The Project Gutenberg EBook of The Mirror of Literature, Amusement, and Instruction, Vol. 10, Issue 266, July 28, 1827, by Various This eBook is for the use of anyone anywhere at no cost and with almost no restrictions whatsoever. You may copy it, give it away or re-use it under the terms of the Project Gutenberg License included with this eBook or online at www.gutenberg.org Title: The Mirror of Literature, Amusement, and Instruction, Vol. 10, Issue 266, July 28, 1827 Author: Various Posting Date: December 6, 2011 [EBook #9919] Release Date: February, 2006 First Posted: October 31, 2003 Language: English Character set encoding: ISO-8859-1 *** START OF THIS PROJECT GUTENBERG EBOOK MIRROR OF LITERATURE, JULY 28, 1827 *** Produced by Jonathan Ingram and Project Gutenberg Distributed Proofreaders
Transcriber's note: In "A Churchyard Scene" the word "iugrate" occurs in the original text. This was probably a typographical error, and the correct word was likely "ingrate."
| Vol. 10, No. 266.] | SATURDAY, JULY 28, 1827. | [PRICE 2d. |
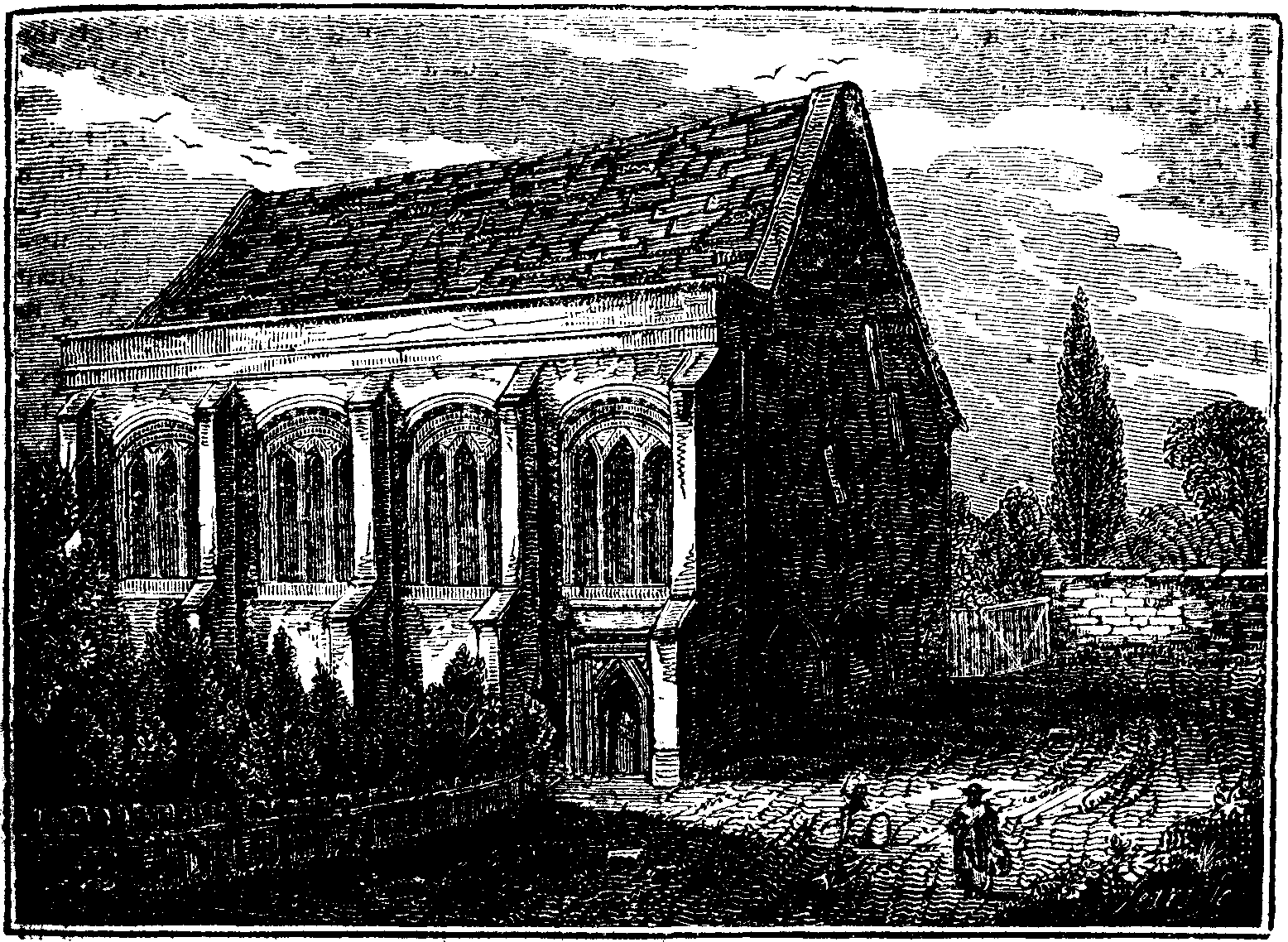
The palace of Croydon is a building of great antiquity, and was for several centuries the magnificent abode of the haughty dignitaries of Canterbury. At the period of the Conquest, Lanfranc resided here, and most of the decrees and audits of his successors were issued from, and held at, this palace. It was here that Archbishop Parker entertained his queen, Elizabeth and her august court, with great splendour and festivity; as also did the celebrated Whitgift, who refused to accept of the high office of lord chancellor. Courtney received his pall here with great solemnity and pomp in the presence of the chief nobility of the realm; and Chichley, Stafford, Laud, Juxon, Wake, and Herring, made it their frequent residence, and were liberal contributors to its architectural beauties. The remains of this interesting fabric are, with the exception of the hall, composed entirely of brick, occupying a considerable space on the south-west side of Croydon church, and are in some points peculiarly striking in local appearance; but on account of their unconnected state, with the intervening screens of garden walls, &c. the view is confined and partial.
The grand hall is a lofty imposing structure, and at a casual computation appears to contain an area of eight hundred square yards; between which and the cornice, at the height of about fifteen feet, a moulding or frieze is carried over the surface of each wall, from whence, resting their bases on angels bearing, shields variously blazoned, issue in the alternate spaces of twelve feet, five ligneous pillars, supporting immense beams traversing the intervening distances of the confronting sides. The roof is formed of large solid pieces of timber, running diagonally to a point; the upper compartment of which (springing from perpendicular posts), is ribbed so as to make it have the appearance of a polygonal ellipsis.
On the right of the southern entrance an escutcheon, surmounted by a canopy, is fixed at a considerable height from the pavement, and must have had formerly a splendid appearance, as faint traces even now of its original pomp are discernible [pg 66]in the faint glittering of the gilding, and the exquisite symmetry of its execution. The bearings appeared to me as—party per pall,—dexter division.—Sapphire a cross gules ensigned with fleur de lis between six martlets topaz.—Sinister—quarterly sapphire and ruby, first and third, three fleur de lis; topaz, second and fourth, three lions passant gardant of the same, supported by two angels, and surmounted by a coronet; the whole resting on an angel bearing a scroll with a motto in old English text, but illegible.1
This hall is now occupied by a carpenter, and is almost filled with old furniture and timber; other parts of the building are appropriated for charity-schools, and the trade of bleaching is practised in its precincts.
SAGITTARIUS.
The first attempt to form an academy for the encouragement of the fine arts in this country was made in Great Queen-street, in the year 1697. The laudable design was undertaken by Sir Godfrey Kneller, and by the most respectable artists of the day, who endeavoured to imitate the French Academy founded by Lewis XIV. Their undertaking, however, was wholly without success; jealousies arose among the members, and they were ultimately compelled to relinquish the project as fruitless. Sir James Thornhill, a few years afterwards, commenced an academy in a room he had built for the purpose at the back of his own residence, near Covent-garden theatre; but his attempt, likewise, proved abortive. Notwithstanding these failures, Mr. Vanderbank, a Dutchman, headed a body of artists, and converted an old Presbyterian meeting-house into an academy. Besides plaster figures, Mr. Vanderbank and his associates procured a living female figure for study, which circumstance tended to gain a few subscribers; but, in a very short space of time, for want of money sufficient to defray the necessary expenses, all the effects belonging to the establishment were seized for rent, and the members, in disgust, accordingly separated.
On the demise of Sir James Thornhill, in 1734, the celebrated William Hogarth became possessed of part of his property.2 Although much averse to the principles on which academies were generally founded, Mr. Hogarth considered that one conducted wisely would probably be of great advantage to the public, as well as to the artists in general. He, therefore, proposed, that a body of artists should enter into a subscription for the purchase of a house sufficiently large and capacious to admit thirty or forty persons to draw from a naked figure. This proposition being unanimously agreed to, a place was forthwith taken in St. Martin's-lane; and Hogarth, to forward the undertaking as far as he could, lent them the furniture, &c. formerly belonging to Sir James Thornhill's academy.
The failure of all preceding attempts to form an academy was attributed by Mr. Hogarth to the principal members assuming too much authority over their brother artists; he, therefore, proposed, that every member should contribute an equal sum of money to the establishment, and should have an equal right to vote on every question relative to the society. He considered electing presidents, directors, and professors, to be a ridiculous imitation of the forms of the French Academy, and liable to create jealousies.3 Under Hogarth's guidance, the Academy continued for thirty years, with little alteration, to the high satisfaction of its several members, and the public in general.
On ascending the British throne, George III. evinced so much interest for the arts, that most of the members of the academy (though contrary to the wishes of their leader, who possessed a most independent spirit,) solicited the royal patronage to a plan they had in view of establishing an academy for painting, sculpture, and architecture. The success of this appeal is too well known to English readers to need much comment. His majesty was pleased to appropriate those very splendid apartments in Somerset-house for the use of artists, who shortly formed a new society, over which, by his majesty's special command, the great Sir Joshua Reynolds presided.
G.W.N.
