
The Project Gutenberg EBook of The Tales Of The Heptameron, Complete, Vol. I to V, by Margaret, Queen Of Navarre This eBook is for the use of anyone anywhere at no cost and with almost no restrictions whatsoever. You may copy it, give it away or re-use it under the terms of the Project Gutenberg License included with this eBook or online at www.gutenberg.org Title: The Tales Of The Heptameron, Complete I to V Author: Margaret, Queen Of Navarre Illustrator: Freudenberg and Dunker Translator: George Saintsbury: From The Authentic Text Of M. Le Roux De Lincy With An Essay Upon The Heptameron by the Translator Release Date: February 7, 2006 [EBook #28858] Last Updated: June 15, 2018 Language: English Character set encoding: UTF-8 *** START OF THIS PROJECT GUTENBERG EBOOK THE TALES OF THE HEPTAMERON *** Produced by David Widger


| Volume II. | Volume III. | Volume IV. | Volume V. |


CONTENTS
Explanation of the Initials appended to the Notes.
MARGARET OF ANGOULÊME, QUEEN OF NAVARRE.
Peter Boaistuau, surnamed Launay, To the Reader
List of Illustrations
039a.jpg Du Mesnil Learns his Mistress’s Infidelity from Her Maid
057a.jpg the Muleteer’s Servant Attacking his Mistress
079a.jpg Hurrying to Her Mistress’s Assistance
095a.jpg the Boatwoman of Coulon Outwitting The Friars
103a.jpg the Wife’s Ruse to Secure The Escape of Her Lover
109.jpg the Merchant Transferring his Caresses from The Daughter to the Mother
|
FIRST DAY. Tale I. The pitiful history of a Proctor of Alençon, named St. Aignan, and of his wife, who caused her husband to assassinate her lover, the son of the Lieutenant-General Tale II. The fate of the wife of a muleteer of Amboise, who suffered herself to be killed by her servant rather than sacrifice her chastity Tale III. The revenge taken by the Queen of Naples, wife to King Alfonso, for her husband’s infidelity with a gentleman’s wife Tale IV. The ill success of a Flemish gentleman who was unable to obtain, either by persuasion or force, the love of a great Princess Tale V. How a boatwoman of Coulon, near Nyort, contrived to escape from the vicious designs of two Grey Friars Tale VI. How the wife of an old valet of the Duke of Alençon’s succeeded in saving her lover from her husband, who was blind of one eye Tale VII. The craft of a Parisian merchant, who saved the reputation of the daughter by offering violence to the mother |
The first printed version of the famous Tales of Margaret of Navarre, issued in Paris in the year 1558, under the title of “Histoires des Amans Fortunez,” was extremely faulty and imperfect. It comprised but sixty-seven of the seventy-two tales written by the royal author, and the editor, Pierre Boaistuau, not merely changed the order of those narratives which he did print, but suppressed numerous passages in them, besides modifying much of Margaret’s phraseology. A somewhat similar course was adopted by Claude Gruget, who, a year later, produced what claimed to be a complete version of the stories, to which he gave the general title of the Heptameron, a name they have ever since retained. Although he reinstated the majority of the tales in their proper sequence, he still suppressed several of them, and inserted others in their place, and also modified the Queen’s language after the fashion set by Boaistuau. Despite its imperfections, however, Gruget’s version was frequently reprinted down to the beginning of the eighteenth century, when it served as the basis of the numerous editions of the Heptameron in beau langage, as the French phrased it, which then began to make their appearance. It served, moreover, in the one or the other form, for the English and other translations of the work, and down to our own times was accepted as the standard version of the Queen of Navarre’s celebrated tales. Although it was known that various contemporary MSS. were preserved at the French National Library in Paris, no attempt was made to compare Gruget’s faulty version with the originals until the Société des Bibliophiles Français entrusted this delicate task to M. Le Roux de Lincy, whose labours led to some most valuable discoveries, enabling him to produce a really authentic version of Margaret’s admired masterpiece, with the suppressed tales restored, the omitted passages reinstated, and the Queen’s real language given for the first time in all its simple gracefulness.
It is from the authentic text furnished by M. Le Roux de Lincy that the present translation has been made, without the slightest suppression or abridgment. The work moreover contains all the more valuable notes to be found in the best French editions of the Heptameron, as well as numerous others from original sources, and includes a résumé of the various suggestions made by MM. Félix Frank, Le Roux de Lincy, Paul Lacroix, and A. de Montaiglon, towards the identification of the narrators of the stories, and the principal actors in them, with well-known personages of the time. An Essay on the Heptameron from the pen of Mr. George Saintsbury, M.A., and a Life of Queen Margaret, are also given, as well as the quaint Prefaces of the earlier French versions; and a complete bibliographical summary of the various editions which have issued from the press.
It may be supposed that numerous illustrated editions have been published of a work so celebrated as the Heptameron, which, besides furnishing scholars with a favourite subject for research and speculation, has, owing to its perennial freshness, delighted so many generations of readers. Such, however, is not the case. Only two fully illustrated editions claim the attention of connoisseurs. The first of these was published at Amsterdam in 1698, with designs by the Dutch artist, Roman de Hooge, whose talent has been much overrated. To-day this edition is only valuable on account of its comparative rarity. Very different was the famous edition illustrated by Freudenberg, a Swiss artist—the friend of Boucher and of Greuze—which was published in parts at Berne in 1778-81, and which among amateurs has long commanded an almost prohibitive price.
The Full-page Illustrations to the present translation are printed from the actual copperplates engraved for the Berne edition by Lon-geuil, Halbou, and other eminent French artists of the eighteenth century, after the designs of S. Freudenberg. There are also the one hundred and fifty elaborate head and tail pieces executed for the Berne edition by Dunker, well known to connoisseurs as one of the principal engravers of the Cabinet of the Duke de Choiseul.
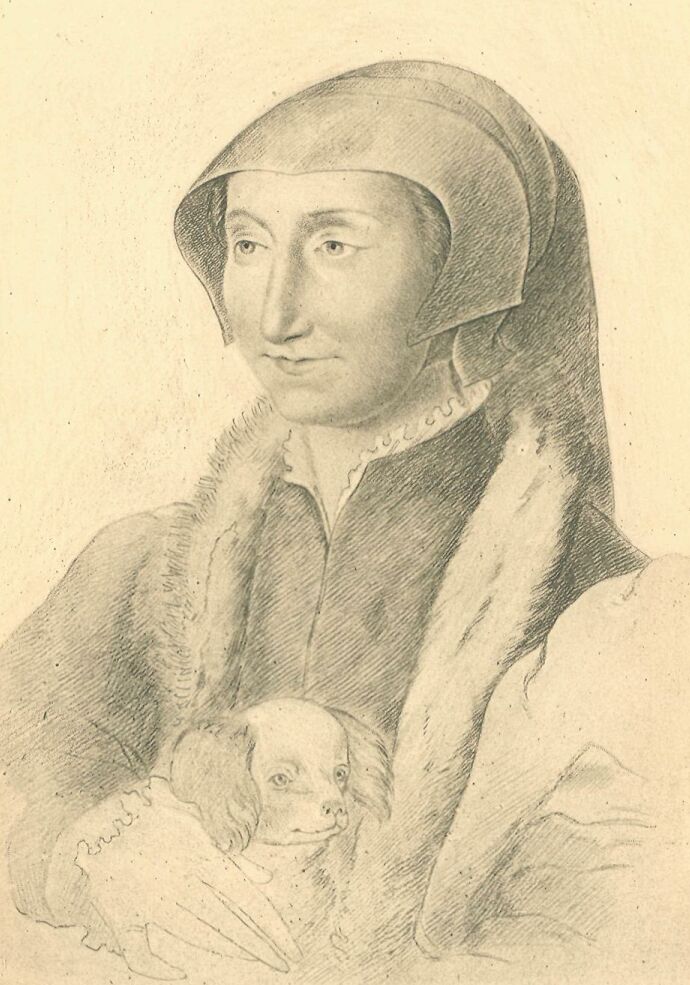
The Portrait of Queen Margaret placed as frontispiece to the present volume is from a crayon drawing by Clouet, preserved at the Bibliothèque Nationale, Paris.
Ernest A. Vizetelly.
London,
|
B.J...Bibliophile Jacob, i.e. Paul Lacroix. D.....F. Dillaye. F.....Félix Frank. L.....Le Roux de Lincy. M.....Anatole de Montaiglon. Ed....E. A. Vizetelly. |
Louise of Savoy; her marriage with the Count of Angouleme—
Birth of her children Margaret and Francis—Their father’s
early death—Louise and her children at Amboise—Margaret’s
studies and her brother’s pastimes—Marriage of Margaret
with the Duke of Alençon—Her estrangement from her husband—
Accession of Francis I.—The Duke of Alençon at Marignano—
Margaret’s Court at Alençon—Her personal appearance—Her
interest in the Reformation and her connection with Clement
Marot—Lawsuit between Louise of Savoy and the Constable de
Bourbon.
In dealing with the life and work of Margaret of Angouleme (1) it is necessary at the outset to refer to the mother whose influence and companionship served so greatly to mould her daughter’s career.
1 This Life of Margaret is based upon the memoir by M, Le
Roux de Lincy prefixed to the edition of the Heptameron
issued by the Société des Bibliophiles Français, but various
errors have been rectified, and advantage has been taken of
the researches of later biographers.
Louise of Savoy, daughter of Count Philip of Bresse, subsequently Duke of Savoy, was born at Le Pont d’Ain in 1477, and upon the death of her mother, Margaret de Bourbon, she married Charles d’Orléans, Count of Angoulême, to whom she brought the slender dowry of thirty-five thousand livres. (1) She was then but twelve years old, her husband being some twenty years her senior. He had been banished from the French Court for his participation in the insurrection of Brittany, and was living in straitened circumstances. Still, on either side the alliance was an honourable one. Louise belonged to a sovereign house, while the Count of Angoulême was a prince of the blood royal of France by virtue of his descent from King Charles V., his grandfather having been that monarch’s second son, the notorious Duke Louis of Orleans, (2) who was murdered in Paris in 1417 at the instigation of John the Bold of Burgundy.
1 The value of the Paris livre at this date was twenty
sols, so that the amount would be equivalent to about L1400.
2 This was the prince described by Brantôme as a “great
débaucher of the ladies of the Court, and invariably of the
greatest among them.”—Vies des Dames galantes (Disc. i.).
Louise, who, although barely nubile, impatiently longed to become a mother, gave birth to her first child after four years of wedded life. “My daughter Margaret,” she writes in the journal recording the principal events of her career, “was born in the year 1492, the eleventh day of April, at two o’clock in the morning; that is to say, the tenth day, fourteen hours and ten minutes, counting after the manner of the astronomers.” This auspicious event took place at the Château of Angoulême, then a formidable and stately pile, of which nowadays there only remains a couple of towers, built in the fourteenth and fifteenth centuries. Soon afterwards Cognac became the Count of Angoulême’s favourite place of residence, and it was there that Louise gave birth, on September 12th, 1494, to her second child, a son, who was christened Francis.
Louise’s desires were now satisfied, but her happiness did not long remain complete. On January 1st, 1496, when she was but eighteen years old, she lost her amiable and accomplished husband, and forthwith retiring to her Château of Romorantin, she resolved to devote herself entirely to the education of her children. The Duke of Orleans, who, on the death of Charles VIII. in 1498, succeeded to the throne as Louis XII., was appointed their guardian, and in 1499 he invited them and their mother to the royal Château of Amboise, where they remained for several years.
The education of Francis, who had become heir-presumptive to the throne, was conducted at Amboise by the Marshal de Gié, one of the King’s favourites, whilst Margaret was intrusted to the care of a venerable lady, whom her panegyrist does not mention by name, but in whom he states all virtues were assembled. (1) This lady took care to regulate not only the acts but also the language of the young princess, who was provided with a tutor in the person of Robert Hurault, Baron of Auzay, great archdeacon and abbot of St. Martin of Autun. (2) This divine instructed her in Latin and French literature, and also taught her Spanish and Italian, in which languages Brantôme asserts that she became proficient. “But albeit she knew how to speak good Spanish and good Italian,” he says, “she always made use of her mother tongue for matters of moment; though when it was necessary to join in jesting and gallant conversation she showed that she was acquainted with more than her daily bread.” (3)
1 Sainte-Marthe’s Oraison funèbre de la Royne de Navarre,
p. 22. Margaret’s modern biographers state that this lady was
Madame de Chastillon, but it is doubtful which Madame
de Chastillon it was. The Rev. James Anderson assumes it was
Louise de Montmorency, the mother of the Colignys, whilst
Miss Freer asserts it was Anne de Chabannes de Damniartin,
wife of James de Chastillon, killed in Italy in 1572. M.
Franck has shown, in his edition of the Heptameron, that
Anne de Chabannes died about 1505, and that James de
Chastillon then married Blanche de Tournon. Possibly his
first wife may have been Margaret’s governess, but what is
quite certain is that the second wife became her lady of
honour, and that it is she who is alluded to in the
Heptameron.
2 Odolant Desnos’s Mémoires historiques sur Alençon,
vol. ii.
3 Brantôme’s Rodomontades espagnoles, 18mo, 1740, vol.
xii. p. 117.
Such was Margaret’s craving for knowledge that she even wished to obtain instruction in Hebrew, and Paul Paradis, surnamed Le Canosse, a professor at the Royal College, gave her some lessons in it. Moreover, a rather obscure passage in the funeral oration which Sainte-Marthe devoted to her after her death, seemingly implies that she acquired from some of the most eminent men then flourishing the precepts of the philosophy of the ancients.
The journal kept by Louise of Savoy does not impart much information as to the style of life which she and her children led in their new abode, the palatial Château of Amboise, originally built by the Counts of Anjou, and fortified by Charles VII. with the most formidable towers in France. (1)
1 The Château of Amboise, now the private property of the
Count de Paris, is said to occupy the site of a Roman
fortress destroyed by the Normans and rebuilt by Foulques
the Red of Anjou. When Francis I. ascended the French throne
he presented the barony of Amboise with its hundred and
forty-six fiefs to his mother, Louise of Savoy.
Numerous authorities state, however, that Margaret spent most of her time in study with her preceptors and in the devotional exercises which then had so large a place in the training of princesses. Still she was by no means indifferent to the pastimes in which her brother and his companions engaged. Gaston de Foix, the nephew of the King, William Gouffier, who became Admiral de Bonnivet, Philip Brion, Sieur de Chabot, Fleurange, “the young adventurer,” Charles de Bourbon, Count of Montpensier, and Anne de Montmorency—two future Constables of France—surrounded the heir to the throne, with whom they practised tennis, archery, and jousting, or played at soldiers pending the time when they were to wage war in earnest. (1)
Margaret was a frequent spectator of these pastimes, and took a keen interest in her brother’s efforts whenever he was assailing or defending some miniature fortress or tilting at the ring. It would appear also that she was wont to play at chess with him; for we have it on high authority that it is she and her brother who are represented, thus engaged, in a curious miniature preserved at the Bibliothèque Nationale in Paris. (2) In this design—executed by an unknown artist—only the back of Francis is to be seen, but a full view of Margaret is supplied; the personage standing behind her being Artus Gouffier, her own and her brother’s governor.
1 Fleurange’s Histoire des Choses mémorables advenues du
Reigne de Louis XII. et François I.
2 Paulin Paris’s Manuscrits françois de la Bibliothèque du
Roi, &c., Paris, 1836, vol. i. pp. 279-281. The miniature
in question is contained in MS. No. 6808: Commentaire sur
le Livre des Échecs amoureux et Archiloge Sophie.
Whatever time Margaret may have devoted to diversion, she was certainly a very studious child, for at fifteen years of age she already had the reputation of being highly accomplished. Shortly after her sixteenth birthday a great change took place in her life. On August 3rd, 1508, Louise of Savoy records in her journal that Francis “this day quitted Amboise to become a courtier, and left me all alone.” Margaret accompanied her brother upon his entry into the world, the young couple repairing to Blois, where Louis XII. had fixed his residence. There had previously been some unsuccessful negotiations in view of marrying Margaret to Prince Henry of England (Henry VIII.), and at this period another husband was suggested in the person of Charles of Austria, Count of Flanders, and subsequently Emperor Charles V. Louis XII., however, had other views as regards the daughter of the Count of Angoulême, for he knew that if he himself died without male issue the throne would pass to Margaret’s brother. Hence he decided to marry her to a prince of the royal house, Charles, Duke of Alençon.
This prince, born at Alençon on September 2nd, 1489, had been brought up at the Château of Mauves, in Le Perche, by his mother, the pious and charitable Margaret of Lorraine, who on losing her husband had resolved, like Louise of Savoy, to devote herself to the education of her children. (1)
1 Hilarion de Coste’s Vies et Éloges des Dames illustres,
vol. ii. p. 260.
It had originally been intended that her son Charles should marry Susan, daughter of the Duke and Duchess of Bourbon—the celebrated Peter and Anne de Beaujeu—but this match fell through owing to the death of Peter and the opposition of Anne, who preferred the young Count of Montpensier (afterwards Constable de Bourbon) as a son-in-law. A yet higher alliance then presented itself for Charles: it was proposed that he should marry Anne of Brittany, the widow of King Charles VIII., but she was many years his senior, and, moreover, to prevent the separation of Brittany from France, it had been stipulated that she should marry either her first husband’s successor (Louis XII.) or the heir-presumptive to the throne. Either course seemed impracticable, as the heir, Francis of Angoulême, was but a child, while the new King was already married to Jane, a daughter of Louis XI. Brittany seemed lost to France, when Louis XII., by promising the duchy of Valentinois to Cæsar Borgia, prevailed upon Pope Alexander VI. to divorce him from his wife. He then married Anne of Brittany, while Charles of Alençon proceeded to perfect his knightly education, pending other matrimonial arrangements.
In 1507, when in his eighteenth year, he accompanied the army which the King led against the Genoese, and conducted himself bravely; displaying such courage, indeed, at the battle of Agnadel, gained over the Venetians—who were assailed after the submission of Genoa—that Louis XII. bestowed upon him the Order of St. Michael. It was during this Italian expedition that his mother negotiated his marriage with Margaret of Angoulême. The alliance was openly countenanced by Louis XII., and the young Duke of Valois—as Francis of Angoulême was now called—readily acceded to it. Margaret brought with her a dowry of sixty thousand livres, payable in four instalments, and Charles, who was on the point of attaining his twenty-first year, was declared a major and placed in possession of his estates. (1) The marriage was solemnised at Blois in October 1509.
1 Odolant Desnos’s Mémoires historiques sur Alençon,
vol. ii. p. 231
Margaret did not find in her husband a mind comparable to her own. Differences of taste and temper brought about a certain amount of coolness, which did not, however, hinder the Duchess from fulfilling the duties of a faithful, submissive wife. In fact, although but little sympathy would appear to have existed between the Duke and Duchess of Alençon, their domestic differences have at least been singularly exaggerated.
During the first five years of her married life Margaret lived in somewhat retired style in her duchy of Alençon, while her husband took part in various expeditions, and was invested with important functions. In 1513 he fought in Picardy against the English and Imperialists, commanded by Henry VIII., being present at the famous “Battle of Spurs;” and early in 1514 he was appointed Lieutenant-General and Governor of Brittany. Margaret at this period was not only often separated from her husband, but she also saw little of her mother, who had retired to her duchy of Angoulême. Louise of Savoy, as mother of the heir-presumptive, was the object of the homage of all adroit and politic courtiers, but she had to behave with circumspection on account of the jealousy of the Queen, Anne of Brittany, whose daughters, Claude and Renée, were debarred by the Salic Law from inheriting the crown. Louis XII. wished to marry Claude to Francis of Angoulême, but Anne refusing her consent, it was only after her death, in 1514, that the marriage was solemnised.
It now seemed certain that Francis would in due course ascend the throne; but Louis XII. abruptly contracted a third alliance, marrying Mary of England, the sister of Henry VIII. Louise of Savoy soon deemed it prudent to keep a watch on the conduct of this gay young Queen, and took up her residence at the Court in November 1514. Shortly afterwards Louis XII. died of exhaustion, as many had foreseen, and the hopes of the Duchess of Angoulême were realised. She knew the full extent of her empire over her son, now Francis I., and felt both able and ready to exercise a like authority over the affairs of his kingdom.
The accession of Francis gave a more important position to Margaret and her husband. The latter was already one of the leading personages of the state, and new favours increased his power. He did not address the King as “Your Majesty,” says Odolant Desnos, but styled him “Monseigneur” or “My Lord,” and all the acts which he issued respecting his duchy of Alençon began with the preamble, “Charles, by the grace of God.” Francis had scarcely become King than he turned his eyes upon Italy, and appointing his mother as Regent, he set out with a large army, a portion of which was commanded by the Duke of Alençon. At the battle of Marignano the troops of the latter formed the rearguard, and, on perceiving that the Swiss were preparing to surround the bulk of the French army, Charles marched against them, overthrew them, and by his skilful manouvres decided the issue of the second day’s fight. (1) The conquest of the duchy of Milan was the result of this victory, and peace supervening, the Duke of Alençon returned to France.
1 Odolant Desnos’s Mémoires historiques sur Alençon, vol.
ii. p. 238.
It was at this period that Margaret began to keep a Court, which, according to Odolant Desnos, rivalled that of her brother. We know that in 1517 she and her husband entertained the King with a series of magnificent fêtes at their Château of Alençon, which then combined both a palace and a fortress. But little of the château now remains, as, after the damage done to it during the religious wars between 1561 and 1572, it was partially demolished by Henry IV. when he and Biron captured it in 1590. Still the lofty keep built by Henry I. of England subsisted intact till in 1715 it was damaged by fire, and finally in 1787 razed to the ground.
The old pile was yet in all its splendour in 1517, when Francis I. was entertained there with jousts and tournaments. At these gay gatherings Margaret appeared apparelled in keeping with her brother’s love of display; for, like all princesses, she clothed herself on important occasions in sumptuous garments. But in every-day life she was very simple, despising the vulgar plan of impressing the crowd by magnificence and splendour. In a portrait executed about this period, her dark-coloured dress is surmounted by a wimple with a double collar and her head covered with a cap in the Bearnese style. This portrait (1) tends, like those of a later date, to the belief that Margaret’s beauty, so celebrated by the poets of her time, consisted mainly in the nobility of her bearing and the sweetness and liveliness spread over her features. Her eyes, nose, and mouth were very large, but although she had been violently attacked with small-pox while still young, she had been spared the traces which this cruel illness so often left in those days, and she even preserved the freshness of her complexion until late in life. (2)
1 It is preserved at the Bibliothèque Nationale in Paris,
where it will be found in the Recueil de Portraits au
crayon par Clouett Dumonstier, &c, fol. xi.
2 Referring to this subject, she says in one of her letters:
“You can tell it to the Count and Countess of Vertus, whom
you will go and visit on my behalf; and say to the Countess
that I am sorely vexed that she has this loathsome illness.
However, I had it as severely as ever was known. And if it
be that she has caught it as I have been told, I should like
to be near her to preserve her complexion, and do for her
what Ï did for myself.”—Génin’s lettres de Marguerite
d’Angoulême, Paris, 1841, p. 374.
Like her brother, whom she greatly resembled, she was very tall. Her gait was solemn, but the dignified air of her person was tempered by extreme affability and a lively humour, which never left her. (1)
1 Sainte-Marthe says on this subject: “For in her face, in
her gestures, in her walk, in her words, in all that she did
and said, a royal gravity made itself so manifest and
apparent, that one saw I know not what of majesty which
compelled every one to revere and dread her. In seeing her
kindly receive every one, refuse no one, and patiently
listen to all, you would have promised yourself easy and
facile access to her; but if she cast eyes upon you, there
was in her face I know not what of gravity, which made you
so astounded that you no longer had power, I do not say to
walk a step, but even to stir a foot to approach her.”—
Oraison-funèbre, &c, p. 53.
Francis I. did not allow the magnificent reception accorded to him at Alençon to pass unrewarded. He presented his sister with the duchy of Berry, where she henceforward exercised temporal control, though she does not appear to have ever resided there for any length of time. In 1521, when her husband started to the relief of Chevalier Bayard, attacked in Mézières by the Imperial troops, she repaired to Meaux with her mother so as to be near to the Duke. Whilst sojourning there she improved her acquaintance with the Bishop, William Briçonnet, who had gathered around him Gerard Roussel, Michael d’Arande, Lefèvre d’Etaples, and other celebrated disciples of the Reformation. The effect of Luther’s preaching had scarcely reached France before Margaret had begun to manifest great interest in the movement, and had engaged in a long correspondence with Briçonnet, which is still extant. Historians are at variance as to whether Margaret ever really contemplated a change of religion, or whether the protection she extended to the Reformers was simply dictated by a natural feeling of compassion and a horror of persecution. It has been contended that she really meditated a change of faith, and even attempted to convert her mother and brother; and this view is borne out by some passages in the letters which she wrote to Bishop Briçonnet after spending the winter of 1521 at Meaux.
Whilst she was sojourning there, her husband, having contributed to the relief of Mézières, joined the King, who was then encamped at Fervacques on the Somme, and preparing to invade Hainault. It was at this juncture that Clement Marot, the poet, who, after being attached to the person of Anne of Brittany, had become a hanger-on at the Court of Francis I., applied to Margaret to take him into her service. (1)
1 Epistle ii.: Le Despourveu à Madame la Duchesse
d’Alençon, in the OEuvres de Clément Marot, 1700, vol. i.
p. 99.
Shortly afterwards we find him furnishing her with information respecting the royal army, which had entered Hainault and was fighting there. (1)
1 Epistle iii.: Du Camp d’ Attigny à ma dite Dame d’
Alençon, ibid., vol. i. p. 104.
Lenglet-Dufresnoy, in his edition of Marot’s works, originated the theory that the numerous poems composed by Marot in honour of Margaret supply proofs of an amorous intrigue between the pair. Other authorities have endorsed this view; but M. Le Roux de Lincy asserts that in the pieces referred to, and others in which Marot incidentally speaks of Margaret, he can find no trace either of the fancy ascribed to her for the poet or of the passion which the latter may have felt for her. Like all those who surrounded the Duchess of Alençon, Marot, he remarks, exalted her beauty, art, and talent to the clouds; but whenever it is to her that his verses are directly addressed, he does not depart from the respect he owes to her. To give some likelihood to his conjectures, Lenglet-Dufresnoy had to suppose that Marot addressed Margaret in certain verses which were not intended for her. In the epistles previously mentioned, and in several short pieces, rondeaux, epigrams, new years’ addresses, and epitaphs really written to or for the sister of Francis I., one only finds respectful praise, such as the humble courtier may fittingly offer to his patroness. There is nothing whatever, adds M. Le Roux de Lincy, to promote the suspicion that a passion, either unfortunate or favoured, inspired a single one of these compositions.
The campaign in which Francis I. was engaged at the time when Marot’s connection with Margaret began, and concerning which the poet supplied her with information, was destined to influence the whole reign, since it furnished the occasion of the first open quarrel between Francis I. and the companion of his childhood, Charles de Bourbon, Count of Montpensier, and Constable of France. Yielding too readily on this occasion to the persuasions of his mother, Francis intrusted to Margaret’s husband the command of the vanguard, a post which the Constable considered his own by virtue of his office. He felt mortally offended at the preference given to the Duke of Alençon, and from that day forward he and Francis were enemies for ever.
Whilst the King was secretly jealous of Bourbon, who was one of the handsomest, richest, and bravest men in the kingdom, Louise of Savoy, although forty-four years of age, was in love with him. The Constable, then thirty-two, had lost his wife, Susan de Bourbon, from whom he had inherited vast possessions. To these Louise of Savoy, finding her passion disregarded, laid claim, as being a nearer relative of the deceased. A marriage, as Chancellor Duprat suggested, would have served to reconcile the parties, but the Constable having rejected the proposed alliance—with disdain, so it is said—the suit was brought before the Parliament and decided in favour of Louise. Such satisfaction as she may have felt was not, however, of long duration, for Charles de Bourbon left France, entered the service of Charles V., and in the following year (1524) helped to drive the French under Bonnivet out of Italy.
The Regency of Louise of Savoy—Margaret and the royal
children—The defeat of Pavia and the death of the Duke of
Alençon—The Royal Trinity—“All is lost save honour”—
Margaret’s journey to Spain and her negotiations with
Charles V.—Her departure from Madrid—The scheme to arrest
her, and her flight on horseback—Liberation of Francis I.—
Clever escape of Henry of Navarre from prison—Margaret’s
secret fancy for him—Her personal appearance at this
period—Marriage of Henry and Margaret at St. Germain.
The most memorable events of Margaret’s public life date from this period. Francis, who was determined to reconquer the Milanese, at once made preparations for a new campaign. Louise of Savoy was again appointed Regent of the kingdom, and as Francis’s wife, Claude, was dying of consumption, the royal children were confided to the care of Margaret, whose husband accompanied the army. Louise of Savoy at first repaired to Lyons with her children, in order to be nearer to Italy, but she and Margaret soon returned to Blois, where the Queen was dying. Before the royal army had reached Milan Claude expired, and soon afterwards Louise was incapacitated by a violent attack of gout, while the children of Francis also fell ill. The little ones, of whom Margaret had charge, consisted of three boys and three girls, the former being Francis, the Dauphin, who died in 1536, Charles, Duke of Orleans, who died in 1545, and Henry, Count of Angoulême, who succeeded his father on the throne. The girls comprised Madeleine, afterwards the wife of James V. of Scotland, Margaret, subsequently Duchess of Savoy, and the Princess Charlotte. The latter was particularly beloved by her aunt Margaret, who subsequently dedicated to her memory her poem Le Miroir de l’Ame Pécheresse. While the other children recovered from their illness, little Charlotte, as Margaret records in her letters to Bishop Briçonnet, was seized “with so grievous a malady of fever and flux,” that after a month’s suffering she expired, to the deep grief of her aunt, who throughout her illness had scarcely left her side.
This affliction was but the beginning of Margaret’s troubles. Soon afterwards the Constable de Bourbon, in conjunction with Pescara and Lannoy, avenged his grievances under the walls of Pavia. On this occasion, as at Marignano, the Duke of Alençon commanded the French reserves, and had charge of the fortified camp from which Francis, listening to Bonnivet, sallied forth, despite the advice of his best officers. The King bore himself bravely, but he was badly wounded and forced to surrender, after La Palisse, Lescun, Bonnivet, La Trémoïlle, and Bussy d’Amboise had been slain before his eyes. Charles of Alençon was then unable to resist the advice given him to retreat, and thus save the few Frenchmen who had escaped the arms of the Imperialists. With four hundred lances he abandoned the camp, crossed the Ticino, and reaching France by way of Piedmont, proceeded to Lyons, where he found Louise of Savoy and Margaret.
It has been alleged that they received him with harsh reproaches, and that, unable to bear the shame he felt for his conduct, he died only a few days after the battle. (1)
1 See Garnier’s Histoire de France, vol. xxiv.; Gaillard’s
Histoire de France, &c. Odolant Desnos, usually well
informed, falls into the same error, and asserts that when
the Duke, upon his arrival, asked Margaret to kiss him, she
replied, “Fly, coward! you have feared death. You might find
it in my arms, as I do not answer for myself.”—Mémoires
historiques, vol. ii. p. 253.
There are several errors in these assertions, which a contemporary document enables us to rectify. The battle of Pavia was fought on February 14th, 1525, and Charles of Alençon did not die till April 11th, more than a month after his arrival at Lyons. He was carried off in five days by pleurisy, and some hours before his death was still able to rise and partake of the communion. Margaret bestowed the most tender care upon him, and the Regent herself came to visit him, the Duke finding strength enough to say to her, “Madam, I beg of you to let the King know that since the day he was made a prisoner I have been expecting nothing but death, since I was not sufficiently favoured by Heaven to share his lot or to be slain in serving him who is my king, father, brother, and good master.” After kissing the Regent’s hand he added, “I commend to you her who has been my wife for fifteen years, and who has been as good as she is virtuous towards me.” Then, as Louise of Savoy wished to take Margaret away, Charles turned towards the latter and said to her, “Do not leave me.”
The Duchess refused to follow her mother, and embracing her dying husband, showed him the crucifix placed before his eyes. The Duke, having summoned one of his gentlemen, M. de Chan-deniers, instructed him to bid farewell on his part to all his servants, and to thank them for their services, telling them that he had no longer strength to see them. He asked God aloud to forgive his sins, received the extreme unction from the Bishop of Lisieux, and raising his eyes to heaven, said “Jesus,” and expired. (1)
Whilst tending her dying husband, Margaret was also deeply concerned as to the fate of her captive brother, for whom she always evinced the warmest affection. Indeed, so close were the ties uniting Louise of Savoy and her two children that they were habitually called the “Trinity,” as Clement Marot and Margaret have recorded in their poems. (2)
1 From a MS. poem in the Bibliothèque Nationale entitled
Les Prisons, probably written by William Philander or
Filandrier, a canon of Rodez.
2 See OEuvres de Clément Marot, 1731, vol. v. p. 274; and
A. Champoîlion-Figeac’s Poésies de François Ier, &c.,
Paris, 1847, p. 80.
In this Trinity Francis occupied the highest place; his mother called him “her Cæsar and triumphant hero,” while his sister absolutely reverenced him, and was ever ready to do his bidding. Thus the intelligence that he was wounded and a prisoner threw them into consternation, and they were yet undecided how to act when they received that famous epistle in which Francis wrote—not the legendary words, “All is lost save honour,” but—“Of all things there have remained to me but honour and life, which is safe.” After begging his mother and sister to face the extremity by employing their customary prudence, the King commended his children to their care, and expressed the hope that God would not abandon him. (1) This missive revived the courage of the Regent and Margaret, for shortly afterwards we find the latter writing to Francis: “Your letter has had such effect upon the health of Madame [Louise], and of all those who love you, that it has been to us as a Holy Ghost after the agony of the Passion.... Madame has felt so great a renewal of strength, that whilst day and evening last not a moment is lost over your business, so that you need have no grief or care about your kingdom and children.” (2)
1 See extract from the Registers of the Parliament of Paris
(Nov. 10, 1525) in Dulaure’s Histoire de Paris, Paris,
1837, vol. iii. p. 209; and Lalanne’s Journal d’un
Bourgeois de Paris, Paris, 1854, p. 234. The original of
the letter no longer exists, but the authenticity of the
text cannot be disputed, as all the more essential portions
are quoted in the collective reply of Margaret and Louise of
Savoy, which is still extant. See Champollion-Figeac’s
Captivité de François Ier, pp. 129, 130.
2 Génin’s Nouvelles Lettres de la Peine de Navarre,
Paris, 1842, p. 27.
Louise of Savoy was indeed now displaying courage and ability. News shortly arrived that the King had been transferred to Madrid, and that Charles demanded most onerous conditions for the release of his prisoner. At this juncture Francis wrote to his mother that he was very ill, and begged of her to come to him. Louise, however, felt that she ought not to accede to this request, for it would be jeopardising the monarchy to place the Regent as well as the King of France in the Emperor’s hands; accordingly she resolved that Margaret should go instead of herself.
The Baron of St. Blancard, general of the King’s galleys, who had previously offered to rescue Francis while the latter was on his way to Spain, received orders to make the necessary preparations for Margaret’s voyage, of which she defrayed the expense, as is shown by a letter she wrote to John Brinon, Chancellor of Alençon. In this missive she states that the Baron of St. Blancard has made numerous disbursements on account of her journey which are to be refunded to him, “so that he may know that I am not ungrateful for the good service he has done me, for he hath acquitted himself thereof in such a way that I have occasion to be gratified.” (1)
1 Génin’s Lettres de Marguerite, &c., p. 193.—Génin’s
Notice, ibid., p. 19.
Despite adverse winds, Margaret embarked on August 27th, 1525, at Aigues-Mortes, with the President de Selves, the Archbishop of Embrun, the Bishop of Tarbes, and a fairly numerous suite of ladies. The Emperor had granted her a safe-conduct for six months, and upon landing in Spain she hurried to Madrid, where she found her brother very sick both in mind and body. She eagerly caressed and tended him, and with a good result, as she knew his nature and constitution much better than the doctors. To raise his depressed spirits she had recourse to religious ceremonies, giving orders for an altar to be erected in the room where he was lying. She then requested the Archbishop of Embrun to celebrate mass, and received the communion in company of all the French retainers about the prisoner. It is stated that the King, who for some hours had given no sign of life, opened his eyes at the moment of the consecration of the elements, and asked for the communion, saying, “God will cure me, soul and body.” From this time forward he began to recover his health, though he remained fretful on account of his captivity.
It was a difficult task to obtain his release. The Court and the Emperor were extremely polite, but Margaret soon recognised the emptiness of their protestations of good-will. “They all tell me that they love the King,” she wrote, “but I have little proof of it. If I had to do with honest folks, who understand what honour is, I should not care, but it is the contrary.” (1)
1 Lettres de Marguerite, &c., p. 21.
She was not the woman to turn back at the first obstacle, however; she began by endeavouring to gain over several high personages, and on perceiving that the men avoided speaking with her on serious business, she addressed herself to their mothers, wives, or daughters. In a letter to Marshal de Montmorency, then with the King, she thus refers to the Duke del Infantado, who had received her at his castle of Guadalaxara. “You will tell the King that the Duke has been warned from the Court that if he wishes to please the Emperor neither he nor his son is to speak to me; but the ladies are not forbidden me, and to them I will speak twofold.” (1)
Throughout the negotiations for her brother’s release Margaret always maintained the dignity and reserve fitting to her sex and situation. Writing to Francis on this subject she says: “The Viceroy (Lannoy) has sent me word that he is of opinion I should go and see the Emperor, but I have told him through M. de Senlis that I have not yet stirred from my lodging without being asked, and that whenever it pleases the Emperor to see me I shall be found there.” (2)
1 Lettres de Marguerite, &c., p. 197.
2 Captivité de François Ier, p. 358.
Margaret was repeatedly admitted to the Imperial council to discuss the conditions of her brother’s ransom. She showed as much ability as loftiness of mind on these occasions, and several times won Charles V. himself and the sternest of his Ministers to her opinion. (1)
1 Brantôme states that the Emperor was greatly impressed and
astonished by her plain speaking. She reproached him for
treating Francis so harshly, declaring that this course
would not enable him to attain his ends. “For although he
(the King) might die from the effects of this rigorous
treatment, his death would not remain unpunished, as he had
children who would some day become men and wreak signal
vengeance.” “These words,” adds Brantôme, “spoken so bravely
and in such hot anger, gave the Emperor occasion for
thought, insomuch that he moderated himself and visited the
King and made him many fine promises, which he did not keep,
however.” With the Ministers Margaret was even more
outspoken; but we are told that she turned her oratorical
powers “to such good purpose that she rendered herself
agreeable rather than odious or unpleasant; the more readily
as she was also good-looking, a widow, and in the flower of
her age.”—OEuvres de Brantôme, 8vo, vol. v. (Les Dames
illustres).
She highly favoured the proposed marriage between Francis and his rival’s sister, Eleanor of Austria, detecting in this alliance the most certain means of a speedy release. Eleanor, born at Louvain in 1498, had in 1519 married Emanuel, King of Portugal, who died two years afterwards. Since then she had been promised to the Constable de Bourbon, but the Emperor did not hesitate to sacrifice the latter to his own interests.
He himself, being fascinated by Margaret’s grace and wit, thought of marrying her, and had a letter sent to Louise of Savoy, plainly setting forth the proposal. In this missive, referring to the Constable de Bourbon, Charles remarked that “there were good matches in France in plenty for him; for instance, Madame Renée, (1) with whom he might very well content himself.” (2) These words have led to the belief that there had been some question of a marriage between Margaret and the Constable; however, there is no mention of any such alliance in the diplomatic documents exchanged between France and Spain on the subject of the King’s release. These documents comprise an undertaking to restore the Constable his estates, and even to arrange a match for him in France, (3) but Margaret is never mentioned. She herself, in the numerous letters handed down to us, does not once refer to the famous exile, and the intrigue described by certain historians and romancers evidently rests upon no solid foundation. (4)
1 Renée, the younger daughter of Louis XII. and Anne of
Brittany, subsequently celebrated as Renée of Ferrara.
2 This letter is preserved at the Bibliothèque Nationale,
Béthune MSS., No. 8496, fol. xiii.
3 Captivité de Francois Ier, &c., pp. 167-207.
4 Varillas is the principal historian who has mentioned
this supposed intrigue, which also furnished the subject of
a romance entitled Histoire de Marguerite, Reine de
Navarre, &c., 1696.
After three months of negotiations, continually broken off and renewed, Margaret and her brother, feeling convinced of Charles V.‘s evil intentions, resolved to take steps to ensure the independence of France. By the King’s orders Robertet, his secretary, drew up letters-patent, dated November 1525 by which it was decreed that the young Dauphin should be crowned at once, and that the regency should continue in the hands of Louise of Savoy, but that in the event of her death the same power should be exercised by Francis’s “very dear and well-beloved only sister, Margaret of France, Duchess of Alençon and Berry.” (1) However, all these provisions were to be deemed null and void in the event of Francis obtaining his release.
It has been erroneously alleged that Margaret on leaving Spain took this deed of abdication with her, and that the Emperor, informed of the circumstance, gave orders for her to be arrested as soon as her safe-conduct should expire. (2) However, it was the Marshal de Montmorency who carried the deed to France, and Charles V. in ordering the arrest of Margaret had no other aim than that of securing an additional hostage in case his treaty with Francis should not be fulfilled.
1 Captivité de François 1er, &c., p. 85.
2 Génin’s Notice in the Lettres de Marguerite, &c., p.
25.
Margaret, pressed by her brother, at last asked for authorisation to leave Spain. By the manner in which the permission was granted she perceived that the Emperor wished to delay rather than hasten her journey. During November she wrote Francis a letter in which this conviction was plainly expressed, and about the 19th of the month she left Madrid upon her journey overland to France.
At first she travelled very leisurely, but eventually she received a message from her brother, advising her to hasten her speed, as the Emperor, hoping that she would still be in Spain in January, when her safe-conduct would expire, had given orders for her arrest. Accordingly, on reaching Medina-Celi she quitted her litter and mounted on horseback, accomplishing the remainder of her journey in the saddle. Nine or ten days before the safe-conduct expired she passed Perpignan and reached Salces, where some French nobles were awaiting her.
Soon after her return to France she again took charge of the royal children, who once more fell ill, this time with the measles, as Margaret related in the following characteristic letter addressed to her brother, still a prisoner in Spain:—
“My Lord,—The fear that I have gone through about your children, without saying anything of it to Madame (Louise of Savoy), who was also very ill, obliges me to tell you in detail the pleasure I feel at their recovery. M. d’Angoulême caught the measles, with a long and severe fever; afterwards the Duke of Orleans took them with a little fever; and then Madame Madeleine without fever or pain; and by way of company the Dauphin without suffering or fever. And now they all are quite cured and very well; and the Dauphin does marvels in the way of studying, mingling with his schooling a hundred thousand other occupations. And there is no more question of passions, but rather of all the virtues; M. d’Orléans is nailed to his book, and says that he wants to be good; but M. d’Angoulême does more than the others, and says things that are to be esteemed rather as prophecies than childish utterances, which you, my lord, would be amazed to hear. Little Margot resembles myself; she will not be ill; but I am assured here that she has very graceful ways, and is getting prettier than ever Mademoiselle d’Angoulême (1) was.”
1 Génin’s Lettres de Marguerite, &c, p. 70. The
Mademoiselle d’Angoulême alluded to at the end of the letter
is Margaret herself.
Francis having consented to the onerous conditions imposed by Charles V., was at last liberated. On March 17th, 1526, he was exchanged for his two elder sons, who were to serve as hostages for his good faith, and set foot upon the territory of Beam. He owed Margaret a deep debt of gratitude for her efforts to hasten his release, and one of his first cares upon leaving Spain was to wed her again in a fitting manner. He appears to have opened matrimonial negotiations with Henry VIII. of England, (1) but, fortunately for Margaret, without result. She, it seems, had already made her choice. There was then at the French Court a young King, without a kingdom, it is true, but endowed with numerous personal qualities. This was Henry d’Albret, Count of Beam, and legitimate sovereign of Navarre, then held by Charles V. in defiance of treaty rights. Henry had been taken prisoner with Francis at Pavia and confined in the fortress there, from which, however, he had managed to escape in the following manner.
Having procured a rope ladder in view of descending from the castle, he ordered Francis de Rochefort, his page, to get into his bed and feign sleep. Then he descended by the rope, the Baron of Arros and a valet following him. In the morning, when the captain on duty came to see Henry, as was his usual custom, he was asked by a page to let the King sleep on, as he had been very ill during the night. Thus the trick was only discovered when the greater part of the day had gone by, and the fugitives were already beyond pursuit. (2)
1 Lettres de Marguerite, &c, p. 31.
2 Olhagaray’s Histoire de Faix, Beam, Navarre, &c,
Paris, 1609. p. 487.
As the young King of Navarre had spent a part of his youth at the French Court, he was well known to Margaret, who apparently had a secret fancy for him. He was in his twenty-fourth year, prepossessing, and extremely brave. (1) There was certainly a great disproportion of age between him and Margaret, but this must have served to increase rather than attenuate her passion. She herself was already thirty-five, and judging by a portrait executed about this period, (2) in which she is represented in mourning for the Duke of Alençon, with a long veil falling from her cap, her personal appearance was scarcely prepossessing.
The proposed alliance met with the approval of Francis, who behaved generously to his sister. He granted her for life the enjoyment of the duchies of Alençon and Berry, with the counties of Armagnac and Le Perche and several other lordships. Finally, the marriage was celebrated on January 24th, 1527, at St. Germain-en-Laye, where, as Sauvai records, “there were jousts, tourneying, and great triumph for the space of eight days or thereabouts.” (3)
1 He was born at Sanguesa, April 1503, and became King of
Navarre in 1517.
2 This portrait is at the Bibliothèque Nationale in the
Recueil de Portraits au crayon by Clouet, Dumonstier, &c.
(fol. 88).
3 Antiquités de Paris, vol. ii. p. 688.
The retirement of King Henry to Beam—Margaret’s intercourse with her brother—The inscription at Chambord—Margaret’s adventure with Bonnivet—Margaret’s relations with her husband—Her opinions upon love and conjugal fidelity—Her confinements and her children—The Court in Beam and the refugee Reformers—Margaret’s first poems—Her devices, pastorals, and mysteries—The embellishment of Pau—Margaret at table and in her study—Reforms and improvements in Beam—Works of defence at Navarreinx—Scheme of refortifying Sauveterre.
Some historians have stated that in wedding his sister to Henry d’Albret, Francis pledged himself to compel Charles V. to surrender his brother-in-law’s kingdom of Navarre. This, however, was but a political project, of which no deed guaranteed the execution. Francis no doubt promised Margaret to make every effort to further the restitution, and she constantly reminded him of his promise, as is shown by several of her letters. However, political exigencies prevented Francis from carrying out his plans, and in a diplomatic document concerning the release of the children whom Charles held as hostages the following clause occurs: “Item, the said Lord King promises not to help or favour the King of Navarre (although he has married his only and dear beloved sister) in reconquering his kingdom.” (1)
The indifference shown by Francis for the political fortunes of his brother-in-law, despite the numerous and signal services the latter had rendered him, justly discontented Henry, who at last resolved to withdraw from the Court, where Montmorency, Brion, and several other personages, his declared enemies, were in favour. Margaret apparently had to follow her husband in his retirement, for Sainte-Marthe remarks: “When the King of Navarre, disgusted with the Court, and seeing none of the promises that his brother-in-law had made him realised, resolved to withdraw to Beam, Margaret, although the keen air of the mountains was hurtful to her health, and her doctors had threatened her with a premature death if she persevered in braving the rigours of the climate, preferred to put her life in peril rather than to fail in her duty by not accompanying her husband.” (2)
1 Bibliothèque Nationale, MS. No. 8546 (Béthune), fol. 107.
2 Oraison funèbre, &c, p. 70.
Various biographers express the opinion that this retirement took place in 1529, shortly after the Peace of Cambray, and others give 1530 as the probable date. Margaret, we find, paid a flying visit to Beam with her husband in 1527; on January 7th, 1528, she was confined of her first child, Jane, at Fontainebleau, and the following year she is found with her little daughter at Longray, near Alençon. In 1530 she is confined at Blois of a second child, John, Prince of Viana, who died at Alençon on Christmas Day in the same year, when but five and a half months old. Then in 1531 her letters show her with her mother at Fontainebleau; and Louise of Savoy being stricken with the plague, then raging in France, Margaret closes her eyes at Gretz, a little village between Fontainebleau and Nemours, on September 22nd in that year.
It was after this event that the King and Queen of Navarre determined to proceed to Beam, but so far as Margaret herself is concerned, it is certain that retirement was never of long duration whilst her brother lived. She is constantly to be found at Alençon, Fontainebleau, and Paris, being frequently with the King, who did not like to remain separated from her for any length of time. He was wont to initiate her into his political intrigues in view of availing himself of her keen and subtle mind. Brantôme, referring to this subject, remarks that her wisdom was such that the ambassadors who “spoke to her were greatly charmed by it, and made great report of it to those of their nation on their return; in this respect she relieved the King her brother, for they (the ambassadors) always sought her after delivering the chief business of their embassy, and often when there was important business the King handed it over to her, relying upon her for its definite resolution. She understood very well how to entertain and satisfy the ambassadors with fine speeches, of which she was very lavish, and also very clever at worming their secrets out of them, for which reason the King often said that she helped him right well and relieved him of a great deal.” (1)
1 OEuvres de Brantôme, 8vo, vol. v. p. 222.
Margaret’s own letters supply proof of this. She is constantly to be found intervening in state affairs and exercising her influence. She receives the deputies from Basle, Berne, and Strasburg who came to Paris in 1537 to ask Francis I. for the release of the imprisoned Protestants. She joins the King at Valence when he is making preparations for a fresh war against Charles V.; then she visits Montmorency at the camp of Avignon, which she praises to her brother; next, hastening to Picardy, when the Flemish troops are invading it, she writes from Amiens and speaks of Thérouenne and Boulogne, which she has found well fortified.
Francis, however, did not value her society and counsel solely for political reasons; he was also fond of conversing with her on literature, and at times they composed amatory verses together. According to an oft-repeated tradition, one day at the Château of Chambord, whilst Margaret was boasting to her brother of the superiority of womankind in matters of love, the King took a diamond ring from his finger and wrote on one of the window panes this couplet:—
“Souvent femme varie, Bien fol est qui s’y fie.” (1)
Brantôme, who declares that he saw the inscription, adds, however, that it consisted merely of three words, “Toute femme varie” (all women are fickle), inscribed in large letters at the side of the window. (2) He says nothing of any pane of glass (all window panes were then extremely small) or of a diamond having been used; (3) and in all probability Francis simply traced these words with a piece of chalk or charcoal on the side of one of the deep embrasures, which are still to be seen in the windows of the château.
1 “Woman is often fickle,
Crazy indeed is he who trusts her.”
2 Vies des Dames galantes, Disc. iv.
3 The practice of cutting glass with diamonds does not seem
to have been resorted to until the close of the sixteenth
century. See Les Subtiles et Plaisantes Inventions de J.
Prévost, Lyons, 1584, part i. pp. 30, 31.
Margaret carried her complaisance for her brother so far as to excuse his illicit amours, and she was usually on the best of terms with his favourites. (1) It has been asserted that improper relations existed between the brother and sister, but this charge rests solely upon an undated letter from her to Francis, which may be interpreted in a variety of ways. Count de la Ferrière, in his introduction to Margaret’s record of her expenditure, (2) expresses the opinion that it was penned in 1525, prior to her hasty departure from Spain; while M. Le Roux de Lincy assigns it to a later date, remarking that it was probably written during one of the frequent quarrels which arose between Margaret’s brother and her husband. However, they are both of opinion that the letter does not bear the interpretation which other writers have placed upon it. (3)
1 E. Fournier’s L’Esprit dans l’Histoire, Paris,
1860, p. 132 et seq.
2 Livre de Dépenses de Marguerite d’Angoulême, &c.
(Introduction).
3 See Lettres de Marguerite, &c., p. 246.
The only really well-authenticated love intrigue in which Margaret was concerned—and in that she played a remarkably virtuous part—was her adventure with the Admiral de Bonnivet, upon which the fourth story of the Heptameron is based. (1) She was certainly unfortunate in both her marriages. Her life with the Duke of Alençon has already been spoken of; and as regards her second union, although contracted under apparently favourable auspices, it failed to yield Margaret the happiness she had hoped for. But four years after its celebration she wrote to the Marshal de Montmorency: “Since you are with the King of Navarre, I have no fear but that all will go well, provided you can keep him from falling in love with the Spanish ladies.” (2) And again: “My nephew, I have received the letters you wrote to me, by which I have learnt that you are a much better relation than the King of Navarre is a good husband, for you alone have given me news of the King (Francis) and of him, without his being willing to give pleasure to a poor wife, big with child, by writing a single word to her.” (3)
1 Particulars concerning this adventure will be found in
the notes to Tale iv., and also in the Appendix to the
present volume (C).
2 Lettres de Marguerite, &c., p. 246.
3 Ibid., p. 248.
In another letter written to the Marshal at the same period she says: “If you listen to the King of Navarre, he will make you commit so many disorders that he will ruin you.” (1) Perhaps these words should not be taken literally; still they furnish cause for reflection when it is remembered that they were written by a woman just turned forty concerning her husband who was not yet thirty years old.
Margaret’s views upon love and the affinity of souls were somewhat singular, but they indicate an elevated and generous nature. In several passages of the Heptameron she has expressed her opinion on these matters, ardently defending the honour of her sex and condemning those wives who show themselves indulgent as regards their husbands’ infidelities. (2) She blames those who sow dissension between husbands and wives, leading them on to blows; (3) and when some one asked her what she understood perfect love to be, she made answer, “I call perfect lovers those who seek some perfection in the object of their love, be it beauty, kindness, or good grace, tending to virtue, and who have such high and honest hearts that they will not even for fear of death do base things that honour and conscience blame.”
1 Lettres de Marguerite, &c, p. 251.
2 Epilogue of Tale xxxvii.
3 Epilogue of Tale xlvi.
In reference to this subject of conjugal fidelity a curious story is told of Margaret. One day at Mont-de-Marsan, upon seeing a young man convicted of having murdered his father being led to execution, she remarked to those about her that it was very wrong to put to death a young fellow who had not committed the crime imputed to him. It was pointed out to her that the judges had only condemned him upon conclusive proofs and the acknowledgments that he himself had made. Margaret, however, persisted in her remark, whereupon some of her intimates begged of her to justify it, for it seemed to them at least singular. “I do not doubt,” she replied, “that this poor wretch killed his mother’s husband, but he certainly did not kill his own father.” (1)
Besides being unfortunate as regards her husbands, Margaret was also denied a mother’s privileges. She experienced great suffering at her confinements, (2) and on two occasions she was delivered of still-born infants of the female sex.
1 Gabriel de Minut’s De la Beauté, Discours divers, &c.,
Lyons, 1587. p. 74.
2 Nouvelles Lettres de Marguerite, pp. 84 and 93.
She had centred many hopes upon her little boy, John, of whom she was confined without accident, but he died, as already stated, in infancy, and this misfortune was a great shock to her, though she tried to conceal it by having the Te Deum sung at the funeral in lieu of the ordinary service, and by setting up in the streets of Alençon the inscription, “God gave him, God has taken him away.” However, from that time forward she never laid aside her black dress, though later on she wore it trimmed with marten’s fur. Her best known portrait (1) represents her attired in this style with the quaint Bearnese cap, which she had also adopted, set upon her head.
1 Bibliothèque Nationale, Recueil de Portraits au crayon,
&c., fol. 46.
Not only did Margaret lose her son by death, but she was prevented from enjoying the companionship of her daughter Jane. Francis, who never once lost sight of his own interests, deemed it advisable to possess himself of this child, who was the heiress to the throne of Navarre. Accordingly when Jane was but two years old she was sent by the King to the Château of Plessis-lès-Tours, where she was carefully brought up in strict seclusion.
To the fact that Margaret was never really happy with either of her husbands, and that she was precluded from discharging a mother’s duties, one may ascribe, in part, her fondness for gathering round her a Court in which divines, scholars, and wits prominently figured. The great interest which she took in religious matters, as is shown by so many of her letters, (1) led her to shelter many of the persecuted Reformers in Beam; others she saved from the stake, and frequently in writing to the King and Marshal de Montmorency she begs for the release of some imprisoned heretic.
1 One of these letters, written by her either to Philiberta
of Savoy, Duchess of Nemours, or to Charlotte d’Orléans,
Duchess of Nemours, both of whom were her aunts, may be thus
rendered in English: “My aunt, on leaving Paris to escort
the King, Monsieur de Meaux (Bishop Briçonnet), sent me the
Gospels in French, translated by Fabry, word for word, which
he says we should read with as much reverence and as much
preparation to receive the Spirit of God, such as He has
left it us in His Holy Scriptures, as when we go to receive
it in the form of Sacrament. And inasmuch as Monsieur de
Villeroy has promised to deliver them to you, I have
requested him to do so, for these words (the Gospels) must
not fall into evil hands. I beg, my aunt, that if by their
means God grants you some grace, you will not forget her who
is above all else your good niece and sister, Margaret.”
Fabry’s translation of the Gospels was made in 1523-24.
Margaret’s religious views frequently caused dissension between her and her husband, in whose presence she abstained from giving expression to them. Hilarion de Coste mentions that “King Henry having one day been informed that a form of prayer and instruction contrary to that of his fathers was held in the chamber of the Queen, his wife, entered it intending to chastise the minister, and finding that he had been hurried away, the remains of his anger fell upon his wife, who received a blow from him, he remarking, ‘Madam, you want to know too much about it,’ and he at once sent word of the matter to King Francis.”
It was at Nérac that most of the divines protected by Margaret found a refuge from the persecutions of the Sorbonne. Here she kept court in a castle of which there now only remains a vaulted fifteenth-century gallery formerly belonging to the northern wing. Nérac has, however, retained intact a couple of quaint mediaeval bridges, which Margaret must have ofttimes crossed in her many journeyings. Moreover, the townsfolk still point out the so-called Palace of Marianne, said to have been built by Margaret’s husband for one of his mistresses, and also the old royal baths, which the Queen no doubt frequented.
It was at the castle of Nérac that Margaret’s favourite protégé, the venerable Lefèvre d’Étaples, died at the age of one hundred and one, in the presence of his patroness, to whom before expiring he declared that he had never known a woman carnally in his life. However, he regretfully added that in his estimation he had been guilty of a greater sin, for he had neglected to lay down his life for his faith. Another partisan of the Reform, Gerard Roussel, whom Margaret had almost snatched from the stake and appointed Bishop of Oloron, had no occasion to express any such regret. His own flock speedily espoused the doctrines of the Reformation, but when he proceeded to Mauléon and tried to preach there, the Basques refused to listen to him, and hacked the pulpit to pieces, the Bishop being precipitated upon the flagstones, and so grievously injured that he died.
Beside the divines who sought an asylum at Nérac, there were various noted men of letters, foremost among whom we may class the Queen’s two secretaries, Clement Marot, the poet, and Peter Le Maçon, the translator of Boccaccio’s Decameron. This translation was undertaken at the Queen’s request, as Le Maçon states in his dedication to her, and it has always been considered one of the most able literary works of the period. With Marot and Le Maçon, but in the more humble capacity of valet, at the yearly wages of one hundred and ten livres, there came the gay Bonaventure Despériers, the author of Les Joyeux Devis; (1) other writers, such as John Frotté, John de la Haye and Gabriel Chapuis, were also among Margaret’s retainers.
1 Livre de Dépenses de Marguerite d’Angoulême.
She herself had long practised the writing of verses. It was in 1531, and at Alençon, that she issued her first volume of poems, the Miroir de l’Ame Pécheresse, (1) which created a great stir at the time, for when it was re-issued in Paris by Augereau in 1533 (2) the Sorbonne denounced it as unorthodox, and Margaret would have been branded as a heretic if Francis had not intervened and ordered the Rector of the Sorbonne to withdraw the decree censuring his sister’s work. Nor did that content the King, for he caused Noël Béda, the syndic of the Faculty of Theology, to be arrested and confined in a dungeon at Mont St. Michel, where he perished miserably.
1 Brunet’s Manual, 4th ed., vol. iii. p. 275.
2 A second edition also appeared at Alençon in the same
year.
Margaret thus gained the day, but the annoyance she had been subjected to doubtless taught her to be prudent, for although she steadily went on writing, sixteen years elapsed before any more of her poems were published. In the meantime various manuscript copies, some of which are still in existence, were made of them, notably one of the poem called “Débat d’Amour” by Margaret, and re-christened “La Coche” by her secretary, John de la Haye, when he subsequently published it in the Marguerites de la Marguerite. This manuscript is enriched with eleven curious miniatures, the last of which represents the Queen handing the volume bound in white velvet (1) to the Duchess of Etampes, her brother’s mistress, whose qualities the poem extols. The Queen of Navarre was on the best of terms with this favourite, to whom in one of her letters she recommends certain servants.
Margaret was not only given to versifying, but was fond of’ framing devices, which she inscribed upon her books and furniture. At one time she adopted as her device a marigold turning towards the sun’s rays, with the motto, “Non inferiora secutus,” implying that she turned “all her acts, thoughts, will, and affections towards the great Sun of Justice, God Almighty.” (2)
1 From the Queen’s Livre de Dépenses, published by M. de
la Ferrière, we learn that this MS., with the miniatures and
binding, cost Margaret fifty golden crowns. It was formerly
in the possession of M. Jérôme Pichon, and was afterwards
acquired by M. Didot, at the sale of whose library it
realised £804. The MS. was recently in the possession of M.
de La Roche-la-Carelle.
2 Claude Paradin’s Dévises héroïques, Lyons, 1557, p. 41.
In her Miroir de l’Ame Pécheresse, previously referred to, there figures another device composed merely of the three words “Ung pour tout;” and in the manuscript of “La Coche” presented to the Duchess of Etampes, the motto “Plus vous que moys” is inscribed beneath each of the miniatures. Margaret also composed a series of devices for some jewels which her brother presented to his favourite, Madame de Châteaubriant. Respecting these Brantôme tells the following curious anecdote:—
“I have heard say, and hold on good authority, that when King Francis I. had left Madame de Châteaubriant, his favourite mistress, to take Madame d’Etampes, as one nail drives out another, Madame d’Etampes begged the King to take back from the said Madame de Châteaubriant all the finest jewels that he had given her, not on account of their cost and value, for pearls and precious stones were not then so fashionable as they have been since, but for the love of the fine devices that were engraved and impressed upon them; which devices the Queen of Navarre, his sister, had made and composed, for she was a mistress in such matters.
“King Francis granted the request, and promised that he would do it. Having with this intent sent a gentleman to Madame de Châteaubriant to ask for the jewels, she at once feigned illness, and put the gentleman off for three days, when he was to have what he asked for. However, out of spite, she sent for a goldsmith, and made him melt down all these jewels without exception, and without having any respect for the handsome devices engraved upon them. And afterwards, when the said gentleman returned, she gave him all the jewels converted into gold ingots.
“‘Go,’ said she, ‘and take these to the King, and tell him that since he has been pleased to take back from me that which he had given me so freely, I restore it and send it back in golden ingots. As for the devices, I have impressed them so firmly on my mind and hold them so dear in it, that I could not let any one have and enjoy them save myself.’
“When the King had received all this, the ingots and the lady’s remark, he only said, ‘Take her back all. What I did was not for the value, for I would have restored her that twofold, but for the love of the devices, and since she has thus destroyed them, I do not want the gold, and send it back. She has shown in this matter more courage and generosity than it would have been thought could come from a woman.’” (1)
Besides writing verses and framing devices, Margaret, as Brantôme tells us, “often composed comedies and moralities, which were in those days styled pastorals, and which she had played by the young ladies of her Court.” (2)
1 OEuvres de Brantôme, 8vo, vol. vii. p. 567.
2 Ibid., 8vo, vol. v. p. 219.
Hilarion de Coste states, moreover, that “she composed a tragi-comic translation of almost the whole of the New Testament, which she caused to be played before the King, her husband, having assembled with this object some of the best actors of Italy; and as these buffoons are only born to give pleasure and make time pass away, in order to amuse the company they invariably introduced rondeaux and virelais against the ecclesiastics, especially the monks and village priests.” (1)
1 M. Le Roux de Lincy points out that this statement is
exaggerated, for Margaret, instead of turning the whole of
the New Testament into verse, merely wrote four Mysteries
which mainly dealt with the childhood of Christ.
These performances took place at the Château of Pau, which Margaret and her husband seem to have preferred to that of Nérac, though political reasons often compelled them to fix their abode at the latter. Pau, however, possessed the advantage of a mild climate, necessary for Margaret’s health, besides being delightfully situated on the Bearnese Gave, the view from the château extending over a fertile valley limited by the snow-capped Pyrenees. There had been a château at Pau as early as the tenth century, but the oldest portions of the structure now subsisting date from the time of Edward III., when Pau was the capital of the celebrated Gaston-Phoebus. The château was considerably enlarged and embellished in the fifteenth century, but it was not until after Margaret’s marriage with Henry d’Albret that the more remarkable decorative work was executed. Upon leaving Nérac to reside at Pau, Margaret summoned a number of Italian artists and confided the embellishment of the château to them.(1)
It was not, however, merely the château which Margaret beautified at Pau. Already at Alençon she had laid out a charming park, which a contemporary poet called a terrestrial paradise,(2) and upon coming to reside at Pau she transformed the surrounding woods into delightful gardens, pronounced to be the finest then existing in Europe.(3)
1 Some of the doors and windows of the château are
elaborately ornamented in the best style of the Renaissance,
whilst the grand staircase, although dating from Margaret’s
time, has vaulted arches, sometimes in the Romanesque and at
others in the Gothic style. Entwined on the friezes are the
initials H and M (Henry and Margaret), occasionally
accompanied by the letter R, implying Rex or Regina. On
the first floor of the chateau is the bedroom occupied by
Margaret’s husband, remarkable for its Renaissance chimney-
piece, and also a grand reception hall, now adorned with
tapestry made for Francis I. in Flanders. It was in this
latter room that the Count of Montgomery—the same who had
thrust out the eye of Henry II. at a tournament, and thereby
caused that monarch’s death—acting at the instigation of
Margaret’s daughter Jane, assembled the Catholic noblemen of
Beam on August 24, 1569, and, after entertaining them with a
banquet, had them treacherously massacred. Bascle de
Lagrèze’s Château de Pau, Paris, 1854.
2 Le Recueil de l’Antique pré-excellence de Gaule, &c., by
G. Le Roville, Paris, 1551 (fol. 74).
3 Hilarion de Coste’s Vies et Éloges des Dames illustres,
&c., vol. ii. p. 272.
Some idea of their appearance may be gained from a couple of the miniatures adorning a curious manuscript catechism composed for Margaret and now in the Arsenal Library at Paris.(1)
1 Manuscrits théologiques français, No. 60, Initiatoire
Instruction en la Religion chrétienne, &c. In one of these
miniatures the Saviour is represented carrying the cross,
followed by Henry of Navarre, his brother Charles d’Albret,
Margaret, and other personages, all of whom bear crosses,
whilst in the background are some pleasure-grounds with a
castle, a little waterfall, and a lake. Another miniature in
the same manuscript shows King Henry of Navarre with a
flower in his hand, which he seems to be offering to the
Queen, who stands in the background among a party of
courtiers. The King wears a surtout of cloth of gold, edged
with ermine, over a blue jerkin, and a red cap with a white
feather. Margaret is also arrayed in cloth of gold, but with
a black cap and wimple. She is standing in a garden enclosed
by a railing, and adorned with a fountain in the form of a
temple which rises among groves and arbours. Beyond a white
crenellated wall is a castle which has been identified with
that of Pau. On fol. 1 of the same MS. the artist has
depicted Queen Margaret’s escutcheon, by which we find that
she quartered the arms of France with those of Navarre,
Aragon, Castile, Leon, Beam, Bigorre, Evreux, and Albret.
The Court which Margaret kept in turns at Alençon, Nérac, and Pau does not appear to have been so sumptuous and gay as some of her biographers assert. Brantôme mentions that the Queen’s two tables were always served with frugality, and Sainte-Marthe states that “she talked at dinner and supper now of medicine, of food wholesome or unwholesome for the human body, and of objects of nature with Masters Schyron, Cormier, and Esterpin, her expert and learned doctors, who carefully watched her eat and drink, as is done with princes; now she would speak of history or of the precepts of philosophy with other very erudite personages, with whom her house was never unfurnished; at another time she would enter into conversation on her faith and the Christian religion with Monsieur Gerard, Bishop of Oloron. Altogether there was not a single moment that was not employed by her in honest, pleasant, and useful conversation.” (1)
The same panegyrist tells us of Margaret’s favourite occupations, mentioning that when she was alone in her room she more often held a book in her hand than a distaff, a pen than a spindle, and the ivory of her tablets than a needle. He then adds: “And if she applied herself to tapestry or other needlework, such as was to her a pleasant occupation, she had beside her some one who read to her, either from a historian or a poet, or some other notable and useful author; or else she dictated some meditation which was written down.” (2)
1 Oraison funèbre, &c., p. 60.
2 Ibid., p. 68.
Margaret’s time was far from being wholly occupied in this manner, for she actively assisted her husband in carrying out improvements and reforms in Beam. The result was that the country, naturally good and fertile, but left in bad condition, uncultivated and sterile through the carelessness of its inhabitants, soon changed its appearance owing to the efforts of Henry and his wife. From all the provinces of France labourers were attracted who settled there and improved and fertilised the fields.(1)
1 Vies el Éloges des Dames illustres, vol. ii. p. 272.
Henry d’Albret also devoted himself to the placing of the country in a proper state of defence, and fortified several of the towns. Navarreinx, commanding the valley of the Gave of Oloron, was virtually rebuilt by him and transformed into a perfect stronghold, as was evidenced during the religious wars, when it successfully withstood the artillery of Terrade, the Catholic commander. Long afterwards, when Vauban inaugurated his new system of fortification, he came to Navarreinx, and on seeing the ramparts raised by Margaret’s husband was so favourably impressed, that instead of levelling them to the ground he contented himself with adding to them and making various improvements. Henry d’Albret was also anxious to refortify Sauveterre, which the Prince of Orange, with one of the Imperial armies, had captured in 1523, when he half-demolished the old castle of Montreal, then the most formidable citadel in Beam. However, as time and money were lacking, Henry had to abandon his plans, and the ruins left by the Imperialists, the ivy-clad keep, and mutilated bridge over the Gave soon fell into irremediable decay.(1)
1 M. Paul Perret’s Pyrénées françaises, vol. ii. p. 303.
Margaret’s attachment to her daughter—Refusal of Jane to
marry the Duke of Clevés—Intervention of Margaret—The
wedding at Châtelherault and the fall of the Constable de
Montmorency—Margaret and her husband at Caulerets—The
“Heptameron”—Illness and death of Francis I.—Margaret’s
anxiety and grief—Her “Marguerites de la Marguerite”—Jane
d’Albret’s second marriage—Death of Margaret at Odos or
Audaux——Her funeral at Lescar—Destruction of her tomb.
Whilst Margaret was living amongst divines and scholars at Pau and Nérac, her mind, as her letters indicate, constantly turned to her daughter Jane, whom Aimée de la Fayette, wife of the Bailiff of Caen, was bringing up at Plessis-lès-Tours. Margaret was only able to see Jane at rare intervals during some of her trips to France, and she was mainly indebted to sympathising friends for news of the little Princess’s condition and health. All her maternal tenderness was concentrated on this daughter, and whenever the child was ailing she became distracted.
Sainte-Marthe records that in December 1537, while Margaret was sojourning in Paris, her daughter, then scarcely nine years old, fell seriously ill at the royal house of Plessis-lès-Tours; and as it was rumoured amongst the Court, then at Paris, that the Princess was threatened with death, her virtuous mother, Margaret, at about four o’clock in the evening, ordered her litter to be brought, saying that she would go and see her daughter, and that all her people should prepare to start. There was nothing ready, the officials and servants were absent, and scattered about the town of Paris and the neighbouring villages. It was already dark, for this was during the shortest days of the year, the weather too was adverse on account of the rain, and neither her litter nor her baggage mules were at hand. Seeing this, the courageous Queen borrowed the litter of Madame Margaret, her niece,(1) got in it, and contenting herself with scant escort, started from Paris and went as far as Bourg-la-Reine.
1 The daughter of Francis I., subsequently Duchess of Savoy.
“When they had arrived there she did not alight at her lodgings, but went straight to the church, which she at once entered, saying to those about her, that her heart told her I know not what concerning her daughter’s fate, and affectionately begging them all to withdraw and leave her alone for an hour in the church. All obeyed and in great uneasiness waited for their mistress at the church door; the Sénéchale de Poitou,(1) a very faithful lady, and very solicitous about Margaret, alone entering with her. Margaret having gone in, kneels down before the image of Jesus crucified, prays to God from the depths of her heart, sighs, weeps, confesses all her transgressions, and laying to herself alone the cause of her daughter’s illness, humbly asks pardon, and begs that the sufferer’s restoration to health may be granted. After this act of faith Margaret felt relieved, and she had scarcely arrived at her lodgings when the Bishop of Mende came to announce to her that her daughter was in the way of recovery.” (2)
1 Brantôme’s grandmother.
2 Oraison funèbre, &c, p. 38.
When Jane was barely twelve years old Charles V. asked her in marriage for his son Philip, but Francis, who was by no means anxious to see the Spaniards established on the northern side of the Pyrenees, preferred that the girl should marry William III., Duke of Cleves. It has frequently been asserted that Francis on this occasion exercised compulsion not only upon his niece, but also upon the King and Queen of Navarre, who vainly protested against this abuse of power. The truth is, that Margaret not only favoured the marriage, but threatened to have Jane whipped if she persisted in her refusal. Moreover, the little bride having declared to Francis I. that she protested against the alliance, Margaret wrote to her brother as follows:—
“My Lord, in my extreme desolation, I have only one single comfort, it is that of knowing with certainty that neither the King of Navarre nor myself have ever had any other wish or intention than that of obeying you, not only as regards a marriage, but in whatever you might order. But now, my lord, having heard that my daughter, neither recognising the great honour you do her in deigning to visit her, nor the obedience that she owes you, nor that a girl should have no will of her own, has spoken to you so madly as to say to you that she begged of you she might not be married to M. de Cleves, I do not know, my lord, either what I ought to think of it, or what I ought to say to you about it, for I am grieved to the heart, and have neither relative nor friend in the world from whom I can seek advice or consolation. And the King of Navarre is on his part so amazed and grieved at it that I have never seen him before so provoked. I cannot imagine whence comes this great boldness, of which she had never spoken to us. She excuses herself towards us in that she is more intimate with you than with ourselves, but this intimacy should not give rise to such boldness, without ever as I know seeking advice from any one, for if I knew any creature who had put such an idea into her head, I would make such a demonstration that you, my lord, would know that this madness is contrary to the will of the father and mother, who have never had, and never will have, any other than your own.” (1)
The rebellion of Jane did not prevent the marriage, which was solemnised at Châtelherault on July 15th, 1540. According to some authorities, Francis was so determined upon the alliance that he required the Duke of Cleves to enter his bride’s bed in the presence of witnesses, so that the marriage should be deemed beyond annulment.(2)
1 Nouvelles Lettres, &c., p. 176.
2 Henri Martin’s Histoire de France. The marriage,
however, was not really consummated (Nouvelles Lettres,
&c., pp. 236, 237), and it was eventually annulled by Pope
Paul III., to whom Francis applied for a divorce when the
Duke of Cleves deserted his cause for that of Charles V.
It was at Châtelherault on this occasion that Margaret triumphed over the Constable de Montmorency, who in earlier years had been her close friend, and with whom she had carried on such a voluminous correspondence. Montmorency had requited her good services with ingratitude, repeatedly endeavouring to estrange Francis from her. Brantôme gives an instance of this in the following passage:—“I have heard related,” he says, “by a person of good faith that the Constable de Montmorency, then in the highest favour, speaking of this matter of religion one day with the King, made no difficulty or scruple about telling him, that ‘if he really wished to exterminate the heretics of his kingdom, he ought to begin at his Court and with his nearest relatives, mentioning the Queen his sister,’ to which the King replied, ‘Do not speak of her; she loves me too much. She will never believe anything save what I believe, and will never take up a religion prejudicial to the State.’” (1)
1 OEuvres de Brantôme, 8vo, vol. v. (Dames illustres),
p. 219.
As soon as Margaret became aware of Montmorency’s conduct she ceased all correspondence with him and steadily endeavoured to effect his overthrow, which was brought about on the occasion of Jane’s marriage. “It was necessary to carry the little bride to the church,” says Brantôme, “as she was laden with jewels and a dress of gold and silver, and owing to this and the weakness of her body, was not able to walk. So the King ordered the Constable to take his little niece and carry her to the church, at which all the Court were greatly astonished, for at such a ceremony this was a duty little suited and honourable for a Constable, and might very well have been given to another. However, the Queen of Navarre was in no way displeased, but said, ‘Behold! he who wished to ruin me with the King my brother now serves to carry my daughter to church.’ The Constable,” adds Brantôme, “was greatly displeased at the task, and sorely vexed to serve as such a spectacle to every one; and he began to say, ‘It is now all over with my favour. Farewell to it.’ Thus it happened, for after the wedding festival and dinner he had his dismissal and left at once.” (1)
After the marriage of her daughter Margaret returned to Paris, and thence repaired to Mont-de-Marsan to spend the winter of 1540-41. Late in the following spring she went to Cauterets in the Pyrenees to take the baths. Writing during Lent to her brother she states that her husband having had a fall will repair to Cauterets by the advice of his doctors,(2) and that she intends to accompany him to prevent him from worrying and to transact his business for him, “for when one is at the baths one must live like a child without any care.” (3)
1 OEuvres de Brantôme, 8vo, vol. v. (Dames illustres),
p. 220.
2 Henry d’Albret had already undergone treatment at the
Pyrenean baths after his escape from Pavia, when, however,
he stayed at Eaux-Bonnes.
3 Génin’s Nouvelles Lettres, &c., p. 189.
This was not her only motive in going to Cauterets apparently, for in a letter to Duke William of Cleves, her daughter’s husband, dated April 1541, she states that as she is suffering from a caterre which “has fallen upon half her neck,” and compels her to keep her bed, the doctors have advised her to take “the natural baths,” and hope that she will be cured by the end of May, providing she follows all their prescriptions.(1)
1 A. de Ruble’s Mariage de Jeanne d’ Albret,
Paris, 1877, p. 86, et seq.
That this visit to Cauterets left a deep impression upon the mind of Margaret is evidenced by the work upon which her literary fame rests. The scene selected for the prologue of the Heptameron is Cauterets and the surrounding country; still it is evident that the book was not commenced upon the occasion referred to, for in the prologue Margaret alludes to historical events which took place in 1543 and 1544, and she speaks of them as being of recent occurrence at her time of writing. Now we know that in April 1544 she met her brother at Alençon, and made a long stay in the duchy, and the probability is that she commenced the Heptameron at that time. It was the work of several years, penned in a desultory style whilst Margaret was travelling about her northern duchy or her southern kingdom. Like all persons of high station, she journeyed in a litter, and Brantôme informs us that her equipage was a modest one, for “she never had more than three baggage-mules and six for her two litters, though she had two, three, or four chariots for her ladies.” (1) Brantôme—who it may be mentioned was brought up at Margaret’s Court under the care of his grandmother, Louise de Daillon, wife of Andrew de Vivonne, Seneschal of Poitou—also states that the Queen composed the Heptameron mainly “in her litter, while journeying about, for she had more important occupations when she was at home. I have thus heard it related by my grandmother, who always went with her in her litter as her lady of honour, and held the escritoire with which she wrote, and she set them (the stories) down in writing as speedily and skilfully as if they had been dictated to her, if not more so.” (2)
1 Lalanne’s OEuvres de Brantôme, 1875, vol. ii. p. 214.
2 Ibid., vol. viii. p. 226.
In 1545 and 1546 we find Margaret in Beam, whence she addresses New Year epistles to her brother expressing her sorrow at being separated from him. In the spring of the latter year she visits him at Plessis-lès-Tours. The King of France—contrary to all tradition—enjoys at this period as good health as the most robust man in his kingdom.(1) In 1547 Margaret repairs to a convent at Tusson in the Angoumois to spend Lent there, and soon afterwards is despatching courier after courier to the Court at Rambouillet for news of Francis, who is dying. Such is her anguish of suspense that she exclaims, “Whoever comes to my door to announce to me the cure of the King my brother, were such a messenger weary, tired, muddy, and dirty, I would embrace and kiss him like the cleanest prince and gentleman in France; and if he lacked a bed and could not find one to repose upon, I would give him mine, and would sleep on the floor for the sake of the good news he brought me.” (2)
1 Lettres de Marguerite, &c., p. 473.
2 OEuvres de Brantôme, 8vo, vol. v. p. 233.
No one, however, had the courage to tell her the truth. It was a poor maniac who by her tears gave her to understand that the King was no longer alive. Sainte-Marthe records the incident as follows: “Now the day that Francis was taken away from us (Margaret herself has since told me so), she thought whilst sleeping that she saw him looking pale, and calling for her in a sad voice, which she took for a very evil sign; and feeling doubtful about it, she sent several messengers to the Court to ascertain the condition of the King her brother, but not a single one of them returned to her. One day, her brother having again appeared to her while she was asleep (he had already been dead fifteen days), (1) she asked the members of her household if they had heard any news of the King.
1 Francis I. died March 31, 1547.
“They replied to her that he was very well, and she then went to the church. On her way there she summoned Thomas le Coustellier, a young man of good intelligence and her secretary, and as she was telling him the substance of a letter that she wished to write to a Princess of the Court, to obtain from her some news of the King’s health, she heard on the other side of the cloister a nun, whose brain was somewhat turned, lamenting and weeping loudly. Margaret, naturally inclined to pity, hastened to this woman, asked her why she was weeping, and encouraged her to tell her whether she wished for anything. Then the nun began to lament still more loudly, and looking at the Queen, told her that she was deploring her ill-fortune. When Margaret heard these words she turned towards those who were with her, and said to them, ‘You were hiding the King’s death from me, but the Spirit of God has revealed it to me through this maniac.’ This said, she turned to her room, knelt down, and humbly thanked the Lord for all the goodness He was pleased to show her.” (1)
After losing her brother, Margaret remained in retirement at the convent of Tusson. She stayed there, says Brantôme, for four months, leading a most austere life and discharging the duties of abbess. She still continued in retirement on her return to Beam, mainly occupying herself with literary work. It was in 1547, subsequent to the death of Francis, that John de la Haye, her secretary, published at Lyons her Marguerites de la Marguerite, poems which she had composed at various periods, and which De la Haye probably transcribed at her dictation.(2)
1 Oraison funèbre, &c., p. 103.
2 Sainte-Marthe states that she would sit with two
secretaries, one on either side, and dictate poetry to the
one and letters to the other.
Margaret’s daughter Jane was at this period at the Court of France, living in extravagant style, as is shown by the letters in which Margaret declares that the Princess’s expenditure is insupportable. She herself spent but little money upon personal needs, though she devoted considerable sums to charity. In October 1548 she emerged from her seclusion to attend the second marriage of her daughter, who now became the wife of Anthony de Bourbon, Duke of Vendôme. From Moulins, where the ceremony took place, Margaret repaired to the Court at Fontainebleau. Here all was changed: there was a new King, and Diana of Poitiers occupied the position of the Duchess of Etampes. After returning to Beam for Christmas, Margaret spent the Lent of 1549 in retreat at Tusson, where she apparently divided her time between prayer and literary labour. She was still writing the Heptameron, as is shown by the sixty-sixth tale, which chronicles an adventure that befell her daughter and Anthony de Bourbon on their marriage trip during the winter of 1548-49. It may be noted, too, that the scene of the sixty-ninth story is laid at the Castle of Odos near Tarbes, and as Margaret came to reside at the castle in the autumn of 1549, this tale was probably written during her sojourn there. Whilst adding fresh stories to the Heptameron, she was not neglecting poetry, for from this period also dates the Miroir de Jésus Christ crucifié, which Brother Olivier published in 1556, stating that it was the Queen’s last work, and that she had handed it to him a few days before her death.
Margaret had long been in failing health and was growing extremely weak. Brantôme, on the authority of his grandmother, states that when her approaching death was announced to her, she found the monition a very bitter one, saying that she was not yet so aged but that she might live some years longer. She was then in her fifty-eighth year. Sainte-Marthe relates that shortly before her death she saw in a dream a very beautiful woman holding in her hand a crown of all sorts of flowers which she showed to her, telling her that she would soon be crowned with it.(1)
1 Oraison funèbre, &c., p. 104.
She interpreted this dream as signifying that her end was near, and from that day forward abandoned the administration of her property to the King of Navarre, refusing to occupy herself with any other matter than that of her approaching end. After dictating her will she fell into her final illness, which lasted twenty days according to some authorities, and eight according to others. It seized her one night at Odos whilst she was watching a comet, which it was averred had appeared to notify the death of Pope Paul III. “It was perhaps to presage her own,” naively remarks Brantôme, who adds that while she was looking at the comet her mouth suddenly became partially paralysed, whereupon her doctor, M. d’Escuranis, led her away and made her go to bed. Her death took place on December 21st, 1549, and just before expiring she grasped a crucifix that lay beside her and murmured, “Jesus, Jesus, Jesus.” (1)
Although the King of Navarre had not always lived in perfect accord with his wife, he none the less keenly felt the loss he had sustained by her death. Olhagaray represents him when deprived of Margaret as no longer showing the same firm purpose of life, but as sad, discontented, and altering his plans at every trifle.(2) He gave orders that Margaret’s remains should be interred in the Cathedral of Lescar, some four and a half miles from the Château of Pau, with which it is said to have been at that time connected by a subterranean passage. Several of the Navarrese sovereigns had already been buried there, for the See was a kind of primacy, the Bishops being ex-officio presidents of the States of Beam.(3)
1 M. Lalanne, in his edition of Brantôme’s works, maintains
that Margaret did not die at Odos, near Tarbes, but at
Audaux, near Orthez, basing this contention on the fact that
Brantôme calls the castle “Audos in Beam,” and that Odos is
in Bigorre. Tradition, however, has always pointed to the
latter locality, though, on the other hand, it is stated
that less than half a century after Margaret’s death Odos
was nothing but a ruin, and had long been in that condition.
In 1596 Henry IV. gave the property to John de Lassalle, by
whose descendants the château was restored (Bascle de
Lagrèze’s Chateau de Pau, &c.).
2 Histoire de Foix et de Béarn, &c., p. 506.
3 Lescar having ceased to be a bishopric since 1790, its
church, which still exists, no longer ranks as a cathedral.
It was in this quaint old cathedral church, dating, so archaeologists assert, from the eleventh century, that Margaret’s remains were interred with all due pomp and ceremony. The Duchess of Estouteville headed the procession, followed by the Duke of Montpensier, the Duke of Nevers, the Duke of Aumale, the Duke of Etampes, the Marquis of Maine, and M. de Rohan. Then came the grands deuils or chief mourners, led by the Duke of Vendôme, and three lords carrying the crown, sceptre, and hand of justice. The Viscount of Lavedan officiated as grand master of the ceremonies, and special seats were assigned to the States of Navarre, Foix, Beam, and Bigorre, and to the chancellor, counsellors, and barons of the country; whilst on a platform surrounded by lighted tapers there was displayed an effigy of the Queen robed in black.(1) After the ceremony a banquet was served in accordance with Bearnese custom, the chief mourners being invited to the Duke of Vendôme’s table, whilst the others were served in different rooms.(2)
1 Lettres de Marguerite (Pièces justificatives. No. xi.).
2 Bascle de Lagrèze’s Château de Pau, &c.
A few years later—in June 1555—the remains of King Henry, Margaret’s husband, were in turn brought to Lescar for burial. The tombs of husband and wife, however, have alike vanished, having been swept away during the religious wars, when Lescar was repeatedly stormed and sacked, when Huguenot and Catholic, in turn triumphant, vented their religious frenzy upon the graves of their former sovereigns; and to-day the only tombs to be found in the old cathedral are those of personages interred there since the middle of the seventeenth century.
January 1893.
WITH SOME NOTICE OF PRECEDENT COLLECTIONS OF TALES IN FRANCE, OF THE AUTHOR, AND OF HER OTHER WORKS.
It is probable that every one who has had much to do with the study of literature has conceived certain preferences for books which he knows not to belong absolutely to the first order, but which he thinks to have been unjustly depreciated by the general judgment, and which appeal to his own tastes or sympathies with particular strength. One of such books in my own case is THE HEPTAMERON of Margaret of Navarre. I have read it again and again, sometimes at short intervals, sometimes at longer, during the lapse of some five-and-twenty years since I first met with it. But the place which it holds in my critical judgment and in my private affections has hardly altered at all since the first reading. I like it as a reader perhaps rather more than I esteem it as a critic; but even as a critic, and allowing fully for the personal equation, I think that it deserves a far higher place than is generally accorded to it.
Three mistakes, as it seems to me, pervade most of the estimates, critical or uncritical, of the Heptameron, the two first of old date, the third of recent origin. The first is that it is a comparatively feeble imitation of a great original, and that any one who knows Boccaccio need hardly trouble himself to know Margaret of Navarre. The second is that it is a loose if not obscene book, disgraceful for a lady to have written (or at least mothered), and not very creditable for any one to read. The third is that it is interesting as the gossip of a certain class of modern newspapers is interesting, because it tells scandal about distinguished personages, and has for its interlocutors other distinguished personages, who can be identified without much difficulty, and the identification of whom adds zest to the reading. All these three seem to me to be mistakes of fact and of judgment. In the first place, the Heptameron borrows from its original literally nothing but plan. Its stories are quite independent; the similarity of name is only a bookseller’s invention, though a rather happy one; and the personal setting, which is in Boccaccio a mere framework, has here considerable substance and interest. In the second place, the accusation of looseness is wildly exaggerated. There is one very coarse but not in the least immoral story in the Heptameron; there are several broad jests on the obnoxious cloister and its vices, there are many tales which are not intended virginibus puerisque, and there is a pervading flavour of that half-French, half-Italian courtship of married women which was at the time usual everywhere out of England. The manners are not our manners, and what may be called the moral tone is distinguished by a singular cast, of which more presently. But if not entirely a book for boys and girls, the Heptameron is certainly not one which Southey need have excepted from his admirable answer in the character of author of “The Doctor,” to the person who wondered whether he (Southey) could have daughters, and if so, whether they liked reading. “He has daughters: they love reading: and he is not the man I take him for if they are not ‘allowed to open’ any book in his library.” The last error, if not so entirely inconsistent with intelligent reading of the book as the first and second, is scarcely less strange to me. For, in the first place, the identification of the personages in the framework of the Heptameron depends upon the merest and, as it seems to me, the idlest conjecture; and, in the second, the interest of the actual tittle-tattle, whether it could be fathered on A or B or not, is the least part of the interest of the book. Indeed, the stories altogether are, as I think, far less interesting than the framework.
Let us see, therefore, if we cannot treat the Heptameron in a somewhat different fashion from that in which any previous critic, even Sainte-Beuve, has treated it. The divisions of such treatment are not very far to seek. In the first place, let us give some account of the works of the same class which preceded and perhaps patterned it. In the second, let us give an account of the supposed author, of her other works, and of the probable character of her connection with this one. In the third, without attempting dry argument, let us give some sketch of the vital part, which we have called the framework, and some general characteristics of the stories. And, in the fourth and last, let us endeavour to disengage that peculiar tone, flavour, note, or whatever word may be preferred, which, as it seems to me at least, at once distinguishes the Heptameron from other books of the kind, and renders it peculiarly attractive to those whose temperament and taste predisposes them to be attracted. For there is a great deal of pre-established harmony in literature and literary tastes; and I have a kind of idea that every man has his library marked out for him when he comes into the world, and has then only got to get the books and read them.
Margaret herself refers openly enough to the example of the Decameron, which had been translated by her own secretary, Anthony le Maçon, a member of her literary coterie, and not improbably connected with the writing or redacting of the Heptameron itself. Nor were later Italian tale-tellers likely to be without influence at a time when French was being “Italianated” in every possible way, to the great disgust of some Frenchmen. But the Italian ancestors or patterns need not be dealt with here, and can be discovered with ease and pleasure by any one who wishes in the drier pages of Dunlop, or in the more flowery and starry pages of Mr. Symonds’ “History of the Renaissance in Italy.” The next few pages will deal only with the French tale-tellers, whose productions before Margaret’s days were, if not very numerous, far from uninteresting, and whose influence on the slight difference of genre which distinguishes the tales before us from Italian tales was by no means slight.
In France, as everywhere else, prose fiction, like prose of all kinds, was considerably later in production than verse, and short tales of the kind before us were especially postponed by the number, excellence, and popularity of the verse fabliaux. Of these, large numbers have come down to us, and they exactly correspond in verse to the tales of the Decameron and the Heptameron in prose, except that the satirical motive is even more strongly marked, and that touches of romantic sentiment are rarer. This element of romance, however, appears abundantly in the long prose versions of the Arthurian and other legends, and we have a certain number of short prose stories of the thirteenth and fourteenth centuries, of which the most famous is that of Aucassin et Nicolette. These latter, however, are rather short romances than distinct prose tales of our kind. Of that kind the first famous book in French, and the only famous book, besides the one before us, is the Cent Nouvelles Nouvelles. The authorship of this book is very uncertain. It purports to be a collection of stories told by different persons of the society of Louis XI., when he was but Dauphin, and was in exile in Flanders under the protection of the Duke of Burgundy. But it has of late years been very generally assigned (though on rather slender grounds of probability, and none of positive evidence), to Anthony de la Salle, the best French prose writer of the fifteenth century, except Comines, and one on whom, with an odd unanimity, conjectural criticism has bestowed, besides his acknowledged romance of late chivalrous society, Petit Jehan de Saintré (a work which itself has some affinities with the class of story before us), not only the Cent Nouvelles Nouvelles, but the famous satirical treatise of the Quinze Joyes du Mariage, and the still more famous farce of Pathelin. Some of the Nouvelles, moreover, have been putatively fathered on Louis XI. himself, in which case the royal house of France would boast of two distinguished taletellers instead of one. However this may be, they all display the somewhat hard and grim but keen and practical humour which seems to have distinguished that prince, which was a characteristic of French thought and temper at the time, and which perhaps arose with the misfortunes and hardships of the Hundred Years’ War. The stories are decidedly amusing, with a considerably greater, though also a much ruder, vis comica than that of the Heptameron; and they are told in a style unadorned indeed, and somewhat dry, lacking the simplicity of the older French, and not yet attaining to the graces of the newer, but forcible, distinct, and sculpturesque, if not picturesque. A great license of subject and language, and an enjoyment of practical jokes of the roughest, not to say the most cruel character, prevail throughout, and there is hardly a touch of anything like romance; the tales alternating between jests as broad as those of the Reeve’s and Miller’s tales in Chaucer (themselves exactly corresponding to verse fabliaux, of which the Cent Nouvelles are exact prose counterparts, and perhaps prose versions), and examples of what has been called “the humour of the stick,” which sometimes trenches hard upon the humour of the gallows and the torture-chamber. These characteristics have made the Cent Nouvelles Nouvelles no great favourites of late, but their unpopularity is somewhat undeserved. For all their coarseness, there is much genuine comedy in them, and if the prettiness of romantic and literary dressing-up is absent from them, so likewise is the insincerity thereof. They make one of the most considerable prose books of what may be called middle French literature, and they had much influence on the books that followed, especially on this of Margaret’s. Indeed, one of the few examples to be found between the two, the Grand Paragon de Nouvelles Nouvelles of Nicolas de Troyes (1535), obviously takes them for model. But Nicolas was a dull dog, and neither profited by his model nor gave any one else opportunity to profit by himself.
Rabelais, the first book of whose Pantagruel anticipated the Paragon by three years, while the Gargantua coincided with it, was a great authority at the Court of Margaret’s brother Francis, dedicated one of the books (the third) of Pantagruel to her, before her death, in high-flown language, as esprit abstrait, ravy et ecstatic, and must certainly have been familiar reading of hers, and of all the ladies and gentlemen, literary and fashionable, of her Court. But there is little resemblance to be found in his style and hers. The short stories which Master Francis scatters about his longer work are, indeed, models of narration, but his whole tone of thought and manner of treatment are altogether alien from those of the “ravished spirit” whom he praises. His deliberate coarseness is not more different from her deliberate delicacy than his intensely practical spirit from her high-flown romanticism (which makes one think of, and may have suggested, the Court of La Quinte), and her mixture of devout and amatory quodlibetation from his cynical criticism and all-dissolving irony. But there was a contemporary of Rabelais who forms a kind of link between him and Margaret, whose work in part is very like the Heptameron, and who has been thought to have had more than a hand in it. This was Bonaventure Despériers, a man whose history is as obscure as his works are interesting. Born in or about the year 1500, he committed suicide in 1544, either during a fit of insanity, or, as has been thought more likely, in order to escape the danger of the persecution which, in the last years of the reign of Francis, threatened the unorthodox, and which Margaret, who had more than once warded it off from them, was then powerless to avert. Despériers, to speak truth, was in far more danger of the stake than most of his friends. The infidelity of Rabelais is a matter of inference only, and some critics (among whom the present writer ranks himself) see in his daring ridicule of existing abuses nothing inconsistent with a perfectly sound, if liberally conditioned, orthodoxy. Despériers, like Rabelais, was a Lucianist, but his modernising of Lucian (the remarkable book called Cymbalum Mundï), though pretending to deal with ancient mythology, has an almost unmistakable reference to revealed religion. It is not, however, by this work or by this side of his character at all that Despériers is brought into connection with the work of Margaret, who, if learned and liberal, and sometimes tending to the new ideas in religion, was always devout and always orthodox in fundamentals. Besides the Cymbalum Mundi, he has left a curious book, not published, like the Heptameron itself, till long after his own death, and entitled Nouvelles Récréations et Joyeux Devis. The tales of which it consists are for the most part very short, some being rather sketches or outlines of tales than actually worked-out stories, so that, although there are no less than a hundred and twenty-nine of them, the whole book is probably not half the bulk of the Heptameron itself. But they are extremely well written, and the specially interesting thing about them is, that in them there appears, and appears for the first time (unless we take the Heptameron itself as earlier, which is contrary to all probability), the singular and, at any rate to some persons, very attractive mixture of sentiment and satire, of learning and a love of refined society, of joint devotion to heavenly and earthly love, of voluptuous enjoyment of the present, blended and shadowed with a sense of the night that cometh, which delights us in the prose of the Heptameron, and in the verse not only of all the Pléiade poets in France, but of Spenser, Donne, and some of their followers in England. The scale of the stories, which are sometimes mere anecdotes, is so small, the room for miscellaneous discourse in them is so scanty, and the absence of any connecting Alinks, such as those of Margaret’s own plan, checks the expression of personal feeling so much, that it is only occasionally that this cast of thought can be perceived. But it is there, and its presence is an important element in determining the question of the exact authorship of the Heptameron itself.
It can hardly be said that, except translations from the Italian (of which the close intercourse between France and Italy in the days of the later Valois produced many), Margaret had many other examples before her. For such a book as the Propos Rustiques of Noël du Fail, though published before her death, is not likely to have exercised any influence over her; and most other books of the kind are later than her own. One such (for, despite its bizarre title and its distinct intention of attacking the Roman Church, Henry Estienne’s Apologie pour Hérodote is really a collection of stories) deserves mention, not because of its influence upon the Queen of Navarre, but because of the Queen of Navarre’s influence upon it. Estienne is constantly quoting the Heptameron, and though to a certain extent the inveteracy with which the friars are attacked here must have given the book a special attraction for him, two things may be gathered from his quotations and attributions. The first is that the book was a very popular one; the second, that there was no doubt among well-informed persons, of whom and in whose company Estienne most certainly was, that the Heptameron was in more than name the work of its supposed author.
From what went before it Margaret could, and could not, borrow certain well-defined things. Models both Italian and French gave her the scheme of including a large number of short and curtly, but not skimpingly, told stories in one general framework, and of subdividing them into groups dealing more or less with the same subject or class of subject. She had also in her predecessors the example of drawing largely on that perennial and somewhat facile source of laughter—the putting together of incidents and phrases which even by those who laugh at them are regarded as indecorous. But of this expedient she availed herself rather less than any of her forerunners. She had further the example of a generally satirical intent; but here, too, she was not content merely to follow, and her satire is, for the most part, limited to the corruptions and abuses of the monastic orders. It can hardly be said that any of the other stock subjects, lawyers, doctors, citizens, even husbands (for she is less satirical on marriage than encomiastic of love), are dealt with much by her. She found also in some, but chiefly in older books of the Chartier and still earlier traditions, and rather in Italian than in French, a certain strain of romance proper and of adventure; but of this also she availed herself but rarely. What she did not find in any example (unless, and then but partially, in the example of her own servant, Bonaventure Des-périers) was first the interweaving of a great deal not merely of formal religious exercise, but of positive religious devotion in her work; and secondly, the infusing into it of the peculiar Renaissance contrast, so often to be noticed, of love and death, passion and piety, voluptuous enjoyment and sombre anticipation.
But it is now time to say a little more about the personality and work of this lady, whose name all this time we have been using freely, and who was indeed a very notable person quite independently of her literary work. Nor was she in literature by any means an unnotable one, quite independently of the collection of unfinished stories, which, after receiving at its first posthumous publication the not particularly appropriate title of Les Amants Fortunés, was more fortunately re-named, albeit by something of a bull (for there is the beginning of an eighth day as well as the full complement of the seven), the Heptameron.
Few ladies have been known in history by more and more confusing titles than the author of the Heptameron, the confusion arising partly from the fact that she had a niece and a great-niece of the same charming Christian name as herself. The second Margaret de Valois (the most appropriate name of all three, as it was theirs by family right) was the daughter of Francis I., the patroness of Ronsard, and, somewhat late in life, the wife of the Duke of Savoy—a marriage which, as the bride carried with her a dowry of territory, was not popular, and brought some coarse jests on her. Not much is said of her personal appearance after her infancy; but she inherited her aunt’s literary tastes, if not her literary powers, and gave Ronsard powerful support in his early days. The third was the daughter of Henry II., the “Grosse Margot” of her brother, Henry III., the “Reine Margot” of Dumas’ novel, the idol of Brantôme, the first wife of Henry IV., the beloved of Guise, La Mole, and a long succession of gallants, the rival of her sister-in-law Mary Stuart, not in misfortunes, but as the most beautiful, gracious, learned, accomplished, and amiable of the ladies of her time. This Margaret would have been an almost perfect heroine of romance (for she had every good quality except chastity), if she had not unluckily lived rather too long.
Her great-aunt, our present subject, was not the equal of her great-niece in beauty, her portraits being rendered uncomely by a portentously long nose, longer even than Mrs. Siddons’s, and by a very curious expression of the eyes, going near to slyness. But the face is one which can be imagined as much more beautiful than it seems in the not very attractive portraiture of the time, and her actual attractions are attested by her contemporaries with something more than the homage-to-order which literary men have never failed to pay to ladies who are patronesses of letters. Besides Margaret of Valois, she is known as Margaret of Angoulême, from her place of birth and her father’s title; Margaret of Alençon, from the fief of her first husband; Margaret of Navarre, of which country, like her grand-niece, she was queen, by her second marriage with Henry d’Albret; and even Margaret of Orleans, as belonging to the Orleans branch of the royal house. She was not, like her nieces, Margaret of France, as her father never reigned, and Brantôme properly denies her the title, but others sometimes give it. When it is necessary to call her anything besides the simple “Margaret,” Angoulême is at once the most appropriate and the most distinctive designation. She was born on the 11th or 12th of April 1492, her father being Charles, Count of Angoulême, and her mother Louise of Savoy. She was their eldest child, and two years older than her brother, the future King Francis. According to, and even in excess of, the custom of the age, she received a very learned education, acquiring not merely the three tongues, French, Italian, and Spanish, which were all in common use at the French Court during her time, but Latin, and even a little Greek and a little Hebrew. She lived in the provinces both before and after her marriage, in 1509, to her relation, Charles, Duke of Alençon, who was older than herself by three years, and though a fair soldier and an inoffensive person, was apparently of little talents and not particularly amiable. The accession of her brother to the throne opened a much more brilliant career to her. She and her mother jointly exercised great influence over Francis; and the Duchess of Alençon, to whom her brother shortly afterwards gave Berry, was for many years one of the most influential persons in the kingdom, using her influence almost invariably for good. Her husband died soon after Pavia, and in the same year (September 1525) she undertook a journey to Spain on behalf of her captive brother. This journey, with some expressions in her letters and in Brantôme, has been wrested by some critics in order to prove that her affection for Francis was warmer than it ought to have been—an imputation wanton in both senses of the word.
She was sought in marriage by or offered in marriage to divers distinguished persons during her widowhood, and this was also the time of her principal diplomatic exercise, an office for which—odd as it now seems for a woman—she had, like her mother, like her niece Catherine of Medicis, like her namesake Margaret of Parma, and like other ladies of the age, a very considerable aptitude and reputation. When she at last married, the match was not a brilliant one, though it proved, contrary to immediate probability, to be the source of the last and the most glorious branch of the royal dynasty of France. The bridegroom bore indeed the title of King of Navarre and possessed Beam, but his kingdom had long been in Spanish hands, and but for his wife’s dowry of Alençon and appanage of Berry (to which Francis had added Armagnac and a large pension) he would have been but a lackland. Furthermore, he was eleven years younger than herself, and it is at least insinuated that the affection, if there was any, was chiefly on her side. At any rate, this earlier Henry of Navarre seems to have had not a few of the characteristics of his grandson, together with a violence and brutality which, to do the Vert Galant justice, formed no part of his character. The only son of the marriage died young, and a girl, Jane d’Albret, mother of the great Bourbon race of the next two centuries, was taken away from her parents by “reasons of state” for a time. The domestic life of Margaret, however, concerns us but little, except in one way. Her husband disliked administration, and she was the principal ruler in their rather extensive estates or dominions. Moreover, she was able at her quasi-Court to extend the literary coteries which she had already begun to form at Paris. The patronage to men of letters for which her brother is famous was certainly more due to her than to himself; and to her also was due the partial toleration of religious liberty which for a time distinguished his reign. It was not till her influence was weakened that intolerance prevailed, and she was able even then for a time to save Marot and other distinguished persons from persecution. It is rather a moot-point how far she inclined to the Reformed doctrines, properly so called. Her letters, her serious and poetical work, and even the Heptameron itself, show a fervently pietistic spirit, and occasionally seem to testify to a distinct inclination towards Protestantism, which is also positively attested by Brantôme and others; but this Protestantism must have been, so far as it was consistent and definite at all, the Protestantism of Erasmus rather than of Luther, of Rabelais rather than of Calvin. She had a very strong objection to the coarseness, the vices, the idleness, the brutish ignorance of the cloister; she had aspirations after a more spiritual form of religion than the ordinary Catholicism of her day provided, and as a strong politician she may have had something of that Gallicanism which has always been well marked in some of the best Frenchmen, and which at one time nearly prevailed with her great-great-grandson, Louis XIV. But there is no doubt that, as her brother said to the fanatical Montmorency, she would always have been and always was of his religion, the religion of the State. The side of the Reformation which must have most appealed to her was neither its austere morals, nor its bare ritual, nor its doctrines, properly so called, but its spiritual pietism and its connection with profane learning and letters; for of literature Margaret was an ardent devotee and a constant practitioner.
Her best days were done by the time of her second marriage. After the King’s return from Spain persecution broke out, and Margaret’s influence became more and more weak to stop it. As early as 1533 her own Miroir de l’Ame Pécheresse, then in a second edition, provoked the fanaticism of the Sorbonne, and the King had to interfere in person to protect his sister’s work and herself from gross insult. The Medici marriage increased the persecuting tendency, and for a time there was even an attempt to suppress printing, and with it all that new literature which was the Queen’s delight. She was herself in some danger, but Francis had not sunk so low as to permit any actual attack to be made on her. Yet all the last years of her life were unhappy, though she continued to keep Court at Nérac in Pau, to accompany her brother in his progresses, and, as we know from documents, to play Lady Bountiful over a wide area of France. Her husband appears to have been rather at variance with her; and her daughter, who married first, and in name only, the Duke of Cleves in 1540, and later (1548) Anthony de Bourbon, was also not on cordial terms with her mother. By the date of this second marriage Francis was dead, and though he had for many years been anything but wholly kind, Margaret’s good days were now in truth done. Her nephew Henry left her in possession of her revenues, but does not seem to have been very affectionately disposed towards her; and even had she been inclined to attempt any recovery of influence, his wife and his mistress, Catherine de Medici and Diana of Poitiers, two women as different from Margaret as they were from one another, would certainly have prevented her from obtaining it. As a matter of fact, however, she had long been in ill-health, and her brother’s death seems to have dealt her the final stroke. She survived it two years, even as she had been born two years before him, and died on the 21 st December 1549, at the Castle of Odos, near Tarbes, having lived in almost complete retirement for a considerable time. Her husband is said to have regretted her dead more than he loved her living, and her literary admirers, such of them as death and exile had spared, were not ungrateful. Tombeaux, or collections of funeral verses, were not lacking, the first being in Latin, and, oddly enough, nominally by three English sisters, Anne, Margaret, and Jane Seymour, nieces of Henry VIII.‘s queen and Edward VI.‘s mother, with learned persons like Dorât, Sainte-Marthe, and Baïf. This was re-issued in French and in a fuller form later.
Some reference has been made to an atrocious slur cast without a shred of evidence on her moral character. There is as little foundation for more general though milder charges of laxity. It is admitted that she had little love for her first husband, and it seems to be probable that her second had not much love for her. She was certainly addressed in gallant strains by men of letters, the most audacious being Clement Marot; but the almost universal reference of the well-known and delightful lines beginning—
“Un doux nenny avec un doux sourire,”
to her method of dealing not merely with this lover but with others, argues a general confidence in her being a virtuous coquette, if somewhat coquettishly virtuous. It may be added that the whole tone of the Heptameron points to a very similar conclusion.
Her literary work was very considerable, and it falls under three divisions: letters, the book before us, and the very curious and interesting collection of poems known by the charming if fantastic title of Les Marguerites de la Marguerite des Princesses, a play on the meanings, daisy, pearl, and Margaret, which had been popular in the artificial school of French poetry since the end of the thirteenth century in a vast number of forms.
The letters are naturally of the very first importance for determining the character of Margaret’s life as a woman of business, a diplomatist, and so forth. They show her to us in all these capacities, and also in that of an enlightened and always ready patroness of letters and of men of letters. Further, they are of value, though their value is somewhat affected by a reservation to be made immediately, as to her mental and moral characteristics. But they are not of literary interest at all equal to that of either of the other divisions. They are, if not spoilt, still not improved, by the fact that the art of easy letter-writing, in which Frenchwomen of the next century were to show themselves such proficients, had not yet been developed, and that most of them are couched in a heavy, laborious, semiofficial style, which smells, as far as mere style goes, of the cumbrous refinements of the rhétoriqueurs, in whose flourishing time Margaret herself grew up, and which conceals the writer’s sentiments under elaborate forms of ceremonial courtesy. Something at least of the groundless scandal before referred to is derived in all probability, if not in all certainty, from the lavish use of hyperbole in addressing her brother; and generally speaking, the rebuke of the Queen to Polonius, “More matter with less art,” is applicable to the whole correspondence.
Something of the same evil influence is shown in the Marguerites. It must be remembered that the writer died before the Pléiade movement had been fully started, and that she was older by five years than Marot, the only one of her own contemporaries and her own literary circle who attained to a poetic style easier, freer, and more genuine than the cumbrous rhetoric, partly derived from the allegorising style of the Roman de la Rose and its followers, partly influenced by corrupt following of the re-discovered and scarcely yet understood classics, partly alloyed with Flemish and German and Spanish stiffness, of which Chastellain, Crétin, and the rest have been the frequently quoted and the rarely read exponents to students of French literature. The contents of the Marguerites, to take the order of the beautiful edition of M. Félix Frank, are as follows: Volume I. contains first a long and singular religious poem entitled Le Miroir de l’Ame Pécheresse, in rhymed decasyllables, in which pretty literal paraphrases of a large number of passages of Scripture are strung together with a certain amount of pious comment and reflection. This is followed (after a shorter piece on the contest in the human soul between the laws of the spirit and of the flesh) by another poem of about the same length as the Miroir, and of no very different character, entitled Oraison de L’Ame Fidèle à son Seigneur Dieu, and a shorter Oraison à Notre Seigneur Jésus Christ completes the volume. The second volume yields four so-called “comedies,” but really mysteries on the old mediæval model, only distinguishable from their forerunners by slightly more modern language and a more scriptural tone. The subjects are the Nativity, the Adoration of the Three Kings, the Massacre of the Innocents, and the Flight into Egypt. The third volume contains a third poem in the style of the Miroir, but much superior, Le Triomphe de l’Agneau, a considerable body of spiritual songs, a miscellaneous poem or two, and some epistles, chiefly addressed to Francis. These last begin the smaller and secular division of the Marguerites, which is completed in the fourth volume by Les Quatre Dames et les Quatre Gentilhommes, composed of long monologues after the fashion of the Froissart-Chartier school, by a “comédie profane,” a farce entitled Trop, Prou [much], Peu, Moins; a long love poem, again in the Chartier style, entitled La Coche, and some minor pieces.
Opinion as to these poems has varied somewhat, but their merit has never been put very high, nor, to tell the truth, could it be put high by any one who speaks critically. In the first place, they are written for the most part on very bad models, both in general plan and in particular style and expression. The plan is, as has been said, taken from the long-winded allegorical erotic poetry of the very late thirteenth, the fourteenth, and the fifteenth centuries—poetry which is now among the most difficult to read in any literature. The groundwork or canvas being transferred from love to religion, it gains a little in freshness and directness of purpose, but hardly in general readableness. Thus, for instance, two whole pages of the Miroir, or some forty or fifty lines, are taken up with endless playings on the words mort and vie and their derivatives, such as mortifiez, and mort fiez, mort vivifiée and vie mourante. The sacred comedies or mysteries have the tediousness and lack of action of the older pieces of the same kind without their naïveté; and pretty much the same may be said of the profane comedy (which is a kind of morality), and of the farce. Of La Coche, what has been said of the long sacred poems may be said, except that here we go back to the actual subject of the models, not on the whole with advantage: while in the minor pieces the same word plays and frigid conceits are observable.
But if this somewhat severe judgment must be passed on the poems as wholes, and from a certain point of view, it may be considerably softened when they are considered more in detail. In not a few passages of the religious poems Margaret has reached (and as she had no examples before her except Marot’s psalms, which were themselves later than at least some of her work, may be said to have anticipated) that grave and solemn harmony of the French Huguenots of the sixteenth century, which in Du Bartas, in Agrippa d’Aubigné, and in passages of the tragedian Montchrestien, strikes notes hardly touched elsewhere in French literature. The Triomphe de l’Agneau displays her at her best in this respect, and not unfrequently comes not too far off from the apocalyptic resonance of d’Aubigné himself. Again, the Bergerie included in the Nativity comedy or mystery, though something of a Dresden Bergerie (to use a later image), is graceful and elegant enough in all conscience. But it is on the minor poems, especially the Epistles and the Chansons Spirituelles, that the defenders of Margaret’s claim to be a poet rest most strongly. In the former her love, not merely for her brother, but for her husband, appears unmistakably, and suggests graceful thoughts. In the latter the force and fire which occasionally break through the stiff wrappings of the longer poems appear with less difficulty and in fuller measure.
It is, however, undoubtedly curious, and not to be explained merely by the difference of subject, that the styles of the letters and of the poems, agreeing well enough between themselves, differ most remarkably from that of the Heptameron. The two former are decidedly open to the charges of pedantry, artificiality, heaviness. There is a great surplusage of words and a seeming inability to get to the point. The Heptameron if not equal in narrative vigour and lightness to Boccaccio before and La Fontaine afterwards, is not in the least exposed to the charge of clumsiness of any kind, employs a simple, natural, and sufficiently picturesque vocabulary, avoids all verbiage and roundabout writing, and both in the narratives and in the connecting conversation displays a very considerable advance upon nearly all the writers of the time, except Rabelais, Marot, and Despériers, in easy command of the vernacular. It is, therefore, not wonderful that there has, at different times (rather less of late years, but that is probably an accident), been a disposition if not to take away from Margaret all the credit of the book, at any rate to give a share of it to others. In so far as this share is attempted to be bestowed on ladies and gentlemen of her Court or family there is very little evidence for it; but in so far as the pen may be thought to have been sometimes held for her by the distinguished men of letters just referred to (there is no reason why Master Francis himself should not have sometimes guided it), and by others only less distinguished, there is considerable internal reason to favour the idea. At all times and in all places—in France perhaps more than anywhere else—kings and queens, lords and ladies, have found no difficulty (we need not use the harsh Voltairian-Carlylian phrase, and say in getting their literary work “buckwashed,” but) in getting it pointed and seasoned, trimmed and ornamented by professional men of letters. The form of the Heptameron lends itself more than any other to such assistance; and while I should imagine that the setting, with its strong colour, both of religiosity and amorousness, is almost wholly Margaret’s work, I should also think it so likely as to be nearly certain that in some at least of the tales the hands of the authors of the Cymbalum Mundi and the Adolescence Clémentine, of Le Maçon and Brodeau, may have worked at the devising, very likely re-shaped and adjusted by the Queen herself, of the actual stories as we have them now.
The book, as we have it, consists of seven complete days of ten novels each, and of an eighth containing two novels only. The fictitious scheme of the setting is somewhat less lugubrious than that of the Decameron, but still not without an element of tragedy. On the first of September, “when the hot springs of the Pyrenees begin to enter upon their virtue,” a company of persons of quality assembled at Cauterets, we are told, and abode there three weeks with much profit. But when they tried to return, rain set in with such severity that they thought the Deluge had come again, and they found their roads, especially that to the French side, almost entirely barred by the Gave de Béarn and other rivers. So they scattered in different directions, most of them taking the Spanish side, either along the mountains and across to Roussillon or straight to Barcelona, and thence home by sea. But a certain widow, named Oisille, made her way with much loss of men and horses to the Abbey of Notre Dame de Serrance. Here she was joined by divers gentlemen and ladies, who had had even worse experiences of travel than herself, with bears and brigands, and other evil things, so that one of them, Longarine, had lost her husband, murdered in an affray in one of the cut-throat inns always dear to romance. Besides this disconsolate person and Oisille, the company consisted of a married pair, Hircan and Parlamente; two young cavaliers, Dagoucin and Saffredent; two young ladies, Nomerfide and Ennasuite; Simontault, a cavalier-servant of Parlamente; and Geburon, a knight older and discreeter than the rest of the company except Oisille.(1)
1 These names have been accommodated to M. Le Roux de
Lincy’s orthography, from MS. No. 1512; but for myself I
prefer the spellings, especially “Emarsuitte,” more usual in
the printed editions.—G. S.
These form the party, and it is to be noted that idle and contradictory as all the attempts made to identify them have been (for instance, the most confident interpreters hesitate between Oisille and Parlamente, an aged widow and a youthful wife, for Margaret herself), it is not to be denied that the various parts are kept up with much decision and spirit. Of the men, indeed, Hircan is the only one who has a very decided character, and is represented as fond of his wife, Parlamente, but a decided libertine and of a somewhat rough and ruthless general character—points which have made the interpreters sure that he must be Henry d’Albret. The others, except that Geburon is, as had been said, older than his companions, and that Simontault sighs vainly after Parlamente, are merely walking gentlemen of the time, accomplished enough, but not individual. The women are much more distinct and show a woman’s hand. Oisille is, as our own seventeenth-century ancestors would have said, ancient and sober, very devout, regarded with great respect by the rest of the company, and accepted as a kind of mistress both of the revels and of more serious matters, but still a woman of the world, and content to make only an occasional and mild protest against tolerably free stories and sentiments. Parlamente, considerably younger, and though virtuous, not by any means ignorant of or wholly averse to the devotion of Simontault, indulging occasionally in a kind of mild conjugal sparring with her husband, Hircan, but apparently devoted to him, full of religion and romance and refinement at once, is a very charming character, resembling Madame de Sévigné as she may have been in her unknown or hardly known youth, when husband and lovers alike were attracted by the flame of her beauty and charm, only to complain that it froze and did not burn. Longarine is discreetly unhappy for her dead husband, but appears decidedly consolable; Ennasuite is a haughty damsel, disdainful of poor folk, and Nomerfide is a pure madcap, a Catherine Seyton of the generation before Catherine herself, the feminine Dioneo of the party, and, if a little too free-spoken for prudish modern taste, a very delightful girl.
Now when this good company had assembled at Serrance and told each other their misadventures, the waters on inquiry seemed to be out more widely and more dangerously than before, so that it was impossible to think of going farther for the time. They deliberated accordingly how they should employ themselves, and, after allowing, on the proposal of Oisille, an ample space for sacred exercises, they resolved that every day, after dinner and an interval, they should assemble in a meadow on the bank of the Gave at midday and tell stories. The device is carried out with such success that the monks steal behind the hedges to hear them, and an occasional postponement of vespers takes place. Simontault begins, and the system of tale-telling goes round on the usual plan of each speaker naming him or her who shall follow. It should be observed that no general subject is, as in the Decameron, prescribed to the speakers of each day, though, as a matter of course, one subject often suggests another of not dissimilar kind. Nor is there the Decameronic arrangement of the “king.” Between the stories, and also between the days, there is often a good deal of conversation, in which the divers characters, as given above, are carried out with a minuteness very different from the chief Italian original.
From what has been said already, it will be readily perceived that the novels, or rather their subjects, are not very easy to class in any rationalised order. The great majority, if they do not answer exactly to the old title of Les Histoires des Amants Fortunés, are devoted to the eternal subject of the tricks played by wives to the disadvantage of husbands, by husbands to the disadvantage of wives, and sometimes by lovers to the disadvantage of both. “Subtilité” is a frequent word in the titles, and it corresponds to a real thing. Another large division, trenching somewhat upon the first, is composed of stories to the discredit of the monks (something, though less, is said against the secular clergy), and especially of the Cordeliers or Franciscans, an Order who, for their coarse immorality and their brutal antipathy to learning, were the special black (or rather grey) beasts of the literary reformers of the time. In a considerable number there are references to actual personages of the time—references which stand on a very different footing of identification from the puerile guessings at the personality of the interlocutors so often referred to. Sometimes these references are avowed: “Un des muletiers de la Reine de Navarre,” “Le Roi François montre sa générosité,” “Un Président de Grenoble,” “Une femme d’Alençon,” and so forth. At other times the reference is somewhat more covert, but hardly to be doubted, as in the remarkable story of a “great Prince” (obviously Francis himself) who used on his journeyings to and from an assignation of a very illegitimate character, to turn into a church and piously pursue his devotions. There are a few curious stories in which amatory matters play only a subordinate part or none at all, though it must be confessed that this last is a rare thing. Some are mere anecdote plays on words (sometimes pretty free, and then generally told by Nomer-fide), or quasi-historical, such as that already noticed of the generosity of Francis to a traitor, or deal with remarkable trials and crimes, or merely miscellaneous matters, the best of the last class being the capital “Bonne invention pour chasser le lutin.”
In so large a number of stories with so great a variety of subjects, it naturally cannot but be the case that there is a considerable diversity of tone. But that peculiarity at which we have glanced more than once, the combination of voluptuous passion with passionate regret and a mystical devotion, is seldom absent for long together. The general note, indeed, of the Heptameron is given by more than one passage in Brantôme—at greatest length by one which Sainte-Beuve has rightly quoted, at the same time and also rightly rebuking the sceptical Abbé’s determination to see in it little more than a piece of précieuse mannerliness (though, indeed, the Précieuses were not yet). Yet even Sainte-Beuve has scarcely pointed out quite strongly enough how entirely this is the keynote of all Margaret’s work, and especially of the Heptameron. The story therefore may be worth telling again, though it may be found in the “Cinquième Discours” of the Vies des Dames Galantes.
Brantôme’s brother, not yet a captain in the army, but a student travelling in Italy, had in sojourning at Ferrara, when Renée of France was Duchess, fallen in love with a certain Mademoiselle de la Roche. For love of him she had returned to France, and, visiting his own country of Gascony, had attached herself to the Court of Margaret, where she had died. And it happened that Bourdeilles, six months afterwards, and having forgotten all about his dead love, came to Pau and went to pay his respects to the Queen. He met her coming back from vespers, and she greeted him graciously, and they talked of this matter and of that. But, as they walked together hither and thither, the Queen drew him, without cause shown, into the church she had just left, where Mademoiselle de la Roche was buried. “Cousin,” said she, “do you feel nothing stirring beneath you and under your feet?” But he said, “Nothing, Madame.” “Think, cousin,” then said she once again. But he said, “Madame, I have thought well, but I feel nought; for under me there is but a stone, hard and firmly set.” “Now, do I tell you,” said the Queen, leaving him no longer at study, “that you are above the tomb and the body of Mademoiselle de la Roche, who is buried beneath you, and whom you loved so much in her lifetime. And since our souls have sense after our death, it cannot be but that this faithful one, dead so lately, felt your presence as soon as you came near her; and if you have not perceived it, because of the thickness of the tomb, doubt not that none the less she felt it. And forasmuch as it is a pious work to make memory of the dead, and notably of those whom we loved, I pray you give her a pater and an ave, and likewise a de profundis, and pour out holy water. So shall you make acquist of the name of a right faithful lover and a good Christian.” And she left him that he might do this.
Brantôme (though he had an admiration for Margaret, whose lady of honour his grandmother had been, and who, according to the Bourdeilles tradition, composed her novels in travelling) thought this a pretty fashion of converse. “Voilà,” he says, “l’opinion de cette bonne princesse; laquelle la tenait plus par gentillesse et par forme de devis que par créance à mon avis.” Sainte-Beuve, on the contrary, and with better reason, sees in it faith, graciousness, feminine delicacy, and piety at once. No doubt; but there is something more than this, and that something more is what we are in search of, and what we shall find, now in one way, now in another, throughout the book: something whereof the sentiment of Donne’s famous thoughts on the old lover’s ghost, on the blanched bone with its circlet of golden tresses, is the best known instance in English. The madcap Nomerfide indeed lays it down, that “the meditation of death cools the heart not a little.” But her more experienced companions know better. The worse side of this Renaissance peculiarity is told in the last tale, a rather ghastly story of monkish corruption; its lighter side appears in the story, already referred to, of the “Grand Prince” and his pious devotions on the way to not particularly pious occupation. But touches of the more poetical and romantic effects of it are all over the book. It is to be found in the story of the gentleman who forsook the world because of his beloved’s cruelty, whereat she repenting did likewise (“he had much better have thrown away his cowl and married her,” quoth the practical Nomerfide); in that of the wife who, to obtain freedom of living with her paramour, actually allowed herself to be buried; in that (very characteristic of the time, especially for the touch of farce in it) of the unlucky person to whom phlebotomy and love together were fatal; and in not a few others, while it emerges in casual phrases of the intermediate conversations and of the stories themselves, even when it is not to be detected in the general character of the subjects.
And thus we can pretty well decide what is the most interesting and important part of the whole subject. The question, What is the special virtue of the Heptameron? I have myself little hesitation in answering. There is no book, in prose and of so early a date, which shows to me the characteristic of the time as it influenced the two great literary nations of Europe so distinctly as this book of Margaret of Angoulême. Take it as a book of Court gossip, and it is rather less interesting than most books of Court gossip, which is saying much. Take it as the performance of a single person, and you are confronted with the difficulty that it is quite unlike that other person’s more certain works, and that it is in all probability a joint affair. Take its separate stories, and, with rare exceptions, they are not of the first order of interest, or even of the second. But separate the individual purport of these stories from the general colour or tone of them; take this general colour or tone in connection with the tenor of the intermediate conversations, which form so striking a characteristic of the book, and something quite different appears. It is that same peculiarity which appears in places and persons and things so different as Spenser, as the poetry of the Pléiade, as Montaigne, as Raleigh, as Donne, as the group of singers known as the Caroline poets. It is a peculiarity which has shown itself in different forms at different times, but never in such vigour and precision as at this time. It combines a profound and certainly sincere—almost severe—religiosity with a very vigorous practice of some things which the religion it professes does not at all countenance. It has an almost morbidly pronounced simultaneous sense of the joys and the sorrows of human life, the enjoyment of the joys being perfectly frank, and the feeling of the sorrows not in the least sentimental. It unites a great general refinement of thought, manners, opinion, with an almost astonishing occasional coarseness of opinion, manners, thought. The prevailing note in it is a profound melancholy mixed with flashes and intervals of a no less profound delight. There is in it the sense of death, to a strange and, at first sight, almost unintelligible extent. Only when one remembers the long night of the religious wars which was just about to fall on France, just as after Spenser, Puritan as he was, after Carew and Herrick still more, a night of a similar character was about to fall on England, does the real reason of this singular idiosyncrasy appear. The company of the Heptameron are the latest representatives, at first hand, and with no deliberate purpose of presentment, of the mediaeval conception of gentlemen and ladies who fleeted the time goldenly. They are not themselves any longer mediaeval; they have been taught modern ways; they have a kind of uneasy sense (even though one and another of themselves may now and then flout the idea) of the importance of other classes, even of some duty on their own part towards other classes. Their piety is a very little deliberate, their voluptuous indulgence has a grain of conscience in it and behind it, which distinguishes it not less from the frank indulgence of a Greek or a Roman than from the still franker naïveté of purely mediaeval art, from the childlike, almost paradisiac, innocence of the Belli-cents and Nicolettes and of the daughter of the great Soldan Hugh in that wonderful serio-comic chanson of the Voyage à Constantinople. The mark of modernity is on them, and yet they are so little conscious of it, and so perfectly free from even the slightest touch of at least its anti-religious influence. Nobody, not even Hircan, the Grammont of the sixteenth century; not even Nomerfide, the Miss Notable of her day and society; not even the haughty lady Ennasuite, who wonders whether common folk can be supposed to have like passions with us, feels the abundant religious services and the periods of meditation unconscionable or tiresome.
And so we have here three notes constantly sounding together or in immediate sequence. There is the passion of that exquisite rondeau of Marot’s, which some will have, perhaps not impossibly, to refer to Margaret herself—
En la baisant m’a dit: “Amy sans blasme,
Ce seul baiser, qui deux bouches embasme,
Les arrhes sont du bien tant espéré,”
Ce mot elle a doulcement proféré,
Pensant du tout apaiser ma grand flamme.
Mais le mien cour adonc plus elle enflamme,
Car son alaine odorant plus que basme
Souffloit le feu qu’Amour m’a préparé,
En la baisant.
Bref, mon esprit, sans congnoissance d’âme,
Vivoit alors sur la bouche à ma dame,
Dont se mouroit le corps énamouré;
Et si la lèvre eust guères demouré
Contre la mienne, elle m’eust succé l’âme,
En la baisant.
There is the devout meditation of Oisille, and that familiarity with the Scriptures which, as Hircan himself says, “I trow we all read and know.” And then there is the note given by two other curious stories of Brantôme. One tells how the Queen of Navarre watched earnestly for hours by the bedside of a dying maid of honour, that she might see whether the parting of the soul was a visible fact or not. The second tells how when some talked before her of the joys of heaven, she sighed and said, “Well, I know that this is true; but we dwell so long dead underground before we arise thither.” There, in a few words, is the secret of THE HEPTAMERON: the fear of God, the sense of death, the voluptuous longing and voluptuous regret for the good things of life and love that pass away.
George Saintsbury.(1)
London, October 1892.
1 As I have spoken so strongly of the attempts to identify
the personages of the Heptameron, it might seem
discourteous not to mention that one of the most
enthusiastic and erudite English students of Margaret,
Madame Darmesteter (Miss Mary Robinson), appears to be
convinced of the possibility and advisableness of
discovering these originals. Everything that this lady
writes is most agreeable to read; but I fear I cannot say
that her arguments have converted me.—G. S.
To the most Illustrious, most Humble, and most Excellent Princess,
Madame Margaret de Bourbon,
Duchess of Nevers, Marchioness of Illes, Countess of Eu, of Dreux, Rételois, Columbiers, and Beaufort, Lady of Aspremont, of Cham-Regnault, of Arches, Rencaurt, Monrond, and La Chapelle-d’Angylon, Peter Boaistuau surnamed Launay, offers most humble salutation and perpetual obedience.(1)
1 This dedicatory preface appeared in the first edition of
Queen Margaret’s Tales, published by Boaistuau in 1558 under
the title of Histoires des Amans Fortunez. The Princess
addressed was the daughter of Charles, Duke of Vendôme; she
was wedded in 1538 to Francis of Cleves, Duke of Nevers, and
by this marriage became niece to the Queen of Navarre.—Ed.
Madam, That great oracle of God, St. John Chrysostom, deplores with infinite compassion in some part of his works the disaster and calamity of his century, in which not only was the memory of an infinity of illustrious persons cut off from among mankind, but, what is more, their writings, by which the rich conceptions of their souls and the divine ornaments of their minds were to have been consecrated to posterity, did not survive them. And certainly with most manifest reason did this good and holy man address such a complaint to the whole Christian Republic, touched as he was with just grief for an infinity of thousands of books, of which some have been lost and buried in eternal forgetfulness by the negligence of men, others dispersed and destroyed by the cruel incursions of war, others rotted and spoiled as much by the rigour of time as by carelessness to collect and preserve them; whereof the ancient Histories and Annals furnish a sufficient example in the memorable library of that great King of Egypt, Ptolemy Phila-delphus, which had been formed with the sweat and blood of so many notable philosophers, and maintained, ordered, and preserved by the liberality of that great monarch. And yet in less than a day, by the monstrous and abominable cruelty of the soldiers of Cæsar, when the latter followed Pompey to Alexandria, it was burned and reduced to ashes. Zonarius, the ecclesiastical historian, writes that the same happened at Constantinople in the time of Zeno, when a superb and magnificent palace, adorned with all sorts of manuscript books, was burnt, to the eternal regret and insupportable detriment of all those who made a profession of letters. And without amusing ourselves too curiously in recounting the destruction among the ancients, we have in our time experienced a similar loss—of which the memory is so recent that the wounds thereof still bleed in all parts of Europe—namely, when the Turks besieged Buda, the capital of Hungary, where the most celebrated library of the good King Matthias was pillaged, dispersed, and destroyed; a library which, without sparing any expense, he had enriched with all the rarest and most excellent books, Greek, Latin, Hebrew, and Arabic, that he had been able to collect in all the most famous provinces of the earth.
Again, he who would particularise and closely examine things will find that Theophrastes, as he himself declares, wrote and composed three hundred volumes, Chrysippus sixty, Empedocles fifty, Servus Sulpicius two hundred on civil law, Gallienus one hundred and thirty on the art of medicine, and Origenes six thousand, all of which St. Jerome attests having read; and yet, of so many admirable and excellent authors, there now remain to us only some little fragments, so debased and vitiated in several places, that they seem abortive, and as if they had been torn from their author’s hands by force.
On account of which, my Lady, since the occasion has offered, I have been minded to present all these examples, with the object of exhorting all those who treasure books and keep them sequestered in their sanctuaries and cabinets, to henceforth publish them and bring them to light, not only so that they may not keep back and bury the glory of their ancestors, but also that they may not deprive their descendants of the profit and pleasure which they might derive from the labour of others.
In regard to myself, I will set forth more amply in the notice which I will give to the reader the motive that induced me to put my hand to the work of the present author, who has no need of trumpet and herald to exalt and magnify her(1) greatness, inasmuch as there is no human eloquence that could portray her more forcibly than she has portrayed herself by the celestial strokes of her own brush; I mean by her other writings, in which she has so well expressed the sincerity of her doctrines, the vivacity of her faith, and the uprightness of her morals, that the most learned men who reigned in her time were not ashamed to call her a prodigy and miracle of nature. And albeit that Heaven, jealous of our welfare, has snatched her from this mortal habitation, yet her virtues rendered her so admirable and so engraved her in the memory of every one, that the injury and lapse of time cannot efface her from it; for we shall ceaselessly mourn and lament for her, like Antimachus the Greek poet wept for Lysidichea, his wife, with sad verses and delicate elegies which describe and reveal, her virtues and merits.
1 In the French text Boaistuau invariably refers to the
author as a personage of the masculine sex, with the evident
object of concealing the real authorship of the work.
Feminine pronouns have, however, been substituted in the
translation, as it is Queen Margaret who is referred to.
—Ed.
Therefore, my Lady, as this work is about to be exposed to the doubtful judgment of so many thousands of men, may it please you to take it under your protection and into your safe keeping; for, whereas you are the natural and legitimate heiress of all the excellencies, ornaments, and virtues which enriched the author while she adorned by her presence the surprise of the earth, and which now by some marvellous ray of divinity live and display themselves in you, it is not possible that you should be defrauded of the fruit of the labour which justly belongs to you, and for which the whole universe will be indebted to you now that it comes forth into the light under the resplendent shelter of your divine and heroic virtues.
May it therefore please you, my Lady, to graciously accept of this little offering, as an eternal proof of my obedience and most humble devotion to your greatness, pending a more important sacrifice which I prepare for the future.
1 This notice follows the dedicatory preface in the edition
of 1558.
Gentle Reader, I can tell thee verily and with good right assert (even prove by witnesses worthy of belief) when this work was presented to me that I might fulfil the office of a sponge and cleanse it of a multitude of manifest errors that were found in a copy written by hand, I was only requested to take out or copy eighteen or twenty of the more notable tales, reserving myself to complete the rest at a more convenient season and at greater leisure.
However, as men are fond of novelties, I was solicited with very pressing requests to pursue my point, to which I consented, rather by reason of the importunity than of my own will, and my enterprise was conducted in such fashion, that so as not to show myself in any wise disobedient, I added some more tales, to which again others have since been adjoined.
In regard to myself, I can assure thee that it would have been less difficult for me to build the whole edifice anew than to mutilate it in several places, change, innovate, add and suppress in others, but I was almost perforce compelled to give it a new form, which I have done, partly for the requirements and the adornment of the stories, partly to conform to the times and the infelicity of our century, when most human things are so exulcerated that there is no work, however well digested, polished, and filed, but it is badly interpreted and slandered by the malice of fastidious persons. Take, therefore, in good part our hasty labour, and be not too close a censor of another’s work until thou hast examined thine own.
Queen of Navarre,
Claud Gruget, her very humble servant, presents salutation and wishes of felicity. (1)
I would not have interfered, Madam, to present you with this book of the Tales of the late Queen, your mother, if the first edition had not omitted or concealed her name, and almost entirely changed its form, to such a point that many did not recognise it; on which account, to render it worthy of its author, I, as soon as it was divulged, gathered together from all sides the copies I could collect of it written by hand, verifying them by my copy, and acting in such wise that I arranged the book in the real order in which she had drawn it up. Then, with the permission of the King and your consent, it was sent to the press to be published such as it should be.
Concerning it, I am reminded of what Count Balthazar says of Boccaccio in the Preface to his Courtier(2) that what he had done by way of pastime, namely, his Decameron, had brought him more honour than all his other works in Latin or Tuscan, which he esteemed the most serious.
1 This preface was inserted in the edition issued in 1559
by Claud Gruget, who gave the title of “Heptameron” to
Queen Margaret’s tales.
2 The Libro del Cortegiano, by Count Baldassare
Castiglione, was the nobleman’s vade-mecum of the period.
First published at Venice in 1528, it was translated into
French in 1537 by J. Colin, secretary to Francis I.—Ed.
Thus, the Queen, that true ornament of our century, from whom you do not derogate in the love and knowledge of good letters, while amusing herself with the acts of human life, has left such beauteous instructions that there is no one who does not find matter of erudition in them; and, indeed, according to all good judgment, she has surpassed Boccaccio in the beautiful Discourses which she composes upon each of her tales. For which she deserves praise, not only over the most excellent ladies, but also among the most learned men; for of the three styles of oration described by Cicero, she has chosen the simple one, similar to that of Terence in Latin, which to every one seems very easy to imitate, though it is anything but that to him who tries it.
It is true that such a present will not be new to you, and that you will only recognise in it the maternal inheritance. However, I feel assured that you will receive it favourably, at seeing it, in this second impression, restored to its original state, for according to what I have heard the first displeased you. Not that he who put his hand to it was not a learned man, or did not take trouble; indeed it is easy to believe that he was not minded to disguise it thus, without some reason; nevertheless his work has proved unpleasing.
I present it to you then, Madam, not that I pretend to any share in it, but only as having unmasked it to restore it to you in its natural state. It is for Your Royal Greatness to favour it since it proceeds from your illustrious House, whereof it bears the mark upon the front, which will serve it as a safe-conduct throughout the world and render it welcome among good company.
As for myself, recognising the honour that you will do me in receiving from my hand the work thus restored to its right state, I shall ever feel obliged to render you most humble duty.

