
NAPOLEON AND EUGENE.
Napoleon Bonaparte.
Lima and the Limanians.
Ally Somers.—A Tale of the Coast-Guard.
Misers.
The Cricket.
The Right One.—A Lesson for Lovers.
Lord Brougham as a Judge.
The Household of Sir Thos. More.
Bookworms.
Incidents of Dueling.
Maurice Tiernay, The Soldier of Fortune.
Recollections of Colton, The Author of "Lacon."
Never Despair.
Incident During the Mutiny of 1797.
Woman's Offices and Influence.
The Town-Ho's Story.
My Novel, Or, Varieties in English Life.
The Fortunes of the Reverend Caleb Ellison.
Lamartine on The Restoration.
The Captain's Self-Devotion.
The Eagle and the Swan.
Monthly Record of Current Events.
Editor's Table.
Editor's Drawer.
Editor's Easy Chair.
Literary Notices.
A Leaf from Punch.
Fashions for October.
BY JOHN S. C. ABBOTT.
The discomfiture of the insurgent sections at Paris, and the energy, tact, and humanity which Napoleon displayed in the subsequent government of the tumultuous city, caused his name to be as familiar as a household word in all parts of the metropolis. His slight and slender figure, so feminine and graceful in its proportions; his hand, so small and white and soft that any lady might covet it; his features, so mild and youthful in their expression, and all these combined in strange alliance with energies as indomitable, and a will as imperious as were ever enshrined in mortal form, invested the young general with a mysterious and almost supernatural fascination.
Famine was rioting in the streets of Paris. All industry was at an end. The poor, unemployed, were perishing. The rich were gathering the wrecks of their estates, and flying from France. There was no law but such as was proclaimed by the thunders of Napoleon's batteries. The National Guard he immediately reorganized, and soon efficient order was established. Napoleon was incessantly occupied in visiting all parts of the city, and words of kindness and sympathy with suffering he combined with the strong and inexorable arm of military rule. More than a hundred families, says the Duchess of Abrantes, were saved from perishing by his personal exertions. He himself climbed to the garrets of penury, and penetrated the cellars of want and woe, and, with a moistened eye, gazed upon the scenes of fearful wretchedness with which Paris was filled. He caused wood and bread to be distributed to the poor, and totally regardless of ease or self-indulgence, did every thing in his power to alleviate suffering.
One day when alighting from his carriage to dine at Madame Permon's, he was addressed by a woman who held a dead infant in her arms. Grief and hunger had dried up the fountain of life in her bosom, and her unweaned child had perished of starvation. Her husband was dead, and five children were mourning for food at home. "If I can not obtain relief," said the famished mother, "I must take my remaining five children and drown myself with them." Napoleon questioned her very minutely, ascertained her place of residence, and giving her some money to meet her immediate wants, entered the house and sat down with the guests at the brilliant entertainment. He was, however, so deeply impressed with the scene of wretchedness which he had just witnessed, that he could not obliterate it from his mind, and all were struck with his absent manner and the sadness of his countenance. Immediately after dinner he took measures to ascertain the truth of the statements which the poor woman had made to him, and finding all her assertions verified, he took the family immediately under his protection. He obtained employment for the girls in needlework among his friends, and the family ever expressed the most profound gratitude for their preserver. It was by the unceasing exhibition of such traits of character that Napoleon entwined around him the hearts of the French people.
There was, at this time in Paris, a lady, who was rendered quite prominent in society, by her social attractions, her personal loveliness, and her elevated rank. She was a widow, twenty-eight years of age. Her husband, the Viscount Beauharnais, had recently perished upon the scaffold, an illustrious victim of revolutionary fury. Josephine Tascher Beauharnais, who subsequently became the world-renowned bride of Napoleon, was born on the island of Martinice in the West Indies. When almost a child she was married to the Viscount Beauharnais, who had visited the island on business and was captivated by the loveliness of the fair young Creole. Upon entering Paris she was immediately introduced to all the splendors of the court of Maria-Antoinette. The revolutionary storm soon burst upon her dwelling with merciless fury. She experienced the most afflictive reverses of friendlessness, bereavement, imprisonment, and penury. The storm had, however, passed over her, and she was left a widow, with two children, Eugene and Hortense. From the wreck of her fortune she had saved an ample competence, and was surrounded by influential and admiring friends.
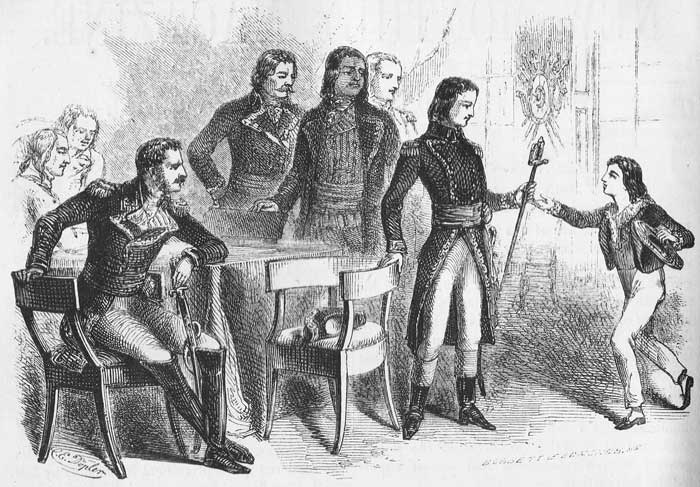
Napoleon, in obedience to the orders of the Convention, to prevent the possibility of another outbreak of lawless violence, had proceeded to the disarming of the populace of Paris. In the performance of this duty the sword of M. Beauharnais was taken. A few days afterward Eugene, a very intelligent and graceful child, twelve years of age, obtained access to Napoleon, and with most engaging artlessness and depth of emotion, implored that the sword of his father might be restored to him. Napoleon had no heart to deny such a request. He sent for the sword, and speaking with kind words of com[Pg 578]mendation, presented it with his own hand to Eugene. The grateful boy burst into tears and, unable to articulate a word, pressed the sword to his bosom, bowed in silence and retired. Napoleon was much interested in this exhibition of filial love, and his thoughts were immediately directed to the mother who had formed the character of such a child. Josephine, whose whole soul was absorbed in love for her children, was so grateful, for the kindness with which the distinguished young general had treated her fatherless Eugene, that she called, in her carriage, the next day, to express to him a mother's thanks. She was dressed in deep mourning. Her peculiarly musical voice was tremulous with emotion. The fervor and the delicacy of her maternal love, and the perfect grace of manner and of language, with which she discharged her mission, excited the admiration of Napoleon. He soon called upon her. The acquaintance rapidly ripened into an unusually strong and ardent affection.

