| Vol. XIX. No. 542.] | SATURDAY, APRIL 14, 1832. | [PRICE 2d. |
Our attention has been invited to the Beulah Spa by a brochure lately published, from the very competent pen of Dr. George Hume Weatherhead; the details of which will be read with interest by all who are in quest of "healing founts." "The Spa," observes Dr. Weatherhead, "has long been resorted to by the country people of the neighbourhood, who, from experiencing its beneficial effects in a variety of diseases, have sustained its sanative character, and kept it from sinking into total neglect." We trust, however, that its virtues may soon enjoy more extensive celebrity, especially as the attractions of the scenery amidst which the spring is situate are of no common-place character, and the distance from the metropolis both easy and inviting. The Spa has already acquired some popularity; for, we learned on our visit a few days since, that, although it was only opened to the public towards the close of the month of August, in the past year, it was visited during the autumn by several hundred persons weekly.
Dr. Weatherhead has described the local scenery with accuracy. Beulah, the estate upon which the spring is situate, is within the village of Norwood, seven miles south of London, upon one of those elevations known as the Norwood hills. "From trigonometrical observation," observes Dr. Weatherhead, "it has been computed that the height of these hills is about 390 feet above the level of the sea at low water. 1 Thus placed above the fogs of the plain, and removed from the smoky and contaminated atmosphere of the metropolis, the air has long been celebrated for its pure and invigorating qualities." Norwood was in the memory of several of the inhabitants still living, an entire forest of oaks, and the well-known resort of tribes of gipsies. 2 The country from Camberwell thence is, therefore, in [pg 226] great part a newly-peopled district. Its outline is very uneven, perhaps more so than any other portion of the environs of the metropolis. The road runs over or through many little crests or hills, and sinks into sheltered valleys, where you see newly-built habitations nestling together, and almost reminding one of the aboriginal contrivances for warmth and comfort in less civilized countries. The road-side is set with "suburban villas" which would make the spleen of Cowper blaze into madness; though few of them exhibit any pretensions to elegance or snugness. Neither would two newly-built churches in the prospect allay the anti-urban poet; their starved proportions contrasting but coldly with the primitive simplicity of a village church. The country itself is nevertheless picturesque; the prospect is of enchanting beauty, and as you approach Beulah, you obtain occasional glimpses of the subjacent valley which you enjoy more at leisure and at a coup d'oeil in the Spa grounds.
The Spring lies embowered in a wood of oaks, open to the south-west whose dense foliage shelters and protects it. It is now the sole vestige of the gipsy haunts, and comprises a space of more than twenty-five acres; the gentle inclination of the ground keeping the foot-paths always dry.
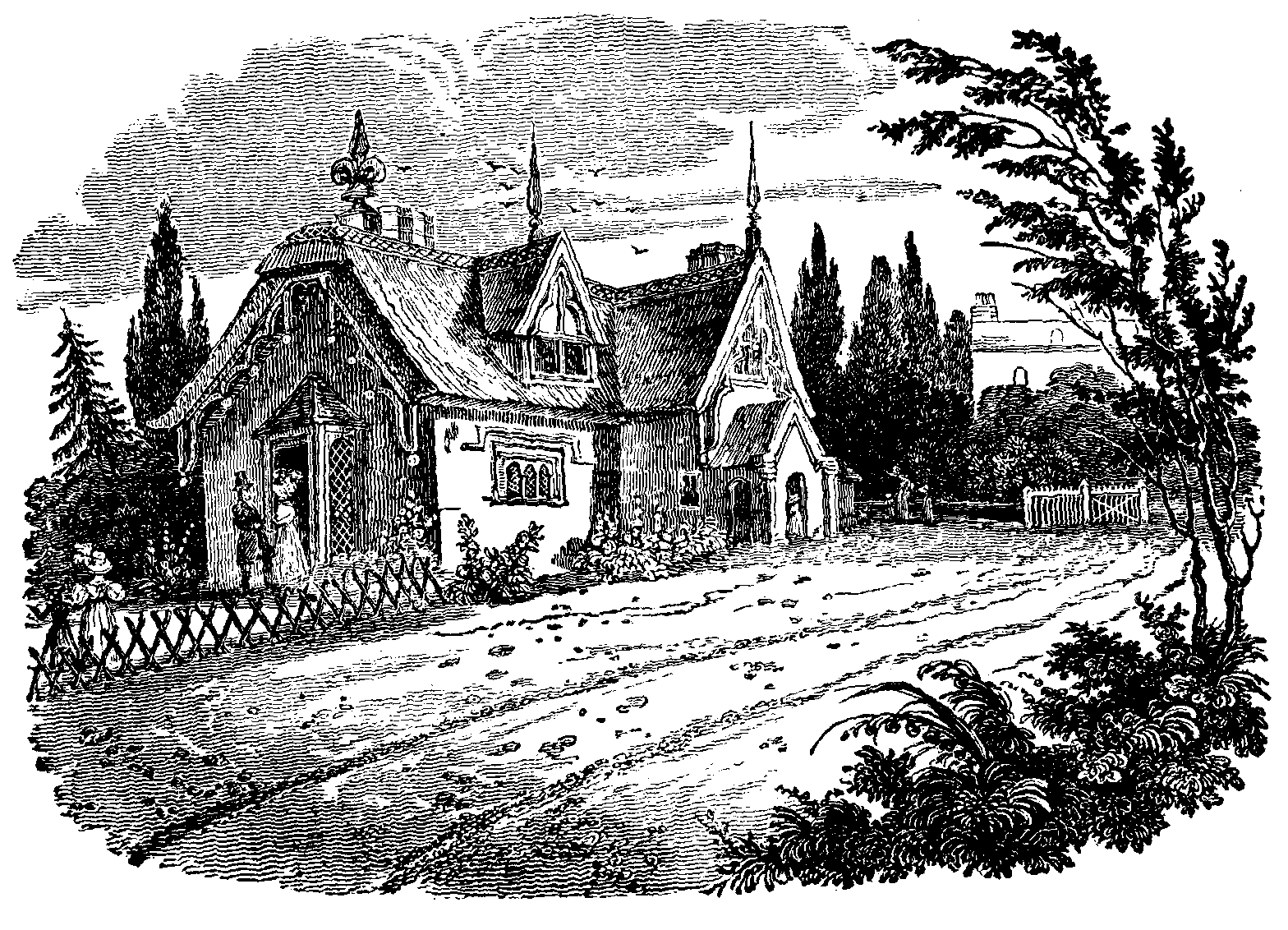
We entered the grounds at an elegant rustic lodge (see the Cut,) where commences a new carriage-road 3 to Croydon; which winds round the flank of the hill, and is protected by hanging woods. The lodge is in the best taste of ornate rusticity, with the characteristic varieties of gable, dripstone, portico, bay-window, and embellished chimney: of the latter there are some specimens in the best style of our olden architects. This building, as well as the other rural edifices in the grounds, and the whole disposal of the latter, have been planned by Mr. Decimus Burton, the originator of the architectural embellishments of the Zoological Gardens in the Regent's Park.
Passing the lodge, we descended by a winding path through the wood to a small lawn or glade, at the highest point of which is a circular rustic building, used as a confectionery and reading-room; near which is the Spa, within a thatched apartment. The spring rises about 14 feet, within a circular rockwork enclosure; the water is drawn by a contrivance, at once ingenious and novel; a glass urn-shaped pail, terminating with a cock of the same material, and having a stout rim and cross-handle of silver, is attached to a thick worsted rope, and let down into the spring by a pulley, when the vessel being taken up full, the water is drawn off by the cock. We quote Dr. Weatherhead's analytical description of the water:
"The water drawn fresh from the well is beautifully transparent and sparkling. Innumerable bubbles of fixed air are seen rising to the surface, when allowed to stand. Its taste is distinctly bitter, without being at all disagreeable, leaving on the palate [pg 227] the peculiar flavour of its predominant saline ingredient, the sulphate of magnesia. The temperature of the water, at the bottom of the well, is 52 deg. of Fahrenheit; its specific gravity 1011; and, by an analysis of its composition by those distinguished scientific chemists, Messrs. Faraday and Hume, the following are the solid contents of a quart of the water:—
BEULAH SALINE.