On the first day of September, when the baths in the Pyrenees Mountains begin to be possessed of their virtue, there were at those of Cauterets(1) many persons as well of France as of Spain, some to drink the water, others to bathe in it, and again others to make trial of the mud; all these being remedies so marvellous that persons despaired of by the doctors return thence wholly cured. My purpose is not to speak to you of the situation or virtue of the said baths, but only to set forth as much as relates to the matter of which I desire to write.
1 There are no fewer than twenty-six sources at Cauterets,
the waters being either of a sulphureous or a saline
character. The mud baths alluded to by Margaret were
formerly taken at the Source de César Vieux, half-way up
Mount Peyraute, and so called owing to a tradition that
Julius Cæsar bathed there. It is at least certain that these
baths were known to the Romans.—Ed.
Cauterets is frequently mentioned by the old authors, and
Rabelais refers to it in this passage: “Pantagruel’s urine
was so hot that ever since that time it has not cooled, and
you have some of it in France, at divers places, at
Coderetz, Limous, Dast, Ballerue, Bourbonne, and
elsewhere”(Book ii. chap, xxxiii.).—M.
All the sick persons continued at the baths for more than three weeks, until by the amendment in their condition they perceived that they might return home again. But while they were preparing to do so, there fell such extraordinary rains that it seemed as though God had forgotten the promise He made to Noah never to destroy the world with water again; for every cottage and every lodging in Cauterets was so flooded with water that it was no longer possible to continue there. Those who had come from the side of Spain returned thither across the mountains as best they could, and such of them as knew whither the roads led fared best in making their escape.
The French lords and ladies thought to return to Tarbes as easily as they had come, but they found the streamlets so deep as to be scarcely fordable. When they came to pass over the Bearnese Gave,(1) which at the time of their former passage had been less than two feet in depth, they found it so broad and swift that they turned aside to seek for the bridges. But these being only of wood, had been swept away by the turbulence of the water.
1 The Basques give the name of Gave to those watercourses
which become torrents in certain seasons. The Bearnese Gave,
so named because it passes through the territory of the
ancient city of Beam, takes its source in the Pyrenees, and
flows past Pau to Sorde, where it joins the Adour, which
falls into the sea at Bayonne. It is nowadays generally
known as the Gave of Pau.—L. & M.
Then certain of the company thought to stem the force of the current by crossing in a body, but they were quickly carried away, and the others who had been about to follow lost all inclination to do so. Accordingly they separated, as much because they were not all of one mind as to find some other way. Some crossed over the mountains, and passing through Aragon came to the county of Rousillon, and thence to Narbonne; whilst others made straight for Barcelona, going thence by sea, some to Marseilles and others to Aigues-Mortes.
But a widow lady of long experience, named Oisille, resolved to lay aside all fear of bad roads and to betake herself to Our Lady of Serrance.(3)
3 The Abbey of Our Lady of Serrance, or more correctly
Sarrances, in the valley of Aspe, was occupied by monks of
the Prémontré Order, who were under the patronage of St.
Mary. An apparition of the Virgin having been reported in
the vicinity, pilgrimages were made to Sarrances on the
feasts of her nativity (Sept. 8) and her assumption (Aug.
15). In 1385 Gaston de Foix, who greatly enriched the abbey,
built a residence in the neighbourhood, his example being
followed by the Gramonts, the Miollens, and other nobles.
The pilgrimages had become very celebrated in the fifteenth
century, when Louis XI. repaired to Sarrances, accompanied
by Coictier, his physician. In 1569, however, the
Huguenots pillaged and burned down the abbey, together with
the royal and other residences. The monks who escaped the
flames were put to the sword.—M. & Ed.
She was not, indeed, so superstitious as to think that the glorious Virgin would leave her seat at her Son’s right hand to come and dwell in a desolate country, but she was desirous to see the hallowed spot of which she had so often heard, and further she was sure that if there were a means of escaping from a danger, the monks would certainly find it out. At last she arrived, after passing through places so strange, and so difficult in the going up and coming down, that, in spite of her years and weight, she had perforce gone most of the way on foot But the most piteous thing was, that the greater part of her servants and horses were left dead on the way, and she had but one man and one woman with her on arriving at Serrance, where she was charitably received by the monks.
There were also among the French two gentlemen who had gone to the baths rather that they might be in the company of the ladies whose lovers they were, than because of any failure in their health. These gentlemen, seeing that the company was departing and that the husbands of their ladies were taking them away, resolved to follow them at a distance without making their design known to any one. But one evening, while the two married gentlemen and their wives were in the house of one who was more of a robber than a peasant, the two lovers, who were lodged in a farmhouse hard by, heard about midnight a great uproar. They got up, together with their serving-men, and inquired what this tumult meant. The poor man, in great fear, told them that it was caused by certain evil-doers who were come to share the spoil which was in the house of their fellow-bandit. Thereupon the gentlemen immediately took their arms, and with their serving-men set forth to succour the ladies, esteeming it a happier thing to die for them than to outlive them.
When they reached the house, they found the first door broken through, and the two gentlemen with their servants defending themselves valiantly. But inasmuch as they were outnumbered by the robbers, and were also sorely wounded, they were beginning to fall back, having already lost many of their servants. The two gentlemen, looking in at the windows, perceived the ladies shrieking and sobbing so bitterly that their hearts swelled with pity and love at the sight; and, like two enraged bears coming down from the mountains, they fell upon the bandits with such fury that many of them were slain, while the remainder, unwilling to await their onset, fled to a hiding-place which was known to them.
When the gentlemen had worsted these rogues and had slain the host himself among the rest, they heard that the man’s wife was even worse than her husband; and they therefore sent her after him with a sword-thrust. Then they entered a lower room, where they found one of the married gentlemen on the point of death. The other had received no hurt, save that his clothes were all pierced with thrusts and that his sword was broken in two. The poor gentleman, perceiving what help the two had afforded him, embraced and thanked them, and besought them not to abandon him, which was to them a very agreeable request. When they had buried the dead gentleman, and had comforted his wife as well as they were able, they took the road which God set before them, not knowing whither they were going.
If it pleases you to know the names of the three gentlemen, the married one was called Hircan, and his wife Parlamente, the name of the widow being Longarine; of the two lovers one was called Dagoucin and the other Saffredent. After having been the whole day on horseback, towards evening they descried a belfry, whither with toil and trouble they made the best of their way, and on their arrival were kindly received by the Abbot and the monks. The abbey is called St. Savyn.(4)
4 The Abbey of St. Savin of Tarbes, situated between Argelèz
and Pierrefitte, in what was formerly called the county of
Lavedan, is stated to have been founded by Charlemagne; and
here the Paladin Roland is said to have slain the giants
Alabaster and Passamont to recompense the monks for their
hospitality. The abbey took its name from a child (the son
of a Count of Barcelona) who led a hermit’s life, and is
accredited with having performed several miracles in the
neighbourhood. About the year 1100 the Pope, siding with the
people of the valley of Aspe in a quarrel between them and
the Abbot of St. Savin, issued a bull forbidding the women
of Lavedan to conceive for a period of seven years. The
animals, moreover, were not to bring forth young, and the
trees were not to bear fruit for a like period. The edict
remained in force for six years, when the Abbot of St. Savin
compromised matters by engaging to pay an annual tribute to
Aspe. This tribute was actually paid until the Revolution of
1789. On the other hand, the abbey was entitled to the right
shoulder of every stag, boar, and izard (the Pyrenean
chamois) killed in the valley, with other tributes of trout,
cheese, and flowers, which last the Abbot acknowledged by
kissing the prettiest maiden of Argelèz. Amongst various
privileges possessed by the monks was that of having their
beds made by the girls of the neighbourhood on certain high
days and holidays.
In the tenth century Raymond of Bigorre presented the abbey
with the valley of Cauterets on condition that a church
should be built there and “sufficient houses kept in repair
to facilitate the using of the baths.” In 1290 Edward III.
of England confirmed the monks of St. Savin in possession of
Cauterets. In 1316, when the inhabitants of the latter place
wished to change the situation of their village, the Abbot
of St. Savin consented, but a woman opposed her veto (all
women had the right of vote) and this sufficed to frustrate
the scheme. The abbey derived a considerable income from
Cauterets, the baths and the houses built there for the
accommodation of visitors being let out on lease. The leases
of 1617 and 1697 are preserved in the archives of Pau. In
the time of Queen Margaret the abbey was extremely wealthy;
the Abbot to whom she refers, according to M. Le Roux de
Lincy, was probably Raymond de Fontaine, who ruled St. Savin
from 1534 to 1540, under the authority of the commendatory
abbots, Anthony de Rochefort and Nicholas Dangu, Bishop of
Séez. Some of the commentators of the Heptameron believe
the latter to have been the original “Dagoucin” who is
supposed to tell several of the tales.—Ed.
The Abbot, who came of an ancient line, lodged them honourably, and when taking them to their apartments inquired of them concerning their adventures. When he had heard the truth, he told them that others had fared as badly as they, for in one of his rooms he had two ladies who had escaped a like danger, or perchance a greater, inasmuch as they had had to do with beasts, and not with men. (5) Half a league on this side of Peyrechitte (6) the poor ladies had met with a bear coming down from the mountain, before whom they had fled with such speed that their horses fell dead under them at the abbey gates. Further, two of their women who arrived a long time afterwards had made report that the bear had killed all the serving-men.
5 In two MS. copies of the Heptameron in the Bibliothèque
Nationale, Paris, numbered respectively 1520 and 1524, after
the words “not with men” there follows “in men there is some
mercy, but in animals none.”—L.
6 Peyrechitte is evidently intended for Pierrefitte, a
village on the left bank of the Gave, between Argelèz and
Cauterets.—Ed.
Then the two ladies and the three gentlemen entered the room where these unhappy travellers were, and found them weeping. They recognised them to be Nomerfide and Ennasuite, whereupon they all embraced and recounted what had befallen them. At the exhortations of the good Abbot they began to take comfort in having found one another again, and in the morning they heard mass with much devotion, praising God for the perils from which they had escaped.
While they were all at mass there came into the church (7) a man clad only in a shirt, fleeing as though he were pursued, and crying out for aid. Forthwith Hircan and the other gentlemen went to meet him to see what the affair might mean, and perceived two men behind him with drawn swords.
(7) This church is still in existence. It is mainly in the
Romanesque style and almost destitute of ornamentation.
There are, however, some antique paintings of St. Savin’s
miracles; and the saint’s tomb, which is still preserved, is
considered to be some twelve hundred years old. The village
is gathered about the church, and forms a wide street lined
with houses of the fifteenth century, which Margaret and her
friends must have gazed upon during their sojourn here.—Ed.
These, on seeing so great a company, sought to fly, but they were hotly pursued by Hircan and his companions, and so lost their lives. When Hircan came back, he found that the man in the shirt was one of his companions named Geburon, who related to them how while he was in bed at a farmhouse near Peyrechitte three men came upstairs, and how he, although he was in his shirt and had no other weapon but his sword, had stretched one of them on the ground mortally wounded. While the other two were occupied in raising their companion, he, perceiving himself to be naked and the others armed, bethought him that he could not outdo them except it were by flight, as being the least encumbered with clothes. And so he had escaped, and for this he praised God and those who had avenged him.
When they had heard mass and had dined they sent to see if it was possible to cross the river Gave, and on learning that it was not, they were in great dismay. However, the Abbot urgently entreated them to stay with him until the water had abated, and they agreed to remain for that day.
In the evening, as they were going to bed, there arrived an aged monk who was wont to come in September of every year to Our Lady of Serrance. They inquired of him concerning his journey, and he told them that on account of the floods he had come over the mountains and by the worst roads he had ever known. On the way he had seen a very pitiful sight. He had met a gentleman named Simontault, who, wearied by his long waiting for the river to subside, and trusting to the goodness of his horse, had tried to force a passage, and had placed all his servants round about him to break the force of the current. But when they were in the midst of the stream, those who were the worst mounted were swept away, horses and men, down the stream, and were never seen again. The gentleman, finding himself alone, turned his horse to go back, but before he could reach the bank his horse sank under him. Nevertheless, God willed that this should happen so close to the bank that the gentleman was able, by dragging himself on all fours and not without swallowing a great deal of water, to scramble out on to the hard stones, though he was then so weak and weary that he could not stand upright.
By good fortune a shepherd, bringing back his sheep at even, found him seated among the stones, wet to the skin, and sad not only for himself but on account of his servants whom he had seen perish before his eyes. The shepherd, who understood his need even better from his appearance than from his speech, took him by the hand and led him to his humble dwelling, where he kindled some faggots, and so dried him in the best way that he could. The same evening God led thither this good monk, who showed him the road to Our Lady of Serrance assuring him that he would be better lodged there than anywhere else, and would there find an aged widow named Oisille who had been as unfortunate as himself.
When all the company heard tell of the good Lady Oisille and the gentle knight Simontault, they were exceedingly glad, and praised the Creator, who, content with the sacrifice of serving-folk, had preserved their masters and mistresses. And more than all the rest did Parlamente give hearty praise to God, for Simontault had long been her devoted lover.
Then they made diligent inquiry concerning the road to Serrance, and although the good old man declared it to be very difficult, they were not to be debarred from attempting to proceed thither that very day. They set forth well furnished with all that was needful, for the Abbot provided them with wine and abundant victuals,(8) and with willing companions to lead them safely over the mountains.
8 According to MS. No. 1520 (Bib. Nat., Paris), the Abbot
also furnished them with the best horses of Lavedan and good
“cappes” of Beam. The Lavedan horses were renowned for their
speed and spirit, and the Bearnese cappe was a cloak
provided with a hood.—B. J.
These they crossed more often on foot than on horseback, and after much toil and sweat came to Our Lady of Serrance. Here the Abbot, although somewhat evilly disposed, durst not deny them lodging for fear of the Lord of Beam,(9) who, as he was aware, held them in high esteem. Being a true hypocrite, he showed them as fair a countenance as he could, and took them to see the Lady Oisille and the gentle knight Simontault.
9 The Kings of Navarre had been Lords of Beam for two
centuries, but Beam still retained its old customs and had
its special government. The Lord of Beam here referred to
was Henry d’Albret, Margaret’s second husband.—B. J.
The joyfulness of all this company who had been thus miraculously brought together was so great that the night seemed short to them while praising God in the Church for the goodness that He had shown to them. When towards morning they had taken a little rest, they all went to hear mass and receive the holy sacrament of fellowship, in which all Christians are joined together as one, imploring Him who of His mercy had thus united them, that He would further their journey to His glory. After they had dined they sent to learn whether the waters were at all abated, and found that, on the contrary, they were rather increased, and could not be crossed with safety for a long time to come. They therefore determined to make a bridge resting on two rocks which come very close together, and where there are still planks for those foot-passengers who, coming from Oleron, wish to avoid crossing at the ford. The Abbot was well pleased that they should make this outlay, to the end that the number of pilgrims might be increased, and he furnished them with workmen, though he was too avaricious to give them a single farthing.
The workmen declared that they could not finish the bridge in less than ten or twelve days, and all the company, both ladies and gentlemen, began to grow weary. But Parlamente, who was Hircan’s wife, and who was never idle or melancholy, asked leave of her husband to speak, and said to the aged Lady Oisille—
“I am surprised, madam, that you who have so much experience, and now fill the place of mother to all of us women, do not devise some pastime to relieve the weariness we shall feel during our long stay; for if we have not some pleasant and virtuous occupation we shall be in danger of falling ill.”
“Nay,” added the young widow Longarine, “worse than that, we shall become ill-tempered, which is an incurable disease; for there is not one among us but has cause to be exceeding downcast, having regard to our several losses.”
Ennasuite laughing replied—
“Every one has not lost her husband like you, and the loss of servants need not bring despair, since others may readily be found. Nevertheless, I too am of opinion that we should have some pleasant exercise with which to while away the time, for otherwise we shall be dead by to-morrow.”
All the gentlemen agreed with what these ladies said, and begged Oisille to tell them what they should do.
“My children,” she replied, “you ask me for something which I find very difficult to teach you, namely, a pastime that may deliver you from your weariness. I have sought for such a remedy all my life and have never found but one, which is the reading of the Holy Scriptures. In them the mind may find that true and perfect joy from which repose and bodily health proceed. If you would know by what means I continue so blithe and healthy in my old age, it is because on rising I immediately take up the Holy Scriptures (10) and read therein, and so perceive and contemplate the goodness of God, who sent His Son into the world to proclaim to us the Sacred Word and glad tidings by which He promises the remission of all sins and the satisfaction of all debts by the gift that He has made us of His love, passion, and merits.
10 Margaret read a portion of the Scriptures every day,
saying that the perusal preserved one “from all sorts of
evils and diabolical temptations” (Histoire de Foix, Béarn,
et Navarre, by P. Olhagaray, Paris, 1609, p. 502).—L.
“The thought of this gives me such joy that I take my Psalter and in all humility sing with my heart and utter with my lips the sweet psalms and canticles which the Holy Spirit put into the heart of David and of other writers. And so acceptable is the contentment that this brings to me, that any evils which may befall me during the day I look upon as blessings, seeing that I have in my heart, through faith, Him who has borne them all for me. In the same way before supper I retire to feed my soul by reading, and then in the evening I call to mind all I have done during the past day, in order that I may ask forgiveness for my sins, thank Him for His mercies, and, feeling safe from all harm, take my rest in His love, fear, and peace. This, my children, is the pastime I have long practised, after making trial of all others and finding in none contentment of spirit. I believe that if you give an hour every morning to reading and then offer up devout prayers during mass, you will find in this lonely place all the beauty that any town could afford. One who knows God sees all things fair in Him, and without Him everything seems uncomely; wherefore, I pray you, accept my advice, if you would live in gladness.”
Then Hircan took up the discourse and said—
“Those, madam, who have read the Holy Scriptures, as I believe we all have done, will acknowledge that what you have said is true. You must, however, consider that we are not yet so mortified that we have not need of some pastime and bodily exercise. When we are at home we have the chase and hawking, which cause us to lay aside a thousand foolish thoughts, and the ladies have their household cares, their work, and sometimes the dance, in all which they find honourable exercise. So, speaking on behalf of the men, I propose that you, who are the oldest, read to us in the morning about the life that was led by Our Lord Jesus Christ and the great and wonderful works that He did for us; and that between dinner and vespers we choose some pastime that shall be pleasant to the body and yet not hurtful to the soul. In this way we shall pass the day cheerfully.”
The Lady Oisille replied that she had been at pains to forget every description of worldly vanity, and she therefore feared that she should succeed but ill in the choice of such an entertainment. The matter must be decided by the majority of opinions, and she begged Hircan to set forth his own first.
“For my part,” said he, “if I thought that the pastime I should choose would be as agreeable to the company as to myself, my opinion would soon be given. For the present, however, I withhold it, and will abide by what the rest shall say.”
His wife Parlamente, thinking he referred to her, began to blush, and, half in anger and half laughing, replied—
“Perhaps, Hircan, she who you think would find it most dull might readily find means of compensation had she a mind for it. But let us leave aside a pastime in which only two can share, and speak of one that shall be common to all.”
“Since my wife has understood the meaning of my words so well,” said Hircan to all the ladies, “and a private pastime is not to her liking, I think she will be better able than any one else to name one that all may enjoy; and I herewith give in to her opinion, having no other of my own.”
To this all the company agreed.
Parlamente, perceiving that it had fallen to her to decide, spoke as follows—
“Did I find myself as capable as the ancients who invented the arts, I should devise some sport or pastime in fulfilment of the charge you lay upon me. But knowing as I do my knowledge and capacity, which are scarcely able to recall the worthy performances of others, I shall think myself happy if I can follow closely such as have already satisfied your request. Among the rest, I think there is not one of you who has not read the Hundred Tales of Boccaccio, (11) lately translated from the Italian into French. So highly were these thought of by King Francis, first of that name, Monseigneur the Dauphin, (12) Madame the Dauphiness, and Madame Margaret, that could Boccaccio have only heard them from the place where he lay, the praise of such illustrious persons would have raised him from the dead.
11 Margaret here alludes to the French translation of the
Decameron made by her secretary, Anthony le Maçon, and
first issued in Paris in 1545. Messrs. De Lincy and
Montaiglon accordingly think that the prologue of the
Heptameron was written subsequently to that date; but M.
Dillaye states that Le Maçon’s translation was circulated at
Court in manuscript long before it was printed. This
contention is in some measure borne out by Le Maçon’s
dedication to Margaret, of which the more interesting
passages are given in the Appendix to this volume (A).—ED.
12 The Dauphin here mentioned is Francis I.‘s second son,
who subsequently reigned as Henry II. He became Dauphin by
the death of his elder brother on August 10, 1536. The
Dauphiness is Catherine de’ Medici, the wife of Henry, whom
he married in 1533; whilst Madame Margaret, according to M.
de Montaiglon, is the Queen of Navarre herself, she being
usually called by that name at her brother’s Court. M.
Dillaye, who is of a different opinion, maintains that the
Queen would not write so eulogistically of herself, and that
she evidently refers to her brother’s daughter, Margaret de
Berry, born in 1523, and married to the Duke of Savoy.—Ed.
Now I heard not long since that the two ladies I have mentioned, together with several others of the Court, determined to do like Boccaccio, with, however, one exception—they would not write any story that was not a true one. And the said ladies, and Monseigneur the Dauphin with them, undertook to tell ten stories each, and to assemble in all ten persons, from among those whom they thought the most capable of relating something. Such as had studied and were people of letters were excepted, for Monseigneur the Dauphin would not allow of their art being brought in, fearing lest the flowers of rhetoric should in some wise prove injurious to the truth of the tales. But the weighty affairs in which the King had engaged, the peace between him and the King of England, the bringing to bed of the Dauphiness,(13) and many other matters of a nature to engross the whole Court, caused the enterprise to be entirely forgotten.
13 The confinement mentioned here is that of Catherine de
Medici, who, after remaining childless during ten years of
wedlock, gave birth to a son, afterwards Francis II., in
January 1543. The peace previously spoken of would appear to
be that signed at Crespy in September 1544. Both M. de
Montaiglon and M. Dillaye are of opinion, however, that a
word or two is deficient in the MS., and that Margaret
intended to imply the rupture of peace in 1543, when Henry
VIII. allied himself with the Emperor Charles V. against
Francis I.—Ed.
By reason, however, of our now great leisure, it can be accomplished in ten days, whilst we wait for our bridge to be finished. If it so pleased you, we might go every day from noon till four of the clock into yonder pleasant meadow beside the river Gave. The trees there are so leafy that the sun can neither penetrate the shade nor change the coolness to heat. Sitting there at our ease, we might each one tell a story of something we have ourselves seen, or heard related by one worthy of belief. At the end of ten days we shall have completed the hundred,(14) and if God wills it that our work be found worthy in the eyes of the lords and ladies I have mentioned, we will on our return from this journey present them with it, in lieu of images and paternosters,(15) and feeling assured that they will hold this to be a more pleasing gift. If, however, any one can devise some plan more agreeable than mine, I will fall in with his opinion.”
14 This passage plainly indicates that the Queen meant to
pen a Decameron.—Ed.
15 This is an allusion to the holy images, medals, and
chaplets which people brought back with them from
pilgrimages.—B. J.
All the company replied that it was not possible to give better advice, and that they awaited the morning in impatience, in order to begin.
Thus they spent that day joyously, reminding one another of what they had seen in their time. As soon as the morning was come they went to the room of Madame Oisille, whom they found already at her prayers. They listened to her reading for a full hour, then piously heard mass, and afterwards went to dinner at ten o’clock.(16)
16 At that period ten o’clock was the Court dinner-hour.
Fifty years earlier people used to dine at eight in the
morning. Louis XII., however, changed the hour of his meals
to suit his wife, Mary of England, who had been accustomed
to dine at noon.—B. J.
After dinner each one withdrew to his chamber, and did what he had to do. According to their plan, at noon they failed not to return to the meadow, which was so fair and pleasant that it would need a Boccaccio to describe it as it really was; suffice to say that a fairer was never seen.
When the company were all seated on the green grass, which was so fine and soft that they needed neither cushion nor carpet, Simontault commenced by saying—
“Which of us shall begin before the others?”
“Since you were the first to speak,” replied Hircan,” ’tis reasonable that you should rule us; for in sport we are all equal.”
“Would to God,” said Simontault, “I had no worse fortune in this world than to be able to rule all the company present.”
On hearing this Parlamente, who well knew what it meant, began to cough. Hircan, therefore, did not perceive the colour that came into her cheeks, but told Simontault to begin, which he did as presently follows.


On the First Day are recounted the ill-turns which have been done by Women to Men and by Men to Women.
The wife of a Proctor, having been pressingly solicited by
the Bishop of Sees, took him for her profit, and, being as
little satisfied with him as with her husband, found a means
to have the son of the Lieutenant-General of Alençon for her
pleasure. Some time afterwards she caused the latter to be
miserably murdered by her husband, who, although he obtained
pardon for the murder, was afterwards sent to the galleys
with a sorcerer named Gallery; and all this was brought
about by the wickedness of his wife.(1)
1 The incidents of this story are historical, and occurred
in Alençon and Paris between 1520 and 1525.—L.
Ladies, said Simontault, I have been so poorly rewarded for my long service, that to avenge myself upon Love, and upon her who treats me so cruelly, I shall be at pains to make a collection of all the ill turns that women hath done to hapless men; and moreover I will relate nothing but the simple truth.
In the town of Alençon, during the lifetime of Charles, the last Duke,(2) there was a Proctor named St. Aignan, who had married a gentlewoman of the neighbourhood. She was more beautiful than virtuous, and on account of her beauty and light behaviour was much sought after by the Bishop of Sees,(3) who, in order to compass his ends, managed the husband so well, that the latter not only failed to perceive the vicious conduct of his wife and of the Bishop, but was further led to forget the affection he had always shown in the service of his master and mistress.
2 The Duke Charles here alluded to is Margaret’s first
husband.—Ed.
3 Sees or Séez, on the Orne, thirteen miles from Alençon,
and celebrated for its Gothic cathedral, is one of the
oldest bishoprics in Normandy. Richard Coeur-de-Lion is said
to have here done penance and obtained absolution for his
conduct towards his father, Henry II. At the time of this
story the Bishop of Sees was James de Silly, whose father,
also James de Silly, Lord of Lonray, Vaux-Pacey, &c, a
favourite and chamberlain of King Louis XII., became Master
of the Artillery of France in 1501. The second James de
Silly—born at Caen—was ordained Bishop of Sees on February
26th, 1511; he was also Abbot of St. Vigor and St. Pierre-
sur-Dives, where he restored and beautified the abbatial
church. In 1519 he consecrated a convent for women of noble
birth, founded by Margaret and her first husband at Essey,
twenty miles from Alençon, the ruins of which still exist. A
year later Francis Rometens dedicated to him an edition of
the letters of Pico della Mirandola. He died April 24th,
1539, at Fleury-sur-Aiidellé, about fifteen miles from
Rouen, and was buried in his episcopal church. (See Gallia
Christiana, vol. xi. p. 702.) His successor in the See of
Sees was Nicholas Danguye, or Dangu (a natural son of
Cardinal Duprat), with whom M. Frank tries to identify
Dagoucin, one of the narrators of the Heptameron.—L. and
Ed.
Thus, from being a loyal servant, he became utterly adverse to them, and at last sought out sorcerers to procure the death of the Duchess.(4) Now for a long time the Bishop consorted with this unhappy woman, who submitted to him from avarice rather than from love, and also because her husband urged her to show him favour. But there was a youth in the town of Alençon, son of the Lieutenant-General,(5) whom she loved so much that she was half crazy regarding him; and she often availed herself of the Bishop to have some commission intrusted to her husband, so that she might see the son of the Lieutenant, who was named Du Mesnil, at her ease.
4 This was of course Margaret herself.—Ed
5 Gilles du Mesnil, Lieutenant-General of the presidial
bailiwick and Sénéchaussée of Alençon.—B. J.
This mode of life lasted a long time, during which she had the Bishop for her profit and the said Du Mesnil for her pleasure. To the latter she swore that she showed a fair countenance to the Bishop only that their own love might the more freely continue; that the Bishop, in spite of appearances, had obtained only words, from her; and that he, Du Mesnil, might rest assured that no man, save himself, should ever receive aught else.
One day, when her husband was setting forth to visit the Bishop, she asked leave of him to go into the country, saying that the air of the town was injurious to her; and, when she had arrived at her farm, she forthwith wrote to Du Mesnil to come and see her, without fail, at about ten o’clock in the evening. This the young man did; but as he was entering at the gate he met the maid who was wont to let him in, and who said to him, “Go elsewhere, friend, for your place is taken.”
Supposing that the husband had arrived, he asked her how matters stood. The woman, seeing that he was so handsome, youthful, and well-bred, and was withal so loving and yet so little loved, took pity upon him and told him of his mistress’s wantonness, thinking that on hearing this he would be cured of loving her so much. She related to him that the Bishop of Sees had but just arrived, and was now in bed with the lady, a thing which the latter had not expected, for he was not to have come until the morrow. However, he had detained her husband at his house, and had stolen away at night to come secretly and see her. If ever man was in despair it was Du Mesnil, who nevertheless was quite unable to believe the story. He hid himself, however, in a house near by, and watched until three hours after midnight, when he saw the Bishop come forth disguised, yet not so completely but that he could recognise him more readily than he desired.
Du Mesnil in his despair returned to Alençon, whither, likewise, his wicked mistress soon came, and went to speak to him, thinking to deceive him according to her wont. But he told her that, having touched sacred things, she was too holy to speak to a sinner like himself, albeit his repentance was so great that he hoped his sin would very soon be forgiven him. When she learnt that her deceit was found out, and that excuses, oaths, and promises never to act in a like way again were of no avail, she complained of it to her Bishop. Then, having weighed the matter with him, she went to her husband and told him that she could no longer dwell in the town of Alençon, for the Lieutenant’s son, whom he had so greatly esteemed among his friends, pursued her unceasingly to rob her of her honour. She therefore begged of him to abide at Argentan,(6) in order that all suspicion might be removed.
6 Argentan, on the Orne, twenty-six miles from Alençon, had
been a distinct viscounty, but at this period it belonged to
the duchy of Alençon.—Ed.
The husband, who suffered himself to be ruled by his wife, consented; but they had not been long at Argentan when this bad woman sent a message to Du Mesnil, saying that he was the wickedest man in the world, for she knew full well that he had spoken evilly (sic.) of her and of the Bishop of Sees; however, she would strive her best to make him repent of it.
The young man, who had never spoken of the matter except to herself, and who feared to fall into the bad graces of the Bishop, repaired to Argentan with two of his servants, and finding his mistress at vespers in the church of the Jacobins,(7) he went and knelt beside her, and said—
“I am come hither, madam, to swear to you before God that I have never spoken of your honour to any person but yourself. You treated me so ill that I did not make you half the reproaches you deserved; but if there be man or woman ready to say that I have ever spoken of the matter to them, I am here to give them the lie in your presence.”
7 The name of Jacobins was given to the monks of the
Dominican Order, some of whom had a monastery in the suburbs
of Argentan.—Ed.
Seeing that there were many people in the church, and that he was accompanied by two stout serving-men, she forced herself to speak as graciously as she could. She told him that she had no doubt he spoke the truth, and that she deemed him too honourable a man to make evil report of any one in the world; least of all of herself, who bore him so much friendship; but since her husband had heard the matter spoken of, she begged him to say in his presence that he had not so spoken and did not so believe.
To this he willingly agreed, and, wishing to attend her to her house, he offered to take her arm; but she told him it was not desirable that he should come with her, for her husband would think that she had put these words into his mouth. Then, taking one of his serving-men by the sleeve, she said—
“Leave me this man, and as soon as it is time I will send him to seek you. Meanwhile do you go and rest in your lodging.”
He, having no suspicion of her conspiracy against him, went thither.
She gave supper to the serving-man whom she had kept with her, and who frequently asked her when it would be time to go and seek his master; but she always replied that his master would come soon enough. When it was night, she sent one of her own serving-men to fetch Du Mesnil; and he, having no suspicion of the mischief that was being prepared for him, went boldly to St. Aignan’s house. As his mistress was still entertaining his servant there, he had but one with himself.
Just as he was entering the house, the servant who had been sent to him told him that the lady wished to speak with him before he saw her husband, and that she was waiting for him in a room where she was alone with his own serving-man; he would therefore do well to send his other servant away by the front door. This he did. Then while he was going up a small, dark stairway, the Proctor St. Aignan, who had placed some men in ambush in a closet, heard the noise, and demanded what it was; whereupon he was told that a man was trying to enter secretly into his house.
At the moment, a certain Thomas Guérin, a murderer by trade, who had been hired by the Proctor for the purpose, came forward and gave the poor young man so many sword-thrusts that whatever defence he was able to make could not save him from falling dead in their midst.
Meanwhile the servant who was waiting with the lady, said to her—
“I hear my master speaking on the stairway. I will go to him.”
But the lady stopped him and said—
“Do not trouble yourself; he will come soon enough.”
A little while afterwards the servant, hearing his master say, “I am dying, may God receive my soul!” wished to go to his assistance, but the lady again withheld him, saying—
“Do not trouble yourself; my husband is only chastising him for his follies. We will go and see what it is.”
Then, leaning over the balustrade at the top of the stairway, she asked her husband—
“Well, is it done?”
“Come and see,” he replied. “I have now avenged you on the man who put you to such shame.”
So saying, he drove a dagger that he was holding ten or twelve times into the belly of a man whom, alive, he would not have dared to assail.
When the murder had been accomplished, and the two servants of the dead man had fled to carry the tidings to the unhappy father, St. Aignan bethought himself that the matter could not be kept secret. But he reflected that the testimony of the dead man’s servants would not be believed, and that no one in his house had seen the deed done, except the murderers, and an old woman-servant, and a girl fifteen years of age. He secretly tried to seize the old woman, but, finding means to escape out of his hands, she sought sanctuary with the Jacobins,(8) and was afterwards the most trustworthy witness of the murder. The young maid remained for a few days in St. Aignan’s house, but he found means to have her led astray by one of the murderers, and had her conveyed to a brothel in Paris so that her testimony might not be received.(9)
8 It was still customary to take sanctuary in churches,
monasteries, and convents at this date, although but little
respect was shown for the refugees, whose hiding-places were
often surrounded so that they might be kept without food and
forced to surrender. After being considerably restricted by
an edict issued in 1515, the right of sanctuary was
abolished by Francis I. in 1539.—B. J. and D.
9 Prostitutes were debarred from giving evidence in French
courts of law at this period.—D.
To conceal the murder, he caused the corpse of the hapless dead man to be burnt, and the bones which were not consumed by the fire he caused to be placed in some mortar in a part of his house where he was building. Then he sent in all haste to the Court to sue for pardon, setting forth that he had several times forbidden his house to a person whom he suspected of plotting his wife’s dishonour, and who, notwithstanding his prohibition, had come by night to see her in a suspicious fashion; whereupon, finding him in the act of entering her room, his anger had got the better of his reason and he had killed him.
But before he was able to despatch his letter to the Chancellor’s, the Duke and Duchess had been apprised by the unhappy father of the matter, and they sent a message to the Chancellor to prevent the granting of the pardon. Finding he could not obtain it, the wretched man fled to England with his wife and several of his relations. But before setting out he told the murderer who at his entreaty had done the deed, that he had seen expresses from the King directing that he should be taken and put to death. Nevertheless, on account of the service that he had rendered him, he desired to save his life, and he gave him ten crowns wherewith to leave the kingdom. The murderer did this, and was afterwards seen no more.
The murder was so fully proven by the servants of the dead man, by the woman who had taken refuge with the Jacobins, and by the bones that were found in the mortar, that legal proceedings were begun and completed in the absence of St. Aignan and his wife. They were judged by default and were both condemned to death. Their property was confiscated to the Prince, and fifteen hundred crowns were to be given to the dead man’s father to pay the costs of the trial.
St. Aignan being in England and perceiving that in the eyes of the law he was dead in France, by means of his services to divers great lords and by the favour of his wife’s relations, induced the King of England (10) to request the King of France (11) to grant him a pardon and restore him to his possessions and honours. But the King of France, having been informed of the wickedness and enormity of the crime, sent the process to the King of England, praying him to consider whether the offence was one deserving of pardon, and telling him that no one in the kingdom but the Duke of Alençon had the right to grant a pardon in that duchy. However, notwithstanding all his excuses, he failed to appease the King of England, who continued to entreat him so very pressingly that, at his request, the Proctor at last received a pardon and so returned to his own home.(12) There, to complete his wickedness, he consorted with a sorcerer named Gallery, hoping that by this man’s art he might escape payment of the fifteen hundred crowns to the dead man’s father.
10 Henry VIII.
11 Francis I.
12 The letters of remission which were granted to St. Aignan
on this occasion will be found in the Appendix to the First
Day (B). It will be noted that Margaret in her story gives
various particulars which St. Aignan did not fail to conceal
in view of obtaining his pardon.—L.
To this end he went in disguise to Paris with his wife. She, finding that he used to shut himself up for a great while in a room with Gallery without acquainting her with the reason thereof, spied upon him one morning, and perceived Gallery showing him five wooden images, three of which had their hands hanging down, whilst two had them lifted up.(13)
“We must make waxen images like these,” said Gallery, speaking to the Proctor. “Such as have their arms hanging down will be for those whom we shall cause to die, and the others with their arms raised will be for the persons from whom you would fain have love and favour.”
“This one,” said the Proctor, “shall be for the King by whom I would fain be loved, and this one for Monseigneur Brinon, Chancellor of Alençon.” (14)
13 This refers to the superstitious practice called
envoûtement, which, according to M. Léon de Laborde, was
well known in France in 1316, and subsisted until the
sixteenth century. In 1330 the famous Robert d’Artois, upon
retiring to Brabant, occupied himself with pricking waxen
images which represented King Philip VI., his brother-in-
law, and the Queen, his sister. (Mémoires de l’Académie des
Inscriptions, vol. xv. p. 426.) During the League the
enemies of Henri III. and the King of Navarre revived this
practice.—(L.) It would appear also from a document in the
Harley MSS. (18,452, Bib. N’at., Paris) that Cosmo Ruggieri,
the Florentine astrologer, Catherine de’ Medici’s
confidential adviser, was accused in 1574 of having made a
wax figure in view of casting a spell upon Charles IX.—M.
14 John Brinon, Councillor of the King, President of the
Parliament of Rouen, Chancellor of Alençon and Berry, Lord
of Villaines (near Dreux), Remy, and Athueuil (near
Montfort-l’Amaury), belonged to an old family of judicial
functionaries. He was highly esteemed by Margaret, several
of whose letters are addressed to him, and he was present at
the signing of her marriage contract with Henry II. of
Navarre (Génin’s Lettres de Marguerite, p. 444). He
married Pernelle Perdrier, who brought him the lordship of
Médan, near Poissy, and other important fiefs, which after
his death she presented to the King. His praises were sung
by Le Chandelier, the poet; and M. Floquet, in his History
of the Parliament of Normandy, states that Brinon rendered
most important services to France as a negotiator in Italy
in 1521, and in England in 1524. The Journal d’un Bourgeois
de Paris mentions that he died in Paris in 1528, aged
forty-four, and was buried in the Church of St. Severin.—L.
According to La Croix du Maine’s Bibliothèque Françoise,
Brinon was the author of a poem entitled Les Amours de
Sydire.—B. J.
“The images,” said Gallery, “must be set under the altar, to hear mass, with words that I will presently tell you to say.”
Then, speaking of those images that had their arms lowered, the Proctor said that one should be for Master Gilles du Mesnil, father of the dead man, for he knew that as long as the father lived he would not cease to pursue him. Moreover, one of the women with their hands hanging down was to be for the Duchess of Alençon, sister to the King; for she bore so much love to her old servant, Du Mesnil, and had in so many other matters become acquainted with the Proctor’s wickedness, that except she died he could not live. The second woman that had her arms hanging down was his own wife, who was the cause of all his misfortune, and who he felt sure would never amend her evil life.
When his wife, who could see everything through the keyhole, heard him placing her among the dead, she resolved to send him among them first. On pretence of going to borrow some money, she went to an uncle she had, named Neaufle, who was Master of Requests to the Duke of Alençon, and informed him of what she had seen and heard. Neaufle, like the old and worthy servant that he was, went forthwith to the Chancellor of Alençon and told him the whole story.
As the Duke and Duchess of Alençon were not at Court that day, the Chancellor related this strange business to the Regent,(15) mother of the King and the Duchess, and she sent in all haste for the Provost of Paris,(16) who made such speed that he at once seized the Proctor and his sorcerer, Gallery. Without constraint or torture they freely confessed their guilt, and their case was made out and laid before the King.
15 Louise of Savoy.
16 John de la Barre, a favourite of Francis I. See note to
Tale lxiii. (vol. v.), in which he plays a conspicuous
part.—Ed.
Certain persons, wishing to save their lives, told him that they had only sought his good graces by their enchantments; but the King, holding his sister’s life as dear as his own, commanded that the same sentence should be passed on them as if they had made an attempt on his own person.
However, his sister, the Duchess of Alençon, entreated that the Proctor’s life might be spared, and the sentence of death be commuted to some heavy punishment. This request was granted her, and St. Aignan and Gallery were sent to the galleys of St. Blancart at Marseilles,(17) where they ended their days in close captivity, and had leisure to ponder on the grievousness of their crimes. The wicked wife, in the absence of her husband, continued in her sinful ways even more than before, and at last died in wretchedness.
17 This passage is explained by Henri Bouché, who states in
his Histoire Chronologique de Provence (vol. ii. p. 554),
that after Francis I.‘s voyage in captivity to Spain it was
judged expedient that France should have several galleys in
the Mediterranean, and that “orders were accordingly given
for thirteen to be built at Marseilles—four for the Baron
de Saint-Blancart, as many for Andrew Doria, &c.” The Baron
de Saint-Blancart here referred to was Bernard d’Ormezan,
Admiral of the seas of the Levant, Conservator of the ports
and tower of Aigues-Mortes, and General of the King’s
galleys. In 1523 he defeated the naval forces of the Emperor
Charles V., and in 1525 conducted Margaret to Spain.—L.
(See Memoir of Margaret, p. xli.)
“I pray you, ladies, consider what evil is caused by a wicked woman, and how many evils sprang from the sins of the one I have spoken of. You will find that ever since Eve caused Adam to sin, all women have set themselves to bring about the torment, slaughter and damnation of men. For myself, I have had such experience of their cruelty that I expect to die and be damned simply by reason of the despair into which one of them has cast me. And yet so great a fool am I, that I cannot but confess that hell coming from her hand is more pleasing than Paradise would be from the hand of another.”
Parlamente, pretending she did not understand that it was touching herself he spoke in this fashion, said to him—
“Since hell is as pleasant as you say, you ought not to fear the devil who has placed you in it.”
“If my devil were to become as black as he has been cruel to me,” answered Simontault angrily, “he would cause the present company as much fright as I find pleasure in looking upon them; but the fires of love make me forget those of this hell. However, to speak no further concerning this matter, I give my vote to Madame Oisille to tell the second story. I feel sure she would support my opinion if she were willing to say what she knows about women.”
Forthwith all the company turned towards Oisille, and begged of her to proceed, to which she consented, and, laughing, began as follows—
“It seems to me, ladies, that he who has given me his vote has spoken so ill of our sex in his true story of a wicked woman, that I must call to mind all the years of my long life to find one whose virtue will suffice to gainsay his evil opinion. However, as I have bethought me of one worthy to be remembered, I will now relate her history to you.”



The wife of a muleteer of Amboise chose rather to die
cruelly at the hands of her servant than to fall in with his
wicked purpose.(1)
In the town of Amboise there was a muleteer in the service of the Queen of Navarre, sister to King Francis, first of that name. She being at Blois, where she had been brought to bed of a son, the aforesaid muleteer went thither to receive his quarterly payment, whilst his wife remained at Amboise in a lodging beyond the bridges.(2)
1 The incidents of this story probably took place at
Amboise, subsequent, however, to the month of August 1530,
when Margaret was confined of her son John.—L.
2 Amboise is on the left bank of the Loire, and there have
never been any buildings on the opposite bank. However,
the bridge over the river intersects the island of St. Jean,
which is covered with houses, and here the muleteer’s wife
evidently resided.—M.
Now it happened that one of her husband’s servants had long loved her exceedingly, and one day he could not refrain from speaking of it to her. She, however, being a truly virtuous woman, rebuked him so severely, threatening to have him beaten and dismissed by her husband, that from that time forth he did not venture to speak to her in any such way again or to let his love be seen, but kept the fire hidden within his breast until the day when his master had gone from home and his mistress was at vespers at St. Florentin,(3) the castle church, a long way from the muleteer’s house.
3 The Church of St. Florentin here mentioned must not be
confounded with that of the same name near one of the gates
of Amboise. Erected in the tenth century by Foulques Nera of
Anjou, it was a collegiate church, and was attended by the
townsfolk, although it stood within the precincts of the
château. For this reason Queen Margaret calls it the castle
church.—Ed.
Whilst he was alone the fancy took him that he might obtain by force what neither prayer nor service had availed to procure him, and accordingly he broke through a wooden partition which was between the chamber where his mistress slept and his own. The curtains of his master’s bed on the one side and of the servant’s bed on the other so covered the walls as to hide the opening he had made; and thus his wickedness was not perceived until his mistress was in bed, together with a little girl eleven or twelve years old.
When the poor woman was in her first sleep, the servant, in his shirt and with his naked sword in his hand, came through the opening he had made in the wall into her bed; but as soon as she felt him beside her, she leaped out, addressing to him all such reproaches as a virtuous woman might utter. His love, however, was but bestial, and he would have better understood the language of his mules than her honourable reasonings; indeed, he showed himself even more bestial than the beasts with whom he had long consorted. Finding she ran so quickly round a table that he could not catch her, and that she was strong enough to break away from him twice, he despaired of ravishing her alive, and dealt her a terrible sword-thrust in the loins, thinking that, if fear and force had not brought her to yield, pain would assuredly do so.
The contrary, however, happened, for just as a good soldier, on seeing his own blood, is the more fired to take vengeance on his enemies and win renown, so her chaste heart gathered new strength as she ran fleeing from the hands of the miscreant, saying to him the while all she could think of to bring him to see his guilt. But so filled was he with rage that he paid no heed to her words. He dealt her several more thrusts, to avoid which she continued running as long as her legs could carry her.
When, after great loss of blood, she felt that death was near, she lifted her eyes to heaven, clasped her hands and gave thanks to God, calling Him her strength, her patience, and her virtue, and praying Him to accept her blood which had been shed for the keeping of His commandment and in reverence of His Son, through whom she firmly believed all her sins to be washed away and blotted out from the remembrance of His wrath.
As she was uttering the words, “Lord, receive the soul that has been redeemed by Thy goodness,” she fell upon her face to the ground.
Then the miscreant dealt her several thrusts, and when she had lost both power of speech and strength of body, and was no longer able to make any defence, he ravished her.(4)
4 Brantôme, in his account of Mary Queen of Scots, quotes
this story. After mentioning that the headsman remained
alone with the Queen’s decapitated corpse, he adds: “He then
took off her shoes and handled her as he pleased. It is
suspected that he treated her in the same way as that
miserable muleteer, in the Hundred Stories of the Queen of
Navarre, treated the poor woman he killed. Stranger
temptations than this come to men. After he (the
executioner) had done as he chose, the (Queen’s) body was
carried into a room adjoining that of her servants.”
Lalanne’s OEuvres de Brantôme, vol. vii. p. 438.—M.
Having thus satisfied his wicked lust, he fled in haste, and in spite of all pursuit was never seen again.
The little girl, who was in bed with the muleteer’s wife, had hidden herself under the bed in her fear; but on seeing that the man was gone, she came to her mistress. Finding her to be without speech or movement, she called to the neighbours from the window for aid; and as they loved and esteemed her mistress as much as any woman that belonged to the town, they came forthwith, bringing surgeons with them. The latter found that she had received twenty-five mortal wounds in her body, and although they did what they could to help her, it was all in vain.
Nevertheless she lingered for an hour longer without speaking, yet making signs with eye and hand to show that she had not lost her understanding. Being asked by a priest in what faith she died, she answered, by signs as plain as any speech, that she placed her hope of salvation in Jesus Christ alone; and so with glad countenance and eyes upraised to heaven her chaste body yielded up its soul to its Creator.
Just as the corpse, having been laid out and shrouded,(5) was placed at the door to await the burial company, the poor husband arrived and beheld his wife’s body in front of his house before he had even received tidings of her death. He inquired the cause of this, and found that he had double occasion to grieve; and his grief was indeed so great that it nearly killed him.
5 Common people were then buried in shrouds, not in coffins.
—Ed.
This martyr of chastity was buried in the Church of St. Florentin, and, as was their duty, all the upright women of Amboise failed not to show her every possible honour, deeming themselves fortunate in belonging to a town where so virtuous a woman had been found. And seeing the honour that was shown to the deceased, such women as were wanton and unchaste resolved to amend their lives.
“This, ladies, is a true story, which should incline us more strongly to preserve the fair virtue of chastity. We who are of gentle blood should die of shame on feeling in our hearts that worldly lust to avoid which the poor wife of a muleteer shrank not from so cruel a death. Some esteem themselves virtuous women who have never like this one resisted unto the shedding of blood. It is fitting that we should humble ourselves, for God does not vouchsafe His grace to men because of their birth or riches, but according as it pleases His own good-will. He pays no regard to persons, but chooses according to His purpose; and he whom He chooses He honours with all virtues. And often He chooses the lowly to confound those whom the world exalts and honours; for, as He Himself hath told us, ‘Let us not rejoice in our merits, but rather because our names are written in the Book of Life, from which nor death, nor hell, nor sin can blot them out.’” (6)
6 These are not the exact words of Scripture, but a
combination of several passages from the Book of
Revelation.—Ed.
There was not a lady in the company but had tears of compassion in her eyes for the pitiful and glorious death of the muleteer’s wife. Each thought within herself that, should fortune serve her in the same way, she would strive to imitate this poor woman in her martyrdom. Oisille, however, perceiving that time was being lost in praising the dead woman, said to Saffredent—
“Unless you can tell us something that will make the company laugh, I think none of them will forgive me for the fault I have committed in making them weep; wherefore I give you my vote for your telling of the third story.”
Saffredent, who would gladly have recounted something agreeable to the company, and above all to one amongst the ladies, said that it was not for him to speak, seeing that there were others older and better instructed than himself, who should of right come first. Nevertheless, since the lot had fallen upon himself, he would rather have done with it at once, for the more numerous the good speakers before him, the worse would his own tale appear.



The Queen of Naples, being wronged by King Alfonso, her
husband, revenged herself with a gentleman whose wife was
the King’s mistress; and this intercourse lasted all their
lives without the King at any time having suspicion of
it.(1)
I have often desired, ladies, to be a sharer in the good fortune of the man whose story I am about to relate to you. You must know that in the time of King Alfonso,(2) whose lust was the sceptre of his kingdom,(3) there lived in the town of Naples a gentleman, so honourable, comely, and pleasant that his perfections induced an old gentleman to give him his daughter in marriage.
1 This story is historical. The events occurred at Naples
cir. 1450.—L.
2 The King spoken of in this story must be Alfonso V., King
of Aragon, who was born in 1385, and succeeded his father,
Ferdinand the Just, in 1416. He had already made various
expeditions to Sardinia and Corsica, when, in 1421, Jane II.
of Naples begged of him to assist her in her contest against
Louis of Anjou. Alfonso set sail for Italy as requested, but
speedily quarrelled with Jane, on account of the manner in
which he treated her lover, the Grand Seneschal Caraccioli.
Jane, at her death in 1438, bequeathed her crown to René,
brother of Louis of Anjou, whose claims Alfonso immediately
opposed. Whilst blockading Gaëta he was defeated and
captured, but ultimately set at liberty, whereupon he
resumed the war. In 1442 he at last secured possession of
Naples, and compelled René to withdraw from Italy. From that
time Alfonso never returned to Spain, but settling himself
in his Italian dominions, assumed the title of King of the
Two Sicilies. He obtained the surname of the Magnanimous,
from his generous conduct towards some conspirators, a list
of whose names he tore to pieces unread, saying, “I will
show these noblemen that I have more concern for their lives
than they have themselves.” The surname of the Learned was
afterwards given to him from the circumstance that, like his
rival René of Anjou, he personally cultivated letters, and
also protected many of the leading learned men of Italy.
Alfonso was fond of strolling about the streets of Naples
unattended, and one day, when he was cautioned respecting
this habit, he replied, “A father who walks abroad in the
midst of his children has no cause for fear.” Whilst
possessed of many remarkable qualities, Alfonso, as Muratori
and other writers have shown, was of an extremely licentious
disposition. That he had no belief in conjugal fidelity is
evidenced by his saying that “to ensure domestic happiness
the husband should be deaf and the wife blind.” He himself
had several mistresses, and lived at variance with his wife,
respecting whom some particulars are given in a note on page
69. He died in 1458, at the age of seventy-four, bequeathing
his Italian possessions to Ferdinand, Duke of Calabria, his
natural son by a Spanish beauty named Margaret de Hijar. It
may be added that Brantôme makes a passing allusion to this
tale of the Heptameron in his Vies des Dames Galantes
(Disc, i.), styling it “a very fine one.”—L. and Ed.
3 Meaning that he employed his sovereign authority for the
accomplishment of his amorous desires.—M.
She vied with her husband in grace and comeliness, and there was great love between them, until a certain day in Carnival time, when the King went masked from house to house. All strove to give him the best welcome they could, but when he came to this gentleman’s house he was entertained better than anywhere else, what with sweetmeats, and singers, and music, and, further, the fairest woman that, to his thinking, he had ever seen. At the end of the feast she sang a song with her husband in so graceful a fashion that she seemed more beautiful than ever.
The King, perceiving so many perfections united in one person, was not over pleased at the gentle harmony between the husband and wife, and deliberated how he might destroy it. The chief difficulty he met with was in the great affection which he observed existed between them, and on this account he hid his passion in his heart as deeply as he could. To relieve it in some measure, he gave many entertainments to the lords and ladies of Naples, and at these the gentleman and his wife were not forgotten. Now, inasmuch as men willingly believe what they desire, it seemed to the King that the glances of this lady gave him fair promise of future happiness, if only she were not restrained by her husband’s presence. Accordingly, that he might learn whether his surmise was true, the King intrusted a commission to the husband, and sent him on a journey to Rome for a fortnight or three weeks.
As soon as the gentleman was gone, his wife, who had never before been separated from him, was in great distress; but the King comforted her as often as he was able, with gentle persuasions and presents, so that at last she was not only consoled, but well pleased with her husband’s absence. Before the three weeks were over at the end of which he was to be home again, she had come to be so deeply in love with the King that her husband’s return was no less displeasing to her than his departure had been. Not wishing to be deprived of the King’s society, she agreed with him that whenever her husband went to his country-house she would give him notice of it. He might then visit her in safety, and with such secrecy that her honour, which she regarded more than her conscience, would not suffer.(4)
4 The edition of 1558 is here followed, the MSS. being
rather obscure.—M.
Having this hope, the lady continued of very cheerful mind, and when her husband arrived she welcomed him so heartily that, even had he been told that the King had sought her in his absence, he would have had no suspicion. In course of time, however, the flame, that is so difficult of concealment, began to show itself, and the husband, having a strong inkling of the truth, kept good watch, by which means he was well-nigh convinced. Nevertheless, as he feared that the man who wronged him would treat him still worse if he appeared to notice it, he resolved to dissemble, holding it better to live in trouble than to risk his life for a woman who had ceased to love him.
In his vexation of spirit, however, he resolved, if he could, to retort upon the King, and knowing that women, especially such as are of lofty and honourable minds, are more moved by resentment than by love, he made bold one day while speaking with the Queen (5) to tell her that it moved his pity to see her so little loved by the King.
5 This was Mary (daughter of Henry III. of Castile), who was
married to King Alfonso at Valencia on June 29, 1415. Juan
de Mariana, the Spanish historian, records that the ceremony
was celebrated with signal pomp by the schismatical Pope
Benedict XIII. The bride brought her husband a dowry of
200,000 ducats, and also various territorial possessions.
The marriage, however, was not a happy one, on account of
Alfonso’s licentious disposition, and the Queen is said to
have strangled one of his mistresses, Margaret de Hijar, in
a fit of jealousy. Alfonso, to escape from his wife’s
interference, turned his attention to foreign expeditions.
According to the authors of L’Art de Vérifier les Dates,
Queen Mary never once set foot in Italy, and this statement
is borne out by Mariana, who shows that whilst Alfonso was
reigning in Naples his wife governed the kingdom of Aragon,
making war and signing truces and treaties of peace with
Castile. In the Heptameron, therefore, Margaret departs
from historical accuracy when she represents the Queen as
residing at Naples with her husband. Moreover, judging by
the date of Mary’s marriage, she could no longer have been
young when Alfonso secured the Neapolitan throne. It is to
be presumed that the Queen of Navarre designedly changed the
date of her story, and that the incidents referred to really
occurred in Spain prior to Alfonso’s departure for Italy.
There is no mention of Mary in her husband’s will, a
remarkable document which is still extant. A letter written
to her by Pope Calixtus II. shows that late in life the King
was desirous of repudiating her to marry an Italian mistress
named Lucretia Alania. The latter repaired to Rome to
negotiate the affair, but the Pope refused to treat with
her, and wrote to Mary saying that she must be prudent, but
that he would not dissolve the marriage, lest God should
punish him for participating in so great a crime. Mary died
a few months after her husband in 1458, and was buried in a
convent at Valencia.—L. and Ed.
The Queen, who had heard of the affection that existed between the King and the gentleman’s wife, replied—
“I cannot have both honour and pleasure together. I well know that I have the honour whilst another has the pleasure; and in the same way she who has the pleasure has not the honour that is mine.”
Thereupon the gentleman, who understood full well at whom these words were aimed, replied—
“Madam, honour is inborn with you, for your lineage is such that no title, whether of queen or empress, could be an increase of nobility; yet your beauty, grace, and virtue are well deserving of pleasure, and she who robs you of what is yours does a greater wrong to herself than to you, seeing that for a glory which is turned to her shame, she loses as much pleasure as you or any lady in the realm could enjoy. I can truly tell you, madam, that were the King to lay aside his crown, he would not possess any advantage over me in satisfying a lady; nay, I am sure that to content one so worthy as yourself he would indeed be pleased to change his temperament for mine.”
The Queen laughed and replied—
“The King may be of a less vigorous temperament than you, yet the love he bears me contents me well, and I prefer it to any other.”
“Madam,” said the gentleman, “if that were so, I should have no pity for you. I feel sure that you would be well pleased if the like of your own virtuous love were found in the King’s heart; but God has withheld this from you in order that, not finding what you desire in your husband, you may not make him your god on earth.”
“I confess to you,” said the Queen, “that the love I bear him is so great that the like could not be found in any other heart but mine.”
“Pardon me, madam,” said the gentleman; “you have not fathomed the love of every heart. I will be so bold as to tell you that you are loved by one whose love is so great and measureless that your own is as nothing beside it. The more he perceives that the King’s love fails you, the more does his own wax and increase, in such wise that, were it your pleasure, you might be recompensed for all you have lost.”
The Queen began to perceive, both from these words and from the gentleman’s countenance, that what he said came from the depth of his heart. She remembered also that for a long time he had so zealously sought to do her service that he had fallen into sadness. She had hitherto deemed this to be on account of his wife, but now she was firmly of belief that it was for love of herself. Moreover, the very quality of love, which compels itself to be recognised when it is unfeigned, made her feel certain of what had been hidden from every one. As she looked at the gentleman, who was far more worthy of being loved than her husband, she reflected that he was forsaken by his wife, as she herself was by the King; and then, beset by vexation and jealousy against her husband, as well as moved by the love of the gentleman, she began with sighs and tearful eyes to say—
“Ah me! shall revenge prevail with me where love has been of no avail?”
The gentleman, who understood what these words meant, replied—
“Vengeance, madam, is sweet when in place of slaying an enemy it gives life to a true lover.(6) Methinks it is time that truth should cause you to abandon the foolish love you bear to one who loves you not, and that a just and reasonable love should banish fear, which cannot dwell in a noble and virtuous heart. Come, madam, let us set aside the greatness of your station and consider that, of all men and women in the world, we are the most deceived, betrayed, and bemocked by those whom we have most truly loved. Let us avenge ourselves, madam, not so much to requite them in the way they deserve as to satisfy that love which, for my own part, I cannot continue to endure and live. And I think that, unless your heart be harder than flint or diamond, you cannot but feel some spark from the fires which only increase the more I seek to conceal them. If pity for me, who am dying of love for you, does not move you to love me, at least pity for yourself should do so. You are so perfect that you deserve to win the heart of every honourable man in the world, yet you are contemned and forsaken by him for whose sake you have scorned all others.”
6 The above sentence being omitted in the MS. followed in
this edition, it has been supplied from MS. No. 1520 in the
Bibliothèque Nationale.—L.
On hearing these words the Queen was so greatly moved that, for fear of showing in her countenance the trouble of her mind, she took the gentleman’s arm and went forth into a garden that was close to her apartment. There she walked to and fro for a long time without being able to say a word to him. The gentleman saw that she was half won, and when they were at the end of the path, where none could see them, he made a very full declaration of the love which he had so long hidden from her. They found that they were of one mind in the matter, and enacted (7) the vengeance which they were no longer able to forego. Moreover, they there agreed that whenever the husband went into the country, and the King left the castle to visit the wife in the town, the gentleman should always return and come to the castle to see the Queen. Thus, the deceivers being themselves deceived, all four would share in the pleasures that two of them had thought to keep to themselves.
7 This expression has allusion to the mysteries or religious
plays so frequently performed in the fifteenth and sixteenth
centuries. The Mystery of Vengeance, which depicted the
misfortunes which fell upon those who had taken part in the
crucifixion of Jesus Christ, such as Pontius Pilate, &c, and
ended by the capture and destruction of Jerusalem, properly
came after the Mysteries of the Passion and the
Resurrection.—L.
When the agreement had been made, the Queen returned to her apartment and the gentleman to his house, both being so well pleased that they had forgotten all their former troubles. The jealousy they had previously felt at the King’s visits to the lady was now changed to desire, so that the gentleman went oftener than usual to his house in the country, which was only half a league distant. As soon as the King was advised of his departure, he never failed to go and see the lady; and the gentleman, when night was come, betook himself to the castle to the Queen, where he did duty as the King’s lieutenant, and so secretly that none ever discovered it.
This manner of life lasted for a long time; but as the King was a person of public condition, he could not conceal his love sufficiently well to prevent it from coming at length to the knowledge of every one; and all honourable people felt great pity for the gentleman, though divers malicious youths were wont to deride him by making horns at him behind his back. But he knew of their derision, and it gave him great pleasure, so that he came to think as highly of his horns as of the King’s crown.
One day, however, the King and the gentleman’s wife, noticing a stag’s head that was set up in the gentleman’s house, could not refrain in his presence from laughing and saying that the head was suited to the house. Soon afterwards the gentleman, who was no less spirited than the King, caused the following words to be written over the stag’s head:—
“Io porto le corna, ciascun lo vede, Ma tal le porta che no lo
crede.” (8)
8 “All men may see the horns I’ve got, But one wears horns
and knows it not.”
When the King came again to the house, he observed these lines newly written, and inquired their meaning of the gentleman, who said—
“If the King’s secret be hidden from the subject, it is not fitting that the subject’s secret should be revealed to the King. Be content with knowing that those who wear horns do not always have their caps raised from their heads. Some horns are so soft that they never uncap one, and especially are they light to him who thinks he has them not.”
The King perceived by these words that the gentleman knew something of his own behaviour, but he never had any suspicion of the love between him and the Queen; for the more pleased the latter was with the life led by her husband, the more did she feign to be distressed by it. And so on either side they lived in this love, until at last old age took them in hand.
“Here, ladies, is a story by which you may be guided, for, as I willingly confess, it shows you that when your husbands give you bucks’ horns you can give them stags’ horns in return.”
“I am quite sure, Saffredent,” began Ennasuite laughing, “that if you still love as ardently as you were formerly wont to do, you would submit to horns as big as oak-trees if only you might repay them as you pleased. However, now that your hair is growing grey, it is time to leave your desires in peace.”
“Fair lady,” said Saffredent, “though I be robbed of hope by the woman I love, and of ardour by old age, yet it lies not in my power to weaken my inclination. Since you have rebuked me for so honourable a desire, I give you my vote for the telling of the fourth tale, that we may see whether you can bring forward some example to refute me.”
During this converse one of the ladies fell to laughing heartily, knowing that she who took Saffredent’s words to herself was not so loved by him that he would have suffered horns, shame, or wrong for her sake. When Saffredent perceived that the lady who laughed understood him, he was well satisfied and became silent, so that Ennasuite might begin; which she did as follows—
“In order, ladies, that Saffredent and the rest of the company may know that all ladies are not like the Queen he has spoken of, and that all foolhardy and venturesome men do not compass their ends, I will tell you a story in which I will acquaint you with the opinion of a lady who deemed the vexation of failure in love to be harder of endurance than death itself. However, I shall give no names, because the events are so fresh in people’s minds that I should fear to offend some who are near of kin.”



A young gentleman sought to discover whether the offer of
an honour-able love would be displeasing to his master’s
sister, a lady of the most illustrious lineage in Flanders,
who had been twice widowed, and was a woman of muck spirit.
Meeting with a reply contrary to his desires, he attempted
to possess her by force; but she resisted him successfully,
and by the advice of her lady of honour, without seeming to
take notice of his designs and efforts, gradually ceased to
regard him with the favour with which she had been wont to
treat him. Thus, by his foolhardy presumption, he lost the
honourable and habitual companionship which, more than
others, he had had with her.(1)
1 This story is historical, and the incidents must have
occurred between 1520 and 1525.—L.
There lived in the land of Flanders a lady of such high lineage, that none more illustrious could be found. She was a widow, both her first and second husbands being dead, and she had no children living. During her widowhood she lived in retirement with her brother, by whom she was greatly loved, and who was a very great lord and married to the daughter of a King. This young Prince was a man much given to pleasure, fond of hunting, pastimes, and women, as his youth inclined him. He had a wife, however, who was of a very froward disposition, (2) and found no pleasure in her husband’s pursuits; wherefore this Lord always took his sister along with his wife, for she was a most joyous and pleasant companion, and withal a discreet and honourable woman.
In this Lord’s household there was a gentleman who, for stature, comeliness, and grace, surpassed all his fellows. This gentleman, (3) perceiving that his master’s sister was of merry mood and always ready for a laugh, was minded to try whether the offer of an honourable love would be displeasing to her.
2 The young prince here mentioned is Francis I., who at
this period was between twenty-five and thirty years old.
The froward wife is Claude of France (daughter of Louis XII.
and Anne of Brittany), whom Francis married in 1514, and who
died of consumption at Blois ten years later, while the King
was on his way to conquer Milan. (See the Memoir of
Margaret, pp. xxvi. and xxxv.)—Ed.
3 According to Brantôme, the Lady of Flanders, the young
Prince’s sister, was Queen Margaret herself, and the
gentleman who paid court to her was William Gouffier, Lord
of Bonnivet, of Crevecoeur, Thois, and Querdes, and also a
favourite of Francis I., with whom he was brought up, and by
whom he was employed in all the great enterprises of the
time. Bonnivet became Admiral of France in 1517, and two
years later he was created governor of Dauphiné, and
guardian of the Dauphin’s person. He negotiated the peace
and alliance with Henry VIII., and arranged all the
preliminaries of the interview known as the Field of the
Cloth of Gold (1520). In 1521, says Anselme in his Histoire
Généalogique, Bonnivet became governor of Guienne,
commanded the army sent to Navarre, and captured Fontarabia.
In 1524 he was despatched to Italy as lieutenant-general,
and besieged Milan, but was repeatedly repulsed, and finally
fell back on the Ticino. He was killed at Pavia (February
24, 1525), and was largely responsible for that disastrous
defeat, having urged Francis I. to give battle, contrary to
the advice of the more experienced captains. Bonnivet, as
mentioned by Queen Margaret in this story, had the
reputation of being one of the handsomest men of his time.—
L.
He made this offer, but the answer that he received from her was contrary to his desires. However, although her reply was such as beseemed a Princess and a woman of true virtue, she readily pardoned his hardihood for the sake of his comeliness and breeding, and let him know that she bore him no ill-will for what he had said. But she charged him never to speak to her after that fashion again; and this he promised, that he might not lose the pleasure and honour of her conversation. Nevertheless, as time went on, his love so increased that he forgot the promise he had made. He did not, however, risk further trial of words, for he had learned by experience, and much against his will, what virtuous replies she was able to make. But he reflected that if he could take her somewhere at a disadvantage, she, being a widow, young, lusty, and of a lively humour, would perchance take pity on him and on herself.
To compass his ends, he told his master that excellent hunting was to be had in the neighbourhood of his house, and that if it pleased him to repair thither and hunt three or four stags in the month of May, he could have no finer sport. The Lord granted the gentleman’s request, as much for the affection he bore him as for the pleasure of the chase, and repaired to his house, which was as handsome and as fairly ordered as that of the richest gentleman in the land.
The Lord and his Lady were lodged on one side of the house, and she whom the gentleman loved more than himself on the other. Her apartment was so well arranged, tapestried above and matted below,(4) that it was impossible to perceive a trap-door which was by the side of her bed, and which opened into a room beneath, that was occupied by the gentleman’s mother.(5)
4 In most palaces and castles at this period the walls were
covered with tapestry and the floors with matting. This
remark is necessary to enable one to understand Bonnivet’s
stratagem.—D.
5 Philippa de Montmorency, second wife of William Gouffier,
Lord of Boissy, who was Bonnivet’s father (Anselme’s
Histoire Généalogique, vol. vii. p. 880).—L.
She being an old lady, somewhat troubled by rheum, and fearful lest the cough she had should disturb the Princess, made exchange of chambers with her son. In the evening this old lady was wont to bring sweetmeats to the Princess for her collation,(6) at which the gentleman was present; and being greatly beloved by her brother and intimate with him, he was also suffered to be present when she rose in the morning and when she retired to bed, on which occasions he always found reasons for an increase of his affection.
6 At that period the collation, as the supper was called,
was served at seven in the evening, shortly before the
curfew.—B. J.
Thus it came to pass that one evening he made the Princess stay up very late, until at last, being desirous of sleep, she bade him leave her. He then went to his own room, and there put on the handsomest and best-scented shirt he had, and a nightcap so well adorned that nothing was lacking in it. It seemed, to him, as he looked at himself in his mirror, that no lady in the world could deny herself to one of his comeliness and grace. He therefore promised himself a happy issue to his enterprise, and so lay down on his bed, where in his desire and sure hope of exchanging it for one more honourable and pleasant, he looked to make no very long stay.
As soon as he had dismissed all his attendants he rose to fasten the door after them; and for a long time he listened to hear whether there were any sound in the room of the Princess, which was above his own. When he had made sure that all was quiet, he wished to begin his pleasant task, and little by little let down the trap-door, which was so excellently wrought, and so well covered with cloth, that it made not the least noise. Then he ascended into the room and came to the bedside of his lady, who was just falling asleep.
Forthwith, having no regard for the duty that he owed his mistress or for the house to which she belonged, he got into bed with her, without entreating her permission or making any kind of ceremony. She felt him in her arms before she knew that he had entered the room; but being strong, she freed herself from his grasp, and fell to striking, biting, and scratching him, demanding the while to know who he was, so that for fear lest she should call out he sought to stop her mouth with the bedclothes. But this he found it impossible to do, for when she saw that he was using all his strength to work her shame she did as much to baffle him. She further called as loudly as she could to her lady of honour,(7) who slept in her room; and this old and virtuous woman ran to her mistress in her nightdress.
7 The lady in question was Blanche de Tournon, daughter of
James de Tournon, by Jane de Polignac, and sister of
Cardinal de Tournon, Minister of Francis I. She first
married Raymond d’Agout, Baron of Sault in Provence, who
died in 1503; and secondly James de Chastillon, Chamberlain
to Charles VIII. and Louis XII., killed at the siege of
Ravenna in 1512. Brantôme states, moreover, that she
subsequently married Cardinal John du Bellay. (See Appendix
to the’present volume, C.) In this story, Margaret describes
the Princess of Flanders as having lost two husbands, with
the view of disguising the identity of her heroine. Her own
husband (the Duke of Alençon) was still alive; but Madame de
Chastillon had twice become a widow, and the Queen, who was
well aware of this, designedly ascribed to the Princess the
situation of the lady of honour. This story should be
compared with the poem “Quatre Dames et Quatre
Gentilhommes” in the Marguerites de la Marguerite.—F.
When the gentleman saw that he was discovered, he was so fearful of being recognised by the lady, that he descended in all haste through his trap-door; his despair at returning in such an evil plight being no less than his desire and assurance of a gracious reception had previously been. He found his mirror and candle on his table,(8) and looking at his face, all bleeding from the lady’s scratches and bites, whence the blood was trickling over his fine shirt, which had now more blood than gold (9) about it, he said—
8 It is not surprising that the mirror should have been
lying on the table. Mirrors were for a long time no larger
than our modern hand-glasses. That of Mary de’ Medici,
offered to her by the Republic of Venice, and now in the
Galerie d’Apollon at the Louvre, is extremely small, though
it has an elaborate frame enriched with precious cameos.
Even the mirrors placed by Louis XIV. in the celebrated
Galerie des Glaces at Versailles were no larger than
ordinary window-panes.—M.
9 Shirts were then adorned at the collar and in front with
gold-thread embroidery, such as is shown in some of Clouet’s
portraits. In M. de Laborde’s Comptes des Bâtiments du Roi
au XVIème Siècle (vol. ii.) mention is made of “a shirt
with gold work,” “a shirt with white work,” &c.; and also of
two beautiful women’s chemises in Holland linen “richly
worked with gold thread and silk, at the price of six crowns
apiece.”—M.
“Beauty! now hast thou been rewarded according to thy deserts. By reason of thy vain promises I attempted an impossible undertaking, and one that, instead of increasing my happiness, will perchance double my misfortune. I feel sure that if she knows I made this foolish attempt contrary to the promise I gave her, I shall lose the honourable and accustomed companionship which more than any other I have had with her. And my folly has well deserved this, for if I was to turn my good looks and grace to any account, I ought not to have hidden them in the darkness. I should not have sought to take that chaste body by force, but should have waited in long service and humble patience till love had conquered her. Without love, all man’s merits and might are of no avail.”
Thus he passed the night in tears, regrets, and sorrowings such as I cannot describe; and in the morning, finding his face greatly torn, he feigned grievous sickness and to be unable to endure the light, until the company had left his house.
The lady, who had come off victorious, knew that there was no man at her brother’s Court that durst attempt such an enterprise save him who had had the boldness to declare his love to her. She therefore concluded that it was indeed her host, and made search through the room with her lady of honour to discover how he could have entered it. But in this she failed, whereupon she said to her companion in great anger—
“You may be sure that it can have been none other than the lord of this house, and I will make such report of him to my brother in the morning that his head shall bear witness to my chastity.”
Seeing her in such wrath, the lady of honour said to her—
“Right glad am I, madam, to find you esteem your honour so highly that, to exalt it, you would not spare the life of a man who, for the love he bears you, has put it to this risk. But it often happens that one lessens what one thinks to increase; wherefore, I pray you, madam, tell me the truth of the whole matter.”
When the lady had fully related the business, the lady of honour said to her—
“You assure me that he had nothing from you save only scratches and blows?”
“I do assure you that it was so,” said the lady; “and, unless he find a rare surgeon, I am certain his face will bear the marks tomorrow.”
“Well, since it is thus, madam,” said the lady of honour, “it seems to me that you have more reason to thank God than to think of vengeance; for you may well believe that, since the gentleman had spirit enough to make such an attempt, his grief at having failed will be harder of endurance than any death you could award him. If you desire to be revenged on him, let love and shame do their work; they will torment him more grievously than could you. And if you would speak out for your honour’s sake,(10) beware, madam, lest you fall into a mishap like to his own.
10 In Boaistuau’s edition this passage runs: “Let love and
shame do their work, they will know better than you how to
torment him; and do this for your honour’s sake. Beware,”
&c.—L.
He, instead of obtaining the greatest delight he could imagine, has encountered the gravest vexation any gentleman could endure. So you, madam, thinking to exalt your honour, may perchance diminish it. If you make complaint, you will bring to light what is known to none, for you may rest assured that the gentleman on his side will never reveal aught of the matter. And even if my lord, your brother, should do justice to him at your asking, and the poor gentleman should die, yet would it everywhere be noised abroad that he had had his will of you, and most people would say it was unlikely a gentleman would make such an attempt unless the lady had given him great encouragement. You are young and fair; you live gaily with all; and there is no one at Court but has seen the kind treatment you have shown to the gentleman whom you suspect. Hence every one will believe that if he did this deed it was not without some fault on your side; and your honour, for which you have never had to blush, will be freely questioned wherever the story is related.”
On hearing the excellent reasoning of her lady of honour, the Princess perceived that she spoke the truth, and that she herself would, with just cause, be blamed on account of the close friendship which she had always shown towards the gentleman. Accordingly she inquired of her lady of honour what she ought to do.
“Madam,” replied the other, “since you are pleased to receive my counsels, having regard for the affection whence they spring, it seems to me you should be glad at heart to think that the most comely and gallant gentleman I have ever seen was not able, whether by love or by force, to turn you from the path of true virtue. For this, madam, you should humble yourself before God, and confess that it was not through your own merit, for many women who have led straighter lives than you have been humiliated by men less worthy of love than he. And you should henceforth be more than ever on your guard against proposals of love; for many have the second time yielded to dangers which on the first occasion they were able to avoid. Be mindful, madam, that love is blind, and that it makes people blind in such wise that the way appears safest just when it is most slippery. Further, madam, it seems to me that you should give no sign of what has befallen you, whether to him or to any one else, and that if he seeks to say anything on the matter, you should feign not to understand him. In this way you will avoid two dangers, the one of vain-glory in the victory you have won, and the other of recalling things so pleasant to the flesh that at mention of them the chastest can only with difficulty avoid feeling some sparks of the flame, though they strive their utmost to escape them. (11)
11 We here follow MS. No. 1520.—L.
Besides this, madam, in order that he may not think he has done anything pleasing in your sight, I am of opinion you should little by little withdraw the friendship you have been in the habit of showing him. In this way he will know how much you scorn his rashness, and how great is your goodness, since, content with the victory that God has given you, you seek no further vengeance upon him. And may God give you grace, madam, to continue in the virtue He has placed in your heart; and, knowing that all good things come from Him, may you love and serve Him better than before.”
The Princess determined to abide by the advice of her lady of honour, and then fell asleep with joy as great as was the sadness of her waking lover.
On the morrow, the lord, her brother, wishing to depart, inquired for his host, and was told that he was too ill to bear the light or to hear any one speak. The Prince was greatly astonished at this, and wished to go and see the gentleman; however, learning that he was asleep, he would not awake him, but left the house without bidding him farewell. He took with him his wife and sister, and the latter, hearing the excuses sent by the gentleman, who would not see the Prince or any of the company before their departure, felt convinced that it was indeed he who had so tormented her, and that he durst not let the marks which she had left upon his face be seen. And although his master frequently sent for him, he did not return to Court until he was quite healed of all his wounds, save only one—namely, that which love and vexation had dealt to his heart.
When he did return, and found himself in presence of his victorious foe, he could not but blush; and such was his confusion, that he who had formerly been the boldest of all the company, was often wholly abashed before her. Accordingly, being now quite certain that her suspicion was true, she estranged herself from him little by little, though not so adroitly that he did not perceive it; but he durst not give any sign for fear of meeting with something still worse, and so he kept his love concealed, patiently enduring the disgrace he had so well deserved.(12)
12 This story is referred to by Brantôme, both in his Vies
des Homines illustres et grands Capitaines français, and in
his Vies des Dames galantes. See Appendix to the
present volume (C. ).
“This, ladies, is a story which should be a warning to those who would grasp at what does not belong to them, and which, further, should strengthen the hearts of ladies, since it shows the virtue of this young Princess, and the good sense of her lady of honour. If the like fortune should befall any among you, the remedy has now been pointed out.”
“It seems to me,” said Hircan, “that the tall gentleman of whom you have told us was so lacking in spirit as to be unworthy of being remembered. With such an opportunity as that, he ought not to have suffered any one, old or young, to baffle him in his enterprise. It must be said, also, that his heart was not entirely filled with love, seeing that fear of death and shame found place within it.”
“And what,” replied Nomerfide, “could the poor gentleman have done with two women against him?”
“He ought to have killed the old one,” said Hircan, “and when the young one found herself without assistance she would have been already half subdued.”
“To have killed her!” said Nomerfide. “Then you would turn a lover into a murderer? Since such is your opinion, it would indeed be a fearful thing to fall into your hands.”
“If I had gone so far,” said Hircan, “I should have held it dishonourable not to achieve my purpose.”
Then said Geburon—
“You think it strange that a Princess, bred in all honour, should prove difficult of capture to one man. You should then be much more astonished at a poor woman who escaped out of the hands of two.”
“Geburon,” said Ennasuite, “I give my vote to you to tell the fifth tale, for I think you know something concerning this poor woman that will not be displeasing to us.”
“Since you have chosen me,” said Geburon, “I will tell you a story which I know to be true from having made inquiries concerning it on the spot. By this story you will see that womanly sense and virtue are not in the hearts and heads of Princesses alone, nor love and cunning in such as are most often deemed to possess them.”


Two Grey Friars, when crossing the river at the haven of
Coulon, sought to ravish the boatwoman who was taking them
over. She, however, being virtuous and Clever, so beguiled
them with words that, whilst promising to grant their
request, she deceived them and handed them over to justice.
They were then delivered up to their warden to receive such
punishment as they deserved.
At the haven of Coulon,(1) near Nyort, there lived a boatwoman who, day or night, did nothing but convey passengers across the ferry.
1 The village of Coulon, in Poitou (department of the Deux-
Sèvres), lies within seven miles of Niort, on the Niortaise
Sevre, which at this point is extremely wide.—L.
Now it chanced that two Grey Friars from Nyort were crossing the river alone with her, and as the passage is one of the longest in France, they began to make love to her, that she might not feel dull by the way. She returned them the answer that was due; but they, being neither fatigued by their journeying, nor cooled by the water, nor put to shame by her refusal, determined to take her by force, and, if she clamoured, to throw her into the river. She, however, was as virtuous and clever as they were gross and wicked, and said to them—
“I am not so ill-disposed as I seem to be, but I pray you grant me two requests. You shall then see that I am more ready to give than you are to ask.”
The friars swore to her by their good St. Francis that she could ask nothing that they would not grant in order to have what they desired of her.
“First of all,” she said, “I require you both to promise on oath that you will inform no man living of this matter.” This they promised right willingly.
“Then,” she continued, “I would have you take your pleasure with me one after the other, for it would be too great a shame for me to have to do with one in presence of the other. Consider which of you will have me first.”
They deemed her request a very reasonable one, and the younger friar yielded the first place to the elder. Then, as they were drawing near a little island, she said to the younger one—
“Good father, say your prayers here until I have taken your companion to another island. Then, if he praises me when he comes back, we will leave him here, and go away in turn together.”
The younger friar leapt out on to the island to await the return of his comrade, whom the boat-woman took away with her to another island. When they had reached the bank she said to him, pretending the while to fasten her boat to a tree—
“Look, my friend, and see where we can place ourselves.”
The good father stepped on to the island to seek for a convenient spot, but no sooner did she see him on land than she struck her foot against the tree and went off with her boat into the open stream, leaving both the good fathers to their deserts, and crying out to them as loudly as she could—
“Wait now, sirs, till the angel of God comes to console you; for you shall have nought that could please you from me to-day.”
The two poor monks, perceiving that they had been deceived, knelt down at the water’s edge and besought her not to put them to such shame; and they promised that they would ask nothing of her if she would of her goodness take them to the haven. But, still rowing away, she said to them—
“I should be doubly foolish if, after escaping out of your hands, I were to put myself into them again.”
When she had come to the village, she went to call her husband and the ministers of justice that they might go and take these fierce wolves, from whose fangs she had by the grace of God escaped. They set out accompanied by many people, for there was no one, big or little, but wished to share in the pleasure of this chase.
When the poor brethren saw such a large company approaching, they hid themselves each in his island, even as Adam did when he perceived his nakedness in the presence of God.(2) Shame set their sin clearly before them, and the fear of punishment made them tremble so that they were half dead. Nevertheless, they were taken prisoners amid the mockings and hootings of men and women.
Some said, “These good fathers preach chastity to us and then rob our wives of theirs.” (3)
2 See Genesis iii. 8-10.
3 The editions of 1558 and 1560 here contain this
additional phrase: “They do not dare to touch money with
bare hands, and yet they willingly finger the thighs of our
wives, which are more dangerous.”—L.
Others said, “They are like unto whited sepulchres, which indeed appear beautiful outward, but are within full of dead men’s bones and uncleanness.” (4) Then another voice cried, “By their fruits shall ye know what manner of trees they are.” (5)
You may be sure that all the passages in the Gospel condemning hypocrites were brought forward against the unhappy prisoners, who were, however, rescued and delivered by their Warden,(6) who came in all haste to claim them, assuring the ministers of justice that he would visit them with a greater punishment than laymen would venture to inflict, and that they should make reparation by saying as many masses and prayers as might be required. The judge granted the Warden’s request and gave the prisoners up to him; and the Warden, who was an upright man, so dealt with them that they never afterwards crossed a river without making the sign of the cross and recommending themselves to God.(7)
4 St. Matthew xxiii. 27.
5 “For every tree is known by his own fruit.”—St. Luke vi.
45.
6 The Father Superior of the Grey Friars was called the
Warden.—B.J.
7 Henry Etienne quotes this story in his Apologie pour
Hérodote, and praises the Queen for thus denouncing the
evil practices of the friars.—F.
“I pray you, ladies, consider, since this poor boatwoman had the wit to deceive two such evil men, what should be done by those who have read of and witnessed so many fair examples, and who have had the goodness of virtuous ladies ever before their eyes? Indeed, the virtue of well-bred women is not so much to be called virtue as habit. It is in the women who know nothing, who hear scarcely two good sermons during the whole year, who have no leisure to think of aught save the gaining of their miserable livelihood, and who nevertheless jealously guard their chastity, hard-pressed as they may be (8)—it is in such women as these that one discovers the virtue that is natural to the heart. Where man’s wit and might are smallest, there the Spirit of God performs the greatest work. And unhappy indeed is the lady who keeps not close ward over the treasure which brings her so much honour if it be well guarded, and so much shame if it be neglected.”
8 Boaistuau’s edition of 1558 here contains the following
interpolation: “As should be done by those who, having their
lives provided for, have no occupation save that of studying
Holy Writ, listening to sermons and preaching, and exerting
themselves to act virtuously in all things.”—L.
“It seems to me, Geburon,” said Longarine, “that there is no great virtue in refusing a Grey Friar, and that it would rather be impossible to love one.”
“Longarine,” replied Geburon, “they who are not accustomed to such lovers as yours do by no means despise the Grey Friars, for the latter are as handsome and as strong as we are, and they are readier and fresher also, for we are worn-out with our service. Moreover, they talk like angels and are as importunate as the devil, so that such women as have never seen other robes than their coarse drugget ones,(9) are truly virtuous when they escape out of their hands.”
9 Meaning who have never seen gallants in gay apparel.—Ed.
“In faith,” said Nomerfide, in a loud voice, “you may say what you like, but I would rather be thrown into the river than lie with a Grey Friar.‘’
“So you can swim well?” said Oisille, laughing.
Nomerfide took this question in bad part, for she thought that she was esteemed by Oisille less highly than she desired. Accordingly she answered in anger—
“There are some who have refused more agreeable men than Grey Friars without blowing a trumpet about it.”
Oisille laughed to see her so wrathful, and said to her—
“Still less do they beat a drum about what they have done and granted.”
“I see,” said Geburon, “that Nomerfide wishes to speak. I therefore give her my vote that she may relieve her heart in telling us some excellent story.”
“What has just been said,” replied Nomerfide, “touches me so little that it affords me neither pleasure nor pain. However, since I have your vote, I pray you listen to me whilst I show that, although one woman used cunning for a good purpose, others have been crafty for evil’s sake. Since we have sworn to tell the truth I will not hide it, for just as the boatwoman’s virtue brings no honour to other women unless they follow her example, so the vice of another cannot disgrace her. Wherefore, listen.”



An old one-eyed valet in the service of the Duke of Alençon
being advised that his wife was in love with a young man,
desired to know the truth, and feigned to go away into the
country for a few days. He returned, however, so suddenly
that his wife, on whom he was keeping watch, perceived how
matters stood, and whilst thinking to deceive her, he was
himself deceived.
There was in the service of Charles, last Duke of Alençon, an old valet who had lost an eye, and who was married to a wife much younger than himself. Now, since his master and mistress liked him as well as any man of his condition that was in their service, he was not able to visit his wife as often as he could have wished. Owing to this she so far forgot her honour and conscience as to fall in love with a young man, and the affair being at last noised abroad, the husband heard of it. He could not believe it, however, on account of the many notable tokens of love that were shown him by his wife.
Nevertheless, he one day determined to put the matter to the test, and to take revenge, if he were able, on the woman who had put him to such shame. For this purpose he pretended to go away to a place a short distance off for the space of two or three days.
As soon as he was gone, his wife sent for her lover, but he had not been with her for half-an-hour when the husband arrived and knocked loudly at the door. The wife well knew who it was and told her lover, who was so greatly confounded that he would fain have been in his mother’s womb, and cursed both his mistress and the love that had brought him into such peril. However, she bade him fear nothing, for she would devise a means to get him away without harm or shame to him, and she told him to dress himself as quickly as he could. All this time the husband was knocking at the door and calling to his wife at the top of his voice; but she feigned not to recognise him, and cried out to the people of the house—
“Why do you not get up and silence those who are making such a clamour at the door? Is this an hour to come to the houses of honest folk? If my husband were here he would soon make them desist.”
On hearing his wife’s voice the husband called to her as loudly as he could—
“Wife, open the door. Are you going to keep me waiting here till morning?”
Then, when she saw that her lover was ready to set forth, she opened the door.
“Oh, husband!” she began, “how glad I am that you are come. I have just had a wonderful dream, and was so pleased that I never before knew such delight, for it seemed to me that you had recovered the sight of your eye.” (1)
1 This is taken from No. xvi. of the Cent Nouvelles
Nouvelles, in which the wife exclaims: “Verily, at the very
moment when you knocked, my lord, I was greatly occupied
with a dream about you.”—“And what was it, sweetheart?”
asks the husband.—“By my faith, my lord,” replies the wife,
“it really seemed to me that you were come back, that you
were speaking to me, and that you saw as clearly with one
eye as with the other.”—Ed.
Then, embracing and kissing him, she took him by the head and covering his good eye with one hand, she asked him—
“Do you not see better than you did before?”
At that moment, whilst he saw not a whit, she made her lover sally forth. The husband immediately suspected the trick, and said to her—
“‘Fore God, wife, I will keep watch on you no more, for in thinking to deceive you, I have myself met with the cunningest deception that ever was devised. May God mend you, for it is beyond the power of man to put a stop to the maliciousness of a woman, unless by killing her outright. However, since the fair treatment I have accorded you has availed nothing for your amendment, perchance the scorn I shall henceforward hold you in will serve as a punishment.”
So saying he went away, leaving his wife in great distress. Nevertheless by the intercession of his friends and her own excuses and tears, he was persuaded to return to her again.(2)
2 Although Queen Margaret ascribes the foregoing adventure
to one of the officers of her husband’s household, and
declares that the narrative is quite true, the same subject
had been dealt with by most of the old story-tellers prior
to her time, and Deslongchamps points out the same incidents
even in the early Hindoo fables (see the Pantcha Tantra,
book I., fable vi.). A similar tale is to be found in the
Gesta Romanorum (cap. cxxii.), in the fabliaux collected
by Legrand d’Aussy (vol. iv., “De la mauvaise femme”), in P.
Alphonse’s Disciplina Clericalis (fab. vii.), in the
Decameron (day vii., story vi.), and in the Cent
Nouvelles Nouvelles (story xvi.). Imitations are also to be
found in Bandello (part i., story xxiii.), Malespini (story
xliv.), Sansovino (Cento Novelle), Sabadino (Novelle),
Etienne (Apologiepour Hérodote, ch. xv. ), De la Monnoye
(vol. ii.), D’Ouville (Contes, vol. ii.), &c.—L. & B. J.
“By this tale, ladies, you may see how quick and crafty a woman is in escaping from danger. And if her wit be quick to discover the means of concealing a bad deed, it would, in my belief, be yet more subtle in avoiding evil or in doing good; for I have always heard it said that wit to do well is ever the stronger.”
“You may talk of your cunning as much as you please,” said Hircan, “but my opinion is that had the same fortune befallen you, you could not have concealed the truth.”
“I had as lief you deemed me the most foolish woman on earth,” she replied.
“I do not say that,” answered Hircan, “but I think you more likely to be confounded by slander than to devise some cunning means to silence it.”
“You think,” said Nomerfide, “that every one is like you, who would use one slander for the patching of another; but there is danger lest the patch impair what it patches and the foundation be so overladen that all be destroyed. However, if you think that the subtlety, of which all believe you to be fully possessed, is greater than that found in women, I yield place to you to tell the seventh story; and, if you bring yourself forward as the hero, I doubt not that we shall hear wickedness enough.”
“I am not here,” replied Hircan, “to make myself out worse than I am; there are some who do that rather more than is to my liking.”
So saying he looked at his wife, who quickly said—
“Do not fear to tell the truth on my account. I can more easily bear to hear you relate your crafty tricks than to see them played before my eyes, though none of them could lessen the love I bear you.”
“For that reason,” replied Hircan, “I make no complaint of all the false opinions you have had of me. And so, since we understand each other, there will be more security for the future. Yet I am not so foolish as to relate a story of myself, the truth of which might be vexatious to you. I will tell you one of a gentleman who was among my dearest friends.”



By the craft and subtlety of a merchant an old woman was
deceived and the honour of her daughter saved.
In the city of Paris there lived a merchant who was in love with a young girl of his neighbourhood, or, to speak more truly, she was more in love with him than he with her. For the show he made to her of love and devotion was but to conceal a loftier and more honourable passion. However, she suffered herself to be deceived, and loved him so much that she had quite forgotten the way to refuse.
After the merchant had long taken trouble to go where he could see her, he at last made her come whithersoever it pleased himself. Her mother discovered this, and being a very virtuous woman, she forbade her daughter ever to speak to the merchant on pain of being sent to a nunnery. But the girl, whose love for the merchant was greater than her fear of her mother, went after him more than ever.
It happened one day, when she was in a closet all alone, the merchant came in to her, and finding himself in a place convenient for the purpose, fell to conversing with her as privily as was possible. But a maid-servant, who had seen him go in, ran and told the mother, who betook herself thither in great wrath. When the girl heard her coming, she said, weeping, to the merchant—“Alas! sweetheart, the love that I bear you will now cost me dear. Here comes my mother, who will know for certain what she has always feared and suspected.”
The merchant, who was not a bit confused by this accident, straightway left the girl and went to meet the mother. Stretching out his arms, he hugged her with all his might, and, with the same ardour with which he had begun to entertain the daughter, threw the poor old woman on to a small bed. She was so taken aback at being thus treated that she could find nothing to say but—“What do you want? Are you dreaming?”
For all that he ceased not to press her as closely as if she had been the fairest maiden in the world, and had she not cried out so loudly that her serving-men and women came to her aid, she would have gone by the same road as she feared her daughter was treading.
However, the servants dragged the poor old woman by main force out of the merchant’s arms, and she never knew for what reason he had thus used her. Meanwhile, her daughter took refuge in a house hard by where a wedding was going on. Since then she and the merchant have ofttimes laughed together at the expense of the old woman, who was never any the wiser.
“By this story, ladies, you may see how, by the subtlety of a man, an old woman was deceived and the honour of a young one saved. Any one who would give the names, or had seen the merchant’s face and the consternation of the old woman, would have a very tender conscience to hold from laughing. It is sufficient for me to prove to you by this story that a man’s wit is as prompt and as helpful at a pinch as a woman’s, and thus to show you, ladies, that you need not fear to fall into men’s hands. If your own wit should fail you, you will find theirs prepared to shield your honour.”
“In truth, Hircan,” said Longarine, “I grant that the tale is a very pleasant one and the wit great, but the example is not such as maids should follow. I readily believe there are some whom you would fain have approve it, but you are not so foolish as to wish that your wife, or her whose honour you set higher than her pleasure,(1) should play such a game. I believe there is none who would watch them more closely or shield them more readily than you.”
1 M. Frank, adopting the generally received opinion that
Hircan is King Henry of Navarre, believes this to be an
allusion to one of the King’s sisters—Ann, who married the
Count of Estrac, or Isabel, who married M. de Rohan—but it
is more likely that Henry’s daughter, Jane d’Albret, is the
person referred to.—Ed.
“By my conscience,” said Hircan, “if she whom you mention had done such a thing, and I knew nothing about it, I should think none the less of her. For all I know, some one may have played as good a trick on me; however, knowing nothing, I am unconcerned.”
At this Parlamente could not refrain from saying—
“A wicked man cannot but be suspicious; happy are those who give no occasion for suspicion.”
“I have never seen a great fire from which there came no smoke,” said Longarine, “but I have often seen smoke where there was no fire. The wicked are as suspicious when there is no mischief as when there is.”
“Truly, Longarine,” Hircan forthwith rejoined, “you have spoken so well in support of the honour of ladies wrongfully suspected, that I give you my vote to tell the eighth tale. I hope, however, that you will not make us weep, as Madame Oisille did, by too much praise of virtuous women.”
At this Longarine laughed heartily, and thus began:—“You want me to make you laugh, as is my wont, but it shall not be at women’s expense. I will show you, however, how easy it is to deceive them when they are inclined to be jealous and esteem themselves clever enough to deceive their husbands.”

The dedication with which Anthony Le Maçon prefaces his translation of Boccaccio contains several curious passages. In it Margaret is styled “the most high and most illustrious Princess Margaret of France, only sister of the King, Queen of Navarre, Duchess of Alençon and of Berry;” while the author describes himself as “Master Anthoine Le Maçon, Councillor of the King, Receiver General of his finances in Burgundy, and very humble secretary to this Queen.” He then proceeds to say:—
“You remember, my lady, the time when you made a stay of four or five months in Paris, during which you commanded me, seeing that I had freshly arrived from Florence, where I had sojourned during an entire year, to read to you certain stories of the Decameron of Boccaccio, after which it pleased you to command me to translate the whole book into our French language, assuring me that it would be found beautiful and entertaining. I then made you reply that I felt my powers were too weak to undertake such a work.... My principal and most reasonable excuse was the knowledge that I had of myself, being a native of the land of Dauphiné, where the maternal language is too far removed from good French.... However, it did not please you to accept any of my excuses, and you showed me that it was not fitting that the Tuscans should be so mistaken as to believe that their Boccaccio could not be rendered in our language as well as it is in theirs, ours having become so rich and so copious since the accession of the King, your brother, to the crown, that nothing has ever been written in any language that could not be expressed in this; and thus your will still was that I should translate it (the Decameron) when I had the leisure to do so. Seeing this and desiring, throughout my life, to do, if I can, even more than is possible to obey you, I began some time afterwards to translate one of the said stories, then two, then three, and finally to the number of ten or twelve, the best that I could choose, which I afterwards showed as much to people of the Tuscan nation as to people of ours, who all made me believe that the stories were, if not perfectly, at least very faithfully translated. Wherefore, allowing myself to be thus pleasantly deceived, if deceit there was, I have since set myself to begin the translation at one end and to finish it at the other....”
This dedicatory preface is followed by an epistle, written in Italian by Emilio Ferretti, and dated from Lyons, May I, 1545; and by a notice to the reader signed by Etienne Rosset, the bookseller, who in the King’s license, dated from St. Germain-en-Laye, Nov. 2, 1544, is described as “Rosset called the Mower, bookseller, residing in Paris, on the bridge of St. Michael, at the sign of the White Rose.” The first edition of Le Maçon’s translation (1545) was in folio; the subsequent ones of 1548, 1551, and 1553 being in octavo. It should be remembered that Le Maçon’s was by no means the first French version of the Decameron. Laurent du Premier-Faict had already rendered Boccaccio’s masterpiece into French in the reign of Charles VI., but unfortunately his translation, although of a pleasing naïveté, was not at all correct, having been made from a Latin version of the original. Manuscript copies of Laurent’s translation were to be found in the royal and most of the princely libraries of the fifteenth century.—Ed.
The letters of remission which at the instance of Henry VIII. were granted to Michael de St. Aignan in respect of the murder of James du Mesnil are preserved in the National Archives of France (Register J. 234, No. 191), and after the usual preamble, recite the culprit’s petition in these terms:—
“Whereas it appears from the prayer of Michael de St. Aignan, lord of the said place, (1) that heretofore he for a long time lived and resided in the town of Alençon in honour and good repute; but, to the detriment of his prosperity, life, and conduct there were divers evil-minded and envious persons who by sinister, cunning, and hidden means persecuted him with all the evils, wiles, and deceits that it is possible to conceive, albeit the said suppliant had never caused them displeasure, injury, or detriment; among others, one named James Dumesnil, a young man, to whom the said suppliant had procured all the pleasure and advantages that were in his power, and whom he had customarily admitted to his house, thinking that the said Dumesnil was his loyal friend, and charging his wife and his servants to treat him when he came as though he were his brother; by which means St. Aignan hoped to induce the said Dumesnil to espouse one of his relatives.
1 This was in all probability the village of St. Aignan on
the Sarthe, between Moulins-la-Marche and Bazoches, and
about twenty miles from Alençon. The personage here
mentioned should not be confounded with Emery de
Beauvilliers, whom Francis I. created Count of St. Aignan
(on the Cher), and whose descendants, many of whom were
distinguished generals and diplomatists, became dukes of the
same place.—Ed.
“But Dumesnil ill-requited the aforesaid good services and courtesies, and rendering evil for good, as is the practice of iniquity, endeavoured to and did cause an estrangement between the said St. Aignan and his wife, who had always lived together in good, great, and perfect affection. And the better to effect his purpose he (Dumesnil) gave the said wife to understand, among other things, that St. Aignan bore her no affection; that he daily desired her death; that she was mistaken in trusting him; and other evil things not fitting to be repeated, which the wife withstood, enjoining Dumesnil not to use such language again, as should he do so she would repeat it to her husband; but Dumesnil, persevering, on divers occasions when St. Aignan had absented himself, gave the wife of the latter to understand that he (St. Aignan) was dead, devising proofs thereof and conjectures, and thinking that by this means he would win her favour and countenance. But she still resisted him, which seeing, the said Dumesnil gave her to understand that St. Aignan would often absent himself, and that she would be happier if she had a husband who remained with her. And plotting to compass the death of the said St. Aignan, Dumesnil gave her to understand that if she would consent to the death of her husband he would marry her; and, in fact, he promised to marry her. And whereas she still refused to consent, the said Dumesnil found a means to gain a servant woman of the house, who, St. Aignan being absent and his wife in bed, opened the door to Dumesnil, who compelled the said wife to let him lie with her. And thenceforward Dumesnil made divers presents to the servant woman, so that she should poison the said suppliant; and she consented to his face; but at Easter confessed the matter to St. Aignan, entreating his forgiveness, and also saying and declaring it to the neighbours. And the said Dumesnil, knowing that he would incur blame and reproach if the matter were brought forward, seized and abducted the said servant woman in all diligence, and took her away from the town, whereby a scandal was occasioned.
“Moreover, it would appear that the said Dumesnil had been found several times by night watching the gardens and the door in view of slaying St. Aignan, as is notorious in Alençon, by virtue of the admission of the said Dumesnil himself. Whereupon St. Aignan, seeing his wife thus made the subject of scandal by Dumesnil, enjoined him to abstain from coming to his house to see his wife, and to consider the outrage and injury he had already inflicted upon him; declaring moreover that he could endure no more. To which Dumesnil refused to listen, declaring that he would frequent the house in spite of every one; albeit, in doing so, he might come by his death. Thereupon St. Aignan, being acquainted with the evil obstinacy of Dumesnil and desirous of avoiding greater misfortune, departed from the town of Alençon, and went to reside in the town of Argentan, ten leagues distant, whither he took his wife, thinking that Dumesnil would abstain from coming. Withal he did not abstain, but came several times to the said town of Argentan, and frequented his (St. Aignan’s) wife; whereby the people of Argentan were scandalised. And the said St. Aignan endeavoured to prevent him from coming, and employed the nurse of his child to remonstrate with Dumesnil, but the latter persevered, saying and declaring that he would kill St. Aignan, and would still go to Argentan, albeit it might cause his death. Insomuch that the said Dumesnil, on the eighth day of this month, departed from Alençon between two and three o’clock in the morning, a suspicious hour, having disguised himself and assumed attire unsuited to his calling, which is that of the law; wearing a Bearnese cloak,(2) a jacket of white woollen stuff underneath, all torn into strips, with a feathered cap upon his head, and having his face covered. In this wise he arrived at the said town of Argentan, accompanied by two young men, and lodged in the faubourgs at the sign of Notre Dame, and remained there clandestinely from noon till about eleven o’clock in the evening, when he asked the host for the key of the backdoor, so that he might go out on his private affairs, not wishing to be recognised.
“At the said suspicious hour, with his sword at his side,(3) and dressed and accoutred in the said garments, he started from his lodging with one of the said young men.
2 See ante, p. 24, note 8.
3 The French word is basion, which in the sixteenth
century was often used to imply a sword; arquebuses and
musketoons being termed basions à feu by way of
distinction. Moreover, it is expressly stated farther on
that Dumesnil had a sword.—Ed.
“In this wise Dumesnil reached the house of St. Aignan, which he found a means of entering, and gained a closet up above, near the room where the said St. Aignan and his wife slept. St. Aignan was without thought of this, inasmuch as he was ignorant of the enterprise of the said Dumesnil, being in the living room with one Master Thomas Guérin, who had come upon business. Now, as St. Aignan was disposing himself to go to bed, he told one of his servants, named Colas, to bring him his cas (4) and the servant having occasion to go up into a closet in which St. Aignan’s wife was sleeping, and in which the said Dumesnil was concealed, the latter, fearing that he might be recognised, suddenly came out with a drawn sword in his hand; whereupon the said Colas cried: ‘Help! There is a robber!’ And he declared to St. Aignan that he had seen a strange man who did not seem to be there for any good purpose; whereupon St. Aignan said to him: ‘One must find out who it is. Is there occasion for any one to come here at this hour?’ Thereupon Colas went after the said personage, whom he found in a little alley near the courtyard behind the house; and the said personage, having suddenly perceived Colas, endeavoured to strike him on the body with his weapon; but Colas withstood him and gave him a few blows,(5) for which reason he cried out ‘Help! Murder!’ Thereupon St. Aignan arrived, having a sword in his hand; and after him came the said Guérin. St. Aignan, who as yet did not know Dumesnil on account of his disguise, and also because it was wonderfully dark, found him calling out: ‘Murder! Confession!’ By which cry the said St. Aignan knew him, and was greatly perplexed, astonished, and angered, at seeing his enemy at such an hour in his house, he having been found there, with a weapon, in the closet. And the said St. Aignan recalling to memory the trouble and worry that Dumesnil had caused him, dealt him two or three thrusts in hot anger, and then said to him: ‘Hey! Wretch that thou art, what hast brought thee here? Wert thou not content with the wrong thou didst me in coming here previously? I never did thee an ill office.’ Whereupon the said Dumesnil said: ‘It is true, I have too grievously offended you, and am too wicked; I entreat your pardon.’ And thereupon he fell to the ground as if dead; which seeing, the said St. Aignan, realising the misfortune that had happened, said not a word, but recommended himself to God and withdrew into his room, where he found his wife in bed, she having heard nothing.
4 The en cas was a kind of light supper provided in case
one felt hungry at night-time. Most elaborate en cas,
consisting of several dishes, were frequently provided for
the kings of France.—Ed.
5 In the story Margaret asserts that it was Thomas Guérin
who attacked Dumesnil.—D.
“On the night of the said dispute, and a little later, St. Aignan went to see what the said Dumesnil was doing, and finding him in the courtyard dead, he helped to carry him into the stable, being too greatly incensed to act otherwise. And upon the said Colas asking him what should be done with the body, St. Aignan paid no heed to this question, because he was not master of himself; but merely said to Colas that he might do as he thought fit, and that the body might be interred in consecrated ground or placed in the street. After which St. Aignan withdrew into his room and slept with his wife, who had her maids with her. And on the morrow this same Colas declared to St. Aignan that he had taken the said body to be buried, so as to avoid a scandal. To all of which things St. Aignan paid no heed, but on the morrow sent to fetch the two young men in the service of the said Dumesnil, who were at his lodging, and had the horses removed from the said lodging, and gave orders to one of the young men to take them back.
“On account of all which occurrences he (St. Aignan) absented himself, &c, &c, but humbly entreating us, &c, &c. Wherefore we now give to the Bailiffs of Chartres and Caen, or to their Lieutenants, and to each of them severally and to all, &c, &c. Given at Châtelherault, in the month of July, the year of Grace, one thousand five hundred and twenty-six, and the twelfth of our reign.
“Signed: By the King on the report of the Council:
“De Nogent.“Visa: contentor.
“De Nogent.”
It will be seen that the foregoing petition contains various
contradictory statements. The closet, for instance, is at
first described as being near the room in which St. Aignan
and his wife slept, then it is asserted that the wife slept
in the closet, but ultimately the husband is shown joining
his wife in the bed-chamber, where she had heard nothing.
The character of the narrative is proof of its falsity, and
Margaret’s account of the affair may readily be accepted as
the more correct one.—Ed.
Les Vies des Dames galantes contains the following passage bearing upon Margaret’s 4th Tale. See Lalanne’s edition of Brantôme’s Works, vol. ix. p. 678 et sec.:—
“I have heard a lady of great and ancient rank relate that the late Cardinal du Bellay, whilst a Bishop and Cardinal, married Madame de Chastillon, and died married; and this lady said it in conversing with Monsieur de Manne, a Provençal of the house of Seulal, and Bishop of Frejus, who had attended the said Cardinal during fifteen years at the Court of Rome, and had been one of his private protonotaries. The conversation turning upon the said Cardinal, this lady asked Monsieur de Manne if he (the Cardinal) had ever said and confessed to him that he had been married. It was Monsieur de Manne who was astonished at such a question. He is still alive and can say if I am telling an untruth, for I was there. He replied that he had never heard the matter spoken of either to himself or to others. ‘Then it is I who inform you of it,’ said she, ‘for nothing could be more true but that he was married, and died really married to Madame de Chastillon.’
“I assure you that I laughed heartily, contemplating the astonished countenance of Monsieur de Manne, who was most conscientious and religious, and thought that he had known all the secrets of his late master; but he was as ignorant as a Gibuan as regards that one, which was indeed scandalous on account of the holy rank which he (Cardinal du Bellay) had held.
“This Madame de Chastillon was the widow of the late Monsieur de Chastillon, of whom it was said that he governed the little King Charles VIII., with Bourdillon and Bonneval, who governed the royal blood. He died at Ferrara, where he had been taken to have his wounds dressed, having been wounded at the siege of Ravenna.
“This lady became a widow when very young and beautiful, and on account of her being sensible and virtuous she was elected as lady of honour to the late Queen of Navarre. It was she who gave that fine advice to that lady and great princess, which is recorded in the hundred stories of the said Queen—the story of herself and a gentleman who had slipped into her bed during the night by a trap-door at the bedside, and who wished to enjoy her, but only obtained by it some fine scratches upon his handsome face. She (the Queen) wishing to complain to her brother, Madame de Chastillon made her that fine remonstrance which will be seen in the story, and gave her that beautiful advice which is one of the finest, most judicious, and most fitting that could be given to avoid scandal: did it come even from a first president of (the Parliament of) Paris. Yet it well showed that the lady was quite as artful and shrewd in such secret matters as she was sensible and prudent; and for this reason there is no need for doubt as to whether she kept her affair with the Cardinal a secret. My grandmother, Madame la Sénéchale of Poitou, had her place after her death, by election of King Francis who chose and elected her, and sent to fetch her even in her house, and gave her with his own hand to the Queen his sister, for he knew her to be a very well-advised and very virtuous lady, but not so shrewd, or artful, or ready-witted in such matters as her predecessor, or married either a second time.
“And if you wish to know to whom the story applies, it is to the Queen of Navarre herself and Admiral de Bonnivet, as I hold it from my late grandmother; and yet it seems to me that the said Queen should not have concealed her name, since the other could not obtain aught from her chastity, but went off in confusion, and since she herself had meant to divulge the matter had it not been for the fine and sensible remonstrance which was made to her by the said lady of honour, Madame de Chastillon. Whoever has read the story will find that she was a lady of honour, and I think that the Cardinal, her said husband, who was one of the best speakers and most learned, eloquent, wise, and shrewd men of his time, must have instilled into her this science of speaking and remonstrating so well.”
Brantôme also refers to the story in question in his Vies des Hommes illustres et grands Capitaines français (vol. ii. p. 162), wherein he says:—
“There is a tale in the stories of the Queen of Navarre, which speaks of a lord, the favourite of a king, whom he invited with all his court to one of his houses, where he made a trap-door in his room conducting to the bedside of a great princess, in view of lying with her, as he did, but, as the story relates, he obtained only scratches from her.”
END OF VOL. I. LONDON: PRINTED FOR THE SOCIETY OF ENGLISH BIBLIOPHILISTS
| Volume II. | Volume III. | Volume IV. | Volume V. |


| Volume I. | Volume III. | Volume IV. | Volume V. |
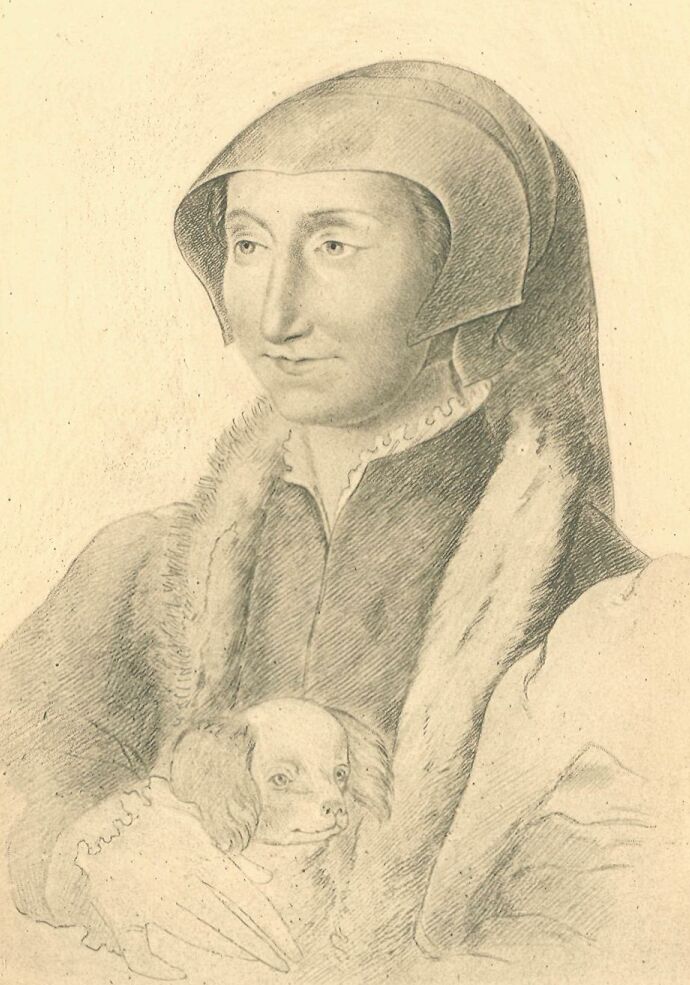


Contents
List of Illustrations
001a.jpg Bornet’s Concern on Discovering That his Wife Is Without Her Ring
013a.jpg the Dying Gentleman Receiving The Embraces Of His Sweetheart
025a.jpg the Countess Asking an Explanation from Amadour
095a.jpg the Grey Friar Telling his Tales
101a.jpg the Gentleman Killing The Duke
119a.jpg the Sea-captain Talking to The Lady
141a.jpg Bonnivet and the Lady of Milan
157a.jpg the Lady Taking Oath As to Her Conduct
183a.jpg the Gentleman Discovering The Trick
195a.jpg the King Showing his Sword
FIRST DAY—Continued.
Tale VIII. The misadventure of Bornet, who, planning with a friend of
his that both should lie with a serving-woman, discovers too late that
they have had to do with his own wife.
Tale IX. The evil fortune of a gentleman of Dauphiné, who dies of
despair because he cannot marry a damsel nobler and richer than himself.
Tale X. The Spanish story of Florida, who, after withstanding the love
of a gentleman named Amadour for many years, eventually becomes a nun.
SECOND DAY.
Prologue
Tale XI. (A). Mishap of the Lady de Roncex in the Grey Friars’ Convent
at Thouars.
Tale XI. (B). Facetious discourse of a Friar of Touraine.
Tale XII. Story of Alexander de’ Medici, Duke of Florence, whom his
cousin, Lorenzino de’ Medici, slew in order to save his sister’s honour.
Tale XIII. Praiseworthy artifice of a lady to whom a sea Captain sent
a letter and diamond ring, and who, by forwarding them to the Captain’s
wife as though they had been intended for her, united husband and wife
once more in all affection.
Tale XIV. The Lord of Bonnivet, after furthering the love entertained
by an Italian gentleman for a lady of Milan, finds means to take
the other’s place and so supplant him with the lady who had formerly
rejected himself.
Tale XV. The troubles and evil fortune of a virtuous lady who, after
being long neglected by her husband, becomes the object of his jealousy.
Tale XVI. Story of a Milanese Countess, who, after long rejecting the
love of a French gentleman, rewards him at last for his faithfulness,
but not until she has put his courage to the proof.
Tale XVII. The noble manner in which King Francis the First shows Count
William of Furstemberg that he knows of the plans laid by him against
his life, and so compels him to do justice upon himself and to leave
France.
Tale XVIII. A young gentleman scholar at last wins a lady’s love, after
enduring successfully two trials that she had made of him.
Appendix to Vol. II

A certain Bornet, less loyal to his wife than she to him,
desired to lie with his maidservant, and made his enterprise
known to a friend, who, hoping to share in the spoil, so
aided and abetted him, that whilst the husband thought to
lie with his servant he in truth lay with his wife. Unknown
to the latter, he then caused his friend to participate in
the pleasure which rightly belonged to himself alone, and
thus made himself a cuckold without there being any guilt on
the part of his wife. (1)
In the county of Alletz (2) there lived a man named Bornet, who being married to an upright and virtuous wife, had great regard for her honour and reputation, as I believe is the case with all the husbands here present in respect to their own wives. But although he desired that she should be true to him, he was not willing that the same law should apply to both, for he fell in love with his maid-servant, from whom he had nothing to gain save the pleasure afforded by a diversity of viands.
1 For a list of tales similar to this one, see post,
Appendix A.
2 Alletz, now Alais, a town of Lower Languedoc (department
of the Gard), lies on the Gardon, at the foot of the
Cevennes mountains. It was formerly a county, the title
having been held by Charles, Duke of Angoulême, natural son
of Charles IX.—M.
Now he had a neighbour of the same condition as his own, named Sandras, a tabourer (3) and tailor by trade, and there was such friendship between them that, excepting Bornet’s wife, they had all things in common. It thus happened that Bornet told his friend of the enterprise he had in hand against the maid-servant; and Sandras not only approved of it, but gave all the assistance he could to further its accomplishment, hoping that he himself might share in the spoil.
3 Tabourers are still to be found in some towns of Lower
Languedoc and in most of those of Provence, where they
perambulate the streets playing their instruments. They are
in great request at all the country weddings and other
festive gatherings, as their instruments supply the
necessary accompaniment to the ancient Provençal dance, the
farandole.—Ed.
The maid-servant, however, was loth to consent, and finding herself hard pressed, she went to her mistress, told her of the matter, and begged leave to go home to her kinsfolk, since she could no longer endure to live in such torment. Her mistress, who had great love for her husband and had often suspected him, was well pleased to have him thus at a disadvantage, and to be able to show that she had doubted him justly. Accordingly, she said to the servant—
“Remain, my girl, but lead my husband on by degrees, and at last make an appointment to lie with him in my closet. Do not fail to tell me on what night he is to come, and see that no one knows anything about it.”
The maid-servant did all that her mistress had commanded her, and her master in great content went to tell the good news to his friend. The latter then begged that, since he had been concerned in the business, he might have part in the result. This was promised him, and, when the appointed hour was come, the master went to lie, as he thought, with the maid-servant; but his wife, yielding up the authority of commanding for the pleasure of obeying, had put herself in the servant’s place, and she received him, not in the manner of a wife, but after the fashion of a frightened maid. This she did so well that her husband suspected nothing.
I cannot tell you which of the two was the better pleased, he at the thought that he was deceiving his wife, or she at really deceiving her husband. When he had remained with her, not as long as he wished, but according to his powers, which were those of a man who had long been married, he went out of doors, found his friend, who was much younger and lustier than himself, and told him gleefully that he had never met with better fortune. “You know what you promised me,” said his friend to him.
“Go quickly then,” replied the husband, “for she may get up, or my wife have need of her.”
The friend went off and found the supposed maid-servant, who, thinking her husband had returned, denied him nothing that he asked of her, or rather took, for he durst not speak. He remained with her much longer than her husband had done, whereat she was greatly astonished, for she had not been wont to pass such nights. Nevertheless, she endured it all with patience, comforting herself with the thought of what she would say to him on the morrow, and of the ridicule that she would cast upon him.
Towards daybreak the man rose from beside her, and toying with her as he was going away, snatched from her finger the ring with which her husband had espoused her, and which the women of that part of the country guard with great superstition. She who keeps it till her death is held in high honour, while she who chances to lose it, is thought lightly of as a person who has given her faith to some other than her husband.
The wife, however, was very glad to have it taken, thinking it would be a sure proof of how she had deceived her husband. When the friend returned, the husband asked him how he had fared. He replied that he was of the same opinion as himself, and that he would have remained longer had he not feared to be surprised by daybreak. Then they both went to the friend’s house to take as long a rest as they could. In the morning, while they were dressing, the husband perceived the ring that his friend had on his finger, and saw that it was exactly like the one he had given to his wife at their marriage. He thereupon asked his friend from whom he had received the ring, and when he heard he had snatched it from the servant’s finger, he was confounded and began to strike his head against the wall, saying—“Ah! good Lord! have I made myself a cuckold without my wife knowing anything about it?”
“Perhaps,” said his friend in order to comfort him, “your wife gives her ring into the maid’s keeping at night-time.”
The husband made no reply, but took himself home, where he found his wife fairer, more gaily dressed, and merrier than usual, like one who rejoiced at having saved her maid’s conscience, and tested her husband to the full, at no greater cost than a night’s sleep. Seeing her so cheerful, the husband said to himself—
“If she knew of my adventure she would not show me such a pleasant countenance.”
Then, whilst speaking to her of various matters, he took her by the hand, and on noticing that she no longer wore the ring, which she had never been accustomed to remove from her finger, he was quite overcome.
“What have you done with your ring?” he asked her in a trembling voice.
She, well pleased that he gave her an opportunity to say what she desired, replied—
“O wickedest of men! From whom do you imagine you took it? You thought it was from my maid-servant, for love of whom you expended more than twice as much of your substance as you ever did for me. The first time you came to bed I thought you as much in love as it was possible to be; but after you had gone out and were come back again, you seemed to be a very devil. Wretch! think how blind you must have been to bestow such praises on my person and lustiness, which you have long enjoyed without holding them in any great esteem. ‘Twas, therefore, not the maid-servant’s beauty that made the pleasure so delightful to you, but the grievous sin of lust which so consumes your heart and so clouds your reason that in the frenzy of your love for the servant you would, I believe, have taken a she-goat in a nightcap for a comely girl! Now, husband, it is time to amend your life, and, knowing me to be your wife, and an honest woman, to be as content with me as you were when you took me for a pitiful strumpet. What I did was to turn you from your evil ways, so that in your old age we might live together in true love and repose of conscience. If you purpose to continue your past life, I had rather be severed from you than daily see before my eyes the ruin of your soul, body, and estate. But if you will acknowledge the evil of your ways, and resolve to live in fear of God and obedience to His commandments, I will forget all your past sins, as I trust God will forget my ingratitude in not loving Him as I ought to do.”
If ever man was reduced to despair it was this unhappy husband. Not only had he abandoned this sensible, fair, and chaste wife for a woman who did not love him, but, worse than this, he had without her knowledge made her a strumpet by causing another man to participate in the leasure which should have been for himself alone; and thus he had made himself horns of everlasting derision. However, seeing his wife in such wrath by reason of the love he had borne his maid-servant, he took care not to tell her of the evil trick that he had played her; and entreating her forgiveness, with promises of full amendment of his former evil life, he gave her back the ring which he had recovered from his friend. He entreated the latter not to reveal his shame; but, as what is whispered in the ear is always proclaimed from the housetop, the truth, after a time, became known, and men called him cuckold without imputing any shame to his wife.
“It seems to me, ladies, that if all those who have committed like offences against their wives were to be punished in the same way, Hircan and Saffredent would have great cause for fear.”
“Why, Longarine,” said Saffredent, “are none in the company married save Hircan and I?”
“Yes, indeed there are others,” she replied, “but none who would play a similar trick.”
“Whence did you learn,” asked Saffredent, “that we ever solicited our wives’ maid-servants?”
“If the ladies who are in question,” said Longarine, “were willing to speak the truth, we should certainly hear of maid-servants dismissed without notice.”
“Truly,” said Geburon, “you are a most worthy lady! You promised to make the company laugh, and yet are angering these two poor gentlemen.”
“Tis all one,” said Longarine: “so long as they do not draw their swords, their anger will only serve to increase our laughter.”
“A pretty business indeed!” said Hircan. “Why, if our wives chose to believe this lady, she would embroil the seemliest household in the company.”
“I am well aware before whom I speak,” said Longarine. “Your wives are so sensible and bear you so much love, that if you were to give them horns as big as those of a deer, they would nevertheless try to persuade themselves and every one else that they were chaplets of roses.”
At this the company, and even those concerned, laughed so heartily that their talk came to an end. However, Dagoucin, who had not yet uttered a word, could not help saying—
“Men are very unreasonable when, having enough to content themselves with at home, they go in search of something else. I have often seen people who, not content with sufficiency, have aimed at bettering themselves, and have fallen into a worse position than they were in before. Such persons receive no pity, for fickleness is always blamed.”
“But what say you to those who have not found their other half?” asked Simontault. “Do you call it fickleness to seek it wherever it may be found?”
“Since it is impossible,” said Dagoucin, “for a man to know the whereabouts of that other half with whom there would be such perfect union that one would not differ from the other, he should remain steadfast wherever love has attached him. And whatsoever may happen, he should change neither in heart nor in desire. If she whom you love be the image of yourself, and there be but one will between you, it is yourself you love, and not her.”
“Dagoucin,” said Hircan, “you are falling into error. You speak as though we should love women without being loved in return.”
“Hircan,” replied Dagoucin, “I hold that if our love be based on the beauty, grace, love, and favour of a woman, and our purpose be pleasure, honour, or profit, such love cannot long endure; for when the foundation on which it rests is gone, the love itself departs from us. But I am firmly of opinion that he who loves with no other end or desire than to love well, will sooner yield up his soul in death than suffer his great love to leave his heart.”
“In faith,” said Simontault, “I do not believe that you have ever been in love. If you had felt the flame like other men, you would not now be picturing to us Plato’s Republic, which may be described in writing but not be put into practice.”
“Nay, I have been in love,” said Dagoucin, “and am so still, and shall continue so as long as I live. But I am in such fear lest the manifestation of this love should impair its perfection, that I shrink from declaring it even to her from whom I would fain have the like affection. I dare not even think of it lest my eyes should reveal it, for the more I keep my flame secret and hidden, the more does my pleasure increase at knowing that my love is perfect.”
“For all that,” said Geburon, “I believe that you would willingly have love in return.”
“I do not deny it,” said Dagoucin, “but even were I beloved as much as I love, my love would not be increased any more than it could be lessened, were it not returned with equal warmth.”
Upon this Parlamente, who suspected this fantasy of Dagoucin’s, said—
“Take care, Dagoucin; I have known others besides you who preferred to die rather than speak.”
“Such persons, madam;” said Dagoucin, “I deem very happy.”
“Doubtless,” said Saffredent, “and worthy of a place among the innocents of whom the Church sings:
‘Non loquendo sed moriendo confessi sunt.’ (4)
4 From the ritual for the Feast of the Holy Innocents.—M.
I have heard much of such timid lovers, but I have never yet seen one die. And since I myself have escaped death after all the troubles I have borne, I do not think that any one can die of love.”
“Ah, Saffredent!” said Dagoucin, “how do you expect to be loved since those who are of your opinion never die? Yet have I known a goodly number who have died of no other ailment than perfect love.”
“Since you know such stories,” said Longarine, “I give you my vote to tell us a pleasant one, which shall be the ninth of to-day.”
“To the end,” said Dagoucin, “that signs and miracles may lead you to put faith in what I have said, I will relate to you something which happened less than three years ago.”



The perfect love borne by a gentleman to a damsel, being too deeply concealed and disregarded, brought about his death, to the great regret of his sweetheart.
Between Dauphiné and Provence there lived a gentleman who was far richer in virtue, comeliness, and honour than in other possessions, and who was greatly in love with a certain damsel. I will not mention her name, out of consideration for her kinsfolk, who are of good and illustrious descent; but you may rest assured that my story is a true one. As he was not of such noble birth as herself, he durst not reveal his affection, for the love he bore her was so great and perfect that he would rather have died than have desired aught to her dishonour. Seeing that he was so greatly beneath her, he had no hope of marrying her; in his love, therefore, his only purpose was to love her with all his strength and as perfectly as he was able. This he did for so long a time that at last she had some knowledge of it; and, seeing that the love he bore her was so full of virtue and of good intent, she felt honoured by it, and showed him in turn so much favour that he, who sought nothing better than this, was well contented.
But malice, which is the enemy of all peace, could not suffer this honourable and happy life to last, and certain persons spoke to the maiden’s mother of their amazement at this gentleman being thought so much of in her house. They said that they suspected him of coming there more on account of her daughter than of aught else, adding that he had often been seen in converse with her. The mother, who doubted the gentleman’s honour as little as that of any of her own children, was much distressed on hearing that his presence was taken in bad part, and, dreading lest malicious tongues should cause a scandal, she entreated that he would not for some time frequent her house as he had been wont to do. He found this hard to bear, for he knew that his honourable conversation with her daughter did not deserve such estrangement. Nevertheless, in order to silence evil gossip, he withdrew until the rumours had ceased; then he returned as before, his absence having in no wise lessened his love.
One day, however, whilst he was in the house, he heard some talk of marrying the damsel to a gentleman who did not seem to him to be so very rich that he should be entitled to take his mistress from him. So he began to pluck up courage, and engaged his friends to speak for him, believing that, if the choice were left to the damsel, she would prefer him to his rival. Nevertheless, the mother and kinsfolk chose the other suitor, because he was much richer; whereupon the poor gentleman, knowing his sweetheart to be as little pleased as himself, gave way to such sorrow, that by degrees, and without any other distemper, he became greatly changed, seeming as though he had covered the comeliness of his face with the mask of that death, to which hour by hour he was joyously hastening.
Meanwhile, he could not refrain from going as often as was possible to converse with her whom he so greatly loved. But at last, when strength failed him, he was constrained to keep his bed; yet he would not have his sweetheart know of this, lest he should cast part of his grief on her. And giving himself up to despair and sadness, he was no longer able to eat, drink, sleep, or rest, so that it became impossible to recognise him by reason of his leanness and strangely altered features.
Some one brought the news of this to his sweetheart’s mother, who was a lady full of charity, and who had, moreover, such a liking for the gentleman, that if all the kinsfolk had been of the same opinion as herself and her daughter, his merits would have been preferred to the possessions of the other. But the kinsfolk on the father’s side would not hear of it. However, the lady went with her daughter to see the unhappy gentleman, and found him more dead than alive. Perceiving that the end of his life was at hand, he had that morning confessed and received the Holy Sacrament, thinking to die without seeing anybody more. But although he was at death’s door, when he saw her who for him was the resurrection and the life come in, he felt so strengthened that he started up in bed.
“What motive,” said he to the lady, “has inclined you to come and see one who already has a foot in the grave, and of whose death you are yourself the cause?”
“How is it possible,” said the lady, “that the death of one whom we like so well can be brought about by our fault? Tell me, I pray, why you speak in this manner?”
“Madam,” he replied, “I concealed my love for your daughter as long as I was able; and my kinsfolk, in speaking of a marriage between myself and her, made known more than I desired, since I have thereby had the misfortune to lose all hope; not, indeed, in regard to my own pleasure, but because I know that she will never have such fair treatment and so much love from any other as she would have had from me. Her loss of the best and most loving friend she has in the world causes me more affliction than the loss of my own life, which I desired to preserve for her sake only. But since it cannot in any wise be of service to her, the loss of it is to me great gain.”
Hearing these words, the lady and her daughter sought to comfort him.
“Take courage, my friend,” said the mother. “I pledge you my word that, if God gives you back your health, my daughter shall have no other husband but you. See, she is here present, and I charge her to promise you the same.”
The daughter, weeping, strove to assure him of what her mother promised. He well knew, however, that even if his health were restored he would still lose his sweetheart, and that these fair words were only uttered in order somewhat to revive him. Accordingly, he told them that had they spoken to him thus three months before, he would have been the lustiest and happiest gentleman in France; but that their aid came so late, it could bring him neither belief nor hope. Then, seeing that they strove to make him believe them, he said—
“Well, since, on account of my feeble state, you promise me a blessing which, even though you would yourselves have it so, can never be mine, I will entreat of you a much smaller one, for which, however, I was never yet bold enough to ask.”
They immediately vowed that they would grant it, and bade him ask boldly.
“I entreat you,” he said, “to place in my arms her whom you promise me for my wife, and to bid her embrace and kiss me.”
The daughter, who was unaccustomed to such familiarity, sought to make some difficulty, but her mother straightly commanded her, seeing that the gentleman no longer had the feelings or vigour of a living man. Being thus commanded, the girl went up to the poor sufferer’s bedside, saying—
“I pray you, sweetheart, be of good cheer.”
Then, as well as he could, the dying man stretched forth his arms, wherein flesh and blood alike were lacking, and with all the strength remaining in his bones embraced her who was the cause of his death. And kissing her with his pale cold lips, he held her thus as long as he was able. Then he said to her—
“The love I have borne you has been so great and honourable, that, excepting in marriage, I have never desired of you any other favour than the one you are granting me now, for lack of which and with which I shall cheerfully yield up my spirit to God. He is perfect love and charity. He knows the greatness of my love and the purity of my desire, and I beseech Him, while I hold my desire within my arms, to receive my spirit into His own.”
With these words he again took her in his arms, and with such exceeding ardour that his enfeebled heart, unable to endure the effort, was deprived of all its faculties and life; for joy caused it so to swell that the soul was severed from its abode and took flight to its Creator.
And even when the poor body had lain a long time without life, and was thus unable to retain its hold, the love which the damsel had always concealed was made manifest in such a fashion that her mother and the dead man’s servants had much ado to separate her from her lover. However, the girl, who, though living, was in a worse condition than if she had been dead, was by force removed at last out of the gentleman’s arms. To him they gave honourable burial; and the crowning point of the ceremony was the weeping and lamentation of the unhappy damsel, who having concealed her love during his lifetime, made it all the more manifest after his death, as though she wished to atone for the wrong that she had done him. And I have heard that although she was given a husband to comfort her, she has never since had joy in her heart. (1)
1 By an expression made use of by Dagoucin (see ante),
Queen Margaret gives us to understand that the incidents
here related occurred three years prior to the writing of
the story. It may be pointed out, however, that there is
considerable analogy between the conclusion of this tale and
the death of Geffroy Rudel de Blaye, one of the earliest
troubadours whose name has been handed down to us. Geffroy,
who lived at the close of the twelfth century, became so
madly enamoured of the charms of the Countess of Tripoli,
after merely hearing an account of her moral and physical
perfections, that, although in failing health, he embarked
for Africa to see her. On reaching the port of Tripoli, he
no longer had sufficient strength to leave the vessel,
whereupon the Countess, touched by his love, visited him on
board, taking his hand and giving him a kindly greeting.
Geffroy could scarcely say a few words of thanks; his
emotion was so acute that he died upon the spot. See J. de
Nostredame’s Vies des plus Célèbres et Anciens Poëtes
Provençaux(Lyons, 1575, p. 25); Raynouard’s Choix des
Poésies des Troubadours (vol. v. p. 165); and also
Raynouard’s Histoire Littéraire de la France (vol. xiv. p.
559).—L.
“What think you of that, gentlemen, you who would not believe what I said? Is not this example sufficient to make you confess that perfect love, when concealed and disregarded, may bring folks to the grave? There is not one among you but knows the kinsfolk on the one and the other side, (2) and so you cannot doubt the story, although nobody would be disposed to believe it unless he had some experience in the matter.”
2 This certainly points to the conclusion that the tale is
founded upon fact, and not, as M. Leroux de Lincy suggests,
borrowed from the story of Geffroy Rudel de Blaye. It will
have been observed (ante) that the Queen of Navarre
curiously enough lays the scene of her narrative between
Provence and Dauphiné. These two provinces bordered upon one
another, excepting upon one point where they were separated
by the so-called Comtat Venaissin or Papal state of Avignon.
Here, therefore, the incidents of the story, if authentic,
would probably have occurred. The story may be compared with
Tale L. (post).—Ed.
When the ladies heard this they all had tears in their eyes, but Hircan said to them—
“He was the greatest fool I ever heard of. By your faith, now, I ask you, is it reasonable that we should die for women who are made only for us, or that we should be afraid to ask them for what God has commanded them to give us? I do not speak for myself nor for any who are married. I myself have all that I want or more; but I say it for such men as are in need. To my thinking, they must be fools to fear those whom they should rather make afraid. Do you not perceive how greatly this poor damsel regretted her folly? Since she embraced the gentleman’s dead body—an action repugnant to human nature—she would not have refused him while he was alive had he then trusted as much to boldness as he trusted to pity when he lay upon his death-bed.”
“Nevertheless,” said Oisille, “the gentleman most plainly showed that he bore her an honourable love, and for this he will ever be worthy of all praise. Chastity in a lover’s heart is something divine rather than human.”
“Madam,” said Saffredent, “in support of Hircan’s opinion, which is also mine, I pray you believe that Fortune favours the bold, and that there is no man loved by a lady but may at last, in whole or in part, obtain from her what he desires, provided he seek it with wisdom and passion. But ignorance and foolish fear cause men to lose many a good chance; and then they impute their loss to their mistress’s virtue, which they have never verified with so much as the tip of the finger. A fortress was never well assailed but it was taken.”
“Nay,” said Parlamente, “I am amazed that you two should dare to talk in this way. Those whom you have loved owe you but little thanks, or else your courting has been carried on in such evil places that you deem all women to be alike.”
“For myself, madam,” said Saffredent, “I have been so unfortunate that I am unable to boast; but I impute my bad luck less to the virtue of the ladies than to my own fault, in not conducting my enterprises with sufficient prudence and sagacity. In support of my opinion I will cite no other authority than the old woman in the Romance of the Rose, who says—
‘Of all, fair sirs, it truly may be said,
Woman for man and man for woman’s made.’ (3)
3 From John de Mehun’s continuation of the poem.—M. 2
Accordingly I shall always believe that if love once enters a woman’s heart, her lover will have fair fortune, provided he be not a simpleton.”
“Well,” said Parlamente, “if I were to name to you a very loving woman who was greatly sought after, beset and importuned, and who, like a virtuous lady, proved victorious over her heart, flesh, love and lover, would you believe this true thing possible?”
“Yes,” said he, “I would.”
“Then,” said Parlamente, “you must all be hard of belief if you do not believe this story.”
“Madam,” said Dagoucin, “since I have given an example to show how the love of a virtuous gentleman lasted even until death, I pray you, if you know any such story to the honour of a lady, to tell it to us, and so end this day. And be not afraid to speak at length, for there is yet time to relate many a pleasant matter.”
“Then, since I am to wind up the day,” said Parlamente, “I will make no long preamble, for my story is so beautiful and true that I long to have you know it as well as I do myself. Although I was not an actual witness of the events, they were told to me by one of my best and dearest friends in praise of the man whom of all the world he had loved the most. But he charged me, should I ever chance to relate them, to change the names of the persons. Apart, therefore, from the names of persons and places the story is wholly true.”