Josephine was two years older than Napoleon. But her form and features had resisted the encroachments of time, and her cheerfulness and vivacity invested her with all the charms of early youth. Barras, now one of the five Directors, who had been established in power by the guns of Napoleon, was a very ardent friend of Josephine. He warmly advocated the contemplated connection, deeming it mutually advantageous. Napoleon would greatly increase his influence by an alliance with one occupying so high a position in society and surrounded by friends so influential. And Barras clearly foresaw that the energetic young general possessed genius which would insure distinction. Josephine thus speaks, in a letter to a friend, of her feelings in view of the proposed marriage.
"I am urged to marry again. My friends counsel the measure, my aunt almost lays her injunctions to the same effect, and my children entreat my compliance. You have met General Bonaparte at my house. He it is who would supply a father's place to the orphans of Alexander Beauharnais, and a husband to his widow. I admire the general's courage, the extent of his information, for on all subjects he talks equally well, and the quickness of his judgment, which enables him to seize the thoughts of others almost before they are expressed. But I confess that I shrink from the despotism he seems desirous of exercising over all who approach him. His searching glance has something singular and inexplicable, which imposes even upon our Directors; judge if it may not intimidate a woman.
"Barras gives assurance that if I marry the general, he will secure his appointment to the command of the army of Italy. Yesterday, Bonaparte speaking of this favor, said to me, 'Think they then, that I have need of their protection to arrive at power? Egregious mistake! They will all be but too happy, one day, should I condescend to grant them mine.'
"What think you of this self-confidence? Is it not a proof of excess of vanity? A general of brigade protect the heads of government! That truly is an event highly probable! I know not how it is, but sometimes this waywardness gains upon me to such a degree, that almost I believe possible whatever this singular man may take into his head to attempt. And with his imagination, who can calculate what he will not undertake."
Though the passion with which Josephine had inspired Napoleon, was ardent and impetuous in the highest degree, it interfered not in the least with his plans of towering ambition. During[Pg 579] the day he was vigorously employed in his professional duties and in persevering study. But each evening found him at the mansion of Josephine, where he met, and dazzled by his commanding genius and his brilliant conversational powers, the most distinguished and the most influential men of the metropolis. In these social entertainments, Josephine testified that Napoleon possessed unlimited powers of fascination, whenever he saw fit to employ them. His acquaintance and his influence was thus extended among those who would be most available in the furtherance of his plans. On the 6th of March, 1796, Napoleon and Josephine were married, Napoleon being then twenty-five years of age. It was a union of very sincere affection on both sides. It can not be doubted that next to ambition, Josephine was to Napoleon the dearest object of his admiration and homage. Marriage had then ceased to be regarded in infidel France as a religious rite. It was a mere partnership which any persons could form or dissolve at pleasure. The revolutionary tribunals had closed the churches, banished the clergy, and dethroned God. The parties, contemplating marriage, simply recorded their intention in the state register of Paris, with two or three friends to sign the record as witnesses. By this simple ceremony Napoleon was united to Josephine. But neither of the parties approved of this mercantile aspect of a transaction so sacred. They were both, in natural disposition serious, thoughtful, and prone to look to the guidance of a power higher than that of man. Surrounded by infidelity, and by that vice with which public infidelity is invariably accompanied, they both instinctively reverenced all that is grand and imposing in the revelations of Christianity.
"Man, launched into life," said Napoleon, "asks himself, whence do I come? What am I? Whither do I go? Mysterious questions which draw him toward religion; our hearts crave the support and guidance of religious faith. We believe in the existence of God because every thing around us proclaims his being. The greatest minds have cherished this conviction—Bossuet, Newton, Leibnitz. The heart craves faith as the body food; and, without doubt, we believe most frequently without exercising our reason. Faith wavers as soon as we begin to argue. But even then our hearts say, 'Perhaps I shall again believe instinctively. God grant it. For we feel that this belief in a protecting deity must be a great happiness; an immense consolation in adversity, and a powerful safeguard when tempted to immorality.
"The virtuous man never doubts of the existence of God, for if his reason does not suffice to comprehend it, the instinct of his soul adopts the belief. Every intimate feeling of the soul is in sympathy with the sentiments of religion."
These are profound thoughts and it is strange that they should have sprung up in the mind of one educated in the midst of the violence, and the clangor, and the crime of battle, and accustomed to hear from the lips of all around him, every religious sentiment ridiculed as the superstition of the most weak and credulous.
When at St. Helena, Napoleon, one evening, called for the New Testament, and read to his friends the address of Jesus to his disciples upon the mountain. He expressed himself as having been ever struck with the highest admiration in view of the purity, the sublimity, and the beauty of the morality which it contained. Napoleon seldom spoke lightly even of the corruptions of the church. But he always declared his most exalted appreciation of the religion of Jesus Christ.
When Napoleon was crowned Emperor he was privately married again by Cardinal Fesch, in accordance with the forms of the church which the Emperor had re-established. "Josephine," said Napoleon, "was truly a most lovely woman; refined, affable, and charming. She was the goddess of the toilet. All the fashions originated with her. Every thing she put on appeared elegant. She was so kind, so humane—she was the most graceful lady and the best woman in France. I never saw her act inelegantly during the whole time we lived together. She possessed a perfect knowledge of the different shades of my character, and evinced the most exquisite tact in turning this knowledge to the best account. For example, she never solicited any favor for Eugene, or thanked me for any that I conferred upon him. She never showed any additional complaisance or assiduity when he was receiving from me the greatest honors. Her grand aim was to assume that all this was my affair—that Eugene was our son, not hers. Doubtless she entertained the idea that I would adopt Eugene as my successor."
Again, he said, of Josephine, "we lived together like honest citizens in our mutual relations, and always retired together till 1805, a period in which political events obliged me to change my habits, and to add the labors of the night to those of the day. This regularity is the best guarantee for a good establishment. It ensures the respectability of the wife, the dependence of the husband, and maintains intimacy of feelings and good morals. If this is not the case, the smallest circumstances make people forget each other. A son by Josephine would have rendered me happy, and would have secured the reign of my dynasty. The French would have loved him very much better than they could love the son of Maria Louisa; and I never would have put my foot on that abyss covered with flowers, which was my ruin. Let no one after this rely upon the wisdom of human combinations. Let no one venture to pronounce, before its close, upon the happiness or misery of life. My Josephine had the instinct of the future when she became terrified at her own sterility. She knew well that a marriage is only real when there is an offspring; and in proportion as fortune smiled her anxiety increased. I was the object of her deepest attachment. If I went into my carriage at midnight for a long journey, there, to my surprise, I found her, seated before[Pg 580] me, and awaiting my arrival. If I attempted to dissuade her from accompanying me, she had so many good and affectionate reasons to urge, that it was almost always necessary to yield. In a word she always proved to me a happy and affectionate wife, and I have preserved the tenderest recollections of her.
