follow the prohibition.
The annual consumption of France, as stated by a person who has good opportunities of knowing it, is as follows.
lbs. pesant. quinteaux. tons.
Paris, according to the registers of 1786,.................................2,800,000 28,000 1750
Twenty-seven other cities, lighted by M. Sangrain,........................ 800,000 8,000 500
Rouen,..................................500,000 5,000 312
Bordeaux,...............................600,000 6,000 375
Lyons,..................................300,000 3,000 187
Other cities, leather and light,......3,000,000 30,000 1875
————- ——— ——
8,000,000 80,000 5,000
Other calculations, or say rather, conjectures, reduce the consumption to about half this. It is treating these conjectures with great respect, to place them on an equal footing with the estimate of the person before alluded to, and to suppose the truth half way between them. But we will do it, and call the present consumption of France only sixty thousand quintals, or three thousand seven hundred and fifty tons a year. This consumption is increasing fast, as the practice of lighting cities is becoming more general, and the superior advantages of lighting them with whale-oil are but now beginning to be known.
What do the fisheries of France furnish? She has employed, this year, fifteen vessels in the southern, and two in the northern fishery, carrying forty-five hundred tons in the whole, or two hundred and sixty-five each, on an average. The English ships, led by Nantuckois as well as the French, have never averaged in the southern fishery, more than one fifth of their burthen, in the best year. The fifteen ships of France, according to this ground of calculation, and supposing the present to have been one of the best years, should have brought, one with another, one fifth of two hundred and sixty-five tons, or fifty-three tons each. But we are told, they have brought near the double of that, to wit, one hundred tons each, and fifteen hundred tons in the whole. Supposing the two northern vessels to have brought home the cargo which is common from the northern fishery, to wit, twenty-five tons each, the whole produce this year will then be fifteen hundred and fifty tons. This is five and a half months’provision, or two fifths of the annual consumption. To furnish for the whole year, would require forty ships of the same size, in years as fortunate as the present, and eighty-five, communibus annis; forty-four tons, or one sixth of the burthen, being as high an average as should be counted on, one year with another: and the number must be increased, with the increasing consumption. France, then, is evidently not yet in a condition to supply her own wants. It is said, indeed, she has a large stock on hand, unsold, occasioned by the English competition. Thirty-three thousand quintals, including this year’s produce, are spoken of: this is between six and seven months’provision; and supposing by the time this is exhausted that the next year’s supply comes in, that will enable her to go on five or six months longer; say a twelvemonth in the whole. But, at the end of the twelvemonth, what is to be done? The manufacturers depending on this article, cannot maintain their competition against those of other countries, if deprived of their equal means. When the alternative, then, shall be presented, of letting them drop, or opening the ports to foreign whale-oil, it is presumable the latter will be adopted, as the lesser evil. But it will be too late for America. Her fishery, annihilated during the late war, only began to raise its head, on the prospect of a market held out by this country. Crushed by the Arrêt of September the 28th, in its first feeble effort to revive, it will rise no more. Expeditions, which require the expense of the outfit of vessels, and from nine to twelve months’ navigation, as the southern fishery does, most frequented by the Americans, cannot be undertaken in sole reliance on a market, which is opened and shut from one day to another, with little or no warning. The English alone, then, will remain to furnish these supplies, and they must be received, even from them. We must accept bread from our enemies, if our friends cannot furnish it. This comes exactly to the point, to which that government has been looking. She fears no rival in the whale-fishery, but America: or rather, it is the whale-fishery of America, of which she is endeavoring to possess herself. It is for this object, she is making the present extraordinary efforts, by bounties and other encouragements: and her success, so far, is very flattering. Before the war, she had not one hundred vessels in the whale-trade, while America employed three hundred and nine. In 1786, Great Britain employed one hundred and fifty-one vessels; in 1787, two hundred and eighty-six; in 1788, three hundred and fourteen, nearly the ancient American number: while the latter has fallen to about eighty. They have just changed places then; England having gained, exactly what America has lost. France, by her ports and markets, holds the balance between the two contending parties, and gives the victory, by opening and shutting them, to which she pleases. We have still precious remains of seamen, educated in this fishery, and capable by their poverty, their boldness, and address, of recovering it from the English, in spite of their bounties. But this Arret endangers the transferring to Great Britain every man of them, who is not invincibly attached to his native soil. There is no other nation in present condition to maintain a competition with Great Britain in the whale-fishery. The expense, at which it is supported on her part, seems enormous. Two hundred and fifty-five vessels, of seventy-five thousand four hundred and thirty-six tons, employed by her, this year, in the northern fishery, at forty-two men each; and fifty-nine in the southern, at eighteen men each, make eleven thousand seven hundred and seventy-two men. These are known to have cost the government fifteen pounds each, or one hundred and seventy-six thousand five hundred and eighty pounds, in the whole, and that, to employ the principal part of them from three to four months only. The northern ships have brought home twenty, and the southern sixty tons of oil, on an average; making eighty-six hundred and forty tons. Every ton of oil, then, has cost the government twenty pounds in bounty. Still, if they can beat, us out of the field, and have it to themselves, they will think their money well employed. If France undertakes, solely, the competition against them, she must do it at equal expense. The trade is too poor to support itself. The eighty-five ships, necessary to supply even her present consumption, bountied, as the English are, will require a sacrifice of twelve hundred and eighty-five thousand two hundred livres a year, to maintain three thousand five hundred and seventy seamen, and that, a part of the year only; and if she will put it to twelve thousand men, in competition with England, she must sacrifice, as they do, four or five millions a year. The same number of men might, with the same bounty, be kept in as constant employ, carrying stone from Bayonne to Cherburg, or coal from Newcastle to Havre, in which navigations they would be always at hand, and become as good seamen. The English consider among their best sailors, those employed to carry coal from Newcastle to London. France cannot expect to raise her fishery, even to the supply of her own consumption, in one year, or in several years. Is it not better, then, by keeping her ports open to the United States, to enable them to aid in maintaining the field against the common adversary, till she shall be in condition to take it herself, and to supply her own wants? Otherwise her supplies must aliment that very force, which is keeping her under. On our part, we can never be dangerous competitors to France. The extent to which we can exercise this fishery, is limited to that of the barren island of Nantucket, and a few similar barren spots; its duration, to the pleasure of this government, as we have no other market. A material observation must be added here: sudden vicissitudes of opening and shutting ports, do little injury to merchants settled on the opposite coast, watching for the opening, like the return of a tide, and ready to enter with it. But they ruin the adventurer, whose distance requires six months’ notice. Those who are now arriving from America, in consequence of the Arret of December the 29th, will consider it as the false light which has led them to their ruin. They will be apt to say, that they come to the ports of France by invitation of that Arrêt, that the subsequent one of September the 28th, which drives them from those ports, founds itself on a single principle, viz. ‘that the prohibition of foreign oils is the most useful encouragement which can be given to that branch of industry.’ They will say, that, if this be a true principle, it was as true on the 29th of December 1787, as on the 20th of September, 1788: it was then weighed against other motives, judged weaker and overruled, and it is hard it should be now revived, to ruin them.
The refinery for whale-oil, lately established at Rouen, seems to be an object worthy of national attention. In order to judge of its importance, the different qualities of whale-oil must be noted. Three qualities are known in the American and English markets. 1st. That of the spermaceti whale. 2nd. Of the Greenland whale. 3rd. Of the Brazil whale. 1. The spermaceti whale found by the Nantuckois, in the neighborhood of the Western Islands, to which they had gone in pursuit of other whales, retired thence to the coast of Guinea, afterwards to that of Brazil, and begins now to be best found in the latitude of the Cape of Good Hope, and even of Cape Horn. He is an active, fierce animal, and requires vast address and boldness in the fisherman. The inhabitants of Brazil make little expeditions from their coast, and take some of these fish. But the Americans are the only distant people, who have been in the habit of seeking and attacking him, in numbers. The British, however, led by the Nantuckois, whom they have decoyed into their service, have begun this fishery. In 1785, they had eighteen ships in it; in 1787, thirty-eight; in 1788, fifty-four, or, as some say, sixty-four. I have calculated on the middle number, fifty-nine. Still they take but a very small proportion of their own demand; we furnish the rest. Theirs is the only market to which we carry that oil, because it is the only one where its properties are known. It is luminous, resists coagulation by cold, to the forty-first degree of Fahrenheit’s thermometer, and fourth of Reaumur’s, and yields no smell at all: it is used, therefore, within doors, to lighten shops, and even in the richest houses, for antichambers, stairs, galleries, &c. It sells at the London market for treble the price of common whale-oil. This enables the adventurer to pay the duty of eighteen pounds five shillings sterling the ton, and still to have a living profit. Besides the mass of oil produced from the whole body of the whale, his head yields three or four barrels of what is called head-matter, from which is made the solid spermaceti, used for medicine and candles. This sells by the pound at double the price of the oil. The disadvantage of this fishery is, that the sailors are from nine to twelve months absent on the voyage; of course, they are not at hand on any sudden emergency, and are even liable to be taken, before they know that war is begun. It must be added, on the subject of this whale, that he is rare and shy, soon abandoning the grounds where he is hunted. This fishery, less losing than the other, and often profitable, will occasion it to be so thronged, soon, as to bring it on a level with the other. It will then require the same expensive support, or to be abandoned.
2. The Greenland whale-oil is next in quality. It resists coagulation by cold, to thirty-six degrees of Fahrenheit, and two of Reaumur, but it has a smell insupportable within doors, and is not luminous. It sells, therefore, in London, at about sixteen pounds the ton. This whale is clumsy and timid; he dives when struck, and comes up to breathe by the first cake of ice, where the fishermen need little address or courage to find and take him. This is the fishery mostly frequented by European nations; it is this fish which yields the fin in quantity, and the voyages last about three or four months.
The third quality is that of the small Brazil whale. He was originally found on the coast of Nantucket, and first led that people to this pursuit: he retired, first to the Banks of Newfoundland, then to the Western Islands, and is now found within soundings on the coast of Brazil, during the months of December, January, February, and March. His oil chills at fifty-two degrees of Fahrenheit, and eight of Reaumur, is black and offensive; worth, therefore, but thirteen pounds the ton, in London. In warm summer nights, however, it burns better than the Greenland oil.
To the qualities of the oils thus described, it is to be added, that an individual has discovered methods, 1. of converting a great part of the oils of the spermaceti-whale, into the solid substance called spermaceti, heretofore produced from his head alone; 2. of refining the Greenland whale-oil, so as to take from it all smell, and render it limpid and luminous as that of the spermaceti-whale; 3. of curdling the oil of the Brazil whale into tallow, resembling that of beef, and answering all its purposes. This person is engaged by the company, which has established the refinery at Rouen: their works will cost them half a million of livres; will be able to refine all the oil which can be used in the kingdom, and even to supply foreign markets. The effects of the refinery, then, would be, 1. to supplant the solid spermaceti of all other nations, by theirs, of equal quality and lower price; 2. to substitute, instead of spermaceti-oil, their black whale-oil refined, of equal quality and lower price; 3. to render the worthless oil of the Brazil, equal in value to tallow; and 4. by accommodating these oils to uses, to which they could never otherwise have been applied, they will extend the demand beyond its present narrow limits, to any supply which can be furnished, and thus give the most effectual encouragement and extension to the whale-fishery. But these works were calculated on the Arrêt of December the 29th, which admitted here, freely and fully, the produce of the American fishery. If confined to that of the French fishery alone, the enterprise may fail, for want of matter to work on.
After this review of the whale-fishery as a political institution, a few considerations shall be added on its produce, as a basis of commercial exchange between France and the United States. The discussions it has undergone, on former occasions, in this point of view, leaves little new to be now urged.
The United States, not possessing mines of the precious metals, can purchase necessaries from other nations, so far only as their produce is received in exchange. Without enumerating our smaller articles, we have three of principal importance, proper for the French market; to wit, tobacco, whale-oil, and rice. The first and most important, is tobacco. This might furnish an exchange for eight millions of the productions of this country; but it is under a monopoly, and that not of a mercantile, but of a financiering company, whose interest is, to pay in money and not in merchandise, and who are so much governed by the spirit of simplifying their purchases and proceedings, that they find means to elude every endeavor on the part of government, to make them diffuse their purchases among the merchants in general. Little profit is derived from this, then, as an article of exchange for the produce and manufactures of France. Whale-oil might be next in importance; but that is now prohibited. American rice is not yet of great, but it is of growing consumption in France, and being the only article of the three which is free, it may become a principal basis of exchange. Time and trial may add a fourth, that is, timber. But some essays, rendered unsuccessful by unfortunate circumstances, place that, at present, under a discredit, which it will be found hereafter not to have merited. The English know its value, and were supplied with it, before the war. A spirit of hostility, since that event, led them to seek Russian rather than American supplies; a new spirit of hostility has driven them back from Russia, and they are now making contracts for American timber. But of the three articles before mentioned, proved by experience to be suitable for the French market, one is prohibited, one under monopoly, and one alone free, and that the smallest and of very limited consumption. The way to encourage purchasers, is, to multiply their means of payment. Whale-oil might be an important one. In one scale, are the interests of the millions who are lighted, shod, or clothed with the help of it, and the thousands of laborers and manufacturers, who would be employed in producing the articles which might be given in exchange for it, if received from America: in the other scale, are the interests of the adventurers in the whale-fishery each of whom, indeed, politically considered, may be of more importance to the State, than a simple laborer or manufacturer; but to make the estimate with the accuracy it merits, we should multiply the numbers in each scale into their individual importance, and see which preponderates.
Both governments have seen with concern, that their commercial intercourse does not grow as rapidly as they would wish. The system of the United States is, to use neither prohibitions nor premiums. Commerce, there, regulates itself freely, and asks nothing better. Where a government finds itself under the necessity of undertaking that regulation, it would seem, that it should conduct it as an intelligent merchant would; that is to say, invite customers to purchase, by facilitating their means of payment, and by adapting goods to their taste. If this idea be just, government here has two operations to attend to, with respect to the commerce of the United States; 1. to do away, or to moderate, as much as possible, the prohibitions and monopolies of their materials for payment; 2. to encourage the institution of the principal manufactures, which the necessities, or the habits of their new customers call for. Under this latter head, a hint shall be suggested, which must find its apology in the motive from which it flows; that is, a desire of promoting mutual interests and close friendship. Six hundred thousand of the laboring poor of America, comprehending slaves under that denomination, are clothed in three of the simplest manufactures possible; to wit, oznaburgs, plains, and duffel blankets. The first is a linen; the two last, woollens. It happens, too, that they are used exactly by those who cultivate the tobacco and rice, and in a good degree by those employed in the whale-fishery. To these manufactures they are so habituated, that no substitute will be received. If the vessels which bring tobacco, rice, and whale-oil, do not find them in the ports of delivery, they must be sought where they can be found; that is, in England, at present. If they were made in France, they would be gladly taken in exchange there. The quantities annually used by this description of people, and their value, are as follows:
Oznaburgs 2,700,000 aunes, at sixteen sous the aune, worth
2,160,000
Plains 1,350,000 aunes, at two livres the aune,
2,700,000
Duffel Blankets 300,000 aunes, at seven and 4/5ths livres each
2,160,000
—————
7,020,000
It would be difficult to say, how much should be added, for the consumption of inhabitants of other descriptions; a great deal surely. But the present view shall be confined to the one description named. Seven millions of livres, are nine millions of days’ work, of those who raise, spin, and weave the wool and flax; and, at three hundred working days to the year, would maintain thirty thousand people. To introduce these simple manufactures, suppose government to give five per cent, on the value of what should be exported of them, for ten years to come: if none should be exported, nothing would be to be paid: but on the other hand, if the manufactures, with this encouragement, should rise to the full demand, it will be a sacrifice of three hundred and fifty-one thousand livres a year, for ten years only, to produce a perpetual subsistence for more than thirty thousand people (for the demand will grow with our population); while she must expend perpetually one million two hundred and eighty-five thousand livres a year, to maintain the three thousand five hundred and seventy seamen, who would supply her with whale-oil. That is to say, for each seaman, as much as for thirty laborers and manufacturers.
But to return to our subject, and to conclude.
Whether, then, we consider the Arrêt of September the 28th, in a political or a commercial light, it would seem, that the United States should be excepted from its operation. Still more so, when they invoke against it the amity subsisting between the two nations, the desire of binding them together by every possible interest and connection, the several acts in favor of this exception, the dignity of legislation, which admits not of changes backwards and forwards, the interests of commerce, which requires steady regulations, the assurances of the friendly motives which have led the King to pass these acts, and the hope, that no cause will arise, to change either his motives or his measures towards us.
TO JOHN JAY.
Paris, November 29, 1788.
Sir,
In the hurry of making up my letter of the 19th instant, I omitted the enclosed printed paper, on the subject of whale-oil. That omission is now supplied by another conveyance, by the way of London. The explanatory Arrêt is not yet come out. I still take for granted, it will pass, though there be an opposition to it in the Council. In the mean time, orders are given to receive our oils which may arrive. The apprehension of a want of corn has induced them to turn their eyes to foreign supplies; and to show their preference of receiving them from us, they have passed the enclosed Arrêt, giving a premium on wheat and flour from the United States, for a limited time. This, you will doubtless think proper to have translated and published. The Notables are still in session: the votes of the separate bureaux have not yet been reduced to a joint act, in an assembly of the whole. I see no reason to suppose they will change the separate votes relative to the representation of the Tiers Etat in the States General. In the mean time, the stream of public indignation, heretofore directed against the court, sets strongly against the Notables. It is not yet decided when the States will meet: but certainly they cannot, till February or March. The Turks have retired across the Danube. This movement indicates their going into winter-quarters, and the severity of the weather must hasten it. The thermometer was yesterday at eight degrees of Fahrenheit, that is, twenty-four degrees below freezing; a degree of cold equal to that of the year 1740, which they count here among their coldest winters. This having continued many days, and being still likely to continue, and the wind from northeast, render it probable, that all enterprise must be suspended between the three great belligerent powers. Poland is likely to be thrown into great convulsions. The Empress of Russia has peremptorily demanded such aids from Poland, as might engage it in the war. The King of Prussia, on the other hand, threatens to march an army on their borders. The vote of the Polish confederacy for one hundred thousand men, was a coalition of the two parties, in that single act only. The party opposed to the King, have obtained a majority, and have voted that this army shall be independent of him. They are supported by Prussia, while the King depends on Russia. Authentic information from England leaves not a doubt, that the King is lunatic; and that, instead of the effect, is the cause of the illness, under which he has been so near dying. I mention this, because the English newspapers, speaking by guess on that as they do on all other subjects, might mislead you as to his true situation; or rather, might mislead others, who know less than you do, that a thing is not rendered the more probable, by being mentioned in those papers.
I enclose those of Leyden to the present date, with the gazettes of France, and have the honor to be, with sentiments of the most perfect esteem and respect, Sir, your most obedient, humble servant,
Th: Jefferson
TO GENERAL WASHINGTON.
Paris, December 4, 1788.
Sir,
Your favor of August the 31st came to hand yesterday; and a confidential conveyance offering, by the way of London, I avail myself of it, to acknowledge the receipt.
I have seen, with infinite pleasure, our new constitution accepted by eleven States, not rejected by the twelfth; and that the thirteenth happens to be a state of the least importance. It is true, that the minorities in most of the accepting States have been very respectable; so much so, as to render it prudent, were it not otherwise reasonable, to make some sacrifice to them. I am in hopes, that the annexation of a bill of rights to the constitution will alone draw over so great a proportion of the minorities, as to leave little danger in the opposition of the residue; and that this annexation may be made by Congress and the Assemblies, without calling a convention, which might endanger the most valuable parts of the system. Calculation has convinced me, that circumstances may arise, and probably will arise, wherein all the resources of taxation will be necessary for the safety of the State. For though I am decidedly of opinion, we should take no part in European quarrels, but cultivate peace and commerce with all, yet who can avoid seeing the source of war in the tyranny of those nations, who deprive us of the natural right of trading with our neighbors? The produce of the United States will soon exceed the European demand: what is to be done with the surplus, when there shall be one? It will be employed, without question, to open, by force, a market for itself, with those placed on the same continent with us, and who wish nothing better. Other causes, too, are obvious, which may involve us in war; and war requires every resource of taxation and credit. The power of making war often prevents it, and in our case, would give efficacy to our desire of peace. If the new government wears the front which I hope it will, I see no impossibility in the availing ourselves of the wars of others, to open the other parts of America to our commerce, as the price of our neutrality.
The campaign between the Turks and two Empires has been clearly in favor of the former. The Emperor is secretly trying to bring about a peace. The alliance between England, Prussia, and Holland, (and some suspect Sweden also) renders their mediation decisive, wherever it is proposed. They seemed to interpose it so magisterially between Denmark and Sweden, that the former submitted to its dictates, and there was all reason to believe, that the war in the northwestern parts of Europe would be, quieted. All of a sudden, a new flame bursts out in Poland. The King and his party are devoted to Russia. The opposition rely on the protection of Prussia. They have lately become the majority in the confederated diet, and have passed a vote for subjecting their army to a commission independent of the King, and propose a perpetual diet, in which case he will be a perpetual cipher. Russia declares against such a change in their constitution, and Prussia has put an army into readiness, for marching, at a moment’s warning, on the frontier of Poland. These events are too recent, to see, as yet, what turn they will take, or what effect they will have on the peace of Europe. So is that also, of the lunacy of the King of England, which is a decided fact, notwithstanding all the stuff the English papers publish, about his fevers, his deliriums, &c. The truth is, that the lunacy declared itself almost at once, and with as few concomitant complaints, as usually attend the first developement of that disorder. I suppose a regency will be established, and if it consists of a plurality of members, it will, probably, be peaceable. In this event, it will much favor the present wishes of this country, which are so decidedly for peace, that they refused to enter into the mediation between Sweden and Russia, lest it should commit them. As soon as the convocation of the States General was announced, a tranquillity took place through the whole kingdom: happily, no open rupture had taken place, in any part of it. The parliament were re-instated in their functions, at the same time. This was all they desired; and they had called for the States General, only through fear that the crown could not otherwise be forced to re-instate them. Their end obtained, they began to foresee danger to themselves, in the States General. They began to lay the foundation for caviling at the legality of that body, if its measures should be hostile to them. The court, to clear itself of the dispute, convened the Notables, who had acted with general approbation on the former occasion, and referred to them the forms of calling and organizing the States General. These Notables consist principally of Nobility and Clergy; the few of the Tiers Etat among them, being either parliament men, or other privileged persons. The court wished, that, in the future States General, the members of the Tiers Etat should equal those of both the other orders, and that they should form but one House, all together, and vote by persons, not by orders. But the Notables, in the true spirit of Priests and Nobles, combining together against the people, have voted, by five bureaux out of six, that the people, or Tiers Etat, shall have no greater number of deputies, than each of the other orders separately, and that they shall vote by orders: so that two orders concurring in a vote, the third will be overruled; for it is not here as in England, where each of the three branches has a negative on the other two. If this project of theirs succeeds, a combination between the two Houses of Clergy and Nobles will render the representation of the Tiers Etat merely nugatory. The bureaux are to assemble together, to consolidate their separate votes: but I see no reasonable hope of their changing this. Perhaps the King, knowing that he may count on the support of the nation, and attach it more closely to him, may take on himself to disregard the opinion of the Notables in this instance, and may call an equal representation of the people, in which precedents will support him. In every event, I think the present disquiet will end well. The nation has been awaked by our Revolution; they feel their strength, they are enlightened, their lights are spreading, and they will not retrograde. The first States General may establish three important points, without opposition from the court; 1. their own periodical convocation; 2. their exclusive right of taxation (which has been confessed by the King); 3. the right of registering laws, and of previously proposing amendments to them, as the parliaments have, by usurpation, been in the habit of doing. The court will consent to this, from its hatred to the parliaments, and from the desire of having to do with one, rather than many legislatures. If the States are prudent, they will not aim at more than this at first, lest they should shock the dispositions of the court, and even alarm the public mind, which must be left to open itself, by degrees, to successive improvements. These will follow, from the nature of things: how far they can proceed, in the end, towards a thorough reformation of abuse, cannot be foreseen. In my opinion, a kind of influence, which none of their plans of reform take into account, will elude them all; I mean the influence of women in the government. The manners of the nation allow them to visit, alone, all persons in office, to solicit the affairs of the husband, family, or friends, and their solicitations bid defiance to laws and regulations. This obstacle may seem less to those, who, like our countrymen, are in the precious habit of considering right, as a barrier against all solicitation. Nor can such an one, without the evidence of his own eyes, believe in the desperate state to which things are reduced in this country, from the omnipotence of an influence, which, fortunately for the happiness of the sex itself, does not endeavor to extend itself, in our country, beyond the domestic line.
Your communications to the Count de Moustier, whatever they may have been, cannot have done injury to my endeavors here, to open the West Indies to us. On this head, the ministers are invincibly mute, though I have often tried to draw them into the subject. I have therefore found it necessary to let it lie, till war, or other circumstances, may force it on. Whenever they are in war with England, they must open the islands to us, and perhaps, during that war, they may see some price which might make them agree to keep them always open. In the mean time, I have laid my shoulder to the opening the markets of this country to our produce, and rendering its transportation a nursery for our seamen. A maritime force is the only one, by which we can act on Europe. Our navigation law (if it be wise to have any) should be the reverse of that of England. Instead of confining importations to home-bottoms, or those of the producing nation, I think we should confine exportations to home-bottoms, or to those of nations having treaties with us. Our exportations are heavy, and would nourish a great force of our own, or be a tempting price to the nation to whom we should offer a participation of it, in exchange for free access to all their possessions. This is an object to which our government alone is adequate, in the gross; but I have ventured to pursue it here, so far as the consumption of our productions by this country extends. Thus, in our arrangements relative to tobacco, none can be received here, but in French or American bottoms. This is employment for near two thousand seamen, and puts nearly that number of British out of employ. By the Arrêt of December, 1787, it was provided, that our whale-oils should not be received here, but in French or American bottoms; and by later regulations, all oils, but those of France and America, are excluded. This will put one hundred English whale vessels immediately out of employ, and one hundred and fifty ere long; and call so many of French and American into service. We have had six thousand seamen formerly in this business, the whole of whom we have been likely to lose. The consumption of rice is growing fast in this country, and that of Carolina gaining ground on every other kind. I am of opinion, the whole of the Carolina rice can be consumed here. Its transportation employs two thousand five hundred sailors, almost all of them English at present; the rice being deposited at Cowes, and brought from thence here. It would be dangerous to confine this transportation to French and American bottoms, the ensuing year, because they will be much engrossed by the transportation of wheat and flour hither, and the crop of rice might lie on hand for want of vessels; but I see no objections to the extension of our principle to this article also, beginning with the year 1790. However, before there is a necessity of deciding on this, I hope to be able to consult our new government in person, as I have asked of Congress a leave of absence for six months, that is to say, from April to November next. It is necessary for me to pay a short visit to my native country, first, to reconduct my family thither, and place them in the hands of their friends, and secondly, to place my private affairs under certain arrangements. When I left my own house, I expected to be absent but five months, and I have been led by events to an absence of five years. I shall hope, therefore, for the pleasure of personal conferences with your Excellency, on the subject of this letter, and others interesting to our country; of getting my own ideas set to rights by a communication of yours, and of taking again the tone of sentiment of my own country, which we lose in some degree, after a certain absence. You know, doubtless, of the death of the Marquis de Chastellux. The Marquis de la Fayette is out of favor with the court, but high in favor with the nation. I once feared for his personal liberty, but I hope he is on safe ground at present.
On the subject of the whale-fishery, I enclose you some observations I drew up for the ministry here, in order to obtain a correction of their Arrêt of September last, whereby they had involved our oils with the English, in a general exclusion from their ports. They will accordingly correct this, so that our oils will participate with theirs, in the monopoly of their markets. There are several things incidentally introduced, which do not seem pertinent to the general question: they were rendered necessary by particular circumstances, the explanation of which would add to a letter already too long. I will trespass no further, than to assure you of the sentiments of sincere attachment and respect, with which I have the honor to be your Excellency’s most obedient, humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
P. S. The observations enclosed, though printed, have been put into confidential hands only. T. J.
TO JOHN ADAMS.
Paris, December 5, 1788.
Dear Sir,
I had the pleasure of writing to you on the 2nd of August, and of adding a Postscript of August the 6th.
You recollect well the Arrêt of December the 29th, 1787, in favor of our commerce, and which, among other things, gave free admission to our whale-oil, under a duty of about two louis a ton. In consequence of the English treaty, their oils flowed in, and over-stocked the market. The light duty they were liable to under the treaty, still lessened by false estimates and aided by the high premiums of the British government, enabled them to undersell the French and American oils. This produced an outcry of the Dunkirk fishery. It was proposed to exclude all European oils, which would not infringe the British treaty. I could not but encourage this idea, because it would give to the French and American fisheries a monopoly of the French market. The Arrêt was so drawn up; but, in the very moment of passing it, they struck out the word European, so that our oils became involved. This, I believe, was the effect of a single person in the ministry. As soon as it was known to me, I wrote to Monsieur de Montmorin, and had conferences with him and the other ministers. I found it necessary to give them information on the subject of the whale-fishery, of which they knew little but from the partial information of their Dunkirk adventurers. I therefore wrote the observations (of which I enclose you a printed copy), had them printed to entice them to read them, and particularly developed the expense at which they are carrying on that fishery, and at which they must continue it, if they do continue it. This part was more particularly intended for Mr. Necker, who was quite a stranger to the subject, who has principles of economy, and will enter into calculations. Other subjects are incidentally introduced; though little connected with the main question, they had been called for by other circumstances. An immediate order was given for the present admission of our oils, till they could form an Arrêt; and, at a conference, the draught of an Arrêt was communicated to me, which re-established that of December the 29th. They expressed fears, that, under cover of our name, the Nova Scotia oils would be introduced; and a blank was left in the draught for the means of preventing that. They have since proposed, that the certificate of their consul shall accompany the oils, to authorize their admission, and this is what they will probably adopt. It was observed, that if our States would prohibit all foreign oils from being imported into them, it would be a great safeguard, and an encouragement to them to continue the admission. Still there remains an expression in the Arrêt, that it is provisory only. However, we must be contented with it as it is; my hope being, that the legislature will be transferred to the National Assembly, in whose hands it will be more stable, and with whom it will be more difficult to obtain a repeal, should the ministry hereafter desire it. If they could succeed in drawing over as many of our Nantucket men as would supply their demands of oil, we might then fear an exclusion; but the present Arrêt, as soon as it shall be passed, will, I hope, place us in safety till that event, and that event may never happen. I have entered into all these details, that you may be enabled to quiet the alarm which must have been raised by the Arrêt of September the 28th, and assure the adventurers that they may pursue their enterprises as safely as if that had never been passed, and more profitably, because we participate now of a monopolized, instead of an open market. The enclosed observations, though printed, have only been given to the ministers, and one or two other confidential persons. You will see that they contain matter which should be kept from the English, and will therefore trust them to the perusal only of such persons as you can confide in. We are greatly indebted to the Marquis de la Fayette for his aid on this, as on every other occasion. He has paid the closest attention to it, and combated for us with the zeal of a native.
The necessity of reconducting my family to America, and of placing my affairs there under permanent arrangements, has obliged me to ask of Congress a six months’ absence, to wit, from April to November next. I hope, therefore, to have the pleasure of seeing you there, and particularly, that it will be at New York that I shall find you. Be so good as to present my sincere esteem to Mrs. Adams, and believe me to be, with very affectionate attachment, Dear Sir, your friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MR. SHORT.
Paris, December 8, 1788.
Dear Sir,
My last to you was of the 21st of November, addressed to Milan, poste restante, according to the desire expressed through Mrs. Paradise. I have lately received yours of the 19th of November, and sincerely felicitate you on your recovery. I wish you may have suffered this to be sufficiently established before you set out on your journey. The present letter will probably reach you amidst the classical enjoyments of Rome. I feel myself kindle at the reflection, to make that journey; but circumstances will oblige me to postpone it at least. We are here under a most extraordinary degree of cold. The thermometer has been ten degrees of Reaumur below freezing: this is eight degrees of Fahrenheit above zero, and was the degree of cold here in the year 1740. The long continuance of this severity, and the snow now on the ground, give physical prognostications of a hard winter. You will be in a privileged climate, and will have had an enviable escape from this. The Notables are not yet separated, nor is their treasonable vote against the people yet consolidated; but it will be. The parliament have taken up the subject, and passed a very laudable vote in opposition. They have made it the occasion of giving sketches of what should be a bill of rights. Perhaps this opposition of authority may give the court an option between the two. Stocks are rising slowly, but steadily. The loan of 1784 is at thirteen loss; the caisse d’escompte, four thousand and seventy-five. The Count de Bryenne has retired, and M. de Puysegur succeeded to his place. Madame de Chambonois (sister of M. de Langear) is dead of the small-pox. Pio is likely to receive a good appointment in his own country, which will take him from us. Corn is likely to become extremely scarce in France, Spain, and England. This country has offered a premium of forty sous the quintal on flour of the United States, and thirty sous the quintal on our wheat, to be brought here between February and June.
General Washington writes me, that industry and economy begin to take place of that idleness and extravagance which had succeeded the close of the war. The Potomac canal is in great forwardness. J. M. writes me word, that Mr. Jay and General Knox are talked of in the Middle States for Vice-Presidents, but he queries whether both will not prefer their present births. It seems agreed, that some emendations will be made to the new constitution. All are willing to add a bill of rights; but they fear the power of internal taxation will be abridged. The friends of the new government will oppose the method of amendment by a federal convention, which would subject the whole instrument to change, and they will support the other method, which admits Congress, by a vote of two thirds, to submit specific changes to the Assemblies, three fourths of whom must concur to establish them.
The enclosed letter is from Pallegrino, one of the Italian laborers established in our neighborhood. I fancy it contains one for his father. I have supposed it would not be unpleasant to you to have the delivery of it, as it may give you a good opportunity of conferring with one of that class as much as you please. I obey at the same time my own wishes to oblige the writer. Mazzei is at this time ill, but not in danger. I am impatient to receive further letters from you, which may assure me of the solidity of your recovery, being, with great anxiety for your health and happiness, Dear Sir, your affectionate friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
[The annexed is here inserted in the Author’s MS. To whom
addressed, does not appear.]
The Minister Plenipotentiary for the United States of America finds himself under the necessity of declining to authenticate writings destined to be sent to the United States, for this main reason, that such authentication is not legal evidence there. After a reason so sufficient, it seems superfluous to add, that, were his authentication admissible in the courts of the United States, he could never give it to any seal or signature, which had not been put in his presence; that he could never certify a copy, unless both that and the original were in a hand-writing legible to him, and had been compared together by him, word by word: that so numerous are the writings presented, that their authentication alone would occupy the greater part of his time, and, withdrawing him from his proper duties, would change the nature of his office to that of a notary. He observes to those who do him the honor of addressing themselves to him on this subject, that the laws for the authentication of foreign writings are not the same through all the United States, some requiring an authentication under the seal of the Prevoté of a city, and others admitting that of a Notary: but that writings authenticated in both these manners, will, under the one or the other, be admitted in most, if not all of the United States. It would seem advisable, then, to furnish them with this double authentication.
TO DOCTOR GILMER.
Paife, December 16, 1788.
Dear Doctor,
Your last letter of December the 23rd was unlucky, like the former one, in arriving while I was absent on a call of public business in Holland. I was discouraged from answering the law part of it on my return, because I foresaw such a length of time between the date of that and receipt of the answer, as would give it the air of a prescription after the death of the patient. I hope the whole affair is settled, and that you are established in good titles to all the lands. Still, however, being on the subject, I cannot help adding a word, in answer to the objection which you say is raised on the words ‘the estate,’ instead of ‘my estate.’ It has long been confessed in the courts, that the first decision, that a devise of lands to a person without words of inheritance, should carry an estate for life only, was an absurd decision, founded on feudal principles, after feudal ideas had long been lost by the unlettered writers of their own wills: and it has often been said, that were the matter to begin again, it should be decided that such a devise should carry a fee simple, as every body is sensible testators intend, by these expressions. The courts, therefore, circumscribe the authority of this chain of decisions, all hanging on the first link, as much as possible; and they avail themselves of every possible circumstance which may render any new case unlike the old one, and authorize them to conform their judgments to common sense, and the will of the testator. Hence they decide, that in a devise of ‘my estate at M.’ to such a one, without words of inheritance, the word estate is descriptive of the duration of the interest bequeathed, as well as its locality. From the same desire of getting back into the paths of common sense, they would not suffer the particle ‘the’ instead of ‘my’, to make a difference. ‘My estate at M.’ means not only my lands at M., but my fee simple in them. ‘The estate at M.’ means not only ‘the lands the testator holds at M., but the fee simple he has in them.’ Another objection will be made, perhaps, viz. that the testator devises in the same clause his estate called Marrow-bone, his tract called Horse-pasture, and his tract called Poison-field; that it is probable he intended to give the same interest in all; and as it is confessed that the word tract conveys but an estate for life, we must conclude that the word estate was meant to convey the same. I should reverse the argument, and say, as it confessed the word estate, conveys an estate in fee simple, we must conclude the word tract was meant to convey the same; that this conclusion coincides with the wishes of the courts, as bringing them back to what is right and consentaneous to the intention of the testator, as furnishing them a circumstance to distinguish the case from the original one, and withdraw it from its authority; whereas, the contrary conclusion tends to lead them further from the meaning of testators, and to fix them in error.
But I perceive that my wishes to see the weight of no objection where you are interested, are leading me to write an argument, where I had promised I would say only a word. I will, therefore, talk the subject over with you at Monticello, or Pen-park. I have asked of Congress a leave of five or six months’ absence next year, that I may carry my daughters home, and assist in the arrangement of my affairs. I shall pass two of the months at Monticello, that is to say, either June and July, or July and August, according to the time I may sail, which I hope will be in April: and then go on to New York and Boston, from whence I shall embark again for Europe, so as to get here before the winter sets in. I look forward with great fondness to the moment, when I can again see my own country and my own neighbors, and endeavor to anticipate as little as possible the pain of another separation from them. I hope I shall find you all under the peaceable establishment of the new constitution, which, as far as I can judge from public papers, seems to have become necessary for the happiness of our country. I thank you for your kind inquiries about my wrist. I followed advice with it, till I saw, visibly, that the joint had never been replaced, and that it was absurd to expect that cataplasms and waters would reduce dislocated bones. From that moment I have done nothing. I have for ever lost the use of my hand, except that I can write: and a withered hand and swelled and crooked fingers, still remaining twenty-seven months after the accident, make me fear I do not yet know the worst of it. But this, too, we will talk over at Monticello, and endeavor that it be the only pain to which our attention may be recalled. Adieu, my dear friend. Kiss and bless every body for me, Mrs. Gilmer especially. Assure her and yourself of the sincere and constant attachment of, Dear Doctor, your affectionate friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO THOMAS PAINE.
Paris, December 23,1788.
Dear Sir,
It is true that I received very long ago your favors of September the 9th and 15th, and that I have been in daily intention of answering them, fully and confidentially; but you know such a correspondence between you and me cannot pass through the post, nor even by the couriers of ambassadors. The French packet-boats being discontinued, I am now obliged to watch opportunities by Americans going to London, to write my letters to America. Hence it has happened, that these, the sole opportunities by which I can write to you without fear, have been lost, by the multitude of American letters I had to write. I now determine, without foreseeing any such conveyance, to begin my letter to you, so that when a conveyance occurs, I shall only have to add recent occurrences. Notwithstanding the interval of my answer which has taken place, I must beg a continuance of your correspondence; because I have great confidence in your communications, and since Mr. Adams’s departure, I am in need of authentic information from that country.
I will begin with the subject of your bridge, in which I feel myself interested; and it is with great pleasure that I learn, by your favor of the 16th, that the execution of the arch of experiment exceeds your expectations. In your former letter you mention, that, instead of arranging your tubes and bolts as ordinates to the cord of the arch, you had reverted to your first idea, of arranging them in the direction of radii. I am sure it will gain both in beauty and strength. It is true that the divergence of these radii recurs as a difficulty, in getting the rails on upon the bolts; but I thought this fully removed by the answer you first gave me, when I suggested that difficulty, to wit, that you should place the rails first, and drive the bolts through them, and not, as I had imagined, place the bolts first, and put the rails on them. I must doubt whether what you now suggest will be as good as your first idea; to wit, to have every rail split into two pieces longitudinally, so that there shall be but the halves of the holes in each, and then to clamp the two halves together. The solidity of this method cannot be equal to that of the solid rail, and it increases the suspicious parts of the whole machine, which, in a first experiment, ought to be rendered as few as possible. But of all this the practical iron men are much better judges than we theorists. You hesitate between the catenary and portion of a circle. I have lately received from Italy a treatise on the equilibrium of arches, by the Abbe Mascheroni. It appears to be a very scientifical work. I have not yet had time to engage in it; but I find that the conclusions of his demonstrations are, that every part of the catenary is in perfect equilibrium. It is a great point, then, in a new experiment, to adopt the sole arch, where the pressure will be equally borne by every point of it. If any one point is pushed with accumulated pressure, it will introduce a danger, foreign to the essential part of the plan. The difficulty you suggest, is, that the rails being all in catenaries, the tubes must be of different lengths, as these approach nearer or recede farther from each other, and therefore you recur to the portions of concentric circles, which are equidistant in all their parts. But I would rather propose, that you make your middle rail an exact catenary, and the interior and exterior rails parallels to that. It is true, they will not be exact catenaries, but they will depart very little from it; much less than portions of circles will. Nothing has been done here on the subject since you went away. There is an Abbe D’Arnal at Nismes, who had obtained an exclusive privilege for navigating the rivers of this country by the aid of the steam-engine. This interests Mr. Rumsey, who had hoped the same thing. D’Arnal’s privilege was published in a paper of the 10th of November. Probably, therefore, his application for it was previous to the delivery of Mr. Rumsey’s papers to the secretary of the Academy of Sciences, which was in the latter part of the month of August. However, D’Arnal is not a formidable competitor. He is not in circumstances to make any use himself of his privilege, and he has so illy succeeded with a steam-mill he erected at Nismes, that he is not likely to engage others to venture in his projects. To say another word of the catenarian arch, without caring about mathematical demonstrations, its nature proves it to be in equilibrio in every point. It is the arch formed by a string fixed at both ends, and swaying loose in all the intermediate points. Thus at liberty, they must finally take that position, wherein every one will be equally pressed; for if any one was more pressed than the neighboring point, it would give way, from the flexibility of the matter of the string.
I am, with sentiments of sincere esteem and attachment, Dear Sir, your friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN JAY.
Paris, January 11, 1789.
Sir,
My last letters were of the 14th, 19th, and 29th of November, by the way of London. The present will go the same way, through a private channel.
All military operations in Europe seem to have been stopped, by the excessive severity of the weather. In this country, it is unparalleled in so early a part of the winter, and in duration, having continued since the middle of November, during which time it has been as low as nine degrees below nought, that is to say, forty degrees below freezing, by Fahrenheit’s thermometer; and it has increased the difficulties of the administration here. They had, before, to struggle with the want of money, and want of bread for the people, and now, the want of fuel for them, and want of employment. The siege of Oczakow is still continued, the soldiers sheltering themselves in the Russian manner, in subterraneous barracks; and the Captain Pacha has retired with his fleet. The death of the King of Spain has contributed, with the insanity of the English King, to render problematical the form which the affairs of Europe will ultimately take. Some think a peace possible between the Turks and two Empires, with the cession of Crimea to the former, as less important to Russia than Poland, which she is in danger of losing. In this case, the two Empires might attack the King of Prussia, and the scene of war be only changed. He is certainly uneasy at the accident happened to his principal ally. There seems no doubt, but that the Prince of Wales will be sole regent; but it is also supposed, they will not give him the whole executive power, and particularly, that of declaring war without the consent of the parliament. Should his personal dispositions, therefore, and that of a new ministry, be the same which the King had, of co-operating with Prussia, yet the latter cannot count on their effect. Probably, the parliament will not consent to war, so that I think we may consider the two great powers of France and England as absolutely at rest for some time.
As the character of the Prince of Wales is becoming interesting, I have endeavored to learn what it truly is. This is less difficult in his case, than in that of other persons of his rank, because he has taken no pains to hide himself from the world. The information I most rely on, is from a person here, with whom I am intimate, who divides his time between Paris and London, an Englishman by birth, of truth, sagacity, and science. He is of a circle, when in London, which has had good opportunities of knowing the Prince; but he has also, himself, had special occasions of verifying their information, by his own personal observation. He happened, when last in London, to be invited to a dinner of three persons. The Prince came by chance, and made the fourth. He ate half a leg of mutton; did not taste of small dishes, because small; drank Champagne and Burgundy as small beer during dinner, and Bordeaux after dinner, as the rest of the company. Upon the whole, he ate as much as the other three, and drank about two bottles of wine without seeming to feel it. My informant sat next him, and being till then unknown to the Prince, personally, (though not by character), and lately from France, the Prince confined his conversation almost entirely to him. Observing to the Prince that he spoke French without the least foreign accent, the Prince told him, that when very young, his father had put only French servants about him, and that it was to that circumstance he owed his pronunciation. He led him from this to give an account of his education, the total of which was the learning a little Latin. He has not a single element of Mathematics, of Natural or Moral Philosophy, or of any other science on earth, nor has the society he has kept been such as to supply the void of education. It has been that of the lowest, the most illiterate and profligate persons of the kingdom, without choice of rank or mind, and with whom the subjects of conversation are only horses, drinking-matches, bawdy houses, and in terms the most vulgar. The young nobility, who begin by associating with him, soon leave him, disgusted with the insupportable profligacy of his society; and Mr. Fox, who has been supposed his favorite, and not over nice in the choice of company, would never keep his company habitually. In fact, he never associated with a man of sense. He has not a single idea of justice, morality, religion, or of the rights of men, or any anxiety for the opinion of the world. He carries that indifference for fame so far, that he would probably not be hurt were he to lose his throne, provided he could be assured of having always meat, drink, horses, and women. In the article of women, nevertheless, he is become more correct, since his connection with Mrs. Fitzherbert, who is an honest and worthy woman: he is even less crapulous than he was. He had a fine person, but it is becoming coarse. He possesses good native common sense; is affable, polite, and very good humored. Saying to my informant on another occasion, ‘your friend, such a one, dined with me yesterday, and I made him damned drunk;’ he replied, ‘I am sorry for it; I had heard that your royal highness had left off drinking;’ the Prince laughed, tapped him on the shoulder very good-naturedly, without saying a word, or ever after showing any displeasure. The Duke of York, who was for some time cried up as the prodigy of the family, is as profligate, and of less understanding. To these particular traits, from a man of sense and truth, it would be superfluous to add the general terms of praise or blame, in which he is spoken of by other persons, in whose impartiality and penetration, I have less confidence. A sample is better than a description. For the peace of Europe, it is best that the King should give such gleamings of recovery, as would prevent the regent or his ministry from thinking themselves firm, and yet, that he should not recover. This country advances with a steady pace towards the establishment of a constitution, whereby the people will resume the great mass of those powers, so fatally lodged in the hands of the King. During the session of the Notables, and after their votes against the rights of the people, the Parliament of Paris took up the subject, and passed a vote in opposition to theirs, (which I send you.) This was not their genuine sentiment: it was a manoeuvre of the young members, who are truly well disposed, taking advantage of the accidental absence of many old members, and bringing others over by the clause, which, while it admits the negative of the States General in legislation, reserves still to the parliament the right of enregistering, that is to say, another negative. The Notables persevered in their opinion. The Princes of the blood (Monsieur and the Duke d’Orleans excepted) presented and published a memoire, threatening a scission. The parliament were proposing to approve of that memoire (by way of rescinding their former vote), and were prevented from it by the threat of a young member, to impeach (denoncer) the memoire and the Princes who signed it. The vote of the Notables, therefore, remaining balanced by that of the parliament, the voice of the nation becoming loud and general for the rights of the Tiers-Etat, a strong probability that if they were not allowed one half the representation, they would send up their members with express instructions to agree to no tax and to no adoption of the public debts, and the court really wishing to give them a moiety of the representation, this was decided on ultimately. You are not to suppose that these dispositions of the court proceed from any love of the people, or justice towards their rights. Courts love the people always, as wolves do the sheep. The fact is this. The court wants money. From the Tiers-Etat they cannot get it, because they are already squeezed to the last drop. The clergy and the nobles, by their privileges and their influence, have hitherto screened their property, in a great degree, from public contribution. That half of the orange, then, remains yet to be squeezed, and for this operation there is no agent powerful enough, but the people. They are, therefore, brought forward as the favorites of the court, and will be supported by them. The moment of crisis will be the meeting of the States; because their first act will be, to decide whether they shall vote by persons or by orders. The clergy will leave nothing unattempted to obtain the latter; for they see that the spirit of reformation will not confine itself to the political, but will extend to the ecclesiastical establishment also. With respect to the nobles, the younger members are generally for the people, and the middle aged are daily coming over to the same side: so that by the time the States meet, we may hope there will be a majority of that body, also, in favor of the people, and consequently for voting by persons, and not by orders.
You will perceive, by the report of Mr. Necker (in the gazette of France), 1. a renewal of the renunciation of the power of imposing a new tax by the King, and a like renunciation of the power of continuing any old one; 2. an acknowledgment that the States are to appropriate the public monies, which will go to the binding the court to a civil list; 3. a consent to the periodical meeting of the States; 4. to consider of the restrictions of which lettres de cachet are susceptible; 5. the degree of liberty to be given to the press; 6. a bill of rights; and 7. there is a passage which looks towards the responsibility of ministers. Nothing is said of communicating to them a share in the legislation. The ministry, perhaps, may be unwilling to part with this, but it will be insisted on in the States. The letters of convocation will not appear till towards the latter end of the month: neither time nor place are yet declared, but Versailles is talked of, and we may well presume that some time in April will be fixed on. In the mean time, Mr. Necker gets money to keep the machine in motion. Their funds rose slowly, but steadily, till within these few days, when there was a small check. However, they stand very well, and will rise. The caisse d’escompte lent the government twenty-five millions, two days ago. The navy of this country sustained a heavy loss lately, by the death of the Bailli de Suffrein. He was appointed Generalissimo of the Atlantic, when war was hourly expected with England, and is certainly the officer on whom the nation would have reposed its principal hopes, in such a case. We just now hear of the death of the Speaker of the House of Commons, before the nomination of a regent, which adds a new embarrassment to the re-establishment of government in England. Since writing mine of November the 29th, yours of the 23rd of September has come to hand. As the General of the Mathurins was to be employed in the final redemption of our captives, I thought that their previous support had better be put into his hands, and conducted by himself in such a way as not to counterwork his plan of redemption, whenever we can enable him to begin on it. I gave him full powers as to the amount and manner of subsisting them. He has undertaken it, informing me, at the same time, that it will be on a very low scale, to avoid suspicion of its coming from the public. He spoke of but three sous a day per man, as being sufficient for their physical necessaries, more than which, he thinks it not advisable to give. I have no definitive answer yet from our bankers, whether we may count on the whole million last agreed to be borrowed, but I have no doubt of it, from other information, though I have not their formal affirmative. The gazettes of Leyden and France to this date, accompany this. I have the honor to be, with sentiments of the most perfect esteem and respect, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JAMES MADISON.
Paris, January 12, 1789.
Dear Sir,
My last to you was of the 18th of November; since which, I have received yours of the 21st of September, and October the 8th, with the pamphlet on the Mohicon language, for which, receive my thanks. I endeavor to collect all the vocabularies I can of the American Indians, as of those of Asia, persuaded, that if they ever had a common parentage, it will appear in their languages.
I was pleased to see the vote of Congress, of September the 16th, on the subject of the Mississippi, as I had before seen, with great uneasiness, the pursuit of other principles, which I could never reconcile to my own ideas of probity or wisdom, and from which, and my knowledge of the character of our western settlers, I saw that the loss of that country was a necessary consequence. I wish this return to true policy may be in time to prevent evil. There has been a little foundation for the reports and fears relative to the Marquis de la Fayette. He has, from the beginning, taken openly part with those who demand a constitution; and there was a moment that we apprehended the Bastile: but they ventured on nothing more, than to take from him a temporary service, on which he had been ordered; and this, more to save appearances for their own authority, than any thing else; for at the very time they pretended that they had put him into disgrace, they were constantly conferring and communicating with him. Since this, he has stood on safe ground, and is viewed as among the foremost of the patriots. Every body here is trying their hand at forming declarations of rights. As something of that kind is going on with you also, I send you two specimens from hence. The one is by our friend of whom I have just spoken. You will see that it contains the essential principles of ours, accommodated as much as could be, to the actual state of things here. The other is from a very sensible man, a pure theorist, of the sect called the Economists, of which Turgot was considered as the head. The former is adapted to the existing abuses, the latter goes to those possible, as well as to those existing.
With respect to Doctor Spence, supposed to have been taken by the Algerines, I think the report extremely improbable. O’Bryan, one of our captives there, has constantly written to me, and given me information on every subject he thought interesting. He could not have failed to know if such a capture had been made, though before his time, nor to inform me of it. I am under perpetual anxiety for our captives there. The money, indeed, is not yet ready at Amsterdam; but when it shall be, there are no orders from the board of treasury to the bankers, to furnish what may be necessary for the redemption of the captives: and it is so long since Congress approved the loan, that the orders of the treasury for the application of the money would have come, if they had intended to send any. I wrote to them early on the subject, and pointedly. I mentioned it to Mr. Jay also, merely that he might suggest it to them. The payments to the foreign officers will await the same formality.
I thank you for your attention to the case of Mrs. Burke. We have no news of Doctor Franklin since July last, when he was very ill. Though the silence of our letters on that subject is a proof that he is well, yet there is an anxiety here among his friends. We have lately had three books published, which are of great merit, in different lines. The one is in seven volumes, octavo, by an Abbe Barthelemy, wherein he has collected every subject of Grecian Literature, after a labor of thirty years. It is called ‘Les Voyages d’Anacharsis.’ I have taken a copy for you, because the whole impression was likely to be run off at once. The second is a work on government, by the Marquis de Condorcet, two volumes, octavo. I shall secure you a copy. The third are the works of the King of Prussia, in sixteen volumes, octavo. These were a little garbled at Berlin, before printed. The government lays its hands on all which come here, and change some leaves. There is a genuine edition published at Basle, where even the garblings of Berlin are re-established. I doubt the possibility of getting a copy, so vigilant is the government as to this work. I shall obtain you one, if it be possible. As I write all the public news to Mr. Jay, I will not repeat it to you. I have just received the Flora Caroliniana of Walter, a very learned and good work. I am, with very sincere esteem and respect, Dear Sir, your friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN JAY.
Sir,
Paris, January 14, 1789.
In my letter of the 11th, I have said nothing of the Arrêt explanatory of that of September the 28th, on the subject of whale-oils, which my letter of November the 19th gave you reason to expect. Though this explanatory Arrêt has been passed so long ago as the 7th of December, it has not been possible for me to obtain an authentic copy of it, till last night. I now enclose that to you, with a copy of a letter to me from Mr. Necker, on the subject. The reception of our oils in the mean time, is provided for by an intermediate order. You will observe, that in the Arrêt it is said to be passed ‘provisoirement,’ and that Mr. Necker expressly holds up to us in his letter, a repeal, whenever the national fishery supplies their wants. The Arrêt, however, is not limited in its duration, and we have several chances against its repeal. It may be questioned, whether Mr. Necker thinks the fishery worth the expense. It may be well questioned, whether, either with or without encouragement, the nation, whose navigation is the least economical of all in Europe, can ever succeed in the whale-fishery, which calls for the most rigorous economy. It is hoped that a share in the legislation will pass immediately into the hands of the States General, so as to be no longer in the power of the commis of a bureau, or even of his minister, to smuggle a law through, unquestioned; and we may even hope that the national demand for this oil will increase faster than both their and our fisheries together will supply. But in spite of all these hopes, if the English should find means to cover their oils under our name, there will be great danger of a repeal. It is essential, then, that our government take effectual measures to prevent the English from obtaining genuine sea-papers, that they enable their consuls in the ports of France (as soon as they shall be named) to detect counterfeit papers, and that we convince this government that we use our best endeavors, with good faith, as it is clearly our interest to do; for the rivalship of the English is the only one we have to fear. It had already begun to render our oils invendible in the ports of France. You will observe that Mr. Necker renews the promise of taking off the ten sous pour livre, at the end of the next year.
Oczakow is at length taken by assault. The assailants were fourteen thousand, and the garrison twelve thousand, of whom seven thousand were cut to pieces before they surrendered. The Russians lost three thousand men. This is the Russian version, of which it is safe to believe no part, but that Oczakow is taken. The Speaker of the English House of Commons, having died suddenly, they have chosen Mr. Grenville, a young man of twenty-seven years of age. This proves that. Mr. Pitt is firm with the present parliament.
I have the honor to be, with sentiments of the most perfect esteem and respect, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MADAME NECKER.
Paris, January 24, 1789.
I have received, Madam, with a great deal of sensibility, the letter of the 22nd instant, with which you were pleased to honor me on the claims of Monsieur Klein against the United States; and immediately endeavored to inform myself of their foundation, by an examination of the journals of Congress. Congress consisting of many persons, can only speak by the organ of their records. If they have any engagements, they are to be found there. If not found there, they can never have existed. I proceeded to this examination, with all the partialities which were naturally inspired by the interest you are so good as to take in his behalf, the desire of doing what will be agreeable to you, and a disposition to obtain for him the justice which might be his due. I have extracted, literally, from those journals, every thing I find in them on his subject, and I take the liberty of enclosing you those extracts. From them, as well as from what I recollect of the ordinary train of business about the years 1778 and 1779, I presume the following to be very nearly the history of Monsieur Klein’s case.
Congress were generally desirous of adding to their army during the war. Among other methods attempted, it was usual for foreigners (multitudes of whom went to ask command), when they found there was no vacancy, to propose to raise troops themselves, on condition they should have commissions to command them. I suppose that Messrs. Klein, Fearer, and Kleinsmit (named in the resolution of Congress of 1778, and whom, from their names, I conjecture to be Germans) offered to enlist a body of men from among the German prisoners taken with General Burgoyne at Saratoga, on condition that Fearer and Kleinsmit should be captains over them, and Klein, lieutenant colonel. Three months seem to have been allowed them for raising their corps. However, at the end of ten months it seems they had engaged but twenty-four men, and that all of these, except five, had deserted. Congress, therefore, put an end to the project, June the 21st, 1779, (and not in July, 1780, as Monsieur Klein says) by informing him they had no further use for his services, and giving him a year’s pay and subsistence to bring him to Europe. He chose to stay there three and a half longer, as he says, to solicit what was due to him. Nothing could ever have been due to him, but pay and subsistence for the ten months he was trying to enlist men, and the donation of a year’s pay and subsistence; and it is not probable he would wait three years and a half to receive these. I suppose he has staid, in hopes of finding some other opening for employment. If these articles of pay and subsistence have not been paid to him, he has the certificates of the paymaster and commissary to prove it; because it was an invariable rule, when demands could not be paid, to give the party a certificate, to establish the sum due to him. If he has not such a certificate, it is a proof he has been paid. If he has it, he can produce it, and in that case, I will undertake to represent his claim to our government, and will answer for their justice.
It would be easy to correct several inaccuracies in the letter of Monsieur Klein, such as that Congress engaged to give him a regiment; that he paid the recruiting money out of his own pocket; that his soldiers had nothing but bread and water; that Congress had promised him they would pay his soldiers in specie, &c.; some of which are impossible, and others very improbable; but these would be details too lengthy, Madam, for you to be troubled with. Klein’s object is to be received at the hospital of invalids. I presume he is not of the description of persons entitled to be received there, and that his American commission and American grievances are the only ground he has, whereon to raise a claim to reception. He has therefore tried to make the most of them. Few think there is any immorality in scandalizing governments or ministers; and M. Klein’s distresses render this resource more innocent in him, than it is in most others.
Your commands, Madam, to give what information I could, have drawn thus much from me. I would not wish to weaken the hopes he so justly rests on your, known goodness and benevolence. On the contrary, the weaker his claims elsewhere, the stronger they will plead in your bosom to procure him relief; and whatever may be done for him here, I repeat it, that if he has any just demand against the United States, and will furnish me with proofs of it, I will solicit it with zeal, and, I trust, with effect. To procure him justice will be one gratification, and a great additional one will be, that he has procured me the occasion of offering you my portion of the general tribute so justly due, for all the good you have done, and all you are perpetually endeavoring to do. Accept then, Madam, I pray you, this homage from one, whose motives are pure truth and justice, when he assures you of the sincerity of those sentiments of esteem and respect, with which he has the honor to be, Madam, your most obedient and most
humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN JAY.
Paris, February 1, 1789.
Sir,
My last letters have been of the 11th, 14th, and 21st of January. The present conveyance being through the post to Havre, from whence a vessel is to sail for New York, I avail myself of it, principally to send you the newspapers. That of Leyden of the 24th, contains a note of the Chargé des Affaires of France, at Warsaw, which is interesting. It shows a concert between France and Russia; it is a prognostication that Russia will interfere in the affairs of Poland, and if she does, it is most probable that the King of Prussia must be drawn into the war. The revolution which has taken place in Geneva, is a remarkable and late event. With the loss of only two or three lives, and in the course of one week, riots, begun at first on account of a rise in the price of bread, were improved and pointed to a reformation of their constitution; and their ancient constitution has been almost completely re-established. Nor do I see any reason to doubt of the permanence of the re-establishment. The King of England has shown such marks of returning reason, that the regency bill was postponed in the House of Lords, on the 19th instant. It seems now probable, there may be no change of the ministry, perhaps no regent. We may be sure, however, that the present ministry make the most of those favorable symptoms. There has been a riot in Brittany, begun on account of the price of bread, but converted into a quarrel between the Noblesse and Tiers-Etat. Some few lives were lost in it. All is quieted for the present moment. In Burgundy and Franche Compte, the opposition of the nobles to the views of government is very warm. Every where else, however, the revolution is going on quietly and steadily, and the public mind ripening so fast, that there is great reason to hope a good result from the States General. Their numbers (about twelve hundred) give room to fear, indeed, that they may be turbulent. Having never heard of Admiral Paul Jones since the action, in which he took a part before Oczakow, I began to be a little uneasy. But I have now received a letter from him, dated at St. Petersburg, the 31 st of January, where he had just arrived, at the desire of the Empress. He has hitherto commanded on the Black Sea. He does not know whether he shall be employed there, or where, the ensuing campaign. I have no other interesting intelligence, which would not lead me into details, improper for the present mode of conveyance. After observing, therefore, that the gazettes of France and Leyden, to the present date, accompany this, I shall only add assurance of the sincere esteem and respect, with which I have the honor to be, Dear Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN JAY.
Paris, February 4, 1789.
Sir,
Your favor of November the 25th, by Gouverneur Morris, is duly received. I must beg you to take the trouble of deciphering yourself what follows, and to communicate it to nobody but the President, at least for the present.
We had before understood, through different channels, that the conduct of the Count de Moustier was politically and morally offensive. It was delicate for me to speak on the subject to the Count de Montmorin. The invaluable mediation of our friend, the Marquis de la Fayette, was therefore resorted to, and the subject explained, though not pressed. Later intelligence showing the necessity of pressing it, it was yesterday resumed, and represented through the same medium to the Count de Montmorin, that recent information proved to us, that his minister’s conduct had rendered him personally odious in America, and might even influence the dispositions of the two nations; that his recall was become a matter of mutual concern; that we had understood he was instructed to remind the new government of their debt to this country, and that he was in the purpose of doing it in very harsh terms; that this could not increase their desire of hastening payment, and might wound their affections: that, therefore, it was much to be desired that his discretion should not be trusted to, as to the form in which the demand should be made, but that the letter should be written here, and he instructed to add nothing but his signature: nor was his private conduct omitted. The Count de Montmorin was sensibly impressed. He very readily determined that the letter should be formed here, but said that the recall was a more difficult business: that as they had no particular fact to allege against the Count de Moustier, they could not recall him from that ministry, without giving him another, and there was no vacancy at present. However, he would hazard his first thoughts on the subject, saving the right of correcting them by further consideration. They were these: that there was a loose expression in one of de Moustier’s letters, which might be construed into a petition for leave of absence; that he would give him permission to return to France; that it had been before decided, on the request of the Marquis de la Luzerne, that Otto should go to him to London; that they would send a person to America as Chargé des Affaires in place of Otto, and that if the President (General Washington) approved of him, he should be afterwards made minister. He had cast his eye on Colonel Ternant, and desired the Marquis to consult me, whether he would be agreeable. At first I hesitated, recollecting to have heard Ternant represented in America, as an hypochondriac, discontented man, and paused for a moment between him and Barthelemy, at London, of whom I have heard a great deal of good. However, I concluded it safer to take one whom we knew and who knew us. The Marquis was decidedly of this opinion. Ternant will see that his predecessor is recalled for unconciliatory deportment, and that he will owe his own promotion to the approbation of the President. He established a solid reputation in Europe, by his conduct when Generalissimo of one of the United Provinces, during their late disturbances; and it is generally thought, that if he had been put at the head of the principal province, instead of the Rhingrave de Salm, he would have saved that cause. Upon the whole, I believe you may expect that the Count de Moustier will have an immediate leave of absence, which will soon after become a recall in effect. I will try also to have the consuls admonished as to the line of conduct they should observe. I shall have the honor of writing you a general letter, within a few days. I have now that of assuring you of the sentiments of sincere esteem and respect, with which I am, Dear Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO WILLIAM SHORT.
Paris, February 9,1789.
Dear Sir,
I wrote you last on the 22nd of January, on which day I received yours of December the 31st, and since that, the other of January the 14th. We have now received news from America down to the middle of December. They had then had no cold weather. All things relative to our new constitution were going on well. Federal senators are; New Hampshire, President Langdon and Bartlett. Massachusetts, Strong and Dalton. Connecticut, Dr. Johnson and Ellsworth. New Jersey, Patterson and Ellmer. Pennsylvania, Robert Morris and M’Clay. Delaware, Reed and Bassett. Virginia, Richard Henry Lee and Grayson. Maryland, Charles Carroll, of Carrolton, and John Henry. All of these are federalists, except those of Virginia; so that a majority of federalists are secured in the Senate, and expected in the House of Representives. General Washington will be President, and probably Mr. Adams Vice-President. So that the constitution will be put under way by those who will give it a fair trial. It does not seem probable that the attempt of New York, to have another convention to make amendments, will succeed, though Virginia concurs in it. It is tolerably certain that Congress will propose amendments to the Assemblies, as even the friends of the constitution are willing to make amendments; some from a conviction they are necessary, others, from a spirit of conciliation. The addition of a bill of rights will, probably, be the most essential change. A vast majority of anti-federalists have got into the Assembly of Virginia, so that Mr. Henry is omnipotent there. Mr. Madison was left out as a senator by eight or nine votes; and Henry has so modeled the districts for representatives, as to tack Orange to counties where himself has great influence, that Madison may not be elected into the lower federal House, which was the place he had wished to serve in, and not the Senate. Henry pronounced a philippic against Madison in open Assembly, Madison being then at Philadelphia. Mifflin is President of Pennsylvania, and Peters, Speaker. Colonel Howard is Governor of Maryland. Beverly Randolph, Governor of Virginia; (this last is said by a passenger only, and he seems not very sure.) Colonel Humphreys is attacked in the papers for his French airs, for bad poetry, bad prose, vanity, &c. It is said his dress, in so gay a style, gives general disgust against him. I have received a letter from him. He seems fixed with General Washington. Mayo’s bridge, at Richmond, was completed, and carried away in a few weeks. While up, it was so profitable that he had great offers for it. A turnpike is established at Alexandria, and succeeds. Rhode Island has again refused to call a convention. Spain has granted to Colonel Morgan, of New Jersey, a vast tract of land on the western side of the Mississippi, with the monopoly of the navigation of that river. He is inviting settlers, and they swarm to him. Even the settlement of Kentucky is likely to be much weakened by emigrations to Morgan’s grant. Warville has returned, charmed with our country. He is going to carry his wife and children to settle there. Gouverneur Morris has just arrived here; deputed, as is supposed, to settle Robert Morris’s affairs, which continue still deranged. Doctor Franklin was well when he left America, which was about the middle of December.
I send Mr. Rutledge two letters by this post. Be so good as to present him my esteem, and to be assured yourself, of the sincere esteem and attachment with which I am and shall ever be? Dear Sir, your affectionate friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO M. DE VILLEDEUIL.
Paris, February 10, 1789.
Sir,
I take the liberty of troubling your Excellency with the following case, which I understand to be within your department. Mr. Jay, secretary for Foreign Affairs, to the United States of America, having occasion to send me despatches of great importance, and by a courier express, confided them to a Mr. Nesbitt, who offered himself in that character. He has delivered them safely: but, in the moment of delivering them, explained to me his situation, which is as follows. He was established in commerce at L’Orient, during the war. Losses by shipwreck, by capture, and by the conclusion of the peace at a moment when he did not expect it, reduced him to bankruptcy, and he returned to America, with the consent of his creditors, to make the most of his affairs there. He has been employed in this ever since, and now wishing to see his creditors, and to consult them on their mutual interests, he availed himself of Mr. Jay’s demand for a courier, to come under the safe conduct of that character to Paris, where he flattered himself he might obtain that of your Excellency, for the purpose of seeing his creditors, settling, and arranging with them. He thinks a twelvemonth will be necessary for this. Understanding that it is not unusual to grant safe conducts in such cases, and persuaded it will be for the benefit of his creditors, I take the liberty of enclosing his memoir to your Excellency, and of soliciting your favorable attention to it, assured that it will not be denied him, if it be consistent with the established usage; and if inadmissible, praying that your Excellency will have the goodness to give me as early an answer as the other arduous occupations in which you are engaged, will admit, in order that he may know whether he may see his creditors, or must return without. I am encouraged to trouble your Excellency with this application, by the goodness with which you have been pleased to attend to our interests on former occasions, and by the desire of availing myself of every occasion of proffering to you the homage of those sentiments of attachment and respect, with which I have the honor to be your Excellency’s most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MR. CARNES.
Paris, February 15,1789.
Sir,
I am now to acknowledge the receipt of your favors of January the 23rd, and February the 9th and 10th. Your departure for America so soon, puzzles me as to the finishing the affair of Schweighaeuser and Dobree, in which I could have reposed myself on you. It remains, that I ask you to recommend some person who may be perfectly relied on, in that business. In fact, it is probably the only one I shall have occasion to trouble them with before my own departure for America, which I expect to take place in May; and I fix my return to Paris, in December. While I ask your recommendation of a person to finish Dobree’s business with fidelity, I must ask your secrecy on the subject of that very business, so as not to name it at all, even to the person you shall recommend.
With respect to the distressed American who needs one hundred and forty livres to enable him to return to America, I have no authority to apply any public monies to that purpose, and the calls of that nature are so numerous, that I am obliged to refuse myself to them in my private capacity. As to Captain Newell’s case, you are sensible, that being in the channel of the laws of the land, to ask a special order from government, would expose us, in reciprocity to like demands from them in America, to which our laws would never permit us to accede. Speaking conscientiously, we must say it is wrong in any government to interrupt the regular course of justice. A minister has no right to intermeddle in a private suit, but when the laws of the country have been palpably perverted to the prejudice of his countryman.
When you shall be so kind as to recommend to me a correspondent in your port during your absence, I will ask the favor of you also to give me some idea of the time you expect to return.
I have the honor, after wishing you pleasant and prosperous voyages, to assure you of the esteem and attachment, with which I am, Sir, your most obedient, humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO DR. BANCROFT.
Paris, March 2, 1789
Dear Sir,
I have just received a letter of January the 31st from Admiral Paul Jones, at Petersburg, which charging me with the execution of some commissions, and these requiring money, he tells me you will answer my drafts, to the amount of four or five thousand livres, on his account. Be so good as to inform me whether you will pay such drafts.
A Monsieur Foulloy, who has been connected with Deane, lately offered me for sale two volumes of Deane’s letter books and account books, that he had taken instead of money, which Deane owed him. I have purchased them on public account. He tells me Deane has still six or eight volumes more, and being to return soon to London, he will try to get them also, in order to make us pay high for them. You are sensible of the impropriety of letting such books get into hands which might make an unfriendly use of them. You are sensible of the immorality of an ex-minister’s selling his secrets for money and, consequently, that there can be no immorality in tempting him with money to part with them; so that they may be restored to that government to whom they properly belong. Your former acquaintance with Deane may, perhaps, put it in your power to render our country the service of recovering those books. It would not do to propose it to him as for Congress. What other way would best bring it about, you know best. I suppose his distresses and his crapulous habits will not render him difficult on this head. On the supposition that there are six or eight volumes, I think you might venture as far as fifty guineas, and proportionably for fewer. I will answer your draft to this amount and purpose, or you may retain it out of any monies you may propose to pay me for admiral Jones. There is no time to lose in this negotiation, as, should Foulloy arrive there before it is closed, he will spoil the bargain. If you should be able to recover these books, I would ask the favor of you to send them to me by the Diligence, that I may carry them back with me to America. I make no apology for giving you this trouble. It is for our common country, and common interest.
I am, with sincere and great esteem and attachment, Dear Sir, your most obedient, humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO M. DE MALESHERBES.
Sir,
Paris, March 11, 1789.
Your zeal to promote the general good of mankind, by an interchange of useful things, and particularly in the line of agriculture, and the weight which your rank and station would give to your interposition, induce me to ask it, for the purpose of obtaining one of the species of rice which grows in Cochin-China on high lands, and which needs no other watering than the ordinary rains. The sun and soil of Carolina are sufficiently powerful to insure the success of this plant, and Monsieur de Poivre gives such an account of its quality, as might induce the Carolinians to introduce it instead of the kind they now possess, which, requiring the whole country to be laid under water during a certain season of the year, sweeps off numbers of the inhabitants annually, with pestilential fevers. If you would be so good as to interest yourself in the procuring for me some seeds of the dry rice of Cochin-China, you would render the most precious service to my countrymen, on whose behalf I take the liberty of asking your interposition: very happy, at the same time, to have found such an occasion of repeating to you the homage of those sentiments of respect and esteem, with which I have the honor to be, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
Sir,
Paris, March 12, 1789.
I had the honor of addressing you, on the 1st instant, through the post. I write the present, uncertain whether Mr. Nesbitt, the bearer of your last, will be the bearer of this, or whether it may not have to wait some other private occasion. They have reestablished their packet-boats here, indeed; but they are to go from Bordeaux, which, being between four and five hundred miles from hence, is too far to send a courier with any letters but on the most extraordinary occasions and without a courier, they must pass through the post-office. I shall, therefore, not make use of this mode of conveyance, but prefer sending my letters by a private hand by the way of London. The uncertainty of finding private conveyances to London, is the principal objection to this.
On the receipt of your letter, advising me to purchase the two volumes of Deane’s letters and accounts, I wrote to the person who had them, and after some offers and refusals, he let me have them for twenty-five louis, instead of twenty louis asked at first. He told me that Deane had still six or eight volumes more, and that when he should return to London he would try to get them, in order to make himself whole for the money he had lent Deane. As I knew he would endeavor to make us pay dear for them, and it appeared to be your opinion, and that of the members you had consulted, that it was an object worthy attention, I wrote immediately to a friend in London to endeavor to purchase them from Deane himself, whose distresses and crapulous habits will probably render him more easy to deal with. I authorized him to go as far as fifty guineas. I have as yet no answer from him. I enclose you a letter which I wrote last month to our bankers in Holland. As it will itself explain the cause of its being written, I shall not repeat its substance here. In answer to my proposition, to pay bills for the medals and the redemption of our captives, they quote a resolution of Congress (which, however, I do not find in the printed journals), appropriating the loans of 1787 and 1788 to the payment of interest on the Dutch loans till 1790, inclusive, and the residue to salaries and contingencies in Europe, and they argue, that, according to this, they are not to pay any thing in Europe till they shall first have enough to pay all the interest which will become due to the end of the year 1790; and that it is out of personal regard, that they relax from this so far as to pay diplomatic salaries. So that here is a clear declaration they will answer no other demands, till they have in hand money enough for all the interest to the end of the year 1790. It is but a twelvemonth since I have had occasion to pay attention to the proceedings of those gentlemen; but during that time I have observed, that as soon as a sum of interest is becoming due, they are able to borrow just that, and no more; or at least only so much more as may pay our salaries, and keep us quiet. Were they not to borrow for the interest, the failure to pay that would sink the value of the capital, of which they are considerable sharers. So far their interests and ours concur. But there, perhaps, they may separate. I think it possible they may choose to support our credit to a certain point, and let it go no further, but at their will; to keep it so poised, as that it may be at their mercy. By this, they will be sure to keep us in their own hands. They write word to the treasury, that in order to raise money for the February interest, they were obliged to agree with the subscribers, that Congress should open no other loan at Amsterdam this year, till this one be filled up, and that this shall not be filled but by the present subscribers, and they not obliged to fill it. This is delivering us, bound hand and foot, to the subscribers, that is, to themselves. Finding that they would not raise money for any other purposes, without being pushed, I wrote the letter I enclose you. They answer, as I have stated, by refusing to pay, alleging the appropriation of Congress. I have written again to press them further, and to propose to them the payment of thirty thousand florins only, for the case of our captives, as I am in hopes this may do. In the close of my letter to them, you will observe I refer them, as to the article of foreign officers, to the board of treasury. I had, in truth, received the printed journals a few days before, but had not yet had time to read them carefully, and, particularly, had not then noted the vote of Congress of August the 20th, directing me to attend to that article. I shall not fail to do what I can in it; but I am afraid they will consider this also as standing on the same ground with the other contingent articles.
This country, being generally engaged in its elections, affords nothing new and worthy of communication. The hopes of accommodation between Turkey and the two empires do not gain strength. The war between Russia and Denmark on the one hand, and Sweden on the other, is likely also to go on, the mediation of England being rendered of little force by the accident to its Executive. The progress of this war, and also of the broils in Poland, may possibly draw the King of Prussia into it during the ensuing campaign: and it must, before it be finished, take in this country, and perhaps England. The ill humor on account of the Dutch revolution continues to rankle here. They have recalled their ambassador from the Hague, manifestly to show their dissatisfaction with that court, and some very dry memorials have lately been exchanged on the subject of the money this country assumed to pay the Emperor for the Dutch. I send you very full extracts of these, which will show you the dispositions of the two courts towards each other. Whether, and when this country will be able to take an active part, will depend on the issue of their States General. If they fund their public debts judiciously, and will provide further funds for a war, on the English plan, 1 believe they will be able to borrow any sums they please. In the mean time, the situation of England will leave them at leisure to settle their internal affairs well. That ministry, indeed, pretend their King is perfectly re-established. No doubt they will make the most of his amendment, which is real, to a certain degree. But as, under pretence of this, they have got rid of the daily certificate of the physicians, and they are possessed of the King’s person, the public must judge hereafter from such facts only as they can catch. There are several at present, which, put together, induce a presumption that the King is only better, not well. And should he be well, time will be necessary to give a confidence, that it is not merely a lucid interval. On the whole, I think we may conclude that that country will not take a part in the war this year, which was by no means certain before.
M. del Pinto, formerly minister of Portugal at London, and the same who negotiated the treaty with us, being now put at the head of the ministry of that country, I presume that negotiation may be renewed successfully, if it be the desire of our government. Perhaps an admission of our flour into their ports may be obtained now, as M. del Pinto seemed impressed with our reasoning on that subject, and promised to press it on his court, though he could not then venture to put it into the treaty. There is not the same reason to hope any relaxation as to our reception in Brazil, because he would scarcely let us mention that at all. I think, myself, it is their interest to take away all temptations to our cooperation in the emancipation of their colonies; and I know no means of doing this, but the making it our interest that they should continue dependant, nor any other way of making this our interest, but by allowing us a commerce with them. However, this is a mode of reasoning which their ministry, probably, could not bear to listen to. I send herewith the gazettes of France and Leyden, and have the honor to be, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO F. HOPKINSON.
Paris, March 13, 1789.
Dear Sir,
Since my last, which was of December the 21st, yours of December the 9th and 21st are received. Accept my thanks for the papers and pamphlets which accompanied them, and mine and my daughters for the book of songs. I will not tell you how much they have pleased us, nor how well the last of them merits praise for its pathos, but relate a fact only, which is, that while my elder daughter was playing it on the harpsichord, I happened to look towards the fire, and saw the younger one all in tears. I asked her if she was sick? She said, ‘No; but the tune was so mournful.’
The Editor of the Encyclopédie has published something as to an advanced price on his future volumes, which, I understand, alarms the subscribers. It was in a paper which I do not take, and therefore I have not yet seen it, nor can I say what it is. I hope that by this time you have ceased to make wry faces about your vinegar, and that you have received it safe and good. You say that I have been dished up to you as an anti-federalist, and ask me if it be just. My opinion was never worthy enough of notice, to merit citing; but since you ask it, I will tell it to you. I am not a federalist, because I never submitted the whole system of my opinions to the creed of any party of men whatever, in religion, in philosophy, in politics, or in any thing else, where I was capable of thinking for myself. Such an addiction is the last degradation of a free and moral agent. If I could not go to heaven but with a party, I would not go there at all. Therefore, I protest to you, I am not of the party of federalists. But I am much farther from that of the anti-federalists. I approved, from the first moment, of the great mass of what is in the new constitution; the consolidation of the government; the organization into executive, legislative, and judiciary; the subdivision of the legislative; the happy compromise of interests between the great and little States, by the different manner of voting in the different Houses; the voting by persons instead of States; the qualified negative on laws given to the executive, which, however, I should have liked better if associated with the judiciary also, as in New York; and the power of taxation. I thought at first that the latter might have been limited. A little reflection soon convinced me it ought not to be. What I disapproved from the first moment, also, was the want of a bill of rights, to guard liberty against the legislative as well as executive branches of the government; that is to say, to secure freedom in religion, freedom of the press, freedom from monopolies, freedom from unlawful imprisonment, freedom from a permanent military, and a trial by jury, in all cases determinable by the laws of the land. I disapproved, also, the perpetual re-eligibility of the President. To these points of disapprobation I adhere. My first wish was, that the nine first conventions might accept the constitution, as the means of securing to us the great mass of good it contained, and that the four last might reject it, as the means of obtaining amendments. But I was corrected in this wish, the moment I saw the much better plan of Massachusetts, and which had never occurred to me. With respect to the declaration of rights, I suppose the majority of the United States are of my opinion: for I apprehend all the anti-federalists, and a very respectable proportion of the federalists, think that such a declaration should now be annexed. The enlightened part of Europe have given us the greatest credit for inventing this instrument of security for the rights of the people, and have been not a little surprised to see us so soon give it up. With respect to the re-eligibility of the President, I find myself differing from the majority of my countrymen; for I think there are but three States of the eleven which have desired an alteration of this. And, indeed, since the thing is established, I would wish it not to be altered during the life of our great leader, whose executive talents are superior to those, I believe, of any man in the world, and who, alone, by the authority of his name, and the confidence reposed in his perfect integrity, is fully qualified to put the new government so under way, as to secure it against the efforts of opposition. But having derived from our error all the good there was in it, I hope we shall correct it, the moment we can no longer have the same name at the helm.
These, my dear friend, are my sentiments, by which you will see I was right in saying, I am neither federalist nor anti-federalist; that I am of neither party, nor yet a trimmer between parties. These, my opinions, I wrote, within a few hours after I had read the constitution, to one or two friends in America. I had not then read one single word printed on the subject. I never had an opinion in politics or religion, which I was afraid to own. A costive reserve on these subjects might have procured me more esteem from some people, but less from myself. My great wish is, to go on in a strict but silent performance of my duty: to avoid attracting notice, and to keep my name out of newspapers, because I find the pain of a little censure, even when it is unfounded, is more acute than the pleasure of much praise. The attaching circumstance of my present office, is, that I can do its duties unseen by those for whom they are done. You did not think, by so short a phrase in your letter, to have drawn on yourself such an egotistical dissertation. I beg your pardon for it, and will endeavor to merit that pardon by the constant sentiments of esteem and attachment, with which I am, Dear Sir, your sincere friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MADAME DE BREHAN.
Paris, March 14, 1789.
Dear Madam,
I had the honor of writing to you on the 15th of February; soon after which, I had that of receiving your favor of December the 29th. I have a thousand questions to ask you about your journey to the Indian treaty, how you like their persons, their manners, their costumes, cuisine, &c. But this I must defer till I can do it personally in New York, where I hope to see you for a moment in the summer, and to take your commands for France. I have little to communicate to you from this place. It is deserted: every body being gone into the country to choose or be chosen deputies to the States General. I hope to see that great meeting before my departure. It is to be on the 27th of next month. A great political revolution will take place in your country, and that without bloodshed. A King with two hundred thousand men at his orders, is disarmed by the force of the public opinion and the want of money. Among the economies becoming necessary, perhaps one may be the opera. They say, it has cost the public treasury an hundred thousand crowns the last year. A new theatre is established since your departure; that of the Opera Buffone, where Italian operas are given, and good music. It is in the Château des Tuileries. Paris is every day enlarging and beautifying. I do not count among its beauties, however, the wall with which they have enclosed us. They have made some amends for this, by making fine boulevards within and without the walls. These are in considerable forwardness, and will afford beautiful rides round the city, of between fifteen and twenty miles in circuit. We have had such a winter, Madam, as makes me shiver yet, whenever I think of it. All communications, almost, were cut off. Dinners and suppers were suppressed, and the money laid out in feeding and warming the poor, whose labors were suspended by the rigor of the season. Loaded carriages passed the Seine on the ice, and it was covered with thousands of people from morning till night, skating and sliding. Such sights were never seen before, and they continued two months. We have nothing new and excellent in your charming art of painting. In fact, I do not feel an interest in any pencil but that of David. But I must not hazard details on a subject wherein I am so ignorant, and you such a connoisseur. Adieu, my dear Madam; permit me always the honor of esteeming and being esteemed by you, and of tendering you the homage of that respectful attachment with which I am, and shall ever be, Dear Madam, your most obedient, humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JAMES MADISON.
Paris, March 15, 1789.
Dear Sir,
I wrote you last on the 12th of January; since which I have received yours of October the 17th, December the 8th and 12th. That of October the 17th came to hand only February the 23rd.
How it happened to be four months on the way, I cannot tell, as I never knew by what hand it came. Looking over my letter of January the 12th, I remark an error of the word ‘probable’ instead of’ improbable,’ which, doubtless, however, you had been able to correct.
Your thoughts on the subject of the declaration of rights, in the letter of October the 17th, I have weighed with great satisfaction. Some of them had not occurred to me before, but were acknowledged just, in the moment they were presented to my mind. In the arguments in favor of a declaration of rights, you omit one which has great weight with me; the legal check which it puts into the hands of the judiciary. This is a body, which, if rendered independent and kept strictly to their own department, merits great confidence for their learning and integrity. In fact, what degree of confidence would be too much, for a body composed of such men as Wythe, Blair, and Pendleton? On characters like these, the ‘civium ardor prava jubentium’ would make no impression. I am happy to find that, on the whole, you are a friend to this amendment. The declaration of rights is, like all other human blessings, alloyed with some inconveniences, and not accomplishing fully its object. But the good, in this instance, vastly overweighs the evil. I cannot refrain from making short answers to the objections which your letter states to have been raised. 1. That the rights in question are reserved, by the manner in which the federal powers are granted. Answer. A constitutive act, may, certainly, be so formed, as to need no declaration of rights. The act itself has the force of a declaration, as far as it goes; and if it goes to all material points, nothing more is wanting. In the draught of a constitution which I had once a thought of proposing in Virginia, and printed afterwards, I endeavored to reach all the great objects of public liberty, and did not mean to add a declaration of rights. Probably the object was imperfectly executed; but the deficiencies would have been supplied by others, in the course of discussion. But in a constitutive act which leaves some precious articles unnoticed, and raises implications against others, a declaration of rights becomes necessary, by way of supplement. This is the case of our new federal constitution. This instrument forms us into one State, as to certain objects, and gives us a legislative and executive body for these objects. It should, therefore, guard us against their abuses of power, within the field submitted to them. 2. A positive declaration of some essential rights could not be obtained in the requisite latitude. Answer. Half a loaf is better than no bread. If we cannot secure all our rights, let us secure what we can. 3. The limited powers of the federal government, and jealousy of the subordinate governments, afford a security which exists in no other instance. Answer. The first member of this seems resolvable into the first objection before stated. The jealousy of the subordinate governments is a precious reliance. But observe that those governments are only agents. They must have principles furnished them, whereon to found their opposition. The declaration of rights will be the text, whereby they will try all the acts of the federal government. In this view, it is necessary to the federal government also; as by the same text, they may try the opposition of the subordinate governments. 4. Experience proves the inefficacy of a bill of rights. True. But though it is not absolutely efficacious under all circumstances, it is of great potency always, and rarely inefficacious. A brace the more will often keep up the building which would have fallen, with that brace the less. There is a remarkable difference between the characters of the inconveniences which attend a declaration of rights, and those which attend the want of it. The inconveniences of the declaration are, that it may cramp government in its useful exertions. But the evil of this is short-lived, moderate, and reparable. The inconveniences of the want of a declaration are permanent, afflicting, and irreparable. They are in constant progression from bad to worse. The executive, in our governments, is not the sole, it is scarcely the principal object of my jealousy. The tyranny of the legislatures is the most formidable dread at present, and will be for many years. That of the executive will come in its turn; but it will be at a remote period. I know there are some among us, who would now establish a monarchy. But they are inconsiderable in number and weight of character. The rising race are all republicans. We were educated in royalism; no wonder, if some of us retain that idolatry still. Our young people are educated in republicanism; an apostacy from that to royalism is unprecedented and impossible. I am much pleased with the prospect that a declaration of rights will be added; and I hope it will be done in that way, which will not endanger the whole frame of government, or any essential part of it.
I have hitherto avoided public news in my letters to you, because your situation insured you a communication of my letters to Mr. Jay. This circumstance being changed, I shall, in future, indulge myself in these details to you. There had been some slight hopes that an accommodation might be effected between the Turks and two empires; but these hopes do not strengthen, and the season is approaching which will put an end to them, for another campaign at least. The accident to the King of England has had great influence on the affairs of Europe. His mediation, joined with that of Prussia, would certainly have kept Denmark quiet, and so have left the two empires in the hands of the Turks and Swedes. But the inactivity to which England is reduced, leaves Denmark more free, and she will probably go on in opposition to Sweden. The King of Prussia, too, had advanced so far, that he can scarcely retire. This is rendered the more difficult by the troubles he has excited in Poland. He cannot, well abandon the party he had brought forward there; so that it is very possible he may be engaged in the ensuing campaign. France will be quiet this year, because this year, at least, is necessary for settling her future constitution. The States will meet the 27th of April: and the public mind will. I think, by that time, be ripe for a just decision of the question, whether they shall vote by orders or persons. I think there is a majority of the Nobles already for the latter. If so, their affairs cannot but go on well. Besides settling for themselves a tolerably free constitution, perhaps as free a one as the nation is as yet prepared to bear, they will fund their public debts. This will give them such a credit, as will enable them to borrow any money they may want, and of course, to take the field again, when they think proper. And I believe they mean to take the field as soon as they can. The pride of every individual in the nation suffers under the ignominies they have lately been exposed to, and I think the States General will give money for a war, to wipe off the reproach. There have arisen new bickerings between this court and that of the Hague; and the papers which have passed, show the most bitter acrimony rankling at the heart of this ministry. They have recalled their ambassador from the Hague, without appointing a successor. They have given a note to the Diet of Poland, which shows a disapprobation of their measures. The insanity of the King of England has been fortunate for them, as it gives them time to put their house in order. The English papers tell you the King is well; and even the English ministry say so. They will naturally set the best foot foremost; and they guard his person so well, that it is difficult for the public to contradict them. The King is probably better, but not well, by a great deal. 1. He has been bled, and judicious physicians say, that in his exhausted state, nothing could have induced a recurrence to bleeding, but symptoms of relapse. 2. The Prince of Wales tells the Irish deputation, he will give them a definitive answer in some days; but if the King had been well, he could have given it at once. 3. They talk of passing a standing law, for providing a regency in similar cases. They apprehend then, they are not yet clear of the danger of wanting a regency.
4. They have carried the King to church; but it was his private chapel. If he be well, why do not they show him publicly to the nation, and raise them from that consternation into which they have been thrown, by the prospect of being delivered over to the profligate hands of the Prince of Wales. In short, judging from little facts, which are known in spite of their teeth, the King is better, but not well. Possibly he is getting well, but still time will be wanting to satisfy even the ministry, that it is not merely a lucid interval. Consequently, they cannot interrupt France this year in the settlement of her affairs, and after this year it will be too late.
As you will be in a situation to know when the leave of absence will be granted me, which I have asked, will you be so good as to communicate it, by a line, to Mr. Lewis and Mr. Eppes? I hope to see you in the summer, and that if you are not otherwise engaged, you will encamp with me at Monticello for a while.
I am, with great and sincere attachment, Dear Sir, your affectionate friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
Paris, March 17,1789.
Dear Sir,
My last letter to you extended from December the 23rd to January the 11th. A confidential opportunity now arising, I can acknowledge the receipt of yours of January the 15th, at the date of which you could not have received mine.
You knew, long ago, that the meeting of the States is to be at Versailles, on the 27th of April. This country is entirely occupied in its elections, which go on quietly and well. The Duke d’Orleans is elected for Villers Cotterets. The Prince of Conde has lost the election he aimed at; nor is it certain he can be elected any where. We have no news from Auvergne, whither the Marquis de la Fayette is gone. In general, all the men of influence in the country are gone into the several provinces, to get their friends elected, or be elected themselves. Since my letter to you, a tumult arose in Bretagne, in which four or five lives were lost. They are now quieter, and this is the only instance of a life lost, as yet, in this revolution. The public mind is now so far ripened by time and discussion, that there seems to be but one opinion on the principal points. The question of voting by persons or orders is the most controverted; but even that seems to have gained already a majority among the Nobles. I fear more from the number of the Assembly, than from any other cause. Twelve hundred persons are difficult to keep to order, and will be so, especially, till they shall have had time to frame rules of order. Their funds continue stationary, and at the level they have stood at for some years past. We hear so little of the parliaments for some time past, that one is hardly sensible of their existence. This unimportance is probably the forerunner of their total re-modification by the nation. The article of legislation is the only interesting one on which the court has not explicitly declared itself to the nation. The Duke d’Orleans has given instructions to his proxies in the bailliages, which would be deemed bold in England, and are reasonable beyond the reach of an Englishman, who, slumbering under a kind of half reformation in politics and religion, is not excited by any thing he sees or feels, to question the remains of prejudice. The writers of this country, now taking the field freely, and unrestrained, or rather revolted by prejudice, will rouse us all from the errors in which we have been hitherto rocked.
We had, at one time, some hope, that an accommodation would have been effected between the Turks and two empires. Probably the taking Oczakow, while it has attached the Empress more to the Crimea, is not important enough to the Turks, to make them consent to peace. These hopes are vanishing. Nor does there seem any prospect of peace between Russia and Sweden. The palsied condition of England leaves it probable, that Denmark will pursue its hostilities against Sweden. It does not seem certain whether the King of Prussia has advanced so far in that mediation, and in the troubles he has excited in Poland, as to be obliged to become a party. Nor will his becoming a party draw in this country, the present year, if England remains quiet. Papers which have lately passed between this court and the government of Holland, prove that this nourishes its discontent, and only waits to put its house in order, before it interposes. They have recalled their ambassador from the Hague, without naming a successor. The King of Sweden, not thinking that Russia and Denmark are enough for him, has arrested a number of his Nobles, of principal rank and influence. It is a bold measure, at least, and he is too boyish a character to authorize us to presume it a wise one, merely because he has adopted it. His army was before disgusted. He now puts the Nobles and all their dependants on the same side, and they are sure of armed support, by Russia on the north, and Denmark on the south. He can have no salvation but in the King of Prussia.
I have received two letters from Ledyard, the one dated Alexandria, August the 15th, the other Grand Cairo, September the 10th; and one lately from Admiral Paul Jones, dated St. Petersburg, January the 31st. He was just arrived there, on the call of the Empress, and was uncertain where he should be employed the next campaign. Mr. Littlepage has returned from the Black Sea to Warsaw, where he has been perfectly received by the King. I saw this from under the King’s own hand, and was pleased with the parental expressions towards him.
We have no news from America later than the middle of January. My letters inform me, that even the friends of the new constitution have come over to the expediency of adding a declaration of rights. There is reason to hope that this will be proposed by Congress to the several legislatures, and that the plan of New York for calling a new convention, will be rejected. Hitherto, no State had acceded to it but Virginia, in which Henry and anti-federalism had got full possession of their legislature. But the people are better disposed. My departure for America is likely to be retarded, by the want of a Congress to give me permission. I must attend it from the new government. I am anxious to know how much we ought to believe of the recovery of the King of England. By putting little facts together, I see that he is not well. Mr. Rumsey (who came in while I was writing the preceding page) tells me you have a long letter ready for me. I shall be happy to receive it.
I am, with great and sincere attachment, Dear Sir, your affectionate friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO COLONEL HUMPHREYS.
Paris, March 18, 1789.
Dear Sir,
Your favor of November the 29th, 1788, came to hand the last month. How it happened that mine of August, 1787, was fourteen months on its way, is inconceivable. I do not recollect by what conveyance I sent it. I had concluded, however, either that it had miscarried, or that you had become indolent, as most of our countrymen are, in matters of correspondence.
The change in this country since you left it, is such as you can form no idea of. The frivolities of conversation have given way entirely to politics. Men, women, and children talk nothing else: and all, you know, talk a great deal. The press groans with daily productions, which, in point of boldness, make an Englishman stare, who hitherto has thought himself the boldest of men. A complete revolution in this government, has, within the space of two years (for it began with the Notables of 1787), been effected merely by the force of public opinion, aided, indeed, by the want of money, which the dissipations of the court had brought on. And this revolution has not cost a single life, unless we charge to it a little riot lately in Bretagne, which began about the price of bread, became afterwards political, and ended in the loss of four or five lives. The assembly of the States General begins the 27th of April. The representation of the people will be perfect. But they will be alloyed by an equal number of nobility and clergy. The first great question they will have to decide, will be, whether they shall vote by orders or persons. And I have hopes, that the majority of the Nobles are already disposed to join the Tiers-Etat, in deciding that the vote shall be by persons. This is the opinion a la mode at present, and mode has acted a wonderful part in the present instance. All the handsome young women, for example, are for the Tiers-Etat and this is an army more powerful in France, than the two hundred thousand men of the King. Add to this, that the court itself is for the Tiers-Etat, as the only agent which can relieve their wants: not by giving money themselves (they are squeezed to the last drop), but by pressing it from the non-contributing orders. The King stands engaged to pretend no more to the power of laying, continuing, or appropriating taxes; to call the States General periodically; to submit lettres de cachet to legal restrictions; to consent to freedom of the press; and that all this shall be fixed by a fundamental constitution, which shall bind his successors. He has not offered a participation in the legislature, but it will surely be insisted on. The public mind is so ripened on all these subjects, that there seems to be now but one opinion. The clergy, indeed, think separately, and the old men among the Nobles: but their voice is suppressed by the general one of the nation. The writings published on this occasion are, some of them, very valuable; because, unfettered by the prejudices under which the English labor, they give a full scope to reason, and strike out truths, as yet unperceived and unacknowledged on the other side the channel. An Englishman, dozing under a kind of half reformation, is not excited to think by such gross absurdities as stare a Frenchman in the face, wherever he looks, whether it be towards the throne or the altar. In fine, I believe this nation will, in the course of the present year, have as full a portion of liberty dealt out to them, as the nation can bear at present, considering how uninformed the mass of their people is. This circumstance will prevent the immediate establishment of the trial by jury. The palsied state of the executive in England is a fortunate circumstance for France, as it will give her time to arrange her affairs internally. The consolidation and funding their debts, will give government a credit which will enable them to do what they please. For the present year the war will be confined to the two empires and Denmark, against Turkey and Sweden. It is not yet evident, whether Prussia will be engaged. If the disturbances of Poland break out into overt acts, it will be a power divided in itself, and so of no weight. Perhaps by the next year England and France may be ready to take the field. It will depend on the former principally, for the latter, though she may be then able, must wish still a little time to see her new arrangements well under way. The English papers and English ministry say the King is well. He is better, but not well: no malady requires a longer time to insure against its return than insanity. Time alone can distinguish accidental insanity from habitual lunacy.
The operations which have taken place in America lately fill me with pleasure. In the first place, they realize the confidence I had, that, whenever our affairs go obviously wrong, the good sense of the people will interpose, and set them to rights. The example of changing a constitution, by assembling the wise men of the State, instead of assembling armies, will be worth as much to the world as the former examples we had given them. The constitution, too, which was the result of our deliberations, is unquestionably the wisest ever yet presented to men, and some of the accommodations of interest which it has adopted are greatly pleasing to me, who have before had occasions of seeing how difficult those interests were to accommodate. A general concurrence of opinion seems to authorize us to say it has some defects. I am one of those who think it a defect, that the important rights, not placed in security by the frame of the constitution itself, were not explicitly secured by a supplementary declaration. There are rights which it is useless to surrender to the government, and which governments have yet always been fond to invade. These are the rights of thinking, and publishing our thoughts by speaking or writing; the right of free commerce; the right of personal freedom. There are instruments for administering the government so peculiarly trust-worthy, that we should never leave the legislature at liberty to change them. The new constitution has secured these in the executive and legislative departments; but not in the judiciary. It should have established trials by the people themselves, that is to say, by jury. There are instruments so dangerous to the rights of the nation, and which place them so totally at the mercy of their governors, that those governors, whether legislative or executive, should be restrained from keeping such instruments on foot, but in well defined cases. Such an instrument is a standing army. We are now allowed to say, such a declaration of rights, as a supplement to the constitution, where that is silent, is wanting, to secure us in these points. The general voice has legitimated this objection. It has not, however, authorized me to consider as a real defect, what I thought, and still think one, the perpetual re-eligibility of the President. But three States out of eleven having declared against this, we must suppose we are wrong, according to the fundamental law of every society, the lex majoris partis, to which we are bound to submit. And should the majority change their opinion, and become sensible that this trait in their constitution is wrong, I would wish it to remain uncorrected, as long as we can avail ourselves of the services of our great leader, whose talents and whose weight of character, I consider as peculiarly necessary to get the government so under way, as that it may afterwards be carried on by subordinate characters.
I must give you sincere thanks for the details of small news contained in your letter. You know how previous that kind of information is to a person absent from his country, and how difficult it is to be procured. I hope to receive soon permission to visit America this summer, and to possess myself anew, by conversation with my countrymen, of their spirit and their ideas. I know only the Americans of the year 1784. They tell me this is to be much a stranger to those of 1789. This renewal of acquaintance is no indifferent matter to one, acting at such a distance, as that instructions cannot be received hot and hot. One of my pleasures, too, will be that of talking over the old and new with you.
In the mean time, and at all times, I have the honor to be, with great and sincere esteem. Dear Sir, your friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson,
TO DOCTOR WILLARD.
Paris, March 24, 1789.
Sir,
I have been lately honored with your letter of September the 24th, 1788, accompanied by a diploma for a Doctorate of Laws, which the University of Harvard has been pleased to confer on me. Conscious how little I merit it, I am the more sensible of their goodness and indulgence to a stranger, who has had no means ef serving or making himself known to them. I beg you to return them my grateful thanks, and to assure them that this notice from so eminent a seat of science is very precious to me.
The most remarkable publications we have had in France, for a year or two past, are the following. Les Voyages d’Anacharsis, par Abbe Barthelemi, seven volumes, octavo. This is a very elegant digest of whatever is known of the Greeks; useless, indeed, to him who has read the original authors, but very proper for one who reads modern languages only. The works of the King of Prussia. The Berlin edition is in sixteen volumes, octavo. It is said to have been gutted at Berlin; and here it has been still more mangled. There are one or two other editions published abroad, which pretend to have rectified the maltreatment both of Berlin and Paris. Some time will be necessary to settle the public mind as to the best edition.
Montignot has given us the original Greek, and a French translation of the seventh book of Ptolemy’s great work, under the title of Etat des Etoiles fixes au second siecle, in quarto. He has given the designation of the same stars by Flamsteed and Bayer, and their position in the year 1786. A very remarkable work is the Mechanique Analytique of La Grange, in quarto. He is allowed to be the greatest mathematician now living, and his personal worth is equal to his science. The object of his work is to reduce all the principles of mechanics to the single one of the equilibrium, and to give a simple formula applicable to them all. The subject is treated in the algebraic method, without diagrams to assist the conception. My present occupations not permitting me to read any thing which requires a long and undisturbed attention, I am not able to give you the character of this work from my own examination. It has been received with great approbation in Europe. In Italy, the works of Spallanzani on Digestion and Generation are valuable. Though, perhaps, too minute, and therefore tedious, he has developed some useful truths, and his book is well worth attention; it is in four volumes, octavo. Clavigero, an Italian also, who has resided thirty-six years in Mexico, has given us a History of that country, which certainly merits more respect than any other work on the same subject. He corrects many errors of Dr. Robertson; and though sound philosophy will disapprove many of his ideas, we must still consider it as an useful work, and assuredly the best we possess on the same subject. It is in four thin volumes, small quarto. De la Lande has not yet published a fifth volume.
The chemical dispute about the conversion and reconversion of air and water, continues still undecided. Arguments and authorities are so balanced, that we may still safely believe, as our fathers did before us, that these principles are distinct. A schism of another kind has taken place among the chemists. A particular set of them here have undertaken to remodel all the terms of the science, and to give to every substance a new name, the composition, and especially the termination of which, shall define the relation in which it stands to other substances of the same family. But the science seems too much in its infancy as yet, for this reformation; because, in fact, the reformation of this year must be reformed again the next year, and so on, changing the names of substances as often as new experiments develope properties in them undiscovered before. The new nomenclature has, accordingly, been already proved to need numerous and important reformations. Probably it will not prevail. It is espoused by the minority only here, and by very few, indeed, of the foreign chemists. It is particularly rejected in England.
In the arts, I think two of our countrymen have presented the most important inventions. Mr. Paine, the author of ‘Common Sense,’ has invented an iron bridge, which promises to be cheaper by a great deal than stone, and to admit of a much greater arch. He supposes it may be ventured for an arch of five hundred feet. He has obtained a patent for it in England, and is now executing the first experiment with an arch of between ninety and one hundred feet. Mr. Rumsey has also obtained a patent for his navigation by the force of steam in England, and is soliciting a similar one here. His principal merit is in the improvement of the boiler, and instead of the complicated machinery of oars and paddles, proposed by others, the substitution of so simple a thing as the reaction of a stream of water on his vessel. He is building a sea-vessel at this time in England, and she will be ready for an experiment in May. He has suggested a great number of mechanical improvements in a variety of branches, and, upon the whole, is the most original and the greatest mechanical genius I have ever seen. The return of La Peyrouse (whenever that shall happen) will probably add to our knowledge in Geography, Botany, and Natural History. What a field have we at our doors to signalize ourselves in! The Botany of America is far from being exhausted, its Mineralogy is untouched, and its Natural History or Zoology totally mistaken and misrepresented. As far as I have seen, there is not one single species of terrestrial birds common to Europe and America, and I question if there be a single species of quadrupeds. (Domestic animals are to be excepted.) It is for such institutions as that over which you preside so worthily, Sir, to do justice to our country, its productions, and its genius. It is the work to which the young men, whom you are forming, should lay their hands. We have spent the prime of our lives in procuring them the precious blessing of liberty. Let them spend theirs in showing that it is the great parent of science and of virtue; and that a nation will be great in both, always in proportion as it is free. Nobody wishes more warmly for the success of your good exhortations on this subject, than he who has the honor to be, with sentiments of great esteem and respect, Sir, your most obedient, humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO J. SARSFIELD.
Paris, April 3, 1789.
Sir,
I could not name to you the day of my departure from Paris, because I do not know it. I have not yet received my congé, though I hope to receive it soon, and to leave this some time in May, so that I may be back before the winter.
Impost is a duty paid on any imported article, in the moment of its importation, and of course, it is collected in the sea-ports only. Excise is a duty on any article, whether imported or raised at home, and paid in the hands of the consumer or retailer; consequently, it is collected through the whole country. These are the true definitions of these words as used in England, and in the greater part of the United States. But in Massachusetts, they have perverted the word excise to mean a tax on all liquors, whether paid in the moment of importation or at a later moment, and on nothing else. So that in reading the debates of the Massachusetts convention, you must give this last meaning to the word excise.
Rotation is the change of officers required by the laws at certain epochs, and in a certain order: thus, in Virginia, our justices of the peace are made sheriffs one after the other, each remaining in office two years, and then yielding it to his next brother in order of seniority. This is the just and classical meaning of the word. But in America we have extended it (for want of a proper word) to all cases of officers who must be necessarily changed at a fixed epoch, though the successor be not pointed out in any particular order, but comes in by free election. By the term rotation in office, then, we mean an obligation on the holder of that office to go out at a certain period. In our first Confederation, the principle of rotation was established in the office of President of Congress, who could serve but one year in three, and in that of a member of Congress, who could serve but three years in six.
I believe all the countries in Europe determine their standard of money, in gold as well as silver. Thus, the laws of England direct that a pound Troy of gold, of twenty-two carats fine, shall be cut into forty-four and a half guineas, each of which shall be worth twenty-one and a half shillings, that is, into 956 3/4 shillings. This establishes the shilling at 5.518 grains of pure gold. They direct that a pound of silver, consisting of 11 1/10 ounces of pure silver, and 9/10 of an ounce alloy, shall be cut into sixty-two shillings. This establishes the shilling at 85.93 grains of pure silver, and, consequently, the proportion of gold to silver as 85.93 to 5.518, or as 15.57 to 1. If this be the true proportion between the value of gold and silver at the general market of Europe, then the value of the shilling, depending on two standards, is the same, whether a payment be made in gold or in silver. But if the proportion at the general market of Europe be as fifteen to one, then the Englishman who owes a pound weight of gold at Amsterdam, if he sends the pound of gold to pay it, sends 1043.72 shillings; if he sends fifteen pounds of silver, he sends only 1030.5 shillings; if he pays half in gold and half in silver, he pays only 1037.11 shillings. And this medium between the two standards of gold and silver, we must consider as furnishing the true medium value of the shilling. If the parliament should now order the pound of gold (of one-twelfth alloy as before) to be cut into a thousand shillings instead of nine hundred and fifty-six and three fourths, leaving the silver as it is, the medium or true value of the shilling would suffer a change of half the difference; and in the case before stated, to pay a debt of a pound weight of gold, at Amsterdam, if he sent the pound weight of gold, he would send 1090.9 shillings; if he sent fifteen pounds of silver, he would send 1030.5 shillings; if half in gold and half in silver, he would send 1060.7 shillings; which shows, that this parliamentary operation would reduce the value of the shilling in the proportion of 1060.7 to 1037.11.
Now this is exactly the effect of the late change in the quantity of gold contained in your louis. Your marc d’argent fin is cut into 53.45 livres (fifty-three livres and nine sous), the marc de l’or fin was cut, heretofore, by law, into 784.6 livres (seven hundred and eighty-four livres and twelve sous); gold was to silver, then, as 14.63 to 1. And if this was different from the proportion at the markets of Europe, the true value of your livre stood half way between the two standards. By the ordinance of October the 30th, 1785, the marc of pure gold has been cut into 828.6 livres. If your standard had been in gold alone, this would have reduced the value of the livre, in the proportion of 828.6 to 784.6. But as you had a standard of silver as well as gold, the true standard is the medium between the two; consequently, the value of the livre is reduced only one half the difference, that is, as 806.6 to 784.6, which is very nearly three per cent. Commerce, however, has made a difference of four per cent., the average value of the pound sterling, formerly twenty-four livres, being now twenty-five livres. Perhaps some other circumstance has occasioned an addition of one per cent, to the change of your standard.
I fear I have tired you by these details. I did not mean to be so lengthy when I began. I beg you to consider them as an appeal to your judgment, which I value, and from which I will expect a correction, if they are wrong.
I have the honor to be, with very great esteem and attachment, Dear Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO THE MARQUIS DE LA FAYETTE.
Paris, May 6,1789.
My Dear Friend,
As it becomes more and more possible that the Noblesse will go wrong, I become uneasy for you. Your principles are decidedly with the Tiers-Etat, and your instructions against them. A complaisance to the latter on some occasions, and an adherence to the former on others, may give an appearance of trimming between the two parties, which may lose you both. You will, in the end, go over wholly to the Tiers-Etat, because it will be impossible for you to live in a constant sacrifice of your own sentiments to the prejudices of the Noblesse. But you would be received by the Tiers-Etat, at any future day, coldly, and without confidence. This appears to me the moment to take at once that honest and manly stand with them, which your own principles dictate. This will win their hearts for ever, be approved by the world, which marks and honors you as the man of the people, and will be an eternal consolation to yourself. The Noblesse, and especially the Noblesse of Auvergne, will always prefer men who will do their dirty work for them. You are not made for that. They will therefore soon drop you, and the people, in that case, will perhaps not take you up. Suppose a scission should take place. The Priests and Nobles will secede, the nation will remain in place, and, with the King, will do its own business. If violence should be attempted, where will you be? You cannot then take side with the people in opposition to your own vote, that very vote which will have helped to produce the scission. Still less can you array yourself against the people. That is impossible. Your instructions are indeed a difficulty. But to state this at its worst, it is only a single difficulty, which a single effort surmounts. Your instructions can never embarrass you a second time, whereas an acquiescence under them will re-produce greater difficulties every day, and without end. Besides, a thousand circumstances offer as many justifications of your departure from your instructions. Will it be impossible to persuade all parties, that (as for good legislation two Houses are necessary) the placing the privileged classes together in one House, and the unprivileged in another, would be better for both than a scission? I own I think it would. People can never agree without some sacrifices; and it appears but a moderate sacrifice in each party, to meet on this middle ground. The attempt to bring this about might satisfy your instructions, and a failure in it would justify your siding with the people, even to those who think instructions are laws of conduct. Forgive me, my dear friend, if my anxiety for you makes me talk of things I know nothing about. You must not consider this as advice. I know you and myself too well to presume to offer advice. Receive it merely as the expression of my uneasiness, and the effusion of that sincere friendship, with which I am, my dear Sir, yours affectionately,
Th: Jefferson.
TO WILLIAM CARMICHAEL.
Paris, May 8, 1789.
Dear Sir,
Your favor of January the 26th, to March the 27th, is duly received, and I thank you for the interesting papers it contained. The answer of Don Ulloa, however, on the subject of the canal through the American isthmus, was not among them, though mentioned to be so. If you have omitted it through accident, I shall thank you for it at some future occasion, as I wish much to understand that subject thoroughly. Our American information comes down to the 16th of March. There had not yet been members enough assembled of the new Congress, to open the tickets. They expected to do it in a day or two. In the mean time, it was said from all the States, that their vote had been unanimous for General Washington, and a good majority in favor of Mr. Adams, who is certainly, therefore, Vice-President. The new government would be supported by very cordial and very general dispositions in its favor from the people. I have not yet seen a list of the new Congress. This delay in the meeting of the new government has delayed the determination on my petition for leave of absence. However, I expect to receive it every day, and am in readiness to sail the instant I receive it, so that this is probably the last letter I shall write you hence, till my return. While there, I shall avail government of the useful information I have received from you, and shall not fail to profit of any good occasion which may occur, to show the difference between your real situation, and what it ought to be. I consider Paris and Madrid as the two only points, at which Europe and America should touch closely, and that a connection at these points should be fostered.
We have had in this city a very considerable riot, in which about one hundred people have been probably killed. It was the most unprovoked, and is therefore, justly, the most unpitied catastrophe of that kind I ever knew. Nor did the wretches know what they wanted, except to do mischief. It seems to have had no particular connection with the great national question now in agitation. The want of bread is very seriously dreaded through the whole kingdom. Between twenty and thirty ship-loads of wheat and flour has already arrived from the United States, and there will be about the same quantity of rice sent from Charleston to this country directly, of which about half has arrived. I presume that, between wheat and rice, one hundred ship-loads may be counted on in the whole from us. Paris consumes about a ship-load a day, (say two hundred and fifty tons.) The total supply of the West Indies, for this year, rests with us, and there is almost a famine in Canada and Nova Scotia. The States General were opened the day before yesterday. Viewing it as an opera, it was imposing; as a scene of business, the King’s speech was exactly what it should have been, and very well delivered; not a word of the Chancellor’s was heard by any body, so that, as yet, I have never heard a single guess at what it was about. Mr. Necker’s was as good as such a number of details would permit it to be. The picture of their resources was consoling, and generally plausible. I could have wished him to have dwelt more on those great constitutional reformations, which his Rapport au Roy had prepared us to expect. But they observe, that these points are proper for the speech of the Chancellor. We are in hopes, therefore, they were in that speech, which, like the Revelations of St. John, were no revelations at all. The Noblesse, on coming together, show that they are not as much reformed in their principles as we had hoped they would be. In fact, there is real danger of their totally refusing to vote by persons. Some found hopes on the lower clergy, which constitute four-fifths of the deputies of that order. If they do not turn the balance in favor of the Tiers-Etat, there is real danger of a scission. But I shall not consider even that event as rendering things desperate. If the King will do business with the Tiers-Etat, which constitutes the nation, it may be well done without Priests or Nobles. From the best information I can obtain, the King of England’s madness has terminated in an imbecility, which may very possibly be of long continuance. He is going with his Queen to Germany. England chained to rest, the other parts of Europe may recover or retain tranquillity.
I have the honor to be, with great and sincere esteem, Dear Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson..
TO JOHN JAY.
Paris, May 9, 1789.
Sir,
Since my letter of March the 1st, by the way of Havre, and those of March the 12th and 15th, by the way of London, no opportunity of writing has occurred, till the present to London.
There are no symptoms of accommodation between the Turks and two empires, nor between Russia and Sweden. The Emperor was, on the 16th of the last month, expected to die, certainly; he was, however, a little better when the last news came away, so that hopes were entertained of him; but it is agreed that he cannot get the better of his complaints ultimately, so that his life is not at all counted on. The Danes profess, as yet, to do no more against Sweden than furnish their stipulated aid. The agitation of Poland is still violent, though somewhat moderated by the late change in the demeanor of the King of Prussia. He is much less thrasonic than he was. This is imputed to the turn which the English politics may be rationally expected to take. It is very difficult to get at the true state of the British King j but from the best information we can get, his madness has gone off, but he is left in a state of imbecility and melancholy. They are going to carry him to Hanover, to see whether such a journey may relieve him. The Queen accompanies him. If England. should, by this accident, be reduced to inactivity, the southern countries of Europe may escape the present war. Upon the whole, the prospect for the present year, if no unforeseen accident happens, is certain peace for the powers not already engaged, a probability that Denmark will not become a principal, and a mere possibility that Sweden and Russia may be accommodated. The interior disputes of Sweden are so exactly detailed in the Leyden gazette, that I have nothing to add on that subject.
The revolution of this country has advanced thus far without encountering any thing which deserves to be called a difficulty. There have been riots in a few instances, in three or four different places, in which there may have been a dozen or twenty lives lost. The exact truth is not be got at. A few days ago, a much more serious riot took place in this city, in which it became necessary for the troops to engage in regular action with the mob, and probably about one hundred of the latter were killed. Accounts vary from twenty to two hundred. They were the most abandoned banditti of Paris, and never was a riot more unprovoked and unpitied. They began, under a pretence that a paper manufacturer had proposed in an assembly, to reduce their wages to fifteen sous a day. They rifled his house, destroyed every thing in his magazines and shops, and were only stopped in their career of mischief, by the carnage above mentioned. Neither this nor any other of the riots, have had a professed connection with the great national reformation going on. They are such as have happened every year since I have been here, and as will continue to be produced by common incidents. The States General were opened on the 4th instant, by a speech from the throne, one by the Garde des Sceaux, and one from Mr. Necker. I hope they will be printed in time to send you herewith: lest they should not, I will observe, that that of Mr, Necker stated the real and ordinary deficit to be fifty-six millions, and that he showed that this could be made up without a new tax, by economies and bonifications which he specified. Several articles of the latter are liable to the objection, that they are proposed on branches of the revenue, of which the nation has demanded a suppression. He tripped too lightly over the great articles of constitutional reformation, these being not as clearly announced in this discourse as they were in his Rapport au Roy, which I sent you some time ago. On the whole, his discourse has not satisfied the patriotic party. It is now, for the first time, that their revolution is likely to receive a serious check, and begins to wear a fearful appearance. The progress of light and liberality in the order of the Noblesse has equalled expectation in Paris only, and its vicinities. The great mass of deputies of that order, which come from the country, show that the habits of tyranny over the people, are deeply rooted in them. They will consent, indeed, to equal taxation; but five-sixths of that chamber are thought to be, decidedly, for voting by orders; so that, had this great preliminary question rested on this body, which formed heretofore the sole hope, that hope would have been completely disappointed. Some aid, however, comes in from a quarter whence none was expected. It was imagined the ecclesiastical elections would have been generally in favor of the higher clergy; on the contrary, the lower clergy have obtained five-sixths of these deputations. These are the sons of peasants, who have done all the drudgery of the service, for ten, twenty, and thirty guineas a year, and whose oppressions and penury, contrasted with the pride and luxury of the higher clergy, have rendered them perfectly disposed to humble the latter. They have done it, in many instances, with a boldness they were thought insusceptible of. Great hopes have been formed, that these would concur with the Tiers-Etat, in voting by persons. In fact, about half of them seem as yet so disposed; but the bishops are intriguing, and drawing them over with the address which has ever marked ecclesiastical intrigue. The deputies of the Tiers-Etat seem, almost to a man, inflexibly determined against the vote by orders. This is the state of parties, as well as can be judged from conversation only, during the fortnight they have been now together. But as no business has been yet begun, no votes as yet taken, this calculation cannot be considered as sure. A middle proposition is talked of, to form the two privileged orders into one chamber. It is thought more possible to bring them into it, than the Tiers-Etat. Another proposition is, to distinguish questions, referring those of certain descriptions to a vote by persons, others to a vote by orders. This seems to admit of endless altercation, and the Tiers-Etat manifest no respect for that, or any other modification whatever. Were this single question accommodated, I am of opinion, there would not occur the least difficulty in the great and essential points of constitutional reformation. But on this preliminary question the parties are so irreconcilable, that it is impossible to foresee what issue it will have. The Tiers-Etat, as constituting the nation, may propose to do the business of the nation, either with or without the minorities in the Houses of Clergy and Nobles, which side with them. In that case, if the King should agree to it, the majorities in those two Houses would secede, and might resist the tax-gatherers. This would bring on a civil war. On the other hand, the privileged orders, offering to submit to equal taxation, may propose to the King to continue the government in its former train, resuming to himself the power of taxation. Here, the tax-gatherers might be resisted by the people. In fine, it is but too possible, that between parties so animated, the King may incline the balance as he pleases. Happy that he is an honest, unambitious man, who desires neither money nor power for himself; and that his most operative minister, though he has appeared to trim a little, is still, in the main, a friend to public liberty.
I mentioned to you in a former letter, the construction which our bankers at Amsterdam had put on the resolution of Congress, appropriating the last Dutch loan, by which the money for our captives would not be furnished till the end of the year 1790. Orders from the board of treasury have now settled this question. The interest of the next month is to be first paid, and after that, the money for the captives and foreign officers is to be furnished, before any other payment of interest. This insures it when the next February interest becomes payable. My representations to them, on account of the contracts I had entered into for making the medals, have produced from them the money for that object, which is lodged in the hands of Mr. Grand.
Mr. Necker, in his discourse, proposes among his bonifications of revenue, the suppression of our two free ports of Bayonne and L’Orient, which, he says, occasion a loss of six hundred thousand livres annually, to the crown, by contraband. (The speech being not yet printed, I state this only as it struck my ear when he delivered it. If I have mistaken it, I beg you to receive this as my apology, and to consider what follows, as written on that idea only.) I have never been able to see that these free ports were worth one copper to us. To Bayonne our trade never went, and it is leaving L’Orient. Besides, the right of entrepot is a perfect substitute for the right of free port. The latter is a little less troublesome only, to the merchants and captains. I should think, therefore, that a thing so useless to us and prejudicial to them might be relinquished by us, on the common principles of friendship. I know the merchants of these ports will make a clamor, because the franchise covers their contraband with all the world. Has Monsieur de Moustier said any thing to you on this subject? It has never been mentioned to me. If not mentioned in either way, it is rather an indecent proceeding, considering that this right of free port is founded in treaty. I shall ask of M. de Montmorin, on the first occasion, whether he has communicated this to you through his minister; and if he has not, I will endeavor to notice the infraction to him in such manner, as neither to reclaim nor abandon the right of free port, but leave our government free to do either.
The gazettes of France and Leyden, as usual, will accompany this. I am in hourly expectation of receiving from you my leave of absence, and keep my affairs so arranged, that I can leave Paris within eight days after receiving the permission.
I have the honor to be, with sentiments of the most perfect esteem and respect, Sir, your most obedient and most humble
servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO GENERAL WASHINGTON.
Paris, May 10, 1780,
Sir,
I am now to acknowledge, the honor of your two letters of November the 27th and February the 13th, both of which have come to hand since my last to you of December the 4th and 5th. The details you are so good as to give me on the subject of the navigation of the waters of the Potomac and Ohio, are very pleasing to me, as I consider the union of those two rivers, as among the strongest Blinks of connection between the eastern and western sides of our confederacy. It will, moreover, add to the commerce of Virginia, in particular, all the upper parts of the Ohio and its waters. Another vast object, and of much less difficulty, is to add also, all the country on the lakes and their waters. This would enlarge our field immensely, and would certainly be effected by an union of the upper waters of the Ohio and lake Erie. The Big Beaver and Cayahoga offer the most direct line, and according to information I received from General Hand, and which I had the honor of writing you in the year 1783, the streams in that neighborhood head in lagoons, and the country is flat. With respect to the doubts which you say are entertained by some, whether the upper waters of Potomac can be rendered capable of navigation, on account of the falls and rugged banks, they are answered, by observing, that it is reduced to a maxim, that whenever there is water enough to float a batteau, there may be navigation for a batteau. Canals and locks may be necessary, and they are expensive; but I hardly know what expense would be too great for the object in question. Probably, negotiation with the Indians, perhaps even settlement, must precede the execution of the Cayahoga canal. The States of Maryland and Virginia should make a common object of it. The navigation, again, between Elizabeth River and the Sound is of vast importance, and in my opinion, it is much better that these should be done at public than private expense.
Though we have not heard of the actual opening of the new Congress, and consequently, have not official information of your election as President of the United States, yet, as there never could be a doubt entertained of it, permit me to express here my felicitations, not to yourself, but to my country. Nobody who has tried both public and private life, can doubt but that you were much happier on the banks of the Potomac than you will be at New York. But there was nobody so well qualified as yourself, to put our new machine into a regular course of action; nobody, the authority of whose name could have so effectually crushed opposition at home, and produced respect abroad. I am sensible of the immensity of the sacrifice on your part. Your measure of fame was full to the brim; and therefore, you have nothing to gain. But there are cases wherein it is a duty to risk all against nothing, and I believe this was exactly the case. We may presume, too, according to every rule of probability, that after doing a great deal of good, you will be found to have lost nothing but private repose.
In a letter to Mr. Jay, of the 19th of November, I asked a leave of absence to carry my children back to their own country, and to settle various matters of a private nature, which were left unsettled, because I had no idea of being absent so long. I expected that letter would have been received in time to be decided on by the government then existing. I know now that it would arrive when there was no Congress, and consequently, that if must have awaited your arrival at New York. I hope you found the request not an unreasonable one. I am excessively anxious to receive the permission without delay, that I may be able to get back before the winter sets in. Nothing can be so dreadful to me, as to be shivering at sea for two or three months, in a winter passage. Besides, there has never been a moment at which the presence of a minister here could be so well dispensed with, from certainty of no war this summer, and that the government will be so totally absorbed in domestic arrangements, as to attend to nothing exterior. Mr. Jay will, of course, communicate to you some ciphered letters lately written, and one of this date. My public letter to him contains all the interesting public details. I enclose with the present, some extracts of a letter from Mr. Paine, which he desired me to communicate: your knowledge of the writer will justify my giving you the trouble of these communications, which their interesting nature and his respectability will jointly recommend to notice. I am in great pain for the Marquis de la Fayette. His principles, you know, are clearly with the people; but having been elected for the Noblesse of Auvergne, they have laid him under express instructions to vote for the decision by orders and not persons. This would ruin him with the Tiers-Etat, and it is not possible he could continue long to give satisfaction to the Noblesse. I have not hesitated to press on him to burn his instructions, and follow his conscience as the only sure clue, which will eternally guide a man clear of all doubts and inconsistencies. If he cannot effect a conciliatory plan, he will surely take his stand manfully at once with the Tiers-Etat. He will in that case be what he pleases with them, and I am in hopes that base is now too solid to render it dangerous to be mounted on it. In hopes of being able, in the course of the summer, to pay my respects to you personally in New York, I have the honor to be, with sentiments of the most perfect respect and attachment, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
[Extract of the letter from Thomas Paine, referred to in the
preceding, to General Washington.]
‘London, March the 12th, 1789. I do not think it is worth while for Congress to appoint any minister at this court. The greater distance Congress observes on this point, the better. It will be all money thrown away to go to any expense about it, at least during the present reign. I know the nation well, and the line of acquaintance I am in enables me to judge better on this matter than any other American can judge, especially at a distance. I believe I am not so much in the good graces of the Marquis of Lansdowne as I used to be. I do not answer his purpose. He was always talking of a sort of re-connection of England and America, and my coldness and reserve on this subject checked communication. I believe he would be a good minister for England, with respect to a better agreement with France.’
(Same letter continued) ‘April 10. The acts for regulating the trade with America are to be continued as last year. A paper from the Privy Council respecting the American fly is before parliament. I had some conversation with Sir Joseph Banks upon this subject, as he was the person whom the Privy Council referred to. I told him that the Hessian fly attacked only the green plant, and did not exist in the dry grain. He said, that with respect to the Hessian fly they had no apprehension, but it was the weevil they alluded to. I told him the weevil had always, more or less, been in the wheat countries of America, and that if the prohibition was on that account, it was as necessary fifty or sixty years ago as now; that I believed it was only a political manoeuvre of the ministry to please the landed interest, as a balance for prohibiting the exportation of wool, to please the manufacturing interest. He did not reply, and as we are on very sociable terms, I went farther, by saying, the English ought not to complain of the non-payment of debts from America, while they prohibit the means of payment. I suggest to you a thought on this subject.
The debts due before the war ought to be distinguished from the debts contracted since, and all and every mode of payment and remittance under which they might have been discharged at the time they were contracted, ought to accompany those debts so long as any of them shall continue unpaid, because the circumstances of payment became united with the debt, and cannot be separated by subsequent acts of one side only. If this was taken up in America, and insisted on as a right coeval with, and inseparable from those debts, it would force some of the restrictions here to give way. While writing this, I am informed that the minister has had a conference with some of the American creditors, and proposed to them to assume the debts, and give them ten shillings in the pound. The conjecture is, that he means, when the new Congress is established, to demand the payment. If you are writing to General Washington, it may not be amiss to mention this, and if I hear further on this matter, I will inform you. But as, being a money matter, it cannot come forward but through parliament; there will be notice given of the business. This would be a proper time to show that the British acts since the peace militate against the payment, by narrowing the means by which those debts might have been paid when they were contracted, and which ought to be considered as constituent parts of the contract.’
TO JAMES MADISON.
Paris, May 11,1789.
Dear Sir,
My last to you was of the 15th of March. I am now in hourly expectation of receiving my leave of absence. The delay of it a little longer will endanger the throwing my return into the winter, the very idea of which is horror itself to me. I am in hopes this is the last letter I shall have the pleasure of writing you before my departure.
The madness of the King of England has gone off, but left him in a state of imbecility and melancholy. They talk of carrying him to Hanover. If they do, it will be a proof he does not mend, and that they take that measure, to authorize them to establish a regency. But if he grows better, they will perhaps keep him at home, to avoid the question, Who shall be regent? As that country cannot be relied on in the present state of its executive, the King of Prussia has become more moderate; he throws cold water on the fermentation he had excited in Poland. The King of Sweden will act as nobody, not even himself, can foresee; because he acts from the caprice of the moment, and because the discontents of his army and nobles may throw him under internal difficulties, while struggling with external ones. Denmark will probably only furnish its stipulated aid to Russia. France is fully occupied with internal arrangements. So that, on the whole, the prospect of this summer is, that the war will continue between the powers actually engaged in the close of the last campaign, and extend to no others; certainly it will not extend, this year, to the southern States of Europe. The revolution of France has gone on with the most unexampled success, hitherto. There have been some mobs, occasioned by the want of bread, in different parts of the kingdom, in which there may have been some lives lost; perhaps a dozen or twenty. These had no professed connection, generally, with the constitutional revolution. A more serious riot happened lately in Paris, in which about one hundred of the mob were killed. This execution has been universally approved, as they seemed to have no view but mischief and plunder. But the meeting of the States General presents serious difficulties, which it had been hoped the progress of reason would have enabled them to get over. The nobility of and about Paris have come over, as was expected, to the side of the people, in the great question of voting by persons or orders. This had induced a presumption, that those of the country were making the same progress, and these form the great mass of the deputies of that order. But they are found to be where they were centuries ago, as to their disposition to keep distinct from the people, and even to tyrannize over them. They agree, indeed, to abandon their pecuniary privileges. The clergy seem at present much divided. Five-sixths of that representation consists of the lower clergy, who, being the sons of the peasantry, are very well with the Tiers-Etat. But the Bishops are intriguing, and drawing them over daily. The Tiers-Etat is so firm to vote by persons or to go home, that it is impossible to conjecture what will be the result. This is the state of parties, as well as we can conjecture from the conversation of the members; for as yet no vote has been given, which will enable us to calculate on certain ground.
Having formerly written to you on the subject of our finances, I enclose you now an abstract of a paper on that subject, which Gouverneur Morris communicated to me. You will be a better judge of its merit than I am. It seems to me worthy good attention.
I have a box of books packed for you, which I shall carry to Havre, and send by any ship bound to New York or Philadelphia. I have been so inexact, as to take no list of them before nailing up the box. Be so good as to do this, and I will take with me my bookseller’s account, which will enable us to make a statement of them. They are chiefly Encyclopédies, from the 23rd to the 30th livraison. Paul Jones has desired me to send to yourself and Colonel Carrington each, his bust. They are packed together in the same box. There are three other boxes, with two in each, for other gentlemen. I shall send them all together, and take the liberty of addressing them to you. I rejoice extremely to hear you are elected, in spite of all cabals. I fear your post will not permit me to see you but in New York, and consequently for a short time only. I shall much regret this.
I am, with sentiments of sincere attachment and respect, Dear Sir, your friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MONSIEUR DE PONTIERE.
Paris, May 17, 1789.
Sir,
I am honored with your letter of the 6th instant, and am sincerely sorry that you should experience inconveniences for the want of the arrearages due to you from the United States. I have never ceased to take every measure, which could promise to procure to the foreign officers the payment of these arrears. At present the matter stands thus. Congress have agreed to borrow a sum of money in Holland, to enable them to pay the individual demands in Europe. They have given orders that these arrearages shall be paid out of this money, when borrowed, and certain bankers in Amsterdam are charged to borrow the money. I am myself of opinion, they will certainly procure the money in the course of the present year; but it is not for me to affirm this, nor to make any engagement. The moment the money is ready, it shall be made known to Colonel Gourion, who, at the desire of many of the officers, has undertaken to communicate with me on the subject, and to inform them, from time to time, of the progress of this business. He will readily answer your letters on this subject. I depart in a few days for America, but shall leave such instructions here, as that this matter will suffer no delay on that account.
I have the honor to be. Sir, your most obedient, humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MR. VAUGHAN.
Paris, May 17, 1789.
Dear Sir,
I am to acknowledge, all together, the receipt of your favors of March the 17th, 26th, and May the 7th, and to return you abundant thanks for your attention to the article of dry rice, and the parcel of seeds you sent me. This is interesting, because, even should it not take place of the wet rice, in South Carolina, it will enable us to cultivate this grain in Virginia, where we have not lands disposed for the wet rice. The collection of the works of Monsieur de Poivre has not, as I believe, been ever published. It could hardly have escaped my knowledge, if they had been ever announced. The French translation of the book on trade has not yet come to my hands. Whenever I receive the copies, they shall be distributed, and principally among the members of the Etats Generaux. I doubt whether, at this session, they will take up the subject of commerce. Whenever they do, they will find better principles no where than in that book. I spoke with Mr. Stewart yesterday on the subject of the distribution, and if I should be gone before the books come to hand, he will execute the commission. Your nation is very far from the liberality that treatise inculcates. The proposed regulation on the subject of our wheat is one proof. The prohibition of it in England would, of itself, be of no great moment, because I do not know that it is much sent there. But it is the publishing a libel on our wheat, sanctioned with the name of parliament, and which can have no object but to do us injury, by spreading a groundless alarm in those countries of Europe where our wheat is constantly and kindly received. It is a mere assassination. If the insect they pretend to fear, be the Hessian fly, it never existed in the grain. If it be the weevil, our grain always had that; and the experience of a century has proved, that either the climate of England is not warm enough to hatch the egg and continue the race, or that some other unknown cause prevents any evil from it. How different from this spirit, my dear Sir, has been your readiness to help us to the dry rice, to communicate to us the bread tree, &tc. Will any of our climates admit the cultivation of the latter? I am too little acquainted with it to judge. I learn that your newspapers speak of the death of Ledyard, at Grand Cairo. I am anxious to know whether there be foundation for this. I have not yet had time to try the execution of the wood hygrometer proposed by Dr. Franklin. Though I have most of the articles ready made, I doubt now whether I shall be able to do it before my departure for America, the permission for which I expect every hour; and I shall go off the instant I receive it. While there, I shall have the pleasure of seeing your father and friends. I expect to return in the fall.
In the mean time, I have the honor to be, with very great esteem and respect, Dear Sir, your most obedient, humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
Paris, May 19,1789.
Dear Sir,
Your favors of February the 16th to April the 13th, and of May the 3rd and 10th, are received; and the two last are sent to Mr. Leroy, who will communicate them to the Academy.
You know that the States General have met, and probably have seen the speeches at the opening of them. The three orders sit in distinct chambers. The great question, whether they shall vote by orders or persons can never be surmounted amicably. It has not yet been proposed in form; but the votes which have been taken on the outworks of that question show, that the Tiers-Etat are unanimous, a good majority of the Clergy (consisting of the Curés) disposed to side with the Tiers-Etat, and in the chamber of the Noblesse there are only fifty-four in that sentiment, against one hundred and ninety, who are for voting by orders. Committees to find means of conciliation are appointed by each chamber; but conciliation is impossible. Some think the Nobles could be induced to unite themselves with the higher Clergy into one House, the lower Clergy and Tiers-Etat forming another. But the Tiers-Etat are immovable. They are not only firm, but a little disdainful. The question is, what will ensue? One idea is to separate, in order to consult again their constituents, and to take new instructions. This would be doing nothing, for the same instructions would be repeated; and what, in the mean time, is to become of a government absolutely without money, and which cannot be kept in motion with less than a million of livres a day? The more probable expectation is as follows. As soon as it shall become evident, that no amicable determination of the manner of voting can take place, the Tiers-Etat will send an invitation to the two other orders, to come and take their places in the common chamber. A majority of the Clergy will go, and the minority of the Noblesse. The chamber thus composed, will declare that the States General are constituted, will notify it to the King, and that they are ready to proceed to business. If the King refuses to do business with them, and adheres to the Nobles, the common chamber will declare all taxes at an end, will form a declaration of rights, and do such other acts as the circumstances will permit, and go home. The tax-gatherers will then be resisted, and it may well be doubted whether the soldiery and their officers will not divide, as the Tiers-Etat and Nobles. But it is more likely that the King will agree to do business with the States General, so constituted, professing that the necessities of the moment force this, and that he means to negotiate (as they go along) a reconciliation between the seceding members, and those which remain. If the matter takes this turn, there may be small troubles and ebullitions excited by the seceding Noblesse and higher Clergy; but no serious difficulty can arise. M. de Lamoignon, the Garde des Sceaux of the last year, has shot himself. The Emperor’s complaint is pulmonary, and incurable. The Grand Seignior is dead; his successor, young and warlike. I congratulate you sincerely on the success of your bridge. I was sure of it before from theory: yet one likes to be assured from practice also. I am anxious to see how Mr. Rumsey’s experiment succeeds.
May the 21st. I have this moment received a letter from Ledyard, dated Cairo, November the 15th. He therein says, ‘I am doing up my baggage, and most curious baggage it is, and I leave Cairo in two or three days. I travel from hence southwest, about three hundred leagues, to a black King: there my present conductors leave me to my fate. Beyond, I suppose, I go alone. I expect to hit the continent across, between the parallels of twelve and twenty degrees north latitude. I shall, if possible, write you from the kingdom of this black gentleman.’ This seems to contradict the story of his having died at Cairo, in January, as he was then, probably, in the interior parts of Africa. If Sir Joseph Banks has no news from him later than the letter of September, it may do him pleasure, if you will communicate the above. If he or any other person knows whether there is any foundation for the story of his death, I will thank you to inform me of it. My letter being to go off to-morrow, I shall only add assurances of the esteem and respect, with which I am, Dear Sir, your friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MONSIEUR DE ST. ETIENNE.
Paris, June 3, 1789.
Sir,
After you quitted us yesterday evening, we continued our conversation (Monsieur de la Fayette, Mr. Short, and myself) on the subject of the difficulties which environ you. The desirable object being to secure the good which the King has offered, and to avoid the ill which seems to threaten, an idea was suggested, which appearing to make an impression on Monsieur de la Fayette, I was encouraged to pursue it on my return to Paris, to put it into form, and now to send it to you and him. It is this; that the King, in a seance royale, should come forward with a Charter of Rights in his hand, to be signed by himself and by every member of the three orders. This charter to contain the five great points which the Resultat of December offered on the part of the King; the abolition of pecuniary privileges offered by the privileged orders, and the adoption of the national debt, and a grant of the sum of money asked from the nation. This last will be a cheap price for the preceding articles; and let the same act declare your immediate separation till the next anniversary meeting. You will carry back to your constituents more good than ever was effected before without violence, and you will stop exactly at the point where violence would otherwise begin. Time will be gained, the public mind will continue to ripen and to be informed, a basis of support may be prepared with the people themselves, and expedients occur for gaining still something further at your next meeting, and for stopping again at the point of force. I have ventured to send yourself and Monsieur de la Fayette a sketch of my ideas of what this act might contain, without endangering any dispute. But it is offered merely as a canvass for you to work on, if it be fit to work on at all. I know too little of the subject, and you know too much of it, to justify me in offering any thing but a hint. I have done it, too, in a hurry: insomuch, that since committing it to writing, it occurs to me that the fifth article may give alarm; that it is in a good degree included in the fourth, and is, therefore, useless. But after all, what excuse can I make, Sir, for this presumption. I have none but an unmeasurable love for your nation, and a painful anxiety lest despotism, after an unaccepted offer to bind its own hands, should seize you again with tenfold fury. Permit me to add to these, very sincere assurances of the sentiments of esteem and respect, with which I have the honor to be, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
[The annexed is the Charter accompanying the preceding letter.]
A Charter of Rights, solemnly established by the King and Nation.
1. The States General shall assemble, uncalled, on the first day of November, annually, and shall remain together so long as they shall see cause. They shall regulate their own elections and proceedings, and until they shall ordain otherwise, their elections shall be in the forms observed in the present year, and shall be triennial.
2. The States General alone shall levy money on the nation, and shall appropriate it.
3. Laws shall be made by the States General only, with the consent of the King.
4. No person shall be restrained of his liberty, but by regular process from a court of justice, authorized by a general law. (Except that a Noble may be imprisoned by order of a court of justice, on the prayer of twelve of his nearest relations.) On complaint of an unlawful imprisonment, to any judge whatever, he shall have the prisoner immediately brought before him, and shall discharge him, if his imprisonment be unlawful. The officer, in whose custody the prisoner is, shall obey the orders of the judge; and both judge and officer shall be responsible, civilly and criminally, for a failure of duty herein.
5. The military shall be subordinate to the civil authority.
7. Printers shall be liable to legal prosecution for printing and publishing false facts, injurious to the party prosecuting; but they shall be under no other restraint.
7. All pecuniary privileges and exemptions, enjoyed by any description of persons, are abolished.
8. All debts already contracted by the King, are hereby made the debts of the nation; and the faith thereof is pledged for their payment in due time.
9. Eighty millions of livres are now granted to the King, to be raised by loan, and reimbursed by the nation: and the taxes heretofore paid, shall continue to be paid to the end of the present year, and no longer.
10. The States General shall now separate, and meet again on the 1st day of November next.
Done, on behalf of the whole nation, by the King and their representatives in the States General, at Versailles, this ——— day of June, 1789.
Signed by the King, and by every member individually, and in his presence.
TO THE MARQUIS DE LA FAYETTE.
Paris, June 12, 1789.
My Dear Sir,
As I may not be able to get at you at Versailles, I write this to deliver it myself at your door. With respect to the utility or inutility of your minority’s joining the Commons, I am unable to form an opinion for myself. I know too little of the subject to see what may be its consequences.
I never knew an instance of the English parliament’s undertaking to relieve the poor by a distribution of bread in time of scarcity. In fact, the English commerce is so extensive and so active, that though bread may be a little more or less plenty, there can never be an absolute failure. The island is so narrow, that corn can be readily carried from the sea-ports to its interior parts. But were an absolute want to happen, and were the parliament to undertake a distribution of corn, I think, that according to the principles of their government, they would only vote a sum of money, and address the King to employ it for the best. The business is, in its nature, executive, and would require too great a variety of detail to be managed by an act of parliament. However, I repeat it, that I never heard or read of an instance of the parliament’s interfering to give bread. If I see you at Versailles to-day, I can be more particular.
I am with great sincerity, my dear Sir, your affectionate friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson,
TO JOHN JAY.
Sir
Paris, June 17, 1789.
I had the honor of addressing you on the 9th and 12th of May, by the way of London. This goes through the same channel to the care of Mr. Trumbull. Having received no letter from you of later date than the 25th of November, I am apprehensive that there may have been miscarriages, and the more so, as I learn, through another channel, that you have particularly answered mine of November the 19th.
The death of the Grand Seignior, which has happened, renders the continuance of the war more probable, as it has brought to the throne a successor of a more active and ardent temper, and who means to put himself at the head of his armies. He has declared the Captain Pacha his Generalissimo. The prospects for Russia, on the other hand, are less encouraging. Her principal ally, the Emperor, is at death’s door, blazing up a little indeed, from time to time like an expiring taper, but certainly to extinguish soon. Denmark, too, is likely to be restrained by the threats of England and Prussia, from contributing even her stipulated naval succors. It is some time since I have been able to obtain any account of the King of England, on which I can rely with confidence. His melancholy continues, and to such a degree, as to render him absolutely indifferent to every thing that passes, so that he seems willing to let his ministers do every thing they please, provided they will let him alone. When forced to speak, his comprehension seems better than it was in the first moments after his phrensy went off. His health is bad: he does not go into public at all, and very few are admitted to see him. This is his present state, according to the best accounts I have been able to get lately. His ministers dictate boldly in the north, because they know it is impossible they should be engaged in the war, while this country is so completely palsied.
You will have seen by my former letters, that the question, whether the States General should vote by persons or by orders, had stopped their proceedings in the very first instance in which it could occur, that is, as to the verification of their powers, and that they had appointed committees to try if there were any means of accommodation. These could do nothing. The King then proposed that they should appoint others, to meet persons whom he should name, on the same subject. These conferences also proved ineffectual. He then proposed a specific mode of verifying. The clergy accepted it unconditionally; the Noblesse, with such conditions and modifications, as did away their acceptance altogether. The Commons, considering this as a refusal, came to the resolution of the 10th instant (which I have the honor to send you), inviting the two other orders to come and take their places in the common room, and notifying that they should proceed to the verification of powers, and to the affairs of the nation, either with or without them. The Clergy have, as yet, given no answer. A few of their members have accepted the invitation of the Commons, and have presented themselves in their room, to have their powers verified; but how many it will detach, in the whole, from that body, cannot be known till an answer be decided on. The Noblesse adhered to their former resolutions, and even the minority, well disposed to the Commons, thought they could do more good in their own chamber, by endeavoring to increase their numbers and fettering the measures of the majority, than by joining the Commons. An intrigue was set on foot, between the leaders of the majority in that House, the Queen, and Princes. They persuaded the King to go for some time to Marly: he went. On the same day, the leaders moved in the chamber of Nobles, that they should address the King, to declare his own sentiments on the great question between the orders. It was intended that this address should be delivered to him at Marly, where, separated from his ministers, and surrounded by the Queen and Princes, he might be surprised into a declaration for the Nobles. The motion was lost, however, by a very great majority, that chamber being not yet quite ripe for throwing themselves into the arms of despotism. Necker and Montmorin, who had discovered this intrigue, had warned some of the minority to defeat it, or they could not answer for what would happen. These two and St. Priest, are the only members of the Council in favor of the Commons. Luzerne, Puy-Segur, and the others, are high aristocrats. The Commons having verified their powers, a motion was made the day before yesterday, to declare themselves constituted, and to proceed to business. I left them at two o’clock yesterday; the debates not then finished. They differed only about forms of expression, but agreed in the substance, and probably decided yesterday, or will decide to-day. Their next move, I fancy, will be to suppress all taxes, and instantly re-establish them till the end of their session, in order to prevent a premature dissolution: and then they will go to work on a declaration of rights and a constitution. The Noblesse, I suppose, will be employed altogether in counter operations; the Clergy, that is to say, the higher Clergy, and such of the Curés as they can bring over to their side, will be waiting and watching, merely to keep themselves in their saddles. Their deportment, hitherto, is that of meekness and cunning. The fate of the nation depends on the conduct of the King and his ministers. Were they to side openly with the Commons, the revolution would be completed without a convulsion, by the establishment of a constitution, tolerably free, and in which the distinction of Noble and Commoner would be suppressed. But this is scarcely possible. The King is honest, and wishes the good of his people; but the expediency of an hereditary aristocracy is too difficult a question for him. On the contrary, his prejudices, his habits, and his connections decide him in his heart to support it. Should they decide openly for the Noblesse, the Commons, after suppressing taxes, and finishing their declaration of rights, would probably go home; a bankruptcy takes place in the instant, Mr. Necker must go out, a resistance to the tax-gatherers follows, and probably a civil war. These consequences are too evident and violent, to render this issue likely. Though the Queen and Princes are infatuated enough to hazard it, the party in the ministry would not. Something, therefore, like what I hinted in my letter of May the 12th, is still the most likely to take place. While the Commons, either with or without their friends of the other two Houses, shall be employed in framing a constitution, perhaps the government may set the other two Houses to work on the same subject: and when the three schemes shall be ready, joint committees may be negotiated, to compare them together, to see in what parts they agree; and probably they will agree in all, except the organization of the future States General. As to this, it may be endeavored, by the aid of wheedling and intimidation, to induce the two privileged chambers to melt themselves into one, and the Commons, instead of one, to agree to two Houses of legislation. I see no other middle ground to which they can be brought.
It is a tremendous cloud, indeed, which hovers over this nation, and he at the helm has neither the courage nor the skill necessary to weather it. Eloquence in a high degree, knowledge in matters of account, and order, are distinguishing traits in his character. Ambition is his first passion, virtue his second. He has not discovered that sublime truth, that a bold, unequivocal virtue is the best handmaid even to ambition, and would carry him further, in the end, than the temporizing, wavering policy he pursues. His judgment is not of the first order, scarcely even of the second; his resolution frail; and upon the whole, it is rare to meet an instance of a person so much below the reputation he has obtained. As this character, by the post and times in which Providence has placed it, is important to be known, I send it to you as drawn by a person of my acquaintance, who knows him well. He is not, indeed, his friend, and allowance must, therefore, be made for the high coloring. But this being abated, the facts and groundwork of the drawing are just. If the Tiers separate, he goes at the same time; if they stay together, and succeed in establishing a constitution to their mind, as soon as that is placed in safety, they will abandon him to the mercy of the court, unless he can recover the confidence which he has lost at present, and which, indeed, seems to be irrecoverable.
The inhabitants of St. Domingo, without the permission of the government, have chosen and sent deputies to the States General. The question of their admission is to be discussed by the States. In the mean time, the government had promised them an Assembly in their own Island, in the course of the present year. The death of the Dauphin, so long expected, has at length happened. Montmorin told Ternant the other day, that De Moustier had now asked a congé, which would be sent him immediately. So that unless a change of ministry should happen, he will, probably, be otherwise disposed of. The gazettes of France and Leyden accompany this. I have the honor to be, with the most perfect esteem and respect, Sir, your most obedient, humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
P. S. June 18. The motion under debate with the Commons, for constituting their Assembly, passed yesterday by a majority of four hundred and odd, against eighty odd. The latter were for it in substance, but wished some particular amendment. They proceeded instantly to the subject of taxation. A member who called on me this moment, gave me a state of the proceedings of yesterday, from memory, which I enclose you. He left the House a little before the question was put, because he saw there was no doubt of its passing, and his brother, who remained till the decision, informed him of it. So that we may expect, perhaps, in the course of to-morrow, to see whether the government will interpose with a bold hand, or will begin a negotiation. But in the mean time, this letter must go off. I will find some other opportunity, however, of informing you of the issue. T. J.
^^^ [Character of Mr. Necker, accompanying the preceding letter.]
Nature bestowed on Mr. Necker an ardent passion for glory, without, at the same time, granting him those qualities required for its pursuit by direct means. The union of a fruitful imagination with a limited talent, with which she has endowed him, is always incompatible with those faculties of the mind which qualify their possessor to penetrate, to combine, and to comprehend all the relations of objects.
He had probably learned in Geneva, his native country, the influence which riches exercise on the success of ambition, without having recourse to the school of Paris, where he arrived about the twenty-eighth year of his age. A personal affair with his brother, in which the chiefs of the republic conducted themselves unjustly towards him, the circumstances of which, moreover, exposed him to ridicule, determined him to forsake his country. On taking his leave, he assured his mother that he would make a great fortune at Paris. On his arrival, he engaged himself as clerk, at a salary of six hundred livres, with the banker Thelusson, a man of extreme harshness in his intercourse with his dependants. The same cause which obliged other clerks to abandon the service of Thelusson, determined Necker to continue in it. By submitting to the brutality of his master with a servile resignation, whilst, at the same time, he devoted the most unremitting attention to his business, he recommended himself to his confidence, and was taken into partnership. Ordinary abilities only were requisite to avail him of the multitude of favorable circumstances, which, before he entered into the administration, built up a fortune of six millions of livres. He owed much of his good fortune to his connections with the Abbe Terrai, of whose ignorance he did not scruple to profit. His riches, his profession, his table, and a virtuous, reasonable, and well informed wife, procured him the acquaintance of many persons of distinction, among whom were many men of letters, who celebrated his knowledge and wisdom.
The wise and just principles by which Turgot aimed to correct the Abuses of the administration, not having been received with favor, he seized the occasion to flatter ignorance and malignity, by publishing his work against the freedom of the corn trade.
He had published, two years before, an eulogy on Colbert. Both these productions exhibited the limited capacity of a banker, and, in no degree, the enlarged views of a statesman. Not at all delicate in the choice of his means, he succeeded to his wish in his object, which was the establishing himself in public opinion. Elevated by a secret cabal to the direction of the finances, he began by refusing the salaries of his office. He affected a spirit of economy and austerity, which imposed even on foreign nations, and showed the possibility of making war without laying new taxes. Such at least was his boast; but, in reality, they have been increased under his administration, about twenty millions, partly by a secret augmentation of the bailies and of the poll-tax, partly by some verifications of the twentieths, and partly by the natural progression, which is tested by the amount of taxes on consumption, the necessary result of the successive increase of population, of riches, and of expensive tastes.
All these circumstances reared for him an astonishing reputation, which his fall has consecrated. People will not reflect, that, in the short period of his ministry, he had more than doubled his fortune. Not that he had peculated on the public treasury; his good sense and pride forbade a resort to this manoeuvre of weak minds; but by resorting to loans and the costly operations of the bank, to provide the funds of war, and being still connected with the house to which he addressed himself for much the greater part of his negotiations. They have not remarked that his great principles of economy have nothing more than a false show, and that the loans resorted to, in order to avoid the imposition of taxes, have been the source of the mischief which has reduced the finances to their present alarming condition.
As to his compte rendu; he has been forgiven the nauseous panegyric which he has passed upon himself, and the affectation of introducing his wife into it, for the purpose of praising her; and we are spared the trouble of examining his false calculations. M. de Calonne has undertaken this investigation. Without being able to vindicate himself, he has already begun to unmask his antagonist, and he promises to do it effectually.
Necessity has recalled this man to the ministry: and it must be confessed, that he is beyond comparison a less mischievous minister than his predecessors. I would compare him to a steward, who, by his management, does not entirely ruin his master, but who enriches himself at his expense. The desire of glory should inspire him as much as possible with the energy requisite for the public business. There is every likelihood that his ministry will not endure long enough, to cause it to feel the effects of his false principles of administration: and it is he alone who is able, if any one can, to preserve order in the finances, until the reform is effected which we hope from the assembling of the States General. In the mean time, the public estimation of his talents and virtue is not so high as it has been. There are persons who pretend that he is more firmly established in public opinion than he ever was. They deceive themselves. The ambitious desire he has always manifested of getting again into the administration, his work on the Importance of Religious Opinions, and the Memoires of M. de Calonne, have greatly impaired his reputation.
TO JAMES MADISON.
Paris, June 18, 1789.
Sir,
My last to you was of May the 11th. Yours of March the 29th came to hand ten days ago; and about two days ago, I received a cover of your hand-writing, under which were a New York paper of May the 4th, and a letter from Mr. Page to Mazzei. There being no letter from you, makes me hope there is one on the way, which will inform me of my congé. I have never received Mr. Jay’s answer to my public letter of November the 19th, which you mention him to have written, and which I fear has been intercepted. I know only from you, that my letter got safe to hand. My baggage has been made up more than a month, so that I shall leave Paris almost in the instant of receiving the permission.
The campaign begins under unfavorable auspices for Russia. The death of the Grand Seignior, who was personally disposed for peace, has brought a young and ardent successor to the throne, determined to push the war to extremity. Her only ally, the Emperor, is in articulo mortis, and the grand Duke of Tuscany, should he succeed, loves peace and money. Denmark is forbidden by England and Prussia to furnish even its stipulated maritime aid. There is no appearance of any other power’s engaging in the war. As far as I can discover, the King of England is somewhat better in his head, but under such a complete depression of spirits, that he does not care how the world goes, and leaves his ministers to do as they please. It is impossible for you to conceive how difficult it is to know the truth relative to him, he is environed in such an atmosphere of lies. Men who would not speak a falsehood on any other subject, lie on this, from a principle of duty; so that even eye-witnesses cannot be believed without scanning their principles and connections; and few will stand this, of the very few permitted to see him.
Committees of conciliation having failed in their endeavors to bring together the three chambers of the States General, the King proposed a specific mode of verifying their powers; for that having been the first question which presented itself to them, was the one in which the question of voting by persons or orders was first brought on. The clergy accepted unconditionally. The Noblesse accepted on conditions which reduced the acceptance to nothing at all. The Commons considered this as a refusal on the part of the Nobles, and thereupon took their definitive resolution, to invite the other two orders to come and verify their powers in common, and to notify them they should proceed with or without them to verify, and to do the business of the nation. This was on the 10th. On the 15th, they moved to declare themselves the National Assembly. The debates on this were finished yesterday, when the proposition was agreed to, by four hundred and odd, against eighty odd. The minority agreed in substance, but wished some particular amendment. They then immediately made the proposition relative to taxes, which I enclose you, as this moment stated to me, by memory, by a member who left the Assembly a little before the question, because there was no opposition to the matter, but only to the form. He assures me, on the information of another member who was present, that Target’s motion passed. We shall know, I think, within a day or two, whether the government will risk a bankruptcy and civil war, rather than see all distinction of orders done way, which is what the Commons will push for. If the fear of the former alternative prevails, they will spin the matter into negotiation. The Commons have in their chamber almost all the talents of the nation; they are firm and bold, yet moderate. There is indeed, among them, a number of very hot-headed members; but those of most influence are cool, temperate, and sagacious. Every step of this House has been marked with caution and wisdom. The Noblesse, on the contrary, are absolutely out of their senses. They are so furious, they can seldom debate at all. They have few men of moderate talents, and not one of great, in the majority. Their proceedings have been very injudicious. The Clergy are waiting to profit of every incident to secure themselves, and have no other object in view. Among the Commons, there is an entire unanimity on the great question of voting by persons. Among the Noblesse, there are about sixty for the Commons, and about three times that number against them. Among the Clergy, about twenty have already come over and joined the Commons, and in the course of a few days, they will be joined by many more, not indeed making the majority of that House, but very near it. The Bishops and Archbishops have been very successful by bribes and intrigues, in detaching the Curés from the Commons, to whom they were at first attached to a man. The Commons are about, five hundred and fifty-four in number, of whom three hundred and forty-four are of the Jaw. These do not possess an influence founded in property; but in their habits of business and acquaintance with the people, and in their means of exciting them as they please. The Curés, throughout the kingdom, form the mass of the Clergy; they are the only part favorably known to the people, because solely charged with the duties of baptism, burial, confession, visitation of the sick, instruction of the children, and aiding the poor; they are themselves of the people, and united with them. The carriages and equipage only of the higher Clergy, not their persons, are known to the people, and are in detestation with them. The soldiers will follow their officers, that is to say, their captains, lieutenants, and ensigns. These are of the lower nobility, and therefore much divided. The colonels and higher officers are of the higher nobility, are seldom with the soldiers, little known to them, not possessing their attachment. These circumstances give them little weight in the partition of the army.
I give you these miscellaneous observations, that knowing somewhat the dispositions of the parties, you may be able to judge of the future for yourself, as I shall not be here to continue its communication to you.
In hopes to see you soon, I conclude with assurances of the perfect esteem and respect, with which I am, Dear Sir, your friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN JAY.
Sir,
Paris, June 24,1789.
My letter of the 17th and 18th instant gave you the progress of the States General to the 17th, when the Tiers had declared the illegality of all the existing taxes, and their discontinuance from the end of their present session. The next day, being a jour de fete, could furnish no indication of the impression that vote was likely to make on the government. On the 19th, a Council was held at Marly, in the afternoon. It was there proposed, that the King should interpose by a declaration of his sentiments in a seance royale. The declaration prepared by M. Necker, while it censured, in general, the proceedings both of the Nobles and Commons, announced the King’s views, such as substantially to coincide with the Commons. It was agreed to in Council, as also that the seance royale should be held on the 22nd, and the meetings till then be suspended. While the Council was engaged in this deliberation at Marly, the chamber of the Clergy was in debate, whether they should accept the invitation of the Tiers to unite with them in the common chamber. On the first question, to unite simply and unconditionally, it was decided in the negative by a very small majority. As it was known however, that some members who had voted in the negative, would be for the affirmative, with some modifications, the question was put with these modifications, and it was determined by a majority of eleven members, that their body should join the Tiers. These proceedings of the Clergy were unknown to the Council at Marly, and those of the Council were kept secret from every body. The next morning (the 20th), the members repaired to the House as usual, found the doors shut and guarded, and a proclamation posted up for holding a seance royale on the 22nd, and a suspension of their meetings till then. They presumed, in the first moment, that their dissolution was decided, and repaired to another place, where they proceeded to business. They there bound themselves to each other by an oath, never to separate of their own accord, till they had settled a constitution for the nation on a solid basis, and if separated by force, that they would re-assemble in some other place. It was intimated to them, however, that day, privately, that the proceedings of the seance royale would be favorable to them. The next day they met in a church, and were joined by a majority of the Clergy. The heads of the aristocracy saw that all was lost without some violent exertion. The King was still at Marly. Nobody was permitted to approach him but their friends. He was assailed by lies in all shapes. He was made to believe that the Commons were going to absolve the army from their oath of fidelity to him, and to raise their pay.
They procured a committee to be held, consisting of the King and his ministers, to which Monsieur and the Count d’Artois should be admitted. At this committee, the latter attacked Mr. Necker personally, arraigned his plans, and proposed one which some of his engines had put into his hands. Mr. Necker, whose characteristic is the want of firmness, was browbeaten and intimidated, and the King shaken. He determined that the two plans should be deliberated on the next day, and the seance royale put off a day longer. This encouraged a fiercer attack on Mr. Necker the next day; his plan was totally dislocated, and that of the Count d’Artois inserted into it. Himself and Monsieur de Montmorin offered their resignation, which was refused; the Count d’Artois saying to Mr. Necker, ‘No, Sir, you must be kept as the hostage; we hold you responsible for all the ill which shall happen.’ This change of plan was immediately whispered without doors. The nobility were in triumph, the people in consternation. When the King passed, the next day, through the lane they formed from the Chateau to the Hotel des Etats (about half a mile), there was a dead silence. He was about an hour in the House, delivering his speech and declaration, copies of which I enclose you. On his coming out, a feeble cry of ‘Vive le Roy’ was raised by some children, but the people remained silent and sullen. When the Duke d’Orleans followed, however, their applauses were excessive. This must have been sensible to the King. He had ordered, in the close of his speech, that the members should follow him, and resume their deliberations the next day. The Noblesse followed him, and so did the Clergy, except about thirty, who, with the Tiers, remained in the room and entered into deliberation. They protested against what the King had done, adhered to all their former proceedings, and resolved the inviolability of their own persons. An officer came twice to order them out of the room, in the King’s name, but they refused to obey. In the afternoon, the people, uneasy, began to assemble in great numbers in the courts and vicinities of the palace. The Queen was alarmed, and sent for Mr. Necker. He was conducted amidst the shouts and acclamations of the multitude, who filled all the apartments of the palace. He was a few minutes only with the Queen, and about three quarters of an hour with the King. Not a word has transpired of what passed at these interviews. The King was just going to ride out. He passed through the crowd to his carriage, and into it, without being in the least noticed. As Mr. Necker followed him, universal acclamations were raised of ‘Vive Monsieur Necker, vive le sauveur de la France opprimée.’ He was conducted back to his house with the same demonstrations of affection and anxiety. About two hundred deputies of the Tiers, catching the enthusiasm of the moment, went to his house, and extorted from him a promise that he would not resign. These circumstances must wound the heart of the King, desirous as he is, to possess the affections of his subjects. As soon as the proceedings at Versailles were known at Paris, a run began on the caisse d’escompte, which is the first symptom always of the public diffidence and alarm. It is the less in condition to meet the run, as Mr. Necker has been forced to make free with its funds, for the daily support of the government. This is the state of things as late as I am able to give them with certainty, at this moment. My letter not being to go off till to-morrow evening, I shall go to Versailles to-morrow, and be able to add the transactions of this day and to-morrow.
June 25. Just returned from Versailles, I am enabled to continue my narration. On the 24th, nothing remarkable passed, except an attack by the mob of Versailles on the Archbishop of Paris, who had been one of the instigators of the court, to the proceedings of the, seance royale. They threw mud and stones at his carriage, broke the windows of it, and he in a fright promised to join the Tiers.
This day (the 25th) forty-eight of the Nobles have joined the Tiers. Among these is the Duke d’Orleans. The Marquis de la Fayette could not be of the number, being restrained by his instructions. He is writing to his constituents, to change his instructions or to accept his resignation. There are with the Tiers now one hundred and sixty-four members of the Clergy, so that the common chamber consists of upwards of eight hundred members. The minority of the Clergy, however, call themselves the Chamber of the Clergy, and pretend to go on with business. I found the streets of Versailles much embarrassed with soldiers. There was a body of about one hundred horse drawn up in front of the Hotel of the States, and all the avenues and doors guarded by soldiers. Nobody was permitted to enter but the members, and this was by order of the King; for till now, the doors of the common room have been open, and at least two thousand spectators attending their debates constantly. They have named a deputation to wait on the King, and desire a removal of the soldiery from their doors, and seem determined, if this is not complied with, to remove themselves elsewhere.
Instead of being dismayed with what has passed, they seem to rise in their demands, and some of them to consider the erasing every vestige of a difference of order, as indispensable to the establishment and preservation of a good constitution. I apprehend there is more courage than calculation in this project. I did imagine, that seeing that Mr. Necker and themselves were involved as common enemies in the hatred of the aristocrats, they would have been willing to make common cause with him, and to wish his continuance in office; and that Mr. Necker, seeing that all the trimming he has used towards the court and Nobles has availed him nothing, would engage himself heartily and solely on the popular side, and view his own salvation in that alone. The confidence which the people place in him, seems to merit some attention. However, the mass of the common chamber are absolutely indifferent to his remaining in office. They consider his head as unequal to the planning a good constitution, and his fortitude to a co-operation in the effecting it. His dismission is more credited to-day than it was yesterday. If it takes place, he will retain his popularity with the nation, as the members of the States will not think it important to set themselves against it, but on the contrary, will be willing that he should continue on their side, on his retirement. The run on the caisse d’escompte continues. The members of the States admit, that Mr. Necker’s departure out of office will occasion a stoppage of public payments. But they expect to prevent any very ill effect, by assuring the public against any loss, and by taking immediate measures for continuing payment. They may, perhaps, connect these measures with their own existence, so as to interest the public in whatever catastrophe may be aimed at them. The gazettes of France and Leyden accompany this. During the continuance of this crisis and my own stay, I shall avail myself of every private conveyance to keep you informed of what passes.
I have the honor to be, with the most perfect esteem and respect, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN JAY.
Paris, June 29, 1789.
Sir,
My letter of the 25th gave you the transactions of the States General to the afternoon of that day. On the next, the Archbishop of Paris joined the Tiers, as did some others of the Clergy and Noblesse. On the 27th, the question of the St. Domingo deputation came on, and it was decided that it should be received. I have before mentioned to you the ferment into which the proceedings at the seance royale of the 23rd had thrown the people. The soldiery also were affected by it. It began in the French guards, extended to those of every other denomination (except the Swiss), and even to the body-guards of the King. They began to quit their barracks, to assemble in squads, to declare they would defend the life of the King, but would not cut the throats of their fellow-citizens. They were treated and caressed by the people, carried in triumph through the streets, called themselves the soldiers of the nation, and left no doubt on which side they would be, in case of a rupture. Similar accounts came in from the troops in other parts of the kingdom, as well those which had not heard of the seance royale, as those which had, and gave good reason to apprehend that the soldiery, in general, would side with their fathers and brothers, rather than with their officers. The operation of this medicine, at Versailles, was as sudden as it was powerful. The alarm there was so complete, that in the afternoon of the 27th, the King wrote a letter to the President of the Clergy, the Cardinal de la Rochefoucault, in these words: [* A translation is here given.]
* My Cousin, Wholly engaged in promoted the general good of
my kingdom, and desirous, above all things, that the
Assembly of the States General should apply themselves to
objects of general interest, after the voluntary acceptance
by your order of my declaration of the 23rd of the present
month; I pass my word that my faithful Clergy will, without
delay, unite themselves with the other two orders, to hasten
the accomplishment of my paternal views. Those whose powers
are too limited, may decline voting until new powers are
procured. This will be a new mark of attachment which my
Clergy will give me. I pray God, my Cousin, to have you in
his holy keeping. LOUIS.’
A like letter was written to the Duke de Luxemburgh, President of the Noblesse. The two chambers entered into debate on the question, whether they should obey the letter of the King. There was a considerable opposition; when notes written by the Count d’Artois to sundry members, and handed about among the rest, decided the matter, and they went in a body and took their seats with the Tiers, and thus rendered the union of the orders in one chamber complete. As soon as this was known to the people of Versailles, they assembled about the palace, demanded the King and Queen, who came and showed themselves in a balcony. They rent the skies with cries of ‘Vive la Roy,’ ‘Vive la Reine.’ They, called for the Dauphin, who was also produced, and was the subject of new acclamations. After feasting themselves and the royal family with this tumultuary reconciliation, they went to the house of Mr. Necker and M. de Montmorin, with shouts of thankfulness and affection. Similar emotions of joy took place in Paris, and at this moment, the triumph of the Tiers is considered as complete. Tomorrow they will recommence business, voting by persons on all questions: and whatever difficulties may be opposed in debate by the malcontents of the Clergy and Nobility, every thing must be finally settled at the will of the Tiers. It remains to see whether they will leave to the nobility any thing but their titulary appellations. I suppose they will not. Mr. Necker will probably remain in office. It would seem natural that he should endeavor to have the hostile part of the Council removed, but I question if he finds himself firm enough for that. A perfect co-operation with the Tiers will be his wisest game. This great crisis being now over, I shall not have matter interesting enough to trouble you with, as often as I have done lately. There has nothing remarkable taken place in any other part of Europe.
I have the honor to be, with the most perfect esteem and respect, Sir, your most; obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO THE MARQUIS DE LA FAYETTE.
Paris, July 6, 1789.
Dear Sir,
I never made an offer to any body to have corn or flour brought here from America: no such idea ever entered my head. Mr. Necker desired me to give information in America, that there would be a want of flour. I did so in a letter to Mr. Jay, which he published with my name to it, for the encouragement of the merchants. Those here, who have named me on this subject, must have mistaken me for Mr. Parker. I have heard him say, he offered to Mr. Necker to bring a large supply, yet I do not think I ever repeated this: or if I did, it must have been in a company I relied on. I will thank you to satisfy Mr. Necker of the truth. It would be disagreeable, and perhaps mischievous, were he to have an idea that I encouraged censures on him. I will bring you the paper you desire to-morrow; and shall dine at the Dutchess Danville’s, where I shall be happy to meet you.
Adieu. Yours affectionately.
Th: Jefferson.
TO THE MARQUIS DE LA FAYETTE.
Paris, July 7,1789.
Dear Sir,
Your letter of yesterday gave me the first information that Monsieur de Mirabeau had suggested to the honorable the Assembly of the Nation, that I had made an offer to Mr. Necker to obtain from America a quantity of corn or flour, which had been refused. I know not how Monsieur de Mirabeau has been led into this error. I never in my life made any proposition to Mr. Necker on the subject: I never said I had made such a proposition. Some time last autumn, Mr. Necker did me the honor to desire I would have notified in the United States, that corn and flour would meet with a good sale in France. I conveyed this notice, in a letter to Mr. Jay, Secretary for Foreign Affairs, as you will see by the extract of my letter published by him in an American gazette, which I have the honor to send you. I must beg leave to avail myself of your friendship and of your position to have a communication of these facts made to the honorable Assembly of the Nation, of which you are a member, and to repeat to you those sentiments of respect and attachment, with which I have the honor to be, my dear Sir, your most obedient and most
humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MR. NECKER.
Paris, July 8, 1789
Sir,
I have the honor to enclose you a copy of my letter to Monsieur de la Fayette. When I called on him yesterday, he had already spoken to Monsieur de Mirabeau, who acknowledged he had been in an error in what he had advanced in the Assembly of the Nation, as to the proposition supposed to have been made by me to your Excellency, and undertook to declare his error, when the subject should be resumed by the Assembly, to whom my letter to the Marquis de la Fayette will be also read.
I have thought it a duty, Sir, thus to correct, in the first moment, an error, by which your name had been compromitted by an unfounded use of mine, and shall be happy in every occasion of proving to you those sentiments of profound respect and attachment, with which I have the honor to be, your Excellency’s most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO THE COUNT DE MONTMORIN.
Paris, July 8, 1789.
Sir,
My hotel having been lately robbed for the third time, I take the liberty of uniting my wish with that of the inhabitants of this quarter, that it might coincide with the arrangements of police, to extend to us the protection of a guard. While the Douane remained here, no accident of that kind happened, but since their removal, other houses in the neighborhood have been robbed as well as mine. Perhaps it may lessen the difficulties of this request, that the house occupied by the people of the Douane, will lodge abundantly a corps de garde. On the one side of that house is Chaillot, on the other the Roule, on the third the Champs Elysees, where accidents are said to happen very frequently, all of which are very distant from any corps de garde.
I have the honor to be, with sentiments of the most perfect respect and esteem, your Excellency’s most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO THE MARQUIS DE LA FAYETTE.
Paris, July 9, 1789.
Dear Sir,
Having been curious to form some estimate of the quantity of corn and flour which have been supplied to France this year, I applied to a person in the Farms to know upon what quantities the premium had been paid. He could not give me information, but as to the Atlantic ports, into which there have been imported from the United States, from March to May inclusive, forty-four thousand one hundred and sixteen quintals of corn, twelve thousand two hundred and twenty-one quintals of flour, making fifty-six thousand three hundred and thirty-seven quintals in the whole. Add to this what has been imported since May, suppose nearly twenty thousand quintals a month, and what has been furnished to the French islands, which has prevented an equal quantity being exported from France, and you will have the proportion drawn from us. Observe, that we have regular and constant markets for our corn and flour in Spain, Portugal, and all the West India islands, except the French. These take nearly our whole quantity. This year, France, the French West Indies, and Canada were added. But a regular course of trade is not quitted in an instant, nor constant customers deserted for accidental ones. This is the reason that so small a proportion has come here.
I am, Dear Sir, with great sincerity, your affectionate friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO THE MARQUIS DE LA FAYETTE.
Paris, July 10, 1789.
Dear Sir,
The acknowledgment by Monsieur de Mirabeau to the National Assembly, that he had been in an error as to the offer he supposed me to have made, and the reading to them my letter, seem to be all that was requisite for any just purpose. As I was unwilling my name should be used to injure the minister, I am also unwilling it should be used to injure Monsieur de Mirabeau. I learn that his enemies in Paris are framing scandalous versions of my letter. I think, therefore, with you, it may be better to print it, and I send you a copy of it. I gave copies of it to Monsieur de Montmorin and Monsieur Necker, as was my duty.
I am, with sincere affection, my Dear Sir, your friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO THOMAS PAINE.
Paris, July 11, 1789.
Dear Sir,
Since my last, which was of May the 19th, I have received yours of June the 17th and 18th. I am struck with the idea of the geometrical wheel-barrow, and will beg of you a farther account, if it can be obtained. I have no news yet of my congé.
Though you have doubtless heard most of the proceedings of the States General since my last, I will take up the narration where that left it, that you may be able to separate the true from the false accounts you have heard. A good part of what was conjecture in that letter, is now become true history.
The National Assembly, then, (for that is the name they take,) having shown through every stage of these transactions a coolness, wisdom, and resolution to set fire to the four corners of the kingdom, and to perish with it themselves, rather than to relinquish an iota from their plan of a total change of government, are now in complete and undisputed possession of the sovereignty. The executive and aristocracy are at their feet; the mass of the nation, the mass of the clergy, and the army are with them: they have prostrated the old government, and are now beginning to build one from the foundation. A committee, charged with the arrangement of their business, gave in, two days ago, the following order of proceedings.
‘1. Every government should have for its only end, the preservation of the rights of man: whence it follows, that to recall constantly the government to the end proposed, the constitution should begin by a declaration of the natural and imprescriptible rights of man.
‘2. Monarchical government being proper to maintain those rights, it has been chosen by the French nation. It suits especially a great society; it is necessary for the happiness of France. The declaration of the principles of this government, then, should follow immediately the declaration of the rights of man.
‘3. It results from the principles of monarchy, that the nation, to assure its own rights, has yielded particular rights to the monarch: the constitution, then, should declare, in a precise manner, the rights of both. It should begin by declaring the rights of the French nation, and then should declare the rights of the King.
‘4. The rights of the King and nation not existing but for the happiness of the individuals who compose it, they lead to an examination of the rights of citizens.
‘5. The French nation not being capable of assembling individually to exercise all its rights, it ought to be represented. It is necessary, then, to declare the form of its representation and the rights of its representatives.
‘6. From the union of the powers of the nation and King, should result the enacting and execution of the laws: thus, then, it should first be determined how the laws shall be established; afterwards should be considered, how they shall be executed.
‘7. Laws have for their object the general administration of the kingdom, the property, and the actions of the citizens. The execution of the laws which concern the general administration, requires Provincial and Municipal Assemblies. It is necessary to examine, therefore, what should be the organization of the Provincial Assemblies, and what of the Municipal.
‘8. The execution of the laws, which concern the property and actions of the citizens, calls for a judiciary power. It should be determined how that should be confided, and then its duties and limits.
‘9. For the execution of the laws and the defence of the kingdom, there exists a public force. It is necessary, then, to determine the principles which should direct it, and how it should be employed.
‘Recapitulation.
‘Declaration of the rights of man. Principles of the monarchy. Rights of the nation. Rights of the King. Rights of the citizens.
‘Organization and rights of the National Assembly. Forms necessary for the enaction of laws. Organization and functions of the Provincial and Municipal Assemblies. Duties and limits of the judiciary power. Functions and duties of the military power.’
You see that these are the materials of a superb edifice, and the hands which have prepared them are perfectly capable of putting them together, and of filling up the work, of which these are only the outlines. While there are some men among them of very superior abilities, the mass possess such a degree of good sense, as enables them to decide well. I have always been afraid their numbers might lead to confusion. Twelve hundred men in one room are too many. I have still that fear. Another apprehension is, that a majority cannot be induced to adopt the trial by jury, and I consider that as the only anchor ever yet imagined by man, by which a government can be held to the principles of its constitution. Mr. Paradise is the bearer of this letter. He can supply those details which it would be so tedious to write.
I am, with great esteem, Dear Sir, your friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.

| Contents |
| Illustrations |
| Volume I. |
| Volume II. |
| Volume IV. |


CONTENTS
LETTER I. TO JOHN JAY, July 19, 1789
LETTER II. TO M. L’ABBE ARNOND, July 19, 1789
LETTER III. TO JOHN JAY, July 23, 1789
LETTER IV. TO JOHN JAY, July 29, 1789
LETTER V. TO JOHN JAY, August 5, 1789
LETTER VI. TO MR. CARMICHAEL, August 9, 1789
LETTER VII. TO JOHN JAY, August 12, 1789
LETTER VIII. TO COLONEL GOUVION, August 15,1789
LETTER IX. TO JOHN JAY, August 27, 1789
LETTER X. TO JAMES MADISON, August 28,1789
LETTER XI. TO JAMES MADISON, September 6, 1789
LETTER XII. TO DR. GEM
LETTER XIII. TO GENERAL KNOX, September 12,1789
LETTER XIV. TO E. RUTLEDGE, September 18, 1789
LETTER XV. TO JOHN JAY, September 19, 1789
LETTER XVI. TO MR. NECKER, September 26,1789
LETTER XVII. TO JOHN JAY, September 30, 1789
LETTER XVIII. TO THE PRESIDENT, December 15,1789
LETTER XIX. TO HENRY LAURENS, ESQUIRE, March 31, 1790
LETTER XX. TO MR. VANDERKEMP, March 31, 1799
LETTER XXI. TO GEORGE JOY, March 31, 1790
LETTER XXII. TO THE COUNT DE MONTMORIN, April 6, 1790
LETTER XXIII. TO THE COUNT DE MONTMORIN, April 6,1790
LETTER XXIV. TO WILLIAM SHORT, April 6, 1790
LETTER XXV. TO THE COUNT DE FLORIDA BLANCA, April 11, 1790
LETTER XXVI. TO WILLIAM CARMICHAEL, April 11, 1789
LETTER XXVII. TO MR. GRAND, April 23, 1790
LETTER XXVIII. TO THE MARQUIS DE LA LUZERNE, April 30,1790
LETTER XXIX. TO WILLIAM SHORT, April 30, 1790
LETTER XXX. TO MR. DUMAS, June 23, 1790
LETTER XXXI. TO MR. DUMAS, July 13,1790
LETTER XXXII TO WILLIAM SHORT, July 26, 1790
LETTER XXXIII. TO WILLIAM CARMICHAEL, August 2, 1790
LETTER XXXIV. TO M. DE PINTO, August 7, 1790
LETTER XXXV. TO JOSHUA JOHNSON, August 7,1790
LETTER XXXVI. TO WILLIAM SHORT, August 10,1790
LETTER XXXVII. TO COLONEL DAVID HUMPHREYS, August 11, 1790
LETTER XXXVIII. TO GOUVERNEUR MORRIS, August 12, 1790
LETTER XXXIX. TO GOVERNOR HANCOCK, August 24, 1790
LETTER XL. TO SYLVANUS BOURNE, August 25, 1790
LETTER XLI. CIRCULAR TO THE CONSULS, August 26, 1790
LETTER XLII. TO WILLIAM SHORT, August 26, 1790
LETTER XLIII. TO M. LA FOREST, August 30, 1790
LETTER XLIV. TO WILLIAM SHORT, August 31,1790
LETTER XLV. TO GOUVERNEUR MORRIS, December 17, 1790
LETTER XLVI. TO JOSHUA JOHNSON, December 17, 1790
LETTER XLVII. TO JOSHUA JOHNSON, December 23, 1790
LETTER XLVIII. TO CHARLES HELLSTEDT, February 14,1791
LETTER XLIX. TO M. DE PINTO, February 21,1791
LETTER L. TO WILLIAM SHORT, March 8,1791
LETTER LI. TO THE PRESIDENT OF THE NATIONAL ASSEMBLY, March 8, 1791
LETTER LII. TO WILLIAM CARMICHAEL, March 12, 1791
LETTER LIII. TO WILLIAM SHORT, March 12,1791
LETTER LIV. TO WILLIAM SHORT, March 15, 1791
LETTER LV. TO WILLIAM CARMICHAEL, March 17,1791
LETTER LVI. TO WILLIAM SHORT, March 19, 1791
LETTER LVII. TO MR. OTTO, March 29, 1791
LETTER FROM THE PRESIDENT, April 4, 1791
LETTER LVIII. TO COLONEL HUMPHREYS, April 11, 1791
LETTER LIX. TO WILLIAM CARMICHAEL, April 11,1791
LETTER LX. TO WILLIAM SHORT, April 25, 1791
LETTER LXI. TO MR. OTTO, May 7, 1791
LETTER LXII. TO THE ATTORNEY OF THE DISTRICT OF KENTUCKY, May 7,1791
LETTER LXIII. TO THOMAS BARCLAY, May 13,1791
LETTER LXIV. TO FULWAR SKIPWITH, May 13,1791
LETTER LXV. TO WILLIAM CARMICHAEL, May 16, 1791
LETTER LXVI. TO COLONEL HUMPHREYS, July 13,1791
LETTER LXVII. TO M. VAN BERKEL, July 14,1791
LETTER LXVIII. TO GOUVERNEUR MORRIS, July 26,1791
LETTER LXIX. TO WILLIAM SHORT, July 28,1791
LETTER LXX. TO THE PRESIDENT, July 30,1791
LETTER LXXI. TO GENERAL KNOX, August 10, 1791
LETTER LXXII. TO THE MINISTER OF FRANCE, August 12, 1791
LETTER LXXIII. TO SYLVANUS BOURNE, August 14,1791
LETTER LXXIV. TO WILLIAM SHORT, August 29, 1791
LETTER LXXV. TO M. LA MOTTE, August 30, 1791
LETTER LXXVI. TO GOUVERNEUR MORRIS, August 30, 1791
LETTER LXXVII. TO MONSIEUR DE TERNANT, September 1, 1791
LETTER LXXVIII. TO T. NEWTON, September 8, 1791
LETTER LXXIX. TO MR. HAMMOND, October 26,1791
LETTER LXXX. TO WILLIAM CARMICHAEL, November 6, 1791
LETTER LXXXI. TO THE PRESIDENT, November 6, 1791
LETTER LXXXII. TO MAJOR THOMAS PINCKNEY, November 6, 1791
LETTER LXXXIII. TO THE PRESIDENT, November 7, 1791
LETTER LXXXIV. TO WILLIAM SHORT, November 24, 1791
LETTER LXXXV. TO THE ATTORNEY GENERAL, December 5,1791
LETTER LXXXVI. TO MR. HAMMOND, December 5, 1791
LETTER LXXXVII. TO MR. HAMMOND, December 12, 1791
LETTER LXXXVIII. TO MR. HAMMOND, December 13, 1791
LETTER LXXXIX. TO THE PRESIDENT, December 23, 1791
LETTER XC. TO THE PRESIDENT, January 4, 1792
LETTER XCI. TO THOMAS PINCKNEY, January 17, 1792
LETTER XCII. TO WILLINKS, VAN STAPHORSTS, AND HUBARD, Jan. 23,1792
LETTER XCIII. TO WILLIAM SHORT, January 23, 1792
LETTER XCIV. TO GOUVERNEUR MORRIS, January 23, 1792
LETTER XCV. TO MR. HAMMOND, February 2, 1792
LETTER XCVI. TO MR. HAMMOND, February 25, 1792
LETTER XCVII. TO MESSRS. JOHNSON, CARROL, AND STEWART, March 6, 1792
LETTER XCVIII. TO GOUVERNEUR MORRIS,
LETTER XCIX. TO MESSRS. CARMICHAEL AND SHORT, March 18, 1792
LETTER C. TO COLONEL PICKERING, March 28, 1792
LETTER CI. TO MR. HAMMOND, March 31, 1792
LETTER CII. TO GOVERNOR PINCKNEY, April 1, 1792
LETTER CIII. TO COLONEL HUMPHREYS, April 9, 1792
LETTER CIV. TO MR. HAMMOND, April 12, 1792
LETTER CV. TO MR. HAMMOND, April 13,1792
LETTER CVI. TO THE PRESIDENT, April 13, 1792
LETTER CVII. TO MESSRS. CARMICHAEL AND SHORT, April 24, 1792
LETTER CVIII. TO GOUVERNEUR MORRIS, April 28,1792
LETTER CIX. CIRCULAR TO THE AMERICAN CONSULS, May 31, 1792
LETTER CX. TO JOHN PAUL JONES, June 1, 1792
LETTER CXI. TO MR. PINCKNEY, June 11, 1792
LETTER CXII. TO THOMAS PINCKNEY, June 11, 1792
LETTER CXIII. TO MR. PINCKNEY, June 14, 1792
LETTER CXIV. TO GOUVERNEUR MORRIS, June 16, 1792
LETTER CXV. TO MR. VAN BERCKEL, July 2,1792
LETTER CXVI. TO MR. PALESKE, August 19,1792
LETTER CXVII. TO THE PRESIDENT, August 19, 1792
LETTER CXVIII. TO M. DE TERNANT, September 27,1792
LETTER CXIX. TO MR. PINCKNEY, October 12,1792
LETTER CXX. TO MESSRS. CARMICHAEL AND SHORT, October 14,1792
LETTER CXXI. TO GOUVERNEUR MORRIS, October 15, 1792
LETTER CXXII. TO M. DE TERNANT, October 16,1792
LETTER CXXIII. TO MESSRS. VIAR AND JAUDENES, November 1, 1792
LETTER CXXIV. TO THE PRESIDENT, November 2,1792
LETTER CXXV. TO MESSRS. CARMICHAEL AND SHORT, November 3, 1792
LETTER CXXVI. TO GOUVERNEUR MORRIS, November 7, 1792
LETTER CXXVII. TO M. DE TERNANT, November 20, 1792
LETTER CXXVIII. TO MR. RUTHERFORD, December 25, 1792
LETTER CXXIX. TO THE SPEAKER OF THE HOUSE, January 2, 1793
LETTER CXXX. CIRCULAR TO THE MINISTERS, February 13, 1793
LETTER CXXXI. TO MR. HAMMOND, February 16, 1793
LETTER CXXXII. TO M. DE TERNANT, February 17, 1793
LETTER CXXXIII. TO M. DE TERNANT, February 20, 1793
LETTER CXXXIV. TO THE SPEAKER OF THE HOUSE, February 20, 1793
LETTER CXXXV. TO GOUVERNEUR MORRIS, March 12,1793
LETTER CXXXVI. TO GOUVERNEUR MORRIS, March 15, 1793
LETTER CXXXVII. TO MR. PINCKNEY, March 16, 1793
LETTER CXXXVIII. TO COLONEL HUMPHREYS, March 21, 1793
LETTER CXXXIX. TO COLONEL HUMPHREYS, March 22, 1793
LETTER CXL.* TO MESSRS. CARMICHAEL AND SHORT, March 23, 1793
LETTER CXLI. TO MR. HAMMOND, April 18, 1793
LETTER CXLII. TO MR. PINCKNEY, April 20, 1793
LETTER CXLIII. CIRCULAR TO MORRIS, PINCKNEY, AND SHORT, April 26,1793
LETTER CXLIV. TO M. DE TERNANT, April 27,1793
LETTER CXLV. TO M. DE TERNANT, May 3,1793
LETTER CXLVI. TO MR. PINCKNEY, May 7, 1793
LETTER CXLVII. TO MR. HAMMOND, May 15, 1793
LETTER CXLVIII.* TO M. DE TERNANT, May 15, 1793
LETTER CXLIX. TO THE GOVERNOR OF VIRGINIA, May 21,1793
LETTER CL. TO MR. VAN BERCKEL, May 29,1793
LETTER CLI. TO MESSRS. CARMICHAEL AND SHORT, May 31, 1793
LETTER CLII. TO MR. GENET, June 5,1793
LETTER CLIII. TO MR. HAMMOND, June 5, 1793
LETTER CLIV. TO GOUVERNEUR MORRIS, June 13, 1793
LETTERS RE THE LOST MILLION, June 10, 1793
LETTER CLV. TO GOUVERNEUR MORRIS, June 13, 1793
LETTER CLVI. TO MR. PINCKNEY, June 14, 1793
LETTER CLVII. TO MR. GENET, June 17, X
LETTER CLVIII. TO MR. HAMMOND, June 19, 1793
LETTER CLIX. TO MESSRS. CARMICHAEL AND SHORT, June 30, 1793
LETTER CLX. TO THE SUPREME COURT OF THE UNITED STATES, July 18,1793
LETTER CLXI. TO MR. GENET, July 24,1793
LETTER CLXII. TO MR. GENET, August 7, 1793
LETTER CLXIII. TO GOUVERNEUR MORRIS, August 16,1793
LETTER CLXIV. CIRCULAR TO THE MERCHANTS OF THE U.S., August 23, 1793
LETTER CLXV. TO MR. GORE, September 2, 1793
LETTER CLXVI. TO MR. HAMMOND, September 5, 1793
LETTER CLXVII. TO MR. PINCKNEY, September 7,1793
LETTER CLXVIII. TO MR. HAMMOND, September 9, 1793
LETTER CLXIX. TO MR. GENET, September 9, 1793
LETTER CLXX. TO COLONEL HUMPHREYS, September 11, 1793
LETTER CLXXI. TO MR. GENET, October 3, 1793
LETTER CLXXII. TO MR. GENET, November 8,1793
LETTER CLXXIII. TO MR. GENET, November 22, 1793
LETTER CLXXIV. TO MR. GENET, December 9, 1793
LETTER CLXXV. TO THE ATTORNEY GENERAL OF THE U.S., December 18, 1793
LETTER CLXXVI. TO E. RANDOLPH, February 3, 1794
LETTER CLXXVII. TO JAMES MADISON, April 3, 1794
LETTER CLXXVIII. TO TENCH COXE, May 1,1794
LETTER CLXXIX. TO THE PRESIDENT, May 14, 1794
LETTER CLXXX. TO THE SECRETARY OF STATE, September 7, 1794
LETTER CLXXXI. TO JAMES MADISON, December 28, 1794
LETTER CLXXXII. TO M. D’IVERNOIS, February 6,1795
LETTER CLXXXIII. TO JAMES MADISON, April 27, 1795
LETTER CLXXXIV. TO WILLIAM B. GILES, April 27, 1795
LETTER CLXXXV. TO MANN PAGE, August 30, 1795
LETTER CLXXXVI. TO JAMES MADISON
LETTER CLXXXVII. TO EDWARD RUTLEDGE, November 30, 1795
LETTER CLXXXVIII. TO WILLIAM B. GILES, December 31, 1795
LETTER CLXXXIX. TO JAMES MADISON, March 6, 1796
LETTER CXC. TO WILLIAM B. GILES, March 19,1796.
LETTER CXCI. TO COLONEL MONROE, March 21, 1796
LETTER CXCII. TO JAMES MADISON, March 27,1796
LETTER CXCIII. TO JAMES MADISON, April 19, 1796
LETTER CXCIV.* TO P. MAZZEI, April 24, 1796
LETTER CXCV. TO COLONEL MONROE, June 12, 1796
LETTER CXCVI. TO THE PRESIDENT, June 19, 1796
LETTER CXCVII. TO M. DE LA FAYETTE, June 19, 1796
LETTER CXCVIII. TO JONATHAN WILLIAMS, July 3,1796
LETTER CXCIX. TO COLONEL MONROE, July 10, 1796
LETTER CC. TO JAMES MADISON
LETTER CCI. TO EDWARD RUTLEDGE, December 27, 1796
LETTER CCII. TO JOHN ADAMS, December 28,1796
LETTER CCIII. to James Madison, January 1, 1797
LETTER CCIV. TO MR. VOLNEY, January 8, 1797
LETTER CCV. TO HENRY TAZEWELL, January 16, 1797
LETTER CCVI. TO JAMES MADISON, January 16, 1797
LETTER CCVII. TO JAMES MADISON, January 22, 1797
LETTER CCVIII. TO JAMES MADISON, January 30, 1797
LETTER CCIX. TO JAMES SULLIVAN, February 9, 1797
LETTER CCX. TO ELBRIDGE GERRY, May 13, 1797
LETTER CCXI. TO GENERAL GATES, May 30,1797
LETTER CCXII. TO JAMES MADISON, June 1, 1797
LETTER CCXIII. TO COLONEL BURR, June 17,1797
LETTER CCXIV. TO ELBRIDGE GERRY, June 21, 1797
LETTER CCXV. TO EDWARD RUTLEDGE, June 24, 1797
LETTER, CCXVI. TO JAMES MADISON, August 3, 1797
LETTER CCXVII. TO COLONEL ARTHUR CAMPBELL, September 1, 1797
LETTER CCXVIII. TO JAMES MONROE, September 7, 1797
LETTER CCXIX. TO JAMES MADISON, January 3, 1798
LETTER CCXX. TO JAMES MADISON, January 25, 1798
LETTER CCXXI. TO JAMES MADISON, February 8, 1798
LETTER CCXXII. TO JAMES MADISON, February 15, 1798
LETTER CCXXIII. TO GENERAL GATES, February 21, 1798
LETTER CCXXIV. TO JAMES MADISON, February 22, 1798
LETTER CCXXV. TO JAMES MADISON, March 2, 1798
LETTER CCXXVI. TO JAMES MADISON, March 15, 1798
LETTER CCXXVII. TO JAMES MADISON, March 21, 1798
LETTER CCXXVIII. TO JAMES MADISON, March 29, 1798
LETTER CCXXIX. TO JAMES MADISON, April 5, 1798
LETTER CCXXX. TO JAMES MADISON, April 6, 1798
LETTER CCXXXI. TO JAMES MADISON, April 12, 1798
LETTER CCXXXII. TO JAMES MADISON, April 26, 1798
LETTER CCXXXIII. TO JAMES MADISON, May 3, 1798
LETTER CCXXXIV. TO JAMES LEWIS, JUNIOR, May 9, 1798
LETTER CCXXXV. TO JAMES MADISON, May 31, 1798
LETTER CCXXXVI. TO JOHN TAYLOR, June 1, 1798
LETTER CCXXXVII. TO GENERAL KOSCIUSKO, June 1, 1798
LETTER CCXXXVIII. TO JAMES MADISON, June 21, 1798
LETTER CCXXXIX. TO SAMUEL SMITH, August 22, 1798
LETTER CCXL. TO A. H. ROWAN, September 26, 1798
LETTER CCXLI. TO STEPHENS THOMPSON MASON, October 11, 1798
LETTER CCXLII. TO JOHN TAYLOR, November 26, 1798
LETTER CCXLIII. TO JAMES MADISON, January 3, 1799
LETTER CCXLIV. TO JAMES MADISON, January 16, 1799
LETTER CCXLV. TO ELBRIDGE GERRY
LETTER CCXLVI. TO EDMUND PENDLETON, January 29, 1799
LETTER CCXLVII. TO JAMES MADISON, February 5, 1799
LETTER CCXLVIII. TO EDMUND PENDLETON, February 14, 1799
LETTER CCXLIX. TO JAMES MADISON, February 19, 1799
LETTER CCL. TO GENERAL KOSCIUSKO, February 21, 1799
LETTER CCLI. TO JAMES MADISON, February 26, 1799
LETTER CCLII. TO T. LOMAX, March 12, 1799
LETTER CCLIII. TO EDMUND RANDOLPH, August 18, 1799
LETTER CCLIV. TO WILSON C. NICHOLAS, September 5, 1799
LETTER CCLV. TO JAMES MADISON, November 22, 1799
LETTER CCLVI. TO COLONEL MONROE, January 12, 1800
LETTER CCLVII. TO SAMUEL ADAMS
LETTER CCLVIII. TO JAMES MADISON, March 4, 1800
LETTER CCLIX. TO JAMES MADISON, May 12, 1800
LETTER CCLX. TO GIDEON GRANGER, August 13, 1800
LETTER CCLXI. TO URIAH M’GREGORY, August 13, 1800
LETTER CCLXII. TO DOCTOR RUSH, September 23, 1800
LETTER, CCLXIII. TO ROBERT R. LIVINGSTON, December 14, 1800
LETTER CCLXIV. TO COLONEL BURR, December 15,1800
LETTER CCLXV. TO JUDGE BRECKENRIDGE, December 18,1800
LETTER CCLXVI. TO JAMES MADISON, December 19,1800
LETTER CCLXVII. TO JAMES MADISON, December 26, 1800
LETTER CCLXVIII. TO COLONEL BURR, February 1, 1801
LETTER CCLXIX. TO GOVERNOR M’KEAN, February 2, 1801
LETTER CCLXX. TO TENCH COXE, February 11,1801
LETTER CCLXXI. TO JAMES MONROE, February 15, 1801
LETTER CCLXXII. TO JAMES MADISON, February 18,1801
LETTER CCLXXIII. TO JOHN DICKINSON, March 6, 1801
LETTER CCLXXIV. TO COLONEL MONROE, March 7, 1801
LETTER CCLXXV. TO GOVERNOR M’KEAN, March 9, 1801
LETTER CCLXXVI. TO JOEL BARLOW, March 14, 1801
LETTER CCLXXVII. TO THOMAS PAINE, March 18, 1801
LETTER CCLXXVIII. TO M. DE REYNEVAL, March 20, 1801
LETTER CCLXXIX. TO DOCTOR JOSEPH PRIESTLEY, March 21, 1801
LETTER CCLXXX. TO MOSES ROBINSON, March 23,1801
LETTER CCLXXXI. TO WILLIAM B. GILES, March 23, 1801
LETTER CCLXXXII. TO SAMUEL ADAMS, March 29, 1801
LETTER CCLXXXIII. TO ELBRIDGE GERRY, March 29, 1801
LETTER CCLXXXIV. TO GIDEON GRANGER, May 3, 1801
LETTER CCLXXXV. TO NATHANIEL MACON, May 14, 1801
LETTER CCLXXXVI. TO LEVI LINCOLN, July 11, 1801
LETTER CCLXXXVII. TO GOVERNOR MONROE, July 11, 1801
LETTER CCLXXXVIII. TO A COMMITTEE OF MERCHANTS, July 12, 1801
LETTER CCLXXXIX. TO LEVI LINCOLN, August 26, 1801
LETTER CCXC. TO ROBERT R. LIVINGSTON, September 9, 1801
LETTER CCXCI. TO WILLIAM SHORT, October 3, 1801
LETTER CCXCII. TO THE HEADS OF THE DEPARTMENTS, November 6, 1801
LETTER CCXCIII. TO JOHN DICKINSON, December 19, 1801
LETTER CCXCIV. TO ALBERT GALLATIN, April 1,1802
LETTER CCXCV. TO GENERAL KOSCIUSKO, April 2,1802
LETTER CCXCVI. TO ROBERT R. LIVINGSTON, April 18, 1802
LETTER CCXCVII. TO GOVERNOR MONROE, July 15, 1802
LETTER CCXCVIII. TO GOVERNOR MONROE, July 17, 1802
LETTER CCXCIX. TO ROBERT R. LIVINGSTON, October 10, 1802
LETTER CCC. TO ALBERT GALLATIN, October 13, 1802
LETTER CCCI. TO LEVI LINCOLN, October 25, 1802
LETTER CCCII. TO GOVERNOR MONROE, January 13,1803
LETTER CCCIII. TO M. DUPONT, February 1, 1803
LETTER CCCIV. TO DOCTOR BENJAMIN RUSH, April 21, 1803
LETTER CCCV. TO GENERAL GATES, July 11, 1803
LETTER CCCVI. TO MR. BRECKENRIDGE, August 12, 1803
List of Illustrations
Book Spines, 1829 Set of Jefferson Papers
Steel Engraving by Longacre from Painting of G. Stuart
TO JOHN JAY.
Paris, July 19, 1789.
Dear Sir,
I am become very uneasy, lest you should have adopted some channel for the conveyance of your letters to me, which is unfaithful. I have none from you of later date than November the 25th, 1788, and of consequence, no acknowledgment of the receipt of any of mine, since that of August the 11th, 1788. Since that period, I have written to you of the following dates. 1788. August the 20th, September the 3rd, 5th, 24th, November the 14th, 19th, 29th. 1789. January the 11th, 14th, 21st, February the 4th, March the 1st, 12th, 14th, 15th, May the 9th, 11th, 12th, June the 17th, 24th, 29th. I know, through another person, that you have received mine of November the 29th, and that you have written an answer; but I have never received the answer, and it is this which suggests to me the fear of some general source of miscarriage.
The capture of three French merchant ships by the Algerines, under different pretexts, has produced great sensation in the seaports of this country, and some in its government. They have ordered some frigates to be armed at Toulon to punish them. There is a possibility that this circumstance, if not too soon set to rights by the Algerines, may furnish occasion to the States General, when they shall have leisure to attend to matters of this kind, to disavow any future tributary treaty with them. These pirates respect still less their treaty with Spain, and treat the Spaniards with an insolence greater than was usual before the treaty.
The scarcity of bread begins to lessen in the southern parts of France, where the harvest has commenced. Here it is still threatening, because we have yet three weeks to the beginning of harvest, and I think there has not been three days’ provision beforehand in Paris, for two or three weeks past. Monsieur de Mirabeau, who is very hostile to Mr. Necker, wished to find a ground for censuring him, in a proposition to have a great quantity of flour furnished from the United States, which he supposed me to have made to Mr. Necker, and to have been refused by him; and he asked time of the States General to furnish proofs. The Marquis de la Fayette immediately gave me notice of this matter, and I wrote him a letter to disavow having ever made any such proposition to Mr. Necker, which I desired him to communicate to the States. I waited immediately on Mr. Necker and Monsieur de Montmorin, satisfied them that what had been suggested was absolutely without foundation from me; and indeed they had not needed this testimony. I gave them copies of my letter to the Marquis de la Fayette, which was afterwards printed. The Marquis, on the receipt of my letter, showed it to Mirabeau. who turned then to a paper from which he had drawn his information, and found he had totally mistaken it. He promised immediately that he would himself declare his error to the States General, and read to them my letter, which he did. I state this matter to you, though of little consequence in itself, because it might go to you misstated in the English papers.
Our supplies to the Atlantic ports of France, during the months of March, April, and May, were only twelve thousand two hundred and twenty quintals, thirty-three pounds of flour, and forty-four thousand one hundred and fifteen quintals, forty pounds of wheat, in twenty-one vessels.
My letter of the 29th of June, brought down the proceedings of the States and government to the re-union of the orders, which took place on the 27th. Within the Assembly, matters went on well. But it was soon observed, that troops, and particularly the foreign troops, were on their march towards Paris from various quarters, and that this was against the opinion of Mr. Necker. The King was probably advised to this, under pretext of preserving peace in Paris and Versailles, and saw nothing else in the measure. That his advisers are supposed to have had in view, when he should be secured and inspirited by the presence of the troops to take advantage of some favorable moment, and surprise him into an act of authority for establishing the declaration of the 23rd of June, and perhaps dispersing the States General, is probable. The Marshal de Broglio was appointed to command all the troops within the Isle of France, a high-flying aristocrat, cool and capable of everything. Some of the French guards were soon arrested under other pretexts, but in reality, on account of their dispositions in favor of the national cause. The people of Paris forced the prison, released them, and sent a deputation to the States General, to solicit a pardon. The States, by a most moderate and prudent Arrêtè, recommended these prisoners to the King, and peace to the people of Paris. Addresses came in to them from several of the great cities, expressing sincere allegiance to the King, but a determined resolution to support the States General. On the 8th of July, they voted an address to the King to remove the troops. This piece of masculine eloquence,* written by Monsieur de Mirabeau, is worth attention on account of the bold matter it expresses and discovers through the whole. The King refused to remove the troops, and said they might remove themselves, if they pleased, to Noyon or Soissons. They proceeded to fix the order in which they will take up the several branches of their future constitution, from which it appears, they mean to build it from the bottom, confining themselves to nothing in their ancient form, but a King. A declaration of rights, which forms the first chapter of their work, was then proposed by the Marquis de la Fayette. This was on the 11th. In the mean time troops, to the number of about twenty-five or thirty thousand, had arrived, and were posted in and between Paris and Versailles. The bridges and passes were guarded. At three o’clock in the afternoon, the Count de la Luzerne was sent to notify Mr. Necker of his dismission, and to enjoin him to retire instantly, without saying a word of it to any body. He went home, dined, proposed to his wife a visit to a friend, but went in fact to his country-house at St. Ouen, and at midnight set out from thence, as is supposed, for Brussels. This was not known till the next day, when the whole ministry was changed, except Villedeuil, of the domestic department, and Barentin, Garde des Sceaux. These changes were as follows. The Baron de Breteuil, president of the council of finance; and De la Galaisière, Comptroller General in the room of Mr. Necker; the Marshal de Broglio, minister of war, and Foulon under him, in the room of Puy-Ségur; Monsieur de la Vauguyon, minister of foreign affairs, instead of Monsieur de Montmorin; De la Porte, minister of marine, in place of the Count de la Luzerne; St. Priest was also removed from the Council. It is to be observed, that Luzerne and Puy-Ségur had been strongly of the aristocratical party in Council; but they were not considered as equal to bear their shares in the work now to be done. For this change, however sudden it may have been in the mind of the King, was, in that of his advisers, only one chapter of a great plan, of which the bringing together the foreign troops had been the first. He was now completely in the hands of men, the principal among whom had been noted through their lives for the Turkish despotism of their characters, and who were associated about the King, as proper instruments for what was to be executed. The news of this change began to be known in Paris about one or two o’clock. In the afternoon, a body of about one hundred German cavalry were advanced and drawn up in the Place Louis XV., and about two hundred Swiss posted at a little distance in their rear. This drew the people to that spot, who naturally formed themselves in front of the troops, at first merely to look at them. But as their numbers increased, their indignation arose; they retired a few steps, posted themselves on and behind large piles of loose stone, collected in that place for a bridge adjacent to it, and attacked the horse with stones. The horse charged, but the advantageous position of the people, and the showers of stones, obliged them to retire, and even to quit the field altogether, leaving one of their number on the ground. The Swiss in their rear were observed never to stir. This was the signal for universal insurrection, and this body of cavalry, to avoid being massacred, retired towards Versailles. The people now armed themselves with such weapons as they could find in armorers’ shops and private houses, and with bludgeons, and were roaming all night through all parts of the city, without any decided practicable object. The next day, the States pressed on the King to send away the troops, to permit the Bourgeois of Paris to arm for the preservation of order in the city, and offered to send a deputation from their body to tranquillize them. He refused all their propositions. A committee of magistrates and electors of the city were appointed by their bodies, to take upon them its government. The mob, now openly joined by the French guards, forced the prison of St. Lazare, released all the prisoners, and took a great store of corn, which they carried to the corn market. Here they got some arms, and the French guards began to form and train them. The committee determined to raise forty-eight thousand Bourgeois, or rather to restrain their numbers to forty-eight thousand. On the 14th, they sent one of their members (Monsieur de Corny, whom we knew in America) to the Hôtel des Invalides, to ask arms for their Garde Bourgeoise. He was followed by, or he found there, a great mob. The Governor of the Invalides came out, and represented the impossibility of his delivering arms, without the orders of those from whom he received them. De Corny advised the people then to retire, and retired himself; and the people took possession of the arms. It was remarkable, that not only the Invalides themselves made no opposition, but that a body of five thousand foreign troops, encamped within four hundred yards, never stirred. Monsieur de Corny and five others were then sent to ask arms of Monsieur de Launai, Governor of the Bastile. They found a great collection of people already before the place, and they immediately planted a flag of truce, which was answered by a like flag hoisted on the parapet. The deputation prevailed on the people to fall back a little, advanced themselves to make their demand of the Governor, and in that instant a discharge from the Bastile killed four people of those nearest to the deputies. The deputies retired: the people rushed against the place, and almost in an instant were in possession of a fortification, defended by one hundred men, of infinite strength, which in other times had stood several regular sieges, and had never been taken. How they got in, has as yet been impossible to discover. Those who pretend to have been of the party tell so many different stories, as to destroy the credit of them all. They took all the arms, discharged the prisoners, and such of the garrison as were not killed in the first moment of fury, carried the Governor and Lieutenant Governor to the Greve (the place of public execution), cut off their heads, and sent them through the city in triumph to the Palais Royal. About the same instant, a treacherous correspondence having been discovered in Monsieur de Flesselles, Prévôt des Marchands, they seized him in the Hotel de Ville, where he was in the exercise of his office, and cut off his head. These events, carried imperfectly to Versailles, were the subject of two successive deputations from the States to the King, to both of which he gave dry and hard answers; for it has transpired, that it had been proposed and agitated in Council, to seize on the principal members of the States General, to march the whole army down upon Paris, and to suppress its tumults by the sword. But, at night, the Duke de Liancourt forced his way into the King’s bed-chamber, and obliged him to hear a full and animated detail of the disasters of the day in Paris. He went to bed deeply impressed. The decapitation of De Launai worked powerfully through the night on the whole aristocratical party, insomuch that, in the morning, those of the greatest influence on the Count d’Artois, represented to him the absolute necessity that the King should give up every thing to the States. This according well enough with the dispositions of the King, he went about eleven o’clock, accompanied only by his brothers, to the States General, and there read to them a speech, in which he asked their interposition to re-establish order. Though this be couched in terms of some caution, yet the manner in which it was delivered, made it evident that it was meant as a surrender at discretion. He returned to the Chateau afoot, accompanied by the States. They sent off a deputation, the Marquis de la Fayette at their head, to quiet Paris. He had, the same morning, been named Commandant in Chief of the Milice Bourgeoise, and Monsieur Bailly, former President of the States General, was called for as Prévôt des Marchands. The demolition of the Bastile was now ordered, and begun. A body of the Swiss guards of the regiment of Ventimille, and the city horse-guards joined the people. The alarm at Versailles increased instead of abating. They believed that the aristocrats of Paris were under pillage and carnage, that one hundred and fifty thousand men were in arms, coming to Versailles to massacre the royal family, the court, the ministers, and all connected with them, their practices, and principles. The aristocrats of the Nobles and Clergy in the States General, vied with each other in declaring how sincerely they were converted to the justice of voting by persons, and how determined to go with the nation all its lengths. The foreign troops were ordered off instantly. Every minister resigned. The King confirmed Bailly as Prévôt des Marchands, wrote to Mr. Necker to recall him, sent his letter open to the States General, to be forwarded by them, and invited them to go with him to Paris the next day, to satisfy the city of his dispositions: and that night and the next morning, the Count d’Artois, and Monsieur de Montisson (a deputy connected with him), Madame de Polignac, Madame de Guiche, and the Count de Vaudreuil, favorites of the Queen, the Abbe de Vermont, her confessor, the Prince of Conde, and Duke de Bourbon, all fled; we know not whither. The King came to Paris, leaving the Queen in consternation for his return. Omitting the less important figures of the procession, I will only observe, that the King’s carriage was in the centre, on each side of it the States General, in two rank, afoot, and at their head the Marquis de la Fayette, as Commander in Chief, on horseback, and Bourgeois guards before and behind. About sixty thousand citizens of all forms and colors, armed with the muskets of the Bastile and Invalids, as far as they would go, the rest with pistols, swords, pikes, pruning-hooks, scythes, &c. lined all the streets through which the procession passed, and, with the crowds of people in the streets, doors, and windows, saluted them every where with cries of ‘Vive la Nation;’ but not a single ‘Vive le Roy’ was heard. The King stopped at the Hôtel de Ville. There Monsieur Bailly presented and put into his hat the popular cockade, and addressed him. The King being unprepared and unable to answer, Bailly went to him, gathered from him some scraps of sentences, and made out an answer, which he delivered to the audience as from the King. On their return, the popular cries were ‘Vive le Roy et la Nation.’ He was conducted by a Garde Bourgeoise to his palace at Versailles, and thus concluded such an amende honorable, as no sovereign ever made, and no people ever received. Letters written with his own hand to the Marquis de la Fayette remove the scruples of his position. Tranquillity is now restored to the capital: the shops are again opened; the people resuming their labors, and if the want of bread does not disturb our peace, we may hope a continuance of it. The demolition of the Bastile is going on, and the Milice Bourgeoise organizing and training. The ancient police of the city is abolished by the authority of the people, the introduction of the King’s troops will probably be proscribed, and a watch or city guards substituted, which shall depend on the city alone. But we cannot suppose this paroxysm confined to Paris alone. The whole country must pass successively through it, and happy if they get through it as soon and as well as Paris has done.
I went yesterday to Versailles, to satisfy myself what had passed there; for nothing can be believed but what one sees, or has from an eye-witness. They believe there still, that three thousand people have fallen victims to the tumults of Paris. Mr. Short and myself have been every day among them, in order to be sure of what was passing. We cannot find, with certainty, that any body has been killed but the three before mentioned, and those who fell in the assault or defence of the Bastile. How many of the garrison were killed, nobody pretends to have ever heard. Of the assailants, accounts vary from six to six hundred. The most general belief is, that there fell about thirty. There have been many reports of instantaneous executions by the mob, on such of their body as they caught in acts of theft or robbery. Some of these may perhaps be true. There was a severity of honesty observed, of which no example has been known. Bags of money offered on various occasions through fear or guilt, have been uniformly refused by the mobs. The churches are now occupied in singing ‘De projundis’ and ‘Requiems,’ ‘for the repose of the souls of the brave and valiant citizens who have sealed with their blood the liberty of the nation.’ Monsieur de Montmorin is this day replaced in the department of foreign affairs, and Monsieur de St. Priest is named to the home department. The gazettes of France and Leyden accompany this. I send also a paper (called the Point du Jour) which will give you some idea of the proceedings of the National Assembly. It is but an indifferent thing; however, it is the best.
I have the honor to be, with great esteem and respect, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
P. S. July 21. Mr. Necker had left Brussels for Frankfort, before the courier got there. We expect, however, to hear of him in a day or two. Monsieur le Comte de la Luzerne has resumed the department of the marine this day. Either this is an office of friendship effected by Monsieur de Montmorin (for though they had taken different sides, their friendship continued), or he comes in as a stop-gap, till somebody else can be found. Though very unequal to his office, all agree that he is an honest man. The Count d’Artois was at Valenciennes. The Prince of Conde and Duke de Bourbon had passed that place. T. J.
TO M. L’ABBE ARNOND.
Paris, July 19, 1789.
Dear Sir,
The annexed is a catalogue of all the books I recollect, on the subject of juries. With respect to the value of this institution, I must make a general observation. We think, in America, that it is necessary to introduce the people into every department of government, as far as they are capable of exercising it: and that this is the only way to insure a long continued and honest administration of its powers.
1. They are not qualified to exercise themselves the executive department, but they are qualified to name the person who shall exercise it. With us, therefore, they choose this officer every four years. 2. They are not qualified to legislate. With us, therefore, they only choose the legislators. 3. They are not qualified to judge questions of law, but they are very capable of judging questions of fact. In the form of juries, therefore, they determine all matters of fact, leaving to the permanent judges to decide the law resulting from those facts. But we all know, that permanent judges acquire an esprit de corps; that being known, they are liable to be tempted by bribery; that they are misled by favor, by relationship, by a spirit of party, by a devotion to the executive or legislative power; that it is better to leave a cause to the decision of cross and pile, than to that of a judge biassed to one side; and that the opinion of twelve honest jurymen gives still a better hope of right, than cross and pile does. It is in the power, therefore, of the juries, if they think the permanent judges are under any bias whatever, in any cause, to take on themselves to judge the law as well as the fact. They never exercise this power but when they suspect partiality in the judges; and by the exercise of this power, they have been the firmest bulwarks of English liberty. Were I called upon to decide, whether the people had best be omitted in the legislative or judiciary department, I would say it is better to leave them out of the legislative. The execution of the laws is more important than the making them. However, it is best to have the people in all the three departments, where that is possible.
I write in great haste, my Dear Sir, and have, therefore, only time to add wishes for the happiness of your country, to which a new order of things is opening; and assurances of the sincere esteem with which 1 have the honor to be, Dear Sir, your most obedient and humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
Books, on the subject of Juries.
Complete Juryman, or a Compendium of the Laws relating to Jurors.
Guide to English Juries.
Hawles’s Englishman’s Right.
Jurors Judges both of Law and Fact, by Jones.
Security of Englishmen’s Lives, or the Duty of Grand Juries.
Walwin’s Juries Justified.
TO JOHN JAY.
Paris, July 23, 1789.
SIR,
The bearer of my letters (a servant of Mr. Morris) not going off till to-day, I am enabled to add to their contents. The spirit of tumult seemed to have subsided, when, yesterday, it was excited again, by a particular incident. Monsieur Foulon, one of the obnoxious ministry, who, as well as his brethren, had absconded, was taken in the country, and, as is said, by his own tenants, and brought to Paris. Great efforts were exerted by popular characters, to save him. He was at length forced out of the hands of the Garde. Bourgeoise, hung immediately, his head cut off, and his body drawn through the principal streets of the city. The Intendant of Paris, Monsieur de Chauvigny, accused of having entered into the designs of the same ministry, has been taken at Compiegne, and a body of two hundred men on horseback have gone for him. If he be brought here, it will be difficult to save him. Indeed, it is hard to say, at what distance of time the presence of one of those ministers, or of any of the most obnoxious of the fugitive courtiers, will not rekindle the same blood-thirsty spirit. I hope it is extinguished as to every body else, and yesterday’s example will teach them to keep out of its way. I add two other sheets of the Point du Jour, and am, with the most perfect esteem and respect, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
P. S. I just now learn that Bertier de Chauvigny was brought to town last night, and massacred immediately.
TO JOHN JAY.
Paris, July 29, 1789.
Sir,
I have written you lately, on the 24th of June, with a postscript of the 25th; on the 29th of the same month; the 19th of July, with a postscript of the 21st; and again on the 23rd. Yesterday I received yours of the 9th of March, by the way of Holland.
Mr. Necker has accepted his appointment, and will arrive today from Switzerland, where he had taken refuge. No other ministers have been named since my last. It is thought that Mr. Necker will choose his own associates. The tranquillity of Paris has not been disturbed, since the death of Foulon and Bertier, mentioned in my last. Their militia is in a course of organization. It is impossible to know the exact state of the supplies of bread. We suppose them low and precarious, because, some days, we are allowed to buy but half or three fourths of the daily allowance of our families. Yet as the wheat harvest must begin within ten days or a fortnight, we are in hopes there will be subsistence found till that time. This is the only source from which I should fear a renewal of the late disorders; for I take for granted, the fugitives from the wrath of their country, are all safe in foreign countries. Among these are numbered seven Princes of the house of Bourbon, and six ministers; the seventh (the Marshal de Broglio) being shut up in the fortified town of Metz, strongly garrisoned with foreign soldiers. I observed to you, in a preceding letter, that the storm which had begun in Paris, on the change of the ministry, would have to pass over the whole country, and consequently, would, for a short time, occasion us terrible details from the different parts of it. Among these, you will find a horrid one retailed from Vesoul, in Franche Compte. The atrociousness of the fact would dispose us rather to doubt the truth of the evidence on which it rests, however regular that appears. There is no question, that a number of people were blown up; but there are reasons for suspecting that it was by accident and not design. It is said the owner of the chateau sold powder by the pound, which was kept in the cellar of the house blown up; and it is possible, some one of the guests may have taken this occasion to supply himself, and been too careless in approaching the mass. Many idle stories have also been propagated and believed here, against the English, as that they have instigated the late tumults with money, that they had taken or were preparing to take Cherbourg, Brest, &c.; and even reasonable men have believed, or pretended to believe, all these. The British ambassador has thought it necessary to disavow them in a public letter, which you will find in one of the papers accompanying this.
I have lately had an opportunity of knowing with certainty the present state of the King of England. His recovery was slow; he passed through a stage of profound melancholy; but this has at length dissipated, and he is at present perfectly re-established. He talks now as much as ever, on the same trifling subjects, and has recovered even his habitual inquisitiveness into the small news of the families about him. His health is also good, though he is not as fleshy as he used to be. I have multiplied my letters to you lately, because the scene has been truly interesting; so much so, that had I received my permission to pay my projected visit to my own country, I should have thought, and should still think it my duty to defer it a while. I presume it cannot now be long, before I receive your definitive answer to my request. I send herewith the public papers, as usual; and have the honor to be, with the most perfect esteem and respect, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
Paris, August 5, 1789.
Sir,
I wrote you on the 19th of the last month, with a postscript of the 21st; and again on the 23rd and 29th. Those letters went by private conveyances. This goes by the London post. Since my last, some small and momentary tumults have taken place in this city, in one of which a few of the rioters were killed by the city militia. No more popular executions have taken place. The capture of the Baron de Besenval, commandant of the Swiss troops, as he was flying to Switzerland, and of the Duke de la Vauguyon, endeavoring to escape by sea, would endanger new interpositions of the popular arm, were they to be brought to Paris. They are, therefore, confined where they were taken. The former of these being unpopular with the troops under his command, on account of oppressions, occasioned a deputation from their body, to demand justice to be done on him, and to avow the devotion of the Swiss troops to the cause of the nation. They had before taken side in part only. Mr. Necker’s return contributed much to re-establish tranquillity, though not quite as much as was expected. His just intercessions for the Baron de Besenval and other fugitives, damped very sensibly the popular ardor towards him. Their hatred is stronger than their love.
Yesterday, the other ministers were named. The Archbishop of Bordeaux is Garde des Sceaux, Monsieur de la Tour du Pin, minister of war, the Prince of Beauvou is taken into the Council, and the feuille des bénéfices given to the Archbishop of Bordeaux. These are all the popular party; so that the ministry (M. de la Luzerne excepted) and the Council, being all in reformation principles, no further opposition may be expected from that quarter. The National Assembly now seriously set their hands to the work of the constitution. They decided, a day or two ago, the question, whether they should begin by a declaration of rights, by a great majority in the affirmative. The negatives were of the Clergy, who fear to trust the people with the whole truth. The declaration itself is now on the carpet. By way of corollary to it, they last night mowed down a whole legion of abuses, as you will see by the Arrêté which I have the honor to inclose you. This will stop the burning of chateaux, and tranquillize the country more than all the addresses they could send them. I expressed to you my fears of the impractibility of debate and decision in a room of one thousand and two hundred persons, as soon as Mr. Necker’s determination to call that number, was known. The inconveniences of their number have been distressing to the last degree, though, as yet, they have been employed in work which could be done in the lump. They are now proceeding to instruments, every word of which must be weighed with precision. Heretofore, too, they were hooped together by a common enemy. This is no longer the case. Yet a thorough view of the wisdom and rectitude of this assembly disposes me more to hope they will find some means of surmounting the difficulty of their numbers, than to fear that yielding to the unmanageableness of debate in such a crowd, and to the fatigue of the experiment, they may be driven to adopt, in the gross, some one of the many projects which will be proposed.
There is a germ of schism in the pretensions of Paris to form its municipal establishment independently of the authority of the nation. It has not yet proceeded so far, as to threaten danger. The occasion does not permit me to send the public papers; but nothing remarkable has taken place in the other parts of Europe.
I have the honor to be, with the most perfect respect and esteem, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MR. CARMICHAEL.
Paris, August 9, 1789.
Dear Sir,
Since your last of March the 27th, I have only written that of May the 3th. The cause of this long silence, on both parts has been the expectation I communicated to you of embarking for America. In fact, I have expected permission for this, every hour since the month of March, and therefore always thought that by putting off writing to you a few days, my letter, while it should communicate the occurrences of the day, might be a letter of adieu. Should my permission now arrive, I should put off my departure till after the equinox. They write me that my not receiving it, has proceeded from the ceasing of the old government in October last, and the organization of the higher departments in the new, which had not yet taken place when my last letters came away. Bills had been brought in, for establishing departments of Foreign Affairs, Finance, and War. The last would certainly be given to General Knox. Mr. Jay would probably have his choice of the first and second; and it was supposed Hamilton would have that which Mr. Jay declined. Some thought Mr. Jay would prefer and obtain the head of the law department, for which Wilson would be a competitor. In such a case, some have supposed C. Thomson would ask the Foreign Affairs. The Senate and Representatives differed about the title of the President. The former wanted to style him ‘His Highness George Washington, President of the United States, and Protector of their Liberties.’ The latter insisted and prevailed, to give no title but that of office, to wit, ‘George Washington, President of the United States.’ I hope the terms of Excellency, Honor, Worship, Esquire, for ever disappear from among us, from that moment: I wish that of Mr. would follow them. In the impost bill, the Representatives had, by almost an unanimous concurrence, made a difference between nations in treaty with us, and those not in treaty. The Senate had struck out this difference, and lowered all the duties. Quære, whether the Representatives would yield? Congress were to proceed, about the 1st of June, to propose amendments to the new constitution. The principal would be the annexing a declaration of rights to satisfy the minds of all, on the subject of their liberties. They waited the arrival of Brown, Delegate from Kentucky, to take up the receiving that district as a fourteenth State. The only objections apprehended, were from the partisans of Vermont, who might insist on both coming in together. This would produce a delay, though probably not a long one.
To detail to you the events of this country, would require a volume. It would be useless too; because those given in the Leyden gazette, though not universally true, have so few and such unimportant errors mixed with them, that you may give a general faith to them. I will rather give you, therefore, what that paper cannot give, the views of the prevailing power, as far as they can be collected from conversation and writings. They will distribute the powers of government into three parts, legislative, judiciary, and executive. The legislative will certainly have no hereditary branch, probably not even a select one, (like our Senate). If they divide it into two chambers at all, it will be by breaking the representative body into two equal halves by lot. But very many are for a single House, and particularly the Turgotists. The imperfection of their legislative body, I think, will be, that not a member of it will be chosen by the people directly. Their representation will be an equal one, in which every man will elect and be elected as a citizen, not as of a distinct order. Quære, whether they will elect placemen and pensioners? Their legislature will meet periodically, and sit at their own will, with a power in the executive to call them extraordinarily, in case of emergencies. There is a considerable division of sentiment whether the executive shall have a negative on the laws. I think they will determine to give such a negative, either absolute or qualified. In the judiciary, the parliaments will be suppressed, less numerous judiciary bodies instituted, and trial by jury established in criminal, if not in civil cases. The executive power will be left entire in the hands of the King. They will establish the responsibility of ministers, gifts and appropriations of money by the National Assembly alone; consequently a civil list, freedom of the press, freedom of religion, freedom of commerce and industry, freedom of person against arbitrary arrests, and modifications, if not a total prohibition, of military agency in civil cases. I do not see how they can prohibit, altogether, the aid of the military in cases of riot, and yet I doubt whether they can descend from the sublimity of ancient military pride, to let a Marechal of France, with his troops, be commanded by a magistrate. They cannot conceive that General Washington, at the head of his army, during the late war, could have been commanded by a common constable to go as his posse comitates, to suppress a mob, and that Count Rochambeau, when he was arrested at the head of his army by a sheriff, must have gone to jail if he had not given bail to appear in court. Though they have gone astonishing lengths, they are not yet thus far. It is probable, therefore, that not knowing how to use the military as a civil weapon, they will do too much or too little with it.
I have said that things will be so and so. Understand by this, that these are only my conjectures, the plan of the constitution not being proposed yet, much less agreed to. Tranquillity is pretty well established in the capital; though the appearance of any of the refugees here would endanger it. The Baron de Besenval is kept away: so is M. de la Vauguyon. The latter was so short a time a member of the obnoxious administration, that probably he might not be touched were he here. Seven Princes of the house of Bourbon, and seven ministers, fled into foreign countries, is a wonderful event indeed.
I have the honor to be, with great respect and attachment, Dear Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN JAY.
Paris, August 12, 1789.
Sir,
I wrote you on the 19th, 23rd, 29th of the last, and 5th of the present month. The last occasions not having admitted the forwarding to you the public papers, I avail myself of the present, by a gentleman going to London, to furnish you with them to the present date. It is the only use I can prudently make of the conveyance. I shall, therefore, only observe, that the National Assembly has been entirely occupied since my last, in developing the particulars which were the subject of their resolutions of the 4th instant, of which I send you the general heads.
The city is as yet not entirely quieted. Every now and then summary execution is done on individuals, by individuals, and nobody is in condition to ask for what, or by whom. We look forward to the completion of the establishment of the city militia, as that which is to restore protection to the inhabitants. The details from the country are as distressing as I had apprehended they would be. Most of them are doubtless false, but many must still be true. Abundance of chateaux are certainly burnt and burning, and not a few lives sacrificed. The worst is probably over in this city; but I do not know whether it is so in the country. Nothing important has taken place in the rest of Europe.
I have the honor to be, with the most perfect esteem and respect, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO COLONEL GOUVION.
Paris, August 15,1789.
Sir,
I have the pleasure to inform you, that money is now deposited in the hands of Messrs. Grand and company, for paying the arrears of interest due to the foreign officers who served in the American army. I will beg the favor of you to notify thereof as many of them as you find convenient; and if you can furnish the addresses of any others to Messrs. Grand and company, they will undertake to give notice to them. The delays which have attended the completion of this object, have been greater than I expected. This has not proceeded from any inattention of Congress or any of their servants to the justice due to those officers. This has been sufficiently felt. But it was not till the present moment, that their efforts to furnish such a sum of money have been successful. The whole amount of arrears to the beginning of the present year, is about ten thousand louis d’ors.
I have the honor to be, with sentiments of the most perfect esteem and attachment, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN JAY.
Paris, August 27, 1789.
Sir,
I am honored with your favor of June the 19th, informing me that permission is given me to make a short visit to my native country, for which indulgence I beg leave to return my thanks to the President, and to yourself, Sir, for the expedition with which you were so good as to forward it, after it was obtained. Being advised that October is the best month of the autumn for a passage to America, I shall wish to sail about the first of that month and as I have a family with me, and their baggage is considerable I must endeavor to find a vessel bound directly for Virginia if possible.
My last letters to you have been of the 5th and 12th instant. Since these, I received information from our bankers in Holland, that they had money in hand sufficient to answer the demands for the foreign officers, and for the captives; and that, moreover, the residue of the bonds of the last loan were engaged. I hereupon wrote to Mr. Grand for an exact estimate of the sum necessary for the officers. He had stated it to me as being forty-five thousand six hundred and fifty-two livres eleven sous six deniers a year, when I was going to Holland to propose the loan to Mr. Adams, and at that sum, you will see it was stated in the estimate we sent you from Amsterdam. He now informed me it was sixty thousand three hundred and ninety-three livres seventeen sous ten deniers a year. I called on him for an explanation. He showed me that his first information agreed with the only list of the officers and sums then in his possession, and his last with a new list lately sent from the treasury board, in which other officers were set down, who had been omitted in the first. I wrote to our bankers on account of this error, and desired to know whether, after receiving the money necessary for the captives, they were in condition to furnish two hundred and fifty-four thousand,livres for the officers. They answered me by sending the money, and the additional sum of twenty-six thousand livres, to complete the business of the medals. I delivered the bills to Messrs. Grand and company, to negotiate and pay away; and the arrears to the officers, to the first day of the present year, are now in a course of payment. While on this subject, I will ask that an order may be forwarded to the bankers in Holland to furnish, and to Mr. Grand to pay, the arrearages which may be due on the first of January next. The money being in hand, it would be a pity that we should fail in payment a single day, merely for want of an order. The bankers further give it as their opinion, that our credit is so much advanced on the exchange of Amsterdam, that we may probably execute any money arrangements we may have occasion for, on this side the water. I have the honor to send you a copy of their letter. They have communicated to me apprehensions, that another house was endeavoring to obtain the business of our government. Knowing of no such endeavors myself, I have assured them that I am a stranger to any applications on the subject. At the same time, I cannot but suspect that this jealousy has been one of the spurs, at least, to the prompt completion of our loan. The spirited proceedings of the new Congress in the business of revenue, has doubtless been the principal one.
An engagement has taken place between the Russian and Swedish fleets in the Baltic, which has been not at all decisive, no ship having been lost on either side. The Swedes claim a victory, because they remained in the field till the Russians quitted it. The latter effected a junction soon after with another part of their fleet, and being now about ten ships strongest, the Swedes retired into port, and it is imagined they will not appear again under so great disparity; so that the campaign by sea is supposed to be finished. Their commerce will be at the mercy of their enemies: but they have put it out of the power of the Russians to send any fleet to the Mediterranean this year.
A revolution has been effected very suddenly in the bishoprick of Liege. Their constitution had been changed by force, by the reigning sovereign, about one hundred years ago. This subject had been lately revived and discussed in print. The people were at length excited to assemble tumultuously. They sent for their Prince, who was at his country-seat, and required him to come to the town-house to hear their grievances. Though in the night, he came instantly, and was obliged to sign a restitution of their ancient constitution, which took place on the spot, and all became quiet without a drop of blood spilt. This fact is worthy notice, only as it shows the progress of the spirit of revolution.
No act of violence has taken place in Paris since my last, except on account of the difference between the French and Swiss guards, which gave rise to occasional single combats, in which five or six were killed. The difference is made up. Some misunderstandings had arisen between the committees of the different districts of Paris, as to the form of the future municipal government. These gave uneasiness for a while, but have been also reconciled. Still there is such a leaven of fermentation remaining in the body of the people, that acts of violence are always possible, and are quite unpunishable; there being, as yet, no judicature which can venture to act in any case, however small or great. The country is becoming more calm. The embarrassments of the government, for want of money, are extreme. The loan of thirty millions, proposed by Mr. Necker, has not succeeded at all. No taxes are paid. A total stoppage of all payment to the creditors of the State is possible every moment. These form a great mass in the city as well as country, and among the lower class of people too, who have been used to carry their little savings of their service into the public funds, upon life rents of five, ten, twenty guineas a year, and many of whom have no other dependence for daily subsistence. A prodigious number of servants are now also thrown out of employ by domestic reforms, rendered necessary by the late events. Add to this the want of bread, which is extreme. For several days past, a considerable proportion of the people have been without bread altogether; for though the new harvest is begun, there is neither water nor wind to grind the grain. For some days past the people have besieged the doors of the bakers, scrambled with one another for bread, collected in squads all over the city, and need only some slight incident to lead them to excesses which may end in, nobody can tell what. The danger from the want of bread, however, which is the most imminent, will certainly lessen in a few days. What turn that may take which arises from the want of money, is difficult to be foreseen. Mr. Necker is totally without influence in the National Assembly, and is, I believe, not satisfied with this want of importance. That Assembly has just finished their bill of rights. The question will then be, whether to take up first the constitution or the business of finance.
No plan of a constitution has been yet given in. But I can state to you the outlines of what the leading members have in contemplation. The executive power in a hereditary King, with power of dissolving the legislature and a negative on their laws; his authority in forming treaties to be greatly restrained. The legislative to be a single House of Representatives, chosen for two or three years. They propose a body whom they call a Senate, to be chosen by the Provincial Assemblies, as our federal Senate is, but with no power of negativing or amending laws; they may only remonstrate on them to the representatives, who will decide by a simple majority the ultimate event of the law. This body will therefore be a mere council of revision. It is proposed that they shall be of a certain age and property, and be for life. They may make them also their court of impeachment. They will suppress the parliaments, and establish a system of judicature somewhat like that of England, with trial by jury in criminal cases, perhaps also in civil. Each province will have a subordinate provincial government, and the great cities, a municipal one on a free basis. These are the ideas and views of the most distinguished members. But they may suffer great modifications from the Assembly, and the longer the delay, the greater will be the modifications. Considerable interval having taken place since any popular execution, the aristocratic party is raising its head. They are strengthened by a considerable defection from the patriots, in consequence of the general suppression of the abuses of the 4th of August, in which many were interested. Another faction too, of the most desperate views, has acquired strength in the Assembly, as well as out of it. These wish to dethrone the reigning branch, and transfer the crown to the Duke d’Orleans. The members of this faction are mostly persons of wicked and desperate fortunes, who have nothing at heart but to pillage from the wreck of their country. The Duke himself is as unprincipled as his followers; sunk in debaucheries of the lowest kind, and incapable of quitting them for business; not a fool, yet not head enough to conduct any thing. In fact, I suppose him used merely as a tool, because of his immense wealth, and that he acquired a certain degree of popularity by his first opposition to the government, then credited to him as upon virtuous motives. He is certainly borrowing money on a large scale. He is in understanding with the court of London, where he had been long in habits of intimacy. The ministry here are apprehensive, that that ministry will support his designs by war. I have no idea of this, but no doubt, at the same time, that they will furnish him money liberally to aliment a civil war, and prevent the regeneration of this country.
It was suggested to me, some days ago, that the court of Versailles were treating with that of London, for a surrender of their West India possessions, in consideration of a great sum of money to relieve their present distress. Every principle of common sense was in opposition to this fact; yet it was so affirmed as to merit inquiry. I became satisfied the government had never such an idea; but that the story was not without foundation altogether; that something like this was in contemplation between the faction of Orleans and the court of London, as a means of obtaining money from that court. In a conversation with the Count de Montmorin, two days ago, he told me their colonies were speaking a language which gave them uneasiness, and for which there was no foundation. I asked him if he knew any thing of what I have just mentioned. He appeared unapprized of it, but to see at once that it would be a probable speculation between two parties circumstanced and principled as those two are. I apologized to him for the inquiries I had made into this business, by observing that it would be much against our interest, that any one power should monopolize all the West India islands. ‘Parde, assurément,’ was his answer.
The emancipation of their islands is an idea prevailing in the minds of several members of the National Assembly, particularly those most enlightened and most liberal in their views. Such a step by this country would lead to other emancipations or revolutions in the same quarter. I enclose you some papers received from Mr. Carmichael, relative to the capture of one of our vessels by a Morocco cruiser, and restitution by the Emperor. I shall immediately write to M. Chiappe, to express a proper sense of the Emperor’s friendly dispositions to us. I forward also the public papers to the present date; and have the honor to be, with sentiments of the most perfect esteem and respect, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JAMES MADISON.
Paris, August 28,1789.
Dear Sir,
My last to you was of July the 22nd. Since that, I have received yours of May the 27th, June 13th and 30th. The tranquillity of the city has not been disturbed since my last. Dissensions between the French and Swiss guards occasioned some private combats, in which five or six were killed. These dissensions are made up. The want of bread for some days past has greatly endangered the peace of the city. Some get a little, some none at all. The poor are the best served, because they besiege perpetually the doors of the bakers. Notwithstanding this distress, and the palpable impotence of the city administration to furnish bread to the city, it was not till yesterday, that general leave was given to the bakers to go into the country and buy flour for themselves, as they can. This will soon relieve us, because the wheat harvest is well advanced.’ Never was there a country where the practice of governing too much, had taken deeper root and done more mischief. Their declaration of rights is finished. If printed in time, I will enclose a copy with this. It is doubtful whether they will now take up the finance or the constitution first. The distress for money endangers every thing. No taxes are paid, and no money can be borrowed. Mr. Necker was yesterday to give in a memoir to the Assembly, on this subject. I think they will give him leave to put into execution any plan he pleases, so as to debarrass themselves of this, and take up that of the constitution. No plan is yet reported; but the leading members (with some small difference of opinion) have in contemplation the following. The executive power in a hereditary King, with a negative on laws, and power to dissolve the legislature; to be considerably restrained in the making of treaties, and limited in his expenses. The legislative in a House of Representatives. They propose a Senate also, chosen on the plan of our federal Senate, by the Provincial Assemblies, but to be for life, of a certain age, (they talk of forty years), and certain wealth (four or five hundred guineas a year), but to have no other power as to laws but to remonstrate against them to the representatives, who will then determine their fate by a simple majority. This you will readily perceive is a mere council of revision, like that of New York, which, in order to be something, must form an alliance with the King, to avail themselves of his veto. The alliance will be useful to both, and to the nation. The representatives to be chosen every two or three years. The judiciary system is less prepared than any other part of the plan; however, they will abolish the parliaments, and establish an order of judges and justices, general and provincial, a good deal like ours, with trial by jury in criminal cases certainly, perhaps also in civil. The provinces will have Assemblies for their provincial government, and the cities a municipal body for municipal government, all founded on the basis of popular election. These subordinate governments, though completely dependent on the general one, will be intrusted with almost the whole of the details which our State governments exercise. They will have their own judiciary, final in all but great cases, the executive business will principally pass through their hands, and a certain local legislature will be allowed them. In short, ours has been professedly their model, in which such changes are made as a difference of circumstances rendered necessary, and some others neither necessary nor advantageous, but into which men will ever run, when versed in theory and new in the practice of government, when acquainted with man only as they see him in their books and not in the world. This plan will undoubtedly undergo changes in the Assembly, and the longer it is delayed, the greater will be the changes; for that Assembly, or rather the patriotic part of it, hooped together heretofore by a common enemy, are less compact since their victory. That enemy (the civil and ecclesiastical aristocracy) begins to raise its head. The lees, too, of the patriotic party, of wicked principles and desperate fortunes, hoping to pillage something in the wreck of their country, are attaching themselves to the faction of the Duke of Orleans: that faction is caballing with the populace, and intriguing at London, the Hague, and Berlin, and have evidently in view the transfer of the crown to the Duke of Orleans. He is a man of moderate understanding, of no principle, absorbed in low vice, and incapable of abstracting himself from the filth of that, to direct any thing else. His name and his money, therefore, are mere tools in the hands of those who are duping him.
They may produce a temporary confusion, and even a temporary civil war, supported, as they will be, by the money of England; but they cannot have success ultimately. The King, the mass of the substantial people of the whole country, the army, and the influential part of the clergy, form a firm phalanx which must prevail. Should those delays which necessarily attend the deliberations of a body of one thousand two hundred men, give time to this plot to ripen and burst, so as to break up the Assembly before any thing definitive is done, a constitution, the principles of which are pretty well settled in the minds of the Assembly, will be proposed by the national militia, (*****) urged by the individual members of the Assembly, signed by the King and supported by the nation, to prevail till circumstances shall permit its revision and more regular sanction. This I suppose the pis aller of their affairs, while their probable event is a peaceable settlement of them. They fear a war from England, Holland, and Prussia. I think England will give money, but not make war. Holland would soon be afire, internally, were she to be embroiled in external difficulties. Prussia must know this, and act accordingly.
It is impossible to desire better dispositions towards us, than prevail in this Assembly. Our proceedings have been viewed as a model for them on every occasion; and though in the heat of debate men are generally disposed to contradict every authority urged by their opponents, ours has been treated like that of the Bible, open to explanation, but not to question. I am sorry that in the moment of such a disposition, any thing should come from us to check it. The placing them on a mere footing with the English, will have this effect. When of two nations, the one has engaged herself in a ruinous war for us, has spent her blood and money to save us, has opened her bosom to us in peace, and received us almost on the footing of her own citizens, while the other has moved heaven, earth, and hell to exterminate us in war, has insulted us in all her councils in peace, shut her doors to us in every part where her interests would admit it, libelled us in foreign nations, endeavored to poison them against the reception of our most precious commodities; to place these two nations on a footing, is to give a great deal more to one than to the other, if the maxim be true, that to make unequal quantities equal, you must add more to one than the other. To say, in excuse, that gratitude is never to enter into the motives of national conduct, is to revive a principle which has been buried for centuries with its kindred principles of the lawfulness of assassination, poison, perjury, &c. All of these were legitimate principles in the dark ages which intervened between ancient and modern civilization, but exploded and held in just horror in the eighteenth century. I know but one code of morality for men, whether acting singly or collectively. He who says I will be a rogue when I act in company with a hundred others, but an honest man when I act alone, will be believed in the former assertion, but not in the latter. I would say with the poet, ‘Hie niger est; hunc tu, Romane, caveto.’ If the morality of one man produces a just line of conduct in him, acting individually, why should not the morality of one hundred men produce a just line of conduct in them, acting together? But I indulge myself in these reflections because my own feelings run me into them; with you they were always acknowledged. Let us hope that our new government will take some other occasion to show, that they mean to proscribe no virtue from the canons of their conduct with other nations. In every other instance, the new government has ushered itself to the world as honest, masculine, and dignified. It has shown genuine dignity, in my opinion, in exploding adulatory titles; they are the offerings of abject baseness, and nourish that degrading vice in the people.
I must now say a word on the declaration of rights, you have been so good as to send me. I like it, as far as it goes; but I should have been for going further. For instance, the following alterations and additions would have pleased me. Article 4. The people shall not be deprived of their right to speak, to write, or otherwise to publish any thing but false facts affecting injuriously the life, liberty, property, or reputation of others, or affecting the peace of the confederacy with foreign nations. Article 7. All facts put in issue before any judicature, shall be tried by jury, except, 1. in cases of admiralty jurisdiction, wherein a foreigner shall be interested; 2. in cases cognizable before a court martial, concerning only the regular-officers and soldiers of the United States, or members of the militia in actual service in time of war or insurrection; and 3. in impeachments allowed by the constitution. Article 8. No person shall be held in confinement more than ——— days after he shall have demanded and been refused a writ of habeas corpus by the judge appointed by law, nor more than ——— days after such a writ shall have been served on the person holding him in confinement, and no order given on due examination for his remandment or discharge, nor more than ——— hours in any place at a greater distance than ——— miles from the usual residence of some judge authorized to issue the writ of habeas corpus; nor shall that writ be suspended for any term exceeding one year, nor in any place more than ——— miles distant from the State or encampment of enemies or of insurgents. Article 9. Monopolies may be allowed to persons for their own productions in literature, and their own inventions in the arts, for a term not exceeding ——— years, but for no longer term, and no other purpose. Article 10. All troops of the United States shall stand ipso facto disbanded, at the expiration of the term for which their pay and subsistence shall have been last voted by Congress, and all officers and soldiers, not natives of the United States, shall be incapable of serving in their armies by land, except during a foreign war. These restrictions I think are so guarded, as to hinder evil only. However, if we do not have them now, I have so much confidence in my countrymen, as to be satisfied that we shall have them as soon as the degeneracy of our government shall render them necessary.
I have no certain news of Paul Jones. I understand only, in a general way, that some persecution on the part of his officers occasioned his being called to Petersburg, and that though protected against them by the Empress, he is not yet restored to his station. Silas Deane is coming over to finish his days in America, not having one sous to subsist on, elsewhere. He is a wretched monument of the consequences of a departure from right. I will, before my departure, write Colonel Lee fully the measures I pursued to procure success in his business, and which as yet offer little hope; and I shall leave it in the hands of Mr. Short to be pursued, if any prospect opens on him. I propose to sail from Havre as soon after the first of October as I can get a vessel; and shall consequently leave this place a week earlier than that. As my daughters will be with me, and their baggage somewhat more than that of mere voyageures, I shall endeavor, if possible, to obtain a passage for Virginia directly. Probably I shall be there by the last of November. If my immediate attendance at New York should be requisite for any purpose, I will leave them with a relation near Richmond, and proceed immediately to New York. But as I do not foresee any pressing purpose for that journey immediately on my arrival, and as it will be a great saving of time, to finish at once in Virginia, so as to have no occasion to return there after having once gone on to the northward, I expect to proceed to my own house directly. Staying there two months (which I believe will be necessary), and allowing for the time I am on the road, I may expect to be at New York in February, and to embark from thence or some eastern port. You ask me if I would accept any appointment on that side of the water? You know the circumstances which led me from retirement, step by step, and from one nomination to another, up to the present. My object is a return to the same retirement. Whenever, therefore, I quit the present, it will not be to engage in any other office, and most especially any one which would require a constant residence from home. The books I have collected for you will go off for Havre in three or four days, with my baggage. From that port, I shall try to send them by a direct occasion to New York.
I am, with great and sincere esteem, Dear Sir, your affectionate friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
P. S. I just now learn that Mr. Necker proposed yesterday to the National Assembly a loan of eighty millions, on terms more tempting to the lender than the former, and that they approved it, leaving him to arrange the details, in order that they might occupy themselves at once about the constitution. T. J.
TO JAMES MADISON.
Paris, September 6, 1789.
Dear Sir,
I sit down to write to you, without knowing by what occasion I shall send my letter. I do it, because a subject comes into my head, which I wrould wish to develope[sp.] a little more than is practicable in the hurry of the moment of making up general despatches.
The question, whether one generation of men has a right to bind another, seems never to have been started either on this, or our side of the water. Yet it is a question of such consequences as not only to merit decision, but place also among the fundamental principles of every government. The course of reflection in which we are immersed here, on the elementary principles of society, has presented this question to my mind; and that no such obligation can be so transmitted, I think very capable of proof. I set out on this ground, which I suppose to be self-evident, that the earth belongs in usufruct to the living: that the dead have neither powers nor rights over it. The portion occupied by any individual ceases to be his when himself ceases to be, and reverts to the society. If the society has formed no rules for the appropriation of its lands in severalty, it will be taken by the first occupants, and these will generally be the wife and children of the decedent. If they have formed rules of appropriation, those rules may give it to the wife and children, or to some one of them, or to the legatee of the deceased. So they may give it to his creditor.
But the child, the legatee, or creditor, takes it not by natural right, but by a law of the society of which he is a member, and to which he is subject. Then, no man can, by natural right, oblige the lands he occupied, or the persons who succeed him in that occupation, to the payment of debts contracted by him. For if he could, he might, during his own life, eat up the usufruct of the lands for several generations to come; and then the lands would belong to the dead, and not to the living, which is the reverse of our principle.
What is true of every member of the society individually, is true of them all collectively; since the rights of the whole can be no more than the sum of the rights of the individuals. To keep our ideas clear when applying them to a multitude, let us suppose a whole generation of men to be born on the same day, to attain mature age on the same day, and to die on the same day, leaving a succeeding generation in the moment of attaining their mature age, all together. Let the ripe age be supposed of twenty-one years, and their period of life thirty-four years more, that being the average term given by the bills of mortality to persons of twenty-one years of age. Each successive generation would, in this way, come and go off the stage at a fixed moment, as individuals do now. Then I say, the earth belongs to each of these generations during its course, fully and in its own right. The second generation receives it clear of the debts and incumbrances of the first, the third of the second, and so on. For if the first could charge it with a debt, then the earth would belong to the dead and not to the living generation. Then no generation can contract debts greater than may be paid during the course of its own existence. At twenty-one years of age, they may bind themselves and their lands for thirty-four years to come; at twenty-two, for thirty-three; at twenty-three, for thirty-two; and at fifty-four, for one year only; because these are the terms of life which remain to them at the respective epochs. But a material difference must be noted, between the succession of an individual and that of a whole generation. Individuals are parts only of a society, subject to the laws of the whole. These laws may appropriate the portion of land occupied by a decedent, to his creditor rather than to any other, or to his child, on condition he satisfies the creditor. But when a whole generation, that is, the whole society, dies, as in the case we have supposed, and another generation or society succeeds, this forms a whole, and there is no superior who can give their territory to a third society, who may have lent money to their predecessors, beyond their faculties of paying. What is true of generations succeeding one another at fixed epochs, as has been supposed for clearer conception, is true for those renewed daily, as in the actual course of nature. As a majority of the contracting generation will continue in being thirty-four years, and a new majority will then come into possession, the former may extend their engagements to that term, and no longer. The conclusion, then, is, that neither the representatives of a nation, nor the whole nation itself assembled, can validly engage debts beyond what they may pay in their own time, that is to say, within thirty-four years from the date of the engagement.
To render this conclusion palpable, suppose that Louis the XIV. and XV. had contracted debts in the name of the French nation, to the amount of ten thousand milliards, and that the whole had been contracted in Holland. The interest of this sum would be five hundred milliards, which is the whole rent-roll or nett[sp.] proceeds of the territory of France. Must the present generation of men have retired from the territory in which nature produces them, and ceded it to the Dutch creditors? No; they have the same rights over the soil on which they were produced, as the preceding generations had. They derive these rights not from them, but from nature. They, then, and their soil are, by nature, clear of the debts of their predecessors. To present this in another point of view, suppose Louis XV. and his cotemporary generation had said to the money-lenders of Holland, Give us money, that we may eat, drink, and be merry in our day; and on condition you will demand no interest till the end of thirty-four years, you shall then, for ever after, receive an annual interest of fifteen per cent. The money is lent on these conditions, is divided among the people, eaten, drunk, and squandered. Would the present generation be obliged to apply the produce of the earth and of their labor, to replace their dissipations? Not at all.
I suppose that the received opinion, that the public debts of one generation devolve on the next, has been suggested by our seeing, habitually, in private life, that he who succeeds to lands is required to pay the debts of his predecessor; without considering that this requisition is municipal only, not moral, flowing from the will of the society, which has found it convenient to appropriate the lands of a decedent on the condition of a payment of his debts: but that between society and society, or generation and generation, there is no municipal obligation, no umpire, but the law of nature.
The interest of the national debt of France being, in fact, but a two thousandth part of its rent-roll, the payment of it is practicable enough; and so becomes a question merely of honor or of expediency. But with respect to future debts, would it not be wise and just for that nation to declare in the constitution they are forming, that neither the legislature nor the nation itself, can validly contract more debt than they may pay within their own age, or within the term of thirty-four years? And that all future contracts shall be deemed void, as to what shall remain unpaid at the end of thirty-four years from their date? This would put the lenders, and the borrowers also, on their guard. By reducing, too, the faculty of borrowing within its natural limits, it would bridle the spirit of war, to which too free a course has been procured by the inattention of money-lenders to this law of nature, that succeeding generations are not responsible for the preceding.
On similar ground it may be proved, that no society can make a perpetual constitution, or even a perpetual law. The earth belongs always to the living generation: they may manage it, then, and what proceeds from it, as they please, during their usufruct. They are masters, too, of their own persons, and consequently may govern them as they please. But persons and property make the sum of the objects of government. The constitution and the laws of their predecessors are extinguished then, in their natural course, with those whose will gave them being. This could preserve that being, till it ceased to be itself, and no longer. Every constitution, then, and every law, naturally expires at the end of thirty-four years. If it be enforced longer, it is an act of force and not of right. It may be said that the succeeding generation exercising, in fact, the power of repeal, this leaves them as free as if the constitution or law had been expressly limited to thirty-four years only. In the first place, this objection admits the right, in proposing an equivalent. But the power of repeal is not an equivalent. It might be, indeed, if every form of government were so perfectly contrived, that the will of the majority could always be obtained, fairly and without impediment. But this is true of no form. The people cannot assemble themselves; their representation is unequal and vicious. Various checks are opposed to every legislative proposition. Factions get possession of the public councils, bribery corrupts them, personal interests lead them astray from the general interests of their constituents; and other impediments arise, so as to prove to every practical man, that a law of limited duration is much more manageable than one which needs a repeal.
This principle, that the earth belongs to the living and not to the dead, is of very extensive application and consequences in every country, and most especially in France. It enters into the resolution of the questions, whether the nation may change the descent of lands holden in tail; whether they may change the appropriation of lands given anciently to the church, to hospitals, colleges, orders of chivalry, and otherwise in perpetuity whether they may abolish the charges and privileges attached on lands, including the whole catalogue, ecclesiastical and feudal; it goes to hereditary offices, authorities, and jurisdictions, to hereditary orders, distinctions, and appellations, to perpetual monopolies in commerce, the arts, or sciences, with a long train of et ceteras; and it renders the question of reimbursement, a question of generosity and not of right. In all these cases, the legislature of the day could authorize such appropriations and establishments for their own time, but no longer; and the present holders, even where they or their ancestors have purchased, are in the case of bonâ fide purchasers of what the seller had no right to convey.
Turn the subject in your mind, my Dear Sir, and particularly as to the power of contracting debts, and develope it with that cogent logic which is so peculiarly yours. Your station in the councils of our country gives you an opportunity of producing it to public consideration, of forcing it into discussion. At first blush it may be laughed at, as the dream of a theorist; but examination will prove it to be solid and salutary. It would furnish matter for a fine preamble to our first law for appropriating the public revenue: and it will exclude, at the threshold of our new government, the ruinous and contagious errors of this quarter of the globe, which have armed despots with means which nature does not sanction, for binding in chains their fellow-men. We have already given, in example, one effectual check to the dog of war, by transferring the power of declaring war from the executive to the legislative body, from those who are to spend, to those who are to pay. I should be pleased to see this second obstacle held out by us also, in the first instance. No nation can make a declaration against the validity of long contracted debts, so disinterestedly as we, since we do not owe a shilling which will not be paid, principal and interest, by the measures you have taken, within the time of our own lives. I write you no news, because when an occasion occurs, I shall write a separate letter for that.