[pg 67]To describe the awful grandeur and terrific phenomena of volcanic eruptions in an adequate manner, is perhaps beyond the power of language. The number of volcanoes now known is about four hundred; nearly all of them are situated a small distance from the sea, and many appear to have been burning from time immemorial.
A certain mixture of sulphur, steel-filings and water, buried a short depth from the ground, will exhibit a kind of miniature volcano; and hence some philosophers have concluded, that in the bowels of burning mountains there are various sorts of bodies which probably ferment by moisture, and being thus expanded, at last produce eruptions and explosions. The mouth or chimney of a burning mountain is, in many instances, upwards of a mile across! from which, in an eruption, are emitted torrents of smoke and flame, rivers of lava, (consisting chiefly of bitumen and melted metal,) and clouds of cinders, stones, &c. to an immense distance. The wonderful quantity of these materials thrown out from the orifice almost exceeds belief; the lava rushes like a fiery torrent at a very rapid pace,—ravages the labours of agriculture, overthrows houses, and in a few seconds utterly destroys the hopes of hundreds of families—the toils of hundreds of years. Nothing impedes its awful course; when interrupted by stone walls, or even rocks, it collects in a few moments to the height of eight or ten feet; its immense heat and violent pressure quickly batter down the obstacle, which is literally made rotten by the fire, and the whole mass seems to melt together into the lava, which again continues its progress until exhausted by the distance of its destructive march.
An English traveller, who was at Naples during the eruption of Mount Vesuvius, on the 10th of September, 1810, thus describes the scene:—
"Curious to witness the volcano as near as possible, I set out for Portici, where I arrived at eight in the evening; from thence to the summit of the mountain the road is long and difficult; having procured a guide about the middle of the distance, we had to climb a mountain of cinders, every step nearly knee-deep; this made it near midnight when we reached the crater, which we approached as near as the heat would permit. The fire of the mountain served us for a beacon, and we set light to our sticks in the lava, which slowly ran through the hollows of the crater. The surface of the inflamed matter nearly resembles metal in a state of fusion, but as it flows it carries a kind of scum, which gradually hardens into scoria and rolls like fire-balls to the bottom of the mountain. We thought ourselves pretty secure in this spot, and had no wish to retire; but shortly a most terrific explosion which launched to an inconceivable height in the air, immense fragments of burning rocks, &c. reminded us of our dangerous situation. We lost not a moment in retreating, and driven on by fear almost with miraculous speed, cleared in about five minutes, a space we had taken two hours to climb; we had hardly gained this spot when a second explosion more terrible, if possible, than the former was heard. The volcano in all its fury vomited forth some thousands of cart-loads of stones and burning lava. As the projection was nearly vertical, the greater part fell back again into the mouth of the mountain and this was again vomited forth as before. On the 11th and 12th, the fury somewhat abated, but on the 13th a fresh eruption commenced, and burning matter flowed down all the sides of the volcano;—all Vesuvius itself seemed on fire,—not a vestige of property for miles could be discovered, and thousands of families were ruined."
JACOBUS.
How sweet and solemn, all alone,
With reverend steps, from stone to stone,
In a small village churchyard lying,
O'er intervening flowers to move!
And as we read the names unknown
Of young and old to judgment gone,
And hear in the calm air above
Time onwards softly flying,
To meditate, in Christian love,
Upon the dead and dying!
Across the silence seem to go
With dream-like motion, wavery, slow,
And shrouded in their folds of snow,
The friends we loved long, long ago!
Gliding across the sad retreat,
How beautiful their phantom feet!
What tenderness is in their eyes,
Turned where the poor survivor lies
'Mid monitory sanctities!
What years of vanished joy are fanned
From one uplifting of that hand
In its white stillness! when the shade
Doth glimmeringly in sunshine fade
From our embrace, how dim appears
This world's life through a mist of tears!
Vain hopes! blind sorrows! needless fears!
Such is the scene around me now:
A little churchyard on the brow
Of a green pastoral hill;
Its sylvan village sleeps below,
And faintly here is heard the flow
Of Woodburn's summer rill;
[pg 68]A place where all things mournful meet,
And yet the sweetest of the sweet,
The stillest of the still!
With what a pensive beauty fall
Across the mossy, mouldering wall
That rose-tree's clustered arches! See
The robin-redbreast warily,
Bright through the blossoms, leaves his nest:
Sweet iugrate! through the winter blest
At the firesides of men—but shy
Through all the sunny summer-hours,
He hides himself among the flowers
In his own wild festivity.
What lulling sound, and shadow cool
Hangs half the darkened churchyard o'er,
From thy green depths so beautiful
Thou gorgeous sycamore!
Oft hath the holy wine and bread
Been blest beneath thy murmuring tent,
Where many a bright and hoary head
Bowed at that awful sacrament.
Now all beneath the turf are laid
On which they sat, and sang, and prayed.
Above that consecrated tree
Ascends the tapering spire, that seems
To lift the soul up silently
To heaven with all its dreams,
While in the belfry, deep and low,
From his heaved bosom's purple gleams
The dove's continuous murmurs flow,
A dirge-like song, half bliss, half woe,
The voice so lonely seems!
Notings, selections,
Anecdote and joke:
Our recollections;
With gravities for graver folk.
It was at the strongly contested election for Westminster, when Sheridan was opposed by Sir Francis Burdett and Lord Cochrane, that the latter, in allusion to the orator's desire of ameliorating his situation on the poll by endeavouring to blend his cause with that of the baronet, characteristically observed, "that the right honourable gentleman sought to have his little skiff taken in tow by the line of battle ship of Sir Francis." Sheridan, in whom the metaphor had awakened the remembrance of the remarkable and successful influence of his speech in the House of Commons on the occasion of the mutiny at the Nore, in calming the irritation of the rebels and reducing them to obedience, in reply to his lordship, bade him "to recollect that it was that little skiff which once brought the whole navy of England safely into port."
The election drew towards its termination, but all the efforts of his friends had proved unavailing to secure Sheridan's return, although his minority was any thing but formidable. The interest that attended the contest had, at its close, become intense; and every spot, whence the candidates might be seen or heard, was crowded in the extreme. A sailor, anxious to acquire a view of the scene of action, after all his exertion to push his way through the crowd had proved fruitless, resorted to the nautical expedient of climbing one of the poles which supported a booth directly in front of the hustings, from the very top of which Jack was enabled to contemplate all that occurred below. As the orator commenced his speech, his eye fell on the elevated mariner, whom he had no sooner observed than he rendered his situation applicable to his own, by stating that "had he but other five hundred voters as upright as the perpendicular gentleman before him, they would yet place him where he was—at the head of the pole."
Often were his addresses to his constituents interrupted by the tumult that arose from the anxiety of the public to get within hearing of him. A person, mounted on horseback, had penetrated to the very centre of the crowd, with more regard for himself than consideration towards others, as the animal he rode, affrighted by the noise, became equally annoying and dangerous to those by whom he was surrounded. The outcry was excessive, and, while some strove to appease the clamour, others urged Sheridan to proceed. "Gentlemen," replied he to the latter, "when the chorus of the horse and his rider is finished, I shall commence."
His good humour was at no time disturbed during the election, although the observations of his noble Caledonian opponent manifested no amicable disposition towards the orator. As it terminated, a mutual friend of the rival candidates expressed a hope that, with the contest, all animosity should cease; and that the gallant officer should drown the memory of differences in a friendly bottle. "With all my heart," said Sheridan, "and will thank his lordship to make it a Scotch pint."
His treatment of Coleridge, the poet, who had submitted a tragedy to his managerial decision, was wholly unmerited by the author, the success of whose piece subsequently so well justified the better claims it had on Sheridan's attention. In the cavern scene, where the silence of the place is presumed to be only broken by the slow dropping of the water from its vault, Sheridan, in reading it to his friends, repeated the words of one of the [pg 69]characters, in a solemn tone, "Drip! drip! drip!" adding, "Why, here's nothing but dripping:" but the story is told by Coleridge himself, in the preface to his tragedy, with that good humour and frankness becoming one sensible of his powers, and conscious that the witty use of an unfortunate expression (were it such) could but little affect the real and numerous beauties of the production.
An author, whose comedies, when returned upon his hands, were generally reduced, by the critical amputation of managers, from the fair proportion of five acts to two, or even one, with the ordinary suggestion of "necessary alteration," &c. complained in wrath and bitterness to Sheridan, who, it is said, attempted to console him, by saying, "Why, my good fellow, what I would advise you is, to present a comedy of a score of acts, and the devil will be in it if five be not saved."
I have heard it said, that, at the first performance of The Critic, Sheridan had adopted, as the representative of Lord Burleigh, an actor whose "looks profound" accorded with his "ignorance;" but who, until then, had only aspired to the livery of the theatre—the placing of chairs, or the presentation of a letter; yet who, in this humble display of histrionic art, generally contrived to commit some egregious blunder. He was remonstrated with, on his choice, by one of the performers, who demonstrated the excessive dulness of apprehension of the would-be Minister of State; and, like other and recent instances in that capacity, his singular aptitude to error, however simple the part he had to enact, or clear and concise the instructions with which it might be accompanied. As Sheridan had planned the character, the face was every thing, and the lengthened, dull, and inexpressive visage of the subject was too strictly ministerial to be lost; and the author would, as he said, "defy him to go wrong," Still his friend was sceptical; nor were his doubts removed by Sheridan's assuring him that the representative of Lord Burleigh "would have only to look wise, shake his head, and hold his tongue;" and he so far persisted as to lay a bet with the author that some capital blunder would nevertheless occur. The wager was accepted, and, in the fulness of his confidence, Sheridan insisted that the actor should not even rehearse the part, and yet that he should get through with it satisfactorily to the public and himself on the night of the first performance. It came. The arbiter of hopes and fears appeared in all the "bearded majesty" of the age of Elizabeth; and, flattered by the preference of the great author, had carefully conned over the following instructions:—"Mr. ——, as Lord Burleigh, will advance from the prompter's side;—proceed to the front of the stage;—fall back to where Mr. G—— stands as Sir Christopher Hatton,—shake his head and exit." The important moment came. With "stately step and slow," Lord Burleigh advanced in face of the audience. "Capital!" exclaimed the gratified author;—with equal correctness he retreated to the side of Sir Christopher, without literally falling back, which Sheridan had for a moment doubted might be the case. "Good! a lucky escape though." half faltered the anxious poet. "Now! now!" he continued, with eager delight at having got so far so well; but, what was his horror, when his unlucky pupil, instead of shaking his own blundering head, in strict but unfortunate interpretation of his orders, took that of Sir Christopher within his hands, shook it long and manfully, and then walked off with a look of exultation at having so exactly complied with his lesson.—New Monthly Magazine.