"Political motives induced me to divorce Josephine, whom I most tenderly loved. She, poor woman, fortunately for herself, died in time to prevent her from witnessing the last of my misfortunes. After her forcible separation from me, she avowed, in most feeling terms, her ardent desire to share with me, my exile and extolled, with many tears, both myself and my conduct to her. The English have represented me as a monster of cruelty. Is this the result of the conduct of a merciless, unfeeling tyrant? A man is known by his treatment of his wife, of his family, and of those under him."
Just before his marriage, Napoleon received the appointment, to him most gratifying, of Commander-in-chief of the army of Italy. His predecessor had been displaced in consequence of excessive intemperance. Napoleon was but twenty-five years of age when placed in this responsible post. "You are rather young," said one of the Directors, "to assume responsibilities so weighty, and to take the command over veteran generals." "In one year," Napoleon replied, "I shall be either old or dead." "We can place you in the command of men alone," said Carnot, "for the troops are destitute of every thing, and we can furnish you with no money to provide supplies." "Give me only men enough," Napoleon replied, "and I ask for nothing more. I will be answerable for the result."
A few days after Napoleon's marriage, he left his bride in Paris, and set out for Nice, the head-quarters of the army of Italy. He passed through Marseilles, that he might pay a short visit to his mother, whose love he ever cherished with the utmost tenderness, and on the 27th of March arrived at the cold and cheerless camps, where the dejected troops of France were enduring every hardship. They were surrounded by numerous foes, who had driven them from the fertile plains of Italy into the barren and dreary fastnesses of the Alps. The Austrian armies, quartered in opulent cities, or encamped upon sunny and vine-clad hill-sides, were living in the enjoyment of security and abundance, while the troops of the distracted and impoverished republic were literally freezing and starving. But here let us pause for a moment to consider the cause of the war, and the motives which animated the contending armies.
France, in the exercise of a right which few in America will question, had, in imitation of the United States, and incited by their example, renounced the monarchical form of government, and established a republic. For centuries uncounted, voluptuous kings and licentious nobles had trampled the oppressed millions into the dust. But now these millions had risen in their majesty, and driving the king from his throne and the nobles from their wide domains, had taken their own interests into their own hands. They were inexperienced and unenlightened in the science of government, and they made many and lamentable mistakes. They were terrified in view of the powerful combination of all the monarchs and nobles of Europe to overwhelm them with invading armies, and in their paroxysms of fear, when destruction seemed to be coming like an avalanche upon them, they perpetrated many deeds of atrocious cruelty. They simply claimed the right of self-government, and when assailed, fell upon their assailants with blind and merciless fury.
The kings of Europe contemplated this portentous change with inexpressible alarm. In consternation they witnessed the uprising of the masses in France, and saw one of their brother monarchs dragged from his palace and beheaded upon the guillotine. The successful establishment of the French Republic would very probably have driven every King in Europe from his throne. England was agitated through all her countries. From the mud cabins of Ireland, from the dark and miry mines, from the thronged streets of the city, and the crowded workshops all over the kingdom, there was a clamorous cry ascending for liberty and equality. The spirit of democracy, radiating from its soul in Paris, was assailing every throne in Europe. There was no alternative for these monarchs but to crush this new power, or to perish before it. There can be no monarchist whose sympathies will not beat high with the allied kings in the fearful conflict which ensued. There can be no republican who will not pray, "God speed the Eagles of France." Both parties believed that they were fighting in self-defense. The kings were attacked by principles triumphant in France, which were undermining their thrones. The French were attacked by bayonets and batteries—by combined armies invading their territories, bombarding their cities, and endeavoring by force of arms, to compel a proud nation of thirty millions of inhabitants to reinstate, at foreign dictation, the rejected Bourbons upon the throne. The allies called upon all the loyalists scattered over France to grasp their arms, to rally beneath the banner of friends coming to their rescue, and to imbrue their country in the blood of a civil war. The French, in trumpet tones, summoned the people of all lands to hail the tri-colored flag, as the harbinger of their deliverance from the servitude of ages. From every city in Europe which Napoleon approached, with his conquering armies, the loyalists fled, while the republicans welcomed him with an adulation amounting almost to religious homage. And the troops of the allies were welcomed, in every city of France which they entered, with tears of gratitude from the eyes of those who longed for the restoration of the monarchy. It was a conflict between the spirit of republicanism on the one side, and of monarchical and ecclesiastical domination upon the other.
England, with her invincible fleet, was hover[Pg 581]ing around the coasts of the republic, assailing every exposed point, landing troops upon the French territory, and arming and inspiriting the loyalists to civil war. Austria had marched an army of nearly two hundred thousand men upon the banks of the Rhine, to attack France upon the north. She had called into requisition all her Italian possessions, and in alliance with the British navy, and the armies of the king of Sardinia, and the fanatic legions of Naples and Sicily had gathered eighty thousand men upon the Alpine frontier. This host was under the command of experienced generals, and was abundantly provided with all the munitions of war. These were the invading foes whom Napoleon was to encounter in fields of blood. It was purely a war of self-defense on the part of the French people. They were contending against the bullets and the bayonets of the armies of monarchical Europe, assailing them at every point. The allied kings felt that they also were engaged in a war of self-defense—that they were struggling against principles which threatened to undermine their thrones. Strange as the declaration to some may appear, it is extremely difficult for a candid and an impartial man severely to censure either side. It is not strange, contemplating frail human nature as it is, that the monarchs of Europe, born to a kingly inheritance, should have made every exertion to retain their thrones, and to secure their kingdoms from the invasion of republican principles. It is not strange that republicanized France, having burst the chains of an intolerable despotism, should have resolved to brave all the horrors of the most desperate war rather than surrender the right of choosing its own form of government. The United States were protected from a similar onset, on the part of allied Europe, only by the wide barrier of the ocean. And had the combined armies of monarchical Europe crossed that barrier, and invaded our shores, to compel us to replace George III. upon his American throne, we should have blest the Napoleon, emerging from our midst, who, contending for the liberties of his country, had driven them back into the sea.
When Napoleon arrived at Nice he found that he had but thirty thousand men with whom to repel the eighty thousand of the allies. The government was impoverished, and had no means to pay the troops. The soldiers were dejected, emaciate, and ragged. The cavalry horses had died upon the bleak and frozen summits of the mountains, and the army was almost entirely destitute of artillery. The young commander-in-chief, immediately upon his arrival, summoned his generals before him. Many of them were veteran soldiers, and they were not a little chagrined in seeing a youth, whom they regarded almost as a beardless boy, placed over them in command. But in the very first hour in which he met them, his superiority was recognized; and he gained a complete and an unquestioned ascendency over all. Berthier, Massena, Augereau, Serrurier, and Lannes were there, men who had already attained renown, and who were capable of appreciating genius. "This is the leader," said one, as he left this first council, "who will surely guide us to fame and fortune."
