
The Project Gutenberg EBook of Pictures of the old French court, by
Catherine Mary Bearne
This eBook is for the use of anyone anywhere in the United States and most
other parts of the world at no cost and with almost no restrictions
whatsoever. You may copy it, give it away or re-use it under the terms of
the Project Gutenberg License included with this eBook or online at
www.gutenberg.org. If you are not located in the United States, you'll have
to check the laws of the country where you are located before using this ebook.
Title: Pictures of the old French court
Jeanne de Bourbon, Isabeau de Bavière, Anne de Bretagne
Author: Catherine Mary Bearne
Illustrator: Edward H. Bearne
Release Date: September 25, 2015 [EBook #50052]
Language: English
Character set encoding: UTF-8
*** START OF THIS PROJECT GUTENBERG EBOOK PICTURES OF THE OLD FRENCH COURT ***
Produced by Clarity, Charlie Howard, and the Online
Distributed Proofreading Team at http://www.pgdp.net (This
file was produced from images generously made available
by The Internet Archive/American Libraries.)

Pictures of the
Old French Court
Jeanne de Bourbon
Isabeau de Bavière
Anne de Bretagne
By
Catherine Bearne
Author of
“Lives and Times of the Early Valois Queens”
ILLUSTRATED BY EDWARD H. BEARNE FROM ANCIENT
PRINTS, ORIGINAL DRAWINGS, &c.
NEW YORK
E. P. DUTTON & COMPANY
1900
In a former book I endeavoured, from information gathered out of the records of the first half of the fourteenth century, to give some idea of the court and social conditions of France at that time, and also of the first three Valois Queens, whose very existence appears unknown to the average English reader. This was no easy matter owing to the scarcity of details, which had to be carefully gleaned from amongst masses of histories and chronicles of battles, sieges, conspiracies, general councils, and other public events.
The present volume treats of the years between the latter part of the fourteenth and beginning of the sixteenth centuries, about which so much more information exists that I have found it necessary to abandon, for want of space, my intention of giving a short account of the courts of Marie d’Anjou and Charlotte de Savoie, wives of Charles VII. and Louis XI., who took very little part in public affairs; and to give a much shorter account of the reign of Anne de Bretagne.
viii Very little has been written about Isabeau de Bavière, and much less still concerning Jeanne de Bourbon, whereas a great deal is known of Anne de Bretagne, the history of whose life has more than once been related. To an interesting biography of her by Louisa Stuart Costello, and an invaluable one by Le Roux de Lincy I am much indebted. I have, as before, consulted many early chronicles, histories, and letters, French, English, German, Italian, and Spanish, besides the works of various excellent modern writers, whose names I quote. Accuracy being of the greatest importance in books like these, I give, in reply to the observation of a critic, that the lines I quoted referring to the siege of Cassel are incorrect, the original of De Nangis:—
“In dicto vero castro, in regis et totius Francorum exercitus derisum et subsannationem, in quodam eminenti loco posuerant Flammingi quemdam gallum permaximum de tela tincta, dicentes: ‘Quando gallus iste cantabit, rex Cassellum capiet vi armorum.’ Unde et gallice in gallo scriptum erat:
‘Quand ce coq chanté aura,
Le Roy Cassel conquestera.’”1
I quoted these lines from the “Grandes Chroniques.”2
ix To another critic who says he has never heard of the “Grand dictionnaire de Morèry,” and suggests that no such book exists, I can only reply that I have it upon my shelves. It is in several folio volumes, was published at Paris 1699, and is quoted by various historians. It is sometimes spelt “Morèri.”
| REIGN OF CHARLES V. AND JEANNE DE BOURBON. | |
| CHAPTER I. | |
| PAGE | |
| The House of Bourbon—Marriage of Pierre de Bourbon and Isabelle de Valois—Birth of their children—Betrothal of Jeanne to the Comte de Savoie—To the Dauphin Humbert—Her marriage with the heir of France—Character of Charles—Death of Philippe VI.—Coronation of King and Queen—Charles invested with Duchy of Normandy—Marriage of the Queen of Spain—Pedro el Cruel—Marriage of the Comtesse de Savoie—Death of the Duc de Bourbon at Poitiers | 1 |
| CHAPTER II. | |
| France after the Battle of Poitiers—The Jacquerie—The Marché de Meaux—The Comte de Foix and the Captal de Buch—Rescue of the Dauphine—Vengeance of the nobles | 16 |
| CHAPTER III. | |
| Return of Charles and Jeanne to Paris—Marriage of Catherine de Bourbon to the Comte de Harcourt—The Céléstins—The Treaty of Bretigny—Marriage of Isabelle de France to Giovanni Visconti—Return of the King—Death of the children of the Dauphine—The plague—The Duchy of xiiBurgundy | 33 |
| CHAPTER IV. | |
| King Jean returns to England—His death—Coronation of Charles V. and Jeanne de Bourbon—Murder of Blanche, Queen of Spain—The Céléstine Church—The Abbey of Chelles—The King’s library—Magnificence of the Court—Birth and death of the second Princess Jeanne | 49 |
| CHAPTER V. | |
| Comet—Meeting of Parliament—Marriage of the Queen’s sister—The Louvre and its gardens—Christine de Pisan—The Dauphin—His christening—War—French victories—Prosperity of France—Hôtel St. Paul—Birth of Marie de France—Capture and liberation of the Queen’s mother—Bonne, Comtesse de Savoie—Birth of Louis and Isabelle de France—Louis, Duc de Bourbon | 68 |
| CHAPTER VI. | |
| Illness of the Queen—Her recovery—Floods in Paris—Death of several princesses of the royal family—Bertrand du Guesclin—Court of Charles V. and Jeanne de Bourbon—The peers of France—The King’s will—Betrothal of his daughters—Visit of the Emperor—The Emperor Charles and the Duchess-dowager de Bourbon—Birth of the Princess Catherine—Death of the Queen—Of the Princess Isabelle—Grief of the King—His death | 89 |
| REIGN OF CHARLES VI. and ISABEAU DE BAVIERE. | |
| CHAPTER I. | |
| The House of Wittelsbach—Stephan von Wittelsbach and Taddea Visconti—Birth of Isabeau—Negotiations for her marriage—Her journey to Brussels—The fair of Amiens—Her interview xiiiwith the King—Her wedding—Charles and Louis de France | 107 |
| CHAPTER II. | |
| Royal Family and Court of France—Birth and death of Charles and Jeanne de France—Dress and amusements—The Abbey of St. Denis—Knighthood of the King of Sicily—The ball—Duchesse de Berry—Valentine Visconti | 124 |
| CHAPTER III. | |
| State entry of Isabeau into Paris—Magnificent fêtes—Southern tour of Charles and Louis—Bad health of Charles—Bonne d’Artois and Jean de Clermont—Dreadful storm—Birth of Dauphin—Death of Blanche, Duchesse d’Orléans—Pierre de Craon and the Constable de Clisson—Madness of the King | 147 |
| CHAPTER IV. | |
| Tyranny of the Duchess of Burgundy—Birth of Marie de France—The Duchesse de Berry saves La Rivière—Doctor Hassely—The King recovers—The Masquerade—Dreadful fire—King ill—The sorcerers—King recovers—Dr. Fréron—King ill again—Accusations against Louis and Valentine d’Orléans—Birth of Louis de France—Betrothal of Isabelle de France to Richard II. of England—Their marriage—Disastrous crusade—Marriage of Jeanne de France to Duc de Bretagne—Marie de France takes the veil | 166 |
| CHAPTER V. | |
| Illness of the King—Execution of the sorcerers—Birth of Jean de France—Death of Queen Blanche de Navarre—Household of Isabeau—Ludwig of Bavaria—Ancient Paris—The Queen’s châteaux—Burgundy and Orléans—Henry of Lancaster—The plague—Revolution in England—The Dauphin Charles | 192 |
| CHAPTER VI. | |
| Courage of the young Queen of England—Death of the Dauphin—Birth of Catherine de France—Intrigues of Louis d’Orléans, and quarrels at Court—Return of the Queen of England—Burgundians and Orléanists—Birth of Charles xivde France—Dreadful storms—Death of Duke of Burgundy—Illness of Duc de Berry—Conduct of Savoisy—Frère Jacques Legrand—The Princess Marie’s choice—Accident in the forest—The King and the Dauphin—Jean Sans-peur—The King ill—Eclipse—Royal weddings—The great winter—Murder of Louis d’Orléans | 212 |
| CHAPTER VII. | |
| Departure of Royal Family—Hundred Years’ War—Valentine d’Orléans—Queen’s return to Louvre—Death of Valentine—Forced reconciliation—Philippe de Bourgogne and Michelle de France—Misconduct of the Duc de Bretagne—Death of Isabelle de France—Of the Duc de Bourbon—Quarrels of the Duke and Duchess of Aquitaine—Of the princes | 242 |
| CHAPTER VIII. | |
| Riots led by Burgundy—The Duc d’Aquitaine’s ball—His quarrels with Burgundy—The Comte de Charolais—The Battle of Azincourt—Death of Louis d’Aquitaine—The Dauphin Jean—His court—His death—Imprisonment of the Queen—Jean Sans-peur rescues her—Enters Paris by night—Massacre of Armagnacs—The Dauphin Charles—Murder of Jean Sans-peur—Marriage of Catherine de France to Henry V.—Departure for England—Birth of a son—Return to Paris—Festivities—Death of Henry V.—Death of Charles VI.—Retirement of the Queen—Henry VI. enters Paris—Treaty of Arras—Death of Isabeau | 260 |
| Marie D’Anjou, wife of Charles VII.; Charlotte de Savoie, wife of Louis XI. | 299 |
| REIGN OF ANNE DE BRETAGNE, WIFE OF CHARLES VIII. and LOUIS XII. | |
| CHAPTER I. | |
| Birth of Anne and Isabelle—Their childhood—Louis d’Orléans—Alain d’Albret—Death of François II.—First council—French xvwar—Marriage ceremony—Siege of Rennes | 303 |
| CHAPTER II. | |
| Joustes before Rennes—Death of Isabelle—Betrothal of Anne—Marguérite of Austria—Marriage of Anne to Charles VIII.—Birth of the Dauphin—Italian war—Return of Charles—Death of Dauphin—Birth and death of other children—Death of Charles VIII. | 316 |
| CHAPTER III. | |
| Despair of the Queen—Resumes duchy—Friendship with Louis XII.—Returns to Bretagne—King’s divorce—Charlotte d’Aragon—Marriage of Anne to Louis XII.—Italian war—Birth of Claude de France—Splendour of the Court—Hôtel des Tournelles—The Maids of Honour—Disasters in Italy | 328 |
| CHAPTER IV. | |
| Ludovico Sforza—Shipbuilding—Queen’s gardens—Library—Treasures—Dress—Betrothal of Claude de France—Archduke’s visit—Illness of King—Maréchal de Gié—Second illness of King—Queen in Bretagne—Second betrothal of Princess Claude | 341 |
| CHAPTER V. | |
| Story of Anne de Graville—Illness of Claude—Court of Anne de Bretagne—Italian war—Marriage of Marguérite d’Angoulême—Dress and customs at Court—Birth of Renée de France—The Prince de Chalais—The Queen ill—Birth and death of a son—League of Cambrai—Sea-fight—Death of the Queen | 353 |
| Amboise | Frontispiece |
| PAGE | |
| Jeanne de Bourbon | 6 |
| Meaux | 25 |
| French Noble, Fourteenth Century | 56 |
| Lady of French Court, Fourteenth Century | 67 |
| The Bastille | 80 |
| Meeting of the Queen and her Mother | 86 |
| Shield of Jeanne de Bourbon | 105 |
| Isabeau de Bavière | 117 |
| Nevers | 186 |
| The Prioress of Poissy | 190 |
| Bedroom of the Fifteenth Century | 197 |
| Old Paris | 202 |
| The Louvre, from the Hôtel de Nesle | 207 |
| Hôtel Barbette | 237 |
| Bourges | 257 |
| Man in Armour, Fifteenth Century | 273 |
| Map of English Possessions in France, 1380–1422 | 287 |
| Shield of Isabeau de Bavière | 298 |
| Marie d’Anjou | 299 |
| Shield of Marie d’Anjou | 300 |
| Charlotte de Savoie | 301 |
| Shield of Charlotte de Savoie | 302 |
| Anne de Bretagne | 310 |
| Trumpeter | 316 |
| Tour d’Amboise | 323 |
| Louis XII. | 330 |
| Bourges | 333 |
| Lady of Fifteenth Century | 339 |
| Blois | 342 |
| Loches | 349 |
| Shield of Anne de Bretagne | 364 |
The House of Bourbon—Marriage of Pierre de Bourbon and Isabelle de Valois—Birth of their children—Betrothal of Jeanne to the Comte de Savoie—To the Dauphin Humbert—Her marriage with the heir of France—Character of Charles—Death of Philippe VI.—Coronation of King and Queen—Charles invested with Duchy of Normandy—Marriage of the Queen of Spain—Pedro el Cruel—Marriage of the Comtesse de Savoie—Death of the Duc de Bourbon at Poitiers.
 The royal house of Bourbon
descends from Saint
Louis through his sixth
son, Robert, Comte de
Clermont and Sire de
Bourbon. The pedigree is
as follows:—
The royal house of Bourbon
descends from Saint
Louis through his sixth
son, Robert, Comte de
Clermont and Sire de
Bourbon. The pedigree is
as follows:—
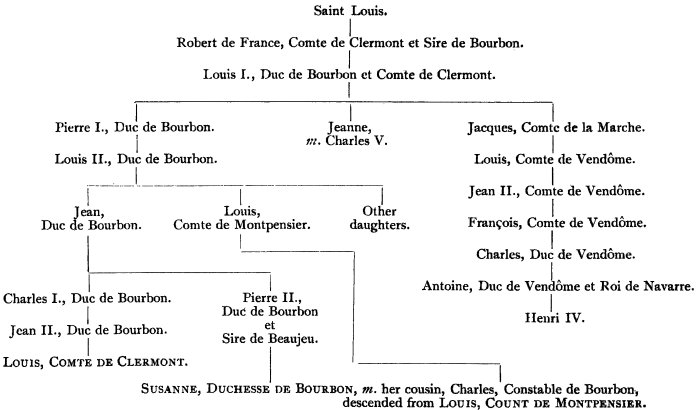
Jeanne de Bourbon was the great-granddaughter of Saint Louis. Her father was Pierre, Duc de Bourbon, and her mother Isabelle, one of the younger daughters of Charles, Comte de Valois.3 Their eldest daughter, Jeanne, was born February 3, 1335, and within a year or so of each other their second daughter, Blanche, and their son Louis.4 The other daughters were Bonne, Catherine, Marguérite, Isabelle (?), and Marie.5
The Duchesse de Bourbon being a half-sister of Philippe, and her husband one of his favourite companions, they spent most of their time and money also, at Paris, Vincennes, and the other royal palaces in the gay, brilliant days when first the Valois came to the throne.
Jeanne was born at Vincennes, and passed her childhood at that magnificent court over which she was so early chosen to reign. She was betrothed at six years old to Amadeo VI. (afterwards called the4 Green Count) of Savoy.6 With the state and splendour that surrounded her earliest years were mingled those national calamities which had already begun to cast their shadow over the kingdom of France.
The Hundred Years’ War had broken out soon after her birth. The disastrous sea-fight ending in the total destruction of the French navy, took place in 1338.
Taxes were high; there had been bad harvests, bringing famine and pestilence. France was already less prosperous than she had been under the Capétiens kings.
The terrors and troubles of the English war must have left a deep impression on the imagination of the gentle child, who seems to have been remarkable for her beauty and sweetness of disposition. She was between nine and ten years old at the time when the English host lay encamped near Paris, when gates and walls were strictly guarded and men were arming in haste, while fugitives poured into Paris all day, and the nights were illumined with flames of burning castles and villages. Her father was in the battle of Crécy, but returned in safety, and not long afterwards her little sister Bonne was married to the younger son of the Duc de Brabant. The Princess Joan, eldest daughter of the Duc de Normandie, was married on the same day to the elder son of the Duc de Brabant, by the desire of the King, who wrote orders that his granddaughter and niece should be ready on a certain day to meet the two boys who were to be their husbands.5 The ceremony took place, but both the boys died a little later of the plague. Joan afterwards became Queen of Navarre, and Bonne Countess of Savoy.
The Duchesse de Bourbon and her children must have left Paris and returned to their home in the Bourbonnais, for the Duke wrote there from Paris on July 22, 1348, to announce to his eldest daughter, whose engagement to the Comte de Savoie had been broken off, that her uncle, Gui, Comte de Forez, had brought proposals of marriage for her from Humbert, Dauphin du Viennois, which he had accepted. But the plague was then raging all over the Lyonnais, so that it was out of the question to run the risk of travelling at that time. The Duke therefore induced the Dauphin to consent to the marriage being deferred for the present. Humbert was scarcely a suitable husband for Jeanne, who was then eleven years old, while he was a widower, whose only son had lost his life by falling from his arms out of a balcony, as he was playing with him. The shock of this accident and the loss of his heir had cast a gloom over the life of the Dauphin, and when a second time the Duc de Bourbon sought to delay the arrangements for the marriage, he replied that in that case he considered himself free from all engagements. The Duc de Bourbon, on hearing this, went to meet the Dauphin, and after an interview between the two princes the negotiations were resumed, in January, 1349, and the middle of February following was fixed upon for their fulfilment. But whether the desire to quit the world and seek the consolations of religion6 in the retirement of the cloister had already taken strong hold upon his mind, or whether the secret ambition and intrigues of the French court had any influence on the matter, it was suddenly given out that the Dauphin had decided to renounce the world and enter the order of St. Dominic, and had arranged for the immediate cession of his estates to the King’s grandson, Charles, eldest son of the Duke of Normandy. Humbert, the last prince of the house of La Tour du Pin, had already, by treaties passed in 1343 and 1344, promised the Viennois, afterwards known as Dauphiné, to Philippe, younger son of Philippe VI. Then the young Philippe had been made Duc d’Orléans instead, and the province was to go to Jean, but at last it was given to the heir of the Duke of Normandy, and from this time forth that province, with the title of Dauphin, was the inheritance of the eldest sons of France. To the Duc de Bourbon the King offered, instead of Humbert de la Tour du Pin, his own grandson, for a son-in-law; an exchange with which it is needless to say the Duke was well content. The treaty was signed at Lyon in July, 1349.

So Jeanne was, after all, to be Dauphine, but her7 husband, instead of a widower old enough to be her father, was to be a young prince of her own age and the future King of France.
They were married at Vincennes in the following year, on the 8th of April, 1350, both of them being about thirteen or fourteen years old. Of course they were not strangers to each other, for they were cousins, and had both been brought up at the court of their grandfather and uncle in Paris, and at that ancient castle in the deep shade of the forest, where generations of the children of France7 had been born, had played in childhood, grown to manhood or womanhood, ruled, loved, suffered and died. The love of the forest and of all beauty in nature and art lay deep in the heart of the young Dauphin, who in no way resembled his father or grandfather. That Philippe and Jean de Valois, the chivalrous King of Bohemia or the warlike Princes of Burgundy should have had such a descendant would surely have seemed impossible at that time and with those surroundings.
Charles had neither inherited the striking beauty nor the martial tastes of the Valois. He was a quiet, delicate lad, tall, pale, dark-eyed and rather timid. He cared very little for riding, and not at all for war and warlike pastimes, but delighted in study and literary pursuits. And he adored the Dauphine, whose bright beauty and charming character made8 her the idol of the court and country. The children had been attached to one another from the first, and as they grew older Charles, both as Dauphin and King, ever turned for sympathy, counsel, or consolation to Jeanne, whom he called “the light of his eyes and the sunshine of the kingdom.”
The plague had now abated, and people were beginning to recover from the fear and depression in which they had lately been living. The royal family had suffered severely. The Dauphin had lost his mother and grandmother; the two little princesses, sisters of himself and the Dauphine, were widows; the Queen of Navarre, whose daughter Blanche the King had just married, was also among the victims of the pestilence. However, for the present the plague was over, and those who had escaped now breathed freely and tried to console themselves in different ways for the calamities of the last two years. The Duke of Normandy was married just after his father to the widowed Comtesse d’Auvergne; there were fêtes again at court, and things seemed to be returning to their usual state. The death of Philippe VI. came as a sudden shock in the midst of the general rejoicing; but then followed the coronation of the new King and Queen, which was celebrated with great magnificence. On the same day the King knighted his two eldest sons, the Dauphin, and Louis, afterwards Duc d’Anjou, his brother Philippe, Duc d’Orléans, his stepson Philippe, Duc de Bourgogne, his cousins the Comtes d’Alençon and d’Etampes, and other young nobles. The King and Queen left Reims on Monday evening and journeyed by Laon, Soissons,9 and Senlis to Paris, which they entered in state on Sunday, the 17th October, after vespers. The town was encourtinée, or hung with costly stuffs, the artisans were dressed each in the costume of their own trade, the citizens of the town in costumes like each other, the Lombards who lived in the city all wore long parti-coloured silk robes, and on their heads tall, pointed hats, parti-coloured like their dresses. “And they followed after each other as was ordered, some on horseback and some on foot, and before them went those playing music, to meet the King, who entered Paris with great joy.”8
The court remained at Paris till the feast of St. Martin in the winter, the time being spent partly in festivities and partly in business connected with parliament. On the accession of a new King all the judicial officers had to be re-invested9 or they were désappointés; a word which became obsolete in French, was adopted by the English, and from them has been re-adopted by the French, but with a different signification.
“In 1352, on Monday the vigil of the Conception,” says the Monk of Saint Denis, “the King gave the duchy of Normandy to Monseigneur Charles, his eldest son, Dauphin de Vienne et Comte de Poitiers, and on the next day, Tuesday, the day of the feast of the Conception beforesaid, Monseigneur Charles did him homage for it, at the hostel of Maistre Martin10 de Mello, canon of Paris, of the cloister of Notre Dame.”
After which the Prince always called himself Duc de Normandie, greatly preferring the title to that of Dauphin.
The Dauphin and Dauphine lived chiefly at Vivier-en-Brie, a castle in the midst of the woods not far from Vincennes. This château had been given to the father of the Dauphin, now King, when he married his mother, Bonne de Luxembourg, by his grandfather, Philippe VI. Here the Dauphin afterwards founded a chantry or chapel with fourteen ecclesiastics to chant the offices and give opportunity to the officers who followed the court to perform their devotions.
Jean, who had been at war with the Spaniards, considering the constant strife which, with short intervals of imperfectly observed truce, was always going on between France and England, was naturally anxious to conclude a peace with the King of Spain, whose subjects were extremely desirous that he should marry a French princess. In 1352 a treaty was arranged between the two countries, in which this was one of the clauses; and it was decided that one of the daughters of the Duc de Bourbon should be selected. Nieces of the late King of France and sisters of the future Queen of that country, one of them would be a suitable wife for their young King. With some difficulty they induced him to consent, and a Spanish embassy was despatched to France to conclude the alliance.
The character of Pedro the Cruel was notorious,11 even for the lawless times in which he lived. His early friend the King of Navarre, though by no means scrupulous, afterwards abandoned his alliance in disgust; and although at this time he was not more than twenty years old, his crimes had already given him a reputation of which the Duc de Bourbon must have known quite well. But the King of France had set his heart upon this alliance, and had promised to give a dowry of three hundred thousand florins. Pedro was to settle various castles, towns, and estates upon the Princess, and the Duke, whose eldest daughter was to be Queen of France, was well contented to see the second Queen of Spain. For it was upon the Princess Blanche that the choice had fallen. As long as one of his girls wore the crown of Spain, the Duke did not care which it might be. He introduced the ambassador into the room where they all were, so that he might choose.10 And as Blanche, the eldest next to the Dauphine of France, seemed to him the most beautiful, he fixed upon her; and the marriage took place during the summer of that year.
Various entries appear among the accounts of the royal expenses for splendid presents and rich dresses purchased “for the marriage of her Majesty the Queen of Spain.” Blanche, then about fourteen or fifteen years old, went to Valladolid to meet her husband. She is said by contemporary historians to have been beautiful, gentle, and attractive, notwithstanding which her fate was one of the most tragic that ever befel a woman sacrificed to political expediency. The destinies of the French princesses who12 have married Kings of Spain have always seemed tinged with melancholy and gloom. The intolerable rigour of that etiquette which reduced the lives of the Spanish queens to a dignified slavery, the cruelty of the national amusements, the jealous tyranny and bigotry of many of the kings, must surely have made these young girls look back with regret and longing to the gay court and “plaisant pays de France.” Even when, as in other cases, the King, however bigoted, morose, or relentless in general, was really fond of his wife, the life of a Queen of Spain can scarcely have been a very cheerful one.
But Blanche de Bourbon was more than usually unfortunate. Pedro, who came to the throne before he was sixteen, began by putting to death various Spanish nobles and gentlemen, and also Eleanor de Guzman, his late father’s mistress, by whom that King had had several sons, and for whom the Queen and her son, the present King, had been slighted and neglected. He also murdered two or three of his natural brothers, and it was by the hand of one of those who escaped from his power that he met the due reward of his crimes.
The Queen-mother had urged Pedro to revenge her wrongs and his own upon Eleanor de Guzman; but when he began not only to imitate but far to surpass the faults of his father, by taking a Jewess named Maria de Padilla for his mistress, deserting his young wife three days after their marriage and keeping her a prisoner, his mother offered the most strenuous opposition to his conduct and warmly espoused the cause of the young Queen, her daughter-in-law. It13 was of no avail, however. Blanche was doomed to wear out her youth in captivity, in one Spanish castle after another, while Pedro carried on intrigues with various women, but remained chiefly under the influence of Maria de Padilla.
The cause of this iniquity has never been certainly known. Whether Pedro, having allowed himself to be persuaded into this marriage against his will, afterwards regretted it and took this way of revenging himself; whether he was, as it has been said actuated by an insane and perfectly groundless jealousy of his younger brother Don Federico, one of the sons of Eleanor de Guzman, whom he had sent to meet Blanche, and whom in a furious rage he stabbed to the heart; or whether it was simply owing to the baneful influence of his Jewish mistress, must remain doubtful. But the story of Blanche de Bourbon will always be considered one of the most pathetic tragedies which history records.
Her sisters were more fortunate. Bonne, the third daughter of the Duc de Bourbon, who had been married when almost a baby to the younger son of the Duc de Brabant and had shortly afterwards become a widow, was married in 1355 to Amadeo VI., Comte de Savoie, then about twenty-two years old. He had been betrothed to Jeanne de Bourgogne sister of the last Capétien Duke, Philippe de Navarre and then to Jeanne de Bourbon, now Dauphine elder sister of Bonne. At ten years old he had succeeded his father, Aimon,11 brother of that Comte de Savoie who married Blanche de Bourgogne and14 left no heirs male. Amadeo VI. was one of the greatest princes of his day, both as warrior and statesman. Bonne de Bourbon, Comtesse de Savoie, was, says an ancient writer, “an ornament to her century, and her goodness caused her to be admired on all occasions.” The wedding was celebrated at Paris in August, and the young Countess set off for Savoy, where she reigned for many years in prosperity and honour. Her life was chequered with many sorrows and also beset by many difficulties, which she surmounted with courage and capacity. As Regent of Savoy during the latter part of her life, she was held in high esteem. She died in the Château de Mâcon in 1402.
In September, 1356, came the disastrous battle of Poitiers. To Jeanne, as to everybody else in France, that must have been a time of fearful anxiety and suspense. Those nearest and dearest to her were with the army; and although the sight of the gallant host that followed the King in such splendid array to meet the enemy might well have filled the hearts of those they left behind with pride and confidence, there was still the remembrance of the time when Paris had waited in breathless expectation for news of Philippe de Valois and his chivalrous army while those who were not prisoners or scattered over the land lay dead on the field of Crécy.
And when tidings came of a defeat more terrible than the former—of the fall of the oriflamme, of the capture of the King and his youngest son by an enemy so inferior in numbers, Jeanne also heard of her father’s death on the field of battle.
15 Pierre, Duc de Bourbon, had died like a brave soldier by the side of the King, whom he shielded from the blows aimed at him. But he had disregarded the commands of the Church, issued at the persuasion of his creditors, that he should pay his debts, and was therefore considered as an excommunicated person, to whom no one dared give Christian burial without permission.
His son and successor, Louis II., undertook to satisfy all claims, and his body was then removed from the convent of the Jacobins at Poitiers, where it had been carried after the battle, to that of the same religious order at Paris.
There the Duc de Bourbon was buried near his father, and his lands and honours passed to his son, known to history as “the good Duke, Louis de Bourbon.”
France after the battle of Poitiers—The Jacquerie—The Marché de Meaux—The Comte de Foix and the Captal de Buch—Rescue of the Dauphine—Vengeance of the nobles.
The captivity of the King and the flight of the Queen, who took refuge with her two children in her son’s duchy of Burgundy, placed Charles and Jeanne at the head of the court and kingdom. The Dauphin, or, as he preferred to call himself, the Duc de Normandie, assumed the government, and, in consideration of his youth, a council was appointed to assist him. Confusion and dismay had taken possession of the country. The three estates were convoked to deliberate on the means to be adopted to provide the ransom of the King. They sat for a fortnight in the hôtel of the Frères Mineurs,12 but Etienne Marcel, at the head of a strong party, demanded the redress of various grievances, and amongst others the immediate release of the King of Navarre, then imprisoned at Arleux. No conclusion, however, was arrived at;17 the estates were dissolved and Charles summoned the three estates of the Languedoc, or southern part of France, but without much more success.13 In December he went to Metz to see his uncle, the son of the King of Bohemia, now the Emperor Charles IV., to take counsel with him; leaving his brother Louis lieutenant at Paris in his place.
Charles IV. had been brought up in the court of Philippe de Valois; his sister, Bonne, had been the first wife of Jean, and he regarded the Valois family with strong affection. But he was too much like them to be of any use as an adviser, although he is said to have reproached his nephew with having, at this time of general distress, ordered for himself a new and splendid crown of gold. He, and probably the Duchesse de Normandie, spent Christmas with their uncle amidst a succession of fêtes, and returned to Paris towards the end of January to find the discontent of the people increased; which was not surprising, for there had been a still further depreciation of the coin of the realm; the seigneurs and knights who had been taken prisoners at Poitiers were returning in crowds to collect their ransoms, which were enormously heavy, and as the Jews and Lombards had been banished they could not borrow money on usury from them, as they might otherwise have done, so that there was no way of getting it but to wring it out of the peasants. As there was scarcely a family that had not at least one member a prisoner, a system of universal extortion was going on. They seized the18 property of their vassals and in many cases endeavoured, by imprisonment and other cruelty, to force them to give up any money they supposed them to have concealed,14 in order that it might be sent to the English to buy back those, many of whom they did not at all wish to see.
And they were profoundly irritated by this new misfortune. At Crécy, at any rate, they grumbled, every one had fought bravely and done their best; no shadow of dishonour had rested on the lilies of France. The nobles might have been proud and extortionate, but in the hour of danger they did not flinch. They lay in heaps on the field of battle, and a life of extravagance and dissipation was redeemed by a hero’s death.
But now there were suspicions of panic; there had been confusion and mismanagement, and there appeared to be an extraordinary number of prisoners. The early flight of four out of the five young princes also displeased the people, who now began to despise the nobles whom hitherto they had only feared and hated. And whereas it had formerly been the custom for them to serve the King in time of war at their own cost and without pay, they had, in the reign of Philippe de Valois, begun to demand money while in the field, and the sums granted by Philippe had to be increased by Jean just at the time when they seemed to be least deserved.
The Hundred Years’ War between France and England in the fourteenth century was destructive to the prosperity and civilisation which, in spite of many19 drawbacks, had characterised the thirteenth. There could be no liberty while the country was full of armed bands led by powerful barons; agriculture was not likely to flourish in such a state of things as has been described; the nobles had no leisure to encourage or interest themselves in literary pursuits while their whole lives were spent in warfare. It was in the monasteries that learning was chiefly cultivated and protected, but many of those great religious establishments in the country, though always possessing some sort of fortification, had been sacked and burned by brigands, and others deserted by their inhabitants, who no longer found that security which the cloister had formerly afforded. The towns had become less free, and many of them had lost the liberties and privileges accorded them by the Capétiens Kings. For the Valois and their followers held the traders and unwarlike citizens in the deepest contempt, and so, as time went on, grew and strengthened a bitter hatred of the lower classes for those of gentle blood, making men the deadly enemies of their own countrymen and causing national calamities far more dreadful and disgraceful than any brought about by foreign invaders.
In other countries nobles and people, united in their sentiments and aspirations, developed in peaceful and harmonious progress to the accomplishment of their destinies;15 whilst in France the deplorable separation that began in the fourteenth century caused the frightful excesses of the Jacquerie, and having produced the Reign of Terror in the days of our great-20grandfathers and the Commune in our own, is still so fatal an injury to the power, stability, and prestige of the French nation.
The first child of the Duke and Duchess of Normandy was born in September of this year (1357), a daughter, named Jeanne.
It was on the 28th of May, 1358,16 that the Jacquerie, or rising of the peasants, broke out at the little town of Saint-Leu, where a number of labourers, joined by small tradesmen, artisans, and other persons of the lower classes, assembled in revolt; and having murdered nine gentlemen who happened to be in the town, spread themselves over the surrounding country, putting to death every man, woman, and child of good blood who came in their way, and plundering and burning the châteaux. They attacked the villages at each end of the forest of Ermenonville, and went to the castle of Beaumont-sur-Oise, where the Duchesse d’Orléans then was. Warned just in time of the approach of the murderers, she fled for her life, was out of the castle before they arrived and set it on fire, and escaped to Meaux, a town on the Marne, where the Duchess of Normandy, the Princess Isabelle de France and more than three hundred ladies had taken refuge, some having escaped in their nightdresses without having had time to dress themselves.
The rebellion spread rapidly over Picardy, Champagne, and the Ile-de-France, and the horrors of it have never been equalled in any Christian country. It was like a revolt of savages. Hordes of bloodthirsty miscreants went about burning castles,21 murdering and torturing men, women, and children. None who fell into their power might escape dishonour and death; any village refusing to join them was exposed to their vengeance.
A band of three thousand Jacques having just destroyed the Château de Poix, were marching on Aumale when they met a hundred and twenty Norman and Picards men-at-arms, led by Guillaume de Picquigny. The latter came forward to parley with them but was treacherously slain by one Jean Petit Cardaine. His followers fell upon the Jacques, killed two thousand of them, and put the remainder to flight. The Jacques had cause to repent of this murder, for Guillaume de Picquigny was a relation of that Jean de Picquigny who delivered the King of Navarre from Arleux. And Charles of Navarre, who was always ready to protect his friends and punish his enemies, took ample vengeance for his death. The Château d’Ermenonville belonged to Robert de Lorris, who had risen from humble life in the village from which he took his name. It is a mistaken notion that in the middle ages people could not and did not rise from the ranks to the highest social position. It was, of course, less frequent than in our own days, but in the fourteenth century there were hundreds of cases of the kind, both ecclesiastic and secular.17
Robert de Lorris was one of them. He was a great authority on French law, and a favourite both of Philippe de Valois and Jean, by whom he had been ennobled, made Chamberlain, Vicomte de Montreuil,22 and Seigneur d’Ermenonville. The Jacques besieged, took, and plundered the Château d’Ermenonville, and the chamberlain only saved his own life and those of his wife and children by renouncing his nobility and declaring himself one of the people.
The atrocities of the Jacquerie did not, fortunately, extend over the whole of France. An attempt was made to produce an insurrection at Caen by one Pierre de Montfort, who paraded the streets with the model of a plough in his hat, proclaiming himself a Jacque, and calling on the people to follow him. This, luckily for themselves, they had too much sense to do, and Pierre de Montfort was soon afterwards slain by three burghers whom he had insulted.18
The rebellion was worst about Amiens, Compiègne, Senlis, Beauvais, and Soissons. The Jacques made an attack upon Compiègne, but were repulsed by the inhabitants and some nobles who had taken refuge in the town. The atrocities committed all over that part of the country which was the scene of the revolt were too frightful to relate. Hundreds of castles were burnt, an immense amount of property destroyed, and numbers of men, women, and children tortured, dishonoured, and slain.
The leader of the Jacques, Guillaume Cale, is said to have disapproved of the most horrible of the excesses of his followers, but to have been unable to restrain them. And Etienne Marcel, with many of the bourgeois of his party, encouraged and gave assistance to these miscreants, though forbidding the23 murder of women and children, which of course he was powerless to prevent. But a letter of remission given subsequently to one Jaquin de Chennevières expressly declares that he had orders from the Prévôt to burn and destroy the châteaux of Beaumont-sur-Oise, Bethemont, Javerny, Montmorency, Enghien, Chaton, and all the houses and fortresses of the nobles between the Seine and the Oise, from Chaton to Beaumont.19
And whatever may be our opinion of the policy of the celebrated Prévôt des Marchands, the murder of the Marshals of Normandy and Champagne (which had already taken place in the presence of the Dauphin) and the assistance he rendered to these wretches are stains which neither good intentions nor expediency can excuse.
Jeanne meanwhile, and her companions, were in the most awful peril. The smaller bourgeoisie, as a rule, hated the gentlemen and sympathised with the Jacques. The Mayor of Meaux, Jean Soulas, was on their side. The gentlemen with them were few in number, the Jacques were coming, and the Duc de Normandie had, a short time before, taken sudden possession of the Marché de Meaux, to the great discontent of the inhabitants of that town. The Mayor had even had the insolence to say to the Comte de Joigny, whom the Duke had sent to perform this duty, that if he had known what he came for he should never have set foot in the place. Informed of this insubordination the Regent had reprimanded and fined the Mayor, which only increased24 his hostility. However, he and the principal officials and burghers had sworn to be faithful to the Regent, and not to allow anything to be done to injure him, and Charles had left Meaux some time in May, leaving his wife and the rest of the ladies in the Marché with a much smaller garrison to protect them than he would have done had he realised the treachery and disloyalty of Soulas and his friends. The Duc d’Orléans was there, the Bègue de Vilaine, the Sires de Trocy and Revel, Héron de Mail, Philippe d’Aulnoy, Regnaud d’Arcy, and Louis de Chambly called Le Borgne.
Scarcely had the Regent quitted Meaux when discord and strife broke out between the inhabitants, led by the Mayor, and the nobles shut up in the Marché. The exasperated bourgeois laid siege to the fortress and sent to Paris to ask for assistance, at the same time summoning all the peasants in the neighbourhood to join them in attacking the Marché.20
They were not slow in answering to the invitation. From all parts of the country round they came swarming to Meaux. The Prévôt des Marchands had responded to their appeal by sending Pierre Gilles, a grocer of Paris and one of the leaders of the insurrection, with a body of armed men from Paris to Meaux. He knew the Regent was absent and the garrison weak, and thought the Marché would fall into their hands by assault. Pierre Gilles and his troop burned all the châteaux on their way, and forced the inhabitants of the villages through which they passed to join them.

26 The Mayor and burghers threw open the gates, and about nine thousand furious ruffians, armed with scythes, pitchforks, and knives, rushed into the town.
The towns people received them with open arms, supplied them with abundance of food and wine, which excited them to still greater ferocity, and joined in the tumult of fearful shouts and cries as the bloodthirsty savages swarmed through the streets looking up with murderous eyes to the towers and walls of the Marché.
Now the Marché de Meaux was on an island formed by the Marne, which flowed on one side of it, and a canal that went round it, coming out of the river on one side of the Marché and going back into it on the other. On the side of Meaux there was a bridge over the Marne from the Marché to the town, and on the opposite side of the Marché another bridge, across the canal to the other shore. Most fortunately, the Dauphin had recently caused the island to be strongly fortified, and his having done so now saved his wife and sister from a horrible death. All round the Marché were high strong walls and towers. Trees could be seen above the parapet inside, and the ground rose high in the middle. It was a strong place, but they were so few to defend it against the furious hordes outside. In it were the young Dauphine, the Princess Isabelle de France, daughter of the King, then about ten or eleven years old; Blanche de France, Duchesse d’Orléans, who had just escaped from Beaumont-sur-Oise; and, as was before said, at least three hundred women,27 girls, and children of the noblest families in France. The gates were closed, the walls guarded as well as could be done with their few defenders, but the position grew every moment more alarming. The streets were crowded to overflowing with these bloodthirsty wretches, and all down them were spread tables with bread, meat and wine for their refreshment. All over the town they were thronging and feasting, while their horrible cries and brutal threats rose to the ears of the besieged women and children who waited in terror and despair, all hope of deliverance seeming to be at an end.
The fortress was always attacked from the town side, and from this direction, when the Jacques had finished feasting, the assault would certainly come.
But the Marché was fortunately not surrounded by the town. On the other side, across the canal, lay the open country of Brie. And suddenly a troop of men in armour was seen approaching at full speed. It was Gaston, Comte de Foix, and Jean de Grailly, Captal de Buch, two of the most famous soldiers in France, with about sixty lances, who rode under the gateway into the beleaguered fortress, and were received with acclamations by those within its walls. The troop was a small one, but a few tried soldiers under such leaders counted for more than hundreds of the rabble outside, and the Dauphine and her companions must have felt that they were saved.
Having no particular fighting to do just then, the two knights had employed their leisure in an expedition against some heathen tribes still to be found in Prussia; and on their way back, passing through28 Châlons, had heard of what was going on at Meaux and of the perilous position of the ladies shut up in the Marché. The Comte de Foix was brother-in-law of the King of Navarre; and the Captal de Buch, a Gascon gentleman, was a subject and follower of King Edward of England. Etienne Marcel, on the other hand, was a strong partisan of Charles of Navarre. But the project of the bourgeois prévôt to throw the wives and children of French gentlemen into the power of a mob of brutal savages was not likely to recommend itself to the two knights, who at once turned their horses’ heads towards Meaux, and pushed on with desperate haste to save the Marché before it fell. The white banner still floated from its walls,21 but they were only just in time. The Jacques, having done feasting, now ranged themselves in order of battle, and in immense numbers, with frightful yells, pressed towards the Marché and began the attack. The shrieks of the terrified women and children mingled with the tumult outside,22 but Jean de Grailly and Gaston de Foix ordered the gate on the side of the town to be thrown open. Then, raising the pennon of the Captal and the banners of Orléans and Foix, they rushed out and fell upon the enemy. Down to the bridge they rode, over which was thronging a multitude like ferocious wild beasts. But before the charge of the knights the Jacques went down in heaps; those behind them hesitated, then drew back and fled before the cavaliers, who pursued them with levelled lances and drawn29 swords through the streets of the town. Several of the nobles were killed, amongst others Louis de Chambly, called Le Borgne, but thousands of the Jacques were slain. Many of the citizens of Meaux were killed in the battle that raged all over the city; the rest were carried prisoners to the citadel. Jean Soulas, the traitorous mayor, was taken during the fighting and hanged when it was over. The nobles then set fire to the town, which was burning for a fortnight. The royal château, with many houses and churches, perished in the flames. Froissart says that seven thousand Jacques were killed. The inhabitants of Meaux, “for their detestable deed,” were declared guilty of high treason, and the town condemned to be and for ever remain uninhabited. The Regent, in consideration of the Dean and Chapter of Meaux, and at the petition of some other towns who interceded with him on behalf of the place, afterwards remitted this sentence. But the commune of Meaux was suppressed and united to the prévôté de Paris.23
Jeanne and her companions watched from the Marché the victory of their friends and the destruction of their enemies, and it must soon have been evident to them that their danger was at an end. The destruction of the Jacques on that day, June 9, 1358, arrested the course of the rebellion. The nobles scoured the country, putting to death all the Jacques they could find. Learning that some of them had taken refuge at Sens, they resolved to inflict on that city the same punishment as on Meaux, and for that purpose a party of them, on the 13th30 of June, presented themselves at the Paris gate of the town, demanding the keys in the name of the Regent. But the inhabitants had received notice beforehand of what was intended, and had taken measures accordingly. Therefore, when the nobles, having been admitted, and thinking themselves masters of the place, advanced with drawn swords and cries of “Ville gagnée! ville prise!” the citizens, and even those nobles who belonged to Sens, pushed down from the top of the street, which was very steep, carts with scythes fastened to the wheels which they had prepared for the purpose, while armed men issued from the houses, and women threw stones, lime, and boiling water from the windows, by which means some were killed and the rest escaped out of the city.
But the defeat at Meaux broke the head of the insurrection. From the terror, the slaughter, and the discouragement of that day the Jacques never recovered, and the finishing stroke was given by the King of Navarre, on whose support some of them had been foolish enough to reckon, because of his hostility to the King and Dauphin.
The gentlemen of Normandy and Picardy sent an invitation to Charles de Navarre, who was then at his castle at Longueville, to be their leader in this contest; he “who was the first gentleman in the world.”24
The King of Navarre was ready enough. He31 placed himself at the head of four hundred lances, and by the time he came up with the Jacques, near Clermont, his troop had increased to a thousand men, many of whom were English. The Jacques were put to flight with great slaughter, and their leader, Guillaume Cale, put to death. Some say that he was arrested by treachery; at any rate Charles of Navarre declared that the Jacques were furious wild beasts, with whom it was not possible to treat or make any terms. The Regent had been in arms ever since the insurrection had broken out, and the attack upon his wife rendered it more hateful to him.
The Jacquerie was soon at an end; it only lasted about a month, and when once the nobles had recovered from the surprise and shock of its outbreak, it was put down and punished with tremendous severity. Pierre Gilles was beheaded at the Halles on the 4th of August. He appears to have been a man of considerable wealth, and in the inventory of his merchandise was a large quantity of sugar in loaves and in powder from Cairo, or, as it was called, Babylon. It came chiefly from Egypt at that time.
That part of Champagne, Ile-de-France, and other districts which had been the scene of these atrocities of the Jacques, was so devastated with fire and sword that for some time it remained almost without inhabitants.25 The towns and villages which had taken part in the Jacquerie were heavily fined, as may be seen by the records in the “Trésor des Chartes.” Chavanges, for instance, was fined a thousand gold florins.26
32 A note, tome vi. p. 117, of the “Grandes Chroniques de France,” M. Paulin Paris, makes the following remarks and gives the following quotation respecting the complicity of Etienne Marcel in the Jacquerie, and the fallacious hopes in which the rebels indulged with regard to the King of Navarre:—
“C’est que ces Marseillais du XIVme siécle avoient été bien réellement soulevés par les anarchistes de Paris. Je demande la permission de citer à l’appui de cette opinion la précieuse chronique manuscrite conservée sous le No. 530, Supplément françois. A l’occasion de l’expédition du roi de Navarre contre les Jacques, on y lit: En ce temps assembla le roy de Navarre grans gens et ala vers Clermont-en-Beauvoisie, et en tuêrent plus de huit cens et fist copper la teste à leur cappitaine qui se vouloit tenir pour roy; et dient aucuns que les Jacques s’attendoient que le roy de Navarre leur deust aidier, pour l’alliance, qu’il avoit au prévost des marchans, par lequel prévost la Jacquerie s’esmeut, si comme on dit.”
Return of Charles and Jeanne to Paris—Marriage of Catherine de Bourbon to the Comte de Harcourt—The Céléstins—The Treaty of Bretigny—Marriage of Isabelle de France to Giovanni Visconti—Return of the King—Death of the children of the Dauphine—The plague—The Duchy of Burgundy.
The Duchess of Normandy and her friends were now free, after the horrible experience of the last few days. The enemy was destroyed, the revolt quelled, and the town, at which they could hardly have looked without shuddering, was half burnt down and deserted; for the inhabitants, who had so lately been raging and clamouring for their blood, were either slain or carried away prisoners. The Duchesse d’Orléans, after this second narrow escape within a few days, set off on her journey towards Paris, which was still in a disturbed state, and in the neighbourhood of which her mother, Queen Jeanne d’Evreux, was busy trying, as she repeatedly did, to patch up a peace between the Duke of Normandy and the King of Navarre, who, although he hated and put down the Jacquerie, was a friend34 and ally of Etienne Marcel and had a powerful party at Paris.
The Duchess of Normandy stayed on for a short time in the fortress of Meaux, waiting for her husband to join her.
On the 19th of July peace was concluded by the efforts of Queen Jeanne d’Evreux, assisted by the young Queen of Navarre, sister of the Duke of Normandy, the Archbishop of Beauvais, and two or three others. The interview took place at Charenton on the Seine, where the Dauphin caused a bridge of boats to be constructed for the occasion.
He then joined the Dauphine at Meaux. The danger in which Jeanne had been and the insult involved in the attack upon her had naturally enraged him against every one in any way connected with the revolt; but various letters of remission to those concerned in it, on several occasions granted to persons forced against their will to take part in it, were signed by him about this time. Meanwhile, reports of the diminishing strength of Etienne Marcel and his party kept arriving from Paris; with invitations to Charles to return and take possession of the capital.
At last came tidings of the death of the prévôt, struck down at night as he was in the act of changing the guard and placing the keys of Paris in the hands of the King of Navarre. His adherents were immediately scattered, imprisoned, or slain, and the royalists sent urgent entreaties to the Duke of Normandy, who lost no time in setting off for Paris, which he entered on the evening of Thursday,35 August 2nd, amidst the acclamations of the people and the illuminations and rejoicings prepared to welcome him.
The next day he sent a messenger to Jeanne with the news of this successful state of affairs, directing her to join him at Paris with the ladies of her court. When she arrived there she found the Duc de Normandie waiting for her at the Louvre, where they took up their abode and where for some time they lived in peace. The King was still a prisoner, and the Regent, freed from the constant enmity of Etienne Marcel, endeavoured to repair the misfortunes that had happened and to get the affairs of the State somewhat into order. The truce with England was soon to expire, but he made another treaty of peace with the King of Navarre, and contrived to win to his side the young Comte de Harcourt, Jean III., who, since the execution of his father by the King of France in the affair of Rouen, had been fighting against that country in the ranks of England and Navarre.
The Dauphin, however, succeeded in making friends with him, and although the precedent of Charles of Navarre was not very encouraging, he tried to attach the Comte de Harcourt to his interests by marrying him to Catherine, one of the Dauphine’s sisters. The wedding took place in October, at the Louvre.27
The favourite monastic order of Charles and Jeanne appears to have been that of the Céléstins.36 It will be remembered that Saint Louis brought from the Holy Land some Carmelites, sometimes called Barrés because of the striped robes or mantles they used at first to wear; and that in the reign of Philippe-le-Long they sold their monastery, or rather the ground on which it stood, to one Jacques Marcel, a citizen of Paris, reserving to themselves all building materials, carved stones, columns, woodwork, and tombs, with the bones of those buried therein; all to be transported by midsummer day to the new place which had been chosen for the larger and more convenient monastery which they now required.
But before they left their old home, the Carmelites, assisted by an agent of the Bishop, carefully pointed out to the new owner those parts which were consecrated ground, and Jacques Marcel, “who was a good man, and feared God,” built two chapels upon them, just at the entrance to the garden, and appointed and endowed two chaplains to serve them.
Jacques Marcel was buried in a tomb of black marble in one of these chapels, and the place went to his son, Garnier Marcel, in 1320.
Now there was a young man named Robert de Jussi, who had been a novice in the Céléstin monastery of St. Pierre, in the forest of Cuisse, not far from Compiègne. But after he had been there a year, his parents by their entreaties and importunity persuaded him to renounce the monastic life and return to the world. Philippe de Valois, who was then king, took a fancy to him, attracted by his talents, good sense, and piety. He chose him, while still very young, to37 be one of his secretaries; and so well did he serve the King and so great was the reputation he acquired at court for his judgment and conduct, that he remained Secretary of State and one of the most distinguished members of Council under Philippe de Valois, Jean, and Charles V., Dauphin. But his worldly success and prosperity did not make him forget the convent in the forest, the holy lessons and examples of the good fathers, and the peaceful days he had spent with them. He spoke of them to the Dauphin, who sent for some of them to come from their monastery to Paris in 1352, when Garnier Marcel presented them with the site of the old Carmelite monastery which had been bought by his father; where they established themselves. Charles both as Dauphin and King showed unvarying kindness and affection to this brotherhood, visiting the convent frequently, and conversing familiarly with the brethren. In this year (1358), seeing that they were in need of help, he granted them a purse of money from the Chancery of France, to be given yearly, and as a proof of his friendship carried the first to them himself, and distributed its contents with his own hands. He afterwards built them a church, and conferred upon them many other benefits.
A curious law made at this time, which in our own days many of us would gladly see re-established, was, that if a tailor or dressmaker spoilt a dress, either by cutting the material badly or by ignorance, so that by their fault it did not fit, they should pay to the owner of the said garment whatever was the value of it, and besides that should pay a fine of five38 solz, of which three should go to the King and two to the confraternity.28
Also that if any one made a doublet to sell, and made it of bad or common thread or stuff, the doublet should be burnt, and the maker should pay six solz to the King and four to the confraternity.29
“On Sunday, the nineteenth day of May,” says the chronicler, “was made a convocation at Paris of the church, the nobles, and the fortified towns,30 by letters of monseigneur the regent, to hear a certain treaty of peace which had been proposed in England between the Kings of France and of England. Which treaty had been brought to the regent by Monseigneur Guillaume de Meleun, Archbishop of Sens, by the Comte de Tanquarville, brother of the said Archbishop, by the Comte de Dampmartin, and by Messire Arnoul d’Odenham, Marshal of France, all prisoners of the English. On which day came few people, partly because they had not been told soon enough of the said convocation, and also because the roads were infested by the English and Navarrais,39 who held fortresses on every road by which one could go to Paris; and also because of the robbers who held French fortresses and were not much better than the English. And the whole kingdom was covered (semé) with them, so that one could not go about the country. The said English and Navarrais held the castle of Meleun, the island and all the town on the side towards Bièvre; and the part towards Brie was French. Item, they held la Ferté-Soubs-Juerre, Oysseri, Nogent-l’Artaut, and at least five or six fortresses on the river Marne; in Brie they held Becoisel and La Houssoie. In Mucien they held Juilly, Creil, and several other places on the river Oyse; on and about the Seine, Poissy, Meullent, Mante, Rais; and more than a hundred others in different parts, as well in Picardie as elsewhere. Which day of the nineteenth was continually put off in the expectation of more people until the following Saturday, the twenty-fifth day of the said month.
“On the which Saturday the said regent was at the palace on the marble staircase in the court; and there, in presence of all the people, he caused the treaty to be read by Maistre Guillaume des Dormares, advocate of the King in parliament, by the which treaty it appeared that the King of England asked for the duchy of Normandy, the duchy of Guienne, the city and castle of Saintes, with all the diocese and country; the cities of Agen, Tarbes, Pierregort, Limoges, Caours, with all the diocese and country; the counties of Bigorre, Poitiers, Anjou, and Maine; the city and castle of Tours, and all the diocese and country of Touraine; the counties of Boulogne,40 Guines, and Pontieu; the town of Monstrueil-sur-Mer and all the chastellenies; the town of Calais and all the land of Merq, without the King of England being, on account of the said lands, in any way subject either to the present King of France or to his successors, but only a neighbour. And besides, the said King of England desired to have the homage and sovereignty of the duchy of Brittany for ever, the same as the other lands before mentioned.
“Besides this he asked for four millions of escus de Philippe, with all the lands that he held in the kingdom of France, upon such condition that the King of France should make recompense of other lands to all those who had anything on the said lands, by alienation made by the Kings of France, or by those who claimed any rights transmitted by them, since the said lands and countries belonged to the Kings of France.
“And also required the said English to be put into possession of the towns and castles of Rouen, Caen, Vernon, Pont-de-l’Arche, Goulet, Gisors, Moliniaux, Arques, Gaillart, Vire, Boulogne, Monstrueil-sur-Mer, and la Rochelle; a hundred thousand pounds sterling and ten seigneurs for hostages on the first of August following. And this done, he would return the King of France to his kingdom and power, but in all manner a loyal prisoner until the above-named things were accomplished.
“Which treaty was very displeasing to the people of France (fu moult deplaisant). And after they had deliberated, they replied to the said regent that the said treaty was neither bearable nor possible (n’estoit41 passable né faisable); and therefore they ordered good war to be made upon the English.
“Item. Sunday, the second day of June following, it was granted to the regent that the nobles should serve him for a month at their own expense, each according to his estate, without counting coming nor going. And that the impositions ordered should be paid by the fortified towns. The clergy offered to pay the said impositions; the town of Paris offered six hundred swords, three hundred archers, and a thousand brigands. And it was ordered that all those who were there should return to their towns, because they could not grant anything without speaking to their towns, and that they should send their answers on the Monday after Trinity. And afterwards several towns sent their answer: but because the flat country was all spoiled by the English and Navarrais enemies, and also by the garrisons of the French fortresses, the said fortified towns (bonnes villes) could not fulfil the number of twelve thousand swords (glaives) which had been granted him by the Langue d’oc.”31
The Duke and Duchess of Normandy had still no son, but another daughter, the Princess Bonne, had been born to them.
The war with England had gone on all the winter, but in the spring of 1360 new proposals of peace were made, and this time accepted. By the treaty signed at Bretigny, May 8, 1360, King Edward renounced his claim to the crown of France, and also to the duchy of Normandy and all the inheritance of the Plantagenets north of the Loire. But the King42 of France ceded to him, no longer as fiefs, but in absolute sovereignty, Poitou, Aquitaine, with all the arrière-fiefs appertaining to it from the Loire to the Pyrenees, and a ransom of three millions of écus d’or, to be paid in sums of four hundred thousand écus annually.
Six English knights were sent to Paris by King Edward, in presence of whom the Dauphin was to swear to the treaty in the most solemn manner. Therefore, when Mass was sung, after the Agnus Dei, Charles, who was then in the Hôtel de Sens, came out of his oratory and took the oath before the altar. Then, from a window of the Hôtel de Sens, peace was proclaimed by a sergeant-at-arms, “the regent went to Notre-Dame de Paris to return thanks for the said peace, and then they chanted the Te Deum, and rang the bells very solemnly.”32
King Edward is said to have been induced to make peace by a frightful storm which overtook his army near Chartres, killing six thousand horses and a thousand cavaliers, amongst whom were the heirs of Warwick and Morley. Thinking that the anger of God was roused against him because of the misery and devastation he was causing, he vowed to put an end to the war.
All over the country the news spread that peace was signed, and in spite of the hard conditions there was a general burst of rejoicing. In the villages and towns church bells rang, thanksgivings were offered, and festivities of all kinds went on everywhere; except in some of the towns and provinces transferred43 to England, who declared that they might yield homage to the English with their lips, but in their hearts never.
To the Princess Isabelle de France the return of the King can have been no subject of congratulation. She was his third daughter, her sisters being the Queen of Navarre and Marie, afterwards Duchesse de Bar. The fourth sister had taken the veil at Poissy, and died the year after in early childhood (1352).
In the deplorable state of the country, it was most difficult to obtain the money required to pay the first instalment of the King’s ransom. Galeazzo Visconti, Vicomte et Prince de Milan,33 offered to give 600,000 florins in exchange for the Princess Isabelle, whom he was anxious to marry to his son, Giovanni. The Visconti were amongst the richest and most powerful of the princes of Italy. They ruled over Milan and the greater part of Lombardy. The two brothers, Galeazzo and Bernabo, chiefs of the family, were stained with countless crimes and cruelties. Of Giovanni nothing could be said, as he was only ten years old. The Princess Isabelle was not quite twelve, but she seems to have had her own ideas, and she hated this Italian marriage. It was no use. The Visconti were eager for the alliance of the King of France, and willing to pay for the honour. King Jean wanted the money, and had been ready to sign the utterly ruinous treaty at first proposed and sacrifice France to gain his own liberty; so that he was not likely to hesitate. The French people did not like the marriage, and there was a murmuring all over the44 country against the King for selling his own blood. But the preparations were hurried on, and the Princess was sent to Italy before the end of that summer, with a splendid cortège.
Villani gives an account of the magnificence of the entertainments given in her honour at the palaces of Galeazzo and Bernabo in Milan. He says she arrived in regal state, splendidly dressed, and received the homage of all before her marriage, but after that, notwithstanding her royal blood, she did reverence to Galeazzo and Bernabo and their wives,34 the former of whom was a Princess of Savoy.35
The splendid fêtes went on for three days and nights in the stately beautiful Italian palaces, which so far surpass those of other lands. Every day there were banquets, where at the chief table dined a thousand guests, princes, ambassadors, nobles and representatives of the citizens. There were jousts in the cortile or courtyard of the palace of Galeazzo, ladies looking on from the windows and loggie.36 The last fête was given by Bernabo.
Meanwhile the King of France, whose freedom had been bought in exchange for his daughter, had been conducted by the Black Prince to Calais, in the castle of which a great supper was given in his honour45 by King Edward, whose sons, with the Duke of Lancaster and the chief barons of England, served bareheaded at the table, and after two days spent at Boulogne in religious ceremonies and festivities King Edward embarked for England, and Jean prepared to return to Paris.
Besides the public misfortunes of this time, a great sorrow befel the Duke and Duchess of Normandy in the death of their two little daughters, Jeanne and Bonne, whom their mother had dedicated to God if the King returned. The historian says God apparently accepted the gift.37 The eldest was about three years old. The former died October 21st at the abbey of St. Antoine des Champs, at Paris, where she had been placed in order to be dedicated to religion, and her little sister rather less than three weeks after her. They were both buried in the church of that abbey, where their effigies in white marble were placed, lying upon their black marble tomb. This grief was all the more bitter to Charles and Jeanne as these were their only children. The chronicler remarks of this event: “Item, on Thursday, the 11th November, were buried the two daughters of the Duke of Normandy, at St. Antoine, near Paris, and was present the said Duke at the funeral, very troubled, for he had no more children.”38 Among those chosen to go to England with King Edward were Louis Duc d’Anjou and Jean Duc de Berry, second46 and third sons of the King, to whom their father had given these two duchies by way of compensation; Philippe, Duc d’Orléans, the King’s brother; Louis, Duc de Bourbon; Pierre d’Alençon and Jean, brother to the Comte d’Etampes, “tous des fleurs-de-lis,” says the monk of St. Denis.
And in December, Jean made his entry into Paris with a pomp and parade rather unsuitable to the occasion and the manner of his return, and again began the usual succession of court festivities and amusements that formed the occupation of the Valois princes and those who surrounded them. As to the peasants, as soon as the peace of Bretigny was signed, they began to take courage and to work in the fields again. After a long cold winter the weather seemed to have cleared up, and they hoped for a good harvest, though the destruction of most of the barns and farm buildings had made it difficult to find places to store it in. The plague, too, was again increasing, not spreading regularly from south to north as it had done in 1348, but appearing irregularly here and there in places which had escaped before, especially in hilly and mountainous districts where the inhabitants had hoped they were safe from it. It attacked first the people who were already weakened from bad food and other hardships; next those who had been suffering, as so many were, from agitation, anxiety or sorrow; and then it began to attack those who were free from any such disadvantages. It spread all about, with the same symptoms as before and attended with the same disastrous consequences. Every one was, of course, dreadfully afraid of catching47 it, so that people shut themselves up, refusing to have communication with each other; there was no one to keep order or to do any work, and the great companies of brigands and disbanded soldiers were all over the country. There were fifteen thousand of them near Lyon alone. The King of England sent orders to those under his allegiance to desist from their depredations, but they would not obey him. The plague was very bad all the spring; seventeen thousand people died of it at Avignon, it was raging in London and was also at Paris, although not quite so violent there.
The Queen and her daughter, the Princess of Burgundy, had died of it in 1360, and now her son Philippe, the last Capétien Duke, fell a victim to the same scourge.
On hearing of the death of his stepson, Jean at once claimed the duchy. As has been already shown, the heirs male of Duke Robert II. were now extinct; the Comtesse de Savoie, his eldest daughter, had no heirs either; of the Duchess de Bar there could be no question, as she had not only renounced her claims on her marriage, but was the youngest daughter. It rested between the King of France, son of the third daughter, Jeanne, and the King of Navarre, grandson of the second daughter, Marguérite. To most people the claim of Charles of Navarre must appear incontestably the right one; but it is true that instances in favour of Jean’s pretensions were not uncommon in these days. At any rate he seized the duchy, and on the 23rd of December entered Dijon; took the oath, before the high altar of Saint48 Bénigne in presence of the chief officials of Burgundy, to observe the constitution and privileges of that state; and was careful to rest his claim to the succession, not on its having lapsed to the crown, but on the right of his mother, Jeanne de Bourgogne, speaking much of his grandfather, Duke Robert, whose heir he declared himself to be and whose laws and system of government he promised to follow.
The great inheritance of Burgundy was now broken up, for Artois and the County Palatine went to Marguérite, Countess dowager of Flanders, second daughter of Philippe-le-Long, Boulogne and Auvergne to the next heir of Guillaume XIII., while Flanders and Hainault remained the inheritance of the child Marguérite, widow of Philippe de Rouvre.