The French, however wretched may be their condition, are attached to life, while the English frequently detest life in the midst of affluence and splendour. English criminals are not dragged, but run to the place of execution, where they laugh, sing, cut jokes, insult the spectators; and if no hangman happens to be present, frequently hang themselves.—Memoirs of Lewis Holberg.
I smiled, for not a cloud was seen o'er the blue heaven's expanse,
As summer's myriad insect tribe led on the winged dance;
The gaudy butterfly was there ranging from flower to flower,
And by its side the wild bee humm'd amid the woodbine bower.
I sighed, for when I looked again the sky was overcast,
The summer insect's winged dance was o'er, yet on I past,
The gaudy butterfly was gone, the bee away had fled,
While on each fairest, brightest flower the wasteful locust fed.
Yet e'en this simple scene to youth a moral shall convey,
Since thus full oft misfortune's clouds obscure life's summer ray;
[pg 70]To-day we smile, for beauty smiles in all her spring-tide bloom—
To-morrow sigh, for beauty's bower has now become her tomb!
H. B.
Gilbert Burns was born about the year 1760. He was eighteen months younger than his brother Robert, Scotland's most gifted bard. With him he was early inured to toil, and rendered familiar with the hardships of the peasant's lot; like him, too, he was much subject to occasional depression of spirits, and from whatever cause, he had contracted a similar bend or stoop in the shoulders; his frame, like that of Robert, was cast in a manly and symmetrical mould. The profile of his countenance resembled that of his brother, and their phrenological developments are said to have been not dissimilar; the principal disparity lay in the form and expression of the eye, which in Gilbert was fixed, sagacious, and steady—in Robert, almost "in a fine frenzy rolling."
Gibert Burns was the archetype of his father, a very remarkable man; his piety was equally warm and sincere; and, in all the private relations of life, as an elder of the church, a husband, a father, a master, and a friend, he was preeminent. His writings want that variety, originality, and ease, which shine so conspicuously even in the prose works of the poet; but they have many redeeming points about them. His taste was as pure as his judgment was masculine. He has been heard to say, that the two most pleasurable moments of his life were—first, when he read Mackenzie's story of La Roche, and secondly, when Robert took him apart, at the breakfast or dinner hour, during harvest, and read to him, while seated on a barley sheaf, his MS. copy of the far-famed Cotter's "Saturday Night."
When Robert Burns was invited by Dr. Blacklock to visit Edinburgh, Gilbert was struggling in the unthrifty farm of Mosgiel, and toiling late and early to keep a house over the heads of his aged mother and unprotected sisters. The poet's success was the first thing that stemmed the ebbing tide of his fortunes. On settling with Mr. Creech, in February, 1788, he received, as the profits of his second publication, about 500l.; and, with that generosity which formed a part of his nature, he immediately presented Gilbert with nearly half of his whole wealth. Thus succoured, Gilbert married a Miss Breconridge, and removed to a better farm at Dinning, in Dumfriesshire. While there, he was recommended to Lady Blantyre, whose estates in East Lothian he subsequently managed for nearly a quarter of a century. He died at Grant's Braes, in the neighbourhood of Haddington, on one of the Blantyre farms, on the 8th of April. He had no fixed complaint; but, for several months preceding his dissolution, a gradual decay of nature had been apparent. It is probable that his death was accelerated by severe domestic afflictions; as, on the 4th of January, he lost a daughter, who had long been the pride of his family hearth; and, on the 26th of February following, his youngest son, a youth of great promise, died at Edinburgh, of typhus fever, on the eve of his being licensed for the ministry. Mrs. Burns, who brought him a family of six sons and five daughters, of whom five sons and one daughter are living, survivors.
It ought to be mentioned that the two hundred pounds which Robert Burns lent to his brother, in the year 1788, was not repaid till 1820. Gilbert was far from affluent; in early life he had to struggle even for existence; and, therefore, to know that his aged mother and one or two sisters, were properly supported, was, in the poet's eyes, a full acquittance of all claims. The children of Robert viewed the subject in the same light. In 1819, Gilbert Burns was invited by Messrs. Cadell and Davies, to revise a new edition of his brother's works; to supply whatever he found wanting, and correct whatever he thought amiss. He accepted the invitation; and, by appending much valuable matter to the late Dr. Currie's biography, he at once vindicated his brother's memory from many aspersions which had been cast upon it, and established his own credit as an author. On receiving payment for his labour, the first thing he did was, to balance accounts, to the uttermost farthing, with the widow and family of his deceased brother. The letter which accompanied the remittance of the money was, in the highest degree, creditable to his feelings.
Monthly Magazine.
Shortly after our arrival at Prome we had an opportunity of witnessing some boxing and wrestling matches, exercises [pg 71]which the Burmahs are very fond of, and which they pride themselves much on excelling in. The challenge is given by stepping to the front, and with the right hand slapping the left shoulder, at the same time taunting the opponent in order to excite him; the struggle does not last long, and when ended, no animosity remains between the parties.
Another amusement of the Burman youth deserves mentioning on account of its singularity. This is a game at ball, played by six or eight young men, formed in a circle; the ball is hollow, and made of wicker work; and the art of the game consists in striking this upwards with the foot, or the leg below the knee. As may be conceived, no little skill is required to keep the ball constantly in motion; and I have often been much entertained in watching the efforts made by the players to send the ball high in the air, so that it should fall within the limits of the ring, when it is again tossed by the foot of another. The natives of Hindostan are not acquainted with this game, but it is said to be common amongst the Chinese, Japanese, and other nations east of the Ganges. But by far the most favourite amusements of the Burmahs are acting and dancing, accompanied by music, which to my ear appeared very discordant, although occasionally a few rather pleasing notes might be distinguished. The principal instrument used in the Burman bands of music is the kiezoop, which is formed of a number of small gongs, graduated in size and tone on the principle of the harmonica, and suspended in a circular frame about four feet high and five feet wide; within which the performer stands, and extracts a succession of soft tones, by striking on the gongs with two small sticks. Another circular instrument (the boundah) serves as a bass; it contains an equal number of different-sized drums, on which the musician strikes with violence, with a view perhaps to weaken the shrill, discordant notes of a very rude species of flageolet, and of an equally imperfect kind of trumpet, which are usually played with a total disregard of time, tune, or harmony. Two or three other instruments, similar in principle to the violin, complete the orchestra. To Europeans, there was not much to admire in the sounds produced by these instruments; neither did our music appear to have many charms for the Burmahs, whom I have seen present at the performance of some of Rossini's most beautiful airs, and of different martial pieces, by one of our best regimental bands, without expressing, either by their words or gestures, the least satisfaction at what they heard.
In condemning, however, the Bunnaa instrumental music generally, I would observe, that some of the vocal airs have a very pleasing effect when accompanied by the Patola. This is an instrument made in the fantastic shape of an alligator; the body of it is hollow, with openings at the back, and three strings only are used, which are supported by a bridge, as in a violin.
I chanced one day to meet with a young Burman who had been stone blind from his birth, but who, gifted with great talent for music, used to console himself for his misfortune by playing on this species of guitar, and accompanying his voice. When I expressed a wish to hear him perform, he immediately struck out a most brilliant prelude, and then commenced a song, in a bold tone, the subject of which was a prophecy that had been current at Rangoon before we arrived. It predicted the appearance of numerous strangers at that place, and that two-masted ships would sail up the Irrawaddy, when all trouble and sorrow would cease! Animated by his subject, his voice gradually became bolder and more spirited, as well as his performance, and without any hesitation he sung with much facility two or three stanzas composed extempore.
Changing suddenly from the enthusiastic tone, he commenced a soft plaintive love-song, and then, after striking the chords for some time in a wild but masterly manner, retired. I confess I felt much interested in this poor fellow's performance, he seemed so deeply to feel every note he uttered, particularly at one time, when he touched upon his own misfortune, that it appeared Providence, in ordaining he should never see, had endowed him with this "soul-speaking" talent in some measure to indemnify him.
The Burmahs, generally speaking, are fond of singing, and, in some instances, I have heard many very good songs. The war-boat song, for example, is remarkably striking. The recitative of the leading songster, and then the swell of voices when the boatmen join in chorus, keeping time with their oars, seemed very beautiful when wafted down the Irrawaddy by the breeze; and the approach of a war-boat might always be known by the sound of the well-known air.
I have sometimes heard a trio sung in parts by three young girls, with a correctness of ear and voice which would do credit to others than the self-taught Burmahs. Many little songs, amongst others that commencing "Tekien, Tekien," were composed and sung by the Burman fair in compliment to their new and welcome visiters, the white strangers; but [pg 72]these, of course, are long since consigned to oblivion, unless they recollect with pleasure
—"The grateful breath of song,
That once was heard in happier hours;"
for it is very certain that the Bunnahs considered themselves quite happy, when enjoying the transient glimpse of liberty, and the advantages of a just government which were offered them during the short stay of the British army at Prome.