The French were on the cold crests of the mountains. The allies were encamped in the warm and fertile valleys which opened into the Italian plains. The untiring energy of the youthful general, his imperial mind, his unhesitating reliance upon his own mental resources, his perfect acquaintance with the theatre of war, as the result of his previous explorations, his gravity and reserve of manners, his spotless morality, so extraordinary in the midst of all the dissipated scenes of the camp, commanded the reverence of the dissolute and licentious, though brave and talented generals who surrounded him. There was an indescribable something in his manner which immediately inspired respect and awe, and which kept all familiarity at a distance.
Decres had known Napoleon well in Paris, and had been on terms of perfect intimacy with him. He was at Toulon when he heard of Napoleon's appointment to the command of the army of Italy. "When I learned," said he, "that the new general was about to pass through the city, I immediately proposed to introduce my comrades to him, and to turn my acquaintance to the best account. I hastened to meet him full of eagerness and joy. The door of the apartment was thrown open, and I was upon the point of rushing to him with my wonted familiarity. But his attitude, his look, the tone of his voice suddenly deterred me. There was nothing haughty or offensive in his appearance or manner, but the impression he produced was sufficient to prevent me from ever again attempting to encroach upon the distance which separated us."[1]
[1] Decres was afterward elevated by Napoleon to a dukedom, and appointed Minister of the Marine. He was strongly attached to his benefactor. At the time of Napoleon's downfall, he was sounded in a very artful way as to his willingness to conspire against the Emperor. Happening to visit a person of celebrity, the latter drew him aside to the fire-place, and taking up a book, said, "I have just now been reading something that struck me very forcibly. Montesquieu here remarks, 'When the prince rises above the laws, when tyranny becomes insupportable, the oppressed have no alternative but—'" "Enough," exclaimed Decres, putting his hand before the mouth of the reader, "I will hear no more. Close the book." The other coolly laid down the volume, as though nothing particular had occurred, and began to talk on a totally different subject.
A similar ascendency, notwithstanding his feminine stature and the extreme youthfulness of his appearance, he immediately gained over all the soldiers and all the generals of the army. Every one who entered his presence was awed by the indescribable influence of his imperial mind. No one ventured to contend with him for the supremacy. He turned with disgust from the licentiousness and dissipation which ever disgraces the presence of an army, and with a sternness of morality which would have done honor to any of the sages of antiquity, secured that respect which virtue ever commands. There were many very beautiful and dissolute females in Nice, opera singers and dancing girls, who, [Pg 582] trafficking in their charms, were living in great wealth and voluptuousness. They exhausted all their arts of enticement to win the attention of the young commander-in-chief. But their allurements were unavailing. Napoleon proved a Samson whom no Delilah could seduce. And this was the more extraordinary, since his natural temperament was glowing and impetuous in the extreme, and he had no religious scruples to interfere with his indulgences. "My extreme youth," said he, afterward, "when I took command of the army of Italy, rendered it necessary that I should evince great reserve of manners and the utmost severity of morals. This was indispensable to enable me to sustain authority over men so greatly my superiors in age and experience. I pursued a line of conduct in the highest degree irreproachable and exemplary. In spotless morality I was a Cato, and must have appeared such to all. I was a philosopher and a sage. My supremacy could be retained only by proving myself a better man than any other man in the army. Had I yielded to human weaknesses I should have lost my power."
He was temperate in the extreme, seldom allowing himself to take even a glass of wine, and never did he countenance by his presence any scene of bacchanalian revelry. For gaming, in all its branches, he manifested then, and through the whole of his life, the strongest disapproval. He ever refused to repose confidence in any one who was addicted to that vice. One day at St. Helena, he was conversing with Las Casas, when some remark which was made led Napoleon to inquire, "Were you a gamester?" "Alas, sire!" Las Casas replied, "I must confess that I was, but only occasionally." "I am very glad," Napoleon rejoined, "that I knew nothing of it at the time. You would have been ruined in my esteem. A gamester was sure to forfeit my confidence. The moment I heard that a man was addicted to that vice I placed no more confidence in him."
From what source did this young soldier imbibe these elevated principles? Licentiousness, irreligion, gambling had been the trinity of revolutionary France—the substitute which rampant infidelity had adopted, for a benignant Father, a pleading Saviour, a sanctifying Spirit. Napoleon was reared in the midst of these demoralizing influences. And yet how unsullied does his character appear when compared with that of his companions in the camp and on the throne! Napoleon informs us that to his mother he was indebted for every pure and noble sentiment which inspired his bosom.
Letitia, the mother of Napoleon, was a woman of extraordinary endowments. She had herself hardly passed the period of childhood, being but nineteen years of age, when she heard the first wailing cry of Napoleon, her second born, and pressed the helpless babe, with thanksgiving and prayer, to her maternal bosom. She was a young mother to train and educate such a child for his unknown but exalted destiny. She encircled, in protecting arms, the nursing babe, as it fondled a mother's bosom with those little hands, which, in after years, grasped sceptres, and uphove thrones, and hewed down armies with resistless sword. She taught those infant lips to lisp "papa"—"mamma"—those lips at whose subsequent command all Europe was moved, and whose burning, glowing, martial words fell like trumpet-tones upon the world, hurling nation upon nation in the shock of war. She taught those feeble feet to make their first trembling essays upon the carpet, rewarding the successful endeavor with a mother's kiss and a mother's caress—those feet which afterward strode over the sands of the desert, and waded through the blood-stained snow-drifts of Russia, and tottered, in the infirmities of sickness and death, on the misty, barren, storm-swept crags of St. Helena. She instilled into the bosom of her son those elevated principles of honor and self-respect, which, when surrounded by every temptation earth could present, preserved him from the degraded doom of the inebriate, of the voluptuary, and of the gamester, and which made the court of Napoleon, when the most brilliant court this world has ever known, also the most illustrious for the purity of its morals and the decorum of its observances. The sincere, unaffected piety of Letitia rose so high above the corruptions of a corrupt and profligate church, that her distinguished son, notwithstanding the all but universal infidelity of the times, was compelled to respect a religion which had embellished a beloved mother's life. He was thus induced, in his day of power, to bring back a wayward nation of thirty millions from cheerless, brutalizing, comfortless unbelief, to all the consoling, ennobling, purifying influences of Christianity. When at the command of Napoleon the church bells began again to toll the hour of prayer, on every hill-side, and through every valley in France, and the dawn of the Sabbath again guided rejoicing thousands in the crowded city and in the silent country to the temples of religion—when the young, in their nuptials, and the aged in their death were blessed by the solemnities of gospel ministrations, it was a mother's influence which inspired a dutiful son to make the magic change, which thus, in an hour, transformed France from a pagan to nominally a Christian land. It was the calm, gentle, persuasive voice of Letitia which was embodied in the consular decree. Honor to Letitia, the mother of Napoleon!