King Jean returns to England—His death—Coronation of Charles V. and Jeanne de Bourbon—Murder of Blanche, Queen of Spain—The Céléstine Church—The Abbey of Chelles—The King’s library—Magnificence of the Court—Birth and death of the second Princess Jeanne.
Four years had passed away: years a little less unfortunate for France, as although Jean was still upon the throne and passed his time in travelling about his kingdom in search of amusement instead of giving serious attention to the affairs of the State, he allowed himself to be much influenced by the Dauphin. He ceased to meddle with the value of the coinage, he recalled the Jews and forbade private wars among the nobles. There was still peace between France and England, although English subjects were frequently to be found in the ranks of the Navarrais who were continually at war with the French.
50 The country was still in a disturbed state, and infested by troops of brigands who were always attacking the villages and châteaux. The Seigneur de Murs, a little castle near Corbeil, was outside his gates one day, when a party of drovers came up and complained that his servants had taken some pigs of theirs. The seigneur invited them to come inside the gates to see if they could identify any, but no sooner were they over the drawbridge than they threw off their disguise, blew a horn, drew their swords, and being joined by their companions who rushed out of a wood close by, they seized the seigneur, his wife and children, and taking possession of the castle, they made it for some time a centre from which they pillaged the whole countryside.
By the death of the Queen, Jeanne, Duchesse de Normandie, was the head of the court and of society. She was extremely popular, and her beauty the admiration of every one. Froissart in his chronicles always speaks of her as “la belle Duchesse,” or “la bonne Duchesse.” And now the time was drawing near for her to ascend the throne.
The Duc d’Anjou, second son of the King, had broken his parole and returned to France. Jean, horrified at such a breach of honour and of the laws of chivalry, declared his resolution to return to England. Of the true reasons for this journey, which was strongly opposed by his ministers and friends, many different explanations have been given. Modern historians have in many cases adopted the well-known story of his reply that if truth and honour were banished from the earth, they ought still to find51 refuge on the lips and in the hearts of kings. M. Dulaure,39 however, observes that this speech, which was that of Marcus Aurelius, does not belong to the fourteenth century, and has been ascribed by Paradin to François I., and by some other writer to the Emperor Charles V. And neither the writers of the “Grandes Chroniques de France,” De Nangis, nor Froissart, who were the most voluminous chroniclers of that time, make any mention of it. De Nangis says that he went to arrange for the ransom of his third son, the Duc de Berry, and his brother, the Duc d’Orléans. Froissart declares that he wished to see the King and Queen of England and to make excuses for the conduct of his second son. Others have attributed his persisting in this project to his love for some English lady, probably the Countess of Salisbury. M. Paulin Paris, in a note to his edition of the “Grandes Chroniques de France,” agrees with the explanation of De Nangis, and treats the idea of the English love affair as ridiculous and unlikely at the age of the King of France, who was forty-five. But this does not seem an unanswerable objection, considering the character and habits of Jean; especially if we look at the history of certain other kings at a much more advanced age—Henry IV. for instance.
But whatever might be his reasons, Jean left France according to the “Grandes Chroniques,” on Tuesday evening, January 3, 1364, embarking at Boulogne; and arrived at Dover on Thursday, whence after two or three days he pursued his way to London, was52 met by a great company of illustrious persons and lavishly entertained by King Edward and the English royal family, who assigned the Savoy Palace for his dwelling, where, after about three months passed in festivities and diversions of various kinds, he was taken ill and died.
The Dauphin was at Vernon, besieging his step-grandmother, Blanche de Navarre, when the news came of his father’s death. Towards her as well as his eldest sister Jeanne, Queen of Navarre, and his aunt, Jeanne d’Evreux, Charles was often placed in an attitude of hostility in which there was no personal animosity, but which arose from their relationship to and affection for his arch-enemy, the King of Navarre. Charles had no wish at all to injure or frighten his sister, of whom he was very fond, or his aunt, for whom he had the greatest respect, or his step-grandmother, who was also his cousin, and with whom he seems to have been on friendly terms when there was no particular quarrel going on about Charles of Navarre. Nevertheless this was not the first time he had been at open war with these ladies, or engaged in besieging one of their castles. He hastened to come to an arrangement with Queen Blanche, and leaving Bertrand du Guesclin in command of the troops that were actively opposing the Navarrais, he hastened to Paris, where the body of the late King was sent from England. “After the funeral at Saint-Denis,” says the chronicler, “Charles went out into a meadow of the cloister of the said church, and there, leaning against a fig tree in the said meadow, he received the homage of several peers and barons;53 after which he went to dinner, and spent that day and the next at Saint-Denis. And the following Thursday, the 9th May, departed the said King Charles to go to his coronation at Reims, which was to be on the day of the Trinity following.”
Nothing could be more solemn, stately, and imposing than the ceremonial used at the coronation of the Kings and Queens of France; and it must have made a strong impression upon the religious and cultivated minds of Charles and Jeanne. By the regulations made to a great extent by Louis le Jeune in 1179, and afterwards added to and confirmed by St. Louis, the King and Queen, on their arrival at Reims, the city consecrated by the baptism of the first Christian King of France and the coronation of so many generations of his successors, were met by a procession of the canons and other ecclesiastics of the cathedral, churches, and convents of the town. On Saturday, the day before the coronation, after complines, the church was committed to the care of guards appointed by the King, with those belonging there. Then the King, in the silence of the night, came to the church and remained alone in prayer and watching.
When matins rang, at the dawning of the day, the King’s guards were marshalled to keep the great entrance, the other doors being closed. Then matins were chanted, and after them prime. And then the King arrived and the coronation began.
On the spot where Clovis was baptised stands the church of St. Remy, second only to the cathedral in beauty and grandeur. In it was always kept the54 ampoulle of holy oil with which the Kings of France were anointed, and to which was attached the ancient legend of its having miraculously appeared, being brought down from heaven by a white dove at the baptism of Clovis. This tradition was then firmly believed, and the ampoulle was brought in solemn procession by the monks of St. Remy with cross and candles, carried with great reverence by the Abbot of that monastery under a silk canopy borne by four of the brotherhood. The Archbishop of Reims, with the bishops and canons, came to the door, when the Archbishop received it from the hand of the Abbot with a promise to restore it, and carried it to the altar accompanied by the Abbot and four monks. It was afterwards taken back to St. Remy.
Two thrones were placed in the middle of the cathedral, joining the choir. Around the highest, which was that of the King, were ranged the peers of France, and all those whose rank and office entitled them to such places.
The Archbishop girded on his sword, charging him to keep the army of God, and defend the Church and kingdom committed to him, with the blessing of God, by the virtue of the Holy Spirit and the help of Jesus Christ the invincible Conqueror. Then with prayers and benediction he was anointed with oil from the ampoulle, the ring placed on his finger, the sceptre and hand or rod of justice in his hands, and finally the Archbishop took the crown from the altar and placed it on his head, supported by the peers of France during the prayers and solemn benediction. When the King was crowned and seated on his throne, the55 Queen arrived at the cathedral. She prostrated herself before the altar and was raised from her knees by the bishops. After some prayers she was anointed, but with a different oil; a smaller sceptre, and a rod of justice like the King’s were given to her, and the ring placed on her finger with these words, “Take the ring of faith, the sign of the Holy Trinity by which thou mayest escape all heresy and malice, and by the virtue given to thee call heathen nations to the knowledge of the truth.”
And never could the benediction of the Archbishop have been more fully re-echoed in the hearts of all around him than when he placed the crown on the head of Jeanne de Bourbon, saying, “Take the crown of glory, honour, and felicity, that thou mayest shine with splendour and be crowned with joy immortal.”
The Queen was conducted to her throne by the barons who supported the crown, and surrounded by the ladies of highest rank; after which the King and Queen kneeling at the altar, received the Communion from the hands of the Archbishop, who at the conclusion of Mass took off their crowns and put smaller ones on their heads, and they proceeded to the palace with a drawn sword carried before them.40
They left Reims after their coronation, and on the 28th of May, Tuesday, entered Paris. The King made his entry at one o’clock, went to the church of Notre Dame and then to the palace, and “about the hour of nine” the Queen’s procession arrived at the gate. Her beauty and grace were the admiration of the multitudes that thronged to see her as she rode56 into Paris, the crown on her head, her dress covered with jewels and the trappings of her horse embroidered with gold. Philippe, Duc de Touraine, the King’s favourite brother, walked by her side holding the bridle of her horse. With her were the Princess Marie de France, afterwards Duchesse de Bar, the Duchesse d’Anjou and the Duchesse d’Orléans, by whose horses walked princes of the blood royal, the ladies of her court with a brilliant cortège of nobles, chevaliers, and guards, winding through the crowded, decorated streets to the Palais de la Cité.
Just after the King and Queen had entered Paris there arrived in triumph from the battlefield Bertrand du Guesclin. He had won a victory at Cocherel, and had brought not only the news of his success but the famous Captal de Buch, whom he had taken prisoner, to greet the King on the opening of his reign.

There was a great banquet next day at the palace, at which the Captal, who was placed on parole, dined with the King.41 And much honour was shown to Sir Bertrand du Guesclin. After dinner there were jousts in the courtyard of the palace, at which the King of Cyprus and many of the greatest nobles jousted.
On Friday, the last day of May, the King invested57 his youngest brother, the Duc de Touraine, with the duchy of Burgundy. It had been promised to him by his father in remembrance of the day when, as a mere child, he stood alone by his side in the battle of Poitiers. He afterwards married the heiress of Flanders and Hainault.
The Duchess-dowager, mother of Jeanne, lived a good deal at court, and her brother Louis, Duc de Bourbon, was a great favourite with the King, who extended his affection for Jeanne to every one belonging to her. Louis de Bourbon was one of the best and noblest characters of his century. When a hostage in England, he made himself so beloved that he was allowed to go about wherever he chose, and even to return to France on parole. His estates were managed during his absence by his mother.
The youngest sister of the Queen, Marie de Bourbon, was a nun at Poissy, and for her also both Jeanne and Charles had much affection.
But a constant source of anxiety and grief to them all had been the unfortunate marriage of their sister Blanche, Queen of Spain, who lingered in captivity in one castle after another in spite of the indignation and remonstrances of the Spanish people, the French King, and the royal family her relations. At last came the news that she had been poisoned by Pedro el Cruel, and her death excited the horror and execration of France and Spain against her murderer. Blanche seems to have passed these years in saintly resignation to the will of God. Her brother the Duc de Bourbon and her brother-in-law the King of France did not suffer her death to remain unavenged.
58 Charles V. declared war upon Pedro, and sent French troops to Spain commanded by Bertrand du Guesclin, the Bègue de Vilaine, and other officers, and after a short time he paid for his crimes with the loss of his throne and his life.
One cannot help being struck by the extraordinary discrepancy in the accounts given of the Kings of France by ancient and modern writers. According to the former, they all appear to have been models of every virtue and talent under the sun; while if one reads the descriptions of some of the latter, especially of those who are republican in principles, one finds that, with the exception perhaps of Saint Louis, no King of France ever had any good qualities at all but courage, and that, while all the misfortunes that happened were entirely his fault, any success he might have in the management of his affairs and the government of his kingdom was either the result of accident or was due to somebody else.
Charles V., however, may be said to have done considerably more to deserve his name “le Sage” than Jean did to earn that of “le Bon.” In all respects different from his father and grandfather, he set himself to try to repair the ruin and distress in which the kingdom was plunged. He was, as Sismondi remarks, the first modern King of France. His effigy on the seals is seated in a chair, not mounted on horseback. It is characteristic of his life and habits. His government was the personal government of an intelligent, prudent, and honest King, occupied with the internal and external affairs of the State.42 He found himself surrounded with59 dangers and difficulties. The country was so depopulated by plague and famine that in many parts the inhabitants were reduced to two-thirds and even one-third of their numbers in the beginning of the reign of his grandfather. The neighbouring countries were involved in civil wars and disturbances, into which it was difficult for France to escape being drawn. Italy was full of discord. Spain was divided between the factions of Pedro el Cruel and his brother, Enrique de Trastamare, who had risen against that tyrant to avenge the murders of his mother and brothers.
Charles found no help in his own family. His eldest sister was married to his enemy the King of Navarre, to whom she was devoted. The Duc de Bar, who had just married Marie, the second sister, was likely to be more trouble than assistance; the Visconti had paid his father a large sum of money for the marriage of Isabelle, but were too far off to have anything to do with affairs in France. Of his brothers, the two elder ones had all the faults and scarcely any of the good qualities of the Valois. They were arrogant, rapacious, violent and cruel. The Duke of Burgundy was the best of them.
Charles had always been delicate, and people said he had been poisoned when he was young by the King of Navarre. It was one of those absurd accusations heaped upon Charles of Navarre by his enemies. He could have had no object in poisoning the Dauphin, for if he had died the crown would have passed, not to him, but to the Duc d’Anjou, and there were plenty of other princes of the house of Valois60 whose claims would have come before his. The Dukes of Berry and Orléans, the Alençon princes, and even the Duc de Bourbon, all stood before him in the line of succession.43 But it is probable that the King firmly believed that he had been poisoned by his brother-in-law, and therefore was not likely to regard him with very friendly feelings.
Jeanne nursed and consoled Charles in his frequent illnesses, and shared and sympathised with all his tastes.44 Both were devoted to art and literature; Charles V. was the best educated and most learned prince of the fourteenth century. Almost the only existing letter written entirely by the hand of a Valois King of the direct line is by him. It is preserved at the Dépôt Central.45 Jeanne’s love of books caused her to interest herself in the writings and translations of the time; she was also fond of poetry. Many Greek and Latin authors were now translated into French, and by the desire of the King and Queen, Nicolas d’Oresme, Bishop of Lisieux, made a translation of the whole of the Bible, which Charles took with him wherever he went, being in the habit of reading it all through every year. It was in two volumes.
On the 24th March, 1367, Charles laid the foundation stone of the new church of the Céléstins. Besides the church he gave them costly presents, amongst others a great cross of silver gilt. The Queen presented an image of the Virgin, also of silver gilt.61 The church was finished in 1370, and consecrated by the Archbishop of Sens. Charles lavished upon this church the most precious objects of art; chalices, missals, and ornaments of all descriptions; and especially magnificent were two chapels entirely hung with cloth of gold, one being covered with fleurs-de-lis, the other with suns and stars. The benefits and favours conferred by the King and Queen upon this convent were so great as to cause them to be considered as founders of it, and their statues were accordingly placed on the portal of the church. They spent 5,000 francs in building a dormitory, refectory, chapter-house and cloister.46
The hôtel St. Paul, where Charles and Jeanne afterwards lived, was most conveniently near the Céléstine convent. The courtiers, following their example, were always giving presents to this brotherhood. The King’s secretaries founded a confraternity in their church, and all belonged to it. The King exempted this order from all public contributions, even such as were generally paid by the clergy. They continued for several generations to enjoy such great favour and protection from the royal family that they appear to have rather presumed upon their privileges, for in time it grew into a byword, and in speaking of a conceited, arrogant person the exclamation “Voilà un fier Céléstin” became a common figure of speech.
The Céléstins, as time went on, became celebrated for the excellence of their cookery; there were especially certain omelettes for which they were62 much distinguished. But this was long after the time we are now considering.
One of the most fashionable convents for women was that of Chelles, near Paris. It had been founded by Clotilde, wife of Clovis I., and much enlarged by Ste. Bathilde, who dreamed that she saw a ladder raised before the altar of Our Lady, which touched Heaven, and by which she mounted in a cortège of angels. In consequence of this, the Abbey of Chelles bore as arms, a ladder between two fleurs-de-lis, those orders founded by Kings and Queens of France having the right to bear the lilies in their arms. The Abbesses of Chelles bore the greatest names in France, among them were Giselle, sister of Charlemagne, one of his daughters and numbers of widows, sisters, and daughters of kings.
But after a time this rich and distinguished establishment became also very worldly. Some monks built a monastery close to it, and the King had a palace on the other side of its walls. Scandals arose. The nuns got up late, went out hunting and conducted themselves much more after the fashion of the court than the cloister. They were on excellent terms with the brotherhood of the neighbouring monastery, who were mostly poor cadets of noble families. They gave parties and made confitures for these monks; and when Louis le Bègue carried off a nun of sixteen years old over the wall of his palace, his example was so much followed by his courtiers that nearly fifty nuns had eloped in a few months. The Bishop of Paris and Abbot of St. Victor went to preach and try to carry out reforms; but on their63 way back were attacked in the forest and the Abbot killed.47 After Robert II. (996) the palace fell into ruins; but the evil reputation of the sisterhood went on long after. In 1358 they fled to Paris, but returned to their convent, which was besieged by the English. They escaped again with their Abbess, Alix le Passy, and were afterwards collected and reorganised by Jehanne la Forêt.
King Jean, who was not by any means a literary character, had only possessed twenty books, but Charles delighted in collecting them and arranged his library in a tower in the Louvre, which was called La Tour de la Librairie.48 He collected nine hundred volumes, which in those days, before printing was used, made a considerable library. The catalogue of this library was made in 1378 by order of the King, and still exists.49 It was in three rooms, occupying three floors of the tower, the windows of which had iron bars and a trellis of ironwork; with glass painted. The ceilings were of cypress wood and the walls panelled with richly carved oak. Thirty candles and a silver lamp burned all night in each room so that they might be available for study night and day.
In a manuscript, “Bibliothèque du Roy,” No. 7609, are found the names of the different instruments of music of the fourteenth century, among which can be recognised several that are still in use. Here are the names of some of the books contained in the library:—
64 “Dit de la Rose.”
“Le Livre de la Mutation de Fortune.”
“Le chemin de long estude” (translated from the Romance into French).
“La Cité des Dames.”
“Le Livre des trois vertus.”
“Le Livre des faits d’Armes et de Chevalrie divisé en quatres parties.”
“Le Traité de la Paix.”
“Le Corps de Policie.”
Charles V. and Jeanne possessed many beautiful books on parchment with exquisite miniatures and illustrations of the fourteenth century, books of hours and books of psalms, one of which had belonged to Saint Louis.
They commissioned Raôul de Presle to translate the “City of God,” by St. Augustine, and gave him 4,000 francs a year for doing it.50
Besides books and manuscripts, they had an immense collection of magnificent objects of art. Since the days of Louis, the taste for splendour and costly decoration had spread in all classes. Every now and then laws were made to check them, but as the nobles would not obey them and could not be forced to do so, they only acted as restraints on the bourgeoisie. And so the most important of all industrial arts had come to be that of the goldsmith.
It seems extraordinary, considering the impoverished condition of the finances and the dreadful state of affairs in general when they came to the throne, that the King and Queen should have been able to65 spend the sums they did upon buildings, books, treasures of art, and all cultivated and intellectual pursuits. But their wise and good management was so successful in altering the disastrous state of things caused by the follies and misfortunes of their predecessors, that they were able to spend money with royal magnificence upon the aims and objects they preferred.
Jeanne was clear-headed and sensible, and the economy and order she introduced into the royal household was considered an excellent example. She sold a quantity of costly plate to help pay the troops of Du Guesclin in 1369, and so contributed to the successful result of the war with England; after which they began to collect again.

But their daily life was surrounded by magnificence, as may be seen by a list made later on by order of the King, in which appear all sorts of precious and costly things. Statuettes of gold and silver, exquisite carvings in ivory, quantities of gold dishes, plates, candlesticks, basins, salt-cellars, drinking cups, knives and spoons; very few forks—there were only three at Vincennes, of which one belonged to the Queen. Jewels and precious stones in profusion, sets of hangings for rooms—that is to say portières; carpets, hangings, canopies, curtains for windows and beds, some of silk, others cloth of gold or velvet; one is mentioned as being entirely of cloth of gold, with a cross of red velvet embroidered with several coats of arms; another of green with stripes of gold. Spanish leather, richly embroidered cushions, costly tents to put over the Queen’s bath, called66 espreniers. One of these is described as being made of white satin, embroidered with roses and fleurs-de-lis; others were blazoned with the arms of France and Navarre.51 Every now and then some curious little incident seems to give a touch of life and interest to this old list, such as a little gold barrel and chain with the arms of Burgundy, which the King always had with him and which had belonged to his grandmother, Jeanne de Bourgogne; the gold serpents on the salt-cellars with their tongues in the salt, which were supposed to reveal the presence of any poison that might have been put in; a crown à bassinet set with jewels, probably belonging to King Jean, who was in the habit of wearing a crown on his helmet in battle, regardless of the additional danger of proclaiming his rank; and in the midst of this catalogue of splendour “item, an old mattress all torn and the pillow the same, which had belonged to King Jean.” Two banners of France covered with fleurs-de-lis and bordered with pearls, to drive away the flies when the King was at table; dog-collars of velvet and silver, green game bags embroidered with pearls, inkstands, purses, whips, leather lanterns. The contents are given of some coffers or boxes the King always took about with him and of which he kept the keys. Amongst the rare cameos, jewels, gold chaplets, &c., was the holy stone to make women have children, and another stone which cured the gout.
Different things are mentioned as having belonged to Charlemagne and St. Louis. There were also gold basins to wash in, and gold vases to put the67 remains of repasts to give to the poor. Bas-reliefs of gold, generally of sacred subjects, and all the things belonging to the chapels, such as chalices, crucifixes, missals, crosses, statues, hangings, reliquaries, paternosters, &c., most costly and beautiful. An immense number of crowns and coronets seem to have belonged to the King, Queen, and Princesses, and jewelled girdles, clasps, and rings are also enumerated among their possessions.
Charles and Jeanne at the beginning of their reign lived chiefly at the Louvre and at Vincennes, where he ordered four of the inhabitants of the village of Montreuil to watch against poachers every night in the forest. At Vincennes had been born on June 7, 1366, “entre tierce et midi,” another daughter to the King and Queen. She was christened four days afterwards in the chapel there and named Jeanne, her god-parents being the Duc de Berry, the two Queens dowager, Jeanne d’Evreux and Blanche de Navarre, and Marguérite, Countess of Flanders and Artois. But the same ill-luck seemed to pursue the children of Charles and Jeanne as had followed those of Philippe de Valois and Jeanne de Bourgogne; for this little princess also died the following December, and was buried at St. Denis, leaving the King and Queen again childless.
Comet—Meeting of Parliament—Marriage of the Queen’s sister—The Louvre and its gardens—Christine de Pisan—The Dauphin—His christening—War—French victories—Prosperity of France—Hôtel St. Paul—Birth of Marie de France—Capture and liberation of the Queen’s mother—Bonne, Comtesse de Savoie—Birth of Louis and Isabelle de France—Louis, Duc de Bourbon.
A French historian assures us that in this, the year before the war began again, “the presage of it was seen in the heavens, that is to say in the Holy Week a comet between north and west with a long hairy tail stretching towards the east and red rays like a pyramid of fire.”52
The monks went preaching about in all the French provinces for the rights of Charles V.; in the English ones for Edward III.
“In this year the King and Queen sat in parliament on the vigil of the Ascension,” and Jeanne gave her advice and opinion, by special desire of the King, upon the important affairs then discussed. Whenever69 he was ill the secret despatches were all taken to her, and her seal carried the same authority as his own.53
He had detached Armand d’Albret from the English cause and married him to Marguérite, one of the Queen’s sisters, to the indignation of the Black Prince, who spoke “moult rudement” about it.54 As Armand d’Albret had before seized the castle of La Motte d’Epineul, it was made part of the dowry of the young princess, who often appears in descriptions of festivities at her sister’s court.
In 1371 she was godmother, with the Princess Jeanne, daughter of Philippe VI., to her niece, Marie de France. Her husband and son were killed at Azincourt, and, like her sister Bonne, Comtesse de Savoie, she undertook the guardianship of her grandson, Charles d’Albret, for whom in 1416 she obtained letters from Charles VI. admitting him to do homage for his lands though under fifteen years old.
Hitherto every King of France had held his court either in the palais de la Cité or the Louvre. Those who only know the Louvre as the magnificent Renaissance palace of François I. and Henri II., can perhaps hardly picture it as the most romantic royal castle that ever existed. The buildings formed an oblong court, with round towers at the angles and in the middle of the sides, while nearly in the centre of the court stood a massive round keep, and to the south and east were well defended gateways. All this was moated, and on the side towards the river70 were other walls and towers.55 It was outside Paris until Charles included it within the walls. He altered the internal arrangements, heightening the rooms and also the towers, so that it was more beautiful than ever. It was he who built the long line of towers all along the river. They were of all sizes and shapes, and each had a captain of its own. The names of many of them are known from the registers in the Chambre des Comptes. The Tour du Fer-de-cheval, Tour de l’Orgueil, du Bois, de l’Ecluse, Jean de l’Etang, de l’Armoirie, de la Taillerie, de la grande Chapelle, la petite Chapelle, Grosse Tour du Louvre, Tour de la Librairie, and many others. The Grosse Tour, built by Philippe Auguste, was enormously thick and strong, and had a dungeon. The great portal was on the river, flanked with towers; the second entrance was narrow, with two towers, on which were sculptured the figures of Charles V. and Jeanne de Bourbon.
The rooms were large, low, with panels of wood; the windows narrow, barred with iron and filled with glass, on which were painted the arms of the person to whom the apartment belonged—King, Queen, enfants de France, princes of the blood, &c.
The apartment of the Queen was below that of the King, and exactly the same in size and disposition. Sauval remarks that the view of the river from the windows was very beautiful. The apartments of the King, the Queen, and each of their children had a chapel and gallery attached to it. In the apartment71 afterwards given to the Dauphin there was a clock, doubtless made by Jean de Vic, who about that time made one for the King, which was placed in the Tour du Palais and has been supposed to be the only one in Paris under Charles V.56
The great garden of the Louvre was very old: it had treilles or trellised walks from one end to the other, hedges, arbours, and grass. It was planted with roses and other flowers, herbs and vegetables. There were two smaller ones, called the King’s and Queen’s garden.57
The great garden went up to what is now the Rue St. Honoré, and was bounded by the city walls. To any one who is fond of flowers and gardening, it is most interesting to read the old bills and accounts preserved in different registers, and to see something of what these ancient gardens were like.
“Compte 1362, of Pierre Culdöë, lieutenant, and the noble Messire Jean de Damille, chevalier, chastelain of the castle of the Louvre, of the receipts, &c., for certain works which have been done in the gardens of the said Louvre, à la plaisance du Roy, nostre Seigneur, beginning in the month of May ‘362,’ and finishing in the month of March CCCLXIII.”
Then follow many interesting accounts, of which, however, it is impossible to give more than a few specimens. For instance, sums of money are paid to—
“Perin Durant, gardener, for having got many72 good herbs and planted the same in the said gardens of the Louvre in the month of March, 1362.”
“To Pierre Hubert, trellis-maker, for having fastened up the hedges round the said gardens in the month of February, and done up about half the said hedges which the wind had blown down; for wood, osier, and trouble.”58
“To Jean Baril, for having made a heap of earth (mound) with a summer-house of trellised wood on the top, with the arms of the King, Queen and nos seigneurs de France upon it, and having made a drawbridge to it in the month of March, 1362, for wood, osier, and trouble.”
“To Jean Caillon and Geffroy de Febon, gardeners, for their trouble in having planted sage, hyssop, lavender, strawberries, and several other herbs in the gardens of the said Louvre, for having dug the garden all round, put in herbs and seeds, renewed all the paths and grass plots (préaux) and taken away the weeds and rubbish.”
“To Jean Dudoy, gardener, for having ... taken away all the weeds, stones, and rubbish, and made several beds of sage, hyssop, lavender, balsam, strawberries, and violets, and planted bulbs of lilies, double red rose trees, and many other good herbs which he got.”
“To Sevestre Vallerin, the work of his arm (la peine de bras) for his trouble in having weeded the paths which go among the préaux (courts or grass plots), and the beds in which are the rose trees,73 strawberries, violets, sage, hyssop, lavender, balsam, parsley, and other good herbs: and also for having watered four summer-houses and a great square room to make the plants grow (pour faire venir les herbes).”
“To Etienne de la Groye, gardener, for having made in the said gardens certain trellises, arbours, and hedges all along the walls, inside.”59
We hear of some one being paid also for planting a pear tree, and lettuce is mentioned amongst the vegetables that mingled with the flowers growing in the quaint old garden. It must have been a strange place, with its stiff beds of roses, lavender, and sweet herbs, its formal paths and summer-houses, its long trellised walks under the huge, ancient walls, shadowed by a forest of frowning towers.
As the Queen’s apartments in the south wing of the château would not contain all the rooms required, some more were allotted to her looking west; and some to the King, who, out of consideration for the Queen, had given her the first floor and taken the second for himself. One of these was the bedroom of the King, and containing amongst other furniture one of two great beds, “pour le corps du Roy,” furnished by the courtepointier, Richard des Ourmes, at the price of twenty francs of gold each.
The King’s cabinet or study (estude) was lighted by one large window with painted glass, and four small ones, and hung with black drap de Caen. It had a high chair, a bench, a form (escabelle) and74 two bureaux. Green drapery was thrown over the furniture, and a high chimney with mantelpiece of stone warmed the room, which was most likely between his oratory and library. His chapel, or oratory, was vaulted, and heated by a stove in the winter.60
The furniture in the Louvre consisted of enormous cupboards, buffets, and heavy chairs or faudesteuils, all richly carved, illuminated, and sometimes decorated with gold and gems; benches, forms, settles, dossiers or seats with backs, covered with velvet, satin, or cloth of gold; an estendait, or kind of sofa is mentioned as being in one or two of the rooms; the walls were hung with tapestry, and there were plenty of carpets and cushions, some embroidered with pearls. Spanish leather was thrown on the floor in summer.61
The house linen seems to have been kept in chests in the bedrooms: a number of white silk sheets are described as being in a square box with two covers in the large window in the King’s room; and later in his palace called Beauté, in a gilded chest (coffre) in the room where the King slept, there were towels, tablecloths, and sheets of toile de Reims; also richly embroidered pillows, one of which had on it a knight, a lady, two fountains and two lions. There were couvertoers, or warm coverings for winter, and couvertures, or sheets of ornamental stuffs thrown over the beds in the day. One of these is mentioned as being of ermine, fastened to an old sheet75 of marramas, of which the King had caused a breadth to be cut off to make a chasuble.
The chimneys were of course high and open, with great fires on dogs (chenets) on the hearth. There exist bills for three chenets de fer for the Queen’s and other rooms, and for tongs, shovels, and tirtifeux. Also for bellows, “five new bellows carved and ornamented with gold.”
There are also bills from one Marie Lallemande, for blue and white stuff for the window curtains of the King’s and Queen’s bedchambers, and for eighteen feather beds with pillows; and from Jean de Verdelay and Colin de la Baste for six tables of walnut wood and a pair of trestles for the Queen’s rooms, and for the King’s large dining-room an oak bench with columns (un banc de chesne à coulombes) twenty feet long for the King’s larger table, with the daïs of the same length and three feet wide, and a dréçoir with a step round it in the same room (sale),62 “et enfonsé le viez banc Sainct Louis, et une marche autour.”
The King was anxious to attract to his court any literary or talented persons that could be found, and being himself, like every one else of his day, a believer in astrology, he gladly welcomed a learned man and celebrated astrologer named Thomas de Pisan, a native of Bologna, who, delighted at his reception, sent for his wife and daughter and presented them at the Louvre, 1368. Charles took the whole family under his protection. He gave an income to the astrologer, and his daughter, the76 celebrated Christine de Pisan, was brought up at court as a demoiselle de qualité. Her father, seeing her talents, bestowed much care on her education. She was taught Latin and French, and not allowed to forget her native Italian; she also studied science and literature. At fifteen she was married to Etienne du Chastel, a young man of good birth and education, but small fortune, who was made one of the King’s secretaries. She became a distinguished writer, and is best known for her life of Charles V., written, after his death, at the command of the Duke of Burgundy. Her style is exceedingly pompous and fulsome, but some interesting details can be gained from her writings, and if they were not crammed with tiresome, prosy moral sentiments, and absurd flattery of the King, they might have been much more interesting and valuable still. After the death of Charles V., the prosperity of the family waned: her father lost most of his pay and died old and poor; her husband died 1402, and one of her sons died young. Her daughter became a nun at Poissy.
On the 16th of April, 1368, Lionel, Duke of Clarence second son of the King of England, passed through Paris on his way to Italy to marry the daughter of Galeazzo Visconti. The Dukes of Berry and Burgundy went to meet him at St. Denis and conducted him to the Louvre, where his room was “moult bien parée et aournée.” He dined and supped that day with the King, and the next day dined with the Queen “en l’ostel du roy près de Saint-Pol, là où elle estoit lors logiée et y fist-en très grant feste.”63 After dinner77 when they had played and danced, the Princes returned to the Louvre, where Lionel stayed during the few days he was at Paris, being entertained by the different members of the French royal family. Lionel of England was a handsome and courageous Flemish giant, mild-tempered and amiable, possessing no great vigour of intellect.64 Through his daughter married to Edmund Mortimer the line of York derived their claim to the English crown.
The King had a painted barge like a floating house, richly decorated inside and outside, in which he used to go up and down the Seine from the Louvre to his new and favourite palace of St. Paul,65 which he had built chiefly while he was still regent.
Charles and Jeanne had now been married eighteen years, and had no children. They had never had a son, and their three daughters had all died, to their great grief. But on the 3rd of December, 1368, “on the first day of the Advent of our Lord, at the third hour after midnight, the Queen Jehanne, wife of King Charles, then King of France, had her first son in the ostel near St. Pol; and the moon was in the sign of the Virgin in the second phase of the said sign, and the moon was twenty-three days old. For the which birth the King and all the people in France had great joy, and not without cause, for until now the said King had had no male child. And the King gave thanks to God and the Virgin Mary. And that day he went to Notre Dame de Paris, and caused a beautiful mass to Our Lady to be sung before her image at the entrance78 of the choir; and the next day, Monday, he went to Saint Denis in France on pilgrimage, and he caused to be given away at Paris a great heap of florins, to the number of three thousand florins and more.”66
The child was christened on Wednesday, the 6th of December, and the chronicler thus describes the proceedings:—
“The Wednesday following, sixth day of December, in the year one thousand three hundred and sixty-eight aforesaid, the said son of the King was christened in the church of Saint-Pol of Paris, about the hour of prime, in the manner which follows. And the day before were made enclosures of wood in the street before the said church, and also inside the said church about the font, to take care that there should not be too great press of people.
“First: before the said child went two hundred varlés who carried two hundred torches, who all remained in the said street,67 holding the said burning torches, except twenty-six who went inside. And after was Messire Hue de Chasteillon, seigneur de Dampierre, master of the crossbowmen, who carried a candle in his hand, and the Comte de Tanquarville, who carried a cup in which was the salt, and had a towel at his neck with which the said salt was covered. And after was the Queen, Jehanne d’Evreux, who carried the said child in her arms, and Monseigneur Charles, seigneur de Montmorenci, et Monseigneur Charles, comte de Dampmartin, were beside her; and thus they issued from the said hostel of the King of79 Saint-Pol, by the door which is the nearest to the church. And immediately after the said child, were the Duc d’Orléans, the King’s uncle, the Duc de Berry, the Duc de Bourbon, the Queen’s brother, and many other great seigneurs and ladies; Queen Blanche, the Duchesse d’Orléans, the Comtesse de Harcourt and the Dame de Lebret,68 sisters of the Queen, who were well adorned with coronets and jewels.”69
The chronicler goes on to describe the christening, the cardinals, bishops, and abbots with mitres and crosiers, how the crowd was so great that the child had to be taken home by a back way and how the King gave away money in the coulture Ste. Katherine, where there was also such a crowd that several women were killed.
The Queen seems to have been ill a long time, for the chronicler says that there was a great fête when she recovered (releva de sa gésine) from her confinement, on the 4th February, and after the dinner a dance and other amusements, and the King gave his son the title of Dauphin du Viennois.
Charles had succeeded in getting rid of the Grande Compagnie led by the Archiprêtre, mentioned in the life of Jeanne de Boulogne, Bertrand du Guesclin having persuaded them to go with him to Spain, to fight against Pedro el Cruel, at the request of the King, who said: “If some one would lead ces gens-là against the miscreant and tyrant Pedro, who has killed our sister, let him do so whatever it costs me.”70

The news of the defeat and death of Pedro was brought to Paris in the early summer, and the chronicler remarks, “and certainly many people thought that this had happened to the said Pierre because he was a very bad man and had wickedly and traitorously murdered his good, wedded wife, daughter of the Duc de Bourbon and sister of the Queen of France.” The inhabitants of Guyenne had revolted against the Black Prince, who had been taxing them too heavily; and the war with England had begun again, but this time it seemed to be going in favour of France. Fortress after fortress fell into French hands81 and on the 29th April, Abbeville surrendered to Hue de Châtillon.
This and the next year passed prosperously for the kingdom. Bertrand du Guesclin, created Constable of France, was everywhere winning back towns, castles, and fortresses; the gallant Sir John Chandos was killed in Poitou, and by the end of 1370, Ponthieu, Périgord, Rouergue, Saintonge, Poitou, part of Limousin, and nearly all Guyenne had been won back. The rapid restoration of the kingdom was a marvel to every one. The hero du Guesclin was the idol of the nation; the Duc de Bourbon especially loved him because he had avenged his sister the Queen of Spain. The wise and firm government of the King brought prosperity and order into everything. His Court was magnificent, not with the wild and warlike revelry of Philippe and Jean de Valois, but with the refined and artistic luxury of a prince more cultivated than his time.
All round about Paris he restored and rebuilt the royal châteaux that had been destroyed by the English and Navarrais, taking care to fortify them at the same time. Melun, Creil, Montargis, amongst others, and St. Germain, which had been burnt by the soldiers of King Edward. He gave Paris a new bridge, walls, gates, and the Bastille, of which the first stone was laid by Aubriot, provost of Paris, in April, 1370. He had built two new royal residences, Beauté, a most delightful château at the end of the forest of Vincennes, and the hôtel de St. Paul at Paris, having taken a dislike to the Palais de la Cité, from the scenes of blood and terror that he had witnessed there.82 The Louvre was not large enough for the immense number of suites of apartments he wanted. Gradually it was used in his reign chiefly to entertain and lodge foreign princes. He bought several hôtels, gardens, and meadows and turned the whole into one huge palace, which, with its pleasure grounds, covered nearly all the space between the river, the rue St. Antoine, the rue St. Paul, and the Bastille. The hôtels de Sens, de Saint Maur, d’Etampes, hôtel de la Reine, and others.
The whole were surrounded with a high wall, enclosing, besides all these great hôtels which formed the palace, and were connected by twelve galleries, six meadows, eight gardens, and a number of courts. All the princes of the blood, great nobles and officers of the court had their apartments in this wonderful palace, which the King declared should for ever belong to the Crown, adding that he had there enjoyed many pleasures, endured and recovered from many illnesses, and therefore he regarded it with singular affection.
It was a curious mixture of luxury and simplicity, arm, feudal castle, and palace all in one.71 The King delighted in the gardens and orchards and used to work in them with his own hands. Both he and Jeanne were also very fond of animals, and seem to have had an immense number of pets, for which there were enclosures and aviaries in all their palaces, but especially at their two favourite abodes, St. Paul and Beauté. They had lions and wild boars amongst other creatures, and numbers of birds. Besides the83 great aviaries at the Palais, the Louvre, St. Paul, and the other palaces, there were in every apartment in St. Paul bird-cages of wire painted green, and there is an account of a large octagon cage made at that palace72 for the King’s parrot, which is called “la cage au pape-gaut du Roy.” There were numbers of fowls, pigeons, and peacocks, the wild boars were kept in a garden, the lions, of course, in dens, and there were rooms for the turtle doves and for the Queen’s dogs.
The description of the interior of this palace, or group of palaces, reads like a page out of the “Arabian Nights.” One large hôtel (one of three houses the King gave the Queen) was used for her horses, coches, and the grooms and people belonging to her stables. The conciergerie, lingerie, tapisserie, pâtisserie, pelleterie, fruiterie, lavandrie, saucisserie, panneterie, épicerie, taillerie, maison du four, jeux de paumes, garde-manger, celliers, caves, cuisines charbonnerie fauconnerie, &c., must have formed a little town in themselves. Silk, velvet, tapestry, Spanish leather, and cloth of gold covered the walls, floors, and seats. The furniture, massive and picturesque in form, was ornamented with rich carving, illumination, gold or gems. The beams of the ceiling were decorated with gold fleurs-de-lis. The rooms were heated with stoves (étuves) and huge fires on open hearths, with magnificent chimney pieces of stone sculptured often with colossal statues and figures of animals. The washing basins and all the dinner services, &c., used by the royal family were of gold or silver. All the numerous apartments of the different84 princes, princesses, and great personages had chapels, galleries, bath-rooms, &c., attached to them. The room of the King’s jewels was brilliant with gold, silver, and precious stones.
To say nothing of the art treasures of gold, jewels, and illuminations, what would not a lover of art and antiquity in our own day give for one of the long oak benches, for instance, ending in handles like those of baskets, carved all over with birds and animals, and mounted on many carved columns—especially for the one called “the old bench of St. Louis,” which stood in the King’s dining room at the Louvre.
It was in their favourite hôtel de St. Paul, or as it is called in old writings, St. Pol, that Charles and Jeanne principally lived, and here were born the Dauphin and all their younger children.
The birth of the Princess Marie took place on the 27th of February, 1370, and her godmothers were Jeanne, daughter of Philippe VI. and Queen Blanche, and the Dame d’Albret, sister of the Queen.
With the exception of Blanche, whom she never met again after her disastrous marriage with the King of Spain, Jeanne saw a great deal of her family, especially of her three youngest sisters, the Comtesse de Harcourt, the Dame d’Albret, and the Prieure de Poissy. Bonne, Comtesse de Savoie, was farther away in her beautiful southern home, and being the wife of a greater prince, had more of the occupations and cares of a government upon her hands. Bonne was brave, clever, sensible, and universally admired. Things went prosperously enough with her until, after she had been married about thirty years, in 1385 her85 husband, the Green Count, died of plague in Italy, where he had gone on some warlike expedition. She governed Savoy for her son Amadeo VII., the Red Count, whom she married to a daughter of the Duc de Berry. But the Red Count was killed out hunting in 1391. He left the guardianship of his son and the regency of Savoy to his mother, in whom he might well have the greatest reliance, instead of to his young widow who had neither the talents nor experience to fit her for such a trust, and who, he was quite sure would marry again, as she did. In spite of her opposition the Countess Bonne assumed the guardianship of her grandson Amadeo VIII. and the State. After he came of age she could not get her dowry properly paid, so she sent for her brother Louis, Duc de Bourbon, who came at once with a troop of soldiers and threatened to make war upon the Savoyards. Thereupon the dowry was paid without any further trouble. Bonne died at the Château de Mâcon, 1402. In 1372 the Duchess-dowager de Bourbon, mother of the Queen, was at the castle of Belle Perche, in the Bourbonnais, when one night it was surprised by three captains of brigands or free companies, who got in by scaling the walls. Louis de Bourbon assembled his vassals and friends and laid siege to the place where his mother was a prisoner. The Duchess managed to let him know that she was afraid of the things the engines threw in and the damage they caused, and that she wished him to blockade the castle. He did so accordingly, but the Earls of Cambridge and Pembroke arrived with a large force and carried off the Duchess and her86 ladies to a château in Limousin. She was soon afterwards exchanged for Simon Burke, a favourite of the Black Prince. She went to Clermont, a hunting château of her son, and in the forest close by she met her daughters coming to see her.73 In a miniature representing their meeting the Queen advances wearing a dress covered with fleurs-de-lis and emblazoned with the arms of France and Bourbon, holding a bird, the sign of high rank and led by Jean de Bourbon, Comte de la Marche. Her little daughter Marie, bearing the same arms accompanies her, then come the young Duchess, wife of Louis, and the Queen’s sisters, Comtesses de Savoie and Harcourt,87 and Dame d’Albret. Each leads a dog with a long leash, two ladies follow, one carrying the train of the Duchesse de Bourbon. All the princesses have the arms of their husbands and of Bourbon emblazoned on their dresses, including the Duchess-dowager, Isabelle de Valois, who also wears a long widow’s veil.74