The Burman plays do not appear to be remarkable for the number of their dramatis personæ. In most there is a prince, a confidant, a buffoon or two, and a due proportion of female characters, represented by boys dressed in female attire. The dresses are handsome; and in one which I attended, the dialogue appeared to be lively and well supported, as far as I can judge from the roars of laughter which resounded from the Burman part of the audience. One sentimental scene, in which the loving prince takes leave of his mistress, and another where, after much weeping and flirtation, she throws herself into his arms, were sufficiently intelligible to us; but some, in which the jokes of the clown formed the leading feature, were quite lost upon those who did not understand the language. The place chosen for the representation was a spot of ground outside of our houses, the heat being very great; and here a circle was formed of carpets and chairs, lighted by torches dipped in petroleum, which threw a brilliant flare around, though accompanied by a most unpleasant odour.
Dancing succeeded, and one or two young women were the performers; like the Hindostanee Nautch, it merely consisted in throwing the body and arms into numerous graceful and rather voluptuous postures; at the same time advancing slowly, with a short steady step, and occasionally changing it for a more lively figure.
All this time the drums, cymbals, and clarionets were unceasing in their discordant sounds, and, before long, fairly drove me from the field.
Two Years in Ava.
While passing some time in the south of France, I spent a few days at S——, a town on the banks of the Loire, situated in that province, which, from its fertility and beauty, is usually designated the garden of France.
S——, I had been informed, was a place famed alike for its vineyards and its pretty girls, a coincidence certainly natural, since it fairly may be supposed, that the sun which ripens the richest fruit in nature, should alike mature its sweetest flowers, and perfect the beauties and the charms of that sex, which is literally "like the fair flower in its lustre." As the friend, by whom I was accompanied, was well known in the place, we were soon introduced to a circle of respectable families; and among others, to that of Berton, consisting of the father, mother, and daughter.
Rosalie Berton was the belle of S——, or to borrow the far prettier French phrase, she was "la perle de ville." And a sweet and lovely girl she was, as ever the eye of affection hailed with delight. Her charms had something of a peculiar style and character; for, with the bright black eyes, and fine dark hair of the south, were united the fair complexion and delicately tinted cheek of a northern beauty. Her face was of a somewhat more pensive turn than usual, and her meek, mild features, and soft dark eyes, bore traces of tender feeling and of gentle thought; while so expressive was her countenance, that it responded, at will, to her feelings, and the eye and the cheek which were one moment impressed with melancholy, beamed forth the next with all the warmth of intelligence, affection, or delight. Her accomplishments were really of a superior kind; she walked with more than the usual elegance of her country-women, and danced with equal animation and grace. But her most attractive charm consisted in her voice, which, though not particularly powerful, had a sweetness and a melody which were perfectly delightful; so that never methinks have I heard a softer strain, than when that fair girl was wont to sing to her guitar the simple ballads and sweet romances of her native land. And her musical talents were enhanced by her gentle, complying disposition, and by the readiness with which she obeyed every call on her exertions. From her music-master, who was a native of Italy, she also learnt Italian, which she spoke with more fluency and correctness than is usual among the French; she drew, moreover, with considerable taste. So affectionate and so amiable was she, that she deserved all the encomiums of her friends and even their hyperbolical compliments were scarcely extravagant when applied to her. She was literally "douce comme un ange, jolie comme les amours;" and, as the ne plus ultra of merit in France, she was "tout a fait gentille." She possessed also, considerable [pg 73]dramatic skill and tact, and would, I think, have proved a delightful acquisition to the stage, from the skill she displayed in those little playful scenes, with which the French delight to embellish life.
We were favoured with a specimen of her talents in this way, on the evening of our arrival. It was the fête day of madame, the mother of Louise, and we were invited to be present. After some time passed in taking refreshments, varied by dancing, conversation, &c., the little ceremony of the evening commenced; the door opened, and a small but gay procession entered the room. It consisted of several young persons, all friends of the family, headed by Louise, who was charmingly dressed, and looked altogether most lovely. She bore her guitar across her bosom, and the instrument was encircled with a wreath of flowers. Each individual carried some little offering, such as bottles of wine and liqueurs, conserves and sweetmeats, flowers and fruit, &c. &c.; and these were placed on the table, the whole group forming a circle round Rosalie, who advanced to her mother, and sang to the guitar the well-known verses consecrated to such occasions.
Madame c'est aujourdhui votre fete,
C'est aussi celle de nos coeurs;
A vous chanter chacun s'apprete!
Et veut vous courouner de fleurs!
The lovely girl then loosed the garland from her lyre, placed it with light hand on the brow of her mother, and sank in a graceful bending attitude to receive her parent's blessing. She was instantly raised, fondly embraced by both her admiring parents, and with a repetition of the song, the whole party left the room. The scene is long past, but I have often recalled it since; and in many an hour of fancy and of thought, have again beheld that fair girl kneeling to her mother, again beheld her clasped to that mother's heart. Nor was the above the only instance of her skill, every day presented some fresh instance of her feeling and of taste.
A plaisanterie, which proved very successful, was arranged as follows:—We were sitting one evening up stairs, when we were attracted by the performance of three musicians, who were singing in the cour. The party consisted of two young men, and a female, who wore a veil; they accompanied their songs by playing on the guitar; their performance was evidently of a superior character; the music and the words were Italian, and the voice of the female performer was eminently sweet and touching. After listening some time with great delight—
"Go," said I to one of the party, "find Rosalie, and tell her to come and listen to a better singer than herself, who will give her a lecon de chant."
This was said in the hearing of the foreign songstress, for whom it was intended as a compliment, while, at the same time, some silver was thrown upon the ground. But what was our surprise, when the lovely girl threw aside her veil, exclaiming—
"He! bien messieurs et dames! vous ne connaissez donc plus votre pauvre Rosalie!"
Such was one of many pleasantries by which we were diverted and amused. Idle fancies these indeed, and such as sterner judgments may deem trifling or absurd, yet not uninteresting, since many of them evidently afford vestiges of classic times and manners, transmitted through the course of ages; nor unuseful, since they tend to smooth and adorn the rugged way of life, and to strew its flinty path with flowers.
With the charms and accomplishments which I have described, (and the sketch can convey but a faint idea of those which she actually possessed,) it cannot be supposed that Rosalie was destitute of admirers. She had, indeed, had several, but their suits were all unsuccessful. She had been addressed in turn by the medecin of the place—by the son of the President of the Tribunal du Commerce—and by a nephew to a Monsieur de V——, the seigneur who resided at a neighbouring château. But they were all, more or less, improper characters; the medecin was a gamester; the president's son a drunkard, a character utterly despised in these parts; while the nephew to the seigneur, was actually a mauvais sujet! What the French precisely understand by a mauvais sujet, I never could exactly make out; for, when impelled by curiosity to inquire, my queries were always met by such a volley of vituperation, as left one altogether in the dark with regard to the real nature of the charge. On the whole, I presume, we are to consider a mauvais sujet as a culprit, compared with whose transgressions, the several enormities of gaming, drinking, and the like, sink into mere peccadilloes.
The parents of Rosalie (the parents settle all these matters in France), on learning the character of their intended sons-in-law, dismissed them one after the other; and Rosalie acquiesced in their determination with a readiness and a decision, which did equal honour to her affection and her judgment.
So interesting a girl, however, was not likely to remain long without a suitable [pg 74]admirer, and she speedily had another affaire du coeur. A young and handsome militaire, a sous-lieutenant in the royal guard, aspired to gain her hand, and to replace the vacancy in her affections.
Henri Vaucouleurs was a fine, tall, dark, martial-looking young man (the French make fine-looking soldiers), and, with his luxuriant mustachios and the eager glance of his keen black eye, seemed the very beau ideal of a modern hero. Born at Mezieres, in the department of Ardennes, he was cradled in the very lap of war, and was yet a mere boy; when, in the summer of 1813, he joined the corps called the garde d'honneur. He made the campaign of Germany, and was present in the battles of Leipzig and of Hanau, in the last of which he received a ball in the right arm. He shortly, however, resumed his post with the army assembled for the defence of France, and at the battle of Laon received a severe coup de sabre on his forehead, the scar of which added much to the martial aspect of his countenance. At the peace he joined the royal guard, in which corps he still continued. He was really a very estimable and engaging young man; and possessed more candour, intelligence, and good sense, than I think I ever witnessed in a military man among the French. His account of his campaigns was exceedingly modest, unaffected, and intelligent, and his whole conversation and manner were of a superior character. I remember, he spoke with great forbearance of the three principal nations among the allies, the Russians, Prussians, and Austrians; but inveighed, bitterly, against several of the auxiliaries, who, he said, having received only benefits of the French emperor, embraced the first opportunity offered by a reverse of fortune, to desert and betray him. Of Napoleon, he spoke with enthusiasm as a soldier; but with detestation, as an intoxicated and deluded tyrant, a rash and desperate gamester, who sent forth his attached and devoted soldiers, to be devoured by the destroying elements, without provision, or scarcely a thought for their natural and indispensable wants.
Such were the character and pretensions of him who was destined to gain the affections of Rosalie. At first, he seemed to have but little chance of success. Old people commonly entertain a prejudice against the character and profession of military men, and are seldom ambitious of such an alliance for a daughter. The parents of Rosalie were prepossessed against Henri on account of his calling; and, though Rosalie herself early entertained an interest in his favour, yet she was too good and too sage to cherish in herself, or to encourage in her lover, an attachment which her parents might disapprove. Henri was, however, admitted as a visiter at the house, and by degrees his amiable manners and correct deportment won, first on the old lady, and then on the father, till their scruples vanished, and, indeed, they wondered they could ever have entertained any against so estimable a young man and an officer. He was thus speedily received as the lover of Rosalie, and about the time of my visit was installed in all the privileges of a bon ami. He was equally accomplished with herself; spoke German fluently, Italian passably well, and was an excellent performer on the flute and the guitar; so that he was a fit companion for his charming intended, and was able to assist in those refined and elegant recreations, in which she also excelled.
(To be concluded in our next.)
"Dozing very much delights."