The first interview between this almost beardless youth and the veteran generals whom he was to command, must have presented a singular scene. These scarred and war-worn chiefs, when they beheld the "stripling," were utterly amazed at the folly of the Directory in sending such a youth to command an army in circumstances so desperate. Rampon undertook to give the young commander some advice. Napoleon, who demanded obedience not advice, impatiently brushed him away, exclaiming, "Gentlemen! the art of war is in its infancy. The time has passed in which enemies are mutually to appoint the place of combat, advance hat in [Pg 583] hand and say, 'Gentlemen, will you have the goodness to fire.' We must cut the enemy in pieces, precipitate ourselves like a torrent upon their battalions, and grind them to powder. Experienced generals conduct the troops opposed to us! So much the better, so much the better. It is not their experience which will avail them against me. Mark my words; they will soon burn their books on tactics and know not what to do. Yes, gentlemen! the first onset of the Italian army will give birth to a new epoch in military affairs. As for us, we must hurl ourselves on the foe like a thunderbolt, and smite like it. Disconcerted by our tactics, and not daring to put them into execution, they will fly before us as the shades of night before the uprising sun."
The commanding and self-confident tone in which Napoleon uttered these glowing sentences, silenced and confounded the generals. They felt that they had indeed a master. "Well," said Augereau, as he left the council, nodding very significantly to Massena, "we have a man here who will cut out some work for government, I think." "It was necessary for me," Napoleon afterward remarked, "to be a little austere, to prevent my generals from slapping me upon the shoulder."
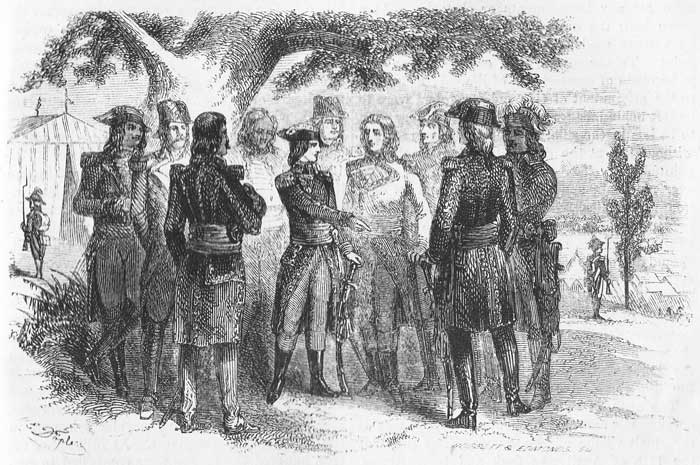

The objects which Napoleon had in view in this campaign were, first, to compel the King of Sardinia to abandon the alliance with Austria; secondly, to assail the Austrians with such vigor as to compel the Emperor to call to his aid the troops upon the Rhine, and thus weaken the powerful hosts then marching against the Republic; and, thirdly, to humble the Pope, who was exerting all his spiritual power to aid the Bourbons in fighting their way back to the throne of France. The Pope had offered an unpardonable insult to the Republic. The French embassador sent to Rome, had been attacked in the streets, and chased home. The mob broke into his house and cruelly assassinated him, unarmed and unresisting. The murderers remained unpunished, and no atonement had been made for the atrocious crime. But how, with thirty thousand troops, unpaid, dejected, famished, and unprovided with the munitions of war, was mortal man to accomplish such results in the face of a foe eighty thousand strong, living in abundance, and flushed with victory!
Napoleon issued his first proclamation. It was read to every regiment in the army, and rang, like trumpet-tones, upon the ears of the troops. "Soldiers! you are hungry and naked; the government owes you much, and can pay you nothing. Your patience, your courage, in the midst of these rocks, are admirable, but they reflect no splendor upon your arms. I come to lead you into the most fertile plains the sun beholds. Rich provinces, opulent cities will soon be at your disposal. There you will find abundant harvests, honor, and glory. Soldiers of Italy, will you fail in courage?" It is not strange that such words, from their young and fearless leader, should have inspired enthusiasm, and should have caused the hearts of the desponding to leap high with hope and confidence. The simple plan which Napoleon adopted, was to direct his whole force against detached portions of the Austrian army, and thus by gaining, at the point of attack, a superiority in numbers, to destroy them by piecemeal. "War," said the young soldier, "is the science of barbarians; and he who has the heaviest battalions will conquer."
[Pg 584]The whole army was instantly on the move. The generals, appreciating the wisdom and the fearlessness of their indomitable leader, imbibed his spirit and emulated his zeal. Napoleon was on horseback night and day. He seemed to take no time to eat or to sleep. He visited the soldiers, sympathized with them in their sufferings, and revealed to them his plans. It was early in the spring. Bleak glaciers and snow-covered ridges of the Alps were between Napoleon and the Austrians. Behind this curtain he assembled his forces. Enormous sacrifices were required to enable the soldiers to move from point to point with that celerity which was essential in operations so hazardous. He made no allowance for any impediments or obstacles. At a given hour the different divisions of the army, by various roads, were to be at a designated point. To accomplish this, every sacrifice was to be made of comfort and of life. If necessary to the attainment of this end stragglers were to be left behind, baggage abandoned, artillery even to be left in the ruts, and the troops were to be, without fail, at the designated place at the appointed hour. Through storms of rain and snow, over mountain and moor, by night and by day, hungry, sleepless, wet, and cold, the enthusiastic host pressed on. It seems incredible that the young Napoleon, so instantaneously as it were, should have been enabled to infuse his almost supernatural energy into the whole army. He had neither mules with which to attempt the passage of the Alps, nor money to purchase the necessary supplies. He therefore decided to turn the mountains, by following down the chain along the shores of the Mediterranean, to a point where the lofty ridges sink almost to a plain.