I am always, with great and sincere esteem, Dear Sir, your affectionate friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
THOMAS JEFFERSON TO DR. GEM.
The hurry in which I wrote my letter to Mr. Madison, which is in your hands, occasioned an inattention to the difference between generations succeeding each other at fixed epochs, and generations renewed daily and hourly. It is true that in the former case, the generation when at twenty-one years of age, may contract a debt for thirty-four yours, because a majority of them will live so long. But a generation consisting of all ages, and which legislates by all its members above the age of twenty-one years, cannot contract for so long a time, because their majority will be dead much sooner. Buffon gives us a table of twenty-three thousand nine hundred and ninety-four deaths, stating the ages at which they happened. To draw from these the result I have occasion for, I suppose a society in which twenty-three thousand nine hundred and ninety-four persons are born every year, and live to the age stated in Buffon’s table. Then, the following inferences may be drawn. Such a society will consist constantly of six hundred and seventeen thousand seven hundred and three persons, of all ages. Of those living at any one instant of time, one half will be dead in twenty-four years and eight months. In such a society, ten thousand six hundred and seventy-five will arrive every year at the age of twenty-one years complete. It will constantly have three hundred and forty-eight thousand four hundred and seventeen persons of all ages above twenty-one years, and the half of those of twenty-one years and upwards living at any one instant of time, will be dead in eighteen years and eight months, or say nineteen years.
Then, the contracts, constitutions, and laws of every such society become void in nineteen years from their date.
TO GENERAL KNOX.
Paris, September 12,1789.
Sir,
In a letter which I had the honor of writing to the Secretary for Foreign Affairs, some three or four years ago, I informed him that a workman here had undertaken by the help of moulds and other means, to make all the parts of the musket so exactly alike, as that, mixed together promiscuously, any one part should serve equally for every musket. He had then succeeded as to the lock both of the officer’s fusil and the soldier’s musket. From a promiscuous collection of parts, I put together myself half a dozen locks, taking the first pieces which came to hand. He has now completed the barrel, stock, and mounting of the officer’s fusil, and is proceeding on those of the soldier’s musket. This method of forming the fire-arm appears to me so advantageous when repairs become necessary, that I thought it my duty not only to mention to you the progress of this artist, but to purchase and send you half a dozen of his officer’s fusils. They are packed in a box marked T. J. No. 36, and are sent to Havre, from whence they shall be forwarded to New York. The barrels and furniture are to their stocks, to prevent the warping of the wood. The locks are in pieces. You will find with them tools for putting them together, also a single specimen of his soldier’s lock. He formerly told me, and still tells me, that he shall be able, after a while, to furnish them cheaper than the common musket of the same quality, but at first, they will not be so cheap in the first cost, though the economy in repairs will make them so in the end. He cannot tell me exactly, at what price he can furnish them. Nor will he be able, immediately, to furnish any great quantity annually; but with the aid of the government, he expects to enlarge his establishment greatly. If the situation of the finances of this country should oblige the government to abandon him, he would prefer removing with all his people and implements to America, if we should desire to establish such a manufacture, and he would expect our government to take all his implements, on their own account, at what they have cost him. He talked of about three thousand guineas. I trouble you with these details, and with the samples, 1. That you may give the idea of such an improvement to our own workmen, if you think it might answer any good end. 2. That all the arms he shall have for sale, may be engaged for our government, if he continues here, and you think it important to engage them. 3. That you may consider, and do me the honor of communicating your determination, whether in the event of his establishment being abandoned by this government, it might be thought worth while to transfer it to the United States, on conditions somewhat like those he has talked of.
I have the honor to be, with sentiments of the most perfect esteem and respect, Sir, your most obedient, humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO E. RUTLEDGE.
Paris, September 18, 1789.
Dear Sir,
I have duly received your favor by Mr. Cutting, enclosing the paper from Doctor Trumbull, for which I am very thankful. The conjecture that inhabitants may have been carried from the coast of Africa to that of America, by the trade winds, is possible enough; and its probability would be greatly strengthened by ascertaining a similarity of language, which I consider as the strongest of all proofs of consanguinity among nations. Still a question would remain between the red men of the eastern and western sides of the Atlantic, which is the stock, and which the shoot. If a fact be true, which I suspect to be true, that there is a much greater number of radical languages among those of America than among those of the other hemisphere, it would be a proof of superior antiquity, which I can conceive no arguments strong enough to overrule.
When I received your letter, the time of my departure was too near to permit me to obtain information from Constantinople, relative to the demand and price of rice there. I therefore wrote to a merchant at Marseilles, concerned in the Levant trade, for the prices current of rice at Constantinople and at Marseilles for several years past. He has sent me only the present price at Marseilles, and that of a particular cargo at Constantinople. I send you a copy of his letter. The Algerines form an obstacle; but the object of our commerce in the Mediterranean is so immense, that we ought to surmount that obstacle, and I believe it could be done by means in our power, and which, instead of fouling us with the dishonorable and criminal baseness of France and England, will place us in the road to respect with all the world.
I have obtained, and enclose to you, a state of all the rice imported into this country in the course of one year, which shows its annual consumption to be between eighty-one and eighty-two thousand quintals. I think you may supplant all the other furnishing States, except as to what is consumed at Marseilles and its neighborhood. In fact, Paris is the place of main consumption. Havre, therefore, is the port of deposit, where you ought to have one or two honest, intelligent, and active consignees. The ill success of a first or second experiment should not damp the endeavors to open this market fully, but the obstacles should be forced by perseverance. I have obtained, from different quarters, seeds of the dry rice; but having had time to try them, I find they will not vegetate, having been too long kept. I have still several other expectations from the East Indies. If this rice be as good, the object of health will render it worth experiment with you. Cotton is a precious resource, and which cannot fail with you. I wish the cargo of olive plants sent by the way of Baltimore, and that which you will perceive my correspondent is preparing now to send, may arrive to you in good order. This is the object for the patriots of your country; for that tree once established there, will be the source of the greatest wealth and happiness. But to insure success, perseverance may be necessary. An essay or two may fail. I think, therefore, that an annual sum should be subscribed, and it need not be a great one. A common country laborer should be engaged to make it his sole occupation, to prepare and pack plants and berries at Marseilles, and in the autumn to go with them himself through the canal of Languedoc to Bordeaux, and there to stay with them till he can put them on board a vessel bound directly to Charleston; and this repeated annually, till you have a sufficient stock insured, to propagate from, without further importation. I should guess that fifty guineas a year would do this, and if you think proper to set such a subscription afoot, write me down for ten guineas of the money, yearly, during my stay in France, and offer my superintendence of the business on this side the water if no better can be had.
Mr. Cutting does full justice to the honorable dispositions of the legislature of South Carolina towards their foreign creditors. None have yet come into the propositions sent to me, except the Van Staphorsts.
The clanger of famine here has not ceased with a plentiful harvest. A new and unskilful administration has not yet got into the way of bringing regular supplies to the capital. We are in danger of hourly insurrection for the want of bread; and an insurrection once begun for that cause, may associate itself with those discontented for other causes, and produce incalculable events. But if the want of bread does not produce a commencement of disorder, I am of opinion the other discontents will be stifled, and a good and free constitution established without opposition. In fact, the mass of the people, the clergy, and army, (excepting the higher orders of the three bodies) are in as compact an union as can be. The National Assembly have decided that their executive shall be hereditary, and shall have a suspensive negative on the laws; that the legislature shall be of one House, annual in its sessions and biennial in its elections. Their declaration of rights will give you their other general views. I am just on my departure for Virginia, where the arrangement of my affairs will detain me the winter; after which (say in February) I shall go on to New York, to embark from some northern port for France. In the mean while and always, I am with great and sincere esteem, Dear Sir, your friend and servant.
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN JAY.
Paris, September 19, 1789.
Sir,
I had the honor of addressing you on the 30th of the last month. Since that, I have taken the liberty of consigning to you a box of officers’ muskets, containing half a dozen, made by the person and on the plan which I mentioned to you in a letter which I cannot turn to at this moment, but I think it was of the year 1785. A more particular account of them you will find in the enclosed copy of a letter which I have written to General Knox. The box is marked T. J. No. 36, is gone to Havre, and will be forwarded to you by the first vessel bound to New York, by Mr. Nathaniel Cutting, an American gentleman establishing himself there.
Recalling to your mind the account I gave you of the number and size of ships fitted out by the English last year, for the northern whale-fishery, and comparing with it what they have fitted out this year, for the same fishery, the comparison will stand thus:
Years. Vessels. Tons. Men.
1788. 255 75,436 10,710
1789. 178 51,473 7,476
Difference. 77 23,963 3,234
By which you will perceive, that they have lost a third of that fishery in one year, which I think almost entirely, if not quite, ascribable to the shutting the French ports against their oil. I have no account of their southern fishery of the present year.
As soon as I was informed that our bankers had the money ready for the redemption of our captives, I went to the General of the order of the Holy Trinity, who retained all his dispositions to aid us in that business. Having a very confidential agent at Marseilles, better acquainted than himself with the details, he wrote to him for his opinion and information on the subject. I enclose you a copy of his answer, the original of which was communicated to me. I thereupon have authorized the General to go as far as three thousand livres a head for our captives, and for this purpose to adopt the plan proposed, of sending one of his own religion at our expense (which will be small), or any other plan he thinks best. The honesty and goodness of his character places us in safety in his hands. To leave him without any hesitation in engaging himself for such a sum of money, it was necessary to deposit it in a banker’s hands here. Mr. Grand’s were agreeable to him, and I have therefore desired our banker at Amsterdam to remit it here. I do not apprehend, in the progress of the present revolution, any thing like a general bankruptcy which should pervade the whole class of bankers. Were such an event to appear imminent, the excessive caution of the house of Grand and Company establishes it in the general opinion as the last that would give way, and consequently would give time to withdraw this money from their hands. Mr. Short will attend to this, and will withdraw the money on the first well-founded appearance of danger. He has asked me what he shall do with it. Because it is evident, that when Grand cannot be trusted, no other individual at Paris can, and a general bankruptcy can only be the effect of such disorders, as would render every private house an insecure deposit, I have not hesitated to say to him, in such an event, ‘Pay it to the government.’ In this case, it becomes only a change of destination and no loss at all. But this has passed between us for greater caution only, and on the worst case supposable: for though a suspension of payment by government might affect the bankers a little, I doubt if any of them have embarked so much in the hands of government as to endanger failure, and especially as they have had such long warning.
You will have known, that the ordinance passed by M. de Chillon in St. Domingo, for opening ports to our importations in another part of the island, was protested against by Marbois. He had always led the Count de la Luzerne by the nose, while Governor of that island. Marbois’ representations, and Luzerne’s prepossessions against our trade with their colonies, occasioned him, as minister of that department, not only to reverse the ordinance, but to recall Chillon and send out a successor. Chillon has arrived here, and having rendered himself very popular in the islands, their deputies in the National Assembly have brought the question before them. The Assembly has done nothing more, as yet, than to appoint a committee of inquiry. So much of Chillon’s ordinance as admitted the importation of our provisions, is continued for a time. M. de Marbois, too, is recalled, I know not why or how. M. de la Luzerne’s conduct will probably come under view only incidentally to the general question urged by the colony deputies, whether they shall not be free in future, to procure provisions where they can procure them cheapest. But the deputies are disposed to treat M. de la Luzerne roughly. This, with the disgrace of his brother, the Bishop de Langres, turned out of the presidentship of the National Assembly, for partiality in office to the aristocratic principles, and the disfavor of the Assembly towards M. de la Luzerne himself, as having been formerly of the plot (as they call it) with Breteuil and Broglio, will probably occasion him to be out of office soon.
The treasury board have no doubt attended to the necessity of giving timely orders for the payment of the February interest at Amsterdam. I am well informed that our credit is now the first at that exchange, (England not borrowing at present.) Our five per cent, bonds have risen to ninety-seven and ninety-nine. They have been heretofore at ninety-three. There are, at this time, several companies and individuals here, in England, and Holland, negotiating to sell large parcels of our liquidated debt. A bargain was concluded by one of these the other day, for six hundred thousand dollars. In the present state of our credit, every dollar of this debt will probably be transferred to Europe within a short time.
September the 20th. The combination of bankers and other ministerial tools had led me into the error (when I wrote my last letter), into which they had led most people, that the loan lately opened here went on well. The truth is, that very little has been borrowed, perhaps not more than six or eight millions. The King and his ministers were yesterday to carry their plate to the mint. The ladies are giving up their jewels to the National Assembly. A contribution of plate in the time of Louis XV. is said to have carried about eight millions to the treasury. Plate is much more common now, and therefore, if the example prevail now in the same degree it did then, it will produce more. The contribution of jewels will hardly be general, and will be unproductive. Mr. Necker is, on the 25th, to go to the Assembly, to make some proposition. The hundreth penny is talked of.
The Assembly proceeds slowly in the forming their constitution. The original vice of their numbers causes this, as well as a tumultuous manner of doing business. They have voted that the elections of the legislature shall be biennial; that it shall be of a single body; but they have not yet decided what shall be its number, or whether they shall be all in one room, or in two (which they call a division into sections). They have determined that the King shall have a suspensive and iterative veto: that is, that after negativing a law, it cannot be presented again till after a new election. If he negatives it then, it cannot be presented a third time till after another new election. If it be then presented, he is obliged to pass it. This is perhaps justly considered as a more useful negative than an absolute one, which a King would be afraid to use. Mr. Necker’s influence with the Assembly is nothing at all. Having written to them, by order of the King, on the subject of the veto, before it was decided, they refused to let his letter be read. Again, lately, when they desired the sanction of the King to their proceedings of the fourth of August, he wrote in the King’s name a letter to them, remonstrating against an immediate sanction to the whole; but they persisted, and the sanction was given. His disgust at this want of influence, together with the great difficulties of his situation, make it believed that he is desirous of resigning. The public stocks were extremely low the day before yesterday. The caisse d’escompte at three thousand six hundred and forty, and the loan of one hundred and twenty-five millions, of 1784, was at fifteen per cent. loss. Yesterday they rose a little. The sloth of the assembly (unavoidable from their number) has done the most sensible injury to the public cause. The patience of a people, who have less of that quality than any other nation in the world, is worn thread-bare. Time has been given to the aristocrats to recover from their panic, to cabal, to sow dissensions in the Assembly, and distrust out of it. It has been a misfortune, that the King and aristocracy together have not been able to make a sufficient resistance, to hoop the patriots in a compact body. Having no common enemy of such force as to render their union necessary, they have suffered themselves to divide. The Assembly now consists of four distinct parties. 1. The aristocrats, comprehending the higher members of the clergy, military, nobility, and the parliaments of the whole kingdom. This forms a head without a body. 2. The moderate royalists, who wish for a constitution nearly similar to that of England. 3. The republicans, who are willing to let their first magistracy be hereditary, but to make it very subordinate to the legislature, and to have that legislature consist of a single chamber. 4. The faction of Orleans. The second and third descriptions are composed of honest, well meaning men, differing in opinion only, but both wishing the establishment of as great a degree of liberty as can be preserved. They are considered together as constituting the patriotic part of the Assembly, and they are supported by the soldiery of the army, the soldiery of the clergy, that is to say, the Cures and monks, the dissenters, and part of the nobility which is small, and the substantial Bourgeoisie of the whole nation. The part of these collected in the cities, have formed themselves into municipal bodies, have chosen municipal representatives, and have organized an armed corps, considerably more numerous in the whole than the regular army. They have also the ministry, such as it is, and as yet, the King. Were the second and third parties, or rather these sections of the same party, to separate entirely, this great mass of power and wealth would be split, no body knows how. But I do not think they will separate; because they have the same honest views; because, each being confident of the rectitude of the other, there is no rancor between them; because they retain the desire of coalescing. In order to effect this, they not long ago proposed a conference, and desired it might be at my house, which gave me an opportunity of judging of their views. They discussed together their points of difference for six hours, and in the course of discussion agreed on mutual sacrifices. The effect of this agreement has been considerably defeated by the subsequent proceedings of the Assembly, but I do not know that it has been through any infidelity of the leaders to the compromise they had agreed on. Another powerful bond of union between these two parties, is our friend the Marquis de la Fayette. He left the Assembly while they as yet formed but one party. His attachment to both is equal, and he labors incessantly to keep them together. Should he be obliged to take part against either, it will be against that which shall first pass the Rubicon of reconciliation with the other. I should hope, in this event, that his weight would be sufficient to turn the scale decidedly in favor of the other. His command of the armed militia of Paris (thirty thousand in number, and comprehending the French guards, who are five thousand regulars), and his influence with the municipality, would secure their city: and though the armed militia and municipalities of the other cities are in no wise subordinate to those of Paris, yet they look up to them with respect, and look particularly to the Marquis de la Fayette, as leading always to the rights of the people. This turn of things is so probable, that I do not think either section of the patriots will venture on any act, which will place themselves in opposition to him.
This being the face of things, troubled as you will perceive, civil war is much talked of and expected; and this talk and expectation has a tendency to beget it. What are the events which may produce it? 1. The want of bread, were it to produce a commencement of disorder, might ally itself to more permanent causes of discontent, and thus continue the effect beyond its first cause. The scarcity of bread, which continues very great amidst a plenty of corn, is an enigma which can be solved only by observing, that the furnishing the city is in the new municipality, not yet masters of their trade. 2. A public bankruptcy. Great numbers of the lower as well as higher classes of the citizens, depend for subsistence on their property in the public funds. 3. The absconding of the King from Versailles. This has for some time been apprehended as possible. In consequence of this apprehension, a person, whose information would have weight, wrote to the Count de Montmorin, adjuring him to prevent it by every possible means, and assuring him that the flight of the King would be the signal of a St. Barthelemi against the aristocrats in Paris, and perhaps through the kingdom. M. de Montmorin showed the letter to the Queen, who assured him solemnly that no such thing was in contemplation. His showing it to the Queen, proves he entertained the same mistrust with the public. It may be asked, What is the Queen disposed to do in the present situation of things? Whatever rage, pride, and fear can dictate in a breast which never knew the presence of one moral restraint.
Upon the whole, I do not see it as yet probable that any actual commotion will take place; and if it does take place, I have strong confidence that the patriotic party will hold together, and their party in the nation be what I have described it. In this case, there would be against them the aristocracy and the faction of Orleans. This consists, at this time, of only the Catilines of the Assembly, and some of the lowest descriptions of the mob. Its force, within the kingdom, must depend on how much of this last kind of people it can debauch with money from its present bias to the right cause. This bias is as strong as any one can be, in a class which must accept its bread from him who will give it. Its resources out of the kingdom are not known. Without doubt, England will give money to produce and to feed the fire which should consume this country; but it is not probable she will engage in open war for that. If foreign troops should be furnished, it would be most probably by the King of Prussia, who seems to offer himself as the bull-dog of tyranny to all his neighbors. He might, too, be disturbed by the contagion of the same principles gaining his own subjects, as they have done those of the Austrian Netherlands, Liege, Cologne, and Hesse-Cassel. The army of the latter Prince, joining with his subjects, are said to have possessed themselves of the treasures he had amassed by hiring troops to conquer us, and by other iniquities. Fifty-four millions of livres is the sum mentioned. But all these means, external and internal must prove inadequate to their ultimate object, if the nation be united as it is at present. Expecting within a few days to leave Paris, and that this is my last letter on public subjects, I have indulged myself in giving you a general view of things, as they appear to me at the time of my leaving them. Mr. Short will have the honor of continuing the narration, and of correcting it, where circumstances unknown or unforseen may give a different turn to events.
I have the honor to be, with sentiments of the most perfect esteem and respect, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MR. NECKER.
Paris, September 26,1789.
Sir,
I had the honor of waiting on you at Versailles, the day before yesterday, in order to present my respects on my departure to America. I was unlucky in the moment, as it was one in which you were gone out.
I wished to have put into your hands, at the same time, the enclosed state of the British northern fishery for the years 1788 and 1789, by which you will see that they have lost in one year, one third of that fishery, the effect, almost solely, of the Arrêt which shut the ports of France to their oils.
I wished also to know, whether, while in America, I could be useful towards encouraging supplies of provision to be brought to this country the ensuing year. I am persuaded a considerable relief to the city of Paris might be obtained, by permitting the importation of salted provisions from the United States. Our salted beef, particularly, (which, since the war, we have learned to prepare in the Irish manner, so as to be as good as the best of that country) could be sold out to the people of Paris, for the half of what they pay for fresh meat. It would seem then, that the laborer paying but half the usual price for his meat, might pay the full price of his bread, and so relieve government from its loss on that article. The interest of the gabelles has been an objection, hitherto, to the importation of salted provisions. But that objection is lessened by the reduction of the price of salt, and done away entirely, by the desire of the present government to consider the ease and happiness of the people as the first object. In every country as fully peopled as France, it would seem good policy to encourage the employment of its lands in the cultivation of corn, rather than in pasturage, and consequently to encourage the use of all kinds of salted provisions, because they can be imported from other countries. It may be apprehended, that the Parisian, habituated to fresh provision, would not use salted. Then he would not buy them, and of course they would not be brought, so that no harm can be done by the permission. On the contrary, if the people of Paris should readily adopt the use of salted provisions, the good would result which is before mentioned. Salt meat is not as good as fresh for soups, but it gives an higher flavor to the vegetables boiled with it. The experience of a great part of America, which is fed almost entirely on it, proves it to be as wholesome as fresh meat. The sea scurvy, ascribed by some to the use of salt meat, is equally unknown in America as in Europe. It is the want of vegetables at sea which produces the scurvy. I have thus hastily mentioned reasons and objections, to save you the time and trouble of recollecting them. To you, Sir, it suffices barely to mention them. Mr. Short, chargé des affaires of the United States, will have the honor of delivering you this, and of giving you any further details which you may be pleased to require.
I shall hope, on my return in the spring, to find your health reestablished, and your mind relieved by a perfect settlement of the affairs of the nation; and with my felicitations on those accounts, to express to you those sentiments of profound respect and attachment, with which I have the honor to be, your Excellency’s most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN JAY.
Havre, September 30, 1789.
Dear Sir,
No convenient ship having offered from any port of France, I have engaged one from London to take me up at Cowes, and am so far on my way thither. She will land me at Norfolk, and as I do not know any service that would be rendered by my repairing immediately to New York, I propose, in order to economize time, to go directly to my own house, get through the business which calls me there, and then repair to New York, where I shall be ready to re-embark for Europe. But should there be any occasion for government to receive any information I can give, immediately on my arrival, I will go to New York on receiving your orders at Richmond. They may probably be there before me, as this goes by Mr. Trumbull, bound directly for New York.
I enclose you herewith the proceedings of the National Assembly on Saturday last, wherein you will perceive that the committee had approved the plan of Mr. Necker. I can add from other sure information received here, that the Assembly adopted it the same evening. This plan may possibly keep their payments alive till their new government gets into motion; though I do not think it very certain. The public stocks lowered so exceedingly the last days of my stay at Paris, that I wrote to our bankers at Amsterdam, to desire they would retain till further orders the thirty thousand guilders, or so much of it as had not yet come on. And as to what might be already coming on, I recommended to Mr. Short to go and take the acceptance himself, and keep the bill in his own hands till the time of payment. He will by that time see what is best to be done with the money.
In taking leave of Monsieur de Montmorin, I asked him whether their West India ports would continue open to us a while. He said they would be immediately declared, open till February, and we may be sure they will be so till the next harvest. He agreed with me, that there would be two or three months’ provision for the whole kingdom wanting for the ensuing year. The consumption of bread for the whole kingdom, is two millions of livres tournois, a day. The people pay the real price of their bread every where, except at Paris and Versailles. There the price is suffered to vary very little as to them, and government pays the difference. It has been supposed that this difference for some time past has cost a million a week. I thought the occasion favorable to propose to Monsieur de Montmorin the free admission of our salted provisions, observing to him, particularly, that our salted beef from the eastern States could be dealt out to the people of Paris for five or six sols the pound, which is but half the common price they pay for fresh beef; that the Parisian paying less for his meat, might pay more for his bread, and so relieve government from its enormous loss on that article. His idea of this resource seemed unfavorable. We talked over the objections of the supposed unhealthiness of that food, its tendency to produce scurvy, the chance of its taking with a people habituated to fresh meat, their comparative qualities of rendering vegetables eatable, and the interests of the gabelles. He concluded with saying the experiment might be tried, and with desiring me to speak with Mr. Necker. I went to Mr. Necker, but he had gone to the National Assembly. On my return to Paris, therefore, I wrote to him on the subject, going over the objections which Monsieur de Montmorin had started. Mr. Short was to carry the letter himself, and to pursue the subject.
Having observed that our commerce to Havre is considerably on the increase, and that most of our vessels coming there, and especially those from the eastward, are obliged to make a voyage round to the neighborhood of the Loire and Garonne for salt, a voyage attended with expense, delay, and more risk, I have obtained from the Farmers General, that they shall be supplied from their magazines at Honfleur, opposite to Havre, at a mercantile price. They fix it at present at sixty livres the muid, which comes to about, fifteen sous, or seven and a half pence sterling our bushel; but it will vary as the price varies at the place from which they bring it. As this will be a great relief to such of our vessels coming to Havre, as might wish to take back salt, it may perhaps be proper to notify it to our merchants. I enclose herewith Mr. Necker’s discourse to the Assembly, which was not printed till I left Paris: and have the honor to be, with sentiments of the most perfect esteem and respect, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO THE PRESIDENT.
Chesterfield, December 15,1789.
Sir,
I have received at this place the honor of your letters of October the 13th and November the 30th, and am truly flattered by your nomination of me to the very dignified office of Secretary of State; for which permit me here to return you my humble thanks. Could any circumstance seduce me to overlook the disproportion between its duties and my talents, it would be the encouragement of your choice. But when I contemplate the extent of that office, embracing as it does the principal mass of domestic administration, together with the foreign, I cannot be insensible of my inequality to it; and I should enter on it with gloomy forebodings from the criticisms and censures of a public, just indeed in their intentions, but sometimes misinformed and misled, and always too respectable to be neglected. T cannot but foresee the possibility that this may end disagreeably for me, who, having no motive to public service but the public satisfaction, would certainly retire the moment that satisfaction should appear to languish. On the other hand, I feel a degree of familiarity with the duties of my present office, as far at least as I am capable of understanding its duties. The ground I have already passed over, enables me to see my way into that which is before me. The change of government too, taking place in the country where it is exercised, seems to open a possibility of procuring from the new rulers some new advantages in commerce, which may be agreeable to our countrymen. So that as far as my fears, my hopes, or my inclination might enter into this question, I confess they would not lead me to prefer a change.
But it is not for an individual to choose his post. You are to marshal us as may best be for the public good; and it is only in the case of its being indifferent to you, that I would avail myself of the option you have so kindly offered in your letter. If you think it better to transfer me to another post, my inclination must be no obstacle; nor shall it be, if there is any desire to suppress the office I now hold, or to reduce its grade. In either of these cases, be so good only as to signify to me by another line your ultimate wish, and I shall conform to it cordially. If it should be to remain at New York, my chief comfort will be to work under your eye, my only shelter the authority of your name, and the wisdom of measures to be dictated by you and implicitly executed by me. Whatever you may be pleased to decide, I do not see that the matters which have called me hither, will permit me to shorten the stay I originally asked; that is to say, to set out on my journey northward till the month of March. As early as possible in that month, I shall have the honor of paying my respects to you in New York. In the mean time, I have that of tendering you the homage of those sentiments of respectful attachment, with which I am, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO HENRY LAURENS, ESQUIRE.
New York, March 31, 1790.
Sir,
Encroachments being made on the eastern limits of the United States, by settlers under the British government, pretending that it is the western and not the eastern river of the bay of Passamaquoddy, which was designated by the name of St. Croix in the treaty of peace with that nation, I have to beg the favor of you to communicate any facts which your memory or papers may enable you to recollect, and which may indicate the true river, the commissioners on both sides had in their view to establish as the boundary between the two nations. It will be of some consequence to be informed by what map they traced the boundary.
I have the honor to be, with the greatest respect, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MR. VANDERKEMP.
New York, March 31, 1799.
Sir,
The letter has been duly received which you addressed to th© President of the United States, praying his interference with the government of the United Netherlands, on the subject of property you left there on coming to America. I have it in charge to inform you that the United States have at present no minister at the Hague, and consequently no channel through which they could express their concern for your interests. However willing, too, we are to receive and protect all persons who come hither, with the property they bring, perhaps it may be doubted, how far it would be expedient to engage ourselves for what they leave behind, or for any other matter retrospective to their becoming citizens. In the present instance, we hope, that no confiscation of the residuum of your property left in the United Netherlands having taken place, the justice of that government will leave you no occasion for that interference which you have been pleased to ask from this.
I have the honor to be, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO GEORGE JOY.
New York, March 31, 1790.
Sir,
I have considered your application for sea-letters for the ship Eliza, and examined into the precedents which you supposed might influence the determination. The resolution of Congress, which imposes this duty on the Secretary for Foreign Affairs, provides expressly, ‘that it be made to appear to him by oath or affirmation, or by such other evidence as shall by him be deemed satisfactory, that the vessel is commanded by officers, citizens of the United States.’ Your affidavit satisfies me that one of the officers is a citizen of the United States; but you are unacquainted with the others, and without evidence as to them, and even without a presumption that they are citizens, except so far as arises on the circumstances of the captain’s being an American, and the ship sailing from an American port. Now, I cannot in my conscience say, that this is evidence of the fact, satisfactory to my mind. The precedents of relaxation by Mr. Jay, were all between the date of the resolution of Congress (February the 12th, 1788) and his public advertisement, announcing the evidence which must be produced. Since this last, the proceedings have been uniform and exact. Having perfect confidence in your good faith, and therefore without a suspicion of any fraud intended in the present case, I could have wished sincerely to grant the sea-letter; but besides the letter of the law which ties me down, the public security against a partial dispensation of justice, depends on its being dispensed by certain rules. The slightest deviation in one circumstance, becomes a precedent for another, that for a third, and so on without bounds. A relaxation in a case where it is certain no fraud is intended, is laid hold of by others, afterwards, to cover fraud. I hope, therefore, you will be sensible of the necessity of my adhering to the rules which have been published and practised by my predecessor; and that I am with great respect, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO THE COUNT DE MONTMORIN.
New York, April 6, 1790.
Sir,
The President of the United States having thought proper to assign to me other functions than those of their Minister Plenipotentiary near the King, I have the honor of addressing to your Excellency my letters of recall, and of beseeching you to be so good as to present them, with the homage of my respectful adieus, to his Majesty.
It is with great satisfaction that I find myself authorized to conclude, as I had begun my mission, with assurances of the attachment of our government to the King and his people, and of its desire to preserve and strengthen the harmony and good understanding, which has hitherto so happily subsisted between the two nations.
Give me leave to place here, also, my acknowledgments to your Excellency, personally, for the facilities you have been pleased always to give in the negotiation of the several matters I have had occasion to treat with you during my residence at your court. They were ever such as to evince, that the friendly dispositions towards our republic which you manifested even from its birth, were still found consistent with that patriotism of which you have continued to give such constant and disinterested proofs. May this union of interests for ever be the patriot’s creed in both countries. Accept my sincere prayers that the King, with life and health, may be long blessed with so faithful and able a servant, and you with a Prince, the model of royal excellence; and permit me to retain, to my latest hours, those sentiments of affectionate respect and attachment, with which I have the honor to be your Excellency’s most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
New York, April 6,1790.
Sir,
The President of the United States having been pleased, in the month of June last, to give me leave of absence for some time from the court of France, and to appoint Mr. William Short chargé des affaires for the United States during my absence, and having since thought proper to call me to the office of Secretary of State, comprehending that of Foreign Affairs, I have now the honor of requesting you to give credence to whatever Mr. Short shall say to you on my part. He knows the interest which our republic takes in the prosperity of France, our strong desire to cultivate its friendship, and my zeal to promote it by whatever may depend on my ministry, and I have no doubt he will so conduct himself as to merit your confidence. I avail myself of this occasion of tendering you assurances of the sentiments of respect and esteem, with which I have the honor to be your Excellency’s most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO WILLIAM SHORT.
New York, April 6, 1790.
Sir,
My last to you was of March the 28th. Since that, yours of the 2nd and 6th of January have come to hand, together with the ratification of the consular convention.
I send you herewith a letter from the President to the King, notifying my recall, with a letter of leave to Monsieur de Montmorin, and another of credence for you to the same, all of which you will be pleased to deliver to him. Copies of them are enclosed for your information.
We are extremely mortified at the prospect there is, that the act of justice and gratitude to the court of France, which Congress, in the first moment it ever was in their power, have been, and still are preparing, may arrive too late, to save that court from the necessity of parting with our debt to a disadvantage. The Secretary of the Treasury, having by order of Congress reported a plan for funding both our foreign and domestic debts, they thought it necessary, by a re-commitment, to subject that part of it which concerned the domestic debt, to maturer discussion. But the clause ‘for making such adequate provision for fulfilling our engagements in respect to our foreign debt,’ was not re-committed, because not susceptible of any abridgment or modification. On the contrary, it was passed without a dissenting voice, and only waits till the residue of that system of which it makes a part, can be digested and put into the form of a law. I send you a copy of the resolution, to be communicated to Monsieur de Montmorin and Monsieur Necker, and anxiously wish it may arrive in time to prevent a disadvantageous alienation, by satisfying these ministers that we are exerting ourselves to repay to that country, in her hour of difficulty, what she generously advanced for us, in ours.
You may remember, I purchased some officer’s fusils, had them packed in my presence, and sent with my own baggage to Havre. When they arrived here, the plates and other principal parts of the locks were no longer in the box. It is necessary, therefore, that the workman send you six new locks, which may be applied to the stocks and barrels we have, and that you be so good as to forward these by the first safe conveyance.
Press the negotiation for our captives, in the line and on the terms I had fixed, not binding us further without further advice, and be pleased to apprize us of its present situation and future progress, as being a subject we have at heart.
The Leyden gazettes furnishing so good information of the interesting scenes now passing in Europe, I must ask your particular attention to the forwarding them as frequently as it is possible to find conveyances. The English papers bring their lies very fresh, and it is very desirable to be provided with an authentic contradiction in the first moment.
You will receive, herewith, the newspapers and other interesting papers, as usual.
I have the honor to be, with the most perfect esteem, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO THE COUNT DE FLORIDA BLANCA.
New York, April 11, 1790.
Sir,
The President of the United States having thought proper to name Mr. William Carmichael their chargé des affaires, near his Catholic Majesty, I have now the honor of announcing the same to your Excellency, and of praying you to give credence to whatever he shall say to you on my part. He knows the concern our republic takes in the interest and prosperity of Spain, our strong desire to cultivate its friendship, and to deserve it by all the good offices which esteem and neighborhood may dictate; he knows also my zeal to promote these by whatever may depend on my ministry. I have no doubt that Mr. Carmichael will so conduct himself as to merit your confidence; and I avail myself with pleasure of this occasion of tendering to you assurances of those sentiments of respect and esteem, with which I have the honor to be, your Excellency’s most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO WILLIAM CARMICHAEL.
New York, April 11, 1789.
Sir,
A vessel being about sail from this port for Cadiz, I avail myself of it to inform you, that under the appointment of the President of the United States, I have entered on the duties of Secretary of State, comprehending the department of Foreign Affairs. Mr. Jay’s letter of October the 2nd acknowledged the receipt of the last of yours which have come to hand. Since that date he wrote you on the 7th of December, enclosing a letter for Mr. Chiappe.
The receipt of his letter of September the 9 th, 1788, having never been acknowledged, the contents of which were important and an answer wished for, I send you herewith a duplicate, lest it should have miscarried.
You will also receive, herewith, a letter of credence for yourself, to be delivered to the Count de Florida Blanca, after putting thereon the proper address, with which I am unacquainted. A copy of it is enclosed for your information.
I beg leave to recommend the case of Don Blas Gonzalez to your good offices with the court of Spain, enclosing you the documents necessary for its illustration. You will perceive, that two vessels were sent from Boston in the year 1787, on a voyage of discovery and commercial experiment in general, but more particularly to try a fur-trade with the Russian settlements, on the northwest coast of our continent, of which such wonders have been published in Captain Cook’s voyages, that it excited similar expeditions from other countries also; and that the American vessels were expressly forbidden to touch at any Spanish port, but in cases of extreme distress. Accordingly, through the whole of their voyage through the extensive latitudes held by that crown, they never put into any port but in a single instance. In passing near the island of Juan Fernandez, one of them was damaged by a storm, her rudder broken, her mast disabled, and herself separated from her companion. She put into the island to refit, and at the same time, to wood and water, of which she began to be in want. Don Blas Gonzalez, after examining her, and finding she had nothing on board but provisions and charts, and that her distress was real, permitted her to stay a few days, to refit and take in fresh supplies of wood and water. For this act of common hospitality, he was immediately deprived of his government, unheard, by superior order, and remains still under disgrace. We pretend not to know the regulations of the Spanish government, as to the admission of foreign vessels into the ports of their colonies; but the generous character of the nation is a security to us, that their regulations can, in no instance, run counter to the laws of nature; and among the first of her laws, is that which bids us to succor those in distress. For an obedience to this law, Don Blas appears to have suffered; and we are satisfied, it is because his case has not been able to penetrate to his Majesty’s ministers, at least, in its true colors. We would not choose to be committed by a formal solicitation, but we would wish you to avail yourself of any good opportunity of introducing the truth to the ear of the minister, and of satisfying him, that a redress of this hardship on the Governor would be received here with pleasure, as a proof of respect to those laws of hospitality which we would certainly observe in a like case, as a mark of attention towards us, and of justice to an individual for whose sufferings we cannot but feel.
With the present letter, you will receive the public and other papers as usual, and I shall thank you in return, for a regular communication of the best gazettes published in Madrid.
I have the honor to be, with sentiments of the most perfect esteem, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MR. GRAND.
New York, April 23, 1790.
Dear Sir,
You may remember that we were together at the Hôtel de la Monnoye, to see Mr. Drost strike coins in his new manner, and that you were so kind as to speak with him afterwards on the subject of his coming to America. We are now in a condition to establish a mint, and should be desirous of engaging him in it. I suppose him to be at present in the service of Watt and Bolton, the latter of whom you may remember to have been present with us at the Monnoye. I know no means of communicating our dispositions to Drost so effectually as through your friendly agency, and therefore take the liberty of asking you to write to him, to know what emoluments he receives from Watts and Bolton, and whether he would be willing to come to us for the same? If he will, you may give him an expectation, but without an absolute engagement, that we will call for him immediately, and that with himself, we may probably take and pay him for all the implements of coinage he may have, suited to our purpose. If he asks higher terms, he will naturally tell you so, and what they are; and we must reserve a right to consider of them. In either case, I will ask your answer as soon as possible. I need not observe to you, that this negotiation should be known to nobody but yourself, Drost, and Mr. Short. The good old Dr. Franklin, so long the ornament of our country, and, I may say, of the world, has at length closed his eminent career. He died on the 17th instant, of an imposthume of his lungs, which having suppurated and burst, he had not strength to throw off the matter, and was suffocated by it. His illness from this imposthume was of sixteen days. Congress wear mourning for him, by a resolve of their body.
I beg you to present my friendly respects to Madame Grand, the elder and younger, and to your son, and believe me to be, with sentiments of great esteem and attachment, Dear Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO THE MARQUIS DE LA LUZERNE.
New York, April 30,1790.
Sir,
When in the course of your legation to the United States, your affairs rendered it necessary that you should absent yourself a while from that station, we flattered ourselves with the hope that that absence was not final. It turned out, in event, that the interests of your sovereign called for your talents and the exercise of your functions, in another quarter. You were pleased to announce this to the former Congress through their Secretary for Foreign Affairs, at a time when, that body was closing its administration, in order to hand it over to a government then preparing on a different model. This government is now formed, organized, and in action; and it considers among its earliest duties, and assuredly among its most cordial, to testify to you the regret which the people and government of the United States felt at your removal from among them; a very general and sincere regret, and tempered only by the consolation of your personal advancement, which accompanied it. You will receive, Sir, by order of the President of the United States, as soon as they can be prepared, a medal and chain of gold, of which he desires your acceptance, in token of their esteem, and of the sensibility with which they will ever recall your legation to their memory.
But as this compliment may hereafter be rendered to other missions, from which yours was distinguished by eminent circumstances, the President of the United States wishes to pay you the distinguished tribute of an express acknowledgment of your services, and our sense of them. You came to us, Sir, through all the perils which encompassed us on all sides. You found us struggling and suffering under difficulties, as singular and trying as our situation was new and unprecedented. Your magnanimous nation had taken side with us in the conflict, and yourself became the centre of our common councils, the link which connected our common operations. In that position you labored without ceasing, till all our labors were crowned with glory to your nation, freedom to ours, and benefit to both. During the whole, we had constant evidence of your zeal, your abilities, and your good faith. We desire to convey this testimony of it home to your own breast, and to that of your sovereign, our best and greatest friend; and this I do, Sir, in the name, and by the express instruction of the President of the United States.
I feel how flattering it is to me, Sir, to be the organ of the public sense on this occasion, and to be justified, by that office, in adding to theirs, the homage of those sentiments of respect and esteem, with which I have the honor to be your Excellency’s most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO WILLIAM SHORT.
New York, April 30, 1790.
Dear Sir,
My last letter to you was of the 6th instant, acknowledging the receipt of your favors of the 2nd and 6th of January. Since that, Mr. Jay has put into my hands yours of the 12th of January, and I have received your note of February the 10th, accompanying some newspapers.
Mine of the 6th covered the President’s letter to the King for my recall, and my letters of leave for myself and of credence to you, for the Count de Montmorin, with copies of them for your information. Duplicates of all these accompany the present; and an original commission for you as chargé des affaires, signed by the President. At the date of my former letters, I had not had time to examine with minuteness the proper form of credentials under our new constitution: I governed myself, therefore, by foreign precedents, according to which a chargé des affaires is furnished with only a letter of credence from one minister of Foreign Affairs to the other. Further researches have shown me, that under our new constitution, all commissions (or papers amounting to that) must be signed by the President. You will judge whether any explanation on this subject to M. de Montmorin be necessary. I enclose you also the copy of a letter written to the Marquis de la Luzerne, to be communicated to the Count de Montmorin, and by him to the King, if he thinks proper.
It has become necessary to determine on a present proper to be given to diplomatic characters on their taking leave of us; and it is concluded that a medal and chain of gold will be the most convenient. I have, therefore, to ask the favor of you to order the dies to be engraved with all the despatch practicable.
The medal must be of thirty lines diameter, with a loop on the edge to receive the chain. On one side, must be the arms of the United States, of which I send you a written description, and several impressions in wax to render that more intelligible; round them, as a legend, must be ‘The United States of America.’ The device of the other side we do not decide on. One suggestion has been a Columbia (a fine female figure), delivering the emblems of peace and commerce to a Mercury, with a legend ‘Peace and Commerce’ circumscribed, and the date of our republic, to wit, IV July ‘MDCCLXXVI,’ subscribed as an exergum: but having little confidence in our own ideas in an art not familiar here, they are only suggested to you, to be altered, or altogether postponed to such better device as you may approve, on consulting with those who are in the habit and study of medals. Duvivier and Dupre seem to be the best workmen; perhaps the last is the best of the two.
The public papers, which accompany this, will give you fully the news of this quarter.
I am with great and sincere esteem, Dear Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MR. DUMAS.
New York, June 23, 1790.
Dear Sir,
I arrived at this place the letter[sp.] end of March, and undertook the office to which the President had been pleased to appoint me, of Secretary of State, which comprehends that of Foreign Affairs. Before I had got through the most pressing matters which had been accumulating, a long illness came upon me, and put it out of my power for many weeks to acknowledge the receipt of your letters.
We are much pleased to learn the credit of our paper at Amsterdam. We consider it as of the first importance, to possess the first credit there, and to use it little. Our distance from the wars of Europe, and our disposition to take no part in them, will, we hope, enable us to keep clear of the debts which they occasion to other powers. It will be well for yourself and our bankers, to keep in mind always, that a great distinction is made here, between our foreign and domestic paper. As to the foreign, Congress is considered as the representative of one party only, and I think I can say with truth, that there is not one single individual in the United States, either in or out of office, who supposes they can ever do any thing which might impair their foreign contracts. But with respect to domestic paper, it is thought that Congress, being the representative of both parties, may shape their contracts so as to render them practicable, only seeing that substantial justice be done. This distinction will explain to you their proceedings on the subject of their debts. The funding their foreign debts, according to express contract, passed without a debate and without a dissenting voice. The modeling and funding the domestic debt occasions great debates and great difficulty. The bill of ways and means was lately thrown out, because an excise was interwoven into its texture; and another ordered to be brought in, which will be clear of that. The assumption of the debts contracted by the States to individuals, for services rendered the Union, is a measure which divides Congress greatly. Some think that the States could much more conveniently levy taxes themselves to pay off these, and thus save Congress from the odium of imposing too heavy burthens in their name. This appears to have been the sentiment of the majority hitherto. But it is possible that modifications may be proposed, which may bring the measure yet into an acceptable form. We shall receive with gratitude the copy of Rymer’s Foedera, which you are so good as to propose for the use of our offices here.
I have the honor to be, with great esteem, Dear Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MR. DUMAS.
New York, July 13,1790.
Sir,
I wrote you last on the 23rd of June, since which I have received yours of March the 24th to the 30th.
Congress are still engaged in their funding bills. The foreign debts did not admit of any difference of opinion. They were settled by a single and unanimous vote: but the domestic debt requiring modifications and settlements, these produce great difference of opinion, and consequently retard the passage of the funding bill. The States had individually contracted considerable debts for their particular defence, in addition to what was done by Congress. Some of the States have so exerted themselves since the war, as to have paid off near the half of their individual debts. Others have done nothing. The State creditors urge, that these debts were as much for general purposes as those contracted by Congress, and insist that Congress shall assume and pay such of them as have not been yet paid by their own States. The States who have exerted themselves most, find, that notwithstanding the great payments they have made, they shall by this assumption, still have nearly as much to pay as if they had never paid any thing. They are therfore opposed to it. I am in hopes a compromise will be effected by a proportional assumption, which may reach a great part of the debts, and leave still a part of them to be paid by those States who have paid few or none of their creditors. This being once settled, Congress will probably adjourn, and meet again in December, at Philadelphia. The appearance of war between our two neighbors, Spain and England, would render a longer adjournment inexpedient.
I have the honor to be, with great esteem, Dear Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO WILLIAM SHORT.
New York, July 26, 1790.
Dear Sir,
My public letters to you have been of the 28th of March, the 6th and 30th of April. Yours, which remain to be acknowledged, are of March the 9th, 17th, 29th, April the 4th, 12th, 23rd, and May the 1st; being from No. 21 to 28, inclusive, except No. 23, which had come to hand before. I will state to you the dates of all your letters received by me, with the times they have been received, and length of their passage.
You will perceive that they average eleven weeks and a half; that the quickest are of nine weeks, and the longest are of near eighteen weeks coming. Our information through the English papers is of about five or six weeks, and we generally remain as long afterwards in anxious suspense, till the receipt of your letters may enable us to decide what articles of those papers have been true. As these come principally by the English packet, I will take the liberty of asking you to write always by that packet, giving a full detail of such events as may be communicated through that channel; and indeed most may. If your letters leave Paris nine or ten days before the sailing of the packet, we shall be able to decide, on the moment, on the facts true or false, with which she comes charged. For communications of a secret nature, you will avail yourself of other conveyances, and you will be enabled to judge which are best, by the preceding statement. News from Europe is very interesting at this moment, when it is so doubtful whether a war will take place between our two neighbors.
Congress have passed an act for establishing the seat of government at Georgetown, from the year 1800, and in the mean time to remove to Philadelphia. It is to that place, therefore, that your future letters had better be addressed. They have still before them the bill for funding the public debts. That has been hitherto delayed by a question, whether the debts contracted by the particular Slates for general purposes should, at once, be assumed by the General Government. A developement of circumstances, and more mature consideration, seem to have produced some change of opinion on the subject. When it was first proposed, a majority was against it. There is reason to believe, by the complexion of some later votes, that the majority will now be for assuming these debts to a fixed amount. Twenty-one millions of dollars are proposed. As soon as this point is settled, the funding bill will pass, and Congress will adjourn. That adjournment will probably be between the 6th and 13th of August. They expect it sooner. I shall then be enabled to inform you, ultimately, on the subject of the French debt, the negotiations for the payment of which will be referred to the executive, and will not be retarded by them an unnecessary moment. A bill has passed, authorizing the President to raise the salary of a Chargé des Affaires to four thousand five hundred dollars, from the first day of July last. I am authorized by him to inform you, that yours will accordingly be at that rate, and that you will be allowed for gazettes, translating or printing papers, where that shall be necessary, postage, couriers, and necessary aids to poor American sailors, in addition to the salary, and no charge of any other description, except where you may be directed to incur it expressly. I have thought it would be most agreeable to you to give you precise information, that you may be in no doubt in what manner to state your accounts. Be pleased to settle your account down to the 1st of July last, and state the balance then due, which will be to be paid out of the former fund. From that day downwards, a new account must be opened, because a new fund is appropriated to it, from that time. The expenses for the medals, directed in my letter of April the 30th, must enter into the new account. As I presume the die will be finished by the time you receive this, I have to desire you will have a medal of gold struck for the Marquis de la Luzerne, and have put to it a chain of three hundred and sixty-five Clinks, each link containing gold to the value of two dollars and a half, or thirteen livres and ten sous. The Clinks to be of plain wire, so that their workmanship may cost as it were nothing. The whole will make a present of little more than one thousand dollars, including the medal and chain. As soon as done, be pleased to forward them by a safe hand to the Marquis de la Luzerne, in the name of the President of the United States, informing him that it is the one spoken of in my letter to him of April the 30th, 1790. Say nothing to any body of the value of the present, because that will not always be the same, in all cases. Be so good as to have a second medal of gold struck in the same die, and to send this second, together with the dies, to Philadelphia, by the first safe person who shall be passing; no chain to be sent with this.
We are impatient to learn the progress and prospect of the Algerine business. Do not let it languish a moment, nor leave us a moment uninformed of any thing relative to it. It is in truth a tender business, and more felt as such in this, than in any other country. The suppression of the Farms of tobacco, and the free importation of our salted provisions, will merit all your attention. They are both of them objects of first rate importance.
The following appointments of Consuls have taken place.
Their jurisdictions, in general, extend to all places within the same allegiance, which are nearer to them than to the residence of any other Consul or Vice-Consul. As yet, only their commissions have been made out. General instructions await the passage of a bill now depending. Mr. La Forest, at this place, remarked our appointment of Consuls in the French islands. In the first project of a convention proposed on the part of France, the expressions reached expressly to the kingdom of France only. I objected to this in writing, as being narrower than the twenty-ninth article of the treaty of amity, which was the basis of the consular convention, and which had granted the appointment of Consuls and Vice-Consuls, in their respective ‘States and ports,’ generally, and without restriction. On this, the word ‘France’ was struck out, and the ‘dominions of the M. C. K.’ inserted every where. See the fifth, ninth, twelfth, thirteenth, and fifteenth articles particularly, of the copy of the draughts of 1784 and 1788, as I had them printed side by side. The object of this alteration was, the appointment of Consuls in the free ports allowed us in the French West Indies, where our commerce has greater need of protection than any where. I mention these things, that you may be prepared, should any thing be said to you on the subject. I am persuaded the appointment will contribute eminently to the preservation of harmony between us. These Consuls will be able to prevent the misunderstandings which arise frequently now between the officers there and our traders, and which are doubtless much exaggerated and misrepresented to us by the latter.
I duly received the copy you were so kind as to send me of the Bishop of Autun’s proposition, on the subject of weights and measures. It happened to arrive in the moment I was about giving in to Congress a report on the same subject, which they had referred to me. In consequence of the Bishop of Autun’s proposition, I made an alteration in my report, substituting forty-five degrees instead of thirty-eight degrees, which I had at first proposed as a standard latitude. I send you a copy of my report for the Bishop, and another for M. Condorcet, Secretary of the Academy of Sciences. By taking the second pendulum or rod of the same latitude for the basis of our measures, it will at least furnish a common measure to which both our systems will refer, provided our experiments on the pendulum or rod of forty-five degrees should yield exactly the same result with theirs.
The newspapers, as usual, will accompany the present, which is to go by Mr. Barrett.
I have the honor to be, with great esteem and attachment, Dear Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO WILLIAM CARMICHAEL.
New York, August 2, 1790.
Dear Sir,
This letter will be delivered to you by Colonel Humphreys, whose character is so well known to you as to need no recommendations from me. The present appearances of war between our two neighbors Spain, and England, cannot but excite all our attention. The part we are to act is uncertain, and will be difficult. The unsettled state of our dispute with Spain may give a turn to it, very different from what we would wish. As it is important that you should be fully apprized of our way of thinking on this subject, I have sketched, in the enclosed paper, general heads of consideration arising from present circumstances. These will be readily developed by your own reflections and in conversations with Colonel Humphreys; who, possessing the sentiments of the executive on this subject, being well acquainted with the circumstances of the western country in particular, and of the state of our affairs in general, comes to Madrid expressly for the purpose of giving you a thorough communication of them. He will, therefore, remain there as many days or weeks, as may be necessary for this purpose. With this information, written and oral, you will be enabled to meet the minister in conversations on the subject of the navigation of the Mississippi, to which we wish you to lead his attention immediately. Impress him thoroughly with the necessity of an early, and even an immediate settlement of this matter, and of a return to the field of negotiation for this purpose: and though it must be done delicately, yet he must be made to understand unequivocally, that a resumption of the negotiation is not desired on our part, unless he can determine, in the first opening of it, to yield the immediate and full enjoyment of that navigation. (I say nothing of the claims of Spain to our territory north of the thirty-first degree, and east of the Mississippi. They never merited the respect of an answer; and you know it has been admitted at Madrid, that they were not to be maintained.) It may be asked, what need of negotiation, if the navigation is to be ceded at all events? You know that the navigation cannot be practised without a port, where the sea and river vessels may meet and exchange loads, and where those employed about them may be safe and unmolested. The right to use a thing, comprehends a right to the means necessary to its use, and without which it would be useless. The fixing on a proper port, and the degree of freedom it is to enjoy in its operations, will require negotiation, and be governed by events. There is danger indeed, that even the unavoidable delay of sending a negotiator here, may render the mission too late for the preservation of peace. It is impossible to answer for the forbearance of our western citizens. We endeavor to quiet them with the expectation of an attainment of their rights by peaceable means. But should they, in a moment of impatience, hazard others, there is no saying how far we may be led: for neither themselves nor their rights will ever be abandoned by us.
You will be pleased to observe, that we press these matters warmly and firmly, under this idea, that the war between Spain and Great Britain will be begun before you receive this; and such a moment must not be lost. But should an accommodation take place, we retain, indeed, the same object and the same resolutions unalterably; but your discretion will suggest, that in that event, they must be pressed more softly, and that patience and persuasion must temper your conferences, till either these may prevail, or some other circumstance turn up, which may enable us to use other means for the attainment of an object, which we are determined, in the end, to obtain at every risk.
I have the honor to be, with great esteem, Dear Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO M. DE PINTO.
New York, August 7, 1790.
Sir, Under cover of the acquaintance I had the honor of contracting with you, during the negotiations we transacted together in London, I take the liberty of addressing you the present letter. The friendly dispositions you were then pleased to express towards this country, which were sincerely and reciprocally felt on my part towards yours, flatter me with the hope you will assist in maturing a subject for their common good. As yet, we have not the information necessary to present it to you formally, as the minister of her Most Faithful Majesty. I beg, therefore, that this letter may be considered as between two individual friends of their respective countries, preliminary to a formal proposition, and meant to give an acceptable shape to that.
It is unnecessary, with your Excellency, to go through the history of our first experiment in government, the result of which was, a want of such tone in the governing powers, as might effect the good of those committed to their care. The nation, become sensible of this, have changed its organization, made a better distribution of its powers, and given to them more energy and independence. The new government has now, for some time, been under way; and, so far, gives a confidence that it will answer its purposes. Abuses under the old forms have led us to lay the basis of the new in a rigorous economy of the public contributions. This principle will show itself in our diplomatic establishments; and the rather, as at such a distance from Europe, and with such an ocean between us, we hope to meddle little in its quarrels or combinations. Its peace and its commerce are what we shall court, and to cultivate these, we propose to place at the courts of Europe most interesting to us, diplomatic characters of economical grade, and shall be glad to receive like ones in exchange. The important commerce carried on between your country and ours, and the proofs of friendly disposition towards us which her Majesty has manifested, induce us to wish for such an exchange with her, to express our sensibility at the intimations heretofore received of her readiness to meet our wish in this point, and our regret at the delay which has proceeded from the circumstances before touched on. The grade to be exchanged is the present question, and that on which I ask a friendly and informal consultation with you. That of Chargé des Affaires is the one we would prefer. It is that we employ at the court of Madrid. But it has been said, that by the etiquette of your court, that grade cannot be received there under a favorable countenance. Something like this existed at the court of Madrid. But his most Catholic Majesty, in consideration of our peculiar circumstances, dispensed with a general rule in our favor and in our particular case; and our Chargé des Affaires there enjoys at court the privileges, the respect, and favor due to a friendly nation, to a nation whom distance and difference of circumstances liberate in some degree, from an etiquette, to which it is a stranger at home as well as abroad. The representative of her Majesty here, under whatever name mutual convenience may designate him, shall be received in the plenitude of friendship and favor. May we not ask a reciprocal treatment of ours with you? The nations of Europe have already seen the necessity of distinguishing America from Europe, even in their treaties; and a difference of commerce, of government, of condition and character, must every day evince more and more the impracticability of involving them under common regulations. Nor ought a difference of arrangement with respect to us to excite claims from others, whose circumstances bear no similitude to ours.
I beg leave to submit these considerations to your Excellency’s wisdom and goodness. You will see them to be such as could not be offered formally. They must shield themselves under the protection of those sentiments of veneration and esteem, with which your character heretofore inspired me, and which I flattered myself were not merely indifferent to you. Be so good as to honor with a conference hereon, the bearer, Colonel Humphreys (who was known to you in London), a gentleman who has long been of the President’s family, and whose worth has acquired so much of our confidence, that whatever shall be arranged with him, on this subject, may be considered as settled. Presuming on a continuance of her Majesty’s dispositions, accept this private assurance that a proper person shall be appointed in due form to reside with you, as soon as we shall know the result of your deliberations with Colonel Humphreys, whom I beg leave to present to your notice; adding the homage of those sentiments of respect and attachment, with which I have the honor to be, your Excellency’s most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOSHUA JOHNSON.
New York, August 7,1790.
Sir,
The President of the United States, desirous of availing his country of the talents of its best citizens in their respective lines, has thought proper to nominate you consul for the United States, at the port of London. The extent of our commercial and political connections with that country, marks the importance of the trust he confides to you, and the more, as we have no diplomatic character at that court. I shall say more to you in a future letter on the extent of the consular functions, which are, in general, to be confined to the superintendence and patronage of commerce and navigation: but in your position, we must desire somewhat more. Political intelligence from that country is interesting to us in a high degree. We must, therefore, ask you to furnish us with this as far as you shall be able; to send us moreover the gazette of the court, Woodfall’s parliamentary paper, Debrett’s parliamentary register; and to serve sometimes as a centre for our correspondences with other parts of Europe, by receiving and forwarding letters sent to your care. It is desirable that we be annually informed of the extent to which the British fisheries are carried on within each year, stating the number and tonnage of the vessels, and the number of men employed in the respective fisheries, to wit, the northern and southern whale-fisheries, and the cod-fishery. I have as yet no statement of them for the year 1789, with which, therefore, I will thank you to begin. While the press of seamen continues, our seamen in ports nearer to you than to Liverpool (where Mr. Maury is consul), will need your protection. The liberation of those impressed should be desired of the proper authority, with due firmness, yet always in temperate and respectful terms, in which way, indeed, all applications to government should be made.
The public papers herein desired may come regularly, once a month, by the British packet, and intermediately, by any vessels bound directly either to Philadelphia or New York. All expenses incurred for papers and postages shall be paid at such intervals as you choose, either here, on your order, or by bill on London, whenever you transmit to me an account.
There was a bill brought into the legislature for the establishment of some regulations in the consular offices: but it is postponed to the next session. That bill proposed some particular fees for particular services. They were, however, so small, as to be no object. As there will be little or no legal emolument annexed to the office of consul, it is, of course, not expected that it shall render any expense incumbent on him.
I have the honor to be, with great esteem, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO WILLIAM SHORT.
New York, August 10,1790.
Dear Sir,
This letter, with the very confidential papers it encloses, will be delivered to you by Mr. Barrett with his own hands. If there be no war between Spain and England, they need be known to yourself alone. But if that war be began, or whenever it shall begin, we wish you to communicate them to the Marquis de la Fayette, on whose assistance we know we can count in matters which interest both our countries. He and you will consider how far the contents of these papers may be communicated to the Count de Montmorin, and his influence be asked with the court of Madrid. France will be called into the war, as an ally, and not on any pretence of the quarrel being in any degree her own. She may reasonably require, then, that Spain should do every thing which depends on her, to lessen the number of her enemies. She cannot doubt that we shall be of that number, if she does not yield our right to the common use of the Mississippi, and the means of using and securing it. You will observe, we state in general the necessity, not only of our having a port near the mouth of the river (without which we could make no use of the navigation at all), but of its being so well separated from the territories of Spain and her jurisdiction, as not to engender daily disputes and broils between us. It is certain, that if Spain were to retain any jurisdiction over our entrepot, her officers would abuse that jurisdiction, and our people would abuse their privileges in it. Both parties must foresee this, and that it will end in war. Hence the necessity of a well defined separation. Nature has decided what shall be the geography of that in the end, whatever it might be in the beginning, by cutting off from the adjacent countries of Florida and Louisiana, and enclosing between two of its channels, a long and narrow slip of land, called the Island of New Orleans. The idea of ceding this could not be hazarded to Spain, in the first step: it would be too disagreeable at first view; because this island, with its town, constitutes, at present, their principal settlement in that part of their dominions, containing about ten thousand white inhabitants of every age and sex. Reason and events, however, may, by little and little, familiarize them to it. That we have a right to some spot as an entrepot for our commerce, may be at once affirmed. The expediency, too, may be expressed, of so locating it as to cut off the source of future quarrels and wars. A disinterested eye looking on a map, will remark how conveniently this tongue of land is formed for the purpose; the Iberville and Amite channel offering a good boundary and convenient outlet, on the one side, for Florida, and the main channel an equally good boundary and outlet, on the other side, for Louisiana; while the slip of land between is almost entirely morass or sandbank; the whole of it lower than the water of the river, in its highest floods, and only its western margin (which is the highest ground) secured by banks and inhabited. I suppose this idea too much even for the Count de Montmorin at first, and that, therefore, you will find it prudent to urge, and get him to recommend to the Spanish court, only in general terms, ‘a port near the mouth of the river, with a circumjacent territory sufficient for its support, well defined, and extra-territorial to Spain,’ leaving the idea to future growth.
I enclose you the copy of a paper distributed by the Spanish commandant on the west side of the Mississippi, which may justify us to M. de Montmorin, for pushing this matter to an immediate conclusion. It cannot be expected we shall give Spain time, to be used by her for dismembering us.
It is proper to apprize you of a circumstance, which may show the expediency of being in some degree on your guard, even in your communications to the court of France. It is believed here, that the Count de Moustier, during his residence with us, conceived a project of again engaging France in a colony upon our continent, and that he directed his views to some of the country on the Mississippi, and obtained and communicated a good deal of matter on the subject to his court. He saw the immediate advantage of selling some yards of French cloths and silks to the inhabitants of New Orleans. But he did not take into account what it would cost France to nurse and protect a colony there, till it should be able to join its neighbors, or to stand by itself; and then what it would cost her to get rid of it. I hardly suspect that the court of France could be seduced by so partial a view of the subject as was presented to them, and I suspect it the less, since the National Assembly has constitutionally excluded conquest from the objects of their government. It may be added too, that the place being ours, their yards of cloth and silk would be as freely sold as if it were theirs.
You will perceive by this letter, and the papers it encloses, what part of the ideas of the Count d’Estain coincide with our views. The answer to him must be a compound of civility and reserve, expressing our thankfulness for his attentions; that we consider them as proofs of the continuance of his friendly dispositions, and that though it might be out of our system to implicate ourselves in trans-Atlantic guarantees, yet other parts of his plans are capable of being improved to the common benefit of the parties. Be so good as to say to him something of this kind, verbally, and so that the matter may be ended as between him and us.
On the whole, in the event of war, it is left to the judgment of the Marquis de la Fayette and yourself, how far you will develope the ideas now communicated, to the Count de Montmorin, and how far you will suffer them to be developed to the Spanish court.
I enclose you a pamphlet by Hutchins for your further information on the subject of the Mississippi; and am, with sentiments of perfect esteem and attachment, Dear Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO COLONEL DAVID HUMPHREYS.
New York, August 11, 1790.
Sir,
The President having thought proper to confide several special matters in Europe to your care, it will be expedient that you take your passage in the first convenient vessel bound to the port of London.
When there, you will be pleased to deliver to Mr. G. Morris and to Mr. Johnson, the letters and papers you will have in charge for them, to communicate to us from thence any interesting public intelligence you may be able to obtain, and then to take as early a passage as possible to Lisbon.
At Lisbon you will deliver the letter with which you are charged for the Chevalier Pinto, putting on it the address proper to his present situation. You know the contents of this letter, and will make it the subject of such conferences with him as may be necessary to obtain our point of establishing there the diplomatic grade, which alone coincides with our system, and of insuring its reception and treatment with the requisite respect. Communicate to us the result of your conferences, and then proceed to Madrid.
There you will deliver the letters and papers which you have in charge for Mr. Carmichael, the contents of all which are known to you. Be so good as to multiply, as much as possible, your conferences with him, in order to possess him fully of the special matters sketched out in those papers, and of the state of our affairs in general.
Your stay there will be as long as its objects may require, only taking care to return to Lisbon by the time you may reasonably expect that our answers to your letters to be written from Lisbon, may reach that place. This cannot be earlier than the first or second week of January. These answers will convey to you the President’s further pleasure.
Through the whole of this business, it will be best that you avoid all suspicion of being on any public business. This need be known only to the Chevalier Pinto and Mr. Carmichael. The former need not know of your journey to Madrid, or if it be necessary, he may be made to understand that it is a journey of curiosity, to fill up the interval between writing your letters and receiving the answers. To every other person, it will be best that you appear as a private traveller.
The President of the United States allows you from this date, at the rate of two thousand two hundred and fifty dollars a year, for your services and expenses, and moreover, what you may incur for the postage of letters; until he shall otherwise order.
Th: Jefferson.
TO GOUVERNEUR MORRIS.
New York, August 12, 1790.
Dear Sir,
Your letter of May the 29th to the President of the United States has been duly received. You have placed their proposition of exchanging a minister on proper ground. It must certainly come from them, and come in unequivocal form. With those who respect their own dignity so much, ours must not be counted at nought. On their own proposal, formally, to exchange a minister, we sent them one. They have taken no notice of that, and talk of agreeing to exchange one now, as if the idea were new. Besides, what they are saying to you, they are talking to us through Quebec; but so informally, that they may disavow it when they please. It would only oblige them to make the fortune of the poor Major, whom they would pretend to sacrifice. Through him, they talk of a minister, a treaty of commerce and alliance. If the object of the latter be honorable, it is useless; if dishonorable, inadmissible. These tamperings prove, they view a war as very possible; and some symptoms indicate designs against the Spanish possessions adjoining us. The consequences of their acquiring all the country on our frontier, from the St. Croix to the St. Mary’s, are too obvious to you, to need developement. You will readily see the dangers which would then environ us. We wish you, therefore, to intimate to them, that we cannot be indifferent to enterprises of this kind. That we should contemplate a change of neighbors with extreme uneasiness; and that a due balance on our borders is not less desirable to us, than a balance of power in Europe has always appeared to them. We wish to be neutral, and we will be so, if they will execute the treaty fairly, and attempt no conquests adjoining us. The first condition is just; the second imposes no hardship on them. They cannot complain that the other dominions of Spain would be so narrow as not to leave them room enough for conquest. If the war takes place, we would really wish to be quieted on these two points, offering in return an honorable neutrality. More than this, they are not to expect. It will be proper that these ideas be conveyed in delicate and friendly terms; but that they be conveyed, if the war takes place: for it is in that case alone, and not till it be begun, that we would wish our dispositions to be known. But in no case, need they think of our accepting any equivalent for the posts.
I have the honor to be, with great respect and esteem, Dear Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO GOVERNOR HANCOCK.
New York, August 24, 1790.
Sir,
The representatives of the United States have been pleased to refer to me the representation from the General Court of Massachusetts, on the subject of the whale and cod fisheries, which had been transmitted by your Excellency, with an instruction to examine the matter thereof, and report my opinion thereupon to the next session of Congress. To prepare such a report as may convey to them the information necessary to lead to an adequate remedy, it is indispensable that I obtain a statement of the fisheries, comprehending such a period before and since the war, as may show the extent to which they were and are carried on. With such a statement under their view, Congress may be able, by comparing the circumstances which existed when the fisheries flourished, with those which exist at this moment of their decline, to discover the cause of that decline, and provide either a remedy for it, or something which may countervail its effect. This information can be obtained no where but in the State over which your Excellency presides, and under no other auspices so likely to produce it. May I, therefore, take the liberty of soliciting your Excellency to charge with the collecting and furnishing me this information, some person or persons who may be competent to the object. Taking a point of commencement at a proper interval before the year of greatest prosperity, there should be stated in a table, year by year, under different columns as follows:
1. The number of vessels fitted out each year for the cod-fishery. 2. Their tonnage. 3. The number of seamen employed. 4. The quantity of fish taken; (I.) of superior quality; (2.) of inferior. 5. The quantity of each kind exported; (1.) to Europe, and to what countries there; (2.) to other, and what parts of America. C. The average prices at the markets, (1.) of Europe; (2.) of America. With respect to the whale-fishery, after the three first articles the following should be substituted. 4. Whether to the northern or southern fishery. 5. The quantity of oil taken; (1.) of the spermaceti whale; (2.) of the other kinds. 6. To what market each kind was sent. 7. The average prices of each. As the ports from which the equipments were made could not be stated in the same table conveniently, they might form a separate one. It would be very material that I should receive this information by the first of November, as I might be able to bestow a more undisturbed attention to the subject before than after the meeting of Congress, and it would be better to present it to them at the beginning, than towards the close of the session.
The peculiar degree of interest with which this subject must affect the State of Massachusetts, the impossibility of obtaining necessary information from any other quarter, and the slender means I should have of acquiring it from thence, without the aid of your Excellency, will, I hope, be a sufficient apology for the trouble I take the liberty of giving you: and I am happy in every occasion of repeating assurances of the respect and attachment with which I have the honor to be your Excellency’s most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO SYLVANUS BOURNE, Consul at Hispaniola.
New York, August 25, 1790.
Sir,
I enclose you herein sundry papers containing a representation from Messrs. Updike and Earle of Providence, who complain that their sloop Nancy was seized in the island of Hispaniola, and though without foundation, as her acquittal proved, yet they were subjected to the payment of very heavy expenses. It is to be observed, that in no country does government pay the costs of a defendant in any prosecution, and that often, though the party be acquitted, there may have been colorable cause for the prosecution. However this may have been in the present case, should the parties think proper to endeavor, by their own agent, to obtain a reimbursement from the government or from individuals of Hispaniola, I take the liberty of recommending their cause to your patronage, so far as evidence and law shall be in their favor. If they address the government, you will support their demands on the ground of right and amity; if they institute process against individuals, counterpoise by the patronage and weight of your public character, any weight of character which may be opposed to their obtaining of justice.
I am, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
Circular to the Consuls and Vice-Consuls of the United States.
New York, August 26, 1790.
Sir,
I expected ere this, to have been able to send you an act of Congress prescribing some special duties and regulations for the exercise of the consular offices of the United States: but Congress not having been able to mature the act sufficiently, it lies over to the next session. In the mean while, I beg leave to draw your attention to some matters of information, which it is interesting to receive.
I must beg the favor of you to communicate to me every six months, a report of the vessels of the United States which enter at the ports of your district, specifying the name and burthen of each vessel, of what description she is (to wit, ship, snow, brig, &c), the names of the master and owners, and number of seamen, the port of the United States from which she cleared, places touched at, her cargo outward and inward, and the owners thereof, the port to which she is bound, and times of arrival and departure; the whole arranged in a table under different columns, and the reports closing on the last days of June and December.
We wish you to use your endeavors that no vessel enter as an American in the ports of your district, which shall not be truly such, and that none be sold under that name, which are not really of the United States.
That you give to me, from time to time, information of all military preparations, and other indications of war which may take place in your ports; and when a war shall appear imminent, that you notify thereof the merchants and vessels of the United States within your district, that they may be duly on their guard; and in general, that you communicate to me such political and commercial intelligence, as you may think interesting to the United States.
The Consuls and Vice-Consuls of the United States are free to wear the uniform of their navy, if they choose to do so. This is a deep-blue coat with red facings, lining, and cuffs, the cuffs slashed and a standing collar; a red waistcoat (laced or not at the election of the wearer) and blue breeches; yellow buttons with a foul anchor, and black cockades and small swords.
Be pleased to observe, that the Vice-Consul of one district is not at all subordinate to the Consul of another. They are equally independent of each other.
The ground of distinction between these two officers is this. Our government thinks, that to whatever there may be either of honor or profit resulting from the consular office, native citizens are first entitled, where such, of proper character, will undertake the duties; but where none such offer, a Vice-Consul is appointed of any other nation. Should a proper native come forward at any future time, he will be named Consul; but this nomination will not revoke the commission of Vice-Consul: it will only suspend his functions during the continuance of the Consul within the limits of his jurisdiction, and on his departure therefrom, it is meant that the vice-consular authority shall revive of course, without the necessity of a re-appointment.
It is understood, that Consuls and Vice-Consuls have authority, of course, to appoint their own agents in the several ports of their district, and that it is with themselves alone those agents are to correspond.
It will be best not fatigue the government in which you reside, or those in authority under it, with applications in unimportant cases. Husband their good dispositions for occasions of some moment, and let all representations to them be couched in the most temperate and friendly terms, never indulging in any case whatever a single expression which may irritate.
I have the honor to be, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO WILLIAM SHORT.
New York, August 26, 1790.
Dear. Sir,
My last letters to you have been of the 26th of July, and 10th instant. Yours of May the 16th, No. 31, has come to hand.
I enclose you sundry papers, by which you will perceive, that the expression in the eleventh article of our treaty of amity and commerce with France, viz. ‘that the subjects of the United States shall not be reputed Aubaines in France, and consequently shall be exempted from the Droit d’Aubaine, or other similar duty, under what name soever,’ has been construed so rigorously to the letter, as to consider us as Aubaines in the colonies of France. Our intercourse with those colonies is so great, that frequent and important losses will accrue to individuals, if this construction be continued. The death of the master or supercargo of a vessel, rendered a more common event by the unhealthiness of the climate, throws all the property which was either his, or under his care, into contest. I presume that the enlightened Assembly now, engaged in reforming the remains of feudal abuse among them, will not leave so inhospitable an one as the Droit d’Aubaine existing in France, or any of its dominions. If this may be hoped, it will be better that you should not trouble the minister with any application for its abolition in the colonies as to us. This would be erecting into a special favor to us, the extinction of a general abuse, which will, I presume, extinguish of itself. Only be so good as to see, that in abolishing this odious law in France, its abolition in the colonies also be not omitted by mere oversight; but if, contrary to expectations, this fragment of barbarism be suffered to remain, then it will become necessary that you bring forward the enclosed case, and press a liberal and just exposition of our treaty, so as to relieve our citizens from this species of risk and ruin hereafter. Supposing the matter to rest on the eleventh article only, it is inconceivable, that he, who with respect to his personal goods is as a native citizen in the mother country, should be deemed a foreigner in its colonies. Accordingly, you will perceive by the opinions of Doctor Franklin and Doctor Lee, two of our ministers who negotiated and signed the treaty, that they considered that rights stipulated for us in France, were meant to exist in all the dominions of France.
Considering this question under the second article of the treaty also, we are exempted from the Droit d’Aubaine in all the dominions of France: for by that article, no particular favor is to be granted to any other nation which shall not immediately become common to the other party. Now, by the forty-fourth article of the treaty between France and England, which was subsequent to ours, it is stipulated, ‘que dans tout ce qui concerne—les successions des biens mobiliers—les sujets des deux hautes parties contractantes auront dans les Etais respectifs les memes privilèges, libertés et droits, que la nation la plus favorisée.’ This gave to the English the general abolition of the Droit d’Aubaine, enjoyed by the Hollanders under the first article of their treaty with France of July the 23rd, 1773, which is in these words. ‘Les sujets des E. G. des P. U. des Pays-Bas ne seront point assujettis au Droit d’Aubaine dans les Etats de S. M. T. C. This favor, then, being granted to the English subsequent to our treaty, we become entitled to it of course by the article in question. I have it not in my power at this moment to turn to the treaty between France and Russia, which was also posterior to ours. If by that, the Russians are exempted from the Droit d’Aubaine, ‘dans les Etats de S. M. T. C. it is a ground the more for our claiming the exemption. To these, you will be pleased to add such other considerations of reason, friendship, hospitality, and reciprocity, as will readily occur to yourself.
About two or three weeks ago, a Mr. Campbell called on me, and introduced himself by observing that his situation was an awkward one, that he had come from Denmark with an assurance of being employed here in a public character, that he was actually in service, though unannounced. He repeated conversations which had passed between Count Bernstorff and him, and asked me when a minister would be appointed to that court, or a character sent to negotiate a treaty of commerce: he had not the scrip of a pen to authenticate himself, however informally. I told him our government had not yet had time to settle a plan of foreign arrangments; that with respect to Denmark particularly, I might safely express to him those sentiments of friendship which our government entertained for that country, and assurances that the King’s subjects would always meet with favor and protection here; and in general, I said to him those things which, being true, might be said to any body. You can perhaps learn something of him from the Baron de Blome. If he be an unauthorized man, it would be well it should be known here, as the respect which our citizens might entertain, and the credit they might give to any person supposed to be honored by the King’s appointment, might lead them into embarrassment.
You know the situation of the new loan of three millions of florins going on at Amsterdam. About one half of this is destined for an immediate payment to France; but advantage may be gained by judiciously timing the payment. The French colonies will doubtless claim, in their new constitution, a right to receive the necessaries of life from whomever will deliver them cheapest; to wit, grain, flour, live stock, salted fish, and other salted provisions. It would be well that you should confer with their deputies, guardedly, and urge them to this demand, if they need urging. The justice of the National Assembly will probably dispose them to grant it, and the clamors of the Bordeaux merchants may be silenced by the clamors and arms of the colonies. It may cooperate with the influence of the colonies, if favorable dispositions towards us can be excited in the moment of discussing this point. It will therefore be left to you to say, when the payment shall be made, in confidence that you will so time it as to forward this great object: and when you make this payment, you may increase its effect, by adding assurances to the minister, that measures have been taken which will enable us to pay up, within a very short time, all arrears of principal and interest now due; and further, that Congress has fully authorized our government to go on and pay even the balance not yet due, which we mean to do, if that money can be borrowed on reasonable terms; and that favorable arrangements of commerce between us and their colonies, might dispose us to effect that payment with less regard to terms. You will, of course, find excuses for not paying the money which is ready and put under your orders, till you see that the moment has arrived when the emotions it may excite, may give a desisive cast to the demands of the colonies.
The newspapers, as usual, will accompany the present.
I have the honor to be, with great esteem and attachment, Dear Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO M. LA FOREST, Consul of France,
New York, August 30, 1790.
Sir,
I asked the favor of the Secretary of the Treasury to consider the fourth article of the consular convention, and to let me know whether he should conclude that Consuls not exercising commerce, were exempt from paying duties on things imported for their own use. I furnished him no explanation whatever, of what had passed on the subject at the time of forming the convention, because I thought it should be decided on the words of the convention, as they are offered to all the world, and that it would only be where these are equivocal, that explanations might be adduced from other circumstances. He considered the naked words of the article, and delivered to me as his opinion, that, according to these, the first paragraph, ‘The Consuls and Vice-Consuls, &c. as the natives are,’ subjected all their property, in whatever form and under whatever circumstances it existed, to the same duties and taxes to which the property of other individuals is liable, and exempts them only from taxes on their persons, as poll-taxes, head-rates for the poor, for town-charges, &c.; and that the second paragraph, ‘Those of the said Consuls, he or other merchants,’ subjected such of them as exercised commerce, even to the same personal taxes as other merchants are: that the second paragraph is an abridgment of the first, not an enlargement of it; and that the exemption of those, not merchants, which seemed implied in the words of the second paragraph, could not be admitted against the contrary meaning, directly and unequivocally expressed in the first.
Such, Sir, was his opinion, and it is exactly conformable to what the negotiators had in view in forming this article. I have turned to the papers which passed on that occasion, and I find that the first paragraph was proposed in the first project given in by myself, by which the distinction between taxes on their property and taxes on their persons, is clearly enounced, and was agreed to: but as our merchants exercising commerce in France, would have enjoyed a much greater benefit from the personal exemption, than those of France do here, M. de Reyneval, in his first counter-project, inserted the second paragraph, to which I agreed. So that the object was, in the first paragraph, to put Consuls, not being merchants, on the same footing with citizens, not being merchants; and in the second, to put Consuls, merchants, on the same footing with citzens, merchants.
This, Sir, we suppose to be the sense of the convention, which has become a part of the law of the land, and the law, you know, in this country, is not under the control of the executive, either in its meaning or course. We must reserve, therefore, for more favorable occasions, our dispositions to render the situation of the Consuls of his Majesty as easy as possible, by indulgences, depending more on us; and of proving the sentiments of esteem and attachment to yourself personally, with which I have the honor to be, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO WILLIAM SHORT.
New York, August 31,1790.
Dear Sir,
Since writing my letter of the 26th, it has been decided to commit to your care the transaction of very important money matters at Amsterdam. It is thought necessary that you should go there immediately, and remain there about three months, to possess yourself of the ground. The Secretary of the Treasury will detail to you the particulars requisite there.
With respect to our affairs at Paris, we trust, in your absence, to the friendship of the Marquis de la Fayette, for such things as are important enough to merit his attention. Two of the subjects lately given you in charge, are of this description. As to all others, do them by letter or otherwise, as you can. It will be necessary for you, doubtless, sometimes to ask the attention of the Marquis by letter; and where you think the moment requires essentially your presence, it is understood you will come to Paris express, returning again to Amsterdam as quickly as circumstances will admit. The facilities of travelling, in Europe, admit of this. Should you think it necessary, you may appoint a secretary during your absence, to remain at Paris and communicate with you, allowing him a salary of four thousand livres a year. If you think this not necessary, you of course will not make the appointment.
I am, with sincere and great esteem, Dear Sir, your most obedient, humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO GOUVERNEUR MORRIS.
Philadelphia, December 17, 1790.
Since mine to you of August the 12th, yours of July the 3rd, August the 16th, and September the 18th, have come to hand. They suffice to remove all doubts which might have been entertained as to the real intentions of the British cabinet, on the several matters confided to you. The view of government in troubling you with this business, was, either to remove from between the two nations all causes of difference, by a fair and friendly adjustment, if such was the intention of the other party, or to place it beyond a doubt that such was not their intention. In result, it is clear enough that further applications would tend to delay, rather than advance our object. It is therefore the pleasure of the President, that no others be made; and that in whatever state this letter may find the business, in that state it be left. I have it in charge at the same time to assure you, that your conduct in these communications with the British ministers has met the President’s entire approbation, and to convey to you his acknowledgments for your services.
As an attendance on this business must, at times, have interfered with your private pursuits, and subjected you also to additional expenses, I have the honor to enclose you a draft on our bankers in Holland for a thousand dollars, as an indemnificatian for those sacrifices.
My letter of August the 12th desired a certain other communication to be made to the same court, if a war should have actually commenced. If the event has not already called for it, it is considered as inexpedient to be made at all.
You will, of course, have the goodness to inform us of whatever may have passed further, since the date of your last.
In conveying to you this testimony of approbation from the President of the United States, I am happy in an occasion of repeating assurances of the sentiments of perfect esteem and respect, with which I have the honor to be, Dear Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
Philadelphia, December 17, 1790.
Sir,
Though not yet informed of your receipt of my letter, covering your commission as Consul for the United States in the port of London, yet knowing that the ship has arrived by which it went, I take for granted the letter and commission have gone safe to hand, and that you have been called into the frequent exercise of your office for the relief of our seamen, upon whom such multiplied acts of violence have been committed in England, by press-gangs, pretending to take them for British subjects, not only without evidence, but against evidence. By what means may be procured for our seamen, while in British ports, that security for their persons which the laws of hospitality require, and which the British nation will surely not refuse, remains to be settled. In the mean time, there is one of these cases, wherein so wilful and so flagrant a violation has been committed by a British officer, on the person of one of our citizens, as requires that it be laid before his government, in friendly and firm reliance of satisfaction for the injury, and of assurance for the future, that the citizens of the United States, entering the ports of Great Britain, in pursuit of a lawful commerce, shall be protected by the laws of hospitality in usage among nations.
It is represented to the President of the United States, that Hugh Purdie, a native of Williamsburg in Virginia, was, in the month of July last, seized in London by a party of men, calling themselves press-officers, and pretending authority from their government so to do, notwithstanding his declarations and the evidence he offered of his being a native citizen of the United States; and that he was transferred on board the Crescent, a British ship of war, commanded by a Captain Young. Passing over the intermediate violences exercised on him, because not peculiar to his case (so many other American citizens having suffered the same), I proceed to the particular one which distinguishes the present representation. Satisfactory evidence having been produced by Mr. John Brown Cutting, a citizen of the United States, to the Lords of the Admiralty, that Hugh Purdie was a native citizen of the same States, they, in their justice, issued orders to the Lord Howe, their Admiral, for his discharge. In the mean time, the Lord Howe had sailed with the fleet of which the Crescent was.
But, on the 27th of August, he wrote to the board of admiralty, that he had received their orders for the discharge of Hugh Purdie, and had directed it accordingly. Notwithstanding these orders, the receipt of which at sea Captain Young acknowledges, notwithstanding Captain Young’s confessed knowledge that Hugh Purdie was a citizen of the United States, from whence it resulted that his being carried on board the Crescent and so long detained there had been an act of wrong, which called for expiatory conduct and attentions, rather than new injuries on his part towards the sufferer, instead of discharging him, according to the orders he had received, on his arrival in port, which was on the 14th of September, he, on the 15th, confined him in irons for several hours, then had him bound and scourged in presence of the ship’s crew, under a threat to the executioner, that if he did not do his duty well, he should take the place of the sufferer. At length he discharged him on the 17th, without the means of subsistence for a single day. To establish these facts, I enclose you copies of papers communicated to me by Mr. Cutting, who laid the case of Purdie before the board of admiralty, and who can corroborate them by his personal evidence. He can especially verify the letter of Captain Young, were it necessary to verify a paper, the original of which is under the command of his Majesty’s ministers, and this paper is so material, as to supersede of itself all other testimony, confessing the orders to discharge Purdie, that yet he had whipped him, and that it was impossible, without giving up all sense of discipline, to avoid whipping a free American citizen. We have such confidence in the justice of the British government, in their friendly regard to these States, in their respect for the honor and good understanding of the two countries, compromitted by this act of their officer, as not to doubt their due notice of him, indemnification to the sufferer, and a friendly assurance to these States that effectual measures shall be adopted in future, to protect the persons of their citizens while in British ports.
By the express command of the President of the United States, you are to lay this case, and our sense of it, before his Britannic Majesty’s Minister for Foreign Affairs, to urge it on his particular notice by all the motives which it calls up, and to communicate to me the result.
I have the honor to be, with great esteem, your most obedient, humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
Philadelphia, December 23, 1790.
Dear Sir,
The vexations of our seamen, and their sufferings under the press-gangs of England, have become so serious, as to oblige our government to take serious notice of it. The particular case has been selected where the insult to the United States has been the most barefaced, the most deliberately intentional, and the proof the most complete. The enclosed letter to you is on that subject, and has been written on the supposition that you would show the original to the Duke of Leeds, and give him a copy of it, but as of your own movement, and not as if officially instructed so to do. You will be pleased to follow up this matter as closely as decency will permit, pressing it in firm but respectful terms, on all occasions. We think it essential that Captain Young’s case may be an example to others. The enclosed, letters are important. Be so good as to have them conveyed by the surest means possible. I am, with great esteem, Dear Sir, you most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
Philadelphia, February 14,1791.
Sir, I now return you the papers you were pleased to put into my hands, when you expressed to me your dissatisfaction that our court of admiralty had taken cognizance of a complaint of some Swedish sailors against their captain for cruelty. If there was error in this proceeding, the law allows an appeal from that to the Supreme Court; but the appeal must be made in the forms of the law, which have nothing difficult in them. You were certainly free to conduct the appeal yourself, without employing an advocate, but then you must do it in the usual form. Courts of justice, all over the world, are held by the laws to proceed according to certain forms, which the good of the suitors themselves requires they should not be permitted to depart from.
I have further to observe to you, Sir, that this question lies altogether with the courts of justice; that the constitution of the United States having divided the powers of government into three branches, legislative, executive, and judiciary, and deposited each with a separate body of magistracy, forbidding either to interfere in the department of the other, the executive are not at liberty to intermeddle in the present question. It must be ultimately decided by the Supreme Court. If you think proper to carry it into that, you may be secure of the strictest justice from them. Partialities they are not at liberty to show. But for whatever may come before the executive, relative to your nation, I can assure you of every favor which may depend on their dispositions to cultivate harmony and a good understanding with it.
I have the honor to be, with great esteem, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO M. DE PINTO.
Philadelphia, February 21,1791.
Sir,
I have duly received the letter of November the 30th, which your Excellency did me the honor to write, informing me that her Most Faithful Majesty had appointed Mr. Freire her minister resident with us, and stating the difficulty of meeting us in the exchange of a chargé des affaires, the grade proposed on our part. It is foreseen that a departure from our system in this instance will materially affect our arrangements with other nations; but the President of the United States has resolved to give her Majesty this proof of his desire to concur in whatever may best tend to promote that harmony and perfect friendship, so interesting to both countries. He has, therefore, appointed Colonel Humphreys to be minister resident for the United States at the court of her Majesty. This gentleman has long been of the President’s own family, and enjoys his particular confidence. I make no doubt he will so conduct himself, as to give perfect satisfaction to her Majesty and yourself, and I therefore recommend him to your friendly attention and respect. Mr. Freire will have every title to the same from us, and will assuredly receive it. It is always with pleasure, that I repeat the homage of those sentiments of respect and esteem with which I have the honor to be your Excellency’s most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO WILLIAM SHORT.
Philadelphia, March 8,1791.
Dear Sir,
A conveyance offering by which we can send large packets, you will receive herewith the following articles.
1. The newspapers.
2. The acts of the second session of Congress.
3. A report on the fisheries of the United States. It is thought that this contains matter which may be usefully communicated. I am persuaded the better this subject is understood in France, the more they will see their interest in favoring our fisheries.
4. A letter from the President to the King, of which an open copy is enclosed for your information.
5. A letter from myself to the Count de Moustier, in answer to his to the President and myself, taking leave.
6. A letter from myself to the President of the National Assembly of France, in answer to his to Congress on the death of Dr. Franklin. Let it be understood, that Congress can only correspond through the executive, whose organ in the case of foreign nations is the Secretary of State. The President of the United States being co-ordinate with Congress, cannot personally be their scribe.
7. Some papers in a case interesting to Dr. M’Henry, of Baltimore. He at first sent them to me, with a desire to commit the subject of them wholly to you. I informed him, we could not consent that you should be used as the agent of private individuals, but that if he would provide an agent on the spot who would undertake the details of solicitation, management, correspondence, &c. I would desire you to patronize the measure so far as you should find it prudent and just. It is put on this footing, as you will see by his answer to me.
8. A correction of the report on weights and measures.
You are desired to have a medal of gold struck from the diplomatic die formerly ordered, and present it with a chain of gold to the Count de Moustier, who is notified that this will be done by you. I formerly informed you, that we proposed to vary the worth of the present, by varying the size of the Clinks of the chain, which are fixed at three hundred and sixty-five in number. Let each link, in the present instance, contain six livres worth of gold, and let it be made of plain wire, so that the value may be in the metal and not at all in the workmanship. I shall hope to receive the dies themselves, when a safe conveyance presents itself. I am, with great esteem, Dear Sir, your friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO THE PRESIDENT OF THE NATIONAL ASSEMBLY OF FRANCE.
Philadelphia, March 8, 1791.
Sir,
I have it in charge from the President of the United States of America, to communicate to the National Assembly of France, the peculiar sensibility of Congress to the tribute paid to the memory of Benjamin Franklin, by the enlightened and free representatives of a great nation, in their decree of the 11th of June, 1790.
That the loss of such a citizen should be lamented by us, among whom he lived, whom he so long and eminently served, and who feel their country advanced and honored by his birth, life, and labors, was to be expected. But it remained for the National Assembly of France to set the first example of the representative of one nation, doing homage, by a public act, to the private citizen of another, and by withdrawing arbitrary lines of separation, to reduce into one fraternity the good and the great, wherever they have lived or died.
That these separations may disappear between us in all times and circumstances, and that the union of sentiment which mingles our sorrows on this occasion, may continue long to cement the friendship and the interests of our two nations, is our constant prayer. With no one is it more sincere than with him, who, in being charged with the honor of conveying a public sentiment, is permitted that of expressing the homage of profound respect and veneration, with which he is, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
Philadelphia, March 12, 1791,
Sir,
I enclose you a statement of the case of Joseph St. Marie, a citizen of the United States of America, whose clerk, Mr. Swimmer, was, in the latter part of the year 1787, seized on the eastern side of the Mississippi, in latitude 34° 40’, together with his goods, of the value of nineteen hundred and eighty dollars, by a party of Spanish soldiers. They justified themselves under the order of a Mr. Valliere, their officer, who avowed authority from the Governor of New Orleans, requiring him to seize and confiscate all property found on either side of the Mississippi, below the mouth of the Ohio. The matter being then carried by St. Marie before the Governor of New Orleans, instead of correcting the injury, he avowed the act and its principle, and pretended orders from his court for this and more. We have so much confidence, however, in the moderation and friendship of the court of Madrid, that we are more ready to ascribe this outrage to officers acting at a distance, than to orders from a just sovereign. We have hitherto considered the delivery of the post of the Natches, on the part of Spain, as only awaiting the result of those arrangements which have been under amicable discussion between us; but the remaining in possession of a post which is so near our limit of thirty-one degrees, as to admit some color of doubt whether it be on our side or theirs, is one thing; while it is a very different one, to launch two hundred and fifty miles further, and seize the persons and property of our citizens; and that too, in the very moment that a friendly accommodation of all differences is under discussion. Our respect for their candor and good faith does not permit us to doubt, that proper notice will be taken of the presumption of their officer, who has thus put to hazard the peace of both nations, and we particularly expect that indemnification will be made to the individual injured. On this you are desired to insist in the most friendly terms, but with that earnestness and perseverance which the complexion of this wrong requires. The papers enclosed will explain the reasons of the delay which has intervened. It is but lately they have been put into the hands of our government.
We cannot omit this occasion of urging on the court of Madrid the necessity of hastening a final acknowledgment of our right to navigate the Mississippi; a right which has been long suspended in exercise, with extreme inconvenience on our part, merely with a desire of reconciling Spain to what it, is impossible for us to relinquish. An accident at this day, like that now complained of, would put further parley beyond our power; yet to such accidents we are every day exposed by the irregularities of their officers, and the impatience of our citizens. Should any spark kindle these dispositions of our borderers into a flame, we are involved beyond recall by the eternal principles of justice to our citizens, which we will never abandon. In such an event, Spain cannot possibly gain; and what may she not lose?
The boldness of this act of the Governor of New Orleans, and of his avowal of it, renders it essential to us to understand the court of Spain on this subject. You will therefore avail yourself of the earliest occasion of obtaining their sentiments, and of communicating them to us.
I have the honor to be, with great esteem, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO WILLIAM SHORT.
Philadelphia, March 12,1791.
Dear Sir,
The enclosed papers will explain to you a case which imminently endangers the peace of the United States with Spain. It is not indeed of recent date, but it has been recently laid before government, and is of so bold a feature, as to render dangerous to our rights a further acquiescence in their suspension. The middle ground held by France between us and Spain, both in friendship and interest, requires that we should communicate with her with the fullest confidence on this occasion. I therefore enclose you a copy of my letter to Mr. Carmichael, and of the papers it refers to, to be communicated to Monsieur de Montmorin, whose efficacious interference with the court of Madrid you are desired to ask. We rely with great confidence on his friendship, justice, and influence.
A cession of the navigation of the Mississippi, with such privileges as to make it useful, and free from future chicane, can be no longer dispensed with on our part: and perhaps while I am writing, something may have already happened to cut off this appeal to friendly accommodation. To what consequences such an event would lead, cannot be calculated. To such, very possibly, as we should lament, without being able to control. Your earnestness with Monsieur de Montmorin, and his with the court of Spain, cannot be more pressing than the present situation and temper of this country requires. The case of St. Marie happens to be the incident presenting itself in the moment, when the general question must otherwise have been brought forward.. We rely, on this occasion, on the good offices of the Marquis de la Fayette, whom you are desired to interest in it.
I am, with sincere and great esteem, Dear Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO WILLIAM SHORT.
Philadelphia, March 15, 1791.
Dear Sir,
In mine of January the 23rd, I acknowledged the receipt of your letters from No. 29 to 48 inclusive, except 31, 44, 45, 46. Since that, I have received Nos. 45 and 50, the former in three months and seven days, the latter in two months and seventeen days, by the English packet, which had an uncommonly long passage. Nos. 31, 44, 46,47, 48, 49, are still missing. They have probably come through merchant vessels and merchants, who will let them lie on their counters two or three months before they will forward them. I wrote you on the 8th and 12th instant, by a private hand, on particular subjects. I am not certain whether this will be in time to go by the same conveyance. In yours of December the 23rd, you suppose we receive regularly the journals of the National Assembly from your secretary at Paris, but we have never received any thing from him. Nothing has been addressed to him, his name being unknown to us.
It gives great satisfaction, that the Arrêt du Conseil of December, 1787, stands a chance of being saved. It is in truth the sheet-anchor of our connection with France, which will be much loosened when that is lost. This Arrêt saved, a free importation of salted meats into France, and of provisions of all kinds into her colonies, will bind our interests to that country more than to all the world besides. It has been proposed in Congress to pass a navigation act, which will deeply strike at that of Great Britain. I send you a copy of it. It is probable the same proposition will be made at the next Congress, as a first step, and for one more extensive at a later period. It is thought the first will be carried: the latter will be more doubtful. Would it not be worth while to have the bill now enclosed, translated, printed, and circulated among the members of the National Assembly? If you think so, have it done at the public expense, with any little comment you may think necessary, concealing the quarter from whence it is distributed; or take any other method you think better, to see whether that Assembly will not pass a similar act. I shall send copies of it to Mr. Carmichael, at Madrid, and to Colonel Humphreys, appointed resident at Lisbon, with a desire for them to suggest similar acts there. The measure is just, perfectly innocent as to all other nations, and will effectually defeat the navigation act of Great Britain, and reduce her power on the ocean within safer limits.
The time of the late Congress having expired on the 3rd instant, they then separated of necessity. Much important matter was necessarily laid over; this navigation act among others. The land law was put off, and nothing further done with the mint than to direct workmen to be engaged. The new Congress will meet on the 4th Monday in October. Their laws shall be sent you by the first opportunity after they shall be printed. You will receive herewith those of their second session. We know that Massachusetts has agreed to the amendments to the constitution, except (as is said) the first, second, and twelfth articles. The others, therefore, are now in force. The articles excepted, will depend on the other legislatures. The late expedition against the northern Indians having been ineffectual, more serious operations against them will be undertaken as soon as the season admits. The President is just now setting out on a tour to the southern States, from whence he will not return till June. The British packet being the quickest mode of conveyance, I shall avail myself of that, as well as of the French packet, to write to you. Are the letters which now pass through the French post-offices opened, as they were under the former government? This is important for me to know.
I am, with great and sincere esteem, Dear Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
P. S. 1 omitted to draw your attention to an additional duty of one cent per gallon on rum, by name. This was intended as some discrimination between England and France. It would have been higher, but for the fear of affecting the revenues in a contrary direction. T.J.
Philadelphia, March 17,1791.
Sir,
The term of the first Congress having expired on the 3rd instant, they separated on that day, much important business being necessarily postponed. New elections have taken place for the most part, and very few changes made. This is one of many proofs, that the proceedings of the new government have given general satisfaction. Some acts, indeed, have produced local discontents; but these can never be avoided. The new Congress will meet on the 4th Monday of October. Enclosed is the copy of an act reported by a committee to the late Congress, who, not having time to go through the subject, referred it to me, to be examined and reported to the next Congress. This measure, therefore, will be proposed to them as a first and immediate step, and perhaps something further at a more distant day. I have sent copies of this act to Mr. Short and Colonel Humphreys, and I enclose this to you, that you may communicate it to the court of Madrid, as a measure in contemplation with us. How far such an one may be politic to be adopted by Spain, France, and Portugal, is for them to consider. The measure is perfectly innocent as to all nations except those, or rather that, which has a navigation act; and to that it retorts only its own principles. Being founded in universal reciprocity, it is impossible it should excite a single complaint. Its consequences on that nation are such as they cannot avoid; for either they must repeal their navigation act, in order to be let in to a share of foreign carriage, or the shipping they now employ in foreign carriage will be out of employ, and this act frustrated, on which their naval power is built. Consequently, that power will be reduced within safer limits, and the freedom of the ocean be better secured to all the world. The more extensive the adoption of this measure is, the more irresistible will be its effect. We would not wish to be declared the exciters of such a concert of measures, but we have thought it expedient to suggest informally to the courts of France, Spain, and Portugal, the measure we propose to take, and to leave with them to decide, on the motives of their own interest, how far it may be expedient for them to adopt a similar measure. Their concurrence will more completely insure the object of our act, and therefore I leave it to yourself to insinuate it with all the discretion and effect you can.
Your letter of May the 6th, 1789, is still the last we have received, and that is now near two years old. A letter from Colonel Humphreys, written within twenty-four hours after his arrival at Madrid, reached us within two months and ten days after its date. A full explanation of the causes of this suspension of all information from you, is expected in answer to my letter of August the 6th. It will be waited for yet a reasonable time, and in the mean while, a final opinion suspended. By the first vessel to Cadiz, the laws and gazettes shall be forwarded.
I have the honor to be, with great esteem, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO WILLIAM SHORT.
Philadelphia, March 19, 1791.
Dear Sir,
Your letter of November the 6th, No. 46, by Mr. Osmont came to hand yesterday, and I have just time before the departure of Mr. Terrasson, the bearer of my letter of the 15th instant, and despatches accompanying it, to acknowledge the receipt, and inform you that it has been laid before the President. On consideration of the circumstances stated in the second page of your letter, he is of opinion, that it is expedient to press at this moment a settlement of our difference with Spain. You are therefore desired, instead of confining your application for the interference of the court of France to the simple case of St. Marie, mentioned in my letter of the 12th, to ask it on the broad bottom of general necessity, that our right of navigating the Mississippi be at length ceded by the court of Madrid, and be ceded in such form, as to render the exercise of it efficacious and free from chicane. This cannot be without an entrepôt in some convenient port of the river, where the river and sea craft may meet and exchange loads, without any control from the laws of the Spanish government. This subject was so fully developed to you in my letter of August the 10th, 1790, that I shall at present only refer to that. We wish you to communicate this matter fully to the Marquis de la Fayette, to ask his influence and assistance, assuring him that a settlement of this matter is become indispensable to us; any further delay exposing our peace, both at home and abroad, to accidents, the results of which are incalculable and must no longer be hazarded. His friendly interposition on this occasion, as well as that of his nation, will be most sensibly felt by us. To his discretion, therefore, and yours, we confide this matter, trusting that you will so conduct it as to obtain our right in an efficacious form, and at the same time, to preserve to us the friendship of France and Spain, the latter of which we value much, and the former infinitely.
Mr. Carmichael is instructed to press this matter at Madrid; yet if the Marquis and yourself think it could be better effected at Paris, with the Count de Nunez, it is left to you to endeavor to draw it there. Indeed, we believe it would be more likely to be settled there than at Madrid or here. Observe always, that to accept the navigation of the river without an entrepot would be perfectly useless, and that an entrepot, if trammeled, would be a certain instrument for bringing on war instead of preventing it.
I am, with great esteem, Dear Sir, your most obedient humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MR. OTTO.
Philadelphia, March 29, 1791.
Sir,
The note of December the 13th, which you did me the honor to address to me, on the acts of Congress of the 20th of July, 1789, and 1790, fixing the tonnage payable by foreign vessels arriving from a foreign port, without excepting those of France, has been submitted to the government of the United States. They consider the conduct of his Most Christian Majesty, in making this the subject of fair discussion and explanation, as a new proof of his justice and friendship, and they have entered on the consideration with all the respect due to whatever comes from his Majesty or his ministers, and with all the dispositions to find grounds for an union of opinion, which a sincere attachment to your nation and a desire to meet their wishes on every occasion, could inspire. But the fifth article of the treaty of amity and commerce is not seen here exactly in the point of view, in which your note places it.
The third and fourth articles subject the vessels of each nation to pay in the ports of the other, only such duties as are paid by the most favored nation; and give them reciprocally, all the privileges and exemptions in navigation and commerce, which are given by either to the most favored nations. Had the contracting parties stopped here, they would have been free to raise or lower their tonnage, as they should find it expedient; only taking care to keep the other on the footing of the most favored nation.
The question then is, whether the fifth article, cited in the note, is any thing more than an application of the principle comprised in the third and fourth, to a particular object: or whether it is an additional stipulation of something not so comprised.
I. That it is merely an application of a principle comprised in the preceding articles, is declared by the express words of the article, to wit, dans l’exemption ci-dessus est nommément compris, &c: ‘In the above exemption is particularly comprised the imposition of one hundred sols per ton, established in France on foreign vessels.’ Here then is at once an express declaration, that the exemption from the duty of one hundred sols is comprised in the third and fourth articles; that is to say, it was one of the exemptions enjoyed by the most favored nations, and, as such, extended to us by those articles. If the exemption spoken of in this first member of the fifth article was comprised in the third and fourth articles, as is expressly declared, then the reservation by France out of that exemption, (which makes the second member of the same article) was also comprised: that is to say, if the whole was comprised, the part was comprised. And if this reservation of France in the second member, was comprised in the third and fourth articles, then the counter reservation by the United States (which constitutes the third and the last member of the same article) was also comprised. Because it is but a corresponding portion of a similar whole, on our part, which had been comprised by the same terms with theirs.
In short, the whole article relates to a particular duty of one hundred sols, laid by some antecedent law of France on the vessels of foreign nations, relinquished as to the most favored, and consequently as to us. It is not a new and additional stipulation then, but a declared application of the stipulations comprised in the preceding articles to a particular case, by way of greater caution.
The doctrine laid down generally in the third and fourth articles, and exemplified specially in the fifth, amounts to this. ‘The vessels of the most favored nation, coming from foreign ports, are exempted from the duty of one hundred sols: therefore, you are exempted from it by the third and fourth articles. The vessels of the most favored nations, coming coastwise, pay that duty: therefore, you are to pay it by the third and fourth articles. We shall not think it unfriendly in you, to lay a like duty on coasters, because it will be no more than we have done ourselves. You are free also to lay that or any other duty on vessels coming from foreign ports, provided they apply to all other nations, even the most favored. We are free to do the same, under the same restriction. Our exempting you from a duty which the most favored nations do not pay, does not exempt you from one which they do pay.’
In this view, it is evident, that the fifth article neither enlarges nor abridges the stipulations of the third and fourth. The effect of the treaty would have been precisely the same, had it been omitted altogether; consequently, it may be truly said that the reservation by the United States, in this article, is completely useless. And it may be added with equal truth, that the equivalent reservation by France is completely useless, as well as her previous abandonment of the same duty: and in short, the whole article. Each party then remains free to raise or lower its tonnage, provided the change operates on all nations, even the most favored.
Without undertaking to affirm, we may obviously conjecture, that this article has been inserted on the part of the United States, from an over caution to guard, nommément, by name, against a particular aggrievance, which they thought could never be too well secured against: and that has happened, which generally happens; doubts have been produced by the too great number of words used to prevent doubt.
II. The court of France, however, understands this article as intended to introduce something to which the preceding articles had not reached, and not merely as an application of them to a particular case. Their opinion seems to be founded on the general rule in the construction of instruments, to leave no words merely useless, for which any rational meaning can be found. They say, that the reservation by the United States of a right to lay a duty equivalent to that of the one hundred sols, reserved by France, would have been completely useless, if they were left free by the preceding articles, to lay a tonnage to any extent whatever; consequently, that the reservation of a part proves a relinquishment of the residue.
If some meaning, and such a one, is to be given to the last member of the article, some meaning, and a similar one, must be given to the corresponding member. If the reservation by the United States of a right to lay an equivalent duty, implies a relinquishment of their right to lay any other, the reservation by France of a right to continue the specified duty, to which it is an equivalent, must imply a relinquishment of the right on her part, to lay or continue any other. Equivalent reservations by both, must imply equivalent restrictions on both. The exact reciprocity stipulated in the preceding articles, and which pervades every part of the treaty, ensures a counter right to each party for every right ceded to the other.
Let it be further considered, that the duty called tonnage, in the United States, is in lieu of the duties for anchorage, for the support of buoys, beacons, and light-houses, to guide the mariner into harbor and along the coast, which are provided and supported at the expense of the United States, and for fees to measurers, weighers, guagers, &c, who are paid by the United States; for which articles, among many others (light excepted), duties are paid by us in the ports of France, under their specific names. That government has hitherto thought these duties consistent with the treaty; and consequently, the same duties under a general instead of specific names, with us, must be equally consistent with it: it is not the name, but the thing, which is essential. If we have renounced the right to lay any port duties, they must be understood to have equally renounced that of either laying new or continuing the old. If we ought to refund the port duties received from their vessels since the date of the act of Congress, they should refund the port duties they have received from our vessels since the date of the treaty, for nothing short of this is the reciprocity of the treaty.
If this construction be adopted, then each party has for ever renounced the right of laying any duties on the vessels of the other coming from any foreign port, or more than one hundred sols on those coming coastwise. Could this relinquishment be confined to the two contracting parties alone, its effect would be calculable. But the exemption once conceded by the one nation to the other, becomes immediately the property of all others who are on the footing of the most favored nations. It is true, that those others would be obliged to yield the same compensation, that is to say, to receive our vessels duty free. Whether France and the United States would gain or lose in the exchange of the measure with them, is not easy to say.
Another consequence of this construction will be, that the vessels of the most favored nations, paying no duties, will be on a better footing than those of natives, which pay a moderate duty: consequently, either the duty on these also must be given up, or they will be supplanted by foreign vessels in our own ports.
The resource, then, of duty on vessels, for the purposes either of revenue or regulation, will be for ever lost to both. It is hardly conceivable that either party, looking forward to all these consequences, would see their interest in them. So that on the whole, Sir, we consider the fifth article of the treaty merely as an illustration of the third and fourth articles, by an application of the principles comprised in them to the case stated in that, and that a contrary construction would exceedingly embarrass and injure both the contracting parties. We feel every disposition on our part to make considerable sacrifices, where they would result to the sole benefit of your nation: but where they would excite from other nations corresponding claims, it becomes necessary to proceed with caution. You probably know, Sir, that the general subject of navigation was before our legislature at their last session, and was postponed merely for the want of time to go through it, before the period arrived to which the constitution had limited their existence. It will be resumed at the meeting of the new legislature, and from a knowledge of the sincere attachment of my countrymen to the prosperity of your nation, and to the increase of our intercourse with it, I may safely say for the new legislature, that the encouragement of that intercourse, for the advantage of both parties, will be considered as among the most interesting branches of the general subject submitted to them. From a perfect conviction of the coincidence of our interests, nobody wishes more sincerely to cultivate the habit of mutual good offices and favors, than he who has the honor to be, with sentiments of the greatest respect and esteem, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
Thomas Jefferson presents his respects to the Vice-President of the United States, and has the honor to enclose him the copy of a letter from the President, just now received.
April 8, 1791.
[The annexed is the letter referred to.]
Mount Vernon, April 4, 1791. Gentlemen,
As the public service may require that communications should be made to me, during my absence from the seat of government, by the most direct conveyances, and as, in the event of any very extraordinary occurrence, it will be necessary to know at what time I may be found in any particular place, I have to inform you, that unless the progress of my journey to Savannah is retarded by unforeseen interruptions, it will be regulated (including days of halt) in the following manner. I shall be,
On the 8th of April, at Fredericksburg,
“11th” Richmond,
“14th” Petersburg,
“16th” Halifax,
“18th” Tarborough,
“20th” Newbern, ‘
“24th” Wilmington,
“29th” Georgetown, South Carolina,
On the 2nd of May, at Charleston, halting five days,
“11th” Savannah, halting two days.
Thence, leaving the line of the mail, I shall proceed to Augusta, and according to the information which I may receive there, my return, by an upper road, will be regulated. The route of my return is at present uncertain, but in all probability it will be through Columbia, Camden, Charlotte, Salisbury, Salem, Guilford, Hillsborough, Harrisburg, Williamsburg to Taylor’s Ferry on the Roanoke, and thence to Fredericksburg by the nearest and best road.
After thus explaining to you, as far as I am able at present, the direction and probable progress of my journey, I have to express my wish, if any serious and important case should arise during my absence (of which the probability is but too strong), that the Secretaries for the departments of State, Treasury, and War, may hold consultations thereon, to determine whether they are of such a nature as to require my personal attendance at the seat of government, and if they should be so considered, I will return immediately from any place at which the information may reach me; or should they determine that measures relevant to the case may be legally and properly pursued, without the immediate agency of the President, I will approve and ratify the measures which may be conformed to such determination.
Presuming that the Vice-President will have left the seat of government for Boston, I have not requested his opinion to be taken on the supposed emergency. Should it be otherwise, I wish him also to be consulted.
I am, Gentlemen, your most obedient servant,
G. Washington.
Thomas Jefferson, Alexander Hamilton, and Henry Knox, Esquires, Secretaries of the United States for the departments of State, Treasury, and War.
TO COLONEL HUMPHREYS.
Philadelphia, April 11, 1791.
Dear Sir,
I wrote you March the 15th, with postscripts of the 18th and 19th. Since that, yours of January the 3rd, No. 10, January the 15th, No. 11, from Madrid, February the 6th, No. 12, and February the 12th, No. 13, from Lisbon, have been received. They covered a letter from Mr. Carmichael, the only one we have from him of later date than May, 1789. You know that my letter to him, of which you were the bearer, took notice of the intermission of his correspondence, and the one enclosed to him in my letter to you of March the 15th, being written when this intermission was felt still stronger, as having continued so much longer, conveyed stronger marks of dissatisfaction. Though his letter, now received, convinces us he has been active in procuring intelligence, yet it does not appear that he has been equally assiduous in procuring means of conveyance, which was the more incumbent on him, in proportion as the government was more jealous and watchful. Still, however, I wish him to receive the letter now enclosed for him, herein, as it softens what had been harder said, and shows a disposition rather to look forward than backward. I hope you will receive it in time to forward with the other. It contains important matter, pressing on him, as I wish to do on you and have done on Mr. Short, to engage your respective courts in a co-operation in our navigation act. Procure us all the information possible, as to the strength, riches, resources, lights, and dispositions of Brazil. The jealousy of the court of Lisbon on this subject, will, of course, inspire you with due caution in making and communicating these inquiries.
The acts of the three sessions of Congress, and Fenno’s papers from April, 1790, were sent you with my last. You will now receive the continuation of Fenno’s paper. I send for Mr. Carmichael, also, laws and newspapers, in hopes you may find some means of conveying them to him. I must sometimes avail myself of your channel to write to him, till we shall have a Consul at Cadiz.
I have the honor to be, with great and sincere esteem, Dear Sir, your most obedient, humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO WILLIAM CARMICHAEL.
Philadelphia, April 11,1791.
Sir,
I wrote you on the 12th of March, and again on the 17th of the same month; since which, I have received your favor of January the 24th, wherein you refer to copies of two letters, also to a paper, No. 1, supposed to be enclosed in that letter; but there was nothing enclosed. You speak particularly of several other letters formerly forwarded, but not a single one was ever received of later date than May the 6th, 1789; and this of January the 24th is all we possess from you since that date. I enclose you a list of letters addressed to you on various subjects, and to which answers were, and are, naturally expected; and send you again copies of the papers in the case of the Dover Cutter, which has been the subject of so many of those letters, and is the subject of the constant solicitation of the parties here. A final decision on that application, therefore, is earnestly desired. When you consider the repeated references of matters to you from hence, and the total suppression of whatever you have written in answer, you will not be surprised if it had excited a great degree of uneasiness. We had inquired whether private conveyances did not occur, from time to time, from Madrid to Cadiz, where we have vessels almost constantly, and we were assured that such conveyances were frequent. On the whole, Sir, you will be sensible, that under the jealous government with which you reside, the conveyance of intelligence requires as much management as the obtaining it; and I am in hopes, that in future you will be on your guard against those infidelities in that line, under which you and we have so much suffered.
The President is absent on a journey through the southern States, from which he will not return till the end of June; consequently, I could not sooner notify him of your desire to return; but even then, I will take the liberty of saying nothing to him on the subject till I hear further from you. The suppression of your correspondence has, in a considerable degree, withdrawn you from the public sight. I sincerely wish that before your return, you could do something to attract their attention and favor, and render your return pleasing to yourself and profitable to them, by introducing you to new proofs of their confidence. My two last letters to you furnish occasions; that of a co-operation against the British navigation act, and the arrangement of our affairs on the Mississippi. The former, if it can be effected, will form a remarkable and memorable epoch in the history and freedom of the ocean. Mr. Short will press it at Paris, and Colonel Humphreys at Lisbon. The latter will show most at first; and as to it, be so good as to observe always, that the right of navigating the Mississippi is considered as so palpable, that the recovery of it will produce no other sensation than that of a gross injustice removed. The extent and freedom of the port for facilitating the use of it, is what will excite the attention and gratification of the public. Colonel Humphreys writes me, that all Mr. Gardoqui’s communications, while here, tended to impress the court of Madrid with the idea, that the navigation of the Mississippi was only demanded on our part, to quiet our western settlers, and that it was not sincerely desired by the maritime States. This is a most fatal error, and must be completely eradicated and speedily, or Mr. Gardoqui will prove to have been a bad peace-maker. It is true, there were characters, whose stations entitled them to credit, and who, from geographical prejudices, did not themselves wish the navigation of the Mississippi to be restored to us, and who believe, perhaps, as is common with mankind, that their opinion was the general opinion. But the sentiments of the great mass of the union were decidedly otherwise then, and the very persons to whom Mr. Gardoqui alluded, have now come over to the opinion heartily, that the navigation of the Mississippi, in full and unrestrained freedom, is indispensably necessary, and must be obtained by any means it may call for. It will be most unfortunate, indeed, if we cannot convince Spain that we make this demand in earnest, but by acts which will render that conviction too late to prevent evil.
Not knowing how better to convey to you the laws and the gazettes, than by committing them to the patronage of Colonel Humphreys, I now send through that channel the laws of the second and third sessions of Congress, and the newspapers.
I have the honor to be, with great esteem, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO WILLIAM SHORT.
Philadelphia, April 25, 1791.
Dear Sir,
My late letters to you have been of the 8th, 12th, 15th, and
19th of March; yours received and acknowledged, are as follows,
******
I consider the consular convention as securing clearly our right to appoint Consuls in the French colonies. The words ‘Etats du roi’ unquestionably extend to all his dominions. If they had been merely synonymous with ‘la France,’ why was the alteration made? When I proposed that alteration, I explained my reasons, and it cannot be supposed I would offer a change of language, but for some matter of substance. Again, in the translation, it is ‘dominions of France.’ This translation was submitted to M. de Montmorin and M. de Reyneval, with a request that they would note any deviation in it from the original, or otherwise it would be considered as faithful. No part was objected to. M. de Reyneval says, we must decide by the instrument itself, and not by the explanations which took place. It is a rule, where expressions are susceptible of two meanings, to recur to other explanations. Good faith is in favor of this recurrence. However, in the present case, the expression does not admit of two constructions; it is co-extensive with the dominions of the King. I insist on this, only as a reservation of our right, and not with a view to exercise it, if it shall be inconvenient or disagreeable to the government of France. Only two appointments have as yet been made (Mr. Skipwith at Martinique and Guadaloupe, and Mr. Bourne in St. Dominique), and they shall be instructed not to ask a regular Exequatur. We certainly wish to press nothing on our friends, which shall be inconvenient. I shall hope that M. de Montmorin will order such attentions to be shown to those gentlemen as the patronage of commerce may call for, and may not be inconvenient to the government. These gentlemen are most pointedly instructed not to intermeddle, by word or deed, with political matters.
My letter of August, 1790, to Mr. Carmichael, was delivered to him by Colonel Humphreys.
The report you mention of the prospect of our captives at Algiers being liberated, has not taken its rise from any authoritative source. Unfortunately for us, there have been so many persons, who (from friendly or charitable motives, or to recommend themselves) have busied themselves about this redemption, as to excite great expectations in the captors, and render our countrymen in fact irredeemable. We have not a single operation on foot for that purpose, but what you know of, and the more all voluntary interpositions are discouraged, the better for our unhappy friends whom they are meant to serve.
You know how strongly we desire to pay off our whole debt to France, and that for this purpose, we will use our credit as far as it will hold good. You know, also, what may be the probability of our being able to borrow the whole sum. Under these dispositions and prospects, it would grieve us extremely to see our debt pass into the hands of speculators, and be subjected ourselves to the chicaneries and vexations of private avarice. We desire you, therefore, to dissuade the government, as far as you can prudently, from listening from any overtures of that kind, and as to the speculators themselves, whether native or foreign, to inform them, without reserve, that our government condemns their projects, and reserves to itself the right of paying nowhere but into the treasury of France, according to their contract.
I enclose you a copy of Mr. Grand’s note to me, stating the conditions on which Drost would come, and also a letter from the Secretary of the Treasury, expressing his ideas as to those terms, with which I agree. We leave to your agency the engaging and sending Mr. Drost as soon as possible, and to your discretion to fix the terms, rendering the allowance for expenses certain, which his first proposition leaves uncertain. Subsistence here costs about one third of what it does in Paris, to a housekeeper. In a lodging house, the highest price for a room and board is a dollar a day, for the master, and half that for the servant. These facts may enable you to settle the article of expenses reasonably. If Mr. Drost undertakes assaying, I should much rather confide it to him, than to any other person who can be sent. It is the most confidential operation in the whole business of coining. We should expect him to instruct a native in it. I think, too, he should be obliged to continue longer than a year, if it should be necessary for qualifying others to continue his operations. It is not important that he be here till November or December, but extremely desirable then. He may come as much sooner as he pleases.
We address to M. la Motte a small box for you, containing a complete set of the journals of the ancient Congress, the acts of the last session of the federal legislature, and a continuation of the newspapers.
I am, with great and sincere esteem, Dear Sir, your affectionate friend and humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MR. OTTO.
Philadelphia, May 7, 1791.
Sir,
I have now the honor to return you the propositions of Messrs. Schweizer, Jeanneret, and Company, which have been submitted to the Secretary of the Treasury. He does not think they can be acceded to on the part of the United States. The greater premium demanded than what we now pay, the change of the place of payment, the change of the bankers whom we have always employed, for others unknown to us, the danger of risking our credit by putting such a mass of our paper into new hands, will, I dare say, appear to you, Sir, substantial reasons for declining this measure; and the more so, as the new instructions given to Mr. Short, are to raise money as fast as our credit will admit: and we have no reason to suppose it cannot be as soon done by our ancient bankers as by others. Our desire to pay our whole debt, principal and interest, to France, is as strong as hers can be to receive it, and we believe, that by the arrangements already taken it will be as soon done for her, and more safely and advantageously for us than by a change of them. We beg you to be assured, that no exertions are sparing on our part to accomplish this desirable object, as it will be peculiarly gratifying to us, that monies advanced to us in critical times, should be reimbursed to France in times equally critical to her.
I have the honor to be, with sentiments of the most perfect esteem and respect, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO THE ATTORNEY OF THE DISTRICT OF KENTUCKY.
Philadelphia, May 7,1791.
Sir,
A certain James O’Fallon is, as we are informed, undertaking to raise, organize, and commission an army, of his own authority, and independent of that of the government, the object of which is, to go and possess themselves of lands which have never yet been granted by any authority, which the government admits to be legal, and with an avowed design to hold them by force against any power, foreign or domestic. As this will inevitably commit our whole nation in war with the Indian nations, and perhaps others, it cannot be permitted that all the inhabitants of the United States shall be involved in the calamities of war, and the blood of thousands of them be poured out, merely that a few adventurers may possess themselves of lands: nor can a well-ordered government tolerate such an assumption of its sovereignty by unauthorized individuals. I send you herein the Attorney General’s opinion of what may legally be done, with a desire that you proceed against the said O’Fallon according to law. It is not the wish, to extend the prosecution to other individuals, who may have given thoughtlessly in to his unlawful proceeding. I enclose you a proclamation to this effect. But they may be assured, that if this undertaking be prosecuted, the whole force of the United States will be displayed to punish the transgression. I enclose you one of O’Fallon’s commissions, signed, as is said, by himself.
I have the honor to be, with great esteem, Sir, your most obedient, humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO THOMAS BARCLAY.
Philadelphia, May 13,1791.
Sir,
You are appointed by the President of the United States, to go to the court of Morocco for the purpose of obtaining from the new Emperor, a recognition of our treaty with his father. As it is thought best that you should go in some definite character, that of Consul has been adopted, and you consequently receive a commission as Consul for the United States, in the dominions of the Emperor of Morocco, which, having been issued during the recess of the Senate, will of course expire at the end of their next session. It has been thought best, however, not to insert this limitation in the commission, as being unnecessary; and it might, perhaps, embarrass. Before the end of the next session of the Senate, it is expected the objects of your mission will be accomplished.
Lisbon being the most convenient port of correspondence between us and Morocco, sufficient authority will be given to Colonel Humphreys, resident of the United States at that place, over funds in Amsterdam, for the objects of your mission. On him, therefore, you will draw for the sums herein allowed, or such parts of them as shall be necessary. To that port, too, you had better proceed in the first vessel which shall be going there, as it is expected you will get a ready passage from thence to Morocco.
On your arrival at Morocco, sound your ground, and know how things stand at present. Your former voyage there, having put you in possession of the characters through whom this may be done, who may best be used for approaching the Emperor and effecting your purpose, you are left to use your own knowledge to the best advantage.
The object being merely to obtain an acknowledgment of the treaty, we rely that you will be able to do this, giving very moderate presents. As the amount of these will be drawn into precedent on future similar repetitions of them, it becomes important. Our distance, our seclusion from the ancient world, its politics, and usages, our agricultural occupations and habits, our poverty, and lastly, our determination to prefer war in all cases to tribute under any form, and to any people whatever, will furnish you with topics for opposing and refusing high or dishonoring pretensions; to which may be added, the advantages their people will derive from our commerce, and their sovereign, from the duties laid on whatever we extract from that country.
Keep us regularly informed of your proceedings and progress, by writing by every possible occasion, detailing to us particularly your conferences, either private or public, and the persons with whom they are held.
We think that Francisco Chiappe has merited well of the United States, by his care of their peace and interests. He has sent an account of disbursements for us, amounting to three hundred and ninety-four dollars. Do not recognise the account, because we are unwilling, by doing that, to give him a color for presenting larger ones hereafter, for expenses which it is impossible for us to scrutinize or control. Let him understand, that our laws oppose the application of public money so informally; but in your presents, treat him handsomely, so as not only to cover this demand, but go beyond it with a liberality which may fix him deeply in our interests. The place he holds near the Emperor, renders his friendship peculiarly important. Let us have nothing further to do with his brothers, or any other person. The money, which would make one good friend, divided among several, will produce no attachment.
The Emperor has intimated that he expects an ambassador from us. Let him understand, that this may be a custom of the old world, but it is not ours; that we never sent an ambassador to any nation.
You are to be allowed, from the day of your departure till your return, one hundred and sixty-six dollars and sixty-six cents and two thirds, a month, for your time and expenses, adding thereto your passage money and sea-stores going and coming.
Remain in your post till the first of April next, and as much longer as shall be necessary to accomplish the objects of your mission, unless you should receive instructions from hence to the contrary.
With your commission, you will receive a letter to the Emperor of Morocco, a cipher, and a letter to Colonel Humphreys.
I have the honor to be, with great esteem, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
A private Instruction which Mr. Barclay is to carry in his memory and not on paper, lest it should come into improper hands.
We rely that you will obtain the friendship of the new Emperor, and his assurances that the treaty shall be faithfully observed, with as little expense as possible. But the sum of ten thousand dollars is fixed as the limit which all your donations together are not to exceed.
May 13, 1791.
[Letter from the President to the Emperor of Morocco, referred to in the letter to Mr Barclay.]
Great and Magnanimous Friend,
Separated by an immense ocean from the more ancient nations of the earth, and little connected with their politics or proceedings, we are late in learning the events which take place among them, and later in conveying to them our sentiments thereon.
The death of the late Emperor, your father and our friend, of glorious memory, is one of those events which, though distant, attracts our notice and concern. Receive, great and good friend, my sincere sympathy with you on that loss; and permit me, at the same time, to express the satisfaction with which I learn the accession of so worthy a successor to the imperial throne of Morocco, and to offer you the homage of my sincere congratulations. May the days of your Majesty’s life be many and glorious, and may they ever mark the era during which a great people shall have been most prosperous and happy, under the best and happiest of sovereigns.
The late Emperor, very soon after the establishment of our infant nation, manifested his royal regard and amity to us by many friendly and generous acts, and particularly by the protection of our citizens in their commerce with his subjects. And as a further instance of his desire to promote our prosperity and intercourse with his realms, he entered into a treaty of amity and commerce with us, for himself and his successors, to continue fifty years. The justice and magnanimity of your Majesty, leave us full confidence that the treaty will meet your royal patronage also; and it will give me great satisfaction to be assured, that the citizens of the United States of America may expect from your imperial Majesty the same protection and kindness, which the example of your illustrious father has taught them to expect from those who occupy the throne of Morocco, and to have your royal word, that they may count on a due observance of the treaty which cements the two nations in friendship.
This will be delivered to your Majesty by our faithful citizen, Thomas Barclay, whom I name Consul for these United States in the dominions of your Majesty, and who, to the integrity and knowledge qualifying him for that office, unites the peculiar advantage of having been the agent, through whom our treaty with the late Emperor was received. I pray your Majesty to protect him in the exercise of his functions for the patronage of the commerce between our two countries, and of those who carry it on.
May that God, whom we both adore, bless your imperial Majesty with long life, health, and success, and have you always, great and magnanimous friend, under his holy keeping.
Written at Philadelphia, the thirty-first day of March, in the fifteenth year of our sovereignty and independence, from your good and faithful friend, George Washington.
By the President.
Th: Jefferson.
TO FULWAR SKIPWITH.
Philadelphia, May 13,1791.
Sir,
You will readily conceive, that the union of domestic with the foreign affairs under the department of State, brings on the head of this department such incessant calls, not admitting delay, as oblige him to postpone whatever will bear postponing: hence, though it is important that I should continue to receive, from time to time, regular information from you of whatever occurs within your notice, interesting to the United States, yet it is not in my power to acknowledge the receipt of your letters, regularly as they come. I mention this circumstance, that you may ascribe the delay of acknowledgment to the real cause, and that it may not produce any relaxation on your part in making all those communications which it is important should be received, and which govern our proceedings, though it is not in my power to note it to you specially.
I had hoped that Congress, at their last session, would have passed a bill for regulating the functions of Consuls. Such an one was laid before them, but there being a considerable difference of opinion as to some of its parts, it was finally lost by the shortness of the session, which the constitution had limited to the 3rd of March. It will be taken up again at the ensuing session of October next: in the mean time, you will be pleased to govern yourself by the instructions already given.
In general, our affairs are proceeding in a train of unparalleled prosperity. This arises from the real improvements of our government; from the unbounded confidence reposed in it by the people, their zeal to support it, and their conviction that a solid union is the best rock of their safety; from the favorable seasons which, for some years past, have co-operated with a fertile soil and genial climate to increase the productions of agriculture; and from the growth of industry, economy, and domestic manufactures. So that I believe I may say, with truth, that there is not a nation under the sun enjoying more present prosperity, nor with more in prospect.
The Indians on our frontier, indeed, still continue to cut off straggling individuals or families falling in their way. An expedition against them the last summer was less successful than there was reason to expect; we lost in it about one hundred men. The operations of the present summer will more probably bring them to peace, which is all we desire of them, it having been a leading object of our present government to guaranty them in their present possessions, and to protect their persons with the same fidelity which is extended to its own citizens. We ask nothing of them but that they will accept our peace, friendship, and services; and we hope soon to make them sensible of this, in spite of the incitements against us, which they have been so much the dupes of. This is the general state of our affairs at present, as faithfully as I am able to give it.
Your favors of August the 30th, September the 18th, October the 10th, and February the 10th, have been duly received. Particular reasons render it improper to press a formal acknowledgment of our Consuls in the French colonies: for this purpose we must wait till circumstances shall render it less inconvenient to their government. In the mean time, as to every thing essential, the same attention will be paid to yourself, your representations, and applications, as if you were formally acknowledged. I am to recommend to you, in the strongest terms, not to intermeddle in the least, by word or deed, in the internal disputes of the colony, or those with the mother country: consider this as a family affair, with which we have neither the right nor the wish to intermeddle. We shall expect, however, narratives of them from time to time.
I have the honor to be, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO WILLIAM CARMICHAEL.
Philadelphia, May 16, 1791.
Sir,
Mr. Swanwick informs me, that the house of Morris, Willing, and Swanwick have suffered a very considerable loss in the port of St. Andero, by an abuse of office, in having a cargo of corn thrown overboard, as being bad, when it was in fact perfectly good. I know that in some countries of Europe it is often difficult to obtain justice against persons protected by court favor. In this, as in all other instances where our citizens shall have occasion to seek justice in the country of your residence, I would wish you to interfere just so far, as by the influence of your character to counterbalance the undue protection of their opponents, so as that equal and impartial justice may be done them.
The regulation by which they suffer, in the present instance, is, in its nature, extremely susceptible of abuse, and prevails, as I am told, only in the ports of the Bay of Biscay. The patronage of our commerce being the chief object of our diplomatic establishments abroad, you would render that an essential service could you obtain a repeal of this regulation, or an impartial exercise of it, if the repeal cannot be obtained; and in any event a permission to re-export a cargo of grain condemned.
I have the honor to be, with great esteem and respect, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
Philadelphia, July 13,1791.
Sir,
Mr. Barclay having been detained longer than was expected, you will receive this as well as my letter of May the 13th, from him. Since the date of that, I have received your No. 15, March the 31st, No. 16, April the 8th, No. 17, April the 30th, No. 18, May the 3rd, and No. 20, May the 21st.
You are not unacquainted with the situation of our captives at Algiers. Measures were taken, and were long depending, for their redemption. During the time of their dependence, we thought it would forward our success to take no notice of the captives. They were maintained by the Spanish Consul, from whom applications for reimbursement, through Mr. Carmichael, often came: no answer of any kind was ever given. A certainty now, that our measures for their redemption will not succeed, renders it unnecessary for us to be so reserved on the subject, and to continue to wear the appearance of neglecting them. Though the government might have agreed to ransom at the lowest price admitted with any nation (as, for instance, that of the French order of Merci), they will not give any thing like the price which has been lately declared to be the lowest by the captors. It remains, then, for us to see what other means are practicable for their recovery. In the mean time, it is our desire that the disbursements hitherto made for their subsistence, by the Spanish Consul or others, be paid off, and that their future comfortable subsistence be provided for. As to past disbursements, I must beg the favor of you to write to Mr. Carmichael, that you are authorized to pay them off, pray him to let you know their amount, and to whom payments are due. With respect to future provision for the captives, I must put it into your hands. The impossibility of getting letters to or from Mr. Carmichael, renders it improper for us to use that channel. As to the footing on which they are to be subsisted, the ration and clothing of a soldier would have been a good measure, were it possible to apply it to articles of food and clothing so extremely different as those used at Algiers. The allowance heretofore made them by the Spanish Consul might perhaps furnish a better rule, as we have it from themselves, that they were then comfortably subsisted. Should you be led to correspond with them at all, it had better be with Captain O’Bryan, who is a sensible man, and whose conduct since he has been there, has been particularly meritorious. It will be better for you to avoid saying any thing which may either increase or lessen their hopes of ransom. I write to our bankers, to answer your drafts for these purposes, and enclose you a duplicate to be forwarded with your first draft. The prisoners are fourteen in number: their names and qualities as follows; Richard O’Bryan and Isaac Stephens, captains; Andrew Montgomery and Alexander Forsyth, mates; Jacob Tessanier, a French passenger; William Patterson, Philip Sloan, Peleg Lorin, John Robertson, James Hall, James Cathcart, George Smith, John Gregory, James Hermel, seamen. They have been twenty-one or twenty-two.
We are in hourly expectation of hearing the event of General Scott’s irruption into the Indian country, at the head of between seven and eight hundred mounted infantry. Perhaps it may yet be known in time to communicate to you by this opportunity. Our bank was filled with subscriptions the moment it was opened. Eight millions of dollars were the whole permitted to be subscribed, of which two millions were deposited in cash, the residue to be public paper. Every other symptom is equally favorable to our credit.
The President has returned from his southern tour in good health. You will receive herewith the newspapers up to the present date.
I have the honor to be, with great esteem Dear Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th; Jefferson.
TO M. VAN BERKEL.
Philadelphia, July 14,1791.
Sir,
I take the liberty of troubling you with the perusal of the enclosed papers from Mr. Shaw, Consul for the United States in the East Indies; wherein you will observe, he complains of a prohibition from the government of Batavia, to American ships, by name, to have any trade in that port, while such trade was permitted to other nations. I do not hesitate to presume, that something has been misunderstood in this case. My presumption is founded on those sentiments of general amity which subsist between our government and that of the United Netherlands, and also on the whole tenor of our treaty, which secures to us always the treatment of the most favored nation. Nevertheless, the refusal by the government of Batavia has been so formal, so deliberate and pointed, as to render it necessary to ask for some explanation. If you will allow me the honor of a moment’s conference on this subject, the first time you come to town, I shall be obliged to you: and in the mean time, have that of assuring you of those sentiments of esteem and respect, with which I am, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO GOUVERNEUR MORRIS.
Philadelphia, July 26,1791.
Dear Sir,
Your favors of February the 26th and March the 16th have been duly received. The conferences which you held last with the British minister needed no apology. At the time of writing my letter desiring that communications with them might cease, it was supposed possible that some might take place before it would be received. They proved to be such as not to vary the opinion formed, and, indeed, the result of the whole is what was to have been expected from known circumstances. Yet the essay was perhaps necessary to justify, as well as induce, the measures proper for the protection of our commerce. The first remittance of a thousand dollars to you, was made without the aid of any facts, which could enable the government to judge what sum might be an indemnification for the interference of the business referred to you, with your private pursuits. Your letter of February the 26th furnishing grounds for correcting the first judgment, I now enclose you a bill on our bankers in Holland for another sum of a thousand dollars. In the original remittance, as in this supplement to it, there has been no view but to do what is right between the public and those who serve them.
Though no authentic account is yet received, we learn through private channels that General Scott has returned from a successful expedition against the Indians; having killed about thirty warriors, taken fifty odd women and children prisoners, and destroyed two or three villages, without the loss of a man, except three, drowned by accident. A similar expedition was to follow immediately after the first, while preparations are making for measures of more permanent effect: so that we hope this summer to bring the Indians to accept of a just and general peace, on which nothing will be asked of them but their peace.
The crops of wheat in the United States are rather abundant, and the quality good. Those of tobacco are not promising as yet. I have heard nothing of the rice crops.
I am, with very great esteem, Dear Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO WILLIAM SHORT.
Philadelphia, July 28,1791.
Dear Sir,
Since my last I have received letters from you as follows:
Mine to you unacknowledged, were of March the 8th, 12th, 15th, 19th, April the 25th, and May the 10th. Your two last letters mention the length of time you have been without intelligence, having then received mine of January the 23rd only. You will perceive by the above, that six letters of a later date were on their way to you. The receipt of these, with the newspapers, journals, laws, and other printed papers accompanying them, will have relieved your anxiety, by answering several articles of your former letters, and opening to you some new and important matters. I scarcely ever miss the opportunity of a private vessel going from hence or New York to any port of France, without writing to you and sending you the newspapers, &c. In the winter, occasions are very rare, this port particularly being blocked up with ice. The reason of so long an interval between the last and present letter, has been the journey of a month, which that informed you I was about to take. This is the first vessel which has offered since my return: she is bound to Havre, and will carry the newspapers as usual.
The difference of sixty-two livres ten sols the hogshead, established by the National Assembly on tobacco brought in their and our ships, is such an act of hostility against our navigation, as was not to have been expected from the friendship of that nation. It is as new in its nature as extravagant in its degree; since it is unexampled, that any nation has endeavored to wrest from another the carriage of its own produce, except in the case of their colonies. The British navigation act, so much and so justly complained of, leaves to all nations the carriage of their own commodities free. This measure, too, is calculated expressly to take our own carriage from us and give the equivalent to other nations: for it is well known, that the shipping of France is not equal to the carriage of their whole commerce; but the freight in other branches of navigation being on an equal footing with only forty livres the hogshead, in ours, and this new arrangement giving them sixty-two livres ten sols the hogshead, in addition to their freight, that is to say, one hundred and two livres ten sols, instead of forty livres, their vessels will leave every other branch of business to fill up this. They will consequently leave a void in those other branches, which will be occupied by English, Dutch, and Swedes, on the spot. They complain of our tonnage duty, but it is because it is not understood. In the ports of France, we pay fees for anchorage, buoys, and beacons, fees to measurers, weighers, and guagers, and in some countries, for light-houses. We have thought it better that the public here should pay all these, and reimburse itself by a consolidation of them into one fee, proportioned to the tonnage of the vessel, and therefore called by that name. They complain that the foreign tonnage is higher than the domestic. If this complaint had come from the English, it would not have been wonderful, because the foreign tonnage operates really as a tax on their commerce, which, under this name, is found to pay sixteen dollars and fifty cents for every dollar paid by France. It was not conceived, that the latter would have complained of a measure calculated to operate so unequally on her rival, and I still suppose she would not complain, if the thing were well understood. The refusing to our vessels the faculty of becoming national bottoms, on sale to their citizens, was never before done by any nation but England. I cannot help hoping that these were wanderings of a moment, founded in misinformation, which reflection will have corrected before you receive this.
Whenever jealousies are expressed as to any supposed views of ours, on the dominion of the West Indies, you cannot go farther than the truth, in asserting we have none. If there be one principle more deeply rooted than any other in the mind of every American, it is, that we should have nothing to do with conquest. As to commerce, indeed, we have strong sensations. In casting our eyes over the earth, we see no instance of a nation forbidden, as we are, by foreign powers, to deal with neighbors, and obliged, with them, to carry into another hemisphere, the mutual supplies necessary to relieve mutual wants. This is not merely a question between the foreign power and our neighbor. We are interested in it equally with the latter, and nothing but moderation, at least with respect to us, can render us indifferent to its continuance. An exchange of surpluses and wants between neighbor nations is both a right and a duty under the moral law, and measures against right should be mollified in their exercise, if it be wished to lengthen them to the greatest term possible. Circumstances sometimes require, that rights the most unquestionable should be advanced with delicacy. It would seem that the one now spoken of would need only a mention, to be assented to by any unprejudiced mind: but with respect to America, Europeans in general have been too long in the habit of confounding force with right. The Marquis de la Fayette stands in such a relation between the two countries, that I should think him perfectly capable of seeing what is just as to both. Perhaps on some occasion of free conversation, you might find an opportunity of impressing these truths on his mind, and that from him they might be let out at a proper moment as matters meriting consideration and weight, when they shall be engaged in the work of forming a constitution for our neighbors. In policy, if not in justice, they should be disposed to avoid oppression, which, falling on us as well as on their colonies, might tempt us to act together.*
[* This paragraph was in cipher, but an explication of it
preserved with the copy.]
The element of measure adopted by the National Assembly excludes, ipso facto, every nation on earth from a communion of measure with them; for they acknowledge themselves, that a due portion for admeasurement of a meridian crossing the forty-fifth degree of latitude, and terminating at both ends in the same level, can be found in no country on earth but theirs. It would follow then, that other nations must trust to their admeasurement, or send persons into their country to make it themselves, not only in the first instance, but whenever afterwards they may wish to verify their measures. Instead of concurring, then, in a measure which, like the pendulum, may be found in every point of the forty-fifth degree, and through both hemispheres, and consequently in all the countries of the earth lying under that parallel, either northern or southern, they adopt one which can be found but in a single point of the northern parallel, and consequently only in one country, and that country is theirs.
I left with you a statement of the case of Schweighaeuser and Dobree, with the original vouchers on which it depends. From these you will have known, that being authorized by Congress to settle this matter, I began by offering to them an arbitration before honest and judicious men of a neutral nation. They declined this, and had the modesty to propose an arbitration before merchants of their own town. I gave them warning then, that as the offer on the part of a sovereign nation to submit to a private arbitration was an unusual condescendence, if they did not accept it then, it would not be repeated, and that the United States would judge the case for themselves hereafter. They continued to decline it, and the case now stands thus. The territorial judge of France has undertaken to call the United States to his jurisdiction, and has arrested their property, in order to enforce appearance, and possess himself of a matter whereon to found a decree; but no court can have jurisdiction over a sovereign nation. This position was agreed to; but it was urged, that some act of Mr. Barclay’s had admitted the jurisdiction. It was denied that there had been any such act by Mr. Barclay, and disavowed, if there was one, as without authority from the United States, the property on which the arrest was made having been purchased by Dr. Franklin, and remaining in his possession till taken out of it by the arrest. On this disavowal, it was agreed that there could be no further contest, and I received assurance that the property should be withdrawn from the possession of the court by an evocation of the cause before the King’s Council, on which, without other proceedings, it should be delivered to the United States. Applications were repeated as often as dignity, or even decency, would permit; but it was never done. Thus the matter rests, and thus it is meant it should rest. No answer of any kind is to be given to Schweighaeuser and Dobree. If they think proper to apply to their sovereign, I presume there will be a communication either through you or their representative here, and we shall have no difficulty to show the character of the treatment we have experienced.
I will observe for your information, that the sustenance of our captives at Algiers is committed to Colonel Humphreys.
You will be so kind as to remember, that your public account from the 1st day of July, 1790, to the last of June, 1791, inclusive, is desired before the meeting of congress, that I may be able to lay before them the general account of the foreign fund for that year.
General Scott has returned from a successful expedition against the northern Indians, having killed thirty-two warriors, taken fifty-eight women and children prisoners, and destroyed three towns and villages, with a great deal of corn in grain and growth. A similar expedition was to follow immediately, while preparation is making for measures of more permanent effect; so that we may reasonably hope the Indians will be induced to accept of peace, which is all we desire.
Our funds have risen nearly to par. The eight millions for the bank was subscribed as fast as it could be written, and that stock is now above par. Our crops of wheat have been rather abundant, and of excellent quality. Those of tobacco are not very promising as yet. The census is not yet completed, but, from what we hear, we may expect our whole numbers will be nearer four than three millions. I enclose a sketch of the numbers as far as we yet know them.
I am, with great and sincere esteem, Dear Sir, your sincere friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
Philadelphia, July 30,1791.
Sir, I have the honor to enclose, for your perusal, a letter which I have prepared for Mr. Short.
The ill humor into which the French colonies are getting, and the little dependence on the troops sent thither, may produce a hesitation in the National Assembly as to the conditions they will impose in their constitution. In a moment of hesitation, small matters may influence their decision. They may see the impolicy of insisting on particular conditions, which, operating as grievances on us as well as on their colonists, might produce a concert of action. I have thought it would not be amiss to trust to Mr. Short the sentiments in the ciphered part of the letter, leaving him to govern himself by circumstances, whether to let them leak out at all or not, and whether so as that it may be known or remain unknown that they come from us. A perfect knowledge of his judgment and discretion leaves me entirely satisfied, that they will be not used, or so used as events shall render proper. But if you think that the possibility that harm may be done, overweighs the chance of good, I would expunge them, as, in cases of doubt, it is better to say too little than too much.
I have the honor to be, with the most perfect respect and attachment, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO GENERAL KNOX.
Philadelphia, August 10, 1791.
Dear Sir,
I have now the honor to return you the petition of Mr. Moultrie on behalf of the South Carolina Yazoo company. Without noticing that some of the highest functions of sovereignty are assumed in the very papers which he annexes as his justification, I am of opinion that government should firmly maintain this ground; that the Indians have a right to the occupation of their lands, independent of the States within whose chartered lines they happen to be; that until they cede them by treaty or other transaction equivalent to a treaty, no act of a State can give a right to such lands; that neither under the present constitution, nor the ancient confederation, had any State or person a right to treat with the Indians, without the consent of the General Government; that that consent has never been given to any treaty for the cession of the lands in question; that the government is determined to exert all its energy for the patronage and protection of the rights of the Indians, and the preservation of peace between the United States and them and that if any settlements are made on lands not ceded by them, without the previous consent of the United States, the government will think itself bound, not only to declare to the Indians that such settlements are without the authority or protection of the United States, but to remove them also by the public force.
It is in compliance with your request, my dear Sir, that I submit these ideas to you, to whom it belongs to give place to them, or such others as your better judgment shall prefer, in answer to Mr. Moultrie.
I have the honor to be, with sentiments of the most sincere and respectful esteem, Dear Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
The Secretary of State has the honor to inform the Minister of France, that the President will receive his letters of credence today, at half after two; that this will be done in a room of private audience, without any ceremony whatever, or other person present than the Secretary of State, this being the usage which will be observed.
As the Secretary of State will be with the President before that hour on business, the Minister will find him there.
August 12,1791.
TO SYLVANUS BOURNE.
Philadelphia, August 14,1791.
Sir,
My letter of May the 13th acknowledged the receipt of yours of November the 30th. Since writing that, I have received yours of April the 29th and June the 30th, addressed to myself, and of July the 14th, to Mr. Remsen. As none of these acknowledge mine of May the 13th, I now enclose you a duplicate of it, fearing the first has miscarried. In this, you will find the sentiments of our government on the subject of your recognition. Subsequent circumstances have rendered it an object still less proper to be pressed. In the present divisions of that country, we wish to avoid every measure which may excite the jealousy of any party, being sincerely the friends and well-wishers of all. As to my writing to the Governor, as pressed in your letter of April the 29th, it would be contrary to the usage established among nations, and therefore cannot be done. We have received Consuls from France, England, Portugal, Sweden, with no other credential but their open commissions; we have sent Consuls to most of the countries of Europe with nothing more. There has never been an instance of a special letter demanded.
Though we have not received an authenticated copy of the decree of the National Assembly of France, extending the repeal of the law of Droit d’Aubaine, by name, to their colonies, yet we know it has been so extended, and doubt not that a notification thereof has been sent to the colonies, so as to relieve us from that oppression.
As Congress have not, as yet, allowed any emoluments to the Consuls of the United States, and perhaps may not mean to do it, we do not expect that any of those gentlemen will think themselves confined to their residence a moment beyond their own convenience. These appointments are given to gentlemen who are satisfied to perform their duties, in consideration of the respect and accidental advantages they may derive from them. When the consideration ceases to be sufficient, the government cannot insist on a continuation of services, because this would found claims which it does not mean to authorize. On these principles, Mr. Skipwith has lately returned from Martinique; on the same, it is my duty to say, that however satisfied we should be with a continuance of your services at St. Domingo, we cannot and do not ask them longer than convenient to yourself.
I have the honor to be, with great regard, Sir, your most obedient, humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO WILLIAM SHORT.
Philadelphia, August 29, 1791.
Dear Sir,
I am to acknowledge the receipt of your No. 67, June the 6th, No. 68, June the 10th, No. 69, June the 22nd, No. 70, June the 26th, No. 71, June the 29th; the three last by the British packet. My last to you was of July the 28th, by a vessel bound to Havre. This goes to the same port, because accompanied by newspapers. It will be the last I shall write you these two months, as I am to set out for Virginia the next week. I now enclose you a copy of my letter of March the 12th, to Mr. Carmichael, which you say was not in that of the same date to you. There was no paper to accompany it but St. Marie’s, which you say you received. I enclose you also a copy of our census, written in black ink, so far as we have actual returns, and supplied by conjecture in red ink, where we have no returns: but the conjectures are known to be very near the truth. Making very small allowance for omissions, which we know to have been very great, we are certainly above four millions, probably about four millions one hundred thousand.
There is a vessel now lying at Philadelphia, advertising to receive emigrants to Louisiana, gratis, on account of the Spanish government. Be so good as to mention this to M. de Montmorin, who will be a judge what we must feel under so impudent a transaction.
You observe, that if Drost does not come, you have not been authorized to engage another coiner. If he does not come, there will probably be one engaged here. If he comes, I should think him a safe hand to send the diplomatic die by, as also all the dies of our medal, which may be used here for striking off what shall be wanting hereafter. But I would not have them trusted at sea, but from April to October inclusive. Should you not send them by Drost, Havre will be the best route. I have not spoken with the Secretary of the Treasury yet, on the subject of the presses, but believe you may safely consider two presses as sufficient for us, and agree for no more without a further request.
The decree of the National Assembly, relative to tobacco carried in French or American ships, is likely to have such an effect in our ports, as to render it impossible to conjecture what may or may not be done. It is impossible to let it go on without a vigorous correction. If that should be administered on our part, it will produce irritation on both sides, and lessen that disposition which we feel cordially to concur in a treaty, which shall melt the two nations as to commercial matters into one, as nearly as possible. It is extremely desirable, that the National Assembly should themselves correct the decree, by a repeal founded on the expectation of an arrangement.
We have, as yet, no news of the event of our second expedition against the Indians.
I am, with great and sincere esteem, Dear Sir, your friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO M. LA MOTTE.
Philadelphia, August 30, 1791.
Sir,
I am now to acknowledge the receipt of your favors of February the 9th, March the 25th, and April the 24th; as also of the several packages of wine, carriages, &c. which came safe to hand, and for your care of which be pleased to accept my thanks.
I am sensible of the difficulties to which our Consuls are exposed by the applications of sailors, calling themselves Americans. Though the difference of dialect between the Irish and Scotch, and the Americans, is sensible to the ear of a native, it is not to that of a foreigner, however well he understands the language; and between the American and English (unless of particular provinces) there is no difference sensible even to a native. Among hundreds of applications to me, at Paris, nine-tenths were Irish, whom I readily discovered. The residue, I think, were English: and I believe not a single instance of a Scotchman or American. The sobriety and order of the two last, preserve them from want. You will find it necessary, therefore, to be extremely on your guard against these applications. The bill of expenses for Huls is much beyond those aids which I should think myself authorized to have advanced habitually, until the law shall make express provision for that purpose. I must, therefore, recommend to you, to hazard only small sums in future, until our legislature shall lay down more precise rules for my government.
The difference of duty on tobacco carried to France in French and American bottoms, has excited great uneasiness. We presume the National Assembly must have been hurried into the measure, without being allowed time to reflect on its consequences. A moment’s consideration must convince any body, that no nation upon earth ever submitted to so enormous an assault on the transportation of their own produce. Retaliation, to be equal, will have the air of extreme severity and hostility. Such would be an additional tonnage of twelve livres ten sous the ton burthen, on all French ships entering Our ports. Yet this would but exactly balance an additional duty of six livres five sous the hogshead of tobacco, brought in American ships entering in the ports of France. I hope, either that the National Assembly will repeal the measure, or the proposed treaty be so hastened, as to get this matter out of the way before it shall be necessary for the ensuing legislature to act on it. Their measure, and our retaliation on it, which is unavoidable, will very illy prepare the minds of both parties for a liberal treaty. My confidence in the friendly dispositions of the National Assembly, and in the sincerity of what they have expressed on the subject, induce me to impute, it to surprise altogether, and to hope it will be repealed before time shall be given to take it up here.
I have the honor to be, with great esteem, Sir, your most obedient humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO GOUVERNEUR MORRIS.
Philadelphia, August 30, 1791.
Dear Sir,
My letter of July the 26th covered my first of exchange for a thousand dollars, and though that went by so sure an opportunity as to leave little doubt of its receipt, yet, for greater security, I enclose a second.
The tranquillity of our country leaves us nothing to relate, which may interest a mind surrounded by such buoyant scenes as yours. No matter; I will still tell you the charming though homespun news, that our crops of wheat have been abundant and of superior quality; that very great though partial drought has destroyed the crops of hay to the north, and corn to the south; that the late rains may recover the tobacco to a middling crop, and that the fields of rice are promising.
I informed you in my last, of the success of our first expedition against the Indians. A second has gone against them, the result of which is not yet known. Our public credit is good, but the abundance of paper has produced a spirit of gambling in the funds, which has laid up our ships at the wharves, as too slow instruments of profit, and has even disarmed the hand of the tailor of his needle and thimble. They say the evil will cure itself. I wish it may; but I have rarely seen a gamester cured, even by the disasters of his vocation. Some new indications of the ideas with which the British cabinet are coming into treaty, confirm your opinions, which I knew to be right, but the Anglomany of some would not permit them to accede to.
Adieu, my dear Sir. Your affectionate, humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MONSIEUR DE TERNANT, Minister Plenipotentiary of France.
Philadelphia, September 1, 1791.
Sir,
I have communicated to the President what passed between us the other day, on the subject of the payments made to France by the United States in the assignats of that country, since they have lost their par with gold and silver; and after conferences, by his instruction, with the Secretary of the Treasury, I am authorized to assure you, that the government of the United States have no idea of paying their debt in a depreciated medium, and that in the final liquidation of the payments which shall have bean made, due regard will be had to an equitable allowance for the circumstance of depreciation.
I have the honor to be, with sentiments of the most perfect esteem and respect, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO T. NEWTON.
Georgetown, September 8, 1791.
Dear Sir,
I was in the moment of my departure from Philadelphia, for Virginia, when I received your favor, inquiring how far the law of nations is to govern in proceedings respecting foreign consuls.
The law of nations does not of itself extend to consuls at all. They are not of the diplomatic class of characters, to which alone that law extends of right. Convention, indeed, may give it to them, and sometimes has done so; but in that case, the convention can be produced. In ours with France, it is expressly declared that consuls shall not have the privileges of that law, and we have no convention with any other nation.
Congress have had before them a bill on the subject of consuls, but have not as yet passed it. Their code then furnishes no law to govern these cases.
Consequently, they are to be decided by the State laws alone. Some of these, I know, have given certain privileges to consuls; and I think those of Virginia did at one time. Of the extent and continuance of those laws, you are a better judge than I am.
Independently of law, consuls are to be considered as distinguished foreigners, dignified by a commission from their sovereign, and specially recommended by him to the respect of the nation with whom they reside. They are subject to the laws of the land, indeed, precisely as other foreigners are, a convention, where there is one, making a part of the laws of the land; but if at any time, their conduct should render it necessary to assert the authority of the laws over them, the rigor of those laws should be tempered by our respect for their sovereign, as far as the case will admit. This moderate and respectful treatment towards foreign-consuls, it is my duty to recommend and press on our citizens, because I ask it for their good towards our own consuls, from the people with whom they reside.
In what I have said, I beg leave to be understood as laying down general principles only, and not as applying them to the facts which may have arisen. Before such application, those facts should be heard from all whom they interest. You, who have so heard them, will be able to make the application yourself, and that, not only in the present, but in future cases.
I have the honor to be, with great esteem, your most obedient, humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
Mr. Jefferson has the honor of presenting his compliments to Mr. Hammond, of expressing his regrets that he happened to be from home when Mr. Hammond did him the honor of calling on him, and was equally unlucky in not finding him at home when he waited on him on Monday. Being informed by Mr. Bond, that Mr. Hammond is charged with a public mission to the government of the United States, relative to which some previous explanations might be proper, Mr. Jefferson has the honor to assure Mr. Hammond, he shall be ready to receive any communications and enter into explanations, either formally or informally, as Mr. Hammond shall choose, and at any time suitable to him. He recollects with pleasure his acquaintance with Mr. Hammond in Paris, and shall be happy in every opportunity of rendering him such offices and attentions as may be acceptable to him.
October 26,1791.
TO WILLIAM CARMICHAEL.
Philadelphia, November 6, 1791.
Sir,
My last letter to you was of the 24th of August. A gentleman going from hence to Cadiz will be the bearer of this, and of the newspapers to the present date, and will take care that the letter be got safe to you, if the papers cannot.
Mr. Mangnal, at length tired out with his useless solicitations at this office, to obtain redress from the court of Spain for the loss of the Dover Cutter, has laid the matter before Congress, and the Senate have desired me to report thereon to them. I am very sorry to know nothing more of the subject, than that letter after letter has been written to you thereon, and that the office is in possession of nothing more than acknowledgments of your receipt of some of them, so long ago as August, 1786, and still to add, that your letter of January the 24th, 1791, is the only one received of later date than May the 6th, 1789. You certainly will not wonder, if the receipt of but one letter in two years and an half inspires a considerable degree of impatience. I have learned through a circuitous channel, that the court of Madrid is at length disposed to yield our right of navigating the Mississippi. I sincerely wish it may be the case, and that this act of justice may be made known, before the delay of it produces any thing intemperate from our western inhabitants.
Congress is now in session. You will see, in the paper herewith sent, the several weighty matters laid before them in the President’s speech. The session will probably continue through the winter. I shall sincerely rejoice to receive from you, not only a satisfactory explanation of the reasons why we receive no letters, but grounds to hope that it will be otherwise in future.
I have the honor to be, with great esteem, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
November 6, 1791.
Sir,
I have the honor to enclose you the draught of a letter to Governor Pinckney, and to observe, that I suppose it to be proper that there should, on fit occasions, be a direct correspondence between the President of the United States and the Governors of the States; and that it will probably be grateful to them to receive from the President, answers to the letters they address to him. The correspondence with them on ordinary business may still be kept up by the Secretary of State, in his own name.
I enclose also a letter to Major Pinckney, with a blank to be filled up, when you shall have made up your mind on it. I have conferred with Mr. M. on the idea of the commissioners of the federal town proceeding to make private sales of the lots, and he thinks it advisable. I cannot but repeat, that if the surveyors will begin on the river, laying off the lots from Rock Creek to the Eastern Branch, and go on, abreast in that way, from the river towards the back part of the town, they may pass the avenue from the President’s house to the Capitol, before the spring; and as soon as they shall have passed it, a public sale may take place, without injustice to either the Georgetown or Carrolsburg interest. Will not the present afford you a proper occasion of assuring the commissioners, that you leave every thing respecting L’Enfant to them?
I have the honor to be, with the most sincere respect, Sir, your most obedient, humble servant,
Th: Jefferson
TO MAJOR THOMAS PINCKNEY.
Philadelphia, November 6, 1791.
Sir,
The mission of a Minister Plenipotentiary to the court of London being now to take place, the President of the United States is desirous of availing the public of your services in that office. I have it in charge, therefore, from him, to ask whether it will be agreeable that he should nominate you for that purpose to the Senate. We know that higher motives will alone influence your mind in the acceptance of this charge. Yet it is proper, at the same time, to inform you, that as a provision for your expenses in the exercise of it, an outfit of nine thousand dollars is allowed, and an annual salary to the same amount, payable quarterly. On receiving your permission, the necessary orders for these sums, together with your credentials, shall be forwarded to you, and it would be expected that you should proceed on the mission as soon as you can have made those arrangements for your private affairs, which such an absence may render indispensable. Let me only ask the favor of you to give me an immediate answer, and by duplicate, by sea and post, that we may have the benefit of both chances for receiving it as early as possible. Though I have not the honor of a personal acquaintance with you, yet I beg you to be assured, that I feel all that anxiety for your entrance on this important mission, which a thorough conviction of your fitness for it can inspire; and that in its relations with my office, I shall always endeavor to render it as agreeable to you as possible.
I have the honor to be, with sentiments of the highest respect and esteem, Sir, your most obedient, humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO THE PRESIDENT.
Philadelphia, November 7, 1791.
Sir,
I have duly considered the letter you were pleased to refer to me, of the 18th of August, from his Excellency Governor Pinckney to yourself, together with the draught of one proposed to be written by him to the Governor of Florida, claiming the re-delivery of certain fugitives from justice, who have been received in that country. The inconveniences of such a receptacle for debtors and malefactors in the neighborhood of the southern States, are obvious and great, and I wish the remedy were as certain and short as the latter seems to suppose.
The delivery of fugitives from one country to another, as practised by several nations, is in consequence of conventions settled between them, defining precisely the cases wherein such deliveries shall take place. I know that such conventions exist between France and Spain, France and Sardinia, France and Germany, France and the United Netherlands; between the several sovereigns constituting the Germanic body, and, I believe, very generally between co-terminous States on the continent of Europe. England has no such convention with any nation, and their laws have given no power to their executive to surrender fugitives of any description; they are, accordingly, constantly refused, and hence England has been the asylum of the Paolis, the La Mottes, the Calonnes, in short, of the most atrocious offenders as well as the most innocent victims, who have been able to get there.
The laws of the United States, like those of England, receive every fugitive, and no authority has been given to our executives to deliver them up. In the case of Longchamp, a subject of France, a formal demand was made by the minister of France, and was refused. He had, indeed, committed an offence within the United States; but he was not demanded as a criminal, but as a subject.
The French government has shown great anxiety to have such a convention with the United States, as might authorize them to demand their subjects coming here: they got a clause in the consular convention signed by Dr. Franklin and the Count de Vergennes, giving their Consuls a right to take and send back captains of vessels, mariners, and passengers. Congress saw the extent of the word passengers, and refused to ratify the convention; a new one was therefore formed, omitting that word. In fact, however desirable it be that the perpetrators of crimes, acknowledged to be such by all mankind, should be delivered up to punishment, yet it is extremely difficult to draw the line between those, and acts rendered criminal by tyrannical laws only; hence the first step always is a convention defining the cases where a surrender shall take place.
If, then, the United States could not deliver up to Governor Quesada, a fugitive from the laws of his country, we cannot claim as a right the delivery of fugitives from us; and it is worthy consideration, whether the demand proposed to be made in Governor Pickney’s letter, should it be complied with by the other party, might not commit us disagreeably, perhaps dishonorably, in event; for I do not think we can take for granted, that the legislature of the United States will establish a convention for the mutual delivery of fugitives; and without a reasonable certainty that they will, I think we ought not to give Governor Quesada any grounds to expect that in a similar case, we would re-deliver fugitives from his government.
I have the honor to be, with the most profound respect and attachment, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO WILLIAM SHORT.
Philadelphia, November 24, 1791.
Dear Sir,
My last to you was of August the 29th, acknowledging the receipt of your Nos. 67, 68, 69, 70, 71, and informing you I was about setting out to Virginia, and should not again write to you till my return. Only one vessel has sailed from hence to Havre since my return, and my notice of her departure was so short, that I could not avail myself of it. Your Nos. 72, 73, 74, 75, 78, came here during my absence, and 79, 80, were received October the 28th. The Nos. 76 and 77 seem to be missing.
You mention that Drost wishes the devices of our money to be sent to him, that he may engrave them there. This cannot be done, because not yet decided on. The devices will be fixed by the law which shall establish the mint. M. de Ternant tells me he has no instructions to propose to us the negotiation of a commercial treaty, and that he does not expect any. I wish it were possible to draw that negotiation to this place. In your letter of July the 24th, is the following paragraph. It is published in the English newspapers, that war is inevitable between the United States and Spain, and that preparations are making for it on both sides.’ M. de Montmorin asked me how the business stood at present, and seemed somewhat surprised at my telling him, that I knew nothing later than what I had formerly mentioned to him. I have, in more than one instance, experienced the inconvenience of being without information. In this, it is disagreeable, as it may have the appearance with M. de Montmorin, of my having something to conceal from him, which not being the case, it would be wrong that he should be allowed to take up such an idea. I observed, that I did not suppose there was any new circumstance, as you had not informed me of it.’ Your observation was certainly just. It would be an Augean task for me to go through the London newspapers, and formally contradict all their lies, even those relating to America. On our side, there have been certainly no preparations for war against Spain; nor have I heard of any on their part, but in the London newspapers. As to the progress of the negotiation, I know nothing of it but from you; having never had a letter from Mr. Carmichael on the subject. Our best newspapers are sent you from my office with scrupulous exactness, by every vessel sailing to Havre or any other convenient port of France. On these I rely for giving you information of all the facts possessed by the public; and as to those not possessed by them, I think there has not been a single instance of my leaving you uninformed of any of them which related to the matters under your charge. In Freneau’s paper of the 21st instant, you will see a small essay on population and emigration, which I think it would be well if the news-writers of Paris would translate and insert in their papers. The sentiments are too just not to make impression.
Some proceedings of the assembly of St. Domingo have lately taken place, which it is necessary for me to state to you exactly, that you may be able to do the same to M. de Montmorin. When the insurrection of their negroes assumed a very threatening appearance, the Assembly sent a deputy here to ask assistance of military stores and provisions. He addressed himself to M. de Ternant, who (the President being then in Virginia, as I was also) applied to the Secretaries of the Treasury and War. They furnished one thousand stand of arms, other military stores, and placed forty thousand dollars in the treasury, subject to the order of M. de Ternant, to be laid out in provisions, or otherwise, as he should think best. He sent the arms and other military stores; but the want of provisions did not seem so instantaneous as to render it necessary, in his opinion, to send any at that time. Before the vessel arrived in St. Domingo, the Assembly, further urged by the appearance of danger, sent two deputies more, with larger demands; viz. eight thousand fusils and bayonets, two thousand musquetoons, three thousand pistols, three thousand sabres, twenty-four thousand barrels of flour, four hundred thousand livres’ worth of Indian meal, rice, pease, and hay, and a large quantity of plank, &c. to repair the buildings destroyed. They applied to M. de Ternant, and then with his consent to me; he and I having previously had a conversation on the subject. They proposed to me, first, that we should supply those wants from the money we owed France; or secondly, from the bills of exchange which they were authorized to draw on a particular fund in France; or thirdly, that we would guaranty their bills, in which case they could dispose of them to merchants, and buy the necessaries themselves. I convinced them the two latter alternatives were beyond the powers of the executive, and the first could only be done with the consent of the minister of France. In the course of our conversation, I expressed to them our sincere attachment to France and all its dominions, and most especially to them who were our neighbors, and whose interests had some common points of union with ours, in matters of commerce; that we wished, therefore, to render them every service they needed, but that we could not do it in any way disagreeable to France; that they must be sensible, that M. de Ternant might apprehend that jealousy would be excited by their addressing themselves directly to foreign powers, and, therefore, that a concert with him in their applications to us was essential. The subject of independence and their views towards it having been stated in the public papers, this led our conversation to it; and, I must say, they appeared as far from these views as any persons on earth. I expressed to them, freely, my opinion that such an object was neither desirable on their part, nor attainable; that as to ourselves, there was one case which would be peculiarly alarming to us, to wit, were there a danger of their falling under any other power; that we conceived it to be strongly our interest, that they should retain their connection with the mother country; that we had a common interest with them, in furnishing them the necessaries of life in exchange for sugar and coffee for our own consumption, but that I thought we might rely on the justice of the mother country towards them, for their obtaining this privilege: and, on the whole, let them see that nothing was to be done, but with the consent of the minister of France.
I am convinced myself, that their views and their application to us are perfectly innocent; however, M. de Ternant, and still more, M. de la Forest, are jealous. The deputies, on the other hand, think that M. de Ternant is not sensible enough of their wants. They delivered me sealed letters to the President and to Congress. That to the President contained only a picture of their distresses, and application for relief. That to Congress, I know no otherwise than through the public papers. The Senate read it, and sent it to the Representatives, who read it, and have taken no other notice of it. The line of conduct I pursue, is, to persuade these gentlemen to be contented with such moderate supplies, from time to time, as will keep them from real distress, and to wait with patience for what would be a surplus, till M. de Ternant can receive instructions from France, which he has reason to expect within a few weeks; and I encourage the latter gentleman even to go beyond their absolute wants of the moment, so far as to keep them in good humor. He is accordingly proposing to lay out ten thousand dollars for them, for the present. It would be ridiculous in the present case, to talk about forms. There are situations when form must be dispensed with. A man attacked by assassins will call for help to those nearest him, and will not think himself bound to silence till a magistrate may come to his aid. It would be unwise in the highest degree, that the colonists should be disgusted with either France or us; for it might then be made to depend on the moderation of another power, whether what appears a chimera may not become a reality. I have thought it necessary to go thus fully into this transaction, and particularly as to the sentiments I have expressed to them, that you may be enabled to place our proceedings in their true light.
Our Indian expeditions have proved successful. As yet, however, they have not led to peace. Mr. Hammond has lately arrived here, as Minister Plenipotentiary from the court of London, and we propose to name one to that court in return. Congress will probably establish the ratio of representation by a bill now before them, at one representative for every thirty thousand inhabitants. Besides the newspapers, as usual, you will receive herewith the census lately taken, by towns and counties as well as by States.
I am, with great and sincere esteem, Dear Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO THE ATTORNEY GENERAL.
Philadelphia, December 5,1791.
Dear Sir,
The enclosed memorial from the British minister, on the case of Thomas Pagan, containing a complaint of injustice in the dispensations of law by the courts of Massachusetts to a British subject, the President approves of my referring it to you, to report thereon your opinion of the proceedings, and whether any thing, and what, can or ought to be done by the government in consequence thereof.
I am, with great and sincere esteem, Dear Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
[The Memorial of the British minister.]
The undersigned, his Britannic Majesty’s Minister Plenipotentiary to the United States of America, has the honor of laying before the Secretary of State, the following brief abstract of the case of Thomas Pagan, a subject of his Britannic Majesty, now confined in the prison of Boston, under an execution issued against him out of the Supreme Judicial Court of Massachusetts Bay. To this abstract, the undersigned has taken the liberty of annexing some observations, which naturally arise out of the statement of the transaction, and which may perhaps tend to throw some small degree of light on the general merits of the case.
In the late war, Thomas Pagan was agent for, and part owner of a privateer called the Industry, which, on the 25th of March, 1783, off Cape Ann, captured a brigantine called the Thomas, belonging to Mr. Stephen Hooper, of Newburyport. The brigantine and cargo were libelled in the Court of Vice-Admiralty in Nova Scotia, and that court ordered the prize to be restored. An appeal was however moved for by the captors, and regularly prosecuted in England before the Lords of Appeals for prize causes, who, in February, 1790, reversed the decree of the Vice-Admiralty Court of Nova Scotia, and condemned the brigantine and cargo as good and lawful prize.
In December, 1788, a judgment was obtained by Stephen Hooper in the Court of Common Pleas for the county of Essex, in Massachusetts, against Thomas Pagan for three thousand five hundred pounds lawful money, for money had and received to the plaintiff’s use. An appeal was brought thereon in May, 1789, to the Supreme Judicial Court of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, held at Ipswich, for the county of Essex, and on the 16th of June, 1789, a verdict was found for Mr. Hooper, and damages were assessed at three thousand and nine pounds two shillings and ten pence, which sum is ‘for the vessel called the brigantine Thomas, her cargo, and every article found on board.’ After this verdict, and before entering the judgment, Mr. Pagan moved for a new trial, suggesting that the verdict was against law; because the merits of the case originated in a question, whether a certain brigantine called the Thomas, with her cargo, taken on the high seas by a private ship of war called the Industry, was prize or no prize, and that the court had no authority to give judgment in a cause, where the point of a resulting or implied promise arose upon a question of this sort. The Supreme Judicial Court refused this motion for a new trial, because it appeared to the court, that, in order to a legal decision, it is not necessary to inquire whether this prize and her cargo were prize or no prize, and because the case did not, in their opinion, involve a question relative to any matter or thing necessarily consequent upon the capture thereof: it was therefore considered by the court, that Hooper should receive of Pagan three thousand and nine pounds two shillings and ten pence, lawful money, damages; and taxed costs, sixteen pounds two shillings and ten pence. From this judgment, Pagan claimed an appeal to the Supreme Judicial Court of the United States of America, for these reasons; that the judgment was given in an action brought by Hooper, who is, and at the time of commencing the action was, a citizen of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, one of the United States, against Pagan, who at the time when the action was commenced, was and ever since has been a subject of the King of Great Britain, residing in and inhabiting his province of New Brunswick. This claim of an appeal was not allowed, because it was considered by the court, that this court was the Supreme Judicial Court of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, from whose judgment there is no appeal; and further, because there does not exist any such court within the United States of America, as that to which Pagan has claimed an appeal from the judgment of this court. Thereupon, execution issued against Pagan on the 9th of October, 1789, and he has been confined in Boston prison ever since. It is to be observed, that in August, 1789, Mr. Pagan petitioned the Supreme Judicial Court of Massachusetts for a new trial, and after hearing the arguments of counsel, a new trial was refused. On the 1st of January, 1791, his Britanic Majesty’s Consul at Boston applied for redress on behalf of Mr. Pagan, to the Governor of Massachusetts Bay, who, in his letter of the 28th of January, 1791, was pleased to recommend this matter to the serious attention of the Senate and House of Representatives of that State. On the 14th of February, 1791, the British Consul memorialized the Senate and House of Representatives on this subject. On the 22nd of February, a committee of both Houses reported a resolution, that the memorial of the Consul and message from the Governor with all the papers, be referred to the consideration of the justices of the Supreme Judicial Court, who were directed, as far as may be, to examine into and consider the circumstances of the case, and if they found that by the force and effect allowed by the law of nations to foreign admiralty jurisdictions, &c. Hooper ought not to have recovered judgment against Pagan, the court was authorized to grant a review of the action. On the 13th of June,’ 1791, the British Consul again represented to the Senate and House of Representatives, that the justices of the Supreme Judicial Court had not been pleased to signify their decision on this subject, referred to them by the resolution of the 22nd of February. This representation was considered by a committee of the Senate and of the House of Representatives, who concluded that one of them should make inquiry of some of the judges to know their determination, and upon being informed that the judges intended to give their opinion, with their reasons, in writing, the committee would not proceed any further in the business. On the 27th of June, 1791, Mr. Pagan’s counsel moved the justices of the Supreme Judicial Court for their opinion in the case of Hooper and Pagan, referred to their consideration by the resolve of the General Court, founded on the British Consul’s memorial. Chief Justice and Justice Dana being absent, Justice Paine delivered it as the unanimous opinion of the judges absent as well as present, that Pagan was not entitled to a new trial for any of the causes mentioned in the said resolve, and added, ‘that the court intended to put their opinions upon paper and to file them in the cause: that the sickness of two of the court had hitherto prevented it, but that it would soon be done.’
It is somewhat remarkable, that the Supreme Judicial Court of Massachusetts Bay should allege, that this case did not necessarily involve a question relative to prize or no prize, when the very jury to whom the court referred the decision of the case established the fact; their verdict was for three thousand and nine pounds two shillings and ten pence, damages, which sum is for the vessel called the brigantine Thomas, her cargo, and every thing found on board. Hence it is evident, that the case did involve a question of prize or no prize, and having received a formal decision by the only court competent to take cognizance thereof (viz. the High Court of Appeals for prize causes in England), every thing that at all related to the property in question or to the legality of the capture, was thereby finally determined. The legality of the capture being confirmed by the High Court of Appeals in England, cannot consistently with the principles of the law of nations be discussed in a foreign court of law; or at least, if a foreign court of common law is, by any local regulations, deemed competent to interfere in matters relating to captures, the decisions of admiralty courts or courts of appeal, should be received and taken as conclusive evidence of the legality or illegality of captures. By such decisions, property is either adjudged to the captors or restored to the owners; if adjudged to the captors, they obtain a permanent property in the captured goods acquired by the rights of war; and this principle originates in the wisdom of nations, and is calculated to prevent endless litigation.
The proceedings of the Supreme Judicial Court of Massachusetts Bay are in direct violation of the rules and usages that have been universally practised among nations in the determination of the validity of captures, and of all collateral questions that may have reference thereto. The General Court of Massachusetts Bay, among other things, kept this point in view, when they referred the case of Mr. Pagan to the consideration of the justices of the Supreme Judicial Court, and authorized the court to grant a review of the action, if it should be found that by the force and effect allowed by the law of nations to foreign admiralty jurisdictions, Mr. Hooper ought not to have recovered judgment against Mr. Pagan. But the Supreme Judicial Court have not only evaded this material consideration, upon which the whole question incontestably turns, but have assumed a fact in direct contradiction to the truth of the case, viz. that the case did not involve a question of prize or no prize. Moreover, they have denied Mr. Pagan the benefit of appeal to that court which is competent to decide on the force of treaties, and which court, by the constitution of the United States, is declared to possess appellate jurisdiction both as to law and fact, in all cases of controversy between citizens of the United States and subjects of foreign countries, to which class this case is peculiarly and strictly to be referred.
From the foregoing abstract of the case of Thomas Pagan, it appears that he is now detained in prison, in Boston, in consequence of a judgment given by a court which is not competent to decide upon his case, or which, if competent, refused to admit the only evidence that ought to have given jurisdiction, and that he is denied the means of appealing to the highest court of judicature known in these States, which exists in the very organization of the constitution of the United States, and is declared to possess appellate jurisdiction in all cases of a nature similar to this.
For these reasons, the undersigned begs leave respectfully to submit the whole matter to the consideration of the Secretary of State, and to request him to take such measures as may appear to him the best adapted for the purpose of obtaining for the said Thomas Pagan, such speedy and effectual redress as his case may seem to require.
George Hammond,
Philadelphia, November 26,1791.
TO MR. HAMMOND, Minister Plenipotentiary of Great Britain,
Philadelphia, December 5, 1791.
Sir,
Your favor of November the 30th remains still unanswered, because the clerks are employed in copying some documents on the subject of the treaty of peace, which I wish to exhibit to you with the answer.
In the mean time, as to that part of your letter which respects matters of commerce, the fear of misunderstanding it induces me to mention my sense of it, and to ask if it be right. Where you are pleased to say, that ‘you are authorized to communicate to this government his Majesty’s readiness to enter into a negotiation for establishing that intercourse (of commerce) upon principles of reciprocal benefit,’ I understand that you are not furnished with any commission or express powers to arrange a treaty with us, or to make any specific propositions on the subject of commerce; but only to assure us that his Britannic Majesty is ready to concur with us, in appointing persons, times, and places for commencing such a negotiation. Be so good as to inform me if there be any misapprehension in this, as some steps on our part may be necessary in consequence of it.
1 have the honor to be, with the most perfect esteem, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson,
Philadelphia, December 12, 1791.
Sir,
I take the liberty of enclosing you an extract of a letter from a respectable character, giving information of a Mr. Bowles, lately come from England into the Creek country, endeavoring to excite that nation of Indians to war against the United States, and pretending to be employed by the government of England. We have other testimony of these his pretensions, and that he carries them much farther than is here stated. We have too much confidence in the justice and wisdom of the British government, to believe they can approve of the proceedings of this incendiary and impostor, or countenance for a moment a person who takes the liberty of using their name for such a purpose; and I make the communication, merely that you may take that notice of the case which in your opinion shall be proper.
I have the honor to be, with great and sincere esteem, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
Philadelphia, December 13, 1791.
Sir,
I have laid before the President of the United States the letters of November the 30th and December the 6th, with which you honored me, and in consequence thereof and particularly of that part of your letter of December the 6th, where you say that you are fully authorized to enter into a negotiation for the purpose of arranging the commercial intercourse between the two countries, I have the honor to inform you, that I am ready to receive a communication of your full powers for that purpose, at any time you shall think proper, and to proceed immediately to their object.
I have the honor to be, with sentiments of the most perfect esteem and respect. Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO THE PRESIDENT.
Philadelphia, December 23, 1791.
Sir,
As the conditions of our commerce with the French and British dominions are important, and a moment seems to be approaching when it may be useful that both should be accurately understood, I have thrown a representation of them into the form of a table, showing at one view how the principal articles, interesting to our agriculture and navigation, stand in the European and American dominions of these two powers. As to so much of it as respects France, I have cited under every article the law on which it depends; which laws, from 1784 downwards, are in my possession.
Port-charges are so different, according to the size of the vessel and the dexterity of the captain, that an examination of a greater number of port-bills might, perhaps, produce a different result. I can only say, that that expressed in the table is fairly drawn from such bills as I could readily get access to, and that I have no reason to suppose it varies much from the truth, nor on which side the variation would lie. Still, I cannot make myself responsible for this article. The authorities cited will vouch the rest.
I have the honor to be, with the most perfect respect and attachment, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
Footing of the Commerce of the United States with France and England, and with the French and English American Colonies.
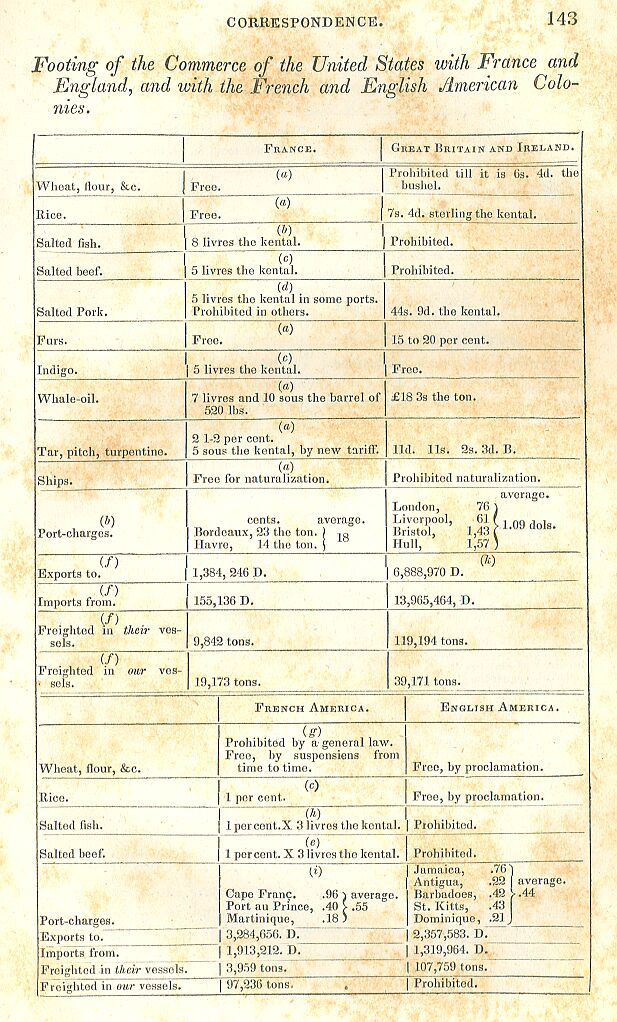
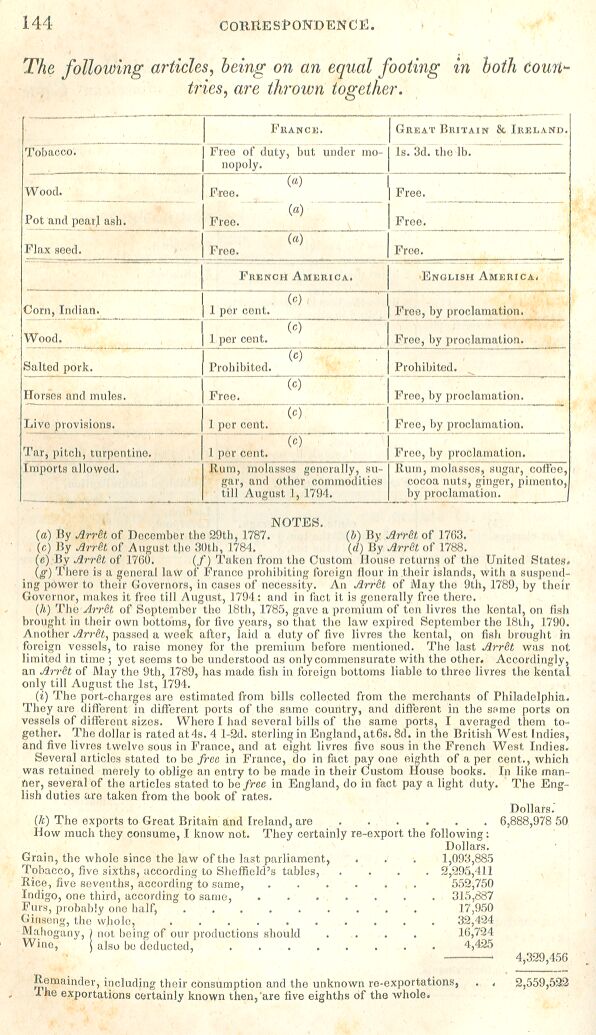
TO THE PRESIDENT.
Philadelphia, January 4, 1792,
Sir,
Having been in conversation to-day with Monsieur Payan, one of the St. Domingo deputies, I took occasion to inquire of him the footing on which our commerce there stands at present, and particularly whether the colonial Arrêt of 1789, permitting a free importation of our flour till 1793, was still in force. He answered, that that Arrêt was revoked in France on the clamors of the merchants there; and with a like permission to carry flour to the three usual ports, and he thinks to bring away coffee and sugar, was immediately renewed by the Governor. Whether this has been regularly kept up by renewed Arrêts, during the present trouble, he cannot say, but is sure that in practice it has never been discontinued, and that not by contraband, but openly and legally, as is understood. The public application to us to send flour there, is a proof of it. Instead, therefore, of resting this permission on a colonial Arrêt till 1793, it should be rested on temporary Arrêts renewed from time to time, as heretofore. This correction of the notes I took the liberty of laying before you with the table containing a comparative view of our commerce with France and England, I thought it my duty to make.
I have the honor to be, with the most perfect respect and attachment, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO THOMAS PINCKNEY.
Philadelphia, January 17, 1792.
Sir,
Your favors of November the 29th, 30th, and December the 1st, came duly to hand, and gave sincere pleasure, by announcing your disposition to accept the appointment to London. The nominations to Paris and the Hague having been detained till yours could be made, they were all immediately sent in to the Senate, to wit, yourself for London, Mr. G. Morris for Paris, Mr. Short for the Hague. Some members of the Senate, apprehending they had a right of determining on the expediency of foreign missions, as well as on the persons named, took that occasion of bringing forward the discussion of that question, by which the nominations were delayed two or three weeks. I am happy to be able to assure you, that not a single personal motive with respect to yourself entered into the objections to these appointments. On the contrary, I believe that your nomination gave general satisfaction. Your commission will be immediately made out, but as the opportunities of conveyance at this season are precarious, and you propose coming to this place, I think it better to retain it.
As to the delay proposed in your letter, it was to be expected: indeed a winter passage from Charleston to this place, or across the Atlantic, is so disagreeable, that if either that circumstance or the arrangement of your affairs should render it in the smallest degree eligible to you to remain at home till the temperate season comes on, stay till after the vernal equinox; there will be no inconvenience to the public attending it. On the contrary, as we are just opening certain negotiations with the British minister here, which have not yet assumed any determinate complexion, a delay till that time will enable us to form some judgment of the issue they may take, and to know exactly in what way your co-operation at the place of your destination may aid us. On this and other accounts it will be highly useful that you take this place in your way, where, or at New York, you will always be sure of finding a convenient, passage to England.
I have the honor to be, with the most perfect esteem and respect, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MESSRS. WILLINKS, VAN STAPHORSTS, AND HUBARD.
Philadelphia, January 23,1792.
Gentlemen,
On the 19th of March last, I had the honor to enclose you a bill for ninety-nine thousand florins, drawn on yourselves by the Treasurer of the United States, in favor of the Secretary of State, and I desired you to raise an account with the Secretary of State, and pass that bill to his credit in the account. In my letter of May the 14th, I enclosed you a duplicate of the same bill, and informed you that this money was destined to pay the salaries and contingent expenses of our ministers and agents of every description, from July the 1st, 1790, and nothing else; and I added these words; ‘I must beg the favor of you, also, to make up your account to the close of the last day of June this present year, into which no expenses are to enter which preceded, the 1st day of July, 1790, these being the dates of the appropriation of the law.’ And lastly, in my letter of August the 5th, I enclosed a triplicate of the same bill, and added, ‘In the mean time, I hope that your account of this fund, from July the 1st, 1790, to June the 30th, 1791, inclusive, is on its way to me, that I may receive it in time to lay before Congress at their meeting:’ but in fact, I have neither received the account so much desired, nor even an acknowledgment of the receipt of any of the said letters or bills; and though Congress have been now sitting upwards of three months, I have it not in my power to lay before them a statement of the administration of this fund. When you consider the delicate situation of those entrusted with the disposal of public monies, and the express injunction under which I am laid by my office to submit this account to a proper and timely examination, I leave you to conceive what my sensations must be under the disability to do it, which the want of your account alone has brought,on me; and I hope I shall soon be relieved by the receipt of it.
I am, with great esteem, Gentlemen, your most obedient servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO WILLIAM SHORT.
Philadelphia, January 23, 1792.
Dear Sir,
I have the pleasure to inform you, that the President of the United States has appointed you Minister Resident for the United. States, at the Hague, which was approved by the Senate on the 16th instant. This new mark of the President’s confidence will be the more pleasing to you, as it imports an approbation of your former conduct, whereon be pleased to accept my congratulations. You will receive herewith, a letter from myself to Monsieur de Montmorin, closing your former mission, your new commission, letters of credence from the President for the States General and Stadtholder, sealed, and copies of them open for your own satisfaction. You will keep the cipher we have heretofore used.
Your past experience in the same line, renders it unnecessary for me to particularize your duties on closing your present, or conducting your future mission. Harmony with our friends being our object, you are sensible how much it will be promoted by attention to the manner as well as the matter of your communications with the government of the United Netherlands. I feel myself particularly bound to recommend, as the most important of your charges, the patronage of our commerce and the extension of its privileges, both in the United Netherlands and their colonies, but most especially the latter.
The allowance to a Minister Resident of the United States, is four thousand five hundred dollars a year, or all his personal services and other expenses, a year’s salary for his outfit and a quarter’s salary for his return. It is understood that the personal services and other expenses here meant, do not extend to the cost of gazettes and pamphlets transmitted to the Secretary of State’s office, to translating or printing necessary papers, postage, couriers, and necessary aids to poor American sailors. These additional charges, therefore, may be inserted in your accounts; but no other of any description, unless where they are expressly directed to be incurred. The salary of your new grade being the same as of your former one, and your services continued, though the scene of them is changed, there will be no intermission of salary; the new one beginning where the former ends, and ending when you shall receive notice of your permission to return. For the same reason, there can be but one allowance of outfit and return, the former to take place now, the latter only on your final return. The funds appropriated to the support of the foreign establishment do not admit the allowance of a secretary to a Minister Resident. I have thought it best to state these things to you minutely, that you may be relieved from all doubt as to the matter of your accounts. I will beg leave to add a most earnest request, that on the 1st day of July next, and on the same day annually afterwards, you make out your account to that day, and send it by the first vessel, and by duplicates. In this I must be very urgent and particular; because at the meeting of the ensuing Congress always, it is expected that I prepare for them a statement of the disbursements from this fund, from July to June inclusive. I shall give orders, by the first opportunity, to our bankers in Amsterdam, to answer your drafts for the allowances herein before mentioned, recruiting them at the same time by an adequate remitment; as I expect that by the time you receive this, they will not have remaining on hand of this fund more than seven or eight thousand dollars.
You shall receive from me, from time to time, the laws and journals of Congress, gazettes, and other interesting papers: for whatever information is in possession of the public, I shall leave you generally to the gazettes, and only undertake to communicate by letter, such, relative to the business of your mission, as the gazetteers cannot, give. From you I shall ask, once or twice a month regularly, a communication of interesting occurrences in Holland, of the general affairs of Europe, and the regular transmission of,the Leyden gazette by every British packet, in the way it now comes, which proves to be very regular. Send also such other publications as may be important enough to be read by one who can spare little time to read any thing, or which may contain matter proper to be turned to, on interesting subjects and occasions. The English packet is the most certain channel for such epistolary communications as are not very secret, and by those packets I would wish always to receive a letter from you by way of corrective to the farrago of news they generally bring. Intermediate letters, secret communications, gazettes, and other printed papers, had better come by private vessels from Amsterdam; which channel I shall use generally for my letters, and always for gazettes and other printed papers.
The President has also joined you in a special and temporary commission with Mr. Carmichael to repair to Madrid, and there negotiate certain matters respecting the navigation of the Mississippi, and other points of common interest between Spain and us. As some time will be necessary to make out the instructions and transcripts necessary in this business, they can only be forwarded by some future occasion; but they shall be soon forwarded, as we wish not to lose a moment in advancing negotiations so essential to our peace. For this reason, I must urge you to repair to the Hague at the earliest day the settlement of your affairs at Paris will admit, that your reception may be over, and the idea of your being established there strengthened, before you receive the new orders.
I have the honor to be, with sincere respect and esteem, Dear Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO GOUVERNEUR MORRIS.
Philadelphia, January 23, 1792.
Dear Sir,
I have the pleasure to inform you, that the President of the United States has appointed you Minister Plenipotentiary for the United States, at the court of France, which was approved by the Senate on the 12th instant; on which be pleased to accept my congratulations. You will receive herewith your commission, a letter of credence for the King, sealed, and a copy of it open for your own satisfaction, as also a cipher, to be used on proper occasions in the correspondence between us.
To you, it would be more than unnecessary for me to undertake a general delineation of the functions of the office to which you are appointed. I shall therefore only express our desire, that they be constantly exercised in that spirit of sincere friendship and attachment which we bear to the French nation; and that in all transactions with the minister, his good dispositions be conciliated by whatever in language or attentions may tend to that effect. With respect to their government, we are under no call to express opinions which might please or offend any party, and therefore it will be best to avoid them on all occasions, public or private. Could any circumstances require unavoidably such expressions, they would naturally be in conformity with the sentiments of the great mass of our countrymen, who, having first, in modern times, taken the ground of government founded on the will of the people, cannot but be delighted on seeing so distinguished and so esteemed a nation arrive on the same ground, and plant their standard by our side.
I feel myself particularly bound to recommend, as the most important of your charges, the patronage of our commerce and the extension of its privileges, both in France and her colonies, but most especially the latter. Our Consuls in France are under general instructions to correspond with the Minister of the United States at Paris; from them you may often receive interesting information. Joseph Fenwick is Consul at Bordeaux, and Burwell Carnes at Nantz; Monsieur de la Motte, Vice-Consul at Havre, and Monsieur Cathalan at Marseilles.
An act of Congress, of July the 1st, 1790, has limited the allowance of a Minster Plenipotentiary to nine thousand dollars a year, for all his personal services and other expenses, a year’s salary for his outfit, and a quarter’s salary for his return. It is understood that the personal services and other expenses here meant, do not extend to the cost of gazettes and pamphlets transmitted to the Secretary of State’s office, to translating or printing necessary papers, postage, couriers, and necessary aids to poor American sailors. These additional charges, therefore, may be inserted in your accounts; but no other of any description, unless where they are expressly directed to be incurred. By an ancient rule of Congress, your salary will commence from the day you receive this letter, if you be then at Paris, or from the day you set out for Paris from any other place at which it may find you: it ceases on receiving notice or permission to return, after which the additional quarter’s allowance takes place. You are free to name your own private secretary, who will receive, from the public a salary of thirteen hundred and fifty dollars a year, without allowance for any extras. I have thought it best to state these things to you minutely, that you may be relieved from all doubt as to the matter of your accounts. I will beg leave to add a most earnest request, that on the 1st day of July next, and on the same day annually afterwards, you make out your account to that day, and send it by the first vessel, and by duplicates. In this I must be very urgent and particular, because at the meeting of the ensuing Congress always, it is expected that I prepare for them a statement of the disbursements from this fund, from July to June inclusive. I shall give orders by the first opportunity to our bankers in Amsterdam, to answer your drafts for the allowances herein before mentioned, recruiting them at the same time by an adequate remitment, as I expect that by the time you receive this, they will not have remaining on hand of this fund more than seven or eight thousand dollars.
You shall receive from me, from time to time, the laws and journals of Congress, gazettes, and other interesting papers: for whatever information is in possession of the public, I shall leave you generally to the gazettes, and only undertake to communicate by letter, such, relative to the business of your mission, as the gazettes cannot give.
From you I shall ask, once or twice a month regularly, a communication of interesting occurrences in France, of the general affairs of Europe, and transmission of the Leyden gazette, the Journal Logographe, and the best paper of Paris for their colonial affairs, with such other publications as may be important enough to be read by one who can spare little time to read any thing, or which may contain matter proper to be turned to on interesting subjects and occasions. The English packet is the most certain channel for such epistolary communications as are not very secret, and by those packets I would wish always to receive a letter from you by way of corrective to the farrago of news they generally bring. Intermediate letters, secret communications, gazettes, and other printed papers, had better come through the channel of Monsieur de la Motte at Havre, to whom I shall also generally address my letters to you, and always the gazettes and other printed papers.
Mr. Short will receive by the same conveyance, his appointment as Minister Resident at the Hague.
I have the honor to be, with great esteem and respect, Dear Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MR. HAMMOND.
Philadelphia, February 2, 1792.
Sir,
On the receipt of your letter of the 14th of December, I communicated it to the President of the United States, and under the sanction of his authority, the principal members of the executive department made it their duty to make known in conversations generally, the explicit disclaimer, in the name of your court, which you had been pleased to give us, that the government of Canada had supported or encouraged the hostilities of our Indian neighbors in the western country. Your favor of January the 30th, to the same purpose, has been, in like manner, communicated to the President, and I am authorized to assure you, that he is duly sensible of this additional proof of the disposition of the court of London to confine the proceedings of their officers in our vicinage within the limits of friendship and good neighborhood, and that a conduct so friendly and just will furnish us a motive the more for those duties and good offices which neighbor nations owe each other.
You have seen too much, Sir, of the conduct of the press in countries where it is free, to consider the gazettes as evidence of the sentiments of any part of the government: you have seen them bestow on the government itself, in all its parts, its full share of inculpation. Of the sentiments of our government on the subject of your letter, I cannot give you better evidence than the statement of the causes of the Indian war, made by the Secretary of War on the 26th of the last month, by order of the President, and inserted in the public papers. No interference on the part of your nation is therein stated among the causes of the war. I am happy however in the hope, that a due execution of the treaty will shortly silence those expressions of public feeling, by removing their cause.
I have the honor to be, with great respect and esteem, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MR. HAMMOND.
Philadelphia, February 25, 1792.
Sir,
I have now the honor to enclose you the answer of the Attorney General to a letter I wrote him on the subject of yours of the 18th instant.
It appears that the judges of the Supreme Court of the United States are open to the application of Mr. Pagan for a writ of error to revise his case. This writ is to be granted, indeed, or refused, at the discretion of the judge; but the discretion of the judge is governed by the rules of law: if these be in favor of Mr. Pagan’s application, his case will be reviewed in the Supreme Court, and the decision against him corrected, if wrong, if these be against his application, he will then be at the end of the ordinary course of law, at which term alone it is usual for nations to take up the cause of an individual, and to inquire whether their judges have refused him justice. At present, therefore, I am not able to say more, than that the judges of the Supreme Court of the United States will receive Mr. Pagan’s application for a writ of error to revise the judgment given against him by the inferior court, and that there can be no doubt they will do on that application what shall be right.
I have the honor to be, with the highest esteem, your most obedient and most humble servant.
Th: Jefferson.
TO MESSRS. JOHNSON, CARROL, AND STEWART.
Philadelphia, March 6, 1792,
Gentlemen,
It having been found impracticable to employ Major L’Enfant about the federal city, in that degree of subordination which was lawful and proper, he has been notified that his services are at an end. It is now proper that he should receive the reward of his past services; and the wish that he should have no just cause of discontent, suggests that it should be liberal. The President thinks of two thousand five hundred, or three thousand dollars, but leaves the determination to you. Ellicot is to go on, the week after, the next, to finish laying off the plan on the ground, and surveying and platting the district. I have remonstrated with him on the excess of five dollars a day and his expenses, and he has proposed striking off the latter; but this also is left to you, and to make the allowance retrospective. He is fully apprized that he is entirely under your orders, and that there will be no person employed but under your orders. The enemies of this enterprise will take advantage of the retirement of L’Enfant, to trumpet an abortion of the whole. This will require double exertions, to be counteracted. I enclose you the project of a loan, which is agreed on, if you approve it. Your answer will be immediately expected, and it is kept entirely secret, till the subscriptions are actually opened. With this money, in aid of your other funds, the works may be pushed with such spirit as to evince to the world that they will not be relaxed.
The immediate employment of a superintendent, of activity and intelligence equal to the nature of his functions and the public expectations, becomes important. You will, doubtless, also consider it as necessary to advertise immediately for plans of the Capitol and President’s house. The sketch of an advertisement for the plan of a Capitol, which Mr. Johnson had sent to the President, is now returned with some alterations, and one also for a President’s house. Both of them are subject to your pleasure, and when accommodated to that, if you will return them, they shall be advertised here and elsewhere. The President thinks it of primary importance to press the providing as great quantities of brick, stone, lime, plank, timber, &c. this year as possible. It will occur to you that the stone should be got by a skilful hand. Knowing what will be your funds, you will be able to decide which of the following works had better be undertaken for the present year.
The cellars of both houses.
The foundation of one, or both.
Bridge over Rock Creek, and the post-road brought over it.
Canal.
Wharves.
The affair of Mr. Carrol of Duddington’s house, seems to call for settlement. The President thinks the most just course would be, to rebuild the house in the same degree, using the same materials as far as they will go, and supplying what are destroyed or rendered unfit; so that the effect will be in fact, only the removal of the house within his lot, and in a position square with the streets. Do you not think it would be expedient to take measures for importing a number of Germans and Highlanders? This need not be to such an extent as to prevent the employment of eastern laborers, which is eligible for particular reasons. If you approve of the importation of Germans, and have a good channel for it, you will use it, of course. If you have no channel, I can help you to one. Though Roberdeau’s conduct has been really blamable, yet we suppose the principal object of the arrest was to remove him off the ground. As the prosecution of him to judgment might give room to misrepresentation of the motives, perhaps you may think it not amiss to discontinue the proceedings. You will receive herewith a packet of papers, among which are several projects and estimates which have been given in by different persons, and which are handed on to you, not as by any means carrying with them any degree of approbation, but merely, that if you find any thing good in them, you may convert it to some account. Some of these contain the views of L’Enfant.
I have the honor to be, with the most perfect esteem and respect, Gentlemen, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO GOUVERNEUR MORRIS.
Philadelphia, March 10, 1792.
Dear Sir,
My letter of January the 23rd, put under cover to Mr. Johnson in London, and sent by a passenger in the British packet of February, will have conveyed to you your appointment as Minister Plenipotentiary of the United States, at the court of France. By the Pennsylvania, Captain Harding, bound to Havre de Grace, and plying pretty regularly between this place and that, you will receive the present letter, with the laws of the United States, journals of Congress, and gazettes to this day, addressed to the care of M. de la Motte. You will also receive a letter from the President to the King of France, in answer to his announcing the acceptance of the constitution, which came to hand only a week ago. A copy of this letter is sent for your own use. You will be pleased to deliver the sealed one (to the minister I presume, according to the ancient etiquette of the court), accompanying it with the assurances of friendship, which the occasion may permit you to express, and which are cordially felt by the President and the great body of our nation. We wish no occasion to be omitted of impressing the National Assembly with this truth. We had expected, ere this, that in consequence of the recommendation of their predecessors, some overtures would have been made to us on the subject of a treaty of commerce. An authentic copy of the recommendation was delivered, but nothing said about carrying it into effect. Perhaps they expect that we should declare our readiness to meet them on the ground of treaty. If they do, we have no hesitation to declare it. In the mean time, if the present communications produce any sensation, perhaps it may furnish a good occasion to endeavor to have matters re-placed in statu quo, by repealing the late innovations as to our ships, tobacco, and whale-oil. It is right that things should be on their ancient footing, at opening the treaty. M. Ternant has applied here for four hundred thousand dollars for the succor of the French colonies. The Secretary of the Treasury has reason to believe, that the late loan at Antwerp has paid up all our arrearages to France, both of principal and interest, and consequently, that there is no part of our debt exigible at this time. However, the legislature having authorized the President to proceed in borrowing to pay off the residue, provided it can be done to the advantage of the United States, it is thought the law will be satisfied with avoiding loss to the United States. This has obliged the Secretary of the Treasury to require some conditions, which may remove from us that loss which we encountered, from an unfavorable exchange, to pay what was exigible, and transfer it to France as to payments not exigible. These shall be fully detailed to you when settled. In the mean time, the money will be furnished as far as it can be done. Indeed, our wishes are cordial for the re-establishment of peace and commerce in those colonies, and to give such proofs of our good faith both to them and the mother country, as to suppress all that jealousy which might oppose itself to the free exchange of our mutual productions, so essential to the prosperity of those colonies, and to the preservation of our agricultural interest. This is our true interest, and our true object, and we have no reason to conceal views so justifiable, though the expression of them may require that the occasions be proper and the terms chosen with delicacy. The gazettes will inform you of the proceedings of Congress, the laws passed and proposed, and generally speaking, of all public transactions. You will perceive that the Indian war calls for sensible exertions. It would have been a trifle had we only avowed enemies to contend with. The British court have disavowed all aid to the Indians. Whatever may have been their orders in that direction, the Indians are fully and notoriously supplied by their agents with every thing necessary to carry on the war. Time will show how all this is to end. Besides the laws, journals, and newspapers, before mentioned, you will receive herewith the State constitutions, the census, and almanac, and an answer to Lord Sheffield on our commerce. A cipher is ready for you, but cannot be sent till we can find a trusty passenger going to Paris.
I am, with great respect and esteem, Dear Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
Since writing the preceding, the two Houses have come to resolutions on the King’s letter, which are enclosed in the President’s, and copies of them accompany this for your use. T.J.
TO MESSRS. CARMICHAEL AND SHORT.
Philadelphia, March 18, 1792.
Gentlemen,
The President having thought proper to appoint you joint commissioners plenipotentiary, on the part of the United States, to treat with the court of Madrid on the subjects of the navigation of the Mississippi, arrangements on our limits, and commerce, you will herewith receive your commission; as also observations on these several subjects, reported to the President and approved by him, which will therefore serve as instructions for you. These expressing minutely the sense of our government and what they wish to have done, it is unnecessary for me to do more here than desire you to pursue these objects unremittingly, and endeavor to bring them to an issue, in the course of the ensuing summer. It is desirable that you should keep an exact journal of what shall pass between yourselves and the court or their negotiator, and communicate it from time to time to me, that your progress and prospects may be known. You will be the best judges whether to send your letters by Lisbon, Cadiz, or what other route; but we shall be anxious to hear from you as often as possible. If no safe conveyance occurs from Madrid to Lisbon, and your matter should be of importance sufficient to justify the expense, a courier must be sent; but do not incur the expense, unless it be to answer some good end.
I have the honor to be, with great and sincere esteem, Gentlemen, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO COLONEL PICKERING.
Philadelphia, March 28, 1792.
Sir,
The President has desired me to confer with you on the proposition I made the other day, of endeavoring to move the posts at the rate of one hundred miles a day. It is believed to be practicable here, because it is practised in every other country. The difference of expense alone appeared to produce doubts with you on the subject. If you have no engagement for dinner to-day, and will do me the favor to come and dine with me, we will be entirely alone, and it will give us time to go over the matter and weigh it thoroughly. I will, in that case, ask the favor of you to furnish yourself with such notes as may ascertain the present expense of the posts, for one day in the week, to Boston and Richmond, and enable us to calculate the savings which may be made by availing ourselves of the stages. Be pleased to observe that the stages travel all the day. There seems nothing necessary for us then, but to hand the mail along through the night till it may fall in with another stage the next day, if motives, of economy should oblige us to be thus attentive to small savings. If a little latitude of expense can be allowed, I should be for only using the stages the first day, and then have our riders. I am anxious that the thing should be begun by way of experiment, for a short distance, because I believe it will so increase the income of the post-office as to show we may go through with it. I shall hope to see you at three o’clock.
I am with great esteem, Sir, your most obedient, humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MR. HAMMOND.
Philadelphia, March 31, 1792.
Sir,
I received yesterday your favor of the day before, and immediately laid it before the President of the United States. I have it in charge from him to express to you the perfect satisfaction which these assurances on the part of your court have given him, that Bowles, who is the subject of them, is an unauthorized impostor. The promptitude of their disavowal of what their candor had forbidden him to credit, is a new proof of their friendly dispositions, and a fresh incitement to us to cherish corresponding sentiments. To these we are led both by interest and inclination, and I am authorized to assure you that no occasion will be omitted, on our part, of manifesting their sincerity.
I have the honor to be, with sentiments of the most perfect esteem and respect, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO GOVERNOR PINCKNEY.
Philadelphia, April 1, 1792.
Sir,
Your letter of January the 8th to the President of the United States having been referred to me, I have given the subject of it as mature consideration as I am able. Two neighboring and free governments, with laws equally mild and just, would find no difficulty in forming a convention for the interchange of fugitive criminals. Nor would two neighboring despotic governments, with laws of equal severity. The latter wish that no door should be opened to their subjects flying from the oppression of their laws. The fact is, that most of the governments on the continent of Europe have such conventions; but England, the only free one till lately, has never yet consented either to enter into a convention for this purpose, or to give up a fugitive. The difficulty between a free government and a despotic one is indeed great. I have the honor to enclose to your Excellency a sketch of the considerations which occurred to me on the subject, and which I laid before the President. He has, in consequence, instructed me to prepare a project of a convention, to be proposed to the court of Madrid, which I have accordingly done, and now enclose a copy of it. I wish it may appear to you satisfactory. Against property we may hope it would be effectual; whilst it leaves a door open to life and liberty except in a single unquestionable case. Messrs. Carmichael and Short will be instructed to make this one of the subjects of their negotiation with the court of Spain. I have the honor to be, with sentiments of the most perfect esteem and respect, your Excellency’s most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO COLONEL HUMPHREYS.
Philadelphia, April 9, 1792.
Dear Sir,
My last to you were of the 29th of November and the 13th of December. I have now to acknowledge the receipt of your Nos. 34 to 44, inclusive. The river here and at New York having remained longer blocked with ice than has been usual, has occasioned a longer interval than usual between my letters. I have particularly to acknowledge, that Mr. Barclay’s receipt of drafts from you on our bankers in Holland for thirty-two thousand one hundred and seventy-five florins has come safely to my hands, and is deposited in my office, where it will be to be found wrapped in the letter in which it came. You have been before informed of the failure of our arms against the Indians, the last year. General St. Clair has now resigned that command. We are raising our western force to five thousand men. The stock-jobbing speculations have occupied some of our countrymen to such a degree, as to give sincere uneasiness to those who would rather see their capitals employed in commerce, manufactures, buildings, and agriculture. The failure of Mr. Duer, the chief of that description of people, has already produced some other bankruptcies, and more are apprehended. He had obtained money from great numbers of small tradesmen and farmers, tempting them by usurious interest, which has made the distress very extensive. Congress will adjourn within a fortnight. The President negatived their representation bill, as framed on principles contrary to the constitution. I suppose another will be passed, allowing simply a representative for every thirty or thirty-three thousand, in each State. The troubles in the French island continue extreme; we have, as yet, heard of the arrival but of a few troops. There begins to be reason to apprehend, the negroes will perhaps never be entirely reduced. A commission has issued to Mr. Carmichael and Mr. Short, to treat with the court of Madrid on the subjects heretofore in negotiation between us. I suppose Mr. Short will be in Madrid by the last of May. We expect Major Pinckney here hourly, on his way to London, as our Minister Plenipotentiary to that court. For a state of our transactions in general, I refer you to the newspapers which accompany this. I put under your cover letters and newspapers for Mr. Carmichael and Mr. Barclay, which I pray you to contrive by some sure conveyances. We must make you, for some time, the common centre of our correspondence.
I am with great and sincere respect and esteem, Dear Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MR. HAMMOND.
Philadelphia, April 12, 1792.
Sir,
I am this moment favored with the letter you did me the honor of writing yesterday, covering the extract of a British statute forbidding the admission of foreign vessels into any ports of the British dominions, with goods or commodities of the growth, production, or manufacture of America. The effect of this appears to me so extensive, as to induce a doubt whether I understand rightly the determination to enforce it, which you notify, and to oblige me to ask of you whether we are to consider it as so far a revocation of the proclamation of your government, regulating the commerce between the two countries, and that henceforth no articles of the growth, production, or manufacture of the United States, are to be received in the ports of Great Britain or Ireland, in vessels belonging to the citizens of the United States.
I have the honor to be, with sentiments of the most perfect esteem and respect, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
The Secretary of State presents his compliments to Mr. Hammond, and encloses him the draught of a letter to the President of the United States, which he has prepared to accompany Mr. Hammond’s communication of the 11th and letter of the 12th. The whole will probably be laid by the President before the legislature, and perhaps communicated to the public, in order to let the merchants know that they need not suspend their shipments, but to the islands of Jersey and Guernsey. Before sending the letter to the President, the Secretary of State has chosen to communicate it to Mr. Hammond in a friendly way, being desirous to know whether it meets his approbation, or whether he would wish any alterations in it.
April 13,1792.
TO THE PRESIDENT.
Philadelphia, April 13, 1792,
Sir,
I have the honor to lay before you a communication from Mr. Hammond, Minister Plenipotentiary of his Britannic Majesty, covering a clause of a statute of that country relative to its commerce with this, and notifying a determination to carry it into execution henceforward. Conceiving that the determination announced could not be really meant as extensively as the words import, I asked and received an explanation from the minister, as expressed in the letter and answer herein enclosed: and on consideration of all circumstances, I cannot but confide in the opinion expressed by him, that its sole object is to exclude foreign vessels from the islands of Jersey and Guernsey. The want of proportion between the motives expressed and the measure, its magnitude, and consequences, total silence as to the proclamation on which the intercourse between the two countries has hitherto hung, and of which, in this broad sense, it would be a revocation, and the recent manifestations of the disposition of that government to concur with this in mutual offices of friendship and good will, support his construction. The minister, moreover, assured me verbally, that he would immediately write to his court for an explanation, and, in the mean time, is of opinion that the usual intercourse of commerce between the two countries (Jersey and Guernsey excepted) need not be suspended.
I have the honor to be, with sentiments of the most profound respect and attachment, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MESSRS. CARMICHAEL AND SHORT.
Philadelphia, April 24, 1792.
Gentlemen,
My letter of March the 18th conveyed to you full powers for treating with Spain on the subjects therein expressed. Since that, our attention has been drawn to the case of fugitive debtors and criminals, whereon it is always well that coterminous States should understand one another, as far as their ideas on the rightful powers of government can be made to go together. Where they separate, the cases may be left unprovided for. The enclosed paper, approved by the President, will explain to you how far we can go, in an agreement with Spain for her territories bordering on us: and the plan of a convention is there stated. You are desired to propose the matter to that court, and establish with them so much of it as they approve, filling up the blank for the manner of the demand by us and compliance by them, in such way, as their laws and the organization of their government may require. But recollect that they bound on us between two and three thousand miles, and consequently, that they should authorize a delivery by some description of officers to be found on every inhabited part of their border. We have thought it best to agree, specially, the manner of proceeding in our country, on a demand of theirs, because the convention will in that way execute itself, without the necessity of a new law for the purpose. Your general powers being comprehensive enough to take in this subject, no new ones are issued.
I have the honor to be, with great respect, Gentlemen, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
[The annexed are the papers referred to in the preceding.]
Project of a Convention with the Spanish Provinces.
Any person having committed murder of malice prepense, not of the nature of treason, within the United States or the Spanish provinces adjoining thereto, and fleeing from the justice of the country, shall be delivered up by the government where he shall be found, to that from which he fled, whenever demanded by the same.
The manner of the demand by the Spanish government, and of the compliance by that of the United States, shall be as follows. The person authorized by the Spanish government, where the murder was committed, to pursue the fugitive, may apply to any justice of the Supreme Court of the United States, or to the district judge of the place where the fugitive is, exhibiting proof on oath that a murder has been committed by the said fugitive within the said government, who shall thereon issue his warrant to the marshal or deputy-marshal of the same place, to arrest the fugitive and have him before the said district judge; or the said pursuer may apply to such marshal or deputy-marshal directly, who on exhibition of proof as aforesaid, shall thereupon arrest the fugitive, and carry him before the said district judge; and when before him in either way, he shall, within not less than ————-days, nor more than ————-, hold a special court of inquiry, causing a grand jury to be summoned thereto, and charging them to inquire whether the fugitive hath committed a murder, not of the nature of treason, within the province demanding him, and on their finding a true bill, the judge shall order the officer in whose custody the fugitive is, to deliver him over to the person authorized as aforesaid to receive him, and shall give such further authorities to aid the said person in safe-keeping and conveying the said fugitive to the limits of the United States, as shall be necessary and within his powers; and his powers shall expressly extend to command the aid of posse of every district through which the said fugitive is to be carried. And the said justices, judges, and other officers, shall use in the premises the same process and proceedings, mutatis mutandis, and govern themselves by the same principles and rules of law, as in cases of murder committed on the high seas.
And the manner of demand by the United States and of compliance by the Spanish government shall be as follows. The person authorized by a justice of the Supreme Court of the United States, or by the district judge where the murder was committed, to pursue the fugitive, may apply to ————-
Evidence on oath, though written and ex parte, shall have the same weight with the judge and grand jury in the preceding cases, as if the same had been given before them orally and in presence of the prisoner.
The courts of justice of the said States and provinces, shall be reciprocally open for the demand and recovery of debts due to any person inhabiting the one, from any person fled therefrom and found in the other, in like manner as they are open to their own citizens; likewise, for the recovery of the property, or the value thereof, carried away from any person inhabiting the one, by any person fled therefrom and found in the other, which carrying away shall give a right of civil action, whether the fugitive came to the original possession lawfully or unlawfully, even feloniously; likewise, for the recovery of damages sustained by any forgery committed by such fugitive. And the same provision shall hold in favor of the representatives of the original creditor or sufferer, and against the representatives of the original debtor, carrier away, or forger; also, in favor of either government or of corporations, as of natural persons. But in no case shall the person of the defendant be imprisoned for the debt, though the process, whether original, mesne, or final, be for the form sake directed against his person. If the time between the flight and the commencement of the action exceed not ——— years, it shall be counted but as one day under any act of limitations.
This convention shall continue in force ————- years, from the exchange of ratifications, and shall not extend to any thing happening previous to such exchange.
Heads of consideration on the establishment of conventions between the United States and their neighbors, for the mutual delivery of fugitives from justice.
Has a nation a right to punish a person who has not offended itself? Writers on the law of nature agree that it has not. That, on the contrary, exiles and fugitives are, to it, as other strangers, and have a right of residence, unless their presence would be noxious; e. g. infectious persons. One writer extends the exception to atrocious criminals, too imminently dangerous to society; namely, to pirates, murderers, and incendiaries. Vattel, L. 1.5. 233.
The punishment of piracy, being provided for by our laws, need not be so by convention.
Murder. Agreed that this is one of the extreme crimes justifying a denial of habitation, arrest, and re-delivery. It should be carefully restrained by definition to homicide of malice prepense, and not of the nature of treason.
Incendiaries, or those guilty of arson. This crime is so rare as not to call for extraordinary provision by a convention. The only rightful subject then of arrest and delivery, for which we have need, is murder. Ought we to wish to strain the natural right of arresting and re-delivering fugitives to other cases?
The punishment of all real crimes is certainly desirable, as a security to society; the security is greater in proportion as the chances of avoiding punishment are less. But does the fugitive from his country avoid punishment? He incurs exile, not voluntary, but under a moral necessity as strong as physical. Exile, in some countries, has been the highest punishment allowed by the laws. To most minds it is next to death; to many beyond it. The fugitive indeed is not of the latter; he must estimate it somewhat less than death. It may be said that to some, as foreigners, it is no punishment.
Answer. These cases are few. Laws are to be made for the mass of cases.
The object of a convention then, in other cases, would be, that the fugitive might not avoid the difference between exile and the legal punishment of the case. Now in what case would this difference be so important, as to overweigh even the single inconvenience of multiplying compacts?
1. Treason. This, when real, merits the highest punishment. But most codes extend their definitions of treason to acts not really against one’s country. They do not distinguish between acts against the government and acts against the oppressions of the government: the latter are virtues; yet have furnished more victims to the executioner than the former; because real treasons are rare, oppressions frequent. The unsuccessful strugglers against tyranny have been the chief martyrs of treason-laws in all countries.
Reformation of government with our neighbors; being as much wanted now as reformation of religion is, or ever was any where, we should not wish then, to give up to the executioner, the patriot who fails, and flees to us. Treasons then, taking the simulated with the real, are sufficiently punished by exile.
2. Crimes against property; the punishment in most countries, immensely disproportionate to the crime.
In England, and probably in Canada, to steal a horse is death, the first offence; to steal above the value of twelve pence is death, the second offence. All excess of punishment is a crime. To remit a fugitive to excessive punishment is to be accessary to the crime. Ought we to wish for the obligation, or the right to do it? Better, on the whole, to consider these crimes as sufficiently punished by the exile.
There is one crime, however, against property, pressed by its consequences into more particular notice, to wit;
Forgery, whether of coin or paper; and whether paper of public or private obligation. But the fugitive for forgery is punished by exile and confiscation of the property he leaves: to which add by convention, a civil action against the property he carries or acquires, to the amount of the special damage done by his forgery.
The carrying away of the property of another, may also be reasonably made to found a civil action. A convention then may include forgery and the carrying away the property of others, under the head of,
3. Flight from debts.
To remit the fugitive in this case, would be to remit him in every case. For in the present state of things, it is next to impossible not to owe something. But I see neither injustice nor inconvenience in permitting the fugitive to be sued in our courts. The laws of some countries punishing the unfortunate debtor by perpetual imprisonment, he is right to liberate himself by flight, and it would be wrong to re-imprison him in the country to which he flies. Let all process, therefore, be confined to his property.
Murder, not amounting to treason, being the only case in which the fugitive is to be delivered;
On what evidence, and by whom, shall he be delivered? In this country let any justice of the Supreme Court of the United States, or other judge of the district where the fugitive is found, use the same proceedings as for a murder committed on the high seas, until the finding of the ‘true bill’ by the grand jury; but evidence on oath from the country demanding him, though in writing and ex parte, should have the same effect as if delivered orally at the examination.
A true bill being found by the grand jury, let the officer in whose custody the fugitive is, deliver him to the person charged to demand and receive him.
In the British provinces adjoining us, the same proceedings will do.
In the Spanish provinces, a proceeding adapted to the course of their laws should be agreed on.
March 22, 1792.
Philadelphia, April 28,1792;
Dear Sir,
My last letter to you was of the 10th of March. The preceding one of January the 23rd had conveyed to you your appointment as Minister Plenipotentiary to the court of France. The present will, I hope, find you there. I now enclose you the correspondence between the Secretary of the Treasury and Minister of France, on the subject of the monies furnished to the distressed of their colonies. You will perceive that the Minister chose to leave the adjustment of the terms to be settled at Paris, between yourself and the King’s ministers. This you will therefore be pleased to do on this principle; that we wish to avoid any loss by the mode of payment, but would not choose to make a gain which should throw loss on them. But the letters of the Secretary of the Treasury will sufficiently explain the desire of the government, and be a sufficient guide to you.
I now enclose you the act passed by Congress for facilitating the execution of the consular convention with France. In a bill which has passed the House of Representatives for raising monies for the support of the Indian war, while the duties on every other species of wine are raised from one to three fourths more than they were, the best wines of France will pay little more than the worst of any other country, to wit, between six and seven cents a bottle; and where this exceeds forty per cent, on their cost, they will pay but the forty per cent. I consider this latter provision as likely to introduce in abundance the cheaper wines of France, and the more so, as the tax on ardent spirits is considerably raised. I hope that these manifestations of friendly dispositions towards that country, will induce them to repeal the very obnoxious laws respecting our commerce, which were passed by the preceding National Assembly. The present session of Congress will pass over, without any other notice of them than the friendly preferences before mentioned. But if these should not produce a retaliation of good on their part, a retaliation of evil must follow on ours. It will be impossible to defer longer than the next session of Congress, some counter regulations for the protection of our navigation and commerce. I must entreat you, therefore, to avail yourself of every occasion of friendly remonstrance on this subject. If they wish an equal and cordial treaty with us, we are ready to enter into it. We would wish that this could be the scene of negotiation, from considerations suggested by the nature of our government which will readily occur to you. Congress will rise on this day se’nnight. I enclose you a letter from Mrs. Greene, who asks your aid in getting her son forwarded by the Diligence to London, on his way to America. The letter will explain to you the mode and the means, and the parentage and genius of the young gentleman will insure your aid to him. As this goes by the French packet, I send no newspapers, laws, or other articles of that kind, the postage of which would be high.
I am with great and sincere esteem, Dear Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
CIRCULAR TO THE AMERICAN CONSULS.
Philadelphia, May 31, 1792.
Sir,
Congress having closed their session on the 8th instant, I have now the honor to forward you a copy of the laws passed thereat. One of these, chapter twenty-four, will require your particular attention, as it contains such regulations relative to the consular office, as it has been thought proper to establish legislatively.
With respect to the security required by the sixth section I would prefer persons residing within the United States, where the party can procure such to be his security. In this case, his own bond duly executed may be sent to me, and his sureties here may enter into a separate bond. Where the party cannot conveniently find sureties within the United States, my distance, and want of means of knowing their sufficiency, oblige me to refer him to the Minister or Chargé des Affaires of the United States, within the same government, if there be one, and if not, then to the Minister of the United States, resident at Paris. The securities which they shall approve, will be admitted as good. In like manner, the account for their disbursements, authorized by this law (and no other can be allowed) are to be settled at stated periods with the Minister or Chargé within their residence, if there be one; if none, then with the Minister of the United States, at Paris. The person who settles the account is authorized to pay it. Our Consuls in America are not meant to be included in these directions as to securityship and the settlement of their accounts, as their situation gives them a more convenient communication with me. It is also recommended to the Consuls to keep an ordinary correspondence with the Minister or Chargé to whom they are thus referred; but it would be also useful, if they could forward directly to me, from time to time, the prices current of their place, and any other circumstances which it might be interesting to make known to our merchants without delay.
The prices of our funds have undergone some variations within the last three months. The six per cents were pushed by gambling adventures up to twenty-six and a half, or twenty-seven and a half shillings the pound. A bankruptcy having taken place among these, and considerably affected the more respectable part of the paper, holders, a greater quantity of paper was thrown suddenly on the market than there was demand or money to take up. The prices fell to nineteen shillings. This crisis has passed, and they are getting up towards their value. Though the price of public paper is considered as the barometer of the public credit, it is truly so only as to the general average of prices. The real credit of the United States depends on their ability, and the immutability of their will, to pay their debts. These were as evident when their paper fell to nineteen shillings, as when it was at twenty-seven shillings. The momentary variation was like that in the price of corn, or any other commodity, the result of a momentary disproportion between the demand and supply.
The unsuccessful issue of our expedition against the savages the last year, is not unknown to you. More adequate preparations are making for the present year, and, in the mean time, some of the tribes have accepted peace, and others have expressed a readiness to do the same.
Another plentiful year has been added to those which had preceded it, and the present bids fair to be equally so. A prosperity built on the basis of agriculture is that which is most desirable to us, because to the efforts of labor it adds the efforts of a greater proportion of soil. The checks, however, which the commercial regulations of Europe have given to the sale of our produce, have produced a very considerable degree of domestic manufacture, which, so far as it is of the household kind, will doubtless continue, and so far as it is more public, will depend on the continuance or discontinuance of the European policy.
I am, with great esteem, Sir, your most obedient, humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN PAUL JONES.
Philadelphia, June 1, 1792.
Sir,
The President of the United States having thought proper to appoint you commissioner for treating with the Dey and government of Algiers, on the subjects of peace and ransom of our captives, I have the honor to enclose you the commissions, of which Mr. Thomas Pinckney, now on his way to London as our Minister Plenipotentiary there, will be the bearer. Supposing that there exists a disposition to thwart our negotiations with the Algerines, and that this would be very practicable, we have thought it advisable that the knowledge of this appointment should rest with the President, Mr. Pinckney, and myself; for which reason you will perceive, that the commissions are all in my own hand-writing. For the same reason, entire secrecy is recommended to you, and that you so cover from the public your departure and destination, as that they may not be conjectured or noticed; and at the same time, that you set out after as short delay as your affairs will possibly permit.
In order to enable you to enter on this business with full information, it will be necessary to give you a history of what has passed.
On the 25th of July, 1785, the schooner Maria, Captain Stevens, belonging to a Mr. Foster, of Boston, was taken off Cape St. Vincent’s, by an Algerine cruiser; and five days afterwards, the ship Dauphin, Captain O’Bryan, belonging to Messrs. Irwins of Philadelphia, was taken by another, about fifty leagues westward of Lisbon. These vessels, with their cargoes and crews, twenty-one persons in number, were carried into Algiers. Mr. John Lambe, appointed agent for treating of peace between the United States and the government of Algiers, was ready to set out from France on that business, when Mr. Adams and myself heard of these two captures. The ransom of prisoners being a case not existing when our powers were prepared, no provision had been made for it. We thought, however, we ought to endeavor to ransom our countrymen, without waiting for orders; but at the same time, that acting without authority, we should keep within the lowest price which had been given by any other nation. We therefore gave a supplementary instruction to Mr. Lambe to ransom our captives, if it could be done for two hundred dollars a man, as we knew that three hundred French captives had been just ransomed by the Mathurins, at a price very little above this sum. He proceeded to Algiers; but his mission proved fruitless. He wrote us word from thence, that the Dey asked fifty-nine thousand four hundred and ninety-six dollars for the twenty-one captives, and that it was not probable he would abate much from that price. But he never intimated an idea of agreeing to give it. As he has never settled the accounts of his mission, no further information has been received. It has been said that he entered into a positive stipulation with the Dey, to pay for the prisoners the price above mentioned, or something near it; and that he came away with an assurance to return with the money. We cannot believe the fact true: and if it were, we disavow it totally, as far beyond his powers. We have never disavowed it formally, because it has never come to our knowledge with any degree of certainty.
In February, 1787, I wrote to Congress to ask leave to employ the Mathurins of France in ransoming our captives; and on the 19th of September, I received their orders to do so, and to call for the money from our bankers at Amsterdam, as soon as it could be furnished. It was long before they could furnish the money, and as soon as they notified that they could, the business was put into train by the General of the Mathurins, not with the appearance of acting for the United States, or with their knowledge, but merely on the usual ground of charity. This expedient was rendered abortive by the revolution of France, the derangement of ecclesiastical orders there, and the revocation of church property, before any proposition, perhaps, had been made in form by the Mathurins to the Dey of Algiers. I have some reason to believe that Mr. Eustace, while in Spain, endeavored to engage the court of Spain to employ their Mathurins in this business; but whether they actually moved in it or not, I have never learned.
We have also been, told, that a Mr. Simpson of Gibraltar, by the direction of the Messrs. Bulkeleys of Lisbon, contracted for the ransom of our prisoners (then reduced by death and ransom to fourteen) at thirty-four thousand seven hundred and ninety-two dollars. By whose orders they did it, we could never learn. I have suspected it was some association in London, which, finding the prices far above their conception, did not go through with their purpose, which probably had been merely a philanthropic one. Be this as it may, it was without our authority or knowledge.
Again Mr. Cathalan, our Consul at Marseilles, without any instruction from the government, and actuated merely, as we presume, by willingness to do something agreeable, set on foot another negotiation for their redemption; which ended in nothing.
These several volunteer interferences, though undertaken with good intentions, run directly counter to our plan; which was, to avoid the appearance of any purpose on our part ever to ransom our captives, and by that semblance of neglect, to reduce the demands of the Algerines to such a price, as might make it hereafter less their interest to pursue our citizens than any others. On the contrary, they have supposed all these propositions directly or indirectly came from us; they inferred from thence the greatest anxiety on our part, where we had been endeavoring to make them suppose there was none; kept up their demands for our captives at the highest prices ever paid by any nation; and thus these charitable, though unauthorized interpositions, have had the double effect of strengthening the chains they were meant to break, and making us at last set a much higher rate of ransom for our citizens, present and future, than we probably should have obtained, if we had been left alone to do our own work in our own way. Thus stands this business then at present. A formal bargain, as I am informed, being registered in the books of the former Dey, on the part of the Bulkeleys of Lisbon, which they suppose to be obligatory on us, but which is to be utterly disavowed, as having never been authorized by us, nor its source even known to us.
In 1790, this subject was laid before Congress fully, and at the late session, monies have been provided, and authority given to proceed to the ransom of our captive citizens at Algiers, provided it shall not exceed a given sum, and provided also, a peace shall be previously negotiated within certain limits of expense. And in consequence of these proceedings, your mission has been decided on by the President.
Since, then, no ransom is to take place without a peace, you will of course take up first the negotiation of peace; or, if you find it better that peace and ransom should be treated of together, you will take care that no agreement for the latter be concluded, unless the former be established before or in the same instant.
As to the conditions, it is understood that no peace can be made with that government, but for a larger sum of money to be paid at once for the whole time of its duration, or for a smaller one to be annually paid. The former plan we entirely refuse, and adopt the latter. We have also understood that peace might be bought cheaper with naval stores than with money: but we will not furnish them naval stores, because we think it not right to furnish them means which we know they will employ to do wrong, and because there might be no economy in it as to Ourselves, in the end, as it would increase the expenses of that coercion which we may in future be obliged to practise towards them. The only question then, is, What sum of money will we agree to pay them annually, for peace? By a letter from Captain O’Bryan, a copy of which you will receive herewith, we have his opinion that a peace could be purchased with money, for sixty thousand pounds sterling, or with naval stores, for one hundred thousand dollars. An annual payment equivalent to the first, would be three thousand pounds sterling, or thirteen thousand and five hundred dollars, the interest of the sum in gross. If we could obtain it for as small a sum as the second, in money, the annual payment equivalent to it would be five thousand dollars. In another part of the same letter, Captain O’Bryan says, ‘If maritime stores and two light cruisers be given, and a tribute paid in maritime stores every two years, amounting to twelve thousand dollars in America,’ a peace can be had. The gift of stores and cruisers here supposed, converted into an annual equivalent, may be stated at nine thousand dollars, and adding to it half the biennial sum, would make fifteen thousand dollars, to be annually paid. You will, of course, use your best endeavors to get it at the lowest sum practicable; whereupon I shall only say, that we should be pleased with ten thousand dollars, contented with fifteen thousand, think twenty thousand a very hard bargain, yet go as far as twenty-five thousand, if it be impossible to get it for less; but not a copper further, this being fixed by law as the utmost limit. These are meant as annual sums. If you can put off the first annual payment to the end of the first year, you may employ any sum not exceeding that, in presents to be paid down; but if the first payment is to be made in hand, that and the presents cannot by law exceed twenty-five thousand dollars.
And here we meet a difficulty, arising from the small degree of information we have respecting the Barbary States. Tunis is said to be tributary to Algiers. But whether the effect of this be, that peace being made with Algiers, is of course with the Tunisians without separate treaty, or separate price, is what we know not. If it be possible to have it placed on this footing, so much the better. In any event, it will be necessary to stipulate with Algiers, that her influence be interposed as strongly as possible with Tunis, whenever we shall proceed to treat with the latter; which cannot be till information of the event of your negotiation, and another session of Congress.
As to the articles and form of the treaty in general, our treaty with Morocco was so well digested that I enclose you a copy of that, to be the model with Algiers, as nearly as it can be obtained, only inserting the clause with respect to Tunis.
The ransom of the captives is next to be considered. They are now thirteen in number; to wit, Richard O’Bryan and Isaac Stevens, captains, Andrew Montgomery and Alexander Forsyth, mates, Jacob Tessanier, a French passenger, William Patterson, Philip Sloan, Peleg Lorin, James Hall, James Cathcart, George Smith, John Gregory, James Hermit, seamen. It has been a fixed principle with Congress, to establish the rate of ransom of American captives in the Barbary States at as low a point as possible, that it may not be the interest of those States to go in quest of our citizens in preference to those of other countries. Had it not been for the danger it would have brought on the residue of our seamen, by exciting the cupidity of those rovers against them, our citizens now in Algiers would have been long ago redeemed, without regard to price. The mere money for this particular redemption neither has been, nor is, an object with any body here. It is from the same regard to the safety of our seamen at large, that they have now restrained us from any ransom unaccompanied with peace. This being secured, we are led to consent to terms of ransom, to which, otherwise, our government never would have consented; that is to say, to the terms stated by Captain O’Bryan in the following passage of the same letter. ‘By giving the minister of the marine (the present Dey’s favorite) the sum of one thousand sequins, I would stake my life that we would be ransomed for thirteen thousand sequins, and all expenses included.’ Extravagant as this sum is, we will, under the security of peace in future, go so far; not doubting, at the same time, that you will obtain It as much lower as possible, and not indeed without a hope that a lower ransom will be practicable, from the assurances given us in other letters from Captain O’Bryan, that prices are likely to be abated by the present Dey, and particularly with us, towards whom he has been represented as well disposed. You will consider this sum, therefore, say twenty-seven thousand dollars, as your ultimate limit, including ransom, duties, and gratifications of every kind.
As soon as the ransom is completed, you will be pleased to have the captives well clothed and sent home at the expense of the United States, with as much economy as will consist with their reasonable comfort. It is thought best, that Mr. Pinckney, our Minister at London, should be the confidential channel of communication between us. He is enabled to answer your drafts for money within the limits before expressed; and as this will be by re-drawing on Amsterdam, you must settle with him the number of days after sight, at which your bills shall be payable in London, so as to give him time, in the mean while, to draw the money from Amsterdam.
We shall be anxious to know, as soon and as often as possible, your prospects in these negotiations. You will receive herewith a cipher, which will enable you to make them with safety. London and Lisbon (where Colonel Humphreys will forward my letters) will be the safest and best ports of communication. I also enclose two separate commissions, for the objects of peace and ransom. To these is added a commission to you as Consul for the United States, at Algiers, on the possibility that it might be useful for you to remain there till the ratification of the treaties shall be returned from hence; though you are not to delay till their return the sending the captives home, nor the necessary payments of money within the limits before prescribed. Should you be willing to remain there, even after the completion of the business, as Consul for the United States, you will be free to do so, giving me notice, that no other nomination may be made. These commissions, being issued during the recess of the Senate, are in force, by the constitution, only till the next session of the Senate. But their renewal then is so much a matter of course and of necessity, that you may consider that as certain, and proceed without interruption. I have not mentioned this in the commissions, because it is in all cases surplusage, and because it might be difficult of explanation to those to whom you are addressed.
The allowance for all your expenses and time (exclusive of the ransom, price of peace, duties, presents, maintenance, and transportation of the captives) is at the rate of two thousand dollars a year, to commence from the day on which you shall set out for Algiers, from whatever place you may take your departure. The particular objects of peace and ransom once out of the way, the two thousand dollars annually are to go in satisfaction of time, services, and expenses of every kind, whether you act as Consul or Commissioner.
As the duration of this peace cannot be counted on with certainty, and we look forward to the necessity of coercion by cruises on their coast, to be kept up during the whole of their cruising season, you will be pleased to inform yourself, as minutely as possible, of every circumstance which may influence or guide us in undertaking and conducting such an operation, making your communications by safe opportunities.
I must recommend to your particular notice Captain O’Bryan, one of the captives, from whom we have received a great deal of useful information. The zeal which he has displayed under the trying circumstances of his present situation, has been very distinguished. You will find him intimately acquainted with the manner in which, and characters with whom, business is to be done there, and perhaps he may be an useful instrument to you, especially in the outset of your undertaking, which will require the utmost caution and the best information. He will be able to give you the characters of the European Consuls there, though you will, probably, not think it prudent to repose confidence in any of them.
Should you be able successfully to accomplish the objects of your mission in time to convey notice of it to us as early as possible during the next session of Congress, which meets in the beginning of November and rises the 4th of March, it would have a very pleasing effect.
I am, with great esteem, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MR. PINCKNEY.
Philadelphia, June 11, 1792.
Dear Sir, I have already had the honor of delivering to you your commission as Minister Plenipotentiary of the United States at the court of London, and have now that of enclosing your letter of credence to the King, sealed, and a copy of it open for your own information. Mr. Adams, your predecessor, seemed to understand, on his being presented to that court, that a letter was expected for the Queen also. You will be pleased to inform yourself whether the custom of that court requires this from us; and to enable you to comply with it, if it should, I enclose a letter sealed for the Queen, and a copy of it open for your own information. Should its delivery not be requisite you will be so good as to return it, as we do not wish to set a precedent which may bind us hereafter to a single unnecessary ceremony. To you, Sir, it will be unnecessary to undertake a general delineation of the duties of the office to which you are appointed. I shall therefore only express a desire that they be constantly exercised in that spirit of sincere friendship which we bear to the English nation, and that in all transactions with the minister, his good dispositions be conciliated by whatever in language or attentions may tend to that effect. With respect to their government, or policy, as concerning themselves or other nations, we wish not to intermeddle in word or deed, and that it be not understood that our government permits itself to entertain either a will or an opinion on the subject.
I particularly recommend to you, as the most important of your charges, the patronage of our commerce, and its liberation from embarrassments in all the British dominions; but most especially in the West Indies. Our Consuls in Great Britain and Ireland are under general instructions to correspond with you, as you will perceive by the copy of a circular letter lately written to them, and now enclosed. From them you may often receive interesting information. Mr. Joshua Johnson is Consul for us at London, James Maury, at Liverpool, Elias Vanderhorst, at Bristol, Thomas Auldjo, Vice-Consul at Pool (resident at Cowes), and William Knox, Consul at Dublin. The jurisdiction of each is exclusive and independent, and extends to all places within the same allegiance nearer to him than to the residence of any other Consul or Vice-Consul of the United States. The settlement of their accounts from time to time, and the payment of them, are referred to you, and in this, the act respecting Consuls and any other laws made, or to be made, are to be your guide. Charges which these do not authorize, you will be pleased not to allow. These accounts are to be settled up to the first day of July in every year and to be transmitted to the Secretary of State.
The peculiar custom in England, of impressing seamen on every appearance of war, will occasionally expose our seamen to peculiar oppressions and vexations. These will require your most active exertions and protection, which we know cannot be effectual without incurring considerable expense; and as no law has as yet provided for this, we think it fairer to take the risk of it on the executive than to leave it on your shoulders. You will, therefore, with all due economy, and on the best vouchers the nature of the case will admit, meet those expenses, transmitting an account of them to the Secretary of State, to be communicated to the legislature. It will be expedient that you take proper opportunities in the mean time, of conferring with the minister on this subject, in order to form some arrangement for the protection of our seamen on those occasions. We entirely reject the mode which was the subject of a conversation between Mr. Morris and him, which was, that our seamen should always carry about them certificates of their citizenship. This is a condition never yet submitted to by any nation, one with which seamen would never have the precaution to comply; the casualties of their calling would expose them to the constant destruction or loss of this paper evidence, and thus, the British government would be armed with legal authority to impress the whole of our seamen. The simplest rule will be, that the vessel being American, shall be evidence that the seamen on board her are such. If they apprehend that our vessels might thus become asylums for the fugitives of their own nation from impress-gangs, the number of men to be protected by a vessel may be limited by her tonnage, and one or two officers only be permitted to enter the vessel in order to examine the numbers on board; but no press-gang should be allowed ever to go on board an American vessel, till after it shall be found that there are more than their stipulated number on board, nor till after the master shall have refused to deliver the supernumeraries (to be named by himself) to the press-officer who has come on board for that purpose; and, even then, the American Consul should be called in. In order to urge a settlement of this point, before a new occasion may arise, it may not be amiss to draw their attention to the peculiar irritation excited on the last occasion, and the difficulty of avoiding our making immediate reprisals on their seamen here. You will be so good as to communicate to me what shall pass on this subject, and it may be made an article of convention, to be entered into either there or here.
You will receive herewith a copy of the journals of the ancient Congress, and of the laws, journals, and reports of the present. Those for the future, with gazettes and other interesting papers, shall be sent you from time to time; and I shall leave you generally to the gazettes, for whatever information is in possession of the public, and shall especially undertake to communicate by letter, such only relative to the business of your mission as the gazetteers cannot give. From you I ask, once or twice a month, a communication of interesting occurrences in England, of the general affairs of Europe, the court gazette, the best paper in the interest of the ministry, and the best of the opposition party, most particularly, that one of each which shall give the best account of the debates of parliament, the parliamentary register annually, and such other political publications as may be important enough to be read by one who can spare little time to read any thing, or which may contain matter proper to be kept and turned to, on interesting subjects and occasions. The English packet is the most certain channel for such epistolary communications as are not very secret, and intermediate occasions by private vessels may be resorted to for secret communications, and for such as would come too expensively burthened with postage, by the packets. You are furnished with a cipher for greater secrecy of communication. To the papers before mentioned, I must desire you to add the Leyden gazette, paper by paper as it comes out, by the first vessel sailing after its receipt.
I enclose you the papers in the case of a Mr. Wilson, ruined by the capture of his vessels after the term limited by the armistice. They will inform you of the circumstances of his case, and where you may find him personally, and I recommend his case to your particular representations to the British court. It is possible that other similar cases may be transmitted to you. You have already received some letters of Mr. Adams’s explanations of the principles of the armistice, and of what had passed between him and the British minister on the subject.
Mr. Greene of Rhode Island will deliver you his papers, and I am to desire that you may patronize his claims so far as shall be just and right, leaving to himself and his agent to follow up the minute details of solicitation, and coming forward yourself only when there shall be proper occasion for you to do so in the name of your nation.
Mr. Cutting has a claim against the government, vouchers for which he is to procure from England. As you are acquainted with the circumstances of it, I have only to desire that you will satisfy yourself as to any facts relative thereto, the evidence of which cannot be transmitted, and that you will communicate the same to me, that justice may be done between the public and the claimant.
We shall have occasion to ask your assistance in procuring a workman or two for our mint; but this shall be the subject of a separate letter after I shall have received more particular explanations from the director of the mint.
I have the honor to be, with great and sincere esteem, Dear sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO THOMAS PINCKNEY.
Philadelphia, June 11, 1792.
Sir,
The letter I have addressed to Admiral Jones, of which you have had the perusal, has informed you of the mission with which the President has thought proper to charge him at Algiers, and how far your agency is desired for conveying to him the several papers, for receiving and paying his drafts to the amount therein permitted, by re-drawing yourself on our bankers in Amsterdam, who are instructed to honor your bills, and by acting as a channel of correspondence between us. It has been some time, however, since we have heard of Admiral Jones. Should any accident have happened to his life, or should you be unable to learn where he is, or should distance, refusal to act, or any other circumstance deprive us of his services on this occasion, or be likely to produce too great a delay, of which you are to be the judge, you will then be pleased to send all the papers confided to you for him, to Mr. Thomas Barclay, our Consul at Morocco, with the letter addressed to him, which is delivered you open, and by which you will perceive that he is, in that event, substituted to every intent and purpose in the place of Admiral Jones. You will be pleased not to pass any of the papers confided to you on this business, through any post-office.
I have the honor to be, with great and sincere esteem, Sir, your most obedient, humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MR. PINCKNEY.
Philadelphia, June 14, 1792.
Sir,
The United States being now about to establish a mint, it becomes necessary to ask your assistance in procuring persons to carry on some parts of it; and to enable you to give it, you must be apprized of some facts.
Congress, some time ago, authorized the President to take measures for procuring some artists from any place where they were to be had. It was known that a Mr. Drost, a Swiss, had made an improvement in the method of coining, and some specimens of his coinage were exhibited here, which were superior to any thing we had ever seen. Mr. Short was therefore authorized to engage Drost to come over, to erect the proper machinery, and instruct persons to go on with the coinage; and as he supposed this would require but about a year, we agreed to give him a thousand louis a year and his expenses. The agreement was made, two coining mills, or screws, were ordered by him; but in the end he declined coming. We have reason to believe he was drawn off by the English East India Company, and that he is now at work for them in England. Mr. Bolton had also made a proposition to coin for us in England, which was declined. Since this, the act has been passed for establishing our mint, which authorizes, among other things, the employment of an assayer at fifteen hundred dollars a year, a chief coiner at the same, and an engraver at twelve hundred dollars. But it admits of the employment of one person, both as engraver and chief coiner; this we expect may be done, as we presume that any engraver who has been used to work for a coinage, must be well enough acquainted with all the operations of coinage to direct them; and it is an economy worth attention, if we can have the services performed by one officer instead of two, in which case, it is proposed to give him the salary of the chief coiner, that is to say, fifteen hundred dollars a year. I have therefore to request that you will endeavor, on your arrival in Europe, to engage and send us an assayer of approved skill and well attested integrity, and a chief coiner and engraver, in one person, if possible, acquainted with all the improvements in coining, and particularly those of Drost and Bolton. Their salaries may commence from the day of their sailing for America. If Drost be in England, I think he will feel himself under some obligation to aid you in procuring persons. How far Bolton will do it, seems uncertain. You will doubtless make what you can of the good dispositions of either of these or any other person. Should you find it impracticable to procure an engraver capable of performing the functions of chief coiner also, we must be content that you engage separate characters. Let these persons bring with them all the implements necessary for carrying on the business, except such as you shall think too bulky and easily made here. It would be proper, therefore, that they should consult you as to the necessary implements and their prices, that they may act under your control. The method of your paying for these implements and making reasonable advances to the workmen, shall be the subject of another letter, after the President shall have decided thereon. It should be a part of the agreement of these people, that they will faithfully instruct all persons in their art, whom we shall put under them for that purpose. Your contract with them may be made for any term not exceeding four years.
I have the honor to be, with great respect and much esteem, Dear Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
P. S. Should you not be able to procure persons of eminent qualifications for their business, in England, it will be proper to open a correspondence with Mr. Morris on the subject, and see whether he cannot get such from France. Next to the obtaining the ablest artists, a very important circumstance is to send them to us as soon as possible. T. J.
TO GOUVERNEUR MORRIS.
Philadelphia, June 16, 1792.
Dear Sir,
My last to you was of March the 28th. Yours of April the 6th and 10th came to hand three days ago.
With respect to the particular objects of commerce susceptible of being placed on a better footing, on which you ask my ideas, they will show themselves by the enclosed table of the situation of our commerce with France and England. That with France is stated as it stood at the time I left that country, when the only objects whereon change was still desirable, were those of salted provisions, tobacco and tar, pitch and turpentine. The first was in negotiation when I came away, and was pursued by Mr. Short with prospects of success, till their general tariff so unexpectedly deranged our commerce with them as to other articles. Our commerce with their West Indies had never admitted amelioration during my stay in France. The temper of that period did not allow even the essay, and it was as much as we could do to hold the ground given us by the Marshal de Castries’ Arrêt, admitting us to their colonies with salted provisions, &c. As to both these branches of commerce, to wit, with France and her colonies, we have hoped they would pursue their own proposition of arranging them by treaty, and that we could draw that treaty to this place. There is no other where the dependence of their colonies on our States for their prosperity is so obvious as here, nor where their negotiator would feel it so much. But it would be imprudent to leave to the uncertain issue of such a treaty, the re-establishment of our commerce with France on the footing on which it was in the beginning of their revolution. That treaty may be long on the anvil; in the mean time, we cannot consent to the late innovations, without taking measures to do justice to our own navigation. This object, therefore, is particularly recommended to you, while you will also be availing yourself of every opportunity which may arise, of benefiting our commerce in any other part. I am in hopes you will have found the moment favorable on your arrival in France, when Monsieur Claviere was in the ministry, and the dispositions of the National Assembly favorable to the ministers. Your cipher has not been sent hitherto, because it required a most confidential channel of conveyance. It is now committed to Mr. Pinckney, who also carries the gazettes, laws, and other public papers for you. We have been long without any vessel going to Havre. Some of the Indian tribes have acceded to terms of peace. The greater part, however, still hold off, and oblige us to pursue more vigorous measures for war. I enclose you an extract from a circular letter to our Consuls, by which you will perceive, that those in countries where we have no diplomatic representative, are desired to settle their accounts annually with the Minister of the United States at Paris. This business I must desire you to undertake. The act concerning Consuls will be your guide, and I shall be glad that the 1st of July be the day to which their accounts shall be annually settled and paid, and that they may be forwarded as soon after that as possible to the office of the Secretary of State, to enter into the general account of his department, which it is necessary he should make up always before the meeting of Congress.
I am with great sincere esteem Dear Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
P.S. I have said nothing of our whale-oil, because I believe it is on a better footing since the tariff than before. T. J.
TO MR. VAN BERCKEL.
Philadelphia, July 2,1792.
Sir,
It was with extreme concern that I learned from your letter of June the 25th, that a violation of the protection, due to you as the representative of your nation had been committed, by an officer of this State entering your house and serving therein a process on one of your servants. There could be no question but that this was a breach of privilege; the only one was, how it was to be punished. To ascertain this, I referred your letter to the Attorney General, whose answer I have the honor to enclose you. By this you will perceive, that from the circumstance of your servant’s not being registered in the Secretary of State’s office, we cannot avail ourselves of the more certain and effectual proceeding which had been provided by an act of Congress for punishing infractions of the law of nations, that act having thought proper to confine the benefit of its provisions to such domestics only, as should have been registered; We are to proceed, therefore, as if that act had never been made, and the Attorney General’s letter indicates two modes of proceeding. 1. By a warrant before a single magistrate, to recover the money paid by the servant under a process declared void by law. Herein the servant must be the actor, and the government not intermeddle at all. The smallness of the sum to be redemanded will place this cause in the class of those in which no appeal to the higher tribunal is permitted, even in the case of manifest error, so that if the magistrate should err, the government has no means of correcting the error. 2. The second mode of proceeding would be, to indict the officer in the Supreme Court of the United States; with whom it would rest to punish him at their discretion, in proportion to the injury done and the malice from which it proceeded; and it would end in punishment alone, and not in a restitution of the money. In this mode of proceeding, the government of the United States is actor, taking the management of the cause into its own hands, and giving you no other trouble than that of bearing witness to such material facts as may not be otherwise supported. You will be so good as to decide in which of these two ways you would choose the proceeding should be; if the latter, I will immediately take measures for having the offender prosecuted according to law.
I have the honor to be, with sentiments of respect, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MR. PALESKE.
Monticello, August 19,1792.
Sir,
I have received at this place your favor of the 9th instant, wherein you request, that agreeably to the treaty of commerce between the United States and his Prussian Majesty, his Consul General be acknowledged as belonging to a most favored nation; that the privileges and immunities due to a Consul General of the most favored nation be granted to his Consul General, and that commissioners be appointed to regulate, by particular convention the functions of the Consuls and Vice-Consuls of the respective nations.
Treaties of the United States duly made and ratified, as is that with his Prussian Majesty, constitute a part of the law of the land, and need only promulgation to oblige all persons to obey them, and to entitle all to those privileges which such treaties confer. That promulgation having taken place, no other act is necessary or proper on the part of our government, according to our rules of proceeding, to give effect to the treaty. This treaty, however, has not specified the privileges or functions of Consuls; it has only provided that these shall be regulated by particular agreement. To the proposition to proceed as speedily as possible to regulate these functions by a convention, my absence from the seat of government does not allow me to give a definitive answer. I know, in general, that it would be agreeable to our government, on account of the recent changes in its form, to suspend for a while the contracting specific engagements with foreign nations, until something more shall be seen of the direction it will take, and of its mode of operation, in order that our engagements may be so moulded to that, as to insure the exact performance of them, which we are desirous ever to observe. Should this be the sentiment of our government on the present occasion, the friendship of his Prussian Majesty is a sufficient reliance to us for that delay which our affairs might require for the present: and the rather, as his vessels are not yet in the habit of seeking our ports, and for the few cases which may occur for some time, our own laws, copied mostly in this respect from those of a very commercial nation, have made the most material of those provisions which could be admitted into a special convention for the protection of vessels, their crews, and cargoes, coming hither. We shall on this, however, and every other occasion, do every thing we can to manifest our friendship to his Prussian Majesty, and our desire to promote commercial intercourse with his subjects; and of this, we hope, he will be fully assured.
I have the honor to be, with great respect, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO THE PRESIDENT.
Monticello, August 19, 1792.