Our corporeal machinery requires an occasional relaxation, as much as the steam engine does the application of oil to its divers springs; and, after a bonâ fide slumber, we rise with a freshness equal to that of flowers in the best regulated flower-pots. But dozing must not be confounded with legitimate sleep, though frequently tending to the same purpose; it may be termed an embryo slumber, that entertaineth the body with the most quiescent gentleness, acting on our senses as a sort of mental warm bath; till, finally, the "material man" himself luxuriates in tepidity.
Nothing can be more ungodly than to enter the church with an express purpose of dozing there. Arm-chairs, sofas, and beds are the legitimate places for dozers. But there is no accounting for that conquering spirit of all-besetting drowsiness that attacks us at sundry times and places. It is in vain that we lengthen our limbs into an awakening stretch—that we yawn with the expressive suavity of yawning no more—that we dislocate our knuckle bones, and ruffle the symmetry of our visage, with a manual application; like the cleft blaze of a candle, drowsiness returns again. Well, then, what manner of reader is he that hath never sinned by drowsing in church time? Let him read [pg 75]on; and I'll realize by description what he has realized by endurance.
It is after the embodying of a good dinner with ourselves, that doziness is most tempting. You have dined at four o'clock to-day. Well, that's a decent Sabbatical hour. After due potations of wine, coffee, &c. your gratitude is awakened; and, like a good Christian, you arrange your beaver, and walk off steadily to church. Now, remember, I give you full credit for your wish to exhibit your external holiness—that you are indeed conscious of the reverence that should accompany all your engagements in the fane of the Deity; and yet I prognosticate that if the Rev. Nabob Narcotic happen to preach this evening, you will, of a surety, doze—infallibly doze—in the midst of his sermon!
'Tis a summer month, and the very church windows seem labouring with a fit perspiration. Horribly boring—isn't it? How your hat clings to your moistened forehead, and the warm gloves droop from your fingers, like roasting chicken! Get as much room as possible; tenderly pass little miss there, and her unbreeched brother, over to their smiling mamma. Now you have the balmy corner to yourself! "Psalms," first lesson—second ditto—prayers—thanksgivings—all reverently attended to; there is a little dreaminess settling on your lids—your lips begin to close with languor; but you have not dozed. Let's hear the sermon. You are seated with tolerable erectness; and, judging from the steady determination of your eyebrows, one would imagine that your eyes would be open for the whole of the discourse. But, alas! 'tis Mr. Narcotic, whose spectacled nose is just verging above the crimson horizon of his pulpit.—"Awake, thou that sleepest!" Why, the text is quite opposed to DOZINESS! But what of this, if the preacher be addicted to drawling, the weather unobligingly sultry, and you yourself have gradually been dwindling from an uncongenial state of wakefulness into a sleepy calm? 'Tis too much for beldame Nature, believe me!
I perceive that you have rubbed the bridge of your nose several times—that you have tried to swell forth your eyes with a full round stare at the parson; but your stoicism "profiteth nothing." The sermon is irreligiously long; and you are nodding—in a doze! Whether there be much pleasure in a church doze, I am not presuming enough to determine. For myself, I have found nothing more tantalizing than the endeavour to restrain from an occasioned doze during church time. After a certain period, I have perceived the parson diminishing, like a phantasmagoric image—all the ladies' black bonnets sinking away, like a cluster of clouds—and (shame on the confession!) I have performed head worship to the front of my seat, instead of keeping an immovable post-like position, before his reverence. However, a church doze is seldom admired by the wakeful. Should an embryo snore escape from one's nose (and this is possible,) some old grandam, or an upright piece of masculine sanctity, is sure to rouse you; the former will either hem you into awakening shame, or drop her prayer-book on the floor; the latter will most likely thump the same with the imperative tip of his boot. How horridly stupid one seems after being aroused! The woman eyes you with the most piquant, self-justifying sneer possible; while all her little IMMACULATES, if she have any, look at you like so many hissing young turkey cocks; and as for the man—bless his holiness!—he'd frown you down to Hades at once.
"My heart leaps up" when I behold a stage coach—that snug, panel painted, comfortable wheel-whirling "thing of life." O ye days of juvenilian sensibilities—ye eye-feeding, heart-rising scenes of remembered felicity!—how glorious was the coach at the school door! The whip—Ajax Mastigoferos never had such a powerful one as the modern Jehu! The spokes of the wheels—they were handled with admiring fingers! That Jupiter-like throne, the coach-box—who would not have risked his neck to have been seated on it? When all was "right," how eloquent the lip-music of coachee! how fine the introductory frisks of the horses' tails, and the arching plunge of the fore-foot—no rainbow-curve ever was so beauteous! "Oh, happy days! who would not be a boy again?" But away with my puerilities. I intend the reader to take a doze in that comfortable repository for the person—the inside of a coach.
With all the reckless simplicity of boyhood, I maintain that travelling by coach is by no means the least of our sublunary pleasures. Man is a wheelable animal as well as walking one. Winter is the time for a nice inside jaunt. What divine evaporations from the coachman's muzzle! What a joyous creak in the down-flying steps!—and, oh! that comfortable alertness with which we deposit ourselves in the padded corner, and fold our coatflaps over our knees, glance at the frosty steam of the window; and then, quite à la Tityre, repose our recumbent bodies at our ease! Such moments as these are snatches of indefinable [pg 76]bliss. It would appear probable, that a coach was a very inconvenient place for a doze; the attendant bustle, the whip-smacks, bickering wheels, and untranquillizing jolts—
"Like angels' visits, few and far between,"—
are not calculated for sleepiness. Notwithstanding these correlative interruptions, a doze in the coach is by no means uncommon, even in the daytime. Let us examine this a little more intellectually.
Suppose a man is returning to his friends, with a mind composed, and "all his business settled." (By-the-by, how vastly comprehensive this speech is!) Suppose he has entered the coach about four in the afternoon, and, by rare luck, finds he is, for the present, the only inside passenger. Such a man, I say, will be likely to doze before twenty miles have run under the coach-wheels—speaking Hibernicè. For the last half-hour, he will be thinking of himself—how many commissions he has performed—how many he has left undone—and how many he intends to do. The next, he will probably give to his home attractions—his anxious wife, sat musingly round the tea-table—his favourite son George (so like his father)—and all the nine hundred and ninety-nine pretty nothings we hear of, after a brief absence. These will send his heart a long way from the coach, and therefore keep him in the full enjoyment of wakefulness. But this train of delectable musing is by no means exhaustless. The roll of the wheels gradually becomes naturalized to the ear, and the body moves in sympathy with the coach; the road gets very monotonously barren; the lounge in the corner—how suitable then to this solitary languor! Lulled here, the traveller for awhile admires the leathern trappings of the coach, hums a tune perhaps, and affects a dubious whistle. Meantime the operations of doziness have been gently applying themselves. His eye is sated with the road and the coach; his hands become stationary on his lap; his feet supinely rested on the opposite seat; his head instinctively motions to the corner—and he dozes! A doze in the coach is the flower of dozes, when you are alone. There, you may twist your person into any shape you please, without the fear of discomposing a silken dress, or a nursemaid's petticoats. No boisterous arguments from snuff-taking sexagenarians: all is placid —Eden-like—just as a dozer's sanctorum ought to be! The only thing attendant on the doze of an inside passenger, is the great chance of being suddenly aroused by the entrance of company. O tell me, ye of the fine nerve, what is more vexing than to be startled from your nest by the creaking slam of the steps, the bleak winter gales galloping along your face, and a whole bundle of human beings pushing themselves into your retreat! There is no rose without its thorn, as myriads have said before me:—
——"O beate Sexti,
Vitæ summa brevis SPEM nos vetat inchoare LONGAM!"
Not all the morose sarcasms of Johnson, on the pleasures of rural life, have ever weakened my capability for enjoying it at convenient intervals. His antipathy to the country resembled his contempt for blank-verse—he could not enjoy it. I have now moped away a considerable number of months in this city of all things—this—this London. "Well?" Pray restrain yourself, reader; I am coming to the point in due season. During my metropolitan existence—although I am neither a tailor, nor any trade, nor anything exactly—I have never beheld a downright intellectual-looking blade of grass. I mean much by an intellectual blade of grass. The Londoners—poor conceited creatures!—have denominated sundry portions of their Babylon "fields." But—I ask it in all the honest pride of sheer ignorance—is there the ghost even of a bit of grass to be seen in many of them? I cannot easily forget my vexation, when, after a tedious walk to one of those misnomered "fields," I found nothing but a weather-beaten, muggy, smoky assemblage of houses of all sizes, circumscribed by appropriate filth and abundant cabbage-stumps. Innocent of London quackeries, I strolled forth with the full hope of laying me down on a velvet carpet of grass—the birds carolling around me—and, perchance, a flock of lambkins, tunefully baying to their mammas!! "Said I to myself," when I reached these fields, "what a fool I am!" I had contemplated a doze on the grass.
But leaving all thoughts of disappointment, who will not allow that there is something exceedingly delightful in dozing calmly beneath the shade of an o'er-arching tree?
——"recubans sub tegmine fagi."
Of course, the weather should be fine, to admit of this luxurious idleness. Let the blue-bosomed clouds be sailing along, like Peter Bell's boat; let the sunbeams be gilding the face of nature, and tinging the landscape with multiform hues; let the breezes be gentle, the spot retired, [pg 77]and the heart at ease. Now, go and stretch yourself on the grassy couch, while the branches of an aged tree shadow forth the imaged leaves around you. What a congenial situation for philosophy—under an old tree, on a sunny summer day! How much more becoming than the immortal tub of the sour-minded Diogenes? Who will be able to refrain from philosophizing. I repeat it, beneath such an old tree? 'Tis at such times that the heart spontaneously unbends itself—that the fancy tranquillizes its thoughts—and that memory awakens her
——"treasured pictures of a thousand scenes."