Parti-coloured dresses were much worn then. The Queen’s second son, Louis, was born March, 1371. Bertrand du Guesclin was his godfather, and put a sword into his hand, praying God and Our Lady to make him a good knight. In July, 1373, was born her daughter Isabelle. The little Dauphin was her godfather and held her at the font; her grandmother, the Duchess Isabelle, was her godmother.
Louis de Bourbon had married in 1371 Anne, daughter of the Comte de Clermont et d’Auvergne. He was a good soldier, just, generous, and religious; his court was as magnificent as those of the Dukes of Burgundy and Orléans. When he returned from being a hostage in England he instituted an order of chivalry called the Ecu d’or. During the fête, after the ceremony, his Procureur-Général, Chavreau, presented to him a register of depredations committed on his lands during his captivity by divers lords, his vassals, most of whom were present, and were seized with consternation; but the Duke replied, “Chavreau, have you also the register of the services they have rendered me?” and without looking at it, threw it into the fire. It is said that when, after the capture of his mother, Anne, Duchesse de Bretagne, fell into88 his hands and exclaimed, “Ah, beau cousin! am I a prisoner?” he replied, “No, madame, we do not make war on ladies.” His subjects adored him, and when, many years afterwards, he died and his body was brought to Moulins to be buried, clergy and people thronged to accompany it wherever the funeral passed, with tears and lamentations.
Illness of the Queen—Her recovery—Floods in Paris—Death of several princesses of the Royal Family—Bertrand du Guesclin—The Court of Charles V. and Jeanne de Bourbon—The peers of France—The King’s will—Betrothal of his daughters—Visit of the Emperor Charles IV.—The Emperor and the Duchess-dowager de Bourbon—Birth of the Princess Catherine—Death of the Queen—Of the Princess Isabelle—Grief of the King—His death.
The beds used at this time were enormous. If only six feet square they were considered very small and called couchettes, but when they were from eight feet and a half by seven and a half to twelve feet by eleven, they were supposed to be of a sufficient size and called couches. These beds were mounted on very wide steps covered with rich carpets, and were hung with exquisite and costly stuffs; alcoves, supposed to be so much later an invention, were then in use. The chronicler of the quatre premiers Valois relates that in 1373 the Queen was seized with a dangerous illness. She seems to have been delirious, as he goes on to say that she lost her90 bonne mémoire, that the King, qui moult l’aimoit, made many pilgrimages about it, and that by the mercy of God and Our Lady she recovered her good health and good senses. In spite of his delicate health Charles often made these pilgrimages to holy places, walking barefoot with the monks.
In the early part of 1373 there were great floods, especially of the Seine, Marne, Yonne, Oise, and Loire. They lasted two months and were said to be the worst that had happened within living memory. The streets of Paris were full of water so that people had to go about in boats. From one gate to another the water flowed; it rose to the bridges and filled the lower rooms in the houses.
Several princesses of the French royal family had died within a short time—the Queen-dowager, Jeanne d’Evreux, of whose will and funeral an account was given in a former volume; Jeanne, Queen of Navarre, eldest sister of the King; the Princess Jeanne, daughter of Philippe VI. and Queen Blanche, who died on her way to Spain to marry the son of the King of Aragon. Also the old Prioress of Poissy, great aunt of the Queen, who was the Princess Marie de Clermont, daughter of Robert, Comte de Clermont, son of St. Louis. In early youth she had been betrothed to the Marquis de Montferrat. But she had set her heart on a monastic life, and she took the veil with the approval of her cousin Philippe le Bel, in the convent he had just founded at Poissy. She became Prioress, but having lost her sight she resigned that dignity, and died in May, 1372, at seventy-three years of age. It was, of course, afterwards91 that Marie de Bourbon, youngest sister of the Queen, was made Prioress of Poissy.
These were years of success and happiness for Charles and Jeanne. They had now four children, two of whom were sons. Prosperity was restored to their kingdom. The people trusted them, so that heavier taxes than those which caused riots under Jean and Charles VI. were paid without opposition by the subjects of Charles V., who knew that the affairs of the State were administered by able hands, and that the money so collected would be used for the defence and welfare of the country, not squandered on court pageants or unworthy favourites.
A truce was made with England, who had lost all the territories won from the late King, and restored to France by the wisdom of Charles le Sage and the valour of Bertrand du Guesclin.
Romance and poetry gather, as well they may, around the career of this heroic leader, the despised, neglected child of a poor Breton gentleman; who swept the English from his country, and died Constable of France, surrounded by his victorious troops, the keys of Châteauneuf-Randon, his last conquest, being laid upon his coffin. His father, a Breton noble, and his mother, who was proud and beautiful, considered their eldest son a disgrace to their family—for Bertrand was ugly, rough, and continually fighting and getting into mischief. Disliked and ill-treated at home he made his escape from his father’s château, and took refuge with an uncle and aunt, who received him with kindness, and with whom he remained. When he was sixteen or92 seventeen there was one day a wrestling match at Rennes, and being resolved to attend it he ran away from church, fought at the match and won the prize, but was so dreadfully hurt that he had to be carried back to the château of his uncle, where he was laid up for some time, during which his aunt, divided between her sorrow and uneasiness about his wounds and her anger at his disobedience, kept coming into his room, alternately reproaching and consoling him. Sometime afterwards there was a tourney at Rennes. Bertrand borrowed a horse and arms of his cousin and presented himself in the lists, challenging the first esquire who would break a lance with him. One of the bravest of the troop came forward, and was overthrown by him at the first shock. The next adversary who advanced was his own father. Recognising the arms of his house upon his father’s shield, Bertrand threw down his own, to the astonishment of all present, who attributed his doing so to fear. But he overthrew the next adversary and then raised his casque. His father embraced him, and his mother and aunt were filled with joy. His father then gave him everything he wanted for the outfit of a cavalier, and by his gallant deeds he soon rose to the height of fame. The story of his death in 1380, when besieging the castle of Châteauneuf-Randon in Gévaudan, as told by ancient chroniclers, is as follows: The Castle was to surrender the day after Du Guesclin died; Marshal de Sancerre summoned the Governor to give up the keys, but he answered that he had sworn to yield them only to Du Guesclin. Being told that he was dead, he replied, “Then I will93 lay them on his tomb.” The Marshal consented, the Governor, at the head of the garrison, issued from the castle, and passing through the ranks of the besieging army knelt before75 the body of Du Guesclin and laid the keys on his coffin.
Before he died Du Guesclin charged his captains to remember that in whatever country they made war, women, children, the poor and les gens de l’église were not their enemies. He had all his life been good to the weak and the poor.
The King and Queen showed all honour and affection to Du Guesclin.
Louis de Harcourt had been one of the foremost captains in the English war, and now came to Paris with the King’s brothers. Charles had suspected him sometime before of being in love with the Queen, and had regarded him with jealousy and anger in consequence, but having become convinced that he had been mistaken and unreasonable, que sans raison il avoit eu cette folle suspicion, he received him moult agréablement et joyeusement.76
While there can be no doubt that the court of Charles V. and Jeanne de Bourbon was much more orderly and more intellectual than those of the two first Valois kings, it does not seem so certain that it was equally amusing. It was stately and magnificent; comfort, luxury, and civilisation had greatly increased; there were splendid banquets, balls, and94 other entertainments, but the accounts of the daily life there, which have come down to us from that time, especially those of Christine de Pisan, who lived among the scenes she describes, show a very different state of things from the brilliant, reckless lives of pleasure and gaiety led by all who belonged to the Court of France in the days of Philippe de Valois and his son Jean.
The King got up at six or seven o’clock in the morning, and when dressed his breviary was brought him and he went to his oratory to hear mass; after which he gave audience to anybody who wished to ask him anything. In these interviews he treated everybody who approached him with the greatest courtesy and kindness. On certain days he then went to the Council Chamber, and at ten o’clock he sat down to dinner, music going on all the time of that repast. When it was over he devoted two hours to interviews with foreign envoys, or with any one bringing news from the seat of war,77 or of any other matters of importance in different parts of his kingdom. Then he went to lie down for an hour, and after that, one reads with a feeling of relief, that he allowed himself a little pleasure. Christine de Pisan takes care to explain that this was only in order that he might work better afterwards, but one may trust that this absurd suggestion was only an idea of her own, and that the mind of Charles was not so saturated with duty and dulness as she would imply.95 At any rate, he amused himself during this part of the day by looking at his books, jewels, and different collections, and talking with his friends. Perhaps the most intimate and the one he loved best was Jean de la Rivière. There is a note of a ring he gave him, with a ruby in it qui tient au violet.
Next, the King went to vespers and then out into his garden, where generally the Queen was with him, and where curious and beautiful things were often brought to them by the merchants. In winter he had different books read to him; stories from the Scriptures, philosophy, romances, &c., till supper, and during the rest of the evening he amused himself. Jeanne also had some one to read aloud to her while she was at dinner.
The King’s devotion to the Queen had never changed. From his boyish days at the court of his grandfather she had been the only woman he had ever loved. Without consulting her he would take no step of importance, and he cared for no pleasure she could not share. They lived, as Christine de Pisan says, en paix et en amour. Charles delighted in finding and giving her beautiful presents of jewels, curiosities, objects of art, or anything that he thought would please her.
Christine de Pisan describes with enthusiasm the way in which Jeanne held her court, the order and magnificence with which everything was arranged, whether in the daily life of her court and household, or in the splendid entertainments and ceremonies of state. She speaks of the beauty and dignity of Jeanne, as she appeared at these festivities, wearing96 her crown, her royal mantle of cloth of gold, or of silk covered with precious stones, and a girdle of jewels, accompanied by two or three queens (the two Queens-dowager, Jeanne and Blanche, and the Queen of Navarre), by her mother the Duchesse de Bourbon and by all the members of the royal family and court.
The peers of France in the time of Charles V. were as follows: Original peers ecclesiastical, called Clercs Ducs, i.e., the Archbishop of Reims and the Bishops of Laon and Langres; Clercs Comtes, i.e., the Bishops of Beauvais, Châlons, and Noyon.
Lay peers, i.e., Dukes of Burgundy, Normandy, and Aquitaine; Counts of Toulouse, Flanders, and Champagne.
But the King held in his hands the Counties of Toulouse and Champagne, and the following new ones had been created.
Comte d’Alençon, Duc de Bourbon, Comte d’Etampes, Comte d’Artois, Duc de Bretagne, Comte de Clermont and Roi de Navarre (as Comte d’Evreux).
The lay peers sat on the right of the King, the ecclesiastical on the left. New peers sat according to creation.78
That Charles should forbid private wars among the nobles was a matter of course. He also made a law forbidding games of hazard. He discouraged all books of licentious tendency and conversation of the same kind, and gave out that those who led scandalous lives would lose his favour and be dismissed97 from court. He was very angry with a young chevalier who had, as Christine de Pisan expresses it, “instructed the Dauphin in love and folly,” and forbade him to enter his presence, or that of the Queen and their children; but he does not seem to have been cruel or very severe. He would by no means allow either his nobles or any one else to condemn their wives to perpetual imprisonment if they were unfaithful to them, “considering the fragility of human nature,” and was with great difficulty persuaded to allow of their being kept under restraint if their conduct was too outrageous.
On one occasion his barber, who was shaving him, kept putting his hand in the pouch or purse the King wore at his side and taking out money. Charles saw what he was about and forgave him; but he repeated his offence twice or thrice. The fourth time, the King dismissed him but would not allow him to be put to death, as by the laws of that time he was liable to be; because he had served him so long. Another time, “it was in the time of the pestilence, before he was crowned,79 as he was entering Paris with a great company, after a great commotion in the town which had been against him,” as he passed through a street one of the rabble cried out, “By God, Sire! if I had been believed, you would not have come in; but they will not do much for you.”
The Comte de Tanquarville, who rode before the King, wanted to go and put the fellow to death, but Charles restrained him, only answering with an indifferent smile. “They will not believe you, beau98 sire.” On being told by some of the princes that he was too easy and too ready to grant pardons, by which he encouraged crime, he replied that he would much rather be too indulgent than too severe. He was exceedingly charitable both to the convents and to the poor and unfortunate of all classes, and gave away an immense amount of money.
The government of Languedoc had been entrusted by the King to the Duc d’Anjou, the eldest and perhaps the worst of his brothers. But his rule was so cruel and oppressive, and such commotions arose from it that Charles interfered; forbade the executions and punishments ordered by the Duke to be carried out, and took the government of the province away from him. The two elder of the King’s brothers were a continual source of uneasiness to him. Believing from his delicate health that his own life would not be a long one, he felt a dread that was only too well founded of what would happen if in the event of his death the kingdom and the Dauphin should fall into their hands. He did what he could to obviate this contingency. He fixed the majority of the Dauphin at fourteen years of age. He gave the guardianship of him and his brother and sisters to the Queen, her brother the Duc de Bourbon, and his third brother the Duc de Bourgogne. The Duc d’Anjou, though he was to be regent, was to swear on the gospels and holy relics to govern loyally for the welfare of the kingdom and his nephew, and was to have no jurisdiction over the town and vicomté of Paris, the towns and baillages of Melun and Sens, and the whole of the duchy of Normandy, which were to99 be administered for the King by his guardians and a council; he also regulated the fortunes of his younger children. The Princess Marie was betrothed to Guillaume de Bavière, Comte de Hollande, et de Hainault, eldest son of the Duke of Bavaria, and the Princess Isabelle to Jean, Duc d’Alençon. The crowns or coronets for these little princesses and several other of their possessions appear in a list made by order of their father.80
In December, 1377, the Emperor Charles IV. came on a visit to the King and Queen. Preparations for his reception were made on the grandest scale. He arrived at Cambrai on Tuesday before Christmas with his son, the King of the Romans, was met by a body of nobles and cavaliers sent by the King to welcome him and entertained by the Bishop. The next night he slept at the abbey of Mont St. Martin. The Duc de Bourbon, the Comte d’Eu, cousin of the King, and the Bishops of Beauvais and Paris came to meet him at Compiègne with three hundred cavaliers in blue and white, the Duke’s colours. The Duc de Bourbon entertained the whole company at supper and the next day, at Senlis, the Emperor was met by another array of cavalry with the Dukes of Burgundy and Berry. As he had been seized on the way with an attack of gout, the King of France sent a litter drawn by mules and “noblement appareilliée”81 belonging to the Queen, which the Emperor received with great satisfaction and in which he travelled to St. Denis. There he was met by a train of prelates and dignitaries who accompanied him to the famous100 church, into which, as he was not well enough to walk, he caused himself to be carried and offered his prayers before the altar of St. Louis. He was then carried to his room and his suite were supplied by the Abbot with “great fish, beef, mutton, rabbits, fowls, fodder for their horses, and abundance of wine.” Many presents were brought by the people of the town, and the Emperor when he had rested was carried to the treasury of the abbey, where priceless collections of relics, crowns, and gems were displayed before him. The robes, crowns, jewels, and everything of the kind used at the coronations were kept by the Abbot and monks of St. Denis.
The Emperor spent that day in the Abbey, and rose very early the next morning, January 4th, as on that day he was to go to Paris. But before he set off he was carried again into the church, where he asked to see the tombs of the kings, especially of Jean and of Philippe de Valois and his wife, Jeanne de Bourgogne. For he was the son of the gallant King of Bohemia, who died at Crécy; his sister, Bonne, was the first wife of Jean, and he himself had been brought up in the court of Philippe de Valois and Jeanne de Bourgogne. As he remarked, “his youth had been nourished in their hostel and much good they had done to him.”82 And he called the Abbot and monks and begged them to pray to God for the “bons seigneurs et dames qui gisoient là.” Then, with much state and ceremony, he began his journey to Paris, to visit once more the splendid scenes of those far-off101 days and the children of those, who had been the friends and companions of his youth. And he said that more than any creature on earth he desired to see the King and Queen and their children, and then let God take him, for he would willingly die.
The Emperor got out of his litter and entered Paris mounted on a black horse richly caparisoned with the arms of France, sent him by the King his nephew, who came out to meet him mounted on a tall white charger wearing a scarlet robe, mantle and hat covered with pearls, with a great train of nobles and chevaliers gorgeously dressed attended by their followers wearing their liveries, the officers of the households of the King and the Dauphin in immense numbers dressed according to their grades. The King had sent a proclamation the day before that no one should dare (que nul ne fust tant hardi) to take up the space in the grant rue by coming to the palace with carts or people, and no one should move from the places where they had put themselves to see the King and Emperor pass. None were allowed to come into the town, and many of the inhabitants had to stay outside in the fields, while sergeants-at-arms were posted in the streets, and thirty of them with swords and maces rode before the King’s bodyguard. The King of France, the Emperor and the King of the Romans rode into Paris side by side in this magnificent procession, and it was three o’clock when they arrived at the marble steps of the palace, when the Emperor, who could hardly hold himself up from the gout, was placed in a chair covered with cloth of gold and with much honour and102 ceremony conducted to the apartment prepared for him.
It would be too long in a work like this to give the details so minutely described and so interesting to the student of history, of the proceedings of the next few days, during which the Emperor remained the guest of the King of France, of the banquets with five dais one above another in great halls where windows, ceiling, and columns were hung with cloth of gold, of the profusion of the feasting, of the spectacle of the conquest of Jerusalem in the vast hall of the Palais de la Cité, of the entertainments at the Louvre, Beauté and Vincennes, offered by the King to the Emperor. It will be sufficient to relate what is perhaps the most interesting event of his sojourn in Paris, his visit to the Queen at the hôtel St. Paul on Sunday, January 10th. The Emperor, accompanied by the King of France, went down to the quay near the Louvre, where they embarked on the King’s barge and proceeded by water to St. Pol, where they landed. They were met in the middle of the court by the Dauphin and his brother Louis Comte de Valois, who knelt before the King and then went to salute the Emperor. The latter took off his hat, kissed the two boys, and was carried on in his chair through such a throng of seigneurs, knights, and people of the Court that the chair could hardly pass, to the salon of the Queen, who was in the midst of a great assemblage of princesses and ladies of the court. As he sat by the Queen the Emperor kept asking for her mother, the Duchesse de Bourbon, Isabelle de Valois, the sister of his first103 wife and friend of his sister Bonne, Duchesse de Normandie, whom he had known so well in the old days at Paris and Vincennes. She had withdrawn to the end of the great room out of the crowd, but when she was told that he was anxious to see her she came up to him.
Then for a moment they looked at each other in silence. The memories of bygone days, of their own youth, of the forms and faces of the dead came back to them and they both burst into tears, so that, as the chronicler says, “it was a piteous thing to see.”83 Finding it impossible to carry on any conversation then, they deferred it till after dinner. After the Emperor had rested in the apartment of the Dauphin, which had been prepared for him, the Kings of France and of the Romans dined, wine and dessert were served, and the banquet was in the great Salle de Sens. Then Charles V. retired to his own rooms; his brothers with the King of the Romans, who wanted to see the lions, went to find Louis, Comte de Valois, who probably wished to go with them, and the Duchesse de Bourbon came to the apartment of the Emperor, her brother-in-law. For a long time they sat together, talking of old times, as people will who were companions in childhood after being separated for half a lifetime. Later on they were joined by the Queen and her two little sons, and they all stayed with the Emperor till the hour of vespers.
They brought him two beautiful dogs with the golden fleur-de-lis on their silken collars, and he gave the Queen a gold reliquary.
104 Towards evening the King came to fetch the Emperor as they were going down to Vincennes and Beauté, whence the latter was to take his departure.84
It was the last fête of the court of Jeanne de Bourbon. For less than a month afterwards, on the 4th of February, at the hôtel St. Paul, she gave birth to a daughter, “dont moult fut grevée de travail.” To allay the violence of the fever with which she was seized the Queen insisted on being put into a cold bath, after which she became alarmingly ill. The child was hastily baptized by the Bishop of Paris and called after her mother’s favourite Saint Catherine. All her life Jeanne had desired to die before her husband, and said she hoped she would never live to be regent. She had her wish,85 for she died in the King’s arms February 6, 1378, about two hours before midnight.
The little Princess Isabelle died a few days after her mother, and was buried by her side at St. Denis.
Jeanne de Bourbon was one of the most charming and spotless characters in history. From her childish marriage to her death she does not seem to have had an enemy or a word of blame ever attached to her. She was always spoken of as “la belle duchesse” or “la bonne reine.” Charles was inconsolable. He never had the frank, open nature nor the graceful charm of manner that made some of the princes of his house adored by their friends and subjects. Quiet and reserved, he was a105 man of few but deep and lasting friendships and affections, and he was capable of a deathless love. The loss of Jeanne broke his heart. From that day his life was over. He never regained either health or spirits, but died rather more than two years after at his château of Beauté at the edge of his beloved forest.
Isabelle de Valois, Duchess-dowager de Bourbon, took charge of her granddaughters and retired into the convent of the Cordelières at Paris, where she ended her days.

The House of Wittelsbach—Stephan von Wittelsbach and Taddea Visconti—Birth of Isabeau—Negotiations for her marriage—Her journey to Brussels—The fair of Amiens—Her interview with the King—Her wedding—Charles and Louis de France.
 During several years after
the death of Jeanne de
Bourbon no Queen sat on
the throne of France, for
her son succeeded as a
child of twelve years old.
And it would have been
difficult to find two kings and queens more totally
unlike each other in every respect than Charles le
Sage and Jeanne de Bourbon, “the sunshine of
France,” were to their son and daughter-in-law,
Charles VI. and Isabeau de Bavière.
During several years after
the death of Jeanne de
Bourbon no Queen sat on
the throne of France, for
her son succeeded as a
child of twelve years old.
And it would have been
difficult to find two kings and queens more totally
unlike each other in every respect than Charles le
Sage and Jeanne de Bourbon, “the sunshine of
France,” were to their son and daughter-in-law,
Charles VI. and Isabeau de Bavière.
An intelligent woman of my acquaintance once108 remarked, on being asked whether she considered women to be better than men, “Oh, certainly! Much better. I know several good women, but I only know one good man.”
It might appear as if some idea of the kind pervaded this and a former volume, in which, with the exception perhaps of Charles V. and Louis XII., none of the Kings of France treated of can be exactly so described; whereas the talents, beauty, and goodness of the Queens seem generally made evident. But all the researches into the history of their times, from which these records are drawn, seem to prove that during the eight reigns in question most of the Queens of France really were distinguished for their excellent qualities, and that except the unlucky Charlotte de Savoie they were all more or less good-looking; Blanche de Navarre, Isabeau de Bavière, and Marie d’Anjou being remarkably beautiful; and that at any rate Blanche de Navarre, the three Jeannes, wives of Philippe de Valois, Jean and Charles V., and Anne de Bretagne, were highly cultivated women, possessing superior talents and strongly-marked characters. In Isabeau de Bavière we find an entirely different personality.
Stephan I., Duke of Bavaria, of the ancient house of Wittelsbach, died in 1375, leaving three sons, between whom he divided his dominions, and from whom descend the three lines of Ingolstadt, Landshut, and Munich.
The strongest ties of affection and friendship united these three brothers, who however, seem to have borne little resemblance to each other.
Stephan of Ingolstadt was short in stature, but good-looking, high-spirited, and full of romance, his chief delight being in love-making and warlike adventures. Friederich of Landshut, a brave, wise, able prince, was by far the most capable member of the family, while Johann, a rough and fearless sportsman, led a wild, jovial life in his own court and castles, which he filled with huntsmen, hawks, dogs, and horses.86 From him descends the Munich line of Bavarian princes.87 Johann took a German wife, but Stephan and Friederich married Taddea and Maddalena, daughters of Bernabo Visconti, one of the chiefs of that family so renowned for splendour, power, and cruelty, then ruling in Milan. After a few years Taddea died, and left Stephan with a son and daughter named Ludwig and Isabeau, or Elizabeth. The latter was born at Ingolstadt 1370 or 1371. By his second marriage he had no children.
In all Germany, and perhaps in all Europe, there is not a more beautiful country than Bavaria, with its lakes, mountains, forests, and ancient castles. Here Isabeau spent her short childhood, idolized by her father and brother, flattered and spoiled by all around her, for her extraordinary beauty was the admiration of the court. It was a brief childhood, for she was only about twelve years old when the first negotiations for her marriage with the King of France were begun. Her uncle, Friederich of Landshut,110 was serving in Flanders with the French against the English army in the year 1383, just at the time when the uncles and guardians of the young Charles VI. were looking for a wife for him, and as his father, the late King Charles V., had desired that he should be married to a German, and thus secure an ally to France against England, they were hesitating between the daughters of Austria, Lorraine, and one or two others that had been suggested, and inquired of Duke Friederich whether there were any marriageable princess of his family who would be suitable.
Friederich was naturally anxious not to let slip the chance of the crown of France for one of his house; so he explained that, although he had no children of the right age, his brother, Stephan, had a daughter in all respects suitable, being extremely beautiful and about two years younger than the King, and he lost no time in writing to inform his brother of the splendid prospect which seemed to be opening before them. But Duke Stephan, less ambitious than his brother, was in no way elated by this proposal. He replied that, in the first place, he did not like unequal alliances, and between himself and the King of France the difference was too great; neither did he wish his daughter to go so far away, but would prefer to marry her to some noble of his own country; besides which objections, there existed a custom that a prospective Queen of France should, like candidates for the army in our own days, pass a sort of medical examination which was conducted by certain matrons chosen from among the ladies of111 highest rank at the French court; and to this the Duke refused to consent. He declared that he was not going to allow either himself or his daughter to be made ridiculous by sending her to France on an uncertainty, or to risk the affront of her being rejected. She should stay in her own country and marry some one nearer home. So, for the time, the negotiations were broken off.
It was indeed most unfortunate that the very sensible decision of Stephan was not adhered to, and also that in the one and only case in which the Dukes of Berry and Burgundy carried out the directions of the late King, their brother, the result should have been so deplorable. In all other respects they disobeyed his injunctions. They brought up his sons in opposition to his wishes, they wasted the treasure he had taken so much time and care to collect, they impoverished the people by their extortions, and incensed them by their misgovernment, so that they were fast bringing France back to that state of anarchy and misery from which she had been rescued by the wise rule of Charles V.
If Isabeau had stayed, as her father wished, at his comparatively simple court and married some German noble, it would probably have been much better both for France and herself; but this was not to be, for the rest of the family and connections of that young princess strongly disapproved of the decision of Duke Stephan, and used all their endeavours to prevail upon him to alter it. For many generations the numerous members of the house of Wittelsbach had married into all the royal and ruling families of112 France, Burgundy, and Flanders. Amongst others, the Duchesse de Brabant was a relation of theirs and was most anxious for the marriage.
In 1385, the wedding of a Bavarian prince with one of the daughters of Philippe, Duke of Burgundy, was to be celebrated with great pomp and rejoicings at Cambrai, in the presence of the King and the whole of the French court. During the festivities the Duchesse de Brabant took the opportunity of reopening the subject with the King’s uncles to whom she pointed out all the alliances and advantages it would bring. The princes were willing to agree to it; for they had not yet decided on a wife for their nephew. A daughter of Lancaster had been suggested, but this was not approved of, and they were still hesitating between an Austrian archduchess and a princess of Lorraine, having, as they said, received88 no further communications from Bavaria. The duchess promised to see about it before the end of the summer. The Duke of Burgundy, himself closely connected with the house of Bavaria, was the chief supporter of this alliance and entered warmly into the plans of the Duchesse de Brabant, who succeeded in overcoming the objections of Stephan and persuaded him to allow his daughter to pay a visit to her and to the Duchesse de Hainault, also a relation, and then to go with them to the fair of Amiens, where she would meet the King. Her uncle, Duke Friederich was to take her, and in order to avoid anything compromising to her dignity, she was to go on the pretext of a pilgrimage to the shrine of Saint Jean d’Amiens,113 where a famous relic was exhibited during the time this fair was going on. A painter was sent to paint the portraits of the three princesses, i.e., of Lorraine, Austria, and Bavaria. The portraits were shown to the King, who at once chose that of Isabeau. It still hangs in the gallery of the Louvre. She wears a red robe trimmed with fur, a tight corsage partly of blue velvet and a high headdress ornamented with gold and jewels.
It was early summer when Isabeau took leave of her father and her country, and set off with her uncle upon her journey. They travelled first to Brussels, where they were warmly received by the Duchesse de Brabant with whom they stayed three days, and then went to Quesnoy to stay three weeks with the Duchesse de Hainault; of whom Froissart remarks, “La duchesse qui fut moult sage, endoctrinait tous les jours, en toutes manières et contenances, la jeune fille de Bavière, quoique, de sa nature, celle-ci estoit propre et pourvue de sens et de doctrine; mais point de françois elle ne sçavoit.”
They also made considerable changes in Isabeau’s dress, which they declared to be far too simple for the future Queen of France. The Duchesse de Brabant ordered an entirely new trousseau for her so that she might be dressed as magnificently as if she had been her own daughter, and having arranged all this she went to Amiens, where she was joined by Isabeau under the care of the Duchesse de Hainault and her uncle, Friederich of Landshut.
The fair of Amiens, which took place every year was one of those mixtures of amusement and devotion114 so characteristic of the Middle Ages. The relic, which they declared to be the head of St. John the Baptist, had been brought from the siege of Constantinople by the Crusaders in 1204; and given by a gentleman of Picardy to the church of St. Jean d’Amiens, of which one of his brothers was a canon. It was always shown at the time of the fair, to which all classes came in crowds. One can form no idea of the splendour and picturesqueness of these mediæval fairs from the squalid spectacles that survive in our own days.
For what do we see now? Uninteresting but harmless crowds, mostly clad in cheap, tasteless imitations of the dress of a higher rank, pressing into shows which one cannot imagine anybody wishing to see, surrounding long rows of monotonous booths filled with ugly, commonplace goods that one cannot imagine anybody wishing to buy, committing no crimes and molesting nobody. But although very few modern fairs in civilised Europe offer anything worth buying or seeing, they were widely different in the Middle Ages. In many towns important fairs took place every year to which people went properly attended and protected, and where beautiful and valuable things of all kinds were to be sold. There the merchants brought jewels, embroideries, and costly stuffs from Italy and the East; pictures, illuminated missals, stamped leather, rich carvings in wood and ivory; delicately wrought cups, flagons, bowls, and other precious works of the gold and silver smiths; weapons of war, objects of art, and curiosities of every description. All sorts of shows and diversions115 were also going on all day and far into the night, which was the time the King and court usually went. It was a wonderful sight: the fitful glare of torches thrown here and there on the booths loaded with costly wares, while mingling in the throng around might be seen gleaming armour, magnificent dresses of silk and velvet, leather jerkins, tall caps, and peasants’ coarse woollen gowns and tunics; dark gabled houses forming a shadowy background. Now and then a fierce quarrel would arise, and there would be a rush and scuffle of armed men, the glitter of swords and daggers, shouts, cries, the fall of some and the dash of others down the dark, narrow streets which afforded their best chance of escape. The most famous of the old French fairs were the Foire de Lendit, or Landit, held between Paris and St. Denis, and perhaps the most ancient of all,89 the fairs of St. Denis and St. Germain, which belonged to the Abbot and monks of St. Germain-des-Près, and was held in the celebrated Pré-aux-clercs, a great meadow or open space going from the Abbey to the Seine. The fair of Amiens was a great resort of all classes at that time, and when Isabeau with her uncle, Duke Friederich, and the Duchesse de Brabant arrived at its gates the town was thronged with people. The King was there with his court and a great array of nobles and ladies, besides numbers of ecclesiastics, merchants bringing their goods on long trains of mules, bourgeois and peasants, wandering minstrels and soldiers, so that the whole place was a scene of bustle, excitement, and festivity, which may well have116 delighted a young girl scarcely out of childhood longing for all the pleasure and magnificence so soon to be laid at her feet. For the King, ever since his uncles had shown him the portrait of Isabeau had not ceased to torment them to let him see the original, and as soon as he heard that she was really close at hand he sent two of his favourite chevaliers, the Seigneurs de la Rivière and de la Tremoille, to receive and conduct her with her relations and suite to the lodgings prepared for them, and assure them of his eagerness for the interview which had been arranged to take place on the following day.
The Duchesses and Isabeau were delighted at all they heard from the two chevaliers of the King’s anxiety and impatience, which promised well for the success of the plan; the beauty of Isabeau being far too striking to leave much doubt of the effect it would produce on a romantic, impressionable lad, who had already fallen in love with her picture.
The next day, Friday, the young princess was magnificently dressed, the Duchesses of Burgundy, Brabant, and Hainault, presiding at her toilette, after which she went with them to the King’s reception.
Charles, who had lain awake all night thinking about her, turned eagerly towards the door as Isabeau entered, and all eyes were fixed on her with interest and curiosity as she passed through the throng of courtiers. It must have been a trying moment for her, though if she felt nervous she did not show it, but only stood in silence before the King, who hastily prevented her, as she was about to bow or kneel117 before him, and raised her up with passionate admiration. All the evening he could not take his eyes from her, and after she had left and the reception was over no one felt any doubt of the result. The Duke of Burgundy told La Rivière, who was going with the King to his room, to find out while he was undressing what he wished to be done. Charles replied: “Tell my uncle, the Duke of Burgundy, to make haste and conclude the affair.”90

The Duke of Burgundy therefore went to the lodgings of the Duchesse de Brabant and Princess Isabeau, and the arrangements were concluded. The Duke, at the council, wished the wedding to be at Arras, but the King declared he would not have any more delay, as he could neither sleep nor rest. He sent the Princess a splendid crown, and the wedding was celebrated at the cathedral of Amiens a few days afterwards, in presence of the whole court, and followed by banquets and various festivities, which lasted for some days. The wedding was so hurried on that there was no time to finish the trousseau ordered for the young queen.91 And thus were two spoilt, self-willed children of fourteen and sixteen placed118 at the head of what, in those days, was the most powerful kingdom in Christendom.
Many people who have a slight acquaintance with French history picture to themselves Charles VI. as the miserable invalid he became in later years, and know nothing about the tall, handsome young Prince, high-spirited, passionate, generous, and as eager for glory, as fond of pleasure, magnificence, and love-making, as his great-grandfather and grandfather the Kings Philippe and Jean, and his great uncle, Duke Philippe d’Orléans. To their own father, the sickly, studious Charles V., who hated riding, war, and rough games, but in whose reign, nevertheless, the English invaders were driven out of France and the French navy re-established; neither Charles VI. nor his young brother Louis bore the slightest resemblance, except that Louis had inherited, with the beauty and gallant grace of the Valois, the love of books, art, and study, which distinguished Charles V.92 By far the most brilliant of the two brothers, he had been, at the time of his father’s death, too young to give much indication of what he would turn out like; indeed about the only details mentioned respecting him are his beauty and the admiration it excited at the last great pageant of court,93 where just before his mother’s death the Emperor was so splendidly received and entertained; and the devout way in which he used to say his prayers, kneeling before the image of the Virgin. But the hasty, impetuous temper of Charles, his incapacity for any serious study, his excitable,119 unstable temperament, his passion for pleasure and display, had been an anxiety and grief to his father, who recognised in the boy all the qualities, attractions, and faults of his race, which had already been so fatal to France. In fact, as it often happens, the lad was everything his father did not want him to be, and Charles V., as long as he lived, used every means in his power to counteract the tendencies which he considered so dangerous. He forbade any love-stories to be told to the Dauphin, and when on one occasion one of the gentlemen of his household disobeyed this order, dismissed him.94 He gave him the best tutors that could be found, and tried to influence and educate him by constant supervision. At the earliest age his tutor observed his delight in anything that had to do with war, and his father, probably seeing that he would never make a scholar or statesman, and thinking that he might perhaps become a great leader and soldier, encouraged this taste. One day he showed him the royal treasury of crowns, jewels, and objects of inestimable value, telling him to choose whatever he liked for himself. The child looked around and pointed to a sword which hung up in a corner of the room, and which was given to him accordingly. Some days afterwards, at a state banquet, the King caused to be placed before him a soldier’s casque and a magnificent crown of gold and precious stones, asking which he would like best—to be crowned King with the one, or to wear the other amidst the dangers of war. Without hesitation the Dauphin replied, “Monseigneur,120 I like the casque better than the crown.” This answer delighted the nobles, who, amidst acclamations of loyalty, swore to serve and defend the boy whenever he should become their King, after which Charles V. ordered the casque and sword to be hung up by the Dauphin’s bed, and a little suit of armour and weapons to be made for him,95 that so gallant a spirit might be encouraged. If Charles V. and Jeanne de Bourbon had lived to look after their sons it seems most likely that the ruin and misery which fell upon them and upon France might have been averted.
For many years Charles V. had felt sure that his life would not be a long one; but his hope was that the Queen, who had good health, would survive him and would be guardian to the children, her brother, Louis de Bourbon—called “the good Duke Louis”—being always at hand to help her. After the irreparable calamity of her death, and finding his own health rapidly breaking up, he did what he could for his children by making the Duc de Bourbon guardian to the young King and his brother, and by preventing the Duc d’Anjou, who, as the eldest of his brothers, had to be regent, from having more power than he could help. The Ducs de Berry and Bourgogne were also joined in the government of the country and the young princes. With many misgivings he entreated them to carry out his directions and to bring up the King properly; nearly his last words to them on the subject having been, “Soignez-le, mes frères, et prenez grande attention de121 le bien former à la royauté, car l’enfant est jeune et de l’esprit léger.”96
Those princes did nothing of the kind. It is true that the Princess Catherine was given into the sole charge of her grandmother, the old Duchesse de Bourbon, who since the Queen’s death had lived a saintly life at the convent of St. Marcel; but Charles and Louis were brought up together at the hôtel St. Paul in an atmosphere of flattery, folly, and corruption, which was eventually fatal to them both. The three brothers of the late King were eager to secure for themselves all the power and wealth they could seize, and would not listen to the Duc de Bourbon, who, as personal guardian only, and not a brother of the late King, had less power and could not oppose them. The lives led by the two boys were what in our own days would be called fast for a man ten years older, and eventually resulted in the madness of Charles and the death of Louis. The aim of their uncles was to keep them ignorant, so that the reins of government might remain as long as possible in their own hands. In this they only partly succeeded, as Louis was very clever and fond of study, but Charles hated books, application, or restraint of any kind. They both rode well and were good at all sorts of games and sports, and the people, who had respected Charles V. and adored Jeanne de Bourbon, now bestowed all their affection on their young King, who was called Charles le Bien-Aimé. To the end of his unfortunate career he never lost either this name or122 the affection of his people, for although he was hot-tempered and imperious, so that he would never bear the slightest opposition, he was brave, open-handed, kind-hearted, and had those free, pleasant, courteous manners that go farther in gaining friends—everywhere, but most especially amongst the lower classes—than a host of benefits and virtues. He was very faithful and affectionate to his friends, never forgot the names of the humblest people,97 but was always polite and ready to talk to any one about anything.98 And amidst the roughness and cruelty of the times it is interesting to come upon the note of a sum paid to Colin le serrurier for an iron fleur-de-lis to hang upon a stag, which had been hunted by the King, had taken refuge in a stable at Choisy, and had been allowed by him to return to the forest—an example of mercy which might well be placed before many people in the present day who ought to be civilised enough not to require it.
The King’s marriage and the beauty of Isabeau delighted the people, and if she had possessed the sense, talents, and good qualities of other queens whose histories have been recorded in these volumes, a great career would indeed have been open before her. Advised and supported by the Duc de Bourbon and the old friends and counsellors of Charles V., she could have retained her influence over the King and held the reins of government when they dropped from his hands. The voice of the nation would have123 been with her, for it was weary of the oppression and cruelty of the princes; and most of the fierce feuds and bloodshed that came from the incapacity and vices of all the chief members of the royal family need never have happened.
The Royal Family and Court of France—Birth and death of Charles and Jeanne de France—Dress and amusements—The Abbey of St. Denis—Knighthood of the King of Sicily—The ball—The Duchesse de Berry—Valentine Visconti.
When Isabeau arrived at the French court the chief members of the royal family were the King, his brother Louis, Comte de Valois, and Duc de Touraine, who, though only fourteen, was already a soldier, having fought at the King’s side in the battle of Rosebecques, in Flanders, when he was scarcely twelve years old, wearing a small suit of armour he had insisted on having made on purpose; and the little Princess Catherine,99 who lived with her grandmother at St. Marcel but came often to Vincennes and the other palaces of her brother. Next in rank were the two uncles of the King, the Dukes of Berry and Burgundy, who, with the Duc de Bourbon, were now regents and guardians of the King and kingdom, for the Duc d’Anjou had been125 adopted as her heir by Giovanna, Queen of Naples and Sicily, and had left France for his new inheritance two or three years before. Chief among the princesses were the famous Queen Blanche of Navarre, widow of Philippe de Valois, the King’s great-grandfather; Blanche, Duchesse d’Orléans, widow of Philippe, the King’s great uncle, and daughter of Charles IV., the last king of the elder Capétienne House; and Marguérite, Duchesse de Bourgogne, the heiress of Flanders, wife of the last Capétien and the first Valois Dukes of Burgundy.100 In the case of the two last-named princesses, Charles left his young wife at Creil when, a few days after their wedding, he started for Flanders to make war upon the contumacious city of Gand, or Ghent. He returned in September and conducted the Queen to Paris; but they did not then make a state entry into the capital, as was usual on such occasions.
Although the majority of the King had been fixed at fourteen years by his father, who considered a boy at that age a less objectionable ruler for France than the Dukes of Berry and Burgundy; they had managed to keep the government in their hands until now. But Charles was exceedingly tired of their interference and strongly urged on by Louis and Isabeau, resolved to get rid of them. He observed one day to his brother: “Beau frère, il est temps que je gouverne comme a fait mon père, et je ne veux souffrir mie l’autorité et volonté des beaux oncles126 de Berry et Bourgogne le peuple aussi trop fort s’en plaint et souffre de leurs faits.”101 And shortly afterwards he informed his two uncles, much to their consternation, that he intended for the future to govern his own kingdom. But he took care to keep with him his uncle Louis, Duc de Bourbon, whom he loved. The frank, loyal, affectionate, and sympathetic nature of the Duke, his chivalrous tastes, and the really paternal care with which he had watched over his nephews, had won their warmest affection102; and now that his influence was no longer weakened by their other uncles, immediate reforms were the result of his wise counsels. Taxes were reduced, certain corrupt officials dismissed, a truce of three years was made with the English, the trusty Juvenal des Ursins was made provost of Paris, and all these measures were received with unqualified approval throughout the kingdom.
The extravagance of the court, and especially of the royal family, prevented any improvements of this kind from lasting long. No queen before her had ever been consumed by such a passion for dress, luxury, and pleasure, as Isabeau de Bavière; never had such boundless extravagance been seen, even at the brilliant court of the Valois.103 Towards the end of September of the year after the marriage of Charles and Isabeau, a son was born to them at the château de Beauté, the favourite resort of Charles V., on the edge of the forest of Vincennes. The birth of the127 Dauphin was, as usual, received with acclamations, and proclaimed by couriers all over the kingdom. It was also usual on such occasions that the King and Queen should endow churches, remit taxes and debts, and distribute alms to the poor. But they did none of these things, and when, shortly after, the little Dauphin Charles died, every one said that was the reason, especially as during all that autumn there were frightful storms, and it was said104 that many crows had been seen flying about, dropping hot ashes from their beaks on the thatched roofs of barns, of which many were set on fire.105
It was the eve of the Holy Innocents when the Dauphin died, and he was carried that night by torchlight, with a grand procession of nobles, to St. Denis, and buried there in the chapel of his grandfather, Charles V. A daughter was Isabeau’s next child, born at the Louvre in 1387. She was called Isabelle, and married Richard II., King of England. In 1388 was born a second daughter, Jeanne, at the Maison Royale de St. Ouen, à l’heure de prime. She died in infancy.
In his interesting study of Isabeau de Bavière, M. Vallet de Viriville says that in the portrait painted of her in 1383 we see a young girl “qui rayonnait d’innocence: telle elle était sortie des mains de l’universel auteur,”106 and goes on to ask by what means she could have fallen from such a height to such a depth of infamy. But it seems improbable128 that this description could ever have applied to Isabeau de Bavière. Except that she was remarkably beautiful, we hear very little about her childhood. The chroniclers of her father’s court indeed said that she possessed admirable beauty, elegant manners, and exquisite virtue. But at the time this was written, Isabeau was probably twelve or thirteen years old; and could hardly have done any great good or harm. During her whole career, beginning at the day when, at fourteen years old, she became Queen of France, there does not seem to have been any great difference in her way of going on; by which we may gather that she was one of the sort of women one meets every now and then who are always surrounded with a turmoil of quarrels, discredit, and difficulties caused by themselves, into which everybody who goes near them is sure to be drawn. We meet them in novels, we meet them in history, we meet them in real life; and when we do, we know that there will be no more peace till they are gone. But, fortunately, we do not meet them as powerful and irresponsible rulers, like Isabeau de Bavière. And we can perhaps imagine what a calamity such a head of society was for France.
Inordinately vain, selfish, capricious, too shallow either really to love or hate, extravagant and yet avaricious, with no sense and no scruples, this young girl, scarcely out of childhood, not knowing a word of French, and having been brought up in the distant castle of a Bavarian noble, was suddenly placed at the head of the court of France, the gayest and most splendid in Europe, with every one at her feet, her will129 supreme except for the nominal control of a dissipated, extravagant boy only two years older than herself, and very much in love with her. Isabeau began by introducing many foolish and exaggerated fashions in dress which, with all their richness, had neither the grace nor the distinction of the costume of the last two or three reigns. For instance, she increased the height of the tall headdresses called hennins so enormously that those who wore them could not get through the doors without stooping; some of them also had horns. Very long pointed open sleeves were worn, large wide sashes of silk or cloth of silver, and a surcot, which was a sort of garment something like a chasuble. Sometimes the surcots had slits and openings to show the dress underneath, of which the preachers loudly complained. These surcots had been worn in the former reigns. Dogskin and chamois-skin boots and gloves lined with fur were also worn. One of the court costumes was a surcot open at the sides and a corsage of cloth of gold.107 Evening dresses were worn for the first time open at the neck and bosom, and arms were no longer blazoned upon the robes.
As to men’s dress, the Valois had made a great change about the middle of the fourteenth century. Long tunics were quite done away with, and they now wore short doublets and justaucorps reaching to the knee, hoods with long points hanging down to the loins, round or pointed hats with plumes and brims looped up behind, cloaks with scolloped edges, open in front or behind, chausses, a kind of stockings of a130 different colour for each leg and sometimes with soles to them instead of shoes. Shoes were still worn with points to the toes.108
The doublets and justaucorps were of silk or velvet, and sometimes padded with wadding so as not to wrinkle; and worn with jewelled girdle, dagger, and purse. They cut their hair short, and wore pointed beards. Charles VI. wore short jackets with large sleeves and short tunic. One of the most costly, fashionable, and, it would seem, comfortable garments was the houppelande, worn both by men and women. This was an enormously long trailing robe or mantle with loose sleeves, made of cloth, silk, or velvet, and trimmed with fur and rich embroideries; high collar and gold chains.109 It had not hitherto been customary for the King himself to take part in the games and sports which were the delight of the court, but Charles who had of course as Dauphin been too young to ride in joustes and tournaments, had no idea of being for ever deprived of his favourite amusement, but distinguished himself in the lists like the other young chevaliers of his court.
The King’s uncles (brothers of Charles V.) were, as has been before observed, most deplorable guides and guardians to their nephews and France. The Duc de Bourgogne was by far the best, as he had many noble qualities, and his overwhelming pride and ambition were at any rate not unsuitable to a great soldier and the most powerful prince in France. The favourite son and brother of the two last kings, he had stood131 by his father’s side at Poitiers at thirteen years old, fighting to the last, had been carried prisoner with him to England, and had been rewarded by the promise of the duchy of Burgundy, which was accordingly conferred on him by his brother, Charles V. At the coronation of his nephew, he had insisted on taking precedence of his elder brother, the Duc d’Anjou, much to the indignation of that prince; as he contended that the duchy of Burgundy made him the premier peer of France. He had married the heiress of Flanders, widow at eleven years old of Philippe de Rouvre, Duc de Bourgogne, and with that haughty and determined princess he lived on terms of such unbroken affection and confidence as to be the wonder of the court. He was much influenced by her, and, unlike most of the princes, no illegitimate child was ever recognised as his.110
The Duc de Berry, without the great qualities of his brother, was greedy after money, and a cruel oppressor of the people, but he spent what he wrung from them with royal magnificence in art, literature, splendid palaces, and a great household.
The Duc d’Anjou was the handsomest of the brothers, and the most unpopular, for he was just as cruel and extortionate as the Duc de Berry, and did not spend his money in Paris, but hoarded it up with a view to providing the means of securing that Italian kingdom of which he had always been dreaming, and to which every one in France rejoiced when he had gone. But he died in 1385, and his widow, Marie de Bretagne, Queen-dowager of Sicily, was now at Paris132 with her two young sons, Louis II. and Charles, whose guardian she was.
In the early part of 1389, the Pope sent word to her that an attempt was being made by another claimant to get possession of the kingdom of Sicily. She went at once to her nephew, asking for help, which Charles was always ready to give on an occasion of this kind, and before the young King of Sicily and his brother started for that country he resolved to give a magnificent fête in honour of their knighthood.
Great were the preparations for this ceremonial. Proclamations were made and invitations issued all over France, England, and Germany. It was arranged that the fêtes should be at St. Denis, the place around which have gathered for centuries the grandest, holiest, and most solemn associations of the history of France. Founded in 630 by Dagobert, the splendid church was restored and decorated by its great Abbot,111 Suger, in 1140. There, according to pious tradition, were transported and buried the remains of St. Denis the martyr, there hung the oriflamme, the flame-coloured banner which had so often led the chivalry of France to victory, there were the tombs of the kings, queens, and royal family from Dagobert downwards, there, at the feet of Charles V., was soon to be laid the hero Du Guesclin. The splendour of the treasure of St. Denis, which had delighted the eyes of the Emperor Charles IV., was unsurpassed. Gold and silver statues, crucifixes, and altar plate set with precious stones, books covered with gold and silver, written in letters of gold and ornamented with gems, gorgeous133 vestments, royal crowns of gold and jewels, the golden sceptre and sword of Charlemagne, the hand of justice, golden spurs, and coronation robes, all were in the keeping of the Abbot of St. Denis, who was independent of any other jurisdiction, and one of the greatest nobles in France. Pope Stephen III. granted to the monks of this great house the privilege of electing one from their number to be consecrated Bishop and receive the power of exercising all episcopal functions in the abbey. The Abbots of St. Denis were also permitted to wear the ring, mitre, and crozier, and the pontifical vestments when they celebrated mass, which on certain high festivals was sung in Greek. From the kings they had the right to pardon criminals, coin money, and hold fairs and markets, and to sit as councillors in the parliament of Paris. Their right, recognised by Louis le Gros, to the country of the Vexin, gave them the oriflamme,112 which belonged to it, and the war-cry of their feudal castle, “Montjoie Saint Denis,” was the war-cry of France.
Those delightful and invaluable historical works, the “Grandes Chroniques de France,” were written by the monks of St. Denis; of whom one used to be chosen by the abbot to go about with the court on purpose to write them. After the invention of printing they were arranged and printed by the Benedictine Jean Chartier, 1496.113
134 The ceremony of conferring knighthood was one of the most interesting and characteristic of the many spectacles of the Middle Ages. In a former volume relating to the French court were described the magnificent fêtes given by Philippe le Bel on the occasion of the knighthood of his three sons and the young Princes of Burgundy, the fame of which had spread all over Christendom. Charles and Isabeau determined that there should be no falling off either in the splendour or the diversions of those they were about to give. During the seventy-six years that had elapsed between those festivities and the ones now in question, wealth and luxury had greatly increased, there was more general cultivation and no gloomy figure severely moral and remorselessly cruel cast a shadow, like Philippe le Bel, upon the universal rejoicing.
135 The Queen, the ladies of the court, and princes of the blood, were to lodge in the abbey itself, which was well suited to receive them. The refectory was of enormous size, with two naves divided by a colonnade, the windows were filled with the most gorgeous stained glass and the tables were of stone. In the cloister was an ancient fountain thirty-six feet in circumference, with sculptured figures from heathen mythology, and over it a vault raised on sixteen columns, mostly of marble, which had been put there by Hugues VI. the forty-second abbot, 1197.114
A huge wooden hall was built for the occasion in the courtyard of the abbey. It was covered with white outside, lined with white and green and decorated with tapestries and cloth of gold. In it was a large dais, and outside a place for tournaments with wooden galleries for the ladies to look on at the spectacle. On Saturday, May 1st, about sunset, the King arrived, and soon after the Queen of Sicily in an open car accompanied by the princes of the blood, her two sons, the King of Sicily, then about twelve years old, and his brother rode by her side in long grey robes without any gold or ornament, carrying pieces of the same stuff rolled up on their saddles as if for a journey, after an ancient custom of esquires. They escorted their mother to the abbey and then proceeded to the priory de l’Estrée, where they undressed136 and bathed. At nightfall they went to salute the King, who took them to the church, where they put on the dress of knighthood. It was of red silk lined with vair, long robes and mantles down to the ground, but no covering on the head. Then a great procession was formed, a cortège of nobles going before and behind the young King of Sicily, who walked between the Dukes of Burgundy and Touraine, and his brother, who was accompanied by the Duc de Bourbon and Pierre de Navarre, Comte de Mortaigne.
After prayers before the holy relics the procession returned with the same state to the great banquet, after which the King went to bed and the King of Sicily and his brother returned to the church to pass the night in prayer and watching before the altar according to the ancient usage. But young as the children were, and tired with the journey and the fatigues of all these ceremonies, it was evident that they would not be able to sit up all night in church saying prayers, so after a little while they were fetched away to rest until daybreak, when they had to go back; and later in the morning came the imposing function in the church. It was crowded with the courtiers and nobles, all the monks were also present, and when the rest were assembled a door was opened out of the cloisters and two of the chief esquires of the King’s household appeared carrying drawn swords and golden spurs, and followed by the King himself in his royal robes and mantle, accompanied by the two young princes.
Immediately after came the Queens of France and137 Sicily with their ladies. A solemn mass was then sung, at the conclusion of which the bishop approached the King, and the two boys knelt before him and demanded admission to knighthood. The King received their vows, girded on their swords, and commanded M. de Chauvigny to put on their spurs, the Bishop gave them his blessing, and the picturesque and touching ceremony was at an end.
Every one returned to the abbey, where there was a grand banquet, in fact two, for the monk of St. Denis who gives the account of it says that they dined and supped in the banqueting hall with the King and court and then danced all night.
It may interest some people to know that a granddaughter of the elder of these boys was the famous and unfortunate Marguérite d’Anjou, wife of Henry VI., King of England.
For four days and nights joustes and tournaments went on, at which the Queen gave away the prizes; followed by banquets and balls. The court was in a frenzy of excitement and the fêtes ended with a masked ball more splendid than any, but so licentious and disorderly that of the brilliant crowds that thronged the torch-lighted halls and wandered in the dim, tapestried galleries and rooms of the great abbey, it has been asserted that few escaped the perils of that night of wild, lawless revelry; and the monk of Saint Denis declares that the scenes enacted there desecrated the holiness of the place.115 A liaison between Isabeau and her brother-in-law138 the Duc de Touraine was said to be one of the results, and it has certainly been the general opinion that whether or not it originated on that occasion, there could be only one explanation to the relations which from that time until the death of the Duke continued to exist between them.
It is true that M. Jarry116 in his interesting work on Louis d’Orléans observes that this has never been proved, and that M. Vallet de Viriville makes the same remark; but he adds “Tout le dit, rien ne le prouve. Louis, duc d’Orléans, etait le vice aimable. Pour cette fille d’Ève, si prête à faillir et trop aisée à charmer, il eut la séduction du Tentateur.”117 Louis was one of the handsomest, most fascinating, and most dissipated men in France, and his liaisons were innumerable. It was said that he wore a magic ring, and that as long as it was on his finger no woman could resist him. It was, in fact, a reproach made by his enemies that he wore it in the Holy Week. Between such a man as this and a woman like Isabeau, can any one believe that the most constant, intimate, and unrestrained companionship was likely to be of a different nature from what was universally believed?
It may here be remarked that the order of knighthood did not in itself confer the right to raise a banner. This privilege belonged only to such gentlemen as bore the rank of “chevalier banneret” and owned enough land to enable them to support it. The others were called “chevalier bachelier” and bore139 a pennon or small pointed flag, whereas the banner was square. If a chevalier bachelier were raised to be a chevalier banneret, he had first to prove that his property was sufficient to qualify him for that dignity. When Sir John Chandos, after having long held high military command, though not a knight banneret, asked the Black Prince for the right to raise a banner, he said, “Thank God I have enough and to spare in lands and in inheritance to keep up that rank as it is fitting.”
The next thing of importance that happened at court was a most absurd marriage made by the Duc de Berry, which, however, seems to have turned out very well.
There was a certain Eléonore, daughter and heiress of the Comte de Comminges, who had married the son of that Comte de Boulogne et d’Auvergne, to whom those two provinces had fallen after the death of the young Philippe de Rouvre and the end of the Capétienne house of Burgundy, which, as will be remembered, took place in the reign of Jean.
The marriage of Eléonore de Comminges turned out unhappily, so she resolved to leave her husband, whose prodigality and neglect she could not bear any longer, and take refuge with her uncle, the Comte d’Urgel, who was a son of the King of Aragon. Taking her only child, a girl of three years old, she contrived to escape out of the dominions of her father-in-law and journeyed south towards those of her uncle. On the way she passed near Orthez, a castle of the famous Gaston, Comte de Foix, who was a cousin of hers and of whom she asked hospitality.
140 Now Gaston Phœbus was that Comte de Foix whose deeds have been described in the life of Blanche de Navarre. He was separated from his wife, the Princess Agnes of Navarre, who had gone back to her own family. He was supposed to have stabbed his only legitimate son in a fit of rage, and he now lived with several illegitimate sons and a mistress who was one of the chief causes of the departure of the Princess Agnes.
But he was a man of many and varied talents; passionately fond of music, a great soldier, an excellent governor of the province entrusted to him by Charles V., and a powerful ally and friend to any one he liked. He received his cousin with great kindness and affection and into his ears she poured the history of her wrongs; her anger against her husband and her resolve to obtain the restitution of Comminges, her inheritance, which had been wrongfully seized by the Comte d’Armagnac. As to her husband, she said, “he cares nothing about it, he is trop mal chevalier, all he cares for is to eat, drink, and waste his property; if he got Comminges he would only sell it for his follies, and besides, I cannot live with him. With great trouble I have taken and extracted my daughter out of the hands and country of my husband’s father, and I have brought her to you to ask you to be her guardian and take care of her. Her father will be rejoiced when he knows she is with you, for he told me he had doubts about her birth.”
Gaston de Foix, who seems to have taken a fancy to the child, willingly agreed, and his cousin continued141 her journey, leaving the child, who was from that time brought up by him as his own daughter in his castle.118
The Comtesse d’Auvergne occasionally came to see her daughter, but she always lived with her adopted father. At the time we are now concerned with, the Duc de Berry, who was a widower, and nearly fifty years of age, attracted by the riches and beauty of the child, now twelve years old, wanted to marry her, much to the disapprobation of the King, who thought it ridiculous. “Bel oncle,” he said, “what can you want with a child (une fillette) like that? She is only twelve years old and you are fifty! It is absurd for you to think of such a thing. Ask for her for my cousin Jean, your son, who is of a proper age for her; the affair would be much more suitable for him than for you.”
To which the Duke replied that he had already done so, but the Comte de Foix would not hear of it, as, by his late mother, Jean descended from the Comtes d’Auvergne, whom he hated; and that if the child were too young the marriage could remain a form for three or four years, until she was grown up.
The King laughed, again advised him not to proceed with the matter, but said that as he persisted he would see to it. Therefore he sent Bureau de la Rivière to treat with the Comte de Foix, to whom142 the Duke gave 3,000 francs for his care of the young girl, who was quite ready to be Duchesse de Berry, did not care a bit for the age of the Duke, but was delighted to marry so exalted a personage as the King’s uncle. The Comte de Foix sent her with an escort of five hundred lances, she was met by five hundred more with litters, chariots, and splendid dresses sent by the Duc de Berry, to whom she was married amid much festivity in presence of her father and other great nobles. And thus was an aunt of twelve years old added to the youthful royal family of France.
The Duc de Berry was delighted with the little Duchess, so were the King and Queen; she became an immense favourite at court, seems to have got on extremely well with the Duke and to have thoroughly enjoyed herself in her new life. She always expressed her gratitude to Bureau de la Rivière for bringing about her marriage, and, as will be seen later, he had every reason to congratulate himself that he had done so. When, after many years, the Duc de Berry died and she married again, she was not happy with her new husband and soon left him.
Just after this marriage came that of Louis, Duc de Touraine with Valentine Visconti, daughter of Gian Galeazzo Visconti and Isabelle de France, and consequently cousin both to the King and Queen. For it will be remembered that the Queen’s mother was a Visconti; while Isabelle de France was that little daughter of King Jean who was married so much against her will to Gian Galeazzo Visconti, but143 who had lived in Italy in great magnificence and honour; for the Visconti were delighted with the alliance, and the birth of her daughter (who was also granddaughter to the King of France) was received with great rejoicings all over the dominions of her father-in-law. Isabelle died in 1373, and Valentine was for a long time the only child of her father, as none of Isabelle’s three sons grew to manhood, and when, seven years later, he married Caterina Visconti, no children were born to them for eight years. Valentine, therefore, was a great heiress, and was sought in marriage all over Europe. But Gian Galeazzo, a quiet, rather shy man of studious tastes, always surrounded with ecclesiastics and learned men from all countries, would not part with the daughter who was his constant companion. For Valentine was clever and fond of learning, she read and spoke Latin, French, and German, and shared in the literary pursuits of her father and the cultivated circle in which they lived. A mysterious and sinister reputation hung over Gian Galeazzo Visconti. He was said to carry his researches beyond the lawful limits of human knowledge. It was whispered that the death of his uncle, Bernabo Visconti, might be traced to a subtle poison administered at his instigation, and what at that time caused even more terror than that of poison and assassination was the suspicion of sorcery that clung to him and attached itself afterwards to his daughter and even his son-in-law. In spite of the roughness, cruelty, and callousness prevailing in those days north of the Alps, the French regarded the Italians with feelings of mingled144 fear, curiosity, and admiration. The glory of Italian art, the splendour of Italian cities, the superior comfort and luxury of life in those immense palaces in that delicious climate, the fearful deeds done in the dungeons of the Italian tyrants, the learning and wisdom of the scholars and students who pored by day over books and manuscripts and watched the heavens from tower and loggia on starry, southern nights, who knew how to read their future from the stars and to destroy their enemies with a ring or a bunch of flowers; all this took firm hold on the imagination of their northern neighbours, and made them look upon Italy as a land full of romance, mystery, and supernatural dangers.
Valentine was twenty years of age when, in 1386, her father consented to her betrothal to the brother of the King of France. The marriage was much desired by the French as, besides Valentine’s enormous fortune, it would bring back to France the county of Vertus, the dowry of Isabelle, and also give her Asti, a whole province of towns, villages, and castles, which would be a footing for the French in Italy.
It was not until the summer of 1389 that Valentine left her father on her journey to France. It was afterwards reported at Paris that the Duke of Milan said to her, “Fair daughter, when I see you again I trust you will be Queen of France;” but this is probably untrue, more especially as Gian Galeazzo, who had kept her as long as he could, rode with her out of the gates of Pavia and then turned, without a word of farewell, and rode silently back, not daring145 to look once more into her beloved face. In the saddest of her tragic life Valentine remembered with tears that silent parting.119
The King, Queen, Duc de Touraine, all the princes and the whole court were waiting at Melun, where the marriage was celebrated with suitable magnificence and much festivity. Valentine fell deeply in love with the Duc de Touraine, although he was five years younger than herself. She was not remarkably handsome, but very attractive, and in spite of the perpetual infidelities of Louis her devotion to him never changed, and she also lived on good terms with the Queen, notwithstanding the disposition of Isabeau to entertain for her a jealousy which might well have been reversed. Isabeau was then eighteen, in the height of her beauty, the idol of the court and people, all the more as she was again enceinte, and the hopes of every one were fixed on the birth of a Dauphin.
Valentine was as superior to Isabeau as light to darkness. Ambitious, cultivated, with brilliant intellectual powers, strong both to love and hate, brave and gentle, no shadow of reproach rests on her name.
The King took a great fancy to her and used to call her his beloved sister. She and Louis seem to have got on very harmoniously and affectionately together on the whole, by which one must conclude she must have been a woman of extraordinary tact and patience in some matters.
She brought with her a most gorgeous trousseau of146 clothes and jewels; amongst her many dresses was a scarlet one sewn thick with pearls and diamonds, and a cap of scarlet and pearls for the hair; another of gold brocade with sleeves and headdress of woven pearls.120