Sulphate of magnesia ............ 123
Sulphate of soda and magnesia .... 32
Muriate of soda .................. 19
Muriate of magnesia .............. 18-1/2
Carbonate of lime ................ 15
Carbonate of soda ................. 3
---
Grains 210-1/2
CHELTENHAM PURE SALINE.
Sulphate of magnesia ............. 22
Sulphate of soda ................. 30
Muriate of soda ..................100
Sulphate of lime .................. 9
---
Grains 161
"As a mean of comparison, the saline contents of a quart of the Cheltenham pure saline, as analyzed by Mr. Brande, the predecessor of Mr. Faraday in the professorship at the Royal Institution, is placed opposite to the Beulah Spring, to enable the reader to judge how much superior, as an aperient water, the latter is to that of Cheltenham. And, first, it may be observed, that the gross amount of the several salts, in the same quantity of the waters, is much greater in the Beulah than in the Cheltenham spring, the difference being forty-nine grains and a half of solid saline matter in a quart—that is, the impregnation is nearly one-third stronger; and, secondly, the nature of the saline ingredients also merits observation. One hundred grains out of one hundred and sixty-one, consist, as we see, in the Cheltenham, of muriate of soda, or common table-salt. Now, this substance, when perfectly freed from other salts adhering to it, possesses comparatively very feeble aperient properties; whereas the mass of the ingredients in the Beulah Spa is composed of two powerful saline substances, the sulphate of magnesia, and that peculiar double salt, the sulphate of soda and magnesia, constituting three-fourths of the whole saline impregnation." 4
The lawn is tastefully varied with parterres of plants; owing to the lateness of the season, we saw but few near flowering, save
Daffodils,
That come before the swallow dares, and take
The winds of March with beauty, violets dim,
But sweeter than the lids of Juno's eyes,
Or Cytherea's breath.
A few yards from the lawn a rustic orchestra is in course of erection: whence "the dulcet and harmonious sounds" of music may attune with the joyful inspiration of the natural beauties of the scene. Our guide, (of a more intelligent and communicative character than guides usually are,) directed us by a descending path through the wood, across a rude bridge, past a maze, by a flight of roughly-formed steps, to a terrace, whence we enjoyed a picturesque prospect of great range and indescribable beauty. The woods were as yet leafless, but primroses enlivened the pathside: how touchingly is their solitude told by our poets. Shakspeare calls them
Pale primroses
That die unmarried ere they can behold
Bright Phoebus in his strength.
Milton describes them as dying forsaken:
Bring the rathe primrose that forsaken dies:
and Mayne calls this flower
Lorn tenant of the peaceful glade,
Emblem of virtue in the shade.
Dr. Weatherhead describes the prospect from this terrace with more minuteness than the hazy state of the atmosphere enabled us to trace its several beauties. The ancient archiepiscopal town of Croydon lies at your feet; more remote, Banstead Downs spread a carpet of blooming verdure to the sight; in the extreme distance Windsor Castle peers its majestic towers above the mist; while elsewhere the utmost verge of the horizon is bounded by the bold range of the Surrey and Hampshire hills. Turning to the left you enjoy a view of Addiscombe Place, the seminary for cadets of the East India Company; of Shirley, the sporting seat of John Maberly, Esq. M.P.; of the Addington hills clothed with heaths; and of the park, the seat of his Grace the Archbishop of Canterbury; when the prospect, deepening in extent, stretches as far as Knockholt Beeches, near Seven Oaks, and, winding round, comprehends the tall spire of Beckenham Church, piercing through the dense woods which surround it; Shooter's Hill, Blackheath, and the villages that intervene.
Immediately beneath you are the grounds of the Spa, every portion of which can be distinctly traced from this spot: the lodge, lawn, refreshment-room, spring, and orchestra, as we have described them, and the paths winding among the woods till they disappear as it were in trackless solitude.
Dr. Weatherhead's pamphlet treats copiously, but in a popular style, of the medicinal properties of the Spa. The terms for drinking the waters are furnished at the lodge, where the visiter may smile at the remedy being set to music, in the melodies of the Beulah Spring Quadrilles. It may prevent some disappointment by stating that the Grounds are not opened to the public on Sundays.
The following quaint observations possess peculiar interest at the present moment:
"Among the ancient Druids," says Mr. Owen Feltham, "it was absolutely forbidden to register their laws in writing. And Caesar, in his Gallique Wars, gives us two reasons for it. One, that their mysteries might not come to be profaned and encommoned by the vulgar: another, that not being written, they might be more careful ever to carry them in their thoughts and memory. Though doubtless it was as well to preserve their own authority, to keep the people to a recourse to them, and to a reverence and esteem of their judgments. Besides, it oft falls out that what is written, though it were a good law when made, yet by the emergency of affairs, and the condition of men and times, it happens to be bad and alterable. And we find it to be evidently true, that, as where there are many physicians, there are many diseases; so where there are many laws, there are likewise many enormities. That nation that swarms with law and lawyers, certainly abounds with vice and corruption. Where you find much fowl resort, you [pg 228] may be sure there is no want of either water, mud, or weeds.
"In the beginning of thriving states, when they are more industrious and innocent, they have then the fewest laws. Rome itself had at first but twelve tables. But after, how infinitely did their number of laws increase! Old states, like old bodies will be sure to contract diseases. And where the law-makers are many, the laws will never be few. That nation is in best estate that hath the fewest laws, and those good. Variety does but multiply snares. If every bush be limed, there is no bird can escape with all his feathers free. And many times when the law did not intend it, men are made guilty by the pleader's oratory; either to express his eloquence, to advance his practice, or out of mastery to carry his cause: like a garment pounced with dust, the business is so smeared and tangled that without a Galilaeus his glass, you can never come to discern the spots of this changeable moon. Sometimes to gratify a powerful party, justice is made blind through corruption, as well as out of impartiality. That indeed, by reason of the non-integrity of men. To go to law, is, for two to contrive the kindling of a fire at their own cost, to warm others, and singe themselves to cinders. Because they cannot agree to what is truth and equity, they will both agree to plume themselves, that others may be stuck with their feathers."
W.G.C.
Rhymes which refer to the weather were probably written by the monks.
If St. Paul be fine and clear,
We shall have a happy year.
If St. Paul be thick with rain,
Then dear will be the price of grain.
After St. Bartholomew
Come long evenings and cold dew.
February fill dyke,
Be it black or be it white,
But if it is white,
It is better to like.
March winds and April showers,
Bring forth May flowers.
He who views his wheat on a weeping May,
Will himself so weeping away;
But he who views it on a weeping June,
Will go away in another tune.
When the sand doth feed the clay,
England woe and well-a-day:
But when the clay doth feed the sand,
Then it is well with Angle Land.
A swarm of bees in May
Is worth a load of hay,
A swarm of bees in June
Is worth a silver spoon.
A swarm of bees in July
Is not worth a fly.
Under a broomstalk silver and gold,
Under a gorsestalk hunger and cold.
When hempe's spun,
England's done.
The latter referred to the reigns of Henry VIII., Edward IV., Mary and Philip, and Queen Elizabeth, but proved false prophecy.
W.