Sir,
I was yesterday honored with yours of the 13th instant, covering the Governor of Vermont’s of July the 16th. I presume it can not now be long before I shall receive his answer to the two letters I wrote him from Philadelphia on the same subject. I now enclose letters received by yesterday’s post from Mr. Hammond, Mr. William Knox, and Mr. Paleske, with answers to the two latter. Should these meet your approbation, you will be so good as to seal and let them go on under the cover to Mr. Taylor, who will have them conveyed according to their address. Should you wish any alteration of them, it shall be made on their being returned. The Prussian treaty is, I believe, within four years of its expiration. I suspect that personal motives alone induce Mr. Paleske to press for a convention, which could hardly be formed and ratified before it would expire; and that his court cannot lay much stress on it. Mr. Hammond’s former explanations of his notification of the 12th of April having been laid before Congress, may perhaps make it proper to communicate to them also his sovereign’s approbation of them.
I have the honor to be, with sentiments of the most perfect respect and attachment, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO M. DE TERNANT.
Philadelphia, September 27,1792.
Sir,
Your letter of the 2d instant, informing me that the legislative body, on the proposition of the King of the French, had declared war against the King of Hungary and Bohemia, has been duly received, and laid before the President of the United States: and I am authorized to convey to you the expression of the sincere concern we feel, on learning that the French nation, to whose friendship and interests we have the strongest attachments, are now to encounter the evils of war. We offer our prayers to Heaven that its duration may be short, and its course marked with as few as may be of those calamities which render the condition of war so afflicting to humanity; and we add assurances, that during its course we shall continue in the same friendly dispositions, and render all those good offices which shall be consistent with the duties of a neutral nation.
I have the honor to be, with sentiments of the most perfect esteem and respect, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MR. PINCKNEY.
Philadelphia, October 12,1792.
Dear Sir,
Your favor of August the 7th came to hand on the 6th instant, and gave me the first certain information of your safe arrival. Mr. Otto, being about to sail for London, furnishes me with an opportunity of sending the newspapers for yourself and Mr Barclay, and I avail myself of it, chiefly for this purpose, as my late return from Virginia and the vacation of Congress furnish little new and important for your information. With respect to the Indian war, the summer has been chiefly employed on our part in endeavoring to persuade them to peace, in an abstinence from all offensive operations, in order to give those endeavors a fairer chance, and in preparation for activity the ensuing season, if they fail. I believe we may say these endeavors have all failed, or probably will do so. The year has been rather a favorable one for our agriculture. The crops of small grain were generally good. Early frosts have a good deal shortened those of tobacco and Indian corn, yet not so as to endanger distress. From the south my information is less certain, but from that quarter you will be informed through other channels. I have a pleasure in noting this circumstance to you, because the difference between a plentiful and a scanty crop more than counterpoises the expenses of any campaign. Five or six plentiful years successively, as we have had, have most sensibly ameliorated the condition of our country, and uniform laws of commerce, introduced by our new government, have enabled us to draw the whole benefits of our agriculture.
I enclose you the copy of a letter from Messrs. Blow and Milhaddo, merchants of Virginia, complaining of the taking away of their sailors on the coast of Africa, by the commander of a British armed vessel. So many instances of this kind have happened, that it is quite necessary that their government should explain themselves on the subject, and be led to disavow and punish such conduct. I leave to your discretion to endeavor to obtain this satisfaction by such friendly discussions as may be most likely to produce the desired effect, and secure to our commerce that protection against British violence, which it has never experienced from any other nation. No law forbids the seaman of any country to engage in time of peace on board a foreign vessel: no law authorizes such seaman to break his contract, nor the armed vessels of his nation to interpose force for his rescue. I shall be happy to hear soon, that Mr. B. has gone on the service on which he was ordered.
I have the honor to be, with great and sincere esteem, Dear Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MESSRS. CARMICHAEL AND SHORT.
Philadelphia, October 14,1792.
Gentlemen,
Since my letters of March the 18th and April the 24th (which have been retarded so unfortunately), another subject of conference-and convention with Spain has occurred. You know that the frontiers of her provinces, as well as of our States, are inhabited by Indians holding justly the right of occupation, and leaving to Spain and to us only the claim of excluding other nations from among them, and of becoming ourselves the purchasers of such portions of land, from time to time, as they choose to sell. We have thought that the dictates of interest as well as humanity enjoined mutual endeavors with those Indians to live in peace with both nations, and we have scrupulously observed that conduct. Our agent with the Indians bordering on the territories of Spain has a standing instruction to use his best endeavors to prevent them from committing acts of hostility against the Spanish settlements. But whatever may have been the conduct or orders of the government of Spain, that of their officers in our neighborhood has been indisputably unfriendly and hostile to us. The papers enclosed will demonstrate this to you. That the Baron de Carondelet, their chief Governor at New Orleans, has excited the Indians to war on us, that he has furnished them with abundance of arms and ammunition, and promised them whatever more shall be necessary, I have from the mouth of him who had it from his own mouth. In short, that he is the sole source of a great and serious war now burst out upon us, and from Indians who, we know, were in peaceable dispositions towards us till prevailed on by him to commence the war, there remains scarcely room to doubt. It has become necessary that we understand the real policy of Spain in this point. You will, therefore, be pleased to extract from the enclosed papers such facts as you think proper to be communicated to that court, and enter into friendly but serious expostulations on the conduct of their officers; for we have equal evidence against the commandants of other posts in West Florida, though, they being subordinate to Carondelet, we name him as the source. If they disavow his conduct, we must naturally look to their treatment of him as the sole evidence of their sincerity. But we must look further. It is a general rule, that no nation has a right to keep an agent within the limits of another, without the consent of that other, and we are satisfied it would be best for both Spain and us, to abstain from having agents or other persons in our employ or pay among the savages inhabiting our respective territories, whether as subjects or independent. You are, therefore, desired to propose and press a stipulation to that effect. Should they absolutely decline it, it may be proper to let them perceive that, as the right of keeping agents exists on both sides or on neither, it will rest with us to reciprocate their own measures. We confidently hope that these proceedings are unauthorized by the government of Spain, and, in this hope, we continue in the dispositions formerly expressed to you, of living on terms of the best friendship and harmony with that country, of making their interests in our neighborhood our own, and of giving them every proof of this, except the abandonment of those essential rights which you are instructed to insist on.
I have the honor to be, with great and sincere esteem, Gentlemen, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
Philadelphia, October 15, 1792.
Sir,
I have received your favor of July the 10th, No. 4, but no other number preceding or subsequent. I fear, therefore, that some miscarriage has taken place. The present goes to Bordeaux under cover to Mr. Fenwick, who I hope will be able to give it a safe conveyance to you. I observe that you say in your letter, that ‘the marine department is to treat with you for supplies to St. Domingo.’ I presume you mean ‘supplies of money,’ and not that our government is to furnish supplies of provisions, &c. specifically, or employ others to do it, this being a business into which they could not enter. The payment of money here, to be employed by their own agents in purchasing the produce of our soil, is a desirable thing. We are informed by the public papers, that the late constitution of France, formally notified to us, is suspended, and a new convention called. During the time of this suspension, and while no legitimate government exists, we apprehend we cannot continue the payments of our debt to France, because there is no person authorized to receive it and to give us an unobjectionable acquittal. You are therefore desired to consider the payment as suspended, until further orders. Should circumstances oblige you to mention this (which it is better to avoid if you can), do it with such solid reasons as will occur to yourself, and accompany it with the most friendly declarations that the suspension does not proceed from any wish in us to delay the payment, the contrary being our wish, nor from any desire to embarrass or oppose the settlement of their government in that way in which their nation shall desire it; but from our anxiety to pay this debt justly and honorably, and to the persons really authorized by the nation (to whom we owe it) to receive it for their use. Nor shall the suspension be continued one moment after we can see our way clear out of the difficulty into which their situation has thrown us. That they may speedily obtain liberty, peace, and tranquillity, is our sincere prayer.
I have the honor to be, with great respect and esteem, Dear Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO M. DE TERNANT.
Philadelphia, October 16,1792.
Sir,
I am to acknowledge the receipt of your letter of the 9th instant, proposing a stipulation for the abolition of the practice of privateering in times of war. The benevolence of this proposition is worthy of the nation from which it comes, and our sentiments on it have been declared in the treaty to which you are pleased to refer, as well as in some others which have been proposed. There are in those treaties some other principles which would probably meet the approbation of your government, as flowing from the same desire to lessen the occasions and the calamities of war. On all of these, as well as on those amendments to our treaty of commerce which might better its conditions with both nations, and which the National Assembly of France has likewise brought into view on a former occasion, we are ready to enter into negotiation with you, only proposing to take the whole into consideration at once. And while contemplating provisions which look to the event of war, we are happy in feeling a conviction that it is yet at a great distance from us, and in believing that the sentiments of sincere friendship which we bear to the nation of France are reciprocated on their part. Of these our dispositions, be so good as to assure them on this and all other occasions; and to accept yourself those sentiments of esteem and respect with which I have the honor to be, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant.
Th: Jefferson.
TO MESSRS. VIAR AND JAUDENES, Commissioners of Spain
Philadelphia, November 1, 1792.
Gentlemen,
I have now to acknowledge the receipt of your favor of October the 29th, which I have duly laid before the President of the United States: and in answer thereto, I cannot but observe that some parts of its contents were truly unexpected. On what foundation it can be supposed that we have menaced the Creek nation with destruction during the present autumn, or at any other time, is entirely inconceivable. Our endeavors, on the contrary, to keep them at peace, have been earnest, persevering, and notorious, and no expense has been spared which might attain that object. With the same views to peace, we have suspended, now more than a twelvemonth, the marking a boundary between them and us, which had been fairly, freely, and solemnly established with the chiefs whom they had deputed to treat with us on that subject: we have suspended it, I say, in the constant hope, that taking time to consider it in the councils of their nation, and recognising the justice and reciprocity of its conditions, they would at length freely concur in carrying it into execution. We agree with you, that the interests which either of us have in the proceedings of the other with this nation of Indians, is a proper subject of discussion at the negotiations to be opened at Madrid, and shall accordingly give the same in charge to our commissioners there. In the mean time, we shall continue sincerely to cultivate the peace and prosperity of all the parties, being constant in the opinion, that this conduct, reciprocally observed, will most increase the happiness of all.
I have the honor to be, with sentiments of great esteem and respect, Gentlemen, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO THE PRESIDENT.
Philadelphia, November 2,1792.
Sir,
The letter of October the 29th, from Messrs. Viar and Jaudenes, not expressing the principle on which their government interests itself between the United States and the Creeks, I thought it of importance to have it ascertained. I therefore called on those Gentlemen, and entered into explanations with them. They assured me, in our conversation, that supposing all question of boundary to be out of the case, they did not imagine their government would think themselves authorized to take under their protection any nations of Indians living within limits confessed to be ours; and they presumed that any interference of theirs, with respect to the Creeks, could only arise out of the question of disputed territory, now existing between us: that, on this account, some part of our treaty with the Creeks had given dissatisfaction. They said, however, that they were speaking from their own sentiments only, having no instructions which would authorize them to declare those of their court: but that they expected an answer to their letters covering mine of July the 9th (erroneously cited by them as of the 11th), from which they would probably know the sentiments of their court. They accorded entirely in the opinion, that it would be better that the two nations should mutually endeavor to preserve each the peace of the other, as well as their own, with the neighboring tribes of Indians.
I shall avail myself of the opportunity by a vessel which is to sail in a few days, of sending proper information and instructions to our commissioners on the subject of the late, as well as of future interferences of the Spanish officers to our prejudice with the Indians, and for the establishment of common rules of conduct for the two nations.
I have the honor to be, with the most perfect respect and attachment, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MESSRS. CARMICHAEL AND SHORT.
Philadelphia, November 3, 1792.
Gentlemen,
I wrote you on the 14th of last month; since which some other incidents and documents have occurred, bearing relation to the subject of that letter. I therefore now enclose you a duplicate of that letter.
Copy of a letter from the Governor of Georgia, with the deposition it covered of a Mr. Hull, and an original passport signed by Olivier, wherein he styles himself Commissary for his Catholic Majesty with the Creeks.
Copy of a letter from Messrs. Viar and Jaudenes to myself, dated October the 29th, with that of the extract of a letter of September the 24th, from the Baron de Carondelet to them.
Copy of my answer of No. 1, to them, and copy of a letter from myself, to the President, stating a conversation with those gentlemen.
From those papers you will find that we have been constantly endeavoring, by every possible means, to keep peace with the Creeks; that in order to do this, we have even suspended and still suspend the running a fair boundary between them and us, as agreed on by themselves, and having for its object the precise definition of their and our lands, so as to prevent encroachment on either side, and that we have constantly endeavored to keep them at peace with the Spanish settlements also: that Spain on the contrary, or at least the officers of her governments, since the arrival of the Baron de Carondelet, have undertaken to keep an agent among the Creeks, have excited them and the other southern Indians to commence a war against us, have furnished them with arms and ammunition for the express purpose of carrying on that war, and prevented the Creeks from running the boundary which would have removed the cause of difference from between us. Messrs. Viar and Jaudenes explain the ground of interference on the fact of the Spanish claim to that territory, and on an article in our treaty with the Creeks, putting themselves under our protection. But besides that you already know the nullity of their pretended claim to the territory, they had themselves set the example of endeavoring to strengthen that claim by the treaty mentioned in the letter of the Baron de Carondelet, and by the employment of an agent among them. The establishment of our boundary, committed to you, will, of course, remove the grounds of all future pretence to interfere with the Indians within our territory, and it was to such only that the treaty of New York stipulated protection: for we take for granted, that Spain will be ready to agree to the principle, that neither party has a right to stipulate protection or interference with the Indian nations inhabiting the territory of the other. But it is extremely material also, with sincerity and good faith, to patronize the peace of each other with the neighboring savages. We are quite disposed to believe that the late wicked excitements to war have proceeded from the Baron de Carondelet himself, without authority from his court. But if so, have we not reason to expect the removal of such an officer from our neighborhood, as an evidence of the disavowal of his proceedings? He has produced against us a serious war. He says in his letter, indeed, that he has suspended it. But this he has not done, nor possibly can he do it. The Indians are more easily engaged in a war than withdrawn from it. They have made the attack in force on our frontiers, whether with or without his consent, and will oblige us to a severe punishment of their aggression. We trust that you will be able to settle principles of a friendly concert between us and Spain, with respect to the neighboring Indians: and if not, that you will endeavor to apprize us of what we may expect, that we may no longer be tied up by principles, which, in that case, would be inconsistent with duty and self-preservation.
I have the honor to be, with sentiments of perfect esteem and respect, Gentlemen, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO GOUVERNEUR MORRIS.
Philadelphia, November 7, 1792.
Dear Sir,
My last to you was of the 15th of October; since which I have received your Nos. 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 7. Though mine went by a conveyance directly to Bordeaux, and may therefore probably get safe to you, yet I think it proper, lest it should miscarry, to repeat to you the following paragraph from it.
I am perfectly sensible that your situation must, ere this reaches you, have been delicate and difficult; and though the occasion is probably over, and your part taken of necessity, so that instructions now would be too late, yet I think it just to express our sentiments on the subject, as a sanction of what you have probably done. Whenever the scene became personally dangerous to you, it was proper you should leave it, as well from personal as public motives. But what degree of danger should be awaited, to what distance or place you should retire, are circumstances which must rest with your own discretion, it being impossible to prescribe them from hence. With what kind of government you may do business, is another question. It accords with our principles to acknowledge any government to be rightful, which is formed by the will of the nation substantially declared. The late government was of this kind, and was accordingly acknowledged by all the branches of ours. So, any alteration of it which shall be made by the will of the nation substantially declared, will doubtless be acknowledged in like manner. With such a government every hind of business may be done. But there are some matters which I conceive might be transacted with a government de facto; such, for instance, as the reforming the unfriendly restrictions on our commerce and navigation. Such cases you will readily distinguish as they occur. With respect to this particular reformation of their regulations, we cannot be too pressing for its attainment, as every day’s continuance gives it additional firmness, and endangers its taking root in their habits and constitution; and indeed, I think they should be told, as soon as they are in a condition to act, that if they do not revoke the late innovations, we must lay additional and equivalent burthens on French ships, by name. Your conduct in the case of M. de Bonne Carrere is approved entirely. We think it of great consequence to the friendship of the two nations, to have a minister here, in whose dispositions we have confidence. Congress assembled the day before yesterday. I enclose you a paper containing the President’s speech, whereby you will see the chief objects of the present session. Your difficulties as to the settlements of our accounts with France and as, to the payment of the foreign officers, will have been removed by the letter of the Secretary of the Treasury, of which, for fear it should have miscarried, I now enclose you a duplicate. Should a conveyance for the present letter offer to any port of France directly, your newspapers will accompany it. Otherwise, I shall send it through Mr. Pinckney, and retain the newspapers as usual, for a direct conveyance.
I am, with great and sincere esteem, Dear Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO M. DE TERNANT.
Philadelphia, November 20, 1792.
Sir,
Your letter on the subject of further supplies to the colony of St. Domingo has been duly received and considered. When the distresses of that colony first broke forth, we thought we could not better evidence our friendship to that and to the mother country also, than to step in to its relief, on your application, without waiting a formal authorization from the National Assembly. As the case was unforeseen, so it was unprovided for on their part, and we did what we doubted not they would have desired us to do, had there been time to make the application, and what we presumed they would sanction as soon as known to them. We have now been going on more than a twelvemonth, in making advances for the relief of the colony, without having, as yet, received any such sanction; for the decree of four millions of livres in aid of the colony, besides the circuitous and informal manner by which we became acquainted with it, describes and applies to operations very different from those which have actually taken place. The wants of the colony appear likely to continue, and their reliance on our supplies to become habitual. We feel every disposition to continue our efforts for administering to those wants; but that cautious attention to forms which would have been unfriendly in the first moment, becomes a duty to ourselves, when the business assumes the appearance of long continuance, and respectful also to the National Assembly itself, who have a right to prescribe the line of an interference so materially interesting to the mother country and the colony.
By the estimate you were pleased to deliver me, we perceive that there will be wanting, to carry the colony through the month of December, between thirty and forty thousand dollars, in addition to the sums before engaged to you. I am authorized to inform you, that the sum of forty thousand dollars shall be paid to your orders at the Treasury of the United States, and to assure you, that we feel no abatement in our dispositions to contribute these aids from time to time, as they shall be wanting, for the necessary subsistence of the colony: but the want of express approbation from the national legislature must ere long produce a presumption that they contemplate perhaps other modes of relieving the colony, and dictate to us the propriety of doing only what they shall have regularly and previously sanctioned. Their decree, before mentioned, contemplates purchases made in the United States only. In this they might probably have in view, as well to keep the business of providing supplies under a single direction, as that these supplies should be bought where they can be had cheapest, and where the same sum will consequently effect the greatest, measure of relief to the colony. It is our wish, as undoubtedly it must be yours, that the monies we furnish be applied strictly in the line they prescribe. We understand, however, that there are in the hands of our citizens, some bills drawn by the administration of the colony, for articles of subsistence delivered there. It seems just, that such of them should be paid as were received before fide bonâ notice that that mode of supply was not bottomed on the funds furnished to you by the United States, and we recommend them to you accordingly.
I have the the honor to be, with sentiments of the most perfect esteem and respect, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MR. RUTHERFORD.
Philadelphia, December 25, 1792.
Sir,
I have considered with all the attention which the shortness of the time would permit, the two motions which you were pleased to put into my hands yesterday afternoon, on the subject of weights and measures, now under reference to a committee of the Senate, and will take the liberty of making a few observations thereon.
The first, I presume, is intended as a basis for the adoption of that alternative of the report on measures and weights, which proposed retaining the present system, and fixing its several parts by a reference to a rod vibrating seconds, under the circumstances therein explained: and to fulfil its object, I think the resolutions there proposed should be followed by this; ‘that the standard by which the said measures of length, surface, and capacity shall be fixed, shall be an uniform cylindrical rod of iron, of such length, as in latitude forty-five degrees, in the level of the ocean, and in a cellar or other place of uniform natural temperature, shall perform its vibrations in small and equal arcs, in one second of mean time, and that rain-water be the substance, to some definite mass of which the said weights shall be referred.’ Without this, the committee employed to prepare a bill on those resolutions, would be uninstructed as to the principle by which the Senate mean to fix their measures of length, and the substance by which they will fix their weights.
The second motion is a middle proposition between the first and the last alternatives in the report. It agrees with the first in some of the present measures and weights, and with the last, in compounding and dividing them decimally. If this should be thought best, I take the liberty of proposing the following alterations of these resolutions.
2nd. For ‘metal’ substitute ‘iron.’ The object is to have one determinate standard. But the different metals having different degrees of expansibility, there would be as many different standards as there are metals, were that generic term to be used. A specific one seems preferable, and ‘iron ‘the best, because the least variable by expansion.
3rd. I should think it better to omit the chain of 66 feet, because it introduces a series which is not decimal, viz. 1. 66. 80. and because it is absolutely useless. As a measure of length, it is unknown to the mass of our citizens; and if retained for the purpose of superficial measure, the foot will supply its place, and fix the acre as in the fourth resolution.
4th. For the same reason I propose to omit the words ‘or shall be ten chains in length and one in breadth.’
5th. This resolution would stand better, if it omitted the words ‘shall be one foot square, and one foot and twenty cents of a foot deep, and,’ because the second description is perfect, and too plain to need explanation. Or if the first expression be preferred, the second may be omitted, as perfectly tautologous.
6th. I propose to leave out the words ‘shall be equal to the pound avoirdupois now in use, and,’ for the reasons suggested on the second resolution, to wit, that our object is, to have one determinate standard. The pound avoirdupois now in use, is an indefinite thing. The committee of parliament reported variations among the standard weights of the exchequer. Different persons weighing the cubic foot of water have made it, some more and some less than one thousand ounces avoirdupois; according as their weights had been tested by the lighter or heavier standard weights of the exchequer. If the pound now in use be declared a standard, as well as the weight of sixteen thousand cubic cents of a foot in water, it may hereafter, perhaps, be insisted that these two definitions are different, and that being of equal authority, either may be used, and so the standard pound be rendered as uncertain as at present.
7th. For the same reasons I propose to omit the words ‘equal to seven grains troy.’ The true ratio between the avoirdupois and troy weights, is a very contested one. The equation of seven thousand grains troy to the pound avoirdupois, is only one of several opinions, and is indebted perhaps to its integral form for its prevalence. The introduction either of the troy or avoirdupois weight into the definition of our unit, will throw that unit under the uncertainties now enveloping the troy and avoirdupois weights.
When the House of Representatives were pleased to refer to me the subject of weights and measures, I was uninformed as to the hypothesis on which I was to take it up; to wit, whether on that, that our citizens would not approve of any material change in the present system, or on the other, that they were ripe for a complete reformation. I therefore proposed plans for each alternative. In contemplating these, I had occasion to examine well all the middle ground between the two, and among others which presented themselves to my mind, was the plan of establishing one of the known weights and measures as the unit in each class; to wit, in the measures of lines, of surfaces, and of solids, and in weights, and to compound and divide them decimally. In the measure of weights, I had thought of the ounce as the best unit, because, calling it the thousandth part of a cubic foot of water, it fell into the decimal series, formed a happy link of connection with the system of measures on the one side, and of coins on the other, by admitting an equality with the dollar, without changing the value of that or its alloy materially. But on the whole, I abandon this middle proposition, on the supposition that if our fellow-citizens were ripe for advancing so great a length towards reformation, as to retain only four known points of the very numerous series to which they were habituated, to wit, the foot, the acre, the bushel, and the ounce, abandoning all the multiples and subdivisions of them, or recurring for their value to the tables which would be formed, they would probably be ripe for taking the whole step, giving up these four points also, and making the reformation complete; and the rather, as in the present series and the one to be proposed, there would be so many points of very near approximation, as, aided in the same manner by tables, would not increase their difficulties, perhaps, indeed, would lessen them by the greater simplicity of the Clinks by which the several members of the system are connected together. Perhaps, however, I was wrong in this supposition. The representatives of the people in Congress are alone competent to judge of the general disposition of the people, and to what precise point of reformation they are ready to go. On this, therefore, I do not presume to give an opinion, nor to pronounce between the comparative expediency of the three propositions; but shall be ready to give whatever aid I can to any of them which shall be adopted by the legislature.
I have the honor to be, with perfect respect, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO THE SPEAKER OF THE HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES.
Philadelphia, January 2, 1793.
Sir,
According to the resolution of the House of Representatives, of the 31st of December, delivered to me yesterday, I have the honor to lay before you a list of the several persons employed in my office, with the salaries allowed to each, as follows:
Dollars. George Taylor, jr. (of New York), chief clerk, his salary fixed by law,................................................. 800
Jacob Blackwell (of New York), clerk,......................... 500
George Pfeiffer (of Pennsylvania), clerk,..................... 500
Philip Freneau (of New York), clerk for foreign languages,.... 250
Sampson Crosby (of Massachusetts), messenger and office-keeper,................................................ 250
The act of Congress of June the 4th, 1790, c. 18, allowed me an additional clerk with the same salary as the chief clerk. After the retirement of the person first appointed, whose services had been particularly desirable, because of his long and intimate acquaintance with the papers of the office, it did not appear necessary to make further use of the indulgence of that law. No new appointment, therefore, has been made.
The clerk for foreign languages has but half the usual salary. I found his clerkship on this establishment when I came into office, and made no change in it, except, that in the time of his predecessor, where translations were required from any language with which he was unacquainted, they were sent to a special translator and paid for by the public. The present clerk is required to defray this expense himself.
I have the honor to be, with the most perfect respect, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
Circular to the Ministers of France, the United Netherlands Great Britain, &c.
Philadelphia, February 13, 1793.
Sir,
The House of Representatives having referred to me, to report to them the nature and extent of the privileges and restrictions on the commerce of the United States with foreign nations, I have accordingly prepared a report on that subject. Being particularly anxious that it may be exact in matters of fact, I take the liberty of putting into your hands, privately and informally, an extract of such as relate to our commerce with your nation, in hopes that if you can either enlarge or correct them, you will do me that favor. It is safer to suppress an error in its first conception, than to trust to any after correction; and a confidence in your sincere desire to communicate or to re-establish any truths which may contribute to a perfect understanding between our two nations, has induced me to make the present request. I wish it had been in my power to have done this sooner, and thereby have obtained the benefit of your having more time to contemplate it: but circumstances have retarded the entire completion of the report till the Congress is approaching its end, which will oblige me to give it in within three or four days.
I am, with great and sincere esteem, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
P. S. The report having been prepared before the late diminution of the duties on our tobacco, that circumstance will be noted in the letter which will cover the report. T. J.
France receives favorably our bread-stuff, rice, wood, pot and pearl ashes.
A duty of five, sous the kental, or nearly four and a half centss paid on our tar, pitch, and turpentine. Our whale-oils pay six livres the kental, and are the only whale-oils admitted. Our indigo pays five livres the kental, their own two and a half; but a difference of quality, still more than a difference of duty, prevents its seeking that market.
Salted beef is received freely for re-exportation; but if for home consumption, it pays five livres the kental. Other salted provisions pay that duty in all cases, and salted fish is made lately to pay the prohibitory one, of twenty livres the kental.
Our ships are free to carry thither all foreign goods, which may be carried in their own or any other vessels, except tobaccos not of our own growth: and they participate with theirs the exclusive carriage of our whale-oils.
During their former government, our tobacco was under a monopoly, but paid no duties; and our ships were freely sold in their ports and converted into national bottoms. The first National Assembly took from our ships this privilege. They emancipated tobacco from its monopoly, but subjected it to duties of eighteen livres fifteen sous the kental, carried in their own vessels, and twenty-five livres, carried in ours; a difference more than equal to the freight of the article.
They and their colonies consume what they receive from us.
France, by a standing law, permits her West India possessions to receive directly our vegetables, live provisions, horses, wood, tar, pitch, and turpentine, rice and maize, and prohibits our other bread-stuff: but a suspension of this prohibition having been left to the colonial legislature, in times of scarcity, it was formerly suspended occasionally, but latterly without interruption.
Our fish and salted provisions (except pork) are received in their islands, under a duty of three colonial livres the kental, and our vessels are as free as their own to carry our commodities thither, and to bring away rum and molasses.
The United Netherlands prohibit our pickled beef and pork, meals and bread of all sorts, and lay a prohibitory duty on spirits distilled from grain.
All other of our productions are received on varied duties, which may be reckoned, on a medium, at about three per cent.
They consume but a small proportion of what they receive. The residue is partly forwarded for consumption in the inland parts of Europe, and partly re-shipped to other maritime countries. On the latter portion, they intercept between us and the consumer, so much of the real value as is absorbed by the charges attending an intermediate deposite.
Foreign goods, except some East India articles, are received in the vessels of any nation.
Our ships may be sold and naturalized there, with exceptions of one or two privileges, which scarcely lessen their value.
In the American possessions of the United Netherlands, and Sweden, our vessels and produce are received, subject to duties, not so heavy as to have been complained of.
Great Britain receives our pot and pearl ashes free, while those of other nations pay a duty of two shillings three pence the kental. There is an equal distinction in favor of our bar-iron, of which article, however, we do not produce enough for our own use. Woods are free from us, whilst they pay some small duty from other countries. Indigo and flaxseed are free from all countries. Our tar and pitch pay eleven pence sterling the barrel. From other alien countries they pay about a penny and a third more.
Our tobacco, for their own consumption, pays one shilling three pence sterling the pound, custom and excise, besides heavy expenses of collection: and rice, in the same case, pays seven shillings four pence sterling the hundred weight, which rendering it too dear as an article of common food, it is consequently used in very small quantity.
Our salted fish, and other salted provisions, except bacon, are prohibited. Bacon and whale-oils are under prohibitory duties: so are our grains, meals, and bread, as to internal consumption, unless in times of such scarcity as may raise the price of wheat to fifty shillings sterling the quarter, and other grains and meals in proportion.
Our ships, though purchased and navigated by their own subjects, are not permitted to be used, even in their trade with us.
While the vessels of other nations are secured by standing laws, which cannot be altered but by the concurrent will of the three branches of the British legislature, in carrying thither any produce or manufacture of the country to which they belong, which may be lawfully carried in any vessels, ours, with the same prohibition of what is foreign, are further prohibited by a standing law (12 Car. 2, c. 18, s. 3.) from carrying thither all and any of our domestic productions and manufactures. A subsequent act, indeed, has authorized their executive to permit the carriage of our own productions in our own bottoms, at its sole discretion: and the permission has been given from year to year, by proclamation; but subject every moment to be withdrawn on that single will, in which event, our vessels having any thing on board, stand interdicted from the entry of all British ports. The disadvantage of a tenure which may be so suddenly discontinued, was experienced by our merchants on a late occasion, when an official notification that this law would be strictly enforced, gave them just apprehensions for the fate of their vessels and cargoes despatched or destined to the ports of Great Britain. It was privately believed, indeed, that the order of that court went further than their intention, and so we were, afterwards, officially informed: but the embarrassments of the moment were real and great, and the possibility of their renewal lays our commerce to that country under the same species of discouragement, as to other countries where it is regulated by a single legislator: and the distinction is too remarkable not to be noticed, that our navigation is excluded from the security of fixed laws, while that security is given to the navigation of others.
Our vessels pay in their ports one shilling nine pence sterling per ton, light and trinity dues, more than is paid by British ships, except in the port of London, where they pay the same as British. The greater part of what they receive from us is re-exported to other countries, under the useless charges of an intermediate deposite and double voyage.
From tables published in England, and composed, as is said, from the books of their Custom-Houses, it appears, that of the indigo imported there in the years 1773-4-5, one third was re-exported; and, from a document of authority, we learn that of the rice and tobacco imported there before the war, four fifths were re-exported. We are assured, indeed, that the quantities sent thither for re-exportation since the war are considerably diminished; yet less so than reason and national interest would dictate. The whole of our grain is re-exported, when wheat is below fifty shillings the quarter, and other grains in proportion.
Great Britain admits in her islands our vegetables, live provisions, horses, wood, tar, pitch, and turpentine, rice and bread-stuff, by a proclamation of her executive, limited always to the term of a year, but hitherto renewed from year to year. She prohibits our salted fish and other salted provisions. She does not permit our vessels to carry thither our own produce. Her vessels alone may take it from us, and bring in exchange, rum, molasses, sugar, coffee, cocoa-nuts, ginger, and pimento. There are, indeed, some freedoms in the island of Dominica, but under such circumstances as to be little used by us. In the British continental colonies, and in Newfoundland, all our productions are prohibited, and our vessels forbidden to enter their ports. Their Governors, however, in times of distress, have power to permit a temporary importation of certain articles in their own bottoms, but not in ours.
Our citizens cannot reside as merchants or factors within any of the British plantations, this being expressly prohibited by the same statute of 12 Car. 2, c. 18, commonly called their navigation act.
Of our commercial objects, Spain receives favorably our breadstuff, salted fish, wood, ships, tar, pitch, and turpentine. On our meals, however, when re-exported to their colonies, they have lately imposed duties, of from half a dollar to two dollars the barrel, the duties being so proportioned to the current price of their own flour, as that both together are to make the constant sum of nine dollars per barrel.
They do not discourage our rice, pot and pearl ash, salted provisions, or whale-oil; but these articles, being in small demand at their markets, are carried thither but in a small degree. Their demand for rice, however, is increasing. Neither tobacco nor indigo are received there.
Themselves and their colonies are the actual consumers of what they receive from us.
Our navigation is free with the kingdom of Spain, foreign goods being received there in our ships on the same conditions as if carried in their own, or in the vessels of the country of which such goods are the manufacture or produce.
Spain and Portugal refuse to those parts of America which they govern, all direct intercourse with any people but themselves. The commodities in mutual demand between them and their neighbors, must be carried to be exchanged in some port of the dominant country, and the transportation between that and the subject state must be in a domestic bottom.
TO MR. HAMMOND.
Philadelphia, February 16, 1793.
I have duly received your letter of yesterday, with the statement of the duties payable on articles imported into Great Britain The object of the report, from which I had communicated some extracts to you, not requiring a minute detail of the several duties on every article, in every country, I had presented both articles and duties in groups, and in general terms, conveying information sufficiently accurate for the object. And I have the satisfaction to find, on re-examining the expressions in the report, that they correspond with your statement as nearly as generals can with particulars. The differences which any nation makes between our commodities and those of other countries, whether favorable or unfavorable to us, were proper to be noted. But they were subordinate to the more important questions, What countries consume most of our produce, exact the lightest duties, and leave to us the most favorable balance?
You seem to think that in the mention made of your official communication of April the 11th, 1792, that the clause in the navigation act (prohibiting our own produce to be carried in our own vessels into the British European dominions) would be strictly enforced in future, and the private belief expressed at the same time, that the intention of that court did not go so far, that the latter terms are not sufficiently accurate. About the fact it is impossible we should differ, because it is a written one. The only difference, then, must be a merely verbal one. For thus stands the fact. In your letter of April the 11th, you say, you have received by a circular despatch from your court, direction to inform this government that it had been determined in future strictly to enforce this clause of the navigation act. This I considered as an official notification. In your answer of April the 12th, to my request of explanation, you say, ‘In answer to your letter of this day, I have the honor of observing that I have no other instructions upon the subject of my communication, than such as are contained in the circular despatch, of which I stated the purport in my letter dated yesterday. I have, however, no difficulty in assuring you, that the result of my personal conviction is, that the determination of his Majesty’s government to enforce the clause of the act, &c. is not intended to militate against the proclamation,’ &c. This personal conviction is expressed in the report as a private belief, in contradistinction of the official declaration. In your letter of yesterday, you chose to call it ‘a formal assurance of your conviction.’ As I am not scrupulous about words when they are once explained, I feel no difficulty in substituting in the report, your own words ‘personal conviction,’ for those of ‘private belief’ which I had thought equivalent. I cannot indeed insert that it was a formal assurance, lest some readers might confound this with an official one, without reflecting that you could not mean to give official assurance that the clause would be enforced, and official assurance, at the same time, of your personal conviction that it would not be enforced.
I had the honor to acknowledge verbally the receipt of your letter of the 3rd of August, when you did me that of making the inquiry verbally about six weeks ago; and I beg leave to assure you, that I am, with due respect, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO M. DE TERNANT.
Philadelphia, February 17, 1793.
Sir,
I have duly received your letter of yesterday, and am sensible of your favor in furnishing me with your observations on the statement of the commerce between our two nations, of which I shall avail myself for the good of both. The omission of our participation with your vessels, in the exclusive transportation of our tobacco, was merely that of the copy, as it was expressed in the original draught where the same circumstance respecting our whale-oil was noted: and I am happy that your notice of it has enabled me to reinstate it before the report goes out of my hand. I must candidly acknowledge to you, that I do not foresee the same effect in favor of our navigation, from the late reduction of duties on our tobaccos in France, which you seem to expect. The difference in favor of French vessels is still so great, as, in my opinion, to make it their interest to quit all other branches of the carrying business, to take up this; and as your stock of shipping is not adequate to the carriage of all your exports, the branches which you abandon will be taken up by other nations: so that this difference thrusts us out of the tobacco carriage, to let other nations in to the carriage of other branches of your commerce. I must therefore avail myself of this occasion to express my hope, that your nation will again revise this subject, and place it on more equal grounds. I am happy in concurring with you more perfectly in another sentiment, that as the principles of our governments become more congenial, the Clinks of affection are multiplied between us. It is impossible they should multiply beyond our wishes. Of the sincere interest we take in the happiness and prosperity of your nation, you have had the most unequivocal proofs.
I pray you to accept assurances of sincere attachment to you personally, and of the sentiments of respect and esteem, with which I am, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO M. DE TERNANT.
Philadelphia, February 20, 1793.
Sir,
I have laid before the President of the United States your notification of the 17th instant, in the name of the Provisory Executive Council charged with the administration of your government, that the French nation has constituted itself into a republic. The President receives with great satisfaction this attention of the Executive Council, and the desire they have manifested of making known to us the resolution entered into by the National Convention, even before a definitive regulation of their new establishment could take place. Be assured, Sir, that the government and the citizens of the United States, view with the most sincere pleasure every advance of your nation towards its happiness, an object essentially connected with its liberty, and they consider the union of principles and pursuits between our two countries, as a link which binds still closer their interests and affections. We earnestly wish on our part, that these our natural dispositions may be improved to mutual good, by establishing our commercial intercourse on principles as friendly to natural right and freedom, as are those of our governments.
I am, with sincere esteem and respect, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO THE SPEAKER OF THE HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES.
Philadelphia, February 20, 1793.
Sir,
The House of Representatives, about the close of the session before the last, referred to me the report of a committee on a message from the President of the United States, of the 14th of February, 1791, with directions to report to Congress the nature and extent of the privileges and restrictions of the commercial intercourse of the United States with foreign nations, and measures for its improvement. The report was accordingly prepared during the ensuing recess, ready to be delivered at the next session, that is to say, at the last. It was thought possible at that time, however, that some changes might take place in the existing state of things, which might call for corresponding changes in measures. I took the liberty of mentioning this in a letter to the Speaker of the House of Representatives, to express an opinion that a suspension of proceedings thereon, for a time, might be expedient, and to propose retaining the report till the present session, unless the House should be pleased to signify their pleasure to the contrary. The changes then contemplated have not taken place, nor, after waiting as long as the term of the session will admit, in order to learn something further on the subject, can any thing definite thereon be now said. If, therefore, the House wishes to proceed on the subject, the report shall be delivered at a moment’s warning. Should they not choose to take it up till their next session, it will be an advantage to be permitted to keep it by me till then, as some farther particulars may perhaps be procured relative to certain parts of our commerce, of which precise information is difficult to obtain. I make this suggestion, however, with the most perfect deference to their will, the first intimation of which shall be obeyed on my part, so as to occasion them no delay.
I have the honor to be, with sentiments of the most perfect esteem and respect, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO GOUVERNEUR MORRIS.
Philadelphia, March 12,1793.
Dear Sir,
Your Nos. 8 to 13, inclusive, have been duly received. I am sensible that your situation must have been difficult during the transition from the late form of government to the re-establishment of some other legitimate authority, and that you may have been at a loss to determine with whom business might be done. Nevertheless, when principles are well understood, their application is less embarrassing. We surely cannot deny to any nation that right whereon our own government is founded, that every one may govern itself according to whatever form it pleases, and change these forms at its own will; and that it may transact its business with foreign nations through whatever organ it thinks proper, whether King, Convention, Assembly, Committee, President, or any thing else it may choose. The will of the nation is the only thing essential to be regarded. On the dissolution of the late constitution in France, by removing so integral a part of it as the King, the National Assembly, to whom a part only of the public authority had been delegated, appear to have considered themselves as incompetent to transact the affairs of the nation legitimately. They invited their fellow-citizens, therefore, to appoint a National Convention. In conformity with this their idea of the defective state of the national authority, you were desired from hence to suspend further payments of our debts to France till new orders, with an assurance, however, to the acting power, that the suspension should not be continued a moment longer than should be necessary for us to see the re-establishment of some person or body of persons authorized to receive payment and give us a good acquittal; (if you should find it necessary to give any assurance or explanation at all.) In the mean time, we went on paying up the four millions of livres which had been destined by the last constituted authorities to the relief of St. Domingo. Before this was completed, we received information that a National Assembly had met, with full powers to transact the affairs of the nation, and soon afterwards, the minister of France here presented an application for three millions of livres, to be laid out in provisions to be sent to France. Urged by the strongest attachment to that country, and thinking it even providential, that monies lent to us in distress, could be repaid under like circumstances, we had no hesitation to comply with the application, and arrangements are accordingly taken, for furnishing this sum at epochs accommodated to the demand and our means of paying it. We suppose this will rather overpay the instalments and interest due on the loans of eighteen, six, and ten millions, to the end of 1792; and we shall certainly use our utmost endeavors to make punctual payments of the instalments and interest hereafter becoming exigible, and to omit no opportunity of convincing that nation how cordially we wish to serve them. Mutual good offices, mutual affection, and similar principles of government, seem to destine the two nations for the most intimate communion: and I cannot too much press it on you, to improve every opportunity which may occur in the changeable scenes which are passing, and to seize them as they occur, for placing our commerce with that nation and its dependencies, on the freest and most encouraging footing possible. Besides what we have furnished publicly for the relief of St. Domingo, individual merchants of the United States have carried considerable supplies thither, which have been sometimes purchased, sometimes taken by force, and bills given by the administration of the colony on the Minister here, which have been protested for want of funds. We have no doubt that justice will be done to these our citizens, and that without a delay which would be ruinous to them. We wish authority to be given to the Minister of France here to pay the just demands of our citizens, out of the monies he may receive from us.
During the fluctuating state of the assignats of France, I must ask the favor of you to inform me, in every letter, of the rate of exchange between them and coin, this being necessary for the regulation of our Custom-Houses.
Congress closed its session on the 2nd instant. You will see their acts in the newspapers forwarded to you, and the body of them shall be sent as soon as the octavo edition is printed. We are to hold a treaty with the western Indians in the ensuing month of May, but not under very hopeful auspices.
You will perceive by the newspapers, a remarkable fall in the price of our public paper. This is owing chiefly to the extraordinary demand for the produce of our country, and a temporary scarcity of cash to purchase it. The merchants holding public paper are obliged to part with it at any price, to raise money.
I sent you, by the way of London, a dozen plans of the city of Washington in the federal territory, hoping you would have them displayed to public view where they would be most seen by those descriptions of men worthy and likely to be attracted to it. Paris, Lyons, Rouen, and the sea-port towns of Havre, Nantes, Bordeaux, and Marseilles, would be proper places to send some of them. I trust to Mr. Taylor to forward you the newspapers by every direct occasion to France. These are rare at all times, and especially in the winter: and to send them through England would cost too much in postage. To these circumstances, as well, probably, as to some miscarriages, you must ascribe the length of intervals sometimes experienced in the receipt of your papers.
I have the honor to be, with great esteem and respect, Dear Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
Philadelphia, March 15, 1793.
Dear Sir,
The President has seen with satisfaction, that the Ministers of the United States in Europe, while they have avoided an useless commitment of their nation on the subject of the Marquis de la Fayette, have nevertheless shown themselves attentive to his situation. The interest which the President himself, and our citizens in general, take in the welfare of this gentleman, is great and sincere, and will entirely justify all prudent efforts to serve him. I am therefore to desire, that you will avail yourself of every opportunity of sounding the way towards his liberation, of finding out whether those in whose power he is are very tenacious of him, or insinuating through such channels as you shall think suitable, the attentions of the government and people of the United States to this object, and the interest they take in it, and of procuring his liberation by informal solicitations, if possible. But if formal ones be necessary, and the moment should arrive when you shall find that they will be effectual, you are authorized to signify through such channel as you shall find suitable, that our government and nation, faithful in their attachments to this gentleman for the services he has rendered them, feel a lively interest in his welfare, and will view his liberation as a mark of consideration and friendship for the United States, and as a new motive for esteem and a reciprocation of kind offices toward the power to whom they shall be indebted for this act.
A like letter being written to Mr. Pinckney, you will of course take care, that however you may act through different channels, there be still a sufficient degree of concert in your proceedings.
I am, with great and sincere esteem, Dear Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson
TO MR. PINCKNEY.
Philadelphia, March 16, 1793.
Dear Sir,
I wrote you on the 30th of December, and again a short letter on the 1st of January, since which I have received yours of October the 2nd and 5th, November the 6th and 9th, and December the 13th, 14th, 15th. I now enclose you the Treasurer’s second of exchange for twenty-four thousand seven hundred and fifty guilders, to be employed in the purchase of copper for the mint, from Sweden, or wherever else it can be got on the best terms; the first of exchange having been enclosed in my letter of December the 30th.
I am in hopes you will have been able to enter into proper arrangements with the British Minister for the protection of our seamen from impressment, before the preparations for war shall have produced inconvenience to them. While he regards so minutely the inconveniences to themselves which may result from a due regulation of this practice, it is just he should regard our inconveniences also, from the want of it. His observations in your letter imply merely, that if they should abstain from injuring us, it might be attended with inconvenience to themselves.
You ask, what should be your conduct, in case you should at any time discover negotiations to be going on, which might eventually be interesting to us. The nature of the particular case will point out what measures, on your part, would be the most for our interest, and to your discretion we must refer the taking such measures, without waiting for instructions, where circumstances would not admit of such a delay. A like necessity to act may arise on other occasions. In the changeable scenes, for instance, which are passing in Europe, were a moment to offer when you could obtain any advantage for our commerce, and especially in the American colonies, you are desired to avail us of it to the best advantage, and not to let the occasion slip by for want of previous instruction.
You ask, what encouragements are given to emigrants by the several States. No other than a permission to become citizens, and to participate of the rights of citizens, except as to eligibility to certain offices in the government. The rules, as to these, are not uniform in the states. I have found it absolutely impracticable to obtain, even for my office, a regular transmission of the laws of the several States: consequently, it would be more so to furnish them to our ministers abroad. You will receive by this or the first proper conveyance, those of Congress, passed at their last session.
It is impossible for me to give any authority for the advance of monies to Mr. Wilson. Were we to do it in his case, we should, on the same principles, be obliged to do it in several others wherein foreign nations decline or delay doing justice to our citizens. No law of the United States would cover such an act of the executive; and all we can do legally is, to give him all the aid which our patronage of his claims with the British court can effect.
With respect to the payment of your allowances, as the laws authorize the payment of a given number of dollars to you, and as your duties place you in London, I suppose we are to pay you the dollars there, or other money of equal value, estimated by the par of the metals. Such has, accordingly, been the practice ever since the close of the war. Your powers to draw on our bankers in Holland, will leave you the master of fixing your drafts by this standard.
The transactions of Europe are now so interesting, that I should be obliged to you, every week, to put the Leyden gazettes of the week under cover to me; and put them into such ship’s bag as shall be first coming to any port north of North Carolina.
Mr. Barclay’s death is just made known to us, and measures are taking in consequence of it.
You will perceive by the newspapers, a remarkable fall in the price of our public paper. This is owing chiefly to the extraordinary demand for the produce of our country, and a temporary scarcity of cash to purchase it. The merchants holding public paper are obliged to part with it at any price, to raise money.
I am, with much respect, Dear Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO COLONEL HUMPHREYS.
Philadelphia, March 21, 1793.
Sir,
The death of Admiral Paul Jones first, and afterwards of Mr. Barclay, to whom the mission to Algiers, explained in the enclosed papers, was successively confided, have led the President to desire you to undertake the execution of it in person. These papers, being copies of what had been delivered to them, will serve as your guide. But Mr. Barclay having been also charged with a mission to Morocco, it will be necessary to give you some trouble with respect to that also.
Mr. Nathaniel Cutting, the bearer hereof, is despatched specially, first to receive from Mr. Pinckney in London any papers or information, which his agency in the Algerine business may have enabled him to communicate to you: he will then proceed to deliver the whole to you, and accompany and aid you in the character of secretary.
It is thought necessary that you should, in the first instance, settle Mr. Barclay’s accounts respecting the Morocco mission, which will probably render it necessary that you should go to Gibraltar. The communications you have had with Mr. Barclay in this mission, will assist you in your endeavors at a settlement. You know the sum received by Mr. Barclay on that account, and we wish as exact a statement as can be made of the manner in which it has been laid out, and what part of its proceeds is now on hand. You will be pleased to make an inventory of these proceeds now existing. If they or any part of them can be used for the Algerine mission, we would have you by all means apply them to that use, debiting the Algerine fund and crediting that of Morocco with the amount of such application. If they cannot be so used, then dispose of the perishable articles to the best advantage, and if you can sell those not perishable for what they cost, do so, and what you cannot so sell, deposite in any safe place under your own power. In this last stage of the business, return us an exact account, 1. Of the specific articles remaining on hand for that mission, and their value. 2. Of its cash on hand. 3. Of any money which may be due to or from Mr. Barclay or any other person on account of this mission: and take measures for replacing the clear balance of cash in the hands of Messrs. W. and J. Willincks, and Nicholas and Jacob Van Staphorsts and Hubard.
This matter being settled, you will be pleased to proceed on the mission to Algiers. This you will do by the way of Madrid, if you think any information you can get from Mr. Carmichael or any other, may be equivalent for the trouble, expense, and delay of the journey. If not proceed in whatever other way you please to Algiers.
Proper powers and credentials for you, addressed to that government, are herewith enclosed. The instructions first given to Admiral Paul Jones are so full that no others need be added, except a qualification in one single article, to wit: should that government finally reject peace on the terms in money, to which you are authorized to go, you may offer to make the first payments for peace and that for ransom in naval stores, reserving the right to make the subsequent annual payments in money.
You are to be allowed your travelling expenses, your salary as minister resident in Portugal going on. Those expenses must be debited to the Algerine mission, and not carried into your ordinary account as resident. Mr. Cutting is allowed one hundred dollars a month and his expenses, which, as soon as he joins you, will of course be consolidated with yours. We have made choice of him as particularly qualified to aid, under your direction, in the matters of account, with which he is well acquainted. He receives here an advance of one thousand dollars, by a draft on our bankers in Holland, in whose hands the fund is deposited. This, and all other sums furnished him, to be debited to the Algerine fund. I enclose you a letter to our bankers giving you complete authority over these funds, which you had better send with your first draft, though I send a copy of it from hence by another opportunity.
This business being done, you will be pleased to return to Lisbon, and to keep yourself and us, thereafter, well informed of the transactions in Morocco; and as soon as you shall find that the succession to that government is settled and stable, so that we may know to whom a commissioner may be addressed, be so good as to give us the information, that we may take measures in consequence.
I have the honor to be, with much respect, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO COLONEL HUMPHREYS.
Philadelphia, March 22, 1793.
Dear Sir,
I have to acknowledge the receipt of your letters from No. 60 to 67, inclusive. You cannot be too vigilant against any such treaty as that mentioned in No. 60, which by giving the exclusive supply of wheat to Naples, would altogether debar the United States from it. This would bear so hard on us, that not only an exclusion of their wines from the United States ought to be expected on their part, but every other measure which might open to us a market in any other part of the world, however Portugal might be affected by it. And I must for ever repeat it, that, instead of excluding our wheat, we must continue to hope that they will open their ports to our flour, and that you will continue to use your efforts, on every good occasion, to obtain this without waiting for a treaty.
As there appears at present a probability of a very general war in Europe, you will be pleased to be particularly attentive to preserve for our vessels all the rights of neutrality, and to endeavor that our flag be not usurped by others to procure to themselves the benefits of our neutrality. This usurpation tends to commit us with foreign nations, to subject those vessels truly ours to rigorous scrutinies and delays to distinguish them from counterfeits, and to take the business of transportation out of our hands.
Continue, if you please, your intelligence relative to the affairs of Spain, from whence we learn nothing but through you: to which it will be acceptable that you add any leading events from other countries, as we have several times received important facts through you, even from London, sooner than they have come from London directly.
The letters enclosed for Mr. Carmichael and Mr. Short are of a very secret nature. If you go by Madrid, you will be the bearer of them yourself; if not, it would be better to retain them than to send them by any conveyance which does not command your entire confidence. I have never yet had a letter from Mr. Carmichael but the one you brought from Madrid. A particular circumstance will occasion forbearance yet a little longer.
Captain Cutting will bring you a copy of the laws of the last session of Congress, and of the gazettes to the time of his departure.
Not yet knowing the actual arrival of Mr. Church at Lisbon, I believe it will be safer that I direct letters for you, during your absence, to Messrs. Bulkeley and son, with whom you will leave what directions on the subject you shall think proper.
I am, with great and sincere esteem and respect, Dear Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MESSRS. CARMICHAEL AND SHORT.
Philadelphia, March 23, 1793.
Gentlemen,
It is intimated to us in such a way as to attract our attention, that France means to send a strong force early this spring to offer independence to the Spanish American colonies, beginning with those on the Mississippi; and that she will not object to the receiving those on the east side into our confederation. Interesting considerations require, that we should keep ourselves free to act in this case according to circumstances, and consequently, that you should not, by any clause of treaty, bind us to guaranty any of the Spanish colonies against their own independence, nor indeed against any other nation. For when we thought we might guaranty Louisiana, on their ceding the Floridas to us, we apprehended it would be seized by Great Britain, who would thus completely encircle us with her colonies and fleets. This danger is now removed by the concert between Great Britain and Spain; and the times will soon enough give independence, and consequently free commerce to our neighbors, without our risking the involving ourselves in a war for them.
I am, with great respect and esteem, your most obedient, humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
** The above meets the approbation of George Washington.
[* This letter was in cipher, but a literal copy of it
preserved.]
[** This is in the hand-writing of General Washington.]
TO MR. HAMMOND.
Philadelphia, April 18, 1793.
Sir,
I have now the honor to enclose you the answer of the Attorney General to my letter covering yours of March the 12th, on the case of Hooper and Pagan, wherein he has stated the proceedings of Pagan for obtaining a writ of error from the Supreme Court of the United States, for revisal of the judgment of the inferior court pronounced against him; and, also, his opinion on the merits of the question, had the writ of error been procured, and the merits thereby been brought into question. From this statement you will be able to judge whether Pagan has, bonâ fide, complied with the rule which requires that a foreigner, before he applies for extraordinary interposition, should use his best endeavors to obtain the justice he claims from the ordinary tribunals of the country. You will perceive also, that had the writ been pressed for and obtained, and the substantial justice of Pagan’s claim thereby brought into discussion, substantial justice would have been against him, according to the opinion of the Attorney General, according to the uniform decisions of the courts of the United States, even in the cases of their own citizens, and according to the decision of this very case in the British provincial court, where the evidence was taken and the trial first had. This does not appear then to be one of those cases of gross and palpable wrong, ascribable only to wickedness of the heart, and not to error of the head, in the judges who have decided on it, and founding a claim of national satisfaction. At least, that it is so, remains yet to be demonstrated.
The readiness with which the government of the United States has entered into inquiries concerning the case of Mr. Pagan, even before that case was ripe for their interposition, according to ordinary rules, will, I hope, satisfy you that they would, with equal readiness, have done for the redress of his case whatever the laws and constitution would have permitted them to do, had it appeared in the result that their courts had been guilty of partiality or other gross wrong against Mr. Pagan. On the contrary, it is hoped, that the marked attentions which have been shown to him by the government of Massachusetts, as well as by that of the United States, have evinced, the most scrupulous dispositions to patronize and effectuate his right, had right been on his side.
I have the honor to be, with due respect, Sir, your most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
[The letter of the Attorney General, referred to in the
preceding.]
TO THE SECRETARY OF STATE.
Philadelphia, April 12, 1793.
Sir,
You will perceive from the two letters marked A. and B. of which I enclose copies, that the subject of Mr. Pagan has been for some time in my view. The former of those letters being intended for you, and containing a summary of facts, I determined to show it to Mr. Tilghman, who was Pagan’s counsel, before it was sent to you, in order that he might correct any misstatement. This produced the latter letter from him to me; and I have thought it more advisable to forward both of them to you even in the unfinished state of my own, than to reduce the case into a form which might be supposed to be less accurate.
As I do not discover an essential difference between Mr. Tilghman and myself, I shall not discuss any seeming variance, but proceed upon his ideas.
It is too obvious to require a diffusive exposition, that the application for a writ of error was not only prudent, but a duty in Pagan. To this Mr. Tilghman explicitly assents, when he says, that he was perfectly ‘satisfied of the prudence of applying for the writ of error, as Pagan could not complain of a defect of justice, until he had tried the writ of error and found that mode ineffectual.’ This remark becomes the more important, as it manifests that the process was not suggested as an expedient for shifting any burthen from the government. Indeed I may with truth add, that the proceedings, taken collectively, appeared to me to present a sufficient intimation of the main question, to serve as a ground of decision.
However, take the case under either aspect; as excluding the consideration of the main question by an omission in the pleadings and record; or as exhibiting it fully to the cognizance of the court.
It never was pretended that a writ of error ought to have been granted, unless the matter was apparent on the record. Whose office was it to make it thus apparent. Of the attorney who managed the pleadings. If, therefore, he has failed to do so, we may presume that he considered the ground untenable, or was guilty of inattention. Either presumption would be fatal to a citizen of the United States; and the condition of a foreigner cannot create a new measure in the administration of justice. It is moreover certain, that those who have been consulted on Pagan’s behalf, as well as others, have seriously doubted whether a cause, which has been pursued to the extent which his had reached before the commencement of our new government, was susceptible of federal relief.
The last observation opens the inquiry, what remedy ought the Supreme Court of the United States to have administered, even if the question had been fairly before them? My opinion is, that the very merits are against Mr. Pagan. In America, the construction of the armistice has been almost universally to compute the places, within which different times were to prevail, by latitude only. Am I misinformed, that such an interpretation has been pressed by our ministers, and not denied by those of London? A second mode has been adopted, by describing a circle, and thereby comprehending longitude as well as latitude: now let either rule be adopted, and the position of the capture in this case will be adverse to Pagan’s pretensions.
But what can be exacted from our government, after repeated trials, before various jurisdictions, none of which can be charged with any symptom of impropriety, and upon a subject, which, to say no more, is at least equipoised? Nothing; and I appeal to the British reasoning on the Silesia loan, as supporting this sentiment, in the following passage. ‘The law of nations, founded upon justice, equity, convenience, and the reason of the thing, and confirmed by long usage, does not allow of reprisals, except in case of violent injuries directed and supported by the State, and justice absolutely denied, in re minime dubid, by all the tribunals, and afterwards by the prince.’ Where the judges are left free, and give sentence according to their consciences, ‘though it should be erroneous, that would be no ground for reprisals. Upon doubtful questions, different men think and judge differently; and all a friend can desire is, that justice should be as impartially administered to him, as it is to the subjects of that prince, in whose courts the matter is tried.’ Under such circumstances, a citizen must acquiesce. So therefore must Pagan; against whom even the court of Nova Scotia, within the dominions of his sovereign, has once decided.
There are many smaller points, arising from the controversy, which might be relied on. But I pass them over, from a hope that the observations already made will induce you to think with me, that government is not bound to interpose farther in the behalf of Pagan. I have the honor, Sir, to be, with respect and esteem, your most obedient servant,
Edmond Randolph.
TO MR. PINCKNEY.
Philadelphia, April 20, 1793.
Dear Sir,
In a postscript to my letter of the 12th, I acknowledged the receipt of yours of January the 3rd; since which, those of January the 30th and February the 5th have been received by the William Penn.
With respect to our negotiation with Mr. Hammond, it is exactly in the state in which it was when you left America, not one single word having been received in reply to my general answer, of which you had a copy. He says, he waits for instructions, which he pretends to expect from packet to packet. But sometimes the ministers are all in the country, sometimes they are absorbed in negotiations nearer home, sometimes it is the hurry of impending war, or attention to other objects, the stock of which is inexhaustible, and can therefore never fail those who desire nothing but that things shall rest as they are. Perhaps, however, the present times may hasten justice.
We shall be glad to receive the assayer you hope to procure, as soon as possible, for we cannot get one in this country equal to the business in all its parts. With respect to Mr. Droz, we retain the same desire to engage him, but we are forced to require an immediate decision, as the officer employed in the interim, and who does tolerably well, will not continue much longer under an uncertainty of permanent employment. I must therefore desire you to press Mr. Morris to bring Droz to an immediate determination; and we place the matter on this ground with him, that if he is not embarked by the first day of July next, we shall give a permanent commission to the present officer, and be free to receive no other. We are likely to be in very great distress for copper for the mint, and must therefore press your expediting what we desired you to order from Sweden.
You may, on every occasion, give assurances which cannot go beyond the real desires of this country, to preserve a fair neutrality in the present war, on condition that the rights of neutral nations are respected in us, as they have been settled in modern times, either by the express declarations of the powers of Europe, or their adoption of them on particular occasions. From our treaties with France and Holland, and that of England and France, a very clear and simple line of conduct can be marked out for us, and I think we are not unreasonable in expecting that England shall recognise towards us the same principles which she has stipulated to recognise towards France, in a state of neutrality.
I have the honor to be, with great and sincere esteem, Dear Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
CIRCULAR TO MESSRS. MORRIS, PINCKNEY, AND SHORT.
Philadelphia, April 26,1793.
Sir,
The public papers giving us reason to believe that the war is becoming nearly general in Europe, and that it has already involved nations with which we are in daily habits of commerce and friendship, the President has thought it proper to issue the proclamation of which I enclose you a copy, in order to mark out to our citizens the line of conduct they are to pursue. That this intimation, however, might not work to their prejudice, by being produced against them as conclusive evidence of their knowledge of the existence of war and of the nations engaged in it, in any case where they might be drawn into courts of justice for acts done without that knowledge, it has been thought necessary to write to the representatives of the belligerent powers here, the letter of which a copy is also enclosed, reserving to our citizens those immunities to which they are entitled, till authentic information shall be given to our government by the parties at war, and be thus communicated, with due certainty, to our citizens. You will be pleased to present to the government where you reside this proceeding of the President, as a proof of the earnest desire of the United States to preserve peace and friendship with all the belligerent powers, and to express his expectation that they will in return extend a scrupulous and effectual protection to all our citizens, wheresoever they may need it, in pursuing their lawful and peaceable concerns with their subjects, or within their jurisdiction. You will, at the same time, assure them, that the most exact reciprocation of this benefit shall be practised by us towards their subjects, in the like cases.
I have the honor to be, with great esteem and respect. Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO M. DE TERNANT.
Philadelphia, April 27,1793.
Sir,
Your letter of the 13th instant, asking monies to answer the expenses and salaries of the consular offices of France, has been duly laid before the President, and his directions thereon taken.
I have in consequence to observe to you, that before the new government of France had time to attend to things on this side the Atlantic, and to provide a deposite of money for the purposes here, there appeared a degree of necessity that we, as the friends and debtors of that nation, should keep their affairs from suffering, by furnishing money for urgent purposes. This obliged us to take on ourselves to judge of the purpose, because on the soundness of that, we were to depend for our justification. Hence we furnished monies for their colonies and their agents here, without express authority, judging from the importance and necessity of the case, that they would approve of our interference.
But this kind of necessity is now at an end: the government has established a deposite of money in the hands of their minister here, and we have nothing now to do but to furnish the money, which we are in the course of doing, without looking into the purposes to which it is to be applied. Their Minister is to be the judge of these, and to pay it to whom and for what he pleases.
If it be urged that they have appropriated all the money we are furnishing, to other objects, and that you are not authorized to divert any of it to any other purpose, and therefore that you need a further sum, it may be answered, that it will not lessen the stretch of authority to add an unauthorized payment by us to an unauthorized application by you; and that it seems fitter that their Minister should exercise a discretion over their appropriations, standing as he does in a place of confidence, authority, and responsibility, than we who are strangers and unamenable to them. It is a respect we owe to their authority, to leave to those acting under that the transaction of their affairs, without an intermeddling on our part, which might justly appear officious.
In this light I hope you will view our conduct, and that the consular officers will be sensible, that in referring them to your care, under which the national authority has placed them, we do but con-form ourselves to that authority.
I have the honor to be, with sentiments of great respect and esteem, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO M. DE TERNANT.
Philadelphia, May 3,1793.
Sir,
The Minister Plenipotentiary of his Britannic Majesty has represented to the government of the United States, that on the 25th of April last, the British ship Grange, while lying at anchor in the bay of the Delaware, within the territory and jurisdiction of the United States, was taken possession of by the Embuscade, a frigate of the French republic, has been brought to this port, where she is now detained as prize and the crew as prisoners, and has made a requisition in form, for a restoration of the vessel and liberation of the crew. I have the honor to furnish you with copies of the evidence given in by the British Minister, and to observe, that the United States, being at peace with all parties, cannot see with indifference its territory or jurisdiction violated by either; that the government will therefore proceed to inquire into the facts, and for that purpose will receive with pleasure, and consider with impartiality, any evidence you will be pleased to have them furnished with on the subject: and the President hopes that you will take effectual measures for detaining here the vessel taken, her crew and cargo, to abide the decision which will be made thereon, and which is desired to be without delay.
I have the honor to be, with great respect, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MR. PINCKNEY.
Philadelphia, May 7, 1793.
Dear Sir,
Since my letter of April the 16th, yours have been received of March the 12th, 12th, 13th, 13th, and 19th. Before the receipt of these, one of which covered the form of your passports, it had been determined here, that passports should be issued in our own ports only, as well to secure us against those collusions which would be fraudulent towards our friends, and would, introduce a competition injurious to our own vessels, as to induce these to remain in our own service, and thereby give to the productions of our own soil the protection of its own flag in its passage to foreign markets. As our citizens are free to purchase and use foreign-built vessels, and these, like all their other lawful property, are entitled to the protection of their government, passports will be issued to them as freely as to home-built vessels. This is strictly within our treaties, the letter of which, as well as their spirit, authorizes passports to all vessels belonging to citizens of the United States. Our laws, indeed, indulge home-built vessels with the payment of a lower tonnage, and to evidence their right to this, permit them alone to take out registers from our own offices, but they do not exclude foreign-built vessels owned by our citizens from any other right. As our home-built vessels are adequate to but a small proportion of our transportation, if we could not suddenly augment the stock of our shipping, our produce would be subject to war-insurance in the vessels of the belligerent powers, though we remain at peace ourselves.
In one of your letters of March the 13th, you express your apprehension that some of the belligerent powers may stop our vessels going with grain to the ports of their enemies, and ask instructions which may meet the question in various points of view, intending, however, in the mean time, to contend for the amplest freedom of neutral nations. Your intention in this is perfectly proper, and coincides with the ideas of our own government in the particular case you put, as in general cases. Such a stoppage to an unblockaded port would be so unequivocal an infringement of the neutral rights, that we cannot conceive it will be attempted. With respect to our conduct, as a neutral nation, it is marked out in our treaties with France and Holland, two of the belligerent powers: and as the duties of neutrality require an equal conduct to both parties, we should, on that ground, act on the same principles towards Great Britain. We presume that this would be satisfactory to her, because of its equality, and because she too has sanctioned the same principles in her treaty with France. Even our seventeenth article with France, which might be disagreeable, as from its nature it is unequal, is adopted exactly by Great Britain in her fortieth article with the same power, and would have laid her, in a like case, under the same unequal obligations against us. We wish then, that it could be arranged with Great Britain, that our treaties with France and Holland, and that of France and Great Britain (which agree in what respects neutral nations), should form the line of conduct for us all, in the present war, in the cases for which they provide. Where they are silent, the general principles of the law of nations must give the rule, as the principles of that law have been liberalized in latter times by the refinement of manners and morals, and evidenced by the declarations, stipulations, and practice of every civilized nation. In our treaty with Prussia, indeed, we have gone ahead of other nations, in doing away restraints on the commerce of peaceful nations, by declaring that nothing shall be contraband. For in truth, in the present improved state of the arts, when every country has such ample means of procuring arms within and without itself, the regulations of contraband answer no other end than to draw other nations into the war. However, as other nations have not given sanction to this improvement, we claim it, at present, with Prussia alone.
You are desired to persevere till you obtain a regulation to guard our vessels from having their hands impressed, and to inhibit the British navy-officers from taking them under the pretext of their being British subjects. There appears but one practicable rule, that the vessel being American, shall be conclusive evidence that the hands are so to a certain number, proportioned to her tonnage. Not more than one or two officers should be permitted to visit a vessel. Mr. Albion Coxe has just arrived.
I have the honor to be, with great and sincere esteem, Dear Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson,
TO MR. HAMMOND.
Philadelphia, May 15, 1793.
Sir,
Your several memorials of the 8th instant have been laid before the President, as had been that of the 2nd, as soon as received. They have been considered with all the attention and the impartiality, which a firm determination to do what is equal and right between all the belligerent powers could inspire.
In one of these, you communicate, on the information of the British Consul at Charleston, that the Consul of France at the same place had condemned, as legal prize, a British vessel, captured by a French frigate, and you justly add, that this judicial act is not warranted by the usage of nations, nor by the stipulations existing between the United States and France. I observe further, that it is not warranted by any law of the land. It is consequently a mere nullity; as such it can be respected in no court, can make no part in the title to the vessel, nor give to the purchaser any other security than what he would have had without it. In short, it is so absolutely nothing, as to give no foundation of just concern to any person interested in the fate of the vessel; and in this point of view, Sir, I am in hopes you will see it. The proceeding, indeed, if the British Consul has been rightly informed (and we have no other information of it), has been an act of disrespect towards the United States, to which its government cannot be inattentive: a just sense of our own rights and duties, and the obviousness of the principle, are a security that no inconveniences will be permitted to arise from repetitions of it.
The purchase of arms and military accoutrements by an agent of the French government, in this country, with an intent to expert them to France, is the subject of another of the memorials. Of this fact we are equally uninformed as of the former. Our citizens have been always free to make, vend, and export arms. It is the constant occupation and livelihood of some of them. To suppress their callings, the only means perhaps of their subsistence, because a war exists in foreign and distant countries, in which we have no concern, would scarcely be expected. It would be hard in principle, and impossible in practice. The law of nations, therefore, respecting the rights of those at peace, does not require from them such an internal derangement in their occupations. It is satisfied with the external penalty pronounced in the President’s proclamation, that of confiscation of such portion of these arms as shall fall into the hands of any of the belligerent powers on their way to the ports of their enemies. To this penalty our citizens are warned that they will be abandoned; and that even private contraventions may work no inequality between the parties at war, the benefits of them will be left equally free and open to all.
The capture of the British ship Grange by the French frigate L’Embuscade has on inquiry been found to have taken place within the bay of Delaware and jurisdiction of the United States, as stated in your memorial of the 2nd instant. The government is, therefore, taking measures for the liberation of the crew and restitution of the ship and cargo.’
It condemns, in the highest degree, the conduct of any of our citizens who may personally engage in committing hostilities at sea against any of the nations, parties to the present war, and will exert all the means with which the laws and constitution have armed them to discover such as offend herein, and bring them to condign punishment. Of these dispositions I am authorized to give assurances to all the parties, without reserve. Our real friendship for them all, our desire to pursue ourselves the path of peace, as the only one leading surely to prosperity, and our wish to preserve the morals of our citizens from being vitiated by courses of lawless plunder and murder, may assure you that our proceedings, in this respect, will be with good faith, fervor, and vigilance. Instructions are consequently given to the proper law officer, to institute such proceedings as the laws will justify, for apprehending and punishing certain individuals of our citizens, suggested to have been concerned in enterprises of this kind, as mentioned in one of your memorials of the 8th instant.
The practice of commissioning, equipping, and manning vessels in our ports, to cruise on any of the belligerent parties, is equally and entirely disapproved; and the government will take effectual measures to prevent a repetition of it. The remaining point in the same memorial is reserved for further consideration.
I trust, Sir, that in the readiness with which the United States have attended to the redress of such wrongs as are committed by their citizens, or within their jurisdiction, you will see proofs of their justice and impartiality to all parties; and that it will insure to their citizens pursuing their lawful business by sea or by land, in all parts of the world, a like efficacious interposition of governing powers to protect them from injury, and redress it, where it has taken place. With such dispositions on both sides, vigilantly and faithfully carried into effect, we may hope that the blessings of peace, on the one part, will be as little impaired, and the evils of war, on the other, as little aggravated, as the nature of things will permit; and that this should be so, is, we trust, the prayer of all.
I have the honor to be, with sentiments of respect, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO M. DE TERNANT.
Philadelphia, May 15, 1793.
Sir,
Having received several memorials from the British Minister on subjects arising out of the present war, I take the liberty of enclosing them to you, and shall add an explanation of the determinations of the government thereon. These will serve to indicate the principles on which it is meant to proceed; and which are to be applied, with impartiality, to the proceedings of both parties. They will form, therefore, as far as they go, a rule of action for them and for us.
In one of these memorials, it is stated, that arms and military accoutrements are now buying up by a French agent in this country, with an intent to export them to France. We have answered, &c.
Another of these memorials complains that the Consul of France at Charleston, has condemned, as legal prize, a British vessel captured by a French frigate, observing that this judicial act is not warranted by the usage of nations nor by the stipulations existing between the United States and France. It is true, &c.
Our information is not perfect on the subject matter of another of these memorials, which states that a vessel has been fitted out at Charleston, manned there, and partly too with citizens of the United States, received a commission there to cruise against nations at peace with us, and has taken and sent a British vessel into this port. Without taking all these facts for granted, we have not hesitated to express our highest disapprobation of the conduct of any of our citizens who may personally engage in committing hostilities at sea against any of the nations, parties to the present war, and to declare, that if the case has happened, or that should it happen, we will exert all the measures with which the laws and constitution have armed us, to discover such offenders and bring them to condign punishment. And that the like conduct shall be observed, should the like enterprises be attempted against your nation, I am authorized to give you the most unreserved assurances.
The capture of the British ship Grange, by the French frigate L’Embuscade, within the Delaware, has been the subject of a former letter to you. On full and mature consideration, the government deems the capture to have been unquestionably within its jurisdiction, and that according to the rules of neutrality and the protection it owes to all persons while within its limits, it is bound to see that the crew be liberated, and the vessel and cargo restored to their former owners. The Attorney General of the United States has made a statement of the grounds of this determination, a copy of which I have the honor to enclose you. I am, in consequence, charged by the President of the United States to express to you his expectation, and at the same time his confidence that you will be pleased to take immediate and effectual measures for having the ship Grange and her cargo restored to the British owners, and the persons taken on board her set at liberty.
I am persuaded, Sir, you will be sensible, on mature consideration, that in forming these determinations, the government of the United States has listened to nothing but the dictates of immutable justice: they consider the rigorous exercise of that virtue as the surest means of preserving perfect harmony between the United States and the powers at war.
I have the honor to be, with sentiments of great respect, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
[* The parts of this letter which are mere repetitions of what is contained in the preceding, to the British Minister, are omitted.]
TO THE GOVERNOR OF VIRGINIA.
Philadelphia, May 21,1793.
Sir,
I have been duly honored with your favor of May the 8th, covering the letter of Mr. Newton, and that of May the 13th, with the letter of the British Consul at Norfolk and the information of Henry Tucker, all of which have been laid before the President.
The putting the several harbors of the United States into a state of defence, having never yet been the subject of deliberation and decision with the legislature, and consequently, the necessary monies not having been appropriated or levied, the President does not find himself in a situation competent to comply with the proposition on the subject of Norfolk.
Mr. Newton supposes, that by the treaties with France and Holland, those powers are authorized to arm vessels within our ports. A careful examination of the treaties will show, however, that no such permission has been stipulated therein. Measures are accordingly taken to correct this error as to the past, and others will be taken to prevent a repetition of it. Proceedings are ordered against Mr. Hooper and other American citizens who have participated in any hostilities against nations at peace with the United States, and circular instructions are given to the District Attorneys of the United States, to institute like prosecutions in all future similar cases. The bringing vessels to, of whatever nation, while within the limits of the protection of the United States, will be pointedly forbidden; the government being firmly determined to enforce a peaceable demeanor among all the parties within those limits, and to deal to all the same impartial measure. I have the honor to be, with the most perfect respect, your Excellency’s most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
Philadelphia, May 29,1793.
Sir,
I am favored with your note of the 22nd instant, stating that under circumstances of invasion and urgent danger, their High Mightinesses, the States General of the United Netherlands, had found it necessary to lay an embargo on all vessels in their ports, and that an American ship, the Hope, being involved in this general order, the master had claimed an exemption under the eighth article of our treaty, which it had been necessary to refuse him.
I have laid this note before the President of the United States, and have it in charge from him to assure you, that the United States having the utmost confidence in the sincerity and good faith with which their High Mightinesses will observe the treaty between the two countries, feel no dissatisfaction at the circumstance mentioned in your note. They are sensible that in human affairs, there are moments of difficulty and necessity, to which it is the office of friendship to accommodate its strict rights.
The President considers the explanation, which their High Mightinesses have instructed you to give of this incident, as a proof of their desire to cultivate harmony and good understanding with these United States, and charges me to assure you that he has nothing more at heart than to convince their High Mightinesses of the same amicable sentiments on the part of this country, and of the certainty with which they may count on its justice and friendship on every occasion.
I have the honor to be, with great respect and esteem, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MESSRS. CARMICHAEL AND SHORT.
Philadelphia, May 31, 1793.
Gentlemen,
In my letters of October the 14th and November the 3rd, 1792, I communicated to you papers and observations on the conduct of the Spanish officers on our southwestern frontier, and particularly of the Baron de Carondelet, the Governor of New Orleans. These made it evident that he had industriously excited the southern Indians to war against us, and had furnished them with arms and ammunition in abundance, for that express purpose. We placed this under the view of the commissioners of Spain here, who undertook to communicate it to their court, and also to write on the subject to the Baron de Carondelet. They have lately made us communications from both these quarters; the aspect of which, however, is by no means such as to remove the causes of our dissatisfaction. I send you these commmunications, consisting of treaties between Spain, the Creeks, Choctaws, Chickasaws, and Cherokees, handed us by express order from their court, a speech of Jiaron de Carondelet to the Cherokees, and a letter from Messrs. de Viar and Jaudenes, covering that speech, and containing in itself very serious matter.
I will first observe to you, that the question stated in that letter to have been proposed to the Cherokees, What part they would take, in the event of a war between the United States and Spain was never proposed by authority from this government. Its instructions to its agents have, on the contrary, been explicitly to cultivate, with good faith, the peace between Spain and the Indians: and from the known prudence and good conduct of Governor Blount, to whom it is imputed, it is not believed to have been proposed by him. This proposition then, you are authorized to disavow to the court of Madrid, in the most unequivocal terms. With respect to the treaties, the speech, and the letter, you will see that they undertake to espouse the concerns of Indians within our limits; to be mediators of boundary between them and us; to guaranty that boundary to them; to support them with their whole power; and hazard to us intimations of acquiescence to avoid disagreeable results. They even propose to extend their intermeddlings to the northern Indians. These are pretensions so totally inconsistent with the usages established among the white nations with respect to Indians living within their several limits, that it is believed no example of them can be produced, in times of peace; and they are presented to us in a manner which we cannot deem friendly. The consequence is, that the Indians, and particularly the Creeks, finding themselves so encouraged, have passed, without the least provocation on our part, from a state of peace, which appeared to be well settled, to that of serious hostility. Their murders and depredations, which, for some months, we were willing to hope were only individual aggressions, now assume the appearance of unequivocal war. Yet such is our desire of courting and cultivating the peace of all our Indian neighbors, that instead of marching at once into their country and taking satisfaction ourselves, we are peaceably requiring punishment of the individual aggressors; and, in the mean time, are holding ourselves entirely on the defensive. But this state of things cannot continue. Our citizens are entitled to effectual protection, and defensive measures are, at the same time, the most expensive and least effectual. If we find then, that peace cannot be obtained by the temperate means we are still pursuing, we must proceed to those which are extreme, and meet all the consequences, of whatever nature, or from whatever quarter, they may be. We have certainly been always desirous to avoid whatever might disturb our harmony with Spain. We should be still more so, at a moment when we see that nation making part of so powerful a confederacy as is formed in Europe, and under particular good understanding with England, our other neighbor. In so delicate a position, therefore, instead of expressing our sense of these things, by way of answer to Messrs. Viar and Jaudenes, the President has thought it better that it should be done to you, and to trust to your discretion the moment, the measure, and the form of communicating it to the court of Madrid. The actual state of Europe at the time you will receive this, the solidity of the confederacy, and especially as between Spain and England, the temper and views of the former, or of both, towards us, the state of your negotiation, are circumstances which will enable you better to decide how far it may be necessary to soften, or even perhaps to suppress, the expressions of our sentiments on this subject. To your discretion, therefore, it is committed by the President, to let the court of Spain see how impossible it is for us to submit with folded arms to be butchered by these savages, and to prepare them to view, with a just eye, the more vigorous measures we must pursue to put an end to their atrocities, if the moderate ones we are now taking should fail of that effect.
Our situation on other accounts and in other quarters is critical. The President is, therefore, constantly anxious to know the state of things with you: and I entreat you to keep him constantly and well informed. Mr. Yznardi, the younger, lately appointed Consul of the United States, at Cadiz, may be a convenient channel of forwarding your letters.
I have the honor to be, with great esteem and respect, Gentlemen, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MR. GENET, Minister Plenipotentiary of France.
Philadelphia, June 5,1793.
Sir,
In my letter of May the 15th, to M. de Ternant, your predecessor, after stating the answer which had been given to the several memorials of the British Minister, of May the 8th, it was observed that a part still remained unanswered of that which respected the fitting out armed vessels in Charleston, to cruise against nations with whom we are at peace.
In a conversation which I had afterwards the honor of holding with you, I observed that one of those armed vessels, the Citizen Genet, had come into this port with a prize: that the President had thereupon taken the case into further consideration, and after mature consultation and deliberation, was of opinion, that the arming and equipping vessels in the ports of the United States to cruise against nations with whom they are at peace, was incompatible with the territorial sovereignty of the United States; that it made them instrumental to the annoyance of those nations, and thereby tended to compromit their peace; and that he thought it necessary as an evidence of good faith to them, as well as a proper reparation to the sovereignty of the country, that the armed vessels of this description should depart from the ports of the United States.
The letter of the 27th instant, with which you have honored me, has been laid before the President, and that part of it which contains your observations on this subject has been particularly attended to. The respect due to whatever comes from you, friendship for the French nation, and justice to all, have induced him to re-examine the subject, and particularly to give your representations thereon the consideration they deservedly claim. After fully weighing again, however, all the principles and circumstances of the case, the result appears still to be, that it is the right of every nation to prohibit acts of sovereignty from being exercised by any other within its limits; and the duty of a neutral nation to prohibit such as would injure one of the warring powers; that the granting military commissions within the United States by any other authority than their own, is an infringement on their sovereignty, and particularly so when granted to their own citizens to lead them to acts contrary to the duties they owe their own country; that the departure of vessels thus illegally equipped from the ports of the United States, will be but an acknowledgment of respect analogous to the breach of it, while it is necessary on their part, as an evidence of their faithful neutrality. On these considerations, Sir, the President thinks that the United States owe it to themselves and to the nations in their friendship, to expect this act of reparation on the part of vessels, marked in their very equipment with offence to the laws of the land, of which the law of nations makes an integral part.
The expressions of friendly sentiments which we have already had the satisfaction of receiving from you, leave no room to doubt that, the conclusion of the President being thus made known to you, these vessels will be permitted to give no further umbrage by their presence in the ports of the United States.
I have the honor to be, with sentiments of perfect esteem and respect, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MR. HAMMOND.
Philadelphia, June 5, 1793.
Sir,
In the letter which I had the honor of writing you on the 15th of May, in answer to your several memorials of the 8th of that month, I mentioned that the President reserved for further consideration, a part of the one which related to the equipment of two privateers in the port of Charleston. The part alluded to was that wherein you express your confidence that the executive government of the United States would pursue measures for repressing such practices in future, and for restoring to their rightful owners any captures, which such privateers might bring into the ports of the United States.
The President, after a full investigation of this subject and the most mature consideration, has charged me to communicate to you, that the first part of this application is found to be just, and that effectual measures are taken for preventing repetitions of the act therein complained of; but that the latter part, desiring restitution of the prizes, is understood to be inconsistent with the rules which govern such cases, and would, therefore, be unjustifiable towards the other party.
The principal agents in this transaction were French citizens. Being within the United States at the moment a war broke out between their own and another country, they determine to go into its defence; they purchase, arm, and equip a vessel with their own money, man it themselves, receive a regular commission from their nation, depart out of the United States, and then commence hostilities by capturing a vessel, If, under these circumstances, the commission of the captors was valid, the property, according to the laws of war, was by the capture transferred to them, and it would be an aggression on their nation, for the United States to rescue it from them, whether on the high seas or on coming into their ports. If the commission was not valid, and, consequently, the property not transferred by the laws of war to the captors, then the case would have been cognizable in our courts of admiralty, and the owners might have gone thither for redress. So that, on neither supposition, would the executive be justifiable in interposing.
With respect to the United States, the transaction can be in nowise imputed to them. It was in the first moment of the war, in one of their most distant ports, before measures could be provided by the government to meet all the cases which such a state of things was to produce, impossible to have been known, and, therefore, impossible to have been prevented by that government.
The moment it was known, the most energetic orders were sent to every State and port of the Union, to prevent a repetition of the accident. On a suggestion that citizens of the United States had taken part in the act, one, who was designated, was instantly committed to prison, for prosecution; one or two others have been since named, and committed in like manner; and should it appear that there were still others, no measure will be spared to bring them to justice. The President has even gone further. He has required, as a reparation of their breach of respect to the United States, that the vessels so armed and equipped, shall depart from our ports.
You will see, Sir, in these proceedings of the President, unequivocal proofs of the line of strict right which he means to pursue. The measures now mentioned, are taken in justice to the one party; the ulterior measure, of seizing and restoring the prizes, is declined in justice to the other; and the evil, thus early arrested, will be of very limited effects; perhaps, indeed, soon disappear altogether.
I have the honor to be, with sentiments of respect, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO GOUVERNEUR MORRIS.
Philadelphia, June 13, 1793,
Dear Sir,
It has long since been observed, that of the three millions of livres given by the court of France to aid us in the commencement of our revolution, one million was unaccounted for by the hands into which it was paid. The date of the payment is fixed to have been the 10th of June, 1776, but to whom it was paid has never been known. Suspicions are, that it was to Beaumarchais; and that with this very money he purchased the supplies furnished us by him, for which large sums have been paid him already, and a further large sum has lately been certified to be due to him as the balance of the account. I enclose you a letter from the Secretary of the Treasury on this subject, with all the papers relative to the same which his office can furnish: and as you are on the spot, I must beg the favor of you to make an immediate and thorough investigation of it. No reasons of State can now exist for covering the transaction longer under mystery.
I have the honor to be, with great and sincere esteem, Dear Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
[The letter of the Secretary of the Treasury, and other papers, relative to the lost million alluded to in the letter to Mr. Morris.]
Treasury Department, June 10, 1793. Sir,
The comptroller of the Treasury has reported to me, that ‘on examining the subsisting contracts between the United States and the government of France and the Farmers General, and a comparison thereof with the foreign accounts and documents transmitted to the Treasury, the following facts appear.
That previous to the treaty of February, 1778, the sum of three millions of livres had been advanced by the government of France to the agents of the United States, under the title of gratuitous, for which no reimbursement was to be made.
That the payments, which composed the before-mentioned sum of three millions of livres, are stated, in a letter of Mr. Durival to Mr. Grand, dated in 1786, to have been made at the following periods:
One million delivered by the Royal Treasury the 10th of June, 1776, and two other millions advanced also by the Royal Treasury in 1777, on four receipts of the Deputies of Congress, of the 17th of January, 3rd of April, 10th of June, and 15th of October of the same year.
In the account of Mr. Ferdinand Grand, banker of the United States, the following sums are credited, viz.
1777.—January 31, .... 500,000 livres.
April 26, ...... 500,000
June 4, ........ 1,000,000
July 3, ........ 500,000
October 10, .... 500,000
Amount in the whole, .. 3,000,000 livres.
The Farmers General of France claim a large balance from the United States, on account of one million of livres which they contend was advanced in June, 1777, in consequence of a special contract with Messrs. Franklin and Deane, to be repaid by the delivery of tobacco at certain stipulated prices, and the advance made by the Farmers General is said to be the same money, as is credited by Mr. Grand on the 4th of June, 1777.
After a careful examination of the foreign accounts, it is found that no more than three millions of livres have been credited by any agents of the United States.
An opinion was entertained by the late officers of the Treasury, that the sum claimed by the Farmers General composed a part of the sum supplied as gratuitous aid by the government. Subsequent explanations have however rendered it probable, that, including the claim of the Farmers General, the sum of four millions of livres were in fact received; it is, however, indispensable that it should be known to whom the money was paid.
The most direct mode of obtaining this information will be, to call for copies of the receipts mentioned in Mr. Durival’s letter of 1786, and more particularly, a copy of that said to have been given on the 10th of June, 1776.’
And as explanatory of the transaction, he has sent me the documents herewith transmitted.
The most likely conjecture, in my mind, considering the period of the advance and the circumstances of that period, is, that the unaccounted-for million went into the hands of M. de Beaumarchais. The supplies which he furnished to the United States exceeded his own probable resources, besides the imprudence of having hazarded so much at that stage of our affairs upon our ability to pay. And there were many symptoms, at the time, of his having been secretly put in motion by the government.
It is now become urgent, that the truth of the case should be known. An account has recently passed the auditor’s office, admitting in favor of M. de Beaumarchais a balance of four hundred and twenty-two thousand two hundred and sixty-five dollars and thirteen cents, with a reservation only of the question of the million. If he has received that million, which has been acknowledged as a free gift from the French government, it is unjust that he should be able to establish a claim against the United States for supplies which must have been the proceeds of that sum. If he has never received the million, every, day’s suspension of his claim, after the immense delays heretofore incurred, is a grievous hardship upon him. It concerns materially the interests, and more the justice, the credit, and the character of the United States, that as speedy a solution as possible of the enigma may be obtained.
With a view to this, I have the honor to make you the present communication, that you may be pleased to take such steps as shall appear to you the most proper and efficacious to procure, as speedily as the nature of the case will admit, the requisite explanations. With respect, I have the honor to be, &c.
Alexander Hamilton.
Letter from Mr. Grand to ——— ———
Paris, September 9, 1786.
Dear Sir,
The letter you honored me with, covered the copies of three letters which Mr. Thomson wrote you to obtain an explanation of a million which is not to be found in my accounts. I should have been very much embarrassed in satisfying him and proving that I had not put that million in my pocket, had I not applied to M. Durival, who, as you will see by the answer enclosed, informs me that there was a million paid by the Royal Treasury on the 10th of June, 1776. This is the very million about which Mr. Thomson inquires, as I have kept an account of the other two millions, which were also furnished by the Royal Treasury, viz.:
The million in January and April, 1777; the other in July and October of the same year; as well as that furnished by the Farmers General in June, 1777.
Here then are the three millions, exactly, which were given by the King before the treaty of 1778, and that furnished by the Farmers General. Nothing then remains to be known but who received the first million in June, 1776. It could not be by me, who was not charged with the business of Congress until January, 1777. I therefore requested of M. Durival the copy of the receipt for the one million. You have the answer which he returned to me. I wrote to him again, renewing my request, but as the carrier is just setting off, I cannot wait to give you his answer, but you will receive it in my next, if I receive one. In the mean while, I beg you will receive the assurances of the sentiments of respect, with which I have the honor to be, my Dear Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Grand.
Letter from Mr. Durival to Mr. Grand.
Versailles, August 30, 1786.
Sir,
I have received the letter which you did me the honor to write the 28th of this month, touching the advance of a million, which you say was made by the General Farm to the United States of America, the 3rd of June, 1777. I have no knowledge of that advance. What I have verified is, that the King by the contract of the 25th of February, 1783, has confirmed the gratuitous gift which his Majesty had previously made of the three millions hereafter mentioned, viz:
One million delivered by the Royal Treasury the 10th of June, 1776, and two other millions advanced also by the Royal Treasury in 1777, on four receipts of the Deputies of Congress of the 17th of January, 3rd of April, 10th of June, and 15th of October, of the same year. This explanation will, Sir, resolve your doubt touching the advance of the 3rd of June, 1777. I farther recommend to you, Sir, to confer on this subject with Mr. Gojard, who ought to be better informed than us, who have no knowledge of any advances but those made by the Royal Treasury.
I have the honor to be, with great respect, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
DU RIVAL.
Postscript from Mr. Grand.
Paris, September 12, 1786.
I hazard a letter in hopes it may be able to join that of the 9th, at L’Orient, in order to forward to you, Sir, the answer I have just received from Mr. Durival. You will therefore see, Sir, that notwithstanding my entreaty, the Minister himself refuses to give me the copy of the receipts which I asked for. I cannot conceive the reason for this reserve, more especially, since if there has been a million paid, he who received it has kept the account, and must in time be known. I shall hear with pleasure that you have been more fortunate in this respect in America than I have been in France, and repeat to you the assurances of the sentiments of regard, with which I have the honor to be, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Grand.
Letter from Mr. Durival to Mr. Grand.
Versailles, September 5, 1786.
I laid before the Count de Vergennes the two letters which you did me the honor, to write, touching the three millions, the free gift of which the King has confirmed in favor of the United States of America.
The Minister, Sir, observed, that this gift has nothing to do with the million which Congress may have received from the General Farm, 1777. Consequently he thinks that the receipt which you desire may be communicated to you, cannot satisfy the object of your view, and that it would be useless to give you the copy which you desire.
I have the honor to be, with perfect attachment, Sir, your most obedient, humble servant,
Durival.
Letter from Mr. Durival to Mr. Grand.
Versailles, September 10, 1786.
I have laid before the Count de Vergennes, as you, Sir, seem to desire, the letter which you did me the honor to write yesterday. The Minister persists in the opinion that the receipt, the copy of which you request, has no relation to the business with which you are entrusted on behalf of Congress, and that this price would be useless in the new point of view in which you have placed it. Indeed, Sir, it is easy for you to prove that the money in question was not delivered by the Royal Treasury into your hands, as you did not begin to be charged with the business of Congress until January, 1777, and the receipt is of the date of the 10th of June, 1776.
I have the honor to be, with perfect attachment, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Durival.
Extract of a letter from Benjamin Franklin to Mr. Grand, banker at Paris, dated Philadelphia, July the 11th, 1786.
‘I send you enclosed some letters that have passed between the Secretary of Congress and me, respecting three millions of livres acknowledged to have been received before the treaty of 1778, as don gratuit, from the King, of which only two millions are found in your accounts; unless the million from the Fanners General be one of the three. I have been assured that all the money received from the King, whether as loan or gift, went through your hands; and as I always looked on the million we had of the Farmers General to be distinct from what we had of the crown, I wonder how I came to sign the contract acknowledging three millions of gift, when in reality there were only two, exclusive of that from the Farmers. And as both you and I examined the project of the contract before I signed it, I am surprised that neither of us took notice of the error. It is possible that the million furnished ostensibly by the Farmers, was in fact a gift of the crown, in which case, as Mr. Thomson observes, they owe us for the two ship-loads of tobacco they received on account of it. I must earnestly request of you to get this,matter explained, that it may stand clear before I die, lest some enemy should afterwards accuse me of having received a million not accounted for.’
Letter from Dr. Franklin to Charles Thomson.
Philadelphia, January 25, 1787.
Dear Friend,
You may remember that in the correspondence between us in June last, on the subject of a million, free gift of the King of France, acknowledged in our contract to have been received, but which did not appear to be accounted for in our banker’s accounts, unless it should be the same with the million said to be received from the Farmers General, I mentioned that an explanation might doubtless be easily obtained, by writing to Mr. Grand or Mr. Jefferson. I know not whether you have accordingly written to either of them. But being desirous that the matter should be speedily cleared up, I wrote myself to Mr. Grand a letter upon it, of which I now enclose a copy with his answer, and several letters from Mr. Durival, who is chef du bureau des fonds (and has under his care la finance des affaires étrangerès). You will see by these letters, that the million in question was delivered to somebody on the 10th of June, 1776, but it does not appear to whom. It is clear that it could not be to Mr. Grand, nor to the commissioners from Congress, for we did not meet in France till the end of December, 1777. That banker was not charged before with our affairs. By the Minister’s refusing him a copy of the receipt, I conjecture it must be money advanced for our use to Mr. Beaumarchais, and that it is a mystère du cabinet, which perhaps should not be further inquired into, unless necessary to guard against more demands than may be just from that agent: for it may well be supposed that if the court furnished him with the means of supplying us, they may not be willing to furnish authentic proofs of such a transaction so early in our dispute with Britain.
Pray tell me, has he dropped his demands, or does he still continue to worry you with them?
I should like to have these original letters returned to me, but you may, if you please, keep copies of them.
It is true, the million in question makes no difference in your accounts with the King of France, it not being mentioned or charged as so much lent and repaid, but stood as freely given. Yet if it was put into the hands of any of our agents or ministers, they ought certainly to account for it. I do not recollect whether Mr. Deane had arrived in France before the 10th of June, 1776, but from his great want of money when I joined him a few months after, I hardly think it could have been paid him.
Possibly Mr. Jefferson may obtain the information, though Mr. Grand could not, and I wish he may be directed to make the inquiry, as I know he would do it directly; I mean, if by Hortales and Co.’ s further demands, or for any other reason, such an inquiry should be thought necessary.
I am ever, my Dear Friend, yours most affectionately,
Benjamin Franklin.
Philadelphia, June 13, 1793.
Dear Sir,
The insulated state in which France is placed with respect to almost all the world, by the present war, has cut off all means of addressing letters to you through other countries. I embrace the present occasion by a private individual going to France directly, to mention, that since the date of my last public letter, which was April the 24th, and which covered the President’s proclamation of April, I have received your Nos. 17 to 24. M. de Ternary notified us of his recall on the 17th of May, and delivered the letter of the Provisory Executive Council to that effect. I now enclose you the President’s answer to the Council, which you will be pleased to deliver; a copy of it is also enclosed, open, for your, information. Mr. Genet delivered his credentials on the same day on which M. de Ternant took his leave, and was received by the President. He found himself immediately immersed in business, the consequence of this war. The incidents to which that gives daily rise, and the questions respecting chiefly France and England, fill the executive with business, equally delicate difficult, and disagreeable. The course intended to be pursued being that of a strict and impartial neutrality, decisions rendered by the President rigorously on that principle, dissatisfy both parties, and draw complaints from both. That you may have a proper idea of them, I enclose you copies of several memorials and letters, which have passed between the executive and the ministers of those two countries, which will at the same time develope the principles of the proceedings, and enable you to satisfy them in your communications, should it be necessary. I enclose also the answer given to Mr. Genet, on a proposition from him to pay up the whole of the French debt at once. While it will enable you to explain the impracticability of the operation proposed, it may put it in your power to judge of the answer which would be given to any future proposition to that effect, and perhaps to prevent their being brought forward. The bill lately passed in England, prohibiting the business of this country with France from passing through the medium of England, is a temporary embarrassment to our commerce, from the unhappy predicament of its all hanging on the pivot of London. It will be happy for us, should it be continued till our merchants may establish connections in the countries in which our produce is consumed, and to which it should go directly.
Our commissioners have proceeded to the treaty with the northwestern Indians. They write, however, that the treaty will be a month later than was expected. This delay, should it be extended, will endanger our losing the benefit of our preparations for the campaign, and consequently bring on a delicate question, whether these shall be relinquished for the result of a treaty in which we never had any confidence. The Creeks have proceeded in their depredations till they assume the appearance of formal war. It scarcely seems possible to avoid its becoming so. They are so strong and so far from us, as to make very serious addition to our Indian difficulties. It is very probable that some of the circumstances arising out of our affairs with the Indians, or with the belligerent powers of Europe, may occasion the convocation of Congress at an earlier day than that to which its meeting stands at present.
I send you the forms of the passports given here. The one in three columns is that now used; the other having been soon discontinued. It is determined that they shall be given in our own ports only, and to serve but for one voyage. It has also been determined, that they shall be given to all vessels bonâ fide owned by American citizens wholly, whether built here or not. Our property, whether in the form of vessels, cargoes, or any thing else, has a right to pass the seas untouched by any nation, by the law of nations; and no one has a right to ask where a vessel was built, but where is she owned? To the security which the law of nations gives to such vessels against all nations, are added particular stipulations with three of the belligerent powers. Had it not been in our power to enlarge our national stock of shipping suddenly in the present exigency, a great proportion of our produce must have remained on our hands for want of the means of transportation to market. At this time, indeed, a great proportion is in that predicament. The most rigorous measures will be taken to prevent any vessel, not wholly and bonâ fide owned by American citizens, from obtaining our passports. It is much our interest to prevent the competition of other nations from taking from us the benefits we have a right to expect from the neutrality of our flag; and I think we may be very sure that few, if any, will be fraudulently obtained within our ports.
Though our spring has been cold and wet, yet the crops of small grain are as promising as they have ever been seen. The Hessian fly, however, to the north, and the weavil to the south of the Potomac, will probably abridge the quantity. Still it seems very doubtful whether we shall not lose more for want of the means of transportation, and I have no doubt that the ships of Sweden and Denmark would find full employment here.
We shall endeavor to get your newspapers under the care of Major Read, the bearer of this letter.
I have the honor to be, with great respect and esteem, Dear Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MR. PINCKNEY.
Philadelphia, June 14, 1793.
My last letters to you have been of the 7th of May and 4th instant. Since the last date, yours of April the 15th has come to hand.
I enclose you several memorials and letters which have passed between the executive and the ministers of France and England. These will develope to you the principles on which we are proceeding between the belligerent powers. The decisions being founded in what is conceived to be rigorous justice, give dissatisfaction to both parties, and produce complaints from both. It is our duty, however, to persevere in them, and to meet the consequences. You will observe that Mr. Hammond proposes to refer to his court the determination of the President, that the prizes taken by the Citoyen Genet, could not be given up. The reasons for this are explained in the papers. Mr. Genet had stated that she was manned by French citizens. Mr. Hammond had not stated the contrary before the decision. Neither produced any proofs. It was therefore supposed that she was manned, principally, with French citizens. After the decision, Mr. Hammond denies the fact, but without producing any proof. I am really unable to say how it was; but I believe it to be certain there were very few Americans. He says, the issuing the commission, Sic. by Mr. Genet within our territory, was an infringement of our sovereignty; therefore, the proceeds of it should be given up to Great Britain. The infringement was a matter between France and us. Had we insisted on any penalty or forfeiture by way of satisfaction to our insulted rights, it would have belonged to us, not to a third party. As between Great Britain and us, considering all the circumstances explained in the papers, we deemed we did enough to satisfy her. We are moreover assured, that it is the standing usage of France, perhaps too of other nations in all wars, to lodge blank commissions with all their foreign consuls, to be given to every vessel of their nation, merchant or armed; without which a merchant vessel would be punished as a pirate, were she to take the smallest thing of the enemy that should fall in her way. Indeed, the place of the delivery of a commission is immaterial. As it may be sent by letter to any one, so it may be delivered by hand to him any where. The place of signature by the Sovereign is the material thing. Were that to be done in any other jurisdiction than his own, it might draw the validity of the act into question. I mention these things, because I think it would be proper, that after considering them and such other circumstances as appear in the papers, or may occur to yourself, you should make it the subject of a conversation with the Minister. Perhaps it may give you an opportunity of touching on another subject. Whenever Mr. Hammond applies to our government on any matter whatever, be it ever so new or difficult, if he does not receive his answer in two or three days or a week, we are goaded with new letters on the subject. Sometimes it is the sailing of the packet, which is made the pretext for forcing us into premature and undigested determinations. You know best how far your applications meet such early attentions, and whether you may with propriety claim a return of them: you can best judge too of the expediency of an intimation, that where despatch is not reciprocal, it may be expedient and justifiable that delay should be so.
I have the honor to be, with great and sincere esteem, Dear Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MR. GENET.
Philadelphia, June 17, 1793.
Sir,
I shall now have the honor of answering your letter of the 1st instant, and so much of that of the 14th (both of which have been laid before the President) as relates to a vessel armed in the port of New York and about to depart from thence, but stopped by order of the government. And here I beg leave to premise, that the case supposed in your letter, of a vessel arming for her own defence, and to repel unjust aggressions, is not that in question, nor that on which I mean to answer, because not having yet happened, as far as is known to the government, I have no instructions on the subject. The case in question is that of a vessel armed, equipped, and manned in a port of the United States, for the purpose of committing hostilities on nations at peace with the United States.
As soon as it was perceived that such enterprises would be attempted, orders to prevent them were despatched to all the States and ports of the Union. In consequence of these, the Governor of New York, receiving information that a sloop heretofore called the Polly, now the Republican, was fitting out, arming, and manning in the port of New York, for the express and sole purpose of cruising against certain nations with whom we are at peace, that she had taken her guns and ammunition aboard and was on the point of departure, seized the vessel. That the Governor was not mistaken in the previous indications of her object, appears by the subsequent avowal of the citizen Hauterive, Consul of France at that port, who, in a letter to the Governor, reclaims her as ‘Un vaisseau arme, en guerre, et pret a mettre a la voile;’ and describes her object in these expressions; ‘Cet usage étrange de la force publique contre les citoyens d’une nation amie qui se réunissent ici pour aller defendre leur frères,’ &c. and again; ‘Je requiers, monsieur, l’autorité dont vous êtes revêtu, pour faire rendre à des Francois, à des allies, &c. la liberte de voler au secours de leur patrie.’ This transaction being reported to the President, orders were immediately sent to deliver over the vessel, and the persons concerned in the enterprise, to the tribunals of the country; that if the act was of those forbidden by the law, it might be punished; if it was not forbidden, it might be so declared, and all persons apprized of what they might or might not do.
This we have reason to believe is the true state of the case, and it is a repetition of that which was the subject of my letter of the 5th instant, which animadverted, not merely on the single fact of the granting commissions of war by one nation within the territory of another, but on the aggregate of the facts: for it states the opinion of the President to be, ‘that the arming and equipping vessels in the ports of the United States, to cruise against nations with whom they are at peace, was incompatible with the sovereignty of the United States; that it made them instrumental to the annoyance of those nations, and thereby tended to commit their peace.’ And this opinion is still conceived to be not contrary to the principles of natural law, the usage of nations, the engagements which unite the two people, nor the proclamation of the President, as you seem to think.
Surely, not a syllable can be found in the last mentioned instrument permitting the preparation of hostilities in the ports of the United States. Its object was to enjoin on our citizens ‘a friendly conduct towards all the belligerent powers;’ but a preparation of hostilities is the reverse of this.
None of the engagements in our treaties stipulate this permission. The XVIIth article of that of commerce, permits the armed vessels of either party to enter the ports of the other, and to depart with their prizes freely: but the entry of an armed vessel into a port, is one act; the equipping a vessel in that port, arming her, and manning her, is a different one, and not engaged by any article of the treaty.
You think, Sir, that this opinion is also contrary to the law of nature and usage of nations. We are of opinion it is dictated by that law and usage; and this had been very maturely inquired into before it was adopted as a principle of conduct. But we will not assume the exclusive right of saying what that law and usage is. Let us appeal to enlightened and disinterested judges. None is more so than Vattel. He says, L. 3, 8, 104. ‘Tant qu’im peuple neutre veut jouir surement de cet état, il doit montrer en toutes choses une exacte impartialité entre ceux qui se font la guerre. Car s’il favorise l’un au préjudice de l’autre, il ne pourra pas se plaindre, quand celui-ci le traitera comme adhérent et associé de son ennemi. Sa neutralité seroit une neutralité frauduleuse, dont personne ne veut être la dupe. Voyons done en quoi consiste cette impartialité qu’un peuple neutre doit garder.
‘Elle se rapport uniquement à la guerre, et comprend deux choses, 1°. Ne point donner de secours quand on n’y est pas obligé; ne fournir librement ni troupes, ni armes, ni munitions, ni rien de ce qui sert directement à la guerre. Je dis ne point donner de secours, et non pas en donner également; car il seroit absurde qu’un etat secourut en même tems deux ennemis. Et puis il seroit impossible de le faire avec égalite; les mêmes choses, le merae nombre de troupes, la même quantite d’armes, de munitions, &c. fournies en des circonstances differentes, ne forment plus des secours equivalents,’ &c. If the neutral power may not, consistent with its neutrality, furnish men to either party, for their aid in war, as little can either enrol them in the neutral territory by the law of nations. Wolf, S. 1174, says, ‘Puisque Je droit de lever des soldats est un droit de majeste, qui ne peut être viole par une nation étrangere, il n’est pas permis de lever des soldats sur le territoire d’autrui, sans le consentement du maitre du territoire.’ And Vattel, before cited, L. 3, 8, 15. ‘Le droit de lever des soldats appartenant uniquement a la nation, ou au souverain, personne ne peut en envoler en pays etranger sans la permission du soverain: Ceux qui entreprennant d’engager des soldats en pays etranger sans la permission du souverain, et en general quiconque debauche les sujets d’autrui, viole un des droits les plus sacres du prince et de la nation. C’est le crime qu’on appelle plagiat, ou vol d’homme. Il n’est aucun état police qui ne le punisse tres sevérement.’ &c. For I choose to refer you to the passage, rather than follow it through all its developements. The testimony of these, and other writers, on the law and usage of nations, with your own just reflections on them, will satisfy you that the United States, in prohibiting all the belligerent powers from equipping, arming, and manning vessels of war in their ports, have exercised a right and a duty, with justice and with great moderation. By our treaties with several of the belligerent powers, which are a part of the laws of our land we have established a state of peace with them. But without appealing to treaties, we are at peace with them all by the law of nature. For by nature’s law, man is at peace with man till some aggression is committed, which, by the same law, authorizes one to destroy another as his enemy. For our citizens then to commit murders and depredations on the members of nations at peace with us, or combine to do it, appeared to the executive, and to those whom they consulted, as much against the laws of the land, as to murder or rob, or combine to murder or rob its own citizens; and as much to require punishment, if done within their limits, where they have a territorial jurisdiction, or on the high seas, where they have a personal jurisdiction, that is to say, one which reaches their own citizens only, this being an appropriate part of each nation on an element where all have a common jurisdiction. So say our laws, as we understand them ourselves. To them the appeal is made; and whether we have construed them well or ill, the constitutional judges will decide. Till that decision shall be obtained, the government of the United States must pursue what they think right with firmness, as is their duty. On the first attempt that was made, the President was desirous of involving in the censures of the law as few as might be. Such of the individuals only, therefore, as were citizens of the United States, were singled out for prosecution. But this second attempt being after full knowledge of what had been done on the first, and indicating a disposition to go on in opposition to the laws, they are to take their course against all persons concerned, whether citizens or aliens; the latter, while within our jurisdiction and enjoying the protection of the laws, being bound to obedience to them, and to avoid disturbances of our peace within, or acts which would commit it without, equally as citizens are.
I have the honor to be, with sentiments of great respect, and esteem, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MR. HAMMOND.
Philadelphia, June 19, 1793.
Sir,
I had the honor to address you a letter on the 29th of May was twelvemonth, on the articles still unexecuted of the treaty of peace between the two nations. The subject was extensive and important, and therefore rendered a certain degree of delay in the reply to be expected. But it has now become such as naturally to generate disquietude. The interest we have in the western posts, the blood and treasure which their detention costs us daily, cannot but produce a corresponding anxiety on our part. Permit me, therefore, to ask when I may expect the honor of a reply to my letter, and to assure you of the sentiments of respect, with which I have the honor to be, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MESSRS. CARMICHAEL AND SHORT.
Philadelphia, June 30, 1793.
Gentlemen,
I have received from Messrs. Viar and Jaudenes, the representatives of Spain at this place, a letter, which, whether considered in itself, or as the sequel of several others, conveys to us very disagreeable prospects of the temper and views of their court towards us. If this letter is a faithful expression of that temper, we presume it to be the effect of egregious misrepresentations by their agents in America. Revising our own dispositions and proceedings towards that power, we can find in them nothing but those of peace and friendship for them; and conscious that this will be apparent from a true statement of facts, I shall proceed to give you such a one, to be communicated to the court of Madrid. If they find it very different from that conveyed to them by others, they may think it prudent to doubt, and to take and to give time for mutual inquiry and explanation. I shall proceed to give you this statement, beginning it from an early period.
At the commencement of the late war, the United States laid down as a rule of their conduct, to engage the Indian tribes within their neighborhood to remain strictly neutral. They accordingly strongly pressed it on them, urging that it was a family quarrel; with which they had nothing to do, and in which we wished them to take no part: and we strengthened these recommendations by doing them every act of friendship and good neighborhood, which circumstances left in our power. With some, these solicitations prevailed; but the greater part of them suffered themselves to be drawn into the war against us. They waged it in their usual cruel manner, murdering and scalping men, women, and children, indiscriminately, burning their houses, and desolating the country. They put us to vast expense, as well by the constant force we were obliged to keep up in that quarter, as by expeditions of considerable magnitude which we were under the necessity of sending into their country from time to time.
Peace being at length concluded with England, we had it also to conclude with them. They had made war on us without the least provocation or pretence of injury. They had added greatly to the cost of that war. They had insulted our feelings by their savage cruelties. They were by our arms completely subdued and humbled. Under all these circumstances, we had a right to demand substantial satisfaction and indemnification. We used that right, however, with real moderation. Their limits with us under the former government were generally ill defined, questionable, and the frequent cause of war. Sincerely desirous of living in their peace, of cultivating it by every act of justice and friendship, and of rendering them better neighbors by introducing among them some of the most useful arts, it was necessary to begin by a precise definition of boundary. Accordingly, at the treaties held with them, our mutual boundaries were settled; and notwithstanding our just right to concessions adequate to the circumstances of the case, we required such only as were inconsiderable; and for even these, in order that we might place them in a state of perfect conciliation, we paid them a valuable consideration, and granted them annuities in money which have been regularly paid, and were equal to the prices for which they have usually sold their lands.
Sensible, as they were, of the wrong they had done, they expected to make some indemnification, and were, for the most part, satisfied with the mode and measure of it. In one or two instances, where a dissatisfaction was observed to remain as to the boundaries agreed on, or doubts entertained of the authority of those with whom they were agreed, the United States invited the parties to new treaties, and rectified what appeared to be susceptible of it. This was particularly the case with the Creeks. They complained of an inconvenient cession of lands on their part, and by persons not duly representing their nation. They were therefore desired to appoint a proper deputation to revise their treaty; and that there might be no danger of any unfair practices, they were invited to come to the seat of the General Government, and to treat with that directly. They accordingly came. A considerable proportion of what had been ceded, was on the revision yielded back to them, and nothing required in lieu of it: and though they would have been better satisfied to have had the whole restored, yet they had obtained enough to satisfy them well. Their nation, too, would have been satisfied, for they were conscious of their aggression, and of the moderation of the indemnity with which we had been contented. But at that time came among them an adventurer of the name of Bowles, who, acting from an impulse with which we are unacquainted, flattered them with the hope of some foreign interference, which should undo what had been done, and force us to consider the naked grant of their peace as a sufficient satisfaction for their having made war on us. Of this adventurer the Spanish government rid us: but not of his principles, his practices, and his excitements against us. These were more than continued by the officers commanding at New Orleans and Pensacola, and by agents employed by them and bearing their commission. Their proceedings have been the subject of former letters to you, and proofs of these proceedings have been sent to you. Those, with others now sent, establish the facts, that they called assemblies of the southern Indians, openly persuaded them to disavow their treaties, and the limits therein established, promised to support them with all the powers which depended on them, assured them of the protection of their sovereign, gave them arms in great quantities for the avowed purpose of committing hostilities on us, and promised them future supplies to their utmost need. The Chickasaws, the most steady and faithful friends of these States, have remained unshaken by these practices. So also have the Chocktaws, for the most part. The Cherokees have been teazed into some expressions of discontent, delivered only to the Spanish Governors, or their agents; while to us, they have continued to speak the language of peace and friendship. One part of the nation only, settled at Cuckamogga and mixed with banditti and outcasts from the Shawanese and other tribes, acknowledging control from none, and never in a state of peace, have readily engaged in the hostilities against us to which they were encouraged. But what was much more important, great numbers of the Creeks, chiefly their young men, have yielded to these incitements, and have now, for more than a twelvemonth, been committing murders and desolations on our frontiers. Really desirous of living in peace with them, we have redoubled our efforts to produce the same disposition in them. We have borne with their aggressions, forbidden all returns of hostility against them, tied up the hands of our people, insomuch that few instances of retaliation have occurred even from our suffering citizens; we have multiplied our gratifications to them, fed them when starving from the produce of our own fields and labor. No longer ago than the last winter, when they had no other resource against famine and must have perished in great numbers, we carried into their country and distributed among them, gratuitously, ten thousand bushels of corn; and that too, at the same time, when their young men were daily committing murders on helpless women and children, on our frontiers. And though these depredations now involve more considerable parts of the nation, we are still demanding punishment of the guilty individuals, and shall be contented with it. These acts of neighborly kindness and support on our part, have not been confined to the Creeks, though extended to them in much the greatest degree. Like wants among the Chickasaws had induced us to send them also, at first, five hundred bushels of corn, and afterwards, fifteen hundred more. Our language to all the tribes of Indians has constantly been, to live in peace with one another, and in a most especial manner, we have used our endeavors with those in the neighborhood of the Spanish colonies, to be peaceable towards those colonies. I sent you on a former occasion the copy of a letter from the Secretary at War to Mr. Seagrove, one of our agents with the Indians, in that quarter, merely to convey to you the general tenor of the conduct marked out for those agents: and I desired you, in placing before the eyes of the Spanish ministry the very contrary conduct observed by their agents here, to invite them to a reciprocity of good offices with our Indian neighbors, each for the other, and to make our common peace the common object of both nations. I can protest that such have hitherto been the candid and zealous endeavors of this government, and that if its agents have in any instance acted in another way, it has been equally unknown and unauthorized by us, and that, were even probable proofs of it produced, there would be no hesitation to mark them with the disapprobation of the government. We expected the same friendly condescension from the court of Spain, in furnishing you with proofs of the practices of the Governor De Carondelet in particular practices avowed by him, and attempted to be justified in his letter.
In this state of things, in such dispositions towards Spain and towards the Indians, in such a course of proceedings with respect to them, and while negotiations were instituted at Madrid for arranging these and all other matters which might affect our friendship and good understanding, we received from Messrs. de Viar and Jaudenes their letter of May the 25th, which was the subject of mine of May the 31st, to you; and now again we have received that of the 18th instant, a copy of which is enclosed. This letter charges us, and in the most disrespectful style, with:
1. Exciting the Chickasaws to war on the Creeks.
2. Furnishing them with provisions and arms.
3. Aiming at the occupation of a post at the Ecores Amargas.
4. Giving medals and marks of distinction to several Indians.
5. Meddling with the affairs of such as are allies of Spain.
6. Not using efficacious means to prevent these proceedings. I shall make short observations on these charges.
1. Were the first true, it would not be unjustifiable. The Creeks have now a second time commenced against us a wanton and unprovoked war, and the present one in the face of a recent treaty, and of the most friendly and charitable offices on our part. There would be nothing out of the common course of proceeding, then, for us to engage allies, if we needed any for their punishment. But we neither need, nor have sought them. The fact itself is utterly false, and we defy the world to produce a single proof of it. The declaration of war by the Chickasaws, as we are informed was a very sudden thing, produced by the murder of some of their people by a party of Creeks, and produced so instantaneously as to give no body time to interfere, either to promote or prevent a rupture. We had, on the contrary, most particularly exhorted that nation to preserve peace, because in truth we have a most particular friendship for them. This will be evident from a copy of the message of the President to them, among the papers now enclosed.
2. The gift of provisions was but an act of that friendship to them, when in the same distress, which had induced us to give five times as much to the less friendly nation of the Creeks. But we have given arms to them. We believe it is the practice of every white nation to give arms to the neighboring Indians. The agents of Spain have done it abundantly, and we suppose not out of their own pockets, and this for purposes of avowed hostility on us; and they have been liberal in promises of further supplies. We have given a few arms to a very friendly tribe, not to make war on Spain, but to defend themselves from the atrocities of a vastly more numerous and powerful people, and one which by a series of unprovoked and even unrepelled attacks on us, is obliging us to look towards war as the only means left of curbing their insolence.
3. We are aiming, as is pretended, at an establishment on the Mississippi, at the Ecores Amargas. Considering the measures of this nature with which Spain is going on, having, since the proposition to treat with us on the subject, established posts at the Walnut Hills and other places for two hundred miles upwards, it would not have been wonderful if we had taken countervailing measures. But the truth is, we have not done it. We wished to give a fair chance to the negotiation going on, and thought it but common candor to leave things in statu quo, to make no innovation pending the negotiation. In this spirit we forbid, and deterred even by military force, a large association of our citizens, under the name of the Yazoo companies, which had formed to settle themselves at those very Walnut Hills, which Spain has since occupied. And so far are we from meditating the particular establishment so boldly charged in this letter, that we know not what place is meant by the Ecores Amargas. This charge then is false also.
4. Giving medals and marks of distinction to the Indian Chiefs. This is but blindly hinted at in this letter, but was more pointedly complained of in the former. This has been an ancient custom from time immemorial. The medals are considered as complimentary things, as marks of friendship to those who come to see us, or who do us good offices, conciliatory of their good-will towards us, and not designed to produce a contrary disposition towards others. They confer no power, and seem to have taken their origin in the European practice of giving medals or other marks of friendship to the negotiators of treaties and other diplomatic characters, or visitors of distinction. The British government, while it prevailed here, practised the giving medals, gorgets, and bracelets to the savages, invariably. We have continued it, and we did imagine, without pretending to know, that Spain also did it.
5. We meddle with the affairs of Indians in alliance with Spain. We are perfectly at a loss to know what this means. The Indians on our frontier have treaties both with Spain and us. We have endeavored to cultivate their friendship, to merit it by presents, charities, and exhortations to peace with their neighbors, and particularly with the subjects of Spain. We have carried on some little commerce with them, merely to supply their wants. Spain too has made them presents, traded with them, kept agents among them, though their country is within the limits established as ours at the general peace. However, Spain has chosen to have it understood that she has some claim to some parts of that country, and that it must be one of the subjects of our present negotiations. Out of respect for her, then, we have considered her pretensions to the country, though it was impossible to believe them serious, as coloring pretensions to a concern with those Indians on the same ground with our own, and we were willing to let them go on till a treaty should set things to rights between us.
6. Another article of complaint is, that we have not used efficacious means to suppress these practices. But if the charge is false, or the practice justifiable, no suppression is necessary.
And lastly, these gentlemen say, that, on a view of these proceedings of the United States with respect to Spain and the Indians, their allies, they foresee that our peace with Spain is very problematical in future. The principal object of the letter being our supposed excitements of the Chickasaws against the Creeks, and their protection of the latter, are we to understand from this, that if we arm to repulse the attacks of the Creeks on ourselves, it will disturb our peace with Spain? That if we will not fold our arms and let them butcher us without resistance, Spain will consider it as a cause of war? This is, indeed, so serious an intimation, that the President has thought it could no longer be treated with subordinate characters, but that his sentiments should be conveyed to the government of Spain itself, through you.
We love and we value peace: we know its blessings from experience. We abhor the follies of war, and are not untried in its distresses and calamities. Unmeddling with the affairs of other nations, we had hoped that our distance and our disposition would have left us free, in the example and indulgence of peace with all the world. We had, with sincere and particular dispositions, courted and cultivated the friendship of Spain. We have made to it great sacrifices of time and interest, and were disposed to believe she would see her interests also in a perfect coalition and good understanding with us. Cherishing still the same sentiments, we have chosen, in the present instance, to ascribe the intimations in this letter to the particular character of the writers, displayed in the peculiarity of the style of their communications, and therefore we have removed the cause from them to their sovereign, in whose justice and love of peace we have confidence. If we are disappointed in this appeal, if we are to be forced into a contrary order of things, our mind is made up. We shall meet it with firmness. The necessity of our position will supersede all appeal to calculation how, as it has done heretofore. We confide in our own strength, without boasting of it; we respect that of others, without fearing it. If we cannot otherwise prevail on the Creeks to discontinue their depredations, we will attack them in force. If Spain chooses to consider our defence against savage butchery as a cause of war to her, we must meet her also in war, with regret, but without fear; and we shall be happier, to the last moment, to repair with her to the tribunal of peace and reason.
The President charges you to communicate the contents of this letter to the court of Madrid, with all the temperance and delicacy which the dignity and character of that court render proper; but with all the firmness and self-respect which befit a nation conscious of its rectitude, and settled in its purpose.
I have the honor to be, with sentiments of the most perfect esteem and respect, Gentlemen, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
To the Chief Justice and Judges of the Supreme Court of the United States.
Philadelphia, July 18,1793.
Gentlemen,
The war which has taken place among the powers of Europe, produces frequent transactions within our ports and limits, on which questions arise of considerable difficulty, and of greater importance to the peace of the United States. These questions depend for their solution on the construction of our treaties, on the laws of nature and nations, and on the laws of the land; and are often presented under circumstances which do not give a cognizance of them to the tribunals of the country. Yet their decision is so little analogous to the ordinary functions of the executive, as to occasion much embarrassment and difficulty to them. The President would, therefore, be much relieved, if he found himself free to refer questions of this description to the opinions of the judges of the Supreme Court of the United States, whose knowledge of the subject would secure us against errors dangerous to the peace of the United States, and their authority insure the respect of all parties. He has therefore asked the attendance of such judges as could be collected in time for the occasion, to know, in the first place, their opinions, whether the public may with propriety be availed of their advice on these questions. And if they may, to present, for their advice, the abstract questions which have already occurred, or may soon occur, from which they will themselves strike out such as any circumstances might, in their opinion, forbid them to pronounce on.
I have the honor to be, with sentiments of great esteem and respect, Gentlemen, your most obedient, humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MR. GENET.
Philadelphia, July 24,1793. Sir,
Your favor of the 9th instant, covering the information of Silvat Ducamp, Pierre Nouvel, Chouquet de Savarence, Gaston de Nogère, and G. Blustier, that being on their passage from the French West Indies to the United States, on board merchant vessels of the United States with slaves and merchandise, of their property, these vessels were stopped by British armed vessels and their property taken out as lawful prize, has been received.
I believe it cannot be doubted, but that by the general law of nations, the goods of a friend found in the vessel of an enemy are free, and the goods of an enemy found in the vessel of a friend are lawful prize. Upon this principle, I presume, the British armed vessels have taken the property of French citzens found in our vessels, in the cases above mentioned, and I confess I should be at a loss on what principle to reclaim it. It is true that sundry nations, desirous of avoiding the inconveniences of having their vessels stopped at sea, ransacked, carried into port, and detained under pretence of having enemy goods aboard, have in many instances introduced by their special treaties another principle between them, that enemy bottoms shall make enemy goods, and friendly bottoms friendly goods; a principle much less embarrassing to commerce, and equal to all parties in point of gain and loss. But this is altogether the effect of particular treaty, controlling in special cases the general principle of the law of nations, and therefore taking effect between such nations only as have so agreed to control it. England has generally determined to adhere to the rigorous principle, having, in no instance, as far as I recollect, agreed to the modification of letting the property of the goods follow that of the vessel, except in the single one of her treaty with France. We have adopted this modification in our treaties with France, the United Netherlands, and Russia; and therefore, as to them, our vessels cover the goods of their enemies, and we lose our goods when in the vessels of their enemies. Accordingly, you will be pleased to recollect, that in the late case of Holland and Mackie, citizens of the United States, who had laden a cargo of flour on board a British vessel, which was taken by the French frigate L’Ambuscade and brought into this port, when I reclaimed the cargo, it was only on the ground that they were ignorant of the declaration of war when it was shipped. You observed, however, that the 14th article of our treaty had provided that ignorance should not be pleaded beyond two months after the declaration of war, which term had elapsed in this case by some days, and finding that to be the truth, though their real ignorance of the declaration was equally true, I declined the reclamation, as it never was in my view to reclaim the cargo, nor apparently in yours to offer to restore it, by questioning the rule established in our treaty, that enemy bottoms make enemy goods. With England, Spain, Portugal, and Austria, we have no treaties: therefore, we have nothing to oppose to their acting according to the general law of nations, that enemy goods are lawful prize, though found in the bottom of a friend. Nor do I see that France can suffer on the whole; for though she loses her goods in our vessels when found therein by England, Spain, Portugal, or Austria, yet she gains our goods when found in the vessels of England, Spain, Portugal, Austria, the United Netherlands, or Prussia: and I believe I may safely affirm that we have more goods afloat in the vessels of these six nations, than France has afloat in our vessels; and consequently, that France is the gainer and we the loser by the principle of our treaty. Indeed, we are losers in every direction of that principle; for when it works in our favor, it is to save the goods of our friends; when it works against us, it is to lose our own; and we shall continue to lose while the rule is only partially established. When we shall have established it with all nations, we shall be in condition neither to gain nor lose, but shall be less exposed to vexatious searches at sea. To this condition we are endeavoring to advance; but as it depends on the will of other nations as well as our own, we can only obtain it when they shall be ready to concur.
I cannot, therefore, but flatter myself, that on revising the cases of Ducamp and others, you will perceive that their losses result from the state of war, which has permitted their enemies to take their goods, though found in our vessels; and consequently, from circumstances over which we have no control.
The rudeness to their persons, practised by their enemies, is certainly not favorable to the character of the latter. We feel for it as much as for the extension of it to our own citizens, their companions, and find in it a motive the more for requiring measures to be taken which may prevent repetitions of it.
I have the honor to be, with great respect, Sir, your most obedient, humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MR. GENET.
Philadelphia, August 7, 1793.
Sir,
In a letter of June the 5th, I had the honor to inform you that the President, after reconsidering, at your request, the case of vessels armed within our ports to commit hostilities on nations at peace with the United States, had finally determined that it could not be admitted, and desired that all those which had been so armed should depart from our ports. It being understood afterwards, that these vessels either still remained in our ports, or had only left them to cruise on our coasts and return again with their prizes, and that another vessel, the Little Democrat, had been since armed at Philadelphia, it was desired in my letter of the 12th of July, that such vessels, with their prizes, should be detained, till a determination should be had of what was to be done under these circumstances. In disregard, however, of this desire, the Little Democrat went out immediately on a cruise.
I have it now in charge to inform you, that the President considers the United States as bound, pursuant to positive assurances given in conformity to the laws of neutrality, to effectuate the restoration of or to make compensation for prizes, which shall have been made of any of the parties at war with France, subsequent to the fifth day of June last, by privateers fitted out of our ports.
That it is consequently expected, that you will cause restitution to be made of all prizes taken and brought into our ports subsequent to the above mentioned day by such privateers, in defect of which, the President considers it as incumbent upon the United States to indemnify the owners of those prizes; the indemnification to be reimbursed by the French nation.
That besides taking efficacious measures to prevent the future fitting out of privateers in the ports of the United States, they will not give asylum therein to any which shall have been at any time so fitted out, and will cause restitution of all such prizes as shall be hereafter brought within their ports by any of the said privateers.
It would have been but proper respect to the authority of the country, had that been consulted before these armaments were undertaken. It would have been satisfactory, however, if their sense of them, when declared, had been duly acquiesced in. Reparation of the injury to which the United States have been made so involuntarily instrumental is all which now remains, and in this your compliance cannot but be expected.
In consequence of the information given in your letter of the 4th instant, that certain citizens of St. Domingo, lately arrived in the United States, were associating for the purpose of undertaking a military expedition from the territory of the United States, against that island, the Governor of Maryland, within which State the expedition is understood to be preparing, is instructed to take effectual measures to prevent the same.
I have the honor to be, with great respect, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO GOUVERNEUR MORRIS.
Philadelphia, August 16,1793.
Sir,
In my letter of January the 13th, I enclosed to you copies of several letters which had passed between Mr. Ternant, Mr. Genet, and myself, on the occurrences to which the present war had given rise within our ports. The object of this communication was to enable you to explain the principles on which our government was conducting itself towards the belligerent parties; principles which might not in all cases be satisfactory to all, but were meant to be just and impartial to all. Mr. Genet had been then but a little time with us; and but a little more was necessary to develope in him a character and conduct so unexpected and so extraordinary, as to place us in the most distressing dilemma, between our regard for his nation, which is constant and sincere, and a regard for our laws, the authority of which must be maintained; for the peace of our country, which the executive magistrate is charged to preserve; for its honor, offended in the person of that magistrate; and for its character grossly traduced, in the conversations and letters of this gentleman. In the course of these transactions, it has been a great comfort to us to believe, that none of them were within the intentions or expectations of his employers. These had been too recently expressed in acts which nothing could discolor, in the letters of the Executive Council, in the letter and decrees of the National Assembly, and in the general demeanor of the nation towards us, to ascribe to them things of so contrary a character. Our first duty, therefore, was, to draw a strong line between their intentions and the proceedings of their Minister; our second, to lay those proceedings faithfully before them.
On the declaration of war between France and England, the United States being at peace with both, their situation was so new and unexperienced by themselves, that their citizens were not, in the first instant, sensible of the new duties resulting therefrom, and of the restraints it would impose even on their dispositions towards the belligerent powers. Some of them imagined (and chiefly their transient sea-faring citizens) that they were free to indulge those dispositions, to take side with either party, and enrich themselves by depredations on the commerce of the other, and were meditating enterprises of this nature, as there was reason to believe. In this state of the public mind, and before it should take an erroneous direction, difficult to be set right and dangerous to themselves and their country, the President thought it expedient, through the channel of a proclamation, to remind our fellow citizens that we were in a state of peace with all the belligerent powers, that in that state it was our duty neither to aid nor injure any, to exhort and warn them against acts which might contravene this duty, and particularly those of positive hostility, for the punishment of which the laws would be appealed to; and to put them on their guard also, as to the risks they would run, if they should attempt to carry articles of contraband to any. This proclamation, ordered on the 19th and signed the 22nd day of April, was sent to you in my letter of the 26th of the same month.
On the day of its publication, we received, through the channel of the newspapers, the first intimation that Mr. Genet had arrived on the 8th of the month at Charleston, in the character of Minister Plenipotentiary from his nation to the United States, and soon after, that he had sent on to Philadelphia the vessel in which he came, and would himself perform the journey by land. His landing at one of the most distant ports of the Union from his points both of departure and destination, was calculated to excite attention; and very soon afterwards, we learned that, he was undertaking to authorize the fitting and arming vessels in that port, enlisting men, foreigners and citizens, and giving them commissions to cruise and commit hostilities on nations at peace with us; that these vessels were taking and bringing prizes into our ports; that the Consuls of France were assuming to hold courts of admiralty on them, to try, condemn, and authorize their sale as legal prize, and all this before Mr. Genet had presented himself or his credentials to the President, before he was received by him, without his consent or consultation, and directly in contravention of the state of peace existing, and declared to exist in the President’s proclamation, and incumbent on him to preserve till the constitutional authority should otherwise declare. These proceedings became immediately, as was naturally to be expected, the subject of complaint by the representative here of that power against whom they would chiefly operate. The British minister presented several memorials thereon, to which we gave the answer of May the 15th, heretofore enclosed to you, corresponding in substance with a letter of the same date written to Mr. Ternant, the Minister of France then residing here, a copy of which I send herewith. On the next day Mr. Genet reached this place, about five or six weeks after he had arrived at Charleston, and might have been at Philadelphia, if he had steered for it directly. He was immediately presented to the President, and received by him as the Minister of the Republic; and as the conduct before stated seemed to bespeak a design of forcing us into the war without allowing us the exercise of any free will in the case, nothing could be more assuaging than his assurance to the President at his reception, which he repeated to me afterwards in conversation, and in public to the citizens of Philadelphia in answer to an address from them, that on account of our remote situation and other circumstances, France did not expect that we should become a party to the war, but wished to see us pursue our prosperity and happiness in peace. In a conversation a few days after, Mr. Genet told me that M. de Ternant had delivered him my letter of May the 15th. He spoke something of the case of the Grange, and then of the armament at Charleston, explained the circumstances which had led him to it before he had been received by the government and had consulted its will, expressed a hope that the President had not so absolutely decided against the measure but that he would hear what was to be said in support of it, that he would write me a letter on the subject, in which he thought he could justify it under our treaty; but that if the President should finally determine otherwise, he must submit; for that assuredly his instructions were to do what would be agreeable to us. He accordingly wrote the letter of May the 27th. The President took the case again into consideration, and found nothing in that letter which could shake the grounds of his former decision. My letter of June the 5th notifying this to him, his of June the 8th and 14th, mine of the 17th, and his again of the 22nd, will show what further passed on this subject, and that he was far from retaining his disposition to acquiesce in the ultimate will of the President.
It would be tedious to pursue this and our subsequent correspondence through all their details. Referring therefore for these to the letters themselves, which shall accompany this, I will present a summary view only of the points of difference which have arisen, and the grounds on which they rest.
1. Mr. Genet asserts his right of arming in our ports and of enlisting our citizens, and that we have no right to restrain him or punish them. Examining this question under the law of nations, founded on the general sense and usage of mankind, we have produced proofs, from the most enlightened and approved writers on the subject, that a neutral nation must, in all things relating to the war, observe an exact impartiality towards the parties; that favors to one to the prejudice of the other would import a fraudulent neutrality, of which no nation would be the dupe; that no succor should be given to either, unless stipulated by treaty, in men, arms, or any thing else directly serving for war; that the right of raising troops being one of the rights of sovereignty, and consequently appertaining exclusively to the nation itself, no foreign power or person can levy men within its territory without its consent; and he who does, may be rightfully and severely punished; that if the United States have a right to refuse the permission to arm vessels and raise men within their ports and territories, they are bound by the laws of neutrality to exercise that right, and to prohibit such armaments and enlistments. To these principles of the law of nations Mr. Genet answers, by calling them ‘diplomatic subtleties,’ and ‘aphorisms of Vattel and others.’ But something more than this is necessary to disprove them; and till they are disproved, we hold it certain that the law of nations and the rules of neutrality forbid our permitting either party to arm in our ports.
But Mr. Genet says, that the twenty-second article of our treaty allows him expressly to arm in our ports. Why has he not quoted the very words of that article expressly allowing it? For that would have put an end to all further question. The words of the article are, ‘It shall not be lawful for any foreign privateers not belonging to subjects of the M. C. King, nor citizens of the said United States, who have commissions from any foreign Prince or State in enmity with either nation, to fit their ships in the ports of either the one or the other of the aforesaid parties.’ Translate this from the general terms in which it here stands, into the special case produced by the present war. ‘Privateers not belonging to France or the United States, and having commissions from the enemies of one of them,’ are, in the present state of things,’ British, Dutch, and Spanish privateers.’ Substituting these then for the equivalent terms, it will stand thus, ‘It shall not be lawful for British, Dutch, or Spanish privateers, to fit their ships in the ports of the United States.’ Is this an express permission to France to do it? Does the negative to the enemies of France, and silence as to France herself, imply an affirmative to France? Certainly not; it leaves the question as to France open, and free to be decided according to circumstances. And if the parties had meant an affirmative stipulation, they would have provided for it expressly; they would never have left so important a point to be inferred from mere silence or implications. Suppose they had desired to stipulate a refusal to their enemies, but nothing to themselves; what form of expression would they have used? Certainly the one they have used; an express stipulation as to their enemies, and silence as to themselves. And such an intention corresponds not only with the words, but with the circumstances of the times. It was of value to each party to exclude its enemies from arming in the ports of the other, and could in no case embarrass them. They therefore stipulated so far mutually. But each might be embarrassed by permitting the other to arm in its ports. They therefore would not stipulate to permit that. Let us go back to the state of things in France when this treaty was made, and we shall find several cases wherein France could not have permitted us to arm in her ports. Suppose a war between these States and Spain. We know, that by the treaties between France and Spain, the former could not permit the enemies of the latter to arm in her ports. It was honest in her, therefore, not to deceive us by such a stipulation. Suppose a war between these States and Great Britain. By the treaties between France and Great Britain, in force at the signature of ours, we could not have been permitted to arm in the ports of France. She could not then have meant in this article to give us such a right. She has manifested the same sense of it in her subsequent treaty with England, made eight years after the date of ours, stipulating in the sixteenth article of it, as in our twenty-second, that foreign privateers, not being subjects of either crown, should not arm against either in the ports of the other. If this had amounted to an affirmative stipulation that the subjects of the other crown might arm in her ports against us, it would have been in direct contradiction to her twenty-second article with us. So that to give to these negative stipulations an affirmative effect, is to render them inconsistent with each other, and with good faith; to give them only their negative and natural effect, is to reconcile them to one another and to good faith, and is clearly to adopt the sense in which France herself has expounded them. We may justly conclude then, that the article only obliges us to refuse this right, in the present case, to Great Britain and the other enemies of France. It does not go on to give it to France, either expressly or by implication. We may then refuse it. And since we are bound by treaty to refuse it to the one party, and are free to refuse it to the other, we are bound by the laws of neutrality to refuse it to that other. The aiding either party then with vessels, arms, or men, being unlawful by the law of nations, and not rendered lawful by the treaty, it is made a question whether our citizens, joining in these unlawful enterprises, may be punished.
The United States being in a state of peace with most of the belligerent powers by treaty, and with all of them by the laws of nature, murders and robberies committed by our citizens within our territory, or on the high seas, on those with whom we are so at peace, are punishable equally as if committed on our own inhabitants. If I might venture to reason a little formally, without being charged with running into ‘subtleties and aphorisms,’ I would say, that if one citizen has a right to go to war of his own authority, every citizen has the same. If every citizen has that right, then the nation (which is composed of all its citizens) has a right to go to war, by the authority of its individual citizens. But this is not true either on the general principles of society, or by our constitution, which gives that power to Congress alone, and not to the citizens individually. Then the first position was not true; and no citizen has a right to go to war of his own authority, and for what he does without right, he ought to be punished. Indeed, nothing can be more obviously absurd than to say, that all the citizens may be at war, and yet the nation at peace.
It has been pretended, indeed, that the engagement of a citizen in an enterprise of this nature, was a divestment of the character of citizen, and a transfer of jurisdiction over him to another sovereign. Our citizens are certainly free to divest themselves of that character by emigration and other acts manifesting their intention, and may then become the subjects of another power, and free to do whatever the subjects of that power may do. But the laws do not admit that the bare commission of a crime amounts of itself to a divestment of the character of citizen, and withdraws the criminal from their coercion. They would never prescribe an illegal act among the legal modes by, which a citizen might disfranchise himself; nor render treason, for instance, innocent by giving it the force of a dissolution of the obligation of the criminal to his country. Accordingly, in the case of Henfeild, a citizen of these States, charged with having engaged in the port of Charleston, in an enterprise against nations at peace with us, and with having joined in the actual commission of hostilities, the Attorney General of the United States, in an official opinion, declared, that the act with which he was charged was punishable by law. The same thing has been unanimously declared by two of the Circuit Courts of the United States, as you will see in the charges of Chief Justice Jay, delivered at Richmond, and Judge Wilson, delivered at Philadelphia, both of which are herewith sent. Yet Mr. Genet, in the moment he lands at Charleston, is able to tell the Governor, and continues to affirm in his correspondence here, that no law of the United States authorizes their government to restrain either its own citizens or the foreigners inhabiting its territory, from warring against the enemies of France. It is true, indeed, that in the case of Henfeild, the jury which tried, absolved him. But it appeared on the trial, that the crime was not knowingly and wilfully committed; that Henfeild was ignorant of the unlawfulness of his undertaking; that in the moment he was apprized of it, he showed real contrition; that he had rendered meritorious services during the late war, and declared he would live and die an American. The jury, therefore, in absolving him, did no more than the constitutional authority might have done, had they found him guilty: the constitution having provided for the pardon of offences in certain cases, and there being no case where it would have been more proper than where no offence was contemplated. Henfeild, therefore, was still an American citizen, and Mr. Genet’s reclamation of him was as unauthorized as the first enlistment of him.
2. Another doctrine advanced by Mr. Genet is, that our courts can take no cognizance of questions whether vessels, held by theirs, as prizes, are lawful prizes or not; that this jurisdiction belongs exclusively to their consulates here, which have been lately erected by the National Assembly into complete courts of admiralty. Let us consider, first, what is the extent of jurisdiction which the consulates of France may rightfully exercise here. Every nation has of natural right, entirely and exclusively, all the jurisdiction which may be rightfully exercised in the territory it occupies. If it cedes any portion of that jurisdiction to judges appointed by another nation, the limits of their power must depend on the instrument of cession. The United States and France have, by their consular convention, given mutually to their Consuls jurisdiction in certain cases especially enumerated. But that convention gives to neither the power of establishing complete courts of admiralty within the territory of the other, nor even of deciding the particular question of prize, or not prize. The consulates of France, then, cannot take judicial cognizance of those questions here. Of this opinion Mr. Genet was, when he wrote his letter of May the 27th, wherein he promises to correct the error of the Consul at Charleston, of whom, in my letter of the 15th instant, I had complained, as arrogating to himself that jurisdiction; though in his subsequent letters he has thought proper to embark in the errors of his Consuls.
But the United States, at the same time, do not pretend any right to try the validity of captures made on the high seas, by France, or any other nation, over its enemies. These questions belong of common usage to the sovereignty of the captor, and whenever it is necessary to determine them, resort must be had to his courts. This is the case provided for in the seventeenth article of the treaty, which says, that such prizes shall not be arrested, nor cognizance taken of the validity thereof; a stipulation much insisted on by Mr. Genet and the Consuls, and which we never thought of infringing or questioning. As the validity of captures then, made on the high seas by France over its enemies, cannot be tried within the United States by their Consuls, so neither can it by our own courts. Nor is this the question between us, though we have been misled into it.
The real question is, whether the United States have not a right to protect vessels within their waters and on their coasts? The Grange was taken within the Delaware, between the shores of Jersey and of the Delaware State, and several miles above its mouth. The seizing her was a flagrant violation of the jurisdiction of the United States. Mr. Genet, however, instead of apologizing, takes great merit in his letters for giving her up. The William is said to have been taken within two miles of the shores of the United States. When the admiralty declined cognizance of the case, she was delivered to the French Consul according to my letter of June the 25th, to be kept till the executive of the United States should examine into the case; and Mr. Genet was desired by my letter of June the 29th, to have them furnished with the evidence on behalf of the captors, as to the place of capture. Yet to this day it has never been done. The brig Fanny was alleged to be taken within five miles from our shore; the Catharine within two miles and a half. It is an essential attribute of the jurisdiction of every country to preserve peace, to punish acts in breach of it, and to restore property taken by force within its limits. Were the armed vessel of any nation to cut away one of our own from the wharves of Philadelphia, and to choose to call it a prize, would this exclude us from the right of redressing the wrong? Were it the vessel of another nation, are we not equally bound to protect it, while within our limits? Were it seized in any other of our waters, or on the shores of the United States, the right of redressing is still the same: and humble indeed would be our condition, were we obliged to depend for that on the will of a foreign Consul, or on negotiation with diplomatic agents. Accordingly, this right of protection within its waters and to a reasonable distance on its coasts, has been acknowledged by every nation, and denied to none: and if the property seized be yet within their power, it is their right and duty to redress the wrong themselves. France herself has asserted the right in herself and recognised it in us, in the sixth article of our treaty, where we mutually stipulate that we will, by all the means in our power (not by negotiation), protect and defend each other’s vessels and effects in our ports or roads, or on the seas near our countries, and recover and restore the same to the right owners. The United Netherlands, Prussia, and Sweden, have recognised it also in treaties with us; and indeed it is a standing formula, inserted in almost all the treaties of all nations, and proving the principle to be acknowledged by all nations.
How, and by what organ of the government, whether judiciary or executive, it shall be redressed, is not yet perfectly settled with us. One of the subordinate courts of admiralty has been of opinion, in the first instance, in the case of the ship William, that it does not belong to the judiciary. Another, perhaps, may be of a contrary opinion. The question is still subjudice, and an appeal to the court of last resort will decide it finally. If finally the judiciary shall declare that it does not belong to the civil authority, it then results to the executive, charged with the direction of the military force of the Union, and the conduct of its affairs with foreign nations. But this is a mere question of internal arrangement between the different departments of the government, depending on the particular diction of the laws and constitution; and it can in no wise concern a foreign nation to which department these have delegated it.
3. Mr. Genet, in his letter of July the 9th, requires that the ship Jane, which he calls an English privateer, shall be immediately ordered to depart; and to justify this, he appeals to the 22nd article of our treaty, which provides that it shall not be lawful for any foreign privateer to fit their ships in our ports, to sell what they have taken, or purchase victuals, &c. The ship Jane is an English merchant vessel, which has been many years employed in the commerce between Jamaica and these States. She brought here a cargo of produce from that island, and was to take away a cargo of flour. Knowing of the war when she left Jamaica, and that our coast was lined with small French privateers, she armed for her defence, and took one of those commissions usually called letters of marque. She arrived here safely without having had any reencounter of any sort. Can it be necessary to say that a merchant vessel is not a privateer? That though she has arms to defend herself in time of war, in the course of her regular commerce, this no more makes her a privateer, than a husbandman following his plough in time of war, with a knife or pistol in his pocket, is thereby made a soldier? The occupation of a privateer is attack and plunder, that of a merchant vessel is commerce and self-preservation. The article excludes the former from our ports, and from selling what she has taken, that is what she has acquired by war, to show it did not mean the merchant vessel and what she had acquired by commerce. Were the merchant vessels coming for our produce forbidden to have any arms for their defence, every adventurer who had a boat, or money enough to buy one, would make her a privateer, our coasts would swarm with them, foreign vessels must cease to come, our commerce must be suppressed, our produce remain on our hands, or at least that great portion of it which we have not vessels to carry away, our ploughs must be laid aside, and agriculture suspended. This is a sacrifice no treaty could ever contemplate, and which we are not disposed to make out of mere complaisance to a false definition of the term privateer. Finding that the Jane had purchased new carriages to mount two or three additional guns, which she had brought in her hold, and that she had opened additional port-holes for them, the carriages were ordered to be relanded, the additional port-holes stopped, and her means of defence reduced, to be exactly the same at her departure as at her arrival. This was done on the general principle of allowing no party to arm within our ports.
4. The seventeenth article of our treaty leaves armed vessels free to conduct, whithersoever they please, the ships and goods taken from their enemies without paying any duty, and to depart and be conducted freely to the places expressed in their commissions, which the captain shall be obliged to show. It is evident, that this article does not contemplate a freedom to sell their prizes here; but on the contrary, a departure to some other place, always to be expressed in their commission, where their validity is to be finally adjudged. In such case, it would be as unreasonable to demand duties on the goods they had taken from an enemy, as it would be on the cargo of a merchant vessel touching in our ports for refreshment or advices; and against this the article provides. But the armed vessels of France have been also admitted to land and sell their prize-goods here for a consumption, in which case, it is as reasonable they should pay duties, as the goods of a merchantman landed and sold for consumption. They have however demanded, and as a matter of right, to sell them free of duty, a right, they say, given by this article of the treaty, though the article does not give the right to sell at all. Where a treaty does not give the principal right of selling, the additional one of selling duty free cannot be given: and the laws, in admitting the principal right of selling, may withhold the additional one of selling duty free. It must be observed, that our revenues are raised almost wholly on imported goods. Suppose prize-goods enough should be brought in to supply our whole consumption. According to their construction we are to lose our whole revenue. I put the extreme case to evince, more extremely, the unreasonableness of the claim. Partial supplies would affect the revenue but partially. They would lessen the evil, but not the error, of the construction: and I believe we may say, with truth, that neither party had it in contemplation, when penning this article, to abandon any part of its revenue for the encouragement of the sea-robbers of the other.
5. Another source of complaint with Mr. Genet has been, that the English take French goods out of American vessels, which he says is against the law of nations, and ought to be prevented by us. On the contrary, we suppose it to have been long an established principle of the law of nations, that the goods of a friend are free in an enemy’s vessel, and an enemy’s goods lawful prize in the vessel of a friend. The inconvenience of this principle, which subjects merchant vessels to be stopped at sea, searched, ransacked, led out of their course, has induced several nations latterly to stipulate against it by treaty, and to substitute another in its stead, that free bottoms shall make free goods, and enemy bottoms enemy goods; a rule equal to the other in point of loss and gain, but less oppressive to commerce. As far as it has been introduced, it depends on the treaties stipulating it, and forms exceptions, in special cases, to the general operation of the law of nations. We have introduced it into our treaties with France, Holland, and Prussia; and French goods found by the two latter nations in American bottoms are not made prize of. It is our wish to establish it with other nations. But this requires their consent also, is a work of time, and in the mean while, they have a right to act on the general principle, without giving to us or to France cause of complaint. Nor do I see that France can lose by if on the whole. For though she loses her goods when found in our vessels by the nations with whom we have no treaties, yet she gains our goods, when found in the vessels of the same and all other nations: and we believe the latter mass to be greater than the former. It is to be lamented, indeed, that the general principle has operated so cruelly in the dreadful calamity which has lately happened in St. Domingo. The miserable fugitives, who, to save their lives, had taken asylum in our vessels, with such valuable and portable things as could be gathered in the moment out of the ashes of their houses and wrecks of their fortunes, have been plundered of these remains by the licensed sea-rovers of their enemies. This has swelled, on this occasion, the disadvantages of the general principle, that ‘an enemy’s goods are free prize in the vessels of a friend.’ But it is one of those deplorable and unforeseen calamities to which they expose themselves who enter into a state of war, furnishing to us an awful lesson to avoid it by justice and moderation, and not a cause or encouragement to expose our own towns to the same burnings and butcheries, nor of complaint because we do not.
6. In a case like the present, where the missionary of one government construes differently from that to which he is sent, the treaties and laws which are to form a common rule of action for both, it would be unjust in either to claim an exclusive right of construction. Each nation has an equal right to expound the meaning of their common rules; and reason and usage have established, in such cases, a convenient and well understood train of proceeding. It is the right and duty of the foreign missionary to urge his own constructions, to support them with reasons which may convince, and in terms of decency and respect which may reconcile the government of the country to a concurrence. It is the duty of that government to listen to his reasonings with attention and candor, and to yield to them when just. But if it shall still appear to them that reason and right are on their side, it follows of necessity, that exercising the sovereign powers of the country, they have a right to proceed on their own constructions and conclusions as to whatever is to be done within their limits. The minister then refers the case to his own government, asks new instructions, and, in the mean time, acquiesces in the authority of the country. His government examines his constructions, abandons them if wrong, insists on them if right, and the case then becomes a matter of negotiation between the two nations. Mr. Genet, however, assumes a new and bolder line of conduct. After deciding for himself ultimately, and without respect to the authority of the country, he proceeds to do what even his sovereign could not authorize, to put himself within the country on a line with its government, to act as co-sovereign of the territory; he arms vessels, levies men, gives commissions of war, independently of them, and in direct opposition to their orders and efforts. When the government forbids their citizens to arm and engage in the war, he undertakes to arm and engage them. When they forbid vessels to be fitted in their ports for cruising on nations with whom they are at peace, he commissions them to fit and cruise. When they forbid an unceded jurisdiction to be exercised within their territory by foreign agents, he undertakes to uphold that exercise, and to avow it openly. The privateers Citoyen Genet and Sans Culottes having been fitted out at Charleston (though without the permission of the government, yet before it was forbidden) the President only required they might leave our ports, and did not interfere with their prizes. Instead, however, of their quitting our ports, the Sans Culottes remains still, strengthening and equipping herself, and the Citoyen Genet went out only to cruise on our coast, and to brave the authority of the country by returning into port again with her prizes. Though in the letter of June the 5th, the final determination of the President was communicated, that no future armaments in our ports should be permitted, the Vainqueur de la Bastille was afterwards equipped and commissioned in Charleston, the Anti-George in Savannah, the Carmagnole in Delaware, a schooner and a sloop in Boston, and the Polly or Republican was attempted to be equipped in New York, and was the subject of reclamation by Mr. Genet, in a style which certainly did not look like relinquishing the practice. The Little Sarah or Little Democrat was armed, equipped, and manned, in the port of Philadelphia, under the very eye of the government, as if meant to insult it. Having fallen down the river, and being evidently on the point of departure for a cruise, Mr. Genet was desired in my letter of July the 2th, on the part of the President, to detain her till some inquiry and determination on the case should be had. Yet within three or four days after, she was sent out by orders from Mr. Genet himself, and is, at this time, cruising on our coasts, as appears by the protest of the master of one of our vessels maltreated by her.
The government thus insulted and set at defiance by Mr. Genet, and committed in its duties and engagements to others, determined still to see in these proceedings but the character of the individual, and not to believe, and it does not believe, that they are by instructions from his employers. They had assured the British Minister here, that the vessels already armed in our ports should be obliged to leave them, and that no more should be armed in them. Yet more had been armed, and those before armed had either not gone away, or gone only to return with new prizes. They now informed him that the order for departure should be enforced, and the prizes made contrary to it should be restored or compensated. The same thing was notified to Mr. Genet in my letter of August the 7th, and that he might not conclude the promise of compensation to be of no concern to him, and go on in his courses, he was reminded that it would be a fair article of account against his nation.
Mr. Genet, not content with using our force, whether we will or not, in the military line against nations with whom we are at peace, undertakes also to direct the civil government; and particularly, for the executive and legislative bodies, to pronounce what powers may or may not be exercised by the one or the other. Thus in his letter of June the 8th, he promises to respect the political opinions of the President, till the Representatives shall have confirmed or rejected them; as if the President had undertaken to decide what belonged to the decision of Congress. In his letter of June the 4th, he says more openly, that the President ought not to have taken on himself to decide on the subject of the letter, but that it was of importance enough to have consulted Congress thereon; and in that of June the 22nd, he tells the President in direct terms, that Congress ought already to have been occupied on certain questions which he had been too hasty in deciding: thus making himself, and not the President, the judge of the powers ascribed by the constitution to the executive, and dictating to him the occasion when he should exercise the power of convening Congress at an earlier day than their own act had prescribed.
On the following expressions no commentary shall be made.
July 9. ‘Les principes philosophiques proclames par le Président.’
June 22. ‘Les opinions privées ou publiques de M. le Président, et cette égide ne paroissant pas suffisante.’
June 22. ‘Le gouvernement fédéral s’est empressé, poussé par je ne se gais quelle influence.’
June 22. ‘Je ne puis attribuer des démarches de cette nature qu’a des impressions étrangeres dont le terns et la vérité triompheront.’
June 25. ‘On poursuit avec acharnement, en vertu des instructions de M. le Président, les armateurs Francais.’
June 14. ‘Ce refus tend a accomplir le système infernal du roi d’Angleterre, et des autres rois ses accomplices, pour faire perir par la famine les Républicans Francais avec la liberté.
June 8. ‘La lache abandon de ses amis.’
July 25. ‘En vain le desirde conserver la paix fait-il sacrifier les interets de la France a cet interêt du moment; en vain la soif des richesses l’emporte-t-elle sur l’honneur dans la balance politique de l’Amérique. Tous ces menagemens, toute cette condescendance, toute cette humilité n’aboutissent a rien: nos ennemis en rient, et les Francais trop confiants sont punis pour avoir cru que la nation Américaine avoit un pavilion, qu’elle avoit quelque egard pours ses loix, quelque conviction de ses forces, et qu’elle tenoit au sentiment de sa dignité. Il ne m’est pas possible de peindre toute ma sensibilité sur ce scandale, qui tend à la diminution de votre commerce, à l’oppression du notre, et à l’abaissement, à l’avilissement des republiques. Si nos concitoyens ont été trompes, si vous n’êtes point en état de soutenir la souveraineté de votre peuple, parlez; nous l’avons garantie quand nous étions esclaves, nous saurons la rendre rédoubtable étant devenus libres.’ We draw a veil over the sensations which these expressions excite. No words can render them; but they will not escape the sensibility of a friendly and magnanimous nation, who will do us justice. We see in them neither the portrait of ourselves, nor the pencil of our friends; but an attempt to embroil both; to add still another nation to the enemies of his country, and to draw on both a reproach, which it is hoped will never stain the history of either. The written proofs, of which Mr. Genet was himself the bearer, were too unequivocal to leave a doubt that the French nation are constant in their friendship to us. The resolves of their National Convention, the letters of their Executive Council attest this truth, in terms which render it necessary to seek in some other hypothesis, the solution of Mr. Genet’s machinations against our peace and friendship.
Conscious, on our part, of the same friendly and sincere dispositions, we can with truth affirm, both for our nation and government, that we have never omitted a reasonable occasion of manifesting them. For I will not consider as of that character, opportunities of sallying forth from our ports to way-lay, rob, and murder defenceless merchants and others, who have done us no injury, and who were coming to trade with us in the confidence of our peace and amity. The violation of all the laws of order and morality which bind mankind together, would be an unacceptable offering to a just nation. Recurring then only to recent things, after so afflicting a libel we recollect with satisfaction, that in the course of two years, by unceasing exertions, we paid up seven years’ arrearages and instalments of our debt to France, which the inefficiency of our first form of government had suffered to be accumulating: that pressing on still to the entire fulfilment of our engagements, we have facilitated to Mr. Genet the effect of the instalments of the present year, to enable him to send relief to his fellow citizens in France, threatened with famine: that in the first moment of the insurrection which threatened the colony of St. Domingo, we stepped forward to their relief with arms and money, taking freely on ourselves the risk of an unauthorized aid, when delay would have been denial: that we have received, according to our best abilities, the wretched fugitives from the catastrophe of the principal town of that colony, who, escaping from the swords and flames of civil war, threw themselves on us naked and houseless, without food or friends, money or other means, their faculties lost and absorbed in the depth of their distresses: that the exclusive admission to sell here the prizes made by France on her enemies, in the present war, though unstipulated in our treaties, and unfounded in her own practice or in that of other nations, as we believe; the spirit manifested by the late grand jury in their proceedings against those who had aided the enemies of France with arms and implements of war; the expressions of attachment to his nation, with which Mr. Genet was welcomed on his arrival and journey from south to north, and our long forbearance under his gross usurpations and outrages of the laws and authority of our country, do not bespeak the partialities intimated in his letters. And for these things he rewards us by endeavors to excite discord and distrust between our citizens and those whom they have entrusted with their government, between the different branches of our government, between our nation and his. But none of these things, we hope, will be found in his power. That friendship which dictates to us to bear with his conduct yet a while, lest the interests of his nation here should suffer injury, will hasten them to replace an agent, whose dispositions are such a misrepresentation of theirs, and whose continuance here is inconsistent with order, peace, respect, and that friendly correspondence which we hope will ever subsist between the two nations. His government will see too that the case is pressing. That it is impossible for two sovereign and independent authorities to be going on within our territory at the same time, without collision. They will foresee that if Mr. Genet perseveres in his proceedings, the consequences would be so hazardous to us, the example so humiliating and pernicious, that we may be forced even to suspend his functions before a successor can arrive to continue them. If our citizens have not already been shedding each other’s blood, it is not owing to the moderation of Mr. Genet, but to the forbearance of the government. It is well known that if the authority of the laws had been resorted to, to stop the Little Democrat, its officers and agents were to have been resisted by the crew of the vessel, consisting partly of American citizens. Such events are too serious, too possible, to be left to hazard, or to what is more than hazard, the will of an agent whose designs are so mysterious.
Lay the case then immediately before his government. Accompany it with assurances, which cannot be stronger than true, that our friendship for the nation is constant and unabating; that faithful to our treaties, we have fulfilled them in every point to the best of our understanding; that if in any thing, however, we have construed them amiss, we are ready to enter into candid explanations, and to do whatever we can be convinced is right; that in opposing the extravagances of an agent, whose character they seem not sufficiently to, have known, we have been urged by motives of duty to ourselves and justice to others, which cannot but be approved by those who are just themselves; and finally, that after independence and self-government, there is nothing we more sincerely wish than perpetual friendship with them.
I have the honor to be, with great respect and esteem, Dear Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.*
* A copy of the preceding letter was sent, enclosed by the
Secretary of State, to Mr. Genet.
CIRCULAR TO THE MERCHANTS OF THE UNITED STATES.
Philadelphia, August 23, 1793,
Gentlemen,
Complaint having been made to the government of the United States, of some instances of unjustifiable vexation and spoliation committed on our merchant vessels by the privateers of the powers at war, and it being possible that other instances may have happened of which no information has been given to the government, I have it in charge from the President to assure the merchants of the United States, concerned in foreign commerce or navigation, that due attention will be paid to any injuries they may suffer on the high seas or in foreign countries, contrary to the law of nations or to existing treaties: and that on their forwarding hither well authenticated evidence of the same, proper proceedings will be adopted for their relief. The just and friendly dispositions of the several belligerent powers, afford well-founded expectation that they will not hesitate to take effectual measures for restraining their armed vessels from committing aggressions and vexations on our citizens or their property.
There being no particular portion or description of the mercantile body pointed out by the laws for receiving communications of this nature, I take the liberty of addressing it to the merchants of ———— for the state of ————- requesting that through them, it may be made known to all those of their State whom it may concern. Information will be freely received either from the individuals aggrieved, or from any associations of merchants who will be pleased to take the trouble of giving it, in a case so interesting to themselves and their country.
I have the honor to be, with great respect, Gentlemen, your most obedient servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MR. GORE.
Philadelphia, September 2, 1793.
Sir,
The President is informed through the channel of a letter from yourself to Mr. Lear, that M. Duplaine, Consul of France at Boston, has lately, with an armed force, seized and rescued a vessel from the officer of a court of justice, by process from which she was under arrest in his custody: and that he has in like manner, with an armed force, opposed and prevented the officer, charged with process from a court against another vessel, from serving that process. This daring violation of the laws requires the more attention, as it is by a foreigner clothed with a public character, arrogating an unfounded right to admiralty jurisdiction, and probably meaning to assert it by this act of force. You know that by the law of nations, consuls are not diplomatic characters, and have no immunities whatever against the laws of the land. To put this altogether out of dispute, a clause was inserted in our consular convention with France, making them amenable to the laws of the land, as other inhabitants. Consequently, M. Duplaine is liable to arrest, imprisonment, and other punishments, even capital, as other foreign subjects resident here. The President therefore desires that you will immediately institute such a prosecution against him, as the laws will warrant. If there be any doubt as to the character of his offence, whether of a higher or lower grade, it will be best to prosecute for that which will admit the least doubt, because an acquittal, though it might be founded merely on the opinion that the grade of offence with which he is charged is higher than his act would support, yet it might be construed by the uninformed to be a judiciary decision against his amenability to the law, or perhaps in favor of the jurisdiction these Consuls are assuming. The process, therefore, should be of the surest kind, and all the proceedings well grounded. In particular, if an arrest, as is probable, be the first step, it should be so managed as to leave room neither for escape nor rescue. It should be attended with every mark of respect, consistent with safe custody, and his confinement as mild and comfortable also, as that would permit. These are the distinctions to which a Consul is entitled, that is to say, of a particular decorum of deportment towards him, indicative of respect to the sovereign whose officer he is.
The President also desires you will immediately obtain the best evidence it shall be in your power to procure, under oath or affirmation, of the transaction stated in your letter, and that in this, you consider yourself as acting as much on behalf of M. Duplaine as the public, the candid truth of the case being exactly that which is desired, as it may be the foundation of an act, the justice of which should be beyond all question. This evidence I shall be glad to receive with as few days, or even hours, of delay as possible.
I am also instructed to ask the favor of you to communicate copies of any memorials, representations, or other written correspondence which may have passed between the Governor and yourself, with respect to the privateers and prizes which have been the subject of your letters to Mr. Lear.
I have the honor to be, with great respect, Sir, your most obedient servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MR. HAMMOND.
Philadelphia, September 5, 1793.
I am honored with yours of August the 30th. Mine of the 7th of that month assured you that measures were taking for excluding from all further asylum in our ports, vessels armed in them to cruise on nations with which we are at peace, and for the restoration of the prizes, the Lovely Lass, Prince William Henry, and the Jane of Dublin and that should the measures for restitution fail in their effect, the President considers it as incumbent on the United States, to make compensation for the vessels. We are bound by our treaties with three of the belligerent nations, by all the means in our power to protect and defend their vessels and effects in our ports or waters, or on the seas near our shores, and to recover and restore the same to the right owners when taken from them. If all the means in our power are used and fail in their effect, we are not bound by our treaties with those nations to make compensation.
Though we have no similar treaty with Great Britain, it was the opinion of the President that we should use towards that nation the same rule, which, under this article, was to govern us with the other nations; and even to extend it to captures made on the high seas and brought into our ports, if done by vessels which had been armed within them.
Having, for particular reasons, forborne to use all the measures in our power for the restitution of the three vessels mentioned in my letter of August the 7th, the President thought it incumbent on the United States to make compensation for them: and though nothing was said in that letter of other vessels taken under like circumstances, and brought in after the 5th of June and before the date of that letter, yet where the same forbearance had taken place, it was and is his opinion that compensation would be equally due.
As to prizes made under the same circumstances, and brought in after the date of that letter, the President determined that all the means in our power should be used for their restitution If these fail us, as we should not be bound by our treaties to make compensation to the other powers, in the analogous case he did not mean to give an opinion that it ought to be done to Great Britain. But still, if any cases shall arise subsequent to that date the circumstances of which shall place them on similar ground with those before it, the President would think compensation equally incumbent on the United States.
Instructions are given to the Governors of the different States, to use all the means in their power for restoring prizes of this last description, found within their ports. Though they will of course take measures to be informed of them, and the General Government has given them the aid of the Custom House officers for this purpose, yet you will be sensible of the importance of multiplying the channels of their information, as far as shall depend on yourself or any person under your direction, in order that the government may use the means in their power, for making restitution. Without knowledge of the capture, they cannot restore it. It will always be best to give the notice to them directly: but any information which you shall be pleased to send to me also, at any time, shall be forwarded to them as quickly as the distance will permit. Hence you will perceive, Sir, that the President contemplates restitution or compensation, in the cases before the seventh of August, and, after that date, restitution, if it can be effected by any means in our power: and that it will be important that you should substantiate the fact that such prizes are in our ports or waters.
Your list of the privateers illicitly armed in our ports, is, I believe, correct.
With respect to losses by detention, waste, spoliation, sustained by vessels taken as before mentioned between the dates of June the 5th and August the 7th, it is proposed, as a provisional measure, that the collector of the customs of the district, and the British Consul, or any other person you please, shall appoint persons to establish the value of the vessel and cargo, at the times of her capture and of her arrival in the port into which she is brought, according to their value in that port. If this shall be agreeable to you, and you will be pleased to signify it to me, with the names of the prizes understood to be of this description, instructions will be given, accordingly, to the collectors of the customs where the respective vessels are.
I have the honor to be, with great respect, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
Philadelphia, September 7,1793.
Sir,
We have received, through a channel which cannot be considered as authentic, the copy of a paper, styled ‘Additional instructions to the commanders of his Majesty’s ships of war and privateers, &c.’ dated at St. James’s, June 8, 1793. If this paper be authentic, I have little doubt but that you will have taken measures to forward it to me. But as your communication of it may miscarry, and time in the meanwhile be lost, it has been thought better that it should be supposed authentic: that on that supposition I should notice to you its very exceptionable nature, and the necessity of obtaining explanations on the subject from the British government; desiring at the same time, that you will consider this letter as provisionally written only, and as if never written, in the event that the paper which is the occasion of it be not genuine.
The first article of it permits all vessels, laden wholly or in part with corn, flour, or meal, bound to any port in France, to be stopped, and sent into any British port, to be purchased by that government, or to be released only on the condition of security given by the master, that he will proceed to dispose of his cargo in the ports of some country in amity with his Majesty.
This article is so manifestly contrary to the law of nations, that nothing more would seem necessary than to observe that it is so. Reason and usage have established that when two nations go to war, those who choose to live in peace retain their natural right to pursue their agriculture, manufactures, and other ordinary vocations, to carry the produce of their industry for exchange to all nations, belligerent or neutral, as usual, to go and come freely without injury or molestation, and in short, that the war among others shall be, for them, as if it did not exist. One restriction on their natural rights has been submitted to by nations at peace, that is to say, that of not furnishing to either party implements merely of war for the annoyance of the other, nor any thing whatever to a place blockaded by its enemy. What these implements of war are, has been so often agreed and is so well understood as to leave little question about them at this day. There does not exist, perhaps, a nation in our common hemisphere, which has not made a particular enumeration of them in some or all of their treaties, under the name of contraband. It suffices for the present occasion, to say, that corn, flour, and meal are not of the class of contraband, and consequently remain articles of free commerce. A culture which, like that of the soil, gives employment to such a proportion of mankind, could never be suspended by the whole earth, or interrupted for them, whenever any two nations should think proper to go to war.
The state of war then existing between Great Britain and France, furnishes no legitimate right either to interrupt the agriculture of the United States, or the peaceable exchange of its produce with all nations; and consequently, the assumption of it will be as lawful hereafter as now, in peace as in war. No ground, acknowledged by the common reason of mankind, authorizes this act now, and unacknowledged ground may be taken at any time, and at all times. We see then a practice begun, to which no time, no circumstances prescribe any limits, and which strikes at the root of our agriculture, that branch of industry which gives food, clothing, and comfort to the great mass of the inhabitants of these States. If any nation whatever has a right to shut up to our produce all the ports of the earth except her own and those of her friends, she may shut up these also, and so confine us within our own limits. No nation can subscribe to such pretensions; no nation can agree, at the mere will or interest of another, to have its peaceable industry suspended, and its citizens reduced to idleness and Want. The loss of our produce destined for foreign markets, or that loss which would result from an arbitrary restraint of our markets, is a tax too serious for us to acquiesce in. It is not enough for a nation to say, we and our friends will buy your produce. We have a right to answer, that it suits us better to sell to their enemies as well as their friends. Our ships do not go to France to return empty. They go to exchange the surplus of one produce which we can spare, for surplusses of other kinds which they can spare and we want; which they can furnish on better terms, and more to our mind, than Great Britain or her friends. We have a right to judge for ourselves what market best suits us, and they have none to forbid to us the enjoyment of the necessaries and comforts which we may obtain from any other independent country.
This act, too, tends directly to draw us from that state of peace in which we are wishing to remain. It is an essential character of neutrality to furnish no aids (not stipulated by treaty) to one party, which we are not equally ready to furnish to the other. If we permit corn to be sent to Great Britain and her friends, we are equally bound to permit it to France. To restrain it would be a partiality which might lead to war with France; and between restraining it ourselves, and permitting her enemies to restrain it unrightfully, is no difference. She would consider this as a mere pretext, of which she would not be the dupe; and on what honorable ground could we otherwise explain it? Thus we should see ourselves plunged by this unauthorized act of Great Britain into a war with which we meddle not, and which we wish to avoid, if justice to all parties and from all parties will enable us to avoid it. In the case where we found ourselves obliged by treaty to withhold from the enemies of France the right of arming in our ports, we thought ourselves in justice bound to withhold the same right from France also, and we did it. Were we to withhold from her supplies of provisions, we should in like manner be bound to withhold them from her enemies also; and thus shut to ourselves all the ports of Europe where corn is in demand, or make ourselves parties in the war. This is a dilemma which Great Britain has no right to force upon us, and for which no pretext can be found in any part of our conduct. She may indeed feel the desire of starving an enemy nation: but she can have no right of doing it at our loss, nor of making us the instruments of it.
The President therefore desires, that you will immediately enter into explanations on this subject with the British government. Lay before them in friendly and temperate terms all the demonstrations of the injury done us by this act, and endeavor to obtain a revocation of it, and full indemnification, to any citizens of these States who may have suffered by it in the mean time. Accompany your representations by every assurance of our earnest desire to live on terms of the best friendship and harmony with them, and to found our expectations of justice on their part, on a strict observance of it on ours.
It is with concern, however, I am obliged to observe, that so marked has been the inattention of the British court to every application which has been made to them on any subject, by this government (not a single answer I believe having ever been given to one of them, except in the act of exchanging a minister), that it may become unavoidable, in certain cases, where an answer of some sort is necessary, to consider their silence as an answer. Perhaps this is their intention. Still, however, desirous of furnishing no color of offence, we do not wish you to name to them any term for giving an answer. Urge one as much as you can without commitment, and on the first day of December be so good as to give us information of the state in which this matter is, that it may be received during the session of Congress.
The second article of the same instruction allows the armed vessels of Great Britain to seize for condemnation all vessels, on their first attempt to enter a blockaded port, except those of Denmark and Sweden, which are to be prevented only, but not seized, on their first attempt. Of the nations inhabiting the shores of the Atlantic ocean, and practising its navigation, Denmark, Sweden, and the United States alone are neutral. To declare then all neutral vessels (for as to the vessels of the belligerent powers no order was necessary) to be legal prize, which shall attempt to enter a blockaded port, except those of Denmark and Sweden, is exactly to declare that the vessels of the United States shall be lawful prize, and those of Denmark and Sweden shall not. It is of little consequence that the article has avoided naming the United States, since it has used a description applicable to them, and to them alone, while it exempts the others from its operation by name. You will be pleased to ask an explanation of this distinction: and you will be able to say, in discussing its justice, that in every circumstance, we treat Great Britain on the footing of the most favored nation where our treaties do not preclude us, and that even these are just as favorable to her, as hers are to us. Possibly she may be bound by treaty to admit this exception in favor of Denmark and Sweden. But she cannot be bound by treaty to withhold it from us. And if it be withheld merely because not established with us by treaty, what might not we, on the same ground, have withheld from Great Britain during the short course of the present war, as well as the peace which preceded it?
Whether these explanations with the British government shall be verbal or in writing, is left to yourself. Verbal communications are very insecure; for it is only to deny them or to change their terms, in order to do away their effect at any time. Those in writing have as many and obvious advantages, and ought to be preferred, unless there be obstacles of which we are not apprized. I have the honor to be, with great and sincere esteem, Dear Sir, your most obedient, humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MR. HAMMOND.
Philadelphia, September 9, 1793.
Sir,
I have the honor to acknowledge the receipt of your two memorials of the 4th and 6th instant, which have been duly laid before the President of the United States.
You cannot be uninformed of the circumstances which have occasioned the French squadron now in New York to seek asylum in the ports of the United States. Driven from those where they were on duty, by the superiority of the adverse party in the civil war which has so unhappily afflicted the colonies of France, filled with the wretched fugitives from the same scenes of distress and desolation, without water or provisions for the shortest voyage, their vessels scarcely in a condition to keep the sea at all, they were forced to seek the nearest ports in which they could be received and supplied with necessaries. That they have ever been out again to cruise, is a fact we have never learned, and which we believe to be impossible, from the information received of their wants and other impediments to active service. This case has been noted specially, to show that no inconvenience can have been produced to the trade of the other belligerent powers, by the presence of this fleet in our harbors. I shall now proceed to more general ground.
France, England, and all other nations have a right to cruise on our coasts; a right not derived from our permission, but from the law of nature. To render this more advantageous, France has secured to herself, by a treaty with us, (as she has done also by a treaty with Great Britain, in the event of a war with us or any other nation) two special rights. 1. Admission for her prizes and privateers into our ports. This, by the seventeenth and twenty-second articles, is secured to her exclusively of her enemies, as is done for her in the like case by Great Britain, were her present war with us instead of Great Britain. 2. Admission for her public vessels of war into our ports, in cases of stress of weather, pirates, enemies, or other urgent necessity, to refresh, victual, repair, &c. This is not exclusive. As then we are bound by treaty to receive the public armed vessels of France, and are not bound to exclude those of her enemies, the executive has never denied the same right of asylum in our ports to the public armed vessels of your nation. They, as well as the French, are free to come into them in all cases of weather, piracies, enemies, or other urgent necessity, and to refresh, victual, repair, &c. And so many are these urgent necessities, to vessels far from their own ports, that we have thought inquiries into the nature as well as the degree of the necessities, which drive them hither, as endless as they would be fruitless, and therefore have not made them. And the rather, because there is a third right, secured to neither by treaty, but due to both on the principles of hospitality between friendly nations, that of coming into our ports, not under the pressure of urgent necessity, but whenever their comfort or convenience induces them. On this ground, also, the two nations are on a footing.
As it has never been conceived that either would detain their ships of war in our ports when they were in a condition for action, we have never conceived it necessary to prescribe any limits to the time of their stay. Nor can it be viewed as an injury to either party, to let their enemies lie still in our ports from year’s end to year’s end, if they choose it. Thus, then, the public ships of war of both nations enjoy a perfect equality in our ports; first, in cases of urgent necessity; secondly, in cases of comfort or convenience; and thirdly, in the time they choose to continue; and all a friendly power can ask from another is, to extend to her the same indulgences which she extends to other friendly powers. And though the admission of the prizes and privateers of France is exclusive, yet it is the effect of treaty made long ago, for valuable considerations, not with a view to the present circumstances, nor against any nation in particular, but all in general, and may, therefore, be faithfully observed without offence to any; and we mean faithfully to observe it. The same exclusive article has been stipulated, as was before observed, by Great Britain in her treaty with France, and indeed is to be found in the treaties between most nations.
With respect to the usurpation of admiralty jurisdiction by the Consuls of France, within these States, the honor and rights of the States themselves were sufficient motives for the executive to take measures to prevent its continuance, as soon as they were apprized of it. They have been led by particular considerations to await the effect of these measures, believing they would be sufficient; but finding at length they were not, such others have been lately taken as can no longer fail to suppress this irregularity completely.
The President is duly sensible of the character of the act of opposition made to the serving of legal process on the brig William Tell, and he presumes the representations made on that subject to the Minister of France, will have the effect of opening a free access to the officer of justice, when he shall again present himself with the precept of his court.
I have the honor to be, with great respect, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MR. GENET.
Philadelphia, September 9, 1793.
Sir,
In my letter of June the 25th, on the subject of the ship William, and generally of vessels suggested to be taken within the limits of the protection of the United States by the armed vessels of your nation, I undertook to assure you it would be more agreeable to the President, that such vessels should be detained under the orders of yourself or the Consul of France, than by a military guard, until the government of the United States should be able to inquire into and decide on the fact. In two separate letters of the 29th of the same month, I had the honor to inform you of the claims lodged with the executive for the same ship William and the brig Fanny, to enclose you the evidence on which they were founded, and to desire that if you found it just, you would order the vessels to be delivered to the owners; or if overweighed in your judgment by any contradictory evidence which you might have or acquire, you would do me the favor to communicate that evidence: and that the Consuls of France might retain the vessels in their custody, in the mean time, until the executive of the United States should consider and decide finally on the subject.
When that mode of proceeding was consented to for your satisfaction, it was by no means imagined it would have occasioned such delays of justice to the individuals interested. The President is still without information, either that the vessels are restored, or that you have any evidence to offer as to the place of capture. I am, therefore, Sir, to repeat the request of early information on this subject, in order that if any injury has been done those interested, it maybe no longer aggravated by delay.
The intention of the letter of June the 25th having been, to permit such vessels to remain in the custody of the Consuls, instead of that of a military guard (which in the case of the ship William appeared to have been disagreeable to you), the indulgence was of course to be understood as going only to cases which the executive might take, or keep possession of, with a military guard, and not to interfere with the authority of the courts of justice in any case wherein they should undertake to act. My letter of June the 29th, accordingly, in the same case of the ship William, informed you that no power in this country could take a vessel out of the custody of the courts, and that it was only because they decided not to take cognizance of that case, that it resulted to the executive to interfere in it. Consequently, this alone put it in their power to leave the vessel in the hands of the Consul. The courts of justice exercise the sovereignty of this country in judiciary matters; are supreme in these, and liable neither to control nor opposition from any other branch of the government. We learn, however, from the enclosed paper, that the Consul of New York, in the first instance, and yourself in a subsequent one, forbid an officer of justice to serve the process with which he was charged from his court, on the British brig William Tell, taken by a French armed vessel within a mile of our shores, as has been deposed on oath, and brought into New York, and that you had even given orders to the French squadron there, to protect the vessel against any person who should attempt to take her from their custody. If this opposition were founded, as is there suggested, on the indulgence of the letters before cited, it was extending that to a case not within their purview; and even had it been precisely the case to which they were to be applied, is it possible to imagine you might assert it within the body of the country by force of arms?
I forbear to make the observations which such a measure must suggest, and cannot but believe that a moment’s reflection will evince to you the depth of the error committed in this opposition to an officer of justice, and in the means proposed to be resorted to in support of it. I am therefore charged to declare to you, expressly, that the President expects and requires that the officer of justice be not obstructed in freely and peaceably serving the process of his court, and that in the mean time, the vessel and her cargo be not suffered to depart till the judiciary, if it will undertake it, or himself if not, shall decide whether the seizure has been made within the limits of our protection.
I have the honor to be, with great respect, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO COLONEL HUMPHREYS.
Philadelphia, September 11, 1793.
Dear Sir,
I have to acknowledge yours of May the 19th and 29th, and July 20th; being Nos. 72, 73, and 76. It is long since I wrote to you, because I know you must be where you could not receive my letters: and perhaps it may be some time before I write to you again, on account of a contagious and mortal fever which has arisen here, and is driving us all away. It is called a yellow fever, but is like nothing known or read of by the physicians. The week before last the deaths were about forty; the last week about eighty; and this week, I think they will be two hundred; and it goes on spreading. All persons who can find asylum elsewhere, are flying from the city: this will doubtless extend it to other towns, and spread it through the country, unless an early winter should stop it. Colonel Hamilton is ill of it, but is on the recovery.
The Indians have refused to meet our commissioners unless they would agree to the Ohio as our boundary, by way of preliminary article. This being impossible, because of the army locations and sales to individuals beyond the Ohio, the war is to go on, and we may soon expect to hear of General Wayne’s being in motion.
The President set out yesterday for Mount Vernon, according to an arrangement of some time ago. General Knox is setting out for Massachusetts, and I am thinking to go to Virginia in some days. When and where we shall re-assemble, will depend on the course of this malady.
I have the honor to be, with great and sincere esteem and respect, Dear Sir, your affectionate friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MR. GENET.
Monticello, October 3, 1793.
Sir,
In a former letter which I had the honor of writing you, I mentioned that information had been received that M. Duplaine, Vice-Consul of France, at Boston, had been charged with an opposition to the laws of the land, of such a character, as, if true, would render it the duty of the President immediately to revoke the Exequatur, whereby he is permitted to exercise the functions of Vice-Consul in these United States. The fact has been since inquired into, and I now enclose you copies of the evidence establishing it; whereby you will perceive how inconsistent with peace and order it would be, to permit, any longer, the exercise of functions in these United States by a person capable of mistaking their legitimate extent so far, as to oppose, by force of arms, the course of the laws within the body of the country. The wisdom and justice of the government of France, and their sense of the necessity in every government, of preserving the course of the laws free and unobstructed, render us confident that they will approve this necessary arrestation of the proceedings of one of their agents; as we would certainly do in the like case, were any Consul or Vice-Consul of ours to oppose with an armed force, the course of their laws within their own limits. Still, however, indispensable as this act has been, it is with the most lively concern, the President has seen that the evil could not be arrested otherwise than by an appeal to the authority of the country.
I have the honor to be, with great esteem and respect, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson,
TO MR. GENET.
Germantown, November 8,1793.
Sir,
I have now to acknowledge and answer your letter of September the 13th, wherein you desire that we may define the extent of the line of territorial protection on the coasts of the United States, observing that governments and jurisconsults have different views on this subject.
It is certain, that heretofore, they have been much divided in opinion, as to the distance from their sea-coast to which they might reasonably claim a right of prohibiting the commitment of hostilities. The greatest distance to which any respectable assent among nations has been at any time given, has been the extent of the human sight, estimated at upwards of twenty miles; and the smallest distance, I believe, claimed by any nation whatever, is the utmost range of a cannon ball, usually stated at one sea league. Some intermediate distances have also been insisted on, and that of three sea leagues has some authority in its favor. The character of our coast, remarkable in considerable parts of it for admitting no vessels of size to pass the shores, would entitle us in reason to as broad a margin of protected navigation as any nation whatever. Not proposing, however, at this time, and without a respectful and friendly communication with the powers interested in this navigation, to fix on the distance to which we may ultimately insist on the right of protection, the President gives instructions to the officers acting under his authority, to consider those heretofore given them as restrained, for the present, to the distance of one sea league, or three geographical miles, from the sea-shore. This distance can admit of no opposition, as it is recognised by treaties between some of the powers with whom we are connected in commerce and navigation, and is as little or less than is claimed by any of them on their own coasts.
Future occasions will be taken to enter into explanations with them, as to the ulterior extent to which we may reasonably carry our jurisdiction. For that of the rivers and bays of the United States, the laws of the several States are understood to have made provision, and they are moreover, as being land-locked, within the body of the United States.
Examining by this rule the case of the British brig Fanny, taken on the 8th of May last, it appears from the evidence that the capture was made four or five miles from the land; and consequently, without the line provisionally adopted by the President, as before mentioned.
I have the honor to be, with sentiments of respect and esteem, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MR. GENET.
Germantown, November 22, 1793.
Sir,
In my letter of October the 2nd, I took the liberty of noticing to you, that the commission of Consul to M. Dannery, ought to have been addressed to the President of the United States. He being the only channel of communication between this country and foreign nations, it is from him alone that foreign nations, or their agents, are to learn what is or has been the will of the nation, and whatever he communicates as such, they have a right and are bound to consider as the expression of the nation, and no foreign agent can be allowed to question it, to interpose between him and any other branch of government, under the pretext of either’s transgressing their functions, nor to make himself the umpire and final judge between them. I am, therefore, Sir, not authorized to enter into any discussions with you on the meaning of our constitution in any part of it, or to prove to you that it has ascribed to him alone the admission or interdiction of foreign agents. I inform you of the fact by authority from the President. I had observed to you, that we were persuaded, in the case of the Consul Dannery, the error in the address had proceeded from no intention in the Executive Council of France to question the functions of the President, and therefore no difficulty was made in issuing the commissions. We are still under the same persuasion. But in your letter of the 14th instant, you personally question the authority of the President, and in consequence of that, have not addressed to him the commission of Messrs. Pennevert and Chervi. Making a point of this formality on your part, it becomes necessary to make a point of it on ours also; and I am therefore charged to return you those commissions, and to inform you, that bound to enforce respect to the order of things established by our constitution, the President will issue no Exequatur to any Consul or Vice-Consul, not directed to him in the usual form, after the party from whom it comes has been apprized that such should be the address.
I have the honor to be, with respect, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MR. GENET.
Philadelphia, December 9, 1793.
Sir,
I have to acknowledge the receipt of your letter of the 3rd instant, which has been duly laid before the President.
We are very far from admitting your principle, that the government on either side has no other right, on the presentation of a consular commission, than to certify, that having examined it, they find it according to rule. The governments of both nations have a right, and that of yours has exercised it as to us, of considering the character of the person appointed, the place for which he is appointed, and other material circumstances; and of taking precautions as to his conduct, if necessary: and this does not defeat the general object of the convention, which, in stipulating that consuls shall be permitted on both sides, could not mean to supersede reasonable objections to particular persons, who might at the moment be obnoxious to the nation to which they were sent, or whose conduct might render them so at any time after. In fact, every foreign agent depends on the double will of the two governments, of that which sends him, and of that which is to permit the exercise of his functions within their territory; and when either of these wills is refused or withdrawn, his authority to act within that territory becomes incomplete. By what member of the government the right of giving or withdrawing permission is to be exercised here, is a question on which no foreign agent can be permitted to make himself the umpire. It is sufficient for him, under our government, that he is informed of it by the executive.
On an examination of the commissions from your nation, among our records, I find that before the late change in the form of our government, foreign agents were addressed, sometimes to the United States, and sometimes to the Congress of the United States, that body being then executive as well as legislative. Thus the commissions of Messrs. L’Etombe, Holker, Dauneraanis, Marbois, Crevecoeur and Chateaufort, have all this clause, ‘Prions et requerons nos tres chers et grands amis et allies, les Etat-Unis de l’Amerique Septentrionale, leurs gouverneurs, et autres officiers, &c. de laisser jouir, &c. le dit sieur, &c. de la charge de notre Consul,’ &c. On the change in the form of our government, foreign nations, not undertaking to decide to what member of the new government their agents should be addressed, ceased to do it to Congress, and adopted the general address to the United States, before cited. This was done by the government of your own nation, as appears by the commissions of Messrs. Mangourit and La Forest, which have in them the clause before cited. So your own commission was, not as M. Gerond’s and Luzerne’s had been, ‘a nos tres chers, &c. le President et membres du Congres general des Etats-Unis,’ &c. but ‘a nos tres chers, &c. les Etats-Unis de l’Amerique,’ &c. Under this general address, the proper member of the government was included, and could take it up. When, therefore, it was seen in the commissions of Messrs. Dupont and Hauterive, that your executive had returned to the ancient address to Congress, it was conceived to be an inattention, insomuch, that I do not recollect (and I do not think it material enough to inquire) whether I noticed it to you either verbally or by letter. When that of M. Dannery was presented with the like address, being obliged to notice to you an inaccuracy of another kind, I then mentioned that of the address, not calling it an innovation, but expressing my satisfaction, which is still entire, that it was not from any design in your Executive Council. The Exequatur was therefore sent. That they will not consider our notice of it as an innovation, we are perfectly secure. No government can disregard formalities more than ours. But when formalities are attacked with a view to change principles, and to introduce an entire independence of foreign agents on the nation with whom they reside, it becomes material to defend formalities. They would be no longer trifles, if they could, in defiance of the national will, continue a foreign agent among us, whatever might be his course of action. Continuing, therefore, the refusal to receive any commission from yourself, addressed to an improper member of the government, you are left free to use either the general one to the United States, as in the commissions of Messrs. Mangourit and La Forest before cited, or the special one, to the President of the United States.
I have the honor to be, with respect, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO THE ATTORNEY GENERAL OF THE UNITED STATES.
Philadelphia, December 18, 1793.
Sir,
The Minister Plenipotentiary of France has enclosed to me a copy of a letter of the 16th instant, which he addressed to you, stating that some libellous publications had been made against him by Mr. Jay, Chief Justice of the United States, and Mr. King, one of the Senators for the State of New York, and desiring that they might be prosecuted. This letter has been laid before the President, according to the request of the Minister; and the President, never doubting your readiness on all occasions to perform the functions of your office, yet thinks it incumbent on him to recommend it specially on the present occasion, as it concerns a public character peculiarly entitled to the protection of the laws. On the other hand, as our citizens ought not to be vexed with groundless prosecutions, duty to them requires it to be added, that if you judge the prosecution in question to be of that nature, you consider this recommendation as not extending to it; its only object being to engage you to proceed in this case according to the duties of your office, the laws of the land, and the privileges of the parties concerned.
I have the honor to be, with great respect and esteem, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
Monticello, February 3, 1794.
Dear Sir,
I have to thank you for the transmission of the letters from General Gates, La Motte, and Hauterive. I perceive by the latter, that the partisans of the one or the other principle (perhaps of both) have thought my name a convenient cover for declarations of their own sentiments. What those are to which Hauterive alludes, I know not, having never seen a newspaper since I left Philadelphia (except those of Richmond), and no circumstances authorize him to expect that I should inquire into them, or answer him. I think it is Montaigne who has said, that ignorance is the softest pillow on which a man can rest his head. I am sure it is true as to every thing political, and shall endeavor to estrange myself to every thing of that character. I indulge myself on one political topic only, that is, in declaring to my countrymen the shameless corruption of a portion of the Representatives in the first and second Congresses, and their implicit devotion to the treasury. I think I do good in this, because it may produce exertions to reform the evil, on the success of which the form of the government is to depend.
I am sorry La Motte has put me to the expense of one hundred and forty livres for a French translation of an English poem, as I make it a rule never to read translations where I can read the original. However, the question now is, how to get the book brought here, as well as the communications with Mr. Hammond which you were so kind as to promise me.
This is the first letter I have written to Philadelphia since my arrival at home, and yours the only ones I have received.
Accept assurances of my sincere esteem and respect. Yours affectionately,
Th: Jefferson.
Monticello, April 3, 1794.
Dear Sir,
Our post having ceased to ride ever since the inoculation began in Richmond, till now, I received three days ago, and all together, your friendly favors of March the 2nd, 9th, 12th, 14th, and Colonel Monroe’s of March the 3rd and 16th. I have been particularly gratified by the receipt of the papers containing yours and Smith’s discussion of your regulating propositions. These debates had not been seen here but in a very short and mutilated form. I am at no loss to ascribe Smith’s speech to its true father. Every tittle of it is Hamilton’s except the introduction. There is scarcely any thing there which I have not heard from him in our various private, though official discussions. The very turn of the arguments is the same, and others will see as well as myself that the style is Hamilton’s. The sophistry is too fine, too ingenious, even to have been comprehended by Smith, much less devised by him. His reply shows he did not understand his first speech; as its general inferiority proves its legitimacy, as evidently as it does the bastardy of the original. You know we had understood that Hamilton had prepared a counter report, and that some of his humble servants in the Senate were to move a reference to him in order to produce it. But I suppose they thought it would have a better effect, if fired off in the House of Representatives. I find the report, however, so fully justified, that the anxieties with which I left it are perfectly quieted. In this quarter, all espouse your propositions with ardor, and without a dissenting voice.
The rumor of a declaration of war has given an opportunity of seeing, that the people here, though attentive to the loss of value of their produce in such an event, yet find in it a gratification of some other passions, and particularly of their ancient hatred to Great Britain. Still I hope it will not come to that; but that the proposition will be carried, and justice be done ourselves in a peaceable way. As to the guarantee of the French islands, whatever doubts may be entertained of the moment at which we ought to interpose, yet I have no doubt but that we ought to interpose at a proper time, and declare both to England and France, that these islands are to rest with France, and that we will make a common cause with the latter for that object. As to the naval armament, the land armament, and the marine fortifications which are in question with you, I have no doubt they will all be carried. Not that the monocrats and papermen in Congress want war; but they want armies and debts; and though we may hope that the sound part of Congress is now so augmented as to insure a majority in cases of general interest merely, yet I have always observed that in questions of expense, where members may hope either for offices or jobs for themselves or their friends, some few will be debauched, and that is sufficient to turn the decision where a majority is, at most, but small. I have never seen a Philadelphia paper since I left it, till those you enclosed me; and I feel myself so thoroughly weaned from the interest I took in the proceedings there, while there, that I have never had a wish to see one, and believe that I never shall take another newspaper of any sort. I find my mind totally absorbed in my rural occupations.
Accept sincere assurances of affection.
Th: Jefferson.
Monticello, May 1,1794.
Dear Sir,
Your several favors of February the 22nd, 27th, and March the 16th, which had been accumulating in Richmond during the prevalence of the small pox in that place, were lately brought to me, on the permission given the post to resume his communication. I am particularly to thank you for your favor in forwarding the Bee. Your letters give a comfortable view of French affairs, and later events seem to confirm it. Over the foreign powers I am convinced they will triumph completely, and I cannot but hope that that triumph, and the consequent disgrace of the invading tyrants, is destined, in the order of events, to kindle the wrath of the people of Europe against those who have dared to embroil them in such wickedness, and to bring at length, kings, nobles, and priests to the scaffolds which they have been so long deluging with human blood. I am still warm whenever I think of these scoundrels, though I do it as seldom as I can, preferring infinitely to contemplate the tranquil growth of my lucerne and potatoes. I have so completely withdrawn myself from these spectacles of usurpation and misrule, that I do not take a single newspaper, nor read one a month: and I feel myself infinitely the happier for it.
We are alarmed here with the apprehensions of war; and sincerely anxious that it may be avoided; but not at the expense either of our faith or honor. It seems much the general opinion here, the latter has been too much wounded not to require reparation, and to seek it even in war, if that be necessary. As to myself, I love peace, and I am anxious that we should give the world still another useful lesson, by showing to them other modes of punishing injuries than by war, which is as much a punishment to the punisher as to the sufferer. I love therefore, Mr. Clarke’s proposition of cutting off all communication with the nation which has conducted itself so atrociously. This you will say may bring on war. If it does, we will meet it like men; but it may not bring on war, and then the experiment will have been a happy one. I believe this war would be vastly more unanimously approved than any one we ever were engaged in; because the aggressions have been so wanton and bare-faced, and so unquestionably against our desire. I am sorry Mr. Cooper and Priestley did not take a more general survey of our country before they fixed themselves. I think they might have promoted their own advantage by it, and have aided the introduction of improvement where it is more wanting. The prospect of wheat for the ensuing year is a bad one. This is all the sort of news you can expect from me. From you I shall be glad to hear all sorts of news, and particularly any improvements in the arts applicable to husbandry or household manufacture.
I am, with very sincere affection, Dear Sir, your friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO THE PRESIDENT.
Monticello, May 14, 1794.
Dear Sir,
I am honored with your favor of April the 24th, and received at the same time Mr. Bertrand’s agricultural prospectus. Though he mentions my having seen him at a particular place, yet I remember nothing of it, and observing that he intimates an application for lands in America, I conceive his letter meant for me as Secretary of State, and therefore I now send it to the Secretary of State. He has given only the heads of his demonstrations, so that nothing can be conjectured of their details. Lord Kaims once proposed an essence of dung, one pint of which should manure an acre. If he or Mr. Bertrand could have rendered it so portable, I should have been one of those who would have been greatly obliged to them. I find on a more minute examination of my lands that the short visits heretofore made to them, permitted, that a ten years’ abandonment of them to the ravages of overseers, has brought on them a degree of degradation far beyond what I had expected. As this obliges me to adopt a milder course of cropping, so I find that they have enabled me to do it, by having opened a great deal of lands during my absence. I have therefore determined on a division of my farms into six fields, to be put under this rotation: first year, wheat; second, corn, potatoes, peas; third, rye, or wheat, according to circumstances; fourth and fifth, clover where the fields will bring it, and buckwheat dressings where they will not; sixth, folding, and buckwheat dressings. But it will take me from three to six years to get this plan under way. I am not yet satisfied that my acquisition of overseers from the head of Elk has been a happy one, or that much will be done this year towards rescuing my plantations from their wretched condition. Time, patience, and perseverance must be the remedy: and the maxim of your letter, ‘slow and sure,’ is not less a good one in agriculture than in politics. I sincerely wish it may extricate us from the event of a war, if this can be done saving our faith and our rights. My opinion of the British government is, that nothing will force them to do justice but the loud voice of their people, and that this can never be excited but by distressing their commerce. But I cherish tranquillity too much, to suffer political things to enter my mind at all. I do not forget that I owe you a letter for Mr. Young; but I am waiting to get full information. With every wish for your health and happiness, and my most friendly respects for Mrs. Washington, I have the honor to be, Dear Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO THE SECRETARY OF STATE.
Monticello, September 7, 1794.
Dear Sir,
Your favor of August the 28th finds me in bed under a paroxysm of the rheumatism which has now kept me for ten days in constant torment, and presents no hope of abatement. But the express and the nature of the case requiring immediate answer, I write to you in this situation. No circumstances, my Dear Sir, will ever more tempt me to engage in any thing public. I thought myself perfectly fixed in this determination when I left Philadelphia, but every day and hour since has added to its inflexibility. It is a great pleasure to me to retain the esteem and approbation of the President, and this forms the only ground of any reluctance at being unable to comply with every wish of his. Pray convey these sentiments and a thousand more to him, which my situation does not permit me to go into. But however suffering by the addition of every single word to this letter, I must add a solemn declaration that neither Mr. J. nor Mr. ———- ever mentioned to me one word of any want of decorum in Mr. Carmichael, nor any thing stronger or more special than stated in my notes of the conversation. Excuse my brevity, my dear Sir, and accept assurances of the sincere esteem and respect, with which I have the honor to be your affectionate friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JAMES MADISON.
Monticello, December 28, 1794.
Dear Sir,
I have kept Mr. Jay’s letter a post or two, with an intention of considering attentively the observations it contains: but I have really now so little stomach for any thing of that kind, that I have not resolution enough even to endeavor to understand the observations. I therefore return the letter, not to delay your answer to it, and beg you in answering for yourself, to assure him of my respects and thankful acceptance of Chalmers’ Treaties, which I do not possess, and if you possess yourself of the scope of his reasoning, make any answer to it you please for me. If it had been on the rotation of my crops, I would have answered myself, lengthily perhaps, but certainly con gusto.
The denunciation of the democratic societies is one of the extraordinary acts of boldness of which we have seen so many from the faction of monocrats. It is wonderful indeed, that the President should have permitted himself to be the organ of such an attack on the freedom of discussion, the freedom of writing, printing, and publishing. It must be a matter of rare curiosity to get at the modifications of these rights proposed by them, and to see what line their ingenuity would draw between democratical societies, whose avowed object is the nourishment of the republican principles of our constitution, and the society of the Cincinnati, a self-created one, carving out for itself hereditary distinctions, lowering over our constitution eternally, meeting together in all parts of the Union, periodically, with closed doors, accumulating a capital in their separate treasury, corresponding secretly and regularly, and of which society the very persons denouncing the democrats are themselves the fathers, founders, and high officers. Their sight must be perfectly dazzled by the glittering of crowns and coronets, not to see the extravagance of the proposition to suppress the friends of general freedom, while those who wish to confine that freedom to the few are permitted to go on in their principles and practices. I here put out of sight the persons whose misbehavior has been taken advantage of to slander the friends of popular rights; and I am happy to observe, that as far as the circle of my observation and information extends, every body has lost sight of them, and views the abstract attempt on their natural and constitutional rights in all its nakedness. I have never heard, or heard of, a single expression or opinion which did not condemn it as an inexcusable aggression. And with respect to the transactions against the excise law, it appears to me that you are all swept away in the torrent of governmental opinions, or that we do not know what these transactions have been. We know of none which, according to the definitions of the law, have been any thing more than riotous. There was indeed a meeting to consult about a separation. But to consult on a question does not amount to a determination of that question in the affirmative, still less to the acting on such a determination: but we shall see, I suppose, what the court lawyers, and courtly judges, and would-be ambassadors will make of it. The excise law is an infernal one. The first error was to admit it by the constitution; the second, to act on that admission; the third and last will be, to make it the instrument of dismembering the Union, and setting us all afloat to choose what part of it we will adhere to. The information of our militia, returned from the westward, is uniform, that though the people there let them pass quietly, they were objects of their laughter, not of their fear; that one thousand men could have cut off their whole force in a thousand places of the Allegany; that their detestation of the excise law is universal, and has now associated to it a detestation of the government; and that separation which perhaps was a very distant and problematical event, is now near, and certain, and determined in the mind of every man. I expected to have seen some justification of arming one part of the society against another; of declaring a civil war the moment before the meeting of that body which has the sole right of declaring war; of being so patient of the kicks and scoffs of our enemies, and rising at a feather against our friends; of adding a million to the public debt and deriding us with recommendations to pay it if we can, &c. &c. But the part of the speech which was to be taken as a justification of the armament, reminded me of Parson Saunders’s demonstration why minus into minus makes plus. After a parcel of shreds of stuff from Æsop’s fables and Tom Thumb, he jumps all at once into his ergo, minus multiplied into minus makes phis. Just so the fifteen thousand men enter after the fables, in the speech.
However, the time is coming when we shall fetch up the leeway of our vessel. The changes in your House, I see, are going on for the better, and even the Augean herd over your heads are slowly purging off their impurities. Hold on then, my dear friend, that we may not shipwreck in the mean while. I do not see, in the minds of those with whom I converse, a greater affliction than the fear of your retirement; but this must not be, unless to a more splendid and a more efficacious post. There I should rejoice to see you; I hope I may say, I shall rejoice to see you. I have long had much in my mind to say to you on that subject. But double delicacies have kept me silent. I ought perhaps to say, while I would not give up my own retirement for the empire of the universe, how I can justify wishing one whose happiness I have so much at heart as yours, to take the front of the battle which is fighting for my security. This would be easy enough to be done, but not at the heel of a lengthy epistle.
Present me respectfully to Mrs. Madison, and pray her to keep you where you are for her own satisfaction and the public good, and accept the cordial affections of us all. Adieu.
Th: Jefferson.
Monticello, February 6,1795.
Dear Sir,
Your several favors on the affairs of Geneva found me here, in the month of December last. It is now more than a year that I have withdrawn myself from public affairs, which I never liked in my life, but was drawn into by emergencies which threatened our country with slavery, but ended in establishing it free. I have returned, with infinite appetite, to the enjoyment of my farm, my family, and my books, and had determined to meddle in nothing beyond their limits. Your proposition, however, for transplanting the college of Geneva to my own country, was too analogous to all my attachments to science, and freedom, the first-born daughter of science, not to excite a lively interest in my mind, and the essays which were necessary to try its practicability. This depended altogether on the opinions and dispositions of our State legislature, which was then in session. I immediately communicated your papers to a member of the legislature, whose abilities and zeal pointed him out as proper for it, urging him to sound as many of the leading members of the legislature as he could, and if he found their opinions favorable, to bring forward the proposition; but if he should find it desperate, not to hazard it: because I thought it best not to commit the honor either of our State or of your college, by an useless act of eclat. It was not till within these three days that I have had an interview with him, and an account of his proceedings. He communicated the papers to a great number of the members, and discussed them maturely, but privately, with them. They were generally well disposed to the proposition, and some of them warmly: however, there was no difference of opinion in the conclusion, that it could not be effected. The reasons which they thought would with certainty prevail against it, were, 1. that our youth, not familiarized but with their mother tongue, were not prepared to receive instructions in any other; 2. that the expense of the institution would excite uneasiness in their constituents, and endanger its permanence; and 3. that its extent was disproportioned to the narrow state of the population with us. Whatever might be urged on these several subjects, yet as the decision rested with others, there remained to us only to regret that circumstances were such, or were thought to be such, as to disappoint your and our wishes.
I should have seen with peculiar satisfaction the establishment of such a mass of science in my country, and should probably have been tempted to approach myself to it, by procuring a residence in its neighborhood, at those seasons of the year at least when the operations of agriculture are less active and interesting. I sincerely lament the circumstances which have suggested this emigration. I had hoped that Geneva was familiarized to such a degree of liberty, that they might without difficulty or danger fill up the measure to its maximum; a term, which, though in the insulated man, bounded only by his natural powers, must, in society, be so far restricted as to protect himself against the evil passions of his associates, and consequently, them against him. I suspect that the doctrine, that small States alone are fitted to be republics, will be exploded by experience, with some other brilliant fallacies accredited by Montesquieu and other political writers. Perhaps it will be found, that to obtain a just republic (and it is to secure our just rights that we resort to government at all) it must be so extensive as that local egoisms may never reach its greater part; that on every particular question a majority may be found in its councils free from particular interests, and giving, therefore, an uniform prevalence to the principles of justice. The smaller the societies, the more violent and more convulsive their schisms. We have chanced to live in an age which will probably be distinguished in history, for its experiments in government on a larger scale than has yet taken place. But we shall not live to see the result. The grosser absurdities, such as hereditary magistracies, we shall see exploded in our day, long experience having already pronounced condemnation against them. But what is to be the substitute? This our children or grandchildren will answer. We may be satisfied with the certain knowledge that none can ever be tried, so stupid, so unrighteous, so oppressive, so destructive of every end for which honest men enter into government, as that which their forefathers had established, and their fathers alone venture to tumble headlong from the stations they have so long abused. It is unfortunate, that the efforts of mankind to recover the freedom of which they have been so long deprived, will be accompanied with violence, with errors, and even with crimes. But while we weep over the means we must pray for the end.
But I have been insensibly led, by the general complexion of the times, from the particular case of Geneva, to those to which it bears no similitude. Of that we hope good things. Its inhabitants must be too much enlightened, too well experienced in the blessings of freedom and undisturbed industry, to tolerate long a contrary state of things. I shall be happy to hear that their government perfects itself, and leaves room for the honest, the industrious, and wise; in which case, your own talents, and those of the persons for whom you have interested yourself, will, I am sure, find welcome and distinction. My good wishes will always attend you, as a consequence of the esteem and regard with which I am, Dear Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JAMES MADISON.
Monticello, April 27, 1795.
Dear Sir,
Your letter of March the 23rd came to hand the 7th of April, and notwithstanding the urgent reasons for answering a part of it immediately, yet as it mentioned that you would leave Philadelphia within a few days, I feared that the answer might pass you on the road. A letter from Philadelphia by the last post having announced to me your leaving that place the day preceding its date, I am in hopes this will find you in Orange. In mine, to which yours of March the 23rd was an answer, I expressed my hope of the only change of position I ever wished to see you make, and I expressed it with entire sincerity, because there is not another person in the United States, who being placed at the helm of our affairs, my mind would be so completely at rest for the fortune of our political bark. The wish too was pure, and unmixed with any thing respecting myself personally.
For as to myself, the subject had been thoroughly weighed and decided on, and my retirement from office had been meant from all office, high or low, without exception. I can say, too, with truth, that the subject had not been presented to my mind by any vanity of my own. I know myself and my fellow citizens too well to have ever thought of it. But the idea was forced upon me by continual insinuations in the public papers, while I was in office. As all these came from a hostile quarter, I knew that their object was to poison the public mind as to my motives, when they were not able to charge me with facts. But the idea being once presented to me, my own quiet required that I should face it and examine it. I did so thoroughly, and had no difficulty to see that every reason which had determined me to retire from the office I then held, operated more strongly against that which was insinuated to be my object. I decided then on those general grounds which could alone be present to my mind at that time, that is to say, reputation, tranquillity, labor; for as to public duty, it could not be a topic of consideration in my case. If these general considerations were sufficient to ground a firm resolution never to permit myself to think of the office, or be thought of for it, the special ones, which have supervened on my retirement, still more insuperably bar the door to it. My health is entirely broken down within the last eight months; my age requires that I should place my affairs in a clear state; these are sound if taken care of, but capable of considerable dangers if longer neglected; and above all things, the delights I feel in the society of my family, and in the agricultural pursuits in which I am so eagerly engaged. The little spice of ambition which I had in my younger days has long since evaporated, and I set still less store by a posthumous than present name. In stating to you the heads of reasons which have produced my determination, I do not mean an opening for future discussion, or that I may be reasoned out of it. The question is for ever closed with me; my sole object is to avail myself of the first opening ever given me from a friendly quarter (and I could not with decency do it before) of preventing any division or loss of votes, which might be fatal to the republican interest. If that has any chance of prevailing, it must be by avoiding the loss of a single vote, and by concentrating all its strength on one object. Who this should be, is a question I can more freely discuss with any body than yourself. In this I painfully feel the loss of Monroe. Had he been here, I should have been at no loss for a channel through which to make myself understood; if I have been misunderstood by any body through the instrumentality of Mr. Fenno and his abettors. I long to see you. I am proceeding in my agricultural plans with a slow but sure step. To get under full way will require four or five years. But patience and perseverance, will accomplish it. My little essay in red-clover, the last year, has had the most encouraging success. I sowed then about forty acres. I have sowed this year about one hundred and twenty, which the rain now falling comes very opportunely on. From one hundred and sixty to two hundred acres, will be my yearly sowing. The seed-box described in the agricultural transactions of New York, reduces the expense of seeding from six shillings to two shillings and three pence the acre, and does the business better than is possible to be done by the human hand. May we hope a visit from you? If we may, let it be after the middle of May, by which time I hope to be returned from Bedford. I have had a proposition to meet Mr. Henry there this month, to confer on the subject of a convention, to the calling of which he is now become a convert. The session of our district court furnished me a just excuse for the time; but the impropriety of my entering into consultation on a measure in which I would take no part, is a permanent one.
Present my most respectful compliments to Mrs. Madison, and be assured of the warm attachment of, Dear Sir, yours affectionately,
Th: Jefferson.
TO WILLIAM B. GILES.
Monticello, April 27, 1795,
Dear Sir,
Your favor of the 16th came to hand by the last post. I sincerely congratulate you on the great prosperities of our two first allies, the French and Dutch. If I could but see them now at peace with the rest of their continent, I should have little doubt of dining with Pichegru in London, next autumn; for I believe I should be tempted to leave my clover for a while, to go and hail the dawn of liberty and republicanism in that island. I shall be rendered very happy by the visit you promise me. The only thing wanting to make me completely so, is the more frequent society of my friends. It is the more wanting, as I am become more firmly fixed to the glebe. If you visit me as a farmer, it must be as a condisciple: for I am but a learner; an eager one indeed, but yet desperate, being too old now to learn a new art. However, I am as much delighted and occupied with it, as if I was the greatest adept. I shall talk with you about it from morning till night, and put you on very short allowance as to political aliment. Now and then a pious ejaculation for the French and Dutch republicans, returning with due despatch to clover, potatoes, wheat, &c. That I may not lose the pleasure promised me, let it not be till the middle of May, by which time I shall be returned from a trip I meditate to Bedford.
Yours affectionately,
Th: Jefferson.
THOMAS JEFFERSON TO MANN PAGE.
Monticello, August 30, 1795.
It was not in my power to attend at Fedricksburg according to the kind invitation in your letter, and in that of Mr. Ogilvie. The heat of the weather, the business of the farm, to which I have made myself necessary, forbade it; and to give one round reason for all, maturè sanus, I have laid up my Rosinante in his stall, before his unfitness for the road shall expose him faltering to the world. But why did not I answer you in time? Because, in truth, I am encouraging myself to grow lazy, and I was sure you would ascribe the delay to any thing sooner than a want of affection or respect to you, for this was not among the possible causes. In truth, if any thing could ever induce me to sleep another night out of my own house, it would have been your friendly invitation and my solicitude for the subject of it, the education of our youth. I do most anxiously wish to see the highest degrees of education given to the higher degrees of genius, and to all degrees of it, so much as may enable them to read and understand what is going on in the world, and to keep their part of it going on right: for nothing can keep it right but their own vigilant and distrustful superintendence. I do not believe with the Rochefoucaults and Montaignes, that fourteen out of fifteen men are rogues: I believe a great abatement from that proportion may be made in favor of general honesty. But I have always found that rogues would be uppermost, and I do not know that the proportion is, too strong for the higher orders, and for those who, rising above the swinish multitude, always contrive to nestle themselves into the places of power and profit. These rogues set out with stealing the peoples’ good opinion, and then steal from them the right of withdrawing it, by contriving laws and associations against the power of the people themselves. Our part of the country is in considerable fermentation on what they suspect to be a recent roguery of this kind. They say that while all hands were below deck mending sails, splicing ropes, and every one at his own business, and the captain in his cabin attending to his log-book and chart, a rogue of a pilot has run them into an enemy’s port. But metaphor apart, there is much dissatisfaction with Mr. Jay and his treaty. For my part, I consider myself now but as a passenger, leaving the world and its government to those who are likely to live longer in it. That you may be among the longest of these, is my sincere prayer. After begging you to be the bearer of my compliments and apologies to Mr. Ogilvie, I bid you an affectionate farewell, always wishing to hear from you.
THOMAS JEFFERSON TO JAMES MADISON.
Monticello, September 21,1795.
I received, about three weeks ago, a box containing six dozen volumes, of two hundred and eighty-three pages, 12mo. with a letter from Lambert, Beckley’s clerk, that they came from Mr. Beckley, and were to be divided between yourself, J. Walker, and myself. I have sent two dozen to J. Walker, and shall be glad of a conveyance for yours. In the mean time, I send you by post, the title-page, table of contents, and one of the pieces, Curtius, lest it should not have come to you otherwise. It is evidently written by Hamilton, giving a first and general view of the subject, that the public mind might be kept a little in check, till he could resume the subject more at large from the beginning, under his second signature of Camillas. The piece called ‘The Features of the Treaty,’ I do not send, because you have seen it in the newspapers. It is said to be written by Coxe, but I should rather suspect by Beckley. The antidote is certainly not strong enough for the poison of Curtius. If I had not been informed the present came from Beckley, I should have suspected it from Jay or Hamilton. I gave a copy or two, by way of experiment, to honest, sound-hearted men of common understanding, and they were not able to parry the sophistry of Curtius. I have ceased, therefore, to give them. Hamilton is really a colossus to the anti-republican party. Without numbers, he is an host within himself. They have got themselves into a defile, where they might be finished; but too much security on the republican part will give time to his talents and indefatigableness to extricate them. We have had only middling performances to oppose to him. In truth when he comes forward, there is nobody but yourself who can meet him. His adversaries having begun the attack, he has the advantage of answering them, and remains unanswered himself. A solid reply might yet completely demolish what was too feebly attacked, and has gathered strength from the weakness of the attack. The merchants were certainly (except those of them who are English) as open-mouthed at first against the treaty, as any. But the general expression of indignation has alarmed them for the strength of the government. They have feared the shock would be too great, and have chosen to tack about and support both treaty and government, rather than risk the government. Thus it is, that Hamilton, Jay, &c. in the boldest act they ever ventured on to undermine the government, have the address to screen themselves, and direct the hue and cry against those who wished to drag them into light. A bolder party-stroke was never struck. For it certainly is an attempt of a party, who find they have lost their majority in one branch of the legislature, to make a law by the aid of the other branch and of the executive, under color of a treaty, which shall bind up the hands of the adverse branch from ever restraining the commerce of their patron-nation. There appears a pause at present in the public sentiment, which may be followed by a revulsion. This is the effect of the desertion of the merchants, of the President’s chiding answer to Boston and Richmond, of the writings of Curtius and Camillus, and of the quietism into which people naturally fall after first sensations are over. For God’s sake take up your pen, and give a fundamental reply to Curtius and Camillus. Adieu affectionately.
TO EDWARD RUTLEDGE.
Monticello, November 30, 1795,
My Dear Sir,
I received your favor of October the 12th by your son, who has been kind enough to visit me here, and from whose visit I have received all that pleasure which I do from whatever comes from you, and especially from a subject so deservedly dear to you. He found me in a retirement I doat on, living like an antediluvian patriarch among my children and grandchildren, and tilling my soil. As he had lately come from Philadelphia, Boston, &c. he was able to give me a great deal of information of what is passing in the world, and I pestered him with questions pretty much as our friends Lynch, Nelson, &c. will us, when we step across the Styx, for they will wish to know what has been passing above ground since they left us. You hope I have not abandoned entirely the service of our country. After five and twenty years’ continual employment in it, I trust it will be thought I have fulfilled my tour, like a punctual soldier, and may claim my discharge. But I am glad of the sentiment from you, my friend, because it gives a hope you will practise what you preach, and come forward in aid of the public vessel. I will not admit your old excuse, that you are in public service though at home. The campaigns which are fought in a man’s own house are not to be counted. The present situation of the President, unable to get the offices filled, really calls with uncommon obligation on those whom nature has fitted for them. I join with you in thinking the treaty an execrable thing. But both negotiators must have understood, that as there were articles in it which could not be carried into execution without the aid of the legislatures on both sides, therefore it must be referred to them, and that these legislatures, being free agents, would not give it their support if they disapproved of it. I trust the popular branch of our legislature will disapprove of it, and thus rid us of this infamous act, which is really nothing more than a treaty of alliance between England and the Anglomen of this country, against the legislature and people of the United States. I am, my dear friend, yours affectionately,
Th: Jefferson.
TO WILLIAM B. GILES.
Monticello, December 31, 1795.
Dear Sir,
Your favors of December the 15th and 20th came to hand by the last post. I am well pleased with the manner in which your House have testified their sense of the treaty: while their refusal to pass the original clause of the reported answer proved their condemnation of it, the contrivance to let it disappear silently respected appearances in favor of the President, who errs as other men do, but errs with integrity. Randolph seems to have hit upon the true theory of our constitution; that when a treaty is made, involving matters confided by the constitution to the three branches of the legislature conjointly, the Representatives are as free as the President and Senate were, to consider whether the national interest requires or forbids their giving the forms and force of law to the articles over which they have a power. I thank you much for the pamphlet. His narrative is so straight and plain, that even those who did not know him will acquit him of the charge of bribery. Those who knew him had done it from the first. Though he mistakes his own political character in the aggregate, yet he gives it to you in the detail. Thus he supposes himself a man of no party (page 57); that his opinions not containing any systematic adherence to party, fell sometimes on one side and sometimes on the other (page 58). Yet he gives you these facts, which show that they fall generally on both sides, and are complete inconsistencies.
1. He never gave an opinion in the cabinet against the rights of the people (page 97); yet he advised the denunciation of the popular societies (page 67).
2. He would not neglect the overtures of a commercial treaty with France (page 79); yet he always opposed it while Attorney General, and never seems to have proposed it while Secretary of State.
3. He concurs in resorting to the militia to quell the pretended insurrections in the west (page 81), and proposes an augmentation from twelve thousand five hundred to fifteen thousand, to march against men at their ploughs (page 80); yet on the 5th of August he is against their marching (pages 83, 101), and on the 25th of August he is for it (page 84).
4. He concurs in the measure of a mission extraordinary to London (as is inferred from page 58), but objects to the men, to wit, Hamilton and Jay (page 50).
5. He was against granting commercial powers to Mr. Jay (page 58); yet he besieged the doors of the Senate to procure their advice to ratify.
6. He advises the President to a ratification on the merits of the treaty (page 97), but to a suspension till the provision order is repealed (page 98). The fact is, that he has generally given his principles to the one party, and his practice to the other; the oyster to one, the shell to the other. Unfortunately, the shell was generally the lot of his friends, the French and republicans, and the oyster of their antagonists. Had he been firm to the principles he professes in the year 1793, the President would have been kept from an habitual concert with the British and anti-republican party. But at that time, I do not know which R. feared most, a British fleet, or French disorganizers. Whether his conduct is to be ascribed to a superior view of things, and adherence to right without regard to party, as he pretends, or to an anxiety to trim between both, those who know his character and capacity will decide. Were parties here divided merely by a greediness for office, as in England, to take a part with either would be unworthy of a reasonable or moral man. But where the principle of difference is as substantial, and as strongly pronounced, as between the republicans and the monocrats of our country, I hold it as honorable to take a firm and decided part, and as immoral to pursue a middle line, as between the parties of honest men and rogues, into which every country is divided.
A copy of the pamphlet came by this post to Charlottesville. I suppose we shall be able to judge soon what kind of impression it is likely to make. It has been a great treat to me, as it is a continuation of that cabinet history, with the former part of which I was intimate. I remark, in the reply of the President, a small travestie of the sentiment contained in the answer of the Representatives. They acknowledge that he has contributed a great share to the national happiness by his services. He thanks them for ascribing to his agency a great share of those benefits. The former keeps in view the co-operation of others towards the public good. The latter presents to view his sole agency. At a time when there would have been less anxiety to publish to the people a strong approbation from your House, this strengthening of your expression would not have been noticed.
Our attentions have been so absorbed by the first manifestation of the sentiments of your House, that we have lost sight of our own legislature; insomuch, that I do not know whether they are sitting or not. The rejection of Mr. Rutledge by the Senate is a bold thing; because they cannot pretend any objection to him but his disapprobation of the treaty. It is, of course, a declaration that they will receive none but tories hereafter into any department of the government. I should not wonder if Monroe were to be recalled, under the idea of his being of the partisans of France, whom the President considers as the partisans of war and confusion, in his letter of July the 31st, and as disposed to excite them to hostile measures, or at least to unfriendly sentiments; a most infatuated blindness to the true character of the sentiments entertained in favor of France. The bottom of my page warns me that it is time to end my commentaries on the facts you have furnished me. You would of course, however, wish to know the sensations here on those facts.
My friendly respects to Mr. Madison, to whom the next week’s dose will be directed. Adieu affectionately.
Th: Jefferson.
TO JAMES MADISON.
Monticello, March 6, 1796.
Dear Sir,
I wrote you February the 21st, since which I have received yours of the same day. Indeed, mine of that date related only to a single article in yours of January the 31st and February the 7th. I do not at all wonder at the condition in which the finances of the United States are found. Hamilton’s object from the beginning, was to throw them into forms which should be utterly undecipherable. I ever said he did not understand their condition himself, nor was able to give a clear view of the excess of our debts beyond our credits, nor whether we were diminishing or increasing the debt. My own opinion was, that from the commencement of this government to the time I ceased to attend to the subject, we had been increasing our debt about a million of dollars annually. If Mr. Gallatin would undertake to reduce this chaos to order, present us with a clear view of our finances, and put them into a form as simple as they will admit, he will merit immortal honor. The accounts of the United States ought to be, and may be, made as simple as those of a common farmer, and capable of being understood by common farmers.
Disapproving, as I do, of the unjustifiable largess to the demands of the Count de Grasse, I will certainly not propose to rivet it by a second example on behalf of M. de Chastellux’s son. It will only be done in the event of such a repetition of the precedent, as will give every one a right to share in the plunder. It is, indeed, surprising you have not yet received the British treaty in form. I presume you would never receive it were not your cooperation on it necessary. But this will oblige the formal notification of it to you.
My salutations to Mrs. Madison, friendly esteem to Mr. Giles, Page, &c. I am, with sincere affection, yours,
Th: Jefferson.
P. S. Have you considered all the consequences of your proposition respecting post-roads? I view it as a source of boundless patronage to the executive, jobbing to members of Congress and their friends, and a bottomless abyss of public money. You will begin by only appropriating the surplus of the post-office revenues: but the other revenues will soon be called in to their aid, and it will be a source of eternal scramble among the members, who can get the most money wasted in their State; and they will always get most who are meanest. We have thought, hitherto, that the roads of a State could not be so well administered even by the State legislature as by the magistracy of the county, on the spot. How will they be when a member of New Hampshire is to mark out a road for Georgia? Does the power to establish post-roads, given you by the constitution, mean that you shall make the roads, or only select from those already made those on which there shall be a post? If the term be equivocal (and I really do not think it so), which is the safest construction; that which permits a majority of Congress to go to cutting down mountains and bridging of rivers, or the other, which if too restricted may be referred to the States for amendment, securing still due measures and proportion among us, and providing some means of information to the members of Congress tantamount to that ocular inspection, which, even in our county determinations, the magistrate finds cannot be supplied by any other evidence? The fortification of harbors was liable to great objection. But national circumstances furnished some color. In this case there is none. The roads of America are the best in the world, except those of France and England. But does the state of our population, the extent of our internal commerce, the want of sea and river navigation, call for such expense on roads here, or are our means adequate to it? Think of all this, and a great deal more which your good judgment will suggest, and pardon my freedom. T. J.
THOMAS JEFFERSON TO WILLIAM B. GILES.
I know not when I have received greater satisfaction than on reading the speech of Dr. Leib, in the Pennsylvania Assembly. He calls himself a new member. I congratulate honest republicanism on such an acquisition, and promise myself much from a career which begins on such elevated ground. We are in suspense here to see the fate and effect of Mr. Pitt’s bill against democratic societies. I wish extremely to get at the true history of this effort to suppress freedom of meeting, speaking, writing, and printing. Your acquaintance with Sedgwick will enable you to do it. Pray get the outlines of the bill he intended to have brought in for this purpose. This will enable us to judge whether we have the merit of the invention; whether we were really beforehand with the British Minister on this subject; whether he took his hint from our proposition, or whether the concurrence in sentiment is merely the result of the general truth that great men will think alike and act alike, though without intercommunication. I am serious in desiring extremely the outlines of the bill intended for us. From the debates on the subject of our seamen, I am afraid as much harm as good will be done by our endeavors to arm our seamen against impressments. It is proposed to register them and give them certificates. But these certificates will be lost in a thousand ways: a sailor will neglect to take his certificate: he is wet twenty times in a voyage; if he goes ashore without it, he is impressed; if with it, he gets drunk, it is lost, stolen from him, taken from him, and then the want of it gives authority to impress, which does not exist now. After ten years’ attention to the subject, I have never been able to devise any thing effectual, but that the circumstance of an American bottom be made, ipso facto, a protection for a number of seamen proportioned to her tonnage; that American captains be obliged, when called on by foreign officers, to parade the men on deck, which would show whether they exceeded their own quota, and allow the foreign officer to send two or three persons aboard and hunt for any suspected to be concealed. This, Mr. Pinckney was instructed to insist upon with Great Britain; to accept of nothing short of it; and, most especially, not to agree that a certificate of citizenship should be requirable from our seamen; because it would be made a ground for the authorized impressment of them. I am still satisfied that such a protection will place them in a worse situation than they are at present. It is true, the British Minister has not shown any disposition to accede to my proposition; but it was not totally rejected: and if he still refuses, lay a duty of one penny sterling a yard on British oznaburgs, to make a fund for paying the expenses of the agents you are obliged to employ to seek out our suffering seamen. I congratulate you on the arrival of Mr. Ames and the British treaty. The newspapers had said they would arrive together. We have had a fine winter. Wheat looks well. Corn is scarce and dear. Twenty-two shillings here, thirty shillings in Amherst. Our blossoms are but just opening. I have begun the demolition of my house, and hope to get through its re-edification in the course of the summer. We shall have the eye of a brick-kiln to poke you into, or an octagon to air you in. Adieu affectionately. March 19,1796.
Monticello, March 21, 1796.
Dear Sir,
I wrote you on the 2nd instant, and now take the liberty of troubling you, in order to have the enclosed letter to M. Gautier safely handed to him. I will thank you for information that it gets safely to hand, as it is of considerable importance to him, to the United States, to the State of Virginia, and to myself, by conveying to him the final arrangement of the accounts of Grand and company with all those parties.
The British treaty has been formally, at length, laid before Congress. All America is a tiptoe to see what the House of Representatives will decide on it. We conceive the constitutional doctrine to be, that though the President and Senate have the general power of making treaties, yet wherever they include in a treaty matters confided by the constitution to the three branches of legislature, an act of legislation will be requisite to confirm these articles, and that the House of Representatives, as one branch of the legislature, are perfectly free to pass the act or to refuse it, governing themselves by their own judgment whether it is for the good of their constituents to let the treaty go into effect or not. On the precedent now to be set will depend the future construction of our constitution, and whether the powers of legislation shall be transferred from the President, Senate, and House of Representatives, to the President and Senate, and Piamingo or any-other Indian, Algerine, or other chief. It is fortunate that the first decision is to be in a case so palpably atrocious, as to have been predetermined by all America. The appointment of Elsworth Chief Justice, and Chase one of the judges, is doubtless communicated to you. My friendly respects to Mrs. Monroe. Adieu affectionately.
Th: Jefferson.
Monticello, March 27,1796.
Dear Sir,
I am much pleased with Mr. Gallatin’s speech in Bache’s paper of March the 14th. It is worthy of being printed at the end of the Federalist, as the only rational commentary on the part of the constitution to which it relates. Not that there may not be objections, and difficult ones, to it, and which I shall be glad to see his answers to; but if they are never answered, they are more easily to be gulped down than those which lie to the doctrines of his opponents, which do in fact annihilate the whole of the powers given by the constitution to the legislature. According to the rule established by usage and common sense, of construing one part of the instrument by another, the objects on which the President and Senate may exclusively act by treaty are much reduced, but the field on which they may act with the sanction of the legislature, is large enough: and I see no harm in rendering their sanction necessary, and not much harm in annihilating the whole treaty-making power, except as to making peace. If you decide in favor of your right to refuse co-operation in any case of treaty, I should wonder on what occasion it is to be used, if not in one where the rights, the interest, the honor, and faith of our nation are so grossly sacrificed; where a faction has entered into a conspiracy with the enemies of their country to chain down the legislature at the feet of both; where the whole mass of your constituents have condemned this work in the most unequivocal manner, and are looking to you as their last hope to save them from the effects of the avarice and corruption of the first agent, the revolutionary machinations of others, and the incomprehensible acquiescence of the only honest man who has assented to it. I wish that his honesty and his political errors may not furnish a second occasion to exclaim, ‘Curse on his virtues, they have undone his country.’ Cold weather, mercury at twenty degrees in the morning. Corn fallen at Richmond to twenty shillings; stationary here. Nicholas sure of his election, R. Jouett and Jo. Monroe in competition for the other vote of the county. Affection to Mrs. M. and yourself. Adieu.
Th: Jefferson.
Monticello, April 19, 1796.
Dear Sir,
Yours of the 4th instant came to hand the day before yesterday. I have turned to the Conventional history, and enclose you an exact copy of what is there on the subject you mentioned. I have also turned to my own papers, and send you some things extracted from them, which show that the recollection of the President has not been accurate, when he supposed his own opinion to have been uniformly that declared in his answer of March the 30th. The records of the Senate will vouch for this. My respects to Mrs. Madison. Adieu affectionately.
Th: Jefferson.
[The papers referred to in the preceding.]
Extract, verbatim, from last page but one and the last page.
‘Mr. King suggested that the journals of the Convention should be either destroyed, or deposited in the custody of the President. He thought, if suffered to be made public, a bad use would be made of them by those who would wish to prevent the adoption of the constitution.
‘Mr. Wilson preferred the second expedient. He had at one time liked the first best: but as false suggestions may be propagated, it should not be made impossible to contradict them.
‘A question was then put on depositing the journals and other papers of the Convention in the hands of the President, on which New Hampshire, aye, Massachusetts, aye, Connecticut, aye, New Jersey, aye, Pennsylvania, aye, Delaware, aye, Maryland, no, Virginia, aye, North Carolina, aye, South Carolina, aye, and Georgia, aye. This negative of Maryland was occasioned by the language of the instructions to the Deputies of that State, which required them to report to the State the proceedings of the Convention.
‘The President having asked what the Convention meant should be done with the journals, &c. whether copies were to be allowed to the members, if applied for, it was resolved nem. con., “that he retain the journals and other papers subject to the order of the Congress, if ever formed under the constitution.”
‘The members then proceeded to sign the instrument,’ &c.
‘In Senate, February 1, 1791.
‘The committee, to whom was referred that part of the speech of the President of the United States, at the opening of the session, which relates to the commerce of the Mediterranean, and also the letter from the Secretary of State, dated the 20th of January, 1791, with the papers accompanying the same, reported; whereupon,
‘Resolved, That the Senate do advise and consent, that the President of the United States take such measures as he may think necessary for the redemption of the citizens of the United States, now in captivity at Algiers, provided the expense shall not exceed forty thousand dollars, and also, that measures be taken to confirm the treaty now existing between the United States and the Emperor of Morocco.’
The above is a copy of a resolve of the Senate, referred to me by the President, to propose an answer to, and I find immediately following this, among my papers, a press copy, from an original written fairly in my own hand, ready for the President’s signature, and to be given in to the Senate, of the following answer.
‘Gentlemen of the Senate,
‘I will proceed to take measures for the ransom of our citizens in captivity at Algiers, in conformity with your resolution of advice of the 1st instant, so soon as the monies necessary shall be appropriated by the legislature, and shall be in readiness.
‘The recognition of our treaty with the new Emperor of Morocco requires also previous appropriation and provision. The importance of this last to the liberty and property of our citizens, induces me to urge it on your earliest attention.’
Though I have no memorandum of the delivery of this to the Senate, yet I have not the least doubt it was given in to them, and will be found among their records.
I find, among my press copies, the following in my hand-writing.
‘The committee to report, that the President does not think that circumstances will justify, in the present instance, his entering into absolute engagements for the ransom of our captives in Algiers, nor calling for money from the treasury, nor raising it by loan, without previous authority from both branches of the legislature.
‘April 9, 1792.’
I do not recollect the occasion of the above paper with certainty; but I think there was a committee appointed by the Senate to confer with the President on the subject of the ransom, and to advise what is there declined, and that a member of the committee advising privately with me as to the report they were to make to the House, I minuted down the above, as the substance of what he observed to be the proper report, after what had passed with the President, and gave the original to the member, preserving the press copy. I think the member was either Mr. Izard or Mr. Butler, and have no doubt such a report will be found on the files of the Senate.
On the 8th of May following, in consequence of questions proposed by the President to the Senate, they came to a resolution, on which a mission was founded.
TO P. MAZZEI.
Monticello, April 24, 1796.
Mr Dear Friend,
[* The first part of this letter is on private business, and is therefore omitted.]
The aspect of our politics has wonderfully changed since you left us. In place of that noble love of liberty and republican government which carried us triumphantly through the war, an Anglican monarchical and aristocratical party has sprung up, whose avowed object is to draw over us the substance, as they have already done the forms, of the British government. The main body of our citizens, however, remain true to their republican principles: the whole landed interest is republican, and so is a great mass of talents. Against us are the executive, the judiciary, two out of three branches of the legislature, all the officers of the government, all who want to be officers, all timid men who prefer the calm of despotism to the boisterous sea of liberty, British merchants and Americans trading on British capitals, speculators and holders in the banks and public funds, a contrivance invented for the purposes of corruption, and for assimilating us in all things to the rotten as well as the sound parts of the British model. It would give you a fever, were I to name to you the apostates who have gone over to these heresies, men who were Samsons in the field and Solomons in the council, but who have had their heads shorn by the harlot England. In short, we are likely to preserve the liberty we have obtained only by unremitting labors and perils. But we shall preserve it; and our mass of weight and wealth on the good side is so great, as to leave no danger that force will ever be attempted against us. We have only to awake and snap the Lilliputian cords with which they have been entangling us during the first sleep which succeeded our labors.
I will forward the testimonial of the death of Mrs. Mazzei, which I can do the more incontrovertibly as she is buried in my grave-yard, and I pass her gravel daily. The formalities of the proof you require, will occasion delay. I begin to feel the effects of age. My health has suddenly broken down, with symptoms which give me to believe I shall not have much to encounter of the tedium vita. While it remains, however, my heart will be warm in its friendships, and, among these, will always foster the affections with which I am, Dear Sir, your friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO COLONEL MONROE.
Monticello, June 12, 1796.
Dear Sir,
Congress have risen. You will have seen by their proceedings the truth of what I always observed to you, that one man outweighs them all in influence over the people, who have supported his judgment against their own and that of their representatives. Republicanism must lie on its oars, resign the vessel to its pilot, and themselves to the course he thinks best for them. I had always conjectured, from such facts as I could get hold of, that our public debt was increasing about a million of dollars a year. You will see by Gallatin’s speeches that the thing is proved. You will see farther, that we are completely saddled and bridled, and that the bank is so firmly mounted on us that we must go where they will guide. They openly publish a resolution, that the national property being increased in value, they must by an increase of circulating medium furnish an adequate representation of it, and by further additions of active capital promote the enterprises of our merchants. It is supposed that the paper in circulation in and around Philadelphia amounts to twenty millions of dollars, and that in the whole Union, to one hundred millions. I think the last too high. All the imported commodities are raised about fifty per cent. by the depreciation of the money. Tobacco shares the rise, because it has no competition abroad. Wheat has been extraordinarily high from other causes. When these cease, it must fall to its ancient nominal price, notwithstanding the depreciation of that, because it must contend in market with foreign wheats. Lands have risen within the vortex of the paper, and as far out as that can influence. They have not risen at all here. On the contrary, they are lower than they were twenty years ago. Those I had mentioned to you, to wit, Carter’s and Colle, were sold before your letter came. Colle at two dollars the acre. Carter’s had been offered me for two French crowns (13s. 2d.) Mechanics here get from a dollar to a dollar and a half a day, yet are much worse off than at the old prices.
Volney is with me at present. He is on his way to the Illinois. Some late appointments, judiciary and diplomatic, you will have heard, and stared at. The death of R. Jouett is the only small news in our neighborhood.
Our best affections attend Mrs. Monroe, Eliza, and yourself. Adieu affectionately.
Th: Jefferson.
TO THE PRESIDENT.
Monticello, June 19, 1796.
In Bache’s Aurora of the 9th instant, which came here by the last post, a paper appears, which having been confided, as I presume, to but few hands, makes it truly wonderful how it should have got there. I cannot be satisfied as to my own part, till I relieve my mind by declaring, and I attest every thing sacred and honorable to the declaration, that it has got there neither through me nor the paper confided to me. This has never been from under my own lock and key, or out of my own hands. No mortal ever knew from me, that these questions had been proposed. Perhaps I ought to except one person, who possesses all my confidence, as he has possessed yours. I do not remember, indeed, that I communicated it even to him. But as I was in the habit of unlimited trust and counsel with him, it is possible I may have read it to him; no more: for the quire of which it makes a part was never in any hand but my own, nor was a word ever copied or taken down from it, by any body. I take on myself, without fear, any divulgation on his part. We both know him incapable of it. From myself, then, or my paper, this publication has never been derived. I have formerly mentioned to you, that from a very early period of my life, I had laid it down as a rule of conduct never to write a word for the public papers. From this, I have never departed in a single instance; and on a late occasion, when all the world seemed to be writing, besides a rigid adherence to my own rule, I can say with truth, that not a line for the press was ever communicated to me, by any other, except a single petition referred for my correction; which I did not correct, however, though the contrary, as I have heard, was said in a public place, by one person through error, through malice by another. I learn that this last has thought it worth his while to try to sow tares between you and me, by representing me as still engaged in the bustle of politics, and in turbulence and intrigue against the government. I never believed for a moment that this could make any impression on you, or that your knowledge of me would not overweigh the slander of an intriguer, dirtily employed in sifting the conversations of my table, where alone he could hear of me; and seeking to atone for his sins against you by sins against another, who had never done him any other injury than that of declining his confidences. Political conversations I really dislike, and therefore avoid where I can without affectation. But when urged by others, I have never conceived that having been in public life requires me to belie my sentiments, or even to conceal them. When I am led by conversation to express them, I do it with the same independence here, which I have practised every where, and which is inseparable from my nature. But enough of this miserable tergiversator, who ought indeed either to have been of more truth, or less trusted by his country.*
[* Here, in the margin of the copy, is written, apparently
at a later date, * General H. Lee.‘]
While on the subject of papers, permit me to ask one from you. You remember the difference of opinion between Hamilton and Knox on the one part, and myself on the other, on the subject of firing on the Little Sarah, and that we had exchanged opinions and reasons in writing. On your arrival in Philadelphia I delivered you a copy of my reasons, in the presence of Colonel Hamilton. On our withdrawing, he told me he had been so much engaged that he had not been able to prepare a copy of his and General Knox’s for you, and that if I would send you the one he had given me, he would replace it in a few days. I immediately sent it to you, wishing you should see both sides of the subject together. I often after applied to both the gentlemen, but could never obtain another copy. I have often thought of asking this one, or a copy of it, back from you, but have not before written on subjects of this kind to you. Though I do not know that it will ever be of the least importance to me, yet one loves to possess arms, though they hope never to have occasion for them. They possess my paper in my own hand-writing. It is just I should possess theirs. The only thing amiss is, that they should have left me to seek a return of the paper, or a copy of it, from you.
I put away this disgusting dish of old fragments, and talk to you of my pease and clover. As to the latter article, I have great encouragement from the friendly nature of our soil. I think I have had, both the last and present year, as good clover from common grounds, which had brought several crops of wheat and corn without ever having been manured, as I ever saw on the lots around Philadelphia. I verily believe that a field of thirty-four acres, sowed on wheat April was twelvemonth, has given me a ton to the acre at its first cutting this spring. The stalks extended, measured three and a half feet long very commonly. Another field, a year older, and which yielded as well the last year, has sensibly fallen off this year. My exhausted fields bring a clover not high enough for hay, but I hope to make seed from it. Such as these, however, I shall hereafter put into pease in the broadcast, proposing that one of my sowings of wheat shall be after two years of clover, and the other after two years of pease. I am trying the white boiling pea of Europe (the Albany pea) this year, till I can get the hog-pea of England, which is the most productive of all. But the true winter-vetch is what we want extremely. I have tried this year the Caroline drill. It is absolutely perfect. Nothing can be more simple, nor perform its office more perfectly for a single row. I shall try to make one to sow four rows at a time of wheat or peas, at twelve inches distance. I have one of the Scotch threshing-machines nearly finished. It is copied exactly from a model of Mr. Pinckney sent me, only that I have put the whole works (except the horse-wheel) into a single frame, moveable from one field to another on the two axles of a wagon. It will be ready in time for the harvest which is coming on, which will give it a full trial. Our wheat and rye are generally fine, and the prices talked of bid fair to indemnify us for the poor crops of the two last years.
I take the liberty of putting under your cover a letter to the son of the Marquis de la Fayette, not exactly knowing where to direct to him.
With very affectionate compliments to Mrs. Washington, I have the honor to be, with great and sincere esteem and respect, Dear Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
Monticello, June 19, 1796.
Dear Sir,
The inquiries of Congress were the first intimation which reached my retirement of your being in this country, and from M. Volney, now with me, I first learned where you are. I avail myself of the earliest moments of this information, to express to you the satisfaction with which I learn that you are in the land of safety, where you will meet in every person the friend of your worthy father and family. Among these I beg leave to mingle my own assurances of sincere attachment to him, and my desire to prove it by every service I can render you. I know, indeed, that you are already under too good a patronage to need any other, and that my distance and retirement render my affections unavailing to you. They exist, nevertheless, in all their purity and warmth towards your father and every one embraced by his love; and no one has wished with more anxiety to see him once more in the bosom of a nation, who, knowing his works and his worth, desire to make him and his family for ever their own. You were, perhaps, too young to remember me personally when in Paris. But I pray you to remember, that should any occasion offer wherein I can be useful to you, there is no one on whose friendship and zeal you may more confidently count. You will, some day perhaps, take a tour through these States. Should any thing in this part of them attract your curiosity, it would be a circumstance of great gratification to me to receive you here, and to assure you in person of those sentiments of esteem, and attachment with which I am, Dear Sir, your friend and humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JONATHAN WILLIAMS.
Monticello, July 3,1796.
Dear Sir,
I take shame to myself for having so long left unanswered your valuable favor on the subject of the mountains. But in truth, I am become lazy as to every thing except agriculture. The preparations for harvest, and the length of the harvest itself, which is not yet finished, would have excused the delay however, at all times and under all dispositions. I examined, with great satisfaction, your barometrical estimate of the heights of our mountains; and with the more, as they corroborated conjectures on this subject which I had made before. My estimates had made them a little higher than yours (I speak of the Blue Ridge.) Measuring with a very nice instrument the angle subtended vertically by the highest mountain of the Blue Ridge opposite to my own house, a distance of about eighteen miles south westward, I made the highest about two thousand feet, as well as I remember, for I can no longer find the notes I made. You make the south side of the mountain near Rockfish Gap, one thousand seven hundred and twenty-two feet above Woods. You make the other side of the mountain seven hundred and sixty-seven feet. Mr. Thomas Lewis, deceased, an accurate man, with a good quadrant, made the north side of the highest mountain opposite my house something more (I think) than one thousand feet; but the mountain estimated by him and myself is probably higher than that next Rockfish Gap. I do not remember from what principles I estimated the Peaks of Otter at four thousand feet; but some late observations of Judge Tucker’s coincided very nearly with my estimate. Your measures confirm another opinion of mine that the Blue Ridge, on its south side, is the highest ridge in our country compared with its base. I think your observations on these mountains well worthy of being published, and hope you will not scruple to let them be communicated to the world.
You wish me to present to the Philosophical Society the result of my philosophical researches since my retirement. But, my good Sir, I have made researches into nothing but what is connected with agriculture. In this way, I have a little matter to communicate, and will do it ere long. It is the form of a mould-board of least resistance. I had some years ago conceived the principles of it, and I explained them to Mr. Rittenhouse. I have since reduced the thing to practice, and have reason to believe the theory fully confirmed. I only wish for one of those instruments used in England for measuring the force exerted in the draughts of different ploughs, &c, that I might compare the resistance of my mould-board with that, of others. But these instruments are not to be had here. In a letter of this date to Mr. Rittenhouse, I mention a discovery in animal history very signal indeed, of which I shall lay before the Society the best account I can, as soon as I shall have received some other materials collecting for me.
I have seen, with extreme indignation, the blasphemies lately vended against the memory of the father of American philosophy. But his memory will be preserved and venerated as long as the thunder of heaven shall be heard or feared.
With good wishes to all of his family, and sentiments of great respect and esteem for yourself, I am, Dear Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO COLONEL MONROE.
Monticello, July 10, 1796.
Dear Sir,
The campaign of Congress has closed. Though the Anglomen have in the end got their treaty through, and so far have triumphed over the cause of republicanism, yet it has been to them a dear-bought victory. It has given the most radical shock to their party which it has ever received: and, there is no doubt, they would be glad to be replaced on the ground they possessed the instant before Jay’s nomination extraordinary. They see that nothing can support them but the colossus of the President’s merits with the people, and the moment he retires, that his successor, if a monocrat, will be overborne by the republican sense of his constituents; if a republican, he will of course give fair play to that sense, and lead things into the channel of harmony between the governors and governed. In the mean time, patience.
Among your neighbors there is nothing new. Mr. Rittenhouse is lately dead. We have had the finest harvest ever known in this part of the country. Both the quantity and quality of wheat are extraordinary. We got fifteen shillings a bushel for the last crop, and hope two thirds of that at least for the present one.
Most assiduous court is paid to Patrick Henry. He has been offered every thing which they knew he would not accept. Some impression is thought to be made, but we do not believe it is radical. If they thought they could count upon him, they would run him for their Vice-President; their first object being to produce a schism in the State. As it is, they will run Mr. Pinckney; in which they regard his southern position rather than his principles. Mr. Jay and his advocate Camillus are completely treaty-foundered.
We all join in love to Mrs. Monroe; and accept for yourself assurances of sincere and affectionate friendship. Adieu.
Th: Jefferson.
THOMAS JEFFERSON TO JAMES MADISON.
Monticello, December 17, 1796.
Your favor of the 5th came to hand last night. The first wish of my heart was, that you should have been proposed for the administration of the government. On your declining it, I wish any body rather than myself: and there is nothing I so anxiously hope, as that my name may come out either second or third. These would be indifferent to me; as the last would leave me at home the whole year, and the other, two thirds of it. I have no expectation that the eastern States will suffer themselves to be so much outwitted, as to be made the tools for bringing in P. instead of A. I presume they will throw away their second vote. In this case, it begins to appear possible, that there may be an equal division where I had supposed the republican vote would have been considerably minor. It seems also possible, that the Representatives may be divided. This is a difficulty from which the constitution has provided no issue. It is both my duty and inclination, therefore, to relieve the embarrassment, should it happen: and in that case, I pray you and authorize you fully, to solicit on my behalf that Mr. Adams may be preferred. He has always been my senior, from the commencement of our public life, and the expression of the public will being equal, this circumstance ought to give him the preference. And when so many motives will be operating to induce some of the members to change their vote, the addition of my wish may have some effect to preponderate the scale. I am really anxious to see the speech. It must exhibit a very different picture of our foreign affairs from that presented in the adieu, or it will little correspond with my views of them. I think they never wore so gloomy an aspect since the year 1783. Let those come to the helm who think they can steer clear of the difficulties. I have no confidence in myself for the undertaking.
We have had the severest weather ever known in November. The thermometer was at twelve degrees here and in Goochland, and I suppose generally. It arrested my buildings very suddenly, when eight days more would have completed my walls, and permitted us to cover in. The drought is excessive. From the middle of October to the middle of December, not rain enough to lay the dust. A few days ago there fell a small rain, but the succeeding cold has probably prevented it from sprouting the grain sown during the drought.
Present me in friendly terms to Messrs. Giles, Venable, and Page. Adieu affectionately.
Monticello, December 27, 1796.
Mr Dear Sir,
You have seen my name lately tacked to so much of eulogy and of abuse, that I dare say you hardly thought it meant your old acquaintance of ‘76. In truth, I did not know myself under the pens either of my friends or foes. It is unfortunate for our peace that unmerited abuse wounds, while unmerited praise has not the power to heal. These are hard wages for the services of all the active and healthy years of one’s life. I had retired after five and twenty years of constant occupation in public affairs, and total abandonment of my own. I retired much poorer than when I entered the public service, and desired nothing but rest and oblivion. My name, however, was again brought forward, without concert or expectation on my part; (on my salvation I declare it.) I do not as yet know the result, as a matter of fact; for in my retired canton we have nothing later from Philadelphia than of the second week of this month. Yet I have never one moment doubted the result I knew it was impossible Mr. Adams should lose a vote north of the Delaware, and that the free and moral agency of the south would furnish him an abundant supplement. On principles of public respect I should not have refused; but I protest before my God that I shall, from the bottom of my heart, rejoice at escaping. I know well that no man will ever bring out of that office the reputation which carries him into it. The honey-moon would be as short in that case as in any other, and its moments of extacy would be ransomed by years of torment and hatred. I shall highly value indeed, the share which I may have had in the late vote, as an evidence of the share I hold in the esteem of my countrymen. But in this point of view, a few votes more or less will be little sensible, and in every other, the minor will be preferred by me to the major vote. I have no ambition to govern men; no passion which would lead me to delight to ride in a storm. Flumina amo sylvasque, inglorius. My attachment to my home has enabled me to make the calculation with rigor, perhaps with partiality, to the issue which keeps me there. The newspapers will permit me to plant my corn, pease, &c. in hills or drills as I please (and my oranges by the bye when you send them), while our eastern friend will be struggling with the storm which is gathering over us; perhaps be shipwrecked in it. This is certainly not a moment to covet the helm.
I have often doubted whether most to praise or to blame your line of conduct. If you had lent to your country the excellent talents you possess, on you would have fallen those torrents of abuse which have lately been poured forth on me. So far, I praise the wisdom which has descried and steered clear of a waterspout ahead. But now for the blame. There is a debt of service due from every man to his country, proportioned to the bounties which nature and fortune have measured to him. Counters will pay this from the poor of spirit; but from you, my friend, coin was due. There is no bankrupt-law in heaven, by which you may get off with shillings in the pound; with rendering to a single State what you owed to the whole confederacy. I think it was by the Roman law that a father was denied sepulture, unless his son would pay his debts. Happy for you and us, that you have a son whom genius and education have qualified to pay yours. But as you have been a good father in every thing else, be so in this also. Come forward and pay your own debts. Your friends, the Mr. Pinckneys, have at length undertaken their tour. My joy at this would be complete if you were in gear with them. I love to see honest and honorable men at the helm, men who will not bend their politics to their purses, nor pursue measures by which they may profit, and then profit by their measures. Au diable les Bougres! I am at the end of my curse and bottom of my page, so God bless you and yours. Adieu affectionately.
Th: Jefferson.
Statement, from memory, of a Letter I wrote to John Adams; copy omitted to be retained.
Dear Sir,
The public, and the public papers, have been much occupied lately in placing us in a point of opposition to each other. I confidently trust we have felt less of it ourselves. In the retired canton where I live, we know little of what is passing. Our last information from Philadelphia is of the 16th instant. At that date, the issue of the late election seems not to have been known as a matter of fact. With me, however, its issue was never doubted. I knew the impossibility of your losing a single vote north of the Delaware; and even if you should lose that of Pennsylvania in the mass, you would get enough south of it to make your election sure. I never for a single moment expected any other issue, and though I shall not be believed, yet it is not the less true, that I never wished any other. My neighbors, as my compurgators, could aver this fact, as seeing my occupations and my attachment to them. It is possible, indeed, that even you may be cheated of your succession by a trick worthy the subtlety of your arch friend of New York, who has been able to make of your real friends tools for defeating their and your just wishes. Probably, however, he will be disappointed as to you; and my inclinations put me out of his reach. I leave to others the sublime delights of riding in the storm, better pleased with sound sleep and a warmer birth below it, encircled with the society of my neighbors, friends, and fellow-laborers of the earth, rather than with spies and sycophants. Still, I shall value highly the share I may have had in the late vote, as a measure of the share I hold in the esteem of my fellow-citizens. In this point of view, a few votes less are but little sensible, while a few more would have been in their effect very sensible and oppressive to me. I have no ambition to govern men. It is a painful and thankless office. And never since the day you signed the treaty of Paris, has our horizon been so overcast. I devoutly wish you may be able to shun for us this war, which will destroy our agriculture, commerce, and credit. If you do, the glory will be all your own. And that your administration may be filled with glory and happiness to yourself, and advantage to us, is the sincere prayer of one, who, though in the course of our voyage, various little incidents have happened or been contrived to separate us, yet retains for you the solid esteem of the times when we were working for our independence, and sentiments of sincere respect and attachment.
Th: Jefferson.
Statement, from memory, of a Letter I wrote to James Madison; copy omitted to be retained.
Dear Sir,
Yours of December the 19th is safely received. I never entertained a doubt of the event of the election. I knew that the eastern troops were trained in the schools of their town-meetings, to sacrifice little differences of opinion to the solid advantages of operating in phalanx, and that the more free and moral agency of the other States would fully supply their deficiency. I had no expectation, indeed, that the vote would have approached so near an equality. It is difficult to obtain full credit to declarations of disinclination to honors, and most so with those who still remain in the world. But never was there a more solid unwillingness, founded on rigorous calculation, formed in the mind of any man, short of peremptory refusal. No arguments, therefore, Were necessary to reconcile me to a relinquishment of the first office, or acceptance of the second. No motive could have induced me to undertake the first, but that of putting our vessel upon her republican tack, and preventing her being driven too far to leeward of her true principles. And the second is the only office in the world about which I cannot decide in my own mind, whether I had rather have it or not have it. Pride does not enter into the estimate. For I think with the Romans of old, that the General of to-day should be a common soldier to-morrow, if necessary. But as to Mr. Adams, particularly, I could have no feelings which would revolt at being placed in a secondary station to him. I am his junior in life, I was his junior in Congress, his junior in the diplomatic line, and lately his junior in our civil government. I had written him the enclosed letter before the receipt of yours. I had intended it for some time, but had put it off, from time to time, from the discouragement of despair to make him believe me sincere. As the information by the last post does not make it necessary to change any thing in the letter, I enclose it open for your perusal, as well that you may be possessed of the true state of dispositions between us, as that if there be any circumstance which might render its delivery ineligible, you may return it to me. If Mr. Adams could be induced to administer the government on its true principles, quitting his bias for an English constitution, it would be worthy consideration whether it would not be for the public good, to come to a good understanding with him as to his future elections. He is the only sure barrier against Hamilton’s getting in.