State entry of Isabeau into Paris—Magnificent fêtes—Southern tour of Charles and Louis—Bad health of Charles—Bonne d’Artois and Jean de Clermont—Dreadful storm—Birth of Dauphin—Death of Blanche, Duchesse d’Orléans—Pierre de Craon and the Constable de Clisson—Madness of the King.
Although it was now four years since her marriage with Charles VI., Isabeau had never been crowned; and although she had of course often been in Paris, she had not made any ceremonial entry into that city.
But she had no idea of giving up the honours usually conferred on the Queens of France; and the King, always delighted at the idea of any new festival, made inquiries as to how these state entries had been arranged in the times of his predecessors, so that nothing might be wanting in magnificence on the present occasion.
There was one member of the royal family who148 was considered a great authority on these and many other matters. The famous Blanche de Navarre, although she had been Queen-dowager for forty-one years and was the widow of the King’s great-grandfather, Philippe de Valois, was only about fifty-nine years old, had been in her youth the brightest star of the Valois court, and all her life one of the most brilliant, powerful, and popular women of her century.121 To her Charles applied for advice, and into her hands he gave authority to regulate every detail of the whole ceremony. She consulted the records kept at St. Denis, and from those and her own recollections she arranged one of the most splendid pageants known to history.
The Queen went from Melun to St. Denis, where she stayed two days until the royal family and court were assembled. On Sunday, August 17th, at midday, the procession started for Paris. Isabeau, dressed in a silk robe covered with golden fleur-de-lis, was in a gorgeous open litter, followed by Queen Blanche, the Duchesses of Burgundy, Berry, and Bar, the Comtesse de Nevers, and the Dame de Coucy, all in their litters. The royal dukes on horseback surrounded the Queen’s litter, and among them rode Valentine, Duchesse de Touraine, on a horse covered with trappings embroidered with gold. Each litter was escorted by a troop of cavaliers, and burghers dressed in red and green, and mounted on horses with trappings of the same colours, lined the road from St. Denis to Paris, from the gates of which issued149 a brilliant crowd, shouting, “Vive le roi! Vive la reine! Noël! Noël!”
The cortège entered Paris by the Porte aux Peintres into the rue St. Denis, which was draped from top to bottom with crimson and green covered with gold stars. At every turn was some new spectacle. As Isabeau entered Paris she passed under an artificial sky, with clouds, stars, the three Persons of the Trinity, and a troop of children dressed like angels, two of whom descended singing a verse in her honour, and placed a crown of gold and jewels on her head; and as she passed over one of the bridges which had been covered with silken curtains, they were suddenly divided, and a man with another crown flew down a cord from the tower of Notre Dame, and flew up again with a lighted torch in each hand, which, as it was already getting dark, could be seen by all Paris. Wine was flowing all day and night from fountains and taps in the streets and carrefours; in open-air theatres plays and “mysteries” were acted, the houses were hung with rich stuffs and costly tapestries. The procession had stopped at St. Lazare, where the Queen put on her crown and the princesses and duchesses their coronets, the princes of the blood and nobles dismounting and ranging themselves by the litters of the Queen and ladies; then proceeding to Notre Dame they entered the church, made a short prayer, and went on to the Palais de la Cité, where they supped.122
Next day the King in his royal robes, scarlet mantle glittering with jewels, and crown on his150 head, entered the chapel of the Palais. The Queen, also covered with scarlet and jewels, and with her hair flowing on her shoulders, knelt before the altar, saluted the King, mounted on to a high dais covered with cloth of gold, and was anointed and crowned by the Archbishop of Rouen.123
Then there was a splendid fête in the great hall of the Palais de la Cité, the most ancient of all the palaces of the Kings of France. This hall was considered one of the largest and finest in the world. It was paved with black and white marble and panelled and vaulted with wood, rows of columns went down it, decorated with gold and blue and adorned with the statues of the Kings of France; those who were distinguished and fortunate having their hands raised, while the hands of those who were bad rulers, weak, or unlucky hung down. At one end, going right down it, was an enormous table, so long, so wide, and so thick that it was said that never were there such huge blocks of marble as those of which it was composed. It stood there for hundreds of years, and was used for great banquets. At it dined only Emperors, Kings, and other Princes and Princesses of the blood royal, peers of France and their wives; the rest of the nobles and courtiers sat at other tables. This huge table was also used as a stage for the clercs de la Basoche for their plays and mummeries during two or three hundred years.124
It was very hot, and there was a great crowd at the joustes and banquet, the Queen and several of the151 ladies nearly fainted. The King ordered a barrier to be broken down to let in air, and the tables withdrawn (“levées”) to let them go out “without wine or spices” (dessert).
The King, who took no part in the entry, which was in honour of the Queen alone, had nevertheless managed to amuse himself very well, and had seen the whole spectacle in disguise. “Savoisy,” he said to his chamberlain, “I want you to get on a good horse, and I will get up behind you; we will disguise ourselves so that no one will know us, and go and see my wife’s entry.”125
They mingled in the crowd, seeing and hearing much that diverted them, and the King afterwards told the Queen and ladies all his adventures with great delight.
Some of the ladies left and went to their own hôtels when the King and Queen retired, but many remained all night, and the next morning the Queen and court moved to the hôtel St. Paul, where the revels went on for six days more, with a license that again called forth the reproaches and indignation of the preachers.126
Splendid presents were given by the City of Paris and by different people to the Queen and the Duchesse de Touraine, whose first appearance among them had excited great curiosity and interest.152 The Duc de Berry gave Isabeau a large house in the faubourg St. Marcel, with courts, galleries, moats, gardens, meadows, and a rabbit warren.127
The fatigue and excitement of all these gaieties seem to have told upon her, for she could not be present at a banquet and dance given by the King to the ladies of the court during the festivities at St. Paul, but stayed in her room and supped there.
She did not accompany the King when early in October he set off on a journey south. He had received great complaints from Aquitaine128 of the oppressions and extortions of the Duc de Berry, and he also wanted to attend the coronation at Avignon of the young King of Sicily. The Queen being enceinte could not take a long and tiring journey, besides which it is more than probable that Charles on this occasion greatly preferred her absence. For his progress through Provence, Guyenne, and Languedoc, though ostensibly for political objects, such as the extinction of the schism at Avignon, the coronation of the King of Sicily, and the reformation of the abuses in Aquitaine, had also its social side. There, in the land of troubadours, poetry, and courts of love, where the sun was burning and the nights were bright, where the imagination was more vivid and the hot blood of the south ran quicker through the veins, where manners and morals were easy and had a tinge of orientalism derived from contact with the East; the progress of the young King from one town to another was a saturnalia of dancing, feasting, love-making, and153 violent exercise in games and tournaments, which for the first time seem to have taken visible effect upon him.
Some symptoms he must have felt which troubled and alarmed him, for while at Avignon he caused an effigy of himself to be made life-size in wax and placed under a tabernacle close to the relics of the young Cardinal Pierre de Luxembourg, of saintly reputation, to whose tomb people were flocking to be cured of epilepsy and other maladies.129
There was no royal post at that time; it was not instituted till the reign of Louis XI. Charles sent a courier to the Queen two or three weeks after his departure, to ask for news of her; he was then in Dauphiné, and from that time until his return in March she seems to have had no more letters or communications from him.130
During his absence another daughter was born and named Jeanne, like the first one. Isabeau had now two daughters still living. This second Jeanne afterwards married the Duc de Bretagne.
M. Vallet de Viriville says of Isabeau that although frivolous, capricious, and fantastic, she seems to have been liked by her ladies, and was certainly just as fond of her children as other women usually are. While they were little she had them always with her, caressed and watched over them, wept and prayed when they were ill, and redoubled her lamentations when any of them died. Her neglect of them a little later on, however, seems to contradict this; but154 then Isabeau was a person so inconsistent and selfish that neither her affection nor her dislike could ever be reckoned upon; and her extravagance and folly was the cause of the penury to which the royal children were at one time reduced. Her quarrels with her sons in later years were long after they had passed childhood; with those of her daughters who lived to grow up she does not seem to have disagreed.
The Queen and the Duchesse de Touraine had been left together at Beauté by their husbands when they started for the south.
After an absence of several months, spent as has been described, those young princes turned their steps northwards again. When they arrived at Montpellier the King told his brother that he felt so impatient to see the Queen and Duchesse de Touraine again that he could not wait any longer, but proposed that they should race back to Paris; a bet of 5,000 francs to be paid to the winner. Louis agreed, and they set off, riding day and night, changing horses very frequently and being carried in litters when it was absolutely necessary to take a little rest. The race was won by Louis, who got on to a boat at Troyes and went down the Seine to Melun, thus getting rest all that part of the way. At Melun he disembarked and rode on to Paris, where he arrived some hours before the King, having done it in four days and a half.
Louis went straight to see the Queen, and then presented himself before his brother and claimed the 5,000 francs.
155 This adventure does not seem to have done Louis any harm, but it was declared by the doctors to have been most injurious to Charles, and to have helped to over-excite and unsettle his brain.
The King returned from his southern tour weakened, exhausted, and very angry with all he had found out about the oppressions and cruelties of the Duc de Berry. He had held a Parliament at Toulouse, punished some of the officials, dismissed others, and tried to redress some of the worst grievances. But though Charles was generous and kind-hearted, neither he nor his brother nor any of his uncles, except the Duc de Bourbon, had any idea how to govern, and the latter was entirely opposed to the Dukes of Berry and Burgundy; so much so, indeed, that a melancholy romance was the result of their dissensions.
The youngest daughter of the Duke of Burgundy had been, in 1386, betrothed to the Comte de Clermont, son of the Duc de Bourbon. But they were too young at the time for the marriage to take place, and meanwhile the quarrels of their families caused it to be broken off. They appear, however, to have been deeply attached to each other, for Bonne de Bourgogne, or, as she is named in her epitaph, Bonne d’Artois, declared that she would have no other husband than the Comte de Clermont, and, after refusing every other alliance suggested to her, died at Arras, 1399. The Comte de Clermont also refused to marry any one else as long as she lived.131
The Queen was again enceinte, and the court were156 at Saint Germain-en-Laye for the summer. Money was wanted, as usual, for the extravagant follies of the royal household, and in spite of the compassion of the King for the suffering of the people, it was proposed to levy new taxes.
It was a calm, cloudless day in July; the Council was sitting, the King presiding, and the Queen had gone to mass in her private chapel, when suddenly the sky became black with clouds, forked lightning flashed through the darkness accompanied by awful claps of thunder, and a violent wind tore the windows from their hinges and shattered all the panes of glass in the Queen’s Chapel. Mass had to be finished low and hurriedly lest the Host132 be torn out of the hands of the officiating priest, the palace seemed to shake, and everybody was prostrate with terror. The Queen went trembling to the King, saying that this was an expression of the anger of God for their oppression of the people, and they had better give up the new taxes. The Council was dismissed accordingly and the taxes abandoned. Many trees were torn up in the forest, and four officers of the royal household killed by the lightning.133 Isabeau had always the greatest terror of a thunderstorm; she had a vaulted cellar under the Palais de la Cité on purpose to take refuge in on those occasions.134
The much longed for Dauphin was born on the157 6th of February, 1391, at the hôtel St. Paul. The King was asleep, for it was in the middle of the night, but the tidings were soon brought to him and to all Paris, which was at once plunged into a tumult of rejoicing. The bells of all the churches were ringing, couriers were starting for all parts of the kingdom, the streets were filled with people and torches, and set with tables covered with wine and food at which stood ladies of the highest rank, offering them freely to all who passed.
The Dauphin was baptized next day in the church of St. Paul, his god-parents being Blanche, Duchess-dowager of Orléans, the Duke of Burgundy, and Comte de Daumartin.
In the following May was born, also at the hôtel St. Paul, the eldest son of Louis and Valentine. He was also named Charles. The Duc de Bourbon was his godfather. He afterwards married the Princess Isabelle, eldest daughter of Charles VI.135
The Duchess-dowager of Orléans, Blanche de France, died in February, 1392, after a long and painful illness. She was greatly respected and honoured, and her funeral at St. Denis was attended by the whole of the royal family and court. She was daughter of Charles IV. and Jeanne d’Evreux, and, as she on one occasion remarked to King Philippe de Valois, if she had been a man she would have been king instead of him. She was proud, high-spirited, and so charitable that she had given away nearly all her fortune before she died.136
158 The King gave the duchy of Orléans to his brother instead of that of Touraine.
A conference was held at Amiens between the Dukes of Lancaster and York, uncles of Richard II., and the French King with the Dukes of Burgundy and Berry. The four dukes entered Amiens riding side by side so as to avoid questions of precedence. It was remarked that the English dukes were dressed with great simplicity in cloth of greenish brown, while the Duke of Burgundy had his clothes covered with pearls, rubies, and sapphires. They could not agree on terms of lasting peace, so they arranged a truce for a year longer, and then separated. But Charles, who, during the whole fortnight had not troubled himself at all about the negotiations, but passed the time in feasting and amusements, had made himself very ill with an attack of fever and had to be taken in a litter to Beauvais, where he stayed in the bishop’s palace till he was well again.137
Amongst the constant companions of the King and the Duc d’Orléans was a certain Pierre de Craon. He was a particular favourite of Louis, they often dressed alike, and Craon was the confidant of all the duke’s love affairs, which were innumerable. There was a girl in Paris whose beauty he had for some time admired and to whom he had offered 1,000 crowns if she would consent to become his mistress. She appears to have been hesitating about the matter, and meanwhile, Louis took Craon to see her. Craon had the rashness to go and tell the whole story to the Duchesse d’Orléans, with the result he might have159 expected. Valentine was very angry and sent for the girl, who appeared before her trembling with fear.
“Well,” said Valentine, “so you wish to take monseigneur away from me?”
“No, no, Madame, God forbid,” answered the girl, beginning to cry, “I should not dare even to think of such a thing.”
“That is true,” said Valentine, “I know all about it. Monseigneur loves you and you love him, things have even gone so far that he has offered you 1,000 crowns, but you have refused and you have done well. For this time I forgive you, and I forbid you, as you value your life, to have for the future anything to do with monseigneur. Dismiss him.”138
The girl retired, thankful to have escaped so well, and the next time the Duke called she fled from him, refusing to show him the least sign of affection. Much astonished and disappointed he asked what was the matter. She began to cry and reproached him with having betrayed her either to the Duchess or to somebody else who had told her, and went on to say, “you had better try to recollect to whom you have been making confidences. I am dreadfully afraid of Madame la Duchesse, and I have promised160 and sworn never to have any communication with you. I am not going to excite her jealousy.”
“Ma belle dame,” replied Louis, “I swear to you that I would rather lose a hundred thousand francs than betray you. Since you have promised, keep your oath, but at any cost I will find out who has revealed our secrets.”
Therefore Louis went that night to supper with his wife, to whom he made himself as pleasant as he well knew how to do. By soft words, love-making and persuasion he prevailed upon her to tell him that it was Pierre de Craon who had revealed the affair to her.
Next morning he rode to the Louvre in a furious rage and met the King going to Mass. Charles, who was very fond of him, seeing his disturbed looks, stopped and asked what was the cause of them. Louis poured out his indignation to his brother, adding that besides this, Craon was always reproaching him with his love of necromancy. “To hear him,” he said, “one would think I was a wizard. By the faith I owe you, monseigneur, if it were not for my respect for you I would kill him.”
“Do not do that,” replied Charles. “I will send him word that I have no further occasion for his services and he is to leave my hôtel; you can turn him out of yours too.” Accordingly that day the Sires de la Rivière and de Noviant from the King, and two gentlemen of the household of the Duc d’Orléans, brought orders to Craon to retire.
He demanded an explanation, but neither the King nor the Duke would see him. Unable to get161 any information, and vowing vengeance against the unknown enemy, he retired to the court of his cousin, the Duc de Bretagne, and, after consulting together, they came to the conclusion that it must have been the Constable de Clisson who had done this, and resolved to avenge themselves on him.
Pierre de Craon therefore returned secretly to Paris and concealed himself in his hôtel, which was a splendid house, and which he had well stored with food and necessaries, and in his anxiety that his presence should not be known, he even took the precaution of locking up the wife and daughter of his concierge for fear they should disclose it.
On the 13th June there was a fête at the hôtel St. Paul. There were joustes in the afternoon and then a supper, followed by a ball which went on until about an hour after midnight.
The Constable de Clisson was the last to depart. He took leave of the King and Duc d’Orléans, and then, with eight valets of whom two carried torches, he proceeded towards the rue St. Catherine, at the corner of which Craon was lying in wait for him with a band of forty brigands. As he rode down the street, on a sudden the torches were snatched from his men and thrown to the ground. Clisson thought it was a trick of Louis d’Orléans and called out, “By my faith, monseigneur, this is too bad, but I forgive you because you are young and think of nothing but jokes.” But to his astonishment the answer was, “A mort! à mort Clisson! Si vous faut mourir,” as Craon drew his sword and with the gang of assassins162 attacked the Constable, who, after defending himself desperately, was flung from his horse against the door of a baker’s shop which gave way and he fell down two steps into the house. The baker and his people rushed out to pick him up, and the assassins, most of whom only now discovered that they had been hired to murder the Constable of France, fled in terror. Craon rode for his life through the Porte Saint Antoine, gained his own castle of Sablé, and from thence got safe to Bretagne. Meanwhile, the news spread rapidly through the city. The King who was going to bed, was just undressing in the hôtel St. Paul, when he was told that his Constable had been murdered.
“Murdered! My Constable! By whom?” he exclaimed.
“It is not known, but it is close by, in the rue St. Catherine.”
“Torches! quick!” cried the King. “I shall go and see him.” And without waiting for guards or suite, he threw a houppelande round him, and rushed out, arriving at the shop just as the Constable was beginning to recover his senses. He opened his eyes and they fell upon the young King leaning anxiously over him. “Ah, Constable, how do you feel?”
“Cher sire, bien faiblement et petitement.”
“Et qui vous a mis en ce parti?”
“Sire, Pierre de Craon et ses complices, trâitreusement et sans défense.”139
163 Charles turned to the doctor who had been hastily called in and said, “Look at my Constable, and tell me what there is to fear.”140 Delighted to hear that although Clisson was covered with wounds, his life was in no danger, and swearing that never had a crime been punished and avenged as this should be; Charles sent in pursuit of Craon and his companions, of whom some were taken and executed, but most of them escaped.
The King confiscated his dominions, took possession of his treasures, and divided his lands between the Duc d’Orléans and some of his friends. The wife and daughter of Craon fled, and the King ordered the Duc de Bretagne to give up the traitor who had attacked his Constable.
The Duke pretended not to know where he was, so Charles assembled his troops to go to war with him, ordering his uncles of Berry and Burgundy to join him with their vassals. They both hated this project as the Duke of Burgundy was a great friend of the Duc de Bretagne, and the Duc de Berry, who was in Paris at the time, had been told of the conspiracy the very day it was carried out, but as he could not bear the Constable he said nothing about it to the King on pretence of not wishing to disturb the festivities going on at the palace. However, they were forced to obey the King, who would not listen to their assurances that Craon was not there at all, but in Spain. He threw himself into a violent passion whenever the matter was discussed, and seemed to be growing so164 violent and so unreasonable that all who approached him were filled with alarm.141
The weather was very hot, and Charles was in a perfectly unfit state to bear the fatigue and excitement of a campaign. During the whole summer it had been so dry that the large rivers, the chief roads for merchandise, had been so low that boats could not go on them, wells and springs were dried up, the parched earth cracked; there was great distress, for no rain fell.
One broiling day he insisted, in spite of the advice of his uncles, on leaving Le Mans with the troops. He was dressed in black velvet, and almost suffocated with the heat.
As they were entering a wood a tall figure rushed out and caught his horse by the bridle, crying out that he was betrayed (which by the by is the typical exclamation of the modern Frenchman). This particular man, however, appears to have been mad, and while he was raving and warning the King not to go further he was seized by the guards.
Charles said nothing at first, but rode on for about an hour till the troop came out of the wood on to a sandy plain where the dust and heat were overpowering. One of the pages, who was so exhausted that he was falling asleep, let his spear fall against some one else’s armour. The clang it made startled the King, who suddenly gave a shout and rode furiously forward striking at everybody. He struck down several men, killing four, and rushed at the Duc d’Orléans, who fled for his life and escaped. The165 Duke of Burgundy rode up exclaiming, “Haro! le grand meschef! monseigneur est tout dévoyé!” They tried to catch the King, but it was most difficult and dangerous. However, at last a cavalier who was very fond of him got behind him and threw his arms round him. He was laid on the ground, the paroxysm passed off and he fell back insensible. They placed him in a litter, and the whole troop turned back to Le Mans. The expedition was at an end, and the King was mad.142
Tyranny of Duchess of Burgundy—Birth of Marie de France—Duchesse de Berry saves La Rivière—Doctor Hassely—King recovers—The masquerade—Dreadful fire—King ill—The sorcerers—King recovers—Dr. Fréron—King ill again—Accusations against Louis and Valentine—Birth of Louis de France—Betrothal of Isabelle de France to Richard II. of England—Their marriage—Disastrous crusade—Marriage of Jeanne de France to Duc de Bretagne—Marie de France takes the veil.
The consternation of everybody and the confusion into which the kingdom fell can scarcely be imagined. The King was taken to Creil where he slowly improved, but was by no means fit to have anything to do with affairs; indeed for some time he only had partially lucid intervals, and was altogether much weakened.
The Queen was on the eve of her confinement, so the news of what had happened was obliged to be kept from her, in fact it was forbidden to be told her on pain of death.143 The Duke of Burgundy seized167 the government,144 to which he had no right, the Duc de Berry being his elder brother, and the Duc d’Orléans the nearest in blood to the King. But, as Sismondi remarks, the Duke of Burgundy was the least incapable of the three, and the people, who hated them all, made no opposition.
The Duchess of Burgundy established herself with the Queen on pretence of taking care of her, and remained there, dictating, meddling, and taking precedence of every one. A daughter was born to the Queen very soon afterwards, and as an offering for the restoration of the King, Isabeau, when she heard of the calamity, named the child Marie and dedicated her to religion.145
Meanwhile the court was in a ferment. The King’s uncles, directly they got the power into their own hands, began to persecute those of the party opposed to them.146 The Duchess of Burgundy, furious against Clisson for causing the King to go to war with the Duc de Bretagne, who was her cousin and great friend, incited her husband against him. Clisson fled from the country, so did several others, including the Seigneur de Noviant who had incurred the enmity of the Duke of Burgundy by refusing to give him thirty thousand crowns out of the treasury without the King’s knowledge.147 He and Bureau de la Rivière, who had been a most intimate friend of Charles V., were caught, thrown into the Bastille, and condemned168 to death. But, fortunately for the latter, the little Duchesse de Berry, whose marriage he had arranged, and whom he had himself fetched from the castle of Gaston de Foix, had ever since that time been exceedingly fond of him. When she heard that he was arrested and in danger of his life, with the Duke and Duchess of Burgundy resolved on his destruction, the Queen absolutely indifferent, and the King powerless to help him, she resolved to save him herself. She was then about fifteen years old, and she hurried to the Duc de Berry, threw herself on her knees before him crying and declaring that La Rivière was falsely accused, that no one dared speak for him but herself, that he had made her marriage, for which she was much obliged to him, that the duke ought to feel the same, that it would be the deepest ingratitude to desert him to whom they owed their happiness, and that if he were put to death she would never be happy again, but would spend every day “en tristesse et douleur.”148 The Duke, who adored her, comforted her and promised that his life should be spared. He went to the King who, though not recovered, was in a state sufficiently rational to be made to understand and give a command, and got from him the order for his pardon, in which the Seigneur de Noviant shared. They were exiled, but later on the Duchesse de Berry, of whom the King was very fond, got all their castles restored to them.149 The Duke and Duchess of Burgundy were furious, but they could do nothing.
The Seigneur de Coucy had a celebrated doctor, a169 certain Guillaume de Hassely,150 who at his recommendation was called in to the King, and so skilful was his treatment that Charles gradually improved, slept, ate, and drank as usual, went out hunting and hawking, and at last asked for the Queen and Dauphin, who were brought to him at Creil, where he received them with delight and affection. He was horrified to find he had killed and wounded several of his followers in his paroxysm. After a little he was allowed to see his brother and uncles, to whom Dr. Hassely said, “Thank God I restore you the King in good health; but he must not be irritated, worried, or troubled with state affairs. His head is not strong yet, but it will get stronger; meanwhile amusements and distractions are better for him than councils and work.” The Queen and Princes were anxious to keep Dr. Hassely at court, but he was an old man and could not bear the fatigue of that life. He retired to Laon, covered with honours and rewards, and died soon afterwards.151
The King’s uncles were very glad to persuade him that he was not well enough to do anything but amuse himself and had better leave the government in their hands. Charles inquired for various friends of his, and was told that they were traitors and in prison. He ordered them to be at once set free and their property restored, but had not strength and clearness of understanding to go more into the matter, and they were safer away from Paris. He sent after Clisson and tried to get him to return; but170 the Constable knew well enough that if the King had another attack he would fall into the hands of the Duke of Burgundy again, so he stayed away, keeping in communication with the Duc d’Orléans and his party, who were called “Marmousets” by the friends of the Dukes of Burgundy and Berry. Charles did not think about business at all; but only amused himself; and Isabeau, careless, apathetic, indifferent to everything but dress, luxury, pleasure, and amassing riches, for some time submitted to the domineering influence of the Duchess of Burgundy, which was vehemently resisted by the Duke and Duchess d’Orléans. Louis claimed the regency during the King’s incapacity to govern, and Valentine was indignant at the presumption of the Duchess of Burgundy in taking precedence over her, the wife of the King’s only brother and, as she imprudently remarked, possibly the future Queen of France.
The King was declared to be well again the following winter; he and the Queen came back and took up their abode at St. Paul, and the Court was once more in a whirl of gaiety.
There are various records of purchases made by Isabeau about this time; amongst others a gold goblet in the form of a rose, her favourite flower; pearls to ornament the collar of the Queen’s squirrel, a chaise à pignier or chair to have her hair dressed in, having a low back. Most chairs of that time had very high backs; they were made low for that purpose. Also some shoes for the Queen’s fool and her mother. And soon after it is stated that the Queen not having obtained money enough for divers things171 necessary and desired by her, would in future have her own “argentier” for herself and her children, by order of the King.
It was January, 1393. The King, delighted to be well again and eager to catch at any new prospect of amusement, was told by one of the gentlemen of his household named De Gensay, of a disguise he had planned whereby people were made to look like naked savages or wild men covered with long hair like that of wild beasts, which Paradin remarks was “chose plaisante à veoir.” These costumes were made of linen covered all over with tow, very long and combed out to look like hair from head to foot. They fitted tightly to the figure, and were stuck on “fort proprement,” as Paradin again remarks. De Gensay proposed that the masquerade should take place at the wedding festivities of one of the Queen’s ladies, who was a countrywoman and great favourite of hers. Now this lady had been married before, and at that time in France extreme licence was permitted at the re-marriage of a widow.152 Speeches, songs, dances, and general behaviour were alike improper to a degree that, even in those days, would not have been allowed on other occasions. The ball was to take place at a large house which belonged to Queen Blanche de Navarre. It stood at the corner of the rue de la Reine Blanche, and was called hôtel de la Reine Blanche.153 When the King saw this preposterous172 disguise he was so delighted that he insisted on being one of the six who were to wear it, the others being the Comte de Joüy, the écuyer d’honneur de Gensay, the bastard De Foix, and the sons of the Comte de Valentinois and Seigneur de Nantoillet.
They all begged the King to give orders that at the ball at which they were to appear no light of any kind should be allowed to approach them on account of the inflammable nature of these absurd costumes. Charles accordingly sent a proclamation ordering all lights, torches, and flambeaux to retire behind and far from six savage men who were to enter the saloon where the ladies were. Unfortunately the Duc d’Orléans had not been told of the intended masquerade, of which indeed no one knew but those who were to take part in it, those who dressed them, and the Queen. The Duc d’Orléans arrived at the ball after the proclamation about the lights, and just then the six savages entered the room all fastened together with cords except the King, who led them. The novelty of this ridiculous spectacle was so successful that everybody crowded round to see them and try to find out who they were, and in their excitement forgot all about the order respecting the lights. The King left his companions fastened together, and, passing before the Queen, went up to the young Duchesse de Berry and began to make173 love to her (luy faisant infinies caresses). She caught hold of his hand, saying that she would not let him go until she knew who he was. Just at that moment the Duc d’Orléans, also desiring to find out who the mummers were, snatched a torch from one of his pages and held it down close to them so as to see better—the dry tow caught fire, in a moment they were all in flames and being fastened together, they could neither escape nor could any one help them. The Duchesse de Berry, when she saw the whole place on fire, threw her long robe round the King and so saved him. The Queen, seeing the flames, hearing the dreadful cries and tumult, and knowing that the King was one of the six, fell fainting with terror. The young De Nantoillet managed to unfasten himself from the others, and happening to remember a tank or cistern of water in one of the rooms of service close by, used for washing the plate, rushed into that room, threw himself into the tank, and was saved; of the rest, De Gensay (the inventor of the mummery) and Charles de Poitiers, son of the Comte de Valentinois, were burnt to death on the spot, and the other two only survived their injuries for two days. There was a general cry of “Save the King!” but the Duchesse de Berry, hastily exclaiming, “Go and change your clothes at once, the Queen is in terror about you,” had hurried him out of the ballroom. Isabeau was carried fainting to her room, where Charles, having pulled off the fatal disguise, hastened to reassure her. Every one was accusing and blaming the Duc d’Orléans, who, nearly beside himself with horror and remorse, and crying out that he had done174 it and it was all his fault, fled out of the ballroom and rushed up to the apartments of the King and Queen.154
The Dukes of Burgundy and Berry had left the ball before the arrival of the mummers, finding it rather late, and had returned to their own hôtels. They knew nothing about what had happened until the next morning, when there was a great outcry all over Paris, and the report reached their ears that there had been a great fire after they had left the ball and that the King had been burnt to death with the others. Even after they had ascertained the truth the people would not believe it, but insisted on seeing the King for themselves, and it was not until he had gone in public procession with his brother and uncles to Notre Dame to give thanks for his safety, that they were pacified; and when they found out in what an idiotic way the King’s life had nearly been sacrificed they broke into denunciations of the goings on at court and threats against the princes of the blood. Some people even declared that Louis d’Orléans had done it on purpose, hoping to destroy the King and thus have the chance of succeeding himself if the Dauphin, who was delicate, did not live to grow up; which, by the by, would certainly have come to pass, for he died before he was ten years old. But there is not the slightest proof or even probability of the truth of this accusation. With all his faults Louis was not capable of so monstrous a crime as this, even supposing he had not been, as he always175 appears to have been, on affectionate terms with his brother.
The catastrophe excited the greatest horror in the minds of everybody except the tenants and people belonging to the Comte de Joüy, who was so outrageously tyrannical and cruel that they were all delighted when they heard that they were so unexpectedly delivered from him.
The late calamity seems to have had a sobering effect upon the court, and for a little while after this shock things went on more quietly. But in June the King had a relapse, and this time he was worse, or at any rate the aggravated symptoms lasted longer. He did not recognise the Queen, and when she came near and spoke to him affectionately would ask who she was and even seemed to take a dislike to her, and told those surrounding him to take her away for he did not know what she wanted. He declared that he was not King, that his name was not Charles but George, that his arms were a lion pierced with a spear and not the fleur-de-lis, the very sight of which threw him into a rage, and which he would try to efface or tear out of tapestries, plate, or anything upon which they were. He declared he was not married and had no children, and the only person he knew was the Duchesse d’Orléans whom he insisted on seeing every day, and called “ma sœur bien-aimée.” People began, as usual, to talk about sorcery. Some said it was to witchcraft that Valentine owed her influence, others declared that the King’s illness came from his having been bewitched. Dr. Hassely was dead, and the Queen insisted on sending for a sorcerer to try and176 cure him. The sorcerer or wizard was, as the monk of St. Denis says, “coarse, brutal, and vulgar.” He had a magic book, which he said God had given to Adam, and by which he professed to be able to control the stars, so that if any planet had a malign influence on the King he could cause another to appear to counteract it. All the clergy, doctors, and professors were very angry and the sorcerer did no good; some said it was folly, others, that it was sin; there was a great outcry and he was got rid of. Then a learned doctor called Fréron was called in, under whom Charles began to get better. All over the kingdom they had litanies, prayers, and processions followed by crowds of barefooted people; priests in splendid robes going from one church to another. The King said he would go too, and after persisting several times, he went to St. Denis with a great cortège of nobles, heard mass, where he behaved very well, “d’une manière décente et sans commettre aucune extravagance.”155 After dinner he went away, leaving the Bishop of Senlis to make a neuvaine for him. The Queen ordered them at many churches. In January, 1394, he was well again. Early in the same month the Princess Michelle was born.
In honour of her the King changed into “Porte Ste. Michelle” the name of the “Porte de l’Enfer” so called on account of the haunted convent of the Chartreux of Vauvert just outside it, with its weird tales of moving lights, unearthly sounds, and phantoms, spoken of in the former volume treating of the Valois Queens.
177 The Hundred Years’ War with England still dragged on, and brigands again began to infest the country, and great distress prevailed; to the alleviation of which Charles now turned his attention for a short time. For Dr. Fréron, either finding that the treatment ordered by his predecessor had been carried much too far, or else because he thought quiet, and rational occupation with the affairs of the State would do the King more good than the ceaseless, reckless, dissipation,156 which was the original cause of his illness, ordered him a tranquil life, occupation for his mind, rest, and various other changes which certainly appeared to succeed; for the King was quite restored under his care, and as well as he had been before his first seizure. No one could now say that he was not capable of giving proper orders, nor dispute the validity of those he gave, as the Duke of Burgundy had done when the King had granted some permissions to hunt in the royal forests.
Charles went several pilgrimages and, his own sufferings having made him more compassionate to others, he recalled fugitives chased away by the tyranny of his uncles, exempted them from taxation for six years, and, abolishing the games of chance in the villages, he established practice in shooting with the bow and crossbow, in order that the peasants should be able to help defend the country which now was obliged to hire mercenaries to oppose the English archers. The people were delighted at this, and already, says M. Sismondi, becoming so skilful that the nobles in alarm took the first opportunity of178 putting a stop to the archery and re-opening the gambling houses. The remembrance of the Jacquerie was naturally in the minds of the French gentlemen as was that of their tyranny in the hearts of the people. That unfortunate class hatred between the upper and lower ranks which, as was remarked in our former volume, had caused the disgrace and downfall of France, was still growing and establishing itself as time passed on, while other nations were slowly becoming stronger and more closely united to their own countrymen as they advanced in civilisation.
The King went on very well until about the middle of the summer of 1395, by which time he had grown very tired of the restraints imposed on him by Dr. Fréron, the trouble of attending to serious affairs, and the comparative dulness of his court. Also it is probable that the symptoms of the terrible malady so long kept at bay by the skill of the great doctor were making themselves felt and deprived him of the little self-control and sense he had ever had. At any rate he dismissed Dr. Fréron, who retired with his property to Cambrai,157 and when he had gone the frenzy returned and Charles was again mad.
It had been a bad summer, with violent winds, doing much damage. Misfortunes and troubles seemed to be gathering again over France. The deepest disappointment was felt by high and low at the relapse of the King, confusion and misgovernment began again, the air was full of evil rumours and terrors as it had been in the years before the battles of Crécy and Poitiers. It was reported that179 in Languedoc had been seen a great star, followed by five little ones which seemed to attack it for about the space of half an hour, while voices and dreadful cries were heard in the heavens; and there appeared the gigantic form of a man who shone like copper, transfixed the great star with a spear and vanished.
In Guyenne unearthly voices were heard in the air, accompanied by the clang of armour and the tramp of combatants.158
The court was rent by the quarrels of the Queen and Duchesse d’Orléans with the Duchess of Burgundy, whom neither of them could bear, and whose interference Isabeau was now roused up to resist. In fact, the arrogance and encroachments of the Burgundian party had become alike intolerable and alarming. The state of the King from this time grew gradually worse. He was not always mad, but his attacks grew more frequent, lasted longer, and took different forms on different occasions. Sometimes even in the middle of them he would have lucid intervals in which his commands were absolutely obeyed. After a period of sanity and health, he could tell by the symptoms when the attack was coming on again, and would desire that all arms, knives, &c., should be taken out of his reach, and sometimes that he should be forcibly restrained lest he should hurt any one. He begged every one he knew, if they had bewitched him, as some said, to have pity upon him and reverse the spell. The whole state of things was heartbreaking, and when he was180 mad he did not know the Queen, it was not safe for her to go near him, he struck at her and ran after her so that she fled in terror. Sometimes he knew every one except the Queen and her children, but one person he always knew, and that was the Duchesse d’Orléans.
He was always calling for her. She would go to him without the least fear and sit with him for hours. Her voice seemed to have a strange fascination for him, and he would do anything she wished. There is not the slightest idea that between Charles and Valentine there was ever any such love as between Louis and Isabeau, but they had always been fond of each other as brother and sister. The populace, however, chose to attribute her influence to magic; they said she came from Lombardy, where it was practised to a great extent; that her father himself was a magician, and that it was from no devotional reasons that the Duc d’Orléans went so often to the Céléstins, but to see one of the brotherhood, a certain Philippe de Mezière, looked upon with suspicion on account of his studies, who had been a great friend of the late King. Louis d’Orléans would sit up half the night talking with him about books, music, or metaphysical subjects. He was a strange mixture of the most opposite qualities and vices, and he added to the inconsistencies of his character that of being extremely devotional. In all intellectual tastes he and Valentine suited each other very well; as to Isabeau, she knew nothing about such matters. There is a record of an historical manuscript which the Duke of Burgundy gave her, probably with the181 hope of inducing her to take more interest in literary subjects, but it was of no use.159
The injurious reports concerning Louis and Valentine were diligently circulated by the Burgundian party. She was said, and by many believed, to have bewitched the King. The monk of St. Denis remarks, “Pour moi, je mis loin de partager l’opinion vulgaire au sujet des sortilèges, opinion repandue par les sots, les nécromanciers, et les gens superstitieux; les médecins et les théologiens s’accordent à dire que les maléfices n’ont aucune puissance, et que la maladie du roi provenait des excés de sa jeunesse.”160
Things, however, came to a climax at last when Valentine was accused of attempting to poison the Dauphin in order to open the way to the throne for her husband and children. The story was that one day when the children of the King and the Duc d’Orléans were playing together in the apartments of Valentine some one had thrown an apple amongst them close to the Dauphin, who was about to pick it up, but that one of the children of the Duc d’Orléans got it, bit a piece out, was taken ill, and died in a few days, the apple being poisoned. The only thing that is certainly true about this story is that a little son of Louis and Valentine did die about this time; but whether he ate an apple shortly before his death, whether it was thrown among the children when at play, or whether there was any reason for attributing his death to such a cause does not seem to have been182 shown. It does not appear that there was a shadow of probability about it, but that it was nothing more than a spiteful calumny got up by the Burgundian party and believed by the fierce and credulous Parisian mob. However, there was a great outcry: the Dauphin was not allowed to go to the apartments of the Duchesse d’Orléans, and the Duc d’Orléans and his friends thought Valentine would be safer out of Paris for the present. Therefore she left that city with her children in great pomp for Blois, where she remained for a time till the storm blew over.
Her father, the Duke of Milan, was furious when he heard of these accusations against his daughter and himself, for he was also said to have bewitched the King, to have asked the French ambassador how he was, and on being told “well,” to have exclaimed, “You tell me a diabolic thing, and one that is impossible.161 The King cannot be well”—clearly pointing either to sorcery or secret poisoning. He offered to send a champion to fight to the death any man who accused his daughter, and threatened to invade France.
In January, 1396, the Queen gave birth to a son, who was named Louis, and in February the King recovered his senses. It had been arranged that the little Princess Isabella, eldest daughter of Charles and Isabeau, should be married to Richard II., King of England, instead of to the son of the Duc de183 Bretagne, to whom she had at first been betrothed. Richard was thirty years old and a widower, but it was felt that the splendour and advantages of such an alliance as this, not only for the Princess, but still more for France, were not to be lost. The English ambassadors, therefore, when in 1395 they came to Paris, where the King was at that time living at the Louvre, and the Queen and her children at the hôtel St. Paul, were received with great honour and favour, and having paid their respects to the Queen, they turned to the Princess Isabelle. The Marshal of England knelt before her saying, “Madame, s’il plaît à Dieu, vous serez notre dame et Reine d’Angleterre.” To which the pretty, graceful child, who was only about seven years old, replied, “Sire s’il plaît à Dieu et à monseigneur mon père, je le serai volontiers; car on m’a bien dit que je serais une grande dame.” Then giving him her hand she raised him and led him to her mother.162
The ambassadors were enchanted with the little princess, who was the especial darling of her parents and the whole Court. All the daughters of Charles and Isabeau seem to have been remarkable for good looks and charm, and very superior to their sons. The second one, Jeanne, was promised to the son of the Duc de Bretagne instead, and the marriage of Isabelle took place in October, 1397.
Magnificent preparations were of course made beforehand for the wedding of the eldest daughter of the Valois with the great enemy of her country, by which it was hoped to close the Hundred Years’ War and restore184 prosperity to France. The King sent for the most skilful jewellers and ordered for her a profusion of rings, bracelets, necklaces, chains, and all kinds of jewels of great price, cloth of gold and other costly stuffs, covered chariots, saddles and bridles covered with gold and silver. He was fortunately quite well, and sane just then, so that he was able to attend his daughter’s wedding. He went with the Queen, princes, and court to meet the King of England between Calais and Ardres, where the French and English camps were pitched near each other, the French one containing a hundred and twenty tents surrounded by a palisade, and in front a large tent like a great hall, more magnificent than the rest, over which floated the lilies of France.
The English camp contained the same number of tents, but the one that stood in front of it, with the standard bearing the leopards of England, was like a vast round tower.
The most stringent regulations were proclaimed in both camps to avoid the slightest danger of any disputes arising to endanger the harmony of the meeting on which hung the peace and welfare of two kingdoms.
None but the immediate escorts were to be armed; it was forbidden to throw stones, pick quarrels, or play any game that could lead to them, and the conferences went on amicably for several days, being disturbed only by a violent storm which tore up many tents in the French camp, tearing the silk lining of them to shreds, while only four of the English tents suffered. Torrents of rain fell, and185 superstitious fears were entertained that some calamity was about to happen. “But,” says the worthy chronicler of St. Denis, “on learning the result of the conference, they rather thought the enemy of the repose of mankind who dwells among the shades of darkness had thus given vent to his fury because he had not been able to throw any obstacle in the way of peace.”163
The young Queen, who had been married by proxy to Richard in Paris, set off for St. Denis with great pomp, where she performed her devotions according to the ancient custom, and then continued her journey.

The King of England had been dining with the King of France, waited upon by the Dukes of Burgundy, Berry, and Bourbon, both monarchs having been much entertained by the amusing conversation of the last-mentioned prince, when the sound of trumpets and other music announced the approach of the young Queen of England, who entered the camp with a procession of surpassing magnificence, wearing royal robes covered with fleurs-de-lis, a gentleman of her train carrying a crown of gold before her carriage. The Duchesses of Lancaster and Gloucester came forward to pay their homage, and the Dukes of Burgundy, Berry, and Orléans advanced, and one of them taking her in his arms carried her to her father, who led her by the hand to the King of England, saying, “Mon fils, voici ma fille que je vous avais promise, je vous la laisse, en vous priant de l’aimer désormais comme votre femme.” Richard II. was a most imposing personage. To186 the stately bearing of the Plantagenets he united the far-famed beauty of his mother, the Fair Maid of Kent. As the little Queen bent before him he raised her up and kissed her, after which he took his leave.164 She was placed in a splendid litter in which she was to proceed to her husband’s town of Calais, accompanied by the Duchesses of Lancaster, York, Gloucester, and other great English ladies, with the Dame de Coucy, who was to go with her to England. She began to cry and sob at parting from her187 father and uncles; Charles VI., who was extremely fond of her, cried too, and the Dukes also shed tears.165 The King and Queen were married again at the Church of St. Nicolas at Calais, and the day after that embarked for England. Before going on board ship, finding that her French attendants were to be dismissed, the poor little thing began to cry again, and begged King Richard to let them go with her, to which he at once consented, so they accompanied her to England.166
An expedition had been for some time in preparation to assist Sigismond, King of Hungary, against the Turks under Bajazet, who had invaded Europe and threatened to push on to Rome and feed his horse upon the high altar of St. Peter. The troop consisted of a thousand men, amongst whom were many young cavaliers of the noblest houses in France, led by Jean, Comte de Nevers, eldest son of the Duke of Burgundy, then about twenty-two years old. The troop was splendidly equipped, Philippe of Burgundy having by means of heavy taxes on his vassals collected a great sum of money with which, had he spent it rationally, he could have put an army into the field. The troop had set forth in March, and the luxury and extravagance of the French nobles astonished their Hungarian and German allies.188 Their tents were of green satin, their banners and the trappings of their horses were covered with gold and silver, their armour, dresses, and plate were magnificent. They marched across Germany and joined their allies at Buda-Pesth. The army then marched along the banks of the Danube, upon which great barges accompanied them loaded with choice wines and delicacies for the French.167
But evil rumours began to be afloat after some time regarding the expedition, and the chroniclers of the time relate various supernatural occurrences which filled with terror the superstitious minds of the people. The garrisons of various fortresses in Guyenne were awakened in the night by the clash of arms. Fearing a surprise, they seized their weapons, and beheld a battle fought in the air by phantoms in the forms of cavaliers in armour, which filled them with dread. They sent messengers to inform the King, the court, and the university of these prodigies, which seemed to portend divers calamities. “For my part,” remarks the monk of St. Denis, “I leave the secret of all these supernatural events to Him who knows all and who commands the heavens, the earth, and the sea.”168
But on Christmas night, 1396, when the King and all the court were assembled in the hôtel St. Paul,169 one Jacques de Helly entered the hall in boots, spurs, and all the disorder of a hasty journey, and throwing himself on his knees before the King, told him of the189 disastrous defeat of the French by Bajazet and the massacre or captivity of the whole troop. It appeared that the French, furious at being obliged to raise the siege of Nicopolis, had murdered in cold blood and in violation of their plighted word all their prisoners who had surrendered on parole, and that Bajazet, enraged at their treachery, had naturally retaliated, and having by overwhelming numbers defeated them and killed four hundred, had taken prisoners the Comte de Nevers and about three hundred others. He had ordered them all to be beheaded except twenty-eight of the highest rank, for whom he could exact enormous ransoms, and among whom of course was the Comte de Nevers. It was to obtain these ransoms, that Jacques de Helly had been sent. It then appeared that some unfortunate fugitives had already come with the tidings, but had been shut up in the Châtelet to prevent the news being disclosed, with threats of being drowned if they told it. History certainly repeats itself.
However, no amount of lies would now avail to make the Parisians think a defeat was a victory, besides which it was necessary again to wring money from the people to pay the ransoms.
This misfortune had such an effect upon the King, that instead of his being all right until the summer as before, an attack of madness came on early in the spring, to cure which Marshal de Sancerre sent from Languedoc two Augustine monks, who had the reputation of being magicians. This was, of course, in direct opposition to the rules of the Church, but190 the clergy did not exactly like to prevent their endeavours; they contented themselves with murmuring that it would be much better to burn them as wizards than to offer them rewards. In July the King recovered his reason, for which the monks imprudently took the credit, forgetting what would be likely to befall them should he have a relapse.
The second daughter of Charles and Isabeau, the Princess Jeanne, was married to the son of the Duc de Bretagne; and the third, the Princess Marie, who had been dedicated from her infancy to the religious life, was now received into the convent of Poissy.