In the days of Monks and Friars, the following lines in bad Latin, were composed on Crowland, Lincolnshire, or the adjoining Abbey:
In Hollandia stat Crowland;
Ibi vinium talequale,
Ibi foenum gladiale
Ibi lecti lapidale,
Ibi viri boreali,
Ibi vale sine vale.
They are thus translated in the Beauties of England and Wales (1767):—
"In Holland stands Crowland
Built on dirty low land.
Where you'll find, if you go,
The wine's but so so;
The blades of the hay
Are like swords one may say,
The beds are like stones,
And break a man's bones;
The men rough and sturdy,
Compliments will afford me
But bid you good b'w'y,
When both hungry and dry."
W.H.
Bromley Pagets was remarkable for a very singular sport on New Year's Day and Twelfth Day, called the Hobby Horse Dance: a person rode upon the image of a horse, with a bow and arrow in his hands, with which he made a snapping noise, keeping time with the music, whilst six others danced the hay and other country dances, with as many rein-deer's heads on their shoulders. To this hobby-horse belonged a pot, which the Reeves of the town kept and filled with cakes and ale, towards which the spectators contributed a penny, and with the remainder maintained their poor and repaired the church.—W.H.
Ramsey Island, near St. David's Head, is said to have been inhabited by so many saints, that no less than twenty thousand are stated in ancient histories to lie interred there. Near this place are the rocks styled the Bishop and his Clerks, which, says an ancient author "preache deadly doctrine to their winter audience, such poor sea-faring men as are forcyd thether by tempest, onelie in one thing they are to be commended, [pg 229] they keepe residence better than the rest of the canons of that see (St. David's) are wont to do."
W.H.
After the Britons retired into Wales, it was enacted that no man should guide a plough that could not make one; and that the driver should make the ropes of twisted willows, with which it was drawn. It was usual for six or eight persons to form themselves into a society for fitting out one of these ploughs, providing it with oxen, and every thing necessary for ploughing; and many curious laws were made for the regulation of such societies. If any person laid dung on the field with the consent of the proprietor, he was by law allowed the use of that land for one year. If the dung was carried out in a cart in great abundance, he was to have the use of the land for three years. Whoever cut down a wood, and converted the ground into arable, with the consent of the owner, was to have the use of it for five years. If any one folded his cattle for one year, upon a piece of ground belonging to another, with the owner's consent, he was allowed the use of the ground for four years. Thus, though the Britons had in a great measure lost the knowledge of agriculture, they appear to have been very assiduous in giving encouragement to such as would attempt the revival of it.
T. GILL.
We continue our extracts from this very entertaining work, the following being from the second volume.
At Boossà, the travellers receive a visit from "the noted widow Zuma." She must be an Amazonian lady, for, having quarrelled with her prince, the ruler of Wowow, she was obliged to fly, and actually to climb over the city wall in the night, and travel on foot to Boossà. Female politicians in Africa are not so safe as in the coteries of civilized Europe: they have to fight their own battles, and we conclude, to raise their own supplies: "the widow complained sadly of poverty and the hardness of the times; she had fought with the Yarribeans against Alòrie; but instead of receiving a recompense for her bravery, she had lost half her slaves in an engagement, which so disgusted her with the military profession, that she immediately abandoned it and returned home. Yet, in spite of all her losses and misfortunes, she has gained so much in corpulency, that it was with the utmost difficulty, she could squeeze herself into the doorway of our hut, although it is by no means small. The widow Zuma is a very good-looking, elderly person of matronly appearance. Her skin is of a light copper colour." Should this meet the eye of any soldier of fortune, &c.
At Boossà, they hear some tidings of
"Our visiters remained with us a considerable time, and in the course of conversation, one of them observed that they had in their possession a tobe, which belonged to a white man who came from the north many years ago, and from whom it had been purchased by the king's father. We expressed great curiosity to see this tobe, and it was sent us as a present a short time after their departure. Contrary to our expectations, we found it to be made of rich crimson damask, and very heavy from the immense quantity of gold embroidery with which it was covered. As the time when the late king was said to have purchased this tobe corresponds very nearly to the supposed period of Mr. Park's death, and as we never heard of any other white man having come from the north so far south as Boossà, we are inclined to believe it to be part of the spoil obtained from the canoe of that ill-fated traveller. Whether Mr. Park wore the tobe himself, which is scarcely probable on account of its weight, or whether he intended it as a present to a native chief, we are at a loss to determine. At all events, the article is a curiosity in itself; and if we should live to return to England, we shall easily learn whether it was made there or not. The chief himself has never worn the tobe, nor did his predecessor, from a superstitious feeling; 'besides,' observed the king, 'it might excite the cupidity of the neighbouring powers.'
"Sunday, June 20th.—The king sent a messenger this morning, to inform us that he was a tailor, and that he would thank us for some thread and a few needles for his own private use. By this man he likewise sent a musket for [pg 230] us to repair; but as it is Sunday, we have declined doing it till to-morrow. Eager as we are to obtain even the slightest information relative to the unhappy fate of Mr. Park and his companions, as well as to ascertain if any of their books or papers are now in existence at this place, we had almost made up our minds to refrain from asking any questions on the subject, because we were apprehensive that it might be displeasing to the king, and involve us in many perplexities. Familiarity, however, having in some measure worn off this impression, and the king being an affable, obliging, and good-natured person, we were emboldened to send Paskoe to him this morning, with a message expressive of the interest we felt on the subject, in common with all our countrymen; and saying that, if any books or papers which belonged to Mr. Park were yet in his possession, he would do us a great service, by delivering them into our hands, or at least by granting us permission to see them. To this the king returned for answer, that when Mr. Park was lost in the Niger, he was a very little boy, and that he knew not what had become of his effects; that the deplorable event had occurred in the reign of the late king's predecessor, who died shortly after; and that all traces of the white man had been lost with him. This answer disappointed our hopes, for to us it appeared final and decisive. But in the evening they were again raised by a hint from our host, who is the king's drummer, and one of the principal men in the country: he assured us, that there was certainly one book at least saved from Mr. Park's canoe, which is now in the possession of a very poor man in the service of his master, to whom it had been entrusted by the late king during his last illness. He said moreover, that if but one application were made to the king, on any subject whatever, very little was thought of it; but if a second were made, the matter would be considered of sufficient importance to demand his whole attention,—such being the custom of the country. The drummer therefore recommended us to persevere in our inquiries, for he had no doubt that something to our satisfaction would be elicited. At his own request, we sent him to the king immediately, desiring him to repeat our former statement, and to assure the king, that should he be successful in recovering the book we wanted, our monarch would reward him handsomely. He desired the drummer to inform us, that he would use every exertion, and examine the man who was reported to have the white man's book in his possession, at an early hour to-morrow. Here the matter at present rests.
"In the afternoon, the king came to see us, followed by a man with a book under his arm, which was said to have been picked up in the Niger after the loss of our countryman. It was enveloped in a large cotton cloth, and our hearts beat high with expectation as the man was slowly unfolding it, for by its size we guessed it to be Mr. Park's journal; but our disappointment and chagrin were great, when, on opening the book, we discovered it to be an old nautical publication of the last century. The title-page was missing, but its contents were chiefly tables of logarithms. It was a thick royal quarto, which led us to conjecture that it was a journal; between the leaves we found a few loose papers of very little consequence indeed; one of them contained two or three observations on the height of the water in the Gambia; one was a tailor's bill on a Mr. Anderson; and another was addressed to Mr. Mungo Park, and contained an invitation to dinner,—the following is a copy of it:—
'Mr. and Mrs. Watson would be happy to have the pleasure of Mr. Park's company at dinner on Tuesday next, at half-past five o'clock. 'An answer is requested. 'Strand, 9th Nov. 1804.'