The Political Progress is a work of value and of a singular complexion. The author’s eye seems to be a natural achromatic, divesting every object of the glare of color. The former work of the same title possessed the same kind of merit. They disgust one, indeed, by opening to his view the ulcerated state of the human mind. But to cure an ulcer you must go to the bottom of it, which no author does more radically than this. The reflections into which it leads us are not very flattering to the human species. In the whole animal kingdom I recollect no family but man, steadily and systematically employed in the destruction of itself. Nor does what is called civilization produce any other effect than to teach him to pursue the principle of the bellum omnium in omnia on a greater scale, and instead of the little contests between tribe and tribe, to comprehend all the quarters of the earth in the same work of destruction. If to this we add, that, as to other animals, the lions and tigers are mere lambs compared with man as a destroyer, we must conclude that nature has been able to find in man alone a sufficient barrier against the too great multiplication of other animals and of man himself, an equilibrating power against the fecundity of generation. While, in making these observations, my situation points my attention to the warfare of man in the physical world, yours may perhaps present him as equally warring in the moral one.
Adieu. Yours affectionately.
Th: Jefferson.
TO MR. VOLNEY.
Monticello, January 8, 1797.
Dear Sir,
I received yesterday your two favors of December the 26th and 29th. Your impatience to receive your valise and its key was natural: and it is we who have been to blame; Mr. Randolph, for not taking information of the vessel and address to which your valise was committed, and myself, for having waited till I heard of your being again immerged into the land of newspapers before forwarded your key. However, as you have at length got them safe, I claim absolution under the proverb, that ‘all is well which ends well.’
About the end of 1793, I received from Mr. Dombey (then at Lyons) a letter announcing his intention to come here. And in May, 1794, I received one from a M. L’Epine, dated from New York, and stating himself to be master of the brig De Boon, Captain Brown, which had sailed from Havre with Mr. Dombey on board, who had sealed up his baggage and wrote my address on them, to save them in case of capture; and that when they were taken, the address did in fact protect them. He mentioned then the death of Mr. Dombey, and that he had delivered his baggage to the Custom-House at New York. I immediately wrote to M. L’Epine, disclaiming any right or interest in the packages under my address, and authorizing, as far as depended on me, the Consul at New York, or any person the representative of Mr. Dombey to open the packages and dispose of them according to right. I enclosed this letter open to Mr. Randolph, then Secretary of State, to get his interference for the liberation of the effects. It may have happened that he failed to forward the letter, or that M. L’Epine may have gone before it reached New York. In any event, I can do no more than repeat my disclaimer of any right to Mr. Dombey’s effects, and add all the authority which I can give to yourself, or to the Consul of France at New York, to do with those effects whatever I might do. Certainly it would be a great gratification to me to receive the Mètre and Grave committed to Mr. Dombey for me, and that you would be so good as to be the channel of my acknowledgments to Bishop Gregoire, or any one else to whom I should owe this favor.
You wish to know the state of the air here during the late cold spell, or rather the present one, for it is at this moment so cold that the ink freezes in my pen, so that my letter will scarcely be legible.
The following is copied from my diary:
In the winter of 1779-80, the mercury in Fahrenheit’s thermometer fell at Williamsburg once to six degrees above zero. In 1783-84, I was at Annapolis without a thermometer, and I do not know that there was one in that State: I heard from Virginia, that the mercury was again down to six degrees. In 1789-90, I was at Paris. The mercury here was as low as eighteen degrees below zero, of Fahrenheit. These have been the most remarkably cold winters ever known in America. We are told, however, that in 1762, at Philadelphia, it was twenty-two degrees below zero: in December, 1793, it was three degrees below zero there by my thermometer. On the 31st of January, 1796, it was one and three-fourth degrees above zero at Monticello. I shall therefore have to change the maximum of our cold, if ever I revise the Notes on Virginia; as six degrees above zero was the greatest which had ever been observed.
It seems possible, from what we hear of the votes at the late election, that you may see me in Philadelphia about the beginning of March, exactly in that character which, if I were to re-appear at Philadelphia, I would prefer to all others; for I change the sentiment of Clorinda to ‘L’alte temo, l’humili non sdegno.’ I have no inclination to govern men. I should have no views of my own in doing it; and as to those of the governed, I had rather that their disappointment (which must always happen) should be pointed to any other cause, real or supposed, than to myself. I value the late vote highly; but it is only as the index of the place I hold in the esteem of my fellow citizens. In this point of view, the difference between sixty-eight and seventy-one votes is little sensible, and still less that between the real vote, which was sixty-nine and seventy; because one real elector in Pennsylvania was excluded from voting by the miscarriage of the votes, and one who was not an elector was admitted to vote. My farm, my family, my books, and my building give me much more pleasure than any public office would, and, especially, one which would keep me constantly from them. I had hoped, when you were here, to have finished the walls of my house in the autumn, and to have covered it early in winter. But we did not finish them at all. I have to resume the work, therefore, in the spring, and to take off the roof of the old part during the summer, to cover the whole. This will render it necessary for me to make a very short stay in Philadelphia, should the late vote have given me any public duty there. My visit there will be merely out of respect to the public, and to the new President.
I am sorry you have received so little information on the subject of our winds. I had once (before our revolutionary war) a project on the same subject. As I had then an extensive acquaintance over this State, I meant to have engaged some person in every county of it, giving them each a thermometer, to observe that and the winds twice a day, for one year, to wit, at sunrise and at four P. M. (the coldest and the warmest point of the twenty-four hours) and to communicate their observations to me at the end of the year. I should then have selected the days in which it appeared that the winds blew to a centre within the State, and have made a map of them, and seen how far they had analogy with the temperature of the air. I meant this to be merely a specimen to be communicated to the Philosophical Society at Philadelphia, in order to engage them, by means of their correspondents, to have the same thing done in every State, and through a series of years. By seizing the days when the winds centred in any part of the United States, we might, in time, have come at some of the causes which determine the direction of the winds, which I suspect to be very various. But this long-winded project was prevented by the war which came upon us, and since that I have been far otherwise engaged. I am sure you will have viewed the subject from much higher ground, and I shall be happy to learn your views in some of the hours of délassement, which I hope we are yet to pass together. To this must be added your observations on the new character of man, which you have seen in your journey, as he is in all his shapes a curious animal, on whom no one is better qualified to judge than yourself; and no one will be more pleased to participate of your views of him than one, who has the pleasure of offering you his sentiments of sincere respect and esteem.
Th: Jefferson.
TO HENRY TAZEWELL.
Monticello, January 16, 1797.
Dear Sir,
As far as the public papers are to be credited, I may suppose that the choice of Vice-President has fallen on me. On this hypothesis I trouble you, and only pray, if it be wrong, that you will consider this letter as not written. I believe it belongs to the Senate to notify the Vice-President of his election. I recollect to have heard, that on the first election of President and Vice-President, gentlemen of considerable office were sent to notify the parties chosen. But this was the inauguration of our new government, and ought not to be drawn into example. At the second election, both gentlemen were on the spot and needed no messengers. On the present occasion, the President will be on the spot, so that what is now to be done respects myself alone: and considering that the season of notification will always present one difficulty, that the distance in the present case adds a second, not inconsiderable, and which may in future happen to be sometimes much more considerable, I hope the Senate will adopt that method of notification, which will always be least troublesome and most certain. The channel of the post is certainly the least troublesome, is the most rapid, and, considering also that it may be sent by duplicates and triplicates, is unquestionably the most certain. Indorsed to the postmaster at Charlottesville, with an order to send it by express, no hazard can endanger the notification. Apprehending, that should there be a difference of opinion on this subject in the senate, my ideas of self-respect might be supposed by some to require something more formal and inconvenient, I beg leave to avail myself of your friendship to declare, if a different proposition should make it necessary, that I consider the channel of the post-office as the most eligible in every respect, and that it is to me the most desirable; which I take the liberty of expressing, not with a view of encroaching on the respect due to that discretion which the Senate have a right to exercise on the occasion, but to render them the more free in the exercise of it, by taking off whatsoever weight the supposition of a contrary desire in me might have on the mind of any member.
I am, with sincere respect, Dear Sir, your friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
Monticello, January 16, 1797.
Dear Sir,
The several accidents of the winter, ice, floods, rains, prevented the Orange post from coming to Charlottesville the last post-day, so that we have nothing from Philadelphia the last week. I see however, by the Richmond papers, a probability that the choice of Vice-President has fallen on me. I have written the enclosed letter therefore to Mr. Tazewell, as a private friend, and have left it open for your perusal. It will explain its own object, and I pray you and Mr. Tazewell to decide in your own discretion how it may best be used for its object, so as to avoid the imputation of an indecent forwardness in me.
I observe doubts are still expressed as to the validity of the Vermont election. Surely, in so great a case, substance, and not form, should prevail. I cannot suppose that the Vermont constitution has been strict in requiring particular forms of expressing the legislative will. As far as my disclaimer may have any effect, I pray you to declare it on every occasion, foreseen or not foreseen by me, in favor of the choice of the people substantially expressed, and to prevent the phenomenon of a pseudo-President at so early a day. Adieu. Yours affectionately,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JAMES MADISON.
Monticello, January 22, 1797.
Dear Sir,
Yours of the 8th came to hand yesterday. I was not aware of any necessity of going on to Philadelphia immediately, yet I had determined to do it as a mark of respect to the public, and to do away the doubts which have spread, that I should consider the second office as beneath my acceptance. The journey, indeed, for the month of February, is a tremendous undertaking for me, who have not been seven miles from home since my re-settlement. I will see you about the rising of Congress; and presume I need not stay there a week. Your letters written before the 7th of February will still find me here. My letters inform me that Mr. Adams speaks of me with great friendship, and with satisfaction in the prospect of administering the government in concurrence with me. I am glad of the first information, because though I saw that our ancient friendship was affected by a little leaven, produced partly by his constitution, partly by the contrivance of others, yet I never felt a diminution of confidence in his integrity, and retained a solid affection for him. His principles of government I knew to be changed, but conscientiously changed. As to my participating in the administration, if by that he meant the executive cabinet, both duty and inclination will shut that door to me. I cannot have a wish to see the scenes of 1793 revived as to myself, and to descend daily into the arena like a gladiator, to suffer martyrdom in every conflict. As to duty, the constitution will know me only as the member of a legislative body: and its principle is, that of a separation of legislative, executive, and judiciary functions, except in cases specified. If this principle be not expressed in direct terms, yet it is clearly the spirit of the constitution, and it ought to be so commented and acted on by every friend to free government.
I sincerely deplore the situation of our affairs with France. War with them, and consequent alliance with Great Britain, will completely compass the object of the executive council, from the commencement of the war between France and England; taken up by some of them from that moment, by others, more latterly. I still, however, hope it will be avoided. I do not believe Mr. Adams wishes war with France; nor do I believe he will truckle to England as servilely as has been done. If he assumes this front at once, and shows that he means to attend to self-respect and national dignity with both the nations, perhaps the depredations of both on our commerce may be amicably arrested. I think we should begin first with those who first began with us, and, by an example on them, acquire a right to re-demand the respect from which the other party has departed.
I suppose you are informed of the proceeding commenced by the legislature of Maryland, to claim the south branch of the Potomac as their boundary, and thus of Albemarle, now the central county of the State, to make a frontier. As it is impossible, upon any consistent principles, and after such a length of undisturbed possession, that they can expect to establish their claim, it can be ascribed to no other than an intention to irritate and divide; and there can be no doubt from what bow the shaft is shot. However, let us cultivate Pennsylvania, and we need not fear the universe. The Assembly have named me among those who are to manage this controversy. But I am so averse to motion and contest, and the other members are so fully equal to the business, that I cannot undertake to act in it. I wish you were added to them. Indeed, I wish and hope you may consent to be added to our Assembly itself. There is no post where you can render greater services, without going out of your State. Let but this block stand firm on its basis, and Pennsylvania do the same, our Union will be perpetual, and our General Government kept within the bounds and form of the constitution. Adieu affectionately.
Th: Jefferson.
Monticello, January 30, 1797.
Yours of the 18th came to hand yesterday. I am very thankful for the discretion you have exercised over the letter. That has happened to be the case, which I knew to be possible, that the honest expression of my feelings towards Mr. Adams might be rendered mal-apropos from circumstances existing, and known at the seat of government, but not known by me in my retired situation. Mr. Adams and myself were cordial friends from the beginning of the revolution. Since our return from Europe, some little incidents have happened, which were capable of affecting a jealous mind like his. His deviation from that line of politics on which we had been united, has not made me less sensible of the rectitude of his heart: and I wished him to know this, and also another truth, that I am sincerely pleased at having escaped the late draught for the helm, and have not a wish which he stands in the way of. That he should be convinced of these truths, is important to our mutual satisfaction, and perhaps to the harmony and good of the public service. But there was a difficulty in conveying them to him, and a possibility that the attempt might do mischief there or somewhere else; and I would not have hazarded the attempt, if you had not been in place to decide upon its expediency. It has now become unnecessary to repeat it by a letter.
I have turned to the constitution and laws, and find nothing to warrant the opinion that I might not have been qualified here, or wherever else I could meet with a Senator; any member of that body being authorized to administer the oath, without being confined to time or place, and consequently to make a record of it, and to deposit it with the records of the Senate. However, I shall come on, on the principle which had first determined me, respect to the public. I hope I shall be made a part of no ceremony whatever. I shall escape into the city as covertly as possible. If Governor Mifflin should show any symptoms of ceremony, pray contrive to parry them. We have now fine mild weather here. The thermometer is above the point which renders fires necessary. Adieu affectionately.
Th: Jefferson.
TO JAMES SULLIVAN.
Monticello, February 9, 1797.
Dear Sir,
I have many acknowledgments to make for the friendly anxiety you are pleased to express in your letter of January the 12th, for my undertaking the office to which I have been elected. The idea that I would accept the office of President, but not that of Vice-President of the United States, had not its origin with me. I never thought of questioning the free exercise of the right of my fellow-citizens, to marshal those whom they call into their service according to their fitness, nor ever presumed that they were not the best judges of that. Had I indulged a wish in what manner they should dispose of me, it would precisely have coincided with what they have done. Neither the splendor, nor the power, nor the difficulties, nor the fame, or defamation, as may happen, attached to the first magistracy, have any attractions for me. The helm of a free government is always arduous, and never was ours more so, than at a moment when two friendly people are like to be committed in war by the ill temper of their administrations. I am so much attached to my domestic situation, that I would not have wished to leave it at all. However, if I am to be called from it, the shortest absences and most tranquil station suit me best. I value highly, indeed, the part my fellow-citizens gave me in their late vote, as an evidence of their esteem, and I am happy in the information you are so kind as to give, that many in the eastern quarter entertain the same sentiment.
Where a constitution, like ours, wears a mixed aspect of monarchy and republicanism, its citizens will naturally divide into two classes of sentiment, according as their tone of body or mind, their habits, connections, and callings, induce them to wish to strengthen either the monarchical or the republican features of the constitution. Some will consider it as an elective monarchy, which had better be made hereditary, and therefore endeavor to lead towards that all the forms and principles of its administration. Others will view it as an energetic republic, turning in all its points on the pivot of free and frequent elections. The great body of our native citizens are unquestionably of the republican sentiment. Foreign education, and foreign connections of interest, have produced some exceptions in every part of the Union, north and south; and perhaps other circumstances in your quarter, better known to you, may have thrown into the scale of exceptions a greater number of the rich. Still there, I believe, and here, I am sure, the great mass is republican. Nor do any of the forms in which the public disposition has been pronounced in the last half dozen years, evince the contrary. All of them, when traced to their true source, have only been evidences of the preponderant popularity of a particular great character. That influence once withdrawn, and our countrymen left to the operation of their own unbiassed good sense, I have no doubt we shall see a pretty rapid return of general harmony, and our citizens moving in phalanx in the paths of regular liberty, order, and a sacrosanct adherence to the constitution. Thus I think it will be, if war with France can be avoided. But if that untoward event comes athwart us in our present point of deviation, no body, I believe, can foresee into what port it will drive us.
I am always glad of an opportunity of inquiring after my most ancient and respected friend Mr. Samuel Adams. His principles, founded on the immovable basis of equal right and reason, have continued pure and unchanged. Permit me to place here my sincere veneration for him, and wishes for his health and happiness; and to assure yourself of the sentiments of esteem and respect, with which I am, Dear Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO ELBRIDGE GERRY.
Philadelphia, May 13, 1797.
My Dear Friend,
Your favor of the 4th instant came to hand yesterday. That of the 4th of April, with the one for Monroe, has never been received. The first, of March the 27th, did not reach me till April the 21st, when I was within a few days of setting out for this place, and I put off acknowledging it till I should come here. I entirely commend your dispositions towards Mr. Adams; knowing his worth as intimately and esteeming it as much as any one, and acknowledging the preference of his claims, if any I could have had, to the high office conferred on him. But in truth, I had neither claims nor wishes on the subject, though I know it will be difficult to obtain belief of this. When I retired from this place and the office of Secretary of State, it was in the firmest contemplation of never more returning here. There had indeed been suggestions in the public papers, that I was looking towards a succession to the President’s chair, but feeling a consciousness of their falsehood, and observing that the suggestions came from hostile quarters, I considered them as intended merely to excite public odium against me. I never in my life exchanged a word with any person on the subject, till I found my name brought forward generally, in competition with that of Mr. Adams. Those with whom I then communicated, could say, if it were necessary, whether I met the call with desire, or even with a ready acquiescence, and whether from the moment of my first acquiescence, I did not devoutly pray that the very thing might happen which has happened. The second office of this government is honorable and easy, the first is but a splendid misery.
You express apprehensions that stratagems will be used, to produce a misunderstanding between the President and myself. Though not a word having this tendency has ever been hazarded to me by any one, yet I consider as a certainty that nothing will be left untried to alienate him from me. These machinations will proceed from the Hamiltonians by whom he is surrounded, and who are only a little less hostile to him than to me. It cannot but damp the pleasure of cordiality, when we suspect that it is suspected. I cannot help thinking, that it is impossible for Mr. Adams to believe that the state of my mind is what it really is; that he may think I view him as an obstacle in my way. I have no supernatural power to impress truth on the mind of another, nor he any to discover that the estimate which he may form, on a just view of the human mind as generally constituted, may not be just in its application to a special constitution. This may be a source of private uneasiness to us; I honestly confess that it is so to me at this time. But neither of us is capable of letting it have effect on our public duties. Those who may endeavor to separate us, are probably excited by the fear that I might have influence on the executive councils: but when they shall know that I consider my office as constitutionally confined to legislative functions, and that I could not take any part whatever in executive consultations, even were it proposed, their fears may perhaps subside, and their object be found not worth a machination.
I do sincerely wish with you, that we could take our stand on a ground perfectly neutral and independent towards all nations. It has been my constant object through my public life: and with respect to the English and French, particularly, I have too often expressed to the former my wishes, and made to them propositions verbally and in writing, officially and privately, to official and private characters, for them to doubt of my views, if they would be content with equality. Of this they are in possession of several written and formal proofs, in my own hand-writing. But they have wished a monopoly of commerce and influence with us; and they have in fact obtained it. When we take notice that theirs is the workshop to which we go for all we want; that with them centre either immediately or ultimately all the labors of our hands and lands; that to them belongs either openly or secretly the great mass of our navigation; that even the factorage of their affairs here, is kept to themselves by factitious citizenships; that these foreign and false citizens now constitute the great body of what are called our merchants, fill our sea-ports, are planted in every little town and district of the interior country, sway every thing in the former places by their own votes, and those of their dependents, in the latter, by their insinuations and the influence of their ledgers; that they are advancing fast to a monopoly of our banks and public funds, and thereby placing our public finances under their control; that they have in their alliance the most influential characters in and out of office; when they have shown that by all these bearings on the different branches of the government, they can force it to proceed in whatever direction they dictate, and bend the interests of this country entirely to the will of another; when all this, I say, is attended to, it is impossible for us to say we stand on independent ground, impossible for a free mind not to see and to groan under the bondage in which it is bound. If anything after this could excite surprise, it would be that they have been able so far to throw dust in the eyes of our own citizens, as to fix on those who wish merely to recover self-government the charge of subserving one foreign influence because they resist submission to another. But they possess our printing presses, a powerful engine in their government of us. At this very moment, they would have drawn us into a war on the side of England, had it not been for the failure of her bank. Such was their open and loud cry, and that of their gazettes, till this event. After plunging us in all the broils of the European nations, there would remain but one act to close our tragedy, that is, to break up our union; and even this they have ventured seriously and solemnly to propose and maintain by arguments in a Connecticut paper. I have been happy, however, in believing, from the stifling of this effort, that that dose was found too strong, and excited as much repugnance there as it did horror in other parts of our country, and that whatever follies we may be led into as to foreign nations, we shall never give up our Union, the last anchor of our hope, and that alone which is to prevent this heavenly country from becoming an arena of gladiators. Much as I abhor war, and view it as the greatest scourge of mankind, and anxiously as I wish to keep out of the broils of Europe, I would yet go with my brethren into these, rather than separate from them. But I hope we may still keep clear of them, notwithstanding our present thraldom, and that time may be given us to reflect on the awful crisis we have passed through, and to find some means of shielding ourselves in future from foreign influence, political, commercial, or in whatever other form it may be attempted. I can scarcely withhold myself from joining in the wish of Silas Deane, that there were an ocean of fire between us and the old world.
A perfect confidence that you are as much attached to peace and union as myself, that you equally prize independence of all nations and the blessings of self-government, has induced me freely to unbosom myself to you, and let you see the light in which I have viewed what has been passing among us from the beginning of the war. And I shall be happy, at all times, in an intercommunication of sentiments with you, believing that the dispositions of the different parts of our country have been considerably misrepresented and misunderstood in each part, as to the other, and that nothing but good can result from an exchange of information and opinions between those whose circumstances and morals admit no doubt of the integrity of their views.
I remain, with constant and sincere esteem, Dear Sir, your affectionate friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO GENERAL GATES.
Philadelphia, May 30,1797.
Dear General,
I thank you for the pamphlet of Erskine enclosed in your favor of the 9th instant, and still more for the evidence which your letter affords me of the health of your mind, and I hope of your body also. Erskine has been reprinted here, and has done good. It has refreshed the memory of those who had been willing to forget how the war between France and England had been produced; and who, aping St. James’s, called it a defensive war on the part of England. I wish any events could induce us to cease to copy such a model, and to assume the dignity of being original. They had their paper system, stockjobbing, speculations, public debt, monied interest, &c, and all this was contrived for us. They raised their cry against jacobinism and revolutionists, we against democratic societies and anti-federalists; their alarmists sounded insurrection, ours marched an army to look for one, but they could not find it. I wish the parallel may stop here, and that we may avoid, instead of imitating, a general bankruptcy and disastrous war.
Congress, or rather the Representatives, have been a fortnight debating between a more or less irritating answer to the President’s speech. The latter was lost yesterday, by forty-eight against fifty-one or fifty-two. It is believed, however, that when they come to propose measures leading directly to war, they will lose some of their numbers. Those who have no wish but for the peace of their country, and its independence of all foreign influence, have a hard struggle indeed, overwhelmed by a cry as loud and imposing as if it were true, of being under French influence, and thus raised by a faction composed of English subjects residing among us, or such as are English in all their relations and sentiments. However, patience will bring all to rights, and we shall both live to see the mask taken from their faces, and our citizens sensible on which side true liberty and independence are sought. Should any circumstance draw me further from home, I shall with great cordiality pay my respects to you at Rose-Hill, and am not without hope of meeting you here some time.
Here, there, and every where else, I am, with great and sincere attachment and respect, your friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JAMES MADISON.
Philadelphia, June 1, 1797.
Dear Sir, I wrote you on the 18th of May. The address of the Senate was soon after that. The first draught was responsive to the speech, and higher toned. Mr. Henry arrived the day it was reported; the addressers had not yet their strength around them. They listened therefore to his objections, recommitted the papers, added him and Tazewell to the committee, and it was reported with considerable alterations; but one great attack was made on it, which was to strike out the clause approving every thing heretofore done by the executive. This clause was retained by a majority of four. They received a new accession of members, held a caucus, took up all the points recommended in the speech, except the raising money, agreed the list of every committee, and on Monday passed the resolutions and appointed the committees, by an uniform vote of seventeen to eleven. (Mr. Henry was accidentally absent; Ross not then come.) Yesterday they took up the nomination of John Quincy Adams to Berlin, which had been objected to as extending our diplomatic establishment. It was approved by eighteen to fourteen. (Mr. Tatnall accidentally absent.) From the proceedings we are able to see, that eighteen on the one side and ten on the other, with two wavering votes, will decide every question. Schuyler is too ill to come this session, and Gunn has not yet come. Pinckney (the General), John Marshall, and Dana are nominated Envoys Extraordinary to France. Charles Lee consulted a member from Virginia, to know whether Marshall would be agreeable. He named you, as more likely to give satisfaction. The answer was,’ Nobody of Mr. Madison’s way of thinking will be appointed.’
The representatives have not yet got through their addresses. An amendment of Mr. Nicholas’s, which you will have seen in the papers, was lost by a division of forty-six to fifty-two. A clause by Mr. Dayton, expressing a wish that France might be put on an equal footing with other nations, was inserted by fifty-two against forty-seven. This vote is most worthy of notice, because the moderation and justice of the proposition being unquestionable, it shows that there are forty-seven decided to go to all lengths to
They have received a new orator from the district of Mr. Ames. He is the son of the Secretary of the Senate. They have an accession from South Carolina also, that State being exactly divided. In the House of Representatives I learned the following facts, which give me real concern. When the British treaty arrived at Charleston, a meeting, as you know, was called, and a committee of seventeen appointed, of whom General Pinckney was one. He did not attend. They waited for him, sent for him: he treated the mission with great hauteur, and disapproved of their meddling. In the course of subsequent altercations, he declared that his brother T. Pinckney, approved of every article of the treaty, under the existing circumstances, and since that time the politics of
[* A few lines ave here unintelligible.]
Charleston have been assuming a different hue. Young Rutledge joining Smith and Harper, is an ominous fact as to that whole interest.
Tobacco is at nine dollars, and flour very dull of sale. A great stagnation in commerce generally. During the present bankruptcy in England, the merchants seem disposed to lie on their oars. It is impossible to conjecture the rising of Congress, as it will depend on the system they decide on; whether of preparation for war, or inaction. In the vote of forty-six to fifty-two, Morgan, Machir, and Evans were of the majority, and Clay kept his seat, refusing to vote with either. In that of forty-seven to fifty-two, Evans was the only one of our delegation who voted against putting France on an equal footing with other nations.
P. M. So far I had written in the morning. I now take up my pen to add, that the addresses having been reported to the House, it was moved to disagree to so much of the amendment as went to the putting France on an equal footing with other nations, and Morgan and Machir turning tail (in consequence, as is said, of having been closeted last night by Charles Lee), the vote was forty-nine to fifty. So the principle was saved by a single vote. They then proposed that compensations for spoliations shall be a sine qua non, and this will be decided on to-morrow,
Yours affectionately,
Th: Jefferson.
TO COLONEL BURR.
Philadelphia, June 17,1797.
Dear Sir,
The newspapers give, so minutely what is passing in Congress, that nothing of detail can be wanting for your information. Perhaps, however, some general view of our situation and prospects, since you left us, may not be unacceptable. At any rate, it will give me an opportunity of recalling myself to your memory, and of evidencing my esteem for you. You well know how strong a character of division had been impressed on the Senate by the British treaty. Common error, common censure, and common efforts of defence had formed the treaty majority into a common band, which feared to separate even on other subjects. Towards the close of the last Congress, however, it had been hoped that their ties began to loosen, and their phalanx to separate a little.
This hope was blasted at the very opening of the present session, by the nature of the appeal which the President made to the nation; the occasion for which had confessedly sprung from the fatal British treaty. This circumstance rallied them again to their standard, and hitherto we have had pretty regular treaty votes on all questions of principle. And indeed I fear, that as long as the same individuals remain, so long we shall see traces of the same division. In the House of Representatives the republican body has also lost strength. The non-attendance of five or six of that description has left the majority very equivocal indeed. A few individuals of no fixed system at all, governed by the panic or the prowess of the moment, flap as the breeze blows against the republican or the aristocratic bodies, and give to the one or the other a preponderance entirely accidental. Hence the dissimilar aspect of the address, and of the proceedings subsequent to that. The inflammatory composition of the speech excited sensations of resentment which had slept under British injuries, threw the wavering into the war scale, and produced the war address. Bonaparte’s victories and those on the Rhine, the Austrian peace, British bankruptcy, mutiny of the seamen, and Mr. King’s exhortations to pacific measures, have cooled them down again, and the scale of peace preponderates. The threatening propositions therefore, founded in the address, are abandoned one by one, and the cry begins now to be, that we have been called together to do nothing. The truth is, there is nothing to do, the idea of war being scouted by the events of Europe: but this only proves that war was the object for which we were called. It proves that the executive temper was for war; and that the convocation of the Representatives was an experiment of the temper of the nation, to see if it was in unison. Efforts at negotiation indeed were promised; but such a promise was as difficult to withhold, as easy to render nugatory. If negotiation alone had been meant, that might have been pursued without so much delay, and without calling the Representatives; and if strong and earnest negotiation had been meant, the additional nomination would have been of persons strongly and earnestly attached to the alliance of 1778. War then was intended. Whether abandoned or not, we must judge from future indications and events: for the same secrecy and mystery are affected to be observed by the present, which marked the former administration. I had always hoped, that the popularity of the late President being once withdrawn from active effect, the natural feelings of the people towards liberty would restore the equilibrium between the executive and legislative departments, which had been destroyed by the superior weight and effect of that popularity; and that their natural feelings of moral obligation would discountenance the ungrateful predilection of the executive in favor of Great Britain. But unfortunately, the preceding measures had already alienated the nation who were the object of them, had excited reaction from them, and this reaction has on the minds of our citizens an effect which supplies that of the Washington popularity. This effect was sensible on some of the late congressional elections, and this it is which has lessened the republican majority in Congress. When it will be reinforced, must depend on events, and these are so incalculable, that I consider the future character of our republic as in the air; indeed its future fortune will be in the air, if war is made on us by France, and if Louisiana becomes a Gallo-American colony.
I have been much pleased to see a dawn of change in the spirit of your State. The late elections have indicated something, which, at a distance, we do not understand. However, what with the English influence in the lower, and the Patroon influence in the upper parts of your State, I presume little is to be hoped. If a prospect could be once opened upon us of the penetration of truth into the Eastern States: if the people there, who are unquestionably republicans, could discover that they have been duped into the support of measures calculated to sap the very foundations of republicanism, we might still hope for salvation, and that it would come, as of old, from the East. But will that region ever awake to the true state of things? Can the middle, southern, and western States hold on till they awake? These are painful and doubtful questions: and if, in assuring me of your health, you can give me a comfortable solution of them, it will relieve a mind devoted to the preservation of our republican government in the true form and spirit in which it was established, but almost oppressed with apprehensions that fraud will at length effect what force could not, and that what with currents and counter-currents, we shall in the end, be driven back to the land from which we launched twenty years ago. Indeed, my dear Sir, we have been but a sturdy fish on the hook of a dexterous angler who letting us flounce till we have spent Our force, brings us up at last.
I am tired of the scene, and this day se’nnight shall change it for one, where, to tranquillity of mind, may be added pursuits of private utility, since none public are admitted by the state of things. I am with great and sincere esteem, Dear Sir, your friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson,
P. S. Since writing the above, we have received a report that the French Directory has proposed a declaration of war against the United States to the Council of Ancients, who have rejected it. Thus we see two nations who love one another affectionately, brought by the ill temper of their executive administrations, to the very brink of a necessity to imbrue their hands in the blood of each other. T. J.
TO ELBRIDGE GERRY.
Philadelphia, June 21, 1797.
My Dear Friend,
It was with infinite joy to me, that you were yesterday announced to the Senate, as Envoy Extraordinary, jointly with General Pinckney and Mr. Marshall, to the French republic. It gave me certain assurances that there would be a preponderance in the mission, sincerely disposed to be at peace with the French government and nation. Peace is undoubtedly at present the first object of our nation. Interest and honor are also national considerations. But interest, duly weighed, is in favor of peace even at the expense of spoliations past and future; and honor cannot now be an object. The insults and injuries committed on, us by both the belligerent parties, from, the beginning of 1793 to this day, and still continuing, cannot now be wiped off by engaging in war with one of them. As there is great reason to expect this is the last campaign in Europe, it would certainly be better for us to rub through this year, as we have done through the four preceding ones, and hope that, on the restoration of peace, we may be able to establish some plan for our foreign connections more likely to secure our peace, interest, and honor, in future. Our countrymen have divided themselves by such strong affections, to the French and the English, that nothing will secure us internally but a divorce from both nations; and this must be the object of every real American, and its attainment is practicable without much self-denial. But, for this, peace is necessary. Be assured of this, my dear Sir, that if we engage in a war during our present passions, and our present weakness in some quarters, our Union runs the greatest risk of not coming out of that war in the shape in which it enters it. My reliance for our preservation is in your acceptance of this mission. I know the tender circumstances which will oppose themselves to it. But its duration will be short, and its reward long. You have it in your power, by accepting and determining the character of the mission, to secure the present peace and eternal union of your country. If you decline, on motives of private pain, a substitute may be named who has enlisted his passions in the present contest, and by the preponderance of his vote in the mission may entail on us calamities, your share in which, and your feelings, will outweigh whatever pain a temporary absence from your family could give you. The sacrifice will be short, the remorse would be never-ending. Let me then, my dear Sir, conjure your acceptance, and that you will, by this act, seal the mission with the confidence of all parties. Your nomination has given a spring to hope, which was dead before.
I leave this place in three days, and therefore shall not here have the pleasure of learning your determination. But it will reach me in my retirement, and enrich the tranquillity of that scene. It will add to the proofs which have convinced me that the man who loves his country on its own account, and not merely for its trappings of interest or power, can never be divorced from it, can never refuse to come forward when he finds that she is engaged in dangers which he has the means of warding off. Make then an effort, my friend, to renounce your domestic comforts for a few months, and reflect that to be a good husband and good father at this moment, you must be also a good citizen. With sincere wishes for your acceptance and success, I am, with unalterable esteem, Dear Sir, your affectionate friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO EDWARD RUTLEDGE.
Philadelphia, June 24, 1797.
My Dear Sir,
I have to acknowledge your two favors of May the 4th and 19th, and to thank you for your attentions to the commissions for the pease and oranges, which I learn have arrived in Virginia. Your draft I hope will soon follow on Mr. John Barnes, merchant here, who, as I before advised you, is directed to answer it.
When Congress first met, the assemblage of facts presented in the President’s speech, with the multiplied accounts of spoliations by the French West-Indians, appeared, by sundry votes on the address, to incline a majority to put themselves in a posture of war. Under this influence the address was formed, and its spirit would probably have been pursued by corresponding measures, had the events of Europe been of an ordinary train. But this has been so extraordinary, that numbers have gone over to those, who, from the first, feeling with sensibility the French insults, as they had felt those of England before, thought now as they thought then, that war measures should be avoided, and those of peace pursued. Their favorite engine, on the former occasion, was commercial regulations, in preference to negotiations, to war preparation, and increase of debt. On the latter, as we have no commerce with France, the restriction of which could press on them, they wished for negotiation. Those of the opposite sentiment had, on the former occasion, preferred negotiation, but at the same time voted for great war preparations, and increase of debt: now also they were for negotiation, war preparations, and debt. The parties have in debate mutually charged each other with inconsistency, and with being governed by an attachment to this or that of the belligerent nations, rather than the dictates of reason and pure Americanism. But in truth, both have been consistent: the same men having voted for war measures who did before, and the same against them now who did before. The events of Europe coming to us in astonishing and rapid succession, to wit, the public bankruptcy of England, Bonaparte’s successes, the successes on the Rhine, the Austrian peace, mutiny of the British fleet, Irish insurrection, a demand of forty-three millions for the current services of the year, and above all, the warning voice, as is said, of Mr. King, to abandon all thought of connection with Great Britian, that she is going down irrecoverably, and will sink us also, if we do not clear ourselves, have brought over several to the pacific party, so as, at present, to give majorities against all threatening measures. They go on with frigates and fortifications, because they were going on with them before. They direct eighty thousand of their militia to hold themselves in readiness for service. But they reject the propositions to raise cavalry, artillery, and a provisional army, and to trust private ships with arms in the present combustible state of things. They believe the present is the last campaign of Europe, and wish to rub through this fragment of a year as they have through the four preceding ones, opposing patience to insult, and interest to honor. They will, therefore, immediately adjourn. This is indeed a most humiliating state of things, but it commenced in 1793. Causes have been adding to causes, and effects accumulating on effects, from that time to this. We had, in 1793, the most respectable character in the universe. What the neutral nations think of us now, I know not; but we are low indeed with the belligerents. Their kicks and cuffs prove their contempt. If we weather the present storm, I hope we shall avail ourselves of the calm of peace, to place our foreign connections under a new and different arrangement. We must make the interest of every nation stand surety for their justice, and their own loss to follow injury to us, as effect follows its cause. As to every thing except commerce, we ought to divorce ourselves from them all. But this system would require time, temper, wisdom, and occasional sacrifice of interest: and how far all of these will be ours, our children may see, but we shall not. The passions are too high at present, to be cooled in our day. You and I have formerly seen warm debates and high political passions. But gentlemen of different politics would then speak to each other, and separate the business of the Senate from that of society. It is not so now. Men who have been intimate all their lives, cross the streets to avoid meeting, and turn their heads another way, lest they should be obliged to touch their hats. This may do for young men with whom passion is enjoyment. But it is afflicting to peaceable minds. Tranquillity is the old man’s milk. I go to enjoy it in a few days, and to exchange the roar and tumult of bulls and bears, for the prattle of my grand-children and senile rest. Be these yours, my dear friend, through long years, with every other blessing, and the attachment of friends as warm and sincere, as yours affectionately,
Th: Jefferson.
THOMAS JEFFERSON TO JAMES MADISON.
Monticello, August 3, 1797.
I scribbled you a line on the 24th ultimo: it missed of the post, and so went by a private hand. I perceive from yours by Mr. Bringhurst, that you had not received it. In fact, it was only an earnest exhortation to come here with Monroe, which I still hope you will do. In the mean time, I enclose you a letter from him, and wish your opinion on its principal subject. The variety of other topics the day I was with you, kept out of sight the letter to Mazzei imputed to me in the papers, the general substance of which is mine, though the diction has been considerably altered and varied in the course of its translations from English into Italian, from Italian into French, and from French into English. I first met with it at Bladensburg, and for a moment conceived I must take the field of the public papers. I could not disavow it wholly, because the greatest part was mine in substance, though not in form. I could not avow it as it stood, because the form was not mine, and, in one place, the substance very materially falsified. This, then, would render explanations necessary; nay, it would render proofs of the whole necessary, and draw me at length into a publication of all (even the secret) transactions of the administration, while I was of it: and embroil me personally with every member of the executive, with the judiciary, and with others still. I soon decided in my own mind, to be entirely silent. I consulted with several friends at Philadelphia, who, every one of them, were clearly against my avowing or disavowing, and some of them conjured me most earnestly to let nothing provoke me to it. I corrected in conversation with them, a substantial misrepresentation in the copy published. The original has a sentiment like this (for I have it not before me), ‘They are endeavoring to submit us to the substance, as they already have to the forms of the British government;’ meaning by forms, the birth-days, levees, processions to parliament, inauguration pomposities, fee. But the copy published says, ‘as they have already submitted us to the form of the British,’ &c.; making me express hostility to the form of our government, that is to say, to the constitution itself. For this is really the difference of the word form, used in the singular or plural, in that phrase, in the English language. Now it would be impossible for me to explain this publicly, without bringing on a personal difference between General Washington and myself, which nothing before the publication of this letter has ever done. It would embroil me also with all those with whom his character is still popular, that is to say, nine tenths of the people of the United States; and what good would be obtained by avowing the letter with the necessary explanations? Very little indeed, in my opinion, to counterbalance a good deal of harm. From my silence in this instance, it cannot be inferred that I am afraid to own the general sentiments of the letter. If I am subject to either imputation, it is to that of avowing such sentiments too frankly both in private and public, often when there is no necessity for it, merely because I disdain every thing like duplicity. Still, however, I am open to conviction. Think for me on the occasion, and advise me what to do, and confer with Colonel Monroe on the subject.
Let me entreat you again to come with him; there are other important things to consult on. One will be his affair. Another is the subject of the petition now enclosed to you, to be proposed to our district, on the late presentment of our representative by the grand jury: the idea it brings forward is still confined to my own breast. It has never been mentioned to any mortal, because I first wish your opinion on the expediency of the measure. If you approve it, I shall propose to ——— or some other, to father it, and to present it to the counties at their general muster. This will be in time for our Assembly. The presentment going in the public papers just at the moment when Congress was together, produced a great effect both on its friends and foes in that body, very much to the disheartening and mortification of the latter. I wish this petition, if approved, to arrive there under the same circumstances, to produce the counter effect so wanting for their gratification. I could have wished to receive it from you again at our court on Monday, because ——— and ——— will be there, and might also be consulted, and commence measures for putting it into motion. If you can return it then, with your opinion, it will be of importance. Present me affectionately to Mrs. Madison, and convey to her my entreaties to interpose her good offices and persuasives with you to bring her here, and before we uncover our house, which will yet be some weeks. Salutations and adieu.
TO COLONEL ARTHUR CAMPBELL.
Monticello, September 1, 1797.
Dear Sir,
I have to acknowledge the receipt of your favor of July the 4th, and to recognise in it the sentiments you have ever held, and worthy of the day on which it is dated. It is true that a party has risen up among us, or rather has come among us, which is endeavoring to separate us from all friendly connection with France, to unite our destinies with those of Great Britian, and to assimilate our government to theirs. Our lenity in permitting the return of the old tories, gave the first body to this party; they have been increased by large importations of British merchants and factors, by American merchants dealing on British capital, and by stock-dealers and banking-companies, who, by the aid of a paper system are enriching themselves to the ruin of our country, and swaying the government by their possession of the printing-presses, which their wealth commands, and by other means, not always honorable to the character of our countrymen. Hitherto, their influence and their system have been irresistible, and they have raised up an executive power which is too strong for the legislature. But I flatter myself they have passed their zenith. The people, while these things were doing, were lulled into rest and security from a cause which no longer exists. No prepossessions now will shut their ears to truth. They begin to see to what port their leaders were steering during their slumbers, and there is yet time to haul in, if we can avoid a war with France. All can be done peaceably, by the people confining their choice of Representatives and Senators to persons attached to republican government and the principles of 1776, not office-hunters, but farmers, whose interests are entirely agricultural. Such men are the true representatives of the great American interest, and are alone to be relied on for expressing the proper American sentiments. We owe gratitude to France, justice to England, good-will to all, and subservience to none. All this must be brought about by the people, using their elective rights with prudence and self-possession, and not suffering themselves to be duped by treacherous emissaries. It was by the sober sense of our citizens that we were safely and steadily conducted from monarchy to republicanism, and it is by the same agency alone we can be kept from falling back. I am happy in this occasion of reviving the memory of old things, and of assuring you of the continuance of the esteem and respect of, Dear Sir, your friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
Monticello, September 7, 1797.
The doubt which you suggest as to our jurisdiction over the case of the Grand Jury vs. Cabell had occurred to me, and naturally occurs on first view of the question. But I knew, that to send the petition to the House of Representatives in Congress, would make bad worse; that a majority of that House would pass a vote of approbation. On examination of the question, too, it appeared to me that we could maintain the authority of our own government over it.
A right of free correspondence between citizen and citizen, on their joint interests, whether public or private, and under whatsoever laws these interests arise (to wit, of the State, of Congress, of France, Spain, or Turkey), is a natural right: it is not the gift of any municipal law, either of England, of Virginia, or of Congress: but in common with all our other natural rights, it is one of the objects for the protection of which society is formed, and municipal laws established.
The courts of this commonwealth (and among them the General Court, as a court of impeachment) are originally competent to the cognizance of all infractions of the rights of one citizen by another citizen: and they still retain all their judiciary cognizances not expressly alienated by the federal constitution.
The federal constitution alienates from them all cases arising, 1st, under the constitution; 2ndly, under the laws of Congress; 3rdly, under treaties, &c. But this right of free correspondence, whether with a public representative in General Assembly, in Congress, in France, in Spain, or with a private one charged with pecuniary trust, or with a private friend, the object of our esteem, or any other, has not been given to us under, 1st, the federal constitution; 2ndly, any law of Congress; or 3rdly, any treaty; but, as before observed, by nature. It is therefore not alienated, but remains under the protection of our courts.
Were the question even doubtful, that is no reason for abandoning it. The system of the General Government is to seize all doubtful ground. We must join in the scramble, or get nothing. Where first occupancy is to give right, he who lies still loses all. Besides, it is not right for those who are only to act in a preliminary form, to let their own doubts preclude the judgment of the court of ultimate decision. We ought to let it go to the House of Delegates for their consideration, and they, unless the contrary be palpable, ought to let it go to the General Court, who are ultimately to decide on it.
It is of immense consequence that the States retain as complete authority as possible over their own citizens. The withdrawing themselves under the shelter of a foreign jurisdiction, is so subversive of order and so pregnant of abuse, that it may not be amiss to consider how far a law of præmunire should be revised and modified, against all citizens who attempt to carry their causes before any other than the State courts, in cases where those other courts have no right to their cognizance. A plea to the jurisdiction of the courts of their State, or a reclamation of a foreign jurisdiction, if adjudged valid, would be safe; but if adjudged invalid, would be followed by the punishment of præmunire for the attempt.
Think further of the preceding part of this letter, and we will have further conference on it. Adieu.
P. S. Observe, that it is not the breach of Mr. Cabell’s privilege which we mean to punish: that might lie with Congress. It is the wrong done to the citizens of our district. Congress have no authority to punish that wrong. They can only take cognizance of it in vindication of their member.
TO JAMES MADISON.
Philadelphia, January 3, 1798
Dear Sir,
Your favor of the 25th came to hand yesterday. I shall observe your direction with respect to the post-day. I have spoken with the Deputy Postmaster-General on the subject of our Fredericksburg post. He never knew before that the Fredericksburg printer had taken the contract of the rider. He will be glad, if either in your neighborhood or ours, some good person will undertake to ride from April next. The price given this year is three hundred and thirty dollars, and it will go to the lowest bidder, who can be depended on. I understand (though not from him) that Wyatt will be changed; and in general they determine that printers shall not be postmasters or riders.
Our weather has been, here as with you, cold and dry. The thermometer has been at eight degrees. The river closed here the first week of December, which has caught a vast number of vessels destined for departure. It deadens also the demand for wheat. The price at New York is one dollar seventy-five cents, and of flour eight dollars fifty cents to nine dollars; tobacco eleven to twelve dollars; there need be no doubt of greater prices. The bankruptcies here continue: the prison is full of the most reputable merchants, and it is understood that the scene has not yet got to its height. Prices have fallen greatly. The market is cheaper than it has been for four years. Labor and house-rent much reduced. Dry goods somewhat. It is expected that they will fall till they get nearly to old prices. Money scarce beyond all example.
The Representatives have rejected the President’s proposition for enabling him to prorogue them. A law has passed putting off the stamp-act till July next. The land-tax will not be brought on. The Secretary of the Treasury says he has money enough. No doubt these two measures may be taken up more boldly at the next session, when most of the elections will be over. It is imagined the stamp-act will be extended or attempted on every possible object. A bill has passed the Representatives to suspend for three years the law arresting the currency of foreign coins. The Senate propose an amendment, continuing the currency of the foreign gold only. Very possibly the bill may be lost. The object of opposing the bill is to make the French crowns a subject of speculation (for it seems they fell on the President’s proclamation to a dollar in most of the States), and to force bank-paper (for want of other medium) through all the States generally. Tench Coxe is displaced, and no reason even spoken of. It is therefore understood to be for his activity during the late election. It is said that the people from hence, quite to the eastern extremity, are beginning to be sensible, that their government has been playing a foul game. In Vermont, Chipman was elected Senator by a majority of one, against the republican candidate. In Maryland, Loyd by a majority of one, against Winder, the republican candidate. Tichenor chosen Governor of Vermont by a very small majority. The House of Representatives of this State has become republican by a firm majority of six. Two counties, it is said, have come over generally to the republican side. It is thought the republicans have also a majority in the New York House of Representatives. Hard elections are expected there between Jay and Livingston, and here between Ross and M’Kean. In the House of Representatives of Congress, the republican interest has at present, on strong questions, a majority of about half a dozen, as is conjectured, and there are as many of their firmest men absent; not one of the anti-republicans is from his post. The bill for permitting private vessels to arm, was put off to the first Monday in February by a sudden vote, and a majority of five. It was considered as an index of their dispositions on that subject, though some voted both ways on other ground. It is most evident that the anti-republicans wish to get rid of Blount’s impeachment. Many metaphysical niceties are handing about in conversation, to show that it cannot be sustained. To show the contrary, it is evident, must be the task of the republicans, or of nobody. Monroe’s book is considered as masterly by all those who are not opposed in principle, and it is deemed unanswerable. An answer, however, is commenced in Fenno’s paper of yesterday, under the signature of Scipio. The real author not yet conjectured. As I take these papers merely to preserve them, I will forward them to you, as you can easily return them to me on my arrival at home; for I shall not see you on my way, as I mean to go by the Eastern Shore and Petersburg. Perhaps the paragraphs in some of these abominable papers may draw from you now and then a squib. A pamphlet of Fauchet’s appeared yesterday. I send you a copy under another cover. A hand-bill has just arrived here from New York, where they learn from a vessel which left Havre about the 9th of November, that the Emperor had signed the definitive articles, given up Mantua, evacuated Mentz, agreed to give passage to the French troops to Hanover, and that the Portuguese ambassador had been ordered to quit Paris, on account of the seizure of fort St. Julian’s by the, English, supposed with the connivance of Portugal. Though this is ordinary mercantile news, it looks like truth. The latest official intelligence from Paris, is from Talleyrand to the French Consul here (Lastombe), dated September the 28th, saying that our Envoys were arrived, and would find every disposition on the part of his government to accommodate with us.
My affectionate respects to Mrs. Madison; to yourself, health and friendship. Adieu.
Th: Jefferson.
TO JAMES MADISON.
Philadelphia, January 25, 1798.
Dear Sir,
I wrote you last on the 2nd instant, on which day I received yours of December the 25th. I have not resumed my pen, because there has really been nothing worth writing about, but what you would see in the newspapers. There is, as yet, no certainty what will be the aspect of our affairs with France. Either the Envoys have not written to the government, or their communications are hushed up. This last is suspected, because so many arrivals have happened from Bordeaux and Havre. The letters from American correspondents in France have been always to Boston: and the experience we had last summer of their adroitness in counterfeiting this kind of intelligence, inspires doubts as to their late paragraphs. A letter is certainly received here by an individual, from Talleyrand, which says our Envoys have been heard, that their pretensions are high, that possibly no arrangement may take place, but that there will be no declaration of war by France. It is said that Bournonville has written that he has hopes of an accommodation (three audiences having then, November, been had), and to be himself a member of a new diplomatic mission to this country. On the whole, I am entirely suspended as to what is to be expected. The Representatives have been several days in debate on the bill for foreign intercourse. A motion has been made to reduce it to what it was before the extension of 1796. The debate will probably have good effects, in several ways, on the public mind, but the advocates for the reformation expect to lose the question. They find themselves deceived in the expectation entertained in the beginning of the session, that they had a majority. They now think the majority is on the other side by two or three, and there are moreover two or three of them absent. Blount’s affair is to come on next. In the mean time, the Senate have before them a bill for regulating proceedings in impeachment. This will be made the occasion of offering a clause for the introduction of juries into these trials. (Compare the paragraph in the constitution which says, that all crimes, except in cases of impeachment, shall be by jury, with the eighth amendment, which says, that in all criminal prosecutions, the trial shall be by jury.) There is no expectation of carrying this; because the division in the Senate is of two to one, but it will draw forth the principles of the parties, and concur in accumulating proofs on which side all the sound principles are to be found.
Very acrimonious altercations are going on between the Spanish Minister and the executive, and at the Natchez something worse than mere altercation. If hostilities have not begun there, it has not been for want of endeavors to bring them on, by our agents. Marshall, of Kentucky, this day proposed in Senate some amendments to the constitution. They were barely read just as we were adjourning, and not a word of explanation given. As far as I caught them in my ear, they went only to modifications of the elections of President and Vice-President, by authorizing voters to add the office for which they name each, and giving to the Senate the decision of a disputed election of President, and to the Representatives that of Vice-President. But I am apprehensive I caught the thing imperfectly, and probably incorrectly. Perhaps this occasion may be taken of proposing again the Virginia amendments, as also to condemn elections by the legislatures, themselves to transfer the power of trying impeachments from the Senate to some better constituted court, &c. &c.
Good tobacco here is thirteen dollars, flour eight dollars and fifty cents, wheat one dollar and fifty cents, but dull, because only the millers buy. The river, however, is nearly open, and the merchants will now come to market and give a spur to the price. But the competition will not be what it has been. Bankruptcies thicken, and the height of them has by no means yet come on. It is thought this, winter will be very trying.
Friendly salutations to Mrs. Madison. Adieu affectionately.
Th: Jefferson.
January 28. I enclose Marshall’s propositions. They have been this day postponed to the 1st of June, chiefly by the vote of the anti-republicans, under the acknowledged fear that other amendments would be also proposed, and that this is not the time for agitating the public mind. T. J.
TO JAMES MADISON.
Philadelphia, February 8, 1798.
Dear Sir,
I wrote you last on the 25th ultimo; since which yours of the 21st has been received. Bache had put five hundred copies of Monroe’s book on board a vessel, which was stopped by the early and unexpected freezing of the river. He tried in vain to get them carried by fifties at a time, by the stage. The river is now open here, the vessels are falling down, and if they can get through the ice below, the one with Bache’s packet will soon be at Richmond. It is surmised here that Scipio is written by C. Lee. Articles of impeachment were yesterday given in against Blount. But many great preliminary questions will arise. Must not a formal law settle the oath of the Senators, form of pleadings, process against person or goods, &c. May he not appear by attorney? Must he not be tried by a jury? Is a Senator impeachable? Is an ex-Senator impeachable? You will readily conceive that these questions, to be settled by twenty-nine lawyers, are not likely to come to speedy issue. A very disagreeable question of privilege has suspended all other proceedings for some days. You will see this in the newspapers. The question of arming vessels came on, on Monday last; that morning, the President sent in an inflammatory message about a vessel taken and burnt by a French privateer, near Charleston. Of this he had been possessed some time, and it had been through all the newspapers. It seemed to come in now apropos for spurring on the disposition to arm. However, the question has not come on. In the mean time the general spirit, even of the merchants, is becoming adverse to it. In New Hampshire and Rhode Island they are unanimously against arming; so in Baltimore. This place is becoming more so. Boston divided and desponding. I know nothing of New York; but I think there is no danger of the question being carried, unless something favorable to it is received from our Envoys. From them we hear nothing. Yet it seems reasonably believed that the executive has heard, and that it is something which would not promote their views of arming. For every action of theirs shows they are panting to come to blows. Giles has arrived.
My friendly salutations to Mrs. Madison. Adieu affectionately.
Th: Jefferson.
TO JAMES MADISON.
Philadelphia, February 15, 1798.
Dear Sir,
I wrote you last on the 8th. We have still not a word from our Envoys. This long silence (if they have been silent) proves things are not going on very roughly. If they have not been silent, it proves their information, if made public, would check the disposition to arm. I had flattered myself, from the progress of the public sentiment against arming, that the same progress had taken place in the legislature. But I am assured by those who have better opportunities of forming a good judgment, that if the question against arming is carried at all, it will not be by more than a majority of two: and particularly, that there will not be more than four votes against it from the five eastern states, or five votes at the utmost. You will have perceived that Dayton has gone over completely. He expects to be appointed Secretary of War in the room of M’Henry, who it is said will retire. He has been told, as report goes, that they would not have confidence enough in him to appoint him. The desire of inspiring them with more, seems the only way to account for the eclat which he chooses to give to his conversion. You will have seen the disgusting proceedings in the case of Lyon: if they would have accepted even of a commitment to the Serjeant it might have been had. But to get rid of his vote was the most material object. These proceedings must degrade the General Government, and lead the people to lean more on their State governments, which have been sunk under the early popularity of the former. This day the question of the jury in cases of impeachment comes on. There is no doubt how it will go. The general division of the Senate is twenty-two and ten; and under the probable prospect of what it will for ever be, I see nothing in the mode of proceeding by impeachment but the most formidable weapon for the purposes of dominant faction that ever was contrived. It would be the most effectual one of getting rid of any man whom they consider as dangerous to their views, and I do not know that we could count on one third in an emergency. All depends then on the House of Representatives, who are the impeachers; and there the majorities are of one, two, or three only; and these sometimes one way and sometimes another: in a question of pure party they have the majority, and we do not know what circumstances may turn up to increase that majority temporarily, it not permanently. I know of no solid purpose of punishment which the courts of law are not equal to, and history shows, that, in England, impeachment has been an engine more of passion than justice. A great ball is to be given here on the 22nd, and in other great towns of the Union. This is, at least, very indelicate, and probably excites uneasy sensations in some. I see in it, however, this useful deduction, that the birth-days which have been kept, have been, not those of the President, but of the General. I enclose, with the newspapers, the two acts of parliament passed on the subject of our commerce, which are interesting. The merchants here, say, that the effect of the countervailing tonnage on American vessels, will throw them completely out of employ as soon as there is peace. The eastern members say nothing but among themselves. But it is said that it is working like grave in their stomachs. Our only comfort is, that they have brought it on themselves. My respectful salutations to Mrs. Madison; and to yourself, friendship and adieu.
Th: Jefferson.
TO GENERAL GATES.
Philadelphia, February 21, 1798.
Dear General,
I received duly your welcome favor of the 15th, and had an opportunity of immediately delivering the one it enclosed to General Kosciusko. I see him often, and with great pleasure mixed with commiseration. He is as pure a son of liberty as I have ever known, and of that liberty which is to go to all, and not to the few or the rich alone. We are here under great anxiety to hear from our Envoys.
I agree with you that some of our merchants have been milking the cow: yet the great mass of them have become deranged, they are daily falling down by bankruptcies, and on the whole, the condition of our commerce far less firm and really prosperous, than it would have been by the regular operations and steady advances which a state of peace would have occasioned. Were a war to take place, and throw our agriculture into equal convulsions with our commerce, our business would be done at both ends. But this I hope will not be. The good news from the Natchez has cut off the fear of a breach in that quarter, where a crisis was brought on which has astonished every one. How this mighty duel is to end between Great Britain and France, is a momentous question. The sea which divides them makes it a game of chance; but it is narrow, and all the chances are not on one side. Should they make peace, still our fate is problematical.
The countervailing acts of Great Britain, now laid before Congress, threaten, in the opinion of merchants, the entire loss of our navigation to England. It makes a difference, from the present state of things, of five hundred guineas on a vessel of three hundred and fifty tons. If, as the newspapers have told us, France has renewed her Arrêt of 1789, laying a duty of seven livres a hundred on all tobacco brought in foreign bottoms (even our own), and should extend it to rice and other commodities, we are done, as navigators, to that country also. In fact, I apprehend that those two great nations will think it their interest not to permit us to be navigators. France had thought otherwise, and had shown an equal desire to encourage our navigation as her own, while she hoped its weight would at least not be thrown into the scale of her enemies. She sees now that that is not to be relied on, and will probably use her own means, and those of the nations under her influence, to exclude us from the ocean. How far it may lessen our happiness to be rendered merely agricultural, how far that state is more friendly to principles of virtue and liberty, are questions yet to be solved. Kosciusko has been disappointed by the sudden peace between France and Austria. A ray of hope seemed to gleam on his mind for a moment, that the extension of the revolutionary spirit through Italy and Germany, might so have occupied the remnants of monarchy there, as that his country might have risen again. I sincerely rejoice to find that you preserve your health so well. That you may so go on to the end of the chapter, and that it may be a long one, I sincerely pray. Make my friendly salutations acceptable to Mrs. Gates, and accept yourself assurances of the great and constant esteem and respect of, Dear Sir, your friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JAMES MADISON.
Philadelphia, February 22, 1798.
Dear Sir,
Yours of the 12th is received. I wrote you last on the 15th, but the letter getting misplaced, will only go by this post. We still hear nothing from our Envoys. Whether the executive hear, we know not. But if war were to be apprehended, it is impossible our Envoys should not find means of putting us on our guard, or that the executive should hold back their information. No news, therefore, is good news. The countervailing act, which I sent you by the last post, will, confessedly, put American bottoms out of employ in our trade with Great Britain. So say well informed merchants. Indeed, it seems probable, when we consider that hitherto, with the advantage of our foreign tonnage, our vessels could only share with the British, and the countervailing duties will, it is said, make a difference of five hundred guineas to our prejudice on a ship of three hundred and fifty tons. Still the eastern men say nothing. Every appearance and consideration render it probable, that on the restoration of peace, both France and Britain will consider it their interest to exclude us from the ocean, by such peaceable means as are in their power. Should this take place, perhaps it may be thought just and politic to give to our native capitalists the monopoly of our internal commerce. This may at once relieve us from the dangers of wars abroad and British thraldom at home. The news from the Natchez, of the delivery of the posts, which you will see in the papers, is to be relied on. We have escaped a dangerous crisis there. The great contest between Israel and Morgan, of which you will see the papers full, is to be decided this day. It is snowing fast at this time, and the most sloppy walking I ever saw. This will be to the disadvantage of the party which has the most invalids. Whether the event will be known this evening, I am uncertain. I rather presume not, and, therefore, that you will not learn it till next post.
You will see in the papers, the ground on which the introduction of the jury into the trial by impeachment was advocated by Mr. Tazewell, and the fate of the question. Reader’s motion, which I enclosed you, will probably be amended and established, so as to declare a Senator unimpeachable, absolutely; and yesterday an opinion was declared, that not only officers of the State governments, but every private citizen of the United States, are impeachable. Whether they will think this the time to make the declaration, I know not; but if they bring it on, I think there will be not more than two votes north of the Potomac against the universality of the impeaching power. The system of the Senate may be inferred from their transactions heretofore, and from the following declaration made to me personally by their oracle.* ‘No republic Can ever be of any duration without a Senate, and a Senate deeply and strongly rooted, strong enough to bear up against all popular storms and passions. The only fault in the constitution of our Senate is, that their term of office is not durable enough. Hitherto they have done well, but probably they will be forced to give way in time.’ I suppose their having done well hitherto, alluded to the stand they made on the British treaty. This declaration may be considered as their text: that they consider themselves as the bulwarks of the government, and will be rendering that the more secure, in proportion as they can assume greater powers. The foreign intercourse bill is set for to-day: but the parties are so equal on that in the House of Representatives, that they seem mutually to fear the encounter.
My friendly salutations to Mrs. Madison and the family. To
yourself, friendly adieus.
Th: Jefferson.
[* Here, in the margin of the copy filed, is written by the
author, in pencil, ‘Mr, Adams.‘]
TO JAMES MADISON.
Philadelphia, March 2, 1798.
Dear Sir,
I wrote to you last on the 22nd ultimo; since which I have received yours without date, but probably of April the 18th or 19th. An arrival to the eastward brings us some news, which you will see detailed in the papers. The new partition of Europe is sketched, but how far authentic we know not. It has some probability in its favor. The French appear busy in their preparations for the invasion of England; nor is there any appearance of movements on the part of Russia and Prussia which might divert them from it.
The late birth-night has certainly sown tares among the exclusive federalists. It has winnowed the grain from the chaff. The sincerely Adamites did not go. The Washingtonians went religiously, and took the secession of the others in high dudgeon. The one sect threatens to desert the levees, the other the parties. The whigs went in number, to encourage the idea that the birth-nights hitherto kept had been for the General and not the President, and of course that time would bring an end to them. Goodhue, Tracy, Sedgwick, &c. did not attend; but the three Secretaries and Attorney General did.
We were surprised, the last week, with a symptom of a disposition to repeal the stamp act. Petitions for that purpose had come from Rhode Island and Virginia, and had been committed to rest with the Ways and Means. Mr. Harper, the chairman, in order to enter on the law for amending it, observed it would be necessary first to put the petitions for repeal out of the way, and moved an immediate decision on this. The Rhode-Islanders begged and prayed for a postponement; that not knowing that this was the next question to be called up, they were not at all prepared: but Harper would show no mercy; not a moment’s delay would be allowed. It was taken up, and, on question without debate, determined in favor of the petitions by a majority of ten. Astonished and confounded, when an order to bring in a bill for revisal was named, they began in turn to beg for time; two weeks, one week, three days, one day; not a moment would be yielded. They made three attempts for adjournment. But the majority appeared to grow. It was decided, by a majority of sixteen, that the bill should be brought in. It was brought in the next day, and on the day after passed and was sent up to the Senate, who instantly sent it back rejected by a vote of fifteen to twelve. Rhode Island and New Hampshire voted for the repeal in Senate. The act will therefore go into operation July the 1st, but probably without amendments. However, I am persuaded it will be shortlived. It has already excited great commotion in Vermont, and grumblings in Connecticut. But they are so priest-ridden, that nothing is to be expected from them, but the most bigoted passive obedience.
No news yet from our commissioners; but their silence is admitted to augur peace. There is no talk yet of the time of adjourning, though it is admitted we have nothing to do, but what could be done in a fortnight or three weeks. When the spring opens, and we hear from our commissioners, we shall probably draw pretty rapidly to a conclusion. A friend of mine here wishes to get a copy of Mazzei’s ‘Recherches Historiques et Politiques.’ Where are they?
Salutations and adieu.
Th: Jefferson.
Philadelphia, March 15, 1798.
Dear Sir,
I wrote you last on the 2nd instant. Yours of the 4th is now at hand. The public papers will give you the news of Europe. The French decree making the vessel friendly or enemy, according to the hands by which the cargo was manufactured, has produced a great sensation among the merchants here. Its operation is not yet perhaps well understood; but probably it will put our shipping out of competition, because British bottoms, which can come under convoy, will alone be trusted with return cargoes. Ours, losing this benefit, would need a higher freight out, in which, therefore, they will be underbid by the British. They must then retire from the competition. Some no doubt will try other channels of commerce, and return cargoes from other countries. This effect would be salutary. A very well informed merchant, too, (a Scotchman, entirely in the English trade) told me, bethought it would have another good effect, by checking and withdrawing our extensive commerce and navigation (the fruit of our natural position) within those bounds to which peace must necessarily bring them. That this being done by degrees, will probably prevent those numerous failures produced generally by a peace coming on suddenly. Notwithstanding this decree, the sentiments of the merchants become more and more cooled and settled down against arming. Yet it is believed the Representatives do not cool; and though we think the question against arming will be carried, yet probably by a majority of only four or five. Their plan is to have convoys furnished for our vessels going to Europe, and smaller vessels for the coasting defence. On this condition, they will agree to fortify southern harbors and build some galleys. It has been concluded among them, that if war takes place, Wolcott is to be retained in office, that the President must give up M’Henry, and as to Pickering they are divided, the eastern men being determined to retain him, their middle and southern brethren wishing to get rid of him. They have talked of General Pinckney as successor to M’Henry. This information is certain. However, I hope we shall avoid war, and save them the trouble of a change of ministry. The President has nominated John Quincy Adams Commissioner Plenipotentiary to renew the treaty with Sweden. Tazewell made a great stand against it, on the general ground that we should let our treaties drop, and remain without any. He could only get eight votes against twenty. A trial will be made today in another form, which he thinks will give ten or eleven against sixteen or seventeen, declaring the renewal inexpedient. In this case, notwithstanding the nomination has been confirmed, it is supposed the President would perhaps not act under it, on the probability that more than the third would be against the ratification. I believe, however, that he would act, and that a third could not be got to oppose the ratification. It is acknowledged we have nothing to do but to decide the question about arming. Yet not a word is said about adjourning; and some even talk of continuing the session permanently; others talk of July and August. An effort, however, will soon be made for an early adjournment. My friendly salutations to Mrs. Madison; to yourself an affectionate adieu.
Th: Jefferson.
TO JAMES MADISON.
Philadelphia, March 21, 1798.
Dear Sir,
I wrote you last on the 15th; since that, yours of the 12th has been received. Since that, too, a great change has taken place in the appearance of our political atmosphere. The merchants, as before, continue, a respectable part of them, to wish to avoid arming. The French decree operated on them as a sedative, producing more alarm than resentment: on the Representatives, differently. It excited indignation highly in the war party, though I do not know that it had added any new friends, to that side of the question. We still hoped a majority of about four: but the insane message which you will see in the public papers has had great effect. Exultation on the one side, and a certainty of victory; while the other is petrified with astonishment. Our Evans, though his soul is wrapt up in the sentiments of this message, yet afraid to give a vote openly for it, is going off to-morrow, as is said. Those who count, say there are still two members of the other side who will come over to that of peace. If so, the members will be for war measures, fifty-two, against them fifty-three; if all are present except Evans. The question is, what is to be attempted, supposing we have a majority: I suggest two things: 1. As the President declares he has withdrawn the executive prohibition to arm, that Congress should pass a legislative one. If that should fail in the Senate, it would heap coals of fire on their heads. 2. As, to do nothing and to gain time is everything with us, I propose, that they shall come to a resolution of adjournment, ‘in order to go home and consult their constituents on the great crisis of American affairs now existing.’ Besides gaining time enough by this, to allow the descent on England to have its effect here as well as there, it will be a means of exciting the whole body of the people from the state of inattention in which they are; it will require every member to call for the sense of his district by petition or instruction; it will show the people with which side of the House their safety as well as their rights rest, by showing them which is for war and which for peace; and their representatives will return here invigorated by the avowed support of the American people. I do not know, however, whether this will be approved, as there has been little consultation on the subject. We see a new instance of the inefficiency of constitutional guards.
We had relied with great security on that provision, which requires two thirds of the legislature to declare war. But this is completely eluded by a majority’s taking such measures as will be sure to produce war. I wrote you in my last, that an attempt was to be made on that day in Senate, to declare the inexpediency of renewing our treaties. But the measure is put off under the hope of its being attempted under better auspices. To return to the subject of war, it is quite impossible, when we consider all the existing circumstances, to find any reason in its favor resulting from views either of interest or honor, and plausible enough to impose even on the weakest mind; and especially, when it would be undertaken by a majority of one or two only. Whatever then be our stock of charity or liberality, we must resort to other views. And those so well known to have been entertained at Annapolis, and afterwards at the grand convention, by a particular set of men, present themselves as those alone which can account for so extraordinary a degree of impetuosity. Perhaps, instead of what was then in contemplation, a separation of the Union, which has been so much the topic to the eastward of late, may be the thing aimed at. I have written so far, two days before the departure of the post. Should any thing more occur to-day or to-morrow, it shall be added. Adieu affectionately.
Th: Jefferson.
TO JAMES MADISON.
Philadelphia, March 29, 1798.
Dear Sir,
I wrote you last on the 21st. Yours of the 12th, therein acknowledged, is the last received. The measure I suggested in mine, of adjourning for consultation with their constituents, was not brought forward; but on Tuesday three resolutions were moved, which you will see in the public papers. They were offered in committee to prevent their being suppressed by the previous question, and in the committee on the state of the Union, to put it out of their power, by the rising of the committee and not sitting again, to get rid of them. They were taken by surprise, not expecting to be called to vote on such a proposition as ‘that it is inexpedient to resort to war against the French republic’. After spending the first day in seeking on every side some hole to get out at, like an animal first put into a cage, they gave up their resource. Yesterday they came forward boldly, and openly combated the proposition. Mr. Harper and Mr. Pinckney pronounced bitter philippics against France, selecting such circumstances and aggravations as to give the worst picture they could present. The latter, on this, as in the affair of Lyon and Griswold, went far beyond that moderation he has on other occasions recommended. We know not how it will go. Some think the resolution will be lost, some, that it will be carried; but neither way, by a majority of more than, one or two. The decision of the Executive, of two thirds of the Senate, and half the House of Representatives, is too much for the other half of that House. We therefore fear it will be borne down, and are under the most gloomy apprehensions. In fact, the question of war and peace depends now on a toss of cross and pile. If we could but gain this season, we should be saved. The affairs of Europe would of themselves save us. Besides this, there can be no doubt that a revolution of opinion in Massachusetts and Connecticut is working. Two whig presses have been set up in each of those States. There has been for some days a rumor, that a treaty of alliance, offensive and defensive with Great Britain, has arrived. Some circumstances have occasioned it to be listened to; to wit, the arrival of Mr. King’s secretary, which is affirmed, the departure of Mr. Liston’s secretary, which I know is to take place on Wednesday next, the high tone of the executive measures at the last, and present session, calculated to raise things to the unison of such a compact, and supported so desperately in both Houses in opposition to the pacific wishes of the people, and at the risk of their approbation at the ensuing election. Langdon yesterday, in debate, mentioned this current report. Tracy, in reply, declared he knew of no such thing, did not believe it, nor would be its advocate.
An attempt has been made to get the Quakers to come forward with a petition, to aid with the weight of their body the feeble band of peace. They have, with some effort, got a petition signed by a few of their society; the main body of their society refuse it. M’Lay’s peace motion in the Assembly of Pennsylvania was rejected with an unanimity of the Quaker vote, and it seems to be well understood, that their attachment to England is stronger than to their principles or their country. The revolution war was a first proof of this. Mr. White, from the federal city, is here, soliciting money for the buildings at Washington. A bill for two hundred thousand dollars has passed the House of Representatives, and is before the Senate, where its fate is entirely uncertain. He has become perfectly satisfied that Mr. Adams is radically against the government’s being there. Goodhue (his oracle) openly said in committee, in presence of White, that he knew the government was obliged to go there, but they would not be obliged to stay there. Mr. Adams said to White, that it would be better that the President should rent a common house there, to live in; that no President would live in the one now building. This harmonizes with Goodhue’s idea of a short residence. I wrote this in the morning, but need not part with it till night. If any thing occurs in the day, it shall be added. Adieu.
Th: Jefferson.
TO JAMES MADISON.
Philadelphia, April 5, 1798.
Dear Sir,
I wrote you last on the 29th ultimo; since which I have no letter from you. These acknowledgments regularly made and attended to will show whether any of my letters are intercepted, and the impression of my seal on wax (which shall be constant hereafter) will discover whether they are opened by the way. The nature of some of my communications furnishes ground of inquietude for their safe conveyance. The bill for the federal buildings labors hard in Senate, though, to lessen opposition, the Maryland Senator himself proposed to reduce the two hundred thousand dollars to one third of that sum. Sedgwick and Hill-house violently oppose it. I conjecture that the votes will be either thirteen for and fifteen against it, or fourteen and fourteen. Every member declares he means to go there, but though charged with an intention to come away again, not one of them disavow it. This will engender incurable distrust. The debate on Mr. Sprigg’s resolutions has been interrupted by a motion to call for papers. This was carried by a great majority. In this case, there appeared a separate squad, to wit, the Pinckney interest, which is a distinct thing, and will be seen sometimes to lurch the President. It is in truth the Hamilton party, whereof Pinckney is only made the stalking-horse. The papers have been sent in and read, and it is now under debate in both Houses, whether they shall be published. I write in the morning, and if determined in the course of the day in favor of publication, I will add in the evening a general idea of their character. Private letters from France, by a late vessel which sailed from Havre, February the 5th, assure us that France, classing us in her measures with the Swedes and Danes, has no more notion of declaring war against us than them. You will see a letter in Bache’s paper of yesterday, which came addressed to me. Still the fate of Spring’s resolutions seems in perfect equilibrio. You will see in Fenno, two numbers of a paper signed Marcellus. They promise much mischief, and are ascribed, without any difference of opinion, to Hamilton. You must, my dear Sir, take up your pen against this champion. You know the ingenuity of his talents; and there is not a person but yourself who can foil him. For Heaven’s sake, then, take up your pen, and do not desert the public cause altogether. Thursday evening. The Senate have, to-day, voted the publication of the communications from our Envoys. The House of Representatives decided against the publication by a majority of seventy-five to twenty-four. The Senate adjourned, over to-morrow (good Friday), to Saturday morning: but as the papers cannot be printed within that time, perhaps the vote of the House of Representatives may induce the Senate to reconsider theirs. For this reason, I think it my duty to be silent on them. Adieu.
Th: Jefferson.
TO JAMES MADISON.
Philadelphia, April 6, 1798.
Dear Sir,
So much of the communications from our Envoys has got abroad, and so partially, that there can now be no ground for reconsideration with the Senate. I may therefore, consistently with duty do what every member of the body is doing. Still, I would rather you would use the communication with reserve till you see the whole papers. The first impressions from them are very disagreeable and confused. Reflection, however, and analysis resolve them into this. Mr. Adams’s speech to Congress in May is deemed such a national affront, that no explanation on other topics can be entered on till that, as a preliminary, is wiped away by humiliating disavowals or acknowledgments. This working hard with our Envoys, and indeed seeming impracticable for want of that sort of authority, submission to a heavy amercement (upwards of a million sterling) was, at an after meeting, suggested as an alternative, which might be admitted if proposed by us. These overtures had been through informal agents; and both the alternatives bringing the Envoys to their ne plus, they resolve to have no more communication through inofficial characters, but to address a letter directly to the government, to bring forward their pretensions. This letter had not yet, however, been prepared. There were interwoven with these overtures some base propositions on the part of Talleyrand, through one of his agents, to sell his interest and influence with the Directory towards soothing difficulties with them, in consideration of a large sum (fifty thousand pounds sterling); and the arguments to which his agent resorted to induce compliance with this demand were very unworthy of a great nation (could they be imputed to them), and calculated to excite disgust and indignation in Americans generally, and alienation in the republicans particularly, whom they so far mistake, as to presume an attachment to France and hatred to the federal party, and not the love of their country, to be their first passion. No difficulty was expressed towards an adjustment of all differences and misunderstandings, or even ultimately a payment for spoliations, if the insult from our executive should be first wiped away. Observe, that I state all this from only a single hearing of the papers, and therefore it may not be rigorously correct. The little slanderous imputation before mentioned, has been the bait which hurried the opposite party into this publication. The first impressions with the people will be disagreeable, but the last and permanent one will be, that the speech in May is now the only obstacle to accommodation, and the real cause of war, if war takes place. And how much will be added to this by the speech of November, is yet to be learned. It is evident however, on reflection, that these papers do not offer one motive the more for our going to war. Yet such is their effect on the minds of wavering characters, that I fear, that, to wipe off the imputation of being French partisans, they will go over to the war measures so furiously pushed by the other party. It seems, indeed, as if they were afraid they should not be able to get into war till Great Britain shall be blown up, and the prudence of our countrymen from that circumstance, have, influence enough to prevent it. The most artful misrepresentations of the contents of these papers were published yesterday, and produced such a shock in the republican mind, as had never been seen since our independence. We are to dread the effects of this dismay till their fuller information. Adieu.
Th: Jefferson.
TO JAMES MADISON.
Philadelphia, April 12, 1798.
Dear Sir, I wrote you two letters on the 5th and 6th instant; since which I have received yours of the 2nd. I send you, in a separate package, the instructions to our Envoys and their communications. You will find that my representation of their contents from memory, was substantially just. The public mind appears still in a state of astonishment. There never was a moment in which the aid of an able pen was so important to place things in their just attitude. On this depend the inchoate movement in the eastern mind, and the fate of the elections in that quarter, now beginning and to continue through the summer. I would not propose to you such a task on any ordinary occasion. But be assured that a well digested analysis of these papers would now decide the future turn of things, which are at this moment on the creen. The merchants here are meeting under the auspices of Fitzsimmons, to address the President and approve his propositions. Nothing will be spared on that side. Sprigg’s first resolution against the expediency of war, proper at the time it was moved, is now postponed as improper, because to declare that, after we have understood it has been proposed to us to try peace, would imply an acquiescence under that proposition. All. therefore, which the advocates of peace can now attempt, is to prevent war measures externally, consenting to every rational measure of internal defence and preparation. Great expenses will be incurred; and it will be left to those whose measures render them necessary, to provide to meet them. They already talk of stopping all payments of interest, and of a land-tax. These will probably not be opposed. The only question will be, how to modify the land-tax. On this there may be a great diversity of sentiment. One party will want to make it a new source of patronage and expense. If this business is taken up, it will lengthen our session. We had pretty generally, till now, fixed on the beginning of May for adjournment. I shall return by my usual routes, and not by the Eastern-shore, on account of the advance of the season. Friendly salutations to Mrs. Madison and yourself. Adieu.
Th: Jefferson.
TO JAMES MADISON,
Philadelphia, April 26, 1798.
Dear Sir,
The bill for the naval armament (twelve vessels) passed by a majority of about four to three in the House of Representatives: all restrictions on the objects for which the vessels should be used were struck out. The bill for establishing a department of Secretary of the Navy was tried yesterday, on its passage to the third reading, and prevailed by forty-seven against forty-one. It will be read the third time to-day. The provisional army of twenty thousand men will meet some difficulty. It would surely be rejected if our members were all here. Giles, Clopton, Cabell, and Nicholas have gone, and Clay goes to-morrow. He received here news of the death of his wife. Parker has completely gone over to the war-party. In this state of things they will carry what they please. One of the war-party, in a fit of unguarded passion, declared some time ago they would pass a citizen-bill, an alien-bill, and a sedition-bill: accordingly, some days ago, Coit laid a motion on the table of the House of Representatives for modifying the citizen-law. Their threats pointed at Gallatin, and it is believed they will endeavor to reach him by this bill. Yesterday Mr. Hillhouse laid on the table of the Senate a motion for giving power to send away suspected aliens. This is understood to be meant for Volney and Collot. But it will not stop there when it gets into a course of execution. There is now only wanting, to accomplish the whole declaration before mentioned, a sedition-bill, which we shall certainly soon see proposed. The object of that, is the suppression of the whig presses. Bache’s has been particularly named. That paper and also Carey’s totter for want of subscriptions. We should really exert ourselves to procure them, for if these papers fall, republicanism will be entirely brow-beaten. Carey’s paper comes out three times a week, at five dollars. The meeting of the people which was called at New York, did nothing. It was found that the majority would be against the address. They therefore chose to circulate it individually. The committee of Ways and Means have voted a land-tax. An additional tax on salt will certainly be proposed in the House, and probably prevail to some degree. The stoppage of interest on the public debt will also, perhaps, be proposed, but not with effect. In the mean time, that paper cannot be sold. Hamilton is coming on as Senator from New York. There have been so much contrivance and combination in that, as to show there is some great object in hand. Troup, the district judge of New York, resigns towards the close of the session of their Assembly. The appointment of Mr. Hobart, then Senator, to succeed Troup, is not made by the President till after the Assembly had risen. Otherwise, they would have chosen the Senator in place of Hobart. Jay then names Hamilton Senator, but not till a day or two before his own election as Governor was to come on, lest the unpopularity of the nomination should be in time to affect his own election. We shall see in what all this is to end; but surely in something. The popular movement in the Eastern States is checked, as we expected, and war addresses are showering in from New Jersey and the great trading towns. However, we still trust that a nearer view of war and a land-tax will oblige the great mass of the people to attend. At present, the war-hawks talk of septembrizing, deportation, and the examples for quelling sedition set by the French executive. All the firmness of the human mind is now in a state of requisition.
Salutations to Mrs. Madison; and to yourself, friendship and adieu.
Th: Jefferson.
Philadelphia, May 3, 1798.
Dear Sir,
I wrote you last on the 26th; since which yours of the 22nd of April has been received, acknowledging mine of the 12th; so that all appear to have been received to that date. The spirit kindled up in the towns is wonderful. These and New Jersey are pouring in their addresses, offering life and fortune. Even these addresses are not the worst things. For indiscreet declarations and expressions of passion may be pardoned to a multitude acting from the impulse of the moment. But we cannot expect a foreign nation to show that apathy to the answers of the President, which are more thrasonic than the addresses. Whatever chance for peace might have been left us after the publication of the despatches, is completely lost by these answers. Nor is it France alone, but his own fellow-citizens, against whom his threats are uttered. In Fenno, of yesterday, you will see one, wherein he says to the address from Newark, ‘The delusions and misrepresentations which have misled so many citizens, must be discountenanced by authority as well as by the citizens at large’; evidently alluding to those letters from the Representatives to their constituents, which they have been in the habit of seeking after and publishing: while those sent by the tory part of the House to their constituents, are ten times more numerous, and replete with the most atrocious falsehoods and calumnies. What new law they will propose on this subject, has not yet leaked out. The citizen-bill sleeps. The alien-bill, proposed by the Senate, has not yet been brought in. That proposed by the House of Representatives has been so moderated, that it will not answer the passionate purposes of the war gentlemen. Whether, therefore, the Senate will push their bolder plan, I know not. The provisional army does not go down so smoothly in the House as it did in the Senate. They are whittling away some of its choice ingredients; particularly that of transferring their own constitutional discretion over the raising of armies to the President. A committee of the Representatives have struck out his discretion, and hang the raising of the men on the contingencies of invasion, insurrection, or declaration of war. Were all our members here, the bill would not pass. But it will, probably, as the House now is. Its expense is differently estimated, from five to eight millions of dollars a year. Their purposes before voted, require two millions above all the other taxes, which, therefore, are voted to be raised on lands, houses, and slaves. The provisional army will be additional to this. The threatening appearances from the alien-bills have so alarmed the French who are among us, that they are going off. A ship, chartered by themselves for this purpose, will sail within about a fortnight for France, with as many as she can carry. Among these I believe will be Volney, who has in truth been the principal object aimed at by the law.
Notwithstanding the unfavorableness of the late impressions, it is believed the New York elections, which are over, will give us two or three republicans more than we now have. But it is supposed Jay is re-elected. It is said Hamilton declines coming to the Senate. He very soon stopped his Marcellus. It was rather the sequel which was feared than what actually appeared. He comes out on a different plan in his Titus Manlius, if that be really his. The appointments to the Mississippi were so abominable that the Senate could not swallow them. They referred them to a committee to inquire into characters, and the President withdrew the nomination.
As there is nothing material now to be proposed, we generally expect to rise in about three weeks. However, I do not venture to order my horses.
My respectful salutations to Mrs. Madison. To yourself affectionate friendship, and adieu,
Th: Jefferson.
P. S. Perhaps the President’s expression before quoted, may look to the sedition-bill which has been spoken of, and which may be meant to put the printing-presses under the imprimatur of the executive. Bache is thought a main object of it. Cabot, of Massachusetts, is appointed Secretary of the Navy. T. J.
Philadelphia, May 9, 1798.
Dear Sir,
I am much obliged by your friendly letter of the 4th instant. As soon as I saw the first of Mr. Martin’s letters, I turned to the newspapers of the day, and found Logan’s speech, as translated by a common Indian interpreter. The version I had used, had been made by General Gibson. Finding from Mr. Martin’s style, that his object was not merely truth, but to gratify party passions, I never read another of his letters. I determined to do my duty by searching into the truth, and publishing it to the world, whatever it should be. This I shall do at a proper season. I am much indebted to many persons, who, without any acquaintance with me, have voluntarily sent me information on the subject. Party passions are indeed high. Nobody has more reason to know it than myself. I receive daily bitter proofs of it from people who never saw me, nor know any thing of me but through Porcupine and Fenno. At this moment all the passions are boiling over, and one who keeps himself cool and clear of the contagion, is so far below the point of ordinary conversation, that he finds himself insulated in every society. However, the fever will not last. War, land-tax, and stamp-tax are sedatives which must cool its ardor. They will bring on reflection, and that, with information, is all which our countrymen need, to bring themselves and their affairs to rights. They are essentially republicans. They retain unadulterated the principles of ‘75, and those who are conscious of no change in themselves have nothing to fear in the long run. It is our duty still to endeavor to avoid war: but if it shall actually take place, no matter by whom brought on, we must defend ourselves. If our house be on fire, without inquiring whether it was fired from within or without, we must try to extinguish it. In that, I have no doubt, we shall act as one man. But if we can ward off actual war till the crisis of England is over, I shall hope we may escape it altogether.
I am, with much esteem, Dear Sir, your must obedient, humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JAMES MADISON.
Philadelphia, May 31, 1798.
Dear Sir,
I wrote you last on the 24th; since which yours of the 20th has been received. I must begin by correcting two errors in my last. It was false arithmetic to say, that two measures therein mentioned to have been carried by majorities of eleven, would have failed if the fourteen absentees (wherein a majority of six is ours) had been present. Six coming over from the other side would have turned the scale, and this was the idea floating in my mind, which produced the mistake. The second error was in the version of Mr. Adams’s expression, which I stated to you. His real expression was, ‘that he would not unbrace a single nerve for any treaty France could offer; such was their entire want of faith, morality, &c.’
The bill from the Senate for capturing French armed vessels found hovering on our coast, was passed in two days by the lower House, without a single alteration; and the Ganges, a twenty-gun sloop, fell down the river instantly to go on a cruise. She has since been ordered to New York, to convoy a vessel from that to this port. The alien-bill will be ready to-day, probably, for its third reading in the Senate. It has been considerably modified, particularly by a proviso saving the rights of treaties. Still, it is a most detestable thing. I was glad, in yesterday’s discussion, to hear it admitted on all hands, that laws of the United States, subsequent to a treaty, control its operation, and that the legislature is the only power which can control a treaty. Both points are sound beyond doubt. This bill will unquestionably pass the House of Representatives; the majority there being very decisive, consolidated, and bold enough to do any thing. I have no doubt from the hints dropped, they will pass a bill to declare the French treaty void. I question if they will think a declaration of war prudent, as it might alarm, and all its effects are answered by the act authorizing captures. A bill is brought in for suspending all communication with the dominions of France, which will no doubt pass. It is suspected they mean to borrow money of individuals in London, on the credit of our land-tax, and perhaps the guarantee of Great Britain. The land-tax was yesterday debated, and a majority of six struck out the thirteenth section of the classification of houses, and taxed them by a different scale from the lands. Instead of this, is to be proposed a valuation of the houses and lands together. Macon yesterday laid a motion on the table for adjourning on the 14th. Some think they do not mean to adjourn; others, that they wait first the return of the Envoys, for whom it is now avowed the brig Sophia was sent. It is expected she would bring them off about the middle of this month. They may, therefore, be expected here about the second week of July. Whatever be their decision as to adjournment, I think it probable my next letter will convey orders for my horses, and that I shall leave this place from the 20th to the 25th of June: for I have no expectation they will actually adjourn sooner. Volney and a ship-load of others sail on Sunday next. Another ship-load will go off in about three weeks. It is natural to expect they go under irritations calculated to fan the flame. Not so Volney. He is most thoroughly impressed with the importance of preventing war, whether considered with reference to the interests of the two countries, of the cause of republicanism, or of man on the broad scale. But an eagerness to render this prevention impossible, leaves me without any hope. Some of those who have insisted that it was long since war on the part of France, are candid enough to admit that it is now begun on our part also. I enclose for your perusal a poem on the alien-bill, written by Mr. Marshall. I do this, as well for your amusement, as to get you to take care of this copy for me till I return; for it will be lost by lending it, if I retain it here, as the publication was suppressed after the sale of a few copies, of which I was fortunate enough to get one. Your locks hinges, &c. shall be immediately attended to.
My respectful salutations and friendship to Mrs. Madison, to the family, and to yourself. Adieu.
Th: Jefferson.
P. S. The President, it is said, has refused an Exequatur to the Consul General of France, Dupont. T. J.
Philadelphia, June 1, 1798.
Mr. New showed me your letter on the subject of the patent, which gave me an opportunity of observing what you said as to the effect, with you, of public proceedings, and that it was not unwise now to estimate the separate mass of Virginia and North Carolina, with a view to their separate existence. It is true that we are completely under the saddle of Massachusetts and Connecticut, and that they ride us very hard, cruelly insulting our feelings, as well as exhausting our strength and subsistence. Their natural friends, the three other eastern States, join them from a sort of family pride, and they have the art to divide certain other parts of the Union so as to make use of them to govern the whole. This is not new, it is the old practice of despots; to use a part of the people to keep the rest in order. And those who have once got an ascendency, and possessed themselves of all the resources of the nation, their revenues and offices, have immense means for retaining their advantage. But our present situation is not a natural one. The republicans, through every part of the Union, say, that it was the irresistible influence and popularity of General Washington played off by the cunning of Hamilton, which turned the government over to anti-republican hands, or turned the republicans chosen by the people into anti-republicans. He delivered it over to his successor in this state, and very untoward events since, improved with great artifice, have produced on the public mind the impressions we see. But still I repeat it, this is not the natural state. Time alone would bring round an order of things more correspondent to the sentiments of our constituents. But are there no events impending, which will do it within a few months? The crisis with England, the public and authentic avowal of sentiments hostile to the leading principles of our constitution, the prospect of a war, in which we shall stand alone, land-tax, stamp-tax, increase of public debt, &c. Be this as it may, in every free and deliberating society, there must, from the nature of man, be opposite parties, and violent dissensions and discords; and one of these, for the most part, must prevail over the other for a longer or shorter time. Perhaps this party division is necessary to induce each to watch and delate to the people the proceedings of the other. But if on a temporary superiority of the one party, the other is to resort to a scission of the Union, no federal government can ever exist. If to rid ourselves of the present rule of Massachusetts and Connecticut, we break the Union, will the evil stop there? Suppose the New England States alone cut off, will our natures be changed? Are we not men still to the south of that, and with all the passions of men? Immediately, we shall see a Pennsylvania and a Virginia party arise in the residuary confederacy, and the public mind will be distracted with the same party-spirit. What a game too will the one party have in their hands, by eternally threatening the other, that unless they do so and so, they will join their northern neighbors. If we reduce our Union to Virginia and North Carolina, immediately the conflict will be established between the representatives of these two States, and they will end by breaking into their simple units. Seeing, therefore, that an association of men who will not quarrel with one another is a thing which never yet existed, from the greatest confederacy of nations down to a town-meeting or a vestry; seeing that we must have somebody to quarrel with, I had rather keep our New England associates for that purpose, than to see our bickerings transferred to others. They are circumscribed within such narrow limits, and their population so full, that their numbers will ever be the minority, and they are marked, like the Jews, with such a perversity of character, as to constitute, from that circumstance, the natural division of our parties. A little patience, and we shall see the reign of witches pass over, their spells dissolved, and the people recovering their true sight, restoring their government to its true principles. It is true, that in the mean time, we are suffering deeply in spirit, and incurring the horrors of a war, and long oppressions of enormous public debt. But who can say what would be the evils of a scission, and when and where they would end? Better keep together as we are, haul off from Europe as soon as we can, and from all attachments to any portions of it; and if they show their powers just sufficiently to hoop us together, it will be the happiest situation in which we can exist. If the game runs sometimes against us at home, we must have patience till luck turns, and then we shall have an opportunity of winning back the principles we have lost For this is a game where principles are the stake. Better luck, therefore, to us all, and health, happiness, and friendly salutations to yourself. Adieu.
P. S. It is hardly necessary to caution you to let nothing of mine get before the public; a single sentence got hold of by the Porcupines, will suffice to abuse and persecute me in their papers for months. T. J.
TO GENERAL KOSCIUSKO.
Philadelphia, June 1, 1798.
Dear Sir,
Mr. Volney’s departure for France gives me an opportunity of writing to you. I was happy in observing, for many days after your departure, that our winds were favorable for you. I hope, therefore, you quickly passed the cruising grounds on our coast, and have safely arrived at the term of your journey. Your departure is not yet known, or even suspected.* Niemsevioz was much affected. He is now at the federal city. He desired me to have some things taken care of for you. There were some kitchen furniture, backgammon table, and chess men, and a pelisse of fine fur. The latter I have taken to my own apartment and had packed in hops, and sewed up; the former are put into a warehouse of Mr. Barnes; all subject to your future orders. Some letters came for you soon after your departure: the person who delivered them said there were enclosed in them some for your friend whom you left here, and desired I would open them. I did so in his presence, found only one letter for your friend, took it out and sealed the letters again in the presence of the same person, without reading a word or looking who they were from. I now forward them to you, as I do this to my friend.
[* Shortly before, Mr. Jefferson had obtained passports for
General Kosciusko, under an assumed name, from the foreign
ministers in this country. The annexed is the note addressed
to Mr. Liston, soliciting one from him.
‘Thomas Jefferson presents his respects to Mr. Liston, and
asks the favor of the passport for his friend Thomas
Kanberg, of whom he spoke to him yesterday. He is a native
of the north of Europe (perhaps of Germany), has been known
to Thomas Jefferson these twenty years in America, is of a
most excellent character, stands in no relation whatever to
any of the belligerent powers, as to whom Thomas Jefferson
is not afraid to be responsible for his political innocence,
as he goes merely for his private affairs. He will sail from
Baltimore, if he finds there a good opportunity for France;
and if not, he wi I come on here. March 27, 1798.‘]
Jacob Van Staphorst at Paris. Our alien-bill struggles hard for a passage. It has been considerably mollified. It is not yet through the Senate. We are proceeding further and further in war-measures. I consider that event as almost inevitable. I am extremely anxious to hear from you, to know what sort of a passage you had, how you find yourself and the state and prospect of things in Europe. I hope I shall not be long without hearing from you. The first dividend which will be drawn for you and remitted, will be in January, and as the winter passages are dangerous, it will not be forwarded till April: after that, regularly, from six months to six months. This will be done by Mr. Barnes. I shall leave this place in three weeks. The times do not permit an indulgence in political disquisitions. But they forbid not the effusion of friendship, and not my warmest towards you, which no time will alter. Your principles and dispositions were made to be honored, revered, and loved. True to a single object, the freedom and happiness of man, they have not veered about with the changelings and apostates of our acquaintance. May health and happiness ever attend you. Accept sincere assurances of my affectionate esteem and respect. Adieu.
Th: Jefferson.
Philadelphia, June 21, 1798.
Dear Sir,
Yours of the 10th instant is received. I expected mine of the 14th would have been my last from hence, as I had proposed to set out on the 20th; but on the morning of the 19th, we heard of the arrival of Marshall at New York, and I concluded to stay and see whether that circumstance would produce any new projects. No doubt he there received more than hints from Hamilton as to the tone required to be assumed. Yet I apprehend he is not hot enough for his friends. Livingston came with him from New York. Marshall told him they had no idea in France of a war with us. That Talleyrand sent passports to him and Pinckney, but none for Gerry. Upon this, Gerry stayed, without explaining to them the reason. He wrote, however, to the President by Marshall, who knew nothing of the contents of the letter. So that there must have been a previous understanding between Talleyrand and Gerry. Marshall was received here with the utmost eclat. The Secretary of State and many carriages, with all the city cavalry, went to Frankfort to meet him, and on his arrival here in the evening, the bells rung till late in the night, and immense crowds were collected to see and make part of the show, which was circuitously paraded through the streets before he was set down at the City tavern. All this was to secure him to their views, that he might say nothing which would oppose the game they have been playing. Since his arrival I can hear of nothing directly from him, while they are disseminating through the town, things, as from him, diametrically opposite to what he said to Livingston. Doctor Logan, about a fortnight ago, sailed for Hamburgh. Though for a twelvemonth past he had been intending to go to Europe as soon as he could get money enough to carry him there, yet when he had accomplished this, and fixed a time for going, he very unwisely made a mystery of it; so that his disappearance without notice excited conversation. This was seized by the war-hawks, and given out as a secret mission from the Jacobins here to solicit an army from France, instruct them as to their landing, he. This extravagance produced a real panic among the citizens; and happening just when Bache published Talleyrand’s letter, Harper, on the 18th, gravely announced to the House of Representatives, that there existed a traitorous correspondence between the Jacobins here and the French Directory; that he had got hold of some threads and clues of it, and would soon be able to develope the whole. This increased the alarm; their libelists immediately set to work, directly and indirectly to implicate whom they pleased. Porcupine gave me a principal share in it, as I am told, for I never read his papers. This state of things added to my reasons for not departing at the time I intended. These follies seem to have died away in some degree already. Perhaps I may renew my purpose by the 25th. Their system is, professedly, to keep up an alarm. Tracy, at the meeting of the joint committee for adjournment, declared it necessary for Congress to stay together to keep up the inflammation of the public mind; and Otis has expressed a similar sentiment since. However, they will adjourn. The opposers of an adjournment in Senate, yesterday agreed to adjourn on the 10th of July. But I think the 1st of July will be carried. That is one of the objects which detain myself, as well as one or two more of the Senate, who had got leave of absence. I imagine it will be decided tomorrow or next day. To separate Congress now, will be withdrawing the fire from under a boiling pot.
My respectful salutations to Mrs. Madison, and cordial friendship to yourself.
Th: Jefferson.
P.M. A message to both Houses this day from the President, with the following communications.
March 23. Pickering’s letter to the Envoys, directing them, if they are not actually engaged in negotiation with authorized persons, or if it is not conducted bonâ fide, and not merely for procrastination, to break up and come home, and at any rate to consent to no loan.
April 3. Talleyrand to Gerry. He supposes the other two gentlemen, perceiving that their known principles are an obstacle to negotiation, will leave the republic, and proposes to renew the negotiations with Gerry immediately.
April 4. Gerry to Talleyrand. Disclaims a power to conclude any thing separately, can only confer informally and as an unaccredited person or individual, reserving to lay every thing before the government of the United States for approbation.
April 14. Gerry to the President. He communicates the preceding, and hopes the President will send other persons instead of his colleagues and himself, if it shall appear that any thing can be done.
The President’s message says, that as the instructions were not to consent to any loan, he considers the negotiation as at an end, and that he will never send another minister to France, until he shall be assured that he will be received and treated with the respect due to a great, powerful, free, and independent nation.
A bill was brought into the Senate this day, to declare the treaties with France void, prefaced by a list of grievances in the style of a manifesto. It passed to the second reading by fourteen to five.
A bill for punishing forgeries of bank-paper passed to the third reading by fourteen to six. Three of the fourteen (Laurence, Bingham, and Read) bank directors.
TO SAMUEL SMITH.
Monticello, August 22, 1798.
Dear Sir,
Your favor of August the 4th came to hand by our last post, together with the ‘extract of a letter from a gentleman of Philadelphia, dated July the 10th,’ cut from a newspaper, stating some facts which respect me. I shall notice these facts. The writer says, that ‘the day after the last despatches were communicated to Congress, Bache, Leib, &c, and a Dr. Reynolds, were closeted with me.’ If the receipt of visits in my public room, the door continuing free to every one who should call at the same time, may be called closeting, then it is true that I was closeted with every person who visited me; in no other sense is it true as to any person. I sometimes received visits from Mr. Bache and Dr. Leib. I received them always with pleasure, because they are men of abilities, and of principles the most friendly to liberty and our present form of government. Mr. Bache has another claim on my respect, as being the grandson of Dr. Franklin, the greatest man and ornament of the age and country in which he lived. Whether I was visited by Mr. Bache or Dr. Leib the day after the communication referred to, I do not remember. I know that all my motions at Philadelphia, here, and every where, are watched and recorded. Some of these spies, therefore, may remember, better than I do, the dates of these visits. If they say these two gentlemen visited me the day after the communication, as their trade proves their accuracy, I shall not contradict them, though I affirm that I do not recollect it. However, as to Dr. Reynolds, I can be more particular, because I never saw him but once, which was on an introductory visit he was so kind as to pay me. This, I well remember, was before the communication alluded to, and that during the short conversation I had with him, not one word was said on the subject of any of the communications. Not that I should not have spoken freely on their subject to Dr. Reynolds, as I should also have done to the letter-writer, or to any other person who should have introduced the subject. I know my own principles to be pure, and therefore am not ashamed of them. On the contrary, I wish them known, and therefore willingly express them to every one. They are the same I have acted on from the year 1775 to this day, and are the same, I am sure, with those of the great body of the American people. I only wish the real principles of those who censure mine were also known. But warring against those of the people, the delusion of the people is necessary to the dominant party. I see the extent to which that delusion has been already carried, and I see there is no length to which it may not be pushed by a party in possession of the revenues and the legal authorities of the United States, for a short time indeed, but yet long enough to admit much particular mischief. There is no event, therefore, however atrocious, which may not be expected. I have contemplated every event which the Maratists of the day can perpetrate, and am prepared to meet every one in such a way, as shall not be derogatory either to the public liberty or my own personal honor. This letter-writer says, I am ‘for peace; but it is only with France.’ He has told half the truth. He would have told the whole, if he had added England. I am for peace with both countries. I know that both of them have given, and are daily giving, sufficient cause of war; that in defiance of the laws of nations, they are every day trampling on the rights of the neutral powers, whenever they can thereby do the least injury, either to the other. But, as I view a peace between France and England the ensuing winter to be certain, I have thought it would have been better for us to have continued to bear from France through the present summer, what we have been bearing both from her and England these four years, and still continue to bear from England, and to have required indemnification in the hour of peace, when I verily believe it would have been yielded by both. This seems to be the plan of the other neutral nations; and whether this, or the commencing war on one of them, as we have done, would have been wisest, time and events must decide. But I am quite at a loss on what ground the letter-writer can question the opinion, that France had no intention of making war on us, and was willing to treat with Mr. Gerry, when we have this from Talleyrand’s letter, and from the written and verbal information of our Envoys. It is true then, that, as with England, we might of right have chosen either war or peace, and have chosen peace, and prudently in my opinion, so with France, we might also of right have chosen either peace or war, and we have chosen war. Whether the choice may be a popular one in the other States, I know not. Here it certainly is not; and I have no doubt the whole American people will rally ere long to the same sentiment, and re-judge those, who, at present, think they have all judgment in their own hands.
These observations will show you how far the imputations in the paragraph sent me approach the truth. Yet they are not intended for a newspaper. At a very early period of my life, I determined never to put a sentence into any newspaper. I have religiously adhered to the resolution through my life, and have great reason to be contented with it. Were I to undertake to answer the calumnies of the newspapers, it would be more than all my own time and that of twenty aids could effect. For while I should be answering one, twenty new ones would be invented. I have thought it better to trust to the justice of my countrymen, that they would judge me by what they see of my conduct on the stage where they have placed me, and what they knew of me before the epoch, since which a particular party has supposed it might answer some view of theirs to vilify me in the public eye. Some, I know, will not reflect how apocryphal is the testimony of enemies so palpably betraying the views with which they give it. But this is an injury to which duty requires every one to submit whom the public think proper to call into its councils. I thank you, my dear Sir, for the interest you have for me on this occasion. Though I have made up my mind not to suffer calumny to disturb my tranquillity, yet I retain all my sensibilities for the approbation of the good and just. That is, indeed, the chief consolation for the hatred of so many, who, without the least personal knowledge, and on the sacred evidence of Porcupine and Fenno alone, cover me with their implacable hatred. The only return I will ever make them, will be to do them all the good I can, in spite of their teeth.
I have the pleasure to inform you that all your friends in this quarter are well, and to assure you of the sentiments of sincere esteem and respect with which I am, Dear Sir, your friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
Monticello, September 26, 1798.
Sir,
To avoid the suspicions and curiosity of the post-office, which would have been excited by seeing your name and mine on the back of a letter, I have delayed acknowledging the receipt of your favor of July last, till an occasion to write to an inhabitant of Wilmington gives me an opportunity of putting my letter under cover to him. The system of alarm and jealousy which has been so powerfully played off in England, has been mimicked here, not entirely without success. The most long-sighted politician could not, seven years ago, have imagined that the people of this wide extended country could have been enveloped in such delusion, and made so much afraid of themselves and their own power, as to surrender it spontaneously to those who are manoeuvring them into a form of government, the principal branches of which may be beyond their control. The commerce of England, however, has spread its roots over the whole face of our country. This is the real source of all the obliquities of the public mind: and I should have had doubts of the ultimate term they might attain; but happily, the game, to be worth the playing of those engaged in it, must flush them with money. The authorized expenses of this year are beyond those of any year in the late war for independence, and they are of a nature to beget great and constant expenses. The purse of the people is the real seat of sensibility. It is to be drawn upon largely, and they will then listen to truths which could not excite them through any other organ. In this State, however, the delusion has not prevailed. They are sufficiently on their guard to have justified the assurance, that should you choose it for your asylum, the laws of the land, administered by upright judges, would protect you from any exercise of power unauthorized by the constitution of the United States. The habeas corpus secures every man here, alien or citizen, against every thing which is not law, whatever shape it may assume. Should this, or any other circumstance, draw your footsteps this way, I shall be happy to be among those who may have an opportunity of testifying, by every attention in our power, the sentiments of esteem and respect which the circumstances of your history have inspired, and which are peculiarly felt by, Sir, your most obedient and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
Monticello, October 11, 1798.
Dear Sir,
I have to thank you for your favor of July the 6th, from Philadelphia. I did not immediately acknowledge it, because I knew you would have come away. The X. Y. Z. fever has considerably abated through the country, as I am informed, and the alien and sedition laws are working hard. I fancy that some of the State legislatures will take strong ground on this occasion. For my own part, I consider those laws as merely an experiment on the American mind, to see how far it will bear an avowed violation of the constitution. If this goes down, we shall immediately see attempted another act of Congress, declaring that the President shall continue in office during life, reserving to another occasion the transfer of the succession to his heirs, and the establishment of the Senate for life. At least, this may be the aim of the Oliverians, while Monk and the Cavaliers (who are perhaps the strongest) may be playing their game for the restoration of his Most Gracious Majesty George the Third. That these things are in contemplation, I have no doubt; nor can I be confident of their failure, after the dupery of which our countrymen have shown themselves susceptible.
You promised to endeavor to send me some tenants. I am waiting for them, having broken up two excellent farms with twelve fields in them of forty acres each, some of which I have sowed with small grain. Tenants of any size may be accommodated with the number of fields suited to their force. Only send me good people, and write me what they are. Adieu.
Yours affectionately,
Th: Jefferson.
Monticello, November 26, 1798,
Dear Sir,
We formerly had a debtor and creditor account of letters on farming: but the high price of tobacco, which is likely to continue for some short time, has tempted me to go entirely into that culture, and in the mean time, my farming schemes are in abeyance, and my farming fields at nurse against the time of my resuming them. But I owe you a political letter. Yet the infidelities of the post-office and the circumstances of the times are against my writing fully and freely, whilst my own dispositions are as much against mysteries, innuendoes, and half confidences. I know not which mortifies me most, that I should fear to write what I think, or my country bear such a state of things. Yet Lyon’s judges, and a jury of all nations, are objects of national fear. We agree in all the essential ideas of your letter. We agree particularly in the necessity of some reform, and of some better security for civil liberty. But perhaps we do not see the existing circumstances in the same point of view. There are many considerations dehors of the State, which will occur to you without enumeration. I should not apprehend them, if all was sound within. But there is a most respectable part of our State who have been enveloped in the X. Y. Z. delusion, and who destroy our unanimity for the present moment. This disease of the imagination will pass over, because the patients are essentially republicans. Indeed, the Doctor is now on his way to cure it, in the guise of a tax-gatherer. But give time for the medicine to work, and for the repetition of stronger doses, which must be administered. The principle of the present majority is excessive expense, money enough to fill all their maws, or it will not be worth the risk of their supporting. They cannot borrow a dollar in Europe, or above two or three millions in America. This is not the fourth of the expenses of this year, unprovided for. Paper money would be perilous even to the paper men. Nothing then but excessive taxation can get us along: and this will carry reason and reflection to every man’s door, and particularly in the hour of election.
I wish it were possible to obtain a single amendment to our constitution. I would be willing to depend on that alone for the reduction of the administration of our government to the genuine principles of its constitution; I mean an additional article, taking from the federal government the power of borrowing. I now deny their power of making paper money or any thing else a legal tender. I know that to pay all proper expenses within the year, would, in case of war, be hard on us. But not so hard as ten wars instead of one. For wars would be reduced in that proportion; besides that the State governments would be free to lend their credit in borrowing quotas. For the present, I should be for resolving the alien and sedition laws to be against the constitution and merely void, and for addressing the other States to obtain similar declarations; and I would not do any thing at this moment which should commit us further, but reserve ourselves to shape our future measures or no measures, by the events which may happen. It is a singular phenomenon, that while our State governments are the very best in the world, without exception or comparison, our General Government has, in the rapid course of nine or ten years, become more arbitrary, and has swallowed more of the public liberty, than even that of England. I enclose you a column, cut out of a London paper, to show you that the English, though charmed with our making their enemies our enemies, yet blush and weep over our sedition-law. But I enclose you something more important. It is a petition for a reformation in the manner of appointing our juries, and a remedy against the jury of all nations, which is handing about here for signature, and will be presented to your House. I know it will require but little ingenuity to make objections to the details of its execution; but do not be discouraged by small difficulties; make it as perfect as you can at a first essay, and depend on amending its defects as they develope themselves in practice. I hope it will meet with your approbation and patronage. It is the only thing which can yield us a little present protection against the dominion of a faction, while circumstances are maturing for bringing and keeping the government in real unison with the spirit of their constituents. I am aware that the act of Congress has directed that juries shall be appointed by lot or otherwise, as the laws now (at the date of the act) in force in the several States provide. The New England States have always had them elected by their selectmen, who are elected by the people. Several or most of the other States have a large number appointed (I do not know how) to attend, out of whom twelve for each cause are taken by lot. This provision of Congress will render it necessary for our Senators or Delegates to apply for an amendatory law, accommodated to that prayed for in the petition. In the mean time, I would pass the law as if the amendatory one existed, in reliance, that our select jurors attending, the federal judge will under a sense of right direct the juries to be taken from among them. If he does not, or if Congress refuses to pass the amendatory law, it will serve as eye-water for their constituents. Health, happiness, safety, and esteem to yourself and my ever honored and ancient friend Mr. Pendleton. Adieu.
Th: Jefferson.
Philadelphia, January 3, 1799.
Dear Sir,
I have suffered the post hour to come so nearly on me, that I must huddle over what I have more than appears in the public papers. I arrived here on Christmas day, not a single bill or other article of business having yet been brought into Senate. The President’s speech, so unlike himself in point of moderation, is supposed to have been written by the military conclave, and particularly Hamilton. When the Senate gratuitously hint Logan to him, you see him in his reply come out in his genuine colors. The debates on that subject and Logan’s declaration you will see in the papers. The republican spirit is supposed to be gaining ground in this State and Massachusetts. The tax-gatherer has already excited discontent. Gerry’s correspondence with Talleyrand, promised by the President at the opening of the session, is still kept back. It is known to show France in a very conciliatory attitude, and to contradict some executive assertions. Therefore, it is supposed they will get their war measures well taken before they will produce this damper. Vans Murray writes them, that the French government is sincere in their overtures for reconciliation, and have agreed, if these fail, to admit the mediation offered by the Dutch government.
General Knox has become bankrupt for four hundred thousand dollars, and has resigned his military commission. He took in General Lincoln for one hundred and fifty thousand dollars, which breaks him. Colonel Jackson also sunk with him. It seems generally admitted, that several cases of the yellow fever still exist in the city, and the apprehension is, that it will re-appear early in the spring. You promised me a copy of McGee’s bill of prices. Be so good as to send it on to me here. Tell Mrs. Madison her friend Madame d’Yrujo is as well as one can be so near to a formidable crisis. Present my friendly respects to her, and accept yourself my sincere and affectionate salutations. Adieu.
Th: Jefferson.
P.S. I omitted to mention that a petition has been presented to the President, signed by several thousand persons in Vermont, praying a remitment of Lyon’s fine. He asked the bearer of the petition if Lyon himself had petitioned, and being answered in the negative, said, ‘Penitence must precede pardon.’ T.J.
Philadelphia, January 16, 1799.
Dear Sir,
The forgery lately attempted to be played off by Mr. H. on the House of Representatives, of a pretended memorial presented by Logan to the French government, has been so palpably exposed, as to have thrown ridicule on the whole of the clamors they endeavored to raise as to that transaction. Still, however, their majority will pass the bill. The real views in the importance they have given to Logan’s enterprise are mistaken by nobody. Mr. Gerry’s communications relative to his transactions after the departure of his colleagues, though he has now been returned five months, and they have been promised to the House six or seven weeks, are still kept back. In the mean time, the paper of this morning promises them from the Paris papers. It is said, they leave not a possibility to doubt the sincerity and the anxiety of the French government to avoid the spectacle of a war with us. Notwithstanding this is well understood, the army and a great addition to our navy are steadily intended. A loan of five millions is opened at eight per cent. interest!
In a society of members, between whom and yourself are great mutual esteem and respect, a most anxious desire is expressed that you would publish your debates of the convention. That these measures of the army, navy, and direct-tax, will bring about a revolution of public sentiment is thought certain and that the constitution will then receive a different explanation. Could those debates be ready to appear critically, their effect would be decisive. I beg of you to turn this subject in your mind. The arguments against it will be personal; those in favor of it moral; and something is required from you as a set-off against the sin of your retirement. Your favor of December the 29th came to hand January the 5th; seal sound. I pray you always to examine the seals of mine to you, and the strength of the impression. The suspicions against the government on this subject are strong. I wrote you January the 5th. Accept for yourself and Mrs. Madison my affectionate salutations. Adieu.
Th: Jefferson.
Philadelphia, January 26, 1799.
Mr Dear Sir,
Your favor of November the 12th was safely delivered to me by Mr. Binney; but not till December the 28th, as I arrived here only three days before that date. It was received with great satisfaction. Our very long intimacy as fellow-laborers in the same cause, the recent expressions of mutual confidence which had preceded your mission, the interesting course which that had taken, and particularly and personally as it regarded yourself, made me anxious to hear from you on your return. I was the more so too, as I had myself during the whole of your absence, as well as since your return, been a constant butt for every shaft of calumny which malice and falsehood could form, and the presses, public speakers, or private letters disseminate. One of these, too, was of a nature to touch yourself; as if, wanting confidence in your efforts, I had been capable of usurping powers committed to you, and authorizing negotiations private and collateral to yours. The real truth is, that though Doctor Logan, the pretended missionary, about four or five days before he sailed for Hamburg, told me he was going there, and thence to Paris, and asked and received from me a certificate of his citizenship, character, and circumstances of life, merely as a protection, should he be molested on his journey in the present turbulent and suspicious state of Europe, yet I had been led to consider his object as relative to his private affairs; and though, from an intimacy of some standing, he knew well my wishes for peace and my political sentiments in general, he nevertheless received then no particular declaration of them, no authority to communicate them to any mortal, nor to speak to any one in my name, or in any body’s name, on that, or any other subject whatever; nor did I write by him a scrip of a pen to any person whatever. This he has himself honestly and publicly declared since his return; and from his well known character and every other circumstance, every candid man must perceive that his enterprise was dictated by his own enthusiasm, without consultation or communication with any one; that he acted in Paris on his own ground, and made his own way. Yet to give some color to his proceedings, which might implicate the republicans in general, and myself particularly, they have not been ashamed to bring forward a supposititious paper, drawn by one of their own party in the name of Logan, and falsely pretended to have been presented by him to the government of France; counting that the bare mention of my name therein, would connect that in the eye of the public with this transaction. In confutation of these and all future calumnies, by way of anticipation, I shall make to you a profession of my political faith; in confidence that you will consider every future imputation on me of a contrary complexion, as bearing on its front the mark of falsehood and calumny.
I do then, with sincere zeal, wish an inviolable preservation of our present federal constitution, according to the true sense in which it was adopted by the States, that in which it was advocated by its friends, and not that which its enemies apprehended, who, therefore, became its enemies: and I am opposed to the monarchizing its features by the forms of its administration, with a view to conciliate a first transition to a President and Senate for life, and from that to an hereditary tenure of these offices, and thus to worm out the elective principle. I am for preserving to the States the powers not yielded by them to the Union, and to the legislature of the Union its constitutional share, in the division of powers; and I am not for transferring all the powers of the States to the General Government, and all those of that government to the executive branch. I am for a government rigorously frugal and simple, applying all the possible savings of the public revenue to the discharge of the national debt: and not for a multiplication of officers and salaries merely to make partisans, and for increasing, by every device, the public debt, on the principle of its being a public blessing. I am for relying, for internal defence, on our militia solely, till actual invasion, and for such a naval force only as may protect our coasts and harbors from such depredations as we have experienced: and not for a standing army in time of peace, which may overawe the public sentiment; nor for a navy, which, by its own expenses and the eternal wars in which it will implicate us, will grind us with public burthens, and sink us under them. I am for free commerce with all nations; political connection with none; and little or no diplomatic establishment. And I am not for Clinking ourselves by new treaties with the quarrels of Europe; entering that field of slaughter to preserve their balance, or joining in the confederacy of kings to war against the principles of liberty. I am for freedom of religion, and against all manoeuvres to bring about a legal ascendency of one sect over another: for freedom of the press and against all violations of the constitution to silence by force and not by reason the complaints or criticisms, just or unjust, of our citizens against the conduct of their agents. And I am for encouraging the progress of science in all its branches: and not for raising a hue and cry against the sacred name of philosophy; for awing the human mind by stories of raw-head and bloody-bones to a distrust of its own vision, and to repose implicitly on that of others; to go backwards instead of forwards to look for improvement; to believe that government, religion, morality, and every other science were in the highest perfection in ages of the darkest ignorance, and that nothing can ever be devised more perfect than what was established by our forefathers. To these I will add, that I was a sincere well-wisher to the success of the French revolution, and still wish it may end in the establishment of a free and well-ordered republic: but I have not been insensible under the atrocious depredations they have committed on our commerce. The first object of my heart is my own country. In that is embarked my family, my fortune, and my own existence. I have not one farthing of interest, nor one fibre of attachment out of it, nor a single motive of preference of anyone nation to another, but in proportion as they are more or less friendly to us. But though deeply feeling the injuries of France, I did not think war the surest means of redressing them. I did believe, that a mission, sincerely disposed to preserve peace, would obtain for us a peaceable and honorable settlement and retribution; and I appeal to you to say, whether this might not have been obtained, if either of your colleagues had been of the same sentiment with yourself.
These, my friend, are my principles; they are unquestionably the principles of the great body of our fellow-citizens, and I know there is not one of them which is not yours also. In truth, we never differed but on one ground, the funding system; and as, from the moment of its being adopted by the constituted authorities, I became religiously principled in the sacred discharge of it to the uttermost farthing, we are united now even on that single ground of difference.
I turn now to your inquiries. The enclosed paper will answer one of them. But you also ask for such political information as may be possessed by me, and interesting to yourself in regard to your embassy. As a proof of my entire confidence in you, I shall give it fully and candidly. When Pinckney, Marshall, and Dana were nominated to settle our differences with France, it was suspected by many, from what was understood of their dispositions, that their mission would not result in a settlement of differences; but would produce circumstances tending to widen the breach, and to provoke our citizens to consent to a war with that nation, and union with England. Dana’s resignation and your appointment gave the first gleam of hope of a peaceable issue to the mission. For it was believed that you were sincerely disposed to accommodation: and it was not long after your arrival there, before symptoms were observed of that difference of views which had been suspected to exist. In the mean time, however, the aspect of our government towards the French republic had become so ardent, that the people of America generally took the alarm. To the southward, their apprehensions were early excited. In the Eastern States also, they at length began to break out. Meetings were held in many of your towns, and addresses to the government agreed on in opposition to war. The example was spreading like a wild-fire. Other meetings were called in other places, and a general concurrence of sentiment against the apparent inclinations of the government was imminent; when, most critically for the government, the despatches of October the 22nd, prepared by your colleague Marshall, with a view to their being made public, dropped into their laps. It was truly a God-send to them, and they made the most of it. Many thousands of copies were printed and dispersed gratis, at the public expense; and the zealots for war co-operated so heartily, that there were instances of single individuals who printed and dispersed ten or twelve thousand copies at their own expense. The odiousness of the corruption supposed in those papers excited a general and high indignation among the people. Unexperienced in such manoeuvres, they did not permit themselves even to suspect that the turpitude of private swindlers might mingle itself unobserved, and give its own hue to the communications of the French government, of whose participation there was neither proof nor probability. It served, however, for a time, the purpose intended. The people, in many places, gave a loose to the expressions of their warm indignation, and of their honest preference of war to dishonor. The fever was long and successfully kept up, and in the mean time, war measures as ardently crowded. Still, however, as it was known that your colleagues were coming away, and yourself to stay, though disclaiming a separate power to conclude a treaty, it was hoped by the lovers of peace, that a project of treaty would have been prepared, ad referendum, on principles which would have satisfied our citizens, and overawed any bias of the government towards a different policy. But the expedition of the Sophia, and, as was supposed, the suggestions of the person charged with your despatches, and his probable misrepresentations of the real wishes of the American people, prevented these hopes. They had then only to look forward to your return for such information, either through the executive, or from yourself, as might present to our view the other side of the medal. The despatches of October 22nd, 1797, had presented one face. That information, to a certain degree, is now received, and the public will see from your correspondence with Talleyrand, that France, as you testify, ‘was sincere and anxious to obtain a reconciliation, not wishing us to break the British treaty, but only to give her equivalent stipulations; and in general, was disposed to a liberal treaty.’ And they will judge whether Mr. Pickering’s report shows an inflexible determination to believe no declarations the French government can make, nor any opinion which you, judging on the spot and from actual view, can give of their sincerity, and to meet their designs of peace with operations of war. The alien and sedition acts have already operated in the south as powerful sedatives of the X. Y. Z. inflammation. In your quarter, where violations of principle are either less regarded or more concealed, the direct tax is likely to have the same effect, and to excite inquiries into the object of the enormous expenses and taxes we are bringing on. And your information supervening, that we might have a liberal accommodation if we would, there can be little doubt of the reproduction of that general movement which had been changed, for a moment, by the despatches of October the 22nd. And though small checks and stops, like Logan’s pretended embassy, may be thrown in the way, from time to time, and may a little retard its motion, yet the tide is already turned and will sweep before it all the feeble obstacles of art. The unquestionable republicanism of the American mind will break through the mist under which it has been clouded, and will oblige its agents to reform the principles and practices of their administration.
You suppose, that you have been abused by both parties. As far as has come to my knowledge, you are misinformed. I have never seen or heard a sentence of blame uttered against you by the republicans; unless we were so to construe their wishes that you had more boldly co-operated in a project of a treaty, and would more explicitly state, whether there was in your colleagues that flexibility, which persons earnest after peace would have practised. Whether, on the contrary, their demeanor was not cold, reserved, and distant, at least, if not backward; and whether, if they had yielded to those informal conferences which Talleyrand seems to have courted, the liberal accommodation you suppose, might not have been effected, even with their agency. Your fellow-citizens think they have a right to full information, in a case of such great concernment to them. It is their sweat which is to earn all the expenses of the war, and their blood which is to flow in expiation of the causes of it. It may be in your power to save them from these miseries by full communications and unrestrained details, postponing motives of delicacy to those of duty. It rests with you to come forward independently; to make your stand on the high ground of your own character; to disregard calumny, and to be borne above it on the shoulders of your grateful fellow-citizens; or to sink into the humble oblivion to which the federalists (self-called) have secretly condemned you; and even to be happy if they will indulge you with oblivion, while they have beamed on your colleagues meridian splendor. Pardon me, my dear Sir, if my expressions are strong. My feelings are so much more so, that it is with difficulty I reduce them even to the tone I use. If you doubt the dispositions towards you, look into the papers, on both sides, for the toasts which were given throughout the States on the fourth of July. You will there see whose hearts were with you, and whose were ulcerated against you. Indeed, as soon as it was known that you had consented to stay in Paris, there was no measure observed in the execrations of the war-party. They openly wished you might be guillotined, or sent to Cayenne, or any thing else. And these expressions were finally stifled from a principle of policy only, and to prevent you from being urged to a justification of yourself. From this principle alone proceed the silence and cold respect they observe towards you. Still, they cannot prevent at times the flames bursting from under the embers, as Mr. Pickering’s letters, report, and conversations testify, as well as the indecent expressions respecting you, indulged by some of them in the debate on these despatches. These sufficiently show that you are never more to be honored or trusted by them, and that they wait to crush you for ever, only till they can do it without danger to themselves.
When I sat down to answer your letter, but two courses presented themselves, either to say nothing or every thing; for half confidences are not in my character. I could not hesitate which was due to you. I have unbosomed myself fully; and it will certainly be highly gratifying if I receive like confidence from you. For even if we differ in principle more than I believe we do, you and I know too well the texture of the human mind, and the slipperiness of human reason, to consider differences of opinion otherwise than differences of form or feature. Integrity of views, more than their soundness, is the basis of esteem. I shall follow your direction in conveying this by a private hand; though I know not as yet when one worthy of confidence will occur. And my trust in you leaves me without a fear that this letter, meant as a confidential communication of my impressions, may ever go out of your own hand, or be suffered in any wise to commit my name. Indeed, besides the accidents which might happen to it even under your care, considering the accident of death to which you are liable, I think it safest to pray you, after reading it as often as you please, to destroy at least the second and third leaves. The first contains principles only, which I fear not to avow; but the second and third contain facts stated for your information, and which, though sacredly conformable to my firm belief, yet would be galling to some, and expose me to illiberal attacks. I therefore repeat my prayer to burn the second and third leaves. And did we ever expect to see the day, when, breathing nothing but sentiments of love to our country and its freedom and happiness, our correspondence must be as secret as if we were hatching its destruction? Adieu, my friend, and accept my sincere and affectionate salutations. I need not add my signature.
Philadelphia, January 29, 1799.
Dear Sir,
Your patriarchal address to your country is running through all the republican papers, and has a very great effect on the people. It is short, simple, and presents things in a view they readily comprehend. The character and circumstances too of the writer leave them without doubts of his motives. If, like the patriarch of old, you had but one blessing to give us, I should have wished it directed to a particular object. But I hope you have one for this also. You know what a wicked use has been made of the French negotiation; and particularly, the X. Y. Z. dish, cooked up by ——— , where the swindlers are made to appear as the French government. Art and industry combined, have certainly wrought out of this business a wonderful effect on the people. Yet they have been astonished more than they have understood it, and now that Gerry’s correspondence comes out, clearing the French government of that turpitude, and showing them ‘sincere in their dispositions for peace, not wishing us to break the British treaty, and willing to arrange a liberal one with us,’ the people will be disposed to suspect they have been duped. But these communications are too voluminous for them, and beyond their reach. A recapitulation is now wanting of the whole story, stating every thing according to what we may now suppose to have been the truth, short, simple, and levelled to every capacity. Nobody in America can do it so well as yourself, in the same character of the father of your country, or any form you like better, and so concise, as, omitting nothing material, may yet be printed in handbills, of which we could print and disperse ten or twelve thousand copies under letter covers, through all the United States, by the members of Congress when they return home. If the understanding of the people could be rallied to the truth on this subject, by exposing the dupery practised on them, there are so many other things about to bear on them favorably for the resurrection of their republican spirit, that a reduction of the administration to constitutional principles cannot fail to be the effect. These are the alien and sedition laws, the vexations of the stamp-act, the disgusting particularities of the direct tax, the additional army without an enemy, and recruiting officers lounging at every Court-House to decoy the laborer from his plough, a navy of fifty ships, five millions to be raised to build it, on the usurious interest of eight per cent., the perseverance in war on our part, when the French government shows such an anxious desire to keep at peace with us, taxes often millions now paid by four millions of people, and yet a necessity, in a year or two, of raising five millions more for annual expenses. These things will immediately be bearing on the public mind, and if it remain not still blinded by a supposed necessity, for the purposes of maintaining our independence and defending our country, they will set things to rights. I hope you will undertake this statement. If any body else had possessed your happy talent for this kind of recapitulation, I would have been the last to disturb you with the application; but it will really be rendering our country a service greater than it is in the power of any other individual to render. To save you the trouble of hunting the several documents from which this statement is to be taken, I have collected them here completely, and enclose them to you.
Logan’s bill has passed. On this subject it is hardly necessary for me to declare to you, on every thing sacred, that the part they ascribed to me was entirely a calumny. Logan called on me, four or five days before his departure, and asked and received a certificate (in my private capacity) of his citizenship and circumstances of life, merely as a protection, should he be molested in the present turbulent state of Europe. I have given such to an hundred others, and they have been much more frequently asked and obtained by tories than whigs.
Accept my sincere prayers for long and happy years to you still, and my affectionate salutations and adieu.
Th: Jefferson.
Philadelphia, February 5, 1799.
Dear Sir,
I wrote you last on the 30th of January; since which yours of the 25th has been received.
*********
The bill for continuing the suspension of intercourse with France and her dependencies, is still before the Senate, but will pass by a very great vote. An attack is made on what is called the Toussaint’s clause, the object of which, as is charged by the one party and admitted by the other, is to facilitate the separation of the island from France. The clause will pass, however, by about nineteen to eight, or perhaps eighteen to nine. Rigaud, at the head of the people of color, maintains his allegiance. But they are only twenty-five thousand souls, against five hundred thousand, the number of the blacks. The treaty made with them by Maitland is (if they are to be separated from France) the best thing for us. They must get their provisions from us. It will indeed be in English bottoms, so that we shall lose the carriage. But the English will probably forbid them the ocean, confine them to their island, and thus prevent their becoming an American Algiers. It must be admitted, too, that they may play them off on us when they please. Against this there is no remedy but timely measures on our part, to clear ourselves, by degrees, of the matter on which that lever can work.
A piece published in Bache’s paper on foreign influence, has had the greatest currency and effect. To an extraordinary first impression, they have been obliged to make a second, and of an extraordinary number. It is such things as these the public want. They say so from all quarters, and that they wish to hear reason instead of disgusting blackguardism. The public sentiment being now on the creen, and many heavy circumstances about to fall into the republican scale, we are sensible that this summer is the season for systematic energies and sacrifices. The engine is the press. Every man must lay his purse and his pen under contribution. As to the former, it is possible I may be obliged to assume something for you. As to the latter, let me pray and beseech you to set apart a certain portion of every post-day to write what may be proper for the public. Send it to me while here, and when I go away I will let you know to whom you may send, so that your name shall be sacredly secret. You can render such incalculable services in this way, as to lessen the effect of our loss of your presence here. I shall see you on the 5th or 6th of March.
Affectionate salutations to Mrs. Madison and yourself. Adieu.
Th: Jefferson.
Philadelphia, February 14, 1799.
Dear Sir,
I wrote you a petition on the 29th of January. I know the extent of this trespass on your tranquillity, and how indiscreet it would have been under any other circumstances. But the fate of this country, whether it shall be irretrievably plunged into a form of government rejected by the makers of the constitution, or shall get back to the true principles of that instrument, depends on the turn which things may take within a short period of time ensuing the present moment. The violations of the constitution, propensities to war, to expense, and to a particular foreign connection, which we have lately seen, are becoming evident to the people, and are dispelling that mist which X. Y. Z. had spread before their eyes. This State is coming forward with a boldness not yet seen. Even the German counties of York and Lancaster, hitherto the most devoted, have come about, and by petitions with four thousand signers remonstrate against the alien and sedition laws, standing armies, and discretionary powers in the President. New York and Jersey are also getting into great agitation. In this State, we fear that the ill-designing may produce insurrection. Nothing could be so fatal. Any thing like force would check the progress of the public opinion and rally them round the government. This is not the kind of opposition the American people will permit. But keep away all show of force, and they will bear down the evil propensities of the government, by the constitutional means of election and petition. If we can keep quiet, therefore, the tide now turning will take a steady and proper direction. Even in New Hampshire there are strong symptoms of a rising inquietude. In this state of things, my dear Sir, it is more in your power than any other man’s in the United States, to give the coup de grace to the ruinous principles and practices we have seen. In hopes you have consented to it, I shall furnish to you some additional matter which has arisen since my last.
I enclose you a part of a speech of Mr. Gallatin on the naval bill. The views he takes of our finances, and of the policy of our undertaking to establish a great navy, may furnish some hints. I am told, something on the same subject from Mr. J. Nicholas will appear in the Richmond and Fredericksburg papers. I mention the real author, that you may respect it duly, for I presume it will be anonymous. The residue of Gallatin’s speech shall follow when published. A recent fact proving the anxiety of France for a reconciliation with us, is the following. You know that one of the armed vessels which we took from her was refitted by us, sent to cruise against her, re-captured, and carried into Guadaloupe under the name of the Retaliation. ‘On the arrival there of Desfourneaux, the new commissioner, he sent Victor Hughes home in irons; called up our captain; told him that he found he had a regular commission as an officer of the United States; that his vessel was then lying in the harbor; that he should inquire into no fact preceding his own arrival (by this he avoided noticing that the vessel was really French property), and that, therefore, himself and crew were free to depart with their vessel; that as to the differences between France and the United States, commissioners were coming out to settle them, and, in the mean time, no injury should be done on their part. The captain insisted on being a prisoner; the other disclaimed; and so he arrived here with vessel and crew the day before yesterday. Within an hour after this was known to the Senate, they passed the retaliation bill, of which I enclose you a copy. This was the more remarkable, as the bill was founded expressly on the Arrêt of October the 29th, which had been communicated by the President as soon as received, and he remarked, ‘that it could not be too soon communicated to the two Houses and the public’. Yet he almost in the same instant received, through the same channel, Mr. King’s information that that Arrêt was suspended, and though he knew we were making it the foundation of a retaliation bill, he has never yet communicated it. But the Senate knew the fact informally from the Secretary of State, and knowing it, passed the bill.
The President has appointed, and the Senate approved, Rufus King, to enter into a treaty of commerce with the Russians, at London, and William Smith (Phocion), Envoy Extraordinary and Minister Plenipotentiary, to go to Constantinople to make one with the Turks. So that as soon as there is a coalition of Turks, Russians, and English, against France, we seize that moment to countenance it as openly as we dare, by treaties, which we never had with them before. All this helps to fill up the measure of provocation towards France, and to get from them a declaration of war, which we are afraid to be the first in making. It is certain the French have behaved atrociously towards neutral nations, and us particularly; and though we might be disposed not to charge them with all the enormities committed in their name in the West Indies, yet they are to be blamed for not doing more to prevent them. A just and rational censure ought to be expressed on them, while we disapprove the constant billingsgate poured on them officially. It is at the same time true, that their enemies set the first example of violating neutral rights, and continue it to this day: insomuch, that it is declared on all hands, and particularly by the insurance companies, and denied by none, that the British spoliations have considerably exceeded the French during the last six months. Yet not a word of these things is said officially to the legislature.
Still further, to give the devil his due (the French), it should be observed that it has been said without contradiction, and the people made to believe, that their refusal to receive our Envoys was contrary to the law of nations, and a sufficient cause of war: whereas every one who ever read a book on the law of nations knows, that it is an unquestionable right in every power, to refuse to receive any minister who is personally disagreeable. Martens, the latest and a very respected writer, has laid it down so clearly and shortly in his ‘Summary of the Law of Nations,’ B. 7. ch. 2. sect. 9. that I will transcribe the passage verbatim. ‘Section 9. Of choice in the person of the minister. The choice of the person to be sent as minister depends of right on the sovereign who sends him, leaving the right, however, of him to whom he is sent, of refusing to acknowledge any one, to whom he has a personal dislike, or who is inadmissible by the laws and usages of the country.’ And he adds notes proving by instances, &c. This is the whole section.
Notwithstanding all these appearances of peace from France, we are, besides our existing army of five thousand men, and additional army of nine thousand (now officered and levying), passing a bill for an eventual army of thirty regiments (thirty thousand) and for rigimenting, brigading, officering, and exercising at the public expense our volunteer army, the amount of which we know not. I enclose you a copy of the bill, which has been twice read and committed in Senate. To meet this expense, and that of the six seventy-fours and six eighteens, part of the proposed fleet, we have opened a loan of five millions at eight per cent., and authorize another of two millions: and, at the same time, every man voting for these measures acknowledges there is no probability of an invasion by France. While speaking of the restoration of our vessel, I omitted to add, that it is said that our government contemplate restoring the Frenchmen taken originally in the same vessel, and kept at Lancaster as prisoners. This has furnished the idea of calling her a cartel vessel, and pretending that she came as such for an exchange of prisoners, which is false. She was delivered free and without condition, but it does not suit to let any new evidence appear of the desire of conciliation in France.
I believe it is now certain that the commissioners on the British debts can proceed together no longer. I am told that our two have prepared a long report, which will perhaps be made public. The result will be, that we must recur again to negotiation, to settle the principles of the British claims. You know that Congress rises on the 3rd of March, and that if you have acceded to my prayers, I should hear from you at least a week before our rising. Accept my affectionate salutations, and assurances of the sincere esteem with which I am, Dear Sir, your friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
Philadelphia, February 19, 1799.
Dear Sir,
I wrote you last on the 11th; yesterday the bill for the eventual army of thirty regiments (thirty thousand) and seventy-five thousand volunteers, passed the Senate. By an amendment, the President was authorized to use the volunteers for every purpose for which he can use militia, so that the militia are rendered completely useless. The friends of the bill acknowledge that the volunteers are a militia, and agreed that they might properly be called the ‘Presidential militia.’ They are not to go out of their State without their own consent. Consequently, all service out of the State is thrown on the constitutional militia, the Presidential militia being exempted from doing duty with them. Leblane, an agent from Desfourneaux, of Guadaloupe, came in the Retaliation. You will see in the papers Desfourneaux’s letter to the President, which will correct some immaterial circumstances of the statement in my last. You will see the truth of the main fact, that the vessel and crew were liberated without condition. Notwithstanding this, they have obliged Leblane to receive the French prisoners, and to admit, in the papers, the terms, ‘in exchange for prisoners taken from us,’ he denying at the same time that they consider them as prisoners, or had any idea of exchange. The object of his mission was not at all relative to that; but they choose to keep up the idea of a cartel, to prevent the transaction from being used as evidence of the sincerity of the French government towards a reconciliation. He came to assure us of a discontinuance of all irregularities in French privateers from Guadaloupe. He has been received very cavalierly. In the mean time, a Consul General is named to St. Domingo: who may be considered as our Minister to Toussaint.
But the event of events was announced to the Senate yesterday. It is this: it seems that soon after Gerry’s departure, overtures must have been made by Pichon, French Chargé d’Affaires at the Hague, to Murray. They were so soon matured, that on the 28th of September, 1798, Talleyrand writes to Pichon, approving what had been done, and particularly of his having assured Murray that whatever Plenipotentiary the government of the United States should send to France to end our differences, would undoubtedly be received with the respect due to the representative of a free, independent, and powerful nation; declaring that the President’s instructions to his Envoys at Paris, if they contain the whole of the American government’s intentions, announce dispositions which have been always entertained by the Directory; and desiring him to communicate these expressions to Murray, in order to convince him of the sincerity of the French government, and to prevail on him to transmit them to his government. This is dated September the 28th, and may have been received by Pichon October the 1st; and nearly five months elapse before it is communicated. Yesterday the President nominated to the Senate William Vans Murray Minister Plenipotentiary to the French republic, and added, that he shall be instructed not to go to France, without direct and unequivocal assurances from the French government that he shall be received in character, enjoy the due privileges, and a minister of equal rank, title, and power, be appointed to discuss and conclude our controversy by a new treaty. This had evidently been kept secret from the federalists of both Houses, as appeared by their dismay. The Senate have passed over this day without taking it up. It is said they are graveled and divided; some are for opposing, others do not know what to do. But in the mean time, they have been permitted to go on with all the measures of war and patronage, and when the close of the session is at hand it is made known. However, it silences all arguments against the sincerity of France, and renders desperate every further effort towards war. I enclose you a paper with more particulars. Be so good as to keep it till you see me, and then return it, as it is the copy of one I sent to another person, and is the only copy I have. Since I began my letter I have received yours of February the 7th and 8th, with its enclosures; that referred to my discretion is precious, and shall be used accordingly.
Affectionate salutations to Mrs. Madison and yourself, and adieu.
Th: Jefferson,
TO GENERAL KOSCIUSKO.
Philadelphia, February 21, 1799.
My Dear Friend,
On politics I must write sparingly, lest it should fall into the hands of persons who do not love either you or me. The wonderful irritation produced in the minds of our citizens by the X. Y. Z. story, has in a great measure subsided. They begin to suspect and to see it coolly in its true light. Mr. Gerry’s communications, with other information, prove to them that France is sincere in her wishes for reconciliation; and a recent proposition from that country, through Mr. Murray, puts the matter out of doubt. What course the government will pursue, I know not. But if we are left in peace, I have no doubt the wonderful turn in the public opinion now manifestly taking place and rapidly increasing, will, in the course of this summer, become so universal and so weighty, that friendship abroad and freedom at home will be firmly established by the influence and constitutional powers of the people at large. If we are forced into war, we must give up political differences of opinion, and unite as one man to defend our country. But whether at the close of such a war, we should be as free as we are now, God knows. In fine, if war takes place, republicanism has every thing to fear; if peace, be assured that your forebodings and my alarms will prove vain; and that the spirit of our citizens now rising as rapidly as it was then running crazy, and rising with a strength and majesty which show the loveliness of freedom, will make this government in practice, what it is in principle, a model for the protection of man in a state of freedom and order. May Heaven have in store for your country a restoration of these blessings, and you be destined as the instrument it will use for that purpose. But if this be forbidden by fate, I hope we shall be able to preserve here an asylum where your love of liberty and disinterested patriotism will be for ever protected and honored, and where you will find in the hearts of the American people, a good portion of that esteem and affection which glow in the bosom of the friend who writes this; and who with sincere prayers for your health, happiness, and success, and cordial salutations, bids you, for this time, adieu.
Th: Jefferson.
Philadelphia, February 26, 1799.
Dear Sir,
My last to you was of the 19th; it acknowledged yours of the 8th. In mine I informed you of the nomination of Murray. There is evidence that the letter of Talleyrand was known to one of the Secretaries, therefore probably to all; the nomination, however, is declared by one of them to have been kept secret from them all. He added, that he was glad of it, as, had they been consulted, the advice would have been against making the nomination. To the rest of the party, however, the whole was a secret till the nomination was announced. Never did a party show a stronger mortification, and consequently, that war had been their object. Dana declared in debate (as I have from those who were present) that we had done every thing which might provoke France to war; that we had given her insults which no nation ought to have borne; and yet she would not declare war. The conjecture as to the executive is, that they received Talleyrand’s letter before or about the meeting of Congress: that not meaning to meet the overture effectually, they kept it secret, and let all the war measures go on; but that just before the separation of the Senate, the President, not thinking he could justify the concealing such an overture, nor indeed that it could be concealed, made a nomination, hoping that his friends in the Senate would take on their own shoulders the odium of rejecting it; but they did not choose it. The Hamiltonians would not, and the others could not, alone. The whole artillery of the phalanx, therefore, was played secretly on the President, and he was obliged himself to take a step which should parry the overture while it wears the face of acceding to it. (Mark that I state this as conjecture; but founded on workings and indications which have been under our eyes.) Yesterday, therefore, he sent in a nomination of Oliver Ellsworth, Patrick Henry, and William Vans Murray, Envoys Extraordinary and Ministers Plenipotentiary to the French Republic, but declaring the two former should not leave this country till they should receive from the French Directory assurances that they should be received with the respect due by the law of nations to their character, &c. This, if not impossible, must at least keep off the day, so hateful and so fatal to them, of reconciliation, and leave more time for new projects of provocation. Yesterday witnessed a scandalous scene in the House of Representatives. It was the day for taking up the report of their committee against the alien and sedition laws, &.c. They held a caucus and determined that not a word should be spoken on their side, in answer to any thing which should be said on the other. Gallatin took up the alien, and Nicholas the sedition law; but after a little while of common silence, they began to enter into loud conversations, laugh, cough, &c., so that for the last hour of these gentlemen’s speaking, they must have had the lungs of a vendue-master to have been heard. Livingston, however, attempted to speak. But after a few sentences, the speaker called him to order, and told him what he was saying was not to the question. It was impossible to proceed. The question was taken and carried in favor of the report, fifty-two to forty-eight; the real strength of the two parties is fifty-six to fifty. But two of the latter have not attended this session. I send you the report of their committee. I still expect to leave this on the 1st, and be with you on the 7th of March. But it is possible I may not set out till the 4th, and then shall not be with you till the 10th. Affectionately adieu.
Th: Jefferson.
Monticello, March 12, 1799.
Dear Sir,
Your welcome favor of last month came to my hands in Philadelphia. So long a time has elapsed since we have been separated by events, that it was like a letter from the dead, and recalled to my memory very dear recollections. My subsequent journey through life has offered nothing which, in comparison with those, is not cheerless and dreary. It is a rich comfort sometimes to look back on them.
I take the liberty of enclosing a letter to Mr. Baylor, open, because I solicit your perusal of it. It will, at the same time, furnish the apology for my not answering you from Philadelphia. You ask for any communication I may be able to make, which may administer comfort to you. I can give that which is solid. The spirit of 1776 is not dead. It has only been slumbering. The body of the American people is substantially republican. But their virtuous feelings have been played on by some fact with more fiction; they have been the dupes of artful manoeuvres, and made for a moment to be willing instruments in forging chains for themselves. But time and truth have dissipated the delusion, and opened their eyes. They see now that France has sincerely wished peace, and their seducers have wished war, as well for the loaves and fishes which arise out of war expenses, as for the chance of changing the constitution, while the people should have time to contemplate nothing but the levies of men and money. Pennsylvania, Jersey, and New York are coming majestically round to the true principles. In Pennsylvania, thirteen out of twenty-two counties had already petitioned on the alien and sedition laws. Jersey and New York had begun the same movement, and though the rising of Congress stops that channel for the expression of their sentiment, the sentiment is going on rapidly, and before their next meeting those three States will be solidly embodied in sentiment with the six southern and western ones. The atrocious proceedings of France towards this country had well nigh destroyed its liberties. The Anglomen and monocrats had so artfully confounded the cause of France with that of freedom, that both went down in the same scale. I sincerely join you in abjuring all political connection with every foreign power: and though I cordially wish well to the progress of liberty in all nations, and would for ever give it the weight of our countenance, yet they are not to be touched without contamination, from their other bad principles. Commerce with all nations, alliance with none, should be our motto.
Accept assurances of the constant and unaltered affection of, Dear Sir, your sincere friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
TO EDMUND RANDOLPH.
Monticello, August 18, 1799
Dear Sir,
I received only two days ago your favor of the 12th, and as it was on the eve of the return of our post, it was not possible to make so prompt a despatch of the answer. Of all the doctrines which have ever been broached by the federal government, the novel one, of the common law being in force and cognizable as an existing law in their courts, is to me the most formidable. All their other assumptions of ungiven powers have been in the detail. The bank-law, the treaty-doctrine, the sedition-act, alien-act, the undertaking to change the State laws of evidence in the State courts by certain parts of the stamp-act, &c. &c. have been solitary, inconsequential, timid things, in comparison with the audacious, barefaced, and sweeping pretension to a system of law for the United States, without the adoption of their legislature, and so infinitely beyond their power to adopt. If this assumption be yielded to, the State courts may be shut up, as there will then be nothing to hinder citizens of the same State suing each other in the federal courts in every case, as on a bond for instance, because the common law obliges payment of it, and the common law they say is their law. I am happy you have taken up the subject; and I have carefully perused and considered the notes you enclosed, and find but a single paragraph which I do not approve. It is that wherein (page 2) you say, that laws being emanations from the legislative department, and, when once enacted, continuing in force from a presumption that their will so continues, that that presumption fails, and the laws of course fall, on the destruction of that legislative department. I do not think this is the true bottom on which laws and the administering them rest. The whole body of the nation is the sovereign legislative, judiciary, and executive power for itself. The inconvenience of meeting to exercise these powers in person, and their inaptitude to exercise them, induce them to appoint special organs to declare their legislative will, to judge, and to execute it. It is the will of the nation which makes the law obligatory; it is their will which creates or annihilates the organ which is to declare and announce it. They may do it by a single person, as an Emperor of Russia (constituting his declarations evidence of their will), or by a few persons, as the aristocracy of Venice, or by a complication of councils, as in our former regal government, or our present republican one. The law being law because it is the will of the nation, is not changed by their changing the organ through which they choose to announce their future will; no more than the acts I have done by one attorney lose their obligation by my changing or discontinuing that attorney. This doctrine has been, in a certain degree, sanctioned by the federal executive. For it is precisely that on which the continuance of obligation from our treaty with France was established, and the doctrine was particularly developed in a letter to Gouverneur Morris, written with the approbation of President Washington and his cabinet. Mercer once prevailed on the Virginia Assembly to declare a different doctrine in some resolutions. These met universal disapprobation in this, as well as the other States, and if I mistake not, a subsequent Assembly did something to do away the authority of their former unguarded resolutions. In this case, as in all others, the true principle will be quite as effectual to establish the just deductions. Before the revolution, the nation of Virginia had, by the organs they then thought proper to constitute, established a system of laws, which they divided into three denominations of, 1. common law; 2. statute law; 3. chancery: or if you please, into two only, of 1. common law; 2. chancery. When by the Declaration of Independence, they chose to abolish their former organs of declaring their will, the acts of will already formally and constitutionally declared, remained untouched. For the nation was not dissolved, was not annihilated; its will, therefore, remained in full vigor: and on the establishing the new organs, first of a convention, and afterwards a more complicated legislature, the old acts of national will continued in force, until the nation should, by its new organs, declare its will changed. The common law, therefore, which was not in force when we landed here, nor till we had formed ourselves into a nation, and had manifested by the organs we constituted that the common law was to be our law, continued to be our law; because the nation continued in being, and because, though it changed the organs for the future declarations of its will, yet it did not change its former declarations that the common law was its law. Apply these principles to the present case. Before the revolution there existed no such nation as the United States: they then first associated as a nation, but for special purposes only. They had all their laws to make, as Virginia had on her first establishment as a nation. But they did not, as Virginia had done, proceed to adopt a whole system of laws ready made to their hand. As their association as a nation was only for special purposes, to wit, for the management of their concerns with one another and with foreign nations, and the States composing the association chose to give it powers for those purposes and no others, they could not adopt any general system, because it would have embraced objects on which this association had no right to form or declare a will. It was not the organ for declaring a national will in these cases. In the cases confided to them, they were free to declare the will of the nation, the law, but till it was declared there could be no law. So that the common law did not become, ipso facto, law on the new association; it could only become so by a positive adoption, and so far only as they were authorized to adopt.
I think it will be of great importance, when you come to the proper part, to portray at full length the consequences of this new doctrine, that the common law is the law of the United States and that their courts have, of course, jurisdiction co-extensive with that law, that is to say, general over all cases and persons. But great heavens! Who could have conceived in 1789, that within ten years we should have to combat such windmills. Adieu. Yours affectionately.
Th: Jefferson.
TO WILSON C. NICHOLAS.
Monticello, September 5, 1799.
Dear Sir,
Yours of August the 30th came duly to hand. It was with great regret we gave up the hope of seeing you here, but, could not but consider the obstacle as legitimate. I had written to Mr. Madison, as I had before informed you, and had stated to him some general ideas for consideration and consultation when we should meet. I thought something essentially necessary to be said, in order to avoid the inference of acquiescence; that a resolution or declaration should be passed, 1. answering the reasonings of such of the States as have ventured into the field of reason, and that of the committee of Congress, taking some notice, too, of those States who have either not answered at all, or answered without reasoning. 2. Making firm protestation against the precedent and principle, and reserving the right to make this palpable violation of the federal compact the ground of doing in future whatever we might now rightfully do, should repetitions of these and other violations of the compact render it expedient. 3. Expressing in affectionate and conciliatory language our warm attachment to union with our sister States, and to the instrument and principles by which we are united; that we are willing to sacrifice to this every thing but the rights of self-government in those important points which we have never yielded, and in which alone we see liberty, safety, and happiness; that not at all disposed to make every measure of error or of wrong, a cause of scission, we are willing to look on with indulgence, and to wait with patience, till those passions and delusions shall have passed over, which the federal government have artfully excited to cover its own abuses and conceal its designs, fully confident that the good sense of the American people, and their attachment to those very rights which we are now vindicating, will, before it shall be too late, rally with us round the true principles of our federal compact. This was only meant to give a general idea of the complexion and topics of such an instrument. Mr. M. who came, as had been proposed, does not concur in the reservation proposed above; and from this I recede readily, not only in deference to his judgment, but because, as we should never think of separation but for repeated and enormous violations, so these, when they occur, will be cause enough of themselves.
To these topics, however, should be added animadversions on the new pretensions to a common law of the United States. I proposed to Mr. M. to write to you but he observed that you knew his sentiments so perfectly from a former conference, that it was unnecessary. As to the preparing any thing, I must decline it, to avoid suspicions (which were pretty strong in some quarters on the late occasion), and because there remains still (after their late loss) a mass of talents in Kentucky sufficient for every purpose. The only object of the present communication is to procure a concert in the general plan of action, as it is extremely desirable that Virginia and Kentucky should pursue the same track on this occasion. Besides, how could you better while away the road from hence to Kentucky, than in meditating this very subject and preparing something yourself, than whom nobody will do it better. The loss of your brother, and the visit of the apostle ——— to Kentucky, excite anxiety. However, we doubt not that his poisons will be effectually counterworked. Wishing you a pleasant journey and happy return, I am with great and sincere esteem, Dear Sir, your affectionate friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
Monticello, November 22, 1799.
Dear Sir,
I have never answered your letter by Mr. Polk, because I expected to have paid you a visit. This has been prevented by various causes, till yesterday. That being the day fixed for the departure of my daughter Eppes, my horses were ready for me to have set out to see you: an accident postponed her departure to this day, and my visit also. But Colonel Monroe dined with me yesterday, and on my asking his commands for you, he entered into the subject of the visit and dissuaded it entirely, founding the motives on the espionage of the little ———in ——— who would make it a subject of some political slander, and perhaps of some political injury. I have yielded to his representations, and therefore shall not have the pleasure of seeing you till my return from Philadelphia. I regret it sincerely, not only on motives of attention but of affairs. Some late circumstances changing considerably the aspect of our situation, must affect the line of conduct to be observed. I regret it the more too, because from the commencement of the ensuing session, I shall trust the post-offices with nothing confidential, persuaded that during the ensuing twelve months they will lend their inquisitorial aid to furnish matter for newspapers. I shall send you as usual printed communications, without saying any thing confidential on them. You will of course understand the cause.
In your new station let me recommend to you the jury system: as also the restoration of juries in the court of chancery, which a law not long since repealed, because ‘the trial by jury is troublesome and expensive.’ If the reason be good, they should abolish it at common law also. If Peter Carr is elected in the room of ——— he will undertake the proposing this business, and only need your support. If he is not elected, I hope you will get it done otherwise. My best respects to Mrs. Madison, and affectionate salutations to yourself.
Th: Jefferson.
TO COLONEL MONROE.
Philadelphia, January 12, 1800.
Dear Sir,
Yours of January the 4th was received last night. I had then no opportunity of communicating to you confidentially information of the state of opinions here; but I learn to-night that two Mr. Randolphs will set out to-morrow morning for Richmond. If I can get this into their hands I shall send it; otherwise it may wait longer. On the subject of an election by a general ticket or by districts, most persons here seem to have made up their minds. All agree that an election by districts wrould be best, if it could be general: but while ten States choose either by their legislatures or by a general ticket, it is folly and worse than folly for the other six not to do it. In these ten States the minority is certainly unrepresented; and their majorities not only have the weight of their whole State in their scale, but have the benefit of so much of our minorities as can succeed at a district election. This is, in fact, insuring to our minorities the appointment of the government. To state it in another form; it is merely a question, whether we will divide the United States into sixteen or one hundred and thirty-seven districts. The latter being more chequered, and representing the people in smaller sections, would be more likely to be an exact representation of their diversified sentiments. But a representation of a part by great, and a part by small sections, would give a result very different from what would be the sentiment of the whole people of the United States, were they assembled together. I have to-day had a conversation with ——— who has taken a flying trip here from New York. He says, they have really now a majority of the House of Representatives, but, for want of some skilful person to rally round, they are disjointed, and will lose every question. In the senate there is a majority of eight or nine against us. But in the new election which is to come on in April, three or four in the Senate will be changed in our favor; and in the House of Representatives the county elections will still be better than the last: but still all will depend on the city election, which is of twelve members. At present there would be no doubt of our carrying our ticket there; nor does there seem to be time for any events arising to change that disposition. There is therefore the best prospect possible of a great and decided majority on a joint vote of the two Houses. They are so confident of this, that the republican party there will not consent to elect either by districts or a general ticket. They choose to do it by their legislature. I am told the republicans of New Jersey are equally confident, and equally anxious against an election either by districts or a general ticket. The contest in this State will end in a separation of the present legislature without passing any election law (and their former one has expired), and in depending on the new one, which will be elected October the 14th, in which the republican majority will be more decided in the Representatives, and instead of a majority of five against us in the Senate, will be of one for us. They will, from the necessity of the case, choose the electors themselves. Perhaps it will be thought I ought in delicacy to be silent on this subject. But you, who know me, know that my private gratifications would be most indulged by that issue, which should leave me most at home. If any thing supersedes this propensity, it is merely the desire to see this government brought back to its republican principles. Consider this as written to Mr. Madison as much as yourself and communicate it, if you think it will do any good to those possessing our joint confidence or any others where it may be useful and safe. Health and affectionate salutations.
Th: Jefferson.
TO SAMUEL ADAMS.
Philadelphia, February 26,1800.
Dear Sir,
Mr. Erving delivered me your favor of January the 31st, and I thank you for making me acquainted with him. You will always do me a favor in giving me an opportunity of knowing gentlemen as estimable in their principles and talents, as I find Mr. Erving to be. I have not yet seen Mr. Winthrop. A letter from you, my respectable friend, after three and twenty years of separation, has given me a pleasure I cannot express. It recalls to my mind the anxious days we then passed in struggling for the cause of mankind. Your principles have been tested in the crucible of time, and have come out pure. You have proved that it was monarchy, and not merely British monarchy, you opposed. A government by representees, elected by the people at short periods, was our object, and our maxim at that day was, ‘Where annual election ends, tyranny begins’; nor have our departures from it been sanctioned by the happiness of their effects. A debt of an hundred millions growing by usurious interest, and an artificial paper phalanx overruling the agricultural mass of our country, with other et ceteras, have a portentous aspect.
I fear our friends on the other side the water, laboring in the same cause, have yet a great deal of crime and of misery to wade through. My confidence had been placed in the head, not in the heart of Bonaparte. I hoped he would calculate truly the difference between the fame of a Washington and a Cromwell. Whatever his views may be, he has at least transferred the destinies of the republic from the civil to the military arm. Some will use this as a lesson against the practicability of republican government. I read it as a lesson against the danger of standing armies. Adieu, my ever respected and venerable friend. May that kind overruling Providence which has so long spared you to our country, still foster your remaining years with whatever may make them comfortable to yourself and soothing to your friends. Accept the cordial salutations of your affectionate friend,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JAMES MADISON.
Philadelphia, March 4, 1800.
Dear Sir,
I have never written to you since my arrival here, for reasons which were explained. Yours of December the 29th, January the 4th, 9th, 12th, 18th, and February the 14th, have therefore remained unacknowledged. I have at different times enclosed to you such papers as seemed interesting. To-day I forward Bingham’s amendment to the election bill formerly enclosed to you, Mr. Pinckney’s proposed amendment to the constitution, and the report of the Ways and Means. Bingham’s amendment was lost by the usual majority of two to one. A very different one will be proposed, containing the true sense of the minority, viz. that the two Houses, voting by heads, shall decide such questions as the constitution authorizes to be raised. This may probably be taken up in the other House under better auspices, for though the federalists have a great majority there, yet they are of a more moderate temper than for some time past. The Senate, however, seem determined to yield to nothing which shall give the other House greater weight in the decision on elections than they have.
Mr. Pinckney’s motion has been supported, and is likely to have some votes which were not expected. I rather believe he will withdraw it, and propose the same thing in the form of a bill; it being the opinion of some that such a regulation is not against the present constitution. In this form it will stand a better chance to pass, as a majority only in both Houses will be necessary. By putting off the building the seventy-fours and stopping enlistments, the loan will be reduced to three and a half millions. But I think it cannot be obtained. For though no new bankruptcies have happened here for some weeks, or in New York, yet they continue to happen in Baltimore, and the whole commercial race are lying on their oars, and gathering in their affairs, not knowing what new failures may put their resources to the proof. In this state of things they cannot lend money. Some foreigners have taken asylum among us, with a good deal of money, who may perhaps choose that deposite. Robbins’s affair has been under agitation for some days. Livingston made an able speech of two and a half hours yesterday. The advocates of the measure feel it pressure heavily; and though they may be able to repel Livingston’s motion of censure, I do not believe they can carry Bayard’s of approbation. The landing of our Envoys at Lisbon will risk a very dangerous consequence, insomuch as the news of Truxton’s aggression will perhaps arrive at Paris before our commissioners will. Had they gone directly there, they might have been two months ahead of that news. We are entirely without further information from Paris. By letters from Bordeaux, of December the 7th, tobacco was then from twenty-five to twenty-seven dollars per hundred. Yet did Marshall maintain on the non-intercourse bill, that its price at other markets had never been affected by that law. While the navigating and provision States, who are the majority, can keep open all the markets, or at least sufficient ones for their objects, the cries of the tobacco-makers, who are the minority, and not at all in favor, will hardly be listened to. It is truly the fable of the monkey pulling the nuts out of the fire with the cat’s paw; and it shows that G. Mason’s proposition in the convention was wise, that on laws regulating commerce, two thirds of the votes should be requisite to pass them. However, it would have been trampled under foot by a triumphant majority.
March 8. My letter has lain by me till now, waiting Mr. Trist’s departure. The question has been decided to-day on Livingston’s motion respecting Robbins; thirty-five for it, about sixty against it. Livingston, Nicholas, and Gallatin distinguished themselves on one side, and J. Marshall greatly on the other. Still it is believed they will not push Bayard’s motion of approbation. We have this day also decided in: Senate on the motion for overhauling the editor of the Aurora. It was carried, as usual, by about two to one; H. Marshall voting of course with them, as did, and frequently does ———: of ——— , who is perfectly at market. It happens that the other party are so strong, that they do not think either him or ——— worth buying. As the conveyance is confidential, I can say something on a subject which, to those who do not know my real dispositions respecting it, might seem indelicate. The federalists begin to be very seriously alarmed about their election next fall. Their speeches in private, as well as their public and private demeanor to me, indicate it strongly. This seems to be the prospect. Keep out Pennsylvania, Jersey, and New York, and the rest of the States are about equally divided; and in this estimate it is supposed that North Carolina and Maryland added together are equally divided. Then the event depends on the three middle States before mentioned. As to them, Pennsylvania passes no law for an election at the present session. They confide that the next election gives a decided majority in the two houses when joined together.
McKean, therefore, intends to call the legislature to meet immediately after the new election, to appoint electors themselves. Still you will be sensible there may arise a difficulty between the two Houses about voting by heads or by Houses. The republican members here from Jersey are entirely confident that their two Houses, joined together, have a majority of republicans; their Council being republican by six or eight votes, and the lower House federal by only one or two; and they have no doubt the approaching election will be in favor of the republicans. They appoint electors by the two Houses voting together. In New York all depends on the success of the city election, which is of twelve members, and of course makes a difference of twenty-four, which is sufficient to make the two Houses, joined together, republican in their vote. Governor Clinton, General Gates, and some other old revolutionary characters, have been put on the republican ticket. Burr, Livingston, &c. entertain no doubt on the event of that election. Still these are the ideas of the republicans only in these three States, and we must make great allowance for their sanguine views. Upon the whole, I consider it as rather more doubtful than the last election, in which I was not deceived in more than a vote or two. If Pennsylvania votes, then either Jersey or New York giving a republican vote, decides the election. If Pennsylvania does not vote, then New York determines the election. In any event, we may say that if the city election of New York is in favor of the republican ticket, the issue will be republican; if the federal ticket for the city of New York prevails, the probabilities will be in favor of a federal issue, because it would then require a republican vote both from Jersey and Pennsylvania to preponderate against New York, on which we could not count with any confidence. The election of New York being in April, it becomes an early and interesting object. It is probable the landing of our Envoys in Lisbon will add a month to our session; because all that the eastern men are anxious about, is to get away before the possibility of a treaty’s coming in upon us.
Present my respectful salutations to Mrs. Madison, and be assured of my constant and affectionate esteem,
Th: Jefferson.
Philadelphia, May 12, 1800.
Dear Sir,
Congress will rise to-day or to-morrow. Mr. Nicholas proposing to call on you, you will get from him the Congressional news. On the whole, the federalists have not been able to carry a single strong measure in the lower House the whole session. When they met, it was believed they had a majority of twenty; but many of these were new and moderate men, and soon saw the true character of the party to which they had been well disposed while at a distance. The tide, too, of public opinion sets so strongly against the federal proceedings, that this melted off their majority, and dismayed the heroes of the party. The Senate alone remained undismayed to the last. Firm to their purposes, regardless of public opinion, and more disposed to coerce than to court it, not a man of their majority gave way in the least; and on the election bill they adhered to John Marshall’s amendment, by their whole number; and if there had been a full Senate, there would have been but eleven votes against it, which include H. Marshall, who has voted with the republicans this session.
Accept assurances of constant and affectionate esteem to Mrs. Madison and yourself from, Dear Sir, your sincere friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
Monticello, August 13, 1800.
Dear Sir,
I received with great pleasure your favor of June the 4th, and am much comforted by the appearance of a change of opinion in your State; for though we may obtain, and I believe shall obtain a majority in the legislature of the United States, attached to the preservation of the federal constitution according to its obvious principles, and those on which it was known to be received; attached equally to the preservation to the States of those rights unquestionably remaining with them; friends to the freedom of religion, freedom of the press, trial by jury, and to economical government; opposed to standing armies, paper systems, war, and all connection, other than commerce, with any foreign nation; in short, a majority firm in all those principles which we have espoused and the federalists have opposed uniformly; still, should the whole body of New England continue in opposition to these principles of government, either knowingly or through delusion, our government will be a very uneasy one. It can never be harmonious and solid, while so respectable a portion of its citizens support principles which go directly to a change of the federal constitution, to sink the State governments, consolidate them into one, and to monarchize that. Our country is too large to have all its affairs directed by a single government. Public servants at such a distance, and from under the eye of their constituents, must, from the circumstance of distance, be unable to administer and overlook all the details necessary for the good government of the citizens, and the same circumstance, by rendering detection impossible to their constituents, will invite the public agents to corruption, plunder, and waste. And I do verily believe, that if the principle were to prevail, of a common law being in force in the United States, (which principle possesses the General Government at once of all the powers of the State governments, and reduces us to a single consolidated government) it would become the most corrupt government on the earth. You have seen the practices by which the public servants have been able to cover their conduct, or, where that could not be done, delusions by which they have varnished it for the eye of their constituents. What an augmentation of the field for jobbing, speculating, plundering, office-building, and office-hunting Would be produced by an assumption of all the State powers into the hands of the General Government. The true theory of our constitution is surely the wisest and best, that the States are independent as to every thing within themselves, and united as to every thing respecting foreign nations. Let the General Government be reduced to foreign concerns only, and let our affairs be disentangled from those of all other nations, except as to commerce, which the merchants will manage the better, the more they are left free to manage for themselves, and our General Government may be reduced to a very simple organization, and a very unexpensive one; a few plain duties to be performed by a few servants. But I repeat, that this simple and economical mode of government can never be secured, if the New England States continue to support the contrary system. I rejoice, therefore, in every appearance of their returning to those principles which I had always imagined to be almost innate in them. In this State, a few persons were deluded by the X. Y. Z. duperies. You saw the effect of it in our last Congressional representatives, chosen under their influence. This experiment on their credulity is now seen into, and our next representation will be as republican as it has heretofore been. On the whole, we hope, that by a part of the Union having held on to the principles of the constitution, time has been given to the States to recover from the temporary phrenzy into which they had been decoyed, to rally round the constitution, and to rescue it from the destruction with which it had been threatened even at their own hands. I see copied from the American Magazine two numbers of a paper signed Don Quixote, most excellently adapted to introduce the real truth to the minds even of the most prejudiced.
I would, with great pleasure, have written the letter you desired in behalf of your friend, but there are existing circumstances which render a letter from me to that magistrate as improper as it would be unavailing. I shall be happy, on some more fortunate occasion, to prove to you my desire of serving your wishes.
I some time ago received a letter from a Mr. M’Gregory of Derby, in your State; it is written with such a degree of good sense and appearance of candor, as entitles it to an answer. Yet the writer being entirely unknown to me, and the stratagems of the times very multifarious, I have thought it best to avail myself of your friendship, and enclose the answer to you. You will see its nature. If you find from the character of the person to whom it is addressed, that no improper use would probably be made of it, be so good as to seal and send it. Otherwise suppress it.
How will the vote of your State and Rhode Island be as to A. and P.?
I am, with great and sincere esteem, Dear Sir, your friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
Monticello, August 13, 1800.
Sir,
Your favor of July the 19th has been received, and received with the tribute of respect due to a person, who, unurged by motives of personal friendship or acquaintance, and unaided by particular information, will so far exercise his justice as to advert to the proofs of approbation given a public character by his own State and by the United States, and weigh them in the scale against the fatherless calumnies he hears uttered against him. These public acts are known even to those who know nothing of my private life, and surely are better evidence to a mind disposed to truth, than slanders which no man will affirm on his own knowledge, or ever saw one who would. From the moment that a portion of my fellow-citizens looked towards me with a view to one of their highest offices, the floodgates of calumny have been opened upon me; not where I am personally known, where their slanders would be instantly judged and suppressed, from a general sense of their falsehood; but in the remote parts of the Union, where the means of detection are not at hand, and the trouble of an inquiry is greater than would suit the hearers to undertake. I know that I might have filled the courts of the United States with actions for these slanders, and have ruined perhaps many persons who are not innocent. But this would be no equivalent to the loss of character. I leave them, therefore, to the reproof of their own consciences. If these do not condemn them, there will yet come a day when the false witness will meet a judge who has not slept over his slanders. If the reverend Cotton Mather Smith of Shena believed this as firmly as I do, he would surely never have affirmed that ‘I had obtained my property by fraud and robbery; that in one instance I had defrauded and robbed a widow and fatherless children of an estate to which I was executor of ten thousand pounds sterling, by keeping the property and paying them in money at the nominal rate, when it was worth no more than forty for one: and that all this could be proved.’ Every tittle of it is fable; there not having existed a single circumstance of my life to which any part of it can hang. I never was executor but in two instances, both of which having taken place about the beginning of the revolution, which withdrew me immediately from all private pursuits, I never meddled in either executorship. In one of the cases only, were there a widow and children. She was my sister. She retained and managed the estate in her own hands, and no part of it was ever in mine. In the other, I was a coparcener, and only received on a division the equal portion allotted me. To neither of these executorships, therefore, could Mr. Smith refer. Again, my property is all patrimonial except about seven or eight hundred pounds’ worth of lands, purchased by myself and paid for, not to widows and orphans, but to the very gentleman from whom I purchased. If Mr. Smith therefore, thinks the precepts of the Gospel intended for those who preach them as well as for others, he will doubtless some day feel the duties of repentance, and of acknowledgment in such forms as to correct the wrong he has done. Perhaps he will have to wait till the passions of the moment have passed away. All this is left to his own conscience.
These, Sir, are facts, well known to every person in this quarter, which I have committed to paper for your own satisfaction, and that of those to whom you may choose to mention them. I only pray that my letter may not go out of your own hands, lest it should get into the newspapers, a bear-garden scene into which I have made it a point to enter on no provocation.
I am, Sir, your most obedient, humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
Monticello, September 23, 1800.
Dear Sir,
I have to acknowledge the receipt of your favor of August the 22nd, and to congratulate you on the healthiness of your city. Still Baltimore, Norfolk, and Providence admonish us that we are not clear of our new scourge. When great evils happen, I am in the habit of looking out for what good may arise from them as consolations to us, and Providence has in fact so established the order of things, as that most evils are the means of producing some good. The yellow fever will discourage the growth of great cities in our nation, and I view great cities as pestilential to the morals, the health, and the liberties of man. True, they nourish some of the elegant arts, but the useful ones can thrive elsewhere, and less perfection in the others, with more health, virtue, and freedom, would be my choice.
I agree with you entirely, in condemning the mania of giving names to objects of any kind after persons still living. Death alone can seal the title of any man to this honor, by putting it out of his power to forfeit it. There is one other mode of recording merit, which I have often thought might be introduced, so as to gratify the living by praising the dead. In giving, for instance, a commission of Chief Justice to Bushrod Washington, it should be in consideration of his integrity, and science in the laws, and of the services rendered to our country by his illustrious relation, &c. A commission to a descendant of Dr. Franklin, besides being in consideration of the proper qualifications of the person, should add, that of the great services rendered by his illustrious ancestor, Benjamin Franklin, by the advancement of science, by inventions useful to man, &c. I am not sure that we ought to change all our names. And, during the regal government, sometimes indeed they were given through adulation; but often also as the reward of the merit of the times, sometimes for services rendered the colony. Perhaps, too, a name when given, should be deemed a sacred property.
I promised you a letter on Christianity, which I have not forgotten. On the contrary, it is because I have reflected on it, that I find much more time necessary for it than I can at present dispose of. I have a view of the subject which ought to displease neither the rational Christian nor Deist, and would reconcile many to a character they have too hastily rejected. I do not know that it would reconcile the genus irritabile vatum, who are all in arms against me. Their hostility is on too interesting ground to be softened. The delusion into which the X. Y. Z. plot showed it possible to push the people; the successful experiment made under the prevalence of that delusion on the clause of the constitution, which, while it secured the freedom of the press, covered also the freedom of religion, had given to the clergy a very favorite hope of obtaining an establishment of a particular form of Christianity through the United States; and as every sect believes its own form the true one, every one perhaps hoped for his own, but especially the Episcopalians and Congregationalists. The returning good sense of our country threatens abortion to their hopes, and they believe that any portion of power confided to me, will be exerted in opposition to their schemes. And they believe rightly: for I have sworn, upon the altar of God, eternal hostility against every form of tyranny over the mind of man. But this is all they have to fear from me: and enough too in their opinion. And this is the cause of their printing lying pamphlets against me, forging conversations for me with Mazzei, Bishop Madison, &c. which are absolute falsehoods without a circumstance of truth to rest on; falsehoods, too, of which I acquit Mazzei and Bishop Madison, for they are men of truth.
But enough of this: it is more than I have before committed to paper on the subject of all the lies which have been preached and printed against me. I have not seen the work of Sonnini which you mention, but I have seen another work on Africa, Park’s, which I fear will throw cold-water on the hopes of the friends of freedom. You will hear an account of an attempt at insurrection in this state. I am looking with anxiety to see what will be its effect on our State. We are truly to be pitied. I fear we have little chance to see you at the federal city or in Virginia, and as little at Philadelphia. It would be a great treat to receive you here. But nothing but sickness could effect that; so I do not wish it. For I wish you health and happiness, and think of you with affection. Adieu.
Th: Jefferson.
TO ROBERT R. LIVINGSTON.
Washington, December 14, 1800.
Dear Sir,
Your former communications on the subject of the steam-engine, I took the liberty of laying before the American Philosophical Society, by whom they will be printed in their volume of the present year. I have heard of the discovery of some large bones, supposed to be of the mammoth, at about thirty or forty miles distance from you: and among the bones found, are said to be some which we have never yet been able to procure. The first interesting question is, whether they are the bones of the mammoth? The second, What are the particular bones, and could I possibly procure them? The bones I am most anxious to obtain, are those of the head and feet, which are said to be among those found in your State, as also the ossa innominata, and scapula. Others would also be interesting, though similar ones may be possessed, because they would show by their similarity that the set belong to the mammoth. Could I so far venture to trouble you on this subject, as to engage some of your friends, near the place, to procure for me the bones above mentioned? If they are to be bought, I will gladly pay for them whatever you shall agree to as reasonable; and will place the money in New York as instantaneously after it is made known to me, as the post can carry it, as I will all expenses of package, transportation, &c. to New York and Philadelphia, where they may be addressed to John Barnes, whose agent (he not being on the spot) will take care of them for me.
But I have still a more important subject whereon to address you. Though our information of the votes of the several States be not official, yet they are stated on such evidence as to satisfy both parties that the republican vote has been successful. We may, therefore, venture to hazard propositions on that hypothesis, without being justly subjected to raillery or ridicule. The constitution, to which we are all attached, was meant to be republican, and we believe to be republican according to every candid interpretation. Yet we have seen it so interpreted and administered, as to be truly what the French have called it, a monarchic masque. Yet so long has the vessel run on this way and been trimmed to it, that to put her on her republican tack will require all the skill, the firmness, and the zeal of her ablest and best friends. It is a crisis which calls on them to sacrifice all other objects, and repair to her aid in this momentous operation. Not only their skill is wanting, but their names also. It is essential to assemble in the outset persons to compose our administration, whose talents, integrity, and revolutionary name and principles may inspire the nation, at once, with unbounded confidence, and impose an awful silence on all the maligners of republicanism; as may suppress in embryo the purpose avowed by one of their most daring and effective chiefs, of beating down the administration. These names do not abound at this day. So few are they, that yours, my friend, cannot be spared among them without leaving a blank which cannot be filled. If I can obtain for the public the aid of those I have contemplated, I fear nothing. If this cannot be done, then are we unfortunate indeed! We shall be unable to realize the prospects which have been held out to the people, and we must fall back into monarchism, for want of heads, not hands, to help us out of it. This is a common cause, my dear Sir, common to all republicans. Though I have been too honorably placed in front of those who are to enter the breach so happily made, yet the energies of every individual are necessary, and in the very place where his energies can most serve the enterprise. I can assure you that your colleagues will be most acceptable to you; one of them, whom you cannot mistake, peculiarly so. The part which circumstances constrain us to propose to you, is the secretaryship of the navy. These circumstances cannot be explained by letter. Republicanism is so rare in those parts which possess nautical skill, that I cannot find it allied there to the other qualifications. Though you are not nautical by profession, yet your residence and your mechanical science qualify you as well as a gentleman can possibly be, and sufficiently to enable you to choose under-agents perfectly qualified, and to superintend their conduct. Come forward then, my dear Sir, and give us the aid of your talents and the weight of your character towards the new establishment of republicanism; I say, for its new establishment; for hitherto, we have seen only its travestie. I have urged thus far, on the belief that your present office would not be an obstacle to this proposition. I was informed, and I think it was by your brother, that you wished to retire from it, and were only restrained by the fear that a successor of different principles might be appointed. The late change in your council of appointment will remove this fear. It will not be improper to say a word on the subject of expense. The gentlemen who composed General Washington’s first administration took up, too universally, a practice of general entertainment, which was unnecessary, obstructive of business, and so oppressive to themselves, that it was among the motives for their retirement. Their successors profited from the experiment, and lived altogether as private individuals, and so have ever continued to do. Here, indeed, it cannot be otherwise our situation being so rural, that during the vacations of the legislature we shall have no society but of the officers of government, and in time of sessions the legislature is become and becoming so numerous, that for the last half dozen years nobody but the President has pretended to entertain them. I have been led to make the application before official knowledge of the result of our election, because the return of Mr. Van Benthuysen, one of your electors and neighbors, offers me a safe conveyance, at a moment when the post-offices will be peculiarly suspicious and prying. Your answer may come by post without danger, if directed in some other hand-writing than your own: and I will pray you to give me an answer as soon as you can make up your mind.
Accept assurances of cordial esteem and respect, and my friendly salutations.
Th: Jefferson.
Washington, December 15,1800.
Dear Sir,
Although we have not official information of the votes for President and Vice-President, and cannot have until the first week in February, yet the state of the votes is given on such evidence, as satisfies both parties that the two republican candidates stand highest. From South Carolina we have not even heard of the actual vote; but we have learned who were appointed electors, and with sufficient certainty how they would vote. It is said they would withdraw from yourself one vote. It has also been said that a General Smith, of Tennessee, had declared he would give his second vote to Mr. Gallatin, not from any indisposition towards you, but extreme reverence to the character of Mr. Gallatin. It is also surmised that the vote of Georgia will not be entire. Yet nobody pretends to know these things of a certainty, and we know enough to be certain that what it is surmised will be withheld, will still leave you four or five votes at least above Mr. Adams. However, it was badly managed not to have arranged with certainty what seems to have been left to hazard. It was the more material, because I understand several of the highflying federalists have expressed their hope that the two republican tickets may be equal, and their determination in that case to prevent a choice by the House of Representatives (which they are strong enough to do) and let the government devolve on a President of the Senate. Decency required that I should be so entirely passive during the late contest, that I never once asked whether arrangements had been made to prevent so many from dropping votes intentionally, as might frustrate half the republican wish; nor did I doubt, till lately, that such had been made.
While I must congratulate you, my dear Sir, on the issue of this contest, because it is more honorable, and doubtless more grateful to you than any station within the competence of the chief magistrate, yet for myself, and for the substantial service of the public, I feel most sensibly the loss we sustain of your aid in our new administration. It leaves a chasm in my arrangements, which cannot be adequately filled up. I had endeavored to compose an administration, whose talents, integrity, names, and dispositions, should at once inspire unbounded confidence in the public mind, and insure a perfect harmony in the conduct of the public business. I lose you from the list, and am not sure of all the others. Should the gentlemen who possess the public confidence decline taking a part in their affairs, and force us to take persons unknown to the people, the evil genius of this country may realize his avowal that ‘he will beat down the administration.’ The return of Mr. Van Benthuysen, one of your electors, furnishes me a confidential opportunity of writing this much to you, which I should not have ventured through the post-office at this prying season. We shall of course see you before the fourth of March. Accept my respectful and affectionate salutations.
Th: Jefferson.
TO JUDGE BRECKENRIDGE.
Washington, December 18,1800.
Dear Sir,
I received, while at home, the letter you were so kind as to write me. The employments of the country have such irresistible attractions for me, that while I am at home I am not very punctual in acknowledging the letters of my friends. Having no refuge here from my room and writing-table, it is my regular season for fetching up the lee-way of my correspondence.
Before you receive this, you will have understood that the State of South Carolina (the only one about which there was uncertainty) has given a republican vote, and saved us from the consequences of the annihilation of Pennsylvania. But we are brought into dilemma by the probable equality of the two republican candidates, The federalists in Congress mean to take advantage of this, and either to prevent an election altogether, or reverse what has been understood to have been the wishes of the people as to the President and Vice-President; wishes which the constitution! did not permit them specially to designate. The latter alternative still gives us a republican administration; the former, a suspension of the federal government, for want of a head. This opens to us an abyss at which every sincere patriot must shudder. General Davie has arrived here with the treaty formed (under the name of a convention) with France. It is now before the Senate for ratification, and will encounter objections. He believes firmly that a continental peace in Europe will take place, and that England also may be comprehended.
Accept assurances of the great respect of, Dear Sir, your most obedient servant,
Th: Jefferson.
Washington, December 19,1800.
Dear Sir,
Mrs. Brown’s departure for Virginia enables me to write confidentially what I could not have ventured by the post at this prying season. The election in South Carolina has in some measure decided the great contest. Though as yet we do not know the actual votes of Tennessee, Kentucky, and Vermont, yet we believe the votes to be on the whole, J. seventy-three, B. seventy-three, A. sixty-five, P. sixty-four. Rhode Island withdrew one from P. There is a possibility that Tennessee may withdraw one from B., and Burr writes that there may be one vote in Vermont for J. But I hold the latter impossible, and the former not probable; and that there will be an absolute parity between the two republican candidates. This has produced great dismay and gloom on the republican gentlemen here, and exultation in the federalists, who openly declare they will prevent an election, and will name a President of the Senate, pro tem, by what they say would only be a stretch of the constitution. The prospect of preventing this, is as follows. Georgia, North Carolina, Tennessee, Kentucky, Vermont, Pennsylvania, and New York, can be counted on for their vote in the, House of Representatives, and it is thought by some, that Baer of Maryland, and Linn of New Jersey will come over. Some even count on Morris of Vermont. But you must know the uncertainty of such a dependence under the operation of caucuses and other federal engines. The month of February, therefore, will present us storms of a new character. Should they have a particular issue, I hope you will be here a day or two, at least, before the 4th of March. I know that your appearance on the scene before the departure of Congress, would assuage the minority, and inspire in the majority confidence and joy unbounded, which they would spread far and wide on their journey home. Let me beseech you then to come with a view of staying perhaps a couple of weeks, within which time things might be put into such a train, as would permit us both to go home for a short time, for removal. I wrote to R. R. L. by a confidential hand three days ago. The person proposed for the Treasury has not come yet.
Davie is here with the convention, as it is called; but it is a real treaty, and without limitation of time. It has some disagreeable features, and will endanger the compromitting us with Great Britain. I am not at liberty to mention its contents, but I believe it will meet with opposition from both sides of the House. It has been a bungling negotiation. Ellsworth remains in France for his health. He has resigned his office of Chief Justice. Putting these two things together, we cannot misconstrue his views. He must have had great confidence in Mr. Adams’s continuance to risk such a certainty as he held. Jay was yesterday nominated Chief Justice. We were afraid of something worse. A scheme of government for the territory is cooking by a committee of each House, under separate authorities, but probably a voluntary harmony. They let out no hints. It is believed that the judiciary system will not be pushed, as the appointments, if made by the present administration, could not fall on those who create them. But I very much fear the road system will be urged. The mines of Peru would not supply the monies which would be wasted on this object, nor the patience of any people stand the abuses which would be incontrollably committed under it. I propose, as soon as the state of the election is perfectly ascertained, to aim at a candid understanding with Mr. Adams. I do not expect that either his feelings or his views of interest will oppose it. I hope to induce in him dispositions liberal and accommodating. Accept my affectionate salutations.
Th: Jefferson.
TO JAMES MADISON.
Washington, December 26, 1800.
Dear Sir,
All the votes have now come in, except of Vermont and Kentucky, and there is no doubt that the result is a perfect parity between the two republican characters. The federalists appear determined to prevent an election, and to pass a bill giving the government to Mr. Jay, appointed Chief Justice, or to Marshall as Secretary of State. Yet I am rather of opinion that Maryland and Jersey will give the seven republican majorities. The French treaty will be violently opposed by the federalists; the giving up the vessels is the article they cannot swallow. They have got their judiciary bill forwarded to commitment. I dread this above all the measures meditated, because appointments in the nature of free-hold render it difficult to undo what is done. We expect a report for a territorial government which is to pay little respect to the rights of man.
****
Cordial and affectionate salutations. Adieu.
Th: Jefferson.
Washington, February 1, 1801.
Dear Sir,
It was to be expected that the enemy would endeavor to sow tares between us, that they might divide us and our friends. Every consideration satisfies me you will be on your guard against this, as I assure you I am strongly. I hear of one stratagem so imposing and so base, that it is proper I should notice it to you. Mr. Munford, who is here, says he saw at New York before he left it, an original letter of mine to Judge Breckenridge, in which are sentiments highly injurious to you. He knows my hand-writing, and did not doubt that to be genuine. I enclose you a copy taken from the press copy of the only letter I ever wrote to Judge Breckenridge in my life: the press copy itself has been shown to several of our mutual friends here. Of consequence the letter seen by Mr. Munford must be a forgery, and if it contains a sentiment unfriendly or disrespectful to you, I affirm it solemnly to be a forgery; as also if it varies, from the copy enclosed. With the common trash of slander I should not think of troubling you; but the forgery of one’s hand-writing is too imposing to be neglected. A mutual knowledge of each other furnishes us with the best test of the contrivances which will be practised by the enemies of both.
Accept assurances of my high respect and esteem.
Th: Jefferson.
TO GOVERNOR M’KEAN.
Washington, February 2, 1801.
Dear Sir,
I have long waited for an opportunity to acknowledge the receipt of your favor of December the 15th, as well as that by Dr. Mendenhall. None occurring, I shall either deliver the present to General Muhlenburg or put it under cover to Dr. Wistar, to whom I happen to be writing, to be sent to your house in Philadelphia, or forwarded confidentially to Lancaster.
The event of the election is still in dubio. A strong portion in the House of Representatives will prevent an election if they can. I rather believe they will not be able to do it, as there are six individuals of moderate character, any one of whom coming over to the republican vote will make a ninth state. Till this is known, it is too soon for me to say what should be done in such atrocious cases as those you mention of federal officers obstructing the operation of the State governments. One thing I will say, that as to the future, interferences with elections, whether of the State or General Government, by officers of the latter, should be deemed cause of removal; because the constitutional remedy by the elective principle becomes nothing, if it may be smothered by the enormous patronage of the General Government. How far it may be practicable, prudent, or proper, to look back, is too great a question to be decided but by the united wisdom of the whole administration when formed. Our situation is so different from yours, that it may render proper some differences in the practice. Your State is a single body, the majority clearly one way. Ours is of sixteen integral parts, some of them all one way, some all the other, some divided. Whatever my be decided as to the past, they shall give no trouble to the State governments in future, if it shall depend on me; and be assured, particularly as to yourself, that I should consider the most perfect harmony and interchange of accommodations and good offices with those governments as among the first objects.
Accept assurances of my high consideration, respect, and esteem.
Th: Jefferson.
Washington, February 11,1801.
Dear Sir,
Your favor of January the 25th came to hand some days ago, and yesterday a gentleman put into my hand, at the door of the Senate chamber, the volume of the American Museum for 1798. As no letter accompanied it, I took it for granted it was to bring under my eye some of its contents. I have gone over it with satisfaction.
This is the morning of the election by the House of Representatives. For some time past a single individual had declared he would by his vote make up the ninth State. On Saturday last he changed, and it stands at present eight one way, six the other, and two divided. Which of the two will be elected, and whether either, I deem perfectly problematical: and my mind has long been equally made up for either of the three events. If I can find out the person who brought me the volume for you, I shall return it by him, because I presume it makes one of a set. If not by him, I will find some other person who may convey it to Philadelphia if not to Lancaster. Very possibly it may go by a different conveyance from this letter. Very probably you will learn before the receipt of either, the result, or progress at least, of the election. We see already at the threshold, that if it falls on me, I shall be embarrassed by finding the offices vacant, which cannot be even temporarily filled but with advice of Senate, and that body is called on the fourth of March, when it is impossible for the new members of Kentucky, Georgia, and South Carolina to receive notice in time to be here. The summons for Kentucky, dated, as all were, January the 31st, could not go hence till the 5th, and that for Georgia did not go till the 6th. If the difficulties of the election, therefore, are got over, there are more and more behind, until new elections shall have regenerated the constituted authorities. The defects of our constitution under circumstances like the present, appear very great. Accept assurances of the esteem and respect of, Dear Sir, your most obedient servant,
Th: Jefferson.
Washington, February 15, 1801.
Dear Sir,
I have received several letters from you which have not been acknowledged. By the post I dare not, and one or two confidential opportunities have passed me by surprise. I have regretted it the less, because I know you could be more safely and fully informed by others. Mr. Tyler, the bearer of this, will give you a great deal more information personally than can be done by letter. Four days of balloting have produced not a single change of a vote. Yet it is confidently believed by most that to-morrow there is to be a coalition. I know of no foundation for this belief. However, as Mr. Tyler waits the event of it, he will communicate it to you. If they could have been permitted to pass a law for putting the government into the hands of an officer, they would certainly have prevented an election. But we thought it best to declare openly and firmly, one and all, that the day such an act passed, the middle States would arm, and that no such usurpation, even for a single day, should be submitted to. This first shook them; and they were completely alarmed at the resource for which we declared, to wit, a convention to re-organize the government, and to amend it. The very word convention gives them the horrors, as in the present democratical spirit of America, they fear they should lose some of the favorite morsels of the constitution. Many attempts have been made to obtain terms and promises from me. I have declared to them unequivocally, that I would not receive the government on capitulation, that I would not go into it with my hands tied. Should they yield the election, I have reason to expect in the outset the greatest difficulties as to nominations. The late incumbents running away from their offices and leaving them vacant, will prevent my filling them without the previous advice of Senate. How this difficulty is to be got over I know not. Accept for Mrs. Monroe and yourself my affectionate salutations. Adieu.
Th: Jefferson.
TO JAMES MADISON.
Washington, February 18,1801.
Dear Sir,
Notwithstanding the suspected infidelity of the post, I must hazard this communication. The minority of the House of Representatives, after seeing the impossibility of electing Burr, the certainty that a legislative usurpation would be resisted by arms, and a recourse to a convention to re-organize and amend the government, held a consultation on this dilemma, whether it would be better for them to come over in a body and go with the tide of the times, or by a negative conduct suffer the election to be made by a bare majority, keeping their body entire and unbroken, to act in phalanx on such ground of opposition as circumstances shall offer: and I know their determination on this question only by their vote of yesterday. Morris of Vermont withdrew, which made Lyon’s vote that of his State. The Maryland federalists put in four blanks, which made the positive ticket of their colleagues the vote of the State. South Carolina and Delaware put in six blanks. So there were ten states for one candidate, four for another, and two blanks. We consider this, therefore, as a declaration of war, on the part of this band. But their conduct appears to have brought over to us the whole body of federalists, who, being alarmed with the danger of a dissolution of the government, had been made most anxiously to wish the very administration they had opposed, and to view it when obtained, as a child of their own.
Mr. A. embarrasses us. He keeps the offices of State and War vacant, but has named Bayard Minister Plenipotentiary to France, and has called an unorganized Senate to meet the fourth of March. As you do not like to be here on that day, I wish you would come within a day or two after. I think that between that and the middle of the month we can so far put things under way, as that we may go home to make arrangements for our final removal. Come to Conrad’s, where I will bespeak lodgings for you. Yesterday Mr. A. nominated Baynard to be Minister Plenipotentiary of the United States to the French republic; to-day, Theophilus Parsons, Attorney General of the United States in the room of C. Lee, who, with Keith Taylor cum multis aliis, are appointed judges under the new system. H. G. Otis is nominated a District Attorney. A vessel has been waiting for some time in readiness to carry the new Minister to France. My affectionate salutations to Mrs. Madison.
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN DICKINSON.
Washington, March 6, 1801.
Dear Sir,
No pleasure can exceed that which I received from reading your letter of the 21st ultimo. It was like the joy we expect in the mansions of the blessed, when received with the embraces of our forefathers, we shall be welcomed with their blessing as having done our part not unworthily of them. The storm through which we have passed, has been tremendous indeed. The tough sides of our Argosie have been thoroughly tried. Her strength has stood the waves into which she was steered, with a view to sink her. We shall put her on her republican tack, and she will now show by the beauty of her motion the skill of her builders. Figure apart, our fellow-citizens have been led hood-winked from their principles by a most extraordinary combination of circumstances. But the band is removed, and they now see for themselves. I hope to see shortly a perfect consolidation, to effect which, nothing shall be spared on my part, short of the abandonment of the principles of our revolution. A just and solid republican government maintained here, will be a standing monument and example for the aim and imitation of the people of other countries; and I join with you in the hope and belief that they will see, from our example, that a free government is of all others the most energetic; that the inquiry which has been excited among the mass of mankind by our revolution and its consequences, will ameliorate the condition of man over a great portion of the globe. What a satisfaction have we in the contemplation of the benevolent effects of our efforts, compared with those of the leaders on the other side, who have discountenanced all advances in science as dangerous innovations, have endeavored to render philosophy and republicanism terms of reproach, to persuade us that man cannot be governed but by the rod, &c. I shall have the happiness of living and dying in the contrary hope. Accept assurances of my constant and sincere respect and attachment, and my affectionate salutations.
Th: Jefferson.
Washington, March 7, 1801.
Dear Sir,
I had written the enclosed letter to Mrs. Trist, and was just proceeding to begin one to you, when your favor of the 6th was put into my hands. I thank you sincerely for it, and consider the views of it so sound, that I have communicated it to my coadjutors as one of our important evidences of the public sentiment, according to which we must shape our course. I suspect, partly from this, but more from a letter of J. Taylor’s which has been put into my hands, that an incorrect idea of my views has got abroad. I am in hopes my inaugural address will in some measure set this to rights, as it will present the leading objects to be conciliation and adherence to sound principle. This I know is impracticable with the leaders of the late faction, whom I abandon as incurables, and will never turn an inch out of my way to reconcile them. But with the main body of the federalists, I believe it very practicable. You know that the manoeuvres of the year X. Y. Z. carried over from us a great body of the people, real republicans, and honest men under virtuous motives. The delusion lasted a while. At length the poor arts of tub-plots, &c. were repeated till the designs of the party became suspected. From that moment those who had left us began to come back. It was by their return to us that we gained the victory in November, 1800, which we should not have gained in November, 1799. But during the suspension of the public mind from the 11th to the 17th of February, and the anxiety and alarm lest there should be no election, and anarchy ensue, a wonderful effect was produced on the mass of federalists who had not before come over. Those who had before become sensible of their error in the former change, and only wanted a decent excuse for coming back, seized that occasion for doing so. Another body, and a large one it is, who from timidity of constitution had gone with those who wished for a strong executive, were induced by the same timidity to come over to us rather than risk anarchy: so that, according to the evidence we receive from every direction, we may say that the whole of that portion of the people which were called federalists, were made to desire anxiously the very event they had just before opposed with all their energies, and to receive the election which was made, as an object of their earnest wishes, a child of their own. These people (I always exclude their leaders) are now aggregated with us, they look with a certain degree of affection and confidence to the administration, ready to become attached to it, if it avoids in the outset acts which might revolt and throw them off. To give time for a perfect consolidation seems prudent. I have firmly refused to follow the counsels of those who have desired the giving offices to some of their leaders, in order to reconcile. I have given, and will give, only to republicans, under existing circumstances. But I believe with others, that deprivations of office, if made on the ground of political principles alone, would revolt our new converts, and give a body to leaders who now stand alone. Some, I know, must be made. They must be as few as possible, done gradually, and bottomed on some malversation or inherent disqualification. Where we shall draw the line between retaining all and none, is not yet settled, and will not be till we get our administration together; and perhaps even then, we shall proceed à tatons, balancing our measures according to the impression we perceive them to make.
This may give you a general view of our plan. Should you be in Albemarle the first week in April, I shall have the pleasure of seeing you there, and of developing things more particularly, and of profiting by an intercommunication of views. Dawson sails for France about the 15th, as the bearer only of the treaty to Ellsworth and Murray. He has probably asked your commands, and your introductory letters.
Present my respects to Mrs. Monroe, and accept assurances of my high and affectionate consideration and attachment.
Th: Jefferson.
TO GOVERNOR M’KEAN.
Washington, March 9, 1801.
Dear Sir,
I have to acknowledge the receipt of your favor of February the 20th, and to thank you for your congratulations on the event of the election. Had it terminated in the elevation of Mr. Burr every republican would, I am sure, have acquiesced in a moment; because, however it might have been variant from the intentions of the voters, yet it would have been agreeable to the constitution. No man would more cheerfully have submitted than myself, because I am sure the administration would have been republican, and the chair of the Senate permitting me to be at home eight months in the year, would, on that account, have been much more consonant to my real satisfaction. But in the event of an usurpation, I was decidedly with those who were determined not to permit it. Because that precedent, once set, would be artificially reproduced, and end soon in a dictator. Virginia was bristling up, I believe. I shall know the particulars from Governor Monroe, whom I expect to meet in a short visit I must make home, to select some books, &c. necessary here, and make other domestic arrangements.
Accept assurances of my high esteem and regard.
Th: Jefferson.
Washington, March 14, 1801.
Dear Sir,
Not having my papers here, it is not in my power to acknowledge the receipt of your letters by their dates, but T am pretty certain I have received two in the course of the last twelve months, one of them covering your excellent second letter. Nothing can be sounder than the principles it inculcates, and I am not without hopes they will make their way. You have understood that the revolutionary movements in Europe had, by industry and artifice, been wrought into objects of terror even to this country, and had really involved a great portion of our well-meaning citizens in a panic which was perfectly unaccountable, and during the prevalence of which they were led to support measures the most insane. They are now pretty thoroughly recovered from it, and sensible of the mischief which was done, and preparing to be done, had their minds continued a little longer under that derangement. The recovery bids fair to be complete, and to obliterate entirely the line of party division which had been so strongly drawn. Not that their late leaders have come over, or ever can come over. But they stand, at present, almost without followers. The principal of them have retreated into the judiciary, as a strong hold, the tenure of which renders it difficult to dislodge them. For all the particulars I must refer you to Mr. Dawson, a member of Congress, fully informed and worthy of entire confidence. Give me leave to ask for him your attentions and civilities, and a verbal communication of such things on your side the water as you know I feel a great interest in, and as may not with safety be committed to paper. I am entirely unable to conjecture the issue of things with you.
Accept assurances of my constant esteem and high consideration.
Th: Jefferson
TO THOMAS PAINE.
Washington, March 18, 1801,
Dear Sir,
Your letters of October the 1st, 4th, 6th, and 16th, came duly to hand, and the papers which they covered were, according to your permission, published in the newspapers and in a pamphlet, and under your own name. These papers contain precisely our principles, and I hope they will be generally recognised here. Determined as we are to avoid, if possible, wasting the energies of our people in war and destruction, we shall avoid implicating ourselves with the powers of Europe, even in support of principles which we mean to pursue. They have so many other interests different from ours, that we must avoid being entangled in them. We believe we can enforce those principles, as to ourselves, by peaceable means, now that we are likely to have our public councils detached from foreign views. The return, of our citizens from the phrenzy into which they had been wrought, partly by ill conduct in France, partly by artifices practised on them, is almost entire, and will, I believe, become quite so. But these details, too minute and long for a letter, will be better developed by Mr. Dawson, the bearer of this, a member of the late Congress, to whom I refer you for them. He goes in the Maryland, a sloop of war, which will wait a few days at Havre to receive his letters, to be written on his arrival at Paris. You expressed a wish to get a passage to this country in a public vessel. Mr. Dawson is charged with orders to the captain of the Maryland to receive and accommodate you with a passage back, if you can be ready to depart at such short warning. Robert R. Livingston is appointed Minister Plenipotentiary to the republic of France, but will not leave this till we receive the ratification of the convention by Mr. Dawson. I am in hopes you will find us returned generally to sentiments worthy of former times. In these it will be your glory to have steadily labored, and with as much effect as any man living. That you may long live to continue your useful labors, and to reap their reward in the thankfulness of nations, is my sincere prayer.
Accept assurances of my high esteem and affectionate attachment.
Th: Jefferson.
TO M. DE REYNEVAL.
Washington, March 20, 1801.
Dear Sir,
Mr. Pichon, who arrived two days ago, delivered me your favor of January the 1st, and I had before received one by Mr. Dupont, dated August the 24th, 1799, both on the subject of lands, claimed on behalf of your brother, Mr. Girard, and that of August the 24th containing a statement of the case. I had verbally explained to Mr. Dupont at the time, what I presumed to have been the case, which must, I believe, be very much mistaken in the statement sent with that letter; and I expected he had communicated it to you.
During the regal government, two companies called the Loyal, and the Ohio companies had obtained grants from the crown for eight hundred thousand, or one million of acres of land, each, on the Ohio, on condition of settling them in a given number of years. They surveyed some and settled them; but the war of 1755 came on and broke up the settlements. After it was over they petitioned for a renewal. Four other large companies then formed themselves, called the Mississippi, the Illinois, the Wabash, and the Indiana companies, each praying for immense quantities of land, some amounting to two hundred miles square, so that they proposed to cover the whole country north between the Ohio and Mississippi, and a great portion of what is south. All these petitions were depending, without any answer whatever from the crown, when the revolution war broke out. The petitioners had associated to themselves some of the nobility of England, and most of the characters in America of great influence. When Congress assumed the government, they took some of their body in as partners, to obtain their influence; and I remember to have heard at the time, that one of them took Mr. Girard as a partner, expecting by that to obtain the influence of the French court; to obtain grants of those lands which they had not been able to obtain from the British government. All these lands were within the limits of Virginia, and that State determined peremptorily, that they never should be granted to large companies, but left open equally to all: and when they passed their land law (which I think was in 1778) they confirmed only so much of the lands of the Loyal company as they had actually surveyed, which was a very small proportion, and annulled every other pretension. And when that State conveyed the lands to Congress (which was not till 1784), so determined were they to prevent their being granted to these or any other large companies, that they made it an express condition of the cession, that they should be applied first towards the soldiers’ bounties, and the residue sold for the payment of the national debt, and for no other purpose. This disposition has been, accordingly, rigorously made, and is still going on, and Congress considers itself as having no authority to dispose of them otherwise.
I sincerely wish, Sir, it had been in my power to have given you a more agreeable account of this claim. But as the case actually is, the most substantial service is to state it exactly, and not to foster false expectations. I remember with great sensibility all the attentions you were so good as to render me while I resided in Paris, and shall be made happy by every occasion which can be given me of acknowledging them, and the expressions of your friendly recollection are particularly soothing to me.
Accept, I pray you, the assurances of my high consideration and constant esteem.
Th: Jefferson.
TO DOCTOR JOSEPH PRIESTLEY.
Washington, March 21, 1801.
Dear Sir,
I learned some time ago that you were in Philadelphia, but that it was only for a fortnight; and I supposed you were gone. It was not till yesterday I received information that you were still there, had been very ill, but were on the recovery. I sincerely rejoice that you are so. Yours is one of the few lives precious to mankind, and for the continuance of which every thinking man is solicitous. Bigots may be an exception. What an effort, my dear Sir, of bigotry in politics and religion have we gone through. The barbarians really flattered themselves they should be able to bring back the times of Vandalism, when ignorance put every thing into the hands of power and priestcraft. All advances in science were proscribed as innovations. They pretended to praise and encourage education, but it was to be the education of our ancestors. We were to look backwards not forwards for improvement: the President himself declaring in one of his answers to addresses, that we were never to expect to go beyond them in real science. This was the real ground of all the attacks on you: those who live by mystery and charlatanerie, fearing you would render them useless by simplifying the Christian philosophy, the most sublime and benevolent but most perverted system that ever shone on man, endeavored to crush your well-earned and well-deserved fame. But it was the Lilliputians upon Gulliver. Our countrymen have recovered from the alarm into which art and industry had thrown them; science and honesty are replaced on their high ground; and you, my dear Sir, as their great apostle, are on its pinnacle. It is with heartfelt satisfaction that, in the first moments of my public action, I can hail you with welcome to our land, tender to you the homage of its respect and esteem, cover you under the protection of those laws which were made for the wise and good like you, and disclaim the legitimacy of that libel on legislation, which under the form of a law was for some time placed among them.*
[* In the margin, is written by the author, ‘Alien law.‘]
As the storm is now subsiding and the horizon becoming serene, it is pleasant to consider the phenomenon with attention. We can no longer say there is nothing new under the sun. For this whole chapter in the history of man is new. The great extent of our republic is new. Its sparse habitation is new. The mighty wave of public opinion which has rolled over it is new. But the most pleasing novelty is, its so quietly subsiding over such an extent of surface to its true level again. The order and good sense displayed in this recovery from delusion, and in the momentous crisis which lately arose, really bespeak a strength of character in our nation which augurs well for the duration of our republic: and I am much better satisfied now of its stability, than I was before it was tried, I have been above all things solaced by the prospect which opened on us, in the event of a non-election of a President; in which case, the federal government would have been in the situation of a clock or watch run down. There was no idea of force, nor of any occasion for it. A convention, invited by the republican members of Congress with the virtual President and Vice-President, would have been on the ground in eight weeks, would have repaired the constitution where it was defective, and wound it up again. This peaceable and legitimate resource, to which we are in the habit of implicit obedience, superseding all appeal to force, and being always within our reach, shows a precious principle of self-preservation in our composition, till a change of circumstances shall take place, which is not within prospect at any definite period.
But I have got into a long disquisition on politics when I only meant to express my sympathy in the state of your health, and to tender you all the affections of public and private hospitality. I should be very happy indeed to see you here. I leave this about the 30th instant, to return about the 25th of April. If you do not leave Philadelphia before that, a little excursion hither would help your health. I should be much gratified with the possession of a guest I so much esteem, and should claim a right to lodge you, should you make such an excursion.
Accept the homage of my high consideration and respect, and assurances of affectionate attachment.
Th: Jefferson.
TO MOSES ROBINSON.
Washington, March 23,1801.
Dear Sir,
I have to acknowledge the receipt of your favor of the 3rd instant, and to thank you for the friendly expressions it contains. I entertain real hope that the whole body of your fellow-citizens (many of whom had been carried away by the X. Y. Z. business) will shortly be consolidated in the same sentiments. When they examine the real principles of both parties, I think they will find little to differ about. I know, indeed, that there are some of their leaders who have so committed themselves, that pride, if no other passion, will prevent their coalescing. We must be easy with them. The eastern States will be the last to come over on account of the dominion of the clergy, who had got a smell of union between Church and State, and began to indulge reveries which can never be realized in the present state of science. If, indeed, they could have prevailed on us to view all advances in science as dangerous innovations, and to look back to the opinions and practices of our forefathers, instead of looking forward, for improvement, a promising groundwork would have been laid. But I am in hopes their good sense will dictate to them, that since the mountain will not come to them, they had better go to the mountain: that they will find their interest in acquiescing in the liberty and science of their country, and that the Christian religion, when divested of the rags in which they have enveloped it, and brought to the original purity and simplicity of its benevolent institutor, is a religion of all others most friendly to liberty, science, and the freest expansion of the human mind.
I sincerely wish with you, we could see our government so secured as to depend less on the character of the person in whose hands it is trusted. Bad men will sometimes get in, and, with such an immense patronage, may make great progress in corrupting the public mind and principles. This is a subject with which wisdom and patriotism should be occupied.
I pray you to accept assurances of my high respect and esteem.
Th: Jefferson.
TO WILLIAM B. GILES.
Washington, March 23, 1801.
Dear Sir,
I received two days ago your favor of the 16th, and thank you for your kind felicitations on my election: but whether it will be a subject of felicitation permanently, will be for chapters of future history to say. The important subjects of the government I meet with some degree of courage and confidence, because I do believe the talents to be associated with me, the honest line of conduct we will religiously pursue at home and abroad, and the confidence of my fellow-citizens dawning on us, will be equal to these objects.
But there is another branch of duty which I must meet with courage too, though I cannot without pain; that is, the appointments and disappointments as to offices. Madison and Gallatin being still absent, we have not yet decided on our rules of conduct as to these. That some ought to be removed from office, and that all ought not, all mankind will agree. But where to draw the line, perhaps no two will agree. Consequently, nothing like a general approbation on this subject can be looked for. Some principles have been the subject of conversation, but not of determination; e.g. all appointments to civil offices during pleasure, made after the event of the election was certainly known to Mr. Adams, are considered as nullities. I do not view the persons appointed as even candidates for the office, but make others without noticing or notifying them. Mr. Adams’s best friends have agreed this is right. 2. Officers who have been guilty of official mal-conduct are proper subjects of removal. 3. Good men, to whom there is no objection but a difference of political principle, practised on only as far as the right of a private citizen will justify, are not proper subjects of removal, except in the case of attorneys and marshals. The courts being so decidedly federal and irremovable, it is believed that republican attorneys and marshals, being the doors of entrance into the courts, are indispensably necessary as a shield to the republican part of our fellow-citizens, which, I believe, is the main body of the people.
These principles are yet to be considered of, and I sketch them to you in confidence. Not that there is objection to your mooting them as subjects of conversation, and as proceeding from yourself, but not as matters of executive determination. Nay, farther, I will thank you for your own sentiments and those of others on them. If received before the 20th of April, they will be in time for our deliberation on the subject. You know that it was in the year X. Y. Z. that so great a transition from us to the other side took place, and with as real republicans as we were ourselves; that these, after getting over that delusion, have been returning to us, and that it is to that return we owe a triumph in 1800, which in 1799 would have been the other way. The week’s suspension of the election before Congress, seems almost to have completed that business, and to have brought over nearly the whole remaining mass. They now find themselves with us, and separated from their quondam leaders. If we can but avoid shocking their feelings by unnecessary acts of severity against their late friends, they will in a little time cement and from one mass with us, and by these means harmony and union be restored to our country, which would be the greatest good we could effect. It was a conviction that these people did not differ from us in principle, which induced me to define the principles which I deemed orthodox, and to urge a re-union on these principles; and I am induced to hope it has conciliated many. I do not speak of the desperadoes of the quondam faction in and out of Congress. These I consider as incurables, on whom all attentions would be lost, and therefore will not be wasted. But my wish is, to keep their flock from returning to them.
On the subject of the marshal of Virginia, I refer you confidentially to Major Egglestone for information. I leave this about this day se’nnight, to make some arrangements at home preparatory to my final removal to this place, from which I shall be absent about three weeks.
Accept assurances of my constant esteem and high consideration and respect.
Th: Jefferson.
TO SAMUEL ADAMS.
Washington, March 29, 1801.
I addressed a letter to you, my very dear and ancient friend, on the 4th of March: not indeed to you by name, but through the medium of some of my fellow-citizens, whom occasion called on me to address. In meditating the matter of that address, I often asked myself, Is this exactly in the spirit of the patriarch, Samuel Adams? Is it as he would express it? Will he approve of it? I have felt a great deal for our country in the times we have seen. But individually for no one so much as yourself. When I have been told that you were avoided, insulted, frowned on, I could but ejaculate, ‘Father, forgive them, for they know not what they do.’ I confess I felt an indignation for you, which for myself I have been able, under every trial, to keep entirely passive. However, the storm is over, and we are in port. The ship was not rigged for the service she was put on. We will show the smoothness of her motions on her republican tack. I hope we shall once more see harmony restored among our citizens, and an entire oblivion of past feuds. Some of the leaders, who have most committed themselves, cannot come into this. But I hope the great body of our fellow-citizens will do it. I will sacrifice every thing but principle to procure it. A few examples of justice on officers who have perverted their functions to the oppression of their fellow-citizens, must, in justice to those citizens, be made. But opinion, and the just maintenance of it, shall never be a crime in my view; nor bring injury on the individual. Those whose misconduct in office ought to have produced their removal even by my predecessor, must not be protected by the delicacy due only to honest men. How much I lament that time has deprived me of your aid. It would have been a day of glory which should have called you to the first office of the administration. But give us your counsel, my friend, and give us your blessing: and be assured that there exists not in the heart of man a more faithful esteem than mine to you, and that I shall ever bear you the most affectionate veneration and respect.
Th: Jefferson*
TO ELBRIDGE GERRY.
Washington, March 29, 1801,
My Dear Sir,
Your two letters of January the 5th and February the 24th came safely to hand, and I thank you for the history of a transaction which will ever be interesting in our affairs. It has been very precisely as I had imagined. I thought, on your return, that if you had come forward boldly, and appealed to the public by a full statement, it would have had a great effect in your favor personally, and that of the republican cause then oppressed almost unto death. But I judged from a tact of the southern pulse. I suspect that of the north was different, and decided your conduct: and perhaps it has been as well. If the revolution of sentiment has been later, it has perhaps been not less sure. At length it has arrived. What with the natural current of opinion which has been setting over to us for eighteen months, and the immense impetus which was given it from the 11th to the 17th of February, we may now say that the United States, from New York southwardly, are as unanimous in the principles of ‘76, as they were in ‘76. The only difference is, that the leaders who remain behind are more numerous and colder than the apostles of toryism in ‘76. The reason is, that we are now justly more tolerant than we could safely have been then, circumstanced as we were. Your part of the Union, though as absolutely republican as ours, had drunk deeper of the delusion, and is therefore slower in recovering from it. The aegis of government, and the temples of religion and of justice, have all been prostituted there to toll us back to the times when we burnt witches. But your people will rise again. They will awake like Samson from his sleep, and carry away the gates and the posts of the city. You, my friend, are destined to rally them again under their former banners, and when called to the post, exercise it with firmness and with inflexible adherence to your own principles. The people will support you, notwithstanding the howlings of the ravenous crew from whose jaws they are escaping. It will be a great blessing to our country if we can once more restore harmony and social love among its citizens. I confess, as to myself, it is almost the first object of my heart, and one to which I would sacrifice every thing but principle. With the people I have hopes of effecting it. But their Coryphæi are incurables. I expect little from them.
I was not deluded by the eulogiums of the public papers in the first moments of change. If they could have continued to get all the loaves and fishes, that is, if I would have gone over to them, they would continue to eulogize. But I well knew that the moment that such removals should take place, as the justice of the preceding administration ought to have executed, their hue and cry would be set up, and they would take their old stand. I shall disregard that also. Mr. Adams’s last appointments, when he knew he was naming counsellors and aids for me and not for himself, I set aside as far as depends on me. Officers who have been guilty of gross abuses of office, such as marshals packing juries, &c, I shall now remove, as my predecessor ought in justice to have done. The instances will be few, and governed by strict rule, and not party passion. The right of opinion shall suffer no invasion from me. Those who have acted well, have nothing to fear, however they may have differed from me in opinion: those who have done ill, however, have nothing to hope; nor shall I fail to do justice lest it should be ascribed to that difference of opinion. A coalition of sentiments is not for the interest of the printers. They, like the clergy, live by the zeal they can kindle, and the schisms they can create. It is contest of opinion in politics as well as religion which makes us take great interest in them, and bestow our money liberally on those who furnish aliment to our appetite. The mild and simple principles of the Christian philosophy would produce too much calm, too much regularity of good, to extract from its disciples a support for a numerous priesthood, were they not to sophisticate it, ramify it, split it into hairs, and twist its texts till they cover the divine morality of its author with mysteries, and require a priesthood to explain them. The Quakers seem to have discovered this. They have no priests, therefore no schisms. They judge of the text by the dictates of common sense and common morality. So the printers can never leave us in a state of perfect rest and union of opinion. They would be no longer useful, and would have to go to the plough. In the first moments of quietude which have succeeded the election, they seem to have aroused their lying faculties beyond their ordinary state, to re-agitate the public mind. What appointments to office have they detailed which had never been thought of, merely to found a text for their calumniating commentaries. However, the steady character of our countrymen is a rock to which we may safely moor: and notwithstanding the efforts of the papers to disseminate early discontents, I expect that a just, dispassionate, and steady conduct will at length rally to a proper system the great body of our country. Unequivocal in principle, reasonable in manner, we shall be able, I hope, to do a great deal of good to the cause of freedom and harmony. I shall be happy to hear from you often, to know your own sentiments and those of others on the course of things, and to concur with you in efforts for the common good. Your letters through the post will now come safely. Present my best respects to Mrs. Gerry, and accept yourself assurances of my constant esteem and high consideration.
Th: Jefferson.
TO GIDEON GRANGER.
Washington, May 3, 1801.
Dear Sir,
I wrote you on the 29th of March. Yours of the 25th of that month, with the address it covered, had not reached this place on the 1st of April, when I set out on a short visit to my residence in Virginia, where some arrangements were necessary previous to my settlement here. In fact, your letter came to me at Monticello only the 24th of April, two days before my departure from thence. This, I hope, will sufficiently apologize for the delay of the answer, which those unapprized of these circumstances will have thought extraordinary.
A new subject of congratulation has arisen. I mean the regeneration of Rhode Island. I hope it is the beginning of that resurrection of the genuine spirit of New England which rises for life eternal. According to natural order, Vermont will emerge next, because least, after Rhode Island, under the yoke of hierocracy. I have never dreamed that all opposition was to cease. The clergy, who have missed their union with the State, the Anglomen, who have missed their union with England, and the political adventurers, who have lost the chance of swindling and plunder in the waste of public money, will never cease to bawl, on the breaking up of their sanctuary. But among the people, the schism is healed, and with tender treatment the wound will not re-open. Their quondam leaders have been astounded with the suddenness of the desertion: and their silence and appearance of acquiescence have proceeded not from a thought of joining us, but the uncertainty what ground to take. The very first acts of the administration, the nominations, have accordingly furnished something to yelp on; and all our subsequent acts will furnish them fresh matter, because there is nothing against which human ingenuity will not be able to find something to say.
Accept assurances of my sincere attachment and high respect.
Th: Jefferson.
TO NATHANIEL MACON.
Washington, May 14, 1801.
Dear Sir,
Your favors of April the 20th and 23rd had been received, and the commission made out for Mr. Potts, before I received the letter of the 1st instant. I have still thought it better to forward the commission, in the hope that reconsideration, or the influence of yourself and friends, might induce an acceptance of it. Should it be otherwise, you must recommend some other good person, as I had rather be guided by your opinion than that of the person you refer me to. Perhaps Mr. Potts may be willing to stop the gap till you meet and repeal the law. If he does not, let me receive a recommendation from you as quickly as possible. And in all cases, when an office becomes vacant in your State, as the distance would occasion a great delay, were you to wait to be regularly consulted, I shall be much obliged to you to recommend the best characters. There is nothing I am so anxious about as making the best possible appointments, and no case in which the best men are more liable to mislead us, by yielding to the solicitations of applicants. For this reason your own spontaneous recommendation would be desirable. Now to answer your particulars, seriatim.
Levees are done away.
The first communication to the nest Congress will be, like all subsequent ones, by message, to which no answer will be expected.
The diplomatic establishment in Europe will be reduced to three ministers.
The compensations to collectors depend on you, and not on me.
The army is undergoing a chaste reformation.
The navy will be reduced to the legal establishment by the last of this month.
Agencies in every department will be revised.
We shall push you to the uttermost in economizing.
A very early recommendation had been given to the Postmaster-General to employ no printer, foreigner, or revolutionary tory in any of his offices. This department is still untouched.
The arrival of Mr. Gallatin, yesterday, completed the organization of our administration.
Accept assurances of my sincere esteem and high respect.
Th: Jefferson.
TO LEVI LINCOLN.
Washington, July 11, 1801,
Dear Sir,
Your favor of the 15th came to hand on the 25th of June, and conveyed a great deal of that information which I am anxious to receive. The consolidation of our fellow-citizens in general is the great object we ought to keep in view; and that being once obtained, while we associate with us in affairs, to a certain degree, the federal sect of republicans, we must strip of all the means of influence the Essex junto, and their associate monocrats in every part of the Union. The former differ from us only in the shades of power to be given to the executive, being, with us, attached to republican government. The latter wish to sap the republic by fraud, if they cannot destroy it by force, and to erect an English monarchy in its place; some of them (as Mr. Adams) thinking its corrupt parts should be cleansed away, others (as Hamilton) thinking that would make it an impracticable machine. We are proceeding gradually in the regeneration of offices, and introducing republicans to some share in them. I do not know that it will be pushed further than was settled before you went away, except as to Essex men. I must ask you to make out a list of those in office in yours and the neighboring States, and to furnish me with it. There is little of this spirit south of the Hudson. I understand that Jackson is a very determined one, though in private life amiable and honorable. But amiable monarchists are not safe subjects of republican confidence. What will be the effect of his removal? How should it be timed? Who his successor? What place can General Lyman properly occupy? Our gradual reformations seem to produce good effects every where except in Connecticut. Their late session of legislature has been more intolerant than all others. We must meet them with equal intolerance. When they will give a share in the State offices, they shall be replaced in a share of the General offices. Till then we must follow their example. Mr. Goodrich’s removal has produced a bitter remonstrance, with much personality against the two Bishops. I am sincerely sorry to see the inflexibility of the federal spirit there, for I cannot believe they are all monarchists.
I observe your tory papers make much of the Berceau. As that is one of the subjects to be laid before Congress, it is material to commit to writing, while fresh in memory, the important circumstances. You possess more of these than any other person. I pray you, therefore, immediately to state to me all the circumstances you recollect. I will aid you with the following hints, which you can correct and incorporate. Pichon, I think, arrived about the 12th of March. I do not remember when he first proposed the question about the Insurgente and Berceau. On the 20th of March, Mr. Stoddart wrote to his agent at Boston to put the Berceau into handsome order to be restored, but whether he did that of his own accord, or after previous consultation with you or myself, I do not recollect. I set out for Monticello April the 1st. About that time General Smith sent new directions to put her precisely into the state in which she was before the capture. Do you recollect from what fund it was contemplated to do this? I had trusted for this to Stoddart who was familiar with all the funds, being myself entirely new in office at that time. What will those repairs have cost? Did we not leave to Le Tombe to make what allowance he thought proper to the officers, we only advancing money on his undertaking repayment? I shall hope to receive from you as full a statement as you can make. It may be useful to inquire into the time and circumstances of her being dismantled. When you shall have retraced the whole matter in your memory, would it not be well to make a summary statement of the important circumstances for insertion in the Chronicle in order to set the minds of the candid part of the public to rights? Mr. Madison has had a slight bilious attack. I am advising him to get off by the middle of this month. We who have stronger constitutions shall stay to the end of it. But during August and September, we also must take refuge in climates rendered safer by our habits and confidence. The post will be so arranged as that letters will go hence to Monticello, and the answer return here in a week. I hope I shall continue to hear from you there.
Accept assurances of my affectionate esteem and high respect.
Th: Jefferson.
P. S. The French convention was laid before the Senate December the 16th. I think the Berceau arrived afterwards. If so, she was dismantled when it was known she was to be restored. When did she arrive? By whose orders was she dismantled? T.J.
TO GOVERNOR MONROE.
Washington, July 11, 1801.
Dear Sir,
As to the mode of correspondence between the general and particular executives, I do not think myself a good judge. Not because my position gives me any prejudice on the occasion; for if it be possible to be certainly conscious of any thing, I am conscious of feeling no difference between writing to the highest and lowest being on earth; but because I have ever thought that forms should yield to whatever should facilitate business. Comparing the two governments together, it is observable that in all those cases where the independent or reserved rights of the States are in question, the two executives, if they are to act together, must be exactly co-ordinate; they are, in these cases, each the supreme head of an independent government. In other cases, to wit, those transferred by the constitution to the General Government, the general executive is certainly pre-ordinate; e.g. in a question respecting the militia, and others easily to be recollected. Were there, therefore, to be a stiff adherence to etiquette, I should say that in the former cases the correspondence should be between the two heads, and that in the latter, the Governor must be subject to receive orders from the war department as any other subordinate officer would. And were it observed that either party set up unjustifiable pretensions, perhaps the other might be right in opposing them by a tenaciousness of his own rigorous rights. But I think the practice in General Washington’s administration was most friendly to business, and was absolutely equal; sometimes he wrote to the Governors, and sometimes the heads of departments wrote. If a letter is to be on a general subject, I see no reason why the President should not write; but if it is to go into details, these being known only to the head of the department, it is better he should write directly. Otherwise, the correspondence must involve circuities. If this be practised promiscuously in both classes of cases, each party setting examples of neglecting etiquette, both will stand on equal ground, and convenience alone will dictate through whom any particular communication is to be made. On the whole, I think a free correspondence best, and shall never hesitate to write myself to the Governors, in every federal case, where the occasion presents itself to me particularly. Accept assurances of my sincere and constant affection and respect.
Th: Jefferson,
To Elias Shipman and Others, a Committee of the Merchants of New Haven.
Washington, July 12, 1801.
Gentlemen,
I have received the remonstrance you were pleased to address to me, on the appointment of Samuel Bishop to the office of Collector of New Haven, lately vacated by the death of David Austin. The right of our fellow-citizens to represent to the public functionaries their opinion on proceedings interesting to them, is unquestionably a constitutional right, often useful, sometimes necessary, and will always be respectfully acknowledged by me.
Of the various executive duties, no one excites more anxious concern than that of placing the interests of our fellow-citizens in the hands of honest men, with understandings sufficient for their stations. No duty, at the same time, is more difficult to fulfil. The knowledge of characters possessed by a single individual is, of necessity, limited. To seek out the best through the whole Union, we must resort to other information, which from the best of men, acting disinterestedly and with the purest motives, is sometimes incorrect. In the case of Samuel Bishop, however, the subject of your remonstrance, time was taken, information was sought, and such obtained as could leave no room for doubt of his fitness. From private sources it was learned that his understanding was sound, his integrity pure, his character unstained. And the offices, confided to him within his own State, are public evidences of the estimation in which he is held by the State in general, and the city and township particularly in which he lives. He is said to be the town clerk, a justice of the peace, mayor of the city of New Haven, an office held at the will of the legislature, chief judge of the court of common pleas for New Haven county, a court of high criminal and civil jurisdiction, wherein most causes are decided without the right of appeal or review, and sole judge of the court of probate, wherein he singly decides all questions of wills, settlement of estates, testate and intestate, appoints guardians, settles their accounts, and in fact has under his jurisdiction and care all the property, real and personal, of persons dying. The two last offices, in the annual gift of the legislature, were given to him in May last. Is it possible that the man to whom the legislature of Connecticut has so recently committed trusts of such difficulty and magnitude, is ‘unfit to be the collector of the district of New Haven,’ though acknowledged in the same writing, to have obtained all this confidence ‘by a long life of usefulness?’ It is objected, indeed, in the remonstrance, that he is seventy-seven years of age; but at a much more advanced age, our Franklin was the ornament of human nature. He may not be able to perform in person, all the details of his office; but if he gives us the benefit of his understanding, his integrity, his watchfulness, and takes care that all the details are well performed by himself or his necessary assistants, all public purposes will be answered. The remonstrance, indeed, does not allege that the office has been illy conducted, but only apprehends that it will be so. Should this happen in event, be assured I will do in it what shall be just and necessary for the public service. In the mean time, he should be tried without being prejudged.
The removal, as it is called, of Mr. Goodrich, forms another subject of complaint. Declarations by myself in favor of political tolerance, exhortations to harmony and affection in social intercourse, and to respect for the equal rights of the minority, have, on certain occasions, been quoted and misconstrued into assurances that the tenure of offices was to be undisturbed. But could candor apply such a construction? It is not indeed in the remonstrance that we find it; but it leads to the explanations which that calls for. When it is considered, that during the late administration, those who were not of a particular sect of politics were excluded from all office; when, by a steady pursuit of this measure, nearly the whole offices of the United States were monopolized by that sect; when the public sentiment at length declared itself, and burst open the doors of honor and confidence to those whose opinions they more approved; was it to be imagined that this monopoly of office was still to be continued in the hands of the minority? Does it violate their equal rights, to assert some rights in the majority also? Is it political intolerance to claim a proportionate share in the direction of the public affairs? Can they not harmonize in society unless they have every thing in their own hands? If the will of the nation, manifested by their various elections, calls for an administration of government according with the opinions of those elected; if, for the fulfilment of that will, displacements are necessary, with whom can they so justly begin as with persons appointed in the last moments of an administration, not for its own aid, but to begin a career at the same time with their successors, by whom they had never been approved, and who could scarcely expect from them a cordial co-operation? Mr Goodrich was one of these. Was it proper for him to place himself in office, without knowing whether those whose agent he was to be, would have confidence in his agency? Can the preference of another as the successor to Mr. Austin, be candidly called a removal of Mr. Goodrich? If a due participation of office is a matter of right, how are vacancies to be obtained? Those by death are few; by resignation none. Can any other mode than that of removal be proposed? This is a painful office. But it is made my duty, and I meet it as such. I proceed in the operation with deliberation and inquiry, that it may injure the best men least, and effect the purposes of justice and public utility with the least private distress; that it may be thrown, as much as possible, on delinquency, on oppression, on intolerance, on anti-revolutionary adherence to our enemies.
The remonstrance laments ‘that a change in the administration must produce a change in the subordinate officers;’ in other words, that it should be deemed necessary for all officers to think with their principal? But on whom does this imputation bear? On those who have excluded from office every shade of opinion which was not theirs? Or on those who have been so excluded? I lament sincerely that unessential differences of opinion should ever have been deemed sufficient to interdict half the society from, the rights and the blessings of self-government, to proscribe them as unworthy of every trust. It would have been to me a circumstance of great relief, had I found a moderate participation of office in the hands of the majority. I would gladly have left to time and accident to raise them to their just share. But their total exclusion calls for prompter corrections. I shall correct the procedure: but that done, return with joy to that state of things, when the only questions concerning a candidate shall be, Is he honest? Is he capable? Is he faithful to the constitution?
I tender you the homage of my high respect.
Th: Jefferson.
TO LEVI LINCOLN.
Monticello, August 26, 1801.
Dear Sir,
Your favor of July the 28th was received here on the 20th instant. The superscription of my letter of July the 11th, by another hand, was to prevent danger to it from the curious. Your statement respecting the Berceau coincided with my own recollection, in the circumstances recollected by me, and I concur with you in supposing it may not now be necessary to give any explanations on the subject in the papers. The purchase was made by our predecessors, and the repairs begun by them. Had she been to continue ours, we were authorized to put and keep her in good order out of the fund of the naval contingencies, and when in good order, we obeyed a law of the land, the treaty, in giving her up. It is true the treaty was not ratified; but when ratified it is validated retrospectively. We took on ourselves this risk, but France had put more into our hands on the same risk. I do not know whether the clamor, as to the allowance to the French officers of their regular pay, has been rectified by a statement that it was on the request of the French Consul, and his promise to repay it. So that they cost the United States, on this arrangement, nothing.
I am glad to learn from you that the answer to New Haven had a good effect in Massachusetts on the republicans, and no ill effects on the sincere federalists. I had foreseen, years ago, that the first republican President who should come into office after all the places in the government had become exclusively occupied by federalists, would have a dreadful operation to perform. That the republicans would consent to a continuation of every thing in federal hands, was not to be expected, because neither just nor politic. On him then was to devolve the office of an executioner, that of lopping off. I cannot say that it has worked harder than I expected. You know the moderation of our views in this business, and that we all concurred in them. We determined to proceed with deliberation. This produced impatience in the republicans, and a belief we meant to do nothing. Some occasion of public explanation was eagerly desired, when the New Haven remonstrance offered us that occasion. The answer was meant as an explanation to our friends. It has had on them, everywhere, the most wholesome effect. Appearances of schismatizing from us have been entirely done away. I own I expected it would check the current, with which the republican federalists were returning to their brethren, the republicans. I extremely lamented this effect. For the moment which should convince me that a healing of the nation into one, is impracticable, would be the last moment of my wishing to remain where I am. (Of the monarchical federalists, I have no expectations. They are incurables, to be taken care of in a mad-house if necessary, and on motives of charity.) I am much pleased, therefore, with your information that the republican federalists are still coming in to the desired union. The eastern newspapers had given me a different impression, because I supposed the printers knew the taste of their customers, and cooked their dishes to their palates. The Palladium is understood to be the clerical paper, and from the clergy I expect no mercy. They crucified their Savior who preached that their kingdom was not of this world, and all who practise on that precept must expect the extreme of their wrath. The laws of the present day withhold their hands from blood. But lies and slander still remain to them.
I am satisfied that the heaping of abuse on me personally, has been with the design and the hope of provoking me to make a general sweep of all federalists out of office. But as I have carried no passion into the execution of this disagreeable duty, I shall suffer none to be excited. The clamor which has been raised will not provoke me to remove one more, nor deter me from removing one less, than if not a word had been said on the subject. In Massachusetts you may be assured, great moderation will be used. Indeed, Connecticut, New York, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, and Delaware are the only States where any thing considerable is desired. In the course of the summer all which is necessary will be done; and we may hope that this cause of offence being at an end, the measures we shall pursue and propose for the amelioration of the public affairs, will be so confessedly salutary as to unite all men not monarchists in principle.
We have considerable hopes of republican Senators from South Carolina, Maryland, and Delaware, and some as to Vermont. In any event we are secure of a majority in the Senate; and consequently that there will be a concert of action between the legislature and executive. The removal of excrescences from the judiciary, is the universal demand. We propose to re-assemble at Washington on the last day of September. Accept assurances of my affectionate esteem and high respect.
Th: Jefferson.
TO ROBERT R. LIVINGSTON.
Monticello, September 9, 1801.
Dear Sir,
You will receive, probably by this post, from the Secretary of State, his final instructions for your mission to France. We have not thought it necessary to say any thing in them on the great question of the maritime law of nations, which at present agitates Europe, that is to say, whether free ships shall make free goods; because we do not mean to take any side in it during the war. But as I had before communicated to you some loose thoughts on that subject, and have since considered it with somewhat more attention, I have thought it might be useful that you should possess my ideas in a more matured form than that in which they were before given. Unforeseen circumstances may perhaps oblige you to hazard an opinion on some occasion or other, on this subject, and it is better that it should not be at variance with Ours. I write this too, myself, that it may not be considered as official, but merely my individual opinion, unadvised by those official counsellors whose opinions I deem my safest guide, and should unquestionably take in form were circumstances to call for a solemn decision of the question.
When Europe assumed the general form in which it is occupied by the nations now composing it, and turned its attention to maritime commerce, we find among its earliest practices, that of taking the goods of an enemy from the ship of a friend; and that into this practice every maritime State went sooner or later, as it appeared on the theatre of the ocean. If, therefore, we are to consider the practice of nations as the sole and sufficient evidence of the law of nature among nations, we should unquestionably place this principle among those of the natural laws. But its inconveniences, as they affected neutral nations peaceably pursuing their commerce, and its tendency to embroil them with the powers happening to be at war, and thus to extend the flames of war, induced nations to introduce by special compacts, from time to time, a more convenient rule; that ‘free ships should make free goods’: and this latter principle has by every maritime nation of Europe been established, to a greater or less degree, in its treaties with other nations; insomuch, that all of them have, more or less frequently, assented to it, as a rule of action in particular cases. Indeed, it is now urged, and I think with great appearance of reason, that this is the genuine principle dictated by national morality; and that the first practice arose from accident, and the particular convenience of the States [* Venice and Genoa] which first figured on the water, rather than from well digested reflections on the relations of friend and enemy, on the rights of territorial jurisdiction, and on the dictates of moral law applied to these. Thus it had never been supposed lawful, in the territory of a friend to seize the goods of an enemy. On an element which nature has not subjected to the jurisdiction of any particular nation, but has made common to all for the purposes to which it is fitted, it would seem that the particular portion of it which happens to be occupied by the vessel of any nation, in the course of its voyage, is, for the moment, the exclusive property of that nation, and, with the vessel, is exempt from intrusion by any other, and from its jurisdiction, as much as if it were lying in the harbor of its sovereign. In no country, we believe, is the rule otherwise, as to the subjects of property common to all. Thus the place occupied by an individual in a highway, a church, a theatre, or other public assembly, cannot be intruded on, while its occupant holds it for the purposes of its institution. The persons on board a vessel traversing the ocean, carrying with them the laws of their nation, have among themselves a jurisdiction, a police, not established by their individual will, but by the authority of their nation, of whose territory their vessel still seems to compose a part, so long as it does not enter the exclusive territory of another. No nation ever pretended a right to govern by their laws the ships of another nation navigating the ocean. By what law then can it enter that ship while in peaceable and orderly use of the common element? We recognise no natural precept for submission to such a right; and perceive no distinction between the movable and immovable jurisdiction of a friend, which would authorize the entering the one and not the other, to seize the property of an enemy.
It may be objected that this proves too much, as it proves you cannot enter the ship of a friend to search for contraband of war. But this is not proving too much. We believe the practice of seizing what is called contraband of war, is an abusive practice, not founded in natural right. War between two nations cannot diminish the rights of the rest of the world remaining at peace. The doctrine that the rights of nations remaining quietly in the exercise of moral and social duties, are to give way to the convenience of those who prefer plundering and murdering one another, is a monstrous doctrine; and ought to yield to the more rational law, that ‘the wrong which two nations endeavor to inflict on each other, must not infringe on the rights or conveniences of those remaining at peace.’ And what is contraband, by the law of nature? Either every thing which may aid or comfort an enemy, or nothing. Either all commerce which would accommodate him is unlawful, or none is. The difference between articles of one or another description, is a difference in degree only. No line between them can be drawn. Either all intercourse must cease between neutrals and belligerents, or all be permitted. Can the world hesitate to say which shall be the rule? Shall two nations turning tigers, break up in one instant the peaceable relations of the whole world? Reason and nature clearly pronounce that the neutral is to go on in the enjoyment of all its rights, that its commerce remains free, not subject to the jurisdiction of another, nor consequently its vessels to search, or to inquiries whether their contents are the property of an enemy, or are of those which have been called contraband of war.
Nor does this doctrine contravene the right of preventing vessels from entering a blockaded port. This right stands on other ground. When the fleet of any nation actually beleaguers the port of its enemy, no other has a right to enter their line, any more than their line of battle in the open sea, or their lines of circumvallation, or of encampment, or of battle-array on land. The space included within their lines in any of those cases, is either the property of their enemy, or it is common property assumed and possessed for the moment, which cannot be intruded on, even by a neutral, without committing the very trespass we are now considering, that of intruding into the lawful possession of a friend.
Although I consider the observance of these principles as of great importance to the interests of peaceable nations, among whom I hope the United States will ever place themselves, yet in the present state of things they are not worth a war. Nor do I believe war the most certain means of enforcing them. Those peaceable coercions which are in the power of every nation, if undertaken in concert and in time of peace, are more likely to produce the desired effect.
The opinions I have here given, are those which have generally been sanctioned by our government. In our treaties with France, the United Netherlands, Sweden, and Prussia, the principle of free bottom, free goods, was uniformly maintained. In the instructions of 1784, given by Congress to their Ministers appointed to treat with the nations of Europe generally, the same principle, and the doing away contraband of war, were enjoined, and were acceded to in the treaty signed with Portugal. In the late treaty with England, indeed, that power perseveringly refused the principle of free bottoms, free goods; and it was avoided in the late treaty with Prussia, at the instance of our then administration, lest it should seem to take side in a question then threatening decision by the sword. At the commencement of the war between France and England, the representative of the French republic then residing in the United States, complaining that the British armed ships captured French property in American bottoms, insisted that the principle of ‘free bottoms, free goods,’ was of the acknowledged law of nations; that the violation of that principle by the British was a wrong committed on us, and such an one as we ought to repel by joining in the war against that country. We denied his position, and appealed to the universal practice of Europe, in proof that the principle of ‘free bottoms, free goods,’ was not acknowledged as of the natural law of nations, but only of its conventional law. And I believe we may safely affirm, that not a single instance can be produced where any nation of Europe, acting professedly under the law of nations alone, unrestrained by treaty, has, either by its executive or judiciary organs, decided on the principle of ‘free bottoms, free goods.’ Judging of the law of nations by what has been practised among nations, we were authorized to say that the contrary principle was their rule, and this but an exception to it, introduced by special treaties in special cases only; that having no treaty with England substituting this instead of the ordinary rule, we had neither the right nor the disposition to go to war for its establishment. But though we would not then, nor will we now, engage in war to establish this principle, we are nevertheless sincerely friendly to it. We think that the nations of Europe have originally set out in error; that experience has proved the error oppressive to the rights and interests of the peaceable part of mankind; that every nation but one has acknowledged this, by consenting to the change, and that one has consented in particular cases; that nations have a right to correct an erroneous principle, and to establish that which is right as their rule of action; and if they should adopt measures for effecting this in a peaceable way, we shall wish them success, and not stand in their way to it. But should it become, at any time, expedient for us to co-operate in the establishment of this principle, the opinion of the executive, on the advice of its constitutional counsellors, must then be given; and that of the legislature, an independent and essential organ in the operation, must also be expressed; in forming which, they will be governed, every man by his own judgment, and may, very possibly, judge differently from the executive. With the same honest views, the most honest men often form different conclusions. As far, however, as we can judge, the principle of ‘free bottoms, free goods,’ is that which would carry the wishes of our nation.
Wishing you smooth seas and prosperous gales, with the enjoyment of good health, I tender you the assurances of my constant friendship and high consideration and respect.
Th: Jefferson
TO WILLIAM SHORT.
Washington, October 3, 1801.
Dear Sir,
I trusted to Mr. Dawson to give you a full explanation, verbally, on a subject which I find he has but slightly mentioned to you. I shall therefore now do it. When I returned from France, after an absence of six or seven years, I was astonished at the change which I found had taken place in the United States in that time. No more like the same people; their notions, their habits and manners, the course of their commerce, so totally changed, that I, who stood in those of 1784, found myself not at all qualified to speak their sentiments, or forward their views in 1790. Very soon, therefore, after entering on the office of Secretary of State, I recommended to General Washington to establish as a rule of practice, that no person should be continued on foreign mission beyond an absence of six, seven, or eight years. He approved it. On the only subsequent Missions which took place in my time, the persons appointed were notified that they could not be continued beyond that period. All returned within it except Humphreys. His term was not quite out when General Washington went out of office. The succeeding administration had no rule for any thing: so he continued. Immediately on my coming to the administration, I wrote to him myself, reminded him of the rule I had communicated to him on his departure; that he had then been absent about eleven years, and consequently must return. On this ground solely he was superseded. Under these circumstances, your appointment was impossible after an absence of seventeen years. Under any others, I should never fail to give to yourself and the world proofs of my friendship for you, and of my confidence in you. Whenever you shall return, you will be sensible in a greater, of what I was in a smaller degree, of the change in this nation from what it was when we both left it in 1784. We return like foreigners, and, like them, require a considerable residence here to become Americanized.
The state of political opinion continues to return steadily towards republicanism. To judge from the opposition papers, a stranger would suppose that a considerable check to it had been produced by certain removals of public officers. But this is not the case. All offices were in the hands of the federalists. The injustice of having totally excluded republicans was acknowledged by every man. To have removed one half, and to have placed republicans in their stead, would have been rigorously just, when it was known that these composed a very great majority of the nation. Yet such was their moderation in most of the States that they did not desire it. In these, therefore, no removals took place but for malversation. In the middle States the contention had been higher, spirits were more sharpened and less accommodating. It was necessary in these to practise a different treatment, and to make a few changes to tranquillize the injured party. A few have been made there, a very few still remain to be made. When this painful operation shall be over, I see nothing else ahead of us which can give uneasiness to any of our citizens, or retard that consolidation of sentiment so essential to our happiness and our strength. The tory papers will still find fault with every thing. But these papers are sinking daily, from their dissonance with the sentiments of their subscribers, and very few will shortly remain to keep up a solitary and ineffectual barking.
There is no point in which an American, long absent from his country, wanders so widely from its sentiments as on the subject of its foreign affairs. We have a perfect horror at every thing like connecting ourselves with the politics of Europe. It would indeed be advantageous to us to have neutral rights established on a broad ground; but no dependence can be placed in any European coalition for that. They have so many other by-interests of greater weight, that some one or other will always be bought off. To be entangled with them would be a much greater evil than a temporary acquiescence in the false principles which have prevailed. Peace is our most important interest, and a recovery from debt. We feel ourselves strong, and daily growing stronger. The census just now concluded, shows we have added to our population a third of what it was ten years ago. This will be a duplication in twenty three or twenty-four years. If we can delay but for a few years the necessity of vindicating the laws of nature on the ocean, we shall be the more sure of doing it with effect. The day is within my time as well as yours, when we may say by what laws other nations shall treat us on the sea. And we will say it. In the meantime, we wish to let every treaty we have drop off without renewal. We call in our diplomatic missions, barely keeping up those to the most important nations. There is a strong disposition in our countrymen to discontinue even these; and very possibly it may be done. Consuls will be continued as usual. The interest which European nations feel, as well as ourselves, in the mutual patronage of commercial intercourse, is a sufficient stimulus on both sides to insure that patronage. A treaty, contrary to that interest, renders war necessary to get rid of it.
I send this by Chancellor Livingston, named to the Senate the day after I came into office, as our Minister Plenipotentiary to France. I have taken care to impress him with the value of your society. You will find him an able and honorable man; unfortunately, so deaf that he will have to transact all his business by writing. You will have known long ago, that Mr. Skipwith is reinstated in his consulship, as well as some others who had been set aside. I recollect no domestic news interesting to you. Your letters to your brother have been regularly transmitted, and I lately forwarded one from him, to be carried you by Mr. Livingston.
Present my best respects to our amiable and mutual friend, and accept yourself assurances of my sincere and constant affection.
Th: Jefferson.
Circular to the Heads of the Departments, and private.
Washington, November 6, 1801.
Dear Sir,
Coming all of us into executive office, new, and unfamiliar with the course of business previously practised, it was not to be expected, we should, in the first outset, adopt in every part a line of proceeding so perfect as to admit no amendment. The mode and degrees of communication, particularly between the President and heads of departments, have not been practised exactly on the same scale in all of them. Yet it would certainly be more safe and satisfactory for ourselves as well as the public, that not only the best, but also an uniform course of proceeding as to manner and degree, should be observed. Having been a member of the first administration under General Washington, I can state with exactness what our course then was. Letters of business came addressed sometimes to the President, but most frequently to the heads of departments. If addressed to himself, he referred them to the proper department to be acted on: if to one of the secretaries, the letter, if it required no answer, was communicated to the President, simply for his information. If an answer was requisite, the secretary of the department communicated the letter and his proposed answer to the President. Generally they were simply sent back after perusal; which signified his approbation. Sometimes he returned them with an informal note, suggesting an alteration or a query. If a doubt of any importance arose, he reserved it for conference. By this means, he was always in accurate possession of all facts and proceedings in every part of the Union, and to whatsoever department they related; he formed a central point for the different branches; preserved an unity of object and action among them; exercised that participation in the gestion of affairs which his office made incumbent on him; and met himself the due responsibility for whatever was done. During Mr. Adams’s administration, his long and habitual absences from the seat of government, rendered this kind of communication impracticable, removed him from any share in the transaction of affairs, and parcelled out the government, in fact, among four independent heads, drawing sometimes in opposite directions. That the former is preferable to the latter course, cannot be doubted. It gave, indeed, to the heads of departments the trouble of making up, once a day, a packet of all their communications for the perusal of the President; it commonly also retarded one day their despatches by mail. But in pressing cases, this injury was prevented by presenting that case singly for immediate attention; and it produced us in return the benefit of his sanction for every act we did. Whether any change of circumstances may render a change in this procedure necessary, a little experience will show us. But I cannot withhold recommending to the heads of departments, that we should adopt this course for the present, leaving any necessary modifications of it to time and trial. I am sure my conduct must have proved, better than a thousand declarations would, that my confidence in those whom I am so happy as to have associated with me, is unlimited, unqualified, and unabated. I am well satisfied that every thing goes on with a wisdom and rectitude which I could not improve. If I had the universe to choose from, I could not change one of my associates to my better satisfaction. My sole motives are those before expressed, as governing the first administration in chalking out the rules of their proceeding; adding to them only a sense of obligation imposed on me by the public will, to meet personally the duties to which they have appointed me. If this mode of proceeding shall meet the approbation of the heads of departments, it may go into execution without giving them the trouble of an answer: if any other can be suggested which would answer our views and add less to their labors, that will be a sufficient reason for my preferring it to my own proposition, to the substance of which only, and not the form, I attach any importance.
Accept for yourself particularly, my Dear Sir, assurances of my constant and sincere affection and respect.
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN DICKINSON.
Washington, December 19, 1801.
Dear Sir,
The approbation of my ancient friends is above all things the most grateful to my heart. They know for what objects we relinquished the delights of domestic society, tranquillity, and science, and committed ourselves to the ocean of revolution, to wear out the only life God has given us here, in scenes, the benefits of which will accrue only to those who follow us. Surely we had in view to obtain the theory and practice of good government; and how any, who seemed so ardent in this pursuit, could as shamelessly have apostatized, and supposed we meant only to put our government into other hands, but not other forms, is indeed wonderful. The lesson we have had will probably be useful to the people at large, by showing to them how capable they are of being made the instruments of their own bondage. A little more prudence and moderation in those who had mounted themselves on their fears, and it would have been long and difficult to unhorse them. Their madness had done in three years what reason alone acting against them would not have effected in many; and the more, as they might have gone on forming new entrenchments for themselves from year to year. My great anxiety at present is, to avail ourselves of our ascendency to establish good principles, and good practices: to fortify republicanism behind as many barriers as possible, that the outworks may give time to rally and save the citadel, should that be again in danger. On their part, they have retired into the judiciary as a strong hold. There the remains of federalism are to be preserved and fed from the treasury, and from that battery all the works of republicanism are to be beaten down and erased. By a fraudulent use of the constitution, which has made judges irremovable, they have multiplied useless judges merely to strengthen their phalanx.
You will perhaps have been alarmed, as some have been, at the proposition to abolish the whole of the internal taxes. But it is perfectly safe. They are under a million of dollars, and we can economize the government two or three millions a year. The impost alone gives us ten or eleven millions annually, increasing at a compound ratio of six and two thirds per cent, per annum, and consequently doubling in ten years. But leaving that increase for contingencies, the present amount will support the government, pay the interest of the public debt, and discharge the principal in fifteen years. If the increase proceeds, and no contingencies demand it, it will pay off the principal in a shorter time. Exactly one half of the public debt, to wit, thirty-seven millions of dollars, is owned in the United States. That capital then will be set afloat, to be employed in rescuing our commerce from the hands of foreigners, or in agriculture, canals, bridges, or other useful enterprises. By suppressing at once the whole internal taxes, we abolish three fourths of the offices now existing, and spread over the land. Seeing the interest you take in the public affairs, I have indulged myself in observations flowing from a sincere and ardent desire of seeing our affairs put into an honest and advantageous train. Accept assurances of my constant and affectionate esteem and high respect.
Th: Jefferson.
TO ALBERT GALLATIN.
Washington, April 1,1802.
Dear Sir,
I have read and considered your report on the operations of the sinking fund, and entirely approve of it, as the best plan on which we can set out. I think it an object of great importance, to be kept in view and to be undertaken at a fit season, to simplify our system of finance, and bring it within the comprehension of every member of Congress. Hamilton set out on a different plan. In order that he might have the entire government of his machine, he determined so to complicate it as that neither the President nor Congress should be able to understand it, or to control him. He succeeded in doing this, not only beyond their reach, but so that he at length could not unravel it himself. He gave to the debt, in the first instance, in funding it, the most artificial and mysterious form he could devise. He then moulded up his appropriations of a number of scraps and remnants, many of which were nothing at all, and applied them to different objects in reversion and remainder, until the whole system was involved in impenetrable fog; and while he was giving himself the airs of providing for the payment of the debt, he left himself free to add to it continually, as he did in fact, instead of paying it. I like your idea of kneading all his little scraps and fragments into one batch, and adding to it a complementary sum, which, while it forms it into a single mass from which every thing is to be paid, will enable us, should a breach of appropriation ever be charged on us, to prove that the sum appropriated, and more, has been applied to its specific object.
But there is a point beyond this, on which I should wish to keep my eye, and to which I should aim to approach by every tack which previous arrangements force on us. That is, to form into one consolidated mass all the monies received into the treasury, and to marshal the several expenditures, giving them a preference of payment according to the order in which they should be arranged. As for example. 1. The interest of the public debt. 2. Such portions of principal as are exigible. 3. The expenses of government. 4. Such other portions of principal as, though not exigible, we are still free to pay when we please. The last object might be made to take up the residuum of money remaining in the treasury at the end of every year, after the three first objects were complied with, and would be the barometer whereby to test the economy of the administration. It would furnish a simple measure by which every one could mete their merit, and by which every one could decide when taxes were deficient or superabundant. If to this can be added a simplification of the form of accounts in the treasury department, and in the organization of its officers, so as to bring every thing to a single centre, we might hope to see the finances of the Union as clear and intelligible as a merchant’s books, so that every member of Congress, and every man of any mind in the Union, should be able to comprehend them, to investigate abuses, and consequently to control them. Our predecessors have endeavored by intricacies of system, and shuffling the investigator over from one officer to another, to cover every thing from detection, I hope we shall go in the contrary direction, and that, by our honest and judicious reformations, we may be able, within the limits of our time, to bring things back to that simple and intelligible system, on which they should have been organized at first.
I have suggested only a single alteration in the report, which is merely verbal and of no consequence. We shall now get rid of the commissioner of the internal revenue, and superintendant of stamps. It remains to amalgamate the comptroller and auditor into one, and reduce the register to a clerk of accounts; and then the organization will consist, as it should at first, of a keeper of money, a keeper of accounts, and the head of the department. This constellation of great men in the treasury department was of a piece with the rest of Hamilton’s plans. He took his own stand as a Lieutenant General, surrounded by his Major Generals, and stationing his Brigadiers and Colonels under the name of Supervisors, Inspectors, &tc. in the different States. Let us deserve well of our country by making her interests the end of all our plans, and not our own pomp, patronage, and irresponsibility. I have hazarded these hasty and crude ideas, which occurred on contemplating your report. They may be the subject of future conversation and correction. Accept my affectionate salutations.
Th: Jefferson.
TO GENERAL KOSCIUSKO.
Washington, April 2,1802.