On the day of the Nativity of the Virgin, the King and Queen, with a brilliant company, arrived at Poissy. There was a grand procession, the Bishop of Bayeux bearing a splendid jewel presented by the King, who with the Queen and a brilliant cortège of nobles and ladies formed part of the procession, the Sire d’Albret carrying in his arms the Princess Marie, who wore a gold crown and long robe and mantle of cloth of gold, and whom he placed before the chapter, where the spiritual director of the convent addressed the novice, who, it must be remembered, was not yet five years old, and explained to her the rules of the order and the vow of poverty, chastity, and obedience, to which the child “answered humbly that she submitted191 herself.” The Prioress, who was a sister of the Duc de Bourbon, and had taken the veil at this convent at about the age of the Princess Marie, then dressed her in the habit of the order, after which she was conducted to the church by all the nuns, singing hymns to the Holy Spirit. After mass she received the episcopal benediction, and then there was a splendid banquet given by the King. At the close of the proceedings a dispute arose between the Prioress and the Abbot and monks of St. Denis respecting the crown worn by the little princess which was of gold set with jewels of great price, and which, with the robes, jewels, &c., worn by her, the Prioress claimed according, as she said, to the usual custom, for the convent. But it appeared that this crown belonged to the abbey of St. Denis, and had been only lent for the occasion; therefore the monks would by no means give it up. The King, being appealed to, declared the crown had been borrowed by his orders, and settled the matter by paying the convent 600 gold crowns to redeem it, and sending it back to St. Denis.170
The King and Queen arranged the household of the young princess, appointing certain nuns to be her ladies, and then returned to Paris.
Illness of the King—Execution of sorcerers—Birth of Jean de France—Death of Queen Blanche de Navarre—Household of Isabeau—Ludwig of Bavaria—Ancient Paris—The Queen’s châteaux—Burgundy and Orléans—Henry of Lancaster—The plague—Revolution in England—The Dauphin Charles.
In 1398 things did not improve. The King had fewer lucid intervals, during one of which, however, he went to Reims and entertained with lavish hospitality the Emperor Wenceslas. The two monks were still at the Bastille occupied with their necromancy, but as it had no effect upon the King, who had more attacks than ever this year, the terror they inspired began to diminish, while the horror excited by their supposed dealings with the powers of darkness remained. Seeing the danger of their position they tried to propitiate the Duke of Burgundy by laying the blame of their failure on the Duc d’Orléans, saying that the diabolic arts he employed against the King were too strong for them to counteract. But by this outrageous accusation against the193 King’s brother, they had gone too far. The Duc d’Orléans complained, the monks were arrested and given over to the clergy, who delivered them to the provost of Paris, and they were soon afterwards beheaded.
In August another son was born to the King and Queen and named Jean.171
In October died Queen Blanche de Navarre, alike beloved and honoured by the royal family, the court, and the people. The adventures of her brilliant youth when she shared the throne of Philippe de Valois, or the fortunes of her brothers, the gallant Princes of Navarre, have been related in a former volume. She had always been rich and powerful, but never through oppressing her subjects or vassals, so that they loved and venerated her as a mother. She was the providence of the poor and suffering, and a good friend to the religious houses. With every earthly gift and advantage, brilliant beauty, an irresistible fascination, distinguished talents, high rank and great riches, living in the midst of the most dissipated court in Europe, no taint of dishonour ever sullied her name; she seemed, in the midst of all the cruelty, violence, and corruption with which she was surrounded, like a bright star in a dark and stormy sky. For fifty years she had been Queen-dowager, and she had been present certainly at the marriage of the eldest, and almost certainly at the marriage of the second, and the consecration of the third of the great-great-granddaughters of her husband. Her dowry reverted to the crown, her personal property, which194 was large, she divided between her favourite nephew, Pierre de Navarre, and certain charities. But as to the relic she left to the Carmelite Church, the worthy monk of St. Denis earnestly declares that she “was deceived by vain and lying tongues of those who brought it from Constantinople, for the only true and undoubted nail which pierced our Lord belongs to St. Denis and nowhere else, as is proved by the history of Charlemagne and by continued miracles which for five hundred years have been done by contact of that relic.”172
The officers of her household went to ask the Dukes of Burgundy, Berry, and Orléans whether, not having been crowned Queen, her funeral was to be at St. Denis with royal pomp. To which (the King being probably ill then) they replied at once that it was undoubtedly to be so, and it was attended by all the royal family and court.173
The health of the King gradually grew worse. The attacks came oftener and lasted longer. But whenever they subsided, as they often did quite suddenly, he became sane again, resumed the government, went out hunting and hawking, and took part in everything, whether amusement or business, as usual. During his intervals of insanity, the Queen ought of course to have been a most important part of the government, but she cared nothing about that or any rational thing; what interested her were only the dissipations of the court, her dress, the sums of money and treasure she could collect, eating and drinking, and the constant society of Louis d’Orléans.195 The only praiseworthy or harmless tastes she had were a sort of natural affection for her children and a fondness for animals of which she had a good many for pets. She was also fond of music. Amongst the accounts of the period we find sums paid to the “varlet de chambre” of Madame Michelle de France for having, during her absence at Poissy (probably to attend the consecration of her little sister) mended her gold cup which the monkey had broken; to Guillaume Juvel “varlet de chambre de la royne,” for money lent the Queen to give a poor man who had given her a goldfinch that would eat out of her hand; also for a milch cow for Monseigneur Jehan de France and for a tent for him with tapestries with histories on them; for the harpist of the Queen and the minstrels of the Dauphin; and for a large box of wood and iron with holes in it to burn a candle by night in the room of Madame Jehanne de France. Among the same accounts come splendid clothes for the Queen’s relevailles on getting up after her confinement; baths of oak; sums for putting iron on two large cupboards in the Queen’s stables at St. Paul to keep the harness of pearls and embroidery of her horses; for two pair of wheels for her “char”; for mending some tapestries bearing the histories of nine heroes, that is to say, Joshua, David, Judas Maccabeus, Hector, Alexander, Cæsar, Arthur, Charlemagne, and Godefroi de Bouillon; histories of the seven deadly sins, of the seven ages of man; of Godefroi de Bouillon, of the Dukes of Aquitaine; and the history of stags.
And for making a chair of red Cordova leather196 fringed with silk, gilt nails, and two gold chains, decorated and painted with choice colours.
Isabeau had much more idea of comfort than had hitherto been usual even in the palaces of the Kings of France. Mingled with the splendour that had been more or less customary for some generations we see various attempts at convenience not yet introduced. She is said to have been the first to use a “suspended carriage,” and those she had were luxurious and commodious to a degree never seen before, and drawn by very swift horses. She had one chariot on purpose for thunderstorms, “pour le tonnerre,” but in what the safety of it consisted is not stated.174
She had calorifères like little iron chariots filled with red-hot ashes wheeled about the cold galleries of the palaces, and hollow balls of gold and silver full of red-hot cinders to hold in the hand as chaufferettes. In hot weather she caused herself to be fanned by huge fans to keep her cool and drive away the flies; her rooms were hung with costly tapestry and stuffs which were taken down and went with her from one palace to another. She had one room entirely hung with white satin, another with green satin, and her plate was almost always of gold. She used an Eastern talisman against poison, fastened with a silver gilt chain to her goblet and salt-cellar, and an officer of her household tried every dish before she tasted it. She had a cupboard painted and decorated by a skilful artist, in which she kept her relics and perfumes. For the latter she had a197 mania. She always kept damask rose water about her, and used also a great quantity of what were called “oiselets de Chypre.” These were little bottles something the shape of birds, filled with different Oriental perfumes. She and her ladies were constantly eating all sorts of sweetmeats, of which there seem to have been innumerable kinds.175

Carpets were sometimes, but not generally used, the floors were still strewn with rushes and fresh boughs, especially the great halls and banqueting rooms. It was, however, usual to lay them on the steps going up to the great beds, and the floors of many of the rooms in the palaces were of wood, often inlaid.
They must have looked both magnificent and comfortable, those great bedrooms in the palaces and hôtels of the nobles. The huge bed in an alcove or corner, steps covered with rich carpets going up to it, and curtains of silk or some costly material, carved cupboards, chests and seats, beams of the ceilings painted or gilded, walls hung with tapestry, windows protected by trellises of iron and filled with stained glass, a huge chimney-place, sculptured all over with figures and armorial bearings, on the hearth of which blazed great logs, while by it at right angles a tall carved settle kept away the draught.
The Queen’s bath was of carved oak, furnished or lined with bath sheets or towels. Over it was a canopy with curtains, which drew all round.176
One thing appears to be certain, and that is that, although at this time houses were insanitary and the199 streets narrow and dirty, with open sewers in them, people were personally far cleaner than at a later day.177 All through the Valois times, down to 1600, there were plenty of étuves, or public bath-houses, to which every one who had not baths in their own houses used often to go. There were hot and vapour baths, and some of these establishments were extremely luxurious and elegant, and were used for other purposes besides bathing. People who were starting on a journey often slept at them the night before, setting off from them in the morning; they were often much resorted to as rendezvous, and many were the scenes of license and revelry which took place in them when the young nobles and courtiers, led often by Louis d’Orléans, adjourned there after some supper or banquet.178
The priests were very angry with them, and often preached against them, and so, later on, did the Huguenot ministers. By 1600 they had much diminished in number and importance, and soon after they disappeared,179 which was a great pity, for of course it did no good at all; people were just as immoral as before, and not nearly so clean. But this is another instance of the mischief done by the misplaced activity of those busy, fanatical folks, who, with the most excellent intentions in their attempts to reform either religion or morals, direct their attacks upon something which is in itself perfectly harmless, or even valuable to the majority of people, doing all200 they can to deprive them of it, simply because they see some persons make an improper use of it. The early Christians were always preaching against those magnificent Roman baths, the destruction of which was such an irreparable loss to the people.180 The Puritans, thinking that the morals of many plays and the lives of many actors left much to be desired, would, even in the last generation, have done away with all theatres if they had been allowed. And in our own days have we not many instances of the same kind?
In spite of all the suffering she caused and the harm she did, we do not gather that Isabeau was at all actively harsh, cruel, or disagreeable. She seems to have been liked by the companions of her follies, the servants of her household, and her ladies, of whom she had four dames, four demoiselles de corps, and two others. Her vices, faults, and deficiencies were just the worst she could have had in the present crisis, for they made her not only useless, but mischievous. If she had had brains, decision of character, courage, and common sense, she might also have been proud, passionate, vindictive, or ambitious, to any extent, and yet have been a great queen, and perhaps the salvation of France.
But Isabeau’s faults were not those of a great character. She was selfish, lazy, frivolous, vain, and avaricious. She let the reins of government remain without an effort or complaint in the hands of the Duke of Burgundy, she allowed the overbearing201 interference of the Duchess until it became perfectly insupportable. She now occupied herself in amassing for herself an enormous private fortune, considering that the health of the King gave every cause for fear, and that she had had no dowry on her marriage. She had certainly secured to herself by letters of the King, 1394, a revenue of 25,000 livres, representing at that time an enormous sum;181 but besides this she was constantly collecting and storing away in chests, gold, jewels, plate, unset diamonds, and other precious stones, title deeds of lands, everything she could lay her hands upon, in which she was assisted by her brother, Ludwig of Bavaria, who was constantly in France, getting a large share of the spoils, wrung by taxation from the people. Isabeau seems to have had more affection for him than for any one else, and never appears to have changed towards him. From what little can be known about him he must have been very much like her, he was generally with her and Louis d’Orléans, and the people hated him, perhaps, most of all. Isabeau caused him to be grand maître d’hôtel to the King for some years, and married him first to Anne de Bourbon, Comtesse de Montpensier, and then to Catherine d’Alençon, widow of Pierre de Navarre, both princesses of the blood. He was apparently corrupt, dissipated, greedy after money, shallow, and useless.
Though the streets of Paris were narrow and winding, yet both city and faubourgs had many large gardens and enclosures, or clos, as they were202 called, which belonged to the abbeys, convents, palaces, and hotels of the King and nobles. First, there was the famous Prè aux clercs, renowned in romance, mentioned several times in this and a former volume, which was so large that De Sauval says: “Il se va perdu bien loin dans la campagne,” and which only began to be built upon in 1630. The clos des Jacobins was nine acres, where now are the streets of la Madeleine, St. Thomas, St. Dominique, &c., and it was said that before part of it was cut through to make the moats and fortifications in the reign of Jean, it went up to the walls of the university.182 The203 clos des Cordeliers was also enormous, and in fact the great enclosures, gardens, vineyards, meadows, and even preserves for rabbits and other game, were so numerous as to form an important feature in the ancient capital.
For those who care for the history of Paris there still remain in the byeways antique houses, picturesque corners, and old streets, around which cling the historic memories dear to their hearts, but to the great majority to whom it appears as nothing but an endless succession of broad streets and boulevards lined with trees, superb, monotonous, uninteresting houses copied from the Italian, and splendid shops; it would be impossible to picture to themselves mediæval Paris as it existed at the time of which this book treats.
Mr. Harrison, in an interesting essay on the transformation of Paris, says: “The modern streets, to which our tourists confine their walks, form after all only a gigantic screen, behind which much of old Paris still remains untouched.”
Until 1789 Paris remained a mediæval city. It would, of course, be out of the question in a work like this to attempt to give any real account of it, but it is possible to catch just a glimpse of what the aspect and life of the city must then have been by careful researches into the many splendid works in the Bibliothèque Nationale, the British Museum, and other places, which are filled with pictures and descriptions of it.
With its lofty walls, towers, gates, and moats, old Paris looked, as it was, a fortress. Inside it was a204 dense, tangled network of dark lanes, narrow, crooked streets, huge palaces, mediæval fortresses and conventual enclosures. Here and there came a tower or Gothic portal, churches, bridges, and quays crowded with confused piles of lofty wooden houses, walled gardens with terraces, courts, and colonnades; while those great royal and feudal castles, the Châtelet, the Bastille, the Temple, and the Louvre, frowned over the city.
The sanitary state of Paris was such that it is difficult to understand why any one was left alive. Narrow, unpaved streets, with open sewers running down the middle of them, cemeteries and charnel houses in the heart of the city, drinking water taken direct from the Seine, it is no wonder that there were such numbers of deaths of children and young people, and that so few attained to old age. Of all the children of Philippe de Valois only two lived to grow up; out of the numerous family of Charles V. only two survived their childhood. Charles VI. had twelve children, and though only four died in childhood, scarcely one reached forty-five years. The sons and daughters of King Jean must have been exceptionally strong, for all except one grew up, and one or two lived to be quite old. And if this were the case with the royal family, it was not likely to be better with those who lived under much less favourable conditions.
Not only within the walls, but for many miles outside them stood a profusion of churches, convents, abbeys, chapels, oratories of all sizes, from the mighty St. Germain des Près to the smallest chantry on the205 pier of a bridge. Rich in works of art, gorgeous in colour, paintings, frescoes, mosaics, stained glass, carved statues, coloured marbles, gold and silver plate, bronzes, ivories, silks, velvets, tapestries, embroideries, illuminated books, bells, clocks, perfumes, organs, instruments of music, choirs of singers, every beautiful and delightful thing was crowded together with the relics of saints and tombs of great men, miraculous images, lamps, candles on thousands of altars, offerings dedicated to countless saints and martyrs. The Church was school, art museum, place of instruction, prayer, confession of sin, preaching, and civilising. The great convents and monasteries were the schools, colleges, hospitals and poorhouses. They existed in design for the poor, diseased, and wretched. Christ loved the weak and suffering, and the doors of His house stood ever open to the weak, the suffering, the halt, the blind, and the lame. The poorest, the weakest, the most abject, were welcome there. The priest, the monk, and the nun taught, clothed, and nursed the suffering poor and their children; there was consolation in heaven for those who had found earth a hell.183
Strange and characteristic were the names of many of the streets and houses, such as Cherche-midi, Trois-morts-et-trois-vifs, L’Ymage-de-Saint Nicolas, Quatre-fils-Aymon, Ami-du-cœur, Panier-vert, Hospice des Quinze-Vingts,184 beside the Croissant, Lyon206 d’or, Gerbe d’or, Croix blanche, Homme sauvage, Couronne, Cheval blanc, and many others still in use. Isabeau had several hôtels of her own amongst this tangled labyrinth of streets, buildings, and gardens. First, the hôtel de la Reine, which was one of the group of hôtels connected by galleries and colonnades, surrounded by gardens, built by Charles V., and called St. Paul. Then she had one in the faubourg St. Marcel, given her by the Duc de Berry, and another out in the country near Pouilly, called Val-la-Reine. Some years later she bought another, called Bagnolet, with a good deal of land and a windmill, besides all other accessories; it had also about six thousand elms and many other trees. And in this year she bought the hôtel Barbette, in the vieille rue du Temple. This she enlarged, bought all the ground about it to turn into gardens, and used it as a place of diversion.185

During this year one Salmon, a gentleman of the household of the Queen of England, who had gone with her to that country on her marriage, arrived with letters from King Richard, who wished to send the King and Queen of France news of the welfare and happiness of their daughter. Charles and Isabeau, delighted to hear about her, received the messenger with great honour. Richard appears to have felt some uneasiness at the friendship between Henry, son of the Duke of Lancaster, and the Duc207 d’Orléans. For Henry of Lancaster was already his secret enemy and dangerous rival, and the Duc d’Orléans was extremely powerful and ambitious; the Venetians sent ambassadors to him, and European princes appealed to him as to an independent sovereign. Year after year the dissension grew deeper between him and his uncle of Burgundy, who persisted in retaining the regency, which Louis declared ought to be his, during the King’s frequent attacks of insanity.
The year 1399 was an unfortunate one in every way. Troubles and dangers were beginning to gather in England, threatening the safety of Richard and Isabelle, and causing the greatest anxiety to the King and Queen of France. In March and April there were great floods. The Seine overflowed the whole country and destroyed the seeds, so that the crops were ruined and the country made so unhealthy that the plague began again. For eight days a dreadful comet flamed in the sky, which every one said foreboded evil.186
Henry of Lancaster, Earl of Hereford and Derby, had become Duke of Lancaster through his father’s death, and having been exiled for treasonable practices by King Richard was spending some months at the French court. Richard seized the duchy of Lancaster and wrote to the King of France, complaining of the disloyalty of Henry and begging him not to consent to his marriage with Marie, daughter of the Duc de Berry, who, though only twenty-three, was a widow for the second time, and would have brought him great riches and powerful alliances.187
209 The Duc de Berry was quite willing to agree to the marriage, but Charles spoke to the Duke of Burgundy, who, when Henry, still called Earl of Derby, took occasion, the King, princes, and court being assembled, to speak of the matter, said in the name of the King: “Cousin, we cannot give our cousin to a traitor.” Henry replied indignantly that he was no traitor, and defied any one who should call him so; whereupon Charles, who really liked him, and besides was weak and confused with illness, softened the refusal by assuring him that the words of his uncle of Burgundy were inspired by England, and that no one in France doubted his honour. That as to the marriage, it could be spoken of another time, but first it was necessary that he should be invested with his duchy of Lancaster. After which wine and dessert (épices) were served and the subject dropped.188 Henry of Lancaster, who was crafty enough, succeeded in deluding and making friends with the King and princes, even gaining over the Duke of Burgundy; and then returned to England.
The plague grew worse and worse; so fatal was the epidemic that it was forbidden at Paris to publish the lists of the dead. The court moved for a time into Normandy, there were litanies, sermons, and processions, but as the monk of St. Denis says, “many abbeys were nearly depopulated, though the abbey of St. Denis only lost one brother, who passed without doubt to the abode of the blessed.” The plague was about in the country for two years.
Disquieting reports were brought from England to210 the French coast by some merchants of Bruges.189 It was rumoured that a revolution had taken place, that King Richard had been deposed, and that both he and the young queen were in captivity. The King and Queen of France were in the deepest anxiety about their daughter and nobody could tell what had happened (which is a strange reflection, in this, the five-hundredth year after these events). The court returned to the capital, and suddenly all Paris was thrown into excitement by the news that the Dame de Coucy, grande-maitresse to the Queen of England, had arrived unexpectedly at her family hôtel. Directly Charles heard of it he rushed to the hôtel de Coucy to see her. He found her in great alarm and dismay, having been banished from England, and all that she told him of the dethronement, imprisonment, and danger of his son-in-law and the captivity of his daughter so distressed and incensed him that although he had been rather unusually well for some little time, he fell into a frenzy of madness which for the present rendered him incapable of doing anything.190
The astonishment and anger of all the French princes at these events knew no bounds. They cursed the insolent London burghers who had dared to rebel against their King, were furious with Henry of Lancaster, of whose resistance to Richard they had never contemplated such a result; and tried to stir up against him the inhabitants of the remaining English possessions in France, but without success; for although attached to Richard, who was born at211 Bordeaux, the inhabitants of Bordeaux, Bayonne, &c., were so much better governed, less taxed, and more prosperous than their French neighbours that they declined to exchange the English for the French rule.
The people of Paris, discontented and uneasy at the King’s illness and the various misfortunes that kept happening, bethought themselves that they never saw anything of the Dauphin, who was delicate and did not appear much in public. They therefore insisted on his being shown to them, and his uncles, in consequence, made him ride through Paris to St. Denis, attended by a cortège of nobles. There was a state banquet there, and the people, delighted with the Dauphin and the splendid pageant, thronged the whole way, singing hymns and litanies, and praying for the little lad who rode in state for the first and last time as the heir of France.191
Courage of the young Queen of England—Death of the Dauphin—Birth of Catherine de France—Intrigues of Louis d’Orléans, and quarrels at court—Return of the Queen of England—Burgundians and Orléanists—Birth of Charles de France—Dreadful storms—Death of Burgundy—Illness of Duc de Berry—Conduct of Savoisy—Frère Jacques Legrand—The Princess Marie’s choice—Accident in the forest—The King and the Dauphin—Jean Sans-peur—King ill—Eclipse—Royal weddings—The great winter—Murder of Louis d’Orléans.
“The marriage of King Richard with Isabelle was unadvised, and so I declared when it was proposed,” said the Duke of Burgundy. “Since the English have imprisoned King Richard, they will assuredly put him to death, for they always hated him because he preferred peace to war.”192
His words were not long in being fulfilled. No one can doubt that it was by the order of Henry that Richard was secretly murdered, and thus came to an end the project of uniting the Valois and Plantagenets and closing by this alliance the Hundred Years’ War.
The fate of Isabelle was of course what now occupied the royal family of France. Her father sent ambassadors to see her and demanded that she should immediately be sent back to France with all her dowry and possessions. Henry IV., on the other hand, was most anxious that she should marry his son, now Prince of Wales, who was, as he truly remarked, of a much more suitable age for her than Richard had been. But Isabelle would not hear of this plan. She had been extremely fond of King Richard, whose visits to her at Windsor or wherever she happened to be pursuing her studies under the care of her ladies had been her greatest pleasure and holidays, and she doubtless looked forward to the time when, free from every restraint, she would live and reign always with the handsome, magnificent hero of romance who treated her with affectionate kindness and unlimited indulgence. If, as Sainte-Marthe and other French historians say, and as seems certain, Isabelle was the eldest daughter of Charles VI. and was born in 1388, she could not at this time have been more than twelve years old, but she appears to have felt for King Richard the kind of romantic worship that very young girls occasionally feel for a man much older than themselves. At any rate, she took an extraordinarily prominent part in a conspiracy to restore Richard, tore the badge of Lancaster from the liveries of her household, issued a proclamation declaring that she did not recognise Henry as king, went with the barons of Richard’s party to Cirencester, and after his death vehemently refused to marry the Prince of Wales, asking only214 to be sent back to France to her father and mother; and a constant interchange of letters upon that subject went on between the royal families of France and England during the whole of this year.
In January the Dauphin Charles, who had been gradually growing thinner and weaker, faded away and died. His doctors could not find out what was the matter nor do him any good. The King, who was just then in his right mind, went to St. Denis to pray for him; the Dukes of Burgundy, Bourbon, and Orléans went to Ste. Catherine and Notre Dame for the same purpose, and prayers and processions went on everywhere, but he died on the 11th of January in the middle of the night.193
The next brother, Louis, became Dauphin, and the youngest, Jean, then two years old, was created Duc de Touraine. The duchy of Guyenne was also added to the territory of the Dauphin.
The Queen’s father, Stephan of Bavaria, came to France this year and remained some time. He was again a widower and Isabeau wanted to marry him to the widow of the last Sire de Coucy who had great possessions, but the princes objected to placing a Bavarian in a powerful position close to Paris, so it had to be given up.
The King’s attacks got no better; he had six during 1399. Sometimes he was childish, played, laughed, and ran about all over the hôtel St. Paul or wherever he happened to be, so that they had to wall up a great many of the entrances and places he could fall out of. At other times he was raving and215 furious, so that it was dangerous to approach him, and sometimes sad and melancholy. The Queen was not entirely separated from him, because every now and then he got well and then they were together and he gave his orders and often tried to put to rights the mischief and wrong done in his absence, and recalled friends who had been exiled or imprisoned. He had insisted on Juvenal des Ursins, provost of Paris, being left with him and not molested, and it was of no use for his enemies to try to prevent it. He would not listen to them, but exclaimed angrily, “Where is my provost? I will have my provost!” He was well for part of the summer of 1400, and was at services of thanksgiving in consequence at St. Denis and Notre Dame, but was soon after taken ill again and not well till Christmas. The Princess Catherine was born October 27th, at St. Paul.
In spite of the King’s frequent attacks of madness, the Queen contrived to amuse herself very well. From what one can gather from the records of the times she seems to have been generally on good terms with him when he was well, and not to have allowed the pleasures and diversions of her life to be interfered with when he was ill. The court was still disturbed and excited by the rivalry of the Duchesses of Burgundy and Orléans, but Isabeau, who, if she had been a different sort of woman, could and ought to have ruled them both, did nothing of the kind. She hated the Duchess of Burgundy and was rather inclined to be jealous of Valentine, but still on the whole seems to have got on well enough with her notwithstanding her liaison with the Duc d’Orléans.216 Louis and Isabeau were nearly always together; they made excursions and gave balls and dinners and suppers at St. Paul, the hôtel Barbette, and other places; they hunted and drove in the royal forests and their proceedings created continual gossip and scandal in society and all over Paris. Louis at the same time was carrying on a more than usually scandalous intrigue194 with the beautiful wife of the Sire de Canny, which is noticeable because the result of it was the birth of the great Dunois, the far-famed Bastard of Orléans, renowned in French song and story.
The Queen and her children lived chiefly at the hôtel St. Paul, going backwards and forwards between it and the Palais, spending two or three weeks at one and then at the other, making excursions and visits to other of the royal castles in the neighbourhood. The plague, or, as they called it, “the mortality,” was still a good deal about, and there are notices of men sent to find out if it was safe to go to different places, as for instance, Jehan Charron was sent by the Queen to Crécy with letters to the receveur to ask if “the mortality” was there, and another man on another occasion to ride all night somewhere to make the same inquiry; and as Isabeau again sent two or three times in April to different places it must have still been going on. She also went to St. Ouen and borrowed a litter from the Abbot of Coulons.195 On May 31st she seems to have217 returned from some excursion, for she dined and supped at the hôtel Barbette and went to St. Paul to sleep. Isabeau and Louis, with their suites, would often go out to dine and sup at one of these châteaux, especially as the days grew long and the weather hot. Baignolet, or Bagnolet, near Romainville, with its wood of elms and other trees, was another of the Queen’s country-places where they sometimes went, returning to Paris at night. But the distress, confusion, and poverty in the kingdom were increasing rapidly, and the people murmured as the sounds of music and merriment were heard from the windows of the hôtel Barbette or the cavalcades of Louis and Isabeau, with their splendid dresses, trappings, and horses swept through the streets or passed out of the gates of Paris.
They were both very fond of horses and rode well, and wherever she was Isabeau had numbers of pet animals. Plenty of dogs, both large and small, monkeys which played about in her rooms, an enormous aviary of all sorts of birds, French and foreign, which sang and chattered all about her palaces, for there were parrots amongst them as well as doves and little birds. When she moved she took them with her, and was always buying more or having them given to her.196
All her children were with her at this time except the Queen of England, who was expected before long, and the little nun at Poissy—that is to say, her two boys, her second daughter, Jeanne, Duchesse de Bretagne, who still lived with her, and the little218 Michelle and Catherine. There is an account of the offerings made by the Queen and the four elder children at Circumcision, Epiphany, Candlemas, Easter, and all the great festivals. The children all gave the same.
Also of enormous quantities of sweetmeats and bonbons made “for the Queen and enfants de France (at the New Year); that is to say, for nos seigneurs the Dukes of Guyenne and Touraine, and nos dames the Duchesse de Bretagne et Michelle de France.” Dragées, coriander, paste du roy, preparations of cinnamon, rose sugar, sugared nuts (perhaps pralines), and various others in great quantities and several times; sometimes twenty pounds, sometimes forty, and then, as one can well imagine, medicines for the Dukes of Guyenne and Touraine.
Also frequently paper and bottles of ink for the Queen, and money paid to the messengers who carried her letters on many occasions to the King, the Duc and Duchesse d’Orléans, to various abbots, abbesses, and different people.197
She also had some fools and dwarfs. One called Grand Jehan le fol died some time before, and there is a bill for 12 lbs. of wax for his funeral at St. Germain d’Auxerrois. These fools were both male and female; she had one fool, her mother, and grandmother, besides a Saracen woman some one had given her, of whom she afterwards made a sister (sœur converse) in a convent.
219 In August the young Queen of England came home. Henry IV. had behaved very badly to her and to her family, for it was not until after long and tedious negotiations that he would send her at all, and when he did he kept nearly all her jewels and the whole of her dowry. He went to take leave of and console her and sent her to Calais with a brilliant escort of nobles and ladies. Her father was just then in his right senses, and delighted at her coming. He sent his uncle the Duke of Burgundy to fetch her. The Duke met her halfway between Calais and Boulogne, where a magnificent tent was pitched in which she took wine and refreshments with her English ladies, who sobbed and cried as she embraced them all, gave them presents, and took leave of them. She then joined the Duke of Burgundy, who waited for her with an escort of six hundred cavalry, and journeyed by Boulogne, Abbeville, then to Picardy, and by St. Denis to Paris, where she was restored to her parents, brothers, and sisters at the hôtel St. Paul. Charles and Isabeau received her with joy and affection. The Queen took charge of her and re-arranged her household, which she diminished in numbers but placed ladies of higher rank about her.198
The Duc d’Orléans had raised a troop of fifteen hundred men to go to the assistance of the Emperor Wenceslas, who had been dethroned by his subjects; but although he was joined in Luxembourg by the Duc de Gueldre, who was rash, hot-headed, and a great friend of his, the expedition came to nothing, and they returned to Paris together, with the Duc220 d’Orléans’s troop and five hundred men of the Duc de Gueldre. They were soon joined by the Bretons who were friends of Clisson, by some Scottish and Welsh companies in the French service, and by a number of Normans and all the vassals of Orléans, ready to fight in his quarrel against the party of Burgundy.
For the rivalry and hatred between the uncle and nephew and their families had arrived at such a pitch that they seemed to be on the verge of a civil war. Besides the question of the regency between Philippe and Louis, and the mortal hatred between the Duchesses of Orléans and Burgundy, it was whispered that a new cause of offence had arisen. Louis d’Orléans had a private room—cabinet, study, or drawing-room—the walls of which he had hung with the portraits of women who he declared had been his mistresses. This room he generally kept closed, but one day by chance, Jean, Comte de Nevers, eldest son of the Duke of Burgundy, went into it and found his wife’s portrait among the others. That this was nothing but an infamous boast on the part of Louis, and that no blame whatever was attached to the Comtesse de Nevers seems certain, that is to say, if the story be true at all. At any rate it was reported and believed at court and related by French historians, and has been given as a reason for the tragic climax to the feud between Burgundy and Orléans. For Jean Sans-peur, as the Comte de Nevers was nick-named, swore vengeance against his cousin for this insult; and the Dukes of Orléans and Burgundy, each with his followers and vassals, fortified221 themselves in their dwellings—Louis in his hôtel near the porte St. Antoine, and the Burgundians in their hôtel d’Artois199—while the citizens trembled at the thought of these fierce and violent men in the midst of them longing to be at each other’s throats and making no secret of their delight at the prospect of sacking Paris. Seven or eight thousand men on each side were waiting the signal to draw their swords; the King was just then mad, and the Queen and Duc de Berry vainly tried to mediate between them. So matters went on all through December, but at the beginning of January, 1402, the Duc de Berry, who was then living at the hôtel de Nesle, managed to get his brother and nephew to meet there. It was no easy matter, as although they sat at the council together they refused to speak to or salute one another, and each vehemently opposed whatever the other proposed. However, he persuaded them at last to embrace, and ride together through the streets to proclaim their reconciliation to the people, and dismiss their soldiers, to the great relief of the court and Parisians, and at the same time the King returned to his senses, so there was a general thanksgiving at St. Denis, and for a time every one breathed more freely.200
In February Isabeau had another boy, and for the third time the King and Queen chose the name of Charles for their son, who was made Comte de Ponthieu and was afterwards Charles VII.
222 In May the Queen gave a great fête at the hôtel Barbette to the Duc de Gueldre, at which Louis, Valentine, and several other seigneurs were present.201
One would almost suppose that serious thunderstorms in those days must have been more frequent than at present in the north of Europe, for three of truly southern violence took place in May and June of this year. The first, accompanied by a furious wind and a shower of hailstones as big as a goose’s egg, destroyed the vines and other crops for sixteen leagues; in the second the lightning struck the hôtel St. Paul, penetrated into the Queen’s room, where that night she was not sleeping,202 and consumed the magnificent curtains of her bed. As a thank-offering for her escape she sent offerings to several churches, and to the monks of St. Denis a sum to say three masses a year for the soul of the late Dauphin. The third storm, on the last day of June, did more harm than either of the others; it tore up trees, unroofed houses, and destroyed a great part of the halle du Lendit, near St. Denis, but left the part untouched where the judges of the royal contributions resided. The people, who were vexed and harassed by them, remarked that the devil had spared his own abode. The great cross on the priory de l’Estrée was struck down.
223 The King went on much the same, being tolerably well for a few weeks, and then ill for several weeks more. The Duc d’Orléans had persuaded him to appoint him regent, and to give him absolute power over all the Langue d’Oïl, or northern part of France. Some time after he had an attack of madness, and Orléans, directly he had the government in his hands, levied enormous taxes, forced loans from everybody, seized provisions both of lay and ecclesiastics, and published a decree for another heavy and universal tax throughout the kingdom, to which he attached the signatures of his uncles of Burgundy and Berry, both of whom at once publicly denied them, saying that the secretary of their nephew was a forger. There was a general commotion; Louis was declared unfit to govern, and even the Queen and Duchesse d’Orléans saw that this sort of thing could not possibly go on. So directly the King was better a council was called, in which the Queen, the Duchesse d’Orléans, all the princes of the blood, the Constable, Chancellor, the chief minister, and some of the nobles took part. By them it was settled that in case of the King’s death the chief authority should be in the hands of the Queen until the majority of her son. Meanwhile the Queen was president of the Council. The direction of affairs was taken away from the Duc d’Orléans, and the Duke of Burgundy regained his power next time the King was ill.
It had been promised by the King and Queen that the late Dauphin should marry the eldest daughter of the Comte de Nevers, and she was now betrothed to the Dauphin Louis, commonly called Duc224 d’Aquitaine,203 and it was further arranged that the Princess Michelle should be married to Philippe, eldest son of the Comte de Nevers, but that she should be left to be brought up by the Queen her mother. The marriage of the Dauphin and Marguérite of Burgundy was celebrated with great pomp at Paris in the cathedral of Notre Dame in August 1404. There had been some talk of marrying Jean, the second son of the King, to another daughter of the Comte de Nevers, but this idea was given up and he was betrothed to Jacqueline, only child of Guillaume, Comte de Hainault, and Marguérite de Bourgogne, a great heiress.
Not long afterwards the Duke of Burgundy was taken ill on a journey from Arras, where he had left the Duchess, to Brussels, in order to visit his aunt, the Duchesse de Brabant. The roads were very bad, and though pioneers were sent on before his litter to smooth and mend them, he could not go on much further, but stopped at an inn called the “Stag,” and sent for his three sons, Jean, Antoine, and Philippe. He expressed repentance for his oppressions, exhorted his sons to fear God, to be good brothers to each other, loyal subjects to the King, and to live at peace with the rest of the royal family, after which he arranged his affairs and died.
So extravagant had he been that, in spite of his immense possessions, it was doubtful whether he had left enough money to pay his debts, for which reason the Duchess of Burgundy formally renounced communauté de biens, laying her girdle, purse and keys225 upon his coffin, according to the custom. She died very soon after.204
At the same time the Duc de Berry was very ill, and when he recovered and found the Duke of Burgundy was dead he was deeply grieved. While the former was ill and the King mad, the Duc d’Orléans, at the head of an armed band, broke into the Palais one night and carried away nearly all the money to be found there. The Hundred Years’ War had begun again, and there were constant fights going on, towns and castles attacked and taken, seaports and villages surprised and sacked by warships. The new Duke of Burgundy was much worse than the old one, and had not, of course, the same authority in the council or royal family. The Duc d’Orléans, though he hated his uncle, was obliged to have a certain respect for him as a sort of representative of his father,205 and the King, in spite of putting a stop every now and then to his tyrannical proceedings, looked up to him with an amount of consideration which neither he nor his brother entertained for Jean Sans-peur, who was as ambitious and extravagant as his father, without his great qualities, and was harder, more unscrupulous, more cruel, and more crafty. The chief princes of the blood who ruled in council were now the Queen, the Duc de Berry (the last surviving son of King Jean), Louis le Bon, Duc de Bourbon, Louis II., King of Sicily (son of the late Duc d’Anjou, and a much better man226 than his father), Charles III., King of Navarre (also an excellent character), and Jean Sans-peur, Duke of Burgundy, besides, of course, the Duc d’Orléans. But unfortunately the two most influential were the Dukes of Burgundy and Orléans, the latter being always supported by the Queen and her brother, Ludwig of Bavaria.
The brigands had reappeared all over the country and great distress prevailed, large tracts of land went out of cultivation, travelling was unsafe owing to the highwaymen who infested the roads, but the fêtes at court grew more brilliant and licentious and the royal favourites more insolent. Charles de Savoisy, who had long been a favourite of the King, and was grand-maître d’hôtel to the Queen, was one of the most conspicuous. One of his pages, galloping down the streets as a procession belonging to the university was going by, knocked down some of the students, out of insolent bravado. The others surrounded and gave him a blow. The page fled to the hôtel Savoisy and demanded vengeance, whereupon the retainers of Savoisy attacked the procession which was already entering the church of Ste. Catherine, striking with sticks and swords those who were still outside, and firing off cross-bows into the church, wounding several people and injuring the sacred images, ornaments, and vestments of the priests. When first Savoisy heard of it, he said his men had done quite right to maintain the honour of his house; but finding that the University had laid a complaint before the Queen and the Dukes of Burgundy and Orléans, he was frightened and offered227 to give up the culprits to be hanged. The University, however, proceeded with the case, the Duc d’Orléans took it up, and just then the King came to his senses and was very angry. He ordered Savoisy to be banished, his hôtel razed to the ground, and a chapel built there at his expense instead. Savoisy was, after a time, recalled and enriched again.206
Meanwhile Louis d’Orléans, Isabeau, and her brother were amassing an enormous amount of treasure, which they kept in safe places distributed about. A convoy drawn by six horses and loaded entirely with gold coin was stopped near Metz, being on the way to Germany, sent by Isabeau. The people learned from the drivers of it that several others207 of these convoys had safely reached their destination. But they did not pay their tradesmen nor any of their debts. The servants of the household of the King, Dauphin, and other royal children, could not get their wages, so that thus it was nearly impossible to procure them proper food, clothes, and attendance. An Augustine monk named Jacques Legrand, preaching before the Queen on Ascension Day, harangued against the dissolute habits of the court, where he declared that Venus reigned and corruption was general. He said that drunkenness, debauchery, and licentious dances went on all night, that the Queen had introduced the excessive luxury and extravagance in dress which everywhere prevailed, as she would hear if she went out in disguise.228 The Queen was very angry and some of her ladies told the monk that they could not imagine why he was not afraid to say such things, to which he replied that he could still less understand why they dared to do them. He treated with indifference the threats aimed at him, and when some of the courtiers told the King that he had been speaking disrespectfully of the Queen and her goings on, he said he was very glad of it, and that the monk should preach to him in his oratory on Whitsunday. Charles listened with much attention to his sermon on the excesses of the court and society, and when it was over praised him for his fidelity and courage, took him under his protection, and resolved to reform the state of things he complained of. But he fell ill again in June and remained so during half July, so nothing was done.208
There was a spell of very bad weather just then. The melting of snow in the mountains of Haute Bourgogne caused a torrent to rush down from the gorges carrying stones and rocks. It drowned many people, broke down the walls of the great abbey of Cluny, and rushed in, driving the monks up to the higher stories, where they remained till, in sixteen hours, the flood went down, and they descended to dig out the dead bodies from the ruins.209
The Queen and Duc d’Orléans had formed the project of attaching to their party the Duc de Bar, cousin of the King, by marrying his son to one of the daughters of France. As the only available one was the Princess Marie, notwithstanding her vows229 and dedication of the child at Poissy, Isabeau, accompanied by Louis, set out for that convent to see her daughter and talk to her on the subject. She found, however, that instead of a ready consent, which she doubtless expected, the Princess Marie, then about twelve years old, absolutely refused to leave the convent. The Queen talked for a long time to her daughter, and the Duc d’Orléans added his persuasions, but it was no use, she would not hear of it. She said to the Queen that she had placed her there, she was dedicated to God, and she should stay there, adding, “You have made a gift to God and you cannot recall it.”
The King was ill just then, but when he got better they persuaded him to try his influence. He consented rather reluctantly, but said she should do as she chose. He went to see her and asked whether she would consent to leave the convent and marry (she had, of course, not yet taken the irrevocable vows). But the child replied that she had promised to be the bride of Christ, and would hold to her vow unless her father could find her a better and more powerful bridegroom.210 The Queen and Duc d’Orléans, after their unsuccessful visit to the young princess, went to hunt in the forest of St. Germain. There a frightful storm came on. Isabeau, as usual, was terrified. Louis got off his horse and took refuge in her carriage. The horses took fright and ran away down to the river, into which they would certainly have plunged had not a man caught hold of them and cut the traces, or whatever were the straps that230 fastened them to the carriage. The lightning struck the room where the Dauphin was in Paris, and killed one of his favourite esquires. The Dauphin was dreadfully frightened but not hurt. His attendants consoled him and had holy water thrown about the room.211 The people said that these floods and storms were caused by the conduct of the Queen and Duc d’Orléans, who seem to have been of the same opinion, for they were for a short time seized with remorse and declared they would pay their debts. Louis even went so far as to summon his creditors to his hôtel to receive their money, but when they came he had changed his mind and would not pay them—at least, only those who had come from a great distance.
One day the King, recovering suddenly from an attack of insanity, and finding everything in a state of confusion and discomfort, began to inquire the meaning of this condition of things. The Queen and the Duc d’Orléans were away, so he questioned the governess of the Dauphin, who told him that she really could not get proper clothes and scarcely proper food for the Dauphin and his brothers and sisters, that the Queen would not attend to the matter, and she did not know what to do. Charles was exceedingly angry and grieved, for he was very fond of his children, and he sent for the Dauphin and asked him if it were true. The boy hesitated, but after a little persuasion told his father that it was, only that his mother had by caresses and entreaties made him promise not to tell his father. Charles231 then asked him how long it was since he had been with his mother, to which he replied, about three months. The King thanked the governess for her faithfulness, begged her to take care of the children, gave her a gold cup he had been drinking from to reward her services, promising to do more for her afterwards. Then he called a council and sent for the Duke of Burgundy.212
The Queen and the Duc d’Orléans, when they heard he was coming, fled to Melun and fortified themselves there; which was easy enough as it was a very strong place on an island in the Seine. It had been the headquarters of the party of Navarre, as it had belonged to Queen Blanche in the reign of Jean and Charles V.213
In order to prevent the Dauphin from falling into the hands of the Duke of Burgundy, they sent word to Ludwig of Bavaria, the Queen’s brother, to bring not only him but the children of Burgundy also, to the Queen’s country house at Pouilly, where they went to wait for them. But the Parisians got to hear of it, and sent in haste to meet the Duke of Burgundy and tell him to come as fast as he could, for the Queen had sent for the Dauphin and they were afraid she was going to take him to Germany. Jean Sans-peur, at the head of a strong body of armed men, pushed on at full speed, but found when he got there that they had already started. He rode after them and caught them up at about a league and a half from Paris. They had been taken by boat to232 Vitry and had slept at Villejuif. It was pouring with rain. The Duke of Bavaria represented that the Queen had sent for the children and begged the Duke of Burgundy, who had much the stronger party of the two, not to prevent his obeying her orders. The Duke of Burgundy rode up to the Dauphin’s litter, and, opening the portière, asked him if it were by his own free will that he had left Paris. The Dauphin replied that he would much rather go back there to his father; upon which the Duke of Burgundy ordered him to return at once, and himself took hold of the bridles of the horses and turned them back towards Paris. The Duke of Bavaria accompanied him, and the Dauphin was soon lodged in the Louvre while the Duke of Burgundy fortified himself in his hôtel d’Artois.
The rest of the party returned to Pouilly, where they found Isabeau and Louis just going to dinner. But on hearing what had happened they were so alarmed that, without even waiting to dine, they fled to Melun and took refuge there.214
There was now open war between the Queen and Duc d’Orléans and the Burgundian party, and the royal family was divided and perplexed. The King of Sicily and Duc de Bourbon tried to make peace and came to Melun for that purpose, but it was no use; the Queen would not see them and the Duc d’Orléans would not listen to them. He said the capture of the Dauphin was an insult to the Queen and to himself. They went back in despair, and begged the Duc de Berry to try. He also went to233 Melun, but it was no use; the Queen would not go back to Paris.
She was at this time very angry with some of the members of her household who had been spreading scandal about her. She dismissed several of her maids-of-honour, among them one who had been her great favourite, whom she often consulted, and who kept her seal. She put two of the gentlemen of her household in prison and kept them there for some time, in spite of the entreaties of their friends that they might be brought to trial.215
However, a conference was held at Vincennes, peace was patched up, and they all returned to Paris, where the Queen took up her abode again with the King at St. Paul, the Duc d’Orléans at his hôtel near the Bastille, the Duke of Burgundy occupied the hôtel d’Artois, the King of Sicily the hôtel d’Anjou, and the Duc de Berry the hôtel de Nesle. Each of these hôtels was a fortress, and all the streets around them were defended with chains and wooden doors.
Meanwhile, the King had another attack worse than ever. He was very fierce, so that no one dared go near him, and refused to undress or wash. This went on so long, and he got into such a dreadful state, that the doctor said it must be stopped somehow. Ten or twelve men therefore disguised themselves, wore armour under their clothes, and blackened their faces. Then they rushed into the King’s room, “terrible to see,” as the chronicler remarks. The King was so frightened that he let234 them get close to him, and then they seized him, undressed and washed him, and put clean clothes on him. He soon began to get better, but for some time did not know any one but Juvenal des Ursins, who used to go to see him, and whom he would recognise and talk to. Shortly after he recovered his senses.216
On the 16th of June, 1406, there was a total eclipse of the sun between six and seven in the morning. It lasted half an hour, “and,” says the chronicler, “nothing whatever could one see, any more than if it had been night and there had been no moon.” People crowded into the churches, and every one thought the world was coming to an end. “However, the thing passed off, and the astronomers assembled and said that the thing was very strange and the sign of a great evil to come.”217
Two more royal marriages took place. Isabelle, Queen of England, was married to Charles, eldest son of the Duc d’Orléans, and her little brother Jean, to Jacqueline, daughter of the Comte de Hainault and niece of the Duke of Burgundy. Isabelle hated this marriage and cried all the time, it was said at court, because she thereby lost the title of Queen of England. Miss Strickland, in her life of that Queen, observes that if she had been so anxious to keep the crown of England, she could easily have done so by marrying King Henry V., and that her grief was caused by her love for King Richard. But at any rate, it is not difficult to understand that a girl of seventeen might well object to be married to a boy of235 fifteen,218 and her cousin, besides the fact of his being a subject while she had been a queen. Miss Strickland goes on to state that after a short time she became reconciled to this marriage, Charles of Orléans being accomplished and precocious beyond his years, and devoted to her, but it was cut short by her early death.
After the weddings the Comtesse de Hainault wished to take the Duc de Touraine back with her. The Queen objected, and a dispute arose, but as it had been agreed in the contract that he should be under her care, she got her way, took leave of the Queen (the King was then ill), and returned to Hainault. The Count came to meet them with a brilliant suite and received the young prince with great ceremony, and in every place through which they passed was music and rejoicing. The children had the household of sovereign princes, and the Count tried to educate his son-in-law in the ways of the country, that he might live in harmony with his future subjects. The King, when he recovered, made no objection, but consented to the Count’s request that his son should be brought up in Hainault.219
Never within the memory of any one alive had been seen such a winter as that of 1407. The snow lay deep on the ground, wells were frozen to an extraordinary depth, wine was frozen in the barrel236 and bread at the bakers. Many people died of the cold, and it was known as “le grand hiver.”220 The frost lasted sixty-six days, beginning in November. Louis d’Orléans had been ill on and off all the autumn, and had been staying at Beauté for the benefit of the fresh air of the forest which his father had so loved. Valentine and her children were still in the country, and the King at the Louvre. Isabeau had for some time been living in the hôtel Barbette, where she had given birth to her twelfth and last child, who was christened Philippe and died soon after. Isabeau was still weak, and had not recovered from her illness; she had displayed extraordinary grief at the death of this baby, for whom it was said she showed more affection than for any of her other children. She was altogether low and depressed in spirits, and Louis came every day to see and console her.
He was just then living at the hôtel de Nesle, not the great palace opposite the Louvre, but the one afterwards called the hôtel de Soissons, whence he and his daily rides to the hôtel Barbette were known and watched by the men of Burgundy.

On Wednesday evening, November 23, 1407, Louis and Isabeau were having supper and spending the evening together at the hôtel Barbette. Isabeau was splendidly dressed in long robes and an enormous headdress with horns, covered with jewels. It was only eight o’clock, but the night was dark and all the shops in that quarter were closed. Suddenly a messenger from the King was announced for the237 Duc d’Orléans, who said that he desired at once to see the Duke, as he had an important matter to speak to him about.
Louis rose, took his leave, and went out. Mounting his mule,221 he rode carelessly along, swinging his embroidered glove and humming a song as he went. He was only accompanied by two esquires, both riding the same horse, a young German page or esquire, and four or five varlets carrying torches. As they passed a dark corner by a wall close to the house of the Maréchal d’Evreux the horse of the two esquires seems to have been aware of the presence of some men concealed in the darkness, snorted violently, and ran away. The assassins rushed out and assailed the Duke, who, thinking it was a mistake, exclaimed, “I am the Duc d’Orléans,” to which, however, the reply was, “It is you we want.” The two esquires looked round, expecting he was following them, and seeing the struggle, managed to stop their horse, and returned. Louis d’Orléans lay dead on the ground, covered with wounds; his German page, who had defended him to the last, died as they came up, muttering, “Mon maître.” The assassins rode off at full speed, laughing and strewing chaussetrapes, or calthrops, behind them, and setting fire to a house to divert attention from their flight. In a moment cries of alarm resounded on all sides; the street was full of torches; some of the followers of the Duke rushed back to the hôtel Barbette to tell the Queen, who heard the tumult239 with terror and did not know what was happening.
Félibien says that the murderers came out of a house called Notre Dame, because over the door was an image of our Lady, and that it was opposite that of the Maréchal de Rieux. This house they had hired for the purpose, and had been hidden in it for a fortnight. They were eighteen in number. The wife of a shoemaker said that she opened her window, and looking out into the street, she saw the Duke and his little group of attendants come out of the hôtel Barbette; then the attack of the murderers, the short fight, the fall of the Duke, his page, and another of his followers; and that after all was over a tall man wrapped in a cloak, with a red hood drawn over his face, came out of a house opposite, which had lately been bought by the Duke of Burgundy, and pushing with his foot the body of Orléans, said, “Il est mort, éteignez tous et allons nous en.” She shouted, “Murder! Fire!” out of the window, but they turned with threatening words and ordered her to be silent. The Maréchal de Rieux, a friend and partisan of Louis d’Orléans, hearing the clamour and cries, came out of his hôtel with a torch, and to his horror found him lying dead, with his German page also dead and another of his followers dying; the rest had fled. The body of Louis was carried to the nearest church, and then to that of the Céléstins, and laid in the chapelle d’Orléans, which he had founded.222
Isabeau, wild with fear, ordered her litter at once, got into it, and was carried to the hôtel St. Paul,240 where she took refuge with the King, taking up her abode in the room adjoining his; while the news spread through Paris, and the nobles, hastily arming, flocked to St. Paul to guard the King, all the gates of Paris were closed but two, which were strictly guarded and count kept of all who passed out or in.
The King, filled with grief and anger, sent for the provost of Paris and ordered him to find out the assassins, and there was a general wonder who was the instigator of this crime. Suspicions fell upon the Sieur de Canny, who had cause enough to hate Louis d’Orléans, but it appeared that he had not been in or near Paris at the time; and on the 25th the provost of Paris presented himself at the hôtel St. Paul where the princes were assembled, as a council was about to be held, and came into the apartment where they were all waiting for the time for it to begin. The King of Sicily and the Dukes of Burgundy, Berry, and Bourbon were present, besides other princes of the blood.223
The Duke of Burgundy was standing by a window talking to the King of Sicily when the provost of Paris appeared and said that he believed he could find out the author of the crime if he might have permission to search the hôtels of all the princes.224 It appeared that a scullion who had acted as spy for the murderers had been seen to escape and enter the hôtel d’Artois, or Burgundy.
All the princes at once gave leave for their palaces241 to be searched except the Duke of Burgundy, who hesitated and changed colour, and the King of Sicily asked him if he knew anything of the affair. Taking him and the Duc de Berry aside, he confessed his guilt. “C’est moi qui ai fait le coup et ne sais comme il s’est fait, il faut que le diable m’ait tenté et surpris.” The princes looked at each other in consternation. “Dieu!” exclaimed the Duc de Berry, “je perds aujourd’hui mes deux neveux!”
Next day, when he presented himself to attend the council at the hôtel de Nesle, the Duc de Berry stopped him, saying he had better not go in, as it would please no one to see him there; he had better go back to his hôtel. The Duke of Burgundy left the palace, the Comte de Saint-Pol refusing to accompany him, got fresh horses, and fled to the nearest fortress belonging to him, cutting the Pont Saint Maxence behind him to stop pursuit. The Duc de Bourbon indignantly asked the Duc de Berry, “Why did you let him go?” He grieved sincerely for his nephew, and never again would sit at a council, or enter a room, or go to any place where the Duke of Burgundy was.
Departure of royal family—Hundred Years’ War—Valentine d’Orléans—Queen returns to Louvre—Death of Valentine—Forced reconciliation—Philippe de Bourgogne and Michelle de France—Misconduct of the Duc de Bretagne—Death of Isabelle de France—Of the Duc de Bourbon—Quarrels of the Duke and Duchess of Aquitaine—Of the princes.
Never did there appear to be a more conspicuous example of successful crime than the one recorded in the last chapter. Jean Sans-peur had satisfied his vengeance and got rid of his rival, and although retribution eventually fell upon him, he was for many years able to rejoice in his deed and escape the punishment of it by reason of his powerful position and the weakness of those opposed to him.
For Charles VI. was in a much worse state of health than he had been at the time of the attack on Clisson, and though he was transported with sorrow and indignation and swore vengeance upon the murderers, he almost immediately fell into one of his fits of madness, and when he got better he was so243 confused and weak as to be unable to take any decided measures. The Queen had implored him to punish the assassins, but she had no power to do so when he was again mad, and, fearing for her own safety, she left Paris with the Duke of Aquitaine, his wife, her other children and her brother, and took up her abode at Melun with them.225 The other members of the royal family were afraid of the Duke of Burgundy,226 who besides his violent character and immense power, could easily have endangered France by throwing in his lot with the English, who were carrying on the war, notwithstanding the absurd injustice of the claim they put forward to the crown of France.
It will be remembered that, as was explained in the former volume,227 Edward III. of England claimed that throne through his mother, Isabella, daughter of Philippe IV., and persisted in it, although it was finally decided that the Valois, as nearest heirs male, descending from Charles, brother of that King, were the lawful possessors of the throne ascending to the loi salique or Salic law, which henceforward was adopted by the country; and notwithstanding the existence of daughters and grandsons through them, who would have come before the sister of the then last Kings, Louis Hutin, Philippe-le-Long and Charles-le-Bel, supposing the female line to have been admitted at all.
But Henry IV. had still less pretensions than Edward III., for he was not the lawful heir even of244 the English King. If, as has been shown, the claim of King Edward was an unjust one, of course he had no ground to stand upon. If, on the other hand, it were a just one, then it would belong, not to the descendant of his third son, John of Gaunt, Duke of Lancaster, but to the Mortimers, who descended by the female line from Lionel, Duke of Clarence, his second son, Richard II., son of the Black Prince, having left no children. In fact, the Mortimers were the right heirs to the crown of England.228
However, the English were still a very serious danger for France, and the Duke of Burgundy would have been an invaluable ally, whom, in consequence, they did not dare to drive to desperation. And as he always posed as a friend of the people when he wanted to injure Louis d’Orléans, who was supposed to be their chief oppressor, he was very popular with the credulous mob, who did not, after the first horror caused by the assassination of the King’s brother, trouble themselves much about it, but said, alluding to the knotted stick which had been the emblem of Orléans, and the plane of Burgundy, “Le bâton noueux est enfin raboté.”229
Louis d’Orléans had been buried with great solemnity in the Chapelle d’Orléans of the Céléstins, all the princes of the blood, including his murderer, attending in white mantles, the day before the council at which the Duke of Burgundy had owned his guilt. Valentine was still in the country when the news was245 brought to her, with her children. Overwhelmed with grief, she sent her daughter and her two eldest boys, the young Duc d’Orléans and the Comte de Vertus, for safety, to the strong castle of Blois, and with her youngest son and her daughter-in-law, the Princess Isabelle, she set off, in spite of the fearful cold, to Paris, where they arrived on December 10th, went to the hôtel St. Paul, threw themselves at the feet of the King, who had got better again, and implored justice on the murderer. Charles received his daughter and sister-in-law with kindness and affection, and promised all they asked, but early in January another of his attacks came on, and Valentine seeing that nothing could be done and not thinking herself safe, as the Duke of Burgundy seemed all powerful at Paris where he had returned amid the acclamations of the mob, retired to Blois, and fortified herself there with her children.230
The great frost broke up and the melting of the snow and ice swelled the rivers into frightful torrents, carrying away houses, trees, and cattle. The monk of St. Denis says that he saw in the Seine masses of ice three hundred feet long dashing against each other, destroying boats and bridges. At Paris, on the second day of the thaw, the pont St. Michel was swept away, with all the houses on it, and so was a wooden bridge on the other branch of the Seine. Much it was feared that the Grand Pont also would246 give way, as it shook terribly with the icicles, but only fourteen shops fell. The roads were impassable by reason of the rocks and trees with which they were covered by the floods. Many mills were destroyed, and the price of bread rose. The King ordered all bakers to sell flour at the same price, but great distress prevailed, and no one alive had ever seen such a winter.231
About May the Princess Marie took the perpetual vows at Poissy, in presence of the King, Queen, and court.
The King went to Melun to visit the Queen, who had sent for the provost of Paris and made him tell her all that had been done there, and found that the Duke of Burgundy had been trying to throw upon her the same suspicions of magic that he had formerly done upon the Duchesse d’Orléans. He had now left Paris, and Isabeau, greatly incensed, resolved to return there in state. Charles was taken ill again the day after his visit to Melun, and Isabeau sent for several of the princes, including Berry, Bourbon, Alençon, and the young Duc de Bretagne, husband of her second daughter Jeanne, and went to Paris escorted by them, in a gilded coach, the Dauphin Louis, who was usually called Duc d’Aquitaine, riding in the procession for the first time, with a guard of three thousand men in armour. Proclamations were issued that any one misbehaving or causing any disturbance would be imprisoned in the Châtelet, which was indeed no desirable place of abode.232
247 The Queen took up her residence in the strong fortress of the Louvre with her children, where she doubtless felt safer than in the hôtel St. Paul, and had herself appointed regent in case of the King’s illness.
The princes were divided between their anger at the murder of Orléans and their fear of Burgundy, but as he was now absent, the Duchesse d’Orléans and her children came to Paris and appealed to the Duc d’Aquitaine and other princes for vengeance on the murderer of their husband and father. The King was just then ill again. As he, when in his mad state, either did not know Isabeau at all, or else was so fierce that she could not go near him without danger to her life, she had ceased to take much trouble about him. In fact, a young girl called Odette had been chosen, with the full consent of the Queen, to be his mistress and constant companion. She seems to have been the only consolation of Charles, who was devoted to her; always listened to her in his most insane moments, and did whatever she told him. She was called by the household and courtiers, “La petite reine.” Their daughter, named Marguérite de Valois, was recognised by the King, and afterwards married to a French noble.
The monk of St. Denis says she was of low origin, and such has been the general opinion; but M. Vallet de Viriville says there is good reason to suppose her to have been the daughter of Odin de Champdivers, a Burgundian gentleman who had a château near Dôle, where, after the death of Charles, she took refuge.233
248 While the Queen and princes were deliberating on the means of punishing Jean Sans-peur, the news of his victorious return from an expedition to Flanders filled them with consternation. The Queen first tried to borrow money to escape with the King and her children, but no one would lend her any. The King, therefore, left Paris with the Duc de Bourbon on the 3rd of November, and went by boat to the Céléstins, and thence to St. Victor with 1,500 men. The Queen, with the Duke and Duchess of Aquitaine,234 the rest of the children, the Duc de Berry, the Kings of Sicily and Navarre left two days later, went down the Loire to Tours and joined the King. The Duke of Burgundy entered Paris amidst cries of “Noël! Noël!” from the populace.235
Valentine Visconti, Duchesse d’Orléans, despairing of getting either justice or vengeance, returned to Blois with her children, and also the little son of Louis d’Orléans and the Dame de Canny, the afterwards famous Dunois, the Bastard of Orléans.
Jean Sans-peur, finding the King, Queen, and royal family all gone, was much disturbed. He resolved to negotiate, and persuaded his brother-in-law, the Comte de Hainault, who was also father-in-law to the King’s second son, to go to Tours for that purpose.
Perhaps what made peace with Burgundy more possible was the death of Valentine Visconti on the249 4th of December, at Blois. Overcome with grief, disappointment, and anxiety, her health had given way. She took for her device a chante-pleurs236 dropping tears, and the motto “Rien ne m’est plus; plus ne m’est rien,” which she had embroidered on the black hangings of her room. She always charged her sons to avenge their father, and pointing to the little Jean (afterwards Dunois), then six years old, she said, “Celui-là m’a été enlevé, il n’y a point d’enfant si bien taillé pour venger la mort de son père.”
As the result of the negotiations an interview was arranged in solemn state in the church of Notre Dame de Chartres. A platform was raised before the great crucifix, all around sat the King, Queen, Kings of Sicily and Navarre, Dukes de Berry and Bourbon, the Cardinal de Bar, the Archbishop of Sens, and all the princes and great nobles. The Duke of Burgundy, with his advocate, then came forward and knelt before the King, the advocate making a speech of which the arrogance was only thinly veiled by the formal respect for the sovereign, ending by asking pardon for the Duke of Burgundy, to which the latter added, “Sire, de ce ie vous prie.” The King was silent, but the Duc de Berry knelt before the Queen, whispering something to her, upon which she rose, and with the Duc d’Aquitaine and the Kings of Sicily and Navarre, knelt and joined in the request, to which he replied, “Nous le voulons et accordons pour l’amour de vous.” The Duke of Burgundy and his advocate then approached the young princes of Orléans, who in deep mourning250 and with tearful eyes stood behind the King; the advocate saying: “Messeigneurs voici le Duc de Bourgogne qui vous prie qu’il vous plaise oster de vos cœurs la vengeance ou hayne que porriez avoir contre luy pour l’éxcés fait et perpetré en la personne de Monseigneur d’Orléans vostre père et que doresnavant vous demourez et soyez bons amys ensemble;” to which Burgundy added, “et de ce ie vous en prie.” The princes of Orléans, of whom the eldest, the young Duke, was then seventeen, stood in silence, and it was only in obedience to the desire of the King that they reluctantly, and with tears, answered, “Sire, puisqu’il vous plait commander, nous luy accordons sa requeste, et luy pardonnons toute la maleveillance que aurions contre luy car en rien ne voulons désobéir à chose qui soit à vostre plaisir.”237 Peace was then signed, sealed, and sworn upon the gospels, but in spite of the grandeur and solemnity of the scene and the intense interest and importance of the occasion, the whole thing was a hollow and worthless form. There was no repentance in the heart of Jean Sans-peur, and no forgiveness in those of the sons, friends, and followers of Louis and Valentine d’Orléans. As to the Queen, she was too weak and shallow for any lasting passion or feeling, in which her son the Duc d’Aquitaine closely resembled her. He expressed great anger at the murder of his uncle, and yet he persuaded his father to appoint the Duke of Burgundy his guardian. It is true that at this time he was only twelve years old, but the same vacillating, unreliable character was the despair of his friends and of France251 during his life. Burgundian one week and Armagnac the next, he, like his mother, was neither to be trusted by friends nor feared by enemies.
The King and Queen returned to Paris in March. All the Queen’s ladies were dressed in white, and there was much feasting at the palaces of the King and Queen, and the hôtels of the nobles and chief burghers.238
In June the Princess Michelle was married to the eldest son of the Duke of Burgundy, Philippe, Comte de Charolais, and this marriage turned out very happily, for Michelle, then seventeen years old, was a charming character, like her sisters, and Philippe was in most respects unlike his fierce, unscrupulous father. Gay, kind-hearted, and affectionate, he was known as Philippe-le-Bon, and was adored by his subjects as no other duke had been since all Burgundy mourned for Philippe de Rouvre, the last of the beloved Capétienne house.
In August the Duke of Burgundy was hastily summoned by the King and Queen to come to Paris and bring a strong body of men-at-arms who might be wanted, as there was a serious quarrel going on with the Duc de Bretagne, husband of their second daughter Jeanne; who had not only brought over239 a number of English and made war on the Comtesse de Penthièvre, but had quarrelled with his wife because she opposed his proceedings, and was even said to have struck her. Her father and mother were, of252 course, much incensed at this, so they resolved to send the Duke of Burgundy and some of the other princes to attack and subdue him. Jean Sans-peur was all the more willing as the Comte de Penthièvre had married one of his daughters, so he came at once with his troops, and preparations were going on vigorously for the invasion of Bretagne; but the Duke, hearing of the indignation of his mother-in-law, “et de ceux qui gouvernoit le roi,” became so frightened that he came to Paris and made his submission. All the princes were very angry, and the Duc d’Orléans, his brother-in-law, told him that the lion in his heart was not bigger than that of a child of a year old.240 In fact, he seems to have been what some in these days would call “well hustled,” and it would appear that the quarrel between him and the Princess Jeanne was made up. One may imagine that at any rate he must have altered his conduct as we find years after, that the Penthièvres having taken him prisoner and threatened his life, she persuaded her brother, the Dauphin, to forbid them to do him any injury, and taking up arms herself she besieged and took their castles and forced them to set him at liberty.
The next calamity that happened was the death, at Blois, of the Princess Isabelle, Duchesse d’Orléans, in giving birth to her first child. The young duke was overwhelmed with grief, and the only consolation he seemed to find at first was in the infant daughter who survived.241 In her “Life of Isabelle de Valois,” Miss Strickland declares that the second marriage of Isabelle had been an extremely happy one, and253 remarks upon the talents and virtues of the young Charles d’Orléans, the well-known poet, of whose despairing verses on the death of Isabelle she gives a translation, also of a later poem, which she declares to have been written on the same subject.242 The young duke gave the rich dresses belonging to her to make vestments for the abbey of St. Denis, where prayers were said for her.
But none of the misfortunes that befel the royal family or the country stopped the gaieties of the court. The King was at the Palais for Christmas and sent for the Queen, who was at Vincennes, to come and join him and bring the Duc d’Aquitaine, who had hitherto remained under her care. The princes went to meet her and various splendid entertainments took place when she arrived. She formally gave the Duc d’Aquitaine into the care of the King, who appointed the Duke of Burgundy his governor. Nothing, however, could be done in council without consent of the Queen. The Ducs de Berry and Bourbon, disapproving of the overweening power of Jean Sans-peur, left Paris and retired to their châteaux.
Jeanne, Duchesse de Bretagne, who had a son in this year, was very anxious that her brother the Duc d’Aquitaine should come and attend her “lever.” He was not allowed to do so, but a seigneur was sent instead, with splendid jewels as presents for her.243254 The monk of St. Denis in his chronicle tells us that in the early part of July there was a strange omen in Hainault. Innumerable flocks of birds of prey assembled and fought in the air, as if leagued against each other. Storks, herons, and magpies attacked rooks, crows, and jays, and a fierce battle ended in the victory of the former, the ground being strewn with the bodies of the latter, and causing people “of learning and experience” to say that bloody battles would soon be going on.244
It was a tolerably safe prediction to make at that time, more especially as the death of Louis had not, as the Duke of Burgundy supposed it would, annihilated the party of his opponents. On the contrary the Orléanists married the young Duke Charles, now a widower, to Bonne, daughter of Bernard, Comte d’Armagnac, one of the most powerful nobles in the kingdom. He claimed descent from Clovis and had married a daughter of the Duc de Berry. Brave, liberal, unscrupulous, a faithful friend, and a relentless foe, he was the man chosen by the princes to take the leadership of the party which none of them were capable of holding themselves. From this time the name of the party changed from Orléanist to Armagnac, and the strife became fiercer and more desperate than it had ever been under the leadership of the more gentle, easy going Louis.
The royal family and court had sustained a great loss in the death of the Duc de Bourbon, who died in August, 1410, on his way to help the Armagnacs at the head of his troops, for he had never for an instant255 been persuaded to condone the murder of his nephew by the Duke of Burgundy. The lofty character and noble life of Louis II., Duc de Bourbon, stand out conspicuously amidst the corruption and depravity with which he was surrounded during his later years. When the court and rule of his brother-in-law and sister had fallen to his nephews, Isabeau, and the brothers of Charles V., the Duchesse de Bourbon withdrew from court and lived almost entirely with her children on their own estates in the Bourbonnais, where he also spent a great deal of his time, although obliged to be frequently at Paris and elsewhere with his nephews, to whom he was always a good friend and who were extremely fond of him. The only letter existing in the handwriting of Charles VI. is to him. As a son, brother, husband, father, soldier, statesman, and ruler, he was idolised, and after his death his funeral train, as it travelled through the country was followed by crowds of people weeping and lamenting. He had, with the consent of the Duchess, intended after this last expedition to retire to the monastery of the Céléstins at Vichy, and after his death two knotted cords were found under his clothes, which he wore secretly. He knew he could not recover, received the last sacraments and prayed constantly, dying peacefully at the age of seventy-three, leaving a stainless name and a heroic example.245
Meanwhile the dissensions amongst the different members of the royal family only increased. The marriage of the Duc d’Aquitaine with Marguérite de Bourgogne had turned out as badly as possible. He256 slighted and neglected her and made open love to other people. One of the ladies of the Queen’s household especially was his mistress, he wore her colours and device to the great indignation of the Duke of Burgundy, who took the part of his daughter. Isabeau seems to have done the same, for it is frequently mentioned that the Duchesse d’Aquitaine was with the Queen while the Duke was elsewhere.
There was open war between Burgundians and Armagnacs. The Duke of Burgundy had placed his own people in the household of his son-in-law, and tried by all means to gain influence over him, which seemed to be easy enough, and to retain it, which was not easy at all, as no dependence whatever could be placed on any friendship, affection, or opinion of his lasting a single week. The Comte de Clermont, Duc de Bourbon by the death of his father, was like him, an Orléanist. In company with the Ducs de Berry and Orléans, the Comtes d’Alençon and Armagnac, and the Sire d’Albret he had entered into a treaty with the English, offering, among other concessions, to restore to them the duchy of Aquitaine. This treaty was discovered and the above-named princes, who had taken refuge in Bourges, were besieged there by the Burgundians about the end of June, 1412.