Florida, after virtuously resisting Amadour, who had assailed her honour almost to the last extremity, repaired, upon her husbands death, to the convent of Jesus, and there took the veil. (1)
1 This tale appears to be a combination of fact and fiction.
Although Queen Margaret states that she has changed the
names of the persons, and also of the places where the
incidents happened, several historical events are certainly
brought into the narrative, the scene of which is laid in
Spain during the reign of Ferdinand and Isabella. M. Le Roux
de Lincy is of opinion, however, that Margaret really refers
to some affair at the Court of Charles VIII. or Louis XII.,
and he remarks that there is great similarity between the
position of the Countess of Aranda, left a widow at an early
age with a son and a daughter, and that of Louise of Savoy
with her two children. M. Lacroix and M. Dillaye believe the
hero and heroine to be Admiral de Bonnivet and Margaret. It
has often been suspected that the latter regarded her
brother’s favourite with affection until after the attempt
related in Tale IV.—Ed.
In the county of Aranda, (2) in Aragon, there lived a lady who, while still very young, was left a widow, with a son and a daughter, by the Count of Aranda, the name of the daughter being Florida. This lady strove to bring up her children in all the virtues and qualities which beseem lords and gentlemen, so that her house was reputed to be one of the most honourable in all the Spains. She often went to Toledo, where the King of Spain dwelt, and when she came to Saragossa, which was not far from her house, she would remain a long while with the Queen and the Court, by whom she was held in as high esteem as any lady could be.
2 Aranda, in the valley of the Duero, between Burgos
and Madrid, is one of the most ancient towns in Spain, but of
miserable aspect, although a large trade is carried on there
in cheap red wines. (Ferdinand and Isabella resided for some
time at Aranda.—Ed.)
Going one day, according to her custom, to visit the King, then at his castle of La Jasserye, (3) at Saragossa, this lady passed through a village belonging to the Viceroy of Catalonia, (4) who, by reason of the great wars between the kings of France and Spain, had not been wont to stir from the frontier at Perpignan. But for the time being there was peace, so that the Viceroy and all his captains had come to do homage to the King. The Viceroy, learning that the Countess of Aranda was passing through his domain, went to meet her, not only for the sake of the ancient friendship he bore her, but in order to do her honour as a kinswoman of the King’s.
3 This castle is called La Jafferie in Boaistuau’s edition
of 1558, and several learned commentators have speculated as
to which is the correct spelling. Not one of them seems to
have been aware that in the immediate vicinity of Saragossa
there still stands an old castle called El Jaferia or
Aljaferia, which, after being the residence of the Moorish
sovereigns, became that of the Spanish kings of Aragon. It
has of modern times been transformed into barracks.—Ed.
4 Henry of Aragon, Duke of Segorbe and Count of Ribagorce,
was Viceroy of Catalonia at this period. He was called the
Infante of Fortune, on account of his father having died
before his birth in 1445.—B. J.
Now he had in his train many honourable gentlemen, who, in the long waging of war, had gained such great honour and renown that all who saw them and consorted with them deemed themselves fortunate. Among others there was one named Amadour, who, although but eighteen or nineteen years old, was possessed of such well-assured grace and of such excellent understanding that he would have been chosen from a thousand to hold a public office. It is true that this excellence of understanding was accompanied by such rare and winsome beauty that none could look at him without pleasure. And if his comeliness was of the choicest, it was so hard pressed by his speech that one knew not whether to give the greatest honour to his grace, his beauty, or the excellence of his conversation.
What caused him, however, to be still more highly esteemed was his great daring, which was no whit diminished by his youth. He had already shown in many places what he could do, so that not only the Spains, but France and Italy also made great account of his merits. For in all the wars in which he had taken part he had never spared himself, and when his country was at peace he would go in quest of wars in foreign lands, where he was loved and honoured by both friend and foe.
This gentleman, for the love he bore his commander, had come to the domain where the Countess of Aranda had arrived, and remarking the beauty and grace of her daughter Florida, who was then only twelve years old, he thought to himself that she was the fairest maiden he had ever seen, and that if he could win her favour it would give him greater satisfaction than all the wealth and pleasure he might obtain from another. After looking at her for a long time he resolved to love her, although his reason told him that what he desired was impossible by reason of her lineage as well as of her age, which was such that she could not yet understand any amorous discourse. In spite of this, he fortified himself with hope, and reflected that time and patience might bring his efforts to a happy issue. And from that moment the kindly love, which of itself alone had entered Amadour’s heart, assured him of all favour and the means of attaining his end.
To overcome the greatest difficulty before him, which consisted in the remoteness of his own home and the few opportunities he would have of seeing Florida again, he resolved to get married. This was contrary to what he had determined whilst with the ladies of Barcelona and Perpignan, in which places he was in such favour that little or nothing was refused him; and, indeed, by reason of the wars, he had dwelt so long on the frontiers that, although he was born near Toledo, he seemed rather a Catalan than a Castillan. He came of a rich and honourable house, but being a younger son, he was without patrimony; and thus it was that Love and Fortune, seeing him neglected by his kin, determined to make him their masterpiece, endowing him with such qualities as might obtain what the laws of the land had refused him. He was of much experience in the art of war, and was so beloved by all lords and princes that he refused their favours more frequently than he had occasion to seek them.
The Countess, of whom I have spoken, arrived then at Saragossa and was well received by the King and all his Court. The Governor of Catalonia often came to visit her, and Amadour failed not to accompany him that he might have the pleasure of merely seeing Florida, for he had no opportunity of speaking with her. In order to establish himself in this goodly company he paid his addresses to the daughter of an old knight, his neighbour. This maiden was named Avanturada, and was so intimate with Florida that she knew all the secrets of her heart. Amadour, as much for the worth which he found in Avanturada as for the three thousand ducats a year which formed her dowry, determined to address her as a suitor, and she willingly gave ear to him. But as he was poor and her father was rich, she feared that the latter would never consent to the marriage except at the instance of the Countess of Aranda. She therefore had recourse to the lady Florida and said to her—
“You have seen, madam, that Castilian gentleman who often talks to me. I believe that all his aim is to have me in marriage. You know, however, what kind of father I have; he will never consent to the match unless he be earnestly entreated by the Countess and you.”
Florida, who loved the damsel as herself, assured her that she would lay the matter to heart as though it were for her own benefit; and Avanturada then ventured so far as to present Amadour to her. He was like to swoon for joy on kissing Florida’s hand, and although he was accounted the readiest speaker in Spain, yet in her presence he became dumb. At this she was greatly surprised, for, although she was only twelve years old, she had already often heard it said that there was no man in Spain who could speak better or with more grace. So, finding that he said nothing to her, she herself spoke.
“Senor Amadour,” she began, “the renown you enjoy throughout all the Spains has made you known to everybody here, and all are desirous of affording you pleasure. If therefore I can in any way do this, you may dispose of me.”
Amadour was in such rapture at sight of the lady’s beauty that he could scarcely utter his thanks. However, although Florida was astonished to find that he made no further reply, she imputed it rather to some whim than to the power of love; and so she withdrew, without saying anything more.
Amadour, who perceived the qualities which even in earliest youth were beginning to show themselves in Florida, now said to her whom he desired to marry—
“Do not be surprised if I lost the power of utterance in presence of the lady Florida. I was so astonished at finding such qualities and such sensible speech in one so very young that I knew not what to say to her. But I pray you, Avanturada, you who know her secrets, tell me if she does not of necessity possess the hearts of all the gentlemen of the Court. Any who know her and do not love her must be stones or brutes.”
Avanturada, who already loved Amadour more than any other man in the world, could conceal nothing from him, but told him that Florida was loved by every one. However, by reason of the custom of the country, few spoke to her, and only two had as yet made any show of love towards her. These were two princes of Spain, and they desired to marry her, one being the son of the Infante of Fortune (5) and the other the young Duke of Cardona. (6)
5 M. Lacroix asserts that the Infante of Fortune left no son
by his wife, Guyomare de Castro y Norogna; whereas M. Le
Roux de Lincy contends that he had a son—Alfonso of Aragon—
who in 1506 was proposed as a husband for Crazy Jane.
Alfonso would therefore probably be the prince referred to
by Margaret.—Ed.
6 Cardona, a fortified town on the river Cardoner, at a few
miles from Barcelona, was a county in the time of Ferdinand
and Isabella, and was raised by them to the rank of a duchy
in favour of Ramon Folch I. To-day it has between two and
three thousand inhabitants, and is chiefly noted for its
strongly built castillo. The young Duke spoken of by Queen
Margaret would be Ramon Folch’s son, who was also named
Ramon.—B. J. and Ed.
“I pray you,” said Amadour, “tell me which of them you think she loves the most.”
“She is so discreet,” said Avanturada, “that on no account would she confess to having any wish but her mother’s. Nevertheless, as far as can be judged, she likes the son of the Infante of Fortune far more than she likes the young Duke of Cardona. But her mother would rather have her at Cardona, for then she would not be so far away. I hold you for a man of good understanding, and, if you are so minded, you may judge of her choice this very day, for the son of the Infante of Fortune, who is one of the handsomest and most accomplished princes in Christendom, is being brought up at this Court. If we damsels could decide the marriage by our opinions, he would be sure of having the Lady Florida, for they would make the comeliest couple in all Spain. You must know that, although they are both young, she being but twelve and he but fifteen, it is now three years since their love for each other first began; and if you would secure her favour, I advise you to become his friend and follower.”
Amadour was well pleased to find that Florida loved something, hoping that in time he might gain the place not of husband but of lover. He had no fear in regard to her virtue, but was rather afraid lest she should be insensible to love. After this conversation he began to consort with the son of the Infante of Fortune, and readily gained his favour, being well skilled in all the pastimes that the young Prince was fond of, especially in the handling of horses, in the practice of all kinds of weapons, and indeed in every diversion and pastime befitting a young man.
However, war broke out again in Languedoc, and it was necessary that Amadour should return thither with the Governor. This he did, but not without great regret, since he could in no wise contrive to return to where he might see Florida. Accordingly, when he was setting forth, he spoke to a brother of his, who was majordomo to the Queen of Spain, and told him of the good match he had found in the Countess of Aranda’s house, in the person of Avanturada; entreating him, in his absence, to do all that he could to bring about the marriage, by employing his credit with the King, the Queen, and all his friends. The majordomo, who was attached to his brother, not only by reason of their kinship, but on account of Amadour’s excellent qualities, promised to do his best. This he did in such wise that the avaricious old father forgot his own nature to ponder over the qualities of Amadour, as pictured to him by the Countess of Aranda, and especially by the fair Florida, as well as by the young Count of Aranda, who was now beginning to grow up, and to esteem people of merit. When the marriage had been agreed upon by the kinsfolk, the Queen’s majordomo sent for his brother, there being at that time a truce between the two kings. (7)
Meanwhile, the King of Spain withdrew to Madrid to avoid the bad air which prevailed in divers places, and, by the advice of his Council, as well as at the request of the Countess of Aranda, he consented to the marriage of the young Count with the heiress Duchess of Medina Celi. (8) He did this no less for their contentment and the union of the two houses than for the affection he bore the Countess of Aranda; and he caused the marriage to be celebrated at the castle of Madrid. (9)
7 There had been a truce in 1497, but Queen Margaret
probably alludes to that of four months’ duration towards
the close of 1503.—B.J.
8 Felix-Maria, widow of the Duke of Feria, and elder sister
of Luis Francisco de la Cerda, ninth of the name. She became
heiress to the titles and estates of the house of Medina-
Celi upon her brother’s death. If, however, Queen Margaret
is really describing some incident in her own life, she must
refer to Louis XII.‘s daughter, Claude, married in 1514 to
Francis I.—D.
9 The castle here referred to was the Moorish Alcazar,
destroyed by fire in 1734. The previous statement that King
Ferdinand withdrew to Madrid on account of the bad air
prevailing in other places is borne out by the fact that the
town enjoyed a most delightful climate prior to the
destruction of the forests which surrounded it.—Ed.
Amadour was present at this wedding, and succeeded so well in furthering his own union, that he married Avanturada, whose affection for him was far greater than his was for her. But this marriage furnished him with a very convenient cloak, and gave him an excuse for resorting to the place where his spirit ever dwelt. After he was married he became very bold and familiar in the Countess of Aranda’s household, so that he was no more distrusted than if he had been a woman. And although he was now only twenty-two years of age, he showed such good sense that the Countess of Aranda informed him of all her affairs, and bade her son consult with him and follow his counsel.
Having gained their esteem thus far, Amadour comported himself so prudently and calmly that even the lady he loved was not aware of his affection for her. By reason, however, of the love she bore his wife, to whom she was more attached than to any other woman, she concealed none of her thoughts from him, and was pleased to tell him of all her love for the son of the Infante of Fortune. Although Amadour’s sole aim was to win her entirely for himself, he continually spoke to her of the Prince; indeed, he cared not what might be the subject of their converse, provided only that he could talk to her for a long time. However, he had not remained a month in this society after his marriage when he was constrained to return to the war, and he was absent for more than two years without returning to see his wife, who continued to live in the place where she had been brought up.
Meanwhile Amadour often wrote to her, but his letters were for the most part messages to Florida, who on her side never failed to return them, and would with her own hand add some pleasant words to the letters which Avanturada wrote. It was on this account that the husband of the latter wrote to her very frequently; yet of all this Florida knew nothing except that she loved Amadour as if he had been her brother. Several times during the course of five years did Amadour return and go away again; yet so short was his stay that he did not see Florida for two months altogether. Nevertheless, in spite of distance and length of absence, his love continued to increase.
At last it happened that he made a journey to see his wife, and found the Countess far removed from the Court, for the King of Spain was gone into Andalusia, (10) taking with him the young Count of Aranda, who was already beginning to bear arms.
10 There had been a revolt at Granada in 1499, and in the
following year the Moors rose in the Alpujarras, whereupon
King Ferdinand marched against them in person.—L.
Thus the Countess had withdrawn to a country-house belonging to her on the frontiers of Aragon and Navarre. She was well pleased on seeing Amadour, who had now been away for nearly three years. He was made welcome by all, and the Countess commanded that he should be treated like her own son. Whilst he was with her she informed him of all the affairs of her household, leaving most of them to his judgment. And so much credit did he win in her house that wherever he visited all doors were opened to him, and, indeed, people held his prudence in such high esteem that he was trusted in all things as though he had been an angel or a saint.
Florida, by reason of the love she bore his wife and himself, sought him out wherever he went. She had no suspicion of his purpose, and was unrestrained in her manners, for her heart was free from love, save that she felt great contentment whenever she was near Amadour. To more than this she gave not a thought.
Amadour, however, had a hard task to escape the observation of those who knew by experience how to distinguish a lover’s looks from another man’s; for when Florida, thinking no evil, came and spoke familiarly to him, the fire that was hidden in his heart so consumed him that he could not keep the colour from rising to his face or sparks of flame from darting from his eyes. Thus, in order that none might be any the wiser, he began to pay court to a very beautiful lady named Paulina, a woman so famed for beauty in her day that few men who saw her escaped from her toils.
This Paulina had heard how Amadour had made love at Barcelona and Perpignan, insomuch that he had gained the affection of the highest and most beautiful ladies in the land, especially that of a certain Countess of Palamos, who was esteemed the first for beauty among all the ladies of Spain; and she told him that she greatly pitied him, since, after so much good fortune, he had married such an ugly wife. Amadour, who well understood by these words that she had a mind to supply his need, made her the fairest speeches he could devise, seeking to conceal the truth by persuading her of a falsehood. But she, being subtle and experienced in love, was not to be put off with mere words; and feeling sure that his heart was not to be satisfied with such love as she could give him, she suspected he wished to make her serve as a cloak, and so kept close watch upon his eyes. These, however, knew so well how to dissemble, that she had nothing to guide her but the barest suspicion.
Nevertheless, her observation sorely troubled Amadour; for Florida, who was ignorant of all these wiles, often spoke to him before Paulina in such a familiar fashion that he had to make wondrous efforts to compel his eyes to belie his heart. To avoid unpleasant consequences, he one day, while leaning against a window, spoke thus to Florida—
“I pray you, sweetheart, counsel me whether it is better for a man to speak or die?”
Florida forthwith replied—
“I shall always counsel my friends to speak and not to die. There are few words that cannot be mended, but life once lost can never be regained.”
“Will you promise me, then,” said Amadour, “that you will not be displeased by what I wish to tell you, nor yet alarmed at it, until you have heard me to the end?”
“Say what you will,” she replied; “if you alarm me, none can reassure me.”
“For two reasons,” he then began, “I have hitherto been unwilling to tell you of the great affection that I feel for you. First, I wished to prove it to you by long service, and secondly, I feared that you might deem it presumption in me, who am but a simple gentleman, to address myself to one upon whom it is not fitting that I should look. And even though I were of royal station like your own, your heart, in its loyalty, would suffer none save the son of the Infante of Fortune, who has won it, to speak to you of love. But just as in a great war necessity compels men to devastate their own possessions and to destroy their corn in the blade, that the enemy may derive no profit therefrom, so do I risk anticipating the fruit which I had hoped to gather in season, lest your enemies and mine profit by it to your detriment. Know, then, that from your earliest youth I have devoted myself to your service and have ever striven to win your favour. For this purpose alone I married her whom I thought you loved best, and, being acquainted with the love you bear to the son of the Infante of Fortune, I have striven to serve him and consort with him, as you yourself know. I have sought with all my power for everything that I thought could give you pleasure. You see that I have won the esteem of your mother, the Countess, and of your brother, the Count, and of all you love, so that I am regarded here, not as a dependant, but as one of the family. All my efforts for five years past have had no other end than that I might spend my whole life near you.
“Understand that I am not one of those who would by these means seek to obtain from you any favour or pleasure otherwise than virtuous. I know that I cannot marry you, and even if I could, I would not do so in face of the love you bear him whom I would fain see your husband. And as for loving you with a vicious love like those who hope that long service will bring them a reward to the dishonour of a lady, that is far from my purpose. I would rather see you dead than know that you were less worthy of being loved, or that your virtue had diminished for the sake of any pleasure to me. For the end and reward of my service I ask but one thing, namely, that you will be so faithful a mistress to me, as never to take your favour from me, and that you will suffer me to continue as I now am, trusting in me more than in any other, and accepting from me the assurance that if for your honour’s sake, or for aught concerning you, you ever have need of a gentleman’s life, I will gladly place mine at your disposal. You may be sure also that whatever I may do that is honourable and virtuous, will be done solely for love of you. If for the sake of ladies less worthy than you I have ever done anything that has been considered of account, be sure that, for a mistress like yourself, my enterprise will so increase, that things I heretofore found impossible will become very easy to me. If, however, you will not accept me as wholly yours, I am resolved to lay aside my arms and to renounce the valour which has failed to help me in my need. So I pray you grant me my just request, for your honour and conscience cannot refuse it.”
The maiden, hearing these unwonted words, began to change colour and to cast down her eyes like a woman in alarm. However, being sensible and discreet, she replied—
“Since you already have what you ask of me, Amadour, why make me such a long harangue? I fear me lest beneath your honourable words there be some hidden guile to deceive my ignorance and youth, and I am sorely perplexed what to reply. Were I to refuse the honourable love you offer, I should do contrary to what I have hitherto done, for I have always trusted you more than any other man in the world. Neither my conscience nor my honour oppose your request, nor yet the love I bear the son of the Infante of Fortune, for that is founded on marriage, to which you do not aspire. I know of nothing that should hinder me from answering you according to your desire, if it be not a fear arising from the small need you have for talking to me in this wise; for if what you ask is already yours, why speak of it so ardently?”
Amadour, who was at no loss for an answer, then said to her—
“Madam, you speak very discreetly, and you honour me so greatly by the trust which you say you have in me, that if I were not satisfied with such good fortune I should be quite unworthy of it. But consider, madam, that he who would build an edifice to last for ever must be careful to have a sure and stable foundation. In the same way I, wishing to continue for ever in your service, must not only take care to have the means of remaining near to you, but also to prevent any one from knowing of the great affection that I bear you. Although it is honourable enough to be everywhere proclaimed, yet those who know nothing of lovers’ hearts often judge contrary to the truth, and thence come reports as mischievous as though they were true. I have been prompted to say this, and led to declare my love to you, because Paulina, feeling in her heart that I cannot love her, holds me in suspicion and does nought but watch my face wherever I may be. Hence, when you come and speak to me so familiarly in her presence, I am in great fear lest I should make some sign on which she may ground her judgment, and should so fall into that which I am anxious to avoid. For this reason I am lead to entreat you not to come and speak to me so suddenly before her or before others whom you know to be equally malicious, for I would rather die than have any living creature know the truth. Were I not so regardful of your honour, I should not have sought this converse with you, for I hold myself sufficiently happy in the love and trust you bear me, and I ask nothing more save that they may continue.”
Florida, who could not have been better pleased, began to be sensible of an unwonted feeling in her heart. She saw how honourable were the reasons which he laid before her; and she told him that virtue and honour replied for her, and that she granted him his request. Amadour’s joy at this no true lover can doubt.
Florida, however, gave more heed to his counsel than he desired, for she became timid not only in presence of Paulina but elsewhere, and ceased to seek him out as she had been accustomed to do. While they were thus separated she took Amadour’s constant converse with Paulina in bad part, for, seeing that the latter was beautiful, she could not believe that Amadour did not love her. To beguile her sorrow she conversed continually with Avanturada, who was beginning to feel very jealous of her husband and Paulina, and often complained of them to Florida, who comforted her as well as she could, being herself smitten with the same disease. Amadour soon perceived the change in Florida’s demeanour, and forthwith thought that she was keeping aloof from him not merely by his own advice, but also on account of some bitter fancies of her own.
One day, when they were coming from vespers at a monastery, he spoke to her, and asked—
“What countenance is this you show me, madam?”
“That which I believe you desire,” replied Florida.
Thereupon, suspecting the truth, and desiring to know whether he was right, he said to her—
“I have used my time so well, madam, that Paulina no longer has any suspicion of you.”
“You could not do better,” she replied, “both for yourself and for me. While giving pleasure to yourself you bring me honour.”
Amadour gathered from this speech that she believed he took pleasure in conversing with Paulina, and so great was his despair that he could not refrain from saying angrily to her—
“In truth, madam, you begin betimes to torment your lover and pelt him with hard words. I do not think I ever had a more irksome task than to be obliged to hold converse with a lady I do not love. But since you take what I have done to serve you in bad part, I will never speak to her again, happen what may. And that I may hide my wrath as I have hidden my joy, I will betake me to some place in the neighbourhood, and there wait till your caprice has passed away. I hope, however, I shall there receive tidings from my captain and be called back to the war, where I will remain long enough to show you that nothing but yourself has kept me here.”
So saying, he forthwith departed without waiting for her reply.
Florida felt the greatest vexation and sorrow imaginable; and love, meeting with opposition, began to put forth its mighty strength. She perceived that she had been in the wrong, and wrote continually to Amadour entreating him to return, which he did after a few days, when his anger had abated.
I cannot undertake to tell you minutely all that they said to each other in order to destroy this jealousy. But at all events he won the victory, and she promised him that not only would she never believe he loved Paulina, but that she would ever be convinced he found it an intolerable martyrdom to speak either to Paulina or to any one else except to do herself a service.
When love had conquered this first suspicion, and while the two lovers were beginning to take fresh pleasure in conversing together, news came that the King of Spain was sending all his army to Salces. (11)
11 Salces, a village about fifteen miles north of Perpignan,
noted for its formidable fortress, still existing and
commanding a pass through the Corbière Mountains, which in
the fifteenth and sixteenth centuries separated France from
Roussillon, then belonging to Spain. The French burnt the
village and demolished the fort of Salces in 1496, but the
latter was rebuilt by the Spaniards in the most massive
style. The walls of the fort are 66 feet thick at the base
and 54 feet thick at the summit. When Queen Margaret
returned from Spain in 152,5 she reached France by the pass
of Salces. (See vol. i. p. xlvi.).—Ed.
Amadour, accustomed ever to be the first in battle, failed not to seize this opportunity of winning renown; but in truth he set forth with unwonted regret, both on account of the pleasure he was losing and because he feared that he might find a change on his return. He knew that Florida, who was now fifteen or sixteen years old, was sought in marriage by many great princes and lords, and he reflected that if she were married during his absence he might have no further opportunity of seeing her, unless, indeed, the Countess of Aranda gave her his wife, Avanturada, as a companion. However, by skilful management with his friends, he obtained a promise from both mother and daughter that wherever Florida might go after her marriage thither should his wife, Avanturada, accompany her. Although it was proposed to marry Florida in Portugal, it was nevertheless resolved that Avanturada should never leave her. With this assurance, yet not without unspeakable regret, Amadour went away and left his wife with the Countess.
When Florida found herself alone after his departure, she set about doing such good and virtuous works as she hoped might win her the reputation that belongs to the most perfect women, and might prove her to be worthy of such a lover as Amadour. He having arrived at Barcelona, was there welcomed by the ladies as of old; but they found a greater change in him than they believed it possible for marriage to effect in any man. He seemed to be vexed by the sight of things he had formerly desired; and even the Countess of Palamos, whom he had loved exceedingly, could not persuade him to visit her.
Amadour remained at Barcelona as short a time as possible, for he was impatient to reach Salces, where he alone was now awaited. When he arrived, there began between the two kings that great and cruel war which I do not purpose to describe. (12) Neither will I recount the noble deeds that were done by Amadour, for then my story would take up an entire day; but you must know that he won renown far above all his comrades. The Duke of Najera (13) having arrived at Perpignan in command of two thousand men, requested Amadour to be his lieutenant, and so well did Amadour fulfil his duty with this band, that in every skirmish the only cry was “Najera!” (14)
12 In 1503 the French, under Marshals de Rieux and de Gié,
again besieged Salces, which had a garrison of 1200 men. The
latter opposed a vigorous defence during two months, and
upon the arrival of the old Duke of Alba with an army of
succour the siege had to be raised.—B. J.
13 Pedro Manriquez de Lara, Count of Trevigno, created Duke
of Najera by Ferdinand and Isabella in 1501.—B. J.
14 The Duke’s war-cry, repeated by his followers as a
rallying signal in the mêlée. War-cries varied greatly.
“Montjoie St. Denis” was that of the kings of France, and
“Passavant le meilleur” (the best to the front) that of the
Counts of Champagne. In other instances the war-cry
consisted of a single word, “Bigorre” being that of the
kings of Navarre, and “Flanders” that of the Princess of
Beaujeu. When the war-cry was merely a name, as in the case
of the Duke of Najera, it belonged to the head of the
family.—D.
Now it came to pass that the King of Tunis, who for a long time had been at war with the Spaniards, heard that the kings of France and Spain were warring with each other on the frontiers of Perpignan and Narbonne, and bethought himself that he could have no better opportunity of vexing the King of Spain. Accordingly, he sent a great number of light galleys and other vessels to plunder and destroy all such badly-guarded places as they could find on the coasts of Spain. (15)The people of Barcelona seeing a great fleet passing in front of their town, sent word of the matter to the Viceroy, who was at Salces, and he forthwith despatched the Duke of Najera to Palamos. (16) When the Moors saw that place so well guarded, they made a feint of passing on; but returning at midnight, they landed a large number of men, and the Duke of Najera, being surprised by the enemy, was taken prisoner.
15 The above two sentences, deficient in the MS. followed by
M. Le Roux de Lincy, have been borrowed from MS. No. 1520
(Bib. Nat.). It was in 1503 that a Moorish flotilla ravaged
the coast of Catalonia.—Ed.
16 The village of Palamos, on the shores of the
Mediterranean, south of Cape Bagur, and within fifteen miles
from Gerona.—Ed.
Amadour, who was on the alert and heard the din, forthwith assembled as many of his men as possible, and defended himself so stoutly that the enemy, in spite of their numbers, were for a long time unable to prevail against him. But at last, hearing that the Duke of Najera was taken, and that the Turks had resolved to set fire to Palamos and burn him in the house which he was holding against them, he thought it better to yield than to cause the destruction of the brave men who were with him. He also hoped that by paying a ransom he might yet see Florida again. Accordingly, he gave himself up to a Turk named Dorlin, a governor of the King of Tunis, who brought him to his master. By the latter he was well received and still better guarded; for the King deemed that in him he held the Achilles of all the Spains.
Thus Amadour continued for two years in the service of the King of Tunis. The news of the captures having reached Spain, the kinsfolk of the Duke of Najera were in great sorrow; but those who held the country’s honour dear deemed Amadour the greater loss. The rumour came to the house of the Countess of Aranda, where the hapless Avanturada at that time lay grievously sick. The Countess, who had great misgivings as to the affection which Amadour bore to her daughter, though she suffered it and concealed it for the sake of the merits she perceived in him, took Florida apart and told her the mournful tidings. Florida, who was well able to dissemble, replied that it was a great loss to the entire household, and that above all she pitied his poor wife, who was herself so ill. Nevertheless, seeing that her mother wept exceedingly, she shed a few tears to bear her company; for she feared that if she dissembled too far the feint might be discovered. From that time the Countess often spoke to her of Amadour, but never could she surprise a look to guide her judgment.
I will pass over the pilgrimages, prayers, supplications, and fasts which Florida regularly performed to ensure the safety of Amadour. As soon as he had arrived at Tunis, he failed not to send tidings of himself to his friends, and by a trusty messenger he apprised Florida that he was in good health, and had hopes of seeing her again. This was the only consolation the poor lady had in her grief, and you may be sure that, since she was permitted to write, she did so with all diligence, so that Amadour had no lack of her letters to comfort him.
The Countess of Aranda was about this time commanded to repair to Saragossa, where the King had arrived; and here she found the young Duke of Cardona, who so pressed the King and Queen that they begged the Countess to give him their daughter in marriage. (17) The Countess consented, for she was unwilling to disobey them in anything, and moreover she considered that her daughter, being so young, could have no will of her own.
17 The Spanish historians state that in 1513 the King, to
put an end to a quarrel between the Count of Aranda and the
Count of Ribagorce, charged Father John of Estuniga,
Provincial of the Order of St. Francis, to negotiate a
reconciliation between them, based on the marriage of the
eldest daughter of the Count of Aranda with the eldest son
of the Count of Ribagorce. The latter refusing his consent,
was banished from the kingdom.—D.
When all was settled, she told Florida that she had chosen for her the match which seemed most suitable. Florida, knowing that when a thing is once done there is small room for counsel, replied that God was to be praised for all things; and, finding her mother look coldly upon her, she sought rather to obey her than to take pity on herself. It scarcely comforted her in her sorrows to learn that the son of the Infante of Fortune was sick even to death; but never, either in presence of her mother or of any one else, did she show any sign of grief. So strongly did she constrain herself, that her tears, driven perforce back into her heart, caused so great a loss of blood from the nose that her life was endangered; and, that she might be restored to health, she was given in marriage to one whom she would willingly have exchanged for death.
After the marriage Florida departed with her husband to the duchy of Cardona, taking with her Avanturada, whom she privately acquainted with her sorrow, both as regards her mother’s harshness and her own regret at having lost the son of the Infante of Fortune; but she never spoke of her regret for Amadour except to console his wife.
This young lady then resolved to keep God and honour before her eyes. So well did she conceal her grief, that none of her friends perceived that her husband was displeasing to her.
In this way she spent a long time, living a life that was worse than death, as she failed not to inform her lover Amadour, who, knowing the virtue and greatness of her heart, as well as the love that she had borne to the son of the Infante of Fortune, thought it impossible that she could live long, and mourned for her as for one that was more than dead. This sorrow was an increase to his former grief, and forgetting his own distress in that which he knew his sweetheart was enduring, he would willingly have continued all his life the slave he was if Florida could thereby have had a husband after her own heart. He learnt from a friend whom he had gained at the Court of Tunis that the King, wishing to keep him if only he could make a good Turk of him, intended to give him his choice between impalement and the renunciation of his faith. Thereupon he so addressed himself to his master, the governor who had taken him prisoner, that he persuaded him to release him on parole. His master named, however, a much higher ransom than he thought could be raised by a man of such little wealth, and then, without speaking to the King, he let him go.
When Amadour reached the Court of the King of Spain, he stayed there but a short time, and then, in order to seek his ransom among his friends, he repaired to Barcelona, whither the young Duke of Cardona, his mother, and Florida had gone on business. As soon as Avanturada heard that her husband was returned, she told the news to Florida, who rejoiced as though for love of her friend. Fearing, however, that her joy at seeing Amadour might make her change her countenance, and that those who did not know her might think wrongly of her, she remained at a window in order to see him coming from afar. As soon as she perceived him she went down by a dark staircase, so that none could see whether she changed colour, and embracing Amadour, led him to her room, and thence to her mother-in-law, who had never seen him. He had not been there for two days before he was loved as much as he had been in the household of the Countess of Aranda.
I leave you to imagine the conversation that he and Florida had together, and how she complained to him of the misfortunes that had come to her in his absence. After shedding many tears of sorrow, both for having been married against her will and also for having lost one she loved so dearly without any hope of seeing him again, she resolved to take consolation from the love and trust she had towards Amadour. Though she durst not declare the truth, he suspected it, and lost neither time nor opportunity to show her how much he loved her.
Just when Florida was all but persuaded to receive him, not as a lover, but as a true and perfect friend, a misfortune came to pass, for the King summoned Amadour to him concerning some important matter.
His wife was so grieved on hearing these tidings that she swooned, and falling down a staircase on which she was standing, was so hurt that she never rose again. Florida having by this death lost all her consolation, mourned like one who felt herself bereft of friends and kin. But Amadour grieved still more; for on the one part he lost one of the best wives that ever lived, and on the other the means of ever seeing Florida again. This caused him such sorrow that he was near coming by a sudden death. The old Duchess of Cardona visited him incessantly, reciting the arguments of philosophers why he should endure his loss with patience. But all was of no avail; for if on the one hand his wife’s death afflicted him, on the other his love increased his martyrdom. Having no longer any excuse to stay when his wife was buried, and his master again summoned him, his despair was such that he was like to lose his reason.
Florida, who thinking to comfort him, was herself the cause of his greatest grief, spent a whole afternoon in the most gracious converse with him in order to lessen his sorrow, and assured him that she would find means to see him oftener than he thought. Then, as he was to depart on the following morning, and was so weak that he could scarcely stir from his bed, he prayed her to come and see him in the evening after every one else had left him. This she promised to do, not knowing that love in extremity is void of reason.
Amadour altogether despaired of ever again seeing her whom he had loved so long, and from whom he had received no other treatment than I have described. Racked by secret passion and by despair at losing all means of consorting with her, he resolved to play at double or quits, and either lose her altogether or else wholly win her, and so pay himself in an hour the reward which he thought he had deserved. Accordingly he had his bed curtained in such a manner that those who came into the room could not see him; and he complained so much more than he had done previously that all the people of the house thought he had not twenty-four hours to live.
After every one else had visited him, Florida, at the request of her husband himself, came in the evening, hoping to comfort him by declaring her affection and by telling him that, so far as honour allowed, she was willing to love him. She sat down on a chair beside the head of his bed, and began her consolation by weeping with him. Amadour, seeing her filled with such sorrow, thought that in her distress he might the more readily achieve his purpose, and raised himself up in the bed. Florida, thinking that he was too weak to do this, sought to prevent him, but he threw himself on his knees before her saying, “Must I lose sight of you for ever?” Then he fell into her arms like one exhausted. The hapless Florida embraced him and supported him for a long time, doing all she could to comfort him. But what she offered him to cure his pain only increased it; and while feigning to be half dead, he, without saying a word, strove to obtain that which the honour of ladies forbids.
When Florida perceived his evil purpose, in which she could hardly believe after all his honourable conversation, she asked him what he sought to do. Amadour, fearing her reply, which he knew could not be otherwise than chaste and virtuous, said nothing, but pursued his attempt with all the strength that he could muster. Florida, greatly astonished, suspected rather that he had lost his senses than that he was really bent upon her dishonour, and called out to a gentleman whom she knew to be in the room; whereupon Amadour in extreme despair flung himself back upon his bed so suddenly that the gentleman thought him dead.
Florida, who had risen from her chair, then said to the gentleman—
“Go quickly for some strong vinegar.”
This the gentleman did, whereupon Florida said—
“What madness, Amadour, has mounted to your brain? What was it you thought and wished to do?”
Amadour, who had lost all reason in the vehemence of his love, replied—
“Does so long a service merit so cruel a reward?”
“And what of the honour of which you have so often preached to me?” said Florida.
“Ah! madam,” said Amadour, “it would be impossible to hold your honour more dear than I have held it. Before you were married, I was able so to subdue my heart that you knew nothing of my desires, but now that you are wedded and your honour may be shielded, do I wrong you in asking for what is mine? By the strength of my love I have won you. He who first possessed your heart had so little desire for your person that he deserved to lose both. He who now owns your person is not worthy to have your heart, and hence even your person does not properly belong to him. But for five or six years I have for your sake borne many pains and woes, which must show you that your body and heart belong to me alone. Think not to defend yourself by speaking of conscience, for when love constrains body and heart sin is never imputed. Those who are driven by frenzy so far as to slay themselves cannot sin, for passion leaves no room for reason; and if the passion of love be more intolerable than any other, and more blinding to the senses, what sin could you fasten upon one who yields to the conduct of such indomitable power? I am going away, and have no hope of ever seeing you again; but if before my departure I could have of you that assurance which the greatness of my love deserves, I should be strengthened sufficiently to endure in patience the sorrows of a long separation. If you will not grant me my request you will ere long learn that your harshness has brought me to a miserable and a cruel death.” (18)
18 The passage commencing “Those who are driven” and ending
“a cruel death” is deficient in the earlier editions of the
Heptameron, which give the following in place of it: “Do
not doubt but what those who have felt the power of love
will cast the blame on you who have so robbed me of my
liberty and dazzled my senses with your divine graces, that
not knowing what to do henceforth, I am constrained to go
away without the hope of ever seeing you again; certain,
however, that wherever I may be, you will still have part of
my heart, which will ever remain yours, be I on land, on the
sea, or in the hands of my most cruel enemies.” The above is
one of various instances of the liberty taken by Boaistuau
and Gruget with Margaret’s text.—Ed.
Florida was not less grieved than astonished to hear these words from one whom she had never imagined capable of such discourse, and, weeping, she thus replied—
“Alas, Amadour, is this the honourable converse that we used to have together while I was young? Is this the honour or conscience which many a time you counselled me to value more than life? Have you forgotten both the worthy examples you set before me of virtuous ladies who withstood unholy love, and also your own contempt for erring women? I cannot believe you so changed, Amadour, that regard for God, your own conscience, and my honour is wholly dead within you. But if it indeed be as you say, I praise the divine goodness which has prevented the misfortune into which I was about to fall, and has revealed to me by your own words the heart of which I was so ignorant. Having lost the son of the Infante of Fortune, not only by my marriage, but also, as is known to me, by reason of his love for another, and finding myself wedded to a man whom, strive as I may, I cannot love, I resolved to set heart and affection entirely on loving you. This love I built upon that virtue which I had so often perceived in you, and to which by your own assistance I think I have attained—I mean the virtue of loving one’s honour and conscience more than life. I came hither thinking to make this rock of virtue a sure foundation of love. But you have in a moment shown me, Amadour, that instead of a pure and cleanly rock, this foundation would have been one of shifting sand or filthy mire; and although a great part of the house in which I hoped always to dwell had already been raised, you have suddenly demolished it. Lay aside, therefore, any hope you had concerning me, and make up your mind not to seek me by look or word wherever I may be, or to hope that I shall ever be able or willing to change my resolve. It is with the deepest sorrow that I tell you this, though had I gone so far as to swear eternal love with you, I know that my heart could not have lived through this meeting. Even now I am so confounded to find myself deceived, that I am sure my life will be either short or sad. With these words I bid you farewell, and for ever.”
I will not try to describe to you the grief that Amadour felt on hearing this speech. It is impossible not only to describe it, but even to conceive it, except indeed to such as have experienced the like. Seeing that with this cruel conclusion she was about to leave him, he seized her by the arm, knowing full well that, if he did not remove her evil opinion of him, he would lose her for ever. Accordingly he dissembled his looks as well as he could, and said—
“During my whole life, madam, I have desired to love a woman of virtue, and having found so few of them, I was minded to put you to proof, and so discover whether you were as well worthy of esteem as of love. Now I know for certain that you are; and therefore I give praise to God, who has inclined my heart to the love of such great perfection. I entreat you to pardon my mad and foolhardy attempt, seeing that the issue of it has turned to your honour and to my great satisfaction.”
Florida was beginning to learn through him the deceitfulness of men; and, just as she had formerly found it difficult to believe in evil where it existed, so did she now find it even more difficult to believe in virtue where there was none.
“Would to God you spoke the truth,” she said to him; “but I am not so ignorant as not to know by my experience in marriage that the blindness of strong passion led you to act as you did. Had God given me a loose rein I am sure that you would not have drawn bridle. Those who go in quest of virtue are wont to take a different road to yours. But enough; if I have been too hasty in crediting you with some goodness, it is time I learned the truth, by which I am now delivered out of your hands.”
So saying, Florida left the room. As long as the night lasted she did nought but weep; for the change that had taken place caused her intense grief, and her heart had much ado to hold out against the sorrowing of love. Although, guided by reason, she had resolved to love no more, yet the heart, which cannot be subdued, would in no wise permit this. Thus she was unable to love him less than before, and knowing that love had been the cause of his offence, she made up her mind to satisfy love by continuing to love him with her whole heart, and to obey honour by never giving any sign of her affection either to him or to any one else.
In the morning Amadour departed in the distress that I have described. Nevertheless his heart, which was so lofty that there was none like it in the world, suffered him not to despair, but prompted him to new devices for seeing Florida again and winning her favour. So as he proceeded to the King of Spain, who was then at Toledo, he took his way through the county of Aranda, where he arrived very late one evening, and found the Countess in great sadness on account of the absence of her daughter.
When she saw Amadour she kissed and embraced him as though he had been her own son, and this no less for the love she herself bore him as for that which she suspected he had for Florida. She asked minutely for news of her daughter, and he told her what he could, though not the entire truth. However, he confessed the love which existed between them, and which Florida had always concealed; and he begged the Countess to aid him in hearing often of Florida, and to take her as speedily as possible to Aranda.
At daybreak he went on his way, and when he had despatched his business with the King he left for the war. So sad was he and so changed in every way that ladies, captains, and acquaintances alike could scarcely recognise him.
He now wore nothing but black, and this of a heavier pile than was needful as mourning for his dead wife; but indeed her death served only as a cloak for the sorrow that was in his heart. Thus Amadour spent three or four years without returning to Court.
The Countess of Aranda hearing that Florida was changed and that it was pitiful to see her, sent for her, hoping that she would return home. The contrary, however, happened. When Florida learned that Amadour had told her mother of their love, and that she, although so discreet and virtuous, had approved of it, she was in extraordinary perplexity. On the one hand she perceived that if her mother, who had such great esteem for Amadour, were told the truth some mischief might befall the latter; and this even to save her life she would not have brought to pass, for she felt strong enough to punish his folly herself without calling on her kinsfolk for assistance. On the other hand she saw that, if she concealed the evil she knew of him, she would be constrained by her mother and all her friends to speak to him and show him favour, and this she feared would only strengthen his evil purpose. However, as he was a long way off, she kept her own counsel, and wrote to him whenever the Countess commanded her. Still her letters were such that he could see they were written more out of obedience than goodwill; and the grief he felt in reading them was as great as his joy had been in reading the earlier ones.
At the end of two or three years, when he had performed so many noble deeds that all the paper in Spain could not contain the records of them, (19) he conceived a very skilful device, not indeed to win Florida’s heart, which he looked upon as lost, but to gain the victory over his enemy, since such she had shown herself to be. He put aside all the promptings of reason and even the fear of death, and at the risk of his life resolved to act in the following way. He persuaded the chief Governor (20) to send him on an embassy to the King concerning some secret attempt against Leucate; (21) and he procured a command to take counsel with the Countess of Aranda about the matter before communicating it to the King.
19 Margaret, perhaps, wrote “All the paper of Spain could
not contain them,” simply because Spanish paper was then of
very small size. Paper-making had, however, been almost
monopolised by Spain until the end of the thirteenth
century, the cotton used in the manufacture being imported
from the East.—M.
20 The Viceroy of Catalonia.—D.
21 Leucate, now a village, but said to have been a
flourishing town in the fourteenth century, lies near the
Mediterranean, at a few miles from Salces, and gives its
name to a large salt-water lake. Formerly fortified, it was
repeatedly besieged and burnt by the Spaniards; notably by
the Duke of Alba in 1503, after he had relieved Salces.—Ed.
Then he came post haste to the county of Aranda, where he knew Florida to be, and secretly sent a friend to inform the Countess of his coming, praying her to keep it secret, and to grant him audience at nightfall without the knowledge of any one.
The Countess, who was very pleased at his coming, spoke of it to Florida, and sent her to undress in her husband’s room, that she might be ready when sent for after every one was gone to bed. Florida had not yet recovered from her first alarm, but she said nothing of it to her mother, and withdrew to an oratory in order to commend herself to Our Lord. While she was praying that her heart might be preserved from all evil affection, she remembered that Amadour had often praised her beauty, and that in spite of long illness it had not been impaired. Being, therefore, more willing to injure her beauty than suffer it to kindle an evil flame in the heart of an honourable gentleman, she took a stone which lay in the chapel and struck herself a grievous blow on the face so that her mouth, nose, and eyes were quite disfigured. Then, in order that no one might suspect it to be of her own doing, she let herself fall upon her face on leaving the chapel when summoned by the Countess, and cried out loudly. The Countess coming thither found her in this pitiful state, and forthwith caused her face to be dressed and bandaged.
Then the Countess led her to her own apartment, and begged her to go to her room and entertain Amadour until she herself had got rid of her company. This Florida did, thinking that there were others with him.
But when she found herself alone with him, and the door closed upon her, she was as greatly troubled as he was pleased. He thought that, by love or violence, he would now have what he desired; so he spoke to her, and finding that she made the same reply as before, and that even to save her life she would not change her resolve, he was beside himself with despair.
“Before God, Florida,” he said to her, “your scruples shall not rob me of the fruits of my labour. Since love, patience, and humble entreaty are of no avail, I will spare no strength of mine to gain the boon, upon which all its existence depends.”
Florida saw that his eyes and countenance were altered exceedingly, so that his complexion, naturally the fairest in the world, was now as red as fire, and his look, usually so gentle and pleasant, had become as horrible and furious as though fierce flames were blazing in his heart and face. In his frenzy he seized her delicate, weak hands in his own strong, powerful ones; and she, finding herself in such bondage that she could neither defend herself nor fly, thought that her only chance was to try whether he had not retained some traces of his former love, for the sake of which he might forego his cruelty. She therefore said to him—
“If you now look upon me, Amadour, in the light of an enemy, I entreat you, by that pure love which I once thought was in your heart, to hearken to me before you put me to torture.”
Seeing that he became attentive, she continued—
“Alas! Amadour, what can prompt you to seek after a thing that can afford you no satisfaction, and thus afflict me with the profoundest grief? You made trial of my inclinations in the days of my youth and earliest beauty, and they perhaps served to excuse your passion; but I am amazed that now, when I am old, and ugly, and sorrow-stricken, you should seek for what you know you can never find. I am sure you do not doubt that my mind is as it used to be, and so by force alone can you obtain what you desire. If you observe the condition of my face, and lay aside the memory of the beauty that once you saw in it, you will have no inclination to draw any nearer; and if you still retain within you any remnants of your past love, it is impossible that pity will not subdue your frenzy. To this pity, which I have often found in you, I appeal with prayers for mercy. Suffer me to live in peace, and in that honour which by your own counsel I have resolved to preserve. But if the love you once bore me is now turned to hate, and you desire, in vengeance rather than in love, to make me the unhappiest woman alive, I protest to you that it shall not be so. You will force me against my will to make your evil purpose known to her who thinks so highly of you; and you may be sure that, when she learns it, your life will not be safe.”
But Amadour interrupted her.
“If I must die,” he said, “I shall be the sooner rid of my torment. The disfigurement of your face, which I believe is of your own seeking, shall not restrain me from making you mine. Though I could have nothing but your bones, I would yet hold them close to me.”
When Florida saw that prayers, reasoning, and tears were alike of no avail, and that while he cruelly pursued his evil purpose she lacked the strength to resist him, she summoned the aid which she dreaded as greatly as death, and in a sad and piteous voice called as loudly as she could upon her mother. The Countess, hearing her daughter’s cries, had grave misgivings of the truth, and hastened into the room with all possible speed.
Amadour, who was not so ready to die as he affirmed, desisted promptly from his enterprise; and when the lady opened the door she found him close beside it, and Florida some distance from him. “Amadour,” said the Countess, “what is the matter? Tell me the truth.”
Amadour, who was never at a loss for invention, replied with a pale and daunted face—
“Alas! madam, what change is this in the lady Florida? I was never so astonished before, for, as I have told you, I thought I had a share in her favour; but I now see clearly that I have lost it all. While she was being brought up by you, she was, I think, no less discreet or virtuous than she is at present; however, she had then no qualms of conscience about speaking with any one. But now, when I sought to look at her, she would not suffer me to do so. When I saw this behaviour on her part I thought I must be dreaming, and asked her for her hand to kiss it after the manner of the country. This she utterly refused me. I acknowledge, madam, that then I acted wrongfully, and I entreat your pardon for it; for I took her hand, as it were by force, and kissed it. I asked nothing more of her, but I believe that she intends my death, for she called out to you as you know. Why she did this I cannot tell, unless indeed she feared that I had some other purpose in view. Nevertheless, madam, be this as it may, I confess that I am in the wrong; for although she ought to love all who are devoted to you, fortune wills it that I, who am of all most attached to her, am banished from her good graces. Still, I shall ever continue the same both to you and to her; and I entreat you to continue me in your good favour since, by no fault of my own, I have now lost hers.”
The Countess, who partly believed and partly suspected him, went up to her daughter and asked—“Why did you call me so loudly?”
Florida replied that she had felt afraid; and, although the Countess questioned her minutely on many points, she would give no other reply. Finding that she had escaped from her enemy she deemed him sufficiently punished by the failure of his attempt.
After the Countess had had a long conversation with Amadour, she suffered him to speak again in her presence with Florida, to see how he would behave. He said but little, save that he thanked her for not having confessed the truth to her mother, and begged that since she had expelled him from her heart, she would at least allow no other to take his place.
“If my voice had not been my only means of defending myself,” she replied, “it would never have been heard; and from me you shall have no worse punishment, if you do not force me to it by troubling me again as you have done. Do not fear that I can ever love another; since I have not found the good I wished for in a heart that I considered to be the most virtuous in the world, I do not expect to find it in any man. This evil fortune will henceforth free me of all the passion that love can give.”
With these words she bade him farewell.
Her mother, who had been watching her face, was unable to form any opinion; though from that time forth she clearly saw that her daughter had lost all affection for Amadour. She imagined her so devoid of reason as to hate everything that she herself loved; and from that hour she warred with her in a strange way, spending seven years without speaking to her except in anger, all which she did at Amadour’s request.
Meanwhile, on account of her mother’s harsh treatment, Florida’s former dread of being with her husband was changed into a desire of never leaving him. Seeing, however, that all her efforts were useless, she resolved to deceive Amadour, and laying aside her coldness for a day or two, she advised him to pay court to a lady who, she said, had been speaking of their love.
This lady lived with the Queen of Spain, and was called Loretta. Amadour believed the story, and, thinking that he might in this way regain Florida’s good graces, he made love to Loretta, who was the wife of a captain, one of the viceroys of the King of Spain. She, in her pleasure at having gained such a lover, showed so much elation that the affair was rumoured abroad. Even the Countess of Aranda, who was at Court, had knowledge of it, and thenceforward treated Florida less harshly than before.
One day Florida heard that the captain, Loretta’s husband, had grown jealous, and was resolved to kill Amadour in one way or another as best he might. In spite of her altered treatment of Amadour, Florida did not desire that evil should befall him, and so she immediately informed him of what she had heard. He was quite ready to hark back again to his first love, and thereupon told her that, if she would grant him three hours of her conversation every day, he would never again speak to Loretta. But this she would not grant. “Then,” said Amadour, “if you will not give me life, why prevent me from dying, unless indeed you hope to make me suffer more pain during life than any death could cause? But though death shun me, I will seek it until I find it; then only shall I have rest.”
While they were on this footing, news came that the King of Granada (22) was entering upon a great war against the King of Spain. The latter, therefore, sent the Prince, his son, (23) to the war, and with him the Constable of Castille and the Duke of Alba, (24) two old and prudent lords. The Duke of Cardona and the Count of Aranda were unwilling to remain behind, and prayed the King to give them some command. This he did as befitted their rank, and gave them into the safe keeping of Amadour, who performed such extraordinary deeds during the war, that they seemed to be acts as much of despair as of bravery.
22 The last King of Granada was Mahomed Boabdil, dethroned
in 1493. The title may have been assumed, however, by the
leader of an insurrection.—D.
23 As Ferdinand and Isabella had no son, the reference must
be to their daughter’s husband, Philip the Fair of Austria,
son of the Emperor Maximilian I. and father of Charles V.—
B. J.
24 Frederick of Toledo, Marquis of Coria and Duke of Alba,
generally called the old Duke of Alba to distinguish him
from his son.—B. J.
Coming now to the point of my story, I have to relate how his overboldness was proved by his death. The Moors had made a show of offering battle, and finding the Christian army very numerous had feigned a retreat. The Spaniards started in pursuit, but the old Constable and the Duke of Alba, who suspected the trickery of the Moors, restrained the Prince of Spain against his will from crossing the river. The Count of Aranda, however, and the Duke of Cardona crossed, although it was forbidden; and when the Moors saw that they were pursued by only a few men they faced about again. The Duke of Cardona was struck down and killed with a blow of a scimitar, and the Count of Aranda was so grievously wounded that he was left for dead. Thereupon Amadour came up filled with rage and fury, and bursting through the throng, caused the two bodies to be taken up and carried to the camp of the Prince, who mourned for them as for his own brothers. On examining their wounds the Count of Aranda was found to be still alive, and was sent in a litter to his home, where he lay ill for a long time. On the other hand, the Duke’s body was sent back to Cardona.
Meanwhile Amadour, having made this effort to rescue the two bodies, had thought so little of his own safety that he found himself surrounded by a large number of Moors. Not desiring his person to be captured any more than he had captured that of his mistress, nor to break his faith with God as he had broken faith with her—for he knew that, if he were taken to the King of Granada, he must either die a cruel death or renounce Christianity—he resolved to withhold from his enemies the glory either of his death or capture. So kissing the cross of his sword and commending his body and soul to God, he dealt himself such a thrust as to be past all help.
Thus died the unhappy Amadour, lamented as deeply as his virtues deserved. The news spread through the whole of Spain; and the rumour of it came to Florida, who was at Barcelona, where her husband had formerly commanded that he should be buried. She gave him an honourable funeral, (25) and then, without saying anything to her mother or mother-in-law, she became a nun in the Convent of Jesus, taking for husband and lover Him who had delivered her from such a violent love as that of Amadour’s, and from such great affliction as she had endured in the company of her husband. Thus were all her affections directed to the perfect loving of God; and, after living for a long time as a nun, she yielded up her soul with gladness, like that of the bride when she goes forth to meet the bridegroom.
25 The Franciscan monastery of the little village cf
Bellpuig, near Lerida, contains the tomb of Ramon de
Cardona, termed one of the marvels of Catalonia on account
of the admirable sculptures adorning it. One of the
beautiful white marble bas-reliefs shows a number of galleys
drawn up in line of battle, whilst some smaller boats are
conveying parties of armed men to a river-bank on which the
Moors are awaiting them in hostile array. On the frieze of
an arch the Spaniards and Moors are shown fighting, many of
the former retreating towards the water. An inscription
records that the tomb was raised to the best of husbands by
Isabella, his unhappy spouse.
Margaret gives the name of Florida to the wife of the Duke
whom she mentions, but it should be borne in mind that she
has systematically mingled fact with fiction throughout this
story; and that she was alluding to the Duke buried at
Bellpuig seems evident from an examination of the bas-
reliefs mentioned above. Ramon de Cardona was, however, a
more important personage than she pictures him. He became
Charles V.‘s viceroy in Naples, and did not die till 1520,
whereas Margaret’s story appears to end in or about 1513.
Possibly she saw the tomb when in Spain.—Ed.
“I am well aware, ladies, that this long tale may have been wearisome to some among you, but had I told it as it was told to me it would have been longer still. Take example, I beg you, by the virtue of Florida, but be somewhat less cruel; and think not so well of any man that, when you are undeceived, you occasion him a cruel death and yourselves a life of sorrow.”
Having had a long and fair hearing Parlamente said to Hircan—
“Do you not think that this lady was pressed to extremities and that she held out virtuously?”
“No,” said Hircan; “a woman can make no more feeble resistance than to cry out. If she had been in a place where none could hear her I do not know how she would have fared. And if Amadour had had more love and less fear he would not have desisted from his attempt for so little. So this story will not cause me to change my firm opinion that no man ever perfectly loved a lady, or was loved by her, that he did not prove successful if only he went the right way to work. Nevertheless, I must praise Amadour for having in part done his duty.”
“What duty?” asked Oisille. “Do you call it a lover’s duty to try and take his mistress by force when he owes her all reverence and submission?”
Here Saffredent took up the discourse.
“Madam,” he said, “when our mistresses hold their state in chamber or hall, seated at their ease as though they were our judges, we lead them to the dance in fear; we wait upon them with all diligence and anticipate their commands; and we are so afraid of offending them and so desirous of doing them service that those who see us pity us, and often deem us more witless than brutes. They account us dull and void of understanding, and give praise to the ladies, whose faces are so imperious and their speech so fair that they make themselves feared, loved, and honoured by those who only know them outwardly. But when we are together in private, and love alone can judge our behaviour, we know full well that they are women and we are men. Then is the name ‘mistress’ changed to ‘sweetheart,’ and the ‘slave’ becomes a ‘lover.’ As the proverb says—‘By service true and loyalty, do servants rise to mastery.’ They have honour equally with men, who can give it to them and can take it away; and seeing us suffer in patience, they should reward us when they can do so without hurt to their honour.”
“You do not speak of that true honour,” said Longarine, “which is the greatest happiness this world can give. If every one calls me a virtuous woman, and I myself know the contrary, the praise I receive only increases my shame and puts me in secret to still greater confusion. In the same way, if people condemn me and I know that I am innocent, their condemnation will only make me the better pleased with myself.”
“In spite of what you all have said,” interposed Geburon, “it seems to me that Amadour was as noble and virtuous a knight as ever lived, and I think I can recognise him under his feigned name. Since Parlamente would not name him, neither will I. But you may rest assured that, if he be the man whom I have in mind, his heart never knew fear, nor was ever void of love and bravery.”
“The day has been spent so pleasantly,” said Oisille, “that if the others are like it I think our talk will make the time pass quickly by. But see where the sun is, and listen to the abbey bell, which has long been calling us to vespers. I did not mention this to you before, for I was more inclined to hear the end of the story than to go to prayers.”
At these words they all rose, and when they reached the abbey they found that the monks had been waiting for them a full hour and more. After vespers they went to supper, and during the whole evening they conversed about the stories they had heard, all of them searching every corner of their memories to try and make the second day as pleasant as the first. And after playing many games in the meadow they went to bed, and so made a glad and happy ending of the first day.

On the Second Day is recounted the first conceit
that presents
itself to each.
On the morrow they rose in great eagerness to return to the place where they had had so much pleasure on the previous day. Each one was ready with a tale, and was impatient for the telling of it. They listened to the reading of Madame Oisille, and then heard mass, all commending themselves to God, and praying Him to grant them speech and grace for the continuance of their fellowship. Afterwards they went to dinner, reminding one another the while of many stories of the past.
After dinner, they rested in their apartments, and at the appointed time returned to the meadow, where day and season alike seemed favourable to their plans. They all sat down on the natural seat afforded by the green sward, and Parlamente said—
“Yesterday I told the tenth and last tale; it is therefore for me to choose who shall begin to-day. Madame Oisille was the first of the ladies to speak, as being the oldest and wisest, and so I now give my vote to the youngest—I do not also say the flightiest—for I am sure that if we all follow her leading we shall not delay vespers so long as we did yesterday. Wherefore, Nomerfide, you shall lead us, but I beg that you will not cause us to begin our second day in tears.”
“There was no need to make that request,” said Nomerfide, “for one of our number has made me choose a tale which has taken such a hold on me that I can tell no other; and should it occasion sadness in you, your natures must be melancholy ones indeed.”

Madame de Roncex, while at the monastery of the Grey Friars
at Thouars, (1) was constrained to go in great haste to a
certain place, and, not looking to see whether the seats
were clean, sat down in a filthy spot and befouled both her
person and clothes; whereupon crying out for assistance, in
the hope that some woman would come and cleanse her, she was
waited on by men, who beheld her in the worst plight in
which a woman could be found. (2)
1 In the department of the Deux-Sèvres.—Ed.
2 This story, given in Boaistuau’s version of Margaret’s
tales, and to be found in most of the MS. copies of the
Heptameron at the ‘Paris Bibliothèque Nationale’, was not
included in the edition issued by Gruget, who replaced it by
a story called The jests made by a Grey Friar, for which
see post, p. 95 et seq.—Ed.
In the household of Madame de la Trémoille there was a lady named Roncex, who one day, when her mistress had gone to visit the monastery of the Grey Friars, found herself in great need to go to a certain place whither her maid could not go in her stead. She took with her a girl named La Mothe to keep her company, but being modest and unwilling to be seen, left her in the room, and went alone into a darksome privy, a place used in common by all the friars, who had given such a good account therein of all their victuals, that seat and floor, and in sooth the whole place, were thickly covered with the must of Bacchus and Ceres that had passed through the friars’ bellies.
The unhappy lady, who was so hard pressed that she had scarcely time to lift her dress, chanced to sit down in the foulest, dirtiest spot in the whole place, where she found herself stuck fast as though with glue, her poor hips, garments, and feet being so contaminated that she durst not take a step or turn on any side, for fear lest she should meet with something worse. Thereupon she began to call out as loudly as she could—
“La Mothe, my child, I am ruined and undone!”
The poor girl, who had formerly heard tell of the wickedness of the Grey Friars, and imagined that some of them were hidden there and were trying to take her mistress by force, thereupon ran off as hard as she could, saying to every one she met—
“Come and help Madame de Roncex; the Grey Friars are trying to ravish her in yonder privy.”
They thereupon hastened thither with all speed, and found the unhappy lady crying out for assistance, longing for some woman to come and cleanse her, and with her back parts all uncovered, for she feared to touch them with her garments lest these also should be defiled.
The gentlemen, coming in at her cries, beheld this fine sight, but could see nought of the Grey Friars, unless it were their ordure clinging to her hips; nor did this pass without laughter on their part and great shame on hers, for instead of having women to cleanse her, she was waited on by men, who saw her naked, and in the sorriest plight in which a woman could be found. For this reason, on perceiving them, she soiled what was still clean, by dropping her garments in order to cover herself, forgetting the filth that she was in for the shame she felt at sight of the men. And when she had come out of that foul place it was necessary to strip her naked and change all her garments before she could leave the monastery. She was minded to be angry with La Mothe for the aid that she had brought her, but finding that the poor girl had thought her in a yet more evil plight, she put aside her wrath and laughed like the rest. (3)
3 It is impossible to identify the lady mentioned in this
story, her name being spelt in so many ways in the various
MSS. of the Heptameron. It is given as Roncex in the copy
here followed, as Roubex in a copy that belonged to Louis
XVIII., and as Roncci in the De Thou MS., whilst Boaistuau
printed it as Roucey. The Madame de la Trémoille, alluded to
at the outset, is believed by Lacroix and Dillaye to have
been Anne de Laval (daughter of Guy XV., Count of Laval, and
of Charlotte of Aragon, Princess of Tarento), who married
Francis de la Trémoille, Viscount of Thouars, in 1521, and
was by her mother a cousin of Queen Margaret. Possibly,
however, the reference is to Gabrielle de Bourbon, wife of
Louis II. de la Trémoille, a lady of exemplary piety, who
erected the beautiful Renaissance chapel of the château of
Thouars.—L. & Ed.
“I think, ladies,” said Nomerfide, “that this story has proved neither long nor melancholy, and that I have given you what you expected.”
At this the company laughed heartily, and Oisille said—“The story is indeed nasty and unclean, yet, knowing the persons who fared in this manner, we cannot consider it unwelcome. Gladly would I have seen the faces of La Mothe and of the lady to whom she brought such timely aid. But now,” she added to Nomerfide, “since you have finished so soon, give your vote to some one whose thoughts are of a graver turn.”
“Since you desire me to atone for my fault,” answered Nomerfide, “I give my vote to Dagoucin, whose discretion is such that he would die rather than say anything foolish.”
Dagoucin then thanked her for the esteem in which she held his good sense, and thus began—“The story I am minded to relate is intended to show you how love blinds the greatest and most honourable hearts, and how hard it is to overcome wickedness by any kindness whatsoever.”



Of the jests made by a Grey Friar in his sermons. (1)
1 See ante, p. 89, note 2, and post. Appendix B.
Near the town of Bléré in Touraine there is a village called St. Martin-le-Beau, whither a Grey Friar belonging to the monastery at Tours was summoned to preach during the seasons of Advent and Lent. This friar, who was more garrulous than learned, and now and then found himself at a loss for matter to eke out his hour, would thereupon begin telling tales which more or less agreeably satisfied the good villagers.
One Holy Thursday he preached about the Paschal Lamb, and while speaking of how it was eaten at night, seeing that there were present at the preaching some handsome young ladies of Amboise, who were newly arrived to keep Easter at the village, and to stay there for a few days afterwards, he wished to surpass himself, and thereupon asked all the women-folk whether they knew what it was to eat raw flesh at night. “I will tell you what it is, ladies,” he said, whereat the young men of Amboise, who had just arrived with their wives, sisters, and nieces, and who had no knowledge of the pilgrim’s humour, began to be scandalised; though on listening further their indignation gave place to laughter, even when he said that to eat the lamb it was needful to have one’s loins girt, one’s feet in one’s shoes, and one’s hand on one’s staff.
The friar, seeing them laugh at this, and guessing the reason, immediately corrected himself. “Well,” said he, “to have shoes on one’s feet and a staff in one’s hand; ‘tis all one.”
That this sally was received with laughter you will readily believe. Even the ladies could not refrain from merriment, and for them he added other diverting sayings. Then finding the time was nearly up, and wishing the ladies to be well pleased with him when they departed, he said to them—“Now, fair ladies, when you are chatting presently with your gossips, you will be asking one another: ‘Who, pray, is this Master Friar, that speaks out so boldly? He must be a brisk fellow.’ I will tell you, ladies, yes, I will tell you, and be not astonished if I speak out boldly, for I am of Anjou, at your service.”
With these words he ended his sermon, leaving his hearers more disposed to laugh at his foolish speeches than to weep in memory of our Lord’s Passion which was then being commemorated.
The other sermons that he preached during the festival had much the same value. You are aware that these friars never fail to go begging for their Easter eggs, and receive not only eggs, but many other things, such as linen, yarn, chitterlings, hams, chines, and similar trifles. So when Easter Tuesday came, and the friar was making those exhortations to charity of which such folks as he are no niggards, he said—
“I am bound to thank you, ladies, for the liberality you have shown to our poor monastery, and yet I cannot forbear telling you that you have hitherto not duly considered the nature of our wants. You have for the most part given us chitterlings, but of these we ourselves have no lack. God be praised, our monastery is indeed full of them. What then can we do with so many? I will tell you. My advice, ladies, is that you should mix your hams with our chitterlings; in this way you would bestow fine alms.”
Then, continuing his sermon, he brought into it certain scandalous matter, and, whilst discoursing upon it somewhat bluntly and quoting sundry examples, he said in apparent amazement—
“Truly, ladies and gentlemen of Saint-Martin, I am greatly astonished that you should be scandalised so unreasonably at what is less than nothing, and should tell tales of me wherever you go, saying: ‘It is a big business; who could have thought that the father would have got his landlady’s daughter with child?’ A monk get a girl with child!” he continued; “forsooth, what a wonder! But hark you, fair ladies, would you not rather have had cause for wonderment, had the girl acted thus by the monk?”
“Such, ladies, was the wholesome food on which this worshipful shepherd fed the Lord’s flock. And so brazen was he, that after committing the sin, he spake openly of it in the pulpit, where nought should be said that tends to aught but the edification of one’s neighbour, and above all to the glory of God.”
“Truly,” said Saffredent, “he was a master monk—I should have liked him nearly as well as Brother Anjibaut, who gets credit for all the jests that are spoken in merry company.”
“For my part, I can see nothing laughable in such mockery,” said Oisille, “especially in such a place.”
“You forget, madam,” said Nomerfide, “that at that time, though it was not so very long ago, the good villagers, and indeed most of the dwellers in the large towns, who think themselves cleverer than other people, had greater regard for such preachers as he than for those who purely and simply preached the holy Gospel to them.”
“However that may be,” said Hircan, “he was not wrong in asking for hams in exchange for chitterlings, for in hams there is far more eating. And even if some devout creature had understood him amphibologically, as I believe he wished to be understood, neither he nor his brethren would have fared badly any more than the wench that had her bag full.”
“But how impudent of him,” said Oisille, “to pervert the meaning of the text to suit his fancy, thinking that he had to do with beasts like himself, and shamelessly trying to entice the poor little women so that he might teach them how to eat raw flesh at night.”
“True,” said Simontault; “but you forget that he saw before him those young tripe-sellers of Amboise in whose tub he would fain have washed his ——— shall I name it? No, but you understand me—and have treated them to a taste of it, not roasted, but stirring and frisking, so as to please them the more.”
“Softly, softly, Simontault,” said Parlamente; “you forget yourself. Have you laid aside your accustomed modesty to don it only in time of necessity?”
“No, madam, no,” said he; “‘twas the unworthy monk that led me astray. Wherefore, that we may return to the matter in hand, I beg Nomerfide, who caused my offence, to give her vote to some one who will make the company forget our common fault.”
“Since you include me in your transgression,” said Nomerfide, “I will choose one who will atone for our failings, that is Dagoucin. He is so discreet that to save his life he would not say a foolish thing.”



The Duke of Florence, having continually failed to make
known to a certain lady the love he bore her, confided in
her brother, and begged his assistance that he might attain
his ends. This, after many remonstrances, the brother agreed
to give, but it was a lip-promise only, for at the moment
when the Duke was expecting to vanquish her whom he had
deemed invincible, the gentleman slew him in his bed, in
this fashion freeing his country from a tyrant, and saving
both his own life and the honour of his house. (1)
1 The basis of this story is historical. The event here
described—one of the most famous in the annals of
Florence—furnished Alfred de Musset with the subject of his
play Lorenzaccio, and served as the foundation of The
Traitor, considered to be Shirley’s highest achievement as
a dramatic poet. As Queen Margaret’s narrative contains
various errors of fact, Sismondi’s account of the affair, as
borrowed by him from the best Italian historians, is given
in the Appendix, C—Eu.
Ten years ago there reigned in the city of Florence a Duke of the house of Medici who had married the Emperor’s natural daughter, Margaret. (2) She was still so young that the marriage could not be lawfully consummated, and, waiting till she should be of a riper age, the Duke treated her with great gentleness, and to spare her, made love to various ladies of the city, whom he was wont to visit at night, whilst his wife was sleeping.
2 The Duke here referred to was Alexander de’ Medici, first
Duke of Florence, in which city he was born in 1510. His
mother, a slave named Anna, was the wife of a Florentine
coachman, but Lorenzo II. de’ Medici, one of this woman’s
lovers, acknowledged him as his offspring, though, according
to some accounts, his real father was one of the popes,
Clement VII. or Julius II. After the Emperor Charles V. had
made himself master of Florence in 1530, he confided the
governorship of the city to Alexander, upon whom he bestowed
the title of Duke. Two years later Alexander threw off the
imperial control, and soon afterwards embarked on a career
of debauchery and crime. In 1536, Charles V., being desirous
of obtaining the support of Florence against France, treated
with Alexander, and gave him the hand of his illegitimate
daughter, Margaret. The latter—whose mother was Margaret
van Gheenst, a Flemish damsel of noble birth—was at that
time barely fourteen, having been born at Brussels in 1522.
The Queen of Navarre’s statements concerning the
youthfulness of the Duchess are thus corroborated by fact.
After the death of Alexander de’ Medici, his widow was
married to Octavius Farnese, Duke of Parma, who was then
only twelve years old, but by whom she eventually became the
mother of the celebrated Alexander Farnese. Margaret of
Austria occupies a prominent place in the history of the
Netherlands, which she governed during a lengthy period for
her brother Philip II. She died in retirement at Ortonna in
Italy in 1586.—L. and Ed.
Among these there was one very beautiful, discreet, and honourable lady, sister to a gentleman whom the Duke loved even as himself, and to whom he gave such authority in his household that his orders were feared and obeyed equally with the Duke’s own. And moreover the Duke had no secrets that he did not share with this gentleman, so that the latter might have been called his second-self. (3)
3 The gentleman here mentioned was the Duke’s cousin,
Lorenzo di Pier-Francesco de’ Medici, commonly called
Lorenzino on account of his short stature. He was born at
Florence in 1514, and, being the eldest member of the junior
branch of the Medici family, it had been decided by the
Emperor Charles V. that he should succeed to the Dukedom of
Florence, if Alexander died without issue. Lorenzino
cultivated letters, and is said to have possessed
considerable wit, but, on the other hand, instead of being a
high-minded man, as Queen Margaret pictures him, he was a
thorough profligate, and willingly lent a hand in
Alexander’s scandalous amours. The heroine of this story is
erroneously described as Lorenzino’s sister; in point of
fact she was his aunt, Catherine Ginori. See Appendix, C.—
Ed.
Finding the gentleman’s sister to be a lady of such exemplary virtue that he was unable to declare his passion to her, though he sought all possible opportunities for doing so, the Duke at last came to his favourite and said to him—
“If there were anything in this world, my friend, that I might be unwilling to do for you, I should hesitate to tell you what is in my mind, and still more to beg your assistance. But such is the affection I bear you that had I wife, mother, or daughter who could avail to save your life, I would sacrifice them rather than allow you to die in torment. I believe that your love for me is the counterpart of mine for you, and that if I, who am your master, bear you so much affection, you, on your part, can have no less for me. I will therefore tell you a secret, the keeping of which has brought me to the condition you see. I have no hope of any improvement except it be through death or else the service which you are in a position to render me.”
On hearing these words from the Duke, and seeing his face unfeignedly bathed in tears, the gentleman felt such great pity for him that he said—
“Sir, I am your creature: all the wealth and honour that I am possessed of in this world come from you. You may speak to me as to your own soul, in the certainty that all that it be in my power to do is at your command.”
Thereupon the Duke began to tell him of the love he bore his sister, a love so deep and strong that he feared he could not live much longer unless, by the gentleman’s help, he succeeded in satisfying his desire. He was well aware that neither prayers nor presents would be of any avail with the lady, wherefore he begged the gentleman—if he cared for his master’s life as much as he, his master, cared for his—to devise some means of procuring him the good fortune which, without such assistance, he could never hope to obtain.
The brother, who loved his sister and the honour of his house far more than the Duke’s pleasure, endeavoured to remonstrate with him, entreating that he might be employed for any other purpose save the cruel task of soliciting the dishonour of his own kin, and declaring that the rendering of such a service was contrary alike to his inclinations and his honour.
Inflamed with excessive wrath, the Duke raised his hand to his mouth and bit his nails.
“Well,” said he in a fury, “since I find that you have no friendship for me, I know what I have to do.”
The gentleman, who was acquainted with his master’s cruelty, felt afraid, and answered—
“My lord, since such is your pleasure, I will speak to her, and tell you her reply.”
“If you show concern for my life, I shall show it for yours,” replied the Duke, and thereupon he went away.
The gentleman well understood the meaning of these words, and spent a day or two without seeing the Duke, considering what he should do. On the one hand he was confronted by the duty he owed his master, and the wealth and honours he had received from him; on the other by the honour of his house, and the fair fame and chastity of his sister. He well knew that she would never submit to such infamy unless through his own treachery she were overcome by violence, so unnatural a deed that if it were committed he and his kindred would be disgraced for ever. In this dilemma he decided that he would sooner die than so ill use his sister, who was one of the noblest women in all Italy, and ought rather to deliver his country of this tyrant who, abusing his power, sought to cast such a slur upon his family; for he felt sure that if the Duke were suffered to live, neither his own life nor the lives of his kindred would be safe. So without speaking of the matter to his sister or to any living creature, he determined to save his life and vindicate his honour at one and the same time. Accordingly, when a couple of days had gone by, he went to the Duke and told him that with infinite difficulty he had so wrought upon his sister that she had at last consented to do his will, provided that the matter were kept secret, and none but he, her brother, knew of it.
The Duke, who was longing for these tidings, readily believed them, and embracing the ambassador, promised him anything that he might ask. He begged him to put his scheme quickly into execution, and they agreed together upon the time when this should be done. The Duke was in great joy, as may well be imagined; and on the arrival of that wished-for night when he hoped to vanquish her whom he had deemed invincible, he retired early, accompanied only by the lady’s brother, and failed not to attire himself in a perfumed shirt and head-gear. Then, when every one was gone to rest, he went with the gentleman to the lady’s abode, where he was conducted into a well-appointed apartment.
Having undressed him and put him to bed, the gentleman said—
“My lord, I will now go and fetch you one who will assuredly not enter this room without blushing; but I hope that before morning she will have lost all fear of you.”
Leaving the Duke, he then went to his own room, where he found one of his servants, to whom he said—
“Are you brave enough to follow me to a place where I desire to avenge myself upon my greatest living enemy?”
The other, who was ignorant of his master’s purpose, replied—
“Yes, sir, though it were the Duke himself.”
Thereupon the gentleman led him away in such haste as to leave him no time to take any weapon except a poignard that he was wearing.
The Duke, on hearing the gentleman coming back again, thought that he was bringing the loved one with him, and, opening his eyes, drew back the curtains in order to see and welcome the joy for which he had so long been waiting. But instead of seeing her who, so he hoped, was to preserve his life, he beheld something intended to take his life away, that is, a naked sword which the gentleman had drawn, and with which he smote the Duke. The latter was wearing nothing but his shirt, and lacked weapons, though not courage, for sitting up in the bed he seized the gentleman round the body, saying—
“Is this the way you keep your promise?”
Then, armed as he was only with his teeth and nails, he bit the gentleman’s thumb, and wrestled with him so stoutly that they both fell down beside the bed.
The gentleman, not feeling altogether confident, called to his servant, who, finding the Duke and his master so closely twined together that he could not tell the one from the other, dragged them both by the feet into the middle of the room, and then tried to cut the Duke’s throat with his poignard. The Duke defended himself until he was so exhausted through loss of blood that he could do no more, whereupon the gentleman and his servant lifted him upon the bed and finished him with their daggers. They then drew the curtain and went away, leaving the dead body shut up in the room.
Having vanquished his great enemy, by whose death he hoped to free his country, the gentleman reflected that his work would be incomplete unless he treated five or six of the Duke’s kindred in the same fashion. The servant, however, who was neither a dare-devil nor a fool, said to him—
“I think, sir, that you have done enough for the present, and that it would be better to think of saving your own life than of taking the lives of others, for should we be as long in making away with each of them as we were in the case of the Duke, daylight would overtake our enterprise before we could complete it, even should we find our enemies unarmed.”
Cowed by his guilty conscience, the gentleman followed the advice of his servant, and taking him alone with him, repaired to a Bishop (4) whose office it was to have the city gates opened, and to give orders to the guard-posts.
4 Probably Cardinal Cybo, Alexander’s chief minister, who
according to Sismondi, was the first to discover the
murder.—Ed.
“I have,” said the gentleman to the Bishop, “this evening received tidings that one of my brothers is at the point of death. I have just asked leave of the Duke to go to him, and he has granted it me; and I beg you to send orders that the guards may furnish me with two good horses, and that the gatekeeper may let me through.”
The Bishop, who regarded the gentleman’s request in the same light as an order from his master the Duke, forthwith gave him a note, by means of which the gate was opened for him, and horses supplied to him as he had requested; but instead of going to see his brother he betook himself straight to Venice, where he had himself cured of the bites that he had received from the Duke, and then passed over into Turkey. (5)
5 On leaving Florence, Lorenzo repaired first to Bologna
and then to Venice, where he informed Philip Strozzi of how
he had rid his country of the tyrant. After embracing him in
a transport, and calling him the Tuscan Brutus, Strozzi
asked the murderer’s sisters, Laudamina and Magdalen de’
Medici, in marriage for his own sons, Peter and Robert. From
Venice Lorenzino issued a mémoire justificatif, full of
quibbles and paradoxes, in which he tried to explain his
lack of energy after the murder by the indifference shown by
the Florentines. He took no part in the various enterprises
directed against Cosmo de’ Medici, who had succeeded
Alexander at Florence. Indeed his chief concern was for his
own safety, which was threatened alike by Cosmo and the
Emperor Charles V., and to escape their emissaries he
proceeded to Turkey, and thence to France, ultimately
returning to Venice, where, despite all his precautions
against danger, he was assassinated in 1547, together with
his uncle, Soderini, by some spadassins in the pay of Cosmo
I.—Ed.
In the morning, finding that their master delayed his return so long, all the Duke’s servants suspected, rightly enough, that he had gone to see some lady; but at last, as he still failed to return, they began seeking him on all sides. The poor Duchess, who was beginning to love him dearly, was sorely distressed on learning that he could not be found; and as the gentleman to whom he bore so much affection was likewise nowhere to be seen, some went to his house in quest of him. They found blood on the threshold of the gentleman’s room, which they entered, but he was not there, nor could any servant or other person give any tidings of him. Following the blood-stains, however, the Duke’s servants came at last to the room in which their master lay. The door of it was locked, but this they soon broke open, and on seeing the floor covered with blood they drew back the bed-curtain, and found the unhappy Duke’s body lying in the bed, sleeping the sleep from which one cannot awaken.
You may imagine the mourning of these poor servants as they carried the body to the palace, whither came the Bishop, who told them how the gentleman had departed with all speed during the night under pretence of going to see his brother. And by this it was clearly shown that it was he who had committed the murder. And it was further proved that his poor sister had known nothing whatever of the matter. For her part, albeit she was astounded by what had happened, she could but love her brother the more, seeing that he had not shrunk from risking his life in order to save her from so cruel a tyrant. And so honourable and virtuous was the life that she continued leading, that although she was reduced to poverty by the confiscation of the family property, both she and her sister found as honourable and wealthy husbands as there were in all Italy, and lived ever afterwards in high and good repute.
“This, ladies, is a story that should make you dread that little god who delights in tormenting Prince and peasant, strong and weak, and so far blinds them that they lose all thought of God and conscience, and even of their own lives. And greatly should Princes and those in authority fear to offend such as are less than they; for there is no man but can wreak injury when it pleases God to take vengeance on a sinner, nor any man so great that he can do hurt to one who is in God’s care.”
This tale was commended by all in the company, (6) but it gave rise to different opinions among them, for whilst some maintained that the gentleman had done his duty in saving his own life and his sister’s honour, as well as in ridding his country of such a tyrant, others denied this, and said it was rank ingratitude to slay one who had bestowed on him such wealth and station. The ladies declared that the gentleman was a good brother and a worthy citizen; the men, on the contrary, that he was a treacherous and wicked servant.
6 In MS. No. 1520 (Bib. Nat.) this sentence begins: “The
tale was attentively listened to by all,” &c.—L.
And pleasant was it to hear the reasons which were brought forward on both sides; but the ladies, as is their wont, spoke as much from passion as from judgment, saying that the Duke was so well worthy of death that he who struck him down was a happy man indeed.
Then Dagoucin, seeing what a controversy he had set on foot, said to them—
“In God’s name, ladies, do not quarrel about a thing that is past and gone. Take care rather that your own charms do not occasion more cruel murders than the one which I have related.”
“‘La belle Dame sans Mercy,’” (7) replied Parlamente, “has taught us to say that but few die of so pleasing an ailment.”
7 La belle Dame sans Merci (The Pitiless Beauty) is one
of Alain Chartier’s best known poems. It is written in the
form of a dialogue between a lady and her lover: the former
having obstinately refused to take compassion on the
sufferings of her admirer, the latter is said to have died
of despair. The lines alluded to by Margaret are spoken by
the lady, and are to the following effect—“So graceful a
malady seldom puts men to death; yet the sooner to obtain
comfort, it is fitting one should say that it did. Some
complain and worry greatly who have not really felt the most
bitter affliction; and if indeed Love doth cause such great
torment, surely it were better there should be but one
sufferer rather than two.” The poem, as here quoted, will be
found in André Duchesne’s edition of the OEuvres de Maistre
Alain Chartier, Paris, 1617, p. 502.—L.
“Would to God, madam,” answered Dagoucin, “that all the ladies in this company knew how false that saying is. I think they would then scarcely wish to be called pitiless, or to imitate that unbelieving beauty who suffered a worthy lover to die for lack of a gracious answer to his suit.”
“So,” said Parlamente, “you would have us risk honour and conscience to save the life of a man who says he loves us.”
“That is not my meaning,” replied Dagoucin, “for he who loves with a perfect love would be even more afraid of hurting his lady’s honour than would she herself. I therefore think that an honourable and graceful response, such as is called for by perfect and seemly love, must tend to the increase of honour and the satisfaction of conscience, for no true lover could seek the contrary.”
“That is always the end of your speeches,” said Ennasuite; “they begin with honour and end with the contrary. However, if all the gentlemen present will tell the truth of the matter, I am ready to believe them on their oaths.”
Hircan swore that for his own part he had never loved any woman but his own wife, and even with her had no desire to be guilty of any gross offence against God.
Simontault declared the same, and added that he had often wished all women were froward excepting his own wife.
“Truly,” said Geburon to him, “you deserve that your wife should be what you would have the others. For my own part, I can swear to you that I once loved a woman so dearly that I would rather have died than have led her to do anything that might have diminished my esteem for her. My love for her was so founded upon her virtues, that for no advantage that I might have had of her would I have seen them blemished.”
At this Saffredent burst out laughing.
“Geburon,” he said, “I thought that your wife’s affection and your own good sense would have guarded you from the danger of falling in love elsewhere, but I see that I was mistaken, for you still use the very phrases with which we are wont to beguile the most subtle of women, and to obtain a hearing from the most discreet. For who would close her ears against us when we begin our discourse by talking of honour and virtue? (8) But if we were to show them our hearts just as they are, there is many a man now welcome among the ladies whom they would reckon of but little account. But we hide the devil in our natures under the most angelic form we can devise, and in this disguise receive many favours before we are found out. And perhaps we lead the ladies’ hearts so far forward, that when they come upon vice while believing themselves on the high road to virtue, they have neither opportunity nor ability to draw back again.”
8 This sentence is borrowed from MS. No. 1520 (Bib. Nat.)—
L.
“Truly,” said Geburon, “I thought you a different man than your words would show you to be, and fancied that virtue was more pleasing to you than pleasure.”
“What!” said Saffredent. “Is there any virtue greater than that of loving in the way that God commands? It seems to me that it is much better to love one woman as a woman than to adore a number of women as though they were so many idols. For my part, I am firmly of opinion that use is better than abuse.”
The ladies, however, all sided with Geburon, and would not allow Saffredent to continue, whereupon he said—
“I am well content to say no more on this subject of love, for I have been so badly treated with regard to it that I will never return to it again.”
“It is your own maliciousness,” said Longarine, “that has occasioned your bad treatment; for what virtuous woman would have you for a lover after what you have told us?”
“Those who did not consider me unwelcome,” answered Saffredent, “would not care to exchange their virtue for yours. But let us say no more about it, that my anger may offend neither myself nor others. Let us see to whom Dagoucin will give his vote.”
“I give it to Parlamente,” said Dagoucin, “for I believe that she must know better than any one else the nature of honourable and perfect love.”
“Since I have been chosen to tell the third tale,” said Parlamente, “I will tell you something that happened to a lady who has always been one of my best friends, and whose thoughts have never been hidden from me.”


A sea-captain, being greatly in love with a lady, sent her a diamond; but she despatched it to his wife, whom he had long neglected, and in this wise so atoned for his conduct that his wife was reconciled to him in perfect affection. (1)
1 M. Le Roux de Lincy believes that this story has some
historical basis, and, Louise of Savoy being termed the
Regent, he assigns the earlier incidents to the year 1524.
But Louise was Regent, for the first time, in 1515, and we
incline to the belief that Queen Margaret alludes to this
earlier period. Note the reference to a Court journey to
Normandy (post, p. 136), which was probably the journey that
Francis I. and his mother are known to have made to Rouen
and Alençon in the autumn of 1517. See vol. i. p. xxviii.—
Ed. 2 119
In the household of the Lady-Regent, mother of King Francis, there was a very pious lady married to a gentleman of like mind with herself, and, albeit her husband was old and she was young and pretty, she served and loved him as though he had been the handsomest and youngest man in the world. So that she might give him no cause for sorrow, she set herself to live as though she were of the same age as himself, eschewing all such company, dress, dances, and amusements as young women are wont to love, and finding all her pleasure and recreation in the service of God; on which account her husband so loved and trusted her, that she ruled him and his household as she would.
One day it happened that the gentleman told his wife that from his youth up he had desired to make a journey to Jerusalem, and asked her what she thought of it. She, whose only wish was to please him, replied—
“Since God has withheld children from us, sweetheart, and has granted us sufficient wealth, I would willingly use some portion of it in making this sacred journey with you, for indeed, whether you go thither or elsewhere, I am resolved never to leave you.”
At this the good man was so pleased, that it seemed to him as though he were already on Mount Calvary.
While they were deliberating on this matter, there came to the Court a gentleman, the Captain of a galley, who had often served in the wars against the Turks, (2) and was now soliciting the King of France to undertake an expedition against one of their cities, which might yield great advantage to Christendom. The old gentleman inquired of him concerning this expedition, and after hearing what he intended to do, asked him whether, on the completion of this business, he would make another journey to Jerusalem, whither he himself and his wife had a great desire to go. The Captain was well pleased on hearing of this laudable desire, and he promised to conduct them thither, and to keep the matter secret.
2 M. Paul Lacroix, who believes that the heroine of this
tale is Margaret herself (she is described as telling it
under the name of Parlamente), is also of opinion that the
gentleman referred to is the Baron de Malleville, a knight
of Malta, who was killed at Beyrout during an expedition
against the Turks, and whose death was recounted in verse by
Clement Marot (OEuvres, 1731, vol. ii. p. 452-455).
Margaret’s gentleman, however, is represented as being
married, whereas M. de Malleville, as a knight of Malta, was
necessarily a bachelor. Marot, moreover, calls Malleville a
Parisian, whereas the gentleman in the tale belonged to
Normandy (see post, p. 136).—B. J. and L.
The old gentleman was all impatience to find his wife and tell her of what he had done. She was as anxious to make the journey as her husband, and on that account often spoke about it to the Captain, who, paying more attention to her person than her words, fell so deeply in love with her, that when speaking to her of the voyages he had made, he often confused the port of Marseilles with the Archipelago, and said “horse” when he meant to say “ship,” like one distracted and bereft of sense. Her character, however, was such that he durst not give any token of the truth, and concealment kindled such fires in his heart that he often fell sick, when the lady showed as much solicitude for him as for the cross and guide of her road, (3) sending to inquire after him so often that the anxiety she showed cured him without the aid of any other medicine.
3 This may simply be an allusion to wayside crosses which
serve to guide travellers on their road. M. de Montaiglon
points out, however, that in the alphabets used for teaching
children in the olden time, the letter A was always preceded
by a cross, and that the child, in reciting, invariably
began: “The cross of God, A, B, C, D,” &c. In a like way, a
cross figured at the beginning of the guide-books of the
time, as a symbol inviting the traveller to pray, and
reminding him upon whom he should rely amid the perils of
his journey. The best known French guide-book of the
sixteenth century is Charles Estienne’s Guide des Chemins
de France.—M. and Ed.
Several persons who knew that this Captain had been more renowned for valour and jollity than for piety, were amazed that he should have become so intimate with this lady, and seeing that he had changed in every respect, and frequented churches, sermons, and confessions, they suspected that this was only in order to win the lady’s favour, and could not refrain from hinting as much to him.
The Captain feared that if the lady should hear any such talk he would be banished from her presence, and accordingly he told her husband and herself that he was on the point of being despatched on his journey by the King, and had much to tell them, but that for the sake of greater secrecy he did not desire to speak to them in the presence of others, for which reason he begged them to send for him when they had both retired for the night. The gentleman deemed this to be good advice, and did not fail to go to bed early every evening, and to make his wife also undress. When all their servants had left them, they used to send for the Captain, and talk with him about the journey to Jerusalem, in the midst of which the old gentleman would oft-times fall asleep with his mind full of pious thoughts. When the Captain saw the old gentleman asleep in bed, and found himself on a chair near her whom he deemed the fairest and noblest woman in the world, his heart was so rent between his desires and his dread of speaking that he often lost the power of speech. In order that she might not perceive this, he would force himself to talk of the holy places of Jerusalem where there were such signs of the great love that Jesus Christ bore us; and he would speak of this love, using it as a cloak for his own, and looking at the lady with sighs and tears which she never understood. By reason of his devout countenance she indeed believed him to be a very holy man, and begged of him to tell her what his life had been, and how he had come to love God in that way.
He told her that he was a poor gentleman, who, to arrive at riches and honour, had disregarded his conscience in marrying a woman who was too close akin to him, and this on account of the wealth she possessed, albeit she was ugly and old, and he loved her not; and when he had drawn all her money from her, he had gone to seek his fortune at sea, and had so prospered by his toil, that he had now come to an honourable estate. But since he had made his hearer’s acquaintance, she, by reason of her pious converse and good example, had changed all his manner of life, and should he return from his present enterprise he was wholly resolved to take her husband and herself to Jerusalem, that he might thereby partly atone for his grievous sins which he had now put from him; save that he had not yet made reparation to his wife, with whom, however, he hoped that he might soon be reconciled.
The lady was well pleased with this discourse, and especially rejoiced at having drawn such a man to the love and fear of God. And thus, until the Captain departed from the Court, their long conversations together were continued every evening without his ever venturing to declare himself. However, he made the lady a present of a crucifix of Our Lady of Pity, (4) beseeching her to think of him whenever she looked upon it.
4 “Our Lady of Pity” is the designation usually applied to
the Virgin when she is shown seated with the corpse of
Christ on her knees. Michael Angelo’s famous group at St.
Peter’s is commonly known by this name. In the present
instance, however, Queen Margaret undoubtedly refers to a
crucifix showing the Virgin at the foot of the Cross,
contemplating her son’s sufferings. Such crucifixes were
formerly not uncommon.—M.
The hour of his departure arrived, and when he had taken leave of the husband, who was falling asleep, and came to bid his lady farewell, he beheld tears standing in her eyes by reason of the honourable affection which she entertained for him. The sight of these rendered his passion for her so unendurable that, not daring to say anything concerning it, he almost fainted, and broke out into an exceeding sweat, so that he seemed to weep not only with his eyes, but with his entire body. And thus he departed without speaking, leaving the lady in great astonishment, for she had never before seen such tokens of regret. Nevertheless she did not change in her good opinion of him, and followed him with her prayers.
After a month had gone by, however, as the lady was returning to her house, she met a gentleman who handed her a letter from the Captain, and begged her to read it in private.
He told her how he had seen the Captain embark, fully resolved to accomplish whatever might be pleasing to the King and of advantage to Christianity. For his own part, the gentleman added, he was straightway going back to Marseilles to set the Captain’s affairs in order.
The lady withdrew to a window by herself, and opening the letter, found it to consist of two sheets of paper, covered on either side with writing which formed the following epistle:—
“Concealment long and silence have, alas!
Brought me all comfortless to such a pass,
That now, perforce, I must, to ease my grief,
Either speak out, or seek in death relief.
Wherefore the tale I long have left untold
I now, in lonely friendlessness grown bold,
Send unto thee, for I must strive to say
My love, or else prepare myself to slay.
And though my eyes no longer may behold
The sweet, who in her hand my life doth hold,
Whose glance sufficed to make my heart rejoice,
The while my ear did listen to her voice,—
These words at least shall meet her beauteous eyes,
And tell her all the plaintive, clamorous cries
Pent in my heart, to which I must give breath,
Since longer silence could but bring me death.
And yet, at first, I was in truth full fain
To blot the words I’d written out again,
Fearing, forsooth, I might offend thine ear
With foolish phrases which, when thou wast near,
I dared not utter; and ‘Indeed,’ said I,
‘Far better pine in silence, aye, and die,
Than save myself by bringing her annoy
For whose sweet sake grim death itself were joy.’
And yet, thought I, my death some pain might give
To her for whom I would be strong, and live:
For have I not, fair lady, promised plain,
My journey ended, to return again
And guide thee and thy spouse to where he now
Doth yearn to call on God from Sion’s brow?
And none would lead thee thither should I die.
If I were dead, methinks I see thee sigh
In sore distress, for then thou couldst not start
Upon that journey, dear unto thy heart.
So I will live, and, in a little space,
Return to lead thee to the sacred place.
Aye, I will live, though death a boon would be
Only to be refused for sake of thee.
But if I live, I needs must straight remove
The burden from my heart, and speak my love,
That love more loyal, tender, deep, and true,
Than, ever yet, the fondest lover knew.
And now, bold words about to wing your flight,
What will ye say when ye have reached her sight?
Declare her all the love that fills my heart?
Too weak ye are to tell its thousandth part!
Can ye at least not say that her clear eyes
Have torn my hapless heart forth in such wise,
That like a hollow tree I pine and wither
Unless hers give me back some life and vigour?
Ye feeble words! ye cannot even tell
How easily her eyes a heart compel;
Nor can ye praise her speech in language fit,
So weak and dull ye are, so void of wit.
Yet there are some things I would have you name—
How mute and foolish I oft time became
When all her grace and virtue I beheld;
How from my ‘raptured eyes tears slowly welled
The tears of hopeless love; how my tongue strayed
From fond and wooing speech, so sore afraid,
That all my discourse was of time and tide,
And of the stars which up in Heav’n abide.
O words, alas! ye lack the skill to tell
The dire confusion that upon me fell,
Whilst love thus wracked me; nor can ye disclose
My love’s immensity, its pains and woes.
Yet, though, for all, your powers be too weak,
Perchance, some little, ye are fit to speak—
Say to her thus: “Twas fear lest thou shouldst chide
That drove me, e’en so long, my love to hide,
And yet, forsooth, it might have openly
Been told to God in Heaven, as unto thee,
Based as it is upon thy virtue—thought
That to my torments frequent balm hath brought,
For who, indeed, could ever deem it sin
To seek the owner of all worth to win?
Deserving rather of our blame were he
Who having seen thee undisturbed could be.’
None such was I, for, straightway stricken sore,
My heart bowed low to Love, the conqueror.
And ah! no false and fleeting love is mine,
Such as for painted beauty feigns to pine;
Nor doth my passion, although deep and strong,
Seek its own wicked pleasure in thy wrong.
Nay; on this journey I would rather die
Than know that thou hadst fallen, and that I
Had wrought thy shame and foully brought to harm
The virtue which thy heart wraps round thy form.
‘Tis thy perfection that I love in thee,
Nought that might lessen it could ever be
Desire of mine—indeed, the nobler thou,
The greater were the love I to thee vow.
I do not seek an ardent flame to quench
In lustful dalliance with some merry wench,
Pure is my heart, ‘neath reason’s calm control
Set on a lady of such lofty soul,
That neither God above nor angel bright,
But seeing her, would echo my delight.
And if of thee I may not be beloved,
What matter, shouldst thou deem that I have proved
The truest lover that did ever live?
And this I know thou wilt, one day, believe,
For time, in rolling by, shall show to thee
No change in my heart’s faith and loyalty.
And though for this thou mayst make no return,
Yet pleased am I with love for thee to burn,
And seek no recompense, pursue no end,
Save, that to thee, I meekly recommend
My soul and body, which I here consign
In sacrifice to Love’s consuming shrine.
If then in safety I sail back the main
To thee, still artless, I’ll return again;
And if I die, then there will die with me
A lover such as none again shall see.
So Ocean now doth carry far away
The truest lover seen for many a day;
His body ‘tis that journeys o’er the wave,
But not his heart, for that is now thy slave,
And from thy side can never wrested be,
Nor of its own accord return to me.
Ah! could I with me o’er the treach’rous brine
Take aught of that pure, guileless heart of thine,
No doubt should I then feel of victory,
Whereof the glory would belong to thee.
But now, whatever fortune may befall,
I’ve cast the die; and having told thee all,
Abide thereby, and vow my constancy—
Emblem of which, herein, a diamond see,
By whose great firmness and whose pure glow
The strength and pureness of my love thou’lt know.
Let it, I pray, thy fair white finger press,
And thou wilt deal me more than happiness.
And, diamond, speak and say: ‘To thee I come
From thy fond lover, who afar doth roam,
And strives by dint of glorious deeds to rise
To the high level of the good and wise,
Hoping some day that haven to attain,
Where thy sweet favours shall reward his pain.”
The lady read the letter through, and was the more astonished at the Captain’s passion as she had never before suspected it. She looked at the cutting of the diamond, which was a large and beautiful one, set in a ring of black enamel, and she was in great doubt as to what she ought to do with it. After pondering upon the matter throughout the night, she was glad to find that since there was no messenger, she had no occasion to send any answer to the Captain, who, she reflected, was being sufficiently tried by those matters of the King, his master, which he had in hand, without being angered by the unfavourable reply which she was resolved to make to him, though she delayed it until his return. However, she found herself greatly perplexed with regard to the diamond, for she had never been wont to adorn herself at the expense of any but her husband. For this reason, being a woman of excellent understanding, she determined to draw from the ring some profit to the Captain’s conscience. She therefore despatched one of her servants to the Captain’s wife with the following letter, which was written as though it came from a nun of Tarascon:—
“MADAM,—Your husband passed this way but a short time before he embarked, and after he had confessed himself and received his Creator like a good Christian, he spoke to me of something which he had upon his conscience, namely, his sorrow at not having loved you as he should have done. And on departing, he prayed and besought me to send you this letter, with the diamond which goes with it, and which he begs of you to keep for his sake, assuring you that if God bring him back again in health and strength, you shall be better treated than ever woman was before. And this stone of steadfastness shall be the pledge thereof.
“I beg you to remember him in your prayers; in mine he will have a place as long as I live.”
This letter, being finished and signed with the name of a nun, was sent by the lady to the Captain’s wife. And as may be readily believed, when the excellent old woman saw the letter and the ring, she wept for joy and sorrow at being loved and esteemed by her good husband when she could no longer see him. She kissed the ring a thousand times and more, watering it with her tears, and blessing God for having restored her husband’s affection to her at the end of her days, when she had long looked upon it as lost. Nor did she fail to thank the nun who had given her so much happiness, but sent her the fairest reply that she could devise. This the messenger brought back with all speed to his mistress, who could not read it, nor listen to what her servant told her, without much laughter. And so pleased was she at having got rid of the diamond in so profitable a fashion as to bring about a reconciliation between the husband and wife, that she was as happy as though she had gained a kingdom.
A short time afterwards tidings came of the defeat and death of the poor Captain, and of how he had been abandoned by those who ought to have succoured him, and how his enterprise had been revealed by the Rhodians who should have kept it secret, so that he and all who landed with him, to the number of eighty, had been slain, among them being a gentleman named John, and a Turk to whom the lady of my story had stood godmother, both of them having been given by her to the Captain that he might take them with him on his journey. The first named of these had died beside the Captain, whilst the Turk, wounded by arrows in fifteen places, had saved himself by swimming to the French ships.
It was through him alone that the truth of the whole affair became known. A certain gentleman whom the poor Captain had taken to be his friend and comrade, and whose interests he had advanced with the King and the highest nobles of France, had, it appeared, stood out to sea with his ships as soon as the Captain landed; and the Captain, finding that his expedition had been betrayed, and that four thousand Turks were at hand, had thereupon endeavoured to retreat, as was his duty. But the gentleman in whom he put such great trust perceived that his friend’s death would leave the sole command and profit of that great armament to himself, and accordingly pointed out to the officers that it would not be right to risk the King’s vessels or the lives of the many brave men on board them in order to save less than a hundred persons, an opinion which was shared by all those of the officers that possessed but little courage.
So the Captain, finding that the more he called to the ships the farther they drew away from his assistance, faced round at last upon the Turks; and, albeit he was up to his knees in sand, he did such deeds of arms and valour that it seemed as though he alone would defeat all his enemies, an issue which his traitorous comrade feared far more than he desired it.
But at last, in spite of all that he could do, the Captain received so many wounds from the arrows of those who durst not approach within bowshot, that he began to lose all his blood, whereupon the Turks, perceiving the weakness of these true Christians, charged upon them furiously with their scimitars; but the Christians, so long as God gave them strength and life, defended themselves to the bitter end.
Then the Captain called to the gentleman named John, whom his lady love had given him, and to the Turk as well, and thrusting the point of his sword into the ground, fell upon his knees beside it, and embraced and kissed the cross, (5) saying—
“Lord, receive into Thy hands the soul of one who has not spared his life to exalt Thy name.”
5 As is well known, before swords were made with shell and
stool hilts, the two guards combined with the handle and
blade formed a cross. Bayard, when dying, raised his sword
to gaze upon this cross, and numerous instances, similar to
that mentioned above by Queen Margaret, may be found in the
old Chansons de Geste.—M.
The gentleman called John, seeing that his master’s life was ebbing away as he uttered these words, thought to aid him, and took him into his arms, together with the sword which he was holding. But a Turk who was behind them cut through both his thighs, whereupon he cried out, “Come, Captain, let us away to Paradise to see Him for whose sake we die,” and in this wise he shared the poor Captain’s death even as he had shared his life.
The Turk, seeing that he could be of no service to either of them, and being himself wounded by arrows in fifteen places, made off towards the ships, and requested to be taken on board. But although of all the eighty he was the only one who had escaped, the Captain’s traitorous comrade refused his prayer. Nevertheless, being an exceeding good swimmer, he threw himself into the sea, and exerted himself so well that he was at last received on board a small vessel, where in a short time he was cured of his wounds. And it was by means of this poor foreigner that the truth became fully known, to the honour of the Captain and the shame of his comrade, whom the King and all the honourable people who heard the tidings deemed guilty of such wickedness toward God and man that there was no death howsoever cruel which he did not deserve. But when he returned he told so many lies, and gave so many gifts, that not only did he escape punishment, but even received the office of the man whose unworthy servant he had been.
When the pitiful tidings reached the Court, the Lady-Regent, who held the Captain in high esteem, mourned for him exceedingly, as did the King and all the honourable people who had known him. And when the lady whom he had loved the best heard of his strange, sad, and Christian death, she changed the chiding she had resolved to give him into tears and lamentations, in which her husband kept her company, all hopes of their journey to Jerusalem being now frustrated.
I must not forget to say that on the very day when the two gentlemen were killed, a damsel in the lady’s service, who loved the gentleman called John better than herself, came and told her mistress that she had seen her lover ir a dream; he had appeared to her clad in white, and had bidden her farewell, telling her that he was going to Paradise with his Captain. And when the damsel heard that her dream had come true, she made such lamentation that her mistress had enough to do to comfort her. (6)
6 The Queen of Navarre was a firm believer in the truth and
premonitory character of dreams, and according to her
biographers she, herself, had several singular ones, two of
which are referred to in the Memoir prefixed to the present
work (vol. i. pp. lxxxiii. and Ixxxvii.). In some of her
letters, moreover, she relates that Francis I., when under
the walls of Pavia, on three successive nights beheld his
little daughter Charlotte (then dying at Lyons) appear to
him in a dream, and on each occasion repeat the words,
“Farewell, my King, I am going to Paradise.”—Ed.
A short time afterwards the Court journeyed into Normandy, to which province the Captain had belonged. His wife was not remiss in coming to pay homage to the Lady-Regent, and in order that she might be presented to her, she had recourse to the same lady whom her husband had so dearly loved.
And while they were waiting in a church for the appointed hour, she began bewailing and praising her husband, saying among other things to the lady—
“Alas, madam! my misfortune is the greatest that ever befell a woman, for just when he was loving me more than he had ever done, God took him from me.”
So saying, and with many tears, she showed the ring which she wore on her finger as a token of her husband’s perfect love, whereat the other lady, finding that her deception had resulted in such a happy issue, was, despite her sorrow for the Captain’s death, so moved to laughter, that she would not present the widow to the Regent, but committed her to the charge of another lady, and withdrew into a side chapel, where she satisfied her inclination to laugh.
“I think, ladies, that those who receive such gifts ought to seek to use them to as good a purpose as did this worthy lady. They would find that benefactions bring joy to those who bestow them. And we must not charge this lady with deceit, but esteem her good sense which turned to good that which in itself was worthless.”
“Do you mean to say,” said Nomerfide, “that a fine diamond, costing two hundred crowns, is worthless? I can assure you that if it had fallen into my hands, neither his wife nor his relations would have seen aught of it. Nothing is more wholly one’s own than a gift. The gentleman was dead, no one knew anything about the matter, and she might well have spared the poor old woman so much sorrow.”
“By my word,” said Hircan, “you are right. There are women who, to make themselves appear of better heart than others, do things that are clearly contrary to their notions, for we all know that women are the most avaricious of beings, yet their vanity often surpasses their avarice, and constrains their hearts to actions that they would rather not perform. My belief is that the lady who gave the diamond away in this fashion was unworthy to wear it.”
“Softly, softly,” said Oisille; “I believe I know who she is, and I therefore beg that you will not condemn her unheard.”
“Madam,” said Hircan, “I do not condemn her at all; but if the gentleman was as virtuous as you say, it were an honour to have such a lover, and to wear his ring; but perhaps some one less worthy of being loved than he held her so fast by the finger that the ring could not be put on.”
“Truly,” said Ennasuite, “she might well have kept it, seeing that no one knew anything about it.”
“What!” said Geburon; “are all things lawful to those who love, provided no one knows anything about them?”
“By my word,” said Saffredent, “the only misdeed that I have ever seen punished is foolishness. There is never a murderer, robber, or adulterer condemned by the courts or blamed by his fellows, if only he be as cunning as he is wicked. Oft-time, however, a bad man’s wickedness so blinds him that he becomes a fool; and thus, as I have just said, it is the foolish only that are punished, not the vicious.”
“You may say what you please,” said Oisille, “only God can judge the lady’s heart; but for my part, I think that her action was a very honourable and virtuous one. (7) However, to put an end to the debate, I pray you, Parlamente, to give some one your vote.”
7 In our opinion this sentence disposes of Miss Mary
Robinson’s supposition (The Fortunate Lovers, London,
1887, p. 159) that Oisille (i.e., Louise of Savoy) is the
real heroine of this tale. Queen Margaret would hardly have
represented her commending her own action. If any one of the
narrators of the Heptameron be the heroine of the story,
the presumptions are in favour of Longarine (La Dame de
Lonray), Margaret’s bosom friend, whose silence during the
after-converse is significant.—Ed.
“I give it willingly,” she said, “to Simontault, for after two such mournful tales we must have one that will not make us weep.”
“I thank you,” said Simontault. “In giving me your vote you have all but told me that I am a jester. It is a name that is extremely distasteful to me, and in revenge I will show you that there are women who with certain persons, or for a certain time, make a great pretence of being chaste, but the end shows them in their real colours, as you will see by this true story.”



The Lord of Bonnivet, desiring to revenge himself upon a
Milanese lady for her cruelty, made the acquaintance of an
Italian gentleman whom she loved, but to whom she had never
granted anything save fair words and assurances of
affection. To accomplish his purpose he gave this gentleman
such good advice that the lady granted him what he had so
long sought, and this the gentleman made known to Bonnivet,
who, having cut both hair and beard, and dressed himself in
clothes like those of the other, went at midnight and put
his vengeance into execution. Then the lady, having learnt
from him the plan that he had devised to win her, promised
to desist from loving those of her own nation, and to hold
fast to him.
At the time when the Grand-Master of Chaumont was Governor of the Duchy of Milan, (1) there lived there a gentleman called the Lord of Bonnivet, who by reason of his merits was afterwards made Admiral of France. Being greatly liked by the Grand-Master and every one else on account of the qualities he possessed, he was a welcome guest at the banquets where the ladies of Milan assembled, and was regarded by them with more favour than ever fell to a Frenchman’s lot, either before or since; and this as much on account of his handsome countenance, grace of manner, and pleasant converse, as by reason of the renown which he had gained among all as being one of the most skilful and valorous soldiers of his time. (2)
1 M. de Lincy is of opinion that the incidents recorded in
this story took place between 1501 and 1503; but according
to M. Lacroix, the Grand-Master of Chaumont did not become
Governor of the Milanese till 1506. This personage, to whom
Queen Margaret frequently alludes in her tales, was Charles
d’Amboise, nephew of the famous Cardinal d’Amboise, minister
to Louis XII. In turn admiral and marshal, Governor of
Paris, and Grand-Master, in France, of the Order of St. John
of Jerusalem, he figured prominently in the Italian wars of
the time, and notably at the battle of Aignadel. In 1510 he
commanded the troops which fought on behalf of the Duke of
Ferrara against the Emperor and Pope Julius II., and the
latter having excommunicated him for bearing arms against
the Holy See, his mind is said to have become unhinged. He
died at Correggio in February 1511, when only thirty-eight
years of age, some biographers asserting that he was
poisoned, whilst others contend that he fell from a bridge
during a military expedition. Whilst on his death-bed, he
sent messengers to the Pope, begging that the decree of
excommunication against him might be annulled, but before
the Papal absolution arrived he had expired. The name of
Chaumont, by which he is generally known, is that of an
estate he possessed, between Blois and Amboise, on the
Loire. The reputation he enjoyed of being one of the
handsomest men of his time was well deserved, if one may
judge by a painting at the Louvre which is said to be his
portrait. This picture, long ascribed to Leonardo da Vinci,
and supposed to represent Charles VIII. of France, has been
identified as the work of Andreas Solario, who executed
numerous paintings for Cardinal d’Amboise at the famous
château of Gaillon.—L. M. and Eu.
2 Some particulars concerning William Gouffier, Lord of
Bonnivet, have been given in vol. i. (Tale IV. n. 3). It
may here be mentioned that the domain whence he derived the
name by which he is generally known was in the neighbourhood
of Poitiers, around the village of Vendeuvre, where he built
himself a vast château, destroyed at the close of the
eighteenth century. Some fragments of the sculptured work
adorning it, remarkable for their elegance of design and
delicacy of workmanship, are in the Poitiers Museum. It is
not unlikely that the incidents related in Tale IV. occurred
at this château; or else at that of Oiron, another domain of
the Gouffiers, between Loudun and Bressuire. In the chapel
of Oiron were buried Bonnivet, his mother, his brother
Artus, and his nephew Claud. Their tombs, large marble
mausoleums of Italian workmanship, surmounted by recumbent
statues, were opened and mutilated by the Huguenots in 1568,
when the bones they contained were scattered to the winds.
Bon-nivet’s statue is probably the most damaged of the four.
The château of Oiron, with its marble staircases, quaint
frescoes, sculptured medallions, &c, testifies to the great
wealth possessed by the Gouffier family, and justifies the
cynical motto assumed by Bonnivet’s nephew: “Others have
beaten the bushes, but we have the birds.”—Ed.
One day during the carnival, when he was among the maskers, he danced with one of the most beautiful and bravely attired ladies to be found in the whole city; and whenever a pause occurred in the music of the hautboys, he did not fail to address her with love speeches, in which he excelled all others. But she (3) having no favourable reply to give him, suddenly checked his discourse by assuring him that she neither loved nor ever would love any man but her husband, and that he must by no means expect that she would listen to him.
3 This lady may perhaps be the “Sennora Clerice” (Clarissa)
of whom Brantôme writes as follows in his Capitaines
François:—“It was Bonnivet alone who advised King Francis
to cross the mountains and follow M. de Bourbon, and in this
he had less his master’s advantage and service at heart than
his desire to return and see a great and most beautiful lady
of Milan, whom he had made his mistress some years
previously.... It is said that this was the ‘Sennora
Clerice,’ then accounted one of the most beautiful ladies of
Italy.... A great lady of the time, from whom I heard this
story, told me that he, Bonnivet, had commended this lady
Clerice to the King so highly as to make him desirous of
seeing and winning her; and this was the principal cause of
this expedition of the King’s.”—Lalanne’s OEuvres de
Brantôme, vol. ii. p. 167-8.—L.
The gentleman, however, would not take this answer for a refusal, and continued to press his suit with great energy until mid-Lent. But he found her still firm in her declaration that she would love neither himself nor another, which he could not believe, however, seeing how ill-favoured was her husband, and how great her own beauty. Convinced that she was practising dissimulation, he resolved, on his own side, to have recourse to deception, and accordingly he ceased to urge his suit, and inquired so closely concerning her manner of life that he discovered she was in love with a most discreet and honourable Italian gentleman.
Little by little the Lord of Bonnivet insinuated himself into the friendship of this gentleman, and did so with so much discretion and skill, that the other remained ignorant of his motive, and became so much attached to him that, after the lady of his heart, there was no one in the world whom he loved more. In order that he might pluck his secret from his breast, the Lord of Bonnivet pretended to tell him his own, declaring that he loved a certain lady to whom he had in truth never given a thought, and begging that he would keep the matter secret, and that they might have but one heart and one mind together. Wishing to show in return a like affection, the poor Italian gentleman thereupon proceeded to disclose at length the love that he bore the lady on whom Bonnivet wished to be revenged; and after this they would meet somewhere once every day in order to recount the favours that had befallen them during the past four and twenty hours; with this difference, however, that one lied, and the other spoke the truth. And the Italian confessed that he had loved this lady for three years, but had never obtained anything of her save fair words and the assurance of her love.
Bonnivet then gave him all the advice that he could to enable him to attain his end, and to such good purpose that in a few days the lady consented to grant all that was sought of her. It only remained to devise a plan for their meeting, and through the counsels of Bonnivet this was soon accomplished. And so one day before supper the Italian said to him—
“I am more beholden to you, sir, than to any other man living, for, thanks to your good advice, I expect to obtain to-night that which I have coveted so many years.”
“I pray you, my friend,” thereupon said Bonnivet, “tell me the manner of your undertaking, so that if there be any risk in it, or craft required, I may serve you in all friendship.”
The Italian gentleman then began to tell him that the lady had devised a means of having the principal door of the house left open that night, availing herself as a pretext of the illness of one of her brothers for whose requirements it was necessary to send into the town at all hours. He might enter the courtyard, but he was to be careful not to go up by the principal staircase. Instead of this he was to take a small flight on his right hand, and enter the first gallery he came to, into which the rooms of the lady’s father-in-law and brothers-in-law opened; and he was to choose the third door from the head of the stairs, and if on trying it gently he found that it was locked, he was to go away again, for in that case he might be sure that her husband had returned, though not expected back for two days. If, however, he found that the door was open, he was to enter softly, and boldly bolt it behind him, for in that case there would be none but herself in the room. And above all, he was to get himself felt shoes, in order that he might make no noise, and he was to be careful not to come earlier than two hours after midnight, for her brothers-in-law, who were fond of play, never went to bed until after one of the clock.
“Go, my friend,” replied Bonnivet, “and may God be with you and preserve you from mischief. If my company can be of any service to you, I am wholly at your disposal.”
The Italian gentleman thanked him warmly, but said that in an affair of this nature he could not be too much alone; and thereupon he went away to set about his preparations.
Bonnivet, on his part, did not go to sleep, for he saw that the time had come for revenging himself upon his cruel love. Going home betimes, he had his beard trimmed to the same length and breadth as the Italian’s, and also had his hair cut, so that, on touching him, no difference between himself and his rival might be perceived. Nor did he forget the felt shoes, nor garments such as the Italian was wont to wear. Being greatly liked by the lady’s father-in-law, he was not afraid to go to the house at an early hour, for he made up his mind that if he were perceived, he would go straight to the chamber of the old gentleman, with whom he had some business on hand.
About midnight he entered the lady’s house, and although there were a good many persons going to and fro, he passed them unnoticed and thus reached the gallery. Trying the first two doors, he found them shut; the third, however, was not, and he softly pushed it open. And having thus entered the lady’s room, he immediately bolted the door behind him. He found that the whole chamber was hung with white linen, the floor and ceiling also being covered with the same; and there was a bed draped with cloth so fine and soft and so handsomely embroidered in white, that nothing better were possible. And in the bed lay the lady alone, wearing her cap and night-gown, and covered with pearls and gems. This, before he was himself perceived by her, he was able to see by peeping round the curtain; for there was a large wax candle burning, which made the room as bright as day. And fearful lest he should be recognised by her, he first of all put out the light. Then he undressed himself and got into bed beside her.
The lady, taking him to be the Italian who had so long loved her, gave him the best possible reception; but he, not forgetting that he was there in another’s stead, was careful not to say a single word. His only thought was to execute his vengeance at the cost of her honour and chastity without being beholden to her for any boon. And although this was contrary to her intention, the lady was so well pleased with this vengeance that she deemed him rewarded for all she thought he had endured. At last it struck one of the clock, and it was time to say good-bye. Then, in the lowest tones he could employ, he asked her if she were as well pleased with him as he was with her. She, believing him to be her lover, said that she was not merely pleased but amazed at the greatness of his love, which had kept him an hour without answering her.
Then he began to laugh aloud, and said to her—
“Now, madam, will you refuse me another time, as you have hitherto been wont to do?”
The lady, recognising him by his speech and laughter, was in such despair with grief and shame, that she called him villain, traitor, and deceiver a thousand times over, and tried to throw herself out of bed to search for a knife in order to kill herself, since she was so unfortunate as to have lost her honour through a man whom she did not love, and who to be revenged on her might publish the matter to the whole world.
But he held her fast in his arms, and in fair soft words declared that he would love her more than her lover, and would so carefully conceal all that affected her honour that she should never be brought to reproach. This the poor foolish thing believed, and on hearing from him the plan that he had devised and the pains that he had taken to win her, she swore to him that she would love him better than the other, who had not been able to keep her secret. She now knew, said she, how false was the repute in which the French were held; they were more sensible, persevering, and discreet than the Italians; wherefore she would henceforward lay aside the erroneous opinions of her nation and hold fast to him. But she earnestly entreated him not to show himself for some time at any entertainment or in any place where she might be unless he were masked; for she was sure she should feel so much ashamed that her countenance would betray her to every one.
This he promised to do, and he then begged that she would give her lover a good welcome when he came at two o’clock, getting rid of him afterwards by degrees. This she was very loth to do, and but for the love she bore to Bonnivet would on no account have consented. However, when bidding her farewell, he gave her so much cause for satisfaction that she would fain have had him stay with her some time longer.
Having risen and donned his garments again, he departed, leaving the door of the room slightly open, as he had found it. And as it was now nearly two o’clock, and he was afraid of meeting the Italian gentleman, he withdrew to the top of the staircase, whence he not long afterwards saw the other pass by and enter the lady’s room.
For his own part, he then betook himself home to rest, in such wise that at nine of the clock on the following morning he was still in bed. While he was rising, there arrived the Italian gentleman, who did not fail to recount his fortune, which had not been so great as he had hoped; for on entering the lady’s chamber, said he, he had found her out of bed, wearing her dressing-gown, and in a high fever, with her pulse beating quick and her countenance aflame, and a perspiration beginning to break out upon her. She had therefore begged him to go away forthwith, for fearing a mishap, she had not ventured to summon her women, and was in consequence so ill that she had more need to think of death than of love, and to be told of God than of Cupid. She was distressed, she added, that he should have run such risk for her sake, since she was wholly unable to grant what he sought in a world she was so soon to leave. He had felt so astonished and unhappy on hearing this that all his fire and joy had been changed to ice and sadness, and he had immediately gone away. However, he had sent at daybreak to inquire about her, and had heard that she was indeed very ill. While recounting his griefs he wept so piteously that it seemed as though his soul must melt away in his tears.
Bonnivet, who was as much inclined to laugh as the other was to weep, comforted him as well as he could, telling him that affections of long duration always had a difficult beginning, and that Love was causing him this delay only that he might afterwards have the greater joy. And so the two gentlemen parted. The lady remained in bed for some days, and on regaining her health dismissed her first suitor, alleging as her reason the fear of death that had beset her and the prickings of her conscience. But she held fast to my lord Bonnivet, whose love, as is usual, lasted no longer than the field flowers bloom.
“I think, ladies, that the gentleman’s craftiness was a match for the hypocrisy of the lady, who, after playing the prude so long, showed herself such a wanton in the end.”
“You may say what you please about women,” said Ennasuite, “but the gentleman played an evil trick. Is it allowable that if a lady loves one man, another may obtain her by craft?”
“You may be sure,” said Geburon, “that when such mares are for sale they are of necessity carried off by the last and highest bidder. Do not imagine that wooers take such great pains for the ladies’ sakes. It is for their own sakes and their own pleasure.”
“By my word,” said Longarine, “I believe you; for, truth to tell, all the lovers that I have ever had have always begun their speeches by talking about me, declaring that they cherished my life, welfare, and honour; but in the end they only thought of themselves, caring for nought but their own pleasure and vanity. The best plan, therefore, is to dismiss them as soon as the first portion of their discourse is ended; for when they come to the second, there is not so much credit in refusing them, seeing that vice when recognised must needs be rejected.”
“So as soon as a man opens his mouth,” said Ennasuite, “we ought to refuse him, without knowing what he is going to say?”
“Nay,” replied Parlamente, “my friend does not mean that. We know that at first a woman should never appear to understand what the man desires, or even to believe him when he has declared what it is; but when he comes to strong protestations, I think it were better for ladies to leave him on the road rather than continue to the end of the journey with him.”
“That may be,” said Nomerfide; “but are we to believe that they love us for evil? Is it not a sin to judge our neighbours?”
“You may believe what you please,” said Oisille; “but there is so much cause for fearing it to be true, that as soon as you perceive the faintest spark, you should flee from this fire, lest it should burn up your heart before you even know it.”
“Truly,” said Hircan, “the laws you lay down are over harsh. If women, whom gentleness beseems so well, were minded to prove as rigorous as you would have them be, we men, on our part, would exchange our gentle entreaties for craft and force.”
“In my opinion,” said Simontault, “the best advice is that each should follow his natural bent. Whether he love or not, let him do so without dissimulation.”
“Would to God,” said Saffredent, “that such a rule would bring as much honour as it would give pleasure.”
Dagoucin, however, could not refrain from saying—
“Those who would rather die than make their desire known could not comply with your law.”
“Die!” thereupon said Hircan; “the good knight has yet to be born that would die for the publishing of such a matter. But let us cease talking of what is impossible, and see to whom Simontault will give his vote.”
“I give it,” said Simontault, “to Longarine, for I observed her just now talking to herself. I imagine that she was recalling some excellent matter, and she is not wont to conceal the truth, whether it be against man or woman.”
“Since you deem me so truthful,” replied Longarine, “I will tell you a tale which, though it be not so much to the praise of women as I could wish it to be, will yet show you that there are some possessed of as much spirit, wit, and craft as men. If my tale be somewhat long, you will bear with it in patience.”


Through the favour of King Francis, a simple gentleman of
the Court married a very rich woman, of whom, however, as
much by reason of her extreme youth as of the bestowal of
his own heart elsewhere, he made but little account;
whereat, after trying every plan to please him, she was so
moved with resentment and overcome by despair, that she
resolved to console herself with another for the indignities
which she endured from her husband. (1)
1 The incidents referred to in this story must have
occurred between 1515 and 1543, during the reign of Francis
I.—L.
At the Court of King Francis the First there was a gentleman whose name I know right well, but will not mention. He was poor, having less than five hundred livres a year, but he was so well liked by the King for his many qualities that he at last married a lady of such wealth that a great lord would have been pleased to take her. As she was still very young, he begged one of the greatest ladies of the Court to receive her into her household, and this the lady very willingly did.
Now this gentleman was so courteous, so handsome, and so full of grace that he was held in great regard by all the ladies of the Court, and among the rest by one whom the King loved, and who was neither so young nor so handsome as his own wife. And by reason of the great love that the gentleman bore this lady, he made such little account of his wife, that he slept scarcely one night in the year with her, and, what she found still harder to endure, he never spoke to her or showed her any sign of love. And although he enjoyed her fortune, he allowed her so small a share in it, that she was not dressed as was fitting for one of her station, or as she herself desired. The lady with whom she abode would often reproach the gentleman for this, saying to him—
“Your wife is handsome, rich, and of a good family, yet you make no more account of her than if she were the opposite. In her extreme youth and childishness she has hitherto submitted to your neglect; but I fear me that when she finds herself grown-up and handsome, her mirror and some one that loves you not will so set before her eyes that beauty by which you set so little store, that resentment will lead her to do what she durst not think of had you treated her well.”
The gentleman, however, having bestowed his heart elsewhere, made light of what the lady said, and notwithstanding her admonitions, continued to lead the same life as before.
But when two or three years had gone by, his wife became one of the most beautiful women ever seen in France, so that she was reputed to have no equal at the Court. And the more she felt herself worthy of being loved, the more distressed she was to find that her husband paid no attention to her; and so great became her affliction that, but for the consolations of her mistress, she had well-nigh been in despair. After trying every possible means to please her husband, she reflected that his inclinations must needs be directed elsewhere, for otherwise he could not but respond to the deep love that she bore him. Thereupon she made such skilful inquiries that she discovered the truth, namely, that he was every night so fully occupied in another quarter that he could give no thought to his wife or to his conscience.
Having thus obtained certain knowledge of the manner of life he led, she fell into such deep melancholy, that she would not dress herself otherwise than in black or attend any place of entertainment. Her mistress, who perceived this, did all that in her lay to draw her from such a mood, but could not. And although her husband was made acquainted with her state, he showed himself more inclined to make light of it than to relieve it.
You are aware, ladies, that just as extreme joy will give occasion to tears, so extreme grief finds an outlet in some joy. In this wise it happened that a great lord who was near akin to the lady’s mistress, and who often visited her, hearing one day of the strange fashion in which she was treated by her husband, pitied her so deeply that he desired to try to console her; and on speaking to her, found her so handsome, so sensible, and so virtuous, that he became far more desirous of winning her favour than of talking to her about her husband, unless it were to show her what little cause she had to love him.
The lady, finding that, though forsaken by the man who ought to have loved her, she was on the other hand loved and sought after by so handsome a Prince, deemed herself very fortunate in having thus won his favour. And although she still desired to preserve her honour, she took great pleasure in talking to him and in reflecting that she was loved and prized, for these were two things for which, so to speak, she hungered.
This friendship continued for some time, until it came to the knowledge of the King, who had so much regard for the lady’s husband that he was unwilling he should be put to any shame or vexation. He therefore earnestly begged the Prince to forego his inclinations, threatening him with his displeasure should he continue to press his suit.
The Prince, who set the favour of the King above all the ladies in the world, promised for his sake to lay aside the enterprise, and to go that very evening and bid the lady farewell. This he did as soon as he knew that she had retired to her own apartments, over which was the room of the gentleman, her husband. And the husband being that evening at his window, saw the Prince going into his wife’s room beneath. The Prince saw him also, but went in for all that, and in bidding farewell to her whose love was but beginning, pleaded as his sole reason the King’s command.
After many tears and lamentations and regrets, which lasted until an hour after midnight, the lady finally said—
“I praise God, my lord, that it pleases Him you should lose your love for me, since it is so slight and weak that you are able to take it up and lay it down at the command of man. For my own part, I have never asked mistress or husband or even myself for permission to love you; Love, aided by your good looks and courtesy, gained such dominion over me that I could recognise no God or King save him. But since your heart is not so full of true love that fear may not find room in it, you can be no perfect lover, and I will love none that is imperfect so perfectly as I had resolved to love you. Farewell, then, my lord, seeing that you are too timorous to deserve a love as frank as mine.”
The Prince went away in tears, and looking back he again noticed the husband, who was still at the window, and had thus seen him go in and come out again. Accordingly he told him on the morrow why he had gone to see his wife, and of the command that the King had laid upon him, whereat the gentleman was well pleased, and gave thanks to the King.
However, finding that his wife was becoming more beautiful every day, whilst he himself was growing old and less handsome than before, he began to change his tactics, and to play the part which he had for a long time imposed upon his wife, bestowing some attention upon her and seeking her more frequently than had been his wont. But the more she was sought by him the more was he shunned by her; for she desired to pay him back some part of the grief that he had caused her by his indifference.
Moreover, being unwilling to forego so soon the pleasure that love was beginning to afford her, she addressed herself to a young gentleman, who was so very handsome, well-spoken, and graceful that he was loved by all the ladies of the Court. And by complaining to him of the manner in which she had been treated, she lured him to take pity upon her, so that he left nothing untried in his attempts to comfort her. She, on her part, to console herself for the loss of the Prince who had forsaken her, set herself to love this gentleman so heartily that she came to forget her former grief, and to think of nothing but the skilful conduct of her new amour, in which she succeeded so well that her mistress perceived nought of it, for she was careful not to speak to her lover in her mistress’s presence. When she wished to talk with him she would betake herself to the rooms of some ladies who lived at the Court, amongst whom was one that her husband made a show of being in love with.
Now one dark evening she stole away after supper, without taking any companion with her, and repaired to the apartment belonging to these ladies, where she found the man whom she loved better than herself. She sat down beside him, and leaning upon a table they conversed together while pretending to read in the same book. Some one whom her husband had set to watch then went and reported to him whither his wife was gone. Being a prudent man, he said nothing, but as quickly as possible betook himself to the room, where he found his wife reading the book. Pretending, however, not to see her, he went straight to speak to the other ladies, who were in another part of the room. But when his poor wife found herself discovered by him in the company of a gentleman to whom she had never spoken in his presence, she was in such confusion that she quite lost her wits; and being unable to pass along the bench, she leaped upon the table and fled as though her husband were pursuing her with a drawn sword. And then she went in search of her mistress, who was just about to withdraw to her own apartments.
When her mistress was undressed, and she herself had retired, one of her women brought her word that her husband was inquiring for her. She answered plainly that she would not go, for he was so harsh and strange that she dreaded lest he should do her some harm.
At last, however, for fear of worse, she consented to go. Her husband said not a word to her until they were in bed together, when being unable to dissemble so well as he, she began to weep. And when he asked her the cause of this, she told him that she was afraid lest he should be angry at having found her reading in company with a gentleman.
He then replied that he had never forbidden her to speak to a man, and did not take it ill that she had done so; but he did indeed take it ill that she had run from him as though she had done something deserving of censure, and her flight and nothing else had led him to think that she was in love with the gentleman. He therefore commanded her never to speak to him again in public or in private, and assured her that the first time she did so he would slay her without mercy or compassion. She very readily promised to obey, and made up her mind not to be so foolish another time.
But things are desired all the more for being forbidden, and it was not long before the poor woman had forgotten her husband’s threats and her own promises. That very same evening she sent to the gentleman, begging him to visit her at night. But the husband, who was so tormented by jealousy that he could not sleep, and who had heard say that the gentleman visited his wife at night, wrapped himself in a cloak, and taking a valet with him, went to his wife’s apartment and knocked at the door. She, not in the least expecting him, got up alone, put on furred slippers and a dressing-gown which were lying close at hand, and finding that the three or four women whom she had with her were asleep, went forth from her room and straight to the door at which she had heard the knocking. On her asking, “Who is there?” she received in answer the name of her lover; but to be still more certain, she opened a little wicket, saying—
“If you be the man you say you are, show me your hand, and I shall recognise it.”
And when she touched her husband’s hand she knew who it was, and quickly shutting the wicket, cried out—
“Ha, sir! it is your hand.”
The husband replied in great wrath—
“Yes; it is the hand that will keep faith with you. Do not fail, therefore, to come when I send for you.”
With these words he went away to his own apartment, whilst she, more dead than alive, went back into her room, and cried out aloud to her servant-women, “Get up, my friends; you have slept only too well for me, for thinking to trick you, I have myself been tricked.”
With these words she swooned away in the middle of the room. The women rose at her cry, and were so astonished at seeing their mistress stretched upon the floor, as well as at hearing the words, she had uttered, that they were at their wits’ end, and sought in haste for remedies to restore her. When she was able to speak, she said to them—
“You see before you, my friends, the most unhappy creature in the world.”
And thereupon she went on to tell them the whole adventure, and begged of them to help her, for she counted her life as good as lost.
While they were seeking to comfort her, a valet came with orders that she was to repair to her husband instantly. Thereupon, clinging to two of her women, she began to weep and wail, begging them not to suffer her to go, for she was sure she would be killed. But the valet assured her to the contrary, offering to pledge his life that she should receive no hurt. Seeing that she lacked all means of resistance, she at last threw herself into the servant’s arms, and said to him—
“Since it may not be otherwise, you must e’en carry this hapless body to its death.”
Half fainting in her distress, she was then at once borne by the valet to his master’s apartment. When she reached it, she fell at her husband’s feet, and said to him—
“I beseech you, sir, have pity on me, and I swear to you by the faith I owe to God that I will tell you the whole truth.”
“‘Fore God you shall,” he replied, like one beside himself, and forthwith he drove all the servants from the room.
Having always found his wife very devout, he felt sure that she would not dare to forswear herself on the Holy Cross. He therefore sent for a very beautiful crucifix that belonged to him, and when they were alone together, he made her swear upon it that she would return true replies to his questions. Already, however, she had recovered from her first dread of death, and taking courage, she resolved that if she was to die she would make no concealment of the truth, but at the same time would say nothing that might injure the gentleman she loved. Accordingly, having heard all the questions that her husband had to put to her, she replied as follows—
“I have no desire, sir, either to justify myself or to lessen to you the love that I have borne to the gentleman you suspect; for if I did, you could not and you should not believe me. Nevertheless, I desire to tell you the cause of this affection. Know, then, sir, that never did wife love husband more than I loved you, and that from the time I wedded you until I reached my present age, no other passion ever found its way into my heart. You will remember that while I was still a child, my parents wished to marry me to one richer and more highly born than yourself, but they could never gain my consent to this from the moment I had once spoken to you. In spite of all their objections I held fast to you, and gave as little heed to your poverty as to their remonstrances. You cannot but know what treatment I have had at your hands hitherto, and the fashion in which you have loved and honoured me; and this has caused me so much grief and discontent that but for the succour of the lady with whom you placed me, I should have been in despair. But at last, finding myself fully grown and deemed beautiful by all but you, I began to feel the wrong you did me so keenly that the love I had for you changed into hate, and the desire of obeying you into one for revenge. In this despairing condition I was found by a Prince who, being more anxious to obey the King than Love, forsook me just as I was beginning to feel my pangs assuaged by an honourable affection. When the Prince had left me, I lighted upon this present gentleman; and he had no need to entreat me, for his good looks, nobleness, grace, and virtue are well worthy of being sought after and courted by all women of sound understanding. At my instance, not at his own, he has loved me in all virtue, so that never has he sought from me aught that honour might refuse. And although I have but little cause to love you, and so might be absolved from being loyal and true to you, my love of God and of my honour has hitherto sufficed to keep me from doing aught that would call for confession or shame. I will not deny that I went into a closet as often as I could to speak with him, under pretence of going thither to say my prayers, for I have never trusted the conduct of this matter to any one, whether man or woman. Further, I will not deny that when in so secret a place and safe from all suspicion I have kissed him with more goodwill than I kiss you. But as I look to God for mercy, no other familiarity has passed between us; he has never urged me to it, nor has my heart ever desired it; for I was so glad at seeing him that methought the world contained no greater pleasure.
“And now, sir, will you, who are the sole cause of my misfortune, take vengeance for conduct of which you have yourself long since set me an example, with, indeed, this difference, that in your case you thought nought of either honour or conscience; for you know and I know too that the woman you love does not rest content with what God and reason enjoin. And albeit the law of man deals great dishonour to wives who love other men than their husbands, the law of God does not exempt from punishment the husbands who love other women than their wives. And if my offences are to be weighed against yours, you are more to blame than I, for you are a wise and experienced man, and of an age to know and to shun evil, whilst I am young and have no experience of the might and power of love. You have a wife who desires you, honours you, and loves you more than her own life; while I have a husband who avoids me, hates me, and rates me as lightly as he would a servant maid. You are in love with a woman who is already old, of meagre figure, and less fair than I; whilst I love a gentleman younger, handsomer, and more amiable than you. You love the wife of one of the best friends you have in the world, the mistress, moreover, of your King and master, so that you offend against the friendship that is due to the first, and the respect that is due to the second; whereas I am in love with a gentleman whose only tie is his love for me. Judge then fairly which of us two is the more worthy of punishment or pardon: you, a man of wisdom and experience, who through no provocation on my part have acted thus ill not only towards me, but towards the King, to whom you are so greatly indebted; or I, who am young and ignorant, who am slighted and despised by you, and loved by the handsomest and most worshipful gentleman in France, a gentleman whom I have loved in despair of ever being loved by you.”
When the husband heard her utter these truths with so fair a countenance, and with such a bold and graceful assurance as clearly testified that she neither dreaded nor deserved any punishment, he was overcome with astonishment, and could find nothing to reply except that a man’s honour and a woman’s were not the same thing. However, since she swore to him that there had been nothing between herself and her lover but what she had told him, he was not minded to treat her ill, provided she would act so no more, and that they both put away the memory of the past. To this she agreed, and they went to bed in harmony together.
Next morning an old damosel who was in great fear for her mistress’s life came to her at her rising, and asked—
“Well, madam, and how do you fare?”
“I would have you know,” said her mistress, laughing, “that there is not a better husband than mine, for he believed me on my oath.”
And so five or six days passed by.
Meanwhile the husband had such care of his wife that he caused a watch to be kept on her both night and day. But for all his care he could not prevent her from again speaking with her lover in a dark and suspicious place. However, she contrived matters with such secrecy that no one, whether man or woman, could ever learn the truth, though a rumour was started by some serving-man about a gentleman and a lady whom he had found in a stable underneath the rooms belonging to the mistress of the lady in question. At this her husband’s suspicions were so great that he resolved to slay the gentleman, and gathered together a large number of his relations and friends to kill him if he was anywhere to be found. But the chief among his kinsmen was so great a friend of the gentleman whom they sought, that instead of surprising him he gave him warning of all that was being contrived against him, for which reason the other, being greatly liked by the whole Court, was always so well attended that he had no fear of his enemy’s power, and could not be taken unawares and attacked.
However, he betook himself to a church to meet his lady’s mistress, who had heard nothing of all that had passed, for the lovers had never spoken together in her presence. But the gentleman now informed her of the suspicion and ill-will borne him by the lady’s husband, and told her that although he was guiltless he had nevertheless resolved to go on a long journey in order to check the rumours, which were beginning greatly to increase. The Princess, his lady’s mistress, was much astonished on hearing this tale, and protested that the husband was much in the wrong to suspect so virtuous a wife, and one in whom she had ever found all worth and honour. Nevertheless, considering the husband’s authority, and in order to quell these evil reports, she advised him to absent himself for a time, assuring him that for her part she would never believe such foolish suspicions.
Both the gentleman and the lady, who was present, were well pleased at thus preserving the favour and good opinion of the Princess, who further advised the gentleman to speak with the husband before his departure. He did as he was counselled, and meeting with the husband in a gallery close to the King’s apartment, he assumed a bold countenance, and said to him with all the respect due to one of high rank—
“All my life, sir, I have desired to do you service, and my only reward is to hear that last evening you lay in wait to kill me. I pray you, sir, reflect that while you have more authority and power than I have, I am nevertheless a gentleman even as you are. It would be grievous to me to lose my life for naught. I pray you also reflect that you have a wife of great virtue, and if any man pretend the contrary I will tell him that he has foully lied. For my part, I can think of nothing that I have done to cause you to wish me ill. If, therefore, it please you, I will remain your faithful servant; if not, I am that of the King, and with that I may well be content.”
The husband replied that he had in truth somewhat suspected him, but he deemed him so gallant a man that he would rather have his friendship than his enmity; and bidding him farewell, cap in hand, he embraced him like a dear friend. You may imagine what was said by those who, the evening before, had been charged to kill the gentleman, when they beheld such tokens of respect and friendship. And many and diverse were the remarks that each one made.
In this manner the gentleman departed, and as he had far less money than good looks, his mistress delivered to him a ring that her husband had given her of the value of three thousand crowns; and this he pledged for fifteen hundred.
Some time after he was gone, the husband came to the Princess, his wife’s mistress, and prayed her to grant his wife leave to go and dwell for a while with one of his sisters. This the Princess thought very strange, and so begged him to tell her the reasons of his request, that he told her part of them, but not all. When the young lady had taken leave of her mistress and of the whole Court without shedding any tears or showing the least sign of grief, she departed on her journey to the place whither her husband desired her to go, travelling under the care of a gentleman who had been charged to guard her closely, and above all not to suffer her to speak on the road to her suspected lover.
She knew of these instructions, and every day was wont to cause false alarms, scoffing at her custodians and their lack of care. Thus one day, on leaving her lodging, she fell in with a Grey Friar on horseback, with whom, being herself on her palfrey, she talked on the road the whole time from the dinner to the supper hour. And when she was a quarter of a league from the place where she was to lodge that night, she said to him—
“Here, father, are two crowns which I give you for the consolation you have afforded me this afternoon. They are wrapped in paper, for I well know that you would not venture to touch them. (2) And I beg you to leave the road as soon as you have parted from me, and to take care that you are not seen by those who are with me. I say this for your own welfare, and because I feel myself beholden to you.”
2 The Grey Friars belonging to a mendicant order were
prohibited from demanding or accepting money; it was only
allowable for them to receive gifts in kind, mainly edible
produce. It was for this reason that the lady gave the friar
the two crowns wrapped in paper, knowing that he ought not
to touch the coins.—M. See also vol. i. p. 98, note 3.
The friar, well pleased with the two crowns, set off across the fields at full gallop; and when he was some distance away the lady said aloud to her attendants—
“You may well deem yourselves good servants and diligent guards. He as to whom you were to be so careful has been speaking to me the whole day, and you have suffered him to do so. Your good master, who puts so much trust in you, should give you the stick rather than give you wages.”
When the gentleman who had charge of her heard these words he was so angry that he could not reply, but calling two others to him, set spurs to his horse, and rode so hard that he at last reached the friar, who on perceiving his pursuers had fled as fast as he could. However, the poor fellow was caught, being less well mounted than they were. He was quite ignorant of what it all meant, and cried them mercy, taking off his hood in order that he might entreat them with bareheaded humility. Thereupon they realised that he was not the man whom they sought, and that their mistress had been mocking them. And this she did with even better effect upon their return to her.
“You are fitting fellows,” said she, “to receive ladies in your charge. You suffer them to talk to any stranger, and then, believing whatever they may say, you go and insult the ministers of God.”
After all these jests they arrived at the place that her husband had commanded, and here her two sisters-in-law, with the husband of one of them, kept her in great subjection.
In the meanwhile her husband had heard how his ring had been pledged for fifteen hundred crowns, whereat he was exceedingly wrathful, and in order to save his wife’s honour and to get back the ring, he bade his sisters tell her to redeem it, he himself paying the fifteen hundred crowns.
She cared nought for the ring since her lover had the money, but she wrote to him saying that she was compelled by her husband to redeem it, and in order that he might not suppose she was doing this through any lessening of her affection, she sent him a diamond which her mistress had given, her, and which she liked better than any ring she had.
Thereupon the gentleman forwarded her the merchant’s bond right willingly; deeming himself fortunate in having fifteen hundred crowns and a diamond, (3) and at being still assured of his lady’s favour. However, as long as the husband lived, he had no means of communing with her save by writing.
When the husband died, expecting to find her still what she had promised him to be, he came in all haste to ask her in marriage; but he found that his long absence had gained him a rival who was loved better than himself. His sorrow at this was so great that he henceforth shunned the companionship of ladies and sought out scenes of danger, and so at last died in as high repute as any young man could have. (4)
3 The gentleman deemed it only natural that the woman he
honoured with his love should present him with money. In the
seventeenth century similar opinions were held, if one may
judge by some passages in Dancourt’s comedies, and by the
presents which the Duchess of Cleveland made to Henry
Jerrayn and John Churchill, afterwards Duke of Marlborough,
as chronicled in the Memoirs of the Count de Gramont.—M.
4 Brantôme tells a somewhat similar tale to this in his
Vies des Dames Galantes (Dis. I.): “I knew,” he writes,
“two ladies of the Court, sisters-in-law to one another, one
of whom was married to a courtier, high in favour and very
skilful, but who did not make as much account of his wife as
by reason of her birth he should have done, for he spoke to
her in public as he might have spoken to a savage, and
treated her most harshly. She patiently endured this for
some time, until indeed her husband lost some of his credit,
when, watching for and taking the opportunity, she quickly
repaid him for all the disdain that he had shown her. And
her sister-in-law imitated her and did likewise; for having
been married when of a young and tender age, her husband
made no more account of her than if she had been a little
girl.... But she, advancing in years, feeling her heart beat
and becoming conscious of her beauty, paid him back in the
same coin, and made him a present of a fine pair of horns,
by way of interest for the past”—Lalanne’s OEuvres de
Brantôme, vol. ix. p. 157.—L.
“In this tale, ladies, I have tried, without sparing our own sex, to show husbands that wives of spirit yield rather to vengeful wrath than to the sweetness of love. The lady of whom I have told you withstood the latter for a great while, but in the end succumbed to despair. Nevertheless, no woman of virtue should yield as she did, for, happen what may, no excuse can be found for doing wrong. The greater the temptations, the more virtuous should one show oneself, by resisting and overcoming evil with good, instead of returning evil for evil; and this all the more because the evil we think to do to another often recoils upon ourselves. Happy are those women who display the heavenly virtues of chastity, gentleness, meekness, and long-suffering.”
“It seems to me, Longarine,” said Hircan, “that the lady of whom you have spoken was impelled by resentment rather than by love; for had she loved the gentleman as greatly as she appeared to do, she would not have forsaken him for another. She may therefore be called resentful, vindictive, obstinate, and fickle.”
“It is all very well for you to talk in that way,” said Ennasuite, “but you do not know the heartbreak of loving without return.”
“It is true,” said Hircan, “that I have had but little experience in that way. If I am shown the slightest disfavour, I forthwith forego lady and love together.”
“That,” said Parlamente, “is well enough for you who love only your own pleasure; but a virtuous wife cannot thus forsake her husband.”
“Yet,” returned Simontault, “the lady in the story forgot for a while that she was a woman. No man could have taken a more signal revenge.”
“It does not follow,” said Oisille, “because one woman lacks discretion that all the rest are the same.”
“Nevertheless,” said Saffredent, “you are all women, as any one would find who looked carefully, despite all the fine clothes you may wear.”
“If we were to listen to you,” said Nomerlide, “we should spend the day in disputes. For my part, I am so impatient to hear another tale, that I beg Longarine to give some one her vote.”
Longarine looked at Geburon and said:—
“If you know anything about a virtuous woman, I pray you set it forth.”
“Since I am to do what I can,” said Geburon, “I will tell you a tale of something that happened in the city of Milan.”