Dear General,
It is but lately that I have received your letter of the 25th Frimaire (December 15th), wishing to know whether some officers of your country could expect to be employed in this country. To prevent a suspense injurious to them, I hasten to inform you, that we are now actually engaged in reducing our military establishment one third, and discharging one third of our officers. We keep in service no more than men enough to garrison the small posts dispersed at great distances on our frontiers, which garrisons will generally consist of a captain’s company only, and in no case of more than two or three, in not one, of a sufficient number to require a field-officer; and no circumstance whatever can bring these garrisons together, because it would be an abandonment of their forts. Thus circumstanced, you will perceive the entire impossibility of providing for the persons you recommend. I wish it had been in my power to give you a more favorable answer; but next to the fulfilling your wishes, the most grateful thing I can do is to give a faithful answer. The session of the first Congress convened since republicanism has recovered its ascendency, is now drawing to a close. They will pretty completely fulfil all the desires of the people. They have reduced the army and navy to what is barely necessary. They are disarming executive patronage and preponderance, by putting down one half the offices of the United States, which are no longer necessary. These economies have enabled them to suppress all the internal taxes, and still to make such provision for the payment of their public debt as to discharge that in eighteen years. They have lopped off a parasite limb, planted by their predecessors on their judiciary body for party purposes; they are opening the doors of hospitality to the fugitives from the oppressions of other countries; and we have suppressed all those public forms and ceremonies which tended to familiarize the public eye to the harbingers of another form of government. The people are nearly all united; their quondam leaders, infuriated with the sense of their impotence, will soon be seen or heard only in the newspapers, which serve as chimneys to carry off noxious vapors and smoke, and all is now tranquil, firm, and well, as it should be. I add no signature because unnecessary for you. God bless you, and preserve you still for a season of usefulness to your country.
TO ROBERT R. LIVINGSTON.
Washington, April 18, 1802.
Dear Sir,
A favorable and confidential opportunity offering by M. Dupont de Nemours, who is re-visiting his native country, gives me an opportunity of sending you a cipher to be used between us, which will give you some trouble to understand, but once understood, is the easiest to use, the most indecipherable, and varied by a new key with the greatest facility, of any I have ever known. I am in hopes the explanation enclosed will be sufficient.
But writing by Mr. Dupont, I need use no cipher. I require from him to put this into your own and no other hand, let the delay occasioned by that be what it will.
The cession of Louisiana and the Floridas by Spain to France, works most sorely on the United States. On this subject the Secretary of State has written to you fully, yet I cannot forbear recurring to it personally, so deep is the impression it makes on my mind. It completely reverses all the political relations of the United States, and will form a new epoch in our political course. Of all nations of any consideration, France is the one, which, hitherto, has offered the fewest points on which we could have any conflict of right, and the most points of a communion of interests. From these causes we have ever looked to her as our natural friend, as one with which we never could have an occasion of difference. Her growth, therefore, we viewed as our own, her misfortunes ours. There is on the globe one single spot, the possessor of which is our natural and habitual enemy. It is New Orleans, through which the produce of three eighths of our territory must pass to market, and from its fertility it will ere long yield more than half of our whole produce, and contain more than half of our inhabitants. France, placing herself in that door, assumes to us the attitude of defiance. Spain might have retained it quietly for years. Her pacific dispositions, her feeble state, would induce her to increase our facilities there, so that her possession of the place would be hardly felt by us, and it would not, perhaps, be very long before some circumstances might arise, which might make the cession of it to us the price of something of more worth to her. Not so can it ever be in the hands of France: the impetuosity of her temper, the energy and restlessness of her character, placed in a point of eternal friction with us, and our character, which, though quiet and loving peace and the pursuit of wealth, is high-minded, despising wealth in competition with insult or injury, enterprising and energetic as any nation on earth; these circumstances render it impossible that France and the United States can continue long friends, when they meet in so irritable a position. They, as well as we, must be blind, if they do not see this, and we must be very improvident if we do not begin to make arrangements on that hypothesis. The day that France takes possession of New Orleans, fixes the sentence which is to restrain her for ever within her low-water mark. It seals the union of two nations, who, in conjunction, can maintain exclusive possession of the ocean. From that moment we must marry ourselves to the British fleet and nation. We must turn all our attentions to a maritime force, for which our resources place us on very high ground: and having formed and connected together a power which may render reinforcement of her settlements here impossible to France, make the first cannon which shall be fired in Europe the signal for tearing up any settlement she may have made, and for holding the two continents of America in sequestration for the common purposes of the United British and American nations. This is not a state of things we seek or desire. It is one which this measure, if adopted by France, forces on us as necessarily, as any other cause, by the laws of nature, brings on its necessary effect. It is not from a fear of France that we deprecate this measure proposed by her. For however greater her force is than ours, compared in the abstract, it is nothing in comparison of ours, when to be exerted on our soil. But it is from a sincere love of peace, and a firm persuasion, that, bound to France by the interests and the strong sympathies still existing in the minds of our citizens, and holding relative positions which insure their continuance, we are secure of a long course of peace. Whereas, the change of friends, which will be rendered necessary if France changes that position, embarks us necessarily as a belligerent power in the first war of Europe. In that case, France will have held possession of New Orleans during the interval of a peace, long or short, at the end of which it will be wrested from her. Will this short-lived possession have been an equivalent to her for the transfer of such a weight into the scale of her enemy? Will not the amalgamation of a young, thriving nation, continue to that enemy the health and force which are at present so evidently on the decline? And will a few years’ possession of New Orleans add equally to the strength of France? She may say she needs Louisiana for the supply of her West Indies. She does not need it in time of peace, and in war she could not depend on them, because they would be so easily intercepted. I should suppose that all these considerations might, in some proper form, be brought into view of the government of France. Though stated by us, it ought not to give offence; because we do not bring them forward as a menace, but as consequences not controllable by us, but inevitable from the course of things. We mention them, not as things which we desire by any means, but as things we deprecate; and we beseech a friend to look forward and to prevent them for our common interests.
If France considers Louisiana, however, as indispensable for her views, she might perhaps be willing to look about for arrangements which might reconcile it to our interests. If any thing could do this, it would be the ceding to us the island of New Orleans and the Floridas. This would certainly, in a great degree, remove the causes of jarring and irritation between us, and perhaps for such a length of time, as might produce other means of making the measure permanently conciliatory to our interests and friendships. It would, at any rate, relieve us from the necessity of taking immediate measures for countervailing such an operation by arrangements in another quarter. But still we should consider New Orleans and the Floridas as no equivalent for the risk of a quarrel with France, produced by her vicinage.
I have no doubt you have urged these considerations, on every proper occasion, with the government where you are. They are such as must have effect, if you can find means of producing thorough reflection on them by that government. The idea here is, that the troops sent to St. Domingo, were to proceed to Louisiana after finishing their work in that island. If this were the arrangement, it will give you time to return again and again to the charge.
For the conquest of St. Domingo will not be a short work. It will take considerable time, and wear down a great number of soldiers. Every eye in the United States is now fixed on the affairs of Louisiana. Perhaps nothing, since the revolutionary war, has produced more uneasy sensations through the body of the nation. Notwithstanding temporary bickerings have taken place with France, she has still a strong hold on the affections of our citizens generally. I have thought it not amiss, by way of supplement to the letters of the Secretary of State, to write you this private one, to impress you with the importance we affix to this transaction. I pray you to cherish Dupont. He has the best dispositions for the continuance of friendship between the two nations, and perhaps you may be able to make a good use of him.
Accept assurances of my affectionate esteem and high consideration.
Th: Jefferson.
Washington, July 15, 1802.
Dear Sir,
Your favor of the 7th has been duly received. I am really mortified at the base ingratitude of Callender. It presents human nature in a hideous form. It gives me concern, because I perceive that relief, which was afforded him on mere motives of charity, may be viewed under the aspect of employing him as a writer. When the ‘Political Progress of Britain’ first appeared in this country, it was in a periodical publication called the ‘Bee,’ where I saw it. I was speaking of it in terms of strong approbation to a friend in Philadelphia, when he asked me, if I knew that the author was then in the city, a fugitive from prosecution on account of that work, and in want of employ for his subsistence. This was the first of my learning that Callender was the author of the work. I considered him as a man of science fled from persecution, and assured my friend of my readiness to do whatever could serve him. It was long after this before I saw him; probably not till 1798. He had, in the mean time, written a second part of the ‘Political Progress,’ much inferior to the first, and his ‘History of the United States.’ In 1798, I think, I was applied to by Mr. Lieper to contribute to his relief. I did so. In 1799, I think, S. T. Mason applied for him. I contributed again. He had, by this time, paid me two or three personal visits. When he fled in a panic from Philadelphia to General Mason’s, he wrote to me that he was a fugitive in want of employ, wished to know if he could get into a counting-house or a school, in my neighborhood or in that of Richmond; that he had materials for a volume, and if he could get as much money as would buy the paper, the profit of the sale would be all his own. I availed myself of this pretext to cover a mere charity, by desiring him to consider me a subscriber for as many copies of his book as the money inclosed (fifty dollars) amounted to; but to send me two copies only, as the others might lie till called for. But I discouraged his coming into my neighborhood. His first writings here had fallen far short of his original ‘Political Progress,’ and the scurrilities of his subsequent ones began evidently to do mischief. As to myself, no man wished more to see his pen stopped: but I considered him still as a proper object of benevolence. The succeeding year he again wanted money to buy paper for another volume. I made his letter, as before, the occasion of giving him another fifty dollars. He considers these as proofs of my approbation of his writings, when they were mere charities, yielded under a strong conviction that he was injuring us by his writings. It is known to many, that the sums given to him were such, and even smaller than I was in the habit of giving to others in distress, of the federal as well as the republican party, without attention to political principles. Soon after I was elected to the government, Callender came on here, wishing to be made post-master at Richmond. I knew him to be totally unfit for it: and however ready I was to aid him with my own charities (and I then gave him fifty dollars), I did not think the public offices confided to me to give away as charities. He took it in mortal offence, and from that moment has been hauling off to his former enemies, the federalists. Besides the letter I wrote him in answer to the one from General Mason’s, I wrote him another containing answers to two questions he addressed to me; 1. whether Mr. Jay received salary as Chief Justice and Envoy at the same time; and 2. something relative to the expenses of an embassy to Constantinople. I think these were the only letters I ever wrote him in answer to volumes he was perpetually writing to me. This is the true state of what has passed between him and me. I do not know that it can be used without committing me in controversy, as it were, with one too little respected by the public to merit that notice. I leave to your judgment what use can be made of these facts. Perhaps it will be better judged of, when we see what use the tories will endeavor to make of their new friend. I shall leave this on the 21st, and be at Monticello probably on the 24th, or within two or three days of that, and shall hope, ere long, to see you there. Accept assurances of my affectionate attachment.
Th: Jefferson.
TO GOVERNOR MONROE.
Washington, July 17, 1802.
Dear Sir,
After writing you on the 15th, I turned to my letter-file to see what letters I had written to Callender, and found them to have been of the dates of 1798, October the 11th, and 1799, September the 6th, and October the 6th; but on looking for the letters they were not in their places, nor to be found. On recollection, I believe I sent them to you a year or two ago. If you have them, I shall be glad to receive them at Monticello, where I shall be on this day se’nnight. I enclose you a paper, which shows the tories mean to pervert these charities to Callender as much as they can. They will probably first represent me as the patron and support of the ‘Prospect before Us,’ and other things of Callender’s, and then picking out all the scurrilities of the author against General Washington, Mr. Adams, and others, impute them to me. I, as well as most other republicans who were in the way of doing it, contributed what I could afford to the support of the republican papers and printers, paid sums of money for the ‘Bee,’ the ‘Albany Register,’ &c. when they were staggering under the sedition-law, contributed to the fines of Callender himself, of Holt, Brown, and others, suffering under that law. I discharged, when I came into office, such as were under the persecution of our enemies, without instituting any prosecutions in retaliation. They may, therefore, with the same justice, impute to me, or to every republican contributor, every thing which was ever published in those papers or by those persons. I must correct a fact in mine of the 15th. I find I did not enclose the fifty dollars to Callender himself while at General Mason’s, but authorized the General to draw on my correspondent at Richmond, and to give the money to Callender. So the other fifty dollars of which he speaks, were by order on my correspondent at Richmond.
Accept assurances of my affectionate esteem and respect.
Th: Jefferson.
TO ROBERT R. LIVINGSTON.
Washington, October 10, 1802.
Dear Sir,
The departure of Madame Brugnard for France furnishes me a safe conveyance of a letter, which I cannot avoid embracing, although I have nothing particular for the subject of it. It is well, however, to be able to inform you, generally, through a safe channel, that we stand completely corrected of the error, that either the government or the nation of France has any remains of friendship for us. The portion of that country which forms an exception, though respectable in weight, is weak in numbers. On the contrary, it appears evident, that an unfriendly-spirit prevails in the most important individuals of the government, towards us. In this state of things, we shall so take our distance between the two rival nations, as, remaining disengaged till necessity compels us, we may haul finally to the enemy of that which shall make it necessary. We see all the disadvantageous consequences of taking a side, and shall be forced into it only by a more disagreeable alternative; in which event we must countervail the disadvantages by measures which will give us splendor and power, but not as much happiness as our present system. We wish, therefore, to remain well with France. But we see that no consequences, however ruinous to them, can secure us with certainty against the extravagance of her present rulers. I think, therefore, that while we do nothing which the first nation on earth would deem crouching, we had better give to all our communications with them a very mild, complaisant, and even friendly complexion, but always independent. Ask no favors, leave small and irritating things to be conducted by the individuals interested in them, interfere ourselves but in the greatest cases, and then not push them to irritation. No matter at present existing between them and us is important enough to risk a breach of peace; peace being indeed the most important of all things for us, except the preserving an erect and independent attitude. Although I know your own judgment leads you to pursue this line identically, yet I thought it just to strengthen it by the concurrence of my own. You will have seen by our newspapers, that, with the aid of a lying renegado from republicanism, the federalists have opened all their sluices of calumny. They say we lied them out of power, and openly avow they will do the same by us. But it was not lies or arguments on our part which dethroned them, but their own foolish acts, sedition-laws, alien-laws, taxes, extravagancies, and heresies. Porcupine, their friend, wrote them down. Callender, their new recruit, will do the same. Every decent man among them revolts at his filth: and there cannot be a doubt, that were a Presidential election to come on this day, they would certainly have but three New England States, and about half a dozen votes from Maryland and North Carolina; these two States electing by districts. Were all the States to elect by a general ticket, they would have but three out of sixteen States. And these three are coming up slowly. We do, indeed, consider Jersey and Delaware as rather doubtful. Elections which have lately taken place there, but their event not yet known here, will show the present point of their varying condition.
My letters to you being merely private, I leave all details of business to their official channel.
Accept assurances of my constant friendship and high respect.
Th: Jefferson.
P. S. We have received your letter announcing the arrival of Mr. Dupont.
THOMAS JEFFERSON TO ALBERT GALLATIN.
You know my doubts, or rather convictions, about the unconstitutionality of the act for building piers in the Delaware, and the fears that it will lead to a bottomless expense, and to the greatest abuses. There is, however, one intention of which the act is susceptible, and which will bring it within the constitution; and we ought always to presume that the real intention which is alone consistent with the constitution. Although the power to regulate commerce does not give a power to build piers, wharves, open ports, clear the beds of rivers, dig canals, build warehouses, build manufacturing machines, set up manufactories, cultivate the earth, to all of which the power would go if it went to the first, yet a power to provide and maintain a navy is a power to provide receptacles for it, and places to cover and preserve it. In choosing the places where this money should be laid out, I should be much disposed, as far as contracts will permit, to confine it to such place or places as the ships of war may lie at, and be protected from ice: and I should be for stating this in a message to Congress, in order to prevent the effect of the present example. This act has been built on the exercise of the power of building light-houses, as a regulation of commerce. But I well remember the opposition, on this very ground, to the first act for building a light-house. The utility of the thing has sanctioned the infraction. But if on that infraction we build a second, on that second a third, &c, any one of the powers in the constitution may be made to comprehend every power of government. Will you read the enclosed letters on the subject of New Orleans, and think what we can do or propose in the case?
Accept my affectionate salutations. October 13, 1802.
TO LEVI LINCOLN.
Washington, October 25, 1802.
Dear Sir,
Your favor of the 16th is received, and that of July the 24th had come to hand while I was at Monticello. I sincerely condole with you on the sickly state of your family, and hope this will find them re-established with the approach of the cold season. As yet, however, we have had no frost at this place, and it is believed the yellow fever still continues in Philadelphia, if not in Baltimore. We shall all be happy to see you here whenever the state of your family admits it. You will have seen by the newspapers that we have gained ground generally in the elections, that we have lost ground in not a single district of the United States except Kent county in Delaware, where a religious dissension occasioned it. In Jersey the elections are always carried by small majorities, consequently the issue is affected by the smallest accidents. By the paper of the last night we have a majority of three in their Council, and one in their House of Representatives: another says it is only of one in each House: even the latter is sufficient for every purpose. The opinion I originally formed has never been changed, that such of the body of the people as thought themselves federalists, would find that they were in truth republicans, and would come over to us by degrees; but that their leaders had gone too far ever to change. Their bitterness increases with their desperation. They are trying slanders now which nothing could prompt but a gall which blinds their judgments as well as their consciences. I shall take no other revenge, than, by a steady pursuit of economy and peace, and by the establishment of republican principles in substance and in form, to sink federalism into an abyss from which there shall be no resurrection for it. I still think our original idea as to office is best: that is, to depend for the obtaining a just participation, on deaths, resignations, and delinquencies. This will least affect the tranquillity of the people, and prevent their giving in to the suggestion of our enemies, that ours has been a contest for office, not for principle. This is rather a slow operation, but it is sure, if we pursue it steadily, which, however, has not been done with the undeviating resolution I could have wished. To these means of obtaining a just share in the transaction of the public business, shall be added one other, to wit, removal for electioneering activity, or open and industrious opposition to the principles of the present government, legislative and executive. Every officer of the government may vote at elections according to his conscience; but we should betray the cause committed to our care, were we to permit the influence of official patronage to be used to overthrow that cause. Your present situation will enable you to judge of prominent offenders in your State, in the case of the present election. I pray you to seek them, to mark them, to be quite sure of your ground, that we may commit no error or wrong, and leave the rest to me. I have been urged to remove Mr. Whittemore, the surveyor of Gloucester, on grounds of neglect of duty and industrious opposition. Yet no facts are so distinctly charged as to make the step sure which we should take in this. Will you take the trouble to satisfy yourself on this point? I think it not amiss that it should be known that we are determined to remove officers who are active or open-mouthed against the government, by which I mean the legislature as well as the executive. Accept assurances of my sincere friendship and high respect.
Th: Jefferson.
TO GOVERNOR MONROE.
Washington, January 13,1803.
Dear Sir,
I dropped you a line on the 10th, informing you of a nomination I had made of you to the Senate, and yesterday I enclosed you their approbation, not then having time to write. The agitation of the public mind on occasion of the late suspension of our right of deposite at New Orleans is extreme. In the western country it is natural, and grounded on honest motives. In the sea-ports it proceeds from a desire for war, which increases the mercantile lottery: in the federalists, generally, and especially those of Congress, the object is to force us into war if possible, in order to derange our finances, or, if this cannot be done, to attach the western country to them, as their best friends, and thus get again into power. Remonstrances, memorials, &c. are now circulating through the whole of the western country, and signed by the body of the people. The measures we have been pursuing, being invisible, do not satisfy their minds. Something sensible, therefore, has become necessary; and indeed our object of purchasing New Orleans and the Floridas is a measure liable to assume so many shapes, that no instructions could be squared to fit them. It was essential then, to send a minister extraordinary, to be joined with the ordinary one, with discretionary powers; first, however, well impressed with all our views, and therefore qualified to meet and modify to these every form of proposition which could come from the other party. This could be done only in full and frequent oral communications. Having determined on this, there could not be two opinions among the republicans as to the person. You possessed the unlimited confidence of the administration and of the western people; and generally of the republicans every where; and were you to refuse to go, no other man can be found who does this. The measure has already silenced the federalists here. Congress will no longer be agitated by them: and the country will become calm as fast as the information extends over it. All eyes, all hopes are now fixed on you; and were you to decline, the chagrin would be universal, and would shake under your feet the high ground on which you stand with the public. Indeed, I know nothing which would produce such a shock. For on the event of this mission depend the future destinies of this republic. If we cannot, by a purchase of the country, insure to ourselves a course of perpetual peace and friendship with all nations, then, as war cannot be distant, it behoves us immediately to be preparing for that course, without, however, hastening it; and it may be necessary (on your failure on the continent) to cross the channel. We shall get entangled in European politics, and figuring more, be much less happy and prosperous. This can only be prevented by a successful issue to your present mission. I am sensible after the measures you have taken for getting into a different line of business, that it will be a great sacrifice on your part, and presents from the season and other circumstances serious difficulties. But some men are born for the public. Nature, by fitting them for the service of the human race on a broad scale, has stamped them with the evidences of her destination and their duty.
But I am particularly concerned, that, in the present case, you have more than one sacrifice to make. To reform the prodigalities of our predecessors is understood to be peculiarly our duty, and to bring the government to a simple and economical course. They, in order to increase expense, debt, taxation, and patronage, tried always how much they could give. The outfit given to ministers resident to enable them to furnish their house, but given by no nation to a temporary minister, who is never expected to take a house or to entertain, but considered on the footing of a voyageur, they gave to their extraordinary missionaries by wholesale. In the beginning of our administration, among other articles of reformation in expense, it was determined not to give an outfit to missionaries extraordinary, and not to incur the expense with any minister of sending a frigate to carry or bring him. The Boston happened to be going to the Mediterranean, and was permitted, therefore, to take up Mr. Livingston and touch in a port of France. A frigate was denied to Charles Pinckney, and has been refused to Mr. King for his return. Mr. Madison’s friendship and mine to you being so well known, the public will have eagle eyes to watch if we grant you any indulgences out of the general rule; and on the other hand, the example set in your case will be more cogent on future ones, and produce greater approbation to our conduct. The allowance, therefore, will be in this, and all similar cases, all the expenses of your journey and voyage, taking a ship’s cabin to yourself, nine thousand dollars a year from your leaving home till the proceedings of your mission are terminated, and then the quarter’s salary for the expenses of your return, as prescribed by law. As to the time of your going, you cannot too much hasten it, as the moment in France is critical. St. Domingo delays their taking possession of Louisiana, and they are in the last distress for money for current purposes. You should arrange your affairs for an absence of a year at least, perhaps for a long one. It will be necessary for you to stay here some days on your way to New York. You will receive here what advance you choose.
Accept assurances of my constant and affectionate attachment.
Th: Jefferson.
TO M. DUPONT.
Washington, February 1, 1803.
Dear Sir,
I have to acknowledge the receipt of your favors of August the 16th and October the 4th. The latter I received with peculiar satisfaction; because, while it holds up terms which cannot be entirely yielded, it proposes such as a mutual spirit of accommodation and sacrifice of opinion may bring to some point of union. While we were preparing on this subject such modifications of the propositions of your letter of October the 4th, as we could assent to, an event happened, which obliged us to adopt measures of urgency. The suspension of the right of deposite at New Orleans, ceded, to us by our treaty with Spain, threw our whole country into such a ferment as imminently threatened its peace. This, however, was believed to be the act of the Intendant, unauthorized by his government. But it showed the necessity of making effectual arrangements, to secure the peace of the two countries against the indiscreet acts of subordinate agents. The urgency of the case, as well as the public spirit, therefore, induced us to make a more solemn appeal to the justice and judgment of our neighbors, by sending a minister extraordinary to impress them with the necessity of some arrangement. Mr. Monroe has been selected. His good dispositions cannot be doubted. Multiplied conversations with him, and views of the subject taken in all the shapes in which it can present itself, have possessed him with our estimates of every thing relating to it, with a minuteness which no written communication to Mr. Livingston could ever have attained. These will prepare them to meet and decide on every form of proposition which can occur, without awaiting new instructions from hence, which might draw to an indefinite length a discussion where circumstances imperiously oblige us to a prompt decision. For the occlusion of the Mississippi is a state of things in which we cannot exist. He goes, therefore, joined with Chancellor Livingston, to aid in the issue of a crisis the most important the United States have ever met since their independence, and which is to decide their future character and career. The confidence which the government of France reposes in you, will undoubtedly give great weight to your information. An equal confidence on our part, founded on your knowledge of the subject, your just views of it, your good dispositions towards this country, and my long experience of your personal faith and friendship, assures me that you will render between us all the good offices in your power. The interests of the two countries being absolutely the same as to this matter, your aid may be conscientiously given. It will often, perhaps, be possible for you, having a freedom of communication, omnibus horis, which diplomatic gentlemen will be excluded from by forms, to smooth difficulties by representations and reasonings, which would be received with more suspicion from them. You will thereby render great good to both countries. For our circumstances are so imperious as to admit of no delay as to our course; and the use of the Mississippi so indispensable, that we cannot hesitate one moment to hazard our existence for its maintenance. If we fail in this effort to put it beyond the reach of accident, we see the destinies we have to run, and prepare at once for them. Not but that we shall still endeavor to go on in peace and friendship with our neighbors as long as we can, if our rights of navigation and deposite are respected; but as we foresee that the caprices of the local officers, and the abuse of those rights by our boatmen and navigators, which neither government can prevent, will keep up a state of irritation which cannot long be kept inactive, we should be criminally improvident not to take at once eventual measures for strengthening ourselves for the contest. It may be said, if this object be so all-important to us, why do we not offer such a sum as to insure its purchase? The answer is simple. We are an agricultural people, poor in money, and owing great debts. These will be falling due by instalments for fifteen years to come, and require from us the practice of a rigorous economy to accomplish their payment: and it is our principle to pay to a moment whatever we have engaged, and never to engage what we cannot, and mean not, faithfully to pay. We have calculated our resources, and find the sum to be moderate which they would enable us to pay, and we know from late trials that little can be added to it by borrowing. The country, too, which we wish to purchase, except the portion already granted, and which must be confirmed to the private holders, is a barren sand, six hundred miles from east to west and from thirty to forty and fifty miles from north to south, formed by deposition of the sands by the Gulf Stream in its circular course round the Mexican Gulf, and which being spent after performing a semicircle, has made from its last depositions the sand-bank of East Florida. In West Florida, indeed, there are on the borders of the rivers some rich bottoms, formed by the mud brought from the upper country. These bottoms are all possessed by individuals. But the spaces between river and river are mere banks of sand: and in East Florida, there are neither rivers nor consequently any bottoms. We cannot then make any thing by a sale of the lands to individuals. So that it is peace alone which makes it an object with us, and which ought to make the cession of it desirable to France. Whatever power, other than ourselves, holds the country east of the Mississippi, becomes our natural enemy. Will such a possession do France as much good, as such an enemy may do her harm? And how long would it be hers, were such an enemy, situated at its door, added to Great Britain? I confess, it appears to me as essential to France to keep at peace with us, as it is to us to keep at peace with her: and that, if this cannot be secured without some compromise as to the territory in question, it will be useful for both to make sacrifices to effect the compromise.
You see, my good friend, with what frankness I communicate with you on this subject; that I hide nothing from you, and that I am endeavoring to turn our private friendship to the good of our respective countries. And can private friendship ever answer a nobler end than by keeping two nations at peace, who, if this new position which one of them is taking were rendered innocent, have more points of common interest, and fewer of collision than any two on earth; who become natural friends, instead of natural enemies, which this change of position would make them. My letters of April the 25th, May the 5th, and this present one have been written, without any disguise, in this view; and while safe in your hands they can never do any thing but good. But you and I are now at that time of life when our call to another state of being cannot be distant, and may be near. Besides, your government is in the habit of seizing papers without notice. These letters might thus get into hands, which, like the hornet which extracts poison from the same flower that yields honey to the bee, might make them the ground of blowing up a flame between our two countries, and make our friendship and confidence in each other effect exactly the reverse of what we are aiming at. Being yourself thoroughly possessed of every idea in them, let me ask from your friendship an immediate consignment of them to the flames. That alone can make all safe, and ourselves secure.
I intended to have answered you here, on the subject of your agency in the transacting what money matters we may have at Paris, and for that purpose meant to have conferred with Mr. Gallatin. But he has, for two or three days, been confined to his room, and is not yet able to do business. If he is out before Mr. Monroe’s departure, I will write an additional letter on that subject. Be assured that it will be a great additional satisfaction to me to render services to yourself and sons by the same acts which shall at the same time promote the public service. Be so good as to present my respectful salutations to Madame Dupont, and to accept yourself assurances of my constant and affectionate friendship and great respect.
Th: Jefferson.
TO DOCTOR BENJAMIN RUSH.
Washington, April 21, 1803.
Dear Sir,
In some of the delightful conversations with you, in the evenings of 1798-99, and which served as an anodyne to the afflictions of the crisis through which our country was then laboring, the Christian religion was sometimes our topic: and I then promised you, that, one day or other, I would give you my views of it. They are the result of a life of inquiry and reflection, and very different from that anti-Christian system imputed to me by those who know nothing of my opinions. To the corruptions of Christianity I am indeed opposed; but not to the genuine precepts of Jesus himself. I am a Christian, in the only sense in which he wished any one to be; sincerely attached to his doctrines, in preference to all others; ascribing to himself every human excellence; and believing he never claimed any other. At the short intervals since these conversations, when I could justifiably abstract my mind from public affairs, the subject has been under my contemplation. But the more I considered it, the more it expanded beyond the measure of either my time or information. In the moment of my late departure from Monticello, I received from Doctor Priestely his little treatise of ‘Socrates and Jesus compared.’ This being a section of the general view I had taken of the field, it became a subject of reflection while on the road, and unoccupied otherwise. The result was, to arrange in my mind a syllabus, or outline of such an estimate of the comparative merits of Christianity, as I wished to see executed by some one of more leisure and information for the task, than myself. This I now send you, as the only discharge of my promise I can probably ever execute. And in confiding it to you, I know it will not be exposed to the malignant perversions of those who make every word from me a text for new misrepresentations and calumnies. I am moreover averse to the communication of my religious tenets to the public; because it would countenance the presumption of those who have endeavored to draw them before that tribunal, and to seduce public opinion to erect itself into that inquisition over the rights of conscience, which the laws have so justly proscribed. It behoves every man who values liberty of conscience for himself, to resist invasions of it in the case of others; or their case may, by change of circumstances, become his own. It behoves him, too, in his own case, to give no example of concession, betraying the common right of independent opinion, by answering questions of faith, which the laws have left between God and himself. Accept my affectionate salutations.
Th: Jefferson.
Syllabus of an Estimate of the Merit of the Doctrines of Jesus, compared with those of others.
In a comparative view of the Ethics of the enlightened nations of antiquity, of the Jews, and of Jesus, no notice should be taken of the corruptions of reason among the ancients, to wit, the idolatry and superstition of the vulgar, nor of the corruptions of Christianity by the learned among its professors.
Let a just view be taken of the moral principles inculcated by the most esteemed of the sects of ancient philosophy, or of their individuals; particularly Pythagoras, Socrates, Epicurus, Cicero, Epictetus, Seneca, Antoninus.
I. Philosophers. 1. Their precepts related chiefly to ourselves, and the government of those passions which, unrestrained, would disturb our tranquillity of mind.* In this branch of philosophy they were really great.
* To explain, I will exhibit the heads of Seneca’s and Cicero’s philosophical works, the most extensive of any we have received from the ancients. Of ten heads in Seneca, seven relate to ourselves, viz. de irâ, consolatio, de tranquillitate, de constantiâ sapientis, de otio sapientis, de vitâ beatâ, de brevitate vitæ; two relate to others, de clementiâ, de beneficiis; and one relates to the government of the world, de pruvidentiâ. Of eleven tracts of Cicero, five respect ourselves, viz. definibus, Tusculana, academica, paradoxa, de senectute, one, de officiis, relates partly to ourselves, partly to others; one, de amicitiâ, relates to others; and four are on different subjects, to wit, de naturâ deorum, de dimnatione, defato, and somnium Scipionis.
2. In developing our duties to others, they were short and defective. They embraced, indeed, the circles of kindred and friends, and inculcated patriotism, or the love of our country in the aggregate, as a primary obligation: towards our neighbors and countrymen they taught justice, but scarcely viewed them as within the circle of benevolence. Still less have they inculcated peace, charity, and love to our fellow-men, or embraced with benevolence the whole family of mankind.
II. Jews. 1. Their system was Deism; that is, the belief in one only God. But their ideas of him and of his attributes were degrading and injurious.
2. Their Ethics were not only imperfect, but often irreconcilable with the sound dictates of reason and morality, as they respect intercourse with those around us; and repulsive and anti-social, as respecting other nations. They needed reformation, therefore, in an eminent degree.
III. Jesus. In this state of things among the Jews, Jesus appeared. His parentage was obscure; his condition poor; his education null; his natural endowments great; his life correct and innocent: he was meek, benevolent, patient, firm, disinterested, and of the sublimest eloquence.
The disadvantages under which his doctrines appear are remarkable.
1. Like Socrates and Epictetus, he wrote nothing himself.
2. But he had not, like them, a Xenophon or an Arrian to write for him. I name not Plato, who only used the name of Socrates to cover the whimsies of his own brain. On the contrary, all the learned of his country, entrenched in its power and riches, were opposed to him, lest his labors should undermine their advantages; and the committing to writing his life and doctrines fell on unlettered and ignorant men; who wrote, too, from memory, and not till long after the transactions had passed.
3. According to the ordinary fate of those who attempt to enlighten and reform mankind, he fell an early victim to the jealousy and combination of the altar and the throne, at about thirty-three years of age, his reason having not yet attained the maximum of its energy, nor the course of his preaching, which was but of three years at most, presented occasions for developing a complete system of morals.
4. Hence the doctrines which he really delivered were defective as a whole, and fragments only of what he did deliver have come to us, mutilated, misstated, and often unintelligible.
5. They have been still more disfigured by the corruptions of schismatizing followers, who have found an interest in sophisticating and perverting the simple doctrines he taught, by engrafting on them the mysticisms of a Grecian sophist, frittering them into subtleties, and obscuring them with jargon, until they have caused good men to reject the whole in disgust, and to view Jesus himself as an impostor.
Notwithstanding these disadvantages, a system of morals is presented to us, which, if filled up in the style and spirit of the rich fragments he left us, would be the most perfect and sublime that has ever been taught by man.
The question of his being a member of the God-head, or in direct communication with it, claimed for him by some of his followers, and denied by others, is foreign to the present view, which is merely an estimate of the intrinsic merit of his doctrines.
1. He corrected the Deism of the Jews, confirming them in their belief of one only God, and giving them juster notions of his attributes and government.
2. His moral doctrines, relating to kindred and friends, were more pure and perfect than those of the most correct of the philosophers, and greatly more so than those of the Jews; and they went far beyond both in inculcating universal philanthropy, not only to kindred and friends, to neighbors and countrymen, but to all mankind, gathering all into one family, under the bonds of love charity, peace, common wants, and common aids. A developement of this head will evince the peculiar superiority of the system of Jesus over all others.
3. The precepts of philosophy, and of the Hebrew code, laid hold of actions only. He pushed his scrutinies into the heart of man; erected his tribunal in the region of his thoughts, and purified the waters at the fountain head.
4. He taught, emphatically, the doctrine of a future state, which was either doubted, or disbelieved by the Jews; and wielded it with efficacy, as an important incentive, supplementary to the other motives to moral conduct.
TO GENERAL GATES.
Washington, July 11, 1803.
Dear General,
I accept with pleasure, and with pleasure reciprocate your congratulations on the acquisition of Louisiana: for it is a subject of mutual congratulation, as it interests every man of the nation. The territory acquired, as it includes all the waters of the Missouri and Mississippi, has more than doubled the area of the United States, and the new part is not inferior to the old in soil, climate, productions, and important communications. If our legislature dispose of it with the wisdom we have a right to expect, they may make it the means of tempting all our Indians on the east side of the Mississippi to remove to the west, and of condensing instead of scattering our population. I find our opposition is very willing to pluck feathers from Monroe, although not fond of sticking them into Livingston’s coat. The truth is, both have a just portion of merit; and were it necessary or proper, it would be shown that each has rendered peculiar services, and of important value. These grumblers, too, are very uneasy lest the administration should share some little credit for the acquisition, the whole of which they ascribe to the accident of war. They would be cruelly mortified could they see our files from May, 1801, the first organization of the administration, but more especially from April, 1802. They would see, that though we could not say when war would arise, yet we said with energy what would take place when it should arise. We did not, by our intrigues, produce the war; but we availed ourselves of it when it happened. The other party saw the case now existing, on which our representations were predicated, and the wisdom of timely sacrifice. But when these people make the war give us everything, they authorize us to ask what the war gave us in their day? They had a war; what did they make it bring us? Instead of making our neutrality the ground of gain to their country, they were for plunging into the war. And if they were now in place, they would now be at war against the atheists and disorganizers of France. They were for making their country an appendage to England. We are friendly, cordially and conscientiously friendly to England, but we are not hostile to France. We will be rigorously just and sincerely friendly to both. I do not believe we shall have as much to swallow from them as our predecessors had.
Present me respectfully to Mrs. Gates, and accept yourself my affectionate salutations, and assurances of great respect and esteem.
Th: Jefferson.
Monticello, August 12, 1803.
Dear Sir,
The enclosed letter, though directed to you, was intended to me also, and was left open with a request, that when forwarded, I would forward it to you. It gives me occasion to write a word to you on the subject of Louisiana, which being a new one, an interchange of sentiments may produce correct ideas before we are to act on them.
Our information as to the country is very incomplete: we have taken measures to obtain it full as to the settled part, which I hope to receive in time for Congress. The boundaries, which I deem not admitting question, are the high lands on the western side of the Mississippi enclosing all its waters, the Missouri of course, and terminating in the line drawn from the northwestern point of the Lake of the Woods to the nearest source of the Mississippi, as lately settled between Great Britain and the United States. We have some claims, to extend on the sea-coast westwardly to the Rio Norte or Bravo, and better, to go eastwardly to the Rio Perdido, between Mobile and Pensacola, the ancient boundary of Louisiana. These claims will be a subject of negotiation with Spain, and if, as soon as she is at war, we push them strongly with one hand, holding out a price in the other, we shall certainly obtain the Floridas, and all in good time. In the mean while, without waiting for permission, we shall enter into the exercise of the natural right we have always insisted on with Spain, to wit, that of a nation holding the upper part of streams, having a right of innocent passage through them to the ocean. We shall prepare her to see us practise on this, and she will not oppose it by force.
Objections are raising to the eastward against the vast extent of our boundaries, and propositions are made to exchange Louisiana, or a part of it, for the Floridas. But, as I have said, we shall get the Floridas without, and I would not give one inch of the waters of the Mississippi to any nation, because I see in a light very important to our peace the exclusive right to its navigation, and the admission of no nation into it, but as into the Potomac or Delaware, with our consent and under our police. These federalists see in this acquisition the formation of a new confederacy, embracing all the waters of the Mississippi, on both sides of it, and a separation of its eastern waters from us. These combinations depend on so many circumstances, which we cannot foresee, that I place little reliance on them. We have seldom seen neighborhood produce affection among nations. The reverse is almost the universal truth. Besides, if it should become the great interest of those nations to separate from this, if their happiness should depend on it so strongly as to induce them to go through that convulsion, why should the Atlantic States dread it? But especially why should we, their present inhabitants, take side in such a question? When I view the Atlantic States, procuring for those on the eastern waters of the Mississippi friendly instead of hostile neighbors on its western waters, I do not view it as an Englishman would the procuring future blessings for the French nation, with whom he has no relations of blood or affection. The future inhabitants of the Atlantic and Mississippi States will be our sons. We leave them in distinct but bordering establishments. We think we see their happiness in their union, and we wish it. Events may prove it otherwise; and if they see their interest in separation, why should we take side with our Atlantic rather than our Mississippi descendants? It is the elder and the younger son differing. God bless them both, and keep them in union, if it be for their good, but separate them, if it be better. The inhabited part of Louisiana, from Point Coupee to the sea, will of course be immediately a territorial government, and soon a State. But above that, the best use we can make of the country for some time, will be to give establishments in it to the Indians on the east side of the Mississippi, in exchange for their present country, and open land-offices in the last, and thus make this acquisition the means of filling up the eastern side, instead of drawing off its population. When we shall be full on this side, we may lay off a range of States on the western bank from the head to the mouth, and so, range after range, advancing compactly as we multiply.
This treaty must of course be laid before both Houses, because both have important functions to exercise respecting it. They, I presume, will see their duty to their country in ratifying and paying for it, so as to secure a good which would otherwise probably be never again in their power. But I suppose they must then appeal to the nation for an additional article to the constitution, approving and confirming an act which the nation had not previously authorized. The constitution has made no provision for our holding foreign territory, still less for incorporating foreign nations into our Union. The executive in seizing the fugitive occurrence which so much advances the good of their country, have done an act beyond the constitution. The legislature in casting behind them metaphysical subtleties, and risking themselves like faithful servants, must ratify and pay for it, and throw themselves on their country for doing for them unauthorized, what we know they would have done for themselves had they been in a situation to do it. It is the case of a guardian, investing the money of his ward in purchasing an important adjacent territory; and saying to him when of age, I did this for your good; I pretend to no right to bind you; you may disavow me, and I must get out of the scrape as I can: I thought it my duty to risk myself for you. But we shall not be disavowed by the nation, and their act of indemnity will confirm and not weaken the constitution, by more strongly marking out its lines.
We have nothing later from Europe than the public papers give. I hope yourself and all the western members will make a sacred point of being at the first day of the meeting of Congress; for vestra res regitur.
Accept my affectionate salutations and assurances of esteem and respect.
Th: Jefferson.

| Contents |
| Illustrations |
| Volume I. |
| Volume II. |
| Volume III. |


CONTENTS
LETTER I. TO LEVI LINCOLN, August 30, 1803
LETTER II. TO WILSON C NICHOLAS, September 7, 1803
LETTER III. TO DOCTOR BENJAMIN RUSH, October 4, 1803
LETTER IV. TO M. DUPONT DE NEMOURS, November 1, 1803
LETTER V. TO ROBERT R. LIVINGSTON, November 4,1803
LETTER VI. TO DAVID WILLIAMS, November 14, 1803
LETTER VII. TO JOHN RANDOLH, December 1, 1803
LETTER VIII. TO MR. GALLATIN, December 13, 1803
LETTER IX. TO DOCTOR PRIESTLEY, January 29, 1804
LETTER X. TO ELBRIDGE GERRY, March 3, 1804
LETTER XI. TO GIDEON GRANGER, April 16, 1804
LETTER XII. TO MRS. ADAMS, June 13,1804
LETTER XIII. TO GOVERNOR PAGE, June 25, 1804
LETTER, XIV. TO P. MAZZEI, July 18, 1804
LETTER XV. TO MRS. ADAMS, July 22, 1804
LETTER XVI. TO JAMES MADISON, August 15, 1804
LETTER XVII. TO GOVERNOR CLAIBORNE, August 30, 1804
LETTER XVIII. TO MRS. ADAMS, September 11, 1804
LETTER XIX. TO MR. NICHOLSON, January 29, 1805
LETTER XX. TO MR. VOLNEY, February 8, 1805
LETTER XXI. TO JUDGE TYLER, March 29, 1805
LETTER XXII. TO DOCTOR LOGAN, May 11, 1805
LETTER XXIII. TO JUDGE SULLIVAN, May 21, 1805
LETTER XXIV. TO THOMAS PAINE, June 5, 1805
LETTER XXV. TO DOCTORS ROGERS AND SLAUGHTER, March 2, 1806
LETTER XXVI. TO MR. DUANE, March 22, 1806
LETTER XXVII. TO WILSON C. NICHOLAS, March 24,1806
LETTER XXVIII. TO WILSON C. NICHOLAS, April 13, 1806
LETTER XXIX. TO MR. HARRIS, April 18, 1806
LETTER XXX. TO THE EMPEROR OF RUSSIA
LETTER XXXI. TO COLONEL MONROE, May 4, 1806
LETTER XXXII. TO GENERAL SMITH, May 4,1806
LETTER XXXIII. TO MR DIGGES, July 1, 1806
LETTER XXXIV. TO MR. BIDWELL, July 5, 1806
LETTER XXXV. TO MR. BOWDOIN, July 10, 1806
LETTER XXXVI. TO W. A. BURWELL, September 17, 1806
LETTER XXXVII. TO ALBERT GALLATIN, October 12, 1806
LETTER XXXVIII. TO JOHN DICKINSON, January 13, 1807
LETTER XXXIX, TO WILSON C. NICHOLAS, February 28,1807
LETTER XL. TO JAMES MONROE, March 21, 1807
LETTER XLI. M. LE COMTE DIODATI, March 29, 1807
LETTER XLII. TO MR. BOWDOIN, April 2, 1807
LETTER XLIII. TO WILLIAM B. GILES, April 20, 1807
LETTER XLIV. TO GEORGE HAY, June 2, 1807
LETTER XLV. TO ALBERT GALLATIN, June 3, 1807
LETTER XLVI. TO GEORGE HAY, June 5, 1807
LETTER XLVII. TO DOCTOR HORATIO TURPIN, June 10, 1807
LETTER XLVIII. TO JOHN NORVELL, June 11, 1807
LETTER XLIX. TO WILLIAM SHORT, June 12, 1807
LETTER L. TO GEORGE HAY, June 12, 1807
LETTER LI. TO GEORGE HAY, June 17, 1807
LETTER LII. TO GEORGE HAY, June 19,1807
LETTER LIII. TO GOVERNOR SULLIVAN, June 19, 1807
LETTER LIV. TO GEORGE HAY, June 20, 1807
LETTER LV. TO DOCTOR WISTAR, June 21, 1807
LETTER LVI. TO MR. BOWDOIN, July 10, 1807
LETTER LVII. TO THE MARQUIS DE LA FAYETTE, July 14, 1807
LETTER LVIII. TO JOHN PAGE, July 17, 1807
LETTER LIX. TO WILLIAM DUANE, July 20, 1807
LETTER LX. TO GEORGE HAY, August 20, 1807
LETTER LXI. TO GEORGE HAY, September 4, 1807
LETTER LXII. TO GEORGE HAY, September 7, 1807
LETTER LXIII. TO THE REV. MR. MILLAR, January 23, 1808
LETTER LXIV. TO COLONEL MONROE, February 18, 1808
LETTER LXV. TO COLONEL MONROE, March 10, 1808
LETTER LXVI. TO RICHARD M. JOHNSON, March 10, 1808
LETTER LXVII. TO LEVI LINCOLN, March 23, 1808
LETTER LXVIII. TO CHARLES PINCKNEY, March 30, 1808
LETTER LXIX. TO DOCTOR LEIB, June 23, 1808
LETTER LXX. TO ROBERT L. LIVINGSTON, October 15, 1808
LETTER LXXI. TO DOCTOR JAMES BROWN, October 27, 1808
LETTER LXXII. TO LIEUTENANT GOVERNOR LINCOLN, November 13, 1808
LETTER LXXIII. TO THOMAS JEFFERSON RANDOLPH, November 24, 1808
LETTER LXXIV. TO DOCTOR EUSTIS, January 14, 1809
LETTER LXXV. TO COLONEL MONROE, January 28, 1809
LETTER LXXVI. TO THOMAS MANN RANDOLPH, February 7, 1809
LETTER LXXVII. TO JOHN HOLLINS, February 19, 1809
LETTER LXXVIII. TO M. DUPONT DE NEMOURS, March 2, 1809
LETTER LXXIX. TO THE PRESIDENT, March 17, 1809
LETTER LXXX. TO THE INHABITANTS OF ALBEMARLE COUNTY, April 3, 1809
LETTER LXXXI. TO WILSON C. NICHOLAS, June 13, 1809
LETTER LXXXII. TO THE PRESIDENT, August 17, 1809
LETTER LXXXIII. TO DOCTOR BARTON, September 21, 1809
LETTER LXXXIV. TO DON VALENTINE DE FORONDA, October 4, 1809
LETTER LXXXV. TO ALBERT GALLATIN, October 11, 1809
LETTER LXXXVI. TO CÆSAR A. RODNEY, February 10, 1810
LETTER LXXXVII.* TO SAMUEL KERCHEVAL, February 19,1810
LETTER LXXXVIII. TO GENERAL KOSCIUSKO, February 26, 1810
LETTER LXXXIX. TO DOCTOR JONES, March 5, 1810
LETTER XC. TO GOVERNOR LANGDON, March 5, 1810
LETTER XCI. TO GENERAL DEARBORN, July 16,1810
LETTER XCII. TO J. B. COLVIN, September 20, 1810
LETTER XCIII. TO MR. LAW, January 15, 1811
LETTER XCIV. TO DOCTOR BENJAMIN RUSH, January 16, 1811
LETTER XCV. TO M. DESTUTT TRACY, January 26, 1811
LETTER XCVI. TO COLONEL MONROE, May 5, 1811
LETTER XCVII. TO GENERAL DEARBORN, August 14, 1811
LETTER XCVIII. TO DOCTOR BENJAMIN RUSH
LETTER XCIX. TO JOHN ADAMS, January 21, 1812
LETTER C. TO JOHN ADAMS, April 20, 1812
LETTER CI. TO JAMES MAURY, April 25, 1812
LETTER CII. TO THE PRESIDENT, May 30, 1812
LETTER CIII. TO ELBRIDGE GERRY, June 11, 1812
LETTER CIV. TO JUDGE TYLER, June 17,1812
LETTER CV. TO COLONEL WILLIAM DUANE, October 1, 1812
LETTER CVI. TO MR. MELISH, January 13, 1813
LETTER CVII. TO MADAME DE STAEL-HOLSTEIN, May 24, 1818
LETTER CVIII. TO JOHN ADAMS, May 27, 1813
LETTER CIX. TO JOHN ADAMS, June 15, 1813
LETTER CX. TO JOHN W. EPPES, June 24, 1813
LETTER CXI. TO JOHN ADAMS, June 21, 1813
LETTER CXII. TO JOHN ADAMS, August 22, 1813
LETTER CXIII. TO JOHN W. EPPES, November 6, 1813
LETTER CXIV. TO JOHN ADAMS, October 13, 1813
LETTER CXV. TO JOHN ADAMS, October 28, 1813
LETTER CXVI. TO THOMAS LIEPER, January 1, 1814
LETTER CXVII. TO DOCTOR WALTER JONES, January 2,1814
LETTER CXVIII. TO JOSEPH C. CABELL, January 31, 1814
LETTER CXIX. TO JOHN ADAMS, July 5, 1814
LETTER CXX. TO COLONEL MONROE, January 1, 1815
LETTER CXXI. TO THE MARQUIS DE LA FAYETTE, February 14, 1815
LETTER CXXII.* TO MR. WENDOVER, March 13, 1815
LETTER CXXIII. TO CÆSAR A. RODNEY, March 16, 1815
LETTER CXXIV. TO GENERAL DEARBORN, March 17, 1815
LETTER CXXV. TO THE PRESIDENT, March 23,1815
LETTER CXXVI. TO JOHN ADAMS, June 10,1815
LETTER CXXVII. TO MR. LEIPER, June 12, 1815
LETTER CXXVIII. TO JOHN ADAMS, August 10,1815
LETTER CXXIX. TO DABNEY CARR, January 19, 1816
LETTER CXXX. TO JOHN ADAMS, April 8, 1816
LETTER CXXXI. TO JOHN TAYLOR, May 28,1816
LETTER CXXXII. TO FRANCIS W. GILMER, June 7,1816
LETTER CXXXIII.* TO BENJAMIN AUSTIN, January 9, 1816
LETTER CXXXIV. TO WILLIAM H. CRAWFORD, June 20, 1816
LETTER CXXXV. TO SAMUEL KERCHIVAL, July 12, 1816
LETTER CXXXVI. TO JOHN TAYLOR, July 21, 1816
LETTER CXXXVII. TO SAMUEL KERCHIVAL, September 5, 1816
LETTER CXXXVIII. TO JOHN ADAMS, October 14, 1816
LETTER CXXXIX. TO JOHN ADAMS, TO JOHN ADAMS
LETTER CXL. TO JOHN ADAMS, May 5, 1817
LETTER CXLI. TO MARQUIS DE LA FAYETTE, May 14, 1817
LETTER CXLII. TO ALBERT GALLATIN, June 16, 1817
LETTER CXLIII. TO JOHN ADAMS, May 17, 1818
LETTER CXLIV. TO JOHN ADAMS, November 13, 1818
LETTER CXLV. TO ROBERT WALSH, December 4, 1818
LETTER CXLVI. TO M. DE NEUVILLE, December 13, 1818
LETTER CXLVII. TO DOCTOR VINE UTLEY, March 21, 1819
LETTER CXLVIII. TO JOHN ADAMS, July 9, 1819
LETTER CXLIX. TO JUDGE ROANE, September 6,1819
LETTER CL. TO JOHN ADAMS, December 10, 1819
LETTER CLI. TO WILLIAM SHORT, April 13, 1820
LETTER CLII. TO JOHN HOLMES, April 22, 1820
LETTER CLIII. TO WILLIAM SHORT, August 4, 1820
LETTER CLIV. TO JOHN ADAMS, August 15, 1820
LETTER CLV. TO JOSEPH C. CABELL, November 28, 1820
LETTER CLVI. TO THOMAS RITCHIE, December, 25, 1820
LETTER CLVII. TO JOHN ADAMS, January 22, 1821
LETTER CLVIII. TO JOSEPH C CABELL, January 31, 1821
LETTER CLIX. TO GENERAL BRECKENRIDGE, February 15, 1821
LETTER CLX. TO — — — NICHOLAS, December 11,1821
LETTER CLXI. TO JEDIDIAH MORSE, March 6, 1822
LETTER CLXII. TO DOCTOR BENJAMIN WATERHOUSE, June 26, 1822
LETTER CLXIII. TO JOHN ADAMS
LETTER CLXIV. TO WILLIAM T. BARRY, July 2, 1822
LETTER CLXV. TO DOCTOR WATERHOUSE, July 19, 1822
LETTER CLXVI. TO JOHN ADAMS
LETTER CLXVII. TO DOCTOR COOPER, November 2, 1822
LETTER CLXVIII. TO JAMES SMITH, December 8, 1822
LETTER, CLXIX. TO JOHN ADAMS, February 25, 1823
LETTER CLXX. TO JOHN ADAMS, April 11, 1823
LETTER CLXXI. TO THE PRESIDENT, June 11, 1823
LETTER CLXXII. TO JUDGE JOHNSON, June 12, 1823
LETTER CLXXIII. TO JAMES MADISON, August 30,1823
LETTER CLXXIV. TO JOHN ADAMS, September 4, 1823
LETTER CLXXV. TO JOHN ADAMS, October 12, 1823
LETTER CLXXVI. TO THE PRESIDENT, October 24,1823
LETTER CLXXVII. TO THE MARQUIS DE LA FAYETTE, November 4, 1823
LETTER CLXXVIII. TO JOSEPH C CABELL, February 3, 1824
LETTER CLXXIX. TO JARED SPARKS, February 4, 1824
LETTER CLXXX. TO EDWARD LIVINGSTON, April 4, 1824
LETTER CLXXXI. TO MAJOR JOHN CARTWRIGHT, June 5,1824
LETTER CLXXXII. TO MARTIN VAN BUREN, June 29, 1824
LETTER CLXXXIII. TO EDWARD EVERETT, October 15, 1824
LETTER CLXXXIV. TO JOSEPH C. CABELL, January 11, 1825
LETTER CLXXXV. TO THOMAS JEFFERSON SMITH, February 21, 1825
LETTER CLXXXVI. TO JAMES MADISON, December 24, 1825
LETTER CLXXXVII. TO WILLIAM B. GILES, December 25, 1825
LETTER CLXXXVIII. TO WILLIAM B. GILES, December 26, 1825
LETTER CLXXXIX. TO CLAIBORNE W. GOOCH, January 9, 1826
LETTER CXC. TO [ANONYMOUS], January 21, 1826
LETTER CXCI. TO JAMES MADISON, February 17,1826
THOUGHTS ON LOTTERIES.
LETTER CXCII. TO JOHN QUINCY ADAMS, March 30, 1826
LETTER CXCIII. TO MR. WEIGHTMAN, June 24, 1826
ANA. EXPLANATION OF VOLUMES IN MARBLED PAPER
List of Illustrations
Steel Engraving by Longacre from Painting of G. Stuart
Titlepage of Volume Three (of Four)
Pages With Greek Phrases and Tables:
TO LEVI LINCOLN.
Monticello, August 30, 1803.
Deak. Sir,
The enclosed letter came to hand by yesterday’s post. You will be sensible of the circumstances which make it improper that I should hazard a formal answer, as well as of the desire its friendly aspect naturally excites, that those concerned in it should understand that the spirit they express is friendly viewed. You can judge also from your knowledge of the ground, whether it may be usefully encouraged. I take the liberty, therefore, of availing myself of your neighborhood to Boston, and of your friendship to me, to request you to say to the Captain and others verbally whatever you think would be proper, as expressive of my sentiments on the subject. With respect to the day on which they wish to fix their anniversary, they may be told, that disapproving myself of transferring the honors and veneration for the great birthday of our republic to any individual, or of dividing them with individuals, I have declined letting my own birthday be known, and have engaged my family not to communicate it. This has been the uniform answer to every application of the kind.
On further consideration as to the amendment to our constitution respecting Louisiana, I have thought it better, instead of enumerating the powers which Congress may exercise, to give them the same powers they have as to other portions of the Union generally, and to enumerate the special exceptions, in some such form as the following.
‘Louisiana, as ceded by France to the United States, is made a part of the United States, its white inhabitants shall be citizens, and stand, as to their rights and obligations, on the same footing with other citizens of the United States, in analogous situations. Save only that as to the portion thereof lying north of an east and west line drawn through the mouth of Arkansas river, no new State shall be established, nor any grants of land made, other than to Indians, in exchange for equivalent portions of land occupied by them, until an amendment of the constitution shall be made for these purposes.
‘Florida also, whensoever it may be rightfully obtained, shall become a part of the United States, its white inhabitants shall thereupon be citizens, and shall stand, as to their rights and obligations, on the same footing with other citizens of the United States, in analogous situations.’
I quote this for your consideration, observing that the less that is said about any constitutional difficulty, the better: and that it will be desirable for Congress to do what is necessary, in silence. I find but one opinion as to the necessity of shutting up the country for some time. We meet in Washington the 25th of September to prepare for Congress. Accept my affectionate salutations, and great esteem and respect.
Th: Jefferson.
TO WILSON C NICHOLAS.
Monticello, September 7, 1803.
Dear Sir,
Your favor of the 3rd was delivered me at court; but we were much disappointed at not seeing you here, Mr. Madison and the Governor being here at the time. 1 enclose you a letter from Monroe on the subject of the late treaty. You will observe a hint in it, to do without delay what we are bound to do. There is reason, in the opinion of our ministers, to believe, that if the thing were to do over again, it could not be obtained, and that if we give the least opening, they will declare the treaty void. A warning amounting to that has been given to them, and an unusual kind of letter written by their minister to our Secretary of State, direct. Whatever Congress shall think it necessary to do, should be done with as little debate as possible, and particularly so far as respects the constitutional difficulty. I am aware of the force of the observations you make on the power given by the constitution to Congress, to admit new States into the Union, without restraining the subject to the territory then constituting the United States. But when I consider that the limits of the United States are precisely fixed by the treaty of 1783, that the constitution expressly declares itself to be made for the United States, I cannot help believing the intention was not to permit Congress to admit into the Union new States, which should be formed out of the territory for which, and under whose authority alone, they were then acting. I do not believe it was meant that they might receive England, Ireland, Holland, &tc. into it, which would be the case on your construction. When an instrument admits two constructions, the one safe, the other dangerous, the one precise, the other indefinite, I prefer that which is safe and precise. I had rather ask an enlargement of power from the nation, where it is found necessary, than to assume it by a construction which would make our powers boundless. Our peculiar security is in the possession of a written constitution. Let us not make it a blank paper by construction. I say the same as to the opinion of those who consider the grant of the treaty-making power as boundless. If it is, then we have no constitution. If it has bounds, they can be no others than the definitions of the powers which that instrument gives. It specifies and delineates the operations permitted to the federal government, and gives all the powers necessary to carry these into execution. Whatever of these enumerated objects is proper for a law, Congress may make the law; whatever is proper to be executed by way of a treaty, the President and Senate may enter into the treaty; whatever is to be done by a judicial sentence, the judges may pass the sentence. Nothing is more likely than that their enumeration of powers is defective. This is the ordinary case of all human works. Let us go on then perfecting it, by adding, by way of amendment to the constitution, those powers which time and trial show are still wanting. But it has been taken too much for granted, that by this rigorous construction the treaty power would be reduced to nothing. I had occasion once to examine its effect on the French treaty, made by the old Congress, and found that out of thirty odd articles which that contained, there were one, two, or three only, which could not now be stipulated under our present constitution. I confess, then, I think it important, in the present case, to set an example against broad construction, by appealing for new power to the people. If, however, our friends shall think differently, certainly I shall acquiesce with satisfaction; confiding, that the good sense of our country will correct the evil of construction when it shall produce ill effects.
No apologies for writing or speaking to me freely are necessary. On the contrary, nothing my friends can do is so dear to me, and proves to me their friendship so clearly, as the information they give me of their sentiments and those of others on interesting points where I am to act, and where information and warning is so essential to excite in me that due reflection which ought to precede action. I leave this about the 21st, and shall hope the District Court will give me an opportunity of seeing you. Accept my affectionate salutations, and assurances of cordial esteem and respect.
Th: Jefferson.
TO DOCTOR BENJAMIN RUSH.
Washington, October 4, 1803.
Dear Sir,
No one would more willingly than myself pay the just tribute due to the services of Captain Barry, by writing a letter of condolence to his widow, as you suggest. But when one undertakes to administer justice, it must be with an even hand, and by rule; what is done for one, must be done for every one in equal degree. To what a train of attentions would this draw a President? How difficult would it be to draw the line between that degree of merit entitled to such a testimonial of it, and that not so entitled? If drawn in a particular case differently from what the friends of the deceased would judge right, what offence would it give, and of the most tender kind? How much offence would be given by accidental inattentions, or want of information? The first step into such an undertaking ought to be well weighed. On the death of Dr. Franklin, the King and Convention of France went into mourning. So did the House of Representatives of the United States: the Senate refused. I proposed to General Washington that the executive departments should wear mourning; he declined it, because he said he should not know where to draw the line, if he once began that ceremony. Mr. Adams was then Vice-President, and I thought General Washington had his eye on him, whom he certainly did not love. I told him the world had drawn so broad a line between himself and Dr. Franklin, on the one side, and the residue of mankind, on the other, that we might wear mourning for them, and the question still remain new and undecided as to all others. He thought it best, however, to avoid it. On these considerations alone, however well affected to the merit of Commodore Barry, I think it prudent not to engage myself in a practice which may become embarrassing.
Tremendous times in Europe! How mighty this battle of lions and tigers? With what sensations should the common herd of cattle look on it? With no partialities certainly. If they can so far worry one another as to destroy their power of tyrannizing the one over the earth, the other the waters, the world may perhaps enjoy peace, till they recruit again.
Affectionate and respectful salutations.
Th: Jefferson.
TO M. DUPONT DE NEMOURS.
Washington, November 1, 1803.
My Dear Sir,
Your favors of April the 6th and June the 27th were duly received, and with the welcome which every thing brings from you. The treaty which has so happily sealed the friendship of our two countries, has been received here with general acclamation. Some inflexible federalists have still ventured to brave the public opinion. It will fix their character with the world and with posterity, who, not descending to the other points of difference between us, will judge them by this fact, so palpable as to speak for itself, in all times and places. For myself and my country I thank you for the aids you have given in it; and I congratulate you on having lived to give those aids in a transaction replete with blessings to unborn millions of men, and which will mark the face of a portion on the globe so extensive as that which now composes the United States of America. It is true that at this moment a little cloud hovers in the horizon. The government of Spain has protested against the right of France to transfer; and it is possible she may refuse possession, and that this may bring on acts of force. But against such neighbors as France there, and the United States here, what she can expect from so gross a compound of folly and false faith, is not to be sought in the book of wisdom. She is afraid of her enemies in Mexico. But not more than we are. Our policy will be to form New Orleans and the country on both sides of it on the Gulf of Mexico, into a State; and, as to all above that, to transplant our Indians into it, constituting them a Marechaussee to prevent emigrants crossing the river, until we shall have filled up all the vacant country on this side. This will secure both Spain and us as to the mines of Mexico, for half a century, and we may safely trust the provisions for that time to the men who shall live in it.
I have communicated with Mr. Gallatin on the subject of using your house in any matters of consequence we may have to do at Paris. He is impressed with the same desire I feel to give this mark of our confidence in you, and the sense we entertain of your friendship and fidelity. Mr. Behring informs him that none of the money which will be due from us to him, as the assignee of France, will be wanting at Paris. Be assured that our dispositions are such as to let no occasion pass unimproved, of serving you, where occurrences will permit it.
Present my respects to Madame Dupont, and accept yourself assurances of my constant and warm friendship.
Th: Jefferson.
Washington, November 4,1803.
Dear Sir,
A report reaches us this day from Baltimore (on probable, but not certain grounds), that Mr. Jerome Bonaparte, brother of the First Consul, was yesterday* married to Miss Patterson of that city. The effect of this measure on the mind of the First Consul, is not for me to suppose; but as it might occur to him primâ facie, that the executive of the United States ought to have prevented it, I have thought it advisable to mention the subject to you, that if necessary, you may by explanations set that idea to rights. You know that by our laws, all persons are free to enter into marriage, if of twenty-one years of age, no one having a power to restrain it, not even their parents; and that under that age, no one can prevent it but the parent or guardian. The lady is under age, and the parents, placed between her affections which were strongly fixed, and the considerations opposing the measure, yielded with pain and anxiety to the former.
* November 8. It is now said that it did not take place on
the 3rd, but will this day.
Mr. Patterson is the President of the bank of Baltimore, the wealthiest man in Maryland, perhaps in the United States, except Mr. Carroll; a man of great virtue and respectability; the mother is the sister of the lady of General Samuel Smith; and, consequently, the station of the family in society is with the first of the United States. These circumstances fix rank in a country where there are no hereditary titles. Your treaty has obtained nearly a general approbation. The federalists spoke and voted against it, but they are now so reduced in their numbers as to be nothing. The question on its ratification in the Senate was decided by twenty-four against seven, which was ten more than enough. The vote in the House of Representatives for making provision for its execution, was carried by eighty-nine against twenty-three, which was a majority of sixty-six, and the necessary bills are going through the Houses by greater majorities. Mr. Pichon, according to instructions from his government, proposed to have added to the ratification a protestation against any failure in time or other circumstances of execution, on our part. He was told, that in that case we should annex a counter protestation, which would leave the thing exactly where it was; that this transaction had been conducted from the commencement of the negotiation to this stage of it, with a frankness and sincerity honorable to both nations, and comfortable to the heart of an honest man to review; that to annex to this last chapter of the transaction such an evidence of mutual distrust, was to change its aspect dishonorably for us both, and contrary to truth as to us; for that we had not the smallest doubt that France would punctually execute its part; and I assured Mr. Pichon that I had more confidence in the word of the First Consul than in all the parchment we could sign. He saw that we had ratified the treaty; that both branches had passed by great majorities one of the bills for execution, and would soon pass the other two; that no circumstances remained that could leave a doubt of our punctual performance; and like an able and an honest minister (which he is in the highest degree) he undertook to do, what he knew his employers would do themselves, were they here spectators of all the existing circumstances, and exchanged the ratification’s purely and simply; so that this instrument goes to the world as an evidence of the candor and confidence of the nations in each other, which will have the best effects. This was the more justifiable, as Mr. Pichon knew that Spain had entered with us a protestation against our ratification of the treaty, grounded, first, on the assertion that the First Consul had not executed the conditions of the treaties of cession, and secondly, that he had broken a solemn promise not to alienate the country to any nation. We answered, that these were private questions between France and Spain, which they must settle together; that we derived our title from the First Consul, and did not doubt his guarantee of it: and we, four days ago, sent off orders to the Governor of the Mississippi territory and General Wilkinson, to move down with the troops at hand to New Orleans, to receive the possession from Mr. Laussat. If he is heartily disposed to carry the order of the Consul into execution, he can probably command a volunteer force at New Orleans, and will have the aid of ours also, if he desires it, to take the possession and deliver it to us. If he is not so disposed, we shall take the possession, and it will rest with the government of France, by adopting the act as their own and obtaining the confirmation of Spain, to supply the non-execution of their stipulation to deliver, and to entitle themselves to the complete execution of our part of the agreements. In the mean time, the legislature is passing the bills, and we are preparing every thing to be done on our part towards execution, and we shall not avail ourselves of the three months’ delay after possession of the province, allowed by the treaty for the delivery of the stock, but shall deliver it the moment that possession is known here, which will be on the eighteenth day after it has taken place.
Accept my affectionate salutations, and assurances of my constant esteem and respect.
Th: Jefferson.
Washington, November 14, 1803.
Sir,
I have duly received the volume on the claims of literature; which you did me the favor to send me through Mr. Monroe: and have read with satisfaction the many judicious reflections it contains, on the condition of the respectable class of literary men. The efforts for their relief, made by a society of private citizens, are truly laudable: but they are, as you justly observe, but a palliation of an evil, the cure of which calls for all the wisdom and the means of the nation. The greatest evils of populous society have ever appeared to me to spring from the vicious distribution of its members among the occupations called for. I have no doubt that those nations are essentially right, which leave this to individual choice, as a better guide to an advantageous distribution, than any other which could be devised. But when, by a blind concourse, particular occupations are ruinously overcharged, and others left in want of hands, the national authorities can do much towards restoring the equilibrium. On the revival of letters, learning became the universal favorite. And with reason, because there was not enough of it existing to manage the affairs of a nation to the best advantage, nor to advance its individuals to the happiness of which they were susceptible, by improvements in their minds, their morals, their health, and in those conveniences which contribute to the comfort and embellishment of life. All the efforts of the society, therefore, were directed to the increase of learning, and the inducements of respect, ease, and profit were held up for its encouragement. Even the charities of the nation forgot that misery was their object, and spent themselves in founding schools to transfer to science the hardy sons of the plough. To these incitements were added the powerful fascinations of great cities. These circumstances have long since produced an overcharge in the class of competitors for learned occupation, and great distress among the supernumerary candidates; and the more, as their habits of life have disqualified them for re-entering into the laborious class. The evil cannot be suddenly, nor perhaps ever entirely cured: nor should I presume to say by what means it may be cured. Doubtless there are many engines which the nation might bring to bear on this object. Public opinion and public encouragement are among these. The class principally defective is that of agriculture. It is the first in utility, and ought to be the first in respect. The same artificial means which have been used to produce a competition in learning, may be equally successful in restoring agriculture to its primary dignity in the eyes of men. It is a science of the very first order. It counts among its handmaids the most respectable sciences, such as Chemistry, Natural Philosophy, Mechanics, Mathematics generally, Natural History, Botany. In every College and University, a professorship of agriculture, and the class of its students, might be honored as the first. Young men closing their academical education with this, as the crown of all other sciences, fascinated with its solid charms, and at a time when they are to choose an occupation, instead of crowding the other classes, would return to the farms of their fathers, their own, or those of others, and replenish and invigorate a calling, now languishing under contempt and oppression. The charitable schools, instead of storing their pupils with a lore which the present state of society does not call for, converted into schools of agriculture, might restore them to that branch, qualified to enrich and honor themselves, and to increase the productions of the nation instead of consuming them. A gradual abolition of the useless offices, so much accumulated in all governments, might close this drain also from the labors of the field, and lessen the burthens imposed on them. By these, and the better means which will occur to others, the surcharge of the learned, might in time be drawn off to recruit the laboring class of citizenss the sum of industry be increased, and that of misery diminished.
Among the ancients, the redundance of population was sometimes checked by exposing infants. To the moderns, America has offered a more humane resource. Many, who cannot find employment in Europe, accordingly come here. Those who can labor do well, for the most part. Of the learned class of emigrants, a small portion find employments analogous to their talents. But many fail, and return to complete their course of misery in the scenes where it began. Even here we find too strong a current from the country to the towns; and instances beginning to appear of that species of misery, which you are so humanely endeavoring to relieve with you. Although we have in the old countries of Europe the lesson of their experience to warn us, yet I am not satisfied we shall have the firmness and wisdom to profit by it. The general desire of men to live by their heads rather than their hands, and the strong allurements of great cities to those who have any turn for dissipation, threaten to make them here, as in Europe, the sinks of voluntary misery. I perceive, however, that I have suffered my pen to run into a disquisition, when I had taken it up only to thank you for the volume you had been so kind as to send me, and to express my approbation of it. After apologizing, therefore, for having touched on a subject so much more familiar to you, and better understood, I beg leave to assure you of my high consideration and respect.
Th: Jefferson.
Washington, December 1, 1803.
Dear Sir,
The explanations in your letter of yesterday were quite unnecessary to me. I have had too satisfactory proofs of your friendly regard, to be disposed to suspect any thing of a contrary aspect.
I understood perfectly the expressions stated in the newspaper to which you allude, to mean, that ‘though the proposition came from the republican quarter of the House, yet you should not concur with it.’ I am aware, that in parts of the Union, and even with persons to whom Mr. Eppes and Mr. Randolph are unknown, and myself little known, it will be presumed from their connection, that what comes from them comes from me. No men on earth are more independent in their sentiments than they are, nor any one less disposed than I am to influence the opinions of others. We rarely speak of politics, or of the proceedings of the House, but merely historically; and I carefully avoid expressing an opinion on them in their presence, that we may all be at our ease. With other members, I have believed that more unreserved communications would be advantageous to the public. This has been, perhaps, prevented by mutual delicacy. I have been afraid to express opinions unasked, lest I should be suspected of wishing to direct the legislative action of members. They have avoided asking communications from me, probably, lest they should be suspected of wishing to fish out executive secrets. I see too many proofs of the imperfection of human reason, to entertain wonder or intolerance at any difference of opinion on any subject; and acquiesce in that difference as easily as on a difference of feature or form: experience having long taught me the reasonableness of mutual sacrifices of opinion among those who are to act together for any common object, and the expediency of doing what good we can, when we cannot do all we would wish.
Accept my friendly salutations, and assurances of great esteem and respect.
Th: Jefferson.
THOMAS JEFFERSON TO MR. GALLATIN.
The Attorney General having considered and decided, that the prescription in the law for establishing a bank, that the officers in the subordinate offices of discount and deposit, shall be appointed ‘on the same terms and in the same manner practised in the principal bank,’ does not extend to them the principle of rotation, established by the legislature in the body of directors in the principal bank, it follows that the extension of that principle has been merely a voluntary and prudential act of the principal bank, from which they are free to depart. I think the extension was wise and proper on their part, because the legislature having deemed rotation useful in the principal bank constituted by them, there would be the same reason for it in the subordinate banks to be established by the principal. It breaks in upon the esprit de corps, so apt to prevail in permanent bodies; it gives a chance for the public eye penetrating into the sanctuary of those proceedings and practices, which the avarice of the directors may introduce for their personal emolument, and which the resentments of excluded directors, or the honesty of those duly admitted, might betray to the public; and it gives an opportunity at the end of the year, or at other periods, of correcting a choice, which, on trial, proves to have been unfortunate; an evil of which themselves complain in their distant institutions. Whether, however, they have a power to alter this or not, the executive has no right to decide; and their consultation with you has been merely an act of complaisance, or from a desire to shield so important an innovation under the cover of executive sanction. But ought we to volunteer our sanction in such a case? Ought we to disarm ourselves of any fair right of animadversion, whenever that institution shall be a legitimate subject of consideration? I own I think the most proper answer would be, that we do not think ourselves authorized to give an opinion on the question.
From a passage in the letter of the President, I observe an idea of establishing a branch bank of the United States in New Orleans. This institution is one of the most deadly hostility existing, against the principles and form of our constitution. The nation is, at this time, so strong and united in its sentiments, that it cannot be shaken at this moment. But suppose a series of untoward events should occur, sufficient to bring into doubt the competency of a republican government to meet a crisis of great danger, or to unhinge the confidence of the people in the public functionaries; an institution like this, penetrating by its branches every part of the Union, acting by command and in phalanx, may, in a critical moment, upset the government. I deem no government safe which is under the vassalage of any self-constituted authorities, or any other authority than that of the nation, or its regular functionaries. What an obstruction could not this bank of the United States, with all its branch banks, be in time of war? It might dictate to us the peace we should accept, or withdraw its aids. Ought we then to give further growth to an institution so powerful, so hostile? That it is so hostile we know, 1. from a knowledge of the principles of the persons composing the body of directors in every bank, principal or branch; and those of most of the stock-holders: 2. from their opposition to the measures and principles of the government, and to the election of those friendly to them: and, 3. from the sentiments of the newspapers they support. Now, while we are strong, it is the greatest duty we owe to the safety of our constitution, to bring this powerful enemy to a perfect subordination under its authorities. The first measure would be to reduce them to an equal footing only with other banks, as to the favors of the government. But, in order to be able to meet a general combination of the banks against us, in a critical emergency, could we not make a beginning towards an independent use of our own money, towards holding our own bank in all the deposits where it is received, and letting the Treasurer give his draft or note for payment at any particular place, which, in a well conducted government, ought to have as much credit as any private draft, or bank note, or bill, and would give us the same facilities which we derive from the banks? I pray you to turn this subject in your mind, and to give it the benefit of your knowledge of details; whereas, I have only very general views of the subject. Affectionate salutations.
Washington, December 13, 1803.
TO DOCTOR PRIESTLEY.
Washington, January 29, 1804.
Dear Sir,
Your favor of December the 12th came duly to hand, as did the second letter to Doctor Linn, and the treatise on Phlogiston, for which I pray you to accept my thanks. The copy for Mr. Livingston has been delivered, together with your letter to him, to Mr. Harvie, my secretary, who departs in a day or two for Paris, and will deliver them himself to Mr. Livingston, whose attention to your matter cannot be doubted. I have also to add my thanks to Mr. Priestley, your son, for the copy of your Harmony, which I have gone through with great satisfaction. It is the first I have been able to meet with, which is clear of those long repetitions of the same transaction, as if it were a different one because related with some different circumstances.
I rejoice that you have undertaken the task of comparing the moral doctrines of Jesus with those of the ancient Philosophers. You are so much in possession of the whole subject, that you will do it easier and better than any other person living. I think you cannot avoid giving, as preliminary to the comparison, a digest of his moral doctrines, extracted in his own words from the Evangelists, and leaving out every thing relative to his personal history and character. It would be short and precious. With a view to do this for my own satisfaction, I had sent to Philadelphia to get two Testaments (Greek) of the same edition, and two English, with a design to cut out the morsels of morality, and paste them on the leaves of a book, in the manner you describe as having been pursued in forming your Harmony. But I shall now get the thing done by better hands.
I very early saw that Louisiana was indeed a speck in our horizon, which was to burst in a tornado; and the public are un-apprized how near this catastrophe was. Nothing but a frank and friendly developement of causes and effects on our part, and good sense enough in Bonaparte to see that the train was unavoidable, and would change the face of the world, saved us from that storm. I did not expect he would yield till a war took place between France and England, and my hope was to palliate and endure, if Messrs. Ross, Morris, &c. did not force a premature rupture until that event. I believed the event not very distant, but acknowledge it came on sooner than I had expected. Whether, however, the good sense of Bonaparte might not see the course predicted to be necessary and unavoidable, even before a war should be imminent, was a chance which we thought it our duty to try: but the immediate prospect of rupture brought the case to immediate decision. The denouement has been happy: and I confess I look to this duplication of area for the extending a government so free and economical as ours, as a great achievement to the mass of happiness which is to ensue. Whether we remain in one confederacy, or form into Atlantic and Mississippi confederacies, I believe not very important to the happiness of either part. Those of the western confederacy will be as much our children and descendants as those of the eastern, and I feel myself as much identified with that country, in future time, as with this: and did I now foresee a separation at some future day, yet I should feel the duty and the desire to promote the western interests as zealously as the eastern, doing all the good for both portions of our future family which should fall within my power.
Have you seen the new work of Malthus on Population? It is one of the ablest I have ever seen. Although his main object is to delineate the effects of redundancy of population, and to test the poor laws of England, and other palliations for that evil, several important questions in political economy, allied to his subject incidentally, are treated with a masterly hand. It is a single octavo volume, and I have been only able to read a borrowed copy, the only one I have yet heard of. Probably our friends in England will think of you, and give you an opportunity of reading it.
Accept my affectionate salutations, and assurances of great esteem and respect.
Th: Jefferson.
Washington, March 3, 1804.
Dear Sir,
Although it is long since I received your favor of October the 27th, yet I have not had leisure sooner to acknowledge it. In the Middle and Southern States, as great an union of sentiment has now taken place as is perhaps desirable. For as there will always be an opposition, I believe it had better be from avowed monarchists than republicans. New York seems to be in danger of republican division; Vermont is solidly with us; Rhode Island with us on anomalous grounds; New Hampshire on the verge of the republican shore; Connecticut advancing towards it very slowly, but with steady step; your State only uncertain of making port at all. I had forgotten Delaware, which will be always uncertain from the divided character of her citizens. If the amendment of the constitution passes Rhode Island (and we expect to hear in a day or two), the election for the ensuing four years seems to present nothing formidable. I sincerely regret that the unbounded calumnies of the federal party have obliged me to throw myself on the verdict of my country for trial, my great desire having been to retire at the end of the present term, to a life of tranquillity; and it was my decided purpose when I entered into office. They force my continuance. If we can keep the vessel of State as steadily in her course for another four years, my earthly purposes will be accomplished, and I shall be free to enjoy, as you are doing, my family, my farm, and my books. That your enjoyments may continue as long as you shall wish them, I sincerely pray, and tender you my friendly salutations, and assurances of great respect and esteem.
Th: Jefferson.
TO GIDEON GRANGER.
Monticello, April 16, 1804.
Dear Sir,
In our last conversation you mentioned a federal scheme afloat, of forming a coalition between the federalists and republicans, of what they called the seven eastern States. The idea was new to me, and after time for reflection, I had no opportunity of conversing with you again. The federalists know that, eo nomine, they are gone for ever. Their object, therefore, is, how to return into power under some other form. Undoubtedly they have but one means, which is to divide the republicans, join the minority, and barter with them for the cloak of their name. I say, join the minority; because the majority of the republicans, not needing them, will not buy them. The minority, having no other means of ruling the majority, will give a price for auxiliaries, and that price must be principle. It is true that the federalists, needing their numbers also, must also give a price, and principle is the coin they must pay in. Thus a bastard system of federo-republicanism will rise on the ruins of the true principles of our revolution. And when this party is formed, who will constitute the majority of it, which majority is then to dictate? Certainly the federalists. Thus their proposition of putting themselves into gear with the republican minority, is exactly like Roger Sherman’s proposition to add Connecticut to Rhode Island. The idea of forming seven eastern States is moreover clearly to form the basis of a separation of the Union. Is it possible that real republicans can be gulled by such a bait? And for what? What do they wish, that they have not? Federal measures? That is impossible. Republican measures? Have they them not? Can any one deny, that in all important questions of principle, republicanism prevails? But do they want that their individual will shall govern the majority? They may purchase the gratification of this unjust wish, for a little time, at a great price; but the federalists must not have the passions of other men, if, after getting thus into the seat of power, they suffer themselves to be governed by their minority. This minority may say, that whenever they relapse into their own principles, they will quit them, and draw the seat from under them. They may quit them, indeed, but, in the mean time, all the venal will have become associated with them, and will give them a majority sufficient to keep them in place, and to enable them to eject the heterogeneous friends by whose aid they get again into power. I cannot believe any portion of real republicans will enter into this trap; and if they do, I do not believe they can carry with them the mass of their States, advancing so steadily as we see them, to an union of principle with their brethren. It will be found in this, as in all other similar cases, that crooked schemes will end by overwhelming their authors and coadjutors in disgrace, and that he alone who walks strict and upright, and who in matters of opinion will be contented that others should be as free as himself, and acquiesce when his opinion is fairly overruled, will attain his object in the end. And that this may be the conduct of us all, I offer my sincere prayers, as well as for your health and happiness.
Th: Jefferson.
TO MRS. ADAMS.
Washington, June 13,1804.
Dear Madam,
The affectionate sentiments which you have had the goodness to express in your letter of May the 20th, towards my dear departed daughter, have awakened in me sensibilities natural to the occasion, and recalled your kindnesses to her, which I shall ever remember with gratitude and friendship. I can assure you with truth, they had made an indelible impression on her mind, and that to the last, on our meetings after long separations, whether I had heard lately of you, and how you did, were among the earliest of her inquiries. In giving you this assurance, I perform a sacred duty for her, and, at the same time, am thankful for the occasion furnished me, of expressing my regret that circumstances should have arisen, which have seemed to draw a line of separation between us. The friendship with which you honored me has ever been valued, and fully reciprocated; and although events have been passing which might be trying to some minds, I never believed yours to be of that kind, nor felt that my own was. Neither my estimate of your character, nor the esteem founded in that, has ever been lessened for a single moment, although doubts whether it would be acceptable may have forbidden manifestations of it.
Mr. Adams’s friendship and mine began at an earlier date. It accompanied us through long and important scenes. The different conclusions we had drawn from our political reading and reflections, were not permitted to lessen mutual esteem; each party being conscious they were the result of an honest conviction in the other. Like differences of opinion existing among our fellow citizens, attached them to the one or the other of us, and produced a rivalship in their minds which did not exist in ours. We never stood in one another’s way. For if either had been withdrawn at any time, his favorers would not have gone over to the other, but would have sought for some one of homogeneous opinions. This consideration was sufficient to keep down all jealousy between us, and to guard our friendship from any disturbance by sentiments of rivalship: and I can say with truth, that one act of Mr. Adams’s life, and one only, ever gave me a moment’s personal displeasure. I did consider his last appointments to office as personally unkind. They were from among my most ardent political enemies, from whom no faithful co-operation could ever be expected; and laid me under the embarrassment of acting through men, whose views were to defeat mine, or to encounter the odium of putting others in their places. It seems but common justice to leave a successor free to act by instruments of his own choice. If my respect for him did not permit me to ascribe the whole blame to the influence of others, it left something for friendship to forgive, and after brooding over it for some little time, and not always resisting the expression of it, I forgave it cordially, and returned to the same state of esteem and respect for him which had so long subsisted. Having come into life a little later than Mr. Adams, his career has preceded mine, as mine is followed by some other; and it will probably be closed at the same distance after him which time originally placed between us. I maintain for him, and shall carry into private life, an uniform and high measure of respect and good will, and for yourself a sincere attachment.
I have thus, my dear Madam, opened myself to you without reserve, which I have long wished an opportunity of doing; and without knowing how it will be received, I feal[sp.] relief from being unbosomed. And I have now only to entreat your forgiveness for this transition from a subject of domestic affliction, to one which seems of a different aspect. But though connected with political events, it has been viewed by me most strongly in its unfortunate bearings on my private friendships. The injury these have sustained has been a heavy price for what has never given me equal pleasure. That you may both be favored with health, tranquillity, and long life, is the prayer of one who tenders you the assurance of his highest consideration and esteem.
Th: Jefferson.
TO GOVERNOR PAGE.
Washington, June 25, 1804.
Your letter, my dear friend, of the 25th ultimo, is a new proof of the goodness of your heart, and the part you take in my loss marks an affectionate concern for the greatness of it. It is great indeed. Others may lose of their abundance, but I, of my want, have lost even the half of all I had. My evening prospects now hang on the slender thread of a single life. Perhaps I maybe destined to see even this last cord of parental affection broken! The hope with which I had looked forward to the moment, when, resigning public cares to younger hands, I was to retire to that domestic comfort from which the last great step is to be taken, is fearfully blighted. When you and I look back on the country over which we have passed, what a field of slaughter does it exhibit! Where are all the friends who entered it with us, under all the inspiring energies of health and hope? As if pursued by the havoc of war, they are strewed by the way, some earlier, some later, and scarce a few stragglers remain to count the numbers fallen, and to mark yet, by their own fall, the last footsteps of their party. Is it a desirable thing to bear up through the heat of the action to witness the death of all our companions, and merely be the last victim? I doubt it. We have, however, the traveller’s consolation. Every step shortens the distance we have to go; the end of our journey is in sight, the bed wherein we are to rest, and to rise in the midst of the friends we have lost. ‘We sorrow not, then, as others who have no hope’; but look forward to the day which ‘joins us to the great majority.’ But whatever is to be our destiny, wisdom, as well as duty, dictates that we should acquiesce in the will of Him whose it is to give and take away, and be contented in the enjoyment of those who are still permitted to be with us. Of those connected by blood, the number does not depend on us. But friends we have, if we have merited them. Those of our earliest years stand nearest in our affections. But in this too, you and I have been unlucky. Of our college friends (and they are the dearest) how few have stood with us in the great political questions which have agitated our country: and these were of a nature to justify agitation. I did not believe the Lilliputian fetters of that day strong enough to have bound so many. Will not Mrs. Page, yourself, and family, think it prudent to seek a healthier region for the months of August and September? And may we not flatter ourselves that you will cast your eye on Monticello? We have not many summers to live. While fortune places us then within striking distance, let us avail ourselves of it, to meet and talk over the tales of other times.
Present me respectfully to Mrs. Page, and accept yourself my friendly salutations, and assurances of constant affection.
Th: Jefferson.
TO P. MAZZEI.
Washington, July 18, 1804.
My Dear Sir,
It is very long, I know, since I wrote you. So constant is the pressure of business that there is never a moment, scarcely, that something of public importance is not waiting for me. I have, therefore, on a principle of conscience, thought it my duty to withdraw almost entirely from all private correspondence, and chiefly the trans-Atlantic; I scarcely write a letter a year to any friend beyond sea. Another consideration has led to this, which is the liability of my letters to miscarry, be opened, and made ill use of. Although the great body of our country are perfectly returned to their ancient principles, yet there remains a phalanx of old tories and monarchists, more envenomed, as all their hopes become more desperate. Every word of mine which they can get hold of, however innocent, however orthodox even, is twisted, tormented, perverted, and, like the words of holy writ, are made to mean every thing but what they were intended to mean. I trust little, therefore, unnecessarily in their way, and especially on political subjects. I shall not, therefore, be free to answer all the several articles of your letters.
On the subject of treaties, our system is to have none with any nation, as far as can be avoided. The treaty with England has therefore, not been renewed, and all overtures for treaty with other nations have been declined. We believe, that with nations as with individuals, dealings may be carried on as anvantageously[sp.], perhaps more so, while their continuance depends on a voluntary good treatment, as if fixed by a contract, which, when it becomes injurious to either, is made, by forced constructions, to mean what suits them, and becomes a cause of war instead of a bond of peace.
We wish to be on the closest terms of friendship with Naples, and we will prove it by giving to her citizens, vessels, and goods all the privileges of the most favored nation; and while we do this voluntarily, we cannot doubt they will voluntarily do the same for us. Our interests against the Barbaresques being also the same, we have little doubt she will give us every facility to insure them, which our situation may ask and hers admit. It is not, then, from a want of friendship that we do not propose a treaty with Naples, but because it is against our system to embarrass ourselves with treaties, or to entangle ourselves at all with the affairs of Europe. The kind offices we receive from that government are more sensibly felt, as such, than they would be, if rendered only as due to us by treaty.
Five fine frigates left the Chesapeake the 1st instant for Tripoli, which, in addition to the force now there, will, I trust, recover the credit which Commodore Morris’s two years’ sleep lost us, and for which he has been broke. I think they will make Tripoli sensible, that they mistake their interest in choosing war with us; and Tunis also, should she have declared war, as we expect, and almost wish.
Notwithstanding this little diversion, we pay seven or eight millions of dollars annually of our public debt, and shall completely discharge it in twelve years more. That done, our annual revenue, now thirteen millions of dollars, which by that time will be twenty-five, will pay the expenses of any war we may be forced into, without new taxes or loans. The spirit of republicanism is now in almost all its ancient vigor, five sixths of the people being with us. Fourteen of the seventeen States are completely with us, and two of the other three will be in one year. We have now got back to the ground on which you left us. I should have retired at the end of the first four years, but that the immense load of tory calumnies which have been manufactured respecting me, and have filled the European market, have obliged me to appeal once more to my country for a justification. I have no fear but that I shall receive honorable testimony by their verdict on those calumnies. At the end of the next four years I shall certainly retire. Age, inclination, and principle all dictate this. My health, which at one time threatened an unfavorable turn, is now firm. The acquisition of Louisiana, besides doubling our extent, and trebling our quantity of fertile country, is of incalculable value, as relieving us from the danger of war. It has enabled us to do a handsome thing for Fayette. He had received a grant of between eleven and twelve thousand acres north of the Ohio, worth, perhaps, a dollar an acre. We have obtained permission of Congress to locate it in Louisiana. Locations can be found adjacent to the city of New Orleans, in the island of New Orleans and in its vicinity, the value of which cannot be calculated. I hope it will induce him to come over and settle there with his family. Mr. Livingston having asked leave to return, General Armstrong, his brother-in-law, goes in his place: he is of the first order of talents.
Remarkable deaths lately, are, Samuel Adams, Edmund Pendleton, Alexander Hamilton, Stephens Thompson Mason, Mann Page, Bellini, and Parson Andrews. To these I have the inexpressible grief of adding the name of my youngest daughter, who had married a son of Mr. Eppes, and has left two children. My eldest daughter alone remains to me, and has six children. This loss has increased my anxiety to retire, while it has dreadfully lessened the comfort of doing it. Wythe, Dickinson, and Charles Thomson are all living, and are firm republicans. You informed me formerly of your marriage, and your having a daughter, but have said nothing in you late letters on that subject. Yet whatever concerns your happiness is sincerely interesting to me, and is a subject of anxiety, retaining, as I do, cordial sentiments of esteem and affection for you. Accept, I pray you, my sincere assurances of this, with my most friendly salutations.
Th: Jefferson.
TO MRS. ADAMS.
Washington, July 22, 1804.
Dear Madam,
Your favor of the 1st instant was duly received, and I would not again have intruded on you, but to rectify certain facts which seem not to have been presented to you under their true aspect. My charities to Callendar are considered as rewards for his calumnies. As early, I think, as 1796, I was told in Philadelphia, that Callendar, the author of the ‘Political Progress of Britain,’ was in that city, a fugitive from persecution for having written that book, and in distress. I had read and approved the book; I considered him as a man of genius, unjustly persecuted. I knew nothing of his private character, and immediately expressed my readiness to contribute to his relief, and to serve him. It was a considerable time after, that, on application from a person who thought of him as I did, I contributed to his relief, and afterwards repeated the contribution. Himself I did not see till long after, nor ever more than two or three times. When he first began to write, he told some useful truths in his coarse way; but nobody sooner disapproved of his writing than I did, or wished more that he would be silent. My charities to him were no more meant as encouragements to his scurrilities, than those I give to the beggar at my door are meant as rewards for the vices of his life, and to make them chargeable to myself. In truth, they would have been greater to him, had he never written a word after the work for which he fled from Britain. With respect to the calumnies and falsehoods which writers and printers at large published against Mr. Adams, I was as far from stooping to any concern or approbation of them, as Mr. Adams was respecting those of Porcupine, Fenno, or Russell, who published volumes against me for every sentence vended by their opponents against Mr. Adams. But I never supposed Mr. Adams had any participation in the atrocities of these editors, or their writers. I knew myself incapable of that base warfare, and believed him to be so. On the contrary, whatever I may have thought of the acts of the administration of that day, I have ever borne testimony to Mr. Adams’s personal worth; nor was it ever impeached in my presence, without a just vindication of it on my part. I never supposed that any person who knew either of us, could believe that either of us meddled in that dirty work. But another fact is, that I ‘liberated a wretch who was suffering for a libel against Mr. Adams.’ I do not know who was the particular wretch alluded to; but I discharged every person under punishment or prosecution under the sedition law, because I considered, and now consider, that law to be a nullity, as absolute and as palpable as if Congress had ordered us to fall down and worship a golden image; and that it was as much my duty to arrest its execution in every stage, as it would have been to have rescued from the fiery furnace those who should have been cast into it for refusing to worship the image. It was accordingly done in every instance, without asking what the offenders had done, or against whom they had offended, but whether the pains they were suffering were inflicted under the pretended sedition law. It was certainly possible that my motives for contributing to the relief of Callendar, and liberating sufferers under the sedition law might have been to protect, encourage, and reward slander; but they may also have been those which inspire ordinary charities to objects of distress, meritorious or not, or the obligation of an oath to protect the constitution, violated by an unauthorized act of Congress. Which of these were my motives, must be decided by a regard to the general tenor of my life. On this I am not afraid to appeal to the nation at large, to posterity, and still less to that Being who sees himself our motives, who will judge us from his own knowledge of them, and not on the testimony of Porcupine or Fenno.
You observe, there has been one other act of my administration personally unkind, and suppose it will readily suggest itself to me. I declare on my honor, Madam, I have not the least conception what act is alluded to. I never did a single one with an unkind intention. My sole object in this letter being to place before your attention, that the acts imputed to me are either such as are falsely imputed, or as might flow from good as well as bad motives, I shall make no other addition, than the assurances of my continued wishes for the health and happiness of yourself and Mr. Adams.
Th: Jefferson.
TO JAMES MADISON.
Monticello, August 15, 1804.
Dear Sir,
Your letter dated the 7th should probably have been of the 14th, as I received it only by that day’s post. I return you Monroe’s letter, which is of an awful complexion; and I do not wonder the communications it contains made some impression on him. To a person placed in Europe, surrounded by the immense resources of the nations there, and the greater wickedness of their courts, even the limits which nature imposes on their enterprises are scarcely sensible. It is impossible that France and England should combine for any purpose; their mutual distrust and deadly hatred of each other admit no co-operation. It is impossible that England should be willing to see France re-possess Louisiana, or get footing on our continent, and that France should willingly see the United States re-annexed to the British dominions. That the Bourbons should be replaced on their throne and agree to any terms of restitution, is possible: but that they and England joined, could recover us to British dominion, is impossible. If these things are not so, then human reason is of no aid in conjecturing the conduct of nations. Still, however, it is our unquestionable interest and duty to conduct ourselves with such sincere friendship and impartiality towards both nations, as that each may see unequivocally, what is unquestionably true, that we may be very possibly driven into her scale by unjust conduct in the other. I am so much impressed with the expediency of putting a termination to the right of France to patronize the rights of Louisiana, which will cease with their complete adoption as citizens of the United States, that I hope to see that take place on the meeting of Congress. I enclose you a paragraph from a newspaper respecting St. Domingo, which gives me uneasiness. Still I conceive the British insults in our harbor as more threatening. We cannot be respected by France as a neutral nation, nor by the world or ourselves as an independent one, if we do not take effectual measures to support, at every risk, our authority in our own harbors. I shall write to Mr. Wagner directly (that a post may not be lost by passing through you) to send us blank commissions for Orleans and Louisiana, ready sealed, to be filled up, signed, and forwarded by us. Affectionate salutations and constant esteem.
Th: Jefferson.
TO GOVERNOR CLAIBORNE.
Monticello, August 30, 1804.
Dear Sir,
Various circumstances of delay have prevented my forwarding till now the general arrangements of the government of the territory of Orleans. Enclosed herewith you will receive the commissions. Among these is one for yourself as Governor. With respect to this I will enter into frank explanations. This office was originally destined for a person * whose great services and established fame would have rendered him peculiarly acceptable to the nation at large. Circumstances, however, exist, which do not now permit his nomination, and perhaps may not at any time hereafter. That, therefore, being suspended, and entirely contingent, your services have been so much approved, as to leave no desire to look elsewhere to fill the office. Should the doubts you have sometimes expressed, whether it would be eligible for you to continue, still exist in your mind, the acceptance of the commission gives you time to satisfy yourself by further experience, and to make the time and manner of withdrawing, should you ultimately determine on that, agreeable to yourself. Be assured, that whether you continue or retire, it will be with every disposition on my part to be just and friendly to you.
I salute you with friendship and respect.
Th: Jefferson.
[* In the margin is written by the author, ‘La Fayette.‘]
TO MRS. ADAMS.
Monticello, September 11, 1804,
Your letter, Madam, of the 18th of August has been some days received, but a press of business has prevented the acknowledgment of it: perhaps, indeed, I may have already trespassed too far on your attention. With those who wish to think amiss of me, I have learned to be perfectly indifferent; but where I know a mind to be ingenuous, and to need only truth to set it to rights, I cannot be as passive. The act of personal unkindness alluded to in your former letter, is said in your last to have been the removal of your eldest son from some office to which the judges had appointed him. I conclude, then, he must have been a commissioner of bankruptcy. But I declare to you, on my honor, that this is the first knowledge I have ever had that he was so. It may be thought, perhaps, that I ought to have inquired who were such, before I appointed others. But it is to be observed, that the former law permitted the judges to name commissioners occasionally only, for every case as it arose, and not to make them permanent officers. Nobody, therefore, being in office, there could be no removal. The judges, you well know, have been considered as highly federal; and it was noted that they confined their nominations exclusively to federalists. The legislature, dissatisfied with this, transferred the nomination to the President, and made the offices permanent. The very object in passing the law was, that he should correct, not confirm, what was deemed the partiality of the judges. I thought it therefore proper to inquire, not whom they had employed, but whom I ought to appoint to fulfil the intentions of the law. In making these appointments, I put in a proportion of federalists, equal, I believe, to the proportion they bear in numbers through the Union generally. Had I known that your son had acted, it would have been a real pleasure to me to have preferred him to some who were named in Boston, in what was deemed the same line of politics. To this I should have been led by my knowledge of his integrity, as well as my sincere dispositions towards yourself and Mr. Adams.
You seem to think it devolved on the judges to decide on the validity of the sedition law. But nothing in the constitution has given them a right to decide for the executive, more than to the executive to decide for them. Both magistracies are equally independent in the sphere of action assigned to them. The judges, believing the law constitutional, had a right to pass a sentence of fine and imprisonment, because the power was placed in their hands by the constitution. But the executive, believing the law to be unconstitutional, were bound to remit the execution of it; because that power has been confided to them by the constitution. That instrument meant that its co-ordinate branches should be checks on each other. But the opinion which gives to the judges the right to decide what laws are constitutional, and what not, not only for themselves in their own sphere of action, but for the legislature and executive also in their spheres, would make the judiciary a despotic branch. Nor does the opinion of the unconstitutionality, and consequent nullity of that law, remove all restraint from the overwhelming torrent of slander, which is confounding all vice and virtue, all truth and falsehood, in the United States. The power to do that is fully possessed by the several State legislatures. It was reserved to them, and was denied to the General Government, by the constitution, according to our construction of it. While we deny that Congress have a right to control the freedom of the press, we have ever asserted the right of the States, and their exclusive right, to do so. They have, accordingly, all of them made provisions for punishing slander, which those who have time and inclination resort to for the vindication of their characters. In general, the State laws appear to have made the presses responsible for slander as far as is consistent with its useful freedom. In those States where they do not admit even the truth of allegations to protect the printer, they have gone too far.
The candor manifested in your letter, and which I ever believed you to possess, has alone inspired the desire of calling your attention once more to those circumstances of fact and motive by which I claim to be judged. I hope you will see these intrusions on your time to be, what they really are, proofs of my great, respect for you. I tolerate with the utmost latitude the right of others to differ from me in opinion, without imputing to them criminality. I know too well the weakness and uncertainty of human reason, to wonder at its different results. Both of our political parties, at least the honest part of them, agree conscientiously in the same object, the public good: but they differ essentially in what they deem the means of promoting that good. One side believes it best done by one composition of the governing powers; the other, by a different one. One fears most the ignorance of the people; the other, the selfishness of rulers independent of them. Which is right, time and experience will prove. We think that one side of this experiment has been long enough tried, and proved not to promote the good of the many: and that the other has not been fairly and sufficiently tried. Our opponents think the reverse. With whichever opinion the body of the nation concurs, that must prevail. My anxieties on this subject will never carry me beyond the use of fair and honorable means of truth and reason; nor have they ever lessened my esteem for moral worth, nor alienated my affections from a single friend, who did not first withdraw himself. Wherever this has happened, I confess I have not been insensible to it: yet have ever kept myself open to a return of their justice. I conclude with sincere prayers for your health and happiness, that yourself and Mr. Adams may long enjoy the tranquillity you desire and merit, and see in the prosperity of your family what is the consummation of the last and warmest of human wishes,
Th: Jefferson.
TO MR. NICHOLSON.
Washington, January 29, 1805.
Dear Sir,
Mr. Eppes has this moment put into my hands your letter of yesterday, asking information on the subject of the gun-boats proposed to be built. I lose no time in communicating to you fully my whole views respecting them, premising a few words on the system of fortifications. Considering the harbors which, from their situation and importance, are entitled to defence, and the estimates we have seen of the fortifications planned for some of them, this system cannot be completed on a moderate scale for less than fifty millions of dollars, nor manned in time of war with less than fifty thousand men, and in peace, two thousand. And when done, they avail little; because all military men agree, that wherever a vessel may pass a fort without tacking under her guns, which is the case at all our sea-port towns, she may be annoyed more or less, according to the advantages of the position, but can never be prevented. Our own experience during the war proved this on different occasions. Our predecessors have, nevertheless, proposed to go into this system, and had commenced it. But, no law requiring us to proceed, we have suspended it.
If we cannot hinder vessels from entering our harbors, we should turn our attention to the putting it out of their power to lie, or come to, before a town, to injure it. Two means of doing this may be adopted in aid of each other. 1. Heavy cannon on travelling carriages, which may be moved to any point on the bank or beach most convenient for dislodging the vessel. A sufficient number of these should be lent to each sea-port town, and their militia trained to them. The executive is authorized to do this; it has been done in a smaller degree, and will now be done more competently.
2. Having cannon on floating batteries or boats, which may be so stationed as to prevent a vessel entering the harbor, or force her after entering to depart. There are about fifteen harbors in the United States, which ought to be in a state of substantial defence. The whole of these would require, according to the best opinions, two hundred and forty gun-boats. Their cost was estimated by Captain Rogers at two thousand dollars each; but we had better say four thousand dollars. The whole would cost one million of dollars. But we should allow ourselves ten years to complete it, unless circumstances should force it sooner. There are three situations in which the gun-boat may be. 1. Hauled up under a shed, in readiness to be launched and manned by the seamen and militia of the town on short notice. In this situation she costs nothing but an enclosure, or a centinel to see that no mischief is done to her. 2. Afloat, and with men enough to navigate her in harbor and take care of her, but depending on receiving her crew from the town on short warning. In this situation, her annual expense is about two thousand dollars, as by an official estimate at the end of this letter. 3. Fully manned for action. Her annual expense in this situation is about eight thousand dollars, as per estimate subjoined. ‘When there is general peace, we should probably keep about six or seven afloat in the second situation; their annual expense twelve to fourteen thousand dollars; the rest all hauled up. When France and England are at war, we should keep, at the utmost, twenty-five in the second situation, their annual expense fifty thousand dollars. When we should be at war ourselves, some of them would probably be kept in the third situation, at an annual expense of eight thousand dollars; but how many, must depend on the circumstances of the war. We now possess ten, built and building. It is the opinion of those consulted, that fifteen more would enable us to put every harbor under our view into a respectable condition; and that this should limit the views of the present year. This would require an appropriation of sixty thousand dollars, and I suppose that the best way of limiting it, without declaring the number, as perhaps that sum would build more. I should think it best not to give a detailed report, which exposes our policy too much. A bill, with verbal explanations, will suffice for the information of the House. I do not know whether General Wilkinson would approve the printing his paper. If he would, it would be useful. Accept affectionate and respectful salutations.
Th: Jefferson.
TO MR. VOLNEY.
Washington, February 8, 1805.
Dear Sir,
Your letter of November the 26th came to hand May the 14th; the books some time after, which were all distributed according to direction. The copy for the East Indies went immediately by a safe conveyance. The letter of April the 28th, and the copy of your work accompanying that, did not come to hand till August. That copy was deposited in the Congressional library. It was not till my return here from my autumnal visit to Monticello, that I had an opportunity of reading your work. I have read it, and with great satisfaction. Of the first part I am less a judge than most people, having never travelled westward of Staunton, so as to know any thing of the face of the country; nor much indulged myself in geological inquiries, from a belief that the skin-deep scratches, which we can make or find on the surface of the earth, do not repay our time with as certain and useful deductions, as our pursuits in some other branches. The subject of our winds is more familiar to me. On that, the views you have taken are always great, supported in their outlines by your facts; and though more extensive observations, and longer continued, may produce some anomalies, yet they will probably take their place in this first great canvass which you have sketched. In no case, perhaps, does habit attach our choice or judgment more than in climate. The Canadian glows with delight in his sleigh and snow, the very idea of which gives me the shivers. The comparison of climate between Europe and North America, taking together its corresponding parts, hangs chiefly on three great points. 1. The changes between heat and cold in America are greater and more frequent, and the extremes comprehend a greater scale on the thermometer in America than in Europe. Habit, however, prevents these from affecting us more than the smaller changes of Europe affect the European. But he is greatly affected by ours. 2. Our sky is always clear; that of Europe always cloudy. Hence a greater accumulation of heat here than there, in the same parallel. 3. The changes between wet and dry are much more frequent and sudden in Europe than in America. Though we have double the rain, it falls in half the time. Taking all these together, I prefer much the climate of the United States to that of Europe. I think it a more cheerful one. It is our cloudless sky which has eradicated from our constitutions all disposition to hang ourselves, which we might otherwise have inherited from our English ancestors. During a residence of between six and seven years in Paris, I never but once saw the sun shine through a whole day, without being obscured by a cloud in any part of it: and I never saw the moment, in which, viewing the sky through its whole hemisphere, I could say there was not the smallest speck of a cloud in it. I arrived at Monticello, on my return from France, in January, and during only two months’ stay there, I observed to my daughters, who had been with me to France, that twenty odd times within that term, there was not a speck of a cloud in the whole hemisphere. Still I do not wonder that an European should prefer his grey to our azure sky. Habit decides our taste in this, as in most other cases.
The account you give of the yellow fever, is entirely agreeable to what we then knew of it. Further experience has developed more and more its peculiar character. Facts appear to have established, that it is originated here by a local atmosphere, which is never generated but in the lower, closer, and dirtier parts of our large cities, in the neighborhood of the water; and that, to catch the disease, you must enter the local atmosphere. Persons having taken the disease in the infected quarter, and going into the country, are nursed and buried by their friends, without an example of communicating it. A vessel going from the infected quarter, and carrying its atmosphere in its hold into another State, has given the disease to every person who there entered her. These have died in the arms of their families, without a single communication of the disease. It is certainly, therefore, an epidemic, not a contagious disease; and calls on the chemists for some mode of purifying the vessel by a decomposition of its atmosphere, if ventilation be found insufficient. In the long scale of bilious fevers, graduated by many shades, this is probably the last and most mortal term. It seizes the native of the place equally with strangers. It has not been long known in any part of the United States. The shade next above it, called the stranger’s fever, has been coeval with the settlement of the larger cities in the southern parts, to wit, Norfolk, Charleston, New Orleans. Strangers going to these places in the months of July, August, or September, find this fever as mortal as the genuine yellow fever. But it rarely attacks those who have resided in them some time. Since we have known that kind of yellow fever which is no respecter of persons, its name has been extended to the stranger’s fever, and every species of bilious fever which produces a black vomit, that is to say, a discharge of very dark bile. Hence we hear of yellow fever on the Allegany mountains, in Kentucky, &c. This is a matter of definition only: but it leads into error those who do not know how loosely and how interestedly some physicians think and speak. So far as we have yet seen, I think we are correct in saying, that the yellow fever, which seizes on all indiscriminately, is an ultimate degree of bilious fever, never known in the United States till lately, nor farther south, as yet, than Alexandria, and that what they have recently called the yellow fever in New Orleans, Charleston, and Norfolk, is what has always been known in those places as confined chiefly to strangers, and nearly as mortal to them, as the other is to all its subjects. But both grades are local: the stranger’s fever less so, as it sometimes extends a little into the neighborhood; but the yellow fever rigorously so, confined within narrow and well defined limits, and not communicable out of those limits. Such a constitution of atmosphere being requisite to originate this disease as is generated only in low, close, and ill-cleansed parts of a town, I have supposed it practicable to prevent its generation by building our cities on a more open plan. Take, for instance, the chequer-board for a plan. Let the black squares only be building squares, and the white ones be left open, in turf and trees. Every square of houses will be surrounded by four open squares, and every house will front an open square. The atmosphere of such a town would be like that of the country, insusceptible of the miasmata which produce yellow fever. I have accordingly proposed that the enlargements of the city of New Orleans, which must immediately take place, shall be on this plan. But it is only in case of enlargements to be made, or of cities to be built, that his means of prevention can be employed.
The genus irritabile vatum could not let the author of the Ruins publish a new work, without seeking in it the means of discrediting that puzzling composition. Some one of those holy calumniators has selected from your new work every scrap of a sentence, which, detached from its context, could displease an American reader. A cento has been made of these, which has run through a particular description of newspapers, and excited a disapprobation even in friendly minds, which nothing but the reading of the book will cure. But time and truth will at length correct error.
Our countrymen are so much occupied in the busy scenes of life, that they have little time to write or invent. A good invention here, therefore, is such a rarity as it is lawful to offer to the acceptance of a friend. A Mr. Hawkins of Frankford, near Philadelphia, has invented a machine, which he calls a polygraph, and which carries two, three, or four pens. That of two pens, with which I am now writing, is best; and is so perfect that I have laid aside the copying-press, for a twelvemonth past, and write always with the polygraph. I have directed one to be made, of which I ask your acceptance. By what conveyance I shall send it while Havre is blockaded, I do not yet know. I think you will be pleased with it, and will use it habitually as I do; because it requires only that degree of mechanical attention which I know you to possess. I am glad to hear that M. Cabanis is engaged in writing on the reformation of medicine. It needs the hand of a reformer, and cannot be in better hands than his. Will you permit my respects to him and the Abbe de la Roche to find a place here.
A word now on our political state. The two parties which prevailed with so much violence when you were here, are almost wholly melted into one. At the late Presidential election I have received one hundred and sixty-two votes against fourteen only. Connecticut is still federal by a small majority; and Delaware on a poise, as she has been since 1775, and will be till Anglomany with her yields to Americanism. Connecticut will be with us in a short time. Though the people in mass have joined us, their leaders had committed themselves too far to retract. Pride keeps them hostile; they brood over their angry passions, and give them vent in the newspapers which they maintain. They still make as much noise as if they were the whole nation. Unfortunately, these being the mercantile papers, published chiefly in the seaports, are the only ones which find their way to Europe, and make very false impressions there. I am happy to hear that the late derangement of your health is going off, and that you are reestablished. I sincerely pray for the continuance of that blessing, and with my affectionate salutations, tender you assurances of great respect and attachment.
Th: Jefferson.
P. S. The sheets which you receive are those of the copying-pen of the polygraph, not of the one with which I have written.
TO JUDGE TYLER.
Monticello, March 29, 1805.
Dear Sir,
Your favor of the 17th found me on a short visit to this place, and I observe in it with great pleasure a continuance of your approbation of the course we are pursuing, and particularly the satisfaction you express with the last inaugural address. The first was, from the nature of the case, all profession and promise. Performance, therefore, seemed to be the proper office of the second. But the occasion restricted me to mention only the most prominent heads, and the strongest justification of these in the fewest words possible. The crusade preached against philosophy by the modern disciples of steady habits, induced me to dwell more in showing its effect with the Indians than the subject otherwise justified.
The war with Tripoli stands on two grounds of fact. 1st. It is made known to us by our agents with the three other Barbary States, that they only wait to see the event of this, to shape their conduct accordingly. If the war is ended by additional tribute, they mean to offer us the same alternative. 2ndly. If peace was made, we should still, and shall ever, be obliged to keep a frigate in the Mediterranean to overawe rupture, or we must abandon that market. Our intention in sending Morris with a respectable force, was to try whether peace could be forced by a coercive enterprise on their town. His inexecution of orders baffled that effort. Having broke him, we try the same experiment under a better commander. If in the course of the summer they cannot produce peace, we shall recall our force, except one frigate and two small vessels, which will keep up a perpetual blockade. Such a blockade will cost us no more than a state of peace, and will save us from increased tributes, and the disgrace attached to them. There is reason to believe the example we have set, begins already to work on the dispositions of the powers of Europe to emancipate themselves from that degrading yoke. Should we produce such a revolution there, we shall be amply rewarded for what we have done. Accept my friendly salutations, and assurances of great respect and esteem.
Th: Jefferson.
TO DOCTOR LOGAN.
Washington, May 11, 1805.
Dear Sir,
I see with infinite pain the bloody schism which has taken place among our friends in Pennsylvania and New York, and will probably take place in other States. The main body of both sections mean well, but their good intentions will produce great public evil. The minority, whichever section shall be the minority, will end in coalition with the federalists, and some compromise of principle; because these will not sell their aid for nothing. Republicanism will thus lose, and royalism gain, some portion of that ground which we thought we had rescued to good government. I do not express my sense of our misfortunes from any idea that they are remediable. I know that the passions of men will take their course, that they are not to be controlled but by despotism, and that this melancholy truth is the pretext for despotism. The duty of an upright administration is to pursue its course steadily, to know nothing of these family dissensions, and to cherish the good principles of both parties. The war ad internecionem which we have waged against federalism, has filled our latter times with strife and unhappiness. We have met it, with pain indeed, but with firmness, because we believed it the last convulsive effort of that Hydra, which in earlier times we had conquered in the field. But if any degeneracy of principle should ever render it necessary to give ascendancy to one of the rising sections over the other, I thank my God it will fall to some other to perform that operation. The only cordial I wish to carry into my retirement, is the undivided good will of all those with whom I have acted.
Present me affectionately to Mrs. Logan, and accept my salutations, and assurances of constant friendship and respect.
Th: Jefferson.
TO JUDGE SULLIVAN.
Washington, May 21, 1805.
Dear Sir,
An accumulation of business, which I found on my return here from a short visit to Monticello, has prevented till now my acknowledgment of your favor of the 14th ultimo. This delay has given time to see the result of the contest in your State, and I cannot but congratulate you on the advance it manifests, and the certain prospect it offers that another year restores Massachusetts to the general body of the nation. You have indeed received the federal unction of lying and slandering. But who has not? Who will ever again come into eminent office, unanointed with this chrism? It seems to be fixed that falsehood and calumny are to be their ordinary engines of opposition; engines which will not be entirely without effect. The circle of characters equal to the first stations is not too large, and will be lessened by the voluntary retreat of those whose sensibilities are stronger than their confidence in the justice of public opinion. I certainly have known, and still know, characters eminently qualified for the most exalted trusts, who could not bear up against the brutal hackings and hewings of these heroes of Billingsgate. I may say, from intimate knowledge, that we should have lost the services of the greatest character of our country, had he been assailed with the degree of abandoned licentiousness now practised. The torture he felt under rare and slight attacks, proved that under those of which the federal bands have shown themselves capable, he would have thrown up the helm in a burst of indignation. Yet this effect of sensibility must not be yielded to. If we suffer ourselves to be frightened from our post by mere lying, surely the enemy will use that weapon; for what one so cheap to those of whose system of politics morality makes no part? The patriot, like the Christian, must learn that to bear revilings and persecutions is a part of his duty; and in proportion as the trial is severe, firmness under it becomes more requisite and praiseworthy. It requires, indeed, self-command. But that will be fortified in proportion as the calls for its exercise are repeated. In this I am persuaded we shall have the benefit of your good example. To the other falsehoods they have brought forward, should they add, as you expect, insinuations of want of confidence in you from the administration generally, or myself particularly, it will, like their other falsehoods, produce in the public mind a contrary inference.
*********
I tender you my friendly and respectful salutations.
Th: Jefferson.
TO THOMAS PAINE.
Washington, June 5, 1805.
Dear Sir,
Your letters, Nos. 1, 2, 3, the last of them dated April the 20th, were received April the 26th. I congratulate you on your retirement to your farm, and still more that it is of a character so worthy of your attention. I much doubt whether the open room on your second story will answer your expectations. There will be a few days in the year in which it will be delightful, but not many. Nothing but trees, or Venetian blinds, can protect it from the sun. The semi-cylindrical roof you propose will have advantages. You know it has been practised on the cloth market at Paris. De Lorme, the inventor, shows many forms of roofs in his book, to which it is applicable. I have used it at home for a dome, being one hundred and twenty degrees of an oblong octagon, and in the capitol we unite two quadrants of a sphere by a semi-cylinder: all framed in De Lorme’s manner. How has your planing machine answered? Has it been tried and persevered in by any workman?
France has become so jealous of our conduct as to St. Domingo (which in truth is only the conduct of our merchants), that the offer to become a mediator would only confirm her suspicions. Bonaparte, however, expressed satisfaction at the paragraph in my message to Congress on the subject of that commerce. With respect to the German redemptioners, you know I can do nothing, unless authorized by law. It would be made a question in Congress, whether any of the enumerated objects to which the constitution authorizes the money of the Union to be applied, would cover an expenditure for importing settlers to Orleans. The letter of the revolutionary sergeant was attended to by General Dearborn, who wrote to him informing him how to proceed to obtain his land.
Doctor Eustis’s observation to you, that ‘certain paragraphs in the National Intelligencer,’ respecting my letter to you, ‘supposed to be under Mr. Jefferson’s direction, had embarrassed Mr. Jefferson’s friends in Massachusetts; that they appeared like a half denial of the letter, or as if there was something in it not proper to be owned, or that needed an apology,’ is one of those mysterious half confidences difficult to be understood. That tory printers should think it advantageous to identify me with that paper, the Aurora, &c. in order to obtain ground for abusing me, is perhaps fair warfare. But that any one who knows me personally should listen one moment to such an insinuation, is what I did not expect. I neither have, nor ever had, any more connection with those papers than our antipodes have; nor know what is to be in them until I see it in them, except proclamations and other documents sent for publication. The friends in Massachusetts who could be embarrassed by so weak a weapon as this, must be feeble friends indeed. With respect to the letter, I never hesitated to avow and to justify it in conversation. In no other way do I trouble myself to contradict any thing which is said. At that time, however, there were certain anomalies in the motions of some of our friends, which events have at length reduced to regularity.
It seems very difficult to find out what turn things are to take in Europe. I suppose it depends on Austria, which knowing it is to stand in the way of receiving the first hard blows, is cautious of entering into a coalition. As to France and England we can have but one wish, that they may disable one another from injuring others.
Accept my friendly salutations, and assurances of esteem and respect.
Th: Jefferson.
[The following, in the hand-writing of the Author, is inserted in his MS. of this period. Whether it was published, or where, is not stated.]
Richmond, 1780, December 31. At 8 A. M. the Governor receives the first intelligence that twenty-seven sail of ships had entered Chesapeake Bay, and were in the morning of the 29th just below Willoughby’s point (the southern cape of James river); their destination unknown.
1781, January 2. At 10 A. M. information received that they had entered James river, their advance being at Warrasqueak bay. Orders were immediately given for calling in the militia, one fourth from some, and one half from other counties. The members of the legislature, which rises this day, are the bearers of the orders to their respective counties. The Governor directs the removal of the records into the country, and the transportation of the military stores from Richmond to Westham (on the river seven miles above); there to be carried across the river.
January 3. At 8 P. M. the enemy are said to be a little below Jamestown; convenient for landing, if Williamsburg is their object.
January 4. At 5 A. M. information is received that they had passed Kennon’s and Hood’s the evening before, with a strong; easterly wind, which determines their object to be either Petersburg or Richmond. The Governor now calls in the whole militia from the adjacent counties.
At 5 P. M. information, that at 2 P. M. they were landed and drawn up at Westover (on the north side of the river, and twenty-five miles below Richmond); and consequently Richmond their destination. Orders are now given to discontinue wagoning the military stores from Richmond to Westham, and to throw them across the river directly at Richmond.
The Governor having attended to this till an hour and a half in the night, then rode up to the foundery (one mile below Westham), ordered Captains Boush and Irish, and Mr. Hylton, to continue all night wagoning to Westham the arms and stores still at the foundery, to be thrown across the river at Westham, then proceeded to Westham to urge the pressing the transportation there across the river, and thence went to Tuckahoe (eight miles above and on the same side of the river) to see after his family, which he had sent that far in the course of the day. He arrived there at 1 o’clock in the night.
January 5. Early in the morning, he carried his family across the river there, and sending them to Fine Creek (eight miles higher up) went himself to Britton’s on the south side of the river, (opposite to Westham). Finding the arms, &c. in a heap near the shore, and exposed to be destroyed by cannon from the north bank, he had them removed under cover of a point of land near by. He proceeded to Manchester (opposite to Richmond). The enemy had arrived at Richmond at 1 P. M. Having found that nearly the whole arms had been got there from Richmond, he set out for Chetwood’s to meet with Baron Steuben, who had appointed that place as a rendezvous and head-quarters; but not finding him there, and understanding he would be at Colonel Fleming’s (six miles above Britton’s), he proceeded thither. The enemy had now a detachment at Westham, and sent a deputation from the city of Richmond to the Governor, at Colonel Fleming’s, to propose terms for ransoming the safety of the city, which terms he rejected.
January 6. The Governor returned to Britton’s, had measures taken more effectually to secure the books and papers there. The enemy, having burnt some houses and stores, left Richmond after twenty-four hours’ stay there, and encamped at Four Mile Creek (eight or ten miles below); and the Governor went to look to his family at Fine Creek.
January 7. He returned to Britton’s to see further to the arms there, exposed on the ground to heavy rains which had fallen the night before, and thence proceeded to Manchester and lodged there. The enemy encamped at Westover.
January 8. At half after 7 A. M. he crossed over to Richmond, and resumed his residence there. The enemy are still retained in their encampment at Westover by an easterly wind. Colonel John Nicholas has now three hundred militia at the Forest (six miles off from Westover); General Nelson, two hundred at Charles City Court-House (eight miles below Westover); Gibson, one thousand, and Baron Steuben, eight hundred, on the south side of the river.
January 9. The enemy are still encamped at Westover.
January 10. At 1 P. M. they embark: and the wind having shifted a little to the north of west, and pretty fresh, they fall down the river. Baron Steuben marches for Hood’s, where their passage may be checked. He reaches Bland’s mills in the evening, within nine miles of Hood’s.
January 11. At 8 A. M. the wind due west and strong, they make good their retreat.
During this period, time and place have been minutely cited, in order that those who think there was any remissness in the movements of the Governor, may lay their finger on the point, and say, when and where it was. Hereafter, less detail will suffice.
Soon after this, General Phillips having joined Arnold with a reinforcement of two thousand men, they advanced again up to Petersburg, and about the last of April to Manchester. The Governor had remained constantly in and about Richmond, exerting all his powers for collecting militia, and providing such means for the defence of the State as its exhausted resources admitted. Never assuming a guard, and with only the river between him and the enemy, his lodgings were frequently within four, five, or six miles of them.
M. de la Fayette about this time arrived at Richmond with some continental troops, with which, and the militia collected, he continued to occupy that place, and the north bank of the river, while Phillips and Arnold held Manchester and the south bank. But Lord Cornwallis, about the middle of May, joining them with the main southern army, M. de la Fayette was obliged to retire. The enemy crossed the river, and advanced up into the country about fifty miles, and within thirty miles of Charlottesville, at which place the legislature being to meet in June, the Governor proceeded to his seat at Monticello, two or three miles from it. His office was now near expiring, the country under invasion by a powerful army, no services but military of any avail; unprepared by his line of life and education for the command of armies, he believed it right not to stand in the way of talents better fitted than his own to the circumstances under which the country was placed. He therefore himself proposed to his friends in the legislature, that General Nelson, who commanded the militia of the State, should be appointed Governor, as he was sensible that the union of the civil and military power in the same hands, at this time, would greatly facilitate military measures. This appointment accordingly took place on the 12th of June, 1781.
This was the state of things, when, his office having actually expired, and no successor yet in place, Colonel Tarleton, with his regiment, of horse, was detached by Lord Cornwallis to surprise Mr. Jefferson (whom they thought still in office) and the legislature now sitting in Charlottesville. The Speakers of the two Houses, and some other members of the legislature, were lodging with Mr. Jefferson at Monticello. Tarleton, early in the morning, (June 23, I believe,) when within ten miles of that place, detached a company of horse to secure him and his guests, and proceeded himself rapidly with his main body to Charlottesville, where he hoped to find the legislature unapprized of his movement. Notice of it, however, had been brought both to Monticello and Charlottesville about sunrise. The Speakers, with their colleagues, returned to Charlottesville, and, with the other members of the legislature, had barely time to get out of his way. Mr. Jefferson sent off his family, to secure them from danger, and was himself still at Monticello, making arrangements for his own departure, when Lieutenant Hudson arrived there at half speed, and informed him the enemy were then ascending the hill of Monticello. He departed immediately, and knowing that he would be pursued if he took the high road, he plunged into the woods of the adjoining mountain, where, being at once safe, he proceeded to overtake his family. This is the famous adventure of Carter’s Mountain, which has been so often resounded through the slanderous chronicles of Federalism. But they have taken care never to detail the facts, lest these should show that this favorite charge amounted to nothing more, than that he did not remain in his house, and there singly fight a whole troop of horse, or suffer himself to be taken prisoner. Having accompanied his family one day’s journey, he returned to Monticello. Tarleton had retired after eighteen hours’ stay in Charlottesville. Mr. Jefferson then rejoined his family, and proceeded with them to an estate he had in Bedford, about eighty miles southwest, where, riding in his farm some time after, he was thrown from his horse, and disabled from riding on horseback for a considerable time. But Mr. Turner finds it more convenient to give him this fall in his retreat before Tarleton, which had happened some weeks before, as a proof that he withdrew from a troop of horse with a precipitancy which Don Quixote would not have practised.
The facts here stated most particularly, with date of time and place, are taken from the notes made by the writer hereof, for his own satisfaction, at the time: the others are from memory, but so well recollected, that he is satisfied there is no material fact misstated. Should any person undertake to contradict any particular, on evidence which may at all merit the public respect, the writer will take the trouble (though not at all in the best situation for it) to produce the proofs in support of it. He finds, indeed, that, of the persons whom he recollects to have been present on these occasions, few have survived the intermediate lapse of four and twenty years. Yet he trusts that some, as well as himself, are yet among the living; and he is positively certain, that no man can falsify any material fact here stated. He well remembers, indeed, that there were then, as there are at all times, some who blamed every thing done contrary to their own opinion, although their opinions were formed on a very partial knowledge of facts. The censures, which have been hazarded by such men as Mr. Turner, are nothing but revivals of these half-informed opinions. Mr. George Nicholas, then a very young man, but always a very honest one, was prompted by these persons to bring specific charges against Mr. Jefferson. The heads of these, in writing, were communicated through a mutual friend to Mr. Jefferson, who committed to writing also the heads of justification on each of them. I well remember this paper, and believe the original of it still exists; and though framed when every real fact was fresh in the knowledge of every one, this fabricated flight from Richmond was not among the charges stated in this paper, nor any charge against Mr. Jefferson for not fighting, singly, the troop of horse. Mr. Nicholas candidly relinquished further proceeding. The House of Representatives of Virginia pronounced an honorable sentence of entire approbation of Mr. Jefferson’s conduct, and so much the more honorable, as themselves had been witnesses to it. And Mr. George Nicholas took a conspicuous occasion afterwards, of his own free will, and when the matter was entirely at rest, to retract publicly the erroneous opinions he had been led into on that occasion, and to make just reparation by a candid acknowledgment of them.
TO DOCTORS ROGERS AND SLAUGHTER.
Washington, March 2, 1806.
Gentlemen,
I have received the favor of your letter of February the 2nd, and read with thankfulness its obliging expressions respecting myself. I regret that the object of a letter from persons whom I so much esteem, and patronized by so many other respectable names, should be beyond the law which a mature consideration of circumstances has prescribed for my conduct. I deem it the duty of every man to devote a certain portion of his income for charitable purposes; and that it is his further duty to see it so applied as to do the most good of which it is capable. This I believe to be best insured, by keeping within the circle of his own inquiry and information, the subjects of distress to whose relief his contributions shall be applied. If this rule be reasonable in private life, it becomes so necessary in my situation, that to relinquish it would leave me without rule or compass. The applications of this kind from different parts of our own, and from foreign countries, are far beyond any resources within my command. The mission of Serampore, in the East Indies, the object of the present application, is but one of many items. However disposed the mind may feel to unlimited good, our means having limits, we are necessarily circumscribed by them. They are too narrow to relieve even the distresses under our own eye: and to desert these for others which we neither see nor know, is to omit doing a certain good for one which is uncertain. I know, indeed, there have been splendid associations for effecting benevolent purposes in remote regions of the earth. But no experience of their effect has proved that more good would not have been done by the same means employed nearer home. In explaining, however, my own motives of action, I must not be understood as impeaching those of others. Their views are those of an expanded liberality. Mine may be too much restrained by the law of usefulness. But it is a law to me, and with minds like yours, will be felt as a justification. With this apology, I pray you to accept my salutations, and assurances of high esteem and respect.
Th: Jefferson.
TO MR. DUANE.
Washington, March 22, 1806.
I thank you, my good Sir, cordially, for your letter of the 12th; which, however, I did not receive till the 20th. It is a proof of sincerity, which I value above all things; as, between those who practise it, falsehood and malice work their efforts in vain. There is an enemy somewhere endeavoring to sow discord among us. Instead of listening first, then doubting, and lastly believing anile tales handed round without an atom of evidence, if my friends will address themselves to me directly, as you have done, they shall be informed with frankness and thankfulness. There is not a truth on earth which I fear or would disguise. But secret slanders cannot be disarmed, because they are secret. Although you desire no answer, I shall give you one to those articles admitting a short answer, reserving those which require more explanation than the compass of a letter admits, to conversation on your arrival here. And as I write this for your personal satisfaction, I rely that my letter will, under no circumstances, be communicated to any mortal, because you well know how every syllable from me is distorted by the ingenuity of political enemies.
In the first place, then, I have had less communication, directly or indirectly, with the republicans of the east, this session, than I ever had before. This has proceeded from accidental circumstances, not from design. And if there be any coolness between those of the south and myself, it has not been from me towards them. Certainly there has been no other reserve, than to avoid taking part in the divisions among our friends. That Mr. R. has openly attacked the administration is sufficiently known. We were not disposed to join in league with Britain, under any belief that she is fighting for the liberties of mankind, and to enter into war with Spain, and consequently France. The House of Representatives were in the same sentiment, when they rejected Mr. R.‘s resolutions for raising a body of regular troops for the western service. We are for a peaceable accommodation with all those nations, if it can be effected honorably. This, perhaps, is not the only ground of his alienation; but which side retains its orthodoxy, the vote of eighty-seven to eleven republicans may satisfy you: but you will better satisfy yourself on coming here, where alone the true state of things can be known, and where you will see republicanism as solidly embodied on all essential points, as you ever saw it on any occasion.
That there is only one minister who is not opposed to me, is totally unfounded. There never was a more harmonious, a more cordial administration, nor ever a moment when it has been otherwise. And while differences of opinion have been always rare among us, I can affirm, that as to present matters, there was not a single paragraph in my message to Congress, or those supplementary to it, in which there was not a unanimity of concurrence in the members of the administration. The fact is, that in ordinary affairs every head of a department consults me on those of his department, and where any thing arises too difficult or important to be decided between us, the consultation becomes general.
That there is an ostensible cabinet and a concealed one, a public profession and concealed counteraction, is false.
That I have denounced republicans by the epithet of Jacobins, and declared I would appoint none but those called moderates of both parties, and that I have avowed or entertain any predilection for those called the third party, or Quids, is in every tittle of it false.
That the expedition of Miranda was countenanced by me is an absolute falsehood, let it have gone from whom it might; and I am satisfied it is equally so as to Mr. Madison. To know as much of it as we could was our duty, but not to encourage it.
Our situation is difficult; and whatever we do, is liable to the criticisms of those who wish to represent it awry. If we recommend measures in a public message, it may be said that members are not sent here to obey the mandates of the President, or to register the edicts of a sovereign. If we express opinions in conversation, we have then our Charles Jenkinsons, and back-door counsellors. If we say nothing, ‘we have no opinions, no plans, no cabinet.’ In truth, it is the fable of the old man, his son, and ass, over again.
These are short facts, which may suffice to inspire you with caution, until you can come here and examine for yourself. No other information can give you a true insight into the state of things; but you will have no difficulty in understanding them when on the spot. In the mean time, accept my friendly salutations and cordial good wishes.
Th: Jefferson.
TO WILSON C. NICHOLAS.—[Confidential.]
Washington, March 24,1806.
Dear Sir,
A last effort at friendly settlement with Spain is proposed to be made at Paris, and under the auspices of France. For this purpose, General Armstrong and Mr. Bowdoin (both now at Paris) have been appointed joint commissioners: but such a cloud of dissatisfaction rests on General Armstrong in the minds of many persons, on account of a late occurrence stated in all the public papers, that we have in contemplation to add a third commissioner, in order to give the necessary measure of public confidence to the commission. Of these two gentlemen, one being of Massachusetts and one of new York, it is thought the third should be a southern man; and the rather, as the interests to be negotiated are almost entirely southern and western. This addition is not yet ultimately decided on; but I am inclined to believe it will be adopted. Under this expectation, and my wish that you may be willing to undertake it, I give you the earliest possible intimation of it, that you may be preparing both your mind and your measures for the mission. The departure would be required to be very prompt; though the absence, I think, will not be long, Bonaparte not being in the practice of procrastination. This particular consideration will, I hope, reconcile the voyage to your affairs and your feelings. The allowance to an extra mission, is salary from the day of leaving home, and expenses to the place of destination, or in lieu of the latter, and to avoid settlements, a competent fixed sum may be given. For the return, a continuance of the salary for three months after fulfilment of the commission. Be so good as to make up your mind as quickly as possible, and to answer me as early as possible. Consider the measure as proposed provisionally only, and not to be communicated to any mortal until we see it proper. Affectionate salutations.
Th: Jefferson.
TO WILSON C. NICHOLAS.
Washington, April 13, 1806.
Dear Sir,
The situation of your affairs certainly furnishes good cause for your not acceding to my proposition of a special mission to Europe. My only hope had been, that they could have gone on one summer without you. An unjust hostility against General Armstrong will, I am afraid, show itself whenever any treaty made by him shall be offered for ratification. I wished, therefore, to provide against this, by joining a person who would have united the confidence of the whole Senate. General Smith was so prominent in the opposition to Armstrong, that it would be impossible for them to act together. We conclude, therefore, to leave the matter with Armstrong and Bowdoin. Indeed, my dear Sir, I wish sincerely you were back in the Senate; and that you would take the necessary measures to get yourself there. Perhaps, as a preliminary, you should go to our legislature. Giles’s absence has been a most serious misfortune. A majority of the Senate means well. But Tracy and Bayard are too dexterous for them, and have very much influenced their proceedings. Tracy has been of nearly every committee during the session, and for the most part the chairman, and of course drawer of the reports. Seven federalists voting always in phalanx, and joined by some discontented republicans, some oblique ones, some capricious, have so often made a majority, as to produce very serious embarrassment to the public operations; and very much do I dread the submitting to them, at the next session, any treaty which can be made with either England or Spain, when I consider that five joining the federalists, can defeat a friendly settlement of our affairs. The House of Representatives is as well disposed as I ever saw one. The defection of so prominent a leader threw them into dismay and confusion for a moment; but they soon rallied to their own principles, and let him go off with five or six followers only. One half of these are from Virginia. His late declaration of perpetual opposition to this administration, drew off a few others, who at first had joined him, supposing his opposition occasional only, and not systematic. The alarm the House has had from this schism, has produced a rallying together, and a harmony, which carelessness and security had begun to endanger. On the whole, this little trial of the firmness of our representatives in their principles, and that of the people also, which is declaring itself in support of their public functionaries, has added much to my confidence in the stability of our government; and to my conviction, that should things go wrong at any time, the people will set them to rights by the peaceable exercise of their elective rights. To explain to you the character of this schism, its objects and combinations, can only be done in conversation; and must be deferred till I see you at Monticello, where I shall probably be about the 10th or 12th of May, to pass the rest of the month there. Congress has agreed to rise on Monday the 21st.
Accept my affectionate salutations.
Th: Jefferson.
Washington, April 18, 1806.
Sir,
It is now some time since I received from you, through the house of Smith and Buchanan, at Baltimore, a bust of the Emperor Alexander, for which I have to return you my thanks. These are the more cordial, because of the value the bust derives from the great estimation in which its original is held by the world, and by none more than by myself. It will constitute one of the most valued ornaments of the retreat I am preparing for myself at my native home. Accept, at the same time, my acknowledgments for the elegant work of Atkinson and Walker on the customs of the Russians. I had laid it down as a law for my conduct while in office, and hitherto scrupulously observed, to accept of no present beyond a book, a pamphlet, or other curiosity of minor value; as well to avoid imputations on my motives of action, as to shut out a practice susceptible of such abuse. But my particular esteem for the character of the Emperor places his image in my mind above the scope of law. I receive it, therefore, and shall cherish it with affection. It nourishes the contemplation of all the good placed in his power, and of his disposition to do it.
A little before Dr. Priestley’s death, he informed me that he had received intimations, through a channel he confided in, that the Emperor entertained a wish to know something of our constitution. I have therefore selected the two best works we have on that subject, for which I pray you to ask a place in his library. They are too much in detail to occupy his time; but they will furnish materials for an abstract, to be made by others, on such a scale as may bring the matter within the compass of the time which his higher callings can yield to such an object.
At a very early period of my life, contemplating the history of the aboriginal inhabitants of America, I was led to believe that if there had ever been a relation between them and the men of color in Asia, traces of it would be found in their several languages. I have therefore availed myself of every opportunity which has offered, to obtain vocabularies of such tribes as have been within my reach, corresponding to a list then formed of about two hundred and fifty words. In this I have made such progress, that within a year or two more I think to give to the public what I then shall have acquired. I have lately seen a report of Mr. Volney’s to the Celtic Academy, on a work of Mr. Pallas, entitled Vocabulaires Comparés des Langues de toute la Terre; with a list of one hundred and thirty words, to which the vocabulary is limited. I find that seventy-three of these words are common to that and to my vocabulary, and therefore will enable us, by a comparison of language, to make the inquiry so long desired, as to the probability of a common origin between the people of color of the two continents. I have to ask the favor of you to procure me a copy of the above work of Pallas, to inform me of the cost, and permit me to pay it here to your use; for I presume you have some mercantile correspondent here, to whom a payment can be made for you. A want of knowledge what the book may cost, as well as of the means of making so small a remittance, obliges me to make this proposition, and to restrain it to the sole condition that I be permitted to reimburse it here.
I enclose you a letter for the Emperor, which be pleased to deliver or have delivered: it has some relation to a subject which the Secretary of State will explain to you.
Accept my salutations, and assurances of esteem and consideration.
Th: Jefferson.
TO THE EMPEROR OF RUSSIA.
Washington, April 19, 1806.
I owe an acknowledgment to your Imperial Majesty, of the great satisfaction I have received from your letter of August the 20th, 1805, and sincere expressions of the respect and veneration I entertain for your character. It will be among the latest and most soothing comforts of my life, to have seen advanced to the government of so extensive a portion of the earth, and at so early a period of his life, a sovereign, whose ruling passion is the advancement of the happiness and prosperity of his people; and not of his own people only, but who can extend his eye and his good will to a distant and infant nation, unoffending in its course, unambitious in its views.
The events of Europe come to us so late, and so suspiciously, that observations on them would certainly be stale, and possibly wide of their actual state. From their general aspect, however, I collect that your Majesty’s interposition in them has been disinterested and generous, and having in view only the general good of the great European family. When you shall proceed to the pacification which is to re-establish peace and commerce, the same dispositions of mind will lead you to think of the general intercourse of nations, and to make that provision for its future maintenance, which, in times past, it has so much needed. The northern nations of Europe, at the head of which your Majesty is distinguished, are habitually peaceable. The United States of America, like them, are attached to peace. We have then with them a common interest in the neutral rights. Every nation, indeed, on the continent of Europe, belligerent as well as neutral, is interested in maintaining these rights, in liberalizing them progressively with the progress of science and refinement of morality, and in relieving them from restrictions which the extension of the arts has long since rendered unreasonable and vexatious.
Two personages in Europe, of which your Majesty is one, have it in their power, at the approaching pacification, to render eminent service to nations in general, by incorporating into the act of pacification, a correct definition of the rights of neutrals on the high seas. Such a definition, declared by all the powers lately or still belligerent, would give to those rights a precision and notoriety, and cover them with an authority, which would protect them in an important degree against future violation; and should any further sanction be necessary, that of an exclusion of the violating nation from commercial intercourse with all the others, would be preferred to war, as more analogous to the offence, more easy and likely to be executed with good faith. The essential articles of these rights, too, are so few and simple as easily to be defined.
Having taken no part in the past or existing troubles of Europe, we have no part to act in its pacification. But as principles may then be settled in which we have a deep interest, it is a great happiness for us that they are placed under the protection of an umpire, who, looking beyond the narrow bounds of an individual nation, will take under the cover of his equity the rights of the absent and unrepresented. It is only by a happy concurrence of good characters and good occasions, that a step can now and then be taken to advance the well being of nations. If the present occasion be good, I am sure your Majesty’s character will not be wanting to avail the world of it. By monuments of such good offices may your life become an epoch in the history of the condition of man, and may He who called it into being for the good of the human family, give it length of days and success, and have it always in his holy keeping.
Th: Jefferson.
Washington, May 4, 1806.
Dear Sir,
I wrote you on the 16th of March by a common vessel, and then expected to have had, on the rising of Congress, an opportunity of peculiar confidence to you. Mr. Beckley then supposed he should take a flying trip to London, on private business. But I believe he does not find it convenient. He could have let you into the arcana rerum, which you have interests in knowing. Mr. Pinckney’s pursuits having been confined to his peculiar line, he has only that general knowledge of what has passed here, which the public possess. He has a just view of things so far as known to him. Our old friend, Mercer, broke off from us some time ago, at first professing to disdain joining the federalists, yet from the habit of voting together, becoming soon identified with them. Without carrying over with him one single person, he is now in a state of as perfect obscurity as if his name had never been known. Mr. J. Randolph is in the same track, and will end in the same way. His course has excited considerable alarm. Timid men consider it as a proof of the weakness of our government, and that it is to be rent into pieces by demagogues and to end in anarchy. I survey the scene with a different eye, and draw a different augury from it. In a House of Representatives of a great mass of good sense, Mr. Randolph’s popular eloquence gave him such advantages as to place him unrivalled as the leader of the House; and, although not conciliatory to those whom he led, principles of duty and patriotism induced many of them to swallow humiliations he subjected them to, and to vote as was right, as long as he kept the path of right himself. The sudden defection of such a man could not but produce a momentary astonishment, and even dismay; but for a moment only. The good sense of the House rallied around its principles, and, without any leader, pursued steadily the business of the session, did it well, and by a strength of vote which has never before been seen. Upon all trying questions, exclusive of the federalists, the minority of republicans voting with him, has been from four to six or eight, against from ninety to one hundred; and although he yet treats the federalists with ineffable contempt, yet having declared eternal opposition to this administration, and consequently associated with them in his votes, he will, like Mercer, end with them. The augury I draw from this is that there is a steady good sense in the legislature, and in the body of the nation, joined with good intentions, which will lead them to discern and to pursue the public good under all circumstances which can arise, and that no ignis faiuus will be able to lead them long astray. In the present case, the public sentiment, as far as declarations of it have yet come in, is, without a single exception, in firm adherence to the administration. One popular paper is endeavoring to maintain equivocal ground; approving the administration in all its proceedings, and Mr. Randolph in all those which have heretofore merited approbation, carefully avoiding to mention his late aberration. The ultimate view of this paper is friendly to you, and the editor, with more judgment than him who assumes to be at the head of your friends, sees that the ground of opposition to the administration is not that on which it would be advantageous to you to be planted. The great body of your friends are among the firmest adherents to the administration, and in their support of you will suffer Mr. Randolph to have no communications with them. My former letter told you the line which both duty and inclination would lead me sacredly to pursue. But it is unfortunate for you, to be embarrassed with such a soi-disant friend. You must not commit yourself to him. These views may assist you to understand such details as Mr. Pinckney will give you. If you are here at any time before the fall, it will be in time for any object you may have, and by that time the public sentiment will be more decisively declared. I wish you were here at present, to take your choice of the two governments of Orleans and Louisiana, in either of which I could now place you; and I verily believe it would be to your advantage to be just that much withdrawn from the focus of the ensuing contest, until its event should be known. The one has a salary of five thousand dollars, the other of two thousand dollars; both with excellent hotels for the Governor. The latter at St. Louis, where there is good society, both French and American, a healthy climate, and the finest field in the United States for acquiring property. The former not unhealthy, if you begin a residence there in the month of November. The Mrs. Trists and their connections are established there. As I think you can within four months inform me what you say to this, I will keep things in their present state till the last day of August, for your answer.
The late change in the ministry I consider as insuring us a just settlement of our differences, and we ask no more. In Mr. Fox, personally, I have more confidence than in any man in England, and it is founded in what, through unquestionable channels, I have had opportunities of knowing of his honesty and his good sense. While he shall be in the administration, my reliance on that government will be solid. We had committed ourselves in a line of proceedings adapted to meet Mr. Pitt’s policy and hostility, before we heard of his death, which self-respect did not permit us to abandon afterwards; and the late unparalleled outrage on us at New York excited such sentiments in the public at large, as did not permit us to do less than has been done. It ought not to be viewed by the ministry as looking towards them at all, but merely as the consequences of the measures of their predecessors, which their nation has called on them to correct. I hope, therefore, they will come to just arrangements. No two countries upon earth have so many points of common interest and friendship; and their rulers must be great bunglers indeed, if, with such dispositions, they break them asunder. The only rivalry that can arise, is on the ocean. England may by petty larceny thwartings check us on that element a little, but nothing she can do will retard us there one year’s growth. We shall be supported there by other nations, and thrown into their scale to make a part of the great counterpoise to her navy. If, on the other hand, she is just to us, conciliatory, and encourages the sentiment of family feelings and conduct, it cannot fail to befriend the security of both. We have the seamen and materials for fifty ships of the line, and half that number of frigates, and were France to give us the money, and England the dispositions to equip them, they would give to England serious proofs of the stock from which they are sprung, and the school in which they have been taught, and added to the efforts of the immensity of sea-coast lately united under one power, would leave the state of the ocean no longer problematical. Were, on the other hand, England to give the money, and France the dispositions to place us on the sea in all our force, the whole world, out of the continent of Europe, might be our joint monopoly. We wish for neither of these scenes. We ask for peace and justice from all nations, and we will remain uprightly neutral in fact, though leaning in belief to the opinion that an English ascendancy on the ocean is safer for us than that of France. We begin to broach the idea that we consider the whole Gulf Stream as of our waters, in which hostilities and cruising are to be frowned on for the present, and prohibited so soon as either consent or force will permit us. We shall never permit another privateer to cruise within it, and shall forbid our harbors to national cruisers. This is essential for our tranquillity and commerce. Be so good as to have the enclosed letters delivered, to present me to your family, and be assured yourself of my unalterable friendship.
For fear of accidents I shall not make the unnecessary addition of my name.
TO GENERAL SMITH.
Washington, May 4,1806.
Dear Sir,
I received your favor covering some papers from General Wilkinson. I have repented but of one appointment there, that of Lucas, whose temper I see overrules every good quality and every qualification he has. Not a single fact has appeared, which occasions me to doubt that I could have made a fitter appointment than General Wilkinson. One qualm of principle I acknowledge I do feel, I mean the union of the civil and military authority. You remember that when I came into office, while we were lodging together at Conrad’s, he was pressed on me to be made Governor of the Mississippi territory; and that I refused it on that very principle. When, therefore, the House of Representatives took that ground, I was not insensible to its having some weight. But in the appointment to Louisiana, I did not think myself departing from my own principle, because I consider it not as a civil government, but merely a military station. The legislature had sanctioned that idea by the establishment of the office of Commandant, in which were completely blended the civil and military powers. It seemed, therefore, that the Governor should be in suit with them. I observed too, that the House of Representatives, on the very day they passed the stricture on this union of authorities, passed a bill making the Governor of Michigan, commander of the regular troops which should at any time be within his government. However, on the subject of General Wilkinson nothing is in contemplation at this time. We shall see what turn things take at home and abroad in the course of the summer. Monroe has had a second conversation with Mr. Fox, which gives me hopes that we shall have an amicable arrangement with that government. Accept my friendly salutations, and assurances of great esteem and respect.
Th: Jefferson.
THOMAS JEFFERSON TO MR DIGGES.
Thomas Jefferson salutes Mr. Digges with friendship and respect, and sends him the newspapers received last night. He is sorry that only the latter part of the particular publication which Mr. Digges wished to see, is in them. He will be happy to see Mr. Digges and his friends on the fourth of July, and to join in congratulations on the return of the day which divorced us from the follies and crimes of Europe, from a dollar in the pound at least of six hundred millions sterling, and from all the ruin of Mr. Pitt’s administration. We, too, shall encounter follies; but if great, they will be short, if long, they will be light: and the vigor of our country will get the better of them. Mr. Pitt’s follies have been great, long, and inflicted on a body emaciated with age, and exhausted by excesses beyond its power to bear. July 1, 1806.
TO MR. BIDWELL.
Washington, July 5, 1806.
Sir,
Your favor of June the 21st has been duly received. We have not as yet heard from General Skinner on the subject of his office. Three persons are proposed on the most respectable recommendations, and under circumstances of such equality as renders it difficult to decide between them. But it shall be done impartially. I sincerely congratulate you on the triumph of republicanism in Massachusetts. The Hydra of Federalism has now lost all its heads but two. Connecticut I think will soon follow Massachusetts. Delaware will probably remain what it ever has been, a mere county of England, conquered indeed, and held under by force, but always disposed to counter-revolution. I speak of its majority only.
Our information from London continues to give us hopes of an accommodation there on both the points of ‘accustomed commerce and impressment.’ In this there must probably be some mutual concession, because we cannot expect to obtain every thing and yield nothing. But I hope it will be such an one as may be accepted. The arrival of the Hornet in France is so recently known, that it will yet be some time before we learn our prospects there. Notwithstanding the efforts made here, and made professedly to assassinate that negotiation in embryo, if the good sense of Bonaparte should prevail over his temper, the present state of things in Europe may induce him to require of Spain, that she should do us justice at least. That he should require her to sell us East Florida, we have no right to insist: yet there are not wanting considerations which may induce him to wish a permanent foundation for peace laid between us. In this treaty, whatever it shall be, our old enemies the federalists, and their new friends, will find enough to carp at. This is a thing of course, and I should suspect error where they found no fault. The buzzard feeds on carrion only. Their rallying point is ‘war with France and Spain, and alliance with Great Britain’: and every thing is wrong with them which checks their new ardor to be fighting for the liberties of mankind; on the sea always excepted. There one nation is to monopolize all the liberties of the others.
I read, with extreme regret, the expressions of an inclination on your part to retire from Congress. I will not say that this time, more than all others, calls for the service of every man; but I will say, there never was a time when the services of those who possess talents, integrity, firmness, and sound judgment, were more wanted in Congress. Some one of that description is particularly wanted to take the lead in the House of Representatives, to consider the business of the nation as his own business, to take it up as if he were singly charged with it, and carry it through. I do not mean that any gentleman, relinquishing his own judgment, should implicitly support all the measures of the administration; but that, where he does not disapprove of them, he should not suffer them to go off in sleep, but bring them to the attention of the House, and give them a fair chance. Where he disapproves, he will of course leave them to be brought forward by those who concur in the sentiment. Shall I explain my idea by an example? The classification of the militia was communicated to General Varnum and yourself merely as a proposition, which, if you approved, it was trusted you would support. I knew, indeed, that General Varnum was opposed to any thing which might break up the present organization of the militia: but when so modified as to avoid this, I thought he might, perhaps, be reconciled to it. As soon as I found it did not coincide with your sentiments, I could not wish you to support it; but using the same freedom of opinion, I procured it to be brought forward elsewhere. It failed there also, and for a time, perhaps, may not prevail: but a militia can never be used for distant service on any other plan; and Bonaparte will conquer the world, if they do not learn his secret of composing armies of young men only, whose enthusiasm and health enable them to surmount all obstacles. When a gentleman, through zeal for the public service, undertakes to do the public business, we know that we shall hear the cant of backstairs counsellors. But we never heard this while the declaimer was himself a backstairs man, as he calls it, but in the confidence and views of the administration, as may more properly and respectfully be said. But if the members are to know nothing but what is important enough to be put into a public message, and indifferent enough to be made known to all the world; if the executive is to keep all other information to himself, and the House to plunge on in the dark, it becomes a government of chance and not of design. The imputation was one of those artifices used to despoil an adversary of his most effectual arms; and men of mind will place themselves above a gabble of this order. The last session of Congress was indeed an uneasy one for a time: but as soon as the members penetrated into the views of those who were taking a new course, they rallied in as solid a phalanx as I have ever seen act together. Indeed I have never seen a House of better dispositions.
Perhaps I am not entitled to speak with so much frankness; but it proceeds from no motive which has not a right to your forgiveness. Opportunities of candid explanation are so seldom afforded me, that I must not lose them when they occur. The information I receive from your quarter agrees with that from the south; that the late schism has made not the smallest impression on the public, and that the seceders are obliged to give to it other grounds than those which we know to be the true ones. All we have to wish is, that, at the ensuing session, every one may take the part openly which he secretly befriends. I recollect nothing new and true, worthy communicating to you. As for what is not true, you will always find abundance in the newspapers. Among other things, are those perpetual alarms as to the Indians, for no one of which has there ever been the slightest ground. They are the suggestions of hostile traders, always wishing to embroil us with the Indians, to perpetuate their own extortionate commerce. I salute you with esteem and respect.
Th: Jefferson.
TO MR. BOWDOIN.
Washington, July 10, 1806.
Dear Sir,
I believe that when you left America, the invention of the polygraph had not yet reached Boston. It is for copying with one pen while you write with the other, and without the least additional embarrassment or exertion to the writer. I think it the finest invention of the present age, and so much superior to the copying machine, that the latter will never be continued a day by any one who tries the polygraph. It was invented by a Mr. Hawkins of Frankford, near Philadelphia, who is now in England, turning it to good account. Knowing that you are in the habit of writing much, I have flattered myself that I could add acceptably to your daily convenience by presenting you with one of these delightful machines. I have accordingly had one made, and to be certain of its perfection I have used it myself some weeks, and have the satisfaction to find it the best one I have ever tried; and in the course of two years’ daily use of them, I have had opportunities of trying several. As a secretary, which copies for us what we write without the power of revealing it, I find it a most precious possession to a man in public-business. I enclose directions for unpacking and using the machine when you receive it; but the machine itself must await a special and sure conveyance under the care of some person going to Paris. It is ready packed, and shall go by the first proper conveyance.
As we heard two or three weeks ago of the safe arrival of the Hornet at L’Orient, we are anxiously waiting to learn from you the first impressions on her mission. If you can succeed in procuring us Florida, and a good western boundary, it will fill the American mind with joy. It will secure to our fellow-citizens one of their most ardent wishes, a long peace with Spain and France. For be assured, the object of war with them and alliance with England, which, at the last session of Congress, drew off from the republican band about half a dozen of its members, is universally reprobated by our native citizens from north to south. I have never seen the nation stand more firm to its principles, or rally so firmly to its constituted authorities, and in reprobation of the opposition to them. With England, I think we shall cut off the resource of impressing our seamen to fight her battles, and establish the inviolability of our flag in its commerce with her enemies.
We shall thus become what we sincerely wish to be, honestly neutral, and truly useful to both belligerents. To the one, by keeping open a market for the consumption of her manufactures, while they are excluded from all the countries under the power of her enemy; to the other, by securing for her a safe carriage of all her productions, metropolitan or colonial, while her own means are restrained by her enemy, and may, therefore, be employed in other useful pursuits. We are certainly more useful friends to France and Spain as neutrals, than as allies. I hope they will be sensible of it, and by a wise removal of all grounds of future misunderstanding to another age, enable you to present us such an arrangement, as will insure to our fellow-citizens long and permanent peace and friendship with them. With respect to our western boundary, your instructions will be your guide. I will only add, as a comment to them, that we are attached to the retaining the Bay of St. Bernard, because it was the first establishment of the unfortunate La Sale, was the cradle of Louisiana, and more incontestibly covered and conveyed to us by France, under that name, than any other spot in the country. This will be secured to us by taking for our western boundary the Guadaloupe, and from its head around the sources of all waters eastward of it, to the highlands embracing the waters running into the Mississippi. However, all these things I presume will be settled before you receive this; and I hope so settled as to give peace and satisfaction to us all.
Our crops of wheat are greater than have ever been known, and are now nearly secured. A caterpillar gave for a while great alarm, but did little injury. Of tobacco, not half a crop has been planted for want of rain; and even this half, with cotton and Indian corn, has yet many chances to run.
This summer will place our harbors in a situation to maintain peace and order within them. The next, or certainly the one following that, will so provide them with gunboats and common batteries, as to be hors d’insulte. Although our prospect is peace, our policy and purpose is to provide for defence by all those means to which our resources are competent.
I salute you with friendship, and assure you of my high respect and consideration.
Th: Jefferson.
TO W. A. BURWELL.
Monticello, September 17, 1806.
Dear Sir,
Yours of August the 7th, from Liberty, never got to my hands till the 9th instant. About the same time, I received the Enquirer in which Decius was so judiciously answered. The writer of that paper observed, that the matter of Decius consisted, first of facts; secondly, of inferences from these facts: that he was not well enough informed to affirm or deny his facts, and he therefore examines his inferences, and in a very masterly manner shows that even were his facts true, the reasonable inferences from them are very different from those drawn by Decius. But his facts are far from truth, and should be corrected. It happened that Mr. Madison and General Dearborn were here when I received your letter. I therefore, with them, took up Decius and read him deliberately; and our memories aided one another in correcting his bold and unauthorized assertions. I shall note the most material of them in the order of the paper.
1. It is grossly false that our ministers, as is said in a note, had proposed to surrender our claims to compensation for Spanish spoliations, or even for French. Their instructions were to make no treaty in which Spanish spoliations were not provided for; and although they were permitted to be silent as to French spoliations carried into Spanish ports, they were not expressly to abandon even them. 2. It is not true that our ministers, in agreeing to establish the Colorado as our western boundary, had been obliged to exceed the authority of their instructions. Although we considered our title good as far as the Rio Bravo, yet in proportion to what they could obtain east of the Mississippi, they were to relinquish to the westward, and successive sacrifices were marked out, of which even the Colorado was not the last. 3. It is not true that the Louisiana treaty was antedated, lest Great Britain should consider our supplying her enemies with money as a breach of neutrality. After the very words of the treaty were finally agreed to, it took some time, perhaps some days, to make out all the copies in the very splendid manner of Bonaparte’s treaties. Whether the 30th of April, 1803, the date expressed, was the day of the actual compact, or that on which it was signed, our memories do not enable us to say. If the former, then it is strictly conformable to the day of the compact; if the latter, then it was postdated, instead of being antedated. The motive assigned, too, is as incorrect as the fact. It was so far from being thought, by any party, a breach of neutrality, that the British minister congratulated Mr. King on the acquisition, and declared that the King had learned it with great pleasure: and when Baring, the British banker, asked leave of the minister to purchase the debt and furnish the money to France, the minister declared to him, that so far from throwing obstacles in the way, if there were any difficulty in the payment of the money, it was the interest of Great Britain to aid it. 4. He speaks of a double set of opinions and principles; the one ostensible, to go on the journals and before the public, the other efficient, and the real motives to action. But where are these double opinions and principles? The executive informed the legislature of the wrongs of Spain, and that preparation should be made to repel them, by force, if necessary. But as it might still be possible to negotiate a settlement, they asked such means as might enable them to meet the negotiation, whatever form it might take. The first part of this system was communicated publicly, the second, privately; but both were equally official, equally involved the responsibility of the executive, and were equally to go on the journals. 5. That the purchase of the Floridas was in direct opposition to the views of the executive, as expressed in the President’s official communication. It was not in opposition even to the public part of the communication, which did not recommend war, but only to be prepared for it. It perfectly harmonized with the private part, which asked the means of negotiation in such terms as covered the purchase of Florida as evidently as it was proper to speak it out. He speaks of secret communications between the executive and members, of backstairs influence, &tc.. But he never spoke of this while he and Mr. Nicholson enjoyed it almost solely. But when he differed from the executive in a leading measure, and the executive, not submitting to him, expressed their sentiments to others, the very sentiments (to wit, for the purchase of Florida), which he acknowledges they expressed to him, then he roars out upon backstairs influence. 6. The committee, he says, forbore to recommend offensive measures. Is this true? Did not they recommend the raising ———- regiments? Besides, if it was proper for the committee to forbear recommending offensive measures, was it not proper for the executive and legislature to exercise the same forbearance? 7. He says Monroe’s letter had a most important bearing on our Spanish relations. Monroe’s letter related, almost entirely, to our British relations. Of those with Spain he knew nothing particular since he left that country. Accordingly, in his letter he simply expressed an opinion on our affairs with Spain, of which he knew we had better information than he could possess. His opinion was no more than that of any other sensible man; and his letter was proper to be communicated with the English papers, and with them only. That the executive did not hold it up on account of any bearing on Spanish affairs, is evident from the fact, that it was communicated when the Senate had not yet entered on the Spanish affairs, and had not yet received the papers relating to them from the other House. The moment the Representatives were ready to enter on the British affairs, Monroe’s letter, which peculiarly related to them, and was official solely as to them, was communicated to both Houses, the Senate being then about entering on the Spanish affairs.
These, my dear Sir, are the principal facts worth correction. Make any use of them you think best, without letting your source of information be known. Can you send me some cones or seeds of the cucumber-tree? Accept affectionate salutations, and assurances of great esteem and respect.
Th: Jefferson.
Washington, October 12, 1806.
Dear Sir,
You witnessed, in the earlier part of the administration, the malignant and long continued efforts which the federalists exerted in their newspapers, to produce misunderstanding between Mr. Madison and myself. These failed completely. A like attempt was afterwards made, through other channels, to effect a similar purpose between General Dearborn and myself, but with no more success. The machinations of the last session to put you at cross questions with us all, were so obvious as to be seen at the first glance of every eye. In order to destroy one member of the administration, the whole were to be set to loggerheads to destroy one another. I observe in the papers lately, new attempts to revive this stale artifice, and that they squint more directly towards you and myself. I cannot, therefore, be satisfied, till I declare to you explicitly, that my affections and confidence in you are nothing impaired, and that they cannot be impaired by means so unworthy the notice of candid and honorable minds. I make the declaration, that no doubts or jealousies, which often beget the facts they fear, may find a moment’s harbor in either of our minds. I have so much reliance on the superior good sense and candor of all those associated with me, as to be satisfied they will not suffer either friend or foe to sow tares among us. Our administration now drawing towards a close, I have a sublime pleasure in believing it will be distinguished as much by having placed itself above all the passions which could disturb its harmony, as by the great operations by which it will have advanced the well-being of the nation.
Accept my affectionate salutations, and assurances of my constant and unalterable respect and attachment.
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN DICKINSON.
Washington, January 13, 1807.
My Dear and Ancient Friend,
I have duly received your favor of the 1st instant, and am ever thankful for communications which may guide me in the duties which I wish to perform as well as I am able. It is but too true, that great discontents exist in the territory of Orleans. Those of the French inhabitants have for their sources, 1. the prohibition of importing slaves. This may be partly removed by Congress permitting them to receive slaves from the other States, which, by dividing that evil, would lessen its danger. 2. The administration of justice in our forms, principles, and language, with all of which they are unacquainted, and are the more abhorrent, because of the enormous expense, greatly exaggerated by the corruption of bankrupt and greedy lawyers, who have gone there from the United States and engrossed the practice. 3. The call on them by the land commissioners to produce the titles of their lands. The object of this is really to record and secure their rights. But as many of them hold on rights so ancient that the title papers are lost, they expect the land is to be taken from them wherever they cannot produce a regular deduction of title in writing. In this they will be undeceived by the final result, which will evince to them a liberal disposition of the government towards them. Among the American inhabitants it is the old division of federalists and republicans. The former, are as hostile there as they are every where, and are the most numerous and wealthy. They have been long endeavoring to batter down the Governor, who has always been a firm republican. There were characters superior to him, whom I wished to appoint, but they refused the office: I know no better man who would accept of it, and it would not be right to turn him out for one not better. But it is the second cause, above mentioned, which is deep seated and permanent. The French members of the legislature, being the majority in both Houses, lately passed an act, declaring that the civil, or French laws, should be the laws of their land, and enumerated about fifty folio volumes, in Latin, as the depositories of these laws. The Governor negatived the act. One of the Houses thereupon passed a vote for self-dissolution of the legislature as a useless body, which failed in the other House by a single vote only. They separated, however, and have disseminated all the discontent they could. I propose to the members of Congress in conversation, the enlisting thirty thousand volunteers, Americans by birth, to be carried at the public expense, and settled immediately on a bounty of one hundred and sixty acres of land each, on the west side of the Mississippi, on the condition of giving two years of military service, if that country should be attacked within seven years. The defence of the country would thus be placed on the spot, and the additional number would entitle the territory to become a State, would make the majority American, and make it an American instead of a French State. This would not sweeten the pill to the French; but in making that acquisition we had some view to our own good as well as theirs, and I believe the greatest good of both will be promoted by whatever will amalgamate us together.
I have tired you, my friend, with a long letter. But your tedium will end in a few lines more. Mine has yet two years to endure. I am tired of an office where I can do no more good than many others, who would be glad to be employed in it. To myself, personally, it brings nothing but unceasing drudgery, and daily loss of friends. Every office becoming vacant, every appointment made, me donne un ingrat, et cent ennemis. My only consolation is in the belief, that my fellow-citizens at large give me credit for good intentions. I will certainly endeavor to merit the continuance of that good will which follows well intended actions, and their approbation will be the dearest reward I can carry into retirement.
God bless you, my excellent friend, and give you yet many healthy and happy years.
Th: Jefferson.
TO WILSON C. NICHOLAS.
Washington, February 28,1807.
Dear Sir,
Your letter of January the 20th was received in due time. But such has been the constant pressure of business, that it has been out of my power to answer it. Indeed, the subjects of it would be almost beyond the extent of a letter, and as I hope to see you ere long at Monticello, it can then be more effectually done verbally. Let me observe, however, generally, that it is impossible for my friends ever to render me so acceptable a favor, as by communicating to me, without reserve, facts and opinions. I have none of that sort of self-love which winces at it; indeed, both self-love and the desire to do what is best strongly invite unreserved communication. There is one subject which will not admit a delay till I see you. Mr. T. M. Randolph is, I believe, determined to retire from Congress, and it is strongly his wish, and that of all here, that you should take his place. Never did the calls of patriotism more loudly assail you than at this moment. After excepting the federalists, who will be twenty-seven, and the little band of schismatics, who will be three or four (all tongue), the residue of the House of Representatives is as well disposed a body of men as I ever saw collected. But there is no one whose talents and standing, taken together, have weight enough to give him the lead. The consequence is, that there is no one who will undertake to do the public business, and it remains undone. Were you here, the whole would rally round you in an instant, and willingly co-operate in whatever is for the public good. Nor would it require you to undertake drudgery in the House. There are enough, able and willing to do that. A rallying point is all that is wanting. Let me beseech you then to offer yourself. You never will have it so much in your power again to render such eminent service.
Accept my affectionate salutations and high esteem.
Th: Jefferson.
TO JAMES MONROE.
Washington, March 21, 1807.
Dear Sir,
A copy of the treaty with Great Britain came to Mr. Erskine’s hands on the last day of the session of Congress, which he immediately communicated to us; and since that, Mr. Purviance has arrived with an original. On the subject of it you will receive a letter from the Secretary of State, of about this date, and one more in detail hereafter. I should not have written, but that I perceive uncommon efforts, and with uncommon wickedness, are making by the federal papers to produce mischief between myself, personally, and our negotiators; and also to irritate the British government, by putting a thousand speeches into my mouth, not one word of which I ever uttered. I have, therefore, thought it safe to guard you, by stating the view which we have given out on the subject of the treaty, in conversation and otherwise; for ours, as you know, is a government which will not tolerate the being kept entirely in the dark, and especially on a subject so interesting as this treaty. We immediately stated in conversation, to the members of the legislature and others, that having, by a letter received in January, perceived that our ministers might sign a treaty not providing satisfactorily against the impressment of our seamen, we had, on the 3rd of February, informed you, that should such an one have been forwarded, it could not be ratified, and recommending, therefore, that you should resume negotiations for inserting an article to that effect; that we should hold the treaty in suspense until we could learn from you the result of our instructions, which probably would not be till summer, and then decide on the question of calling the Senate. We observed, too, that a written declaration of the British commissioners, given in at the time of signature, would of itself, unless withdrawn, prevent the acceptance of any treaty, because its effect was to leave us bound by the treaty, and themselves totally unbound. This is the statement we have given out, and nothing more of the contents of the treaty has been made known. But depend on it, my dear Sir, that it will be considered as a hard treaty when it is known. The British commissioners appear to have screwed every article as far as it would bear, to have taken every thing, and yielded nothing. Take out the eleventh article, and the evil of all the others so much overweighs the good, that we should be glad to expunge the whole. And even the eleventh article admits only that we may enjoy our right to the indirect colonial trade, during the present hostilities. If peace is made this year, and war resumed the next, the benefit of this stipulation is gone, and yet we are bound for ten years, to pass no non-importation or non-intercourse laws, nor take any other measures to restrain the unjust pretensions and practices of the British. But on this you will hear from the Secretary of State. If the treaty cannot be put into an acceptable form, then the next best thing is to back out of the negotiation as well as we can, letting that die away insensibly; but, in the mean time, agreeing informally, that both parties shall act on the principles of the treaty, so as to preserve that friendly understanding which we so sincerely desire, until the one or the other may be disposed to yield the points which divide us. This will leave you to follow your desire of coming home, as soon as you see that the amendment of the treaty is desperate. The power of continuing the negotiations will pass oyer to Mr. Pinckney, who, by procrastinations, can let it die away, and give us time, the most precious of all things to us. The government of New Orleans is still without such a head as I wish. The salary of five thousand dollars is too small; but I am assured the Orleans legislature would make it adequate, would you accept it. It is the second office in the United States in importance, and I am still in hopes you will accept it. It is impossible to let you stay at home while the public has so much need of talents. I am writing under a severe indisposition of periodical headache, without scarcely command enough of my mind to know what I write. As a part of this letter concerns Mr. Pinckney as well as yourself, be so good as to communicate so much of it to him; and with my best respects to him, to Mrs. Monroe, and your daughter, be assured yourself, in all cases, of my constant and affectionate friendship and attachment.
Th: Jefferson.
M. LE COMTE DIODATI.
Washington, March 29, 1807.
My Dear and Antient Friend,
Your letter of August the 29th reached me the 18th of February. It enclosed a duplicate of that written from Brunswick five years before, but which I never received, or had notice of, but by this duplicate. Be assured, my friend, that I was incapable of such negligence towards you, as a failure to answer it would have implied. It would illy have accorded with those sentiments of friendship I entertained for you at Paris, and which neither time nor distance has lessened. I often pass in review the many happy hours I spent with Madame Diodati and yourself on the banks of the Seine, as well as at Paris, and I count them among the most pleasing I enjoyed in France. Those were indeed days of tranquillity and happiness. They had begun to cloud a little before I left you; but I had no apprehension that the tempest, of which I saw the beginning, was to spread over such an extent of space and time. I have often thought of you with anxiety, and wished to know how you weathered the storm, and into what port you had retired. The letters now received give me the first information, and I sincerely felicitate you on your safe and quiet retreat. Were I in Europe, pax et panis would certainly be my motto. Wars and contentions, indeed, fill the pages of history with more matter. But more blest is that nation whose silent course of happiness furnishes nothing for history to say. This is what I ambition for my own country, and what it has fortunately enjoyed now upwards of twenty years, while Europe has been in constant volcanic eruption. I again, my friend, repeat my joy that you have escaped the overwhelming torrent of its lava.
At the end of my present term, of which two years are yet to come, I propose to retire from public life, and to close my days on my patrimony of Monticello, in the bosom of my family. I have hitherto enjoyed uniform health; but the weight of public business begins to be too heavy for me, and I long for the enjoyments of rural life, among my books, my farms, and my family. Having performed my quadragena stipendia, I am entitled to my discharge, and should be sorry, indeed, that others should be sooner sensible than myself when I ought to ask it. I have, therefore, requested my fellow-citizens to think of a successor for me, to whom I shall deliver the public concerns with greater joy than I received them. I have the consolation too of having added nothing to my private fortune, during my public service, and of retiring with hands as clean as they are empty. Pardon me these egoisms, which, if ever excusable, are so when writing to a friend to whom our concerns are not uninteresting. I shall always be glad to hear of your health and happiness, and having been out of the way of hearing of any of our cotemporaries of the corps diplomatique at Paris, any details of their subsequent history, which you will favor me with, will be thankfully received. I pray you to make my friendly respects acceptable to Madame la Comtesse Diodati, to assure M. Tronchin of my continued esteem, and to accept yourself my affectionate salutations, and assurances of constant attachment and respect.
Th: Jefferson.
Washington, April 2, 1807.
Dear Sir,
I wrote you on the 10th of July last; but neither your letter of October the 20th nor that of November the 15th mentioning the receipt of it, I fear it has miscarried. I therefore now enclose a duplicate. As that was to go under cover of the Secretary of State’s despatches by any vessel going from our distant ports, I retained the polygraph therein mentioned for a safer conveyance. None such has occurred till now, that the United States’ armed brig the Wasp, on her way to the Mediterranean is to touch at Falmouth, with despatches for our ministers at London, and at Brest, with others for yourself and General Armstrong.
You heard in due time from London of the signature of a treaty there between Great Britain and the United States. By a letter we received in January from our ministers at London, we found they were making up their minds to sign a treaty, in which no provision was made against the impressment of our seamen, contenting themselves with a note received in the course of their correspondence, from the British negotiators, assuring them of the discretion with which impressments should be conducted, which could be construed into a covenant only by inferences, against which its omission in the treaty was a strong inference; and in its terms totally unsatisfactory. By a letter of February the 3rd, they were immediately informed that no treaty, not containing a satisfactory article on that head, would be ratified, and desiring them to resume the negotiations on that point. The treaty having come to as actually in the inadmissible shape apprehended, we, of course, hold it up until we know the result of the instructions of February the 3rd. I have but little expectation that the British government will retire from their habitual wrongs in the impressment of our seamen, and am certain, that without that we will never tie up our hands by treaty, from the right of passing a non-importation or non-intercourse act, to make it her interest to become just. This may bring on a war of commercial restrictions. To show, however, the sincerity of our desire for conciliation, I have suspended the non-importation act. This state of things should be understood at Paris, and every effort used on your part to accommodate our differences with Spain, under the auspices of France, with whom it is all-important that we should stand in terms of the strictest cordiality. In fact, we are to depend on her and Russia for the establishment of neutral rights by the treaty of peace, among which should be that of taking no persons by a belligerent out of a neutral ship, unless they be the soldiers of an enemy. Never did a nation act towards another with more perfidy and injustice than Spain has constantly practised against us: and if we have kept our hands off of her till now, it has been purely out of respect to France, and from the value we set on the friendship of France. We expect, therefore, from the friendship of the Emperor, that he will either compel Spain to do us justice, or abandon her to us. We ask but one month to be in possession of the city of Mexico.
No better proof of the good faith of the United States could have been given, than the vigor with which we have acted, and the expense incurred, in suppressing the enterprise meditated lately by Burr against Mexico. Although at first he proposed a separation of the western country, and on that ground received encouragement and aid from Yrujo, according to the usual spirit of his government towards us, yet he very early saw that the fidelity of the western country was not to be shaken, and turned himself wholly towards Mexico. And so popular is an enterprise on that country in this, that we had only to lie still, and he would have had followers enough to have been in the city of Mexico in six weeks. You have doubtless seen my several messages to Congress, which gave a faithful narrative of that conspiracy. Burr himself, after being disarmed by our endeavors of all his followers, escaped from the custody of the court of Mississippi, but was taken near Fort Stoddart, making his way to Mobile, by some country people, who brought him on as a prisoner to Richmond, where he is now under a course for trial. Hitherto we have believed our law to be, that suspicion on probable grounds was sufficient cause to commit a person for trial, allowing time to collect witnesses till the trial. But the judges here have decided, that conclusive evidence of guilt must be ready in the moment of arrest, or they will discharge the malefactor. If this is still insisted on, Burr will be discharged; because his crimes having been sown from Maine, through the whole line of the western waters, to New Orleans, we cannot bring the witnesses here under four months. The fact is, that the federalists make Burr’s cause their own, and exert their whole influence to shield him from punishment, as they did the adherents of Miranda. And it is unfortunate that federalism is still predominent in our judiciary department, which is consequently in opposition to the legislative and executive branches, and is able to baffle their measures often.
Accept my friendly salutations, and assurances of great esteem and respect.
Th: Jefferson.
TO WILLIAM B. GILES.
Monticello, April 20, 1807.
Dear Sir,
Your favor of the 6th instant, on the subject of Burr’s offences, was received only four days ago. That there should be anxiety and doubt in the public mind, in the present defective state of the proof, is not wonderful; and this has been sedulously encouraged by the tricks of the judges to force trials before it is possible to collect the evidence, dispersed through a line of two thousand miles from Maine to Orleans. The federalists, too, give all their aid, making Burr’s cause their own, mortified only that he did not separate the union or overturn the government, and proving, that had he had a little dawn of success, they would have joined him to introduce his object, their favorite monarchy, as they would any other enemy, foreign or domestic, who could rid them of this hateful republic for any other government in exchange.
The first ground of complaint was the supine inattention of the administration to a treason stalking through the land in open day. The present one, that they have crushed it before it was ripe for execution, so that no overt acts can be produced. This last may be true; though I believe it is not. Our information having been chiefly by way of letter, we do not know of a certainty yet what will be proved. We have set on foot an inquiry through the whole of the country which has been the scene of these transactions, to be able to prove to the courts, if they will give time, or to the public by way of communication to Congress, what the real facts have been. For obtaining this, we are obliged to appeal to the patriotism of particular persons in different places, of whom we have requested to make the inquiry in their neighborhood, and on such information as shall be voluntarily offered. Aided by no process or facilities from the federal courts, but frowned on by their new-born zeal for the liberty of those whom we would not permit to overthrow the liberties of their country, we can expect no revealments from the accomplices of the chief offender. Of treasonable intentions, the judges have been obliged to confess there is probable appearance. What loop-hole they will find in the case, when it comes to trial, we cannot foresee. Eaton, Stoddart, Wilkinson, and two others whom I must not name, will satisfy the world, if not the judges, of Burr’s guilt. And I do suppose the following overt acts will be proved. 1. The enlistment of men, in a regular way. 2. The regular mounting of guard round Blannerhassett’s island, when they expected Governor Tiffin’s men to be on them modo guerrino arraiati. 3. The rendezvous of Burr with his men at the mouth of Cumberland. 4. His letter to the acting Governor of Mississippi, holding up the prospect of civil war. 5. His capitulation, regularly signed with the aid of the Governor, as between two independent and hostile commanders.
But a moment’s calculation will show that this evidence cannot be collected under four months, probably five, from the moment of deciding when and where the trial shall be. I desired Mr. Rodney expressly to inform the Chief Justice of this, inofficially. But Mr. Marshall says, ‘More than five weeks have elapsed since the opinion of the Supreme Court has declared the necessity of proving the overt acts, if they exist. Why are they not proved.’ In what terms of decency can we speak of this? As if an express could go to Natchez, or the mouth of Cumberland, and return in five weeks, to do which has never taken less than twelve. Again, ‘If, in November or December last, a body of troops had been assembled on the Ohio, it is impossible to suppose the affidavits, establishing the fact, could not have been obtained by the last of March.’ But I ask the Judge, where they should have been lodged? At Frankfort? at Cincinnati? at Nashville? St. Louis? Natchez? New Orleans? These were the probable places of apprehension and examination. It was not known at Washington till the 26th of March, that Burr would escape from the western tribunals, be retaken and brought to an eastern one: and in five days after (neither five months nor five weeks, as the Judge calculated) he says, it is ‘impossible to suppose the affidavits could not have been obtained.’ Where? At Richmond he certainly meant, or meant only to throw dust in the eyes of his audience. But all the principles of law are to be perverted which would bear on the favorite offenders, who endeavor to overturn this odious republic. ‘I understand,’ says the Judge, ‘probable cause of guilt to be a case made out of proof furnishing good reason to believe,’ &c. Speaking as a lawyer, he must mean legal proof, i.e. proof on oath, at least. But this is confounding probability and proof. We had always before understood that where there was reasonable ground to believe guilt, the offender must be put on his trial. That guilty intentions were probable, the Judge believed. And as to the overt acts, were not the bundle of letters of information in Mr. Rodney’s hands, the letters and facts published in the local newspapers, Burr’s flight, and the universal belief or rumor of his guilt, probable ground for presuming the facts of enlistment, military guard, rendezvous, threat of civil war, or capitulation, so as to put him on trial? Is there a candid man in the United States who does not believe some one, if not all, of these overt acts to have taken place?
If there ever had been an instance in this or the preceding administrations, of federal judges so applying principles of law as to condemn a federal or acquit a republican offender, I should have judged them in the present case with more charity. All this, however, will work well. The nation will judge both the offender and judges for themselves. If a member of the executive or legislature does wrong, the day is never far distant when the people will remove him. They will see then, and amend the error in our constitution, which makes any branch independent of the nation. They will see that one of the great co-ordinate branches of the government, setting itself in opposition to the other two, and to the common sense of the nation, proclaims impunity to that class of offenders which endeavors to overturn the constitution, and are themselves protected in it by the constitution itself: for impeachment is a farce which will not be tried again. If their protection of Burr produces this amendment, it will do more good than his condemnation would have done. Against Burr, personally, I never had one hostile sentiment. I never, indeed, thought him an honest, frank-dealing man, but considered him as a crooked gun, or other perverted machine, whose aim or shot you could never be sure of. Still, while he possessed the confidence of the nation, I thought it my duty to respect in him their confidence, and to treat him as if he deserved it: and if his punishment can be commuted now for an useful amendment of the constitution, I shall rejoice in it. My sheet being full, I perceive it is high time to offer you my friendly salutations, and assure you of my constant and affectionate esteem and respect.
Th: Jefferson.
TO GEORGE HAY.
Washington, June 2, 1807.
Dear Sir,
While Burr’s case is depending before the court, I will trouble you from time to time with what occurs to me. I observe that the case of Marbury v. Madison has been cited, and I think it material to stop at the threshold the citing that case as authority, and to have it denied to be law. 1. Because the judges, in the outset, disclaimed all cognizance of the case; although they then went on to say what would have been their opinion, had they had cognizance of it. This then was confessedly an extra-judicial opinion, and, as such, of no authority. 2. Because, had it been judicially pronounced, it would have been against law; for to a commission, a deed, a bond, delivery is essential to give validity. Until, therefore, the commission is delivered out of the hands of the executive and his agents, it is not his deed. He may withhold or cancel it at pleasure, as he might his private deed in the same situation. The constitution intended that the three great branches of the government should be co-ordinate, and independent of each other. As to acts, therefore, which are to be done by either, it has given no control to another branch. A judge, I presume, cannot sit on a bench without a commission, or a record of a commission: and the constitution having given to the judiciary branch no means of compelling the executive either to deliver a commission, or to make a record of it, shows it did not intend to give the judiciary that control over the executive, but that it should remain in the power of the latter to do it or not. Where different branches have to act in their respective lines, finally and without appeal, under any law, they may give to it different and opposite constructions. Thus in the case of William Smith, the House of Representatives determined he was a citizen, and in the case of William Duane (precisely the same in every material circumstance) the judges determined he was no citizen. In the cases of Callender and others, the judges determined the sedition act was valid under the constitution, and exercised their regular powers of sentencing them to fine and imprisonment. But the executive determined that the sedition act was a nullity under the constitution, and exercised his regular power of prohibiting the execution of the sentence, or rather of executing the real law, which protected the acts of the defendants. From these different constructions of the same act by different branches, less mischief arises, than from giving to any one of them a control over the others. The executive and Senate act on the construction, that until delivery from the executive department, a commission is in their possession, and within their rightful power; and in cases of commissions not revocable at will, where, after the Senate’s approbation and the President’s signing and sealing, new information of the unfitness of the person has come to hand before the delivery of the commission, new nominations have been made and approved, and new commissions have issued.
On this construction I have hitherto acted; on this I shall ever act, and maintain it with the powers of the government, against any control which may be attempted by the judges in subversion of the independence of the executive and Senate within their peculiar department. I presume, therefore, that in a case where our decision is by the constitution the supreme one, and that which can be carried into effect, it is the constitutionally authoritative one, and that that by the judges was coram non judice, and unauthoritative, because it cannot be carried into effect. I have long wished for a proper occasion to have the gratuitous opinion in Marbury v. Madison brought before the public, and denounced as not law: and I think the present a fortunate one, because it occupies such a place in the public attention. I should be glad, therefore, if, in noticing that case, you could take occasion to express the determination of the executive, that the doctrines of that case were given extra-judicially and against law, and that their reverse will be the rule of action with the executive. If this opinion should not be your own, I would wish it to be expressed merely as that of the executive. If it is your own also, you would of course give to the arguments such a developement, as a case, incidental only, might render proper.
I salute you with friendship and respect.
Th: Jefferson.
THOMAS JEFFERSON TO ALBERT GALLATIN.
I gave you, some time ago, a project of a more equal tariff on wines, than that which now exists. But in that I yielded considerably to the faulty classification of them in our law. I have now formed one with attention, and according to the best information I possess, classing them more rigorously. I am persuaded, that were the duty on cheap wines put on the same ratio with the dear, it would wonderfully enlarge the field of those who use wine, to the expulsion of whiskey. The introduction of a very cheap wine (St. George) into my neighborhood, within two years past, has quadrupled in that time the number of those who keep wine, and will ere long increase them tenfold. This would be a great gain to the treasury, and to the sobriety of our country. I will here add my tariff, wherein you will be able to choose any rate of duty you please; and to decide whether it will not, on a fit occasion, be proper for legislative attention. Affectionate salutations.
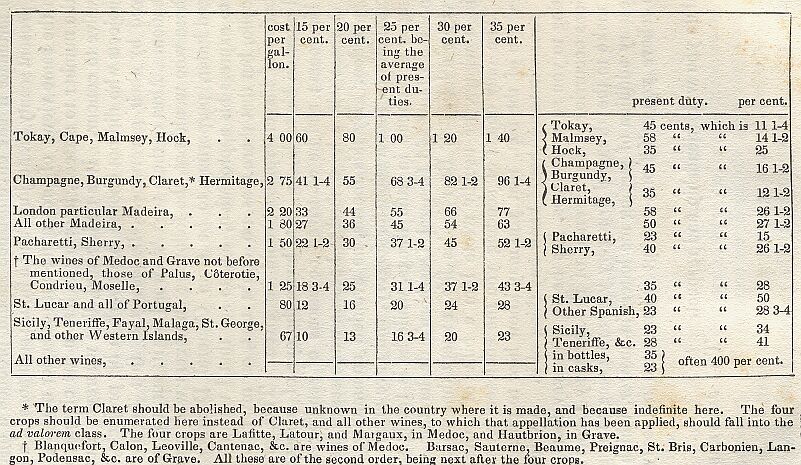
TO GEORGE HAY.
Washington, June 5, 1807.
Dear Sir,
Your favor of the 31st instant has been received, and I think it will be fortunate if any circumstance should produce a discharge of the present scanty grand jury, and a future summons of a fuller: though the same views of protecting the offender may again reduce the number to sixteen, in order to lessen the chance of getting twelve to concur. It is understood, that wherever Burr met with subjects who did not choose to embark in his projects, unless approved by their government, he asserted that he had that approbation. Most of them took his word for it, but it is said that with those who would not, the following stratagem was practised. A forged letter, purporting to be from General Dearborn, was made to express his approbation, and to say that I was absent at Monticello, but that there was no doubt that, on my return, my approbation of his enterprises would be given. This letter was spread open on his table, so as to invite the eye of whoever entered his room; and he contrived occasions of sending up into his room, those whom he wished to become witnesses of his acting under sanction. By this means, he avoided committing himself to any liability to prosecution for forgery, and gave another proof of being a great man in little things, while he is really small in great ones. I must add General Dearborn’s declaration, that he never wrote a letter to Burr in his life, except that when here, once in a winter, he usually wrote him a billet of invitation to dine. The only object of sending you the enclosed letters is to possess you of the fact, that you may know how to pursue it, if any of your witnesses should know any thing of it. My intention in writing to you several times, has been to convey facts or observations occurring in the absence of the Attorney General, and not to make to the dreadful drudgery you are going through the unnecessary addition of writing me letters in answer, which I beg you to relieve yourself from, except when some necessity calls for it.
I salute you with friendship and respect.
Th: Jefferson.
TO DOCTOR HORATIO TURPIN.
Washington, June 10, 1807.
Dear Sir,
Your favor of June the 1st has been duly received. To a mind like yours, capable in any question of abstracting it from its relation to yourself, I may safely hazard explanations, which I have generally avoided to others, on questions of appointment. Bringing into office no desires of making it subservient to the advancement of my own private interests, it has been no sacrifice, by postponing them, to strengthen the confidence of my fellow-citizens. But I have not felt equal indifference towards excluding merit from office, merely because it was related to me. However, I have thought it my duty so to do, that my constituents may be satisfied, that, in selecting persons for the management of their affairs, I am influenced by neither personal nor family interests, and especially, that the field of public office will not be perverted by me into a family property. On this subject, I had the benefit of useful lessons from my predecessors, had I needed them, marking what was to be imitated and what avoided. But, in truth, the nature of our government is lesson enough. Its energy depending mainly on the confidence of the people, in their Chief Magistrate, makes it his duty to spare nothing which can strengthen him with that confidence.
Accept assurances of my constant friendship and respect.
Th: Jefferson.
Washington, June 11, 1807.
Sir,
Your letter of May the 9th has been duly received. The subjects it proposes would require time and space for even moderate developement. My occupations limit me to a very short notice of them. I think there does not exist a good elementary work on the organization of society into civil government: I mean a work which presents in one full and comprehensive view the system of principles on which such an organization should be founded, according to the rights of nature. For want of a single work of that character, I should recommend Locke on Government, Sidney, Priestley’s Essay on the First Principles of Government, Chipman’s Principles of Government, and the Federalist. Adding, perhaps, Beccaria on Crimes and Punishments, because of the demonstrative manner in which he has treated that branch of the subject. If your views of political inquiry go further, to the subjects of money and commerce, Smith’s Wealth of Nations is the best book to be read, unless Say’s Political Economy can be had, which treats the same subjects on the same principles, but in a shorter compass, and more lucid manner. But I believe this work has not been translated into our language.
History, in general, only informs us what bad government is. But as we have employed some of the best materials of the British constitution in the construction of our own government, a knowledge of British history becomes useful to the American politician. There is, however, no general history of that country which can be recommended. The elegant one of Hume seems intended to disguise and discredit the good principles of the government, and is so plausible and pleasing in its style and manner, as to instil its errors and heresies insensibly into the minds of unwary readers. Baxter has performed a good operation on it. He has taken the text of Hume as his ground-work, abridging it by the omission of some details of little interest, and wherever he has found him endeavoring to mislead, by either the suppression of a truth, or by giving it a false coloring, he has changed the text to what it should be, so that we may properly call it Hume’s history republicanized. He has, moreover, continued the history (but indifferently) from where Hume left it, to the year 1800. The work is not popular in England, because it is republican; and but a few copies have ever reached America. It is a single quarto volume. Adding to this Ludlow’s Memoirs, Mrs. Macaulay’s and Belknap’s histories, a sufficient view will be presented of the free principles of the English constitution.
To your request of my opinion of the manner in which a newspaper should be conducted, so as to be most useful, I should answer, ‘by restraining it to true, facts and sound principles only.’ Yet I fear such a paper would find few subscribers. It is a melancholy truth, that a suppression of the press could not more completely deprive the nation of its benefits, than is done by its abandoned prostitution to falsehood. Nothing can now be believed which is seen in a newspaper. Truth itself becomes suspicious by being put into that polluted vehicle. The real extent of this state of misinformation is known only to those who are in situations to confront facts within their knowledge with the lies of the day. I really look with commiseration over the great body of my fellow-citizens, who, reading newspapers, live and die in the belief, that they have known something of what has been passing in the world in their time; whereas the accounts they have read in newspapers are just as true a history of any other period of the world as of the present, except that the real names of the day are affixed to their fables. General facts may indeed be collected from them, such as that Europe is now at war, that Bonaparte has been a successful warrior, that he has subjected a great portion of Europe to his will, &c. &c.; but no details can be relied on. I will add, that the man who never looks into a newspaper is better informed than he who reads them; inasmuch as he who knows nothing is nearer to truth than he whose mind is filled with falsehoods and errors. He who reads nothing will still learn the great facts, and the details are all false.
Perhaps an editor might begin a reformation in some such way as this. Divide his paper into four chapters, heading the 1st, Truths. 2nd, Probabilities. 3rd, Possibilities. 4th, Lies. The 1st chapter would be very short, as it would contain little more than authentic papers, and information from such sources, as the editor would be willing to risk his own reputation for their truth. The 2nd would contain what, from a mature consideration of all circumstances, his judgment should conclude to be probably true. This, however, should rather contain too little than too much. The 3rd and 4th should be professedly for those readers who would rather have lies for their money than the blank paper they would occupy.
Such an editor too, would have to set his face against the demoralizing practice of feeding the public mind habitually on slander, and the depravity of taste which this nauseous aliment induces. Defamation is becoming a necessary of life; insomuch, that a dish of tea in the morning or evening cannot be digested without this stimulant. Even those who do not believe these abominations, still read them with complaisance to their auditors, and instead of the abhorrence and indignation which should fill a virtuous mind, betray a secret pleasure in the possibility that some may believe them, though they do not themselves. It seems to escape them, that it is not he who prints, but he who pays for printing a slander, who is its real author.
These thoughts on the subjects of your letter are hazarded at your request. Repeated instances of the publication of what has not been intended for the public eye, and the malignity with which political enemies torture every sentence from me into meanings imagined by their own wickedness only, justify my expressing a solicitude, that this hasty communication may in nowise be permitted to find its way into the public papers. Not fearing these political bull-dogs, I yet avoided putting myself in the way of being baited by them, and do not wish to volunteer away that portion of tranquillity, which a firm execution of my duties will permit me to enjoy.
I tender you my salutations, and best wishes for your success.
Th: Jefferson.
Washington, June 12, 1807.
Dear Sir,
******
The proposition in your letter of May the 16th, of adding an umpire to our discordant negotiators at Paris, struck me favorably on reading it, and reflection afterwards strengthened my first impressions. I made it therefore a subject of consultation with my coadjutors, as is our usage. For our government, although in theory subject to be directed by the unadvised will of the President, is, and from its origin has been, a very different thing in practice. The minor business in each department is done by the Head of the department, on consultation with the President alone. But all matters of importance or difficulty are submitted to all the Heads of departments composing the cabinet; sometimes by the President’s consulting them separately and successively, as they happen to call on him; but in the greatest cases, by calling them together, discussing the subject maturely, and finally taking the vote, in which the President counts himself but as one. So that in all important cases the executive is, in fact, a directory, which certainly the President might control: but of this there was never an example either in the first or the present administration. I have heard, indeed, that my predecessor sometimes decided things against his council.
I adopted in the present case the mode of separate consultation. The opinion of each member, taken separately, was, that the addition of a third negotiator was not at this time advisable. For the present, therefore, the question must rest. Mr. Bowdoin, we know, is anxious to come home, and is detained only by the delicacy of not deserting his post. In the existing temper between him and his colleague, it would certainly be better that one of them should make an opening for re-composing the commission more harmoniously. I salute you with affection and respect.
Th: Jefferson.
TO GEORGE HAY.
Washington, June 12, 1807.
Dear Sir,
Your letter of the 9th is this moment received. Reserving the necessary right of the President of the United States to decide, independently of all other authority, what papers, coming to him as President, the public interests permit to be communicated, and to whom, I assure you of my readiness, under that restriction, voluntarily to furnish, on all occasions, whatever the purposes of justice may require. But the letter of General Wilkinson, of October the 21st, requested for the defence of Colonel Burr, with every other paper relating to the charges against him, which were in my possession when the Attorney General went on to Richmond in March, I then delivered to him; and I have always taken for granted he left the whole with you. If he did, and the bundle retains the order in which I had arranged it, you will readily find the letter desired, under the date of its receipt, which was November the 25th: but lest the Attorney General should not have left those papers with you, I this day write to him to forward this one by post. An uncertainty whether he is at Philadelphia, Wilmington, or New Castle, may produce delay in his receiving my letter, of which it is proper you should be apprized. But, as I do not recollect the whole contents of that letter, I must beg leave to devolve on you the exercise of that discretion which it would be my right and duty to exercise, by withholding the communication of any parts of the letter, which are not directly material for the purposes of justice.
With this application, which is specific, a prompt compliance is practicable. But when the request goes to ‘copies of the orders issued in relation to Colonel Burr, to the officers at Orleans, Natchez, &c. by the Secretaries of the War and Navy departments,’ it seems to cover a correspondence of many months, with such a variety of officers, civil and military, all over the United States, as would amount to the laying open the whole executive books. I have desired the Secretary of War to examine his official communications; and on a view of these, we may be able to judge what can and ought to be done towards a compliance with the request. If the defendant alleges that there was any particular order, which, as a cause, produced any particular act on his part, then he must know what this order was, can specify it, and a prompt answer can be given. If the object had been specified, we might then have had some guide for our conjectures, as to what part of the executive records might be useful to him: but, with a perfect willingness to do what is right, we are without the indications which may enable us to do it. If the researches of the Secretary at War should produce any thing proper for communication, and pertinent to any point we can conceive in the defence before the court, it shall be forwarded to you. I salute you with respect and esteem.
Th: Jefferson.
TO GEORGE HAY.
Washington, June 17, 1807.
Sir,
In answering your letter of the 9th, which desired a communication of one to me from General Wilkinson, specified by its date, I informed you in mine of the 12th that I had delivered it, with all other papers respecting the charges against Aaron Burr, to the Attorney General, when he went to Richmond; that I had supposed he had left them in your possession, but would immediately write to him, if he had not, to forward that particular letter without delay. I wrote to him accordingly on the same day, but having no answer, I know not whether he has forwarded the letter. I stated in the same letter, that I had desired the Secretary at War, to examine his office, in order to comply with your further request, to furnish copies of the orders which had been given respecting Aaron Burr and his property; and in a subsequent letter of the same day, I forwarded to you copies of two letters from the Secretary at War, which appeared to be within the description expressed in your letter. The order from the Secretary of the Navy, you said, you were in possession of. The receipt of these papers had, I presume, so far anticipated, and others this day forwarded will have substantially fulfilled, the object of a subpoena from the District Court of Richmond, requiring that those officers and myself should attend the Court in Richmond, with the letter of General Wilkinson, the answer to that letter, and the orders of the departments of War and the Navy, therein generally described. No answer to General Wilkinson’s letter, other than a mere acknowledgment of its receipt, in a letter written for a different purpose, was ever written by myself or any other. To these communications of papers, I will add, that if the defendant supposes there are any facts within the knowledge of the Heads of departments, or of myself, which can be useful for his defence, from a desire of doing any thing our situation will permit in furtherance of justice, we shall be ready to give him the benefit of it, by way of deposition, through any persons whom the Court shall authorize to take our testimony at this place. I know, indeed, that this cannot be done but by consent of parties; and I therefore authorize you to give consent on the part of the United States. Mr. Burr’s consent will be given of course, if he supposes the testimony useful.
As to our personal attendance at Richmond, I am persuaded the Court is sensible, that paramount duties to the nation at large control the obligation of compliance with their summons in this case; as they would, should we receive a similar one, to attend the trials of Blannerhassett and others, in the Mississippi territory, those instituted at St. Louis and other places on the western waters, or at any place, other than the seat of government. To comply with such calls would leave the nation without an executive branch, whose agency, nevertheless, is understood to be so constantly necessary, that it is the sole branch which the constitution requires to be always in function. It could not then mean that it should be withdrawn from its station by any co-ordinate authority.
With respect to papers, there is certainly a public and a private side to our offices. To the former belong grants of land, patents for inventions, certain commissions, proclamations, and other papers patent in their nature. To the other belong mere executive proceedings. All nations have found it necessary, that for the advantageous conduct of their affairs, some of these proceedings, at least, should remain known to their executive functionary only. He, of course, from the nature of the case, must be the sole judge of which of them the public interests will permit publication. Hence, under our constitution, in requests of papers, from the legislative to the executive branch, an exception is carefully expressed, as to those which he may deem the public welfare may require not to be disclosed; as you will see in the enclosed resolution of the House of Representatives, which produced the message of January 22nd, respecting this case. The respect mutually due between the constituted authorities, in their official intercourse, as well as sincere dispositions to do for every one what is just, will always insure from the executive, in exercising the duty of discrimination confided to him, the same candor and integrity to which the nation has in like manner trusted in the disposal of its judiciary authorities. Considering you as the organ for communicating these sentiments to the Court, I address them to you for that purpose, and salute you with esteem and respect.
Th: Jefferson.
TO GEORGE HAY.
Washington, June 19,1807.
Dear Sir,
Yours of the 17th was received last night. Three blank pardons had been (as I expect) made up and forwarded by the mail of yesterday, and I have desired three others to go by that of this evening. You ask what is to be done if Bollman finally rejects his pardon, and the Judge decides it to have no effect? Move to commit him immediately for treason or misdemeanor, as you think the evidence will support; let the court decide where he shall be sent for trial; and on application, I will have the marshal aided in his transportation, with the executive means. And we think it proper, further, that when Burr shall have been convicted of either treason or misdemeanor, you should immediately have committed all those persons against whom you should find evidence sufficient, whose agency has been so prominent as to mark them as proper objects of punishment, and especially where their boldness has betrayed an inveteracy of criminal disposition. As to obscure offenders and repenting ones, let them lie for consideration.
I enclose you the copy of a letter received last night, and giving singular information. I have inquired into the character of Graybell. He was an old revolutionary captain, is now a flour merchant in Baltimore, of the most respectable character, and whose word would be taken as implicitly as any man’s for whatever he affirms. The letter-writer, also, is a man of entire respectability. I am well informed, that for more than a twelvemonth it has been believed in Baltimore, generally, that Burr was engaged in some criminal enterprise, and that Luther Martin knew all about it. We think you should immediately despatch a subpoena for Graybell; and while that is on the road, you will have time to consider in what form you will use his testimony; e.g. shall Luther Martin be summoned as a witness against Burr, and Graybell held ready to confront him? It may be doubted whether we could examine a witness to discredit our own witness. Besides, the lawyers say that they are privileged from being forced to breaches of confidence, and that no others are. Shall we move to commit Luther Martin, as particeps criminis with Burr? Graybell will fix upon him misprision of treason at least. And at any rate, his evidence will put down this unprincipled and impudent federal bull-dog, and add another proof that the most clamorous defenders of Burr are all his accomplices. It will explain why Luther Martin flew so hastily to the aid of ‘his honorable friend,’ abandoning his clients and their property during a session of a principal court in Maryland, now filled, as I am told, with the clamors and ruin of his clients. I believe we shall send on Latrobe as a witness. He will prove that Aaron Burr endeavored to get him to engage several thousand men, chiefly Irish emigrants, whom he had been in the habit of employing in the works he directs, under pretence of a canal opposite Louisville, or of the Washita, in which, had he succeeded, he could with that force alone have carried every thing before him, and would not have been where he now is. He knows, too, of certain meetings of Burr, Bollman, Yrujo, and one other whom we have never named yet, but have him not the less in our view.
I salute you with friendship and respect.
Th: Jefferson.
P. S. Will you send us half a dozen blank subpoenas?
Since writing the within I have had a conversation with Latrobe. He says it was five hundred men he was desired to engage. The pretexts were to work on the Ohio canal, and be paid in Washita lands. Your witnesses will some of them prove that Burr had no interest in the Ohio canal, and that consequently this was a mere pretext to cover the real object from the men themselves, and all others. Latrobe will set out in the stage of to-morrow evening, and be with you Monday evening. T. J.
Washington, June 19, 1807.
Dear Sir,
In acknowledging the receipt of your favor of the 3rd instant, I avail myself of the occasion it offers of tendering to yourself, to Mr. Lincoln, and to your State, my sincere congratulations on the late happy event of the election of a republican executive to preside over its councils. The harmony it has introduced between the legislative and executive branches, between the people and both of them, and between all and the General Government, are so many steps towards securing that union of action and effort in all its parts, without which no nation can be happy or safe. The just respect, with which all the States have ever looked to Massachusetts, could leave none of them without anxiety while she was in a state of alienation from her family and friends. Your opinion of the propriety and advantage of a more intimate correspondence between the executives of the several States, and that of the Union, as a central point, is precisely that which I have ever entertained; and on coming into office I felt the advantages which would result from that harmony. I had it even in contemplation, after the annual recommendation to Congress of those measures called for by the times, which the constitution had placed under their power, to make communications in like manner to the executives of the States, as to any parts of them to which their legislatures might be alone competent. For many are the exercises of power reserved to the States, wherein an uniformity of proceeding would be advantageous to all. Such are quarantines, health laws, regulations of the press, banking institutions, training militia, &c. &c. But you know what was the state of the several governments when I came into office. That a great proportion of them were federal, and would have been delighted with such opportunities of proclaiming their contempt, and of opposing republican men and measures. Opportunities so furnished and used by some of the State governments, would have produced an ill effect, and would have insured the failure of the object of uniform proceeding. If it could be ventured even now (Connecticut and Delaware being still hostile) it must be on some greater occasion than is likely to arise within my time. I look to it, therefore, as a course which will probably be to be left to the consideration of my successor.
I consider, with you, the federalists as completely vanquished, and never more to take the field under their own banners. They will now reserve themselves to profit by the schisms among republicans, and to earn favors from minorities, whom they will enable to triumph over their more numerous antagonists. So long as republican minorities barely accept their votes, no great harm will be done; because it will only place in power one shade of republicanism, instead of another. But when they purchase the votes of the federalists, by giving them a participation of office, trust, and power, it is a proof that anti-monarchism is not their strongest passion. I do not think that the republican minority in Pennsylvania has fallen into this heresy, nor that there are in your State materials of which a minority can be made who will fall into it.
With respect to the tour my friends to the north have proposed that I should make in that quarter, I have not made up a final opinion. The course of life which General Washington had run, civil and military, the services he had rendered, and the space he therefore occupied in the affections of his fellow-citizens, take from his examples the weight of precedents for others, because no others can arrogate to themselves the claims which he had on the public homage. To myself, therefore, it comes as a new question, to be viewed under all the phases it may present. I confess, that I am not reconciled to the idea of a chief magistrate parading himself through the several States as an object of public gaze, and in quest of an applause, which, to be valuable, should be purely voluntary. I had rather acquire silent good will by a faithful discharge of my duties, than owe expressions of it to my putting myself in the way of receiving them. Were I to make such a tour to Portsmouth or Portland, I must do it to Savannah, perhaps to Orleans and Frankfort. As I have never yet seen the time when the public business would have permitted me to be so long in a situation in which I could not carry it on, so I have no reason to expect that such a time will come while I remain in office. A journey to Boston or Portsmouth, after I shall be a private citizen, would much better harmonize with my feelings, as well as duties; and, founded in curiosity, would give no claims to an extension of it. I should see my friends, too, more at our mutual ease, and be left more exclusively to their society. However, I end as I began, by declaring I have made up no opinion on the subject, and that I reserve it as a question for future consideration and advice.
In the mean time, and at all times, I salute you with great respect and esteem,
Th: Jefferson.
TO GEORGE HAY.
Washington, June 20, 1807.
Dear Sir,
Mr. Latrobe now comes on as a witness against Burr. His presence here is with great inconvenience dispensed with, as one hundred and fifty workmen require his constant directions on various public works of pressing importance. I hope you will permit him to come away as soon as possible. How far his testimony will be important as to the prisoner, I know not; but I am desirous that those meetings of Yrujo with Burr and his principal accomplices should come fully out, and judicially, as they will establish the just complaints we have against his nation.
I did not see till last night the opinion of the Judge on the subpoena duces tecum against the President. Considering the question there as coram non judice, I did not read his argument with much attention. Yet I saw readily enough, that, as is usual, where an opinion is to be supported, right or wrong, he dwells much on smaller objections, and passes over those which are solid. Laying down the position generally, that all persons owe obedience to subpoenas, he admits no exception unless it can be produced in his law books. But if the constitution enjoins on a particular officer to be always engaged in a particular set of duties imposed on him, does not this supersede the general law, subjecting him to minor duties inconsistent with these? The constitution enjoins his constant agency in the concerns of six millions of people. Is the law paramount to this, which calls on him on behalf of a single one? Let us apply the Judge’s own doctrine to the case of himself and his brethren. The sheriff of Henrico summons him from the bench, to quell a riot somewhere in his county. The federal judge is, by the general law, a part of the posse of the State sheriff. Would the Judge abandon major duties to perform lesser ones? Again; the court of Orleans or Maine commands, by subpoenas, the attendance of all the judges of the Supreme Court. Would they abandon their posts as judges, and the interests of millions committed to them, to serve the purposes of a single individual? The leading principle of our constitution is the independence of the legislature, executive, and judiciary, of each other, and none are more jealous of this than the judiciary. But would the executive be independent of the judiciary, if he were subject to the commands of the latter, and to imprisonment for disobedience; if the several courts could bandy him from pillar to post, keep him constantly trudging from north to south, and east to west, and withdraw him entirely from his constitutional duties? The intention of the constitution, that each branch should be independent of the others, is further manifested by the means it has furnished to each, to protect itself from enterprises of force attempted on them by the others, and to none has it given more effectual or diversified means than to the executive. Again; because ministers can go into a court in London, as witnesses, without interruption to their executive duties, it is inferred that they would go to a court one thousand or one thousand five hundred miles off, and that ours are to be dragged from Maine to Orleans by every criminal who will swear that their testimony ‘may be of use to him.’ The Judge says, ‘it is apparent that the President’s duties, as chief magistrate, do not demand his whole time, and are not unremitting.’ If he alludes to our annual retirement from the seat of government, during the sickly season, he should be told that such arrangements are made for carrying on the public business, at and between the several stations we take, that it goes on as unremittingly there, as if we were at the seat of government. I pass more hours in public business at Monticello than I do here, every day; and it is much more laborious, because all must be done in writing. Our stations being known, all communications come to them regularly, as to fixed points. It would be very different were we always on the road, or placed in the noisy and crowded taverns where courts are held. Mr. Rodney is expected here every hour, having been kept away by a sick child. I salute you with friendship and respect.
Th: Jefferson.
TO DOCTOR WISTAR.
Washington, June 21, 1807.
Dear Sir,
I have a grandson, the son of Mr. Randolph, now about fifteen years of age, in whose education I take a lively interest.
I am not a friend to placing young men in populous cities, because they acquire there habits and partialities which do not contribute to the happiness of their after life. But there are particular branches of science, which are not so advantageously taught any where else in the United States as in Philadelphia. The garden at the Woodlands for Botany, Mr. Peale’s Museum for Natural History, your Medical School for Anatomy, and the able professors in all of them, give advantages not to be found elsewhere. We propose, therefore, to send him to Philadelphia to attend the schools of Botany, Natural History, Anatomy, and perhaps Surgery; but not of Medicine. And why not of Medicine, you will ask? Being led to the subject, I will avail myself of the occasion to express my opinions on that science, and the extent of my medical creed. But, to finish first with respect to my grandson, I will state the favor I ask of you, and which is the object of this letter.
This subject dismissed, I may now take up that which it led to, and further tax your patience with unlearned views of medicine; which, as in most cases, are, perhaps, the more confident in proportion as they are less enlightened.
We know, from what we see and feel, that the animal body is in its organs and functions subject to derangement, inducing pain, and tending to its destruction. In this disordered state, we observe nature providing for the re-establishment of order, by exciting some salutary evacuation of the morbific matter, or by some other operation which escapes our imperfect senses and researches. She brings on a crisis, by stools, vomiting, sweat, urine, expectoration, bleeding, &c, which, for the most part, ends in the restoration of healthy action. Experience has taught us also, that there are certain substances, by which, applied to the living body, internally or externally, we can at will produce these same evacuations, and thus do, in a short time, what nature would do but slowly, and do effectually, what perhaps she would not have strength to accomplish. Where, then, we have seen a disease, characterized by specific signs or phenomena, and relieved by a certain natural evacuation or process, whenever that disease recurs under the same appearances, we may reasonably count on producing a solution of it, by the use of such substances as we have found produce the same evacuation or movement. Thus, fulness of the stomach we can relieve by emetics; diseases of the bowels, by purgatives; inflammatory cases, by bleeding; intermittents, by the Peruvian bark; syphilis, by mercury; watchfulness, by opium; &c. So far, I bow to the utility of medicine. It goes to the well defined forms of disease, and happily, to those the most frequent. But the disorders of the animal body, and the symptoms indicating them, are as various as the elements of which the body is composed. The combinations, too, of these symptoms are so infinitely diversified, that many associations of them appear too rarely to establish a definite disease: and to an unknown disease, there cannot be a known remedy. Here, then, the judicious, the moral, the humane physician should stop. Having been so often a witness to the salutary efforts which nature makes to re-establish the disordered functions, he should rather trust to their action, than hazard the interruption of that, and a greater derangement of the system, by conjectural experiments on a machine so complicated and so unknown as the human body, and a subject so sacred as human life. Or, if the appearance of doing something be necessary to keep alive the hope and spirits of the patient, it should be of the most innocent character. One of the most successful physicians I have ever known, has assured me, that he used more bread pills, drops of colored water, and powders of hickory ashes, than of all other medicines put together. It was certainly a pious fraud. But the adventurous physician goes on, and substitutes presumption for knowledge. From the scanty field of what is known, he launches into the boundless region of what is unknown. He establishes for his guide some fanciful theory of corpuscular attraction, of chemical agency, of mechanical powers, of stimuli, of irritability accumulated or exhausted, of depletion by the lancet, and repletion by mercury, or some other ingenious dream, which lets him into all nature’s secrets at short hand. On the principle which he thus assumes, he forms his table of nosology, arrays his diseases into families, and extends his curative treatment, by analogy, to all the cases he has thus arbitrarily marshaled together. I have lived myself to see the disciples of Hoffman, Boerhaave, Stahl, Cullen, Brown, succeed one another like the shifting figures of a magic-lanthern, and their fancies like the dresses of the annual doll-babies from Paris, becoming, from their novelty, the vogue of the day, and yielding to the next novelty their ephemeral favor. The patient, treated on the fashionable theory, sometimes gets well in spite of the medicine. The medicine therefore restored him, and the young doctor receives new courage to proceed in his bold experiments on the lives of his fellow creatures. I believe we may safely affirm, that the inexperienced and presumptuous band of medical tyros let loose upon the world, destroys more of human life in one year, than all the Robin-hoods, Cartouches, and Macheaths do in a century. It is in this part of medicine that I wish to see a reform, an abandonment of hypothesis for sober facts, the first degree of value set on clinical observation, and the lowest on visionary theories. I would wish the young practitioner, especially, to have deeply impressed on his mind the real limits of his art, and that when the state of his patient gets beyond these, his office is to be a watchful, but quiet spectator of the operations of nature, giving them fair play by a well regulated regimen, and by all the aid they can derive from the excitement of good spirits and hope in the patient. I have no doubt, that some diseases not yet understood may in time be transferred to the table of those known. But, were I a physician, I would rather leave the transfer to the slow hand of accident, than hasten it by guilty experiments on those who put their lives into my hands. The only sure foundations of medicine are, an intimate knowledge of the human body, and observation on the effects of medicinal substances on that. The anatomical and clinical schools, therefore, are those in which the young physician should be formed. If he enters with innocence that of the theory of medicine, it is scarcely possible he should come out untainted with error. His mind must be strong indeed, if, rising above juvenile credulity, it can maintain a wise infidelity against the authority of his instructers, and the bewitching delusions of their theories. You see that I estimate justly that portion of instruction, which our medical students derive from your labors; and, associating with it one of the chairs which my old and able friend, Doctor Rush, so honorably fills, I consider them as the two fundamental pillars of the edifice. Indeed, I have such an opinion of the talents of the professors in the other branches which constitute the school of medicine with you, as to hope and believe, that it is from this side of the Atlantic, that Europe, which has taught us so many other things, will at length be led into sound principles in this branch of science, the most important of all others, being that to which we commit the care of health and life.
I dare say, that by this time you are sufficiently sensible that old heads, as well as young, may sometimes be charged with ignorance and presumption. The natural course of the human mind is certainly from credulity to scepticism: and this is perhaps the most favorable apology I can make for venturing so far out of my depth, and to one, too, to whom the strong as well as the weak points of this science are so familiar. But having stumbled on the subject in my way, I wished to give a confession of my faith to a friend; and the rather, as I had perhaps, at times, to him as well as others, expressed my scepticism in medicine, without defining its extent or foundation. At any rate, it has permitted me, for a moment, to abstract myself from the dry and dreary waste of politics, into which I have been impressed by the times on which I happened, and to indulge in the rich fields of nature, where alone I should have served as a volunteer, if left to my natural inclinations and partialities.
I salute you at all times with affection and respect.
Th: Jefferson.
TO MR. BOWDOIN.
Washington, July 10, 1807.
Dear Sir,
I wrote you on the 10th of July, 1806; but supposing, from your not acknowledging the receipt of the letter, that it had miscarried, I sent a duplicate with my subsequent one of April the 2nd. These having gone by the Wasp, you will doubtless have received them. Since that, yours of May the 1st has come to hand. You will see by the despatches from the department of State, carried by the armed vessel the Revenge, into what a critical state our peace with Great Britain is suddenly brought, by their armed vessels in our waters. Four vessels of war (three of them two-deckers) closely blockade Norfolk at this instant. Of the authority under which this aggression is committed, their minister here is unapprized. You will see by the proclamation of July the 2nd, that (while we are not omitting such measures of force as are immediately necessary) we propose to give Great Britain an opportunity of disavowal and reparation, and to leave the question of war, non-intercourse, or other measures, uncommitted, to the legislature. This country has never been in such a state of excitement since the battle of Lexington. In this state of things, cordial friendship with France, and peace at least with Spain, become more interesting. You know the circumstances respecting this last power, which have rendered it ineligible that you should have proceeded heretofore to your destination. But this obstacle is now removed by their recall of Yrujo, and appointment of another minister, and, in the mean time, of a chargé des affaires, who has been received. The way being now open for taking your station at Madrid, it is certainly our wish you should do so, and that this may be more agreeable to you than your return home, as is solicited in yours of May the 1st. It is with real unwillingness we should relinquish the benefit of your services. Nevertheless, if your mind is decidedly bent on that, we shall regret, but not oppose your return. The choice, therefore, remains with yourself. In the mean time, your place in the joint commission being vacated by either event, we shall take the measures rendered necessary by that. We have seen, with real grief, the misunderstanding which has taken place between yourself and General Armstrong. We are neither qualified nor disposed to form an opinion between you. We regret the pain which must have been felt by persons, both of whom hold so high a place in our esteem, and we have not been without fear that the public interest might suffer by it. It has seemed, however, that the state of Europe has been such as to admit little to be done, in matters so distant from them.
The present alarm has had the effect of suspending our foreign commerce. No merchant ventures to send out a single vessel; and I think it probable this will continue very much the case till we get an answer from England. Our crops are uncommonly plentiful. That of small grain is now secured south of this, and the harvest is advancing here.
Accept my salutations, and assurances of affectionate esteem and respect.
Th: Jefferson.
TO THE MARQUIS DE LA FAYETTE.
Washington, July 14, 1807.
My Dear Friend,
I received last night your letters of February the 20th and April the 29th, and a vessel just sailing from Baltimore enables me hastily to acknowledge them; to assure you of the welcome with which I receive whatever comes from you, and the continuance of my affectionate esteem for yourself and family. I learn with much concern, indeed, the state of Madame de la Fayette’s health. I hope I have the pleasure yet to come of learning its entire re-establishment. She is too young not to give great confidence to that hope.
Measuring happiness by the American scale, and sincerely wishing that of yourself and family, we had been anxious to see them established on this side of the great water. But I am not certain that any equivalent can be found for the loss of that species of society, to which our habits have been formed from infancy. Certainly had you been, as I wished, at the head of the government of Orleans, Burr would never have given me one moment’s uneasiness. His conspiracy has been one of the most flagitious of which history will ever furnish an example. He meant to separate the western States from us, to add Mexico to them, place himself at their head, establish what he would deem an energetic government, and thus provide an example and an instrument for the subversion of our freedom. The man who could expect to effect this, with American materials, must be a fit subject for Bedlam. The seriousness of the crime, however, demands more serious punishment. Yet, although there is not a man in the United States who doubts his guilt, such are the jealous provisions of our laws in favor of the accused against the accuser, that I question if he is convicted. Out of forty-eight jurors to be summoned, he is to select the twelve who are to try him, and if there be any one who will not concur in finding him guilty, he is discharged of course. I am sorry to tell you that Bollman was Burr’s right hand man in all his guilty schemes. On being brought to prison here, he communicated to Mr. Madison and myself the whole of the plans, always, however, apologetically for Burr as far as they would bear. But his subsequent tergiversations have proved him conspicuously base. I gave him a pardon, however, which covers him from every thing but infamy. I was the more astonished at his engaging in this business, from the peculiar motives he should have felt for fidelity. When I came into the government, I sought him out on account of the services he has rendered you, cherished him, offered him two different appointments of value, which, after keeping them long under consideration, he declined for commercial views, and would have given him any thing for which he was fit. Be assured he is unworthy of ever occupying again the care of any honest man. Nothing has ever so strongly proved the innate force of our form of government, as this conspiracy. Burr had probably engaged one thousand men to follow his fortunes, without letting them know his projects, otherwise than by assuring them the government approved of them. The moment a proclamation was issued, undeceiving them, he found himself left with about thirty desperadoes only. The people rose in mass wherever he was or was suspected to be, and by their own energy the thing was crushed in one instant, without its having been necessary to employ a man of the military but to take care of their respective stations. His first enterprise was to have been to seize New Orleans, which he supposed would powerfully bridle the upper country, and place him at the door of Mexico. It is with pleasure I inform you that not a single native Creole, and but one American of those settled there before we received the place, took any part with him. His partisans were the new emigrants from the United States and elsewhere, fugitives from justice or debt, and adventurers and speculators of all descriptions.
I enclose you a proclamation, which will show you the critical footing on which we stand, at present, with England. Never, since the battle of Lexington, have I seen this country in such a state of exasperation as at present. And even that did not produce such unanimity. The federalists themselves coalesce with us as to the object, although they will return to their old trade of condemning every step we take towards obtaining it. ‘Reparation for the past, and security for the future,’ is our motto. Whether these will be yielded freely, or will require resort to non-intercourse, or to war, is yet to be seen. We have actually near two thousand men in the field, covering the exposed parts of the coast, and cutting off supplies from the British vessels.
I am afraid I have been very unsuccessful in my endeavors to serve Madame de Tesse in her taste for planting. A box of seeds, &c. which I sent her in the close of 1805, was carried with the vessel into England, and discharged so late that I fear she lost their benefit, for that season. Another box, which I prepared in the autumn of 1806, has, I fear, been equally delayed from other accidents. However, I will persevere in my endeavors.
Present me respectfully to her, M. de Tesse, Madame de la Fayette, and your family, and accept my affectionate salutations, and assurances of constant esteem and respect.
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN PAGE.
Washington, July 17, 1807.
My Dear Friend,
Yours of the 11th is received. In appointments to public offices of mere profit, I have ever considered faithful service in either our first or second revolution as giving preference of claim, and that appointments on that principle would gratify the public, and strengthen that confidence so necessary to enable the executive to direct the whole public force to the best, advantage of the nation. Of Mr. Boiling Robertson’s talents and integrity I have long been apprized, and would gladly use them where talents and integrity are wanting. I had thought of him for the vacant place of secretary of the Orleans territory, but supposing the salary of two thousand dollars not more than he makes by his profession, and while remaining with his friends, I have, in despair, not proposed it to him. If he would accept it, I should name him instantly with the greatest satisfaction. Perhaps you could inform me on this point.
With respect to Major Gibbons, I do indeed recollect, that in some casual conversation, it was said that the most conspicuous accomplices of Burr were at home at his house; but it made so little impression on me, that neither the occasion nor the person is now recollected. On this subject, I have often expressed the principles on which I act, with a wish they might be understood by the federalists in office. I have never removed a man merely because he was a federalist: I have never wished them to give a vote at an election, but according to their own wishes. But as no government could discharge its duties to the best advantage of its citizens, if its agents were in a regular course of thwarting instead of executing all its measures, and were employing the patronage and influence of their offices against the government and its measures, I have only requested they would be quiet, and they should be safe: and if their conscience urges them to take an active and zealous part in opposition, it ought also to urge them to retire from a post which they could not conscientiously conduct with fidelity to the trust reposed in them; and on failure to retire, I have removed them; that is to say, those who maintained an active and zealous opposition to the government. Nothing which I have yet heard of Major Gibbons places him in danger from these principles.
I am much pleased with the ardor displayed by our countrymen on the late British outrage. It gives us the more confidence of support in the demand of reparation for the past, and security for the future, that is to say, an end of impressments. If motives of either justice or interest should produce this from Great Britain, it will save a war: but if they are refused, we shall have gained time for getting in our ships and property, and at least twenty thousand seamen now afloat on the ocean, and who may man two hundred and fifty privateers. The loss of these to us would be worth to Great Britain many victories of the Nile and Trafalgar. The mean time may also be importantly employed in preparations to enable us to give quick and deep blows.
Present to Mrs. Page, and receive yourself my affectionate and respectful salutations.
Th: Jefferson.
TO WILLIAM DUANE.
Washington, July 20, 1807.
Sir,
Although I cannot always acknowledge the receipt of communications, yet I merit their continuance by making all the use of them of which they are susceptible. Some of your suggestions had occurred, and others will be considered. The time is coming when our friends must enable us to hear every thing, and expect us to say nothing; when we shall need all their confidence that every thing is doing which can be done, and when our greatest praise shall be, that we appear to be doing nothing. The law for detaching one hundred thousand militia, and the appropriation for it, and that for fortifications, enable us to do every thing for land service, as well as if Congress were here; and as to naval matters, their opinion is known. The course we have pursued, has gained for our merchants a precious interval to call in their property and our seamen, and the postponing the summons of Congress will aid in avoiding to give too quick an alarm to the adversary. They will be called, however, in good time. Although we demand of England what is merely of right, reparation for the past, security for the future, yet as their pride will possibly, nay probably, prevent their yielding them to the extent we shall require, my opinion is, that the public mind, which I believe is made up for war, should maintain itself at that point. They have often enough, God knows, given us cause of war before; but it has been on points which would not have united the nation. But now they have touched a chord which vibrates in every heart. Now then is the time to settle the old and the new.
I have often wished for an occasion of saying a word to you on the subject of the Emperor of Russia, of whose character and value to us, I suspect you are not apprized correctly. A more virtuous man, I believe, does not exist, nor one who is more enthusiastically devoted to better the condition of mankind. He will probably, one day, fall a victim to it, as a monarch of that principle does not suit a Russian noblesse. He is not of the very first order of understanding, but he is of a high one. He has taken a peculiar affection to this country and its government, of which he has given me public as well as personal proofs. Our nation being like his, habitually neutral, our interests as to neutral rights, and our sentiments, agree. And whenever conferences for peace shall take place, we are assured of a friend in him. In fact, although in questions of restitution he will be with England, in those of neutral rights he will be with Bonaparte and every other power in the world, except England: and I do presume that England will never have peace until she subscribes to a just code of marine law. I have gone into this subject, because I am confident that Russia (while her present monarch lives) is the most cordially friendly to us of any power on earth, will go furthest to serve us, and is most worthy of conciliation. And although the source of this information must be a matter of confidence with you, yet it is desirable that the sentiments should become those of the nation. I salute you with esteem and respect.
Th: Jefferson.
TO GEORGE HAY.
Monticello, August 20, 1807.
Dear Sir,
I received yesterday your favor of the 11th. An error of the post-office had occasioned the delay. Before an impartial jury Burr’s conduct would convict himself, were not one word of testimony to be offered against him. But to what a state will our law be reduced by party feelings in those who administer it? Why do not Blannerhasset, Dayton, &c. demand private and comfortable lodgings? In a country where an equal application of law to every condition of man is fundamental, how could it be denied to them? How can it ever be denied to the most degraded malefactor? The enclosed letter of James Morrison, covering a copy of one from Alston to Blannerhasset, came to hand yesterday. I enclose them, because it is proper all these papers should be in one deposite, and because you should know the case and all its bearings, that you may understand whatever turns up in the cause. Whether the opinion of the letter-writer is sound, may be doubted. For however these, and other circumstances which have come to us, may induce us to believe that the bouncing letter he published, and the insolent one he wrote to me, were intended as blinds, yet they are not sufficient for legal conviction. Blannerhasset and his wife could possibly tell us enough. I commiserate the sufferings you have to go through in such a season, and salute you with great esteem and respect.
Th: Jefferson.
TO GEORGE HAY.
Monticello, September 4, 1807.
Dear Sir,
Yours of the 1st came to hand yesterday. The event has been ——— that is to say, not only to clear Burr, but to prevent the evidence from ever going before the world. But this latter case must not take place. It is now, therefore, more than ever indispensable, that not a single witness be paid or permitted to depart, until his testimony has been committed to writing, either as delivered in court, or as taken by yourself in the presence of any of Burr’s counsel, who may choose to attend to cross-examine. These whole proceedings will be laid before Congress, that they may decide, whether the defect has been in the evidence of guilt, or in the law, or in the application of the law, and that they may provide the proper remedy for the past and the future. I must pray you also to have an authentic copy of the record made out (without saying for what) and to send it to me: if the Judge’s opinions make not a part of it, then I must ask a copy of them, either under his hand, if he delivers one signed, or duly proved by affidavit.
This criminal is preserved to become the rallying point of all the disaffected and the worthless of the United States, and to be the pivot on which all the intrigues and the conspiracies which foreign governments may wish to disturb us with, are to turn. If he is convicted of the misdemeanor, the Judge must in decency give us respite by some short confinement of him; but we must expect it to be very short. Be assured yourself, and communicate the same assurances to your colleagues, that your and their zeal and abilities have been displayed in this affair to my entire satisfaction and your own honor.
I salute you with great esteem and respect.
Th: Jefferson.
TO GEORGE HAY.
Monticello, September 7, 1807.
Dear Sir,
I received, late last night, your favor of the day before, and now re-enclose you the subpoena. As I do not believe that the district courts have a power of commanding the executive government to abandon superior duties and attend on them, at whatever distance, I am unwilling, by any notice of the subpoena, to set a precedent which might sanction a proceeding so preposterous. I enclose you, therefore, a letter, public and for the court, covering substantially all they ought to desire. If the papers which were enclosed in Wilkinson’s letter may, in your judgment, be communicated without injury, you will be pleased to communicate them. I return you the original letter.
I am happy in having the benefit of Mr. Madison’s counsel on this occasion, he happening to be now with me. We are both strongly of opinion, that the prosecution against Burr for misdemeanor should proceed at Richmond. If defeated, it will heap coals of fire on the head of the Judge: if successful, it will give time to see whether a prosecution for treason against him can be instituted in any, and what other court. But, we incline to think, it may be best to send Blannerhasset and Smith (Israel) to Kentucky, to be tried both for the treason and misdemeanor. The trial of Dayton for misdemeanor may as well go on at Richmond.
I salute you with great esteem and respect.
Th: Jefferson.
TO THE REV. MR. MILLAR,
Washington, January 23, 1808.
Sir,
I have duly received your favor of the 18th, and am thankful to you for having written it, because it is more agreeable to prevent than to refuse what I do not think myself authorized to comply with. I consider the government of the United States as interdicted by the constitution from intermeddling with religious institutions, their doctrines, discipline, or exercises. This results not only from the provision that no law shall be made respecting the establishment or free exercise of religion, but from that also which reserves to the States the powers not delegated to the United States. Certainly, no power to prescribe any religious exercise, or to assume authority in religious discipline, has been delegated to the General Government. It must then rest with the States, as far as it can be in any human authority. But it is only proposed that I should recommend, not prescribe, a day of fasting and prayer. That is, that I should indirectly assume to the United States an authority over religious exercises, which the constitution has directly precluded them from. It must be meant, too, that this recommendation is to carry some authority, and to be sanctioned by some penalty on those who disregard it; not indeed of fine and imprisonment, but of some degree of proscription, perhaps in public opinion. And does the change in the nature of the penalty make the recommendation the less a law of conduct for those to whom it is directed? I do not believe it is for the interest of religion to invite the civil magistrate to direct its exercises, its discipline, or its doctrines; nor of the religious societies, that the General Government should be invested with the power of effecting any uniformity of time or matter among them. Fasting and prayer are religious exercises; the enjoining them an act of discipline. Every religious society has a right to determine for itself the times for these exercises, and the objects proper for them, according to their own particular tenets; and this right can never be safer than in their own hands, where the constitution has deposited it.
I am aware that the practice of my predecessors may be quoted. But I have ever believed, that the example of State executives led to the assumption of that authority by the General Government, without due examination, which would have discovered that what might be a right in a State government, was a violation of that right when assumed by another. Be this as it may, every one must act according to the dictates of his own reason, and mine tells me that civil powers alone have been given to the President of the United States, and no authority to direct the religious exercises of his constituents.
I again express my satisfaction that you have been so good as to give me an opportunity of explaining myself in a private letter, in which I could give my reasons more in detail than might have been done in a public answer: and I pray you to accept the assurances of my high esteem and respect.
Th: Jefferson.
TO COLONEL MONROE.
Washington, February 18, 1808.
My Dear Sir,
You informed me that the instruments you had been so kind as to bring for me from England, would arrive at Richmond with your baggage, and you wished to know what was to be done with them there. I will ask the favor of you to deliver them to Mr. Jefferson, who will forward them to Monticello in the way I shall advise him. And I must intreat you to send me either a note of their amount, or the bills, that I may be enabled to reimburse you. There can be no pecuniary matter between us, against which this can be any set-off. But if, contrary to my recollection or knowledge, there were any thing, I pray that that may be left to be settled by itself. If I could have known the amount beforehand, I should have remitted it, and asked the advance only under the idea that it should be the same as ready money to you on your arrival. I must again, therefore, beseech you to let me know its amount.
I see with infinite grief a contest arising between yourself and another, who have been very dear to each other, and equally so to me. I sincerely pray that these dispositions may not be affected between you; with me I confidently trust they will not. For independently of the dictates of public duty, which prescribes neutrality to me, my sincere friendship for you both will insure its sacred observance. I suffer no one to converse with me on the subject. I already perceive my old friend Clinton estranging himself from me. No doubt lies are carried to him, as they will be to the other two candidates, under forms, which, however false he can scarcely question. Yet I have been equally careful as to him also, never to say a word on his subject. The object of the contest is a fair and honorable one, equally open to you all; and I have no doubt the personal conduct of all will be so chaste, as to offer no ground of dissatisfaction with each other. But your friends will not be as delicate. I know too well from experience the progress of political controversy, and the exacerbation of spirit into which it degenerates, not to fear for the continuance of your mutual esteem. One piquing thing said, draws on another, that a third, and always with increasing acrimony, until all restraint is thrown off, and it becomes difficult for yourselves to keep clear of the toils in which your friends will endeavor to interlace you, and to avoid the participation in their passions which they will endeavor to produce. A candid recollection of what you know of each other will be the true corrective. With respect to myself, I hope they will spare me. My longings for retirement are so strong, that I with difficulty encounter the daily drudgeries of my duty. But my wish for retirement itself is not stronger than that of carrying into it the affections of all my friends. I have ever viewed Mr. Madison and yourself as two principal pillars of my happiness. Were either to be withdrawn, I should consider it as among the greatest calamities which could assail my future peace of mind. I have great confidence that the candor and high understanding of both will guard me against this misfortune, the bare possibility of which has so far weighed on my mind, that I could not be easy without unburthening it.
Accept my respectful salutations for yourself and Mrs. Monroe, and be assured of my constant and sincere friendship.
Th: Jefferson.
TO COLONEL MONROE.
Washington, March 10, 1808.
Dear Sir,
From your letter of the 27th ultimo, I perceive that painful impressions have been made on your mind during your late mission, of which I had never entertained a suspicion. I must, therefore, examine the grounds, because explanations between reasonable men can never but do good. 1. You consider the mission of Mr. Pinckney as an associate, to have been in some way injurious to you. Were I to take that measure on myself, I might say in its justification, that it has been the regular and habitual practice of the United States to do this, under every form in which their government has existed. I need not recapitulate the multiplied instances, because you will readily recollect them. I went as an adjunct to Dr. Franklin and Mr. Adams, yourself as an adjunct first to Mr. Livingston, and then to Mr. Pinckney, and I really believe there has scarcely been a great occasion which has not produced an extraordinary mission. Still, however, it is well known, that I was strongly opposed to it in the case of which you complain. A committee of the Senate called on me with two resolutions of that body on the subject of impressment and spoliations by Great Britain, and requesting that I would demand satisfaction. After delivering the resolutions, the committee entered into free conversation, and observed, that although the Senate could not, in form, recommend any extraordinary mission, yet that as individuals, there was but one sentiment among them on the measure, and they pressed it. I was so much averse to it, and gave them so hard an answer, that they felt it, and spoke of it. But it did not end here. The members of the other House took up the subject, and set upon me individually, and these the best friends to you, as well as myself, and represented the responsibility which a failure to obtain redress would throw on us both, pursuing a conduct in opposition to the opinion of nearly every member of the legislature. I found it necessary, at length, to yield my own opinion, to the general sense of the national council, and it really seemed to produce a jubilee among them; not from any want of confidence in you, but from a belief in the effect which an extraordinary mission would have on the British mind, by demonstrating the degree of importance which this country attached to the rights which we considered as infracted.
2. You complain of the manner in which the treaty was received. But what was that manner? I cannot suppose you to have given a moment’s credit to the stuff which was crowded in all sorts of forms into the public papers, or to the thousand speeches they put into my mouth, not a word of which I had ever uttered. I was not insensible at the time of the views to mischief, with which these lies were fabricated. But my confidence was firm, that neither yourself nor the British government, equally outraged by them, would believe me capable of making the editors of newspapers the confidants of my speeches or opinions. The fact was this. The treaty was communicated to us by Mr. Erskine on the day Congress was to rise. Two of the Senators inquired of me in the evening, whether it was my purpose to detain them on account of the treaty. My answer was, ‘that it was not: that the treaty containing no provision against the impressment of our seamen, and being accompanied by a kind of protestation of the British ministers, which would leave that government free to consider it as a treaty or no treaty, according to their own convenience, I should not give them the trouble of deliberating on it.’ This was substantially, and almost verbally, what I said whenever spoken to about it, and I never failed when the occasion would admit of it, to justify yourself and Mr. Pinckney, by expressing my conviction, that it was all that could be obtained from the British government; that you had told their commissioners that your government could not be pledged to ratify, because it was contrary to their instructions; of course, that it should be considered but as a projet; and in this light I stated it publicly in my message to Congress on the opening of the session. Not a single article of the treaty was ever made known beyond the members of the administration, nor would an article of it be known at this day, but for its publication in the newspapers, as communicated by somebody from beyond the water, as we have always understood. But as to myself, I can solemnly protest, as the most sacred of truths, that I never, one instant, lost sight of your reputation and favorable standing with your country, and never omitted to justify your failure to attain our wish, as one which was probably unattainable. Reviewing, therefore, this whole subject, I cannot doubt you will become sensible, that your impressions have been without just ground. I cannot, indeed, judge what falsehoods may have been written or told you; and that, under such forms as to command belief. But you will soon find, my dear Sir, that so inveterate is the rancor of party spirit among us, that nothing ought to be credited but what we hear with our own ears. If you are less on your guard than we are here, at this moment, the designs of the mischief-makers will not fail to be accomplished, and brethren and friends will be made strangers and enemies to each other, without ever having said or thought a thing amiss of each other. I presume that the most insidious falsehoods are daily carried to you, as they are brought to me, to engage us in the passions of our informers, and stated so positively and plausibly as to make even doubt a rudeness to the narrator; who, imposed on himself, has no other than the friendly view of putting us on our guard. My answer is, invariably, that my knowledge of your character is better testimony to me of a negative, than any affirmative which my informant did not hear from yourself with his own ears. In fact, when you shall have been a little longer among us, you will find that little is to be believed which interests the prevailing passions, and happens beyond the limits of our own senses. Let us not then, my dear friend, embark our happiness and our affections on the ocean of slander, of falsehood, and of malice, on which our credulous friends are floating. If you have been made to believe that I ever did, said, or thought a thing unfriendly to your fame and feelings, you do me injury as causeless as it is afflicting to me. In the present contest in which you are concerned, I feel no passion, I take no part, I express no sentiment. Whichever of my friends is called to the supreme cares of the nation, I know that they will be wisely and faithfully administered, and as far as my individual conduct can influence, they shall be cordially supported,
For myself I have nothing further to ask of the world, than to preserve in retirement so much of their esteem as I may have fairly earned, and to be permitted to pass in tranquillity, in the bosom of my family and friends, the days which yet remain for me. Having reached the harbor myself, I shall view with anxiety (but certainly not with a wish to be in their place) those who are still buffeting the storm, uncertain of their fate. Your voyage has so far been favorable, and that it may continue with entire prosperity, is the sincere prayer of that friendship which I have ever borne you, and of which I now assure you, with the tender of my high respect and affectionate salutations.
Th: Jefferson,
TO RICHARD M. JOHNSON.
Washington, March 10, 1808.
Sir,
I am sure you can too justly estimate my occupations, to need an apology for this tardy acknowledgment of your favor of February the 27th. I cannot but be deeply sensible of the good opinion you are pleased to express of my conduct in the administration of our government. This approbation of my fellow-citizens is the richest reward I can receive. I am conscious of having always intended to do what was best for them: and never, for a single moment, to have listened to any personal interest of my own. It has been a source of great pain to me, to have met with so many among our opponents, who had not the liberality to distinguish between political and social opposition; who transferred at once to the person, the hatred they bore to his political opinions. I suppose, indeed, that in public life, a man whose political principles have any decided character, and who has energy enough to give them effect, must always expect to encounter political hostility from those of adverse principles. But I came to the government under circumstances calculated to generate peculiar acrimony. I found all its offices in the possession of a political sect, who wished to transform it ultimately into the shape of their darling model, the English government; and in the mean time, to familiarize the public mind to the change, by administering it on English principles, and in English forms. The elective interposition of the people had blown all their designs, and they found themselves and their fortresses of power and profit put in a moment into the hands of other trustees. Lamentations and invective were all that remained to them. This last was naturally directed against the agent selected to execute the multiplied reformations, which their heresies had rendered necessary. I became of course the butt of every thing which reason, ridicule, malice, and falsehood could supply. They have concentrated all their hatred on me, till they have really persuaded themselves, that I am the sole source of all their imaginary evils. I hope, therefore, that my retirement will abate some of their disaffection to the government of their country, and that my successor will enter on a calmer sea than I did. He will at least find the vessel of state in the hands of his friends, and not of his foes. Federalism is dead, without even the hope of a day of resurrection. The quondam leaders, indeed, retain their rancor and principles; but their followers are amalgamated with us in sentiment, if not in name. If our fellow-citizens, now solidly republican, will sacrifice favoritism towards men for the preservation of principle, we may hope that no divisions will again endanger a degeneracy in our government.
I pray you to accept my salutations, and assurances of great esteem and respect.
Th: Jefferson.
TO LEVI LINCOLN.
Washington, March 23, 1808.
Dear Sir,
Your letter on the subject of Mr. Lee came safely to hand. You know our principles render federalists in office safe, if they do not employ their influence in opposing the government, but only give their own vote according to their conscience. And this principle we act on as well with those put in office by others, as by ourselves.
We have received from your presses a very malevolent and incendiary denunciation of the administration, bottomed on absolute falsehood from beginning to end. The author would merit exemplary punishment for so flagitious a libel, were not the torment of his own abominable temper punishment sufficient for even as base a crime as this. The termination of Mr. Rose’s mission, re infectâ, put it in my power to communicate to Congress yesterday, every thing respecting our relations with England and France, which will effectually put down Mr. Pickering, and his worthy coadjutor Quincy. Their tempers are so much alike, and really their persons, as to induce a supposition that they are related. The embargo appears to be approved, even by the federalists of every quarter except yours. The alternative was between that and war, and, in fact, it is the last card we have to play, short of war. But if peace does not take place in Europe, and if France and England will not consent to withdraw the operation of their decrees and orders from us, when Congress shall meet in December, they will have to consider at what point of time the embargo, continued, becomes a greater evil than war. I am inclined to believe, we shall have this summer and autumn to prepare for the defence of our sea-port towns, and hope that in that time the works of defence will be completed, which have been provided for by the legislature. I think Congress will rise within three weeks. I salute you with great affection and respect.
Th: Jefferson.
Washington, March 30, 1808.
Dear Sir,
Your letter of the 8th was received on the 25th, and I proceed to state to you my views of the present state and prospect of foreign affairs, under the confidence that you will use them for your own government and opinions only, and by no means let them get out as from me. With France we are in no immediate danger of war. Her future views it is impossible to estimate. The immediate danger we are in of a rupture with England, is postponed for this year. This is effected by the embargo, as the question was simply between that and war. That may go on a certain time, perhaps through the year, without the loss of their property to our citizens, but only its remaining unemployed on their hands. A time would come, however, when war would be preferable to a continuance of the embargo. Of this Congress may have to decide at their next meeting. In the mean time, we have good information, that a negotiation for peace between France and England is commencing through the medium of Austria. The way for it has been smoothed by a determination expressed by France (through the Moniteur, which is their government paper), that herself and her allies will demand from Great Britain no renunciation of her maritime principles; nor will they renounce theirs. Nothing shall be said about them in the treaty, and both sides will be left in the next war to act on their own. No doubt the meaning of this is, that all the Continental powers of Europe will form themselves into an armed neutrality, to enforce their own principles. Should peace be made, we shall have safely rode out the storm in peace and prosperity. If we have any thing to fear, it will be after that. Nothing should be spared from this moment in putting our militia into the best condition possible, and procuring arms. I hope, that this summer, we shall get our whole sea-ports put into that state of defence, which Congress has thought proportioned to our circumstances and situation; that is to say, put hors d’insulte from a maritime attack, by a moderate squadron. If armies are combined with their fleets, then no resource can be provided, but to meet them in the field. We propose to raise seven regiments only for the present year, depending always on our militia for the operations of the first year of war. On any other plan, we should be obliged always to keep a large standing army. Congress will adjourn in about three weeks. I hope Captain McComb is going on well with your defensive works. We shall be able by mid-summer, to give you a sufficient number of gun-boats to protect Charleston from any vessels which can cross the bar; but the militia of the place must be depended on to fill up the complement of men necessary for action in the moment of an attack, as we shall man them, in ordinary, but with their navigating crew of eight or ten good seamen. I salute you with great esteem and respect.
Th: Jefferson.
TO DOCTOR LEIB.
Washington, June 23, 1808.
Sir,
I have duly received your favor covering a copy of the talk to the Tammany society, for which I thank you, and particularly for the favorable sentiments expressed towards myself. Certainly, nothing will so much sweeten the tranquillity and comfort of retirement, as the knowledge that I carry with me the good will and approbation of my republican fellow-citizens, and especially of the individuals in unison with whom I have so long acted. With respect to the federalists, I believe we think alike; for when speaking of them, we never mean to include a worthy portion of our fellow-citizens, who consider themselves as in duty bound to support the constituted authorities of every branch, and to reserve their opposition to the period of election. These having acquired the appellation of federalists, while a federal administration was in place, have not cared about throwing off their name, but, adhering to their principle, are the supporters of the present order of things. The other branch of the federalists, those who are so in principle as well as in name, disapprove of the republican principles and features of our constitution, and would, I believe, welcome any public calamity (war with England excepted) which might lessen the confidence of our country in those principles and forms. I have generally considered them rather as subjects for a madhouse. But they are now playing a game of the most mischievous tendency, without perhaps being themselves aware of it. They are endeavoring to convince England, that we suffer more by the embargo than they do, and that, if they will but hold out a while, we must abandon it. It is true, the time will come when we must abandon it. But if this is before the repeal of the orders of council, we must abandon it only for a state of war. The day is not distant, when that will be preferable to a longer continuance of the embargo. But we can never remove that, and let our vessels go out and be taken under these orders, without making reprisal. Yet this is the very state of things which these federal monarchists are endeavoring to bring about; and in this it is but too possible they may succeed. But the fact is, that if we have war with England, it will be solely produced by their manoeuvres. I think that in two or three months we shall know what will be the issue. I salute you with esteem and respect.
Th: Jefferson.
TO ROBERT L. LIVINGSTON.
Washington, October 15, 1808.
Sir,
Your letter of September the 22nd waited here for my return, and it is not till now that I have been able to acknowledge it. The explanation of his principles, given you by the French Emperor, in conversation, is correct as far as it goes. He does not wish us to go to war with England, knowing we have no ships to carry on that war. To submit to pay to England the tribute on our commerce which she demands by her orders of council, would be to aid her in the war against him, and would give him just ground to declare war with us. He concludes, therefore, as every rational man must, that the embargo, the only remaining alternative, was a wise measure. These are acknowledged principles, and should circumstances arise, which may offer advantage to our country in making them public, we shall avail ourselves of them. But as it is not usual nor agreeable to governments to bring their conversations before the public, I think it would be well to consider this on your part as confidential, leaving to the government to retain or make it public, as the general good may require. Had the Emperor gone further, and said that he condemned our vessels going voluntarily into his ports in breach of his municipal laws, we might have admitted it rigorously legal, though not friendly. But his condemnation of vessels taken on the high seas by his privateers, and carried involuntarily into his ports, is justifiable by no law, is piracy, and this is the wrong we complain of against him.
Supposing that you may be still at Clermont, from whence your letter is dated, I avail myself of this circumstance to request your presenting my friendly respects to Chancellor Livingston.
I salute you with esteem and respect.
Th: Jefferson.
TO DOCTOR JAMES BROWN.
Washington, October 27, 1808.
Dear Sir,
You will wonder that your letter of June the 3rd should not be acknowledged till this date. I never received it till September the 12th, and coming soon after to this place, the accumulation of business I found here has prevented my taking it up till now. That you ever participated in any plan for a division of the Union, I never for one moment believed. I knew your Americanism too well. But as the enterprise against Mexico was of a very different character, I had supposed what I heard on that subject to be possible. You disavow it; that is enough for me, and I for ever dismiss the idea. I wish it were possible to extend my belief of innocence to a very different description of men in New Orleans; but I think there is sufficient evidence of there being there a set of foreign adventurers, and native malcontents, who would concur in any enterprise to separate that country from this. I did wish to see these people get what they deserved; and under the maxim of the law itself, that inter arma silent leges, that in an encampment expecting daily attack from a powerful enemy, self-preservation is paramount to all law, I expected that instead of invoking the forms of the law to cover traitors, all good citizens would have concurred in securing them. Should we have ever gained our Revolution, if we had bound our hands by manacles of the law, not only in the beginning, but in any part of the revolutionary conflict? There are extreme cases where the laws become inadequate even to their own preservation, and where the universal resource is a dictator, or martial law. Was New Orleans in that situation? Although we knew here that the force destined against it was suppressed on the Ohio, yet we supposed this unknown at New Orleans at the time that Burr’s accomplices were calling in the aid of the law to enable them to perpetrate its suppression, and that it was reasonable, according to the state of information there, to act on the expectation of a daily attack. Of this you are the best judge.
Burr is in London, and is giving out to his friends that that government offers him two millions of dollars the moment he can raise an ensign of rebellion as big as an handkerchief. Some of his partisans will believe this, because they wish it. But those who know him best will not believe it the more because he says it. For myself, even in his most flattering periods of the conspiracy, I never entertained one moment’s fear. My long and intimate knowledge of my countrymen satisfied and satisfies me, that, let there ever be occasion to display the banners of the law, and the world will see how few and pitiful are those who shall array themselves in opposition. I as little fear foreign invasion. I have indeed thought it a duty to be prepared to meet even the most powerful, that of a Bonaparte, for instance, by the only means competent, that of a classification of the militia, and placing the junior classes at the public disposal: but the lesson he receives in Spain extirpates all apprehensions from my mind. If, in a peninsula, the neck of which is adjacent to him, and at his command, where he can march any army without the possibility of interception or obstruction from any foreign power, he finds it necessary to begin with an army of three hundred thousand men, to subdue a nation of five millions, brutalized by ignorance, and enervated by long peace, and should find constant reinforcements of thousands after thousands necessary to effect at last a conquest as doubtful as deprecated, what numbers would be necessary against eight millions of free Americans, spread over such an extent of country as would wear him down by mere marching, by want of food, autumnal diseases, &c.? How would they be brought, and how reinforced, across an ocean of three thousand miles, in possession of a bitter enemy, whose peace, like the repose of a dog, is never more than momentary? And for what? For nothing but hard blows. If the Orleanese Creoles would but contemplate these truths, they would cling to the American Union, soul and body, as their first affection, and we should be as safe there as we are every where else. I have no doubt of their attachment to us in preference of the English.
I salute you with sincere friendship and respect.
Th: Jefferson.
TO LIEUTENANT GOVERNOR LINCOLN.
Washington, November 13, 1808.
Dear Sir,
I enclose you a petition from Nantucket, and refer it for your decision. Our opinion here is, that that place has been so deeply concerned in smuggling, that if it wants, it is because it has illegally sent away what it ought to have retained for its own consumption. Be so good as to bear in mind that I have asked the favor of you to see that your State encounters no real want, while, at the same time, where applications are made merely to cover fraud, no facilities towards that be furnished. I presume there can be no want in Massachusetts, as yet, as I am informed that Governor Sullivan’s permits are openly bought and sold here and in Alexandria, and at other markets. The Congressional campaign is just opening: three alternatives alone are to be chosen from. 1. Embargo. 2. War. 3. Submission and tribute. And, wonderful to tell, the last will not want advocates. The real question, however, will lie between the two first, on which there is considerable division. As yet the first seems most to prevail; but opinions are by no means yet settled down. Perhaps the advocates of the second may, to a formal declaration of war, prefer general letters of mark and reprisal, because, on a repeal of their edicts by the belligerent, a revocation of the letters of mark restores peace without the delay, difficulties, and ceremonies of a treaty. On this occasion, I think it fair to leave to those who are to act on them, the decisions they prefer, being to be myself but a spectator. I should not feel justified in directing measures which those who are to execute them would disapprove. Our situation is truly difficult. We have been pressed by the belligerents to the very wall, and all further retreat is impracticable. I salute you with sincere friendship.
Th: Jefferson.
TO THOMAS JEFFERSON RANDOLPH.
Washington, November 24, 1808.
My Dear Jefferson,
Your situation, thrown at such a distance from us and alone, cannot but give us all great anxieties for you. As much has been secured for you, by your particular position and the acquaintance to which you have been recommended, as could be done towards shielding you from the dangers which surround you. But thrown on a wide world, among entire strangers, without a friend or guardian to advise, so young, too, and with so little experience of mankind, your dangers are great, and still your safety must rest on yourself. A determination never to do what is wrong, prudence, and good humor, will go far towards securing to you the estimation of the world. When I recollect that at fourteen years of age, the whole care and direction of myself was thrown on myself entirely, without a relation or friend qualified to advise or guide me, and recollect the various sorts of bad company with which I associated from time to time, I am astonished I did not turn off with some of them, and become as worthless to society as they were. I had the good fortune to become acquainted very early with some characters of very high standing, and to feel the incessant wish that I could ever become what they were. Under temptations and difficulties, I would ask myself what would Dr. Small, Mr. Wythe, Peyton Randolph do in this situation? What course in it will insure me their approbation? I am certain that this mode of deciding on my conduct, tended more to its correctness than any reasoning powers I possessed. Knowing the even and dignified line they pursued, I could never doubt for a moment which of two courses would be in character for them. Whereas, seeking the same object through a process of moral reasoning, and with the jaundiced eye of youth, I should often have erred. From the circumstances of my position, I was often thrown into the society of horse-racers, card-players, fox-hunters, scientific and professional men, and of dignified men; and many a time have I asked myself, in the enthusiastic moment of the death of a fox, the victory of a favorite horse, the issue of a question eloquently argued at the bar, or in the great council of the nation, well, which of these kinds of reputation should I prefer? That of a horse-jockey? a fox-hunter? an orator? or the honest advocate of my country’s rights? Be assured, my dear Jefferson, that these little returns into ourselves, this self-catechizing habit, is not trifling, nor useless, but leads to the prudent selection and steady pursuit of what is right.