But the Duc d’Aquitaine began to get tired of these constant quarrels of Burgundians and Armagnacs, for whose sake the kingdom, which was his own inheritance, was being wasted and destroyed, and he resolved to put a stop to the war. To the consternation of his father-in-law he forbade the gunners and engineers to fire any more, or to demolish or destroy the walls,257 gates, or fortifications of Bourges, saying that the war had gone on long enough. The Duke of Burgundy said that the sooner it was finished the better, only it must be by the complete subjection of the Armagnacs. To which the Duc d’Aquitaine rejoined that he would doubtless welcome their submission to the King, his father, but that in any case this had gone on too long already, to the detriment of the kingdom; that the discredit would fall upon him, the heir of France, and that the opposing party were his uncles, cousins, and near relations, against whom he refused any longer to fight. The Duke of Burgundy was obliged to submit, the siege was raised and peace for a short time restored.246
The princes and court returned to Paris, where the usual amusements and festivities began again. The Duc d’Aquitaine was the leader of all the follies and dissipation that went on. He was as extravagant and licentious as his uncle Louis d’Orléans had been, without his intellect or charm.
Louis d’Orléans, in spite of his countless infidelities, lived on good terms with his wife, but the Duc d’Aquitaine seems not only to have been unfaithful, but brutal. He was not without cultivation, spoke Latin almost as well as French, and was exceedingly fond of music, but he cared nothing for the affairs of state, spent his nights in balls, suppers, and entertainments, and stayed in bed all day. His life seemed even more full of dissipation and debauchery than those of his father and uncle, while it was not redeemed by any of the gallant, warlike deeds of a259 soldier’s life, such as had won them popularity even in early boyhood. Every one complained of the Duc d’Aquitaine; his father-in-law was indignant at his behaviour to his wife, very serious apprehensions were entertained for his health amongst the members of the royal family, the people pointed to the example of his father, whose manner of life had caused his madness, and predicted that if he went on so he would lose his reason in the same way, and even the Queen several times threatened that unless he reformed his conduct in some degree the succession to the throne should be transferred to his brother Jean, Duc de Touraine, who, in the charge of his father-in-law, the Comte de Hainault, was being better brought up.
Riots led by Burgundy—The Duc d’Aquitaine’s ball—His quarrels with Burgundy—The Comte de Charolais—Battle of Azincourt—Death of Aquitaine—The Dauphin Jean—His court—His death—Imprisonment of the Queen—Jean Sans-peur rescues her—Enters Paris by night—Massacre of Armagnacs—The Dauphin Charles—Murder of Jean Sans-peur—Marriage of Catherine de France to Henry V.—Departure for England—Birth of a son—Return to Paris—Festivities—Death of Henry V.—Death of Charles VI.—Retirement of the Queen—Henry VI. enters Paris—Treaty of Arras—Death of Isabeau.
It was May, 1413, the court was at Saint Paul. The King had just recovered from one of his attacks. Every one had been, dressed in white hoods, to Notre Dame to give thanks, and now the important event was the wedding to be celebrated on the following day between the Queen’s brother, Duke Ludwig of Bavaria, and Catherine d’Alençon, widow of Pierre de Navarre, Comte de Mortaigne.
There had been a good deal of uneasiness in the air for some time and the war with England was going on. When peace was made between Burgundians and Armagnacs, the latter were obliged to break their261 alliance with the English king, whose troops under his second son, the Duke of Clarence, had ever since been ravaging Normandy, Picardy, and Maine, notwithstanding that the little Comte d’Angoulême, the youngest of the Orléans princes, had been given them as a hostage. They were also attacking some of the southern parts of France, and swore they would regain the duchy of Aquitaine, their ancient patrimony. Two months ago Henry IV. had died, and the Prince of Wales, now Henry V., hitherto remarkable chiefly for his fast, disorderly, somewhat scandalous life, seemed likely to be a powerful and dangerous enemy. The populace of Paris were deeply discontented, as well they might be, for it was openly declared that the expenses of the King’s household, which used to be 94,000 francs were now 450,000, and yet the tradesmen were not paid; that although the allowance for the King and Queen’s alms went on, scarcely any alms were ever given; that some of the royal servants and officers received enormous salaries, while others could never get any wages paid at all; and that, in spite of the sums allowed for the repair of the King’s castles and palaces, they were in such a state that they would soon fall into ruins.
The Duke of Burgundy had his own reasons for wishing to stir up the people. He was afraid of certain transactions by which he had got hold of a large sum of money being made known by Pierre des Essarts, provost of Paris, who held his receipts for them, and now belonged to the Orléanists; he was uneasy about the power and favour of that party and the estrangement of the Duc d’Aquitaine, who262 disliked him because he was so overbearing and disagreeable.
The Duc d’Aquitaine had been warned that an attack upon the hôtel St. Paul was intended, and advised to arm his household, raise the banner with the fleur-de-lis over the entrance and defend himself. But while he was deliberating with the other princes, instead of taking immediate action, as any of his forefathers would have done, a dreadful noise began to be heard, and a shouting, howling, desperate mob was seen to be rushing down the streets towards the hôtel St. Paul. They surrounded that palace, planted the standard of the city, and with loud cries and threats demanded to speak to the Duc d’Aquitaine.
Among the chief characteristics that distinguish the history of France from that of any other Christian or civilised nation are the furious, credulous, ferocious mobs, whose atrocious deeds continually appear in her annals, and who seem to belong to no particular century; for whether we see them murdering nobles and gentlemen with their wives and children in the fourteenth century, Huguenots in the sixteenth, waggon loads of women, young girls, and little children in the eighteenth—or priests and unarmed hostages in the nineteenth, whether they are called Jacques, or Leaguers, or Septembriseurs, or Communists—they evidently do not excite either abhorrence or shame in the minds of the great mass of their countrymen who have just raised a statue in Paris in honour of one of the most bloodthirsty of the wretches who acted as their leader in the perpetration of those cowardly263 and brutal crimes against which the rest of civilised humanity revolts.
One of these mobs, not a whit more cruel and savage than those which yelled and howled and danced through the streets of Paris in our own and our fathers’ and grandfathers’ days, was now pressing round the hôtel of the Duc d’Aquitaine at Saint Paul. They had certainly much reason for their anger and complaints, but whether their cause is a bad or a good one the means by which they carry it out are always atrocious. On this occasion they put forward a Carmelite monk called Eustace, who gave a harangue on the calamities, bad government, and generally disastrous state of things. The Duke of Burgundy came down, said the King was only just recovered and could not bear this agitation, and advised them to go away. But they clamoured for the Duc d’Aquitaine, who, terrified by the tumult and urged by the Duke of Burgundy, appeared at a window and promised all they asked.
One of their leaders, named Jean de Troyes, then imposed silence, and in a speech received with enthusiastic applause by the people and with scarcely concealed indignation by the nobles, declared that they would do no harm to the Duc d’Aquitaine, but demanded that his evil counsellors should be given up to them; and on his chancellor imprudently asking to whom they referred handed up a list of fifty names, including not only the principal gentlemen of his household, but Ludwig of Bavaria, the Queen’s brother, Edouard, Duc de Bar, cousin of the King, and several of the Queen’s ladies. The princes could264 not pacify them, the Queen wept and raved, the King remonstrated in vain; the Duc d’Aquitaine, turning with a furious look to the Duke of Burgundy, exclaimed, “Father-in-law, this outrage is your doing, for the leaders of it are the people of your house. Know surely that the day will come when you shall repent of it, for things will not always go on according to your pleasure.”
Some of the nobles and ladies came down and gave themselves up, the others were seized by the mob, who broke into the palace and hunted all over the rooms and galleries to find them, tearing one gentleman out of the arms of the Duchesse d’Aquitaine, who tried to protect him. They were carried away on horseback and shut up, some in the Palais, some in the Louvre.
When they were gone, the King went to dinner and the Duc d’Aquitaine retired with the Queen into her room, where they shut themselves up and cried.
Something, however, had to be done, so they sent the Comte de Vertus, who escaped to his brother, the Duc d’Orléans, told him what had happened, and how some of the princes were in prison, and the King, Queen, and Duc d’Aquitaine like prisoners in the hands of the Parisians, and desired the rest of the princes to make haste to come and deliver them.
The King of Sicily, the Ducs d’Orléans, Bourbon, and Bretagne, the Comtes de Vertus and Alençon accordingly assembled at Vernon, and sent a message to the populace that unless the prisoners were immediately set free they would put all Paris to fire and sword.
265 The Duke of Burgundy saw he had gone too far, having infuriated the Duc d’Aquitaine and set all the princes against him, the University of Paris hastened to disassociate herself with the riots, and the chief bourgeois, frightened at what had been done tried by all means and with many apologies, to divert and appease the anger of the royal family. The city was still very unquiet, frère Eustache went on preaching against Aquitaine, saying that the licentiousness and debauchery of such a life as he was leading had already caused the madness of his father and the death of his uncle, and that it would be better to declare his brother, Jean de Touraine, the heir of France; while one Léon de Jacqueville forced his way into the ballroom of his hôtel one night in the middle of a ball and loudly declaimed against him, saying that he dishonoured his rank. The Duke struck him three times with his dagger, but his cuirass saved him. The ballroom was a scene of confusion, the mob rushed to attack the hôtel and were only stopped by the opportune arrival of the Duke of Burgundy, who dispersed them. The Duc d’Aquitaine was so agitated by the scene that he spit blood for days afterwards.247
Burgundy, however, saw that he was rapidly losing friends, and thought it well to send his son, the Comte de Charolais, away. That young prince, therefore, with his wife, the Princess Michelle, set off for Gand, accompanied as far as Lendit by a great body of the bourgeois of Paris of whom she took266 leave affectionately, begging them to deliver her uncle, the Duke of Bavaria, and then she proceeded to St. Denis with her husband, after which they went with a brilliant train to Gand.248
While all these commotions were going on the English made a descent upon the county of Eu, sacked and burnt Tréport and several other towns, took to their ships and sailed for England with their plunder. The Armagnacs were devastating the country, and the Parisians more and more terrified at the threats of the princes. Their party grew stronger and stronger, the King ordered the Duc d’Aquitaine to go and liberate the prisoners, which he did, riding to the Palais and the Louvre and bringing them all away with him except the ladies, who had been liberated soon after they were taken, and two or three gentlemen who had been killed in the riots. Bells rang, feasting went on, the rioters were either seized and punished or else fled, and the princes entered Paris in triumph.249
The Duc d’Aquitaine ordered all the favourites of Burgundy to be seized, one only was spared at the entreaty of the Duchesse d’Aquitaine, the rest were arrested or fled. Jean Sans-peur himself, warned that the streets round the hôtel d’Artois were being watched by night by the Orléanists who were crowding into Paris to join the Duc d’Aquitaine, fled from a hunting party with one gentleman only, rode at full speed in doubt and fear through the forest of Bondy, and next day meeting one of his followers267 with a band of men-at-arms pursued his journey safely to Flanders.
For a little while the Armagnacs were triumphant. The marriage of the Duke of Bavaria took place, and what was more important, Charles, Comte de Ponthieu, youngest son of the King, was betrothed to Marie d’Anjou, daughter of the King of Sicily, at the Louvre in presence of the Queen and Princes, the King being ill at the time.
There was also a talk of marrying the Princess Catherine, youngest daughter of the King and Queen, to Henry V. of England.
In February of 1414, with bitterly cold winds appeared a disease that seems just like the modern influenza. It was attended by cold, cough, loss of appetite, violent pains in the head and general languour. It attacked all classes; judges and lawyers had to suspend their courts, the malady spread and was very dangerous.
A foolish step of the Queen’s had just re-opened the routs and quarrels that always seemed now to rage amongst the royal family. There were certain gentlemen in the household of her son, the Duc d’Aquitaine, whom she distrusted because they had been placed there by his father-in-law, and she wished to remove them. She was just then living at the hôtel St. Paul, and the Duchesse d’Aquitaine with her; the Duke was at the Louvre. Having consulted with the Armagnac chiefs, who were silly enough to countenance her plans, she went suddenly to the Louvre taking the Duchess with her, seized Jean de Croy, and three other officers of her son’s household,268 and threw them into prison. The Duc d’Aquitaine, who liked them, flew into a great rage and the princes could hardly prevent him from rushing out to appeal to the mob, and could not stop him from writing secretly to the Duke of Burgundy to come back.
With two such people as Isabeau and her son what could be done? Jean Sans-peur set off at once with a body of troops—but before he could arrive Isabeau and the princes had contrived to pacify the Duc d’Aquitaine and persuade him to contradict everything he had said, and write to the fortified towns proclaiming the Duke of Burgundy an enemy of the King. Infuriated by this treatment, the Duke of Burgundy produced and displayed his son-in-law’s letters, and continued his march towards Paris, the civil war beginning again with much cruelty and slaughter.
The domestic quarrels of the royal family were worse than ever. The old Duc de Berry disputed the regency during the King’s frequent attacks, with the Duc d’Aquitaine, just as he and his brother had done with Louis d’Orléans, and on the same pretence, his youth and inexperience. Aquitaine was at daggers drawn with his father-in-law, and so far justified his great-uncle’s assertions that besides possessing all the faults of his uncle, Louis d’Orléans and his father, he had no taste for military affairs, no attraction or charm, though he was rather good-looking. He was exceedingly unpopular, hated appearing in public, and shut himself up all day (when he was not in bed) playing the harp and épinette with his musical friends. If the King gave him any business to do he neglected it, and was so ill-tempered269 that he could not bear to be found the least fault with. Music, horses, and dissipation were all he cared for. He had now separated from his wife and reduced her household to a very low estate; he had always disliked her. Historians say that she gave no cause whatever for complaint, but that people made mischief between them.250 The Duke of Burgundy sent a message requiring him to dismiss La Cassinelle and take his wife back, which only made him more angry. He had removed her from his mother’s care and sent her to St. Germain-en-Laye,251 also seizing some treasure kept by Isabeau at the houses of confidential agents, taking advantage of the illness of the King his father to do as he chose. This was the beginning of the Queen’s dislike for Armagnac, who was mixed up in the affair, and her inclining towards the Burgundian party.
In March, 1415, the Emperor of Germany paid a visit to the French Court, where he was entertained with the usual lavish profusion. He, in return, gave a great banquet at the Louvre to the ladies of the court and bourgeoises of Paris, “and to each one was laid a German knife, and the strongest wine that could be got. And everything was so spiced they could hardly eat it. There were many minstrels, and after dinner they danced and some sang. And when they left to each was given a gold ring, which, however was not of much value.”252
When the summer came round the truce with270 England expired. English troops from Calais and other places began to attack the French provinces, and it was rumoured that King Henry was gathering a great host at Southampton to invade France.
It was nearly sixty years since the battle of Poitiers, and seventy since that of Crécy, and there were old people alive who could remember the confusion, dismay, and terror of that time. The Duc de Berry had himself been in the battle of Poitiers, from which he had fled; while the Duke of Burgundy, then a boy of thirteen, had fought to the last beside their father, King Jean, and been carried prisoner with him to England.
Times were still more disastrous now. With a mad King, a worthless heir-apparent, and a number of princes of the blood without either capacity or conduct, there were no leaders whom the people could trust or love, or whom they would follow and die for as their fathers and grandfathers did for Philippe de Valois, King Jean, the Duc de Bourbon, the gallant Princes of Navarre, the heroic King of Bohemia, or the noble chiefs of the Capétienne house of Burgundy.
However, it was necessary to make preparations. Enormous taxes were levied in haste, and everywhere bands of soldiers were hurrying up to join the army, and plundering the villages on their way. What the tax collectors left they carried off, and the people in terror and despair left their homes and hid in the woods, longing only that the campaign might be over, whichever side won.253
271 Charles d’Albret was appointed commander-in-chief, and all the highest commands were given to Armagnacs. Jean Sans-peur took no post in the army at all, and forbade the Comte de Charolais to join; being, besides politically hostile, resolved not to risk his only son as had been done to their cost by the former house of Burgundy.
Early in August the English fleet sailed from Southampton, and sixteen hundred ships entered the Seine, passed up between Honfleur and Harfleur, and landed the troops, who proceeded to invest the latter town, which was an important commercial place and the key of Normandy, being a strong fortress surrounded with deep moats and massive walls and towers.254 It was bravely defended, but as no help came from the French army which was slowly gathering at Vernon, the town surrendered on September 22nd.
King Henry repaired, provisioned, and garrisoned the place, and then began his victorious march through France. Charles, who just then was in his right mind, came to Rouen with the Duc d’Aquitaine and the rest of the princes in October, and at a hurried council it was decided that a battle must be fought, but that the King and his son should not be present for fear of a calamity such as befel King Jean at Poitiers. All over France the nobles were summoned to join the royal standard with their vassals, but the princes were stupid enough to refuse a body of six thousand armed men offered by the city of Paris whose services they disdained.
272 The Comte de Charolais, who knew there was going to be a battle but did not know when, was wild to get away and join the army. His tutors, however, had been warned by the terrible Duke of Burgundy that he made them responsible for his not doing so, and they were at their wits’ end what to do. They did not like to tell the young Philippe, lest he should find some way of circumventing them, and when a summons arrived for him from the Constable d’Albret, he declared he would go. He was then at Arras, and in much perplexity they pretended to consent, and leaving that city got him to the castle of Aire, where the Constable again sent several seigneurs and Montjoye, King-at-arms, to fetch him. As long as they could the distracted tutors put off his departure, carefully concealing from him the time when the battle was to take place, but most of his people kept escaping secretly to go to the front, and at last they were obliged to tell him, to appease his anger, of his father’s orders, which he dared not disobey but retired to his room in despair and shut himself up there crying. (“Moult fort pleurant.”)255

The King of England desired to cross by the ford of Blanchetache, where his great-grandfather, Edward III., had passed over the river seventy years ago, but the place was too strongly guarded, so he marched along the bank for some distance and came up with the French army which was waiting for him at a place enclosed with little woods between the villages of Rousseauville and Azincourt. It was Thursday, October 24th, about the hour of vespers, when the273 two armies confronted each other. Philippe, Comte de Nevers, and several young nobles had just been knighted by the hand of Boucicault, Marshal of France. The Constable had arrived with the royal banner, the Oriflamme.256 Around it rose the banners of the princes, barons, and chevaliers with their274 followers who had flocked to the standard of France. Great fires were lighted, for the night was cold; a drizzling rain had begun to fall, and they were waiting for the English army which must pass on its way to Calais.
The English were hungry and tired with their long march, but they came up with the sound of trumpets and martial music, and the heavy tramp of horses and armed men, so that the earth seemed to tremble with the echo. Silently and composedly they took up their perilous position, well aware of the danger which lay before them, for the French host outnumbered them by at least three to one, and had a much larger proportion of cavalry. But they thought of Crécy and Poitiers, passed the night in attending to their horses, bows, and armour, and prepared for death by confessing their sins, and receiving the Sacrament of the Body of Christ.257
The French had scarcely any musical instruments to rejoice their spirits, and their horses did not neigh, but made scarcely a sound all night, which many considered an evil omen. The rain and mud and cold depressed their spirits which sank lower as they, too, remembered Crécy and Poitiers. All night they were calling to each other in the darkness, and many who had been at enmity made friends again, forgave each other, embraced, and drank out of the same cup, as they thought that perhaps they were about to see the dawn of their last day.258
Still, when morning broke and they saw their own275 great superiority in numbers and strength, they gathered confidence, and thought indeed that the English army could not escape them. And between nine and ten they advanced to battle, bending their heads so that the arrows might not pierce through their visors.
King Henry had heard mass at the break of day, and then mounting his grey charger had arranged his troops for the battle, the archers forming the right and left wings. He rode through the ranks and harangued the soldiers, pointing out the danger of their position, from which the only escape was victory. He reminded them of those other battles in which their fathers and grandfathers, wearied and outnumbered, had fought and conquered, and then dismounting from his horse he placed himself at the head of the infantry and led the attack. Twice they halted to take breath, and twice they came on with a great shout, while a shower of arrows rushed through the air into the vanguard of the French army. The English archers were slightly armed and poorly dressed, but strong and active; they wore an axe or sword at their girdle and carried a pike to force their way through the thickest of the fight. In the French army there was neither order nor discipline. The King and his sons were not present as at Crécy and Poitiers, and the princes would obey no other leader. Those who were not placed in the vanguard refused to stay with their men but pressed forward to join the line of cavaliers in heavy armour who bore the noblest names in France, and stood in the front of the battle.
276 A squadron of cavalry was ordered to charge; they were the flower of the French troops. They came on impetuously at a gallop, but the ground was soft with deep mud, the horses slipped, floundered, and became unmanageable, a flight of arrows falling amongst them added to their confusion, they turned and fled. Then the English throwing down bows and pikes, seized their swords and axes and rushed into the thick of the fight. They broke through the first division, but when they came to the second and third there were no leaders, as they had all gone to the front ranks. The subalterns could not lead the soldiers, who hesitated, wavered, and at last gave way, and the battle became a rout. The English were too few in number to pursue as they dared not separate, and Henry seeing a troop coming up, and thinking the enemy were being reinforced, gave the order to put the prisoners to death, which command began to be carried out, but presently, seeing that the troop was also retreating, the King ordered the massacre to be stopped, which was at once done, but not before many lives had been sacrificed, and a deep stain inflicted upon his name.
The English lost sixteen hundred men, including the Duke of York and Earl of Oxford, but the losses of the French are said to have been ten thousand men and fifteen hundred prisoners. Among the dead were the Duc de Brabant and Comte de Nevers, brothers of the Duke of Burgundy, the Duc de Bar and his two brothers, the Constable d’Albret and the Duc d’Alençon, all nearly related to the King, and numbers of other nobles and gentlemen. Among the277 prisoners were the Ducs d’Orléans and Bourbon, the Comtes de Richemont and Eu, Marshal Boucicault, and many others of high degree.
But the army of King Henry was too small and too exhausted to push its victory any further; in fact, its safety appeared to him so doubtful that he ordered all the plunder taken to be burnt, and taking their prisoners with them the English troops turned their steps towards Calais and embarked for Dover a week after the victory.259 The Queen was at Melun when the news of the disaster arrived. She was ill at the time, and had also become so stout that she had been obliged to give up riding, therefore in haste and consternation she had herself carried in a litter to Paris, taking with her the Duchesse d’Aquitaine, for fear of falling into the hands of the Duke of Burgundy, who directly he heard of the result of the battle and the losses of the Armagnacs, started for the capital at the head of ten thousand cavalry. The Queen and Duchesse d’Aquitaine were at the hôtel d’Orléans,260 and the Duc d’Aquitaine, who now returned in haste to Paris, went to the hôtel de Bourbon; the King, the Duc de Berry, and Comte d’Armagnac also hurried back; the King of Sicily took refuge at Angers, to get out of the way of Jean Sans-peur, who was his bitter enemy, because he had first betrothed his son to the278 daughter of the latter, a little child, and then changed his mind and sent her back to her father.
The Duc d’Aquitaine sent to forbid Burgundy to advance, and not liking to set his son-in-law at defiance he arrested his march, but in the midst of all the anxiety and commotion that was going on, Louis Duc d’Aquitaine died after a few days’ illness, having, as had always been foretold, utterly destroyed his constitution by the excesses of his life. Before his death he expressed his remorse at his conduct to his wife.261 Of course there were some who declared that he had been poisoned, and that Jean Sans-peur had done it, but as his death prevented the Duke of Burgundy’s daughter from being Queen of France this is not at all likely, however angry he might have been at Aquitaine’s treatment of her and disregard of his own counsels.
The next Dauphin, Jean Duc de Touraine, lived with his wife and her family in Hainault, where the Queen and Council (the King being ill) sent, to desire him to come at once to Paris. But Jean, brought up by the near relations and firm allies of Burgundy, was far more Burgundian than his elder brother, the son-in-law of Jean Sans-peur. He refused to receive the deputation except in the presence of the Burgundian ambassadors, and he would not go to Paris unless his uncle of Burgundy might go too. Louis d’Aquitaine had died at the beginning of 1416, and it was not until early in 1417 that, after much discussion279 and exchange of letters and messengers he set off with his father-in-law for Compiègne, as the Queen absolutely refused to come to St. Quentin as they wished.262
They established themselves in the royal palace of Compiègne, where they were joined by the Dauphine and Comtesse de Hainault, and where they lived in state and splendour as Jean always had done, for the Hainaults were very rich. Jacqueline was their only child, and they were exceedingly proud of the alliance with the son of the King, especially now he had become Dauphin. He was now eighteen, and seems to have had more constancy of purpose than his brother, but to have been entirely under the influence of the Comte de Hainault and Duke of Burgundy. What he was really like is impossible to say. De Mézeray calls him “un jeune homme capriceux, acriastre, déplaisant en mœurs et façons.” Juvenal des Ursins and Paradin observe that it was a pity he did not live to be King, as he had been well brought up and taught by the Comte de Hainault who was a wise prince. The monk of St. Denis declares that he was a noble character, but he generally appears to have had that opinion of the fleurs-de-lis. It was very likely that he was better than his eldest brother, as he easily might have been. He was extravagant and magnificent like all his family, and those who surrounded him and had charge of his education were always praising his lavish generosity and inciting him to280 hold a more brilliant court than his parents the King and Queen.263
That the Dauphin and Dauphine lived in great splendour at Compiègne is proved by many of the bills and accounts still existing, the costly stuffs of their dresses, the magnificent plate and jewels, and the presents they made to each other and to the members of their households. Messengers went perpetually between Compiègne, Senlis, Paris, and other places to fetch things and to carry letters. There is a record of a sum paid to the Provost of Senlis for having escorted “pour la doubte et péril des chemins,” a sum of money from Senlis to Compiègne. Sums of money are also given to the King’s minstrels, to the choristers of the Dauphin’s chapel, and to Hennequin who takes care of his pet dogs; also for tapestry hangings for his room, nine pieces, with a stag hunt and boat hunt on green worked with silk, gold, and silver.264
Isabeau must have been estranged from the son who had been so separated from her; for we find that when she came to Senlis with her youngest son Charles, who had been made Duc de Touraine, Governor of Paris, and Duc de Berry (the old Duke having just died), although the Dauphine was taken there to pay her homage, and spent some hours with her “en grande léeses,” Isabeau returned to Paris with the Comte de Hainault without seeing the Dauphin. Possibly she may have been irritated against him, for281 he still refused to come to Paris, now in the hands of the Armagnacs, and demanded the regency during the King’s malady.
But amongst the schemes, disputes, and rivalry of the two parties, one of which put its trust in the Dauphin, and the other fixed its hopes on his brother, the Duc de Touraine, then between fourteen and fifteen years old—a sudden change raised the spirits of the one and filled the other with dismay. The Dauphin began to be ill. Doctors were sent for; we read of “chevaucheurs” sent to ride “haste hastivement” to fetch fruit and medicines from Paris; and prayers and masses said and sung in chapels and convents for his recovery.
Early in April the Comte de Hainault, secretly warned that he would be arrested by the Armagnacs, escaped early in the morning from Paris on pretence of a pilgrimage to St. Maur-des-fossés, in the forest of Vincennes, from whence he rode in haste to Compiègne. But he found the Dauphin ill in bed “with a swollen body and other symptoms of poison,” according to some historians, or, as others say, with an abscess in the ear. At any rate he died in a few days,265 and there was an outcry of poison, perhaps with more probability than usual, for he had not ruined his health like his brother, and though it could be nothing but an outrageous calumny that the Queen had done it by means of a gold chain she sent him, it was more likely that if there had been foul play at all it came from the Armagnacs who had282 everything to gain by the death of the Burgundian Jean and the succession of the Armagnac Charles, the son-in-law of the King of Sicily and bitter enemy of Burgundy.
Isabeau was certainly most unlucky in her relations with her sons. Three of them died in early childhood, with Louis she latterly had frequent quarrels, Jean was estranged from her; but the unnatural strife and hatred between her and her remaining son Charles was the crown of all the calamities of her reign. It seems to have been caused in the first place by Armagnac, who, in consequence of the death soon after each other of the King’s two elder sons, the Duc de Berry, the King of Sicily, and the Comte de Hainault, had become exceedingly powerful and, the only person whose power and influence might stand in his way being the Queen, proceeded to make mischief between her, the Dauphin, a weak, characterless boy, and the King, whose mind was now more clouded and his intellect feebler during the intervals between the attacks of his terrible malady.
Added to all this, the King of England threatened that he would soon be in Paris and there were hurried preparations to resist him. All the places that lay on the road by which he would pass were strengthened, moats deepened, walls repaired, batteries of wood and stone made, and stores of provisions laid in. St. Denis was especially fortified, and the monks had to contribute largely to the defence fund, for which purpose they were obliged to sell two large gold crowns and a quantity of silver plate. The holy relics, including the body of St.283 Denis, were taken by some of the monks to Paris and hidden in a safe but secular place, which, however, caused so much scandal that they had to be brought back again; and the monk who writes of this time says that for eleven months the trumpets of the enemy were continually in their ears.266
The Queen was holding her court at Vincennes and had placed in command of the troops who acted as her guards, Louis de Bosredon, and the Sires de Graville and Giac, dissolute young nobles, who spent enormous sums of money and passed their time in feasting, revelry, and in carrying on intrigues with the Queen’s ladies, and, it was rumoured, even with the Queen herself. At least it was said by Armagnac and his party, to whose interest it was to circulate such a report, and who succeeded in making the Dauphin and the King, who then had a lucid interval, believe the story. Being at the same time weak and violent, and so, as is always the case, more dangerous and mischievous than a person who, though violent, is also strong, they listened to the words of Armagnac, and the King riding in haste one evening to Vincennes, passed Bosredon, who instead of dismounting according to the usual etiquette, saluted slightly and rode on. This put a finishing stroke to the anger of Charles, who ordered him to be arrested. He was put to the “question” or torture, and was said to have made compromising confessions respecting the Queen. He was thrown into the Seine and drowned; the other young nobles escaped. It is very likely, whatever admissions were wrung by these284 iniquitous means from Bosredon, that he was not guilty; as to Isabeau she was about forty-seven years old, had grown fat, and was suffering from gout, which circumstances make such an accusation as far as she was concerned highly improbable, though the disorders of her court were doubtless deplorable. However, the conspiracy had succeeded, she was sent to Tours with the Duchess of Bavaria her sister-in-law, and not allowed as she wished, to go to Melun, where she had much treasure, a great deal of which was seized by the Dauphin, and the part he took in this outrage aroused in the Queen that undying hatred which caused such disaster to him and to France.
It would have been better for the Dauphin Charles if he had let his mother and her friends and her treasure alone, for Isabeau, though capricious and foolish, was not a woman to submit tamely to such an outrage as this. And Jean Sans-peur was neither capricious, foolish, nor weak, and it was to him that her thoughts turned in this crisis.
For about six months Isabeau led an intolerable life at Tours in close captivity, guarded by Jean Picard, who had been her own secretary, and had betrayed to the Dauphin the existence of a collection of gold, silver, pearls, and diamonds which she had entrusted to the keeping of the Abbot of St. Denis; Guillaume Toreau, her chancellor, and Laurent du Puy, whom she hated more than any of them, as he prevented her from writing or receiving letters without his leave and treated her with disrespect, even speaking to her without taking his hat off.
She managed however to send a secret message to285 the Duke of Burgundy with her seal. Jean Sans-peur was besieging Corbeil, but he knew that the Queen was worth more to him than the possession of that or any other town, so he raised the siege and rode day and night to Tours where he arrived on the Feast of All Souls.
The Queen meanwhile had signified her intention of performing her devotions at the abbey of Marmoutiers on the banks of the Loire, near Tours. The three gaolers did not venture to object to this act of religion. While prayers were going on they approached the Queen and said that a great company of Burgundians and English were close at hand. Just then Hector de Saveuse, lieutenant of the Duke of Burgundy, having posted armed men all round, entered the church and saluted the Queen in the name of his master who was close at hand. Isabeau pointed to her three gaolers saying, “Arrest these three men.” This was immediately done, but Laurent du Puy, who knew it was all over with him, broke away, ran down to the Loire, tried to jump into a boat that lay moored to the shore, fell into the water and was drowned. In two hours the Queen and the Duke of Burgundy had met and become reconciled; the Queen assumed the regency, and under the powerful escort of the Duke of Burgundy, having been recognised by the authorities of Tours, made a progress through central France with her ladies, and fixed her court and parliament at Troyes. She had a seal engraved with the arms of France and Bavaria and issued proclamations beginning, “Isabelle, par la grace de Dieu Royne de France.” The civil war now286 raged as fiercely as ever, and the English had conquered most of Normandy and were besieging Rouen.
In May, 1418, a party of young men, partisans of the Queen and Burgundy, led by Perrinet le Clerc, whose father kept the keys of the porte S. Germain-des-Près, went to Seigneur de L’Isle Adam, and offered to admit the Burgundian troops by night into Paris. It was arranged that the latter should be at the gate with eight hundred men, and Perrinet should contrive to steal the keys from his father who always kept them under his pillow, and who would have distrusted any one rather than his son. With a band of the conspirators Perrinet crept secretly in the darkness to the Porte St. Germain and awaited the coming of the soldiers. It was nearly two hours after midnight when the gate was unlocked, L’Isle Adam and his troops in order of battle passed stealthily through, and Perrinet le Clerc locked the gate behind them and threw the keys over the wall into the moat, while the Burgundians began their silent march through the dark, narrow streets, no word being spoken until they stood before the Châtelet where a body of four hundred armed men waited for them, and then began the attack on the houses of the Armagnacs with a sudden rush amid cries for the King and Burgundy. Forcing their way to the palace they seized the King, induced him to grant all their demands and rode away with him. Armagnac escaped in disguise; Tanneguy du Chastel, provost of Paris, aroused by the noise and tumult, hastened to the hôtel of the Dauphin, wrapped him in a cloak,287 and hurried him and the Dauphine into the Bastille where some of their party had taken refuge. Doors were flung open, people rushed out of their houses with arms in their hands, torches gleamed and cries resounded in the streets, plunder, fighting, and slaughter went on all night, and in the morning both King and capital were in the hands of the Burgundians. Armagnac was betrayed by the man who had sheltered him and carried off to prison; Tanneguy du Chastel escaped with the Dauphin to Corbeil and thence to Melun; the town was given up to violence, pillage, and murder; the Armagnacs fled in confusion; and the Duke of Burgundy went to Troyes and brought back the Queen in triumph. All the chiefs of the Burgundian party came to meet them with six hundred of the principal citizens, bringing velvet robes covered with crosses of St. Andrew for Burgundy and his nephew which they put on to enter Paris. The Queen was seated on a “char,” the streets so lately running with blood were strewn with flowers, and the King received the Queen with affection and satisfaction.

But very soon the approach of the English army compelled them to take refuge at Troyes, while a dreadful pestilence was ravaging the country. The Abbot of St. Denis died, and many other people of importance. Many fled from the country, and for four months there was a dreadful mortality.267 The Duke of Burgundy was now declared Captain of Paris instead of the Dauphin, who remained at Bourges. The King, Queen, and Princess Catherine were completely288 under the influence of Burgundy, whose eldest son was, it will be remembered, married to another daughter of the King, and whose aim now was to get the Dauphin also under his guidance, which did not seem to be at all impossible, Charles being only fifteen, and having no more brains, capacity, nor decision of character than his brother Louis; being absolutely guided by whoever he was with, and at present surrounded by persons of no particular rank or weight. The young Comte de Clermont, son of the Duc de Bourbon, who was about the age of the Dauphin and had just returned from captivity in England, had come over to the Burgundians, saying that wherever the King was, there was his place, and it was hoped the Dauphin would do the same. Armagnac was dead, and his chief counsellor was Tanneguy du Chastel, a Breton gentleman. Burgundy had sent his young wife Marie d’Anjou back to him and was anxious for a reconciliation.
The English conquests were spreading. Rouen was besieged and taken, and though negotiations were going on for the marriage of the Princess Catherine, Henry V. demanded as her dowry all the provinces conceded to his great-grandfather by the peace of Bretigny, to which the King and Duke of Burgundy would not agree.
As the King and Queen started to take the Princess Catherine to meet Henry V. at Pontoise, however, the King was seized with an attack of frenzy, so he had to be left there while the Duke of Burgundy went on to Melun with the Queen and Princess.
289 Henry V. met them, and at once fell in love with the Princess who was just nineteen and extremely beautiful; but he would not come to terms about the dowry, and Isabeau, thinking to inflame his passion for her, only let them meet once and then sent her back to Pontoise. However, this only infuriated Henry, who told Burgundy that he would have the Princess and the lands too, in spite of them, “et je vous chasseray de France, vous et vostre Roy.”268
The negotiations not having resulted in much good the King desired the Dauphin and Duke of Burgundy to make peace. The Duc de Bretagne went to and fro between the Dauphin, his brother-in-law, and the Queen and Burgundy. “Everywhere there was a great longing for the success of the arrangements for there was great desolation in all parts of the kingdom for the war was of father against son, brother against brother, uncle against nephew. And the worst was when in one town were held the two factions of Burgundy and Armagnac, and thieves and robbers were everywhere and merchandise always and everywhere lost.”269
It was difficult enough to persuade the Dauphin to agree to terms, but the Queen sent the Dame de Giac, an old lady the Dauphin had been very fond of from his childhood, and who was said to have been at one time the mistress of the Duke of Burgundy, to Pouilly where the conference was going on. She went from one tent to the other and managed so to arrange matters as to bring about a reconciliation.290 The Dauphin, who, though he had no sense, had very pleasant manners, showed great courtesy to the Duke and when they separated frantic rejoicings took place at Paris, bells ringing, feasting in the streets, singing and dancing going on all night long.270
But, as at the marriage festivities of Richard II. and Isabelle, a great storm came on during the conference, “and,” says the monk of St. Denis, “the heavens were black with clouds, there was thunder and lightning and torrents of rain and huge hailstones which destroyed the vines and crops. Some said this storm arose from natural causes, but it was most generally believed that the evil spirits could sometimes produce these disorders and that perhaps the interviews of the princes were disagreeable to them. Therefore people did not believe in the stability or durability of the treaty concluded. It was also the opinion of several of the learned astrologers. For my part I leave their judgment to Him who reigns in the heavens.”271
The truce with England expired and the war broke out again. The English troops took many towns and castles, the Duke of Burgundy retired with the King and Queen to Troyes, and no adequate measures were taken against the enemy. The Dauphin returned from Touraine in September, and sent Tanneguy du Chastel to Troyes to ask for another conference with the Duke of Burgundy, who at first refused, saying that there was peace between them and the Dauphin had much better come to Troyes to291 his father and mother. However, he allowed himself to be persuaded and consented to meet the Dauphin at Montereau, in spite of the entreaties and warnings of his own friends and followers who dreaded the vengeance of the Armagnacs for all his deeds, from the murder of Louis d’Orléans to the late massacres of their friends and relations in Paris, besides their fear of his gaining over the Dauphin the influence he already possessed over the King and Queen.
The interview was to take place on the bridge of Montereau, to which the Duke of Burgundy rode on the 10th of September, about three in the afternoon. As he dismounted to go on to the bridge, three of his servants who had been upon it examining the barrier across it, which they did not like the look of, came up to him and again begged him not to risk himself on it, but it was no use. At the barrier in the middle of the bridge he met the Dauphin, the one through which he himself passed having been locked behind him. After a few words of conversation, the Dauphin, as the Duke knelt before him, began to reproach him with having done nothing to oppose the English. At that moment one of the Armagnacs pushed him from behind, Burgundy laid his hand on his sword which had got behind him to pull it forward. Robert de Loir, who had pushed him, exclaimed, “Mettez-vous la main à vostre épée en la présence de Monseigneur le Dauphin?” Tanneguy du Chastel approached, made a sign, and saying “Il est temps” struck the Duke with an axe. He tried to draw his sword but it was too late, there was a cry of292 “Tuez! tuez!” a fierce scuffle; then Jean Sans-peur lay dead at the feet of the Dauphin, and Louis d’Orléans was avenged.
The rage, consternation, and mischief caused by this event throughout the country, just as every one thought there was going to be a little peace, cannot be described. The Queen and her son-in-law Philippe, Comte de Charolais, now Duke of Burgundy, prepared to take their revenge. Philippe, overwhelmed with grief, would scarcely see or speak to any one for days. To his wife he said, “Michelle, your brother has murdered my father”; and then finding that she was fretting and making herself miserable fearing to lose his affection he comforted and reassured her. The Queen and Duke of Burgundy sent proclamations to all the chief towns in France denouncing the Dauphin for the murder of Jean Sans-peur; and made a treaty with the King of England at Troyes, by which they agreed that he should marry the Princess Catherine and not only act as regent of France during the King’s illnesses but succeed to the crown to the exclusion of the Dauphin.
Isabeau, who was then at Troyes, sent the Bishop of Arras secretly to Henry to invite him to come there, and to take him a love-letter from the Princess Catherine, with which he was delighted.272 The young princess was deeply in love with Henry V. and very anxious to be Queen of England, and had all along persuaded her mother, whose great favourite she was,293 to help her in the matter and forward the alliance. Isabeau was glad enough to do so for she loved her daughter and hated her son, and this marriage fell in with her views regarding them both. The wedding was celebrated at Troyes, June 3, 1420, with extraordinary magnificence. The Kings and Queens of France and England and the young Duke of Burgundy entered Paris, and spent Christmas there; after which Henry and Catherine went on a visit to England. The young Queen seems to have felt bitterly the separation from her parents and country; an ancient chronicle says of her: “Item, ce jour party la fille de France nommée Catherine que le roy d’Engleterre avoit espousée et fut menée en Engleterre, et fut une piteuse départie, especialement du roy de France et de sa fille.”273
Just before Christmas, 1421, came the news of the birth of a son to the King and Queen of England. In Paris as in London bells rang and bonfires blazed in the streets; for the child, afterwards the unfortunate Henry VI., was born the heir of both England and France. The winter was an unusually cold one, the frost being so severe that no corn could be ground except in windmills, all the watermills being frozen up.
In May, 1422, Queen Catherine came back escorted in great pomp by a great body of English troops. She arrived at Vincennes, where she stayed some weeks with her parents and husband who received her, as an ancient chronicler observes, “as if she had been an angel.” The court kept Whitsuntide at294 Paris, Charles VI. and Isabeau at the hôtel St. Paul, Henry V. and Catherine at the Louvre. The people thronged to see the great banquets at which the King and Queen of England feasted in splendid robes, crowns, and jewels; while those of the King and Queen of France were neglected, and at neither were food and wine given away according to ancient custom, which caused much discontent. But these were the last great fêtes of the French court in the reigns of Charles and Henry. In the following August the King of England, who had for some time been suffering from a dangerous and, in those days, incurable malady, died at Vincennes, and his death was followed in October by that of Charles VI. at the hôtel St. Paul. Henry died at thirty-six, in the midst of a brilliant and victorious career King of England and almost King of France, leaving a widow of twenty-one overwhelmed with grief, an infant heir to two kingdoms, and a nation in mourning. Charles, whose reign began so magnificently, passed away in the half-deserted palace of St. Paul. Although Isabeau was living there at the time, only his confessor, almoner, and the first gentleman of his household were with him when he died, at the age of fifty-three.
The Queen does not seem to have been present at the funeral, the Dauphin was an exile and an enemy, and the chief mourner was the Duke of Bedford, Regent of France for Henry of Lancaster. The funeral waited till his arrival at Paris and there was much dispute as to what the arrangements should be, it having been so long since a King of France295 had been buried that very few people remembered, and there were no records on the subject.
The litter was so constructed, that it could be made narrower to pass through the doors of St. Paul, Notre Dame, and the narrow streets, and widened in the broader thoroughfares. On it was placed the coffin covered with a pall of cloth of gold and scarlet with deep border of blue velvet embroidered with golden fleurs-de-lis, which fell down to the ground. It was surmounted by an image of the King dressed in royal robes, with mantle of ermine, crown, and sceptre. The litter was carried by the “varlets” of the King and followed by two hundred gentlemen of his household in black, bearing torches and shields with the arms of France. Next came the mendicant orders, Jacobins, Carmelites, Cordeliers, and Augustins, then the colleges, parochial clergy, ecclesiastics of the collegiate churches and university, bishops, abbots and nobles, members of Parliament, the four presidents in mantles of scarlet and vair holding the four corners of the pall, the King’s chamberlain, esquires, and many of the chief citizens; the Duke of Bedford, Regent of France, rode behind the litter. The streets and windows were crowded with people mourning and lamenting, and so, at the hour of vespers the body of Charles le Bien-aimé was carried to Notre Dame. The church was hung with costly stuffs covered with fleurs-de-lis, and blazing with torches, the psalms and vigils for the dead were chanted “et fut nuict.” Next morning, after mass, the procession formed again and the body was carried in state to St. Denis, where all night the monks296 chanted psalms and vigils for the dead; and then next day, after a magnificent requiem, Charles VI. was buried by his father and mother, and through the dim aisles and cloister of the great abbey resounded the cry, “Pray for the soul of the most excellent prince, Charles VI., King of France.”
After the religious rites were over the Duke of Bedford dined in his own room, but there was a great dinner in the vast hall of the abbey to which crowded prelates, nobles, gentlemen, and officials, maîtres d’hôtel restraining those who were pressing to the chief table and had no right there, and alms being distributed while the banquet was going on to more than five thousand poor people.
Isabeau survived her husband twelve years, but this latter part of her life contains scarcely anything of sufficient interest to record. After the death of her son-in-law Henry V., with whom she always got on well, the departure of her daughter Catherine for England, and the death of Charles VI., she lived in the half-deserted palace of St. Paul with a diminished household and shattered fortune. Her daughter the Duchess of Burgundy died in 1423, and of her twelve children there only remained the son she hated, the Queen of England, now far away, and her second and third daughters, Jeanne, Duchesse de Bretagne, and Marie, Prioress of Poissy, whom it is to be supposed she sometimes saw.
Her brother, Ludwig of Bavaria, also survived her. But war and famine and pestilence had devastated the kingdom. Grass grew in the streets of Paris, and wolves came and attacked children outside the297 walls and even within the city.274 One event of interest happened in 1431, which was the state entry of her grandson Henry VI. into Paris. While Isabeau stood at the window of the hôtel St. Paul watching the pageant, the child looked up at her as he rode by, and, some one saying to him, “That is the Queen-dowager of France, your grandmother,” he took off his cap and saluted her. At the sight of the young King, the son of her favourite daughter, riding as she herself had done amid the acclamations of the people through the streets which had once been decorated and thronged to do her honour, Isabeau burst into tears and turned from the window. The King, then ten years old, afterwards went to visit his grandmother at the hôtel St. Paul.275
Isabeau died there in 1435, September 29th. She had a favourite old German lady who lived with her to the last and with her other ladies followed her funeral cortège to Notre Dame on the 13th of October. Very little pomp was displayed on that occasion, but the clergy of that cathedral came in procession to St. Paul, and spared nothing to make the office worthy of a sovereign, lending a crown, sceptre, and other royal ornaments. There were present the Chancellor of France, the Bishop of Paris, and certain French and English nobles. After the ceremony the body was placed in a boat by the presidents of Parliament and taken to St. Denis to be buried by her husband Charles VI.276
298 Paris was still in possession of the English, but just before the Queen’s death the treaty of Arras was signed between the Duke of Burgundy and Charles VII.

 Round Marie d’Anjou and
Charlotte de Savoie, wives of
Charles VII. and Louis XI.,
partly from their own
personality and partly
from
the circumstances amidst which
they were placed, so much less
interest gathers than around the
two Queens who precede or the
one who follows them, that I
have preferred to pass over their
reigns, and to conclude this
volume with a sketch of the more
interesting character and eventful
life of Anne de Bretagne, whose
death closes the annals of the
early Queens of the house of
Valois.
Round Marie d’Anjou and
Charlotte de Savoie, wives of
Charles VII. and Louis XI.,
partly from their own
personality and partly
from
the circumstances amidst which
they were placed, so much less
interest gathers than around the
two Queens who precede or the
one who follows them, that I
have preferred to pass over their
reigns, and to conclude this
volume with a sketch of the more
interesting character and eventful
life of Anne de Bretagne, whose
death closes the annals of the
early Queens of the house of
Valois.

Marie was the granddaughter of Louis, Duc d’Anjou, the second, handsomest, and300 perhaps worst of the sons of King Jean. Although she was exceedingly beautiful, and in many ways gifted, she had no influence with Charles VII., whom she had married as a child, when, his elder brothers being alive, there appeared no prospect of his becoming King. After his accession he constantly neglected her for Agnes Sorel and other mistresses. She seems not to have been wanting in judgment or capacity, and under different circumstances might have made an excellent queen; but her idea of duty was the submission of a slave, and her gentle, saintly character was more fitted for the cloister than the throne. She was the only human being her son, Louis XI., really loved,277 and would never oppose, and her death soon after his accession to the throne was considered a public calamity. She had twelve children, of whom seven died young.