A lady of Milan, widow of an Italian Count, had resolved never again to marry or to love. But for three years she was so earnestly wooed by a French gentleman, that after repeated proof of the steadfastness of his love, she granted him what he had so greatly desired, and they vowed to each other everlasting affection. (l)
In the days of the Grand Master of Chaumont, (2) there lived a lady who was reckoned one of the most honourable women that there were at that time in the city of Milan. She had married an Italian Count, and being left a widow, lived in the house of her brothers-in-law, refusing to hear speak of another marriage. And so discreetly and piously did she demean herself that there was none in the Duchy, whether French or Italian, but held her in high esteem.
1 According to M. de Lincy, who points out that Bonnivet
must be the hero of the adventure here related, the
incidents referred to would have occurred at Milan between
1501 and 1503; but in M. Lacroix’s opinion they would be
posterior to 1506.—Ed.
2 See ante, note 1 to Tale XIV.
One day when her brothers and sisters-in-law offered an entertainment to the Grand Master of Chaumont, this widow lady was obliged to be present, though she made it her rule not to attend such gatherings when held in other places. And when the Frenchmen saw her, they were all admiration for her beauty and grace, especially one among them whose name I shall not mention; for it will suffice for you to know that there was no Frenchman in Italy more worthy of love than he, for he was endowed with all the beauties and graces that a gentleman could have. And though he saw that the lady wore black crape, and remained with several old women in a corner apart from the young ones, yet, having never known what it was to fear either man or woman, he set himself to converse with her, taking off his mask, and leaving the dance in order to remain in her company.
Throughout the whole of the evening he did not cease talking to her and to the old women, and found more pleasure in doing so than if he had been with the most youthful and bravely attired ladies of the Court. So much, indeed, was this the case, that when the hour came to withdraw he seemed to have not yet had time even to sit down. And although he only spoke to the lady on such common matters as were suited to such company, she knew very well that he desired to win her favour, and this she resolved to guard against by all means in her power, so that he was never afterwards able to see her at any banquet or assembly.
He inquired about the manner of her life, and found that she often went to churches and convents; whereupon he kept such good watch that she could never visit them so secretly but he was there before her. And he would remain in the church as long as he had the happiness to see her, and all the time that she was present would gaze at her so affectionately that she could not remain in ignorance of the love he bore her. In order to avoid him, she resolved to feign illness for a time, and to hear mass in her own house; and at this the gentleman was most sorely grieved, for he had no other means of seeing her than at church.
Thinking that she had cured him of his habit, she at last returned to the churches as before, but love quickly brought tidings of this to the French gentleman, who then renewed his habits of devotion. He feared, however, that she might again throw some hindrance in his way, and that he might not have time to tell her what he would; and so one morning, when she thought herself well concealed in a chapel, he placed himself at the end of the altar at which she was hearing mass; and seeing that she was but scantily attended, he turned towards her just as the priest was elevating the host, and in a soft and loving voice said to her—
“May I be sent to perdition, madam, by Him whom the priest has now in his hands, if you are not causing my death. Though you take from me all means of speaking with you, you cannot be ignorant of my desire; my wearied eyes and my deathly face must make the truth apparent to you.” (3)
3 The Queen of Navarre is known to have had a considerable
knowledge of the Italian language, and it is therefore quite
possible that she was acquainted with the story of
Poliphilus and Polia, which, although no French translation
of it appeared until 1554, had been issued at Venice as
early as 1499. In any case, however, there is a curious
similarity between the speech of the French gentleman given
above and the discourse which Poliphilus addresses to Polia
when he finds her saying her prayers in the temple. A
considerable portion of the Italian story is in keeping with
the character of the Heptameron tales.—M.
The lady pretended not to understand him, and replied—
“God’s name should not thus be taken in vain; but the poets say that the gods laugh at the oaths and lies of lovers, and so women who regard their honour should not show themselves credulous or compassionate.”
With these words she rose up and returned home.
The gentleman’s anger at these words may well be imagined by such as have experienced the like fortune. But having no lack of spirit, he held it better to have received this unfavourable reply than to have failed in declaring his love, to which he held fast during three years, losing neither time nor opportunity in wooing her by letters and in other ways.
For three years, however, she vouchsafed him no reply, but shunned him as the wolf shuns the hound that is to take him; and this she did through fear for her honour and fair fame, and not because she hated him. He perceived this so clearly that he pursued her more eagerly than ever; and at last, after many refusals, troubles, tortures and despairs, the lady took pity upon him for the greatness and steadfastness of his love, and so granted him what he had so greatly desired and so long awaited.
When they had agreed concerning the means to be employed, the French gentleman failed not to repair to her house, although in doing so he placed his life in great danger, seeing that she and her relations lived all together.
However, being as skilful as he was handsome, he contrived the matter so prudently that he was able to enter the lady’s room at the hour which she had appointed, and found her there all alone, lying in a beautiful bed; but as he was hasting to put off his clothes in order to join her, he heard a great whispering at the door, and a noise of swords scraping against the wall.
Then the widow said to him, with the face of one nigh to death—
“Now is your life and my honour in as great danger as well can be, for I hear my brothers outside seeking you to slay you. I pray you, therefore, hide yourself under this bed, and when they fail to find you I shall have reason to be angry with them for alarming me without just cause.”
The gentleman, who had never yet known fear, replied—
“And what, pray, are your brothers that they should frighten a man of mettle? If the whole breed of them were there together, I am sure they would not tarry for the fourth thrust of my sword. Do you, therefore, rest quietly in bed, and leave the guarding of this door to me.”
Then he wrapped his cloak about his arm, took his drawn sword in his hand, and opened the door so that he might have a closer view of the swords that he had heard. When the door was opened, he saw two serving-women, who, holding a sword in each hand, had raised this alarm.
“Sir,” they said to him, “forgive us. We were commanded by our mistress to act in this manner, but you shall be hindered by us no more.”
Seeing that they were women, the gentleman could do no more than bid them go to the devil, and shut the door in their faces. Then he got into bed to the lady with all imaginable speed, his passion for her being in no wise diminished by fear; and forgetting to inquire the reason of this skirmish, he thought only of satisfying his desire.
But when daybreak was drawing nigh, he begged his mistress to tell him why she had treated him so ill, both in making him wait so long, and in having played this last trick upon him.
“My intention,” she answered, laughing, “had been never to love again, and I had observed it from the time I became a widow; but, after you had spoken to me at the entertainment, your worth led me to change my resolve, and to love you as much as you loved me. It is true that honour, which had ever guided me, would not suffer me to be led by love to do aught to the disparagement of my reputation. But as the poor hind when wounded unto death thinks by change of place to change the pain it carries with it, so did I go from church to church thinking to flee from him whom I carried in my heart, and the proof of whose perfect devotion has reconciled honour and love. However, that I might be the more certain that I was giving my heart and love to a true man, I desired to make this last proof by means of my serving-women. And I vow to you that had I found you so timorous as to hide beneath my bed, either for fear of your life or for any other reason, I was resolved to rise and go into another room and never see you more. But since I have found that you are possessed of more beauty, and grace, and virtue, and valour than rumour had given you, and that fear has no power over your heart, nor can cool one whit the love you bear me, I am resolved to cleave to you for the remainder of my days. I feel sure that I could not place life and honour in better hands than those of one whom I deem unmatched in every virtue.”
And, just as though the human will could be unchangeable, they vowed and promised what was not in their power, namely, perpetual affection. For this is a thing that can neither spring up nor abide in the heart of man, as only those ladies know who have had experience of how long such feelings last. (4)
4 In Boaistuau’s edition of the Heptameron the final part
of the above sentence is given as follows: “And those women
that have had experience of it know this, and also how long
such fancies last.” An extract from Brantôme in connection
with the story will be found in the Appendix to this volume,
D.
“So, ladies, if you are wise, you will beware of us even as the stag, had he understanding, would beware of the hunter; for our glory, happiness, and delight is to see you captured in order to rob you of that which is more precious to you than life.”
“Why, Geburon,” said Hircan, “since when have you turned preacher? I can remember a time when you did not talk after that fashion.”
“It is quite true,” said Geburon, “that I have just spoken contrary to what I have always said my life long; but since my teeth are no longer able to chew venison, I warn the hapless deer to beware of the hunters, in order that I may atone in my old age for all the mischief which I sought to do in my youth.”
“We thank you, Geburon,” said Nomerfide, “for warning us to our profit, but for all that we do not feel very greatly beholden to you. You never spoke in that way to one you truly loved, and this is a proof that you have little love for us, and, moreover, would not have us loved. Nevertheless, we hold ourselves as discreet and as virtuous as the ladies whom you so long pursued in your youth. But old folk are commonly vain enough to think that they have been wiser in their time than those who come after them.”
“Well, Nomerfide,” said Geburon, “will you believe that I have told you the truth when the faithlessness of one of your lovers has made you acquainted with the evil nature of men?”
“It seems to me,” said Oisille to Geburon, “that the gentleman whom you praise so highly for his boldness ought rather to be praised for the ardour of his love. So strong is this passion, that it impels the most cowardly to embark on enterprises about which the bravest would think twice.”
“If, madam,” said Saffredent, “he’had not deemed the Italians to be better at talking than acting, me-thinks he had reason to be afraid.”
“Yes,” said Oisille, “if he had not had in his heart the fire that consumes fear.”
“Since you do not deem the boldness of this gentleman altogether worthy of praise,” said Hircan, “you doubtless know of some one else more deserving of commendation.”
“Nay,” said Oisille, “the gentleman in the story deserves praise, but I do know of one who is more worthy of being admired.”
“I pray you, madam,” said Geburon, “if that be so, take my place and tell us the tale.”
“If,” began Oisille, “a man who showed such boldness against the Milanese to save his own life and his mistress’s honour is to be esteemed so very brave, what shall be said of one who, without any need for it, and from pure and simple valour, performed the deed of which I will now tell you?”


King Francis, being urged to banish Count William, who was said to have received money to bring about his death, did not suffer it to appear that he had any inkling of the scheme, but played the Count so shrewd a trick that he himself took leave of the King and went into banishment. (1)
To the town of Dijon, in the Duchy of Burgundy, there came a German Count to take service with King Francis. He was named William, (2) and was of the House of Saxony, which is so closely allied with that of Savoy that formerly they were but one. This Count, who was held for as handsome and valiant a gentleman as Germany ever knew, was right well received by the King, who not only took him into his service, but kept him close to himself as a groom of the chamber.
1 The incidents of this story are historical. Francis I. is
known to have sojourned at Dijon in June and July 1521.—L.
2 This is William, eldest son of Wolfgang von Furstemberg,
chamberlain to Maximilian I., and privy counsellor to Philip
of Austria.—B. J. Various particulars concerning him are
given in the Appendix to this volume, E.
Now the Lord de la Trémoille, (3) Governor of Burgundy, an old knight and a loyal servant to the King, was ever jealous and anxious for his master’s safety, and was wont to have spies at all points to learn what the King’s enemies were doing; and so prudently did he contrive matters, that but few things were hidden from him. Among his informations there came to him one day a letter from a friend telling him that Count William had received a sum of money, with promise of more, for putting the King to death in any such manner as he might find possible. (4)
3 This is Louis II., Sire de la Trémoille, Viscount of
Thouars and Prince of Talmont, born in 1460. The son of
Louis I. de la Trémoille and of Margaret d’Amboise, he
became one of the most remarkable men of his time. Favoured
by Anne de Beaujeu, who arranged his marriage with Gabrielle
de Bourbon, he commanded the royal troops at the battle of
St. Aubin du Cormier, in Brittany (1488), at which the
rebellious Duke of Orleans (afterwards Louis XII.) and the
Prince of Orange, with a large number of the nobles, their
partisans, were made prisoners. They were all invited to La
Trémoille’s table after the engagement, and, according to
Godefroi’s Latin history of Louis XII., at the close of the
repast two Franciscan monks entered the hall, whereupon La
Trémoille rose and said: “Princes, I refer your judgments to
the King, but as for you, Knights, who have broken your
faith and falsified your knightly oath, you shall pay for
your crime with your heads. If you have any remorse on your
consciences, here are monks who will shrive you.” The hall
resounded with lamentations, but the unhappy nobles were
promptly dragged into the courtyard, and there put to death;
both Orleans and Orange being too terror-stricken to
intercede for them. When the former came to the throne, he
forgave La Trémoille for his conduct in this affair, and
showed him great favour, appointing him Governor of Burgundy
in 1501. La Trémoille also became Admiral of Guienne and
Brittany, and figured conspicuously in the various Italian
campaigns of the period. He was killed at Pavia in 1525.
Jean Bouchet, a contemporary, wrote a curious life of this
remarkable man, entitled Panegyric du Chevalier sans
reproche. It will be found in Michaud and Poujoulat’s
Collection de Mitnoires,—L. and Ed.
4 It has been suggested that the instigator of this plot
was Charles V.‘s famous minister, Cardinal Granvelle.—Ed.
The Lord de la Trémoille failed not to give speedy notice of the affair to the King, and further made it known to the King’s mother, Louise of Savoy, who, forgetting that she and this German were akin, begged the King to banish him forthwith. But the King bade her speak no more of it, saying that it was impossible so upright and honourable a gentleman would undertake so vile a deed.
Some time afterwards a second warning arrived in confirmation of the first, and the Governor, burning with love for his master, sought permission either to banish the Count or else take him in hand in some other fashion; but the King charged him expressly to keep the affair secret, being persuaded that he might discover the truth by some other means.
One day when going a-hunting, the King, as his sole weapon, buckled on the finest sword it were possible to see, and took Count William along with him, desiring that he would follow him close. After hunting the stag for some time, seeing that all his people save the Count were far off, he turned out of all the roads and tracks, till he found himself alone with the Count in the deepest part of the forest, (5) when, drawing his sword, he said:—
“Think you that this sword be handsome and trusty?”
5 This may be either the forest of Argilly or that of
Mondragon, both in the vicinity of Dijon.—ED.
The Count took it by the point, and answered that he had never seen one that he liked better.
“You are right,” said the King; “and I think that, if a gentleman had resolved to slay me, he would think twice before he attacked me if he knew the strength of my arm, the stoutness-of my heart, and the excellence of this sword. Yet, for all that, I should count him but a craven scoundrel if, when we were face to face and alone, he durst not execute what he had dared to undertake.”
“Sire,” replied Count William, with astonished countenance, “the wickedness of the undertaking would be very great, but the folly of seeking to execute it would be no less.”
The King laughed, sheathed his sword again, and hearing the hunt hard by, spurred after it with all speed. When he reached his train he spoke to none of what had passed, but he felt convinced that, although Count William was as brave and ready a gentleman as might be, he was not the man to carry out so high an enterprise.
However, Count William, fearing that he had been discovered or was at least suspected, repaired the next morning to Robertet, Secretary for the King’s Finances, (6) and told him that he had considered the privileges and pay offered him to continue in the King’s service, and that they would not suffice to support him for half the year. Unless therefore it pleased the King to give him double, he would be forced to depart; and he accordingly begged the said Robertet to acquaint him as soon as might be with the will of the King. To this the Secretary replied that he could not better advance the business than by going to the King straightway; and he undertook the mission right willingly, for he had seen the warnings that the Governor had received.
6 This is Florimond Robertet, the first of that family of
statesmen who served the French crown from Charles VIII. to
Henri III. It was Charles VIII. who appointed Florimond
Treasurer of France and Secretary of Finances, offices in
which he displayed great skill and honesty. Louis XII., who
confirmed him in his functions, habitually consulted him on
important political affairs. He acquired considerable
wealth, and was often called “the great baron,” after the
barony of Alluye, which he possessed in Le Perche. One of
the curiosities of Blois is the Hôtel d’Alluye, a house of
semi-Moorish style, erected by Robertet at the close of the
fifteenth century. Another of his residences was the château
of Bury, near Blois, where he set up Michael Angelo’s famous
bronze statue of David, presented to him by the city of
Florence, and the fate of which has furnished material for
so much speculation. Under Francis I. Robertet enjoyed the
same credit as during the two previous reigns. Fleuranges
declares that no one else was so intimate with the King, and
commends him as being the most experienced and competent
statesman of the times. According to the Journal d’un
Bourgeois de Paris, Robertet died “at the Palais (de
Justice) in Paris, of which he was concierge,” on November
29, 1527. Francis repeatedly visited him during his illness,
and, on his death, ordered that his remains should lie in
state, and be interred with great pomp and ceremony. Clement
Marot’s works contain a poem, four hundred lines in length,
celebrating Robertet’s virtues and talents.—L., B. J., and
Ed.
As soon, therefore, as the King was awake he failed not to lay the matter before him in the presence of the Lord de la Trémoille and the Admiral de Bonnivet, who were ignorant of the trick that the King had played the Count the day before.
Then the King laughed, and said to them—“You desired to banish Count William, and you see he is banishing himself. Wherefore, tell him that if he be not content with the establishment which he accepted on entering my service, and which many men of good families have deemed themselves fortunate to have, he must e’en seek a better fortune elsewhere. For my part, I will in no wise hinder him, but shall be well pleased if he can find some condition wherein to live according to his deserts.”
Robertet was as prompt to bear this answer to the Count as he had been to prefer his request to the King. The Count replied that with the King’s permission he was resolved to depart, and, like one whom fear urges to flight, he did not tarry even four and twenty hours; but, just as the King was sitting down to table, came to take leave of him, feigning much sorrow that his need should force him from the Royal presence.
He also went to take leave of the King’s mother, who parted from him no less joyfully than she had formerly received him as a kinsman and friend. And thus he returned to his own country; and the King, seeing his mother and courtiers in amazement at his sudden departure, told them of the fright he had given him, saying that, even if the Count were innocent of that which was laid against him, his fear had been sufficiently great to constrain him to leave a master whose temper he had not yet come to know.
“For my part, ladies, I can see no reason why the King should have been moved to risk himself thus against so famous a captain, except that, forsaking the company and places where Kings find no inferiors ready to give them battle, he desired to place himself on an equal footing with one whom he suspected to be his enemy; and this that he might have the satisfaction of testing the stoutness and valour of his own heart.”
“Without a doubt,” said Parlamente, “he was in the right; for all the praise of man cannot so well satisfy a noble heart as its own particular knowledge and experience of the virtues that God has placed in it.”
“The ancients,” said Geburon, “long ago showed us that to reach the Temple of Fame it was necessary to pass through the Temple of Virtue, and I, who am acquainted with the two persons in your tale, know right well that the King is indeed one of the most valiant men in his kingdom.”
“By my word,” said Hircan, “at the time when Count William came to France, I should have feared his [the King’s] sword more than those of the four most accomplished Italian gentlemen at Court.”
“We well know,” said Ennasuite, “that he is too famous for our praises to equal his merit, and that the day would be spent before we each could say all the good we think of him. And so, madam, I pray you, give your vote to one who will tell us some further good of men, if such there be.”
Then said Oisille to Hircan—
“It seems to me that, as you are so wont to speak ill of women, you will find it easy to tell us some good story in praise of a man. I therefore give you my vote.”
“That can I easily do,” said Hircan, “for but a little while since I was told a story in praise of a gentleman whose love, constancy and patience are so meritorious that I must not suffer them to be forgotten.”



A young student of noble birth, being smitten with love for
a very beautiful lady, subdued both love and himself in
order to achieve his end, and this in spite of many such
temptations as might have sufficed to make him break his
promise. And so all his woes were turned to joy by a reward
suitable to his constant, patient, loyal and perfect love.
(1)
1 This story seems to be based on fact, being corroborated
in its main lines by Brantôme, but there is nothing in the
narrative to admit of the personages referred to being
identified.—Ed.
In one of the goodly towns of the kingdom of France there dwelt a nobleman of good birth, who attended the schools that he might learn how virtue and honour are to be acquired among virtuous men. But although he was so accomplished that at the age of seventeen or eighteen years he was, as it were, both precept and example to others, Love failed not to add his lesson to the rest; and, that he might be the better hearkened to and received, concealed himself in the face and the eyes of the fairest lady in the whole country round, who had come to the city in order to advance a suit-at-law. But before Love sought to vanquish the gentleman by means of this lady’s beauty, he had first won her heart by letting her see the perfections of this young lord; for in good looks, grace, sense and excellence of speech he was surpassed by none.
You, who know what speedy way is made by the fire of love when once it fastens on the heart and fancy, will readily imagine that between two subjects so perfect as these it knew little pause until it had them at its will, and had so filled them with its clear light, that thought, wish and speech were all aflame with it. Youth, begetting fear in the young lord, led him to urge his suit with all the gentleness imaginable; but she, being conquered by love, had no need of force to win her. Nevertheless, shame, which tarries with ladies as long as it can, for some time restrained her from declaring her mind. But at last the heart’s fortress, which is honour’s abode, was shattered in such sort that the poor lady consented to that which she had never been minded to refuse.
In order, however, to make trial of her lover’s patience, constancy and love, she only granted him what he sought on a very hard condition, assuring him that if he fulfilled it she would love him perfectly for ever; whereas, if he failed in it, he would certainly never win her as long as he lived. And the condition was this:—she would be willing to talk with him, both being in bed together, clad in their linen only, but he was to ask nothing more from her than words and kisses.
He, thinking there was no joy to be compared to that which she promised him, agreed to the proposal, and that evening the promise was kept; in such wise that, despite all the caresses she bestowed on him and the temptations that beset him, he would not break his oath. And albeit his torment seemed to him no less than that of Purgatory, yet was his love so great and his hope so strong, sure as he felt of the ceaseless continuance of the love he had thus painfully won, that he preserved his patience and rose from beside her without having done anything contrary to her expressed wish. (2)
2 Brantôme’s Dames Galantes contains an anecdote which is
very similar in character to this tale: “I have heard
speak,” he writes, “of a very beautiful and honourable lady,
who gave her lover an assignation to sleep with her, on the
condition that he should not touch her... and he actually
obeyed her, remaining in a state of ecstasy, temptation and
continence the whole night long; whereat she was so well
pleased with him that some time afterwards she consented to
become his mistress, giving as her reason that she had
wished to prove his love by his obedience to her
injunctions; and on this account she afterwards loved him
the more, for she felt sure that he was capable of even a
greater feat than this, though it were a very great one.”—
Lalanne’s OEuvres de Brantôme, vol. ix. pp. 6, 7.—L.
The lady was, I think, more astonished than pleased by such virtue; and giving no heed to the honour, patience and faithfulness her lover had shown in the keeping of his oath, she forthwith suspected that his love was not so great as she had thought, or else that he had found her less pleasing than he had expected.
She therefore resolved, before keeping her promise, to make a further trial of the love he bore her; and to this end she begged him to talk to a girl in her service, who was younger than herself and very beautiful, bidding him make love speeches to her, so that those who saw him come so often to the house might think that it was for the sake of this damsel and not of herself.
The young lord, feeling sure that his own love was returned in equal measure, was wholly obedient to her commands, and for love of her compelled himself to make love to the girl; and she, finding him so handsome and well-spoken, believed his lies more than other truth, and loved him as much as though she herself were greatly loved by him.
The mistress finding that matters were thus well advanced, albeit the young lord did not cease to claim her promise, granted him permission to come and see her at one hour after midnight, saying that after having so fully tested the love and obedience he had shown towards her, it was but just that he should be rewarded for his long patience. Of the lover’s joy on hearing this you need have no doubt, and he failed not to arrive at the appointed time.
But the lady, still wishing to try the strength of his love, had said to her beautiful damsel—
“I am well aware of the love a certain nobleman bears to you, and I think you are no less in love with him; and I feel so much pity for you both, that I have resolved to afford you time and place that you may converse together at your ease.”
The damsel was so enchanted that she could not conceal her longings, but answered that she would not fail to be present.
In obedience, therefore, to her mistress’s counsel and command, she undressed herself and lay down on a handsome bed, in a room the door of which the lady left half-open, whilst within she set a light so that the maiden’s beauty might be clearly seen. Then she herself pretended to go away, but hid herself near to the bed so carefully that she could not be seen.
Her poor lover, thinking to find her according to her promise, failed not to enter the room as softly as he could, at the appointed hour; and after he had shut the door and put off his garments and fur shoes, he got into the bed, where he looked to find what he desired. But no sooner did he put out his arms to embrace her whom he believed to be his mistress, than the poor girl, believing him entirely her own, had her arms round his neck, speaking to him the while in such loving words and with so beautiful a countenance, that there is not a hermit so holy but he would have forgotten his beads for love of her.
But when the gentleman recognised her with both eye and ear, and found he was not with her for whose sake he had so greatly suffered, the love that had made him get so quickly into the bed, made him rise from it still more quickly. And in anger equally with mistress and damsel, he said—
“Neither your folly nor the malice of her who put you there can make me other than I am. But do you try to be an honest woman, for you shall never lose that good name through me.”
So saying he rushed out of the room in the greatest wrath imaginable, and it was long before he returned to see his mistress. However love, which is never without hope, assured him that the greater and more manifest his constancy was proved to be by all these trials, the longer and more delightful would be his bliss.
The lady, who had seen and heard all that passed, was so delighted and amazed at beholding the depth and constancy of his love, that she was impatient to see him again in order to ask his forgiveness for the sorrow that she had caused him to endure. And as soon as she could meet with him, she failed not to address him in such excellent and pleasant words, that he not only forgot all his troubles but even deemed them very fortunate, seeing that their issue was to the glory of his constancy and the perfect assurance of his love, the fruit of which he enjoyed from that time forth as fully as he could desire, without either hindrance or vexation. (3)
3 In reference to this story, Montaigne says in his Essay
on Cruelty: “Such as have sensuality to encounter, willingly
make use of this argument, that when it is at the height it
subjects us to that degree that a man’s reason can have no
access... wherein they conceive that the pleasure doth so
transport us that our reason cannot perform its office
whilst we are so benumbed and extacied in delight.... But I
know that a man may triumph over the utmost effort of this
pleasure: I have experienced it in myself, and have not
found Venus so imperious a goddess as many—and some more
reformed than I—declare. I do not consider it as a miracle,
as the Queen of Navarre does in one of the Tales of her
Heptameron (which is a marvellous pretty book of the
kind), nor for a thing of extreme difficulty to pass over
whole nights, where a man has all the convenience and
liberty he can desire, with a long-coveted mistress, and yet
be just to his faith first given to satisfy himself with
kisses and innocent embraces only, without pressing any
further.”—Cotton’s “Montaigne’s Essays”, London, 1743, vol
ii. pp. 109-10.
“I pray you, ladies, find me if you can a woman who has ever shown herself as constant, patient and true as was this man. They who have experienced the like temptations deem those in the pictures of Saint Antony very small in comparison; for one who can remain chaste and patient in spite of beauty, love, opportunity and leisure, will have virtue enough to vanquish every devil.”
“Tis a pity,” said Oisille, “that he did not address his love to a woman possessing as much virtue as he possessed himself. Their amour would then have been the most perfect and honourable that was ever heard of.”
“But prithee tell me,” said Geburon, “which of the two trials do you deem the harder?”
“I think the last,” said Parlamente, “for resentment is the strongest of all temptations.”
Longarine said she thought that the first was the most arduous to sustain, since to keep his promise it was needful he should subdue both love and himself.
“It is all very well for you to talk,” said Simontault, “it is for us who know the truth of the matter to say what we think of it. For my own part, I think he was stupid the first time and witless the second; for I make no doubt that, while he was keeping his promise, to his mistress, she was put to as much trouble as himself, if not more. She had him take the oath only in order to make herself out a more virtuous woman than she really was; she must have well known that strong love will not be bound by commandment or oath, or aught else on earth, and she simply sought to give a show of virtue to her vice, as though she could be won only through heroic virtues. And the second time he was witless to leave a woman who loved him, and who was worth more than his pledged mistress, especially when his displeasure at the trick played upon him had been a sound excuse.”
Here Dagoucin put in that he was of the contrary opinion, and held that the gentleman had on the first occasion shown himself constant, patient and true, and on the second occasion loyal and perfect in his love.
“And how can we tell,” asked Saffredent, “that he was not one of those that a certain chapter calls de frigidis et malificiatis?” (4)
4 This is an allusion to the penalties pronounced by
several ecclesiastical Councils, and specified in the
Capitularies, against those who endeavoured to suspend the
procreative faculties of their enemies by resorting to
magic. On this matter Baluze’s collection of Capitularies
(vol. i.) may be consulted. The “chapter” referred to by
Margaret is evidently chapter xv. (book vi.) of the
Decretals of Pope Boniface VIII., which bears the title of
De frigidis et maleficiatis, and which is alluded to by
Rabelais in Pantagruel. The belief in the practices in
question dates back to ancient times, and was shared by
Plato and Pliny, the latter of whom says that to guard
against any spell of the kind some wolf fat should be rubbed
upon the threshold and door jambs of one’s bed-chamber. In
the sixteenth century sorcery of this description was so
generally believed in, in some parts of France, that
Cardinal du Perron inserted special prayers against it in
the ritual. Some particulars on the subject will be found in
the Admirables Secrets du Petit Albert, and also in a
Traité d’Enchantement, published at La Rochelle in 1591,
which gives details concerning certain practices alleged to
take place on the solemnisation of marriage among those of
the Reformed Church.—D. and L.
“To complete his eulogy, Hircan ought to have told us how he comported himself when he obtained what he wanted, and then we should have been able to judge whether it was virtue or impotence that made him observe so much discretion.”
“You may be sure,” said Hircan, “that had he told me this I should have concealed it as little as I did the rest. Nevertheless, from seeing his person and knowing his temper, I shall ever hold that his conduct was due to the power of love rather than to any impotence or coldness.”
“Well, if he was such as you say,” said Simontault, “he ought to have broken his oath; for, had the lady been angered by such a trifle, it would have been easy to appease her.”
“Nay,” said Ennasuite, “perhaps she would not then have consented.”
“And pray,” said Saffredent, “would it not have been easy enough to compel her, since she had herself given him the opportunity?”
“By Our Lady!” said Nomerfide, “how you run on! Is that the way to win the favour of a lady who is accounted virtuous and discreet?”
“In my opinion,” said Saffredent, “the highest honour that can be paid to a woman from whom such things are desired is to take her by force, for there is not the pettiest damsel among them but seeks to be long entreated. Some indeed there are who must receive many gifts before they are won, whilst there are others so stupid that hardly any device or craft can enable one to win them, and with these one must needs be ever thinking of some means or other. But when you have to do with a woman who is too clever to be deceived, and too virtuous to be gained by words or gifts, is there not good reason to employ any means whatever that may be at your disposal to vanquish her? When you hear it said that a man has taken a woman by force, you may be sure that the woman has left him hopeless of any other means succeeding, and you should not think any the worse of a man who has risked his life in order to give scope to his love.”
Geburon burst out laughing.
“In my day,” said he, “I have seen besieged places stormed because it was impossible to bring the garrison to a parley either by money or by threats; ‘tis said that a place which begins to treat is half taken.”
“You may think,” said Ennasuite, “that every love on earth is based upon such follies as these, but there are those who have loved, and who have long persevered in their love, with very different aims.”
“If you know a story of that kind,” said Hircan, “I will give place to you for the telling of it.”
“I do know one,” said Ennasuite, “and I will very willingly relate it.”

Tales of a similar character to this will be found in the following works written prior to Margaret’s time:—
Legrand d’Aussy’s collection of Fabliaux ou Contes du XIIème et XIIIème siècles (vol. iii.).
Boccaccio’s Decameron (day viii., story iv.).
Enguerrand d’Oisy’s Le Meunier d’Aleu.
Poggio’s Facetio ( Vir sibi cornua promovens).
Sacchetti’s Novelle (vol. ii., No. ccvi.).
Morlini’s Novelle (No. lxxix.).
Les Cent Nouvelles Nouvelles (story ix.).
Malespini’s Ducento Novelle (part ii., No. xcvi.).
Of the foregoing, says M. de Montaiglon, Margaret could only have been acquainted with the Decameron, the Cent Nouvelles, and Poggio’s Facetio, which had been translated into French by Tardix (see Nos. cv. and ex. of that translation).
A similar story in Latin verse is also contained in a fourteenth century MS. at Monte Cassino. See I codici e le arti a Monte Cassino, by D. Andrea Caravita (vol. ii. p. 289).
Since Margaret’s time stories of the same character have appeared in the following works:—
Melander’s Jocondia (p. 298).
Phil. Béroalde’s Contes Latins (see Poggii Imitationes, Noel’s éd., vol. ii. p. 245).
Guicciardini’s Hore di Recreazione (p. 103).
J. Bouchet’s Serées (No. 8; Roybet’s éd., vol. ii. p. 115).
Gabrielle Chapuys’ Facétieuses Journées (p. 213).
La Fontaine’s Contes (book v., No. viii.: Les Quiproquo). Le Passe-Temps Agréable (p. 27).
Moreover, a song written on the same subject will be found, says M. de Lincy, on folio 44 of the Premier Recueil de toutes les chansons nouvelles (Troyes, Nicholas du Ruau, 1590). It is there called “The facetious and recreative story of a certain labourer of a village near Paris, who, thinking that he was enjoying his servant, lay with his wife.” This song was reprinted in various other collections of the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries.
An anecdote in keeping with this story will be found in Brantôme’s miscellaneous works (Petitot’s éd., vol. viii. pp. 382-4). The author of Les Dames Galantes, after alluding to his aunt Louise de Bourdeille—who was brought up at Court by Anne of Brittany—proceeds to say:—
“A certain Grey Friar, who habitually preached before the Queen, fell so deeply in love with Mademoiselle de Bourdeille that he completely lost his wits, and sometimes in his sermons, whilst speaking of the beauty of the holy virgins of past times, he would so forget himself as to say some words respecting the beauty of my said aunt, not to mention the soft glances which he cast at her. And sometimes, whilst in the Queen’s room, he would take great pleasure in discoursing to her, not with words of love however, for he would have incurred a whipping, but with other covert words which tended towards love. My aunt in no wise approved of his discourses, and made some mention of them to her own and her companions’ governess. The Queen heard of the matter and could not believe it, on account of this man’s cloth and holiness. For this reason she kept silent until a certain Good Friday, when, in accordance with custom, this friar preached before her on the Holy Passion. The ladies and the maids, including my aunt, being seated as was their wont before the reverend father, in full view of him, he, as though giving out the text and introit of his sermon, began to say: ‘It is for you, lovely humanity, it is for you that I suffer this day. Thus on a certain occasion spake our Lord Jesus Christ.’ Then proceeding with his sermon the friar chronicled all the sufferings and afflictions which Jesus endured for mankind at His death upon the Cross, and these he compared to the sufferings that he himself endured on account of my aunt; but in such covert, such disguised words that even the most enlightened might have failed to understand their meaning. Queen Anne, however, who was very expert both in mind and judgment, laid hold of this, and took counsel as to the real meaning of the sermon, both with certain lords and ladies and certain learned men who were there present. They all pronounced the sermon to be most scandalous, and the Grey Friar most deserving of punishment; for which reason he was secretly chastised and whipped, and then driven away, without any scandal being made. Such was the Queen’s reply to the amours of this Grey Friar; and thus was my aunt well avenged on him for the way in which he had so often importuned her. In those times it was not allowable, under divers penalties, either to contradict or to refuse to speak to such people, who, so it was thought, conversed only of God and the salvation of the soul.”
In Mérimée’s Chronique de Charles IX., there will be found a facetious sermon by another Grey Friar; this, however, is less in keeping with the Heptameron, than with the character of the discourses delivered by the preachers of the League.—M.
The following account of the assassination of Alexander de’ Medici is taken from Sismondi’s Histoire des Républiques Italiennes du Moyen Age, Paris, 1826, vol. xvi. p. 95 et seq.:—
“But few months had elapsed since Alexander’s marriage, and he had employed them in his wonted debauchery, carrying depravity and dishonour alternately into the convents and noblest abodes of Florence, when, on January 6, 1537, he was assassinated by the man whom, of all men, he the least mistrusted. This was his cousin, Lorenzino de’ Medici.... Lorenzino had already helped Alexander to seduce several women of noble birth; and to facilitate his assignations had often lent him his house, which adjoined the ducal residence in the Via Larga. He engaged to bring the Duke the wife of Leonardo Ginori—sister to his own mother, but much younger than she was. Alexander had long been struck with this lady’s beauty, but so far she had virtuously repulsed him. After supper, however, on the day of the feast of the Epiphany, when the Carnival begins, Lorenzino informed the Duke that if he would repair to his house, unaccompanied and observing the greatest secrecy, he would find Catherine Ginori there. Alexander accepted the assignation, dismissed all his guards, rid himself of all those who wished to keep a watch upon him, and entered Lorenzino’s house without being perceived. He was tired and wished to rest awhile, but before throwing himself on the bed he unbuckled his sword, and Lorenzino, on taking it from him to hang it at the head of the bedstead, wound the belt around the hilt in such a fashion that the weapon could not be easily drawn from its scabbard. After telling the Duke to rest whilst he went to fetch his aunt, he went away, locking the door of the room behind him; but returned shortly afterwards with a spadassin, nicknamed Scoronconcolo, whom he had previously engaged, for the purpose, he said, of ridding him of a great personage of the Court whose name he had prudently not given. In fact Lorenzino had carried his design to the very point of execution without taking a single person into his confidence. On returning into the room, followed by Scoronconcolo, he called to the Duke: ‘Are you asleep, my lord?’ and at the same moment transpierced him with a short sword which he was carrying. Alexander, although mortally wounded, tried to resist his murderer, whereupon Lorenzino, to prevent him from crying out, thrust two of his fingers into his mouth, at the same time exclaiming: ‘Be not afraid, my lord.’ Alexander, it appears, bit his assailant’s fingers with all the strength of his jaws, and holding him in a tight embrace, rolled with him about the bed, so that Scoronconcolo was unable to strike the one without striking the other. He endeavoured to get at the Duke from between Lorenzino’s legs, but only succeeded in piercing the mattress, till at last he remembered that he had a knife about him, and drove it into the Duke’s throat, turning it round and round until he eventually killed him. (1)
1 Bened. Varchi, lib. xv.; Bern. Segni, 1. vii.; Filippo de
Nerli, 1. xii.; Gio. Batt. Adriani, 1. i.; Scipione
Ammirato, 1. xxxi.; Pauli Jovii. Hist. 1. xxxviii.; Istorie
di Marco Guazzo, fol. 159.
“Lorenzino failed to reap the fruits of the crime, which he had planned with so much skill and such profound secrecy. By the life he had led, he had aroused the distrust of all honest folks, he had no friends to whom he could apply for advice or help, he had no party behind him, he had never been known to display that zeal for liberty which he subsequently affected. Although he was the first of the Medici in the order of succession, no one thought of him. For his own part, he only thought of ensuring his safety. He locked the door of the room, taking the key away with him, and having obtained an order for the city gates to be opened, and for post-horses to be provided for him, under pretence that he had just learned that his brother was ill, in the country, he started for Bologna, whence he proceeded to Venice, accompanied by Scoronconcolo.”
With reference to this story Brantôme writes as follows in the Sixth Discourse of his Vies des Dames Galantes:—
“In the hundred stories of Queen Margaret of Navarre we have a very fine tale of that lady of Milan who, having one night given an assignation to the late M. de Bonnivet, afterwards Admiral of France, posted her maids with drawn swords on the stairs so that they might make a noise there; which they did right well, in obedience to the orders of their mistress, who for her part feigned great affright, saying that her brothers-in-law must have remarked something amiss, that she herself was lost, and that he, Bonnivet, ought to hide under the bed or behind the hangings. But M. de Bonnivet, without evincing any fear, wrapped his cape round his arm, and taking his sword replied: ‘Well, where are these brave brothers who want to frighten me, or do me harm? When they see me they will not even dare to look at the point of my sword.’ Then opening the door he rushed out, and just as he was about to charge down the staircase he espied the women making all this noise; and they, taking fright at sight of him, began to cry out and confess everything. M. de Bonnivet, seeing that it was nothing more serious, left them, bidding them betake themselves to the devil; and then, returning into the room, he closed the door after him and went to find his lady, who began to laugh and embrace him, and confess to him that it was a trick devised by herself, assuring him that if he had behaved as a poltroon, and had not thus displayed the valour which he was said to possess, he should never have had her favours.... She was one of the most beautiful women of Milan, and he had had a deal of trouble to win her.
“I knew a brave gentleman who, one day at Rome, was alone with a pretty Roman lady—her husband being away—and she gave him a similar alarm, causing one of her women to come in hastily to warn her that her husband had returned from the country. The lady, feigning astonishment, begged the gentleman to hide himself in a closet, as otherwise she would be lost. ‘No, no,’ said the gentleman; ‘I would not do that for all the wealth in the world; if he comes I will kill him.’ And as he seized upon his sword the lady began to laugh and confess that she had contrived this to try him so as to see how he would act, and if he would defend her well should her husband seek to do her any harm.
“I also knew a very beautiful lady who suddenly left a lover she had, because she did not find him brave, and took another who did not resemble him, but who was extremely feared and redoubted on account of his sword, he being one of the best swordsmen that could then be found.”—Lalanne’s OEuvres de Brantôme, vol. ix. pp. 388-90.
Brantome, in the Thirtieth Discourse of his Capitaines Étrangers, writes of Furstemberg as follows:—
“Count William von Furstemberg was accounted a good and valiant captain, and would have been more highly esteemed had he not been deficient in faith, over greedy and too much addicted to pillage, as he showed once in France, when he passed along with his troops; for after his passage there was nothing left. He served King Francis for the space of six or seven years [not more than six.—Ed.] with some five companies always numbering from six to seven thousand men; however, after this long term of services, or rather ravages and pillage, he was suspected of having designs against the King’s person, as I have elsewhere related, and those who would learn more of the matter will find the story in the hundred tales of Queen Margaret of Navarre, wherein the valour, generosity and magnanimity of that great King are clearly shown. The other, in great fear, left his service and entered that of the Emperor (Charles V.). If he had not been related to Madame la Régente (Louise of Savoy), through the House of Saxony, whence sprang that of Savoy, he would possibly have met with the fate he merited, had the King been minded to it; but on this occasion the King wished to show his magnanimity rather than have him put to death by the officers of justice. Again the King pardoned him when, on the arrival of the Emperor at St. Dizier in Champagne, he was taken, sounding the river Marne, (2) which he had on other occasions well reconnoitred, in coming to or on leaving France with his troops. He was on this occasion merely sent to the Bastille, and got quit for a ransom of 30,000 crowns. Some great captains said and opined that he ought not to have been thus treated as a prisoner of war but as a real vile spy, for he had professedly acted as such; and they said, moreover, that he got off too cheaply at such a ransom, which did not represent the smallest of the larcenies that he had perpetrated in France.”—Lalanne’s OEuvres de Brantôme, vol. i. pp. 349-50.
Prior to this affair Furstemberg apparently showed some regret for his earlier schemes against Francis I., for Queen Margaret, writing to her brother in 1536, remarked:—
“Count William has asked me to write and tell you that there is a great difference between the shameful purgatory of Italy and the glorious paradise of this camp, (3) and he spoke to me of his past misdeeds, which I would rather he should speak of to you,” &c.—Génin’s Lettres de Marguerite, p. 321.
2 This occurred in September 1544. From an unpublished MS.
in the public library at Rheims it appears that Furstemberg
was wearing a disguise when captured. The Emperor had sent
him forward expressly to sound the river. Another
unpublished MS. at the Bibliothèque Nationale, Paris (anc.
fol. 8561. f. 22), gives some particulars of his operations
about this time.—Ed.
3 That of Avignon. See vol. i. p. liv.—Ed.
In a poetic epistle sent by Margaret to Francis I. in January 1543, to celebrate the New Year, there is an allusion to a “Conte Guillaume,” whom Messrs. de Lincy and Montaiglon conjecture to be Furstemberg, though other commentators think that the Queen refers to William Poyet, the dishonest chancellor, who was sent to the Bastille in 1542 for peculation. We share, however, the opinion of Messrs. de Lincy and Montaiglon, as in various contemporary MSS. which we have referred to, we have frequently found Furstemberg alluded to as “Conte” and “Comte Guillaume,” without any mention of his surname. The passage in Margaret’s epistle alluded to above may be thus rendered in prose:—
“God, fighting for the King in every spot, curses his enemies and brings them to shame and ruin, so that none hold them of account; as witness ‘Compte [“Conte” in the MS.] Guillaume,’ who, in serving the King and the kingdom, became rich, feared and highly esteemed. Now, however, a fugitive, poor and contemned, he may well meditate as to whence came his honours, who it was that maintained him wealthy, happy and feared; and thus it is that all the King’s enemies are cursed by God in Paradise.”—Les Marguerites de la Marguerite, 1873, vol. ii. p. 203.
Apropos of Furstemberg the following entry occurs in M. de Laborde’s Comptes des Bâtiments du Roi (vol. ii. p. 229):—
“Paid to Francis de Cadenet, doctor to Count William of Furstemberg, as a gift and favour for his services, 30 crowns, value 67 livres 10 sols.”—L., M. and Ed.
END OF VOL. II.
| Volume I. | Volume III. | Volume IV. | Volume V. |


| Volume I. | Volume II. | Volume IV. | Volume V. |
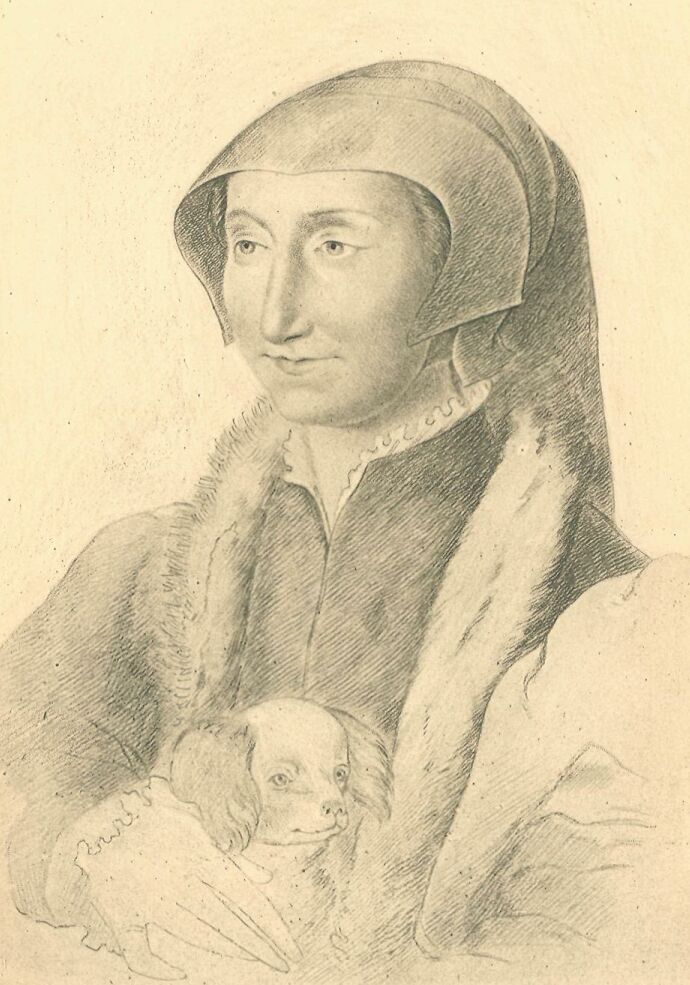


Contents
001a.jpg the Parting Between Pauline and The Gentlemen
021a.jpg the Lord de Riant Finding The Widow With Her Groom
035a.jpg Rolandine Conversing With Her Husband
073a.jpg Sister Marie and the Prior
097a.jpg the Grey Friar Deceiving The Gentleman of Périgord
113a.jpg Elisor Showing the Queen Her Own Image
131a.jpg the Advocate’s Wife Attending on The Prince
143a.jpg the Lord of Avannes Paying his Court in Disguise
171a.jpg the Secretary Imploring The Lady Not to Tell of his Wickedness
177a.jpg the Secretary Opening The Pasty
185a.jpg the Husbandman Surprised by The Fall of The Winnowing Fan
191a.jpg the Young Gentleman Embracing his Mother
SECOND DAY—Continued.
Tale XIX. The honourable love of a gentleman, who, when his sweetheart
is forbidden to speak with him, in despair becomes a monk of the
Observance, while the lady, following in his footsteps, becomes a nun of
St. Clara
Tale XX. How the Lord of Riant is cured of his love fora beautiful widow
through surprising her in the arms of a groom
THIRD DAY.
Prologue
Tale XXI. The affecting history of Rolandine, who, debarred from
marriage by her father’s greed, betrothes herself to a gentleman to
whom, despite his faithlessness, she keeps her plighted word, and does
not marry until after his death
Tale XXII. How Sister Marie Heroet virtuously escapes the attempts of
the Prior of St. Martin in-the-Fields
Tale XXIII. The undeserved confidence which a gentleman of Perigord
places in the monks of the Order of St. Francis, causes the death of
himself, his wife and their little child
Tale XXIV. Concerning the unavailing love borne to the Queen of Castile
by a gentleman named Elisor, who in the end becomes a hermit
Tale XXV. How a young Prince found means to conceal his intrigue with
the wife of a lawyer of Paris
Tale XXVI. How the counsels of a discreet lady happily withdrew the
young Lord of Avannes from the perils of his foolish love for a lady of
Pampeluna
Tale XXVII. How the wife of a man who was valet to a Princess rid
herself of the solicitations of one who was among the same Princess’s
servants, and at the same time her husband’s guest
Tale XXVIII. How a Gascon merchant, named Bernard du Ha, while
sojourning at Paris, deceived a Secretary to the Queen of Navarre who
had thought to obtain a pasty from him
Tale XXIX. How the Priest of Carrelles, in Maine, when surprised with
the wife of an old husbandman, gets out of the difficulty by pretending
to return him a winnowing fan
Tale XXX. How a gentleman marries his own daughter and sister unawares


Pauline, being in love with a gentleman no less than he was with her, and finding that he, because forbidden ever again to speak with her, had entered the monastery of the Observance, gained admittance for her own part into the convent of St. Clara, where she took the veil; thus fulfilling the desire she had conceived to bring the gentleman’s love and her own to a like ending in respect of raiment, condition and manner of life. (1)
In the time of the Marquis of Mantua, (2) who had married the sister of the Duke of Ferrara, there lived in the household of the Duchess a damsel named Pauline, who was greatly loved by a gentleman in the Marquis’s service, and this to the astonishment of every one; for being poor, albeit handsome and greatly beloved by his master, he ought, in their estimation, to have wooed some wealthy dame, but he believed that all the world’s treasure centred in Pauline, and looked to his marriage with her to gain and possess it.
1 The incidents related in this tale appear to have taken
place at Mantua and Ferrara. M. de Montaiglon, however,
believes that they happened at Lyons, and that Margaret laid
the scene of her story in Italy, so that the personages she
refers to might not be identified. The subject of the tale
is similar to that of the poem called L’Amant rendu
Cordelier à l’Observance et Amour, which may perhaps have
supplied the Queen of Navarre with the plot of her
narrative.—M. and Ed.
2 This was John Francis II. of Gonzaga, who was born in
1466, and succeeded his father, Frederic I., in 1484. He
took an active part in the wars of the time, commanding the
Venetian troops when Charles VIII. invaded Italy, and
afterwards supporting Ludovico Sforza in the defence of
Milan. When Sforza abandoned the struggle against France,
the Marquis of Mantua joined the French king, for whom he
acted as viceroy of Naples. Ultimately, however, he espoused
the cause of the Emperor Maximilian, when the latter was at
war with Venice in 1509, and being surprised and defeated
while camping on the island of La Scala, he fled in his
shirt and hid himself in a field, where, by the treachery of
a peasant who had promised him secrecy, he was found and
taken prisoner. By the advice of Pope Julius II., the
Venetians set him at liberty after he had undergone a year’s
imprisonment. In 1490 John Francis married Isabella d’Esté,
daughter of Hercules I. Duke of Ferrara, by whom he had
several children. He died at Mantua in March 1519, his widow
surviving him until 1539. Among the many dignities acquired
by the Marquis in the course of his singularly chequered
life was that of gonfalonier of the Holy Church, conferred
upon him by Julius II.—L. and En.
The Marchioness, who desired that Pauline should through her favour make a more wealthy marriage, discouraged her as much as she could from wedding the gentleman, and often hindered the two lovers from talking together, pointing out to them that, should the marriage take place, they would be the poorest and sorriest couple in all Italy. But such argument as this was by no means convincing to the gentleman, and though Pauline, on her side, dissembled her love as well as she could, she none the less thought about him as often as before.
With the hope that time would bring them better fortune, this love of theirs continued for a long while, during which it chanced that a war broke out (3) and that the gentleman was taken prisoner along with a Frenchman, whose heart was bestowed in France even as was his own in Italy.
3 This would be the expedition which Louis XII. made into
Italy in 1503 in view of conquering the Kingdom of Naples,
and which was frustrated by the defeats that the French army
sustained at Seminara, Cerignoles, and the passage of the
Garigliano.—D.
Finding themselves comrades in misfortune, they began to tell their secrets to one another, the Frenchman confessing that his heart was a fast prisoner, though he gave not the name of its prison-house. However, as they were both in the service of the Marquis of Mantua, this French gentleman knew right well that his companion loved Pauline, and in all friendship for him advised him to lay his fancy aside. This the Italian gentleman swore was not in his power, and he declared that if the Marquis of Mantua did not requite him for his captivity and his faithful service by giving him his sweetheart to wife, he would presently turn friar and serve no master but God. This, however, his companion could not believe, perceiving in him no token of devotion, unless it were that which he bore to Pauline.
At the end of nine months the French gentleman obtained his freedom, and by his diligence compassed that of his comrade also, who thereupon used all his efforts with the Marquis and Marchioness to bring about his marriage with Pauline. But all was of no avail; they pointed out to him the poverty wherein they would both be forced to live, as well as the unwillingness of the relatives on either side; and they forbade him ever again to speak with the maiden, to the end that absence and lack of opportunity might quell his passion.
Finding himself compelled to obey, the gentleman begged of the Marchioness that he might have leave to bid Pauline farewell, promising that he would afterwards speak to her no more, and upon his request being granted, as soon as they were together he spoke to her as follows:—
“Heaven and earth are both against us, Pauline, and hinder us not only from marriage but even from having sight and speech of one another. And by laying on us this cruel command, our master and mistress may well boast of having with one word broken two hearts, whose bodies, perforce, must henceforth languish; and by this they show that they have never known love or pity, and although I know that they desire to marry each of us honourably and to worldly advantage,—ignorant as they are that contentment is the only true wealth,—yet have they so afflicted and angered me that never more can I do them loyal service. I feel sure that had I never spoken of marriage they would not have shown themselves so scrupulous as to forbid me from speaking to you; but I would have you know that, having loved you with a pure and honourable love, and wooed you for what I would fain defend against all others, I would rather die than change my purpose now to your dishonour. And since, if I continued to see you, I could not accomplish so harsh a penance as to restrain myself from speech, whilst, if being here I saw you not, my heart, unable to remain void, would fill with such despair as must end in woe, I have resolved, and that long since, to become a monk. I know, indeed, full well that men of all conditions may be saved, but would gladly have more leisure for contemplating the Divine goodness, which will, I trust, forgive me the errors of my youth, and so change my heart that it may love spiritual things as truly as hitherto it has loved temporal things. And if God grant me grace to win His grace, my sole care shall be to pray to Him without ceasing for you; and I entreat you, by the true and loyal love that has been betwixt us both, that you will remember me in your prayers, and beseech Our Lord to grant me as full a measure of steadfastness when I see you no more, as he has given me of joy in beholding you. Finally, I have all my life hoped to have of you in wedlock that which honour and conscience allow, and with this hope have been content; but now that I have lost it and can never have you to wife, I pray you at least, in bidding me farewell, treat me as a brother, and suffer me to kiss you.”
When the hapless Pauline, who had always treated him somewhat rigorously, beheld the extremity of his grief and his uprightness, which, amidst all his despair, would suffer him to prefer but this moderate request, her sole answer was to throw her arms around his neck, weeping so bitterly that speech and strength alike failed her, and she swooned away in his embrace. Thereupon, overcome by pity, love and sorrow, he must needs swoon also, and one of Pauline’s companions, seeing them fall one on one side and one on the other, called aloud for aid, whereupon remedies were fetched and applied, and brought them to themselves.
Then Pauline, who had desired to conceal her love, was ashamed at having shown such transports; yet were her pity for the unhappy gentleman a just excuse. He, unable to utter the “Farewell for ever!” hastened away with heavy heart and set teeth, and, on entering his apartment, fell like a lifeless corpse upon his bed. There he passed the night in such piteous lamentations that his servants thought he must have lost all his relations and friends, and whatsoever he possessed on earth.
In the morning he commended himself to Our Lord, and having divided among his servants what little worldly goods he had, save a small sum of money which he took, he charged his people not to follow him, and departed all alone to the monastery of the Observance, (4) resolved to take the cloth there and never more to quit it his whole life long.
4 The monastery of the Observance here referred to would
appear to be that at Ferrara, founded by Duke Hercules I.,
father of the Marchioness of Mantua. The name of
“Observance” was given to those conventual establishments
where the rules of monastic life were scrupulously observed,
however rigorous they might be. The monastery of the
Observance at Ferrara belonged to the Franciscan order,
reformed by the Pope in 1363.—D. and L.
The Warden, who had known him in former days, at first thought he was being laughed at or was dreaming, for there was none in all the land that less resembled a Grey Friar than did this gentleman, seeing that he was endowed with all the good and honourable qualities that one would desire a gentleman to possess. Albeit, after hearing his words and beholding the tears that flowed (from what cause he knew not) down his face, the Warden compassionately took him in, and very soon afterwards, finding him persevere in his desire, granted him the cloth: whereof tidings were brought to the Marquis and Marchioness, who thought it all so strange that they could scarcely believe it.
Pauline, wishing to show herself untrammelled by any passion, strove as best she might to conceal her sorrow, in such wise that all said she had right soon forgotten the deep affection of her faithful lover. And so five or six months passed by without any sign on her part, but in the meanwhile some monk had shown her a song which her lover had made a short time after he had taken the cowl. The air was an Italian one and pretty well known; as for the words, I have put them into our own tongue as nearly as I can, and they are these:—
What word shall be
Hers unto me,
When I appear in convent guise
Before her eyes?
Ah! sweet maiden,
Lone, heart-laden,
Dumb because of days that were;
When the streaming
Tears are gleaming
‘Mid the streaming of thy hair,
Ah! with hopes of earth denied thee,
Holiest thoughts will heavenward guide thee
To the hallowing cloister’s door.
What word shall be, &c.
What shall they say,
Who wronged us, they
Who have slain our heart’s desire,
Seeing true love
Doth flawless prove,
Thus tried as gold in fire?
When they see my heart is single,
Their remorseful tears shall mingle,
Each and other weeping sore.
What word shall be, &c.
And should they come
To will us home,
How vain were all endeavour!
“Nay, side by side,
“We here shall bide
“Till soul from soul shall sever.
“Though of love your hate bereaves us
“Yet the veil and cowl it leaves us,
“We shall wear till life be o’er.”
What word shall be, &c.
And should they move
Our flesh to love
Once more the mockers, singing
Of fruits and flowers
In golden hours
For mated hearts upspringing;
We shall say: “Our lives are given,
Flower and fruit, to God in Heaven,
Who shall hold them evermore.”
What word shall be, &c.
O victor Love!
Whose might doth move
My wearied footsteps hither,
Here grant me days
Of prayer and praise,
Grant faith that ne’er shall wither;
Love of each to either given,
Hallowed by the grace of Heaven,
God shall bless for evermore.
What word shall be, &c.
Avaunt Earth’s weal!
Its bands are steel
To souls that yearn for Heaven;
Avaunt Earth’s pride!
Deep Hell shall hide
Hearts that for fame have striven.
Far be lust of earthly pleasure,
Purity, our priceless treasure,
Christ shall grant us of His store.
What word shall be, &c.
Swift be thy feet,
My own, my sweet,
Thine own true lover follow;
Fear not the veil,
The cloister’s pall
Keeps far Earth’s spectres hollow.
Sinks the fire with fitful flashes,
Soars the Phoenix from his ashes,
Love yields Life for evermore.
What word shall be, &c.
Love, that no power
Of dreariest hour,
Could change, no scorn, no rage,
Now heavenly free
From Earth shall be,
In this, our hermitage.
Winged of love that upward, onward,
Ageless, boundless, bears us sunward,
To the heavens our souls shall soar.
What word shall be, &c.
On reading these verses through in a chapel where she was alone, Pauline began to weep so bitterly that all the paper was wetted with her tears. Had it not been for her fear of showing a deeper affection than was seemly, she would certainly have withdrawn forthwith to some hermitage, and never have looked upon a living being again; but her native discretion moved her to dissemble for a little while longer. And although she was now resolved to leave the world entirely, she feigned the very opposite, and so altered her countenance, that in company she was altogether unlike her real self. For five or six months did she carry this secret purpose in her heart, making a greater show of mirth than had ever been her wont.
But one day she went with her mistress to the Observance to hear high mass, and when the priest, the deacon and the sub-deacon came out of the vestry to go to the high altar, she saw her hapless lover, who had not yet fulfilled his year of novitiate, acting as acolyte, carrying the two vessels covered with a silken cloth, and walking first with his eyes upon the ground. When Pauline saw him in such raiment as did rather increase than diminish his comeliness, she was so exceedingly moved and disquieted, that to hide the real reason of the colour that came into her face, she began to cough. Thereupon her unhappy lover, who knew this sound better than that of the cloister bells, durst not turn his head; still on passing in front of her he could not prevent his eyes from going the road they had so often gone before; and whilst he thus piteously gazed on Pauline, he was seized in such wise by the fire which he had considered well-nigh quelled, that whilst striving to conceal it more than was in his power, he fell at full length before her. However, for fear lest the cause of his fall should be known, he was led to say that it was by reason of the pavement of the church being broken in that place.
When Pauline perceived that the change in his dress had not wrought any change in his heart, and that so long a time had gone by since he had become a monk, that every one believed her to have forgotten him, she resolved to fulfil the desire she had conceived to bring their love to a like ending in respect of raiment, condition and mode of life, even as these had been akin at the time when they abode together in the same house, under the same master and mistress. More than four months previously she had carried out all needful measures for taking the veil, and now, one morning she asked leave of the Marchioness to go and hear mass at the convent of Saint Clara, (5) which her mistress granted her, not knowing the reason of her request. But in passing by the monastery of the Grey Friars, she begged the Warden to summon her lover, saying that he was her kinsman, and when they met in a chapel by themselves, she said to him:—
5 There does not appear to have been a church of St. Clara
at Mantua, but there was one attached to a convent of that
name at Ferrara.—M. and D.
“Had my honour suffered me to seek the cloister as soon as you, I should not have waited until now; but having at last by my patience baffled the slander of those who are more ready to think evil than good, I am resolved to take the same condition, raiment and life as you have taken. Nor do I inquire of what manner they are; if you fare well, I shall partake of your welfare, and if you fare ill, I would not be exempt. By whatsoever path you are journeying to Paradise I too would follow; for I feel sure that He who alone is true and perfect, and worthy to be called Love, has drawn us to His service by means of a virtuous and reasonable affection, which He will by His Holy Spirit turn wholly to Himself. Let us both, I pray you, put from us the perishable body of the old Adam, and receive and put on the body of our true Spouse, who is the Lord Jesus Christ.”
The monk-lover was so rejoiced to hear of this holy purpose, that he wept for gladness and did all that he could to strengthen her in her resolve, telling her that since the pleasure of hearing her words was the only one that he might now seek, he deemed himself happy to dwell in a place where he should always be able to hear them. He further declared that her condition would be such that they would both be the better for it; for they would live with one love, with one heart and with one mind, guided by the goodness of God, whom he prayed to keep them in His hand, wherein none can perish. So saying, and weeping for love and gladness, he kissed her hands; but she lowered her face upon them, and then, in all Christian love, they gave one another the kiss of hallowed affection.
And so, in this joyful mood Pauline left him, and came to the convent of Saint Clara, where she was received and took the veil, whereof she sent tidings to her mistress, the Marchioness, who was so amazed that she could not believe it, but came on the morrow to the convent to see Pauline and endeavour to turn her from her purpose. But Pauline replied that she, her mistress, had had the power to deprive her of a husband in the flesh, the man whom of all men she had loved the best, and with that she must rest content, and not seek to sever her from One who was immortal and invisible, for this Was neither in her power nor in that of any creature upon earth.
The Marchioness, finding her thus steadfast in her resolve, kissed her and left her, with great sorrow.
And thenceforward Pauline and her lover lived such holy and devout lives, observing all the rules of their order, that we cannot doubt that He whose law is love told them when their lives were ended, as He had told Mary Magdalene: “Your sins are forgiven, for ye have loved much;” and doubtless He removed them in peace to that place where the recompense surpasses all the merits of man.
“You cannot deny, ladies, that in this case the man’s love was the greater of the two; nevertheless, it was so well requited that I would gladly have all lovers equally rewarded.”
“Then,” said Hircan, “there would be more manifest fools among men and women than ever there were.”
“Do you call it folly,” said Oisille, “to love virtuously in youth and then to turn this love wholly to God?”
“If melancholy and despair be praiseworthy,” answered Hircan, laughing, “I will acknowledge that Pauline and her lover are well worthy of praise.”
“True it is,” said Geburon, “that God has many ways of drawing us to Himself, and though they seem evil in the beginning, yet in the end they are good.”
“Moreover,” said Parlamente, “I believe that no man can ever love God perfectly that has not perfectly loved one of His creatures in this world.”
“What do you mean by loving perfectly?” asked Saffredent. “Do you consider that those frigid beings who worship their mistresses in silence and from afar are perfect lovers?”
“I call perfect lovers,” replied Parlamente, “those who seek perfection of some kind in the objects of their love, whether beauty, or goodness, or grace, ever tending to virtue, and who have such noble and upright hearts that they would rather die than do base things, contrary and repugnant to honour and conscience. For the soul, which was created for nothing but to return to its sovereign good, is, whilst enclosed in the body, ever desirous of attaining to it. But since the senses, through which the soul receives knowledge, are become dim and carnal through the sin of our first parent, they can show us only those visible things that approach towards perfection; and these the soul pursues, thinking to find in outward beauty, in a visible grace and in the moral virtues, the supreme, absolute beauty, grace and virtue. But when it has sought and tried these external things and has failed to find among them that which it really loves, the soul passes on to others; wherein it is like a child, which, when very young, will be fond of dolls and other trifles, the prettiest its eyes can see, and will heap pebbles together in the idea that these form wealth; but as the child grows older he becomes fond of living dolls, and gathers together the riches that are needful for earthly life. And when he learns by greater experience that in all these earthly things there is neither perfection nor happiness, he is fain to seek Him who is the Creator and Author of happiness and perfection. Albeit, if God should not give him the eye of Faith, he will be in danger of passing from ignorance to infidel philosophy, since it is Faith alone that can teach and instil that which is right; for this, carnal and fleshly man can never comprehend.” (6)
6 The whole of this mystical dissertation appears to have
been inspired by some remarks in Castiglione’s Libro del
Cortegiano—which Margaret was no doubt well acquainted
with, as it was translated into French in 1537 by Jacques
Colin, her brother’s secretary. This work, which indeed
seems to have suggested several passages in the
Heptameron, was at that time as widely read in France as
in Italy and Spain.—B. J. and D.
“Do you not see,” said Longarine, “that uncultivated ground which bears plants and trees in abundance, however useless they may be, is valued by men, because it is hoped that it will produce good fruit if this be sown in it? In like manner, if the heart of man has no feeling of love for visible things, it will never arrive at the love of God by the sowing of His Word, for the soul of such a heart is barren, cold and worthless.”
“That,” said Saffredent, “is the reason why most of the doctors are not spiritual. They never love anything but good wine and dirty, ill-favoured serving-women, without making trial of the love of honourable ladies.”
“If I could speak Latin well,” said Simontault, “I would quote you St. John’s words: ‘He that loveth not his brother whom he hath seen, how can he love God whom he hath not seen?’ (7) From visible things we are led on to love those that are invisible.”
“If,” said Ennasuite, “there be a man as perfect as you say, quis est ille et laudabimus eum?” (8)
7 I St. John, iv. 20.
8 We have been unable to find this anywhere in the
Scriptures.—Ed.
“There are men,” said Dagoucin, “whose love is so strong and true that they would rather die than harbour a wish contrary to the honour and conscience of their mistress, and who at the same time are unwilling that she or others should know what is in their hearts.”
“Such men,” said Saffredent, “must be of the nature of the chameleon, which lives on air. (9) There is not a man in the world but would fain declare his love and know that it is returned; and further, I believe that love’s fever is never so great, but it quickly passes off when one knows the contrary. For myself, I have seen manifest miracles of this kind.”
9 A popular fallacy. The chameleon undoubtedly feeds upon
small insects.—D.
“I pray you then,” said Ennasuite, “take my place and tell us about some one that was recalled from death to life by having discovered in his mistress the very opposite of his desire.”
“I am,” said Saffredent, “so much afraid of displeasing the ladies, whose faithful servant I have always been and shall always be, that without an express command from themselves I should never have dared to speak of their imperfections. However, in obedience to them, I will hide nothing of the truth.”



The Lord of Riant, being greatly in love with a widow lady and finding her the contrary of what he had desired and of what she had often declared herself to be, was so affected thereby that in a moment resentment had power to extinguish the flame which neither length of time nor lack of opportunity had been able to quench. (1)
1 The unpleasant discovery related in this tale is
attributed by Margaret to a gentleman of Francis I.‘s
household, but a similar incident figures in the
introduction to the Arabian Nights. Ariosto also tells
much the same tale in canto xxviii. of his Rolando
Furioso, and another version of it will be found in No. 24
of Morlini’s Novella, first issued at Naples in 1520.
Subsequent to the Heptameron it supplied No. 29 of the
Comptes du Monde Adventureux, figured in a rare imitation
of the Cent Nouvelles Nouvelles printed at Rouen early in
the seventeenth century, and was introduced by La Fontaine
into his well-known tale Joconde. On the other hand, there
is certainly a locality called Rians in Provence, just
beyond the limits of Dauphiné, and moreover among Francis
I.‘s “equerries of the stable” there was a Monsieur dc Rian
who received a salary of 200 livres a year from 1522 to
1529.—See the roll of the officers of the King’s Household
in the French National Archives, Sect. Histor., K. 98.
Some extracts from Brantôme bearing on the story will be
found in the Appendix to this vol. (A).—L. and En.
In the land of Dauphiné there lived a gentleman named the Lord of Riant; he belonged to the household of King Francis the First, and was as handsome and worshipful a gentleman as it was possible to see. He had long been the lover of a widow lady, whom he loved and revered so exceedingly that, for fear of losing her favour, he durst not solicit of her that which he most desired. Now, since he knew himself to be a handsome man and one worthy to be loved, he fully believed what she often swore to him—namely, that she loved him more than any living man, and that if she were led to do aught for any gentleman, it would be for him alone, who was the most perfect she had ever known. She at the same time begged him to rest satisfied with this virtuous love and to seek nothing further, and assured him that if she found him unreasonably aiming at more, he would lose her altogether. The poor gentleman was not only satisfied, but he deemed himself very fortunate in having gained the heart of a lady who appeared to him so full of virtue.
It would take too long to tell you his love-speeches, his lengthened visits to her, and the journeys he took in order to see her; it is enough to say that this poor martyr, consumed by so pleasing a fire that the more one burns the more one wishes to burn, continually sought for the means of increasing his martyrdom.
One day the fancy took him to go post-haste to see the lady whom he loved better than himself, and whom he prized beyond every other woman in the world. On reaching her house, he inquired where she was, and was told that she had just come from vespers, and was gone into the warren to finish her devotions there. He dismounted from his horse and went straight to the warren where she was to be found, and here he met with some of her women, who told him that she had gone to walk alone in a large avenue.
He was more than ever beginning to hope that some good fortune awaited him, and continued searching for her as carefully and as quietly as he could, desiring above all things to find her alone. He came in this way to a summer-house formed of bended boughs, the fairest and pleasantest place imaginable, (2) and impatient to see the object of his love, he went in; and there beheld the lady lying on the grass in the arms of a groom in her service, who was as ill-favoured, foul and disreputable as the Lord of Riant was handsome, virtuous and gentle.
2 For a description of a summer-house of the kind referred
to, see Cap’s edition of Palissy’s Dessein du Jardin
Délectable, p. 69. Palissy there describes some summer-
houses formed of young elmtrees, with seats, columns,
friezes, and a roofing so cunningly contrived of bent boughs
that the rain could not penetrate into the interior. It is
to some such construction that Queen Margaret refers.—M.
I will not try to depict to you his resentment, but it was so great that in a moment it had power to extinguish the flame which neither length of time nor lack of opportunity had been able to impair.
“Madam,” he said to her, being now as full of indignation as once he had been of love, “much good may this do you! (3) The revelation of your wickedness has to-day cured me, and freed me from the continual anguish that was caused by the virtue I believed to be in you.” (4)
3 The French words here are “prou face,” which in Margaret’s
time were very generally used in lieu of “Amen” or “So be
it.”—M.
4 In Joconde La Fontaine gives the end of the adventure as
follows:—
“Sans rencontrer personne et sans etre entendu
Il monte dans sa chambre et voit près de la dame
Un lourdaud de valet sur son sein étendu.
Tous deux dormaient. Dans cet abord Joconde
Voulut les envoyer dormir en l’autre monde,
Mais cependant il n’en fit rien
Et mon avis est qu’il fit bien.”
Both in La Fontaine’s Conte and in Ariosto’s Rolando the
lady is the Queen, and the favoured lover the King’s dwarf.
—Ed.
And with this farewell he went back again more quickly than he had come.
The unhappy woman made him no other reply than to put her hand to her face; for being unable to hide her shame, she covered her eyes that she might not see him who in spite of her deceit now perceived it only too clearly.
“And so, ladies, if you are not minded to love perfectly, do not, I pray you, seek to deceive and annoy an honest man for vanity’s sake; for hypocrites are rewarded as they deserve, and God favours those who love with frankness.”
“Truly,” said Oisille, “you have kept us a proper tale for the end of the day. But that we have all sworn to speak the truth, I could not believe that a woman of that lady’s condition could be so wicked both in soul and in body, and leave so gallant a gentleman for so vile a muleteer.”
“Ah, madam,” said Hircan, “if you knew what a difference there is between a gentleman who has worn armour and been at the wars all his life, and a well-fed knave that has never stirred from home, you would excuse the poor widow.”
“I do not believe,” said Oisille, “whatever you may say, that you could admit any possible excuse for her.”
“I have heard,” said Simontault, “that there are women who like to have apostles to preach of their virtue and chastity, and treat them as kindly and familiarly as possible, saying that but for the restraints of honour and conscience they would grant them their desire. And so these poor fools, when speaking in company of their mistresses, swear that they would thrust their fingers into the fire without fear of burning in proof that these ladies are virtuous women, since they have themselves thoroughly tested their love. Thus are praised by honourable men, those who show their true nature to such as are like themselves; and they choose such as would not have courage to speak, or, if they did, would not be believed by reason of their low and degraded position.”
“That,” said Longarine, “is an opinion which I have before now heard expressed by jealous and suspicious men, but it may indeed be called painting a chimera. And even although it be true of one wretched woman, the same suspicion cannot attach to all.”
“Well,” said Parlamente, “the longer we talk in this way, the longer will these good gentlemen play the critics over Simontault’s tale, and all at our own expense. So in my opinion we had better go to vespers, and not cause so much delay as we did yesterday.”
The company agreed to this proposal, and as they were going Oisille said:—
“If any one gives God thanks for having told the truth to-day, Saffredent ought to implore His forgiveness for having raked up so vile a story against the ladies.”
“By my word,” replied Saffredent, “what I told you was true, albeit I only had it upon hearsay. But were I to tell you all that I have myself seen of women, you would have need to make even more signs of the cross than the priests do in consecrating a church.”
“Repentance is a long way off,” said Geburon, “when confession only increases the sin.”
“Since you have so bad an opinion of women,” said Parlamente, “they ought to deprive you of their honourable society and friendship.”
“There are some women,” he returned, “who have acted towards me so much in accordance with your advice, in keeping me far away from things that are honourable and just, that could I do and say worse to them, I should not neglect doing so, in order that I might stir them up to revenge me on her who does me so much wrong.”
Whilst he spoke these words, Parlamente put on her mask (5) and went with the others into the church, where they found that although the bell had rung for vespers, there was not a single monk, present to say them.
5 Little masks hiding only the upper part of the face, and
called tourets-de-nez, were then frequently worn by ladies
of rank. Some verses by Christine de Pisan show them to have
been in vogue already in the fourteenth century. In the MS.
copy of Margaret’s poem of La Coche presented to the
Duchess of Etampes, the ladies in the different miniatures
are frequently shown wearing masks of the kind referred to.
Some curious particulars concerning these tourets will be
found in M. Léon do Laborde’s Le Palais Mazarin et les
grandes habitations de ville et de campagne au XVIIe
Siècle, Paris, 1846, 8vo, p. 314.—L.
The monks, indeed, had heard that the company assembled in the meadow to tell the pleasantest tales imaginable, and being fonder of pleasure than of their prayers, they had gone and hidden themselves in a ditch, where they lay flat on their bellies behind a very thick hedge; and they had there listened so eagerly to the stories that they had not heard the ringing of the monastery bell, as was soon clearly shown, for they returned in such great haste that they almost lacked breath to begin the saying of vespers.
After the service, when they were asked why they had been so late and had chanted so badly, they confessed that they had been to listen to the tales; whereupon, since they were so desirous of hearing them, it was granted that they might sit and listen at their ease every day behind the hedge.
Supper-time was spent joyously in discoursing of such matters as they had not brought to an end in the meadow. And this lasted through the evening, until Oisille begged them to retire so that their minds might be the more alert on the morrow, after a long, sound sleep, one hour of which before midnight was, said she, better than three after it. Accordingly the company parted one from another, betaking themselves to their respective rooms; and in this wise ended the Second Day.

On the Third Day are recounted Tales of the
Ladies who have only
sought what was
honourable in Love, and of the
hypocrisy and
wickedness
of the Monks.
Though it was yet early when the company entered the hall on the morrow, they found Madame Oisille there before them. She had been meditating for more than half-an-hour upon the lesson that she was going to read; and if she had contented them on the first and second days, she assuredly did no less on the third; indeed, but that one of the monks came in search of them they would not have heard high mass, for so intent were they upon listening to her that they did not even hear the bell.
When they had piously heard mass, and had dined with temperance to the end that the meats might in no sort hinder the memory of each from acquitting itself as well as might be when their several turns came, they withdrew to their apartments, there to consult their note-books until the wonted hour for repairing to the meadow was come. When it had arrived they were not slow to make the pleasant excursion, and those who were prepared to tell of some merry circumstance already showed mirthful faces that gave promise of much laughter. When they were seated, they asked Saffredent to whom he would give his vote for the beginning of the Third Day.
“I think,” said he, “that since my offence yesterday was as you say very great, and I have knowledge of no story that might atone for it, I ought to give my vote to Parlamente, who, with her sound understanding, will be able to praise the ladies sufficiently to make you forget such truth as you heard from me.”
“I will not undertake,” said Parlamente, “to atone for your offences, but I will promise not to imitate them. Wherefore, holding to the truth that we have promised and vowed to utter, I propose to show you that there are ladies who in their loves have aimed at nought but virtue. And since she of whom I am going to speak to you came of an honourable line, I will just change the names in my story but nothing more; and I pray you, ladies, believe that love has no power to change a chaste and virtuous heart, as you will see by the tale I will now begin to tell.”


Having remained unmarried until she was thirty years of
age, Rolandine, recognising her father’s neglect and her
mistress’s disfavour, fell so deeply in love with a bastard
gentleman that she promised him marriage; and this being
told to her father he treated her with all the harshness
imaginable, in order to make her consent to the dissolving
of the marriage; but she continued steadfast in her love
until she had received certain tidings of the Bastard’s
death, when she was wedded to a gentleman who bore the same
name and arms as did her own family.
There was in France a Queen (1) who brought up in her household several maidens belonging to good and noble houses. Among others there was one called Rolandine, (2) who was near akin to the Queen; but the latter, being for some reason unfriendly with the maiden’s father, showed her no great kindness.
Now, although this maiden was not one of the fairest—nor yet indeed was she of the ugliest—she was nevertheless so discreet and virtuous that many persons of great consequence sought her in marriage. They had, however, but a cold reply; for the father (3) was so fond of his money that he gave no thought to his daughter’s welfare, while her mistress, as I have said, bore her but little favour, so that she was sought by none who desired to be advanced in the Queen’s good graces.
1 This is evidently Anne of Brittany, elder daughter of Duke
Francis II. and wife in turn of Charles VIII. and Louis XII.
Brantôme says: “She was the first to form that great Court
of ladies which we have seen since her time until now; she
always had a very great suite of ladies and maids, and never
refused fresh ones; far from it, indeed, for she would
inquire of the noblemen at Court if they had daughters, and
would ask that they might be sent to her.”—Lalanne’s
OEuvres de Brantôme, vol. vii. p. 314—L.
2 This by the consent of all the commentators is Anne de
Rohan, elder daughter of John II. Viscount de Rohan, Count
of Porhoët, Léon and La Garnache, by Mary of Brittany,
daughter of Duke Francis I. The date of Anne de Rohan’s
birth is not exactly known, but she is said to have been
about thirty years of age at the time of the tale, though
the incidents related extend over a somewhat lengthy period.
However, we know that Anne was ultimately married to Peter
de Rohan in 1517, when, according to her marriage contract,
she was over thirty-six years old (Les Preuves de Histoire
ecclésiastique et civile de Bretagne, 1756, vol. v. col.
940). From this we may assume that she was thirty in or
about 1510. The historical incidents alluded to in the tale
would, however, appear to have occurred (as will be shown by
subsequent notes) between 1507 and 1509, and we are of
opinion that the Queen of Navarre has made her heroine
rather older than she really was, and that the story indeed
begins in or about 1505, when Rolandine can have been little
more than five or six and twenty.—Ed.
3 See notes to Tale XL. (vol. iv).
Thus, owing to her father’s neglect and her mistress’s disdain, the poor maiden continued unmarried for a long while; and this at last made her sad at heart, not so much because she longed to be married as because she was ashamed at not being so, wherefore she forsook the vanities and pomps of the Court and gave herself up wholly to the worship of God. Her sole delight consisted in prayer or needlework, and thus in retirement she passed her youthful years, living in the most virtuous and holy manner imaginable.
Now, when she was approaching her thirtieth year, there was at Court a gentleman who was a Bastard of a high and noble house; (4) he was one of the pleasantest comrades and most worshipful men of his day, but he was wholly without fortune, and possessed of such scant comeliness that no lady would have chosen him for her lover.
4 One cannot absolutely identify this personage; but judging
by what is said of him in the story—that he came of a great
house, that he was very brave but poor, neither rich enough
to marry Rolandine nor handsome enough to be made a lover
of, and that a lady, who was a near relative of his, came to
the Court after his intrigue had been going on for a couple
of years—he would certainly appear to be John, Bastard of
Angoulôme, a natural son of Count John the Good, and
consequently half-brother to Charles of Angoulôme ( who
married Louise of Savoy) and uncle to Francis I. and Queen
Margaret. In Père Anselme’s Histoire Généalogique de la
Maison de France, vol. i. p. 210 B. there is a record of
the letters of legitimisation granted to the Bastard of
Angoulême at his father’s request in June 1458, and M. Paul
Lacroix points out that if Rolandine’s secret marriage to
him took place in or about 1508, he would then have been
about fifty years old, hardly the age for a lover. The
Bastard is, however, alluded to in the tale as a man of
mature years, and as at the outset of the intrigue (1505) he
would have been but forty-seven, we incline with M. de Lincy
to the belief that he is the hero of it.—Eu.
Thus this poor gentleman had continued unmated, and as one unfortunate often seeks out another, he addressed himself to Rolandine, whose fortune, temper and condition were like his own. And while they were engaged in mutually lamenting their woes, they became very fond of each other, and finding that they were companions in misfortune, sought out one another everywhere, so that they might exchange consolation, in this wise setting on foot a deep and lasting attachment.
Those who had known Rolandine so very retiring that she would speak to none, were now greatly shocked on seeing her unceasingly with the well-born Bastard, and told her governess that she ought not to suffer their long talks together. The governess, therefore, remonstrated with Rolandine, and told her that every one was shocked at her conversing so freely with a man who was neither rich enough to marry her nor handsome enough to be her lover.
To this Rolandine, who had always been rebuked rather for austereness than for worldliness, replied—
“Alas, mother, you know that I cannot have a husband of my own condition, and that I have always shunned such as are handsome and young, fearing to fall into the same difficulties as others. And since this gentleman is discreet and virtuous, as you yourself know, and tells me nothing that is not honourable and right, what harm can I have done to you and to those that have spoken of the matter, by seeking from him some consolation in my grief?”
The poor old woman, who loved her mistress more than she loved herself, replied—
“I can see, my lady, that you speak the truth, and know that you are not treated by your father and mistress as you deserve to be. Nevertheless, since people are speaking about your honour in this way, you ought to converse with him no longer, even were he your own brother.”
“Mother,” said Rolandine, “if such be your counsel I will observe it; but ‘tis a strange thing to be wholly without consolation in the world.”
The Bastard came to talk with her according to his wont, but she told him everything that her governess had said to her, and, shedding tears, besought him to have no converse with her for a while, until the rumour should be past and gone; and to this he consented at her request.
Being thus cut off from all consolation, they both began, however, to feel such torment during their separation as neither had ever known before. For her part she did not cease praying to God, journeying and fasting; for love, heretofore unknown to her, caused her such exceeding disquiet as not to leave her an hour’s repose. The well-born Bastard was no better off; but, as he had already resolved in his heart to love her and try to wed her, and had thought not only of his love but of the honour that it would bring him if he succeeded in his design, he reflected that he must devise a means of making his love known to her and, above all, of winning the governess to his side. This last he did by protesting to her the wretchedness of her poor mistress, who was being robbed of all consolation. At this the old woman, with many tears, thanked him for the honourable affection that he bore her mistress, and they took counsel together how he might speak with her. They planned that Rolandine should often feign to suffer from headache, to which noise is exceedingly distressful; so that, when her companions went into the Queen’s apartment, she and the Bastard might remain alone, and in this way hold converse together.
The Bastard was overjoyed at this, and, guiding himself wholly by the governess’s advice, had speech with his sweetheart whensoever he would. However, this contentment lasted no great while, for the Queen, who had but little love for Rolandine, inquired what she did so constantly in her room. Some one replied that it was on account of sickness, but another, who possessed too good a memory for the absent, declared that the pleasure she took in speaking with the Bastard must needs cause her headache to pass away.
The Queen, who deemed the venial sins of others to be mortal ones in Rolandine, sent for her and forbade her ever to speak to the Bastard except it were in the royal chamber or hall. The maiden gave no sign, but replied—
“Had I known, madam, that he or any one beside were displeasing to you, I should never have spoken to him.”
Nevertheless she secretly cast about to find some other plan of which the Queen should know nothing, and in this she was successful. On Wednesdays, Fridays and Saturdays she was wont to fast, and would then stay with her governess in her own room, where, while the others were at supper, she was free to speak with the man whom she was beginning to love so dearly.
The more they were compelled to shorten their discourse, the more lovingly did they talk; for they stole the time even as a robber steals something that is of great worth. But, in spite of all their secrecy, a serving-man saw the Bastard go into the room one fast day, and reported the matter in a quarter where it was not concealed from the Queen. The latter was so wroth that the Bastard durst enter the ladies’ room no more. Yet, that he might not lose the delight of converse with his love, he often made a pretence of going on a journey, and returned in the evening to the church or chapel of the castle (5) dressed as a Grey Friar or a Jacobin, or disguised so well in some other way that none could know him; and thither, attended by her governess, Rolandine would go to have speech with him.
5 This would be either the château of Amboise or that of
Blois, we are inclined to think the latter, as Louis XII.
more frequently resided there.—Ed.
Then, seeing how great was the love she bore him, he feared not to say—
“You see, fair lady, what risk I run in your service, and how the Queen has forbidden you to speak with me. You see, further, what manner of man is your father, who has no thought whatsoever of bestowing you in marriage. He has rejected so many excellent suitors, that I know of none, whether near or far, that can win you. I know that I am poor, and that you could not wed a gentleman that were not richer than I; yet, if love and good-will were counted wealth, I should hold myself for the richest man on earth. God has given you great wealth, and you are like to have even more. Were I so fortunate as to be chosen for your husband, I would be your husband, lover and servant all my life long; whereas, if you take one of equal consideration with yourself—and such a one it were hard to find—he will seek to be the master, and will have more regard for your wealth than for your person, and for the beauty of others than for your virtue; and, whilst enjoying the use of your wealth, he will fail to treat you, yourself, as you deserve. And now my longing to have this delight, and my fear that you will have none such with another, impel me to pray that you will make me a happy man, and yourself the most contented and best treated wife that ever lived.”
When Rolandine heard the very words that she herself had purposed speaking to him, she replied with a glad countenance—
“I am well pleased that you have been the first to speak such words as I had a long while past resolved to say to you. For the two years that I have known you I have never ceased to turn over in my mind all the arguments for you and against you that I was able to devise; but now that I am at last resolved to enter into the married state, it is time that 1 should make a beginning and choose some one with whom I may look to dwell with tranquil mind. And I have been able to find none, whether handsome, rich, or nobly born, with whom my heart and soul could agree excepting yourself alone. I know that in marrying you I shall not offend God, but rather do what He enjoins, while as to his lordship my father, he has regarded my welfare so little, and has rejected so many offers, that the law suffers me to marry without fear of being disinherited; though, even if I had only that which is now mine, I should, in marrying such a husband as you, account myself the richest woman in the world. As to the Queen, my mistress, I need have no qualms in displeasing her in order to obey God, for never had she any in hindering me from any blessing that I might have had in my youth. But, to show you that the love I bear you is founded upon virtue and honour, you must promise that if I agree to this marriage, you will not seek its consummation until my father be dead, or until I have found a means to win his consent.”
To this the Bastard readily agreed, whereupon they exchanged rings in token of marriage, and kissed each other in the church in the presence of God, calling upon Him to witness their promise; and never afterwards was there any other familiarity between them save kissing only.
This slender delight gave great content to the hearts of these two perfect lovers; and, secure in their mutual affection, they lived for some time without seeing each other. There was scarcely any place where honour might be won to which the Bastard did not go, rejoicing that he could not now continue a poor man, seeing that God had bestowed on him a rich wife; and she during his absence steadfastly cherished their perfect love, and made no account of any other living man. And although there were some who asked her in marriage, the only answer they had of her was that, since she had remained unwedded for so long a time, she desired to continue so for ever. (6)
6 The speeches of Rolandine and the Bastard should be
compared with some of Clement Marot’s elegies, notably with
one in which he complains of having been surprised while
conversing with his mistress in a church.—B. J.
This reply came to the ears of so many people, that the Queen heard of it and asked her why she spoke in that way. Rolandine replied that it was done in obedience to herself, who had never been pleased to marry her to any man who would have well and comfortably provided for her; accordingly, being taught by years and patience to be content with her present condition, she would always return a like answer whensoever any one spoke to her of marriage.
When the wars were over, (7) and the Bastard had returned to Court, she never spoke to him in presence of others, but always repaired to some church and there had speech with him under pretence of going to confession; for the Queen had forbidden them both, under penalty of death, to speak together except in public. But virtuous love, which recks naught of such a ban, was more ready to find them means of speech than were their enemies to spy them out; the Bastard disguised himself in the habit of every monkish order he could think of, and thus their virtuous intercourse continued, until the King repaired to a pleasure house he had near Tours. (8)
7 The wars here referred to would be one or another of Louis
XII.‘s Italian expeditions, probably that of 1507, when the
battle of Aignadel was fought.—Ed.
8 This would no doubt be the famous château of Plessis-lez-
Tours, within a mile of Tours, and long the favourite
residence of Louis XI. Louis XII. is known to have sojourned
at Plessis in 1507, at the time when the States-general
conferred upon him the title of “Father of the People.”
English tourists often visit Plessis now adays in memory of
Scott’s “Quentin Durward,” but only a few shapeless ruins of
the old structure are left.—M. and Ed.
This, however, was not near enough for the ladies to go on foot to any other church but that of the castle, which was built in such a fashion that it contained no place of concealment in which the confessor would not have been plainly recognised.
But if one opportunity failed them, love found them another and an easier one, for there came to the Court a lady to whom the Bastard was near akin. This lady was lodged, together with her son, (9) in the King’s abode; and the young Prince’s room projected from the rest of the King’s apartments in such a way that from his window it was possible to see and to speak to Rolandine, for his window and hers were just at the angle made by the two wings of the house.
9 This lady would be Louise of Savoy. She first came to the
Court at Amboise in 1499, a circumstance which has led some
commentators to place the incidents of this story at that
date. But she was at Blois on various occasions between 1507
and 1509, to negotiate and attend the marriage of her
daughter Margaret with the Duke of Alençon. Louis XII.
having gone from Blois to Plessis in 1507, Louise of Savoy
may well have followed him thither. Her son was, of course,
the young Duke de Valois, afterwards Francis I.—Ed.
In this room of hers, which was over the King’s presence-chamber, all the noble damsels that were Rolandine’s companions were lodged with her. She, having many times observed the young Prince at his window, made this known to the Bastard through her governess; and he, having made careful observation of the place, feigned to take great pleasure in reading a book about the Knights of the Round Table (10) which was in the Prince’s room.
10 Romances of chivalry were much sought after at this time.
Not merely were there MS. copies of these adorned with
miniatures, but we find that L’Histoire du Saint Gréai, La
Vie et les Prophéties de Merlin, and Les Merveilleux Faits
et Gestes du Noble Chevalier Lancelot du Lac were printed
in France in the early years of the sixteenth century.—B.J.
And when every one was going to dinner, he would beg a valet to let him finish his reading, shut up in the room, over which he promised to keep good guard. The servants knew him to be a kinsman of his master and one to be trusted, let him read as much as he would. Rolandine, on her part, would then come to her window; and, so that she might be able to make a long stay at it, she pretended to have an infirmity in the leg, and accordingly dined and supped so early that she no longer frequented the ladies’ table. She likewise set herself to work a coverlet of crimson silk, (11) and fastened it at the window, where she desired to be alone; and, when she saw that none was by, she would converse with her husband, who contrived to speak in such a voice as could not be overheard; and whenever any one was coming, she would cough and make a sign, so that the Bastard might withdraw in good time.
11 In the French, “Ung lût de reseul:” reticella—i.e., a
kind of open work embroidery very fashionable in those days,
and the most famous designers of which were Frederic
Vinciolo, Dominic de Sara, and John Cousin the painter.
Various sixteenth and seventeenth century books on
needlework, still extant, give some curious information
concerning this form of embroidery.—M.
Those who kept watch upon them felt sure that their love was past, for she never stirred from the room in which, as they thought, he could assuredly never see her, since it was forbidden him to enter it.
One day, however, the young Prince’s mother, (12) being in her son’s room, placed herself at the window where this big book lay, and had not long been there when one of Rolandine’s companions, who was at the window in the opposite room, greeted her and spoke to her. The lady asked her how Rolandine did; whereon the other replied that she might see her if she would, and brought her to the window in her nightcap. Then, when they had spoken together about her sickness, they withdrew from the window on either side.
12 Louise of Savoy.
The lady, observing the big book about the Round Table, said to the servant who had it in his keeping—
“I am surprised that young folk can waste their time in reading such foolishness.”
The servant replied that he marvelled even more that people accounted sensible and of mature age should have a still greater liking for it than the young; and he told her, as matter for wonderment, how her cousin the Bastard would spend four or five hours each day in reading this fine book. Straightway there came into the lady’s mind the reason why he acted thus, and she charged the servant to hide himself somewhere, and take account of what the Bastard might do. This the man did, and found that the Bastard’s book was the window to which Rolandine came to speak with him, and he, moreover, heard many a love-speech which they had thought to keep wholly secret.
On the morrow he related this to his mistress, who sent for the Bastard, and after chiding him forbade him to return to that place again; and in the evening she spoke of the matter to Rolandine, and threatened, if she persisted in this foolish love, to make all these practices known to the Queen.
Rolandine, whom nothing could dismay, vowed that in spite of all that folks might say she had never spoken to him since her mistress had forbidden her to do so, as might be learned both from her companions and from her servants and attendants. And as for the window, she declared that she had never spoken at it to the Bastard. He, however, fearing that the matter had been discovered, withdrew out of harm’s way, and was a long time without returning to Court, though not without writing to Rolandine, and this in so cunning a manner that, in spite of the Queen’s vigilance, never a week went by but she twice heard from him.
When he no longer found it possible to employ monks as messengers, as he had done at first, he would send a little page, dressed now in one colour and now in another; and the page used to stand at the doorways through which the ladies were wont to pass, and deliver his letters secretly in the throng. But one day, when the Queen was going out into the country, it chanced that one who was charged to look after this matter recognised the page, and hastened after him; but he, being keen-witted and suspecting that he was being pursued, entered the house of a poor woman who was boiling her pot on the fire, and there forthwith burned his letters. The gentleman who followed him stripped him naked and searched through all his clothes; but he could find nothing, and so let him go. And the boy being gone, the old woman asked the gentleman why he had so searched him.
“To find some letters,” he replied, “which I thought he had upon him.”
“You could by no means have found them,” said the old woman, “they were too well hidden for that.”
“I pray you,” said the gentleman, in the hope of getting them before long, “tell me where they were.”
However, when he heard that they had been thrown into the fire, he perceived that the page had proved more crafty than himself, and forthwith made report of the matter to the Queen.
From that time, however, the Bastard no longer employed the page or any other child, but sent an old servant of his, who, laying aside all fear of the death which, as he well knew, was threatened by the Queen against all such as should interfere in this matter, undertook to carry his master’s letters to Rolandine. And having come to the castle where she was, he posted himself on the watch at the foot of a broad staircase, beside a doorway through which all the ladies were wont to pass. But a serving-man, who had aforetime seen him, knew him again immediately and reported the matter to the Queen’s Master of the Household, who quickly came to arrest him. However, the discreet and wary servant, seeing that he was being watched from a distance, turned towards the wall as though he desired to make water, and tearing the letter he had into the smallest possible pieces, threw them behind a door. Immediately afterwards he was taken and thoroughly searched, and nothing being found on him, they asked him on his oath whether he had not brought letters, using all manner of threats and persuasions to make him confess the truth; but neither by promises nor threats could they draw anything from him.
Report of this having been made to the Queen, some one in the company bethought him that it would be well to look behind the door near which the man had been taken. This was done, and they found what they sought, namely the pieces of the letter. Then the King’s confessor was sent for, and he, having put the pieces together on a table, read the whole of the letter, in which the truth of the marriage, that had been so carefully concealed, was made manifest; for the Bastard called Rolandine nothing but “wife.” The Queen, who was in no mind, as she should have been, to hide her neighbour’s transgressions, made a great ado about the matter, and commanded that all means should be employed to make the poor man confess the truth of the letter. And indeed, when they showed it to him, he could not deny it; but for all they could say or show, he would say no more than at first. Those who had him in charge thereupon brought him to the brink of the river, and put him into a sack, declaring that he had lied to God and to the Queen, contrary to proven truth. But he was minded to die rather than accuse his master, and asked for a confessor; and when he had eased his conscience as well as might be, he said to them—
“Good sirs, I pray you tell the Bastard, my master, that I commend the lives of my wife and children to him, for right willingly do I yield up my own in his service. You may do with me what you will, for never shall you draw from me a word against my master.”
Thereupon, all the more to affright him, they threw him in the sack into the water, calling to him—
“If you will tell the truth, you shall be saved.”
Finding, however, that he answered nothing, they drew him out again, and made report of his constancy to the Queen, who on hearing of it declared that neither the King nor herself were so fortunate in their followers as was this gentleman the Bastard, though he lacked even the means to requite them. She then did all that she could to draw the servant into her own service, but he would by no means consent to forsake his master. However, by the latter’s leave, he at last entered the Queen’s service, in which he lived in happiness and contentment.
The Queen, having learnt the truth of the marriage from the Bastard’s letter, sent for Rolandine, whom with a wrathful countenance she several times called “wretch” instead of “cousin,” reproaching her with the shame that she had brought both upon her father’s house and her mistress by thus marrying without her leave or commandment.
Rolandine, who had long known what little love her mistress bore her, gave her but little in return. Moreover, since there was no love between them, neither was there fear; and as Rolandine perceived that this reprimand, given her in presence of several persons, was prompted less by affection than by a desire to put her to shame, and that the Queen felt more pleasure in chiding her than grief at finding her in fault, she replied with a countenance as glad and tranquil as the Queen’s was disturbed and wrathful—
“If, madam, you did not know your own heart, such as it is, I would set forth to you the ill-will that you have long borne my father (13) and myself; but you do, indeed, know this, and will not deem it strange that all the world should have an inkling of it too. For my own part, madam, I have perceived it to my dear cost, for had you been pleased to favour me equally as you favour those who are not so near to you as myself, I were now married to your honour as well as to my own; but you passed me over as one wholly a stranger to your favour, and so all the good matches I might have made passed away before my eyes, through my father’s neglect and the slenderness of your regard. By reason of this treatment I fell into such deep despair, that, had my health been strong enough in any sort to endure a nun’s condition, I would have willingly entered upon it to escape from the continual griefs your harshness brought me.
13 Of all those with pretensions to the Duchy of Brittany,
the Viscount de Rohan had doubtless the best claim, though
he met with the least satisfaction. It was, however, this
reason that led the Queen [Anne of Brittany] to treat him
with such little regard. It was with mingled grief and
resentment that this proud princess realised how real were
the Viscount’s rights; moreover, she never forgave him for
having taken up arms against her in favour of France; and
seeking an opportunity to avenge herself, she found one in
giving the Viscount but little satisfaction in the matter of
his pretensions.”—Dora Morice’s Histoire ecclésiastique et
civile de Bretagne, Paris, 1756, vol. ii. p. 231.—L.
“Whilst in this despair I was sought by one whose lineage would be as good as my own if mutual love were rated as high as a marriage ring; for you know that his father would walk before mine. He has long wooed and loved me; but you, madam, who have never forgiven me the smallest fault nor praised me for any good deed, you—although you knew from experience that I was not wont to speak of love or worldly things, and that I led a more retired and religious life than any other of your maids—forthwith deemed it strange that I should speak with a gentleman who is as unfortunate in this life as I am myself, and one, moreover, in whose friendship I thought and looked to have nothing save comfort to my soul. When I found myself wholly baffled in this design, I fell into great despair, and resolved to seek my peace as earnestly as you longed to rob me of it; whereupon we exchanged words of marriage, and confirmed them with promise and ring. Wherefore, madam, methinks you do me a grievous wrong in calling me wicked, seeing that in this great and perfect love, wherein opportunity, had I so desired, would not have been lacking, no greater familiarity has passed between us than a kiss. I have waited in the hope that, before the consummation of the marriage, I might by the grace of God win my father’s heart to consent to it. I have given no offence to God or to my conscience, for I have waited till the age of thirty to see what you and my father would do for me, and have kept my youth in such chastity and virtue that no living man can bring up aught against me. But when I found that I was old and without hope of being wedded suitably to my birth and condition, I used the reason that God has given me, and resolved to marry a gentleman after my own heart. And this I did not to gratify the lust of the eye, for you know that he is not handsome; nor the lust of the flesh, for there has been no carnal consummation of our marriage; nor the ambition and pride of life, for he is poor and of small rank; but I took account purely and simply of the worth that is in him, for which every one is constrained to praise him, and also of the great love that he bears me, and that gives me hope of having a life of quietness and kindness with him. Having carefully weighed all the good and the evil that may come of it, I have done what seems to me best, and, after considering the matter in my heart for two years, I am resolved to pass the remainder of my days with him. And so firm is my resolve that no torment that may be inflicted upon me, nor even death itself, shall ever cause me to depart from it. Wherefore, madam, I pray you excuse that which is indeed very excusable, as you yourself must realise, and suffer me to dwell in that peace which I hope to find with him.”
The Queen, finding her so steadfast of countenance and so true of speech, could make no reply in reason, but continued wrathfully rebuking and reviling her, bursting into tears and saying—
“Wretch that you are! instead of humbling yourself before me, and repenting of so grievous a fault, you speak hardily with never a tear in your eye, and thus clearly show the obstinacy and hardness of your heart. But if the King and your father give heed to me, they will put you into a place where you will be compelled to speak after a different fashion.”
“Madam,” replied Rolandine, “since you charge me with speaking too hardily, I will e’en be silent if you give me not permission to reply to you.”
Then, being commanded to speak, she went on—
“‘Tis not for me, madam, to speak to you, my mistress and the greatest Princess in Christendom, hardily and without the reverence that I owe to you, nor have I purposed doing so; but I have no defender to speak for me except the truth, and as this is known to me alone, I am forced to utter it fearlessly in the hope that, when you know it, you will not hold me for such as you have been pleased to name me. I fear not that any living being should learn how I have comported myself in the matter that is laid to my charge, for I know that I have offended neither against God nor against my honour. And this it is that enables me to speak without fear; for I feel sure that He who sees my heart is on my side, and with such a Judge in my favour, I were wrong to fear such as are subject to His decision. Why should I weep? My conscience and my heart do not at all rebuke me, and so far am I from repenting of this matter, that, were it to be done over again, I should do just the same. But you, madam, have good cause to weep both for the deep wrong that you have done me throughout my youth, and for that which you are now doing me, in rebuking me publicly for a fault that should be laid at your door rather than at mine. Had I offended God, the King, yourself, my kinsfolk or my conscience, I were indeed obstinate and perverse if I did not greatly repent with tears; but I may not weep for that which is excellent, just and holy, and which would have received only commendation had you not made it known before the proper time. In doing this, you have shown that you had a greater desire to compass my dishonour than to preserve the honour of your house and kin. But, since such is your pleasure, madam, I have nothing to say against it; command me what suffering you will, and I, innocent though I am, will be as glad to endure as you to inflict it. Wherefore, madam, you may charge my father to inflict whatsoever torment you would have me undergo, for I well know that he will not fail to obey you. It is pleasant to know that, to work me ill, he will wholly fall in with your desire, and that as he has neglected my welfare in submission to your will, so will he be quick to obey you to my hurt. But I have a Father in Heaven, and He will, I am sure, give me patience equal to all the evils that I foresee you preparing for me, and in Him alone do I put my perfect trust.”
The Queen, beside herself with wrath, commanded that Rolandine should be taken from her sight and put into a room alone, where she might have speech with no one. However, her governess was not taken from her, and through her Rolandine acquainted the Bastard with all that had befallen her, and asked him what he would have her do. He, thinking that his services to the King might avail him something, came with all speed to the Court. Finding the King at the chase, he told him the whole truth, entreating him to favour a poor gentleman so far as to appease the Queen and bring about the consummation of the marriage.
The King made no reply except to ask—
“Do you assure me that you have wedded her?”
“Yes, sire,” said the Bastard, “but by word of mouth alone; however, if it please you, we’ll make an ending of it.”
The King bent his head, and, without saying anything more, returned straight towards the castle, and when he was nigh to it summoned the Captain of his Guard, and charged him to take the Bastard prisoner.
However, a friend who knew and could interpret the King’s visage, warned the Bastard to withdraw and betake himself to a house of his that was hard by, saying that if the King, as he expected, sought for him, he should know of it forthwith, so that he might fly the kingdom; whilst if, on the other hand, things became smoother, he should have word to return. The Bastard followed this counsel, and made such speed that the Captain of the Guards was not able to find him.
The King and Queen took counsel together as to what they should do with the hapless lady who had the honour of being related to them, and by the Queen’s advice it was decided that she should be sent back to her father, and that he should be made acquainted with the whole truth.
But before sending her away they caused many priests and councillors to speak with her and show her that, since her marriage consisted in words only, it might by mutual agreement readily be made void; and this, they urged, the King desired her to do in order to maintain the honour of the house to which she belonged.
She made answer that she was ready to obey the King in all such things as were not contrary to her conscience, but that those whom God had brought together man could not put asunder. She therefore begged them not to tempt her to anything so unreasonable; for if love and goodwill founded on the fear of God were the true and certain marriage ties, she was Clinked by bonds that neither steel nor flame nor water could sever. Death alone might do this, and to death alone would she resign her ring and her oath. She therefore prayed them to gainsay her no more; for so strong of purpose was she that she would rather keep faith and die than break it and live.
This steadfast reply was repeated to the King by those whom he had appointed to speak with her, and when it was found that she could by no means be brought to renounce her husband, she was sent to her father, and this in so pitiful a plight that all who beheld her pass wept to see her. And although she had done wrong, her punishment was so grievous and her constancy so great, that her wrongdoing was made to appear a virtue.
When her father heard the pitiful tale, he would not see her, but sent her away to a castle in a forest, which he had aforetime built for a reason well worthy to be related. (14) There he kept her in prison for a long time, causing her to be told that if she would give up her husband he would treat her as his daughter and set her free.
14 The famous château of Josselin in Morbihan. See notes to
Tale XL., vol. lv.—Ed.
Nevertheless she continued firm, for she preferred the bonds of prison together with those of marriage, to all the freedom in the world without her husband. And, judging from her countenance, all her woes seemed but pleasant pastimes to her, since she was enduring them for one she loved.
And now, what shall I say of men? The Bastard, who was so deeply beholden to her, as you have seen, fled to Germany where he had many friends, and there showed by his fickleness that he had sought Rolandine less from true and perfect love than from avarice and ambition; for he fell deeply in love with a German lady, and forgot to write to the woman who for his sake was enduring so much tribulation. However cruel Fortune might be towards them, they were always able to write to each other, until he conceived this foolish and wicked love. And Rolandine’s heart gaining an inkling of it, she could no longer rest.
And afterwards, when she found that his letters were colder and different from what they had been before, she suspected that some new love was separating her from her husband, and doing that which all the torments and afflictions laid upon herself had been unable to effect. Nevertheless, her perfect love would not pass judgment on mere suspicion, so she found a means of secretly sending a trusty servant, not to carry letters or messages to him, but to watch him and discover the truth. When this servant had returned from his journey, he told her that the Bastard was indeed deeply in love with a German lady, and that according to common report he was seeking to marry her, for she was very rich.
These tidings brought extreme and unendurable grief to Rolandine’s heart, so that she fell grievously sick. Those who knew the cause of her sickness, told her on behalf of her father that, with this great wickedness on the part of the Bastard before her eyes, she might now justly renounce him. They did all they could to persuade her to that intent, but, notwithstanding her exceeding anguish, she could not be brought to change her purpose, and in this last temptation again gave proof of her great love and surpassing virtue. For as love grew less and less on his part, so did it grow greater on hers, and in this way make good that which was lost. And when she knew that the entire and perfect love that once had been shared by both remained but in her heart alone, she resolved to preserve it there until one or the other of them should die. And the Divine Goodness, which is perfect charity and true love, took pity upon her grief and long suffering, in such wise that a few days afterwards the Bastard died while occupied in seeking after another woman. Being advised of this by certain persons who had seen him laid in the ground, she sent to her father and begged that he would be pleased to speak with her.
Her father, who had never spoken to her since her imprisonment, came without delay. He listened to all the pleas that she had to urge, and then, instead of rebuking her or killing her as he had often threatened, he took her in his arms and wept exceedingly.
“My daughter,” he said, “you are more in the right than I, for if there has been any wrongdoing in this matter, I have been its principal cause. But now, since God has so ordered it, I would gladly atone for the past.”
He took her home and treated her as his eldest daughter. A gentleman who bore the same name and arms as did her own family sought her in marriage; he was very sensible and virtuous, (15) and he thought so much of Rolandine, whom he often visited, that he gave praise to what others blamed in her, perceiving that virtue had been her only aim. The marriage, being acceptable both to Rolandine and to her father, was concluded without delay.
It is true, however, that a brother she had, the sole heir of their house, would not grant her a portion, for he charged her with having disobeyed her father. And after his father’s death he treated her so harshly that she and her husband (who was a younger son) had much ado to live. (16)
15 Peter de Rohan-Gié, Lord of Frontenay, third son of
Peter de Rohan, Lord of Gié, Marshal of Prance and preceptor
to Francis I. As previously stated, the marriage took place
in 1517, and eight years later the husband was killed at
Pavia.—Ed.
16 Anne de Rohan (Rolandine) had two brothers, James and
Claud. Both died without issue. Some particulars concerning
them will be found in the notes to Tale XL. The father’s
death, according to Anselme, took place in 1516, that is,
prior to Anne’s marriage.—Ed.
However, God provided for them, for the brother that sought to keep everything died suddenly one day, leaving behind him both her wealth, which he was keeping back, and his own.
Thus did she inherit a large and rich estate, whereon she lived piously and virtuously and in her husband’s love. And after she had brought up the two sons that God gave to them, (17) she yielded with gladness her soul to Him in whom she had at all times put her perfect trust.
17 Anne’s sons were René and Claud. Miss Mary Robinson (The
Fortunate Lovers, London, 1887) believes René to be
“Saffredent,” and his wife Isabel d’Albret, sister of Queen
Margaret’s husband Henry of Navarre, to be “Nomerfide.”—Ed.
“Now, ladies, let the men who would make us out so fickle come forward and point to an instance of as good a husband as this lady was a good wife, and of one having like faith and steadfastness. I am sure they would find it so difficult to do this, that I will release them from the task rather than put them to such exceeding toil. But as for you, ladies, I would pray you, for the sake of maintaining your own fair fame, either to love not at all, or else to love as perfectly as she did. And let none among you say that this lady offended against her honour, seeing that her constancy has served to heighten our own.”
“In good sooth, Parlamente,” said Oisille, “you have indeed told us the story of a woman possessed of a noble and honourable heart; but her constancy derives half its lustre from the faithlessness of a husband that could leave her for another.”
“I think,” said Longarine, “that the grief so caused must have been the hardest to bear. There is none so heavy that the love of two united lovers cannot support it; but when one fails in his duty, and leaves the whole of the burden to the other, the load becomes too heavy to be endured.”
“Then you ought to pity us,” said Geburon, “for we have to bear the whole burden of love, and you will not put out the tip of a finger to relieve us.”
“Ah, Geburon,” said Parlamente, “the burdens of men and of women are often different enough. The love of a woman, being founded on godliness and honour, is just and reasonable, and any man that is false to it must be reckoned a coward, and a sinner against God and man. On the other hand, most men love only with reference to pleasure, and women, being ignorant of their ill intent, are sometimes ensnared; but when God shows them how vile is the heart of the man whom they deemed good, they may well draw back to save their honour and reputation, for soonest ended is best mended.”
“Nay, that is a whimsical idea of yours,” said Hircan, “to hold that an honourable woman may in all honour betray the love of a man; but that a man may not do as much towards a woman. You would make out that the heart of the one differs from that of the other; but for my part, in spite of their differences in countenance and dress, I hold them to be alike in inclination, except indeed that the guilt which is best concealed is the worst.”
Thereto Parlamente replied with some heat—
“I am well aware that in your opinion the best women are those whose guilt is known.”
“Let us leave this discourse,” said Simontault; “for whether we take the heart of man or the heart of woman, the better of the twain is worth nothing. And now let us see to whom Parlamente is going to give her vote, so that we may hear some fine tale.”
“I give it,” she said, “to Geburon.”
“Since I began,” (18) he replied, “by talking about the Grey friars, I must not forget those of Saint Benedict, nor an adventure in which they were concerned in my own time. Nevertheless, in telling you the story of a wicked monk, I do not wish to hinder you from having a good opinion of such as are virtuous; but since the Psalmist says ‘all men are liars,’ and in another place, ‘there is none that doeth good, no not one,’ (19) I think we are bound to look upon men as they really are. If there be any virtue in them, we must attribute it to Him who is its source, and not to the creature. Most people deceive themselves by giving overmuch praise or glory to the latter, or by thinking that there is something good in themselves. That you may not deem it impossible for exceeding lust to exist under exceeding austerity, listen to what befel in the days of King Francis the First.”
18 See the first tale he tells, No. 5, vol. i.—Ed.
19 Psalms cxvi. 11 and xiv. 3.



Sister Marie Heroet, being unchastely solicited by a Prior
of Saint-Martin-in-the-Fields, was by the grace of God
enabled to overcome his great temptations, to the Prior’s
exceeding confusion and her own glory. (1)
1 This story is historical, and though M. Frank indicates
points of similarity between it and No. xxvii. of St. Denis’
Comptes du Monde Adventureux, and No. vi. of Masuccio de
Solerac’s Novellino, these are of little account when one
remembers that the works in question were written posterior
to the Heptameron. The incidents related in the tale must
have occurred between 1530 and 1535. The Abbey of Saint-
Martin-in-the-Fields stood on the site of the present
Conservatoire des Arts et Métiers, Paris.—Ed.
In the city of Paris there was a Prior of Saint-Martin-in-the-Fields, whose name I will keep secret for the sake of the friendship I bore him. Until he reached the age of fifty years, his life was so austere that the fame of his holiness was spread throughout the entire kingdom, and there was not a prince or princess but showed him high honour when he came to visit them. There was further no monkish reform that was not wrought by his hand, so that people called him the “father of true monasticism.” (2)
He was chosen visitor to the illustrious order of the “Ladies of Fontevrault,” (3) by whom he was held in such awe that, when he visited any of their convents, the nuns shook with very fear, and to soften his harshness towards them would treat him as though he had been the King himself in person. At first he would not have them do this, but at last, when he was nearly fifty-five years old, he began to find the treatment he had formerly contemned very pleasant; and reckoning himself the mainstay of all monasticism, he gave more care to the preservation of his health than had heretofore been his wont. Although the rules of his order forbade him ever to partake of flesh, he granted himself a dispensation (which was more than he ever did for another), declaring that the whole burden of conventual affairs rested upon him; for which reason he feasted himself so well that, from being a very lean monk he became a very fat one.
2 This prior was Stephen Gentil, who succeeded Philip
Bourgoin on December 15, 1508, and died November 6, 1536.
The Gallia Christiana states that in 1524 he reformed an
abbey of the diocese of Soissons, but makes no mention of
his appointment as visitor to the abbey of Fontevrault.
Various particulars concerning him will be found in Manor’s
Monasterii Regalis S. Martini de Campis, &c. Parisiis,
1636, and in Gallia Christiana, vol. vii. col. 539.—L.
3 The abbey of Fontevrault, near Saumur, Maine-et-Loire, was
founded in 1100 by Robert d’Arbrissel, and comprised two
conventual establishments, one for men and the other for
women. Prior to his death, d’Arbrissel abdicated his
authority in favour of Petronilla de Chemillé, and from her
time forward monks and nuns alike were always under the sway
of an abbess—this being the only instance of the kind in
the history of the Roman Catholic Church. Fourteen of the
abbesses were princesses, and several of these were of the
blood royal of France. In the abbey church were buried our
Henry II., Eleanor of Guienne, Richard Coeur-de-Lion, and
Isabella of Angoulême; their tombs are still shown, though
the abbey has become a prison, and its church a refectory.—
Ed.
Together with this change of life there was wrought also a great change of heart, so that he now began to cast glances upon countenances which aforetime he had looked at only as a duty; and, contemplating charms which were rendered even more desirable by the veil, he began to hanker after them. Then, to satisfy this longing, he sought out such cunning devices that at last from being a shepherd he became a wolf, so that in many a convent, where there chanced to be a simple maiden, he failed not to beguile her. But after he had continued this evil life for a long time, the Divine Goodness took compassion upon the poor, wandering sheep, and would no longer suffer this villain’s triumph to endure, as you shall hear.
One day he went to visit the convent of Gif, (4) not far from Paris, and while he was confessing all the nuns, it happened that there was one among them called Marie Heroet, whose speech was so gentle and pleasing that it gave promise of a countenance and heart to match.
4 Gif, an abbey of the Benedictine order, was situated at
five leagues from Paris, in the valley of Chevreuse, on the
bank of the little river Yvette. A few ruins of it still
remain. It appears to have been founded in the eleventh
century.—See Le Beuf s Histoire du Diocèse de Paris, vol.
viii. part viii. p. 106, and Gallia Christiana, vol. vii.
col. 596.—L. and D.
The mere sound of her voice moved him with a passion exceeding any that he had ever felt for other nuns, and, while speaking to her, he bent low to look at her, and perceiving her rosy, winsome mouth, could not refrain from lifting her veil to see whether her eyes were in keeping therewith. He found that they were, and his heart was filled with so ardent a passion that, although he sought to conceal it, his countenance became changed, and he could no longer eat or drink. When he returned to his priory, he could find no rest, but passed his days and nights in deep disquiet, seeking to devise a means whereby he might accomplish his desire, and make of this nun what he had already made of many others. But this, he feared, would be difficult, seeing that he had found her to be prudent of speech and shrewd of understanding; moreover, he knew himself to be old and ugly, and therefore resolved not to employ words but to seek to win her by fear.
Accordingly, not long afterwards, he returned to the convent of Gif aforesaid, where he showed more austerity than he had ever done before, and spoke wrathfully to all the nuns, telling one that her veil was not low enough, another that she carried her head too high, and another that she did not do him reverence as a nun should do. So harsh was he in respect of all these trifles, that they feared him as though he had been a god sitting on the throne of judgment.
Being gouty, he grew very weary in visiting all the usual parts of the convent, and it thus came to pass that about the hour for vespers, an hour which he had himself fixed upon, he found himself in the dormitory, when the Abbess said to him—
“Reverend father, it is time to go to vespers.”
“Go, mother,” he replied, “do you go to vespers. I am so weary that I will remain here, yet not to rest but to speak to Sister Marie, of whom I have had a very bad report, for I am told that she prates like a worldly-minded woman.”
The Abbess, who was aunt to the maiden’s mother, begged him to reprove her soundly, and left her alone with him and a young monk who accompanied him.
When he found himself alone with Sister Marie, he began to lift up her veil, and to tell her to look at him. She answered that the rule of her order forbade her to look at men.
“It is well said, my daughter,” he replied, “but you must not consider us monks as men.”
Then Sister Marie, fearing to sin by disobedience, looked him in the face; but he was so ugly that she though it rather a penance than a sin to look at him.
The good father, after telling her at length of his goodwill towards her, sought to lay his hand upon her breasts; but she repulsed him, as was her duty; whereupon, in great wrath, he said to her—
“Should a nun know that she has breasts?”
“I know that I have,” she replied, “and certes neither you nor any other shall ever touch them. I am not so young and ignorant that I do not know the difference between what is sin and what is not.”
When he saw that such talk would not prevail upon her, he adopted a different plan, and said—
“Alas, my daughter, I must make known to you my extreme need. I have an infirmity which all the physicians hold to be incurable unless I have pleasure with some woman whom I greatly love. For my part, I would rather die than commit a mortal sin; but, when it comes to that, I know that simple fornication is in no wise to be compared with the sin of homicide. So, if you love my life, you will preserve it for me, as well as your own conscience from cruelty.”
She asked him what manner of pleasure he desired to have. He replied that she might safely surrender her conscience to his own, and that he would do nothing that could be a burden to either.
Then, to let her see the beginning of the pastime that he sought, he took her in his arms and tried to throw her upon a bed. She, recognising his evil purpose, defended herself so well with arms and voice that he could only touch her garments. Then, when he saw that all his devices and efforts were being brought to naught, he behaved like a madman and one devoid not only of conscience but of natural reason, for, thrusting his hand under her dress, he scratched wherever his nails could reach with such fury that the poor girl shrieked out, and fell swooning at full length upon the floor.
Hearing this cry, the Abbess came into the dormitory; for while at vespers she had remembered that she had left her niece’s daughter alone with the good father, and feeling some scruples of conscience, she had left the chapel and repaired to the door of the dormitory in order to learn what was going on. On hearing her niece’s voice, she pushed open the door, which was being held by the young monk.
And when the Prior saw the Abbess coming, he pointed to her niece as she lay in a swoon, and said—
“Assuredly, mother, you are greatly to blame that you did not inform me of Sister Marie’s condition. Knowing nothing of her weakness, I caused her to stand before me, and, while I was reproving her, she swooned away as you see.”
They revived her with vinegar and other remedies, and found that she had wounded her head in her fall. When she was recovered, the Prior, fearing that she would tell her aunt the reason of her indisposition, took her aside and said to her—
“I charge you, my daughter, if you would be obedient and hope for salvation, never to speak of what I said to you just now. You must know that it was my exceeding love for you that constrained me, but since I see that you do not wish to love me, I will never speak of it to you again. However, if you be willing, I promise to have you chosen Abbess of one of the three best convents in the kingdom.”
She replied that she would rather die in perpetual imprisonment than have any lover save Him who had died for her on the cross, for she would rather suffer with Him all the evils the world could inflict than possess without Him all its blessings. And she added that he must never again speak to her in such a manner, or she would inform the Abbess; whereas, if he kept silence, so would she.
Thereupon this evil shepherd left her, and in order to make himself appear quite other than he was, and to again have the pleasure of looking upon her he loved, he turned to the Abbess and said—
“I beg, mother, that you will cause all your nuns to sing a Salve Regina in honour of that virgin in whom I rest my hope.”
While this was being done, the old fox did nothing but shed tears, not of devotion, but of grief at his lack of success. All the nuns, thinking that it was for love of the Virgin Mary, held him for a holy man, but Sister Marie, who knew his wickedness, prayed in her heart that one having so little reverence for virginity might be brought to confusion.
And so this hypocrite departed to St. Martin’s, where the evil fire that was in his heart did not cease burning night and day alike, prompting him to all manner of devices in order to compass his ends. As he above all things feared the Abbess, who was a virtuous woman, he hit upon a plan to withdraw her from the convent, and betook himself to Madame de Vendôme, who was at that time living at La Fère, where she had founded and built a convent of the Benedictine order called Mount Olivet. (5)
5 This is Mary of Luxemburg, Countess of St. Paul-de-
Conversan, Marie and Soissons, who married, first, James of
Savoy, and secondly, Francis de Bourbon, Count of Vendôme.
The latter, who accompanied Charles VIII. to Italy, was
killed at Vercelli in October 1495, when but twenty-five
years old. His widow did not marry again, but retired to her
château of La Fère near Laon (Aisne), where late in 1518 she
founded a convent of Benedictine nuns, which, according to
the Gallia Christiana, she called the convent of Mount
Calvary. This must be the establishment alluded to by Queen
Margaret, who by mistake has called it Mount Olivet, i.e.,
the Mount of Olives. Madame de Vendôme died at a very
advanced age on April 1, 1546.—See Anselme’s Histoire
Généalogique, vol. i. p. 326.—L.
Speaking in the quality of a prince of reformers, he gave her to understand that the Abbess of the aforesaid Mount Olivet lacked the capacity to govern such a community. The worthy lady begged him to give her another that should be worthy of the office, and he, who asked nothing better, counselled her to have the Abbess of Gif, as being the most capable in France. Madame de Vendôme sent for her forthwith, and set her over the convent of Mount Olivet.
As the Prior of St. Martin’s had every monastic vote at his disposal, he caused one who was devoted to him to be chosen Abbess of Gif, and this being accomplished, he went to Gif to try once more whether he might win Sister Marie Heroet by prayers or honied words. Finding that he could not succeed, he returned in despair to his priory of St. Martin’s, and in order to achieve his purpose, to revenge himself on her who was so cruel to him, and further to prevent the affair from becoming known, he caused the relics of the aforesaid convent of Gif to be secretly stolen at night, and accusing the confessor of the convent, a virtuous and very aged man, of having stolen them, he cast him into prison at St. Martin’s.
Whilst he held him captive there, he stirred up two witnesses who in ignorance signed what the Prior commanded them, which was a statement that they had seen the confessor in a garden with Sister Marie, engaged in a foul and wicked act; and this the Prior sought to make the old monk confess. But he, who knew all the Prior’s misdoings, entreated him to bring him before the Chapter, saying that there, in presence of all the monks, he would tell the truth of all that he knew. The Prior, fearing that the confessor’s justification would be his own condemnation, would in no wise grant this request; and, finding him firm of purpose, he treated him so ill in prison that some say he brought about his death, and others that he forced him to lay aside his robe and betake himself out of the kingdom of France. Be that as it may, the confessor was never seen again.
The Prior, thinking that he had now a sure hold upon Sister Marie, repaired to the convent, where the Abbess, chosen for this purpose, gainsaid him in nothing. There he began to exercise his authority as visitor, and caused all the nuns to come one after the other into a room that he might hear them, as is the fashion at a visitation. When the turn of Sister Marie, who had now lost her good aunt, had come, he began speaking to her in this wise—
“Sister Marie, you know of what crime you are accused, and that your pretence of chastity has availed you nothing, since you are well known to be the very contrary of chaste.”
“Bring here my accuser,” replied Sister Marie, with steadfast countenance, “and you will see whether in my presence he will abide by his evil declaration.”
“No further proof is needed,” he said, “since the confessor has been found guilty.”
“I hold him for too honourable a man,” said Sister Marie, “to have confessed so great a lie; but even should he have done so, bring him here before me, and I will prove the contrary of what he says.”
The Prior, finding that he could in no wise move her, thereupon said—
“I am your father, and seek to save your honour. For this reason I will leave the truth of the matter to your own conscience, and will believe whatever it bids you say. I ask you and conjure you on pain of mortal sin to tell me truly whether you were indeed a virgin when you were placed in this house?”
“My father,” she replied, “I was then but five years old, and that age must in itself testify to my virginity.”
“Well, my daughter,” said the Prior, “have you not since that time lost this flower?”
She swore that she had kept it, and that she had had no hindrance in doing so except from himself. Whereto he replied that he could not believe it, and that the matter required proof.
“What proof,” she asked, “would you have?”
“The same as from the others,” said the Prior; “for as I am visitor of souls, even so am I visitor of bodies also. Your abbesses and prioresses have all passed through my hands, and you need have no fear if I visit your virginity. Wherefore throw yourself upon the bed, and lift the forepart of your garments over your face.”
“You have told me so much of your wicked love for me,” Sister Marie replied in wrath, “that I think you seek rather to rob me of my virginity than to visit it. So understand that I shall never consent.”
Thereupon he said to her that she was excommunicated for refusing him the obedience which Holy Church commanded, and that, if she did not consent, he would dishonour her before the whole Chapter by declaring the evil that he knew of between herself and the confessor.
But with fearless countenance she replied—
“He that knows the hearts of His servants shall give me as much honour in His presence as you can give me shame in the presence of men; and since your wickedness goes so far, I would rather it wreaked its cruelty upon me than its evil passion; for I know that God is a just judge.”
Then the Prior departed and assembled the whole Chapter, and, causing Sister Marie to appear on her knees before him, he said to her with wondrous malignity—
“Sister Marie, it grieves me to see that the good counsels I have given you have been of no effect, and to find you fallen into such evil ways that, contrary to my wont, I must needs lay a penance upon you. I have examined your confessor concerning certain crimes with which he is charged, and he has confessed to me that he has abused your person in the place where the witnesses say that they saw him. And so I command that, whereas I had formerly raised you to honourable rank as Mistress of the Novices, you shall now be the lowest placed of all, and further, shall eat only bread and water on the ground, and in presence of all the Sisters, until you have shown sufficient penitence to receive forgiveness.”
Sister Marie had been warned by one of her companions, who was acquainted with the whole matter, that if she made any reply displeasing to the Prior, he would put her in pace—that is, in perpetual imprisonment—and she therefore submitted to this sentence, raising her eyes to heaven, and praying Him who had enabled her to withstand sin, to grant her patience for the endurance of tribulation. The Prior of St. Martin’s further commanded that for the space of three years she should neither speak with her mother or kinsfolk when they came to see her, nor send any letters save such as were written in community.
The miscreant then went away and returned no more, and for a long time the unhappy maiden continued in the tribulation that I have described. But her mother, who loved her best of all her children, was much astonished at receiving no tidings from her; and told one of her sons, who was a prudent and honourable gentleman, (6) that she thought her daughter was dead, and that the nuns were hiding it from her in order that they might receive the yearly payment. She, therefore, begged him to devise some means of seeing his sister.
6 It is conjectured by M. Lacroix that this “prudent and
honourable gentleman,” Mary Heroet’s brother, was Antoine
Heroet or Hérouet, alias La Maisonneuve, who at one time was
a valet and secretary to Queen Margaret, and so advanced
himself in life that he died Bishop of Digne in 1544. He was
the author of La Parfaite Amie, L’Androgyne, and De n’aimer
point sans être aimé, poems of a semi-metaphysical, semi-
amorous character such as might have come from Margaret’s
own pen. Whether he was Mary Heroet’s brother or not, it is
at least probable that he was her relative.-B. J. and L.
He went forthwith to the convent, where he met with the wonted excuses, being told that for three years his sister had not stirred from her bed. But this did not satisfy him, and he swore that, if he did not see her, he would climb over the walls and force his way into the convent. Thereupon, being in great fear, they brought his sister to him at the grating, though the Abbess stood so near that she could not tell her brother aught that was not heard. But she had prudently set down in writing all that I have told you, together with a thousand others of the Prior’s devices to deceive her, which ‘twould take too long to relate.
Yet I must not omit to mention that at the time when her aunt was Abbess, the Prior, thinking that his ugliness was the cause of her refusal, had caused Sister Marie to be tempted by a handsome young monk, in the hope that if she yielded to this man through love, he himself might afterwards obtain her through fear. The young monk aforesaid spoke to her in a garden with gestures too shameful to be mentioned, whereat the poor maiden ran to the Abbess, who was talking with the Prior, and cried out—
“Mother, they are not monks, but devils, who visit us here!”
Thereupon the Prior, in great fear of discovery, began to laugh, and said—
“Assuredly, mother, Sister Marie is right.”
Then, taking Sister Marie by the hand, he said to her in presence of the Abbess—
“I had heard that Sister Marie spoke very well, and so constantly that she was deemed to be worldly-minded. For this reason I constrained myself, contrary to my natural inclination, to speak to her in the way that worldly men speak to women—at least in books, for in point of experience I am as ignorant as I was on the day when I was born. Thinking, however, that only my years and ugliness led her to discourse in so virtuous a fashion, I commanded my young monk to speak to her as I myself had done, and, as you see, she has virtuously resisted him. So highly, therefore, do I think of her prudence and virtue, that henceforward she shall rank next after you and shall be Mistress of the Novices, to the intent that her excellent disposition may ever increase in virtue.”
This act, with many others, was done by this worthy monk during the three years that he was in love with the nun. She, however, as I have said, gave her brother in writing, through the grating, the whole story of her pitiful fortunes; and this her brother brought to her mother, who came, overwhelmed with despair, to Paris. Here she found the Queen of Navarre, only sister to the King, and showing her the piteous story, said—
“Madam, trust no more in these hypocrites. I thought that I had placed my daughter within the precincts of Paradise, or on the high road thither, whereas I have placed her in the precincts of Hell, and in the hands of the vilest devils imaginable. The devils, indeed, do not tempt us unless temptation be our pleasure, but these men will take by force when they cannot win by love.”
The Queen of Navarre was in great concern, for she trusted wholly in the Prior of St. Martin’s, to whose care she had committed her sisters-inlaw, the Abbesses of Montivilliers and Caen. (7) On the other hand, the enormity of the crime so horrified her and made her so desirous of avenging the innocence of this unhappy maiden, that she communicated the matter to the King’s Chancellor, who happened also to be Legate in France. (8)
7 The abbess of Montivilliers was Catherine d’Albret,
daughter of John d’Albret, King of Navarre and sister of
Queen Margaret’s husband, Henry. At first a nun at the abbey
of St. Magdalen at Orleans, she became twenty-eighth abbess
of Montivilliers near Havre. She was still living in 1536.
(Gallia Christ., vol. xi. col. 285). The abbess of Caen
was Magdalen d’Albret, Catherine’s sister. She took the veil
at Fontevrault in 1527, subsequently became thirty-third
abbess of the Trinity at Caen, and died in November 1532.
(Gallia Christ., vol. xi. col. 436).—L.
8 This is the famous Antony Duprat, Francis I.‘s favourite
minister. Born in 1463, he became Chancellor in 1515, and
his wife dying soon afterwards, he took orders, with the
result that he was made Archbishop of Sens and Cardinal. It
was in 1530 that he was appointed Papal Legate in France, so
that the incidents related in this tale cannot have occurred
at an earlier date. Duprat died in July 1535, of grief, it
is said, because Francis I. would not support him in his
ambitious scheme to secure possession of the papal see, as
successor to Clement VII.-B. J. and Ed.
The Prior was sent for, but could find nothing to plead except that he was seventy years of age, and addressing himself to the Queen of Navarre he begged that, for all the good she had ever wished to do him, and in token of all the services he had rendered or had desired to render her, she would be pleased to bring these proceedings to a close, and he would acknowledge that Sister Marie was a pearl of honour and chastity.
On hearing this, the Queen of Navarre was so astonished that she could make no reply, but went off and left him there. The unhappy man then withdrew in great confusion to his monastery, where he would suffer none to see him, and where he lived only one year afterwards. And Sister Marie Heroet, now reputed as highly as she deserved to be, by reason of the virtues that God had given her, was withdrawn from the convent of Gif, where she had endured so much evil, and was by the King made Abbess of the the convent of Giy (9) near Montargis.
9 Giy-les-Nonains, a little village on the river Ouanne, at
two leagues and a half from Montargis, department of the
Loiret.—L.
This convent she reformed, and there she lived like one filled with the Spirit of God, whom all her life long she ever praised for having of His good grace restored to her both honour and repose.
“There, ladies, you have a story which clearly proves the words of the Gospel, that ‘God hath chosen the weak things of the world to confound the things which are mighty, and things which are despised of men hath God chosen to bring to nought the glory of those who think themselves something but are in truth nothing.’ (10) And remember, ladies, that without the grace of God there is no good at all in man, just as there is no temptation that with His assistance may not be overcome. This is shown by the abasement of the man who was accounted just, and the exaltation of her whom men were willing to deem a wicked sinner. Thus are verified Our Lord’s words, ‘Whosoever exalteth himself shall be abased; and he that humbleth himself shall be exalted.’” (11)
10 I Corinthians i. 27, 28, slightly modified.
11 St. Luke xiv. 11 and xviii. 14.
“Alas,” said Oisille, “how many virtuous persons did that Prior deceive! For I saw people put more trust in him than even in God.”
“I should not have done so,” said Nomerfide, “for such is my horror of monks that I could not confess to one. I believe they are worse than all other men, and never frequent a house without leaving disgrace or dissension behind them.”
“There are good ones among them,” said Oisille, “and they ought not to be judged by the bad alone; but the best are those that least often visit laymen’s houses and women.”
“You are right,” said Ennasuite. “The less they are seen, the less they are known, and therefore the more highly are they esteemed; for companionship with them shows what they really are.”
“Let us say no more about them,” said Nomerfide, “and see to whom Geburon will give his vote.”
“I shall give it,” said he, “to Madame Oisille, that she may tell us something to the credit of Holy Church.” (12)
12 In lieu of this phrase, the De Thou MS. of the
Heptameron gives the following: “To make amends for his
fault, if fault there were in laying bare the wretched and
abominable life of a wicked Churchman, so as to put others
on their guard against the hypocrisy of those resembling
him, Geburon, who held Madame Oysille in high esteem, as one
should hold a lady of discretion, who was no less reluctant
to speak evil than prompt to praise and publish the worth
which she knew to exist in others, gave her his vote,
begging her to tell something to the honour of our holy
religion.”—L.
“We have sworn,” said Oisille, “to speak the truth, and I cannot therefore undertake such a task. Moreover, in telling your tale you have reminded me of a very pitiful story which I feel constrained to relate, seeing that I am not far from the place where, in my own time, the thing came to pass. I shall tell it also, ladies, to the end that the hypocrisy of those who account themselves more religious than their neighbours, may not so beguile your understanding as to turn your faith out of the right path, and lead you to hope for salvation from any other than Him who has chosen to stand alone in the work of our creation and redemption. He is all powerful to save us unto life eternal, and, in this temporal life, to comfort us and deliver us from all our tribulations. And knowing that Satan often transforms himself into an angel of light so that the outward eye, blinded by the semblance of holiness and devotion, cannot apprehend that from which we ought to flee, I think it well to tell you this tale, which came to pass in our own time.”