Place the palms of your hands beneath your pole, and survey the skies!—calm, beautifully unconscious! By-gone times, and by-gone friends—the thousand commingling scenes of varied life—how they all recur to you now! You fancy you could lie beneath the tree for eternity—so soothing is the employment of doing nothing—or field philosophy! Yet, to speak correctly, you are doing a great deal; your imagination is flying in all directions—from the death of Caesar to the last cup of Congou that you took with a regretted friend. What a mystery your existence is! The world turns round as gently as ever; the flowers bud into life; and the winter nips them. Man lives, thinks, and dies. All very wondrous truisms. Well, after a half-hour—or perchance more—you will be gradually relapsing into a state of soporific nothing-at-all-ness (the best word I can find to express my meaning.) May there be some clear little stream just behind you, laughing along its idle way;—some chirping birds, singing their roundelay—some buzzing flies—you will then be lulled into doziness. However, with or without the purling murmur of the brook—the joyous warbling of the birds—the busy bustling flies—you will not be able to resist the dozing temptations that will steal over you. Your eyes will close gently as flower-leaflets—your thoughts die away in a heavenly confusion—and then you doze!—neither sleeping nor waking, but absolved in delicious dreaminess! O, for such a doze!—Monthly Magazine.
Notwithstanding the aversion of the Chinese to the profession of the Roman Catholic religion, which has been shown, first by persecuting, and then by expelling the Jesuits from the empire, the Chinese government is, however, obliged to keep at least some missionaries at Pekin to compile the almanac. While astrology has led in other nations to the study of astronomy, the Chinese, though they have studied astrology for some thousand years, have made no progress in the real knowledge of the stars. Their ancient boasted observations, and the instruments which they make use of, were brought by the learned men, whom Koubilaï, the grandson of Gingis Khan, had invited from Balk and Samarcand. The government, at present, considers the publication of an annual calendar of the first importance and utility. It must do every thing in its power, not only to point out to its numerous subjects the distribution of the seasons, the knowledge of which is essentially necessary to them, to arrange the manner of gaining their livelihood, and distributing their labour; but on account of the general superstition, it must mark in the almanac, the lucky and unlucky days, the best days for being married, for undertaking a journey, for making their dresses, for buying, or building, for presenting petitions to the emperor, and for many other cases of ordinary life. By this means, the government keeps the people within the limits of humble obedience; it is for this reason that the emperors of China established the academy of astronomy, but we must not expect to find men really acquainted with that science. When this illustrious body, composed of Mantchoos, and in which Europeans, though subordinate, are the most active, condescended to look at the planetarium, which was among the presents which the king of England sent to the emperor of China by lord Macartney, Mr. Barrow was not able to make the president of this learned society understand the real merit of that instrument. Besides, how should a people be able to comprehend astronomy, to know the position of the heavenly bodies, and determine the orbits of the planets, while it is ignorant of the elements of mathematics, and makes its calculations by the help of vertical arithmetical tables, like those used by the shop-keepers in Russia, and who are ignorant both of analysis and geometry?—Timkowski's Mission to China.
The following are points of comparison which may be remarked in the characters [pg 78]of the French and English. The French are great talkers, the English great thinkers; the former excel in vivacity, the latter in solidity of intellect. The French dress with splendour, the English with neatness; the French live almost exclusively on bread, the English on meat. Both are passionate; but it is the blood which rouses the passion of a Frenchman, and the bile which exasperates an Englishman. The anger of a Frenchman is more violent, that of an Englishman more pertinacious. A Frenchman spends his money on his clothes, an Englishman on his belly. A Frenchman follows the stream, an Englishman delights in struggling against it. The friendships of the French are quickly formed, and as quickly dissolved; those of the English are formed slowly, and as slowly relinquished. The French respect their superiors, the English respect themselves; the former are better citizens, the latter better men. The mental endowments of the French are of a more refined, those of the English of a loftier, character. The French practise virtue for the sake of reputation, and seek the reward of meritorious actions in popular applause; the English practise it for its own sake, and seek no reward but that which springs from the consciousness of rectitude. There is the same relative difference in their vices as in their virtues. Both commit crimes; the French from the love of gain, the desire of vengeance or similar motives; but the English are often criminal for the mere sake of committing crime. The French, like the people of other countries, often commit crimes in the hope of escaping punishment, but the English frequently commit crimes because they know they cannot escape unpunished; so that the very severity of the law, which deters others from crime, often operates as an additional stimulus on the English for the commission of offences, "I would commit this offence," exclaims the Frenchman, "if the law permitted it." "I would not commit this offence, if it were not prohibited by law," is frequently the language of the Englishman.—Memoirs of Lewis Holberg.
With tender vine-leaves wreathe thy brow,
And I shall fancy that I see,
In the bright eye that laughs below,
The dark grape on its parent tree.
'Tis but a whim—but, oh! entwine
Thy brow with this green wreath of mine.
Weave of the clover-leaves a wreath,
Fresh sparkling with a summer-shower,
And I shall, in my fair one's breath,
Find the soft fragrance of the flower.
'Tis but a whim—but, oh! do thou
Twine the dark leaves around thy brow.
Oh, let sweet-leaved geranium be
Entwined amidst thy clustering hair,
Whilst thy red lips shall paint to me,
How bright its scarlet blossoms are.
'Tis but a whim—but, oh! do thou
Crown with my wreath thy blushing brow.
Oh, twine young rose-leaves round thy head,
And I shall deem the flowers are there,—
The red rose on thy rich cheek spread,
The white upon thy forehead fair.
'Tis but a whim—but, oh! entwine
My wreath round that dear brow of thine.
The Draught of Immortality, &c.
At the Academy of Sciences at Paris, a memoir was read by Captain Duperrey, on the experiments made with the invariable pendulum, during the voyage of the Coquille round the world. He states that various experiments confirmed the fact of the flattening of the terrestrial globe, conjectured by several travellers, who had remarked that the number of oscillations which the pendulum made at certain places, differed from what had been observed in the extent of the same parallel. The principal anomalies observed by Captain Duperrey were at the Isle of France, Mons, Guam, and the Island of Ascension. At the Isle of France, the invariable pendulum (as had been remarked by M. Freycinet) made in one day, upon an average, thirteen or fourteen oscillations more than it ought, supposing the depression to be 1.305, according to the lunar theory. At Ascension, the acceleration, as noticed by Captain Sabine, was five or six oscillations, even supposing the depression to be 1.228. At other stations the difference was almost nothing; and in some, the motion of the pendulum was retarded. Such differences, Captain Duperry remarks, between the results of experiment and those given by theory, cannot be attributed to errors of observation. He is disposed to refer the cause of the phenomena, with Captain Sabine, to the want of homogeneousness in the earth, considered as a mass, or to the mere variations of density in the superficial strata. What tends to confirm this hypothesis, he says, is, that all observations show that an acceleration of the pendulum generally takes place on volcanic ground [pg 79]and a retardation on such as is sandy and argillaceous. A very important question to ascertain is, whether the flattening is exactly the same in both hemispheres. From the observations of Captains Duperrey and Freycinet, it appears that in the southern hemisphere it is 1.291, and in the northern 1.288; that is to say, it is sensibly the same, or 1.290 in both.
The following curious observations on the habits of plants, were made by General Walker, in his address to the Agricultural Society of St. Helena, in February last:—"The functions of plants, as well as of animals, depend upon the air in which they live. I have observed that those of St. Helena, which have been brought from another hemisphere, are very irregular in their annual progress; many of them, in the development of their foliage, have adopted the law of nature peculiar to the country into which they have been transplanted. Others, more obstinate, remain faithful to their own habits, and continue to follow the stated changes to which they had been accustomed. They all appear to maintain a struggle either before they adopt the habits which belong to the seasons of their new country, or decide on retaining their relations with the old. In yielding to external circumstances, they appear to have different tempers. This appearance of contention is often observed in plants of the same species; they seem to hesitate and deliberate, ere they adopt the mode of performing the functions of life. At length when the decision is made, apparently not without pain and effort, we are at a loss to discover an adequate cause. An oak, for instance, which loses its leaves in a St. Helena winter of 68 degrees, scarcely experiences the difference of temperature, which, reasoning by analogy, could cause that change. It would have continued to maintain inflexibility, in its original climate, its old habits, though exposed to far greater irregularity and severity of climate. But though the law is obeyed by many plants, it does not determine the periodical changes of the whole, nor do they all submit to it with equal readiness and regularity. It would add, I conceive, to the natural history of vegetation, and improve our knowledge of the geography of plants, were the facts concerning their habits and changes, under different temperatures, carefully collected."
The wonderful miracles wrought by Bridget Bostock, of Cheshire, who healed all diseases by prayer, faith, and an embrocation of fasting spittle, induced multitudes to resort to her from all parts of the country, and kept her salival glands in full employ. Sir John Pryce, with a high spirit of enthusiasm, wrote to this woman to make him a visit at Newton Hall, in order to restore to him his third, a favourite, wife. His letter will best tell the foundation on which he built his strange hope, and every uncommon request.
To Mrs. Bridget Bostock.
Madam,—Having received information, by repeated advices, both public and private, that you have of late performed many wonderful cures, even where the best physicians have failed; and that the means used appear to be very inadequate to the effect produced; I cannot but look upon you as an extraordinary and highly favoured person. And why may not the same most merciful God, who enables you to restore sight to the blind, hearing to the deaf, and strength to the same, also enable you to raise the dead to life? Now, having lately lost a wife, whom I most tenderly loved, my children a most excellent step-mother, and our acquaintances a most dear and valuable friend, you will lay us all under the highest obligations; and I earnestly entreat you, for God Almighty's sake, that you will put up your petitions to the Throne of Grace on our behalf, that the deceased may be restored to us, and the late dame Eleanor Pryce be raised from the dead. If your personal attendance appears to you to be necessary, I will send my coach and six, with proper servants to wait on you hither, whenever you please to appoint. Recompense of any kind that you may please to propose would be made with the utmost gratitude; but I wish the bare mention of it is not offensive to both God and you.
I am, madam,
Your most obedient, and very much afflicted, humble servant,
JOHN PRYCE.