"The king, as well as the owner of the book, looked as greatly mortified as ourselves, when they were told that the one produced was not that of which we were in quest, because the reward promised would not of course be obtained. As soon as our curiosity had been fully satisfied, the papers were carefully collected and placed again between the leaves, and the book as carefully folded in its envelope as before, and taken away by its owner, who values it as much as a household god. Thus all our hopes of obtaining Mr. Park's journal or papers, in this city, are entirely defeated. The inquiry, on our part, has not been prosecuted without much trouble and anxiety, and some little personal sacrifices likewise, which, had they been ten times as great, we would gladly have made whilst a single hope remained of their being effectual."
After much ado at Boossà, owing to the canoe not being ready—the "King of the Canoe," a sort of Lord of the Admiralty, informing the travellers with the utmost unconcern that it was out of repair—they
[pg 231]"About mid-day the workmen having finished our canoe, the luggage was presently put into it, and between twelve and one we embarked with our people, and were launched out into the river. The direction of this branch was nearly east and west; and we proceeded some distance down the stream for the purpose of getting into the main branch of the Niger, where there is deeper water. This object was soon attained, and we found it flowing from north to south, through a rich and charming country, which seemed to improve in appearance the further we advanced. We were propelled at a good rate up a channel, which, from half a mile in breadth, gradually widened to rather better than a mile. Beautiful, spreading, and spiry trees adorned the country on each side of the river, like a park; corn, nearly ripe, waved over the water's edge; large, open villages appeared every half-hour; and herds of spotted cattle were observed grazing and enjoying the cool of the shade. The appearance of the river, for several miles, was no less enchanting than its borders; it was as smooth as a lake; canoes laden with sheep and goats, were paddled by women down its almost imperceptible current; swallows, and a variety of aquatic birds, were sporting over its glassy surface, which was ornamented by a number of pretty little islands.
"Friday, June 25th.—The most remarkable object which we saw on rising this morning, was a rugged and romantic range of hills, appearing to the eastward of our encampment; it is called Engarskie, from a country of the same name in which the hills are situated, and which was formerly an independent kingdom, but is now become a province of Yàoorie. At a little before seven, A.M., our canoe was pushed off the sandy beach on which it had been secured last evening, and propelled down a very narrow channel, between a large sand-bank and the shore. This conducted us into the main branch of the Niger, and we again admired its delightful and magnificent appearance.
"We had proceeded only a few hundred yards when the river gradually widened to two miles, and continued so as far as the eye could reach. It looked very much like an artificial canal; the banks having the appearance of a dwarf wall, with vegetation beyond. In most places the water was extremely shallow, but in others it was deep enough to float a frigate. During the first two hours of the day, the scenery was as interesting and picturesque as can be imagined. The banks were literally covered with hamlets and villages; fine trees, bending under the weight of their dark and impenetrable foliage, everywhere relieved the eye from the glare of the sun's rays, and, contrasted with the lively verdure of the little hills and plains, produced the most pleasing effect. Afterwards, however, there was a decided change; the banks, which before consisted of dark earth, clay, or sand, were now composed of black rugged rocks; large sand-banks and islands were scattered in the river, which diverted it into a variety of little channels, and effectually destroyed its appearance.
"We had heard so unfavourable an account of the state of the river at one particular place which we should have to pass, that our people were compelled to disembark and walk along the banks a considerable way till we had passed it, when we took them in again. We found the description to be in no wise exaggerated; it presented a most forbidding appearance, and yields only to the state of the Niger near Boossà in difficulty and danger. On our arrival at this formidable place, we discovered a range of black rocks running directly across the stream, and the water, finding only one narrow passage, rushed through it with great impetuosity, over-turning and carrying away everything in its course. Our boatmen, with the assistance of a number of the natives, who planted themselves on the rocks on each side of the only channel, and in the stream at the stern of the canoe, lifted it by main force into smoother and safer water. The last difficulty with respect to rocks and sand-banks was now overcome, and in a very little time we came to the termination of all the islands, after which, it is said, there is not a single dangerous place up the Niger. The river here presented its noblest appearance; not a single rock nor sand-bank was anywhere perceptible; its borders resumed their beauty, and a strong, refreshing breeze, which had blown during the whole of the morning, now gave it the motion of a slightly-agitated sea. In the course of the morning we passed two lovely little islands, clothed in verdure, which at a short distance looked as charming as the fabled gardens of Hesperia; indeed no spot on earth can excel them in beauty of appearance. These islands are inhabited by a few individuals."
Upon leaving Yàoorie, a venerable Arab chief pretended great regard for the travellers, though he used them [pg 232] deceitfully; they had, however, "enjoyed an innocent kind of revenge, in administering to him a powerful dose of medicine, which though harmless in its effects, had yet been very troublesome to him. Indeed, it was not till we had 'jalaped' the sultan, his sister, and all the royal family, that we were permitted to take our farewell of Yàoorie."
The incident of physicking the royal family at Yàoorie by way of leave-taking, is only equalled by the following oddity:—"The captain of the palm oil brig, Elizabeth, now in the Calabar river, actually white-washed his crew from head to foot, while they were sick with fever and unable to protect themselves; his cook suffered so much in the operation, that the lime totally deprived him of the sight of one of his eyes, and rendered the other of little service to him."
The account of the Travellers' visit to Fernando Po, in the third volume, will be read with interest, as indeed will every page of the whole narrative; and to this commendation of the Messrs. Landers' Journal of their past adventures we cheerfully add our best wishes for the success of their future enterprize.
Among the musical novelties of the day, we notice with much pleasure, a pretty volume of Lyrics, written by Mr. Moncrieff, the music by Mr. S. Nelson. The poetry is throughout sparkling and characteristic, and "an Historical Introduction on the origin and customs of Gipsies," prefixed to the Songs, is so attractive as to be likely to share the popularity of the piano-forte accompaniments. It is written with considerable care and neatness, and the peculiar tact requisite to produce an interesting paper on a dry subject.
We are only enabled to quote from the lyrics, an opening carol, as
Liberty, liberty!
Search the world round,
'Tis with the Gipsy
Alone thou art found.
Then in the gay greenwood
We worship thee now,
The free, oh the free!
Still live under the bough.
Trarah! Trarah!
Hark, the deep dingles ring,
Free hearts, with the bird
And the deer are on wing;
Joy claims in the greenwood
The Gipsy's glad vow,
The blithe, oh the blithe!
Still live under the bough.
And the first song entire.
Oh! 'tis I am the Gipsy Queen!
And where is there queen like me,
That can revel upon the green,
In boundless liberty?
What though my cheek be brown,
And wild my raven hair,
A red cloth hood my crown,
And my sceptre the wand I bear!
Yet, 'tis I am the Gipsy Queen!
With my kingdom I'm well content,
Though my realm's but the hawthorn glade;
And my palace a tatter'd tent
Beneath the willow's shade:
Though my banquet I'm forc'd to make
On haws and berries store,
And the game that by chance we take
From some neighbouring hind's barn door!
Yet, 'tis I am the Gipsy Queen!
'Tis true I must ply my art,
And share in my subjects' toils;
But of all their gains I've part,
I've the choice of all their spoils;
And, by love and duty led,
Ere from my jet black eye
One sad tear should be shed,
A thousand hearts would die!
For, 'tis I am the Gipsy Queen!
Come, take our boy, and we will go
Before our cabin door;
The winds shall bring us, as they blow,
The murmurs of the shore;
And we will kiss his young blue eyes,
And I will sing him as he lies,
Songs that were made of yore:
I'll sing, in his delighted ear,
The island-lays thou lov'st to hear.
And thou, while stammering I repeat,
Thy country's tongue shalt teach;
'Tis not so soft, but far more sweet
Than my own native speech;
For thou no other tongue didst know,
When, scarcely twenty moons ago,
Upon Tahité's beach,
Thou cam'st to woo me to be thine,
With many a speaking look and sign.