I have mentioned good humor as one of the preservatives of our peace and tranquillity. It is among the most effectual, and its effect is so well imitated and aided, artificially, by politeness, that this also becomes an acquisition of first-rate value. In truth, politeness is artificial good humor, it covers the natural want of it, and ends by rendering habitual a substitute nearly equivalent to the real virtue. It is the practice of sacrificing to those whom we meet in society, all the little conveniences and preferences which will gratify them, and deprive us of nothing worth a moment’s consideration; it is the giving a pleasing and flattering turn to our expressions, which will conciliate others, and make them pleased with us as well as themselves. How cheap a price for the good will of another! When this is in return for a rude thing said by another, it brings him to his senses, it mortifies and corrects him in the most salutary way, and places him at the feet of your good nature, in the eyes of the company. But in stating prudential rules for our government in society I must not omit the important one of never entering into dispute or argument with another. I never yet saw an instance of one of two disputants convincing the other by argument. I have seen many, of their getting warm, becoming rude, and shooting one another. Conviction is the effect of our own dispassionate reasoning, either in solitude, or weighing within ourselves, dispassionately, what we hear from others, standing uncommitted in argument ourselves. It was one of the rules, which, above all others, made Doctor Franklin the most amiable of men in society, ‘never to contradict any body.’ If he was urged to announce an opinion, he did it rather by asking questions, as if for information, or by suggesting doubts. When I hear another express an opinion which is not mine, I say to myself, he has a right to his opinion, as I to mine; why should I question it? His error does me no injury, and shall I become a Don Quixote, to bring all men by force of argument to one opinion? If a fact be misstated, it is probable he is gratified by a belief of it, and I have no right to deprive him of the gratification. If he wants information, he will ask it, and then I will give it in measured terms; but if he still believes his own story, and shows a desire to dispute the fact with me, I hear him, and say nothing. It is his affair, not mine, if he prefers error. There are two classes of disputants most frequently to be met with among us. The first is of young students, just entered the threshold of science, with a first view of its outlines, not yet filled up with the details and modifications which a further progress would bring to their knowledge. The other consists of the ill-tempered and rude men in society, who have taken up a passion for politics. (Good humor and politeness never introduce into mixed society a question on which they foresee there will be a difference of opinion.) From both of those classes of disputants, my dear Jefferson, keep aloof, as you would from the infected subjects of yellow fever or pestilence. Consider yourself, when with them, as among the patients of Bedlam, needing medical more than moral counsel. Be a listener only, keep within yourself, and endeavor to establish with yourself the habit of silence, especially on politics. In the fevered state of our country, no good can ever result from any attempt to set one of these fiery zealots to rights, either in fact or principle. They are determined as to the facts they will believe, and the opinions on which they will act. Get by them, therefore, as you would by an angry bull: it is not for a man of sense to dispute the road with such an animal. You will be more exposed than others to have these animals shaking their horns at you, because of the relation in which you stand with me. Full of political venom, and willing to see me and to hate me as a chief in the antagonist party, your presence will be to them what the vomit-grass is to the sick dog, a nostrum for producing ejaculation. Look upon them exactly with that eye, and pity them as objects to whom you can administer only occasional ease. My character is not within their power. It is in the hands of my fellow-citizens at large, and will be consigned to honor or infamy by the verdict of the republican mass of our country, according to what themselves will have seen, not what their enemies and mine shall have said. Never, therefore, consider these puppies in politics as requiring any notice from you, and always show, that you are not afraid to leave my character to the umpirage of public opinion. Look steadily to the pursuits which have carried you to Philadelphia, be very select in the society you attach yourself to, avoid taverns, drinkers, smokers, idlers, and dissipated persons generally; for it is with such that broils and contentions arise; and you will find your path more easy and tranquil. The limits of my paper warn me that it is time for me to close with my affectionate adieu.
Th: Jefferson.
P. S. Present me affectionately to Mr. Ogilvie, and in doing the same to Mr. Peale, tell him I am writing with his polygraph, and shall send him mine the first moment I have leisure enough to pack it. T. J.
TO DOCTOR EUSTIS.
Washington, January 14, 1809.
Sir,
I have the pleasure to acknowledge the receipt of your letter of December the 24th, and of the resolutions of the republican citizens of Boston, of the 19th of that month. These are worthy of the ancient character of the sons of Massachusetts, and of the spirit of concord with her sister States, which, and which alone, carried us successfully through the revolutionary war, and finally placed us under that national government, which constitutes the safety of every part, by uniting for its protection the powers of the whole. The moment for exerting these united powers, to repel the injuries of the belligerents of Europe, seems likely to be pressed upon us. They have interdicted our commerce with nearly the whole world. They have declared it shall be carried on with such places, in such articles, and in such measure only, as they shall dictate; thus prostrating all the principles of right, which have hitherto protected it. After exhausting the cup of forbearance and conciliation to its dregs, we found it necessary, on behalf of that commerce, to take time to call it home into a state of safety, to put the towns and harbors which carry it on into a condition of defence, and to make further preparation for enforcing the redress of its wrongs, and restoring it to its rightful freedom. This required a certain measure of time, which, although not admitting specific limitation, must, from its avowed objects, have been obvious to all: and the progress actually made towards the accomplishment of these objects, proves it now to be near its term.
While thus endeavoring to secure, and preparing to vindicate that commerce, the absurd opinion has been propagated, that this temporary and necessary arrangement was to be a permanent system, and was intended for its destruction. The sentiments expressed in the paper you were so kind as to enclose me, show that those who have concurred in them, have judged with more candor the intentions of their government, and are sufficiently aware of the tendency of the excitements and misrepresentations which have been practised on this occasion. And such, I am persuaded, will be the disposition of the citizens of Massachusetts at large, whenever truth can reach them. Associated with her sister States in a common government, the fundamental principle of which is, that the will of the majority is to prevail, sensible, that in the present difficulty, that will has been governed by no local interests or jealousies, that to save permanent rights, temporary sacrifices were necessary, that these have fallen as impartially on all, as in a situation so peculiar they could be made to do, she will see, in the existing measures, a legitimate and honest exercise of the will and wisdom of the whole. And her citizens, faithful to themselves and their associates, will not, to avoid a transient pressure, yield to the seductions of enemies to their independence, foreign or domestic, and take a course equally subversive of their well-being, as of that of their brethren.
The approbation expressed by the republican citizens of the town of Boston, of the course pursued by the national government, is truly consoling to its members: and, encouraged by the declaration of the continuance of their confidence, and by the assurance of their support, they will continue to pursue the line of their high duties according to the best of their understandings, and with undeviating regard to the good of the whole. Permit me to avail myself of this occasion of tendering you personally the assurances of my great esteem and respect.
Th: Jefferson.
TO COLONEL MONROE.
Washington, January 28, 1809.
Dear Sir,
Your favor of the 18th was received in due time, and the answer has been delayed as well by a pressure of business, as by the expectation of your absence from Richmond.
The idea of sending a special mission to France or England is not entertained at all here. After so little attention to us from the former, and so insulting an answer from Canning, such a mark of respect as an extraordinary mission, would be a degradation against which all minds revolt here. The idea was hazarded in the House of Representatives a few days ago, by a member, and an approbation expressed by another, but rejected indignantly by every other person who spoke, and very generally in conversation by all others: and I am satisfied such a proposition would get no vote in the Senate. The course the legislature means to pursue, may be inferred from the act now passed for a meeting in May, and a proposition before them for repealing the embargo in June, and then resuming and maintaining by force our right of navigation. There will be considerable opposition to this last proposition, not only from the federalists, old and new, who oppose every thing, but from sound members of the majority. Yet it is believed it will obtain a good majority, and that it is the only proposition which can be devised that could obtain a majority of any kind. Final propositions, will, therefore, be soon despatched to both the belligerents through the resident ministers, so that their answers will be received before the meeting in May, and will decide what is to be done. This last trial for peace is not thought desperate. If, as is expected, Bonaparte should be successful in Spain, however every virtuous and liberal sentiment revolts at it, it may induce both powers to be more accommodating with us. England will see here the only asylum for her commerce and manufactures, worth more to her than her orders of council. And Bonaparte, having Spain at his feet, will look immediately to the Spanish colonies, and think our neutrality cheaply purchased by a repeal of the illegal parts of his decrees, with perhaps the Floridas thrown into the bargain. Should a change in the aspect of affairs in Europe produce this disposition in both powers, our peace and prosperity may be revived and long continue. Otherwise, we must again take the tented field, as we did in 1776 under more inauspicious circumstances.
There never has been a situation of the world before, in which such endeavors as we have made would not have secured our peace. It is probable there never will be such another. If we go to war now, I fear we may renounce for ever the hope of seeing an end of our national debt. If we can keep at peace eight years longer, our income, liberated from debt, will be adequate to any war, without new taxes or loans, and our position and increasing strength will put us hors d’insulte from any nation. I am now so near the moment of retiring, that I take no part in affairs beyond the expression of an opinion. I think it fair, that my successor should now originate those measures of which he will be charged with the execution and responsibility, and that it is my duty to clothe them with the forms of authority. Five weeks more will relieve me from a drudgery to which I am no longer equal, and restore me to a scene of tranquillity, amidst my family and friends, more congenial to my age and natural inclinations. In that situation, it will always be a pleasure to me to see you, and to repeat to you the assurances of my constant friendship and respect.
Th: Jefferson.
TO THOMAS MANN RANDOLPH.
Washington, February 7, 1809.
Dear Sir,
I thought Congress had taken their ground firmly for continuing their embargo till June, and then war. But a sudden and unaccountable revolution of opinion took place the last week, chiefly among the New England and New York members, and in a kind of panic, they voted the 4th of March for removing the embargo, and by such a majority as gave all reason to believe, they would not agree either to war or non-intercourse. This, too, was after we had become satisfied, that the Essex Junto had found their expectation desperate, of inducing the people there to either separation or forcible opposition. The majority of Congress, however, has now rallied to the removing the embargo on the 4th of March, non-intercourse with France and Great Britain, trade every where else, and continuing war preparations. The further details are not yet settled, but I believe it is perfectly certain that the embargo will be taken off the 4th of March. Present my warmest affections to my dearest Martha, and the young ones, and accept the assurances of them to yourself.
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN HOLLINS.
Washington, February 19, 1809.
Dear Sir,
A little transaction of mine, as innocent an one as I ever entered into, and where an improper construction was never less expected, is making some noise, I observe, in your city. I beg leave to explain it to you, because I mean to ask your agency in it. The last year, the Agricultural Society of Paris, of which I am a member, having had a plough presented to them, which, on trial with a graduated instrument, did equal work with half the force of their best ploughs, they thought it would be a benefit to mankind to communicate it. They accordingly sent one to me, with a view to its being made known here, and they sent one to the Duke of Bedford also, who is one of their members, to be made use of for England, although the two nations were then at war. By the Mentor, now going to France, I have given permission to two individuals in Delaware and New York, to import two parcels of Merino sheep from France, which they have procured there, and to some gentlemen in Boston, to import a very valuable machine which spins cotton, wool, and flax equally. The last spring, the Society informed me they were cultivating the cotton of the Levant and other parts of the Mediterranean, and wished to try also that of our southern States. I immediately got a friend to have two tierces of seed forwarded to me. They were consigned to Messrs. Falls and Brown of Baltimore, and notice of it being given me, I immediately wrote to them to re-ship them to New York, to be sent by the Mentor. Their first object was to make a show of my letter, as something very criminal, and to carry the subject into the newspapers. I had, on a like request, some time ago (but before the embargo), from the President of the Board of Agriculture of London, of which I am also a member, to send them some of the genuine May wheat of Virginia, forwarded to them two or three barrels of it. General Washington, in his time, received from the same Society the seed of the perennial succory, which Arthur Young had carried over from France to England, and I have since received from a member of it the seed of the famous turnip of Sweden, now so well known here. I mention these things, to show the nature of the correspondence which is carried on between societies instituted for the benevolent purpose of communicating to all parts of the world whatever useful is discovered in any one of them. These societies are always in peace, however their nations may be at war. Like the republic of letters, they form a great fraternity spreading over the whole earth, and their correspondence is never interrupted by any civilized nation. Vaccination has been a late and remarkable instance of the liberal diffusion of a blessing newly discovered. It is really painful, it is mortifying, to be obliged to note these things, which are known to every one who knows any thing, and felt with approbation by every one who has any feeling. But we have a faction to whose hostile passions the torture even of right into wrong is a delicious gratification. Their malice I have long learned to disregard, their censure to deem praise. But I observe, that some republicans are not satisfied (even while we are receiving liberally from others) that this small return should be made. They will think more justly at another day: but, in the mean time, I wish to avoid offence. My prayer to you, therefore, is, that you will be so good, under the enclosed order, as to receive these two tierces of seed from Falls and Brown, and pay them their disbursements for freight, &c. which I will immediately remit you on knowing the amount. Of the seed, when received, be so good as to make manure for your garden. When rotted with a due mixture of stable manure or earth, it is the best in the world. I rely on your friendship to excuse this trouble, it being necessary I should not commit myself again to persons of whose honor, or the want of it, I know nothing.
Accept the assurances of my constant esteem and respect.
Th: Jefferson.
TO M. DUPONT DE NEMOURS.
Washington, March 2, 1809.
Dear Sir,
My last to you was of May the 2nd; since which I have received yours of May the 25th, June the 1st, July the 23rd, 24th, and September the 5th, and distributed the two pamphlets according to your desire. They are read with the delight which every thing from your pen gives.
After using every effort which could prevent or delay our being entangled in the war of Europe, that seems now our only resource. The edicts of the two belligerents, forbidding us to be seen on the ocean, we met by an embargo. This gave us time to call home our seamen, ships, and property, to levy men and put our sea-ports into a certain state of defence. We have now taken off the embargo, except as to France and England and their territories, because fifty millions of exports annually sacrificed, are the treble of what war would cost us; besides, that by war we should take something, and lose less than at present. But to give you a true description of the state of things here, I must refer you to Mr. Coles, the bearer of this, my secretary, a most worthy, intelligent, and well-informed young man, whom I recommend to your notice, and conversation on our affairs. His discretion and fidelity may be relied on. I expect he will find you with Spain at your feet, but England still afloat, and a barrier to the Spanish colonies. But all these concerns I am now leaving to be settled by my friend Mr. Madison. Within a few days I retire to my family, my books, and farms; and having gained the harbor myself, I shall look on my friends still buffeting the storm, with anxiety indeed, but not with envy. Never did a prisoner, released from his chains, feel such relief as I shall on shaking off the shackles of power. Nature intended me for the tranquil pursuits of science, by rendering them my supreme delight. But the enormities of the times in which I have lived, have forced me to take a part in resisting them, and to commit myself on the boisterous ocean of political passions. I thank God for the opportunity of retiring from them without censure, and carrying with me the most consoling proofs of public approbation. I leave every thing in the hands of men so able to take care of them, that if we are destined to meet misfortunes, it will be because no human wisdom could avert them. Should you return to the United States, perhaps your curiosity may lead you to visit the hermit of Monticello. He will receive you with affection and delight; hailing you in the mean time with his affectionate salutations, and assurances of constant esteem and respect.
Th: Jefferson.
P. S. If you return to us, bring a couple of pair of true-bred shepherd’s dogs. You will add a valuable possession to a country now beginning to pay great attention to the raising sheep.
TO THE PRESIDENT.
Monticello, March 17, 1809.
Dear Sir,
On opening my letters from France, in the moment of my departure from Washington, I found from their signatures that they were from literary characters, except one from Mr. Short, which mentioned in the outset that it was private, and that his public communications were in the letter to the Secretary of State, which I sent you. I find, however, on reading his letter to me (which I did not do till I got home) a passage of some length, proper to be communicated to you, and which I have therefore extracted.
I had a very fatiguing journey, having found the roads excessively bad, although I have seen them worse. The last three days I found it better to be on horseback, and travelled eight hours through as disagreeable a snow storm as I was ever in. Feeling no inconvenience from the expedition but fatigue, I have more confidence in my vis vitæ than I had before entertained. The spring is remarkably backward. No oats sown, not much tobacco seed, and little done in the gardens. Wheat has suffered considerably. No vegetation visible yet but the red maple, weeping-willow, and lilac. Flour is said to be at eight dollars at Richmond, and all produce is hurrying down.
I feel great anxiety for the occurrences of the ensuing four or five months. If peace can be preserved, I hope and trust you will have a smooth administration. I know no government which would be so embarrassing in war as ours. This would proceed very much from the lying and licentious character of our papers; but much, also, from the wonderful credulity of the members of Congress in the floating lies of the day. And in this no experience seems to correct them. I have never seen a Congress during the last eight years, a great majority of which I would not implicitly have relied on in any question, could their minds have been purged of all errors of fact. The evil, too, increases greatly with the protraction of the session, and I apprehend, in case of war, their session would have a tendency to become permanent. It is much, therefore, to be desired that war may be avoided, if circumstances will admit. Nor in the present maniac state of Europe, should I estimate the point of honor by the ordinary scale. I believe we shall, on the contrary, have credit with the world, for having made the avoidance of being engaged in the present unexampled war, our first object. War, however, may become a less losing business than unresisted depredation. With every wish that events may be propitious to your administration, I salute you with sincere affection and every sympathy of the heart.
Th: Jefferson.
TO THE INHABITANTS OF ALBEMARLE COUNTY, IN VIRGINIA,
Returning to the scenes of my birth and early life, to the society of those with whom I was raised, and who have been ever dear to me, I receive, fellow-citizens and neighbors, with inexpressible pleasure, the cordial welcome you are so good as to give me. Long absent on duties which the history of a wonderful era made incumbent on those called to them, the pomp, the turmoil, the bustle, and splendor of office, have drawn but deeper sighs for the tranquil and irresponsible occupations of private life, for the enjoyment of an affectionate intercourse with you, my neighbors and friends, and the endearments of family love, which nature has given us all, as the sweetener of every hour. For these I gladly lay down the distressing burthen of power, and seek, with my fellow-citizens, repose and safety under the watchful cares, the labors, and perplexities of younger and abler minds. The anxieties you express to administer to my happiness, do, of themselves, confer that happiness; and the measure will be complete, if my endeavors to fulfil my duties in the several public stations to which I have been called, have obtained for me the approbation of my country. The part which I have acted on the theatre of public life, has been before them; and to their sentence I submit it: but the testimony of my native county, of the individuals who have known me in private life, to my conduct in its various duties and relations, is the more grateful, as proceeding from eye-witnesses and observers, from triers of the vicinage. Of you, then, my neighbors, I may ask, in the face of the world, ‘Whose ox have I taken, or whom have I defrauded? Whom have I oppressed, or of whose hand have I received a bribe to blind mine eyes therewith?’ On your verdict I rest with conscious security. Your wishes for my happiness are received with just sensibility, and I offer sincere prayers for your own welfare and prosperity.
Th: Jefferson.
April 3, 1809.
TO WILSON C. NICHOLAS.
Monticello, June 13, 1809.
Dear Sir,
I did not know till Mr. Patterson called on us, a few days ago, that you had passed on to Washington. I had recently observed in the debates of Congress, a matter introduced, on which I wished to give explanations more fully in conversation, which I will now do by abridgment in writing. Mr. Randolph has proposed an inquiry into certain prosecutions at common law in Connecticut, for libels on the government, and not only himself, but others have stated them with such affected caution, and such hints at the same time, as to leave on every mind the impression that they had been instituted either by my direction, or with my acquiescence, at least. This has not been denied by my friends, because probably the fact is unknown to them. I shall state it for their satisfaction, and leave it to be disposed of as they think best.
I had observed in a newspaper (some years ago, I do not recollect the time exactly), some dark hints of a prosecution in Connecticut, but so obscurely hinted, that I paid little attention to it. Some considerable time after, it was again mentioned, so that I understood that some prosecution was going on in the federal court there, for calumnies uttered from the pulpit against me by a clergyman. I immediately wrote to Mr. Granger, who, I think, was in Connecticut at the time, stating that I had laid it down as a law to myself, to take no notice of the thousand calumnies issued against me, but to trust my character to my own conduct, and the good sense and candor of my fellow-citizens; that I had found no reason to be dissatisfied with that course, and I was unwilling it should be broke through by others as to any matter concerning me; and I therefore requested him to desire the district attorney to dismiss the prosecution. Some time after this, 1 heard of subpoenas being served on General Lee, David M. Randolph, and others, as witnesses to attend the trial. I then, for the first time, conjectured the subject of the libel. I immediately wrote to Mr. Granger, to require an immediate dismission of the prosecution. The answer of Mr. Huntington, the district attorney, was, that these subpoenas had been issued by the defendant without his knowledge, that it had been his intention to dismiss all the prosecutions at the first meeting of the court, and to accompany it with an avowal of his opinion, that they could not be maintained, because the federal court had no jurisdiction over libels. This was accordingly done. I did not till then know that there were other prosecutions of the same nature, nor do I now know what were their subjects. But all went off together; and I afterwards saw, in the hands of Mr. Granger, a letter written by the clergyman, disavowing any personal ill will towards me, and solemnly declaring he had never uttered the words charged. I think Mr. Granger either showed me, or said there were affidavits of at least half a dozen respectable men who were present at the sermon, and swore no such expressions were uttered, and as many equally respectable who swore the contrary. But the clergyman expressed his gratification at the dismission of the prosecution. I write all this from memory, and after too long an interval of time to be certain of the exactness of all the details; but I am sure there is no variation material, and Mr. Granger, correcting small lapses of memory, can confirm every thing substantial. Certain it is, that the prosecutions had been instituted, and had made considerable progress, without my knowledge; that they were disapproved by me as soon as known, and directed to be discontinued. The attorney did it on the same ground on which I had acted myself in the cases of Duane, Callender, and others; to wit, that the sedition law was unconstitutional and null, and that my obligation to execute what was law, involved that of not suffering rights secured by valid laws, to be prostrated by what was no law. I always understood that these prosecutions had been invited, if not instituted, by Judge Edwards, and the marshal, being republican, had summoned a grand jury partly or wholly republican: but that Mr. Huntington declared from the beginning against the jurisdiction of the court, and had determined to enter nolle-prosequis before he received my directions.
I trouble you with another subject. The law making my letters post free, goes to those to me only, not those from me. The bill had got to its passage before this was observed (and first I believe by Mr. Dana), and the house under too much pressure of business near the close of the session to bring in another bill. As the privilege of freedom was given to the letters from as well as to both my predecessors, I suppose no reason exists for making a distinction. And in so extensive a correspondence as I am subject to, and still considerably on public matters, it would be a sensible convenience to myself, as well as those who have occasion to receive letters from me. It happens, too, as I was told at the time (for I have never looked into it myself), that it was done by two distinct acts on both the former occasions. Mr. Eppes, I think, mentioned this to me. I know from the Post Master General, that Mr. Adams franks all his letters. I state this matter to you as being my representative, which must apologize for the trouble of it. We have been seasonable since you left us. Yesterday evening and this morning we have had refreshing showers, which will close and confirm the business of planting. Affectionately yours,
Th: Jefferson.
TO THE PRESIDENT.
Monticello, August 17, 1809.
Dear Sir,
I never doubted the chicanery of the Anglomen, on whatsoever measures you should take in consequence of the disavowal of Erskine; yet I am satisfied that both the proclamations have been sound. The first has been sanctioned by universal approbation; and although it was not literally the case foreseen by the legislature, yet it was a proper extension of their provision to a case similar, though not the same. It proved to the whole world our desire of accommodation, and must have satisfied every candid federalist on that head. It was not only proper on the well-grounded confidence that the arrangement would be honestly executed, but ought to have taken place even had the perfidy of England been foreseen. Their dirty gain is richly remunerated to us by our placing them so shamefully in the wrong, and by the union it must produce among ourselves. The last proclamation admits of quibbles, of which advantage will doubtless be endeavored to be taken, by those to whom gain is their god, and their country nothing. But it is soundly defensible. The British minister assured us, that the orders of council would be revoked before the 10th of June. The executive, trusting in that assurance, declared by proclamation that the revocation was to take place, and that on that event the law was to be suspended. But the event did not take place, and the consequence, of course, could not follow. This view is derived from the former non-intercourse law only, having never read the latter one. I had doubted whether Congress must not be called; but that arose from another doubt, whether their second law had not changed the ground, so as to require their agency to give operation to the law. Should Bonaparte have the wisdom to correct his injustice towards us, I consider war with England as inevitable. Our ships will go to France and its dependencies, and they will take them. This will be war on their part, and leaves no alternative but reprisal. I have no doubt you will think it safe to act on this hypothesis, and with energy. The moment that open war shall be apprehended from them, we should take possession of Baton Rouge. If we do not, they will, and New Orleans becomes irrecoverable, and the western country blockaded during the war. It would be justifiable towards Spain on this ground, and equally so on that of title to West Florida, and reprisal extended to East Florida. Whatever turn our present difficulty may take, I look upon all cordial conciliation with England as desperate during the life of the present King. I hope and doubt not that Erskine will justify himself. My confidence is founded in a belief of his integrity, and in the ——— of Canning. I consider the present as the most shameless ministry which ever disgraced England. Copenhagen will immortalize their infamy. In general their administrations are so changeable, and they are obliged to descend to such tricks to keep themselves in place, that nothing like honor or morality can ever be counted on in transactions with them. I salute you with all possible affection.
Th: Jefferson.
TO DOCTOR BARTON.
Monticello, September 21, 1809.
Dear Sir,
I received last night your favor of the 14th, and would with all possible pleasure have communicated to you any part or the whole of the Indian vocabularies which I had collected, but an irreparable misfortune has deprived me of them. I have now been thirty years availing myself of every possible opportunity of procuring Indian vocabularies to the same set of words: my opportunities were probably better than will ever occur again to any person having the same desire. I had collected about fifty, and had digested most of them in collateral columns, and meant to have printed them the last year of my stay in Washington. But not having yet digested Captain Lewis’s collection, nor having leisure then to do it, I put it off till I should return home. The whole, as well digest as originals, were packed in a trunk of stationery, and sent round by water with about thirty other packages of my effects, from Washington, and while ascending James river, this package, on account of its weight and presumed precious contents, was singled out and stolen. The thief, being disappointed on opening it, threw into the river all its contents, of which he thought he could make no use. Among these were the whole of the vocabularies. Some leaves floated ashore, and were found in the mud; but these were very few, and so defaced by the mud and water, that no general use can ever be made of them. On the receipt of your letter I turned to them, and was very happy to find, that the only morsel of an original vocabulary among them, was Captain Lewis’s of the Pani language, of which you say you have not one word. I therefore enclose it to you as it is, and a little fragment of some other, which I see is in his hand-writing, but no indication remains on it of what language it is. It is a specimen of the condition of the little which was recovered. I am the more concerned at this accident, as of the two hundred and fifty words of my vocabularies, and the one hundred and thirty words of the great Russian vocabularies of the languages of the other quarters of the globe, seventy-three were common to both, and would have furnished materials for a comparison, from which something might have resulted. Although I believe no general use can ever be made of the wrecks of my loss, yet I will ask the return of the Pani vocabulary when you are done with it. Perhaps I may make another attempt to collect, although I am too old to expect to make much progress in it.
I learn, with pleasure, your acquisition of the pamphlet on the astronomy of the ancient Mexicans. If it be ancient and genuine, or modern and rational, it will be of real value. It is one of the most interesting countries of our hemisphere, and merits every attention.
I am thankful for your kind offer of sending the original Spanish for my perusal. But I think it a pity to trust it to the accidents of the post, and whenever you publish the translation, I shall be satisfied to read that which shall be given by your translator, who is, I am sure, a greater adept in the language than I am.
Accept the assurances of my great esteem and respect.
Th: Jefferson.
TO DON VALENTINE DE FORONDA.
Monticello, October 4, 1809.
Dear Sir,
Your favor of August the 26th came to hand in the succeeding month, and have now to thank you for the pamphlet it contained. I have read it with pleasure, and find the constitution proposed would probably be as free as is consistent with hereditary institutions. It has one feature which I like much; that which provides that when the three co-ordinate branches differ in their construction of the constitution, the opinion of two branches shall overrule the third. Our constitution has not sufficiently solved this difficulty.
Among the multitude of characters with which public office leads us to official intercourse, we cannot fail to observe many, whose personal worth marks them as objects of particular esteem, whom we would wish to select for our society in private life. I avail myself gladly of the present occasion, of assuring you that I was peculiarly impressed with your merit and talents, and that I have ever entertained for them a particular respect. To those whose views are single and direct, it is a great comfort to have to do business with frank and honorable minds. And here give me leave to make an avowal, for which, in my present retirement, there can be no motive but a regard for truth. Your predecessor, soured on a question of etiquette against the administration of this country, wished to impute wrong to them in all their actions, even where he did not believe it himself. In this spirit, he wished it to be believed that we were in unjustifiable co-operation in Miranda’s expedition. I solemnly, and on my personal truth and honor, declare to you, that this was entirely without foundation, and that there was neither co-operation nor connivance on our part. He informed us he was about to attempt the liberation of his native country from bondage, and intimated a hope of our aid, or connivance at least. He was at once informed, that, although we had great cause of complaint against Spain, and even of war, yet whenever we should think proper to act as her enemy, it should be openly and above board, and that our hostility should never be exercised by such petty means. We had no suspicion that he expected to engage men here, but merely to purchase military stores. Against this there was no law, nor consequently any authority for us to interpose obstacles. On the other hand, we deemed it improper to betray his voluntary communication to the agents of Spain. Although his measures were many days in preparation at New York, we never had the least intimation or suspicion of his engaging men in his enterprise, until he was gone; and I presume the secrecy of his proceedings kept them equally unknown to the Marquis Yrujo at Philadelphia, and the Spanish Consul at New York, since neither of them gave us any information of the enlistment of men, until it was too late for any measures taken at Washington to prevent their departure. The officer in the Customs, who participated in this transaction with Miranda, we immediately removed, and should have had him and others further punished, had it not been for the protection given them by private citizens at New York, in opposition to the government, who, by their impudent falsehoods and calumnies, were able to overbear the minds of the jurors. Be assured, Sir, that no motive could induce me, at this time, to make this declaration so gratuitously, were it not founded in sacred truth: and I will add further, that I never did, or countenanced, in public life, a single act inconsistent with the strictest good faith; having never believed there was one code of morality for a public, and another for a private man.
I receive, with great pleasure, the testimonies of personal esteem which breathe through your letter; and I pray you to accept those equally sincere with which I now salute you.
Th: Jefferson.
TO ALBERT GALLATIN.
Monticello, October 11, 1809.
Dear Sir,
I do not know whether the request of Monsieur Moussier, explained in the enclosed letter, is grantable or not. But my partialities in favor of whatever may promote either the useful or liberal arts, induce me to place it under your consideration, to do in it whatever is right, neither more nor less. I would then ask you to favor me with three lines, in such form as I may forward him by way of answer.
I have reflected much and painfully on the change of dispositions which has taken place among the members of the cabinet, since the new arrangement, as you stated to me in the moment of our separation. It would be, indeed, a great public calamity, were it to fix you in the purpose which you seemed to think possible. I consider the fortunes of our republic as depending, in an eminent degree, on the extinguishment of the public debt before we engage in any war: because, that done, we shall have revenue enough to improve our country in peace, and defend it in war, without recurring either to new taxes or loans. But if the debt should once more be swelled to a formidable size, its entire discharge will be despaired of, and we shall be committed to the English career of debt, corruption, and rottenness, closing with revolution. The discharge of the debt, therefore, is vital to the destinies of our government, and it hangs on Mr. Madison and yourself alone. We shall never see another President and Secretary of the Treasury making all other objects subordinate to this. Were either of you to be lost to the public, that great hope is lost. I had always cherished the idea that you would fix on that object the measure of your fame, and of the gratitude which our country will owe you. Nor can I yield up this prospect to the secondary considerations which assail your tranquillity. For sure I am, they never can produce any other serious effect. Your value is too justly estimated by our fellow-citizens at large, as well as their functionaries, to admit any remissness in their support of you. My opinion always was, that none of us ever occupied stronger ground in the esteem of Congress than yourself, and I am satisfied there is no one who does not feel your aid to be still as important for the future, as it has been for the past. You have nothing, therefore, to apprehend in the dispositions of Congress, and still less of the President, who, above all men, is the most interested and affectionately disposed to support you. I hope, then, you will abandon entirely the idea you expressed to me, and that you will consider the eight years to come as essential to your political career. I should certainly consider any earlier day of your retirement, as the most inauspicious day our new government has ever seen. In addition to the common interest in this question, I feel particularly for myself the considerations of gratitude which I personally owe you for your valuable aid during my administration of the public affairs, a just sense of the large portion of the public approbation which was earned by your labors, and belongs to you, and the sincere friendship and attachment which grew out of our joint exertions to promote the common good; and of which I pray you now to accept the most cordial and respectful assurances.
Th: Jefferson.
TO CÆSAR A. RODNEY.
Monticello, February 10, 1810.
My Dear Sir,
I have to thank you for your favor of the 31st ultimo, which is just now received. It has been peculiarly unfortunate for us, personally, that the portion in the history of mankind, at which we were called to take a share in the direction of their affairs, was such an one as history has never before presented. At any other period, the even-handed justice we have observed towards all nations, the efforts we have made to merit their esteem by every act which candor or liberality could exercise, would have preserved our peace, and secured the unqualified confidence of all other nations in our faith and probity. But the hurricane which is now blasting the world, physical and moral, has prostrated all the mounds of reason as well as right. All those calculations which, at any other period, would have been deemed honorable, of the existence of a moral sense in man, individually or associated, of the connection which the laws of nature have established between his duties and his interests, of a regard for honest fame and the esteem of our follow-men, have been a matter of reproach on us, as evidences of imbecility. As if it could be a folly for an honest man to suppose that others could be honest also, when it is their interest to be so. And when is this state of things to end? The death of Bonaparte would, to be sure, remove the first and chiefest apostle of the desolation of men and morals, and might withdraw the scourge of the land. But what is to restore order and safety on the ocean? The death of George III? Not at all. He is only stupid; and his ministers, however weak and profligate in morals, are ephemeral. But his nation is permanent, and it is that which is the tyrant of the ocean. The principle that force is right, is become the principle of the nation itself. They would not permit an honest minister, were accident to bring such an one into power, to relax their system of lawless piracy. These were the difficulties when I was with you. I know they are not lessened, and I pity you.
It is a blessing, however, that our people are reasonable; that they are kept so well informed of the state of things as to judge for themselves, to see the true sources of their difficulties, and to maintain their confidence undiminished in the wisdom and integrity of their functionaries. Macte virtute therefore. Continue to go straight forward, pursuing always that which is right, as the only clue which can lead us out of the labyrinth. Let nothing be spared of either reason or passion, to preserve the public confidence entire, as the only rock of our safety. In times of peace the people look most to their representatives; but in war, to the executive solely. It is visible that their confidence is even now veering in that direction; that they are looking to the executive to give the proper direction to their affairs, with a confidence as auspicious as it is well founded.
I avail myself of this, the first occasion of writing to you, to express all the depth of my affection for you; the sense I entertain of your faithful co-operation in my late labors, and the debt I owe for the valuable aids I received from you. Though separated from my fellow-laborers in place and pursuit, my affections are with you all, and I offer daily prayers that ye love one another, as I love you. God bless you.
Th: Jefferson.
Monticello, February 19,1810.
[* This letter is endorsed, ‘not sent.‘]
Sir,
Yours of the 7th instant has been duly received, with the pamphlet enclosed, for which I return you my thanks. Nothing can be more exactly and seriously true than what is there stated; that but a short time elapsed after the death of the great reformer of the Jewish religion, before his principles were departed from by those who professed to be his special servants, and perverted into an engine for enslaving mankind, and aggrandizing their oppressors in Church and State; that the purest system of morals ever before preached to man, has been adulterated and sophisticated by artificial constructions, into a mere contrivance to filch wealth and power to themselves; that rational men not being able to swallow their impious heresies, in order to force them down their throats, they raise the hue and cry of infidelity, while themselves are the greatest obstacles to the advancement of the real doctrines of Jesus, and do in fact constitute the real Anti-Christ.
You expect that your book will have some effect on the prejudices which the society of Friends entertain against the present and late administrations. In this I think you will be disappointed. The Friends are men, formed with the same passions, and swayed by the same natural principles and prejudices as others. In cases where the passions are neutral, men will display their respect for the religious professions of their sect. But where their passions are enlisted, these professions are no obstacle. You observe very truly, that both the late and present administration conducted the government on principles professed by the Friends. Our efforts to preserve peace, our measures as to the Indians, as to slavery, as to religious freedom, were all in consonance with their professions. Yet I never expected we should get a vote from them, and in this I was neither deceived nor disappointed. There is no riddle in this, to those who do not suffer themselves to be duped by the professions of religious sectaries. The theory of American Quakerism is a very obvious one. The mother society is in England. Its members are English by birth and residence, devoted to their own country, as good citizens ought to be. The Quakers of these States are colonies or filiations from the mother society, to whom that society sends its yearly lessons. On these the filiated societies model their opinions, their conduct, their passions, and attachments. A Quaker is, essentially an Englishman, in whatever part of the earth he is born or lives. The outrages of Great Britain on our navigation and commerce have kept us in perpetual bickerings with her. The Quakers here have taken side against their own government; not on their profession of peace, for they saw that peace was our object also; but from devotion to the views of the mother society. In 1797 and 8, when an administration sought war with France, the Quakers were the most clamorous for war. Their principle of peace, as a secondary one, yielded to the primary one of adherence to the Friends in England, and what was patriotism in the original became treason in the copy. On that occasion, they obliged their good old leader, Mr. Pemberton, to erase his name from a petition to Congress, against war, which had been delivered to a Representative of Pennsylvania, a member of the late and present administration. He accordingly permitted the old gentleman to erase his name. You must not, therefore, expect that your book will have any more effect on the society of Friends here, than on the English merchants settled among us. I apply this to the Friends in general, not universally. I know individuals among them as good patriots as we have.
I thank you for the kind wishes and sentiments towards myself, expressed in your letter, and sincerely wish to yourself the blessings of health and happiness.
Th: Jefferson.
TO GENERAL KOSCIUSKO.
Monticello, February 26, 1810.
My Dear General and Friend,
I have rarely written to you; never but by safe conveyances; and avoiding every thing political, lest coming from one in the station I then held, it might be imputed injuriously to our country, or perhaps even excite jealousy of you. Hence my letters were necessarily dry. Retired now from public concerns, totally unconnected with them, and avoiding all curiosity about what is done or intended, what I say is from myself only, the workings of my own mind, imputable to nobody else.
The anxieties which I know you have felt, on seeing exposed to the justlings of a warring world, a country to which, in early life, you devoted your sword and services when oppressed by foreign dominion, were worthy of your philanthropy and disinterested attachment to the freedom and happiness of man. Although we have not made all the provisions which might be necessary for a war in the field of Europe, yet we have not been inattentive to such as would be necessary here. From the moment that the affair of the Chesapeake rendered the prospect of war imminent, every faculty was exerted to be prepared for it, and I think I may venture to solace you with the assurance, that we are, in a good degree, prepared. Military stores for many campaigns are on hand, all the necessary articles (sulphur excepted), and the art of preparing them among ourselves, abundantly; arms in our magazines for more men than will ever be required in the field, and forty thousand new stand yearly added, of our own fabrication, superior to any we have ever seen from Europe; heavy artillery much beyond our need; an increasing stock of field-pieces, several founderies casting one every other day each; a military school of about fifty students, which has been in operation a dozen years; and the manufacture of men constantly going on, and adding forty thousand young soldiers to our force every year that the war is deferred: at all our sea-port towns of the least consequence we have erected works of defence, and assigned them gunboats, carrying one or two heavy pieces, either eighteen, twenty-four, or thirty-two pounders, sufficient in the smallest harbors to repel the predatory attacks of privateers or single armed ships, and proportioned in the larger harbors to such more serious attacks as they may probably be exposed to. All these were nearly completed, and their gunboats in readiness, when I retired from the government. The works of New York and New Orleans alone, being on a much larger scale, are not yet completed. The former will be finished this summer, mounting four hundred and thirty-eight guns, and, with the aid of from fifty to one hundred gunboats, will be adequate to the resistance of any fleet which will ever be trusted across the Atlantic. The works for New Orleans are less advanced. These are our preparations. They are very different from what you will be told by newspapers, and travellers, even Americans. But it is not to them the government communicates the public condition. Ask one of them if he knows the exact state of any particular harbor, and you will find probably that he does not know even that of the one he comes from. You will ask, perhaps, where are the proofs of these preparations for one who cannot go and see them. I answer, in the acts of Congress, authorizing such preparations, and in your knowledge of me, that, if authorized, they would be executed.
Two measures have not been adopted which I pressed on Congress repeatedly at their meetings. The one, to settle the whole ungranted territory of Orleans, by donations of land to able bodied young men, to be engaged and carried there at the public expense, who would constitute a force always ready on the spot to defend New Orleans. The other was, to class the militia according to the years of their birth, and make all those from twenty to twenty-five liable to be trained and called into service at a moment’s warning. This would have given us a force of three hundred thousand young men, prepared, by proper training, for service in any part of the United States; while those who had passed through that period would remain at home, liable to be used in their own or adjacent States. These two measures would have completed what I deemed necessary for the entire security of our country. They would have given me, on my retirement from the government of the nation, the consolatory reflection, that having found, when I was called to it, not a single sea-port town in a condition to repel a levy of contribution by a single privateer or pirate, I had left every harbor so prepared by works and gun-boats, as to be in a reasonable state of security against any probable attack; the territory of Orleans acquired, and planted with an internal force sufficient for its protection; and the whole territory of the United States organized by such a classification of its male force, as would give it the benefit of all its young population for active service, and that of a middle and advanced age for stationary defence. But these measures will, I hope, be completed by my successor, who, to the purest principles of republican patriotism, adds a wisdom and foresight second to no man on earth.
So much as to my country. Now a word as to myself. I am retired to Monticello, where, in the bosom of my family, and surrounded by my books, I enjoy a repose to which I have been long a stranger. My mornings are devoted to correspondence. From breakfast to dinner, I am in my shops, my garden, or on horseback among my farms; from dinner to dark, I give to society and recreation with my neighbors and friends; and from candle-light to early bed-time, I read. My health is perfect; and my strength considerably reinforced by the activity of the course I pursue; perhaps it is as great as usually falls to the lot of near sixty-seven years of age. I talk of ploughs and harrows, seeding and harvesting, with my neighbors, and of politics too, if they choose, with as little reserve as the rest of my fellow-citizens, and feel, at length, the blessing of being free to say and do what I please, without being responsible for it to any mortal. A part of my occupation, and by no means the least pleasing, is the direction of the studies of such young men as ask it. They place themselves in the neighboring village, and have the use of my library and counsel, and make a part of my society. In advising the course of their reading, I endeavor to keep their attention fixed on the main objects of all science, the freedom and happiness of man. So that coming to bear a share in the councils and government of their country, they will keep ever in view the sole objects of all legitimate government.
Instead of the unalloyed happiness of retiring unembarrassed and independent, to the enjoyment of my estate, which is ample for my limited views, I have to pass such a length of time in a thraldom of mind never before known to me. Except, for this, my happiness would have been perfect. That yours may never know disturbance, and that you may enjoy as many years of life, health, and ease as yourself shall wish, is the sincere prayer of your constant and affectionate friend.
Th: Jefferson.
TO DOCTOR JONES.
Monticello, March 5, 1810.
Dear Sir,
I received duly your favor of the 19th ultimo, and I salute you with all antient and recent recollections of friendship. I have learned, with real sorrow, that circumstances have risen among our executive counsellors, which have rendered foes those who once were friends. To themselves it will be a source of infinite pain and vexation, and therefore chiefly I lament it, for I have a sincere esteem for both parties. To the President it will be really inconvenient: but to the nation I do not know that it can do serious injury, unless we were to believe the newspapers, which pretend that Mr. Gallatin will go out. That indeed would be a day of mourning for the United States: but I hope that the position of both gentlemen may be made so easy as to give no cause for either to withdraw. The ordinary business of every day is done by consultation between the President and the Head of the department alone to which it belongs. For measures of importance or difficulty, a consultation is held with the Heads of departments, either assembled, or by taking their opinions separately in conversation or in writing. The latter is most strictly in the spirit of the constitution. Because the President, on weighing the advice of all, is left free to make up an opinion for himself. In this way they are not brought together, and it is not necessarily known to any what opinion the others have given. This was General Washington’s practice for the first two or three years of his administration, till the affairs of France and England threatened to embroil us, and rendered consideration and discussion desirable. In these discussions, Hamilton and myself were daily pitted in the cabinet like two cocks. We were then but four in number, and, according to the majority, which of course was three to one, the President decided. The pain was for Hamilton and myself, but the public experienced no inconvenience. I practised this last method, because the harmony was so cordial among us all, that we never failed, by a contribution of mutual views of the subject, to form an opinion acceptable to the whole. I think there never was one instance to the contrary, in any case of consequence. Yet this does, in fact, transform the executive into a directory, and I hold the other method to be more constitutional. It is better calculated, too, to prevent collision and irritation, and to cure it, or at least suppress its effects when it has already taken place. It is the obvious and sufficient remedy in the present case, and will doubtless be resorted to.
Our difficulties are indeed great, if we consider ourselves alone. But when viewed in comparison with those of Europe, they are the joys of Paradise. In the eternal revolution of ages, the destinies have placed our portion of existence amidst such scenes of tumult and outrage, as no other period, within our knowledge, had presented. Every government but one on the continent of Europe, demolished, a conqueror roaming over the earth with havoc and destruction, a pirate spreading misery and ruin over the face of the ocean. Indeed, my friend, ours is a bed of roses. And the system of government which shall keep us afloat amidst this wreck of the world, will be immortalized in history. We have, to be sure, our petty squabbles and heart-burnings, and we have something of the blue devils at times, as to these raw heads and bloody bones who are eating up other nations. But happily for us, the Mammoth cannot swim, nor the Leviathan move on dry land: and if we will keep out of their way, they cannot get at us. If, indeed, we choose to place ourselves within the scope of their tether, a gripe of the paw, or flounce of the tail, may be our fortune. Our business certainly was to be still. But a part of our nation chose to declare against this, in such a way as to control the wisdom of the government. I yielded with others, to avoid a greater evil. But from that moment, I have seen no system which could keep us entirely aloof from these agents of destruction. If there be any, I am certain that you, my friends, now charged with the care of us all, will see and pursue it. I give myself, therefore, no trouble with thinking or puzzling about it. Being confident in my watchmen, I sleep soundly. God bless you all, and send you a safe deliverance.
Th: Jefferson.
Monticello, March 5, 1810.
Your letter, my dear friend, of the 18th ultimo, comes like the refreshing dews of the evening on a thirsty soil. It recalls antient as well as recent recollections, very dear to my heart. For five and thirty years we have walked together through a land of tribulations. Yet these have passed away, and so I trust will those of the present day. The toryism with which we struggled in ‘77, differed but in name from the federalism of ‘99, with which we struggled also; and the Anglicism, of 1808, against which we are now struggling, is but the same thing still, in another form. It is a longing for a King, and an English King, rather than any other. This is the true source of their sorrows and wailings.
The fear that Bonaparte will come over to us and conquer us also, is too chimerical to be genuine. Supposing him to have finished Spain and Portugal, he has yet England and Russia to subdue. The maxim of war was never sounder than in this case, not to leave an enemy in the rear; and especially where an insurrectionary flame is known to be under the embers, merely smothered, and ready to burst at every point. These two subdued (and surely the Anglomen will not think the conquest of England alone a short work), ancient Greece and Macedonia, the cradle of Alexander, his prototype, and Constantinople, the seat of empire for the world, would glitter more in his eye than our bleak mountains and rugged forests. Egypt, too, and the golden apples of Mauritania, have for more than half a century fixed the longing eyes of France; and with Syria, you know, he has an old affront to wipe out. Then come ‘Pontus and Galatia, Cappadocia, Asia, and Bithynia,’ the fine countries on the Euphrates and Tigris, the Oxus and Indus, and all beyond the Hyphasis, which bounded the glories of his Macedonian rival; with the invitations of his new British subjects on the banks of the Ganges, whom, after receiving under his protection the mother country, he cannot refuse to visit. When all this is done and settled, and nothing of the old world remains unsubdued, he may turn to the new one. But will he attack us first, from whom he will get but hard knocks, and no money? Or will he first lay hold of the gold and silver of Mexico and Peru, and the diamonds of Brazil? A republican Emperor, from his affection to republics, independent of motives of expediency, must grant to ours the Cyclops’ boon of being the last devoured. While all this is doing, we are to suppose the chapter of accidents read out, and that nothing can happen to cut short or disturb his enterprises.
But the Anglomen, it seems, have found out a much safer dependence, than all these chances of death or disappointment. That is, that we should first let England plunder us, as she has been doing for years, for fear Bonaparte should do it; and then ally ourselves with her, and enter into the war. A conqueror, whose career England could not arrest when aided by Russia, Austria, Prussia, Sweden, Spain, and Portugal, she is now to destroy, with all these on his side, by the aid of the United States alone. This, indeed, is making us a mighty people. And what is to be our security, that when embarked for her in the war, she will not make a separate peace, and leave us in the lurch? Her good faith! The faith of a nation of merchants! The Punica fides of modern Carthage! Of the friend and protectress of Copenhagen! Of the nation who never admitted a chapter of morality into her political code! And is now boldly avowing, that whatever power can make hers, is hers of right. Money, and not morality, is the principle of commerce and commercial nations. But, in addition to this, the nature of the English government forbids, of itself, reliance on her engagements; and it is well known she has been the least faithful to her alliances of any nation of Europe, since the period of her history wherein she has been distinguished for her commerce and corruption, that is to say, under the houses of Stuart and Brunswick. To Portugal alone she has steadily adhered, because, by her Methuin treaty, she had made it a colony, and one of the most valuable to her. It may be asked, what, in the nature of her government, unfits England for the observation of moral duties? In the first place, her King is a cipher; his only function being to name the oligarchy which is to govern her. The parliament is, by corruption, the mere instrument of the will of the administration. The real power and property in the government is in the great aristocratical families of the nation. The nest of office being too small for all of them to cuddle into at once, the contest is eternal, which shall crowd the other out. For this purpose they are divided into two parties, the Ins and the Outs, so equal in weight, that a small matter turns the balance. To keep themselves in, when they are in, every stratagem must be practised, every artifice used, which may flatter the pride, the passions, or power of the nation. Justice, honor, faith, must yield to the necessity of keeping themselves in place. The question, whether a measure is moral, is never asked; but whether it will nourish the avarice of their merchants, or the piratical spirit of their navy, or produce any other effect which may strengthen them in their places. As to engagements, however positive, entered into by the predecessors of the Ins, why, they were their enemies; they did every thing which was wrong; and to reverse every thing they did, must, therefore, be right. This is the true character of the English government in practice, however different its theory; and it presents the singular phenomenon of a nation, the individuals of which are as faithful to their private engagements and duties, as honorable, as worthy, as those of any nation on earth, and whose government is yet the most unprincipled at this day known. In an absolute government there can be no such equiponderant parties. The despot is the government. His power, suppressing all opposition, maintains his ministers firm in their places. What he has contracted, therefore, through them, he has the power to observe with good faith; and he identifies his own honor and faith with that of his nation.
When I observed, however, that the King of England was a cipher, I did not mean to confine the observation to the mere individual now on that throne. The practice of Kings marrying only into the families of Kings, has been that of Europe for some centuries. Now, take any race of animals, confine them in idleness and inaction, whether in a sty, a stable, or a state-room, pamper them with high diet, gratify all their sexual appetites, immerse them in sensualities, nourish their passions, let every thing bend before them, and banish whatever might lead them to think, and in a few generations they become all body, and no mind: and this, too, by a law of nature, by that very law by which we are in the constant practice of changing the characters and propensities of the animals we raise for our own purposes. Such is the regimen in raising Kings, and in this way they have gone on for centuries. While in Europe, I often amused myself with contemplating the characters of the then reigning sovereigns of Europe. Louis the XVI. was a fool, of my own knowledge, and in despite of the answers made for him at his trial. The King of Spain was a fool, and of Naples the same. They passed their lives in hunting, and despatched two couriers a week, one thousand miles, to let each other know what game they had killed the preceding days. The King of Sardinia was a fool. All these were Bourbons. The Queen of Portugal, a Braganza, was an idiot by nature. And so was the King of Denmark. Their sons, as regents, exercised the powers of government. The King of Prussia, successor to the great Frederick, was a mere hog in body as well as in mind. Gustavus of Sweden, and Joseph of Austria, were really crazy, and George of England you know was in a straight waistcoat. There remained, then, none but old Catherine, who had been too lately picked up to have lost her common sense. In this state Bonaparte found Europe; and it was this state of its rulers which lost it with scarce a struggle. These animals had become without mind and powerless; and so will every hereditary monarch be after a few generations. Alexander, the grandson of Catherine, is as yet an exception. He is able to hold his own. But he is only of the third generation. His race is not yet worn out. And so endeth the book of Kings, from all of whom the Lord deliver us and have you, my friend, and all such good men and true, in his holy keeping.
Th: Jefferson.
Monticello, July 16,1810.
Dear General and Friend,
Your favor of May the 31st was duly received, and I join in congratulations with you on the resurrection of republican principles in Massachusetts and New Hampshire, and the hope that the professors of these principles will not again easily be driven off their ground. The federalists, during their short-lived ascendancy, have, nevertheless, by forcing us from the embargo, inflicted a wound on our interests which can never be cured, and on our affections which will require time to cicatrize. I ascribe all this to one pseudo-republican, Story. He came on (in place of Crowningshield, I believe) and staid only a few days; long enough, however, to get complete hold of Bacon, who giving in to his representations, became panic-struck, and communicated his panic to his colleagues, and they to a majority of the sound members of Congress. They believed in the alternative of repeal or civil war, and produced the fatal measure of repeal. This is the immediate parent of all our present evils, and has reduced us to a low standing in the eyes of the world. I should think that even the federalists themselves must now be made, by their feelings, sensible of their error. The wealth which the embargo brought home safely, has now been thrown back into the laps of our enemies; and our navigation completely crushed, and by the unwise and unpatriotic conduct of those engaged in it. Should the orders prove genuine, which are said to have been given against our fisheries, they, too, are gone: and if not true as yet, they will be true on the first breeze of success which England shall feel: for it has now been some years, that I am perfectly satisfied her intentions have been to claim the ocean as her conquest, and prohibit any vessel from navigating it, but on such a tribute as may enable her to keep up such a standing navy as will maintain her dominion over it. She has hauled in, or let herself out, been bold or hesitating, according to occurrences, but has in no situation done any thing which might amount to an acknowledged relinquishment of her intentions. I have ever been anxious to avoid a war with England, unless forced by a situation more losing than war itself. But I did believe we could coerce her to justice by peaceable means, and the embargo, evaded as it was, proved it would have coerced her, had it been honestly executed. The proof she exhibited on that occasion, that she can exercise such an influence in this country, as to control the will of its government and three fourths of its people, and oblige the three fourths to submit to one fourth, is to me the most mortifying circumstance which has occurred since the establishment of our government. The only prospect I see of lessening that influence, is in her own conduct, and not from any thing in our power. Radically hostile to our navigation and commerce, and fearing its rivalry, she will completely crush it, and force us to resort to agriculture, not aware that we shall resort to manufactures also, and render her conquests over our navigation and commerce useless, at least, if not injurious to herself in the end, and perhaps salutary to us, as removing out of our way the chief causes and provocations to war.
But these are views which concern the present and future generation, among neither of which I count myself. You may live to see the change in our pursuits, and chiefly in those of your own State, which England will effect. I am not certain that the change on Massachusetts, by driving her to agriculture, manufactures, and emigration, will lessen her happiness. But once more to be done with politics. How does Mrs. Dearborn do? How do you both like your situation? Do you amuse yourself with a garden, a farm, or what? That your pursuits, whatever they be, may make you both easy, healthy, and happy, is the prayer of your sincere friend,
Th: Jefferson.
Monticello, September 20, 1810.
Sir,
Your favor of the 14th has been duly received, and I have to thank you for the many obliging things respecting myself which are said in it. If I have left in the breasts of my fellow-citizens a sentiment of satisfaction with my conduct in the transaction of their business, it will soften the pillow of my repose through the residue of life.
The question you propose, whether circumstances do not sometimes occur, which make it a duty in officers of high trust, to assume authorities beyond the law, is easy of solution in principle, but sometimes embarrassing in practice. A strict observance of the written laws, is doubtless one of the high duties of a good citizen: but it is not the highest. The laws of necessity, of self-preservation, of saving our country when in danger, are of higher obligation. To lose our country by a scrupulous adherence to written law, would be to lose the law itself, with life, liberty, property, and all those who are enjoying them with us; thus absurdly sacrificing the end to the means. When, in the battle of Germantown, General Washington’s army was annoyed from Chew’s house, he did not hesitate to plant his cannon against it, although the property of a citizen. When he besieged Yorktown, he leveled the suburbs, feeling that the laws of property must be postponed to the safety of the nation. While the army was before York, the Governor of Virginia took horses, carriages, provisions, and even men, by force, to enable that army to stay together till it could master the public enemy; and he was justified. A ship at sea in distress for provisions, meets another having abundance, yet refusing a supply; the law of self-preservation authorizes the distressed to take a supply by force. In all these cases, the unwritten laws of necessity, of self-preservation, and of the public safety, control the written laws of meum and tuum. Further to exemplify the principle, I will state an hypothetical case. Suppose it had been made known to the executive of the Union in the autumn of 1805, that we might have the Floridas for a reasonable sum, that that sum had not indeed been so appropriated by law, but that Congress were to meet within three weeks, and might appropriate it on the first or second day of their session. Ought he, for so great an advantage to his country, to have risked himself by transcending the law and making the purchase? The public advantage offered, in this supposed case, was indeed immense: but a reverence for law, and the probability that the advantage might still be legally accomplished by a delay of only three weeks, were powerful reasons against hazarding the act. But suppose it foreseen that a John Randolph would find means to protract the proceeding on it by Congress, until the ensuing spring, by which time new circumstances would change the mind of the other party. Ought the executive, in that case, and with that foreknowledge, to have secured the good to his country, and to have trusted to their justice for the transgression of the law? I think he ought, and that the act would have been approved. After the affair of the Chesapeake, we thought war a very possible result. Our magazines were illy provided with some necessary articles, nor had any appropriations been made for their purchase. We ventured, however, to provide them, and to place our country in safety; and stating the case to Congress, they sanctioned the act.
To proceed to the conspiracy of Burr, and particularly to General Wilkinson’s situation in New Orleans. In judging this case, we are bound to consider the state of the information, correct and incorrect, which he then possessed. He expected Burr and his band from above, a British fleet from below, and he knew there was a formidable conspiracy within the city. Under these circumstances, was he justifiable, 1. In seizing notorious conspirators? On this there can be but two opinions; one, of the guilty and their accomplices; the other, that of all honest men. 2. In sending them to the seat of government, when the written law gave them a right to trial in the territory? The danger of their rescue, of their continuing their machinations, the tardiness and weakness of the law, apathy of the judges, active patronage of the whole tribe of lawyers, unknown disposition of the juries, an hourly expectation of the enemy, salvation of the city, and of the Union itself, which would have been convulsed to its centre, had that conspiracy succeeded; all these constituted a law of necessity and self-preservation, and rendered the salus populi supreme over the written law. The officer who is called to act on this superior ground, does indeed risk himself on the justice of the controlling powers of the constitution, and his station makes it his duty to incur that risk. But those controlling powers, and his fellow-citizens generally, are bound to judge according to the circumstances under which he acted. They are not to transfer the information of this place or moment to the time and place of his action; but to put themselves into his situation. We knew here that there never was danger of a British fleet from below, and that Burr’s band was crushed before it reached the Mississippi. But General Wilkinson’s information was very different, and he could act on no other.
From these examples and principles you may see what I think on the question proposed. They do not go to the case of persons charged with petty duties, where consequences are trifling, and time allowed for a legal course, nor to authorize them to take such cases out of the written law. In these, the example of overleaping the law is of greater evil than a strict adherence to its imperfect provisions. It is incumbent on those only who accept of great charges, to risk themselves on great occasions, when the safety of the nation, or some of its very high interests are at stake.
An officer is bound to obey orders: yet he would be a bad one who should do it in cases for which they were not intended, and which involved the most important consequences. The line of discrimination between cases may be difficult; but the good officer is bound to draw it at his own peril, and throw himself on the justice of his country, and the rectitude of his motives.
I have indulged freer views on this question, on your assurances that they are for your own eye only, and that they will not get into the hands of news-writers. I met their scurrilities without concern, while in pursuit of the great interests with which I was charged. But in my present retirement, no duty forbids my wish for quiet.
Accept the assurances of my esteem and respect.
Th: Jefferson.
Monticello, January 15, 1811.
Dear Sir,
An absence from home of some length has prevented my sooner acknowledging the receipt of your letter, covering the printed pamphlet, which the same absence has as yet prevented me from taking up, but which I know I shall read with great pleasure. Your favor of December the 22nd is also received.
Mr. Wagner’s malignity, like that of the rest of his tribe of brother printers, who deal out calumnies for federal readers, gives me no pain. When a printer cooks up a falsehood, it is as easy to put it into the mouth of a Mr. Fox, as of a smaller man, and safer into that of a dead than a living one. Your sincere attachment to this country, as well as to your native one, was never doubted by me; and in that persuasion, I felt myself free to express to you my genuine sentiments with respect to England. No man was more sensible than myself of the just value of the friendship of that country. There are between us so many of those circumstances which naturally produce and cement kind dispositions, that if they could have forgiven our resistance to their usurpations, our connections might have been durable, and have insured duration to both our governments. I wished, therefore, a cordial friendship with them, and I spared no occasion of manifesting this in our correspondence and intercourse with them; not disguising, however, my desire of friendship with their enemy also. During the administration of Mr. Addington, I thought I discovered some friendly symptoms on the part of that government; at least, we received some marks of respect from the administration, and some of regret at the wrongs we were suffering from their country. So, also, during the short interval of Mr. Fox’s power. But every other administration since our Revolution has been equally wanton in their injuries and insults, and has manifested equal hatred and aversion. Instead, too, of cultivating the government itself, whose principles are those of the great mass of the nation, they have adopted the miserable policy of teazing and embarrassing it, by allying themselves with a faction here, not a tenth of the people, noisy and unprincipled, and which never can come into power while republicanism is the spirit of the nation, and that must continue to be so, until such a condensation of population shall have taken place as will require centuries. Whereas, the good will of the government itself would give them, and immediately, every benefit which reason or justice would permit it to give. With respect to myself, I saw great reason to believe their ministers were weak enough to credit the newspaper trash about a supposed personal enmity in myself towards England. This wretched party imputation was beneath the notice of wise men. England never did me a personal injury, other than in open war, and for numerous individuals there, I have great esteem and friendship. And I must have had a mind far below the duties of my station, to have felt either national partialities or antipathies in conducting the affairs confided to me. My affections were first for my own country, and then, generally, for all mankind; and nothing but minds placing themselves above the passions, in the functionaries of this country, could have preserved us from the war to which their provocations have been constantly urging us. The war interests in England include a numerous and wealthy part of their population; and their influence is deemed worth courting by ministers wishing to keep their places. Continually endangered by a powerful opposition, they find it convenient to humor the popular passions at the expense of the public good. The shipping interest, commercial interest, and their janizaries of the navy, all fattening on war, will not be neglected by ministers of ordinary minds. Their tenure of office is so infirm that they dare not follow the dictates of wisdom, justice, and the well calculated interests of their country. This vice, in the English constitution, renders a dependance on that government very unsafe. The feelings of their King, too, fundamentally averse to us, have added another motive for unfriendliness in his ministers. This obstacle to friendship, however, seems likely to be soon removed; and I verily believe the successor will come in with fairer and wiser dispositions towards us; perhaps on that event their conduct may be changed. But what England is to become on the crush of her internal structure, now seeming to be begun, I cannot foresee. Her monied interest, created by her paper system, and now constituting a baseless mass of wealth equal to that of the owners of the soil, must disappear with that system, and the medium for paying great taxes thus failing, her navy must be without support. That it shall be supported by permitting her to claim dominion of the ocean, and to levy tribute on every flag traversing that, as lately attempted and not yet relinquished, every nation must contest, even ad internecionem. And yet, that, retiring from this enormity, she should continue able to take a fair share in the necessary equilibrium,of power on that element, would be the desire of every nation.
I feel happy in withdrawing my mind from these anxieties, and resigning myself, for the remnant of life, to the care and guardianship of others. Good wishes are all an old man has to offer to his country or friends. Mine attend yourself, with sincere assurances of esteem and respect, which, however, I should be better pleased to tender you in person, should your rambles ever lead you into the vicinage of Monticello.
Th: Jefferson.
TO DOCTOR BENJAMIN RUSH.
Monticello, January 16, 1811.
Dear Sir,
I had been considering for some days, whether it was not time by a letter, to bring myself to your recollection, when I received your welcome favor of the 2nd instant. I had before heard of the heart-rending calamity you mention, and had sincerely sympathized with your afflictions. But I had not made it the subject of a letter, because I knew that condolences were but renewals of grief. Yet I thought, and still think, this is one of the cases wherein we should ‘not sorrow, even as others who have no hope.’
You ask if I have read Hartley? I have not. ‘My present course of life admits less reading than I wish. From breakfast, or noon at latest, to dinner, I am mostly on horseback, attending to my farms or other concerns, which I find healthful to my body, mind, and affairs; and the few hours I can pass in my cabinet, are devoured by correspondences; not those with my intimate friends, with whom I delight to interchange sentiments, but with others, who, writing to me on concerns of their own in which I have had an agency, or from motives of mere respect and approbation, are entitled to be answered with respect and a return of good will. My hope is that this obstacle to the delights of retirement will wear away with the oblivion which follows that, and that I may at length be indulged in those studious pursuits, from which nothing but revolutionary duties would ever have called me.
I shall receive your proposed publication, and read it with the pleasure which every thing gives me from your pen. Although much of a sceptic in the practice of medicine, I read with pleasure its ingenious theories.
I receive with sensibility your observations on the discontinuance of friendly correspondence between Mr. Adams and myself, and the concern you take in its restoration. This discontinuance has not proceeded from me, nor from the want of sincere desire, and of effort on my part, to renew our intercourse. You know the perfect coincidence of principle and of action, in the early part of the Revolution, which produced a high degree of mutual respect and esteem between Mr. Adams and myself. Certainly no man was ever truer than he was, in that day, to those principles of rational republicanism, which, after the necessity of throwing off our monarchy, dictated all our efforts in the establishment of a new government. And although he swerved, afterwards, towards the principles of the English constitution, our friendship did not abate on that account. While he was Vice-President, and I Secretary of State, I received a letter from President Washington, then at Mount Vernon, desiring me to call together the Heads of departments, and to invite Mr. Adams to join us (which, by the bye, was the only instance of that being done) in order to determine on some measure which required despatch; and he desired me to act on it, as decided, without again recurring to him. I invited them to dine with me, and after dinner, sitting at our wine, having settled our question, other conversation came on, in which a collision of opinion arose between Mr. Adams and Colonel Hamilton, on the merits of the British Constitution, Mr. Adams giving it as his opinion, that, if some of its defects and abuses were corrected, it would be the most perfect constitution of government ever devised by man. Hamilton, on the contrary, asserted, that with its existing vices, it was the most perfect model of government that could be formed; and that the correction of its vices would render it an impracticable government. And this you may be assured was the real line of difference between the political principles of these two gentlemen. Another incident took place on the same occasion, which will further delineate Hamilton’s political principles. The room being hung around with a collection of the portraits of remarkable men, among them were those of Bacon, Newton, and Locke. Hamilton asked me who they were. I told him they were my trinity of the three greatest men the world had ever produced, naming them. He paused for some time: ‘The greatest man,’ said he, ‘that ever lived, was Julius Caesar.’ Mr. Adams was honest as a politician, as well as a man; Hamilton honest as a man, but, as a politician, believing in the necessity of either force or corruption to govern men.
You remember the machinery which the federalists played off, about that time, to beat down the friends to the real principles of our constitution, to silence by terror every expression in their favor, to bring us into war with France and alliance with England, and finally to homologize our constitution with that of England. Mr. Adams, you know, was overwhelmed with feverish addresses, dictated by the fear, and often by the pen of the bloody buoy, and was seduced by them into some open indications of his new principles of government, and in fact, was so elated as to mix with his kindness a little superciliousness towards me. Even Mrs. Adams, with all her good sense and prudence, was sensibly flushed. And you recollect the short suspension of our intercourse, and the circumstance which gave rise to it, which you were so good as to bring to an early explanation, and have set to rights, to the cordial satisfaction of us all. The nation at length passed condemnation on the political principles of the federalists, by refusing to continue Mr. Adams in the Presidency. On the day on which we learned in Philadelphia the vote of the city of New York, which it was well known would decide the vote of the State, and that, again, the vote of the Union, I called on Mr. Adams on some official business. He was very sensibly affected, and accosted me with these words. ‘Well, I understand that you are to beat me in this contest, and I will only say that I will be as faithful a subject as any you will have.’ ‘Mr. Adams,’ said I, ‘this is no personal contest between you and me. Two systems of principles on the subject of government divide our fellow-citizens into two parties. With one of these you concur, and I with the other. As we have been longer on the public stage than most of those now living, our names happen to be more generally known. One of these parties, therefore, has put your name at its head, the other mine. Were we both to die to-day, to-morrow two other names would be in the place of ours, without any change in the motion of the machine. Its motion is from its principle, not from you or myself. ‘I believe you are right,’ said he, ‘that we are but passive instruments, and should not suffer this matter to affect our personal dispositions.’ But he did not long retain this just view of the subject. I have always believed that the thousand calumnies which the federalists, in bitterness of heart, and mortification at their ejection, daily invented against me, were carried to him by their busy intriguers, and made some impression. When the election between Burr and myself was kept in suspense by the federalists, and they were meditating to place the President of the Senate at the head of the government, I called on Mr. Adams with a view to have this desperate measure prevented by his negative. He grew warm in an instant, and said with a vehemence he had not used towards me before, ‘Sir, the event of the election is within your own power. You have only to say you will do justice to the public creditors, maintain the navy, and not disturb those holding offices, and the government will instantly be put into your hands. We know it is the wish of the people it should be so.‘ ‘Mr. Adams,’ said I, ‘I know not what part of my conduct, in either public or private life, can have authorized a doubt of my fidelity to the public engagements. I say, however, I will not come into the government by capitulation. I will not enter on it, but in perfect freedom to follow the dictates of my own judgment.’ I had before given the same answer to the same intimation from Gouverneur Morris. ‘Then,’ said he, ‘things must take their course.’ I turned the conversation to something else, and soon took my leave. It was the first time in our lives we had ever parted with any thing like dissatisfaction. And then followed those scenes of midnight appointment, which have been condemned by all men. The last day of his political power, the last hours, and even beyond the midnight, were employed in filling all offices and especially permanent ones, with the bitterest federalists, and providing for me the alternative, either to execute the government by my enemies, whose study it would be to thwart and defeat all my measures, or to incur the odium of such numerous removals from office, as might bear me down. A little time and reflection effaced in my mind this temporary dissatisfaction with Mr. Adams, and restored me to that just estimate of his virtues and passions, which a long acquaintance had enabled me to fix. And my first wish became that of making his retirement easy by any means in my power; for it was understood he was not rich. I suggested to some republican members of the delegation from his State, the giving him, either directly or indirectly, an office, the most lucrative in that State, and then offered to be resigned, if they thought he would not deem it affrontive. They were of opinion he would take great offence at the offer; and, moreover, that the body of republicans would consider such a step in the outset, as auguring very ill of the course I meant to pursue. I dropped the idea, therefore, but did not cease to wish for some opportunity of renewing our friendly understanding.
Two or three years after, having had the misfortune to lose a daughter, between whom and Mrs. Adams there had been a considerable attachment, she made it the occasion of writing me a letter, in which, with the tenderest expressions of concern at this event, she carefully avoided a single one of friendship towards myself, and even concluded it with the wishes ‘of her who once took pleasure in subscribing herself your friend, Abigail Adams.’ Unpromising as was the complexion of this letter, I determined to make an effort towards removing the clouds from between us. This brought on a correspondence which I now enclose for your perusal, after which be so good as to return it to me, as I have never communicated it to any mortal breathing, before. I send it to you, to convince you I have not been wanting either in the desire, or the endeavor to remove this misunderstanding. Indeed, I thought it highly disgraceful to us both, as indicating minds not sufficiently elevated to prevent a public competition from affecting our personal friendship. I soon found from the correspondence that conciliation was desperate, and yielding to an intimation in her last letter, I ceased from further explanation. I have the same good opinion of Mr. Adams which I ever had. I know him to be an honest man, an able one with his pen, and he was a powerful advocate on the floor of Congress. He has been alienated from me, by belief in the lying suggestions contrived for electioneering purposes, that I perhaps mixed in the activity and intrigues of the occasion. My most intimate friends can testify that I was perfectly passive. They would sometimes, indeed, tell me what was going on; but no man ever heard me take part in such conversations; and none ever misrepresented Mr. Adams in my presence without my asserting his just character. With very confidential persons I have doubtless disapproved of the principles and practices of his administration. This was unavoidable. But never with those with whom it could do him any injury. Decency would have required this conduct from me, if disposition had not: and I am satisfied Mr. Adams’s conduct was equally honorable towards me. But I think it part of his character to suspect foul play in those of whom he is jealous, and not easily to relinquish his suspicions.
I have gone, my dear friend, into these details, that you might know every thing which had passed between us, might be fully possessed of the state of facts and dispositions, and judge for yourself whether they admit a revival of that friendly intercourse for which you are so kindly solicitous. I shall certainly not be wanting in any thing on my part which may second your efforts; which will be the easier with me, inasmuch as I do not entertain a sentiment of Mr. Adams, the expression of which could give him reasonable offence. And I submit the whole to yourself, with the assurance, that whatever be the issue, my friendship and respect for yourself will remain unaltered and unalterable.
Th: Jefferson.
Monticello, January 26, 1811.
Sir,
The length of time your favor of June the 12th, 1809, was on its way to me, and my absence from home the greater part of the autumn, delayed very much the pleasure which awaited me of reading the packet which accompanied it. I cannot express to you the satisfaction which I received from its perusal. I had, with the world, deemed Montesquieu’s a work of much merit; but saw in it, with every thinking man, so much of paradox, of false principle, and misapplied fact, as to render its value equivocal on the whole. Williams and others had nibbled only at its errors. A radical correction of them, therefore, was a great desideratum. This want is now supplied, and with a depth of thought, precision; of idea, of language, and of logic, which will force conviction into every mind. I declare to you, Sir, in the spirit of truth and sincerity, that I consider it the most precious gift the present age has received. But what would it have been, had the author, or would the author, take up the whole scheme of Montesquieu’s work, and following the correct analysis he has here developed, fill up all its parts according to his sound views of them. Montesquieu’s celebrity would be but a small portion of that which would immortalize the author. And with whom? With the rational and high-minded spirits of the present and all future ages. With those whose approbation is both incitement and reward to virtue and ambition. Is then the hope desperate? To what object can the occupation of his future life be devoted so usefully to the world, so splendidly to himself? But I must leave to others who have higher claims on his attention, to press these considerations.
My situation, far in the interior of the country, was not favorable to the object of getting this work translated and printed. Philadelphia is the least distant of the great towns of our States, where there exists any enterprise in this way; and it was not till the spring following the receipt of your letter, that I obtained an arrangement for its execution. The translation is just now completed. The sheets came to me by post, from time to time, for revisal; but not being accompanied by the original, I could not judge of verbal accuracies. I think, however, it is substantially correct, without being an adequate representation of the excellences of the original; as indeed no translation can be. I found it impossible to give it the appearance of an original composition in our language. I therefore think it best to divert inquiries after the author towards a quarter where he will not be found; and with this view, propose to prefix the prefatory epistle now enclosed. As soon as a copy of the work can be had, I will send it to you by duplicate. The secret of the author will be faithfully preserved during his and my joint lives; and those into whose hands my papers will fall at my death will be equally worthy of confidence. When the death of the author, or his living consent shall permit the world to know their benefactor, both his and my papers will furnish the evidence. In the mean time, the many important truths the works so solidly establishes, will, I hope, make it the political rudiment of the young, and manual of our older citizens.
One of its doctrines, indeed, the preference of a plural over a singular executive, will probably not be assented to here. When our present government was first established, we had many doubts on this question, and many leanings towards a supreme executive council. It happened that at that time the experiment of such an one was commenced in France, while the single executive was under trial here. We watched the motions and effects of these two rival plans, with an interest and anxiety proportioned to the importance of a. choice between them. The experiment in France failed after a short course, and not from any circumstance peculiar to the times or nation, but from those internal jealousies and dissensions in the Directory, which will ever arise among men equal in power, without a principal to decide and control their differences. We had tried a similar experiment in 1784, by establishing a committee of the States, composed of a member from every State, then thirteen, to exercise the executive functions during the recess of Congress. They fell immediately into schisms and dissensions, which became at length so inveterate as to render all co-operation among them impracticable: they dissolved themselves, abandoning the helm of government, and it continued without a head, until Congress met the ensuing winter. This was then imputed to the temper of two or three individuals; but the wise ascribed it to the nature of man. The failure of the French Directory, and from the same cause, seems to have authorized a belief that the form of a plurality, however promising in theory, is impracticable with men constituted with the ordinary passions. While the tranquil and steady tenor of our single executive, during a course of twenty-two years of the most tempestuous times the history of the world has ever presented, gives a rational hope that this important problem is at length solved. Aided by the counsels of a cabinet of Heads of departments, originally four, but now five, with whom the President consults, either singly or all together, he has the benefit of their wisdom and information, brings their views to one centre, and produces an unity of action and direction in all the branches of the government. The excellence of this construction of the executive power has already manifested itself here under very opposite circumstances. During the administration of our first President, his cabinet of four members was equally divided, by as marked an opposition of principle, as monarchism and republicanism could bring into conflict. Had that cabinet been a directory, like positive and negative quantities in Algebra, the opposing wills would have balanced each other, and produced a state of absolute inaction. But the President heard with calmness the opinions and reasons of each, decided the course to be pursued, and kept the government steadily in it, unaffected by the agitation. The public knew well the dissensions of the cabinet, but never had an uneasy thought on their account; because they knew also they had provided a regulating power, which would keep the machine in steady movement. I speak with an intimate knowledge of these scenes, quorum pars fui; as I may of others of a character entirely opposite. The third administration, which was of eight years, presented an example of harmony in a cabinet of six persons, to which perhaps history has furnished no parallel. There never arose, during the whole time, an instance of an unpleasant thought or word between the members. We sometimes met under differences of opinion, but scarcely ever failed, by conversing and reasoning, so to modify each other’s ideas, as to produce an unanimous result. Yet, able and amiable as these members were, I am not certain this would have been the case, had each possessed equal and independent powers. Ill defined limits of their respective departments, jealousies, trifling at first, but nourished and strengthened by repetition of occasions, intrigues without doors of designing persons to build an importance to themselves on the divisions of others, might, from small beginnings, have produced persevering oppositions. But the power of decision in the President left no object for internal dissension, and external intrigue was stifled in embryo by the knowledge which incendiaries possessed, that no divisions they could foment would change the course of the executive power. I am not conscious that my participations in executive authority have produced any bias in favor of the single executive; because the parts I have acted have been in the subordinate, as well as superior stations, and because, if I know myself, what I have felt, and what I have wished, I know that I have never been so well pleased, as when I could shift power from my own, on the shoulders of others; nor have I ever been able to conceive how any rational being could propose happiness to himself from the exercise of power over others.
I am still, however, sensible of the solidity of your principle, that, to insure the safety of the public liberty, its depository should be subject to be changed with the greatest ease possible, and without suspending or disturbing for a moment the movements of the machine of government. You apprehend that a single executive, with, eminence of talent, and destitution of principle, equal to the object, might, by usurpation, render his powers hereditary. Yet I think history furnishes as many examples of a single usurper arising out of a government by a plurality, as of temporary trusts of power in a single hand rendered permanent by usurpation. I do not believe, therefore, that this danger is lessened in the hands of a plural executive. Perhaps it is greatly increased, by the state of inefficiency to which they are liable from feuds and divisions among themselves. The conservative body you propose might be so constituted, as, while it would be an admirable sedative in a variety of smaller cases, might also be a valuable sentinel and check on the liberticide views of an ambitious individual. I am friendly to this idea. But the true barriers of our liberty in this country are our State governments: and the wisest conservative power ever contrived by man, is that of which our Revolution and present government found us possessed. Seventeen distinct States, amalgamated into one as to their foreign concerns, but single and independent as to their internal administration, regularly organized with a legislature and governor resting on the choice of the people, and enlightened by a free press, can never be so fascinated by the arts of one man, as to submit voluntarily to his usurpation. Nor can they be constrained to it by any force he can possess. While that may paralyze the single State in which it happens to be encamped, sixteen others, spread over a country of two thousand miles diameter, rise up on every side, ready organized for deliberation by a constitutional legislature, and for action by their governor, constitutionally the commander of the militia of the State, that is to say, of every man in it, able to bear arms; and that militia, too, regularly formed into regiments and battalions, into infantry, cavalry, and artillery, trained under officers general and subordinate, legally appointed, always in readiness, and to whom they are already in habits of obedience. The republican government of France was lost without a struggle, because the party of ‘un et indivisible’ had prevailed: no provincial organizations existed to which the people might rally under authority of the laws, the seats of the directory were virtually vacant, and a small force sufficed to turn the legislature out of their chamber and to salute its leader chief of the nation. But with us, sixteen out of seventeen States rising in mass, under regular organization and legal commanders, united in object and action by their Congress, or, if that be in duresse, by a special convention, present such obstacles to an usurper as for ever to stifle ambition in the first conception of that object.
Dangers of another kind might more reasonably be apprehended from this perfect and distinct organization, civil and military, of the States; to wit, that certain States, from local and occasional discontents, might attempt to secede from the Union. This is certainly possible; and would be befriended by this regular organization. But it is not probable that local discontents can spread to such an extent, as to be able to face the sound parts of so extensive an union: and if ever they could reach the majority, they would then become the regular government, acquire the ascendancy in Congress, and be able to redress their own grievances by laws peaceably and constitutionally passed. And even the States in which local discontents might engender a commencement of fermentation, would be paralyzed and self-checked by that very division into parties into which we have fallen, into which all States must fall wherein men are at liberty to think, speak, and act freely, according to the diversities of their individual conformations, and which are, perhaps, essential to preserve the purity of the government, by the censorship which these parties habitually exercise over each other.
You will read, I am sure, with indulgence, the explanations of the grounds on which I have ventured to form an opinion differing from yours. They prove my respect for your judgment, and diffidence of my own, which have forbidden me to retain, without examination, an opinion questioned by you. Permit me now to render my portion of the general debt of gratitude, by acknowledgments in advance for the singular benefaction which is the subject of this letter, to tender my wishes for the continuance of a life so usefully employed, and to add the assurances of my perfect esteem and respect.
Th: Jefferson.
Monticello, May 5, 1811.
Dear Sir,
Your favor on your departure from Richmond came to hand in due time. Although I may not have been among the first, I am certainly with the sincerest, who congratulate you on your re-entrance into the national councils. Your value there has never been unduly estimated by those whom personal feelings did not misguide. The late misunderstandings at Washington have been a subject of real concern to me. I know that the dissolutions of personal friendships are among the most painful occurrences in human life. I have sincere esteem for all who have been affected by them, having passed with them eight years of great harmony and affection. These incidents are rendered more distressing in our country than elsewhere, because our printers ravin on the agonies of their victims, as wolves do on the blood of the lamb. But the printers and the public are very different personages. The former may lead the latter a little out of their track, while the deviation is insensible: but the moment they usurp their direction and that of their government, they will be reduced to their true places. The two last Congresses have been the theme of the most licentious reprobation for printers thirsting after war, some against France, and some against England. But the people wish for peace with both. They feel no incumbency on them to become the reformers of the other hemisphere, and to inculcate, with fire and sword, a return to moral order. When, indeed, peace shall become more losing than war, they may owe to their interest, what these Quixottes are clamoring for on false estimates of honor. The public are unmoved by these clamors, as the re-election of their legislators shows, and they are firm to their executive on the subject of the more recent clamors.
We are suffering here both in the gathered and the growing crop. The lowness of the river, and great quantity of produce brought to Milton this year, render it almost impossible to get our crops to market. This is the case of mine as well as yours: and the Hessian fly appears alarmingly in our growing crop. Every thing is in distress for the want of rain.
Present me respectfully to Mrs. Monroe, and accept yourself assurances of my constant and affectionate esteem.
Th: Jefferson.
TO GENERAL DEARBORN.
Poplar Forest, August 14, 1811.
Dear General and Friend,
I am happy to learn that your own health is good, and I hope it will long continue so. The friends we left behind us have fallen out by the way. I sincerely lament it, because I sincerely esteem them all, and because it multiplies schisms where harmony is safety. As far as I have been able to judge, however, it has made no sensible impression against the government. Those who were murmuring before are a little louder now; but the mass of our citizens is firm and unshaken. It furnishes, as an incident, another proof that they are perfectly equal to the purposes of self-government, and that we have nothing to fear for its stability. The spirit, indeed, which manifests itself among the tories of your quarter, although I believe there is a majority there sufficient to keep it down in peaceable times, leaves me not without some disquietude. Should the determination of England, now formally expressed, to take possession of the ocean, and to suffer no commerce on it but through her ports, force a war upon us, I foresee a possibility of a separate treaty between her and your Essex men, on the principles of neutrality and commerce. Pickering here, and his nephew Williams there, can easily negotiate this. Such a lure to the quietists in our ranks with you, might recruit theirs to a majority. Yet, excluded as they would be from intercourse with the rest of the Union and of Europe, I scarcely see the gain they would propose to themselves, even for the moment. The defection would certainly disconcert the other States, but it could not ultimately endanger their safety. They are adequate, in all points, to a defensive war. However, I hope your majority, with the aid it is entitled to, will save us from this trial, to which I think it possible we are advancing. The death of George may come to our relief; but I fear the dominion of the sea is the insanity of the nation itself also. Perhaps, if some stroke of fortune were to rid us at the same time from the Mammoth of the land as well as the Leviathan of the ocean, the people of England might lose their fears, and recover their sober senses again. Tell my old friend, Governor Gerry, that I gave him glory for the rasping with which he rubbed down his herd of traitors. Let them have justice and protection against personal violence, but no favor. Powers and pre-eminences conferred on them are daggers put into the hands of assassins, to be plunged into our own bosoms in the moment the thrust can go home to the heart. Moderation can never reclaim them. They deem it timidity, and despise without fearing the tameness from which it flows. Backed by England, they never lose the hope that their day is to come, when the terrorism of their earlier power is to be merged in the more gratifying system,of deportation and the guillotine. Being now hors de combat myself, I resign to others these cares. A long attack of rheumatism has greatly enfeebled me, and warns me, that they will not very long be within my ken. But you may have to meet the trial, and in the focus of its fury. God send you a safe deliverance, a happy issue out of all afflictions, personal and public, with long life, long health, and friends as sincerely attached, as yours affectionately,
Th: Jefferson.
Poplar Forest, December 5, 1811.
Dear Sir,
While at Monticello I am so much engrossed by business or society, that I can only write on matters of strong urgency. Here I have leisure, as I have every where the disposition, to think of my friends. I recur, therefore, to the subject of your kind letters relating to Mr. Adams and myself, which a late occurrence has again presented to me. I communicated to you the correspondence which had parted Mrs. Adams and myself, in proof that I could not give friendship in exchange for such sentiments as she had recently taken up towards myself, and avowed and maintained in her letters to me. Nothing but a total renunciation of these could admit a reconciliation, and that could be cordial only in proportion as the return to ancient opinions was believed sincere. In these jaundiced sentiments of hers I had associated Mr. Adams, knowing the weight which her opinions had with him, and notwithstanding she declared in her letters that they were not communicated to him. A late incident has satisfied me that I wronged him as well as her in not yielding entire confidence to this assurance on her part. Two of the Mr. ———, my neighbors and friends, took a tour to the northward during the last summer. In Boston they fell into company with Mr. Adams, and by his invitation passed a day with him at Braintree. He spoke out to them every thing which came uppermost, and as it occurred to his mind, without any reserve, and seemed most disposed to dwell on those things which happened during his own administration. He spoke of his masters, as he called his Heads of departments, as acting above his control, and often against his opinions. Among many other topics, he adverted to the unprincipled licentiousness of the press against myself, adding, ‘I always loved Jefferson, and still love him.’
This is enough for me. I only needed this knowledge to revive towards him all the affections of the most cordial moments of our lives. Changing a single word only in Dr. Franklin’s character of him, I knew him to be always an honest man, often a great one, but sometimes incorrect and precipitate in his judgments: and it is known to those who have ever heard me speak of Mr. Adams, that I have ever done him justice myself, and defended him when assailed by others, with the single exception as to his political opinions. But with a man possessing so many other estimable qualities, why should we be dissocialized by mere differences of opinion in politics, in religion, in philosophy, or any thing else. His opinions are as honestly formed as my own. Our different views of the same subject are the result of a difference in our organization and experience. I never withdrew from the society of any man on this account, although many have done it from me; much less should I do it from one with whom I had gone through, with hand and heart, so many trying scenes. I wish, therefore, but for an apposite occasion to express to Mr. Adams my unchanged affections for him. There is an awkwardness which hangs over the resuming a correspondence so long discontinued, unless something could arise which should call for a letter. Time and chance may perhaps generate such an occasion, of which I shall not be wanting in promptitude to avail myself. From this fusion of mutual affections, Mrs. Adams is of course separated. It will only be necessary that I never name her. In your letters to Mr. Adams, you can, perhaps, suggest my continued cordiality towards him, and knowing this, should an occasion of writing first present itself to him, he will perhaps avail himself of it, as I certainly will, should it first occur to me. No ground for jealousy now existing, he will certainly give fair play to the natural warmth of his heart. Perhaps I may open the way in some letter to my old friend Gerry, who I know is in habits of the greatest intimacy with him.
I have thus, my friend, laid open my heart to you, because you were so kind as to take an interest in healing again revolutionary affections, which have ceased in expression only, but not in their existence. God ever bless you, and preserve you in life and health.
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN ADAMS.
Monticello, January 21, 1812.
Dear Sir,
I thank you beforehand (for they are not yet arrived) for the specimens of homespun you have been so kind as to forward me by post. I doubt not their excellence, knowing how far you are advanced in these things in your quarter. Here we do little in the fine way, but in coarse and middling goods a great deal. Every family in the country is a manufactory within itself, and is very generally able to make within itself all the stouter and middling stuffs for its own clothing and household use. We consider a sheep for every person in the family as sufficient to clothe it, in addition to the cotton, hemp, and flax, which we raise ourselves. For fine stuff we shall depend on your northern manufactories. Of these, that is to say, of company establishments, we have none. We use little machinery. The spinning jenny, and loom with the flying shuttle, can be managed in a family; but nothing more complicated. The economy and thriftiness resulting from our household manufactures are such that they will never again be laid aside; and nothing more salutary for us has ever happened than the British obstructions to our demands for their manufactures. Restore free intercourse when they will, their commerce with us will have totally changed its form, and the articles we shall in future want from them will not exceed their own consumption of our produce.
A letter from you calls up recollections very dear to my mind. It carries me back to the times when, beset with difficulties and dangers, we were fellow-laborers in the same cause, struggling for what is most valuable to man, his right of self-government. Laboring always at the same oar, with some wave ever ahead threatening to overwhelm us, and yet passing harmless under our bark, we knew not how, we rode through the storm with heart and hand, and made a happy port. Still we did not expect to be without rubs and difficulties; and we have had them. First the detention of the western posts: then the coalition of Pilnitz, outlawing our commerce with France, and the British enforcement of the outlawry. In your day, French depredations: in mine, English, and the Berlin and Milan decrees: now, the English orders of council, and the piracies they authorize. When these shall be over, it will be the impressment of our seamen, or something else: and so we have gone on, and so we shall go on, puzzled and prospering beyond example in the history of man. And I do believe we shall continue to growl, to multiply, and prosper, until we exhibit an association, powerful, wise, and happy, beyond what has yet been seen by men. As for France and England, with all their pre-eminence in science, the one is a den of robbers, and the other of pirates. And if science produces no better fruits than tyranny, murder, rapine, and destitution of national morality, I would rather wish our country to be ignorant, honest, and estimable, as our neighboring savages are. But whither is senile garrulity leading me? Into politics, of which I have taken final leave. I think little of them, and say less. I have given up newspapers in exchange for Tacitus and Thucydides, for Newton and Euclid, and I find myself much the happier. Sometimes, indeed, I look back to former occurrences, in remembrance of our old friends and fellow-laborers, who have fallen before us. Of the signers of the Declaration of Independence, I see now living not more than half a dozen on your side of the Potomac, and on this side, myself alone. You and I have been wonderfully spared, and myself with remarkable health, and a considerable activity of body and mind. I am on horseback three or four hours of every day; visit three or four times a year a possession I have ninety miles distant, performing the winter journey on horseback. I walk little, however, a single mile being too much for me; and I live in the midst of my grandchildren, one of whom has lately promoted me to be a great-grandfather. I have heard with pleasure that you also retain good health, and a greater power of exercise in walking than I do. But I would rather have heard this from yourself, and that, writing a letter like mine, full of egotisms, and of details of your health, your habits, occupations, and enjoyments, I should have the pleasure of knowing, that in the race of life, you do not keep, in its physical decline, the same distance ahead of me, which you have done in political honors and achievements. No circumstances have lessened the interest I feel in these particulars respecting yourself; none have suspended for one moment my sincere esteem for you, and I now salute you with unchanged affection and respect.
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN ADAMS.
Monticello, April 20, 1812.
Dear Sir,
I have it now in my power to send you a piece of homespun in return for that I received from you. Not of the fine texture, or delicate character of yours, or, to drop our metaphor, not filled as that was with that display of imagination which constitutes excellence in Belles Lettres, but a mere sober, dry, and formal piece of logic. Ornari res ipsa negat. Yet you may have enough left of your old taste for law reading, to cast an eye over some of the questions it discusses. At any rate, accept it as the offering of esteem and friendship.
You wish to know something of the Richmond and Wabash prophets. Of Nimrod Hews I never before heard. Christopher Macpherson I have known for twenty years. He is a man of color, brought up as a book-keeper by a merchant, his master, and afterwards enfranchised. He had understanding enough to post up his leger from his journal, but not enough to bear up against hypochrondriac affections, and the gloomy forebodings they inspire. He became crazy, foggy, his head always in the clouds, and rhapsodizing what neither himself nor any one else could understand. I think he told me he had visited you personally while you were in the administration, and wrote you letters, which you have probably forgotten in the mass of the correspondences of that crazy class, of whose complaints, and terrors, and mysticisms, the several Presidents have been the regular depositories. Macpherson was too honest to be molested by any body, and too inoffensive to be a subject for the mad-house; although, I believe, we are told in the old book, that ‘every man that is mad, and maketh himself a prophet, thou shouldst put him in prison and in the stocks.’
The Wabash prophet is a very different character, more rogue than fool, if to be a rogue is not the greatest of all follies. He arose to notice while I was in the administration, and became, of course, a proper subject of inquiry for me. The inquiry was made with diligence. His declared object was the reformation of his red brethren, and their return to their pristine manner of living. He pretended to be in constant communication with the Great Spirit; that he was instructed by him to make known to the Indians that they were created by him distinct from the whites, of different natures, for different purposes, and placed under different circumstances, adapted to their nature and destinies; that they must return from all the ways of the whites to the habits and opinions of their forefathers; they must not eat the flesh of hogs, of bullocks, of sheep, &c. the deer and buffalo having been created for their food; they must not make bread of wheat, but of Indian corn; they must not wear linen nor woollen, but dress like their fathers in the skins and furs of animals; they must not drink ardent spirits: and I do not remember whether he extended his inhibitions to the gun and gunpowder, in favor of the bow and arrow. I concluded from all this that he was a visionary, enveloped in the clouds of their antiquities, and vainly endeavoring to lead back his brethren to the fancied beatitudes of their golden age. I thought there was little danger of his making many proselytes from the habits and comforts they had learned from the whites, to the hardships and privations of savagism, and no great harm if he did. We let him go on, therefore, unmolested. But his followers increased till the English thought him worth corruption, and found him corruptible. I suppose his views were then changed; but his proceedings in consequence of them were after I left the administration, and are, therefore, unknown to me; nor have I ever been informed what were the particular acts on his part, which produced, an actual commencement of hostilities on ours. I have no doubt, however, that his subsequent proceedings are but a chapter apart, like that of Henry and Lord Liverpool, in the book of the Kings of England.
Of this mission of Henry, your son had got wind in the time of the embargo, and communicated it to me. But he had learned nothing of the particular agent, although, of his workings, the information he had obtained appears now to have been correct. He stated a particular which Henry has not distinctly brought forward, which was, that the eastern States were not to be required to make a formal act of separation from the Union, and to take a part in the war against it; a measure deemed much too strong for their people: but to declare themselves in a state of neutrality, in consideration of which they were to have peace and free commerce, the lure most likely to insure popular acquiescence. Having no indications of Henry as the intermediate in this negotiation of the Essex junto, suspicions fell on Pickering, and his nephew Williams in London. If he was wronged in this, the ground of the suspicion is to be found in his known practices and avowed opinions, as that of his accomplices in the sameness of sentiment and of language with Henry, and subsequently by the fluttering of the wounded pigeons.
This letter, with what it encloses, has given you enough, I presume, of law and the prophets. I will only add to it, therefore, the homage of my respects to Mrs. Adams, and to yourself the assurances of affectionate esteem and respect.
Th: Jefferson.
TO JAMES MAURY.
Monticello, April 25, 1812.
My Dear and Ancient Friend and Classmate,
Often has my heart smote me for delaying acknowledgments to you, receiving, as I do, such frequent proofs of your kind recollection in the transmission of papers to me. But instead of acting on the good old maxim of not putting off to to-morrow what we can do to-day, we are too apt to reverse it, and not to do today what we can put off to to-morrow. But this duty can be no longer put off. To-day we are at peace; to-morrow war. The curtain of separation is drawing between us, and probably will not be withdrawn till one, if not both of us, will be at rest with our fathers. Let me now, then, while I may, renew to you the declarations of my warm attachment, which in no period of life has ever been weakened, and seems to become stronger as the remaining objects of our youthful affections are fewer.
Our two countries are to be at war, but not you and I. And why should our two countries be at war, when by peace we can be so much more useful to one another? Surely the world will acquit our government of having sought it. Never before has there been an instance of a nation’s bearing so much as we have borne. Two items alone in our catalogue of wrongs will for ever acquit us of being the aggressors; the impressment of our seamen, and the excluding us from the ocean. The first foundations of the social compact would be broken up, were we definitively to refuse to its members the protection of their persons and property, while in their lawful pursuits. I think the war will not be short, because the object of England, long obvious, is to claim the ocean as her domain, and to exact transit duties from every vessel traversing it. This is the sum of her orders of council, which were only a step in this bold experiment, never meant to be retracted if it could be permanently maintained. And this object must continue her in war with all the world. To this I see no termination, until her exaggerated efforts, so much beyond her natural strength and resources, shall have exhausted her to bankruptcy. The approach of this crisis is, I think, visible in the departure of her precious metals, and depreciation of her paper medium. We, who have gone through that operation, know its symptoms, its course, and consequences. In England they will be more serious than elsewhere, because half the wealth of her people is now in that medium, the private revenue of her money-holders, or rather of her paper-holders, being, I believe, greater than that of her land-holders. Such a proportion of property, imaginary and baseless as it is, cannot be reduced to vapor, but with great explosion. She will rise out of its ruins, however, because her lands, her houses, her arts, will remain, and the greater part of her men. And these will give her again that place among nations which is proportioned to her natural means, and which we all wish her to hold. We believe that the just standing of all nations is the health and security of all. We consider the overwhelming power of England on the ocean, and of France on the land, as destructive of the prosperity and happiness of the world, and wish both to be reduced only to the necessity of observing moral duties. We believe no more in Bonaparte’s fighting merely for the liberty of the seas, than in Great Britain’s fighting for the liberties of mankind. The object of both is the same, to draw to themselves the power, the wealth, and the resources of other nations. We resist the enterprises of England first, because they first come vitally home to us. And our feelings repel the logic of bearing the lash of George the III. for fear of that of Bonaparte at some future day. When the wrongs of France shall reach us with equal effect, we shall resist them also. But one at a time is enough: and having offered a choice to the champions, England first takes up the gauntlet.
The English newspapers suppose me the personal enemy of their nation. I am not so. I am an enemy to its injuries, as I am to those of France. If I could permit myself to have national partialities, and if the conduct of England would have permitted them to be directed towards her, they would have been so. I thought that, in the administration of Mr. Addington, I discovered some dispositions towards justice, and even friendship and respect for us, and began to pave the way for cherishing these dispositions, and improving them into ties of mutual good will. But we had then a federal minister there, whose dispositions to believe himself, and to inspire others with a belief, in our sincerity, his subsequent conduct has brought into doubt; and poor Merry, the English minister here, had learned nothing of diplomacy but its suspicions, without head enough to distinguish when they were misplaced. Mr. Addington and Mr. Fox passed away too soon to avail the two countries of their dispositions. Had I been personally hostile to England, and biassed in favor of either the character or views of her great antagonist, the affair of the Chesapeake put war into my hand. I had only to open it, and let havoc loose. But if ever I was gratified with the possession of power, and of the confidence of those who had entrusted me with it, it was on that occasion, when I was enabled to use both for the prevention of war, towards which the torrent of passion here was directed almost irresistibly, and when not another person in the United States, less supported by authority and favor, could have resisted it. And now that a definitive adherence to her impressments and orders of council renders war no longer avoidable, my earnest prayer is, that our government may enter into no compact of common cause with the other belligerent, but keep us free to make a separate peace, whenever England will separately give us peace, and future security. But Lord Liverpool is our witness, that this can never be but by her removal from our neighborhood.
I have thus, for a moment, taken a range into the field of politics, to possess you with the view we take of things here. But in the scenes which are to ensue, I am to be but a spectator. I have withdrawn myself from all political intermeddlings, to indulge the evening of my life with what have been the passions of every portion of it, books, science, my farms, my family, and friends.
To these every hour of the day is now devoted. I retain a good activity of mind, not quite as much of body, but uninterrupted health. Still the hand of age is upon me. All my old friends are nearly gone. Of those in my neighborhood, Mr. Divers and Mr. Lindsay alone remain. If you could make it a partie quarrée, it would be a comfort indeed. We would beguile our lingering hours with talking over our youthful exploits, our hunts on Peter’s Mountain, with a long train of et cetera in addition, and feel, by recollection at least, a momentary flash of youth. Reviewing the course of a long and sufficiently successful life, I find in no portion of it happier moments than those were. I think the old hulk in which you are, is near her wreck, and that like a prudent rat, you should escape in time. However, here, there, and every where, in peace or in war, you will have my sincere affections, and prayers for your life, health, and happiness.
Th: Jefferson.
TO THE PRESIDENT.
Monticello, May 30, 1812.
Dear Sir,
Another communication is enclosed, and the letter of the applicant is the only information I have of his qualifications. I barely remember such a person as the secretary of Mr. Adams, and messenger to the Senate while I was of that body. It enlarges the sphere of choice by adding to it a strong federalist. The triangular war must be the idea of the Anglomen and malcontents; in other words, the federalists and quids. Yet it would reconcile neither. It would only change the topic of abuse with the former, and not cure the mental disease of the latter. It would prevent our eastern capitalists and seamen from employment in privateering, take away the only chance of conciliating them, and keep them at home, idle, to swell the discontents; it would completely disarm us of the most powerful weapon we can employ against Great Britain, by shutting every port to our prizes, and yet would not add a single vessel to their number; it would shut every market to our agricultural productions, and engender impatience and discontent with that class which, in fact, composes the nation; it would insulate us in general negotiations for peace, making all the parties our opposers, and very indifferent about peace with us, if they have it with the rest of the world; and would exhibit a solecism worthy of Don Quixotte only, that of a choice to fight two enemies at a time, rather than to take them by succession. And the only motive for all this is a sublimated impartiality, at which the world will laugh, and our own people will turn upon us in mass as soon as it is explained to them, as it will be by the very persons who are now laying that snare. These are the hasty views of one who rarely thinks on these subjects. Your own will be better, and I pray to them every success, and to yourself every felicity.
Th: Jefferson.
TO ELBRIDGE GERRY.
Monticello, June 11, 1812.
Dear Sir,
It has given me great pleasure to receive a letter from you. It seems as if, our ancient friends dying off, the whole mass of the affections of the heart survives undiminished to the few who remain. I think our acquaintance commenced in 1764, both then just of age. We happened to take lodgings in the same house in New York. Our next meeting was in the Congress of 1775, and at various times afterwards in the exercise of that and other public functions, until your mission to Europe. Since we have ceased to meet, we have still thought and acted together, ‘et idem velle, atque idem nolle, ea demum amicitia est.’ Of this harmony of principle, the papers you enclosed me are proof sufficient. I do not condole with you on your release from your government. The vote of your opponents is the most honorable mark by which the soundness of your conduct could be stamped. I claim the same honorable testimonial. There was but a single act of my whole administration of which that party approved. That was the proclamation on the attack of the Chesapeake. And when I found they approved of it, I confess I began strongly to apprehend I had done wrong, and to exclaim with the Psalmist, ‘Lord, what have I done, that the wicked should praise me!’
What, then, does this English faction with you mean? Their newspapers say rebellion, and that they will not remain united with us unless we will permit them to govern the majority. If this be their purpose, their anti-republican spirit, it ought to be met at once. But a government like ours should be slow in believing this, should put forth its whole might when necessary to suppress it, and promptly return to the paths of reconciliation. The extent of our country secures it, I hope, from the vindictive passions of the petty incorporations of Greece. I rather suspect that the principal office of the other seventeen States will be to moderate and restrain the local excitement of our friends with you, when they (with the aid of their brethren of the other States, if they need it) shall have brought the rebellious to their feet. They count on British aid. But what can that avail them by land? They would separate from their friends, who alone furnish employment for their navigation, to unite with their only rival for that employment. When interdicted the harbors of their quondam brethren, they will go, I suppose, to ask a share in the carrying-trade of their rivals, and a dispensation with their navigation act. They think they will be happier in an association under the rulers of Ireland, the East and West Indies, than in an independent government, where they are obliged to put up with their proportional share only in the direction of its affairs. But I trust that such perverseness will not be that of the honest and well meaning mass of the federalists of Massachusetts; and that when the questions of separation and rebellion shall be nakedly proposed to them, the Gores and the Pickerings will find their levees crowded with silk-stocking gentry, but no yeomanry; an army of officers without soldiers. I hope, then, all will still end well: the Anglomen will consent to make peace with their bread and butter, and you and I shall sink to rest, without having been actors or spectators in another civil war.
How many children have you? You beat me, I expect, in that count; but I you in that of our grand-children. We have not timed these things well together, or we might have begun a re-alliance between Massachusetts and the Old Dominion, faithful companions in the war of Independence, peculiarly tallied in interests, by each wanting exactly what the other has to spare; and estranged to each other, in latter times, only by the practices of a third nation, the common enemy of both. Let us live only to see this re-union, and I will say with old Simeon, ‘Lord, now lettest thou thy servant depart in peace, for mine eyes have seen thy salvation.’ In that peace may you long remain, my friend, and depart only in the fulness of years, all passed in health and prosperity. God bless you.
Th: Jefferson.
P.S. June 13. I did not condole with you on the reprobation of your opponents, because it proved your orthodoxy. Yesterday’s post brought me the resolution of the republicans of Congress, to propose you as Vice-President. On this I sincerely congratulate you. It is a stamp of double proof. It is a notification to the factionaries that their nay is the yea of truth, and its best test. We shall be almost within striking distance of each other. Who knows but you may fill up some short recess of Congress with a visit to Monticello, where a numerous family will hail you with a hearty country welcome. T.J.
TO JUDGE TYLER.
Monticello, June 17,1812.
Dear Sir,
On the other subject of your letter, the application of the common law to our present situation, I deride with you the ordinary doctrine, that we brought with us from England the common law rights. This narrow notion was a favorite in the first moment of rallying to our rights against Great Britain. But it was that of men who felt their rights before they had thought of their explanation. The truth is, that we brought with us the rights of men; of expatriated men. On our arrival here, the question would at once arise, by what law will we govern ourselves? The resolution seems to have been, by that system with which we are familiar, to be altered by ourselves occasionally, and adapted to our new situation. The proofs of this resolution are to be found in the form of the oaths of the judges, 1 Hening’s Stat. 169, 187; of the Governor, ib. 504; in the act for a provisional government, ib. 372; in the preamble to the laws of 1661-2; the uniform current of opinions and decisions; and in the general recognition of all our statutes framed on that basis. But the state of the English law at the date of our emigration, constituted the system adopted here. We may doubt, therefore, the propriety of quoting in our courts English authorities subsequent to that adoption; still more, the admission of authorities posterior to the Declaration of Independence, or rather to the accession of that King, whose reign, ab initio, was that very tissue of wrongs which rendered the Declaration at length necessary. The reason for it had inception at least as far back as the commencement of his reign. This relation to the beginning of his reign, would add the advantage of getting us rid of all Mansfield’s innovations, or civilizations of the common law. For however I admit the superiority of the civil, over the common law code, as a system of perfect justice, yet an incorporation of the two would be like Nebuchadnezzar’s image of metals and clay, a thing without cohesion of parts. The only natural improvement of the common law, is through its homogeneous ally, the chancery, in which new principles are to be examined, concocted, and digested. But when, by repeated decisions and modifications, they are rendered pure and certain, they should be transferred by statute to the courts of common law, and placed within the pale of juries. The exclusion from the courts of the malign influence of all authorities after the Georgium sidus became ascendant, would uncanonize Blackstone, whose book, although the most elegant and best digested of our law catalogue, has been perverted more than all others to the degeneracy of legal science. A student finds there a smattering of every thing, and his indolence easily persuades him, that if he understands that book, he is master of the whole body of the law. The distinction between these and those who have drawn their stores from the deep and rich mines of Coke’s Littleton, seems well understood even by the unlettered common people, who apply the appellation of Blackstone-lawyers to these ephemeral insects of the law.
Whether we should undertake to reduce the common law, our own, and so much of the English statutes as we have adopted, to a text, is a question of transcendant difficulty. It was discussed at the first meeting of the committee of the revised code, in 1776, and decided in the negative, by the opinions of Wythe, Mason, and myself, against Pendleton and Thomas Lee. Pendleton proposed to take Blackstone for that text, only purging him of what was inapplicable, or unsuitable to us. In that case, the meaning of every word of Blackstone would have become a source of litigation, until it had been settled by repeated legal decisions. And to come at that meaning, we should have had produced, on all occasions, that very pile of authorities from which it would be said he drew his conclusion, and which, of course, would explain it, and the terms in which it is couched. Thus we should have retained the same chaos of law-lore from which we wished to be emancipated, added to the evils of the uncertainty which a new text and new phrases would have generated. An example of this may be found in the old statutes, and commentaries on them, in Coke’s second institute; but more remarkably, in the institute of Justinian, and the vast masses, explanatory or supplementary of that, which fill the libraries of the civilians. We were deterred from the attempt by these considerations, added to which, the bustle of the times did not permit leisure for such an undertaking.
Your request of my opinion on this subject has given you the trouble of these observations. If your firmer mind in encountering difficulties, would have added your vote to the minority of the committee, you would have had on your side one of the greatest men of our age, and, like him, have detracted nothing from the sentiments of esteem and respect which I bore to him, and tender with sincerity the assurance of to yourself.
Th: Jefferson.
TO COLONEL WILLIAM DUANE.
Monticello, October 1, 1812.
Dear Sir,
Your favor of September the 20th has been duly received, and I cannot but be gratified by the assurance it expresses, that my aid in the councils of our government would increase the public confidence in them; because it admits an inference that they have approved of the course pursued, when I heretofore bore a part in those councils. I profess, too, so much of the Roman principle, as to deem it honorable for the general of yesterday to act as a corporal to-day, if his services can be useful to his country; holding that to be false pride, which postpones the public good to any private or personal considerations. But I am past service. The hand of age is upon me. The decay of bodily faculties apprizes me that those of the mind cannot be unimpaired, had I not still better proofs. Every year counts by increased debility, and departing faculties keep the score. The last year it was the sight, this it is the hearing, the next something else will be going, until all is gone. Of all this I was sensible before I left Washington, and probably my fellow-laborers saw it before I did. The decay of memory was obvious: it is now become distressing. But the mind, too, is weakened. When I was young, mathematics was the passion of my life. The same passion has returned upon me, but with unequal powers. Processes which I then read off with the facility of common discourse, now cost me labor, and time, and slow investigation. When I offered this, therefore, as one of the reasons deciding my retirement from office, it was offered in sincerity and a consciousness of its truth. And I think it a great blessing that I retain understanding enough to be sensible how much of it I have lost, and to avoid exposing myself as a spectacle for the pity of my friends; that I have surmounted the difficult point of knowing when to retire. As a compensation for faculties departed, nature gives me good health, and a perfect resignation to the laws of decay which she has prescribed to all the forms and combinations of matter.
The detestable treason of Hull has, indeed, excited a deep anxiety in all breasts. The depression was in the first moment gloomy and portentous. But it has been succeeded by a revived animation, and a determination to meet the occurrence with increased efforts; and I have so much confidence in the vigorous minds and bodies of our countrymen, as to be fearless as to the final issue. The treachery of Hull, like that of Arnold, cannot be matter of blame on our government. His character, as an officer of skill and bravery, was established on the trials of the last war, and no previous act of his life had led to doubt his fidelity. Whether the Head of the war department is equal to his charge, I am not qualified to decide. I knew him only as a pleasant, gentlemanly man in society; and the indecision of his character rather added to the amenity of his conversation. But when translated from the colloquial circle to the great stage of national concerns, and the direction of the extensive operations of war, whether he has been able to seize at one glance the long line of defenceless border presented by our enemy, the masses of strength which we hold on different points of it, the facility this gave us of attacking him, on the same day, on all his points, from the extremity of the lakes to the neighborhood of Quebec, and the perfect indifference with which this last place, impregnable as it is, might be left in the hands of the enemy to fall of itself; whether, I say, he could see and prepare vigorously for all this, or merely wrapped himself in the cloak of cold defence, I am uninformed. I clearly think with you on the competence of Monroe to embrace great views of action. The decision of his character, his enterprise, firmness, industry, and unceasing vigilance, would, I believe, secure, as I am sure they would merit, the public confidence, and give us all the success which our means can accomplish. If our operations have suffered or languished from any want of energy in the present head which directs them, I have so much confidence in the wisdom and conscientious integrity of Mr. Madison, as to be satisfied, that, however torturing to his feelings, he will fulfil his duty to the public and to his own reputation, by making the necessary change. Perhaps he may be preparing it while we are talking about it: for of all these things I am uninformed. I fear that Hull’s surrender has been more than the mere loss of a year to us. Besides bringing on us the whole mass of savage nations, whom fear and not affection had kept in quiet, there is danger that in giving time to an enemy who can send reinforcements of regulars faster than we can raise them, they may strengthen Canada and Halifax beyond the assailment of our lax and divided powers. Perhaps, however, the patriotic efforts from Kentucky and Ohio, by recalling the British force to its upper posts, may yet give time to Dearborn to strike a blow below. Effectual possession of the river from Montreal to the Chaudiere, which is practicable, would give us the upper country at our leisure, and close for ever the scenes of the tomahawk and scalping-knife.
But these things are for others to plan and achieve. The only succor from the old, must lie in their prayers. These I offer up with sincere devotion; and in my concern for the great public, I do not overlook my friends, but supplicate for them, as I do for yourself, a long course of freedom, happiness, and prosperity.
Th: Jefferson.
TO MR. MELISH.
Monticello, January 13, 1813.
Dear Sir,
I received duly your favor of December the 15th, and with it the copies of your map and travels, for which be pleased to accept my thanks. The book I have read with extreme satisfaction and information. As to the western States, particularly, it has greatly edified me; for of the actual condition of that interesting portion of our country, I had not an adequate idea. I feel myself now as familiar with it as with the condition of the maritime States. I had no conception that manufactures had made such progress there, and particularly of the number of carding and spinning machines dispersed through the whole country. We are but beginning here to have them in our private families. Small spinning-jennies of from half a dozen to twenty spindles, will soon, however, make their way into the humblest cottages, as well as the richest houses; and nothing is more certain, than that the coarse and middling clothing for our families, will for ever hereafter continue to be made within ourselves. I have hitherto myself depended entirely on foreign manufactures: but I have now thirty-five spindles a going, a hand carding-machine, and looms with the flying shuttle, for the supply of my own farms, which will never be relinquished in my time. The continuance of the war will fix the habit generally, and out of the evils of impressment and of the orders of council, a great blessing for us will grow. I have not formerly been an advocate for great manufactories. I doubted whether our labor, employed in agriculture, and aided by the spontaneous energies of the earth, would not procure us more than we could make ourselves of other necessaries. But other considerations entering into the question, have settled my doubts.
The candor with which you have viewed the manners and condition of our citizens, is so unlike the narrow prejudices of the French and English travellers preceding you, who, considering each the manners and habits of their own people as the only orthodox, have viewed every thing differing from that test as boorish and barbarous, that your work will be read here extensively, and operate great good.
Amidst this mass of approbation which is given to every other part of the work, there is a single sentiment which I cannot help wishing to bring to what I think the correct one; and, on a point so interesting, I value your opinion too highly not to ambition its concurrence with my own. Stating in volume first, page sixty-third, the principle of difference between the two great political parties here, you conclude it to be, ‘whether the controlling power shall be vested in this or that set of men.’ That each party endeavors to get into the administration of the government, and to exclude the other from power, is true, and may be stated as a motive of action: but this is only secondary; the primary motive being a real and radical difference of political principle. I sincerely wish our differences were but personally who should govern and that the principles of our constitution were those of both parties. Unfortunately, it is otherwise; and the question of preference between monarchy and republicanism, which has so long divided mankind elsewhere, threatens a permanent division here.
Among that section of our citizens called federalists, there are three shades of opinion. Distinguishing between the leaders and people who compose it, the leaders consider the English constitution as a model of perfection, some, with a correction of its vices, others, with all its corruptions and abuses. This last was Alexander Hamilton’s opinion, which others, as well as myself, have often heard him declare, and that a correction of what are called its vices, would render the English an impracticable government.. This government they wished to have established here, and only accepted and held fast, at first, to the present constitution, as a stepping-stone to the final establishment of their favorite model. This party has therefore always clung to England, as their prototype, and great auxiliary in promoting and effecting this change. A weighty minority, however, of these leaders, considering the voluntary conversion of our government into a monarchy as too distant, if not desperate, wish to break off from our Union its eastern fragment, as being, in truth, the hot-bed of American monarchism, with a view to a commencement of their favorite government, from whence the other States may gangrene by degrees, and the whole be thus brought finally to the desired point. For Massachusetts, the prime mover in this enterprise, is the last State in the Union to mean a final separation, as being of all the most dependant on the others. Not raising bread for the sustenance her own inhabitants, not having a stick of timber for the construction of vessels, her principal occupation, nor an article to export in them, where would she be, excluded from the ports of the other States, and thrown into dependance on England, her direct and natural, but now insidious, rival? At the head of this minority is what is called the Essex Junto of Massachusetts. But the majority of these leaders do not aim at separation. In this they adhere to the known principle of General Hamilton, never, under any views, to break the Union. Anglomany, monarchy, and separation, then, are the principles of the Essex federalists; Anglomany and monarchy, those of the Hamiltonians, and Anglomany alone, that of the portion among the people who call themselves federalists. These last are as good republicans as the brethren whom they oppose, and differ from them only in the devotion to England and hatred of France, which they have imbibed from their leaders. The moment that these leaders should avowedly propose a separation of the Union, or the establishment of regal government, their popular adherents would quit them to a man, and join the republican standard; and the partisans of this change, even in Massachusetts, would thus find themselves an army of officers without a soldier.
The party called republican is steadily for the support of the present constitution. They obtained, at its commencement, all the amendments to it they desired. These reconciled them to it perfectly, and if they have any ulterior view, it is only, perhaps, to popularize it further, by shortening the Senatorial term, and devising a process for the responsibility of judges, more practicable than that of impeachment. They esteem the people of England and France equally, and equally detest the governing powers of both.
This I verily believe, after an intimacy of forty years with the public councils and characters, is a true statement of the grounds on which they are at present divided, and that it is not merely an ambition for power. An honest man can feel no pleasure in the exercise of power over his fellow-citizens. And considering as the only offices of power those conferred by the people directly, that is to say, the executive and legislative functions of the General and State governments, the common refusal of these, and multiplied resignations, are proofs sufficient that power is not alluring to pure minds, and is not, with them, the primary principle of contest. This is my belief of it; it is that on which I have acted; and had it been a mere contest who should be permitted to administer the government according to its genuine republican principles, there has never been a moment of my life, in which I should not have relinquished for it the enjoyments of my family, my farm, my friends, and books.
You expected to discover the difference of our party principles in General Washington’s Valedictory, and my Inaugural Address. Not at all. General Washington did not harbor one principle of federalism. He was neither an Angloman, a monarchist, nor a separatist. He sincerely wished the people to have as much self-government as they were competent to exercise themselves. The only point in which he and I ever differed in opinion, was, that I had more confidence than he had in the natural integrity and discretion of the people, and in the safety and extent to which they might trust themselves with a control over their government. He has asseverated to me a thousand times his determination that the existing government should have a fair trial, and that in support of it he would spend the last drop of his blood. He did this the more repeatedly, because he knew General Hamilton’s political bias, and my apprehensions from it. It is a mere calumny, therefore, in the monarchists, to associate General Washington with their principles. But that may have happened in this case which has been often seen in ordinary cases, that, by often repeating an untruth, men come to believe it themselves. It is a mere artifice in this party, to bolster themselves up on the revered name of that first of our worthies. If I have dwelt longer on this subject than was necessary, it proves the estimation in which I hold your ultimate opinions, and my desire of placing the subject truly before them. In so doing, I am certain I risk no use of the communication which may draw me into contention before the public. Tranquillity is the summum bonum of a Septagénaire.
To return to the merits of your work; I consider it as so lively a picture of the real state of our country, that if I can possibly obtain opportunities of conveyance, I propose to send a copy to a friend in France, and another to one in Italy, who, I know, will translate and circulate it as an antidote to the misrepresentations of former travellers. But whatever effect my profession of political faith may have on your general opinion, a part of my object will be obtained, if it satisfies you as to the principles of my own action, and of the high respect and consideration with which I tender you my salutations.
Th: Jefferson.
TO MADAME LA BARONNE DE STAEL-HOLSTEIN.
United States of America,
May 24, 1818.
I received with great pleasure, my dear Madam and friend, your letter of November the 10th, from Stockholm, and am sincerely gratified by the occasion it gives me of expressing to you the sentiments of high respect and esteem which I entertain for you. It recalls to my remembrance a happy portion of my life, passed in your native city; then the seat of the most amiable and polished society of the world, and of which yourself and your venerable father were such distinguished members. But of what scenes has it since been the theatre, and with what havoc has it overspread the earth! Robespierre met the fate, and his memory the execration, he so justly merited. The rich were his victims, and perished by thousands. It is by millions that Bonaparte destroys the poor, and he is eulogized and deified by the sycophants—even of science. These merit more than the mere oblivion to which they will be consigned; and the day will come when a just posterity will give to their hero the only pre-eminence he has earned, that of having been the greatest of the destroyers of the human race. What year of his military life has not consigned a million of human beings to death, to poverty, and wretchedness? What field in Europe may not raise a monument of the murders, the burnings, the desolations, the famines, and miseries, it has witnessed from him! And all this to acquire a reputation, which Cartouche attained with less injury to mankind, of being fearless of God or man.
To complete and universalize the desolation of the globe, it has been the will of Providence to raise up, at the same time, a tyrant as unprincipled and as overwhelming, for the ocean. Not in the poor maniac George, but in his government and nation. Bonaparte will die, and his tyrannies with him. But a nation never dies. The English government and its piratical principles and practices, have no fixed term of duration. Europe feels, and is writhing under the scorpion whips of Bonaparte. We are assailed by those of England. The one continent thus placed under the gripe of England, and the other of Bonaparte, each has to grapple with the enemy immediately pressing on itself. We must extinguish the fire kindled in our own house, and leave to our friends beyond the water that which is consuming theirs. It was not till England had taken one thousand of our ships, and impressed into her service more than six thousand of our citizens; till she had declared, by the proclamation of her Prince Regent, that she would not repeal her aggressive orders as to us, until Bonaparte should have repealed his as to all nations; till her minister, in formal conference with ours, declared, that no proposition for protecting our seamen from being impressed, under color of taking their own, was practicable or admissible; that, the door to justice and to all amicable arrangement being closed, and negotiation become both desperate and dishonorable, we concluded that the war she had been for years waging against us, might as well become a war on both sides. She takes fewer vessels from us since the declaration of war than before, because they venture more cautiously; and we now make full reprisals where before we made none. England is, in principle, the enemy of all maritime nations, as Bonaparte is of the continental; and I place in the same line of insult to the human understanding, the pretension of conquering the ocean, to establish continental rights, as that of conquering the continent, to restore maritime rights. No, my dear Madam; the object of England is the permanent dominion of the ocean, and the monopoly of the trade of the world. To secure this, she must keep a larger fleet than her own resources will maintain. The resources of other nations, then, must be impressed to supply the deficiency of her own. This is sufficiently developed and evidenced by her successive strides towards the usurpation of the sea. Mark them, from her first war after William Pitt, the little, came into her administration. She first forbade to neutrals all trade with her enemies in time of war, which they had not in time of peace. This deprived them of their trade from port to port of the same nation. Then she forbade them to trade from the port of one nation to that of any other at war with her, although a right fully exercised in time of peace. Next, instead of taking vessels only entering a blockaded port, she took them over the whole ocean, if destined to that port, although ignorant of the blockade, and without intention to violate it. Then she took them returning from that port, as if infected by previous infraction of blockade. Then came her paper blockades, by which she might shut up the whole world without sending a ship to sea, except to take all those sailing on it, as they must, of course, be bound to some port. And these were followed by her orders of council, forbidding every nation to go to the port of any other, without coming first to some port of Great Britain, there paying a tribute to her, regulated by the cargo, and taking from her a license to proceed to the port of destination; which operation the vessel was to repeat with the return cargo on its way home. According to these orders, we could not send a vessel from St. Mary’s to St. Augustine, distant six hour’s sail, on our own coast, without crossing the Atlantic four times, twice with the outward cargo, and twice with the inward. She found this too daring and outrageous for a single step, retracted as to certain articles of commerce, but left it in force as to others which constitute important branches of our exports. And finally, that her views may no longer rest on inference, in a recent debate, her minister declared in open parliament, that the object of the present war is a monopoly of commerce.
In some of these atrocities, France kept pace with her fully in speculative wrong, which her impotence only shortened in practical execution. This was called retaliation by both; each charging the other with the initiation of the outrage. As if two combatants might retaliate on an innocent bystander, the blows they received from each other. To make war on both would have been ridiculous. In order, therefore, to single out an enemy, we offered to both, that if either would revoke its hostile decrees, and the other should refuse, we would interdict all intercourse whatever with that other; which would be war of course, as being an avowed departure from neutrality. France accepted the offer, and revoked her decrees as to us. England not only refused, but declared by a solemn proclamation of her Prince Regent, that she would not revoke her orders even as to us, until those of France should be annulled as to the whole world. We thereon declared war, and with abundant additional cause.
In the mean time, an examination before parliament of the ruinous effects of these orders on her own manufacturers, exposing them to the nation and to the world, their Prince issued a palinodial proclamation, suspending the orders on certain conditions, but claiming to renew them at pleasure, as a matter of right. Even this might have prevented the war, if done and known here before its declaration. But the sword being once drawn, the expense of arming incurred, and hostilities in full course, it would have been unwise to discontinue them, until effectual provision should be agreed to by England, for protecting our citizens on the high seas from impressment by her naval commanders, through, error, voluntary or involuntary; the fact being notorious, that these officers, entering our ships at sea under pretext of searching for their seamen, (which they have no right to do by the law or usage of nations, which they neither do, nor ever did, as to any other nation but ours, and which no nation ever before pretended to do in any case), entering our ships, I say, under pretext of searching for and taking out their seamen, they took ours, native as well as naturalized, knowing them to be ours, merely because they wanted them; insomuch, that no American could safely cross the ocean, or venture to pass by sea from one to another of our own ports. It is not long since they impressed at sea two nephews of General Washington, returning from Europe, and put them, as common seamen, under the ordinary discipline of their ships of war. There are certainly other wrongs to be settled between England and us; but of a minor character, and such as a proper spirit of conciliation on both sides would not permit to continue them at war. The sword, however, can never again be sheathed, until the personal safety of an American on the ocean, among the most important and most vital of the rights we possess, is completely provided for.
As soon as we heard of her partial repeal of her orders of council, we offered instantly to suspend hostilities by an armistice, if she would suspend her impressments, and meet us in arrangements for securing our citizens against them. She refused to do it, because impracticable by any arrangement, as she pretends; but, in truth, because a body of sixty to eighty thousand of the finest seamen in the world, which we possess, is too great a resource for manning her exaggerated navy, to be relinquished, as long as she can keep it open. Peace is in her hand, whenever she will renounce the practice of aggression on the persons of our citizens. If she thinks it worth eternal war, eternal war we must have. She alleges that the sameness of language, of manners, of appearance, renders it impossible to distinguish us from her subjects. But because we speak English, and look like them, are we to be punished? Are free and independent men to be submitted to their bondage?
England has misrepresented to all Europe this ground of the war. She has called it a new pretension, set up since the repeal of her orders of council. She knows there has never been a moment of suspension of our reclamations against it, from General Washington’s time inclusive, to the present day: and that it is distinctly stated in our declaration of war, as one of its principal causes. She has pretended we have entered into the war, to establish the principle of ‘free bottoms, free goods,’ or to protect her seamen against her own right over them. We contend for neither of these. She pretends we are partial to France; that we have observed a fraudulent and unfaithful neutrality between her and her enemy. She knows this to be false, and that if there has been any inequality in our proceedings towards the belligerents, it has been in her favor. Her ministers are in possession of full proofs of this. Our accepting at once, and sincerely, the mediation of the virtuous Alexander, their greatest friend, and the most aggravated enemy of Bonaparte, sufficiently proves whether we have partialities on the side of her enemy. I sincerely pray that this mediation may produce a just peace. It will prove that the immortal character, which has first stopped by war the career of the destroyer of mankind, is the friend of peace, of justice, of human happiness, and the patron of unoffending and injured nations. He is too honest and impartial to countenance propositions of peace derogatory to the freedom of the seas.
Shall I apologize to you, my dear Madam, for this long political letter? But yours justifies the subject, and my feelings must plead for the unreserved expression of them; and they have been the less reserved, as being from a private citizen, retired from all connection with the government of his country, and whose ideas, expressed without communication with any one, are neither known, nor imputable to them.
The dangers of the sea are now so great, and the possibilities of interception by sea and land such, that I shall subscribe no name to this letter. You will know from whom it comes, by its reference to the date of time and place of yours, as well as by its subject in answer to that. This omission must not lessen in your view the assurances of my great esteem, of my sincere sympathies for the share which you bear in the afflictions of your country, and the deprivations to which a lawless will has subjected you. In return, you enjoy the dignified satisfaction of having met them, rather than be yoked, with the abject, to his car; and that, in withdrawing from oppression, you have followed the virtuous example of a father, whose name will ever be dear to your country and to mankind. With my prayers that you may be restored to it, that you may see it re-established in that temperate portion of liberty which does not infer either anarchy or licentiousness, in that high degree of prosperity which would be the consequence of such a government, in that, in short, which the constitution of 1789 would have insured it, if wisdom could have stayed at that point the fervid but imprudent zeal of men, who did not know the character of their own countrymen, and that you may long live in health and happiness under it, and leave to the world a well educated and virtuous representative and descendant of your honored father, is the ardent prayer of the sincere and respectful friend who writes this letter.
TO JOHN ADAMS.
Monticello, May 27, 1813.
Another of our friends of seventy-six is gone, my Dear Sir, another of the co-signers of the Independence of our country. And a better man than Rush could not have left us, more benevolent, more learned, of finer genius, or more honest. We too must go; and that ere long. I believe we are under half a dozen at present; I mean the signers of the Declaration. Yourself, Gerry, Carroll, and myself, are all I know to be living. I am the only one south of the Potomac. Is Robert Treat Paine, or Floyd living? It is long since I heard of them, and yet I do not recollect to have heard of their deaths.
Moreton’s deduction of the origin of our Indians from the fugitive Trojans, stated in your letter of January the 26th, and his manner of accounting for the sprinkling of their Latin with Greeks is really amusing. Adair makes them talk Hebrew. Reinold Foster derives them from the soldiers sent by Kouli Khan to conquer Japan. Brerewood, from the Tartars, as well as our bears, wolves, foxes, &c. which, he says, ‘must of necessity fetch their beginning from Noah’s ark, which rested after the deluge, in Asia, seeing they could not proceed by the course of nature, as the imperfect sort of living creatures do, from putrefaction.’ Bernard Romans is of opinion that God created an original man and woman in this part of the globe. Doctor Barton thinks they are not specifically different from the Persians; but, taking afterwards a broader range, he thinks, ‘that in all the vast countries of America, there is but one language, nay, that it may be proven, or rendered highly probable, that all the languages of the earth bear some affinity together.’ This reduces it to a question of definition, in which every one is free to use his own: to wit, What constitutes identity, or difference in two things, in the common acceptation of sameness? All languages may be called the same, as being all made up of the same primitive sounds, expressed by the letters of the different alphabets. But, in this sense, all things on earth are the same, as consisting of matter. This gives up the useful distribution into genera and species, which we form, arbitrarily indeed, for the relief of our imperfect memories. To aid the question, from whence our Indian tribes descended, some have gone into their religion, their morals, their manners, customs, habits, and physical forms. By such helps it may be learnedly proved, that our trees and plants of every kind are descended from those of Europe; because, like them, they have no locomotion, they draw nourishment from the earth, they clothe themselves with leaves in spring, of which they divest themselves in autumn for the sleep of winter, he. Our animals too must be descended from those of Europe, because our wolves eat lambs, our deer are gregarious, our ants hoard, &c. But when, for convenience, we distribute languages, according to common understanding, into classes originally different, as we choose to consider them, as the Hebrew, the Greek, the Celtic, the Gothic; and these again into genera, or families, as the Icelandic, German, Swedish, Danish, English; and these last into species, or dialects, as English, Scotch, Irish, we then ascribe other meanings to the terms, ‘same’ and ‘different.’ In some one of these senses, Barton, and Adair, and Foster, and Brerewood, and Moreton, may be right, every one according to his own definition of what constitutes ‘identity.’ Romans, indeed, takes a higher stand, and supposes a separate creation. On the same unscriptural ground, he had but to mount one step higher, to suppose no creation at all, but that all things have existed without beginning in time, as they now exist, and may for ever exist, producing and reproducing in a circle, without end. This would very summarily dispose of Mr. Moreton’s learning, and show that the question of Indian origin, like many others, pushed to a certain height, must receive the same answer, ‘Ignoro.’ You ask if the usage of hunting in circles has ever been known among any of our tribes of Indians? It has been practised by them all; and is to this day, by those still remote from the settlements of the whites. But their numbers not enabling them, like Genghis Khan’s seven hundred thousand, to form themselves into circles of one hundred miles diameter, they make their circle by firing the leaves fallen on the ground, which gradually forcing the animals to a centre, they there slaughter them with arrows, darts, and other missiles. This is called fire-hunting, and has been practised in this State within my time, by the white inhabitants. This is the most probable cause of the origin and extension of the vast prairies in the western country, where the grass having been of extraordinary luxuriance, has made a conflagration sufficient to kill even the old as well as the young timber.
I sincerely congratulate you on the successes of our little navy; which must be more gratifying to you than to most men, as having been the early and constant advocate of wooden walls. If I have differed with you on this ground, it was not on the principle, but the time; supposing that we cannot build or maintain a navy, which will not immediately fall into the same gulph which has swallowed not only the minor navies, but even those of the great second-rate powers of the sea. Whenever these can be resuscitated, and brought so near to a balance with England that we can turn the scale, then is my epoch for aiming at a navy. In the mean time, one competent to keep the Barbary States in order is necessary; these being the only smaller powers disposed to quarrel with us. But I respect too much the weighty opinions of others to be unyielding on this point, and acquiesce with the prayer, ‘quod felix faustumque sit’; adding ever a sincere one for your health and happiness.
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN ADAMS.
Monticello, June 15, 1813.
Dear Sir,
I wrote you a letter on the 27th of May, which probably would reach you about the 3rd instant, and on the 9th I received yours of the 29th of May. Of Lindsay’s Memoirs I had never before heard, and scarcely indeed of himself. It could not, therefore, but be unexpected, that two letters of mine should have any thing to do with his life. The name of his editor was new to me, and certainly presents itself for the first time under unfavorable circumstances. Religion, I suppose, is the scope of his book; and that a writer on that subject should usher himself to the world in the very act of the grossest abuse of confidence, by publishing private letters which passed between two friends, with no views to their ever being made public, is an instance of inconsistency as well as of infidelity, of which I would rather be the victim than the author.
By your kind quotation of the dates of my two letters, I have been enabled to turn to them. They had completely vanished from my memory. The last is on the subject of religion, and by its publication will gratify the priesthood with new occasion of repeating their comminations against me. They wish it to be believed, that he can have no religion who advocates its freedom. This was not the doctrine of Priestley; and I honored him for the example of liberality he set to his order. The first letter is political. It recalls to our recollection the gloomy transactions of the times, the doctrines they witnessed, and the sensibilities they excited. It was a confidential communication of reflections on these from one friend to another, deposited in his bosom, and never meant to trouble the public mind. Whether the character of the times is justly portrayed or not, posterity will decide. But on one feature of them, they can never decide, the sensations excited in free yet firm minds by the terrorism of the day. None can conceive who did not witness them, and they were felt by one party only. This letter exhibits their side of the medal. The federalists, no doubt, have presented the other, in their private correspondences, as well as open action. If these correspondences should ever be laid open to the public eye, they will probably be found not models of comity towards their adversaries. The readers of my letter should be cautioned not to confine its view to this country alone. England and its alarmists were equally under consideration. Still less must they consider it as looking personally towards you. You happen, indeed, to be quoted, because you happened to express more pithily than had been done by themselves, one of the mottos of the party. This was in your answer to the address of the young men of Philadelphia. [See Selection of Patriotic Addresses, page 198.] One of the questions, you know, on which our parties took different sides, was on the improvability of the human mind, in science, in ethics, in government, &c. Those who advocated reformation of institutions, pari passu with the progress of science, maintained that no definite limits could be assigned to that progress. The enemies of reform, on the other hand, denied improvement, and advocated steady adherence to the principles, practices, and institutions of our fathers, which they represented as the consummation of wisdom, and acme of excellence, beyond which the human mind could never advance. Although in the passage of your answer alluded to, you expressly disclaim the wish to influence the freedom of inquiry, you predict that that will produce nothing more worthy of transmission to posterity than the principles, institutions, and systems of education received from their ancestors. I do not consider this as your deliberate opinion. You possess yourself too much science, not to see how much is still ahead of you, unexplained and unexplored. Your own consciousness must place you as far before our ancestors, as in the rear of our posterity. I consider it as an expression lent to the prejudices of your friends; and although I happened to cite it from you, the whole letter shows I had them only in view. In truth, my dear Sir, we were far from considering you as the author of all the measures we blamed. They were placed under the protection of your name, but we were satisfied they wanted much of your approbation. We ascribed them to their real authors, the Pickerings, the Wolcotts, the Tracys, the Sedgwicks, et id genus omne, with whom we supposed you in a state of duresse. I well remember a conversation with you in the morning of the day on which you nominated to the Senate a substitute for Pickering, in which you expressed a just impatience under ‘the legacy of Secretaries which General Washington had left you,’ and whom you seemed, therefore, to consider as under public protection. Many other incidents showed how differently you would have acted with less impassioned advisers; and subsequent events have proved that your minds were not together. You would do me great injustice, therefore, by taking to yourself what was intended for men who were then your secret, as they are now your open enemies. Should you write on the subject, as you propose, I am sure we shall see you place yourself farther from them than from us.
As to myself, I shall take no part in any discussions. I leave others to judge of what I have done, and to give me exactly that place which they shall think I have occupied. Marshall has written libels on one side; others, I suppose, will be written on the other side; and the world will sift both, and separate the truth as well as they can. I should see with reluctance the passions of that day rekindled in this, while so many of the actors are living, and all are too near the scene not to participate in sympathies with them. About facts you and I cannot differ; because truth is our mutual guide. And if any opinions you may express should be different from mine, I shall receive them with the liberality and indulgence which I ask for my own, and still cherish with warmth the sentiments of affectionate respect of which I can with so much truth tender you the assurance.
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN W. EPPES.
Monticello, June 24, 1813.
Dear Sir,
This letter will be on politics only. For although I do not often permit myself to think on that subject, it sometimes obtrudes itself, and suggests ideas which I am tempted to pursue. Some of these, relating to the business of finance, I will hazard to you, as being at the head of that committee, but intended for yourself individually, or such as you trust, but certainly not for a mixed committee.
It is a wise rule, and should be fundamental in a government disposed to cherish its credit, and at the same time to restrain the use of it within the limits of its faculties, ‘never to borrow a dollar without laying a tax in the same instant for paying the interest annually, and the principal within a given term; and to consider that tax as pledged to the creditors on the public faith.’ On such a pledge as this, sacredly observed, a government may always command, on a reasonable interest, all the lendable money of their citizens, while the necessity of an equivalent tax is a salutary warning to them and their constituents against oppressions, bankruptcy, and its inevitable consequence, revolution. But the term of redemption must be moderate, and, at any rate, within the limits of their rightful powers. But what limits, it will be asked, does this prescribe to their powers? What is to hinder them from creating a perpetual debt? The laws of nature, I answer. The earth belongs to the living, not to the dead. The will and the power of man expire with his life, by nature’s law. Some societies give it an artificial continuance, for the encouragement of industry; some refuse it, as our aboriginal neighbors, whom we call barbarians. The generations of men may be considered as bodies or corporations. Each generation has the usufruct of the earth during the period of its continuance. When it ceases to exist, the usufruct passes on to the succeeding generation, free and unincumbered, and so on, successively, from one generation to another for ever. We may consider each generation as a distinct nation, with a right, by the will of its majority, to bind themselves, but none to bind the succeeding generation, more than the inhabitants of another country. Or the case may be likened to the ordinary one of a tenant for life, who may hypothecate the land for his debts, during the continuance of his usufruct; but at his death, the reversioner (who is also for life only) receives it exonerated from all burthen. The period of a generation, or the term of its life, is determined by the laws of mortality, which, varying a little only in different climates, offer a general average, to be found by observation. I turn, for instance, to Buffon’s tables, of twenty-three thousand nine hundred and ninety-four deaths, and the ages at which they happened, and I find that of the numbers of all ages living at one moment, half will be dead in twenty-four years and eight months. Bat (leaving out minors, who have not the power of self-government) of the adults (of twenty-one years of age) living at one moment, a majority of whom act for the society, one half will be dead in eighteen years and eight months. At nineteen years then from the date of a contract, the majority of the contractors are dead, and their contract with them. Let this general theory be applied to a particular case. Suppose the annual births of the State of New York to be twenty-three thousand nine hundred and ninety-four: the whole number of its inhabitants, according to Buffon, will be six hundred and seventeen thousand seven hundred and three, of all ages. Of these there would constantly be two hundred and sixty-nine thousand two hundred and eighty-six minors, and three hundred and forty-eight thousand four hundred and seventeen adults, of which last, one hundred and seventy-four thousand two hundred and nine will be a majority. Suppose that majority, on the first day of the year 1794, had borrowed a sum of money equal to the fee simple value of the State, and to have consumed it in eating, drinking, and making merry in their day; or, if you please, in quarrelling and fighting with their unoffending neighbors. Within eighteen years and eight months, one half of the adult citizens were dead. Till then, being the majority, they might rightfully levy the interest of their debt annually on themselves and their fellow-revellers, or fellow-champions. But at that period, say at this moment, a new majority have come into place, in their own right, and not under the rights, the conditions, or laws of their predecessors. Are they bound to acknowledge the debt, to consider the preceding generation as having had a right to eat up the whole soil of their country in the course of a life, to alienate it from them (for it would be an alienation to the creditors), and would they think themselves either legally or morally bound to give up their country, and emigrate to another for subsistence? Every one will say no: that the soil is the gift of God to the living, as much as it had been to the deceased generation; and that the laws of nature impose no obligation on them to pay this debt. And although, like some other natural rights, this has not yet entered into any declaration of rights, it is no less a law, and ought to be acted on by honest governments. It is, at the same time, a salutary curb on the spirit of war and indebtment, which, since the modern theory of the perpetuation of debt, has drenched the earth with blood, and crushed its inhabitants under burthens ever accumulating. Had this principle been declared in the British bill of rights, England would have been placed under the happy disability of waging eternal war, and of contracting her thousand millions of public debt. In seeking, then, for an ultimate term for the redemption of our debts, let us rally to this principle, and provide for their payment within the term of nineteen years, at the farthest. Our government has not, as yet, begun to act on the rule, of loans and taxation going hand in hand. Had any loan taken place in my time, I should have strongly urged a redeeming tax. For the loan which has been made since the last session of Congress, we should now set the example of appropriating some particular tax, sufficient to pay the interest annually, and the principal within a fixed term, less than nineteen years. And I hope yourself and your committee will render the immortal service of introducing this practice. Not that it is expected that Congress should formally declare such a principle. They wisely enough avoid deciding on abstract questions. But they may be induced to keep themselves within its limits.
I am sorry to see our loans begin at so exorbitant an interest. And yet, even at that, you will soon be at the bottom of the loan-bag. We are an agricultural nation. Such an one employs its sparings in the purchase or improvement of land or stocks. The lendable money among them is chiefly that of orphans and wards in the hands of executors and guardians, and that which the farmer lays by till he has enough for the purchase in view. In such a nation there is one and one only resource for loans, sufficient to carry them through the expense of a war; and that will always be sufficient, and in the power of an honest government, punctual in the preservation of its faith. The fund I mean, is the mass of circulating coin. Every one knows, that, although not literally, it is nearly true, that every paper dollar emitted banishes a silver one from the circulation. A nation, therefore, making its purchases and payments with bills fitted for circulation, thrusts an equal sum of coin out of circulation. This is equivalent to borrowing that sum, and yet the vendor, receiving payment in a medium as effectual as coin for his purchases or payments, has no claim to interest. And so the nation may continue to issue its bills as far as its wants require, and the limits of the circulation will admit. Those limits are understood to extend with us, at present, to two hundred millions of dollars, a greater sum than would be necessary for any war. But this, the only resource which the government could command with certainty, the States have unfortunately fooled away, nay corruptly alienated to swindlers and shavers, under the cover of private banks. Say, too, as an additional evil, that the disposable funds of individuals, to this great amount, have thus been withdrawn from improvement and useful enterprise, and employed in the useless, usurious, and demoralizing practices of bank directors and their accomplices. In the war of 1755, our State availed itself of this fund by issuing a paper money, bottomed on a specific tax for its redemption, and, to insure its credit, bearing an interest of five per cent. Within a very short time, not a bill of this emission was to be found in circulation. It was locked up in the chests of executors, guardians, widows, farmers, &tc. We then issued bills, bottomed on a redeeming tax, but bearing no interest. These were readily received, and never depreciated a single farthing. In the revolutionary war, the old Congress and the States issued bills without interest, and without tax. They occupied the channels of circulation very freely, till those channels were overflowed by an excess beyond all the calls of circulation. But although we have so improvidently suffered the field of circulating medium to be filched from us by private individuals, yet I think we may recover it in part, and even in the whole, if the States will co-operate with us. If treasury bills are emitted on a tax appropriated for their redemption in fifteen years, and (to insure preference in the first moments of competition) bearing an interest of six per cent., there is no one who would not take them in preference to the bank-paper now afloat, on a principle of patriotism as well as interest: and they would be withdrawn from circulation into private hoards to a considerable amount. Their credit once established, others might be emitted, bottomed also on a tax, but not bearing interest: and if ever their credit faltered, open public loans, on which these bills alone should be received as specie. These, operating as a sinking fund, would reduce the quantity in circulation, so as to maintain that in an equilibrium with specie. It is not easy to estimate the obstacles which, in the beginning, we should encounter in ousting the banks from their possession of the circulation: but a steady and judicious alternation of emissions and loans, would reduce them in time. But while this is going on, another measure should be pressed, to recover ultimately our right to the circulation. The States should be applied to, to transfer the right of issuing circulating paper to Congress exclusively, in perpetuum, if possible, but during the war at least, with a saving of charter rights. I believe that every State west and south of Connecticut river, except Delaware, would immediately do it; and the others would follow in time.
Congress would, of course, begin by obliging unchartered banks to wind up their affairs within a short time, and the others as their charters expired, forbidding the subsequent circulation of their paper. This they would supply with their own, bottomed, every emission, on an adequate tax, and bearing or not bearing interest, as the state of the public pulse should indicate. Even in the non-complying States, these bills would make their way, and supplant the unfunded paper of their banks, by their solidity, by the universality of their currency, and by their receivability for customs and taxes. It would be in their power, too, to curtail those banks to the amount of their actual specie, by gathering up their paper, and running it constantly on them. The national paper might thus take place even in the non-complying States. In this way, I am not without a hope, that this great, this sole resource for loans in an agricultural country, might yet be recovered for the use of the nation during war: and, if obtained in perpetuum, it would always be sufficient to carry us through any war; provided, that, in the interval between war and war, all the outstanding paper should be called in, coin be permitted to flow in again, and to hold the field of circulation until another war should require its yielding place again to the national medium.
But it will be asked, are we to have no banks? Are merchants and others to be deprived of the resource of short accommodations, found so convenient? I answer, let us have banks: but let them be such as are alone to be found in any country on earth, except Great Britain. There is not a bank of discount on the continent of Europe (at least there was not one when I was there), which offers any thing but cash in exchange for discounted bills. No one has a natural right to the trade of a money-lender, but he who has the money to lend. Let those then among us, who have a monied capital, and who prefer employing it in loans rather than otherwise, set up banks, and give cash or national bills for the notes they discount. Perhaps, to encourage them, a larger interest than is legal in the other cases might be allowed them, on the condition of their lending for short periods only. It is from Great Britain we copy the idea of giving paper in exchange for discounted bills: and while we have derived from that country some good principles of government and legislation, we unfortunately run into the most servile imitation of all her practices, ruinous as they prove to her, and with the gulph yawning before us into which those very practices are precipitating her. The unlimited emission of bank-paper has banished all her specie, and is now, by a depreciation acknowledged by her own statesmen, carrying her rapidly to bankruptcy, as it did France, as it did us, and will do us again, and every country permitting paper to be circulated, other than that by public authority, rigorously limited to the just measure for circulation. Private fortunes, in the present state of our circulation, are at the mercy of those self-created money-lenders, and are prostrated by the floods of nominal money with which their avarice deluges us. He who lent his money to the public or to an individual, before the institution of the United States bank, twenty years ago, when wheat was well sold at a dollar the bushel, and receives now his nominal sum when it sells at two dollars, is cheated of half his fortune: and by whom? By the banks, which, since that, have thrown into circulation ten dollars of their nominal money where there was one at that time.
Reflect, if you please, on these ideas, and use them or not as they appear to merit. They comfort me in the belief, that they point out a resource ample enough, without overwhelming war-taxes, for the expense of the war, and possibly still recoverable; and that they hold up to all future time a resource within ourselves, ever at the command of government, and competent to any wars into which we may be forced. Nor is it a slight object to equalize taxes through peace and war.
Ever affectionately yours.
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN ADAMS.
Monticello, June 21, 1813.

And I too, my dear Sir, like the wood-cutter of Ida, should doubt where to begin, were I to enter the forest of opinions, discussions, and contentions which have occurred in our day. I should say with Theocritus,
But I shall not do it. The summum bonum with me is now truly
epicurean, ease of body and tranquillity of mind; and to these I wish to
consign my remaining days. Men have differed in opinion, and been divided
into parties by these opinions, from the first origin of societies; and in
all governments, where they have been permitted freely to think and to
speak. The same political parties which now agitate the United States,
have existed through all time. Whether the power of the people, or that of
the![]() should prevail, were questions which kept the States of Greece and Rome in
eternal convulsions; as they now schismatize every people whose minds and
mouths are not shut up by the gag of a despot. And in fact, the terms of
whig and tory belong to natural, as well as to civil history. They denote
the temper and constitution of mind of different individuals. To come to
our own country, and to the times when you and I became first acquainted:
we well remember the violent parties which agitated the old Congress, and
their bitter contests. There you and I were together, and the Jays, and
the Dickinsons, and other anti-independents were arrayed against us. They
cherished the monarchy of England, and we the rights of our countrymen.
When our present government was in the mew, passing from Confederation to
Union, how bitter was the schism between the Feds and Antis. Here you and
I were together again. For although, for a moment, separated by the
Atlantic from the scene of action, I favored the opinion that nine States
should confirm the constitution, in order to secure it, and the others
hold off, until certain amendments, deemed favorable to freedom, should be
made. I rallied in the first instant to the wiser proposition of
Massachusetts, that all should confirm, and then all instruct their
delegates to urge those amendments. The amendments were made, and all were
reconciled to the government. But as soon as it was put into motion, the
line of division was again drawn. We broke into two parties, each wishing
to give the government a different direction; the one to strengthen the
most popular branch, the other the more permanent branches, and to extend
their permanence. Here you and I separated for the first time: and as we
had been longer than most others on the public theatre, and our names
therefore were more familiar to our countrymen, the party which considered
you as thinking with them, placed your name at their head; the other, for
the same reason, selected mine. But neither decency nor inclination
permitted us to become the advocates of ourselves, or to take part
personally in the violent contests which followed. We suffered ourselves,
as you so well expressed it, to be passive subjects of public discussion.
And these discussions, whether relating to men, measures, or opinions,
were conducted by the parties with an animosity, a bitterness, and an
indecency, which had never been exceeded. All the resources of reason and
of wrath were exhausted by each party in support of its own, and to
prostrate the adversary opinions; one was upbraided with receiving the
anti-federalists, the other the old tories and refugees, into their bosom.
Of this acrimony, the public papers of the day exhibit ample testimony, in
the debates of Congress, of State legislatures, of stump-orators, in
addresses, answers, and newspaper essays; and to these, without question,
may be added the private correspondences of individuals; and the less
guarded in these, because not meant for the public eye, not restrained by
the respect due to that, but poured forth from the overflowings of the
heart into the bosom of a friend, as a momentary easement of our feelings.
In this way and in answers to addresses, you and I could indulge
ourselves. We have probably done it, sometimes with warmth, often with
prejudice, but always, as we believed, adhering to truth. I have not
examined my letters of that day. I have no stomach to revive the memory of
its feelings. But one of these letters, it seems, has got before the
public, by accident and infidelity, by the death of one friend to whom it
was written, and of his friend to whom it had been communicated, and by
the malice and treachery of a third person, of whom I had never before
heard, merely to make mischief, and in the same Satanic spirit, in which
the same enemy had intercepted and published, in 1776, your letter
animadverting on Dickinson’s character. How it happened that I
quoted you in my letter to Doctor Priestley, and for whom, and not for
yourself, the strictures were meant, has been explained to you in my
letter of the 15th, which had been committed to the post eight days before
I received yours of the 10th, 11th, and 14th. That gave you the reference
which these asked to the particular answer alluded to in the one to
Priestley. The renewal of these old discussions, my friend, would be
equally useless and irksome. To the volumes then written on these
subjects, human ingenuity can add nothing new, and the rather, as lapse of
time has obliterated many of the facts. And shall you and I, my Dear Sir,
at our age, like Priam of old, gird on the
should prevail, were questions which kept the States of Greece and Rome in
eternal convulsions; as they now schismatize every people whose minds and
mouths are not shut up by the gag of a despot. And in fact, the terms of
whig and tory belong to natural, as well as to civil history. They denote
the temper and constitution of mind of different individuals. To come to
our own country, and to the times when you and I became first acquainted:
we well remember the violent parties which agitated the old Congress, and
their bitter contests. There you and I were together, and the Jays, and
the Dickinsons, and other anti-independents were arrayed against us. They
cherished the monarchy of England, and we the rights of our countrymen.
When our present government was in the mew, passing from Confederation to
Union, how bitter was the schism between the Feds and Antis. Here you and
I were together again. For although, for a moment, separated by the
Atlantic from the scene of action, I favored the opinion that nine States
should confirm the constitution, in order to secure it, and the others
hold off, until certain amendments, deemed favorable to freedom, should be
made. I rallied in the first instant to the wiser proposition of
Massachusetts, that all should confirm, and then all instruct their
delegates to urge those amendments. The amendments were made, and all were
reconciled to the government. But as soon as it was put into motion, the
line of division was again drawn. We broke into two parties, each wishing
to give the government a different direction; the one to strengthen the
most popular branch, the other the more permanent branches, and to extend
their permanence. Here you and I separated for the first time: and as we
had been longer than most others on the public theatre, and our names
therefore were more familiar to our countrymen, the party which considered
you as thinking with them, placed your name at their head; the other, for
the same reason, selected mine. But neither decency nor inclination
permitted us to become the advocates of ourselves, or to take part
personally in the violent contests which followed. We suffered ourselves,
as you so well expressed it, to be passive subjects of public discussion.
And these discussions, whether relating to men, measures, or opinions,
were conducted by the parties with an animosity, a bitterness, and an
indecency, which had never been exceeded. All the resources of reason and
of wrath were exhausted by each party in support of its own, and to
prostrate the adversary opinions; one was upbraided with receiving the
anti-federalists, the other the old tories and refugees, into their bosom.
Of this acrimony, the public papers of the day exhibit ample testimony, in
the debates of Congress, of State legislatures, of stump-orators, in
addresses, answers, and newspaper essays; and to these, without question,
may be added the private correspondences of individuals; and the less
guarded in these, because not meant for the public eye, not restrained by
the respect due to that, but poured forth from the overflowings of the
heart into the bosom of a friend, as a momentary easement of our feelings.
In this way and in answers to addresses, you and I could indulge
ourselves. We have probably done it, sometimes with warmth, often with
prejudice, but always, as we believed, adhering to truth. I have not
examined my letters of that day. I have no stomach to revive the memory of
its feelings. But one of these letters, it seems, has got before the
public, by accident and infidelity, by the death of one friend to whom it
was written, and of his friend to whom it had been communicated, and by
the malice and treachery of a third person, of whom I had never before
heard, merely to make mischief, and in the same Satanic spirit, in which
the same enemy had intercepted and published, in 1776, your letter
animadverting on Dickinson’s character. How it happened that I
quoted you in my letter to Doctor Priestley, and for whom, and not for
yourself, the strictures were meant, has been explained to you in my
letter of the 15th, which had been committed to the post eight days before
I received yours of the 10th, 11th, and 14th. That gave you the reference
which these asked to the particular answer alluded to in the one to
Priestley. The renewal of these old discussions, my friend, would be
equally useless and irksome. To the volumes then written on these
subjects, human ingenuity can add nothing new, and the rather, as lapse of
time has obliterated many of the facts. And shall you and I, my Dear Sir,
at our age, like Priam of old, gird on the
Shall we, at our age, become the athletes of party, and exhibit ourselves, as gladiators, in the arena of the newspapers? Nothing in the universe could induce me to it. My mind has been long fixed to bow to the judgment of the world, who will judge by my acts, and will never take counsel from me as to what that judgment shall be. If your objects and opinions have been misunderstood, if the measures and principles of others have been wrongfully imputed to you, as I believe they have been, that you should leave an explanation of them, would be an set of justice to yourself. I will add, that it has been hoped that you would leave such explanations as would place every saddle on its right horse, and replace on the shoulders of others the burdens they shifted to yours.
But all this, my friend, is offered merely for your consideration and judgment, without presuming to anticipate what you alone are qualified to decide for yourself. I mean to express my own purpose only, and the reflections which have led to it. To me, then, it appears, that there have been differences of opinion and party differences, from the first establishment of governments to the present day, and on the same question which now divides our own country: that these will continue through all future time: that every one takes his side in favor of the many, or of the few, according to his constitution, and the circumstances in which he is placed: that opinions, which are equally honest on both sides, should not affect personal esteem or social intercourse: that as we judge between the Claudii and the Gracchi, the Wentworths and the Hampdens of past ages, so, of those among us whose names may happen to be remembered for a while, the next generations will judge, favorably or unfavorably, according to the complexion of individual minds, and the side they shall themselves have taken: that nothing new can be added by you or me to what has been said by others, and will be said in every age in support of the conflicting opinions on government: and that wisdom and duty dictate an humble resignation to the verdict of our future peers. I doing this myself, I shall certainly not suffer moot questions to affect the sentiments of sincere friendship and respect, consecrated to you by so long a course of time, and of which I now repeat sincere assurances,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN ADAMS.
Monticello, August 22, 1813.
Dear Sir,
Since my letter of June the 27th, I am in your debt for many; all of which
I have read with infinite delight. They open a wide field for reflection,
and offer subjects enough to occupy the mind and the pen indefinitely. I
must follow the good example you have set; and when I have not time to
take up every subject, take up a single one. Your approbation of my
outline to Dr. Priestley is a great gratification to me; and I very much
suspect that if thinking men would have the courage to think for
themselves, and to speak what they think, it would be found they do not
differ in religious opinions, as much as is supposed. I remember to have
heard Dr. Priestley say, that if all England would candidly examine
themselves, and confess, they would find that Unitarianism was really the
religion of all: and I observe a bill is now depending in parliament for
the relief of Anti-Trinitarians. It is too late in the day for men of
sincerity to pretend they believe in the Platonic mysticisms that three
are one, and one is three; and yet that the one is not three, and the
three are not one: to divide mankind by a single letter into
![]()
But this constitutes the craft, the power, and the profit of the priests. Sweep away their gossamer fabrics of factitious religion, and they would catch no more flies. We should all then, like the Quakers, live without an order of priests, moralize for ourselves, follow the oracle of conscience, and say nothing about what no man can understand, nor therefore believe; for I suppose belief to be the assent of the mind to an intelligible proposition.
It is with great pleasure I can inform you, that Priestley finished the comparative view of the doctrines of the philosophers of antiquity, and of Jesus, before his death; and that it was printed soon after. And with still greater pleasure, that I can have a copy of his work forwarded from Philadelphia, by a correspondent there, and presented for your acceptance, by the same mail which carries you this, or very soon after. The branch of the work which the title announces, is executed with learning and candor, as was every thing Priestley wrote: but perhaps a little hastily; for he felt himself pressed by the hand of death. The Abbe Batteux had, in fact, laid the foundation of this part in his ‘Causes Premieres’; with which he has given us the originals of Ocellus and Timzeus, who first committed the doctrines of Pythagoras to writing: and Enfield, to whom the Doctor refers, had done it more copiously. But he has omitted the important branch, which, in your letter of August the 9th, you say you have never seen executed, a comparison of the morality of the Old Testament with that of the New. And yet, no two things were ever more unlike. I ought not to have asked him to give it. He dared not. He would have been eaten alive by his intolerant brethren, the Cannibal priests. And yet, this was really the most interesting branch of the work.
Very soon after my letter to Doctor Priestley, the subject being still in my mind, I had leisure, during an abstraction from business for a day or two, while on the road, to think a little more on it, and to sketch more fully than I had done to him, a syllabus of the matter which I thought should enter into the work. I wrote it to Doctor Rush; and there ended all my labor on the subject; himself and Doctor Priestley being the only depositories of my secret. The fate of my letter to Priestley, after his death, was a warning to me on that of Doctor Rush; and at my request, his family were so kind as to quiet me by returning my original letter and syllabus. By this you will be sensible how much interest I take in keeping myself clear of religious disputes before the public; and especially of seeing my syllabus disembowelled by the Aruspices of the modern Paganism. Yet I enclose it to you with entire confidence, free to be perused by yourself and Mrs. Adams, but by no one else; and to be returned to me.
You are right in supposing, in one of yours, that I had not read much of Priestley’s Predestination, his no-soul system, or his controversy with Horsley. But I have read his Corruptions of Christianity, and Early Opinions of Jesus, over and over again; and I rest on them, and on Middleton’s writings, especially his letters from Rome, and to Waterland, as the basis of my own faith. These writings have never been answered, nor can be answered by quoting historical proofs, as they have done. For these facts, therefore, I cling to their learning, so much superior to my own.
I now fly off in a tangent to another subject. Marshall, in the first volume of his history, chapter 3, p. 180, ascribes the petition to the King, of 1774, (1 Journ. Cong. 67) to the pen of Richard Henry Lee. I think myself certain, it was not written by him, as well from what I recollect to have heard, as from the internal evidence of style. He was loose, vague, frothy, rhetorical. He was a poorer writer than his brother Arthur; and Arthur’s standing may be seen in his Monitor’s Letters, to insure the sale of which, they took the precaution of tacking to them a new edition of the Farmer’s Letters; like Mezentius, who ‘mortua jungebat corpora vivis.’ You were of the committee, and can tell me who wrote this petition; and who wrote the Address to the Inhabitants of the Colonies, ib. 45. Of the papers of July 1775, I recollect well that Mr. Dickinson drew the petition to the King, ib. 149; I think Robert R. Livingston drew the Address to the Inhabitants of Great Britain, ib. 152. Am I right in this? And who drew the Address to the People of Ireland, ib. 180? On these questions, I ask of your memory to help mine. Ever and affectionately yours,
Th: Jefferson.
Monticello, November 6, 1813.
Dear Sir,
I had not expected to have troubled you again on the subject of finance; but since the date of my last, I have received from Mr. Law a letter covering a memorial on that subject, which, from its tenor, I conjecture must have been before Congress at their two last sessions. This paper contains two propositions; the one for issuing treasury notes, bearing interest, and to be circulated as money; the other for the establishment of a national bank. The first was considered in my former letter; and the second shall be the subject of the present.
The scheme is for Congress to establish a national bank, suppose of thirty millions capital, of which they shall contribute ten millions in new six per cent, stock, the States ten millions, and individuals ten millions, one half of the two last contributions to be of similar stock, for which the parties are to give cash to Congress: the whole, however, to be under the exclusive management of the individual subscribers, who are to name all the directors; neither Congress nor the States having any power of interference in its administration. Discounts are to be at five per cent., but the profits are expected to be seven per cent. Congress then will be paying six per cent, on twenty millions, and receiving seven per cent, on ten millions, being its third of the institution: so that on the ten millions cash which they receive from the States and individuals, they will, in fact, have to pay but five per cent, interest. This is the bait. The charter is proposed to be for forty or fifty years, and if any future augmentations should take place, the individual proprietors are to have the privilege of being the sole subscribers for that. Congress are further allowed to issue to the amount of three millions of notes, bearing interest, which they are to receive back in payment for lands at a premium of five or ten per cent., or as subscriptions for canals, roads, and bridges, in which undertakings they are, of course, to be engaged. This is a summary of the scheme, as I understand it: but it is very possible I may not understand it in all its parts, these schemes being always made Unintelligible for the gulls who are to enter into them. The advantages and disadvantages shall be noted promiscuously as they occur; leaving out the speculation of canals, &c. which, being an episode only in the scheme, may be omitted, to disentangle it as much as we can.
1. Congress are to receive five millions from the States (if they will enter into this partnership, which few probably will), and five millions from the individual subscribers, in exchange for ten millions of six per cent, stock, one per cent, of which, however, they will make on their ten millions of stock remaining in bank, and so reduce it, in effect, to a loan of ten millions at five per cent, interest. This is good: but
2. They authorize this bank to throw into circulation ninety millions of dollars, (three times the capital), which increases our circulating medium fifty per cent., depreciates proportionably the present value of the dollar, and raises the price of all future purchases in the same proportion.
3. This loan of ten millions at five per cent., is to be once for all, only. Neither the terms of the scheme, nor their own prudence could ever permit them to add to the circulation in the same, or any other way, for the supplies of the succeeding years of the war. These succeeding years then are to be left unprovided for, and the means of doing it in a great measure precluded.
4. The individual subscribers, on paying their own five millions of cash to Congress, become the depositories of ten millions of stock belonging to Congress, five millions belonging to the States, and five millions to themselves, say twenty millions, with which, as no one has a right ever to see their books, or to ask a question, they may choose their time for running away, after adding to their booty the proceeds of as much of their own notes as they shall be able to throw into circulation.
5. The subscribers may be one, two, or three, or more individuals, (many single individuals being able to pay in the five millions,) whereupon this bank oligarchy or monarchy enters the field with ninety millions of dollars, to direct and control the politics of the nation; and of the influence of these institutions on our politics, and into what scale it will be thrown, we have had abundant experience. Indeed, England herself may be the real, while her friend and trustee here shall be the nominal and sole subscriber.
6. This state of things is to be fastened on us, without the power of relief, for forty or fifty years. That is to say, the eight millions of people now existing, for the sake of receiving one dollar and twenty-five cents apiece at five per cent, interest, are to subject the fifty millions of people who are to succeed them within that term, to the payment of forty-five millions of dollars, principal and interest, which will be payable in the course of the fifty years.
7. But the great and national advantage is to be the relief of the present scarcity of money, which is produced and proved by,
1. The additional industry created to supply a variety of articles for the troops, ammunition, he.
2. By the cash sent to the frontiers, and the vacuum occasioned in the trading towns by that.
3. By the late loans.
4. By the necessity of recurring to shavers with good paper, which the existing banks are not able to take up; and
5. By the numerous applications for bank charters, showing that an increase of circulating medium is wanting.
Let us examine these causes and proofs of the want of an increase of medium, one by one.
1. The additional industry created to supply a variety of articles for troops, ammunition, &c. Now I had always supposed that war produced a diminution of industry, by the number of hands it withdraws from industrious pursuits, for employment in arms &c. which are totally unproductive. And if it calls for new industry in the articles of ammunition and other military supplies, the hands are borrowed from other branches on which the demand is slackened by the war; so that it is but a shifting of these hands from one pursuit to another.
2. The cash sent to the frontiers occasions a vacuum in the trading towns, which requires a new supply. Let us examine what are the calls for money to the frontiers. Not for clothing, tents, ammunition, arms, which are all bought in the trading towns. Not for provisions; for although these are bought partly in the intermediate country, bank-bills are more acceptable there than even in the trading towns. The pay of the army calls for some cash; but not a great deal, as bank-notes are as acceptable with the military men, perhaps more so; and what cash is sent must find its way back again, in exchange for the wants of the upper from the lower country. For we are not to suppose that cash stays accumulating there for ever.
3. This scarcity has been occasioned by the late loans. But does the government borrow money to keep it in their coffers? Is it not instantly restored to circulation by payment for its necessary supplies? And are we to restore a vacuum of twenty millions of dollars by an emission of ninety millions?
4. The want of medium is proved by the recurrence of individuals with good paper to brokers at exorbitant interest; and
5. By the numerous applications to the State governments for additional banks; New York wanting eighteen millions, Pennsylvania ten millions, &c. But say more correctly, the speculators and spendthrifts of New York and Pennsylvania, but never consider them as being the States of New York and Pennsylvania. These two items shall be considered together.
It is a litigated question, whether the circulation of paper, rather than of specie, is a good or an evil. In the opinion of England and of English writers it is a good; in that of all other nations it is an evil; and excepting England and her copyist, the United States, there is not a nation existing, I believe, which tolerates a paper circulation. The experiment is going on, however, desperately in England, pretty boldly with us, and at the end of the chapter, we shall see which opinion experience approves: for I believe it to be one of those cases where mercantile clamor will bear down reason, until it is corrected by ruin. In the mean time, however, let us reason on this new call for a national bank.
After the solemn decision of Congress against the renewal of the charter of the bank of the United States, and the grounds of that decision (the want of constitutional power), I had imagined that question at rest, and that no more applications would be made to them for the incorporation of banks. The opposition on that ground to its first establishment, the small majority by which it was overborne, and the means practised for obtaining it, cannot be already forgotten. The law having passed, however, by a majority, its opponents, true to the sacred principle of submission to a majority, suffered the law to flow through its term without obstruction. During this, the nation had time to consider the constitutional question, and when the renewal was proposed, they condemned it, not by their representatives in Congress only, but by express instructions from different organs of their will. Here then we might stop, and consider the memorial as answered. But, setting authority apart, we will examine whether the legislature ought to comply with it, even if they had the power.
Proceeding to reason on this subject, some principles must be premised as forming its basis. The adequate price of a thing depends on the capital and labor necessary to produce it. (In the term capital, I mean to include science, because capital as well as labor has been employed to acquire it.) Two things requiring the same capital and labor should be of the same price. If a gallon of wine requires for its production the same capital and labor with a bushel of wheat, they should be expressed by the same price, derived from the application of a common measure to them. The comparative prices of things being thus to be estimated, and expressed by a common measure, we may proceed to observe, that were a country so insulated as to have no commercial intercourse with any other, to confine the interchange of all its wants and supplies within itself, the amount of circulating medium, as a common measure for adjusting these exchanges, would be quite immaterial. If their circulation, for instance, were of a million of dollars, and the annual produce of their industry equivalent to ten millions of bushels of wheat, the price of a bushel of wheat might be one dollar. If, then, by a progressive coinage, their medium should be doubled, the price of a bushel of wheat might become progressively two dollars, and without, inconvenience. Whatever be the proportion of the circulating medium to the value of the annual produce of industry, it may be considered as the representative of that industry. In the first case, a bushel of wheat will be represented by one dollar; in the second, by two dollars. This is well explained by Hume, and seems admitted by Adam Smith, (B. 2. c. 2. 436, 441, 490.) But where a nation is in a full course of interchange of wants and supplies with all others, the proportion of its medium to its produce is no longer indifferent, (lb. 441.) To trade on equal terms, the common measure of values should be as nearly as possible on a par with that of its corresponding nations, whose medium is in a sound state; that is to say, not in an accidental state of excess or deficiency. Now, one of the great advantages of specie as a medium is, that being of universal value, it will keep itself at a general level, flowing out from where it is too high into parts where it is lower. Whereas, if the medium be of local value only, as paper-money, if too little, indeed, gold and silver will flow in to supply the deficiency; but if too much, it accumulates, banishes the gold and silver not locked up in vaults and hoards, and depreciates itself; that is to say, its proportion to the annual produce of industry being raised, more of it is required to represent any particular article of produce than in the other countries. This is agreed by Smith (B. 2. c. 2. 437.), the principal advocate for a paper circulation; but advocating it on the sole condition that it be strictly regulated. He admits, nevertheless, that ‘the commerce and industry of a country cannot be so secure when suspended on the Daedalian wings of paper-money, as on the solid ground of gold and silver; and that in time of war the insecurity is greatly increased, and great confusion possible where the circulation is for the greater part in paper.‘(B. 2. c. 2. 484.) But in a country where loans are uncertain, and a specie circulation the only sure resource for them, the preference of that circulation assumes a far different degree of importance, as is explained in my former letters.
The only advantage which Smith proposes by substituting paper in the room of gold and silver money (B. 2. c. 2. 434.), is, ‘to replace an expensive instrument with one much less costly, and sometimes equally convenient’; that is to say, (page 437,) to allow the gold and silver to be sent abroad and converted into foreign goods,’ and to substitute paper as being a cheaper measure. But this makes no addition to the stock or capital of the nation. The coin sent out was worth as much, while in the country, as the goods imported and taking its place. It is only, then, a change of form in a part of the national capital, from that of gold and silver to other goods. He admits, too, that while a part of the goods received in exchange for the coin exported, may be materials, tools, and provisions for the employment of an additional industry, a part also may be taken back in foreign wines, silks, &c. to be consumed by idle people who produce nothing; and so far the substitution promotes prodigality, increases expense and consumption, without increasing production. So far also, then, it lessens the capital of the nation. What may be the amount which the conversion of the part exchanged for productive goods, may add to the former productive mass, it is not easy to ascertain, because, as he says, (page 441,) ‘It is impossible to determine what is the proportion which the circulating money of any country bears to the whole value of the annual produce. It has been computed by different authors, from a fifth* to a thirtieth of that value.’
* The real cash or money necessary to carry on the
circulation and barter of a State, is nearly one third part
of all the annual rents of the proprietors of the said
State; that is, one ninth of the whole produce of the land.
Sir William Petty supposes one tenth part of the value of
the whole produce sufficient. Postlethwayt, voce, Cash.
In the United States it must be less than in any other part of the commercial world; because the great mass of their inhabitants being in responsible circumstances, the great mass of their exchanges in the country is effected on credit, in their merchant’s ledger, who supplies all their wants through the year, and at the end of it receives the produce of their farms, or other articles of their industry. It is a fact, that a farmer, with a revenue of ten thousand dollars a year, may obtain all his supplies from his merchant, and liquidate them at the end of the year, by the sale of his produce to him, without the intervention of a single dollar of cash. This, then, is merely barter, and in this way of barter a great portion of the annual produce of the United States is exchanged without the intermediation of cash. We might safely, then, state our medium at the minimum of one thirtieth. But what is one thirtieth of the value of the annual produce of the industry of the United States? Or what is the whole value of the annual produce of the United States? An able writer and competent judge of the subject, in 1799, on as good grounds as probably could be taken, estimated it, on the then population of four and a half millions of inhabitants, to be thirty-seven and a half millions sterling, or one hundred and sixty-eight and three fourths millions of dollars. See Cooper’s Political Arithmetic, page 47. According to the same estimate, for our present population it will be three hundred millions of dollars, one thirtieth of which, Smith’s minimum, would be ten millions, and one fifth, his maximum, would be sixty millions for the quantum of circulation. But suppose, that, instead of our needing the least circulating medium of any nation, from the circumstance before mentioned, we should place ourselves in the middle term of the calculation, to wit, at thirty-five millions. One fifth of this, at the least, Smith thinks should be retained in specie, which would leave twenty-eight millions of specie to be exported in exchange for other commodities; and if fifteen millions of that should be returned in productive goods, and not in articles of prodigality, that would be the amount of capital which this operation would add to the existing mass. But to what mass? Not that of the three hundred millions, which is only its gross annual produce; but to that capital of which the three hundred millions are but the annual produce. But this being gross, we may infer from it the value of the capital by considering that the rent of lands is generally fixed at one third of the gross produce, and is deemed its nett profit, and twenty times that its fee simple value. The profits on landed capital may, with accuracy enough for our purpose, be supposed on a par with those of other capital. This would give us then for the United States, a capital of two thousand millions, all in active employment, and exclusive of unimproved lands lying in a great degree dormant. Of this, fifteen millions would be the hundred and thirty-third part. And it is for this petty addition to the capital of the nation, this minimum of one dollar, added to one hundred and thirty-three and a third, or three fourths per cent., that we are to give up our gold and silver medium, its intrinsic solidity, its universal value, and its saving powers in time of war, and to substitute for it paper, with all its train of evils, moral, political, and physical, which I will not pretend to enumerate.
There is another authority to which we may appeal for the proper quantity of circulating medium for the United States. The old Congress, when we were estimated at about two millions of people, on a long and able discussion, June the 22nd, 1775, decided the sufficient quantity to be two millions of dollars, which sum they then emitted.* According to this, it should be eight millions, now that we are eight millions of people. This differs little from Smith’s minimum of ten millions, and strengthens our respect for that estimate.
* Within five months after this they were compelled, by the
necessities of the war, to abandon the idea of emitting only
an adequate circulation, and to make those necessities the
sole measure of their emissions.
There is, indeed, a convenience in paper; its easy transmission from one place to another. But this may be mainly supplied by bills of exchange, so as to prevent any great displacement of actual coin. Two places trading together balance their dealings, for the most part, by their mutual supplies, and the debtor individuals of either may, instead of cash, remit the bills of those who are creditors in the same dealings; or may obtain them through some third place with which both have dealings. The cases would be rare where such bills could not be obtained, either directly or circuitously, and too unimportant to the nation to overweigh the train of evils flowing from paper circulation.
From eight to thirty-five millions then being our proper circulation, and two hundred millions the actual one, the memorial proposes to issue ninety millions more, because, it says, a great scarcity of money is proved by the numerous applications for banks; to wit, New York for eighteen millions, Pennsylvania ten millions, &c. The answer to this shall be quoted, from Adam Smith (B. 2, c. 2, page 462), where speaking of the complaints of the traders against the Scotch bankers, who had already gone too far in their issues of paper, he says, ‘Those traders and other undertakers having got so much assistance from banks, wished to get still more. The banks, they seem to have thought, could extend their credits to whatever sum might be wanted, without incurring any other expense besides that of a few reams of paper. They complained of the contracted views and dastardly spirit of the directors of those banks, which did not, they said, extend their credits in proportion to the extension of the trade of the country; meaning, no doubt, by the extension of that trade, the extension of their own projects beyond what they could carry on, either with their own capital, or with what they had credit to borrow of private people in the usual way of bond or mortgage. The banks, they seem to have thought, were in honor bound to supply the deficiency, and to provide them with all the capital which they wanted to trade with.’ And again (page 470): ‘When bankers discovered that certain projectors were trading, not with any capital of their own, but with that which they advanced them, they endeavored to withdraw gradually, making every day greater and greater difficulties about discounting. These difficulties alarmed and enraged in the highest degree those projectors. Their own distress, of which this prudent and necessary reserve of the banks was no doubt the immediate occasion, they called the distress of the country; and this distress of the country, they said, was altogether owing to the ignorance, pusillanimity, and bad conduct of the banks, which did not give a sufficiently liberal aid to the spirited undertakings of those who exerted themselves in order to beautify, improve, and enrich the country. It was the duty of the banks, they seemed to think, to lend for as long a time, and to as great an extent, as they might wish to borrow.’ It is, probably, the good paper of these projectors, which, the memorial says, the banks being unable to discount, goes into the hands of brokers, who (knowing the risk of this good paper) discount it at a much higher rate than legal interest, to the great distress of the enterprising adventurers, who had rather try trade on borrowed capital, than go to the plough or other laborious calling. Smith again says, (page 478,) ‘That the industry of Scotland languished for want of money to employ it, was the opinion of the famous Mr. Law. By establishing a bank of a particular kind, which he seems to have imagined might issue paper to the amount of the whole value of all the lands in the country, he proposed to remedy this want of money. It was afterwards adopted, with some variations, by the Duke of Orleans, at that time Regent of France. The idea of the possibility of multiplying paper to almost any extent, was the real foundation of what is called the Mississippi scheme, the most extravagant project both of banking and stockjobbing, that perhaps the world ever saw. The principles upon which it was founded are explained by Mr. Law himself, in a discourse concerning money and trade, which he published in Scotland when he first proposed his project. The splendid but visionary ideas which are set forth in that and some other works upon the same principles, still continue to make an impression upon many people, and have perhaps, in part, contributed to that excess of banking which has of late been complained of both in Scotland and in other places.’ The Mississippi scheme, it is well known, ended in France in the bankruptcy of the public treasury, the crush of thousands and thousands of private fortunes, and scenes of desolation and distress equal to those of an invading army, burning and laying waste all before it.
At the time we were funding our national debt, we heard much about ‘a public debt being a public blessing’; that the stock representing it was a creation of active capital for the aliment of commerce, manufactures, and agriculture. This paradox was well adapted to the minds of believers in dreams, and the gulls of that size entered bonâ fide into it. But the art and mystery of banks is a wonderful improvement on that. It is established on the principle, that ‘private debts are a public blessing;’ that the evidences of those private debts, called bank-notes, become active capital, and aliment the whole commerce, manufactures, and agriculture of the United States. Here are a set of people, for instance, who have bestowed on us the great blessing of running in our debt about two hundred millions of dollars, without our knowing who they are, where they are, or what property they have to pay this debt when called on; nay, who have made us so sensible of the blessings of letting them run in our debt, that we have exempted them by law from the repayment of these debts beyond a given proportion, (generally estimated at one third.) And to fill up the measure of blessing, instead of paying, they receive an interest on what they owe from those to whom they owe; for all the notes, or evidences of what they owe, which we see in circulation, have been lent to somebody on an interest which is levied again on us through the medium of commerce. And they are so ready still to deal out their liberalities to us, that they are now willing to let themselves run in our debt ninety millions more, on our paying them the same premium of six or eight per cent, interest, and on the same legal exemption from the repayment of more than thirty millions of the debt, when it shall be called for. But let us look at this principle in its original form, and its copy will then be equally understood. ‘A public debt is a public blessing.’ That our debt was juggled from forty-three up to eighty millions, and funded at that amount, according to this opinion, was a great public blessing, because the evidences of it could be vested in commerce, and thus converted into active capital, and then the more the debt was made to be, the more active capital was created. That is to say, the creditors could now employ in commerce the money due them from the public, and make from it an annual profit of five per cent., or four millions of dollars. But observe, that the public were at the same time paying on it an interest of exactly the same amount of four millions of dollars. Where then is the gain to either party, which makes it a public blessing? There is no change in the state of things, but of persons only. A has a debt due to him from the public, of which he holds their certificate as evidence, and on which he is receiving an annual interest. He wishes, however, to have the money itself, and to go into business with it. B has an equal sum of money in business, but wishes now to retire, and live on the interest. He therefore gives it to A, in exchange for A’s certificates of public stock. Now, then, A has the money to employ in business, which B so employed before. B has the money on interest to live on, which A lived on before: and the public pays the interest to B, which they paid to A before. Here is no new creation of capital, no additional money employed, nor even a change in the employment of a single dollar. The only change is of place between A and B, in which we discover no creation of capital, nor public blessing. Suppose, again, the public to owe nothing. Then A not having lent his money to the public, would be in possession of it himself, and would go into business without the previous operation of selling stock. Here again, the same quantity of capital is employed as in the former case, though no public debt exists. In neither case is there any creation of active capital, nor other difference than that there is a public debt in the first case, and none in the last; and we may safely ask which of the two situations is most truly a public blessing? If, then, a public debt be no public blessing, we may pronounce a fortiori, that a private one cannot be so. If the debt which the banking companies owe be a blessing to any body, it is to themselves alone, who are realizing a solid interest of eight or ten per cent, on it. As to the public, these companies have banished all our gold and silver medium, which, before their institution, we had without interest, which never could have perished in our hands, and would have been our salvation now in the hour of war; instead of which, they have given us two hundred millions of froth and bubble, on which we are to pay them heavy interest, until it shall vanish into air, as Morris’s notes did. We are warranted, then, in affirming that this parody on the principle of ‘a public debt being a public blessing,’ and its mutation into the blessing of private instead of public debts, is as ridiculous as the original principle itself. In both cases, the truth is, that capital may be produced by industry, and accumulated by economy: but jugglers only will propose to create it by legerdemain tricks with paper. I have called the actual circulation of bank paper in the United States, two hundred millions of dollars. I do not recollect where I have seen this estimate; but I retain the impression that I thought it just at the time. It may be tested, however, by a list of the banks now in the United States, and the amount of their capital. I have no means of recurring to such a list for the present day: but I turn to two lists in my possession for the years of 1803 and 1804.
In 1803, there were thirty-four banks, whose capital was $28,902,000
In 1804, there were sixty-six, consequently thirty-two additional ones. Their capital is not stated, but at the average of the others (excluding the highest, that of the United States, which was of ten millions) they would be of six hundred thousand dollars each, and add.........19,200,000
Making a total of........ $48,102,000
or say, of fifty millions in round numbers. Now every one knows the immense multiplication of these institutions since 1804. If they have only doubled, their capital will be of one hundred millions, and if trebled, as I think probable, it will be of one hundred and fifty millions, on which they are at liberty to circulate treble the amount. I should sooner, therefore, believe two hundred millions to be far below than above the actual circulation. In England, by a late parliamentary document, (see Virginia Argus of October the 18th, 1813, and other public papers of about that date) it appears that six years ago, the bank of England had twelve millions of pounds sterling in circulation, which had increased to forty-two millions in 1812, or to one hundred and eighty-nine millions of dollars. What proportion all the other banks may add to this, I do not know: if we were allowed to suppose they equal it, this would give a circulation of three hundred and seventy-eight millions, or the double of ours on a double population. But that nation is essentially commercial, ours essentially agricultural, and needing, therefore, less circulating medium, because the produce of the husbandman comes but once a year, and is then partly consumed at home, partly exchanged by barter. The dollar, which was of four shillings and six pence sterling, was, by the same document, stated to be then six shillings and nine pence, a depreciation of exactly fifty per cent. The average price of wheat on the continent of Europe, at the commencement of its present war with England, was about a French crown, of one hundred and ten cents, the bushel. With us it was one hundred cents, and consequently we could send it there in competition with their own. That ordinary price has now doubled with us, and more than doubled in England; and although a part of this augmentation may proceed from the war demand, yet from the extraordinary nominal rise in the prices of land and labor here, both of which have nearly doubled in that period, and are still rising with every new bank, it is evident that were a general peace to take place to-morrow, and time allowed for the re-establishment of commerce, justice, and order, we could not afford to raise wheat for much less than two dollars, while the continent of Europe, having no paper circulation, and that of its specie not being augmented, would raise it at their former price of one hundred and ten cents. It follows, then, that with our redundancy of paper, we cannot, after peace, send a bushel of wheat to Europe, unless extraordinary circumstances double its price in particular places, and that then the exporting countries of Europe could undersell us. It is said our paper is as good as silver, because we may have silver for it at the bank where it issues. This is not true. One, two, or three persons might have it: but a general application would soon exhaust their vaults, and leave a ruinous proportion of their paper in its intrinsic worthless form. It is a fallacious pretence, for another reason. The inhabitants of the banking cities might obtain cash for their paper, as far as the cash of the vaults would hold out; but distance puts it out of the power of the country to do this. A farmer having a note of a Boston or Charleston bank, distant hundreds of miles, has no means of calling for the cash. And while these calls are impracticable for the country, the banks have no fear of their being made from the towns; because their inhabitants are mostly on their books, and there on sufferance only and during good behavior.
In this state of things, we are called on to add ninety millions more to the circulation. Proceeding in this career, it is infallible, that we must end where the revolutionary paper ended. Two hundred millions was the whole amount of all the emissions of the old Congress, at which point their bills ceased to circulate. We are now at that sum; but with treble the population, and of course a longer tether. Our depreciation is, as yet, but at about two for one. Owing to the support its credit receives from the small reservoirs of specie in the vaults of the banks, it is impossible to say at what point their notes will stop. Nothing is necessary to effect it but a general alarm; and that may take place whenever the public shall begin to reflect on, and perceive, the impossibility that the banks should repay this sum. At present, caution is inspired no farther than to keep prudent men from selling property on long payments. Let us suppose the panic to arise at three hundred millions, a point to which every session of the legislatures hastens us by long strides. Nobody dreams that they would have three hundred millions of specie to satisfy the holders of their notes. Were they even to stop now, no one supposes they have two hundred millions in cash, or even the sixty-six and two-thirds millions, to which amount alone the law obliges them to repay. One hundred and thirty-three and one-third millions of loss, then, is thrown on the public by law; and as to the sixty-six and two-thirds, which they are legally bound to pay, and ought to have in their vaults, every one knows there is no such amount of cash in the United States, and what would be the course with what they really have there? Their notes are refused. Cash is called for. The inhabitants of the banking towns will get what is in the vaults, until a few banks declare their insolvency; when, the general crush becoming evident, the others will withdraw even the cash they have, declare their bankruptcy at once, and leave an empty house and empty coffers for the holders of their notes. In this scramble of creditors, the country gets nothing, the towns but little. What are they to do? Bring suits? A million of creditors bring a million of suits against John Nokes and Robert Styles, wheresoever to be found? All nonsense. The loss is total. And a sum is thus swindled from our citizens, of seven times the amount of the real debt, and four times that of the factitious one of the United States, at the close of the war. All this they will justly charge on their legislatures; but this will be poor satisfaction for the two or three hundred millions they will have lost. It is time, then, for the public functionaries to look to this. Perhaps it may not be too late. Perhaps, by giving time to the banks, they may call in and pay off their paper by degrees. But no remedy is ever to be expected while it rests with the State legislatures. Personal motives can be excited through so many avenues to their will, that, in their hands, it will continue to go on from bad to worse, until the catastrophe overwhelms us. I still believe, however, that on proper representations of the subject, a great proportion of these legislatures would cede to Congress their power of establishing banks, saving the charter rights already granted. And this should be asked, not by way of amendment to the constitution, because until three fourths should consent, nothing could be done; but accepted from them one by one, singly, as their consent might be obtained. Any single State, even if no other should come into the measure, would find its interest in arresting foreign bank-paper immediately, and its own by degrees. Specie would flow in on them as paper disappeared. Their own banks would call in and pay off their notes gradually, and their constituents would thus be saved from the general wreck. Should the greater part of the States concede, as is expected, their power over banks to Congress, besides insuring their own safety, the paper of the non-conceding States might be so checked and circumscribed, by prohibiting its receipt in any of the conceding States, and even in the non-conceding as to duties, taxes, judgments, or other demands of the United States, or of the citizens of other States, that it would soon die of itself, and the medium of gold and silver be universally restored. This is what ought to be done. But it will not be done. Carthago non delebitur. The overbearing clamor of merchants, speculators, and projectors, will drive us before them with our eyes open, until, as in France, under the Mississippi bubble, our citizens will be overtaken by the crash of this baseless fabric, without other satisfaction than that of execrations on the heads of those functionaries, who, from ignorance, pusillanimity, or corruption, have betrayed the fruits of their industry into the hands of projectors and swindlers.
When I speak comparatively of the paper emissions of the old Congress and the present banks, let it not be imagined that I cover them under the same mantle. The object of the former was a holy one; for if ever there was a holy war, it was that which saved our liberties and gave us independence. The object of the latter, is to enrich swindlers at the expense of the honest and industrious part of the nation.
The sum of what has been said is, that pretermitting the constitutional question on the authority of Congress, and considering this application on the grounds of reason alone, it would be best that our medium should be so proportioned to our produce, as to be on a par with that of the countries with which we trade, and whose medium is in a sound state: that specie is the most perfect medium, because it will preserve its own level; because, having intrinsic and universal value, it can never die in our hands, and it is the surest resource of reliance in time of war: that the trifling economy of paper, as a cheaper medium, or its convenience for transmission, weighs nothing in opposition to the advantages of the precious metals: that it is liable to be abused, has been, is, and for ever will be abused, in every country in which it is permitted; that it is already at a term of abuse in these States, which has never been reached by any other nation, France excepted, whose dreadful catastrophe should be a warning against the instrument which produced it: that we are already at ten or twenty times the due quantity of medium; insomuch, that no man knows what his property is now worth, because it is bloating while he is calculating; and still less what it will be worth when the medium shall be relieved from its present dropsical state: and that it is a palpable falsehood to say we can have specie for our paper whenever demanded. Instead, then, of yielding to the cries of scarcity of medium set up by speculators, projectors, and commercial gamblers, no endeavors should be spared to begin the work of reducing it by such gradual means as may give time to private fortunes to preserve their poise, and settle down with the subsiding medium; and that, for this purpose, the States should be urged to concede to the General Government, with a saving of chartered rights, the exclusive power of establishing banks of discount for paper.
To the existence of banks of discount for cash, as on the continent of Europe, there can be no objection, because there can be no danger of abuse, and they are a convenience both to merchants and individuals. I think they should even be encouraged, by allowing them a larger than legal, interest on short discounts, and tapering thence, in proportion as the term of discount is lengthened, down to legal interest on those of a year or more. Even banks of deposite, where cash should be lodged, and a paper acknowledgment taken out as its representative, entitled to a return of the cash on demand, would be convenient for remittances, travelling persons, he. But, liable as its cash would be to be pilfered and robbed, and its paper to be fraudulently re-issued, or issued without deposite, it would require skilful and strict regulation. This would differ from the bank of Amsterdam, in the circumstance that the cash could be re-demanded on returning the note.
When I commenced this letter to you, my dear Sir, on Mr. Law’s memorial, I expected a short one would have answered that. But as I advanced, the subject branched itself before me into so many collateral questions, that even the rapid views I have taken of each have swelled the volume of my letter beyond my expectations, and, I fear, beyond your patience. Yet on a revisal of it, I find no part which has not so much bearing on the subject as to be worth merely the time of perusal. I leave it then as it is; and will add only the assurances of my constant and affectionate esteem and respect.
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN ADAMS.
Monticello, October 13, 1813.
Dear Sir,
Since mine of August the 22nd, I have received your favors of August the 16th, September the 2nd, 14th, 15th, and, and Mrs. Adams’s, of September the 20th. I now send you, according to your request, a copy of the syllabus. To fill up this skeleton with arteries, with veins, with nerves, muscles, and flesh, is really beyond my time and information. Whoever could undertake it, would find great aid in Enfield’s judicious abridgment of Brucker’s History of Philosophy, in which he has reduced five or six quarto volumes, of one thousand pages each of Latin closely printed, to two moderate octavos of English open type.
To compare the morals of the Old, with those of the New Testament, would require an attentive study of the former, a search through all its books for its precepts, and through all its history for its practices, and the principles they prove. As commentaries, too, on these, the philosophy of the Hebrews must be inquired into, their Mishna, their Gemara, Cabbala, Jezirah, Sonar, Cosri, and their Talmud, must be examined and understood, in order to do them full justice. Brucker, it would seem, has gone deeply into these repositories of their ethics, and Enfield his epitomizer, concludes in these words. ‘Ethics were so little understood among the Jews, that, in their whole compilation called the Talmud, there is only one treatise on moral subjects. Their books of morals chiefly consisted in a minute enumeration of duties. From the law of Moses were deduced six hundred and thirteen precepts, which were divided into two classes, affirmative and negative, two hundred and forty-eight in the former, and three hundred and sixty-five in the latter. It may serve to give the reader some idea of the low state of moral philosophy among the Jews in the middle age, to add, that of the two hundred and forty-eight affirmative precepts, only three were considered as obligatory upon women; and that, in order to obtain salvation, it was judged sufficient to fulfil any one single law in the hour of death; the observance of the rest being deemed necessary, only to increase the felicity of the future life. What a wretched depravity of sentiment and manners must have prevailed, before such corrupt maxims could have obtained credit! It is impossible to collect from these writings a consistent series of moral doctrine. (Enfield, B. 4. chap. 3.) It was the reformation of this wretched depravity of morals which Jesus undertook. In extracting the pure principles which he taught, we should have to strip off the artificial vestments in which they have been muffled by priests who have travestied them into various forms, as instruments of riches and power to themselves. We must dismiss the Platonists and Plotinists, the Stagyrites and Gamalielites, the Eclectics, the Gnostics and Scholastics, their essences and emanations, their Logos and Demiurgos, Æons, and Daemons, male and female, with a long train of &c. &c. &c. or, shall I say at once, of nonsense. We must reduce our volume to the simple evangelists, select, even from them, the very words only of Jesus, paring off the amphiboligisms into which they have been led, by forgetting often, or not understanding, what had fallen from him, by giving their own misconceptions as his dicta, and expressing unintelligibly for others what they had not understood themselves. There will be found remaining the most sublime and benevolent code of morals which has ever been offered to man. I have performed this operation for my own use, by cutting verse by verse out of the printed book, and arranging the matter which is evidently his, and which is as easily distinguishable as diamonds, in a dunghill. The result is an octavo of forty-six pages, of pure and unsophisticated doctrines, such as were professed and acted on by the unlettered Apostles, the Apostolic Fathers, and the Christians, of the first century. Their Platonizing successors, indeed, in after times, in order to legitimate the corruptions which they had incorporated into the doctrines of Jesus, found it necessary to disavow the primitive Christians, who had taken their principles from the mouth of Jesus himself, of his Apostles, and the Fathers cotemporary with them. They excommunicated their followers as heretics, branding them with the opprobrious name of Ebionites and Beggars. For a comparison of the Grecian philosophy with that of Jesus, materials might be largely drawn from the same source. Enfield gives a history and detailed account of the opinions and principles of the different sects. These relate to the Gods, their natures, grades, places, and powers; the demi-Gods and Demons, and their agency with man; the universe, its structure, extent, and duration; the origin of things from the elements of fire, water, air, and earth; the human soul, its essence and derivation; the summum bonum, and finis bonorum; with a thousand idle dreams and fancies on these and other subjects, the knowledge of which is withheld from man; leaving but a short chapter for his moral duties, and the principal section of that given to what he owes himself, to precepts for rendering him impassible, and unassailable by the evils of life, and for preserving his mind in a state of constant serenity.
Such a canvass is too broad for the age of seventy, and especially of one whose chief occupations have been in the practical business of life. We must leave, therefore, to others, younger and more learned than we are, to prepare this euthanasia for Platonic Christianity, and its restoration to the primitive simplicity of its founder. I think you give a just outline of the theism of the three religions, when you say that the principle of the Hebrew was the fear, of the Gentile the honor, and of the Christian the love of God.
An expression in your letter of September the 14th, that ‘the human understanding is a revelation from its maker,’ gives the best solution that I believe can be given of the question, ‘What did Socrates mean by his Daemon?’ He was too wise to believe, and too honest to pretend, that he had real and familiar converse with a superior and invisible being. He probably considered the suggestions of his conscience, or reason, as revelations, or inspirations from the Supreme mind, bestowed, on important occasions, by a special superintending providence.
I acknowledge all the merit of the hymn of Cleanthes to Jupiter, which you ascribe to it. It is as highly sublime as a chaste and correct imagination can permit itself to go. Yet in the contemplation of a being so superlative, the hyperbolic flights of the Psalmist may often be followed with approbation, even with rapture; and I have no hesitation in giving him the palm over all the hymnists of every language, and of every time. Turn to the 148th psalm in Brady and Tate’s version. Have such conceptions been ever before expressed? Their version of the 15th psalm is more to be esteemed for its pithiness than its poetry. Even Sternhold, the leaden Sternhold, kindles, in a single instance, with the sublimity of his original, and expresses the majesty of God descending on the earth, in terms not unworthy of the subject.

The Latin versions of this passage by Buchanan and by Johnston, are but mediocres. But the Greek of Duport is worthy of quotation.
The best collection of these psalms is that of the Octagonian dissenters of Liverpool, in their printed form of prayer; but they are not always the best versions. Indeed, bad is the best of the English versions; not a ray of poetical genius having ever been employed on them. And how much depends on this, may be seen by comparing Brady and Tate’s 15th psalm with Blacklock’s Justum et tenacem propositi virum of Horace, quoted in Hume’s History, Car. 2. ch. 66. A translation of David in this style, or in that of Pompei’s Cleanthes, might give us some idea of the merit of the original. The character, too, of the poetry of these hymns is singular to us; written in monostichs, each divided into strophe and antistrophe, the sentiment of the first member responded with amplification or antithesis in the second.
On the subject of the Postscript of yours of August the 16th and of Mrs. Adams’s letter, I am silent. I know the depth of the affliction it has caused, and can sympathize with it the more sensibly, inasmuch as there is no degree of affliction, produced by the loss of those dear to us, which experience has not taught me to estimate. I have ever found time and silence the only medicine, and these but assuage, they never can suppress, the deep-drawn sigh which recollection for ever brings up, until recollection and life are extinguished together. Ever affectionately yours.
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN ADAMS.
Monticello, October 28, 1813.
Dear Sir,
According to the reservation between us, of taking up one of the subjects of our correspondence at a time, I turn to your letters of August the 16th and September the 2nd.
The passage you quote from Theognis, I think has an ethical rather than a political object. The whole piece is a moral exhortation,

and this passage particularly seems to be a reproof to man, who, while with his domestic animals he is curious to improve the race, by employing always the finest male, pays no attention to the improvement of his own race, but intermarries with the vicious, the ugly, or the old, for considerations of wealth or ambition. It is in conformity with the principle adopted afterwards by the Pythagoreans, and expressed by Ocellus in another form;
which, as literally as intelligibility will admit, may be thus translated;
‘Concerning the interprocreation of men, how, and of whom it shall
be, in a perfect manner, and according to the laws of modesty and
sanctity, conjointly, this is what I think right. First, to lay it down
that we do not commix for the sake of pleasure, but of the procreation of
children. For the powers, the organs, and desires for coition have not
been given by God to man for the sake of pleasure, but for the procreation
of the race. For as it were incongruous for a mortal born to partake of
divine life, the immortality of the race being taken away, God fulfilled
the purpose by making the generations uninterrupted and continuous. This,
therefore, we are especially to lay down as a principle, that coition is
not for the sake of pleasure.’ But nature, not trusting to this
moral and abstract motive, seems to have provided more securely for the
perpetuation of the species, by making it the effect of the oestrum
implanted in the constitution of both sexes. And not only has the commerce
of love been indulged on this unhallowed impulse, but made subservient
also to wealth and ambition by marriages, without regard to the beauty,
the healthiness, the understanding, or virtue of the subject from which we
are to breed. The selecting the best male for a Haram of well chosen
females, also, which Theognis seems to recommend from the example of our
sheep and asses, would doubtless improve the human, as it does the brute
animal, and produce a race of veritable
![]()
For experience proves, that the moral and physical qualities of man,
whether good or evil, are transmissible in a certain degree from father to
son. But I suspect that the equal rights of men will rise up against this
privileged Solomon and his Haram, and oblige us to continue acquiescence
under the
![]() which Theognis complains of, and to content
ourselves with the accidental aristoi produced by the fortuitous
concourse of breeders. For I agree with you, that there is a natural
aristocracy among men. The grounds of this are virtue and talents.
Formerly, bodily powers gave place among the aristoi. But since the
invention of gunpowder has armed the weak as well as the strong with
missile death, bodily strength, like beauty, good humor, politeness, and
other accomplishments, has become but an auxiliary ground of distinction.
There is also an artificial aristocracy, founded on wealth and birth,
without either virtue or talents; for with these it would belong to the
first class. The natural aristocracy I consider as the most precious gift
of nature, for the instruction, the trusts, and government of society.
And, indeed, it would have been inconsistent in creation to have formed
man for the social state, and not to have provided virtue and wisdom
enough to manage the concerns of the society. May we not even say, that
that form of government is the best, which provides the most effectually
for a pure selection of these natural aristoi into the offices of
government? The artificial aristocracy is a mischievous ingredient in
government, and provision should be made to prevent its ascendancy. On the
question, what is the best provision, you and I differ; but we differ as
rational friends, using the free exercise of our own reason, and mutually
indulging its errors. You think it best to put the pseudo-aristoi into a
separate chamber of legislation, where they may be hindered from doing
mischief by their co-ordinate branches, and where, also, they may be a
protection to wealth against the Agrarian and plundering enterprises of
the majority of the people. I think that to give them power in order to
prevent them from doing mischief, is arming them for it, and increasing
instead of remedying the evil. For if the co-ordinate branches can arrest
their action, so may they that of the co-ordinates. Mischief may be done
negatively as well as positively. Of this, a cabal in the Senate of the
United States has furnished many proofs. Nor do I believe them necessary
to protect the wealthy; because enough of these will find their way into
every branch of the legislation, to protect themselves. From fifteen to
twenty legislatures of our own, in action for thirty years past, have
proved that no fears of an equalization of property are to be apprehended
from them. I think the best remedy is exactly that provided by all our
constitutions, to leave to the citizens the free election and separation
of the aristoi from the pseudo-aristoi, of the wheat from
the chaff. In general, they will elect the really good and wise. In some
instances, wealth may corrupt, and birth blind them; but not in sufficient
degree to endanger the society.
which Theognis complains of, and to content
ourselves with the accidental aristoi produced by the fortuitous
concourse of breeders. For I agree with you, that there is a natural
aristocracy among men. The grounds of this are virtue and talents.
Formerly, bodily powers gave place among the aristoi. But since the
invention of gunpowder has armed the weak as well as the strong with
missile death, bodily strength, like beauty, good humor, politeness, and
other accomplishments, has become but an auxiliary ground of distinction.
There is also an artificial aristocracy, founded on wealth and birth,
without either virtue or talents; for with these it would belong to the
first class. The natural aristocracy I consider as the most precious gift
of nature, for the instruction, the trusts, and government of society.
And, indeed, it would have been inconsistent in creation to have formed
man for the social state, and not to have provided virtue and wisdom
enough to manage the concerns of the society. May we not even say, that
that form of government is the best, which provides the most effectually
for a pure selection of these natural aristoi into the offices of
government? The artificial aristocracy is a mischievous ingredient in
government, and provision should be made to prevent its ascendancy. On the
question, what is the best provision, you and I differ; but we differ as
rational friends, using the free exercise of our own reason, and mutually
indulging its errors. You think it best to put the pseudo-aristoi into a
separate chamber of legislation, where they may be hindered from doing
mischief by their co-ordinate branches, and where, also, they may be a
protection to wealth against the Agrarian and plundering enterprises of
the majority of the people. I think that to give them power in order to
prevent them from doing mischief, is arming them for it, and increasing
instead of remedying the evil. For if the co-ordinate branches can arrest
their action, so may they that of the co-ordinates. Mischief may be done
negatively as well as positively. Of this, a cabal in the Senate of the
United States has furnished many proofs. Nor do I believe them necessary
to protect the wealthy; because enough of these will find their way into
every branch of the legislation, to protect themselves. From fifteen to
twenty legislatures of our own, in action for thirty years past, have
proved that no fears of an equalization of property are to be apprehended
from them. I think the best remedy is exactly that provided by all our
constitutions, to leave to the citizens the free election and separation
of the aristoi from the pseudo-aristoi, of the wheat from
the chaff. In general, they will elect the really good and wise. In some
instances, wealth may corrupt, and birth blind them; but not in sufficient
degree to endanger the society.
It is probable that our difference of opinion may, in some measure, be
produced by a difference of character in those among whom we live. From
what I have seen of Massachusetts and Connecticut myself, and still more
from what I have heard, and the character given of the former by yourself,
(Vol. I, page 111,) who know them so much better, there seems to be in
those two States a traditionary reverence for certain families, which has
rendered the offices of government nearly hereditary in those families. I
presume that from an early period of your history, members of these
families happening to possess virtue and talents, have honestly exercised
them for the good of the people, and by their services have endeared their
names to them. In coupling Connecticut with you, I mean it politically
only, not morally. For having made the Bible the common law of their land,
they seem to have modeled their morality on the story of Jacob and Laban.
But although this hereditary succession to office with you may, in some
degree, be founded in real family merit, yet in a much higher degree, it
has proceeded from your strict alliance of Church and State. These
families are canonized in the eyes of the people on the common principle,
‘You tickle me, and I will tickle you.’ In Virginia, we have
nothing of this. Our clergy, before the revolution, having been secured
against rivalship by fixed salaries, did not give themselves the trouble
of acquiring influence over the people. Of wealth, there were great
accumulations in particular families, handed down from generation to
generation, under the English law of entails. But the only object of
ambition for the wealthy was a seat in the King’s Council. All their
court then was paid to the crown and its creatures; and they Philipized in
all collisions between the King and the people. Hence they were unpopular;
and that unpopularity continues attached to their names. A Randolph, a
Carter, or a Burwell must have great personal superiority over a common
competitor, to be elected by the people, even at this day. At the first
session of our legislature after the Declaration of Independence, we
passed a law abolishing entails. And this was followed by one abolishing
the privilege of primogeniture, and dividing the lands of intestates
equally among all their children, or other representatives. These laws,
drawn by myself, laid the axe to the root of pseudo-aristocracy. And had
another which I prepared been adopted by the legislature, our work would
have been complete. It was a bill for the more general diffusion of
learning. This proposed to divide every county into wards of five or six
miles square, like your townships; to establish in each ward a free school
for reading, writing, and common arithmetic; to provide for the annual
selection of the best subjects from these schools, who might receive, at
the public expense, a higher degree of education at a district school; and
from these district schools to select a certain number of the most
promising subjects, to be completed at an University, where all the useful
sciences should be taught. Worth and genius would thus have been sought
out from every condition of life, and completely prepared by education for
defeating the competition of wealth and birth for public trusts. My
proposition had, for a further object, to impart to these wards those
portions of self-government for which they are best qualified, by
confiding to them the care of their poor, their roads, police, elections,
the nomination of jurors, administration of justice in small cases,
elementary exercises of militia; in short, to have made them little
republics, with a warden at the head of each, for all those concerns
which, being under their eye, they would better manage than the larger
republics of the county or State. A general call of ward-meetings by their
wardens on the same day through the State, would at any time produce the
genuine sense of the people on any required point, and would enable the
State to act in mass, as your people have so often done, and with so much
effect, by their town-meetings. The law for religious freedom, which made
a part of this system, having put down the aristocracy of the clergy, and
restored to the citizen the freedom of the mind, and those of entails and
descents nurturing an equality of condition among them, this on education
would have raised the mass of the people to the high ground of moral
respectability necessary to their own safety, and to orderly government;
and would have completed the great object of qualifying them to select the
veritable aristoi, for the trusts of government, to the exclusion of the
pseudalists: and the same Theognis, who has furnished the epigraphs of
your two letters, assures us that
![]() Although this law has not yet been acted on but
in a small and inefficient degree, it is still considered as before the
legislature, with other bills of the revised code, not yet taken up, and I
have great hope that some patriotic spirit will, at a favorable moment,
call it up, and make it the key-stone of the arch of our government.
Although this law has not yet been acted on but
in a small and inefficient degree, it is still considered as before the
legislature, with other bills of the revised code, not yet taken up, and I
have great hope that some patriotic spirit will, at a favorable moment,
call it up, and make it the key-stone of the arch of our government.
With respect to aristocracy, we should further consider, that before the establishment of the American States, nothing was known to history but the man of the old world, crowded within limits either small or overcharged, and steeped in the vices which that situation generates. A government adapted to such men would be one thing; but a very different one, that for the man of these States. Here every one may have land to labor for himself, if he chooses; or, preferring the exercise of any other industry, may exact for it such compensation as not only to afford a comfortable subsistence, but wherewith to provide for a cessation from labor in old age. Every one, by his property or by his satisfactory situation, is interested in the support of law and order. And such men may safely and advantageously reserve to themselves a wholesome control over their public affairs, and a degree of freedom, which, in the hands of the canaille of the cities of Europe, would be instantly perverted to the demolition and destruction of every thing public and private. The history of the last twenty-five years of France, and of the last forty years in America, nay, of its last two hundred years, proves the truth of both parts of this observation.
But even in Europe a change has sensibly taken place in the mind of man. Science had liberated the ideas of those who read and reflect, and the American example had kindled feelings of right in the people. An insurrection has consequently begun, of science, talents, and courage, against rank and birth, which have fallen into contempt. It has failed in its first effort, because the mobs of the cities, the instrument used for its accomplishment, debased by ignorance, poverty, and vice, could not be restrained to rational action. But the world will recover from the panic of this first catastrophe. Science is progressive, and talents and enterprise on the alert. Resort may be had to the people of the country, a more governable power from their principles and subordination; and rank and birth and tinsel-aristocracy will finally shrink into insignificance, even there. This, however, we have no right to meddle with. It suffices for us, if the moral and physical condition of our own citizens qualifies them to select the able and good for the direction of their government, with a recurrence of elections at such short periods as will enable them to displace an unfaithful servant, before the mischief he meditates may be irremediable, I have thus stated my opinion on a point on which we differ, not with a view to controversy, for we are both too old to change opinions which are the result of a long life of inquiry and reflection; but on the suggestion of a former letter of yours, that we ought not to die before we have explained ourselves to each other. We acted in perfect harmony, through a long and perilous contest for our liberty and independence. A constitution has been acquired, which, though neither of us thinks perfect, yet both consider as competent to render our fellow-citizens the happiest and the securest on whom the sun has ever shone. If we do not think exactly alike as to its imperfections, it matters little to our country, which, after devoting to it long lives of disinterested labor we have delivered over to our successors in life, who will be able to take care of it and of themselves.
Of the pamphlet on aristocracy which has been sent to you, or who may be its author, I have heard nothing but through your letter. If the person you suspect, it may be known from the quaint, mystical, and hyperbolical ideas, involved in affected, newfangled, and pedantic terms, which stamp his writings. Whatever it be, I hope your quiet is not to be affected at this day by the rudeness or intemperance of scribblers; but that you may continue in tranquillity to live and to rejoice in the prosperity of our country, until it shall be your own wish to take your seat among the aristoi who have gone before you.
Ever and affectionately yours.
Th: Jefferson.
TO THOMAS LIEPER.
Monticello, January 1, 1814.
Dear Sir,
I had hoped, when I retired from the business of the world, that I should have been permitted to pass the evening of life in tranquillity, undisturbed by the peltings and passions of which the public papers are the vehicles. I see, however, that I have been dragged into the newspapers by the infidelity of one with whom I was formerly intimate, but who has abandoned the American principles out of which that intimacy grew, and become the bigoted partisan of England, and malcontent of his own government. In a letter which he wrote me, he earnestly besought me to avail our country of the good understanding which subsisted between the executive and myself, by recommending an offer of such terms to our enemy as might produce a peace, towards which he was confident that enemy was disposed. In my answer, I stated the aggressions, the insults, and injuries which England had been heaping on us for years, our long forbearance in the hope she might be led by time and reflection to a sounder view of her own interests, and of their connection with justice to us, the repeated propositions for accommodation made by us, and rejected by her, and at length her Prince Regent’s solemn proclamation to the world, that he would never repeal the orders in council as to us, until France should have revoked her illegal decrees as to all the world, and her minister’s declaration to ours, that no admissible precaution against the impressment of our seamen could be proposed: that the unavoidable declaration of war which followed these was accompanied by advances for peace, on terms which no American could dispense with, made through various channels, and unnoticed and unanswered through any: but that if he could suggest any other conditions which we ought to accept, and which had not been repeatedly offered and rejected, I was ready to be the channel of their conveyance to the government: and, to show him that neither that attachment to Bonaparte nor French influence, which they allege eternally without believing it, themselves, affected my mind, I threw in the two little sentences, of the printed extract enclosed in your friendly favor of the 9th ultimo, and exactly these two little sentences, from a letter of two or three pages, he has thought proper to publish, naked, alone, and with my name, although other parts of the letter would have shown that I wished such limits only to the successes of Bonaparte, as should not prevent his completely closing Europe against British manufactures and commerce; and thereby reducing her to just terms of peace with us.
Thus am I situated. I receive letters from all quarters, some from known friends, some from those who write like friends, on various subjects. What am I to do? Am I to button myself up in Jesuitical reserve, rudely declining any answer, or answering in terms so unmeaning, as only to prove my distrust? Must I withdraw myself from all interchange of sentiment with the world? I cannot do this. It is at war with my habits and temper. I cannot act as if all men were unfaithful, because some are so; nor believe that all will betray me, because some do. I had rather be the victim of occasional infidelities, than relinquish my general confidence in the honesty of man.
So far as to the breach of confidence which has brought me into the newspapers, with a view to embroil me with my friends, by a supposed separation in opinion and principle from them. But it is impossible there can be any difference of opinion among us on the two propositions contained in these two little sentences, when explained, as they were explained in the context from which they were insulated. That Bonaparte is an unprincipled tyrant, who is deluging the continent of Europe with blood, there is not a human being, not even the wife of his bosom, who does not see: nor can there, I think, be a doubt as to the line we ought to wish drawn between his successes and those of Alexander. Surely none of us wish to see Bonaparte conquer Russia, and lay thus at his feet the whole continent of Europe. This done, England would be but a breakfast: and although I am free from the visionary fears which the votaries of England have affected to entertain, because I believe he cannot effect the conquest of Europe; yet put all Europe into his hands, and he might spare such a force, to be sent in British ships, as I would as lieve not have to encounter, when I see how much trouble a handful of British soldiers in Canada has given us. No. It cannot be our interest that all Europe should be reduced to a single monarchy. The true line of interest for us is, that Bonaparte should be able to effect the complete exclusion of England from the whole continent of Europe, in order, as the same letter said, ‘by this peaceable engine of constraint, to make her renounce her views of dominion over the ocean, of permitting no other nation to navigate it but with her license, and on tribute to her, and her aggressions on the persons of our citizens who may choose to exercise their right of passing over that element.’ And this would be effected by Bonaparte’s succeeding so far as to close the Baltic against her. This success I wished him the last year, this I wish him this year; but were he again advanced to Moscow, I should again wish him such disasters as would prevent his reaching Petersburg. And were the consequences even to be the longer continuance of our war, I would rather meet them, than see the whole force of Europe wielded by a single hand.
I have gone into this explanation, my friend, because I know you will not carry my letter to the newspapers, and because I am willing to entrust to your discretion the explaining me to our honest fellow-laborers, and the bringing them to pause and reflect, if any of them have not sufficiently reflected on the extent of the success we ought to wish to Bonaparte, with a view to our own interests only; and even were we not men, to whom nothing human should be indifferent. But is our particular interest to make us insensible to all sentiments of morality? Is it then become criminal, the moral wish that the torrents of blood this man is shedding in Europe, the sufferings of so many human beings, good as ourselves, on whose necks he is trampling, the burnings of ancient cities, devastations of great countries, the destruction of law and order, and demoralization of the world, should be arrested, even if it should place our peace a little further distant? No. You and I cannot differ in wishing that Russia, and Sweden, and Denmark, and Germany, and Spain, and Portugal, and Italy, and even England, may retain their independence. And if we differ in our opinions about Towers and his four beasts and ten kingdoms, we differ as friends, indulging mutual errors, and doing justice to mutual sincerity and honesty. In this spirit of sincere confidence and affection, I pray God to bless you here and hereafter.
Th: Jefferson.
TO DOCTOR WALTER JONES.
Monticello, January 2,1814.
Dear Sir,
Your favor of November the 25th reached this place December the 21st, having been near a month on the way. How this could happen I know not, as we have two mails a week both from Fredericksburg and Richmond. It found me just returned from a long journey and absence, during which so much business had accumulated, commanding the first attentions, that another week has been added to the delay.
I deplore, with you, the putrid state into which our newspapers have passed, and the malignity, the vulgarity, and mendacious spirit of those who write for them; and I enclose you a recent sample, the production of a New England judge, as a proof of the abyss of degradation into which we are fallen. These ordures are rapidly depraving the public taste, and lessening its relish for sound food. As vehicles of information, and a curb on our functionaries, they have rendered themselves useless, by forfeiting all title to belief. That this has, in a great degree, been produced by the violence and malignity of party spirit, I agree with you; and I have read with great pleasure the paper you enclosed me on that subject, which I now return. It is at the same time a perfect model of the style of discussion which candor and decency should observe, of the tone which renders difference of opinion even amiable, and a succinct, correct, and dispassionate history of the origin and progress of party among us. It might be incorporated, as it stands, and without changing a word, into the history of the present epoch, and would give to posterity a fairer view of the times than they will probably derive from other sources. In reading it, with great satisfaction, there was but a single passage where I wished a little more developement of a very sound and catholic idea; a single intercalation to rest it solidly on true bottom. It is near the end of the first page, where you make a statement of genuine republican maxims; saying, ‘that the people ought to possess as much political power as can possibly consist with the order and security of society.’ Instead of this, I would say, ‘that the people, being the only safe depository of power, should exercise in person every function which their qualifications enable them to exercise consistently with the order and security of society; that we now find them equal to the election of those who shall be invested with their executive and legislative powers, and to act themselves in the judiciary, as judges in questions of fact; that the range of their powers ought to be enlarged,’ &c. This gives both the reason and exemplification of the maxim you express, ‘that they ought to possess as much political power,’ &c. I see nothing to correct either in your facts or principles.
You say that in taking General Washington on your shoulders, to bear him harmless through the federal coalition, you encounter a perilous topic. I do not think so. You have given the genuine history of the course of his mind through the trying scenes in which it was engaged, and of the seductions by which it was deceived, but not depraved. I think I knew General Washington intimately and thoroughly; and were I called on to delineate his character, it should be in terms like these.
His mind was great and powerful, without being of the very first order; his penetration strong, though not so acute as that of a Newton, Bacon, or Locke; and as far as he saw, no judgment was ever sounder. It was slow in operation, being little aided by invention or imagination, but sure in conclusion. Hence the common remark of his officers, of the advantage he derived from councils of war, where, hearing all suggestions, he selected whatever was best; and certainly no General ever planned his battles more judiciously. But if deranged during the course of the action, if any member of his plan was dislocated by sudden circumstances, he was slow in a re-adjustment. The consequence was, that he often failed in the field, and rarely against an enemy in station, as at Boston and York. He was incapable of fear, meeting personal dangers with the calmest unconcern. Perhaps the strongest feature in his character was prudence, never acting until every circumstance, every consideration, was maturely weighed; refraining if he saw a doubt, but, when once decided, going through with his purpose, whatever obstacles opposed. His integrity was most pure, his justice the most inflexible I have ever known, no motives of interest or consanguinity, of friendship or hatred, being able to bias his decision. He was, indeed, in every sense of the words, a wise, a good, and a great man. His temper was naturally irritable and high-toned; but reflection and resolution had obtained a firm and habitual ascendancy over it. If ever, however, it broke its bonds, he was most tremendous in his wrath. In his expenses he was honorable, but exact; liberal in contributions to whatever promised utility; but frowning and unyielding on all visionary projects, and all unworthy calls on his charity. His heart was not warm in its affections; but he exactly calculated every man’s value, and gave him a solid esteem proportioned to it. His person, you know, was fine, his stature exactly what one would wish, his deportment easy, erect, and noble; the best horseman of his age, and the most, graceful figure that could be seen on horseback. Although in the circle of his friends, where he might be unreserved with safety, he took a free share in conversation, his colloquial talents were not above mediocrity, possessing neither copiousness of ideas, nor fluency of words. In public, when called on for a sudden opinion, he was unready, short, and embarrassed. Yet he wrote readily, rather diffusely, in an easy and correct style. This he had acquired by conversation with the world, for his education was merely reading, writing, and common arithmetic, to which he added surveying at a later day. His time was employed in action chiefly, reading little, and that only in agriculture and English history. His correspondence became necessarily extensive, and, with journalizing his agricultural proceedings, occupied most of his leisure hours within doors. On the whole, his character was, in its mass, perfect, in nothing bad, in few points indifferent; and it may truly be said, that never did nature and fortune combine more perfectly to make a man great, and to place him in the same constellation with whatever worthies have merited from man an everlasting remembrance. For his was the singular destiny and merit, of leading the armies of his country successfully through an arduous war, for the establishment of its independence; of conducting its councils through the birth of a government, new in its forms and principles, until it had settled down into a quiet and orderly train; and of scrupulously obeying the laws through the whole of his career, civil and military, of which the history of the world furnishes no other example. How, then, can it be perilous for you to take such a man on your shoulders? I am satisfied the great body of republicans think of him as I do. We were, indeed, dissatisfied with him on his ratification of the British treaty. But this was short-lived. We knew his honesty, the wiles with which he was encompassed, and that age had already begun to relax the firmness of his purposes; and I am convinced he is more deeply seated in the love and gratitude of the republicans, than in the Pharisaical homage of the federal monarchists. For he was no monarchist from preference of his judgment. The soundness of that gave him correct views of the rights of man, and his severe justice devoted him to them. He has often declared to me that he considered our new constitution as an experiment on the practicability of republican government, and with what dose of liberty man could be trusted for his own good; that he was determined the experiment should have a fair trial, and would lose the last drop of his blood in support of it. And these declarations he repeated to me the oftener and the more pointedly, because he knew my suspicions of Colonel Hamilton’s views, and probably had heard from him the same declarations which I had, to wit, ‘that the British constitution, with its unequal representation, corruption, and other existing abuses, was the most perfect government which had ever been established on earth, and that a reformation of these abuses would make it an impracticable government.’ I do believe that General Washington had not a firm confidence in the durability of our government. He was naturally distrustful of men, and inclined to gloomy apprehensions: and I was ever persuaded that a belief that we must at length end in something like a British constitution, had some weight in his adoption of the ceremonies of levees, birthdays, pompous meetings with Congress, and other forms of the same character, calculated to prepare us gradually for a change which he believed possible, and to let it come on with as little shock as might be to the public mind.
These are my opinions of General Washington, which I would vouch at the judgment-seat of God, having been formed on an acquaintance of thirty years. I served with him in the Virginia legislature from 1769 to the Revolutionary war, and again, a short time in Congress, until he left us to take command of the army. During the war and after it we corresponded Occasionally, and in the four years of my continuance in the office of Secretary of State, our intercourse was daily, confidential, and cordial. After I retired from that office, great and malignant pains were taken by our federal monarchists, and not entirely without effect, to make him view me as a theorist, holding French principles of government, which would lead infallibly to licentiousness and anarchy. And to this he listened the more easily, from my known disapprobation of the British treaty. I never saw him afterwards, or these malignant insinuations should have been dissipated before his just judgment, as mists before the sun. I felt on his death, with my countrymen, that ‘verily a great man hath fallen this day in Israel.’
More time and recollection would enable me to add many other traits of his character; but why add them to you, who knew him well? And I cannot justify to myself a longer detention of your paper.
Vale, proprieque tuum me esse tibi persuadeas.
Th: Jefferson.
Monticello, January 31, 1814.
Dear Sir,
Your favor of the 23d is received. Say had come to hand safely. But I regretted having asked the return of him; for I did not find in him one new idea on the subject I had been contemplating; nothing more than a succinct, judicious digest of the tedious pages of Smith.
You ask my opinion on the question, whether the States can add any qualifications to those which the constitution has prescribed for their members of Congress? It is a question I had never before reflected on; yet had taken up an off-hand opinion, agreeing with your first, that they could not: that to add new qualifications to those of the constitution, would be as much an alteration, as to detract from them. And so I think the House of Representatives of Congress decided in some case; I believe that of a member from Baltimore. But your letter having induced me to look into the constitution, and to consider the question a little, I am again in your predicament, of doubting the correctness of my first opinion. Had the constitution been silent, nobody can doubt but that the right to prescribe all the qualifications and disqualifications of those they would send to represent them, would have belonged to the State. So also the constitution might have prescribed the whole, and excluded all others. It seems to have preferred the middle way. It has exercised the power in part, by declaring some disqualifications, to wit, those of not being twenty-five years of age, of not having been a citizen seven years, and of not being an inhabitant of the State at the time of election. But it does not declare, itself, that the member shall not be a lunatic, a pauper, a convict of treason, of murder, of felony, or other infamous crime, or a non-resident of his district; nor does it prohibit to the State the power of declaring these, or any other disqualifications which its particular circumstances may call for: and these may be different in different States. Of course, then, by the tenth amendment, the power is reserved to the State. If, wherever the constitution assumes a single power out of many which belong to the same subject, we should consider it as assuming the whole, it would vest the General Government with a mass of powers never contemplated. On the contrary, the assumption of particular powers seems an exclusion of all not assumed. This reasoning appears to me to be sound; but, on so recent a change of view, caution requires us not to be too confident, and that we admit this to be one of the doubtful questions on which honest men may differ with the purest motives; and the more readily, as we find we have differed from ourselves on it.
I have always thought, that where the line of demarcation between the powers of the General and State governments was doubtfully or indistinctly drawn, it would be prudent and praiseworthy in both parties, never to approach it but under the most urgent necessity. Is the necessity now urgent, to declare that no non-resident of his district shall be eligible as a member of Congress? It seems to me that, in practice, the partialities of the people are a sufficient security against such an election; and that if, in any instance, they should ever choose a non-resident, it must be in one of such eminent merit and qualifications, as would make it a good, rather than an evil; and that, in any event, the examples will be so rare, as never to amount to a serious evil. If the case then be neither clear nor urgent, would it not be better to let it lie undisturbed? Perhaps its decision may never be called for. But if it be indispensable to establish this disqualification now, would it not look better to declare such others, at the same time, as may be proper? I frankly confide to yourself these opinions, or rather no-opinions, of mine; but would not wish to have them go any farther. I want to be quiet: and although some circumstances now and then excite me to notice them, I feel safe, and happier in leaving events to those whose turn it is to take care of them; and, in general, to let it be understood, that I meddle little or not at all with public affairs. There are two subjects, indeed, which I shall claim a right to further as long as I breathe, the public education and the subdivision of the counties into wards. I consider the continuance of republican government as absolutely hanging on these two hooks. Of the first, you will, I am sure, be an advocate, as having already reflected on it, and of the last, when you shall have reflected. Ever affectionately yours.
Th: Jefferson.
Monticello, July 5, 1814
Dear Sir,
Since mine of January the 24th, yours of March the 14th has been received. It was not acknowledged in the short one of May the 18th, by Mr. Rives, the only object of that having been to enable one of our most promising young men to have the advantage of making his bow to you. I learned with great regret the serious illness mentioned in your letter; and I hope Mr. Rives will be able to tell me you are entirely restored. But our machines have now been running seventy or eighty years, and we must expect that, worn as they are, here a pivot, there a wheel, now a pinion, next a spring, will be giving way; and however we may tinker them up for a while, all will at length surcease motion. Our watches, with works of brass and steel, wear out within that period. Shall you and I last to see the course the seven-fold wonders of the times will take? The Attila of the age dethroned, the ruthless destroyer of ten millions of the human race, whose thirst for blood appeared unquenchable, the great oppressor of the rights and liberties of the world, shut up within the circuit of a little island of the Mediterranean, and dwindled to the condition of an humble and degraded pensioner on the bounty of those he has most injured. How miserably, how meanly, has he closed his inflated career! What a sample of the bathos will his history present! He should have perished on the swords of his enemies, under the walls of Paris.

But Bonaparte was a lion in the field only. In civil life, a cold-blooded, calculating, unprincipled usurper, without a virtue; no statesman, knowing nothing of commerce, political economy, or civil government, and supplying ignorance by bold presumption. I had supposed him a great man until his entrance into the Assembly des Cinq Cens, eighteenth Brumaire (an 8.) From that date, however, I set him down as a great scoundrel only. To the wonders of his rise and fall, we may add that of a Czar of Muscovy, dictating, in Paris, laws and limits to all the successors of the Caesars, and holding even the balance in which the fortunes of this new world are suspended. I own, that while I rejoice, for the good of mankind, in the deliverance of Europe from the havoc which would have never ceased while Bonaparte should have lived in power, I see with anxiety the tyrant of the ocean remaining in vigor, and even participating in the merit of crushing his brother tyrant. While the world is thus turned upside down, on which side of it are we? All the strong reasons, indeed, place us on the side of peace; the interests of the continent, their friendly dispositions, and even the interests of England. Her passions alone are opposed to it. Peace would seem now to be an easy work, the causes of the war being removed. Her orders of council will no doubt be taken care of by the allied powers, and, war ceasing, her impressment of our seamen ceases of course. But I fear there is foundation for the design intimated in the public papers, of demanding a cession of our right in the fisheries. What will Massachusetts say to this? I mean her majority, which must be considered as speaking through the organs it has appointed itself, as the index of its will. She chose to sacrifice the liberty of our sea-faring citizens, in which we were all interested, and with them her obligations to the co-States, rather than war with England. Will she now sacrifice the fisheries to the same partialities? This question is interesting to her alone; for to the middle, the southern, and western States, they are of no direct concern; of no more than the culture of tobacco, rice, and cotton to Massachusetts. I am really at a loss to conjecture what our refractory sister will say on this occasion. I know what, as a citizen of the Union, I would say to her. ‘Take this question ad referendum. It concerns you alone. If you would rather, give up the fisheries than war with England, we give them up. If you had rather fight for them, we will defend your interests to the last drop of our blood, choosing rather to set a good example than follow a bad one.’ And I hope she will determine to fight for them. With this, however, you and I shall have nothing to do; ours being truly the case wherein ‘Non tali auxilio, nec defensoribus istis, tempus eget.’ Quitting this subject, therefore, I will turn over another leaf.
I am just returned from one of my long absences, having been at my other home for five weeks past. Having more leisure there than here for reading, I amused myself with reading seriously Plato’s Republic. I am wrong, however, in calling it amusement, for it was the heaviest task-work I ever went through. I had occasionally before taken up some of his other works, but scarcely ever had patience to go through a whole dialogue. While wading through the whimsies, the puerilities, and unintelligible jargon of this work, I laid it down often to ask myself, how it could have been that the world should have so long consented to give reputation to such nonsense as this. How the soi-disant Christian world, indeed, should have done it, is a piece of historical curiosity. But how could the Roman good sense do it? And particularly, how could Cicero bestow such eulogies on Plato? Although Cicero did not wield the dense logic of Demosthenes, yet he was able, learned, laborious, practised in the business of the world and honest. He could not be the dupe of mere style, of which he was himself the first master in the world. With the moderns, I think, it is rather a matter of fashion and authority. Education is chiefly in the hands of persons who, from their profession, have an interest in the reputation and the dreams of Plato. They give the tone while at school, and few in their after years have occasion to revise their college opinions. But fashion and authority apart, and bringing Plato to the test of reason, take from him, his sophisms, futilities, and incomprehensibilities, and what remains? In truth, he is one of the race of genuine sophists, who has escaped the oblivion of his brethren, first, by the elegance of his diction, but chiefly by the adoption and incorporation of his whimsies into the body of artificial Christianity. His foggy mind is for ever presenting the semblances of objects which, half seen through a mist, can be defined neither in form nor dimension. Yet this, which should have consigned him to early oblivion, really procured him immortality of fame and reverence. The Christian priesthood, finding the doctrines of Christ levelled to every understanding, and too plain to need explanation, saw in the mysticisms of Plato materials with which they might build up an artificial system, which might, from its indistinctness, admit everlasting controversy, give employment for their order, and introduce it to profit, power, and pre-eminence. The doctrines which flowed from the lips of Jesus himself are within the comprehension of a child; but thousands of volumes have not yet explained the Platonisms engrafted on them: and for this obvious reason, that nonsense can never be explained. Their purposes, however, are answered. Plato is canonized: and it is now deemed as impious to question his merits as those of an Apostle of Jesus. He is peculiarly appealed to as an advocate of the immortality of the soul; and yet I will venture to say, that were there no better arguments than his in proof of it, not a man in the world would believe it. It is fortunate for us, that Platonic republicanism has not obtained the same favor as Platonic Christianity; or we should now have been all living, men, women, and children, pell-mell together, like the beasts of the field or forest. Yet ‘Plato is a great philosopher,’ said La Fontaine. But, says Fontenelle, ‘Do you find his ideas very clear.’ ‘Oh, no! he is of an obscurity impenetrable.’ ‘Do you not find him full of contradictions?’ ‘Certainly,’ replied La Fontaine, ‘he is but a sophist.’ Yet immediately after, he exclaims again, ‘Oh, Plato was a great philosopher.’ Socrates had reason, indeed, to complain of the misrepresentations of Plato; for, in truth, his dialogues are libels on Socrates.
But why am I dosing you with these antediluvian topics? Because I am glad to have some one to whom they are familiar, and who will not receive them as if dropped from the moon. Our post-revolutionary youth are born under happier stars than you and I were. They acquire all learning in their mother’s womb, and bring it into the world ready made. The information of books is no longer necessary; and all knowledge which is not innate is in contempt, or neglect at least. Every folly must run its round; and so, I suppose, must that of self-learning and self-sufficiency; of rejecting the knowledge acquired in past ages, and starting on the new ground of intuition. When sobered by experience, I hope our successors will turn their attention to the advantages of education. I mean of education on the broad scale, and not that of the petty academies, as they call themselves, which are starting up in every neighborhood, and where one or two men, possessing Latin, and sometimes Greek, a knowledge of the globes, and the first six books of Euclid, imagine and communicate this as the sum of science. They commit their pupils to the theatre of the world, with just taste enough of learning to be alienated from industrious pursuits, and not enough to do service in the ranks of science. We have some exceptions, indeed. I presented one to you lately, and we have some others. But the terms I use are general truths. I hope the necessity will, at length, be seen of establishing institutions here, as in Europe, where every branch of science, useful at this day, may be taught in its highest degree. Have you ever turned your thoughts to the plan of such an institution? I mean to a specification of the particular sciences of real use in human affairs, and how they might be so grouped as to require so many professors only, as might bring them within the views of a just but enlightened economy? I should be happy in a communication of your ideas on this problem, either loose or digested. But to avoid my being run away with by another subject, and adding to the length and ennui of the present letter, I will here present to Mrs. Adams and yourself, the assurance of my constant and sincere friendship and respect.
Th: Jefferson.
Monticello, January 1, 1815.
Dear Sir,
Your letters of November the 30th and December the 21st have been received with great pleasure. A truth now and then projecting into the ocean of newspaper lies, serves like headlands to correct our course. Indeed, my scepticism as to every thing I see in a newspaper, makes me indifferent whether I ever see one. The embarrassments at Washington, in August last, I expected would be great in any state of things; but they proved greater than expected. I never doubted that the plans of the President were wise and sufficient. Their failure we all impute, 1. To the insubordinate temper of Armstrong: and, 2. To the indecision of Winder. However, it ends well. It mortifies ourselves, and so may check, perhaps, the silly boasting spirit of our newspapers, and it enlists the feelings of the world on our side: and the advantage of public opinion is like that of the weather-gage in a naval action. In Europe, the transient possession of our Capital can be no disgrace. Nearly every Capital there was in possession of its enemy some often and long. But diabolical as they paint that enemy, he burnt neither public edifices nor private dwellings. It was reserved for England to show that Bonaparte, in atrocity, was an infant to their ministers and their generals. They are taking his place in the eyes of Europe, and have turned into our channel all its good will. This will be worth the million of dollars the repairs of their conflagrations will cost us. I hope that to preserve this weather-gage of public opinion, and to counteract the slanders and falsehoods disseminated by the English papers, the government will make it a standing instruction to their ministers at foreign courts, to keep Europe truly informed of occurrences here, by publishing in their papers the naked truth always, whether favorable or unfavorable. For they will believe the good, if we candidly tell them the bad also.
But you have two more serious causes of uneasiness; the want of men and money. For the former, nothing more wise or efficient could have been imagined than what you proposed. It would have filled our ranks with regulars, and that, too, by throwing a just share of the burthen on the purses of those whose persons are exempt either by age or office; and it would have rendered our militia, like those of the Greeks and Romans, a nation of warriors. But the go-by seems to have been given to your proposition, and longer sufferance is necessary to force us to what is best. We seem equally incorrigible in our financial course. Although a century of British experience has proved to what a wonderful extent the funding on specific redeeming taxes enables a nation to anticipitate in war the resources of peace, and although the other nations of Europe have tried and trodden every path of force or folly in fruitless quest of the same object, yet we still expect to find, in juggling tricks and banking dreams, that money can be made out of nothing, and in sufficient quantity to meet the expenses of a heavy war by sea and land. It is said, indeed, that money cannot be borrowed from our merchants as from those of England. But it can be borrowed from our people. They will give you all the necessaries of war they produce, if, instead of the bankrupt trash they now are obliged to receive for want of any other, you will give them a paper-promise funded on a specific pledge, and of a size for common circulation. But you say the merchants will not take this paper. What the people take the merchants must take, or sell nothing. All these doubts and fears prove only the extent of the dominion which the banking institutions have obtained over the minds of our citizens, and especially of those inhabiting cities or other banking places; and this dominion must be broken, or it will break us. But here, as in the other case, we must make up our mind to suffer yet longer before we can get right. The misfortune is, that in the mean time, we shall plunge ourselves into inextinguishable debt, and entail on our posterity an inheritance of eternal taxes, which will bring our government and people into the condition of those of England, a nation of pikes and gudgeons, the latter bred merely as food for the former. But, however these two difficulties of men and money may be disposed of, it is fortunate that neither of them will affect our war by sea. Privateers will find their own men and money. Let nothing be spared to encourage them. They are the dagger which strikes at the heart of the enemy, their commerce. Frigates and seventy-fours are a sacrifice we must make, heavy as it is, to the prejudices of a part of our citizens. They have, indeed, rendered a great moral service, which has delighted me as much as any one in the United States. But they have had no physical effect sensible to the enemy; and now, while we must fortify them in our harbors, and keep armies to defend them, our privateers are bearding and blockading the enemy in their own sea-ports. Encourage them to burn all their prizes, and let the public pay for them. They will cheat us enormously. No matter; they will make the merchants of England feel, and squeal, and cry out for peace.
I much regretted your acceptance of the war department. Not that I know a person who I think would better conduct it. But, conduct it ever so wisely, it will be a sacrifice of yourself. Were an angel from Heaven to undertake that office, all our miscarriages would be ascribed to him. Raw troops, no troops, insubordinate militia, want of arms, want of money, want of provisions, all will be charged to want of management in you. I speak from experience, when I was Governor of Virginia. Without a regular in the State, and scarcely a musket to put into the hands of the militia, invaded by two armies, Arnold’s from the sea-board, and Cornwallis’s from the southward,—when we were driven from Richmond and Charlottesville, and every member of my council fled to their homes, it was not the total destitution of means, but the mismanagement of them, which, in the querulous voice of the public, caused all our misfortunes. It ended, indeed, in the capture of the whole hostile force, but not till means were brought us by General Washington’s army, and the French fleet and army. And although the legislature, who were personally intimate with both the means and measures, acquitted me with justice and thanks, yet General Lee has put all those imputations among the romances of his historical novel, for the amusement of credulous and uninquisitive readers. Not that I have seen the least disposition to censure you. On the contrary, your conduct on the attack of Washington has met the praises of every one, and your plan for regulars and militia, their approbation. But no campaign is as yet opened. No generals have yet an interest in shifting their own incompetence on you, no army agents, their rogueries. I sincerely pray you may never meet censure where you will deserve most praise, and that your own happiness and prosperity may be the result of your patriotic services.
Ever and affectionately yours.
Th: Jefferson.
TO THE MARQUIS DE LA FAYETTE.
Monticello, February 14, 1815.
Mr Dear Friend,
Your letter of August the 14th has been received and read, again and again, with extraordinary pleasure. It is the first glimpse which has been furnished me of the interior workings of the late unexpected but fortunate revolution of your country. The newspapers told us only that the great beast was fallen; but what part in this the patriots acted, and what the egoists, whether the former slept while the latter were awake to their own interests only, the hireling scribblers of the English press said little, and knew less. I see now the mortifying alternative under which the patriot there is placed, of being either silent, or disgraced by an association in opposition with the remains of Bonaparteism. A full measure of liberty is not now perhaps to be expected by your nation; nor am I confident they are prepared to preserve it. More than a generation will be requisite, under the administration of reasonable laws favoring the progress of knowledge in the general mass of the people, and their habituation to an independent security of person and property, before they will be capable of estimating the value of freedom, and the necessity of a sacred adherence to the principles on which it rests for preservation. Instead of that liberty which takes root and growth in the progress of reason, if recovered by mere force or accident, it becomes, with an unprepared people, a tyranny still, of the many, the few, or the one. Possibly you may remember, at the date of the jeu de paume, how earnestly I urged yourself and the patriots of my acquaintance to enter then into a compact with the King, securing freedom of religion, freedom of the press, trial by jury, habeas corpus, and a national legislature, all of which it was known he would then yield, to go home, and let these work on the amelioration of the condition of the people, until they should have rendered them capable of more, when occasions would not fail to arise for communicating to them more. This was as much as I then thought them able to bear, soberly and usefully for themselves. You thought otherwise, and that the dose might still be larger. And I found you were right; for subsequent events proved they were equal to the constitution of 1791. Unfortunately, some of the most honest and enlightened of our patriotic friends (but closet politicians merely, unpractised in the knowledge of man) thought more could still be obtained and borne. They did not weigh the hazards of a transition from one form of government to another, the value of what they had already rescued from those hazards, and might hold in security if they pleased, nor the imprudence of giving up the certainty of such a degree of liberty, under a limited monarch, for the uncertainty of a little more under the form of a republic. You differed from them. You were for stopping there, and for securing the constitution which the National Assembly had obtained. Here, too, you were right; and from this fatal error of the republicans, from their separation from yourself and the constitutionalists, in their councils, flowed all the subsequent sufferings and crimes of the French nation. The hazards of a second change fell upon them by the way. The foreigner gained time to anarchize by gold the government he could not overthrow by arms, to crush in their own councils the genuine republicans, by the fraternal embraces of exaggerated and hired pretenders, and to turn the machine of Jacobinism from the change to the destruction of order: and, in the end, the limited monarchy they had secured was exchanged for the unprincipled and bloody tyranny of Robespierre, and the equally unprincipled and maniac tyranny of Bonaparte. You are now rid of him, and I sincerely wish you may continue so. But this may depend on the wisdom and moderation of the restored dynasty. It is for them now to read a lesson in the fatal errors of the republicans; to be contented with a certain portion of power, secured by formal compact with the nation, rather than, grasping at more, hazard all upon uncertainty, and risk meeting the fate of their predecessor, or a renewal of their own exile. We are just informed, too, of an example which merits, if true, their most profound contemplation. The gazettes say, that Ferdinand of Spain is dethroned, and his father re-established on the basis of their new constitution. This order of magistrates must, therefore, see, that although the attempts at reformation have not succeeded in their whole length, and some secession from the ultimate point has taken place, yet that men have by no means fallen back to their former passiveness; but on the contrary, that a sense of their rights, and a restlessness to obtain them, remain deeply impressed on every mind, and, if not quieted by reasonable relaxations of power, will break out like a volcano on the first occasion, and overwhelm every thing again in its way. I always thought the present King an honest and moderate man: and having no issue, he is under a motive the less for yielding to personal considerations. I cannot, therefore, but hope, that the patriots in and out of your legislature, acting in phalanx, but temperately and wisely, pressing unremittingly the principles omitted in the late capitulation of the King, and watching the occasions which the course of events will create, may get those principles engrafted into it, and sanctioned by the solemnity of a national act.
With us the affairs of war have taken the more favorable turn which was to be expected. Our thirty years of peace had taken off, or superannuated, all our revolutionary officers of experience and grade; and our first draught in the lottery of untried characters had been most unfortunate. The delivery of the fort and army of Detroit, by the traitor Hull; the disgrace at Queenstown, under Van Rensellaer; the massacre at Frenchtown, under Winchester; and surrender of Boerstler in an open field to one third of his own numbers, were the inauspicious beginnings of the first year of our warfare. The second witnessed but the single miscarriage occasioned by the disagreement of Wilkinson and Hampton, mentioned in my letter to you of November the 30th, 1813; while it gave us the capture of York by Dearborn and Pike; the capture of Fort George by Dearborn also; the capture of Proctor’s army on the Thames by Harrison, Shelby, and Johnson; and that of the whole British fleet on Lake Erie by Perry. The third year has been a continued series of victories; to wit, of Brown and Scott at Chippeway; of the same at Niagara; of Gaines over Drummond at Fort Erie; that of Brown over Drummond at the same place; the capture of another fleet on Lake Champlain by M’Donough; the entire defeat of their army under Prevost, on the same day, by M’Comb, and recently their defeats at New Orleans by Jackson, Coffee, and Carroll, with the loss of four thousand men out of nine thousand and six hundred, with their two Generals, Packingham and Gibbs killed, and a third, Keane, wounded, mortally, as is said.
This series of successes has been tarnished only by the conflagrations at Washington, a coup de main differing from that at Richmond, which you remember, in the revolutionary war, in the circumstance only, that we had, in that case, but forty-eight hour’s notice that an enemy had arrived within our capes; whereas at Washington there was abundant previous notice. The force designated by the President was the double of what was necessary; but failed, as is the general opinion, through the insubordination of Armstrong, who would never believe the attack intended until it was actually made, and the sluggishness of Winder before the occasion, and his indecision during it. Still, in the end, the transaction has helped rather than hurt us, by arousing the general indignation of our country, and by marking to the world of Europe the Vandalism and brutal character of the English government. It has merely served to immortalize their infamy. And add further, that through the whole period of the war, we have beaten them single-handed at sea, and so thoroughly established our superiority over them with equal force, that they retire from that kind of contest, and never suffer their frigates to cruise singly. The Endymion would never have engaged the frigate President, but knowing herself backed by three frigates and a razee, who, though somewhat slower sailors, would get up before she could be taken. The disclosure to the world of the fatal secret that they can be beaten at sea with an equal force, the evidence furnished by the military operations of the last year that experience is rearing us officers, who, when our means shall be fully under way, will plant our standard on the walls of Quebec and Halifax, their recent and signal disaster at New Orleans, and the evaporation of their hopes from the Hartford Convention, will probably raise a clamor in the British nation, which will force their ministry into peace. I say force them; because, willingly, they would never be at peace. The British ministers find in a state of war rather than of peace, by riding the various contractors, and receiving douceurs on the vast expenditures of the war supplies, that they recruit their broken fortunes, or make new ones, and therefore will not make peace, as long as by any delusions they can keep the temper of the nation up to the war point. They found some hopes on the state of our finances. It is true, that the excess of our banking institutions, and their present discredit, have shut us out from the best source of credit we could ever command with certainty. But the foundations of credit still remain to us, and need but skill, which experience will soon produce, to marshal them into an order which may carry us through any length of war. But they have hoped more in their Hartford Convention. Their fears of republican France being now done away, they are directed to republican America, and they are playing the same game for disorganization here, which they played in your country. The Marats, the Dantons, and Robespierres of Massachusetts are in the same pay, under the same orders, and making the same efforts to anarchize us, that their prototypes in France did there.
I do not say that all who met at Hartford were under the same motives of money: nor were those of France. Some of them are Outs, and wish to be Ins; some the mere dupes of the agitators, or of their own party passions; while the Maratists alone are in the real secret: but they have very different materials to work on. The yeomanry of the United States are not the canaille of Paris. We might safely give them leave to go through the United States recruiting their ranks, and I am satisfied they could not raise one single regiment (gambling merchants and silk-stocking clerks excepted), who would support them in any effort to separate from the Union. The cement of this Union is in the heart-blood of every American. I do not believe there is on earth a government established on so immovable a basis. Let them, in any State, even in Massachusetts itself, raise the standard of separation, and its citizens will rise in mass, and do justice themselves on their own incendiaries. If they could have induced the government to some effort of suppression, or even to enter into discussion with them, it would have given them some importance, have brought them into some notice. But they have not been able to make themselves even a subject of conversation, either of public or private societies. A silent contempt has been the sole notice they could excite; consoled, indeed, some of them, by the palpable favors of Philip. Have then no fears for us, my friend. The grounds of these exist only in English newspapers, endited or endowed by the Castlereaghs or the Cannings, or some other such models of pure and uncorrupted virtue. Their military heroes, by land and sea, may sink our oyster-boats, rob our hen-roosts, burn our negro-huts, and run off. But a campaign or two more will relieve them from further trouble or expense in defending their American possessions.
You once gave me a copy of the journal of your campaign in Virginia, in 1781, which I must have lent to some one of the undertakers to write the history of the revolutionary war, and forgot to reclaim. I conclude this, because it is no longer among my papers, which I have very diligently searched for it, but in vain. An author of real ability is now writing that part of the history of Virginia. He does it in my neighborhood, and I lay open to him all my papers. But I possess none, nor has he any, which can enable him to do justice to your faithful and able services in that campaign. If you could be so good as to send me another copy, by the very first vessel bound to any port of the United States, it might be here in time; for although he expects to begin to print within a month or two, yet you know the delays of these undertakings. At any rate, it might be got in as a supplement. The old Count Rochambeau gave me also his memoire of the operations at York, which is gone the same way, and I have no means of applying to his family for it. Perhaps you could render them as well as us, the service of procuring another copy.
I learn, with real sorrow, the deaths of Monsieur and Madame de Tesse. They made an interesting part in the idle reveries in which I have sometimes indulged myself, of seeing all my friends of Paris once more, for a month or two; a thing impossible, which, however, I never permitted myself to despair of. The regrets, however, of seventy-three at the loss of friends, may be the less, as the time is shorter within which we are to meet again, according to the creed of our education.
This letter will be handed you by Mr. Ticknor, a young gentleman of Boston, of great erudition, indefatigable industry, and preparation for a life of distinction, in his own country. He passed a few days with me here, brought high recommendations from Mr. Adams and others, and appeared in every respect to merit them. He is well worthy of those attentions which you so kindly bestow on our countrymen, and for those he may receive I shall join him in acknowledging personal obligations.
I salute you with assurances of my constant and affectionate friendship and respect.
Th; Jefferson.
P.S. February 26. My letter had not yet been sealed, when I received news of our peace. I am glad of it, and especially that we closed our war with the eclat of the action at New Orleans. But I consider it as an armistice only, because no security is provided against the impressment of our seamen. While this is unsettled we are in hostility of mind with England, although actual deeds of arms may be suspended by a truce. If she thinks the exercise of this outrage is worth eternal war, eternal war it must be, or extermination of the one or the other party. The first act of impressment she commits on an American, will be answered by reprisal, or by a declaration of war here; and the interval must be merely a state of preparation for it. In this we have much to do, in further fortifying our seaport towns, providing military stores, classing and disciplining our militia, arranging our financial, system, and above all, pushing our domestic manufactures, which have taken such root as never again can be shaken. Once more, God bless you. T.J.
TO MR. WENDOVER.
Monticello, March 13, 1815.
[* This is endorsed;’ not sent.‘]
Sir,
Your favor of January the 30th was received after long delay on the road, and I have to thank you for the volume of Discourses which you have been so kind as to send me. I have gone over them with great satisfaction, and concur with the able preacher in his estimate of the character of the belligerents in our late war, and lawfulness of defensive war. I consider the war, with him, as ‘made on good advice,’ that is, for just causes, and its dispensation as providential, inasmuch, as it has exercised our patriotism and submission to order, has planted and invigorated among us arts of urgent necessity, has manifested the strong and the weak parts of our republican institutions, and the excellence of a representative democracy compared with the misrule of Kings, has rallied the opinions of mankind to the natural rights of expatriation, and of a common property in the ocean, and raised us to that grade in the scale of nations which the bravery and liberality of our citizen soldiers, by land and by sea, the wisdom of our institutions and their observance of justice, entitled us to in the eyes of the world. All this Mr. McLeod has well proved, and from those sources of argument particularly which belong to his profession. On one question only I differ from him, and it is that which constitutes the subject of his first discourse, the right of discussing public affairs in the pulpit. I add the last words, because I admit the right in general conversation and in writing; in which last form it has been exercised in the valuable book you have now favored me with.
The mass of human concerns, moral and physical, is so vast, the field of knowledge requisite for man to conduct them to the best advantage is so extensive, that no human being can acquire the whole himself, and much less in that degree necessary for the instruction of others. It has of necessity, then, been distributed into different departments, each of which, singly, may give occupation enough to the whole time and attention of a single individual. Thus we have teachers of Languages, teachers of Mathematics, of Natural Philosophy, of Chemistry, of Medicine, of Law, of History, of Government, &c. Religion, too, is a separate department, and happens to be the only one deemed requisite for all men, however high or low. Collections of men associate together, under the name of congregations, and employ a religious teacher of the particular sect of opinions of which they happen to be, and contribute to make up a stipend as a compensation for the trouble of delivering them, at such periods as they agree on, lessons in the religion they profess. If they want instruction in other sciences or arts, they apply to other instructers; and this is generally the business of early life. But I suppose there is not an instance of a single congregation which has employed their preacher for the mixt purpose of lecturing them from the pulpit, in Chemistry, in Medicine, in Law, in the science and principles of Government, or in any thing but Religion exclusively. Whenever, therefore, preachers, instead of a lesson in religion, put them off with a discourse on the Copernican system, on chemical affinities, on the construction of government, or the characters or conduct of those administering it, it is a breach of contract, depriving their audience of the kind of service for which they are salaried, and giving them, instead it, what they did not want, or if wanted, would rather seek from better sources in that particular art or science. In choosing our pastor we look to his religious qualifications, without inquiring into his physical or political dogmas, with which we mean to have nothing to do. I am aware that arguments may be found, which may twist a thread of politics into the cord of religious duties. So may they for every other branch of human art or science. Thus, for example, it is a religious duty to obey the laws of our country: the teacher of religion, therefore, must instruct us in those laws, that we may know how to obey them. It is a religious duty to assist our sick neighbors: the preacher must, therefore, teach us medicine, that we may do it understandingly. It is a religious duty to preserve our own health: our religious teacher, then, must tell us what dishes are wholesome, and give us recipes in cookery, that we may learn how to prepare them. And so ingenuity, by generalizing more and more, may amalgamate all the branches of science into any one of them, and the physician who is paid to visit the sick, may give a sermon instead of medicine; and the merchant to whom money is sent for a hat, may send a handkerchief instead of it. But not withstanding this possible confusion of all sciences into one, common sense draws lines between them sufficiently distinct for the general purposes of life, and no one is at a loss to understand that a recipe in medicine or cookery, or a demonstration in geometry, is not a lesson in religion. I do not deny that a congregation may, if they please, agree with their preacher that he shall instruct them in Medicine also, or Law, or Politics. Then, lectures in these, from the pulpit, become not only a matter of right, but of duty also. But this must be with the consent of every individual; because the association being voluntary, the mere majority has no right to apply the contributions of the minority to purposes unspecified in the agreement of the congregation. I agree, too, that on all other occasions the preacher has the right, equally with every other citizen, to express his sentiments, in speaking or writing, on the subjects of Medicine, Law, Politics, he, his leisure time being his own, and his congregation not obliged to listen to his conversation, or to read his writings; and no one would have regretted more than myself, had any scruple as to this right, withheld from us the valuable discourses which have led to the expression of an opinion as to the true limits of the right. I feel my portion of indebtment to the reverend author, for the distinguished learning, the logic, and the eloquence, with which he had proved that religion, as well as reason, confirms the soundness of those principles on which our government has been founded and its rights asserted.