The excessive reverence shown by a gentleman of Périgord to
the Order of St. Francis, brought about the miserable death
of his wife, his little child and himself. (1)
1 Etienne introduces this tale into his Apologie pour
Hérodote, ch. xxi.—B. J.
In the county of Périgord dwelt a gentleman whose devotion to St. Francis was such that in his eyes all who wore the saint’s robe must needs be as holy as the saint himself. To do honour to the latter, he had caused rooms and closets to be furnished in his house for the lodgment of the brethren, and he regulated all his affairs by their advice, even to the most trifling household matters, believing that he must needs pursue the right path if he followed their good counsels.
Now it happened that this gentleman’s wife, who was a beautiful woman and as discreet as she was virtuous, was brought to bed of a fine boy, whereat the love which her husband bore her was increased twofold. One day, in order to entertain his dear, he sent for one of his brothers-in-law, and just as the hour for supper was drawing nigh, there arrived also a Grey Friar, whose name I will keep secret out of regard for his Order. The gentleman was well pleased to see his spiritual father, from whom he had no secrets, and after much talk among his wife, his brother-in-law and the monk, they sat down to supper. While they were at table the gentleman cast his eyes upon his wife, who was indeed beautiful and graceful enough to be desired of a husband, and thereupon asked this question aloud of the worthy father—
“Is it true, father, that a man commits mortal sin if he lies with his wife at the time of her lying-in?” (2)
2 Meaning the period between her delivery and her
churching.—Ed.
The worthy father, whose speech and countenance belied his heart, answered with an angry look—
“Undoubtedly, sir, I hold this to be one of the very greatest sins that can be committed in the married state. The blessed Virgin Mary would not enter the temple until the days of her purification were accomplished, although she had no need of these; and if she, in order to obey the law, refrained from going to the temple wherein was all her consolation, you should of a surety not fail to abstain from such slight pleasure. Moreover, physicians say that there is great risk to the offspring so begotten.”
When the gentleman heard these words, he was greatly downcast, for he had hoped that the good Friar would give him the permission he sought; however, he said no more. Meanwhile the worthy father, who had drunk more than was needful, looked at the lady, (3) thinking to himself that, if he were her husband, he would ask no Friar’s advice before lying with her; and just as a fire kindles little by little until at last it envelops the whole house, so this monk began to burn with such exceeding lust that he suddenly resolved to satisfy a desire which for three years he had carried hidden in his heart.
3 The French word here is damoiselle, by which
appellation the lady is called throughout the story. Her
husband, being a petty nobleman, was a damoiseau, whence
the name given to his wife. The word damoiselle is
frequently employed in the Heptameron, and though
sometimes it merely signifies an attendant on a lady, the
reference is more frequently to a woman of gentle birth,
whether she be spinster, wife or widow. Only women of high
nobility and of the blood royal were at that time called
Madame.—Ed.
After the tables had been withdrawn, he took the gentleman by the hand, and, leading him to his wife’s bedside, (4) said to him in her presence—
“It moves my pity, sir, to see the great love which exists between you and this lady, and which, added to your extreme youth, torments you so sore. I have therefore determined to tell you a secret of our sacred theology which is that, although the rule be made thus strict by reason of the abuses committed by indiscreet husbands, it does not suffer that such as are of good conscience like you should be balked of all intercourse. If then, sir, before others I have stated in all its severity the command of the law, I will now reveal to you, who are a prudent man, its mildness also. Know then, my son, that there are women and women, just as there are men and men. In the first place, my lady here must tell us whether, three weeks having gone by since her delivery, the flow of blood has quite ceased?”
4 The supper would appear to have been served in the
bedroom, and the tables were taken away as soon as the
repast was over. It seems to us very ridiculous when on the
modern stage we see a couple of lackeys bring in a table
laden with viands and carry it away again as soon as the
dramatis personæ have dined or supped. Yet this was the
common practice in France in Queen Margaret’s time.—Ed.
The lady replied that it had.
“Then,” said the Friar, “I permit you to lie with her without scruple, provided that you are willing to promise me two things.”
The gentleman replied that he was willing.
“The first,” said the good father, “is that you speak to no one concerning this matter, but come here in secret. The second is that you do not come until two hours after midnight, so that the good lady’s digestion be not hindered.”
These things the gentleman promised; and he confirmed his promise with so strong an oath that the other, knowing him to be foolish rather than false, was quite satisfied.
After much converse the good father withdrew to his chamber, giving them good-night and an abundant blessing. But, as he was going, he took the gentleman by the hand, and said to him—
“You too, sir, i’ faith must come, nor keep your poor lady longer awake.”
Thereupon the gentleman kissed her. “Sweetheart,” said he, and the good father heard him plainly, “leave the door of your room open for me.”
And so each withdrew to his own chamber.
On leaving them the Friar gave no heed to sleep or to repose, and, as soon as all the noises in the house were still, he went as softly as possible straight to the lady’s chamber, at about the hour when he was wont to go to matins, and finding the door open in expectation of the master’s coming, he went in, cleverly put out the light, and speedily got into bed with the lady, without speaking a single word.
The lady, believing him to be her husband, said—
“How is this, love? you have kept but poorly the promise you gave last evening to our confessor that you would not come here before two o’clock.”
The Friar, who was more eager for action than for contemplation, and who, moreover, was fearful of being recognised, gave more thought to satisfying the wicked desires that had long poisoned his heart than to giving her any reply; whereat the lady wondered greatly. When the friar found the husband’s hour drawing near, he rose from the lady’s side and returned with all speed to his own chamber.
Then, just as the frenzy of lust had robbed him of sleep, so now the fear that always follows upon wickedness would not suffer him to rest. Accordingly, he went to the porter of the house and said to him—
“Friend, your master has charged me to go without delay and offer up prayers for him at our convent, where he is accustomed to perform his devotions. Wherefore, I pray you, give me my horse and open the door without letting any one be the wiser; for the mission is both pressing and secret.”
The porter knew that obedience to the Friar was service acceptable to his master, and so he opened the door secretly and let him out.
Just at that time the gentleman awoke. Finding that it was close on the hour which the good father had appointed him for visiting his wife, he got up in his bedgown and repaired swiftly to that bed whither by God’s ordinance, and without need of the license of man, it was lawful for him to go.
When his wife heard him speaking beside her, she was greatly astonished, and, not knowing what had occurred, said to him—
“Nay, sir, is it possible that, after your promise to the good father to be heedful of your own health and of mine, you not only come before the hour appointed, but even return a second time? Think on it, sir, I pray you.”
On hearing this, the gentleman was so much disconcerted that he could not conceal it, and said to her—
“What do these words mean? I know of a truth that I have not lain with you for three weeks, and yet you rebuke me for coming too often. If you continue to talk in this way, you will make me think that my company is irksome to you, and will drive me, contrary to my wont and will, to seek elsewhere that pleasure which, by the law of God, I should have with you.”
The lady thought that he was jesting, and replied—
“I pray you, sir, deceive not yourself in seeking to deceive me; for although you said nothing when you came, I knew very well that you were here.”
Then the gentleman saw that they had both been deceived, and solemnly vowed to her that he had not been with her before; whereat the lady, weeping in dire distress, besought him to find out with all despatch who it could have been, seeing that besides themselves only his brother-in-law and the Friar slept in the house.
Impelled by suspicion of the Friar, the gentleman forthwith went in all haste to the room where he had been lodged, and found it empty; whereupon, to make yet more certain whether he had fled, he sent for the man who kept the door, and asked him whether he knew what had become of the Friar. And the man told him the whole truth.
The gentleman, being now convinced of the Friar’s wickedness, returned to his wife’s room, and said to her—
“Of a certainty, sweetheart, the man who lay with you and did such fine things was our Father Confessor.”
The lady, who all her life long had held her honour dear, was overwhelmed with despair, and laying aside all humanity and womanly nature, besought her husband on her knees to avenge this foul wrong; whereupon the gentleman immediately mounted his horse and went in pursuit of the Friar.
The lady remained all alone in her bed, with no counsel or comfort near her but her little newborn child. She reflected upon the strange and horrible adventure that had befallen her, and, without making any excuse for her ignorance, deemed herself guilty as well as the unhappiest woman in the world. She had never learned aught of the Friars, save to have confidence in good works, and seek atonement for sins by austerity of life, fasting and discipline; she was wholly ignorant of the pardon granted by our good God through the merits of His Son, the remission of sins by His blood, the reconciliation of the Father with us through His death, and the life given to sinners by His sole goodness and mercy; and so, assailed by despair based on the enormity and magnitude of her sin, the love of her husband and the honour of her house, she thought that death would be far happier than such a life as hers. And, overcome by sorrow, she fell into such despair that she was not only turned aside from the hope which every Christian should have in God, but she forgot her own nature, and was wholly bereft of common sense.
Then, overpowered by grief, and driven by despair from all knowledge of God and herself, this frenzied, frantic woman took a cord from the bed and strangled herself with her own hands.
And worse even than this, amidst the agony of this cruel death, whilst her body was struggling against it, she set her foot upon the face of her little child, whose innocence did not avail to save it from following in death its sorrowful and suffering mother. While dying, however, the infant uttered so piercing a cry that a woman who slept in the room rose in great haste and lit the candle. Then, seeing her mistress hanging strangled by the bed-cord, and the child stifled and dead under her feet, she ran in great affright to the apartment of her mistress’s brother, and brought him to see the pitiful sight.
The brother, after giving way to such grief as was natural and fitting in one who loved his sister with his whole heart, asked the serving-woman who it was that had committed this terrible crime.
She replied that she did not know; but that no one had entered the room excepting her master, and he had but lately left it. The brother then went to the gentleman’s room, and not finding him there, felt sure that he had done the deed. So, mounting his horse without further inquiry, he hastened in pursuit and met with him on the road as he was returning disconsolate at not having been able to overtake the Grey Friar.
As soon as the lady’s brother saw his brother-in-law, he cried out to him—
“Villain and coward, defend yourself, for I trust that God will by this sword avenge me on you this day.”
The gentleman would have expostulated, but his brother-in-law’s sword was pressing so close upon him that he found it of more importance to defend himself than to inquire the reason of the quarrel; whereupon each dealt the other so many wounds that they were at last compelled by weariness and loss of blood to sit down on the ground face to face.
And while they were recovering breath, the gentleman asked—
“What cause, brother, has turned our deep and unbroken friendship to such cruel strife as this?”
“Nay,” replied the brother-in-law, “what cause has moved you to slay my sister, the most excellent woman that ever lived, and this in so cowardly a fashion that under pretence of sleeping with her you have hanged and strangled her with the bed-cord?”
On hearing these words the gentleman, more dead than alive, came to his brother, and putting his arms around him, said—
“Is it possible that you have found your sister in the state you say?”
The brother-in-law assured him that it was indeed so.
“I pray you, brother,” the gentleman thereupon replied, “hearken to the reason why I left the house.”
Forthwith he told him all about the wicked Grey Friar, whereat his brother-in-law was greatly astonished, and still more grieved that he should have unjustly attacked him.
Entreating pardon, he said to him—
“I have wronged you; forgive me.”
“If you were ever wronged by me,” replied the gentleman, “I have been well punished, for I am so sorely wounded that I cannot hope to recover.”
Then the brother-in-law put him on horseback again as well as he might, and brought him back to the house, where on the morrow he died. And the brother-in-law confessed in presence of all the gentleman’s relatives that he had been the cause of his death.
However, for the satisfaction of justice, he was advised to go and solicit pardon from King Francis, first of the name; and accordingly, after giving honourable burial to husband, wife and child, he departed on Good Friday to the Court in order to sue there for pardon, which he obtained through the good offices of Master Francis Olivier, then Chancellor of Alençon, afterwards chosen by the King, for his merits, to be Chancellor of France. (5)
5 M. de Montaiglon has vainly searched the French Archives
for the letters of remission granted to the gentleman. There
is no mention of them in the registers of the Trésor des
Chartes. Francis Olivier, alluded to above, was one of the
most famous magistrates of the sixteenth century. Son of
James Olivier, First President of the Parliament of Paris
and Bishop of Angers, he was born in 1493 and became
successively advocate, member of the Grand Council,
ambassador, Chancellor of Alençon, President of the Paris
Parliament, Keeper of the Seals and Chancellor of France.
This latter dignity was conferred upon him through Queen
Margaret’s influence in April 1545. The above tale must have
been written subsequent to that date. Olivier’s talents were
still held in high esteem under both Henry II. and Francis
II.; he died in 1590, aged 67.—(Blanchard’s Éloges de tous
les Présidents du Parlement, &c., Paris, 1645, in-fol. p.
185.)
Ste. Marthe, in his funeral oration on Queen Margaret,
refers to Olivier in the following pompous strain: “When
Brinon died Chancellor of this duchy of Alençon, Francis
Olivier was set in his place, and so greatly adorned this
dignity by his admirable virtues, and so increased the
grandeur of the office of Chancellor, that, like one of
exceeding merit on whom Divine Providence, disposing of the
affairs of France, has conferred a more exalted office, he
is today raised to the highest degree of honour, and, even
as Atlas upholds the Heavens upon his shoulders, so he by
his prudence doth uphold the entire Gallic commonwealth.”—
M. L. and Ed.
“I am of opinion, ladies, that after hearing this true story there is none among you but will think twice before lodging such knaves in her house, and will be persuaded that hidden poison is always the most dangerous.”
“Remember,” said Hircan, “that the husband was a great fool to bring such a gallant to sup with his fair and virtuous wife.”
“I have known the time,” said Geburon, “when in our part of the country there was not a house but had a room set apart for the good fathers; but now they are known so well that they are dreaded more than bandits.”
“It seems to me,” said Parlamente, “that when a woman is in bed she should never allow a priest to enter the room, unless it be to administer to her the sacraments of the Church. For my own part, when I send for them, I may indeed be deemed at the point of death.”
“If every one were as strict as you are,” said Ennasuite, “the poor priests would be worse than excommunicated, in being wholly shut off from the sight of women.”
“Have no such fear on their account,” said Saffredent; “they will never want for women.”
“Why,” said Simontault, “‘tis the very men that have united us to our wives by the marriage tie that wickedly seek to loose it and bring about the breaking of the oath which they have themselves laid upon us.”
“It is a great pity,” said Oisille, “that those who administer the sacraments should thus trifle with them. They ought to be burned alive.”
“You would do better to honour rather than blame them,” said Saffredent, “and to flatter rather than revile them, for they are men who have it in their power to burn and dishonour others. Wherefore ‘sinite eos,’ and let us see to whom Oisille will give her vote.”
“I give it,” said she, “to Dagoucin, for he has become so thoughtful that I think he must have made ready to tell us something good.”
“Since I cannot and dare not reply as I would,” said Dagoucin, “I will at least tell of a man to whom similar cruelty at first brought hurt but afterwards profit. Although Love accounts himself so strong and powerful that he will go naked, and finds it irksome, nay intolerable, to go cloaked, nevertheless, ladies, it often happens that those who, following his counsel, are over-quick in declaring themselves, find themselves the worse for it. Such was the experience of a Castilian gentleman, whose story you shall now hear.”



Elisor, having unwisely ventured to discover his love to
the Queen of Castile, was by her put to the test in so cruel
a fashion that he suffered sorely, yet did he reap advantage
therefrom.
In the household of the King and Queen of Castile, (1) whose names shall not be mentioned, there was a gentleman of such perfection in all qualities of mind and body, that his like could not be found in all the Spains. All wondered at his merits, but still more at the strangeness of his temper, for he had never been known to love or have connection with any lady. There were very many at Court that might have set his icy nature afire, but there was not one among them whose charms had power to attract Elisor; for so this gentleman was called.
1 M. Lacroix conjectures that the sovereigns referred to
are Ferdinand and Isabella, but this appears to us a
baseless supposition. The conduct of the Queen in the story
is in no wise in keeping with what we know of Isabella’s
character. Queen Margaret doubtless heard this tale during
her sojourn in Spain in 1525. We have consulted many Spanish
works, and notably collections of the old ballads, in the
hope of being able to throw some light on the incidents
related, but have been no more successful than previous
commentators.—Ed.
The Queen, who was a virtuous woman but by no means free from that flame which proves all the fiercer the less it is perceived, was much astonished to find that this gentleman loved none of her ladies; and one day she asked him whether it were possible that he could indeed love as little as he seemed to do.
He replied that if she could look upon his heart as she did his face, she would not ask him such a question. Desiring to know his meaning, she pressed him so closely that he confessed he loved a lady whom he deemed the most virtuous in all Christendom. The Queen did all that she could by entreaties and commands to find out who the lady might be, but in vain; whereupon, feigning great wrath, she vowed that she would never speak to him any more if he did not tell her the name of the lady he so dearly loved. At this he was greatly disturbed, and was constrained to say that he would rather die, if need were, than name her.
Finding, however, that he would lose the Queen’s presence and favour in default of telling her a thing in itself so honourable that it ought not to be taken in ill part by any one, he said to her in great fear—
“I cannot and dare not tell you, madam, but the first time you go hunting I will show her to you, and I feel sure that you will deem her the fairest and most perfect lady in the world.”
This reply caused the Queen to go hunting sooner than she would otherwise have done.
Elisor, having notice of this, made ready to attend her as was his wont, and caused a large steel mirror after the fashion of a corselet to be made for him, which he placed upon his breast and covered with a cloak of black frieze, bordered with purflew and gold braid. He was mounted on a coal-black steed, well caparisoned with everything needful to the equipment of a horse, and such part of this as was metal was wholly of gold, wrought with black enamel in the Moorish style. (2)
2 Damascened.—Ed.
His hat was of black silk, and to it was fastened a rich medal on which by way of device was engraved the god of Love subdued by Force, the whole enriched with precious stones. His sword and dagger were no less handsomely and choicely ordered. In a word, he was most bravely equipped, while so skilled was his horsemanship that all who saw him left the pleasures of the chase to watch the leaps and paces of his steed.
After bringing the Queen in this fashion to the place where the nets were spread, he dismounted from his noble horse and went to assist the Queen to alight from her palfrey. And whilst she was stretching out her hands to him, he threw his cloak back from before his breast, and taking her in his arms, showed her his corselet-mirror, saying—
“I pray you, madam, look here.”
Then, without waiting for her reply, he set her down gently upon the ground.
When the hunt was over, the Queen returned to the castle without speaking to Elisor, but after supper she called him to her and told him that he was the greatest liar she had ever seen; for he had promised to show her at the hunt the lady whom he loved the best, but had not done so, for which reason she was resolved to hold him in esteem no more.
Elisor, fearing that the Queen had not understood the words he had spoken to her, answered that he had indeed obeyed her, for he had shown her not merely the woman but the thing also, that he loved best in all the world.
Pretending that she did not understand him, she replied that he had not, to her knowledge, shown her a single one among her ladies.
“That is true, madam,” said Elisor, “but what did I show you when I helped you off your horse?”
“Nothing,” said the Queen, “except a mirror on your breast.”
“And what did you see in the mirror?” said Elisor.
“I saw nothing but myself,” replied the Queen.
“Then, madam,” said Elisor, “I have kept faith with you and obeyed your command. There is not, nor ever will there be, another image in my heart save that which you saw upon my breast. Her alone will I love, reverence and worship, not as a woman merely, but as my very God on earth, in whose hands I place my life or my death, entreating her withal that the deep and perfect affection, which was my life whilst it remained concealed, may not prove my death now that it is discovered. And though I be not worthy that you should look on me or accept me for your lover, at least suffer me to live, as hitherto, in the happy consciousness that my heart has chosen so perfect and so worthy an object for its love, wherefrom I can have no other satisfaction than the knowledge that my love is deep and perfect, seeing that I must be content to love without hope of return. And if, now knowing this great love of mine, you should not be pleased to favour me more than heretofore, at least do not deprive me of life, which for me consists wholly in the delight of seeing you as usual. I now have from you nought but what my utmost need requires, and should I have less, you will have a servant the less, for you will lose the best and most devoted that you have ever had or could ever look to have.”
The Queen—whether to show herself other than she really was, or to thoroughly try the love he bore her, or because she loved another whom she would not cast off, or because she wished to hold him in reserve to put him in the place of her actual lover should the latter give her any offence—said to him, with a countenance that showed neither anger nor content—“Elisor, I will not feign ignorance of the potency of love, and say aught to you concerning your foolishness in aiming at so high and hard a thing as the love of me; for I know that man’s heart is so little under his own control, that he cannot love or hate at will. But, since you have concealed your feelings so well, I would fain know how long it is since you first entertained them.”
Elisor, gazing at her beauteous face and hearing her thus inquire concerning his sickness, hoped that she might be willing to afford him a remedy. But at the same time, observing the grave and staid expression of her countenance, he became afraid, feeling himself to be in the presence of a judge whose sentence, he suspected, would be against him. Nevertheless he swore to her that this love had taken root in his heart in the days of his earliest youth, though it was only during the past seven years that it had caused him pain,—and yet, in truth, not pain, but so pleasing a sickness that its cure would be his death.
“Since you have displayed such lengthened steadfastness,” said the Queen, “I must not show more haste in believing you, than you have shown in telling me of your affection. If, therefore, it be as you say, I will so test your sincerity that I shall never afterwards be able to doubt it; and having proved your pain, I will hold you to be towards me such as you yourself swear you are; and on my knowing you to be what you say, you, for your part, shall find me to be what you desire.”
Elisor begged her to test him in any way she pleased, there being nothing, he said, so difficult that it would not appear very easy to him, if he might have the honour of proving his love to her; and accordingly he begged her once more to command him as to what she would to have him do.
“Elisor,” she replied, “if you love me as much as you say, I am sure that you will deem nothing hard of accomplishment if only it may bring you my favour. I therefore command you, by your desire of winning it and your fear of losing it, to depart hence to-morrow morning without seeing me again, and to repair to some place where, until this day seven years, you shall hear nothing of me nor I anything of you. You, who have had seven years’ experience of this love, know that you do indeed love me; and when I have had a like experience, I too shall know and believe what your words cannot now make me either believe or understand.”
When Elisor heard this cruel command, he on the one hand suspected that she desired to remove him from her presence, yet, on the other, he hoped that this proof would plead more eloquently for him than any words he could utter. He therefore submitted to her command, and said—
“For seven years I have lived hopeless, bearing in my breast a hidden flame; now, however, that this is known to you, I shall spend these other seven years in patience and trust. But, madam, while I obey your command, which robs me of all the happiness that I have heretofore had in the world, what hope will you give me that at the end of the seven years you will accept me as your faithful and devoted lover?”
“Here is a ring,” said the Queen, drawing one from her finger, “which we will cut in two. I will keep one half, and you shall keep the other, (3) so that I may know you by this token, if the lapse of time should cause me to forget your face.”
3 This was a common practice at the time between lovers, and
even between husbands and wives. There is the familiar but
doubtful story of Frances de Foix, Countess of
Châteaubriant, who became Francis I.‘s mistress, and who is
said to have divided a ring in this manner with her husband,
it being understood between them that she was not to repair
to Court, or even leave her residence in Brittany, unless
her husband sent her as a token the half of the ring which
he had kept. Francis I., we are told, heard of this, and
causing a ring of the same pattern to be made, he sent half
of it to the Countess, who thereupon came to Court,
imagining that it was her husband who summoned her. Whether
the story be true or not, it should be mentioned that the
sole authority for it is Varillas, whose errors and
inventions are innumerable.—Ed.
Elisor took the ring and broke it in two, giving one half of it to the Queen, and keeping the other himself. Then, more corpse-like than those who have given up the ghost, he took his leave, and went to his lodging to give orders for his departure. In doing this he sent all his attendants to his house, and departed alone with one servingman to so solitary a spot that none of his friends or kinsfolk could obtain tidings of him during the seven years.
Of the life that he led during this time, and the grief that he endured through this banishment, nothing is recorded, but lovers cannot be ignorant of their nature. At the end of the seven years, just as the Queen was one day going to mass, a hermit with a long beard came to her, kissed her hand, and presented her with a petition. This she did not look at immediately, although it was her custom to receive in her own hands all the petitions that were presented to her, no matter how poor the petitioners might be.
When mass was half over, however, she opened the petition, and found in it the half-ring which she had given to Elisor. At this she was not less glad than astonished, and before reading the contents she instantly commanded her almoner to bring her the tall hermit who had presented her the petition.
The almoner looked for him everywhere, but could obtain no tidings of him, except that some one said that he had seen him mount a horse, but knew not what road he had taken.
Whilst she was waiting for the almoner’s return, the Queen read the petition, which she found to be an epistle in verse, written in the best style imaginable; and were it not that I would have you acquainted with it, I should never have dared to translate it; for you must know, ladies, that, for grace and expression, the Castilian is beyond compare the tongue which is best fitted to set forth the passion of love. The matter of the letter was as follows:—
“Time, by his puissance stern, his sov’reign might,
Hath made me learn love’s character aright;
And, bringing with him, in his gloomy train,
The speechless eloquence of bitter pain,
Hath caused the unbelieving one to know
What words of love were impotent to show.
Time made my heart, aforetime, meekly bow
Unto the mastery of love; but now
Time hath, at last, revealed love to be
Far other than it once appeared to me;
And Time the frail foundation hath made clear
Whereon I purposed, once, my love to rear—
To wit, your beauty, which but served as sheath
To hide the cruelty that lurked beneath.
Yea, Time hath shown me beauty’s nothingness
And taught me e’en your cruelty to bless,
That cruelty which banished me the place
Where I, at least, had gazed upon your face.
And when no more I saw your beauty beam
The harsher yet your cruelty did seem;
Yet in obedience failed I not, and this
Hath been the means of compassing my bliss.
For Time, love’s parent, pitiful at last,
Upon my woe commiserate eyes hath cast,
And done to me so excellent a turn,
That, if I now come back, think not I yearn
To sigh and dally, and renew the spell—
I only come to bid a last farewell.
Time, the revealer, hath not failed to prove
How base and sorry is all human love,
So that through Time, I now that time regret
When all my fancy upon love was set,
For then Time wasted was, lost in love’s chains,
Sorrow whereof is all that now remains.
And Time in teaching me that love’s deceit
Hath brought another, far more pure and sweet,
To dwell within me, in the lonely spot
Where tears and silence long have been my lot.
Time, to my heart, that higher love hath brought
With which the lower can no more be sought;
Time hath the latter into exile driven,
And, to the first, myself hath wholly given,
And consecrated to its service true
The heart and hand I erst had given to you.
When I was yours you nothing showed of grace,
And I that nothing loved, for your fair face;
Then, death for loyalty, you sought to give,
And I, in fleeing it, have learnt to live.
For, by the tender love that Time hath brought
The other vanquished is, and turned to nought;
Once did it lure and lull me, but I swear
It now hath wholly vanished in thin air.
And so your love and you I gladly leave,
And, needing neither, will forbear to grieve;
The other perfect, lasting love is mine,
To it I turn, nor for the lost one pine.
My leave I take of cruelty and pain,
Of hatred, bitter torment, cold disdain,
And those hot flames which fill you, and which fire
Him, that beholds your beauty, with desire.
Nor can I better part from ev’ry throe,
From ev’ry evil hap, and stress of woe,
And the fierce passion of love’s awful hell,
Than by this single utterance: Farewell.
Learn therefore, that whate’er may be in store,
Each other’s faces we shall see no more.”
This letter was not read without many tears and much astonishment on the Queen’s part, together with regret surpassing belief; for the loss of a lover filled with so perfect a love must needs have been keenly felt; and not all her treasures, nor even her kingdom itself, could hinder the Queen from being the poorest and most wretched lady in the world, seeing that she had lost that which all the world’s wealth could not replace. And having heard mass to the end and returned to her apartment, she there made such mourning as her cruelty had provoked. And there was not a mountain, a rock or a forest to which she did not send in quest of the hermit; but He who had withdrawn him out of her hands preserved him from falling into them again, and took him away to Paradise before she could gain tidings of him in this world.
“This instance shows that a lover should never acknowledge that which may do him harm and in no wise help him. And still less, ladies, should you in your incredulity demand so hard a test, lest in getting your proof you lose your lover.”
“Truly, Dagoucin,” said Geburon, “I had all my life long deemed the lady of your story to be the most virtuous in the world, but now I hold her for the most cruel woman that ever lived.”
“Nevertheless,” said Parlamente, “it seems to me that she did him no wrong in wishing to try him for seven years, in order to see whether he did love her as much as he said. Men are so wont to speak falsely in these matters that before trusting them, if indeed one trust them at all, one cannot put them to the proof too long.”
“The ladies of our day,” said Hircan, “are far wiser than those of past times, for they are as sure of a lover after a seven days’ trial as the others were after seven years.”
“Yet there are those in this company,” said Longarine, “who have been loved with all earnestness for seven years and more, and albeit have not been won.”
“‘Fore God,” said Simontault, “you speak the truth; but such as they ought to be ranked with the ladies of former times, for they cannot be recognised as belonging to the present.”
“After all,” said Oisille, “the gentleman was much beholden to the lady, for it was owing to her that he devoted his heart wholly to God.”
“It was very fortunate for him,” said Saffredent, “that he found God upon the way, for, considering the grief he was in, I am surprised that he did not give himself to the devil.”
“And did you give yourself to such a master,” asked Ennasuite, “when your lady ill used you?”
“Yes, thousands of times,” said Saffredent, “but the devil, seeing that all the torments of hell could bring me no more suffering than those which she caused me to endure, never condescended to take me. He knew full well that no devil is so bad as a lady who is deeply loved and will make no return.”
“If I were you,” said Parlamente to Saffredent, “and held such an opinion as that, I would never make love to woman.”
“My affection,” said Saffredent, “and my folly are always so great, that where I cannot command I am well content to serve. All the ill-will of the ladies cannot subdue the love that I bear them. But, I pray you, tell me on your conscience, do you praise this lady for such great harshness?”
“Ay,” said Oisille, “I do, for I think that she wished neither to receive love nor to bestow it.”
“If such was her mind,” said Simontault, “why did she hold out to him the hope of being loved after the seven years were past?”
“I am of your opinion,” said Longarine, “for ladies who are unwilling to love give no occasion for the continuance of the love that is offered them.”
“Perhaps,” said Nomerfide, “she loved some one else less worthy than that honourable gentleman, and so forsook the better for the worse.”
“‘T faith,” said Saffredent, “I think that she meant to keep him in readiness and take him whenever she might leave the other whom for the time she loved the best.”
“I can see,” said Oisille, (4) “that the more we talk in this way, the more those who would not be harshly treated will do their utmost to speak ill of us. Wherefore, Dagoucin, I pray you give some lady your vote.”
4 Prior to this sentence the following passage occurs in
the De Thou MS.: “When Madame Oysille saw that the men,
under pretence of censuring the Queen of Castille for
conduct which certainly cannot be praised either in her or
in any other, continued saying so much evil of women, that
the most discreet and virtuous were spared no more than the
most foolish and wanton, she could endure it no longer, but
spoke and said,” &c.—L.
“I give it,” he said, “to Longarine, for I feel sure that she will tell us no melancholy story, and that she will speak the truth without sparing man or woman.”
“Since you deem me so truthful,” said Longarine, “I will be so bold as to relate an adventure that befel a very great Prince, who surpasses in worth all others of his time. Lying and dissimulation are, indeed, things not to be employed save in cases of extreme necessity; they are foul and infamous vices, more especially in Princes and great lords, on whose lips and features truth sits more becomingly than on those of other men. But no Prince in the world however great he be, even though he have all the honours and wealth he may desire, can escape being subject to the empire and tyranny of Love; indeed it would seem that the nobler and more high-minded the Prince, the more does Love strive to bring him under his mighty hand. For this glorious God sets no store by common things; his majesty rejoices solely in the daily working of miracles, such as weakening the strong, strengthening the weak, giving knowledge to the simple, taking intelligence from the most learned, favouring the passions, and overthrowing the reason. In such transformations as these does the Deity of Love delight. Now since Princes are not exempt from love’s thraldom, so also are they not free from its necessities, and must therefore perforce be permitted to employ falsehood, hypocrisy and deceit, which, according to the teaching of Master Jehan de Mehun, (5) are the means to be employed for vanquishing our enemies. And, since such conduct is praiseworthy on the part of a Prince in such a case as this (though in any other it were deserving of blame), I will relate to you the devices to which a young Prince resorted, and by which he contrived to deceive those who are wont to deceive the whole world.”
5 John dc Melun, who continued the Roman de la Rose begun
by Lorris.—D.



A young Prince, whilst pretending to visit his lawyer and
talk with him of his affairs, conversed so freely with the
lawyer’s wife, that he obtained from her what he desired.
In the city of Paris there dwelt an advocate who was more highly thought of than any other of his condition, (1) and who, being sought after by every one on account of his excellent parts, had become the richest of all those who wore the gown.
1 In five of the oldest MSS. of the Heptameron, and in
the original editions of 1558, 1559, and 1560, the words are
“than nine others of his condition.” The explanation of this
is, that the advocate’s name, as ascertained by Baron Jerome
Pichon, was Disome, which, written Dix-hommes, would
literally mean “ten men.” Baron Pichon has largely
elucidated this story, and the essential points of his
notice, contributed to the Mélanges de la Société des
Bibliophiles Français, will be found summarized in the
Appendix to this volume, B.—Ed.
Now, although he had had no children by his first wife, he was in hopes of having some by a second; for, although his body was no longer hearty, his heart and hopes were as much alive as ever. Accordingly, he made choice of one of the fairest maidens in the city; she was between eighteen and nineteen years of age, very handsome both in features and complexion, and still more handsome in figure. He loved her and treated her as well as could be; but he had no children by her any more than by his first wife, and this at last made her unhappy. And as youth cannot endure grief, she sought diversion away from home, and betook herself to dances and feasts; yet she did this in so seemly a fashion that her husband could not take it ill, for she was always in the company of women in whom he had trust.
One day, when she was at a wedding, there was also present a Prince of very high degree, who, when telling me the story, forbade me to discover his name. I may, however, tell you that he was the handsomest and most graceful Prince that has ever been or, in my opinion, ever will be in this realm. (2)
2 Francis L, prior to his accession.—Ed.
The Prince, seeing this fair and youthful lady whose eyes and countenance invited him to love her, came and spoke to her with such eloquence and grace that she was well pleased with his discourse.
Nor did she seek to hide from him that she had long had in her heart the love for which he prayed, but entreated that he would spare all pains to persuade her to a thing to which love, at first sight, had brought her to consent. Having, by the artlessness of love, so promptly gained what was well worth the pains of being won by time, the young Prince thanked God for His favour, and forthwith contrived matters so well that they agreed together in devising a means for seeing each other in private.
The young Prince failed not to appear at the time and place that had been agreed upon, and, that he might not injure his lady’s honour, he went in disguise. On account, however, of the evil fellows (3) who were wont to prowl at night through the city, and to whom he cared not to make himself known, he took with him certain gentlemen in whom he trusted.
3 The French expression here is mauvais garsons, a name
generally given to foot-pads at that time, but applied more
particularly to a large band of brigands who, in the
confusion prevailing during Francis I.‘s captivity in Spain,
began to infest the woods and forests around Paris, whence
at night-time they descended upon the city. Several
engagements were fought between them and the troops of the
Queen-Regent, and although their leader, called King
Guillot, was captured and hanged, the remnants of the band
continued their depredations for several years.—B. J.
And on entering the street in which the lady lived, he parted from them, saying—
“If you hear no noise within a quarter of an hour, go home again, and come back here for me at about three or four o’clock.”
They did as they were commanded, and, hearing no noise, withdrew.
The young Prince went straight to his advocate’s house, where he found the door open as had been promised him. But as he was ascending the staircase he met the husband, carrying a candle in his hand, and was perceived by him before he was aware. However Love, who provides wit and boldness to contend with the difficulties that he creates, prompted the young Prince to go straight up to him and say—
“Master advocate, you know the trust which I and all belonging to my house have ever put in you, and how I reckon you among my best and truest servants. I have now thought it well to visit you here in private, both to commend my affairs to you, and also to beg you to give me something to drink, for I am in great thirst. And, I pray you, tell none that I have come here, for from this place I must go to another where I would not be known.”
The worthy advocate was well pleased at the honour which the Prince paid him in coming thus privately to his house, and, leading him to his own room, he bade his wife prepare a collation of the best fruits and confections that she had.
Although the garments she wore, a kerchief and mantle, made her appear more beautiful than ever, the young Prince affected not to look at her or notice her, but spoke unceasingly to her husband about his affairs, as to one who had long had them in his hands. And, whilst the lady was kneeling with the confections before the Prince, and her husband was gone to the sideboard in order to serve him with drink, she told him that on leaving the room he must not fail to enter a closet which he would find on the right hand, and whither she would very soon come to see him.
As soon as he had drunk, he thanked the advocate, who was all eagerness to attend him; but the Prince assured him that in the place whither he was going he had no need of attendance, and thereupon turning to the wife, he said—
“Moreover, I will not do so ill as to deprive you of your excellent husband, who is also an old servant of mine. Well may you render thanks to God since you are so fortunate as to have such a husband, well may you render him service and obedience. If you did otherwise, you would be blameworthy indeed.”
With these virtuous words the young Prince went away, and, closing the door behind him so that he might not be followed to the staircase, he entered the closet, whither also came the fair lady as soon as her husband had fallen asleep.
Thence she led the Prince into a cabinet as choicely furnished as might be, though in truth there were no fairer figures in it than he and she, no matter what garments they may have been pleased to wear. And here, I doubt not, she kept word with him as to all that she had promised.
He departed thence at the hour which he had appointed with his gentlemen, and found them at the spot where he had aforetime bidden them wait.
As this intercourse lasted a fairly long time, the young Prince chose a shorter way to the advocate’s house, and this led him through a monastery of monks. (4) And so well did he contrive matters with the Prior, that the porter used always to open the gate for him about midnight, and do the like also when he returned. And, as the house which he visited was hard by, he used to take nobody with him.
4 If at this period Jane Disome, the heroine of the story,
lived in the Rue de la Pauheminerie, where she is known to
have died some years afterwards, this monastery, in Baron
Jerome Pichon’s opinion, would be the Blancs-Manteaux, in
the Marais district of Paris. We may further point out that
in the Rue Barbette, near by, there was till modern times a
house traditionally known as the “hôtel de la belle
Féronnière.” That many writers have confused the heroine of
this tale with La Belle Féronnière (so called because her
husband was a certain Le Féron, an advocate) seems manifest;
the intrigue in which the former took part was doubtless
ascribed in error to the latter, and the proximity of their
abodes may have led to the mistake. It should be pointed
out, however, that the amour here recorded by Queen Margaret
took place in or about the year 1515, before Francis I.
ascended the throne, whereas La Féronnière was in all her
beauty between 1530 and 1540. The tradition that the King
had an intrigue with La Féronnière reposes on the flimsiest
evidence (see Appendix B), and the supposition, re-echoed by
the Bibliophile Jacob, that it was carried on in the Rue de
l’Hirondelle, is entirely erroneous. The house, adorned with
the salamander device and corneted initials of Francis I.,
which formerly extended from that street to the Rue Git-le-
Coeur, never had any connection with La Féronnière. It was
the famous so-called Palace of Love which the King built for
his acknowledged mistress, Anne de Pisseleu, Duchess of
Étampes.—Ed.
Although he led the life that I have described, he was nevertheless a Prince that feared and loved God, and although he made no pause when going, he never failed on his return to continue for a long time praying in the church. And the monks, who when going to and fro at the hour of matins used to see him there on his knees, were thereby led to consider him the holiest man alive.
This Prince had a sister (5) who often visited this monastery, and as she loved her brother more than any other living being, she used to commend him to the prayers of all whom she knew to be good.
5 This of course is Queen Margaret, then Duchess of
Alençon. On account of her apparent intimacy with the prior,
M. de Montaiglon conjectures that the monastery may have
been that of St. Martin-in-the-Fields.—See ante, Tale
XXII.—Ed.
One day, when she was in this manner commending him lovingly to the Prior of the monastery, the Prior said to her—
“Ah, madam, whom are you thus commending to me? You are speaking to me of a man in whose prayers, above those of all others, I would myself fain be remembered. For if he be not a holy man and a just”—here he quoted the passage which says, “Blessed is he that can do evil and doeth it not”—“I cannot hope to be held for such.”
The sister, wishing to learn what knowledge this worthy father could have of her brother’s goodness, questioned him so pressingly that he at last told her the secret under the seal of the confessional, saying—
“Is it not an admirable thing to see a young and handsome Prince forsake pleasure and repose in order to come so often to hear our matins? Nor comes he like a Prince seeking honour of men, but quite alone, like a simple monk, and hides himself in one of our chapels. Truly such piety so shames both the monks and me, that we do not deem ourselves worthy of being called men of religion in comparison with him.”
When the sister heard these words she was at a loss what to think. She knew that, although her brother was worldly enough, he had a tender conscience, as well as great faith and love towards God; but she had never suspected him of a leaning towards any superstitions or rites save such as a good Christian should observe. (6) She therefore went to him and told him the good opinion that the monks had of him, whereat he could not hold from laughing, and in such a manner that she, knowing him as she did her own heart, perceived that there was something hidden beneath his devotion; whereupon she rested not until she had made him tell her the truth.
6 In Boaistuau’s edition this sentence ends, “But she had
never suspected him of going to church at such an hour as
this.”—L.
And she has made me here set it down in writing, for the purpose, ladies, of showing you that there is no lawyer so crafty and no monk so shrewd, but love, in case of need, gives the power of tricking them both, to those whose sole experience is in truly loving. And since love can thus deceive the deceivers, well may we, who are simple and ignorant folk, stand in awe of him.
“Although,” said Geburon, “I can pretty well guess who the young Prince is, I must say that in this matter he was worthy of praise. We meet with few great lords who reck aught of a woman’s honour or a public scandal, if only they have their pleasure; nay, they are often well pleased to have men believe something that is even worse than the truth.”
“Truly,” said Oisille, “I could wish that all young lords would follow his example, for the scandal is often worse than the sin.”
“Of course,” said Nomerfide, “the prayers he offered up at the monastery through which he passed were sincere.”
“That is not a matter for you to judge,” said Parlamente, “for perhaps his repentance on his return was great enough to procure him the pardon of his sin.”
“‘Tis a hard matter,” said Hircan, “to repent of an offence so pleasing. For my own part I have many a time confessed such a one, but seldom have I repented of it.”
“It would be better,” said Oisille, “not to confess at all, if one do not sincerely repent.”
“Well, madam,” said Hircan, “sin sorely displeases me, and I am grieved to offend God, but, for all that, such sin is ever a pleasure to me.”
“You and those like you,” said Parlamente, “would fain have neither God nor law other than your own desires might set up.”
“I will own to you,” said Hircan, “that I would gladly have God take as deep a pleasure in my pleasures as I do myself, for I should then often give Him occasion to rejoice.”
“However, you cannot set up a new God,” said Geburon, “and so we must e’en obey the one we have. Let us therefore leave such disputes to theologians, and allow Longarine to give some one her vote.”
“I give it,” she said, “to Saffredent, but I will beg him to tell us the finest tale he can think of, and not to be so intent on speaking evil of women as to hide the truth when there is something good of them to relate.”
“In sooth,” said Saffredent, “I consent, for I have here in hand the story of a wanton woman and a discreet one, and you shall take example by her who pleases you best. You will see that just as love leads wicked people to do wicked things, so does it lead a virtuous heart to do things that are worthy of praise; for love in itself is good, although the evil that is in those that are subject to it often makes it take a new title, such as wanton, light, cruel or vile. However, you will see from the tale that I am now about to relate that love does not change the heart, but discovers it to be what it really is, wanton in the wanton and discreet in the discreet.”



By the counsel and sisterly affection of a virtuous lady,
the Lord of Avannes was drawn from the wanton love that he
entertained for a gentlewoman dwelling at Pampeluna.
In the days of King Louis the Twelfth there lived a young lord called Monsieur d’Avannes, (1) son of the Lord of Albret [and] brother to King John of Navarre, with whom this aforesaid Lord of Avannes commonly abode.
1 This is Gabriel d’Albret, Lord of Avesnes and Lesparre,
fourth son of Alan the Great, Sire d’Albret, and brother of
John d’Albret, King of Navarre, respecting whom see post,
note 4 to Tale XXX. Queen Margaret is in error in dating
this story from the reign of Louis XII. The incidents she
relates must have occurred between 1485 and 1490, under the
reign of Charles VIII., by whom Gabriel d’Albret, on
reaching manhood, was successively appointed counsellor and
chamberlain, Seneschal of Guyenne and Viceroy of Naples.
Under Louis XII. he took a prominent part in the Italian
campaigns of 1500-1503, in which latter year he is known to
have made his will, bequeathing all he possessed to his
brother, Cardinal d’Albret. He died a bachelor in 1504.—See
Anselme’s Histoire Généalogique, vol. vi. p. 214.—L. and
Ed.
Now this young lord, who was fifteen years of age, was so handsome and so fully endowed with every excellent grace that he seemed to have been made solely to be loved and admired, as he was indeed by all who saw him, and above all by a lady who dwelt in the town of Pampeluna (2) in Navarre. She was married to a very rich man, with whom she lived in all virtue, inasmuch that, although her husband was nearly fifty years old and she was only three and twenty, she dressed so plainly that she had more the appearance of a widow than of a married woman. Moreover, she was never known to go to weddings or feasts unless accompanied by her husband, whose worth and virtue she prized so highly that she set them before all the comeliness of other men. And her husband, finding her so discreet, trusted her and gave all the affairs of his household into her hands.
2 Pampeluna or Pamplona, the capital of Navarre, wrested
from King John in 1512 by the troops of Ferdinand the
Catholic.—Ed.
One day this rich man was invited with his wife to a wedding among their kinsfolk; and among those who were present to do honour to the bridal was the young Lord of Avannes, who was exceedingly fond of dancing, as was natural in one who surpassed therein all others of his time. When dinner was over and the dances were begun, the rich man begged the Lord of Avannes to do his part, whereupon the said lord asked him with whom he would have him dance.
“My lord,” replied the gentleman, “I can present to you no lady fairer and more completely at my disposal than my wife, and I therefore beg you to honour me so far as to lead her out.”
This the young Prince did; and he was still so young that he took far greater pleasure in frisking and dancing than in observing the beauty of the ladies. But his partner, on the contrary, gave more heed to his grace and beauty than to the dance, though in her prudence she took good care not to let this appear.
The supper hour being come, the Lord of Avannes bade the company farewell, and departed to the castle, (3) whither the rich man accompanied him on his mule. And as they were going, the rich man said to him—
“My lord, you have this day done so much honour to my kinsfolk and to me, that I should indeed be ungrateful if I did not place myself with all that belongs to me at your service. I know, sir, that lords like yourself, who have stern and miserly fathers, are often in greater need of money than we, who, with small establishments and careful husbandry, seek only to save up wealth. Now, albeit God has given me a wife after my own heart, it has not pleased Him to give me all my Paradise in this world, for He has withheld from me the joy that fathers derive from having children. I know, my lord, that it is not for me to adopt you as a son, but if you will accept me for your servant and make known to me your little affairs, I will not fail to assist you in your need so far as a hundred thousand crowns may go.”
3 Evidently the castle of Pampeluna, where Gabriel d’Albret
resided with his brother the King.—Ed.
The Lord of Avannes was in great joy at this offer, for he had just such a father as the other had described; accordingly he thanked him, and called him his adopted father.
From that hour the rich man evinced so much love towards the Lord of Avannes, that morning and evening he failed not to inquire whether he had need of anything, nor did he conceal this devotion from his wife, who loved him for it twice as much as before. Thenceforward the Lord of Avannes had no lack of anything that he desired. He often visited the rich man, and ate and drank with him; and when he found the husband abroad, the wife gave him all that he required, and further spoke to him so sagely, exhorting him to live discreetly and virtuously, that he reverenced and loved her above all other women.
Having God and honour before her eyes, she remained content with thus seeing him and speaking to him, for these are sufficient for virtuous and honourable love; and she never gave any token whereby he might have imagined that she felt aught but a sisterly and Christian affection towards him.
While this secret love continued, the Lord of Avannes, who, by the assistance that I have spoken of, was always well and splendidly apparelled, came to the age of seventeen years, and began to frequent the company of ladies more than had been his wont. And although he would fain have loved this virtuous lady rather than any other, yet his fear of losing her friendship should she hear any such discourse from him, led him to remain silent and to divert himself elsewhere.
He therefore addressed himself to a gentlewoman of the neighbourhood of Pampeluna, who had a house in the town, and was married to a young man whose chief delight was in horses, hawks and hounds. For her sake, he began to set on foot a thousand diversions, such as tourneys, races, wrestlings, masquerades, banquets, and other pastimes, at all of which this young lady was present. But as her husband was very humorsome, and her parents, knowing her to be both fair and frolicsome, were jealous of her honour, they kept such strict watch over her that my Lord of Avannes could obtain nothing from her save a word or two at the dance, although, from the little that had passed between them, he well knew that time and place alone were wanting to crown their loves.
He therefore went to his good father, the rich man, and told him that he deeply desired to make a pilgrimage to our Lady of Montferrat, (4) for which reason he begged him to house his followers, seeing that he wished to go alone.
4 The famous monastery of Montserrate, at eight leagues
from Barcelona, where is preserved the ebony statue of the
Virgin carrying the Infant Jesus, which is traditionally
said to have been carved by St. Luke, and to have been
brought to Spain by St. Peter.—See Libro de la historia y
milagros hechos à invocation de Nuestra Seilora de
Montserrate, Barcelona, 1556, 8vo.—Ed.
To this the rich man agreed; but his wife, in whose heart was that great soothsayer, Love, forthwith suspected the true nature of the journey, and could not refrain from saying—
“My lord, my lord, the Lady you adore is not without the walls of this town, so I pray that you will have in all matters a care for your health.”
At this he, who both feared and loved her, blushed so deeply that, without speaking a word, he confessed the truth; and so he went away.
Having bought a couple of handsome Spanish horses, he dressed himself as a groom, and disguised his face in such a manner that none could know him. The gentleman who was husband to the wanton lady, and who loved horses more than aught beside, saw the two that the Lord of Avannes was leading, and forthwith offered to buy them. When he had done so, he looked at the groom, who was managing the horses excellently well, and asked whether he would enter his service. The Lord of Avannes replied that he would; saying that he was but a poor groom, who knew no trade except the caring of horses, but in this he could do so well that he would assuredly give satisfaction. At this the gentleman was pleased, and having given him the charge of all his horses, entered his house, and told his wife that he was leaving for the castle, and confided his horses and groom to her keeping.
The lady, as much to please her husband as for her own diversion, went to see the horses, and looked at the new groom, who seemed to her to be well favoured, though she did not at all recognise him. Seeing that he was not recognised, he came up to do her reverence in the Spanish fashion and kissed her hand, and, in doing so, pressed it so closely that she at once knew him, for he had often done the same at the dance. From that moment, the lady thought of nothing but how she might speak to him in private; and contrived to do so that very evening, for, being invited to a banquet, to which her husband wished to take her, she pretended that she was ill and unable to go.
The husband, being unwilling to disappoint his friends, thereupon said to her—
“Since you will not come, my love, I pray you take good care of my horses and hounds, so that they may want for nothing.”
The lady deemed this charge a very agreeable one, but, without showing it, she replied that since he had nothing better for her to do, she would show him even in these trifling matters how much she desired to please him.
And scarcely was her husband outside the door than she went down to the stable, where she found that something was amiss, and to set it right gave so many orders to the serving-men on this side and the other, that at last she was left alone with the chief groom, when, fearing that some one might come upon them, she said to him—
“Go into the garden, and wait for me in a summer house that stands at the end of the alley.”
This he did, and with such speed that he stayed not even to thank her.
When she had set the whole stable in order, she went to see the dogs, and was so careful to have them properly treated, that from mistress she seemed to have become a serving-woman. Afterwards she withdrew to her own apartment, where she lay down weariedly upon the bed, saying that she wished to rest. All her women left her excepting one whom she trusted, and to whom she said—
“Go into the garden, and bring here the man whom you will find at the end of the alley.”
The maid went and found the groom, whom she forthwith brought to the lady, and the latter then sent her outside to watch for her husband’s return. When the Lord of Avannes found himself alone with the lady, he doffed his groom’s dress, took off his false nose and beard, and, not like a timorous groom, but like the handsome lord he was, boldly got into bed with her without so much as asking her leave; and he was received as the handsomest youth of his time deserved to be by the handsomest and gayest lady in the land, and remained with her until her husband returned. Then he again took his mask and left the place which his craft and artifice had usurped.
On entering the courtyard the gentleman heard of the diligence that his wife had shown in obeying him, and he thanked her heartily for it.
“Sweetheart,” said the lady, “I did but my duty. Tis true that if we did not keep watch upon these rogues of servants you would not have a dog without the mange or a horse in good condition; but, now that I know their slothfulness and your wishes, you shall be better served than ever you were before.”
The gentleman, who thought that he had chosen the best groom in the world, asked her what she thought of him.
“I will own, sir,” she replied, “that he does his work as well as any you could have chosen, but he needs to be urged on, for he is the sleepiest knave I ever saw.”
So the lord and his lady lived together more lovingly than before, and he lost all the suspicion and jealousy with which he had regarded her, seeing that she was now as careful of her house hold as she had formerly been devoted to banquets, dances and assemblies. Whereas, also, she had formerly been wont to spend four hours in attiring herself, she was now often content to wear nothing but a dressing-gown over her chemise; and for this she was praised by her husband and by every one else, for they did not understand that a stronger devil had entered her and thrust out a weaker one.
Thus did this young lady, under the guise of a virtuous woman, like the hypocrite she was, live in such wantonness that reason, conscience, order and moderation found no place within her. The youth and tender constitution of the Lord of Avannes could not long endure this, and he began to grow so pale and lean that even without his mask he might well have passed unrecognised; yet the mad love that he had for this woman so blunted his understanding that he imagined he had strength to accomplish feats that even Hercules had tried in vain. However, being at last constrained by sickness and advised thereto by his lady, who was not so fond of him sick as sound, he asked his master’s leave to return home, and this his master gave him with much regret, making him promise to come back to service when he was well again.
In this wise did the Lord of Avannes go away, and all on foot, for he had only the length of a street to travel. On arriving at the house of his good father, the rich man, he there found only his wife, whose honourable love for him had been in no whit lessened by his journey. But when she saw him so colourless and thin, she could not refrain from saying to him—
“I do not know, my lord, how your conscience may be, but your body has certainly not been bettered by your pilgrimage. I fear me that your journeyings by night have done you more harm than your journeyings by day, for had you gone to Jerusalem on foot you would have come back more sunburnt, indeed, but not so thin and weak. Pay good heed to this one, and worship no longer such images as those, which, instead of reviving the dead, cause the living to die. I would say more, but if your body has sinned it has been well punished, and I feel too much pity for you to add any further distress.”
When my Lord of Avannes heard these words, he was as sorry as he was ashamed.
“Madam,” he replied, “I have heard that repentance follows upon sin, and now I have proved it to my cost. But I pray you pardon my youth, which could not have been punished save by the evil in which it would not believe.”
Thereupon changing her discourse, the lady made him lie down in a handsome bed, where he remained for a fortnight, taking nothing but restoratives; and the lady and her husband constantly kept him company, so that he always had one or the other beside him. And although he had acted foolishly, as you have heard, contrary to the desire and counsel of the virtuous lady, she, nevertheless, lost nought of the virtuous love that she felt towards him, for she still hoped that, after spending his early youth in follies, he would throw them off and bring himself to love virtuously, and so be all her own.
During the fortnight that he was in her house, she held to him such excellent discourse, all tending to the love of virtue, that he began to loathe the folly that he had committed. Observing, moreover, the lady’s beauty, which surpassed that of the wanton one, and becoming more and more aware of the graces and virtues that were in her, he one day, when it was rather dark, could not longer hold from speaking, but, putting away all fear, said to her—
“I see no better means, madam, for becoming a virtuous man such as you urge me and desire me to be, than by being heart and soul in love with virtue. I therefore pray you, madam, to tell me whether you will give me in this matter all the assistance and favour that you can.”
The lady rejoiced to find him speaking in this way, and replied—
“I promise you, my lord, that if you are in love with virtue as it beseems a lord like yourself to be, I will assist your efforts with all the strength that God has given me.”
“Now, madam,” said my Lord of Avannes, “remember your promise, and consider also that God, whom man knows by faith alone, deigned to take a fleshly nature like that of the sinner upon Himself, in order that, by drawing our flesh to the love of His humanity, He might at the same time draw our spirits to the love of His divinity, thus making use of visible means to make us in all faith love the things which are invisible. In like manner this virtue, which I would fain love all my life long, is a thing invisible except in so far as it produces outward effects, for which reason it must take some bodily shape in order to become known among men. And this it has done by clothing itself in your form, the most perfect it could find. I therefore recognise and own that you are not only virtuous but virtue itself; and now, finding it shine beneath the veil of the most perfect person that was ever known, I would fain serve it and honour it all my life, renouncing for its sake every other vain and vicious love.”
The lady, who was no less pleased than surprised to hear these words, concealed her happiness and said—
“My lord, I will not undertake to answer your theology, but since I am more ready to apprehend evil than to believe in good, I will entreat you to address to me no more such words as lead you to esteem but lightly those who are wont to believe them. I very well know that I am a woman like any other and imperfect, and that virtue would do a greater thing by transforming me into itself than by assuming my form—unless, indeed, it would fain pass unrecognised through the world, for in such a garb as mine its real nature could never be known. Nevertheless, my lord, with all my imperfections, I have ever borne to you all such affection as is right and possible in a woman who reverences God and her honour. But this affection shall not be declared until your heart is capable of that patience which a virtuous love enjoins. At that time, my lord, I shall know what to say, but meanwhile be assured that you do not love your own welfare, person and honour as I myself love them.”
The Lord of Avannes timorously and with tears in his eyes entreated her earnestly to seal her words with a kiss, but she refused, saying that she would not break for him the custom of her country.
While this discussion was going on the husband came in, and my Lord of Avannes said to him—
“I am greatly indebted, father, both to you and to your wife, and I pray you ever to look upon me as your son.”
This the worthy man readily promised.
“And to seal your love,” said the Lord of Avannes, “I pray you let me kiss you.” This he did, after which the Lord of Avannes said—:
“If I were not afraid of offending against the law, I would do the same to your wife and my mother.”
Upon this, the husband commanded his wife to kiss him, which she did without appearing either to like or to dislike what her husband commanded her. But the fire that words had already kindled in the poor lord’s heart, grew fiercer at this kiss which had been so earnestly sought for and so cruelly denied.
After this the Lord of Avannes betook himself to the castle to see his brother, the King, to whom he told fine stories about his journey to Montferrat. He found that the King was going to Oly and Taffares, (5) and, reflecting that the journey would be a long one, he fell into deep sadness, and resolved before going away to try whether the virtuous lady were not better disposed towards him than she appeared to be.
5 Evidently Olite and Tafalla, the former at thirty and the
latter at twenty-seven miles from Pamplona. The two towns
were commonly called la flor de Navarra. King John
doubtless intended sojourning at the summer palaces which
his predecessor Carlos the Noble had built at either
locality, and which were connected, it is said, by a gallery
a league in length. Some ruins of these palaces still exist.
—Ed.
He therefore went to lodge in the street in which she lived, where he hired an old house, badly built of timber. About midnight he set fire to it, and the alarm, which spread through the whole town, reached the rich man’s house. He asked from the window where the fire was, and hearing that it was in the house of the Lord of Avannes, immediately hastened thither with all his servants. He found the young lord in the street, clad in nothing but his shirt, whereat in his deep compassion he took him in his arms, and, covering him with his own robe, brought him home as quickly as possible, where he said to his wife, who was in bed—
“Here, sweetheart, I give this prisoner into your charge. Treat him as you would treat myself.”
As soon as he was gone, the Lord of Avannes, who would gladly have been treated like a husband, sprang lightly into the bed, hoping that place and opportunity would bring this discreet lady to a different mind; but he found the contrary to be the case, for as he leaped into the bed on one side, she got out at the other. Then, putting on her dressing-gown, she came up to the head of the bed and spoke as follows—
“Did you think, my lord, that opportunity could influence a chaste heart? Nay, just as gold is tried in the furnace, so a chaste heart becomes stronger and more virtuous in the midst of temptation, and grows colder the more it is assailed by its opposite. You may be sure, therefore, that had I been otherwise minded than I professed myself to be, I should not have wanted means, to which I have paid no heed solely because I desire not to use them. So I beg of you, if you would have me preserve my affection for you, put away not merely the desire but even the thought that you can by any means whatever make me other than I am.”
While she was speaking, her women came in, and she commanded a collation of all kinds of sweetmeats to be brought; but the young lord could neither eat nor drink, in such despair was he at having failed in his enterprise, and in such fear lest this manifestation of his passion should cost him the familiar intercourse that he had been wont to have with her.
Having dealt with the fire, the husband came back again, and begged the Lord of Avannes to remain at his house for the night. This he did, but in such wise that his eyes were more exercised in weeping than in sleeping. Early in the morning he went to bid them farewell, while they were still in bed; and in kissing the lady he perceived that she felt more pity for the offence than anger against the offender, and thus was another brand added to the fire of his love. After dinner, he set out for Taffares with the King; but before leaving he went again to take yet another farewell of his good father and the lady who, after her husband’s first command, made no difficulty in kissing him as her son.
But you may be sure that the more virtue prevented her eyes and features from testifying to the hidden flame, the fiercer and more intolerable did that flame become. And so, being unable to endure the war between love and honour, which was waging in her heart, but which she had nevertheless resolved should never be made apparent, and no longer having the comfort of seeing and speaking to him for whose sake alone she cared to live, she fell at last into a continuous fever, caused by a melancholic humour which so wrought upon her that the extremities of her body became quite cold, while her inward parts burned without ceasing. The doctors, who have not the health of men in their power, began to grow very doubtful concerning her recovery, by reason of an obstruction that affected the extremities, and advised her husband to admonish her to think of her conscience and remember that she was in God’s hands—as though indeed the healthy were not in them also.
The husband, who loved his wife devotedly, was so saddened by their words that for his comfort he wrote to the Lord of Avannes entreating him to take the trouble to come and see them, in the hope that the sight of him might be of advantage to the patient. On receiving the letter, the Lord of Avannes did not tarry, but started off post-haste to the house of his worthy father, where he found the servants, both men and women, assembled at the door, making such lament for their mistress as she deserved.
So greatly amazed was he at the sight, that he remained on the threshold like one paralysed, until he beheld his good father, who embraced him, weeping the while so bitterly that he could not utter a word. Then he led the Lord of Avannes to the chamber of the sick lady, who, turning her languid eyes upon him, put out her hand and drew him to her with all the strength she had. She kissed and embraced him, and made wondrous lamentation, saying—
“O my lord, the hour has come when all dissimulation must cease, and I must confess the truth which I have been at such pains to hide from you. If your affection for me was great, know that mine for you has been no less; but my grief has been greater than yours, because I have had the anguish of concealing it contrary to the wish of my heart. God and my honour have never, my lord, suffered me to make it known to you, lest I should increase in you that which I sought to diminish; but you must learn that the ‘no’ I so often said to you pained me so greatly in the utterance that it has indeed proved the cause of my death.
“Nevertheless, I am glad it should be so, and that God in His grace should have caused me to die before the vehemence of my love has stained my conscience and my fair fame; for smaller fires have ere now destroyed greater and stronger structures. And I am glad that before dying I have been able to make known to you that my affection is equal to your own, save only that men’s honour and women’s are not the same thing. And I pray you, my lord, fear not henceforward to address yourself to the greatest and most virtuous of ladies; for in such hearts do the deepest and discreetest passions dwell, and moreover, your own grace and beauty and worth will not suffer your love to toil without reward.
“I will not beg you, my lord, to pray God for me, because I know full well that the gate of Paradise is never closed against true lovers, and that the fire of love punishes lovers so severely in this life here that they are forgiven the sharp torment of Purgatory. And now, my lord, farewell; I commend to you your good father, my husband. Tell him the truth as you have heard it from me, that he may know how I have loved God and him. And come no more before my eyes, for I now desire to think only of obtaining those promises made to me by God before the creation of the world.”
With these words she kissed him and embraced him with all the strength of her feeble arms. The young lord, whose heart was as nearly dead through pity as hers was through pain, was unable to say a single word. He withdrew from her sight to a bed that was in the room, and there several times swooned away.
Then the lady called her husband, and, after giving him much virtuous counsel, commended the Lord of Avannes to him, declaring that next to himself she had loved him more than any one upon earth, and so, kissing her husband, she bade him farewell. Then, after the extreme unction, the Holy Sacrament was brought to her from the altar, and this she received with the joy of one who is assured of her salvation. And finding that her sight was growing dim and her strength failing her, she began to utter the “In manus” aloud.
Hearing this cry, the Lord of Avannes raised himself up on the bed where he was lying, and gazing piteously upon her, beheld her with a gentle sigh surrender her glorious soul to Him from whom it had come. When he perceived that she was dead, he ran to the body, which when alive he had ever approached with fear, and kissed and embraced it in such wise that he could hardly be separated from it, whereat the husband was greatly astonished, for he had never believed he bore her so much affection; and with the words, “Tis too much, my lord,” he led him away.
After he had lamented for a great while, the Lord of Avannes related all the converse they had had together during their love, and how, until her death, she had never given him sign of aught save severity. This, while it gave the husband exceeding joy, also increased his grief and sorrow at the loss he had sustained, and for the remainder of his days he rendered service to the Lord of Avannes.
But from that time forward my Lord of Avannes, who was then only eighteen years old, went to reside at Court, where he lived for many years without wishing to see or to speak with any living woman by reason of his grief for the lady he had lost; and he wore mourning for her sake during more than ten years. (6)
6 Some extracts from Brantôme bearing on this story will be
found in the Appendix, C.
“You here see, ladies, what a difference there is between a wanton lady and a discreet one. The effects of love are also different in each case; for the one came by a glorious and praiseworthy death, while the other lived only too long with the reputation of a vile and shameless woman. Just as the death of a saint is precious in the sight of God, so is the death of a sinner abhorrent.”
“In truth, Saffredent,” said Oisille, “you have told us the finest tale imaginable, and any one who knew the hero would deem it better still. I have never seen a handsomer or more graceful gentleman than was this Lord of Avannes.”
“She was indeed a very virtuous woman,” said Saffredent. “So as to appear outwardly more virtuous than she was in her heart, and to conceal her love for this worthy lord which reason and nature had inspired, she must needs die rather than take the pleasure which she secretly desired.”
“If she had felt such a desire,” said Parlamente, “she would have lacked neither place nor opportunity to make it known; but the greatness of her virtue prevented her desire from exceeding the bounds of reason.”
“You may paint her as you will,” said Hircan, “but I know very well that a stronger devil always thrusts out the weaker, and that the pride of ladies seeks pleasure rather than the fear and love of God. Their robes are long and well woven with dissimulation, so that we cannot tell what is beneath, for if their honour were not more easily stained than ours, (7) you would find that Nature’s work is as complete in them as in ourselves. But not daring to take the pleasure they desire, they have exchanged that vice for a greater, which they deem more honourable, I mean a self-sufficient cruelty, whereby they look to obtain everlasting renown.
7 This reading is borrowed from MS. No. 1520. In the MS.
mainly followed for this translation, the passage runs as
follows-“if their honour were not more easily stained than
their hearts.”—L.
By thus glorying in their resistance to the vice of Nature’s law—if, indeed, anything natural be vicious—they become not only like inhuman and cruel beasts, but even like the devils whose pride and subtility they borrow.” (8)
8 This reading is borrowed from MS. No. 1520. In our MS.
the passage runs—“like the devils whose semblance and
subtility they borrow.”—L.
“Tis a pity,” said Nomerfide, “that you should have an honourable wife, for you not only think lightly of virtue, but are even fain to prove that it is vice.”
“I am very glad,” said Hircan, “to have a wife of good repute, just as I, myself, would be of good repute. But as for chastity of heart, I believe that we are both children of Adam and Eve; wherefore, when we examine ourselves, we have no need to cover our nakedness with leaves, but should rather confess our frailty.”
“I know,” said Parlamente, “that we all have need of God’s grace, being all steeped in sin; but, for all that, our temptations are not similar to yours, and if we sin through pride, no one is injured by it, nor do our bodies and hands receive a stain. But your pleasure consists in dishonouring women, and your honour in slaying men in war—two things expressly contrary to the law of God.” (9)
“I admit what you say,” said Geburon, “but God has said, ‘Whosoever looketh with lust, hath already committed adultery in his heart,’ and further, ‘Whosoever hateth his neighbour is a murderer.’ (10) Do you think that women offend less against these texts than we?”
9 This sentence, defective in our MS., is taken from No.
1520.—L.
10 1 St. John iii. 15.—M.
“God, who judges the heart,” said Longarine, “must decide that. But it is an important thing that men should not be able to accuse us, for the goodness of God is so great, that He will not judge us unless there be an accuser. And so well, moreover, does He know the frailty of our hearts, that He will even love us for not having put our thoughts into execution.”
“I pray you,” said Saffredent, “let us leave this dispute, for it savours more of a sermon than of a tale. I give my vote to Ennasuite, and beg that she will bear in mind to make us laugh.”
“Indeed,” said she, “I will not fail to do so; for I would have you know that whilst coming hither, resolved upon relating a fine story to you to-day, I was told so merry a tale about two servants of a Princess, that, in laughing at it, I quite forgot the melancholy story which I had prepared, and which I will put off until to-morrow; for, with the merry face I now have, you would scarce find it to your liking.”



A secretary sought the wife of his host and comrade in
dishonourable and unlawful love, and as she made show of
willingly giving ear to him, he was persuaded that he had
won her. But she was virtuous, and, while dissembling
towards him, deceived his hopes and made known his
viciousness to her husband. (1)
1 The incidents here related would have occurred at Amboise
between 1540 and 1545. The hero of the story would probably
be John Frotté, Queen Margaret’s First Secretary, who also
apparently figures in Tale XXVIII. The Sires de Frotté had
been in the service of the Dukes of Alençon since the early
part of the fifteenth century. Ste-Marthe says of John
Frotté that he was a man of great experience and good wit,
prudent, dutiful and diligent. He died secretary to Francis
I.—L. and B. J.
In the town of Amboise there lived one of this Princess’s servants, an honest man who served her in the quality of valet-de-chambre, and who used readily to entertain those that visited his house, more especially his own comrades; and not long since one of his mistress’s servants came to lodge with him, and remained with him ten or twelve days.
This man was so ugly that he looked more like a King of the cannibals than a Christian, and although his host treated him as a friend and a brother, and with all the courtesy imaginable, he behaved in return not only like one who has forgotten all honour, but as one who has never had it in his heart. For he sought, in dishonourable and unlawful love, his comrade’s wife, who was in no sort attractive to lust but rather the reverse, and was moreover as virtuous a woman as any in the town in which she lived. When she perceived the man’s evil intent, she thought it better to employ dissimulation in order to bring his viciousness to light, rather than conceal it by a sudden refusal; and she therefore made a pretence of approving his discourse. He then believed he had won her, and, paying no heed to her age, which was that of fifty years, or to her lack of beauty, or her reputation as a virtuous woman attached to her husband, he urged his suit continually.
One day, the husband being in the house, the wife and her suitor were in a large room together, when she pretended that he had but to find some safe spot in order to have such private converse with her as he desired. He immediately replied that it was only necessary to go up to the garret. She instantly rose, and begged him to go first, saying that she would follow. Smiling with as sweet a countenance as that of a big baboon entertaining a friend, he went lightly up the stairway; and, on the tip-toe of expectation with regard to that which he so greatly desired, burning with a fire not clear, like that of juniper, but dense like that of coal in the furnace, he listened whether she was coming after him. But instead of hearing her footsteps, he heard her voice saying—
“Wait, master secretary, for a little; I am going to find out whether it be my husband’s pleasure that I should go up to you.”
His face when laughing was ugly indeed, and you may imagine, ladies, how it looked when he wept; but he came down instantly, with tears in his eyes, and besought her for the love of God not to say aught that would destroy the friendship between his comrade and himself.
“I am sure,” she replied, “that you like him too well to say anything he may not hear. I shall therefore go and tell him of the matter.”
And this, in spite of all his entreaties and threats, she did. And if his shame thereat was great as he fled the place, the husband’s joy was no less on hearing of the honourable deception that his wife had practised; indeed, so pleased was he with his wife’s virtue that he took no notice of his comrade’s viciousness, deeming him sufficiently punished inasmuch as the shame he had thought to work in another’s household had fallen upon his own head.
“I think that from this tale honest people should learn not to admit to their houses those whose conscience, heart and understanding know nought of God, honour and true love.”
“Though your tale be short,” said Oisille, “it is as pleasant as any I have heard, and it is to the honour of a virtuous woman.”
“‘Fore God,” said Simontault, “it is no great honour for a virtuous woman to refuse a man so ugly as you represent this secretary to have been. Had he been handsome and polite, her virtue would then have been clear. I think I know who he is, and, if it were my turn, I could tell you another story about him that is no less droll.”
“Let that be no hindrance,” said Ennasuite, “for I give you my vote.”
Thereupon Simontault began as follows:—
“Those who are accustomed to dwell at Court or in large towns value their own knowledge so highly that they think very little of all other men in comparison with themselves; but, for all that, there are subtle and crafty folk to be found in every condition of life. Still, when those who think themselves the cleverest are caught tripping, their pride makes the jest a particularly pleasant one, and this I will try to show by telling you of something that lately happened.”



A secretary, thinking to deceive Bernard du Ha, was by him
cunningly deceived. (1)
1 The incidents of this story must have occurred subsequent
to 1527. The secretary is doubtless John Frotté. We have
failed to identify the Lieutenant referred to.—M. and Ed.
It chanced that when King Francis, first of the name, was in the city of Paris, and with him his sister, the Queen of Navarre, the latter had a secretary called John. He was not one of those who allow a good thing to lie on the ground for want of picking it up, and there was, accordingly, not a president or a councillor whom he did not know, and not a merchant or a rich man with whom he had not intercourse and correspondence.
At this time there also arrived in Paris a merchant of Bayonne, called Bernard du Ha, who, both on account of the nature of his commerce and because the Lieutenant for Criminal Affairs (2) was a countryman of his, was wont to address himself to that officer for counsel and assistance in the transaction of his business. The Queen of Navarre’s secretary used also frequently to visit the Lieutenant as one who was a good servant to his master and mistress.
2 The Provost of Paris, who, in the King’s name,
administered justice at the Châtelet court, and upon whose
sergeants fell the duty of arresting and imprisoning all
vagabonds, criminals and disturbers of the peace, was
assisted in his functions by three lieutenants, one for
criminal affairs, one for civil affairs, and one for
ordinary police duties.—Ed.
One feast-day the secretary went to the Lieutenant’s house, and found both him and his wife abroad; but he very plainly heard Bernard du Ha teaching the serving-women to foot the Gascon dances to the sound of a viol or some other instrument. And when the secretary saw him, he would have had him believe that he was committing the greatest offence imaginable, and that if the Lieutenant and his wife knew of it they would be greatly displeased with him. And after setting the fear of this well before his eyes, until, indeed, the other begged him not to say anything about it, he asked—
“What will you give me if I keep silence?”
Bernard du Ha, who was by no means so much afraid as he seemed to be, saw that the secretary was trying to cozen him, and promised to give him a pasty of the best Basque ham (3) that he had ever eaten. The secretary was well pleased at this, and begged that he might have the pasty on the following Sunday after dinner, which was promised him.
3 So-called Bayonne ham is still held in repute in France.
It comes really from Orthez and Salies in Beam.—D.
Relying upon this promise, he went to see a lady of Paris whom above all things he desired to marry, and said to her—
“On Sunday, mistress, I will come and sup with you, if such be your pleasure. But trouble not to provide aught save some good bread and wine, for I have so deceived a foolish fellow from Bayonne that all the rest will be at his expense; by my trickery you shall taste the best Basque ham that ever was eaten in Paris.”
The lady believed his story, and called together two or three of the most honourable ladies of her neighbourhood, telling them that she would give them a new dish such as they had never tasted before.
When Sunday was come, the secretary went to look for his merchant, and finding him on the Pont-au-Change, (4) saluted him graciously and said—
“The devil take you, for the trouble you have given me to find you.”
4 The oldest of the Paris bridges, spanning the Seine
between the Châtelet and the Palais. Originally called the
Grand-Pont, it acquired the name of Pont-au-Change through
Louis VII. allowing the money-changers to build their houses
and offices upon it in 1141.—Ed.
Bernard du Ha made reply that a good many men had taken more trouble than he without being rewarded in the end with such a dainty dish. So saying, he showed him the pasty, which he was carrying under his cloak, and which was big enough to feed an army. The secretary was so glad to see it that, although he had a very large and ugly mouth, he mincingly made it so small that one would not have thought him capable of biting the ham with it. He quickly took the pasty, and, without waiting for the merchant to go with him, went off with it to the lady, who was exceedingly eager to learn whether the fare of Gascony was as good as that of Paris.
When supper-time was come and they were eating their soup, the secretary said—
“Leave those savourless dishes alone, and let us taste this loveworthy whet for wine.”
So saying, he opened the huge pasty, but, where he expected to find ham, he found such hardness that he could not thrust in his knife. After trying several times, it occurred to him that he had been deceived; and, indeed, he found ‘twas a wooden shoe such as is worn in Gascony. It had a burnt stick for knuckle, and was powdered upon the top with iron rust and sweet-smelling spice.
If ever a man was abashed it was the secretary, not only because he had been deceived by the man whom he himself had thought to deceive, but also because he had deceived her to whom he had intended and thought to speak the truth. Moreover, he was much put out at having to content himself with soup for supper.
The ladies, who were well-nigh as vexed as he was, would have accused him of practising this deception had they not clearly seen by his face that he was more wroth than they.
After this slight supper, the secretary went away in great anger, intending, since Bernard du Ha had broken his promise, to break also his own. He therefore betook himself to the Lieutenant’s house, resolved to say the worst he could about the said Bernard.
Quick as he went, however, Bernard was first afield and had already related the whole story to the Lieutenant, who, in passing sentence, told the secretary that he had now learnt to his cost what it was to deceive a Gascon, and this was all the comfort that the secretary got in his shame.
The same thing befalls many who, believing that they are exceedingly clever, forget themselves in their cleverness; wherefore we should never do unto others differently than we would have them do unto us.
“I can assure you,” said Geburon, “that I have often known similar things to come to pass, and have seen men who were deemed rustic blockheads deceive very shrewd people. None can be more foolish than he who thinks himself shrewd, nor wiser than he who knows his own nothingness.”
“Still,” said Parlamente, “a man who knows that he knows nothing, knows something after all.”
“Now,” said Simontault, “for fear lest time should fail us for our discourse, I give my vote to Nomerfide, for I am sure that her rhetoric will keep us no long while.”
“Well,” she replied, “I will tell you a tale such as you desire.
“I am not surprised, ladies, that love should afford Princes the means of escaping from danger, for they are bred up in the midst of so many well-informed persons that I should marvel still more if they were ignorant of anything. But the smaller the intelligence the more clearly is the inventiveness of love displayed, and for this reason I will relate to you a trick played by a priest through the prompting of love alone. In all other matters he was so ignorant that he could scarcely read his mass.”



A parson, surprised by the sudden return of a husbandman
with whose wife he was making good cheer, quickly devised a
means for saving himself at the expense of the worthy man,
who was never any the wiser. (1)
1 Etienne brings this story into his Apologie pour
Hérodote, ch xv.—B. J.
At a village called Carrelles, (2) in the county of Maine, there dwelt a rich husbandman who in his old age had married a fair young wife. She bore him no children, but consoled herself for this disappointment with several lovers.
2 Carrelles is at six leagues from Mayenne, in the canton of
Gorron. Margaret’s first husband, the Duke of Alençon, held
various fiefs in this part of Maine, which would account for
the incident related in the story coming to her knowledge.—
M. and Ed.
When gentlemen and persons of consequence failed her, she turned as a last resource to the Church, and took for companion in her sin him who could absolve her of it—that is to say, the parson, who often came to visit his pet ewe. The husband, who was dull and old, had no suspicion of the truth; but, as he was a stern and sturdy man, his wife played her game as secretly as she was able, fearing that, if it came to her husband’s knowledge, he would kill her.
One day when he was abroad, his wife, thinking that he would not soon return, sent for his reverence the parson, who came to confess her; and while they were making good cheer together, her husband arrived, and this so suddenly that the priest had not the time to escape out of the house.
Looking about for a means of concealment, he mounted by the woman’s advice into a loft, and covered the trap-door through which he passed with a winnowing fan.
The husband entered the house, and his wife, fearing lest he might suspect something, regaled him exceedingly well at dinner, never sparing the liquor, of which he drank so much, that, being moreover wearied with his work in the fields, he at last fell asleep in his chair in front of the fire.
The parson, tired with waiting so long in the loft, and hearing no noise in the room beneath, leaned over the trap-door, and, stretching out his neck as far as he was able, perceived the goodman to be asleep. However, whilst he was looking at him, he leaned by mischance so heavily upon the fan, that both fan and himself tumbled down by the side of the sleeper. The latter awoke at the noise, but the priest was on his feet before the other had perceived him, and said—
“There is your fan, my friend, and many thanks to you for it.”
With these words he took to flight. The poor husbandman was in utter bewilderment.
“What is this?” he asked of his wife. “‘Tis your fan, sweetheart,” she replied, “which the parson had borrowed, and has just brought back.”
Thereupon in a grumbling fashion the goodman rejoined—
“‘Tis a rude way of returning what one has borrowed, for I thought the house was coming down.”
In this way did the parson save himself at the expense of the goodman, who discovered nothing to find fault with except the rudeness with which the fan had been returned.
“The master, ladies, whom the parson served, saved him that time so that he might afterwards possess and torment him the longer.”
“Do not imagine,” said Geburon, “that simple folk are more devoid of craft than we are; (3) nay, they have a still larger share. Consider the thieves and murderers and sorcerers and coiners, and all the people of that sort, whose brains are never at rest; they are all poor and of the class of artisans.”
“I do not think it strange,” said Parlamente, “that they should have more craft than others, but rather that love should torment them amid their many toils, and that so gentle a passion should lodge in hearts so base.”
“Madam,” replied Saffredent, “you know what Master Jehan de Mehun has said—
“Those clad in drugget love no less
Than those that wear a silken dress.” (4)
3 In MS. No. 1520 this passage runs—“that simple and
humble people are,” &c.—L.
4 This is a free rendering of lines 4925-6 of Méon’s
edition of the Roman de la Rose:—
“Aussy bien sont amourettes
Soubz bureau que soubz brunettes.”
Bureau, the same as dure, is a kind of drugget;
brunette was a silken stuff very fashionable among the
French lords and ladies at the time of St. Louis. It was
doubtless of a brown hue.—B, J. and M.
Moreover, the love of which the tale speaks is not such as makes one carry harness; for, while poor folk lack our possessions and honours, on the other hand they have their natural advantages more at their convenience than we. Their fare is not so dainty as ours, but their appetites are keener, and they live better on coarse bread than we do on delicacies. Their beds are not so handsome or so well appointed as ours, but their sleep is sounder and their rest less broken. They have no ladies pranked out and painted like those whom we idolise, but they take their pleasure oftener than we, without fear of telltale tongues, save those of the beasts and birds that see them. What we have they lack, and what we lack they possess in abundance.”
“I pray you,” said Nomerfide, “let us now have done with this peasant and his wife, and let us finish the day’s entertainment before vespers. ‘Tis Hircan shall bring it to an end.”
“Truly,” said he, “I have kept in reserve as strange and pitiful a tale as ever you heard. And although it grieves me greatly to relate anything to the discredit of a lady, knowing, as I do, that men are malicious enough to blame the whole sex for the fault of one, yet the strangeness of the story prompts me to lay aside my fear. Perhaps, also, the discovery of one woman’s ignorance will make others wiser. And so I will fearlessly tell you the following tale.”



A young gentleman, of from fourteen to fifteen years of
age, thought to lie with one of his mother’s maids, but lay
with his mother herself; and she, in consequence thereof,
was, nine months afterwards, brought to bed of a daughter,
who, twelve or thirteen years later, was wedded by the son;
he being ignorant that she was his daughter and sister, and
she, that he was her father and brother.(1)
In the time of King Louis the Twelfth, the Legate at Avignon being then a scion of the house of Amboise, nephew to George, Legate of France, (2) there lived in the land of Languedoc a lady who had an income of more than four thousand ducats a year, and whose name I shall not mention for the love I bear her kinsfolk.
1 This story is based on an ancient popular tradition
common to many parts of France, and some particulars of
which, with a list of similar tales in various European
languages, will be found in the Appendix, D.—En.
2 The Papal Legate in France here alluded to is the famous
George, Cardinal d’Amboise, favourite minister of Louis XII.
His nephew, the Legate at Avignon, is Louis d’Amboise,
fourth son of Peter d’Amboise, Lord of Chaumont, and brother
of the Grand-Master of Chaumont. Louis d’Amboise became
bishop of Albi, and lieutenant-general of the King of France
in Burgundy, Languedoc and Roussillon, and played an
important part in the public affairs of his time. He died in
1505.—See Gallia Christiana, vol. i. p. 34.—L. and R. J.
While still very young, she was left a widow with one son; and, both by reason of her regret for her husband and her love for her child, she determined never to marry again. To avoid all opportunity of doing so, she had fellowship only with the devout, for she imagined that opportunity makes the sin, not knowing that sin will devise the opportunity.
This young widow, then, gave herself up wholly to the service of God, and shunned all worldly assemblies so completely that she scrupled to be present at a wedding, or even to listen to the organs playing in a church. When her son was come to the age of seven years, she chose for his schoolmaster a man of holy life, so that he might be trained up in all piety and devotion.
When the son was reaching the age of fourteen or fifteen, Nature, who is a very secret schoolmaster, finding him in good condition and very idle, taught him a different lesson to any he had learned from his tutor. He began to look at and desire such things as he deemed beautiful, and among others a maiden who slept in his mother’s room. No one had any suspicion of this, for he was looked upon as a mere child, and, moreover, in that household nothing save godly talk was ever heard.
This young gallant, however, began secretly soliciting the girl, who complained of it to her mistress. The latter had so much love for her son and so high an opinion of him, that she thought the girl spoke as she did in order to make her hate him; but, being strongly urged by the other, she at last said—
“I shall find out whether it is true, and will punish him if it be as you say. But if, on the other hand, you are bringing an untruthful accusation against him, you shall suffer for it.”
Then, in order to test the matter, she bade the girl make an appointment with her son that he might come and lie with her at midnight, in the bed in which she slept alone, beside the door of his mother’s room.
The maid obeyed her mistress, who, when night came, took the girl’s place, resolved, if the story were true, to punish her son so severely that he would never again lie with a woman without remembering it.
While she was thinking thus wrathfully, her son came and got into the bed, but although she beheld him do so, she could not yet believe that he meditated any unworthy deed. She therefore refrained from speaking to him until he had given her some token of his evil intent, for no trifling matters could persuade her that his desire was actually a criminal one. Her patience, however, was tried so long, and her nature proved so frail that, forgetting her motherhood, her anger became transformed into an abominable delight. And just as water that has been restrained by force rushes onward with the greater vehemence when it is released, so was it with this unhappy lady who had so prided herself on the constraint she had put upon her body. After taking the first step downwards to dishonour, she suddenly found herself at the bottom, and thus that night she became pregnant by him whom she had thought to restrain from acting in similar fashion towards another.
No sooner was the sin accomplished than such remorse of conscience began to torment her as filled the whole of her after-life with repentance. And so keen was it at the first, that she rose from beside her son—who still thought that she was the maid—and entered a closet, where, dwelling upon the goodness of her intention and the wickedness of its execution, she spent the whole night alone in tears and lamentation.
But instead of humbling herself, and recognising the powerlessness of our flesh, without God’s assistance, to work anything but sin, she sought by her own tears and efforts to atone for the past, and by her own prudence to avoid mischief in the future, always ascribing her sin to circumstances and not to wickedness, for which there is no remedy save the grace of God. Accordingly she sought to act so as never again to fall into such wrongdoing; and as though there were but one sin that brought damnation in its train, she put forth all her strength to shun that sin alone.
But the roots of pride, which acts of sin ought rather to destroy, grew stronger and stronger within her, so that in avoiding one evil she wrought many others. Early on the morrow, as soon as it was light, she sent for her son’s preceptor, and said—
“My son is beginning to grow up, it is time to send him from home. I have a kinsman, Captain Monteson, (3) who is beyond the mountains with my lord the Grand-Master of Chaumont, and he will be very glad to admit him into his company. Take him, therefore, without delay, and to spare me the pain of parting do not let him come to bid me farewell.”
3 Monteson was one of the bravest captains of his time; as
the comrade of Bayard, he greatly distinguished himself by
his intrepidity in Louis XII.‘s Italian campaigns. Some
particulars concerning him will be found in M. Lacroix’s
edition of Les Chroniques de Jean d’Anton.—B. J.
Respecting the Grand-Master of Chaumont, also mentioned
above, see ante, vol ii., notes to Tale XIV.
So saying, she gave him money for the journey, and that very morning sent the young man away, he being right glad of this, for, after enjoying his sweetheart, he asked nothing better than to set off to the wars.
The lady continued for a great while in deep sadness and melancholy, and, but for the fear of God, had many a time longed that the unhappy fruit of her womb might perish. She feigned sickness, in order that she might wear a cloak and so conceal her condition; and having a bastard brother, in whom she had more trust than in any one else, and upon whom she had conferred many benefits, she sent for him when the time of her confinement was drawing nigh, told him her condition (but without mentioning her son’s part in it), and besought him to help her save her honour. This he did, and, a few days before the time when she expected to be delivered, he begged her to try a change of air and remove to his house, where she would recover her health more quickly than at home. Thither she went with but a very small following, and found there a midwife who had been summoned as for her brother’s wife, and who one night, without recognising her, delivered her of a fine little girl. The gentleman gave the child to a nurse, and caused it to be cared for as his own.
After continuing there for a month, the lady returned in sound health to her own house, where she lived more austerely than ever in fasts and disciplines. But when her son was grown up, he sent to beg his mother’s permission to return home, as there was at that time no war in Italy. She, fearing lest she should fall again into the same misfortune, would not at first allow him, but he urged her so earnestly that at last she could find no reason for refusing him. However, she instructed him that he was not to appear before her until he was married to a woman whom he dearly loved; but to whose fortune he need give no heed, for it would suffice if she were of gentle birth.
Meanwhile her bastard brother, finding that the daughter left in his charge had grown to be a tall maiden of perfect beauty, resolved to place her in some distant household where she would not be known, and by the mother’s advice she was given to Catherine, Queen of Navarre. (4) The maiden thus came to the age of twelve or thirteen years, and was so beautiful and virtuous that the Queen of Navarre had great friendship for her, and much desired to marry her to one of wealth and station. Being poor, however, she found no husband, though she had lovers enough and to spare.
4 This is Catherine, daughter of Gaston and sister of
Francis Phoebus de Foix. On her brother’s death, in 1483,
she became Queen of Navarre, Duchess of Nemours and Countess
of Foix and Bigorre, and in the following year espoused
John, eldest son of Alan, Sire d’Albret. Catherine at this
time was fourteen years old, and her husband, who by the
marriage became King of Navarre, was only one year her
senior. Their title to the crown was disputed by a dozen
pretenders, for several years they exercised but a
precarious authority, and eventually, in July 1512,
Ferdinand the Catholic despatched the Duke of Alva to
besiege Pamplona. On the fourth day of the siege John and
Catherine succeeded in escaping from their capital, which,
three days later, surrendered. Ferdinand, having sworn to
maintain the fueros, was thereupon acknowledged as
sovereign. However, it was only in 1516 that the former
rulers were expelled from Navarrese territory. “Had I been
Don Juan and you Donna Catherine,” said the Queen to her
pusillanimous husband, as they crossed the Pyrenees, “we
should not have lost our kingdom.” From this time forward
the d’Albrets, like their successors the Bourbons, were
sovereigns of Navarre in name only, for an attempt made in
1521 to reconquer the kingdom resulted in total failure, and
their dominions were thenceforth confined to Beam, Bigorre,
and Foix on the French side of the Pyrenees. Queen Catherine
died in 1517, aged 47, leaving several children, the eldest
of whom was Henry, Queen Margaret’s second husband.—M., B.
J., D. and Ed.
Now it happened one day that the gentleman who was her unknown father came to the house of the Queen of Navarre on his way back from beyond the mountains, and as soon as he had set eyes on his daughter he fell in love with her, and having license from his mother to marry any woman that might please him, he only inquired whether she was of gentle birth, and, hearing that she was, asked her of the Queen in marriage. The Queen willingly consented, for she knew that the gentleman was not only rich and handsome, but worshipful to boot.
When the marriage had been consummated, the gentleman again wrote to his mother, saying that she could no longer close her doors against him, since he was bringing with him as fair a daughter-in-law as she could desire. The lady inquired to whom he had allied himself, and found that it was to none other than their own daughter. Thereupon she fell into such exceeding sorrow that she nearly came by a sudden death, seeing that the more she had striven to hinder her misfortune, the greater had it thereby become.
Not knowing what else to do, she went to the Legate of Avignon, to whom she confessed the enormity of her sin, at the same time asking his counsel as to how she ought to act. The Legate, to satisfy his conscience, sent for several doctors of theology, and laid the matter before them, without, however, mentioning any names; and their advice was that the lady should say nothing to her children, for they, being in ignorance, had committed no sin, but that she herself should continue doing penance all her life without allowing it to become known.
Accordingly, the unhappy lady returned home, where not long afterwards her son and daughter-in-law arrived. And they loved each other so much that never were there husband and wife more loving, nor yet more resembling each other; for she was his daughter, his sister and his wife, while he was her father, her brother and her husband. And this exceeding love between them continued always; and the unhappy and deeply penitent lady could never see them in dalliance together without going apart to weep.
“You see, ladies, what befalls those who think that by their own strength and virtue they may subdue Love and Nature and all the faculties that God has given them. It were better to recognise their own weakness, and instead of running a-tilt against such an adversary, to betake themselves to Him who is their true Friend, saying to Him in the words of the Psalmist, ‘Lord, I am afflicted very much; answer Thou for me.’” (5)
5 We have failed to find this sentence in the Psalms.
Probably the reference is to Isaiah xxxviii. 14, “O Lord,
I am oppressed; undertake for me.”—Eu.
“It were impossible,” said Oisille “to hear a stranger story than this. Methinks every man and woman should bend low in the fear of God, seeing that in spite of a good intention so much mischief came to pass.”
“You may be sure,” said Parlamente, “that the first step a man takes in self-reliance, removes him so far from reliance upon God.”
“A man is wise,” said Geburon, “when he knows himself to be his greatest enemy, and holds his own wishes and counsels in suspicion.”
“Albeit the motive might seem to be a good and holy one,” said Longarine, “there were surely none, howsoever worthy in appearance, that should induce a woman to lie beside a man, whatever the kinship between them, for fire and tow may not safely come together.”
“Without question,” said Ennasuite, “she must have been some self-sufficient fool, who, in her friar-like dreaming, deemed herself so saintly as to be incapable of sin, just as many of the Friars would have us believe that we can become, merely by our own efforts, which is an exceeding great error.”
“Is it possible, Longarine,” asked Oisille, “that there are people foolish enough to hold such an opinion?”
“They go further than that,” replied Longarine. “They say that we ought to accustom ourselves to the virtue of chastity; and in order to try their strength they speak with the prettiest women they can find and whom they like best, and by kissing and touching them essay whether their fleshly nature be wholly dead. When they find themselves stirred by such pleasure, they desist, and have recourse to fasts and grievous discipline. Then, when they have so far mortified their flesh that neither speech nor kiss has power to move them, they make trial of the supreme temptation, that, namely, of lying together and embracing without any lustfulness. (6) But for one who has escaped, so many have come to mischief, that the Archbishop of Milan, where this religious practice used to be carried on, (7) was obliged to separate them and place the women in convents and the men in monasteries.”
6 Robert d’Arbrissel, the founder of the abbey of
Fontevrault (see ante, p. 74), was accused of this
practice.—See the article Fontevraud in Desoer’s edition of
Bayle’s Dictionary, vi. 508, 519.—M.
7 Queen Margaret possibly refers to some incidents which
occurred at Milan in the early part of the fourteenth
century, when Matteo and Galeazzo Visconti ruled the city.
In Signor Tullio Dandolo’s work, Sui xxiii. libri delta
Histories Patrice di Giuseppe Ripamonti ragionamento
(Milano, 1856, pp. 52-60), will be found the story of a
woman of the people, Guglielmina, and her accomplice, Andrea
Saramita, who under some religious pretext founded a secret
society of females. The debauchery practised by its members
being discovered, Saramita was burnt alive, and
Guglielmina’s bones were disinterred and thrown into the
fire. The Bishop of Milan at this time (1296-1308) was
Francesco Fontana.—M.
“Truly,” said Geburon, “it were the extremity of folly to seek to become sinless by one’s own efforts, and at the same time to seek out opportunities for sin.”
“There are some,” said Saffredent, “who do the very opposite, and flee opportunities for sin as carefully as they are able; nevertheless, concupiscence pursues them. Thus the good Saint Jerome, after scourging and hiding himself in the desert, confessed that he could not escape from the fire that consumed his marrow. We ought, therefore, to recommend ourselves to God, for unless He uphold us by His power, we are greatly prone to fall.”
“You do not notice what I do,” said Hircan. “While we were telling our stories, the monks behind the hedge here heard nothing of the vesper-bell; whereas, now that we have begun to speak about God, they have taken themselves off, and are at this moment ringing the second bell.”
“We shall do well to follow them,” said Oisille, “and praise God for enabling us to spend this day in the happiest manner imaginable.”
Hereat they rose and went to the church, where they piously heard vespers; after which they went to supper, discussing the discourses they had heard, and calling to mind divers adventures that had come to pass in their own day, in order to determine which of them were worthy to be recounted. And after spending the whole evening in gladness, they betook themselves to their gentle rest, hoping on the morrow to continue this pastime which was so agreeable to them.
And so was the Third Day brought to an end.

Brantôme alludes as follows to this tale, in the Fourth Discourse of his Vies des Dames Galantes:—
“I knew a great lady whose plumpness was the subject of general talk both whilst she was a maid and when she became a wife, but she happened to lose her husband, and gave way to such extreme grief that she became as dry as a stick. Still she did not cease to enjoy herself to her heart’s content, with the assistance of one of her secretaries, and even so it is said of her cook. Nevertheless, she did not regain her plumpness, albeit the said cook, who was all grease and fat, should as it seems to me have made her stout again. Whilst she thus amused herself with one and another of her varlets, she affected more prudery and chastity than any other lady of the Court, having none but words of virtue on her lips, speaking ill of all other women and finding something to be censured in each of them. Very similar to this one was that great lady of Dauphiné who is mentioned in the Hundred Tales of the Queen of Navarre, and who was found, lying on the grass with her stableman or muleteer, by a gentleman who was in love with her to distraction. On finding her thus, however, he was speedily cured of his love-sickness.
“I have read in an old romance about John de Saintré, printed in black-letter, that the late King John brought him up as a page. In the old times it was usual for great personages to send their pages about with messages, as is indeed done nowadays, but at that time they journeyed anywhere across country, on horseback. In fact, I have heard our fathers say that pages were often sent on little embassies, for very often a matter would be settled and expense saved by merely despatching a page with a horse and a piece of silver. This little Jehan de Saintré, as he was long called, was a great favourite with his master King John, for he was full of wit, and it often happened that he was sent with messages to his [the King’s?] sister, who was then a widow, though of whom the book does not say. This lady fell in love with him after several messages that he had delivered to her, and one day finding him alone, she engaged him in converse, and, according to the usual practice of ladies when they wish to engage any one in a love attack, she began to ask him if he were in love with any lady of the Court, and which one pleased him the most. This little John de Saintre, who had never even so much as thought of love, told her that he cared for none at the Court as yet, whereupon she mentioned several other ladies to him, and asked him whether he thought of them. ‘Still less,’ replied he.... Thereupon the lady, seeing that the young fellow was of good appearance, told him that she would give him a mistress who would love him tenderly if he would serve her well, and whilst he stood there feeling greatly ashamed, she made him promise that he would keep the matter secret, and finally declared to him that she herself wished to be his lady and lover, for at that time the word ‘mistress’ was not yet used. The young page was vastly astonished, thinking that the lady was joking, or wished to deceive him or to have him whipped. However, she soon showed him so many signs of the fire and fever of love, saying to him that she wished to tutor him and make a man of him, that he at last realised that it was not a jest. Their love lasted for a long time, both whilst he was a page and afterwards, until at length he had to go upon a long journey, when she replaced him by a big, fat abbot. This is the same story that one finds in the Nouvelles du Monde Advantureux by a valet of the Queen of Navarre [Antoine de St. Denis], in which one sees the abbot insult this same John de Saintré who was so brave and valiant, and who right speedily and liberally paid back my lord the abbot in his own coin.... So you see it is no new thing for ladies to love pages. What inclinations some women have, they will willingly take any number of lovers but they want no husband! All this is through love of liberty, which they deem such a pleasant thing. It seems to them as though they were in Paradise when they are not under a husband’s rule. They have a fine dowry and spend it thriftily, they have all their household affairs in hand, receive their income, everything passing through their hands; and instead of being servants they are mistresses, select their own pleasures and favourites, and amuse themselves as much as they like.”—Lalanne’s OEuvres de Brantôme, vol. xi. pp. 703-6.
Baron Jerome Pichon’s elucidations of this story, as given by him in the Mélanges de la Société des Bibliophiles Français, 1866, may be thus summarised:—
The advocate referred to in the tale is James Disome, who Mézeray declares was the first to introduce Letters to the bar, though this, to my mind, is a very hazardous assertion. Disome was twice married. His first wife, Mary de Rueil, died Sept. 17, 1511, and was buried at the Cordeliers church; he afterwards espoused Jane Lecoq, daughter of John Lecoq, Counsellor of the Paris Parliament, who held the fiefs of Goupillières, Corbeville and Les Porcherons, where he possessed a handsome château, a view of which has been engraved by Israel Silvestre. John Lecoq’s wife was Magdalen Bochart, who belonged like her husband to an illustrious family of lawyers and judges. Their daughter Jane, who is the heroine of the tale, must have been married to James Disome not very long after the death of the latter’s first wife, for her intrigue with Francis I. originated prior to his accession to the throne (1515). This is proved by the tale, in which Disome is spoken of as being the young prince’s advocate. Now none but the Procurors and Advocates-General were counsel to the Crown, and Disome held neither of those offices. He was undoubtedly advocate to Francis as Duke de Valois, and, from certain allusions in the tale, it may be conjectured that he had been advocate to Francis’s father, the Count of Angoulême.
When Francis ascended the throne his intrigue with Jane Disome was already notorious, as is proved by this extract, under date 1515, from the Journal d’un Bourgeois de Paris: “About this time whilst the King was in Paris, there was a priest called Mons. Cruche, a great buffoon, who a little time before with several others had publicly performed in certain entertainments and novelties’ (sic) on scaffolds upon the Place Maubert, there being in turn jest, sermon, morality and farce; and in the morality appeared several lords taking their cloth of gold to the tomb and carrying their lands upon their shoulders into the other world. And in the farce came Monsieur Cruche with his companions, who had a lantern by which all sorts of things were seen, and among others a hen feeding under a salamander, (1) and this hen carried something on her back which would suffice to kill ten men (dix hommes, i.e., Disome).
1 The salamander was Francis I.‘s device.
The interpretation of this was that the King loved and enjoyed a woman of Paris, who was the daughter of a counsellor of the Court of Parliament, named Monsieur le Coq. And she was married to an advocate at the bar of Parliament, a very skilful man, named Monsieur James Disome, who was possessed of much property which the King confiscated. Soon afterwards the King sent eight or ten of his principal gentlemen to sup at the sign of the Castle in the Rue de la Juiverie, and thither, under the false pretence of making him play the said farce, was summoned Messire Cruche, who came in the evening, by torch-light, and was constrained to play the farce by the said gentlemen. But thereupon, at the very beginning, he was stripped to his shirt, and wonderfully well whipped with straps until he was in a state of the utmost wretchedness. At the end there was a sack all ready to put him in, that he might be thrown from the window, and then carried to the river; and this would assuredly have come to pass had not the poor man cried out very loudly and shown them the tonsure on his head. And all these things were done, so it was owned, on the King’s behalf.”
It is probable that this intrigue between the King and Jane Disome ceased soon after the former’s accession; at all events Francis did not evince much indulgence for the man whose wife he had seduced. Under date April, 1518, the Journal dun Bourgeois de Paris mentions the arrest of several advocates and others for daring to discuss the question of the Pragmatic Sanction. Disome was implicated in the matter but appears to have escaped for a time; however in September of that year we find him detained at Orleans and subjected to the interrogatories of various royal Commissioners. The affair was then adjourned till the following year, when no further mention is made of it.
Disome died prior to 1521, for in September of that year we find his wife remarried to Peter Perdrier, Lord of Baubigny, notary and secretary to the King, and subsequently clerk of the council to the city of Paris. Perdrier was a man of considerable means; for when the King raised a forced loan of silver plate in September 1521, we find him taxed to the amount of forty marcs of silver (26 1/2 lbs. troy); or only ten marcs less than each counsellor of Parliament was required to contribute. Five and twenty years later, he lost his wife Jane, the curious record of whose death runs as follows: “The year one thousand five hundred forty-six, after Easter, at her house (hôtel) Rue de la Parcheminerie, called Rue des Blancs-Manteaux, died the late Demoiselle Jane Lecoq, daughter of Master John Lecoq, Counsellor of the Court of Parliament, deceased; in her lifetime wife of noble Master Peter Perdrier, Lord of Baubigny, &c, and previously wife of the late Master James Disome, in his lifetime advocate at the Court of Parliament and Lord of Cernay in Beauvaisis; and the said Demoiselle Jane Lecoq (2) is here—buried with her father and mother, and departed this life on the 23rd day of April 1546. Pray ye God for her soul.”
2 The church of the Celestines.
Less than a twelvemonth afterwards King Francis followed his whilom mistress to the tomb. She left by Peter Perdrier a son named John, Lord of Baubigny, who in 1558 married Anne de St. Simon, grand-aunt of the author of the Memoirs. John Perdrier was possibly the Baubigny who killed Marshal de St. André at the battle of Dreux in 1562.
Such is Baron Pichon’s account of Jane Lecoq and her husbands. We have now to turn to an often-quoted passage of the Diverses Leçons of Louis Guyon, sieur de la Nauthe, a physician of some repute in his time, but whose book it should be observed was not issued till 1610, or more than half-a-century subsequent to King Francis I.‘s death. La Nauthe writes as follows:—
“Francis I. became enamoured of a woman of great beauty and grace, the wife of an advocate of Paris, whom I will not name, for he has left children in possession of high estate and good repute; and this lady would not yield to the King, but on the contrary repulsed him with many harsh words, whereat the King was sorely vexed. And certain courtiers and royal princes who knew of the matter told the King that he might take her authoritatively and by virtue of his royalty, and one of them even went and told this to the lady, who repeated it to her husband. The advocate clearly perceived that he and his wife must needs quit the kingdom, and that he would indeed find it hard to escape without obeying. Finally the husband gave his wife leave to comply with the King’s desire, and in order that he might be no hindrance in the matter, he pretended to have business in the country for eight or ten days; during which time, however, he remained concealed in Paris, frequenting the brothels and trying to contract a venereal disease in order to give it to his wife, so that the King might catch it from her; and he speedily found what he sought, and infected his wife and she the King, who gave it to several other women, whom he kept, and could never get thoroughly cured, for all the rest of his life he remained unhealthy, sad, peevish and inaccessible.”
Brantôme, it may be mentioned, also speaks of the King contracting a complaint through his gallantries, and declares that it shortened his life, but he mentions no woman by name, and does not tell the story of the advocate’s wife. It will have been observed in the extract we have quoted that Guyon de la Nauthe says that the advocate had left children “in possession of high estate and good repute.” Disome, however, had no children either by his first or his second wife. The question therefore arises whether La Nauthe is not referring to another advocate, for instance Le Féron, husband of La belle Féronnière. These would appear to have left posterity (see Catalogue de tous les Conseillers du Parlement de Paris, pp. 120-2-3, and Blanchard’s les Présidents à mortier du Parlement de Paris, etc., 1647, 8vo). But it should be borne in mind that the Féronnière intrigue is purely traditional. The modern writers who speak of it content themselves with referring to Mézeray, a very doubtful authority at most times, and who did not write, it should be remembered, till the middle of the seventeenth century, his Abrégé Chronologique being first published in 1667. Moreover, when we come to consult him we find that he merely makes a passing allusion to La Féronnière, and even this is of the most dubious kind. Here are his words: “In 1538 the King had a long illness at Compiègne, caused by an ulcer.... He was cured at the time, but died [of it?] nine years later. I have sometimes heard say(!) that he caught this disease from La belle Féronnière.”
Against this we have to set the express statement of Louise of Savoy, who writes in her journal, under date 1512, that her son (born in 1494) had already and at an early age had a complaint en secrete nature. Now this was long before the belle Féronnière was ever heard of, and further it was prior to the intrigue with Jane Disome, who, by Queen Margaret’s showing, did not meet with “the young prince” until she had been married some time and was in despair of having children by her husband. The latter had lost his first wife late in 1511, and it is unlikely that he married Jane Lecoq until after some months of widowhood. To our thinking Prince Francis would have appeared upon the scene in or about 1514, his intrigue culminating in the scandal of the following year, in which Mons. Cruche played so conspicuous a part. With reference to the complaint from which King Francis is alleged to have suffered, one must not overlook the statement of a contemporary, Cardinal d’Armagnac, who, writing less than a year before the King’s death, declares that Francis enjoys as good health as any man in his kingdom (Genin’s Lettres de Marguerite, 1841, p. 473). Cardinal d’Armagnac’s intimacy with the King enabled him to speak authoritatively, and his statement refutes the assertions of Brantôme, Guyon de la Nauthe and Mézeray, besides tending to the conclusion that the youthful complaint mentioned by Louise of Savoy was merely a passing disorder.—Ed.
Brantome mentions this tale in both the First and the Fourth Discourse of his Dames Galantes. In the former, after contending that all women are naturally inclined to vice—a view which he borrows from the Roman de la Rose, and which Pope afterwards re-echoed in the familiar line, “Every woman is at heart a rake”—he proceeds to speak of those who overcome their inclinations and remain virtuous:—
“Of this,” says he, “we have a very fine story in the Hundred Tales of the Queen of Navarre; the one in which that worthy Lady of Pampeluna, vicious at heart and by inclination, burning too with love for that handsome Prince, Monsieur d’Avannes, preferred to die consumed by the fire that possessed her rather than seek a remedy for it, as she herself declared in her last words on her deathbed. This worshipful and beautiful lady dealt herself death most iniquitously and unjustly; and as I once heard a worthy man and worthy lady say of this very passage, she did really offend against God, since it was in her power to deliver herself from death; whereas in seeking it and advancing it as she did, she really killed herself. And thus have done many similar to her, who by excessive continence and abstinence have brought about the destruction both of their souls and bodies.”—Lalanne’s OEuvres de Brantôme, vol. ix. pp. 209-n.
In the Fourth Discourse of his work, Brantôme mentions the case of a “fresh and plump” lady of high repute, who, through love-sickness for one of her admirers, so wasted away that she became seriously alarmed, and for fear of worse resolved to satisfy her passion, whereupon she became “plump and beautiful as she had been before.”
“I have heard speak,” adds Brantôme, “of another very great lady, of very joyous humour, and great wit, who fell ill and whose doctor told her that she would never recover unless she yielded to the dictates of nature, whereupon she instantly rejoined: ‘Well then, let it be so;’ and she and the doctor did as they listed.... One day she said to him: ‘It is said everywhere that you have relations with me; but that is all the same to me, since it keeps me in good health... and it shall continue so, as long as may be, since my health depends on it.’ These two ladies in no wise resemble that worthy lady of Pampeluna, in the Queen of Navarre’s Hundred Tales, who, as I have previously said, fell madly in love with Monsieur d’Avannes, but preferred to hide her flame and nurse it in her burning breast rather than forego her honour. And of this I have heard some worthy ladies and lords discourse, saying that she was a fool, caring but little for the salvation of her soul, since she dealt herself death, when it was in her power to drive death away, at very trifling cost."-Lalanne’s OEuvres de Brantôme, vol. xi. pp. 542-5.
To these extracts we may add that the problem discussed by Brantôme, three hundred years ago, is much the same as that which has so largely occupied the attention of modern medical men, namely the great spread of nervous disease and melancholia among women, owing to the unnatural celibacy enforced upon them by the deficiency of husbands.—Ed.
Various French, English and Italian authors have written imitations of this tale, concerning which Dunlop writes as follows in his History of Fiction:—
“The plot of Bandello’s thirty-fifth story is the same as that of Horace Walpole’s comedy The Mysterious Mother, and of the Queen of Navarre’s thirtieth tale. The earlier portion will be found also in Masuccio’s twenty-third tale: but the second part, relating to the marriage, occurs only in Bandello’s work and the Heptameron. It is not likely, however, that the French or the Italian novelist borrowed from one another. The tales of Bandello were first published in 1554, and as the Queen of Navarre died in 1549, it is improbable that she ever had an opportunity of seeing them. On the other hand, the work of the Queen was not printed till 1558, nine years after her death, so it is not likely that any part of it was copied by Bandello, whose tales had been edited some years before.”
Walpole, it may be mentioned, denied having had any knowledge either of the Heptameron or of Bandello when he wrote The Mysterious Mother, which was suggested to him, he declared, by a tale he had heard when very young, of a lady who had waited on Archbishop Tillotson with a story similar to that which is told by Queen Margaret’s heroine to the Legate of Avignon. According to Walpole, Tillotson’s advice was identical with that given by the Legate.
Dunlop mentions that a tale of this character is given in Byshop’s Blossoms (vol. xi.); and other authors whose writings contain similar stories are: Giovani Brevio, Rime e Prose vulgari, Roma, 1545 (Novella iv.); Desfontaine’s L’Inceste innocent, histoire véritable, Paris, 1644 5 Tommaso Grappulo, or Grappolino, Il Convito Borghesiano, Londra, 1800 (Novella vii.); Luther, Colloquia Mens alia (article on auricular confession); and Masuccio de Solerac, Novellino, Ginevra, 1765 (Novella xxiii.).
Curiously enough, Bandello declares that the story was related to him by a lady of Navarre (Queen Margaret?) as having occurred in that country, while Julio de Medrano, a Spanish author of the sixteenth century, asserts that it was told to him in the Bourbonnais as being actual fact, and that he positively saw the house where the lady’s son and his wife resided; but on the other hand we find the tale related, in its broad lines, in Amadis de Gaule as being an old-time legend, and in proof of this, it figures in an ancient French poem of the life of St. Gregory, the MS. of which still exists at Tours, and was printed in 1854.
In support of the theory that the tale is based on actual fact, the following passage from Millin’s Antiquités Nationales (vol. iii. f. xxviii. p. 6) is quoted—
“In the middle of the nave of the collégial church of Ecouis, in the cross aisle, was found a white marble slab on which was inscribed this epitaph:—
“Hore lies the child, here lies the father,
Here lies the sister, here lies the brother,
Here lie the wife and the husband,
Yet there are but two bodies here.”
“The tradition is that a son of Madame d’Écouis had by his mother, without knowing her or being recognised by her, a daughter named Cecilia, whom he afterwards married in Lorraine, she then being in the service of the Duchess of Bar. Thus Cecilia was at one and the same time her husband’s daughter, sister and wife. They were interred together in the same grave at Écouis in 1512.”
According to Millin, a similar tradition will be found with variations in different parts of France. For instance, at the church of Alincourt, a village between Amiens and Abbeville, there was to be seen in Millin’s time an epitaph running as follows:—
“Here lies the son, here lies the mother,
Here lies the daughter with the father;
Here lies the sister, here lies the brother,
Here lie the wife and the husband;
And there are only three bodies here.”
Gaspard Meturas, it may be added, gives the same epitaph in his Hortus Epitaphiomm Selectorum, issued in 1648, but declares that it is to be found at Clermont in Auvergne—a long way from Amiens—and explains it by saying that the mother engendered her husband by intercourse with her own father; whence it follows that he was at the same time her husband, son and brother.—L. M. and Ed.
End of vol. III.
LONDON: PRINTED FOR THE SOCIETY OF ENGLISH BIBLIOPHILISTS
| Volume I. | Volume II. | Volume IV. | Volume V. |


| Volume I. | Volume II. | Volume III. | Volume V. |
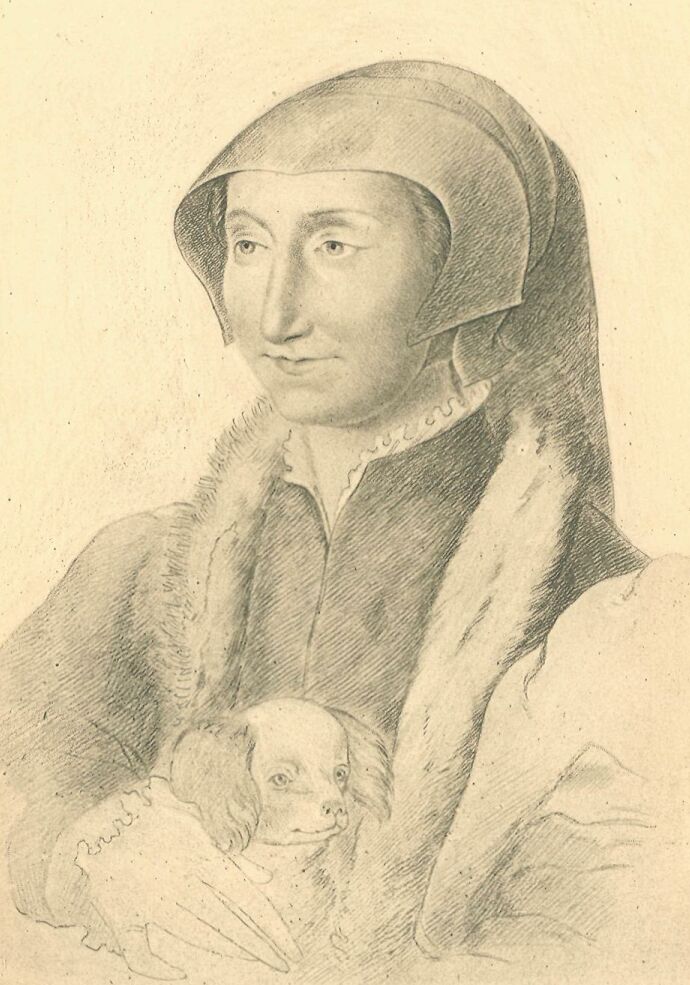


Contents
List of Illustrations
007a.jpg the Wicked Friar Captured
017a.jpg Bernage Observing the German Lady’s Strange Penance
029a.jpg the Execution of The Wicked Priest and his Sister
039a.jpg the Grey Friar Imploring The Butcher to Spare his Life
049a.jpg the Lady Embracing The Supposed Friar
063a.jpg the Clerk Entreating Forgiveness of The President
073a.jpg the Lady of Loué Bringing Her Husband The Basin Of Water
083a.jpg the Lady of Tours Questioning Her Husband’s Mistress
089a.jpg the Lord of Grignaulx Catching The Pretended Ghost
095a.jpg the Count of Jossebelin Murdering his Sister’s Husband
115a.jpg the Beating of The Wicked Grey Friar
123a.jpg the Girl Refusing The Gift of The Young Prince
143a.jpg Jambicque Repudiating Her Lover
163a.jpg the Lovers Returning from Their Meeting in The Garden
177a.jpg the Man of Tours and his Serving-maid in The Snow
195a.jpg the Young Man Beating his Wife
203a.jpg the Gentleman Reproaching his Friend for His Jealousy
213a.jpg the Grey Friars Caught and Punished
219a.jpg the Countess Facing Her Lovers
Prologue
Tale XXXI. Punishment of the wickedness of a Friar who sought to lie
with a gentleman’s wife.
Tale XXXII. How an ambassador of Charles VIII., moved by the repentance
of a German lady, whom her husband compelled to drink out of her lover’s
skull, reconciled husband and wife together.
Tale XXXIII. The hypocrisy of a priest who, under the cloak of sanctity,
had lain with his own sister, is discovered and punished by the wisdom
of the Count of Angoulême.
Tale XXXIV. The terror of two Friars who believed that a butcher
intended to murder them, whereas the poor man was only speaking of his
Pigs.
Tale XXXV. How a husband’s prudence saves his wife from the risks she
incurred while thinking to yield to merely a spiritual love.
Tale XXXVI. The story of the President of Grenoble, who saves the honour
of his house by poisoning his wife with a salad.
Tale XXXVII. How the Lady of Loué regained her husband’s affection.
Tale XXXVIII. The kindness of a townswoman of Tours to a poor
farm-woman who is mistress to her husband, makes the latter so ashamed
of his faithlessness that he returns to his wife.
Tale XXXIX. How the Lord of Grignaulx rid one of his houses of a
pretended ghost.
Tale XL. The unhappy history of the Count de Jossebelin’s sister, who
shut herself up in a hermitage because her brother caused her husband to
be slain.
Prologue
Tale XLI. Just punishment of a Grey Friar for the unwonted penance that
he would have laid upon a maiden.
Tale XLII. The virtuous resistance made by a young woman of Touraine
causes a young Prince that is in love with her, to change his desire to
respect, and to bestow her honourably in marriage.
Tale XLIII. How a little chalk-mark revealed the hypocrisy of a lady
called Jambicque, who was wont to hide the pleasures she indulged in,
beneath the semblance of austerity.
Tale XLIV. (A). Through telling the truth, a Grey Friar receives as alms
from the Lord of Sedan two pigs instead of one.
Tale XLIV. (B). Honourable conduct of a young citizen of Paris, who,
after suddenly enjoying his sweetheart, at last happily marries.
Tale XLV. Cleverness of an upholsterer of Touraine, who, to hide that
he has given the Innocents to his serving-maid, contrives to give them
afterwards to his wife.
Tale XLVI. (A). Wicked acts of a Grey Friar of Angoulême called De Vale,
who fails in his purpose with the wife of the Judge of the Exempts, but
to whom a mother in blind confidence foolishly abandons her daughter.
Tale XLVI. (B). Sermons of the Grey Friar De Vallès, at first against
and afterwards on behalf of husbands that beat their wives.
Tale XLVII. The undeserved jealousy of a gentleman of Le Perche towards
another gentleman, his friend, leads the latter to deceive him.
Tale XLVIII. Wicked act of a Grey Friar of Perigord, who, while a
husband was dancing at his wedding, went and took his place with the
bride.
Tale XLIX. Story of a foreign Countess, who, not content with having
King Charles as her lover, added to him three lords, to wit, Astillon,
Durassier and Valnebon.
Tale L. Melancholy fortune of Messire John Peter, a gentleman of
Cremona, who dies just when he is winning the affection of the lady he
loves.
Appendix to Vol. IV.
On the Fourth Day are chiefly told Tales of the
virtuous patience
and long suffering of
Ladies to win over their husbands;
and of
the prudence that Men
have used towards Women
to save the
honour of
their families and
lineage.
The Lady Oisille, as was her excellent custom, rose up on the morrow very much earlier than the others, and meditating upon her book of Holy Scripture, awaited the company which, little by little, assembled together again. And the more slothful of them excused themselves in the words of the Bible, saying, “I have a wife, and therefore could not come so quickly.” (1) In this wise it came to pass that Hircan and his wife Parlamente found the reading of the lesson already begun. Oisille, however, knew right well how to pick out the passage in the Scriptures, which reproves those who neglect the hearing of the Word, and she not only read the text, but also addressed to them such excellent and pious exhortations that it was impossible to weary of listening to her.
1 “I have married a wife, and therefore I cannot come.”—St.
Luke xiv. 20.—M.
The reading ended, Parlamente said to her—
“I felt sorry for my slothfulness when I came in, but since my error has led you to speak to me in such excellent fashion, my laziness has profited me double, for I have had rest of body by sleeping longer, and satisfaction of spirit by hearing your godly discourse.” “Well,” said Oisille, “let us for penance go to mass and pray Our Lord to give us both will and power to fulfil His commandments; and then may He command us according to His own good pleasure.”
As she was saying these words, they reached the church, where they piously heard mass. And afterwards they sat down to table, where Hircan failed not to laugh at the slothfulness of his wife. After dinner they withdrew to rest and study their parts, (2) and when the hour was come, they all found themselves at the wonted spot.
2 Meaning what they had to relate. The French word is
rolle from rotulus.—M.
Then Oisille asked Hircan to whom he would give his vote to begin the day.
“If my wife,” said he, “had not begun yesterday, I should have given her my vote, for although I always thought that she loved me more than any man alive, she has further proved to me this morning that she loves me better than God or His Word, seeing that she neglected your excellent reading to bear me company. However, since I cannot give my vote to the discreetest lady of the company, I will present it to Geburon, who is the discreetest among the men; and I beg that he will in no wise spare the monks.”
“It was not necessary to beg that of me,” said Geburon; “I was not at all likely to forget them. Only a short while ago I heard Monsieur de Saint-Vincent, Ambassador of the Emperor, tell a story of them which is well worthy of being rememorated and I will now relate it to you.”


A monastery of Grey Friars was burned down, with the monks
that were in it, as a perpetual memorial of the cruelty
practised by one among them that was in love with a lady.
In the lands subject to the Emperor Maximilian of Austria (1) there was a monastery of Grey Friars that was held in high repute, and nigh to it stood the house of a gentleman who was so kindly disposed to these monks that he could withhold nothing from them, in order to share in the benefits of their fastings and disciplines. Among the rest there was a tall and handsome friar whom the said gentleman had taken to be his confessor, and who had as much authority in the gentleman’s house as the gentleman himself. This friar, seeing that the gentleman’s wife was as beautiful and prudent as it was possible to be, fell so deeply in love with her that he lost all appetite for both food and drink, and all natural reason as well. One day, thinking to work his end, he went all alone to the house, and not finding the gentleman within, asked the lady whither he was gone. She replied that he was gone to an estate where he proposed remaining during two or three days, but that if the friar had business with him, she would despatch a man expressly to him. The friar said no to this, and began to walk to and fro in the house like one with a weighty matter in his mind.
1 Maximilian I., grandfather of Charles V. and Ferdinand
I., and Emperor of Germany from 1494 to 1519.—Ed.
When he had left the room, the lady said to one of her women (and there were but two) “Go after the good father and find out what he wants, for I judge by his countenance that he is displeased.”
The serving-woman went to the courtyard and asked the friar whether he desired aught, whereat he answered that he did, and, drawing her into a corner, he took a dagger which he carried in his sleeve, and thrust it into her throat. Just after he had done this, there came into the courtyard a mounted servant who had been gone to receive the rent of a farm. As soon as he had dismounted he saluted the friar, who embraced him, and while doing so thrust the dagger into the back part of his neck. And thereupon he closed the castle gate.
The lady, finding that her serving-woman did not return, was astonished that she should remain so long with the friar, and said to the other—
“Go and see why your fellow-servant does not come back.”
The woman went, and as soon as the good father saw her, he drew her aside into a corner and did to her as he had done to her companion. Then, finding himself alone in the house, he came to the lady, and told her that he had long been in love with her, and that the hour was now come when she must yield him obedience.
The lady, who had never suspected aught of this, replied—
“I am sure, father, that were I so evilly inclined, you would be the first to cast a stone at me.”
“Come out into the courtyard,” returned the monk, “and you will see what I have done.”
When she beheld the two women and the man lying dead, she was so terrified that she stood like a statue, without uttering a word. The villain, who did not seek merely an hour’s delight, would not take her by force, but forthwith said to her—
“Mistress, be not afraid; you are in the hands of him who, of all living men, loves you the most.”
So saying, he took off his long robe, beneath which he wore a shorter one, which he gave to the lady, telling her that if she did not take it, she should be numbered with those whom she saw lying lifeless before her eyes.
More dead than alive already, the lady resolved to feign obedience, both to save her life, and to gain time, as she hoped, for her husband’s return. At the command of the friar, she set herself to put off her head-dress as slowly as she was able; and when this was done, the friar, heedless of the beauty of her hair, quickly cut it off. Then he caused her to take off all her clothes except her chemise, and dressed her in the smaller robe he had worn, he himself resuming the other, which he was wont to wear; then he departed thence with all imaginable speed, taking with him the little friar he had coveted so long.
But God, who pities the innocent in affliction, beheld the tears of this unhappy lady, and it so happened that her husband, having arranged matters more speedily than he had expected, was now returning home by the same road by which she herself was departing. However, when the friar perceived him in the distance, he said to the lady—
“I see your husband coming this way. I know that if you look at him he will try to take you out of my hands. Go, then, before me, and turn not your head in his direction; for, if you make the faintest sign, my dagger will be in your throat before he can deliver you.”
As he was speaking, the gentleman came up, and asked him whence he was coming.
“From your house,” replied the other, “where I left my lady in good health, and waiting for you.”
The gentleman passed on without observing his wife, but a servant who was with him, and who had always been wont to foregather with one of the friar’s comrades named Brother John, began to call to his mistress, thinking, indeed, that she was this Brother John. The poor woman, who durst not turn her eyes in the direction of her husband, answered not a word. The servant, however, wishing to see her face, crossed the road, and the lady, still without making any reply, signed to him with her eyes, which were full of tears.
The servant then went after his master and said—“Sir, as I crossed the road I took note of the friar’s companion. He is not Brother John, but is very like my lady, your wife, and gave me a pitiful look with eyes full of tears.”
The gentleman replied that he was dreaming, and paid no heed to him; but the servant persisted, entreating his master to allow him to go back, whilst he himself waited on the road, to see if matters were as he thought. The gentleman gave him leave, and waited to see what news he would bring him. When the friar heard the servant calling out to Brother John, he suspected that the lady had been recognised, and with a great, iron-bound stick that he carried, he dealt the servant so hard a blow in the side that he knocked him off his horse. Then, leaping upon his body, he cut his throat.
The gentleman, seeing his servant fall in the distance, thought that he had met with an accident, and hastened back to assist him. As soon as the friar saw him, he struck him also with the iron-bound stick, just as he had struck the servant, and, flinging him to the ground, threw himself upon him. But the gentleman being strong and powerful, hugged the friar so closely that he was unable to do any mischief, and was forced to let his dagger fall. The lady picked it up, and, giving it to her husband, held the friar with all her strength by the hood. Then her husband dealt the friar several blows with the dagger, so that at last he cried for mercy and confessed his wickedness. The gentleman was not minded to kill him, but begged his wife to go home and fetch their people and a cart, in which to carry the friar away. This she did, throwing off her robe, and running as far as her house in nothing but her shift, with her cropped hair.
The gentleman’s men forthwith hastened to assist their master to bring away the wolf that he had captured. And they found this wolf in the road, on the ground, where he was seized and bound, and taken to the house of the gentleman, who afterwards had him brought before the Emperor’s Court in Flanders, when he confessed his evil deeds.
And by his confession and by proofs procured by commissioners on the spot, it was found that a great number of gentlewomen and handsome wenches had been brought into the monastery in the same fashion as the friar of my story had sought to carry off this lady; and he would have succeeded but for the mercy of Our Lord, who ever assists those that put their trust in Him. And the said monastery was stripped of its spoils and of the handsome maidens that were found within it, and the monks were shut up in the building and burned with it, as an everlasting memorial of this crime, by which we see that there is nothing more dangerous than love when it is founded upon vice, just as there is nothing more gentle or praiseworthy when it dwells in a virtuous heart. (2)
2 Queen Margaret states (ante, p. 5) that this tale was
told by M. de St.-Vincent, ambassador of Charles V., and
seems to imply that the incident recorded in it was one of
recent occurrence. The same story may be found, however, in
most of the collections of early fabliaux. See OEuvres de
Rutebeuf, vol. i. p. 260 (Frère Denise), Legrand
d’Aussy’s Fabliaux, vol. iv. p. 383, and the Recueil
complet des Fabliaux, Paris, 1878, vol. iii. p. 253. There
is also some similarity between this tale and No. LX. of the
Cent Nouvelles Nouvelles. Estienne quotes it in his
Apologie pour Hérodote, L’Estoile in his Journal du règne
de Henri III. (anno 1577), Malespini uses it in his
Ducento Novelle (No. 75), and it suggested to Lafontaine
his Cordeliers de Catalogne.—L. and M.
“I am very sorry, ladies, that truth does not provide us with stories as much to the credit of the Grey Friars as it does to the contrary. It would be a great pleasure to me, by reason of the love that I bear their Order, if I knew of one in which I could really praise them; but we have vowed so solemnly to speak the truth that, after hearing it from such as are well worthy of belief, I cannot but make it known to you. Nevertheless, I promise you that, whenever the monks shall accomplish a memorable and glorious deed, I will be at greater pains to exalt it than I have been in relating the present truthful history.”
“In good faith, Geburon,” said Oisille, “that was a love which might well have been called cruelty.”
“I am astonished,” said Simontault, “that he was patient enough not to take her by force when he saw her in her shift, and in a place where he might have mastered her.”
“He was not an epicure, but a glutton,” said Saffredent. “He wanted to have his fill of her every day, and so was not minded to amuse himself with a mere taste.”
“That was not the reason,” said Parlamente. “Understand that a lustful man is always timorous, and the fear that he had of being surprised and robbed of his prey led him, wolf-like, to carry off his lamb that he might devour it at his ease.”
“For all that,” said Dagoucin, “I cannot believe that he loved her, or that the virtuous god of love could dwell in so base a heart.”
“Be that as it may,” said Oisille, “he was well punished, and I pray God that like attempts may meet with the same chastisement. But to whom will you give your vote?”
“To you, madam,” replied Geburon; “you will, I know, not fail to tell us a good story.”
“Since it is my turn,” said Oisille, “I will relate to you one that is indeed excellent, seeing that the adventure befel in my own day, and before the eyes of him who told it to me. You are, I am sure, aware that death ends all our woes, and this being so, it may be termed our happiness and tranquil rest. It is, therefore, a misfortune if a man desires death and cannot obtain it, and so the most grievous punishment that can be given to a wrongdoer is not death, but a continual torment, great enough to render death desirable, but withal too slight to bring it nearer. And this was how a husband used his wife, as you shall hear.”



Bernage, learning in what patience and humility a German
lady submitted to the strange penance laid upon her for her
unchastity by her husband, so persuaded the latter that he
forgot the past, showed pity to his wife, and, taking her
back again, afterwards had by her some very handsome
children.
King Charles, eighth of the name, sent into Germany a gentleman called Bernage, Lord of Sivray, near Amboise, (1) who to make good speed spared not to travel both by day and night. In this wise he came very late one evening to a gentleman’s castle, where he asked for lodging, a request which was not granted him without great difficulty.
1 Bernage, Bernaige, or Vernaiges, as the name is diversely
written in the MSS. of the Heptameron, was in 1495 equerry
to Charles VIII., a post which brought him an annual salary
of 300 livres.—See Godefroy’s Histoire de Charles VIII.,
p. 705. Civray, near Chenonceaux, on the Cher, was a fief of
the barony of Amboise. In 1483 we find a certain John
Goussart doing homage for it to the crown.—Archives
Nationales, Section Domaniale, côte 3801.—L.
However, when the gentleman came to know that he was servant to so great a King, he went to him and begged him not to take the churlishness of his servants in bad part, since he was obliged to keep his house thus closed on account of certain of his wife’s kinsfolk who sought to do him hurt. Bernage then told him the nature of his mission, wherein the gentleman offered to serve the interests of the King his master, so far as in him lay; and he forthwith led Bernage into the house, where he lodged and entertained him honourably.
It was the hour for supper, and the gentleman led him into a handsome room, hung with beautiful tapestry, where, as soon as the meats were served, he saw come from behind the hangings the most beautiful woman it were possible to behold; though her head was shorn and she was dressed in black garments of the German fashion.
After the gentleman had washed his hands with Bernage, water was borne to the lady, who also washed hers and then sat down at the end of the table without speaking to the gentleman, or he to her. The Lord de Bernage looked very closely at her, and thought her one of the most beautiful women he had ever seen, except that her face was very pale, and its expression very sad.
After eating a little, she asked for drink, which was brought to her by a servant in a most marvellous vessel, for it was a death’s head, the eyeholes of which were closed with silver; and from this she drank two or three times. When she had supped, the lady washed her hands, made a reverence to the lord of the house, and retired again behind the tapestry without speaking to any one. Bernage was exceedingly amazed at this strange sight, and became very melancholy and thoughtful.
The gentleman, who perceived this, then said to him—
“I perceive that you are astonished at what you have seen at this table; but for the sake of the excellence that I find in you I will explain the matter, so that you may not think I could show such cruelty without reasons of great weight. The lady whom you saw is my wife; I loved her more than ever man loved woman, insomuch that in order to marry her I forgot all fear, and brought her hither in defiance of her relations. On her part, she showed me so many tokens of love that I would have risked ten thousand lives in bringing her hither, to her delight and mine. And here we lived for a while in such peace and gladness that I deemed myself the happiest gentleman in Christendom.
“But it came to pass, upon my undertaking a journey which my honour compelled me to make, she forgot her honour, conscience and love for me to such a degree as to fall in love with a young gentleman whom I had brought up in this house, and this I thought I could perceive when I returned home again. Nevertheless, the love I bore her was so great that I was not able to mistrust her, until at last experience opened my eyes and made me see what I dreaded more than death, whereupon my love for her was turned to frenzy and despair in such wise that I watched her closely, and one day, while feigning to walk abroad, I hid myself in the room in which she now dwells.
“Thither she withdrew soon after my departure, and sent for the young gentleman, whom I saw come in with such familiarity as should have been mine alone. But when I saw him about to get upon the bed beside her, I sprang out, seized him in her very arms, and slew him. And as my wife’s crime seemed to me so great that death would not suffice to punish it, I laid upon her a penalty which she must hold, I think, to be more bitter than death; and this penalty was to shut her up in the room to which she was wont to retire to take her greatest pleasures in the company of him for whom she had more love than she had for me; and there I further placed in a cupboard all her lover’s bones, hanging there even as precious things are hung up in a cabinet.
“That she may not lose the memory of this villain I cause her to be served with his skull, (2) in place of a cup, when she is eating and drinking at table, and this always in my presence, so that she may behold, alive, him whom her guilt has made her mortal enemy, and dead, through love of her, him whose love she did prefer to mine. And in this wise, at dinner and at supper, she sees the two things that must be most displeasing to her, to wit, her living enemy, and her dead lover; and all this through her own great sinfulness.
2 It will be remembered that the Lombard King Alboin forced
his wife Rosamond to drink his health out of a goblet which
had been made from the skull of her father Cunimond,
sovereign of the Gepidæ. To revenge herself for this
affront, Rosamond caused her husband to be murdered one
night during his sleep in his palace at Pavia.—Ed.
“In other matters I treat her as I do myself, save that she goes shorn; for an array of hair beseems not the adulterous, nor a veil the unchaste.
“For this reason is her hair cut, showing that she has lost the honour of virginity and purity. Should it please you to take the trouble to see her, I will lead you to her.”
To this Bernage willingly consented, and going-downstairs they found her in a very handsome apartment, seated all alone in front of the fire. The gentleman drew aside a curtain that hung in front of a large cupboard, wherein could be seen hanging a dead man’s bones. Bernage greatly longed to speak to the lady, but durst not do so for fear of the husband. The gentleman, perceiving this, thereupon said to him—
“If it be your pleasure to say anything to her, you will see what manner of grace and speech is hers.”
Then said Bernage to her—“Lady, your patience is as great as your torment. I hold you to be the most unhappy woman alive.”
With tears in her eyes, and with the humblest grace imaginable, the lady answered—
“Sir, I acknowledge my offence to have been so great that all the woes that the lord of this house (for I am not worthy to call him husband) may be pleased to lay upon me are nothing in comparison with the grief I feel at having offended him.”
So saying, she began to weep bitterly. The gentleman took Bernage by the arm and led him away.
On the following morning Bernage took his leave, in order to proceed on the mission that the King had given him. However, in bidding the gentleman farewell, he could not refrain from saying to him—
“Sir, the love I bear you, and the honour and friendship that you have shown me in your house, constrain me to tell you that, having regard to the deep penitence of your unhappy wife, you should, in my opinion, take compassion upon her. You are, moreover, young and have no children, and it would be a great pity that so fair a lineage should come to an end, and that those who, perhaps, have no love for you, should become your heirs.”
The gentleman, who had resolved that he would never more speak to his wife, pondered a long time on the discourse held to him by the Lord de Bernage, and at last recognised that he had spoken truly, and promised him that, if his wife should continue in her present humility, he would at some time have pity upon her.
Accordingly Bernage departed on his mission, and when he had returned to his master, the King, he told him the whole story, which the Prince, upon inquiry, found to be true. And as Bernage among other things had made mention of the lady’s beauty, the King sent his painter, who was called John of Paris, (3) that he might make and bring him a living portrait of her, which, with her husband’s consent, he did. And when she had long done penance, the gentleman, in his desire to have offspring, and in the pity that he felt for his wife who had submitted to this penance with so much humility, took her back again and afterwards had by her many handsome children. (4)
3 John Perréal, called “Jehan de Paris,” was one of the
most famous painters of the reigns of Charles VIII. and
Louis XII. At the end of 1496 we find him resident at Lyons,
and there enjoying considerable celebrity. From October 1498
to November 1499 he figures in the roll of officers of the
royal household, as valet of the wardrobe, with a salary of
240 livres. In the royal stable accounts for 1508 he appears
as receiving ten livres to defray the expense of keeping a
horse during June and July that year. He is known to have
painted the portrait and planned the obsequies of Philibert
of Savoy in 1509; to have been sent to England in 1514 to
paint a portrait of the Princess Mary, sister of Henry
VIII., who married Louis XII.; and in 1515 to have had
charge of all the decorative work connected with Louis
XII.‘s obsequies. In his Légende des Vénitiens (1509) John
Le Maire de Belges praises Perréal’s skill both in landscape
and portrait painting, and describes him as a most
painstaking and hardworking artist. He had previously
referred to him in his Temple d’Honneur et de Vertu (1504)
as being already at that period painter to the King. In the
roll of the officers of Francis I.‘s household (1522)
Perréal’s name takes precedence of that of the better known
Jehannet Clouet, but it does not appear in that of 1529,
about which time he would appear to have died. Shortly
before that date he had designed some curious initial
letters for the famous Parisian printer and bookseller,
Tory. The Claud Perréal, “Lyonnese,” whom Clement Marot
commemorates in his 36th Rondeau would appear to have been
a relative, possibly the son, of “Jehan de Paris.”—See Léon
de La Borde’s Renaissance des Arts, vol. i., Pericaud
ainé’s Notice sur Jean de Paris, Lyons, 1858, and more
particularly E. M. Bancel’s Jehan Perréal dit Jean de
Paris, peintre et valet-de-chambre des rois Charles VIII.
Louis XII., &c. Paris, Launette, 1884.—L. and M.
4 Brantôme refers to this tale, as an example of marital
cruelty, in his Vies des Dames Galantes, Lalanne’s
edition, vol. ix. p. 38.—L.
“If, ladies, all those whom a like adventure has befallen, were to drink out of similar vessels, I greatly fear that many a gilt cup would be turned into a death’s head. May God keep us from such a fortune, for if His goodness do not restrain us, there is none among us but might do even worse; but if we trust in Him He will protect those who confess that they are not able to protect themselves. Those who confide in their own strength are in great danger of being tempted so far as to be constrained to acknowledge their frailty. Many have stumbled through pride in this way, while those who were reputed less discreet have been saved with honour. The old proverb says truly, ‘Whatsoever God keeps is well kept.’”
“The punishment,” said Parlamente, “was in my opinion a most reasonable one, for, just as the offence was more than death, so ought the punishment to have been.”
“I am not of your opinion,” said Ennasuite. “I would rather see the bones of all my lovers hanging up in my cabinet than die on their account. There is no misdeed that cannot be repaired during life, but after death there is no reparation possible.”
“How can shame be repaired?” said Longarine. “You know that, whatever a woman may do after a misdeed of that kind, she cannot repair her honour.”
“I pray you,” said Ennasuite, “tell me whether the Magdalen has not now more honour among men than her sister who continued a virgin?” (5)
5 Martha, sister of Lazarus and Mary Magdalen.—M.
“I acknowledge,” said Longarine, “that we praise her for the great love she bore to Jesus Christ and for her deep repentance; yet the name of sinner clings to her.”
“I do not care what name men may give me,” said Ennasuite, “if only God forgive me, and my husband do the same. There is nothing for which I should be willing to die.”
“If the lady loved her husband as she ought,” said Dagoucin, “I am amazed that she did not die of sorrow on looking at the bones of the man whom her guilt had slain.”
“Why, Dagoucin,” returned Simontault, “have you still to learn that women know neither love nor even grief?”
“Yes, I have still to learn it,” said Dagoucin, “for I have never made trial of their love, through fear of finding it less than I desired.”
“Then you live on faith and hope,” said Nomerfide, “as the plover does on air. (6) You are easily fed.”
6 This popular error was still so prevalent in France in
the last century, that Buffon, in his Natural History, took
the trouble to refute it at length.—B. J.
“I am content,” he replied, “with the love that I feel within myself, and with the hope that there is the like in the hearts of the ladies. If I knew that my hopes were true, I should have such gladness that I could not endure it and live.”
“Keep clear of the plague,” said Geburon; “as for the other sickness you mention, I will warrant you against it. But I should like to know to whom the Lady Oisille will give her vote?”
“I give it,” she said, “to Simontault, who I know will be sparing of none.”
“That,” he replied, “is as much as to say that I am somewhat given to slander; however, I will show you that reputed slanderers have spoken the truth. I am sure, ladies, that you are not so foolish as to believe all the tales that you are told, no matter what show of sanctity they may possess, if the proof of them be not clear beyond doubt. Many an abuse lurks even under the guise of a miracle, and for this reason I am minded to tell you the story of a miracle that will prove no less to the honour of a pious Prince than to the shame of a wicked minister of the Church.”



The hypocrisy of a priest who, under the cloak of sanctity,
had got his sister with child, was discovered by the wisdom
of the Count of Angoulême, by whose command they both were
visited with punishment by law. (1)
Count Charles of Angoulême, father of King Francis, a pious Prince and one that feared God, happened to be at Coignac when he was told that in a village called Cherues, (2) not far away, there dwelt a maiden who lived a marvellously austere life, and who, for all that, was now great with child. She made no secret of the matter, but assured every one that she had never known a man and that she could not tell how such a fortune should have befallen her, unless indeed it were the work of the Holy Ghost. This explanation the people readily received, and knowing as they all did how virtuous she had been from her youth up, and how she had never given a single token of worldliness, they believed and deemed her a second Virgin Mary. She used to fast not only on the days commanded by the Church, but, from natural devotion, several times a week also; and she never stirred from the church whenever there was a service going on there. For these reasons she was held in such great repute among all the vulgar that every one came to see her as though she were a miracle, and those who succeeded in touching her dress deemed themselves fortunate indeed.
1 This tale is historical, the incidents must have occurred
between 1480 and 1490.—L.
2 Cherves-de-Cognac, now a large village of nearly 3000
inhabitants, within four miles of Cognac. The church, where
some of the incidents recorded in the tale occurred, is
still in existence. It dates from the eleventh and twelfth
centuries, and is surmounted by three cupolas.—Eu.
The priest of the parish was her brother; he was a man advanced in years and of very austere life, and was loved and reverenced by his parishioners, who held him for a holy man. He treated his sister with such harshness as to keep her shut up in a house, to the great discontent of all the people; and so greatly was the matter noised abroad that, as I have told you, the story reached the ear of the Count. He perceived that the people were being deceived, and, wishing to set them right, sent a Master of Requests and an Almoner, two very worthy men, to learn the truth. These repaired to the spot and inquired into the matter with all possible diligence, addressing themselves for information to the priest, who, being weary of the whole affair, begged them to be present at an examination which he hoped to hold on the morrow.
Early the next morning the said priest chanted mass, his sister, who was now far gone with child, being present on her knees; and when mass was over, the priest took the “Corpus Domini,” and in presence of the whole congregation said to his sister—
“Unhappy woman that you are, here is He who suffered death and agony for you, and in His presence I ask you whether, as you have ever affirmed to me, you are indeed a virgin?”
She boldly replied that she was.
“How is it possible that you can be with child and yet be still a virgin?”
“I can give no reason,” she replied, “except that the grace of the Holy Ghost has wrought within me according to His good pleasure; nevertheless, I cannot deny the grace that God has shown me in preserving me a virgin without ever a thought of marriage.”
Forthwith her brother said to her—
“I offer you the precious Body of Jesus Christ, which you will take to your damnation if it be not as you say; and the gentlemen here present on behalf of my lord the Count shall be witnesses thereof.”
The maiden, who was nearly thirty years of age, (3) then swore as follows:—
“I take this Body of Our Lord, here present, to my damnation in the presence of you, gentlemen, and of you, my brother, if ever man has touched me any more than yourself.”
And with these words she received the Body of Our Lord.
Having witnessed this, the Master of Requests and the Almoner went away quite confounded, for they thought that no lie was possible with such an oath. And they reported the matter to the Count, and tried to persuade him even as they were themselves persuaded. But he was a man of wisdom, (4) and, after pondering a long time, bade them again repeat the terms of the oath. And after weighing them well, he said—
“She has told you the truth and yet she has deceived you. She said that no man had ever touched her any more than her brother had done, and I feel sure that her brother has begotten this child and now seeks to hide his wickedness by a monstrous deception. We, however, who believe that Jesus Christ has come, can look for none other. Go, therefore, and put the priest in prison; I am sure that he will confess the truth.”
3 In the MS. followed for this edition, as well as in
Boaistuau’s-version of the Heptameron, the age is given as
“thirteen.” We borrow the word “thirty” from MS. 1518
(Béthune).—L.
4 Charles of Angoulême, father of King Francis and Queen
Margaret, had received for the times a most excellent
education, thanks to the solicitude of his father, Count
John the Good, who further took upon himself to “instruct
him in morality, showing him by a good example how to live
virtuously and honestly, and teaching him to pray God and
obey His commandments.”—Vie de très illustre et vertueux
Prince Jean, Comte d’Angoulême, by Jean du Port, Angoulême,
1589, p. 66. That Count Charles profited by this teaching is
shown in the above tale.—ED.
This was done according to his command, though not without serious remonstrances concerning the putting of this virtuous man to open shame.
Albeit, as soon as the priest had been taken, he made confession of his wickedness, and told how he had counselled his sister to speak as she had done in order to conceal the life they had led together, not only because the excuse was one easy to be made, but also because such a false statement would enable them to continue living honoured by all. And when they set before him his great wickedness in taking the Body of Our Lord for her to swear upon, he made answer that he had not been so daring, but had used a wafer that was unconsecrated and unblessed.
Report was made of the matter to the Count of Angoulême, who commanded that the law should take its course. They waited until the sister had been delivered, and then, after she had been brought to bed of a fine male child, they burned brother and sister together. And all the people marvelled exceedingly at finding beneath the cloak of holiness so horrible a monster, and beneath a pious and praiseworthy life indulgence in so hateful a crime.
“By this you see, ladies, how the faith of the good Count was not lessened by outward signs and miracles. He well knew that we have but one Saviour, who, when He said ‘Consummatum est,’ (5) showed that no room was left for any successor to work our salvation.”
5 “When Jesus therefore had received the vinegar, He said,
It is finished.”—St. John xix. 30.—M.
“It was indeed,” said Oisille, “great daring and extreme hypocrisy to throw the cloak of Godliness and true Christianity over so enormous a sin.”
“I have heard,” said Hircan, “that such as under pretext of a commission from the King do cruel and tyrannous deeds, receive a double punishment for having screened their own injustice behind the justice of the Crown. In the same way, we see that although hypocrites prosper for a time beneath the cloak of God and holiness, yet, when the Lord God lifts His cloak, they find themselves exposed and bare, and then their foul and abominable nakedness is deemed all the more hideous for having had so honourable a covering.”
“Nothing can be pleasanter,” said Nomerfide, “than to speak forth frankly the thoughts that are in the heart.”
“Yes, for profit’s sake,” (6) replied Longarine. “I have no doubt that you give your opinion according to your temper.”
6 This sentence is rather obscure in the MSS., and we have
adopted the reading suggested by M. Frank. M. Lacroix,
however, was of opinion that the sentence should run, “Yes,
for mirth’s sake.”—M.
“I will tell you what it is,” said Nomerfide. “I find that fools, when they are not put to death, live longer than wise folk, and the only reason that I know for this, is that they do not conceal their passions. If they be angry, they strike; if they be merry, they laugh: whereas those that aim at wisdom conceal their imperfections with such exceeding care that they end by thoroughly corrupting their hearts.”
“I think you are right,” said Geburon, “and that hypocrisy, whether towards God, man or Nature, is the cause of all our ills.”
“It would be a glorious thing,” said Parlamente, “if our hearts were so filled with faith in Him, who is all virtue and all joy, that we could freely show them to every one.”
“That will come to pass,” said Hircan, “when all the flesh has left our bones.”
“Yet,” said Oisille, “the Spirit of God, which is stronger than Death, is able to mortify our hearts without changing or destroying the body.”
“Madam,” returned Saffredent, “you speak of a gift of God that is not as yet common among mankind.”
“It is common,” said Oisille, “among those that have faith, but as this is a matter not to be understood by such as are fleshly minded, let us see to whom Simontault will give his vote.”
“I will give it,” said Simontault, “to Nomerfide, for, since her heart is merry, her words cannot be sad.”
“Truly,” said Nomerfide, “since you desire to laugh, I will give you reason to do so. That you may learn how hurtful are ignorance and fear, and how the lack of comprehension is often the cause of much woe, I will tell you what happened to two Grey Friars, who, through failing to understand the words of a butcher, thought that they were about to die.”