Charlotte de Savoie was much less gifted and more unfortunate than her predecessor. Charles VII., with all his faults, was neither cruel, avaricious, nor disagreeable, and his wife was free to amuse herself and direct her children and household as she pleased. But Louis XI. was a cruel, remorseless tyrant, and the only consolation of the unfortunate Charlotte de Savoie was that she seldom saw him. She lived in seclusion and with little state at Loches and Amboise, and when his death gave her freedom she was already in bad health, and only survived him for a few months. Of her six children only three302 lived to grow up: Charles VIII., Anne de Beaujeu, Regent of France, and Jeanne, the deformed wife of Louis XII.

Birth of Anne and Isabelle—Their childhood—Louis d’Orléans—Alain d’Albret—Death of François II.—First Council—French war—Marriage ceremony—Siege of Rennes.
 Anne, eldest
daughter of
François II.,
Duc de Bretagne,
and
his second
wife, Marguérite
de Foix, was born
at Nantes, January 26,
1476,278 and her sister, Isabelle,
four or five years
after.
Anne, eldest
daughter of
François II.,
Duc de Bretagne,
and
his second
wife, Marguérite
de Foix, was born
at Nantes, January 26,
1476,278 and her sister, Isabelle,
four or five years
after.
Their mother died in 1485, leaving the children under the care of Françoise de Dinan, Dame de Laval, a member of one of the greatest families of Bretagne, who had been their governess from their infancy. They continued to be brought up at the court of their father, who seems to have kept them constantly with him, but whose affection for them did not prevent his promising them to anybody whose alliance he thought might be useful to him amidst the difficulties and dangers he had brought upon the duchy which had been so prosperous when he succeeded to it.
Always under the influence of some unworthy favourite, he had for many years been governed by Antoinette de Maignelais, Dame de Villequier, niece of Agnes Sorel, and her successor in the affections of Charles VII. After his death she carried on a liaison with François, which embittered the life of his first wife, daughter of the last Duc de Bretagne, so that the people declared that his having no son to succeed him was a punishment from heaven for his conduct.
Anne, as the heiress of Bretagne, was of especial importance, and proposals for her marriage and her sister’s with the King of the Romans, the young sons of Edward IV. of England, the Infant of Spain, or some of the chief Breton nobles, were perpetually being entertained.
Some French writers have originated a romantic story of love between Anne and Louis, Duc d’Orléans, who had quarrelled with Charles VIII. and his sister, the Regent,279 and was a great deal at the court of305 Bretagne. But as Anne was from eight to eleven years old at that time, by comparing dates and details given by early chroniclers, it becomes evident that this was not possible, and that if Louis, who was then from two to five and twenty, thought of such a child at all, it could only be as the heiress of Bretagne. He was, like his grandfather, the brother of Charles VI., always involved in some love affair, besides being already married to Jeanne, the deformed daughter of Louis XI., who had forced the marriage upon him in childhood, notwithstanding his opposition and that of his parents,280 Charles Duc d’Orléans and Marie de Clèves, hoping thereby to extinguish that branch of the family. And, notwithstanding his aversion to his wife, he could not get rid of her whilst her brother was King and her sister Regent of France.
Jeanne, Duchesse d’Orléans, was greatly to be pitied. She loved Louis as Valentine Visconti had loved his still handsomer and more dissipated grandfather. But Valentine was a brilliant, attractive woman of the world, with whom the Duke, in spite of his frequent infidelities, had got on very well. Jeanne, besides being deformed, was a meek, ascetic person, whose life had been passed in slavish submission to her father, the terrible Louis XI., and despairing love for her husband; her tastes and ideas were those of the cloister.
Although his follies were the cause of many calamities to the duchy, François II. was very popular, he was good-looking and pleasant, encouraged art, literature, and commerce, and spent his money freely.
The greatest danger in which he involved the State arose from his constant enmity to France, whose fugitives he protected, and whose enemies he encouraged and assisted on all occasions; and from the credulous weakness which placed him always under the influence of some objectionable person. Antoinette de Maignelais died in 1475, but still more fatal was his infatuation for one Landais, a man of obscure birth and abominable character, whom he made his treasurer, and whose crimes and cruelties so exasperated the Bretons that they rose in rebellion, surrounded the palace with threats and cries, and demanded that he should be given up to them. The Comte de Foix tried to appease them, but returned in haste, exclaiming, “I would rather be Prince over a million wild boars than over such people as your Bretons; you will certainly have to give up your treasurer, or we shall all be murdered.”281 Landais was accordingly tried, condemned, and executed, but the harm he had done and the disastrous state of affairs still remained.
The young English princes having been murdered by their uncle, Richard III., the Vicomte de Rohan wanted to marry the two princesses to his two sons; other suitors also presented themselves, of whom the one specially detested by Anne was Alain, Comte d’Albret, brother of her governess, the Dame de Laval. He was a widower of forty-five, rough, ugly, disagreeable, ill-tempered, and the father of eight legitimate and four illegitimate children. A more preposterous husband for the young princess could308 not have been thought of; notwithstanding which, the Dame de Laval used all her influence in his favour. But her persuasions were useless. Anne could not bear the sight of him, and would not listen. Besides her personal dislike to him, she said his position was far beneath her. She wanted to marry a King, or the son of a King, not a mere Breton noble who was her father’s subject and would be her own.
There was, however, a strong party who, desiring that their future duchess should marry a Breton and stay in her own country, supported the pretensions of Albret, and so harassed the Duke, her father, that in order to gain allies and help in his difficulties, he consented to this monstrous sacrifice, and desired her to accept him. Anne resisted, but she was then a child of eleven or twelve years of age, and when her father, whom she loved, used reproaches, commands, entreaties, and assured her that the marriage was necessary to the welfare of the country she adored, he succeeded in wringing a reluctant consent from her.
But shortly afterwards he was beaten by the French at St. Aubin, and after signing a treaty giving up Dol, St. Malo, and other important towns, and promising not to marry either of his daughters without permission of Charles VIII., he fell ill and died in September, 1488.
The Princess Anne, now Duchess de Bretagne, was not quite thirteen years old, but in capacity and character far beyond her age. She was well educated, understood Latin and Greek, and wrote very good letters. One to Maximilian of Austria, with an309 account of the war, the troubles in Bretagne, and the battle of St. Aubin is quoted as a surprising production for one so young. But Anne was full of talent and high spirit, her faults and good qualities were those of a noble nature. Brave, proud, impetuous, imperious, passionately attached to her own country, loving her friends and hating her enemies with all her heart, always to be relied on, yielding only to the commands of the Church, or the good of her own Bretagne, a woman to be loved, admired, sometimes feared, but never despised or distrusted.
The Duke left his daughters under the guardianship of the Maréchal de Rieux and the Comte de Comminges, who were also to consult Dunois, son of the famous Bastard of Orléans, and Madame de Laval was to remain their governess.282 She must have been fond of them and good to them in spite of her reprehensible partisanship of her unsuitable brother, for Anne always showed her much affection.
The princesses were taken immediately from Coiron, where the Duke died, to Guérande, which was considered safer. The Breton nobles had sworn allegiance to Anne in her father’s lifetime, among others her natural brother, François Baron d’Avaugour, son of Antoinette de Maignelais. He and Anne were very fond of each other.
An embassy was sent to the King of France and the States hastily summoned. Anne sat at the head of the Council, and her ministers soon discovered that she was no weak, timid girl of whom they could310 dispose at their pleasure, but a high-spirited princess who knew very well that she was their sovereign.
When Rieux brought forward again the project of marrying her to the detested Albret as the best way out of the present difficulties, she immediately, with an eloquence and decision that astonished them, rejected the proposal. An historian remarks, “And the high heart that she had! girl as she was!”283
She said that Albret had not even fulfilled the conditions which alone had induced her to consent to such an engagement, in giving assistance to her father, who had never desired nor approved of the marriage, but had been tormented into consenting when in weak health by Madame de Laval, that she had always protested against it, and that Albret knew he was repugnant to her, and that she never meant to carry it out. That she was the Duchesse de Bretagne and the greatest heiress in Christendom, that the idea of trying to force her to marry against her will was contrary to all propriety, and that sooner than make such a marriage as this she would retire into a convent and take the veil.

She hated Albret all the more, because as she grew older and increased in beauty, he had conceived a violent passion for her, but her courage and firmness put a stop to the tyrannical meddling of her311 ministers and filled them with respect and admiration.
She then sent a messenger to England claiming the protection of Henry VII.
Her chancellor, Montauban, supported her, considering the match far beneath her, and told Albret plainly of the aversion and indignation of the Duchess and the preposterous nature of his claims. The Comte d’Albret flew into a furious rage, but was of course powerless in the matter. And just then Charles VIII. sent to claim the wardship of the Duchess and her sister, saying that he would marry them to the two sons of the Vicomte de Rohan and resign all his claims to the duchy.
But the Bretons, who hated the Rohans because they were considered friends to France and traitors to Bretagne, would not hear of this; Louis d’Orléans was in prison at Bourges, help did not come from England, and the friends of the Duchess, including the Maréchal de Rieux, who saw that it was hopeless to think of the Comte d’Albret, proposed the eldest son of the Emperor Maximilian, King of the Romans, who had been already suggested as a possible husband for her during the lifetime of her father, and to whom she had no objection. For, although Maximilian was also a widower and a great deal older than herself, he was a handsome, courteous, pleasant man in the prime of life, and could give her the most splendid position in Europe.
The duchy was by this time in a condition equally deplorable and dangerous. Charles VIII., exasperated at the English and other foreign troops312 being called in, made vigorous war upon Bretagne, town after town was besieged and taken by his army. Alain d’Albret continued to put forth his claims on the young Duchess, declaring that he had her father’s promise and her own consent, but ignoring the fact that this consent had been wrung from a weak and almost dying man, and a child of ten years old, who directly she was free had made a public protest against this arbitrary act. Madame de Laval for a long time continued her advocacy of her brother’s cause, while Anne steadily persisted that she would take the veil sooner than marry him.
Meanwhile she waited anxiously for help from England, but Henry VII., unwilling to make war on France, lost a great deal of time in correspondence with the French King, hoping to arrange matters by this means. But the war went on, and the young Duchess fled from one town to another, and at length, finding herself in an unsafe position in the unfortified town of Rhédon, with her sister, where there was a great chance of being taken by the French, sent to her guardians, Rieux and Comminges, to come up with the troops and escort them to Nantes. There was no time to lose, for the French were in the neighbourhood, and the place could not be defended.
The princesses were waiting in great anxiety when they were told that Rieux and Comminges had both gone to Nantes, where they had joined Albret. Anne was very angry, all the more as she suspected that they would try to influence the people against her and her friends by making them believe that313 Dunois intended to deliver up both her and the town to the King of France. She set off from Rhédon on horseback with Isabelle and the Chancellor Montauban, with a bodyguard of ten Bretons as an escort, and rode to La Pasquelay, about three leagues from Nantes, where she was joined by Dunois at the head of some troops. She sent a message to Nantes ordering the gates to be opened for her entry, but the reply was that she was welcome to enter with her household and private guards, but not with Montauban, Dunois, or the troops; and seeing that the plan was to throw her into the power of Rieux and Albret, she angrily refused, upon which they marched out of the town with a large force to compel her to enter as they proposed. With undaunted courage Anne mounted on horseback behind Montauban and rode forward, while Dunois and the troops prepared for battle. But the townspeople no sooner saw her than they forbade any force to be used against her, but obliged the nobles to go back into the town. For some days negotiations went on, but Anne sent word that she would only enter Nantes as its sovereign, and turning away after a perilous journey took refuge at Rennes, where the people had begged her to come, and where they received her with bursts of enthusiastic loyalty and abuse of the traitors of Nantes.284
Her cousin, Jean de Châlons, who was taken prisoner with the Duc d’Orléans, but had been released,285 was Anne’s great friend and supporter314 against Albret; and in March, 1490, it was decided to place her under the protection of the Emperor, by marrying her to his son, the King of the Romans. Negotiations were accordingly carried on with profound secrecy. Madame de Laval, seeing that her efforts were vain, abandoned the cause of her brother; Maximilian, King of the Romans, sent the Baron Volfan de Polhaim, with several other nobles, to Bretagne, and a few days after the ceremony of betrothal was gone through, and the marriage celebrated without any one knowing the day on which it took place. According to the old German custom in such cases, the young princess was placed in her bed into which Polhaim, as proxy for Maximilian, put his bare leg up to the knee in presence of the three other envoys, Madame de Laval and some members of the household of the Duchess, and declared the marriage to be consummated.
It was not likely that so important an event could be long concealed. The Chancellor de Montauban was one of the first to let it out by giving Anne, in several official acts, the title of Queen of the Romans. This disclosure caused an outburst of anger and commotion. The French pushed on the war with more activity than ever, Alain d’Albret betrayed Nantes into their hands, and Charles VIII. refused to acknowledge the legality of the marriage, contracted without his consent.
Anne, who was in desperate straits for want of money, sold her plate and jewels, and struck a coinage of leather with a small piece of silver in the315 centre. She gave the command of her army to Rieux, who had left Albret, returned to his allegiance, and for the sake of the country, been pardoned. He drove the French out of Lower Bretagne; Brest, St. Malo, and some other towns held out for her; she had English archers and German and Spanish troops from Maximilian, but was too weak to withstand the French, who, late in the autumn, laid siege to Rennes.
Anne made her Chancellor, Montauban, promise not to leave her for a day; she trusted also in Jean de Châlons and Dunois, who was as brave as his renowned father though his enormous size interfered with his activity.

Joustes before Rennes—Death of Isabelle—Betrothal of Anne—Marguérite of Austria—Marriage of Anne—Charles VIII.—Birth of Dauphin—Italian War—Return of King—Death of Dauphin—Birth and death of other children—Death of Charles VIII.
The French army lay encamped before Rennes. Hostilities began by the Bastard de Foix dressed as St. George, riding up to the walls and challenging any knight to come out and break a lance with him in honour of the ladies. A Breton noble in complete armour at once appeared, lists were made among the moats, Anne had a scaffolding erected from which she with her ladies and court witnessed the combat, first with lances, then with swords, and, after she had supplied hypocras and other refreshments to the French, every one retired.
Next day the siege began. Provisions and money ran short and the Princess Isabelle died. Charles offered Anne a large pension, any place she chose to live in except Rennes or Nantes; and Louis de Luxembourg, the Comte d’Angoulême or the Duc de Nemours for a husband in exchange for the duchy, which she refused. He next offered her foreign troops all the arrears due to them if they would withdraw from Rennes, which they immediately did. Then he tried to induce her to accept a large allowance, give up the duchy and go to the King of the Romans; and finally proposed that she should throw over Maximilian, who could get no money from his father, the Emperor, had never even seen her, and probably cared very little for the marriage (having lately lost Marie de Bourgogne whom he loved passionately), and marry him.
It was far the best way out of this disastrous state of things. Charles was politically her enemy, but she had no personal dislike to him, he was a suitable age and a splendid match, besides which it was evident that she must either accept him or lose Bretagne altogether. And whether it would be better for her or Bretagne that she should be a landless fugitive or Queen of France was a question about which there was no doubt whatever in the minds of any of the sensible people who surrounded her. Her cousin, the Prince of Orange, her guardian, the Maréchal de Rieux, her Chancellor, Montauban, and her governess, Madame de Laval, all told her the same thing, and tried to persuade her to consent to this marriage. The Duc d’Orléans, who had been318 released by the intercession of his wife; and the Comte de Dunois, added their entreaties, and Anne at last began to hesitate. Then Madame de Laval told her confessor and begged him to speak to her. He accordingly assured her that it was required of her by God and the Church to make this sacrifice for the good of her country and the restoration of peace. Anne yielded to the only authority she recognised and consented to an interview with the King.
Charles therefore went, on pretence of a pilgrimage to the chapel of Notre Dame which was at the gate of Rennes. After his devotions were finished, he suddenly entered the town accompanied by the Princess Anne de Beaujeu, and an armed escort. The next day he presented himself at the palace of the Duchess. They had a long private audience in which Charles seems to have succeeded in overcoming any dislike Anne may have had for him, as they were betrothed to each other three days afterwards in the chapel of Notre Dame.
Two solemn contracts had to be broken for the sake of this marriage, so important both to Bretagne and France. Besides the ceremonial marriage of Anne and Maximilian, his daughter Marguérite had not only been for the last eight years the legal wife of Charles VIII., but had been brought up in France and treated as Dauphine and then as Queen. The marriage, which was of course only a form, had been celebrated at Amboise just before the death of Louis XI., with pomp and ceremony in the presence of the court, the Dauphin being then319 twelve and the Princess Marguérite three years old.286
It was a great affront to Maximilian, both on his own account and that of his daughter, who, though so young, was extremely indignant, having long considered herself Queen of France. She was conducted back to her father with great state, and when, as she passed through Arras, the people began the French cry of “Noël, Noël!” she said impatiently, “Do not cry ‘Noël!’ but ‘Vive Bourgogne!’” She was afterwards the famous Regent of the Netherlands, and throughout her life never forgot the slight or felt anything but enmity to France, in which, however, she did not include the Queen, who had sent her splendid jewels and beautiful embroideries, and with whom she was always on friendly terms.287
A chronicler favouring the Austrian party, observes in his writings that with respect to this alliance three things are most surprising: first, that Charles VIII. should have had the audacity to carry it out, being already married to the daughter of Maximilian; secondly, that the Duchesse de Bretagne should have accepted the deadly enemy of her house as her husband; and thirdly, that the Seigneur de Dunois, who had done so much to bring about this marriage, should have fallen dead from his horse as he returned from the betrothal, ce qui épouvanta fort tout le peuple.288
320 For Dunois, one of the most faithful friends of the young Duchess, never saw her crowned Queen, having been seized with apoplexy as just described.
Although by this alliance Anne gained a much higher rank, she lost that of a sovereign princess. Charles was the conqueror, and she had no choice but to submit to the French terms, which were—that the duchy of Bretagne should pass entirely into the hands of the King; that if she should survive him but have no living children, it should again become hers, but that in that case, in order to avoid another war she should bind herself not to marry any one but the King of France or his heir; that she should receive the same dowry as the King’s mother; and, by his special desire, that any jewels, furniture, or property of whatever value, which might be in her possession at the King’s death, should be hers absolutely. The Prince of Orange approved of this contract, which she signed on her wedding day, December 6, 1491.
In spite of her poverty, Anne displayed royal magnificence in her dress and all the accessories of her wedding. It is probable that the States granted her a large sum of money for that occasion. At any rate her wedding-dress of cloth-of-gold with gold embroideries, cost 126,000 francs (present value), and all her travelling appointments were splendid. She gave velvet dresses to the ladies and gentlemen of her household, that of Madame de Laval being of violet velvet, and a costume of cloth-of-gold to the Prince of Orange.289
321 Anne was now fifteen years old and the King twenty. After their wedding, they went to Tours, and then to Paris, splendidly received all the way. Anne was crowned at St. Denis in the following February, on which occasion she was dressed in white satin. The crown was too large and heavy for the young head, and was held by Louis, Duc d’Orléans. The next day she entered Paris.
De Mézeray declares that Anne had an immense influence over the King, and that she ruled her own duchy entirely. But M. Le Roux de Lincy denies this statement, and quotes in support of such contradiction two well-known historians of Bretagne,290 who assert that during the whole of the married life of Charles VIII. and Anne, all the actes de Bretagne are in the name of Charles alone, without that of Anne ever being mentioned.
In spite of the King’s jealous monopoly of her duchy, he was always much attached to the Queen, although this did not prevent his carrying on many love affairs and intrigues with other women, greatly to her displeasure; and every now and then arose quarrels and disputes about this or that person to whom his attentions were too much directed. But they were always together, except when he was at war; he lavished money and every luxury upon her, and was as much influenced by her as he could be by anybody. For Charles was obstinate, rash, and chimerical; and in many matters would take no advice from any one. He was not handsome like most of his family, being short and badly made; but322 he had beautiful eyes, a charming expression and manners so gentle and courteous that it was said that no one had ever heard him say a rude or harsh thing.
Madame de Beaujeu, sister of the King, who had been hitherto the greatest lady in France, began by trying in vain to oppose and interfere with the Queen, who, having from childhood been accustomed to the deference and obedience due to a sovereign princess, declined to allow her authority to be questioned, so that the late Regent had to yield.
Charles and Anne lived chiefly at Plessis and Amboise, which he had caused to be magnificently refurnished and decorated for her reception.
Whenever it was possible Anne travelled by water, the rivers being still the chief highways, and the great barges with wooden houses on board the most comfortable conveyances. On October 10th was born the Dauphin, Charles-Orland, at Plessis, to the great rejoicing of France, Bretagne, and the King; he was christened with splendid ceremonial, his god-parents being the Queen-dowager of Sicily and the Dukes of Orléans and Bourbon. He was dedicated to the Virgin, and always dressed in white and cloth of silver. A few months afterwards the King and Queen set off for Lyon, leaving him at Amboise, surrounded by the strictest precautions, amongst which was one forbidding any one to visit him who had ever been in Italy.
They stayed at Lyon and Grenoble amidst much festivity until the baggage arrived, was unloaded from the chariots and packed on mules to cross the Alps. On September 1st, after attending mass,323 Charles bade the Queen farewell, mounted his horse, placed himself at the head of his army and started, accompanied by Louis d’Orléans.

Anne remained at Lyon, and at first the King’s daily letters brought news of unbroken conquests, which, however, like all the French victories in Italy, melted away, leaving nothing but disaster to France.324 It was fifteen months before Charles returned to Lyon where Anne had waited for him. In spite of his reverses he was in good spirits and resolved on another Italian campaign, for like all the Valois he was an ardent soldier. His favourite charger “Savoie,” a splendid black horse with only one eye, had carried him through all the battles and loved him so much that he would fight for him with his teeth and hoofs. He was given him by the Duc de Savoie.291 Amongst other adventures is told the story of a young girl to whom he took a fancy at Naples. She was brought to his palace there and when left alone with him she explained that she had not come of her own free will, but had been carried off by force, and threw herself on his mercy. Charles assured her that she need fear no violence from him, sent her away in safety, and promised her his protection.
In December, 1495, the Dauphin, then about three years old, was suddenly taken ill and died at Amboise, where he had always lived. Although he had been so little with his parents they were most anxious about him, and constant news of him had always been sent them. M. Le Roux de Lincy gives several letters written by the Queen to his governor, full of inquiries and directions respecting him. He was a beautiful, precocious child,292 and his death was a severe blow to his parents. Philippe de Commines, who had a grudge against Charles because he had been imprisoned by him and the Regent, says that he cared very little, being jealous of the Dauphin, a most absurd supposition regarding a child of three325 years old, and it being most unlikely that he should have293 preferred his heir to be Louis d’Orléans instead of a son of his own. On the contrary, the shock made both Charles and Anne so ill and depressed that the doctors ordered the King to be amused, therefore many more gaieties took place at court than the Queen felt inclined for. She hated being present at them, and quarrelled with the Duc d’Orléans because he seemed to her in such good spirits that she fancied he was glad to be again heir-presumptive and to be called “Monseigneur,” which she could not bear to hear.294 This caused a coolness between Louis and the King and Queen, so that he retired to Blois, where he surrounded himself with literary men and collected a large library, including the books and manuscripts written by his father. Anne had another son next year, also named Charles, the following year one called François, and then a daughter named Anne. But although she got strong Bretonne women to nurse them and took every precaution she could not save any. None of them lived more than a few weeks. They were buried in an exquisitely sculptured tomb of white marble in the cathedral of Tours.
The King and Queen, finding no medicine or cure any use, had tried various superstitious means. They had a whole coffer full of charms and amulets, and the people said it was a curse on them because they had not been free to marry each other. But they were still very young and hoped yet to have living children. Charles began to think that these misfortunes were326 the punishment of Heaven for his dissipated life, and resolved to reform. Anne was so uneasy and jealous of his proceedings that she could not bear him to be out of her sight, and had at one time brought on a miscarriage by persisting in going out hunting when she was enceinte because she did not want him to go without her. Now, however, Charles declared he would have no more love affairs, would give his whole attention to his kingdom and people. He had planned another Italian campaign and a crusade against the unbelievers, but it was strongly represented to him that he ought not to leave France without having an heir. The Queen, who dreaded another long separation, was naturally of the same opinion, and Charles was persuaded to remain in France, and began to alter and decorate his favourite château of Amboise. He had brought books, pictures, statues, and all sorts of treasures from Italy, and had become much influenced by the splendour of the renaissance then prevailing there. He began the great tower with an inclined ascent by which a troop of cavalry can ride to the top, from the lower entrance down by the river.
The splendid old château had become more comfortable and luxurious than ever under the rule of Anne de Bretagne.295 Tapestries hung on the walls, thick carpets lay on the floors, curtains of damask and satin were over the beds and everywhere. The Queen was at Amboise with the King, who could not bear to be separated from her, and in whose pursuits and diversions she always shared. One day, about327 two o’clock in the afternoon, he proposed that they should go and look on at a game of paume which was to be played dans les fossés du château.
She consented, and the King, taking her by the hand, they left her private apartment together. They had to pass through a low, dirty, dilapidated gallery which Charles intended to have pulled down, and in entering which he struck his head violently against its arched doorway.296 He declared, however, that he was not much hurt and they proceeded to the seats from which they were to watch the game. While it was going on the King talked and laughed as usual, but when it was over he complained of pain in his head and said he would go to his own room. The Queen, dreadfully frightened, went with him.297 As they walked back he began to speak of his repentance for the faults and follies of his life, and just as he said, “J’espère bien ne commettre aucun péché, soit mortel, soit véniel,” he suddenly fell to the ground. They were again at the entrance of the fatal gallery, where a straw mattress being hastily thrown on the floor he was laid upon it. They dared not move him, so he lay there until about eleven at night, only recovering consciousness for a few moments, when, after murmuring, “Mon Dieu! Vierge Marie! Monseigneur Saint Claude! Monseigneur Saint Blaise me soient en aide!” he died.298
Despair of the Queen—Resumes duchy—Friendship with Louis XII.—Returns to Bretagne—King’s divorce—Charlotte d’Aragon—Marriage of Anne and Louis XII.—Italian war—Birth of Claude de France—Splendour of Court—Hôtel des Tournelles—Maids of honour—Disaster in Italy.
Charles VIII. died at dawn on Palm Sunday.299 The Queen, who was only two and twenty, had now lost her mother, father, sister, children, and husband. In a frenzy of grief and despair she shut herself up in her own rooms where she remained crying, wringing her hands and refusing to eat.
The Duc d’Orléans, now Louis XII., was still at Blois, and much distressed at the melancholy state of the Queen. He sent the Cardinal Briçonnet and the Bishop of Condon, who had been friends of hers and of Charles VIII., to see her.300 They found her lying on the floor sobbing and crying in a corner of the room. She did not get up when they came in, but the Bishop, a man of holy life and intellectual power,329 succeeded in comforting her so far that she listened to his words of consolation, rose, became calmer, and was persuaded to take some food.
Then she began to think about her beloved Bretagne, now her own again, and directly she had finished that first repast she signed a decree reestablishing the chancellerie which had been suppressed.
Her nearest remaining relation was her brother the Baron d’Avaugour, but she was very fond of her cousin, Jeanne de Laval, Queen-dowager of Sicily, to whom she wrote, telling her of the death of the King; and also of the Prince of Orange, Jean de Châlons, for whom she sent at once and whom she made governor of Bretagne.
Three days after the death of Charles, Louis XII. came to see her. He promised to give a splendid funeral to the late King, which he did. Anne ordered her mourning to be black instead of the white usually worn by Queens of France, and sent to the prelates, nobles, and bourgeois of Bretagne to come and escort her to Paris, where, according to custom, she was to pass the first months of widowhood; the hôtel d’Estampes, one of the group forming the hôtel St. Paul, having been prepared for her.
On May 15th she left Amboise with her great Breton train, paid a state visit to the King, and establishing herself in her hôtel turned her attention to the government of Bretagne, demanding from the Mâitre de la Monnaie at Nantes the gold and silver coinage with the effigies of her father and herself, appointing her brother and other Breton nobles governors of the330 towns, from which the French troops were now withdrawn,301 writing constantly to her relations, friends, and officers, and occasionally seeing Louis XII., who did everything he could to please her.

For although he could not have been in love with her, as some historians assert, before she was ten years old, it is certain that he was now most anxious to marry her, not only as Duchesse de Bretagne but as the woman he admired and loved.302 He was thirty-four, handsome, and extremely attractive, and Anne, besides being ambitious and reluctant to lose the French crown, seems to have returned his affection. A French writer remarks that her love for Charles had arisen from duty, and therefore was not likely to be very lasting,303 which may well have been the case. But it was evident that no such marriage could take place until Louis had obtained a divorce from his present wife, Jeanne de France, for which purpose he began negotiations with the Pope, the friendship between Anne and himself meanwhile increasing as may be seen by the following letter:—
“Monsieur mon bon frère,—Je aye receu par le Sr de la Pomeraye, voz lectres & aveques sa charge331 entendu la singulere benevoleme & amytié que me portés, dont je suys très consolée & vous en remercie de tout mon cueur, vous priant de tousjours ainsi continuer comme c’est la ferme confiance de celle que est & à jamays serra.
“Vostre bonne seure, cosine & allyée,
“Anne.”304
In June they met at Estampes and agreed to marry each other as soon as Louis could get his divorce. Anne went back to Paris, and later in the summer she went to Laval to stay with the Queen-dowager of Sicily, after which she returned to Bretagne, where she was received with great state and universal joy. Delighted to be once more in possession of her own duchy she resolved now that she had recovered the reins of government never again to let them slip out of her hands. Under her supervision a history of Bretagne was written by a learned priest, her almoner, from the papers and records in different monasteries.
She ruled Bretagne as a sovereign princess with much wisdom and capacity, and being generous and charitable she made various excellent laws for the good of the people. Her own household she arranged on a magnificent scale, and appointed a guard of a hundred Breton gentlemen who escorted her wherever she went.
While she was at Nantes her old governess, Madame de Laval, died, to her great sorrow.
The question of the King’s divorce was heard before an ecclesiastical tribunal, and the marriage dissolved by Alexander VI. (Borgia).
Louis made Jeanne Duchesse de Berry and gave her a splendid appanage of lands and money. She retired to Bourges, founded the order of the Annonciades, became Superior of it, and died in 1500, after a life of charity and devotion. The dissolution of a marriage to which he had always had an unconquerable repugnance cannot be considered surprising, but at first many of the people were indignant and pointed at the judges, saying, “There is Caiaphas, there is Herod, there is Pontius Pilate; they have judged against la haute dame that she is not Queen of France.”305
Alexander VI.,306 of the noble Spanish family of Borgia, had in his youth a natural daughter, the famous Lucrezia, Duchess of Ferrara, and four sons. The eldest and youngest he married to daughters of the King of Naples, the second, Giovanni, Duca di Gandia was supposed to have been murdered by his next brother, the Cardinal Cesare, or Cæsar, who had become a soldier and who surpassed most of his contemporaries in the enormity of his crimes. The Pope now sent him to France with a Cardinal’s hat for George d’Amboise, the King’s favourite minister, and the bull for the dissolution of his marriage, Louis promising him the duchy of Valentinois, a large pension and one of his relations in marriage.

The court was at Chinon when he arrived. His333 followers, horses, and mules were covered with silk, velvet, and cloth of gold. The horse he rode had trappings of cloth of gold covered with precious stones; he himself wore a dress of red satin and cloth of gold bordered with pearls and gems; his hat was trimmed with a double row of rubies as big as beans, which shed a strange light; even his boots were covered with gold cords and edged with pearls. Around his neck was a necklace or collar worth 30,000 ducats.307 He gave the cardinal’s hat to the King, telling him that the bull was not ready, although he had it with him, as he hoped to be able to extort something more from Louis. The Pope’s nuncio however told the King that the dispensation had been made out long ago, and that Cæsar had got it. He was therefore obliged to deliver it up, but he invited the nuncio to dinner, and, as he was foolish enough to accept, he died of poison shortly afterwards.
The wife upon whom Borgia fixed his choice was Charlotte d’Aragon, daughter of Frederic III., King of Naples and Sicily, called Princesse de Tarente at the French Court, where her mother, the niece of Queen Charlotte de Savoie, had been brought up. When she died, as Frederic, engaged in perpetual strife, could not look after his daughter, she had been adopted by Charles VIII. when about ten years old, and lived at court ever since.308 She had a complete household, a litter, mule, and several horses, being335 treated as a royal princess,309 and was demoiselle d’honneur to the Queen. She grew up into a most attractive girl—pretty, clever, amusing, kind-hearted; the favourite of the whole court. The Queen, who was extremely fond of her, when, after the death of Charles VIII., she returned to Bretagne, gave her a silver toilette service and parted from her reluctantly.
When Charlotte heard that Cæsar Borgia wanted to marry her she was very much alarmed, very much horrified, and very angry. She declared that she would not marry that abominable man, and entreated her father and every one she knew to protect her. Borgia, who had set his mind on her, and also hoped to get hold of the principality of Tarentum, pressed for an answer. Charlotte positively refused, declaring that she would not have for her husband a priest, the son of a priest, and a fratricide, whose birth and conduct were alike, infamous. Cæsar revenged himself by getting up a league against Frederic, who fled to Ischia and thence to France. The Queen was delighted with her courage, and in 1500 married her to Guy de Laval, a handsome young Breton noble, very rich and a cousin of her own, so that Charlotte not only became still more nearly connected with the Queen, but remained at court.
Anne chose to be married at Nantes in January, and this time the contract secured her entire control of the government and revenues of Bretagne, with power to leave it to her own heirs after the death of the King if they had no children. Besides her dowry336 from Charles she had one of equal amount for her life from Louis.
The King and Queen spent most of the winter in Bretagne, hunting and amusing themselves, and in April travelled slowly to Blois, great festivities attending their progress.
The Queen’s second marriage was much happier than the first. In appearance, intellect, and character Louis was far superior to Charles. The intrigues and dissipations of his former life disappeared before the higher, nobler love of which Charles was incapable. No suspicion of unfaithfulness ever arose between Anne and Louis;310 she had regained her beloved duchy, the management of which was her chief interest and occupation, besides the share she took in the government of France. Though she had no better luck with the sons of her second than of her first marriage her two daughters lived, and upon them she lavished the passionate affection she had given to the first Dauphin. Louis was the idol of France; since the days of St. Louis there had been no such king. To the virtues of Charles V. he united the gallant grace and charm of the Valois, and the people called him “le père du peuple.”
Inheriting also the warlike spirit of his house, he resolved to make an expedition to conquer the duchy of Milan, now seized by Ludovico Sforza, but which he claimed as heir of his grandmother, Valentine Visconti.
The Queen, in her anxiety about the child she was337 expecting, instead of accompanying him to the frontier waited at Romorantin as the plague was at Blois. Even there some of her household had it, and when it abated she proceeded to Blois where her daughter was born and named after Ste. Claude, to whose shrine she had just made a pilgrimage.

Notwithstanding his desire to have a son, Louis received the news with great joy just as he was entering Milan, and both he and the Queen were always devoted to this child, which though small and delicate lived to grow up. Not long afterwards Louis returned with his victorious army, and the court resumed its wonted gaiety, the Queen being anxious that it should be the most magnificent in Europe. She was very rich, exceedingly generous, and always ready to pay any expenses that Louis, who was more economical, thought too great. She held many tournaments, at which she gave splendid prizes; she was a great benefactress to the religious orders, especially to the Cordeliers and Minimes, to whom she gave convents,311 and crowds of poor people waited for alms at her gates.
The hôtel St. Paul, the favourite palace of Charles V. and Charles VI., was now deserted. It was considered unhealthy because of the malaria arising from its many moats and ponds, and Louis XI. gave away most of the splendid hôtels belonging to it.312
Louis XII. and Anne, when in Paris, lived at Les338 Tournelles, a most picturesque and delightful old château near St. Paul, but more healthy. It was built in 1380, and had belonged to Jean Duc de Berry, Charles VI., and Louis d’Orléans. It was named from being a mass of little towers and turrets, was very large and convenient, stood in a wood like a country house, had chapels, galleries and gardens with fountains and seats of turf. The Duke of Bedford lived there during the English rule, and his beautiful wife, Anne of Burgundy; they kept flocks of peacocks and other rare birds.
Louis and Anne were as fond of animals as their predecessors. The Queen kept a large hawking establishment, and numbers of horses and mules; her stables were magnificent, and her litters and chariots branlants (suspended) lined with soft cushions and costly stuffs. She had many dogs of different breeds and sizes.
The position of the Queen’s ladies was very distinguished and important. Already in 1492 she had sixteen dames and eighteen demoiselles, of the noblest families. She was very strict, keeping constant supervision over their books, songs, and amusements, and forbidding them to be alone with the gentlemen of the court, or talk to them about love that had nothing to do with marriage. If they disobeyed her she was implacable, otherwise she treated them with unbounded kindness, gave them the same luxuries she had herself, and took the greatest care of them in illness. An existing account mentions silver plate and a fur-lined coverlet for the night, ordered for Anne de Foix when she was ill. She gave them339 dowries, arranged their marriages, and if their husbands lived far away sent somebody to take care of them and bring her news of them. Some she loved almost like her own children.
Ladislas, King of Hungary, Poland, and Bohemia, being a widower, wanted a French princess for his wife. The Queen selected Anne de Candale and Germaine de Foix, both pretty girls and princesses of Foix, and sent him their portraits. He chose Anne, who did not wish to be Queen of Hungary, but to marry the Comte de Dunois, son of the Queen’s old friend whom he did not resemble, for though handsome and agreeable he was supposed to be wanting in courage. The Queen would not hear of it, and notwithstanding the tears and objections of the young princess the marriage was celebrated by proxy, and she started with a brilliant retinue in charge of Bretagne, King-at-arms, whose account of the grandeur of her reception, presents, &c., still exists in the Bibliothèque Impériale. Ladislas was enchanted with her and wrote with enthusiastic gratitude to the Queen, who was very fond of and anxious about her, and many messengers and letters passed between them; but the princess, who never became reconciled to her splendid exile, died in giving birth to a son.
Germaine de Foix became the second wife of Ferdinand, King of Spain.
The Queen apparently acted in an arbitrary manner towards Anne de Rohan, who clandestinely married a natural son of the house of Bourbon, and who, after a stormy scene with her royal mistress, left the court and was imprisoned by her father at a château in a forest until, hearing that her husband had married somebody else in Germany, she became the wife of her cousin, Pierre de Rohan.313
Cæsar Borgia had insisted on a wife being found for him, and the person so sacrificed was Charlotte, the youngest daughter of Alain d’Albret. His consent was bought by an enormous dowry from the Pope and a cardinal’s hat for one of his family. Five years later Cæsar Borgia was killed in a skirmish, and the Duchess de Valentinois, his widow, who was universally respected, retired in peace with her daughter to a castle in Berry.314
In April came disastrous news from Milan, which had revolted against the French, who now only held the fortress itself.315 The King sent Louis de la Trémoille and the Cardinal d’Amboise immediately to take command, and the wise counsels of the one and the military capacity of the other so rapidly turned the tide that France was again victorious, Sforza was taken prisoner, “and thus,” says the chronicler, “was the duchy of Milan twice conquered in seven months and a half, and for this time the war in Lombardy finished.”316
Ludovico Sforza—Shipbuilding—Queen’s gardens—Library—Treasures—Dress—Betrothal of Claude de France—Archduke and Archduchess—Illness of King—Maréchal de Gié—Second illness of King—Queen in Bretagne—Second betrothal of Princess Claude.
Ludovico Sforza was imprisoned at Loches, at first rigorously, but afterwards with indulgence, being allowed books, paper, ink, cards, paume, &c. He died in captivity.
Louis had a project for the conquest of Naples, which displeased the Queen, by whom he was in most matters greatly influenced, and whom he called “Ma Bretonne.” She saw that these expeditions always caused disasters to France, and had much more sympathy with his desire for a crusade against the Turks, who had invaded Greece. Out of her own revenues she raised soldiers and sailors and had twelve large ships built in the seaports of Bretagne. The largest, Marie la Cordelière, of 2,000 tons, carried 100 guns.317 Anne took the deepest interest in the342 navy, upon which she spent large sums, but managed her affairs so well that in spite of her princely generosity she had no debts but always plenty of money.
This crusade was unsuccessful, the ships being damaged by a tempest.

Anne filled her household with her faithful Bretons. Her guard of gentlemen assembled always on the terrace at Blois, called “la Perche aux Bretons.” She never kept them waiting, but would rise and hasten towards them saying, “There are my Bretons on their perch expecting me.”318 To her the French queens owed the right to have their especial guard, also the right to receive separately all foreign ambassadors.
343 She delighted in flowers and gardening, her favourite gardens being those of Amboise, given her by Charles VIII., and of Blois by Louis XII. She was also extremely fond of books, and had a splendid library, for, besides all she inherited from her father and the French kings, Charles VIII. brought her eleven hundred and forty from Naples and Louis XII. a thousand manuscripts from the library of the Visconti at Milan. She employed a colony of painters, sculptors, scribes, and architects brought from Italy and established at Tours by Charles VIII., and consequently possessed numbers of artistic treasures, including that wonderful illuminated book containing the psalms, prayers, and offices of the Church richly adorned with flowers, animals, landscapes, portraits and scenes in miniature well known as the “Livre d’Heures d’Anne de Bretagne,” and one of the most perfect examples of French art of that day.319
She had a little room with boxes and drawers full of costly jewels to give as presents. For dress personally she cared little, although especially on state occasions she was always magnificent in her toilette. The fashions in her reign were exceedingly graceful and artistic. Fine linen, velvet or satin shoes, long trailing dresses open in front, made of cloth of gold and crimson silk or velvet, with a golden girdle and chaplet of pearls, chains and jewels round the neck, headdress of white silk embroidered with gold and pearls, hoods of cloth, satin, or velvet, scarlet for bourgeoises, black for nobles. Sometimes long dresses344 of black velvet. These were purely French till late in this reign when Italian and Flemish costumes began to be copied.320 Charles VIII., being short and ill-made, re-introduced the long robes of former times, but Louis XII., who was tall and graceful, usually wore short clothes. The Queen created an order for the ladies of the court, called the Cordelière, from the cords that bound Christ: the badge was a jewelled necklace in the form of a cord.
Before the Princess Claude was two years old proposals came from the Emperor Maximilian to marry her to his grandson, the Duke of Luxemburg, son of the Archduke Philip of Austria. In France the general desire was that she should become the wife of the Comte d’Angoulême, heir-presumptive to the throne of that country, but the Queen strongly favoured the Austrian alliance. In November, 1501, the Archduke and Archduchess arrived on a visit. They were mounted on mules covered with trappings of crimson velvet, next rode a long train of ladies, and six hundred horses carried litters and drew waggons after them. The procession entered Blois at night; as it wound up the steep street torches blazed on every house, and the grand staircase of the castle was lined with hundreds of archers of the guard in gilded armour. The King, sitting in a great carved chair by the fire, welcomed them, and asked the Archduchess if it was her pleasure to bestow a kiss upon him, which she did, after asking permission of the Bishop of Cordova. Louis then saying that he345 knew the ladies would like to be alone together, she was taken to the Queen’s rooms, where Anne sat by the fire surrounded by her ladies, who, it may here be remarked generally sat on the floor or on cushions, not many chairs being usual in the rooms. Later, she retired to her bedchamber, where, escorted by six pages in red and yellow with wax candles in gold candlesticks, quantities of all kinds of sweetmeats were carried to her by ladies and gentlemen, with gold and silver boxes of knives, forks, serviettes, &c., which were all placed on buffets and on the bed. The Queen’s apothecary followed, and afterwards came silver warming-pans and washing basins, velvet coffers of brushes, combs, sponges, mirrors, and fine linen.321
The Princess Claude had been brought down, but directly she saw her proposed mother-in-law she cried so loud that she had to be removed by her governess.322
The Archduke had supper downstairs, but the King did not join him as he was keeping the fast of Notre Dame des Avents on bread and water. They stayed five days, and the betrothal of the Princess was concluded.
January 21, 1503, was born a Dauphin, who, however, died immediately, to the general grief and disappointment.
Next came news of reverses in Italy and the loss of two battles, soon after which the King became very ill. The Queen nursed him untiringly, scarcely ever leaving his room; every one was in consternation, and346 the doctors gave up all hope of his recovery. Anne was in despair. Added to her grief for him was the dread of what would be the position of herself and her daughter in the event of his death and the triumph of Louise de Savoie and the hostile party, at the head of which was Pierre de Rohan, Maréchal de Gié, a Breton who had taken the side of France against Bretagne.
She therefore ordered the officers of her household to load two or three great barges on the Loire with all her treasure and take them down to Nantes. Then, if the King died, she could retreat with her child to Bretagne, where they would be safe among their own subjects.
But Gié, thinking the King’s death at hand, had the insolence to stop the Queen’s barges, placing 10,000 archers to watch the Loire and prevent the Princess Claude being carried out of France.323 This attempt of one of her own subjects to take from her guardianship her daughter, the heiress of Bretagne, not of France, and to seize the property settled on her by two kings, was not likely to be forgiven by the Queen. Gié had overreached himself, for Louis suddenly recovered, and on hearing of his conduct, ordered his arrest. The judges who tried him hated him, and condemned him to death, but this sentence was quashed by the King, and Gié was heavily fined, deprived of his post, and banished from court for five years. Some French historians, who seem to think any means justifiable to gain a province for France, approve his conduct, and call347 Anne vindictive for insisting on its punishment; others will probably consider that he got what he deserved.
Gié retired to his magnificent château of Verger, and the clercs de la Basoche gave a play called “Trop chauffer cuit, trop parler nuit” alluding to him. In another they said, “Un Maréchal avait voulu ferrer une Anne (âne), mais elle lui avait donné un si grand coup de pied qu’elle l’avait jeté hors de la cour, pardessus les murailles jusque dedans le verger.”324
They were very witty, often impertinent. When the King was told that they had ventured to represent him, because of some necessary retrenchment, as Avarice, he said that the people might laugh, and he would rather be called avaricious than extravagant; but when they attempted any ridicule of the Queen he sternly forbade it, saying he would suffer no disrespect to his wife, nor for that matter to any woman in his kingdom.
The Queen’s second coronation at St. Denis and entry into Paris took place when the King was convalescent—with the same splendour as the first. It was by torchlight, and after the usual fêtes and banquet at the Palais they returned to Touraine, and spent the rest of the summer at Blois, Loches, and Amboise with the Princess Claude.
The year 1505 opened with an unsatisfactory state of affairs in Italy,325 where many of the best French officers, amongst them the Chevalier Bayard, were348 still engaged. The King became depressed and out of spirits, all the more because of the dispute about his daughter, whose marriage the Emperor kept urging him to celebrate immediately with the Duke of Luxemburg, while the French were so vehemently in favour of François, whom he had created Duc de Valois, that he felt both he and the Queen were for the first time becoming unpopular. These matters so preyed upon his mind as to bring on an illness more serious than the last. He was seized with fever and delirium, and all the country was plunged into grief and alarm. Again the Queen nursed him night and day, the people thronged the churches,326 masses were chanted, long lines of cowled figures carried holy relics, with banners, crosses, and swinging censers through the streets, peasants left their work and multitudes with bare feet, tears and lamentations flocked after the processions. The Queen vowed that if he recovered she would make a pilgrimage to Notre Dame du Foll-Coat in Bretagne before the year was out.327
A romantic incident caused by this calamity was the death of Tommasina Spinola, a beautiful Genoese who had fallen in love with Louis in Italy. It was a platonic, chivalrous romance, to which neither her husband nor the Queen objected, and after the shock of hearing that Louis was dead had been fatal to her, he, having by this time recovered, desired Jean d’Auton to write a record of her, which was presented to him and the Queen at Tours.328

In the summer the Queen set off for Bretagne to fulfil her vow about the pilgrimage, leaving the King at Blois with their child.
When once Anne was in Bretagne it was no easy matter to get her away again, although Louis was now left with Louise de Savoie, and all those who were anxious for the French instead of the Austrian marriage of the Princess Claude.
She took her ladies and a large suite of French nobles, and was joined by numbers of Bretons, her progress through her own dominions being one continual triumph. She visited many of the towns, which were richly decorated, and gave splendid joustes and other fêtes in her honour, and having made her neuvaine and offerings at Foll-Coat, she summoned the States, transacted a great deal of business, and went to Brest to see her favourite ship, Marie-la-Cordelière.
The King, however, got very tired of being without her, and sent her a message to come and join him at Angers. She was then at Morlaix suffering from inflammation in the eye, and sent for a relic supposed to be the finger of St. John Baptist, to cure her. It was kept in a church at Plougarnon, not far off, but she was presently told that it had disappeared on the way, and been found in the church again. Then Anne with all her suite went to Plougarnon, slept in the village, and attended mass at the dawn of day in the ancient church with massive square tower and quaint leaden steeple,351 standing in a green valley by a brook flowing down to the sea.329 The Bishop of Nantes touched the Queen’s eye with the relic when she had received the Communion; she made her offerings, and the pilgrimage was finished.330
The King kept writing to her to come back, and began to get very angry at her delay. The Cardinal d’Amboise, who was very much in the confidence of them both, wrote three sensible and urgent letters,331 assuring her that he had never seen the King so displeased, and begging her to return; saying what a pity it would be if any dissension should arise between them; also that the King was going back to Blois and thence by water to Amboise, taking Princess Claude and the Countess d’Angoulême with him. The Queen therefore brought her Breton tour to an end, and returned to Blois in September.
Her arrival dispelled the King’s vexation, but to her dismay she found him bent upon breaking off the Austrian engagement of their daughter, for many were murmuring against the Queen for allowing her dislike of Louise de Savoie to influence her to the detriment of France. Even the Bretons preferred the future King of France to the grandson of the Emperor, and although the prediction of Anne that François would not care about Claude, who was neither pretty, clever, nor attractive, was certainly verified, there seems no reason to suppose she352 would have been happier with the Duke of Luxemburg, afterwards Charles V. Louis said he was resolved “de n’allier ses souris qu’aux rats de son grenier;” and when Anne impatiently remarked, “To hear you one would think mothers conspired to injure their daughters,” he asked if she thought it was the same thing to rule Bretagne as to wear the crown of France, saying, “Voulez-vous préferer le bât d’un ane (Anne) à la selle d’un cheval?” and as she still seemed unconvinced, he told her that at the Creation God gave horns to hinds as well as stags, but finding they wanted to govern everybody, He took them away as a punishment.332
But not wishing to act in defiance of the Queen, Louis agreed that at the meeting of the States at Tours, in May, 1506, the deputies should implore him on their knees to consent to the marriage of the Princess Claude to François, Duc de Valois. As he had foreseen, the Queen could not then oppose it; and on Ascension Day the children were betrothed in the great hall of the Castle of Plessis les Tours, she being six and he twelve years old.333
Story of Anne de Graville—Illness of Claude—Court of Anne de Bretagne—Italian war—Marriage of Marguérite d’Angoulême—Dress and customs at Court—Birth of Renée de France—The Prince de Chalais—The Queen ill—Birth and death of a son—League of Cambrai—Sea-fight—Death of Queen.
Though much vexed at her daughter’s engagement the Queen still hoped something might happen to prevent the marriage; meanwhile she formed the household of the Princess, and amongst others she placed in it Anne de Graville, one of her demoiselles d’honneur, a sister of whom had been in that of the King’s first wife. To Anne, as to some of her companions, is attached a romance, which, after four hundred years, clings to her memory, and like the scent of rose leaves and lavender in some old-fashioned country house, the refrain of an ancient ballad or the quaint phrases traced in faded ink on some letter yellow with age coming to us from a long-vanished generation, seems to give us a momentary glimpse into the life of those far-off days.
Louis de Malet, Admiral de Graville, bore one of the oldest names in France, and had been the favourite of three kings. That he was a man of great capacity and wisdom is proved by his correspondence, now existing in the Bibliothèque Impériale. He was also extremely cultivated. He gave a bell to Rouen Cathedral, built the portal of Sens and a church near Paris. He collected a valuable library of manuscripts, with illuminations, miniatures, poems in French and Italian, &c., and filled his château of Marcoussy with pictures and splendid furniture.
Marcoussy, about eighteen miles from Paris, was one of the most imposing castles in the Ile-de-France, with its massive walls, huge towers, and deep moats, surrounded by trees and gardens with terraces, fountains, and fishponds. Here he passed most of his time when not occupied in public affairs, and here grew up his children, Louis, Joachim, Jeanne, Louise, and Anne. They studied music, poetry, literature, and received altogether as good an education as was then attainable. The youngest, Anne, was herself the authoress of a poem written on one of the stories of Boccaccio, and many an exquisite embroidery for church or convent was done by the three sisters.
But upon the prosperous, happy lives of the Gravilles sorrow began to fall. Louis and Joachim died, and their loss so affected their mother that she also died in March, 1503, desiring to be buried near Joachim in the monastery of Marcoussy. Louise and Jeanne had made brilliant marriages, and Anne was left alone with her father, whose favourite she355 was, and who dreaded parting with her. However, between marriage and the cloister there was no alternative, and the Admiral wrote to her saying he had received offers from three young nobles, of whom he thought the first frivolous, the second rash and hasty, but the third, though less rich, was sensible and irreproachable in character.334
But meanwhile, Anne fell in love with her cousin Pierre, Baron d’Entragues, illegitimate son of Robert de Balzac, a young soldier of four and twenty who, fearing the Admiral might not allow the marriage, carried her off; some said with, others without her consent. At any rate she forgave him, and their marriage was celebrated without waiting for the permission of the Admiral, who was very angry, threatened to disinherit his daughter and forbade any one to help them. The Baron d’Entragues had no money and when he applied for help to his relations they refused; the young people had nothing to live upon and did not know what to do. So they bethought themselves of the good monks of the Céléstin convent of Marcoussy and took refuge with them. The Prior and brotherhood received them with kindness, sympathy, and promises of help, and they stayed in the monastery waiting till Good Friday, which was now approaching, when the Admiral was sure to come there to church.
Accordingly, when he presented himself at the office of the veneration of the Cross, the Prior stopped him, saying, “Dare you approach with your lips the sacred wood on which the Son of God shed356 His precious blood to reconcile men with His Father; if you have not resolved from your heart to forgive your two children who are here at your knees with profound repentance imploring pardon for their fault?” As he spoke Pierre and Anne threw themselves on their knees before him. The solemn words of the Prior and the sight of the child who had always been so dear to him were too much for the Admiral, he held out his arms to them both, and took them back with him to the castle.335 The marriage proved a very happy one. Anne had a long prosperous life, and one of her children inherited Marcoussy.
In the spring of 1507, Louis went to Genoa, to put down a revolt there, which, having done, he recrossed the Alps and came to Grenoble, where the Queen went to meet him. While he was there the Princess Claude was seized with a kind of continuous fever which greatly alarmed and distressed the Queen, who kept up a constant correspondence with Madame des Bouchage, governess to the little princess, being always fully informed of her condition. The doctors at first declared she would not recover, but as she very soon became much better, the Queen, who did not believe in doctors because they had been altogether wrong about her eldest son, and failed to save either him or any of her other children, was so angry, and so confirmed in her opinion that she wrote to Madame des Bouchage that the child was not to see357 any more of them, for they were no use, she must take care of her herself.336 The Princess Claude soon recovered.
The Italian war dragged on. The league of Cambrai was formed against Venice in 1508, and Louis was eager to be again at the head of the French army. Anne did all she could to dissuade him, and tried to induce him to return to Blois, assuring him that Claude was fretting to see him,337 but it was useless. He recrossed the Alps, and soon came tidings of the victory of Agnadel and conquest of nearly all the Venetian mainland provinces.338
He returned, safe and victorious, to Blois at the end of the summer, and there during that year took place the wedding of Marguérite, sister of François, Duc de Valois, with the Duc d’Alençon. It was celebrated with suitable splendour and followed by a great banquet and ball, after which there were joustes. The Duc de Valois kept the lists with eight others, served by the King himself, the princes who contended were so young that small lances were made on purpose. The Pope’s legate not being well, looked on from a window. Next day they fought again, this time in white armour, the bridegroom dressed in white satin. The Queen and her ladies gave the prizes.339
They all delighted in festivities and amusements,358 fêtes champêtres were often given in the open air, a favourite day being Mid-Lent Sunday, called, especially in the valleys of the Marne and Meuse, dimanche des fontaines. M. Siméon de Luce describes those given in a preceding reign by Beatrix de Bourlemont when young men and girls from the neighbouring châteaux and peasants from the villages hung garlands, dined, sang, and danced under an ancient beech tree said to be haunted by fairies.340
A solemn and important domestic fête in the country was the first mass of a young priest. M. de Ribbe describes one of their mediæval village festivals. Presents were given, relations and friends assembled as for a marriage or christening. They walked to church two and two in a long procession, minstrels playing before them and crowds following. A collection was made in church and then there was a great banquet in the bergerie to which the relations contributed various dishes, the cooking being done in a mill close by.341
On the opening of parliament it was customary to present quantities of roses and violets to the members, one special person being responsible. De Sauval mentions an account owing to Marguérite le Mercier, marchande de roses, for four dozen chapeaux of red roses, eight bouquets of violets, and a great basinful of flowers to cover the table, distributed to the Presidents, Councillors, and other officers of the King, the vigil of the feast of Whitsuntide, who were assembled at the Chastelet for the deliverance of the359 prisoners in the said Chastelet “comme d’anciennté a este coutume de faire.”342
Renée de France was born October, 1509. Amidst the general disappointment at not getting a Dauphin, the King and Queen rejoiced that this child lived. She was afterwards the celebrated Duchess of Ferrara.
The Queen from this time entertained the project of leaving Bretagne to Renée, if she could not break off Claude’s marriage, and constantly endeavoured to gain the consent of the King; but, although, dreading the outcry which would be the consequence, he would not agree to her wishes, it seems very possible, considering her great influence over him, that had she lived longer she would have succeeded in carrying out one or other of these plans. During her lifetime she would never allow the marriage of Claude to take place.
Anne was extremely fond of music; amongst other musicians in her household were four Bretons minstrels. About six months after the birth of Renée, being at Chartres, she was so struck with the voice of a chorister boy in the cathedral that she asked the chapter to give him to her, and in return for their doing so she said, “You have given me a little voice and I will give you a large one,” and accordingly presented them with a great bell, named “Anne de Bretagne” to be rung every day from Easter to Trinity, and 3,000 livres.343
She rather prided herself upon her conversational powers, indeed, writers of her day assert that nobody could talk better, either in society or on State affairs. The King, who liked to have her opinion about everything that went on, always sent the ambassadors to her after an audience with him.
One day she was going to receive the Spanish ambassador, and not understanding Spanish she asked her chamberlain, the Prince de Chalais, who understood several languages, to teach her some sentences to say to him. Chalais, who had a mania for playing practical jokes, without considering whether the Queen was a proper subject for one, taught her some words not possible in any decent society. Fortunately for himself he was so delighted with his trick or so doubtful of the result of it that, just before the audience, he told it to the King. He laughed but hastened to warn the Queen, who was, of course, exceedingly angry, would not receive Chalais for some days, and would have dismissed him had not the King dissuaded her, assuring her that he would never have allowed her to say the words to the ambassador.344
In 1510 Louis and Anne sustained an irreparable loss by the death of the Cardinal d’Amboise.
As usual, the French successes in Italy had been short lived. The Venetians under their famous Doge, Loredan, had reconquered nearly all their territory, and the members of the league of Cambrai had turned against France, the Milanese was lost, and the King of Spain seized the Spanish side of Navarre including Pampeluna. Catherine de Foix, heiress of361 the gallant Princes of Navarre and Queen in her own right, remarked to her husband, Jean d’Albret, “Dom Jean, if you had been born Catherine and I Dom Jean, we should never have lost Navarre.”345
The Queen had so dangerous an illness in March, 1511, that her life was despaired of; but after receiving the Communion she revived and by the middle of April was tolerably well. In the following January she had another son, who died like all his brothers, and the doctors managed the Queen so badly that her health was permanently injured. Late in March the Austrian ambassador, who went to take leave of her, found her still in bed but brave, cheerful, and taking her usual interest in public affairs. She did not get up until May, when she appeared much better, but never really regained her strength, and just then many circumstances combined to depress and trouble her.
A great battle was fought August 10, 1512, between the French and English fleets. The Regent with the English Admiral on board attacked the famous Cordelière, commanded by the Breton Hervé Portzmoguet. The two ships were grappled together, the battle raged fiercely and the dead lay in heaps on the decks. Then Portzmoguet, seeing that all hope was lost, set fire to both vessels, and, clad in complete armour, threw himself from the mast into the sea. The ships went down together with more than two thousand men, the French fleet drew off to Brest, the English to the high seas.346
There was strife between the King and Pope, and the Queen’s views were strongly opposed to those of Louis. The Pope laid France under an interdict from which he excepted Bretagne. In vain the King assured her that women had no voice in Church matters; she had but to point to Bretagne as her answer, and to remind him that at fourteen years old she had successfully opposed Innocent III. when he illegally appointed two of his nephews to benefices in her duchy. Also that her influence had prevented Louis from occupying Rome, when, after the battle of Ravenna, the road to the Eternal City lay open to his victorious troops. She ultimately induced him to subscribe to the Lateran Council, whereby the Roman gained the victory over the Gallican party in the Church.347
Anne was not yet thirty-eight, but her brilliant, eventful life was drawing to a close. For a year or two her health had been failing and on the 2nd of January, 1514, she was taken ill at Blois and died a week afterwards. Knowing that she would not recover, one of her last orders was that her heart should be sent to Nantes and laid in the tomb of her father and mother in the land and among the people she had so faithfully loved.
The King shut himself up alone for days wearing the black mourning he had chosen, contrary to the custom for Kings of France. From the shock of the Queen’s death he never recovered. He only survived for two months the preposterous marriage he was induced to make in the following year with the363 young sister of Henry VIII. for the purpose of stopping the English war. Claude, wife of François I., died ten years after her mother leaving several children, one of whom was Henri II., whose three sons were the last kings of the house of Valois.
The funeral of the Queen at St. Denis was of more than usual magnificence, and when her coffin was lowered into the tomb there stepped forward Champagne King-at-arms who, after calling three times for silence, said, “King-at-arms of the Bretons, do your duty.” Then Bretagne King-at-arms in his coat of mail stepped forward and proclaimed, “The most Christian Queen and Duchess, our sovereign Lady and Mistress, is dead? The Queen is dead! The Queen is dead!” The Chevalier d’honneur with the hand of justice, the Grand Maître de Bretagne (brother of the Queen) with the sceptre, and the grand écuyer with the crown advanced, kissed them, and gave them to the Bretagne King-at-arms, who laid them on the coffin.348
In France, to which she had given a great province, Anne de Bretagne was soon forgotten; but, in the land she loved and ruled so well four hundred years ago, her name and her memory are still honoured and cherished by her own people.