These are my views of this question. They are in opposition to those of the highly respected and able preacher, and are therefore the more doubtingly offered. Difference of opinion leads to inquiry, and inquiry to truth; and that, I am sure, is the ultimate and sincere object of us both. We both value too much the freedom of opinion sanctioned by our constitution, not to cherish its exercise even where in opposition to ourselves.
Unaccustomed to reserve or mystery in the expression of my opinions, I have opened myself frankly on a question suggested by your letter and present. And although I have not the honor of your acquaintance, this mark of attention, and still more the sentiments of esteem so kindly expressed in your letter, are entitled to a confidence that observations not intended for the public will not be ushered to their notice, as has happened to me sometimes. Tranquillity, at my age, is the balm of life. While I know I am safe in the honor and charity of a McLeod, I do not wish to be cast forth to the Marats, the Dantons, and the Robespierres of the priesthood: I mean the Parishes, the Osgoods, and the Gardiners of Massachusetts.
I pray you to accept the assurances of my esteem and respect.
Th: Jefferson.
TO CÆSAR A. RODNEY.
Monticello, March 16, 1815.
My Dear Friend and Ancient Colleague,
Your letter of February the 19th has been received with very sincere pleasure. It recalls to memory the sociability, the friendship, and the harmony of action which united personal happiness with public duties, during the portion of our lives in which we acted together. Indeed, the affectionate harmony of our cabinet is among the sweetest of my recollections. I have just received a letter of friendship from General Dearborn. He writes me that he is now retiring from every species of public occupation, to pass the remainder of life as a private citizen; and he promises me a visit in the course of the summer. As you hold out a hope of the same gratification, if chance or purpose could time your visits together, it would make a real jubilee. But come as you will, or as you can, it will always be joy enough to me. Only you must give me a month’s notice; because I go three or four times a year to a possession ninety miles southwestward, and am absent a month at a time, and the mortification would be indelible of losing such a visit by a mistimed absence. You will find me in habitual good health, great contentedness, enfeebled in body, impaired in memory, but without decay in my friendships.
Great, indeed, have been the revolutions in the world, since you and I have had any thing to do with it. To me they have been like the howlings of the winter storm over the battlements, while warm in my bed. The unprincipled tyrant of the land is fallen, his power reduced to its original nothingness, his person only not yet in the mad-house, where it ought always to have been. His equally unprincipled competitor, the tyrant of the ocean, in the mad-house indeed, in person, but his power still stalking over the deep. ‘Quem deus vult perdere, prius dementat.’ The madness is acknowledged; the perdition of course impending. Are we to be the instruments? A friendly, a just, and a reasonable conduct on their part, might make us the main pillar of their prosperity and existence. But their deep-rooted hatred to us seems to be the means which Providence permits to lead them to their final catastrophe. ‘Nullam enim in terris gentem esse, nullum infestiorem populum, nomini Romano, said the General who erased Capua from the list of powers. What nourishment and support would not England receive from an hundred millions of industrious descendants, whom some of her people now born will live to see here. What their energies are, she has lately tried. And what has she not to fear from an hundred millions of such men, if she continues her maniac course of hatred and hostility to them. I hope in God she will change. There is not a nation on the globe with whom I have more earnestly wished a friendly intercourse on equal conditions. On no other would I hold out the hand of friendship to any. I know that their creatures represent me as personally an enemy to England. But fools only can believe this, or those who think me a fool. I am an enemy to her insults and injuries. I am an enemy to the flagitious principles of her administration, and to those which govern her conduct towards other nations. But would she give to morality some place in her political code, and especially would she exercise decency, and at least neutral passions towards us, there is not, I repeat it, a people on earth with whom I would sacrifice so much to be in friendship. They can do us, as enemies, more harm than any other nation; and in peace and in war, they have more means of disturbing us internally. Their merchants established among us, the bonds by which our own are chained to their feet, and the banking combinations interwoven with the whole, have shown the extent of their control, even during a war with her. They are the workers of all the embarrassments our finances have experienced during the war. Declaring themselves bankrupt, they have been able still to chain the government to a dependence on them; and had the war continued, they would have reduced us to the inability to command a single dollar. They dared to proclaim that they would not pay their own paper obligations, yet our government could not venture to avail themselves of this opportunity of sweeping their paper from the circulation, and substituting their own notes bottomed on specific taxes for redemption, which every one would have eagerly taken and trusted, rather than the baseless trash of bankrupt companies; our government, I say, have still been overawed from a contest with them, and have even countenanced and strengthened their influence, by proposing new establishments, with authority to swindle yet greater sums from our citizens. This is the British influence to which I am an enemy, and which we must subject to our government, or it will subject us to that of Britain.
Come and gratify, by seeing you once more, a friend, who assures you with sincerity of his constant and affectionate attachment and respect.
Th: Jefferson.
TO GENERAL DEARBORN.
Monticello, March 17, 1815.
My Dear General, Friend, and Ancient Colleague,
I have received your favor of February the 27th, with very great pleasure, and sincerely reciprocate congratulations on the late events. Peace was indeed desirable; yet it would not have been as welcome without the successes of New Orleans. These last have established truths too important not to be valued; that the people of Louisiana are sincerely attached to the Union; that their city can be defended; that the western States make its defence their peculiar concern; that the militia are brave; that their deadly aim countervails the manoeuvring skill of their enemy; that we have officers of natural genius now starting forward from the mass; and that, putting together all our conflicts, we can beat the British, by sea and by land, with equal numbers. All this being now proved, I am glad of the pacification of Ghent, and shall still be more so, if, by a reasonable arrangement against impressment, they will make it truly a treaty of peace, and not a mere truce, as we must all consider it, until the principle of the war is settled. Nor, among the incidents of the war, will we forget your services. After the disasters produced by the treason or the cowardice, or both, of Hull, and the follies of some others, your capture of York and Fort George first turned the tide of success in our favor; and the subsequent campaigns sufficiently wiped away the disgraces of the first. If it were justifiable to look to your own happiness only, your resolution to retire from all public business could not but be approved. But you are too young to ask a discharge as yet, and the public counsels too much needing the wisdom of our ablest citizens, to relinquish their claim on you. And surely none needs your aid more than your own State. Oh, Massachusetts! how have I lamented the degradation of your apostacy! Massachusetts, with whom I went with pride in 1776, whose vote was my vote on every public question, and whose principles were then the standard of whatever was free or fearless. But then she was under the counsels of the two Adamses; while Strong, her present leader, was promoting petitions for submission to British power and British usurpation. While under her present counsels, she must be contented to be nothing; as having a vote, indeed, to be counted, but not respected. But should the State once more buckle on her republican harness, we shall receive her again as a sister, and recollect her wanderings among the crimes only of the parricide party, which would have basely sold what their fathers so bravely won from the same enemy. Let us look forward, then, to the act of repentance, which, by dismissing her venal traitors, shall be the signal of return to the bosom and to the principles of her brethren; and if her late humiliation can just give her modesty enough to suppose that her southern brethren are somewhat on a par with her in wisdom, in information, in patriotism, in bravery, and even in honesty, although not in psalm-singing, she will more justly estimate her own relative momentum in the Union. With her ancient principles, she would really be great, if she did not think herself the whole. I should be pleased to hear that you go into her councils, and assist in bringing her back to those principles, and to a sober satisfaction with her proportionable share in the direction of our affairs.
Be so good as to lay my homage at the feet of Mrs. Dearborn, and to be assured that I am ever and affectionately yours.
Th: Jefferson.
TO THE PRESIDENT.
Monticello, March 23,1815.
Deak Sir,
I duly received your favor of the 12th, and with it the pamphlet on the causes and conduct of the war, which I now return. I have read it with great pleasure, but with irresistible desire that it should be published. The reasons in favor of this are strong, and those against it are so easily gotten over, that there appears to me no balance between them. 1. We need it in Europe. They have totally mistaken our character. Accustomed to rise at a feather themselves, and to be always fighting, they will see in our conduct, fairly stated, that acquiescence under wrong, to a certain degree, is wisdom, and not pusillanimity; and that peace and happiness are preferable to that false honor, which, by eternal wars, keeps their people in eternal labor, want, and wretchedness. 2. It is necessary for the people of England, who have been deceived as to the causes and conduct of the war, and do not entertain a doubt, that it was entirely wanton and wicked on our part, and under the order of Bonaparte. By rectifying their ideas, it will tend to that conciliation which is absolutely necessary to the peace and prosperity of both nations. 3. It is necessary for our own people, who, although they have known the details as they went along, yet have been so plied with false facts and false views by; the federalists, that some impression has been left that all has not been right. It may be said that it will be thought unfriendly. But truths necessary for our own character, must not be suppressed out of tenderness to its calumniators. Although written, generally, with great moderation, there may be some things in the pamphlet which may perhaps irritate. The characterizing every act, for example, by its appropriate epithet, is not necessary to show its deformity to an intelligent reader. The naked narrative will present it truly to his mind, and the more strongly, from its moderation, as he will perceive that no exaggeration is aimed at. Rubbing down these roughnesses (and they are neither many nor prominent), and preserving the original date, might, I think, remove all the offensiveness, and give more effect to the publication. Indeed, I think that a soothing postscript, addressed to the interests, the prospects, and the sober reason of both nations, would make it acceptable to both. The trifling, expense of reprinting it ought not to be considered a moment. Mr. Gallatin could have it translated into French, and suffer it to get abroad in Europe without either avowal or disavowal. But it would be useful to print some copies of an appendix, containing all the documents referred to, to be preserved in libraries, and to facilitate to the present and future writers of history, the acquisition of the materials which test the truths it contains.
I sincerely congratulate you on the peace, and more especially on the eclat with which the war was closed. The affair of New Orleans was fraught with useful lessons to ourselves, our enemies, and our friends, and will powerfully influence our future relations with the nations of Europe. It will show them we mean to take no part in their wars, and count no odds when engaged in our own. I presume, that, having spared to the pride of England her formal acknowledgment of the atrocity of impressment in an article of the treaty, she will concur in a convention for relinquishing it. Without this, she must understand that the present is but a truce, determinable on the first act of impressment of an American citizen, committed by any officer of hers. Would it not be better that this convention should be a separate act, unconnected with any treaty of commerce, and made an indispensable preliminary to all other treaty? If blended with a treaty of commerce, she will make it the price of injurious concessions. Indeed, we are infinitely better without such treaties with any nation. We cannot too distinctly detach ourselves from the European system, which is essentially belligerent, nor too sedulously cultivate an American system, essentially pacific. But if we go into commercial treaties at all, they should be with all, at the same time, with whom we have important commercial relations. France, Spain, Portugal, Holland, Denmark, Sweden, Russia, all should proceed pari passu. Our ministers marching in phalanx on the same line, and intercommunicating freely, each will be supported by the weight of the whole mass, and the facility with which the other nations will agree to equal terms of intercourse, will discountenance the selfish higglings of England, or justify our rejection of them. Perhaps with all of them it would be best to have but the single article gentis amicissimæ, leaving every thing else to the usages and courtesies of civilized nations. But all these things will occur to yourself, with their counter considerations.
Mr. Smith wrote to me on the transportation of the library, and particularly, that it is submitted to your direction. He mentioned also, that Dougherty would be engaged to superintend it. No one will more carefully and faithfully execute all those duties which would belong to a wagon-master. But it requires a character acquainted with books, to receive the library. I am now employing as many hours of every day as my strength will permit, in arranging the books, and putting every one in its place on the shelves, corresponding with its order in the catalogue, and shall have them numbered correspondently. This operation will employ me a considerable time yet. Then I should wish a competent agent to attend, and, with the catalogue in his hand, see that every book is on the shelves, and have their lids nailed on, one by one, as he proceeds. This would take such a person about two days; after which, Dougherty’s business would be the mere mechanical removal, at convenience. I enclose you a letter from Mr. Milligan, offering his service, which would not cost more than eight or ten days’ reasonable compensation. This is necessary for my safety, and your satisfaction, as a just caution for the public. You know there are persons, both in and out of the public councils, who will seize every occasion of imputation on either of us, the more difficult to be repelled in this case, in which a negative could not be proved. If you approve of it, therefore, as soon as I am through the review, I will give notice to Mr. Milligan, or any other person whom you will name, to come on immediately. Indeed it would be well worth while to add to his duty, that of covering the books with a little paper (the good bindings at least), and filling the vacancies of the presses with paper-parings, to be brought from Washington. This would add little more to the time, as he could carry on both operations at once.
Accept the assurance of my constant and affectionate friendship and respect,
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN ADAMS.
Monticello, June 10,1815.
Dear Sir,
It is long since we have exchanged a letter, and yet what volumes might have been written on the occurrences even of the last three months. In the first place, peace, God bless it! has returned, to put us all again into a course of lawful and laudable pursuits: a new trial of the Bourbons has proved to the world their incompetence to the functions of the station they have occupied: and the recall of the usurper has clothed him with the semblance of a legitimate autocrat. If adversity should have taught him wisdom, of which I have little expectation, he may yet render some service to mankind, by teaching the ancient dynasties that they can be changed for misrule, and by wearing down the maritime power of England to limitable and safe dimensions. But it is not possible he should love us; and of that our commerce had sufficient proofs during his power. Our military achievements, indeed, which he is capable of estimating, may in some degree moderate the effect of his aversions; and he may perhaps fancy that we are to become the natural enemies of England, as England herself has so steadily endeavored to make us, and as some of our own over-zealous patriots would be willing to proclaim; and in this view, he may admit a cold toleration of some intercourse and commerce between the two nations. He has certainly had time to see the folly of turning the industry of France from the cultures for which nature has so highly endowed her, to those of sugar, cotton, tobacco, and others, which the same creative power has given to other climates: and, on the whole, if he can conquer the passions of his tyrannical soul, if he has understanding enough to pursue from motives of interest, what no moral motives lead him to, the tranquil happiness and prosperity of his country, rather than a ravenous thirst for human blood, his return may become of more advantage than injury to us. And if again some great man could arise in England, who could see and correct the follies of his nation in their conduct as to us, and by exercising justice and comity towards ours, bring both into a state of temperate and useful friendship, it is possible we might thus attain the place we ought to occupy between these two nations, without being degraded to the condition of mere partisans of either.
A little time will now inform us, whether France, within its proper limits, is big enough for its ruler, on the one hand, and whether, on the other, the allied powers are either wicked or foolish enough to attempt the forcing on the French, a ruler and government which they refuse; whether they will risk their own thrones to re-establish that of the Bourbons. If this is attempted, and the European world again committed to war, will the jealousy of England at the commerce which neutrality will give us, induce her again to add us to the number of her enemies, rather than see us prosper in the pursuit of peace and industry? And have our commercial citizens merited from their country its encountering another war to protect their gambling enterprises? That the persons of our citizens shall be safe in freely traversing the ocean, that the transportation of our own produce, in our own vessels, to the markets of our choice, and the return to us of the articles we want for our own use, shall be unmolested, I hold to be fundamental, and that the gauntlet must be for ever hurled at him who questions it. But whether we shall engage in every war of Europe, to protect the mere agency of our merchants and shipowners in carrying on the commerce of other nations, even were those merchants and ship-owners to take the side of their country in the contest, instead of that of the enemy, is a question of deep and serious consideration, with which, however, you and I shall have nothing to do; so we will leave it to those whom it will concern.
I thank you for making known to me Mr. Ticknor and Mr. Gray. They are fine young men, indeed, and if Massachusetts can raise a few more such, it is probable she would be better counselled as to social rights and social duties. Mr. Ticknor is, particularly, the best bibliograph I have met with, and very kindly and opportunely offered me the means of reprocuring some part of the literary treasures which I have ceded to Congress, to replace the devastations of British Vandalism at Washington. I cannot live without books. But fewer will suffice, where amusement, and not use, is the only future object. I am about sending him a catalogue, to which less than his critical knowledge of books would hardly be adequate.
Present my high respects to Mrs. Adams, and accept yourself the assurances of my affectionate attachment.
Th: Jefferson.
TO MR. LEIPER.
Monticello, June 12, 1815.
Dear Sir,
A journey soon after the receipt of your favor of April the 17th and an absence from home of some continuance, have prevented my earlier acknowledgment of it. In that came safely my letter of January the 2nd, 1814. In our principles of government we differ not at all; nor in the general object and tenor of political measures. We concur in considering the government of England as totally without morality, insolent beyond bearing, inflated with vanity and ambition, aiming at the exclusive dominion of the sea, lost in corruption, of deep-rooted hatred towards us, hostile to liberty wherever it endeavors to show its head, and the eternal disturber of the peace of the world. In our estimate of Bonaparte, I suspect we differ. I view him as a political engine only, and a very wicked one; you, I believe, as both political and religious, and obeying, as an instrument, an unseen hand. I still deprecate his becoming sole lord of the continent of Europe, which he would have been, had he reached in triumph the gates of Petersburg. The establishment in our day of another Roman. empire, spreading vassalage and depravity over the face of the globe, is not, I hope, within the purposes of Heaven. Nor does the return of Bonaparte give me pleasure unmixed; I see in his expulsion of the Bourbons, a valuable lesson to the world, as showing that its ancient dynasties may be changed for their misrule. Should the allied powers presume to dictate a ruler and government to France, and follow the example he had set of parcelling and usurping to themselves their neighbor nations, I hope he will give them another lesson in vindication of the rights of independence and self-government, which himself had heretofore so much abused, and that in this contest he will wear down the maritime power of England to limitable and safe dimensions. So far, good. It cannot be denied, on the other hand, that his successful perversion of the force (committed to him for vindicating the rights and liberties of his country) to usurp its government, and to enchain it under an hereditary despotism, is of baneful effect in encouraging future usurpations, and deterring those under oppression from rising to redress themselves. His restless spirit leaves no hope of peace to the world; and his hatred of us is only a little less than that he bears to England, and England to us. Our form of government is odious to him, as a standing contrast between republican and despotic rule; and as much from that hatred, as from ignorance in political economy, he had excluded intercourse between us and his people, by prohibiting the only articles they wanted from us, that is, cotton and tobacco. Whether the war we have had with England, the achievements of that war, and the hope that we may become his instruments and partisans against that enemy, may induce him, in future, to tolerate our commercial intercourse with his people, is still to be seen. For my part, I wish that all nations may recover and retain their independence; that those which are overgrown may not advance beyond safe measures of power, that a salutary balance may be ever maintained among nations, and that our peace, commerce, and friendship may be sought and cultivated by all. It is our business to manufacture for ourselves whatever we can, to keep all markets open for what we can spare or want; and the less we have to do with the amities or enmities of Europe, the better. Not in our day, but at no distant one, we may shake a rod over the heads of all, which may make the stoutest of them tremble. But I hope our wisdom will grow with our power, and teach us that the less we use our power, the greater it will be.
The federal misrepresentation of my sentiments, which occasioned my former letter to you, was gross enough; but that and all others are exceeded by the impudence and falsehood of the printed extract you sent me from Ralph’s paper. That a continuance of the embargo for two months longer would have prevented our war; that the non-importation law which succeeded it was a wise and powerful measure, I have constantly maintained. My friendship for Mr. Madison, my confidence in his wisdom and virtue, and my approbation of all his measures, and especially of his taking up at length the gauntlet against England, is known to all with whom I have ever conversed or corresponded on these measures. The word federal, or its synonyme &c., may therefore be written under every word of Mr. Ralph’s paragraph. I have ransacked my memory to recollect any incident which might have given countenance to any particle of it, but I find none. For if you will except the bringing into power and importance those who were enemies to himself as well as to the principles of republican government, I do not recollect a single measure of the President which I have not approved. Of those under him, and of some very near him, there have been many acts of which we have all disapproved, and he more than we. We have at times dissented from the measures, and lamented the dilatoriness of Congress. I recollect an instance the first winter of the war, when, from sloth of proceedings, an embargo was permitted to run through the winter, while the enemy could not cruise, nor consequently restrain the exportation of our whole produce, and was taken off in the spring, as soon as they could resume their stations. But this procrastination is unavoidable. How can expedition be expected from a body which we have saddled with an hundred lawyers, whose trade is talking? But lies, to sow divisions among us, are so stale an artifice of the federal prints, and are so well understood, that they need neither contradiction nor explanation. As to myself, my confidence in the wisdom and integrity of the administration is so entire, that I scarcely notice what is passing, and have almost ceased to read newspapers. Mine remain in our post-office a week or ten days, sometimes, unasked for. I find more amusement in studies to which I was always more attached, and from which I was dragged by the events of the times in which I have happened to live.
I rejoice exceedingly that our war with England was single-handed. In that of the Revolution, we had France, Spain, and Holland on our side, and the credit of its success was given to them. On the late occasion, unprepared and unexpecting war, we were compelled to declare it, and to receive the attack of England, just issuing from a general war, fully armed, and freed from all other enemies, and have not only made her sick of it, but glad to prevent, by a peace, the capture of her adjacent possessions, which one or two campaigns more would infallibly have made ours. She has found that we can do her more injury than any other enemy on earth, and henceforward will better estimate the value of our peace. But whether her government has power, in opposition to the aristocracy of her navy, to restrain their piracies within the limits of national rights, may well be doubted. I pray, therefore, for peace, as best for all the world, best for us, and best for me, who have already lived to see three wars, and now pant for nothing more than to be permitted to depart in peace. That you also, who have longer to live, may continue to enjoy this blessing with health and prosperity, through as long a life as you desire, is the prayer of yours affectionately.
Th: Jefferson.
P. S. June the 14th. Before I had sent my letter to the post-office, I received the new treaty of the allied powers, declaring that the French nation shall not have Bonaparte, and shall have Louis XVIII for their ruler. They are all then as great rascals, as Bonaparte himself. While he was in the wrong, I wished him exactly as much success as would answer our purposes, and no more. Now that they are wrong and he in the right, he shall have all my prayers for success, and that he may dethrone every man of them.
TO JOHN ADAMS.
Monticello, August 10,1815.
Dear Sir,
The simultaneous movements in our correspondence have been remarkable on several occasions. It would seem as if the state of the air, or state of the times, or some other unknown cause, produced a sympathetic effect on our mutual recollections. I had sat down to answer your letters of June the 19th, 20th, and 22nds with pen, ink, and paper, before me, when I received from our mail that of July the 30th. You ask information on the subject of Camus. All I recollect of him is, that he was one of the deputies sent to arrest Dumourier at the head of his army, who were, however, themselves arrested by Dumourier, and long detained as prisoners. I presume, therefore, he was a Jacobin. You will find his character in the most excellent revolutionary history of Toulongeon. I believe also, he may be the same person who has given us a translation of Aristotle’s Natural History, from the Greek into French. Of his report to the National Institute on the subject of the Bollandists, your letter gives me the first information. I had supposed them defunct with the society of Jesuits, of which they were: and that their works, although above ground, were, from their bulk and insignificance, as effectually entombed on their shelves, as if in the graves of their authors. Fifty-two volumes in folio, of the acta sanctorum, in dog-Latin, would be a formidable enterprise to the most laborious German. I expect, with you, they are the most enormous mass of lies, frauds, hypocrisy, and imposture, that ever was heaped together on this globe. By what chemical process M. Camus supposed that an extract of truth could be obtained from such a farrago of falsehood, I must leave to the chemists and moralists of the age to divine.
On the subject of the history of the American Revolution you ask who shall write it? Who can write it? And who will ever be able to write it? Nobody; except merely its external facts; all its councils, designs, and discussions having been conducted by Congress with closed doors, and no member, as far as I know, having even made notes of them. These, which are the life and soul of history, must for ever be unknown. Botta, as you observe, has put his own speculations and reasonings into the mouths of persons whom he names, but who, you and I know, never made such speeches. In this he has followed the example of the ancients, who made their great men deliver long speeches, all of them in the same style, and in that of the author himself. The work is nevertheless a good one, more judicious, more chaste, more classical, and more true, than the party diatribe of Marshall. Its greatest fault is in having taken too much from him. I possessed the work, and often recurred to considerable portions of it, although I never read it through. But a very judicious and well informed neighbor of mine went through it with great attention, and spoke very highly of it. I have said that no member of the old Congress, as far as I knew, made notes of the discussions. I did not knew of the speeches you mention of Dickinson and Witherspoon But on the questions of Independence, and on the two articles of Confederation respecting taxes and voting, I took minutes of the heads of the arguments. On the first, I threw all into one mass, without ascribing to the speakers their respective arguments; pretty much in the manner of Hume’s summary digests of the reasonings in parliament for and against a measure. On the last, I stated the heads of arguments used by each speaker. But the whole of my notes on the question of Independence does not occupy more than five pages, such as of this letter: and on the other questions, two such sheets. They have never been communicated to any one. Do you know that there exists in manuscript the ablest work of this kind ever yet executed, of the debates of the constitutional convention of Philadelphia in 1788? The whole of every thing said and done there was taken down by Mr. Madison, with a labor and exactness beyond comprehension.
I presume that our correspondence has been observed at the post-offices, and thus has attracted notice. Would you believe, that a printer has had the effrontery to propose to me the letting him publish it? These people think they have a right to every thing, however secret or sacred. I had not before heard of the Boston pamphlet with Priestley’s Letters and mine.
At length Bonaparte has got on the right side of a question. From the time of his entering the legislative hall to his retreat to Elba, no man has execrated him more than myself. I will not except even the members of the Essex Junto; although for very different reasons; I, because he was warring against the liberty of his own country, and independence of others; they, because he was the enemy of England, the Pope, and the Inquisition. But at length, and as far as we can judge, he seems to have become the choice of his nation. At least, he is defending the cause of his nation, and that of all mankind, the rights of every people to independence and self-government. He and the allies have now changed sides. They are parcelling out among themselves Poland, Belgium, Saxony, Italy, dictating a ruler and government to France, and looking askance at our republic, the splendid libel on their governments, and he is fighting for the principles of national independence, of which his whole life hitherto has been a continued violation. He has promised a free government to his own country, and to respect the rights of others; and although his former conduct inspires little confidence in his promises, yet we had better take the chance of his word for doing right, than the certainty of the wrong which his adversaries are doing and avowing. If they succeed, ours is only the boon of the Cyclops to Ulysses, of being the last devoured.
Present me affectionately and respectfully to Mrs. Adams, and Heaven give you both as much more of life as you wish, and bless it with health and happiness.
Th: Jefferson.
P. S. August the 11th. I had finished my letter yesterday, and this morning receive the news of Bonaparte’s second abdication. Very well. For him personally, I have no feeling but reprobation. The representatives of the nation have deposed him. They have taken the allies at their word, that they had no object in the war but his removal. The nation is now free to give itself a good government, either with or without a Bourbon; and France unsubdued, will still be a bridle on the enterprises of the combined powers, and a bulwark to others. T.J.
TO DABNEY CARR.
Monticello, January 19, 1816.
Dear Sir,
At the date of your letter of December the 1st, I was in Bedford, and since my return, so many letters, accumulated during my absence, having been pressing for answers, that this is the first moment I have been able to attend to the subject of yours. While Mr. Girardin was in this neighborhood writing his continuation of Burke’s History, I had suggested to him a proper notice of the establishment of the committee of correspondence here in 1773, and of Mr. Carr, your father, who introduced it. He has doubtless done this, and his work is now in the press. My books, journals of the times, &c. being all gone, I have nothing now but an impaired memory to resort to for the more particular statement you wish. But I give it with the more confidence, as I find that I remember old things better than new. The transaction took place in the session of Assembly of March 1773. Patrick Henry, Richard Henry Lee, Frank Lee, your father, and myself, met by agreement, one evening, about the close of the session, at the Raleigh Tavern, to consult on the measures which the circumstances of the times seemed to call for. We agreed, in result, that concert in the operations of the several Colonies was indispensable; and that to produce this, some channel of correspondence between them must be opened: that, therefore, we would propose to our House the appointment of a committee of correspondence, which should be authorized and instructed to write to the Speakers of the House of Representatives of the several Colonies, recommending the appointment of similar committees on their part, who, by a communication of sentiment on the transactions threatening us all, might promote a harmony of action salutary to all. This was the substance, not pretending to remember words. We proposed the resolution, and your father was agreed on to make the motion. He did it the next day, March the 12th, with great ability, reconciling all to it, not only by the reasonings, but by the temper and moderation with which it was developed. It was adopted by a very general vote. Peyton Randolph, some of us who proposed it, and who else I do not remember, were appointed of the committee. We immediately despatched letters by expresses, to the Speakers of all the other Assemblies. I remember that Mr. Carr and myself, returning home together, and conversing on the subject by the way, concurred in the conclusion, that that measure must inevitably beget the meeting of a Congress of Deputies from all the Colonies, for the purpose of uniting all in the same principles and measures for the maintenance of our rights. My memory cannot deceive me, when I affirm that we did it in consequence of no such proposition from any other Colony. No doubt, the resolution itself, and the journals of the day, will show that ours was original, and not merely responsive to one from any other quarter. Yet, I am certain I remember also, that a similar proposition, and nearly cotemporary, was made by Massachusetts, and that our northern messenger passed theirs on the road. This, too, may be settled by recurrence to the records of Massachusetts. The proposition was generally acceded to by the other Colonies, and the first effect, as expected, was the meeting of a Congress at New York the ensuing year. The committee of correspondence appointed by Massachusetts, as quoted by you from Marshall, under the date of 1770, must have been for a special purpose, and functus officio before the date of 1773, or Massachusetts herself would not then have proposed another. Records should be examined to settle this accurately. I well remember the pleasure expressed in the countenance and conversation of the members generally, on this début of Mr. Carr, and the hopes they conceived as well from the talents as the patriotism it manifested. But he died within two months after, and in him we lost a powerful fellow-laborer. His character was of a high order. A spotless integrity, sound judgment, handsome imagination, enriched by education and reading, quick and clear in his conceptions, of correct and ready elocution, impressing every hearer with the sincerity of the heart from which it flowed. His firmness was inflexible in whatever he thought was right: but when no moral principle stood in the way, never had man more of the milk of human kindness, of indulgence, of softness, of pleasantry in conversation and conduct. The number of his friends, and the warmth of their affection, were proofs of his worth, and of their estimate of it. To give to those now living, an idea of the affliction produced by his death in the minds of all who knew him, I liken it to that lately felt by themselves on the death of his eldest son, Peter Carr, so like him in all his endowments and moral qualities, and whose recollection can never recur without a deep-drawn sigh from the bosom of any one who knew him. You mention that I showed you an inscription I had proposed for the tomb-stone of your father. Did I leave it in your hands to be copied? I ask the question, not that I have any such recollection, but that I find it no longer in the place of its deposite, and think I never took it out but on that occasion. Ever and affectionately yours.
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN ADAMS.
Monticello, April 8, 1816.
Dear Sir,
I have to acknowledge your two favors of February the 16th and March the 2nd, and to join sincerely in the sentiment of Mrs. Adams, and regret that distance separates us so widely. An hour of conversation would be worth a volume of letters. But we must take things as they come.
You ask, if I would agree to live my seventy or rather seventy-three years over again? To which I say, yea. I think with you that it is a good world on the whole; that it has been framed on a principle of benevolence, and more pleasure than pain dealt out to us. There are, indeed, (who might say nay) gloomy and hypochondriac minds, inhabitants of diseased bodies, disgusted with the present, and despairing of the future; always counting that the worst will happen, because it may happen. To these I say, how much pain have cost us the evils which have never happened! My temperament is sanguine. I steer my bark with Hope in the head, leaving Fear astern. My hopes, indeed, sometimes fail; but not oftener than the forebodings of the gloomy. There are, I acknowledge, even in the happiest life, some terrible convulsions, heavy set-offs against the opposite page of the account. I have often wondered for what good end the sensations of grief could be intended. All our other passions, within proper bounds, have an useful object. And the perfection of the moral character is, not in a stoical apathy, so hypocritically vaunted, and so untruly too, because impossible, but in a just equilibrium of all the passions. I wish the pathologists then would tell us what is the use of grief in the economy, and of what good it is the cause, proximate or remote.
Did I know Baron Grimm while at Paris? Yes, most intimately. He was the pleasantest and most conversable member of the diplomatic corps while I was there; a man of good fancy, acuteness, irony, cunning, and egoism. No heart, not much of any science, yet enough of every one to speak its language: his forte was Belles-lettres, painting, and sculpture. In these he was the oracle of the society, and as such, was the Empress Catharine’s private correspondent and factor, in all things not diplomatic. It was through him I got her permission for poor Ledyard to go to Kamschatka, and cross over thence to the western coast of America, in order to penetrate across our continent in the opposite direction to that afterwards adopted for Lewis and Clarke: which permission she withdrew after he had got within two hundred miles of Kamschatka, had him seized, brought back, and set down in Poland. Although I never heard Grimm express the opinion directly, yet I always supposed him to be of the school of Diderot, D’Alembert, D’Holbach; the first of whom committed his system of atheism to writing in ‘Le Bon Sens,’ and the last in his ‘Systeme de la Nature? It was a numerous school in the Catholic countries, while the infidelity of the Protestant took generally the form of theism. The former always insisted that it was a mere question of definition between them, the hypostasis of which on both sides, was ‘Nature,’ or ‘the Universe’: that both agreed in the order of the existing system, but the one supposed it from eternity, the other as having begun in time. And when the atheist descanted on the unceasing motion and circulation of matter through the animal, vegetable, and mineral kingdoms, never resting, never annihilated, always changing form, and under all forms gifted with the power of reproduction; the theist pointing ‘to the heavens above, and to the earth beneath, and to the waters under the earth,’ asked, if these did not proclaim a first cause, possessing intelligence and power; power in the production, and intelligence in the design, and constant preservation of the system; urged the palpable existence of final causes; that the eye was made to see, and the ear to hear, and not that we see because we have eyes, and hear because we have ears; an answer obvious to the senses, as that of walking across the room, was to the philosopher demonstrating the non-existence of motion. It was in D’Holbach’s conventicles that Rousseau imagined all the machinations against him were contrived and he left, in his Confessions, the most biting anecdotes of Grimm. These appeared after I left France; but I have heard that poor Grimm was so much afflicted by them, that he kept his bed several weeks. I have never seen the Memoirs of Grimm. Their volume has kept them out of our market.
I have been lately amusing myself with Levi’s book, in answer to Dr. Priestley. It is a curious and tough work. His style is inelegant and incorrect, harsh and petulant to his adversary, and his reasoning flimsy enough. Some of his doctrines were new to me, particularly that of his two resurrections: the first, a particular one of all the dead, in body as well as soul, who are to live over again, the Jews in a state of perfect obedience to God, the other nations in a state of corporeal punishment for the sufferings they have inflicted on the Jews. And he explains this resurrection of bodies to be only of the original stamen of Leibnitz, or the human calus in semine masculino, considering that as a mathematical point, insusceptible of separation or division. The second resurrection, a general one of souls and bodies, eternally to enjoy divine glory in the presence of the Supreme Being. He alleges that the Jews alone preserve the doctrine of the unity of God. Yet their God would be deemed a very indifferent man with us: and it was to correct their anamorphosis of the Deity, that Jesus preached, as well as to establish the doctrine of a future state. However, Levi insists, that that was taught in the Old Testament, and even by Moses himself and the prophets. He agrees that an anointed prince was prophesied and promised: but denies that the character and history of Jesus had any analogy with that of the person promised. He must be fearfully embarrassing to the Hierophants of fabricated Christianity; because it is their own armor in which he clothes himself for the attack. For example, he takes passages of scripture from their context (which would give them a very different meaning), strings them together, and makes them point towards what object he pleases; he interprets them figuratively, typically, analogically, hyperbolically; he calls in the aid of emendation, transposition, ellipsis, metonymy, and every other figure of rhetoric; the name of one man is taken for another, one place for another, days and weeks for months and years; and finally he avails himself of all his advantage over his adversaries by his superior knowledge of the Hebrew, speaking in the very language of the divine communication, while they can only fumble on with conflicting and disputed translations. Such is this war of giants. And how can such pigmies as you and I decide between them? For myself, I confess, that my head is not formed tantas componere lites. And as you began yours of March the 2nd, with a declaration, that you were about to write me the most frivolous letter I had ever read, so I will close mine by saying, I have written you a full match for it, and by adding my affectionate respects to Mrs. Adams, and the assurance of my constant attachment and consideration for yourself.
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN TAYLOR.
Monticello, May 28,1816.
Dear Sir,
On my return from a long journey and considerable absence from home, I found here the copy of your ‘Enquiry into the Principles of our Government,’ which you had been so kind as to send me; and for which I pray you to accept my thanks. The difficulties of getting new works in our situation, inland and without a single bookstore, are such as had prevented my obtaining a copy before; and letters which had accumulated during my absence, and were calling for answers, have not yet permitted me to give to the whole a thorough reading: yet certain that you and I could not think differently on the fundamentals of rightful government, I was impatient, and availed myself of the intervals of repose from the writing-table, to obtain a cursory idea of the body of the work.
I see in it much matter for profound reflection; much which should confirm our adhesion, in practice, to the good principles of our constitution, and fix our attention on what is yet to be made good. The sixth section on the good moral principles of our government, I found so interesting and replete with sound principles, as to postpone my letter-writing to its thorough perusal and consideration. Besides much other good matter, it settles unanswerably the right of instructing representatives, and their duty to obey. The system of banking we have both equally and ever reprobated. I contemplate it as a blot left in all our constitutions, which, if not covered, will end in their destruction, which is already hit by the gamblers in corruption, and is sweeping away in its progress the fortunes and morals of our citizens. Funding I consider as limited, rightfully, to a redemption of the debt within the lives of a majority of the generation contracting it; every generation coming equally, by the laws of the Creator of the world, to the free possession of the earth he made for their subsistence, unincumbered by their predecessors, who, like them, were but tenants for life. You have successfully and completely pulverized Mr. Adams’s system of orders, and his opening the mantle of republicanism to every government of laws, whether consistent or not with natural right. Indeed, it must be acknowledged, that the term republic is of very vague application in every language. Witness the self-styled republics of Holland, Switzerland, Genoa, Venice, Poland. Were I to assign to this term a precise and definite idea, I would say, that, purely and simply, it means a government by its citizens in mass, acting directly and personally, according to rules established by the majority: and that every other government is more or less republican, in proportion as it has in its composition more or less of this ingredient of the direct action of the citizens. Such a government is evidently restrained to very narrow limits of space and population. I doubt if it would be practicable beyond the extent of a New England township. The first shade from this pure element, which, like that of pure vital air, cannot sustain life of itself, would be where the powers of the government, being divided, should be exercised each by representatives chosen by the citizens either pro hac vice, or for such short terms as should render secure the duty of expressing the will of their constituents. This I should consider as the nearest approach to a pure republic, which is practicable on a large scale of country or population. And we have examples of it in some of our State constitutions, which, if not poisoned by priestcraft, would prove its excellence over all mixtures with other elements; and, with only equal doses of poison, would still be the best. Other shades of republicanism may be found in other forms of government, where the executive, judiciary, and legislative functions, and the different branches of the latter, are chosen by the people more or less directly, for longer terms of years, or for life, or made hereditary; or where there are mixtures of authorities, some dependent on, and others independent of the peopje. The further the departure from direct and constant control by the citizens, the less has the government of the ingredient of republicanism; evidently none where the authorities are hereditary, as in France, Venice, &c. or self-chosen, as in Holland; and little, where for life, in proportion as the life continues in being after the act of election.
The purest republican feature in the government of our own State, is the House of Representatives. The Senate is equally so the first year, less the second, and so on. The Executive still less, because not chosen by the people directly. The Judiciary seriously anti-republican, because for life; and the national arm wielded, as you observe, by military leaders, irresponsible but to themselves. Add to this the vicious constitution of our county courts (to whom the justice, the executive administration, the taxation, police, the military appointments of the county, and nearly all our daily concerns are confided), self-appointed, self-continued, holding their authorities for life, and with an impossibility of breaking in on the perpetual succession of any faction once possessed of the bench. They are, in truth, the executive, the judiciary, and the military of their respective counties, and the sum of the counties makes the State. And add, also, that one half of our brethren who fight and pay taxes, are excluded, like Helots, from the rights of representation, as if society were instituted for the soil, and not for the men inhabiting it; or one half of these could dispose of the rights and the will of the other half, without their consent.
What constitutes a State?
Not high-raised battlements, or lahor’d mound,
Thick wall, or moated gate;
Not cities proud, with spires and turrets crown’d;
No: men, high-minded men;
Men, who their duties know;
But know their rights; and, knowing, dare maintain.
These constitute a State.’
In the General Government, the House of Representatives is mainly republican; the Senate scarcely so at all, as not elected by the people directly, and so long secured even against those who do elect them; the Executive more republican than the Senate, from its shorter term, its election by the people, in practice (for they vote for A only on an assurance that he will vote for B), and because, in practice, also, a principle of rotation seems to be in a course of establishment; the judiciary independent of the nation, their coercion by impeachment being found nugatory.
If, then, the control of the people over the organs of their government be the measure of its republicanism (and I confess I know no other measure), it must be agreed that our governments have much less of republicanism than ought to have been expected; in other words, that the people have less regular control over their agents, than their rights and their interest require. And this I ascribe, not to any want of republican dispositions in those who formed these constitutions, but to a submission of true principle to European authorities, to speculators on government, whose fears of the people have been inspired by the populace of their own great cities, and were unjustly entertained against the independent, the happy, and therefore orderly citizens of the United States. Much I apprehend that the golden moment is past for reforming these heresies. The functionaries of public power rarely strengthen in their dispositions to abridge it, and an unorganized call for timely amendment is not likely to prevail against an organized opposition to it. We are always told that things are going on well; why change them? ‘Chi sta bene, non si muova,’ says the Italian, ‘Let him who stands well, stand still.’ This is true; and I verily believe they would go on well with us under an absolute monarch, while our present character remains, of order, industry, and love of peace, and restrained, as he would be, by the proper spirit of the people. But it is while it remains such, we should provide against the consequences of its deterioration. And let us rest in the hope that it will yet be done, and spare ourselves the pain of evils which may never happen.
On this view of the import of the term republic, instead of saying, as has been said, ‘that it may mean any thing or nothing,’ we may say with truth and meaning, that governments are more or less republican, as they have more or less of the element of popular election and control in their composition: and believing, as I do, that the mass of the citizens is the safest depository of their own rights, and especially, that the evils flowing from the duperies of the people, are less injurious than those from the egoism of their agents, I am a friend to that composition of government which has in it the most of this ingredient. And I sincerely believe, with you, that banking establishments are more dangerous than standing armies; and that the principle of spending money to be paid by posterity, under the name of funding, is but swindling futurity on a large scale.
I salute you with constant friendship and respect.
Th: Jefferson.
TO FRANCIS W. GILMER.
Monticello, June 7,1816.
Dear Sir,
I received a few-days ago from Mr. Dupont the enclosed manuscript, with permission to read it, and a request, when read, to forward it to you, in expectation that you would translate it. It is well worthy of publication for the instruction of our citizens, being profound, sound, and short. Our legislators are not sufficiently apprized of the rightful limits of their powers: that their true office is to declare and enforce only our natural rights and duties, and to take none of them from us. No man has a natural right to commit aggression on the equal rights of another; and this is all from which the laws ought to restrain him: every man is under the natural duty of contributing to the necessities of the society; and this is all the laws should enforce on him: and, no man having a natural right to be the judge between himself and another, it is his natural duty to submit to the umpirage of an impartial third. When the laws have declared and enforced all this, they have fulfilled their functions, and the idea is quite unfounded, that on entering into society we give up any natural right. The trial of every law by one of these texts, would lessen much the labors of our legislators, and lighten equally our municipal codes. There is a work of the first order of merit now in the press at Washington, by Destutt Tracy, on the subject of political economy, which he brings into the compass of three hundred pages, octavo. In a preliminary discourse on the origin of the right of property, he coincides much with the principles of the present manuscript; but is more developed, more demonstrative. He promises a future work on morals, in which I lament to see, that he will adopt the principles of Hobbes, or humiliation to human nature; that the sense of justice and injustice is not derived from our natural organization, but founded on convention only. I lament this the more, as he is unquestionably the ablest writer living, on abstract subjects. Assuming the fact, that the earth has been created in time, and consequently the dogma of final causes, we yield, of course, to this short syllogism. Man was created for social intercourse; but social intercourse cannot be maintained without a sense of justice; then man must have been created with a sense of justice. There is an error into which most of the speculators on government have fallen, and which the well known state of society of our Indians ought, before now, to have corrected. In their hypothesis of the origin of government, they suppose it to have commenced in the patriarchal or monarchical form. Our Indians are evidently in that state of nature which has passed the association of a single family; and not yet submitted to the authority of positive laws, or of any acknowledged magistrate. Every man, with them, is perfectly free to follow his own inclinations. But if, in doing this, he violates the rights of another, if the case be slight, he is punished by the disesteem of his society, or, as we say, by public opinion; if serious, he is tomahawked as a dangerous enemy. Their leaders conduct them by the influence of their character only; and they follow, or not, as they please, him of whose character for wisdom or war they have the highest opinion. Hence the origin of the parties among them adhering to different leaders, and governed by their advice, not by their command. The Cherokees, the only tribe I know to be contemplating the establishment of regular laws, magistrates, and government, propose a government of representatives, elected from every town. But of all things, they least think of subjecting themselves to the will of one man. This, the only instance of actual fact within our knowledge, will be then a beginning by republican, and not by patriarchal or monarchical government, as speculative writers have generally conjectured.
We have to join in mutual congratulations on the appointment of our friend Correa, to be Minister or Envoy of Portugal, here. This, I hope, will give him to us, for life. Nor will it at all interfere with his botanical rambles or journeys. The government of Portugal is so peaceable and inoffensive, that it has never any altercations with its friends. If their minister abroad writes them once a quarter that all is well, they desire no more. I learn (though not from Correa himself) that he thinks of paying us a visit as soon as he is through his course of lectures. Not to lose this happiness again by my absence, I have informed him I shall set out for Poplar Forest the 20th instant, and be back the first week of July. I wish you and he could concert your movements so as to meet here, and that you would make this your headquarters. It is a good central point from which to visit your connections; and you know our practice of placing our guests at their ease, by showing them we are so ourselves, and that we follow our necessary vocations, instead of fatiguing them by hanging unremittingly on their shoulders.
I salute you with affectionate esteem and respect.
Th: Jefferson.
TO BENJAMIN AUSTIN.
Monticello, January 9, 1816.
[* This letter was accidentally misplaced, and is now
inserted out of its regular order.]
Dear Sir,
I acknowledge with pleasure your letter of the 9th of December last.
Your opinions on the events which have taken place in France, are entirely just, so far as these events are yet developed. But we have reason to suppose, that they have not reached their ultimate termination. There is still an awful void between the present, and what is to be the last chapter of that history; and I fear it is to be filled with abominations, as frightful as those which have already disgraced it. That nation is too high-minded, has too much innate force, intelligence, and elasticity, to remain quiet under its present compression. Samson will arise in his strength, and probably will ere long burst asunder the cords and the webs of the Philistines. But what are to be the scenes of havoc and horror, and how widely they may spread between the brethren of one family, our ignorance of the interior feuds and antipathies of the country places beyond our view. Whatever may be the convulsions, we cannot but indulge the pleasing hope, they will end in the permanent establishment of a representative government; a government in which the will of the people will be an effective ingredient. This important element has taken root in the European mind, and will have its growth. Their rulers, sensible of this, are already offering this modification of their governments, under the plausible pretence that it is a voluntary concession on their part. Had Bonaparte used his legitimate power honestly, for the establishment and support of a free government, France would now have been in prosperity and rest, and her example operating for the benefit of mankind, every nation in Europe would eventually have founded a government over which the will of the people would have had a powerful control. His improper conduct, however, has checked the salutary progress of principle; but the object is fixed in the eye of nations, and they will press to its accomplishment, and to the general amelioration of the condition of man. What a germ have the freemen of the United States planted, and how faithfully should they cherish the parent tree at home. Chagrin and mortification are the punishments our enemies receive.
You tell me I am quoted by those who wish to continue our dependence on England for manufactures. There was a time when I might have been so quoted with more candor. But within the thirty years which have since elapsed, how are circumstances changed! We were then in peace; our independent place among nations was acknowledged. A commerce which offered the raw material, in exchange for the same material after receiving the last touch of industry, was worthy of welcome to all nations. It was expected, that those especially to whom manufacturing industry was important, would cherish the friendship of such customers by every favor, and particularly cultivate their peace by every act of justice and friendship. Under this prospect, the question seemed legitimate, whether, with such an immensity of unimproved land, courting the hand of husbandry, the industry of agriculture, or that of manufactures, would add most to the national wealth. And the doubt on the utility of the American manufactures was entertained on this consideration, chiefly, that to the labor of the husbandman a vast addition is made by the spontaneous energies of the earth on which it is employed. For one grain of wheat committed to the earth, she renders twenty, thirty, and even fifty fold; whereas to the labor of the manufacturer nothing is added. Pounds of flax, in his hands, on the contrary, yield but penny weights of lace. This exchange, too, laborious as it might seem, what a field did it promise for the occupation of the ocean; what a nursery for that class of citizens who were to exercise and maintain our equal rights on that element! This was the state of things in 1785, when the Notes on Virginia were first published; when, the ocean being open to all nations, and their common right in it acknowledged and exercised under regulations sanctioned by the assent and usage of all, it was thought that the doubt might claim some consideration.
But who, in 1785, could foresee the rapid depravity which was to render the close of that century a disgrace to the history of man? Who could have imagined that the two most distinguished in the rank of nations, for science and civilization, would have suddenly descended from that honorable eminence, and setting at defiance all those moral laws established by the Author of Nature between nation and nation, as between man and man, would cover earth and sea with robberies and piracies, merely because strong enough to do it with temporal impunity, and that under this disbandment of nations from social order, we should have been despoiled of a thousand ships, and have thousands of our citizens reduced to Algerine slavery. Yet all this has taken place. The British interdicted to our vessels all harbors of the globe, without having first proceeded to some one of hers, there paid a tribute proportioned to the cargo, and obtained her license to proceed to the port of destination. The French declared them to be lawful prize if they had touched at the port, or been visited by a ship of the enemy nation. Thus were we completely excluded from the ocean. Compare this state of things with that of ‘85, and say whether an opinion founded in the circumstances of that day, can be fairly applied to those of the present. We have experienced, what we did not then believe, that there exist both profligacy and power enough to exclude us from the field of interchange with other nations. That to be independent for the comforts of life, we must fabricate them ourselves. We must now place the manufacturer by the side of the agriculturalist. The former question is suppressed, or rather assumes a new form. The grand inquiry now is, Shall we make our own comforts, or go without them at the will of a foreign nation? He, therefore, who is now against domestic manufacture, must be for reducing us either to dependence on that foreign nation, or to be clothed in skins, and to live like wild beasts in dens and caverns. I am not one of these. Experience has taught me that manufactures are now as necessary to our independence as to our comfort; and if those who quote me as of a different opinion, will keep pace with me in purchasing nothing foreign, where an equivalent of domestic fabric can be obtained, without regard to difference of price, it will not be our fault if we do not soon have a supply at home equal to our demand, and wrest that weapon of distress from the hand which has so long wantonly wielded it. If it shall be proposed to go beyond our own supply, the question of ‘85 will then recur, Will our surplus labor be then more beneficially employed, in the culture of the earth, or in the fabrications of art? We have time yet for consideration, before that question will press upon us; and the axiom to be applied will depend on the circumstances which shall then exist. For in so complicated a science as political economy, no one axiom can be laid down as wise and expedient for all times and circumstances. Inattention to this is what has called for this explanation, which reflection would have rendered unnecessary with the candid, while nothing will do it with those who use the former opinion only as a stalking-horse to cover their disloyal propensities to keep us in eternal vassalage to a foreign and unfriendly people.
I salute you with assurances of great respect and esteem.
Th: Jefferson.
TO WILLIAM H. CRAWFORD.
Monticello, June 20, 1816.
Dear Sir,
I am about to sin against all discretion, and knowingly, by adding to the drudgery of your letter-reading, this acknowledgment of the receipt of your favor of May the 31st, with the papers it covered. I cannot, however, deny myself the gratification of expressing the satisfaction I have received, not only from the general statement of affairs at Paris, in yours of December the 12th, 1814, (as a matter of history which I had not before received,) but most especially and superlatively, from the perusal of your letter of the 8th of the same month to Mr. Fisk, on the subject of drawbacks. This most heterogeneous principle was transplanted into ours from the British system, by a man whose mind was really powerful, but chained by native partialities to every thing English; who had formed exaggerated ideas of the superior perfection of the English constitution, the superior wisdom of their government, and sincerely believed it for the good of this country to make them their model in every thing; without considering that what might be wise and good for a nation essentially commercial, and entangled in complicated intercourse with numerous and powerful neighbors, might not be so for one essentially agricultural, and insulated by nature from the abusive governments of the old world.
The exercise, by our own citizens, of so much commerce as may suffice to exchange our superfluities for our wants, may be advantageous for the whole. But it does not follow, that, with a territory so boundless, it is the interest of the whole to become a mere city of London, to carry on the business of one half the world at the expense of eternal war with the other half. The agricultural capacities of our country constitute its distinguishing feature; and the adapting our policy and pursuits to that, is more likely to make us a numerous and happy people, than the mimicry of an Amsterdam, a Hamburgh, or a city of London. Every society has a right to fix the fundamental principles of its association, and to say to all individuals, that, if they contemplate pursuits beyond the limits of these principles, and involving dangers which the society chooses to avoid, they must go somewhere else for their exercise; that we want no citizens, and still less ephemeral and pseudo-citizens, on such terms. We may exclude them from our territory, as we do persons infected with disease. Such is the situation of our country. We have most abundant resources of happiness within ourselves, which we may enjoy in peace and safety, without permitting a few citizens, infected with the mania of rambling and gambling, to bring danger on the great mass engaged in innocent and safe pursuits at home. In your letter to Fisk, you have fairly stated the alternatives between which we are to choose: 1. licentious commerce and gambling speculations for a few, with eternal war for the many; or, 2. restricted commerce, peace, and steady occupations for all. If any State in the Union will declare that it prefers separation with the first alternative, to a continuance in union without it, I have no hesitation in saying, ‘Let us separate.’ I would rather the States should withdraw, which are for unlimited commerce and war, and confederate with those alone which are for peace and agriculture. I know that every nation in Europe would join in sincere amity with the latter, and hold the former at arm’s length, by jealousies, prohibitions, restrictions, vexations, and war. No earthly consideration could induce my consent to contract such a debt as England has by her wars for commerce, to reduce our citizens by taxes to such wretchedness, as that laboring sixteen of the twenty-four hours, they are still unable to afford themselves bread, or barely to earn as much oatmeal or potatoes as will keep soul and body together. And all this to feed the avidity of a few millionary merchants, and to keep up one thousand ships of war for the protection of their commercial speculations. I returned from Europe after our government had got under way, and had adopted from the British code the law of drawbacks. I early saw its effects in the jealousies and vexations of Britain; and that, retaining it, we must become, like her, an essentially warring nation, and meet, in the end, the catastrophe impending over her. No one can doubt that this alone produced the orders of council, the depredations which preceded, and the war which followed them. Had we carried but our own produce, and brought back but our own wants, no nation would have troubled us. Our commercial dashers, then, have already cost us so many thousand lives, so many millions of dollars, more than their persons and all their commerce were worth. When war was declared, and especially after Massachusetts, who had produced it, took side with the enemy waging it, I pressed on some confidential friends in Congress to avail us of the happy opportunity of repealing the drawback; and I do rejoice to find that you are in that sentiment. You are young, and may be in the way of bringing it into effect. Perhaps time, even yet, and change of tone (for there are symptoms of that in Massachusetts), may not have obliterated altogether the sense of our late feelings and sufferings; may not have induced oblivion of the friends we have lost, the depredations and conflagrations we have suffered, and the debts we have incurred, and to have to labor for through the lives of the present generation. The earlier the repeal is proposed, the more it will be befriended by all these recollections and considerations. This is one of three great measures necessary to insure us permanent prosperity. This preserves our peace. A second should enable us to meet any war, by adopting the report of the war department, for placing the force of the nation at effectual command: and a third should insure resources of money by the suppression of all paper circulation during peace, and licensing that of the nation alone during war. The metallic medium of which we should be possessed at the commencement of a war, would be a sufficient fund for all the loans we should need through its continuance; and if the national bills issued, be bottomed (as is indispensable) on pledges of specific taxes for their redemption within certain and moderate epochs, and be of proper denominations for circulation, no interest on them would be necessary or just, because they would answer to every one the purposes of the metallic money withdrawn and replaced by them. But possibly these may be the dreams of an old man, or that the occasions of realizing them may have passed away without return. A government regulating itself by what is wise and just for the many, uninfluenced by the local and selfish views of the few who direct their affairs, has not been seen, perhaps, on earth. Or if it existed, for a moment, at the birth of ours, it would not be easy to fix the term of its continuance. Still, I believe it does exist here in a greater degree than any where else; and for its growth and continuance, as well as for your personal health and happiness, I offer sincere prayers, with the homage of my respect and esteem.
Th: Jefferson.
TO SAMUEL KERCHIVAL.
Monticello, July 12, 1816.
Sir,
I duly received your favor of June the 13th, with the copy of the letters on the calling a convention, on which you are pleased to ask my opinion. I have not been in the habit of mysterious reserve on any subject, nor of buttoning up my opinions within my own doublet. On the contrary, while in public service especially, I thought the public entitled to frankness, and intimately to know whom they employed. But I am now retired: I resign myself, as a passenger, with confidence to those at present at the helm, and ask but for rest, peace, and good will. The question you propose, on equal representation, has become a party one, in which I wish to take no public share. Yet, if it be asked for your own satisfaction only, and not to be quoted before the public, I have no motive to withhold it, and the less from you, as it coincides with your own. At the birth of our republic, I committed that opinion to the world, in the draught of a constitution annexed to the Notes on Virginia, in which a provision was inserted for a representation permanently equal. The infancy of the subject at that moment, and our inexperience of self-government, occasioned gross departures in that draught from genuine republican canons. In truth, the abuses of monarchy had so much filled all the space of political contemplation, that we imagined every thing republican which was not monarchy. We had not yet penetrated to the mother principle, that ‘governments are republican only in proportion as they embody the will of their people, and execute it.’ Hence, our first constitutions had really no leading principle in them. But experience and reflection have but more and more confirmed me in the particular importance of the equal representation then proposed. On that point, then, I am entirely in sentiment with your letters; and only lament that a copyright of your pamphlet prevents their appearance in the newspapers, where alone they would be generally read, and produce general effect. The present vacancy too, of other matter, would give them place in every paper, and bring the question home to every man’s conscience.
But inequality of representation in both Houses of our legislature, is not the only republican heresy in this first essay of our revolutionary patriots at forming a constitution. For let it be agreed that a government is republican in proportion as every member composing it has his equal voice in the direction of its concerns, (not indeed in person, which would be impracticable beyond the limits of a city, or small township, but) by representatives chosen by himself, and responsible to him at short periods, and let us bring to the test of this canon every branch of our constitution.
In the legislature, the House of Representatives is chosen by less than half the people, and not at all in proportion to those who do choose. The Senate are still more disproportionate, and for long terms of irresponsibility. In the Executive, the Governor is entirely independent of the choice of the people, and of their control; his Council equally so, and at best but a fifth wheel to a wagon. In the Judiciary, the judges of the highest courts are dependent on none but themselves. In England, where judges were named and removable at the will of an hereditary executive, from which branch most misrule was feared, and has flowed, it was a great point gained, by fixing them for life, to make them independent of that executive. But in a government founded on the public will, this principle operates in an opposite direction, and against that will. There, too, they were still removable on a concurrence of the executive and legislative branches. But we have made them independent of the nation itself. They are irremovable, but by their own body, for any depravities of conduct, and even by their own body for the imbecilities of dotage. The justices of the inferior courts are self-chosen, are for life, and perpetuate their own body in succession for ever, so that a faction once possessing themselves of the bench of a county, can never be broken up, but hold their county in chains, for ever indissoluble. Yet these justices are the real executive as well as judiciary, in all our minor and most ordinary concerns. They tax us at will; fill the office of sheriff, the most important of all the executive officers of the county; name nearly all our military leaders, which leaders, once named, are removable but by themselves. The juries, our judges of all fact, and of law when they choose it, are not selected by the people, nor amenable to them. They are chosen by an officer named by the court and executive. Chosen, did I say? Picked up by the sheriff from the loungings of the court-yard, after every thing respectable has retired from it. Where then is our republicanism to be found? Not in our constitution certainly, but merely in the spirit of our people. That would oblige even a despot to govern us republicanly. Owing to this spirit, and to nothing in the form of our constitution, all things have gone well. But this fact, so triumphantly misquoted by the enemies of reformation, is not the fruit of our constitution, but has prevailed in spite of it. Our functionaries have done well, because generally honest men. If any were not so, they feared to show it.
But it will be said, it is easier to find faults than to amend them. I do not think their amendment so difficult as is pretended. Only lay down true principles, and adhere to them inflexibly. Do not be frightened into their surrender by the alarms of the timid, or the croakings of wealth against the ascendancy of the people. If experience be called for, appeal to that of our fifteen or twenty governments for forty years, and show me where the people have done half the mischief in these forty years, that a single despot would have done in a single year; or show half the riots and rebellions, the crimes and the punishments, which have taken place in any single nation, under Kingly government, during the same period. The true foundation of republican government is the equal right of every citizen, in his person and property, and in their management. Try by this, as a tally, every provision of our constitution, and see if it hangs directly on the will of the people. Reduce your legislature to a convenient number for full, but orderly discussion. Let every man who fights or pays, exercise his just and equal right in their election. Submit them to approbation or rejection at short intervals. Let the executive be chosen in the same way, and for the same term, by those whose agent he is to be; and leave no screen of a council behind which to skulk from responsibility. It has been thought that the people are not competent electors of judges learned in the law. But I do not know that this is true, and if doubtful, we should follow principle. In this, as in many other elections, they would be guided by reputation, which would not err oftener, perhaps, than the present mode of appointment. In one State of the Union, at least, it has been long tried, and with the most satisfactory success. The judges of Connecticut have been chosen by the people every six months, for nearly two centuries, and I believe there has hardly ever been an instance of change; so powerful is the curb of incessant responsibility. If prejudice, however, derived from a monarchical institution, is still to prevail against the vital elective principle of our own, and if the existing example among ourselves of periodical election of judges by the people be still mistrusted, let us at least not adopt the evil, and reject the good, of the English precedent; let us retain a movability on the concurrence of the executive and legislative branches, and nomination by the executive alone. Nomination to office is an executive function. To give it to the legislature, as we do, is a violation of the principle of the separation of powers. It swerves the members from correctness, by temptations to intrigue for office themselves, and to a corrupt barter of votes; and destroys responsibility by dividing it among a multitude. By leaving nomination in its proper place, among executive functions, the principle of the distribution of power is preserved, and responsibility weighs with its heaviest force on a single head.
The organization of our county administrations may be thought more difficult. But follow principle, and the knot unties itself. Divide the counties into wards of such size as that every citizen can attend when called on, and act in person. Ascribe to them the government of their wards in all things relating to themselves exclusively. A justice, chosen by themselves, in each, a constable, a military company, a patrol, a school, the care of their own poor, their own portion of the public roads, the choice of one or more jurors to serve in some court, and the delivery, within their own wards, of their own votes for all elective officers of higher sphere, will relieve the county administration of nearly all its business, will have it better done, and by making every citizen an acting member of the government, and in the offices nearest and most interesting to him, will attach him by his strongest feelings to the independence of his country, and its republican constitution. The justices thus chosen by every ward, would constitute the county court, would do its judiciary business, direct roads and bridges, levy county and poor rates, and administer all the matters of common interest to the whole county. These wards, called townships in New England, are the vital principle of their governments, and have proved themselves the wisest invention ever devised by the wit of man for the perfect exercise of self-government, and for its preservation. We should thus marshal our government into, 1. The general federal republic, for all concerns foreign and federal; 2. That of the State, for what relates to our own citizens exclusively; 3. The county republics, for the duties and concerns of the county; and, 4. The ward republics, for the small, and yet numerous and interesting concerns of the neighborhood: and in government, as well as in every other business of life, it is by division and sub-division of duties alone, that all matters, great and small, can be managed to perfection. And the whole is cemented by giving to every citizen, personally, a part in the administration of the public affairs.
The sum of these amendments is, 1. General suffrage. 2. Equal representation in the legislature. 3. An executive chosen by the people. 4. Judges elective or amovable. 5. Justices, jurors, and sheriffs elective. 6. Ward divisions. And, 7. Periodical amendments of the constitution.
I have thrown out these, as loose heads of amendment, for consideration and correction: and their object is to secure self-government by the republicanism of our constitution, as well as by the spirit of the people; and to nourish and perpetuate that spirit. I am not among those who fear the people. They, and not the rich, are our dependence for continued freedom. And to preserve their independence, we must not let our rulers load us with perpetual debt. We must make our election between economy and liberty, or profusion and servitude. If we run into such debts, as that we must be taxed in our meat and in our drink, in our necessaries and our comforts, in our labors and our amusements, for our callings and our creeds, as the people of England are, our people, like them, must come to labor sixteen hours in the twenty-four, give the earnings of fifteen of these to the government for their debts and daily expenses; and the sixteenth being insufficient to afford us bread, we must live, as they now do, on oatmeal and potatoes; have no time to think, no means of calling the mismanagers to account; but be glad to obtain subsistence by hiring ourselves to rivet their chains on the necks of our fellow-sufferers. Our land-holders, too, like theirs, retaining indeed the title and stewardship of estates called theirs, but held really in trust for the treasury, must wander, like theirs, in foreign countries, and be contented with penury, obscurity, exile, and the glory of the nation. This example reads to us the salutary lesson that private fortunes are destroyed by public, as well as by private extravagance. And this is the tendency of all human governments. A departure from principle in one instance, becomes a precedent for a second; that second for a third; and so on, till the bulk of the society is reduced to be mere automatons of misery, to have no sensibilities left but for sinning and suffering. Then begins, indeed, the bellum omnium in omnia, which some philosophers observing to be so general in this world, have mistaken it for the natural, instead of the abusive state of man. And the fore-horse of this frightful team is public debt. Taxation follows that, and in its train wretchedness and oppression.
Some men look at constitutions with sanctimonious reverence, and deem them, like the ark of the covenant, too sacred to be touched. They ascribe to the men of the preceding age a wisdom more than human, and suppose what they did to be beyond amendment. I knew that age well: I belonged to it, and labored with it. It deserved well of its country. It was very like the present, but without the experience of the present; and forty years of experience in government is worth a century of book-reading: and this they would say themselves, were they to rise from the dead. I am certainly not an advocate for frequent and untried changes in laws and constitutions. I think moderate imperfections had better be borne with; because, when once known, we accommodate ourselves to them, and find practical means of correcting their ill effects. But I know, also, that laws and institutions must go hand in hand with the progress of the human mind. As that becomes more developed, more enlightened, as new discoveries are made, new truths disclosed, and manners and opinions change with the change of circumstances, institutions must advance also, and keep pace with the times. We might as well require a man to wear still the coat which fitted him when a boy, as civilized society to remain ever under the regimen of their barbarous ancestors. It is this preposterous idea which has lately deluged Europe in blood. Their monarchs, instead of wisely yielding to the gradual changes of circumstances, of favoring progressive accommodation to progressive improvement, have clung to old abuses, entrenched themselves behind steady habits, and obliged their subjects to seek through blood and violence rash and ruinous innovations, which, had they been referred to the peaceful deliberations and collected wisdom of the nation, would have been put into acceptable and salutary forms. Let us follow no such examples, nor weakly believe that one generation is not as capable as another of taking care of itself, and of ordering its own affairs. Let us, as our sister States have done, avail ourselves of our reason and experience, to correct the crude essays of our first and unexperienced, although wise, virtuous, and well-meaning councils. And, lastly, let us provide in our constitution for its revision at stated periods. What these periods should be, nature herself indicates. By the European tables of mortality, of the adults living at any one moment of time, a majority will be dead in about nineteen years. At the end of that period, then, a new majority is come into place; or, in other words, a new generation. Each generation is as independent of the one preceding, as that was of all which had gone before. It has, then, like them, a right to choose for itself the form of government it believes most promotive of its own happiness; consequently, to accommodate to the circumstances in which it finds itself, that received from its predecessors: and it is for the peace and good of mankind, that a solemn opportunity of doing this every nineteen or twenty years, should be provided by the constitution; so that it may be handed on, with periodical repairs, from generation to generation, to the end of time, if any thing human can so long endure. It is now forty years since the constitution of Virginia was formed. The same tables inform us, that, within that period, two thirds of the adults then living are now dead. Have then the remaining third, even if they had the wish, the right to hold in obedience to their will, and to laws heretofore made by them, the other two thirds, who, with themselves, compose the present mass of adults? If they have not, who has? The dead? But the dead have no rights. They are nothing; and nothing cannot own something. Where there is no substance, there can be no accident. This corporeal globe, and every thing upon it, belong to its present corporeal inhabitants, during their generation. They alone have a right to direct what is the concern of themselves alone, and to declare the law of that direction: and this declaration can only be made by their majority. That majority, then, has a right to depute representatives to a convention, and to make the constitution what they think will be best for themselves. But how collect their voice? This is the real difficulty. If invited by private authority to county or district meetings, these divisions are so large, that few will attend; and their voice will be imperfectly or falsely pronounced. Here, then, would be one of the advantages of the ward divisions I have proposed. The mayor of every ward, on a question like the present, would call his ward together, take the simple yea or nay of its members, convey these to the county court, who would hand on those of all its wards to the proper general authority; and the voice of the whole people would be thus fairly, fully, and peaceably expressed, discussed, and decided by the common reason of the society. If this avenue be shut to the call of sufferance, it will make itself heard through that of force, and we shall go on, as other nations are doing, in the endless circle of oppression, rebellion, reformation; and oppression, rebellion, reformation, again; and so on, for ever.
These, Sir, are my opinions of the governments we see among men, and of the principles by which alone we may prevent our own from falling into the same dreadful track. I have given them at greater length than your letter called for. But I cannot say things by halves; and I confide them to your honor, so to use them as to preserve me from the gridiron of the public papers. If you shall approve and enforce them, as you have done that of equal representation, they may do some good. If not, keep them to yourself as the effusions of withered age, and useless time. I shall, with not the Less truth, assure you of my great respect and consideration.
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN TAYLOR.
Monticello, July 21, 1816.
Dear Sir,
Yours of the 10th is received, and I have to acknowledge a copious supply of the turnip-seed requested. Besides taking care myself, I shall endeavor again to commit it to the depository of the neighborhood, generally found to be the best precaution against losing a good thing. I will add a word on the political part of our letters. I believe we do not differ on either of the points you suppose. On education certainly not; of which the proofs are my bill for the diffusion of knowledge, proposed near forty years ago, and my uniform endeavors, to this day, to get our counties divided into wards, one of the principal objects of which is, the establishment of a primary school in each. But education not being a branch of municipal government, but, like the other arts and sciences, an accident only, I did not place it, with election, as a fundamental member in the structure of government. Nor, I believe, do we differ as to the county courts. I acknowledge the value of this institution; that it is in truth our principal executive and judiciary, and that it does much for little pecuniary reward. It is their self-appointment I wish to correct; to find some means of breaking up a cabal, when such a one gets possession of the bench. When this takes place, it becomes the most afflicting of tyrannies, because its powers are so various, and exercised on every thing most immediately around us. And how many instances have you and I known of these monopolies of county administration! I knew a county in which a particular family (a numerous one) got possession of the bench, and for a whole generation. never admitted a man on it who was not of its clan or connection. 1 know a county now of one thousand and five hundred militia, of which sixty are federalists. Its court is of thirty members, of whom twenty are federalists, (every third man of the sect.) There are large and populous districts in it without a justice, because without a federalist for appointment: the militia are as disproportionably under federal officers. And there is no authority on earth which can break up this junto, short of a general convention. The remaining one thousand four hundred and forty, free, fighting, and paying citizens, are governed by men neither of their choice nor confidence, and without a hope of relief. They are certainly excluded from the blessings of a free government for life, and indefinitely, for aught the constitution has provided. This solecism may be called any thing but republican, and ought undoubtedly to be corrected. I salute you with constant friendship and respect.
Th: Jefferson.
Monticello, September 5, 1816.
Sir,
Your letter of August the 16th is just received. That which I wrote to you under the address of H. Tompkinson, was intended for the author of the pamphlet you were so kind as to send me, and therefore, in your hands, found its true destination. But I must beseech you, Sir, not to admit a possibility of its being published. Many good people will revolt from its doctrines, and my wish is to offend nobody; to leave to those who are to live under it, the settlement of their own constitution, and to pass in peace the remainder of my time. If those opinions are sound, they will occur to others, and will prevail by their own weight, without the aid of names. I am glad to see that the Staunton meeting has rejected the idea of a limited convention. The article, however, nearest my heart, is the division of the counties into wards. These will be pure and elementary republics, the sum of all which, taken together, composes the State, and will make of the whole a true democracy as to the business of the wards, which is that of nearest and daily concern. The affairs of the larger sections, of counties, of States, and of the Union, not admitting personal transaction by the people, will be delegated to agents elected by themselves; and representation will thus be substituted, where personal action becomes impracticable. Yet, even over these representative organs, should they become corrupt and perverted, the division into wards constituting the people, in their wards, a regularly organized power, enables them by that organization to crush, regularly and peaceably, the usurpations of their unfaithful agents, and rescues them from the dreadful necessity of doing it insurrectionally. In this way we shall be as republican as a large society can be; and secure the continuance of purity in our government, by the salutary, peaceable, and regular control of the people. No other depositories of power have ever yet been found, which did not end in converting to their own profit the earnings of those committed to their charge. George the III., in execution of the trust confided to him, has, within his own day, loaded the inhabitants of Great Britain with debts equal to the whole fee-simple value of their island, and under pretext of governing it, has alienated its whole soil to creditors who could lend money to be lavished on priests, pensions, plunder, and perpetual war. This would not have been so, had the people retained organized means of acting on their agents. In this example, then, let us read a lesson for ourselves, and not ‘go, and do likewise.’
Since writing my letter of July the 12th, I have been told, that on the question of equal representation, our fellow-citizens in some sections of the State claim peremptorily a right of representation for their slaves. Principle will, in this, as in most other cases, open the way for us to correct conclusion. Were our State a pure democracy, in which all its inhabitants should meet together to transact all their business, there would yet be excluded from their deliberations, 1. Infants, until arrived at years of discretion. 2. Women, who, to prevent depravation of morals, and ambiguity of issue, could not mix promiscuously in the public meetings of men. 3, Slaves, from whom the unfortunate state of things with us takes away the rights of will and of property. Those, then, who have no will, could be permitted to exercise none in the popular assembly; and of course could delegate none to an agent in a representative assembly. The business, in the first case, would be done by qualified citizens only; and, in the second, by the representatives of qualified citizens only. It is true, that in the general constitution, our State is allowed a larger representation on account of its slaves. But every one knows, that that constitution was a matter of compromise; a capitulation between conflicting interests and opinions. In truth, the condition of different descriptions of inhabitants in any country is a matter of municipal arrangement, of which no foreign country has a right to take notice. All its inhabitants are men as to them. Thus, in the New England States, none have the powers of citizens but those whom they call freemen; and none are freemen Until admitted by a vote of the freemen of the town. Yet, in the General Government, these non-freemen are counted in their quantum of representation and of taxation. So, slaves with us have no powers as citizens; yet, in representation in the General Government, they count in the proportion of three to five; and so also in taxation. Whether this is equal, is not here the question. It is a capitulation of discordant sentiments and circumstances, and is obligatory on that ground. But this view shows there is no inconsistency in claiming representation for them from the other States, and refusing it within our own.
Accept the renewal of assurances of my respect.
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN ADAMS,
Monticello, October 14, 1816.
Your letter, dear Sir, of May the 6th, had already well explained the uses of grief. That of September the 3rd, with equal truth, adduces instances of its abuse; and when we put into the same scale these abuses, with the afflictions of soul which even the uses of grief cost us, we may consider its value in the economy of the human being, as equivocal at least. Those afflictions cloud too great a portion of life, to find a counterpoise in any benefits derived from its uses. For setting aside its paroxyms on the occasions of special bereavements, all the latter years of aged men are overshadowed with its gloom. Whither, for instance, can you and I look without seeing the graves of those we have known? And whom can we call up, of our early companions, who has not left us to regret his loss? This, indeed, may be one of the salutary effects of grief; inasmuch as it prepares us to loose ourselves also without repugnance. Doctor Freeman’s instances of female levity cured by grief, are certainly to the point, and constitute an item of credit in the account we examine. I was much mortified by the loss of the Doctor’s visit, by my absence from home. To have shown how much I feel indebted to you for making good people known to me, would have been one pleasure; and to have enjoyed that of his conversation, and the benefits of his information, so favorably reported by my family, would have been another. I returned home on the third day after his departure. The loss of such visits is among the sacrifices which my divided residence costs me.
Your undertaking the twelve volumes of Dupuis, is a degree of heroism to which I could not have aspired even in my younger days. I have been contented with the humble achievement of reading the analysis of his work by Destutt Tracy, in two hundred pages, octavo. I believe I should have ventured on his own abridgment of the work, in one octavo volume, had it ever come to my hands; but the marrow of it in Tracy has satisfied my appetite: and even in that, the preliminary discourse of the analyzer himself, and his conclusion, are worth more in my eye than the body of the work. For the object of that seems to be to smother all history under the mantle of allegory. If histories so unlike as those of Hercules and Jesus, can, by a fertile imagination and allegorical interpretations, be brought to the same tally, no line of distinction remains between fact and fancy. As this pithy morsel will not overburthen the mail in passing and repassing between Quincy and Monticello, I send it for your perusal. Perhaps it will satisfy you, as it has me; and may save you the labor of reading twenty-four times its volume. I have said to you that it was written by Tracy; and I had so entered it on the title-page, as I usually do on anonymous works whose authors are known to me. But Tracy requested me not to betray his anonyme, for reasons which may not yet, perhaps, have ceased to weigh. I am bound, then, to make the same reserve with you. Destutt-Tracy is, in my judgment, the ablest writer living on intellectual subjects, or the operations of the understanding. His three octavo volumes on Ideology, which constitute the foundation of what he has since written, I have not entirely read; because I am not fond of reading what is merely abstract, and unapplied immediately to some useful science. Bonaparte, with his repeated derisions of Ideologists (squinting at this author) has by this time felt that true wisdom does not lie in mere practice without principle. The next work Tracy wrote was the Commentary on Montesquieu, never published in the original, because not safe; but translated and published in Philadelphia, yet without the author’s name. He has since permitted his name to be mentioned. Although called a Commentary, it is, in truth, an elementary work on the principles of government, comprised in about three hundred pages octavo. He has lately published a third work on Political Economy, comprising the whole subject within about the same compass; in which all its principles are demonstrated with the severity of Euclid, and, like him, without ever using a superfluous word. I have procured this to be translated, and have been four years endeavoring to get it printed: but, as yet, without success. In the mean time, the author has published the original in France, which he thought unsafe while Bonaparte was in power. No printed copy, I believe, has yet reached this country. He has his fourth and last work now in the press at Paris, closing, as he conceives, the circle of metaphysical sciences. This work, which is on Ethics, I have not seen, but suspect I shall differ from it in its foundation, although not in its deductions. I gather from his other works that he adopts the principle of Hobbes, that justice is founded in contract solely, and does not result from the constitution of man. I believe, on the contrary, that it is instinct and innate, that the moral sense is as much a part of our constitution as that of feeling, seeing, or hearing; as a wise creator must have seen to be necessary in an animal destined to live in society: that every human mind feels pleasure in doing good to another: that the non-existence of justice is not to be inferred from the fact that the same act is deemed virtuous and right in one society which is held vicious and wrong in another; because, as the circumstances and opinions of different societies vary, so the acts which may do them right or wrong must vary also; for virtue does not consist in the act we do, but in the end it is to effect. If it is to effect the happiness of him to whom it is directed, it is virtuous, while, in a society under different circumstances and opinions, the same act might produce pain, and would be vicious. The essence of virtue is in doing good to others, while what is good may be one thing in one society, and its contrary in another. Yet, however we may differ as to the foundation of morals (and as many foundations have been assumed as there are writers on the subject nearly), so correct a thinker as Tracy will give us a sound system of morals. And, indeed, it is remarkable, that so many writers, setting out from so many different premises, yet meet all in the same conclusions. This looks as if they were guided unconsciously, by the unerring-hand of instinct.
Your history of the Jesuits, by what name of the author or other description is it to be inquired for?
What do you think of the present situation of England? Is not this the great and fatal crush of their funding system, which, like death, has been foreseen by all, but its hour, like that of death, hidden from mortal prescience? It appears to me that all the circumstances now exist which render recovery desperate. The interest of the national debt is now equal to such a portion of the profits of all the land and the labor of the island, as not to leave enough for the subsistence of those who labor. Hence the owners of the land abandon it and retire to other countries, and the laborer has not enough of his earnings left to him to cover his back and to fill his belly. The local insurrections, now almost general, are of the hungry and the naked, who cannot be quieted but by food and raiment. But where are the means of feeding and clothing them? The landholder has nothing of his own to give; he is but the fiduciary of those who have lent him money; the lender is so taxed in his meat, drink, and clothing, that he has but a bare subsistence left. The landholder, then, must give up his land, or the lender his debt, or they must compromise by giving up each one half. But will either consent, peaceably, to such an abandonment of property? Or must it not be settled by civil conflict? If peaceably compromised, will they agree to risk another ruin under the same government unreformed? I think not; but I would rather know what you think; because you have lived with John Bull, and know better than I do the character of his herd. I salute Mrs. Adams and yourself with every sentiment of affectionate cordiality and respect;
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN ADAMS.
Monticello, January 11, 1817.
Dear Sir,
Forty-three volumes read in one year, and twelve of them quarto! Dear Sir, how I envy you! Half a dozen octavos in that space of time are as much as I am allowed. I can read by candlelight only, and stealing long hours from my rest: nor would that time be indulged to me, could I by that light see to write. From sunrise to one or two o’clock, and often from dinner to dark, I am drudging at the writing-table. And all this to answer letters into which neither interest nor inclination on my part enters; and often from persons whose names I have never before heard. Yet, writing civilly, it is hard to refuse them civil answers. This is the burthen of my life, a very grievous one indeed, and one which I must get rid of. Delaplaine lately requested me to give him a line on the subject of his book; meaning, as I well knew, to publish it. This I constantly refuse; but in this instance yielded, that in saying a word for him, I might say two for myself. I expressed in it freely my sufferings from this source; hoping it would have the effect of an indirect appeal to the discretion of those, strangers and others, who, in the most friendly dispositions, oppress me with their concerns, their pursuits, their projects, inventions, and speculations, political, moral, religious, mechanical, mathematical, historical, &c. &c. &c. I hope the appeal will bring me relief, and that I shall be left to, exercise and enjoy correspondence with the friends I love, and on subjects which they, or my own inclinations, present. In that case, your letters shall not be so long on my files unanswered, as sometimes they have been to my great mortification.
To advert now to the subjects of those of December the 12th and 16th. Tracy’s Commentaries on Montesquieu have never been published in the original. Duane printed a translation from the original manuscript a few years ago. It sold, I believe, readily, and whether a copy can now be had, I doubt. If it can, you will receive it from my bookseller in Philadelphia, to whom I now write for that purpose. Tracy comprehends, under the word ‘Ideology’ all the subjects which the French term Morale, as the correlative to Physique, His works on Logic, Government, Political Economy, and Morality, he considers as making up the circle of ideological subjects, or of those which are within the scope of the understanding, and not of the senses. His Logic occupies exactly the ground of Locke’s work on the Understanding. The translation of that on Political Economy is now printing; but it is no translation of mine. I have only had the correction of it, which was, indeed, very laborious. Le premier jet having been by some one who understood neither French nor English, it was impossible to make it more than faithful. But it is a valuable work.
The result of your fifty or sixty years of religious reading in the four words, ‘Be just and good,’ is that in which all our inquiries must end; as the riddles of all the priesthoods end in four more, ‘Ubi panis, ibi deus.’ What all agree in, is probably right; what no two agree in, most probably wrong. One of our fan-coloring biographers, who paints small men as very great, inquired of me lately, with real affection too, whether he might consider as authentic, the change in my religion much spoken of in some circles. Now this supposed that they knew what had been my religion before, taking for it the word of their priests, whom I certainly never made the confidants of my creed. My answer was, ‘Say nothing of my religion. It is known to my God and myself alone. Its evidence before the world is to be sought in my life; if that has been honest and dutiful to society, the religion which has regulated it cannot be a bad one.’ Affectionately adieu.
Th: Jefferson.
Monticello, May 5, 1817.
Dear Sir,
Absences and avocations had prevented my acknowledging your favor of February the 2nd, when that of April the 19th arrived. I had not the pleasure of receiving the former by the hands of Mr. Lyman. His business probably carried him in another direction; for I am far inland, and distant from the great line of communication between the trading cities. Your recommendations are always welcome, for, indeed, the subjects of them always merit that welcome, and some of them in an extraordinary degree. They make us acquainted with what there is excellent in our ancient sister State of Massachusetts, once venerated and beloved, and still hanging on our hopes, for what need we despair of after the resurrection of Connecticut to light and liberality. I had believed that the last retreat of monkish darkness, bigotry, and abhorrence of those advances of the mind which had carried the other States a century ahead of them. They seemed still to be exactly where their forefathers were when they schismatized from the covenant of works, and to consider as dangerous heresies all innovations good or bad. I join you, therefore, in sincere congratulations that this den of the priesthood is at length broken up, and that a Protestant Popedom is no longer to disgrace the American history and character. If by religion, we are to understand sectarian dogmas, in which no two of them agree, then your exclamation on that hypothesis is just, ‘that this would be the best of all possible worlds, if there were no religion in it.’ But if the moral precepts, innate in man, and made a part of his physical constitution, as necessary for a social being, if the sublime doctrines of philanthropism and deism taught us by Jesus of Nazareth, in which all agree, constitute true religion, then, without it, this would be, as you again say, ‘something not fit to be named, even indeed, a hell.’
You certainly acted wisely in taking no notice of what the malice of Pickering could say of you. Were such things to be answered, our lives would be wasted in the filth of fendings and provings, instead of being employed in promoting the happiness and prosperity of our fellow-citizens. The tenor of your life is the proper and sufficient answer. It is fortunate for those in public trust, that posterity will judge them by their works, and not by the malignant vituperations and invectives of the Pickerings and Gardiners of their age. After all, men of energy of character must have enemies; because there are two sides to every question, and taking one with decision, and acting on it with effect, those who take the other will of course be hostile in proportion as they feel that effect. Thus, in the Revolution, Hancock and the Adamses were the raw-head and bloody bones of tories and traitors; who yet knew nothing of you personally but what was good. I do not entertain your apprehensions for the happiness of our brother Madison in a state of retirement. Such a mind as his, fraught with information and with matter for reflection, can never know ennui. Besides, there will always be work enough cut out for him to continue his active usefulness to his country. For example, he and Monroe (the President) are now here on the work of a collegiate institution to be established in our neighborhood, of which they and myself are three of six Visitors. This, if it succeeds, will raise up children for Mr. Madison to employ his attention through life. I say, if it succeeds; for we have two very essential wants in our way: 1. means to compass our views; and 2. men qualified to fulfil them. And these you will agree are essential wants indeed.
I am glad to find you have a copy of Sismondi, because his is a field familiar to you, and on which you can judge him. His work is highly praised, but I have not yet read it. I have been occupied and delighted with reading another work, the title of which did not promise much useful information or amusement, ‘L’Italia avanti il Dominio del Romani, dal Micali. It has often, you know, been a subject of regret that Carthage had no writer to give her side of her own history, while her wealth, power, and splendor prove she must have had a very distinguished policy and government. Micali has given the counterpart of the Roman history, for the nations over which they extended their dominion. For this he has gleaned up matter from every quarter, and furnished materials for reflection and digestion to those who, thinking as they read, have perceived that there was a great deal of matter behind the curtain, could that be fully withdrawn. He certainly gives new views of a nation whose splendor has masked and palliated their barbarous ambition. I am now reading Botta’s History of our own Revolution. Bating the ancient practice which he has adopted, of putting speeches into mouths which never made them, and fancying motives of action which we never felt, he has given that history with more detail, precision, and candor, than any writer I have yet met with. It is, to be sure, compiled from those writers; but it is a good secretion of their matter, the pure from the impure, and presented in a just sense of right, in opposition to usurpation.
Accept assurances for Mrs. Adams and yourself of my affectionate esteem and respect.
Th: Jefferson.
TO MARQUIS DE LA FAYETTE.
Monticello, May 14, 1817.
Although, Dear Sir, much retired from the world, and meddling little in its concerns, yet I think it almost a religious duty to salute at times my old friends, were it only to say and to know that ‘all’s well.’ Our hobby has been politics; but all here is so quiet, and with you so desperate, that little matter is furnished us for active attention. With you too, it has long been forbidden ground, and therefore imprudent for a foreign friend to tread, in writing to you. But although our speculations might be intrusive, our prayers cannot but be acceptable, and mine are sincerely offered for the well-being of France. What government she can bear, depends not on the state of science, however exalted, in a select band of enlightened men, but on the condition of the general mind. That, I am sure, is advanced and will advance, and the last change of government was fortunate, inasmuch as the new will be less obstructive to the effects of that advancement. For I consider your foreign military oppression as an ephemeral obstacle only.
Here all is quiet. The British war has left us in debt; but that is a cheap price for the good it has done us. The establishment of the necessary manufactures among ourselves, the proof that our government is solid, can stand the shock of war, and is superior even to civil schism, are precious facts for us; and of these the strongest proofs were furnished, when, with four eastern States tied to us, as dead to living bodies, all doubt was removed as to the achievements of the war, had it continued. But its best effect has been the complete suppression of party. The federalists who were truly American, and their great mass was so, have separated from their brethren who were mere Anglomen, and are received with cordiality into the republican ranks. Even Connecticut, as a State, and the last one expected to yield its steady habits (which were essentially bigoted in politics as well as religion), has chosen a republican governor, and republican legislature. Massachusetts indeed still lags; because most deeply involved in the parricide crimes and treasons of the war. But her gangrene is contracting, the sound flesh advancing on it, and all there will be well. I mentioned Connecticut as the most hopeless of our States. Little Delaware had escaped my attention. That is essentially a Quaker State, the fragment of a religious sect which, there, in the other States, in England, are a homogeneous mass, acting with one mind, and that directed by the mother society in England. Dispersed, as the Jews, they still form, as those do, one nation, foreign to the land they live in. They are Protestant Jesuits, implicitly devoted to the will of their superior, and forgetting all duties to their country in the execution of the policy of their order. When war is proposed with England, they have religious scruples; but when with France, these are laid by, and they become clamorous for it. They are, however, silent, passive, and give no other trouble than of whipping them along. Nor is the election of Monroe an inefficient circumstance in our felicities. Four and twenty years, which he will accomplish, of administration in republican forms and principles, will so consecrate them in the eyes of the people as to secure them against the danger of change. The evanition of party dissensions has harmonized intercourse, and sweetened society beyond imagination. The war then has done us all this good, and the further one of assuring the world, that although attached to peace from a sense of its blessings, we will meet war when it is made necessary.
I wish I could give better hopes of our southern brethren. The achievement of their independence of Spain is no longer a question. But it is a very serious one, what will then become of them. Ignorance and bigotry, like other insanities, are incapable of self-government. They will fall under military despotisms, and become the murderous tools of the ambition of their respective Bonapartes; and whether this will be for their greater happiness, the rule of one only has taught you to judge. No one, I hope, can doubt my wish to see them and all mankind exercising self-government, and capable of exercising it. But the question is not what we wish, but what is practicable. As their sincere friend and brother, then, I do believe the best thing for them, would be for themselves to come to an accord with Spain, under the guarantee of France, Russia, Holland, and the United States, allowing to Spain a nominal supremacy, with authority only to keep the peace among them, leaving them otherwise all the powers of self-government, until their experience in them, their emancipation from their priests, and advancement in information, shall prepare them for complete independence. I exclude England from this confederacy, because her selfish principles render her incapable of honorable patronage or disinterested co-operation: unless, indeed, what seems now probable, a revolution, should restore to her an honest government, one which will permit the world to live in peace. Portugal grasping at an extension of her dominion in the south, has lost her great northern province of Pernambuco, and I shall not wonder if Brazil should revolt in mass, and send their royal family back to Portugal, Brazil is more populous, more wealthy, more energetic, and as wise as Portugal. I have been insensibly led, my dear friend, while writing to you, to indulge in that line of sentiment in which we have been always associated, forgetting that these are matters not belonging to my time. Not so with you, who have still many years to be a spectator of these events. That these years may indeed be many and happy, is the sincere prayer of your affectionate friend.
Th: Jefferson.
TO ALBERT GALLATIN.
Monticello, June 16, 1817.
Dear Sir,
The importance that the enclosed letters should safely reach their destination, impels me to avail myself of the protection of your cover. This is an inconvenience to which your situation exposes you, while it adds to the opportunities of exercising yourself in works of charity.
According to the opinion I hazarded to you a little before your departure, we have had almost an entire change in the body of Congress. The unpopularity of the compensation law was completed, by the manner of repealing it as to all the world except themselves. In some States, it is said, every member is changed; in all, many. What opposition there was to the original law, was chiefly from southern members. Yet many of those have been left out, because they received the advanced wages. I have never known so unanimous a sentiment of disapprobation; and what is remarkable, is, that it was spontaneous. The newspapers were almost entirely silent, and the people not only unled by their leaders, but in opposition to them. I confess I was highly pleased with this proof of the innate good sense, the vigilance, and the determination of the people to act for themselves.
Among the laws of the late Congress, some were of note: a navigation act, particularly, applicable to those nations only who have navigation acts; pinching one of them especially, not only in the general way, but in the intercourse with her foreign possessions. This part may re-act on us, and it remains for trial which may bear longest. A law respecting our conduct as a neutral between Spain and her contending colonies, was passed by a majority of one only, I believe, and against the very general sentiment of our country. It is thought to strain our complaisance to Spain beyond her right or merit, and almost against the right of the other party, and certainly against the claims they have to our good wishes and neighborly relations. That we should wish to see the people of other countries free, is as natural, and at least as justifiable, as that one King should wish to see the Kings of other countries maintained in their despotism. Right to both parties, innocent favor to the juster cause, is our proper sentiment.
You will have learned that an act for internal improvement, after passing both houses, was negatived by the President. The act was founded, avowedly, on the principle that the phrase in the constitution, which authorizes Congress ‘to lay taxes, to pay the debts and provide for the general welfare,’ was an extension of the powers specifically enumerated to whatever would promote the general welfare; and this, you know, was the federal doctrine. Whereas, our tenet ever was, and, indeed, it is almost the only land-mark which now divides the federalists from the republicans, that Congress had not unlimited powers to provide for the general welfare, but were restrained to those specifically enumerated; and that, as it was never meant they should provide for that welfare but by the exercise of the enumerated powers, so it could not have been meant they should raise money for purposes which the enumeration did not place under their action: consequently, that the specification of powers is a limitation of the purposes for which they may raise money. I think the passage and rejection of this bill a fortunate incident. Every State will certainly concede the power; and this will be a national confirmation of the grounds of appeal to them, and will settle for ever the meaning of this phrase, which, by a mere grammatical quibble, has countenanced the General Government in a claim of universal power. For in the phrase, ‘to lay taxes, to pay the debts and provide for the general welfare,’ it is a mere question of syntax, whether the two last infinitives are governed by the first, or are distinct and co-ordinate powers; a question unequivocally decided by the exact definition of powers immediately following. It is fortunate for another reason, as the States, in conceding the power, will modify it, either by requiring the federal ratio of expense in each State, or otherwise, so as to secure us against its partial exercise. Without this caution, intrigue, negotiation, and the barter of votes might become as habitual in Congress, as they are in those legislatures which have the appointment of officers, and which, with us, is called ‘logging,’ the term of the farmers for their exchanges of aid in rolling together the logs of their newly cleared grounds. Three of our papers have presented us the copy of an act of the legislature of New York, which, if it has really passed, will carry us back to the times of the darkest bigotry and barbarism to find a parallel. Its purport is, that all those who shall hereafter join in communion with the religious sect of Shaking Quakers, shall be deemed civilly dead, their marriages dissolved, and all their children and property taken out of their hands. This act being published nakedly in the papers, without the usual signatures, or any history of the circumstances of its passage, I am not without a hope it may have been a mere abortive attempt. It contrasts singularly with a cotemporary vote of the Pennsylvania legislature, who, on a proposition to make the belief in a God a necessary qualification for office, rejected it by a great majority, although assuredly there was not a single atheist in their body. And you remember to have heard, that, when the act for religious freedom was before the Virginia Assembly, a motion to insert the name of Jesus Christ before the phrase, ‘the author of our holy religion,’ which stood in the bill, was rejected, although that was the creed of a great majority of them.
I have been charmed to see that a Presidential election now produces scarcely any agitation. On Mr. Madison’s election there was little, on Monroe’s all but none. In Mr. Adams’s time and mine, parties were so nearly balanced as to make the struggle fearful for our peace. But since the decided ascendancy of the republican body, federalism has looked on with silent but unresisting anguish. In the middle, southern, and western States, it is as low as it ever can be; for nature has made some men monarchists and tories by their constitution, and some, of course, there always will be.
We have had a remarkably cold winter. At Hallowell, in Maine, the mercury was at thirty-four degrees below zero, of Fahrenheit, which is sixteen degrees lower than it was in Paris in 1788-9. Here it was at six degrees above zero, which is our greatest degree of cold.
Present me respectfully to Mrs. Gallatin, and be assured of my constant and affectionate friendship.
Th: Jefferson.
Monticello, May 17, 1818.
Dear Sir,
I was so unfortunate as not to receive from Mr. Holly’s own hand your favor of January the 28th, being then at my other home. He dined only with my family, and left them with an impression which has filled me with regret that I did not partake of the pleasure his visit gave them. I am glad he is gone to Kentucky. Rational Christianity will thrive more rapidly there than here. They are freer from prejudices than we are, and bolder in grasping at truth. The time is not distant, though neither you nor I shall see it, when we shall be but a secondary people to them. Our greediness for wealth, and fantastical expense have degraded, and will degrade, the minds of our maritime citizens. These are the peculiar vices of commerce.
I had been long without hearing from you, but I had heard of you through a letter from Doctor Waterhouse. He wrote to reclaim against an expression of Mr. Wirt’s, as to the commencement of motion in the revolutionary ball. The lawyers say that words are always to be expounded secundum subjectam materiem, which, in Mr. Wirt’s case, was Virginia. It would, moreover, be as difficult to say at what moment the Revolution began, and what incident set it in motion, as to fix the moment that the embryo becomes an animal, or the act which gives him a beginning. But the most agreeable part of his letter was that which informed me of your health, your activity, and strength of memory; and the most wonderful, that which assured me that you retained your industry and promptness in epistolary correspondence. Here you have entire advantage over me. My repugnance to the writing-table becomes daily and hourly more deadly and insurmountable. In place of this has come on a canine appetite for reading. And I indulge it, because I see in it a relief against the tædium senectutis; a lamp to lighten my path through the dreary wilderness of time before me, whose bourne I see not. Losing daily all interest in the things around us, something else is necessary to fill the void. With me it is reading, which occupies the mind without the labor of producing ideas from my own stock.
I enter into all your doubts as to the event of the revolution of South America. They will succeed against Spain. But the dangerous enemy is within their own breasts. Ignorance and superstition will chain their minds and bodies under religious and military despotism. I do believe it would be better for them to obtain freedom by degrees only; because that would by degrees bring on light and information, and qualify them to take charge of themselves understanding; with more certainty, if, in the mean time, under so much control as may keep them at peace with one another. Surely, it is our duty to wish them independence and self-government, because they wish it themselves, and they have the right, and we none, to choose for themselves: and I wish, moreover, that our ideas may be erroneous, and theirs prove well-founded. But these are speculations, my friend, which we may as well deliver over to those who are to see their developement. We shall only be lookers on, from the clouds above, as now we look down on the labors, the hurry, and bustle of the ants and bees. Perhaps, in that super-mundane region, we may be amused with seeing the fallacy of our own guesses, and even the nothingness of those labors which have filled and agitated our own time here.
En attendant, with sincere affections to Mrs. Adams and yourself, I salute you both cordially.
Th: Jefferson.
Monticello, November 13, 1818.
The public papers, my dear friend, announce the fatal event of which your letter of October the 20th had given me ominous foreboding. Tried myself in the school of affliction, by the loss of every form of connection which can rive the human heart, I know well, and feel what you have lost, what you have suffered, are suffering, and have yet to endure. The same trials have taught me that, for ills so immeasurable, time and silence are the only medicine. I will not, therefore, by useless condolences, open afresh the sluices of your grief, nor, although mingling sincerely my tears with yours, will I say a word more where words are vain, but that it is of some comfort to us both, that the term is not very distant, at which we are to deposit in the same cerement our sorrows and suffering bodies, and to ascend in essence to an ecstatic meeting with the friends we have loved and lost, and whom we shall still love, and never lose again. God bless you, and support you under your heavy affliction.
Th: Jefferson.
TO ROBERT WALSH.
Monticello, December 4, 1818.
Dear Sir,
Yours of November the 8th has been some time received; but it is in my power to give little satisfaction as to its inquiries. Dr. Franklin had many political enemies, as every character must, which, with decision enough to have opinions, has energy and talent to give them effect on the feelings of the adversary opinion. These enmities were chiefly in Pennsylvania and Massachusetts. In the former, they were merely of the proprietary party. In the latter, they did not commence till the Revolution, and then sprung chiefly from personal animosities, which, spreading by little and little, became at length of some extent. Dr. Lee was his principal calumniator, a man of much malignity, who, besides enlisting his whole family in the same hostility, was enabled, as the agent of Massachusetts with the British government, to infuse it into that State with considerable effect. Mr. Izard, the Doctor’s enemy also, but from a pecuniary transaction, never countenanced these charges against him. Mr. Jay, Silas Deane, Mr. Laurens, his colleagues also, ever maintained towards him unlimited confidence and respect. That he would have waived the formal recognition of our independence, I never heard on any authority worthy notice. As to the fisheries, England was urgent to retain them exclusively, France neutral, and I believe, that had they been ultimately made a sine qua non, our commissioners (Mr. Adams excepted) would have relinquished them, rather than have broken off the treaty. To Mr. Adams’s perseverance alone, on that point, I have always understood we were indebted for their reservation. As to the charge of subservience to France, besides the evidence of his friendly colleagues before named, two years of my own service with him at Paris, daily visits, and the most friendly and confidential conversations, convince me it had not a shadow of foundation. He possessed the confidence of that government in the highest degree, insomuch, that it may truly be said, that they were more under his influence, than he under theirs. The fact is, that his temper was so amiable and conciliatory, his conduct so rational, never urging impossibilities, or even things unreasonably inconvenient to them, in short, so moderate and attentive to their difficulties, as well as our own, that what his enemies called subserviency, I saw was only that reasonable disposition, which, sensible that advantages are not all to be on one side, yielding what is just and liberal, is the more certain of obtaining liberality and justice. Mutual confidence produces, of course, mutual influence, and this was all which subsisted between Dr. Franklin and the government of France.
I state a few anecdotes of Dr. Franklin, within my own knowledge, too much in detail for the scale of Delaplaine’s work, but which may find a cadre in some of the more particular views you contemplate. My health is in a great measure restored, and our family join with me in affectionate recollections and assurances of respect.
Th: Jefferson.
TO M. DE NEUVILLE.
Monticello, December 13, 1818.
I thank your Excellency for the notice with which your letters favor me, of the liberation of France from the occupation of the allied powers. To no one, not a native, will it give more pleasure. In the desolation of Europe, to gratify the atrocious caprices of Bonaparte, France sinned much: but she has suffered more than retaliation. Once relieved from the incubus of her late oppression, she will rise like a giant from her slumbers. Her soil and climate, her arts and eminent science, her central position and free constitution, will soon make her greater than she ever was. And I am a false prophet if she does not, at some future day, remind of her sufferings those who have inflicted them the most eagerly. I hope, however, she will be quiet for the present, and risk no new troubles. Her constitution, as now amended, gives as much of self-government as perhaps she can yet bear, and will give more, when the habits of order shall have prepared her to receive more. Besides the gratitude which every American owes her, as our sole ally during the war of independence, I am additionally affectioned by the friendships I contracted there, by the good dispositions I witnessed, and by the courtesies I received.
I rejoice, as a moralist, at the prospect of a reduction of the duties on wine, by our national legislature. It is an error to view a tax on that liquor as merely a tax on the rich. It is a prohibition of its use to the middling class of our citizens, and a condemnation of them to the poison of whiskey, which is desolating their houses. No nation is drunken where wine is cheap; and none sober, where the dearness of wine substitutes ardent spirits as the common beverage. It is, in truth, the only antidote to the bane of whiskey. Fix but the duty at the rate of other merchandise, and we can drink wine here as cheap as we do grog: and who will not prefer it? Its extended use will carry health and comfort to a much enlarged circle. Every one in easy circumstances (as the bulk of our citizens are) will prefer it to the poison to which they are now driven by their government. And the treasury itself will find that a penny a piece from a dozen, is more than a groat from a single one. This reformation, however, will require time. Our merchants know nothing of the infinite variety of cheap and good wines to be had in Europe; and particularly in France, in Italy, and the Grecian islands: as they know little, also, of the variety of excellent manufactures and comforts to be had any where out of England. Nor will these things be known, nor of course called for here, until the native merchants of those countries, to whom they are known, shall bring them forward, exhibit, and vend them at the moderate profits they can afford. This alone will procure them familiarity with us, and the preference they merit in competition with corresponding articles now in use.
Our family renew with pleasure their recollections of your kind visit to Monticello, and join me in tendering sincere assurances of the gratification it afforded us, and of our great esteem and respectful consideration.
Th: Jefferson.
TO DOCTOR VINE UTLEY.
Monticello, March 21, 1819.
Sir,
Your letter of February the 18th came to hand on the 1st instant; and the request of the history of my physical habits would have puzzled me not a little, had it not been for the model with which you accompanied it, of Doctor Rush’s answer to a similar inquiry. I live so much like other people, that I might refer to ordinary life as the history of my own. Like my friend the Doctor, I have lived temperately, eating little animal food, and that not as an aliment, so much as a condiment for the vegetables, which constitute my principal diet. I double, however, the Doctor’s glass and a half of wine, and even treble it with a friend; but halve its effect by drinking the weak wines only. The ardent wines I cannot drink, nor do I use ardent spirits in any form. Malt liquors and cider are my table drinks, and my breakfast, like that also of my friend, is of tea and coffee. I have been blest with organs of digestion, which accept and concoct, without ever murmuring, whatever the palate chooses to consign to them, and I have not yet lost a tooth by age. I was a hard student until I entered on the business of life, the duties of which leave no idle time to those disposed to fulfil them; and now, retired, and at the age of seventy-six, I am again a hard student. Indeed my fondness for reading and study revolts me from the drudgery of letter-writing. And a stiff wrist, the consequence of an early dislocation, makes writing both slow and painful. I am not so regular in my sleep as the Doctor says he was, devoting to it from five to eight hours, according as my company or the book I am reading interests me; and I never go to bed without an hour, or half hour’s previous reading of something moral, whereon to ruminate in the intervals of sleep. But whether I retire to bed early or late, I rise with the sun. I use spectacles at night, but not necessarily in the day, unless in reading small print. My hearing is distinct in particular conversation, but confused when several voices cross each other, which unfits me for the society of the table. I have been more fortunate than my friend in the article of health. So free from catarrhs that I have not had one (in the breast, I mean) on an average of eight or ten years through life. I ascribe this exemption partly to the habit of bathing my feet in cold water every morning for sixty years past. A fever of more than twenty-four hours I have not had above two or three times in my life. A periodical headache has afflicted me occasionally, once, perhaps, in six or eight years, for two or three weeks at a time, which seems now to have left me; and, except on a late occasion of indisposition, I enjoy good health; too feeble, indeed, to walk much, but riding without fatigue six or eight miles a day, and sometimes thirty or forty. I may end these egotisms, therefore, as I began, by saying that my life has been so much like that of other people, that I might say with Horace, to every one, ‘Nomine mutato, narratur fabula de te.’ I must not end, however, without due thanks for the kind sentiments of regard you are so good as to express towards myself; and with my acknowledgments for these, be pleased to accept the assurances of my respect and esteem.
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN ADAMS.
Monticello, July 9, 1819.
Dear Sir,
I am in debt to you for your letters of May the 21st, 27th, and June the 22nd. The first, delivered me by Mr. Greenwood, gave me the gratification of his acquaintance; and a gratification it always is, to be made acquainted with gentlemen of candor, worth, and information, as I found Mr. Greenwood to be. That, on the subject of Mr. Samuel Adams Wells, shall not be forgotten in time and place, when it can be used to his advantage.
But what has attracted my peculiar notice, is the paper from Mecklenburg county, of North Carolina, published in the Essex Register, which you were so kind as to enclose in your last, of June the 22nd. And you seem to think it genuine. I believe it spurious. I deem it to be a very unjustifiable quiz, like that of the volcano, so minutely related to us as having broken out in North Carolina, some half dozen years ago, in that part of the country, and perhaps in that very county of Mecklenburg, for I do not remember its precise locality. If this paper be really taken from the Raleigh Register, as quoted, I wonder it should have escaped Ritchie, who culls what is good from every paper, as the bee from every flower; and the National Intelligencer, too, which is edited by a North-Carolinian: and that the fire should blaze out all at once in Essex, one thousand miles from where the spark is said to have fallen. But if really taken from the Raleigh Register, who is the narrator, and is the name subscribed real, or is it as fictitious as the paper itself? It appeals, too, to an original book, which is burnt, to Mr. Alexander, who is dead, to a joint letter from Caswell, Hughes, and Hooper, all dead, to a copy sent to the dead Caswell, and another sent to Doctor Williamson, now probably dead, whose memory did not recollect, in the history he has written of North Carolina, this gigantic step of its county of Mecklenburg. Horry, too, is silent in his history of Marion, whose scene of action was the country bordering On Mecklenburg. Ramsay, Marshall, Jones, Girardin, Wirt, historians of the adjacent States, all silent. When Mr. Henry’s resolutions, far short of independence, flew like lightning through every paper, and kindled both sides of the Atlantic, this flaming declaration of the same date, of the independence of Mecklenburg county, of North Carolina, absolving it from the British allegiance, and abjuring all political connection with that nation, although sent to Congress, too, is never heard of. It is not known even a twelvemonth after, when a similar proposition is first made in that body. Armed with this bold example, would not you have addressed our timid brethren in peals of thunder, on their tardy fears? Would not every advocate of independence have rung the glories of Mecklenburg county, in North Carolina, in the ears of the doubting Dickinson and others, who hung so heavily on us? Yet the example of independent Mecklenburg county, in North Carolina, was never once quoted. The paper speaks, too, of the continued exertions of their delegation (Caswell, Hooper, Hughes,) ‘in the cause of liberty and independence.’ Now, you remember as well as I do, that we had not a greater tory in Congress than Hooper; that Hughes was very wavering, sometimes firm, sometimes feeble, according as the day was clear or cloudy; that Caswell, indeed, was a good whig, and kept these gentlemen to the notch, while he was present; but that he left us soon, and their line of conduct became then uncertain until Penn came, who fixed Hughes, and the vote of the State. I must not be understood as suggesting any doubtfulness in the State of North Carolina. No State was more fixed or forward. Nor do I affirm, positively, that this paper is a fabrication: because the proof of a negative can only be presumptive. But I shall believe it such until positive and solemn proof of its authenticity shall be produced. And if the name of McKnitt be real, and not a part of the fabrication, it needs a vindication by the production of such proof. For the present, I must be an unbeliever in the apocryphal gospel.
I am glad to learn that Mr. Ticknor has safely returned to his friends; but should have been much more pleased had he accepted the Professorship in our University, which we should have offered him in form. Mr. Bowditch, too, refuses us; so fascinating is the vinculum of the dulce natale solum. Our wish is to procure natives, where they can be found, like these gentlemen, of the first order of acquirement in their respective lines; but preferring foreigners of the first order to natives of the second, we shall certainly have to go, for several of our Professors, to countries more advanced in science than we are.
I set out within three or four days for my other home, the distance of which, and its cross mails, are great impediments to epistolary communications. I shall remain there about two months; and there, here, and every where, I am and shall always be, affectionately and respectfully yours.
Th: Jefferson.
TO JUDGE ROANE.
Poplar Forest, September 6,1819.
Dear Sir,
I had read in the Enquirer, and with great approbation, the pieces signed Hampden, and have read them again with redoubled approbation in the copies you have been so kind as to send me. I subscribe to every tittle of them. They contain the true principles of the revolution of 1800, for that was as real a revolution in the principles of our government as that of 1776 was in its form; not effected indeed by the sword, as that, but by the rational and peaceable instrument of reform, the suffrage of the people. The nation declared its will by dismissing functionaries of one principle, and electing those of another, in the two branches, executive and legislative, submitted to their election. Over the judiciary department, the constitution had deprived them of their control. That, therefore, has continued the reprobated system: and although new matter has been occasionally incorporated into the old, yet the leaven of the old mass seems to assimilate to itself the new; and after twenty years’ confirmation of the federated system by the voice of the nation, declared through the medium of elections, we find the judiciary, on every occasion, still driving us into consolidation.
In denying the right they usurp of exclusively explaining the constitution, I go further than you do, if I understand rightly your quotation from the Federalist, of an opinion that ‘the judiciary is the last resort in relation to the other departments of the government, but not in relation to the rights of the parties to the compact under which the judiciary is derived.’ If this opinion be sound, then indeed is our constitution a complete felo de se. For intending to establish three departments, co-ordinate and independent, that they might check and balance one another, it has given, according to this opinion, to one of them alone, the right to prescribe rules for the government of the others, and to that one too, which is unelected by, and independent of the nation. For experience has already shown that the impeachment it has provided is not even a scare-crow; that such opinions as the one you combat, sent cautiously out, as you observe also, by detachment, not belonging to the case often, but sought for out of it, as if to rally the public opinion beforehand to their views, and to indicate the line they are to walk in, have been so quietly passed over as never to have excited animadversion, even in a speech of any one of the body entrusted with impeachment. The constitution, on this hypothesis, is a mere thing of wax in the hands of the judiciary, which they may twist and shape into any form they please. It should be remembered, as an axiom of eternal truth in politics, that whatever power in any government is independent, is absolute also; in theory only, at first, while the spirit of the people is up, but in practice, as fast as that relaxes. Independence can be trusted no where but with the people in mass. They are inherently independent of all but moral law. My construction of the constitution is very different from that you quote. It is that each department is truly independent of the others, and has an equal right to decide for itself what is the meaning of the constitution in the cases submitted to its action; and especially, where it is to act ultimately and without appeal. I will explain myself by examples, which, having occurred while I was in office, are better known to me, and the principles which governed them.
A legislature had passed the sedition-law. The federal courts had subjected certain individuals to its penalties, of fine and imprisonment. On coming into office, I released these individuals by the power of pardon committed to executive discretion, which could never be more properly exercised than where citizens were suffering without the authority of law, or, which was equivalent, under a law unauthorized by the constitution, and therefore null. In the case of Marbury and Madison, the federal judges declared that commissions, signed and sealed by the President, were valid, although not delivered. I deemed delivery essential to complete a deed, which, as long as it remains in the hands of the party, is as yet no deed, it is in posse only, but not in esse, and I withheld delivery of the commissions. They cannot issue a mandamus* to the President or legislature, or to any of their officers. When the British treaty of 180- arrived, without any provision against the impressment of our seamen, I determined not to ratify it. The Senate thought I should ask their advice. I thought that would be a mockery of them, when I was predetermined against following it, should they advise its ratification. The constitution had made their advice necessary to confirm a treaty, but not to reject it. This has been blamed by some; but I have never doubted its soundness. In the cases of two persons, antenati, under exactly similar circumstances, the federal court had determined that one of them (Duane) was not a citizen; the House of Representatives nevertheless determined that the other (Smith of South Carolina) was a citizen, and admitted him to his seat in their body. Duane was a republican, and Smith a federalist, and these decisions were during the federal ascendancy.
* The constitution controlling the common law in this
particular.
These are examples of my position, that each of the three departments has equally the right to decide for itself what is its duty under the constitution, without any regard to what the others may have decided for themselves under a similar question. But you intimate a wish that my opinion should be known on this subject. No, dear Sir, I withdraw from all contests of opinion, and resign every thing cheerfully to the generation now in place. They are wiser than we were, and their successors will be wiser than they, from the progressive advance of science. Tranquillity is the summum bonum of age. I wish, therefore, to offend no man’s opinions, nor to draw disquieting animadversions on my own. While duty required it, I met opposition with a firm and fearless step. But, loving mankind in my individual relations with them, I pray to be permitted to depart in their peace; and like the superannuated soldier, ‘quadragenis stipendiis emeritis’to hang my arms on the post. I have unwisely, I fear, embarked in an enterprise of great public concern, but not to be accomplished within my term, without their liberal and prompt support. A severe illness the last year and another from which I am just emerged, admonish me that repetitions may be expected, against which a declining frame cannot long bear up. I am anxious therefore to get our University so far advanced as may encourage the public to persevere to its final accomplishment. That secured, I shall sing my Nunc demittas. I hope your labors will be long continued in the spirit in which they have always been exercised, in maintenance of those principles on which I verily believe the future happiness of our country essentially depends. I salute you with affectionate and great respect.
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN ADAMS.
Monticello, December 10, 1819.
Dear Sir,
I have to acknowledge the receipt of your favor of November the 23rd. The banks, bankrupt-law, manufacturers, Spanish treaty, are nothing. These are occurrences which, like waves in a storm, will pass under the ship. But the Missouri question is a breaker on which we lose the Missouri country by revolt, and what more, God only knows. From the battle of Bunker’s Hill to the treaty of Paris, we never had so ominous a question. It even damps the joy with which I hear of your high health, and welcomes to me the consequences of my want of it. I thank God that I shall not live to witness its issue. Sed hæc hactenus.
I have been amusing myself latterly with reading the voluminous letters of Cicero. They certainly breathe the purest effusions of an exalted patriot, while the parricide Caesar is lost in odious contrast. When the enthusiasm, however, kindled by Cicero’s pen and principles, subsides into cool reflection, I ask myself, What was that government which the virtues of Cicero were so zealous to restore, and the ambition of Caesar to subvert? And if Caesar had been as virtuous as he was daring and sagacious, what could he, even in the plenitude of his usurped power, have done to lead his fellow-citizens into good government? I do not say to restore it, because they never had it, from the rape of the Sabines to the ravages of the Caesars. If their people indeed had been, like ourselves, enlightened, peaceable, and really free, the answer would be obvious. ‘Restore independence to all your foreign conquests, relieve Italy from the government of the rabble of Rome, consult it as a nation entitled to self-government, and do its will.’ But steeped in corruption, vice, and venality, as the whole nation was, (and nobody had done more than Caesar to corrupt it,) what could even Cicero, Cato, Brutus, have done, had it been referred to them to establish a good government for their country? They had no ideas of government themselves, but of their degenerate Senate, nor the people of liberty, but of the factious opposition of their tribunes. They had afterwards their Tituses, their Trajans, and Antoninuses, who had the will to make them happy, and the power to mould their government into a good and permanent form. But it would seem as if they could not see their way clearly to do it. No government can continue good, but under the control of the people; and their people were so demoralized and depraved, as to be incapable of exercising a wholesome control. Their reformation then was to be taken up ab incunabulis. Their minds were to be informed by education what is right and what wrong; to be encouraged in habits of virtue, and deterred from those of vice, by the dread of punishments, proportioned indeed, but irremissible; in all cases, to follow truth as the only safe guide, and to eschew error, which bewilders us in one false consequence after another, in endless succession. These are the inculcations necessary to render the people a sure basis for the structure of order and good government. But this would have been an operation of a generation or two, at least, within which period would have succeeded many Neros and Commoduses, who would have quashed the whole process. I confess then, I can neither see what Cicero, Cato, and Brutus, united and uncontrolled, could have devised to lead their people into good government, nor how this enigma can be solved, nor how further shown why it has been the fate of that delightful country never to have known, to this day, and through a course of five and twenty hundred years, the history of which we possess, one single day of free and rational government. Your intimacy with their history, ancient, middle, and modern, your familiarity with the improvements in the science of government at this time, will enable you, if any body, to go back with our principles and opinions to the limes of Cicero, Cato, and Brutus, and tell us by what process these great and virtuous men could have led so unenlightened and vitiated a people into freedom and good government, et eris mihi magnus Apollo. Cura ut valeas, et tibi persuadeas carissimum te mihi esse.
Th: Jefferson.
TO WILLIAM SHORT.
Monticello, April 13, 1820.
Dear Sir,
Your favor of March the 27th is received, and, as you request, a copy of the syllabus is now enclosed. It was originally written to Dr. Rush. On his death, fearing that the inquisition of the public might get hold of it, I asked the return of it from the family, which they kindly complied with. At the request of another friend, I had given him a copy. He lent it to his friend to read, who copied it, and in a few months it appeared in the Theological Magazine of London. Happily that repository is scarcely known in this country; and the syllabus, therefore, is still a secret, and in your hands I am sure it will continue so.
But while this syllabus is meant to place the character of Jesus in its true and high light, as no impostor himself, but a great reformer of the Hebrew code of religion, it is not to be understood that I am with him in all his doctrines. I am a Materialist; he takes the side of Spiritualism: he preaches the efficacy of repentance towards forgiveness of sin; I require a counterpoise of good works to redeem it, &c. &c. It is the innocence of his character, the purity and sublimity of his moral precepts, the eloquence of his inculcations, the beauty of the apologues in which he conveys them, that I so much admire; sometimes, indeed, needing indulgence to eastern hyperbolism. My eulogies, too, may be founded on a postulate which all may not be ready to grant. Among the sayings and discourses imputed to him by his biographers, I find many passages of fine imagination, correct morality, and of the most lovely benevolence; and others again, of so much ignorance, so much absurdity, so much untruth, charlatanism, and imposture, as to pronounce it impossible that such contradictions should have proceeded from the same being. I separate, therefore, the gold from the dross; restore to him the former, and leave the latter to the stupidity of some, and roguery of others of his disciples. Of this band of dupes and impostors, Paul was the great Coryphæus, and first corrupter of the doctrines of Jesus. These palpable interpolations and falsifications of his doctrines led me to try to sift them apart. I found the work obvious and easy, and that his part composed the most beautiful morsel of morality which has been given to us by man. The syllabus is therefore of his doctrine, not all of mine: I read them as I do those of other ancient and modern moralists, with a mixture of approbation and dissent.
I rejoice, with you, to see an encouraging spirit of internal improvement prevailing in the States. The opinion I have ever expressed of the advantages of a western communication through the James River, I still entertain; and that the Cayuga is the most promising of the Dlinks of communication.
The history of our University you know so far. Seven of the ten pavilions destined for the Professors, and about thirty dormitories, will be completed this year, and three others, with six hotels for boarding, and seventy other dormitories, will be completed the next year, and the whole be in readiness then to receive those who are to occupy them. But means to bring these into place, and to set the machine into motion, must come from the legislature. An opposition, in the mean time, has been got up. That of our alma mater, William and Mary, is not of much weight. She must descend into the secondary rank of academies of preparation for the University. The serious enemies are the priests of the different religious sects, to whose spells on the human mind its improvement is ominous. Their pulpits are now resounding with denunciations against the appointment of Doctor Cooper, whom they charge as a monotheist in opposition to their tritheism. Hostile as these sects are, in every other point, to one another, they unite in maintaining their mystical theogony against those who believe there is one God only. The Presbyterian clergy are loudest; the most intolerant of all sects, the most tyrannical and ambitious; ready at the word of the lawgiver, if such a word could be now obtained, to put the torch to the pile, and to rekindle in this virgin hemisphere the flames in which their oracle Calvin consumed the poor Servetus, because, he could not find in his Euclid the proposition which has demonstrated that three are one, and one is three, nor subscribe to that of Calvin, that magistrates have a right to exterminate all heretics to Calvinistic creed. They pant to re-establish, by law, that holy inquisition, which they can now only infuse into public opinion. We have most unwisely committed to the hierophants of our particular superstition the direction of public opinion, that lord of the universe. We have given them stated and privileged days to collect and catechize us, opportunities of delivering their oracles to the people in mass, and of moulding their minds as wax in the hollow of their hands. But in despite of their fulminations against endeavors to enlighten the general mind, to improve the reason of the people, and encourage them in the use of it, the liberality of this State will support this institution, and give fair play to the cultivation of reason. Can you ever find a more eligible occasion of visiting once more your native country, than that of accompanying Mr. Correa, and of seeing with him this beautiful and hopeful institution in ovo.
Although I had laid down as a law to myself, never to write, talk, or even think of politics, to know nothing of public affairs, and therefore had ceased to read newspapers, yet the Missouri question aroused and filled me with alarm. The old schism of federal and republican threatened nothing, because it existed in every State, and united them together by the fraternism of party. But the coincidence of a marked principle, moral and political, with a geographical line, once conceived, I feared would never more be obliterated from the mind; that it would be recurring on every occasion, and renewing irritations, until it would kindle such mutual and mortal hatred, as to render separation preferable to eternal discord. I have been among the most sanguine in believing that our Union would be of long duration. I now doubt it much, and see the event at no great distance, and the direct consequence of this question: not by the line which has been so confidently counted on; the laws of nature control this; but by the Potomac, Ohio, and Missouri, or more probably, the Mississippi upwards to our northern boundary. My only comfort and confidence is, that I shall not live to see this; and I envy not the present generation the glory of throwing away the fruits of their fathers’ sacrifices of life and fortune, and of rendering desperate the experiment which was to decide ultimately whether man is capable of self-government. This treason against human hope will signalize their epoch in future history, as the counterpart of the medal of their predecessors.
You kindly inquire after my health. There is nothing in it immediately threatening, but swelled legs, which are kept down mechanically, by bandages from the toe to the knee. These I have worn for six months. But the tendency to turgidity may proceed from debility alone. I can walk the round of my garden; not more. But I ride six or eight miles a day without fatigue. I shall set out for Poplar Forest within three or four days; a journey from which my physician augurs much good.
I salute you with constant and affectionate friendship and respect.
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN HOLMES.
Monticello, April 22, 1820.
I thank you, dear Sir, for the copy you have been so kind as to send me of the letter to your constituents on the Missouri question. It is a perfect justification to them. I had for a long time ceased to read newspapers, or pay any attention to public affairs, confident they were in good hands, and content to be a passenger in our bark to the shore from which I am not distant. But this momentous question, like a fire-bell in the night, awakened and filled me with terror. I considered it at once as the knell of the Union. It is hushed, indeed, for the moment. But this is a reprieve only, not a final sentence. A geographical line, coinciding with a marked principle, moral and political, once conceived and held up to the angry passions of men, will never be obliterated; and every new irritation will mark it deeper and deeper. I can say, with conscious truth, that there is not a man on earth who would sacrifice more than I would to relieve us from this heavy reproach, in any practicable way. The cession of that kind of property (for so it is misnamed) is a bagatelle which would not cost me a second thought, if, in that way, a general emancipation and expatriation could be effected: and, gradually, and with due sacrifices, I think it might be. But as it is, we have the wolf by the ears, and we can neither hold him, nor safely let him go. Justice is in one scale, and self-preservation in the other. Of one thing I am certain, that as the passage of slaves from one State to another, would not make a slave of a single human being who would not be so without it, so their diffusion over a greater surface would make them individually happier, and proportionally facilitate the accomplishment of their emancipation, by dividing the burthen on a greater number of coadjutors. An abstinence, too, from this act of power, would remove the jealousy excited by the undertaking of Congress to regulate the condition of the different descriptions of men composing a State. This certainly is the exclusive right of every State, which nothing in the constitution has taken from them, and given to the General Government. Could Congress, for example, say, that the non-freemen of Connecticut shall be freemen, or that they shall not emigrate into any other State?
I regret that I am now to die in the belief, that the useless sacrifice of themselves by the generation of 1776, to acquire self-government and happiness to their country, is to be thrown away by the unwise and unworthy passions of their sons, and that my only consolation is to be, that I live not to weep over it. If they would but dispassionately weigh the blessings they will throw away, against an abstract principle more likely to be effected by union than by scission, they would pause before they would perpetrate this act of suicide on themselves, and of treason against the hopes of the world. To yourself, as the faithful advocate of the Union, I tender the offering of my high esteem and respect.
Th: Jefferson.
TO WILLIAM SHORT.
Monticello, August 4, 1820.
Dear Sir,
I owe you a letter for your favor of June the 29th, which was received in due time; and there being no subject of the day, of particular interest, I will make this a supplement to mine of April the 13th. My aim in that was, to justify the character of Jesus against the fictions of his pseudo-followers, which have exposed him to the inference of being an impostor. For if we could believe that he really countenanced the follies, the falsehoods, and the charlatanisms which his biographers father on him, and admit the misconstructions, interpolations, and theorizations of the fathers of the early, and fanatics of the latter ages, the conclusion would be irresistible by every sound mind, that he was an impostor. I give no credit to their falsifications of his actions and doctrines, and to rescue his character, the postulate in my letter asked only what is granted in reading every other historian. When Livy and Siculus, for example, tell us things which coincide with our experience of the order of nature, we credit them on their word, and place their narrations among the records of credible history. But when they tell us of calves speaking, of statues sweating blood, and other things against the course of nature, we reject these as fables not belonging to history. In like manner, when an historian, speaking of a character well known and established on satisfactory testimony, imputes to it things incompatible with that character, we reject them without hesitation, and assent to that only of which we have better evidence. Had Plutarch informed us that Cæsar and Cicero passed their whole lives in religious exercises, and abstinence from the affairs of the world, we should reject what was so inconsistent with their established characters, still crediting what he relates in conformity with our ideas of them. So again, the superlative wisdom of Socrates is testified by all antiquity, and placed on ground not to be questioned. When, therefore, Plato puts into his mouth such paralogisms, such quibbles on words, and sophisms, as a school-boy would be ashamed of, we conclude they were the whimsies of Plato’s own foggy brain, and acquit Socrates of puerilities so unlike his character. (Speaking of Plato, I will add, that no writer, ancient or modern, has bewildered the world with more ignes fatui, than this renowned philosopher, in Ethics, in Politics, and Physics. In the latter, to specify a single example, compare his views of the animal economy, in his Timasus, with those of Mrs. Bryan in her Conversations on Chemistry, and weigh the science of the canonized philosopher against the good sense of the unassuming lady. But Plato’s visions have furnished a basis for endless systems of mystical theology, and he is therefore all but adopted as a Christian saint. It is surely time for men to think for themselves, and to throw off the authority of names so artificially magnified. But to return from this parenthesis.) I say, that this free exercise of reason is all I ask for the vindication of the character of Jesus. We find in the writings of his biographers matter of two distinct descriptions. First, a ground-work of vulgar ignorance, of things impossible, of superstitions, fanaticisms, and fabrications. Intermixed with these, again, are sublime ideas of the Supreme Being, aphorisms, and precepts of the purest morality and benevolence, sanctioned by a life of humility, innocence, and simplicity of manners, neglect of riches, absence of worldly ambition and honors, with an eloquence and persuasiveness which have not been surpassed. These could not be inventions of the grovelling authors who relate them. They are far beyond the powers of their feeble minds. They show that there was a character, the subject of their history, whose splendid conceptions were above all suspicion of being interpolations from their hands. Can we be at a loss in separating such materials, and ascribing each to its genuine author? The difference is obvious to the eye and to the understanding, and we may read as we run to each his part; and I will venture to affirm, that he who, as I have done, will undertake to winnow this grain from its chaff, will find it not to require a moment’s consideration. The parts fall asunder of themselves, as would those of an image of metal and clay.
There are, I acknowledge, passages not free from objection, which we may, with probability, ascribe to Jesus himself; but claiming indulgence from the circumstances under which he acted. His object was the reformation of some articles in the religion of the Jews, as taught by Moses. That sect had presented for the object of their worship, a being of terrific character, cruel, vindictive, capricious, and unjust. Jesus, taking for his type the best qualities of the human head and heart, wisdom, justice, goodness, and adding to them power, ascribed all of these, but in infinite perfection, to the Supreme Being, and formed him really worthy of their adoration. Moses had either not believed in a future state of existence, or had not thought it essential to be explicitly taught to his people. Jesus inculcated that doctrine with emphasis and precision. Moses had bound the Jews to many idle ceremonies, mummeries, and observances, of no effect towards producing the social utilities which constitute the essence of virtue; Jesus exposed their futility and insignificance. The one instilled into his people the most anti-social spirit towards other nations; the other preached philanthropy and universal charity and benevolence. The office of reformer of the superstitions of a nation, is ever dangerous. Jesus had to walk on the perilous confines of reason and religion: and a step to right or left might place him within the gripe of the priests of the superstition, a blood-thirsty race, as cruel and remorseless as the being whom they represented as the family God of Abraham, of Isaac, and of Jacob, and the local God of Israel. They were constantly laying snares, too, to entangle him in the web of the law. He was justifiable, therefore, in avoiding these by evasions, by sophisms, by misconstructions, and misapplications of scraps of the prophets, and in defending himself with these their own weapons, as sufficient, ad homines, at least. That Jesus did not mean to impose himself on mankind as the Son of God, physically speaking, I have been convinced by the writings of men more learned than myself in that lore. But that he might conscientiously believe himself inspired from above, is very possible. The whole religion of the Jews, inculcated on him from his infancy, was founded in the belief of divine inspiration. The fumes of the most disordered imaginations were recorded in their religious code, as special communications of the Deity; and as it could not but happen that, in the course of ages events would now and then turn up to which some of these vague rhapsodies might be accommodated by the aid of allegories, figures, types, and other tricks upon words, they have not only preserved their credit with the Jews of all subsequent times, but are the foundation of much of the religions of those who have schismatized from them. Elevated by the enthusiasm of a warm and pure heart, conscious of the high strains of an eloquence which had not been taught him, he might readily mistake the coruscations of his own fine genius for inspirations of an higher order. This belief, carried, therefore, no more personal imputation, than the belief of Socrates, that himself was under the care and admonitions of a guardian Daemon. And how many of our wisest men still believe in the reality of these inspirations, while perfectly sane on all other subjects. Excusing, therefore, on these considerations, those passages in the gospels which seem to bear marks of weakness in Jesus, ascribing to him what alone is consistent with the great and pure character of which the same writings furnish proofs, and to their proper authors their own trivialities and imbecilities, I think myself authorized to conclude the purity and distinction of his character, in opposition to the impostures which those authors would fix upon him; and that the postulate of my former letter is no more than is granted in all other historical works.
Mr. Correa is here, on his farewell visit to us. He has been much pleased with the plan and progress of our University, and has given some valuable hints to its botanical branch. He goes to do, I hope, much good in his new country; the public instruction there, as I understand, being within the department destined for him. He is not without dissatisfaction, and reasonable dissatisfaction, too, with the piracies of Baltimore; but his justice and friendly dispositions will, I am sure, distinguish between the iniquities of a few plunderers, and the sound principles of our country at large, and of our government especially. From many conversations with him, I hope he sees, and will promote, in his new situation, the advantages of a cordial fraternization among all the American nations, and the importance of their coalescing in an American system of policy, totally independent of, and unconnected with that of Europe. The day is not distant, when we may formally require a meridian of partition through the ocean which separates the two hemispheres, on the hither side of which no European gun shall ever be heard, nor an American on the other; and when, during the rage of the eternal wars of Europe, the lion and the lamb, within our regions, shall lie down together in peace. The excess of population in Europe, and want of room, render war, in their opinion, necessary to keep down that excess of numbers. Here, room is abundant, population scanty, and peace the necessary means for producing men, to whom the redundant soil is offering the means of life and happiness. The principles of society there and here, then, are radically different, and I hope no American patriot will ever lose sight of the essential policy of interdicting in the seas and territories of both Americas, the ferocious and sanguinary contests of Europe. I wish to see this coalition begun. I am earnest for an agreement with the maritime powers of Europe, assigning them the task of keeping down the piracies of their seas and the cannibalisms of the African coasts, and, to us, the suppression of the same enormities within our seas: and for this purpose, I should rejoice to see the fleets of Brazil and the United States riding together as brethren of the same family, and pursuing the same object. And indeed it would be of happy augury to begin at once this concert of action here, on the invitation of either to the other government, while the way might be preparing for withdrawing our cruisers from Europe, and preventing naval collisions there which daily endanger our peace.
Accept assurances of the sincerity of my friendship and respect for you.
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN ADAMS.
Monticello, August 15, 1820.
I am a great defaulter, my Dear Sir, in our correspondence, but prostrate health rarely permits me to write; and when it does, matters of business imperiously press their claims. I am getting better however, slowly, swelled legs being now the only serious symptom, and these, I believe, proceed from extreme debility. I can walk but little; but I ride six or eight miles a day without fatigue; and within a few days, I shall endeavor to visit my other home, after a twelvemonth’s absence from it. Our University, four miles distant, gives me frequent exercise, and the oftener, as I direct its architecture. Its plan is unique, and it is becoming an object of curiosity for the traveller. I have lately had an opportunity of reading a critique on this institution in your North American Review of January last, having been not without anxiety to see what that able work would say of us: and I was relieved on finding in it much coincidence of opinion, and even where criticisms where indulged, I found they would have been obviated had the developements of our plan been fuller. But these were restrained by the character of the paper reviewed, being merely a report of outlines, not a detailed treatise, and addressed to a legislative body, not to a learned academy. For example, as an inducement to introduce the Anglo-Saxon into our plan, it was said that it would reward amply the few weeks of attention which alone would be requisite for its attainment; leaving both term and degree under an indefinite expression, because I know that not much time is necessary to attain it to an useful degree, sufficient to give such instruction in the etymologies of our language as may satisfy ordinary students, while more time would be requisite for those who should propose to attain a critical knowledge of it. In a letter which I had occasion to write to Mr. Crofts who sent you, I believe, as well as myself, a copy of his treatise on the English and German languages, as preliminary to an etymological dictionary he meditated, I went into explanations with him of an easy process for simplifying the study of the Anglo-Saxon, and lessening the terrors and difficulties presented by it’s rude alphabet, and unformed orthography. But this is a subject beyond the bounds of a letter, as it was beyond the bounds of a report to the legislature. Mr. Crofts died, I believe, before any progress was made in the work he had projected.
The reviewer expresses doubt, rather than decision, on our placing military and naval architecture in the department of pure mathematics. Military architecture embraces fortification and field works, which, with their bastions, curtains, hornworks, redoubts, &c. are based on a technical combination of lines and angles. These are adapted to offence and defence, with and against the effects of bombs, balls, escalades, he. But lines and angles make the sum of elementary geometry, a branch of pure mathematics: and the direction of the bombs, balls, and other projectiles, the necessary appendages of military works, although no part of their architecture, belong to the conic sections, a branch of transcendental geometry. Diderot and D’Alembert, therefore, in their Arbor scienciæ, have placed military architecture in the department of elementary geometry. Naval architecture teaches the best form and construction of vessels; for which best form it has recourse to the question of the solid of least resistance; a problem of transcendental geometry. And its appurtenant projectiles belong to the same branch as in the preceding case. It is true, that so far as respects the action of the water on the rudder and oars, and of the wind on the sails, it may be placed in the department of mechanics, as Diderot and D’Alembert have done; but belonging quite as much to geometry, and allied in its military character to military architecture, it simplified our plan to place both under the same head. These views are so obvious, that I am sure they would have required but a second thought to reconcile the reviewer to their location under the head of pure mathematics. For this word location, see Bailey, Johnson, Sheridan, Walker, &c. But if dictionaries are to be the arbiters of language, in which of them shall we find neologism? No matter. It is a good word, well sounding, obvious, and expresses an idea, which would otherwise require circumlocution. The reviewer was justifiable, therefore, in using it; although he noted at the same time, as unauthoritative, centrality, grade, sparse; all which have been long used in common speech and writing. I am a friend to neology. It is the only way to give to a language copiousness and euphony. Without it we should still be held to the vocabulary of Alfred or of Ulphilas; and held to their state of science also: for I am sure they had no words which could have conveyed the ideas of oxygen, cotyledons, zoophytes, magnetism, electricity, hyaline, and thousands of others expressing ideas not then existing, nor of possible communication in the state of their language. What a language has the French become since the date of their revolution, by the free introduction of new words! The most copious and eloquent in the living world; and equal to the Greek, had not that been regularly modifiable almost ad infinitum. Their rule was, that whenever their language furnished or adopted a root, all its branches in every part of speech, were legitimated by giving them their appropriate terminations:
And this should be the law of every language. Thus, having adopted the adjective fraternal, it is a root which should legitimate fraternity, fraternation, fraternization, fraternism, to fratenate, fraternize, fraternally. And give the word neologism to our language, as a root, and it should give us its fellow substantives, neology, neologist, neologization; its adjectives, neologous, neological, neologistical; its verb, neologize; and adverb neologically. Dictionaries are but the depositories of words already legitimated by usage. Society is the work-shop in which new ones are elaborated. When an individual uses a new word, if ill formed, it is rejected in society, if well formed, adopted, and after due time, laid up in the depository of dictionaries. And if, in this process of sound neologization, our trans-Atlantic brethren shall not choose to accompany us, we may furnish, after the Ionians, a second example of a colonial dialect improving on its primitive.
But enough of criticism: let me turn to your puzzling letter of May the 12th, on matter, spirit, motion, &c. Its crowd of scepticisms kept me from sleep. I read it, and laid it down: read it, and laid it down, again and again: and to give rest to my mind, I was obliged to recur ultimately to my habitual anodyne, ‘I feel, therefore I exist.’ I feel bodies which are not myself: there are other existences then. I call them matter. I feel them changing place. This gives me motion. Where there is an absence of matter, I call it void, or nothing, or immaterial space. On the basis of sensation, of matter and motion, we may erect the fabric of all the certainties we can have or need. I can conceive thought to be an action of a particular organization of matter, formed for that purpose by its creator, as well as that attraction is an action of matter, or magnetism of loadstone. When he who denies to the Creator the power of endowing matter with the mode of action called thinking, shall show how he could endow the sun with the mode of action called attraction, which reins the planets in the track of their orbits, or how an absence of matter can have a will, and by that will put matter into motion, then the Materialist may be lawfully required to explain the process by which matter exercises the faculty of thinking. When once we quit the basis of sensation, all is in the wind. To talk of immaterial existences, is to talk of nothings. To say that the human soul, angels, God, are immaterial, is to say, they are nothings, or that there is no God, no angels, no soul. I cannot reason otherwise: but I believe I am supported in my creed of materialism by the Lockes, the Tracys, and the Stewarts. At what age* of the Christian church this heresy of immaterialism, or masked atheism, crept in, I do not exactly know. But a heresy it certainly is. Jesus taught nothing of it. He told us, indeed, that ‘God is a spirit,’ but he has not defined what a spirit is, nor said that it is not matter. And the ancient fathers generally, of the three first centuries, held it to be matter, light and thin indeed, an ethereal gas; but still matter. Origen says. ‘Deus reapse corporalis est; sed graviorum tantum ratione corporum incorporeus.’ Tertullian,’ Quid enim Deus nisi corpus?’ And again, ‘Quis negabit Deum esse corpus? Etsi Deus spiritus, spiritus etiam corpus est, sui generis in sua effigie. St. Justin Martyr,
And St. Macarius, speaking of angels, says, ‘Quamvis enim subtilia sint, tamen in substantia, forma, et figura, secundum tenuitatem naturas eorum, corpora sunt tenuia.’ And St. Austin, St. Basil, Lactantius, Tatian, Athenagoras, and others, with whose writings I pretend not a familiarity, are said by those who are better acquainted with them, to deliver the same doctrine. (Enfield x. 3. 1.) Turn to your Ocellus d’Argens, 97, 105. and to his Timseus 17. for these quotations. In England, these Immaterialists might have been burnt until the 29 Car. 2. when the writ de hæretico comburendo was abolished; and here until the Revolution, that statute not having extended to us. All heresies being now done away with us, these schismatists are merely atheists, differing from the material atheist only in their belief, that ‘nothing made something,’ and from the material deist, who believes that matter alone can operate on matter.
[* That of Athanasius and the Council of Nicasa, anno 324]
Rejecting all organs of information, therefore, but my senses, I rid myself of the pyrrhonisms with which an indulgence in speculations hyperphysical and antiphysical, so uselessly occupy and disquiet the mind. A single sense may indeed be sometimes deceived, but rarely; and never all our senses together, with their faculty of reasoning. They evidence realities, and there are enough of these for all the purposes of life, without plunging into the fathomless abyss of dreams and phantasms. I am satisfied, and sufficiently occupied with the things which are, without tormenting or troubling myself about those which may indeed be, but of which I have no evidence. I am sure that I really know many, many things, and none more surely than that I love you with all my heart, and pray for the continuance of your life until you shall be tired of it yourself.
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOSEPH C. CABELL.
Poplar Forest, November 28, 1820.
Dear Sir,
I sent in due time the Report of the Visitors to the Governor, with a request that he would endeavor to convene the Literary Board in time to lay it before the legislature on the second day of their session. It was enclosed in a letter which will explain itself to you. If delivered before the crowd of other business presses on them, they may act on it immediately, and before there will have been time for unfriendly combinations and manoeuvres by the enemies of the institution. I enclose you now a paper presenting some views which may be useful to you in conversations, to rebut exaggerated estimates of what our institution is to cost, and reproaches of deceptive estimates. One hundred and sixty-two thousand three hundred and sixty-four dollars will be about the cost of the whole establishment, when completed. Not an office at Washington has cost less. The single building of the courthouse of Henrico has cost nearly that: and the massive walls of the millions of bricks of William and Mary could not now be built for a less sum.
Surely Governor Clinton’s display of the gigantic efforts of New York towards the education of her citizens, will stimulate the pride as well as the patriotism of our legislature, to look to the reputation and safety of their own country, to rescue it from the degradation of becoming the Barbary of the Union, and of falling into the ranks of our own negroes. To that condition it is fast sinking. We shall be in the hands of the other States, what our indigenous predecessors were when invaded by the science and arts of Europe. The mass of education in Virginia, before the Revolution, placed her with the foremost of her sister colonies. What is her education now? Where is it? The little we have, we import, like beggars, from other States; or import their beggars to bestow on us their miserable crumbs. And what is wanting to restore us to our station among our confederates? Not more money from the people. Enough has been raised by them, and appropriated to this very object. It is that it should be employed understandingly, and for their greatest good. That good requires, that while they are instructed in general, competently to the common business of life, others should employ their genius with necessary information to the useful arts, to inventions for saving labor and increasing our comforts, to nourishing our health, to civil government, military science, &c.
Would it not have a good effect for the friends of the University to take the lead in proposing and effecting a practical scheme of elementary schools? to assume the character of the friends, rather than the opponents of that object? The present plan has appropriated to the primary schools forty-five thousand dollars for three years, making one hundred and thirty-five thousand dollars. I should be glad to know if this sum has educated one hundred and thirty-five poor children? I doubt it much. And if it has, they have cost us one thousand dollars a piece for what might have been done with thirty dollars. Supposing the literary revenue to be sixty thousand dollars, I think it demonstrable, that this sum, equally divided between the two objects, would amply suffice for both. One hundred counties, divided into about twelve wards each, on an average, and a school in each ward of perhaps ten children, would be one thousand and two hundred schools, distributed proportionably over the surface of the State. The inhabitants of each ward, meeting together (as when they work on the roads), building good log-houses for their school and teacher, and contributing for his provisions, rations of pork, beef, and corn, in the proportion, each of his other taxes, would thus lodge and feed him without feeling it; and those of them who are able, paying for the tuition of their own children, would leave no call on the public fund but for the tuition fee of, here and there, an accidental pauper, who would still be fed and lodged with his parents. Suppose this fee ten dollars, and three hundred dollars apportioned to a county on an average (more or less duly proportioned), would there be thirty such paupers for every county? I think not. The truth is, that the want of common education with us is not from our poverty, but from want of an orderly system. More money is now paid for the education of a part, than would be paid for that of the whole, if systematically arranged. Six thousand common schools in New York, fifty pupils in each, three hundred thousand in all; one hundred and sixty thousand dollars annually paid to the masters; forty established academies, with two thousand two hundred and eighteen pupils; and five colleges, with seven hundred and eighteen students; to which last classes of institutions seven hundred and twenty thousand dollars have been given; and the whole appropriations for education estimated at two and a half millions of dollars! What a pigmy to this is Virginia become, with a population almost equal to that of New York! And whence this difference? From the difference their rulers set on the value of knowledge, and the prosperity it produces. But still, if a pigmy, let her do what a pigmy may do. If among fifty children in each of the six thousand schools of New York, there are only paupers enough to employ twenty-five dollars of public money to each school, surely among the ten children of each of our one thousand and two hundred schools, the same sum of twenty-five dollars to each school will teach its paupers (five times as much as to the same number in New York), and will amount for the whole to thirty thousand dollars a year, the one half only of our literary revenue.
Do then, Dear Sir, think of this, and engage our friends to take in hand the whole subject. It will reconcile the friends of the elementary schools, and none are more warmly so than myself, lighten the difficulties of the University, and promote in every order of men the degree of instruction proportioned to their condition, and to their views in life. It will combine with the mass of our force, a wise direction of it, which will insure to our country its future prosperity and safety. I had formerly thought that visitors of the schools might be chosen by the county, and charged to provide teachers for every ward, and to superintend them. I now think it would be better for every ward to choose its own resident visitor, whose business it would be to keep a teacher in the ward, to superintend the school, and to call meetings of the ward for all purposes relating to it: their accounts to be settled, and wards laid off by the courts. I think ward elections better for many reasons, one of which is sufficient, that it will keep elementary education out of the hands of fanaticizing preachers, who, in county elections, would be universally chosen, and the predominant sect of the county would possess itself of all its schools.
A wrist stiffened by an ancient accident, now more so by the effect of age, renders writing a slow and irksome operation with me. I cannot, therefore, present these views by separate letters to each of our colleagues in the legislature, but must pray you to communicate them to Mr. Johnson and General Breckenridge, and to request them to consider this as equally meant for them. Mr. Gordon, being the local representative of the University and among its most zealous friends, would be a more useful second to General Breckenridge in the House of Delegates, by a free communication of what concerns the University, with which he has had little opportunity of becoming acquainted. So also, would it be as to Mr. Rives, who would be a friendly advocate.
Accept the assurances of my constant and affectionate esteem and respect.
Th: Jefferson.
Monticello, December, 25, 1820.
Dear Sir,
On my return home after a long absence, I find here your favor of November the 23rd, with Colonel Taylor’s ‘Construction Construed,’ which you have been so kind as to send me, in the name of the author as well as yourself. Permit me, if you please, to use the same channel for conveying to him the thanks I render you also for this mark of attention. I shall read it, I know, with edification, as I did his Enquiry, to which I acknowledge myself indebted for many valuable ideas, and for the correction of some errors of early opinion, never seen in a correct light until presented to me in that work. That the present volume is equally orthodox I know before reading it, because I know that Colonel Taylor and myself have rarely, if ever, differed in any political principle of importance. Every act of his life, and every word he ever wrote, satisfies me of this. So, also, as to the two Presidents, late and now in office, I know them both to be of principles as truly republican as any men living. If there be any thing amiss, therefore, in the present state of our affairs, as the formidable deficit lately unfolded to us indicates, I ascribe it to the inattention of Congress to their duties, to their unwise dissipation and waste of the public contributions. They seemed, some little while ago, to be at a loss for objects whereon to throw away the supposed fathomless funds of the treasury. I had feared the result, because I saw among them some of my old fellow-laborers, of tried and known principles, yet often in their minorities. I am aware that in one of their most ruinous vagaries, the people were themselves betrayed into the same phrenzy with their Representatives. The deficit produced, and a heavy tax to supply it, will, I trust, bring both to their sober senses.
But it is not from this branch of government we have most to fear. Taxes and short elections will keep them right. The judiciary of the United States is the subtle corps of sappers and miners constantly working under ground to undermine the foundations of our confederated fabric. They are construing our constitution from a co-ordination of a general and special government to a general and supreme one alone. This will lay all things at their feet, and they are too well versed in English law to forget the maxim, ‘Boni judicis est ampliare jurisdictionem.’ We shall see if they are bold enough to take the daring stride their five lawyers have lately taken. If they do, then, with the editor of our book in his address to the public, I will say, that against this every man should raise his voice, and more, should uplift his arm. Who wrote this admirable address? Sound, luminous, strong, not a word too much, nor one which can be changed but for the worse. That pen should go on, lay bare these wounds of our constitution, expose these decisions seriatim, and arouse, as it is able, the attention of the nation to these bold speculators on its patience. Having found, from experience, that impeachment is an impracticable thing, a mere scare-crow, they consider themselves secure for life; they skulk from responsibility to public opinion, the only remaining hold on them, under a practice first introduced into England by Lord Mansfield. An opinion is huddled up in conclave, perhaps by a majority of one, delivered as if unanimous and with the silent acquiescence of lazy or timid associates, by a crafty chief judge, who sophisticates the law to his mind, by the turn of his own reasoning. A judiciary law was once reported by the Attorney General to Congress, requiring each judge to deliver his opinion seriatim and openly, and then to give it in writing to the clerk to be entered in the record. A judiciary independent of a King or executive alone, is a good thing; but independence of the will of the nation is a solecism, at least in a republican government.
But to return to your letter; you ask for my opinion of the work you send me, and to let it go out to the public. This I have ever made a point of declining (one or two instances only excepted). Complimentary thanks to writers who have sent me their works, have betrayed me sometimes before the public, without my consent having been asked. But I am far from presuming to direct the reading of my fellow-citizens, who are good enough judges themselves of what is worthy their reading. I am, also, too desirous of quiet to place myself in the way of contention. Against this I am admonished by bodily decay, which cannot be unaccompanied by corresponding wane of the mind. Of this I am as yet sensible sufficiently to be unwilling to trust myself before the public, and when I cease to be so, I hope that my friends will be too careful of me to draw me forth and present me, like a Priam in armor, as a spectacle for public compassion. I hope our political bark will ride through all its dangers; but I can in future be but an inert passenger.
I salute you with sentiments of great friendship and respect.
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN ADAMS.
Monticello, January 22, 1821.
I was quite rejoiced, dear Sir, to see that you had health and spirits enough to take part in the late convention of your State, for revising its constitution, and to bear your share in its debates and labors. The amendments of which we have as yet heard, prove the advance of liberalism in the intervening period; and encourage a hope that the human mind will some day get back to the freedom it enjoyed two thousand years ago. This country, which has given to the world the example of physical liberty, owes to it that of moral emancipation also, for as yet it is but nominal with us. The inquisition of public opinion overwhelms, in practice, the freedom asserted by the laws in theory.
Our anxieties in this quarter are all concentrated in the question, what does the Holy Alliance in and out of Congress mean to do with us on the Missouri question? And this, by the bye, is but the name of the case, it is only the John Doe or Richard Roe of the ejectment. The real question, as seen in the States afflicted with this unfortunate population, is, Are our slaves to be presented with freedom and a dagger? For if Congress has the power to regulate the conditions of the inhabitants of the States, within the States, it will be but another exercise of that power, to declare that all shall be free. Are we then to see again Athenian and Lacedæmonian confederacies? To wage another Peloponnesian war to settle the ascendancy between them? Or is this the tocsin of merely a servile war? That remains to be seen: but not, I hope, by you or me. Surely, they will parley awhile, and give us time to get out of the way. What a Bedlamite is man? But let us turn from our own uneasiness to the miseries of our southern friends. Bolivar and Morillo, it seems, have come to a parley, with dispositions at length to stop the useless effusion of human blood in that quarter. I feared from the beginning, that these people were not yet sufficiently enlightened for self-government; and that after wading through blood and slaughter, they would end in military tyrannies, more or less numerous. Yet as they wished to try the experiment, I wished them success in it: they have now tried it, and will possibly find that their safest road will be an accommodation with the mother country, which shall hold them together by the single link of the same chief magistrate, leaving to him power enough to keep them in peace with one another, and to themselves the essential power of self-government and self-improvement, until they shall be sufficiently trained by education and habits of freedom, to walk safely by themselves. Representative government, native functionaries, a qualified negative on their laws, with a previous security by compact for freedom of commerce, freedom of the press, habeas corpus, and trial by jury, would make a good beginning. This last would be the school in which their people might begin to learn the exercise of civic duties as well as rights. For freedom of religion they are not yet prepared. The scales of bigotry have not sufficiently fallen from their eyes, to accept it for themselves individually, much less to trust others with it. But that will come in time, as well as a general ripeness to break entirely from the parent stem. You see, my dear Sir, how easily we prescribe for others a cure for their difficulties, while we cannot cure our own. We must leave both, I believe, to Heaven, and wrap ourselves up in the mantle of resignation, and of that friendship of which I tender to you the most sincere assurances.
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOSEPH C CABELL.
Monticello, January 31, 1821.
Dear Sir,
Your favors of the 18th and 25th came together, three days ago. They fill me with gloom as to the dispositions of our legislature towards the University. I perceive that I am not to live to see it opened. As to what had better be done within the limits of their will, I trust with entire confidence to what yourself, General Breckenridge, and Mr. Johnson shall think best. You will see what is practicable, and give it such shape as you think best. If a loan is to be resorted to, I think sixty thousand dollars will be necessary, including the library. Its instalments cannot begin until those of the former loan are accomplished; and they should not begin later, nor be less than thirteen thousand dollars a year. (I think it safe to retain two thousand dollars a year for care of the buildings, improvement of the grounds, and unavoidable contingencies.) To extinguish the second loan, will require between five and six instalments, which will carry us to the end of 1833, or thirteen years from this time. My individual opinion is, that we had better not open the institution until the buildings, library, and all, are finished, and our funds cleared of incumbrance. These buildings once erected, will secure the full object infallibly at the end of thirteen years, and as much earlier as the legislature shall choose. And if we were to begin sooner, with half funds only, it would satisfy the common mind, prevent their aid beyond that point, and our institution, remaining at that for ever, would be no more than the paltry academies we now have. Even with the whole funds we shall be reduced to six Professors. While Harvard will still prime it over us with her twenty Professors. How many of our youths she now has, learning the lessons of anti-Missourianism, I know not; but a gentleman lately from Princeton told me he saw there the list of the students at that place, and that more than half were Virginians. These will return home, no doubt, deeply impressed with the sacred principles of our Holy Alliance of restrictionists.
But the gloomiest of all prospects, is in the desertion of the best friends of the institution, for desertion I must call it. I know not the necessities which may force this on you. General Cocke, you say, will explain them to me; but I cannot conceive them, nor persuade myself they are uncontrollable. I have ever hoped, that yourself, General Breckenridge, and Mr. Johnson, would stand at your posts in the legislature, until every thing was effected, and the institution opened. If it is so difficult to get along with all the energy and influence of our present colleagues in the legislature, how can we expect to proceed at all, reducing our moving power? I know well your devotion to your country, and your foresight of the awful scenes coming on her, sooner or later. With this foresight, what service can we ever render her equal to this? What object of our lives can we propose so important? What interest of our own which ought not to be postponed to this? Health, time, labor, on what in the single life which nature has given us, can these be better bestowed than on this immortal boon to our country? The exertions and the mortifications are temporary; the benefit eternal. If any member of our college of Visitors could justifiably withdraw from this sacred duty, it would be myself, who quadragenis stipendiis jamdudum peractis, have neither vigor of body nor mind left to keep the field: but I will die in the last ditch, and so I hope you will, my friend, as well as our firm-breasted brothers and colleagues, Mr. Johnson and General Breckenridge. Nature will not give you a second life wherein to atone for the omissions of this. Pray then, dear and very dear Sir, do not think of deserting us, but view the sacrifices which seem to stand in your way, as the lesser duties, and such as ought to be postponed to this, the greatest of all. Continue with us in these holy labors, until, having seen their accomplishment, we may say with old Simeon, ‘Nunc dimittas, Domine. Under all circumstances, however, of praise or blame, I shall be affectionately yours.
Th: Jefferson.
TO GENERAL BRECKENRIDGE.
Monticello, February 15, 1821.
Dear Sir,
I learn with deep affliction, that nothing is likely to be done for our University this year. So near as it is to the shore that one shove more would land it there, I had hoped that would be given; and that we should open with the next year an institution on which the fortunes of our country may depend more than may meet the general eye. The reflections that the boys of this age are to be the men of the next; that they should be prepared to receive the holy charge which we are cherishing to deliver over to them; that in establishing an institution of wisdom for them, we secure it to all our future generations; that in fulfilling this duty, we bring home to our own bosoms the sweet consolation of seeing our sons rising under a luminous tuition, to destinies of high promise; these are considerations which will occur to all; but all, I fear, do not see the speck in our horizon which is to burst on us as a tornado, sooner or later. The line of division lately marked out between different portions of our confederacy, is such as will never, I fear, be obliterated, and we are now trusting to those who are against us in position and principle, to fashion to their own form the minds and affections of our youth. If, as has been estimated, we send three hundred thousand dollars a year to the northern seminaries, for the instruction of our own sons, then we must have there five hundred of our sons, imbibing opinions and principles in discord with those of their own country. This canker is eating on the vitals of our existence, and if not arrested at once, will be beyond remedy. We are now certainly furnishing recruits to their school. If it be asked what are we to do, or said we cannot give the last lift to the University without stopping our primary schools, and these we think most important; I answer, I know their importance. Nobody can doubt my zeal for the general instruction of the people. Who first started that idea? I may surely say, Myself. Turn to the bill in the revised code, which I drew more than forty years ago, and before which the idea of a plan for the education of the people, generally, had never been suggested in this State. There you will see developed the first rudiments of the whole system of general education we are now urging and acting on: and it is well known to those With whom I have acted on this subject, that I never have proposed a sacrifice of the primary to the ultimate grade of instruction. Let us keep our eye steadily on the whole system. If we cannot do every thing at once, let us do one at a time. The primary schools need no preliminary expense; the ultimate grade requires a considerable expenditure in advance. A suspension of proceeding for a year or two on the primary schools, and an application of the whole income, during that time, to the completion of the buildings necessary for the University, would enable us then to start both institutions at the same time. The intermediate branch, of colleges, academies, and private classical schools, for the middle grade, may hereafter receive any necessary aids when the funds shall become competent. In the mean time, they are going on sufficiently, as they have ever yet gone on, at the private expense of those who use them, and who in numbers and means are competent to their own exigencies. The experience of three years has, I presume, left no doubt, that the present plan of primary schools, of putting money into the hands of twelve hundred persons acting for nothing, and under no responsibility, is entirely inefficient. Some other must be thought of; and during this pause, if it be only for a year, the whole revenue of that year, with that of the last three years which has not been already thrown away, would place our University in readiness to start with a better organization of primary schools, and both may then go on, hand in hand, for ever. No diminution of the capital will in this way have been incurred; a principle which ought to be deemed sacred. A relinquishment of interest on the late loan of sixty thousand dollars, would so far, also, forward the University without lessening the capital.
But what may be best done I leave with entire confidence to yourself and your colleagues in legislation, who know better than I do the conditions of the literary fund and its wisest application; and I shall acquiesce with perfect resignation to their will. I have brooded, perhaps with fondness, over this establishment, as it held up to me the hope of continuing to be useful while I continued to live. I had believed that the course and circumstances of my life had placed within my power some services favorable to the outset of the institution. But this may be egoism; pardonable, perhaps, when I express a consciousness that my colleagues and successors will do as well, whatever the legislature shall enable them to do.
I have thus, my dear Sir, opened my bosom, with all its anxieties, freely to you. I blame nobody for seeing things in a different light. I am sure that all act conscientiously, and that all will be done honestly and wisely which can be done. I yield the concerns of the world with cheerfulness to those who are appointed in the order of nature to succeed to them; and for yourself, for our colleagues, and for all in charge of our country’s future fame and fortune, I offer up sincere prayers.
Th: Jefferson.
TO ————- NICHOLAS.
Monticello, December 11,1821,
Dear Sir,
Your letter of December the 19th places me under a dilemma, which I cannot solve but by an exposition of the naked truth. I would have wished this rather to have remained as hitherto, without inquiry; but your inquiries have a right to be answered. I will do it as exactly as the great lapse of time and a waning memory will enable me. I may misremember indifferent circumstances, but can be right in substance.
At the time when the republicans of our country were so much alarmed at the proceedings of the federal ascendancy in Congress, in the executive and the judiciary departments, it became a matter of serious consideration how head could be made against their enterprises on the constitution. The leading republicans in Congress found themselves of no use there, browbeaten, as they were, by a bold and overwhelming majority. They concluded to retire from that field, take a stand in the State legislatures, and endeavor there to arrest their progress. The alien and sedition laws furnished the particular occasion. The sympathy between Virginia and Kentucky was more cordial, and more intimately confidential, than between any other two States of republican policy. Mr. Madison came into the Virginia legislature. 1 was then in the Vice-Presidency, and could not leave my station. But your father, Colonel W. C. Nicholas, and myself happening to be together, the engaging the co-operation of Kentucky in an energetic protestation against the constitutionality of those laws, became a subject of consultation. Those gentlemen pressed me strongly to sketch resolutions for that purpose, your father undertaking to introduce them to that legislature, with a solemn assurance, which I strictly required, that it should not be known from what quarter they came. I drew and delivered them to him, and, in keeping their origin secret, he fulfilled his pledge of honor. Some years after this, Colonel Nicholas asked me if I would have any objection to its being known that I had drawn them. I pointedly enjoined that it should not. Whether he had unguardedly intimated it before to any one, I know not: but I afterwards observed in the papers repeated imputations of them to me; on which, as has been my practice on all occasions of imputation, I have observed entire silence. The question, indeed, has never before been put to me, nor should I answer it to any other than yourself; seeing no good end to be proposed by it, and the desire of tranquillity inducing with me a wish to be withdrawn from public notice. Your father’s zeal and talents were too well known, to derive any additional distinction from the penning these resolutions. That circumstance, surely, was of far less merit than the, proposing and carrying them through the legislature of his State. The only fact in this statement, on which my memory is not distinct, is the time and occasion of the consultation with your father and Colonel Nicholas. It took place here I know; but whether any other person was present, or communicated with, is my doubt. I think Mr. Madison was either with us, or consulted, but my memory is uncertain as to minute details.
I fear, Dear Sir, we are now in such another crisis, with this difference only, that the judiciary branch is alone and single-handed in the present assaults on the constitution. But its assaults are more sure and deadly, as from an agent seemingly passive and unassuming. May you and your cotemporaries meet them with the same determination and effect, as your father and his did the alien and sedition laws, and preserve inviolate a constitution, which, cherished in all its chastity and purity, will prove in the end a blessing to all the nations of the earth. With these prayers, accept those for your own happiness and prosperity.
Th: Jefferson.
TO JEDIDIAH MORSE.
Monticello, March 6, 1822.
Sir,
I have duly received your letter of February the 16th, and have now to express my sense of the honorable station proposed to my ex-brethren and myself, in the constitution of the society for the civilization and improvement of the Indian tribes. The object, too, expressed, as that of the association, is one which I have ever had much at heart, and never omitted an occasion of promoting, while I have been in situations to do it with effect, and nothing, even now, in the calm of age and retirement, would excite in me a more lively interest than an approvable plan of raising that respectable and unfortunate people from the state of physical and moral abjection, to which they have been reduced by circumstances foreign to them. That the plan now proposed is entitled to unmixed approbation, I am not prepared to say, after mature consideration, and with all the partialities which its professed object would rightfully claim from me.
I shall not undertake to draw the line of demarcation between private associations of laudable views and unimposing numbers, and those whose magnitude may rivalize and jeopardize the march of regular government. Yet such a line does exist. I have seen the days, they were those which preceded the Revolution, when even this last and perilous engine became necessary; but they were days which no man would wish to see a second time. That was the case where the regular authorities of the government had combined against the rights of the people, and no means of correction remained to them, but to organize a collateral power, which, with their support, might rescue and secure their violated rights. But such is not the case with our government. We need hazard no collateral power, which, by a change of its original views, and assumption of others we know not how virtuous or how mischievous, would be ready organized, and in force sufficient to shake the established foundations of society, and endanger its peace and the principles on which it is based. Is not the machine now proposed of this gigantic stature? It is to consist of the ex-Presidents of the United States, the Vice-President, the Heads of all the executive departments, the members of the supreme judiciary, the Governors of the several States and Territories, all the members of both Houses of Congress, all the general officers of the army, the commissioners of the navy, all Presidents and Professors of colleges and theological seminaries, all the clergy of the United States, the. Presidents and Secretaries of all associations having relation to Indians, all commanding officers within or near Indian territories, all Indian superintendants and agents; all these ex officio; and as many private individuals as will pay a certain price for membership. Observe, too, that the clergy will constitute * nineteen twentieths of this association, and, by the law of the majority, may command the twentieth part, which, composed of all the high authorities of the United States, civil and military, may be outvoted and wielded by the nineteen parts with uncontrollable power, both as to purpose and process. . Can this formidable array be reviewed without dismay?
* The clergy of the United States may probably be estimated
at eight thousand. The residue of this society at four
hundred; but if the former number be halved, the reasoning
will be the same.
It will be said, that in this association will be all the confidential officers of the government; the choice of the people themselves. No man on earth has more implicit confidence than myself in the integrity and discretion of this chosen band of servants. But is confidence or discretion, or is strict limit, the principle of our constitution? It will comprehend, indeed, all the functionaries of the government: but seceded from their consitutional stations as guardians of the nation, and acting not by the laws of their station, but by those of a voluntary society, having no limit to their purposes but the same will which constitutes their existence. It will be the authorities of the people, and all influential characters from among them, arrayed on one side, and on the other, the people themselves deserted by their leaders. It is a fearful array. It will be said, that these are imaginary fears. I know they are so at present. I know it is as impossible for these agents of our choice and unbounded confidence, to harbor machinations against the adored principles of our constitution, as for gravity to change its direction, and gravid bodies to mount upwards. The fears are indeed imaginary: but the example is real. Under its authority, as a precedent, future associations will arise with objects at which we should shudder at this time. The society of Jacobins, in another country, was instituted on principles and views as virtuous as ever kindled the hearts of patriots. It was the pure patriotism of their purposes which extended their association to the limits of the nation, and rendered their power within it boundless; and it was this power which degenerated their principles and practices to such enormities, as never before could have been imagined. Yet these were men; and we and our descendants will be no more. The present is a case where, if ever, we are to guard against ourselves; not against ourselves as we are, but as we may be; for who can now imagine what we may become under circumstances not now imaginable? The object, too, of this institution, seems to require so hazardous an example as little as any which could be proposed. The government is, at this time, going on with the process of civilizing the Indians, on a plan probably as promising as any one of us is able to devise, and with resources more competent than we could expect to command by voluntary taxation. Is it that the new characters called into association with those of the government, are wiser than these? Is it that a plan originated by a meeting of private individuals, is better than that prepared by the concentrated wisdom of the nation, of men not self-chosen, but clothed with the full confidence of the people? Is it that there is no danger that a new authority, marching independently along side of the government, in the same line and to the same object, may not produce collision, may not thwart and obstruct the operations of the government, or wrest the object entirely from their hands? Might we not as well appoint a committee for each department of the government, to counsel and direct its head separately, as volunteer ourselves to counsel and direct the whole, in mass? And might we not do it as well for their foreign, their fiscal, and their military, as for their Indian affairs? And how many societies, auxiliary to the government, may we expect to see spring up, in imitation of this, offering to associate themselves in this and that of its functions? In a word, why not take the government out of its constitutional hands, associate them indeed with us, to preserve a semblance that the acts are theirs, but insuring them to be our own by allowing them a minor vote only?
These considerations have impressed my mind with a force so irrresistible, that (in duty bound to answer your polite letter, without which I should not have obtruded an opinion) I have not been able to withhold the expression of them. Not knowing the individuals who have proposed this plan, I cannot be conceived as entertaining personal disrespect for them. On the contrary, I see in the printed list persons for whom I cherish sentiments of sincere friendship; and others, for whose opinions and purity of purpose I have the highest respect. Yet thinking, as I do, that this association is unnecessary; that the government is proceeding to the same object under control of the law; that they are competent to it in wisdom, in means, and inclination; that this association, this wheel within a wheel, is more likely to produce collision than aid; and that it is, in its magnitude, of dangerous example; I am bound to say, that, as a dutiful citizen, I cannot in conscience become a member of this society, possessing as it does my entire confidence in the integrity of its views. I feel with awe the weight of opinion to which I may be opposed, and that, for myself, I have need to ask the indulgence of a belief, that the opinion I have given is the best result I can deduce from my own reason and experience, and that it is sincerely conscientious. Repeating, therefore, my just acknowledgments for the honor proposed to me, I beg leave to add the assurances to the society and yourself of my highest confidence and consideration.
Th: Jefferson.
Monticello, June 26, 1822.
Dear Sir,
I have received and read with thankfulness and pleasure your denunciation of the abuses of tobacco and wine. Yet, however sound in its principles, I expect it will be but a sermon to the wind. You will find it is as difficult to inculcate these sanative precepts on the sensualities of the present day, as to convince an Athanasian that there is but one God. I wish success to both attempts, and am happy to learn from you that the latter, at least, is making progress, and the more rapidly in proportion as our Platonizing Christians make more stir and noise about it. The doctrines of Jesus are simple, and tend all to the happiness of man.
1. That there is one only God, and he all perfect.
2. That there is a future state of rewards and punishments.
3. That to love God with all thy heart, and thy neighbor as thyself, is the sum of religion. These are the great points on which he endeavored to reform the religion of the Jews. But compare with these the demoralizing dogmas of Calvin.
1. That there are three Gods.
2. That good works, or the love of our neighbor, are nothing.
3. That faith is everything, and the more incomprehensible the proposition, the more merit in its faith.
4. That reason in religion is of unlawful use.
5. That God, from the beginning, elected certain individuals to be saved, and certain others to be damned; and that no crimes of the former can damn them; no virtues of the latter, save.
Now, which of these is the true and charitable Christian? He who believes and acts on the simple doctrines of Jesus; or the impious dogmatists, as Athanasius and Calvin? Verily I say these are the false shepherds foretold as to enter not by the door into the sheepfold, but to climb up some other way. They are mere usurpers of the Christian name, teaching a counter-religion made up of the deliria of crazy imaginations, as foreign from Christianity as is that of Mahomet. Their blasphemies have driven thinking men into infidelity, who have too hastily rejected the supposed author himself, with the horrors so falsely imputed to him. Had the doctrines of Jesus been preached always as pure as they came from his lips, the whole civilized world would now have been Christian. I rejoice that in this blessed country of free inquiry and belief, which has surrendered its creed and conscience to neither kings nor priests, the genuine doctrine of one only God is reviving, and I trust that there is not a young man now living in the United States, who will not die an Unitarian.
But much I fear, that when this great truth shall be re-established, its votaries will fall into the fatal error of fabricating formulas of creed and confessions of faith, the engines which so soon destroyed the religion of Jesus, and made of Christendom a mere Aceldama; that they will give up morals for mysteries, and Jesus for Plato. How much wiser are the Quakers, who, agreeing in the fundamental doctrines of the Gospel, schismatize about no mysteries, and, keeping within the pale of common sense, suffer no speculative differences of opinion, any more than of feature, to impair the love of their brethren. Be this the wisdom of Unitarians, this the holy mantle which shall cover within its charitable circumference all who believe in one God, and who love their neighbor! I conclude my sermon with sincere assurances of my friendly esteem and respect.
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN ADAMS.
Monticello, June 27, 1822.
Dear Sir,
Your kind letter of the 11th has given me great satisfaction. For although I could not doubt but that the hand of age was pressing heavily on you, as on myself, yet we like to know the particulars and the degree of that pressure. Much reflection, too, has been produced by your suggestion of lending my letter of the 1st, to a printer. I have generally great aversion to the insertion of my letters in the public papers; because of my passion for quiet retirement, and never to be exhibited in scene on the public stage. Nor am I unmindful of the precept of Horace, ‘Solve senescentem, mature sanus, equum, ne peccet ad extremum ridendus.’ In the present case, however, I see a possibility that this might aid in producing the very quiet after which I pant. I do not know how far you may suffer, as I do, under the persecution of letters, of which every mail brings a fresh load. They are letters of inquiry, for the most part, always of good will, sometimes from friends whom I esteem, but much oftener from persons whose names are unknown to me, but written kindly and civilly, and to which, therefore, civility requires answers. Perhaps, the better known failure of your hand in its function of writing, may shield you in greater degree from this distress, and so far qualify the misfortune of its disability. I happened to turn to my letter-list some time ago, and a curiosity was excited to count those received in a single year. It was the year before the last. I found the number to be one thousand two hundred and sixty-seven, many of them requiring answers of elaborate research, and all to be answered with due attention and consideration. Take an average of this number for a week or a day, and I will repeat the question suggested by other considerations in mine of the 1st. Is this life? At best it is but the life of a mill-horse, who sees no end to his circle but in death. To such a life, that of a cabbage is paradise. It occurs, then, that my condition of existence, truly stated in that letter, if better known, might check the kind indiscretions which are so heavily oppressing the departing hours of life. Such a relief would, to me, be an ineffable blessing. But yours of the 11th, equally interesting and affecting, should accompany that to which it is an answer. The two, taken together, would excite a joint interest, and place before our fellow-citizens the present condition of two ancient servants, who, having faithfully performed their forty or fifty campaigns, stipendiis omnibus expletis, have a reasonable claim to repose from all disturbance in the sanctuary of invalids and superannuates. But some device should be thought of for their getting before the public otherwise than by our own publication. Your printer, perhaps, could frame something plausible, ———‘s name, should be left blank, as his picture, should it meet his eye, might give him pain. I consign, however, the whole subject to your consideration, to do in it whatever your own judgment shall approve, and repeat always, with truth, the assurance of my constant and affectionate friendship and respect.
Th: Jefferson.
TO WILLIAM T. BARRY.
Monticello, July 2, 1822.
Sir,
Your favor of the 15th of June is received, and I am very thankful for the kindness of its expressions respecting myself. But it ascribes to me merits which I do not claim. I was only of a band devoted to the cause of independence, all of whom exerted equally their best endeavors for its success, and have a common right to the merits of its acquisition. So also in the civil revolution of 1801. Very many and very meritorious were the worthy patriots who assisted in bringing back our government to its republican tack. To preserve it in that will require unremitting vigilance. Whether the surrender of our opponents, their reception into our camp, their assumption of our name, and apparent accession to our objects, may strengthen or weaken the genuine principles of republicanism, may be a good or an evil, is yet to be seen. I consider the party division of whig and tory the most wholesome which can exist in any government, and well worthy of being nourished, to keep out those of a more dangerous character. We already see the power, installed for life, responsible to no authority (for impeachment is not even a scare-crow), advancing with a noiseless and steady pace to the great object of consolidation. The foundations are already deeply laid by their decisions, for the annihilation of constitutional State rights, and the removal of every check, every counterpoise to the ingulphing* power of which themselves are to make a sovereign part. If ever this vast country is brought under a single government, it will be one of the most extensive corruption, indifferent and incapable of a wholesome care over so wide a spread of surface. This will not be borne, and you will have to choose between reformation and revolution. If I know the spirit of this country, the one or the other is inevitable. Before the canker is become inveterate, before its venom has reached so much of the body politic as to get beyond control, remedy should be applied. Let the future appointments of judges be for four or six years, and renewable by the President and Senate. This will bring their conduct, at regular periods, under revision and probation, and may keep them in equipoise between the general and special governments. We have erred in this point, by copying England, where certainly it is a good thing to have the judges independent of the King. But we have omitted to copy their caution also, which makes a judge removable on the address of both legislative Houses. That there should be public functionaries independent of the nation, whatever may be their demerit, is a solecism in a republic, of the first order of absurdity and inconsistency.
To the printed inquiries respecting our schools, it is not in my power to give an answer. Age, debility, an ancient dislocated, and now stiffened wrist, render writing so slow and painful, that I am obliged to decline every thing possible requiring writing. An act of our legislature will inform you of our plan of primary schools, and the annual reports show that it is becoming completely abortive, and must be abandoned very shortly, after costing us to this day one hundred and eighty thousand dollars, and yet to cost us forty-five thousand dollars a year more until it shall be discontinued; and if a single boy has received the elements of common education, it must be in some part of the country not known to me. Experience has but too fully confirmed the early predictions of its fate. But on this subject I must refer you to others more able than I am to go into the necessary details; and I conclude with the assurances of my great esteem and respect.
Th: Jefferson.
TO DOCTOR WATERHOUSE.
Monticello, July 19, 1822.
Dear Sir,
An anciently dislocated, and now stiffening wrist, makes writing an operation so slow and painful to me, that I should not so soon have troubled you with an acknowledgment of your favor of the 8th, but for the request it contained of my consent to the publication of my letter of June the 26th. No, my dear Sir, not for the world. Into what a nest of hornets would it thrust my head! the genus irritabile vatum, on whom argument is lost, and reason is, by themselves, disclaimed in matters of religion. Don Quixote undertook to redress the bodily wrongs of the world, but the redressment of mental vagaries would be an enterprise more than Quixotic. I should as soon undertake to bring the crazy skulls of Bedlam to sound understanding, as inculcate reason into that of an Athanasian. I am old, and tranquillity is now my summum bonum. Keep me, therefore, from the fire and faggots of Calvin and his victim Servetus. Happy in the prospect of a restoration of primitive Christianity, I must leave to younger athletes to encounter and lop off the false branches which have been engrafted into it by the mycologists of the middle and modern ages. I am not aware of the peculiar resistance to Unitarianism, which you ascribe to Pennsylvania. When I lived in Philadelphia there was a respectable congregation of that sect, with a meeting-house and regular service which I attended, and in which Doctor Priestley officiated to numerous audiences. Baltimore has one or two churches, and their pastor, author of an inestimable book on this subject, was elected chaplain to the late Congress. That doctrine has not yet been preached to us: but the breeze begins to be felt which precedes the storm; and fanaticism is all in a bustle, shutting its doors and windows to keep it out. But it will come, and drive before it the foggy mists of Platonism which have so long obscured our atmosphere. I am in hopes that some of the disciples of your institution will become missionaries to us, of these doctrines truly evangelical, and open our eyes to what has been so long hidden from them. A bold and eloquent preacher would be no where listened to with more freedom than in this State, nor with more firmness of mind. They might need a preparatory discourse on the text of ‘Prove all things, hold fast that which is good,’ in order to unlearn the lesson that reason is an unlawful guide in religion. They might startle on being first awaked from the dreams of the night, but they would rub their eyes at once, and look the spectres boldly in the face. The preacher might be excluded by our hierophants from their churches and meeting-houses, but would be attended in the fields by whole acres of hearers and thinkers. Missionaries from Cambridge would soon be greeted with more welcome, than from the tritheistical school of Andover. Such are my wishes, such would be my welcomes, warm and cordial as the assurances of my esteem and respect for you.
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN ADAMS.
Monticello, November 1, 1822.
Dear Sir,
I have racked my memory and ransacked my papers, to enable myself to answer the inquiries of your favor of October the 15th; but to little purpose. My papers furnish me nothing, my memory, generalities only. I know that while I was in Europe, and anxious about the fate of our seafaring men, for some of whom, then in captivity in Algiers, we were treating, and all were in like danger, I formed, undoubtingly, the opinion that our government, as soon as practicable, should provide a naval force sufficient to keep the Barbary States in order; and on this subject we communicated together, as you observe. When I returned to the United States and took part in the administration under General Washington, I constantly maintained that opinion; and in December, 1790, took advantage of a reference to me from the first Congress which met after I was in office, to report in favor of a force sufficient for the protection of our Mediterranean commerce; and I laid before them an accurate statement of the whole Barbary force, public and private. I think General Washington approved of building vessels of war to that extent. General Knox, I know, did. But what was Colonel Hamilton’s opinion, I do not in the least remember. Your recollections on that subject are certainly corroborated by his known anxieties for a close connection with Great Britain, to which he might apprehend danger from collisions between their vessels and ours. Randolph was then Attorney General; but his opinion on the question I also entirely forget. Some vessels of war were accordingly built and sent into the Mediterranean. The additions to these in your time, I need not note to you, who are well known to have ever been an advocate for the wooden walls of Themistocles. Some of those you added, were sold under an act of Congress passed while you were in office. I thought, afterwards, that the public safety might require some additional vessels of strength, to be prepared and in readiness for the first moment of a war, provided they could be preserved against the decay which is unavoidable if kept in the water, and clear of the expense of officers and men. With this view I proposed that they should be built in dry docks, above the level of the tide waters, and covered with roofs. I further advised, that places for these docks should be selected where there was a command of water on a high level, as that of the Tiber at Washington, by which the vessels might be floated out, on the principle of a lock. But the majority of the legislature was against any addition to the navy, and the minority, although for it in judgment, voted against it on a principle of opposition. We are now, I understand, building vessels to remain on the stocks, under shelter, until wanted, when they will be launched and finished. On my plan they could be in service at an hour’s notice. On this, the finishing, after launching, will be a work of time.
This is all I recollect about the origin and progress of our navy. That of the late war, certainly raised our rank and character among nations. Yet a navy is a very expensive engine. It is admitted, that in ten or twelve years a vessel goes to entire decay; or, if kept in repair, costs as much as would build a new one: and that a nation who could count on twelve or fifteen years’ of peace, would gain by burning its navy and building a new one in time. Its extent, therefore, must be governed by circumstances. Since my proposition for a force adequate to the piracies of the Mediterranean, a similar necessity has arisen in our own seas for considerable addition to that force. Indeed, I wish we could have a convention with the naval powers of Europe, for them to keep down the pirates of the Mediterranean, and the slave ships on the coast of Africa, and for us to perform the same duties for the society of nations in our seas. In this way, those collisions would be avoided between the vessels of war of different nations, which beget wars and constitute the weightiest objection to navies. I salute you with constant affection and respect.
Th: Jefferson.
[The annexed is the letter to which the foregoing is a reply.]
TO THOMAS JEFFERSON.
Montezillo, October 15, 1822. Dear Sir,
I have long entertained scruples about writing this letter, upon a subject of some delicacy. But old age has overcome them at last.
You remember the four ships ordered by Congress to be built, and the four captains appointed by Washington, Talbot, and Truxton, and Barry, &c, to carry an ambassador to Algiers, and protect our commerce in the Mediterranean. I have always imputed this measure to you; for several reasons. First, because you frequently proposed it to me while we were at Paris, negotiating together for peace with the Barbary powers. Secondly, because I knew that Washington and Hamilton were not only indifferent about a navy, but averse to it. There was no Secretary of the Navy; only four Heads of department. You were Secretary of State; Hamilton, Secretary of the Treasury; Knox, Secretary of War; and I believe Bradford was Attorney General. I have always suspected that you and Knox were in favor of a navy. If Bradford was so, the majority was clear. But Washington, I am confident, was against it in his judgment. But his attachment to Knox, and his deference to your opinion, for I know he had a great regard for you, might induce him to decide in favor of you and Knox, even though Bradford united with Hamilton in opposition to you. That Hamilton was averse to the measure, I have personal evidence; for while it was pending, he came in a hurry and a fit of impatience to make a visit to me. He said, he was likely to be called upon for a large sum of money to build ships of war, to fight the Algerines, and he asked my opinion of the measure. I answered him that I was clearly in favor of it. For I had always been of opinion, from the commencement of the Revolution, that a navy was the most powerful, the safest, and the cheapest national defence for this country. My advice, therefore, was, that as much of the revenue as could possibly be spared, should be applied to the building and equipping of ships. The conversation was of some length, but it was manifest in his looks and in his air, that he was disgusted at the measure, as well as at the opinion that I had expressed.
Mrs. Knox not long since wrote a letter to Doctor Waterhouse, requesting him to procure a commision for her son, in the navy; ‘that navy,’ says her ladyship, ‘of which his father was the parent.’ ‘For,’ says she, ‘I have frequently heard General Washington say to my husband, the navy was your child.’ I have always believed it to be Jefferson’s child, though Knox may have assisted in ushering it into the world. Hamilton’s hobby was the army. That Washington was averse to a navy, I had full proof from his own lips, in many different conversations, some of them of length, in which he always insisted that it was only building and arming ships for the English. ‘Si quid novisti rectius istis, candidus imperii; si non, his utere mecum.’
If I am in error in any particular, pray correct your humble servant.
John Adams.
TO DOCTOR COOPER.
Monticello, November 2, 1822.
Dear Sir,
Your favor of October the 18th came to hand yesterday. The atmosphere of our country is unquestionably charged with a threatening cloud of fanaticism, lighter in some parts, denser in others, but too heavy in all. I had no idea, however, that in Pennsylvania, the cradle of toleration and freedom of religion, it could have arisen to the height you describe. This must be owing to the growth of Presbyterianism. The blasphemy and absurdity of the five points of Calvin, and the impossibility of defending them, render their advocates impatient of reasoning, irritable, and prone to denunciation. In Boston, however, and its neighborhood, Unitarianism has advanced to so great strength, as now to humble this haughtiest of all religious sects; insomuch, that they condescend to interchange with them and the other sects, the civilities of preaching freely and frequently in each other’s meeting-houses. In Rhode Island, on the other hand, no sectarian preacher will permit an Unitarian to pollute his desk. In our Richmond there is much fanaticism, but chiefly among the women. They have their night meetings and praying parties, where, attended by their priests, and sometimes by a hen-pecked husband, they pour forth the effusions of their love to Jesus, in terms as amatory and carnal, as their modesty would permit them to use to a mere earthly lover. In our village of Charlottesville, there is a good degree of religion, with a small spice only of fanaticism. We have four sects, but without either church or meeting-house. The court-house is the common temple, one Sunday in the month to each. Here, Episcopalian and Presbyterian, Methodist and Baptist, meet together, join in hymning their Maker, listen with attention and devotion to each others’ preachers, and all mix in society with perfect harmony. It is not so in the districts where Presbyterianism prevails undividedly. Their ambition and tyranny would tolerate no rival, if they had power. Systematical in grasping at an ascendancy over all other sects, they aim, like the Jesuits, at engrossing the education of the country, are hostile to every institution which they do not direct, and jealous at seeing others begin to attend at all to that object. The diffusion of instruction, to which there is now so growing an attention, will be the remote remedy to this fever of fanaticism; while the more proximate one will be the progress of Unitarianism. That this will, ere long, be the religion of the majority from north to south, I have no doubt.
In our University you know there is no professorship of Divinity. A handle has been made of this, to disseminate an idea that this is an institution, not merely of no religion, but against all religion. Occasion was taken at the last meeting of the Visitors, to bring forward an idea that might silence this calumny, which weighed on the minds of some honest friends to the institution. In our annual report to the legislature, after stating the constitutional reasons against a public establishment of any religious instruction, we suggest the expediency of encouraging the different religious sects to establish, each for itself, a professorship of their own tenets, on the confines of the University, so near as that the students may attend the lectures there, and have the free use our own library, and every other accommodation we can give them; preserving, however, their independence of us and of each other. This fills the chasm objected to ours, as a defect in an institution professing to give instruction in all useful sciences. I think the invitation will be accepted, by some sects from candid intentions, and by others from jealousy and rivalship. And by bringing the sects together, and mixing them with the mass of other students, we shall soften their asperities, liberalize and neutralize their prejudices, and make the general religion, a religion of peace, reason, and morality.
The time of opening our University is still as uncertain as ever. All the pavilions, boarding-houses, and dormitories are done. Nothing is now wanting but the central building for a library and other general purposes. For this we have no funds, and the last legislature refused all aid. We have better hopes of the next. But all is uncertain. I have heard with regret of disturbances on the part of the students in your seminary. The article of discipline is the most difficult in American education. Premature ideas of independence, too little repressed by parents, beget a spirit of insubordination, which is the great obstacle to science with us, and a principal cause of its decay since the Revolution. I look to it with dismay in our institution, as a breaker ahead, which I am far from being confident we shall be able to weather. The advance of age, and tardy pace of the public patronage, may probably spare me the pain of witnessing consequences.
I salute you with constant friendship and respect.
Th: Jefferson.
TO JAMES SMITH.
Monticello, December 8, 1822.
Sir,
I have to thank you for your pamphlets on the subject of Unitarianism, and to express my gratification with your efforts for the revival of primitive Christianity in your quarter. No historical fact is better established, than that the doctrine of one God, pure and uncompounded, was that of the early ages of Christianity; and was amoung the efficacious doctrines which gave it triumph over the polytheism of the ancients, sickened with the absurdities of their own theology. Nor was the unity of the Supreme Being ousted from the Christian creed by the force of reason, but by the sword of civil government, wielded at the will of the fanatic Athanasius. The hocus-pocus phantasm of a God like another Cerberus, with one body and three heads, had its birth and growth in the blood of thousands and thousands of martyrs. And a strong proof of the solidity of the primitive faith, is its restoration, as soon as a nation arises which vindicates to itself the freedom of religious opinion, and its external divorce from the civil authority. The pure and simple unity of the Creator of the universe, is now all but ascendant in the eastern States; it is dawning in the west, and advancing towards the south; and I confidently expect that the present generation will see Unitarianism become the general religion of the United States. The eastern presses are giving us many excellent pieces on the subject, and Priestley’s learned writings on it are, or should be, in every hand. In fact, the Athanasian paradox that one is three, and three but one, is so incomprehensible to the human mind, that no candid man can say he has any idea of it, and how can he believe what presents no idea? He who thinks he does, only deceives himself. He proves, also, that man, once surrendering his reason, has no remaining guard against absurdities the most monstrous, and like a ship without rudder, is the sport of every wind. With such persons, gullability, which they call faith, takes the helm from the hand of reason, and the mind becomes a wreck.
I write with freedom, because, while I claim a right to believe in one God, if so my reason tells me, I yield as freely to others that of believing in three. Both religions, I find, make honest men, and that is the only point society has any right to look to. Although this mutual freedom should produce mutual indulgence, yet I wish not to be brought in question before the public on this or any other subject, and I pray you to consider me as writing under that trust. I take no part in controversies, religious or political. At the age of eighty, tranquillity is the greatest good of life, and the strongest of our desires that of dying in the good-will of all mankind. And with the assurances of all my good-will to Unitarian and Trinitarian, to Whig and Tory, accept for yourself that of my entire respect.
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN ADAMS,
Monticello, February 25, 1823.
Dear Sir,
I received, in due time, your two favors of December the 2nd and February the 10th, and have to acknowledge for the ladies of my native State their obligations to you for the encomiums which you are so kind as to bestow on them. They certainly claim no advantages over those of their sister States, and are sensible of more favorable circumstances existing with many of them, and happily availed, which our situation does not offer. But the paper respecting Monticello, to which you allude, was not written by a Virginian, but a visitant from another State; and written by memory at least a dozen years after the visit. This has occasioned some lapses of recollection, and a confusion of some things in the mind of our friend, and particularly as to the volume of slanders supposed to have been cut out of newspapers and preserved. It would not, indeed, have been a single volume, but an Encyclopaedia in bulk. But I never had such a volume; indeed, I rarely thought those libels worth reading, much less preserving and remembering. At the end of every year, I generally sorted all my pamphlets, and had them bound according to their subjects. One of these volumes consisted of personal altercations between individuals, and calumnies on each other. This was lettered on the back, ‘Personalities,’ and is now in the library of Congress. I was in the habit, also, while living apart from my family, of cutting out of the newspapers such morsels of poetry, or tales, as I thought would please, and of sending them to my grandchildren, who pasted them on leaves of blank paper and formed them into a book. These two volumes have been confounded into one in the recollection of our friend. Her poetical imagination, too, has heightened the scenes she visited, as well as the merits of the inhabitants, to whom her society was a delightful gratification.
I have just finished reading O’Meara’s Bonaparte. It places him in a higher scale of understanding than I had allotted him. I had thought him the greatest of all military captains, but an indifferent statesman, and misled by unworthy passions. The flashes, however, which escaped from him in these conversations with O’Meara, prove a mind of great expansion, although not of distinct developement and reasoning. He seizes results with rapidity and penetration, but never explains logically the process of reasoning by which he arrives at them. This book, too, makes us forget his atrocities for a moment, in commiseration of his sufferings. I will not say that the authorities of the world, charged with the care of their country and people, had not a right to confine him for life, as a lion or tiger, on the principles of self-preservation. There was no safety to nations while he was permitted to roam at large. But the putting him to death in cold blood, by lingering tortures of mind, by vexations, insults, and deprivations, was a degree of inhumanity to which the poisonings and assassinations of the school of Borgia and the den of Marat never attained. The book proves, also, that nature had denied him the moral sense, the first excellence of well-organized man. If he could seriously and repeatedly affirm, that he had raised himself to power without ever having committed a crime, it proves that he wanted totally the sense of right and wrong. If he could consider the millions of human lives which he had destroyed or caused to be destroyed, the desolations of countries by plunderings, burnings, and famine, the destitutions of lawful rulers of the world without the consent of their constituents, to place his brothers and sisters on their thrones, the cutting up of established societies of men and jumbling them discordantly together again at his caprice, the demolition of the fairest hopes of mankind for the recovery of their rights and amelioration of their condition, and all the numberless train of his other enormities; the man, I say, who could consider all these as no crimes, must have been a moral monster, against whom every hand should have been lifted to slay him.
You are so kind as to inquire after my health. The bone of my arm is well knitted, but my hand and fingers are in a discouraging condition, kept entirely useless by an oedematous swelling of slow amendment.
God bless you and continue your good health of body and mind.
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN ADAMS.
Monticello, April 11, 1823.
Dear Sir,
The wishes expressed in your last favor, that I may continue in life and health until I become a Calvinist, at least in his exclamation of, ‘Mon Dieu! jusqu’a quand?’ would make me immortal. I can never join Calvin in addressing his God. He was indeed an atheist, which I can never be; or rather his religion was daemonism. If ever man worshipped a false God, he did. The being described in his five points, is not the God whom you and I acknowledge and adore, the Creator and benevolent Governor of the world; but a daemon of malignant spirit. It would be more pardonable to believe in no God at all, than to blaspheme him by the atrocious attributes of Calvin. Indeed, I think that every Christian sect gives a great handle to atheism by their general dogma, that, without a revelation, there would not be sufficient proof of the being of a God. Now one sixth of mankind only are supposed to be Christians: the other five sixths then, who do not believe in the Jewish and Christian revelation, are without a knowledge of the existence of a God! This gives completely a gain de cause to the disciples of Ocellus, Timasus, Spinosa, Diderot, and D’Holbach. The argument which they rest on as triumphant and unanswerable is, that in every hypothesis of cosmogony, you must admit an eternal pre-existence of something; and according to the rule of sound philosophy, you are never to employ two principles to solve a difficulty when one will suffice. They say then, that it is more simple to believe at once in the eternal pre-existence of the world, as it is now going on, and may for ever go on by the principle of reproduction which we see and witness, than to believe in the eternal pre-existence of an ulterior cause, or creator of the world, a being whom we see not and know not, of whose form, substance, and mode, or place of existence, or of action, no sense informs us, no power of the mind enables us to delineate or comprehend. On the contrary, I hold (without appeal to revelation), that when we take a view of the universe, in its parts, general or particular, it is impossible for the human mind not to perceive and feel a conviction of design, consummate skill, and indefinite power in every atom of its composition. The movements of the heavenly bodies, so exactly held in their course by the balance of centrifugal and centripetal forces; the structure of our earth itself, with its distribution of lands, waters, and atmosphere; animal and vegetable bodies, examined in all their minutest particles; insects, mere atoms of life, yet as perfectly organized as man or mammoth; the mineral substances, their generation and uses; it is impossible, I say, for the human mind not to believe, that there is in all this, design, cause, and effect, up to an ultimate cause, a fabricator of all things from matter and motion, their preserver and regulator while permitted to exist in their present forms, and their regenerator into new and other forms. We see, too, evident proofs of the necessity of a superintending power, to maintain the universe in its course and order. Stars, well known, have disappeared, new ones have come into view; comets, in their incalculable courses, may run foul of suns and planets, and require renovation under other laws; certain races of animals are become extinct; and were there no restoring power, all existences might extinguish successively, one by one, until all should be reduced to a shapeless chaos. So irresistible are these evidences of an intelligent and powerful agent, that, of the infinite numbers of men who have existed through all time, they have believed, in the proportion of a million at least to unit, in the hypothesis of an eternal pre-existence of a creator, rather than in that of a self-existent universe. Surely this unanimous sentiment renders this more probable, than that of the few in the other hypothesis. Some early Christians, indeed, have believed in the co-eternal pre-existence of both the creator and the world, without changing their relation of cause and effect. That this was the opinion of St. Thomas, we are informed by Cardinal Toleta, in these words; ‘Deus ab terno fuit jam omnipotens, si cut cum produxit mundum. Ah aternopotuit producers mundum. Si sol ah czterno esset, lumen ah æterno esset; et si pes, similiter vestigium. At lumen et vestigium effectus sunt efficients solis et pedis; potuit ergo cum causa æterna effectus coaternus esse. Cujus sententia, est S. Thomas, theologorum primus.’—Cardinal Toleta.


Of the nature of this being we know nothing. Jesus tells us, that ‘God is a spirit’ (John iv. 24.), but without defining what a spirit is: [Greek phrase] Down to the third century, we know that it was still deemed material but of a lighter, subtler matter than our gross bodies. So says Origen; Deus igitur, cui anima similis est, juxta Originem, reapte corporalis est; sed graviorum tantum ratione corporum incorporeus.’ These are the words of Huet in his commentary on Origen. Origen himself says, [Greek and Latin phrase]
These two fathers were of the third century. Calvin’s character of this Supreme Being seems chiefly copied from that of the Jews. But the reformation of these blasphemous attributes, and substitution of those more worthy, pure, and sublime, seems to have been the chief object of Jesus in his discourses to the Jews: and his doctrine of the cosmogony of the world is very clearly laid down in the three first verses of the first chapter of John, in these words: [Greek phrase] Which, truly translated, means, ‘In the beginning God existed, and reason [or mind] was with God, and that mind was God. This was in the beginning with God. All things were created by it, and without it was made not one thing which was made.’ Yet this text, so plainly declaring the doctrine of Jesus, that the world was created by the supreme intelligent being, has been perverted by modern Christians to build up a second person of their tritheism, by a mistranslation of the word Xoyog. One of its legitimate meanings, indeed, is ‘a word.’ But in that sense it makes an unmeaning jargon: while the other meaning, ‘reason,’ equally legitimate, explains rationally the eternal pre-existence of God, and his creation of, the world. Knowing how incomprehensible it was that ‘a word,’ the mere action or articulation of the organs of speech could create a world, they undertook to make of this articulation a second pre-existing being, and ascribe to him, and not to God, the creation of the universe. The atheist here plumes himself on the uselessness of such a God, and the simpler hypothesis of a self-existent universe. The truth is, that the greatest enemies to the doctrines of Jesus are those calling themselves the expositors of them, who have perverted them for the structure of a system of fancy absolutely incomprehensible, and without any foundation in his genuine words. And the day will come, when the mystical generation of Jesus, by the Supreme Being as his father, in the womb of a virgin, will be classed with the fable of the generation of Minerva in the brain of Jupiter. But we may hope that the dawn of reason, and freedom of thought, in these United States, will do away all this artificial scaffolding, and restore to us the primitive and genuine doctrines of this the most venerated reformer of human errors.
So much for your quotation of Calvin’s ‘Mon Dieu! jusqu’a quand’in which, when addressed to the God of Jesus, and our God, I join you cordially, and await his time and will with more readiness than reluctance. May we meet there again, in Congress, with our ancient colleagues, and receive with them the seal of approbation, ‘Well done, good and faithful servants.’
Th: Jefferson.
TO THE PRESIDENT.
Monticello, June 11, 1823.
Dear Sir,
Considering that I had not been to Bedford for a twelvemonth before, I thought myself singularly unfortunate in so timing my journey, as to have been absent exactly at the moment of your late visit to our neighborhood. The loss, indeed, was all my own; for in these short interviews with you. I generally get my political compass rectified, learn from you whereabouts we are, and correct my course again. In exchange for this, I can give you but newspaper ideas, and little indeed of these, for I read but a single paper, and that hastily. I find Horace and Tacitus so much better writers than the champions of the gazettes, that I lay those down, to take up these, with great reluctance. And on the question you propose, whether we can, in any form, take a bolder attitude than formerly in favor of liberty, I can give you but commonplace ideas. They will be but the widow’s mite, and offered only because requested. The matter which now embroils Europe, the presumption of dictating to an independent nation the form of its government, is so arrogant, so atrocious, that indignation, as well as moral sentiment, enlists all our partialities and prayers in favor of one, and our equal execrations against the other. I do not know, indeed, whether all nations do not owe to one another a bold and open declaration of their sympathies with the one party, and their detestation of the conduct of the other. But farther than this we are not bound to go; and indeed, for the sake of the world, we ought not to increase the jealousies, or draw on ourselves the power, of this formidable confederacy. I have ever deemed it fundamental for the United States, never to take active part in the quarrels of Europe. Their political interests are entirely distinct from ours. Their mutual jealousies, their balance of power, their complicated alliances, their forms and principles of government, are all foreign to us. They are nations of eternal war. All their energies are expended in the destruction of the labor, property, and lives of their people. On our part, never had a people so favorable a chance of trying the opposite system, of peace and fraternity with mankind, and the direction of all our means and faculties to the purposes of improvement instead of destruction. With Europe we have few occasions of collision, and these, with a little prudence and forbearance, may be generally accommodated. Of the brethren of our own hemisphere, none are yet, or for an age to come will be, in a shape, condition, or disposition to war against us. And the foothold, which the nations of Europe had in either America, is slipping from under them, so that we shall soon be rid of their neighborhood. Cuba alone seems at present to hold up a speck of war to us. Its possession by Great Britain would indeed be a great calamity to us. Could we induce her to join us in guarantying its independence against all the world, except Spain, it would be nearly as valuable to us as if it were our own. But should she take it, I would not immediately go to war for it; because the first war on other accounts will give it to us; or the island will give itself to us, when, able to do so. While no duty, therefore, calls on us to take part in the present war of Europe, and a golden harvest offers itself in reward for doing nothing, peace and neutrality seem to be our duty and interest. We may gratify ourselves, indeed, with a neutrality as partial to Spain as would be justifiable without giving cause of war to her adversary; we might and ought to avail ourselves of the happy occasion of procuring and cementing a cordial reconciliation with her, by giving assurance of every friendly office which neutrality admits, and especially, against all apprehension of our intermeddling in the quarrel with her colonies. And I expect daily and confidently to hear of a spark kindled in France, which will employ her at home, and relieve Spain from all further apprehensions of danger.
That England is playing false with Spain cannot be doubted. Her government is looking one way and rowing another. It is curious to look back a little on past events. During the ascendancy of Bonaparte, the word among the herd of Kings was, ‘Sauve qui peut.’ Each shifted for himself, and left his brethren to squander and do the same as they could. After the battle of Waterloo, and the military possession of France, they rallied and combined in common cause, to maintain each other against any similar and future danger. And in this alliance, Louis, now avowedly, and George, secretly but solidly, were of the contracting parties; and there can be no doubt that the allies are bound by treaty to aid England with their armies, should insurrection take place among her people. The coquetry she is now playing off between her people and her allies is perfectly understood by the latter, and accordingly gives no apprehensions to France, to whom it is all explained. The diplomatic correspondence she is now displaying, these double papers fabricated merely for exhibition, in which she makes herself talk of morals and principle, as if her qualms of conscience would not permit her to go all lengths with her Holy Allies, are all to gull her own people. It is a theatrical farce, in which the five powers are the actors, England the Tartuffe, and her people the dupes. Playing thus so dextrously into each other’s hands, and their own persons seeming secured, they are now looking to their privileged orders. These faithful auxiliaries, or accomplices, must be saved. This war is evidently that of the general body of the aristocracy, in which England is also acting her part. ‘Save but the Nobles, and there shall be no war,’ says she, masking her measures at the same time under the form of friendship and mediation, and hypocritically, while a party, offering herself as a judge, to betray those whom she is not permitted openly to oppose. A fraudulent neutrality, if neutrality at all, is all Spain will get from her. And Spain, probably, perceives this, and willingly winks at it rather than have her weight thrown openly into the other scale.
But I am going beyond my text, and sinning against the adage of carrying coals to Newcastle. In hazarding to you my crude and uninformed notions of things beyond my cognizance, only be so good as to remember that it is at your request, and with as little confidence on my part as profit on yours. You will do what is right, leaving the people of Europe to act their follies and crimes among themselves, while we pursue in good faith the paths of peace and prosperity. To your judgment we are willingly resigned, with sincere assurances of affectionate esteem and respect.
Th: Jefferson.
TO JUDGE JOHNSON.
Monticello, June 12, 1823.
Dear Sir,
Our correspondence is of that accommodating character, which admits of suspension at the convenience of either party, without inconvenience to the other. Hence this tardy acknowledgment of your favor of April the 11th. I learn from that with great pleasure, that you have resolved on continuing your history of parties. Our opponents are far ahead of us in preparations for placing their cause favorably before posterity. Yet I hope even from some of them the escape of precious truths, in angry explosions or effusions of vanity, which will betray the genuine monarchism of their principles. They do not themselves believe what they endeavor to inculcate, that we were an opposition party, not on principle, but merely seeking for office. The fact is, that at the formation of our government, many had formed their political opinions on European writings and practices, believing the experience of old countries, and especially of England, abusive as it was, to be a safer guide than mere theory. The doctrines of Europe were, that men in numerous associations cannot be restrained within the limits of order and justice, but by forces physical and moral, wielded over them by authorities independent of their will. Hence their organization of kings, hereditary nobles, and priests. Still further to constrain the brute force of the people, they deem it necessary to keep them down by hard labor, poverty, and ignorance, and to take from them, as from bees, so much of their earnings, as that unremitting labor shall be necessary to obtain a sufficient surplus barely to sustain a scanty and miserable life. And these earnings they apply to maintain their privileged orders in splendor and idleness, to fascinate the eyes of the people, and excite in them an humble adoration and submission, as to an order of superior beings. Although few among us had gone all these lengths of opinion, yet many had advanced, some more, some less, on the way. And in the convention which formed our government, they endeavored to draw the cords of power as tight as they could obtain them, to lessen the dependence of the general functionaries on their constituents, to subject to them those of the States, and to weaken their means of maintaining the steady equilibrium which the majority of the convention had deemed salutary for both branches, general and local. To recover, therefore, in practice, the powers which the nation had refused, and to warp to their own wishes those actually given, was the steady object of the federal party. Ours, on the contrary, was to maintain the will of the majority of the convention, and of the people themselves. We believed, with them, that man was a rational animal, endowed by nature with rights, and with an innate sense of justice; and that he could be restrained from wrong and protected in right, by moderate powers, confided to persons of his own choice, and held to their duties by dependence on his own will. We believed that the complicated organization of kings, nobles, and priests, was not the wisest nor best to effect the happiness of associated man; that wisdom and virtue were not hereditary; that the trappings of such a machinery consumed, by their expense, those earnings of industry they were meant to protect, and, by the inequalities they produced, exposed liberty to sufferance. We believed that men, enjoying in ease and security the full fruits of their own industry, enlisted by all their interests on the side of law and order, habituated to think for themselves, and to follow their reason as their guide, would be more easily and safely governed, than with minds nourished in error, and vitiated and debased, as in Europe, by ignorance, indigence, and oppression. The cherishment of the people then was our principle, the fear and distrust of them, that of the other party. Composed, as we were, of the landed and laboring interests of the country, we could not be less anxious for a government of law and order than were the inhabitants of the cities, the strong holds of federalism. And whether our efforts to save the principles and form of our constitution have not been salutary, let the present republican freedom, order, and prosperity of our country determine. History may distort truth, and will distort it for a time, by the superior efforts at justification of those who are conscious of needing it most. Nor will the opening scenes of our present government be seen in their true aspect, until the letters of the day, now held in private hoards, shall be broken up and laid open to public view. What a treasure will be found in General Washington’s cabinet, when it shall pass into the hands of as candid a friend to truth as he was himself! When no longer, like Caesar’s notes and memorandums in the hands of Anthony, it shall be open to the high priests of federalism only, and garbled to say so much, and no more, as suits their views.
With respect to his Farewell Address, to the authorship of which, it seems, there are conflicting claims, I can state to you some facts. He had determined to decline a re-election at the end of his first term, and so far determined, that he had requested Mr. Madison to prepare for him something valedictory, to be addressed to his constituents on his retirement. This was done: but he was finally persuaded to acquiesce in a second election, to which no one more strenuously pressed him than myself, from a conviction of the importance of strengthening, by longer habit, the respect necessary for that office, which the weight of his character only could effect. When, at the end of this second term, his Valedictory came out, Mr. Madison recognised in it several passages of his draught; several others we were both satisfied were from the pen of Hamilton, and others from that of the President himself. These he probably put into the hands of Hamilton to form into a whole, and hence it may all appear in Hamilton’s hand-writing, as if it were all of his composition.
I have stated above, that the original objects of the federalists were, 1. To warp our government more to the form and principles of monarchy, and 2. To weaken the barriers of the State governments as co-ordinate powers. In the first they have been so completely foiled by the universal spirit of the nation, that they have abandoned the enterprise, shrunk from the odium of their old appellation, taken to themselves a participation of ours, and under the pseudo-republican mask, are now aiming at their second object, and strengthened by unsuspecting or apostate recruits from our ranks, are advancing fast towards an ascendancy. I have been blamed for saying, that a prevalence of the doctrines of consolidation would one day call for reformation or revolution. I answer by asking, if a single State of the Union would have agreed to the constitution, had it given all powers to the General Government? If the whole opposition to it did not proceed from the jealousy and fear of every State, of being subjected to the other States, in matters merely its own? And if there is any reason to believe the States more disposed now than then, to acquiesce in this general surrender of all their rights and powers to a consolidated government, one and undivided?
You request me confidentially, to examine the question, whether the Supreme Court has advanced beyond its constitutional limits, and trespassed on those of the State authorities? I do not undertake it, my dear Sir, because I am unable. Age, and the wane of mind consequent on it, have disqualified me from investigations so severe, and researches so laborious. And it is the less necessary in this case, as having been already done by others with a logic and learning to which I could add nothing. On the decision of the case of Cohens vs. The State of Virginia, in the Supreme Court of the United States, in March, 1821, Judge Roane, under the signature of Algernon Sidney, wrote for the Enquirer, a series of papers on the law of that case. I considered these papers maturely as they came out, and confess, that they appeared to me to pulverize every word which had been delivered by Judge Marshall, of the extra-judicial part of his opinion; and all was extra-judicial, except the decision that the act of Congress had not purported to give to the corporation of Washington the authority claimed by their lottery-law, of controlling the laws of the States within the States themselves. But unable to claim that case, he could not let it go entirely, but went on gratuitously to prove, that notwithstanding the eleventh amendment of the constitution, a State could be brought, as a defendant, to the bar of his court; and again, that Congress might authorize a corporation of its territory to exercise legislation within a State, and paramount to the laws of that State. I cite the sum and result only of his doctrines, according to the impression made on my mind at the time, and still remaining. If not strictly accurate in circumstance, it is so in substance. This doctrine was so completely refuted by Roane, that if he can be answered, I surrender human reason as a vain and useless faculty, given to bewilder, and not to guide us. And I mention this particular case as one only of several, because it gave occasion to that thorough examination of the constitutional limits between the General and State jurisdictions, which you have asked for. There were two other writers in the same paper, under the signatures of Fletcher of Saltoun, and Somers, who in a few essays presented some very luminous and striking views of the question. And there was a particular paper which recapitulated all the cases in which it was thought the federal court had usurped on the State jurisdictions. These essays will be found in the Enquirers of 1821, from May the 10th to July the 13th. It is not in my present power to send them to you, but if Ritchie can furnish them, I will procure and forward them. If they had been read in the other States, as they were here, I think they would have left, there as here, no dissentients from their doctrine. The subject was taken up by our legislature of 1821-22, and two draughts of remonstrances were prepared and discussed. As well as I remember, there was no difference of opinion as to the matter of right; but there was as to the expediency of a remonstrance at that time, the general mind of the States being then under extraordinary excitement by the Missouri question; and it was dropped on that consideration. But this case is not dead; it only sleepeth. The Indian Chief said, he did not go to war for every petty injury by itself, but put it into his pouch, and when that was full, he then made war. Thank Heaven, we have provided a more peaceable and rational mode of redress.
This practice of Judge Marshall, of travelling out of his case to prescribe what the law would be in a moot case not before the court, is very irregular and very censurable. 1 recollect another instance, and the more particularly, perhaps, because it in some measure bore on myself. Among the midnight appointments of Mr. Adams, were commissions to some federal justices of the peace for Alexandria. These were signed and sealed by him, but not delivered. I found them on the table of the department of State, on my entrance into office, and 1 forbade their delivery. Marbury, named in one of them, applied to the Supreme Court for a Mandamus to the Secretary of State (Mr. Madison), to deliver the commission intended for him. The Court determined at once, that being an original process, they had no cognizance of it; and there the question before them was ended. But the Chief Justice went on to lay down what the law would be, had they jurisdiction of the case; to wit, that they should command the delivery.
The object was clearly to instruct any other court having the jurisdiction, what they should do, if Marbury should apply to them. Besides the impropriety of this gratuitous interference, could any thing exceed the perversion of law? For if there is any principle of law never yet contradicted, it is that delivery is one of the essentials to the validity of a deed. Although signed and sealed, yet as long as it remains in the hands of the party himself, it is in fieri only, it is not a deed, and can be made so only by its delivery. In the hands of a third person it may be made an escrow. But whatever is in the executive offices is certainly deemed to be in the hands of the President; and, in this case, was actually in my hands, because, when I countermanded them, there was as yet no Secretary of State. Yet this case of Marbury and Madison is continually cited by bench and bar, as if it were settled law, without any animadversion on its being merely an obiter dissertation of the Chief Justice.
It may be impracticable to lay down any general formula of words which shall decide at once, and with precision, in every case, this limit of jurisdiction. But there are two canons which will guide us safely in most of the cases. 1. The capital and leading object of the constitution was, to leave with the States all authorities which respected their own citizens only, and to transfer to the United States those which respected citizens of foreign or other States: to make us several as to ourselves, but one as to all others. In the latter case, then, constructions should lean to the general jurisdiction, if the words will bear it; and in favor of the States in the former, if possible to be so construed. And indeed, between citizens and citizens of the same State, and under their own laws, I know but a single case in which a jurisdiction is given to the General Government. That is, where any thing but gold or silver is made a lawful tender, or the obligation of contracts is any otherwise impaired. The separate legislatures had so often abused that power, that the citizens themselves chose to trust it to the general, rather than to their own special authorities. 2. On every question of construction, carry ourselves back to the time when the constitution was adopted, recollect the spirit manifested in the debates, and instead of trying what meaning may be squeezed out of the text, or invented against it, conform to the probable one in which it was passed. Let us try Cohen’s case by these canons only, referring always however, for full argument, to the essays before cited.
1. It was between a citizen and his own State, and under a law of his State. It was a domestic case therefore, and not a foreign one.
2. Can it be believed, that under the jealousies prevailing against the General Government, at the adoption of the constitution, the States meant to surrender the authority of preserving order, of enforcing moral duties, and restraining vice, within their own territory? And this is the present case, that of Cohen being under the ancient and general law of gaming. Can any good be effected, by taking from the States the moral rule of their citizens, and subordinating it to the general authority, or to one of their corporations, which may justify forcing the meaning of words, hunting after possible constructions, and hanging inference on inference, from heaven to earth, like Jacob’s ladder? Such an intention was impossible, and such a licentiousness of construction and inference, if exercised by, both governments, as may be done with equal right, would equally authorize both to claim all powers, general and particular, and break up the foundations of the Union. Laws are made for men of ordinary understanding, and should, therefore, be construed by the ordinary rules of common sense. Their meaning is not to be sought for in metaphysical subtleties, which may make any thing mean every thing or nothing, at pleasure. It should be left to the sophisms of advocates, whose trade it is, to prove that a defendant is a plaintiff, though dragged into court, torto collo, like Bonaparte’s volunteers into the field in chains, or that a power has been given, because it ought to have been given, et alia talia. The States supposed, that, by their tenth amendment, they had secured themselves against constructive powers. They were not lessoned yet by Cohen’s case, nor aware of the slipperiness of the eels of the law. I ask for no straining of words against the General Government nor yet against the States. I believe the States can best govern our home concerns, and the General Government our foreign ones. I wish, therefore, to see maintained that wholesome distribution of powers, established by the constitution for the limitation of both; and never to see all offices transferred to Washington, where, further withdrawn from the eyes of the people, they may more secretly be bought and sold, as at market.
But the Chief Justice says, ‘there must be an ultimate arbiter somewhere.’ True, there must; but does that prove it is either party? The ultimate arbiter is the people of the Union, assembled by their deputies in convention, at the call of Congress, or of two thirds of the States. Let them decide to which they mean to give an authority claimed by two of their organs. And it has been the peculiar wisdom and felicity of our constitution, to have provided this peaceable appeal, where that of other nations is at once to force.
I rejoice in the example you set of seriatim opinions. I have heard it often noticed, and always with high approbation. Some of your brethren will be encouraged to follow it occasionally, and in time, it may be felt by all as a duty, and the sound practice of the primitive court be again restored. Why should not every judge be asked his opinion, and give it from the bench, if only by yea or nay? Besides ascertaining the fact of his opinion, which the public have a right to know, in order to judge whether it is impeachable or not, it would show whether the opinions were unanimous or not, and thus settle more exactly the weight of their authority.
The close of my second sheet warns me that it is time now to relieve you from this letter of unmerciful length. Indeed, I wonder how I have accomplished it, with two crippled wrists, the one scarcely able to move my pen, the other to hold my paper. But I am hurried sometimes beyond the sense of pain, when unbosoming myself to friends who harmonize with me in principle. You and I may differ occasionally in details of minor consequence, as no two minds, more than two faces, are the same in every feature. But our general objects are the same; to preserve the republican form and principles of our constitution, and cleave to the salutary distribution of powers which that has established. These are the two sheet anchors of our Union. If driven from either, we shall be in danger of foundering. To my prayers for its safety and perpetuity, I add those for the continuation of your health, happiness, and usefulness to your country.
Th: Jefferson.
TO JAMES MADISON.
Monticello, August 30,1823.
Dear Sir,
I received the enclosed letters from the President, with a request that after perusal I would forward them to you, for perusal by yourself also, and to be returned then to him.
You have doubtless seen Timothy Pickering’s fourth of July observations on the Declaration of Independence. If his principles and prejudices, personal and political, gave us no reason to doubt whether he had truly quoted the information he alleges to have received from Mr. Adams, I should then say, that in some of the particulars, Mr. Adams’s memory has led him into unquestionable error. At the age of eighty-eight, and forty-seven years after the transactions of Independence, this is not wonderful. Nor should I, at the age of eighty, on the small advantage of that difference only, venture to oppose my memory to his, were it not supported by written notes, taken by myself at the moment and on the spot. He says, ‘The committee of five, to wit, Doctor Franklin, Sherman, Livingston, and ourselves, met, discussed the subject, and then appointed him and myself to make the draught; that, we, as a sub-committee, met, and after the urgencies of each on the other, I consented to undertake the task; that, the draught being made, we, the sub-committee, met, and conned the paper over, and he does not remember that he made or suggested a single alteration.’ Now these details are quite incorrect. The committee of five met; no such thing as a sub-committee was proposed, but they unanimously pressed on myself alone to undertake the draught. I consented; I drew it: but before I reported it to the committee, I communicated it separately to Doctor Franklin and Mr. Adams, requesting their corrections, because they were the two members of whose judgments and amendments I wished most to have the benefit, before presenting it to the committee: and you have seen the original paper now in my hands, with the corrections of Doctor Franklin and Mr. Adams interlined in their own hand-writings. Their alterations were two or three only, and merely verbal. I then wrote a fair copy, reported it to the committee, and from them, unaltered, to Congress. This personal communication and consultation with Mr. Adams, he has misremembered into the actings of a sub-committee. Pickering’s observations, and Mr. Adams’s in addition, ‘that it contained no new ideas, that it is a common-place compilation, its sentiments hacknied in Congress for two years before, and its essence contained in Otis’s pamphlet,’ may all be true. Of that I am not to be the judge. Richard Henry Lee charged it as copied from Locke’s Treatise on Government. Otis’s pamphlet I never saw, and whether I had gathered my ideas from reading or reflection I do not know. I know only that I turned to neither book nor pamphlet while writing it. I did not consider it as any part of my charge to invent new ideas altogether, and to offer no sentiment which had ever been expressed before. Had Mr. Adams been so restrained, Congress would have lost the benefit of his bold and impressive advocations of the rights of Revolution. For no man’s confident and fervid addresses, more than Mr. Adams’s, encouraged and supported us through the difficulties surrounding us, which, like the ceaseless action of gravity, weighed on us by night and by day. Yet, on the same ground, we may ask what of these elevated thoughts was new, or can be affirmed never before to have entered the conceptions of man?
Whether, also, the sentiments of Independence, and the reasons for declaring it, which makes so great a portion of the instrument, had been hacknied in Congress for two years before the 4th of July, ‘76, or this dictum also of Mr. Adams be another slip of memory, let history say. This, however, I will say for Mr. Adams, that he supported the Declaration with zeal and ability, fighting fearlessly for every word of it. As to myself, I thought it a duty to be, on that occasion, a passive auditor of the opinions of others, more impartial judges than I could be, of its merits or demerits. During the debate I was sitting by Doctor Franklin, and he observed that I was writhing a little under the acrimonious criticisms on some of its parts; and it was on that occasion, that by way of comfort, he told me the story of John Thomson, the hatter, and his new sign.
Timothy thinks the instrument the better for having a fourth of it expunged. He would have thought it still better, had the other three fourths gone out also, all but the single sentiment (the only one he approves), which recommends friendship to his dear England, whenever she is willing to be at peace with us. His insinuations are, that although ‘the high tone of the instrument was in unison with the warm feelings of the times, this sentiment of habitual friendship to England should never be forgotten, and that the duties it enjoins should especially be borne in mind on every celebration of this anniversary.’ In other words, that the Declaration, as being a libel on the government of England, composed in times of passion, should now be buried in utter oblivion, to spare the feelings of our English friends and Angloman fellow-citizens. But it is not to wound them that we wish to keep it in mind; but to cherish the principles of the instrument in the besoms of our own citizens: and it is a heavenly comfort to see that these principles are yet so strongly felt, as to render a circumstance so trifling as this little lapse of memory of Mr. Adams’s, worthy of being solemnly announced and supported at an anniversary assemblage of the nation on its birth-day. In opposition, however, to Mr. Pickering, I pray God that these principles may be eternal, and close the prayer with my affectionate wishes for yourself of long life, health, and happiness.
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN ADAMS.
Monticello, September 4, 1823.
Dear Sir,
Your letter of August the 15th was received in due time, and with the welcome of every thing which comes from you. With its opinions on the difficulties of revolutions from despotism to freedom, I very much concur. The generation which commences a revolution rarely completes it. Habituated from their infancy to passive submission of body fend mind to their kings and priests, they are not qualified, when called on, to think and provide for themselves; and their inexperience, their ignorance and bigotry, make them instruments often, in the hands of the Bonapartes and Iturbides, to defeat their own rights and purposes. This is the present situation of Europe and Spanish America. But it is not desperate. The light which has been shed on mankind by the art of printing, has eminently changed the condition of the world. As yet, that light has dawned on the middling classes only of the men in Europe. The kings and the rabble, of equal ignorance, have not yet received its rays; but it continues to spread, and while printing is preserved, it can no more recede than the sun return on his course. A first attempt to recover the right of self-government may fail, so may a second, a third, &c. But as a younger and more instructed race comes on, the sentiment becomes more and more intuitive, and a fourth, a fifth, or some subsequent one of the ever-renewed attempts will ultimately succeed. In France, the first effort was defeated by Robespierre, the second by Bonaparte, the third by Louis XVIII., and his holy allies; another is yet to come, and all Europe, Russia excepted, has caught the spirit; and all will attain representative government, more or less perfect. This is now well understood to be a necessary check on Kings, whom they will probably think it more prudent to chain and tame, than to exterminate. To attain all this, however, rivers of blood must yet flow, and years of desolation pass over; yet the object is worth rivers of blood, and years of desolation. For what inheritance so valuable, can man leave to his posterity? The spirit of the Spaniard, and his deadly and eternal hatred to a Frenchman, give me much confidence that he will never submit, but finally defeat this atrocious violation of the laws of God and man, under which he is suffering; and the wisdom and firmness of the Cortes, afford reasonable hope, that that nation will settle down in a temperate representative government, with an executive properly subordinated to that. Portugal, Italy, Prussia, Germany, Greece, will follow suit. You and I shall look down from another world on these glorious achievements to man, which will add to the joys even of heaven.
I observe your toast of Mr. Jay on the 4th of July, wherein you say that the omission of his signature to the Declaration of Independence was by accident. Our impressions as to this fact being different, I shall be glad to have mine corrected, if wrong. Jay, you know, had been in constant opposition to our laboring majority. Our estimate at the time was, that he, Dickinson, and Johnson of Maryland, by their ingenuity, perseverance, and partiality to our English connection, had constantly kept us a year behind where we ought to have been, in our preparations and proceedings. From about the date of the Virginia instructions of May the 15th, 1776, to declare Independence, Mr. Jay absented himself from Congress, and never came there again until December, 1778. Of course, he had no part in the discussions or decision of that question. The instructions to their Delegates by the convention of New York, then sitting, to sign the Declaration, were presented to Congress on the 15th of July only, and on that day the journals show the absence of Mr. Jay, by a letter received from him, as they had done as early as the 29th of May, by another letter. And I think he had been omitted by the convention on a new election of Delegates, when they changed their instructions. Of this last fact, however, having no evidence but an ancient impression, I shall not affirm it. But whether so or not, no agency of accident appears in the case. This error of fact, however, whether yours or mine, is of little consequence to the public. But truth being as cheap as error, it is as well to rectify it for our own satisfaction.
I have had a fever of about three weeks, during the last and preceding month, from which I am entirely recovered except as to strength.
Ever affectionately yours.
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOHN ADAMS.
Monticello, October 12, 1823.
Dear Sir,
I do not write with the ease which your letter of September the 18th supposes. Crippled wrists and fingers make writing slow and laborious. But while writing to you, I lose the sense of these things in the recollection of ancient times, when youth and health made happiness out of every thing. I forget for a while the hoary winter of age, when we can think of nothing but how to keep ourselves warm, and how to get rid of our heavy hours until the friendly hand of death shall rid us of all at once. Against this tedium vita, however, I am fortunately mounted on a hobby, which, indeed, I should have better managed some thirty or forty years ago; but whose easy amble is still sufficient to give exercise and amusement to an octogenary rider. This is the establishment of a University, on a scale more comprehensive, and in a country more healthy and central than our old William and Mary, which these obstacles have long kept in a state of languor and inefficiency. But the tardiness with which such works proceed, may render it doubtful whether I shall live to see it go into action.
Putting aside these things, however, for the present, I write this letter as due to a friendship coeval with our government, and now attempted to be poisoned, when too late in life to be replaced by new affections. I had for some time observed, in the public papers, dark hints and mysterious innuendoes of a correspondence of yours with a friend, to whom you had opened your bosom without reserve, and which was to be made public by that friend or his representative. And now it is said to be actually published. It has not yet reached us, but extracts have been given, and such as seemed most likely to draw a curtain of separation between you and myself. Were there no other motive than that of indignation against the author of this outrage on private confidence, whose shaft seems to have been aimed at yourself more particularly, this would make it the duty of every honorable mind to disappoint that aim, by opposing to its impression a seven-fold shield of apathy and insensibility. With me, however, no such armor is needed. The circumstances of the times in which we have happened to live, and the partiality of our friends at a particular period, placed us in a state of apparent opposition, which some might suppose to be personal also: and there might, not be wanting those who wished to make it so, by filling our ears with malignant falsehoods, by dressing up hideous phantoms of their own creation, presenting them to you under my name, to me under yours, and endeavoring to instil into our minds things concerning each other the most destitute of truth. And if there had been, at any time, a moment when we were off our guard, and in a temper to let the whispers of these people make us forget what we had known of each other for so many years, and years of so much trial, yet all men, who have attended to the workings of the human mind, who have seen the false colors under which passion sometimes dresses the actions and motives of others, have seen also those passions subsiding with time and reflection, dissipating like mists before the rising sun, and restoring to us the sight of all things in their true shape and colors. It would be strange, indeed, if, at our years, we were to go an age back to hunt up imaginary or forgotten facts, to disturb the repose of affections so sweetening to the evening of our lives. Be assured, my dear Sir, that I am incapable of receiving the slightest impression from the effort now made to plant thorns on the pillow of age, worth, and wisdom, and to sow tares between friends who have been such for near half a century. Beseeching you, then, not to suffer your mind to be disquieted by this wicked attempt to poison its peace, and praying you to throw it by among the things which have never happened, I add sincere assurances of my unabated and constant attachment, friendship, and respect.
Th: Jefferson.
TO THE PRESIDENT.
Monticello, October 24,1823.
Dear Sir,
The question presented by the letters you have sent me, is the most momentous which has ever been offered to my contemplation since that of Independence. That made us a nation, this sets our compass, and points the course which we are to steer through the ocean of time opening on us. And never could we embark on it under circumstances more auspicious. Our first and fundamental maxim should be, never to entangle ourselves in the broils of Europe. Our second, never to suffer Europe to intermeddle with cis-Atlantic affairs. America, North and South, has a set of interests distinct from those of Europe, and peculiarly her own.
She should therefore have a system of her own, separate and apart from that of Europe. While the last is laboring to become the domicile of despotism, our endeavor should surely be, to make our hemisphere that of freedom. One nation, most of all, could disturb us in this pursuit; she now offers to lead, aid, and accompany us in it. By acceding to her proposition, we detach her from the band of despots, bring her mighty weight into the scale of free government, and emancipate a continent at one stroke, which might otherwise linger long in doubt and difficulty. Great Britain is the nation which can do us the most harm of any one, or all, on earth; and with her on our side we need not fear the whole world. With her, then, we should most sedulously cherish a cordial friendship; and nothing would tend more to knit our affections, than to be fighting once more, side by side, in the same cause. Not that I would purchase even her amity at the price of taking part in her wars. But the war in which the present proposition might engage us, should that be its consequence, is not her war, but ours. Its object is to introduce and establish the American system, of keeping out of our land all foreign powers, of never permitting those of Europe to intermeddle with the affairs of our nations. It is to maintain our own principle, not to depart from it. And if, to facilitate this, we can effect a division in the body of the European powers, and draw over to our side its most powerful member, surely we should do it. But I am clearly of Mr. Canning’s opinion, that it will prevent instead of provoking war. With Great Britain withdrawn from their scale, and shifted into that of our two continents, all Europe combined would not undertake such a war. For how would they propose to get at either enemy without superior fleets? Nor is the occasion to be slighted which this proposition offers, of declaring our protest against the atrocious violations of the rights of nations, by the interference of any one in the internal affairs of another, so flagitiously begun by Bonaparte, and now continued by the equally lawless Alliance, calling itself Holy.
But we have first to ask ourselves a question. Do we wish to acquire to our own confederacy any one or more of the Spanish provinces? I candidly confess, that I have ever looked on Cuba as the most interesting addition which could ever be made to our system of States. The control which, with Florida Point, this island would give us over the Gulf of Mexico, and the countries and isthmus bordering on it, as well as all those whose waters flow into it, would fill up the measure of our political well-being. Yet, as I am sensible that this can never be obtained, even with her own consent, but by war; and its independence, which is our second interest (and especially its independence of England), can be secured without it, I have no hesitation in abandoning my first wish to future chances, and accepting its independence, with peace and the friendship of England, rather than its association, at the expense of war and her enmity.
I could honestly, therefore, join in the declaration proposed, that we aim not at the acquisition of any of those possessions, that we will not stand in the way of any amicable arrangement between them and the mother country; but that we will oppose, with all our means, the forcible interposition of any other power, as auxiliary, stipendiary, or under any other form or pretext, and most especially, their transfer to any power by conquest, cession, or acquisition in any other way. I should think it, therefore, advisable, that the Executive should encourage the British government to a continuance in the dispositions expressed in these letters, by an assurance of his concurrence with them as far as his authority goes; and that as it may lead to war, the declaration of which requires an act of Congress, the case shall be laid before them for consideration at their first meeting, and under the reasonable aspect in which it is seen by himself.
I have been so long weaned from political subjects, and have so long ceased to take any interest in them, that I am sensible I am not qualified to offer opinions on them worthy of any attention. But the question now proposed involves consequences so lasting, and effects so decisive of our future destinies, as to re-kindle all the interest I have heretofore felt on such occasions, and to induce me to the hazard of opinions, which will prove only my wish to contribute still my mite towards any thing which may be useful to our country. And praying you to accept it at only what it is worth, I add the assurance of my constant and affectionate friendship and respect.
Th: Jefferson.
TO THE MARQUIS DE LA FAYETTE.
Monticello, November 4, 1823.
My Dear Friend,
Two dislocated wrists and crippled fingers have rendered writing so slow and laborious, as to oblige me to withdraw from nearly all correspondence: not, however, from yours, while I can make a stroke with a pen. We have gone through too many trying scenes together, to forget the sympathies and affections they nourished.
Your trials have indeed been long and severe. When they will end, is yet unknown, but where they will end, cannot be doubted. Alliances, Holy or Hellish, may be formed, and retard the epoch of deliverance, may swell the rivers of blood which are yet to flow, but their own will close the scene, and leave to mankind the right of self-government. I trust that Spain will prove, that a nation cannot be conquered which determines not to be so, and that her success will be the turning of the tide of liberty, no more to be arrested by human efforts. Whether the state of society in Europe can bear a republican government, I doubted, you know when with you, and I do now. A hereditary chief, strictly limited, the right of war vested in the legislative body, a rigid economy of the public contributions, and absolute interdiction of all useless expenses, will go far towards keeping the government honest and unoppressive. But the only security o£ all, is in a free press. The force of public opinion cannot be resisted, when permitted freely to be expressed. The agitation it produces must be submitted to. It is necessary to keep the waters pure.
We are all, for example, in agitation even in our peaceful country. For in peace as well as in war, the mind must be kept in motion. Who is to be the next President, is the topic here of every conversation. My opinion on that subject is what I expressed to you in my last letter. The question will be ultimately reduced to the northernmost and southernmost candidates. The former will get every federal vote in the Union, and many republicans; the latter, all those denominated of the old school; for you are not to believe that these two parties are amalgamated, that the lion and the lamb are lying down together. The Hartford convention, the victory of Orleans, the peace of Ghent, prostrated the name of federalism. Its votaries abandoned it through shame and mortification; and now call themselves republicans. But the name alone is changed, the principles are the same. For in truth, the parties of Whig and Tory are those of nature. They exist in all countries, whether called by these names, or by those of Aristocrats and Democrats, Cote Droite and Cote Gauche, Ultras and Radicals, Serviles and Liberals. The sickly, weakly, timid man, fears the people, and is a tory by nature. The healthy, strong, and bold, cherishes them, and is formed a whig by nature. On the eclipse of federalism with us, although not its extinction, its leaders got up the Missouri question, under the false front of lessening the measure of slavery, but with the real view of producing a geographical division of parties, which might insure them the next President. The people of the north went blindfold into the snare, followed their leaders for a while with a zeal truly moral and laudable, until they became sensible that they were injuring instead of aiding the real interests of the slaves, that they had been used, merely as tools for electioneering purposes; and that trick of hypocrisy then fell as quickly as it had been got up. To that is now succeeding a distinction, which, like that of republican and federal, or whig and tory, being equally intermixed through every State, threatens none of those geographical schisms which go immediately to a separation. The line of division now is the preservation of State rights as reserved in the constitution, or by strained constructions of that instrument, to merge all into a consolidated government. The tories are for strengthening the executive and General Government; the whigs cherish the representative branch, and the rights reserved by the States, as the bulwark against consolidation, which must immediately generate monarchy. And although this division excites, as yet, no warmth, yet it exists, is well understood, and will be a principle of voting at the ensuing election, with the reflecting men of both parties.
I thank you much for the two books you were so kind as to send me by Mr. Gallatin. Miss Wright had before favored me with the first edition of her American work: but her ‘Few Days in Athens,’ was entirely new, and has been a treat to me of the highest order. The matter and manner of the dialogue is strictly ancient; the principles of the sects are beautifully and candidly explained and contrasted; and the scenery and portraiture of the interlocutors are of higher finish than any thing in that line left us by the ancients; and like Ossian, if not ancient, it is equal to the best morsels of antiquity. I augur, from this instance, that Herculaneum is likely to furnish better specimens of modern than of ancient genius; and may we not hope more from the same pen?
After much sickness, and the accident of a broken and disabled arm, I am again in tolerable health, but extremely debilitated, so as to be scarcely able to walk into my garden. The hebitude of age too, and extinguishment of interest in the things around me, are weaning me from them, and dispose me with cheerfulness to resign them to the existing generation, satisfied that the daily advance of science will enable them to administer the commonwealth with increased wisdom. You have still many valuable years to give to your country, and with my prayers that, they may be years of health and happiness, and especially that they may see the establishment of the principles of government which you have cherished through life, accept the assurance of my affectionate and constant friendship and respect.
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOSEPH C CABELL.
Monticello, February 3, 1824.
Dear Sir,
I am favored with your two letters of January the 26th and 29th, and am glad that yourself and the friends of the University are so well satisfied, that the provisos amendatory of the University Act are mere nullities. I had not been able to put out of my head the Algebraical equation, which was among the first of my college lessons, that a-a = 0. Yet I cheerfully arrange myself to your opinions. I did not suppose, nor do I now suppose it possible, that both Houses of the legislature should ever consent, for an additional fifteen thousand dollars of revenue, to set all the Professors and students of the University adrift: and if foreigners will have the same confidence which we have in our legislature, no harm will have been done by the provisos.
You recollect that we had agreed that the Visitors who are of the legislature should fix on a certain day of meeting, after the rising of the Assembly, to put into immediate motion the measures which this act was expected to call for. You will of course remind the Governor that a re-appointment of Visitors is to be made on the day following Sunday, the 29th of this month; and as he is to appoint the day of their first meeting, it would be well to recommend to him that which our brethren there shall fix on. It may be designated by the Governor as the third, fourth, &c. day after the rising of the legislature, which will give it certainty enough.
You ask what sum would be desirable for the purchase of books and apparatus. Certainly the largest you can obtain. Forty or fifty thousand dollars would enable us to purchase the most essential books of text and reference for the schools, and such an apparatus for Mathematics, Astronomy, and Chemistry, as may enable us to set out with tolerable competence, if we can, through the banks and otherwise, anticipate the whole sum at once.
I remark what you say on the subject of committing ourselves to any one for the Law appointment. Your caution is perfectly just. I hope, and am certain, that this will be the standing law of discretion and duty with every member of our board, in this and all cases. You know we have all, from the beginning, considered the high qualifications of our Professors, as the only means by which we can give to our institution splendor and pre-eminence over all its sister seminaries. The only question, therefore, we can ever ask ourselves, as to any candidate, will be, Is he the most highly qualified? The college of Philadelphia has lost its character of primacy by indulging motives of favoritism and nepotism, and by conferring the appointments as if the professorships were entrusted to them as provisions for their friends. And even that of Edinburgh, you know, is also much lowered from the same cause. We are next to observe, that a man is not qualified for a Professor, knowing nothing but merely his own profession. He should be otherwise well educated as to the sciences generally; able to converse understandingly with the scientific men with whom he is associated, and to assist in the councils of the Faculty on any subject of science on which they may have occasion to deliberate. Without this, he will incur their contempt, and bring disreputation on the institution. With respect to the professorship you mention, I scarcely know any of our judges personally; but I will name, for example, the late Judge Roane, who, I believe, was generally admitted to be among the ablest of them. His knowledge was confined to the common law chiefly, which does not constitute one half of the qualification of a really learned lawyer, much less that of a Professor of law for an University. And as to any other branches of science, he must have stood mute in the presence of his literary associates, or of any learned strangers or others visiting the University. Would this constitute the splendid stand we propose to take?
In the course of the trusts I have exercised through life with powers of appointment, I can say with truth, and with unspeakable comfort, that I never did appoint a relation to office, and that merely because I never saw the case in which some one did not offer, or occur, better qualified; and I have the most unlimited confidence, that in the appointment of Professors to our nursling institution, every individual of my associates will look with a single eye to the sublimation of its character, and adopt, as our sacred motto, ‘Detur digniori? In this way it will honor us, and bless our country.
I perceive that I have permitted my reflections to run into generalities beyond the scope of the particular intimation in your letter I will let them go, however, as a general confession of faith, not belonging merely to the present case.
Name me affectionately to our brethren with you, and be assured yourself of my constant friendship and respect.
Th: Jefferson.
TO JARED SPARKS.
Monticello, February 4, 1824.
Dear Sir,
I duly received your favor of the 3th, and with it the last number of the North American Review. This has anticipated the one I should receive in course, but have not yet received, under my subscription to the new series. The article on the African colonization of the people of color, to which you invite my attention, I have read with great consideration. It is, indeed, a fine one, and will do much good. I learn from it more, too, than I had before known, of the degree of success and promise of that colony.
In the disposition of these unfortunate people, there are two rational objects to be distinctly kept in view. 1. The establishment of a colony on the coast of Africa, which may introduce among the aborigines the arts of cultivated life, and the blessings of civilization and science. By doing this, we may make to them some retribution for the long course of injuries we have been committing on their population. And considering that these blessings will descend to the ‘nati natorum, et qui nascentur ab illis,’ we shall in the long run have rendered them perhaps more good than evil. To fulfil this object, the colony of Sierra Leone promises well, and that of Mesurado adds to our prospect of success. Under this view, the Colonization Society is to be considered as a missionary society, having in view, however, objects more humane, more justifiable, and less aggressive on the peace of other nations, than the others of that appellation.
The second object, and the most interesting to us, as coming home to our physical and moral characters, to our happiness and safety, is to provide an asylum to which we can, by degrees, send the whole of that population from among us, and establish them under our patronage and protection, as a separate, free, and independent people, in some country and climate friendly to human life and happiness. That any place on the coast of Africa should answer the latter purpose, I have ever deemed entirely impossible. And without repeating the other arguments which have been urged by others, I will appeal to figures only, which admit no controversy. I shall speak in round numbers, not absolutely accurate, yet not so wide from truth as to vary the result materially. There are in the United States a million and a half of people of color in slavery. To send off the whole of these at once, nobody conceives to be practicable for us, or expedient for them. Let us take twenty-five years for its accomplishment, within which time they will be doubled. Their estimated value as property, in the first place, (for actual property has been lawfully vested in that form, and who can lawfully take it from the possessors?) at an average of two hundred dollars each, young and old, would amount to six hundred millions of dollars, which must be paid or lost by somebody. To this, add the cost of their transportation by land and sea to Mesurado, a year’s provision of food and clothing, implements of husbandry and of their trades, which will amount to three hundred millions more, making thirty-six millions of dollars a year for twenty-five years, with insurance of peace all that time, and it is impossible to look at the question a second time. I am aware that at the end of about sixteen years, a gradual detraction from this sum will commence, from the gradual diminution of breeders, and go on during the remaining nine years. Calculate this deduction, and it is still impossible to look at the enterprise a second time. I do not say this to induce an inference that the getting rid of them is for ever impossible. For that is neither my opinion nor my hope. But only that it cannot be done in this way. There is, I think, a way in which it can be done; that is, by emancipating the after born, leaving them, on due compensation, with their mothers, until their services are worth their maintenance, and then putting them to industrious occupations, until a proper age for deportation. This was the result of my reflections on the subject five and forty years ago, and I have never yet been able to conceive any other practicable plan. It was sketched in the Notes on Virginia, under the fourteenth query. The estimated value of the new-born infant is so low (say twelve dollars and fifty cents), that it would probably be yielded by the owner gratis, and would thus reduce the six hundred millions of dollars, the first head of expense, to thirty-seven millions and a half: leaving only the expenses of nourishment while with the mother, and of transportation. And from what fund are these expenses to be furnished? Why not from that of the lands which have been ceded by the very States now needing this relief? And ceded on no consideration, for the most part, but that of the general good of the whole. These cessions already constitute one fourth of the States of the Union. It may be said that these lands have been sold; are now the property of the citizens composing those States; and the money long ago received and expended. But an equivalent of lands in the territories since acquired may be appropriated to that object, or so much at least, as may be sufficient; and the object, although more important to the slave States, is highly so to the others also, if they were serious in their arguments on the Missouri question. The slave States, too, if more interested, would also contribute more by their gratuitous liberation, thus taking on themselves alone the first and heaviest item of expense.
In the plan sketched in the Notes on Virginia, no particular place of asylum was specified; because it was thought possible, that in the revolutionary state of America, then commenced, events might open to us some one within practicable distance. This has now happened. St. Domingo has become independent, and with a population of that color only; and if the public papers are to be credited, their Chief offers to pay their passage, to receive them as free citizens, and to provide them employment. This leaves, then, for the general confederacy, no expense but of nurture with the mother a few years, and would call, of course, for a very moderate appropriation of the vacant lands. Suppose the whole annual increase to be of sixty thousand effective births, fifty vessels, of four hundred tons burthen each, constantly employed in that short run, would carry off the increase of every year, and the old stock would die off in the ordinary course of nature, lessening from the commencement until its final disappearance. In this way no violation of private rights is proposed. Voluntary surrenders would probably come in as fast as the means to be provided for their care would be competent to it. Looking at my own State only, (and I presume not to speak for the others,) I verily believe that this surrender of property would not amount to more, annually, than half our present direct taxes, to be continued fully about twenty or twenty-five years, and then gradually diminishing for as many more until their final extinction; and even this half tax would not be paid in cash, but by the delivery of an object which they have never yet known or counted as part of their property: and those not possessing the object will be called on for nothing. I do not go into all the details of the burthens and benefits of this operation. And who could estimate its blessed effects? I leave this to those who will live to see their accomplishment, and to enjoy a beatitude forbidden to my age. But I leave it with this admonition, to rise and be doing. A million and a half are within their control; but six millions (which a majority of those now living will see them attain), and one million of these fighting men, will say, ‘We will not go.’
I am aware that this subject involves some constitutional scruples. But a liberal construction, justified by the object, may go far, and an amendment of the constitution, the whole length necessary. The separation of infants from their mothers, too, would produce some scruples of humanity. But this would be straining at a gnat, and swallowing a camel.
I am much pleased to see that you have taken up the subject of the duty on imported books. I hope a crusade will be kept up against it, until those in power shall become sensible of this stain on our legislation and shall wipe it from their code, and from the remembrance of man, if possible.
I salute you with assurances of high respect and esteem.
Th: Jefferson
TO EDWARD LIVINGSTON.
Monticello, April 4, 1824.
Dear Sir,
It was with great pleasure I learned that the good people of New Orleans had restored you again to the councils of our country. I did not doubt the aid it would bring to the remains of our old school in Congress, in which your early labors had been so useful. You will find, I suppose, on revisiting our maritime States, the names of things more changed than the things themselves; that though our old opponents have given up their appellation, they have not, in assuming ours, abandoned their views, and that they are as strong nearly as they ever were. These cares, however, are no longer mine. I resign myself cheerfully to the managers of the ship, and the more contentedly, as I am near the end of my voyage. I have learned to be less confident in the conclusions of human reason, and give more credit to the honesty of contrary opinions. The radical idea of the character of the constitution of our government, which I have adopted as a key in cases of doubtful construction, is, that the whole field of government is divided into two departments, domestic and foreign, (the States in their mutual relations being of the latter) that the former department is reserved exclusively to the respective States within their own limits, and the latter assigned to a separate set of functionaries, constituting what may be called the, foreign branch, which, instead of a federal basis, is established as a distinct government quo ad hoc, acting as the domestic branch does on the citizens directly and coercively; that these departments have distinct directories, co-ordinate, and equally independent and supreme, each within its own sphere of action. Whenever a doubt arises to which of these branches a power belongs, I try it by this test. I recollect no case where a question simply between citizens of the same State has been transferred to the foreign department, except that of inhibiting tenders but of metallic money, and ex post facto legislation. The causes of these singularities are well remembered.
I thank you for the copy of your speech on the question of national improvement, which I have read with great pleasure, and recognise in it those powers of reasoning and persuasion of which I had formerly seen from you so many proofs. Yet, in candor, I must say it has not removed, in my mind, all the difficulties of the question. And I should really be alarmed at a difference of opinion with you, and suspicious of my own, were it not that I have, as companions in sentiment, the Madisons, the Monroes, the Randolphs, the Macons, all good men and true, of primitive principles. In one sentiment of the speech I particularly concur. ‘If we have a doubt relative to any power, we ought not to exercise it.’ When we consider the extensive and deep-seated opposition to this assumption, the conviction entertained by so many, that this deduction of powers by elaborate construction prostrates the rights reserved to the States, the difficulties with which it will rub along in the course of its exercise; that changes of majorities will be changing the system backwards and forwards, so that no undertaking under it will be safe; that there is not a State in the Union which would not give the power willingly, by way of amendment, with some little guard, perhaps, against abuse; I cannot but think it would be the wisest course to ask an express grant of the power. A government held together by the bands of reason only, requires much compromise of opinion; that things even salutary should not be crammed down the throats of dissenting brethren, especially when they may be put into a form to be willingly swallowed, and that a great deal of indulgence is necessary to strengthen habits of harmony and fraternity. In such a case, it seems to me it would be safer and wiser to ask an express grant of the power. This would render its exercise smooth and acceptable to all, and insure to it all the facilities which the could contribute, to prevent that kind of abuse which all will fear, because all know it is so much practised in public bodies, I mean the bartering of votes. It would reconcile every one, if limited by the proviso, that the federal proportion of each State should be expended within the State. With this single security against partiality and corrupt bargaining, I suppose there is not a State, perhaps not a man in the Union, who would not consent to add this to the powers of the General Government. But age has weaned me from questions of this kind. My delight is now in the passive occupation of reading; and it is with great reluctance I permit my mind ever to encounter subjects of difficult investigation. You have many years yet to come of vigorous activity, and I confidently trust they will be employed in cherishing every measure which may foster our brotherly union, and perpetuate a constitution of government destined to be the primitive and precious model of what is to change the condition of man over the globe. With this confidence, equally strong in your powers and purposes, I pray you to accept the assurance of my cordial esteem and respect.
Th: Jefferson.
TO MAJOR JOHN CARTWRIGHT.
Monticello, June 5,1824.
Dear and Venerable Sir,
I am much indebted for your kind letter of February the 29th, and for your valuable volume on the English constitution. I have, read this with pleasure and much approbation, and think it has deduced the constitution of the English nation from its rightful root, the Anglo-Saxon, it is really wonderful, that so many able and learned men should have failed in their attempts to define it with correctness. No wonder then, that Paine, who thought more than he read, should have credited the great authorities who have declared, that the will of Parliament is the constitution of England. So Marbois, before the French revolution, observed to me, that the Almanac Royal was the constitution of France. Your derivation of it from the Anglo-Saxons, seems to be made on legitimate principles. Having driven out the former inhabitants of that part of the island called England, they became aborigines as to you, and your lineal ancestors. They doubtless had a constitution; and although they have not left it in a written formula, to the precise text of which you may always appeal, yet they have left fragments of their history and laws, from which it may be inferred with considerable certainty. Whatever their history and laws show to have been practised with approbation, we may presume was permitted by their constitution; whatever was not so practised, was not permitted. And although this constitution was violated and set at nought by Norman force, yet force cannot change right. A perpetual claim was kept up by the nation, by their perpetual demand of a restoration of their Saxon laws; which shows they were never relinquished by the will of the nation. In the pullings and haulings for these ancient rights, between the nation, and its kings of the races of Plantagenets, Tudors, and Stuarts, there was sometimes gain, and sometimes loss, until the final re-conquest of their rights from the Stuarts. The destitution and expulsion of this race broke the thread of pretended inheritance extinguished all regal usurpations, and the nation reentered into all its rights; and although in their bill of rights they specifically reclaimed some only, yet the omission of the others was no renunciation of the right to assume their exercise also, whenever occasion should occur. The new King received no rights or powers, but those expressly granted to him. It has ever appeared to me, that the difference between the whig and the tory of England is, that the whig deduces his rights from the Anglo-Saxon source, and the tory from the Norman. And Hume, the great apostle of toryism, says in so many words, (note AA to chapter 42,) that, in the reign of the Stuarts, ‘it was the people who encroached upon the sovereign, not the sovereign who attempted, as is pretended, to usurp upon the people.’ This supposes the Norman usurpations to be rights in his successors. And again, (C. 159,) ‘the Commons established a principle, which is noble in itself, and seems specious, but is belied by all history and experience, that the people are the origin of all just power.’ And where else will this degenerate son of science, this traitor to his fellow-men, find the origin of just powers, if not in the majority of the society? Will it be in the minority? Or in an individual of that minority?
Our revolution commenced on more favorable ground. It presented us an album on which we were free to write what we pleased. We had no occasion to search into musty records, to hunt up royal parchments, or to investigate the laws and institutions of a semi-barbarous ancestry. We appealed to those of nature, and found them engraved on our hearts. Yet we did not avail ourselves of all the advantages of our position. We had never been permitted to exercise self-government. When forced to assume it, we were novices in its science. Its principles and forms had entered little into our former education. We established however some, although not all its important principles. The constitutions of most of our States assert, that all power is inherent in the people; that they may exercise it by themselves, in all cases to which they think themselves competent (as in electing their functionaries, executive and legislative, and deciding by a jury of themselves, in all judiciary cases in which any fact is involved), or they may act by representatives, freely and equally chosen; that it is their right and duty to be at all times armed; that they are entitled to freedom of person, freedom of religion, freedom of property, and freedom of the press. In the structure of our legislatures, we think experience has proved the benefit of subjecting questions to two separate bodies of deliberants; but in constituting these, natural right has been mistaken, some making one of these bodies, and some both, the representatives of property instead of persons; whereas the double deliberation might be as well obtained without any violation of true principle, either by requiring a greater age in one of the bodies, or by electing a proper number of representatives of persons, dividing them by lots into two chambers, and renewing the division at frequent intervals, in order to break up all cabals. Virginia, of which I am myself a native and resident, was not only the first of the States, but, I believe I may say, the first of the nations of the earth, which assembled its wise men peaceably together to form a fundamental constitution, to commit it to writing, and place it among their archives, where every one should be free to appeal to its text. But this act was very imperfect. The other States, as they proceeded successively to the same work, made successive improvements; and several of them, still further corrected by experience, have, by conventions, still further amended their first forms. My own State has gone on so far with its première ébauch; but it is now proposing to call a convention for amendment. Among other improvements, I hope they will adopt the subdivision of our counties into wards. The former may be estimated at an average of twenty-four miles square; the latter should be about six miles square each, and would answer to the hundreds of your Saxon Alfred. In each of these might be, 1. An elementary school. 2. A company of militia, with its officers. 3. A justice of the peace and constable. 4. Each ward should take care of their own poor. 5. Their own roads. 6. Their own police. 7. Elect within themselves one or more jurors to attend the courts of justice. And, 8. Give in at their Folk-house, their votes for all functionaries reserved to their election. Each ward would thus be a small republic within itself, and every man in the State would thus become an acting member of the common government, transacting in person a great portion of its rights and duties, subordinate indeed, yet important and entirely within his competence. The wit of man cannot devise a more solid basis for a free, durable, and well-administered republic.
With respect to our State and federal governments, I do not think their relations correctly understood by foreigners. They generally suppose the former subordinate to the latter. But this is not the case. They are co-ordinate departments of one simple and integral whole. To the State governments, are reserved all legislation and administration, in affairs which concern their own citizens only, and to the federal government is given whatever concerns foreigners, or the citizens of other States; these functions alone being made federal. The one is the domestic, the other the foreign branch of the same government; neither having control over the other, but within its own department. There are one or two exceptions only to this partition of power. But you may ask, if the two departments should claim each the same subject of power, where is the common umpire to decide ultimately between them? In cases of little importance or urgency, the prudence of both parties will keep them aloof from the questionable ground: but if it can neither be avoided nor compromised, a convention of the States must be called, to ascribe the doubtful power to that department which they may think best. You will perceive by these details, that we have not yet so far perfected our constitutions as to venture to make them unchangeable. But still, in their present state, we consider them not otherwise changeable than by the authority of the people, on a special election of representatives for that purpose expressly: they are until then the lex legum.
But can they be made unchangeable? Can one generation bind another, and all others, in succession for ever? I think not. The Creator has made the earth for the living, not the dead. Rights and powrers can only belong to persons, not to things, not to mere matter, unendowed with will. The dead are not even things. The particles of matter which composed their bodies, make part now of the bodies of other animals, vegetables, or minerals, of a thousand forms. To what then are attached the rights and powers they held while in the form of men? A generation may bind itself as long as its majority continues in life; when that has disappeared, another majority is in place, holds all the rights and powers their predecessors once held, and may change their laws and institutions to suit themselves. Nothing then is unchangeable but the inherent and unalienable rights of man.