The army of Beaulieu was divided into three corps. His centre, ten thousand strong, was at the small village of Montenotte. The night of the 11th of April was dark and tempestuous. Torrents of rain were falling, and the miry roads were almost impassable. But through the long hours of this stormy night, while the Austrians were reposing warmly in their tents, Napoleon and his soldiers, drenched with rain, were toiling through the muddy defiles of the mountains, wading the swollen streams, and climbing the slippery cliffs. Just as the day began to dawn through the broken clouds, the young general stood upon the heights in the rear of Montenotte, and looked down upon the encamped host whom he was now for the first time to encounter in decisive conflict. He had so manœuvred as completely to envelop his unsuspecting enemy. Allowing his weary troops not an hour for repose, he fell upon the allied Austrians and Sardinians like a whirlwind, attacking them, at the same moment, in front, flank, and rear. The battle was long and bloody. The details of these horrid scenes of carnage are sickening. The shout of onset, the shriek of agony; the mutilated and the mangled forms of the young and the noble, trampled beneath the iron hoofs of rushing squadrons; the wounded crushed into the mire, with their bones ground to powder as the wheels of ponderous artillery were dragged mercilessly over them, and the wailing echo of widows and orphans in their distant homes, render these battle-fields revolting to humanity. At length the Austrians were broken and completely routed. They fled in dismay, leaving three thousand dead and wounded upon the field, and their cannon and colors in possession of the French. This was the first battle in which Napoleon had the supreme command; the first victory in which the honor redounded to himself. "My title of nobility," said he proudly to the Emperor of Austria, "dates from the battle of Montenotte." The Austrians fled in one direction to Dego, to meet reinforcements coming to their aid and to protect Milan. The Sardinians retreated in another direction to Millesimo, to cover their own capital of Turin. Thus the two armies were separated as Napoleon desired. The indefatigable general, allowing his exhausted and bleeding army but a few hours of repose, and himself not one, resolved, while his troops were flushed with victory, and the enemy were depressed by defeat and loss, to attack both armies at once. The 13th and the 14th of April were passed in one incessant conflict. The Austrians and Sardinians intrenching themselves in strong fortresses and upon craggy hill-sides, and every hour receiving reinforcements pressing on to their aid, cast showers of stones and rolled heavy rocks upon their assailants, sweeping away whole companies at a time. Napoleon was every where, sharing the toil, incurring the danger, and inspiring his men with his own enthusiastic ardor and courage. In both battles the French were entirely victorious. At Dego, the Austrians were compelled to abandon their artillery and baggage, and escape as they could over the mountains, leaving three thousand prisoners in the hands of the conqueror. At Millesimo, fifteen hundred Sardinians were compelled to surrender. Thus like a thunderbolt Napoleon opened the campaign. In three days, three desperate battles had been fought, and three decisive victories gained. Still Napoleon's situation was perilous in the extreme. He was surrounded by forces vastly superior to his own, crowding down upon him. The Austrians were amazed at his audacity. They deemed it the paroxysm of a madman, who throws himself single-handed into the midst of an armed host. His destruction was sure, unless by almost supernatural rapidity of marching, he could prevent the concentration of these forces and bring superior numbers to attack and destroy the detached portions. A day of inaction, an hour of hesitancy, might have been fatal. It was in the battle at Dego that Napoleon was first particularly struck with the gallantry of a young officer named Lannes. In nothing was the genius of this extraordinary man more manifest, than in the almost intuitive penetration with which he discovered character. Lannes became subsequently Duke of Montebello and one of the marshals of the Empire.[2]
[2] "The education of Lannes had been much neglected but his mind rose to the level of his courage. He became a giant. He adored me as his protector, his superior being, his providence. In the impetuosity of his temper he sometimes allowed hasty expressions against me to escape his lips, but he would probably have broken the head of any one who had joined him in his remarks. When he died he had been in fifty-four pitched battles and three hundred combats of different kinds."—Napoleon.
[Pg 585]In the midst of these marches and counter-marches and these incessant battles, there had been no opportunity to distribute regular rations among the troops. The soldiers, destitute of every thing, began to pillage. Napoleon, who was exceedingly anxious to win the good-will of the people of Italy and to be welcomed by them as their deliverer from proud oppressors, proceeded against the culprits with great severity, and immediately re-established the most rigid discipline in the army.
He had now advanced to the summit of Mt. Zemolo. From that eminence the troops looked down upon the lovely plains of Italy, opening, like a diorama beneath them. The poetic sensibilities of Napoleon were deeply moved by the majestic spectacle. Orchards and vineyards, and fertile fields and peaceful villages lay spread out, a scene of perfect enchantment, in the extended valley. Majestic rivers, reflecting the rays of the sun like ribbons of silver, meandered through meadow and forest; encircling the verdant hill-sides, and bathing the streets of opulent cities. In the distance stupendous mountains, hoary with eternal ice and snow, bounded and seemed to embrace in protecting arms this land of promise. Napoleon, sitting upon his horse, gazed for some time in silent and delighted admiration upon the scene. "Hannibal," he exclaimed, "forced the Alps; but we have turned them."
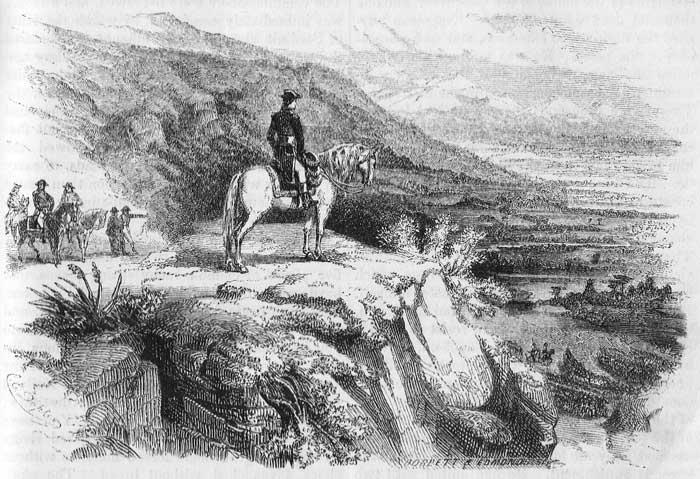

There was, however, not a moment to be lost in rest or reverie. From every direction the Austrians and Sardinians were hurrying to their appointed rendezvous, to combine and destroy this audacious band, which had so suddenly and fatally plunged into their midst. The French troops rushed down the declivities of the mountains and, crossing the Tanaro, rejoiced with trembling as they found themselves in the sunny plains of Italy. Dispatching Augereau to pursue the Austrian army, now effectually separated from their allies, Napoleon, with indefatigable perseverance, pursued the Sardinians in their flight toward Turin. He came up with them on the 18th at Ceva, where they had intrenched themselves, eight thousand strong.
He immediately attacked them in their intrenchments, and during the remainder of the day the sanguinary battle raged without any decisive result. The flash and the roar of artillery and of musketry did not cease, till the darkness rendered it impossible to distinguish friend from foe. The French slept upon their arms, ready to resume the combat in the earliest dawn of the morning. In the night the Sardinians fled, and again took a strong position behind the deep and foaming torrent of the Carsuglia. On the evening of the ensuing day, Napoleon again overtook them. A single bridge crossed the rapid torrent. The Sardinians were so strongly posted that it seemed impossible that they could be dislodged. Large detachments were hastening to reinforce them. The Austrians were accumulating in great strength in Napoleon's rear, and notwithstanding all these brilliant victories the situation of the French was perilous in the extreme. A council of war was held in the night, and it was decided, regardless of the extreme exhaustion of the troops, to make an assault upon the bridge as soon as the morning [Pg 586] should dawn. Before the first gray of the morning the French, in battle array, were moving down upon the bridge, anticipating a desperate struggle. But the Sardinians, in a panic, had again fled during the night, and Napoleon, rejoicing at his good fortune, passed the bridge unobstructed. The indefatigable victor pressed onward in the pursuit, and before nightfall again overtook his fugitive foes, who had intrenched themselves upon some almost inaccessible hills near Mondovi. The French immediately advanced to the assault. The Sardinians fought with desperation, but the genius of Napoleon triumphed, and again the Sardinians fled, leaving two thousand men, eight cannon, and eleven standards in the hands of the conqueror, and one thousand dead upon the field. Napoleon pursued the fugitives to Cherasco, and took possession of the place. He was now within twenty miles of Turin, the capital of the kingdom of Sardinia. All was commotion in the metropolis. There were thousands there, who had imbibed the revolutionary spirit, who were ready to welcome Napoleon as their deliverer, and to implore him to aid them in the establishment of a republic. The king and the nobles were in perfect consternation. The English and Austrian ministers entreated the king to adhere to the alliance, abandon his capital, and continue the conflict. They assured him that the rash and youthful victor was rushing into difficulties from which he could by no possibility extricate himself. But he, trembling for his throne and his crown, believing it to be impossible to resist so rapid a conqueror, and fearing that Napoleon, irritated by a protracted conflict, would proclaim political liberty to the people, and revolutionize the kingdom, determined to throw himself into the arms of the French, and to appeal to the magnanimity of the foe, whose rights he had so unpardonably assailed. By all human rules he deserved the severest punishment. He had united with two powerful nations, England and Austria, to chastise the French for preferring a republic to a monarchy, and had sent an invading army to bombard the cities of France and instigate the royalists to rise in civil war against the established government of the country.