The late Rev. Thomas Toller, an eminent dissenting minister, (joint preacher with the celebrated Dr. James Fordyce, at Monkwell-street,) resided many years in the Lower-street, Islington. One day, when he got into the stage to come to [pg 80]London, he met with two ladies of his acquaintance, and a loquacious young Irishman, who was very obtrusive with his "would-be wit" to the females. The coachman soon stopped to take up another passenger, who, Dutchman-like, was "slow to make haste." A young dog, being confined in the neighbourhood, bewailed its loss of liberty, by making an hideous noise; which all the party agreed was very disagreeable. The Hibernian, desirous to display his wit, and to quiz the parson, said, "The animal was so unpleasantly noisy, it must be a presbyterian dog." Mr. Toller calmly, but with much apparent confidence, said, "I am sure it is an Irish dog."—"How do you know that?" exclaimed the astonished young man with eagerness.—"I know it, sir," (replied the divine,) "by its impudence and its howl." This seasonable retort cured the garrulity of the patient, and gave him a locked-jaw till the stage arrived at the Royal Exchange.
It was his custom, to retire in the evening to what he considered the most comfortable corner in the house, and take his seat close, to the kitchen fireside, in order to draw some plan for the forming a new instrument, or scheme for the improvement of one already made. There, with his drawing implements on the table before him, a cat sitting on the one side, and a certain portion of bread, butter, and a small mug of porter placed on the other side, while four or five apprentices commonly made up the circle, he amused himself with either whistling the favourite air, or sometimes singing the old ballad of
"If she is not so true to me,
What care I to whom she be?
What care I, what care I, to whom she be!"
and appeared, in this domestic group, contentedly happy. When he occasionally sent for a workman, to give him necessary directions concerning what he wished to have done, he first showed the recent finished plan, then explained the different parts of it, and generally concluded by saying, with the greatest good humour, "Now see, man, let us try to find fault with it;" and thus, by putting two heads together, to scrutinize his own performance, some alteration was probably made for the better. But, whatever expense an instrument had cost in forming, if it did not fully answer the intended design, he would immediately say, after a little examination of the work, "Bobs, man! this won't do, we must have at it again;" and then the whole of that was put aside, and a new instrument, begun. By means of such perseverance, he succeeded in bringing various mathematical, philosophical, and astronomical instruments to perfection. The large theodolite for terrestrial measurements, and the equal altitude instrument for astronomy, will always be monuments of his fertile, penetrating, arduous, superior genius! There cannot be a lover (especially of this more difficult part) of philosophy, in any quarter of the globe, but must admire the abilities, and respect the memory, of Jesse Ramsden—Practical Observations on Telescopes.
"I am but a Gatherer and disposer of other men's stuff."—Wotton.
Mr. Kelly, in his "Reminiscences," relates, that in 1792 he was walking in the Place Vendome with two Irish gentlemen, a Colonel Stark Macarthy and a Captain Fagan, the latter possessing "a vast portion of the ready wit of his country." Coming to the celebrated statue of Victory holding the laurel crown over the head of Louis XIV., a French officer was enumerating the splendid achievements of that heroic king, and particularly desired us to observe the attitude of the figure of Victory. "Pray, sir," said Fagan, "may I take the liberty of asking the question—Is Victory putting the laurel on his majesty's head, or taking it off?" The question puzzled the Frenchman, and made us laugh heartily.
Parr carried his compassion towards the inferior tribes so far, that two or three hares found a secure asylum for nearly two years in his garden at Hatton. He said that they were his clients, for they had placed themselves under his protection. He gave strict orders that they should not be shot. "It would be a gross violation," he said, "of a tacit covenant of hospitality."
A few months since, a noble marquis bespoke a play at a country theatre, the representation of which Mr. Canning, prime minister, honoured with his presence. The boxes and other parts of the house were crammed, with the exception of the pit, which looked beggarly; on which an actor observed to a brother of the sock, "We've no pit to-night."—"No Pitt!" rejoined the other, "and none we want while we have a Canning!"
Footnote 1: (return)I should feel highly obliged if any of your valuable correspondents would favour me, through the medium of the MIRROR, with the name of the noble to whom the above arms appertained.
Footnote 2: (return)The remaining part was left to Lady Thornhill, who lived several years with her son-in-law after the death of Sir James.
Footnote 3: (return)Our Royal Academy is now governed precisely on the same principles as is the French Academy. What would Hogarth have said, had he lived at the present day?
Printed and published by J. LIMBIRD, 143, Strand, (near Somerset House,) and sold by all Newsmen and Booksellers.
End of the Project Gutenberg EBook of The Mirror of Literature, Amusement,
and Instruction, Vol. 10, Issue 266, July 28, 1827, by Various
*** END OF THIS PROJECT GUTENBERG EBOOK MIRROR OF LITERATURE, JULY 28, 1827 ***
***** This file should be named 9919-h.htm or 9919-h.zip *****
This and all associated files of various formats will be found in:
https://www.gutenberg.org/9/9/1/9919/
Produced by Jonathan Ingram and Project Gutenberg
Distributed Proofreaders
Updated editions will replace the previous one--the old editions
will be renamed.
Creating the works from public domain print editions means that no
one owns a United States copyright in these works, so the Foundation
(and you!) can copy and distribute it in the United States without
permission and without paying copyright royalties. Special rules,
set forth in the General Terms of Use part of this license, apply to
copying and distributing Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works to
protect the PROJECT GUTENBERG-tm concept and trademark. Project
Gutenberg is a registered trademark, and may not be used if you
charge for the eBooks, unless you receive specific permission. If you
do not charge anything for copies of this eBook, complying with the
rules is very easy. You may use this eBook for nearly any purpose
such as creation of derivative works, reports, performances and
research. They may be modified and printed and given away--you may do
practically ANYTHING with public domain eBooks. Redistribution is
subject to the trademark license, especially commercial
redistribution.
*** START: FULL LICENSE ***
THE FULL PROJECT GUTENBERG LICENSE
PLEASE READ THIS BEFORE YOU DISTRIBUTE OR USE THIS WORK
To protect the Project Gutenberg-tm mission of promoting the free
distribution of electronic works, by using or distributing this work
(or any other work associated in any way with the phrase "Project
Gutenberg"), you agree to comply with all the terms of the Full Project
Gutenberg-tm License (available with this file or online at
https://gutenberg.org/license).
Section 1. General Terms of Use and Redistributing Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic works
1.A. By reading or using any part of this Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic work, you indicate that you have read, understand, agree to
and accept all the terms of this license and intellectual property
(trademark/copyright) agreement. If you do not agree to abide by all
the terms of this agreement, you must cease using and return or destroy
all copies of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works in your possession.
If you paid a fee for obtaining a copy of or access to a Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic work and you do not agree to be bound by the
terms of this agreement, you may obtain a refund from the person or
entity to whom you paid the fee as set forth in paragraph 1.E.8.
1.B. "Project Gutenberg" is a registered trademark. It may only be
used on or associated in any way with an electronic work by people who
agree to be bound by the terms of this agreement. There are a few
things that you can do with most Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works
even without complying with the full terms of this agreement. See
paragraph 1.C below. There are a lot of things you can do with Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic works if you follow the terms of this agreement
and help preserve free future access to Project Gutenberg-tm electronic
works. See paragraph 1.E below.
1.C. The Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation ("the Foundation"
or PGLAF), owns a compilation copyright in the collection of Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic works. Nearly all the individual works in the
collection are in the public domain in the United States. If an
individual work is in the public domain in the United States and you are
located in the United States, we do not claim a right to prevent you from
copying, distributing, performing, displaying or creating derivative
works based on the work as long as all references to Project Gutenberg
are removed. Of course, we hope that you will support the Project
Gutenberg-tm mission of promoting free access to electronic works by
freely sharing Project Gutenberg-tm works in compliance with the terms of
this agreement for keeping the Project Gutenberg-tm name associated with
the work. You can easily comply with the terms of this agreement by
keeping this work in the same format with its attached full Project
Gutenberg-tm License when you share it without charge with others.
1.D. The copyright laws of the place where you are located also govern
what you can do with this work. Copyright laws in most countries are in
a constant state of change. If you are outside the United States, check
the laws of your country in addition to the terms of this agreement
before downloading, copying, displaying, performing, distributing or
creating derivative works based on this work or any other Project
Gutenberg-tm work. The Foundation makes no representations concerning
the copyright status of any work in any country outside the United
States.
1.E. Unless you have removed all references to Project Gutenberg:
1.E.1. The following sentence, with active links to, or other immediate
access to, the full Project Gutenberg-tm License must appear prominently
whenever any copy of a Project Gutenberg-tm work (any work on which the
phrase "Project Gutenberg" appears, or with which the phrase "Project
Gutenberg" is associated) is accessed, displayed, performed, viewed,
copied or distributed:
This eBook is for the use of anyone anywhere at no cost and with
almost no restrictions whatsoever. You may copy it, give it away or
re-use it under the terms of the Project Gutenberg License included
with this eBook or online at www.gutenberg.org
1.E.2. If an individual Project Gutenberg-tm electronic work is derived
from the public domain (does not contain a notice indicating that it is
posted with permission of the copyright holder), the work can be copied
and distributed to anyone in the United States without paying any fees
or charges. If you are redistributing or providing access to a work
with the phrase "Project Gutenberg" associated with or appearing on the
work, you must comply either with the requirements of paragraphs 1.E.1
through 1.E.7 or obtain permission for the use of the work and the
Project Gutenberg-tm trademark as set forth in paragraphs 1.E.8 or
1.E.9.
1.E.3. If an individual Project Gutenberg-tm electronic work is posted
with the permission of the copyright holder, your use and distribution
must comply with both paragraphs 1.E.1 through 1.E.7 and any additional
terms imposed by the copyright holder. Additional terms will be linked
to the Project Gutenberg-tm License for all works posted with the
permission of the copyright holder found at the beginning of this work.