Two Grey Friars, while listening to secrets that did not
concern them, misunderstood the language of a butcher and
endangered their lives. (1)
Between Nyort and Fors there is a village called Grip, (2) which belongs to the Lord of Fors.
1 This story is evidently founded upon fact; the incidents
must have occurred prior to 1530.—L.
2 Gript, a little village on the Courance, eight miles
south of Niort (Deux-Sèvres), produces some of the best
white wine in this part of France. Its church of St. Aubin
stood partly in the diocese of Poitiers, partly in that of
Saintes, the altar being in the former, and the door in the
latter one. This is the only known instance of the kind in
France. Fors, a few miles distant from Gript, was a fief
which Catherine, daughter of Artus de Vivonne, brought in
marriage to James Poussart, knight, who witnessed the Queen
of Navarre’s marriage contract, signing himself, “Seigneur
de Fors, Bailly du Berry.” He is often mentioned in the
Queen’s letters.—See Génin’s Lettres de Marguerite, &c,
pp. 243-244, 258-259, 332.—L. and M.
It happened one day that two Grey Friars, on their way from Nyort, arrived very late at this place, Grip, and lodged in the house of a butcher. Now, as there was nothing between their host’s room and their own but a badly joined partition of wood, they had a mind to listen to what the husband might say to his wife when he was in bed with her, and accordingly they set their ears close to the head of their host’s bed. He, having no thought of his lodgers, spoke privately with his wife concerning their household, and said to her—
“I must rise betimes in the morning, sweetheart, and see after our Grey Friars. One of them is very fat, and must be killed; we will salt him forthwith and make a good profit off him.”
And although by “Grey Friars” he meant his pigs, the two poor brethren, on hearing this plot, felt sure that they themselves were spoken of, (3) and so waited with great fear and trembling for the dawn.
3 The butcher doubtless called his pigs “Grey Friars” in
allusion to the latter’s gluttony and uncleanly habits. Pigs
are even nowadays termed moines (monks) by the peasantry
in some parts of France. Moreover, the French often render
our expression “fat as a pig” by “fat as a monk.”—Ed.
One of them was very fat and the other rather lean. The fat one wished to confess himself to his companion, saying that a butcher who had lost the love and fear of God would think no more of slaughtering him than if he were an ox or any other beast; and adding that as they were shut up in their room and could not leave it without passing through that of their host, they must needs look upon themselves as dead men, and commend their souls to God. But the younger Friar, who was not so overcome with fear as his comrade, made answer that, as the door was closed against them, they must e’en try to get through the window, for, whatever befel them, they could meet with nothing worse than death; to which the fat Friar agreed.
The young one then opened the window, and, finding that it was not very high above the ground, leaped lightly down and fled as fast and as far as he could, without waiting for his companion. The latter attempted the same hazardous jump, but in place of leaping, fell so heavily by reason of his weight, that one of his legs was sorely hurt, and he could not rise from the ground.
Finding himself forsaken by his companion and being unable to follow him, he looked around him to see where he might hide, and could espy nothing save a pigsty, to which he dragged himself as well as he could. And as he opened the door to hide himself within, out rushed two huge pigs, whose place the unhappy Friar took, closing the little door upon himself, and hoping that, when he heard the sound of passers-by, he would be able to call out and obtain assistance.
As soon as the morning was come, however, the butcher got ready his big knives, and bade his wife bear him company whilst he went to slaughter his fat pig. And when he reached the sty in which the Grey Friar lay concealed, he opened the little door and began to call at the top of his voice—
“Come out, Master Grey Friar, come out! I intend to have some of your chitterlings to-day.”
The poor Friar, who was not able to stand upon his leg, crawled on all-fours out of the sty, crying for mercy as loud as he could. But if the hapless Friar was in great terror, the butcher and his wife were in no less; for they thought that St. Francis was wrathful with them for calling a beast a Grey Friar, and therefore threw themselves upon their knees asking pardon of St. Francis and his Order. Thus, the Friar was crying to the butcher for mercy on the one hand, and the butcher to the Friar on the other, in such sort that a quarter of an hour went by before they felt safe from each other.
Perceiving at last that the butcher intended him no hurt, the good father told him the reason why he had hidden himself in the sty. Then was their fear turned to laughter, except, indeed, that the poor Friar’s leg was too painful to suffer him to be merry. However, the butcher brought him into the house, where he caused the hurt to be carefully dressed.
His comrade, who had deserted him in his need, ran all night long, and in the morning came to the house of the Lord of Fors, where he lodged a complaint against the butcher, whom he suspected of killing his companion, seeing that the latter had not followed him. The Lord of Fors forthwith sent to Grip to learn the truth, and this, when known, was by no means the cause of tears. And he failed not to tell the story to his mistress the Duchess of Angoulême, mother of King Francis, first of that name. (4)
4 Many modern stories and anecdotes have been based on this
amusing tale.—Ed.
“You see, ladies, how bad a thing it is to listen to secrets that do not concern us, and to misunderstand what other people say.”
“Did I not know,” said Simontault, “that Nomer-fide would give us no cause to weep, but rather to laugh? And I think that we have all done so very heartily.”
“How comes it,” said Oisille, “that we are more ready to be amused by a piece of folly than by something wisely done?”
“Because,” said Hircan, “the folly is more agreeable to us, for it is more akin to our own nature, which of itself is never wise. And like is fond of like, the fool of folly, and the wise man of discretion. But I am sure,” he continued, “that no one, whether foolish or wise, could help laughing at this story.”
“There are some,” said Geburon, “whose hearts are so bestowed on the love of wisdom that, whatever they may hear, they cannot be made to laugh. They have a gladness of heart and a moderate content such as nought can move.”
“Who are they?” asked Hircan.
“The philosophers of olden days,” said Geburon. “They were scarcely sensible of either sadness or joy, or at least they gave no token of either, so great a virtue did they deem the conquest of themselves and their passions. I too think, as they did, that it is well to subdue a wicked passion, but a victory over a natural passion, and one that tends to no evil, appears useless in my eyes.”
“And yet,” added Geburon, “the ancients held it for a great virtue.”
“It is not maintained,” said Saffredent, “that they all were wise. They had more of the appearance of sense and virtue than of the reality.”
“Nevertheless, you will find that they rebuke everything bad,” said Geburon. “Diogenes himself, even, trod on the bed of Plato, who was too fond (5) of rare and precious things for his taste, and this in order to show that he despised Plato’s vanity and greed, and would put them under foot. ‘I trample with contempt,’ said he, ‘upon the pride of Plato.’”
“But you have not told all,” said Saffredent, “for Plato retorted that he did so from pride of another kind.”
“In truth,” said Parlamente, “it is impossible to accomplish the conquest of ourselves without extraordinary pride. And this is the vice that we should fear most of all, for it springs from the death and destruction of all the virtues.”
“Did I not read to you this morning,” said Oisille, “that those who thought themselves wiser than other men, since by the sole light of reason they had come to recognise a God, creator of all things, were made more ignorant and irrational not only than other men, but than the very brutes, and this because they did not ascribe the glory to Him to whom it was due, but thought that they had gained the knowledge they possessed by their own endeavours? For having erred in their minds by ascribing to themselves that which pertains to God alone, they manifested their errors by disorder of body, forgetting and perverting their natural sex, as St. Paul to-day doth tell us in the Epistle that he wrote to the Romans.” (6)
5 The French word here is curieux, which in Margaret’s
time implied one fond of rare and precious things.—B. J
6 Romans i. 26, 27.—Ed.
“There is none among us,” said Parlamente, “but will confess, on reading that Epistle, that outward sin is but the fruit of infelicity dwelling within, which, the more it is hidden by virtue and marvels, is the more difficult to pluck out.”
“We men,” said Hircan, “are nearer to salvation than you are, for we do not conceal our fruits, and so the root is readily known; whereas you, who dare not display the fruit, and who do so many seemingly fair deeds, are hardly aware of the root of pride that is growing beneath so brave a surface.”
“I acknowledge,” said Longarine, “that if the Word of God does not show us by faith the leprosy of unbelief that lurks in the heart, yet God is very merciful to us when He allows us to fall into some visible wrongdoing whereby the hidden plague may be made manifest. Happy are they whom faith has so humbled that they have no need to test their sinful nature by outward acts.”
“But just look where we are now,” said Simontault. “We started from a foolish tale, and we are now fallen into philosophy and theology. Let us leave these disputes to such as are more fitted for such speculation, and ask Nomerfide to whom she will give her vote.”
“I give it,” she said, “to Hircan, but I commend to him the honour of the ladies.”
“You could not have commended it in a better place,” said Hircan, “for the story that I have ready is just such a one as will please you. It will, nevertheless, teach you to acknowledge that the nature of men and women is of itself prone to vice if it be not preserved by Him to whom the honour of every victory is due. And to abate the pride that you display when a story is told to your honour, I will tell you one of a different kind that is strictly true.”



The affection of a lady of Pampeluna—who, thinking that
there was no danger in spiritual love, had striven to
insinuate herself into the good graces of a Grey Friar—was
subdued by her husband’s prudence in such wise that, without
telling her that he knew aught of the matter, he brought her
mortally to hate that which she had most dearly loved, and
wholly to devote herself to him.
In the town of Pampeluna there lived a lady who was accounted beautiful and virtuous, as well as the chastest and most pious in the land. She loved her husband, and was so obedient to him that he had entire trust in her. This lady was constantly present at Divine service and at sermons, and she used to persuade her husband and children to be hearers with her. She had reached the age of thirty years, at which women are wont to claim discretion rather than beauty, when on the first day of Lent she went to the church to receive the emblem of death. (1) Here she found that the sermon was beginning, the preacher being a Grey Friar, a man esteemed holy by all the people on account of his great austerity and goodness of life, which made him thin and pale, yet not to such a point as to prevent him from being one of the handsomest men imaginable.
The lady listened piously to his sermon, her eyes being fixed on this reverend person, and her ears and mind ready to hearken to what he said. And so it happened that the sweetness of his words passed through the lady’s ears even to her heart, while the comeliness and grace of his countenance passed through her eyes and so smote her soul that she was as one entranced. When the sermon was over, she looked carefully to see where the Friar would celebrate mass, (2) and there she presented herself to take the ashes from his hand. The latter was as fair and white as any lady’s, and this pious lady paid more attention to it than to the ashes which it gave her.
1 To receive the ashes on Ash Wednesday.—M.
2 That is, in which of the chapels. A friar would not
officiate at the high altar.—Ed.
Feeling persuaded that a spiritual love such as this, with any pleasure that she might derive from it, could not wound her conscience, she failed not to go and hear the sermon every day and to take her husband with her; and they both gave such great praise to the preacher, that they spoke of nought beside at table or elsewhere. At last this supposed spiritual fire became so carnal that the poor lady’s heart in which it glowed began to consume her whole body; and just as she had been slow to feel the flame, so did she now swiftly kindle, and feel all the delights of passion, before she knew that she even was in love. Being thus surprised by her enemy, Love, she offered no further resistance to his commands. But the worst was that the physician who might have cured her ills was ignorant of her distemper; for which reason, banishing the dread she should have had of making known her foolishness to a man of wisdom, and her vice and wickedness to a man of virtue and honour, she proceeded to write to him of the love she bore him, doing this, to begin with, as modestly as she could. And she gave her letter to a little page, telling him what he had to do, and saying that he was to be careful above all things that her husband should not see him going to the monastery of the Grey Friars.
The page, desiring to take the shortest way, passed through a street in which his master was sitting in a shop. Seeing him pass, the gentleman came out to observe whither he was going, and when the page perceived him, he was quite confused, and hid himself in a house. Noticing this, his master followed him, took him by the arm and asked him whither he was bound. Finding also that he had a terrified look and made but empty excuses, he threatened to beat him soundly if he did not confess the truth.
“Alas, sir,” said the poor page, “if I tell you, my lady will kill me.”
The gentleman, suspecting that his wife was making some bargain without his knowledge, promised the page that he should come by no hurt, and should be well rewarded, if he told the truth; whereas, if he lied, he should be thrown into prison for life. Thereupon the little page, eager to have the good and to avoid the evil, told him the whole story, and showed him the letter that his mistress had written to the preacher. At this her husband was the more astonished and grieved, as he had all his life long been persuaded of the faithfulness of his wife, in whom he had never discovered a fault.
Nevertheless, being a prudent man, he concealed his anger, and so that he might fully learn his wife’s intention, he sent a reply as though from the preacher, thanking her for her goodwill, and declaring that his was as great towards her. The page, having sworn to his master that he would conduct the matter with discretion, (3) brought the counterfeit letter to his mistress, who was so greatly rejoiced by it that her husband could see that her countenance was changed; for, instead of growing lean from the fasts of Lent, she now appeared fairer and fresher than before they began.
3 This is borrowed from MS. 1520. In our MS. the passage
runs, “The page having shown his master how to conduct this
affair,” &c.—L.
It was now mid-Lent, but no thought of the Passion or Holy Week prevented the lady from writing her frenzied fancies to the preacher according to her wont; and when he turned his eyes in her direction, or spoke of the love of God, she thought that all was done or said for love of her; and so far as her eyes could utter her thoughts, she did not spare them.
The husband never failed to return her similar answers, but after Easter he wrote to her in the preacher’s name, begging her to let him know how he could secretly see her. She, all impatient for the meeting, advised her husband to go and visit some estates of theirs in the country, and this he agreed to do, hiding himself, however, in the house of a friend. Then the lady failed not to write to the preacher that it was time he should come and see her, since her husband was in the country.
The gentleman, wishing thoroughly to try his wife’s heart, then went to the preacher, and begged him for the love of God to lend him his robe. The preacher, who was a man of worth, replied that the rules of his Order forbade it, and that he would never lend his robe for a masquerade. (4) The gentleman assured him, however, that he would make no evil use of it, and that he wanted it for a matter necessary to his happiness and his salvation. Thereupon the Friar, who knew the other to be a worthy and pious man, lent it to him; and with this robe, which covered his face so that his eyes could not be seen, the gentleman put on a false beard and a false nose, each similar to the preacher’s. He also made himself of the same height by means of cork. (5)
4 This may be compared with the episode of Tappe-coue or
Tickletoby in Pantagruel:—“Villon, to dress an old clownish
father grey-beard, who was to represent God the Father [at
the performance of a mystery], begged of Friar Stephen
Tickletoby, sacristan to the Franciscan Friars of the place,
to lend him a cope and a stole. Tickletoby refused him,
alleging that by their provincial statutes it was rigorously
forbidden to give or lend anything to players. Villon
replied that the statute reached no further than farces,
drolls, antics, loose and dissolute games.... Tickletoby,
however, peremptorily bid him provide himself elsewhere, if
he would, and not to hope for anything out of his monastical
wardrobe.... Villon gave an account of this to the players
as of a most abominable action; adding that God would
shortly revenge himself and make an example of Tickletoby.”—
Urquhart’s Works of Rabelais, Pantagruel, (Book IV.
xiii.)—M.
5 In Boaistuau’s edition the sentence runs, “and by putting
some cork in his shoes made himself of the same height as
the preacher.”—L.
Thus garmented, he repaired in the evening to his wife’s apartment, where she was very piously awaiting him. The poor fool did not tarry for him to come to her, but ran to embrace him like a woman bereft of reason. Keeping his face bent down lest he should be recognised, he then began making the sign of the cross, and pretended to flee from her, saying the while nothing but—
“Temptation! temptation!”
“Alas, father,” said the lady, “you are indeed right, for there is no stronger temptation than that which proceeds from love. But for this you have promised me a remedy; and I pray you, now that we have time and opportunity, to take pity upon me.”
So saying, she strove to embrace him, but he ran all round the room, making great signs of the cross, and still crying—
“Temptation! temptation!”
However, when he found that she was urging him too closely, he took a big stick that he had beneath his cloak and beat her so sorely as to end her temptation, and that without being recognised by her. Then he immediately went and returned the robe to the preacher, assuring him that it had brought him good fortune.
On the morrow, pretending to come from a distance, he returned home and found his wife in bed, when, as though he knew nothing of her sickness, he asked her the cause of it; and she replied that it was a catarrh, and that she could move neither hand nor foot. The husband, who was much inclined to laugh, made as though he were greatly grieved, and as if to cheer her told her that he had bidden the saintly preacher to supper that evening. But she quickly replied—
“God forbid, sweetheart, that you should ever invite such folk. They bring misfortune into every house they visit.”
“Why, sweet,” said the husband, “how is this? You have always greatly praised this man, and for my own part I believe that if there be a holy man on earth, it is he.”
“They are good in church and when preaching,” answered the lady, “but in our houses they are very antichrists. I pray you, sweet, let me not see him, for with my present sickness it would be enough to kill me.”
“Since you do not wish to see him,” returned the husband, “you shall not do so, but I must have him here to supper.”
“Do what you will,” she replied, “but let me not see him, for I hate such folk as I do the devil.”
After giving supper to the good father, the husband said to him—
“Father, I believe you to be so beloved of God, that He will refuse you no request. I therefore entreat you to take pity on my poor wife, who for a week past has been possessed by the evil spirit in such a way, that she tries to bite and scratch every one. She cares for neither cross nor holy water, but I verily believe that if you will lay your hand upon her the devil will come forth, and I therefore earnestly entreat you to do so.”
“My son,” said the good father, “all things are possible to a believer. Do you, then, firmly believe that God in His goodness never refuses those that in faith seek grace from Him?”
“I do, father,” said the gentleman.
“Be also assured, my son,” said the friar, “that He can do what He will, and that He is even as powerful as He is good. Let us go, then, strong in faith to withstand this roaring lion, and to pluck from him his prey, whom God has purchased by the blood of Jesus Christ, His Son.”
Accordingly, the gentleman led this worthy man to where his wife lay on a little bed. She, thinking that it was the Friar who had beaten her, was much astonished to see him there and exceedingly wrathful; however, her husband being present, she cast down her eyes, and remained dumb.
“As long as I am with her,” said the husband to the holy man, “the devil scarcely torments her. But sprinkle some holy water upon her as soon as I am gone, and you will soon see how the evil spirit does his work.”
The husband left them alone together, and waited at the door to see how they would behave. When the lady saw no one with her but the good father, she began to cry out like a woman bereft of reason, calling him rascal, villain, murderer, betrayer. At this, the good father, thinking that she was surely possessed by an evil spirit, tried to put his hands upon her head, in order to utter his prayers upon it; but she scratched and bit him in such a fashion, that he was obliged to speak at a greater distance, whence, throwing a great deal of holy water upon her, he pronounced many excellent prayers.
When the husband saw that the Friar had done his duty, he came into the room and thanked him for his trouble. At his entrance his wife ceased her cursings and revilings, and meekly kissed the cross in the fear she had of him. But the holy man, having seen her in so great a frenzy, firmly believed that Our Lord had cast out the devil in answer to his prayer, and he went away, praising God for this wonderful miracle.
The husband, seeing that his wife was well punished for her foolish fancy, did not tell her of what he had done. He was content to have subdued her affection by his own prudence, and to have so dealt with her that she now hated mortally what she had formerly loved, and, loathing her folly, devoted herself to her husband and household more completely than she had ever done before.
“In this story, ladies, you see the good sense of a husband and the frailty of a woman of repute. I think that if you look carefully into this mirror you will no longer trust to your own strength, but will learn to have recourse to Him who holds your honour in His hand.”
“I am well pleased,” said Parlamente, “to find you become a preacher to the ladies, and I should be even more so if you would make these fine sermons to all those with whom you speak.”
“Whenever you are willing to listen to me,” said Hircan, “I promise you that I will say as much.”
“In other words,” said Simontault, “when you are not present, he will speak in a different fashion.”
“He will do as he pleases,” said Parlamente, “but for my content I wish to believe that he always speaks in this way. At all events, the example he has brought forward will be profitable to those who believe that spiritual love is not dangerous. In my opinion it is more so than any other.”
“Yet,” said Oisille, “it seems to me that to love a worthy, virtuous and God-fearing man is in nowise a matter for scorn, and that one cannot but be the better for it.”
“Madam,” said Parlamente, “I pray you believe that no one can be more simple or more easily deceived than a woman who has never loved. For in itself love is a passion that seizes upon the heart before one is aware of it, and so pleasing a passion is it that, if it can make use of virtue as a cloak, it will scarcely be recognised before some mischief has come of it.”
“What mischief,” asked Oisille, “can come of loving a worthy man?”
“Madam,” said Parlamente, “there are a good many men that are esteemed worthy, but to be worthy in respect of the ladies, and to be careful for their honour and conscience—not one such man as that could, I think, be found in these days. Those who think otherwise, and put their trust in men, find at last that they have been deceived, and, having begun such intimacy with obedience to God, will often end it with obedience to the devil. I have known many who, under pretext of speaking about God, began an intimacy from which they could not withdraw when at last they wished to do so, being held in subjection by this semblance of virtue. A vicious love perishes of its own nature, and cannot continue in a good heart, but virtuous love has bonds of silk so fine that one is caught in them before they are seen.”
“According to you,” said Ennasuite, “no woman should ever love a man; but your law is too harsh a one to last.”
“I know that,” said Parlamente, “but none the less must I desire that every one were as content with her own husband as I am with mine.”
Ennasuite, who felt that these words touched her, changed colour and said—
“You ought to believe every one the same at heart as yourself, unless, indeed, you think yourself more perfect than all others.”
“Well,” said Parlamente, “to avoid dispute, let us see to whom Hircan will give his vote.”
“I give it,” Hircan replied, “to Ennasuite, in order to make amends to her for what my wife has said.”
“Then, since it is my turn,” said Ennasuite, “I will spare neither man nor woman, that all may fare alike. I see right well that you are unable to subdue your hearts to acknowledge the virtue and goodness of men, for which reason I am obliged to resume the discourse with a story like to the last.”



By means of a salad a President of Grenoble avenged himself
upon one of his clerks with whom his wife was smitten, and
so saved the honour of his house.
In the town of Grenoble there dwelt a President whose name I shall not mention, but he was not a Frenchman. (1) He had a very beautiful wife, and they lived in great tranquillity together.
1 The personage referred to is Jeffroy Charles or Carles,
Chief President of the Parliament of Grenoble, and President
of the Senate of Turin; his wife’s name was Margaret du
Mottet; she came of a very old family of Embrun. Some
interesting particulars concerning President Charles,
supplied by that erudite scholar M. Jules Roman, will be
found in the Appendix to the present volume (A).—Ed.
This lady, finding that her husband was now old, fell in love with a young clerk, called Nicholas. When the President went to the court in the morning, Nicholas used to enter his room and take his place. This was observed by a servant of the President’s who had served his master well for thirty years, and in his faithfulness he could not refrain from speaking to him of the matter.
The President, being a prudent man, would not lightly believe the story, but said that the servant wished to create contention between himself and his wife. If the matter, said he, were really as the servant declared, he could easily prove it to him, and if proof were not given he would believe that it was a lie contrived in order to destroy the love existing between himself and his wife. The servant promised that he would show him the truth of what he had said, and one morning, as soon as the President was gone to the court and Nicholas had entered the room, he sent one of his fellow-servants to tell his master to come, while he himself remained watching at the door lest Nicholas should come out.
As soon as the President saw the sign that was made to him by one of his servants, he pretended to be ill, left the court and hastened home. Here he found his old servant at the door, and was assured by him that Nicholas was inside and had only just gone in.
“Do not stir from this door,” said his lord to him, “for, as you are aware, there is no other means of going into or out of the room, except indeed by way of a little closet of which I myself alone carry the key.”
The President entered the room and found his wife and Nicholas in bed together. The clerk, clad in nothing but his shirt, threw himself at his feet to entreat forgiveness, while his wife began to weep.
Then said the President—
“Though you have done a deed the enormity of which you may yourself judge, I am yet unwilling that my house should be dishonoured on your account, and the daughters I have had by you made to suffer. Wherefore,” he continued, “cease to weep, I command you, and hearken to what I am going to do; and do you, Nicholas, hide yourself in my closet and make not a single sound.”
When this was done, he opened the door, and calling his old servant, said to him—
“Did you not assure me that you would show me Nicholas in company with my wife? Trusting in your word, I came hither in danger of killing my poor wife, and I have found nothing of what you told me. I have searched the whole room, as I will show you.”
So saying, he caused his servant to look under the beds and in every quarter. The servant, finding nothing, was greatly astonished, and said to his master—
“The devil must have made away with him, for I saw him go in, and he did not come out through the door. But I can see that he is not here.”
Then said his master to him—
“You are a wicked servant to try to create contention in this way between my wife and me. I dismiss you, and will pay you what I owe you for your services to me, and more besides; but be speedily gone, and take care that you are not in the town twenty-four hours from now.”
The President paid him for five or six years in advance, and, knowing him to be a faithful servant, resolved to reward him still further.
When the servant was gone weeping away, the President made Nicholas come forth from the closet, and after telling them both what he thought of their wickedness, he commanded them to give no hint of the matter to anyone. He also charged his wife to dress more bravely than was her wont, and to attend all assemblies, dances and feasts; and he told Nicholas to make more merry than before, but, as soon as he whispered to him, “Begone,” to see that he was out of the town before three hours were over. Having arranged matters in this way, he returned to the court, none being any the wiser. And for a fortnight, contrary to his wont, he entertained his friends and neighbours, and after the banquet had the tabourers, so that the ladies might dance.
One day, seeing that his wife was not dancing, he commanded Nicholas to lead her out. The clerk, thinking that the past had been forgotten, did so gladly, but when the dance was over, the President, under pretence of charging him with some household matter, whispered to him, “Begone, and come back no more.” And albeit Nicholas was grieved to leave his mistress, yet was he no less glad that his life was spared.
When the President had convinced all his kinsfolk and friends and the whole countryside of the deep love that he bore his wife, he went into his garden one fine day in the month of May to gather a salad, of such herbs that his wife did not live for twenty-four hours after eating of them; whereupon he made such a great show of mourning that none could have suspected him of causing her death; and in this way he avenged himself upon his enemy, and saved the honour of his house. (2)
2 Whilst admitting the historical basis of this story, M.
Le Roux de Lincy conceives it to be the same as No. xlvii.
of the Cent Nouvelles Nouvelles, printed half-a-century
before the Heptameron was written. Beyond the
circumstance, however, that in both cases a judge is shown
privily avenging himself on his wife for her infidelity,
there is no resemblance between the two tales. There is good
reason for believing that Queen Margaret’s narrative is
based on absolute fact, and not on the story in the Cent
Nouvelles. Both tales have often been imitated. See for
instance Bonaventure Despéricr’s Contes, Nouvelles, et
joyeux Devis (tale xcii., or, in some editions, xc. ); Les
Heures de Récréation de Louis Guicciardini, p. 28; G.
Giraldi Cinthio’s Hecatommithi, overro cento Novelle, &c.
(dec. iii. nov. vi. ); Malespini’s Ducento Novelle (part
ii. nov. xvi.); Verboquet’s Les Délices, &c, 1623, p. 23;
and Shirley’s Love’s Cruelly. These tales also inspired
some of the Spanish dramatists, notably Calderon.—Ed. and
L.
“I do not mean by this, ladies, to praise the President’s conscience, but rather to bring out the frailty of a woman and the great patience and prudence of a man. And I beg you, ladies, be not angered by the truth, which sometimes speaks as loudly against ourselves as against the men; for vice and virtue are common alike to men and women.”
“If all those,” said Parlamente, “who have fallen in love with their servants were obliged to eat salads of that kind, I know some who would be less fond of their gardens than they are at present, and who would pluck up the herbs to get rid of such as restore the honour of a family by compassing the death of a wanton mother.”
Hircan, who guessed why she had said this, angrily replied—“A virtuous woman should never judge another guilty of what she would not do herself.”
“Knowledge is not judgment nor yet foolishness,” returned Parlamente. “However, this poor woman paid the penalty that many others have deserved, and I think that the President, when desirous of vengeance, comported himself with wondrous prudence and wisdom.”
“And with great malevolence, also,” said Longarine. “‘Twas a slow and cruel vengeance, and showed he had neither God nor conscience before his eyes.”
“Why, what would you have had him do,” said Hircan, “to revenge himself for the greatest wrong that a woman can deal to a man?”
“I would have had him kill her in his wrath,” she replied. “The doctors say that since the first impulses of passion are not under a man’s control, such a sin may be forgiven; so it might have obtained pardon.” “Yes,” said Geburon, “but his daughters and descendants would have always borne the stain.”
“He ought not to have killed her at all,” said Longarine, “for, when his wrath was past, she might have lived with him in virtue, and nothing would ever have been said about the matter.”
“Do you think,” said Saffredent, “that he was appeased merely because he concealed his anger? For my part, I believe that he was as wrathful on the last day, when he made his salad, as he had been on the first, for there are persons whose first impulses have no rest until their passion has worked its will. I am well pleased you say that the theologians deem such sins easy to be pardoned, for I am of their opinion.”
“It is well to look to one’s words,” said Longarine, “in presence of persons so dangerous as you. What I said is to be understood of passion when it is so strong that it suddenly seizes upon all the senses, and reason can find no place.”
“It is so,” said Saffredent, “that I understood your words, and I thence conclude that, whatever a man may do, he can commit only venial sin if he be deeply in love. I am sure that, if Love hold him fast bound, Reason can never gain a hearing, whether from his heart or from his understanding. And if the truth be told, there is not one among us but has had knowledge of such passion; and not merely do I think that sin so committed is readily pardoned, but I even believe that God is not angered by it, seeing that such love is a ladder whereby we may climb to the perfect love of Himself. And none can attain to this save by the ladder of earthly love, (3) for, as St. John says, ‘He that loveth not his brother whom he hath seen, how can he love God whom he hath not seen?’” (4)
3 All this passage is borrowed, almost word for word, from
Castiglione’s Libro del Cortegiano. See ante, vol. i. p.
10.—B.J.
4 i John iv. 20.—M.
“There is not a passage in Scripture,” said Oisille, “too good for you to turn to your own purposes. But beware of doing like the spider, which transforms sound meat into poison. Be advised that it is a perilous matter to quote Scripture out of place and without cause.”
“Do you call speaking the truth out of place and without cause?” said Saffredent. “You hold, then, that when, in speaking to you unbelieving women, we call God to our assistance, we take His name in vain; but if there be any sin in this, you alone must bear the blame, for it is your unbelief that compels us to seek out all the oaths that we can think of. And in spite of it all, we cannot kindle the flame of charity in your icy hearts.”
“That,” said Longarine, “proves that you all speak falsely. If truth were in your words, it is strong enough to make you be believed. Yet there is danger lest the daughters of Eve should hearken too readily to the serpent.”
“I see clearly,” said Saffredent, “that women are not to be conquered by men. So I shall be silent, and see to whom Ennasuite will give her vote.”
“I give it,” she said, “to Dagoucin, for I think he would not willingly speak against the ladies.”
“Would to God,” said Dagoucin, “that they were as well disposed towards me as I am towards them. To show you that I have striven to honour the virtuous among them by recalling their good deeds, I will now tell you the story of such a one. I will not deny, ladies, that the patience of the gentleman at Pampeluna, and of the President at Grenoble was great, but then it was equalled in magnitude by their vengeance. Moreover, when we seek to praise a virtuous man, we ought not so to exalt a single virtue as to make of it a cloak for the concealment of grievous vice; for none are praiseworthy save such as do virtuous things from the love of virtue alone, and this I hope to prove by telling you of the patient virtue of a lady whose goodness had no other object save the honour of God and the salvation of her husband.”



The Lady of Loué so influenced her husband by her great
patience and longsuffering, that she drew him from his evil
ways, and they lived afterwards in greater love than
before.
There was a lady of the house of Loué (1) who was so prudent and virtuous, that she was loved and esteemed by all her neighbours. Her husband trusted her, as well he might, with all his affairs, and she managed them with such wisdom that his house came, by her means, to be one of the wealthiest and best appointed in either the land of Anjou or Touraine.
1 Loué is in Anjou, in the department of the Sarthe, being
the chief locality of a canton of the arrondissement of Le
Mans. The Lady of Loué referred to may be either Philippa de
Beaumont-Bressuire, wife of Peter de Laval, knight, Lord of
Loué, Benars, &c.; or her daughter-in-law, Frances de
Maillé, who in or about 1500 espoused Giles de Laval, Lord
of Loué. Philippa is known to have died in 1525, after
bearing her husband five children. She had been wedded fifty
years. However, the subject of this story is the same as
that of the Lady of Langallier, or Languillier (also in
Anjou), which will be found in chapter xvii. of Le Livre du
Chevalier de la Tour-Landry, an English translation of
which, made in the reign of Henry VI., was edited in 1868 by
Mr. Thomas Wright for the Early English Text Society.—See
also Le Roux de Lincy’s Femmes célèbres de l’ancienne
France, vol i. p. 356. Particulars concerning the Laval-
Loué family will be found in Duchesne’s Histoire de la
Maison de Montmorency.—L. and M.
In this fashion she lived a great while with her husband, to whom she bore several handsome children; but then, as happiness is always followed by its opposite, hers began to be lessened. Her husband, finding virtuous ease to be unendurable, laid it aside to seek for toil, and made it his wont to rise from beside his wife as soon as she was asleep, and not to return until it was nearly morning. The lady of Loué took this conduct ill, and falling into a deep unrest, of which she was fain to give no sign, neglected her household matters, her person and her family, like one that deemed herself to have lost the fruit of her toils, to wit, her husband’s exceeding love, for the preserving of which there was no pain that she would not willingly have endured. But having lost it, as she could see, she became careless of everything else in the house, and the lack of her care soon brought mischief to pass.
Her husband, on the one part, spent with much extravagance, while, on the other, she had ceased to control the management, so that ere long affairs fell into such great disorder, that the timber began to be felled, and the lands to be mortgaged.
One of her kinsfolk that had knowledge of her distemper, rebuked her for her error, saying that if love for her husband did not lead her to care for the advantage of his house, she should at least have regard to her poor children. Hereat her pity for them caused her to recover herself, and she tried all means to win back her husband’s love.
In this wise she kept good watch one night, and, when he rose from beside her, she also rose in her nightgown, let make her bed, and said her prayers until her husband returned. And when he came in, she went to him and kissed him, and brought him a basin full of water that he might wash his hands. He was surprised at this unwonted behaviour, and told her that there was no need for her to rise, since he was only coming from the latrines; whereat she replied that, although it was no great matter, it was nevertheless a seemly thing to wash one’s hands on coming from so dirty and foul a place, intending by these words to make him perceive and abhor the wickedness of his life. But for all that he did not mend his ways, and for a full year the lady continued to act in this way to no purpose.
Accordingly, seeing that this behaviour served her naught, one day, while she was waiting for her husband, who tarried longer than ordinary, she had a mind to go in search of him, and, passing from room to room, found him at last in a closet at the back of the house, lying asleep by the side of the ugliest, vilest, and filthiest serving-woman they had.
Thereupon, thinking she would teach him to leave so excellent a wife for so filthy and vile a woman, she took some straw and set it on fire in the middle of the room; but on seeing that it would as soon kill her husband as awaken him, she plucked him by the arm, crying out—
“Fire! fire!”
If the husband was ashamed and sorry at being found by so virtuous a wife in company with such a slut, he certainly had good reason for it. Then said his wife to him—
“For a year, sir, have I tried by gentle and patient means to draw you from this wickedness, and to show you that whilst washing the outside you should also cleanse that which is within. Finding that all I could do was of no avail, I have sought assistance from that clement which brings all things to an end, and I promise you, sir, that, if this do not mend you, I know not whether I shall a second time be able to deliver you from the danger as I have now done. I pray you remember that the deepest despair is that caused by love, and that if I had not had the fear of God before my eyes I could not have endured so much.”
The husband, glad to get off so easily, promised that he would never again cause her any pain on his account. This the lady was very willing to believe, and with her husband’s consent turned away the servant who had so offended her. And from that time forth they lived most lovingly together, so that even the errors of the past, by the good that had resulted from them, served but to increase their happiness.
“Should God give you such husbands, ladies, I pray you despair not until you have fully tried all means to win them back. There are twenty-four hours in the day in which a man may change his mind, and a wife who has gained her husband over by patience and longsuffering should deem herself more fortunate than if fate and her kinsfolk had given her one more perfect.”
“It is an example,” said Oisille, “that all married women ought to follow.”
“Follow it who will,” said Parlamente; “for my own part, I should find it impossible to be patient so long. Although in every condition patience is a seemly virtue, yet I think that in wedded life it finally produces ill-will. For, when suffering is caused you by your partner, you are compelled to keep yourself as much apart from him as possible; and from such estrangement there springs up contempt for the faithless one; and this contempt gradually lessens love, for a thing is loved in proportion as it is esteemed.”
“But there is a danger,” said Ennasuite, “that the impatient wife may meet with a passionate husband who, instead of patience, will bring her pain.”
“And what more,” said Parlamente, “could a husband do than was done by the husband in the story?”
“What more?” said Ennasuite. “Why, beat his wife soundly, and make her lie in the smaller bed, and his sweetheart in the larger.” (2)
2 At this period, and for some time afterwards, there were
usually two beds in the master’s room, a large one for
himself and his wife, and a small one in which slept a
trusty servant, male or female. These little beds are shown
in some of the designs engraved by Abraham Bosse in the
seventeenth century.—L.
“It is my belief,” said Parlamente, “that a true woman would be less grieved by being beaten in anger than by being contemned for one of less worth than herself. After enduring the severance of love, nothing that her husband could do would be able to cause her any further pain. And in this wise the story says that the trouble she took to regain him was for the sake of her children—which I can well believe.”
“And do you think that it showed great patience on her part,” said Nomerfide, “to kindle a fire beneath the bed on which her husband was sleeping.”
“Yes,” said Longarine; “for when she saw the smoke she waked him, and herein, perhaps, was she most to blame; for the ashes of such a husband as hers would to my thinking have been good for the making of lye.”
“You are cruel, Longarine,” said Oisille, “but those are not the terms on which you lived with your own husband.”
“No,” said Longarine, “for, God be thanked, he never gave me cause. I have reason to regret him all my life long, not to complain of him.”
“But if he had behaved in such a manner towards you,” said Nomerfide, “what would you have done?”
“I loved him so dearly,” said Longarine, “that I believe I should have killed him, and myself as well. To die after taking such a vengeance would have been sweeter to me than to live faithfully with the faithless.”
“So far as I can see,” said Hircan, “you do not love your husbands except for your own sakes. If they are what you want them to be, you are very fond of them; but if they fall into the slightest error towards you, they lose on a Saturday the toil of an entire week. Thus you are minded to rule, and I for my part will consent to it provided, however, that all other husbands agree.”
“It is reasonable,” said Parlamente, “that man should rule us as our head, but not that he should forsake us or treat us ill.”
“God has provided so wisely,” said Oisille, “both for man and for woman, that I hold marriage, if it be not abused, to be the goodliest and securest condition imaginable, and I am sure that, whatever they may seem to do, all here present think the same. And if the man claims to be wiser than the woman, he will be the more severely blamed should the fault come from him. But enough of such talk. Let us now see to whom Dagoucin will give his vote.”
“I give it,” he said, “to Longarine.”
“You do me a great pleasure,” she replied, “for I have read a story that is worthy to follow yours. Since we are set upon praising the virtuous patience of ladies, I will show you one more worthy of praise than she of whom we have just been speaking. And she is the more deserving of esteem in that she was a city dame, and therefore one of those whose breeding is less virtuous than that of others.”



A towns-woman of Tours returned so much good for all the
evil treatment she had received from her husband, that the
latter forsook the mistress whom he was quietly maintaining,
and returned to his wife. (1)
1 It is probable that the incidents related in this tale
occurred between 1460 and 1470. They will be found recorded
in the Ménagier de Paris. (See Baron Pichon’s edition,
1847, vol. i. p. 237). A similar narrative figures in some
editions of Morlini’s tales, notably the Novello, Fabello,
et Comedies, Neapoli, 1520. We further find it in
Gueudeville’s translation of Erasmus’s Colloquies (Dialogue
sur le mariage, collogues, &c., Leyden, 1720, vol. i. p.
87), and Mr. Walter Keily has pointed out (the Heptameron,
Bohn, 1864) that William Warner worked the same incidents
into his poem Albion’s England, his stanzas being
reproduced in Percy’s Reliques under the title of The
Patient Countess.—L. and Ed.
In the city of Tours there dwelt a chaste and comely townswoman, who, by reason of her virtues, was not only loved but feared also and respected by her husband. Nevertheless, with all the fickleness of men who grow weary of ever eating good bread, he fell in love with a farm tenant (2) of his own, and would oft-time leave Tours to visit the farm, where he always remained two or three days; and when he came back to Tours he was always in so sorry a plight that his wife had much ado to cure him, yet, as soon as he was whole again, he never failed to return to the place where pleasure caused him to forget all his ills.
2 The French word here is métayère. The métayer (fem.
métayère) was a farm tenant under the general control of his
landlord, who supplied him with seed and took to himself a
considerable portion of the produce. The system was done
away with at the Revolution, but was revived here and there
under the Restoration, when some of the nobles came to
“their own” again, and there may even nowadays be a few
instances of the kind.—Ed.
When his wife, who was anxious above all things for his life and health, found him constantly return home in so evil a plight, she went to the farm and found there the young woman whom her husband loved. Then, without anger but with graceful courage, she told her that she knew her husband often went to see her, but that she was ill-pleased to find him always return home exhausted in consequence of her sorry treatment of him. The poor woman, influenced as much by respect for her mistress as by regard for the truth, was not able to deny the fact, and craved forgiveness.
The lady asked to see the room and bed in which her husband was wont to sleep, and found it so cold and dirty and ill-appointed that she was moved to pity. Forthwith she sent for a good bed furnished with sheets, blankets and counterpane such as her husband loved; she caused the room to be made clean and neat and hung with tapestries; provided suitable ware for his meat and drink, a pipe of good wine, sweetmeats and confections, and begged the woman to send him back no more in so miserable a state.
It was not long before the husband again went, as was his wont, to see his tenant, and he was greatly amazed to find his poor lodging in such excellent order. And still more was he surprised when the woman gave him to drink in a silver cup; and he asked her whence all these good things had come. The poor woman told him, weeping, that they were from his wife, who had taken such great pity on his sorry treatment that she had furnished the house in this way, and had charged her to be careful of his health.
When the gentleman saw the exceeding generosity of his wife in returning so much good for all the evil turns that he had done her, he looked upon his own wrongdoing as no less great than her kindness; and, after giving some money to his tenant, he begged her to live in future as an honest woman. Then he went back to his wife, acknowledged his wrongdoing, and told her that, but for her great gentleness and generosity, he could never have forsaken the life that he had been leading. And thenceforward, forgetting the past, they lived in all peacefulness together.
“You may be sure, ladies, that there are but few husbands whom a wife’s love and patience cannot win at last, unless they be harder even than stone, which weak and yielding water will in time make hollow.”
“That woman,” said Parlamente, “had neither heart, gall nor liver.”
“What would you have had her do?” said Longarine. “She practised what God commands, and returned good for evil.” (3)
3 “Recompense to no man evil for evil.”—Rom. xii. 17.
“Not rendering evil for evil, or railing for railing.”—1
Pet. iii. 9.—Ed.
“I think,” said Hircan, “she must have been in love with some Grey Friar, who had laid upon her the penance of having her husband well treated in the country, so that, meantime, she might be free to entertain herself well in the town.”
“Therein,” said Oisille, “you clearly show the wickedness of your own heart, judging ill of a good deed. I rather believe her to have been so subdued by the love of God that she cared for naught save the salvation of her husband’s soul.”
“It seems to me,” said Simontault, “that he had more reason to return to his wife when he was so cold at the farm than afterwards when he was treated so well.”
“From what I can see,” said Saffredent, “you are not of the same opinion as the rich man of Paris who, when he lay with his wife, could not put off his gear without being chilled, but who never felt the worse when he went without cap or shoes, in the depth of winter, to see his servant-maid in the cellar. Yet his wife was very beautiful and the maid very ugly.”
“Have you not heard,” said Geburon, “that God always aids lunatics, lovers and sots? Perhaps he was all three in one.”
“Do you thence conclude,” said Pariamente, “that God recks not of the wise, the chaste and the temperate? Help is not needed by those who can help themselves. He who said that He had come for the sick and not for the whole, (4) came by the law of His mercy to succour our infirmities, thereby annulling the decrees of His rigorous justice; and he that deems himself wise is a fool in the sight of God. But, to end the sermon, to whom will Longarine give her vote?”
4 “They that are whole have no need of the physician, but
they that are sick.”—St. Mark ii. 17. See also St.
Luke v. 31.—Ed.
“I give it,” she said, “to Saffredent.”
“Then I hope,” said Saffredent, “to prove to you that God does not favour lovers. For although it has already been said, ladies, that vice is common to men and women alike, yet will a subtle artifice be more readily and adroitly devised by a woman than by a man Of this I am now about to give you an instance.”



The Lord of Grignaulx freed his house from a ghost which
had so tormented his wife that for the space of two years
she had dwelt elsewhere.
A certain Lord of Grignaulx (1) who was gentleman of honour to the Queen of France, Anne, Duchess of Brittany, on returning to his house whence he had been absent during more than two years, found his wife at another estate, near by, and when he inquired the reason of this, she told him that a ghost was wont to haunt the house, and tormented them so much that none could dwell there. (2) Monsieur de Grig-naulx, who had no belief in such absurdities, replied that were it the devil himself he was not afraid of him, and so brought his wife home again.
At night he caused many candles to be lighted that he might see the ghost more clearly, and, after watching for a long time without hearing anything, he fell asleep; but immediately afterwards he was awaked by a buffet upon the cheek, and heard a voice crying, “Brenigne, Brenigne,” which had been the name of his grandmother. (3) Then he called to the serving-woman, who lay near them, (4) to light the candle, for all were now extinguished, but she durst not rise. And at the same time the Lord of Grig-naulx felt the covering pulled from off him, and heard a great noise of tables, trestles and stools falling about the room; and this lasted until morning. However, the Lord of Grignaulx was more displeased at losing his rest than afraid of the ghost, for indeed he never believed it to be any such thing.
1 This is John de Talleyrand, knight, lord of Grignols and
Fouquerolles, Prince of Chalais, Viscount of Fronsac, mayor
and captain of Bordeaux, chamberlain of Charles VIII., first
majordomo and gentleman of honour in turn to two French
Queens, Anne of Brittany and Mary of England. His wife was
Margaret de la Tour, daughter of Anne de la Tour, Viscount
of Turenne, and Mary de Beaufort. She bore him several
children. It was John de Talleyrand who warned Louise of
Savoy that her son Francis, then Count of Angoulême, was
paying court to the young Queen, Mary of England, wife to
Louis XII. Apprehensive lest this intrigue should destroy
her son’s prospects, Louise prevailed on him to relinquish
it (Brantôme’s Dames Illustres).—L. 4 89
2 The house haunted by the ghost would probably be
Talleyrand’s château at Grignols, in the department of the
Gironde. His lordship of Fouquerolles was only a few miles
distant, in the Dordogne, and this would be the estate to
which his wife had retired.—Ed.
3 Talleyrand’s grandmother on the paternal side was Mary of
Brabant; the reference may be to his maternal grandmother,
whose Christian name was possibly “Bénigne.” On the other
hand, Boaistuau gives the name as Revigne, and among the old
French noblesse were the Revigné and Revigny families.—
Ed.
4 See ante, note 2 to Tale XXXVII.
On the following night he resolved to capture this ghost, and so, when he had been in bed a little while, he pretended to snore very loudly, and placed his open hand close to his face. Whilst he was in this wise waiting for the ghost, he felt that something was coming near him, and accordingly snored yet louder than before, whereat the ghost was so encouraged as to deal him a mighty blow. Forthwith, the Lord of Grignaulx caught the ghost’s hand as it rested on his face, and cried out to his wife—
“I have the ghost!”
His wife immediately rose up and lit the candle, and found that it was the serving-woman who slept in their room; and she, throwing herself upon her knees, entreated forgiveness and promised to confess the truth. This was, that she had long loved a serving-man of the house, and had taken this fine mystery in hand in order to drive both master and mistress away, so that she and her lover, having sole charge of the house, might be able to make good cheer as they were wont to do when alone. My Lord of Grignaulx, who was a somewhat harsh man, commanded that they should be soundly beaten so as to prevent them from ever forgetting the ghost, and this having been done, they were driven away. In this fashion was the house freed from the plaguy ghosts who for two years long had played their pranks in it. (5)
5 Talleyrand, who passes for having been the last of the
“Rois des Ribauds” (see the Bibliophile Jacob’s historical
novel of that title), was, like his descendant the great
diplomatist, a man of subtle and caustic humour. Brantôme,
in his article on Anne of Brittany in Les Dames Illustres,
repeatedly refers to him, and relates that on an occasion
when the Queen wished to say a few words in Spanish to the
Emperor’s ambassador—there was a project of marrying her
daughter Claude to Charles V.—she applied to Grignols to
teach her a sentence or two of the Castilian language. He,
however, taught her some dirty expression, but was careful
to warn Louis XII., who laughed at it, telling his wife on
no account to use the Spanish words she had learnt. On
discovering the truth, Anne was so greatly vexed, that
Grignols was obliged to withdraw from Court for some time,
and only with difficulty obtained the Queen’s forgiveness.—
L. and Ed.
“It is wonderful, ladies, to think of the effects wrought by the mighty god of Love. He causes women to put aside all fear, and teaches them to give every sort of trouble to man in order to work their own ends. But if the purpose of the serving-woman calls for blame, the sound sense of the master is no less worthy of praise. He knew that when the spirit departs, it returns no more.” (6)
6 “A wind that passeth away, and cometh not again.”—Psalm
lxxviii. 39.—M.
“In sooth,” said Geburon, “love showed little favour to the man and the maid, but I agree that the sound sense of the master was of great advantage to him.”
“Nevertheless,” said Ennasuite, “the maid through her cunning lived for a long time at her ease.”
“‘Tis but a sorry ease,” said Oisille, “that is founded upon sin and that ends in shame and chastisement.”
“That is true, madam,” said Ennasuite, “but many persons reap pain and sorrow by living righteously, and lacking wit enough to procure themselves in all their lives as much pleasure as these two.”
“It is nevertheless my opinion,” said Oisille, “that there can be no perfect pleasure unless the conscience be at rest.”
“Nay,” said Simontault, “the Italian maintains that the greater the sin the greater the pleasure.” (7)
7 This may be a reference to Boccaccio or Castiglione, but
the expression is of a proverbial character in many
languages.—Ed.
“In very truth,” said Oisille, “he who invented such a saying must be the devil himself. Let us therefore say no more of him, but see to whom Saffredent will give his vote.”
“To whom?” said he. “Only Parlamente now remains; but if there were a hundred others, she should still receive my vote, as being the one from whom we shall certainly learn something.”
“Well, since I am to end the day,” said Parlamente, “and since I promised yesterday to tell you why Rolandine’s father built the castle in which he kept her so long a prisoner, I will now relate it to you.”



The sister of the Count of Jossebelin, after marrying
unknown to her brother a gentleman whom he caused to be put
to death (albeit except for his lowlier rank he had often
desired him for his brother-in-law) did, with great patience
and austerity of life, spend the remainder of her days in a
hermitage. (1)
This lord, who was the father of Rolandine and was called the Count of Jossebelin, had several sisters, some of whom were married to wealthy husbands, others becoming nuns, whilst one, who was beyond comparison fairer than all the rest, dwelt unwedded in his house. (2)
1 The events here narrated would have occurred in or about
1479.—L.
2 The so-called Count of Jossebelin is John II., Viscount
de Rohan, previously referred to in Tale XXI. He was the son
of Alan IX., Vicount of Rohan, by his second wife, Mary of
Lorraine. Alan, by a first marriage with Margaret of
Brittany, had three daughters, Jane, Margaret and Catherine,
all three of whom were married advantageously. Contrary to
Queen Margaret’s assertion above, none of them became nuns;
Alan may, however, have had illegitimate daughters who took
the veil. By his second wife he had a son, John II., and a
daughter christened Catherine, like her half-sister. She
died unmarried, says Anselme’s Histoire Généalogique (vol.
iv. p. 57), and would appear to be the heroine of Queen
Margaret’s tale.—L. and B. J.
And so dearly did she love her brother that he, for his part, preferred her even to his wife and children.
She was asked in marriage by many of good estate, but her brother would never listen to them through dread of losing her, and also because he loved his money too well. She therefore spent a great part of her life un-wedded, living very virtuously in her brother’s house. Now there was a young and handsome gentleman who had been reared from childhood in this same house, and who, growing in comeliness and virtue as well as in years, had come to have a complete and peaceful rule over his master, in such sort that whenever the latter desired to give any charge to his sister he always did so by means of this young gentleman, (3) and he allowed him so much influence and intimacy, sending him morning and evening to his sister, that at last a great love sprang up between the two.
3 This is possibly a Count of Keradreux, whom John II. is
known to have put to death, though the Breton and French
chroniclers do not relate the circumstances of the crime.—
Seepost, p. 100, note 4.—Ed.
But as the gentleman feared for his life if he should offend his master, and the lady feared also for her honour, their love found gladness in speech alone, until the Lord of Jossebelin had often said to his sister that he wished the gentleman were rich and of as good a house as her own, for he had never known a man whom he would so gladly have had for his brother-in-law.
He repeated these sayings so often that, after debating them together, the lovers concluded that if they wedded one another they would readily be forgiven. Love, which easily believes what it desires, persuaded them that nothing but good could come of it; and in this hope they celebrated and consummated the marriage without the knowledge of any save a priest and certain women.
After they had lived for a few years in the delight that man and woman can have together in marriage, and as one of the handsomest and most loving couples in Christendom, Fate, vexed to find two persons so much at their ease, would no longer suffer them to continue in it, but stirred up against them an enemy, who, keeping watch upon the lady, came to a knowledge of her great happiness, and, ignorant the while of her marriage, went and told the Lord of Jossebelin that the gentleman in whom he had so much trust, went too often to his sister’s room, and that moreover at hours when no man should enter it. This the Count would not at first believe for the trust that he had in his sister and in the gentleman.
But the other, like one careful for the honour of the house, repeated the charge so often that a strict watch was set, and the poor folk, who suspected nothing, were surprised. For one evening the Lord of Jossebelin was advised that the gentleman was with his sister, and, hastening thither, found the poor love-blinded pair lying in bed together. His anger at the sight robbed him of speech, and, drawing his sword, he ran after the gentleman to kill him. But the other, being nimble of body, fled in nothing but his shirt, and, being unable to escape by the door, leaped through a window into the garden.
Then the poor lady, clad only in her chemise, threw herself upon her knees before her brother and said to him—
“Sir, spare the life of my husband, for I have indeed married him; and if you are offended punish only me, for what he did was done at my request.”
Her brother, beside himself with wrath, could only reply—
“Even if he be your husband one hundred thousand times over, yet will I punish him as a rascally servant who has deceived me.”
So saying, he went to the window and called out loudly to kill him, which was speedily done before the eyes of himself and his sister. The latter, on beholding the pitiful sight which no prayers on her part had been able to prevent, spoke to her brother like a woman bereft of reason.
“Brother,” she said, “I have neither father nor mother, and I am old enough to marry according to my own pleasure. I chose one whom many a time you said you would gladly have me marry, and for doing by your own counsels that which the law permits me to do without them, you have put to death the man whom you loved best of all the world. Well, since my prayers have been of no avail to preserve his life, I implore you, by all the love you have ever borne me, to make me now a sharer in his death even as I have been a sharer in all his living fortunes. In this way, while sating your unjust and cruel anger, you will give repose to the body and soul of one who cannot and will not live without him.” Although her brother was almost distracted with passion, (4) he had pity upon his sister, and so, without granting or denying her request, withdrew. After weighing well what he had done, and hearing that the gentleman had in fact married his sister, he would gladly have undone his grievous crime. Nevertheless, being afraid that his sister would seek justice or vengeance for it, he caused a castle to be built in the midst of a forest, (5) and, placing her therein, forbade that any should have speech with her.
4 John II. of Rohan was a man of the most passionate,
resentful disposition, and the greater part of his life was
spent in furthering ambitious schemes, stirring up feuds and
factions, and desolating Brittany with civil war. In 1470 we
find him leaving the service of the Duke, his master, to
enter that of Louis XI., on whose side he fought till the
peace of Senlis in 1475. Four years later the Duke of
Brittany caused him to be arrested on the charge of
murdering the Count of Keradreux, and he appears to have
remained in prison till 1484, when it is recorded that he
fled to France, and thence to Lorraine. In 1487 he leagued
himself with several discontented nobles to drive away the
Chancellor of Brittany and various foreign favourites around
the Duke, and carried civil war into several parts of the
duchy. Then for a brief space he made his peace with the
Duke, but again took up arms for the French King, fought at
St. Aubin du Cormier, captured Dinan and besieged and
pillaged Guingamp. Charles VIII. appointed him Lieutenant-
general of Lower Brittany in 1491, and he was first
commissary of the King of France at the States of Brittany
held at Vannes in 1491 and 1501. In 1507 he witnessed the
marriage contract of the Princess Claude with Francis, Duke
of Valois, afterwards Francis I. (Anselme’s Histoire
Généalogique, vol. iv. p. 57). When Anne became Duchess of
Brittany, John II. vainly strove to compel her to marry his
son, James, and this was one of the causes of their life-
long enmity (ante vol. iii. Tale XXI.) John II. died in
1516.—L. and Ed.
5 If this be the chateau of Josselin, as some previous
commentators think, Queen Margaret is in error here, for
records subsist which prove that Josselin, now classed among
the historical monuments of France, was built not by John
II., but by his father, Alan IX. It rises on a steep rock on
the bank of the Oust, at nine miles from Ploèrmel, and on
the sculptured work, both inside and out, the letters A. V.
(Alan, Viscount) are frequently repeated, with the arms of
Rohan and Brittany quartered together, and bearing the proud
device A plus. It seems to us evident that the incidents
recorded in the early part of Queen Margaret’s tale took
place at Josselin, and that Catherine de Rohan was
imprisoned in some other chateau expressly erected by her
brother.—D. and Ed.
Some time afterwards he sought, for the satisfaction of his conscience, to win her back again, and spoke to her of marriage; but she sent him word that he had given her too sorry a breakfast to make her willing to sup off the same dish, and that she looked to live in such sort that he should never murder a second husband of hers; for, she added, she could scarcely believe that he would forgive another man after having so cruelly used the one whom he had loved best of all the world.
And although weak and powerless for revenge, she placed her hopes in Him who is the true Judge, and who suffers no wickedness to go unpunished; and, relying upon His love alone, was minded to spend the rest of her life in her hermitage. And this she did, for she never stirred from that place so long as she lived, but dwelt there with such patience and austerity that her tomb was visited by every one as that of a saint.
From the time that she died, her brother’s house came to such a ruinous state, that of his six sons not one was left, but all died miserably; (6) and at last the inheritance, as you heard in the former story, passed into the possession of Rolandine, who succeeded to the prison that had been built for her aunt.
6 Queen Margaret is in error here. Instead of six sons,
John II., according to the most reliable genealogical
accounts of the Rohan family, had but two, James, Viscount
of Rohan and Lord of Leon, who died childless in 1527, and
Claud, Bishop of Cornouailles, who succeeded him as Viscount
of Rohan (Anselme). These had two sisters, Anne, the
Rolandine of Tale XXI., and Mary, who died in June 1542
(Dillaye).—Ed.
“I pray God, ladies, that this example may be profitable to you, and that none among you will seek to marry for her own pleasure without the consent of those to whom obedience is due; for marriage is a state of such long continuance that it should not be entered upon lightly and without the advice of friends and kin. And, indeed, however wisely one may act, there is always at least as much pain in it as there is pleasure.”
“In good faith,” said Oisille, “were there neither God nor law to teach maidens discretion, this example would suffice to give them more reverence for their kindred, and not to seek marriage according to their own pleasure.”
“Still, madam,” said Nomerfide, “whoso has but one good day in the year, is not unhappy her whole life long. She had the pleasure of seeing and speaking for a long time with him whom she loved better than herself, and she moreover enjoyed the delights of marriage with him without scruple of conscience. I consider such happiness so great, that in my opinion it surpassed the sorrow that she bore.”
“You maintain, then,” said Saffredent, “that a woman has more pleasure in lying with a husband, than pain in seeing him put to death before her eyes.”
“That is not my meaning,” said Nomerfide, “for it would be contrary to my experience of women. But I hold that an unwonted pleasure such as that of marrying the man whom one loves best of all the world, must be greater than that of losing him by death, which is common to all.”
“Yes,” said Geburon, “if the death be a natural one, but that in the story was too cruel. And I think it very strange, considering he was neither her father nor her husband but only her brother, and she had reached an age when the law suffers maidens to marry according to their own pleasure, that this lord should have had the daring to commit so cruel a deed.”
“I do not think it at all strange,” said Hircan, “for he did not kill his sister whom he dearly loved, and who was not subject to his control, but dealt with the gentleman whom he had bred as his son and loved as his brother. He had bestowed honour and wealth upon him in his service, and in return for all this the other sought his sister in marriage, a thing which was in nowise fitting for him to do.”
“Moreover,” said Nomerfide, “it was no ordinary or wonted pleasure for a lady of such high lineage to marry a gentleman servant for love. If the death was extraordinary, the pleasure also was novel, and it was the greater seeing that it had against it the opinions of all wise folk, for it was the happiness of a loving heart with tranquillity of soul, since God was in no wise offended by it And as for the death that you call cruel, it seems to me that, since death is unavoidable, the swifter it comes the better; for we know that it is a road by which all of us must travel. I deem those fortunate who do not long linger on the outksirts of death, but who take a speedy flight from all that can be termed happiness in this world to the happiness that is eternal.”
“What do you mean by the outskirts of death?” said Simontault.
“Such as have deep tribulation of spirit,” replied Nomerfide, “such, too, as have long been ill, and in their extreme bodily or spiritual pain have come to think lightly of death and find its approach too slow, such, I say, as these have passed through the outskirts of death and will tell you of the hostels where they knew more lamentation than rest. The lady of the story could not help losing her husband through death, but her brother’s wrath preserved her from seeing him a long time sick or distressed in mind. And turning the gladness that she had had with him to the service of Our Lord, she might well esteem herself happy.”
“Do you make no account,” said Longarine, “of the shame that she endured, or of her imprisonment?”
“I consider,” said Nomerfide, “that a woman who lives perfectly, with a love that is in keeping with the commands of her God, has no knowledge of shame or dishonour except when they impair or lessen the perfection of her love; for the glory of truly loving knows no shame. As for her imprisonment, I imagine that, with her heart at large and devoted to God and her husband, she thought nothing of it, but deemed her solitude the greatest freedom. When one cannot see what one loves, the greatest happiness consists in thinking constantly upon it, and there is no prison so narrow that thought cannot roam in it at will.”
“Nothing can be truer than what Nomerfide says,” observed Simontault, “but the man who in his passion brought this separation to pass must have deemed himself unhappy indeed, seeing that he offended God, Love and Honour.”
“In good sooth,” said Geburon, “I am amazed at the diversity of woman’s love. I can see that those who have most love have most virtue; but those who have less love conceal it in their desire to appear virtuous.”
“It is true,” said Parlamente, “that a heart which is virtuous towards God and man loves more deeply than a vicious one, and fears not to have its inmost purpose known.”
“I have always heard,” said Simontault, “that men should not be blamed if they seek the love of women, for God has put into the heart of man desire and boldness for asking, and in that of woman fear and chastity for refusal. If, then, a man be punished for using the powers that have been given him, he suffers wrong.”
“But it must be remembered,” said Longarine, “that he had praised this gentleman for a long time to his sister. It seems to me that it would be madness or cruelty in the keeper of a fountain to praise its fair waters to one fainting with thirst, and then to kill him when he sought to taste them.”
“The brother,” thereupon said Parlamente, “did indeed so kindle the flame by gentle words of his own, that it was not meet he should beat it out with the sword.”
“I am surprised,” said Saffredent, “to find it taken ill that a simple gentleman should by dint of love alone, and without deceit, have come to marry a lady of high lineage, seeing that the wisdom of the philosophers accounts the least of men to be of more worth than the greatest and most virtuous of women.”
“The reason is,” said Dagoucin, “that in order to preserve the commonwealth in peace, account is only taken of the rank of families, the age of persons, and the provisions of the laws, without regard to the love and virtue of individuals, and all this so that the kingdom may not be disturbed. Hence it comes to pass that, in marriages made between equals and according to the judgment of kinsfolk and society, the husband and wife often journey to the very outskirts of hell.”
“Indeed it has been seen,” said Geburon, “that those who, being alike in heart, character and temperament, have married for love and paid no heed to diversity of birth and lineage, have ofttime sorely repented of it; for a deep unreasoning love is apt to turn to jealousy and rage.”
“It seems to me,” said Parlamente, “that neither course is worthy of praise, but that folks should submit themselves to the will of God, and pay no heed to glory, avarice or pleasure, and loving virtuously and with the approval of their kinsfolk, seek only to live in the married state as God and nature ordain. And although no condition be free from tribulation, I have nevertheless seen such persons live together without regret; and we of this company are not so unfortunate as to have none of these married ones among the number.”
Hircan, Geburon, Simontault and Saffredent swore that they had wedded after this sort, and had never repented since. Whatever the truth of this declaration may have been, the ladies concerned were exceedingly content with it, and thinking that they could hear nothing to please them better, they rose up to go and give thanks for it to God, and found the monks at the church, ready for vespers.
When the service was over they went to supper, but not without much discourse concerning their marriages; and this lasted all the evening, each one relating the fortune that had befallen him whilst he was wooing his wife.
As it happened, however, that one was interrupted by another, it is not possible to set down these stories in full, albeit they would have been as pleasant to write as those which had been told in the meadow. Such great delight did they take in the converse, and so well did it entertain them, that, before they were aware of it, the hour for rest had come.
The Lady Oisille made the company separate, and they betook themselves to bed so joyously that, what with recounting the loves of the past, and proving those of the present, the married folk, methinks, slept no longer than the others.
And so the night was pleasantly spent until the morning.

On the Fifth Day Tales are told of the virtue of those
maids and
matrons who held their honour in
more consideration than their
pleasure,
also of those who did the contrary,
and of the
simplicity of
certain others.
When morning was come, the Lady Oisille made ready for them a spiritual breakfast of such excellent flavour that it sufficed to strengthen both body and mind. The whole company was very attentive to it; it seemed to them that they had never harkened to a sermon with such profit before. Then, when the last bell rang for mass, they went to meditate upon the pious discourse which they had heard.
After listening to mass, and walking for a little while, they went to table feeling assured that the present day would prove as agreeable as any of the past. Saffredent even said that he would gladly have the bridge building for another month, so great was the pleasure that he took in their entertainment; but the Abbot was pressing the work with all speed, for it was no pleasure to him to live in the company of so many honourable persons, among whom he could not bring his wonted female pilgrims.
Having rested for a time after dinner, they returned to their accustomed diversion. When all were seated in the meadow, they asked Parlamente to whom she gave her vote.
“I think,” she replied, “that Saffredent might well begin this day, for his face does not look as though he wished us to weep.”
“Then, ladies, you will needs be very hard-hearted,” said Saffredent, “if you take no pity on the Grey Friar whose story I am going to relate to you. You may perhaps think, from the tales that some among us have already told of the monks, that misadventures have befallen hapless damsels simply because ease of execution induced the attempt to be fearlessly begun, but, so that you may know that it is the blindness of wanton lust which deprives the friars of all fear and prudence, I will tell you of what happened to one of them in Flanders.”


A Grey Friar to whom a maiden had presented herself on
Christmas night that he might confess her, laid upon her so
strange a penance that she would not submit to it, but rose
from before him without having received absolution; but her
mistress, hearing of the matter, caused the Grey Friar to be
flogged in her kitchen, and then sent him back, bound and
gagged, to his Warden.
In the year when my Lady Margaret of Austria came to Cambray on behalf of her nephew the Emperor, to treat of peace between him and the Most Christian King, who on his part was represented by his mother, my Lady Louise of Savoy, (1) the said Lady Margaret had in her train the Countess of Aiguemont, (2) who won, among this company, the renown of being the most beautiful of all the Flemish ladies.
1 It was in June 1529 that Margaret of Austria came to
Cambrai to treat for peace, on behalf of Charles V. Louise
of Savoy, who represented Francis I., was accompanied on
this occasion by her daughter, Queen Margaret, who appears
to have taken part in the conferences. The result of these
was that the Emperor renounced his claims on Burgundy, but
upheld all the other stipulations of the treaty of Madrid.
Having been brought about entirely by feminine negotiators,
the peace of Cambrai acquired the name of “La Paix des
Dames,” or “the Ladies’ Peace.” Some curious particulars of
the ceremonies observed at Cambrai on this occasion will be
found in Leglay’s Notice sur les fêles et cérémonies à
Cambray depuis le XIe siècle, Cambrai, 1827.—L. and B. J.
2 This is Frances of Luxemburg, Baroness of Fiennes and
Princess of Gavre, wife of John IV., Count of Egmont,
chamberlain to the Emperor Charles V. They were the parents
of the famous Lamoral Count of Egmont, Prince of Gavre and
Baron of Fiennes, born in 1522 and put to death by the Duke
of Alba on June 5, 1568.—B.J.
When this great assembly separated, the Countess of Aiguemont returned to her own house, and, Advent being come, sent to a monastery of Grey Friars to ask for a clever preacher and virtuous man, as well to preach as to confess herself and her whole household. The Warden, remembering the great benefits that the Order received from the house of Aiguemont and that of Fiennes, to which the Countess belonged, sought out the man whom he thought most worthy to fill the said office.
Accordingly, as the Grey Friars more than any other order desire to obtain the esteem and friendship of great houses, they sent the most important preacher of their monastery, and throughout Advent he did his duty very well, and the Countess was well pleased with him.
On Christmas night, when the Countess desired to receive her Creator, she sent for her confessor, and after making confession in a carefully closed chapel, she gave place to her lady of honour, who in her turn, after being shriven, sent her daughter to pass through the hands of this worthy confessor. When the maiden had told all that was in her mind, the good father knew something of her secrets, and this gave him the desire and the boldness to lay an unwonted penance upon her.
“My daughter,” said he, “your sins are so great that to atone for them I command you the penance of wearing my cord upon your naked flesh.”
The maiden, who was unwilling to disobey him, made answer—
“Give it to me, father, and I will not fail to wear it.”
“My daughter,” said the good father, “it will be of no avail from your own hand. Mine, from which you shall receive absolution, must first bind it upon you; then shall you be absolved of all your sins.”
The maiden replied, weeping, that she would not suffer it.
“What?” said the confessor. “Are you a heretic, that you refuse the penances which God and our holy mother Church have ordained?”
“I employ confession,” said the maiden, “as the Church commands, and I am very willing to receive absolution and do penance. But I will not be touched by your hands, and I refuse this mode of penance.”
“Then,” said the confessor, “I cannot give you absolution.”
The maiden rose from before him greatly troubled in conscience, for, being very young, she feared lest she had done wrong in thus refusing to obey the worthy father.
When mass was over and the Countess of Aiguemont had received the “Corpus Domini,” her lady of honour, desiring to follow her, asked her daughter whether she was ready. The maiden, weeping, replied that she was not shriven.
“Then what were you doing so long with the preacher?” asked her mother.
“Nothing,” said the maiden, “for, as I refused the penance that he laid upon me, he on his part refused me absolution.”
Making prudent inquiry, the mother learnt the extraordinary penance that the good father had chosen for her daughter; and then, having caused her to be confessed by another, they received the sacrament together. When the Countess was come back from the church, the lady of honour made complaint to her of the preacher, whereupon the Countess was the more surprised and grieved, since she had thought so well of him. Nevertheless, despite her anger, she could not but feel very much inclined to laugh at the unwonted nature of the penance.
Still her laughter did not prevent her from having the friar taken and beaten in her kitchen, where he was brought by the strokes of the rod to confess the truth; and then she sent him bound hand and foot to his Warden, begging the latter for the future to commission more virtuous men to preach the Word of God.
“Consider, ladies, if the monks be not afraid to display their wantonness in so illustrious a house, what may they not do in the poor places where they commonly make their collections, and where opportunities are so readily offered to them, that it is a miracle if they are quit of them without scandal. And this, ladies, leads me to beg of you to change your ill opinion into compassion, remembering that he (3) who blinds the Grey Friars is not sparing of the ladies when he finds an opportunity.”
3 The demon.—B. J.
“Truly,” said Oisille, “this was a very wicked Grey Friar. A monk, a priest and a preacher to work such wickedness, and that on Christmas day, in the church and under the cloak of the confessional—all these are circumstances which heighten the sin.”
“It would seem from your words,” said Hircan, “that the Grey Friars ought to be angels, or more discreet than other men, but you have heard instances enough to show you that they are far worse. As for the monk in the story, I think he might well be excused, seeing that he found himself shut up all alone at night with a handsome girl.”
“True,” said Oisille, “but it was Christmas night.”
“That makes him still less to blame,” said Simontault, “for, being in Joseph’s place beside a fair virgin, he wished to try to beget an infant and so play the Mystery of the Nativity to the life.”
“In sooth,” said Parlamente, “if he had thought of Joseph and the Virgin Mary, he would have had no such evil purpose. At all events, he was a wickedly-minded man to make so evil an attempt upon such slight provocation.”
“I think,” said Oisille, “that the Countess punished him well enough to afford an excellent example to his fellows.”
“But ‘tis questionable,” said Nomerfide, “whether she did well in thus putting her neighbour to shame, or whether ‘twould not have been better to have quietly shown him his faults, rather than have made them so publicly known.”
“That would, I think, have been better,” said Geburon, “for we are commanded to rebuke our neighbour in secret, before we speak of the matter to any one else or to the Church. When a man has been brought to public disgrace, he will hardly ever be able to mend his ways, but fear of shame withdraws as many persons from sin as conscience does.”
“I think,” said Parlamente, “that we ought to observe the teaching of the Gospel towards all except those that preach the Word of God and act contrary to it. We should not be afraid to shame such as are accustomed to put others to shame; indeed I think it a very meritorious thing to make them known for what they really are, so that we take not a mock stone (4) for a fine ruby. But to whom will Saffredent give his vote?”
4 The French word here is doublet. The doublet was a
piece of crystal, cut after the fashion of a diamond, and
backed with red wax so as to give it somewhat the colour of
a ruby.—B. J.
“Since you ask me,” he replied, “I will give it to yourself, to whom no man of understanding should refuse it.”
“Then, since you give it to me, I will tell you a story to the truth of which I can myself testify. I have always heard that when virtue abides in a weak and feeble vessel, and is assailed by its strong and puissant opposite, it especially deserves praise, and shows itself to be what it really is. If strength withstand strength, it is no very wonderful thing; but if weakness win the victory, it is lauded by every one. Knowing, as I do, the persons of whom I desire to speak, I think that I should do a wrong to virtue, (which I have often seen hidden under so mean a covering that none gave it any heed), if I did not tell of her who performed the praiseworthy actions that I now feel constrained to relate.”



A young Prince set his affections upon a young girl, and
although she was of low and poor parentage, he could not, in
spite of all his efforts, obtain from her what he had hoped
to have. Accordingly, recognising her virtue and honour, the
Prince desisted from his attempt, esteemed her highly all
his life, and, marrying her to a follower of his own,
bestowed great benefits upon her.
In one of the best towns in Touraine there dwelt a lord of illustrious family, who had there been brought up from early youth. Of the perfections, graces, beauty and great virtues of this young Prince (1) I will say nothing, except that in his time his equal could not be found. Being fifteen years of age, he had more pleasure in hunting and hawking than in looking at beautiful ladies.
1 This is undoubtedly Francis I., then Count of Angoulême.
M. de Lincy thinks that the scene of the story must be
Amboise, where Louise of Savoy went to live with her
children in 1499, and remained for several years; Louis XII.
having placed the château there at her disposal. Francis,
however, left Amboise to join the Court at Blois in August
1508, when less than fourteen years old (see Memoir of Queen
Margaret, vol. i. p. xxiii.), and in the tale, above, he is
said to have been fifteen at the time of the incidents
narrated. These, then, would have occurred in the autumn of
1509. It will be seen that in the tale the young Prince’s
sister (Margaret) is described as residing at the castle.
Now Margaret married Charles of Alençon at Blois, in October
1509, and forthwith removed to Alençon. Possibly Francis,
who was very precocious, especially in matters of gallantry,
engaged in the love affair narrated by his sister at a yet
earlier age than she asserts, in which case the town she
refers to would undoubtedly be Amboise.—Ed.
One day in a church he beheld a young maiden who formerly, during her childhood, had been bred in the castle where he dwelt; but after her mother’s death, her father having married again, she had withdrawn into Poitou with her brother. This maiden, who was called Frances, had a bastard sister whom her father dearly loved, and whom he had married to the young Prince’s butler, who maintained her in as excellent a condition as that of any of her family. It came to pass that the father died and left to Frances as her portion what he possessed near the town aforementioned, and thither she returned after his death; nevertheless, being unmarried and only sixteen years of age, she would not live alone in her house, but went to lodge with her sister, the butler’s wife.
On perceiving this girl, who was passably beautiful for a light brunette, and possessed a grace beyond her condition (for, indeed, she seemed rather a lady or princess than a towns-woman), the young Prince gazed at her for a long time, and he, who never yet had loved, now felt in his heart an unwonted delight. On returning to his apartment he inquired concerning the maiden he had seen in the church, and then recollected that formerly in her youth she had come to the castle to have dolls’ play with his sister. He reminded the latter of her; and his sister sent for her, received her kindly, and begged her to come often to see her. This she did whenever there was a feast or entertainment; and the young Prince was so pleased to see her that he had in mind to be deeply in love with her, and, knowing her to be of low and poor parentage, hoped easily to obtain what he sought.
Having no means of speaking with her, he sent a gentleman of his chamber to her to conduct his intrigue. But she, being discreet and fearing God, told the gentleman that she did not believe so handsome and honourable a Prince as his master could have pleasure in looking upon one so ugly as herself, since he had so many beautiful ladies in the castle where he lived, that he had no need to search through the town; and she added that in her opinion the gentleman was speaking of his own authority, and without his master’s command.
When the young Prince received this reply, love, which becomes the more eager the more it meets with resistance, caused him to pursue his enterprise more hotly than before, and to write her a letter in which he begged that she would believe all the gentleman had told her.
Being well able to read and write, she read the letter through, but, in spite of all the gentleman’s entreaties, she would never send an answer to it. It was not for one of such low degree, she said, to write to so noble a Prince, and she begged the gentleman not to deem her foolish enough to believe that the Prince had so much love for her. Moreover, he was deceived if he thought that he could have her at his will by reason of her humble condition; for her heart was as virtuous as that of the greatest Princess in Christendom, and she looked upon all the treasures in the world as naught in comparison with honour and a good conscience. She therefore entreated him not to try to hinder her from keeping these treasures safe her whole life long, for she would never change her mind even were she threatened with death.
The young Prince did not find this reply to his liking, nevertheless he loved her dearly for it, and never failed to have his chair set in the church to which she went to hear mass, where, during the service, he would ever turn his eyes upon the same image. When she perceived this, she changed her place and went to another chapel—not indeed to flee the sight of him, for she would not have been a reasonable being had she not found pleasure in beholding him—but because she dreaded to be seen by him. She did not deem herself worthy to be loved by him in honour or marriage, and, on the other hand, she would not be loved wantonly and for pleasure. When she found that, in whatever part of the church she placed herself, the Prince heard mass close by, she would no longer go to the same church, but repaired every day to the remotest that she could find. And when there was feasting at the castle, although the Prince’s sister often sent for her, she would no longer go thither, but excused herself on the plea of sickness.
Finding that he could not have speech with her, the Prince had recourse to his butler, and promised him great rewards if he would lend assistance in the matter. This the butler, for the sake both of pleasing his master and of the gain that he expected, readily promised to do. Every day he would relate to the Prince what she said or did, telling him that she was especially careful to shun all opportunities of seeing him. However, the great desire that the Prince had of speaking with her at his ease, prompted him to devise the following plan.
One day he took his chargers, which he was beginning to manage excellently well, to a large open space in the town opposite to his butler’s house, in which Frances lived. After making many courses and leaps which she could easily see, he let himself fall from his horse into some deep mire, but so softly that he was not hurt. Nevertheless he uttered passably loud groans, and asked whether there was a house near in which he might change his dress. Every one offered his own, but on some one saying that the butler’s was the nearest and worthiest, it was chosen before all the others.
He found the room well furnished, and, as all his garments were soiled with the mud, he stripped himself to his shirt, and got into a bed. Then, when he saw that, except the gentleman aforementioned, every one was gone to bring him some clothes, he called his host and hostess and asked them where Frances was. They had much ado to find her, for, as soon as she had seen the young Prince coming in, she had gone to hide herself in the most retired nook in the house. Nevertheless her sister found her, and begged her not to be afraid to speak to so worshipful and virtuous a Prince.
“What! sister,” said Frances, “do you, whom I look upon as my mother, advise me to go and speak with a young lord, of whose purpose, as you are aware, I cannot be ignorant?”
However, her sister addressed so many remonstrances to her, and promised so often not to leave her alone, that she at last went with her, showing so pale and sorry a face that she seemed more likely to beget compassion than desire.
When the young Prince saw her by his bedside, he took hold of her hand, which was cold and trembling, and said to her—
“Frances, do you deem me so wicked a man, and so strange and cruel, that I eat the women I look upon? Why have you come to be so afraid of me who seek only your honour and profit? You know that I have sought to hold converse with you in all possible places, but all in vain; and, to grieve me still more, you have even shunned the places where I had been wont to see you at mass, so that my eyes might bring me as little gladness as my tongue. But all this has availed you naught, for I have never rested until I came hither in the manner you have seen, and I have risked my neck, in allowing myself to fall, in order that I might have the joy of speaking to you without hindrance. I therefore entreat you, Frances, that the opportunity gained by so much toil may not be thrown away, and that my deep love may avail to win your own.”
After waiting a long time for her reply, and seeing that her eyes were full of tears and fixed upon the ground, he drew her to him as closely as he could, and tried to embrace and kiss her. But she said to him—
“No, my lord, no; what you desire cannot be, for although I am but a worm of the earth compared with you, I hold my honour dear, and would rather die than lessen it for any pleasure that the world can give. And the dread I have lest those who have seen you come in should suspect the truth, makes me tremble and be afraid as you see. And, since it pleases you to do me the honour of speaking to me, you will also forgive me if I answer you according as my honour requires. I am not so foolish, my lord, nor so blind as not to perceive and recognise the comeliness and grace that God has given you, or not to consider that she who shall possess the person and love of such a Prince must be the happiest woman alive. But what does all this avail me, since it is not for me or any woman of my condition, and since even to long for it would, in me, be utter folly? What reason can I believe to be yours in addressing yourself to me except that the ladies in your house, whom you must love if you have any love for beauty and grace, are so virtuous that you dare not seek or expect from them what the lowliness of my condition has led you to expect from me? I am sure that if you obtained your desire from one such as I, it would afford matter for entertainment to your mistress during two good hours, to hear you tell her of your conquests over the weak. But, my lord, be pleased to bear in mind that I shall never be of their number. I have been brought up in your house, where I have learned what it is to love; my father and my mother were your faithful servants. Since, therefore, God has not made me a Princess to marry you, nor of sufficient rank to be your mistress and love, you will be pleased not to try to number me with the unfortunate, seeing that I deem and would have you to be one of the happiest Princes in Christendom. If for diversion you would have women of my condition, you will find in this town many who are beyond compare more beautiful than I, and who will spare you the pains of so many entreaties. Content yourself, then, with those to whom you will give pleasure by the purchase of their honour, and cease to trouble one who loves you more than she loves herself. For, indeed, if either your life or mine were required of God this day, I should esteem myself fortunate in offering mine to save yours. It is no lack of love that makes me shun your presence, but rather too great a love for your conscience and mine; for I hold my honour dearer than life. I will continue, my lord, if it please you, in your good grace, and will all my life pray God for your health and prosperity. And truly the honour that you have done me will lend me consideration among those of my own rank, for, after seeing you, where is the man of my own condition upon whom I could deign to look? So my heart will continue free save for the duty which shall always be mine of praying to God on your behalf. But no other service can you ever have of me.”
On hearing this virtuous reply, contrary though it was to his desires, the young Prince could not but esteem her as she deserved. He did all that he could to persuade her that he would never love another woman, but she was too prudent to suffer so unreasonable a thought to enter her mind. While they were talking together, word was often brought that his clothes were come from the castle, but such was his present pleasure and comfort, that he caused answer to be given that he was asleep. And this continued until the hour for supper was come, when he durst not fail to appear before his mother, who was one of the discreetest ladies imaginable.
Accordingly, the young man left his butler’s house thinking more highly than ever of the maiden’s virtue. He often spoke of her to the gentleman that slept in his room, and the latter, who deemed money to be more powerful than love, advised his master to offer her a considerable sum if she would yield to his wishes. The young Prince, whose mother was his treasurer, had but little money for his pocket, but, borrowing as much as he was able, he made up the sum of five hundred crowns, which he sent by the gentleman to the girl, begging her to change her mind.
But, when she saw the gift, she said to the gentleman—
“I pray you tell my lord that I have a good and virtuous heart, and that if it were meet to obey his commands his comeliness and grace would ere now have vanquished me; but, since these have no power against my honour, all the money in the world can have none. Take it, therefore, back to him again, for I would rather enjoy virtuous poverty than all the wealth it were possible to desire.”
On beholding so much stubbornness, the gentleman thought that violence must needs be used to win her, and threatened her with his master’s authority and power. But she laughed, and said—
“Make those fear him who have no knowledge of him. For my part, I know him to be so discreet and virtuous that such discourse cannot come from him, and I feel sure that he will disown it when you repeat it to him. But even though he were what you say, there is neither torment nor death that would make me change my mind; for, as I have told you, since love has not turned my heart, no imaginable evil or good can divert me one step from the path that I have chosen.”
The gentleman, who had promised his master to win her, brought him back this reply in wondrous anger, and counselled him to persevere in every possible way, telling him that it was not to his honour to be unable to win a woman of her sort.
The young Prince was unwilling to employ any means but such as honour enjoins, and was also afraid that if the affair made any noise, and so came to his mother’s ears, she would be greatly angered with him. He therefore durst make no attempt, until at last the gentleman proposed to him so simple a plan that he could already fancy her to be in his power. In order to carry it into execution he spoke to the butler; and he, being anxious to serve his master in any way that might be, begged his wife and sister-in-law one day to go and visit their vintages at a house he had near the forest. And this they promised to do.
When the day was come, he informed the Prince, who resolved to go thither alone with the gentleman, and caused his mule to be secretly held in readiness, that they might set out at the proper time. But God willed it that his mother should that day be garnishing a most beautiful cabinet, (2) and needed all her children with her to help her, and thus the young Prince lingered there until the hour was past.
There was, however, no hindrance to the departure of the butler, who had brought his sister-in-law to his house, riding behind him, (3) and had made his wife feign sickness, so that when they were already on horseback she had come and said that she could not go with them. But now, seeing that the hour at which the Prince should have come was gone by, he said to his sister-in-law—
“I think we may now return to the town.”
2 The French word here is cabinet, which some English
translators have rendered as “little room.” We think,
however, with the Bibliophile Jacob, that the allusion is to
an article of furniture, such as we ourselves still call a
cabinet in England, though in France the word has virtually
lost that sense.—Ed.
3 The MSS. do not say whether she rode on a pillion, or
simply bestrode the horse. This last fashion was still
common at this period and long afterwards, even among women
of high degree. See, for instance, several of the enamels in
the Louvre, notably one which depicts Henry II. of France
with Diana of Poitiers riding behind him. The practice is
also referred to in a sixteenth century ballad. “La
Superfluity des habitz des Dames” (Anciennes Poésies
Françaises. Bib. Elzev. 1858, p. 308).—M.
“What is there to hinder us from doing so?” asked Frances.
“Why,” said the butler, “I was waiting here for my lord, who had promised me that he would come.”
When his sister-in-law heard this wickedness, she replied—
“Do not wait for him, brother, for I know that he will not come to-day.”
The brother-in-law believed her and brought her back again, and when she had reached home she let him know her extreme anger, telling him that he was the devil’s servant, and did yet more than he was commanded, for she was sure that the plan had been devised by him and the gentleman and not by the young Prince, whose money he would rather earn by aiding him in his follies, than by doing the duty of a good servant. However, now that she knew his real nature, she would remain no longer in his house, and thereupon indeed she sent for her brother to take her to his own country, and immediately left her sister’s dwelling.
Having thus failed in his attempt, the butler went to the castle to learn what had prevented the arrival of the young Prince, and he had scarcely come thither when he met the Prince himself sallying forth on his mule, and attended only by the gentleman in whom he put so much trust.
“Well,” the Prince asked of him, “is she still there?”
Thereupon the butler related all that had taken place.
The young Prince was deeply vexed at having failed in his plan, which he looked upon as the very last that he could devise, but, seeing that it could not be helped, he sought out Frances so diligently that at last he met her in a gathering from which she could not escape. He then upbraided her very harshly for her cruelty towards him, and for having left her brother-in-law, but she made answer that the latter was, in regard to herself, the worst and most dangerous man she had ever known, though he, the Prince, was greatly beholden to him, seeing that he was served by him not only with body and substance, but with soul and conscience as well.
When the Prince perceived by this that the case was a hopeless one, he resolved to urge her no more, and esteemed her highly all his life.
Seeing this maiden’s goodness, one of the said Prince’s attendants desired to marry her, but to this she would not consent without the command and license of the young Prince, upon whom she had set all her affection; and this she caused to be made known to him, and with his approval the marriage was concluded. And so she lived all her life in good repute, and the young Prince bestowed great benefits upon her. (4)
4 We take this concluding paragraph from MS. 1520; it is
deficient in ours.—L.
“What shall we say to this, ladies? Have we hearts so base as to make our servants our masters—seeing that this woman was not to be subdued either by love or torment? Let us, I pray you, take example by her conduct and conquer ourselves, for this is the most meritorious conquest that we can make.”
“I see but one thing to be regretted,” said Oisille, “which is that these virtuous actions did not take place in the days of the old historians. Those who gave so much praise to their Lucretia would have neglected her to set down at length the virtues of this maiden.”
“They are indeed so great,” said Hircan, “that, were it not for the solemn vow that we have taken to speak the truth, I could not believe her to have been what you describe. We have often seen sick persons turn in disgust from good and wholesome meats to eat such as are bad and hurtful, and in the same way this girl may have had some gentleman of her own estate for whose sake she despised all nobility.”
But to this Parlemente replied that the girl’s whole life showed that she had never loved any living man save him whom she loved more than her very life, though not more than her honour.
“Put that notion out of your head,” said Saffredent, “and learn the origin of the term ‘honour’ as used among women; for perhaps those that speak so much of it are ignorant of how the name was devised. Know then that in the earliest times, when there was but little wickedness among men, love was so frank and strong that it was never concealed, and he who loved the most perfectly received most praise. But when greed and sinfulness fastened upon heart and honour, they drove out God and love, and in their place set up selfishness, hypocrisy and deceit. Then, when some ladies found that they fostered in their hearts the virtue of true love but that the word ‘hypocrisy’ was hateful among men, they adopted instead the word ‘honour.’ At last, too, even those who could feel no honourable love said that ‘honour’ forbade them, and cruelly made this a law for all, so that now even those who love perfectly use concealment, holding virtue for a vice. But such as have an excellent understanding and a sound judgment never fall into any such error. They know the difference between darkness and light, and are aware that true honour consists in manifesting the purity of their hearts, (which should live upon love alone), and not in priding themselves on the vice of dissimulation.”
“Yet,” said Dagoucin, “it is said that the most secret love is the most worthy of praise.”
“Ay, secret,” said Simontault, “from the eyes of those who might misjudge it, but open and manifest at least to the two persons whom it concerns.”
“So I take it,” said Dagoucin, “but it would be better to have one of the two ignorant of it rather than have it known to a third. I believe that the love of the woman in the story was all the deeper for not being declared.”
“Be that as it may,” said Longarine, “virtue should be esteemed, and the highest virtue is to subdue one’s own heart. Considering the opportunities that the maiden had of forgetting conscience and honour, and the virtue she displayed in all these opportunities and temptations by subduing her heart, will, and even him whom she loved better than herself, I say that she might well be called a strong woman. And, since you measure virtue by the mortification of self, I say that the lord deserved higher praise than she, if we remember the greatness of his love, his opportunities, and his power. Yet he would not offend against that rule of true love which renders prince and peasant equal, but employed only such means as honour allows.”
“There are many,” said Hircan, “who would not have acted in the same way.”
“So much the more is he to be esteemed,” said Longarine, “in having subdued the common craftiness of men. He who can do evil and yet does it not is happy indeed.”
“Your words,” said Geburon, “remind me of one who was more afraid of doing wrong in the eyes of men than of offending against God, her honour and love.”
“Then I pray you tell us the story,” said Parlamente, “for I give you my vote.”
“There are some persons,” said Geburon, “who have no God, or, if they believe in one, think Him so far away that He can neither see nor know the wicked acts that they commit; or, if He does, imagine that He pays no heed to things here below, and is too careless to punish them. Of this opinion was a lady, whose name I will alter for the sake of her family, and whom I will call Jambicque.( 5) She used often to say that a woman who had only God to deal with was very fortunate, if for the rest she was able to maintain her honour among men. But you will see, ladies, that her prudence and her hypocrisy did not prevent her secret from being discovered, as will appear from her story, wherein the truth shall be set forth in full, except that the names of persons and places will be changed.”
5 Some of the MSS. give the name as Camele or Camille,
which is also that adopted by Boaistuau.—L.



Jambicque, preferring the praise of the world to a good
conscience, strove to appear before men other than site
really was; but her friend and lover discovered her
hypocrisy by means of a little chalk-mark, and made known to
everybody the wickedness that she was at such pains to
hide.
There dwelt in a very handsome castle a high and mighty Princess, who had in her train a very haughty lady called Jambicque. (1) The latter had so deceived her mistress that the Princess did nothing save by her advice, deeming her the discreetest and most virtuous lady of her day.
1 There are no means of positively identifying this woman.
Brantôme, who refers at length to the above tale in his
Vies des Dames Galantes (Lalanne’s edition, pp. 236-8),
implies that he knew her name but would not tell it. He
says, however, that “she was a widow and lady of honour to a
very great Princess, and knew better how to play the prude
than any other lady at Court.”—M.
This Jambicque used greatly to inveigh against wanton passion, and whenever she perceived any gentleman in love with one of her companions, she would chide them with much harshness, and, by making ill report of them to her mistress, often cause them to be rebuked; hence she was feared far more than she was loved by all the household. As for herself, she never spoke to a man except in a loud voice, and with much haughtiness, and was therefore reputed a deadly enemy to all love. Nevertheless, it was quite otherwise with her heart, for there was a gentleman in her mistress’s service towards whom she entertained so strong a passion that, at last, she could no longer endure it. (2)
2 Brantôme writes as follows concerning the gentleman
referred to above: “According to what I have heard from my
mother, [Anne de Vivonne, wife of Francis de Bourdeille],
who was in the Queen of Navarre’s service and knew some of
her secrets, and was herself one of the narrators [of the
Heptameron, i.e., Ennasuite], this gentleman was my late
uncle La Chastàigneraye, who was brusque, hasty, and rather
fickle. The tale, however, is so disguised as to hide this,
for my said uncle was never in the service of the great
Princess, who was mistress of the lady [Jambicque], but in
that of the King her brother.” This shows the Princess to
have been Queen Margaret herself; and Jambicque, being
described by Brantôme as a widow and lady of honour to the
Princess, might possibly be Blanche de Tournon ( Madame de
Chastillon), concerning whom see vol. i. of the present
work, p. 84 (note 7) and pp. 122-4. Her successor as lady of
honour to Margaret was Brantôme’s own grandmother, of whom
he says that she was not so shrewd, artful, or ready-witted
in love matters as her predecessor. On the other hand,
Blanche de Tournon must have been over forty when La
Chastàigneraye engaged in this adventure, even allowing that
he was only a youth at the time.—Ed.
The regard which she had for honour and good name caused her to conceal her affection, but after she had been consumed by this passion for a full year, being unwilling to find relief as other lovers do in look and speech, she felt her heart so aflame that, in the end, she sought the final cure. And she resolved that it were better to satisfy her desire with none but God in the secret of her heart, rather than speak of it to a man who might some time make it known.
After taking this resolve, she chanced to be one day in her mistress’s apartment, when, looking out upon a terrace, she perceived walking there the man whom she so dearly loved. She gazed upon him until the falling darkness was hiding him from her sight, when she called a little page of hers, and pointing to the gentleman, said—
“Do you see yonder that gentleman who wears a crimson satin doublet and cloak of lynx fur? Go and tell him that one of his friends would speak with him in the garden gallery.”
As soon as the page was gone, she herself passed through her mistress’s wardrobe and into the gallery, having first put on her low hood and half-mask. (3)
3 See ante, vol. iii. p. 27.
When the gentleman was come to where she was waiting, she immediately shut the two doors by which they might have been surprised, and then, without taking off her mask, embraced him very closely, and in the softest whisper imaginable said—
“For a long time, sweetheart, the love I bear you has made me desire time and place for speaking with you, but fearfulness for my honour was for a while so strong as to oblige me, in my own despite, to conceal my passion. Albeit, in the end, the strength of love has vanquished fear, and, in the knowledge that I have of your honour, I protest to you that if you will promise to love me without ever speaking of the matter to any one, or asking of me who I am, I will be your true and faithful sweetheart, and will never love any man but you. But I would rather die than that you should know who I am.”
The gentleman promised her what she asked, which made her very ready to do as much for him, namely, to refuse him nothing he might desire to have. It was between five and six o’clock in winter-time, so that he could see nothing of the lady, but by the touch of her dress he perceived that it was of velvet, which at that time was not worn every day except by ladies of high and mighty lineage. And so far as his hand could let him judge of what was beneath, there was nothing there that was not excellent, trim, and plump. Accordingly, he was at pains to entertain her as well as he was able. She on her part did no less, and the gentleman readily perceived that she was a married woman.
She desired afterwards to return immediately to the place whence she had come, but the gentleman said to her—
“I esteem greatly the undeserved favour that you have shown me, but I shall esteem still more that which you may bestow at my request. So well pleased am I by this your kindness, that I would fain learn whether I may not look for more of the same sort, and, also, in what manner you would have me act; for, knowing you not, I shall be powerless to woo.”
“Have no concern,” said the lady, “about that. You may rest assured that every evening, before my mistress sups, I shall not fail to send for you, and do you be in readiness on the terrace where you were just now. I shall merely send you word to remember what you have promised, and in this way you will know that I am waiting for you here in the gallery. But if you hear talk of going to table, you may withdraw for that day or else come into our mistress’s apartment. Above all things, I pray you will never seek to know me, if you would not forthwith bring our friendship to an end.”
So the lady and the gentleman went their several ways. And although their love affair lasted for a great while, he could never learn who she was. He pondered much upon the matter, wondering within himself who she might be. He could not imagine that any woman in the world would fain be unseen and unloved; and, having heard some foolish preacher say that no one who had looked upon the face of the devil could ever love him, he suspected that his mistress might be some evil spirit.
In this perplexity he resolved to try and find out who it was that entertained him so well, and when next she sent for him he brought some chalk, and, while embracing her, marked the back of her shoulder without her knowledge. Then, as soon as she was gone, the gentleman went with all speed to his mistress’s apartment, and stood beside the door in order to look from behind at the shoulders of those ladies that might go in.
He saw Jambicque enter among the rest, but with so haughty a bearing that he feared to look at her as keenly as at the others, and felt quite sure that it could not have been she. Nevertheless, when her back was turned, he perceived the chalk mark, whereat he was so greatly astonished that he could hardly believe his eyes.
However, after considering both her figure, which was just such a one as his hands had known, and her features, which he recognised in the same way, he perceived that it was indeed none other than herself. And he was well pleased to think that a woman who had never been reputed to have a lover, and who had refused so many worthy gentlemen, should have chosen himself alone.
But Love, which is ever changeful of mood, could not suffer him to live long in such repose, but, filling him with self-conceit and hope, led him to make known his love, in the expectation that she would then hold him still more dear.
One day, when the Princess was in the garden, the lady Jambicque went to walk in a pathway by herself. The gentleman, seeing that she was alone, went up to converse with her, and, as though he had never elsewhere met her, spoke as follows—
“Mistress, I have long borne towards you in my heart an affection which, through dread of displeasing you, I have never ventured to reveal. But now my pain has come to be such that I can no longer endure it and live, for I think that no man could ever have loved you as I do.”
The Lady Jambicque would not allow him to finish his discourse, but said to him in great wrath—
“Did you ever hear or see that I had sweetheart or lover? I trow not, and am indeed astonished to find you bold enough to address such words to a virtuous woman like me. You have lived in the same house long enough to know that I shall never love other than my husband; beware, then, of speaking further after this fashion.”
At this hypocrisy the gentleman could not refrain from laughing and saying to her—
“You are not always so stern, madam, as you are now. What boots it to use such concealment towards me? Is it not better to have a perfect than an imperfect love?”
“I have no love for you,” replied Jambicque, “whether perfect or imperfect, except such as I bear to the rest of my mistress’s servants. But if you speak further to me as you have spoken now, I shall perhaps have such hatred for you as may be to your hurt.”
However, the gentleman persisted in his discourse.
“Where,” said he, “is the kindness that you show me when I cannot see you? Why do you withhold it from me now when the light suffers me to behold both your beauty and your excellent and perfect grace?”
Jambicque, making a great sign of the cross, replied—
“Either you have lost your understanding or you are the greatest liar alive. Never in my life have I to my knowledge shown you more kindness or less than I do at this moment, and I pray you therefore tell me what it is you mean.”
Then the unhappy gentleman, thinking to better his fortune with her, told her of the place where he had met her, and of the chalk-mark which he had made in order to recognise her, on hearing which she was so beside herself with anger as to tell him that he was the wickedest of men, and that she would bring him to repent of the foul falsehood that he had invented against her.
The gentleman, knowing how well she stood with her mistress, sought to soothe her, but he found it impossible to do so; for, leaving him where he stood, she furiously betook herself to her mistress, who, loving Jambicque as she did herself, left all the company to come and speak with her, and, on finding her in such great wrath, inquired of her what the matter was. Thereupon Jambicque, who had no wish to hide it, related all the gentleman’s discourse, and this she did so much to the unhappy man’s disadvantage, that on the very same evening his mistress commanded him to withdraw forthwith to his own home without speaking with anyone and to stay there until he should be sent for. And this he did right speedily, for fear of worse. (4)
4 It has been mentioned in note 2 that the gentleman in
question was Brantôme’s uncle La Chastaigneraye. Born,
according to most accounts, in 1520, Francis de Vivonne,
Lord of La Chastaigneraye, was a godson of Francis I., and
early displayed marked skill and prowess in all bodily
exercises and feats of arms. He was, however, of a very
quarrelsome disposition, and had several duels. A dispute
arising between him and Guy de Chabot, Lord of Jarnac, they
solicited permission to fight, but Francis I. would not
accord it, and it was only after the accession of Henry II.
that the encounter took place. The spot fixed upon was the
park of St. Germain-en-Laye, and the King and the whole
Court were present (July 10, 1547)—In the result, La
Chastaigneraye was literally ham-strung by a back-thrust
known to this day as the coup de Jarnac. The victor
thereupon begged the King to accept his adversary’s life and
person, and Henry, after telling Jamac that “he had fought
like Cæsar and spoken like Cicero,” caused La Chastaigneraye
to be carried to his tent that his wound might be dressed.
Deeply humiliated by his defeat, however, the vanquished
combatant tore off his bandages and bled to death.—Ed.
So long as Jambicque dwelt with her mistress, the gentleman returned not to the Princess’s house, nor did he ever have tidings of her who had vowed to him that he should lose her as soon as he might seek her out. (5)
5 After referring to this tale Brantôme adds that he had
heard tell of another Court lady who was minded to imitate
Jambicque, but who, “every time she returned from her
assignation, went straight to her room, and let one of her
serving maids examine her on all sides to see if she were
marked. By this means she guarded herself against being
surprised and recognised, and indeed was never marked until
at her ninth assignation, when the mark was at once
discovered by her women. And thereupon, for fear of scandal
and opprobrium, she broke off her intrigue and never more
returned to the appointed spot. Some one said ‘twould have
been better if she had let her lover mark her as often as he
liked, and each time have had his marks effaced, for in this
wise she would have reaped a double pleasure—contentment in
love and satisfaction at duping her lover, who, like he who
seeks the Philosopher’s Stone, would have toiled hard to
discover and identify her, without ever succeeding in doing
so.”—(Lalanne’s OEuvres de Brantôme, pp. 236-8).—M.
“By this tale, ladies, you may see how one who preferred the world’s esteem to a good conscience lost both the one and the other. For now may the eyes of all men read what she strove to hide from those of her lover, and so, whilst fleeing the derision of one, she has incurred the derision of all. Nor can she be held excused on the score of simplicity and artless love, for which all men should have pity, but she must be condemned twice over for having concealed her wickedness with the twofold cloak of honour and glory, and for making herself appear before God and man other than she really was. He, however, who gives not His glory to another, took this cloak from off her and so brought her to double shame.”
“Her wickedness,” said Oisille, “was without excuse. None can defend her when God, Honour, and even Love are her accusers.”
“Nay,” said Hircan, “Pleasure and Folly may; they are the true chief advocates of the ladies.”
“If we had no other advocates,” said Parlamente, “than those you name, our cause would indeed be ill supported; but those who are vanquished by pleasure ought no longer to be called women but rather men, whose reputation is merely exalted by frenzy and lust. When a man takes vengeance upon his enemy and slays him for giving him the lie, he is deemed all the more honourable a gentleman for it; and so, too, when he loves a dozen women besides his own wife. But the reputation of women has a different foundation, that, namely, of gentleness, patience and chastity.”
“You speak of the discreet,” said Hircan.
“Yes,” returned Parlamente, “because I will know none others.”
“If none were wanton,” said Nomerfide, “those who would fain be believed by all the world must often have lied.”
“Pray, Nomerfide,” said Geburon, “receive my vote, and forget that you are a woman, in order that we may learn what some men that are accounted truthful say of the follies of your sex.”
“Since virtue compels me to it, and you have made it my turn, I will tell you what I know. I have not heard any lady or gentleman present speak otherwise than to the disadvantage of the Grey Friars, and out of pity I have resolved to speak well of them in the story that I am now about to relate.”


In reward for not having concealed the truth, the Lord of
Sedan doubled the alms of a Grey Friar, who thus received
two pigs instead of one. (1)
To the castle of Sedan once came a Grey Friar to ask my Lady of Sedan, who was of the house of Crouy, (2) for a pig, which she was wont to give to his Order every year as alms.
1 This tale, though it figures in all the MSS., does not
appear in Gruget’s edition of the Heptameron, but is there
replaced by the one that follows, XLIV. (B).—Ed.
2 This Lady of Sedan is Catherine de Croï, daughter of
Philip VI. de Croï, Count of Chimay. In 1491 she married
Robert II. do la Marck, Duke of Bouillon, Lord of Sedan,
Fleuranges, &c., who was long the companion in arms of
Bayard and La Trémoïlle. Robert II. lost the duchy of
Bouillon through the conquests of Charles V., and one of the
clauses of the treaty of Cambrai (the “Ladies’ Peace”) was
that Francis I. would in no wise assist him to regain it.
His eldest son by Catherine de Croï was the celebrated
Marshal de Fleuranges, “the young adventurer,” who left such
curious memoirs behind him. Robert II. died in 1535, his son
surviving him a couple of years.—Anselme’s Histoire
Généalogique, vol. vii. p. 167.—L. and B. J.
My Lord of Sedan, who was a prudent man and a merry talker, had the good father to eat at his table, and in order to put him on his mettle said to him, among other things—
“Good father, you do well to make your collection while you are yet unknown. I greatly fear that, if once your hypocrisy be found out, you will no longer receive the bread of poor children, earned by the sweat of their fathers.”
The Grey Friar was not abashed by these words, but replied—
“Our Order, my lord, is so securely founded that it will endure as long as the world exists. Our foundation, indeed, cannot fail so long as there are men and women on the earth.”
My Lord of Sedan, being desirous of knowing on what foundation the existence of the Grey Friars was thus based, urgently begged the father to tell him.
After making many excuses, the Friar at last replied—
“Since you are pleased to command me to tell you, you shall hear. Know, then, my lord, that our foundation is the folly of women, and that so long as there be a wanton or foolish woman in the world we shall not die of hunger.”
My Lady of Sedan, who was very passionate, was in such wrath on hearing these words, that, had her husband not been present, she would have dealt harshly with the Grey Friar; and indeed she swore roundly that he should not have the pig that she had promised him; but the Lord of Sedan, finding that he had not concealed the truth, swore that he should have two, and caused them to be sent to his monastery.
“You see, ladies, how the Grey Friar, being sure that the favour of the ladies could not fail him, contrived, by concealing nothing of the truth, to win the favour and alms of men. Had he been a flatterer and dissembler, he would have been more pleasing to the ladies, but not so profitable to himself and his brethren.”
The tale was not concluded without making the whole company laugh, and especially such among them as knew the Lord and Lady of Sedan. And Hircan said—“The Grey Friars, then, should never preach with intent to make women wise, since their folly is of so much service to the Order.”
“They do not preach to them,” said Parlamente, “with intent to make them wise, but only to make them think themselves so. Women who are altogether worldly and foolish do not give them much alms; nevertheless, those who think themselves the wisest because they go often to monasteries, and carry paternosters marked with a death’s head, and wear caps lower than others, must also be accounted foolish, for they rest their salvation on their confidence in the holiness of wicked men, whom they are led by a trifling semblance to regard as demigods.”
“But who could help believing them,” said Enna-suite, “since they have been ordained by our prelates to preach the Gospel to us and rebuke our sins?”
“Those who have experienced their hypocrisy,” said Parlamente, “and who know the difference between the doctrine of God and that of the devil.”
“Jesus!” said Ennasuite. “Can you think that these men would dare to preach false doctrine?”
“Think?” replied Parlamente. “Nay, I am sure that they believe anything but the Gospel. I speak only of the bad among them; for I know many worthy men who preach the Scriptures in all purity and simplicity, and live without reproach, ambition, or covetousness, and in such chastity as is unfeigned and free. However, the streets are not paved with such as these, but are rather distinguished by their opposites; and the good tree is known by its fruit.”
“In very sooth,” said Ennasuite, “I thought we were bound on pain of mortal sin to believe all they tell us from the pulpit as truth, that is, when they speak of what is in the Holy Scriptures, or cite the expositions of holy doctrines divinely inspired.”
“For my part,” said Parlamente, “I cannot but see that there are men of very corrupt faith among them. I know that one of them, a Doctor of Theology and a Principal in their Order, (3) sought to persuade many of the brethren that the Gospel was no more worthy of belief than Cæsar’s Commentaries or any other histories written by learned men of authority; and from the hour I heard that I would believe no preacher’s word unless I found it in harmony with the Word of God, which is the true touchstone for distinguishing between truth and falsehood.”
3 In MS. No. 1520 this passage runs, “a Doctor of Theology
named Colimant, a great preacher and a Principal in their
Order.” However, none of the numerous works on the history
of the Franciscans makes any mention of a divine called
Colimant.—B. J.
“Be assured,” said Oisille, “that those who read it constantly and with humility will never be led into error by deceits or human inventions; for whosoever has a mind filled with truth cannot believe a lie.”
“Yet it seems to me,” said Simontault, “that a simple person is more readily deceived than another.”
“Yes,” said Longarine, “if you deem foolishness to be the same thing as simplicity.”
“I affirm,” replied Simontault, “that a good, gentle and simple woman is more readily deceived than one who is wily and wicked.”
“I think,” said Nomerfide, “that you must know of one overflowing with such goodness, and so I give you my vote that you may tell us of her.”
“Since you have guessed so well,” said Simontault, “I will indeed tell you of her, but you must promise not to weep. Those who declare, ladies, that your craftiness surpasses that of men would find it hard to bring forward such an instance as I am now about to relate, wherein I propose to show you not only the exceeding craftiness of a husband, but also the simplicity and goodness of his wife.”



Concerning the subtlety of two lovers in the enjoyment of
their love, and the happy issue of the latter. (1)
1 This is the tale given by Gruget in his edition of the
Heptameron, in lieu of the preceding one.—Ed.
In the city of Paris there lived two citizens of middling condition, of whom one had a profession, while the other was a silk mercer. These two were very old friends and constant companions, and so it happened that the son of the former, a young man, very presentable in good company, and called James, used often by his father’s favour to visit the mercer’s house. This, however, he did for the sake of the mercer’s beautiful daughter named Frances, whom he loved; and so well did James contrive matters with her, that he came to know her to be no less loving than loved.
Whilst matters were in this state, however, a camp was formed in Provence in view of withstanding the descent of Charles of Austria, (2) and James, being called upon the list, was obliged to betake himself to the army. At the very beginning of the campaign his father passed from life into death, the tidings whereof brought him double sorrow, on the one part for the loss of his father, and on the other for the difficulty he should have on his return in seeing his sweetheart as often as he had hoped.
2 Charles V. entered Provence by way of Piedmont in the
summer of 1536, and invested Marseilles. A scarcity of
supplies and much sickness among his troops compelled him,
however, to raise the siege.—M.
As time went on, the first of these griefs was forgotten and the other increased. Since death is a natural thing, and for the most part befalls the father before the children, the sadness it causes gradually disappears; but love, instead of bringing us death, brings us life through the procreation of children, in whom we have immortality, and this it is which chiefly causes our desires to increase.
James, therefore, when he had returned to Paris, thought or cared for nothing save how he might renew his frequent visits to the mercer’s house, and so, under cloak of pure friendship for him, traffic in his dearest wares. On the other hand, during his absence, Frances had been urgently sought by others, both because of her beauty and of her wit, and also because she was long since come to marriageable years; but whether it was that her father was avaricious, or that, since she was his only daughter, he was over anxious to establish her well, he failed to perform his duty in the matter. This, however, tended but little to her honour, for in these days people speak ill of one long before they have any reason to do so, and particularly in aught that concerns the chastity of a beautiful woman or maid. Her father did not shut his ears or eyes to the general gossip, nor seek resemblance with many others who, instead of rebuking wrongdoing, seem rather to incite their wives and children to it, for he kept her with such strictness that even those who sought her with offers of marriage could see her but seldom, and then only in presence of her mother.
It were needless to ask whether James found all this hard of endurance. He could not conceive that such rigour should be without weighty reason, and therefore wavered greatly between love and jealousy. However, he resolved at all risks to learn the cause, but wished first of all to know whether her affection was the same as before; he therefore set about this, and coming one morning to church, he placed himself near her to hear mass, and soon perceived by her countenance that she was no less glad to see him than he was to see her. Accordingly, knowing that the mother was less stern than the father, he was sometimes, when he met them on their way to church, bold enough to accost them as though by chance, and with a familiar and ordinary greeting; all, however, being done expressly so that he might the better work his ends.
To be brief, when the year of mourning for his father was drawing to an end, he resolved, on laying aside his weeds, to cut a good figure and do credit to his forefathers; and of this he spoke to his mother, who approved his design; for having but two children, himself and a daughter already well and honourably mated, she greatly desired to see him suitably married. And, indeed, like the worthy lady that she was, she still further incited his heart in the direction of virtue by countless instances of other young men of his own age who were making their way unaided, or at least were showing themselves worthy of those from whom they sprang.
It now only remained to determine where they should equip themselves, and the mother said—
“I am of opinion, James, that we should go to our friend Master Peter,”—that is, to the father of Frances—“for, knowing us, he will not cheat us.”
His mother was indeed tickling him where he itched; however, he held firm and replied—
“We will go where we may find the cheapest and the best. Still,” he added, “for the sake of his friendship with my departed father, I am willing that we should visit him first.”
Matters being thus contrived, the mother and son went one morning to see Master Peter, who made them welcome; for traders, as you know, are never backward in this respect. They caused great quantities of all kinds of silk to be displayed before them, and chose what they required; but they could not agree upon the price, for James haggled on purpose, because his sweetheart’s mother did not come in. So at last they went away without buying anything, in order to see what could be done elsewhere. But James could find nothing so handsome as in his sweetheart’s house, and thither after a while they returned.
The mercer’s wife was now there and gave them the best reception imaginable, and after such bargaining as is common in shops of the kind, during which Peter’s wife proved even harder than her husband, James said to her—
“In sooth, madam, you are very hard to deal with. I can see how it is; we have lost my father, and our friends recognise us no longer.”
So saying, he pretended to weep and wipe his eyes at thought of his departed father; but ‘twas done in order to further his design.
The good widow, his mother, took the matter in perfect faith, and on her part said—
“We are as little visited since his death as if we had never been known. Such is the regard in which poor widows are held!”
Upon this the two women exchanged fresh declarations of affection, and promised to see each other oftener than ever. While they were thus discoursing, there came in other traders, whom the master himself led into the back shop. Then the young man perceived his opportunity, and said to his mother—
“I have often on feast days seen this good lady going to visit the holy places in our neighbourhood, and especially the convents. Now if, when passing, she would sometimes condescend to take wine with us, she would do us at once pleasure and honour.”
The mercer’s wife, who suspected no harm, replied that for more than a fortnight past she had intended to go thither, that, if it were fair, she would probably do so on the following Sunday, and that she would then certainly visit the lady at her house. This affair being concluded, the bargain for the silk quickly followed, since, for the sake of a little money, ‘twould have been foolish to let slip so excellent an opportunity.
When matters had been thus contrived, and the merchandise taken away, James, knowing that he could not alone achieve so difficult an enterprise, was constrained to make it known to a faithful friend named Oliver, and they took such good counsel together that nothing now remained but to put their plan into execution.
Accordingly, when Sunday was come, the mercer’s wife and her daughter, on returning from worship, failed not to visit the widow, whom they found talking with a neighbour in a gallery that looked upon the garden, while her daughter was walking in the pathways with James and Oliver.
When James saw his sweetheart, he so controlled himself that his countenance showed no change, and in this sort went forward to receive the mother and her daughter. Then, as the old commonly seek the old, the three ladies sat down together on a bench with their backs to the garden, whither the lovers gradually made their way, and at last reached the place where were the other two. Thus meeting, they exchanged some courtesies and then began to walk about once more, whereupon the young man related his pitiful case to Frances, and this so well that, while unwilling to grant, she yet durst not refuse what he sought; and he could indeed see that she was in a sore strait. It must, however, be understood that, while thus discoursing, they often, to take away all ground for suspicion, passed and repassed in front of the shelter-place where the worthy dames were seated—talking the while on commonplace and ordinary matters, and at times disporting themselves through the garden.
At last, in the space of half-an-hour, when the good women had become well accustomed to this behaviour, James made a sign to Oliver, who played his part with the girl that was with him so cleverly, that she did not perceive the two lovers going into a close rilled with cherry trees, and well shut in by tall rose trees and gooseberry bushes. (3) They made show of going thither in order to gather some almonds which were in a corner of the close, but their purpose was to gather plums.
3 Large gardens and enclosures were then plentiful in the
heart of Paris. Forty years ago, when the Boulevard
Sebastopol was laid out, it was found that many of the
houses in the ancient Rues St. Martin and St. Denis had, in
their rear, gardens of considerable extent containing
century-old trees, the existence of which had never been
suspected by the passers-by in those then cramped and dingy
thoroughfares.—M.
Accordingly, James, instead of giving his sweetheart a green gown, gave her a red one, and its colour even came into her face through finding herself surprised sooner than she had expected. And these plums of theirs being ripe, they plucked them with such expedition that Oliver himself had not believed it possible, but that he perceived the girl to droop her gaze and look ashamed. This taught him the truth, for she had before walked with head erect, with no fear lest the vein in her eye, which ought to be red, should take an azure hue. However, when James perceived her perturbation, he recalled her to herself by fitting remonstrances.
Nevertheless, while making the next two or three turns about the garden, she would not refrain from tears and sighs, or from saying again and again—“Alas! was it for this you loved me? If only I could have imagined it! Heavens! what shall I do? I am ruined for life. What will you now think of me? I feel sure you will respect me no longer, if, at least, you are one of those that love but for their own pleasure. Alas, why did I not die before falling into such an error?”
She shed many tears while uttering these words, but James comforted her with many promises and oaths, and so, before they had gone thrice again round the garden, or James had signalled to his comrade, they once more entered the close, but by another path. And there, in spite of all, she could not but receive more delight from the second green gown than from the first; from which moment her satisfaction was such that they took counsel together how they might see each other with more frequency and convenience until her father should see fit to consent.
In this matter they were greatly assisted by a young woman, who was neighbour to Master Peter; she had some kinship with James, and was a good friend to Frances. And in this way, from what I can understand, they continued without scandal until the celebration of the marriage, when Frances, being an only child, proved to be very rich for a trader’s daughter. James had, however, to wait for the greater part of his fortune until the death of his father-in-law, for the latter was so grasping a man that he seemed to think one hand capable of robbing him of that which he held in the other. (4)
4 This reminds one of Moliere’s Harpagon, when he requires
La Flèche to show him his hands. See L’Avare, act i. sc.
iii.—M.
“In this story, ladies, you see a love affair well begun, well carried on, and better ended. For although it is a common thing among you men to scorn a girl or woman as soon as she has freely given what you chiefly seek in her, yet this young man was animated by sound and sincere love; and finding in his sweetheart what every husband desires in the girl he weds, and knowing, moreover, that she was of good birth, and discreet in all respects, save for the error into which he himself had led her, he would not act the adulterer or be the cause of an unhappy marriage elsewhere. And for this I hold him worthy of high praise.”
“Yet,” said Oisille, “they were both to blame, ay, and the third party also who assisted or at least concurred in a rape.”
“Do you call that a rape,” said Saffredent, “in which both parties are agreed? Is there any marriage better than one thus resulting from secret love? The proverb says that marriages are made in heaven, but this does not hold of forced marriages, nor of such as are made for money or are deemed to be completely sanctioned as soon as the parents have given their consent.”
“You may say what you will,” said Oisille, “but we must recognise that obedience is due to parents, or, in default of them, to other kinsfolk. Otherwise, if all were permitted to marry at will, how many horned marriages should we not find? Is it to be presumed that a young man and a girl of twelve or fifteen years can know what is good for them? If we examined into the happiness of marriages on the whole, we should find that at least as many love-matches have turned out ill as those that were made under compulsion. Young people, who do not know what is good for them, attach themselves heedlessly to the first that comes; then by degrees they find out their error and fall into others that are still greater. On the other hand, most of those who act under compulsion proceed by the advice of people who have seen more and have more judgment than the persons concerned, and so when these come to feel the good that was before unknown to them, they rejoice in it and embrace it with far more eagerness and affection.”
“True, madam,” said Hircan, “but you have forgotten that the girl was of full age and marriageable, and that she was aware of her father’s injustice in letting her virginity grow musty rather than rub the rust off his crown pieces. And do you not know that nature is a jade? She loved and was loved; she found her happiness close to her hand, and she may have remembered the proverb, ‘She that will not when she may, when she will she shall have nay.’ All these things, added to her wooer’s despatch, gave her no time to resist. Further, you have heard that immediately afterwards her face showed that some noteworthy change had been wrought in her. She was perhaps annoyed at the shortness of the time afforded her to decide whether the thing were good or bad, for no great pressing was needed to make her try a second time.”
“Now, for my part,” said Longarine, “I can find no excuse for such conduct, except that I approve the good faith shown by the youth who, comporting himself like an honest man, would not forsake her, but took her such as he had made her. In this respect, considering the corruption and depravity of the youth of the present day, I deem him worthy of high praise. I would not for all that seek to excuse his first fault, which, in fact, amounted to rape in respect to the daughter, and subornation with regard to the mother.”
“No, no,” said Dagoucin, “there was neither rape nor subornation. Everything was done by mere consent, both on the part of the mothers, who did not prevent it (though, indeed, they were deceived), and on that of the daughter, who was pleased by it, and so never complained.”
“It was all the result,” said Parlamente, “of the great kindliness and simplicity of the mercer’s wife, who unwittingly led the maiden to the slaughter.”
“Nay, to the wedding,” said Simontault, “where such simplicity was no less profitable to the girl than it once was hurtful to one who suffered herself to be readily duped by her husband.”
“Since you know such a story,” said Nomerfide, “I give you my vote that you may tell it to us.”
“I will indeed do so,” said Simontault, “but you must promise not to weep. Those who declare, ladies, that your craftiness surpasses that of men, would find it hard to bring forward such an instance as I will now relate, wherein I propose to show you not only the great craftiness of a husband, but the exceeding simplicity and goodness of his wife.”



At his wife’s request, an upholsterer of Tours gave the
Innocents to his serving-maid, with whom he was in love; but
he did so after such a fashion as to let her have what
belonged by right only to his wife, who, for her part, was
such a simpleton that she could never believe her husband
had so wronged her, albeit she had abundant warning thereof
from a neighbour.
In the city of Tours dwelt a man of shrewd and sound understanding, who was upholsterer to the late Duke of Orleans, (1) son of King Francis the First; and although this upholsterer had, through sickness, become deaf, he had nevertheless lost nothing of his wit, which, in regard both to his trade and to other matters, was as shrewd as any man’s. And how he was able to avail himself of it you shall hear.
1 Charles of France, Duke of Orleans, Bourbonnais,
Angoumois and Châtelherault, Count of Clermont, La Marche,
and Civray, Governor and Lieutenant-General of Champagne and
Brie. He has been referred to in the Memoir of Queen
Margaret, ante, vol. i. pp. xxxvi., xlvii.-viii. Born at
St. Germain in January 1521, the Duke of Orleans took part
in several military expeditions, and gave proof of much
ability as a commander. He died, according to some accounts,
of a pleurisy, and, according to others, of the plague, in
1545. The above story was evidently written subsequent to
that date, as Queen Margaret refers to him as “the late Duke
of Orleans.”—L.
He had married a virtuous and honourable woman, with whom he lived in great peace and quietness. He was very fearful of displeasing her, whilst she, on her part, sought in all things to obey him. But, for all the affection that he bore her, he was so charitably inclined that he would often give to his female neighbours that which by right belonged to his wife, though this he did as secretly as he was able.
There was in their house a very plump serving-maid with whom the upholsterer fell in love. Nevertheless, dreading lest his wife should know this, he often made show of scolding and rebuking her, saying that she was the laziest wench he had ever known, though this was no wonder, seeing that her mistress never beat her. And thus it came to pass that one day, while they were speaking about giving the Innocents, (2) the upholsterer said to his wife—
“It were a charity to give them to that lazy wench of yours, but it should not be with your hand, for it is too feeble, and in like way your heart is too pitiful for such a task. If, however, I were to make use of mine, she would serve us better than she now does.”
2 Prior to the Reformation it was the custom, not only in
France but throughout Europe, to whip children on the
morning of Innocents’ Day (December 28), in order, says
Gregory in his treatise on the Boy Bishop, “that the
memory of Herod’s murder of the Innocents might stick the
closer.” This custom (concerning which see Haspinian, De
Orig. Festor, Christianor. fol. 160) subsequently
degenerated into a jocular usage, so far as the children
were concerned, and town-gallants and country-swains
commonly sought to surprise young women in bed, and make
them play the part of the Innocents, more frequently than
otherwise to the loss of their virtue. A story is told of a
French nobleman who in taking leave of some ladies to join a
hunting party, heard one of them whisper, “We shall sleep at
our ease, and pass the Innocents without receiving them.”
This put the nobleman, a certain Seigneur du Rivau, on his
mettle. “He kept his appointment,” we are told, “galloped
back twenty leagues at night, arrived at the lady’s house at
dawn on Innocents’ Day, surprised her in bed, and used the
privilege of the season.” (Bonn’s Heptameron, p. 301).
Verses illustrative of the custom will be found in the works
of Clement Marot, Jannet’s edition, 1868, vol iii. p. 7, and
in those of Cholières, Jouaust’s edition, 1879, vol. i. p.
224-6.—L. and Ed.
The poor woman, suspecting no harm, begged him to do execution upon the girl, confessing that she herself had neither strength nor heart for beating her.
The husband willingly accepted this commission, and, playing the part of a stern executioner, had purchase made of the finest rods that could be found. To show, moreover, how anxious he was not to spare the girl, he caused these rods to be steeped in pickle, so that his poor wife felt far more pity for her maid than suspicion of her husband.
Innocents’ Day being come, the upholsterer rose early in the morning, and, going up to the room where the maid lay all alone, he gave her the Innocents in a different fashion to that which he had talked of with his wife. The maid wept full sore, but it was of no avail. Nevertheless, fearing lest his wife should come upon them, he fell to beating the bed-post with the rods which he had with him in such wise that he barked and broke them; and in this condition he brought them back to his wife, saying—
“Methinks, sweetheart, your maid will remember the Innocents.”
When the upholsterer was gone out of the house, the poor servant threw herself upon her knees before her mistress, telling her that her husband had done her the greatest wrong that was ever done to a serving-maid. The mistress, however, thinking that this merely had reference to the flogging which she believed to have been given, would not suffer the girl to finish, but said to her—
“My husband did well, and only what I have for more than a month been urging him to do. If you were hurt I am very glad to hear it. You may lay it all at my door, and, what is more, he did not even do as much as he ought to have done.”
The serving-maid, finding that her mistress approved of the matter, thought that it could not be so great a sin as she had imagined, the more so as it had been brought to pass by a woman whose virtue was held in such high repute. Accordingly she never afterwards ventured to speak of it.
Her master, however, seeing that his wife was as content to be deceived as he was to deceive her, resolved that he would frequently give her this contentment, and so practised on the serving-maid, that she wept no more at receiving the Innocents.
He continued this manner of life for a great while, without his wife being any the wiser, until there came a time of heavy snow, when, having already given the girl the Innocents on the grass in his garden, he was minded to do the same in the snow. Accordingly, one morning before any one in the house was awake, he took the girl clad in nothing but her shift to make the crucifix in the snow, and while they were pelting each other in sport, they did not forget the game of the Innocents.
This sport, however, was observed by one of their female neighbours who had gone to her window, which overlooked the garden, to see what manner of weather it was, and so wrathful was she at the evil sight, that she resolved to tell her good gossip of it, to the end that she might no longer suffer herself to be deceived by a wicked husband or served by a wanton jade.
After playing these fine pranks, the upholsterer looked about him to see whether any one could perceive him, and to his exceeding annoyance observed his neighbour at her window. But just as he was able to give any colour to his tapestry, so he bethought him to give such a colour to what he had done, that his neighbour would be no less deceived than his wife. Accordingly, as soon as he had gone back to bed again, he made his wife rise in nothing but her shift, and taking her into the garden as he had taken his serving-maid, he played with her for a long time in the snow even as he had played with the other. And then he gave her the Innocents in the same way as he had given them to the maid, and afterwards they returned to bed together.
When the good woman went to mass, her neighbour and excellent friend failed not to be there, and, while unwilling to say anything further, zealously begged of her to dismiss her serving-maid, who was, she said, a very wicked and dangerous wench. This, however, the other would not do without knowing why she thought so ill of the girl, and at last her neighbour related how she had seen the wench that morning in the garden with her husband.
At this the good woman fell to laughing heartily, and said—
“Eh! gossip dear, ‘twas myself!”
“What, gossip? Why she wore naught but her shift, and it was only five o’clock in the morning.”
“In faith, gossip,” replied the good woman, “‘twas myself.”
“They pelted each other with snow,” the other went on, “on the breasts and elsewhere, as familiarly as could be.”
“Eh! gossip, eh!” the good woman replied, “‘twas myself.”
“Nay, gossip,” said the other, “I saw them afterwards doing something in the snow that to my mind is neither seemly nor right.”
“Gossip,” returned the good woman, “I have told you, and I tell you again, that it was myself and none other who did all that you say, for my good husband and I play thus familiarly together. And, I pray you, be not scandalised at this, for you know that we are bound to please our husbands.”
So the worthy gossip went away, more wishful to possess such a husband for herself than she had been to talk about the husband of her friend; and when the upholsterer came home again his wife told him the whole story.
“Now look you, sweetheart,” replied the upholsterer, “if you were not a woman of virtue and sound understanding we should long ago have been separated the one from the other. But I hope that God will continue to preserve us in our mutual love, to His own glory and our happiness.”
“Amen to that, my dear,” said the good woman, “and I hope that on my part you will never find aught to blame.” (3)
3 This tale is accounted by most critics and commentators
to be the best in the Heptameron. Dunlop thinks it may
have been borrowed from a fabliau composed by some
Trouvère who had travelled in the East, and points out
that it corresponds with the story of the Shopkeeper s
Wife in Nakshebi’s Persian Tales (Tooti Nameh). Had it
been brought to France, however, in the manner suggested it
would, like other tales, have found its way into the works
of many sixteenth-century story-writers besides Queen
Margaret. Such, however, is not the case, and curiously
enough, so far as we can find, the tale, as given in the
Heptameron, was never imitated until La Fontaine wrote his
Servante Justifiée (Contes, livre ii. No. vi.), in the
opening lines of which he expressly acknowledges his
indebtedness to the Queen of Navarre.—Ed.
“Unbelieving indeed, ladies, must be the man who, after hearing this true story, should hold you to be as crafty as men are; though, if we are not to wrong either, and to give both man and wife the praise they truly deserve, we must needs admit that the better of the two was worth naught.”
“The man,” said Parlamente, “was marvellously wicked, for he deceived his servant on the one side and his wife on the other.”
“Then you cannot have understood the story,” said Hircan. “We are told that he contented them both in the same morning, and I consider it a highly virtuous thing, both for body and mind, to be able to say and do that which may make two opposites content.”
“It was doubly wicked,” said Parlamente, “to satisfy the simplicity of one by falsehood and the wickedness of the other by vice. But I am aware that sins, when brought before such judges as you, will always be forgiven.”
“Yet I promise you,” said Hircan, “that for my own part I shall never essay so great and difficult a task, for if I but render you content my day will not have been ill spent.”
“If mutual love,” said Parlamente, “cannot content the heart, nothing else can.”
“In sooth,” said Simontault, “I think there is no greater grief in the world than to love and not be loved.”
“To be loved,” said Parlamente, “it were needful to turn to such as love. Very often, however, those women who will not love are loved the most, while those men who love most strongly are loved the least.”
“You remind me,” said Oisille, “of a story which I had not intended to bring forward among such good ones.”
“Still I pray you tell it us,” said Simontault. “That will I do right willingly,” replied Oisille.


A Grey Friar named De Vale, being bidden to dinner at the
house of the Judge of the Exempts in Angoulême, perceived
that the Judge’s wife (with whom he was in love) went up
into the garret alone; thinking to surprise her, he followed
her thither; but she dealt him such a kick in the stomach
that he fell from the top of the stairs to the bottom, and
fled out of the town to the house of a lady that had such
great liking for those of his Order (foolishly believing
them possessed of greater virtues than belong to them), that
she entrusted him with the correction of her daughter, whom
he lay with by force instead of chastising her for the sin
of sloth-fulness, as he had promised her mother he would
do. (1)
1 Boaistuau and Gruget omit this tale, and the latter
replaces it by that numbered XLVI. (B). Count Charles of
Angoulême having died on January i, 1496, the incidents
related above must have occurred at an earlier date.—L.
In the town of Angoulême, where Count Charles, father of King Francis, often abode, there dwelt a Grey Friar named De Vale, the same being held a learned man and a great preacher. One Advent this Friar preached in the town in presence of the Count, whereby he won such renown that those who knew him eagerly invited him to dine at their houses. Among others that did this was the Judge of the Exempts (2) of the county, who had wedded a beautiful and virtuous woman. The Friar was dying for love of her, yet lacked the hardihood to tell her so; nevertheless she perceived the truth, and held him in derision.
2 The Exempt was a police officer, and the functions of
the Juge des Exempts were akin to those of a police
magistrate.—Ed.
After he had given several tokens of his wanton purpose, he one day espied her going up into the garret alone. Thinking to surprise her, he followed, but hearing his footsteps she turned and asked whither he was going. “I am going after you,” he replied, “to tell you a secret.”
“Nay, good father,” said the Judge’s wife. “I will have no secret converse with such as you. If you come up any higher, you will be sorry for it.”
Seeing that she was alone, he gave no heed to her words, but hastened up after her. She, however, was a woman of spirit, and when she saw the Friar at the top of the staircase, she gave him a kick in the stomach, and with the words, “Down! down! sir,” (3) cast him from the top to the bottom. The poor father was so greatly ashamed at this, that, forgetting the hurt he had received in falling, he fled out of the town as fast as he was able. He felt sure that the lady would not conceal the matter from her husband; and indeed she did not, nor yet from the Count and Countess, so that the Friar never again durst come into their presence.
3 The French words here are “Dévaliez, dévaliez,
monsieur,” whilst MS. No. 1520 gives, “Monsieur de Vale,
dévalés.” In either case there is evidently a play upon the
friar’s name, which was possibly pronounced Vallès or
Vallès. Adrien de Valois, it maybe pointed out, rendered his
name in Latin as Valesius; the county of Valois and that
of Valais are one and the same; we continue calling the old
French kings Valois, as their name was written, instead of
Valais as it was pronounced, as witness, for instance, the
nickname given to Henry III. by the lampooners of the
League, “Henri dévalé.” See also post, Tale XLVI. (B),
note 2.—M. and Ed.
To complete his wickedness, he repaired to the house of a lady who preferred the Grey Friars to all other folk, and, after preaching a sermon or two before her, he cast his eyes upon her daughter, who was very beautiful. And as the maiden did not rise in the morning to hear his sermon, he often scolded her in presence of her mother, whereupon the latter would say to him—“Would to God, father, that she had some taste of the discipline which you monks receive from one another.”
The good father vowed that if she continued to be so slothful, he would indeed give her some of it, and her mother earnestly begged him to do so.
A day or two afterwards, he entered the lady’s apartment, and, not seeing her daughter there, asked her where she was.
“She fears you so little,” replied the lady, “that she is still in bed.”
“There can be no doubt,” said the Grey Friar, “that it is a very evil habit in young girls to be slothful. Few people think much of the sin of sloth, but for my part, I deem it one of the most dangerous there is, for the body as for the soul. You should therefore chastise her for it, and if you will give me the matter in charge, I will take good care that she does not lie abed at an hour when she ought to be praying to God.”
The poor lady, believing him to be a virtuous man, begged him to be kind enough to correct her daughter, which he at once agreed to do, and, going up a narrow wooden staircase, he found the girl all alone in bed. She was sleeping very soundly, and while she slept he lay with her by force. The poor girl, waking up, knew not whether he were man or devil, but began to cry out as loudly as she could, and to call for help to her mother. But the latter, standing at the foot of the staircase, cried out to the Friar—“Have no pity on her, sir. Give it to her again, and chastise the naughty jade.”
When the Friar had worked his wicked will, he came down to the lady and said to her with a face all afire—“I think, madam, that your daughter will remember my discipline.”
The mother thanked him warmly and then went upstairs, where she found her daughter making such lamentation as is to be expected from a virtuous woman who has suffered from so foul a crime. On learning the truth, the mother had search made everywhere for the Friar, but he was already far away, nor was he ever afterwards seen in the kingdom of France.
“You see, ladies, with how much security such commissions may be given to those that are unfit for them. The correction of men pertains to men and that of women to women; for women in the correction of men would be as pitiful as men in the correction of women would be cruel.”
“Jesus! madam,” said Parlamente, “what a base and wicked Friar!”
“Say rather,” said Hircan, “what a foolish and witless mother to be led by hypocrisy into allowing so much familiarity to those who ought never to be seen except in church.”
“In truth,” said Parlamente, “I acknowledge that she was the most foolish mother imaginable; had she been as wise as the Judge’s wife, she would rather have made him come down the staircase than go up. But what can you expect? The devil that is half-angel is the most dangerous of all, for he is so well able to transform himself into an angel of light, that people shrink from suspecting him to be what he really is; and it seems to me that persons who are not suspicious are worthy of praise.”
“At the same time,” said Oisille, “people ought to suspect the evil that is to be avoided, especially those who hold a trust; for it is better to suspect an evil that does not exist than by foolish trustfulness to fall into one that does. I have never known a woman deceived through being slow to believe men’s words, but many are there that have been deceived through being over prompt in giving credence to falsehood. Therefore I say that possible evil cannot be held in too strong suspicion by those that have charge of men, women, cities or states; for, however good the watch that is kept, wickedness and treachery are prevalent enough, and the shepherd who is not vigilant will always be deceived by the wiles of the wolf.”
“Still,” said Dagoucin, “a suspicious person cannot have a perfect friend, and many friends have been divided by suspicion.”
“If you know any such instance,” said Oisille, “I give you my vote that you may relate it.”
“I know one,” said Dagoucin, “which is so strictly true that you will needs hear it with pleasure. I will tell you, ladies, when it is that a close friendship is most easily severed; ‘tis when the security of friendship begins to give place to suspicion. For just as trust in a friend is the greatest honour that can be shown him, so is doubt of him a still greater dishonour. It proves that he is deemed other than we would have him to be, and so causes many close friendships to be broken off, and friends to be turned into foes. This you will see from the story that I am minded to relate.”