It was with lively satisfaction that Napoleon received the advances of the Sardinian King, for he was fully aware of the peril in which he was placed. The allied armies were still far more numerous than his own. He had neither heavy battering cannon, nor siege equipage to reduce Turin, and the other important fortresses of the kingdom. He was far from home, could expect no immediate reinforcements from France, and his little army was literally in destitution and in rags. The allies, on the contrary, were in the enjoyment of abundance. They could every day augment their strength; and their resources were apparently inexhaustible. "The king of Sardinia," says Napoleon, "had still a great number of fortresses left; and in spite of the victories which had been gained, the slightest check, one caprice of fortune, would have undone every thing." Napoleon, however, with the commissioners who had been sent to treat with him, assumed a very confident and imperious tone. He demanded, as a preliminary to any armistice, that the important fortresses of Coni, Tortona, and Alexandria, "the keys of the Alps," should be surrendered to him. The commissioners hesitated to comply with these requisitions, which would place Sardinia entirely at his mercy, and proposed some modifications. "Your ideas are absurd," exclaimed Napoleon, sternly; "it is for me to state conditions. Listen to the laws which I impose upon you, in the name of the government of my country, and obey, or to-morrow my batteries are erected, and Turin is in flames." The commissioners were overawed, and a treaty was immediately concluded, by which the King of Sardinia abandoned the alliance, surrendered the three fortresses, with all their artillery and military stores, to Napoleon, sent an embassador to Paris to conclude a definitive peace, left the victors in possession of all the places they had already taken, disbanded the militia, and dispersed the regular troops, and allowed the French free use of the military roads, to carry on the war with Austria. Napoleon then issued to his soldiers the following soul-stirring proclamation:
"Soldiers! you have gained in fifteen days six victories, taken one-and-twenty standards, fifty-five pieces of cannon, many strong places, and have conquered the richest part of Piedmont. You have made fifteen thousand prisoners, and killed or wounded ten thousand men. Hitherto you have fought on sterile rocks, illustrious, indeed, by your courage, but of no avail. Now you rival by your services the armies of Holland and of the Rhine. You were utterly destitute; you have supplied all your wants. You have gained battles without cannon; passed rivers without bridges; made forced marches without shoes, bivouacked without bread. The phalanxes of the Republic, the soldiers of liberty were alone capable of such sacrifices. But, soldiers! you have accomplished nothing while any thing remains to be done. Neither Turin nor Milan is in your hands. I am told that there are some among you whose courage is failing, who wish to return to the summits of the Alps and the Apennines. No! I can not believe it. The conquerors of Montenotte, of Millesimo, of Dego, of Mondovi burn to carry still further the glories of the French name. But ere I lead you to conquest there is one condition you must promise to fulfill: that is to protect the people whom you liberate and to repress all acts of lawless violence. Without this you would not be the deliverers, but the scourges of nations. Invested with the national authority, strong in justice and law, I shall not hesitate to enforce the requisitions of humanity and of honor. I will not suffer robbers to sully your laurels. Pillagers shall be shot without mercy.
"People of Italy! The French army advances to break your chains. The French people are the friends of all nations. In them you may [Pg 587] confide. Your property, your religion, your customs shall be respected. We will only make war as generous foes. Our sole quarrel is with the tyrants who enslave you."
A large majority of Napoleon's soldiers and officers severely condemned any treaty of peace with a monarchical government, and were clamorous for the dethronement of the king of Sardinia, and the establishment of a Republic. The people thronged Napoleon with the entreaty that he would lend them his countenance that they might revolutionize the kingdom. They urged that, by the banishment of the king and the nobles, they could establish a free government, which should be the natural and efficient ally of Republican France. He had but to say the word and the work was done. The temptation to utter that word must have been very strong. It required no common political foresight to nerve Napoleon to resist that temptation. But he had a great horror of anarchy. He had seen enough of the working of Jacobin misrule in the blood-deluged streets of Paris. He did not believe that the benighted peasants of Italy possessed either the intelligence or the moral principle essential to the support of a well-organized republic. Consequently, notwithstanding the known wishes of the Directory, the demands of the army, and the entreaties of the populace, with heroic firmness he refused to allow the overthrow of the established government. He diverted the attention of his soldiers from the subject, by plunging them into still more arduous enterprises, and leading them to yet more brilliant victories.
Napoleon had no desire to see the reign of terror re-enacted in the cities of Italy. He was in favor of reform, not of revolution. The kings and the nobles had monopolized wealth and honor, and nearly all the most precious privileges of life. The people were merely hewers of wood and drawers of water. Napoleon wished to break down this monopoly and to emancipate the masses from the servitude of ages. He would do this, however, not by the sudden upheaving of thrones and the transfer of power to unenlightened and inexperienced democracy, but by surrounding the thrones with republican institutions, and conferring upon all people a strong and well-organized government, with constitutional liberty. Eloquently he says, "It would be a magnificent field for speculation to estimate what would have been the destinies of France and of Europe, had England satisfied herself with denouncing the murder of Louis XVI., which would have been for the interests of public morality, and listened to the councils of a philanthropic policy, by accepting revolutionized France as an ally. Scaffolds would not then have been erected over the whole country, and kings would not have trembled on their thrones; but their states would all have passed, more or less, through a revolutionary process, and the whole of Europe, without a convulsion, would have become constitutional and free."