UNWIN BROTHERS, THE GRESHAM PRESS, WOKING AND LONDON.
1 “Chron. Guill. de Nangis,” t. ii. p. 94. Société de l’histoire de France.
2 “Les Grandes Chron.,” confirment la leçon in gallo, mais donnent deux vers un peu différents.
3 Charles de Valois had three wives and fourteen children; two or three of his daughters were named Isabelle. One married Robert d’Artois. Sainte-Marthe says the marriage of Pierre and Isabelle took place in 1322, in her early childhood; but other historians, with more probability, place it in 1332.
4 It is difficult to reconcile the conflicting dates given by historians. There is no doubt that Jeanne was the eldest daughter, yet some place her birth in 1337; and the second daughter Blanche, who in that case would not have been born till 1338, is nevertheless declared to have been sixteen years old when she became Queen of Spain, 1352, which is manifestly impossible.
5 There seems to be some doubt about Isabelle, as we hear nothing about her in after life. One historian confuses her with her sister Marguérite; another states that she married one Guillaume, Sire de Mello; others that she died unmarried; most do not mention her at all. If she ever existed she most probably died in childhood.
6 The Counts of Savoy were, as is well known, ancestors of the Kings of Italy.
7 Only the children of the King and the heir-apparent were called “Enfants de France.” It was for centuries later the rule that only the Enfants de France might ride or drive into the Louvre, Palais, Hôtel St. Paul, Tournelles, or any royal palace. Princes of the blood must get down at the door, nobles in the street. (De Sauval.)
8 “Grandes Chroniques,” t. vi. p. 2.
9 “Grandes Chroniques,” t. vi. p. 2. M. Paulin Paris remarks that the distinction here made between the gens de métier, or workmen, and bourgeois, or burghers, sufficiently proves the existence of the latter as a class.
10 Mariana, “España.”
11 Morèry, “Grand dictionnaire historique,” 1699.
12 “Grandes Chroniques de France,” t. vi. p. 35, Paulin Paris.
13 The northern part of France was the Langue d’oil, the southern the Langue d’oc, so called from the languages spoken there.
14 Sismondi, “Hist. France,” t. vii. p. 78.
15 “Hist. de la Jacquerie,” chap. ii. p. 31. Siméon Luce.
16 “Grandes Chroniques de France,” Paulin Paris, t. vi. p. 110.
17 Siméon de Luce, “Guerre de cent ans.”
18 “Hist. de la Jacquerie,” Siméon Luce.
19 “Hist. de la Jacquerie,” Siméon Luce.
20 “Hist. de la Jacquerie,” p. 135, Siméon Luce.
21 This is the first time the white banner appears in French history.
22 “Hist. de la Jacquerie,” p. 140. Siméon Luce.
23 Siméon de Luce.
24 “Sire, vous etes le plus gentilhomme du monde, ne souffrés pas que gentillesse soit mise à néant. Si ceste gent qui ce dient Jacques durent longuement, et les bonne villes soient de leur aide, ilz mettront gentillesse au néant et du tout destruiront” (“Hist. Jacquerie,” Siméon Luce; et “Chronique des quatre premiers Valois”).
25 Sismondi.
26 A gold florin was worth twenty francs.
27 The “Grandes Chroniques de France” place this marriage in October, 1359.
28 The guild or confraternity of tailors and dressmakers of Paris.
“Item. Que quiconque sera tailleur de robes à Paris, et il mestaille une robe ou une garnement par mal ordonner le drap au tailler, ou par l’ignorance de sa taille, le meffait et dommaige sera veu et regardé par ledis maistres; et s’ilz rapportent que la robe ou garnement soit empiré par mestaille ou par la coulpe du tailleur, le tailleur rendra le dommaige à celui à qui la robe ou le garnement sera; et y paiera cinq solz d’amende, dont les trois seront au roy, et les deux à la dicte confrairie.”
29 “Item. Que nul ne mectent lay ne estouppes en doublet qu’il face pour vendre; et qui fera le contraire; le doublet sera ars, et paiera six solz d’amende au roy, et quatre solz à la confrairie.
“Estouppe était probablement chanvre, filasse, lin.”
30 Bonne villes, i.e., fortified towns.
31 “Grandes Chroniques de France.”
32 “Grandes Chroniques de France.”
33 Sainte-Marthe.
34 “... ma il drappo sopra capo non sofferse, e così stette infino che fu sposata; e da quel punto dinnanzi posto in oltre la reale dignità e nobilità di sangue, reverenza fece a messer Galeazzo e a messer Barnabo e alle donne loro.”
35 Sainte-Marthe.
36 Loggie are arcaded galleries, terraces or balconies generally to be seen in Italian palaces or houses of any antiquity. The vulgar and tasteless buildings that now disfigure modern Italy are frequently without them.
37 De Mézeray.
38 Bonne de France died November 7, 1360. “Item, le jeudi 12 Novembre furent enterrées les deux filles du duc de Normandie à Saint Antoine près de Paris, et fu present le dit duc à l’enterrage moult courroucié qui plus n’avait d’enfants.”
39 Dulaure, “Hist. Paris.”
40 “Hist. du Cérémonial Français,” Godefroy.
41 Soon afterwards released.
42 Guizot, “Hist. France,” t. ii. p. 179.
43 “Trésor des Chartes,” No. 386, p. 221.
44 Dreux du Radier, “Reines et Regentes.”
45 There is also a letter of his son Charles VI.
46 De Sauval, “Sablier.”
47 “Environs de Paris,” Nodier.
48 Sauval, “Antiquitez de Paris.”
49 “Bibliothèque du Roy,” Félibien.
50 Félibien.
51 Douet d’Arcq.
52 “Grandes Chroniques de France.”
53 De Mézeray, “Hist. France.”
54 “Archives Nat. de Bourbon,” No. 1,409.
55 “Paris in its Old and Present Times,” p. 157. Hamerton.
56 “Antiquitez de Paris,” Sauval.
57 “Paris à Travers les Ages,” Fourmier et Hoffbauer.
58 “Comptes du vieux Louvre. Topographie historique du vieux Paris.” A. Berty et Tisserand.
59 “Comptes du vieux Louvre. Topographie historique du vieux Paris.”
60 “Paris à Travers les Ages,” Fourmier et Hoffbauer.
61 Documents inédits, 3me serie: Archéologie.
62 Documents inedits, 3me serie: Archéologie.
63 “Grandes Chroniques de France,” t. vi. p. 251.
64 “Queens of England,” A. Strickland, vol. ii. p. 345.
65 Christine de Pisan.
66 “Grandes Chroniques de France,” t. vi. p. 267.
67 Idem.
68 Marguérite de Bourbon.
69 “Grandes Chroniques de France.”
70 “Chron. de Bertrand du Guesclin,” Cuvelier, 14th century.
71 Martin, “Hist. France.”
72 Sauval.
73 Abbé Choisy, “Hist. Charles V.”
74 Montfaucon, “Monuments de la Monarchie française.”
75 Some doubt has been thrown on the certainty of this occurrence, but an ancient chronicler of Du Guesclin gives an account which confirms the fact of the keys being laid on the coffin of the dead hero. (Guizot, “Hist. France,” t. ii. p. 201.)
76 “Chronique des quatre premiers Valois.”
77 He had couriers who rode night and day and brought him news from a distance of eighty leagues on the following day. (Martin, “Hist. France.”)
78 “Hist. Cérémonial Français.” T. Godefroy.
79 Christine de Pisan.
80 Documents inédits.
81 “Grandes Chroniques de France.”
82 “... en leur hostel avoit esté norry en sa jeunesse et que moult de biens luy avoient fais.”
83 “C’estoit piteuse chose à regarder.”
84 “Grandes Chroniques de France,” t. vi. p. 401.
85 De Mézeray.
86 “Baierischen Geschichten,” Heinrich Zschokke.
87 The house of Wittelsbach claims descent from Charlemagne. The Kings of Bavaria descend from Johann, or John of Munich the third brother.
88 “Chronique de Flandre.”
89 “Antiquitez de Paris,” t. i. p. 667. De Sauval.
90 “Chronique de Flandre.”
91 Froissart.
92 Christine de Pisan.
93 “La Vie politique de Louis de France, Duc d’Orléans,” Jarry.
94 Christine de Pisan.
95 “Chronique du religieux de St. Denis,” t. i. p. 25.
96 Froissart.
97 “Relig. du St. Denis.”
98 “Comptes de l’hôtel de la reine Isabeau de Bavière. Doüet d’Arcq, Archives de l’empire.”
99 The Princess Catherine died in childhood.
100 It is true that the Valois were strictly speaking Capétiens also; but the elder line are generally known as the Capétiens and the younger as the Valois Dukes.
101 Froissart.
102 “Ducs de Bourbon et Comtes de Forez,” J. de la Mure. Notes, Steyert.
103 Brantôme.
104 Relig. de St. Denis, trad., Bellaguet, t. i. livre vii., p. 459.
105 Juvenal des Ursins.
106 “Isabeau de Bavière, étude historique,” Vallet de Viriville, p. 8.
107 “Comment discerner les styles, le costume et la mode du viii. au xix. siècle,” L. Roger-Milés.
108 “Comment discerner les Styles,” etc. L. Roger Milés.
109 Ibid.
110 “Histoire des Ducs de Bourgogne,” t. ii. p. 161. Barante.
111 De Sauval, &c.
112 “Grand Dictionnaire Historique: père Louis Morery, prêtre, docteur en théologie,” pub. Thierry, Rue St. Jacques, devant les Mathurius, 1699, t. iv. This name, when quoted by some writers, is spelt “Morèri.”
113 With this account of St. Denis in mediæval France, let us compare the following account of it in modern France:—
“Most of these persons were still drunk, with the brandy they had swallowed out of chalices—eating mackerel on the patenas! Mounted on asses, which were housed with priests’ cloaks, they reined them with priests’ stoles; they held clutched with the same hand communion-cup and sacred wafer. They stopped at the doors of dram-shops; held out ciboriums: and the landlord, stoup in hand, had to fill them thrice. Next came mules high-laden with crosses, chandeliers, censers, holy-water vessels, hyssops; recalling to mind the priests of Cybele, whose panniers, filled with the instruments of their worship, served at once as storehouse, sacristy, and temple. In such equipage did these profaners advance towards the Convention. They enter there, in an immense train, ranged in two rows; all masked like mummers in fantastic sacerdotal vestments; bearing on hand-barrows their heaped plunder—ciboriums, suns, candelabras, plates of gold and silver.... Not untouched with liquor, they crave to dance the Carmagnole also on the spot: whereto an exhilarated Convention cannot but accede.... Several members, quitting their curule chairs, took the hand of girls flaunting in priests’ vestures, and danced the Carmagnole along with them. Such Old-Hallowtide have they in this year once named of Grace, 1793” (“French Revolution,” Carlyle, vol. iii. p. 193).
114 “Au cloistre d’icelle maison royale se voit un bassin de fontaine fort ancien et admirable pour estre grand et d’une piéce, et relevé tout à l’entour de figures qui representent quelques fables des dieux paiens” (Père du Breul).
115 “Ils souillèrent la sainteté de la maison religieuse” (“Relig. de St. Denis,” liv. x. p. 599).
116 “Vie politique de Louis de France,” &c., Jarry.
117 “Isabeau de Bavière,” Vallet de Viriville, p. 13.
118 “Madame et cousine, je fairay volontiers ce dont vous me priez. Car j’y suis tenus par lignage, et pour ce vostre fille ma cousine je garderay, et penseray bien d’elle comme si ce fust ma propre fille ...” (“L’Art de vérifier les dates,” t. 10, p. 145).
119 “Valentine Visconti,” Mary Robinson, Fortnightly Review.
120 “Valentine Visconti,” Mary Robinson, Fortnightly Review.
121 Blanche de Navarre. “Lives of the Early Valois Queens,” to which this volume is a sequel.
122 “Relig. de St. Denis”; Froissart.
123 “Relig. de St. Denis,” liv. x. p. 615.
124 “Antiquitez de Paris.” De Sauval.
125 “Savoisy, je te pris tant que je puis, que tu montes sur un bon cheval et je monterai derrière toi et nous nous habillerons tellement qu’on ne nous connoistra point et nous allons voir l’entrée de ma femme.”
126 “Relig. de St. Denis,” liv. x. p. 609; also Juvenal des Ursins and Froissart.
127 De Sauval.
128 “Relig. de St. Denis,” liv. x. p. 627.
129 “Archives de l’Art Français, 1858,” p. 342 et suivantes. “Isabeau de Bavière,” Vallet de Viriville.
130 Ibid.
131 “Histoire des Ducs de Bourbon, Comtes de Forez,” La Mure.
132 Juvenal des Ursins, p. 83.
133 “Relig. de St. Denis,” liv. xi. p. 685.
134 “Antiquitez de Paris,” De Sauval.
135 “Hist. de la maison de France,” Sainte-Marthe, t. 1. p. 675.
136 “Relig. de St. Denis,” liv. xiii. p. 63.
137 Froissart, t. xiii. c. 27, p. 45.
138 “Comment! vous voulez donc m’enlever, monseigneur?” “Nenni, Madame, à Dieu ne plaise; je n’oserai seulement pas y penser.” “C’est vrai, je sais tout et suis bien informée; monseigneur vous aime et vous l’aimez, la chose va même si loin qu’il vous a promis 1,000 écus d’or. Mais vous avez refusé, et vous avez fait sagement. Je vous pardonne pour cette fois et vous défends, si vous tenez à la vie d’avoir désormais nul entretien avec monseigneur” (“Ducs de Bourgogne de la maison de Valois,” Barante).
139 Froissart, t. xiii. c. 28, p. 38 to 61. “Relig. de St. Denis,” liv. xii. c. i. p. 214. Juvenal des Ursins, p. 88.
140 “Regardez mon connétable, et sachez me dire ce qu’il y a à craindre, etc.” (“Ducs de Bourgogne de la maison de Valois,” p. 341.)
141 “Relig. de St. Denis,” liv. xiv. Juvenal des Ursins, p. 91.
142 Froissart; “Relig. de St. Denis,” &c.
143 “Chronique de Flandre.”
144 Froissart, xiii. c. 50, p. 102. “Relig. de St. Denis,” liv. xii. c. 4, p. 221. Juvenal des Ursins, p. 91.
145 “Relig. de St. Denis,” liv. xiv. p. 95.
146 Juvenal des Ursins, p. 91.
147 Juvenal des Ursins, p. 91.
148 “Chronique de Flandre.”
149 Ibid.
150 “Chronique de Flandre.” Froissart. Paradin.
151 “Chronique de Flandre.”
152 A curious relic of this ancient custom still survives in villages in the west of England, where, after the marriage of a widow or widower, the villagers will sometimes assemble at night outside their house blowing horns, beating drums, and making hideous noises.
153 The “Religieux de St. Denis” says this ball was at the hôtel St. Paul; but Juvenal des Ursins, who from his position at Court was certain to have known where it took place, and was most likely himself at the ball, declares it was at the hôtel de la Reine Blanche, we will therefore accept his authority, which De Sauval considers conclusive.
154 Froissart, t. xiii. c. 32, p. 240. “Relig. de St. Denis,” liv. xii. c. 9, p. 255. Juvenal des Ursins, p. 93. Monstrelet, t. i. pp. 312 and 423. Also Barante, “Ducs de Bourgogne,” t. ii. p. 197.
155 “Relig. de St. Denis,” liv. xiv. p. 93.
156 Sismondi.
157 “Relig. de St. Denis,” liv. xv. c. 14, p. 324.
158 Juvenal des Ursins. The “Relig. de St. Denis” relates this ghostly story, but places it in 1397.
159 It was the “Chroniques de France.” Philippe de Bourgogne, like all his brothers, was a collector of books, manuscripts, and objects of art.
160 “Relig. de St. Denis,” t. xvi. p. 407.
161 “Diabolicum recitas et quod est impossibile,” Valentine Visconti, M. Robinson, Fortnightly Review. Gian Galeazzo bought the title of Duke from the Emperor, 1395.
162 Froissart.
163 “Relig. de St. Denis,” l. xvii. p. 465.
164 “Relig. de St. Denis,” l. xvii. p. 469. Froissart.
165 Barante, “Ducs de Bourgogne.”
166 “Les demandes du roi Charles VI. avec les réponses de Pierre Salmon, son sécrétaire et intime.” “D’après les Manuscrits de la Bibliothèque du Roi,” p. 17. Salmon was one of these attendants. The Minutes of the Council contain a long list of the French members of Isabelle’s household returning with her some years afterwards to France.
167 Planche, “Hist. de Bourg.,” l. xiv. c. 150, p. 147.
168 “Relig. de St. Denis,” liv. xvii. p. 483.
169 Ibid.
170 “Relig. de St. Denis.”
171 “Relig. de St. Denis.”
172 “Relig. de St. Denis.”
173 Ibid.
174 “Isabeau de Bavière,” Vallet de Viriville.
175 “Isabeau de Bavière,” Vallet de Viriville.
176 Idem.
177 “Isabeau de Bavière,” Vallet de Viriville.
178 “Poésies d’Eustache Deschamps.”
179 “An Idler in Old France,” Tighe Hopkins.
180 I do not, of course, mean to say that the Roman baths were destroyed by the early Christians.
181 Vallet de Viriville.
182 De Sauval, “Antiquitez de Paris.”
183 “The Mediæval City. The Transformation of Paris,” F. Harrison.
184 The hospice of Quinze-Vingts was founded by St. Louis for the blind. A tradition, which is not considered true, says it was so named from three hundred knights who were blinded by the infidels for the Christian faith. They had a cemetery, chapel, chaplain, and two bells, and bore the fleur-de-lis, being a royal foundation. A tavern keeper in Paris having adopted the sign of the “Quinze-Vingts,” they complained to the provost, who ordered him to give it up.
185 “Antiquitez de Paris.” Sauval.
186 “Relig. de St. Denis.” Juvenal des Ursins.
187 Sismondi.
188 Froissart, t. xiv. c. 69, p. 155.
189 Strickland, “Queens of England,” vol. iii. p. 25.
190 Sismondi, “Hist. Français,” t. viii. p. 125.
191 “Relig. de St. Denis,” liv. xx. p. 745.
192 Juvenal des Ursins.
193 “Relig. de St. Denis,” liv. xxi. p. 771, t. ii.
194 The whole history of it may be read in ancient French chronicles, Juvenal des Ursins, Paradin, &c.
195 “Compte de l’hôtel de la reine Isabeau de Bavière,” 1401. “Archives de l’Empire.” “Registre Côté,” R. K. 45, fol. 87 à 101. Doüet d’Arcq.
196 Vallet de Viriville.
197 “Compte de l’hôtel de la reine Isabeau de Bavière,” 1401. “Archives de l’Empire.” “Registre Côté,” R. K. 45, fol. 87 à 101. Doüet d’Arcq.
198 “Relig. de St. Denis,” t. iii. l. xxii. p. 7.
199 Plancher, “Hist. de Bourg.,” l. xiv. p. 182.
200 “Relig. de St. Denis,” liv. xxi. c. 4, p. 442. Juvenal des Ursins.
201 “Compte de l’hôtel de la reine Isabeau de Bavière,” 1401. “Archives de l’Empire.” “Registre Côté,” R. K. 45, fol. 87 à 101. Doüet d’Arcq.
202 “Relig. de St. Denis,” t. iii. l. xxii. p. 9. Another account says the Queen was in bed at the time, but escaped unhurt.
203 Aquitaine was beginning to be called Guyenne about this time.
204 Monstrelet, “Chronique,” t. i. p. 89. Barante, “Ducs de Bourg.,” t. ii. p. 17.
205 Sismondi.
206 “Relig. de St. Denis,” liv. xxiv. c. 8, p. 493. Monstrelet, c. xiii. p. 126.
207 “Isabeau de Bavière,” Vallet de Viriville.
208 “Relig. de St. Denis,” liv. xxvi. p. 275.
209 Ibid., liv. xxvi. p. 281.
210 “Relig. de St. Denis.” Juvenal des Ursins.
211 “Relig. de St. Denis,” liv. xxvi. p. 283.
212 “Relig. de St. Denis.”
213 “Early Valois Queens.”
214 “Relig. de St. Denis,” liv. xxvi. p. 295.
215 “Relig. de St. Denis,” liv. xxvi. p. 331.
216 Juvenal des Ursins, p. 177.
217 Juvenal des Ursins.
218 Many historians make out Isabelle and Charles to have been younger, which is impossible, as she was born in November, 1388, and he in May, 1391.
219 “Relig. de St. Denis,” liv. xxvii. p. 397.
220 “Relig. de St. Denis.”
221 It was the custom to use mules to go about in the town, also for two to ride the same horse on these occasions.
222 Félibien, Monstrelet, Paradin, “Relig. de St. Denis,” &c.
223 De Mézeray, Monstrelet, Félibien, &c.
224 The hôtels of princes of the blood were sanctuary, as well as the churches.
225 Vallet de Viriville.
226 Sismondi, “Hist. France.”
227 “Lives of the Early Valois Queens,” Catherine Bearne, p. 8.
228 The Yorkists claimed the crown of England by a marriage with the heiress of the elder line, i.e., of Lionel.
229 Monstrelet, “Chronique,” t. i. c. 43, p. 165.
230 Monstrelet, c. 37, p. 229. “Relig. de St. Denis.” The Duke of Burgundy before an assembly of princes boldly tried to justify the murder, and employed a friar to speak for that purpose. Charles was induced in his weak state to sign letters of pardon for him.
231 “Relig. de St. Denis,” liv. xxviii. p. 749.
232 Ibid., liv. xxix. p. 59.
233 “Isabeau de Bavière,” p. 15, Vallet de Viriville.
234 Before the final expulsion of the English, Aquitaine was gradually taking the name of Guyenne. But, when it became the settled name, Guyenne did not include Gascony, Limousin, Saintonge, Anjoumois, and Poitou.
235 “Relig. de St. Denis.”
236 Historians differ as to what this meant.
237 Paradin, “Annales de Bourgogne,” liv. iii. p. 518.
238 Juvenal des Ursins.
239 Jeanne de Navarre, mother of the Duc de Bretagne, had, as a widow, become the wife of Henry IV. of England.
240 Monstrelet, “Chron.,” 1. ii. p. 96, édition Buchon.
241 Idem.
242 M. de Maulde de Clavière, however, in his interesting history of Louis XII., son of Charles, says that, with respect to the second at any rate of these poems, it is not known for whom it was meant, it was written during his captivity in England. There is, however, no reason why it should not have been about Isabelle.
243 Monstrelet, “Chroniques,” c. lxv. p. 81, édition Doüet d’Arcq.
244 “Relig. de St. Denis,” liv. xxxi. p. 333.
245 La Mure, “Hist. Ducs de Bourgogne, &c.”
246 Paradin, “Annales de Bourgogne,” liv. iii. p. 560.
247 Paradin. “Relig. de St. Denis.” Monstrelet.
248 Paradin.
249 Paradin. “Relig. de St. Denis.”
250 “Relig. de St. Denis,” xxxvi. 587.
251 “Chronique de Flandre.” Monstrelet, “Chron.,” c. cxliii. p. 85.
252 Juvenal des Ursins, p. 330.
253 “Relig. de St. Denis,” liv. xxxv. p. 1002.
254 Monstrelet, “Chron.,” c. cxliii. p. 85.
255 Monstrelet, c. cxlvii. p. 102.
256 The battle of Azincourt was the last at which the Oriflamme appeared.
257 Monstrelet.
258 “Le Fèvre St. Remi,” t. viii. c. 61, p. 1. Monstrelet.
259 Sismondi in the account he gives of this battle says that Le Fèvre Saint-Remi who writes of it was himself present, and to him most of these details are owing. The description of it is also given by the “Relig. de St. Denis,” Monstrelet, Juvenal des Ursins, Pierre Fenin, Barante, Walsingham, and others.
260 “Mem. Sire de St. Remi, ed. Buchon,” t. viii. p. 27.
261 “Relig. de St. Denis,” liv. xxxv., c. 9, p. 1016. Monstrelet, c. clxiv. p. 168. “Journal d’un bourgeois de Paris,” p. 210. Paradin, Juvenal des Ursins, &c.
262 “Chronique de Flandre.” “Messager des sciences historiques de la Belgique,” 1887.
263 “Relig. de St. Denis,” t. vi. liv. xxxvii. p. 61.
264 “Messager des Sciences historiques de la Belgique,” Leopold de Villers, 1887.
265 “Chronique de Flandre,” “Relig. de St. Denis,” Monstrelet, Juvenal des Ursins, Paradin, De Mézeray, &c.
266 “Relig. de St. Denis.”
267 “Relig. de St. Denis,” liv. xxxix. p. 283.
268 De Mézeray, p. 1023. Monstrelet, c. ccvii., p. 322.
269 “Chronique anonyme.” Bibliothèque imperiale.
270 “Relig. de St. Denis.”
271 Ibid.
272 Strickland, “Queens of England,” vol. iii. p. 135. Katherine de Valois.
273 “Journal d’un bourgeois de Paris,” p. 148.
274 “Journal d’un bourgeois de Paris.”
275 Monstrelet.
276 T. Chastier, t. i. p. 211.
277 Except his eldest daughter in after years, for whom he had a strong affection.
278 Sainte-Marthe. Hilarion de la Coste. Morèry, Grand Dictionnaire. Lobineau, “Hist. Bretagne,” t. i. p. 727.
279 About a game of paume. Commines, Bellefont, &c.
280 De Maulde La Clavière. Louis XII. t. i. p. 115.
281 Lobineau, “Hist. Bretagne,” t. i. p. 745.
282 Lobineau, “Hist. Bretagne,” t. i. p. 790.
283 D’Argentré.
284 Lobineau, “Hist. Bret.,” t. i. p. 796.
285 Ibid., t. i. pp. 798, 807, 808.
286 Philippe de Commines. “Mém.” t. ii. p. 241, note 1, édition Dupont. L’Art de Vérifier les dates.
287 Le Roux de Lincy.
288 Jean Molinet, “Chroniques,” t. iv. p. 577.
289 “Revue des provinces de l’Ouest,” Juillet, 1854, p. 235.
290 Dom Morice; Lobineau, “Hist. Bretagne,” t. ii. col. 1550.
291 Commines.
292 Ibid.
293 Le Roux de Lincy, “Anne de Bretagne,” t. i. p. 133.
294 Brantôme, “Dames illustres,” t. v. p. 4.
295 De Maulde-la-Clavière, “Louis XII.,” t. ii. p. 272.
296 Commines; Brantôme, t. ii. p. 19, ed. Petitot.
297 Villeneuve, “Mem. Anne de Bretagne,” p. 246.
298 Commines, Villeneuve, Godefroy, &c.
299 Villeneuve, “Mem.,” p. 246.
300 Godefroy, “Hist. Charles VIII.,” p. 745.
301 Dom Lobineau, t. i. p. 823.
302 Brantôme, “Hommes illustres,” t. ii. p. 59.
303 Touchard Lafosse.
304 Biblio. Imp., fonds Béthune, MS. 8465, fol. 10, recto (Le Roux de Lincy).
305 Douey d’Attichy, “Madame Jeanne de France de Valois,” &c., p. 143.
306 Moréry.
307 Brantôme, “Capitaines étrangers,” t. l. p. 404.
308 “Etat de la maison d’Anne de Bretagne,” p. 708. “Hist. Charles VIII.” Godefroy.
309 Tomasi, “Bibliophile Jacob, Hist. xvi. Siècle,” i. p. 176. Le Roux de Lincy.
310 Sainte-Marthe, t. ii. p. 620. De Seyssel.
311 De Mézeray.
312 The buildings were sold in 1542 and pulled down; scarcely a trace remains of them except a tower at the corner of the rue St. Paul, which may have belonged to one.
313 Le Roux de Lincy.
314 Hilarion, de la Coste.
315 Guizot, “Hist. France,” t. ii. p. 505.
316 Jean d’Auton.
317 De Mézeray.
318 Brantôme, “Dames illustres,” t. v. p. 8.
319 Musée des Souverains, Louvre.
320 Roger-Milés, “Comment discerner les styles,” &c.
321 Godefroy, “Ceremonial français.”
322 Ibid.
323 Lobineau.
324 Brantôme, D’Argentré, Jean d’Auton.
325 “L’Art de vérifier les dates.”
326 “Jean de Saint Gelais.”
327 Le Roux de Lincy.
328 Spinola was one of the four great Genoese families allowed to build their palaces of striped black and white marble. The others were Grimaldi, Fieschi, and Doria.
329 Le Roux de Lincy.
330 Ibid.
331 These valuable letters were first published by M. Le Roux de Lincy in his work on Anne de Bretagne; they belonged to the collection Lajariette.
332 De Mézeray, “Hist. France,” p. 375.
333 Dane, “Hist. Bretagne,” t. iii. p. 242; Henault, Ste.-Marthe.
334 Letter preserved in Archives of Château de Marcoussy.
335 Archives of Monastery of Marcoussy, “Histoire manuscrites des convent et des seigneurs de Marcoussy &c.,” given by M. Le Roux de Lincy.
336 Bibliothèque Imperiale. MS. 8457, fol. 5, given by Le Roux de Lincy.
337 Jean d’Auton.
338 Guizot, “Hist. France,” t. ii. p. 520. Henault, Sainte-Marthe.
339 Touchard-Lafosse, “Hist. Blois.” St. Gelais.
340 “Revue des deux Mondes,” 1 Mai, 1885.
341 “La Société provençale, à la fin du Moyen Age.”
342 “Antiquitez de Paris.”
343 Le Roux de Lincy quotes “Hist. de l’auguste et vénérable église de Chartres, &c.,” Chartres, 1683.
344 Brantôme, “Dames illustres,” t. v. p. 9.
345 Henault, “Hist. France,” t. i. p. 442.
346 Alain Bouchard, “Chron. de Bretagne,” quoted by Le Roux de Lincy, &c.
347 Louarches, “Les Femmes dans l’hist. France,” p. 105.
348 M. Le Roux de Lincy giving these details says they only exist in a manuscript called “Le trépas de l’Hermine regrettée.” MS. fol. 35. vo.
Punctuation, hyphenation, and spelling were made consistent when a predominant preference was found in this book; otherwise they were not changed. The spelling of non-English words has not been thoroughly checked.
Simple typographical errors were corrected; occasional unbalanced quotation marks retained.
Ambiguous hyphens at the ends of lines were retained.
The original book included a running timeline (years) at the top of most pages. Those years appear here between paragraphs in the form: {year} (where “year” is a number), with consecutive duplicates omitted within each chapter. The dates in the timeline mostly are in ascending sequence, but not always.
Index not checked for proper alphabetization or correct page references. The “See”-type cross-links were added by the Transcriber, and some of them may be incorrect.
Footnotes, originally at the bottom of each page, have been collected and placed at the end of this eBook, following the Index.
Page 2: Small-caps names in the text version of the genealogy chart are shown in all-caps.
Page 45: Closing quotation mark added after “no more children.”
Page 195: Closing quotation mark added after “varlet de chambre”.
Page 310: Closing quotation mark added after “girl as she was!”.
Page 340: Closing quotation mark added after “the war in Lombardy finished.”
Page 363: “Mistress, is dead? The Queen is dead!” was printed with the question mark.
Page 375: No page numbers given for “Michelle de France”.
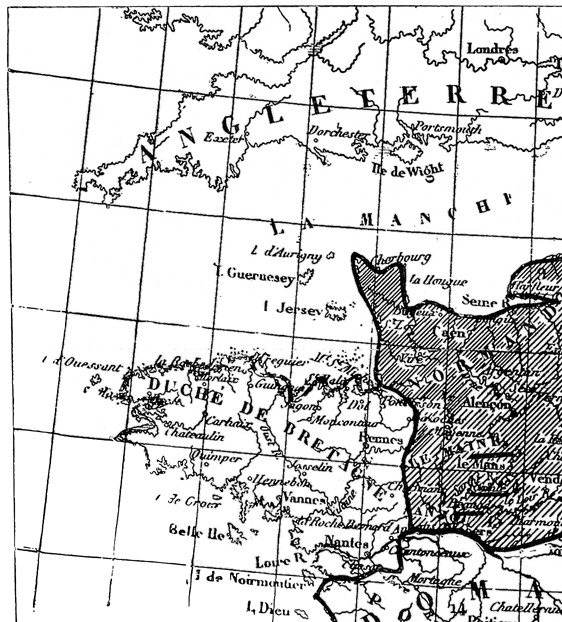
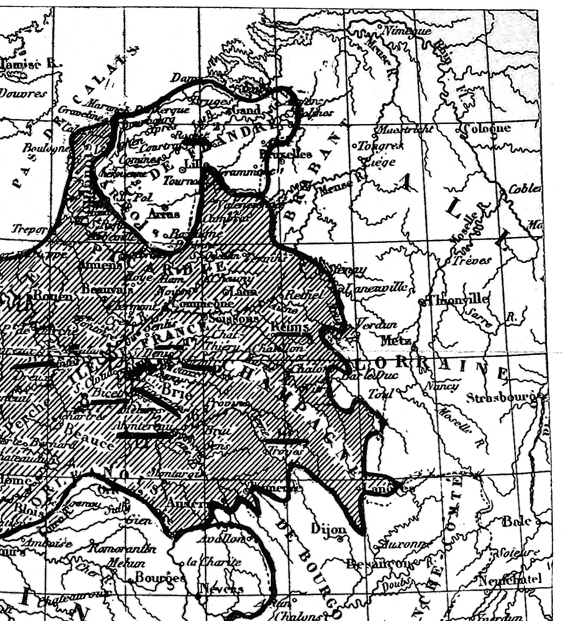
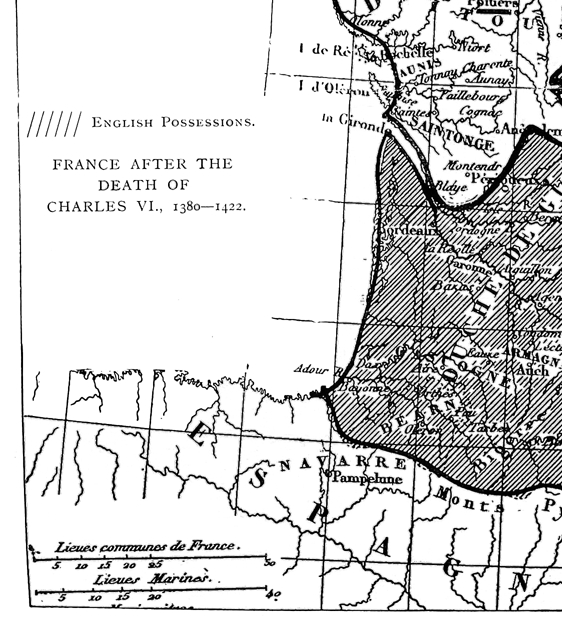
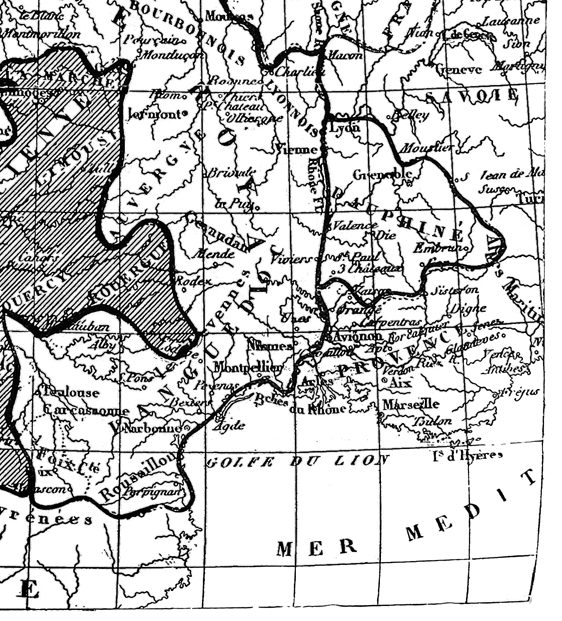
End of the Project Gutenberg EBook of Pictures of the old French court, by
Catherine Mary Bearne
*** END OF THIS PROJECT GUTENBERG EBOOK PICTURES OF THE OLD FRENCH COURT ***
***** This file should be named 50052-h.htm or 50052-h.zip *****
This and all associated files of various formats will be found in:
http://www.gutenberg.org/5/0/0/5/50052/
Produced by Clarity, Charlie Howard, and the Online
Distributed Proofreading Team at http://www.pgdp.net (This
file was produced from images generously made available
by The Internet Archive/American Libraries.)
Updated editions will replace the previous one--the old editions will
be renamed.
Creating the works from print editions not protected by U.S. copyright
law means that no one owns a United States copyright in these works,
so the Foundation (and you!) can copy and distribute it in the United
States without permission and without paying copyright
royalties. Special rules, set forth in the General Terms of Use part
of this license, apply to copying and distributing Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic works to protect the PROJECT GUTENBERG-tm
concept and trademark. Project Gutenberg is a registered trademark,
and may not be used if you charge for the eBooks, unless you receive
specific permission. If you do not charge anything for copies of this
eBook, complying with the rules is very easy. You may use this eBook
for nearly any purpose such as creation of derivative works, reports,
performances and research. They may be modified and printed and given
away--you may do practically ANYTHING in the United States with eBooks
not protected by U.S. copyright law. Redistribution is subject to the
trademark license, especially commercial redistribution.
START: FULL LICENSE
THE FULL PROJECT GUTENBERG LICENSE
PLEASE READ THIS BEFORE YOU DISTRIBUTE OR USE THIS WORK
To protect the Project Gutenberg-tm mission of promoting the free
distribution of electronic works, by using or distributing this work
(or any other work associated in any way with the phrase "Project
Gutenberg"), you agree to comply with all the terms of the Full
Project Gutenberg-tm License available with this file or online at
www.gutenberg.org/license.
Section 1. General Terms of Use and Redistributing Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic works
1.A. By reading or using any part of this Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic work, you indicate that you have read, understand, agree to
and accept all the terms of this license and intellectual property
(trademark/copyright) agreement. If you do not agree to abide by all
the terms of this agreement, you must cease using and return or
destroy all copies of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works in your
possession. If you paid a fee for obtaining a copy of or access to a
Project Gutenberg-tm electronic work and you do not agree to be bound
by the terms of this agreement, you may obtain a refund from the
person or entity to whom you paid the fee as set forth in paragraph
1.E.8.
1.B. "Project Gutenberg" is a registered trademark. It may only be
used on or associated in any way with an electronic work by people who
agree to be bound by the terms of this agreement. There are a few
things that you can do with most Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works
even without complying with the full terms of this agreement. See
paragraph 1.C below. There are a lot of things you can do with Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic works if you follow the terms of this
agreement and help preserve free future access to Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic works. See paragraph 1.E below.
1.C. The Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation ("the
Foundation" or PGLAF), owns a compilation copyright in the collection
of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works. Nearly all the individual
works in the collection are in the public domain in the United
States. If an individual work is unprotected by copyright law in the
United States and you are located in the United States, we do not
claim a right to prevent you from copying, distributing, performing,
displaying or creating derivative works based on the work as long as
all references to Project Gutenberg are removed. Of course, we hope
that you will support the Project Gutenberg-tm mission of promoting
free access to electronic works by freely sharing Project Gutenberg-tm
works in compliance with the terms of this agreement for keeping the
Project Gutenberg-tm name associated with the work. You can easily
comply with the terms of this agreement by keeping this work in the
same format with its attached full Project Gutenberg-tm License when
you share it without charge with others.
1.D. The copyright laws of the place where you are located also govern
what you can do with this work. Copyright laws in most countries are
in a constant state of change. If you are outside the United States,
check the laws of your country in addition to the terms of this
agreement before downloading, copying, displaying, performing,
distributing or creating derivative works based on this work or any
other Project Gutenberg-tm work. The Foundation makes no
representations concerning the copyright status of any work in any
country outside the United States.
1.E. Unless you have removed all references to Project Gutenberg:
1.E.1. The following sentence, with active links to, or other
immediate access to, the full Project Gutenberg-tm License must appear
prominently whenever any copy of a Project Gutenberg-tm work (any work
on which the phrase "Project Gutenberg" appears, or with which the
phrase "Project Gutenberg" is associated) is accessed, displayed,
performed, viewed, copied or distributed:
This eBook is for the use of anyone anywhere in the United States and
most other parts of the world at no cost and with almost no
restrictions whatsoever. You may copy it, give it away or re-use it
under the terms of the Project Gutenberg License included with this
eBook or online at www.gutenberg.org. If you are not located in the
United States, you'll have to check the laws of the country where you
are located before using this ebook.
1.E.2. If an individual Project Gutenberg-tm electronic work is
derived from texts not protected by U.S. copyright law (does not
contain a notice indicating that it is posted with permission of the
copyright holder), the work can be copied and distributed to anyone in
the United States without paying any fees or charges. If you are
redistributing or providing access to a work with the phrase "Project
Gutenberg" associated with or appearing on the work, you must comply
either with the requirements of paragraphs 1.E.1 through 1.E.7 or
obtain permission for the use of the work and the Project Gutenberg-tm
trademark as set forth in paragraphs 1.E.8 or 1.E.9.
1.E.3. If an individual Project Gutenberg-tm electronic work is posted
with the permission of the copyright holder, your use and distribution
must comply with both paragraphs 1.E.1 through 1.E.7 and any
additional terms imposed by the copyright holder. Additional terms
will be linked to the Project Gutenberg-tm License for all works
posted with the permission of the copyright holder found at the
beginning of this work.
1.E.4. Do not unlink or detach or remove the full Project Gutenberg-tm
License terms from this work, or any files containing a part of this
work or any other work associated with Project Gutenberg-tm.
1.E.5. Do not copy, display, perform, distribute or redistribute this
electronic work, or any part of this electronic work, without
prominently displaying the sentence set forth in paragraph 1.E.1 with
active links or immediate access to the full terms of the Project
Gutenberg-tm License.
1.E.6. You may convert to and distribute this work in any binary,
compressed, marked up, nonproprietary or proprietary form, including
any word processing or hypertext form. However, if you provide access
to or distribute copies of a Project Gutenberg-tm work in a format
other than "Plain Vanilla ASCII" or other format used in the official
version posted on the official Project Gutenberg-tm web site
(www.gutenberg.org), you must, at no additional cost, fee or expense
to the user, provide a copy, a means of exporting a copy, or a means
of obtaining a copy upon request, of the work in its original "Plain
Vanilla ASCII" or other form. Any alternate format must include the
full Project Gutenberg-tm License as specified in paragraph 1.E.1.
1.E.7. Do not charge a fee for access to, viewing, displaying,
performing, copying or distributing any Project Gutenberg-tm works
unless you comply with paragraph 1.E.8 or 1.E.9.
1.E.8. You may charge a reasonable fee for copies of or providing
access to or distributing Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works
provided that
* You pay a royalty fee of 20% of the gross profits you derive from
the use of Project Gutenberg-tm works calculated using the method
you already use to calculate your applicable taxes. The fee is owed
to the owner of the Project Gutenberg-tm trademark, but he has
agreed to donate royalties under this paragraph to the Project
Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation. Royalty payments must be paid
within 60 days following each date on which you prepare (or are
legally required to prepare) your periodic tax returns. Royalty
payments should be clearly marked as such and sent to the Project
Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation at the address specified in
Section 4, "Information about donations to the Project Gutenberg
Literary Archive Foundation."
* You provide a full refund of any money paid by a user who notifies
you in writing (or by e-mail) within 30 days of receipt that s/he
does not agree to the terms of the full Project Gutenberg-tm
License. You must require such a user to return or destroy all
copies of the works possessed in a physical medium and discontinue
all use of and all access to other copies of Project Gutenberg-tm
works.
* You provide, in accordance with paragraph 1.F.3, a full refund of
any money paid for a work or a replacement copy, if a defect in the
electronic work is discovered and reported to you within 90 days of
receipt of the work.
* You comply with all other terms of this agreement for free
distribution of Project Gutenberg-tm works.
1.E.9. If you wish to charge a fee or distribute a Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic work or group of works on different terms than
are set forth in this agreement, you must obtain permission in writing
from both the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation and The
Project Gutenberg Trademark LLC, the owner of the Project Gutenberg-tm
trademark. Contact the Foundation as set forth in Section 3 below.
1.F.
1.F.1. Project Gutenberg volunteers and employees expend considerable
effort to identify, do copyright research on, transcribe and proofread
works not protected by U.S. copyright law in creating the Project
Gutenberg-tm collection. Despite these efforts, Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic works, and the medium on which they may be stored, may
contain "Defects," such as, but not limited to, incomplete, inaccurate
or corrupt data, transcription errors, a copyright or other
intellectual property infringement, a defective or damaged disk or
other medium, a computer virus, or computer codes that damage or
cannot be read by your equipment.
1.F.2. LIMITED WARRANTY, DISCLAIMER OF DAMAGES - Except for the "Right
of Replacement or Refund" described in paragraph 1.F.3, the Project
Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation, the owner of the Project
Gutenberg-tm trademark, and any other party distributing a Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic work under this agreement, disclaim all
liability to you for damages, costs and expenses, including legal
fees. YOU AGREE THAT YOU HAVE NO REMEDIES FOR NEGLIGENCE, STRICT
LIABILITY, BREACH OF WARRANTY OR BREACH OF CONTRACT EXCEPT THOSE
PROVIDED IN PARAGRAPH 1.F.3. YOU AGREE THAT THE FOUNDATION, THE
TRADEMARK OWNER, AND ANY DISTRIBUTOR UNDER THIS AGREEMENT WILL NOT BE
LIABLE TO YOU FOR ACTUAL, DIRECT, INDIRECT, CONSEQUENTIAL, PUNITIVE OR
INCIDENTAL DAMAGES EVEN IF YOU GIVE NOTICE OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH
DAMAGE.
1.F.3. LIMITED RIGHT OF REPLACEMENT OR REFUND - If you discover a
defect in this electronic work within 90 days of receiving it, you can
receive a refund of the money (if any) you paid for it by sending a
written explanation to the person you received the work from. If you
received the work on a physical medium, you must return the medium
with your written explanation. The person or entity that provided you
with the defective work may elect to provide a replacement copy in
lieu of a refund. If you received the work electronically, the person
or entity providing it to you may choose to give you a second
opportunity to receive the work electronically in lieu of a refund. If
the second copy is also defective, you may demand a refund in writing
without further opportunities to fix the problem.
1.F.4. Except for the limited right of replacement or refund set forth
in paragraph 1.F.3, this work is provided to you 'AS-IS', WITH NO
OTHER WARRANTIES OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT
LIMITED TO WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR ANY PURPOSE.
1.F.5. Some states do not allow disclaimers of certain implied
warranties or the exclusion or limitation of certain types of
damages. If any disclaimer or limitation set forth in this agreement
violates the law of the state applicable to this agreement, the
agreement shall be interpreted to make the maximum disclaimer or
limitation permitted by the applicable state law. The invalidity or
unenforceability of any provision of this agreement shall not void the
remaining provisions.
1.F.6. INDEMNITY - You agree to indemnify and hold the Foundation, the
trademark owner, any agent or employee of the Foundation, anyone
providing copies of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works in
accordance with this agreement, and any volunteers associated with the
production, promotion and distribution of Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic works, harmless from all liability, costs and expenses,
including legal fees, that arise directly or indirectly from any of
the following which you do or cause to occur: (a) distribution of this
or any Project Gutenberg-tm work, (b) alteration, modification, or
additions or deletions to any Project Gutenberg-tm work, and (c) any
Defect you cause.
Section 2. Information about the Mission of Project Gutenberg-tm
Project Gutenberg-tm is synonymous with the free distribution of
electronic works in formats readable by the widest variety of
computers including obsolete, old, middle-aged and new computers. It
exists because of the efforts of hundreds of volunteers and donations
from people in all walks of life.
Volunteers and financial support to provide volunteers with the
assistance they need are critical to reaching Project Gutenberg-tm's
goals and ensuring that the Project Gutenberg-tm collection will
remain freely available for generations to come. In 2001, the Project
Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation was created to provide a secure
and permanent future for Project Gutenberg-tm and future
generations. To learn more about the Project Gutenberg Literary
Archive Foundation and how your efforts and donations can help, see
Sections 3 and 4 and the Foundation information page at
www.gutenberg.org
Section 3. Information about the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation
The Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation is a non profit
501(c)(3) educational corporation organized under the laws of the
state of Mississippi and granted tax exempt status by the Internal
Revenue Service. The Foundation's EIN or federal tax identification
number is 64-6221541. Contributions to the Project Gutenberg Literary
Archive Foundation are tax deductible to the full extent permitted by
U.S. federal laws and your state's laws.
The Foundation's principal office is in Fairbanks, Alaska, with the
mailing address: PO Box 750175, Fairbanks, AK 99775, but its
volunteers and employees are scattered throughout numerous
locations. Its business office is located at 809 North 1500 West, Salt
Lake City, UT 84116, (801) 596-1887. Email contact links and up to
date contact information can be found at the Foundation's web site and
official page at www.gutenberg.org/contact
For additional contact information:
Dr. Gregory B. Newby
Chief Executive and Director
gbnewby@pglaf.org
Section 4. Information about Donations to the Project Gutenberg
Literary Archive Foundation
Project Gutenberg-tm depends upon and cannot survive without wide
spread public support and donations to carry out its mission of
increasing the number of public domain and licensed works that can be
freely distributed in machine readable form accessible by the widest
array of equipment including outdated equipment. Many small donations
($1 to $5,000) are particularly important to maintaining tax exempt
status with the IRS.
The Foundation is committed to complying with the laws regulating
charities and charitable donations in all 50 states of the United
States. Compliance requirements are not uniform and it takes a
considerable effort, much paperwork and many fees to meet and keep up
with these requirements. We do not solicit donations in locations
where we have not received written confirmation of compliance. To SEND
DONATIONS or determine the status of compliance for any particular
state visit www.gutenberg.org/donate
While we cannot and do not solicit contributions from states where we
have not met the solicitation requirements, we know of no prohibition
against accepting unsolicited donations from donors in such states who
approach us with offers to donate.
International donations are gratefully accepted, but we cannot make
any statements concerning tax treatment of donations received from
outside the United States. U.S. laws alone swamp our small staff.
Please check the Project Gutenberg Web pages for current donation
methods and addresses. Donations are accepted in a number of other
ways including checks, online payments and credit card donations. To
donate, please visit: www.gutenberg.org/donate
Section 5. General Information About Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works.
Professor Michael S. Hart was the originator of the Project
Gutenberg-tm concept of a library of electronic works that could be
freely shared with anyone. For forty years, he produced and
distributed Project Gutenberg-tm eBooks with only a loose network of
volunteer support.
Project Gutenberg-tm eBooks are often created from several printed
editions, all of which are confirmed as not protected by copyright in
the U.S. unless a copyright notice is included. Thus, we do not
necessarily keep eBooks in compliance with any particular paper
edition.
Most people start at our Web site which has the main PG search
facility: www.gutenberg.org
This Web site includes information about Project Gutenberg-tm,
including how to make donations to the Project Gutenberg Literary
Archive Foundation, how to help produce our new eBooks, and how to
subscribe to our email newsletter to hear about new eBooks.