I was glad to find in your book a formal contradiction, at length, of the judiciary usurpation of legislative powers; for such the judges have usurped in their repeated decisions, that Christianity is a part of the common law. The proof of the contrary, which you have adduced, is incontrovertible; to wit, that the common law existed while the Anglo-Saxons were yet Pagans, at a time when they had never yet heard the name of Christ pronounced, or knew that such a character had ever existed. But it may amuse you, to show when, and by what means, they stole this law in upon us. In a case of quare impedit in the Year-book, 34. H. 6. folio 38. (anno 1458,) a question was made, how far the ecclesiastical law was to be respected in a common law court. And Prisot, Chief Justice, gives his opinion in these words. ‘A tiel leis qu’ils de seint eglise ont enancien scripture, covient a nous a donner credence; car ceo common ley stir quels touts manners leis sont fondes. Et auxy, Sir, nous sumus obliges de conustre lour ley de saint eglise: et semblablement ils sont obliges de conustre nostre ley. Et, Sir, si poit apperer or a nous que Pevesque ad fait come un ordinary fera en tiel cas, adong nous devons ceo adju-ger bon,ou auterment nemy,’ &c. See S. C. Fitzh.Abr. Qu. imp. 89. Bro. Abr. Qu. imp. 12. Finch in his first book, c. 3. is the first afterwards who quotes this case, and mistakes it thus. ‘To such laws of the church as have warrant in holy scripture, our law giveth credence.’ And cites Prisot; mistranslating ‘ancien scripture’ into ‘holy scripture.’ Whereas, Prisot palpably says, ‘to such laws as those of holy church have in ancient writing, it is proper for us to give credence;’ to wit, to their ancient written laws. This was in 1613, a century and a half after the dictum of Prisot. Wingate, in 1658, erects this false translation into a maxim of the common law, copying the words of Finch, but citing Prisot. Wing. Max. 3. and Sheppard, title, ‘Religion,’ in 1675, copies the same mistranslation, quoting the Y. B. Finch and Win-gate. Hale expresses it in these words; ‘Christianity is parcel of the laws of England.’ 1 Ventr. 293, 3 Keb. 607. But he quotes no authority. By these echoings and re-echoings from one to another, it had become so established in 1728, that in the case of the King vs. Woolston, 2 Stra. 834, the court would not suffer it to be debated, whether to write against Christianity was punishable in the temporal court at common law. Wood, therefore, 409, ventures still to vary the phrase and say, that all blasphemy and profaneness are offences by the common law; and cites 2 Stra. Then Blackstone, in 1763, IV. 59, repeats the words of Hale, that ‘Christianity is part of the laws of England,’ citing Ventris and Strange. And finally, Lord Mansfield, with a little qualification, in Evans’s case, in 1767, says, that ‘the essential principles of revealed religion are part of the common law.’ Thus ingulphing Bible, Testament, and all into the common law, without citing any authority. And thus we find this chain of authorities hanging link by link, one upon another, and all ultimately on one and the same hook, and that a mistranslation of the words ‘ancien scripture,’ used by Prisot. Finch quotes Prisot; Wingate does the same. Sheppard quotes Prisot, Finch, and Wingate. Hale cites nobody. The court, in Woolston’s case, cite Hale. Wood cites Woolston’s case. Blackstone quotes Woolston’s case and Hale. And Lord Mansfield, like Hale, ventures it on his own authority. Here I might defy the best read lawyer to produce another scrip of authority for this judiciary forgery; and I might go on further to show, how some of the Anglo-Saxon priests interpolated into the text of Alfred’s laws, the 20th, 21st, 22nd, and 23rd chapters of Exodus, and the 15th of the Acts of the Apostles, from the 23rd to the 29th verses. But this would lead my pen and your patience too far. What a conspiracy this, between Church and State! Sing Tantarara, rogues all, rogues all, Sing Tantarara, rogues all!
I must still add to this long and rambling letter, my acknowledgments for your good wishes to the University we are now establishing in this State. There are some novelties in it. Of that of a professorship of the principles of government, you express your approbation. They will be founded in the rights of man. That of agriculture, I am sure, you will approve: and that also of Anglo-Saxon. As the histories and laws left us in that type and dialect, must be the text-books of the reading of the learners, they will imbibe with the language their free principles of government. The volumes you have been so kind as to send, shall be placed in the library of the University. Having at this time in England a person sent for the purpose of selecting some Professors, a Mr. Gilmer of my neighborhood, I cannot but recommend him to your patronage, counsel, and guardianship, against imposition, misinformation, and the deceptions of partial and false recommendations, in the selection of characters. He is a gentleman of great worth and correctness, my particular friend, well educated in various branches of science, and worthy of entire confidence.
Your age of eighty-four and mine of eighty-one years, insure us a speedy meeting. We may then commune at leisure, and more fully, on the good and evil, which in the course of our long lives, we have.both witnessed; and in the mean time, I pray you to accept assurances of my high veneration and esteem for your person and character.
Th: Jefferson.
TO MARTIN VAN BUREN.
Monticello, June 29, 1824.
Dear Sir,
I have to thank you for Mr. Pickering’s elaborate philippic against Mr. Adams, Gerry, Smith, and myself; and I have delayed the acknowledgment until I could read it and make some observations on it.
I could not have believed, that for so many years, and to such a period of advanced age, he could have nourished passions so vehement and viperous. It appears, that for thirty years past, he has been industriously collecting materials for vituperating the characters he had marked for his hatred; some of whom certainly, if enmities towards him had ever existed, had forgotten them all, or buried them in the grave with themselves. As to myself, there never had been any thing personal between us, nothing but the general opposition of party sentiment; and our personal intercourse had been that of urbanity, as himself says. But it seems he has been all this time brooding over an enmity which I had never felt, and that with respect to myself, as well as others, he has been writing far and near, and in every direction, to get hold of original letters, where he could, copies, where he could not, certificates and journals, catching at every gossipping story he could hear of in any quarter, supplying by suspicions what he could find no where else, and then arguing on this motley farrago, as if established on gospel evidence. And while expressing his wonder, ‘at the age of eighty-eight, the strong passions of Mr. Adams should not have cooled ‘; that on the contrary, ‘they had acquired the mastery of his soul,’ (p. 100 ;) that ‘where these were enlisted, no reliance could be placed on his statements,’ (p. 104 ;) the facility and little truth with which he could represent facts and occurrences, concerning persons who were the objects of his hatred, (p. 3 ;) that ‘he is capable of making the grossest misrepresentations, and, from detached facts, and often from bare suspicions, of drawing unwarrantable inferences,’ if suited to his purpose at the instant,’ (p. 174;) while making such charges, I say, on Mr. Adams, instead of his ‘ecce homo,’ (p. 100;) how justly might we say to him, ‘Mutato nomine, de te fabula narratur.’ For the assiduity and industry he has employed in his benevolent researches after matter of crimination against us, I refer to his pages 13, 14, 34, 36, 46, 71, 79, 90, bis. 92, 93, bis. 101, ter. 104, 116, 118, 141, 143, 146,150,151,153, 168, 171, 172. That Mr. Adams’s strictures on him, written and pointed, should have excited some notice on his part, was not perhaps to be wondered at. But the sufficiency of his motive for the large attack on me may be more questionable. He says, (p. 4) ‘of Mr. Jefferson I should have said nothing, but for his letter to Mr. Adams, of October the 12th, 1823.’ Now the object of that letter was to soothe the feelings of a friend, wounded by a publication which I thought an ‘outrage on private confidence.’ Not a word or allusion in it respecting Mr. Pickering, nor was it suspected that it would draw forth his pen in justification of this infidelity, which he has, however, undertaken in the course of his pamphlet, but more particularly in its conclusion.
He arraigns me on two grounds, my actions, and my motives. The very actions, however, which he arraigns, have been such as the great majority of my fellow-citizens have approved. The approbation of Mr. Pickering, and of those who thought with him, I had no right to expect. My motives he chooses to ascribe to hypocrisy, to ambition, and a passion for popularity. Of these the world must judge between us. It is no office of his or mine. To that tribunal I have ever submitted my actions and motives, without ransacking the Union for certificates, letters, journals, and gossiping tales, to justify myself and weary them. Nor shall I do this on the present occasion, but leave still to them these antiquated party diatribes, now newly revamped and paraded, as if they had not been already a thousand times repeated, refuted, and adjudged against him, by the nation itself. If no action is to be deemed virtuous for which malice can imagine a sinister motive, then there never was a virtuous action; no, not even in the life of our Savior himself. But he has taught us to judge the tree by its fruit, and to leave motives to him who can alone see into them.
But whilst I leave to its fate the libel of Mr. Pickering, with the thousands of others like it, to which I have given no other answer than a steady course of similar action, there are two facts or fancies of his which I must set to rights. The one respects Mr. Adams, the other myself. He observes, that my letter of October the 12th, 1823, acknowledges the receipt of one from Mr. Adams, of September the 18th, which, having been written a few days after Cunningham’s publication, he says was no doubt written to apologize to me for the pointed reproaches he had uttered against me in his confidential letters to Cunningham. And thus having ‘no doubt’ of his conjecture, he considers it as proven, goes on to suppose the contents of the letter (19, 22), makes it place Mr. Adams at my feet suing for pardon, and continues to rant upon it, as an undoubted fact. Now I do most solemnly declare, that so far from being a letter of apology, as Mr. Pickering so undoubtingly assumes, there was not a word or allusion in it respecting Cunningham’s publication.
The other allegation respecting myself, is equally false. In page 34, he quotes Doctor Stuart, as having, twenty years ago, informed him that General Washington, ‘when he became a private citizen,’ called me to account for expressions in a letter to Mazzei, requiring, in a tone of unusual severity, an explanation of that letter. He adds of himself, ‘in what manner the latter humbled himself, and appeased the just resentment of Washington, will never be known, as some time after his death, the correspondence was not to be found, and a diary for an important period of his Presidency was also missing.’ The diary being of transactions during his Presidency, the letter to Mazzei not known here until some time after he became a private citizen, and the pretended correspondence of course after that, I know not why this lost diary and supposed correspondence are brought together here, unless for insinuations worthy of the letter itself. The correspondence could not be found, indeed, because it had never existed. I do affirm, that there never passed a word, written or verbal, directly or indirectly, between General Washington and myself on the subject of that letter. He would never have degraded himself so far as to take to himself the imputation in that letter on the ‘Samsons in combat.’ The whole story is a fabrication, and I defy the framers of it, and all mankind, to produce a scrip of a pen between General Washington and myself on the subject, or any other evidence more worthy of credit than the suspicions, suppositions, and presumptions of the two persons here quoting and quoted for it. With Doctor Stuart I had not much acquaintance. I supposed him to be an honest man, knew him to be a very weak one, and, like Mr. Pickering, very prone to antipathies, boiling with party passions, and, under the dominion of these, readily welcoming fancies for facts. But, come the story from whomsoever it might, it is an unqualified falsehood.
This letter to Mazzei has been a precious theme of crimination for federal malice. It was a long letter of business, in which was inserted a single paragraph only of political information as to the state of our country. In this information there was not one word which would not then have been, or would not now be approved by every republican in the United States, looking back to those times, as you will see by a faithful copy now enclosed of the whole of what that letter said on the subject of the United States, or of its government. This paragraph, extracted and translated, got into a Paris paper at a time when the persons in power there were laboring under very general disfavor, and their friends were eager to catch even at straws to buoy them up. ‘To them, therefore, I have always imputed the interpolation of an entire paragraph additional to mine, which makes me charge my own country with ingratitude and injustice to France. There was not a word in my letter respecting France, or any of the proceedings or relations between this country and that. Yet this interpolated paragraph has been the burden of federal calumny, has been constantly quoted by them, made the subject of unceasing and virulent abuse, and is still quoted, as you see, by Mr. Pickering, (page 33,) as if it were genuine, and really written by me. And even Judge Marshall makes history descend from its dignity, and the ermine from its sanctity, to exaggerate, to record, and to sanction this forgery. In the very last note of his book, he says, ‘A letter from Mr. Jefferson to Mr. Mazzei, an Italian, was published in Florence, and republished in the Moniteur, with very severe strictures on the conduct of the United States.’ And instead of the letter itself, he copies what he says are the remarks of the editor, which are an exaggerated commentary on the fabricated paragraph itself, and silently leaves to his reader to make the ready inference that these were the sentiments of the letter. Proof is the duty of the affirmative side. A negative cannot be possibly proved. But, in defect of impossible proof of what was not in the original letter, I have its press-copy still in my possession. It has been shown to several, and is open to any one who wishes to see it. I have presumed only that the interpolation was done in Paris. But I never saw the letter in either its Italian or French dress, and it may have been done here, with the commentary handed down to posterity by the judge. The genuine paragraph, re-translated through Italian and French into English, as it appeared here in a federal paper, besides the mutilated hue which these translations and re-translations of it produced generally, gave a mistranslation of a single word, which entirely perverted its meaning, and made it a pliant and fertile text of misrepresentation of my political principles. The original, speaking of an Anglican, monarchical, and aristocratical party, which had sprung up since he had left us, states their object to be ‘to draw over us the substance, as they had already done the forms of the British government.’ Now the ‘forms’ here meant, were the levees, birth-days, the pompous cavalcade to the State House on the meeting of Congress, the formal speech from the throne, the procession of Congress in a body to re-echo the speech in an answer, &c. &c. But the translator here, by substituting form in the singular number, for forms in the plural, made it mean the frame or organization of our government, or its form of legislative, executive, and judiciary authorities, co-ordinate and independent: to which form it was to be inferred that I was an enemy. In this sense they always quoted it, and in this sense Mr. Pickering still quotes, it (pages 34, 35, 38), and countenances the inference. Now General Washington perfectly understood what I meant by these forms, as they were frequent subjects of conversation between us. When, on my return from Europe, I joined the government in March, 1790, at New York, I was much astonished, indeed, at the mimicry I found established of royal forms and ceremonies, and more alarmed at the unexpected phenomenon, by the monarchical sentiments I heard expressed and openly maintained in every company, and among others by the high members of the government, executive and judiciary (General Washington alone excepted), and by a great part of the legislature, save only some members who had been of the old Congress, and a very few of recent introduction. I took occasion, at various times, of expressing to General Washington my disappointment at these symptoms of a change of principle, and that I thought them encouraged by the forms and ceremonies, which I found prevailing, not at all in character with the simplicity of republican government, and looking as if wishfully to those of European courts. His general explanations to me were, that when he arrived at New York to enter on the executive administration of the new government, he observed to those who were to assist him, that placed as he was in an office entirely new to him, unacquainted with the forms and ceremonies of other governments, still less apprized of those which might be properly established here, and himself perfectly indifferent to all forms, he wished them to consider and prescribe what they should be; and the task was assigned particularly to General Knox, a man of parade, and to Colonel Humphreys, who had resided some time at a foreign court. They, he said, were the author’s of the present regulations, and that others were proposed so highly strained, that he absolutely rejected them. Attentive to the difference of opinion prevailing on this subject, when the term of his second election arrived, he called the Heads of departments together, observed to them the situation in which he had been at the commencement of the government, the advice he had taken, and the course he had observed in compliance with it; that a proper occasion had now arrived of revising that course, of correcting in it any particulars not approved in experience; and he desired us to consult together, agree on any changes we should think for the better, and that he should willingly conform to what we should advise. We met at my office. Hamilton and myself agreed at once that there was too much ceremony for the character of our government, and, particularly, that the parade of the installation at New York ought not to be copied on the present occasion, that the President should desire the Chief Justice to attend him at his chambers, that he should administer the oath of office to him in the presence of the higher officers of the government, and that the certificate of the fact should be delivered to the Secretary of State to be recorded. Randolph and Knox differed from us, the latter vehemently: they thought it not advisable to change any of the established forms, and we authorized Randolph to report our opinions to the President. As these opinions were divided, and no positive advice given as to any change, no change was made. Thus the forms, which I had censured in my letter to Mazzei, were perfectly understood by General Washington, and were those which he himself but barely tolerated. He had furnished me a proper occasion for proposing their reformation, and, my opinion not prevailing, he knew I could not have meant any part of the censure for him.
Mr. Pickering quotes too (page 34) the expression in the letter, of ‘the men who were Samsons in the field, and Solomons in the council, but who had had their heads shorn by the harlot England’ or, as expressed in their re-translation, the men who were Solomons in council, and Samsons in combat, but whose hair had been cut off by the whore England.’ Now this expression also was perfectly understood by General Washington. He knew that I meant it for the Cincinnati generally, and that, from what had passed between us at the commencement of that institution, I could not mean to include him. When the first meeting was called for its establishment, I was a member of the Congress then sitting at Annapolis. General Washington wrote to me, asking my opinion on that proposition, and the course, if any, which I thought Congress would observe respecting it. I wrote him frankly my own disapprobation of it; that I found the members of Congress generally in the same sentiment; that I thought they would take no express notice of it, but that in all appointments of trust, honor, or profit, they would silently pass by all candidates of that order, and give an uniform preference to others. On his way to the first meeting in Philadelphia, which I think was in the spring of 1784, he called on me at Annapolis. It was a little after candle-light, and he sat with me till after midnight, conversing, almost exclusively, on that subject. While he was feelingly indulgent to the motives which might induce the officers to promote it, he concurred with me entirely in condemning it; and when I expressed an idea that, if the hereditary quality were suppressed, the institution might perhaps be indulged during the lives of the officers now living, and who had actually served; ‘No,’ he said, ‘not a fibre of it ought, to be left, to be an eye-sore to the public, a ground of dissatisfaction, and a line of separation between them and their country’: and he left me with a determination to use all his influence for its entire suppression. On his return from the meeting, he called on me again, and related to me the course the thing had taken. He. said, that, from the beginning, he had used every endeavor to prevail on the officers to renounce the project altogether, urging the many considerations which would render it odious to their fellow-citizens, and disreputable and injurious to themselves; that he had at length prevailed on most of the old officers to reject it, although with great and warm opposition from others, and especially the younger ones, among whom he named Colonel W. S. Smith as particularly intemperate. But that in this state of things, when he thought the question safe, and the meeting drawing to a close, Major L’Enfant arrived from France with a bundle of eagles, for which he had been sent there, with letters from the French officers who had served in. America, praying for admission into the order, and a solemn act of their King permitting them to wear its ensign. This, he said, changed the face of matters at once, produced an entire revolution of sentiment, and turned the torrent so strongly in an opposite direction, that it could be no longer withstood: all he could then obtain, was a suppression of the hereditary quality. He added, that it was the French applications, and respect for the approbation of the King, which saved the establishment in its modified and temporary form. Disapproving thus of the institution as much as I did, and conscious that I knew him to do so, he could never suppose that I meant to include him among the Samsons in the field, whose object was to draw over us the form, as they made the letter say, of the British government, and especially its aristocractic member, an hereditary House of Lords. Add to this, that the letter saying, ‘that two out of the three branches of legislature were against us,’ was an obvious exception of him; it being well known that the majorities in the two branches of Senate and Representatives were the very instruments which carried, in opposition to the old and real republicans, the measures which were the subjects of condemnation in this letter. General Washington, then, understanding perfectly what and whom I meant to designate, in both phrases, and that they could not have any application or view to himself, could find in neither any cause of offence to himself; and therefore neither needed, nor ever asked any explanation of them from me. Had it even been otherwise, they must know very little of General Washington, who should believe to be within the laws of his character what Doctor Stuart is said to have imputed to him. Be this, however, as it may, the story is infamously false in every article of it. My last parting with General Washington was at the inauguration of Mr. Adams, in March, 1797, and was warmly affectionate; and I never had any reason to believe any change on his part, as there certainly was none on mine. But one session of Congress intervened between that and his death, the year following, in my passage to and from which, as it happened to be not convenient to call on him, I never had another opportunity; and as to the cessation of correspondence observed during that short interval, no particular circumstance occurred for epistolary communication, and both of us were too much oppressed with letter-writing, to trouble either the other, with a letter about nothing.
The truth is, that the federalists, pretending to be the exclusive friends of General Washington, have ever done what they could to sink his character, by hanging theirs on it, and by representing as the enemy of republicans him, who, of all men, is best entitled to the appellation of the father of that republic which they were endeavoring to subvert, and the republicans to maintain. They cannot deny, because the elections proclaimed the truth, that the great body of the nation approved the republican measures. General Washington was himself sincerely a friend to the republican principles of our constitution. His faith, perhaps, in its duration, might not have been as confident as mine; but he repeatedly declared to me, that he was determined it should have a fair chance for success, and that he would lose the last drop of his blood in its support, against any attempt which, might be made to change it from its republican form. He made these declarations the oftener, because he knew my suspicions that Hamilton had other views, and he wished to quiet my jealousies on this subject. For Hamilton frankly avowed, that he considered the British constitution, with all the corruptions of its administration, as the most perfect model of government which had ever been devised by the wit of man; professing, however, at the same time, that the spirit of this country was so fundamentally republican, that it would be visionary to think of introducing monarchy here, and that, therefore, it was the duty of its administrators to conduct it on the principles their constituents had elected.
General Washington, after the retirement of his first cabinet, and the composition of his second, entirely federal, and at the head of which was Mr. Pickering himself, had no opportunity of hearing both sides of any question. His measures, consequently, took more the hue of the party in whose hands he was. These measures were certainly not approved by the republicans; yet were they not imputed, to him, but to the counsellors around him; and his prudence so far restrained their impassioned course and bias, that no act of strong mark, during the remainder of his administration, excited much dissatisfaction. He lived too short a time after, and too much withdrawn from information, to correct the views into which he had been deluded; and the continued assiduities of the party drew him into the vortex of their intemperate career; separated him still farther from his real friends, and excited him to actions and expressions of dissatisfaction, which grieved them, but could not loosen their affections from him. They would not suffer the temporary aberration to weigh against the immeasurable merits of his life; and although they tumbled his seducers from their places, they preserved his memory embalmed in their hearts, with undiminished love and devotion; and there it for ever will remain embalmed, in entire oblivion of every temporary thing which might cloud the glories of his splendid life. It is vain, then, for Mr. Pickering and his friends to endeavor to falsify his character, by representing him as an enemy to republicans and republican principles, and as exclusively the friend of those who were so; and had he lived longer, he would have returned to his ancient and unbiassed opinions, would have replaced his confidence in those whom the people approved and supported, and would have seen that they were only restoring and acting on the principles of his own first administration.
I find, my dear Sir, that I have written you a very long letter or rather a history. The civility of having sent me a copy of Mr. Pickering’s diatribe, would scarcely justify its address to you. I do not publish these things, because my rule of life has been never to harass the public with fendings and provings of personal slanders; and least of all would I descend into the arena of slander with such a champion as Mr. Pickering. I have ever trusted to the justice and consideration of my fellow-citizens, and have no reason to repent it, or to change my course. At this time of life, too, tranquillity is the summum bonum. But although I decline all newspaper controversy, yet when falsehoods have been advanced, within the knowledge of no one so much as myself, I have sometimes deposited a contradiction in the hands of a friend, which, if worth preservation, may, when I am no more, nor those whom I might offend, throw light on history, and recall that into the path of truth. And if of no other value, the present communication may amuse you with anecdotes not known to every one.
I had meant to have added some views on the amalgamation of parties, to which your favor of the 8th has some allusion; an amalgamation of name, but not of principle. Tories are tories still, by whatever name they may be called. But my letter is already too unmercifully long, and I close it here with assurances of my great esteem and respectful consideration.
Th: Jefferson.
Monticello, October 15, 1824.
Dear Sir,
I have yet to thank you for your O. B. K. oration, delivered in presence of General la Fayette. It is all excellent, much of it sublimely so, well worthy of its author and his subject, of whom we may truly say, as was said of Germanicus, ‘Fruitur famâ sui.’
Your letter of September the 10th gave me the first information that mine to Major Cartwright had got into the newspapers; and the first notice, indeed, that he had received it. I was a stranger to his person, but not to his respectable and patriotic character. I received from him a long and interesting letter, and answered it with frankness, going without reserve into several subjects, to which his letter had led, but on which I did not suppose I was writing for the newspapers. The publication of a letter in such a case, without the consent of the writer, is not a fair practice.
The part which you quote, may draw on me the host of judges and divines. They may cavil, but cannot refute it. Those who read Prisot’s opinion with a candid view to understand, and not to chicane it, cannot mistake its meaning. The reports in the Year-books were taken very short. The opinions of the judges were written down sententiously, as notes or memoranda, and not with all the developement which they probably used in delivering them. Prisot’s opinion, to be fully expressed, should be thus paraphrased. ‘To such laws as those of holy church have recorded, and preserved in their ancient books and writings, it is proper for us to give credence; for so is, or so says, the common law, or law of the land, on which all manner of other laws rest for their authority, or are founded; that is to say, the common law, or the law of the land common to us all, and established by the authority of us all, is that from which is derived the authority of all other special and subordinate branches of law, such as the canon law, law merchant, law maritime, law of Gavelkind, Borough English, corporation laws, local customs and usages, to all of which the common law requires its judges to permit authority in the special or local cases belonging to them. The evidence of these laws is preserved in their ancient treatises, books, and writings, in like manner as our own common law itself is known, the text-of its original enactments having been long lost, and its substance only preserved in ancient and traditionary writings. And if it appears, from their ancient books, writings, and records, that the bishop, in this case, according to the rules prescribed by these authorities, has done what an ordinary would have done, in such case, then we should adjudge it good, otherwise not.’ To decide this question, they would have to turn to the ancient writings and records of the canon law, in which they would find evidence of the laws of advowsons, quare impedit, the duties of bishops and ordinaries, for which terms Prisot could never have meant to refer them to the Old or New Testament, les saincts scriptures, where surely they would not be found. A license which should permit ‘ancien scripture’ to be translated ‘holy scripture,’ annihilates at once all the evidence of language. With such a license, we might reverse the sixth commandment into ‘Thou shalt not omit murder.’ It would be the more extraordinary in this case, where the mistranslation was to effect the adoption of the whole code of the Jewish and Christian laws into the text of our statutes, to convert religious offences into temporal crimes, to make the breach of every religious precept a subject of indictment, submit the question of idolatry, for example, to the trial of a jury, and to a court, its punishment, to the third and fourth generation of the offender. Do we allow to our judges this lumping legislation?
The term ‘common law,’ although it has more than one meaning, is perfectly definite, secundum subjectam materiem. Its most probable origin was on the conquest of the Heptarchy by Alfred, and the amalgamation of their several codes of law into one, which became common to them all. The authentic text of these enactments has not been preserved; but their substance has been committed to many ancient books and writings, so faithfully as to have been deemed genuine from generation to generation, and obeyed as such by all. We have some fragments of them collected by Lambard, Wilkins, and others, but abounding with proofs of their spurious authenticity. Magna Charta is the earliest statute, the text of which has come down to us in an authentic form, and thence downward we have them entire. We do not know exactly when the common law and statute law, the lex scripta et non scripta, began to be contra-distinguished, so as to give a second acceptation to the former term; whether before or after Prisot’s day, at which time we know that nearly two centuries and a half of statutes were in preservation. In later times, on the introduction of the chancery branch of law, the term common law began to be used in a third sense, as the correlative of chancery law. This, however, having been long after Prisot’s time, could not have been the sense in which he used the term. He must have meant the ancient lex, non scripta, because, had he used it as inclusive of the lex scripta, he would have put his finger on the statute which had enjoined on the judges a deference to the laws of holy church. But no such statute existing, he must have referred to the common law in the sense of a lex non scripta. Whenever, then, the term common law is used in either of these senses, and it is never employed in any other, it is readily known in which of them by the context and subject matter under consideration; which, in the present case, leave no room for doubt. I do not remember the occasion which led me to take up this subject, while a practitioner of the law. But I know I went into it with all the research which a very copious law library enabled me to indulge; and I fear not for the accuracy of any of my quotations. The doctrine might be disproved by many other and different topics of reasoning; but having satisfied myself of the origin of the forgery, and found how, like a rolling snow-ball, it had gathered volume, I leave its further pursuit to those who need further proof, and perhaps I have already gone further than the feeble doubt you expressed might require, I salute you with great esteem and respect.
Th: Jefferson.
TO JOSEPH C. CABELL.
Monticello, January 11, 1825.
Dear Sir,
We are dreadfully nonplussed here by the non-arrival of our three Professors. We apprehend that the idea of our opening on the 1st of February prevails so much abroad (although we have always mentioned it doubtfully), as that the students will assemble on that day without awaiting the further notice which was promised. To send them away will be discouraging, and to open an University without Mathematics or Natural Philosophy would bring on us ridicule and disgrace. We therefore publish an advertisement, stating that on the arrival of these Professors, notice will be given of the day of opening the institution.
Governor Barbour writes me hopefully of getting our fifty thousand dollars from Congress. The proposition has been originated in the House of Representatives, referred to the committee of claims, the chairman of which has prepared a very favorable report, and a bill conformable, assuming the repayment of all interest which the State has actually paid. The legislature will certainly owe to us the recovery of this money; for had they not given it in some measure the reverenced character of a donation for the promotion of learning, it would never have been paid. It is to be hoped, therefore, that the displeasure incurred by wringing it from them at the last session, will now give way to a contrary feeling, and even place us on a ground of some merit. Should this sentiment take place, and the arrival of our Professors, and filling our dormitories with students on the 1st of February, encourage them to look more favorably towards us, perhaps it might dispose them to enlarge somewhat their order on the same fund. You observe the Proctor has stated in a letter accompanying our Report, that it will take about twenty-five thousand dollars more than we have to finish the Rotunda. Besides this, an Anatomical theatre (costing about as much as one of our hotels, say about five thousand dollars,) is indispensable to the school of Anatomy. There cannot be a single dissection until a proper theatre is prepared, giving an advantageous view of the operation to those within, and effectually excluding observation from without. Either the additional sums, therefore, of twenty-five thousand and five thousand dollars will be wanting, or we must be permitted to appropriate a part of the fifty thousand to a theatre, leaving the Rotunda unfinished for the present. Yet I should think neither of these objects an equivalent for renewing the displeasure of the legislature. Unless we can carry their hearty patronage with us, the institution can never flourish. I would not, therefore, hint at this additional aid, unless it were agreeable to our friends generally, and tolerably sure of being carried without irritation.
In your letter of December the 31st, you say my ‘hand-writing and my letters have great effect there,’ i.e. at Richmond. I am sensible, my dear Sir, of the kindness with which this encouragement is held up to me. But my views of their effect are very different. When I retired from the administration of public affairs, I thought I saw some evidence that I retired with a good degree of public favor, and that my conduct in office had been considered, by the one party at least, with approbation, and with acquiescence by the other. But the attempt, in which I have embarked so earnestly, to procure an improvement in the moral condition of my native State, although, perhaps, in other States it may have strengthened good dispositions, it has assuredly weakened them within our own. The attempt ran foul of so many local interests, of so many personal views, and so much ignorance, and I have been considered as so particularly its promoter, that I see evidently a great change of sentiment towards myself. I cannot doubt its having dissatisfied with myself a respectable minority, if not a majority of the House of Delegates. I feel it deeply, and very discouragingly. Yet I shall not give way. I have ever found in my progress through life, that, acting for the public, if we do always what is right, the approbation denied in the beginning will surely follow us in the end. It is from posterity we are to expect remuneration for the sacrifices we are making for their service, of time, quiet, and good will. And I fear not the appeal. The multitude of fine young men whom we shall redeem from ignorance, who will feel that they owe to us the elevation of mind, of character, and station they will be able to attain from the result of our efforts, will insure their remembering us with gratitude. We will not, then, be ‘weary in well-doing.’ Usque ad aras amicus tuus,
Th: Jefferson.
THOMAS JEFFERSON TO THOMAS JEFFERSON SMITH.
This letter will, to you, be as one from the dead. The writer will be in the grave before you can weigh its counsels. Your affectionate and excellent father has requested that I would address to you something which might possibly have a favorable influence on the course of life you have to run, and I too, as a namesake, feel an interest in that course. Few words will be necessary, with good dispositions on your part. Adore God. Reverence and cherish your parents. Love your neighbor as yourself, and your country more than yourself. Be just. Be true. Murmur not at the ways of Providence. So shall the life, into which you have entered, be the portal to one of eternal and ineffable bliss. And if to the dead it is permitted to care for the things of this world, every action of your life will be under my regard. Farewell.
Monticello, February 21, 1825.
The Portrait of a Good Man, by the most sublime of Poets, for your imitation.
Lord, who’s the happy man that may to thy blest courts repair;
Not stranger-like to visit them, but to inhabit there?
‘Tis he, whose every thought and deed by rules of virtue moves;
Whose generous tongue disdains to speak the thing his heart
disproves.
Who never did a slander forge, his neighbor’s fame to wound;
Nor hearken to a false report, by malice whispered round.
Who vice, in all its pomp and power, can treat with just neglect;
And piety, though clothed in rags, religiously respect.
Who to his plighted vows and trust has ever firmly stood;
And though he promise to his loss, he makes his promise good.
Whose soul in usury disdains his treasure to employ;
Whom no rewards can ever bribe the guiltless to destroy.
The man, who, by this steady course, has happiness insured,
When earth’s foundations shake, shall stand, by Providence secured.
A Decalogue of Canons for observation in practical life.
1. Never put off till to-morrow what you can do to-day.
2. Never trouble another for what you can do yourself.
3. Never spend your money before you have it.
4. Never buy what you do not want, because it is cheap; it will be dear to you.
5. Pride costs us more than hunger, thirst, and cold.
6. We never repent of having eaten too little.
7. Nothing is troublesome that we do willingly.
8. How much pain have cost us the evils which have never happened.
9. Take things always by their smooth handle.
10. When angry, count ten before you speak; if very angry, an hundred.
TO JAMES MADISON.
Monticello, December 24, 1825.
Dear Sir,
I have for sometime considered the question of internal improvement as desperate. The torrent of general opinion sets so strongly in favor of it as to be irresistible. And I suppose that even the opposition in Congress will hereafter be feeble and formal, unless something can be done which may give a gleam of encouragement to our friends, or alarm their opponents in their fancied security. I learn from Richmond, that those who think with us there are in a state of perfect dismay, not knowing what to do, or what to propose. Mr. Gordon, our representative, particularly, has written to me in very desponding terms, not disposed to yield, indeed, but pressing for opinions and advice on the subject. I have no doubt you are pressed in the same way, and I hope you have devised and recommended something to them. If you have, stop here and read no more, but consider all that follows as non avenue. I shall be better satisfied to adopt implicitly any thing which you may have advised, than any thing occurring to myself. For I have long ceased to think on subjects of this kind, and pay little attention to public proceedings. But if you have done nothing in it, then I risk for your consideration what has occurred to me, and is expressed in the enclosed paper. Bailey’s propositions, which came to hand since I wrote the paper, and which I suppose to have come from the President himself, show a little hesitation in the purposes of his party; and in that state of mind, a bolt shot critically may decide the contest, by its effect on the less bold. The olive-branch held out to them at this moment may be accepted, and the constitution thus saved at a moderate sacrifice. I say nothing of the paper, which will explain itself. The following heads of consideration, or some of them, may weigh in its favor.
It may intimidate the wavering. It may break the western coalition, by offering the same thing in a different form. It will be viewed with favor in contrast with the Georgia opposition and fear of strengthening that. It will be an example of a temperate mode of opposition in future and similar cases. It will delay the measure a year at least. It will give us the chance of better times and of intervening accidents; and in no way place us in a worse than our present situation. I do not dwell on these topics; your mind will develope them.
The first question is, whether you approve of doing any thing of the kind. If not, send it back to me, and it shall be suppressed; for I would not hazard so important a measure against your opinion, nor even without its support. If you think it may be a canvass on which to put something good, make what alterations you please, and I will forward it to Gordon, under the most sacred injunctions that it shall be so used as that not a shadow of suspicion shall fall on you or myself, that it has come from either of us. But what you do, do as promptly as your convenience will admit, lest it should be anticipated by something worse. Ever and affectionately yours,
Th: Jefferson.
The solemn Declaration and Protest of the Commonwealth of Virginia, on the Principles of the Constitution of the United, States of America, and on the Violations of them.
We, the General Assembly of Virginia, on behalf and in the name of the people thereof, do declare as follows.
The States in North America which confederated to establish their independence on the government of Great Britain, of which Virginia was one, became, on that acquisition, free and independent States, and, as such, authorized to constitute governments, each for itself, in such form as it thought best.
They entered into a compact (which is called the Constitution of the United States of America), by which they agreed to unite in a single government as to their relations with each other, and with foreign nations, and as to certain other articles particularly specified. They retained at the same time, each to itself, the other rights of independent government, comprehending mainly their domestic interests.
For the administration of their federal branch, they agreed to appoint, in conjunction, a distinct set of functionaries, legislative, executive, and judiciary, in the manner settled in that compact: while to each, severally and of course, remained its original right of appointing, each for itself, a separate set of functionaries, legislative, executive, and judiciary, also, for administering the domestic branch of their respective governments.
These two sets of officers, each independent of the other, constitute thus a whole of government, for each State separately; the powers ascribed to the one, as specifically made federal, exercised over the whole, the residuary powers, retained to the other, exercisable exclusively over its particular State, foreign herein, each to the others, as they were before the original compact.
To this construction of government and distribution of its powers, the Commonwealth of Virginia does religiously and affectionately adhere, opposing, with equal fidelity and firmness, the usurpation of either set of functionaries on the rightful powers of the other.
But the federal branch has assumed in some cases, and claimed in others, a right of enlarging its own powers by constructions, inferences, and indefinite deductions from those directly given, which this Assembly does declare to be usurpations of the powers retained to the independent branches, mere interpolations into the compact, and direct infractions of it.
They claim, for example, and have commenced the exercise of a right to construct roads, open canals, and effect other internal improvements within the territories and jurisdictions exclusively belonging to the several States, which this Assembly does declare has not been given to that branch by the constitutional compact, but remains to each State among its domestic and unalienated powers, exercisable within itself and by its domestic authorities alone.
This Assembly does further disavow, and declare to be most false and unfounded, the doctrine, that the compact, in authorizing its federal branch to lay and collect taxes, duties, imposts, and excises to pay the debts and provide for the common defence and general welfare of the United States, has given them thereby a power to do whatever they may think, or pretend, would promote the general welfare, which construction would make that, of itself, a complete government, without limitation of powers; but that the plain sense and obvious meaning were, that they might levy the taxes necessary to provide for the general welfare, by the various acts of power therein specified and delegated to them, and by no others.
Nor is it admitted, as has been said, that the people of these States, by not investing their federal branch with all the means of bettering their condition, have denied to themselves any which may effect that purpose; since, in the distribution of these means, they have given to that branch those which belong to its department, and to the States have reserved separately the residue which belong to them separately: and thus by the organization of the two branches taken together, have completely secured the first object of human association, the full improvement of their condition, and reserved to themselves all the faculties of multiplying their own blessings.
Whilst the General Assembly thus declares the rights retained by the States, rights which they have never yielded, and which this State will never voluntarily yield, they do not mean to raise the banner of disaffection, or of separation from their sister States, co-parties with themselves to this compact. They know and value too highly the blessings of their Union, as to foreign nations and questions arising among themselves, to consider every infraction as to be met by actual resistance. They respect too affectionately the opinions of those possessing the same rights, under the same instrument, to make every difference of construction a ground of immediate rupture. They would, indeed, consider such a rupture as among the greatest calamities which could befall them; but not the greatest. There is yet one greater, submission to a government of unlimited powers. It is only when the hope of avoiding this shall become absolutely desperate, that further forbearance could not be indulged. Should a majority of the co-parties, therefore, contrary to the expectation and hope of this Assembly, prefer, at this time, acquiescence in these assumptions of power by the federal member of the government, we will be patient and suffer much, under the confidence that time, ere it be too late, will prove to them also the bitter consequences in which that usurpation will involve us all. In the mean while, we will breast with them, rather than separate from them, every misfortune, save that only of living under a government of unlimited powers. We owe every other sacrifice to ourselves, to our federal brethren, and to the world at large, to pursue with temper and perseverance the great experiment which shall prove that man is capable of living in society, governing itself by laws self-imposed, and securing to its members the enjoyment of life, liberty, property, and peace; and further to show, that even when the government of its choice shall manifest a tendency to degeneracy, we are not at once to despair but that the will and the watchfulness of its sounder parts will reform its aberrations, recall it to original and legitimate principles, and restrain it within the rightful limits of self-government. And these are the objects of this Declaration and Protest.
Supposing then, that it might be for the good of the whole, as some of its co-States seem to think, that the power of making roads and canals should be added to those directly given to the federal branch, as more likely to be systematically and beneficially directed, than by the independent action of the several States, this Commonwealth, from respect to these opinions, and a desire of conciliation with its co-States, will consent, in concurrence with them, to make this addition, provided it be done regularly by an amendment of the compact, in the way established by that instrument, and provided also, it be sufficiently guarded against abuses, compromises, and corrupt practices, not only of possible, but of probable occurrence.
And as a further pledge of the sincere and cordial attachment of this Commonwealth to the union of the whole, so far as has been consented to by the compact called ‘The Constitution of the United States of America,’ (construed according to the plain and ordinary meaning of its language, to the common intendment of the time, and of those who framed it;) to give also to all parties and authorities, time for reflection and for consideration, whether, under a temperate view of the possible consequences, and especially of the constant obstructions which an equivocal majority must ever expect to meet, they will still prefer the assumption of this power rather than its acceptance from the free will of their constituents; and to preserve peace in the mean while, we proceed to make it the duty of our citizens, until the legislature shall otherwise and ultimately decide, to acquiesce under those acts of the federal branch of our government which we have declared to be usurpations, and against which, in point of right, we do protest as null and void, and never to be quoted as precedents of right.
We therefore do enact, and be it enacted by the General Assembly of Virginia, that all citizens of this Commonwealth, and persons and authorities within the same, shall pay full obedience at all times to the acts which may be passed by the Congress of the United States, the object of which shall be the construction of post-roads, making canals of navigation, and maintaining the same, in any part of the United States, in like manner as if the said acts were, totidem verbis, passed by the legislature of this Commonwealth.
TO WILLIAM B. GILES.
Monticello, December 25, 1825.
Dear Sir,
Your favor of the 15th was received four days ago. It found me engaged in what I could not lay aside till this day.
Far advanced in my eighty-third year, worn down with infirmities which have confined me almost entirely to the house for seven or eight months past, it afflicts me much to receive appeals to my memory for transactions so far back as that which is the subject of your letter. My memory is indeed become almost a blank, of which no better proof can probably be given you than by my solemn protestation, that I have not the least recollection of your intervention between Mr. John Q. Adams and myself, in what passed on the subject of the embargo. Not the slightest trace of it remains in my mind. Yet I have no doubt of the exactitude of the statement in your letter. And the less, as I recollect the interview with Mr. Adams, to which the previous communications which had passed between him and yourself were probably and naturally the preliminary. That interview I remember well; not indeed in the very words which passed between us, but in their substance, which was of a character too awful, too deeply engraved in my mind, and influencing too materially the course I had to pursue, ever to be forgotten. Mr. Adams called on me pending the embargo, and while endeavors were making to obtain its repeal. He made some apologies for the call, on the ground of our not being then in the habit of confidential communications, but that that which he had then to make, involved too seriously the interest of our country not to overrule all other considerations with him, and make it his duty to reveal it to myself particularly. I assured him there was no occasion for any apology for his visit; that, on the contrary, his communications would be thankfully received, and would add a confirmation the more to my entire confidence in the rectitude and patriotism of his conduct and principles. He spoke then of the dissatisfaction of the eastern portion of our confederacy with the restraints of the embargo then existing, and their restlessness under it. That there was nothing which might not be attempted, to rid themselves of it. That he had information of the most unquestionable certainty, that certain citizens of the Eastern States (I think he named Massachusetts particularly) were in negotiation with agents of the British government, the object of which was an agreement that the New England States should take no further part in the war then going on; that, without formally declaring their separation from the Union of the States, they should withdraw from all aid and obedience to them, that their navigation and commerce should be free from restraint and interruption by the British; that they should be considered and treated by them as neutrals, and as such might conduct themselves towards both parties; and, at the close of the war, be at liberty to rejoin the confederacy. He assured me that there was imminent danger that the convention would take place; that the temptations were such as might debauch many from their fidelity to the Union; and that, to enable its friends to make head against it, the repeal of the embargo was absolutely necessary. I expressed a just sense of the merit of this information, and of the importance of the disclosure to the safety and even the salvation of our country: and however reluctant I was to abandon the measure (a measure which persevered in a little longer, we had subsequent and satisfactory assurance would have effected its object completely), from that moment, and influenced by that information, I saw the necessity of abandoning it, and instead of effecting our purpose by this peaceful weapon, we must fight it out, or break the Union. I then recommended to my friends to yield to the necessity of a repeal of the embargo, and to endeavor to supply its place by the best substitute, in which they could procure a general concurrence.
I cannot too often repeat, that this statement is not pretended to be in the very words which passed; that it only gives faithfully the impression remaining on my mind. The very words of a conversation are too transient and fugitive to be so long retained in remembrance. But the substance was too important to be forgotten, not only from the revolution of measures it obliged me to adopt, but also from the renewals of it in my memory on the frequent occasions I have had of doing justice to Mr. Adams, by repeating this proof of his fidelity to his country, and of his superiority over all ordinary considerations when the safety of that was brought into question.
With this best exertion of a waning memory which I can command, accept assurances of my constant and affectionate friendship and respect.
Th: Jefferson.
TO WILLIAM B. GILES.
Monticello, December 26, 1825.
Dear Sir,
I wrote you a letter yesterday, of which you will be free to make what use you please. This will contain matters not intended for the public eye. I see, as you do, and with the deepest affliction, the rapid strides with which the federal branch of our government is advancing towards the usurpation of all the rights reserved to the States, and the consolidation in itself of all powers, foreign and domestic; and that too, by constructions which, if legitimate, leave no limits to their power. Take together the decisions of the federal court, the doctrines of the President, and the misconstructions of the constitutional compact acted on by the legislature of the federal branch, and it is but too evident, that the three ruling branches of that department are in combination to strip their colleagues, the State authorities, of the powers reserved by them, and to exercise themselves all functions, foreign and domestic. Under the power to regulate commerce, they assume indefinitely that also over agriculture and manufactures, and call it regulation to take the earnings of one of these branches of industry, and that too the most depressed, and put them into the pockets of the other, the most flourishing of all. Under the authority to establish post-roads, they claim that of cutting down mountains for the construction of roads, of digging canals, and aided by a little sophistry on the words ‘general welfare,’ a right to do, not only the acts to effect that, which are specifically enumerated and permitted, but whatsoever they shall think or pretend will be for the general welfare. And what is our resource for the preservation of the constitution? Reason and argument? You might as well reason and argue with the marble columns encircling them. The representatives chosen by ourselves? They are joined in the combination, some from incorrect views of government, some from corrupt ones, sufficient, voting together, to outnumber the sound parts; and with majorities only of one, two, or three, bold enough to go forward in defiance. Are we then to stand to our arms, with the hot-headed Georgian? No. That must be the last resource, not to be thought of until much longer and greater sufferings. If every infraction of a compact of so many parties is to be resisted at once, as a dissolution of it, none can ever be formed which would last one year. We must have patience and longer endurance then with our brethren while under delusion; give them time for reflection and experience of consequences; keep ourselves in a situation to profit by the chapter of accidents; and separate from our companions only when the sole alternatives left, are the dissolution of our Union with them, or submission to a government without limitation of powers. Between these two evils, when we must make a choice, there can be no hesitation. But in the mean while, the States should be watchful to note every material usurpation on their rights; to denounce them as they occur in the most peremptory terms; to protest against them as wrongs to which our present submission shall be considered, not as acknowledgments or precedents of right, but as a temporary yielding to the lesser evil, until their accumulation shall overweigh that of separation. I would go still further, and give to the federal member, by a regular amendment of the constitution, a right to make roads and canals of intercommunication between the States, providing sufficiently against corrupt practices in Congress (log-rolling, &c.), by declaring that the federal proportion of each State of the monies so employed, shall be in works within the State, or elsewhere with its consent, and with a due salvo of jurisdiction. This is the course which I think safest and best as yet. You ask my opinion of the propriety of giving publicity to what is stated in your letter, as having passed between Mr. John Q. Adams and yourself. Of this no one can judge but yourself. It is one of those questions which belong to the forum of feeling. This alone can decide on the degree of confidence implied in the disclosure; whether under no circumstances it was to be communicated to others. It does not seem to be of that character, or at all to wear that aspect. They are historical facts, which belong to the present, as well as future times. I doubt whether a single fact, known to the world, will carry as clear conviction to it, of the correctness of our knowledge of the treasonable views of the federal party of that day, as that disclosed by this, the most nefarious and daring attempt to dissever the Union, of which the Hartford Convention was a subsequent chapter: and both of these having failed, consolidation becomes the first chapter of the next book of their history. But this opens with a vast accession of strength from their younger recruits, who, having nothing in them of the feelings or principles of ‘76, now look to a single and splendid government of an aristocracy, founded on banking institutions, and monied incorporations under the guise and cloak of their favored branches of manufactures, commerce, and navigation, riding and ruling over the plundered ploughman and beggared yeomanry. This will be to them a next best blessing to the monarchy of their first aim, and perhaps the surest stepping-stone to it.
I learn with great satisfaction that your school is thriving well, and that you have at its head a truly classical scholar. He is one of three or four whom I can hear of in the State. We were obliged the last year to receive shameful Latinists into the classical school of the University; such as we will certainly refuse as soon as we can get from better schools a sufficiency of those properly instructed to form a class. We must get rid of this Connecticut Latin, of this barbarous confusion of long and short syllables, which renders doubtful whether we are listening to a reader of Cherokee, Shawnee, Iroquois, or what. Our University has been most fortunate in the five Professors procured from England. A finer selection could not have been made. Besides their being of a grade of science which has left little superior behind, the correctness of their moral character, their accommodating dispositions, and zeal for the prosperity of the institution, leave us nothing more to wish. I verily believe that as high a degree of, education can now be obtained here, as in the country they left. And a finer set of youths I never saw assembled for instruction. They committed some irregularities at first, until they learned the lawful length of their tether; since which it has never been transgressed in the smallest degree. A great proportion of them are severely devoted to study, and I fear not to say, that within twelve or fifteen years from this time, a majority of the rulers of our State will have been educated here. They shall carry hence the correct principles of our day, and you may count assuredly that they will exhibit their country in a degree of sound respectability it has never known, either in our days, or those of our forefathers. I cannot live to see it. My joy must only be that of anticipation. But that you may see it in full fruition, is the probable consequence of the twenty years I am ahead of you in time, and is the sincere prayer of your affectionate and constant friend,
Th: Jefferson.
TO CLAIBORNE W. GOOCH.
Monticello, January 9, 1826.
Dear Sir,
I have duly received your favor of December the 31st, and fear, with you, all the evils which the present lowering aspect of our political horizon so ominously portends. That at some future day, which I hoped to be very distant, the free principles of our government might change, with the change of circumstances, was to be expected. But I certainly did not expect that they would not over-live the generation which established them. And what I still less expected was, that my favorite western country was to be made the instrument of change. I had ever and fondly cherished the interests of that country, relying on it as a barrier against the degeneracy of public opinion from our original and free principles. But the bait of local interests, artfully prepared for their palate, has decoyed them from their kindred attachments, to alliances alien to them. Yet, although I have little hope that the torrent of consolidation can be withstood, I should not be for giving up the ship without efforts to save her. She lived well through the first squall, and may weather the present one. But, Dear Sir, I am not the champion called for by our present dangers; Non tali auxilio, nee defensoribus istis, tempus eget.’ A waning body, a waning mind, and waning memory, with habitual ill health, warn me to withdraw and relinquish the arena to younger and abler athletes. I am sensible myself, if others are not, that this is my duty. If my distant friends know it not, those around me can inform them that they should not, in friendship, wish to call me into conflicts, exposing only the decays which nature has inscribed among her unalterable laws, and injuring the common cause by a senile and puny defence.
I will, however, say one word on the subject. The South Carolina resolutions, Van Buren’s motion, and above all Bailey’s propositions, show that other States are coming forward on the subject, and better for any one to take the lead than Virginia, where opposition is considered as common-place, and a mere matter of form and habit. We shall see what our co-States propose, and before the close of the session we may shape our own course more understandingly.
Accept the assurance of my great esteem and respect.
Th: Jefferson.
Monticello, January 21, 1826.
Dear Sir,
Your favor of January the 15th is received, and I am entirely sensible of the kindness of the motives which suggested the caution it recommended. But I believe what I have done is the only thing I could have done with honor or conscience. Mr. Giles requested me to state a fact which he knew himself, and of which he knew me to be possessed. What use he intended to make of it I knew not, nor had I a right to inquire, or to indicate any suspicion that he would make an unfair one. That was his concern, not mine, and his character was sufficient to sustain the responsibility for it. I knew, too, that if an uncandid use should be made of it, there would be found those who would so prove it. Independent of the terms of intimate friendship on which Mr. Giles and myself have ever lived together, the world’s respect entitled him to the justice of my testimony to any truth he might call for; and how that testimony should connect me with whatever he may do or write hereafter, and with his whole career, as you apprehend, is not understood by me. With his personal controversies I have nothing to do. I never took any part in them, or in those of any other person. Add to this, that the statement I have given him on the subject of Mr. Adams, is entirely honorable to him in every sentiment and fact it contains. There is not a word in it which I would wish to recall. It is one which Mr. Adams himself might willingly quote, did he need to quote any thing. It was simply, that during the continuance of the embargo, Mr. Adams informed me of a combination (without naming any one concerned in it), which had for its object a severance of the Union, for a time at least. That Mr. Adams and myself not being then in the habit of mutual consultation and confidence, I considered it as the stronger proof of the purity of his patriotism, which was able to lift him above all party passions when the safety of his country was endangered. Nor have I kept this honorable fact to myself. During the late canvass, particularly, I had more than one occasion to quote it to persons who were expressing opinions respecting him, of which this was a direct corrective. I have never entertained for Mr. Adams any but sentiments of esteem and respect; and if we have not thought alike on political subjects, I yet never doubted the honesty of his opinions, of which the letter in question, if published, will be an additional proof. Still, I recognise your friendship in suggesting a review of it, and am glad of this, as of every other occasion, of repeating to you the assurance of my constant attachment and respect.
Th: Jefferson.
TO JAMES MADISON.
Monticello, February 17,1826.
Dear Sir,
Immediately on seeing the overwhelming vote of the House of Representatives against giving us another dollar, I rode to the University and desired Mr. Brockenbrough to engage in nothing new, to stop every thing on hand which could be done without, and to employ all his force and funds in finishing the circular room for the books, and the Anatomical theatre. These cannot be done without; and for these and all our debts, we have funds enough. But I think it prudent then to clear the decks thoroughly, to see how we shall stand, and what we may accomplish further. In the mean time, there have arrived for us in different ports of the United States, ten boxes of books, from Paris, seven from London, and from Germany I know not how many; in all, perhaps, about twenty-five boxes. Not one of these can be opened until the book-room is completely finished, and all the shelves ready to receive their charge directly from the boxes, as they shall be opened. This cannot be till May. I hear nothing definitive of the three thousand dollars duty of which we are asking the remission from Congress. In the selection of our Law Professor, we must be rigorously attentive to his political principles. You will recollect, that, before the Revolution, Coke Littleton was the universal elementary book of law students, and a sounder whig never wrote, nor of profounder learning in the orthodox doctrines of the British constitution, or in what were called English liberties. You remember also that our lawyers were then all whigs. But when his black-letter text, and uncouth but cunning learning got out of fashion, and the honied Mansfieldism of Blackstone became the students’ hornbook, from that moment, that profession (the nursery of our Congress) began to slide into toryism, and nearly all the young brood of lawyers now are of that hue. They suppose themselves, indeed, to be whigs, because they no longer know what whigism or republicanism means. It is in our seminary that that vestal flame is to be kept alive; it is thence it is to spread anew over our own and the sister States. If we are true and vigilant in our trust, within a dozen or twenty years a majority of our own legislature will be from our school, and many disciples will have carried its doctrines home with them to their several States, and will have leavened thus the whole mass. New York has taken strong ground in vindication of the constitution; South Carolina had already done the same. Although I was against our leading, I am equally against omitting to follow in the same line, and backing them firmly; and i hope that yourself or some other will mark out the track to be pursued by us.
You will have seen in the newspapers some proceedings in the legislature, which have cost me much mortification. My own debts had become considerable, but not beyond the effect of some lopping of property, which would have been little felt, when our friend —— gave me the coup de grace. Ever since that I have been paying twelve hundred dollars a year interest on his debt, which, with my own, was absorbing so much of my annual income, as that the maintenance of my family was making deep and rapid inroads on my capital, and had already done it. Still, sales at a fair price would leave me competently provided. Had crops and prices for several years been such as to maintain a steady competition of substantial bidders at market, all would have been safe. But the long succession of years of stunted crops, of reduced prices, the general prostration of the farming business, under levies for the support of manufacturers, &c, with the calamitous fluctuations of value in our paper medium, have kept agriculture in a state of abject depression, which has peopled the western States by silently breaking up those on the Atlantic, and glutted the land-market, while it drew off its bidders. In such a state of things, property has lost its character of being a resource for debts. Highland in Bedford, which, in the days of our plethory, sold readily for from fifty to one hundred dollars the acre (and such sales were many then), would not now sell for more than from ten to twenty dollars, or one quarter or one fifth of its former price. Reflecting on these things, the practice occurred to me, of selling, on fair valuation, and by way of lottery, often resorted to before the Revolution to effect large sales, and still in constant usage in every State for individual as well as corporation purposes. If it is permitted in my case, my lands here alone, with the mills, he, will pay every thing, and leave me Monticello and a farm free. If refused, I must sell every thing here, perhaps considerably in Bedford, move thither with my family, where I have not even a log hut to put my head into, and whether ground for burial, will depend on the depredations which, under the form of sales, shall have been committed on my property. The question then with me was, Utrum horum? But why afflict you with these details? Indeed, I cannot tell, unless pains are lessened by communication with a friend. The friendship which has subsisted between us, now half a century, and the harmony of our political principles and pursuits, have been sources of constant happiness to me through that long period. And if I remove beyond the reach of attentions to the University, or beyond the bourne of life itself, as I soon must, it is a comfort to leave that institution under your care, and an assurance that it will not be wanting. It has also been a great solace to me, to believe that you are engaged in vindicating to posterity the course we have pursued for preserving to them, in all their purity, the blessings of self-government, which we had assisted too in acquiring for them. If ever the earth has beheld a system of administration conducted with a single and steadfast eye to the general interest and happiness of those committed to it, one which, protected by truth, can never know reproach, it is that to which our lives have been devoted. To myself you have been a pillar of support through life. Take care of me when dead, and be assured that I shall leave with you my last affections.
Th: Jefferson.
[The following paper it is deemed proper to insert, as well
because of the explanation it contains of the reasons which
led the author to ask permission of the legislature to sell
his property by lottery, as of its otherwise interesting
character.]
It is a common idea that games of chance are immoral. But what is chance? Nothing happens in this world without a cause. If we know the cause, we do not call it chance; but if we do not know it, we say it was produced by chance. If we see a loaded die turn its lightest side up, we know the cause, and that it is not an effect of chance; but whatever side an unloaded die turns up, not knowing the cause, we say it is the effect of chance. Yet the morality of a thing cannot depend on our knowledge or ignorance of its cause. Not knowing why a particular side of an unloaded die turns up, cannot make the act of throwing it, or of betting on it, immoral. If we consider games of chance immoral, then every pursuit of human industry is immoral, for there is not a single one that is not subject to chance; not one wherein you do not risk a loss for the chance of some gain. The navigator, for example, risks his ship in the hope (if she is not lost in the voyage) of gaining an advantageous freight. The merchant risks his cargo to gain a better price for it. A landholder builds a house on the risk of indemnifying himself by a rent. The hunter hazards his time and trouble in the hope of killing game. In all these pursuits, you stake some one thing against another which you hope to win. But the greatest of all gamblers is the farmer. He risks the seed he puts into the ground, the rent he pays for the ground itself, the year’s labor on it, and the wear and tear of his cattle and gear, to win a crop, which the chances of too much or too little rain, and general uncertainties of weather, insects, waste, &c. often make a total or partial loss. These, then, are games of chance. Yet so far from being immoral, they are indispensable to the existence of man, and every one has a natural right to choose for his pursuit such one of them as he thinks most likely to furnish him subsistence. Almost all these pursuits of chance produce something useful to society. But there are some which produce nothing, and endanger the well-being of the individuals engaged in them, or of others depending on them. Such are games with cards, dice, billiards, &c. And although the pursuit of them is a matter of natural right, yet society, perceiving the irresistible bent of some of its members to pursue them, and the ruin produced by them to the families depending on these individuals, consider it as a case of insanity, quoad hoc, step in to protect the family and the party himself, as in other cases of insanity, infancy, imbecility, &c, and suppress the pursuit altogether, and the natural right of following it. There are some other games of chance, useful on certain occasions, and injurious only when carried beyond their useful bounds. Such are insurances, lotteries, raffles, &tc. These they do not suppress, but take their regulation under their own discretion. The insurance of ships on voyages is a vocation of chance, yet useful, and the right to exercise it therefore is left free. So of houses against fire, doubtful debts, the continuance of a particular life, and similar cases. Money is wanting for an useful undertaking, as a school, &c. for which a direct tax would be disapproved. It is raised therefore by a lottery, wherein the tax is laid on the willing only, that is to say, on those who can risk the price of a ticket without sensible injury, for the possibility of a higher prize. An article of property, insusceptible of division at all, or not without great diminution of its worth, is sometimes of so large value as that no purchaser can be found, while the owner owes debts, has no other means of payment, and his creditors no other chance of obtaining it, but by its sale at a full and fair price. The lottery is here a salutary instrument for disposing of it, where many run small risks for the chance of obtaining a high prize. In this way, the great estate of the late Colonel Byrd (in 1756) was made competent to pay his debts, which, had the whole been brought into the market at once, would have overdone the demand, would have sold at half or quarter the value, and sacrificed the creditors, half or three fourths of whom would have lost their debts. This method of selling was formerly very much resorted to, until it was thought to nourish too much a spirit of hazard. The legislature Were therefore induced, not to suppress it altogether, but to take it under their own special regulation. This they did, for the first time, by their act of 1769, c.17., before which time, every person exercised the right freely; and since which time, it is made unlawful but when approved and authorized by a special act of the legislature.
Since then, this right of sale, by way of lottery, has been exercised only under the discretion of the legislature. Let us examine the purposes for which they have allowed it in practice, not looking beyond the date of our independence.
1. It was for a long time an item of the standing revenue of the State.
1813. c. 1. § 3 An act imposing taxes for the support of government, and c. 2. § 10.
1814. Dec. c. 1. § 3. 1814. Feb. c. 1. § 3. 1818. c. 1. § 1. 1819. c. 1. 1820. c. 1.
This then is a declaration by the nation, that an act was not immoral, of which they were in the habitual use themselves as a part of the regular means of supporting the government: the tax on the vender of tickets was their share of the profits, and if their share was innocent, his could not be criminal.
2. It has been abundantly permitted, to raise money by lottery for the purposes of schools; and in this, as in many other cases, the lottery has been permitted to retain a part of the money (generally from ten to fifteen per cent.) for the use to which the lottery has been applied. So that while the adventurers paid one hundred dollars for tickets, they received back eighty-five or ninety dollars only, in the form of prizes, the remaining ten or fifteen being the tax levied on them, with their own consent. Examples are.
1784. c. 34. Authorizing the city of Williamsburg to raise £2000 for a grammar school.
1789. c. 68. For Randolph Academy, £1000.
1789. c. 73. For Fauquier Academy, £500. c. 74. For the Fredericksburg Academy, £4000.
1790. c. 46. For the Transylvania Seminary, £500. For the Southampton Academy, £300.
1796. c. 82. For the New London Academy.
1803. c. 49. For the Fredericksburg Charity School. c» 50. For finishing the Strasburg Seminary. c. 58. For William and Mary College. c. 62. For the Bannister Academy.c. 79. For the Belfield Academy. c. 82. For the Petersburg Academy.
1804. c. 40. For the Hotsprings Seminary. c. 76. For the Stevensburg Academy. c.100. For William and Mary College.
1805. c. 24. For the Rumford Academy.
1812. c. 10. For the Literary Fund. To sell the privilege for $30,000 annually, for seven years.
1816. c. 80. For Norfolk Academy, $12,000. Norfolk Female Society, $2000. Lancastrian School, $6000.
3. The next object of lotteries has been rivers.
1790. c. 46. For a bridge between Gosport and Portsmouth, £400.
1796. c. 83. For clearing Roanoke River.
1804. c. 62. For clearing Quantico Creek.
1805. c. 42. For a toll-bridge over Cheat River.
1816. c. 49. For the Dismal Swamp, $50,000.
4. For roads.
1790. c. 46. For a road to Warminster, £200. For cutting a road from Rockfish gap to Scott’s and Nicholas’s landing, £400. 1796. c. 85. To repair certain roads.
1803. c. 60. For improving roads to Snigger’s and Ashby’s gaps. c. 61. For opening a road to Brock’s gap. c. 65. For opening a road from the town of Monroe to Sweet Springs and Lewisburg.
* The acts not being at hand, the sums allowed are not known.
1803. c. 71. For improving the road to Brock’s gap.
1805. c. 5. For improving the road to Clarksburg. c. 26. For opening a road from Monongalia Glades to Fishing Creek.
1813. c. 44. For opening a road from Thornton’s gap.
5. Lotteries for the benefit of counties.
1796. c. 78. To authorize a lottery in the county of Shenandoah. c. 84. To authorize a lottery in the county of Gloucester.
6. Lotteries for the benefit of towns.
1782. c. 31. Richmond, for a bridge over Shockoe, amount not limited.
1789. c. 75. Alexandria, to pave its streets, £1500.
1790. c. 46. do. do. £5000. 1796. c. 79. Norfolk, one or more lotteries authorized., c. 81. Petersburg, a lottery authorized.
1803. c. 12. Woodstock, a lottery authorized c. 48. Fredericksburg, for improving its main street. c. 73. Harrisonburg, for improving its streets.
7. Lotteries for religious congregations.
1785. c.lll. Completing a church in Winchester. For rebuilding a church in the parish of Elizabeth River.
1791. c. 69. For the benefit of the Episcopal society.
1790. c. 46. For building a church in Warminster, £200. in Halifax, £200. in Alexandria, £500. in Petersburg, £750. in Shepherdstown, £250.
8. Lotteries for private societies.
1790. c. 46. For the Amicable Society in Richmond, £1000.
1791. c. 70. For building a Freemason’s hall in Charlotte, £750.
9. Lotteries for the benefit of private individuals. [To raise money for them.]
1796. c. 80. For the sufferers by fire in the town of Lexington.
1781. c. 6. For completing titles under Byrd’s lottery.
1790. c. 46. To erect a paper-mill in Staunton, £300. To raise £2000 for Nathaniel Twining.
1791. c. 13. To raise £4000 for William Tatham, to enable him to complete his geographical work. To enable————-to complete a literary work.*
* I found such an act, but not noting it at the time, I have not been able to find it again. But there is such an one.
We have seen, then, that every vocation in life is subject to the influence of chance; that so far from being rendered immoral by the admixture of that ingredient, were they abandoned on that account, man could no longer subsist; that, among them, every one has a natural right to choose that which he thinks most likely to give him comfortable subsistence; but that while the greater number of these pursuits are productive of something which adds to the necessaries and comforts of life, others again, such as cards, dice, &ic, are entirely unproductive, doing good to none, injury to many, yet so easy, and so seducing in practice to men of a certain constitution of mind, that they cannot resist the temptation, be the consequences what they may; that in this case, as in those of insanity, idiocy, infancy, &c, it is the duty of society to take them under its protection, even against their own acts, and to restrain their right of choice of these pursuits, by suppressing them entirely; that there are others, as lotteries particularly, which, although liable to chance also, are useful for many purposes, and are therefore retained and placed under the discretion of the legislature, to be permitted or refused according to the circumstances of every special case, of which they are to judge: that between the years 1782 and 1820, a space of thirty-eight years only, we have observed seventy case’s, where the permission of them has been found useful by the legislature, some of which are in progress at this time. These cases relate to the emolument of the whole State, to local benefits of education, of navigation, of roads, of counties, towns, religious assemblies, private societies, and of individuals under particular circumstances which may claim indulgence or favor. The latter is the case now submitted to the legislature, and the question is, whether the individual soliciting their attention, or his situation, may merit that degree of consideration, which will justify the legislature in permitting him to avail himself of the mode of selling by lottery, for the purpose of paying his debts.
That a fair price cannot be obtained by sale in the ordinary way, and in the present depressed state of agricultural industry, is well known. Lands in this State will not now sell for more than a third or fourth of what they would have brought a few years ago, perhaps at the very time of the contraction of the debts for which they are now to be sold. The low price in foreign markets, for a series of years past, of agricultural produce, of wheat generally, of tobacco most commonly, and the accumulation of duties on the articles of consumption not produced within our State, not only disable the farmer or planter from adding to his farm by purchase, but reduce him to sell his own, and remove to the western country, glutting the market he leave’s, while he lessens the number of bidders. To be protected against this sacrifice is the object of the present application, and whether the applicant has any particular claim to this protection, is the present question.
Here the answer must be left to others. It is not for me to give it. I may, however, more readily than others, suggest the offices in which I have served. I came of age in 1764, and was soon put into the nomination of justices of the county in which I live, and at the first election following I became one of its representatives in the legislature.
I was thence sent to the old Congress.
Then employed two years, with Mr. Pendleton and Mr. Wythe, on the revisal and reduction to a single code of the whole body of the British statutes, the acts of our Assembly, and certain parts of the common law.
Then elected Governor.
Next to the legislature, and to Congress again.
Sent to Europe as Minister Plenipotentiary.
Appointed Secretary of State to the new government.
Elected Vice President, and
President.
And lastly, a Visitor and Rector of the University.
In these different offices, with scarcely any interval between them, I have been in the public service now sixty-one years; and during the far greater part of the time, in foreign countries or in other States. Every one knows how inevitably a Virginia estate, goes to ruin, when the owner is so far distant as to be unable to pay attention to it himself; and the more especially, when the line of his employment is of a character to abstract and alienate his mind entirely from the knowledge necessary to good, and even to saving management.
If it were thought worth while to specify any particular services rendered, I would refer to the specification of them made by the legislature itself in their Farewell Address, on my retiring from the Presidency, February, 1809. [This will be found in 2 Pleasant’s Collection, page 144.] There is one, however, not therein specified, the most important in its consequences, of any transaction in any portion of my life; to wit, the head I personally made against the federal principles and proceedings, during the administration of Mr. Adams. Their usurpations and violations of the constitution at that period, and their majority in both Houses of Congress, were so great, so decided, and so daring, that after combating their aggressions, inch by inch, without being able in the least to check their career, the republican leaders thought it would be best for them to give up their useless efforts there, go home, get into their respective legislatures, embody whatever of resistance they could be formed into, and if ineffectual, to perish there as in the last ditch. All, therefore, retired, leaving Mr. Gallatin alone in the House of Representatives, and myself in the Senate, where I then presided as Vice-President. Remaining at our posts, and bidding defiance to the brow-beatings and insults by which they endeavored to drive us off also, we kept the mass of republicans in phalanx together, until the legislatures could be brought up to the charge; and nothing on earth is more certain, than that if myself particularly, placed by my office of Vice-President at the head of the republicans, had given way and withdrawn from my post, the republicans throughout the Union would have given up in despair, and the cause would have been lost for ever. By holding on, we obtained time for the legislatures to come up with their weight; and those of Virginia and Kentucky particularly, but more especially the former, by their celebrated resolutions, saved the constitution, at its last gasp. No person who was not a witness of the scenes of that gloomy period, can form any idea of the afflicting persecutions and personal indignities we had to brook. They saved our country however. The spirits of the people were so much subdued and reduced to despair by the X. Y. Z. imposture, and other stratagems and machinations, that they would have sunk into apathy and monarchy, as the only form of government which could maintain itself.
If legislative services are worth mentioning, and the stamp of liberality and equality, which was necessary to be impressed on our laws in the first crisis of our birth as a nation, was of any value, they will find that the leading and most important laws of that day were prepared by myself, and carried chiefly by my efforts; supported, indeed, by able and faithful coadjutors from the ranks of the House, very effective as seconds, but who would not have taken the field as leaders.
The prohibition of the further importation of slaves, was the first of these measures in time.
This was followed by the abolition of entails, which broke up the hereditary and high-handed aristocracy, which, by accumulating immense masses of property in single lines of families, had divided our country into two distinct orders, of nobles and plebeians.
But further to complete the equality among our citizens so essential to the maintenance of republican government, it was necessary to abolish the principle of primogeniture. I drew the law of descents, giving equal inheritance to sons and daughters which made a part of the revised code.
The attack on the establishment of a dominant religion, was first made by myself. It could be carried at first only by a suspension of salaries for one year, by battling it again at the next session for another year, and so from year to year, until the public mind was ripened for the bill for establishing religious freedom, which I had prepared for the revised code also. This was at length established permanently, and by the efforts chiefly of Mr. Madison, being myself in Europe at the time that work was brought forward.
To these particular services, I think I might add the establishment of our University, as principally my work, acknowledging at the same time, as I do, the great assistance received from my able colleagues of the Visitation. But my residence in the vicinity threw, of course, on me the chief burthen of the enterprise, as well of the buildings, as of the general organization and care of the whole. The effect of this institution on the future fame, fortune, and prosperity of our country, can as yet be seen but at a distance. But an hundred well educated youths, which it will turn out annually, and ere long, will fill all its offices with men of superior qualifications, and raise it from its humble state to an eminence among its associates which it has never yet known; no, not in its brightest days. That institution is now qualified to raise its youth to an order of science unequalled in any other State; and this superiority will be the greater from the free range of mind encouraged there, and the restraint imposed at other seminaries by the shackles of a domineering hierarchy, and a bigoted adhesion to ancient habits. Those now on the theatre of affairs will enjoy the ineffable happiness of seeing themselves succeeded by sons of a grade of science beyond their own ken. Our sister States will also be repairing to the same fountains of instruction, will bring hither their genius to be kindled at our fire, and will carry back the fraternal affections which, nourished by the same alma mater, will knit us to them by the indissoluble bonds of early personal friendships. The good Old Dominion, the blessed mother of us all, will then raise her head with pride among the nations, will present to them that splendor of genius which she has ever possessed, but has too long suffered to rest uncultivated and unknown, and will become a centre of ralliance to the States whose youths she has instructed, and, as it were, adopted.
I claim some share in the merits of this great work of regeneration. My whole labors, now for many years, have been devoted to it, and I stand pledged to follow it up through the remnant of life remaining to me. And what remuneration do I ask? Money from the treasury? Not a cent. I ask nothing from the earnings or labors of my fellow-citizens. I wish no man’s comforts to be abridged for the enlargement of mine. For the services rendered on all occasions, I have been always paid to my full satisfaction. I never wished a dollar more than what the law had fixed on. My request is, only to be permitted to sell my own property freely to pay my own debts. To sell it, I say, and not to sacrifice it, not to have it gobbled up by speculators to make fortunes for themselves, leaving unpaid those who have trusted to my good faith, and myself without resource in the last and most helpless stage of life. If permitted to sell it in a way which will bring me a fair price, all will be honestly and honorably paid, and a competence left for myself, and for those who look to me for subsistence. To sell it in a way which will offend no moral principle, and expose none to risk but the willing, and those wishing to be permitted to take the chance of gain. To give me, in short, that permission which you often allow to others for purposes not more moral.
Will it be objected, that although not evil in itself, it may, as a precedent, lead to evil? But let those who shall quote the precedent bring their case within the same measure. Have they, as in this case, devoted three-score years and one of their lives, uninterruptedly, to the service of their country? Have the times of those services been as trying as those which have embraced our Revolution, our transition from a colonial to a free structure of government? Have the stations of their trial been of equal importance? Has the share they have borne in holding their new government to its genuine principles, been equally marked? And has the cause of the distress, against which they seek a remedy, proceeded, not merely from themselves, but from errors of the public authorities, disordering the circulating medium, over which they had no control, and which have, in fact, doubled and trebled debts, by reducing, in that proportion, the value of the property which was to pay them? If all these circumstances, which characterize the present case, have taken place in theirs also, then follow the precedent. Be assured, the cases will be so rare as to produce no embarrassment, as never to settle into an injurious habit. The single feature of a sixty years’ service, as no other instance of it has yet occurred in our country, so it probably never may again. And should it occur, even once and again, it will not impoverish your treasury, as it takes nothing from that, and asks but a simple permission, by an act of natural right, to do one of moral justice.
In the ‘Thoughts on Lotteries,’ the following paper is referred to. It is here copied to spare the trouble of seeking for the-book.
Farewell Address To Th: Jefferson, President Of The United States.
[Agreed to by both Houses, February 7, 1809.]
Sir, The General Assembly of your native State cannot close their session, without acknowledging your services in the office which you are just about to lay down, and bidding you a respectful and affectionate farewell.
We have to thank you for the model of an administration conducted on the purest principles of republicanism; for pomp and state laid aside; patronage discarded; internal taxes abolished; a host of superfluous officers disbanded; the monarchic maxim that ‘a national debt is a national blessing,’ renounced, and more than thirty-three millions of our debt discharged; the native right to nearly one hundred millions of acres of our national domain extinguished; and, without the guilt or calamities of conquest, a vast and, fertile region added to our country, far more extensive than her original possessions, bringing along with it the Mississippi and the port of Orleans, the trade of the west to the Pacific Ocean, and in the intrinsic value of the land itself, a source of permanent and almost inexhaustible revenue. These are points in your administration which the historian will not fail to seize, to expand, and teach posterity to dwell upon with delight. Nor will he forget our peace with the civilized world, preserved through a season of uncommon difficulty and trial; the good-will cultivated with the unfortunate aborigines of our country, and the civilization humanely extended among them; the lesson taught the inhabitants of the coast of Barbary, that we have the means of chastising their piratical encroachments, and awing them into justice; and that theme, on which, above all others, the historic genius will hang with rapture, the liberty of speech and of the press, preserved inviolate, without which genius and science are given to man in vain.
In the principles on which you have administered the government, we see only the continuation and maturity of the same virtues and abilities, which drew upon you in your youth the resentment of Dunmore. From the first brilliant and happy moment of your resistance to foreign tyranny, until the present day, we mark with pleasure and with gratitude the same uniform, consistent character, the same warm and devoted attachment to liberty and the republic, the same Roman love of your country, her rights, her peace, her honor, her prosperity.
How blessed will be the retirement into which you are about to go! How deservedly blessed will it be! For you carry with you the richest of all rewards, the recollection of a life well spent in the service of your country, and proofs the most decisive, of the love, the gratitude, the veneration of your countrymen.
That your retirement may be as happy as your life has been virtuous and useful; that our youth may see, in the blissful close of your days, an additional inducement to form themselves on your model, is the devout and earnest prayer of your fellow-citizens who compose the General Assembly of Virginia.
TO JOHN QUINCY ADAMS.
Monticello, March 30, 1826.
Dear Sir,
I am thankful for the very interesting message and documents of which you have been so kind as to send me a copy, and will state my recollections as to the particular passage of the message to which you ask my attention. On the conclusion of peace, Congress, sensible of their right to assume independence, would not condescend to ask its acknowledgment from other nations, yet were willing, by some of the ordinary international transactions, to receive what would imply that acknowledgment. They appointed commissioners, therefore, to propose treaties of commerce to the principal nations of Europe. I was then a member of Congress, was of the committee appointed to prepare instructions for the commissioners, was, as you suppose, the draughtsman of those actually agreed to, and was joined with your father and Doctor Franklin to carry them into execution. But the stipulations making part of these instructions, which respected privateering, blockades, contraband, and freedom of the fisheries, were not original conceptions of mine. They had before been suggested by Doctor Franklin, in some of his papers in possession of the public, and had I think, been recommended in some letter of his to Congress I happen only to have been the inserter of them in the first public act which gave the formal sanction of a public authority. We accordingly proposed our treaties, containing these stipulations, to the principal governments of Europe. But we were then just emerged from a subordinate condition; the nations had as yet known nothing of us and had not yet reflected on the relations which it might be their interest to establish with us. Most of them, therefore, listened to our propositions with coyness and reserve; old Frederic alone closing with us without hesitation. The negotiator of Portugal, indeed, signed a treaty with us, which his government did not ratify, and Tuscany was near a final agreement. Becoming sensible, however, ourselves, that we should do nothing with the greater powers, we thought it better not to hamper our country with engagements to those of less significance, and suffered our powers to expire without closing any other negotiation. Austria soon after became desirous of a treaty with us, and her ambassador pressed it often on me; but our commerce with her being no object, I evaded her repeated invitations. Had these governments been then apprized of the station we should so soon occupy among nations, all, I believe, would have met us promptly and with frankness. These principles would then have been established with all, and from being the conventional law with us alone, would have slid into their engagements with one another, and become general. These are the facts within my recollection. They have not yet got into written history; but their adoption by our southern brethren will bring them into observance, and make them, what they should be, a part of the law of the world and of the reformation of principles for which they will be indebted to us. I pray you to accept the homage of my friendly and high consideration.
Th: Jefferson.
Monticello, June 24, 1826.
Respected Sir,
The kind invitation I receive from you, on the part of the citizens of the city of Washington, to be present with them at their celebration on the fiftieth anniversary of American Independence, as one of the surviving signers of an instrument pregnant with our own, and the fate of the world, is most flattering to myself, and heightened by the honorable accompaniment proposed for the comfort of such a journey. It adds sensibly to the sufferings of sickness, to be deprived by it of a personal participation in the rejoicings of that day. But acquiescence is a duty, under circumstances not placed among those we are permitted to control. I should indeed, with peculiar delight, have met and exchanged there congratulations personally with the small band, the remnant of that host of worthies, who joined with us on that day, in the bold and doubtful election we were to make for our country, between submission or the sword; and to have enjoyed with them the consolatory fact, that our fellow-citizens, after half a century of experience and prosperity, continue to approve the choice we made. May it be to the world, what I believe it will be (to some parts sooner, to others later, but finally to all), the signal of arousing men to burst the chains under which monkish ignorance and superstition had persuaded them to bind themselves, and to assume the blessings and security of self-government. That form which we have substituted, restores the free right to the unbounded exercise of reason and freedom of opinion. All eyes are opened, or opening, to the rights of man. The general spread of the light of science has already laid open to every view the palpable truth, that the mass of mankind has not been born with saddles on their backs, nor a favored few booted and spurred, ready to ride them legitimately, by the grace of God. These are grounds of hope for others. For ourselves, let the annual return of this day for ever refresh our recollections of these rights, and an undiminished devotion to them.
I will ask permission here to express the pleasure with which I should have met my ancient neighbors of the city of Washington and its vicinities, with whom I passed so many years of a pleasing social intercourse; an intercourse which so much relieved the anxieties of the public cares, and left impressions so deeply engraved in my affections, as never to be forgotten. With my regret that ill health forbids me the gratification of an acceptance, be pleased to receive for yourself, and those for whom you write, the assurance of my highest respect and friendly attachments.
Th: Jefferson.
Explanation of the Three Volumes bound in Marbled Paper.*
In these three volumes will be found copies of the official opinions given in writing by me to General Washington, while I was Secretary of State, with sometimes the documents belonging to the case. Some of these are the rough draughts, some press copies, some fair ones. In the earlier part of my acting in that office, I took no other note of the passing transactions; but after a while, I saw the importance of doing it in aid of my memory. Very often, therefore, I made memorandums on loose scraps of paper, taken out of my pocket in the moment, and laid by to be copied fair at leisure, which, however, they hardly ever were. These scraps, therefore, ragged, rubbed, and scribbled as they were, I had bound with the others by a binder, who came into my cabinet, did it under my own eye, and without the opportunity of reading a single paper. At this day, after the lapse of twenty-five years, or more, from their dates, I have given to the whole a calm revisal, when the passions of the time are passed away, and the reasons of the transactions act alone on the judgment. Some of the informations I had recorded, are now cut out from the rest, because I have seen that they were incorrect, or doubtful, or merely personal or private, with which we have nothing to do. I should perhaps have thought the rest not worth preserving, but for their testimony against the only history of that period, which pretends to have been compiled from authentic and unpublished documents.
[* These are the volumes containing the Ana to the time that the Author retired from the office of Secretary of State. The official opinions and documents referred to, being very voluminous, are for the most part omitted, to make room for the conversations which the same volumes comprise.]
But a short review of facts ***** will show, that the contests of that day were contests of principle between the advocates of republican, and those of kingly government, and that, had not the former made the efforts they did, our government would have been even at this early day, a very different thing from what the successful issue of those efforts have made it.
The alliance between the States under the old Articles of Confederation, for the purpose of joint defence against the aggressions of Great Britain, was found insufficient, as treaties of alliance generally are, to enforce compliance with their mutual stipulations; and these, once fulfilled, that bond was to expire of itself, and each State to become sovereign and independent in all things. Yet, it could not but occur to every one, that these separate independencies, like the petty States of Greece, would be eternally at war with each other, and would become at length the mere partisans and satellites of the leading powers of Europe. All, then, must have looked forward to some further bond of union, which would insure internal peace, and a political system of our own, independent of that of Europe. Whether all should be consolidated into a single government, or each remain independent as to internal matters, and the whole form a single nation as to what was foreign only, and whether that national government should be a monarchy or republic, would of course divide opinions, according to the constitutions, the habits, and the circumstances of each individual. Some officers of the army, as it has always been said and believed, (and Steuben and Knox have ever been named as the leading agents,) trained to monarchy by military habits, are understood to have proposed to General Washington, to decide this great question by the army before its disbandment, and to assume himself the crown, on the assurance of their support. The indignity with which he is said to have scouted this parricide proposition, was equally worthy of his virtue and wisdom. The next effort was, (on suggestion of the same individuals, in the moment of their separation,) the establishment of an hereditary order, under the name of the Cincinnati, ready prepared by that distinction to be engrafted into the future frame of government, and placing General Washington still at their head. The General wrote to me on this subject, while I was in Congress at Annapolis, and an extract from my letter is inserted in 5th Marshall’s History, page 28. He afterwards called on me at that place, on his way to a meeting of the society, and after a whole evening of consultation, he left that place fully determined to use all his endeavors for its total suppression. But he found it so firmly riveted in the affections of the members, that, strengthened as they happened to be by an adventitious occurrence of the moment, he could effect no more than the abolition of its hereditary principle. He called again on his return, and explained to me fully the opposition which had been made, the effect of the occurrence from France, and the difficulty with which its duration had been limited to the lives of the present members. Further details will be found among my papers, in his and my letters, and some in the Encyclopédic Méthodique et Dictionnaire d’Economic Politique, communicated by myself to M. Meusnier, its author, who had made the establishment of this society the ground, in that work, of a libel on our country.
The want of some authority which should procure justice to the public creditors, and an observance of treaties with foreign nations, produced, some time after, the call of a convention of the States at Annapolis. Although, at this meeting, a difference of opinion was evident on the question of a republican or kingly government, yet, so general through the States was the sentiment in favor of the former, that the friends of the latter confined themselves to a course of obstruction only, and delay, to every thing proposed; they hoped, that nothing being done, and all things going from bad to worse, a kingly government might be usurped, and submitted to by the people, as better than anarchy and wars, internal and external, the certain consequences of the present want of a general government. The effect of their manoeuvres, with the defective attendance of Deputies from the States, resulted in the measure of calling a more general convention, to be held at Philadelphia. At this the same party exhibited the same practices, and with the same views of preventing a government of concord, which they foresaw would be republican, and of forcing: through anarchy their way to monarchy. But the mass of that convention was too honest, too wise, and too steady, to be baffled and misled by their manoeuvres. One of these was a form of government proposed by Colonel Hamilton, which would have been in fact a compromise between the two parties of royalism and republicanism. According to this, the executive and one branch of the legislature were to be during good behavior, i.e. for life, and the governors of the States were to be named by these two permanent organs. This, however, was rejected; on which Hamilton left the convention, as desperate, and never returned again until near its final conclusion. These opinions and efforts, secret or avowed, of the advocates for monarchy, had begotten great jealousy through the States generally; and this jealousy it was, which excited the strong opposition to the conventional constitution; a jealousy which yielded at last only to a general determination to establish certain amendments, as barriers against a government either monarchical or consolidated. In what passed through the whole period of these conventions, I have gone on the information of those who were members of them, being absent myself on my mission to France.
I returned from that mission in the first year of the new government, having landed in Virginia in December, 1789, and proceeded to New York in March, 1790, to enter on the office of Secretary of State. Here, certainly, I found a state of things which, of all I had ever contemplated, I the least expected. I had left France in the first year of her revolution, in the fervor of natural rights, and zeal for reformation. My conscientious devotion to these rights could not be heightened, but it had been aroused and excited by daily exercise. The President received me cordially, and my colleagues and the circle of principal citizens, apparently with welcome. The courtesies of dinner-parties given me, as a stranger newly arrived among them, placed me at once in their familiar society. But I cannot describe the wonder and mortification with which the table conversations filled me. Politics were the chief topic, and a preference of kingly over republican government, was evidently the favorite sentiment. An apostate I could not be, nor yet a hypocrite; and I found myself, for the most part, the only advocate on the republican side of the question, unless among the guests there chanced to be some member of that party from the legislative Houses. Hamilton’s financial system had then passed. It had two objects; 1. as a puzzle, to exclude popular understanding and inquiry; 2. as a machine for the corruption of the legislature: for he avowed the opinion, that man could be governed by one of two motives only, force or interest: force, he observed, in this country, was out of the question, and the interests, therefore, of the members must be laid hold of, to keep the legislature in unison with the executive. And with grief and shame it must be acknowledged that his machine was not without effect; that even in this, the birth of our government, some members were found sordid enough to bend their duty, to their interests, and to look after personal rather than public good.
It is well known that during the war, the greatest difficulty we encountered, was the want of money or means to pay our soldiers who fought, or our farmers, manufacturers, and merchants, who furnished the necessary supplies of food and clothing for them. After the expedient of paper money had exhausted itself, certificates of debt were given to the individual creditors, with assurance of payment, so soon as the United States should be able. But the distresses of these people often obliged them to part with these for the half, the fifth, and even a tenth of their value; and speculators had made a trade of cozening them from the holders, by the most fraudulent practices, and persuasions that they would never be paid. In the bill for funding and paying these, Hamilton made no difference between the original holders, and the fraudulent purchasers of this paper. Great and just repugnance arose at putting these two classes of creditors on the same footing, and great exertions were used to pay the former the full value, and to the latter, the price only which they had paid, with interest. But this would have prevented the game which was to be played, and for which the minds of greedy members were already tutored and prepared. When the trial of strength, on these several efforts, had indicated the form in which the bill would finally pass, this being known within doors sooner than without, and especially, than to those who were in distant parts of the Union, the base scramble began. Couriers and relay-horses by land, and swift-sailing pilot-boats by sea, were flying in all directions. Active partners and agents were associated and employed in every State, town, and country neighborhood, and this paper was bought up at five shillings, and even as low as two shillings in the pound, before the holder knew that Congress had already provided for its redemption at par. Immense sums were thus filched from the poor and ignorant, and fortunes accumulated by those who had themselves been poor enough before. Men thus enriched by the dexterity of a leader, would follow of course the chief who was leading them to fortune, and become the zealous instruments of all his enterprises.
This game was over, and another was on the carpet at the moment of my arrival; and to this I was most ignorantly and innocently made to hold the candle. This fiscal manoeuvre is well known by the name of the Assumption. Independently of the debts of Congress, the States had, during the war, contracted separate and heavy debts; and Massachusetts particularly, in an absurd attempt, absurdly conducted, on the British post of Penobscot: and the more debt Hamilton could rake up, the more plunder for his mercenaries. This money, whether wisely or foolishly spent, was pretended to have been spent for general purposes, and ought, therefore, to be paid from the general purse. But it was objected, that nobody knew what these debts were, what their amount, or what their proofs. No matter; we will guess them to be twenty millions. But of these twenty millions, we do not know how much should be reimbursed to one State, or how much to another. No matter; we will guess. And so another scramble was set on foot among the several States, and some got much, some little, some nothing. But the main object was obtained, the phalanx of the Treasury was reinforced by additional recruits. This measure produced the most bitter and angry contests ever known in Congress, before or since the Union of the States. I arrived in the midst of it. But a stranger to the ground, a stranger to the actors on it, so long absent as to have lost all familiarity with the subject, and as yet unaware of its object, I took no concern in it. The great and trying question, however, was lost in the House of Representatives. So high were the feuds excited by this subject, that on its rejection business was suspended. Congress met and adjourned from day to day without doing any thing, the parties being too much out of temper to do business together. The eastern members particularly, who, with Smith from South Carolina, were the principal gamblers in these scenes, threatened a secession and dissolution. Hamilton was in despair. As I was going to the President’s one day, I met him in the street. He walked me backwards and forwards before the President’s door for half an hour. He painted pathetically the temper into which the legislature had been wrought; the disgust of those who were called the creditor States; the danger of the secession of their members, and the separation of the States. He observed that the members of the administration ought to act in concert; that though this question was not of my department, yet a common duty should make it a common concern; that the President was the centre on which all administrative questions ultimately rested, and that all of us should rally around him, and support, with joint efforts, measures approved by him; and that the question having been lost by a small majority only, it was probable that an appeal from me to the judgment and discretion of some of my friends, might effect a change in the vote, and the machine of government, now suspended, might be again set into motion. I told him that I was really a stranger to the whole subject; that not having yet informed myself of the system of finance adopted, I knew not how far this was a necessary sequence; that undoubtedly, if its rejection endangered a dissolution of our Union at this incipient stage, I should deem that the most unfortunate of all consequences, to avert which all partial and temporary evils should be yielded. I proposed to him, however, to dine with me the next day, and I would invite another friend or two, bring them into conference together, and I thought it impossible that reasonable men, consulting together coolly, could fail, by some mutual sacrifices of opinion, to form a compromise which was to save the Union. The discussion took place. I could take no part in it but an exhortatory one, because I was a stranger to the circumstances which should govern it. But it was finally agreed, that whatever importance had been attached to the rejection of this proposition, the preservation of the Union and of concord among the States was more important, and that therefore it would be better that the vote of rejection should be rescinded, to effect which, some members should change their votes. But it was observed that this pill would be peculiarly bitter to the Southern States, and that some concomitant measure should be adopted to sweeten it a little to them. There had before been propositions to fix the seat of government either at Philadelphia, or at Georgetown on the Potomac; and it was thought that by giving it to Philadelphia for ten years, and to Georgetown permanently afterwards, this might, as an anodyne, calm in some degree the ferment which might be excited by the other measure alone. So two of the Potomac members (White and Lee, but White with a revulsion of stomach almost convulsive,) agreed to change their votes, and Hamilton undertook to carry the other point. In doing this, the influence he had established over the eastern members, with the agency of Robert Morris with those of the middle States, effected his side of the engagement; and so the Assumption was passed, and twenty millions of stock divided among favored States, and thrown in as a pabulum to the stock-jobbing herd. This added to the number of votaries to the Treasury, and made its chief the master of every vote in the legislature, which might give to the government the direction suited to his political views.
I know well, and so must be understood, that nothing like a majority in Congress had yielded to this corruption. Far from it. But a division, not very unequal, had already taken place in the honest part of that body, between the parties styled republican and federal. The latter being monarchists in principle, adhered to Hamilton of course, as their leader in that principle, and this mercenary phalanx added to them, insured him always a majority in both Houses: so that the whole action of the legislature was now under the direction of the Treasury. Still the machine was not complete. The effect of the funding system, and of the Assumption, would be temporary; it would be lost with the loss of the individual members whom it had enriched, and some engine of influence more permanent must be contrived, while these myrmidons were yet in place to carry it through all opposition. This engine was the Bank of the United States. All that history is known, so I shall say nothing about it. While the government remained at Philadelphia, a selection of members of both Houses were constantly kept as directors, who, on every question interesting to that institution, or to the views of the federal head, voted at the will of that head; and, together with the stock-holding members, could always make the federal vote that of the majority. By this combination, legislative expositions were given to the constitution, and all the administrative laws were shaped on the model of England and so passed. And from this influence we were not relieved, until the removal from the precincts of the bank, to Washington. Here then was the real ground of the opposition which was made to the course of administration. Its object was to preserve the legislature pure and independent of the executive, to restrain, the administration to republican forms and principles, and not permit the constitution to be construed into a monarchy, and to be warped, in practice, into all the principles and pollutions of their favorite English model. Nor was this an opposition to General Washington. He was true to the republican charge confided to him; and has solemnly and repeatedly protested to me, in our conversations, that he would lose the last drop of his blood in support of it; and he did this the oftener and with the more earnestness, because he knew my suspicions of Hamilton’s designs against it, and wished to quiet them. For he was not aware of the drift, or of the effect of Hamilton’s schemes. Unversed in financial projects and calculations and budgets, his approbation of them was bottomed on his confidence in the man.
But Hamilton was not only a monarchist, but for a monarchy bottomed on corruption. In proof of this, I will relate an anecdote, for the truth of which I attest the God who made me. Before the President set out on his southern tour in April, 1791, he addressed a letter of the fourth of that month, from Mount Vernon, to the Secretaries of State, Treasury, and War, desiring that if any serious and important cases should arise during his absence, they would consult and act on them. And he requested that the Vice-President should also be consulted. This was the only occasion on which that officer was ever requested to take part in a cabinet question. Some occasion for consultation arising, I invited those gentlemen (and the Attorney General, as well as I remember,) to dine with me, in order to confer on the subject. After the cloth was removed, and our question agreed and dismissed, conversation began on other matters, and, by some circumstance, was led to the British constitution, on which Mr. Adams observed, ‘Purge that constitution of its corruption, and give to its popular branch equality of representation, and it would be the most perfect constitution ever devised by the wit of man.’ Hamilton paused and said, ‘Purge it of its corruption, and give to its popular branch equality of representation, and it would become an impracticable government: as it stands at present, with all its supposed defects, it is the most perfect government which ever existed.’ And this was assuredly the exact line which separated the political creeds of these two gentlemen. The one was for two hereditary branches and an honest elective one: the other, for an hereditary King, with a House of Lords and Commons corrupted to his will, and standing between him and the people. Hamilton was, indeed, a singular character. Of acute understanding, disinterested, honest, and honorable in all private transactions, amiable in society, and duly valuing virtue in private life, yet so bewitched and perverted by the British example, as to be under thorough conviction that corruption was essential to the government of a nation. Mr. Adams had originally been a republican. The glare of royalty and nobility, during his mission to England, had made him believe their fascination a necessary ingredient in government; and Shays’s rebellion, not sufficiently understood where he then was, seemed to prove that the absence of want and oppression, was not a sufficient guarantee of order. His book on the American Constitutions having made known his political bias, he was taken up by the monarchical federalists in his absence, and, on his return to the United States, he was by them made to believe that the general disposition of our citizens was favorable to monarchy. He here wrote his Davila, as a supplement to the former work, and his election to the Presidency confirmed him in his errors. Innumerable addresses too, artfully and industriously poured in upon him, deceived him into a confidence that he was on the pinnacle of popularity, when the gulph was yawning at his feet, which was to swallow up him and his deceivers. For when General Washington was withdrawn, these energumeni of royalism, kept in check hitherto by the dread of his honesty, his firmness, his patriotism, and the authority of his name, now mounted on the car of State and free from control, like Phaeton on that of the sun, drove headlong and wild, looking neither to right nor left, nor regarding any thing but the objects they were driving at; until, displaying these fully, the eyes of the nation were opened, and a general disbandment of them from the public councils took place.
Mr. Adams, I am sure, has been long since convinced of the treacheries with which he was surrounded during his administration. He has since thoroughly seen, that his constituents were devoted to republican government, and whether his judgment is resettled on its ancient basis, or not, he is conformed as a good citizen to the will of the majority, and would now, I am persuaded, maintain its republican structure with the zeal and fidelity belonging to his character. For even an enemy has said, ‘He is always an honest man, and often a great one.’ But in the fervor of the fury and follies of those who made him their stalking-horse, no man who did not witness it can form an idea of their unbridled madness, and the terrorism with which they surrounded themselves. The horrors of the French revolution, then raging, aided them mainly, and using that as a raw-head and bloody-bones, they were enabled by their stratagems of X. Y. Z. in which ——— was a leading mountebank, their tales of tub-plots, ocean-massacres, bloody-buoys, and pulpit-lyings and slanderings, and maniacal ravings of their Gardiners, their Osgoods, and Parishes, to spread alarm into all but the firmest breasts. Their Attorney General had the impudence to say to a republican member, that deportation must be resorted to, of which, said he, ‘you republicans have set the example’; thus daring to identify us with the murderous Jacobins of France. These transactions, now recollected but as dreams of the night, were then sad realities; and nothing rescued us from their liberticide effect, but the unyielding opposition of those firm spirits who sternly maintained their post in defiance of terror, until their fellow-citizens could be aroused to their own danger, and rally and rescue the standard of the constitution. This has been happily done. Federalism and monarchism have languished from that moment, until their treasonable combinations with the enemies of their country during the late war, their plots of dismembering the Union, and their Hartford Convention, have consigned them to the tomb of the dead: and I fondly hope, ‘we may now truly say, We are all republicans, all federalists,’ and that the motto of the standard to which our country will for ever rally, will be, ‘Federal union, and republican government’: and sure I am we may say, that we are indebted for the preservation of this point of ralliance, to that opposition of which so injurious an idea is so artfully insinuated and excited in this history.
Much of this relation is notorious to the world; and many intimate proofs of it will be found in these notes. From the moment where they end, of my retiring from the administration, the federalists * got unchecked hold of General Washington. His memory was already sensibly impaired by age, the firm tone of mind for which he had been remarkable, was beginning to relax, its energy was abated, a listlessness of labor, a desire for tranquillity had crept on him, and a willingness to let others act, and even think for him. Like the rest of mankind, he was disgusted with atrocities of the French revolution, and was not sufficiently aware of the difference between the rabble who were used as instruments of their perpetration, and the steady and rational character of the American people, in which he had not sufficient confidence. The opposition too of the republicans to the British treaty, and the zealous support of the federalists in that unpopular but favorite measure of theirs, had made him all their own. Understanding, moreover, that I disapproved of that treaty, and copiously nourished with falsehoods by a malignant neighbor of mine, who ambitioned to be his correspondent, he had become alienated from myself personally, as from the republican body generally of his fellow-citizens; and he wrote the letters to Mr. Adams and Mr. Carroll, over which, in devotion to his imperishable fame, we must for ever weep as monuments of mortal decay.
Th: Jefferson. February 4th, 1818.
* See conversation with General Washington, of October 1,1792,
****
August the 13th, 1791. Notes of a conversation between Alexander Hamilton and Thomas Jefferson. Th: Jefferson mentioned to him a letter received from John Adams, disavowing Publicola, and denying that he ever entertained a wish to bring this country under an hereditary executive, or introduce an hereditary branch of legislature, &c. See his letter. Alexander Hamilton condemning Mr. Adams’s writings, and most particularly Davila, as having a tendency to weaken the present government, declared in substance as follows: ‘I own it is my own opinion, though I do not publish it in Dan or Beersheba, that the present government is not that which will answer the ends of society, by giving stability and protection to its rights, and that it will probably be found expedient to go into the British form. However, since we have undertaken the experiment, I am for giving it a fair course, whatever my expectations may be. The success, indeed, so far, is greater than I had expected, and therefore, at present, success seems more possible than it had done heretofore, and there are still other and other stages of improvement, which, if the present does not succeed, may be tried, and ought to be tried, before we give up the republican form altogether; for that mind must be really depraved, which would not prefer the equality of political rights, which is the foundation of pure republicanism, if it can be obtained consistently with order. Therefore, whoever by his writings disturbs the present order of things, is really blameable, however pure his intentions may be, and he was sure Mr. Adams’s were pure.’ This is the substance of a declaration made in much more lengthy terms, and which seemed to be more formal than usual for a private conversation between two, and as if intended to qualify some less guarded expressions which had been dropped on former occasions. Th: Jefferson has committed it to writing in the moment of A. Hamilton’s leaving the room.
December the 25th, 1791. Colonel Gunn (of Georgia), dining the other day with Colonel Hamilton, said to him, with that plain freedom he is known to use, ‘I wish, Sir, you would advise your friend King to observe some kind of consistency in his votes. There has been scarcely a question before the Senate on which he has not voted both ways. On the representation bill, for instance, he first voted for the proposition of the Representatives, and ultimately voted against it.’ ‘Why,’ says Colonel Hamilton, ‘I ‘ll tell you as to that, Colonel Gunn, that it never was intended that bill should pass.’ Gunn told this to Butler, who told it to Th: Jefferson.
CONVERSATIONS WITH THE PRESIDENT.
February the 28th, 1792. I was to have been with him long enough before three o’clock (which was the hour and day he received visits) to have opened to him a proposition for doubling the velocity of the post-riders, who now travel about fifty miles a day, and might, without difficulty, go one hundred, and for taking measures (by way-bills) to know where the delay is, when there is any. I was delayed by business, so as to have scarcely time to give him the outlines. I run over them rapidly, and observed afterwards, that I had hitherto never spoken to him on the subject of the post-office, not knowing whether it was considered as a revenue law, or a law for the general accommodation of the citizens: that the law just passed seemed to have removed the doubt, by declaring that the whole profits of the office should be applied to extending the posts, and that even the past profits should be refunded by the Treasury for the same purpose: that I therefore conceived it was now in the department of the Secretary of State: that I thought it would be advantageous so to declare it for another reason, to wit, that the department of the Treasury possessed already such an influence as to swallow up the whole executive powers, and that even the future Presidents (not supported by the weight of character which himself possessed) would not be able to make head against this department. That in urging this measure I had certainly no personal interest, since, if I was supposed to have any appetite for power, yet, as my career would certainly be exactly as short as his own, the intervening time was too short to be an object. My real wish was to avail the public of every occasion, during the residue of the President’s period, to place things on a safe footing. He was now called on to attend his company, and he desired me to come and breakfast with him the next morning.
February the 29th. I did so; and after breakfast we retired to his room, and I unfolded my plan for the post-office, and after such an approbation of it as he usually permitted himself on the first presentment of any idea, and desiring me to commit it to writing, he, during that pause of conversation which follows a business closed, said, in an affectionate tone, that he had felt much concern at an expression which dropped from me yesterday, and which marked my intention of retiring when he should. That as to himself, many motives obliged him to it. He had, through the whole course of the war, and most particularly at the close of it, uniformly declared his resolution to retire from public affairs, and never to act in any public office; that he had retired under that firm resolution: that the government however, which had been formed, being found evidently too inefficacious, and it being supposed that his aid was of some consequence towards bringing the people to consent to one of sufficient efficacy for their own good, he consented to come into the convention, and on the same motive, after much pressing, to take a part in the new government, and get it under way. That were he to continue longer, it might give room to say, that having tasted the sweets of office, he could not do without them: that he really felt himself growing old, his bodily health less firm, his memory, always bad, becoming worse, and perhaps the other faculties of his mind showing a decay to others of which he was insensible himself; that this apprehension particularly oppressed him: that he found, moreover, his activity lessened, business therefore more irksome, and tranquillity and retirement become an irresistible passion. That, however he felt himself obliged, for these reasons, to retire from the government, yet he should consider it as unfortunate, if that should bring on the retirement of the great officers of the government, and that this might produce a shock on the public mind of dangerous consequence.
I told him that no man had ever had less desire of entering into public offices than myself; that the circumstance of a perilous war, which brought every thing into danger, and called for all the services which every citizen could render, had induced me to undertake the administration of the government of Virginia; that I had both before and after refused repeated appointments of Congress to go abroad in that sort of office, which, if I had consulted my own gratification, would always have been the most agreeable to me; that at the end of two years, I resigned the government of Virginia, and retired with a firm resolution never more to appear in public life; that a domestic loss, however, happened, and made me fancy that absence and a change of scene for a time might be expedient for me; that I therefore accepted a foreign appointment, limited to two years; that at the close of that, Doctor Franklin having left France, I was appointed to supply his place, which I had accepted, and though I continued in it three or four years, it was under the constant idea of remaining only a year or two longer; that the revolution in France coming on, I had so interested myself in the event of that, that when obliged to bring my family home, I had still an idea of returning and awaiting the close of that, to fix the era of my final retirement; that on my arrival here I found he had appointed me to my present office; that he knew I had not come into it without some reluctance; that it was, on my part, a sacrifice of inclination to the opinion that I might be more serviceable here than in France, and with a firm resolution in my mind, to indulge my constant wish for retirement at no very distant day; that when, therefore, I had received his letter, written from Mount Vernon, on his way to Carolina and Georgia (April the 1st, 1791), and discovered, from an expression in that, that he meant to retire from the government ere long, and as to the precise epoch there could be no doubt, my mind was immediately made up, to make that the epoch of my own retirement from those labors of which I was heartily tired. That, however, I did not believe there was any idea in either of my brethren in the administration of retiring; that on the contrary, I had perceived at a late meeting of the trustees of the sinking fund, that the Secretary of the Treasury had developed the plan he intended to pursue, and that it embraced years in its view.
He said, that he considered the Treasury department as a much more limited one, going only to the single object of revenue, while that of the Secretary of State, embracing nearly all the objects of administration, was much more important, and the retirement of the officer therefore, would be more noticed: that though the government had set out with a pretty general good will of the public, yet that symptoms of dissatisfaction had lately shown themselves far beyond what he could have expected, and to what height these might arise, in case of too great a change in the administration, could not be foreseen.
I told him that in my opinion, there was only a single source of these discontents. Though they had indeed appeared to spread themselves over the War department also, yet I considered that as an overflowing only from their real channel, which would never have taken place, if they had not first been generated in another department, to wit, that of the Treasury. That a system had there been contrived, for deluging the States with paper-money instead of gold and silver, for withdrawing our citizens from the pursuits of commerce, manufactures, buildings, and other branches of useful industry, to occupy themselves and their capitals in a species of gambling, destructive of morality, and which had introduced its poison into the government itself. That it was a fact, as certainly known as that he and I were then conversing, that particular members of the legislature, while those laws were on the carpet, had feathered their nests with paper, had then voted for the laws, and constantly since lent all the energy of their talents, and instrumentality of their offices, to the establishment and enlargement of this system; that they had chained it about our necks for a great length of time, and in order to keep the game in their hands, had, from time to time, aided in making such legislative constructions of the constitution, as made it a very different thing from what the people thought they had submitted to; that they had now brought forward a proposition far beyond every one ever yet advanced, and to which the eyes of many were turned, as the decision which was to let us know, whether we live under a limited or an unlimited government. He asked me to what proposition I alluded; I answered, to that in the report on manufactures, which, under color of giving bounties for the encouragement of particular manufactures, meant to establish the doctrine, that the power given by the constitution to collect taxes to provide for the general welfare of the United States, permitted Congress to take every thing under their management which they should deem for the public welfare, and which is susceptible of the application of money; consequently, that the subsequent enumeration of their powers was not the description to which resort must be had, and did not at all constitute the limits of their authority: that this was a very different question from that of the bank, which was thought an incident to an enumerated power: that, therefore, this decision was expected with great anxiety; that, indeed, I hoped the proposition would be rejected, believing there was a majority in both Houses against it, and that if it should be, it would be considered as a proof that things were returning into their true channel: and that, at any rate, I looked forward to the broad representation which would shortly take place, for keeping the general constitution on its true ground; and that this would remove a great deal of the discontent which had shown itself. The conversation ended with this last topic. It is here stated nearly as much at length as it really was; the expressions preserved where I could recollect them, and their substance always faithfully stated.
Th: Jefferson.
March 1, 1792.
On the 2nd of January, 1792, Messrs. Fitzsimmons and Gerry (among others) dined with me. These two staid, with a Mr. Learned of Connecticut, after the company was gone. We got on the subject of references by the legislature to the Heads of departments, considering their mischief in every direction. Gerry and Fitzsimmons clearly opposed to them.
Two days afterwards (January the 4th), Mr. Bourne from Rhode Island presented a memorial from his State, complaining of inequality in the Assumption, and moved to refer it to the Secretary of the Treasury. Fitzsimmons, Gerry, and others opposed it; but it was carried.
January the 19th. Fitzsimmons moved, that the President of the United States be requested to direct the Secretary of the Treasury, to lay before the House information to enable the legislature to judge of the additional revenue necessary on the increase of the military establishment. The House, on debate, struck out the words, ‘President of the United States.’
March the 7th. The subject resumed. An animated debate took place on the tendency of references to the Heads of departments; and it seemed that a great majority would be against it: the House adjourned. Treasury greatly alarmed, and much industry supposed to be used before next morning, when it was brought on again, and debated through the day, and on the question, the Treasury carried it by thirty-one to twenty-seven: but deeply wounded, since it was seen that all Pennsylvania, except Jacobs, voted against the reference; that Tucker of South Carolina voted for it, and Sumpter absented himself, debauched for the moment only, because of the connection of the question with a further assumption which South Carolina favored; but showing that they never were to be counted on among the Treasury votes.
Some others absented themselves. Gerry changed sides. On the whole, it showed that Treasury influence was tottering. Committed to writing this 10th of March, 1792.
March the 11th, 1792. Consulted verbally by the President, on whom a committee of the Senate (Izard, Morris, and King) are to wait to-morrow morning, to know whether he will think it proper to redeem our Algerine captives, and make a treaty with the Algerines, on the single vote of the Senate, without taking that of the Representatives.
My opinions run on the following heads.
We must go to Algiers with cash in our hands. Where shall we get it? By loan? By converting money now in the treasury?
Probably a loan might be obtained on the President’s authority: but as this could not be repaid without a subsequent act of legislature, the Representatives might refuse it. So if money in the treasury be converted, they may refuse to sanction it.
The subsequent approbation of the Senate being necessary to validate a treaty, they expect to be consulted beforehand, if the case admits.
So the subsequent act of the Representatives being necessary where money is given, why should not they expect to be consulted in like manner, when the case admits? A treaty is a law of the land. But prudence will point out this difference to be attended to in making them; viz. where a treaty contains such articles only as will go into execution of themselves, or be carried into execution by the judges, they may be safely made; but where there are articles which require a law to be passed afterwards by the legislature, great caution is requisite.
For example; the consular convention with France required a very small legislative regulation. This convention was unanimously ratified by the Senate. Yet the same identical men threw by the law to enforce it at the last session, and the Representatives at this session have placed it among the laws which they may take up or not, at their own convenience, as if that was a higher motive than the public faith.
Therefore, against hazarding this transaction without the sanction of both Houses.
The President concurred. The Senate express the motive for this proposition, to be a fear that the Representatives would not keep the secret. He has no opinion of the secrecy of the Senate. In this very case, Mr. Izard made the communication to him, sitting next to him at table, on one hand, while a lady (Mrs. McLane) was on his other hand, and the French minister next to her; and as Mr. Izard got on with his communication, his voice kept rising, and his stutter bolting the words out loudly at intervals, so that the minister might hear if he would. He said he had a great mind at one time to have got up, in order to put a stop to Mr. Izard.
March the 11th, 1792. Mr. Sterret tells me that sitting round a fire the other day with four or five others, Mr. Smith (of South Carolina) was one. Somebody mentioned that the murderers of Hogeboom, sheriff of Columbia county, New York, were acquitted. ‘Ay,’ says Smith, ‘this is what comes of your damned trial by jury.’
1791. Towards the latter end of November, Hamilton had drawn Ternant into a conversation on the subject of the treaty of commerce recommended by the National Assembly of France to be negotiated with us, and, as he had no ready instructions on the subject, he led him into a proposal that Ternant should take the thing up as a volunteer with me, that we should arrange conditions, and let them go for confirmation or refusal. Hamilton communicated this to the President, who came into it, and proposed it to me. I disapproved of it, observing, that such a volunteer project would be binding on us, and not them; that it would enable them to find out how far we would go, and avail themselves of it. However, the President thought it worth trying, and I acquiesced. I prepared a plan of treaty for exchanging the privileges of native subjects, and fixing all duties for ever as they now stood. Hamilton did not like this way of fixing the duties, because, he said, many articles here would bear to be raised, and therefore, he would prepare a tariff. He did so, raising duties for the French, from twenty-five to fifty per cent. So they were to give us the privileges of native subjects, and we, as a compensation, were to make them pay higher duties. Hamilton, having made his arrangements with Hammond to pretend that though he had no powers to conclude a treaty of commerce, yet his general commission authorized him to enter into the discussion of one, then proposed to the President at one of our meetings, that the business should be taken up with Hammond in the same informal way. I now discovered the trap which he had laid, by first getting the President into the step with Ternant. I opposed the thing warmly. Hamilton observed, if we did it with Ternant we should also with Hammond. The President thought this reasonable. I desired him to recollect, I had been against it with Ternant, and only acquiesced under his opinion. So the matter went off as to both. His scheme evidently was, to get us engaged first with Ternant, merely that he might have a pretext to engage us on the same ground with Hammond, taking care, at the same time, by an extravagant tariff, to render it impossible we should come to any conclusion with Ternant: probably meaning, at the same time, to propose terms so favorable to Great Britain, as would attach us to that country by treaty. On one of those occasions he asserted, that our commerce with Great Britain and her colonies was put on a much more favorable footing than with France and her colonies. I therefore prepared the tabular comparative view of the footing-of our commerce with those nations, which see among my papers. See also my project of a treaty and Hamilton’s tariff. Committed to writing March the 11th, 1792.
It was observable, that whenever, at any of our consultations, any thing was proposed as to Great Britain, Hamilton had constantly ready something which Mr. Hammond had communicated to him, which suited the subject and proved the intimacy of their communications; insomuch, that I believe he communicated to Hammond all our views, and knew from him, in return, the views of the British court. Many evidences of this occurred; I will state some. I delivered to the President my report of instructions for Carmichael and Short, on the subject of navigation, boundary, and commerce, and desired him to submit it to Hamilton. Hamilton made several just criticisms on different parts of it. But where I asserted that the United States had no right to alienate an inch of the territory of any State, he attacked and denied the doctrine. See my report, his note, and my answer. A few days after came to hand Kirkland’s letter, informing us that the British, at Niagara, expected to run a new line between themselves and us; and the reports of Pond and Stedman, informing us it was understood at Niagara, that Captain Stevenson had been sent here by Simcoe to settle that plan with Hammond. Hence Hamilton’s attack of the principle I had laid down, in order to prepare the way for this new line. See minute of March the 9th. Another proof. At one of our consultations, about the last of December, I mentioned that I wished to give in my report on commerce, in which I could not avoid recommending a commercial retaliation against Great Britain. Hamilton opposed it violently: and among other arguments, observed, that it was of more importance to us to have the posts than to commence a commercial war; that this, and this alone, would free us from the expense of the Indian wars; that it would therefore be the height of imprudence in us, while treating for the surrender of the posts, to engage in any thing which would irritate them; that if we did so, they would naturally say, ‘These people mean war; let us therefore hold what we have in our hands.’ This argument, struck me forcibly, and I said, ‘If there is a hope of obtaining the posts, I agree it would be imprudent to risk that hope by a commercial retaliation. I will, therefore, wait till Mr. Hammond gives me in his assignment of breaches, and if that gives a glimmering of hope that they mean to surrender the posts, I will not give in my report till the next session.’ Now, Hammond had received my assignment of breaches on the 15th of December, and about the 22nd or 23rd had made me an apology for not having been able to send me his counter-assignment of breaches; but in terms which showed I might expect it in a few days. From the moment it escaped my lips in the presence of Hamilton, that I would not give in my report till I should see Hammond’s counter-complaint, and judge if there was a hope of the posts, Hammond never said a word to me on any occasion, as to the time he should be ready. At length the President got out of patience, and insisted I should jog him. This I did on the 21st of February, at the President’s assembly: he immediately promised I should have it in a few days, and accordingly, on the 5th of March I received it.
Written March the 11th, 1792.
March the 12th, 1792. Sent for by the President, and desired to bring the letter he had signed to the King of France. Went. He said the House of Representatives had, on Saturday, taken up the communication he had made of the King’s letter to him, and come to a vote in their own name; that he did not expect this when he sent this message and the letter, otherwise he would have sent the message without the letter, as I had proposed. That he apprehended the legislature would be endeavoring to invade the executive. I told him, I had understood the House had resolved to request him to join their congratulations to his on the completion and acceptance of the constitution; on which part of the vote, there were only two dissentients (Barnwell and Benson); that the vote was thirty-five to sixteen on the part which expressed an approbation of the wisdom of the constitution; that in the letter he had signed, I had avoided saying a word in approbation of the constitution, not knowing whether the King, in his heart, approved it. ‘Why, indeed,’ says he,’ I begin to doubt very much of the affairs of France; there are papers from London as late as the 10th of January, which represent them as going into confusion. He read over the letter he had signed, found there was not a word which could commit his judgment about the constitution, and gave it to me back again. This is one of many proofs I have had, of his want of confidence in the event of the French revolution. The fact is, that Gouverneur Morris, a highflying monarchy man, shutting his eyes and his faith to every fact against his wishes, and believing every thing he desires to be true, has kept the President’s mind constantly poisoned with his forebodings. That the President wishes the revolution may be established, I believe from several indications. I remember, when I received the news of the King’s flight and capture, I first told him of it at his assembly. I never saw him so much dejected by any event in my life. He expressed clearly, on this occasion, his disapprobation of the legislature referring things to the Heads of departments.
Written March the 12th.
Eodem die. Ten o’clock, A. M. The preceding was about nine o’clock. The President now sends Lear to me, to ask what answer he shall give to the committee, and particularly, whether he shall add to it, that, ‘in making the communication, it was not his expectation that the House should give any answer.’ I told Mr. Lear, that I thought the House had a right, independently of legislation, to express sentiments on other subjects. That when these subjects did not belong to any other branch particularly, they would publish them by their own authority; that in the present case, which respected a foreign nation, the President being the organ of our nation with other nations, the House would satisfy their duty, if, instead of a direct communication, they should pass their sentiments through the President: that if expressing a sentiment were really an invasion of the executive power, it was so faint a one, that it would be difficult to demonstrate it to the public, and to a public partial to the French revolution, and not disposed to considered the approbation of it from any quarter is improper. That the Senate, indeed, had given many indications of their wish to invade the executive power: the Representatives had done it in one case, which was indeed mischievous and alarming; that of giving orders to the Heads of the executive departments, without consulting the President; but that the late vote for directing the Secretary of the Treasury to report ways and means, though carried, was carried by so small a majority, and with the aid of members so notoriously under local influence on that question, as to give a hope that the practice would be arrested, and the constitutional course be taken up, of asking the President to have information laid before them. But that in the present instance, it was so far from being clearly an invasion of the executive, and would be so little approved by the general voice, that I could not advise the President to express any dissatisfaction at the vote of the House; and I gave Lear, in writing, what I thought should be his answers. See it.
March the 31st. A meeting at the President’s; present, Thomas Jefferson, Alexander Hamilton, Henry Knox, and Edmund Randolph. The subject was the resolution of the House of Representatives, of March the 27th, to appoint a committee to inquire into the causes of the failure of the late expedition under Major General St. Clair, with the power to call for such persons, papers, and records, as may be necessary to assist their inquiries. The committee had written to Knox for the original letters, instructions, &tc. The President had called us to consult, merely because it was the first example, and he wished that so far as it should become a precedent, it should be rightly conducted. He neither acknowledged nor denied, nor even doubted the propriety of what the House were doing, for he had not thought upon it, nor was acquainted with subjects of this kind: he could readily conceive there might be papers of so secret a nature, as that they ought not to be given up. We were not prepared, and wished time to think and inquire.
April the 2nd. Met again at the President’s, on the same subject. We had all considered, and were of one mind, first, that the House was an inquest, and therefore might institute inquiries. Secondly, that it might call for papers generally. Thirdly, that the executive ought to communicate such papers as the public good would permit, and ought to refuse those, the disclosure of which would injure the public: consequently were to exercise a discretion. Fourthly, that neither the committee nor House had a right to call on the Head of a department, who and whose papers were under the President alone; but that the committee should instruct their chairman to move the House to address the President. We had principally consulted the proceedings of the Commons in the case of Sir Robert Walpole, 13 Chandler’s Debates. For the first point, seepages 161, 170, 172,183, 187,207; for the second, pages 153, 173,207; for the third, 81, 173, Appendix, page 44; for the fourth, page 246. Note: Hamilton agreed with us in all these points, except as to the power of the House to call on Heads of departments. He observed, that as to his department, the act constituting it had made it subject to Congress, in some points, but he thought himself not so far subject, as to be obliged to produce all the papers they might call for. They might demand secrets of a very mischievous nature. [Here I thought he began to fear they would go to examining how far their own members and other persons in the government had been dabbling in stocks, banks, &c. and that he probably would choose in this case to deny their power; and, in short, he endeavored to place himself subject to the House, when the executive should propose what he did not like, and subject to the executive, when the House should propose any thing disagreeable.] I observed here a difference between the British parliament and our Congress; that the former was a legislature, an inquest, and a council (S. C. page 91.) for the King. The latter was, by the constitution, a legislature and an inquest, but not a council. Finally agreed, to speak separately to the members of the committee, and bring them by persuasion into the right channel. It was agreed in this case, that there was not a paper which might not be properly produced; that copies only should be sent, with an assurance, that if they should desire it, a clerk should attend with the originals to be verified by themselves. The committee were Fitzsimmons, Steele, Mercer, Clarke, Sedgwick, Giles, and Vining.
April the 9th, 1792. The President had wished to redeem our captives at Algiers, and to make a peace with them on paying an annual tribute. The Senate were willing to approve this, but unwilling to have the lower House applied to previously to furnish the money; they wished the President to take the money from the treasury, or open a loan for it. They thought that to consult the Representatives on one occasion, would give them a handle always to claim it, and would let them into a participation of the power of making treaties, which the constitution had given exclusively to the President and Senate. They said, too, that if the particular sum was noted by the Representatives, it would not be a secret. The President had no confidence in the secrecy of the Senate, and did not choose to take money from the treasury or to borrow. But he agreed he would enter into provisional treaties with the Algerines, not to be binding on us till ratified here. I prepared questions for consultation with the Senate, and added, that the Senate were to be apprized, that on the return of the provisional treaty, and after they should advise the ratification, he would not have the seal put to it till the two Houses should vote the money. He asked me, if the treaty stipulating a sum and ratified by him, with the advice of the Senate, would not be good under the constitution, and obligatory on the Representatives to furnish the money. I answered, it certainly would, and that it would be the duty of the Representatives to raise the money; but that they might decline to do what was their duty, and I thought it might be incautious to commit himself by a ratification with a foreign nation, where he might be left in the lurch in the execution: it was possible too, to conceive a treaty, which it would not be their duty to provide for. He said that he did not like throwing too much into democratic hands, that if they would not do what the constitution called on them to do, the government would be at an end, and must then assume another form. He stopped here; and I kept silence to see whether he would say any thing more in the same line, or add any qualifying expression to soften what he had said: but he did neither. I had observed, that wherever the agency of either, or both Houses would be requisite subsequent to a treaty, to carry it into effect, it would be prudent to consult them previously, if the occasion admitted. That thus it was, we were in the habit of consulting the Senate previously, when the occasion permitted, because their subsequent ratification would be necessary. That there was the same reason for consulting the lower House previously, where they were to be called on afterwards, and especially in the case of money, as they held the purse-strings, and would be jealous of them. However, he desired me to strike out the intimation that the seal would not be put till both Houses should have voted the money.
April the 6th. The President called on me before breakfast, and first introduced some other matter, then fell on the representation bill, which he had now in his possession for the tenth day. I had before given him my opinion in writing, that the method of apportionment was contrary to the constitution. He agreed that it was contrary to the common understanding of that instrument, and to what was understood at the time by the makers of it: that, yet it would bear the construction which the bill put, and he observed that the vote for and against the bill was perfectly geographical, a northern against a southern vote, and he feared he should be thought to be taking side with a southern party. I admitted the motive of delicacy, but that it should not induce him to do wrong: urged the dangers to which the scramble for the fractionary members would always lead. He here expressed his fear that there would, ere long, be a separation of the Union; that the public mind seemed dissatisfied and tending to this. He went home, sent for Randolph, the Attorney General, desired him to get Mr. Madison immediately and come to me, and if we three concurred in opinion that he should negative the bill, he desired to hear nothing more about it, but that we would draw the instrument for him to sign. They came. Our minds had been before made up.
We drew the instrument. Randolph carried it to him, and told him we all concurred in it. He walked with him to the door, and as if he still wished to get off, he said, ‘And you say you approve of this yourself.’ ‘Yes, Sir,’ says Randolph, ‘I do upon my honor.’ He sent it to the House of Representatives instantly. A few of the hottest friends of the bill expressed passion, but the majority were satisfied, and both in and out of doors it gave pleasure to have, at length, an instance of the negative being exercised.
Written this the 9th of April.
July the 10th, 1792. My letter of —— to the President, directed to him at Mount Vernon, had not found him there, but came to him here. He told me of this, and that he would take an occasion of speaking with me on the subject. He did so this day. He began by observing that he had put it off from day to day, because the subject was painful; to wit, his remaining in office, which that letter solicited. He said that the declaration he had made when he quitted his military command, of never again entering into public life, was sincere. That, however, when he was called on to come forward to set the present government in motion, it appeared to him that circumstances were so changed as to justify a change in his resolution: he was made to believe that in two years all would be well in motion, and he might retire. At the end of two years he found some things still to be done. At the end of the third year, he thought it was not worth while to disturb the course of things, as in one year more his office would expire, and he was decided then to retire. Now he was told there would still be danger in it. Certainly, if he thought so, he would conquer his longing for retirement. But he feared it would be said his former professions of retirement had been mere affectation, and that he was like other men, when once in office he could not quit it. He was sensible, too, of a decay of his hearing, perhaps his other faculties might fall off and he not be sensible of it. That with respect to the existing causes of uneasiness, he thought there we’re suspicions against a particular party, which had been carried a great deal too far: there might be desires, but he did not believe there were designs to change the form of government into a monarchy: that there might be a few who wished it in the higher walks of life, particularly in the great cities; but that the main body of the people in the eastern States were as steadily for republicanism as in the southern. That the pieces lately published, and particularly in Freneau’s paper, seemed to have in view the exciting opposition to the government. That this had taken place in Pennsylvania as to the excise-law, according to information he had received from General Hand. That they tended to produce a separation of the Union, the most dreadful of all calamities, and that whatever tended to produce anarchy, tended, of course, to produce a resort to monarchical government. He considered those papers as attacking him directly, for he must be a fool indeed to swallow the little sugar-plumbs here and there thrown out to him. That in condemning the administration of the government, they condemned him, for if they thought there were measures pursued contrary to his sentiments, they must conceive him too careless to attend to them, or too stupid to understand them. That though, indeed, he had signed many acts which he did not approve in all their parts, yet he had never put his name to one which he did not think, on the whole, was eligible. That as to the bank, which had been an act of so much complaint, until there was some infallible criterion of reason, a difference of opinion must be tolerated. He did not believe the discontents extended far from the seat of government. He had seen and spoken with many people in Maryland and Virginia in his late journey. He found the people contented and happy. He wished, however, to be better informed on this head. If the discontents were more extensive than he supposed, it might be, that the desire that he should remain in the government was not general.
My observations to him tended principally to enforce the topics of my letter. I will not, therefore, repeat them, except where they produced observations from him. I said, that the two great complaints were, that the national debt was unnecessarily increased, and that it had furnished the means of corrupting both branches of the legislature; that he must know, and every body knew, there was a considerable squadron in both, whose votes were devoted to the paper and stock-jobbing interest, that the names of a weighty number were known, and several others suspected on good grounds. That on examining the votes of these men, they would be found uniformly for every Treasury measure, and that as most of these measures had been carried by small majorities, they were carried by these very votes. That, therefore, it was a cause of just uneasiness, when we saw a legislature legislating for their own interests, in opposition to those of the people. He said not a word on the corruption of the legislature, but took up the other point, defended the Assumption, and argued that it had not increased the debt, for that all of it was honest debt. He justified the excise-law, as one of the best laws which could be passed, as nobody would pay the tax who did not choose to do it. With respect to the increase of the debt by the Assumption, I observed to him, that what was meant and objected to was, that it increased the debt of the General Government, and carried it beyond the possibility of payment. That if the balances had been settled, and the debtor States directed to pay their deficiencies to the creditor States, they would have done it easily, and by resources of taxation in their power, and acceptable to the people; by a direct tax in the south, and an excise in the north. Still, he said, it would be paid by the people. Finding him decided, I avoided entering into argument with him on those points.
Bladensburg, October the 1st, 1792. This morning, at Mount Vernon, I had the following conversation with the President. He opened it by expressing his regret at the resolution in which I appeared so fixed, in the letter I had written him, of retiring from public affairs. He said, that he should be extremely sorry that I should do it, as long as he was in office, and that he could not see where he should find another character to fill my office. That as yet, he was quite undecided whether to retire in March or not. His inclinations led him strongly to do it. Nobody disliked more the ceremonies of his office, and he had not the least taste or gratification in the execution of its functions. That he was happy at home alone, and that his presence there was now peculiarly called for by the situation of Major Washington, whom he thought irrecoverable, and should he get well, he would remove into another part of the country, which might better agree with him. That he did not believe his presence necessary; that there were other characters who would do the business as well or better. Still, however, if his aid was thought necessary to save the cause to which he had devoted his life principally, he would make the sacrifice of a longer continuance. That he therefore reserved himself for future decision, as his declaration would be in time if made a month before the day of election. He had desired Mr. Lear to find out from conversation, without appearing to make the inquiry, whether any other person would be desired by any body. He had informed him, he judged from conversations that it was the universal desire he should continue, and he believed that those who expressed a doubt of his continuance, did it in the language of apprehension, and not of desire. But this, says he, is only from the north; it may be very different in the south. I thought this meant as an opening to me to say what was the sentiment in the south, from which quarter I came. I told him, that as far as I knew, there was but one voice there, which was for his continuance. That as to myself, I had ever preferred the pursuits of private life to those of public, which had nothing in them agreeable to me. I explained to him the circumstances of the war which had first called me into public life, and those following the war, which had called me from a retirement on which I had determined. That I had constantly kept my eye on my own home, and could no longer refrain from returning to it. As to himself, his presence was important; that he was the only man in the United States who possessed the confidence of the whole; that government was founded in opinion and confidence, and that the longer he remained, the stronger would become the habits of the people in submitting to the government, and in thinking it a thing to be maintained; that there was no other person, who would be thought any thing more than the head of a party. He then expressed his concern at the difference which he found to subsist between the Secretary of the Treasury and myself, of which he said he had not been aware. He knew, indeed, that there was a marked difference in our political sentiments, but he had never suspected it had gone so far in producing a personal difference, and he wished he could be the mediator to put an end to it. That he thought it important to preserve the check of my opinions in the administration, in order to keep things in their proper channel, and prevent them from going too far. That as to the idea of transforming this government into a monarchy, he did not believe there were ten men in the United States whose opinions were worth attention, who entertained such a thought. I told him there were many more than he imagined. I recalled to his memory a dispute at his own table, a little before we left Philadelphia, between General Schuyler on one side and Pinckney and myself on the other, wherein the former maintained the position, that hereditary descent was as likely to produce good magistrates as election. I told him, that though the people were sound, there were a numerous sect who had monarchy in contemplation; that the Secretary of the Treasury was one of these. That I had heard him say that this constitution was a shilly-shally thing, of mere milk and water, which could not last, and was only good as a step to something better. That when we reflected, that he had endeavored in the convention, to make an English constitution of it, and when failing in that, we saw all his measures tending to bring it to the same thing, it was natural for us to be jealous; and particularly, when we saw that these measures had established corruption in the legislature, where there was a squadron devoted to the nod of the Treasury, doing whatever he had directed, and ready to do what he should direct. That if the equilibrium of the three great bodies, legislative, executive, and judiciary, could be preserved, if the legislature could be kept independent, I should never fear the result of such a government; but that I could not but be uneasy, when I saw that the executive had swallowed up the legislative branch. He said, that as to that interested spirit in the legislature, it was what could not be avoided in any government, unless we were to exclude particular descriptions of men, such as the holders of the funds, from all office. I told him, there was great difference between the little accidental schemes of self-interest, which would take place in every body of men, and influence their votes, and a regular system for forming a corps of interested persons, who should be steadily at the orders of the Treasury. He touched on the merits of the funding system, observed there was a difference of opinion about it, some thinking it very bad, others very good; that experience was the only criterion of right which he knew, and this alone would decide which opinion was right. That for himself, he had seen our affairs desperate and our credit lost, and that this was in a sudden and extraordinary degree raised to the highest pitch. I told him, all that was ever necessary to establish our credit, was an efficient government and an honest one, declaring it would sacredly pay our debts, laying taxes for this purpose, and applying them to it. I avoided going further into the subject. He finished by another exhortation to me not to decide too positively on retirement, and here we were called to breakfast.
October the 31st, 1792. I had sent to the President, Viar and Jaudenes’s letter of the 29th instant, whereupon he desired a consultation of Hamilton, Knox, E. Randolph, and myself, on these points. 1. What notice was to be taken hereof to Spain. 2. Whether it should make part of the communication to the legislature. I delivered my opinion, that it ought to be communicated to both Houses, because the communications intended to be made, being to bring on the question, whether they would declare war against any, and which of the nations or parts of the nations of Indians to the south, it would be proper this information should be before them, that they might know how far such a declaration would lead them. There might be some who would be for war against the Indians, if it were to stop there, but who would not be for it, if it were to lead to a war against Spain. I thought it should be laid before both Houses, because it concerned the question of declaring war, which was the function equally of both Houses. I thought a simple acknowledgment of the receipt of the letter should be made by me to the Spanish Charges, expressing that it contained some things very unexpected to us, but that we should refer the whole, as they had proposed, to the negotiators at Madrid. This would secure to us a continuation of the suspension of Indian hostilities, which the Governor of New Orleans said he had brought about till the result of the negotiation at Madrid should be known; would not commit us as to running or not running the line, or imply any admission of doubt about our tentorial right; and would avoid a rupture with Spain, which was much to be desired, while we had similar points to discuss with Great Britain. Hamilton declared himself the advocate for peace. War would derange our affairs greatly; throw us back many years in the march towards prosperity; be difficult for us to pursue, our countrymen not being disposed to become soldiers; a part of the Union feeling no interest in the war, would with difficulty be brought to exert itself; and we had no navy. He was for every thing which would procrastinate the event. A year, even, was a great gain to a nation strengthening as we were. It laid open to us, too, the chapter of accidents, which in the present state of Europe, was a very pregnant one. That while, however, he was for delaying the event of war, he had no doubt it was to take place between us for the object in question: that jealousy and perseverance were remarkable features in the character of the Spanish government, with respect to their American possessions; that so far from receding as to their claims against us, they had been strengthening themselves in them. He had no doubt the present communication was by authority from the court. Under this impression he thought we should be looking forward to the day of rupture, and preparing for it. That if we were unequal to the contest ourselves, it behoved us to provide allies for our aid. That in this view, but two nations could be named, France and England. France was too intimately connected with Spain in other points, and of too great mutual value, ever to separate for us. Her affairs too, were such, that whatever issue they had, she could not be in a situation to make a respectable mediation for us. England alone, then, remained. It would not be easy to effect it with her; however, he was for trying it, and for sounding them on the proposition of a defensive treaty of alliance. The inducements to such a treaty, on their part, might be, 1. The desire of breaking up our former connections, which we knew they had long wished. 2. A continuance of the statu quo in commerce for ten years, which he believed would be desirable to them. 3. An admission to some navigable part of the Mississippi, by some line drawn from the Lake of the Woods to such navigable part. He had not, he said, examined the map to see how such a line might be run, so as not to make too great a sacrifice. The navigation of the Mississippi being a joint possession, we might then take measures in concert for the joint security of it. He was, therefore, for immediately sounding them on this subject through our minister at London; yet so as to keep ourselves unengaged as long as possible, in hopes a favorable issue with Spain might be otherwise effected. But he was for sounding immediately, and for not letting slip an opportunity of securing our object.
E. Randolph concurred, in general, with me. He objected that such a reliance could not be effected without pecuniary consideration probably, which he could not give. And what was to be their aid? If men, our citizens would see their armies get foothold in the United States, with great jealousy; it would be difficult to protect them. Even the French, during the distresses of the late war, excited some jealous sentiments,
Hamilton said, money was often but not always demanded, and the aid he should propose to stipulate would be in ships. Knox non dissentiente.
The President said the remedy would be worse than the disease, and stated some of the disagreeable circumstances which would attend our making such overtures.
November, 1792. Hamilton called on me to speak about our furnishing supplies to the French colony of St. Domingo. He expressed his opinion, that we ought to be cautious, and not go too far in our application of money to their use, lest it should not be recognised by the mother country. He did not even think that some kinds of government they might establish could give a sufficient sanction.* I observed, that the National Convention was now met, and would certainly establish a form of government; that as we had recognised the former government because established by authority of the nation, so we must recognise any other which should be established by the authority of the nation. He said we had recognised the former, because it contained an important member of the ancient, to wit, the King, and wore the appearance of his consent; but if, in any future form, they should omit the King, he did not know that we could with safety recognise it, or pay money to its order.
* There had been a previous consultation at the President’s
(about the first week in November) on the expediency of
suspending payments to France, under her present situation.
I had admitted that the late constitution was dissolved by
the dethronement of the King; and the management of affairs
surviving to the National Assembly only, this was not an
integral legislature, and therefore not competent to give a
legitimate discharge for our payments: that I thought
consequently, that none should be made till some legitimate
body came into place; and that I should consider the
National Convention, called, but not met as we had yet
heard, to be a legitimate body. Hamilton doubted whether it
would be a legitimate body, and whether, if the King should
be re-established, he might not disallow such payments on
good grounds. Knox, for once, dared to differ from Hamilton,
and to express, very submissively, an opinion, that a
convention named by the whole body of the nation, would be
competent to do any thing. It ended by agreeing, that I
should write to Gouverneur Morris to suspend payment
generally, till further orders.
November the 19th, 1792. Beckley brings me the pamphlet written by Hamilton, before the war, in answer to ‘Common Sense.’ It is entitled ‘Plain Truth.’ Melancthon Smith sends it to Beckley, and in his letter says, it was not printed in New York by Loudon, because prevented by a mob, and was printed in Philadelphia, and that he has these facts from Loudon.
November the 21st, 1792. Mr. Butler tells me, that he dined last winter with Mr. Campbell from Denmark, in company with Hamilton, Lawrence, Dr. Shippen, T. Shippen, and one other person whom he cannot recollect. That after dinner political principles became the subject of conversation; that Hamilton declared openly, that ‘there was no stability, no security in any kind of government but a monarchy.’ That Lawrence took him up, and entered the lists of argument against him; that the dispute continued long, and grew warm, remarkably so as between them; that Shippen, at length, joined Lawrence in it; and in fine, that it broke up the company. Butler recommended to the company, that the dispute having probably gone farther than was intended, it ought to be considered as confined to the company.
Thursday, December the 27th, 1792. I waited on the President on some current business. After this was over, he observed to me, that he thought it was time to endeavor to effect a stricter connection with France, and that Gouverneur Morris should be written to on this subject. He went into the circumstances of dissatisfaction between Spain and Great Britain, and us, and observed, there was no nation on whom we could rely, at all times, but France; and that, if we did not prepare in time some support, in the event of rupture with Spain and England, we might be charged with a criminal negligence. I was much pleased with the tone of these observations. It was the very doctrine which had been my polar star, and I did not need the successes of the republican arms in France, lately announced to us, to bring me to these sentiments. For it is to be noted, that on Saturday last, (the 22nd) I received Mr. Short’s letters of October the 9th and 12th, with the Leyden gazettes to October the 13th, giving us the first news of the retreat of the Duke of Brunswick, and the capture of Spires and Worms by Custine, and that of Nice by Anselme. I therefore expressed to the President my cordial approbation of these ideas; told him, I had meant on that day (as an opportunity of writing by the British packet would occur immediately) to take his orders for removing the suspension of payments to France, which had been imposed by my last letter to Gouverneur Morris, but was meant, as I supposed, only for the interval between the abolition of the late constitution by the dethronement of the King, and the meeting of some other body, invested by the will of the nation with powers to transact their affairs; that I considered the National Convention, then assembled, as such a body; and that, therefore, we ought to go on with the payments to them, or to any government they should establish; that, however, I had learned last night, that some clause in the bill for providing reimbursement of the loan made by the bank to the United States, had given rise to a question before the House of Representatives yesterday, which might affect these payments; a clause in that bill proposing, that the money formerly borrowed in Amsterdam, to pay the French debt, and appropriated by law (1790, August 4th, c. 34. § 2.) to that purpose, lying dead as was suggested, should be taken to pay the bank, and the President be authorized to borrow two millions of dollars more, out of which it should be replaced: and if this should be done, the removal of our suspension of payments, as I had been about to propose, would be premature. He expressed his disapprobation of the clause above mentioned; thought it highly improper in the legislature to change an appropriation once made, and added, that no one could tell in what that would end. I concurred, but observed, that on a division of the House, the ayes for striking out the clause were twenty-seven, the noes twenty-six; whereon the Speaker gave his vote against striking out, which divides the House: the clause for the disappropriation remained of course. I mentioned suspicions, that the whole of this was a trick to serve the bank under a great existing embarrassment; that the debt to the bank was to be repaid by instalments; that the first instalment was of two hundred thousand dollars only, or rather one hundred and sixty thousand dollars, (because forty thousand of the two hundred thousand dollars would be the United States’ own dividend of the instalment.) Yet here were two millions to be paid them at once, and to be taken from a purpose of gratitude and honor, to which it had been appropriated.
December the 30th, 1792. I took the occasion furnished by Pinckney’s letter of September the 19th, asking instructions how to conduct himself as to the French revolution, to lay down the catholic principle of republicanism, to wit, that every people may establish what form of government they please, and change it as they please; the will of the nation being the only thing essential. I was induced to do this, in order to extract the President’s opinion on the question which divided Hamilton and myself in the conversation of November, 1792, and the previous one of the first week of November, on the suspension of payments to France: and if favorable to mine, to place the principle on record in the letter-books of my office. I therefore wrote the letter of December the 30th, to Pinckney, and sent it to the President, and he returned me his approbation in writing, in his note of the same date, which see.
February the 7th, 1793. I waited on the President with letters and papers from Lisbon. After going through these, I told him that I had for some time suspended speaking with him on the subject of my going out of office, because I had understood that the bill for intercourse with foreign nations was likely to be rejected by the Senate, in which case, the remaining business of the department would be too inconsiderable to make it worth while to keep it up. But that the bill being now passed, I was freed from the considerations of propriety which had embarrassed me. That &c. [nearly in the words of a letter to Mr. T. M. Randolph, of a few days ago,] and that I should be willing, if he had taken no arrangements to the contrary, to continue somewhat longer, how long I could not say, perhaps till summer, perhaps autumn. He said, so far from taking arrangements on the subject, he had never mentioned to any mortal the design of retiring which I had expressed to him, till yesterday, when having heard that I had given up my house, and that it was rented by another, he thereupon mentioned it to Mr. E. Randolph, and asked him, as he knew my retirement had been talked of, whether he had heard any persons suggested in conversation to succeed me. He expressed his satisfaction at my change of purpose and his apprehensions that my retirement would be a new source of uneasiness to the public. He said Governor Lee had that day informed him of the general discontent prevailing in Virginia, of which he never had had any conception, much less sound information. That it appeared to him very alarming. He proceeded to express his earnest wish that Hamilton and myself could coalesce in the measures of the government, and urged here the general reasons for it, which he had done to me in two former conversations. He said he had proposed the same thing to Hamilton, who expressed his readiness, and he thought our coalition would secure the general acquiescence of the public. I told him my concurrence was of much less importance than he seemed to imagine; that I kept myself aloof from all cabal and correspondence on the subject with the government, and saw and spoke with as few as I could. That as to a coalition with Mr. Hamilton, if by that was meant that either was to sacrifice his general system to the other, it was impossible. We had both, no doubt, formed our conclusions after the most mature consideration; and principles conscientiously adopted, could not be given up on either side. My wish was, to see both Houses of Congress cleansed of all persons interested in the bank or public stocks: and that a pure legislature being given us, I should always be ready to acquiesce under their determinations, even if contrary to my own opinions; for that I subscribe to the principle, that the will of the majority, honestly expressed, should give law. I confirmed him in the fact of the great discontents to the south; that they were grounded on seeing that their judgments and interests were sacrificed to those of the eastern States on every occasion, and their belief that it was the effect of a corrupt squadron of voters in Congress, at the command of the Treasury; and they see that if the votes of those members who had any interest distinct from, and contrary to the general interest of their constituents, had been withdrawn, as in decency and honesty they should have been, the laws would have been the reverse of what they are on all the great questions. I instanced the new Assumption carried in the House of Representatives by the Speaker’s vote. On this subject he made no reply. He explained his remaining in office to have been the effect of strong solicitations after he returned here; declaring that he had never mentioned his purpose of going out but to the Heads of departments and Mr. Madison; he expressed the extreme wretchedness of his existence while in office, and went lengthily into the late attacks on him for levees, &c. and explained to me how he had been led into them by the persons he consulted at New York; and that if he could but know what the sense of the public was, he would most cheerfully conform to it.
February the 16th, 1793. E. Randolph tells J. Madison and myself, a curious fact which he had from Lear. When the President went to New York, he resisted for three weeks the efforts to introduce levees. At length he yielded, and left it to Humphreys and some others to settle the forms. Accordingly, an antechamber and presence-room were provided, and when those who were to pay their court were assembled, the President set out, preceded by Humphreys. After passing through the antechamber, the door of the inner room was thrown open, and Humphreys entered first, calling out with a loud voice, ‘The President of the United States.’ The President was so much disconcerted with it, that he did not recover it the whole time of the levee, and when the company was gone, he said to Humphreys, ‘Well, you have taken me in once, but, by God, you shall never take me in a second time.’
There is reason to believe that the rejection of the late additional Assumption by the Senate was effected by the President through Lear, operating on Langdon. Beckley knows this.
February the 26th, 1793. Notes on the proceedings of yesterday. [See the formal opinions given to the President in writing, and signed.]
First question. We were all of opinion that the treaty should proceed merely to gratify the public opinion, and not from an expectation of success. I expressed myself strongly, that the event was so unpromising, that I thought the preparations for a campaign should go on without the least relaxation, and that a day should be fixed with the commissioners for the treaty, beyond which they should not permit the treaty to be protracted, by which day, orders should be given for our forces to enter into action. The President took up the thing instantly, after I had said this, and declared he was so much in the opinion that the treaty would end in nothing, that he then, in the presence of us all, gave orders to General Knox, not to slacken the preparations for the campaign in the least, but to exert every nerve in preparing for it. Knox said something about the ultimate day for continuing the negotiations. I acknowledged myself not a judge on what day the campaign should begin, but that whatever it was, that day should terminate the treaty. Knox said he thought a winter campaign was always the most efficacious against the Indians. I was of opinion, since Great Britain insisted on furnishing provisions, that we should offer to repay. Hamilton thought we should not.
Second question. I considered our right of preemption of the Indian lands, not as amounting to any dominion, or jurisdiction, or paramountship whatever, but merely in the nature of a remainder after the extinguishment of a present right, which gave us no present right whatever, but of preventing other nations from taking possession, and so defeating our expectancy; that the Indians had the full, undivided, and independent sovereignty as long as they chose to keep it, and that this might be for ever; that as fast as we extend our rights by purchase from them, so fast we extend the limits of our society, and as soon as a new portion became encircled within our line, it became a fixed limit of our society: that the executive, with either or both branches of the legislature, could not alien any part of our territory; that by the law of nations it was settled, that the unity and indivisibility of the society was so fundamental, that it could not be dismembered by the constituted authorities, except, 1. where all power was delegated to them (as in the case of despotic governments,) or, 2. where it was expressly delegated; that neither of these delegations had been made to our General Government, and, therefore, that it had no right to dismember or alienate any portion of territory once ultimately consolidated with us; and that we could no more cede to the Indians than to the English or Spaniards, as it might, according to acknowledged principles, remain as irrevocably and eternally with the one as the other. But I thought, that, as we had a right to sell and settle lands once comprehended within our lines, so we might forbear to exercise that right, retaining the property, till circumstances should be more favorable to the settlement, and this I agreed to do in the present instance, if necessary for peace.
Hamilton agreed to the doctrine of the law of nations, as laid down in Europe, but that it was founded on the universality of settlement there; consequently that no lopping-off of territory could be made without a lopping-off of citizens, which required their consent; but that the law of nations for us, must be adapted to the circumstance of our unsettled country, which he conceived the President and Senate may cede: that the power of treaty was given to them by the constitution, without restraining it to particular objects; consequently that it was given in as plenipotentiary a form as held by any sovereign in any other society. Randolph was of opinion, there was a difference between a cession to Indians and to any others, because it only restored the ceded part to the condition in which it was before we bought it, and consequently, that we might buy it again hereafter: therefore, he thought the executive and Senate could cede it. Knox joined in the main opinion. The President discovered no opinion, but he made some efforts to get us to join in some terms which could unite us all, and he seemed to direct those efforts more towards me: but the thing could not be done.
Third question. We agreed in idea as to the line to be drawn; to wit, so as to retain all lands appropriated, or granted, or reserved.
Fourth question. We all thought, if the Senate should be consulted, and consequently apprized of our line, it would become known to Hammond, and we should lose all chance of saving any thing more at the treaty than our ultimatum.
The President, at this meeting, mentioned the declaration of some person, in a paper of Fenno, that he would commence an attack on the character of Dr. Franklin. He said, the theme was to him excessively disagreeable on other considerations, but most particularly so, as the party seemed to do it as a means of defending him (the President) against the late attacks on him: that such a mode of defence would be peculiarly painful to him, and he wished it could be stopped. Hamilton and Randolph undertook to speak to Fenno to suppress it, without mentioning it as the President’s wish. Both observed, that they had heard this declaration mentioned in many companies, and that it had excited universal horror and detestation.
The paper in Fenno must lie between two persons, viz. Adams and Izard, because they are the only persons who could know such facts as are there promised to be unfolded. Adams is an enemy to both characters, and might choose this ground as an effectual position to injure both. Izard hated Franklin with unparalleled bitterness, but humbly adores the President, because he is in loco regis. If the paper proceeds, we shall easily discover which of these two gentlemen is the champion. In the mean time, the first paper leads our suspicions more towards Izard than Adams, from the circumstance of style, and because he is quite booby enough not to see the injury he would do to the President by such a mode of defence.
February the 28th. Knox, E. Randolph, and myself met at Knox’s, where Hamilton was also to have met, to consider the time, manner, and place of the President’s swearing in. Hamilton had been there before, and had left his opinion with Knox; to wit, that the President should ask a judge to attend him in his own house to administer the oath, in the presence of the Heads of departments; which oath should be deposited in the Secretary of State’s office. I concurred in this opinion. Randolph was for the President’s going to the Senate chamber to take the oath, attended by the marshal of the United States, who should then make proclamation, &c. Knox was for this, and for adding the House of Representatives to the presence, as they would not yet be departed. Our individual opinions were written, to be communicated to the President, out of which he might form one. In the course of our conversation, Knox, stickling for parade, got into great warmth, and swore that our government must either be entirely new modeled, or it would be knocked to pieces in less than ten years; and that, as it is at present, he would not give a copper for it; that it is the President’s character, and not the written constitution which keeps it together.
Same day. Conversation with Lear. He expressed the strongest confidence that republicanism was the universal creed of America, except of a very few; that a republican administration must of necessity immediately overbear the contrary faction; said that he had seen with extreme regret, that a number of gentlemen had for a long time been endeavoring to instil into the President, that the noise against the administration of the government was that of a little faction, which would soon be silent, and which was detested by the people, who were contented and prosperous: that this very party, however, began to see their error, and that the sense of America was bursting forth to their conviction.
March the 2nd, 1793. See, in the papers of this date, Mr. Giles’s resolutions. He and one or two others were sanguine enough to believe, that the palpableness of these resolutions rendered it impossible the House could reject them. Those who knew the composition of the House, 1. of bank directors, 2. holders of bank stock, 3. stock-jobbers, 4. blind devotees, 5. ignorant persons who did not comprehend them, 6. lazy and good-humored persons, who comprehended and acknowledged them, yet were too lazy to examine, or unwilling to pronounce censure; the persons who knew these characters, foresaw, that the three first descriptions making one third of the House, the three latter would make one half of the residue; and of course, that they would be rejected by a majority of two to one. But they thought, that even this rejection would do good, by showing the public the desperate and abandoned dispositions with which their affairs were conducted. The resolutions were proposed, and nothing spared to present them in the fulness of demonstration. There were not more than three or four who voted otherwise than had been expected.
March the 30th, 1793. At our meeting at the President’s, February the 25th, in discussing the question, whether we should furnish to France the three millions of livres desired, Hamilton, in speaking on the subject, used this expression; ‘When Mr. Genet arrives, whether we shall receive him or not, will then be a question for discussion’; which expression I did not recollect till E. Randolph reminded me of it a few days after. Therefore, on the 20th instant, as the President was shortly to set out for Mount Vernon, I observed to him, that as Genet might arrive in his absence, I wished to know beforehand how I should treat him, whether as a person who would or would not be received. He said, he could see no ground of doubt, but that he ought to be received. On the 24th, he asked E. Randolph’s opinion on the subject, saying, he had consulted Colonel Hamilton thereon, who went into lengthy considerations of doubt and difficulty, and viewing it as a very unfortunate thing, that the President should have the decision of so critical a point forced on him; but in conclusion, said, since he was brought into that situation, he did not see but that he must receive Mr. Genet. Randolph told the President, he was clear he should be received, and the President said, he had never had any doubt on the subject in his mind. Afterwards on the same day, he spoke to me again on it, and said, Mr. Genet should unquestionably be received; but he thought not with too much warmth or Cordiality, so only as to be satisfactory to him. I wondered at first at this restriction: but when Randolph afterwards communicated to me his conversation of the 24th, I became satisfied it was a small sacrifice to the opinion of Hamilton.
March the 31st. Mr. Beckley tells me, that the merchants’ bonds for duties on six months’ credit became due the 1st instant, to a very great amount; that Hamilton went to the bank on that day, and directed the bank to discount for those merchants all their bonds at thirty days, and that he would have the collectors credited for the money at the treasury. Hence, the treasury lumping its receipts by the month in its printed accounts, these sums will be considered by the public as only received on the last day; consequently, the bank makes the month’s interest out of it. Beckley had this from a merchant, who had a bond discounted, and who supposes a million of dollars were discounted at the bank here. Mr. Brown got the same information from another merchant, who supposed only six hundred thousand dollars discounted here. But they suppose the same orders went to all the branch banks to a great amount.
Eodem die. Mr. Brown tells me he has it from a merchant here, that during the last winter, the directors of the bank ordered the freest discounts. Every man could obtain it. Money being so flush, the six per cents run up to twenty-one and twenty-two shillings. Then the directors sold out their private stocks. When the discounted notes were becoming due, they stopped discounts, and not a dollar was to be had. This reduced six per cents to eighteen shillings and three pence; then the same directors bought in again.
April the 7th, 1793. Mr. Lear called on me, and introduced of himself a conversation on the affairs of the United States. He laughed at the cry of prosperity, and the deriving it from the establishment of the treasury: he said, that, so far from giving in to this opinion, and that we were paying off our national debt, he was clear the debt was growing on us: that he had lately expressed this opinion to the President, who appeared much astonished at it. I told him I had given the same hint to the President last summer, and lately again had suggested, that we were even depending for the daily subsistence of government on borrowed money. He said, that was certain, and was the only way of accounting for what was become of the money drawn over from Holland to this country. He regretted that the President was not in the way of hearing full information, declared he communicated to him every thing he could learn himself; that the men who vaunted the present government so much on some occasions, were the very men who at other times declared it was a poor thing, and such a one as could not stand, and he was sensible they only esteemed it as a stepping-stone to something else, and had availed themselves of the first moments of the enthusiasm in favor of it, to pervert its principles and make of it what they wanted: and that though they raised the cry of anti-federalism against those who censured the mode of administration, yet he was satisfied, whenever it should come to be tried, that the very men whom they called anti-federalists, were the men who would save the government, and he looked to the next Congress for much rectification.
April the 18th. The President sends a set of questions to be considered, and calls a meeting. Though those sent me were in his own hand-writing, yet it was palpable from the style, their ingenious tissue and suite, that they were not the President’s, that they were raised upon a prepared chain of argument, in short, that the language was Hamilton’s, and the doubts his alone. They led to a declaration of the executive, that our treaty with France is void. E. Randolph, the next day, told me that the day before the date of these questions, Hamilton went with him through the whole chain of reasoning of which these questions are the skeleton, and that he recognised them the moment he saw them.
We met. The first question, whether we should receive the French minister, Genet, was proposed, and we agreed unanimously that he should be received; Hamilton, at the same time, expressing his great regret that any accident had happened, which should oblige us to recognise the government. The next question was, whether he should be received absolutely, or with qualifications. Here Hamilton took up the whole subject, and went through it in the order in which the questions sketch it. See the chain of his reasoning in my opinion of April the 28th. Knox subscribed at once to Hamilton’s opinion that we ought to declare the treaty void, acknowledging, at the same time, like a fool as he is, that he knew nothing about it. I was clear it remained valid. Randolph declared himself of the same opinion, but on Hamilton’s undertaking to present to him the authority in Vattel (which we had not present), and to prove to him, that if the authority was admitted, the treaty might be declared void, Randolph agreed to take further time to consider. It was adjourned. We determined unanimously the last question, that Congress should not be called. There having been an intimation by Randolph, that in so great a question he should choose to give a written opinion, and this being approved by the President, I gave in mine April the 28th. Hamilton gave in his. I believe Knox’s was never thought worth offering or asking for. Randolph gave his May the 6th, concurring with mine. The President told me, the same day, he had never had a doubt about the validity of the treaty; but that since a question had been suggested, he thought it ought to be considered: that this being done, I might now issue passports to sea-vessels in the form prescribed by the French treaty. I had for a week past only issued the Dutch form; to have issued the French, would have been presupposing the treaty to be in existence. The President suggested, that he thought it would be as well that nothing should be said of such a question having been under consideration. Written May the 6th.
May the 6th, 1793. When the question was, whether the proclamation of April the 22nd should be issued, Randolph observed, that there should be a letter written by me to the ministers of the belligerent powers, to declare that it should not be taken as conclusive evidence against our citizens in foreign courts of admiralty, for contraband goods. Knox suddenly adopted the opinion before Hamilton delivered his. Hamilton opposed it pretty strongly. I thought it an indifferent thing, but rather approved Randolph’s opinion. The President was against it; but observed that, as there were three for it, it should go. This was the first instance I had seen of an opportunity to decide by a mere majority, including his own vote.
May the 12th. Lear called on me to-day. Speaking of the lowness of stocks (sixteen shillings), I observed it was a pity we had not money to buy on public account. He said, yes, and that it was the more provoking, as two millions had been borrowed for that purpose, and drawn over here, and yet were not here. That he had no doubt those would take notice of the circumstance whose duty it was to do so. I suppose he must mean the President.
May the 23rd. I had sent to the President, yesterday, draughts of a letter from him to the Provisory Executive Council of France, and of one from myself to Mr. Ternant, both on the occasion of his recall. I called on him to-day. He said there was an expression in one of them, which he had never before seen in any of our public communications, to wit, ‘our republic’ The letter prepared for him to the Council, began thus: ‘The Citizen Ternant has delivered to me the letter wherein you inform me, that yielding &c. you had determined to recall him from his mission, as your Minister Plenipotentiary to our republic.’ He had underscored the words our republic. He said that certainly ours was a republican government, but yet we had not used that style in this way; that if any body wanted to change its form into a monarchy, he was sure it was only a few individuals, and that no man in the United States would set his face against it more than himself: but that this was not what he was afraid of; his fears were from another quarter; that there was more danger of anarchy being introduced. He adverted to a piece in Freneau’s paper of yesterday; he said he despised all their attacks on him personally, but that there never had been an act of the government, not meaning in the executive line only, but in any line, which that paper had not abused. He had also marked the word republic thus X, where it was applied to the French republic. (See the original paper.) He was evidently sore and warm, and I took his intention to be, that I should interpose in some way with Freneau, perhaps withdraw his appointment of translating clerk to my office. But I will not do it. His paper has saved our constitution, which was galloping fast into monarchy, and has been checked by no one means so powerfully as by that paper. It is well and universally known, that it has been that paper which has checked the career of the monocrats; and the President, not sensible of the designs of the party, has not, with his usual good sense and sang froid, looked on the efforts and effects of this free press, and seen that, though some bad things have passed through it to the public, yet the good have preponderated immensely.
June the 7th, 1793. Mr. Beckley, who has returned from New York within a few days, tells me that, while he was there, Sir John Temple, Consul General of the northern States for Great Britain showed him a letter from Sir Gregory Page Turner, a member of parliament for a borough in Yorkshire, who, he said, had been a member for twenty-five years, and always confidential for the ministers in which he permitted him to read particular passages of the following purport: that the government was well apprized of the predominancy of the British interest in the United States; that they considered Colonel Hamilton, Mr. King, and Mr. Smith of South Carolina, as the main supports of that interest; that particularly, they considered Colonel Hamilton, and not Mr. Hammond as their effective minister here; that if the anti-federal interest (that was his term) at the head of which they considered Mr. Jefferson to be should prevail, these gentlemen had secured an asylum to themselves in England.’ Beckley could not understand whether they had secured it themselves* or whether they were only notified that it was secured to them. So that they understand that they may go on boldly in their machinations to change the government, and if they should be overset and choose to withdraw, they will be secure of a pension in England, as Arnold, Deane, &c. had. Sir John read passages of a letter (which he did not put into Beckley’s hand, as he did the other) from Lord Grenville, saying nearly the same things. This letter mentions Sir John, that though they had divided the Consul-Generalship, and given the southern department to Bond, yet he Sir John, was to retain his whole salary. [By this it would seem, as if, wanting to use Bond, they had covered his employment with this cloak.] Mr. Beckley says that Sir John Temple is a strong republican. I had a proof of his intimacy with Sir John in this circumstance. Sir John received his new commission of Consul General for the northern department, and, instead of sending it through Mr. Hammond, got Beckley to enclose it to me for his exequatur I wrote to Sir John that it must come through Mr Hammond enclosing it back to him. He accordingly then sent it to Mr. Hammond.
[* In the margin is written, by Mr. Jefferson; ‘Impossible
as to Hamilton; he was far above that.]
In conversation with the President to-day, and speaking about General Greene, he said that he and General Greene had always differed in opinion about the manner of using militia. Greene always placed them in his front: himself was of opinion, they should always be used as a reserve to improve any advantage, for which purpose they were the finest fellows in the world. He said he was on the ground of the battle of Guilford, with a person who was in the action, and who explained the whole of it to him. That General Greene’s front was behind a fence at the edge of a large field, through which the enemy were obliged to pass to get at them; and that, in their passage through this, they must have been torn all to pieces, if troops had been posted there who would have stood their ground; and that the retreat from that position was through a thicket, perfectly secure. Instead of this he posted the North Carolina militia there who only gave one fire and fell back, so that the whole benefit of their position was lost. He thinks that the regulars, with their field-pieces, would have hardly let a single man get through that field.
Eodem die (June the 7th). Beckley tells me that he has the following fact from Governor Clinton. That before the proposition for the present General Government, i.e. a little before Hamilton conceived a plan for establishing a monarchical government in the United States, he wrote a draught of a circular letter, which was to be sent to about ———-persons, to bring it about. One of these letters in Hamilton’s hand-writing, is now in possession of an old militia General up the North River, who, at that time, was thought orthodox enough to be entrusted in the execution. This General has given notice to Governor Clinton, that he has this paper, and that he will deliver it into his hands, and no one’s else. Clinton intends, the first interval of leisure, to go for it, and he will bring it to Philadelphia. Beckley is a man of perfect truth as to what he affirms of his own knowledge, but too credulous as to what he hears from others.
June the 10th, 1793. Mr. Brown gives me the following specimen of the phrenzy which prevailed at New York on the opening of the new government. The first public ball which took place after the President’s arrival there, Colonel Humphreys, Colonel W. S. Smith, and Mrs. Knox were to arrange the ceremonials. These arrangements were as follows: a sofa at the head of the room, raised on several steps whereon the President and Mrs. Washington were to be seated. The gentlemen were to dance in swords. Each one, when going to dance, was to lead his partner to the foot of the sofa, make a low obeisance to the President and his lady, then go and dance, and when done, bring his partner again to the foot of the sofa for new obeisances, and then to retire to their chairs. It was to be understood, too, that gentlemen should be dressed in bags. Mrs. Knox contrived to come with the President, and to follow him and Mrs. Washington to their destination, and she had the design of forcing an invitation from the President to a seat on the sofa. She mounted up the steps after them unbidden, but unfortunately the wicked sofa was so short, that when the President and Mrs. Washington were seated, there was not room for a third person; she was obliged therefore to descend in the face of the company, and to sit where she could. In other respects the ceremony was conducted rigorously according to the arrangements, and the President made to pass an evening which his good sense rendered a very miserable one to him.
June the 12th. Beckley tells me that Klingham has been with him to-day, and relates to him the following fact. A certificate of the old Congress had been offered at the treasury and refused payment and so endorsed in red ink as usual. This certificate came to the hands of Francis, (the quondam clerk of the treasury who, on account of his being dipped in the infamous case of the Baron Glaubec, Hamilton had been obliged to dismiss, to save appearances, but with an assurance of all future service, and he accordingly got him established in New York). Francis wrote to Hamilton that such a ticket was offered him, but he could not buy it unless he would inform him and give him his certificate that it was good. Hamilton wrote him a most friendly letter, and sent him the certificate. He bought the paper, and came on here and got it recognised, whereby he made twenty-five hundred dollars Klingham saw both the letter and certificate.
Irving, a clerk in the treasury, an Irishman, is the author of the pieces now coming out under the signature of Verita’s and attacking the President. I have long suspected this detestable game was playing by the fiscal party, to place the President on their side.
July the 18th, 1793. Lear calls on me. I told him that Irving, an Irishman, and a writer in the treasury, who, on a former occasion, had given the most decisive proofs of his devotion to his principal, was the author of the pieces signed Veritas: and I wished he could get at some of Irving’s acquaintances and inform himself of the fact, as the person who told me of it would not permit the name of his informer to be mentioned. [Note. Beckley told me of it, and he had it from Swaine, the printer to whom the pieces were delivered]; that I had long before suspected this excessive foul play in that party of writing themselves in the character of the most exaggerated democrats and incorporating with it a great deal of abuse on the President to make him believe it was that party who were his enemies, and so throw him entirely into the scale of the monocrats. Lear said he no longer ago than yesterday expressed to the President his suspicions of the artifices of that party to work on him. He mentioned the following fact as a proof of their writing in the character of their adversaries; to wit, the day after the little incident of Richet’s toasting ‘the man of the people’ (see the gazettes), Mrs. Washington was at Mrs. Powel’s, who mentioned to her that, when the toast was given, there was a good deal of disapprobation appeared in the audience, and that many put on their hats and went out: on inquiry, he had not found the fact true, and yet it was put into ———‘s paper, and written under the character of a republican, though he is satisfied it is altogether a slander of the monocrats. He mentioned this to the President, but he did not mention to him the following fact, which he knows; that in New York, the last summer, when the parties of Jay and Clinton were running so high, it was an agreed point with the former, that if any circumstances should ever bring it to a question, whether to drop Hamilton or the President, they had decided to drop the President. He said that lately one of the loudest pretended friends to the government, damned it, and said it was good for nothing, that it could not support itself, and it was time to put it down and set up a better; and yet the same person, in speaking to the President, puffed off that party as the only friends to the government. He said he really feared, that by their artifices and industry, they would aggravate the President so much against the republicans, as to separate him from the body of the people. I told him what the same cabals had decided to do, if the President had refused his assent to the bank bill; also what Brockhurst Livingston said to ———, that Hamilton’s life was much more precious to the community than the President’s.
August the 1st. Met at the President’s, to consider what was to be done with Mr. Genet. All his correspondence with me was read over. The following propositions were made. 1. That a full statement of Mr. Genet’s conduct be made in a letter to G. Morris, and be sent with his correspondence, to be communicated to the Executive Council of France; the letter to be so prepared, as to serve for the form of communication to the Council. Agreed unanimously. 2. That in that letter his recall be required. Agreed by all, though I expressed a preference of expressing that desire with great delicacy; the others were for peremptory terms. 3. To send him off. This was proposed by Knox; but rejected by every other. 4. To write a letter to Mr. Genet, the same in substance with that written to G. Morris, and let him know we had applied for his recall. I was against this, because I thought it would render him extremely active in his plans, and endanger confusion. But I was overruled by the other three gentlemen and the President. 5. That a publication of the whole correspondence, and statement of the proceedings should be made by way of appeal to the people. Hamilton made a jury speech of three quarters of an hour, as inflammatory and declamatory as if he had been speaking to a jury. E. Randolph opposed it. I chose to leave the contest between them. Adjourned to next day.
August the 2nd. Met again. Hamilton spoke again three quarters of an hour. I answered on these topics. Object of the appeal. The democratic society; this the great circumstance of alarm; afraid it would extend its connections over the continent; chiefly meant for the local object of the ensuing election of Governor. If left alone, would die away after that is over. If opposed, if proscribed, would give it importance and vigor; would give it a new object, and multitudes would join it merely to assert the right of voluntary associations. That the measure was calculated to make the President assume the station of the head of a party, instead of the head of the nation. Plan of the appeal. To consist of facts and the decisions of the President. As to facts we are agreed; but as to the decisions, there have been great differences of opinion among us. Sometimes as many opinions as persons. This proves there will be ground to attack the decision. Genet will appeal also; it will become a contest between the President and Genet—anonymous writers—will be same difference of opinion in public, as in our cabinet—will be same difference in Congress, lot it must be laid before them—would, therefore, work very unpleasantly at home. How would it work abroad? France—unkind—after such proofs of her friendship, should rely on that friendship and her justice. Why appeal to the world? Friendly nations always negotiate little differences in private. Never appeal to the world, but when they appeal to the sword. Confederacy of Pilnitz was to overthrow the government of France. The interference of France to disturb other governments and excite insurrections, was a measure of reprisal. Yet these Princes have been able to make it believed to be the system of France. Colonel Hamilton supposes Mr. Genet’s proceedings here are in pursuance of that system: and we are so to declare it to the world, and to add our testimony to this base calumny of the Princes. What a triumph to them to be backed by our testimony. What a fatal stroke at the cause of liberty; Et tu, Brute? We indispose the French government, and they will retract their offer of the treaty of commerce. The President manifestly inclined to the appeal to the people.* Knox, in a foolish, incoherent sort of a speech, introduced the pasquinade lately printed, called the funeral of George W—n and James W—-n, King and Judge, &c, where the President was placed on a guillotine. The President was much inflamed; got into one of those passions when he cannot command himself; ran on much on the personal abuse which had been bestowed on him; defied any man on earth to produce one single act of his since he had been in the government, which was not done on the purest motives; that he had never repented but once the having slipped the moment of resigning his office, and that was every moment since; that by God he had rather be in his grave than in his present situation; that he had rather be on his farm than to be made Emperor of the world; and yet that they were charging him with wanting to be a King. That that rascal Freneau sent him three of his papers every day, as if he thought he would become the distributor of his papers; that he could see in this, nothing but an impudent design to insult him: he ended in this high tone. There was a pause. Some difficulty in resuming our question; it was, however, after a little while, presented again, and he said there seemed to be no necessity for deciding it now; the propositions before agreed on might be put into a train of execution, and perhaps events would show whether the appeal would be necessary or not. He desired we would meet at my office the next day, to consider what should be done with the vessels armed in our ports by Mr. Genet, and their prizes.
* He said that Mr. Morris, taking a family dinner with him
the other day, went largely, and of his own accord, into
this subject; advised this appeal, and promised, if the
President adopted it, that he would support it himself, and
engage for all his connections. The President repeated this
twice, and with an air of importance. Now Mr. Morris has no
family connections; he engaged then for his political
friends. This shows that the President has not confidence
enough in the virtue and good sense of mankind, to confide
in a government bottomed on them, and thinks other props
necessary.
August the 3rd. We met. The President wrote to take our opinions, whether Congress should be called. Knox pronounced at once against it. Randolph was against it. Hamilton said his judgment was against it, but that if any two were for it, or against it, he would join them to make a majority. I was for it. We agreed to give separate opinions to the President. Knox said we should have had fine work, if Congress had been sitting these two last months. The fool thus let out the secret. Hamilton endeavored to patch up the indiscretion of this blabber, by saying ‘he did not know; he rather thought they would have strengthened the executive arm.’
It is evident they do not wish to lengthen the session of the next Congress, and probably they particularly wish it should not meet till Genet is gone. At this meeting I received a letter from Mr. Remsen at New York, informing me of the event of the combat between the Ambuscade and the Boston. Knox broke out into the most unqualified abuse of Captain Courtnay. Hamilton, with less fury, but with the deepest vexation, loaded him with censures. Both showed the most unequivocal mortification at the event.
August the 6th, 1793. The President calls on me at my house in the country, and introduces my letter of July the 31st, announcing that I should resign at the close of the next month. He again expressed his repentance at not having resigned himself, and how much it was increased by seeing that he was to be deserted by those on whose aid he had counted: that he did not know where he should look to find characters to fill up the offices; that mere talents did not suffice for the department of State, but it required a person conversant in foreign affairs, perhaps acquainted with foreign courts; that without this, the best talents would be awkward and at a loss. He told me that Colonel Hamilton had three or four weeks ago written to him, informing him that private as well as public reasons had brought him to the determination to retire, and that he should do it towards the close of the next session. He said he had often before intimated dispositions to resign, but never as decisively before; that he supposed he had fixed on the latter part of next session, to give an opportunity to Congress to examine into his conduct: that our going out at times so different, increased his difficulty; for if he had both places to fill at once, he might consult both the particular talents and geographical situation of our successors. He expressed great apprehensions at the fermentation which seemed to be working in the mind of the public; that many descriptions of persons, actuated by different causes, appeared to be uniting; what it would end in he knew not; a new Congress was to assemble, more numerous, perhaps of a different spirit; the first expressions of their sentiment would be important; if I would only stay to the end of that, it would relieve him considerably.
I expressed to him my excessive repugnance to public life, the particular uneasiness of my situation in this place, where the laws of society oblige me always to move exactly in the circle which I know to bear me peculiar hatred; that is to say, the wealthy aristocrats, the merchants connected closely with England, the new created paper fortunes; that thus surrounded, my words were caught, multiplied, misconstrued, and even fabricated and spread abroad to my injury; that he saw also, that there was such an opposition of views between myself and another part of the administration, as to render it peculiarly unpleasing, and to destroy the necessary harmony. Without knowing the views of what is called the republican party here, or having any communication with them, I could, undertake to assure him, from my intimacy with that party in the late Congress, that there was not a view in the republican party as spread over the United States, which went to the frame of the government; that I believed the next Congress would attempt nothing material, but to render their own body independent; that that party were firm in their dispositions to support the government; that the manoeuvres of Mr. Genet might produce some little embarrassment, but that he would be abandoned by the republicans the moment they knew the nature of his conduct; and on the whole, no crisis existed which threatened any thing.
He said, he believed the views of the republican party were perfectly pure, but when men put a machine into motion, it is impossible for them to stop it exactly where they would choose, or to say where it will stop. That the constitution we have is an excellent one, if we can keep it where it is; that it was, indeed, supposed there was a party disposed to change it into a monarchical form, but that he could conscientiously declare there was not a man in the United States who would set his face more decidedly against it than himself. Here I interrupted him by saying, ‘No rational man in the United States suspects you of any other disposition; but there does not pass a week, in which we cannot prove declarations dropping from the monarchical party, that our government is good for nothing, is a milk-and-water thing which cannot support itself, we must knock it down, and set up something of more energy. He said, if that was the case, he thought it a proof of their insanity, for that the republican spirit of the Union was so manifest and so solid, that it was astonishing how any one could expect to move it.
He returned to the difficulty of naming my successor; he said Mr. Madison would be his first choice, but that he had always expressed to him such a decision against public office, that he could not expect he would undertake it. Mr. Jay would prefer his present office. He said that Mr. Jay had a great opinion of the talents of Mr. King; that there was also Mr. Smith of South Carolina, and E. Rutledge: but he observed, that, name whom he would, some objections would be made, some would be called speculators, some one thing, some another; and he asked me to mention any characters occurring to me. I asked him if Governor Johnson of Maryland had occurred to him. He said he had; that he was a man of great good sense, an honest man, and, he believed, clear of speculations: but this, says he, is an instance of what I was observing; with all these qualifications, Governor Johnson, from a want of familiarity with foreign affairs, would be in them like a fish out of water; every thing would be new to him, and he awkward in every thing. I confessed to him that I had considered Johnson rather as fit for the Treasury department. ‘Yes,’ says he, ‘for that he would be the fittest appointment that could be made; he is a man acquainted with figures, and having as good a knowledge of the resources of this country as any man.’ I asked him if Chancellor Livingston had occurred to him. He said yes; but he was from New York, and to appoint him while Hamilton was in, and before it should be known he was going out, would excite a newspaper conflagration, as the ultimate arrangement would not be known. He said McLurg had occurred to him as a man of first-rate abilities, but it is said that he is a speculator. He asked me what sort of a man Wolcot was. I told him I knew nothing of him myself; I had heard him characterized as a cunning man. I asked him whether some person could not take my office per interim, till he should make an appointment; as Mr. Randolph, for instance. ‘Yes,’ says he; ‘but there you would raise the expectation of keeping it, and I do not know that he is fit for it, nor what is thought of Mr. Randolph.’ I avoided noticing the last observation, and he put the question to me directly. I then told him, I went into society so little as to be unable to answer it. I knew that the embarrassments in his private affairs had obliged him to use expedients, which had injured him with the merchants and shop-keepers, and affected his character of independence; that these embarrassments were serious, and not likely to cease soon. He said, if I would only stay in till the end of another quarter (the last of December), it would get us through the difficulties of this year, and he was satisfied that the affairs of Europe would be settled with this campaign: for that either France would be overwhelmed by it, or the confederacy would give up the contest. By that time, too, Congress will have manifested its character and views. I told him that I had set my private affairs in motion in a line which had powerfully called for my presence the last spring, and that they had suffered immensely from my not going home; that I had now calculated them to my return in the fall, and to fail in going then, would be the loss of another year, and prejudicial beyond measure. I asked him whether he could not name Governor Johnson to my office, under an express arrangement that at the close of the session he should take that of the Treasury. He said that men never chose to descend; that being once in a higher department, he would not like to go into a lower one. He asked me whether I could not arrange my affairs by going home. I told him I did not think the public business would admit of it; that there never was a day now, in which the absence of the Secretary of State would not be inconvenient to the public. And he concluded by desiring that I would take two or three days to consider whether I could not stay in till the end of another quarter, for that, like a man going, to the gallows, he was willing to put it off as long as he could; but if I persisted, he must then look about him and make up his mind to do the best he could: and so he took leave.
November the 5th, 1793. E. Randolph tells me, that Hamilton, in conversation with him yesterday, said, ‘Sir, if all the people in America were now assembled, and to call on me to say whether I am a friend to the French revolution, I would declare that I have it in abhorrence?’
November the 8th, 1793. At a conference at the President’s, where I read several letters of Mr. Genet; on finishing one of them, I asked what should be the answer. The President thereupon took occasion to observe, that Mr. Genet’s conduct continued to be of so extraordinary a nature, that he meant to propose to our serious consideration, whether he should not have his functions discontinued, and be ordered away. He went lengthily into observations on his conduct, to raise against the executive, 1. the people, 2. the State governments, 3. the Congress. He showed he felt the venom of Genet’s pen, but declared he would not choose his insolence should be regarded any farther, than as might be thought to affect the honor of the country. Hamilton and Knox readily and zealously argued for dismissing Mr. Genet. Randolph opposed it with firmness, and pretty lengthily. The President replied to him lengthily, and concluded by saying he did not wish to have the thing hastily decided, but that we should consider of it, and give our opinions on his return from Reading and Lancaster. Accordingly, November the 18th, we met at his house; read new volumes of Genet’s letters, received since the President’s departure; then took up the discussion of the subjects of communication to Congress. 1. The Proclamation. E. Randolph read the statement he had prepared; Hamilton did not like it; said much about his own views; that the President had a right to declare his opinion to our citizens and foreign nations; that it was not the interest of this country to join in the war, and that we were under no obligation to join in it; that though the declaration would not legally bind Congress, yet the President had a right to give his opinion of it, and he was against any explanation in the speech, which should yield that he did not intend that foreign nations should consider it as a declaration of neutrality, future as well as present; that he understood it as meant to give them that sort of assurance and satisfaction, and to say otherwise now, would be a deception on them. He was for the President’s using such expressions, as should neither affirm his right to make such a declaration to foreign nations, nor yield it. Randolph and myself opposed the right of the President to declare any thing future on the question, Shall there or shall there not be a war? and that no such thing was intended; that Hamilton’s construction of the effect of the proclamation would have been a determination of the question of the guarantee, which we both denied to have intended, and I had at the time declared the executive incompetent to. Randolph said he meant that foreign nations should understand it as an intimation of the President’s opinion, that neutrality would be our interest. I declared my meaning to have been, that foreign nations should understand no such thing; that, on the contrary, I would have chosen them to be doubtful, and to come and bid for our neutrality. I admitted the President, having received the nation at the close of Congress in a state of peace, was bound to preserve them in that state till Congress should meet again, and might proclaim any thing which went no farther. The President declared he never had an idea that he could bind Congress against declaring war, or that any thing contained in his proclamation could look beyond the first day of their meeting. His main view was to keep our people in peace; he apologized for the use of the term neutrality in his answers, and justified it, by having submitted the first of them (that to the merchants, wherein it was used) to our consideration, and we had not objected to the term. He concluded in the end, that Colonel Hamilton should prepare a paragraph on this subject for the speech, and it should then be considered. We were here called to dinner.
After dinner, the renvoi of Genet was proposed by himself. I opposed it on these topics. France, the only nation on earth sincerely our friend. The measure so harsh a one, that no precedent is produced where it has not been followed by war. Our messenger has now been gone eighty-four days; consequently, we may hourly expect the return, and to be relieved by their revocation of him. Were it now resolved on, it would be eight or ten days before the matter on which the order should be founded, could be selected, arranged, discussed, and forwarded. This would bring us within four or five days of the meeting of Congress. Would it not be better to wait and see how the pulse of that body, new as it is, would beat. They are with us now, probably, but such a step as this may carry many over to Genet’s side. Genet will not obey the order, &c. &c. The President asked me what I would do if Genet sent the accusation to us to be communicated to Congress, as he threatened in the letter to Moultrie. I said I would not send it to Congress; but either put it in the newspapers, or send it back to him to be published if he pleased. Other questions and answers were put and returned in a quicker altercation than I ever before saw the President use. Hamilton was for the renvoi; spoke much of the dignity of the nation; that they were now to form their character; that our conduct now would tempt or deter other foreign ministers from treating us in the same manner; touched on the President’s personal feelings; did not believe France would make it a cause of war; if she did, we ought to do what was right, and meet the consequences, &c. Knox on the same side, and said he thought it very possible Mr. Genet would either declare us a department of France, or levy troops here and endeavor to reduce us to obedience. Randolph of my opinion, and argued chiefly on the resurrection of popularity to Genet, which might be produced by this measure. That at present he was dead in the public opinion, if we would but leave him so. The President lamented there was not unanimity among us; that as it was, we had left him exactly where we found him; and so it ended.
November the 21st. We met at the President’s. The manner of explaining to Congress the intentions of the proclamation, was the matter of debate. Randolph produced his way of stating it. This expressed its views to have been, 1. to keep our citizens quiet; 2. to intimate to foreign nations that it was the President’s opinion, that the interests and dispositions of this country were for peace. Hamilton produced his statement, in which he declared his intention to be, to say nothing which could be laid hold of for any purpose; to leave the proclamation to explain itself. He entered pretty fully into all the argumentation of Pacificus; he justified the right of the President to declare his opinion for a future neutrality, and that there existed no circumstances to oblige the United States to enter into the war on account of the guarantee; and that in agreeing to the proclamation, he meant it to be understood as conveying both those declarations; viz. neutrality, and that the casus foederis on the guarantee did not exist. He admitted the Congress might declare war, notwithstanding these declarations of the President. In like manner, they might declare war in the face of a treaty, and in direct infraction of it. Among other positions laid down by him, this was with great positiveness; that the constitution having given power to the President and Senate to make treaties, they might make a treaty of neutrality which should take from Congress the right to declare war in that particular case, and that under the form of a treaty they might exercise any powers whatever, even those exclusively given by the constitution to the House of Representatives. Randolph opposed this position, and seemed to think that where they undertook to do acts by treaty (as to settle a tariff of duties), which were exclusively given to the legislature, that an act of the legislature would be necessary to confirm them, as happens in England, when a treaty interferes with duties established by law. I insisted that in giving to the President and Senate a power to make treaties, the constitution meant only to authorize them to carry into effect, by way of treaty, any powers they might constitutionally exercise. I was sensible of the weak points in this position, but there were still weaker in the other hypothesis; and if it be impossible to discover a rational measure of authority to have been given by this clause, I would rather suppose that the cases which my hypothesis would leave unprovided, were not thought of by the convention, or if thought of, could not be agreed on, or were thought of and deemed unnecessary to be invested in the government. Of this last description, were treaties of neutrality, treaties offensive and defensive, &c. In every event, I would rather construe so narrowly as to oblige the nation to amend, and thus declare what powers they would agree to yield, than too broadly, and, indeed, so broadly as to enable the executive and Senate to do things which the constitution forbids. On the question, which form of explaining the principles of the proclamation should be adopted, I declared for Randolph’s, though it gave to that instrument more objects than I had contemplated. Knox declared for Hamilton’s. The President said he had had but one object, the keeping our people quiet till Congress should meet; that nevertheless, to declare he did not mean a declaration of neutrality, in the technical sense of the phrase, might perhaps be crying peccavi before he was charged. However, he did not decide between the two draughts.
November the 23rd. At the President’s. Present, Knox, Randolph, and Th: Jefferson. Subject, the heads of the speech. One was, a proposition to Congress to fortify the principal harbors. I opposed the expediency of the General Government’s undertaking it, and the expediency of the President’s proposing it. It was amended, by substituting a proposition to adopt means for enforcing respect to the jurisdiction of the United States within its waters. It was proposed to recommend the establishment of a military academy. I objected that none of the specified powers given by the constitution to Congress, would authorize this. It was, therefore, referred for further consideration and inquiry. Knox was for both propositions. Randolph against the former, but said nothing as to the latter. The President acknowledged he had doubted of the expediency of undertaking the former; and as to the latter, though it would be a good thing, he did not wish to bring on any thing which might generate heat and ill-humor. It was agreed that Randolph should draw the speech and the messages.
November the 28th. Met at the President’s. I read over a list of the papers copying, to be communicated to Congress on the subject of Mr. Genet. It was agreed that Genet’s letter of August the 13th to the President, mine of August the 16th, and Genet’s of November to myself and the Attorney General, desiring a prosecution of Jay and King, should not be sent to the legislature: on a general opinion, that the discussion of the fact certified by Jay and King had better be left to the channel of the newspapers, and in the private hands in which it now is, than for the President to meddle in it, or give room to a discussion of it in Congress.
Randolph had prepared a draught of the speech. The clause recommending fortifications was left out; but that for a military academy was inserted. I opposed it, as unauthorized by the constitution. Hamilton and Knox approved it without discussion. Randolph was for it, saying that the words of the constitution anthorizing Congress to lay taxes, &c. for the common defence, might comprehend it. The President said he would not choose to recommend any thing against the constitution, but if it was doubtful, he was so impressed with the necessity of this measure, that he would refer it to Congress, and let them decide for themselves whether the constitution authorized it or not. It was, therefore, left in. I was happy to see that Randolph had, by accident, used the expression ‘our republic,’ in the speech. The President, however, made no objection to it, and so, as much as it had disconcerted him on a former occasion with me, it was now put into his own mouth to be pronounced to the two Houses of legislature.
No material alterations were proposed or made in any part of the draught.
After dinner, I produced the draught of messages on the subject of France and England, proposing that that relative to Spain should be subsequent and secret.
Hamilton objected to the draught in toto; said that the contrast drawn between the conduct of France and England amounted to a declaration of war; he denied that France had ever done us favors; that it was mean for a nation to acknowledge favors; that the dispositions of the people of this country towards France, he considered as a serious calamity; that the executive ought not, by an echo of this language, to nourish that disposition in the people; that the offers in commerce made us by France, were the offspring of the moment, of circumstances which would not last, and it was wrong to receive as permanent, things merely temporary; that he could demonstrate that Great Britain showed us more favors than France. In complaisance to him I whittled down the expressions without opposition; struck out that of ‘favors ancient and recent’ from France; softened some terms, and omitted some sentiments respecting Great Britain. He still was against the whole, but insisted that, at any rate, it should be a secret communication, because the matters it stated were still depending. These were, 1. the inexecution of the treaty; 2. the restraining our commerce to their own ports and those of their friends. Knox joined Hamilton in every thing. Randolph was for the communications; that the documents respecting the first should be given in as public; but that those respecting the second should not be given to the legislature at all, but kept secret. I began to tremble now for the whole, lest all should be kept secret. I urged, especially, the duty now incumbent on the President, to lay before the legislature and the public what had passed on the inexecution of the treaty, since Mr. Hammond’s answer of this month might be considered as the last we should ever have; that, therefore, it could no longer be considered as a negotiation pending. I urged that the documents respecting the stopping our corn ought also to go, but insisted that if it should be thought better to withhold them, the restrictions should not go to those respecting the treaty; that neither of these subjects was more in a state of pendency than the recall of Mr. Genet, on which, nevertheless, no scruples had been expressed. The President took up the subject with more vehemence than I have seen him show, and decided without reserve, that not only what had passed on the inexecution of the treaty should go in as public (in which Hamilton and Knox had divided in opinion from Randolph and myself), but also that those respecting the stopping our corn should go in as public (wherein Hamilton, Knox, and Randolph had been against me.) This was the first instance I had seen of his deciding on the opinion of one against that of three others, which proved his own to have been very strong.
December the 1st, 1793. Beckley tells me he had the following fact from Lear. Langdon, Cabot, and some others of the Senate, standing in a knot before the fire after the Senate had adjourned, and growling together about some measure which they had just lost; ‘Ah!’ said Cabot, ‘things will never go right till you have a President for life, and an hereditary Senate.’ Langdon told this to Lear, who mentioned it to the President. The President seemed struck with it, and declared he had not supposed there was a man in the United States who could have entertained such an idea.
March the 2nd, 1797. I arrived at Philadelphia to qualify as Vice-President, and called instantly on Mr. Adams, who lodged at Francis’s, in Fourth street. The next morning he returned my visit at Mr. Madison’s, where I lodged. He found me alone in my room, and shutting the door himself, he said he was glad to find me alone, for that he wished a free conversation with me. He entered immediately on an explanation of the situation of our affairs with France, and the danger of rupture with that nation, a rupture which would convulse the attachments of this country; that he was impressed with the necessity of an immediate mission to the Directory; that it would have been the first wish of his heart to have got me to go there, but that he supposed it was out of the question, as it did not seem justifiable for him to send away the person destined to take his place in case of accident to himself, nor decent to remove from competition one who was a rival in the public favor. That he had, therefore, concluded to send a mission, which, by its dignity, should satisfy France, and by its selection from the three great divisions of the continent, should satisfy all parts of the United States; in short, that he had determined to join Gerry and Madison to Pinckney, and he wished me to consult Mr. Madison for him. I told him that, as to myself, I concurred in the opinion of the impropriety of my leaving the post assigned me, and that my inclinations, moreover, would never permit me to cross the Atlantic again; that I would, as he desired, consult Mr. Madison, but I feared it was desperate, as he had refused that mission on my leaving it, in General Washington’s time, though it was kept open a twelvemonth for him. He said that if Mr. Madison should refuse, he would still appoint him, and leave the responsibility on him. I consulted Mr. Madison, who declined, as I expected. I think it was on Monday the 6th of March, Mr. Adams and myself met at dinner at General Washington’s, and we happened, in the evening, to rise from table and come away together. As soon as we got into the street, I told him the event of my negotiation with Mr. Madison. He immediately said, that, on consultation, some objections to that nomination had been raised, which he had not contemplated; and was going on with excuses which evidently embarrassed him, when we came to Fifth street, where our road separated, his being down Market street, mine off along Fifth, and we took leave: and he never after that said one word to me on the subject, or ever consulted me as to any measures of the government. The opinion I formed at the time on this transaction was, that Mr. Adams, in the first moments of the enthusiasm of the occasion (his inauguration), forgot party sentiments, and, as he never acted on any system, but was always governed by the feeling of the moment, he thought, for a moment, to steer impartially between the parties; that Monday, the 6th of March, being the first time he had met his cabinet, on expressing ideas of this kind, he had been at once diverted from them, and returned to his former party views.
July, 1797. Murray is rewarded for his services by an appointment to Amsterdam; W. Smith of Charleston, to Lisbon.
August the 24th. About the time of the British treaty, Hamilton and Talleyrand, bishop of Autun, dined together, and Hamilton drank freely. Conversing on the treaty, Talleyrand says, ‘Mais vraiment, Monsieur Hamilton, ce n’est pas Men honnete, after making the Senate ratify the treaty, to advise the President to reject it.’ ‘The treaty,’ says Hamilton, ‘is an execrable one, and Jay was an old woman for making it; but the whole credit of saving us from it must be given to the President.’ After circumstances had led to a conclusion that the President also must ratify it, he said to the same Talleyrand, ‘Though the treaty is a most execrable one, yet when once we have come to a determination on it, we must carry it through thick and thin, right or wrong.’ Talleyrand told this to Volney, who told it to me.
There is a letter now appearing in the papers, from Pickering to Monroe, dated July the 24th, 1797, which I am satisfied is written by Hamilton. He was in Philadelphia at that date.
December the 26th, 1797. Langdon tells me, that at the second election of President and Vice-President of the United States, when there was a considerable vote given to Clinton in opposition to Mr. Adams, he took occasion to remark it in conversation in the Senate chamber with Mr. Adams, who gritting his teeth, said, ‘Damn ‘em, damn ‘em, damn ‘em, you see that an elective government will not do.’ He also tells me that Mr. Adams, in a late conversation,said,’ Republicanism must be disgraced, ‘Sir.’ The Chevalier Yrujo called on him at Braintree, and conversing on French affairs, and Yrujo expressing his belief of their stability, in opposition to Mr. Adamses, the latter lifting up and shaking his finger at him, said, ‘I’ll tell you what, the French republic will not last three months.’ This I had from Yrujo.
Harper, lately in a large company, was saying that the best thing the friends of the French could do, was to pray for the restoration of their monarch. ‘Then,’ says a by-stander, ‘the best thing we could do, I suppose, would be to pray for the establishment of a monarch in the United States.’ ‘Qur people,’ says Harper, ‘are not yet ripe for it, but it is the best thing we can come to, and we shall come to it.’ Something like this was said in presence of Findlay. He now denies it in the public papers, though it can be proved by several members.
December the 27th. Tench Coxe tells me, that a little before Hamilton went out of office, or just as he was going out, taking with him his last conversation, and among other things, on the subject of their differences, ‘For my part,’ says he, ‘I avow myself a monarchist; I have no objection to a trial being made of this thing of a republic, but,’ &c.
January the 5th, 1798. I receive a very remarkable fact indeed, in our history, from Baldwin and Skinner. Before the establishment of our present government, a very extensive combination had taken place in New York and the eastern States, among that description of people who were partly monarchical in principle, or frightened with Shays’s rebellion and the impotence of the old Congress. Delegates in different places had actually had consultations on the subject of seizing on the powers of a government, and establishing them by force; had corresponded with one another, and had sent a deputy to General Washington to solicit his co-operation. He refused to join them. The new convention was in the mean time proposed by Virginia and appointed. These people believed it impossible the States should ever agree on a government, as this must include the impost and all the other powers which the States had, a thousand times, refused to the general authority. They therefore let the proposed convention go on, not doubting its failure, and confiding that on its failure would be a still more favorable moment for their enterprise. They therefore wished it to fail, and especially, when Hamilton, their leader, brought forward his plan of government, failed entirely in carrying it, and retired in disgust from the convention. His associates then took every method to prevent any form of government being agreed to. But the well-intentioned never ceased trying, first one thing, then another, till they could get something agreed to. The final passage and adoption of the constitution completely defeated the views of the combination, and saved us from an attempt to establish a government over us by force. This fact throws a blaze of light on the conduct of several members from New York and the eastern States in the convention of Annapolis, and the grand convention. At that of Annapolis, several eastern members most vehemently opposed Madison’s proposition for a more general convention, with more general powers. They wished things to get more and more into confusion, to justify the violent measure they proposed. The idea of establishing a government by reasoning and agreement, they publicly ridiculed as an Utopian project, visionary and unexampled.
February the 6th, 1798. Mr. Baldwin tells me, that in a conversation yesterday with Goodhue, on the state of our affairs, Goodhue said, ‘I’ll tell you what, I have made up my mind on this subject; I would rather the old ship should go down than not’; (meaning the Union of the States.) Mr. Hillhouse coming up, ‘Well,’ says Mr. Baldwin, ‘I’ll tell my old friend Hillhouse what you say ‘; and he told him. ‘Well,’ says Goodhue, ‘I repeat, that I would rather the old ship should go down, if we are to be always kept pumping so.’ ‘Mr. Hillhouse,’ says Baldwin, ‘you remember when we were learning logic together at school, there was the case categorical and the case hypothetical. Mr. Goodhue stated it to me first as the case categorical. I am glad to see that he now changes it to the case hypothetical, by adding, ‘if we are always to be kept pumping so.’ Baldwin went on then to remind Goodhue what an advocate he had been for our tonnage duty, wanting to make it one dollar instead of fifty cents; and how impatiently he bore the delays of Congress in proceeding to retaliate on Great Britain before Mr. Madison’s propositions came on. Goodhue acknowledged that his opinions had changed since that.
February the 15th, 1798. I dined this day with Mr. Adams, (the President.) The company was large. After dinner I was sitting next to him, and our conversation was first on the enormous price of labor,* house rent, and other things. We both concurred in ascribing it chiefly to the flood of bank paper now afloat, and in condemning those institutions. We then got on the constitution; and in the course of our conversation he said, that no republic could ever last which had not a Senate, and a Senate deeply and strongly rooted, strong enough to bear up against all popular storms and passions; that he thought our Senate as well constituted as it could have been, being chosen by the legislatures; for if these could not support them, he did not know what could do it; that perhaps it might have been as well for them to be chosen by the State at large, as that would insure a choice of distinguished men, since none but such could be known to a whole people; that the only fault in our Senate was, that it was not durable enough; that hitherto, it had behaved very well; however, he was afraid they would give way in the end. That as to trusting to a popular assembly for the preservation of our liberties, it was the merest chimera imaginable; they never had any rule of decision but their own will; that he would as lieve be again in the hands of our old committees of safety, who made the law and executed it at the same time; that it had been observed by some writer (I forget whom he named), that anarchy did more mischief in one night, than tyranny in an age; and that in modern times we might say with truth, that, in France, anarchy had done more harm in one night, than all the despotism of their Kings had ever done in twenty or thirty years. The point in which he views our Senate, as the colossus of the constitution, serves as a key to the politics of the Senate, who are two thirds of them in his sentiments, and accounts for the bold line of conduct they pursue.
* He observed, that eight or ten years ago he gave only
fifty dollars to a common laborer for his farm, finding him
food and lodging. Now he gives one hundred and fifty
dollars, and even two hundred dollars to one.
March the 1st. Mr. Tazewell tells me, that when the appropriations for the British treaty were on the carpet, and very uncertain in the lower House, there being at that time a number of bills in the hands of committees of the Senate, none reported, and the Senate idle for want of them, he, in his place, called on the committees to report, and particularly on Mr. King, who was of most of them. King said that it was true the committees kept back their reports, waiting the event of the question about appropriation: that if that was not carried, they considered legislation as at an end; that they might as well break up and consider the Union as dissolved. Tazewell expressed his astonishment at these ideas, and called on King to know if he had misapprehended him. King rose again and repeated the same words. The next day, Cabot took an occasion in debate, and so awkward a one as to show it was a thing agreed to be done, to repeat the same sentiments in stronger terms, and carried further, by declaring a determination on their side to break up and dissolve the government.
March the 11th. In conversation with Baldwin and Brown of Kentucky, Brown says that in a private company once, consisting of Hamilton, King, Madison, himself, and some one else making a fifth, speaking of the ‘federal government’; ‘Oh!’ says Hamilton, ‘say the federal monarchy; let us call things by their right names, for a monarchy it is.’
Baldwin mentions at table the following fact. When the bank bill was under discussion in the House of Representatives, Judge Wilson came in, and was standing by Baldwin. Baldwin reminded him of the following fact which passed in the grand convention. Among the enumerated powers given to Congress, was one to erect corporations. It was on debate struck out. Several particular powers were then proposed. Among others, Robert Morris proposed to give Congress a power to establish a national bank. Gouverneur Morris opposed it, observing that it was extremely doubtful whether the constitution they were framing could ever be passed at all by the people of America; that to give it its best chance, however, they should make it as palatable as possible and put nothing into it not very essential, which might raise up enemies; that his colleague (Robert Morris) well knew that ‘a bank’ was, in their State (Pennsylvania) the very watch-word of party; that a bank had been the great bone of contention between the two parties of the State, from the establishment of their constitution, having been erected, put down, and erected again, as either party preponderated; that therefore, to insert this power, would instantly enlist against the whole instrument, the whole of the anti-bank party in Pennsylvania. Whereupon it was rejected, as was every other special power, except that of giving copyrights to authors, and patents to inventors; the general power of incorporating being whittled down to this shred. Wilson agreed to the fact.
Mr. Hunter of South Carolina, who lodges with Rutledge, [* J. Rutledge, junior] tells me, that Rutledge was explaining to him the plan they proposed to pursue as to war measures, when Otis came in. Rutledge addressed Otis. ‘Now, Sir,’ says he, ‘you must come forward with something liberal for the southern States, fortify their harbors and build galleys, in order to obtain their concurrence.’ Otis said, ‘We insist on convoys for our European trade, and guarda-costas, on which condition alone, we will give them galleys and fortifications.’ Rutledge observed, that in the event of war, McHenry and Pickering must go out; Wolcott, he thought, might remain, but the others were incapable of conducting a war. Otis said the eastern people would never abandon Pickering; he must be retained; McHenry might go. They considered together whether General Pinckney would accept the office of Secretary of War. They apprehended he would not. It was agreed in this conversation, that Sewall had more the ear of the President than any other person.
March the 12th. When the bill for appropriations was before the Senate, Anderson moved to strike out a clause recognising (by way of appropriation) the appointment of a committee by the House of Representatives, to sit during their recess to collect evidence on Blount’s case, denying they had power, but by a law, to authorize a committee to sit during recess. Tracy advocated the motion, and said, ‘We may as well speak out. The committee was appointed by the House of Representatives, to take care of the British minister, to take care of the Spanish minister, to take care of the Secretary of State, in short, to take care of the President of the United States. They were afraid the President and Secretary of State would not perform the office of collecting evidence faithfully; that there would be collusion, &c. Therefore, the House appointed a committee of their own. We shall have them next sending a committee to Europe to make a treaty, &c. Suppose that the House of Representatives should resolve, that after the adjournment of Congress, they should continue to sit as a committee of the whole House during the whole recess.’ This shows how the appointment of that committee has been viewed by the President’s friends.
April the 5th. Doctor Rush tells me he had it from Mrs. Adams, that not a scrip of a pen has passed between the late and present President, since he came into office.
April the 13th. New instructions of the British government to their armed ships now appear, which clearly infringe their treaty with us, by authorizing them to take our vessels carrying produce of the French colonies from those colonies to Europe, and to lake vessels bound to a blockaded port. See them in Brown’s paper, of April the 18th, in due form.
The President has sent a government brig to France, probably to carry despatches. He has chosen as the bearer of these, one Humphreys, the son of a ship-carpenter, ignorant, under age, not speaking a word of French, most abusive of that nation; whose only merit is, the having mobbed and beaten Bache on board the frigate built here, for which he was indicted and punished by fine.
April the 25th. At a dinner given by the bar to the federal judges, Chase and Peters, present about twenty-four lawyers, and William Tilghman in the chair, this toast was given; ‘Our King in old England.’ Observe the double entendre on the word King. Du Ponceau, who was one of the bar present, told this to Tench Coxe, who told me in presence of H. Tazewell. Dallas was at the dinner; so was Colonel Charles Sims of Alexandria, who is here on a law-suit vs. General Irving.
May the 3rd. The President some time ago appointed Steele, of Virginia, a commissioner to the Indians, and recently Secretary of the Mississippi Territory. Steele was a Counsellor of Virginia, and was voted out by the Assembly because he turned tory. He then offered for Congress, and was rejected by the people. Then offered for the Senate of Virginia, and was rejected. The President has also appointed Joseph Hopkinson commissioner to make a treaty with the Oneida Indians. He is a youth of about twenty-two or twenty-three, and has no other claims to such an appointment than extreme toryism, and the having made a poor song to the tune of the President’s March.
October the 13th, 1798. Littlepage, who has been on one or two missions from Poland to Spain, said that when Gardoqui returned from America, he settled with his court an account of secret service money, of six hundred thousand dollars. Ex relatione Colonel Monroe.
January, 1799. In a conversation between Doctor Ewen and the President, the former said one of his sons was an aristocrat, the other a democrat. The President asked if it were not the youngest who was the democrat. ‘Yes,’ said Ewen. ‘Well,’ said the President, ‘a boy of fifteen who is not a democrat is good for nothing, and he is no better who is a democrat at twenty.’ Ewen told Hurt, and Hurt told me.
January the 14th. Logan tells me that in his conversation with Pickering on his arrival, the latter abused Gerry very much; said he was a traitor to his country, and had deserted the post to which he was appointed; that the French temporized at first with Pinckney, but found him too much of a man for their purpose. Logan observing, that, notwithstanding the pacific declarations of France, it might still be well to keep up. the military ardor of our citizens, and to have the militia in good order: ‘The militia,’ said Pickering, ‘the militia never did any good to this country, except in the single affair of Bunker’s Hill; that we must have a standing army of fifty thousand men, which being stationed in different parts of the continent, might serve as rallying points for the militia, and so render them of some service.’ In his conversation with Mr. Adams, Logan mentioned the willingness of the French to treat with Gerry. ‘And do you know why,’ said Mr. Adams. ‘Why, Sir?’ said Logan. ‘Because,’ said Mr. Adams, ‘they know him to have been an anti-federalist, against the constitution.’
January the 2nd, 1800. Information from Tench Coxe. Mr. Liston had sent two letters to the Governor of Canada by one Sweezy. He had sent copies of them, together with a third, (original) by one Cribs. Sweezy was arrested (being an old horse-thief), and his papers examined. T. Coxe had a sight of them. As soon as a rumor got out that there were letters of Mr. Liston disclosed, but no particulars yet mentioned, Mr. Liston suspecting that Cribs had betrayed him, thought it best to bring all his three letters, and lay them before Pickering, Secretary of State. Pickering thought them all very innocent. In his office they were seen by Mr. Hodgen of New Jersey, commissary of military stores, and the intimate friend of Pickering. It happens that there is some land partnership between Pickering, Hodgen, and Coxe, so that the latter is freely and intimately visited by Hodgen, who, moreover, speaks freely with him on political subjects. They were talking the news of the day, when Mr. Coxe observed that these intercepted letters of Liston were serious things; (nothing being yet out but a general rumor.) Hodgen asked which he thought the most serious. Coxe said the second; (for he knew yet of no other.) Hodgen said he thought little of any of them, but that the third was the most exceptionable. This struck Coxe, who, not betraying his ignorance of a third letter, asked generally what part of that he alluded to. Hodgen said to that wherein he assured the Governor of Canada, that if the French invaded Canada, an army would be marched from these States to his assistance. After this it became known that it was Sweezy who was arrested, and not Cribs; so that Mr. Liston had made an unnecessary disclosure of his third letter to Mr. Pickering, who, however, keeps his secret for him. In the beginning of the conversation between Hodgen and Coxe, Coxe happened to name Sweezy as the bearer of the letters. ‘That ‘s not his name,’ says Hodgen, (for he did not know that two of the letters had been sent by Sweezy also) ‘his name is Cribs.’ This put Coxe on his guard, and set him to fishing for the new matter.
January the 10th. Doctor Rush tells me, that he had it from Samuel Lyman, that during the X. Y. Z. Congress, the federal members held the largest caucus they have ever had, at which he was present, and the question was proposed and debated, whether they should declare war against France, and determined in the negative. Lyman was against it. He tells me, that Mr. Adams told him, that when he came on in the fall to Trenton, he was there surrounded constantly by the opponents of the late mission to France. That Hamilton pressing him to delay it, said, ‘Why, Sir, by Christmas, Louis the XVIII. will be seated on his throne.’ Mr. A. ‘By whom?’ H. ‘By the coalition.’ Mr. A. ‘Ah! then farewell to the independence of Europe. If a coalition, moved by the finger of England, is to give a government to France, there is an end to the independence of every country.’
January the 12th. General Samuel Smith says that Pickering, Wolcott, and McHenry, wrote a joint letter from Trenton to the President, then at Braintree, dissuading him from the mission to France. Stoddard refused to join it. Stoddard says the instructions are such, that if the Directory have any disposition to reconciliation, a treaty will be made. He observed to him also, that Ellsworth looks beyond this mission to the Presidential chair. That with this view, he will endeavor to make a treaty, and a good one. That Davie has the same vanity and views. All this communicated by Stoddard to S. Smith.
January the 13th. Baer and Harrison G. Otis told J. Nicholas, that in the caucus mentioned ante 10th, there wanted but five votes to produce a declaration of war. Baer was against it.
January the 19th. W. C. Nicholas tells me, that in a conversation with Dexter three or four days ago, he asked Dexter whether it would not be practicable for the States to agree on some uniform mode of choosing electors of President. Dexter said, ‘I suppose you would prefer an election by districts.’ ‘Yes,’ said Nicholas, ‘I think it would be best; but would nevertheless agree to any other consistent with the constitution.’ Dexter said he did not know what might be the opinion of his State, but his own was, that no mode of election would answer any good purpose; that he should prefer one for life. ‘On that reasoning,’ said Nicholas, ‘you should prefer an hereditary one.’ ‘No,’ he said, ‘we are not ripe for that yet. I suppose,’ added he, ‘this doctrine is not very popular with you.’ ‘No,’ said Nicholas, ‘it would effectually damn any man in my State.’ ‘So it would in mine,’ said Dexter; ‘but I am under no inducement to belie my sentiment; I have nothing to ask from any body; I had rather be at home than here, therefore I speak my sentiments freely.’ Mr. Nicholas, a little before or after this, made the same proposition of a uniform election to Rossr who replied that he saw no good in any kind of election. ‘Perhaps,’ said he, ‘the present one may last a while.’ On the whole, Mr. Nicholas thinks he perceives, in that party, a willingness and a wish to let every thing go from bad to worse, to amend nothing, in hopes it may bring on confusion, and open a door to the kind of government they wish. In a conversation with Gunn, who goes with them, but thinks in some degree with us, Gunn told him that the very game which the minority of Pennsylvania is now playing with McKean (see substitute of minority in lower House, and address of Senate in upper), was meditated by the same party in the federal government, in case of the election of a republican President; and that the eastern States would in that case throw things into confusion, and break the Union. That they have in a great degree got rid of their paper, so as no longer to be creditors, and the moment they cease to enjoy the plunder of the immense appropriations now exclusively theirs, they would aim at some other order of things.
January the 24th. Mr. Smith, a merchant of Hamburg, gives me the following information. The St. Andrew’s Club, of New York, (all of Scotch tories,) gave a public dinner lately. Among other guests Alexander Hamilton was one. After dinner, the first toast was ‘The President of the United States.’ It was drunk without any particular approbation. The next was, ‘George the Third.’ Hamilton started up on his feet, and insisted on a bumper and three cheers. The whole company accordingly rose and gave the cheers. One of them, though a federalist, was so disgusted at the partiality shown by Hamilton to a foreign sovereign over his own President, that he mentioned it to a Mr. Schwart-house, an American merchant of New York, who mentioned it to Smith.
Mr. Smith also tells me, that calling one evening on Mr. Evans, then Speaker of the House of Representatives of Pennsylvania, and asking the news, Evans said, Harper had just been there, and speaking of the President’s setting out to Braintree, said, ‘he prayed to God that his horses might run away with him, or some other accident happen to break his neck before he reached Braintree.’ This was in indignation at his having named Murray, &c. to negotiate with France. Evans approved of the wish.
February the 1st. Doctor Rush tells me that he had it from Asa Green, that when the clergy addressed General Washington on his departure from the government, it was observed in their consultation, that he had never, on any occasion, said a word to the public which showed a belief in the Christian religion, and they thought they should so pen their address, as to force him at length to declare publicly whether he was a Christian or not. They did so. However, he observed, the old fox was too cunning for them. He answered every article of their address particularly except that, which he passed over without notice. Rush observes, he never did say a word on the subject in any of his public papers, except in his valedictory letter to the Governors of the States when he resigned his commission in the army, wherein he speaks of ‘the benign influence of the Christian religion.’
I know that Gouverneur Morris, who pretended to be in his secrets and believed himself to be so, has often told me that General Washington believed no more of that system than he himself did.
March, 1800. Heretical doctrines maintained in Senate, on the motion against the Aurora. That there is in every legal body of men a right of self-preservation, authorizing them to do whatever is necessary for that purpose: by Tracy, Read, and Lawrence. That the common law authorizes the proceeding proposed against the Aurora, and is in force here: by Read. That the privileges of Congress are and ought to be indefinite: by Read.
Tracy says, he would not say exactly that the common law of England in all its extent is in force here; but common sense reason, and morality, which are the foundations of the common law, are in force here, and establish a common law. He held himself so nearly half way between the common law of England and what every body else has called natural law, and not common law, that he could hold to either the one or the other, as he should find expedient.
Dexter maintained that the common law, as to crimes, is in force in the United States.
Chipman says, that the principles of common right are common law.
March the 11th. Conversing with Mrs. Adams on the subject of the writers in the newspapers, I took occasion to mention that I never in my life had, directly or indirectly, written one sentence for a newspaper; which is an absolute truth. She said that Mr. Adams, she believed, had pretty well ceased to meddle in the newspapers, since he closed the pieces on Davila. This is the first direct avowal of that work to be his, though long and universally understood to be so.
March the 14th. Freneau, in Charleston, had the printing of the laws in his paper. He printed a pamphlet of Pinckney’s letters on Robbins’s case. Pickering has given the printing of the laws to the tory paper of that place, though not of half the circulation. The printing amounted to about one hundred dollars a year.
March the 24th. Mr. Perez Morton of Massachusetts tells me that Thatcher, on his return from the war Congress, declared to him he had been for a declaration of war against France, and many others also; but that on counting noses they found they could not carry it, and therefore did not attempt it.
March the 27th. Judge Breckenridge gives me the following information. He and Mr. Ross were originally very intimate; indeed, he says, he found him keeping a little Latin school, and advised and aided him in the study of the law, and brought him forward. After Ross became a Senator, and particularly at the time of the western insurrection, they still were in concert. After the British treaty, Ross, on his return, informed him there was a party in the United States who wanted to overturn the government, who were in league with France; that France, by a secret article of treaty with Spain, was to have Louisiana; and that Great Britain was likely to be our best friend and dependence.
On this information, he, Breckenridge, was induced to become an advocate for the British treaty. During this intimacy with Ross, he says, that General Collot, in his journey to the western country, called on him, and he frequently led Breckenridge into conversations on their grievances under the government, and particularly the western expedition; that he spoke to him of the advantages that country would have in joining France when she should hold Louisiana; showed him a map he had drawn of that part of the country; pointed out the passes in the mountain, and the facility with which they might hold them against the United States, and with which France could support them from New Orleans. He says, that in these conversations, Collot let himself out without common prudence. He says, Michaux (to whom I, at the request of Genet, had given a letter of introduction to the Governor of Kentucky as a botanist, which was his real profession,) called on him; that Michaux had a commissary’s commission for the expedition, which Genet had planned from that quarter against the Spaniards; that —————, the late Spanish commandant of St. Genevieve, with one Powers, an Englishman, called on him. That from all these circumstances, together with Ross’s stories, he did believe that there was a conspiracy to deliver our country, or some part of it at least, to the French; that he made notes of what passed between himself and Collot and the others, and lent them to Mr. Ross, who gave them to the President, by whom they were deposited in the office of the Board of War; that when he complained to Ross of this breach of confidence, he endeavored to get off by compliments on the utility and importance of his notes. They now cooled towards each other; and his opposition to Ross’s election as Governor has separated them in truth, though not entirely to appearance.
Doctor Rush tells me, that within a few days he has heard a member of Congress lament our separation from Great Britain, and express his sincere wishes that we were again dependent on her.
December the 25th, 1800. Colonel Hitchburn tells me what Colonel Monroe had before told me of, as coming from Hitchburn. He was giving me the characters of persons in Massachusetts. Speaking of Lowell, he said he was, in the beginning of the Revolution, a timid whig, but as soon as he found we were likely to prevail, he became a great office-hunter. And in the very breath of speaking of Lowell, he stopped: says he, I will give you a piece of information which I do not venture to speak of to others. There was a Mr. Hale in Massachusetts, a reputable, worthy man, who becoming a little embarrassed in his affairs, I aided him, which made him very friendly to me. He went to Canada on some business. The Governor there took great notice of him. On his return, he took occasion to mention to me that he was authorized by the Governor of Canada to give from three to five thousand guineas each to himself and some others, to induce them not to do any thing to the injury of their country, but to befriend a good connection between England and it. Hitchburn said he would think of it, and asked Hale to come and dine with him to-morrow. After dinner he drew Hale fully out. He told him he had his doubts, but particularly, that he should not like to be alone in such a business. On that, Hale named to him four others who were to be engaged, two of whom, said Hitchburn, are now dead, and two living. Hitchburn, when he had got all he wanted out of Hale, declined in a friendly way. But he observed those, four men, from that moment, to espouse the interests of England in every point and on every occasion. Though he did not name the men to me, yet as the speaking of Lowell was what brought into his Read to tell me this anecdote, I concluded he was one. From other circumstances respecting Stephen Higginson, of whom he spoke, I conjectured him to be the other living one.
December the 26th. In another conversation, I mentioned to Colonel Hitchburn, that though he had not named names, I had strongly suspected Higginson to be one of Hale’s men. He smiled and said, if I had strongly suspected any man wrongfully from his information, he would undeceive me: that there were no persons he thought more strongly to be suspected himself, than Higginson and Lowell. I considered this as saying they were the men. Higginson is employed in an important business about our navy.
February the 12th, 1801. Edward Livingston tells me, that Bayard applied to-day or last night to General Samuel Smith, and represented to him the expediency of his coming over to the States who vote for Burr, that there was nothing in the way of appointment which he might not command, and particularly mentioned the Secretaryship of the Navy. Smith asked him if he was authorized to make the offer. He said he was authorized. Smith told this to Livingston, and to W. C. Nicholas, who confirms it to me. Bayard in like manner tempted Livingston, not by offering any particular office, but by representing to him his (Livingston’s) intimacy and connection with Burr; that from him he had every thing to expect, if he would come over to him. To Doctor Linn of New Jersey, they have offered the government of New Jersey. See a paragraph in Martin’s Baltimore paper of February the 10th, signed, ‘a looker on,’ staling an intimacy of views between Harper and Burr.
February the 14th. General Armstrong tells me, that Gouverneur Morris, in conversation with him to-day on the scene which is passing, expressed himself thus. ‘How comes it,’ says he, ‘that Burr, who is four hundred miles off (at Albany), has agents here at work with great activity, while Mr. Jefferson, who is on the spot, does nothing?’ This explains the ambiguous conduct of himself and his nephew, Lewis Morris, and that they were holding themselves free for a price; i.e. some office, either to the uncle or nephew.
February the 16th. See in the Wilmington Mirror of February the 14th, Mr. Bayard’s elaborate argument to prove that the common law, as modified by the laws of the respective States at the epoch of the ratification of the constitution, attached to the courts of the United States.
June the 23rd, 1801. Andrew Ellicot tells me, that in a conversation last summer with Major William Jackson of Philadelphia, on the subject of our intercourse with Spain, Jackson said we had managed our affairs badly; that he himself was the author of the papers against the Spanish minister signed Americanus; that his object was irritation; that he was anxious, if it could have been brought, about, to have plunged us into a war with Spain, that the people might have been occupied with that, and not with the conduct of the administration, and other things they had no business to meddle with.
December the 13th, 1803. The Reverend Mr. Coffin of New England, who is now here soliciting donations for a college in Greene county, in Tennessee, tells me that when he first determined to engage in this enterprise, he wrote a paper recommendatory of the enterprise, which he meant to get signed by clergymen, and a similar one for persons in a civil character, at the head of which he wished Mr. Adams to put his name, he being then President, and the application going only for his name, and not for a donation. Mr. Adams, after reading the paper and considering, said, ‘he saw no possibility of continuing the union of the States; that their dissolution must necessarily take place; that he therefore saw no propriety in recommending to New England men to promote a literary institution in the south; that it was in fact giving strength to those who were to be their enemies, and therefore, he would have nothing to do with it.’
December the 31st. After dinner to-day, the pamphlet on the conduct of Colonel Burr being the subject of conversation, Matthew Lyon noticed the insinuations against the republicans at Washington, pending the Presidential election, and expressed his wish that every thing was spoken out which was known; that it would then appear on which side there was a bidding for votes, and he declared that John Brown of Rhode Island, urging him to vote for Colonel Burr, used these words. ‘What is it you want, Colonel Lyon? Is it office, is it money? Only say what you want, and you shall have it.’
January the 2nd, 1804. Colonel Hitchburn, of Massachusetts, reminding me of a letter he had written me from Philadelphia, pending the Presidential election, says he did not therein give the details. That he was in company at Philadelphia with Colonel Burr and ——— that in the course of the conversation on the election, Colonel Burr said, ‘We must have a President, and a constitutional one, in some way.’ ‘How is it to be done,’ says Hitchburn; ‘Mr. Jefferson’s friends will not quit him, and his enemies are not strong enough to carry another.’ ‘Why,’ says Burr, ‘our friends must join the federalists, and give the President.’ ‘The next morning at breakfast, Colonel Burr repeated nearly the same, saying, ‘We cannot be without a President, our friends must join the federal vote.’ ‘But,’ says Hitchburn, ‘we shall then be without a Vice-President; who is to be our Vice-President?’ Colonel Burr answered, ‘Mr. Jefferson.’
January the 26th. Colonel Burr, the Vice-President, calls on me in the evening, having previously asked an opportunity of conversing with me. He began by recapitulating summarily, that he had come to New York a stranger, some years ago; that he found the country in possession of two rich families (the Livingstons and Clintons); that his pursuits were not political, and he meddled not. When the crisis, however, of 1800 came on, they found their influence worn out, and solicited his aid with the people. He lent it without any views of promotion. That his being named as a candidate for Vice-President was unexpected by him. He acceded to it with a view to promote my fame and advancement, and from a desire to be with me, whose company and conversation had always been fascinating to him. That, since, those great families had become hostile to him, and had excited the calumnies which I had seen published. That in this Hamilton had joined, and had even written some of the pieces against him. That his attachment to me had been sincere, and was still unchanged, although many little stories had been carried to him, and he supposed to me also, which he despised; but that attachments must be reciprocal, or cease to exist, and therefore he asked if any change had taken place in mine towards him; that he had chosen to have this conversation with myself directly, and not through any intermediate agent. He reminded me of a letter written to him about the time of counting the votes (say February, 1801), mentioning that his election had left a chasm in my arrangements; that I had lost him from my list in the administration, &c. He observed, he believed it would be for the interest of the republican cause for him to retire; that a disadvantageous schism would otherwise take place; but that were he to retire, it would be said he shrunk from the public sentence, which he never would do; that his enemies were using my name to destroy him, and something was necessary from me to prevent and deprive them of that weapon, some mark of favor from me which would declare to the world that he retired with my confidence.
I answered by recapitulating to him what had been my conduct previous to the election of 1800. That I had never interfered directly or indirectly, with my friends or any others, to influence the election either for him or myself; that I considered it as my duty to be merely passive, except that in Virginia I had taken some measures to procure for him the unanimous vote of that State, because I thought any failure there might be imputed to me. That in the election now coming on, I was observing the same conduct, held no councils with any body respecting it, nor suffered any one to speak to me on the subject, believing it my duty to leave myself to the free discussion of the public; that I do not at this moment know, nor have ever heard, who were to be proposed as candidates for the public choice, except so far as could be gathered from the newspapers. That as to the attack excited against him in the newspapers, I had noticed it but as the passing wind; that I had seen complaints that Cheetham, employed in publishing the laws, should be permitted to eat the public bread and abuse its second officer: that as to this, the publishers of the laws were appointed by the Secretary of State, without any reference to me; that to make the notice general, it was often given to one republican and one federal printer of the same place; that these federal printers did not in the least intermit their abuse of me, though receiving emoluments from the government, and that I have never thought it proper to interfere for myself, and consequently not in the case of the Vice-President. That as to the letter he referred to, I remembered it, and believed he had only mistaken the date at which it was written; that I thought it must have been on the first notice of the event of the election of South Carolina; and that I had taken that occasion to mention to him, that I had intended to have proposed to him one of the great offices, if he had not been elected; but that his election, in giving him a higher station, had deprived me of his aid in the administration. The letter alluded to was, in fact, mine to him of December the 15th, 1800. I now went on to explain to him verbally, what I meant by saying I had lost him from my list. That in General Washington’s time, it had been signified to him that Mr. Adams, the Vice-President, would be glad of a foreign embassy; that General Washington mentioned it to me, expressed his doubts whether Mr. Adams was a fit character for such an office, and his still greater doubts, indeed, his conviction, that it would not be justifiable to send away the person who, in case of his death, was provided by the constitution to take his place: that it would moreover appear indecent for him to be disposing of the public trusts, in apparently buying off a competitor for the public favor. I concurred with him in the opinion, and, if I recollect rightly, Hamilton, Knox, and Randolph were consulted, and gave the same opinions. That when Mr. Adams came to the administration, in his first interview with me, he mentioned the necessity of a mission to France, and how desirable it would have been to him if he could have got me to undertake it; but that he conceived it would be wrong in him to send me away, and assigned the same reasons General Washington had done; and therefore, he should appoint Mr. Madison, &c. That I had myself contemplated his (Colonel Burr’s) appointment to one of the great offices, in case he was not elected Vice-President; but that as soon as that election was known, I saw it could not be done, for the good reasons which had led General Washington and Mr. Adams to the same conclusion; and therefore, in my first letter to Colonel Burr, after the issue was known, I had mentioned to him that a chasm in my arrangements had been produced by this event. I was thus particular in rectifying the date of this letter, because it gave me an opportunity of explaining the grounds on which it was written, which were, indirectly, an answer to his present hints. He left the matter with me for consideration, and the conversation was turned to indifferent subjects. I should here notice, that Colonel Burr must have thought I could swallow strong things in my own favor, when he founded his acquiescence to the nomination as Vice-President, to his desire of promoting my honor, the being with me, whose company and conversation had always been fascinating with him, &c. I had never seen Colonel Burr till he came as a member of Senate. His conduct very soon inspired me with distrust. I habitually cautioned Mr. Madison against trusting him too much. I saw afterwards, that under General Washington’s and Mr. Adams’s administrations, whenever a great military appointment or a diplomatic one was to be made, he came post to Philadelphia to show himself, and in fact that he was always at market, if they had wanted him. He was indeed told by Dayton in 1800, he might be Secretary at War; but this bid was too late! His election as Vice-President was then foreseen. With these impressions of Colonel Burr, there never had been an intimacy between us, and but little association. When I destined him for a high appointment, it was out of respect for the favor he had obtained with the republican party, by his extraordinary exertions and success in the New York election in 1800.
April the 15th, 1806. About a month ago, Colonel Burr called on me, and entered into a conversation, in which he mentioned, that a little before my coming into office, I had written to him a letter intimating that I had destined him for a high employ, had he not been placed by the people in a different one; that he had signified his willingness to resign as Vice-President, to give aid to the administration in any other place; that he had never asked an office, however; he asked aid of nobody, but could walk on his own legs and take care of himself; that I had always used him with politeness, but nothing more; that he aided in bringing on the present order of things; that he had supported the administration; and that he could do me much harm: he wished, however, to be on different ground: he was now disengaged from all particular business—willing to engage in something—should be in town some days, if I should have any thing to propose to him. I observed to him, that I had always been sensible that he possessed talents which might be employed greatly to the advantage of the public, and that, as to myself, I had a confidence that if he were employed, he would use his talents for the public good: but that he must be sensible the public had withdrawn their confidence from him, and that in a government like ours it was necessary to embrace in its administration as great a mass of public confidence as possible, by employing those who had a character with the public, of their own, and not merely a secondary one through the executive. He observed, that if we believed a few newspapers, it might be supposed he had lost the public confidence, but that I knew how easy it was to engage newspapers in any thing. I observed, that I did not refer to that kind of evidence of his having lost the public confidence, but to the late Presidential election, when, though in possession of the office of Vice-President, there was not a single voice heard for his retaining it. That as to any harm he could do me, I knew no cause why he should desire it, but, at the same time, I feared no injury which any man could do me: that I never had done a single act, or been concerned in any transaction, which I feared to have fully laid open, or which could do me any hurt, if truly stated: that I had never done a single thing with a view to my personal interest, or that of any friend, or with any other view than that of the greatest public good: that, therefore, no threat or fear on that head would ever be a motive of action with me. He has continued in town to this time; dined with me this day week, and called on me to take leave two or three days ago.
I did not commit these things to writing at the time, but I do it now, because in a suit between him and Cheetham, he has had a deposition of Mr. Bayard taken, which seems to have no relation to the suit, nor to any other object than to calumniate me. Bayard pretends to have addressed to me, during the pending of the Presidential election in February, 1801, through General Samuel Smith, certain conditions on which my election might be obtained, and that General Smith, after conversing with me, gave answers from me. This is absolutely false. No proposition of any kind was ever made to me on that occasion by General Smith, nor any answer authorized by me. And this fact General Smith affirms at this moment.
For some matters connected with this, see my notes of February the 12th and 14th, 1801, made at the moment. But the following transactions took place about the same time, that is to say, while the Presidential election was in suspense in Congress, which, though I did not enter at the time, they made such an impression on my mind, that they are now as fresh, as to their principal circumstances, as if they had happened yesterday. Coming out of the Senate chamber one day, I found Gouverneur Morris on the steps. He stopped me, and began a conversation on the strange and portentous state of things then existing, and went on to observe, that the reasons why the minority of States was so opposed to my being elected, were, that they apprehended that, 1. I would turn all federalists out of office; 2. put down the navy; 3. wipe off the public debt. That I need only to declare, or authorize my friends to declare, that I would not take these steps, and instantly the event of the election would be fixed. I told him, that I should leave the world to judge of the course I meant to pursue, by that which I had pursued hitherto, believing it to be my duty to be passive and silent during the present scene; that I should certainly make no terms; should never go into the office of President by capitulation, nor with my hands tied by any conditions which should hinder me from pursuing the measures which I should deem for the public good. It was understood that Gouverneur Morris had entirely the direction of the vote of Lewis Morris of Vermont, who, by coming over to Matthew Lyon, would have added another vote, and decided the election. About the same time, I called on Mr. Adams. We conversed on the state of things. I observed to him, that a very dangerous experiment was then in contemplation, to defeat the Presidential election by an act of Congress declaring the right of the Senate to name a President of the Senate, to devolve on him the government during any interregnum: that such a measure would probably produce resistance by force, and incalculable consequences, which it would be in his power to prevent by negativing such an act. He seemed to think such an act justifiable, and observed, it was in my power to fix the election by a word in an instant, by declaring I would not turn out the federal officers, nor put down the navy, nor spunge the national debt. Finding his mind made up as to the usurpation of the government by the President of the Senate, I urged it no further, observed, the world must judge as to myself of the future by the past, and turned the conversation to something else. About the same time, Dwight Foster of Massachusetts called on me in my room one night, and went into a very long conversation on the state of affairs, the drift of which was to let me understand, that the fears above mentioned were the only obstacle to my election, to all of which I avoided giving any answer the one way or the other. From this moment he became most bitterly and personally opposed to me, and so has ever continued. I do not recollect that I ever had any particular conversation with General Samuel Smith on this subject. Very possibly I had, however, as the general subject and all its parts were the constant themes of conversation in the private tête-à-têtes with our friends. But certain I am, that neither he nor any other republican ever uttered the most distant hint to me about submitting to any conditions, or giving any assurances to any body; and still more certainly, was neither he nor any other person ever authorized by me to say what I would or would not do.
[The following official opinion, though inadvertently omitted in its proper place, is deemed of sufficient importance to be inserted here.]
The bill for establishing a National Bank, undertakes, among other things,
1. To form the subscribers into a corporation.
2. To enable them, in their corporate capacities, to receive grants of land; and so far, is against the laws of Mortmain.*
* Though the constitution controls the laws of Mortmain, so
far as to permit Congress itself to hold lands for certain
purposes, yet not so far as to permit them to communicate a
similar right to other corporate bodies.
3. To make alien subscribers capable of holding lands; and so far, is against the laws of Alienage.
4. To transmit these lands, on the death of a proprietor, to a certain line of successors; and so far, changes the course of Descents.
5. To put the lands out of the reach of forfeiture or escheat; and so far, is against the laws of Forfeiture and Escheat.
6. To transmit personal chattels to successors in a certain line; and so far, is against the laws of Distribution.
7. To give them the sole and exclusive right of banking under the national authority; and so far, is against the laws of Monopoly.
8. To communicate to them a power to make laws paramount to the laws of the States; for so they must be construed, to protect the institution from the control of the State legislatures; and so, probably, they will be construed.
I consider the foundation of the constitution as laid on this ground, that all powers not delegated to the United States by the constitution nor prohibited by it to the States, are reserved to the States or to the people.’ (Twelfth amendment.) To take a single step beyond the boundaries thus specially drawn around the powers of Congress, is to take possession of a boundless field of power, no longer susceptible of any definition.
The incorporation of a bank, and the powers assumed by this bill, have not, in my opinion, been delegated to the United States by the constitution.
I. They are not among the powers specially, enumerated. For these are,
1. A power to lay taxes for the purpose of paying the debts of the United States. But no debt is paid by this bill, nor any tax laid. Were it a bill to raise money, its origination in the Senate would condemn it by the constitution.
2. To ‘borrow money.’ But this bill neither borrows money, nor insures the borrowing it. The proprietors of the bank will be just as free as any other money-holders, to lend or not to lend their money to the public. The operation proposed in the bill, first to lend them two millions, and then borrow them back again cannot change the nature of the latter act, which will still be a payment and not a loan, call it by what name you please.
3. ‘To regulate commerce with foreign nations, and among the States, and with the Indian tribes.’ To erect a bank, and to regulate commerce, are very different acts. He who erects a bank creates a subject of commerce in its bills: so does he who makes a bushel of wheat, or digs a dollar out of the mines. Yet neither of these persons regulates commerce thereby. To make a thing which may be bought and sold, is not to prescribe regulations for buying and selling. Besides, if this were an exercise of the power of regulating commerce, it would be void, as extending as much to the internal commerce of every State, as to its external. For the power given to Congress by the constitution, does not extend to the internal regulation, of the commerce of a State (that is to say, of the commerce between citizen and citizen), which remains exclusively with its own legislature; but to its external commerce only, that is to say, its commerce with another State, or with foreign nations, or with the Indian tribes. Accordingly, the bill does not propose the measure as a ‘regulation of trade,’ but as ‘productive of considerable advantage to trade.’
Still less are these powers covered by any other of the special enumerations.
II. Nor are they within either of the general phrases, which are the two following.
1. ‘To lay taxes to provide for the general welfare of the United States’; that is to say, ‘to lay taxes for the purpose of providing for the general welfare.’ For the laying of taxes is the power, and the general welfare the purpose for which the power is to be exercised. Congress are not to lay taxes, ad libitum, for any purpose they please: but only to pay the debts, or provide for the welfare of the Union. In like manner, they are not to do any thing they please, to provide for the general welfare, but only to lay taxes for that purpose. To consider the latter phrase, not as describing the purpose of the first, but as giving a distinct and independent power to do any act they please, which might be for the good of the Union, would render all the preceding and subsequent enumerations of power completely useless. It would reduce the whole instrument to a single phrase, that of instituting a Congress with power to do whatever would be for the good of the United States; and as they would be the sole judges of the good or evil, it would be also a power to do whatever evil they pleased. It is an established rule of construction, where a phrase will bear either of two meanings, to give it that which will allow some meaning to the other parts of the instrument, and not that which will render all the others useless. Certainly no such universal power was meant to be given them. It was intended to lace them up straitly within the enumerated powers, and those without which, as means, these powers could not be carried into effect. It is known that the very power now proposed as a means, was rejected as an end by the convention which formed the constitution. A proposition was made to them, to authorize Congress to open parials, and an amendatory one, to empower them to incorporate. But the whole was rejected; and one of the reasons of rejection urged in debate was, that they then would have a power to erect a bank, which would render the great cities, where there were prejudices and jealousies on that subject, adverse to the reception of the constitution.
2. The second general phrase is, ‘to make all laws necessary and proper for carrying into execution the enumerated powers.’ But they can all be carried into execution without a bank. A bank, therefore, is not necessary, and consequently, not authorized by this phrase.
It has been much urged, that a bank will give great facility or convenience in the collection of taxes. Suppose this were true: yet the constitution allows only the means which are ‘necessary’ not those which are merely ‘convenient’ for effecting the enumerated powers. If such a latitude of construction be allowed to this phrase, as to give any non-enumerated power, it will go to every one; for there is no one which ingenuity may not torture into a convenience, in some way or other, to some one of so long a list of enumerated powers. It would swallow up all the delegated powers, and reduce the whole to one phrase, as before observed. Therefore it was, that the constitution restrained them to the necessary means, that is to say, to those means without which the grant of the power would be nugatory.
But let us examine this ‘convenience,’ and see what it is. The report on this subject, page 2, states the only general convenience to be, the preventing the transportation and re-transportation of money between the States and the treasury. (For I pass over the increase of circulating medium ascribed to it as a merit, and which, according to my ideas of paper money, is clearly a demerit.) Every State will have to pay a sum of tax-money into the treasury; and the treasury will have to pay in every State a part of the interest on the public debt, and salaries to the officers of government resident in that State. In most of the States, there will be still a surplus of tax-money, to come up to the seat of government, for the officers residing there. The payments of interest and salary in each State, may be made by treasury orders on the state collector. This will take up the greater part of the money he has collected in his State and consequently prevent the great mass of it from being drawn out of the state. If there be a balance of commerce in favor of that State, against the one in which the government resides, the surplus of taxes will be remitted by the bills of exchange drawn for that commercial balance. And so it must be if there were a bank. But if there be no balance of commerce, either direct or circuitous, all the banks in the world could not bring us the surplus of taxes but in the form of money. Treasury orders, then, and bills of exchange, may prevent the displacement of the main mass of the money collected, without the aid of any bank: and where these fail, it cannot be prevented even with that aid.
Perhaps, indeed, bank bills may be a more convenient vehicle than treasury orders. But a little difference in the degree of convenience, cannot constitute the necessity which the constitution makes the ground for assuming any non-enumerated power.
Besides; the existing banks will, without doubt, enter into arrangements for lending their agency, and the more favorable, as there will be a competition among them for it. Whereas, this bill delivers us up bound to the national bank, who are free to refuse all arrangements but on their own terms, and the public not free, on such refusal to employ any other bank. That of Philadelphia, I believe, now does this business by their post notes, which, by an arrangement with the treasury, are paid by any State collector to whom they are presented. This expedient alone, suffices to prevent the existence of that necessity which may justify the assumption of a non-enumerated power, as a means for carrying into effect an enumerated one. The thing may be done, and has been done, and well done, without this assumption; therefore, it does not stand on that degree of necessity which can honestly justify it.
It may be said, that a bank, whose bills would have a currency all over the States, would be more convenient than one whose currency is limited to a single State. So it would be still more convenient, that there should be a bank whose bills should have a currency all over the world. But it does not follow from this superior conveniency, that there exists any where a power to establish such a bank, or that the world may not go on very well without it. Can it be thought that the constitution intended, that for a shade or two of convenience, more or less, Congress should be authorized to break down the most ancient and fundamental laws of the several States, such as those against mortmain, the laws of alienage, the rules of descent, the acts of distribution, the laws of escheat and forfeiture, and the laws of monopoly. Nothing but a necessity invincible by any other means, can justify such a prostration of laws, which constitute the pillars of our whole system of jurisprudence. Will Congress be too strait-laced to carry the constitution into honest effect, unless they may pass over the foundation laws of the State governments, for the slightest convenience to theirs?
The negative of the President is the shield provided by the constitution, to protect against the invasions of the legislature, 1. the rights of the Executive; 2. of the Judiciary; 3. of the States and State legislatures. The present is the case of a right remaining exclusively with the States, and is, consequently, one of those intended by the constitution to be placed under his protection.
It must be added, however, that unless the President’s mind, on a view of every thing which is urged for and against this bill, is tolerably clear that it is unauthorized by the constitution, if the pro and the con hang so even as to balance his judgment, a just respect for the wisdom of the legislature would naturally decide the balance in favor of their opinion. It is chiefly for cases where they are clearly misled by error, ambition, or interest, that the constitution has placed a check in the negative of the President.
Th: Jefferson.
February 15, 1791.
End of the Project Gutenberg EBook of The Memoirs, Correspondence, And
Miscellanies, From The Papers Of Thomas Jefferson, by Thomas Jefferson
*** END OF THIS PROJECT GUTENBERG EBOOK THE PAPERS OF THOMAS JEFFERSON ***
***** This file should be named 28860-h.htm or 28860-h.zip *****
This and all associated files of various formats will be found in:
http://www.gutenberg.org/2/8/8/6/28860/
Produced by David Widger
Updated editions will replace the previous one--the old editions
will be renamed.
Creating the works from public domain print editions means that no
one owns a United States copyright in these works, so the Foundation
(and you!) can copy and distribute it in the United States without
permission and without paying copyright royalties. Special rules,
set forth in the General Terms of Use part of this license, apply to
copying and distributing Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works to
protect the PROJECT GUTENBERG-tm concept and trademark. Project
Gutenberg is a registered trademark, and may not be used if you
charge for the eBooks, unless you receive specific permission. If you
do not charge anything for copies of this eBook, complying with the
rules is very easy. You may use this eBook for nearly any purpose
such as creation of derivative works, reports, performances and
research. They may be modified and printed and given away--you may do
practically ANYTHING with public domain eBooks. Redistribution is
subject to the trademark license, especially commercial
redistribution.
*** START: FULL LICENSE ***
THE FULL PROJECT GUTENBERG LICENSE
PLEASE READ THIS BEFORE YOU DISTRIBUTE OR USE THIS WORK
To protect the Project Gutenberg-tm mission of promoting the free
distribution of electronic works, by using or distributing this work
(or any other work associated in any way with the phrase "Project
Gutenberg"), you agree to comply with all the terms of the Full Project
Gutenberg-tm License (available with this file or online at
http://gutenberg.org/license).
Section 1. General Terms of Use and Redistributing Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic works
1.A. By reading or using any part of this Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic work, you indicate that you have read, understand, agree to
and accept all the terms of this license and intellectual property
(trademark/copyright) agreement. If you do not agree to abide by all
the terms of this agreement, you must cease using and return or destroy
all copies of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works in your possession.
If you paid a fee for obtaining a copy of or access to a Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic work and you do not agree to be bound by the
terms of this agreement, you may obtain a refund from the person or
entity to whom you paid the fee as set forth in paragraph 1.E.8.
1.B. "Project Gutenberg" is a registered trademark. It may only be
used on or associated in any way with an electronic work by people who
agree to be bound by the terms of this agreement. There are a few
things that you can do with most Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works
even without complying with the full terms of this agreement. See
paragraph 1.C below. There are a lot of things you can do with Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic works if you follow the terms of this agreement
and help preserve free future access to Project Gutenberg-tm electronic
works. See paragraph 1.E below.
1.C. The Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation ("the Foundation"
or PGLAF), owns a compilation copyright in the collection of Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic works. Nearly all the individual works in the
collection are in the public domain in the United States. If an
individual work is in the public domain in the United States and you are
located in the United States, we do not claim a right to prevent you from
copying, distributing, performing, displaying or creating derivative
works based on the work as long as all references to Project Gutenberg
are removed. Of course, we hope that you will support the Project
Gutenberg-tm mission of promoting free access to electronic works by
freely sharing Project Gutenberg-tm works in compliance with the terms of
this agreement for keeping the Project Gutenberg-tm name associated with
the work. You can easily comply with the terms of this agreement by
keeping this work in the same format with its attached full Project
Gutenberg-tm License when you share it without charge with others.
1.D. The copyright laws of the place where you are located also govern
what you can do with this work. Copyright laws in most countries are in
a constant state of change. If you are outside the United States, check
the laws of your country in addition to the terms of this agreement
before downloading, copying, displaying, performing, distributing or
creating derivative works based on this work or any other Project
Gutenberg-tm work. The Foundation makes no representations concerning
the copyright status of any work in any country outside the United
States.
1.E. Unless you have removed all references to Project Gutenberg:
1.E.1. The following sentence, with active links to, or other immediate
access to, the full Project Gutenberg-tm License must appear prominently
whenever any copy of a Project Gutenberg-tm work (any work on which the
phrase "Project Gutenberg" appears, or with which the phrase "Project
Gutenberg" is associated) is accessed, displayed, performed, viewed,
copied or distributed:
This eBook is for the use of anyone anywhere at no cost and with
almost no restrictions whatsoever. You may copy it, give it away or
re-use it under the terms of the Project Gutenberg License included
with this eBook or online at www.gutenberg.org
1.E.2. If an individual Project Gutenberg-tm electronic work is derived
from the public domain (does not contain a notice indicating that it is
posted with permission of the copyright holder), the work can be copied
and distributed to anyone in the United States without paying any fees
or charges. If you are redistributing or providing access to a work
with the phrase "Project Gutenberg" associated with or appearing on the
work, you must comply either with the requirements of paragraphs 1.E.1
through 1.E.7 or obtain permission for the use of the work and the
Project Gutenberg-tm trademark as set forth in paragraphs 1.E.8 or
1.E.9.
1.E.3. If an individual Project Gutenberg-tm electronic work is posted
with the permission of the copyright holder, your use and distribution
must comply with both paragraphs 1.E.1 through 1.E.7 and any additional
terms imposed by the copyright holder. Additional terms will be linked
to the Project Gutenberg-tm License for all works posted with the
permission of the copyright holder found at the beginning of this work.
1.E.4. Do not unlink or detach or remove the full Project Gutenberg-tm
License terms from this work, or any files containing a part of this
work or any other work associated with Project Gutenberg-tm.
1.E.5. Do not copy, display, perform, distribute or redistribute this
electronic work, or any part of this electronic work, without
prominently displaying the sentence set forth in paragraph 1.E.1 with
active links or immediate access to the full terms of the Project
Gutenberg-tm License.
1.E.6. You may convert to and distribute this work in any binary,
compressed, marked up, nonproprietary or proprietary form, including any
word processing or hypertext form. However, if you provide access to or
distribute copies of a Project Gutenberg-tm work in a format other than
"Plain Vanilla ASCII" or other format used in the official version
posted on the official Project Gutenberg-tm web site (www.gutenberg.org),
you must, at no additional cost, fee or expense to the user, provide a
copy, a means of exporting a copy, or a means of obtaining a copy upon
request, of the work in its original "Plain Vanilla ASCII" or other
form. Any alternate format must include the full Project Gutenberg-tm
License as specified in paragraph 1.E.1.
1.E.7. Do not charge a fee for access to, viewing, displaying,
performing, copying or distributing any Project Gutenberg-tm works
unless you comply with paragraph 1.E.8 or 1.E.9.
1.E.8. You may charge a reasonable fee for copies of or providing
access to or distributing Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works provided
that
- You pay a royalty fee of 20% of the gross profits you derive from
the use of Project Gutenberg-tm works calculated using the method
you already use to calculate your applicable taxes. The fee is
owed to the owner of the Project Gutenberg-tm trademark, but he
has agreed to donate royalties under this paragraph to the
Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation. Royalty payments
must be paid within 60 days following each date on which you
prepare (or are legally required to prepare) your periodic tax
returns. Royalty payments should be clearly marked as such and
sent to the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation at the
address specified in Section 4, "Information about donations to
the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation."
- You provide a full refund of any money paid by a user who notifies
you in writing (or by e-mail) within 30 days of receipt that s/he
does not agree to the terms of the full Project Gutenberg-tm
License. You must require such a user to return or
destroy all copies of the works possessed in a physical medium
and discontinue all use of and all access to other copies of
Project Gutenberg-tm works.
- You provide, in accordance with paragraph 1.F.3, a full refund of any
money paid for a work or a replacement copy, if a defect in the
electronic work is discovered and reported to you within 90 days
of receipt of the work.
- You comply with all other terms of this agreement for free
distribution of Project Gutenberg-tm works.
1.E.9. If you wish to charge a fee or distribute a Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic work or group of works on different terms than are set
forth in this agreement, you must obtain permission in writing from
both the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation and Michael
Hart, the owner of the Project Gutenberg-tm trademark. Contact the
Foundation as set forth in Section 3 below.
1.F.
1.F.1. Project Gutenberg volunteers and employees expend considerable
effort to identify, do copyright research on, transcribe and proofread
public domain works in creating the Project Gutenberg-tm
collection. Despite these efforts, Project Gutenberg-tm electronic
works, and the medium on which they may be stored, may contain
"Defects," such as, but not limited to, incomplete, inaccurate or
corrupt data, transcription errors, a copyright or other intellectual
property infringement, a defective or damaged disk or other medium, a
computer virus, or computer codes that damage or cannot be read by
your equipment.
1.F.2. LIMITED WARRANTY, DISCLAIMER OF DAMAGES - Except for the "Right
of Replacement or Refund" described in paragraph 1.F.3, the Project
Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation, the owner of the Project
Gutenberg-tm trademark, and any other party distributing a Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic work under this agreement, disclaim all
liability to you for damages, costs and expenses, including legal
fees. YOU AGREE THAT YOU HAVE NO REMEDIES FOR NEGLIGENCE, STRICT
LIABILITY, BREACH OF WARRANTY OR BREACH OF CONTRACT EXCEPT THOSE
PROVIDED IN PARAGRAPH F3. YOU AGREE THAT THE FOUNDATION, THE
TRADEMARK OWNER, AND ANY DISTRIBUTOR UNDER THIS AGREEMENT WILL NOT BE
LIABLE TO YOU FOR ACTUAL, DIRECT, INDIRECT, CONSEQUENTIAL, PUNITIVE OR
INCIDENTAL DAMAGES EVEN IF YOU GIVE NOTICE OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH
DAMAGE.
1.F.3. LIMITED RIGHT OF REPLACEMENT OR REFUND - If you discover a
defect in this electronic work within 90 days of receiving it, you can
receive a refund of the money (if any) you paid for it by sending a
written explanation to the person you received the work from. If you
received the work on a physical medium, you must return the medium with
your written explanation. The person or entity that provided you with
the defective work may elect to provide a replacement copy in lieu of a
refund. If you received the work electronically, the person or entity
providing it to you may choose to give you a second opportunity to
receive the work electronically in lieu of a refund. If the second copy
is also defective, you may demand a refund in writing without further
opportunities to fix the problem.
1.F.4. Except for the limited right of replacement or refund set forth
in paragraph 1.F.3, this work is provided to you 'AS-IS' WITH NO OTHER
WARRANTIES OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO
WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTIBILITY OR FITNESS FOR ANY PURPOSE.
1.F.5. Some states do not allow disclaimers of certain implied
warranties or the exclusion or limitation of certain types of damages.
If any disclaimer or limitation set forth in this agreement violates the
law of the state applicable to this agreement, the agreement shall be
interpreted to make the maximum disclaimer or limitation permitted by
the applicable state law. The invalidity or unenforceability of any
provision of this agreement shall not void the remaining provisions.
1.F.6. INDEMNITY - You agree to indemnify and hold the Foundation, the
trademark owner, any agent or employee of the Foundation, anyone
providing copies of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works in accordance
with this agreement, and any volunteers associated with the production,
promotion and distribution of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works,
harmless from all liability, costs and expenses, including legal fees,
that arise directly or indirectly from any of the following which you do
or cause to occur: (a) distribution of this or any Project Gutenberg-tm
work, (b) alteration, modification, or additions or deletions to any
Project Gutenberg-tm work, and (c) any Defect you cause.
Section 2. Information about the Mission of Project Gutenberg-tm
Project Gutenberg-tm is synonymous with the free distribution of
electronic works in formats readable by the widest variety of computers
including obsolete, old, middle-aged and new computers. It exists
because of the efforts of hundreds of volunteers and donations from
people in all walks of life.
Volunteers and financial support to provide volunteers with the
assistance they need, are critical to reaching Project Gutenberg-tm's
goals and ensuring that the Project Gutenberg-tm collection will
remain freely available for generations to come. In 2001, the Project
Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation was created to provide a secure
and permanent future for Project Gutenberg-tm and future generations.
To learn more about the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation
and how your efforts and donations can help, see Sections 3 and 4
and the Foundation web page at http://www.pglaf.org.
Section 3. Information about the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive
Foundation
The Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation is a non profit
501(c)(3) educational corporation organized under the laws of the
state of Mississippi and granted tax exempt status by the Internal
Revenue Service. The Foundation's EIN or federal tax identification
number is 64-6221541. Its 501(c)(3) letter is posted at
http://pglaf.org/fundraising. Contributions to the Project Gutenberg
Literary Archive Foundation are tax deductible to the full extent
permitted by U.S. federal laws and your state's laws.
The Foundation's principal office is located at 4557 Melan Dr. S.
Fairbanks, AK, 99712., but its volunteers and employees are scattered
throughout numerous locations. Its business office is located at
809 North 1500 West, Salt Lake City, UT 84116, (801) 596-1887, email
business@pglaf.org. Email contact links and up to date contact
information can be found at the Foundation's web site and official
page at http://pglaf.org
For additional contact information:
Dr. Gregory B. Newby
Chief Executive and Director
gbnewby@pglaf.org
Section 4. Information about Donations to the Project Gutenberg
Literary Archive Foundation
Project Gutenberg-tm depends upon and cannot survive without wide
spread public support and donations to carry out its mission of
increasing the number of public domain and licensed works that can be
freely distributed in machine readable form accessible by the widest
array of equipment including outdated equipment. Many small donations
($1 to $5,000) are particularly important to maintaining tax exempt
status with the IRS.
The Foundation is committed to complying with the laws regulating
charities and charitable donations in all 50 states of the United
States. Compliance requirements are not uniform and it takes a
considerable effort, much paperwork and many fees to meet and keep up
with these requirements. We do not solicit donations in locations
where we have not received written confirmation of compliance. To
SEND DONATIONS or determine the status of compliance for any
particular state visit http://pglaf.org
While we cannot and do not solicit contributions from states where we
have not met the solicitation requirements, we know of no prohibition
against accepting unsolicited donations from donors in such states who
approach us with offers to donate.
International donations are gratefully accepted, but we cannot make
any statements concerning tax treatment of donations received from
outside the United States. U.S. laws alone swamp our small staff.
Please check the Project Gutenberg Web pages for current donation
methods and addresses. Donations are accepted in a number of other
ways including checks, online payments and credit card donations.
To donate, please visit: http://pglaf.org/donate
Section 5. General Information About Project Gutenberg-tm electronic
works.
Professor Michael S. Hart is the originator of the Project Gutenberg-tm
concept of a library of electronic works that could be freely shared
with anyone. For thirty years, he produced and distributed Project
Gutenberg-tm eBooks with only a loose network of volunteer support.
Project Gutenberg-tm eBooks are often created from several printed
editions, all of which are confirmed as Public Domain in the U.S.
unless a copyright notice is included. Thus, we do not necessarily
keep eBooks in compliance with any particular paper edition.
Most people start at our Web site which has the main PG search facility:
http://www.gutenberg.org
This Web site includes information about Project Gutenberg-tm,
including how to make donations to the Project Gutenberg Literary
Archive Foundation, how to help produce our new eBooks, and how to
subscribe to our email newsletter to hear about new eBooks.