I knew thy meaning—thou didst praise
My eyes, my locks of jet;
Ah! well for me they won thy gaze—
But thine were fairer yet!
I'm glad to see my infant wear
Thy soft blue eyes and sunny hair,
And when my sight is met
By his white brow and blooming cheek,
I feel a joy I cannot speak.
Come talk of Europe's maids with me,
Whose necks and cheeks, they tell,
Outshine the beauty of the sea,
White foam and crimson shell.
I'll shape like theirs my simple dress,
And bind like them each jetty tress,
A sight to please thee well;
And for my dusky brow will braid
A bonnet like an English maid.
Come, for the soft, low sunlight calls—
We lose the pleasant hours;
'Tis lovelier than these cottage walls—
That seat among the flowers.
And I will learn of thee a prayer
To Him who gave a home so fair,
A lot so blest as ours—
The God who made for thee and me
This sweet lone isle amid the sea.
From a volume of American Poetry, William Cullen Bryant.
In the churchyard of Beaconsfield, Bucks, stands the above handsome tribute to the memory of the celebrated poet and politician, EDMUND WALLER. The monument is of marble, with a pyramid rising from the centre, and a votive urn at each corner. On the east side is a Latin inscription, stating that Waller was born March 30, 1605, at Coleshill, in Hertfordshire; his father being Robert Waller, Esq. (of Agmondelsham in Buckingham, whose family was originally a branch of the Kentish Wallers, 5 ) and his mother of the Hampden family; that he was a student at Cambridge; "his first wife was Anne, only daughter and heiress to Edward Banks, twice made a father by his first wife, and thirteen times by his second, whom he survived eight years; he died October 21, 1687." The original inscription is by Rymer, and is to be seen in most editions of the poet's works. The monument was erected by the poet's son's executors, in 1700, and stands on the east side of the churchyard, near the family vault. The above engraving is from a sketch, obligingly furnished by our Correspondent, W.H. of Wycombe.
Waller was proprietor of the manor of Beaconsfield, and that of Hall Barn, in the vicinity, at which latter place he resided.
It is remarkable, that this great man, toward the decline of life bought a small house, with a little land, on his natal spot; observing, "that he should be glad to die like the stag, where he was roused." This, however, did not happen. "When he was at Beaconsfield," says Johnson, "he found his legs grow tumid: he went to Windsor, where Sir Charles Scarborough then attended the king, and requested him, as both a friend and physician, to tell him what that swelling meant. 'Sir,' answered Scarborough, 'your blood will run no longer.' Waller repeated some lines of Virgil, and went home to die. As the disease increased upon him, he composed himself for his departure; and calling upon Dr. Birch to give him the holy sacrament, he desired his children to take it with him, and made an earnest declaration of his faith in Christianity. It now appeared what part of his conversation with the great could be remembered with delight. He related, that being present when the Duke of Buckingham talked profanely before King Charles, he said to him, 'My lord, I am a great deal older than your Grace, and have, I believe, heard more arguments for atheism than ever your Grace did; but I have lived long enough to see there is nothing in them, and so I hope your Grace will."
What will our ticklish correspondent, W.H.H. say to this?
"Kniveing trouts" (they call it tickling in England) is good sport. You go to a stony shallow at night, a companion bearing a torch; then stripping to the thighs and shoulders, wade in; grope with your hands under the stones, sods, and other harbourage, till you find your game, then grip him in your "knieve," and toss him ashore.
I remember, when a boy, carrying the splits for a servant of the family, called Sam Wham. Now Sam was an able young fellow, well-boned and willing; a hard headed cudgel player, and a marvellous tough wrestler, for he had a backbone like a sea-serpent; this gained him the name of the Twister and Twiner. He had got into the river, with his back to me, was stooping over a broad stone, when something bolted from under the bank on which I stood, right through his legs. Sam fell with a great splash upon his face, but in falling, jammed whatever it was against the stone. "Let go, Twister," shouted I, "'tis an otter, he will nip a finger off you."—"Whisht," sputtered he, as he slid his hand under the water; "May I never read a text again, if he isna a sawmont wi' a shouther like a hog!"—"Grip him by the gills, Twister," cried I.—"Saul will I!" cried the Twiner; but just then there was a heave, a roll, a splash, a slap like a pistol-shot; down went Sam, and up went the salmon, spun like a shilling at pitch and toss, six feet into the air. I leaped in just as he came to the water; but my foot caught between two stones, and the more I pulled the firmer it stuck. The fish fell in a spot shallower than that from which he had leaped. Sam saw the chance, and tackled to again: while I, sitting down in the stream as best I might, held up my torch, and cried fair play, as shoulder to shoulder, throughout and about, up and down, roll and tumble, to it they went, Sam and the salmon. The Twister was never so twined before. Yet through crossbuttocks and capsizes innumerable, he still held on; now haled through a pool; now haling up a bank; now heels over head; now head over heels; now head and heels together; doubled up in a corner; but at last stretched fairly on his back, and foaming for rage and disappointment; while the victorious salmon, slapping the stones with his tail, and whirling the spray from his shoulders at every roll, came boring and snoring up the ford. I tugged and strained to no purpose; he flashed by me with a snort, and slid into the deep water. Sam now staggered forward with battered bones and peeled elbows, blowing like a grampus, and cursing like nothing but himself. He extricated me, and we limped home. Neither rose for a week; for I had a dislocated ankle, and the Twister was troubled with a broken rib. Poor Sam! he had his brains discovered at last by a poker in a row, and was worm's meat within three months; yet, ere he died, he had the satisfaction of feasting on his old antagonist, who was man's meat next morning. They caught him in a net. Sam knew him by the twist in his tail.—Blackwood's Magazine.
The operation of working for these precious jems is a very simple one. The alluvial soil (the cascalhao) is dug up from the bed of the river, and removed to a convenient spot on the banks for working. The process is as follows:—a rancho is erected about a hundred feet long, and half that distance in width; down the middle of the area is conveyed a canal, covered with earth; on the other side of the area is a flooring of planks, about sixteen feet in length, extending the whole length of the shed, and to which an inclined direction is given; this flooring is divided into troughs, into which is thrown a portion of the cascalhao; the water is then let in, and the earth raked until the water becomes clear; the earthy particles having been washed away, the gravel is raked up to the end of the trough; the largest stones are thrown out, and afterwards the smaller ones, the whole is then examined with great care for diamonds. When a negro finds one, he claps his hands, stands in an erect posture, holding the diamond between his fore-finger and thumb; it is received by one of the overseers posted on lofty seats, at equal distances, along the line of the work. On the conclusion of the work, the diamonds found during the day are weighed, and registered by the overseer en chef. If a negro has the good fortune to find a stone weighing upwards of seventeen carats, he is immediately manumitted, and for smaller stones proportionate premiums are given. There are, besides, several other works on this river, and on other streams, but the supply of [pg 235] diamonds falls now considerably short of former periods, and their produce scarcely defrays the expenses.
The Diamond District of the Serro do Frio is about twenty leagues in length, and nine in breadth; the soil is barren, but intersected by numerous streams. It was first discovered by some miners, shortly after the establishment of the Villa do Principe. In working for gold in the rivulets of Milho Verde and St. Goncalzes, they discovered some pebbles of geometric form, and of a peculiar hue and lustre. For some years these pebbles were given as pretty baubles to children, or used as counters for marking the points of their favourite game of voltarete. At last an officer, who had been some years at Goa, in the East Indies, arrived in the Commarca: he was struck with the peculiar form of these pebbles, and from several experiments he made, it struck him that they were diamonds. He immediately collected a few, and sent them to Holland, where, to the astonishment of the lapidaries, they were found to be brilliants of the finest water. It will easily be imagined, that on the arrival of this intelligence in Brazil, the hitherto despised counters suddenly became the objects of universal research, and almost immediately disappeared.