Concerning a Grey Friar who made it a great crime on the
part of husbands to beat their wives. (1)
In the town of Angoulême, where Count Charles, father of King Francis, often abode, there dwelt a Grey Friar named De Vallès, (2) the same being a learned man and a very great preacher. At Advent time this Friar preached in the town in presence of the Count, whereby his reputation was still further increased.
1 This is the tale inserted in Gruget’s edition in lieu of
the previous one.—Ed.
2 We had thought that Friar Vallès might possibly be Robert
de Valle, who at the close of the fifteenth century wrote a
work entitled Explanatio in Plinium, but find that this
divine was a Bishop of Rouen, and never belonged to the Grey
Friars. In Gessner’s Biographia Universalis, continued by
Frisius, mention is made of three learned ecclesiastics of
the name of Valle living in or about Queen Margaret’s time:
Baptiste de Valle, who wrote on war and duelling; William de
Valle, who penned a volume entitled De Anima Sorbono; and
Amant de Valle, a Franciscan minorité born at Toulouse, who
was the author of numerous philosophical works, the most
important being Elucidationes Scoti.—B. J.
It happened also that during Advent a hare-brained young fellow, who had married a passably handsome young woman, continued none the less to run at the least as dissolute a course as did those that were still bachelors. The young wife, being advised of this, could not keep silence upon it, so that she very often received payment after a different and a prompter fashion than she could have wished. For all that, she ceased not to persist in lamentation, and sometimes in railing as well; which so provoked the young man that he beat her even to bruises and blood. Thereupon she cried out yet more loudly than before; and in a like fashion all the women of the neighbourhood, knowing the reason of this, could not keep silence, but cried out publicly in the streets, saying—
“Shame, shame on such husbands! To the devil with them!”
By good fortune the Grey Friar De Vallès was passing that way and heard the noise and the reason of it. He resolved to touch upon it the following day in his sermon, and did so. Turning his discourse to the subject of marriage and the affection which ought to subsist in it, he greatly extolled that condition, at the same time censuring those that offended against it, and comparing wedded to parental love. Among other things, he said that a husband who beat his wife was in more danger, and would have a heavier punishment, than if he had beaten his father or his mother.
“For,” said he, “if you beat your father or your mother you will be sent for penance to Rome; but if you beat your wife, she and all the women of the neighbourhood will send you to the devil, that is, to hell. Now look you what a difference there is between these two penances. From Rome a man commonly returns again, but from hell, oh! from that place, there is no return: nulla est redemptio” (3)
After preaching this sermon, he was informed that the women were making a triumph of it, (4) and that their husbands could no longer control them. He therefore resolved to set the husbands right just as he had previously assisted their wives.
3 This was the Pope’s expression apropos of Messer Biagio,
whom Michael Angelo had introduced into his “Last
Judgment.”—M.
4 The French expression is faisaient leur Achilles, the
nearest equivalent to which in English would probably be
“Hectoring” It is curious that the French should have taken
the name of Achilles and we that of Hector to express the
same idea of arrogance and bluster.—Ed.
With this intent, in one of his sermons he compared women and devil together, saying that these were the greatest enemies that man had, that they tempted him without ceasing, and that he could not rid himself of them, especially of women.
“For,” said he, “as far as devils are concerned, if you show them the cross they flee away, whereas women, on the contrary, are tamed by it, and are made to run hither and thither and cause their husbands countless torments. But, good people, know you what you must do? When you find your wives afflicting you thus continually, as is their wont, take off the handle of the cross and with it drive them away. You will not have made this experiment briskly three or four times before you will find yourselves the better for it, and see that, even as the devil is driven off by the virtue of the cross, so can you drive away and silence your wives by virtue of the handle, provided only that it be not attached to the cross aforesaid.”
“You have here some of the sermons by this reverend De Vallès, of whose life I will with good reason relate nothing more. However, I will tell you that, whatever face he put upon the matter—and I knew him—he was much more inclined to the side of the women than to that of the men.”
“Yet, madam,” said Parlamente, “he did not show this in his last sermon, in which he instructed the men to ill-treat them.”
“Nay, you do not comprehend his artifice,” said Hircan. “You are not experienced in war and in the use of the stratagems that it requires; among these, one of the most important is to kindle strife in the camp of the enemy, whereby he becomes far easier to conquer. This master monk well knew that hatred and wrath between husband and wife most often cause a loose rein to be given to the wife’s honour. And when that honour frees itself from the guardianship of virtue, it finds itself in the power of the wolf before it knows even that it is astray.”
“However that may be,” said Parlamente, “I could not love a man who had sown such division between my husband and myself as would lead even to blows; for beating banishes love. Yet, by what I have heard, they [the friars] can be so mincing when they seek some advantage over a woman, and so attractive in their discourse, that I feel sure there would be more danger in hearkening to them in secret than in publicly receiving blows from a husband in other respects a good one.”
“Truly,” said Dagoucin, “they have so revealed their plottings in all directions, that it is not without reason that they are to be feared; (5) although in my opinion persons who are not suspicious are worthy of praise.”
5 From this point the dialogue is almost word for word the
same as that following Tale XLVI. (A).—Ed.
“At the same time,” said Oisille, “people ought to suspect the evil that is to be avoided, for it is better to suspect an evil that does not exist than by foolish trustfulness to fall into one that does. For my part, I have never known a woman deceived by being slow to believe men’s words, but many are through being too prompt in giving credence to falsehood. Therefore I say that possible evil cannot be too strongly suspected by those that have charge of men, women, cities or states; for, however good may be the watch that is kept, wickedness and treachery are prevalent enough, and for this reason the shepherd who is not vigilant will always be deceived by the wiles of the wolf.”
“Still,” said Dagoucin, “a suspicious person cannot have a perfect friend, and many friends have been parted by bare suspicion.”
“If you should know any such instance,” thereupon said Oisille, “I will give you my vote that you may relate it.”
“I know one,” said Dagoucin, “which is so strictly true that you will hear it with pleasure. I will tell you, ladies, when it is that close friendship is most readily broken off; it is when the security of friendship begins to give place to suspicion. For just as to trust a friend is the greatest honour one can do him, so is doubt of him the greatest dishonour, inasmuch as it proves that he is deemed other than one would have him to be, and in this wise many close friendships are broken off and friends turned into foes. This you will see from the story that I am now about to relate.”


Two gentlemen lined in such perfect friendship that for a
great while they had everything excepting a wife in common,
until one was married, when without cause he began to
suspect his companion, who, in vexation at being wrongfully
suspected, withdrew his friendship, and did not rest till he
had made the other a cuckold.
Not far from the province of Le Perche (1) there dwelt two gentlemen who from the days of their childhood had lived in such perfect friendship that they had but one heart, one house, one bed, one table, and one purse. They continued living in this perfect friendship for a long time, without there ever being between them any wish or word such as might betray that they were different persons; so truly did they live not merely like two brothers but like one individual man.
1 Between Normandy and Maine. Its chief town was Mortagne.
Of the two one married, yet did not on that account abate his friendship for his fellow or cease to live with him as had been his wont. And whenever they chanced to lodge where room was scanty, he failed not to make him sleep with himself and his wife; (2) though he did, in truth, himself lie in the middle. Their goods were all in common, so that neither the marriage nor aught else that might betide could impair their perfect friendship.
2 To do honour to a guest it was then a common practice to
invite him to share the same bed as one’s self and one’s
wife. In this wise, long after Queen Margaret s time, we
find Louis XIII. sharing the bed of the Duke and Duchess of
Luynes. Tale vii. of the Cent Nouvelles Nouvelles
(imitated in Malespini’s Ducento Novelle and the Joyeuses
Adventures et nouvelles récréations) relates what befell a
Paris goldsmith who took a carter to bed with him and his
spouse, and neglected to follow the usual custom of sleeping
in the middle. In Queen Margaret’s time, it may be added,
the so-called “beds of honour” in the abodes of noblemen and
gentlemen were large enough to accommodate four or five
persons.—B. J. and Ed.
But after some time, worldly happiness, which is ever changeful in its nature, could no longer abide in this too happy household. The husband, without cause, lost the confidence that he had in his friend and in his wife, and, being unable to conceal the truth from the latter, spoke to her with angry words. At this she was greatly amazed, for he had charged her in all things save one to treat his friend as she did himself, and now he forbade her to speak with him except it were before others. She made the matter known to her husband’s friend, who did not believe her, knowing as he well did that he had never purposed doing aught to grieve his comrade. And as he was wont to hide nothing from him, he told him what he had heard, begging him not to conceal the truth, for neither in this nor in any other matter had he any desire to occasion the severance of the friendship which had so long subsisted between them.
The married gentleman assured him that he had never thought of such a thing, and that those who had spread such a rumour had foully lied.
Thereupon his comrade replied—
“I well know that jealousy is a passion as insupportable as love, and were you inclined to jealousy even with regard to myself, I should not blame you, for you could not help it. But there is a thing that is in your power of which I should have reason to complain, and that is the concealment of your distemper from me, seeing that never before was thought, feeling or opinion concealed between us. If I were in love with your wife, you should not impute it to me as a crime, for love is not a fire that I can hold in my hand to do with it what I will; but if it were so and I concealed it from you, and sought by demonstration to make it known to your wife, I should be the wickedest comrade that ever lived.
“As far as I myself am concerned, I can truly assure you that, although she is an honourable and virtuous woman, she is the last of all the women I have ever seen upon whom, even though she were not yours, my fancy would light. But even though there be no occasion to do so, I ask you, if you have the smallest possible feeling of suspicion, to tell me of it, that I may so act as to prevent a friendship that has lasted so long from being severed for the sake of a woman. For, even if I loved her more dearly than aught in the world beside, I would never speak to her of it, seeing that I set your honour before aught else.”
His comrade swore to him the strongest oaths he could muster, that he had never thought of such a thing, and begged him to act in his house as he had been used to do.
“That will I,” the other replied, “but if after this should you harbour an evil opinion of me and conceal it or bear me ill-will, I will continue no more in fellowship with you.”
Some time afterwards, whilst they were living together as had been their wont, the married gentleman again fell into stronger suspicion than ever, and commanded his wife to no longer show the same countenance to his friend as before. This she at once made known to her husband’s comrade, and begged that he would of his own motion abstain from holding speech with her, since she had been charged to do the like towards him.
The gentleman perceived from her words and from divers tokens on the part of his comrade that the latter had not kept his promise, and so said to him in great wrath—
“If, comrade, you are jealous, ‘tis a natural thing, but, after the oaths you swore to me, I must needs be angered that you have used such concealment towards me. I had always thought that neither obstacle nor mean intervened between your heart and mine, but to my exceeding sorrow, and with no fault on my part, I see that the reverse is true. Not only are you most jealous of your wife and of me, but you seek to hide your distemper from me, until at last it must wholly turn to hate, and the dearest love that our time has known become the deadliest enmity.
“I have done all I could to avoid this mishap, but since you suspect me of being so wicked and the opposite of what I have always proved towards you, I give you my oath and word that I will indeed be such a one as you deem me, and that I will never rest until I have had from your wife that which you believe I seek from her. So I bid you beware of me henceforward, for, since suspicion has destroyed your friendship for me, resentment will destroy mine for you.”
Although his comrade tried to persuade him of the contrary, he would no longer believe him, but removed his portion of the furniture and goods that had been in common between them. And so their hearts were as widely sundered as they had before been closely united, and the unmarried gentleman never rested until, as he had promised, he had made his comrade a cuckold. (3)
3 The idea developed in this tale, that of bringing to pass
by one’s own actions the thing one fears and seeks to avoid
or prevent, has much analogy with that embodied in the
“novel of the Curious Impertinent” which Cervantes
introduces into Don Quixote (Part I. chaps, xxviii.,
xxix). In this tale it will be remembered Anselmo and
Lothario are represented as being two such close friends as
the gentlemen who figured in Queen Margaret’s tale. Anselmo
marries, however, and seized with an insane desire to test
the virtue of his wife, Camilla, by exposing her to
temptation, urges Lothario to pay court to her. Lothario at
first resists these solicitations, pointing out the folly of
such an enterprise, but his friend entreats him so
pressingly that he finally consents, and in the sequel the
passion which he at first simulates for Camilla becomes a
real one and leads to his seducing her and carrying her
away, with the result that both the wretched Anselmo and his
wife soon die of grief, whilst Lothario betakes himself to
the wars and perishes in battle.—M. & Ed.
“Thus, ladies, may it fare with those who wrongfully suspect their wives of evil. Many men make of them what they suspect them to be, for a virtuous woman is more readily overcome by despair than by all the pleasures on earth. And if any one says that suspicion is love, I give him nay, for although it results from love as do ashes from fire, it kills it nevertheless in the same way.”
“I do not think,” said Hircan, “that anything can be more grievous to either man or woman than to be suspected of that which is contrary to fact. For my own part, nothing could more readily prompt me to sever fellowship with my friends than such suspicion.”
“Nevertheless,” said Oisille, “woman is without rational excuse who revenges herself for her husband’s suspicion by her own shame. It is as though a man should thrust his sword through his own body, because unable to slay his foe, or should bite his own fingers because he cannot scratch him. She would have done better had she spoken to the gentleman no more, and so shown her husband how wrongly he had suspected her; for time would have softened them both.”
“Still ‘twas done like a woman of spirit,” said Ennasuite. “If many women acted in the same way, their husbands would not be so outrageous as they are.”
“For all that,” said Longarine, “patience gives a woman the victory in the end, and chastity brings her praise, and more we should not desire.”
“Nevertheless,” said Ennasuite, “a woman may be unchaste and yet commit no sin.”
“How may that be?” said Oisille.
“When she mistakes another man for her husband.”
“And who,” said Parlamente, “is so foolish that she cannot clearly tell the difference between her husband and another man, whatever disguise the latter may wear?”
“There have been and still will be,” said Ennasuite, “a few deceived in this fashion, and therefore still innocent and free from sin.”
“If you know of such a one,” said Dagoucin, “I give you my vote that you may tell us about her, for I think it very strange that innocence and sin can go together.”
“Listen, then,” said Ennasuite. “If, ladies, the foregoing tales have not sufficiently warned you of the danger of lodging in our houses those who call us worldly and consider themselves as something holy and far worthier than we, I will give you yet a further instance of it, that you may see by the errors into which those fall who trust them too much that not only are they human like others, but that there is something devilish in their nature, passing the ordinary wickedness of men. This you will learn from the following story.”



The older and wickeder of two Grey Friars, who were lodged
in an inn where the marriage of the host’s daughter was
being celebrated, perceived the bride being led away,
whereupon he went and took the place of the bridegroom
whilst the latter was still dancing with the company. (1)
1 We have already had an instance of a friar stealing into
a wife’s bed at night-time, in the husband’s absence (see
ante, vol. iii., tale xxili.). For a similar incident see
the Cent Nouvelles Nouvelles, No. xxx.—Ed.
At an inn, in a village of the land of Perigort, there was celebrated the marriage of a maiden of the house, at which all the kinsfolk and friends strove to make as good cheer as might be. On the day of the wedding there arrived at the inn two Grey Friars, to whom supper was given in their own room, since it was not meet for those of their condition to be present at a wedding. However, the chief of the two, who had the greater authority and craft, resolved that, since he was shut out from the board, he would share the bed, and in this way play them one of the tricks of his trade.
When evening was come, and the dances were begun, the Grey Friar continued to observe the bride for a long time, and found her very handsome and to his taste. Then, inquiring carefully of the serving-woman concerning the room in which she was to lie, he found that it was close to his own, at which he was well pleased; and so good a watch did he keep in order to work his end, that he perceived the bride being led from the hall by the old women, as is the custom. As it was yet very early, the bridegroom would not leave the dance, in which he was so greatly absorbed that he seemed to have altogether forgotten his wife.
Not so the Friar, for, as soon as his ears told him that the bride was in bed, he put off his grey robe and went and took the husband’s place. Being fearful of discovery, however, he stayed but a very short time, and then went to the end of a passage where his comrade, who was keeping watch for him, signed to him that the husband was dancing-still.
The Friar, who had not yet satisfied his wicked lust, thereupon went back to bed with the bride, until his comrade gave him a signal that it was time to leave.
The bridegroom afterwards came to bed, and his wife, who had been so tormented by the Friar that she desired naught but rest, could not help saying to him—
“Have you resolved never to sleep or do anything but torment me?”
The unhappy husband, who had but just come in, was greatly astonished at this, and asked what torment he had given her, seeing that he had not left the dance.
“A pretty dance!” said the poor girl. “This is the third time that you have come to bed. I think you would do better to sleep.”
The husband was greatly astonished on hearing these words, and set aside thought of everything else in order that he might learn the truth of what had passed.
When his wife had told him the story, he at once suspected the Grey Friars who were lodged in the house, and forthwith rising, he went into their room, which was close beside his own.
Not finding them there, he began to call out for help in so loud a voice that he speedily drew together all his friends, who, when they had heard the tale, assisted him with candles, lanterns, and all the dogs of the village to hunt for the Grey Friars.
Not finding them in the house, they made all diligence, and so caught them among the vines, where they treated them as they deserved; for, after soundly beating them, they cut off their arms and legs, and left them among the vines to the care of Bacchus and Venus, of whom they had been better disciples than of St. Francis.
“Be not amazed, ladies, if such folk, being cut off from our usual mode of life, do things of which adventurers (2) even would be ashamed. Wonder rather that they do no worse when God withdraws his hand from them, for so little does the habit make the monk, that it often unmakes him through the pride it lends him. For my own part, I go not beyond the religion that is taught by St. James, who has told us to ‘keep the heart pure and unspotted toward God, and to show all charity to our neighbours.’”(3)
2 This is an allusion to the dismissed French Swiss, and
German lansquenets who roamed about France in little bands,
kidnapping, plundering, and at times hiring themselves out
as spadassins. These men, the pests of the country, were
commonly known by the name of adventurers.—B. J.
3 “Pure religion and undefiled before God and the Father is
this, To visit the fatherless and widows in their affliction
and to keep himself unspotted from the world.”—James i.
27.—Ed.
“Heavens!” said Oisille, “shall we never have done with tales about these tiresome Grey Friars?”
Then said Ennasuite—
“If, ladies, princes and gentlemen are not spared, the Grey Friars, it seems to me, are highly honoured by being noticed. They are so useless that, were it not that they often do evil things worthy of remembrance, they would never even be mentioned; and, as the saying goes, it is better to do evil than to do nothing at all. Besides, the more varied the flowers the handsomer will our posy be.”
“If you will promise not to be angry with me,” said Hircan, “I will tell you the story of a great lady whose wantonness was so extreme that you will forgive the poor friar for having taken what he needed, where he was able to find it, seeing that she, who had enough to eat, nevertheless sought for dainties in too monstrous a fashion.”
“Since we have sworn to speak the truth,” said Oisille, “we have also sworn to hear it. You may therefore speak with freedom, for the evil things that we tell of men and women are not uttered to shame those that are spoken of in the story, but to take away all trust in created beings, by revealing the trouble to which these are liable, and this to the end that we may fix and rest our hope on Him alone who is perfect, and without whom every man is only imperfection.”
“Well then,” said Hircan, “I will relate my story without fear.”



Same French gentlemen, perceiving that the King their
master was exceedingly well treated by a foreign Countess
whom he loved, ventured to speak to her, and sought her with
such success, that one after another they had from her what
they desired, each, however, believing that he alone
possessed the happiness in which all the others shared. And
this being discovered by one of their number, they all
plotted together to be revenged on her; but, as she showed a
fair countenance and treated them no worse than before, they
brought away in their own bosoms the shame which they had
thought to bring upon her. (1)
At the Court of King Charles—which Charles I shall not mention, for the sake of the lady of whom I wish to speak, and whom I shall not call by her own name—there was a Countess of excellent lineage, (2) but a foreigner. And as novelties ever please, this lady, both for the strangeness of her attire and for its exceeding richness, was observed by all. Though she was not to be ranked among the most beautiful, she possessed gracefulness, together with a noble assurance that could not be surpassed; and, moreover, her manner of speech and her seriousness were to match, so that there was none but feared to accost her excepting the King, who loved her exceedingly. That he might have still more intimate converse with her, he gave some mission to the Count, her husband, which kept him away for a long time, and meanwhile the King made right good cheer with his wife.
1 The incidents here related must have occurred during the
reign of Charles VIII., probably in or about 1490.—L.
2 This Countess cannot be identified. She was probably the
wife of one of the many Italian noblemen, like the
Caraccioli and San Severini, who entered the French service
about the time of the conquest of Naples. Brantôme alludes
to the story in his Dames Galantes (Fourth Discourse) but
gives no names.—Ed.
Several of the King’s gentlemen, knowing that their master was well treated by her, took courage to speak to her, and among the rest was one called Astillon, (3) a bold man and graceful of bearing.
3 This is James de Chastillon, not, however, J. Gaucher de
Chastillon, “King of Yvetot,” as M. de Lincy supposes, but
J. de Coligny-Chastillon, as has been pointed out by M.
Frank. Brantôme devotes the Nineteenth Discourse of his
Capitaines françois to this personage, and says: “He had
been one of the great favourites and mignons of King
Charles VIII., even at the time of the journey to the
kingdom of Naples; and ‘twas then said, ‘Chastillon,
Bourdillon and Bonneval [see post, note 5] govern the royal
blood.’” Wounded in April 1512 at the battle of Ravenna,
“the most bloody battle of the century,” he was removed to
Ferrara, where he died (May 25). He was the second husband
of Blanche de Tournon, Lady of Honour to Queen Margaret,
respecting whom see ante, vol. i. pp. 84-5, 122-4, and
vol. iv. p. 144, note 2.—L., F. and Ed.
At first she treated him so seriously, threatening to tell of him to the King his master, that he well-nigh became afraid of her. However, as he had not been wont to fear the threats even of the most redoubtable captains, he would not suffer himself to be moved by hers, but pressed her so closely that she at last consented to speak with him in private, and taught him the manner in which he should come to her apartment. This he failed not to do, and, in order that the King might be without suspicion of the truth, he craved permission to go on a journey, and set out from the Court. On the very first day, however, he left all his following and returned at night to receive fulfilment of the promises that the Countess had made him. These she kept so much to his satisfaction, that he was content to remain shut up in a closet for five or six days, without once going out, and living only on restoratives.
During the week that he lay in hiding, one of his companions called Durassier (4) made love to the Countess. At the beginning she spoke to this new lover, as she had spoken to the first, with harsh and haughty speech that grew milder day by day, insomuch that when the time was come for dismissing the first prisoner, she put the second into his place. While he was there, another companion of his, named Valnebon, (5) did the same as the former two, and after these there came yet two or three more to lodge in the sweet prison.
4 This in all probability is the doughty James Galliot de
Genouillac, who—much in the same way as in our own times
the names of the “Iron Duke” and the “Man of Iron” have been
bestowed on Wellington and Bismarck—was called by his
contemporaries the “Seigneur d’Acier” or “Steel Lord,”
whence “Durassier”—hard steel. Born in Le Quercy in or
about 1466, Genouillac accompanied Charles VIII. on his
Italian expeditions, and, according to Brantôme, surpassed
all others in valour and influence. He greatly distinguished
himself at the battle of Fornova (1495), and in 1515 we find
him one of the chief commanders of the French artillery. For
the great skill he displayed at Marignano he was appointed
Grand Master of the Artillery and Seneschal of Armagnac, and
he subsequently became Grand Equerry of France. At Pavia,
where he again commanded the artillery, he would have swept
away the Spaniards had not the French impetuously charged
upon them, preventing him from firing his pieces. Most of
the latter he contrived to save, severe as was the defeat,
and he effectually protected the retreat of the Duke of
Alençon and the Count of Clermont into France. Genouillac
died in 1546, a year after he had been appointed Governor of
Languedoc.—B. J. and Ed.
5 Valnebon is an anagram of the name Bonneval, and Queen
Margaret evidently refers here to a member of the Bonneval
family. In the time of Charles VIII. this illustrious
Limousin house had two principal members, Anthony, one of
the leading counsellors of that king (as of his predecessor
Louis XI. and his successor Louis XII.), and Germain, also a
royal counsellor and chamberlain. The heroes of the above
story being military men and old friends and comrades, it is
probable that the reference is to Germain de Bonneval, he,
like Chastillon and Genouillac, having accompanied Charles
VIII. on his expedition into Italy. Germain de Bonneval,
moreover, was one of the seven noblemen who fought at the
battle of Fornova, clad and armed exactly like the French
king. He perished at the memorable defeat of Pavia in 1525.
From him descended, in a direct line, the famous eighteenth
century adventurer, Claud Alexander, Count de Bonneval.—B.
J. and Ed.
This manner of life continued for a long time, and was so skilfully contrived that none of the lovers knew aught of the others; and although they were aware of the love that each of them bore the lady, there was not one but believed himself to be the only successful suitor, and laughed at his comrades who, as he thought, had failed to win such great happiness.
One day when the gentlemen aforesaid were at a banquet where they made right good cheer, they began to speak of their several fortunes and of the prisons in which they had lain during the wars. Valnebon, however, who found it a hard task to conceal the great good fortune he had met with, began saying to his comrades—
“I know not what prisons have been yours, but for my own part, for love of one wherein I once lay, I shall all my life long give praise and honour to the rest. I think that no pleasure on earth comes near that of being kept a prisoner.”
Astillon, who had been the first captive, had a suspicion of the prison that he meant, and replied—
“What gaoler, Valnebon, man or woman, treated you so well that you became so fond of your prison?”
“Whoever the gaoler may have been,” said Valnebon, “my prisonment was so pleasant that I would willingly have had it last longer. Never was I better treated or more content.”
Durassier, who was a man of few words, clearly perceived that they were discussing the prison in which he had shared like the rest; so he said to Valnebon—
“On what meats were you fed in the prison that you praise so highly?”
“What meats?” said Valnebon. “The King himself has none better or more nourishing.”
“But I should also like to know,” said Durassier, “whether your keeper made you earn your bread properly?”
Valnebon, suspecting that he had been understood, could not hold from swearing.
“God’s grace!” said he. “Had I indeed comrades where I believed myself alone?”
Perceiving this dispute, wherein he had part like the rest, Astillon laughed and said—
“We all serve one master, and have been comrades and friends from boyhood; if, then, we are comrades in the same good fortune, we can but laugh at it. But, to see whether what I imagine be true, pray let me question you, and do you confess the truth to me; for if that which I fancy has befallen us, it is as amusing an adventure as could be found in any book.”
They all swore to tell the truth if the matter were such as they could not deny.
Then said he to them—
“I will tell you my own fortune, and you will tell me, ay or nay, if yours has been the same.”
To this they all agreed, whereupon he said—
“I asked leave of the King to go on a journey.”
“So,” they replied, “did we.”
“When I was two leagues from the Court, I left all my following and went and yielded myself up prisoner.”
“We,” they replied, “did the same.”
“I remained,” said Astillon, “for seven or eight days, and lay in a closet where I was fed on nothing but restoratives and the choicest viands that I ever ate. At the end of a week, those who held me captive suffered me to depart much weaker in body than I had been on my arrival.”
They all swore that the like had happened to them.
“My imprisonment,” said Astillon, “began on such a day and finished on such another.”
“Mine,” thereupon said Durassier, “began on the very day that yours ended, and lasted until such a day.”
Valnebon, who was losing patience, began to swear.
“‘Sblood!” said he, “from what I can see, I, who thought myself the first and only one, was the third, for I went in on such a day and came out on such another.”
Three others, who were at the table, swore that they had followed in like order.
“Well, since that is so,” said Astillon, “I will mention the condition of our gaoler. She is married, and her husband is a long way off.”
“‘Tis even she,” they all replied.
“Well, to put us out of our pain,” said Astillon, “I, who was first enrolled, shall also be the first to name her. It was my lady the Countess, she who was so extremely haughty that in conquering her affection I felt as though I had conquered Cæsar.”
[Said Valnebon—(6)]
6 It is probable that the angry Valnebon is speaking here,
and that his name has been accidentally omitted from the
MSS. At all events the three subsequent paragraphs show that
these remarks are not made by Astillon, who declines the
other speaker’s advice, and proposes a scheme of his own.—
Ed.
“To the devil with the jade, who gave us so much toil, and made us believe ourselves so fortunate in winning her! Never was there such wantonness, for while she kept one in hiding she was practising upon another, so that she might never be without diversion. I would rather die than suffer her to go unpunished.”
Each thereupon asked him what he thought ought to be done to her, saying that they were all ready to do it.
“I think,” said he, “that we ought to tell the King our master, who prizes her as though she were a goddess.
“By no means,” said Astillon; “we are ourselves able to take vengeance upon her, without calling in the aid of our master. Let us all be present to-morrow when she goes to mass, each of us wearing an iron chain about his neck. Then, when she enters the church, we will greet her as shall be fitting.”
This counsel was highly approved by the whole company, and each provided himself with an iron chain. The next morning they all went, dressed in black and with their iron chains twisted like collars round their necks, to meet the Countess as she was going to church. And as soon as she saw them thus attired, she began to laugh and asked them—
“Whither go such doleful folk?”
“Madam,” said Astillon, “we are come to attend you as poor captive slaves constrained to do your service.”
The Countess, feigning not to understand, replied—
“You are not my captives, and I cannot understand that you have more occasion than others to do me service.”
Thereupon Valnebon stepped forward and said to her—
“After eating your bread for so long a time, we should be ungrateful indeed if we did not serve you.”
She made excellent show of not understanding the matter, thinking by this seriousness to confound them; but they pursued their discourse in such sort that she saw that all was discovered. So she immediately devised a means of baffling them, for, having lost honour and conscience, she would in no wise take to herself the shame that they thought to bring upon her. On the contrary, like one who set her pleasure before all earthly honour, she neither changed her countenance nor treated them worse than before, whereat they were so confounded, that they carried away in their own bosoms the shame they had thought to bring upon her.
“If, ladies, you do not consider this story enough to prove that women are as bad as men, I will seek out others of the same kind to relate to you. Nevertheless I think that this one will suffice to show you that a woman who has lost shame is far bolder to do evil than a man.”
There was not a woman in the company that heard this story, who did not make as many signs of the cross as if all the devils in hell were before her eyes. However, Oisille said—
“Ladies, let us humble ourselves at hearing of so terrible a circumstance, and the more so as she who is forsaken by God becomes like him with whom she unites; for even as those who cleave to God have His spirit within them, so is it with those that cleave to His opposite, whence it comes that nothing can be more brutish than one devoid of the Spirit of God.”
“Whatever the poor lady may have done,” said Ennasuite, “I nevertheless cannot praise the men who boasted of their imprisonment.”
“It is my opinion,” said Longarine, “that a man finds it as troublesome to conceal his good fortune as to pursue it. There is never a hunter but delights to wind his horn over his quarry, nor lover but would fain have credit for his conquest.”
“That,” said Simontault, “is an opinion which I would hold to be heretical in presence of all the Inquisitors of the Faith, for there are more men than women that can keep a secret, and I know right well that some might be found who would rather forego their happiness than have any human being know of it. For this reason has the Church, like a wise mother, ordained men to be confessors and not women, seeing that the latter can conceal nothing.”
“That is not the reason,” said Oisille; “it is because women are such enemies of vice that they would not grant absolution with the same readiness as is shown by men, and would be too stern in their penances.”
“If they were as stern in their penances,” said Dagoucin, “as they are in their responses, they would reduce far more sinners to despair than they would draw to salvation; and so the Church has in every sort well ordained. But, for all that, I will not excuse the gentlemen who thus boasted of their prison, for never was a man honoured by speaking evil of a woman.”
“Since they all fared alike,” said Hircan, “it seems to me that they did well to console one another.”
“Nay,” said Geburon, “they should never have acknowledged it for the sake of their own honour. The books of the Round Table (7) teach us that it is not to the honour of a worthy knight to overcome one that is good for naught.”
7 Queen Margaret was well acquainted with these (see
ante, vol. iii. p. 48). In a list drawn up after her
father’s death, of the two hundred volumes of books in his
library, a most remarkable one for the times, we find
specified several copies of “Lancelot,” “Tristan,” &c, some
in MS. with miniatures and illuminated letters, and others
printed on parchment. Besides numerous religious writings,
volumes of Aristotle, Ovid, Mandeville, Dante, the
Chronicles of St. Denis, and the “Book of the Great Khan,
bound in cloth of gold,” the library contained various works
of a character akin to that of the Heptameron. For
instance, a copy of the Cent Nouvelles Nouvelles in print;
a French translation of Poggio’s Facetio, also in print,
and two copies of Boccaccio in MS., one of them bound in
purple velvet, and richly illuminated, each page having a
border of blue and silver. This last if still in existence
would be very valuable.—Eu.
“I am amazed,” said Longarine, “that the unhappy woman did not die of shame in presence of her captives.”
“Those who have lost shame,” said Oisille, “can hardly ever recover it, excepting, however, she that has forgotten it through deep love. Of such have I seen many return.”
“I think,” said Hircan, “that you must have seen the return of as many as went, for deep love in a woman is difficult to find.”
“I am not of your opinion,” said Longarine; “I think that there are some women who have loved to death.”
“So exceedingly do I desire to hear a tale of that kind,” said Hircan, “that I give you my vote in order to learn of a love in women that I had never deemed them to possess.”
“Well, if you hearken,” said Longarine, “you will believe, and will see that there is no stronger passion than love. But while it prompts one to almost impossible enterprises for the sake of winning some portion of happiness in this life, so does it more than any other passion reduce that man or woman to despair, who loses the hope of gaining what is longed for. This indeed you will see from the following story.”



Messire John Peter for a long time wooed in vain a
neighbour of his by whom he was sorely smitten, and to
divert his humour withdrew for a few days from the sight of
her; but this brought so deep a melancholy upon him that the
doctors ordered him to be bled. The lady, who knew whence
his distemper proceeded, then thought to save his life, but
did indeed hasten his death, by granting him that which she
had always refused. Then, reflecting that she was herself
the cause of the loss of so perfect a lover, she dealt
herself a sword-thrust that made her a partner in his fate.
(1)
In the town of Cremona not long ago there lived a gentleman called Messire John Peter, (2) who had long loved a lady that dwelt near to his own house; but strive as he might he was never able to have of her the reply that he desired, albeit he loved her with his whole heart. Being greatly grieved and troubled at this, the poor gentleman withdrew into his lodging with the resolve that he would no longer vainly pursue the happiness the quest of which was devouring his life; and accordingly, to divert his humour, he passed a few days without seeing her. This caused him to fall into deep sadness, so that his countenance was no longer the same. His kinsfolk summoned the doctors, who, finding that his face was growing yellow, thought that he had some obstruction of the liver and ordered a blood-letting.
1 The incidents here narrated probably occurred in or about
1544.—L.
2 “Jehan Piètre” (Pietro) in the MSS.—Ed.
The lady, who had dealt so sternly with him, knew very well that his sickness was caused by her refusal alone, and she sent to him an old woman in whom she trusted, to tell him that, since she saw his love to be genuine and unfeigned, she was now resolved to grant him all that which she had refused him so long. She had therefore devised a means to leave her house and go to a place where he might privately see her.
The gentleman, who that same morning had been bled in the arm, found himself better cured by this message than by any medicine or bloodletting he could have had, and he sent word that he would be at the place without fail at the hour she had appointed. He added that she had wrought an evident miracle, since with one word she had cured a man of a sickness for which all the doctors were not able to find a remedy.
The longed-for evening being come, the gentleman repaired to the appointed place with such extreme joy as must needs come soon to an end, since increase of it were not possible. He had waited but a short time after his arrival, when she whom he loved more dearly than his own soul came to meet him. He did not occupy himself with making long speeches, for the fire that consumed him prompted him to seek with all speed that which he could scarcely believe to be at last within his power. But whilst, intoxicated beyond measure with love and joy, he was in one direction seeking a cure that would give him life, he brought to pass in another the hastening of his death; for, heedless of himself for his sweetheart’s sake, he perceived not that his arm became unbound, and that the newly-opened wound discharged so much blood that he was, poor gentleman, completely bathed in it. Thinking, however, that his weakness had been caused by his excess, he bethought himself of returning home.
Then love, which had too closely united them, so dealt with him that, as he was parting from his sweetheart, his soul parted from his body, and, by reason of his great loss of blood, he fell dead at his lady’s feet.
She, on her side, stood there in astonishment, contemplating the loss of so perfect a lover, of whose death she had herself been the sole cause. Reflecting, on the other hand, on the shame and sorrow that would be hers if the dead body were found in her house, she carried it, with a serving-woman whom she trusted, into the street in order that the matter might not be known. Nevertheless, she felt that she could not leave it there alone. Taking up the dead man’s sword, she was fain to share his fate, and, indeed, to punish her heart, which had been the cause of all his woe, she pierced it through and through, so that her dead body fell upon that of her lover.
When her father and mother came out of their house in the morning, they found this pitiful sight, and, after making such mourning as was natural, they buried the lovers together.
“Thus, ladies, may it be seen that excessive love brings with it other woe.”
“This is what I like to see,” said Simontault, “a love so equal that when one died the other could not live. Had I, by the grace of God, found such a mistress, I think that none could ever have ioved her more perfectly than I.”
“Yet am I of opinion,” said Parlamente, “that you would not have been so blinded by love as not to bind up your arm better than he did. The days are gone when men were wont to forget their lives for the ladies’ sake.”
“But those are not gone,” said Simontault, “when ladies are apt to forget their lovers’ lives for their pleasure’s sake.”
“I think,” said Ennasuite, “that there is no living woman that can take pleasure in the death of a man, no, not even though he were her enemy. Still, if men will indeed kill themselves, the ladies cannot prevent them.”
“Nevertheless,” said Saffredent, “she that denies the gift of bread to a poor starving man is held to be a murderess.”
“If your requests,” said Oisille, “were as reasonable as those of a poor man seeking to supply his needs, it would be over cruel of the ladies to refuse you. God be thanked, however, your sickness kills none but such as must of necessity die within the year.”
“I do not understand, madam,” said Saffredent, “that there can be any greater need than that which causes all others to be forgotten. When love is deep, no bread and no meat whatsoever can be thought of save the glance and speech of the woman whom one loves.”
“If you were allowed to fast,” said Oisille, “with no other meat but that, you would tell a very different tale.”
“I acknowledge,” he replied, “that the body might fail, but not so the heart and will.”
“Then,” said Parlamente, “God has dealt very mercifully with you in leading you to have recourse to a quarter where you find such little contentment that you must needs console yourself with eating and drinking. Methinks in these matters you acquit yourself so well, that you should praise God for the tenderness of His cruelty.”
“I have been so nurtured in torment,” he replied, “that I am beginning to be well pleased with woes of which other men complain.”
“Perhaps,” said Longarine, “our complaints debar you from company where your gladness makes you welcome; for nothing is so vexatious as an importunate lover.”
“Say, rather,” answered Simontault, “as a cruel lady ———‘”
“I clearly see,” said Oisille, “now that the matter touches Simontault, that, if we stay until he brings his reasonings to an end, we shall find ourselves at complines (3) rather than vespers. Let us, therefore, go and praise God that this day has passed without graver dispute.”
3 The last division in the Roman Catholic breviary.—Ed.
She was the first to rise, and all the others followed her, but Simontault and Longarine ceased not to carry on their quarrel, yet so gently that, without drawing of sword, Simontault won the victory, and proved that the strongest passion was the sorest need.
At this point they entered the church, where the monks were waiting for them.
Having heard vespers, they went to sup as much off words as meat, for their converse lasted as long as they were at table, and throughout the evening also, until Oisille told them that they might well retire and give some rest to their minds. The five days that were past had been filled with such brave stories, that she had great fear lest the sixth should not be equal to them; for, even if they were to invent their tales, it was not possible to tell any better than those true ones which had already been related in the company.
Geburon, however, told her that, so long as the world lasted, things would happen worthy of remembrance.
“For,” said he, “the wickedness of wicked men is always what it has been, as also is the goodness of the good. So long as wickedness and good reign upon earth, they will ever fill it with fresh actions, although it be written that there is nothing new under the sun. (4) But we, who have not been summoned to the intimate counsels of God, and who are ignorant of first causes, deem all new things noteworthy in proportion as we would not or could not ourselves accomplish them. So, be not afraid that the days to come will not be in keeping with those that are past, and be sure that on your own part you perform well your duty.”
4 Ecclesiastes i. 9, 10.—M.
Oisille replied that she commended herself to God, and in His name she bade them good-night.
So all the company withdrew, thus bringing to an end the Fifth Day.

The following are the more important particulars, supplied by M. Jules Roman, with reference to President Charles of Grenoble:—
Jeffroy Charles was an Italian, born in the marquisate of Saluzza, where his father, Constant, had been a distinguished jurisconsult. The hero of Queen Margaret’s xxxvith tale always signed his name Jeffroy Charles, but his descendants adopted the spelling Carles. Doubtless the name had originally been Caroli. Before fixing himself in France, Jeffroy Charles had been in the service of Luigi II., Marquis of Saluzza, who had appointed him to the office of “Podesta” and entrusted him with various diplomatic missions to the French Court (see Discorsi sopre alame famiglie nobili del Piemonte by Francesco Agostini della Chiesa, in MS. in the State Archives, at Turin). At the time when Charles VIII. was planning his expedition to Naples, he gave a cordial greeting to all the Italians who presented themselves at his Court, and, securing the services of Jeffroy Charles, he appointed him counsellor of the Parliament of Grenoble (October 5, 1493), and entrusted him with various secret missions, the result being that he sojourned but unfrequently in Dauphiné. On the death of Charles VIII., Jeffroy secured the good graces of his successor, Louis XII., and was appointed (June 16, 1500) President of the Senate of Turin, and some months later Chief President of the Parliament of Grenoble. Charles spent the greater part of that year on missions, both to the Court of the Emperor Maximilian and that of the Pope. It was he who obtained from the former the investiture of Louis XII. as Duke of Milan, which afterwards led to so much warfare. Most of the following years he spent at Milan, seeking to organise the government of the duchy, and contending against the rapacity of both the French and the Italian nobles. In 1508 he was sent by Louis XII. to Cambrai, in company with Cardinal d’Amboise, to conclude an alliance with the Emperor against Venice, and he also repaired the same year to Rome with Marshal Trivulzio to negotiate the Pope’s entry into this league.
On war being declared, he set aside his judicial robes, and took an active part in the campaign against Venice, fighting so bravely at Agnadel that Louis XII. knighted him on the battlefield. His last diplomatic mission was to the Court of Leo X. in 1515, in which year he was, on account of his great learning, appointed to direct the education of the King’s younger daughter, the celebrated Renée of Ferrara. But it is doubtful whether he ever even entered upon these duties, since he died soon after he had been entrusted with them. His family remained in Dauphiné, where it died out, obscurely, during the seventeenth century. Only one of his sons, Anthony, evinced any talent, becoming counsellor of the Rouen Parliament (1519), and ambassador at Milan (1530). Lancelot de Carles, Bishop of Riez, was not, as some biographers assert, a son of Jeffroy Charles, nor was he, it would seem, in any way connected with the Saluzza family.
Jeffroy Charles’s wife, Margaret du Mottet, had borne him eight children before he surprised her in adultery. After the tragical ending of his conjugal mishaps he adopted as his crest the figure of an angel holding the forefinger of one hand to his mouth as if to enjoin secrecy. (1) In the seventeenth century this “angel of silence” was to be seen, carved in stone, and serving as a support of the Charles escutcheon, on the house where the President had resided in the Rue des Clercs at Grenoble (Guy Allard’s Dictionnaire du Dauphiné, &c, Grenoble 1695). Escutcheon and support have nowadays disappeared, but on certain of Charles’s seals, as well as in books that belonged to him, now in the Bibliothèque Nationale, Paris, the emblem of the angel will still be found. The earliest seal on which we find it is one affixed to a receipt dated from Milan, July 31, 1506. Assuming that he adopted this crest in memory of the events narrated by Queen Margaret, it is probable that the latter occurred in the earlier part of 1506 or the latter part of the previous year. (2)
1 The suggestion here presents itself that, apart from the
question of any crime, this emblem of secrecy was a very
fitting one for a diplomatist to assume.—Ed.
2 That is, twenty years after the Cent Nouvelles
Nouvelles, from which some commentators think the
Heptameron story to have been borrowed, was first printed.
—Ed.
Three copies of a medal showing Charles’s energetic, angular profile, with the inscription Jafredus Karoli jurisconsultus preses Delphinatus et Mediolani, are known to exist; one in the Grenoble museum, one in that of Milan, and one in my (M. Roman’s) collection. Three MS. works from the President’s library are in the Bibliothèque Nationale, Paris. The frontispiece of one of these (MSS. Lat. No. 4801) is a miniature painting of his escutcheon, surmounted by the half-length figure of the “angel of silence,” who is clad in dark blue, with wings of red, green and blue feathers. On folio 74 of the same MS. is a full-length figure of the angel, clad in light blue and supporting Charles’s escutcheon with one hand, whilst the forefinger of the other is pressed to his lips. In the libraries of Lyons, Grenoble and Turin are other richly-illuminated works that belonged to the President, who was a distinguished bibliophilist and great patron of letters, several learned Italian writers, and among others, J. P. Parisio, J. M. Cattaneo and P’ranchino Gafforio, having dedicated their principal works to him. He it was, moreover, who saved the life of Aldo Manuzio, the famous Venetian printer, when he was arrested by the French as a spy in 1506.
From the foregoing particulars it will be seen that
President Charles was alike learned, brave and skilful. But
for the Queen of Navarre’s circumstantial narrative it would
be hard to believe that a man with so creditable a public
record killed his wife by means of a salad of poisonous
herbs.—Ed.
THE END OF THE FOURTH VOLUME
| Volume I. | Volume II. | Volume III. | Volume V. |


| Volume I. | Volume II. | Volume III. | Volume IV. |
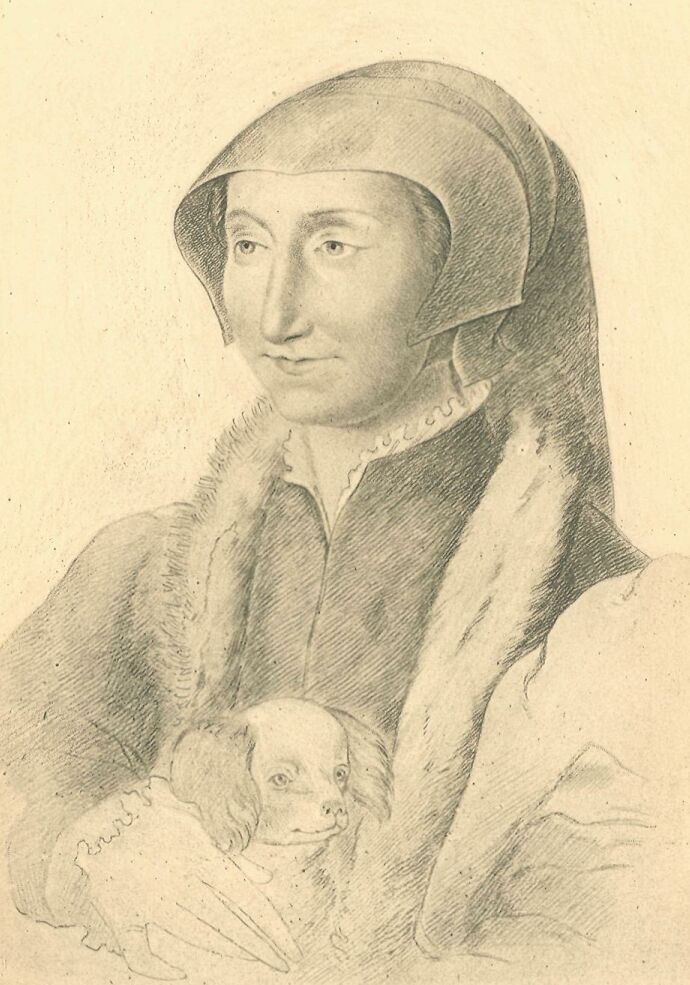


Contents
THE SUPPOSED NARRATORS OF THE HEPTAMERON TALES.
List of Illustrations
005a.jpg the Duke of Urbino Sending The Maiden to Prison for Carrying Messages
015a.jpg the Gentleman and his Friend Annoyed by The Smell of Sugar
023a.jpg the Lord Des Cheriots Flying from The Prince’s Servant
037a.jpg the Lady Watching The Shadow Faces Kissing
043a.jpg the Servant Selling The Horse With The Cat
051a.jpg the Grey Friar Introducing his Comrade to The Lady and Her Daughter
063a.jpg the English Lord Seizing The Lady’s Glove
071a. The Gentleman Mocked by The Ladies when Returning from The False Tryst
079a. The Lady Discovering Her Husband With The Waiting-woman
091a. The Chanter of Blois Delivering his Mistress from The Grave
105a. The Lady Returning to Her Lover, The Canon of Autun
119a. The Gentleman’s Spur Catching in The Sheet
125a. The King Asking The Young Lord to Join his Banquet
133a. The Lady Swooning in The Arms of The Gentleman Of Valencia Who Had Become a Monk
143a. The Old Woman Startled by The Waking of The Soldier
149a. The Old Serving-woman Explaining Her Mistake To The Duke and Duchess of Vendôme
155a. The Wife Reading to Her Husband on The Desert Island
163a. The Apothecary’s Wife Giving The Dose of Cantharides To Her Husband
169a. The Wife Discovering Her Husband in The Hood Of Their Serving-maid
175a. The Gentleman Killing Himself on The Death of his Mistress
219a. The Saddler’s Wife Cured by The Sight of Her Husband Caressing the Serving-maid
225a. The Monk Conversing With The Nun While Shrouding A Dead Body
SIXTH DAY.
Prologue
Tale LI. Cruelty of the Duke of Urbino, who, contrary to the promise he had given to the Duchess, hanged a poor lady that had consented to convey letters to his son’s sweetheart, the sister of the Abbot of Farse.
Tale LII. Merry trick played by the varlet of an apothecary at Alençon on the Lord de la Tirelière and the lawyer Anthony Bacheré, who, thinking to breakfast at his expense, find that they have stolen from him something very different to a loaf of sugar.
Tale LIII. Story of the Lady of Neufchâtel, a widow at the Court of Francis I., who, through not admitting that she has plighted her troth to the Lord des Cheriots, plays him an evil trick through the means of the Prince of Belhoste.
Tale LIV. Merry adventure of a serving-woman and a gentleman named Thogas, whereof his wife has no suspicion.
Tale LV. The widow of a merchant of Saragossa, not wishing to lose the value of a horse, the price of which her husband had ordered to be given to the poor, devises the plan of selling the horse for one ducat only, adding, however, to the bargain a cat at ninety-nine.
Tale LVI. Notable deception practised by an old Grey Friar of Padua, who, being charged by a widow to find a husband for her daughter, did, for the sake of getting the dowry, cause her to marry a young Grey Friar, his comrade, whose condition, however, was before long discovered.
Tale LVII. Singular behaviour of an English lord, who is content merely to keep and wear upon his doublet the glove of a lady whom he loves.
Tale LVIII. A lady at the Court of Francis I., wishing to prove that she has no commerce with a certain gentleman who loves her, gives him a pretended tryst and causes him to pass for a thief.
Tale LIX. Story of the same lady, who, learning that her husband is in love with her waiting-woman, contrives to surprise him and impose her own terms upon him.
Tale LX. A man of Paris, thinking his wife to be well and duly deceased, marries again, but at the end of fifteen years is forced to take his first wife back, although she has been living meantime with one of the chanters of Louis XII.
SEVENTH DAY.
Prologue
Tale LXI. Great kindness of a husband, who consents to take back his wife twice over, spite of her wanton love for a Canon of Autun.
Tale LXII. How a lady, while telling a story as of another, let her tongue trip in such a way as to show that what she related had happened to herself.
Tale LXIII. How the honourable behaviour of a young lord, who feigns sickness in order to be faithful to his wife, spoils a party in which he was to have made one with the King, and in this way saves the honour of three maidens of Paris.
Tale LXIV. Story of a gentleman of Valencia in Spain, whom a lady drove to such despair that he became a monk, and whom afterwards she strove in vain to win back to herself.
Tale LXV. Merry mistake of a worthy woman, who in the church of St. John of Lyons mistakes a sleeping soldier for one of the statues on a tomb, and sets a lighted candle on his forehead.
Tale LXVI. How an old serving-woman, thinking to surprise a Prothonotary with a lady, finds herself insulting Anthony de Bourbon and his wife Jane d’Albret.
Tale LXVII. How the Sire de Robertval, granting a traitor his life at the prayers of the man’s wife, set them both down on a desert island, and how, after the husband’s death, the wife was rescued and brought back to La Rochelle.
Tale LXVIII. The wife of an apothecary at Pau, hearing her husband give some powder of cantharides to a woman who was godmother with himself, secretly administered to him such a dose of the same drug that he nearly died.
Tale LXIX. How the wife of one of the King’s Equerries surprised her husband muffled in the hood of their servant-maid, and bolting meal in her stead.
Tale LXX. Of the love of a Duchess of Burgundy for a gentleman who rejects her advances, for which reason she accuses him to the Duke her husband, and the latter does not believe his oaths till assured by him that he loves the Lady du Vergier. Then the Duchess, having drawn knowledge of this amour from her husband, addresses to the Lady du Vergier in public, an allusion that causes the death of both lovers; and the Duke, in despair at his own lack of discretion, stabs the Duchess himself.
EIGHTH DAY.
Prologue
Tale LXXI. The wife of a saddler of Amboise is saved on her deathbed through a fit of anger at seeing her husband fondle a servant-maid.
Tale LXXII. Kindness of the Duchess of Alençon to a poor nun whom she meets at Lyons, on her way to Rome, there to confess to the Pope how a monk had wronged her, and to obtain his Holiness’s pardon.
On the Sixth Day are related the deceits practised
by Man on
Woman, Woman on Man, or
Woman on Woman, through
greed, revenge,
and
wickedness.
In the morning the Lady Oisille went earlier than was her wont to make ready for her reading in the hall, but the company being advised of this, and eager to hearken to her excellent instruction, used such despatch in dressing themselves that she had not long to wait. Perceiving their fervour, she set about reading them the Epistle of St. John the Evangelist, which is full of naught but love, in the same wise as, on the foregoing days, she had expounded to them St. Paul’s Epistle to the Romans. The company found this fare so much to their taste, that, although they tarried a half-hour longer than on the other days, it seemed to them as if they had not remained there a quarter of an hour altogether. From thence they proceeded to the contemplation of the mass, when one and all commended themselves to the Holy Ghost in order that they might that day be enabled to satisfy their merry audience; and, after they had broken their fast and taken a little rest, they set out to resume their accustomed diversion.
And the Lady Oisille asking who should begin the day, Longarine made answer—
“I give my vote to Madame Oisille; she has this day read to us so beauteous a lesson, that she can but tell us some story apt to crown the glory which she won this morning.”
“I am sorry,” said Oisille, “that I cannot tell you aught so profitable this afternoon as I did in the morning. But at least the purport of my story shall not depart from the teaching of Holy Scripture, where it is written, ‘Trust not in princes, nor in the sons of men, in whom is not our salvation.’ (1) And that this truth may not be forgotten by you for lack of an example, I will tell you a tale which is quite true, and the memory of which is so fresh that the eyes of those that saw the piteous sight are scarcely yet dried.”


Because he would not have his son make a poor marriage, the
Duke of Urbino, contrary to the promise given to his wife,
hanged a young maiden by whom his son was wont to inform his
sweetheart of the love he bore her.
The Duke of Urbino, called the Prefect, (1) the same that married the sister of the first Duke of Mantua, had a son of between eighteen and twenty years of age, who was in love with a girl of an excellent and honourable house, sister to the Abbot of Farse. (2) And since, according to the custom of the country, he was not free to converse with her as he wished, he obtained the aid of a gentleman in his service, who was in love with a very beautiful and virtuous young damsel in the service of his mother. By means of this damsel he informed his sweetheart of the deep affection that he bore her; and the poor girl, thinking no harm, took pleasure in doing him service, believing his purpose to be so good and virtuous that she might honourably be the carrier of his intentions. But the Duke, who had more regard for the profit of his house than for any virtuous affection, was in such great fear lest these dealings should lead his son (3) into marriage, that he caused a strict watch to be kept; whereupon he was informed that the poor damsel had been concerned in carrying some letters from his son to the lady he loved. On hearing this he was in great wrath, and resolved to take the matter in hand.
1 This is Francesco Maria I., della Rovere, nephew to Pope
Julius II., by whom he was created Prefect of Rome. Brought
up at the French Court, he became one of the great captains
of the period, especially distinguishing himself in the
command of the Venetian forces during the earlier part of
his career. He married Leonora Ypolita Gonzaga, daughter of
Francesco II., fourth Marquis of Mantua, respecting whom see
ante, vol. iii., notes to Tale XIX. It was Leonora rather
than her husband who imparted lustre to the Court of Urbino
at this period by encouraging arts and letters. Among those
who flourished there were Raffaelle and Baldassare
Castiglione. Francesco Maria, born in March 1491, died in
1538 from the effects—so it is asserted by several
contemporary writers—of a poisonous lotion which a Mantuan
barber had dropped into his ear. His wife, who bore him two
sons (see post, note 3), died at the age of 72, in 1570.—L.
and Ed.
2 The French words are Abbé de Farse. Farse would appear
to be a locality, as abbots were then usually designated by
the names of their monasteries; still it may be intended for
the Abbot’s surname, and some commentators, adopting this
view, have suggested that the proper reading would be
Farnese.—Ed.
3 The Duke’s two sons were Federigo, born in March 1511,
and Guidobaldo, born in April 1514. The former according to
all authorities died when “young,” and probably long before
reaching man’s estate. Dennistoun, in his searching Memoirs
of the Dukes of Urbino (London, 1851), clearly shows that
for many years prior to Francesco Maria’s death his second
son Guidobaldo was the only child remaining to him. Already
in 1534, when but twenty years old, Guidobaldo was regarded
as his father’s sole heir and successor. In that year
Francesco Maria forced the young man to marry Giulia Varana,
a child of eleven, in order that he might lay claim to her
father’s state of Camerino and annex it to the duchy. There
is no record of Guidobaldo having ever engaged in any such
intrigue as related by Queen Margaret in the above tale,
still it must be to him that she refers, everything pointing
to the conclusion that his brother Federigo died in
childhood. Guidobaldo became Duke of Urbino on his father’s
death.—Ed.
He could not, however, conceal his anger so well that the maiden was not advised of it, and knowing his wickedness, which was in her eyes as great as his conscience was small, she felt a wondrous dread. Going therefore to the Duchess, she craved leave to retire somewhere out of the Duke’s sight until his passion should be past; but her mistress replied that, before giving her leave to do so, she would try to find out her husband’s will in the matter.
Very soon, however, the Duchess heard the Duke’s evil words concerning the affair, and, knowing his temper, she not only gave the maiden leave, but advised her to retire into a convent until the storm was over. This she did as secretly as she could, yet not so stealthily but that the Duke was advised of it. Thereupon, with pretended cheerfulness of countenance, he asked his wife where the maiden was, and she, believing him to be well aware of the truth, confessed it to him. He feigned to be vexed thereat, saying that the girl had no need to behave in that fashion, and that for his part he desired her no harm. And he requested his wife to cause her to come back again, since it was by no means well to have such matters noised abroad.
The Duchess replied that, if the poor girl was so unfortunate as to have lost his favour, it were better for a time that she should not come into his presence; however, he would not hearken to her reasonings, but commanded her to bid the maiden return.
The Duchess failed not to make the Duke’s will known to the maiden; but the latter, who could not but feel afraid, entreated her mistress that she might not be compelled to run this risk, saying that she knew the Duke was not so ready to forgive her as he feigned to be. Nevertheless, the Duchess assured her that she should take no hurt, and pledged her own life and honour for her safety.
The girl, who well knew that her mistress loved her, and would not lightly deceive her, trusted in her promise, believing that the Duke would never break a pledge when his wife’s honour was its warranty. And accordingly she returned to the Duchess.
As soon as the Duke knew this, he failed not to repair to his wife’s apartment. There, as soon as he saw the maiden, he said to his wife, “So such-a-one has returned,” and turning to his gentlemen, he commanded them to arrest her and lead her to prison.
At this the poor Duchess, who by the pledging of her word had drawn the maiden from her refuge, was in such despair that, falling upon her knees before her husband, she prayed that for love of herself and of his house he would not do so foul a deed, seeing that it was in obedience to himself that she had drawn the maiden from her place of safety.
But no prayer that she could utter availed to soften his hard heart, or to overcome his stern resolve to be avenged. Without making any reply, he withdrew as speedily as possible, and, foregoing all manner of trial, and forgetting God and the honour of his house, he cruelly caused the hapless maiden to be hanged.
I cannot undertake to recount to you the grief of the Duchess; it was such as beseemed a lady of honour and a tender heart on beholding one, whom she would fain have saved, perish through trust in her own plighted faith. Still less is it possible to describe the deep affliction of the unhappy gentleman, the maiden’s lover, who failed not to do all that in him lay to save his sweetheart’s life, offering to give his own for hers; but no feeling of pity moved the heart of this Duke, whose only happiness was that of avenging himself on those whom he hated. (4)
4 That Francesco-Maria was a man of a hasty, violent
temperament is certain. Much that Guicciardini relates of
him was doubtless penned in a spirit of resentment, for
during the time the historian lived at Urbino the Duke
repeatedly struck him, and on one occasion felled him to the
ground, with the sneering remark, “Your business is to
confer with pedants.” On the other hand, however, there is
independent documentary evidence in existence—notably
among the Urbino MSS. in the Vatican library—which shows
that Francesco-Maria in no wise recoiled from shedding
blood. He was yet in his teens when it was reported to him
that his sister—the widow of Venanzio of Camerino, killed
by Caesar Borgia—had secretly married a certain Giovanni
Andrea of Verona and borne him a son. Watching his
opportunity, Francesco-Maria set upon the unfortunate Andrea
one day in the ducal chamber and then and there killed him,
though not without resistance, for Andrea only succumbed
after receiving four-and-twenty stabs with his murderer’s
poignard (Urbino MSS. Vat. No. 904). A few years later, in
1511, Francesco-Maria assassinated the Papal Legate
Alidosio, Cardinal Archbishop of Pavia, whom he encountered
in the environs of Bologna riding his mule and followed by a
hundred light horse. Nevertheless Urbino, with only a small
retinue, galloped up to him, plunged a dagger into his
stomach and fled before the soldiery could intervene. From
these examples it will be seen that, although history has
preserved no record of the affair related by Queen Margaret,
her narrative may well be a true one.—Ed.
Thus, in spite of every law of honour, was the innocent maiden put to death by this cruel Duke, to the exceeding sorrow of all that knew her.
“See, ladies, what are the effects of wickedness when this is combined with power.”
“I had indeed heard,” said Longarine, “that the Italians were prone to three especial vices; but I should not have thought that vengeance and cruelty would have gone so far as to deal a cruel death for so slight a cause.”
“Longarine,” said Saffredent, laughing, “you have told us one of the three vices, but we must also know the other two.”
“If you did not know them,” she replied, “I would inform you, but I am sure that you know them all.”
“From your words,” said Saffredent, “it seems that you deem me very vicious.”
“Not so,” said Longarine, “but you so well know the ugliness of vice that, better than any other, you are able to avoid it.”
“Do not be amazed,” said Simontault, “at this act of cruelty. Those who have passed through Italy have seen such incredible instances, that this one is in comparison but a trifling peccadillo.”
“Ay, truly,” said Geburon. “When Rivolta was taken by the French, (5) there was an Italian captain who was esteemed a knightly comrade, but on seeing the dead body of a man who was only his enemy in that being a Guelph he was opposed to the Ghibellines, he tore out his heart, broiled it on the coals and devoured it. And when some asked him how he liked it, he replied that he had never eaten so savoury or dainty a morsel. Not content with this fine deed, he killed the dead man’s wife, and tearing out the fruit of her womb, dashed it against a wall. Then he filled the bodies both of husband and wife with oats and made his horses eat from them. Think you that such a man as that would not surely have put to death a girl whom he suspected of offending him?”
5 Rivolta or Rivoli was captured by the French under Louis
XII. in 1509. An instance of savagery identical in character
with that mentioned by “Geburon” had already occurred at the
time of Charles VIII.‘s expedition to Naples, when the
culprit, a young Italian of good birth, was seized and
publicly executed.—Ed.
“It must be acknowledged,” said Ennasuite, “that this Duke of Urbino was more afraid that his son might make a poor marriage than desirous of giving him a wife to his liking.”
“I think you can have no doubt,” replied Simon-tault, “that it is the Italian nature to love unnaturally that which has been created only for nature’s service.”
“Worse than that,” said Hircan, “they make a god of things that are contrary to nature.”
“And there,” said Longarine, “you have another one of the sins that I meant; for we know that to love money, excepting so far as it be necessary, is idolatry.”
Parlamente then said that St. Paul had not forgotten the vices of the Italians, and of all those who believe that they exceed and surpass others in honour, prudence and human reason, and who trust so strongly to this last as to withhold from God the glory that is His due. Wherefore the Almighty, jealous of His honour, renders’ those who believe themselves possessed of more understanding than other men, more insensate even than wild the beasts, causing them to show by their unnatural deeds that their sense is reprobate.
Longarine here interrupted Parlamente to say that this was indeed the third sin to which the Italians were prone.
“By my faith,” said Nomerfide, “this discourse is very pleasing to me, for, since those that possess the best trained and acutest understandings are punished by being made more witless even than wild beasts, it must follow that such as are humble, and low, and of little reach, like myself, are filled with the wisdom of angels.”
“I protest to you,” said Oisille, “that I am not far from your opinion, for none is more ignorant than he who thinks he knows.”
“I have never seen a mocker,” said Geburon, “that was not mocked, a deceiver that was not deceived, or a boaster that was not humbled.”
“You remind me,” said Simontault, “of a deceit which, had it been of a seemly sort, I would willingly have related.”
“Well,” said Oisille, “since we are here to utter truth, I give you my vote that you may tell it to us whatsoever its nature may be.”
“Since you give place to me,” said Simontault, “I will tell it you.”



An apothecary s man, espying behind him an advocate who was
to plague him, and on whom he desired to be revenged,
dropped from his sleeve a lump of frozen ordure, wrapped in
paper like a sugar-loaf, which a gentleman who was with the
advocate picked up and hid in his bosom, and then went to
breakfast at a tavern, whence he came forth with all the
cost and shame that he had thought to bring upon the poor
varlet.
Near the town of Alençon there lived a gentleman called the Lord of La Tireliere, who one morning came from his house to the town afoot, both because the distance was not great and because it was freezing hard. (1) When he had done his business, he sought out a crony of his, an advocate named Anthony Bacheré, and, after speaking with him of his affairs, he told him that he should much like to meet with a good breakfast, but at somebody else’s expense. While thus discussing, they sat themselves down in front of an apothecary’s shop, where there was a varlet who listened to them, and who forthwith resolved to give them their breakfast.
1 The phraseology of this story varies considerably in the
different MSS. of the Heptameron. In No. 1520, for
instance, the tale begins as follows: “In the town of
Alençon, in the time of the last Duke Charles, there was an
advocate, a merry companion, fond of breakfasting o’
mornings. One day, whilst he sat at his door, he saw pass a
gentleman called the Lord of La Tilleriere, who, by reason
of the extreme cold, had come on foot from his house to the
town in order to attend to certain business there, and in
doing so had not forgotten to put on his great robe, lined
with fox-skin. And when he saw the advocate, who was much
such a man as himself, he told him that he had completed his
business, and had nothing further to do, except it were to
find a good breakfast. The advocate made answer that they
could find breakfasts enough and to spare, provided they had
some one to defray the cost, and, taking the other under the
arm, he said to him, ‘Come, gossip, we may perhaps find some
fool who will pay the reckoning for us both.’ Now behind
them was an apothecary’s man, an artful and inventive
fellow, whom this advocate was always plaguing,” &c.—L.
He went out from his shop into a street whither all repaired on needful occasions, (2) and there found a large lump of ordure standing on end, and so well frozen that it looked like a small loaf of fine sugar. Forthwith he wrapped it in handsome white paper, in the manner he was wont to use for the attraction of customers, and hid it in his sleeve.
2 In olden time, as shown in the Mémoires de l’Académie de
Troyes, there were in most French towns streets specially
set aside for the purpose referred to. At Alençon, in Queen
Margaret’s time, there was a street called the Rue des
Fumiers, as appears from a report dated March 8, 1564
(Archives of the Orne, Series A). Probably it is to this
street that she alludes. (Communicated by M. L. Duval,
archivist of the department of the Orne).—M.
Afterwards he came and passed in front of the gentleman and the advocate, and, letting the sugar-loaf (3) fall near them, as if by mischance, went into a house whither he had pretended to be carrying it.
The Lord of La Tirelière (4) hastened back with all speed to pick up what he thought to be a sugar-loaf, and just as he had done so the apothecary’s man also came back looking and asking for his sugar everywhere.
3 M. Duval, archivist of the Orne, states that La
Tirelière, which is situated near St. Germain-du-Corbois,
within three miles of Alençon, is an old gentilhommière or
manor-house, surrounded by a moat. It was originally a
simple vavassonrie held in fief from the Counts and Dukes
of Alençon by the Pantolf and Crouches families, and in the
seventeenth century was merged into the marquisate of
L’Isle.—M.
4 Sugar was at this period sold by apothecaries, and was a
rare and costly luxury. There were loaves of various sizes,
but none so large as those of the present time.—M.
The gentleman, thinking that he had cleverly tricked him, then went in haste to a tavern with his crony, to whom he said—
“Our breakfast has been paid for at the cost of that varlet.”
When he was come to the tavern he called for good bread, good wine and good meat, for he thought that he had wherewith to pay. But whilst he was eating, as he began to grow warm, his sugar-loaf in its turn began to thaw and melt, and filled the whole room with the smell peculiar to it, whereupon he, who carried it in his bosom, grew wroth with the waiting-woman, and said to her—
“You are the filthiest folks that ever I knew in this town, for either you or your children have strewn all this room with filth.”
“By St. Peter!” replied the woman, “there is no filth here unless you have brought it in yourselves.”
Thereupon they rose, by reason of the great stench that they smelt, and went up to the fire, where the gentleman drew out of his bosom a handkerchief all dyed with the melted sugar, and on opening his robe, lined with fox-skin, found it to be quite spoiled.
And all that he was able to say to his crony was this—
“The rogue whom we thought to deceive has deceived us instead.”
Then they paid their reckoning and went away as vexed as they had been merry on their arrival, when they fancied they had tricked the apothecary’s varlet. (5)
5 In MS. 1520, this tale ends in the following manner:—
“They were no sooner in the street than they perceived the
apothecary’s man going about and making inquiry of every one
whether they had not seen a loaf of sugar wrapped in paper.
They [the advocate and his companion] sought to avoid him,
but he called aloud to the advocate, ‘If you have my loaf of
sugar, sir, I beg that you will give it back to me, for ‘tis
a double sin to rob a poor servant.’ His shouts brought to
the spot many people curious to witness the dispute, and the
true circumstances of the case were so well proven, that the
apothecary’s man was as glad to have been robbed as the
others were vexed at having committed such a nasty theft.
However, they comforted themselves with the hope that they
might some day give him tit for tat.”—Ed.
“Often, ladies, do we see the like befall those who delight in using such cunning. If the gentleman had not sought to eat at another’s expense, he would not have drunk so vile a beverage at his own. It is true, ladies, that my story is not a very clean one, but you gave me license to speak the truth, and I have done so in order to show you that no one is sorry when a deceiver is deceived.”
“It is commonly said,” replied Hircan, “that words have no stink, yet those for whom they are intended do not easily escape smelling them.”
“It is true,” said Oisille, “that such words do not stink, but there are others which are spoken of as nasty, and which are of such evil odour that they disgust the soul even more than the body is disgusted when it smells such a sugar-loaf as you described in the tale.”
“I pray you,” said Hircan, “tell me what words you know of so foul as to sicken both the heart and soul of a virtuous woman.”
“It would indeed be seemly,” replied Oisille, “that I should tell you words which I counsel no woman to utter.”
“By that,” said Saffredent, “I quite understand what those terms are. They are such as women desirous of being held discreet do not commonly employ. But I would ask all the ladies present why, when they dare not utter them, they are so ready to laugh at them when they are used in their presence.”
Then said Parlamente—
“We do not laugh because we hear such pretty expressions, though it is indeed true that every one is disposed to laugh on seeing anybody stumble or on hearing any one utter an unfitting word, as often happens. The tongue will trip and cause one word to be used for another, even by the discreetest and most excellent speakers. But when you men talk viciously, not from ignorance, but by reason of your own wickedness, I know of no virtuous woman who does not feel a loathing for such speakers, and who would not merely refuse to hearken to them, but even to remain in their company.”
“That is very true,” responded Geburon. “I have frequently seen women make the sign of the cross on hearing certain words spoken, and cease not in doing so after these words had been uttered a second time.”
“But how many times,” said Simontault, “have they put on their masks (6) in order to laugh as freely as they pretended to be angry?”
“Yet it were better to do this,” said Parlamente, “than to let it be seen that the talk pleased them.”
“Then,” said Dagoucin, “you praise a lady’s hypocrisy no less than her virtue?”
“Virtue would be far better,” said Longarine, “but, when it is lacking, recourse must be had to hypocrisy, just as we use our slippers (7) to disguise our littleness. And it is no small matter to be able to conceal our imperfections.”
8 Tourets-de-nez. See ante, vol. iii. p. 27, note 5.—Ed.
7 High-heeled slippers or mules were then worn.—B. J.
“By my word,” said Hircan, “it were better sometimes to show some slight imperfection than to cover it so closely with the cloak of virtue.”
“It is true,” said Ennasuitc, “that a borrowed garment brings the borrower as much dishonour when he is constrained to return it as it brought him honour whilst it was being worn, and there is a lady now living who, by being too eager to conceal a small error, fell into a greater.”
“I think,” said Hircan, “that I know whom you mean; in any case, however, do not pronounce her name.”
“Ho! ho!” said Geburon [to Ennasuite], “I give you my vote on condition that when you have related the story you will tell us the names. We will swear never to mention them.”
“I promise it,” said Knnasuite, “for there is nothing that may not be told in all honour.”


By her dissimulation the Lady of Neufchastel caused the
Prince of Belhoste to put her to such proof that it turned
to her dishonour.
King Francis the First was once at a handsome and pleasant castle, whither he had gone with a small following, both for the purpose of hunting and in order to take some repose. With him in his train was a certain Prince of Belhoste, (1) as worshipful, virtuous, discreet and handsome a Prince as any at Court. The wife he had married did not belong to a family of high rank, yet he loved her as dearly and treated her as well as it were possible for a husband to do, and also trusted in her. And when he was in love with anybody he never concealed it from her, knowing that she had no other will than his own.
1 The Bibliophile Jacob surmises that this personage may be
one of the Italian grandees at that period in the service of
France, in which case the allusion may be to John
Caraccioli, Prince of Melphes, created a marshal of France
in 1544. Queen Margaret, however, makes no mention of her
Prince being a foreigner. “Belhoste” is of course a
fictitious name invented to replace that which the Prince
really bore, and admits of so many interpretations that its
meaning in the present instance cannot well be determined.
From the circumstance, however, that the Prince’s wife was
of inferior birth to himself, it is not impossible that the
personage referred to may be either Charles de Bourbon,
Prince of La Roche-sur-Yonne and Duke of Beaupréau, or John
VIII., Lord of Créqui, Canaples and Pontdormi, and Prince of
Poix. The former, who married Philippa de Montespedon, widow
of René de Montéjan, and a lady of honour to Catherine de’
Medici when Dauphiness, took a prominent part in the last
wars of Francis I.‘s reign, and survived till 1565. The
latter, generally known at Court by the name of Canaples,
was a gentleman of the chamber and an especial favourite of
Francis I. Brantôme says of him in his Homines Illustres
that he was “a valiant lord and the strongest man of arms
that in those days existed in all Christendom, for he broke
a lance, no matter its strength, as easily as though it were
a mere switch, and few were able to withstand him.” In 1525
the Prince of Poix married a Demoiselle d’Acigné or Assigny,
of petite noblesse, who in 1532 became a lady of honour to
Queen Eleanor. She died in 1558, surviving her husband by
three years. See Rouard’s rare Notice dun Recueil de
Crayons à la Bibliothèque Méjanes d’Aix, Paris, 1863.—Ed.
Now this Prince conceived a deep affection for a widow lady called Madame de Neufchastel, (2) who was reputed the most beautiful woman it were possible to see; and if the Prince of Bel-hoste loved her well, his wife loved her no less, and would often send and bid her to dinner, for she deemed her so discreet and honourable, that, instead of being grieved by her husband’s love for her, she rejoiced to see him address his attentions to one so full of honour and virtue.
2 M. Lacroix thinks that this lady may be Jane de Hochberg,
only daughter of Philip, sovereign Count of Neufchâtel.
According to the custom of the time, she was commonly called
Madame de Neufchâtel, despite her marriage with Louis
d’Orléans, Duke of Longueville. She died in 1543, after a
lengthy widowhood. We consider the accuracy of M. Lacroix’s
surmise to be extremely doubtful, for the names of both the
men figuring in the story are obviously altered so as to
conceal their identity, and it is therefore not likely that
Queen Margaret would designate the lady by her real name,
and thus publish her shame to the world. The Madame de
Neufchâtel she speaks of may really have been a Madame de
Châteauneuf, Châteauvieux or Maisonneuve; or we may again be
in presence of Margaret’s lady of honour, the widowed
Blanche de Chastillon, née de Tournon, to whom frequent
reference has been made.—Ed.
This affection lasted for a great while, the Prince of Belhoste caring for all the lady’s affairs as though they were his own, and his wife doing no less. By reason, however, of her beauty many great lords and gentlemen earnestly sought the lady’s favour, some only for love’s sake, others for sake of the ring, for, besides being beautiful, she was also very rich.
Among the rest was a young gentleman, called the Lord des Cheriots, (3) who wooed her so ardently that he was never absent from her levee and couchée, and was also with her as much as possible during the day. This did not please the Prince of Belhoste, who thought that a man of such poor estate, and so lacking in grace, did not deserve an honourable and gracious reception, and he often made remonstrances about it to the lady. She, however, being one of Eve’s daughters, (4) excused herself by saying that she spoke with every one in general, and that their own affection was the better concealed, since she never spoke more with one than with another.
3 “Des Cheriots” (occasionally Des Cheriotz in the MS.) may
be a play upon the name of D’Escars, sometimes written Des
Cars. According to La Curne de Ste. Palaye car as well as
char signified chariot. The D’Escars dukedom is modern,
dating from 1815, and in the time of Francis I. the family
was of small estate. Some members of it may well have filled
inferior offices about the court, as in 1536 a Demoiselle
Suzanne d’Escars married Geoffrey de Pompadour, who was both
a prothonotary and cupbearer to Francis I., and lived to
become Governor of the Limousin under Charles IX.—M. and
Ed.
4 We take this expression from MS. 1520. Ours says, “a
daughter of the Duke,” which is evidently an error.—L.
Albeit, after some time, this Lord des Cheriots so pressed her that, more through his importunity than through love, she promised to marry him, begging him, however, not to urge her to reveal the marriage until her daughters were wedded. After this the gentleman was wont to go with untroubled conscience to her chamber at whatsoever hour he chose, and none but a waiting-woman and a serving-man had knowledge of the matter.
When the Prince perceived that the gentleman was growing more and more familiar in the house of her whom he so dearly loved, he took it in ill-part, and could not refrain from saying to the lady—
“I have always prized your honour like that of my own sister, and you are aware of the honourable manner in which I have addressed you, and the happiness that I have in loving a lady as discreet and virtuous as yourself; but did I think that another who deserves it not could win by importunity that which I am not willing to crave, contrary to your own desire, this would be unendurable to me, and in the like degree dishonouring to you. I tell you this because you are beautiful and young, and although hitherto of good repute, are now beginning to gain a very evil fame. Even though he be not your equal in birth or fortune, and have less influence, knowledge and address, yet it were better to have married him than to give all men matter for suspicion. I pray you, therefore, tell me whether you are resolved to love him, for I will not have him as fellow of mine. I would rather leave you altogether to him, and put away from me the feelings that I have hitherto borne you.”
The poor lady, fearful of losing his affection, thereupon began to weep, and vowed to him that she would rather die than wed the gentleman of whom he had spoken, but (she added) he was so importunate that she could not help his entering her chamber at a time when every one else did so.
“Of such times as those,” said the Prince, “I do not speak, for I can go as well as he, and see all what you are doing. But I have been told that he goes after you are in bed, and this I look upon as so extraordinary that, if you should continue in this mode of life without declaring him to be your husband, you will be disgraced more than any woman that ever lived.”
She swore to him with all the oaths she could utter that the other was neither her husband nor her lover, but only as importunate a gentleman as there well could be.
“Since he is troublesome to you,” said the Prince, “I promise you that I will rid you of him.”
“What!” asked the lady. “Would you kill him?”
“No, no,” said the Prince, “but I will give him to understood that it is not in such a place as this, not in such a house as the King’s, that ladies are to be put to shame. And I swear to you by the faith of the lover that I am, that if, after I have spoken with him, he does not correct himself, I will correct him in such a manner as to make him a warning to others.”
So saying he went away, and on leaving the room failed not to meet the Lord des Cheriots on his way in. To him he spoke after the fashion that you have heard, assuring him that the first time he was found there after an hour at which gentlemen might reasonably visit the ladies, he would give him such a fright as he would ever remember. And he added that the lady was of too noble a house to be trifled with after such a fashion.
The gentleman protested that he had never been in the room except in the same manner as the rest, and, if the Prince should find him there, he gave him full leave to do his worst.
One day afterwards, when the gentleman believed the Prince’s words to have been forgotten, he went to see his lady in the evening, and remained sufficiently late.
The Prince [that same evening] told his wife that Madame de Neufchastel had a severe cold, upon hearing which the worthy lady begged that he would visit her on behalf of them both, and make excuse for herself, since she could not go by reason of a certain matter that she must needs attend to in her room.
The Prince waited until the King was in bed, and then went to give the lady good-evening, but as he was going up a stairway he met a serving-man coming down, who, on being asked how his mistress did, swore that she was in bed and asleep.
The Prince went down the stairway, but, suspecting that the servant had lied, looked behind and saw him going back again with all speed. He walked about the courtyard in front of the door to see whether the servant would return. A quarter of an hour later he perceived him come down again and look all about to see who was in the courtyard.
Forthwith the Prince was convinced that the Lord des Cheriots was in the lady’s chamber, but through fear of himself durst not come down, and he therefore again walked about for a long-while.
At last, observing that the lady’s room had a casement which was not at all high up, and which looked upon a little garden, he remembered the proverb which says, “When the door fails the window avails,” and he thereupon called a servant of his own, and said to him—
“Go into the garden there behind, and, if you see a gentleman come down from the window, draw your sword as soon as he reaches the ground, clash it against the wall, and cry out, ‘Slay! slay!’ Be careful, however, that you do not touch him.”
The servant went whither his master had sent him, and the Prince walked about until three hours after midnight.
When the Lord des Cheriots heard that the Prince was still in the yard, he resolved to descend by the window, and, having first thrown clown his cloak, he then, by the help of his good friends, leapt into the garden. As soon as the servant saw him, he failed not to make a noise with his sword, at the same time crying, “Slay! slay!” Upon this the poor gentleman, believing it was his [the servant’s] master, was in such great fear that, without thinking of his cloak, he fled as quickly as he was able.
He met the archers of the watch, who wondered greatly to see him running in this fashion, but he durst say nothing to them, except to beg them to open him the gate [of the castle], or else to lodge him with themselves until morning. And this, as they had not the keys, they did.
Then the Prince went to bed, and, finding his wife asleep, awoke her saying—
“Guess, my wife, what hour it is.‘’
“I have not heard the clock strike since I went to bed,” she replied.
“It is three hours after midnight,” said he.
“If that be so,” said his wife, “where have you been all this time? I greatly fear that your health will be the worse for it.”
“Sweetheart,” said the Prince, “watching will never make me ill when I am engaged in preventing those who try to deceive me from going to sleep.”
So saying, he began to laugh so heartily that his wife begged him to tell her of the matter. This he did at length, showing her the wolf’s skin (4) which his servant had brought him. After making merry at the expense of the hapless lovers, they went to sleep in gentle tranquillity, while the other two passed the night in torment, fearing and dreading lest the affair should be revealed.
However, the gentleman, knowing right well that he could not use concealment with the Prince, came to him in the morning when he was dressing to beg that he would not expose him, and would give orders for the return of his cloak.
The Prince pretended that he knew nothing of the matter, and put such a face on it that the gentleman was wholly at a loss what to think. But in the end he received a rating that he had not expected, for the Prince assured him that, if ever he went to the lady’s room again, he would tell the King of it, and have him banished the Court.
“I pray you, ladies, judge whether it had not been better for this poor lady to have spoken freely to him who did her the honour of loving and esteeming her, instead of leading him by her dissimulation to prove her in a way that brought her so much shame.”
“She knew,” said Geburon, “that if she confessed the truth she would wholly lose his favour, and this she on no account desired to do.”
“It seems to me,” said Longarine, “that when she had chosen a husband to her liking, she ought not to have feared the loss of any other man’s affection.”
“I am sure,” said Parlamente, “that if she had dared to reveal her marriage, she would have been quite content with her husband; but she wished to hide it until her daughters were wed, and so she would not abandon so good a means of concealment.”
“It was not for that reason,” said Saffredent, “but because the ambition of women is so great that they are never satisfied with having only one lover. I have heard that the discreetest of them are glad to have three—one, namely, for honour, one for profit, and one for delight. Each of the three thinks himself loved the best, but the first two are as servants to the last.”
“You speak,” said Oisille, “of such women as have neither love nor honour.”
“Madam,” said Saffredent, “there are some of the kind that I describe, whom you reckon among the most honourable in the land.”
“You may be sure,” said Hircan, “that a crafty woman will be able to live where all others die of hunger.”
“And,” said Longarine, “when their craftiness is discerned, ‘tis death.”
“Nay, ‘tis life,” said Simontault, “for they deem it no small glory to be reputed more crafty than their fellows. And the reputation of ‘crafty,’ gained thus at their own expense, brings lovers more readily under subjection to them than does their beauty, for one of the greatest delights shared by those who are in love is to conduct the affair slyly.”
“You speak,” said Ennasuite, “of wanton love, for the honourable has no need of concealment.”
“Ah!” said Dagoucin, “I pray you put that thought out of your head. The more precious the drug, the less should it be exposed to the air, because of the perverseness of those who trust only to outward signs. These are not different in the case of honourable and faithful affection than in any other case, so they must none the less be hidden when the love is virtuous than when it is the opposite, if one would avoid the evil opinion of those who cannot believe that a man may love a lady in all honour, and who, being themselves slaves to pleasure, think every one else the same. If we were all of good faith, look and speech would be without concealment, at least toward those who would rather die than take them in an evil sense.”
“I protest to you, Dagoucin,” said Hircan, “that your philosophy is too deep for any man here to understand or believe. You would have us think that men are angels, or stones, or devils.”
“I am well aware,” said Dagoucin, “that men are men and subject to every passion, but there are some, nevertheless, who would rather die than that their mistresses should, for their delight, do aught against their consciences.”
“To die means a great deal,” said Geburon. “I would not believe that of them were it uttered by the lips of the austerest monk alive.”
“Nay, I believe,” said Hircan, “that there is none but desires the very opposite. But they make pretence of disliking the grapes when these hang too high to be gathered.”
“Still,” said Nomcrfide, “I am sure that the Prince’s wife was very glad to find that her husband was learning to know women.”
“I assure you it was not so,” said Ennasuite. “She was very sorry on account of the love that she bore the lady.”
“I would as soon,” said Saffredent, “have the lady who laughed when her husband kissed her maid.”
“In sooth,” said Ennasuite, “you shall tell us the story. I give place to you.”
“Although the story is very short,” said Saffredent, “I will still relate it, for I would rather make you laugh than speak myself at length.”



Thogas’s wife, believing that her husband loved none but
herself, was pleased that her serving-woman should amuse
him, and laughed when in her presence he kissed the girl
before her eyes, and with her knowledge.
Between the Pyrenees Mountains and the Alps, there dwelt a gentleman named Thogas, (1) who had a wife and children, with a very beautiful house, and so much wealth and pleasure at his hand, that there was reason he should live in contentment, had it not been that he was subject to great pain beneath the roots of the hair, in such wise that the doctors advised him to sleep no longer with his wife. She, whose chief thought was for her husband’s life and health, readily consented, and caused her bed to be set in another corner of the room directly opposite her husband’s, so that they could neither of them put out their heads without seeing each other.
1 We are unable to trace any family named Thogas, which is
probably a fictitious appellation. Read backwards with the
letter h omitted it forms Sagot, whilst if the syllables be
transposed it suggests Guasto, a well-known Basque or
Navarrese name.—Ed.
This lady had two serving-women, and often when the lord and his lady were in bed, they would each take some diverting book to read, whilst the serving-women held candles, the younger, that is, for the gentleman, and the other for his wife.
The gentleman, finding that the maid was younger and handsomer than her mistress, took such great pleasure in observing her that he would break off his reading in order to converse with her. His wife could hear this very plainly, but believing that her husband loved none but herself, she was well pleased that her servants should amuse him.
It happened one evening, however, when they had read longer than was their wont, that the lady looked towards her husband’s bed where was the young serving-maid holding the candle. Of her she could see nothing but her back, and of her husband nothing at all excepting on the side of the chimney, which jutted out in front of his bed, and the white wall of which was bright with the light from the candle. And upon this wall she could plainly see the shadows both of her husband and of her maid; whether they drew apart, or came near together or laughed, it was all as clear to her as though she had veritably beheld them.
The gentleman, using no precaution since he felt sure that his wife could not see them, kissed her maid, and on the first occasion his wife suffered this to pass without uttering a word. But when she saw that the shadows frequently returned to this fellowship, she feared that there might be some reality beneath it all, and burst into a loud laugh, whereat the shadows were alarmed and separated.
The gentleman then asked his wife why she was laughing so heartily, so that he might have a share in her merriment.
“Husband,” she replied, “I am so foolish that I laugh at my own shadow.”
Inquire as he might, she would never acknowledge any other reason, but, nevertheless, he thenceforward refrained from kissing such shadow-faces.
“That is the story of which I was reminded when I spoke of the lady who loved her husband’s sweetheart.”
“By my faith,” said Ennasuite, “if my maid had treated me in that fashion, I should have risen and extinguished the candle upon her nose.”
“You are indeed terrible,” said Hircan, “but it had been well done if your husband and the maid had both turned upon you and beaten you soundly. There should not be so much ado for a kiss; and ‘twould have been better if his wife had said nothing about it, and had suffered him to take his pastime, which might perchance have cured his complaint.”
“Nay,” said Parlamente, “she was afraid that the end of the pastime would make him worse.”
“She was not one of those,” said Oisille, “against whom our Lord says, ‘We have mourned to you and ye have not lamented, we have sung to you and ye have not danced,’ (2) for when her husband was ill, she wept, and when he was merry, she laughed. In the same fashion every virtuous woman ought to share the good and evil, the joy and the sadness of her husband, and serve and obey him as the Church does Jesus Christ.”
2 “They are like unto children sitting in the market-place,
and calling one to another, and saying, We have piped unto
you, and ye have not danced; we have mourned to you, and ye
have not wept.”—St. Luke vii. 32.—M.
“Then, ladies,” said Parlamente, “our husbands should be to us what Christ is to the Church.”
“So are we,” said Saffredent, “and, if it were possible, something more; for Christ died but once for His Church, whereas we die daily for our wives.”
“Die!” said Longarine. “Methinks that you and the others here present are now worth more crowns than you were worth pence before you were wed.”
“And I know why,” said Saffredent; “it is because our worth is often tried. Still our shoulders are sensible of having worn the cuirass so long.”
“If,” said Ennasuite, “you had been obliged to wear harness for a month and lie on the hard ground, you would greatly long to regain the bed of your excellent wife, and wear the cuirass of which you now complain. But it is said that everything can be endured except ease, and that none know what rest is until they have lost it. This foolish woman, who laughed when her husband was merry, was fond of taking her rest under any circumstances.”
“I am sure,” said Longarine, “that she loved her rest better than her husband, since she took nothing that he did to heart.”
“She did take to heart,” said Parlamente, “those things which might have been hurtful to his conscience and his health, but she would not dwell upon trifles.”
“When you speak of conscience,” said Simontault “you make me laugh. ‘Tis a thing to which I would have no woman give heed.”
“It would be a good thing,” said Nomerfide, “if you had a wife like one who, after her husband’s death, proved that she loved her money better than her conscience.”
“I pray you,” said Saffredent, “tell us that tale. I give you my vote.”
“I had not intended,” said Nomcrfide, “to relate so short a story, but, since it is suited to the occasion, I will do so.”


A merchant’s widow, whilst carrying out her husband’s will,
interpreted its purport to the advantage of herself and her
children. (1)
In the town of Safagossa there lived a rich merchant, who, finding his death draw nigh, and himself no longer able to retain possession of his goods—-which he had perchance gathered together by evil means—thought that if he made a little present to God, he might thus after his death make part atonement for his sins, just as though God sold His pardon for money. Accordingly, when he had settled matters in respect of his house, he declared it to be his desire that a fine Spanish horse which he possessed should be sold for as much as it would bring, and the money obtained for it be distributed among the poor. And he begged his wife that she would in no wise fail to sell the horse as soon as he was dead, and distribute the money in the manner he had commanded.
1 Whether the incidents here related be true or not, it is
probable that this was a story told to Queen Margaret at the
time of her journey to Spain in 1525. It will have been
observed (ante, pp. 36 and 42) that both the previous tale
and this one are introduced into the Heptameron in a semi-
apologetic fashion, as though the Queen had not originally
intended that her work should include such short, slight
anecdotes. However, already at this stage—the fifty-fifth
only of the hundred tales which she proposed writing—she
probably found fewer materials at her disposal than she had
anticipated, and harked back to incidents of her earlier
years, which she had at first thought too trifling to
record. Still, slight as this story may be, it is not
without point. The example set by the wife of the Saragossa
merchant has been followed in modern times in more ways than
one.—Ed.
When the burial was over and the first tears were shed, the wife, who was no more of a fool than Spanish women are used to be, went to the servant who with herself had heard his master declare his desire, and said to him—
“Methinks I have lost enough in the person of a husband I loved so dearly, without afterwards losing his possessions. Yet would I not disobey his word, but rather better his intention; for the poor man, led astray by the greed of the priests, thought to make a great sacrifice to God in bestowing after his death a sum of money, not a crown of which, as you well know, he would have given in his lifetime to relieve even the sorest need. I have therefore bethought me that we will do what he commanded at his death, and in still better fashion than he himself would have done if had he lived a fortnight longer. But no living person must know aught of the matter.”
When she had received the servant’s promise to keep it secret, she said to him—
“You will go and sell the horse, and when you are asked, ‘How much?’ you will reply, ‘A ducat.’ I have, however, a very fine cat which I also wish to dispose of, and you will sell it with the horse for ninety-nine ducats, so that cat and horse together will bring in the hundred ducats for which my husband wished to sell the horse alone.”
The servant readily fulfilled his mistress’s command. While he was walking the horse about the market-place, and holding the cat in his arms, a gentleman, who had seen the horse before, and was desirous of possessing it, asked the servant what price he sought.
“A ducat,” replied the man.
“I pray you,” said the gentleman, “do not mock me.”
“I assure you, sir,” said the servant, “that it will cost you only a ducat. It is true that the cat must be bought at the same time, and for the cat I must have nine and ninety ducats.”
Forthwith, the gentleman, thinking the bargain a reasonable one, paid him one ducat for the horse, and the remainder as was desired of him, and took his goods away.
The servant, on his part, went off with the money, with which his mistress was right well pleased, and she failed not to give the ducat that the horse had brought to the poor Mendicants, (2) as her husband had commanded, and the remainder she kept for the needs of herself and her children. (3)
2 The allusion is not to the ordinary beggars who then, as
now, swarmed in Spain, but to the Mendicant friars.—Ed.
3 In Boaistuau’s and Gruget’s editions of the Heptameron
the dialogue following this tale is replaced by matter of
their own invention. They did not dare to reproduce Queen
Margaret’s bold opinions respecting the clergy, the monastic
orders, &c., at a time when scores of people, including even
Counsellors of Parliament, were being burnt at the stake for
heresy.—L. and Ed.
“What think you? Was she not far more prudent than her husband, and did she not think less of her conscience than of the advantage of her household?”
“I think,” said Parlamente, “that she did love her husband; but, seeing that most men wander in their wits when at the point of death, and knowing his intentions, she tried to interpret them to her children’s advantage. And therein I hold her to have been very prudent.”
“What!” said Geburon. “Do you not hold it a great wrong not to carry out the last wishes of departed friends?”
“Assuredly I do,” said Parlamente; “that is to say if the testator be in his right mind, and not raving.”
“Do you call it raving to give one’s goods to the Church and the poor Mendicants?”
“I do not call it raving,” said Parlamente, “if a man distribute what God has given into his hands among the poor; but to make alms of another person’s goods is, in my opinion, no great wisdom. You will commonly see the greatest usurers build the handsomest and most magnificent chapels imaginable, thinking they may appease God with ten thousand ducats’ worth of building for a hundred thousand ducats’ worth of robbery, just as though God did not know how to count.”
“In sooth,” said Oisille, “I have many a time wondered how they can think to appease God for things which He Himself rebuked when He was on earth, such as great buildings, gildings, pictures and paint. If they really understood the passage in which God says to us that the only offering He requires from us is a contrite and humble heart, (4) and the other in which St. Paul says we are the temples of God wherein He desires to dwell, (5) they would be at pains to adorn their consciences while yet alive, and would not wait for the hour when man can do nothing more, whether good or evil, nor (what is worse) charge those who remain on earth to give their alms to folk upon whom, during their lifetime, they did not deign to look. But He who knows the heart cannot be deceived, and will judge them not according to their works, but according to their faith and charity towards Himself.”
4 “The sacrifices of God are a broken spirit: a broken and
a contrite heart, O God, thou will not despise.”—Psalm
li. 17.—Ed.
5 “For ye are the temple of the living God; as God hath
said, I will dwell in them and walk in them,” &c.—2
Corinthians vi. 16.—Ed.
“Why is it, then,” said Geburon, “that these Grey Friars and Mendicants talk to us at our death of nothing but bestowing great benefits upon their monasteries, assuring us that they will put us into Paradise whether we will or not?”
“How now, Geburon?” said Hircan. “Have you forgotten the wickedness you related to us of the Grey Friars, that you ask how such folk find it possible to lie? I declare to you that I do not think that there can be greater lies than theirs. Those, indeed, who speak on behalf of the whole community are not to be blamed, but there are some among them who forget their vows of poverty in order to satisfy their own greed.”
“Methinks, Hircan,” said Nomerfide, “you must know some such tale, and if it be worthy of this company, I pray you tell it us.”
“I will,” said Hircan, “although it irks me to speak of such folk. Methinks they are of the number of those of whom Virgil says to Dante, ‘Pass on and heed them not.’ (6) Still, to show you that they have not laid aside their passions with their worldly garments, I will tell you of something that once came to pass.”
6 Non ragioniam di lor, ma guarda e passa (Dante’s
Purgatorio, iii. 51). The allusion is to the souls of
those who led useless and idle lives on earth, supporting
neither the Divinity by the observance of virtue, nor the
spirit of evil by the practice of vice. They are thus cast
out both from heaven and hell.—Ed.



A pious lady had recourse to a Grey Friar for his advice in
providing her daughter with a good husband, for whom she
proposed making it so profitable a match that the worthy
father, hoping to get the money she intended for her son-in-
law, married her daughter to a young comrade of his own. The
latter came every evening to sup and lie with his wife, and
in the morning returned in the garb of a scholar to his
convent. But one day while he was chanting mass, his wife
perceived him and pointed him out to her mother; who,
however, could not believe that it was he until she had
pulled off his coif while he was in bed, and from his tonsure
learned the whole truth, and the deceit used by her father
confessor.
A French lady, whilst sojourning at Padua, was informed that there was a Grey Friar in the Bishop’s prison there, and finding that every one spoke jestingly about him, she inquired the reason. She was told that this Grey Friar, who was an old man, had been confessor to a very honourable and pious widow lady, mother of only one daughter, whom she loved so dearly as to be at all pains to amass riches for her, and to find her a good husband. Now, seeing that her daughter was grown up, she was unceasingly anxious to find her a husband who might live with them in peace and quiet, a man, that is, of a good conscience, such as she deemed herself to possess. And since she had heard some foolish preacher say that it were better to do evil by the counsel of theologians than to do well through belief in the inspiration of the Holy Spirit, she had recourse to her father confessor, a man already old, a doctor of theology and one who was held to lead a holy life by the whole town, for she felt sure that, with his counsel and good prayers, she could not fail to find peace both for herself and for her daughter. After she had earnestly begged him to choose for her daughter such a husband as he knew a woman that loved God and her honour ought to desire, he replied that first of all it was needful to implore the grace of the Holy Spirit with prayer and fasting, and then, God guiding his judgment, he hoped to find what she required.
So the Friar retired to think over the matter; and whereas he had heard from the lady that she had got five hundred ducats together to give to her daughter’s husband, and that she would take upon herself the charge of maintaining both husband and wife with lodgment, furniture and clothes, he bethought himself that he had a young comrade of handsome figure and pleasing countenance, to whom he might give the fair maiden, the house, the furniture, maintenance and food, whilst he himself kept the five hundred ducats to gratify his burning greed. And when he spoke to his comrade of the matter, he found that they were both of one mind upon it.
He therefore returned to the lady and said—“I verily believe that God has sent his angel Raphael to me as he did to Tobit, to enable me to find a perfect husband for your daughter. I have in my house the most honourable gentleman in Italy, who has sometimes seen your daughter and is deeply in love with her. And so to-day, whilst I was at prayer, God sent him to me, and he told me of his desire for the marriage, whereupon, knowing his lineage and kindred and notable descent, I promised him to speak to you on the matter. There is, indeed, one defect in him, of which I alone have knowledge, and it is this. Wishing to save one of his friends whom another man was striving to slay, he drew his sword in order to separate them; but it chanced that his friend slew the other, and thus, although he himself had not dealt a blow, yet inasmuch as he had been present at a murder and had drawn his sword, he became a fugitive from his native town. By the advice of his kinsfolk he came hither in the garb of a scholar, and he dwells here unknown until his kinsfolk shall have ended the matter; and this he hopes will shortly be done. For this reason, then, it would be needful that the marriage should be performed in secret, and that you should suffer him to go in the daytime to the public lectures and return home every evening to sup and sleep.”
“Sir,” replied the worthy woman, “I look upon what you tell me as of great advantage to myself, for I shall at least have by me what I most desire in the world.”
Thereupon the Grey Friar brought his comrade, bravely attired with a crimson satin doublet, and the lady was well pleased with him. And as soon as he was come the betrothal took place, and, immediately after midnight, a mass was said and they were married. Then they went to bed together until daybreak, when the bridegroom told his wife that to escape discovery he must needs return to the college.
After putting on his crimson satin doublet and his long robe, without forgetting his coif of black silk, he bade his wife, who was still in bed, good-bye, promising that he would come every evening to sup with her, but that at dinner they must not wait for him. So he went away and left his wife, who esteemed herself the happiest woman alive to have found so excellent a match. And the young wedded Friar returned to the old father and brought him the five hundred ducats, as had been agreed between them when arranging the marriage.
In the evening he failed not to return and sup with her, who believed him to be her husband, and so well did he make himself liked by her and by his mother-in-law, that they would not have exchanged him for the greatest Prince alive.
This manner of life continued for some time, but God in His kindness takes pity upon those that are deceived without fault of their own, and so in His mercy and goodness it came to pass that one morning the lady and her daughter felt a great desire to go and hear mass at St. Francis, (1) and visit their good father confessor through whose means they deemed themselves so well provided, the one with a son-in-law and the other with a husband.
1 The church of the Grey Friars’ monastery, St Francis
being their patron.—B. J.
It chanced that they did not find the confessor aforesaid nor any other that they knew, and, while waiting to see whether the father would come, they were pleased to hear high mass, which was just beginning. And whilst the young wife was giving close heed to the divine service and its mystery, she was stricken with astonishment on seeing the Priest turn himself about to pronounce the Dominus vobiscum, for it seemed to her that it was her husband or else his very fellow. She uttered, however, not a word, but waited till he should turn round again, when, looking still more carefully at him, she had no doubt that it was indeed he. Then she twitched her mother, who was deep in contemplation, and said—
“Alas! madam, what is it that I see?”
“What is it?” said her mother.
“That is my husband,” she replied, “who is singing mass, or else ‘tis one as like him as can be.”
“I pray you, my daughter,” replied the mother, who had not carefully observed him, “do not take such a thought into your head. It is impossible that men who are so holy should have practised such deceit. You would sin grievously against God if you believed such a thing.”
Nevertheless the mother did not cease looking at him, and when it came to the Ite missa est she indeed perceived that no two sons of the same mother were ever so much alike. Yet she was so simple that she would fain have said, “O God, save me from believing what I see.” Since her daughter was concerned in the matter, however, she would not suffer it to remain in uncertainty, and resolved to learn the truth.
When evening was come, and the husband (who had perceived nothing of them) was about to return, the mother said to her daughter—
“We shall now, if you are willing, find out the truth concerning your husband. When he is in bed I will go to him, and then, while he is not thinking, you will pluck off his coif from behind, and we shall see whether he be tonsured like the Friar who said mass.”
As it was proposed, so was it done. As soon as the wicked husband was in bed, the old lady came and took both his hands as though in sport—her daughter took off his coif, and there he was with his fine tonsure. At this both mother and daughter were as greatly astonished as might be, and forthwith they called their servants to seize him and bind him fast till the morning, nor did any of his excuses or fine speeches avail him aught.
When day was come, the lady sent for her confessor, making as though she had some great secret to tell him, whereupon he came with all speed, and then, reproaching him for the deceit that he had practised on her, she had him seized like the other. Afterwards she sent for the officers of justice, in whose hands she placed them both. It is to be supposed that if the judges were honest men they did not suffer the offence to go unpunished. (2)
2 There is some little resemblance between this tale and
the 36th of Morlini’s Novello, De monacho qui duxit
uxorem.—M.
“From this story, ladies, you will see that those who have taken vows of poverty are not free from the temptation of covetousness, which is the cause of so many ills.”
“Nay, of so many blessings,” said Saffredent, “for with the five hundred ducats that the old woman would have stored up there was made much good cheer, while the poor maiden, who had been longing for a husband, was thus enabled to have two, and to speak with more knowledge as to the truth of all hierarchies.”
“You always hold the falsest opinions,” said Oisille, “that ever I knew. You think that all women are of your own temper.”
“Not so, madam, with your good leave,” said Saffredent. “I would give much that they were as easily satisfied as we are.”
“That is a wicked speech,” said Oisille, “and there is not one present but knows the contrary, and that what you say is untrue. The story that has just been told proves the ignorance of poor women and the wickedness of those whom we regard as better than the rest of your sex; for neither mother nor daughter would do aught according to their own fancy, but subjected desire to good advice.”
“Some women are so difficult,” said Longarine, “that they think they ought to have angels instead of men.”
“And for that reason,” said Simontault, “they often meet with devils, more especially those who, instead of trusting to God’s grace, think by their own good sense, or that of others, that they may in this world find some happiness, though this is granted by none save God, from whom alone it can come.”
“How now, Simontault!” said Oisille. “I did not think that you knew so much good.”
“Madam,” said Simontault, “‘tis a pity that I have not been proved, for I see that through lack of knowledge you have already judged ill of me. Yet I may well practise a Grey Friar’s trade, since a Grey Friar has meddled with mine.”
“So you call it your trade,” said Parlamente, “to deceive women? Thus out of your mouth are you judged.”
“Had I deceived a hundred thousand,” said Simontault, “I should yet not have avenged the woes that I have endured for the sake of one alone.”
“I know,” said Parlamente, “how often you complain of women; yet, for all that, we see you so merry and hearty that it is impossible to believe that you have endured all the woes you speak of. But the ‘Compassionless Fair One’ (3) replies that—
“‘Tis as well to say as much
To draw some comfort thence.’”
3 La belle Dame sans mercy, by Alain Chartier.—Ed.
“You quote a truly notable theologian,” said Simontault, “one who is not only froward himself, but makes all the ladies so, who have read and followed his teaching.”
“Yet his teaching,” said Parlamente, “is as profitable for youthful dames as any that I know.”
“If it were indeed true,” said Simontault, “that the ladies were without compassion, we might as well let our horses rest and our armour grow rusty until the next war, and think of nothing but household affairs. And, I pray you, tell me whether it is an excellence in a lady to have the reputation of being without pity, or charity, or love, or mercy.”
“Without charity or love,” said Parlamente, “they should not be, but the word ‘mercy’ sounds so ill among women that they cannot use it without wounding their honour; for properly speaking ‘mercy’ means to grant a favour sought, and we well know what the favour is that men desire.”
“May it please you, madam,” said Simontault, “there are some men who are so reasonable that they crave nought but speech.”
“You remind me,” said Parlamente, “of one who was content with a glove.”
“We must know who this easy lover was,” said Hircan, “and so this time I give my vote to you.”
“It will give me pleasure to tell the tale,” said Parlamente, “for it is full of virtue.”



An English lord for seven years loved a lady without ever
venturing to let her know of it, until one day, when
observing her in a meadow, he lost all colour and control of
feature through a sudden throbbing of the heart that came
upon him. Then she, showing her compassion, at his request
placed her gloved hand upon his heart, whereupon he pressed
it so closely, whilst declaring to her the love he had so
long borne her, that she withdrew it, leaving in its place
her glove. And this glove he afterwards enriched with gems
and fastened upon his doublet above his heart, and showed
himself so graceful and virtuous a lover that he never
sought any more intimate favour of her.
King Louis the Eleventh (1) sent the Lord de Montmorency to England as his ambassador, and so welcome was the latter in that country that the King and all the Princes greatly esteemed and loved him, and even made divers of their private affairs known to him in order to have his counsel upon them.
1 Some of the MS. say Louis XII., but we cannot find that
either the eleventh or twelfth Louis sent any Montmorency as
ambassador to England. Ripault-Desormeaux states, however,
in his history of this famous French family, that William de
Montmorency, who, after fighting in Italy under Charles
VIII. and Louis XII., became, governor of the Orléanais and
chevalier d’honneur to Louise of Savoy was one of the
signatories of the treaty concluded with Henry VIII. of
England, after the-battle of Pavia in 1525. We know that
Louise, as Regent of France, at that time sent John Brinon
and John Joachim de Passano as ambassadors to England, and
possibly William de Montmorency accompanied them, since
Desormeaux expressly states that he guaranteed the loyal
observance of the treaty then negotiated. William was the
father of Anne, the famous Constable of France, and died May
24, 1531. “Geburon,” in the dialogue following the above
tale, mentions that he had well known the Montmorency
referred to, and speaks of him as of a person dead and gone.
It is therefore scarcely likely that Queen Margaret alludes
to Francis de Montmorency, Lord of La Rochepot, who was only
sent on a mission to England in 1546, and survived her by
many years.—L. and Ed.
One day, at a banquet that the King gave to him, he was seated beside a lord (2) of high lineage, who had on his doublet a little glove, such as women wear, fastened with hooks of gold and so adorned upon the finger-seams with diamonds, rubies, emeralds and pearls, that it was indeed a glove of great price.
2 The French word is Millor (Milord) and this is probably
one of the earliest instances of its employment to designate
a member of the English aristocracy. In such of the Cent
Nouvelles Nouvelles in which English nobles figure, the
latter are invariably called seigneurs or chevaliers,
and addressed as Monseigneur, Later on, when Brantôme
wrote, the term un milord anglais had become quite common,
and he frequently makes use of it in his various works.
English critics have often sneered at modern French writers
for employing the expression, but it will be seen from this
that they have simply followed a very old tradition.—Ed.
The Lord de Montmorency looked at it so often that the English lord perceived he was minded to inquire why it was so choicely ordered; so, deeming its story to be greatly to his own honour, he thus began—
“I can see that you think it strange I should have so magnificently arrayed a simple glove, and on my part I am still more ready to tell you the reason, for I deem you an honest gentleman and one who knows what manner of passion love is, so that if I did well in the matter you will praise me for it, and if not, make excuse for me, knowing that every honourable heart must obey the behests of love. You must know, then, that I have all my life long loved a lady whom I love still, and shall love even when I am dead, but, as my heart was bolder to fix itself worthily than were my lips to speak, I remained for seven years without venturing to make her any sign, through fear that, if she perceived the truth, I should lose the opportunities I had of often being in her company; and this I dreaded more than death. However, one day, while I was observing her in a meadow, a great throbbing of the heart came upon me, so that I lost all colour and control of feature. Perceiving this, she asked me what the matter was, and I told her that I felt an intolerable pain of the heart. She, believing it to be caused by a different sickness than love, showed herself pitiful towards me, which prompted me to beg her to lay her hand upon my heart and see how it was beating. This, more from charity than from any other affection, she did, and while I held her gloved hand against my heart, it began to beat and strain in such wise, that she felt that I was speaking the truth. Then I pressed her hand to my breast, saying—
“‘Alas, madam, receive the heart which would fain break forth from my breast to leap into the hand of her from whom I look for indulgence, life and pity, and which now constrains me to make known to you the love that I have so long concealed, for neither my heart nor I can now control this potent God.’
“When she heard those words, she deemed them very strange. She wished to withdraw her hand, but I held it fast, and the glove remained in her cruel hand’s place; and having neither before nor since had any more intimate favour from her, I have fastened this glove upon my heart as the best plaster I could give it. And I have adorned it with the richest rings I have, though the glove itself is wealth that I would not exchange for the kingdom of England, for I deem no happiness on earth so great as to feel it on my breast.”
The Lord de Montmorency, who would have rather had a lady’s hand than her glove, praised his very honourable behaviour, telling him that he was the truest lover he had ever known, and was worthy of better treatment, since he set so much value upon so slight a thing; though perchance, if he had obtained aught better than the glove, the greatness of his love might have made him die of joy. With this the English lord agreed, not suspecting that the Lord de Montmorency was mocking him. (3)
3 Alluding to this story, Brantôme writes as follows in his
Dames Galantes: “You have that English Milord in the
Hundred Tales of the Queen of Navarre, who wore his
mistress’s glove at his side, beautifully adorned. I myself
have known many gentlemen who, before wearing their silken
hose, would beg their ladies and mistresses to try them on
and wear them for some eight or ten days, rather more than
less, and who would then themselves wear them in extreme
veneration and contentment, both of mind and body.”—
Lalanne’s OEuvres de Brantôme, vol. ix. p. 309.—L.
“If all men were so honourable as this one, the ladies might well trust them, since the cost would be merely a glove.”
“I knew the Lord de Montmorency well,” said Geburon, “and I am sure that he would not have cared to fare after the English fashion. Had he been contented with so little, he would not have been so successful in love as he was, for the old song says—
‘Of a cowardly lover
No good is e’er heard.’”
“You may be sure,” said Saffredent, “that the poor lady withdrew her hand with all speed, when she felt the beating of his heart, because she thought that he was about to die, and people say that there is nothing women loathe more than to touch dead bodies.” (4)
4 Most of this sentence, deficient in our MS., is taken
from MS. No. 1520.—L.
“If you had spent as much time in hospitals as in taverns,” said Ennasuite, “you would not speak in that way, for you would have seen women shrouding dead bodies, which men, bold as they are, often fear to touch.”
“It is true,” said Saffredent, “that there is none upon whom penance has been laid but does the opposite of that wherein he formerly had delight, like a lady I once saw in a notable house, who, to atone for her delight in kissing one she loved, was found at four o’clock in the morning kissing the corpse of a gentleman who had been killed the day before, and whom she had never liked more than any other. Then every one knew that this was a penance for past delights. But as all the good deeds done by women are judged ill by men, I am of opinion that, dead or alive, there should be no kissing except after the fashion that God commands.”
“For my part,” said Hircan, “I care so little about kissing women, except my own wife, that I will assent to any law you please, yet I pity the young folk whom you deprive of this trifling happiness, thus annulling the command of St. Paul, who bids us kiss in osculo sancto.” (5)
5 Romans xvi. 16; 1 Corinthians xvi. 20; 2
Corinthians xiii. 12; I Thessalonians v. 26. Also 1
Peter v. 14.—M.
“If St. Paul had been such a man as you are,” said Nomerfide, “we should indeed have required proof of the Spirit of God that spoke in him.”
“In the end,” said Geburon, “you will doubt Holy Scripture rather than give up one of your petty affectations.”
“God forbid,” said Oisille, “that we should doubt Holy Scripture, but we put small faith in your lies. There is no woman but knows what her belief should be, namely, never to doubt the Word of God or believe the word of man.”
“Yet,” said Simontauit, “I believe that there are more men deceived by women than [women] by men. The slenderness of women’s love towards us keeps them from believing our truths, whilst our exceeding love towards them makes us trust so completely in their falsehoods, that we are deceived before we suspect such a thing to be possible.”
“Methinks,” said Parlamente, “you have been hearing some fool complain of being duped by a wanton woman, for your words carry but little weight, and need the support of an example. If, therefore, you know of one, I give you my place that you may tell it to us. I do not say that we are bound to believe you on your mere word, but it will assuredly not make our ears tingle to hear you speak ill of us, since we know what is the truth.”
“Well, since it is for me to speak,” said Dagoucin, “‘tis I who will tell you the tale.”



A gentleman, through putting too much trust in the
truthfulness of a lady whom he had offended by forsaking her
for others just when she was most in love with him, was, by
a false tryst, deceived by her, and bemocked by the whole
Court.
At the Court of King Francis the First there was a lady (1) of excellent wit, who, by her grace, virtue and pleasantness of speech, had won the hearts of several lovers. With these she right well knew how to pass the time, but without hurt to her honour, conversing with them in such pleasant fashion that they knew not what to think, for those who were the most confident were reduced to despair, whilst those that despaired the most became hopeful. Nevertheless, while fooling most of them, she could not help greatly loving one whom she called her cousin, a name which furnished a pretext for closer fellowship.
1 M. de Lincy surmises that Margaret is referring to
herself both here and in the following tale, which concerns
the same lady. His only reason for the supposition, however,
is that the lady’s views on certain love matters are akin to
those which the Queen herself professed.—Ed.
However, as there is nothing in this world of firm continuance, their friendship often turned to anger and then was renewed in stronger sort than ever, so that the whole Court could not but be aware of it.
One day the lady, both to let it be seen that she was wholly void of passion, and to vex him, for love of whom she had endured much annoyance, showed him a fairer countenance than ever she had done before. Thereupon the gentleman, who lacked boldness neither in love nor in war, began hotly to press the suit that he many a time previously had addressed to her.
She, pretending to be wholly vanquished by pity, promised to grant his request, and told him that she would with this intent go into her room, which was on a garret floor, where she knew there was nobody. And as soon as he should see that she was gone he was to follow her without fail, for he would find her ready to give proof of the good-will that she bore him.
The gentleman, believing what she said, was exceedingly well pleased, and began to amuse himself with the other ladies until he should see her gone, and might quickly follow her. But she, who lacked naught of woman’s craftiness, betook herself to my Lady Margaret, daughter of the King, and to the Duchess of Montpensier, (2) to whom she said—
“I will if you are willing, show you the fairest diversion you have ever seen.”
2 The former is Margaret of France, Duchess of Savoy and
Berry. Born in June 1523, she died in September 1574.—
Queen Margaret was her godmother. When only three years old,
she was promised in marriage to Louis of Savoy, eldest son
of Duke Charles III., and he dying, she espoused his younger
brother, Emmanuel Philibert, in July 1549. Graceful and
pretty as a child (see ante, vol. i. p. xlviii.), she
became, thanks to the instruction of the famous Michael de
l’ Hôpital, one of the most accomplished women of her time,
and Brantôme devotes an article to her in his Dames
Illustres (Lalanne, v. viii. pp. 328-37). See also Hilarion
de Coste’s Éloges et Vies des Reines, Princesses, &c.,
Paris, 1647, vol. ii. p. 278.
The Duchess of Montpensier, also referred to above, is
Jacqueline de Longwick (now Longwy), Countess of Bar-sur-
Seine, daughter of J. Ch. de Longwick, Lord of Givry, and of
Jane, bâtarde of Angoulême. In 1538 Jacqueline was
married to Louis II. de Bourbon, Duke of Montpensier. She
gained great influence at the French Court, both under
Francis I. and afterwards, and De Thou says of her that she
was possessed of great wit and wisdom, far superior to the
century in which she lived. She died in August 1561, and was
the mother of Francis I., Duke of Montpensier, sometimes
called the Dauphin of Auvergne, who fought at Jarnac,
Moncontour, Arques, and Ivry, against Henry of Navarre.—L.,
B. J. and Ed.
They, being by no means enamoured of melancholy, begged that she would tell them what it was.
“You know such a one,” she replied, “as worthy a gentleman as lives, and as bold. You are aware how many ill turns he has done me, and that, just when I loved him most, he fell in love with others, and so caused me more grief than I have ever suffered to be seen. Well, God has now afforded me the means of taking revenge upon him.
“I am forthwith going to my own room, which is overhead, and immediately afterwards, if it pleases you to keep watch, you will see him follow me. When he has passed the galleries, and is about to go up the stairs, I pray you come both to the window and help me to cry ‘Thief!’ You will then see his rage, which, I am sure, will not become him badly, and, even if he does not revile me aloud, I am sure he will none the less do so in his heart.”
This plan was not agreed to without laughter, for there was no gentleman that tormented the ladies more than he did, whilst he was so greatly liked and esteemed by all, that for nothing in the world would any one have run the risk of his raillery.
It seemed, moreover, to the two Princesses that they would themselves share in the glory which the other lady looked to win over this gentleman.
Accordingly, as soon as they saw the deviser of the plot go out, they set themselves to observe the gentleman’s demeanour. But little time went by before he shifted his quarters, and, as soon as he had passed the door, the ladies went out into the gallery, in order that they might not lose sight of him.
Suspecting nothing, he wrapped his cloak about his neck, so as to hide his face, and went down the stairway to the court, but, seeing some one whom he did not desire to have for witness, he came back by another way, and then went down into the court a second time. The ladies saw everything without being perceived by him, and when he reached the stairway, by which he thought he might safely reach his sweetheart’s chamber, they went to the window, whence they immediately perceived the other lady, who began crying out ‘Thief!’ at the top of her voice; whereupon the two ladies below answered her so loudly that their voices were heard all over the castle.
I leave you to imagine with what vexation the gentleman fled to his lodgings. He was not so well muffled as not to be known by those who were in the mystery, and they often twitted him with it, as did even the lady who had done him this ill turn, saying that she had been well revenged upon him.
It happened, however, that he was so ready with his replies and evasions as to make them believe that he had quite suspected the plan, and had only consented to visit the lady in order to furnish them with some diversion, for, said he, he would not have taken so much trouble for her sake, seeing that his love for her had long since flown. The ladies would not admit the truth of this, so that the point is still in doubt; nevertheless, it is probable that he believed the lady. And since he was so wary and so bold that few men of his age and time could match and none could surpass him (as has been proved by his very brave and knightly death), (3) you must, it seems to me, confess that men of honour love in such wise as to be often duped, by placing too much trust in the truthfulness of the ladies.
3 This naturally brings Bonnivet to mind, though of course
the gay, rash admiral was not the only Frenchman of the time
who spent his life in making love and waging war.—Ed.
“In good faith,” said Ennasuite, “I commend this lady for the trick she played; for when a man is loved by a lady and forsakes her for another, her vengeance cannot be too severe.”
“Yes,” said Parlamente, “if she is loved by him; but there are some who love men without being certain that they are loved in return, and when they find that their sweethearts love elsewhere, they call them fickle. It therefore happens that discreet women are never deceived by such talk, for they give no heed or belief even to those people who speak truly, lest they should prove to be liars, seeing that the true and the false speak but one tongue.”
“If all women were of your opinion,” said Simon-tault, “the gentlemen might pack up their prayers at once; but, for all that you and those like you may say, we shall never believe that women are as unbelieving as they are fair. And in this wise we shall live as content as you would fain render us uneasy by your maxims.”
“Truly,” said Longarine, “knowing as I well do who the lady is that played that fine trick upon the gentleman, it is impossible for me not to believe in any craftiness on her part. Since she did not spare her husband, ‘twere fitting she should not spare her lover.”
“Her husband, say you?” said Simontault. “You know, then, more than I do, and so, since you wish it, I give you my place that you may tell us your opinion of the matter.”
“And since you wish it,” said Longarine, “I will do so.”



This same lady, finding that her husband took it ill that
she should have lovers with whom she amused herself without
hurt to her honour, kept close watch upon him, and so
discovered how pleasantly he addressed himself to one of her
waiting-women. This woman she gained upon, made her consent
to what her husband solicited, and then surprised him in
such error that to atone for it, he was forced to confess
that he deserved greater punishment than herself; by which
means she was afterwards able to live as her fancy listed.
The lady of your story was wedded to a rich gentleman of high and ancient lineage, and had married him on account of the great affection that they bore to one another.
Being a woman most pleasant of speech, she by no means concealed from her husband that she had lovers whom she made game of for her pastime, and, at first, her husband shared in her pleasure. But at last this manner of life became irksome to him, for on the one part he took it ill that she should hold so much converse with those that were no kinsfolk or friends of his own, and on the other, he was greatly vexed by the expense to which he was put in sustaining her magnificence and in following the Court.
He therefore withdrew to his own house as often as he was able, but so much company came thither to see him that the expenses of his household became scarcely any less, for, wherever his wife might be, she always found means to pass her time in sports, dances, and all such matters as youthful dames may use with honour. And when sometimes her husband told her, laughing, that their expenses were too great, she would reply that she promised never to make him a “coqu” or cuckold, but only a “coquin,” that is, a beggar; for she was so exceedingly fond of dress, that she must needs have the bravest and richest at the Court. (1) Her husband took her thither as seldom as possible, but she did all in her power to go, and to this end behaved in a most loving fashion towards her husband, who would not willingly have refused her a much harder request.
1 As Queen Margaret was by no means over fond of gorgeous
apparel and display, this passage is in contradiction with
M. de Lincy’s surmise that the lady of this and the
preceding tale may be herself. In any case the narrative
could only apply to the period of her first marriage, and
this was in no wise a love-match. Yet we are told at the
outset of the above story that the lady and gentleman had
married on account of the great affection between them. On
the other hand, these details may have been introduced the
better to conceal the identity of the persons referred to.—
Ed.
Now one day, when she had found that all her devices could not induce him to make this journey to the Court, she perceived that he was very pleasant in manner with a chamber-woman (2) she had, and thereupon thought she might turn the matter to her own advantage. Taking the girl apart, she questioned her cleverly, using both wiles and threats, in such wise that the girl confessed that, ever since she had been in the house, not a day had passed on which her master had not sought her love; but (she added) she would rather die than do aught against God and her honour, more especially after the honour which the lady had done her in taking her into her service, for this would make such wickedness twice as great.
2 The French expression here is femme de chambre à
chaperon. The chaperon in this instance was a cap with a
band of velvet worn across it as a sign of gentle and even
noble birth. The attendant referred to above would therefore
probably be a young woman of good descent, constrained by
circumstances to enter domestic service.—B. J. and Ed.
On hearing of her husband’s unfaithfulness, the lady immediately felt both grief and joy. Her grief was that her husband, despite all his show of loving her, should be secretly striving to put her to so much shame in her own household, and this when she believed herself far more beautiful and graceful than the woman whom he sought in her stead. But she rejoiced to think that she might surprise her husband in such manifest error that he would no longer be able to reproach her with her lovers, nor with her desire to dwell at Court; and, to bring this about, she begged the girl gradually to grant her husband what he sought upon certain conditions that she made known to her.
The girl was minded to make some difficulty, but when her mistress warranted the safety both of her life and of her honour, she consented to do whatever might be her pleasure.
The gentleman, on continuing his pursuit of the girl, found her countenance quite changed towards him, and therefore urged his suit more eagerly than had been his wont; but she, knowing by heart the part she had to play, made objection of her poverty, and said that, if she complied with his desire, she would be turned away by her mistress, in whose service she looked to gain a good husband.
The gentleman forthwith replied that she need give no thought to any such matters, since he would bestow her in marriage more profitably than her mistress would be able to do, and further, would contrive the matter so secretly that none would know of it.
Upon this they came to an agreement, and, on considering what place would be most suited for such a fine business, the girl said that she knew of none better or more remote from suspicion than a cottage in the park, where there was a chamber and a bed suitable for the occasion.
The gentleman, who would not have thought any place unsuitable, was content with the one she named, and was very impatient for the appointed day and hour to come.
The girl kept her word to her mistress, and told her in full the whole story of the plan, and how it was to be put into execution on the morrow after dinner. She would not fail, said she, to give a sign when the time came to go to the cottage, and she begged her mistress to be watchful, and in no wise fail to be present at the appointed hour, in order to save her from the danger into which her obedience was leading her.
This her mistress swore, begging her to be without fear, and promising that she would never forsake her, but would protect her from her husband’s wrath.
When the morrow was come and dinner was over, the gentleman was more pleasant with his wife than ever, and although this was not very agreeable to her, she dissembled so well that he did not perceive the truth.
After dinner she asked him how he was minded to pass away the time, and he answered that he knew of nothing better than to play at “cent.” (3) Forthwith everything was made ready for the game, but the lady pretended that she did not care to take part in it, and would find diversion enough in looking at the players.
3 This is probably a reference to the card game now called
piquet, usually played for a hundred points. It is one of
the oldest of its kind. See Rabelais’ Gargantua, book i.
chap, xxii.—L.
Just before he sat down to play, the gentleman failed not to ask the girl to remember her promise to him, and while he was playing she passed through the room, making a sign to her mistress which signified that she was about to set out on the pilgrimage she had to make. The sign was clearly seen by the lady, but her husband perceived nothing of it.
An hour later, however, one of his servants made him a sign from a distance, whereupon he told his wife that his head ached somewhat, and that he must needs rest and take the air. She, knowing the nature of his sickness as well as he did himself, asked him whether she should play in his stead, and he consented, saying that he would very soon return. However, she assured him that she could take his place for a couple of hours without weariness.
So the gentleman withdrew to his room, and thence by an alley into his park.
The lady, who knew another and shorter way, waited for a little while, and then, suddenly feigning to be seized with colic, gave her hand at play to another.
As soon as she was out of the room, she put off her high-heeled shoes and ran as quickly as she could to the place, where she had no desire that the bargain should be struck without her. And so speedily did she arrive, that, when she entered the room by another door, her husband was but just come in. Then, hiding herself behind the door, she listened to the fair and honest discourse that he held to her maid. But when she saw that he was coming near to the criminal point, she seized him from behind, saying—
“Nay, I am too near that you should take another.”
It is needless to ask whether the gentleman was in extreme wrath, both at being balked of the delight he had looked to obtain, and at having his wife, whose affection he now greatly feared to lose for ever, know more of him than he desired. He thought, however, that the plot had been contrived by the girl, and (without speaking to his wife) he ran after her with such fury that, had not his wife rescued her from his hands, he would have killed her. He declared that she was the wickedest jade he had ever known, and that, if his wife had waited to see the end, she would have found that he was only mocking her, for, instead of doing what she expected, he would have chastised her with rods.
But his wife, knowing what words of the sort were worth, set no value upon them, and addressed such reproaches to him that he was in great fear lest she should leave him. He promised her all that she asked, and, after her sage reproaches, confessed that it was wrong of him to complain that she had lovers; since a fair and honourable woman is none the less virtuous for being loved, provided that she do or say nothing contrary to her honour; whereas a man deserves heavy punishment when he is at pains to pursue a woman that loves him not, to the wronging of his wife and his own conscience. He would therefore, said he, never more prevent his wife from going to Court, nor take it ill that she should have lovers, for he knew that she spoke with them more in jest than in affection.
This talk was not displeasing to the lady, for it seemed to her that she had gained an important point. Nevertheless she spoke quite to the contrary, pretending that she had no delight in going to Court, since she no longer possessed his love, without which all assemblies were displeasing to her; and saying that a woman who was truly loved by her husband, and who loved him in return, as she did, carried with her a safe-conduct that permitted her to speak with one and all, and to be derided by none.
The poor gentleman was at so much pains to assure her of the love he bore her, that at last they left the place good friends. That they might not again fall into such trouble, he begged her to turn away the girl through whom he had undergone so much distress. This she did, but did it by bestowing her well and honourably in marriage, and at her husband’s expense.
And, to make the lady altogether forget his folly, the gentleman soon took her to Court, in such style and so magnificently arrayed that she had good reason to be content.
“This, ladies, was what made me say I did not find the trick she played upon one of her lovers a strange one, knowing, as I did, the trick she had played upon her husband.”
“You have described to us a very cunning wife and a very stupid husband,” said Hircan. “Having advanced so far, he ought not to have come to a standstill and stopped on so fair a road.”
“And what should he have done?” said Longarine.
“What he had taken in hand to do,” said Hircan, “for his wife was no less wrathful with him for his intention to do evil than she would have been had he carried the evil into execution. Perchance, indeed, she would have respected him more if she had seen that he was a bolder gallant.”
“That is all very well,” said Ennasuite, “but where will you find a man to face two women at once? His wife would have defended her rights and the girl her virginity.”
“True,” said Hircan, “but a strong bold man does not fear to assail two that are weak, nor will he ever fail to vanquish them.”
“I readily understand,” said Ennasuite, “that if he had drawn his sword he might have killed them both, but otherwise I cannot see that he had any means of escape. I pray you, therefore, tell us what you would have done?”
“I should have taken my wife in my arms,” said Hircan, “and have carried her out. Then I should have had my own way with her maid by love or by force.”
“‘Tis enough, Hircan,” said Parlamente, “that you know how to do evil.”
“I am sure, Parlamente,” he replied, “that I do not scandalise the innocence in whose presence I speak, and by what I have said I do not mean that I support a wicked deed. But I wonder at the attempt, which was in itself worthless, and at the attempter, who, for fear rather than for love of his wife, failed to complete it. I praise a man who loves his wife as God ordains; but when he does not love her, I think little of him for fearing her.”
“Truly,” replied Parlamente, “if love did not render you a good husband, I should make small account of what you might do through fear.”
“You are quite safe, Parlamente,” said Hircan, “for the love I bear you makes me more obedient than could the fear of either death or hell.”
“You may say what you please,” said Parlamente, “but I have reason to be content with what I have seen and known of you. As for what I have not seen, I have never wished to make guess or still less inquiry.”
“I think it great folly,” said Nomerfide, “for women to inquire so curiously concerning their husbands, or husbands concerning their wives. Sufficient unto the day is the evil thereof, without giving so much heed to the morrow.”
“Yet it is sometimes needful,” said Oisille, “to inquire into matters that may touch the honour of a house in order to set them right, though not to pass evil judgment upon persons, seeing that there is none who does not fail.”
“Many,” said Geburon, “have at divers times fallen into trouble for lack of well and carefully inquiring into the errors of their wives.”
“I pray you,” said Longarine, “if you know any such instance, do not keep it from us.”
“I do indeed know one,” said Geburon, “and since you so desire, I will relate it.”



A man of Paris, through not making good inquiry concerning
his wife, whom he believed dead, though she was indeed
making good cheer with a chanter to the King, married a
second wife, whom, after having several children by her and
consorting with her for fourteen or fifteen years, he was
constrained to leave, in order to take his first wife back
again.
In the city of Paris there was a man who was so good-natured that he would have scrupled to believe a man abed with his wife, even if he had seen him with his own eyes. This poor man married a woman whose conduct was as bad as could be; nevertheless he perceived nothing of it, and treated her as though she were the most virtuous woman alive. One day, however, when King Louis XII. came to Paris, his wife surrendered herself to one of the choir-men of the aforesaid sovereign, and when she found that the King was leaving Paris and that she would no longer be able to see the singer, she resolved to follow him and forsake her husband. To this the chanter agreed, and brought her to a house that he had near Blois, (1) where for a long while they lived together. The poor husband, finding that he had lost his wife, sought her everywhere; and at last it was told him that she was gone away with the chanter.
Wishing to recover the lost ewe which he had so badly watched, he wrote many letters to her begging her to return to him, and saying that he would take her back if she were willing to be a virtuous woman. But she took such great delight in listening to the songs of the chanter, that she had forgotten her husband’s voice, and gave no heed to all his excellent words, but mocked at them.
Therefore the husband, in great wrath, gave her to know that, since she would return to him in no other way, he would demand her in legal fashion of the Church. (2) The wife, dreading that if the law should take the matter in hand she and her chanter would fare badly, devised a stratagem worthy of such a woman as herself. Feigning sickness, she sent for some honourable women of the town to come and see her, and this they willingly did, hoping that her illness might be a means of withdrawing her from her evil life, with which purpose they addressed the sagest admonitions to her. Thereupon she, whilst pretending to be grievously sick, made a show of weeping and acknowledging her sinfulness in such sort that she gained the pity of the whole company, who quite believed that she was speaking from the bottom of her heart. And, finding her thus subdued and sorry, they began to comfort her, telling her that God was in no wise so terrible as many preachers represented Him, and that He would never refuse to show her mercy.
1 Louis XII.‘s favourite place of residence.—Ed.
2 Implying the Officialité or episcopal court.—B. J.
After this excellent discourse, they sent for a virtuous man to come and confess her, and on the morrow the priest of the parish came to administer the Holy Sacrament. This she received so piously, that all the virtuous women of the town who were present wept to see her devoutness, praising God, who of His goodness had in this wise shown compassion upon this poor creature.
Afterwards she pretended that she could no longer take food, whereupon the extreme unction was brought by the priest and received by her with many pious signs; for (as they thought) she was scarcely able to speak. She continued thus for a great while, and it seemed as though she were gradually losing her sight, hearing and other senses, whereat there came from all a cry of “Jesus!” As night was at hand and the ladies were far from home, they all withdrew; and just as they were leaving the house it was told them that she was dead, whereupon, saying their De profundis for her, they returned to their houses.
The priest asked the chanter where he would have her buried, and the other replied that she had desired to be buried in the cemetery, and that it would be well to bring her there at night. So the poor unfortunate was shrouded by a serving-woman, who was careful not to hurt her, and then by brave torchlight she was carried to the grave that the chanter had caused to be made.
When the body passed in front of the houses of those who had been present when she received the extreme unction, they all came forth and followed her to the tomb; and there she was soon left by women and priests alike. The chanter, however, did not go away, but, as soon as he saw the company some distance off, he and the serving-woman opened the grave wherein was his sweetheart more alive than ever, and he sent her secretly to his house, where for a long time he kept her concealed.
The husband, who was in pursuit of her, came as far as Blois to demand justice, when he found that she was dead and buried according to the testimony of all the ladies of Blois. They told him, too, what a good end she had made, and the worthy man was rejoiced to think that his wife’s soul was in Paradise, and himself rid of her wicked body.
In this wise well content, he betook himself back to Paris, where he married a beautiful and virtuous young woman, and a good housewife, by whom he had several children, and with whom he lived for fourteen or fifteen years. But at last rumour, which can keep nothing hid, advised him that his wife was not dead, but was still dwelling with the wicked chanter. The poor man concealed the matter as well as he was able, pretending to know nothing about it, and hoping that it was a lie. But his wife, who was a discreet woman, was told of it, and such was her anguish at the tidings that she was like to die of grief. Had it been possible without offence to her conscience, she would gladly have concealed her misfortune, but it was not possible. The Church immediately took the affair in hand, and first of all separated them from each other until the truth of the matter should be known.
Then was this poor man obliged to leave the good and go after the bad, and in this wise he came to Blois shortly after Francis the First had become king. Here he found Queen Claude and my Lady the Regent, (3) to whom he made his complaint, asking for her whom he would gladly not have found, but whom, to the great compassion of the whole company, he was now obliged to see.
3 This shows that the incidents of the tale occurred in the
summer or autumn of 1515, when Francis I. was absent in
Italy conducting the campaign which resulted in the victory
of Marignano and the surrender of Milan.—Ed.
When his wife was brought before him, she strove for a long while to maintain that he was not her husband, which he would willingly have believed had he been able. More disappointed than abashed, she told him that she would rather die than go back with him, and at this he was well pleased; but the ladies in whose presence she spoke in this unseemly fashion condemned her to return, and so rated the chanter with many a threat, that he was obliged to tell his ugly sweetheart to go back with her husband, and to declare that he himself would never see her more.
Rejected thus on all sides, the poor unfortunate withdrew to a home in which she was fated to meet with better treatment from her husband than she had deserved.
“You see, ladies, why I say that if the poor husband had been more watchful over his wife, he would not thus have lost her. A thing that is well guarded is difficult to lose, but heedlessness makes the thief.”
“‘Tis a strange thing,” said Hircan, “how strong love is just where it seems most unreasonable.”
“I have heard,” said Simontault, “that it were easier to break two marriages than to sunder the love of a priest and his serving-maid.”
“I believe it,” said Ennasuite; “for those who bind others together in marriage, are so well able to tie the knot that nought but death can destroy it. Theologians, moreover, hold that spiritual language is of more effect than any other, and in consequence spiritual love surpasses any other kind.”
“It is a thing that I cannot forgive in ladies,” said Dagoucin, “when they forsake an honourable husband or a lover for a priest, however handsome and worthy the latter may be.”
“I pray you, Dagoucin,” said Hircan, “intermeddle not with our Holy Mother Church. Be assured that ‘tis a great delight for timorous and secret-loving women to sin with those who can absolve them; for there are some who are more ashamed to confess a thing than to do it.”
“You speak,” said Oisille, “of those who have no knowledge of God, and who think not that secret matters are one day revealed in presence of the Company of Heaven. But I think that it is not for confession’s sake that they go after confessors; for the Enemy has so blinded them that they are more concerned to attach themselves where they think there is most concealment and security, than anxious to obtain absolution for the wickedness of which they do not repent.”
“Repent, say you?” said Saffredent. “Nay, they deem themselves holier than other women. I am sure that there are some who deem it honourable in themselves that they are constant in such love.”
“You speak in such a manner,” said Oisille to Saffredent, “that I think you know of some one of that kind. I pray you, therefore, begin the Day tomorrow by telling us what you know. But now the last bell for vespers is already ringing; for our friends the monks went off as soon as they had heard the tenth tale, and left us to finish our discussions among ourselves.”
At these words they all rose and came to the church, where they found the monks awaiting them. Then, after hearing vespers, they all supped together, talking the while of many excellent stories. After supper they went, according to their wont, to disport themselves somewhat in the meadow, and then retired to rest, in order that their memories might be the sounder on the morrow.