1.E.4. Do not unlink or detach or remove the full Project Gutenberg-tm
License terms from this work, or any files containing a part of this
work or any other work associated with Project Gutenberg-tm.
1.E.5. Do not copy, display, perform, distribute or redistribute this
electronic work, or any part of this electronic work, without
prominently displaying the sentence set forth in paragraph 1.E.1 with
active links or immediate access to the full terms of the Project
Gutenberg-tm License.
1.E.6. You may convert to and distribute this work in any binary,
compressed, marked up, nonproprietary or proprietary form, including any
word processing or hypertext form. However, if you provide access to or
distribute copies of a Project Gutenberg-tm work in a format other than
"Plain Vanilla ASCII" or other format used in the official version
posted on the official Project Gutenberg-tm web site (www.gutenberg.org),
you must, at no additional cost, fee or expense to the user, provide a
copy, a means of exporting a copy, or a means of obtaining a copy upon
request, of the work in its original "Plain Vanilla ASCII" or other
form. Any alternate format must include the full Project Gutenberg-tm
License as specified in paragraph 1.E.1.
1.E.7. Do not charge a fee for access to, viewing, displaying,
performing, copying or distributing any Project Gutenberg-tm works
unless you comply with paragraph 1.E.8 or 1.E.9.
1.E.8. You may charge a reasonable fee for copies of or providing
access to or distributing Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works provided
that
- You pay a royalty fee of 20% of the gross profits you derive from
the use of Project Gutenberg-tm works calculated using the method
you already use to calculate your applicable taxes. The fee is
owed to the owner of the Project Gutenberg-tm trademark, but he
has agreed to donate royalties under this paragraph to the
Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation. Royalty payments
must be paid within 60 days following each date on which you
prepare (or are legally required to prepare) your periodic tax
returns. Royalty payments should be clearly marked as such and
sent to the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation at the
address specified in Section 4, "Information about donations to
the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation."
- You provide a full refund of any money paid by a user who notifies
you in writing (or by e-mail) within 30 days of receipt that s/he
does not agree to the terms of the full Project Gutenberg-tm
License. You must require such a user to return or
destroy all copies of the works possessed in a physical medium
and discontinue all use of and all access to other copies of
Project Gutenberg-tm works.
- You provide, in accordance with paragraph 1.F.3, a full refund of any
money paid for a work or a replacement copy, if a defect in the
electronic work is discovered and reported to you within 90 days
of receipt of the work.
- You comply with all other terms of this agreement for free
distribution of Project Gutenberg-tm works.
1.E.9. If you wish to charge a fee or distribute a Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic work or group of works on different terms than are set
forth in this agreement, you must obtain permission in writing from
both the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation and Michael
Hart, the owner of the Project Gutenberg-tm trademark. Contact the
Foundation as set forth in Section 3 below.
1.F.
1.F.1. Project Gutenberg volunteers and employees expend considerable
effort to identify, do copyright research on, transcribe and proofread
public domain works in creating the Project Gutenberg-tm
collection. Despite these efforts, Project Gutenberg-tm electronic
works, and the medium on which they may be stored, may contain
"Defects," such as, but not limited to, incomplete, inaccurate or
corrupt data, transcription errors, a copyright or other intellectual
property infringement, a defective or damaged disk or other medium, a
computer virus, or computer codes that damage or cannot be read by
your equipment.
1.F.2. LIMITED WARRANTY, DISCLAIMER OF DAMAGES - Except for the "Right
of Replacement or Refund" described in paragraph 1.F.3, the Project
Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation, the owner of the Project
Gutenberg-tm trademark, and any other party distributing a Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic work under this agreement, disclaim all
liability to you for damages, costs and expenses, including legal
fees. YOU AGREE THAT YOU HAVE NO REMEDIES FOR NEGLIGENCE, STRICT
LIABILITY, BREACH OF WARRANTY OR BREACH OF CONTRACT EXCEPT THOSE
PROVIDED IN PARAGRAPH 1.F.3. YOU AGREE THAT THE FOUNDATION, THE
TRADEMARK OWNER, AND ANY DISTRIBUTOR UNDER THIS AGREEMENT WILL NOT BE
LIABLE TO YOU FOR ACTUAL, DIRECT, INDIRECT, CONSEQUENTIAL, PUNITIVE OR
INCIDENTAL DAMAGES EVEN IF YOU GIVE NOTICE OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH
DAMAGE.
1.F.3. LIMITED RIGHT OF REPLACEMENT OR REFUND - If you discover a
defect in this electronic work within 90 days of receiving it, you can
receive a refund of the money (if any) you paid for it by sending a
written explanation to the person you received the work from. If you
received the work on a physical medium, you must return the medium with
your written explanation. The person or entity that provided you with
the defective work may elect to provide a replacement copy in lieu of a
refund. If you received the work electronically, the person or entity
providing it to you may choose to give you a second opportunity to
receive the work electronically in lieu of a refund. If the second copy
is also defective, you may demand a refund in writing without further
opportunities to fix the problem.
1.F.4. Except for the limited right of replacement or refund set forth
in paragraph 1.F.3, this work is provided to you 'AS-IS' WITH NO OTHER
WARRANTIES OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO
WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTIBILITY OR FITNESS FOR ANY PURPOSE.
1.F.5. Some states do not allow disclaimers of certain implied
warranties or the exclusion or limitation of certain types of damages.
If any disclaimer or limitation set forth in this agreement violates the
law of the state applicable to this agreement, the agreement shall be
interpreted to make the maximum disclaimer or limitation permitted by
the applicable state law. The invalidity or unenforceability of any
provision of this agreement shall not void the remaining provisions.
1.F.6. INDEMNITY - You agree to indemnify and hold the Foundation, the
trademark owner, any agent or employee of the Foundation, anyone
providing copies of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works in accordance
with this agreement, and any volunteers associated with the production,
promotion and distribution of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works,
harmless from all liability, costs and expenses, including legal fees,
that arise directly or indirectly from any of the following which you do
or cause to occur: (a) distribution of this or any Project Gutenberg-tm
work, (b) alteration, modification, or additions or deletions to any
Project Gutenberg-tm work, and (c) any Defect you cause.
Section 2. Information about the Mission of Project Gutenberg-tm
Project Gutenberg-tm is synonymous with the free distribution of
electronic works in formats readable by the widest variety of computers
including obsolete, old, middle-aged and new computers. It exists
because of the efforts of hundreds of volunteers and donations from
people in all walks of life.
Volunteers and financial support to provide volunteers with the
assistance they need are critical to reaching Project Gutenberg-tm's
goals and ensuring that the Project Gutenberg-tm collection will
remain freely available for generations to come. In 2001, the Project
Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation was created to provide a secure
and permanent future for Project Gutenberg-tm and future generations.
To learn more about the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation
and how your efforts and donations can help, see Sections 3 and 4
and the Foundation web page at https://www.pglaf.org.
Section 3. Information about the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive
Foundation
The Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation is a non profit
501(c)(3) educational corporation organized under the laws of the
state of Mississippi and granted tax exempt status by the Internal
Revenue Service. The Foundation's EIN or federal tax identification
number is 64-6221541. Its 501(c)(3) letter is posted at
https://pglaf.org/fundraising. Contributions to the Project Gutenberg
Literary Archive Foundation are tax deductible to the full extent
permitted by U.S. federal laws and your state's laws.
The Foundation's principal office is located at 4557 Melan Dr. S.
Fairbanks, AK, 99712., but its volunteers and employees are scattered
throughout numerous locations. Its business office is located at
809 North 1500 West, Salt Lake City, UT 84116, (801) 596-1887, email
business@pglaf.org. Email contact links and up to date contact
information can be found at the Foundation's web site and official
page at https://pglaf.org
For additional contact information:
Dr. Gregory B. Newby
Chief Executive and Director
gbnewby@pglaf.org
Section 4. Information about Donations to the Project Gutenberg
Literary Archive Foundation
Project Gutenberg-tm depends upon and cannot survive without wide
spread public support and donations to carry out its mission of
increasing the number of public domain and licensed works that can be
freely distributed in machine readable form accessible by the widest
array of equipment including outdated equipment. Many small donations
($1 to $5,000) are particularly important to maintaining tax exempt
status with the IRS.
The Foundation is committed to complying with the laws regulating
charities and charitable donations in all 50 states of the United
States. Compliance requirements are not uniform and it takes a
considerable effort, much paperwork and many fees to meet and keep up
with these requirements. We do not solicit donations in locations
where we have not received written confirmation of compliance. To
SEND DONATIONS or determine the status of compliance for any
particular state visit https://pglaf.org
While we cannot and do not solicit contributions from states where we
have not met the solicitation requirements, we know of no prohibition
against accepting unsolicited donations from donors in such states who
approach us with offers to donate.
International donations are gratefully accepted, but we cannot make
any statements concerning tax treatment of donations received from
outside the United States. U.S. laws alone swamp our small staff.
Please check the Project Gutenberg Web pages for current donation
methods and addresses. Donations are accepted in a number of other
ways including including checks, online payments and credit card
donations. To donate, please visit: https://pglaf.org/donate
Section 5. General Information About Project Gutenberg-tm electronic
works.
Professor Michael S. Hart was the originator of the Project Gutenberg-tm
concept of a library of electronic works that could be freely shared
with anyone. For thirty years, he produced and distributed Project
Gutenberg-tm eBooks with only a loose network of volunteer support.
Project Gutenberg-tm eBooks are often created from several printed
editions, all of which are confirmed as Public Domain in the U.S.
unless a copyright notice is included. Thus, we do not necessarily
keep eBooks in compliance with any particular paper edition.
Most people start at our Web site which has the main PG search facility:
https://www.gutenberg.org
This Web site includes information about Project Gutenberg-tm,
including how to make donations to the Project Gutenberg Literary
Archive Foundation, how to help produce our new eBooks, and how to
subscribe to our email newsletter to hear about new eBooks.