The government of Portugal now issued a decree, declaring all diamonds a monopoly of the crown. For a length of time it was considered that diamonds were confined solely to the district of Serro Frio. But this is an error; they are found in almost every part of the empire, particularly in the remote provinces of Goyazes and Matto Grosso, where there exist several districtos diamantescos. These gems have been even found on the tops of the highest mountains; indeed, it is the opinion of the Brazilian mineralogists that the original diamond formations are in the mountains, and that they will one day or other be discovered in such quantities, as to render them objects of comparatively small value.
The largest diamond in the world was found in the river Abaite; about ninety-two leagues to N.W. of Serro do Frio. The history of its discovery is romantic:—three Brazilians, Ant. de Souza, Jose Felix Gomes, and Thomas de Souza, were sentenced, for some supposed misdemeanour, to perpetual banishment in the wildest part of the interior. Their sentence was a cruel one; but the region of their exile was the richest in the world; every river rolled over a bed of gold, every valley contained inexhaustible mines of diamonds. A suspicion of this kind enabled these unfortunate men to support the horrors of their fate; they were constantly sustained by the golden hope of discovering some rich mine, that would produce a reversion of their hard sentence. Thus they wandered about for nearly six years, in quest of mines; but fortune was at last propitious. An excessive draught had laid dry the bed of the river Abaite, and here, while working for gold, they discovered a diamond of nearly an ounce in weight. Overwhelmed with joy at this providential discovery, they resolved to proceed, at all hazards, to Villa Rica, and trust to the mercy of the crown. The governor, on beholding the magnitude and lustre of the gem, could scarcely credit the evidence of his senses. He immediately appointed a commission of the officers of the Diamond District to report on its nature; and on their pronouncing it a real diamond, it was immediately dispatched to Lisbon. It is needless to add that the sentence of the three "condemnados" was immediately reversed.
This celebrated diamond has been estimated by Romé de l'Isle at the enormous sum of three hundred millions sterling. It is uncut, but the late King of Portugal, who had a passion for precious stones, had a hole bored through it, in order to wear it suspended about his neck on gala days. No sovereign possessed so fine a collection of diamonds as this prince.—Monthly Mag.
Mrs. Trollope's amusing book has furnished us with still another page or two of scenes and sketches:
Crocodiles on the Mississippi.
"It is said that at some points of this dismal river, crocodiles are so abundant as to add the terror of their attacks to the other sufferings of a dwelling there. We were told a story of a squatter, who having 'located' himself close to the river's edge, proceeded to build his cabin. This operation is soon performed, for social feeling and the love of whiskey bring all the scanty neighbourhood round a new comer, to aid him in cutting down trees, and in rolling up the logs, till the mansion is complete. This was done; the wife and five young children were put in possession of their new home, and slept soundly after a long march. Towards day-break the husband and father was awakened by a faint cry, and looking up, beheld relics [pg 236] of three of his children scattered over the floor, and an enormous crocodile, with several young-ones around her, occupied in devouring the remnants of their horrid meal. He looked around for a weapon, but finding none, and aware that unarmed he could do nothing, he raised himself gently on his bed, and contrived to crawl from thence through a window, hoping that his wife, whom he left sleeping, might with the remaining children rest undiscovered till his return. He flew to his nearest neighbour and besought his aid; in less than half an hour two men returned with him, all three well armed; but alas! they were too late! the wife and her two babes lay mangled on their bloody bed. The gorged reptiles fell an easy prey to their assailants, who, upon examining the place, found the hut had been constructed close to the mouth of a large hole, almost a cavern, where the monster had hatched her hateful brood."
Pig Scavengers.
"We were soon settled in our new dwelling, which looked neat and comfortable enough, but we speedily found that it was devoid of nearly all the accommodation that Europeans conceive necessary to decency and comfort. No pump, no cistern, no drain of any kind, no dustman's cart, or any other visible means of getting rid of the rubbish, which vanishes with such celerity in London, that one has no time to think of its existence; but which accumulated so rapidly at Cincinnati, that I sent for my landlord to know in what manner refuse of all kinds was to be disposed of.
"Your Help will just have to fix them all into the middle of the street, but you must mind, old woman, that it is the middle. I expect you don't know as we have got a law what forbids throwing such things at the sides of the streets; they must just all be cast right into the middle, and the pigs soon takes them off.'"
American English.
"I very seldom during my whole stay in the country heard a sentence elegantly turned, and correctly pronounced from the lips of an American. There is always something either in the expression or the accent that jars the feelings and shocks the taste."
Mr. Bullock.
"About two miles below Cincinnati, on the Kentucky side of the river, Mr. Bullock, the well known proprietor of the Egyptian Hall, has bought a large estate, with a noble house upon it. He and his amiable wife were devoting themselves to the embellishment of the house and grounds; and certainly there is more taste and art lavished on one of their beautiful saloons, than all Western America can show elsewhere. It is impossible to help feeling that Mr. Bullock is rather out of his element in this remote spot, and the gems of art he has brought with him, show as strangely there, as would a bower of roses in Siberia, or a Cincinnati fashionable at Almack's. The exquisite beauty of the spot, commanding one of the finest reaches of the Ohio, the extensive gardens, and the large and handsome mansion, have tempted Mr. Bullock to spend a large sum in the purchase of this place, and if any one who has passed his life in London could endure such a change, the active mind and sanguine spirit of Mr. Bullock might enable him to do it; but his frank, and truly English hospitality, and his enlightened and inquiring mind, seemed sadly wasted there. I have since heard with pleasure that Mr. Bullock has parted with this beautiful, but secluded mansion.
"Mr. Bullock was showing to some gentlemen of the first standing, the very élite of Cincinnati, his beautiful collection of engravings, when one among them exclaimed, 'Have you really done all these since you came here? How hard you must have worked!'"
Cows.
"These animals are fed morning and evening at the door of the house, with a good mess of Indian corn, boiled with water; while they eat, they are milked, and when the operation is completed the milk-pail and the meal-tub retreat into the dwelling, leaving the republican cow to walk away, to take her pleasure on the hills, or in the gutters, as may suit her fancy best. They generally return very regularly to give and take the morning and evening meal; though it more than once happened to us, before we were supplied by a regular milk cart, to have our jug sent home empty, with the sad news that 'the cow was not come home, and it was too late to look for her to breakfast now.' Once, I remember, the good woman told us that she had overslept herself, and that the cow had come and gone again, 'not liking, I expect, to hanker about by herself for nothing, poor thing.'"
Health of Cincinnati.
"A gentleman told us, that when a medical man intended settling in a new situation, he always, if he knew his [pg 237] business, walked through the streets at night, before he decided. If he saw the dismal twinkle of the watch-light from many windows he might be sure that disease was busy, and that the 'location' might suit him well."
Marketing.
"It is the custom for the gentlemen to go to market at Cincinnati; the smartest men in the place, and those of the 'highest standing' do not scruple to leave their beds with the sun, six days in the week, and, prepared with a mighty basket, to sally forth in search of meat, butter, eggs, and vegetables. I have continually seen them returning, with their weighty basket on one arm and an enormous ham depending from the other."
Moving Houses.
"One of the sights to stare at in America is that of houses moving from place to place. We were often amused by watching this exhibition of mechanical skill in the streets. They make no difficulty of moving dwellings from one part of the town to another. Those I saw travelling were all of them frame-houses, that is, built wholly of wood, except the chimneys; but it is said that brick buildings are sometimes treated in the same manner. The largest dwelling that I saw in motion was one containing two stories of four rooms each; forty oxen were yoked to it. The first few yards brought down the two stacks of chimneys, but it afterwards went on well. The great difficulties were the first getting it in motion and the stopping exactly in the right place. This locomotive power was extremely convenient at Cincinnati, as the constant improvements going on there made it often desirable to change a wooden dwelling for one of brick; and whenever this happened, we were sure to see the ex No. 100 of Main-street or the ex No. 55 of Second-street creeping quietly out of town, to take possession of a humble suburban station on the common above it."