On the Seventh Day relation is made
of such as have done
quite contrary to
their duty
or desire.
In the morning the Lady Oisille failed not to administer to them wholesome nutriment, which she did by reading of the acts and virtuous deeds of the glorious knights and apostles of Jesus Christ, as related by St. Luke, telling them withal that these relations should suffice to make them long for the return of such a time, and to make them weep for the uncomeliness of this age as compared with that. When she had sufficiently read and expounded to them the beginning of this excellent book, she begged them to go to the church in such union as that in which the Apostles were wont to pray, seeking of God the mercy which is never refused to those who ask for it in faith. Her counsel was approved by all, and they came to the church just as the Mass of the Holy Spirit was beginning; this seemed to them very apt to the occasion, and they hearkened to the service in great devotion.
Afterwards they went to dinner, where they called to mind the apostolic life, and took such great delight in it that it was as though their undertaking had been forgotten. But Nomerfide, who was the youngest, noticed this, and said, “The Lady Oisille has made us so devout that we are letting slip the hour at which we are wont to withdraw, in order to make ready for the relating of our tales.”
Her words caused the whole company to rise, and, after they had been for a while in their rooms, they failed not to repair to the meadow as on the day before. When they were seated at their ease, the Lady Oisille said to Saffredent, “Although I am certain that you will say nothing to the advantage of women, yet I must call upon you to tell the tale that you had in readiness yester evening.”
“I protest, madam,” replied Saffredent, “against winning the repute of a slanderer through telling the truth, or losing the favour of virtuous ladies through relating the deeds of the wanton. I have felt what it is to lack their presence, and had I equally lacked their fair favours, I had not been alive to-day.”
So saying, he turned his eyes away from her who was the cause of his happiness and of his woe; and, looking upon Ennasuite, caused her to blush as deeply as though his words had been directed to her. Yet was he none the less understood by her whom he desired should understand him. The Lady Oisille then assured him that he might freely speak the truth at the cost of any person concerned; whereupon he thus began:—


A husband is reconciled with his wife after she had lived
during fourteen or fifteen years with a Canon of Autun.
Near the town of Autun there lived a very beautiful woman, who was tall, fair, and as handsome of feature as any I have ever seen. She was married to an honest man who seemed somewhat younger than herself, and who loved and treated her well enough to give her reason for content.
A little while after they were married, he took her to the town of Autun, where he had business; and while he was engaged with the law, his wife would go to the church to pray God for him.
She repaired so often to this holy place that a very rich Canon fell in love with her, and wooed her so urgently that the unhappy creature gave herself up to him. Her husband had no suspicion of this, however, for he gave more thought to the guarding of his property than of his wife.
When the time for departure was come, and they must needs return to their home, which was full seven leagues from the town, great was the woman’s sorrow. But the Canon promised that he would often go and see her, and this he did, pretending to be making some journey which led him past the house. The gentleman, however, was not so foolish as not to perceive the truth, and he so skilfully contrived matters, that when the Canon came thither he no longer met the wife, who was too well hidden by her husband to allow of his having any speech with her. The wife, knowing her husband’s jealousy, gave no sign that this was displeasing to her; nevertheless, she resolved to set things to rights, for she felt herself as it were in hell, deprived as she was of the sight of her God.
One day, when her husband was abroad, she found a means to occupy her servants, both men and women, after such a fashion that she was left alone in the house. Immediately, she took what was needful, and, with no company save that of the wanton love she carried with her, she repaired on foot to Autun. Here she arrived none too late to be recognised by her Canon, who kept her shut up in hiding for more than a year, and this in spite of the monitions and excommunications that were procured against him by her husband.
The latter, finding that he had no other remedy, at last complained to the Bishop, who had an Archdeacon, as worthy a man as any at that time in France. This Archdeacon himself searched with great diligence through all the Canon’s houses, until he discovered the one in which the woman was being kept in concealment, whereupon he cast her into prison, and laid heavy penance upon the Canon.
The husband, knowing that his wife had been recovered by the counsels of the Archdeacon and divers other excellent persons, was content to take her back on her swearing to him that she would live for the future as beseemed a virtuous woman.
This the worthy man in his deep love for her readily believed, and, bringing her back to his house, he treated her as honourably as before, except that he gave her two old serving-women who never left her, one or other of them being at all times with her.
But, however kindly her husband might use her, the wicked love she bore towards the Canon caused her to regard all rest as torment. And although she was a very beautiful woman and her husband a man of excellent constitution, vigorous and strong, she never had any children by him, her heart being always seven leagues away from her body; this, however, she concealed so well that it seemed to her husband that, like himself, she had wholly forgotten the past.
But in her great wickedness she was not so minded; for, just when she saw her husband most in love with her and having least suspicion, she pretended to fall ill, and continued in this pretence until her husband was in wondrous distress, and anxious to spare nought that might relieve her.
However, she played her part so exceedingly well that he, and all in the house, thought that she was sick unto death, and was growing by degrees weaker and weaker. Finding that her husband was no less grieved than he should have been glad, she begged of him that he would authorise her to make her will, and this with tears he did.
Having power of bequest, although she had no children, she gave to her husband what she could, craving at the same time his forgiveness for her wrong-doing towards him. Then she sent for the priest, confessed herself, and received the Holy Sacrament of the Altar with such devoutness, that all wept to see so glorious an end.
When the evening was come, she begged her husband to send for the extreme unction, saying that, as she was growing very weak, she was in fear lest she might not live to receive it. Her husband in all haste caused it to be brought by the priest, and she, by receiving it with very great humility, prompted every one to praise her.
After she had got through her brave mysteries, she told her husband that, having through God’s grace received all that the Church commands, she felt great peace of conscience, and would fain take some rest; and she begged him to do the like, seeing that he had great need of it after all his weeping and watching with her.
When her husband was gone, and all his servants with him, the poor old women, who had so long watched her in health and now had no fear of losing her except by death, went contentedly and comfortably to bed. As soon as she heard them asleep and loudly snoring, she rose in nothing but her shift, and went out of the room, listening to hear if any one was yet astir in the house. Taking every precaution, she then (as she well knew how) let herself out through a little garden-gate that was not shut, and, barefooted and in her shift, journeyed all night long towards Autun and the saint, who had preserved her from death.
It happened, however, that as the distance was great, she could not accomplish the whole of it before daylight overtook her. Looking then all along the road, she perceived two horsemen who were galloping at full speed, and thinking that it might be her husband in search of her, she hid herself entirely in a marsh, with her head among the reeds. As her husband (for he it was) passed close beside her, he spoke to a servant who was with him, in tones of deep despair, saying—
“Ah, the wicked woman! Who could have thought that so foul and abominable a deed could be hidden under cloak of the holy sacraments of the Church.”
“If Judas,” replied the servant, “feared not to betray his Master when he was receiving the like, a woman’s treachery is but small matter for wonder.”
At this point the husband passed on, and his wife remained among the rushes, in greater gladness at having deceived and escaped him than she had ever felt at home in a good bed but in subjection.
The poor husband sought her through all the town of Autun, but learning for certain that she had not entered it, he retraced his steps, complaining unceasingly of her and of his loss, and threatening her with nothing short of death if he should find her. Of this she had as little fear in her mind as she had of cold in her body, although the place and season might well have caused her to repent of her evil journey. And any one who did not know how the fire of hell inflames those that are filled with it, must needs wonder how it was that this unhappy woman could so leave a warm bed and continue for a whole day in the piercing cold.
Yet she neither lost courage nor gave up the journey, but, as soon as night was come, went forward once more. Just as the gate at Autun was being closed, this pilgrim arrived thither and repaired straight to the shrine of her saint, who was in great wonder at her coming, and could scarcely believe that it was indeed she. But when he had carefully looked at her and examined her at all points, he found that, unlike a spirit, she was really possessed of bone and flesh, and so became convinced that she was no ghost.
And thenceforward they agreed so well together that she dwelt with the Canon for fourteen or fifteen years.
Although for a time she lived in concealment, in the end she lost all fear, and (what is worse) became so exceedingly proud of her lover that at church she would set herself before most of the honourable women of the town, wives of officials and others. Moreover, she had children by the Canon, and among others a daughter who was married to a rich merchant, and who had so magnificent a wedding that all the women of the town murmured exceedingly, yet were powerless to set the affair to rights.
Now it happened that at this time Queen Claude, wife of King Francis, passed through the town of Autun, having with her my Lady the Regent, mother of the King aforesaid, and the Duchess of Alençon, her daughter. (1) One of the Queen’s waiting-women, named Perrette, came to the Duchess and said—
“Madam, I pray you listen to me, and you will do a better deed than if you went to hear the whole day’s service at the church.”
1 This would have occurred in the late autumn of 1515, when
the Court journeyed southward to meet Francis I. on his
return from the Marignano campaign.—Ed.
The Duchess gave ready heed, knowing that nought but good counsel could come from her. Then Perrette forthwith told her how she had taken a young girl to help her in washing the Queen’s linen, and how, on asking the news of the town, she had heard from her the vexation which all the honourable women endured at seeing the Canon’s mistress go before them, together with some of the history of the wicked woman’s life.
The Duchess went immediately to the Queen and my Lady the Regent, and told them the story; and they, without any form of law, sent for the unhappy woman. The latter sought no concealment, for her shame was turned to pride at being mistress in the household of so rich a man; and hence, with no feeling of confusion or disgrace, she presented herself before the ladies aforesaid, who were so abashed by her hardihood that at first they knew not what to say. After a time, however, my Lady the Regent rebuked her in a fashion which would have made a right-thinking woman weep, though this unhappy creature did not do so, but with great boldness said—
“I pray you, ladies, let my honour go unscathed, for, God be praised, I have lived so well and virtuously with the Canon that no person alive can say aught against me. And let it not be thought that I am living in opposition to the will of God, since, for three years past, the Canon has not come near me, and we live together as chastely and as lovingly as two little angels, without any speech or wish between us to the contrary. And any one separating us will commit a great sin, for the worthy man, who is nigh eighty years old, will not live long without me, who am forty-five.”
You may imagine how the ladies then comported themselves, and what remonstrance they all made with her; but, in spite of the words that were spoken, and her own age, and the honourable indignation of those present, her obstinacy was not softened. That she might be the more effectually humbled, they sent for the good Archdeacon of Autun, and he condemned her to lie in prison for a year, faring on bread and water. The ladies further sent for her husband, and he, after hearing their excellent exhortations, was content to take her back again after she should have performed her penance.
But when she found that she was a prisoner, and that the Canon was resolved to have her back no more, she thanked the ladies for having taken a devil off her shoulders, and showed such deep and perfect contrition that her husband, instead of waiting until the year should have expired, came and asked her of the Archdeacon before a fortnight was over; and since then they have lived together in all peace and affection.
“You see, ladies, how the chains of St. Peter are by wicked ministers converted into those of Satan, which it is so hard to break that even the sacraments, which cast out devils from the body, are here the means of making them abide longer in the conscience; for the best things, when abused, bring about most evil.”
“Truly,” said Oisille, “this woman was a very wicked one, but at the same time she was well punished by her appearance before such judges as the ladies you have named. The mere glance of the Lady Regent had such power that never was there a woman, however virtuous, that did not dread being found unworthy in her sight. Those who were looked upon kindly by her deemed that they had earned a high honour, knowing as they did that none but virtuous women were favoured by her.” (2)
2 We are asked to believe that Oisille is none other than
the Lady Regent (Louise of Savoy), but is it likely she
would thus speak of herself? We can scarcely conceive Queen
Margaret perpetrating such a flagrant anachronism.—Ed.
“It were indeed a fine thing,” said Hircan, “that there should be greater dread of a woman’s eyes than of the Holy Sacrament, which, if it be not received in faith and charity, brings with it eternal damnation.”
“Those,” said Parlamente, “who are not inspired by God are, I promise you, in greater dread of the temporal than of the spiritual powers. And I believe that the poor creature was brought to mend her ways rather by her imprisonment and the thought of seeing her Canon no more, than by any remonstrance that might have been made to her.”
“Nay,” said Simontault, “you have forgotten the chief cause of her return to her husband, which was that the Canon was eighty years old, whilst her husband was younger than herself; so the worthy lady had the best of all her bargains. Had the Canon been young, she would not have been willing to forsake him, and the admonitions of the ladies would have been as ineffectual as the sacraments.”
“Further,” said Nomerfide, “I think she did well not to confess her sin so readily; such an offence ought to be humbly acknowledged to God, but stoutly denied before men. Even though it be true, still, by deception and swearing, doubt may be cast upon it.”
“Not so,” said Longarine. “A sin can scarcely be so secret that it will not become revealed, unless God in His pity conceal it, as in the case of those who for love of Himself have truly repented.”
“And what,” said Hircan, “will you say of those women who have no sooner done a deed of folly than they tell some one about it?”
“I think that a strange thing,” answered Longarine, “and a sign that sin is not displeasing to them. If, as I said, a sin is not covered by the mercy of God, it cannot be denied before men; there are many who, delighting in such talk, glory to make their vices known, whilst others who contradict themselves in this way become their own accusers.”
“If you know any such instance,” said Saffredent, “I give you my place and beg you to tell it us.”
“Listen then,” said Longarine.



A lady’s tongue tripped so awkwardly whilst she was telling
a story, as if of another, to a dame of high degree, that
her honour thenceforward bore a stain which she could never
remove.
In the time of King Francis the First there lived a lady of the blood royal, who was endowed with honour, virtue and beauty, and well knew how to tell a story with grace and to laugh at such as might be told to her. (1) This lady being at one of her houses, all her subjects and neighbours came to see her; for she was as much liked as it were possible for woman to be.
1 M. de Lincy thinks that this lady may be Louise of Savoy,
who was very fond of listening to stories of an equivocal
character. This, it may be pointed out, is one of the
reasons why the commentators of the Heptameron suppose her
to be Oisille, though the latter in the conversational
passages following the tales displays considerable prudery
and devoutness. That Louise was a woman of extremely amorous
tendency is well known; we need, indeed, no better proof of
it than her unseemly passion for the Constable de Bourbon
when she was five-and-forty years of age. If she be the lady
of royal blood spoken of above, the incidents of the tale
may have occurred in the Bourbonnais, a considerable portion
of which passed into her hands after the flight of the
Constable from France. It will be noted that allusion is
made to the lady’s subjects, showing that she exercised a
feudal sway. As one of the commentators of the Heptameron
has pointed out, Queen Margaret always saw her mother—that
“donna terribilissima!” as De Lussy called her—in such an
ideal light that M. de Lincy’s surmise may well be a correct
one despite the attributes of honour, virtue and beauty
bestowed on the lady whom she speaks of.—Ed.
Among others there came a lady who hearkened whilst the rest told every story they could think of in order to amuse the Princess. This lady then resolved that she would not be behind the others, and accordingly said—
“Madam, I will tell you a fine story, but you must promise me not to speak of it.”
Then she forthwith continued—
“The story, madam, is on my conscience a perfectly true one, and concerns a married lady who lived in all honour with her husband, although he was old and she was young. A gentleman who was her neighbour, seeing her married to this old man, fell in love with her, and importuned her for several years; but never received of her any reply save such as a virtuous woman should make. One day the gentleman bethought him that if he could take her at a disadvantage she might perchance be less harsh towards him, and, after he had for a long while weighed the danger that he might run, his love for the lady wholly banished his fears, and he resolved to find a time and place. He kept excellent watch, and so one morning, when the lady’s husband was going to another of his houses, and leaving at daybreak by reason of the heat, the young gallant came to the house, where he found the lady asleep in her bed, and perceived that the serving-women were gone out of the room.
“Then, without having sense enough to fasten the door, he got into the lady’s bed all booted and spurred as he was, and when she awoke, she was as distressed as she could possibly be. But in spite of any remonstrance that she could make to him, he took her by force, saying that if she should make the matter known he would tell every one that she had sent for him; and at this the lady was so greatly afraid that she durst not cry out. Afterwards, on some of her women coming in, he rose in haste and would have been perceived by none if his spur, which had become fastened in the upper sheet, had not drawn it right off, leaving the lady quite naked in her bed.”
So far the lady had told the story as if of another, but at the end she involuntarily said—
“Never was a woman so confounded as I was, when I found myself lying quite naked.”
At these last words the lady, who had hitherto hearkened to the story without laughing, could not refrain from doing so, and said—
“By what I can see, you are well qualified to tell the tale.”
The poor lady tried in every possible way to clear her honour, but it was already flown so far away that she was never able to recall it.
“I assure you, ladies, that had she felt any deep displeasure in doing such a deed, she would have desired to forget it. But, as I have told you, sin will of itself be discovered before it could otherwise be known, unless it be hidden by the mantle which, as David says, makes man blessed.”
“In good sooth,” said Ennasuite, “she was the greatest fool I have ever heard of, to make the others laugh at her own expense.”
“I do not deem it strange,” said Parlamente, “that the word should follow the deed, for it is easier to say than to do.”
“Why,” said Geburon, “what sin had she committed? She was asleep in her bed, he threatened her with shame and death; Lucrèce, who is so highly praised, did just the same.”
“That is true,” said Parlamente, “and I confess that there is none too righteous to fall. But when one has felt great offence in the deed, the same holds good of the recollection; and whereas Lucrèce to efface the latter killed herself, this foolish woman tried to make others laugh.”
“Nevertheless,” said Nomerfide, “it seems that she was a virtuous woman, seeing that she had been many times entreated but would never consent, so that the gentleman must needs resort to treachery and force in order to wrong her.”
“What!” said Parlamente. “Do you think that a woman has answered for her honour, when she gives herself up after refusing two or three times? There would then be many virtuous women among those that are deemed the opposite, for many of them have been known to refuse for a long while those to whom their hearts had been given, some doing this through fear for their honour, and others in order to make themselves still more ardently loved and esteemed. No account, therefore, should be made of a woman unless she stands firm to the end. But if a man refuse a beautiful girl, do you regard that as great virtue?”
“Truly,” said Oisille, “if a young and lusty man so refused, I should hold it worthy of high praise, but none the less difficult of belief.”
“Yet,” said Dagoucin, “I know one who refused to partake in amours that were sought after by all his comrades.”
“I pray you,” said Longarine, “take my place and tell us the tale, yet remember that you must here utter the truth.”
“I promise you,” said Dagoucin, “that I will tell it in all its simplicity, without any colouring or disguise.”



A gentleman’s refusal of an amour that was sought after by
all his comrades, was imputed to him as great virtue, and
his wife loved him and esteemed him in consequence far more
than before. (1)
In the city of Paris there lived four girls, of whom two were sisters, and such was their beauty, youth and freshness, that they were run after by all the gallants. A gentleman, however, who at that time held the office of Provost of Paris (2) from the King, seeing that his master was young, of an age to desire such company, so cleverly contrived matters with all four of the damsels that each, thinking herself intended for the King, agreed to what the aforesaid Provost desired. This was that they should all of them be present at a feast to which he invited his master.
1 This story, omitted by Boaistuau, was included in
Gruget’s edition of the Heptameron.—L.
2 This is John de la Barre, already alluded to in Tale I.
The Journal d’un Bourgeois de Paris tells us that he was
born in Paris of poor parents, and became a favourite of
Francis I., who appointed him Bailiff of the capital,
without requiring him to pay any of the dues attaching to
the office. From the roll of the royal household for 1522,
we also find that he was then a gentleman of the bed chamber
with 1200 livres salary, master of the wardrobe (a post
worth 200 livres) and governor of the pages, for the board
and clothing of whom he received 5000 livres annually. In
1526 he became Provost as well as Bailiff of Paris, the two
offices then being amalgamated. He was further created Count
of Etampes, and acquired the lordship of Veretz, best
remembered by its associations with the murder of Paul Louis
Courier. La Barre fought at Pavia, was taken prisoner with
the King, and remained his constant companion during his
captivity. Several letters of his, dating from this period
and of great historical interest, are still extant; some of
them have been published by Champollion-Figeac (Captivité
de François Ier) and Génin (Lettres de Marguerite, &c).
Under date 1533 (o. s.) the “Bourgeois de Paris” writes in
his Journal: “At the beginning of March there died in
Paris, at the house of Monsieur Poncher, Monsieur le Prévost
de Paris, named de La Barre.... The King was then in Paris,
at his chateau of the Louvre, and there was great pomp at
the obsequies; and he was borne to his lordship of Veretz,
near Tours, that he might be buried there.” Numerous
particulars concerning La Barre will also be found in M. de
Laborde’s Comptes des Bâtiments du Roi au XVIeme Siècle.—
L. and Ed.
He told the latter his plan, which was approved both by the Prince and by two other great personages of the Court, all three agreeing together to share in the spoil.
While they were looking for a fourth comrade, there arrived a handsome and honourable lord who was ten years younger than the others. He was invited to the banquet, but although he accepted with a cheerful countenance, in his heart he had no desire for it. For on the one part he had a wife who was the mother of handsome children, and with whom he lived in great happiness, and in such peacefulness that on no account would he have had her suspect evil of him. And on the other hand he was the lover of one of the handsomest ladies of her time in France, whom he loved and esteemed so greatly that all other women seemed to him ugly beside her.
In his early youth, before he was married, he had found it impossible to gaze upon and associate with other women, however beautiful they might be; for he took more delight in gazing upon his sweetheart, and in perfectly loving her, than in having all that another might have given him.
This lord, then, went to his wife and told her secretly of the enterprise that his master had in hand, saying that he would rather die than do what he had promised. For (he told her) just as there was no living man whom he would not venture to attack in anger, although he would rather die than commit a causeless and wilful murder unless his honour compelled him to it; even so, unless driven by extreme love, such as may serve to blind virtuous men, he would rather die than break his marriage vow to gratify another.
On hearing these words of his, and finding that so much honour dwelt in one so young, his wife loved and esteemed him more than she had ever done before, and inquired how he thought he might best excuse himself, since Princes often frown on those who do not praise what they like.
“I have always heard,” he replied, “that a wise man has a journey or a sickness in his sleeve for use in time of need. I have therefore resolved that I will feign a grievous sickness four or five days beforehand, and in this matter your countenance may render me true service.”
“Tis a worthy and holy hypocrisy,” said his wife, “and I will not fail to serve you with the saddest face I can command; for he who can avoid offending God and angering the Prince is fortunate indeed.”
As it was resolved, so was it done, and the King was very sorry to hear from the wife of her husband’s sickness. This, however, lasted no long time; for, on account of certain business which arose, the King disregarded his pleasure to attend to his duty, and betook himself away from Paris.
However, one day, remembering their unfinished undertaking, he said to the young lord:—
“We were very foolish to leave so suddenly without seeing the four girls who are declared to be the fairest in my kingdom.”
“I am very glad,” replied the young lord, “that you failed in the matter, for I was in great fear that, by reason of my sickness, I should be the only one to miss so pleasant an adventure.”
By reason of this answer the King never suspected the dissimulation of the young lord, who was thenceforward loved by his wife more dearly than he had ever been before.
Hereupon Parlamente began to laugh, and could not hold from saying—
“He would have loved his wife better if he had done this for love of her alone. But in any case he is worthy of great praise.”
“It seems to me,” said Hircan, “that it is no great merit in a man to keep his chastity for love of his wife, inasmuch as there are many reasons which in a manner compel him to do so. In the first place, God commands it; his marriage vow binds him to it, and, further, surfeited nature is not liable to temptation or desire as necessity is. But when the unfettered love that a man bears towards a mistress of whom he has no delight, and no other happiness save that of seeing her and speaking with her, and from whom he often receives harsh replies—when this love is so loyal and steadfast that nothing can ever make it change, I say that such chastity is not simply praiseworthy but miraculous.”
“‘Tis no miracle in my opinion,” said Oisille, “for when the heart is plighted, nothing is impossible to the body.”
“True,” said Hircan; “to bodies which have become those of angels.”
“I do not speak only of those,” said Oisille, “who by the grace of God are wholly transformed into Himself, but of the grosser spirits that we see here below among men. And, if you give heed, you will find that those who have set their hearts and affections upon seeking after the perfection of the sciences, have forgotten not only the lust of the flesh, but even the most needful matters, such as food and drink; for so long as the soul is stirred within the body, so long does the flesh continue as though insensible. Thence comes it that those who love handsome, honourable and virtuous women have such happiness of spirit in seeing them and speaking with them, that the flesh is lulled in all its desires. Those who cannot feel this happiness are the carnally-minded, who, wrapped in their exceeding fatness, cannot tell whether they have a soul or not. But, when the body is in subjection to the spirit, it is as though heedless of the failings of the flesh, and the beliefs of such persons may render them insensible of the same. I knew a gentleman who, to show that he loved his mistress more dearly than did any other man, proved it to all his comrades by holding his bare fingers in the flame of a candle. And then, with his eyes fixed upon his mistress, he remained firm until he had burned himself to the bone, and yet said that he had felt no hurt.”
“Methinks,” said Geburon, “that the devil whose martyr he was ought to have made a St. Lawrence of him; for there are few whose love-flame is hot enough to keep them from fearing that of the smallest taper. But if a lady had suffered me to endure so much hurt for her sake, I should either have sought a rich reward or else have taken my love away from her.”
“So,” said Parlamente, “you would have your hour after the lady had had hers? That was what was done by a gentleman of the neighbourhood of Valencia in Spain, whose story was told to me by a captain, a right worthy man.”
“I pray you, madam,” said Dagoucin, “take my place and tell it us, for I am sure that it must be a good one.”
“This story, ladies,” said Parlamente, “will teach you both to think twice when you are inclined to give a refusal and to lay aside the thought that the present will always continue; and so, knowing that it is subject to mutation, you will have a care for the time to come.”



After a lady had for the space of five or six years made
trial of the love that a certain gentleman bore her, she
desired to have a still stronger proof of it, and reduced
him to such despair that he turned monk, on which account
she was not able to win him back again when she would fain
have done so.
In the city of Valencia there lived a gentleman, who for the space of five or six years had loved a lady so perfectly that the honour and conscience of neither of them had taken any hurt; for his intent was to have her as his wife, and this was reasonable, seeing that he was handsome, rich and of good descent. But, before he became her lover, he first inquired concerning her own mind, whereupon she declared herself willing to marry according to the counsels of her kinsfolk. The latter, being come together for the purpose, deemed the marriage a very reasonable one provided that the maiden was herself disposed to it; but she—whether because she thought to do better or because she wished to hide her love for him—-made some difficulty, and the company separated, not without regret at having failed to conclude a match so well suited to both parties.
The most grieved of all was the poor gentleman, who would have borne his misfortune with patience had he thought that the fault lay with the kinsfolk and not with her; but he knew the truth, and the knowledge was to him worse than death. So, without speaking to his sweetheart or to any other person, he withdrew to his own house, and, after setting his affairs in order, betook himself to a solitary spot, where he strove to forget his love and change it wholly to that love of our Lord which were truly a higher duty than the other.
During this time he received no tidings of his mistress or her kindred, and he therefore resolved that, since he had failed to obtain the happiest life he could hope for, he would choose the most austere and disagreeable that he could imagine. With this sad intent, which might well have been called despair, he went and became a monk in the monastery of St. Francis. This monastery was not far from the dwellings of divers of his kinsfolk, who, on hearing of his desperate condition, did all that in them lay to hinder his purpose; but this was so firmly rooted in his heart that it was not possible to turn him from it.
Nevertheless, as the source of his distemper was known to them, they determined to seek the cure, and so repaired to her who was the cause of his sudden devoutness. She was greatly astonished and grieved by this mischance, for, in refusing for a time, she had thought only to test his affection, not to lose it for ever. Seeing now the evident risk that she ran of doing this last, she sent him a letter, which, ill-translated, was as follows:—
“Since love, if tested not full needfully,
Steadfast and faithful is not shown to be,
By length of time my heart would that assay
Whereon itself was set to love alway—
To wit, a husband with that true love filled
Such as no lapsing time has ever killed.
This, then, was the sole reason that I drew
My kin to hinder for a year or two
That closest tie which lasts till life is not,
And whereby woe is oftentimes begot.
Yet sought I not to have you wholly sent
Away; such was in no wise my intent,
For none save you could I have e’er adored
Or looked to as my husband and my lord.
But woe is me, what tidings reach mine ear!
That you, to lead the cloistered life austere,
Are gone with speech to none; whereat the pain
That ever holds me, now can brook no rein,
But forces me mine own estate to slight
For that which yours aforetime was of right;
To seek him out who once sought me alone,
And win him who myself has sometimes won.
Nay then, my love, life of the life in me,
For loss of whom I fain would cease to be,
Turn hither, graciously, those eyes of pain
And trace those wandering footsteps back again.
Leave the grey robe and its austerity,
Come back and taste of that felicity
Which often you desired, and which to-day
Time has nor slain, nor swept away.
For you alone I’ve kept myself; and I,
Lacking your presence, cannot choose but die.
Come back then; in your sweetheart have belief,
And for past memories find cool relief
In holy marriage-ties. Ah! then, my dear,
To me, not to your pride give ready ear,
And rest of this assured, I had no thought
To give, sweetheart, to you offence in aught,
But only yearned your faithfulness to prove
And then to make you happy with my love.
But now that through this trial, free from scathe,
Are come your steadfastness and patient faith,
And all that loyal love to me is known,
Which at the last has made me yours alone,
Come, my beloved, take what is your due
And wholly yield to me, as I to you!”
This letter, brought by a friend of hers with every remonstrance that it was possible to make, was received and read by the gentleman friar with such sadness of countenance, such sighs and such tears, that it seemed as though he would drown and burn the poor epistle. But he made no reply to it, except to tell the messenger that the mortification of his exceeding passion had cost him so dear as to have taken from him both the wish to live and the fear to die. He therefore requested her who had been the cause of this, that since she had not chosen to satisfy his passionate longings, she would, now that he was rid of them, abstain from tormenting him, and rest content with the evil which was past. For that evil he could find no remedy but the choice of an austere life, which by continual penance might bring him to forget his grief, and, by fasts and disciplines, subdue his body, till the thought of death should be to him but a sovereign consolation. Above all, he begged that he might never hear of her, since he found the mere remembrance of her name a purgatory not to be endured.
The gentleman went back with this mournful reply, and reported it to the maiden who did not hear it without intolerable sorrow. But Love, which will not suffer the spirit utterly to fail, gave her the thought that, if she could see him, her words and presence might be of more effect than the writing. She therefore, with her father and the nearest of her kin, went to the monastery where he abode. She had left nothing in her box that might set off her beauty, for she felt sure that, could he but once look at her and hear her, the fire that had so long dwelt in both their hearts must of necessity be kindled again in greater strength than before.
Coming thus into the monastery towards the end of vespers, she sent for him to come to her in a chapel that was in the cloister. He, knowing not who it was that sought him, went in all ignorance to the sternest battle in which he had ever been. When she saw him so pale and wan that she could hardly recognise him, yet filled with grace, in no whit less winning than of yore, Love made her stretch out her arms to embrace him, whilst her pity at seeing him in such a plight so enfeebled her heart, that she sank swooning to the floor.
The poor monk, who was not void of brotherly charity, lifted her up and set her upon a seat in the chapel. Although he had no less need of aid than she had, he feigned to be unaware of her passion, and so strengthened his heart in the love of God against the opportunities now present with him, that, judging by his countenance, he seemed not to know what was actually before him. Having recovered from her weakness, she turned upon him her beautiful, piteous eyes, which were enough to soften a rock, and began to utter all such discourse as she believed apt to draw him from the place in which he now was. He replied as virtuously as he was able; but at last, finding that his heart was being softened by his sweetheart’s abundant tears, and perceiving that Love, the cruel archer whose pains he long had known, was ready with his golden dart to deal him fresh and more deadly wounds, he fled both from Love and from his sweetheart, like one whose only resource lay, indeed, in flight.
When he was shut up in his room, not desiring to let her go without some settlement of the matter, he wrote her a few words in Spanish, which seem to me so excellent in their matter that I would not by translating them mar their grace. These were brought to her by a little novice, who found her still in the chapel and in such despair that, had it been lawful, she too would have remained there and turned friar. But when she saw the words, which were these—
“Volvete don venesti, anima mia,
Que en las tristas vidas es la mia,” (1)
she knew that all hope was gone, and she resolved to follow the advice of him and her friends, and so returned home, there to lead a life as melancholy as that of her lover in his monastery was austere.
1 “Return whence thou earnest, my soul,
for among the sad lives is mine.”’
“You see, ladies, what vengeance the gentleman took upon his harsh sweetheart, who, thinking to try him, reduced him to such despair that, when she would have regained him, she could not do so.”
“I am sorry,” said Nomerfide, “that he did not lay aside his gown and marry her. It would, I think, have been a perfect marriage.”
“In good sooth,” said Simontault, “I think he was very wise. Anyone who well considers what marriage is will deem it no less grievous than a monkish life. Moreover, being so greatly weakened by fasts and abstinence, he feared to take upon him a burden of that kind which lasts all through life.”
“Methinks,” said Hircan, “she wronged so feeble a man by tempting him to marriage, for ‘tis too much for the strongest man alive; but had she spoken to him of love, free from any obligation but that of the will, there is no friar’s cord that would not have been untied. However, since she sought to draw him out of purgatory by offering him hell, I think that he was quite right to refuse her, and to let her feel the pain that her own refusal had cost him.”
“By my word,” said Ennasuite, “there are many who, thinking to do better than their fellows, do either worse or else the very opposite of what they desire.”
“Truly,” said Geburon, “you remind me—though, indeed, the matter is not greatly to the point—of a woman who did the opposite of what she desired, and so caused a great uproar in the church of St. John of Lyons.”
“I pray you,” said Parlamente, “take my place and tell us about it.”
“My story,” said Geburon, “will not be so long or so piteous as the one we have heard from Parlamente.”



Though the priests of St. John of Lyons would fain have
concealed it, the falsity of a miracle was brought to light
through an old woman’s folly becoming known. (1)
In the church of St. John of Lyons there is a very dark chapel, and inside it a stone tomb with figures of great personages raised life-like upon it, whilst several men-at-arms lie all around it.
1 We believe that the incident here narrated occurred early
in 1525, when Margaret is known to have been at Lyons. She
and her husband (on his return from Pavia) resided there at
the house of the Obédiencier de St. Just, and it was in the
church of St. Just that the Duke of Alençon was buried.
Doubtless it was during his illness that the novena
alluded to in the final tale of the Heptameron was
performed by Queen Margaret at the church of St. John of
Lyons, where the two most important chapels, according to
Quincarnon’s Antiquités et la fondation de la Métropole
des Gaules, &c., Lyons, 1673, were the Most Holy Eucharist,
or Bourbon chapel, built in 1449 by Charles de Bourbon,
Primate of Gaul, and the Holy Sepulchre, or Good Friday
chapel, erected at the beginning of the fifteenth century by
Philip de Turey, Archbishop of Lyons. Unfortunately the
church of St. John was in 1652 devastated by the Huguenots,
who in their insensate fury destroyed almost all the tombs.
It is therefore now impossible to identify the chapel and
tomb to which the Queen of Navarre refers in the above
story, though her allusion to the dimness of the light would
incline us to place the incident she recounts in the
Chapelle du St. Sépulcre.—L. and Ed.
One day a soldier, walking in the church at the very height of summer, felt inclined to sleep, and, looking at this dark, cool chapel, resolved to go and guard the tomb in sleep like the rest; (2) and accordingly he lay down beside them. Now it chanced that a very pious old woman came in while his sleep was the soundest, and having performed her devotions, holding a lighted taper in her hand, she sought to fix this taper to the tomb. Finding that the sleeping man was nearest to her, she tried to set it upon his forehead, thinking that it was of stone; but the wax would not stick to such stone as this, whereupon the worthy dame, believing that the reason of it was the coldness of the statue, applied the flame to the sleeper’s forehead, that she might the better fix the taper on it. At this, however, the statue, which was not without feeling, began to cry out.
2 Meaning the recumbent statues of the men-at-arms.—Ed.
The good woman was then in exceeding fear, and set herself to shout, “A miracle! a miracle!” until all who were in the church ran, some to ring the bells, and the rest to view the miracle. The good woman forthwith took them to see the statue that had stirred, whereupon many found food for laughter; though the greater number were unable to feel any content, inasmuch as they had really determined to make profit out of the tomb, and to gain as much money by it as by the crucifix on their pulpit, which is said to have spoken. (3) But when the woman’s folly became known the farce came to an end. If all knew of their follies, they would not be accounted holy nor their miracles true. And I would beg you, ladies, to see henceforward to what saints you offer your candles. (4)
3 The crucifix in the church of St. John was mainly of
silver, and, according to Quincarnon, at the time of a
Huguenot outbreak at Lyons it was thrown to the ground by a
Calvinist minister named Ruffy, who, after reducing it to
fragments, carried all the precious metal away with him.—M.
4 The latter portion of this story and all the dialogue
that follows it are omitted by Boaistuau in his edition.
Gruget inserted the dialogue, but he did not dare to print
the passage respecting the talking crucifix.—L.
“‘Tis notable,” said Hircan, “that, whatever the matter in question may be, women always do wrong.”
“Is it wrong,” asked Nomerfide, “to bring candles to a tomb?”
“Yes,” said Hircan, “if the flame be turned against a man’s forehead; for nothing good should be called good if it be attended with evil. You may be sure that the poor woman thought she had made a fine gift to God with her little candle.”
“I look not to the gift,” said Oisille, “but to the heart that offers it. Perhaps this worthy woman had more love for God than those who offer great torches; for, as the Gospel says, she gave of her need.”
“Still, I no not believe,” said Saffredent, “that God, who is sovereign wisdom, can be pleased with the foolishness of women. Although simplicity is pleasing to Him, I see from the Scriptures that He despises the ignorant; and if He commands us to be as harmless as the dove, He none the less commands us to be wise like the serpent.”
“For my part,” said Oisille, “I do not call the woman ignorant who brings her candle or burning taper into the presence of God, and makes amends for her wrongdoing on bended knees before her sovereign Lord, confessing her unworthiness and with steadfast hope seeking pity and salvation.”
“Would to God,” said Dagoucin, “that all understood it in the same way as you; but I do not believe that these poor fools do it with the intent you say.”
“The women,” said Oisille, “who are least able to speak are just those who are most sensible of the love and will of God; wherefore ‘tis well to judge none but ourselves.”
Ennasuite laughed and said—“‘Tis no wonderful thing to have frightened a sleeping varlet, since women of as lowly condition have frightened noble Princes, without putting fire to their foreheads.”
“I am sure,” said Geburon, “that you know some such story, which you are willing to relate; wherefore, if it please you, you shall take my place.”
“The tale will not be a long one,” said Ennasuite, “but, could I recount it just as it happened, you would have no desire to weep.”



The Duke of Vendôme and the Princess of Navarre, whilst
resting together one afternoon, were surprised by an old
serving-woman, who took them for a prothonotary and a damsel
between whom she suspected some affection; and, through this
fine justicement, a matter, of which intimates were
ignorant, was made known to strangers.
In the year when the Duke of Vendôme married the Princess of Navarre, (1) the King and Queen, their parents, after feasting at Vendôme, went with them into Guienne, and, visiting a gentleman’s house where there were many honourable and beautiful ladies, the newly married pair danced so long in this excellent company that they became weary, and, withdrawing to their chamber, lay down in their clothes upon the bed and fell asleep, doors and windows being shut and none remaining with them.
1 It was in October 1548, some eighteen months after Henry
II. had succeeded Francis I., that Anthony de Bourbon, Duke
of Vendôme, who after the King’s children held the first
rank in France, was married at Moulins to Margaret’s
daughter Jane of Navarre. The Duke was then thirty and Jane
twenty years old. “I never saw so joyous a bride,” wrote
Henry II. to Montmorency, “she never does anything but
laugh.” She was indeed well pleased with the match, the
better so, perhaps, as her husband had settled 100,000
livres on her, a gift which was the more acceptable by
reason of her extravagant tastes and love of display. Ste.
Marthe, in his Oraison Funèbre on Queen Margaret, speaks
of her daughter’s marriage as “a most fortunate
conjunction,” and refers to her son-in-law as “the most
valiant and magnanimous Prince Anthony, Duke of Vendôme,
whose admirable virtues have so inclined all France to love
and revere him, that princes and nobles, the populace, the
great and the humble alike, no sooner hear his name
mentioned than they forthwith wish him and beg God to bestow
on him all possible health and prosperity.”—Ed
Just, however, when their sleep was at its soundest, they were awakened by their door being opened from without, and the Duke drew the curtain and looked to see who it might be, suspecting indeed that it was one of his friends who was minded to surprise him. But he perceived a tall, old bed-chamber woman come in and walk straight up to their bed, where, for the darkness of the room, she could not recognise them. Seeing them, however, quite close together, she began to cry out—
“Thou vile and naughty wanton! I have long suspected thee to be what thou art, yet for lack of proof spoke not of it to my mistress. But now thy vileness is so clearly shown that I shall in no sort conceal it; and thou, foul renegade, who hast wrought such shame in this house by the undoing of this poor wench, if it were not for the fear of God, I would e’en cudgel thee where thou liest. Get up, in the devil’s name, get up, for methinks even now thou hast no shame.”
The Duke of Vendôme and the Princess hid their faces against each other in order to have the talk last longer, and they laughed so heartily that they were not able to utter a word. Finding that for all her threats they were not willing to rise, the serving-woman came closer in order to pull them by the arms. Then she at once perceived both from their faces and from their dress that they were not those whom she sought, and, recognising them, she flung herself upon her knees, begging them to pardon her error in thus robbing them of their rest.
But the Duke of Vendôme was not content to know so little, and rising forthwith, he begged the old woman to say for whom she had taken them. This at first she was not willing to do; but at last, after he had sworn to her never to reveal it, she told him that there was a girl in the house with whom a prothonotary (2) was in love, and that she had long kept a watch on them, since it pleased her little to see her mistress trusting in a man who was working this shame towards her. She then left the Prince and Princess shut in as she had found them, and they laughed for a long while over their adventure. And, although they afterwards told the story they would never name any of the persons concerned.
2 The office of apostolic prothonotary was instituted by
Pope Clement I., there being at first twelve such officers,
whose duty was to write the lives of the saints and other
apostolic records. Gradually their number so increased, that
in the fifteenth century the title of prothonotary had come
to be merely an honorary dignity, conferred as a matter of
course on doctors of theology of noble family, or otherwise
of note. In the role of Francis I.‘s household for 1522, we
find but one prothonotary mentioned, but in that for 1529
there are twelve. More than one of them might have been
called un letrado que no tenia muchas letras, as Brantôme
wrote of Thomas de Lescun, Prothonotary of Foix and
afterwards Marshal of France. “In those days,” adds the
author of Les Grands Capitaines Français, “it was usual
for prothonotaries and even for those of good family not to
have much learning, but to enjoy themselves, hunt, make love
and seduce the wives of the poor gentlemen who were gone to
the wars.”—OEuvres complètes de Brantôme, 8vo edit., vol.
ii. p. 144.—L. and Ed.
“You see, ladies, how the worthy dame, whilst thinking to do a fine deed of justice, made known to strange princes a matter of which the servants of the house had never heard.”
“I think I know,” said Parlamente, “in whose house it was, and who the prothonotary is; for he has governed many a lady’s house, and when he cannot win the mistress’s favour he never fails to have that of one of the maids. In other matters, however, he is an honourable and worthy man.”
“Why do you say ‘in other matters’?” said Hircan. “Tis for that very behaviour that I deem him so worthy a man.”
“I can see,” said Parlamente, “that you know the sickness and the sufferer, and that, if he needed excuse, you would not fail him as advocate. Yet I would not trust myself to a man who could not contrive his affairs without having them known to the serving-women.”
“And do you imagine,” said Nomerfide, “that men care whether such a matter be known if only they can compass their end? You may be sure that, even if none spoke of it but themselves, it would still of necessity be known.”
“They have no need,” said Hircan angrily, “to say all that they know.”
“Perhaps,” she replied, blushing, “they would not say it to their own advantage.”
“Judging from your words,” said Simontault, “it would seem that men delight in hearing evil spoken about women, and I am sure that you reckon me among men of that kind. I therefore greatly wish to speak well of one of your sex, in order that I may not be held a slanderer by all the rest.”
“I give you my place,” said Ennasuite, “praying you withal to control your natural disposition, so that you may acquit yourself worthily in our honour.”
Forthwith Simontault began—
“Tis no new thing, ladies, to hear of some virtuous act on your part which, methinks, should not be hidden but rather written in letters of gold, that it may serve women as an example, and give men cause for admiration at seeing in the weaker sex that from which weakness is prone to shrink. I am prompted, therefore, to relate something that I heard from Captain Robertval and divers of his company.”



A poor woman risked her own life to save that of her
husband, whom she forsook not until death.
The Captain Robertval aforesaid once made a voyage across the seas to the island of Canadas, (1) himself being chief in command by the appointment of the King, his master. And there, if the air of the country were good, he had resolved to dwell and to build towns and castles. With this work he made such a beginning as is known to all; and to people the country with Christians he took with him all kinds of artificers, among whom was a most wicked man, who betrayed his master and put him in danger of being captured by the natives. But God willed that his attempt should be discovered before any evil befell the Captain, who, seizing the wicked traitor, was minded to punish him as he deserved. And this he would have done but for the man’s wife, who had followed her husband through the perils of the deep and would not now leave him to die, but with many tears so wrought upon the Captain and all his company that, for pity of her and for the sake of the services she had done them, her request was granted. In consequence, husband and wife were left together on a small island in the sea, inhabited only by wild beasts, and were suffered to take with them such things as were needful.
1 Canada had been discovered by Cabot in 1497; and in 1535
James Cartier sailed up the St. Lawrence and, taking
possession of the country in the name of Francis I., called
it La Nouvelle France. Seven years later a gentleman of
Picardy, named John Francis de La Roque, Lord of Robertval,
accompanying Cartier, established a colony on the Isle
Royale, and subsequently built the fort of Charlebourg. One
of his pilots, named Alphonse of Saintonge, meanwhile
reconnoitred the coasts both of Canada and Labrador. About
this time (1542) the incidents related in the above tale
must have occurred.—L.
The poor folk, finding themselves all alone and surrounded by wild and cruel beasts, had no recourse but to God, who had ever been this poor woman’s steadfast hope; and, since she found all her consolation in Him, she carried the New Testament with her for safeguard, nourishment and consolation, and in it read unceasingly. Further, she laboured with her husband to make them a little dwelling as best they might, and when the lions (2) and other animals came near to devour them, the husband with his arquebuss and she with stones made so stout a defence that not only were the beasts afraid to approach, but often some were slain that were very good for food. And on this flesh and the herbs of the land, they lived for some time after their bread failed them.
2 This mention of lions on a small desert island in the
Canadian seas would be rather perplexing did we not know how
great at that time was the general ignorance on most matters
connected with natural history. Possibly the allusion may be
to the lion marin, as the French call the leonine seal.
This, however, is anything but an aggressive animal.
Curiously enough, Florimond de Rémond, the sixteenth century
writer, speaks of a drawing of a “marine lion” given to him
“by that most illustrious lady Margaret Queen of Navarre, to
whom it had been presented by a Spanish gentleman, who was
taking a second copy of it to the Emperor Charles V., then
in Spain.”—Ed.
At last, however, the husband could no longer endure this nutriment, and by reason of the waters that they drank became so swollen that in a short while he died, and this without any service or consolation save from his wife, she being both his doctor and his confessor; and when he had joyously passed out of the desert into the heavenly country, the poor woman, left now in solitude, buried him in the earth as deeply as she was able. Nevertheless the beasts quickly knew of it, and came to eat the dead body; but the poor woman, firing with the arquebuss from her cabin, saved her husband’s flesh from finding such a grave.
Leading thus in regard to her body the life of a brute, and in regard to her soul the life of an angel, she passed her time in reading, meditations, prayers and orisons, having a glad and happy mind in a wasted and half-dead body. But He who never forsakes His own, and who manifests His power when others are in despair, did not suffer the virtue that he had put into this woman to be unknown by men, but willed that it should be made manifest to His own glory. He therefore brought things so to pass, that after some time, when one of the ships of the armament was passing by the island, those that were looking that way perceived some smoke, which reminded them of the persons who had been left there, and they resolved to go and see what God had done with them.
The poor woman, seeing the ship draw nigh, dragged herself to the shore, and there they found her on their arrival. After giving praise to God, she brought them to her poor cottage and showed them on what she had lived during her abode in that place. This would have seemed to them impossible of belief, but for their knowledge that God is as powerful to feed His servants in a desert as at the greatest banquet in the world. As the poor woman could not continue in such a spot, they took her with them straight to La Rochelle, where, their voyage ended, they arrived. And when they had made known to the inhabitants the faithfulness and endurance of this woman, she was very honourably received by all the ladies, who gladly sent their daughters to her to learn to read and write. In this honest calling she maintained herself for the rest of her life, having no other desire save to admonish every one to love and trust Our Lord, and setting forth as an example the great compassion that He had shown towards her.
“Now, ladies, you cannot say I do not praise the virtues which God has given you, and which show the more when possessed by one of lowly condition.”
“Why, we are not sorry,” said Oisille, “to hear you praise the mercies of Our Lord, for in truth all virtue comes from Him; but we must confess that man assists in the work of God as little as women. Neither can by heart or will do more than plant. God alone giveth the increase.”
“If you have studied Scripture,” said Saffredent, “you know that St. Paul says that Apollos planted and he himself watered; (3) but he does not speak of women as having set hand to the work of God.”
3 The text is just the contrary: “I have planted, Apollos
watered; but God gave the increase.”—I Corinthians iii.
6.—Ed.
“You would follow,” said Parlamente, “the opinion of those wicked men who take a passage of Scripture that is in their favour and leave one that is against them. If you had read St. Paul to the end, you would have found that he commends himself to the ladies, who greatly laboured with him in the work of the Gospel.”
“However that may be,” said Longarine, “the woman in the story is well worthy of praise both for the love she bore her husband, on whose behalf she risked her own life, and for the faith she had in God, who, as we see, did not forsake her.”
“I think,” said Ennasuite, “as far as the first is concerned, that there is no woman present but would do as much to save her husband’s life.”
“I think,” said Parlamente, “that some husbands are such brutes that the women who live with them should not find it strange to live among their fellows.”
Ennasuite, who took these words to herself, could not refrain from saying—
“Provided the beasts did not bite me, their company would be more pleasant to me than that of men, who are choleric and intolerable. But I abide by what I have said, that, if my husband were in a like danger, I should not leave him to die.”
“Beware,” said Nomerfide, “of loving too fondly, for excess of love will deceive both him and you. There is a medium in all things, and through lack of knowledge love often gives birth to hate.”
“Methinks,” said Simontault, “you have not carried your discourse so far without having an instance to confirm it. If, then, you know such a one, I give you my place that you may tell it to us.”
“Well,” said Nomerfide, “the tale shall, as is my wont, be a short and a merry one.”



An apothecary’s wife, finding that her husband made no
great account of her, and wishing to be better loved by him,
followed the advice that he had given to a “commère” (1) of
his, whose sickness was of the same kind as her own; but she
prospered not so well as the other, and instead of love
reaped hate.
1 Mr W. Kelly has pointed out (Bohn’s Heptameron, p. 395)
that in France the godfather and godmother of a child are
called in reference to each other compère and commère, terms
implying mutual relations of an extremely friendly kind. “The
same usage exists in all Catholic countries,” adds Mr Kelly,
“and one of the novels of the Decameron is founded on a
very general opinion in Italy that an amorous connection
between a compadre and his commadre partook almost of
the nature of incest.”
In the town of Pau in Beam there was an apothecary whom men called Master Stephen. He had married a virtuous wife and a thrifty, with beauty enough to content him. But just as he was wont to taste different drugs, so did he also with women, that he might be the better able to speak of all kinds. His wife was greatly tormented by this, and at last lost all patience; for he made no account of her except by way of penance during Holy Week.
One day when the apothecary was in his shop, and his wife had hidden herself behind him to listen to what he might say, a woman, who was “commère” to the apothecary, and was stricken with the same sickness as his own wife, came in, and, sighing, said to him—
“Alas, good godfather, I am the most unhappy woman alive. I love my husband better than myself, and do nothing but think of how I may serve and obey him; but all my labour is wasted, for he prefers the wickedest, foulest, vilest woman in the town to me. So, godfather, if you know of any drug that will change his humour, prithee give it me, and, if I be well treated by him, I promise to reward you by all means in my power.”
The apothecary, to comfort her, said that he knew of a powder which, if she gave it to her husband with his broth or roast, after the fashion of Duke’s powder, (2) would induce him to entertain her in the best possible manner. The poor woman, wishing to behold this miracle, asked him what the powder was, and whether she could have some of it. He declared that there was nothing like powder of cantharides, of which he had a goodly store; and before they parted she made him prepare this powder, and took as much of it as was needful for her purpose. And afterwards she often thanked the apothecary, for her husband, who was strong and lusty, and did not take too much, was none the worse for it.
2 Boaistuau and Gruget call this preparation poudre de
Dun, as enigmatical an appellation as poudre de Duc. As
for the specific supplied by the apothecary, the context
shows that this was the same aphrodisiac as the Marquis de
Sades put to such a detestable use at Marseilles in 1772,
when, after fleeing from justice, he was formally sentenced
to death, and broken, in effigy, upon the wheel. See P.
Lacroix’s Curiosités de l’histoire de France, IIème Série,
Paris, 1858.—Ed.
The apothecary’s wife heard all this talk, and thought within herself that she had no less need of the recipe than her husband’s “commère.” Observing, therefore, the place where her husband put the remainder of the powder, she resolved that she would use some of it when she found an opportunity; and this she did within three or four days. Her husband, who felt a coldness of the stomach, begged her to make him some good soup, but she replied that a roast with Duke’s powder would be better for him; whereupon he bade her go quickly and prepare it, and take cinnamon and sugar from the shop. This she did, not forgetting also to take the remainder of the powder given to the “commère,” without any heed to dose, weight or measure.
The husband ate the roast, and thought it very good. Before long, however, he felt its effects, and sought to soothe them with his wife, but this he found was impossible, for he felt all on fire, in such wise that he knew not which way to turn. He then told his wife that she had poisoned him, and demanded to know what she had put into the roast. She forthwith confessed the truth, telling him that she herself required the recipe quite as much as his “commère.” By reason of his evil plight, the poor apothecary could belabour her only with hard words; however, he drove her from his presence, and sent to beg the Queen of Navarre’s apothecary (3) to come and see him. This the Queen’s apothecary did, and whilst giving the other all the remedies proper for his cure (which in a short time was effected) he rebuked him very sharply for his folly in counselling another to use drugs that he was not willing to take himself, and declared that his wife had only done her duty, inasmuch as she had desired to be loved by her husband.
3 It was from her apothecary no doubt that Queen Margaret
heard this story.—Ed.
Thus the poor man was forced to endure the results of his folly in patience, and to own that he had been justly punished in being brought into such derision as he had proposed for another.
“Methinks, ladies, this woman’s love was as indiscreet as it was great.”
“Do you call it loving her husband,” said Hircan, “to give him pain for the sake of the delight that she herself looked to have?”
“I believe,” said Longarine, “she only desired to win back her husband’s love, which she deemed to have gone far astray; and for the sake of such happiness there is nothing that a woman will not do.” “Nevertheless,” said Geburon, “a woman ought on no account to make her husband eat or drink anything unless, either through her own experience or that of learned folk, she be sure that it can do him no harm. Ignorance, however, must be excused, and hers was worthy of excuse; for the most blinding passion is love, and the most blinded of persons is a woman, since she has not strength enough to conduct so weighty a matter wisely.”
“Geburon,” said Oisille, “you are departing from your own excellent custom so as to make yourself of like mind with your fellows; but there are women who have endured love and jealousy in patience.”
“Ay,” said Hircan, “and pleasantly too; for the most sensible are those who take as much amusement in laughing at their husbands’ doings, as their husbands take in secretly deceiving them. If you will make it my turn, so that the Lady Oisille may close the day, I will tell you a story about a wife and her husband who are known to all of us here.”
“Begin, then,” said Nomerfide; and Hircan, laughing, began thus:—


On finding her husband bolting meal in the garb of her
serving-woman, whom he was awaiting in the hope that he
would obtain from her what he desired, a certain lady showed
such good sense that she was content to laugh and make merry
at his folly.
At the castle of Odoz (1) in Bigorre, there dwelt one Charles, equerry to the King and an Italian by birth, who had married a very virtuous and honourable woman. After bearing him many children, she was now grown old, whilst he also was not young. And he lived with her in all peacefulness and affection, for although he would at times speak with his serving-women, his excellent wife took no notice of this, but quietly dismissed them whenever she found that they were becoming too familiar in her house.
1 The scene of this tale is laid at the castle where
Margaret died. Ste. Marthe in his Oraison funèbre,
pronounced at Alençon fifteen days after the Queen’s death,
formally states that she expired at Odos near Tarbes. He is
not likely to have been mistaken, so that Brantome’s
assertion that the Queen died at Audos in Beam may be
accepted as incorrect (ante, vol. i. p. lxxxviii.). It is
further probable that the above tale was actually written at
Odos (ante, vol. i. p. lxxxvi.), but the authenticity of
the incidents is very doubtful, as there is an extremely
similar story in the Cent Nouvelles Nouvelles (No, xvii.
Le Conseiller au bluteau), in which the hero of the
adventure is a “great clerk and knight who presided over the
Court of Accounts in Paris.” For subsequent imitations see
Malespini’s Ducento Novelle (No. xcvii.) and Les Joyeuses
Adventures et Nouvelles Recreations (No. xix.)—L. and Ed.
One day she hired a discreet and worthy girl, telling her of her husband’s temper and her own, and how she was wont to turn away such girls whom she found to be wantons. This maid, wishing to continue in her mistress’s service and esteem, resolved to remain a virtuous woman; and although her master often spoke to her, she on her part gave no heed to his words save that she repeated them to her mistress, and they thus both derived much diversion from his folly.
One day the maid was in a back room bolting meal, and wearing her “sarot,” a kind of hood which, after the fashion of that country, not only formed a coif but covered the whole of the back and shoulders. Her master, finding her in this trim, came and urged her very pressingly, and, although she would not have done such a thing even to save her life, she pretended to consent, and asked leave to go first and see whether her mistress was engaged in some such manner that they might not be surprised together. To this he agreed; whereupon she begged him to put her hood upon his head and to continue bolting whilst she was away, in order that her mistress might still hear the noise of the bolter. And this he gladly did, in the hope of obtaining what he sought.
The maid, who was by no means inclined to melancholy, ran off to her mistress and said to her—
“Come and see your good husband, whom I have taught to bolt in order to be rid of him.”
The wife made all speed to behold this new serving-woman, and when she saw her husband with the hood upon his head and the bolter in his hands, she began to laugh so exceedingly, clapping her hands the while, that she was scarce able to say to him—
“How much dost want a month, wench, for thy labour?”
The husband, on hearing this voice, realised that he had been deceived, and, throwing down both what he was holding and wearing, he ran at the girl, calling her a thousand bad names. Had his wife not set herself in front of the maid, he would have given her wage enough for her quarter; but at last all was settled to the content of the parties concerned, and thenceforward they lived together without quarrelling. (2)
2 The Italian Charles, equerry to the King, to whom the
leading part is assigned in Queen Margaret’s tale, may have
been Charles de San Severino, who figures among the
equerries with a salary of 200 livres, in the roll of the
royal household for 1522. The San Severino family, one of
the most prominent of Naples, had attached itself to the
French cause at the time of the expedition of Charles VIII.,
whom several of its members followed to France. In 1522 we
find a “Monsieur de Saint-Severin” holding the office of
first maître d’hôtel to Francis I., and over a course of
several years his son figures among the enfants
d’honneur.—B. J. and Ed.
“What say you, ladies, of this wife? Was she not sensible to make sport of her husband’s sport?”
“‘Twas no sport,” said Saffredent, “for the husband who failed in his purpose.”
“I believe,” said Ennasuite, “that he had more delight in laughing with his wife, than at killing himself at his age with his serving-woman.”
“Still, I should be sorely vexed,” said Simontault, “to be discovered so bravely coifed.”
“I have heard,” said Parlamente, “that it was not your wife’s fault that she did not once discover you in very much the same attire in spite of all your craft, and that since then she has known no repose.”
“Rest content with what befalls your own house,” said Simontault, “without inquiring into what befalls mine. Nevertheless, my wife has no reason to complain of me, and even did I act as you say, she would never have occasion to notice it through any lack of what she might need.”
“Virtuous women,” said Longarine, “require nothing but the love of their husbands, which alone can satisfy them. Those who seek a brutish satisfaction will never find it where honour enjoins.”
“Do you call it brutish,” asked Geburon, “if a wife desires that her husband should give her her due?”
“I say,” said Longarine, “that a chaste woman, whose heart is filled with true love, is more content to be perfectly loved than to have all the delights that the body can desire.”
“I am of your opinion,” said Dagoucin, “but my lords here will neither hear it nor confess it. I think if mutual love cannot satisfy a woman, her husband alone will not do so; for unless she live in the love that is honourable for a woman, she must be tempted by the infernal lustfulness of brutes.”
“In truth,” said Oisille, “you remind me of a lady who was both handsome and well wedded, but who, through not living in that honourable love, became more carnal than swine and more cruel than lions.”
“I ask you, madam,” said Simontault, “to end the day by telling us her story.”
“That I cannot do,” said Oisille, “and for two reasons. The first is that it is exceedingly long; and the second, that it does not belong to our own day. It is written indeed by an author worthy of belief; but we are sworn to relate nothing that has been written.”
“That is true,” said Parlamente; “but I believe I know the story you mean, and it is written in such old language that methinks no one present except ourselves has ever heard of it. It will therefore be looked upon as new.”
Upon this the whole company begged her to tell it without fear for its length, seeing that a full hour was yet left before vespers. So, at their request, the Lady Oisille thus began:—



The Duchess of Burgundy, not content with the love that her
husband bore her, conceived so great an affection for a
young gentleman that, when looks and glances were not
sufficient to inform him of her passion, she declared it to
him in words which led to an evil ending. (1)
1 This story is borrowed from an old fabliau, known under
the title of the Châtelaine de Vergy, which will be found
in the Recueil de Barbazan (vol iv.) and in Legrand
d’Aussy’s Fabliaux (vol iii.). Margaret calls the lady
Madame du Vergier (literally the lady of the orchard) in her
tale. Bandello imitated the same fabliau in his Novelle
(1554; part iv. nov. v.), but gave it a different ending.
Belleforest subsequently adapted it for his Histoires
Tragiques. Margaret’s tale may also be compared with No.
lxii. of the Cento Novelle antiche, p. 84 of the edition
of Florence, 1825.—L. and M.
In the Duchy of Burgundy there was a Duke who was a very honourable and handsome Prince. He had married a wife whose beauty pleased him so greatly that it kept him from knowledge of her character, and he took thought only how he might please her, whilst she made excellent show of returning his affection. Now the Duke had in his household a gentleman filled with all the perfection that could be sought for in a man. He was loved by all, more especially by the Duke, who had reared him from childhood near his own person; and, finding him possessed of such excellent qualities, the Duke loved him exceedingly and trusted him with all such matters as one of his years could understand.
The Duchess, who had not the heart of a virtuous woman and Princess, and was not content with the love that her husband bore her and the good treatment that she had at his hands, often observed this gentleman, and so much to her liking did she find him, that she loved him beyond measure. This she strove unceasingly to make known to him, as well by soft and piteous glances as by sighs and passionate looks.
But the gentleman, whose inclinations had ever been to virtue alone, could not perceive wickedness in a lady who had so little excuse for it, and so the glances and looks of the poor wanton bore no fruit save her own frenzied despair. This at last drove her to extremes, and forgetting that she was a woman fit to be entreated and yet to refuse, and a Princess made to be worshipped by such lovers and yet to hold them in scorn, she acted with the spirit of a man transported by passion, with a view to rid herself of the fire which she could no longer endure.
Accordingly, one day when her husband was gone to the council, at which the gentleman by reason of his youth was not present, she beckoned him to come to her, which he did, thinking that she had some command to give him. But leaning on his arm, like a woman wearied with repose, she brought him to walk in a gallery, where she said to him—
“I marvel that you who are so handsome and young, and full of excellent grace, have lived in this company, where are so many beautiful ladies, and yet have been lover or true knight to none.” Then, looking at him as graciously as she was able, she waited for his reply.
“Madam,” he said, “if I were worthy that your Highness should stoop to think of me, you would have still greater reason to marvel at seeing a man so little worthy of love as I am, offer his service where it would be rejected or scorned.”
On hearing this discreet reply, the Duchess felt she loved him more than before. She vowed to him that there was not a lady at her Court who would not be only too happy to have such a knight, and that he might well make an adventure of the sort, since there was no danger but he would come out of it with honour. The gentleman kept his eyes downcast, not daring to meet her looks, which were hot enough to melt ice; but, just as he was trying to excuse himself, the Duke sent for the Duchess to come to the council on some matter that concerned her, and thither with much regret she went. The gentleman never afterwards made the slightest sign of having understood a word of what she had said to him, at which she was exceedingly distressed and vexed; and she knew not to what cause to impute her failure, unless it were to the foolish fear of which she deemed the gentleman to be possessed.
A few days afterwards, finding that he gave no sign of understanding what she had said, she resolved on her part to set aside all fear or shame, and to tell him of her love. She felt sure that beauty such as hers could not be otherwise than well received, although she would fain have had the honour of being wooed. However, she set her honour on one side for her pleasure’s sake, and after she had several times attempted the same fashion of discourse as at first, but without receiving any reply to her liking, she one day plucked the gentleman by the sleeve, and told him that she must speak to him on certain matters of weight. The gentleman went with the humility and reverence that were her due to a deep window into which she had withdrawn; and, on perceiving that no one in the room could see her, she began in a trembling voice, that halted between desire and fear, to continue her former discourse, rebuking him for not yet having chosen some lady in the company, and promising him that, no matter who it might be, she would help him to win kindly treatment.
The gentleman, who was no less vexed than astonished by her words, replied—
“Madam, my heart is so tender, that, were I once refused, I should never again have joy in this world; and I know myself to be of such little worth that no lady at this Court would deign to accept my suit.”
The Duchess blushed, and, imagining that at last he was indeed won, vowed to him that she knew the most beautiful lady in the company would, if he were willing, joyfully receive him, and afford him perfect happiness.
“Alas! madam,” he replied, “I do not think that there is any woman in this company so unfortunate and so blind as to find me worthy of her love.”
The Duchess, finding that he would not understand her, drew the veil of her passion somewhat aside, and, by reason of the fears which the gentleman’s virtue caused her, spoke to him in the form of a question.
“If fortune,” she said, “had so far favoured you that it was myself who bore you this goodwill, what would you say?”
The gentleman, who thought that he was dreaming when he heard her speak in this wise, dropped on his knee, and replied—
“Madam, when God by His favour enables me to have both the favour of the Duke, my master, and your own, I shall deem myself the happiest man alive; for ‘tis the reward I crave for the loyal service of one who, more than any other, is bound to give his life in the service of you both. And I am sure, madam, that the love you bear my Lord aforesaid is attended with such chastity and nobleness that, apart from myself, who am but a worm of the earth, not even the greatest Prince and most perfect man to be found could break the union that exists between you. For my own part, my Lord has brought me up from childhood, and made me what I am, and to save my life I could not entertain towards any wife, daughter, sister or mother of his any thought contrary to what is due from a loyal and faithful servant.”
The Duchess would not allow him to continue, but finding that she was in danger of obtaining a dishonourable refusal, she suddenly interrupted him, and said—
“Wicked and boastful fool, who seeks any such thing from you? Do you think that your good looks win you the love of the very flies in the air? Nay, if you were presumptuous enough to address yourself to me, I would show you that I love, and seek to love, none but my husband. What I have said to you was spoken only for my amusement, to try you and laugh at you, as I do at all foolish lovers.”
“Madam,” said the gentleman, “I believed, and do still believe, that it is as you say.”
Then, without listening further, she withdrew in haste to her own apartment, and, finding that she was followed by her ladies, went into her closet, where she sorrowed after a fashion that cannot be described. On the one part, the love wherein she had failed caused her mortal sadness; on the other, her anger, both against herself for having entered upon such foolish talk and against the gentleman for his discreet reply, drove her into such fury that at one moment she wished to make away with herself, and at another, to live that she might avenge herself on one whom she now regarded as her deadly enemy.
When she had wept for a long while, she made pretence of being ill, in order that she might not be present at the Duke’s supper, at which the gentleman was commonly in waiting. The Duke, who loved his wife better than he did himself, came to see her; but the more effectually to work her end, she told him that she believed herself to be with child, and that her pregnancy had caused a rheum to come upon her eyes, which gave her much pain. So passed two or three days, during which the Duchess kept her bed in sadness and melancholy, until at last the Duke thought that something further must be the matter. He therefore came at night to sleep with her; but, finding that for all he could do he could in no sort check her sighs, he said to her—
“You know, sweetheart, that I love you as dearly as my life, and that if yours were lacking I could not endure my own. If therefore you would preserve my health, I pray you tell me what causes you to sigh after this manner; for I cannot believe that such unhappiness can come only because you are with child.”
The Duchess, finding that her husband was disposed to her just as she could have wished him to be, thought that the time was come to seek vengeance for her affliction; and embracing the Duke, she began to weep, and said—
“Alas, my lord, my greatest unhappiness is to see you deceived by those on whom is so deep an obligation to guard your substance and your honour.”
The Duke, on hearing this, was very desirous of knowing why she spoke in that manner, and earnestly begged her to make the truth known to him without fear. After refusing several times, she said—
“I shall never wonder, my lord, that foreigners make war on Princes, when those who are in duty most bound to them, wage upon them a war so cruel that loss of territory were nothing in comparison. I say this, my lord, in reference to a certain gentleman” (naming her enemy) “who, though reared by your own hand and treated more like a son than a servant, has made a cruel and base attempt to ruin the honour of your wife, in which is also bound up the honour of your house and your children. Although for a long time he showed me such looks as pointed to his wicked purpose, yet my heart, which only cares for you, understood nothing of them; and so at last he declared himself in words to which I returned a reply such as beseemed my condition and my chastity. Nevertheless, I now so hate him that I cannot endure to look at him, and for this cause I have continued in my own apartment and lost the happiness of fellowship with you. I entreat you, my lord, keep not this pestilence near your person; for, after such a crime, he might fear lest I should tell you of it, and so attempt worse. This, my lord, is the cause of my sorrow, and methinks it were right and fitting that you should deal with it forthwith.”
The Duke, who on the one hand loved his wife and felt himself grievously affronted, and on the other loved his servant, whose faithfulness he had so fully tried that he could scarce believe this falsehood against him, was in great distress and filled with anger. Repairing to his own room, he sent word to the gentleman to come no more into his presence, but to withdraw to his lodging for a time. The gentleman, being ignorant of the cause of this, was grieved exceedingly, for he knew that he had deserved the opposite of such unworthy treatment. Aware, then, of his own innocence in heart and deed, he sent a comrade to speak to the Duke and take him a letter, humbly entreating that if any evil report had caused his banishment, his master would be pleased to suspend judgment until he had heard from himself the truth of the matter, when it would be found that he had been guilty of no offence.
When the Duke saw this letter, his anger was somewhat abated. He secretly sent for the gentleman to his own room, and with wrathful countenance said—
“I could never have thought that the care I took to rear you as my own child would be changed into regret at having so highly advanced you; but you have attempted what was more hurtful to me than loss of life or substance, and have sought to assail the honour of one who is half myself, and so bring infamy on my house and name. You may be assured that this outrage is so wounding to my heart that, were it not for my doubt whether it be true or not, you would have already been at the bottom of the water, and so have received in secret due punishment for the wrong that in secret you intended against me.”
The gentleman was in no wise dismayed by this discourse, but, ignorant as he was of the truth, spoke forth with confidence and entreated the Duke to name his accuser, since such a charge should be justified rather with the lance than with the tongue.
“Your accuser,” said the Duke, “carries no weapon but chastity. Know, then, that none other but my wife has told me this, and she begged me to take vengeance upon you.”
The poor gentleman, though he then perceived the lady’s great wickedness, would not accuse her.
“My lord,” he replied, “my lady may say what she will. You know her better than I do, and you are aware if ever I saw her when out of your sight, save only on one occasion, when she spoke but little with me. You have, moreover, as sound a judgment as any Prince alive; wherefore I pray you, my lord, judge whether you have ever seen aught in me to cause any suspicion; and remember love is a fire that cannot be hidden so as never to be known of by those who have had a like distemper. So I pray you, my lord, to believe two things of me: first, that my loyalty to you is such that were my lady, your wife, the fairest being in the world, love would never avail to make me stain my honour and fidelity; and secondly, that even were she not your wife, I should be least in love with her of all the women I have ever known, since there are many others to whom I would sooner plight my troth.”
On hearing these words of truth, the Duke began to be softened, and said—
“I assure you, on my part, that I did not believe it. Do, therefore, according to your wont, in the assurance that, if I find the truth to be on your side, I will love you yet better than before. But if it be not so, your life is in my hands.”
The gentleman thanked him and offered to submit to any pain or penalty if he were found guilty.
The Duchess, on seeing the gentleman again in waiting as had formerly been his wont, could not endure it in patience, but said to her husband—
“‘Twould be no more than you deserve, my lord, if you were poisoned, since you put more trust in your deadly enemies than in your friends.”
“I pray you, sweetheart, do not torment yourself in this matter,” said the Duke. “If I find that you have told me true, I promise you he shall not live four and twenty hours. But he has sworn to the contrary, and I have myself never perceived any such fault, and so I cannot believe it without complete proof.”
“In good sooth, my lord,” she replied, “your goodness renders his wickedness the greater. What more complete proof would you have than this, that no love affair has ever been imputed to him? Believe me, my lord, were it not for the lofty purpose that he took into his head of being my lover, he would not have continued so long without a mistress; for never did a young man live solitary as he does in such good company, unless he had fixed his heart so high as to be content merely with his own vain hope. Since, then, you think that he is not hiding the truth from you, put him, I beg you, on oath as regards his love. If he loves another, I am content that you should believe him, and if not, you will know that what I say is true.”
The Duke thought his wife’s reasonings very good, and, taking the gentleman into the country with him, said—
“My wife continues still of the same mind, and has set before me an argument that causes me grave suspicion against you. It is deemed strange that you who are so gallant and young have never been known to love, and this makes me think that you have such affection for her as she says, and that the hope it gives you renders you content to think of no other woman. As a friend, therefore, I pray you, and as a master I command you to tell me whether you are in love with any lady on earth.”
Although the gentleman would have fain concealed his passion yet as he loved his life, he was obliged, on seeing his master’s jealousy, to swear to him that he did indeed love one whose beauty was so great, that the beauty of the Duchess or of any lady of the Court would be simply ugliness beside it. But he entreated that he might never be compelled to name her, since the agreement between himself and his sweetheart was of such a nature that it could not be broken excepting by whichever of them should be the first to make it known.
The Duke promised not to urge him, and being quite satisfied with him, treated him with more kindness than ever before. The Duchess perceived this, and set herself with her wonted craft to find out the reason. The Duke did not hide it from her; whereupon strong jealousy sprang up beside her desire for vengeance, and she begged her husband to command the gentleman to name his sweetheart. She assured him that the story was a lie, and that the course she urged was the best means of testing it. If the gentleman, said she, did not name her whom he deemed so beautiful, and his master believed him on his mere word, he would indeed be the most foolish Prince alive.
The poor Duke, whose wife directed his thoughts at her pleasure, went to walk alone with the gentleman, and told him that he was in even greater trouble than before; for he was greatly minded to believe that he had been given an excuse to keep him from suspecting the truth. This was a greater torment to him than ever; and he therefore begged the gentleman, as earnestly as he was able, to name her whom he loved so dearly. The poor gentleman entreated that he might not be made to commit so great an offence against his mistress as to break the promise he had given her and had kept so long, and thus lose in a day all that he had preserved for seven years. And he added that he would rather suffer death than in this wise wrong one who had been true to him.
The Duke, finding that he would not tell him, became deeply jealous, and with a wrathful countenance exclaimed—
“Well, choose one of two things: either tell me whom you love more than any other, or else go into banishment from the territories over which I rule, under pain of a cruel death if you be found within them after a week is over.”
If ever heart of loyal servant was torn with anguish, it was so with that of this poor gentleman, who might well have said, Angustiæ sunt mihi undique, for on the one part he saw that by telling the truth he would lose his mistress, if she learned that he had failed in his promise to her; while, if he did not confess it, he would be banished from the land in which she dwelt, and be no more able to see her. Hard pressed in this manner on all sides, there came upon him a cold sweat, as on one whose sorrow was bringing him near to death. The Duke, observing his looks, concluded that he loved no other lady than the Duchess, and was enduring this suffering because he was able to name none other. He therefore said to him with considerable harshness—
“If what you say were true, you would not have so much trouble in telling me; but methinks ‘tis your crime that is tormenting you.”
The gentleman, piqued by these words, and impelled by the love that he bore his master, resolved to tell him the truth, believing that he was too honourable a man ever, on any account, to reveal it. Accordingly, throwing himself upon his knees, and clasping his hands, he said—
“My lord, the duty that I owe to you and the love that I bear you constrain me more than the fear of any death. I can see that you imagine and judge falsely concerning me, and, to take this trouble from you, I am resolved to do that to which no torment had compelled me. But I pray you, my lord, swear to me by the honour of God, and promise me by your own faith as a Prince and a Christian, that you will never reveal the secret which, since it so pleases you, I am obliged to tell.”
Upon this the Duke swore to him with all the oaths he could think of that he would never reveal aught of it to any living being, whether by speech, or writing, or feature. Then the young man, feeling confidence in so virtuous a Prince as he knew his master to be, began the building up of his misfortune, and said—
“It is now seven years, my lord, since knowing your niece, the Lady du Vergier, to be a widow and without kindred, I set myself to win her favour. But, since I was of too lowly a birth to wed her, I contented myself with being received by her as her true knight, as indeed I have been. And it has pleased God that the affair has hitherto been contrived with much discretion, so that neither man nor woman knows of it save ourselves alone, and now, my lord, you also. I place my life and honour in your hands, entreating you to keep the matter secret and to esteem your niece none the less; for I think that under heaven there is no more perfect being.”
If ever man was rejoiced it was the Duke, for, knowing as he did the exceeding beauty of his niece, he now had no doubt that she was more pleasing than his wife. However, being unable to understand how so great a mystery could have been contrived, he begged the gentleman to tell him how it was that he was able to see her. The gentleman related to him then that his lady’s chamber looked upon a garden, and that, on the days when he was to visit her, a little gate was left open through which he went in on foot until he heard the barking of a little dog which the lady used to loose in the garden when all her women were withdrawn. Then he went and conversed with her all night long, and, in parting from her, would appoint a day on which he would return; and this appointment, unless for some weighty reason, he never failed to keep. The Duke, who was the most inquisitive man alive, and who had made love in no small degree in his day, wished both to satisfy his suspicions and to fully understand so strange a business; and he therefore begged the gentleman to take him, not as a master but as a companion, the next time he went thither. To this the gentleman, having gone so far already, consented, saying that he had an appointment for that very day; at which the Duke was as glad as if he had gained a kingdom. Making pretence of retiring to rest in his closet, he caused two horses to be brought for himself and the gentleman, and they travelled all night long from Argilly, where the Duke lived, to Le Vergier. (2)
2 At Argilly the Dukes of Burgundy had a castle, which was
destroyed during the religious wars at the close of the
sixteenth century. The place is now a small village in the
arrondissement of Nuits, Côte d’Or. As the crow flies, it is
some ten miles distant from the ruins of the castle of
Vergy, which stands on a steep height, at an altitude of
over 1600 ft., within five miles from Nuits. The castle,
which can only be reached on one side of the hill, by a
narrow, winding and precipitous pathway, is known to have
been in existence already in the tenth century, when the
Lords of Vergy were Counts of Chalons, Beaune, and Nuits.
They appear to have engaged in a struggle for supremacy with
the princes of the first Ducal house of Burgundy, but in
1193 Alix de Vergy espoused Duke Eudes III., to whom she
brought, as dower, the greater part of the paternal
inheritance. The castle of Vergy was dismantled by Henry
IV., and the existing ruins are of small extent. Some
antiquaries believe the fortress to have been originally
built by the Romans.—B.J. and L.
Then they left their horses without the wall, and the gentleman brought the Duke into the garden through the little gate, begging him to remain behind a walnut-tree, whence he might see whether he had been told the truth or not.
They had been but a short time in the garden when the little dog began to bark, and the gentleman walked towards the tower, where his lady failed not to come and meet him. She kissed him, saying that it seemed a thousand years since she had seen him, and then they went into the chamber and shut the door behind them.
Having seen the whole of the mystery, the Duke felt more than satisfied. Nor had he a great while to wait, for the gentleman told his mistress that he must needs return sooner than was his wont, since the Duke was to go hunting at four o’clock, and he durst not fail to attend him.
The lady, who set honour before delight, would not keep him from fulfilling his duty; for what she prized most in their honourable affection was that it was kept secret from all.
So the gentleman departed an hour after midnight, and his lady in cloak and kerchief went with him, yet not so far as she wished, for, fearing lest she should meet the Duke, he obliged her to return. Then he mounted with the Duke and returned to the castle of Argilly, his master unceasingly swearing to him on the way that he would die rather than ever reveal his secret. Moreover, he then put so much trust in the gentleman, and had so much love for him, that no one in his Court stood higher in his favour. The Duchess grew furious at this, but the Duke forbade her ever to speak to him about the gentleman again, saying that he now knew the truth about him and was well pleased, since the lady in question was more worthy of love than herself. These words deeply pierced the heart of the Duchess, and she fell into a sickness that was worse than fever.
The Duke went to see her in order to comfort her, but there was no means of doing this except by telling her the name of this beautiful and dearly loved lady. She pressed him urgently to do this, until at last the Duke went out of the room, saying—
“If you speak to me again after this fashion, we shall part one from the other.”
These words increased the sickness of the Duchess, and she pretended that she felt her infant stirring, at which the Duke was so rejoiced that he came and lay beside her. But, just when she saw him most loving towards her, she turned away, and said—
“I pray you, my lord, since you have no love for either wife or child, leave us to die together.”
With these words she gave vent to many tears and lamentations, and the Duke was in great fear lest she should lose her child. He therefore took her in his arms and begged her to tell him what she would have, since he possessed nothing that was not also hers.
“Ah, my lord,” she replied, weeping, “what hope can I have that you would do a hard thing for me, when you will not do the easiest and most reasonable in the world, which is to name to me the mistress of the wickedest servant you ever had? I thought that you and I had but one heart, one soul, and one flesh. But now I see that you look upon me as a stranger, seeing that your secrets, which should be known to me, are hidden from me as though I were a stranger. Alas! my lord, you have told me many weighty and secret matters, of which you have never known me to speak, you have proved my will to be like to your own, and you cannot doubt but that I am less myself than you. And if you have sworn never to tell the gentleman’s secret to another, you will not break your oath in telling it to me, for I am not and cannot be other than yourself. I have you in my heart, I hold you in my arms, I have in my womb a child in whom you live, and yet I may not have your heart as you have mine. The more faithful and true I am to you, the more cruel and stern are you to me, so that a thousand times a day do I long by a sudden death to rid my child of such a father and myself of such a husband. And I hope that this will be ere long, since you set a faithless servant before a wife such as 1 am to you, and before the life of the mother of your child, which will perish because I cannot have of you that which I most desire to know.”
So saying, she embraced and kissed her husband, and watered his face with her tears, uttering the while such lamentations and sighs that the good Prince feared to lose wife and child together, and resolved to tell her all the truth of the matter. Nevertheless, he first swore to her that if ever she revealed it to a living being she should die by his own hand; and she agreed to and accepted this punishment. Then the poor, deceived husband told her all that he had seen from beginning to end, and she made show of being well pleased. In her heart she was minded very differently, but through fear of the Duke she concealed her passion as well as she was able.
Now on a certain great feast-day the Duke held his Court, to which he had bidden all the ladies of that country, and among the rest his niece. When the dances began, all did their duty save the Duchess, who, tormented by the sight of her niece’s beauty and grace, could neither make merry nor prevent her spleen from being perceived. At last she called all the ladies, and making them scat themselves around her, began to talk of love; and seeing that the Lady du Vergier said nothing, she asked her, with a heart which jealousy was rending—
“And you, fair niece, is it possible that your beauty has found no lover or true knight?”
“Madam,” replied the Lady du Vergier, “my beauty has not yet made such a conquest. Since my husband’s death I have sought to love none but his children, with whom I deem myself happy.”
“Fair niece, fair niece,” replied the Duchess, with hateful spleen, “there is no love so secret that it is not known, and no little dog so well broken in and trained that it cannot be heard to bark.”
I leave you to imagine, ladies, what sorrow the poor Lady du Vergier felt in her heart on finding a matter, so long concealed, thus made known to her great dishonour. Her honour, which had been so carefully guarded and was now wofully lost, tortured her, but still more so her suspicion that her lover had failed in his promise to her. This she did not think he could have done, unless it were that he loved some lady fairer than herself, to whom his love had constrained him to make the whole matter known. Yet so great was her discretion that she gave no sign, but replied laughing to the Duchess that she did not understand the language of animals. However, beneath this prudent concealment her heart was filled with sadness, so that she rose up, and, passing out of the chamber, entered a closet in sight of the Duke, who was walking up and down.
Having thus reached a place where she believed herself to be alone, the poor lady let herself fall helplessly upon a bed, whereat a damsel, who had sat down beside it to sleep, rose up and drew back the curtains to see who this might be. Finding that it was the Lady du Vergier, who believed herself to be alone, she durst say nothing to her, but listened, making as little noise as she was able. And in a stifled voice the poor Lady du Vergier began to lament, saying—
“O unhappy one, what words have I heard? to what decree of death have I hearkened? what final sentence have I received? O best beloved of men, is this the reward of my chaste, honourable and virtuous love? O my heart, hast thou made so parlous an election, and chosen for the most loyal the most faithless, for the truest the most false, for the discreetest the most slanderous? Alas! can it be that a thing hidden from every human eye has been revealed to the Duchess? Alas, my little dog, so well taught and the sole instrument of my love and virtuous affection, it was not you who betrayed me, it was he whose voice is louder than a dog’s bark, and whose heart is more thankless than any brute’s. Tis he who, contrary to his oath and promise, has made known the happy life which, wronging none, we so long have led together. O my beloved, the love of whom alone has entered into my heart, and preserved my life, must you now be declared my deadly foe, while mine honour is given to the winds, my body to the dust, and my soul to its everlasting abode? Is the beauty of the Duchess so exceeding great that, like the beauty of Circe, it has bewitched and transformed you? Has she turned you from virtue to vice, from goodness to wickedness, from being a man to be a beast of prey? O my beloved, though you have failed in your promise to me, yet will I keep mine to you, and, now that our love has been revealed, will never see you more. Nevertheless, I cannot live without your presence, and so I gladly yield to my exceeding sorrow, and will seek for it no cure either in reason or in medicine. Death alone shall end it, and death will be sweeter to me than life on earth without lover, honour or happiness. Neither war nor death has robbed me of my lover; no sin or fault of mine has robbed me of my honour; neither error nor demerit of mine has made me lose my joy. ‘Tis cruel fate that has rendered the most favoured of men thankless, and has caused me to receive the contrary of that which I deserved.
“Ah, my Lady Duchess, what delight it was to you to taunt me with my little dog! Rejoice, then, in the happiness you owe to me alone; taunt her who thought by careful concealment and virtuous love to be free from any taunt. Ah! how those words have bruised my heart! how they have made me blush for shame and pale for jealousy! Alas, my heart, I feel that thou art indeed undone! The wicked love that has discovered me burns thee; jealousy of thee and evil intent towards thee are to thee as ice and death; while wrath and sorrow do not suffer me to comfort thee. Alas, poor soul, that in adoring the creature didst forget the Creator, thou must return into the hands of Him from whom vain love tore thee away. Have trust, my soul, that thou wilt find in Him a Father kinder than was the lover for whose sake thou hast so often forgotten Him. O my God, my Creator, Thou who art the true and perfect love, by whose grace the love I bore to my beloved has been stained by no blemish save that of too great an affection, I implore Thee in mercy to receive the soul-and spirit of one who repents that she has broken thy first and most just commandment. And, through the merits of Him whose love passeth all understanding, forgive the error into which excess of love has led me, for in Thee alone do I put my perfect trust. And farewell, O my beloved, whose empty name doth break my very heart.”
With these words she fell backward, and her face grew pallid, her lips blue, and her extremities cold.
Just at this moment the gentleman she loved came into the hall, and, seeing the Duchess dancing with the ladies, looked everywhere for his sweetheart. Not finding her, he went into the chamber of the Duchess, and there found the Duke, who was walking up and down, and who, guessing his purpose, whispered in his ear—
“She went into that closet, and methought she was ill.”
The gentleman asked whether he would be pleased to let him go in, and the Duke begged him to do so. When he entered the closet he found the Lady du Vergier, come to the last stage of her mortal life; whereat, throwing his arms about her, he said—
“What is this, sweetheart? Would you leave me?”
The poor lady, hearing the voice that she knew so well, recovered a little strength and opened her eyes to look upon him who was the cause of her death; but at this look her love and anguish waxed so great that, with a piteous sigh, she yielded up her soul to God.
The gentleman, more dead than the dead woman herself, asked the damsel who was there how this sickness had come upon his sweetheart, and she told him all the words that she had heard. Then the gentleman knew that the Duke had revealed the secret to his wife, and felt such frenzy that, whilst embracing his sweetheart’s body, he for a long time watered it with his tears, saying—
“O traitorous, wicked and unhappy lover that I am! why has not the punishment of my treachery fallen upon me, and not upon her who is innocent? Why was I not struck by a bolt from heaven on the day when my tongue revealed the secret and virtuous love between us? Why did not the earth open to swallow up this traitor to his troth? O tongue, mayest thou be punished as was the tongue of the wicked rich man in hell!
“O heart, too fearful of death and banishment, mayest thou be torn continually by eagles as was the heart of Ixion! (3)
3 Queen Margaret’s memory plainly failed her here.—Ed.
“Alas, sweetheart, the greatest of all the greatest woes has fallen upon me! I thought to keep you, but I have lost you; I thought to see you for a long time and to abide with you in sweet and honourable content, yet now I embrace your dead body, and you passed away in sore displeasure with me, with my heart and with my tongue. O most loyal and faithful of women, I do confess myself the most disloyal, fickle and faithless of all men. Gladly would I complain of the Duke in whose promise I trusted, hoping thus to continue our happy life; but alas! I should have known that none could keep our secret better than I kept it myself. The Duke had more reason in telling his secret to his wife than I in telling mine to him. I accuse none but myself of the greatest wickedness that was ever done between lovers. I ought to have submitted to be cast into the moat as he threatened to do with me; at least, sweetheart, you would then have lived in widowhood and I have died a glorious death in observing the law that true love enjoins. But through breaking it I am now in life, and you, through perfectness of love, are dead; for your pure, clear heart could not bear to know the wickedness of your lover.
“O my God! why didst Thou endow me with so light a love and so ignorant a heart? Why didst thou not create me as the little dog that faithfully served his mistress? Alas, my little friend, the joy your bark was wont to give me is turned to deadly sorrow, now that another than we twain has heard your voice. Yet, sweetheart, neither the love of the Duchess nor of any living woman turned me aside, though indeed that wicked one did often ask and entreat me. ‘Twas by my ignorance, which thought to secure our love for ever, that I was overcome. Yet for that ignorance am I none the less guilty; for I revealed my sweetheart’s secret and broke my promise to her, and for this cause alone do I see her lying dead before my eyes. Alas, sweetheart, death will to me be less cruel than to you, whose love has ended your innocent life. Methinks it would not deign to touch my faithless and miserable heart; for life with dishonour and the memory of that which I have lost through guilt would be harder to bear than ten thousand deaths. Alas, sweetheart, had any dared to slay you through mischance or malice, I should quickly have clapped hand to sword to avenge you; ‘tis therefore right that I should not pardon the murderer who has caused your death by a more wicked act than any sword-thrust. Did I know a viler executioner than myself, I would entreat him to put your traitorous lover to death. O Love! I have offended thee from not having known how to love, and therefore thou wilt not succour me as thou didst succour her who kept all thy laws. ‘Tis not right that I should die after so honourable a manner; but ‘tis well that I should die by mine own hand. I have washed your face, sweet, with my tears, and with my tongue have craved your forgiveness; and now it only remains for my hand to make my body like unto yours, and send my soul whither yours will go, in the knowledge that a virtuous and honourable love can never end, whether in this world or in the next.”
Rising up from the body he then, like a frenzied man beside himself, drew his dagger and with great violence stabbed himself to the heart. Then he again took his sweetheart in his arms, kissing her with such passion that it seemed as though he were seized rather with love than with death.
The damsel, seeing him deal himself the blow, ran to the door and called for help. The Duke, on hearing the outcry, suspected misfortune to those he loved, and was the first to enter the closet, where he beheld the piteous pair. He sought to separate them, and, if it were possible, to save the gentleman; but the latter clasped his sweetheart so fast that he could not be taken from her until he was dead. Nevertheless he heard the Duke speaking to him and saying—“Alas! what is the cause of this?” To which, with a glance of fury, he replied—“My tongue, my lord, and yours.” So saying, he died, with his face close pressed to that of his mistress.
The Duke, wishing to know more of the matter, made the damsel tell him what she had seen and heard; and this she did at full length, sparing nothing. Then the Duke, finding that he was himself the cause of all this woe, threw himself upon the two dead lovers, and, with great lamentation and weeping, kissed both of them several times and asked their forgiveness. And after that he rose up in fury, and drew the dagger from the gentleman’s body; and, just as a wild boar, wounded with a spear, rushes headlong against him that has dealt the blow, so did the Duke now seek out her who had wounded him to the bottom of his soul. He found her dancing in the hall, and more merry than was her wont at the thought of the excellent vengeance she had wreaked on the Lady du Vergier.
The Duke came upon her in the midst of the dance, and said—
“You took the secret upon your life, and upon your life shall fall the punishment.”
So saying, he seized her by the head-dress and stabbed her with the dagger in the breast. All the company were astonished, and it was thought that the Duke was out of his mind; but, having thus worked his will, he brought all his retainers together in the hall and told them the virtuous and pitiful story of his niece, and the evil that his wife had wrought her. And those who were present wept whilst they listened.
Then the Duke ordered that his wife should be buried in an abbey which he founded partly to atone for the sin that he had committed in killing her; and he caused a beautiful tomb to be built, in which the bodies of his niece and the gentleman were laid together, with an epitaph setting forth their tragic story. And the Duke undertook an expedition against the Turks, in which God so favoured him, that he brought back both honour and profit. On his return, he found his eldest son now able to govern his possessions, and so left all to him, and went and became a monk in the abbey where his wife and the two lovers were buried. And there did he spend his old age happily with God.
“Such, ladies, is the story which you begged me to relate, and which, as I can see from your eyes, you have not heard without compassion. It seems to me that you should take example by it, and beware of placing your affections upon men; for, however honourable or virtuous these affections may be, in the end they have always an aftertaste of evil. You see how St. Paul would not that even married people should so deeply love each other; (4) for the more our hearts are set upon earthly things, the more remote are they from heavenly affection, and the harder is the tie to be broken. I therefore pray you, ladies, ask God for His Holy Spirit, who will so fire your hearts with the love of God, that when death comes, you will not be pained at leaving that which you love too well in this world.”
4 I Corinthians vii. 32-5.—M.
“If their love,” said Geburon, “was as honourable as you describe, why was it needful to keep it so secret?”
“Because,” said Parlamente, “the wickedness of men is so great, that they can never believe deep love to be allied with honour, but judge men and women to be wicked according to their own passions. Hence, if a woman has a dear friend other than one of her nearest kinsfolk, she must speak with him in secret if she would speak long with him; for a woman’s honour is attacked, whether she love virtuously or viciously, since people judge only from appearances.”
“But,” said Geburon, “when a secret of that kind is revealed, people think far worse of it.”
“I grant you that,” said Longarine; “and so it is best not to love at all.”
“We appeal from that sentence,” said Dagoucin, “for, did we believe the ladies to be without love, we would fain be ourselves without life. I speak of those who live but to win love: and, even if they secure it not, yet the hope of it sustains them and prompts them to do a thousand honourable deeds, until old age changes their fair sufferings to other pains. But, did we think that ladies were without love, it were needful we should turn traders instead of soldiers, and instead of winning fame, think only of hea’ping up riches.”
“You would say, then,” said Hircan, “that, were there no women, we should all be dastards, as though we had no courage save such as they put into us. But I am of quite the opposite opinion, and hold that nothing weakens a man’s courage so much as to consort with women or love them too much. For this reason the Jews would not suffer a man to go to the war within a year after his marriage, lest love for his wife should draw him back from the dangers that he ought to seek.” (5)
5 See Deuteronomy xx. 5, 6, 7; and the comments thereon
of Rabelais (book iii. ch. vi.).—M.
“I consider that law,” said Saffredent, “to have been without reason, for nothing will more readily make a man leave his home than marriage. The war without is not harder of endurance than the war within; and I think that, to make men desirous of going into foreign lands instead of lingering by their hearths, it were only needful to marry them.”
“It is true,” said Ennasuite, “that marriage takes from them the care of their houses; for they trust in their wives, and for their own part think only of winning fame, feeling certain that their wives will give due heed to the profit.”
“However that may be,” replied Saffredent, “I am glad that you are of my opinion.”
“But,” said Parlamente, “you are not discussing what is chiefly to be considered, and that is why the gentleman, who was the cause of all the misfortune, did not as quickly die of grief as she who was innocent.”
Nomerfide replied—
“‘Twas because women love more truly than men.”
“Nay,” said Simontault, “‘twas because the jealousy and spitefulness of women make them die without knowing the reason, whereas men are led by their prudence to inquire into the truth of the matter. When this has been learnt through their sound sense, they display their courage, as this gentleman did; for, as soon as he understood the reason of his sweetheart’s misfortune, he showed how truly he loved her and did not spare his own life.”
“Yet,” said Ennasuite, “she died of true love, for her steadfast and loyal heart could not endure to be so deceived.”
“It was her jealousy,” said Simontault, “which would not yield to reason, so that she believed evil of her lover of which he was not guilty at all. Moreover, her death was matter of necessity, for she could not prevent it, whilst her lover’s death was voluntary, after he had recognised his own wrongdoing.”
“Still,” said Nomerfide, “the love must needs be great that causes such deep sorrow.”
“Have no fear of it,” said Hircan, “for you will never die of that kind of fever.”
“Nor,” said Nomerfide, “will you ever kill yourself after recognising your error.”
Here Parlamente, who suspected that the dispute was being carried on at her own expense, said, laughing—
“‘Tis enough that two persons should have died of love, without two others fighting for the same cause. And there is the last bell sounding for vespers, which will have us gone whether you be willing or not.”
By her advice the whole company then rose and went to hear vespers, not forgetting in their fervent prayers the souls of those true lovers, for whom, also, the monks, of their charity, said a De profundis. As long as supper lasted there was no talk save of the Lady du Vergier, and then, when they had spent a little time together, they withdrew to their several apartments, and so brought to an end the Seventh Day.

On the Eighth Day relation is made
of the greatest yet truest
folliesthat each
can remember.
When morning was come they inquired whether their bridge (1) were being well advanced, and found that it might be finished in two or three days. These were not welcome tidings to some among the company, for they would gladly have had the work last a longer time, so as to prolong the happiness that they enjoyed in this pleasant mode of life. Finding, however, that only two or three such days were left, they resolved to turn them to account, and begged the Lady Oisille to give them their spiritual nourishment as had been her wont. This she forthwith did, but she detained them longer than usual, for before setting forth she desired to finish reading the canonical writings of St. John; and so well did she acquit herself of this, that it seemed as if the Holy Spirit in all His love and sweetness spoke by her mouth. Glowing with this heavenly flame, they went to hear high mass, and afterwards dined together, again speaking of the past day, and doubting whether they could make another as fair.
1 The allusion is to the bridge over the Gave spoken of in
the General Prologue (ante, vol. i. p. 25-6).—M.
In order to set about it, they retired to their own rooms until it was time to repair to their Chamber of Accounts on the Board of Green Grass, where they found the monks already arrived and in their places.
When all were seated, the question was put, who should begin; and Saffredent said—
“You did me the honour to have me begin on two days. Methinks we should act wrongly towards the ladies if one of them did not also begin on two.”
“It were then needful,” said the Lady Oisille, “either that we should continue here for a great while, or else that a gentleman and a lady of the company should forego the beginning of a day.”
“For my part,” said Dagoucin, “had I been chosen, I would have given my place to Saffredent.”
“And I,” said Nomerfide, “to Parlamente, for I have been so wont to serve that I know not how to command.”
To this all agreed, and Parlamente thus began—
“Ladies, the days that are past have been filled with so many tales of wisdom, that I would beg you to fill this one with the greatest (yet most real) follies that we can remember. So, to lead the way, I will begin.”


A saddler’s wife, who was grievously sick, was made whole
and recovered the power of speech, which for the space of
two days site had lost, on seeing her husband holding his
serving-maid too familiarly on the bed whilst she herself
was drawing to her end.
In the town of Amboise there lived one Brimbaudier, (1) saddler to the Queen of Navarre, and a man whose colour of feature showed him to be by nature rather a servant of Bacchus than a priest of Diana. He had married a virtuous woman who controlled his household very discreetly, and with whom he was well content.
1 Boaistuau gives the name as Bruribandier, and Gruget
transforms it into Borribaudier. M, Pifteau, after examining
the MSS., is doubtful whether Brimbaudier is the correct
reading. Bromardier, which in old French meant a tippler
(Ducange, Briemardum), would have been an appropriate name
for the individual referred to.—Ed.
One day it was told him that his good wife was sick and in great danger, at which tidings he was in the greatest trouble imaginable. He went with all speed to her aid, and found her so low, poor woman, that she had more need of a confessor than a doctor. Thereupon he made the most pitiful lamentation that could be, but to represent it well ‘twere needful to speak thickly as he did, (2) and better still to paint one’s face like his.
2 Curiously enough, the transcriber of MS. No. 1520
attempts to give some idea of the husband’s pronunciation by
transforming all his r’s into l’s. Here is an example: “Je
pelz ma povle femme, que fesai-ze, moi malhureux?... M’amie
je me meuls, je suis pis que tlepassé... je ne sçai que
faize,” &c.—L.
When he had done all that he could for her, she asked for the cross, and it was brought. On seeing this, the good man flung himself upon a bed in despair, crying and saying in his thick speech—
“Ah God! I am losing my poor wife! What shall I do, unhappy man that I am?”
After uttering many such complaints, he perceived that there was no one in the room but a young servant-maid, passably fair and buxom, and he called to her in a whisper.
“Sweetheart,” he said, “I am dying. I am more than dead to see your mistress dying in this manner. I know not what to do or say, except that I commend myself to you, and beg you to care for my house and my children. Take therefore the keys from my side, and order the household, for I myself can attend to nothing more.”
The poor girl had pity on him and comforted him, begging him not to despair, so that, if she must lose her mistress, she might not also lose her good master.
“Sweetheart,” he replied, “‘tis all of no avail, for I am indeed dying. See yourself how cold my face is; bring your cheeks close to mine and warm them.”
With this he laid his hand upon her breast. She tried to make some difficulty, but he begged her to have no fear, since they must indeed see each other more closely. And speaking in this wise, he took her in his arms and threw her upon the bed.
Then his wife, whose only company was the cross and the holy water, and who had not spoken for two days, began to cry out as loudly as her feeble voice enabled her—
“Ah! ah! ah! I am not dead yet!” And threatening them with her hand, she repeated—“Villain! monster! I am not dead yet!”
On hearing her voice, the husband and maid rose up, but she was in such a rage against them that her anger consumed the catarrhal humour that had prevented her from speaking, and she poured upon them all the abuse that she could think of. And from that hour she began to mend, though not without often reproaching her husband for the little love he bore her. (3)
3 This story was imitated by Noël du Fail de La Hérissaye
in his Contes d’Eutrapel (ch. v. De la Goutte), where
the hero of the incident is called Glaume Esnaut de
Tremeril. “It is said,” writes Du Fail, “that the wife of
that rascal Glaume of Tremeril when at the point of death,
on seeing Glaume too familiar with her serving-woman,
recovered her senses, saying, ‘Ah! wicked man, I am not yet
so low as you thought. By God’s grace, mistress baggage, you
shall go forth at once.’” Curiously enough, the 1585 edition
of the Contes d’Eutrapel was printed at Rennes for Noël
Glame, virtually the same name as Glaume.—M.
“By this you see, ladies, the hypocrisy of men, and how a little consolation will make them forget their sorrow for their wives.”
“How do you know,” said Hircan, “that he had not heard that such was the best remedy his wife could have? Since his kindly treatment availed not to cure her, he wished to try whether the opposite would prove any better, and the trial was a very fortunate one. But I marvel that you who are a woman should have shown how the constitution of your sex is brought to amendment rather by foul means than by fair.”
“Without doubt,” said Longarine, “behaviour of that kind would make me rise not merely from my bed, but from a grave such as that yonder.”
“And what wrong did he do her,” asked Saffre-dent, “by comforting himself when he thought that she was dead? It is known that the marriage-tie lasts only through life, and that when this is ended it is loosed.”
“Ay,” said Oisille, “loosed from oath and bond, but a good heart is never loosed from love. The husband you have told us of was indeed quick to forget his grief, since he could not wait until his wife had breathed her last.”
“What I think strangest of all,” said Nomerfide, “is that, when death and the cross were before his eyes, he should not have lost all desire to offend against God.”
“A brave argument!” said Simontault. “You would therefore not be surprised to see a man act wantonly provided he were a good distance from the church and cemetery?”
“You may laugh at me as much as you please,” said Nomerfide; “nevertheless the contemplation of death must greatly chill a heart, however young it may be.”
“I should indeed be of the same opinion as yourself,” said Dagoucin, “if I had not heard a Princess say the opposite.”
“In other words.” said Parlamente, “she told some story about it. If it be so, I will give you my place that you may relate it to us.”
Then Dagoucin began as follows:—


Whilst engaged in the last deed of charity, the shrouding
of a dead body, a monk did also engage with a nun in the
deeds of the flesh, and made her big with child. (1)
In one of the finest towns of France after Paris there stood an hospital (2) richly endowed—namely, with a Prioress and fifteen or sixteen nuns, while in another building there was a Prior and seven or eight monks. Every day the monks said mass, but the nuns only their paternosters and the Hours of Our Lady, for they were occupied in tending the sick.
1 Gruget first printed this tale, which was not given by
Boaistuau.—L.
2 It is impossible to say what town and hospital Margaret
here refers to. Lyons is the scene of the latter part of the
story; and we are inclined to think that the earlier
incidents may have occurred at Dijon, where there was a
famous hospital under ecclesiastical management, founded by
Eudes III., seventh Duke of Burgundy.—L. and Ed.
One day it chanced that a poor man died, and the nuns, being all assembled with him, after giving him every remedy for his health, sent for one of their monks to confess him. Then, finding that he was growing weaker, they gave him the extreme unction, after which he little by little lost the power of speech.
But as he was a long time in passing away, and it seemed that he could still hear, the nuns continued speaking to him with the most comforting words they knew, until at last they grew weary, and, finding that night was come and that it was late, retired one after another to rest. Thus, to shroud the body, there remained only one of the youngest of the nuns, with a monk whom she feared more than the Prior or any other, by reason of the severity that he displayed in both speech and life.
When they had duly uttered their Hours in the poor man’s ear, they perceived that he was dead, and thereupon laid him out. Whilst engaged on this last deed of charity, the monk began to speak of the wretchedness of life, and the blessedness of death; and in such discourse they continued until after midnight.
The poor girl listened attentively to the monk’s pious utterances, looking at him the while with tears in her eyes; and so pleasing were these to him that, whilst speaking of the life to come, he began to embrace her as though he longed to bear her away in his arms to Paradise.
The poor girl, listening to his discourse and deeming him the most pious of the community, ventured not to say him nay.
Perceiving this, the wicked monk, whilst still speaking of God, accomplished with her the work which the devil suddenly put into their hearts—for before there had been no question of such a thing. He assured her, however, that secret sin was not imputed to men by God, and that two persons who had no ties, could do no wrong in this manner, when no scandal came of it; and, to avoid all scandal, he told her to be careful to confess to none but himself.
So they parted each from the other, she going first. And as she passed through a chapel dedicated to Our Lady, she was minded to make her prayer as was her wont. But when she began with the words, “Mary, Virgin,” she remembered that she had lost the title of virginity not through force or love, but through foolish fear; and she began to weep so bitterly that it seemed as if her heart must break.
The monk, hearing the sighing from a distance, suspected her repentance, which might make him lose his delight, and to prevent this, he came and, finding her prostrate before the image, began to rebuke her harshly, telling her that if she had any scruples of conscience she should confess herself to him, and that she need not so act again unless she desired; for she might behave in either way without sin. The foolish nun, thinking to make atonement to God, confessed herself to the monk; but in respect of penance he swore to her that she did no sin in loving him, and that holy water would suffice to wash away such a peccadillo.
Believing in him more than in God, she again some time afterwards yielded to him, and so became big with child. At this she was in deep grief, and entreated the Prioress to have the monk turned away from his monastery, saying that she knew him to be so crafty that he would not fail to seduce her. The Abbess and the Prior, who understood each other, laughed at her, saying that she was big enough to defend herself against a man, and that the monk she spoke of was too virtuous to do such a deed.
At last, urged by the prickings of her conscience, she craved license to go to Rome, for she thought that, by confessing her sin at the Pope’s feet, she might recover her virginity. This the Prior and Prioress very readily granted her, for they were more willing that she should become a pilgrim contrary to the rules of her order, than be shut up in the convent with her present scruples. They feared also that in her despair she might denounce the life that was led among them, and so gave her money for her journey.
But God brought it to pass that when she came to Lyons, my lady the Duchess of Alençon, afterwards Queen of Navarre, being one evening after vespers in the roodloft of the church of St. John, whither she came secretly to perform a novena with three or four of her women, (3) heard someone mounting the stairway whilst she was kneeling before the crucifix. By the light of the lamp she saw it was a nun, and in order that she might hear her devotions, the Duchess thereupon withdrew to the corner of the altar. The nun, who believed herself to be alone, knelt down and, beating her breast, began weeping so sorrowfully that it was piteous to hear her; and all the while she cried naught but this—“Alas! my God, take pity on this poor sinner.”
3 See ante, Tale LXV., note i.
The Duchess, wishing to learn what it meant, went up to her and said, “Dear heart, what ails you, and whence do you come, and what brings you to this place?”
The poor nun, who did not know her, replied, “Ah, sweet, my woe is such that I have no help but in God; and I pray that He may bring me to speak with the Duchess of Alençon. To her alone will I tell the matter, for I am sure that, if it be possible, she will set it right.”
“Dear heart,” then said the Duchess, “you may speak to me as you would to her, for I am one of her nearest friends.”
“Forgive me,” said the nun; “she alone must know my secret.”
Then the Duchess told her that she might speak freely, since she had indeed found her whom she sought. Forthwith the poor woman threw herself at her feet, and, after she had wept, related what you have heard concerning her hapless fortune. The Duchess consoled her so well, that whilst she took not from her everlasting repentance for her sin, she put from her mind the journeying to Rome, and then sent her back to her priory with letters to the Bishop of the place to have that shameful monk turned away.
“I have this story from the Duchess herself, and from it you may see, ladies, that Nomerfide’s prescription is not good for all, since these persons fell into lewdness even while touching and laying out the dead.”
“‘Twas a device,” said Hircan, “that methinks no man ever used before, to talk of death and engage in the deeds of life.”
“‘Tis no deed of life,” said Oisille, “to sin, for it is well known that sin begets death.”
“You may be sure,” said Saffredent, “that these poor folk gave no thought to any such theology; but just as the daughters of Lot made their father drunk so that the human race might be preserved, so these persons wished to repair what death had spoiled, and to replace the dead body by a new one. I therefore can see no harm in the matter except the tears of the poor nun, who was always weeping and always returning to the cause of her tears.”
“I have known many of the same kind,” said Hircan, “who wept for their sins and laughed at their pleasures both together.”
“I think I know whom you mean,” said Parlamente, “and their laughter has lasted so great a while that ‘twere time the tears should begin.”
“Hush!” said Hircan. “The tragedy that has begun with laughter is not ended yet.”
“To change the subject,” said Parlamente, “it seems to me that Dagoucin departed from our purpose. We were to tell only merry tales, and his was very piteous.”
“You said,” replied Dagoucin, “that you would only tell of follies, and I think that herein I have not been lacking. But, that we may hear a more pleasant story, I give my vote to Nomerfide, in the hope that she will make amends for my error.”
“I have indeed,” she answered, “a story ready which is worthy to follow yours; for it speaks of monks and death. So I pray you give good heed.”
Here end the Tales and Novels of the late Queen of Navarre, that is, all that can be recovered of them.
In his introductory essay to this translation of the Heptameron, Mr. George Saintsbury has called attention to the researches of various commentators who have laboured to identify the supposed narrators of Queen Margaret’s tales. As it may be fairly assumed that the setting of the work is pure invention on the Queen’s part, the researches in question can scarcely serve any useful purpose. Still they appear to have had considerable attraction for several erudite editors, whose opinions, occasionally alluded to in our notes, we will here briefly summarise for the information of those whom the matter may interest:—
OISILLE, a widow lady of long experience, is supposed by Messrs. de Lincy, Lacroix, Génin, Frank, de Montaiglon and Miss Mary Robinson to be Louise of Savoy. In some MSS. the name is written Osyle, the anagram of Loyse, in which fashion Louise was spelt in old French. It may be pointed out, en passant, that Brantôme’s grandmother, the Sénéchale of Poitou, whose connection with the Heptameron is recorded, was also named Louise (see ante, vol. i. p. lxxxii.).
PARLAMENTE, wife of Hircan, is supposed by the same commentators to be Queen Margaret herself; this is assumed mainly because the views which Parlamente expresses on religion, philosophy, men and women, are generally in accord with those which the Queen is known to have professed.
HIRCAN, in M. de Lincy’s opinion, might be the Duke of Alençon, Margaret’s first husband. Messrs. Frank and Mont-aiglon, following M. Lacroix, prefer to identify him as Henry d’Albret, King of Navarre. They conjecture the name of Hircan to be derived from Ilanricus, a not uncommon fashion of spelling Henricus. It might, however, simply come from hircus, a he-goat, for Hircan is a man of gross, sensual tastes.
LONGARINE, a young widow, is supposed by M. de Lincy to be Blanche de Chastillon, née de Tournon (concerning whom see ante, vol. i. p. 84, n. 7, and p. 120 et seq.; vol. iv. p. 144, n. 2; and vol. v. p. 25, n. 2). M. Frank, however, thinks she is Aimée Motier de la Fayette, lady of Longray, widow of Francis de Silly, Bailiff of Caen, and gouvernante to Queen Margaret’s daughter, Jane of Navarre. Miss Robinson shares this opinion, but M. de Montaiglon thinks that Longarine would rather be Aimée Motier de la Fayette’s daughter Frances, married to Frederic d’Almenesches, of one of the branches of the house of Foix.
SIMONTAULT (occasionally Symontaut), a young knight, is thought by M. de Lincy to be Henry d’Albret, Margaret’s second husband, who was of an extremely amorous disposition, and much younger than herself. Messrs. Frank and de Montaiglon, however, fancy Simontault to have been Francis, Baron de Bourdeilles, father of Brantôme. It is admitted, however, that if this be the case, it is curious that Brantôme should not have alluded to it in any of his writings, whereas he does speak both of his mother and of his grandmother in connection with the Heptameron.
ENNASUITE (occasionally Ennasuitte or Ennasuicte, and in some MSS. Emarsuite), is supposed by Messrs. de Lincy, Frank, and de Montaiglon to be Anne de Vivonne, wife of Francis de Bourdeilles and mother of Brantôme (see ante, vol. iv. p. 144, n. 2). It is pointed out that the name may be transformed into the three words Anne et suite.
DAGOUCIN, a young gentleman, is thought by M. Frank to be Nicholas Dangu (see ante, vol. i. p. 20, n. 4, and p. 40, n. 3), who became Chancellor to the King of Navarre. M. Lacroix, however, fancies this personage to be a Count d’Agoust.
GEBURON, apparently an elderly man, would in M. Frank’s opinion be the Seigneur de Burye, a captain of the Italian wars to whom Brantôme (his cousin-german) alludes in his writings. The name of de Burye is also found in a list of the personages present at Queen Margaret’s funeral. M. de Montaiglon shares M. Frank’s views.
NOMERFIDE, so M. de Lincy suggests, may have been the famous Frances de Foix, Countess of Chateaubriand; but M. Frank opines that she is a Demoiselle de Fimarcon or Fiédmarcon (Lat. Feudimarco), who in 1525 married John de Montpczat, called “Captain Carbon,” one of the exquisites of the famous Field of the cloth of gold. Miss Robinson, however, fancies that Nomerfide is Isabel d’Albret, sister of Margaret’s second husband, and wife of René de Rohan.
SAFFREDENT, so M. de Lincy thinks, may be Admiral de Bonnivet; M. Frank suggests John de Montpezat; and Miss Robinson René de Rohan, who, after his father Peter de Rohan-Gié (husband of Rolandine, see ante, vol. iii., Tale XXI, notes 2 and 15), had been killed at Pavia, was for some years entrusted to Queen Margaret’s care. As Miss Robinson points out, Saffredent literally means greedy tooth or sweet tooth.
Those who may be desirous of studying and comparing these various attempts at identification, will find all the evidence and arguments of any value set forth in the writings of M. Frank, M. de Montaiglon and Miss Robinson, which are specified in the Bibliography annexed to this appendix.—Ed.
Fourteen MS. copies of the Heptameron are known to exist. Twelve of these are at the Bibliothèque Nationale, Paris, one is at the town library of Orleans, and one in the Vatican library. We also have some record of four other copies which were in private libraries at the end of the last century.
The twelve MSS. at the Bibliothèque Nationale are the following:—
I. (No. 1511 in the catalogue). A folio volume bound in red morocco, bearing the Béthune arms. This MS. is on ruled paper, and only one leaf, the last, is missing.
II. (No. 1512). A small folio, calf gilt, 350 leaves, from Colbert’s library. The handwriting is that of the middle of the sixteeenth century, and is the same throughout; the last page bearing the signature “Doulcet.” This supplied the text followed in the present translation.
III. (No. 1513). A small folio, half-bound in red morocco, stamped with King Louis Philippe’s monogram. It contains only twenty-eight of the tales.
IV. (No. 1514). A large quarto, calf, from the De Mesmes library. Contains only thirty-four of the tales.
V. (No. 1515). A small folio from Colbert’s library, bound in calf, in Groslier’s style. The text is complete, but there are numerous interlinear and marginal corrections and additions, in the same handwriting as MS. VII.
VI. (Nos. 1516 to 1519). Four quarto vols., red morocco, Béthune arms. The first prologue is deficient, as is also the last leaf of tale lxxi.
VII. (No. 1520). A folio vol., calf and red morocco, stamped with fleurs-de-lys and the monogram of Louis XVIII. This MS. on stout ruled paper, in a beautiful italic handwriting of the end of the sixteenth century, is complete. Unfortunately Queen Margaret’s phraseology has been considerably modified, though, on the other hand, the copyist has inserted a large number of different readings, as marginal notes, which render his work of great value. It is frequently quoted in the present translation.
VIII. (No. 1523). A folio vol., calf, from the De La Marre library. The first two leaves are deficient, and the text ends with the fifth tale of Day IV.
IX. (No. 1522). A small folio, bound in parchment, from the De La Marre library. Only the tales of the first four days are complete, and on folio 259 begins a long poem called Les Prisons, the work probably of William Filandrier, whom Queen Margaret protected. On the first folio of the volume is the inscription, in sixteenth-century handwriting: Pour ma sour Marie Philander. The poem Les Prisons is quoted on pp. xxxviii.-ix. vol. i. of the present work. It concludes with an epitaph on Margaret, dated 1549.
X. (No. 1524). A folio vol. from Colbert’s library, bound in red and yellow morocco, on which is painted, on a blue ground, a vine laden with grapes twining round the trunk of a tree. On either side and in gold letters is the device, Sin e doppo la morte (until and after death). Following the title-page, on which the work is called “The Decameron of the most high and most illustrious Princess, Madame Margaret of France,” is a curious preface signed “Adrian de Thou,” and dated “Paris, August 8, 1553.” This Adrian de Thou, Lord of Hierville and canon of Notre Dame de Paris, counsellor and clerk of the Paris Parliament, was the fourth son of Augustine de Thou and uncle to James Augustus de Thou, the historian. He died in October 1570. His MS. of the Heptameron, a most beautiful specimen of caligraphy, contains a long table of various readings and obscure passages; this was consulted in preparing the text for the present translation. The titles to the tales have also been borrowed from this MS.; they were composed by De Thou himself, and figure in no other MS. copy.
XI. (No. 1525). A small folio, calf, from Colbert’s library, very incomplete and badly written, but containing the Miroir de Jésu Crist crucifié, the last poem Queen Margaret composed (see ante, vol. i. p. lxxxvi.).
XII. (No. 2155). A small quarto, red morocco, from the library of Mazarin, whose escutcheon has been cut off. The text, which is complete and correct, excepting that a portion of the prologue has been accidentally transposed, is followed by an epitaph on the Queen. The handwriting throughout is that of the end of the sixteenth century.
The other MSS. of the Heptameron are the following:—
XIII. (Orleans town library, No. 352). A folio vol. of 440 pp. It is doubtful whether this MS. is of the sixteenth or seventeenth century. It bears the title L’Heptaméron des Nouvelles, &c. There are numerous deficiencies in the text.
XIV. (Vatican library, No. 929; from the library of Queen Christina of Sweden). A folio vol., calf, 95 leaves, handwriting of the end of the sixteenth century. This only contains fifteen of the stories.
XV. (present possessor unknown). A folio vol., red morocco; text (ending with tale lxix. ) in sixteenth-century handwriting, with illuminated initial letters to each tale. Catalogue des livres de feue Mme. la Comtesse de Verrue, Paris, G. Martin, 1737.
XVI. (possessor unknown). MS. supposed to be the original, a large folio, handwriting of the period, antique binding, containing the seventy-two tales. Catalogue des livres, &c., du cabinet de M. Filheul, &c., Paris, Chardin, 1779, pp. xxi. and 280.
XVII. (possessor unknown). A folio vol., blue morocco, gilt. No. 1493 in the catalogue of the Bibliothèque de Simon Bernard, chez Barrois, Paris, 1734; and No. 213 in a Catalogue de manuscrits intéressants qui seront vendus... en la maison de M. Gueret, notaire, Paris, Debure fils jeune, 1776.
XVIII. (possessor unknown). A folio vol., blue morocco, gilt, stamped with the arms of France, from the Randon de Boisset library; the seventy-two tales complete, a very fine copy. Catalogue des livres de la bibliothèqzie de l’Abbé Rive, Marseilles, 1793. (This MS. should not be confounded with No. xvii. See L. J. Hubaud’s Dissertation sur les Contes de la Reine de Navarre, Marseilles, 1850.)
The following are the editions of Queen Margaret’s tales issued from the press from the sixteenth century to the present time. The list has been prepared with great care, and we believe it to be as complete a one as can be furnished; it includes several editions not mentioned in Brunet’s Manual:—
I. Histoires des Amans Fortunez dédiées à très illustre princesse, Mme. Marguerite de Bourbon, etc., par Pierre Boaistuau, dit Launoy, Paris, 1558, 40. The authorisation to print and publish was accorded to Vincent Sertenas, and the work was issued by three different booksellers; some copies bearing the name of Gilles Robinot, others that of Jean Cavyller, and others that of Gilles Gilles.
This, the first edition of the Queen’s work, contains only sixty-seven of the tales, which are not divided into days or printed in their proper sequence; the prologues, moreover, are deficient, and all the bold passages on religious and philosophical questions, &c, in the conversational matter following the stories, are suppressed.
II. L’Heptaméron des Nouvelles de tris illustre et très excellente Princesse Marguerite de Valois, Royne de Navarre, &c., dédié à très illustre et très vertueuse Princesse Jeanne, Royne de Navarre, par Claude Gruget, parisien, Paris, Vincent Certena, or Jean Caveillier, 1559.
This contains all the Queen’s tales excepting Nos. xi., xliv., and xlvi., which Gruget replaced by others, probably written by himself. The other stories are placed in their proper order, but none of the names and passages suppressed by Boaistuau are restored. The phraseology of the MSS., moreover, is still further modified and polished.
The text adopted by Boaistuau and Gruget was followed, with a few additional modifications, in all the editions issued during the later years of the sixteenth century. Most of these are badly printed and contain numerous typographical errors:—
III. L’Heptamêron des Nouvelles, &c. Reprint of Gruget’s edition, sold by Vincent Sertenas, Gilles Robinot & Gilles Gille, and printed by Benoist Prévost, Paris, 1560.
IV. L’Heptamêron des Nouvelles, &c., 1560, 16mo. (No bookseller’s or printer’s name appears in this edition. )
V. L’Heptamêron, &c. (Gruget). Guill. Rouillé, Lyons, 1561, small 12mo; Gilles Gilles, Paris, 1561, 16mo.
VI. The same. Norment & Bruneau, and Gilles Gilles, Paris, 1567, 16mo.
VII. The same. Louys Cloquemin, Lyons, 1572, 16mo (reprinted in 1578 and 1581).
VIII. The same. Michel de Roigny, Paris, 1574, 16mo (round letters).
IX. The same. Gab. Buon, Paris, 1581, 16mo.
X. The same. Abel L’Angelier, Paris, 1581, 18mo.
XI. The same. Jean Osmont, Rouen, 1598, 578 pp., sin. 12mo (good type).
XII. The same. Romain Beauvais, Rouen, 1598, 589 pp. 12mo.
In the seventeenth century the Heptameron was frequently reprinted, Gruget’s text, with a few changes, being still followed until 1698, when it occurred to some obscure literary man to put the tales into so-called beau langage. At the same time the title of Heptameron, devised by Gruget, was discarded (see post, No. XVI.).
XIII. L’Heptaméron, &c., printed by Ch. Chappellein, Paris, 1607, 18mo.
XIV. The same. Sur Pimprimé à Paris, J. Bessin (Holland), 1615, sm. l2mo (reprinted in 1698, 2. vols. 12mo).
XV. The same. David du Petit-Val, Rouen, 1625, 12mo.
XVI. Contes et Nouvelles de Marguerite de Valois, Reine de Navarre, mis en beau langage. Gallet, Amsterdam, 1698, 2 vols, sm. 8vo. This edition is valued not for its beau langage, but for the copperplate engravings illustrating it. These are coarsely executed, and are attributed to Roman de Hooge, but do not bear his name. A reprint of the edition appeared at Amsterdam in 1700.
XVII. The same. Gallet, Amsterdam, 1708, 2 vols. sm. 8vo. Virtually a reprint, but with several of the Roman de Hooge plates deficient, and replaced by others signed Harrewyn.
XVIII. The same. La Haye (Chartres), 1733, 2 vols. sm. 12mo.
XIX. The same. Londres, 1744, 2 vols. 12mo.
XX. Heptaméron Français, ou les Nouvelles de Marguerite, Reine de Navarre; chez la Nouvelle Société Typographique, Berne, 1780-1, 3 vols. 8vo. On some copies the title is simply, Nouvelles de Marguerite, etc., Berne, 1781; on others Béat Louis Walthard is designated as the publisher.
For this edition were executed the copperplate engravings, designed by Freudenberg and Dunker, which illustrate the present translation. It was at first intended to issue the work in parts, but after parts i. and ii. had been published (at 4 livres each) the project was abandoned. A few copies of these two parts are in existence; they bear the date 1778. Freudenberg began his designs in the previous year, and finished them in 1780.
This edition is greatly prized for its illustrations; the text, however, largely modified by Jean Rodolphe de Sinner, is without value. The work was reissued at Paris in 1784 (8 vols, in 8vo, some copies 18mo), at Berne in 1792, and again in Paris in 1807 (8 vols. 18mo).
The following new editions of the Heptameron have appeared during the present century:—
XXI. Contes et Nouvelles de Marguerite, &c. Dauthereau, Paris, 1828, 5 vols. 32mo. (Collection des romans français et étrangers.)
XXII. L’Heptamêron, ou Histoire des Amants fortunés, &c, ancien texte publié par C. Gruget.., revu, corrigé et publié avec des notes, &c., par le bibliophile Jacob. Gosselin (Bibliothèque d’Élite), Paris, 1841, 12mo. In this edition the Bibliophile Jacob (M. P. Lacroix) but slightly modified Gruget’s text, and his annotation was comparatively insignificant. His work was reproduced in a volume of the Panthéon Littéraire: Les vieux Conteurs français, Paris, 1841, 1. 8vo. (double cols.).
XXIII. Heptaméron des Nouvelles de... Margtierile d’Angouléme... publiée sur les manuscrits par la Société des Bibliophiles Français (Le Roux de Lincy, editor), Paris, 1853-4, 3 vols. sm. 18mo.
In this edition the real text of the tales was printed for the first time, M. de Lincy having carefully examined the best MSS. for this purpose. The present English translation is based upon his work. Copies of the “Bibliophiles Français” edition, which contains a portrait of the Queen, a facsimile of a miniature, and an engraving showing her arms and device, cannot be purchased, when in fair condition, for less than £6 in Paris.
XXIV. L’Heptaméron des Nouvelles, etc.... avec des notes et une notice par P. L. Jacob, Bibliophile (Paul Lacroix). Adolphe Delahays, Bibliothèque Gauloise, Paris, 1858, 18mo.
In this edition M. Lacroix, following M. de Lincy’s example, went to the MSS. for his text, which he annotated with care and erudition. All his notes of any importance are reproduced in the present translation. The edition of 1858 was reprinted in 1875.
XXV. L’Heptaméron, &c. Gamier frères, Paris, n.d., 1 vol. 18mo. This was long the “popular” edition in France. The text, which is considerably modernised, is of no value.
XXVI. Les sept Journées de la Reine de Navarre, suivies de la huitième. Paris, Librairie des Bibliophiles (Jouaust), 1872, 4 vols. l6mo.
In this edition Gruget’s text is followed; the notes, &c, are by M. Lacroix. The work is prized for its illustrations (a portrait and eight etchings) by Leopold Flameng. It was originally issued in eight parts. The value of the copies varies according to the paper on which they are printed. Those on India or Whatman paper, with a duplicate set of the engravings, command high prices. The text has been reissued by the same firm in two cr. 8vo vols, under the title of L’Heptaméron des contes, etc.
XXVII. L’Heptaméron des Nouvelles, &c, preface, notes, &c, by Benjamin Pifteau, in the Nouvelle Collection Jannet, Alphonse Lemerre, Paris, 1875, 2 vols. l6mo.
This, undoubtedly the best of all the cheap editions, has been reprinted by Marpon & Flammarion, Paris, n.d. The text is from the MSS.; the notes are mainly abbreviated from those of MM. de Lincy and Lacroix. M. Pifteau supplies an introduction and glossary.
XXVIII. L’Heptaméron, &c., publié avec Introduction, Notes et Glossaire par Félix Frank. Liseux, Paris, 1879, 3 vols. 12mo.
This, from the literary point of view, is one of the most important of modern editions. The text is not taken from the same MS. as was followed by M. de Lincy. The tales are preceded by a lengthy introduction, in which the editor discusses Queen Margaret’s work and seeks to identify the supposed narrators of her tales. He has frequently been quoted in the notes to this translation.
XXIX. L’Heptaméron, &c, avec notes, variantes et glossaire par F. Dillaye et notice par A. France. A. Lemerre, Paris, 1879.
A handy edition based on the MSS. The notes embody the substance of M. de Lincy’s and M. Lacroix’s researches with additional particulars supplied by M. Dillaye, who has been quoted in the course of the present work.
XXX. L’Heptaméron, &c., publié stir les manuscrits avec les notes de MM. Le Poux de Lincy et Anatole de Montaiglon. Auguste Eudes, Paris, 1880, 8 vols. 1. 8vo and 4 vols. cr. 8vo.
The edition in 8 vols, (two copies of which on parchment were issued at £44 each; and twelve on Japanese paper at £20 each) is illustrated with the Freudenberg plates; that in 4 vols, contains the text only. The text is the same as that of No. XXIII.; but with additional notes, prefatory matter, &c. The copyright attaching to this edition was acquired for the present work, in which all M. de Montaiglon’s important notes are reproduced.
Among the English translations of the Heptameron are the following:—
Heptameron, or the History of the Fortunate Lovers, translated by R. Codrington, London, 1654, 12mo. (Dedicated to Thomas Stanley, the translator of Anacreon and editor of Æschylus, and based on Boaistuau’s defective text.)
The Heptameron of Margaret, Queen of Navarre, nota first translated from the original text, by Walter K. Kelly. Bohn (extra volume), London, 1855. This has been several times reprinted. The translation is a very free rendering of M. de Lincy’s text; many passages are deficient.
The Heptameron, &c., translated from the original French by Arthur Machen. Privately printed (G. Redway), London, 1886, 1 vol. 1. 8vo. A scholarly translation, not annotated; illustrated with the etchings by Flameng (see ante, edition xxv.).
The Fortunate Lovers, twenty-seven novels of the Queen of Navarre, translated by Arthur Machen, edited with notes and introduction by A. Mary F. Robinson. G. Redway, London, 1887, 8vo. Etched frontispiece by G. P. Jacomb Hood. This only contains such of the tales as the lady-editor considered unobjectionable. In her introduction she sketches the life of Queen Margaret and discusses the identity of the supposed narrators of the tales. Some of the notes are original, but the majority are based upon the researches of French commentators.—Ed.
| Volume I. | Volume II. | Volume III. | Volume IV. |
End of the Project Gutenberg EBook of The Tales Of The Heptameron,
Complete Vol. I to V, by Margaret, Queen Of Navarre
*** END OF THIS PROJECT GUTENBERG EBOOK THE TALES OF THE HEPTAMERON ***
***** This file should be named 28858-h.htm or 28858-h.zip *****
This and all associated files of various formats will be found in:
http://www.gutenberg.org/2/8/8/5/28858/
Produced by David Widger
Updated editions will replace the previous one--the old editions
will be renamed.
Creating the works from public domain print editions means that no
one owns a United States copyright in these works, so the Foundation
(and you!) can copy and distribute it in the United States without
permission and without paying copyright royalties. Special rules,
set forth in the General Terms of Use part of this license, apply to
copying and distributing Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works to
protect the PROJECT GUTENBERG-tm concept and trademark. Project
Gutenberg is a registered trademark, and may not be used if you
charge for the eBooks, unless you receive specific permission. If you
do not charge anything for copies of this eBook, complying with the
rules is very easy. You may use this eBook for nearly any purpose
such as creation of derivative works, reports, performances and
research. They may be modified and printed and given away--you may do
practically ANYTHING with public domain eBooks. Redistribution is
subject to the trademark license, especially commercial
redistribution.
*** START: FULL LICENSE ***
THE FULL PROJECT GUTENBERG LICENSE
PLEASE READ THIS BEFORE YOU DISTRIBUTE OR USE THIS WORK
To protect the Project Gutenberg-tm mission of promoting the free
distribution of electronic works, by using or distributing this work
(or any other work associated in any way with the phrase “Project
Gutenberg”), you agree to comply with all the terms of the Full Project
Gutenberg-tm License (available with this file or online at
http://gutenberg.org/license).
Section 1. General Terms of Use and Redistributing Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic works
1.A. By reading or using any part of this Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic work, you indicate that you have read, understand, agree to
and accept all the terms of this license and intellectual property
(trademark/copyright) agreement. If you do not agree to abide by all
the terms of this agreement, you must cease using and return or destroy
all copies of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works in your possession.
If you paid a fee for obtaining a copy of or access to a Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic work and you do not agree to be bound by the
terms of this agreement, you may obtain a refund from the person or
entity to whom you paid the fee as set forth in paragraph 1.E.8.
1.B. “Project Gutenberg” is a registered trademark. It may only be
used on or associated in any way with an electronic work by people who
agree to be bound by the terms of this agreement. There are a few
things that you can do with most Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works
even without complying with the full terms of this agreement. See
paragraph 1.C below. There are a lot of things you can do with Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic works if you follow the terms of this agreement
and help preserve free future access to Project Gutenberg-tm electronic
works. See paragraph 1.E below.
1.C. The Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation (“the Foundation”
or PGLAF), owns a compilation copyright in the collection of Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic works. Nearly all the individual works in the
collection are in the public domain in the United States. If an
individual work is in the public domain in the United States and you are
located in the United States, we do not claim a right to prevent you from
copying, distributing, performing, displaying or creating derivative
works based on the work as long as all references to Project Gutenberg
are removed. Of course, we hope that you will support the Project
Gutenberg-tm mission of promoting free access to electronic works by
freely sharing Project Gutenberg-tm works in compliance with the terms of
this agreement for keeping the Project Gutenberg-tm name associated with
the work. You can easily comply with the terms of this agreement by
keeping this work in the same format with its attached full Project
Gutenberg-tm License when you share it without charge with others.
1.D. The copyright laws of the place where you are located also govern
what you can do with this work. Copyright laws in most countries are in
a constant state of change. If you are outside the United States, check
the laws of your country in addition to the terms of this agreement
before downloading, copying, displaying, performing, distributing or
creating derivative works based on this work or any other Project
Gutenberg-tm work. The Foundation makes no representations concerning
the copyright status of any work in any country outside the United
States.
1.E. Unless you have removed all references to Project Gutenberg:
1.E.1. The following sentence, with active Alinks to, or other immediate
access to, the full Project Gutenberg-tm License must appear prominently
whenever any copy of a Project Gutenberg-tm work (any work on which the
phrase “Project Gutenberg” appears, or with which the phrase “Project
Gutenberg” is associated) is accessed, displayed, performed, viewed,
copied or distributed:
This eBook is for the use of anyone anywhere at no cost and with
almost no restrictions whatsoever. You may copy it, give it away or
re-use it under the terms of the Project Gutenberg License included
with this eBook or online at www.gutenberg.org
1.E.2. If an individual Project Gutenberg-tm electronic work is derived
from the public domain (does not contain a notice indicating that it is
posted with permission of the copyright holder), the work can be copied
and distributed to anyone in the United States without paying any fees
or charges. If you are redistributing or providing access to a work
with the phrase “Project Gutenberg” associated with or appearing on the
work, you must comply either with the requirements of paragraphs 1.E.1
through 1.E.7 or obtain permission for the use of the work and the
Project Gutenberg-tm trademark as set forth in paragraphs 1.E.8 or
1.E.9.
1.E.3. If an individual Project Gutenberg-tm electronic work is posted
with the permission of the copyright holder, your use and distribution
must comply with both paragraphs 1.E.1 through 1.E.7 and any additional
terms imposed by the copyright holder. Additional terms will be Alinked
to the Project Gutenberg-tm License for all works posted with the
permission of the copyright holder found at the beginning of this work.
1.E.4. Do not unAlink or detach or remove the full Project Gutenberg-tm
License terms from this work, or any files containing a part of this
work or any other work associated with Project Gutenberg-tm.
1.E.5. Do not copy, display, perform, distribute or redistribute this
electronic work, or any part of this electronic work, without
prominently displaying the sentence set forth in paragraph 1.E.1 with
active Alinks or immediate access to the full terms of the Project
Gutenberg-tm License.
1.E.6. You may convert to and distribute this work in any binary,
compressed, marked up, nonproprietary or proprietary form, including any
word processing or hypertext form. However, if you provide access to or
distribute copies of a Project Gutenberg-tm work in a format other than
“Plain Vanilla ASCII” or other format used in the official version
posted on the official Project Gutenberg-tm web site (www.gutenberg.org),
you must, at no additional cost, fee or expense to the user, provide a
copy, a means of exporting a copy, or a means of obtaining a copy upon
request, of the work in its original “Plain Vanilla ASCII” or other
form. Any alternate format must include the full Project Gutenberg-tm
License as specified in paragraph 1.E.1.
1.E.7. Do not charge a fee for access to, viewing, displaying,
performing, copying or distributing any Project Gutenberg-tm works
unless you comply with paragraph 1.E.8 or 1.E.9.
1.E.8. You may charge a reasonable fee for copies of or providing
access to or distributing Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works provided
that
- You pay a royalty fee of 20% of the gross profits you derive from
the use of Project Gutenberg-tm works calculated using the method
you already use to calculate your applicable taxes. The fee is
owed to the owner of the Project Gutenberg-tm trademark, but he
has agreed to donate royalties under this paragraph to the
Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation. Royalty payments
must be paid within 60 days following each date on which you
prepare (or are legally required to prepare) your periodic tax
returns. Royalty payments should be clearly marked as such and
sent to the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation at the
address specified in Section 4, “Information about donations to
the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation.”
- You provide a full refund of any money paid by a user who notifies
you in writing (or by e-mail) within 30 days of receipt that s/he
does not agree to the terms of the full Project Gutenberg-tm
License. You must require such a user to return or
destroy all copies of the works possessed in a physical medium
and discontinue all use of and all access to other copies of
Project Gutenberg-tm works.
- You provide, in accordance with paragraph 1.F.3, a full refund of any
money paid for a work or a replacement copy, if a defect in the
electronic work is discovered and reported to you within 90 days
of receipt of the work.
- You comply with all other terms of this agreement for free
distribution of Project Gutenberg-tm works.
1.E.9. If you wish to charge a fee or distribute a Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic work or group of works on different terms than are set
forth in this agreement, you must obtain permission in writing from
both the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation and Michael
Hart, the owner of the Project Gutenberg-tm trademark. Contact the
Foundation as set forth in Section 3 below.
1.F.
1.F.1. Project Gutenberg volunteers and employees expend considerable
effort to identify, do copyright research on, transcribe and proofread
public domain works in creating the Project Gutenberg-tm
collection. Despite these efforts, Project Gutenberg-tm electronic
works, and the medium on which they may be stored, may contain
“Defects,” such as, but not limited to, incomplete, inaccurate or
corrupt data, transcription errors, a copyright or other intellectual
property infringement, a defective or damaged disk or other medium, a
computer virus, or computer codes that damage or cannot be read by
your equipment.
1.F.2. LIMITED WARRANTY, DISCLAIMER OF DAMAGES - Except for the “Right
of Replacement or Refund” described in paragraph 1.F.3, the Project
Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation, the owner of the Project
Gutenberg-tm trademark, and any other party distributing a Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic work under this agreement, disclaim all
liability to you for damages, costs and expenses, including legal
fees. YOU AGREE THAT YOU HAVE NO REMEDIES FOR NEGLIGENCE, STRICT
LIABILITY, BREACH OF WARRANTY OR BREACH OF CONTRACT EXCEPT THOSE
PROVIDED IN PARAGRAPH F3. YOU AGREE THAT THE FOUNDATION, THE
TRADEMARK OWNER, AND ANY DISTRIBUTOR UNDER THIS AGREEMENT WILL NOT BE
LIABLE TO YOU FOR ACTUAL, DIRECT, INDIRECT, CONSEQUENTIAL, PUNITIVE OR
INCIDENTAL DAMAGES EVEN IF YOU GIVE NOTICE OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH
DAMAGE.
1.F.3. LIMITED RIGHT OF REPLACEMENT OR REFUND - If you discover a
defect in this electronic work within 90 days of receiving it, you can
receive a refund of the money (if any) you paid for it by sending a
written explanation to the person you received the work from. If you
received the work on a physical medium, you must return the medium with
your written explanation. The person or entity that provided you with
the defective work may elect to provide a replacement copy in lieu of a
refund. If you received the work electronically, the person or entity
providing it to you may choose to give you a second opportunity to
receive the work electronically in lieu of a refund. If the second copy
is also defective, you may demand a refund in writing without further
opportunities to fix the problem.
1.F.4. Except for the limited right of replacement or refund set forth
in paragraph 1.F.3, this work is provided to you ‘AS-IS’ WITH NO OTHER
WARRANTIES OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO
WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTIBILITY OR FITNESS FOR ANY PURPOSE.
1.F.5. Some states do not allow disclaimers of certain implied
warranties or the exclusion or limitation of certain types of damages.
If any disclaimer or limitation set forth in this agreement violates the
law of the state applicable to this agreement, the agreement shall be
interpreted to make the maximum disclaimer or limitation permitted by
the applicable state law. The invalidity or unenforceability of any
provision of this agreement shall not void the remaining provisions.
1.F.6. INDEMNITY - You agree to indemnify and hold the Foundation, the
trademark owner, any agent or employee of the Foundation, anyone
providing copies of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works in accordance
with this agreement, and any volunteers associated with the production,
promotion and distribution of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works,
harmless from all liability, costs and expenses, including legal fees,
that arise directly or indirectly from any of the following which you do
or cause to occur: (a) distribution of this or any Project Gutenberg-tm
work, (b) alteration, modification, or additions or deletions to any
Project Gutenberg-tm work, and (c) any Defect you cause.
Section 2. Information about the Mission of Project Gutenberg-tm
Project Gutenberg-tm is synonymous with the free distribution of
electronic works in formats readable by the widest variety of computers
including obsolete, old, middle-aged and new computers. It exists
because of the efforts of hundreds of volunteers and donations from
people in all walks of life.
Volunteers and financial support to provide volunteers with the
assistance they need, is critical to reaching Project Gutenberg-tm’s
goals and ensuring that the Project Gutenberg-tm collection will
remain freely available for generations to come. In 2001, the Project
Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation was created to provide a secure
and permanent future for Project Gutenberg-tm and future generations.
To learn more about the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation
and how your efforts and donations can help, see Sections 3 and 4
and the Foundation web page at http://www.pglaf.org.
Section 3. Information about the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive
Foundation
The Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation is a non profit
501(c)(3) educational corporation organized under the laws of the
state of Mississippi and granted tax exempt status by the Internal
Revenue Service. The Foundation’s EIN or federal tax identification
number is 64-6221541. Its 501(c)(3) letter is posted at
http://pglaf.org/fundraising. Contributions to the Project Gutenberg
Literary Archive Foundation are tax deductible to the full extent
permitted by U.S. federal laws and your state’s laws.
The Foundation’s principal office is located at 4557 Melan Dr. S.
Fairbanks, AK, 99712., but its volunteers and employees are scattered
throughout numerous locations. Its business office is located at
809 North 1500 West, Salt Lake City, UT 84116, (801) 596-1887, email
business@pglaf.org. Email contact Alinks and up to date contact
information can be found at the Foundation’s web site and official
page at http://pglaf.org
For additional contact information:
Dr. Gregory B. Newby
Chief Executive and Director
gbnewby@pglaf.org
Section 4. Information about Donations to the Project Gutenberg
Literary Archive Foundation
Project Gutenberg-tm depends upon and cannot survive without wide
spread public support and donations to carry out its mission of
increasing the number of public domain and licensed works that can be
freely distributed in machine readable form accessible by the widest
array of equipment including outdated equipment. Many small donations
($1 to $5,000) are particularly important to maintaining tax exempt
status with the IRS.
The Foundation is committed to complying with the laws regulating
charities and charitable donations in all 50 states of the United
States. Compliance requirements are not uniform and it takes a
considerable effort, much paperwork and many fees to meet and keep up
with these requirements. We do not solicit donations in locations
where we have not received written confirmation of compliance. To
SEND DONATIONS or determine the status of compliance for any
particular state visit http://pglaf.org
While we cannot and do not solicit contributions from states where we
have not met the solicitation requirements, we know of no prohibition
against accepting unsolicited donations from donors in such states who
approach us with offers to donate.
International donations are gratefully accepted, but we cannot make
any statements concerning tax treatment of donations received from
outside the United States. U.S. laws alone swamp our small staff.
Please check the Project Gutenberg Web pages for current donation
methods and addresses. Donations are accepted in a number of other
ways including checks, online payments and credit card donations.
To donate, please visit: http://pglaf.org/donate
Section 5. General Information About Project Gutenberg-tm electronic
works.
Professor Michael S. Hart is the originator of the Project Gutenberg-tm
concept of a library of electronic works that could be freely shared
with anyone. For thirty years, he produced and distributed Project
Gutenberg-tm eBooks with only a loose network of volunteer support.
Project Gutenberg-tm eBooks are often created from several printed
editions, all of which are confirmed as Public Domain in the U.S.
unless a copyright notice is included. Thus, we do not necessarily
keep eBooks in compliance with any particular paper edition.
Most people start at our Web site which has the main PG search facility:
http://www.gutenberg.org
This Web site includes information about Project Gutenberg-tm,
including how to make donations to the Project Gutenberg Literary
Archive Foundation, how to help produce our new eBooks, and how to
subscribe to our email newsletter to hear about new eBooks.