Social distinctions.
"My general appellation amongst my neighbours was 'the English old woman,' but in mentioning each other they constantly employed the term 'lady;' and they evidently had a pleasure in using it, for I repeatedly observed, that in speaking of a neighbour, instead of saying Mrs. Such-a-one, they described her as 'the lady over the way what takes in washing,' or as 'that there lady, out by the Gulley, what is making dip-candles.' Mr. Trollope was as constantly called 'the old man,' while dray-men, butchers' boys, and the labourers on the canal were invariably denominated 'them gentlemen;' nay, we once saw one of the most gentlemanlike men in Cincinnati introduce a fellow in dirty shirt sleeves, and all sorts of detestable et cetera, to one of his friends, with this formula, 'D—— let me introduce this gentleman to you.'"
The oriental fable of the Roc has its probable origin in the condor, which is undoubtedly the largest and strongest bird of the vulture tribe in existence, and extremely ravenous. Minerva's bird, the Owl, is well known as one of ill omen; besides the superstitious idea that the screech-owl foretells death by its cry, it was formerly believed to suck the blood of children. The Mongol and Calmuc Tartars have held the White Owl sacred since the days of Genghis Khan, when a bird of this species having settled on a bush in which that prince had hidden himself from his enemies, those who pursued him past it, not believing that a bird would perch on a bush wherein a man was concealed. The Raven has ever been considered by the vulgar as a bird of evil omen, the indicator of misfortunes and death; and, indeed, the superstition is but consonant with a bird of such funereal note and hue, and exhibiting such goule-like propensities. The Swedes, however, regard it as sacred, and no one offers to molest it. In the north of England, one Magpie flying alone, is deemed an ill omen; two together, a fortunate one; three forebode a funeral, and four a wedding; or, when on a journey, to meet two magpies portends a wedding; three, a successful journey; four, unexpected good news; and five, that the person will soon be in company with the great. To kill a magpie, indicates or brings down some terrible misfortune. The Sparrow Hawk was sacred with the Egyptians, and the symbol of Osiris. The Yellow Hammer is superstitiously considered an agent diablerie. The Wheat-Ear is, in the Highlands, a detested bird, and fancied one of evil omen, on account of its frequenting old churchyards, where it nestles amongst the stones, and finds plenty of insects for food. The Woodcock is, we believe, the bird imagined to drop, in its proper season, from the moon. It is a vulgar [pg 238] error, that the song of the Nightingale is melancholy, and that it only sings by night; but to hear the Cuckoo before the Nightingale has been long deemed an unsuccessful omen in love: the saliva of the cuckoo has been thought to preserve all it falls upon.
"The Robin and the Wren
Are God Almighty's cock and hen,"
says the old distich, and whilst it is reckoned wicked to kill either of these (not but that there is an ancient custom of "hunting the wren" still kept up, we believe, in some parts of this country,) it is considered unlucky to kill a Swallow, or House-Martin. The King-fisher is the Halcyon of the ancients, who imagined that during the process of incubation by the female the sea remained unvexed by storms; hence "halcyon days." The feathers of this bird are employed by the Tartars for many superstitious purposes; they consider them amulets of priceless value, enabling them to inspire women with love. In more civilized countries it was once believed, that if the body of a kingfisher were suspended by a thread, some magnetic influence would turn its breast to the north: others thought it a preserver of woollen cloths from moths. The Albatross (by some considered the kingfisher or halcyon,) is fabled to sleep in the air, never to touch the earth; and to kill one is reckoned supremely unlucky. There is an Indian bird, the name of which has unfortunately escaped us, that is feigned to live only on the rain-drops which it can draw with its bill from the clouds; in a dry season, therefore, this bird perishes. Of the Bird of Paradise the following wonders were once credited: viz. that the egg was laid in the air by the female, and there hatched by the male in an orifice of his body; that it had no legs (these however are long, and a disfigurement to the body, which the Indians know, and fearful of their depreciating the value of the bird, upon capturing it, cut them off); that it hung itself by the two long feathers of its tail on a tree when sleeping; that it never touched the ground during any period of its existence, and fed wholly on dew. The Indians also believe that the leader, or king of the birds of paradise is black, with red spots, and that he soars far away from the rest of the flock, which, however, never quit him, but settle where he does. The Gigantic Crane is believed by the Indians to be invulnerable, and animated by the souls of deceased Brahmins; the Africans hold it in equal veneration. Whence arises the classical fable that swans sing their own dirge just previous to death, and expire singing it? The wild swan certainly may be said to whistle, but the tame has no other note than a hiss, and this only when provoked. The Kamschatdales and Kuriles wear round their necks the bills of Puffins, as an amulet which ensures good fortune. Who was Mother Carey?—The wife, perhaps, of "Davy," and keeper of his "locker;" Mother Carey's chickens is the well-known appellation, in tarrish tongue, of Stormy Petrels, not superstitiously supposed to forebode tempests, since they seem their very element; but it is probable that to Mother Carey herself (we crave her pardon—Mistress) some astounding "yarn" is attached. The Stork, the Crane, and the Pelican, are each the subject of idle stories; the latter has been asserted to feed her young with her own bosom's blood, and to fill her pouch with water in order to supply them in the desert. A notion is entertained by the ignorant that the Bittern thrusts its bill into a reed, which serves as a pipe to increase the volume of its natural note, and swell it above pitch; and in some places a tradition prevails that it thrusts its head into water and then blows with all its might. It is erroneous that the Ostrich lays her eggs in the sand, depending solely on the sun's rays to hatch them; the truth is that, as from the heat of her native climate, it is not always necessary for her to sit upon them, she simply does what numerous birds in colder latitudes are well known to do; viz. cover them, that they may not, during her absence, lose their heat.
The popular opinion that the Turtle Dove, of either sex, should it happen to lose its mate, remains ever after in a state of disconsolate celibacy, is, we believe, disproved by the fact, at least as respects these birds in a wild state; but we may remark, that the loss of a companion to more than one kind of domesticated bird, if it has been brought up with one, even though not in the same cage, is sometimes so severely deplored by the survivor, as to occasion its death, if the loss be not speedily supplied. The old story of Swallows passing the winter in a state of torpidity at the bottom of rivers, lakes, and ponds, has been frequently agitated, asserted to be a fact by one party, and totally disproved by the other. The reader may be amused to learn, that very recently we were assured by one, who knew it for an absolute fact, that ducks and even chickens (!!!) had been found in a certain farmer's pond, laid up in winter quarters, which were revived by the [pg 239] warmth of the sun and upper air, upon being fished out of it!! "Regarding Birds' Eggs," says the Naturalist in his interesting Journal, "we have a very foolish superstition here (Gloucestershire:) the boys may take them unrestrained, but their mothers so dislike their being kept in the house, that they usually break them; their presence may be tolerated for a few days, but by the ensuing Sunday they are frequently destroyed, under the idea that they bring bad luck, or prevent the coming of good fortune, as if in some way offensive to the domestic deity of the hearth." Here, then, we pause; some abler hand may, perhaps, be tempted to take up the subject as we leave it, for there are yet gleanings, in the field, of "Superstitions and Fables connected with animals," over which our leisure has allowed us but lightly to pass; gleanings sufficient to reward the industrious and the curious; or, it may even be, that we shall return, some day, to this topic ourselves, time and materials permitting.
Great Marlow, Bucks. M.L.B.
Congreve Rockets.—When the Congreve rockets were first introduced into the navy, the admiral on the Brazil station proposed to exhibit to the king, Don Juan VI., the effect of these formidable projectiles. His majesty consented, and the whole court were accordingly assembled in the balconies of the palace, at the Rio, for the purpose of witnessing the spectacle. By some mishap, of very frequent occurrence in the early history of these missiles, at the moment of firing the tube veered round, and the rocket, instead of flying over to Praia Grande, took the opposite direction, and fell and exploded in the great square, almost beneath the windows of the palace. The consternation of the king was only equalled by the mortification of the admiral, who immediately despatched an officer on shore to explain the cause of the contretemps to his majesty; and offering to let off another, but the terrified monarch would not hear of it. "I have a great respect," said he, "for my good allies, the English, but after dinner they are absolutely fit for nothing;" an observation which clearly indicated to what cause his majesty attributed the unfortunate result of the exhibition.—Monthly Magazine.
Prosperity of America.—The United States of N. America posses an almost undefinable extent of fertile uncultivated land—a highly industrious and intelligent population of 13,000,000—the national debt will be paid this year—and they have a large surplus revenue. That of 1831 was 27,700,000 Spanish dollars; the expenditure for all government purposes 14,700,000.
War.—Were the disputes between great and rival nations to be settled by single combat, by those, through whose ambition, pride, or other cause, they were occasioned, millions of lives might have been saved.
Curious Custom.—There is held in Italy, a kind of feast, or ceremony, in the courts of certain princes, on St. Nicholas's Day, in which people hide presents in the shoes or slippers of those they would do honour to; in such a manner as to surprise them on the morrow, when they come to dress. It is done in imitation of the practice of St. Nicholas; who used, in the night time, to throw purses of money in at the windows, for portions to poor maidens on their marriage. P.T.W.
Experience.—It often happens that the more we see into a man, the less we admire him.—Pliny.
The Romans were so anxious to encourage marriage, that they punished unmarried persons by rendering them incapable of receiving any legacy, or inheritance by will, except from near relatives. And those who were married, and had not any children, could take no more than half the estate.
Etruscan Vases.—The art of making earthenware was transported from Etruria into Greece. The Romans also borrowed this invention from the Etruscans, to whom also Greece was indebted for many of its ceremonies and religious institutions, as well as for its mechanics and artificers.
It is customary in the canton Wallis, Switzerland, for those who have found anything lost, even money, to affix it to a large crucifix in the churchyard, and there is not an example on record, of any object being taken away except by the rightful owner. W.G.C.
Cumberland Titles.—The honorary titles arising from the different degrees of allowed consequence or property in Cumberland, appear (says Britton) singular when compared with their usual acceptation in society. The mistress of the house is a Dame; every owner of a little landed property is a 'Statesman; his eldest son is the Laird; and where there is no son, the eldest daughter is [pg 240] born to the title of Leady. Thus we may see a 'Statesman driving the plough, a Lord attending the market with vegetables, and a Leady labouring at the churn. P.T.W.
A string of echo puns surpassing all others, may be seen in a scarce work, published in the reign of James I. A specimen—a divine, willing to play more with words, than to be serious in the expounding of his text, spoke thus in one part of the sermon:—"This dyall shewes we must die all; yet, notwithstanding, all howses are turned into ale-houses; our cares are turned into cates; our paradise, into, a pair of dice; our marriage, into a merry age; our matrimony, into a matter of money; our divines, into dry vines. It was not so in the days of Noah, Ah no!"—T.G.
Advertisement Extraordinary, from a Newspaper of 1796.—"Whereas the right hon. William Pitt, Chancellor of his Majesty's Exchequer, did on the night of Monday last, and on or about the hour of six o'clock, utter in his place in the House of Commons, certain sentences or phrases, containing several assurances, denials, promises, retractions, persuasions, explanations, hints, insinuations, and intimations, and expressing much hope, fear, joy, sorrow, confidence, and doubt, upon the subject of peace, then and there recommended by Charles Grey, esq., member of the aforesaid House of Commons, for the county of Northumberland; and whereas the entire effectual and certain meaning of the whole of the said sentences, phrases, denials, promises, retractions, persuasions, explanations, hints, insinuations, and intimations, has escaped and fled, so that what remains is to plain understandings incomprehensible, and to many good men is matter of painful contemplation: now this is to promise to any person who shall restore the said lost meaning, or shall illustrate, simplify, and explain the said meaning, the sum of five thousand pounds, to be paid on the first day of April next, at the office of John Bull, esq., Pay-All and Fight-All, to the several high contracting powers, engaged in the present just and necessary war!
"Done at the office of Mr. John Bull's Chief Decypherer, Turnagain Lane, Circumbendibus Street, Obscurity Square, Feb. 18, 1796."
Cheap Soup.—Take ten quarts of water, and stir it with a rush-light till it boils; season it to your liking, and it is ready for use. N.B. The wick may be bolted.—Monthly Mag.
Epitaph on the death of Miss Eliza More, aged 14.
Here lies who never lied before,
And one who will never lie More,
To which there need no more be said
Than More the pity she is dead,
For when alive she charmed us More
Than all the Mores just gone before. 6
On Anne Green, a Quakeress.
Here lies a piece of Christ, a star in dust,
A wedge of gold, a china dish that must
Be used in heaven, when Christ doth feed the just.
Inscribed on the back door of a Tavern, which opened into the Parish Church of St. Michael's, Cambridge, kept by Mr. Burrell, 1639: which door is now taken down, the tavern having been pulled down, and a new street built on its site.
Go on by leave, no way here lies:
But way and leave to those
That hast to taste good wine and fine,
And fear not Burrell's foes.
Copied from the Churchwarden's Book.
The Mother Tongue.—In Mr. Combe's Illustrations of Phrenology, a case is related of a Welsh milkman, in London, who happening to fall down two pair of stairs, received a severe contusion on the head, and was carried to St. George's Hospital, where he lay senseless for several days, and unable to speak. At length he became something better, and began to talk to the nurses, but in such terms that no one could understand him, till it was discovered that he had forgotten his English, and was talking Welsh; a language he had not spoken for eighteen years. Mr. Combe conceives that the blow having hit the store-house in his head, where the Welsh language was garnered, his youthful acquisitions were poured out, whilst the English language, which he had learned much later, was overpowered and obliterated by the force of his mother tongue. W.G.C.
Warning to Betrayers.—St. Bennet's Abbey, in Norfolk, was so well fortified, that William the Conqueror, in vain besieged it, till a monk, upon condition of being made abbot, betrayed the place. The king performed the condition, but hanged the new abbot as a traitor. P.T.W.
Footnote 1: (return)By accurate observation the height of the fog, relatively with the higher edifices, whose elevation is known, it has been ascertained that the fogs of London never rise more than from two hundred to two hundred and forty feet above the same level.
Footnote 2: (return)Who does not remember the traditionary notoriety of Margaret Finch?
Footnote 3: (return)The private property of the estate, and attached to the Spa.
Footnote 4: (return)We drank a half-pint tumbler of the water, which, as Dr. Weatherhead observes, is bitter without being disagreeable. Its flavour is that of Sulphate of Magnesia, or Epsom Salts; and we should say that our modicum might be imitated by dissolving a dram of the above ingredient in half-a-pint of pure water.
Footnote 5: (return)Johnson's Life of Waller, wherein the poet is stated to have been born March 3.
Footnote 6: (return)Her two sisters dying some months before.
Printed and Published by J. LIMBIRD, 143, Strand, (near Somerset House,) London; sold by ERNEST FLEISCHER, 626, New Market, Leipsic; G.G. BENNIS, 55, Rue Neuve, St. Augustin, Paris; and by all Newsmen and Booksellers.