The kingdom of Sardinia was composed of the provinces of Nice, Piedmont, Savoy, and Montferrat. It contained three millions of inhabitants. The king, by extraordinary efforts and by means of subsidies from England, had raised an army of sixty thousand men, trained to service in long continued wars. His numerous fortresses, well armed and amply provisioned, situated at the defiles of all the mountains, placed his frontier in a state which was regarded as impregnable. He was the father-in-law of both of the brothers of Louis XVI.; which brothers subsequently ascended the throne of France as Louis XVIII. and as Charles X. He had welcomed them, in their flight from France to his court in Turin; and had made his court a place of refuge for the emigrant noblesse, where, in fancied security, they matured their plans and accumulated their resources for the invasion of France, in connection with the armies of the allies. And yet Napoleon, with thirty thousand half-starved men, had, in one short fortnight, dispersed his troops, driven the Austrians from the kingdom, penetrated to the very heart of the state, and was threatening the bombardment of his capital. The humiliated monarch, trembling for his crown, was compelled to sue for peace at the feet of an unknown young man of twenty-five. His chagrin was so great, in view of his own fallen fortunes and the hopelessness of his sons-in-law ever attaining the throne of France, that he died, a few days after signing the treaty of Cherasco, of a broken heart.
Napoleon immediately dispatched Murat, his first aid-de-camp, to Paris, with a copy of the armistice, and with twenty-one standards taken from the enemy. The sensation which was produced in France by this rapid succession of astonishing victories was intense and universal. The spirit of antique eloquence which imbued the proclamations of the young conqueror; the modest language of his dispatches to the Directory; the entire absence of boasting respecting his own merits, and the glowing commendation of the enthusiastic bravery of his soldiers and of his generals, excited profound admiration. Bonaparte was a foreign, an Italian name. Few in France had ever heard it, and it was not easily pronounced. Every one inquired, Who is this young general, whose talents thus suddenly, with such meteoric splendor, have blazed upon Europe? His name and his fame were upon every lip, and the eyes of all Europe were concentred upon him. Three times in the course of fifteen days, the Council of Ancients and The Five Hundred had decreed that the army of Italy deserved well of their country, and had appointed festivals to victory in their honor. In very imposing ceremony Murat presented the captured standards to the Directory. Several foreign embassadors were present on the occasion. The Republic, thus triumphant, was invested with new dignity, and elevated, by the victories of the young general, to a position of respect and consideration which it had never attained before.
While these scenes were transpiring Napoleon did not forget the bride he had left in Paris. Though for seven days and nights he had allowed [Pg 588] himself no quiet meal, no regular repose, and had not taken off either his coat or his boots, he found time to send frequent and most affectionate, though very short, notes to Josephine. Immediately after the victory of Montenotte, while the thunders of the cannonade were still ringing in his ears, he dispatched a courier to Josephine with the following lines, written in such haste and under such circumstances as to be scarcely legible.
"My first laurel is due to my country. My second shall be yours. While pursuing the enemy I thought of France. When he was beaten I thought of Josephine. Your son will send you a scarf surrendered to him by Colonel Morback, whom he took prisoner with his own hand. You see, Madame, that our Eugene is worthy of his father. Do not deem me altogether undeserving of having succeeded to that brave and unfortunate general, under whom I should have felt honored to have learned to conquer. I embrace you.
Bonaparte."This delicacy of attention Napoleon ever manifested toward Josephine, even after their unhappy divorce, and until the hour of her death.
Napoleon having, by an advantageous treaty with Sardinia, secured his rear from assault, without a day's delay, commenced the pursuit of the discomfited remains of the Austrian army. Under their commander-in-chief, Beaulieu, they had retreated behind the Po, where they strongly intrenched themselves, awaiting the reinforcements which were hurrying to their aid.
Upon leaving the kingdom of Sardinia Napoleon first entered the states of Parma. The Duke of Parma, who had united with his more powerful neighbors, in the alliance against France, reigned over a population of but about five hundred thousand, and could furnish to the allies but three thousand troops. He was of course powerless, and sent envoys to solicit the clemency of the conqueror. Napoleon granted him an armistice upon his paying five hundred thousand dollars in silver, sixteen hundred artillery horses, and a large supply of corn and provisions. And here commenced one of those characteristic acts of the young general which have been greatly admired by some, and most severely censured by others. Napoleon, a lover and connoisseur of the arts, conscious of the addition they contribute to the splendor of an empire, and of the effect which they produce upon the imagination of men, demanded twenty of the choicest pictures in the galleries of the duke, to be sent to the Museum at Paris. To save one of these works of art, the celebrated picture of St. Jerome, the duke offered two hundred thousand dollars. Napoleon declined the money, stating to the army, "the sum which he offers us will soon be spent; but the possession of such a master-piece, at Paris, will adorn that capital for ages, and give birth to similar exertions of genius." No one objects, according to the laws of war, to the extortion of the money, the horses, the corn, and the beef, but it is represented by some as an unpardonable act of spoliation and rapacity to have taken the pictures. If conquest confers the right to the seizure of any species of property, it is difficult to conceive why works of art, which are subject to barter and sale, should claim exemption. Indeed, there seems to be a peculiar propriety in taking luxuries rather than necessaries. The extortion of money only inflicted a tax upon the people who were the friends of Napoleon and of his cause. The selection of the paintings and the statuary deprived not the people of their food, but caused that very class in the community to feel the evils of war, who had originated the conflict. It was making requisition upon the palace and not upon the cottage. But war, with its extortion, robbery, cruelty, and blood, involves all our ideas of morality in confusion. Whatever may be the decision of posterity respecting the propriety of including works of genius among the trophies of war, the occurrence surely exhibits Napoleon as a man of refined and elevated tastes. An ignoble spirit, moved by avarice, would have grasped the money. Napoleon, regardless of personal indulgence, sought only the glory of France. There is at least grandeur in the motive which inspired the act.
The Austrians were now reinforced to the amount of forty thousand men, and had intrenched themselves upon the other side of the Po, having this magnificent stream flowing between them and the French. It is one of the most difficult operations in war to cross a river in the face of an opposing army. It was difficult to conceive how Napoleon could effect the enterprise. He, however, marched resolutely on toward Valenza, making every demonstration of his intention to cross at that point, in defiance of the foe, arrayed in vastly superior numbers to contest the passage. The Austrians concentrated their strength to give him a warm reception. Suddenly by night Napoleon turned down the river, and with amazing celerity made a march of eighty miles in thirty-six hours, seizing every boat upon the stream as he passed along. He had timed the march of the several divisions of his army so precisely, that all of his forces met at the appointed rendezvous within a few hours of each other. Rapidly crossing the river in boats, he found himself and his army, without the loss of a single man, in the plains of Lombardy.
This beautiful and productive country had been conquered by the Austrians, and was governed by an archduke. It contained one million two hundred thousand inhabitants, and was one of the most fertile and rich provinces in the world. Its inhabitants were much dissatisfied with their foreign masters, and the great majority, longing for political regeneration, were ready to welcome the armies of France. As soon as Beaulieu, who was busily at work upon his fortifications at Valenza, heard that Napoleon had thus out-generaled him, and had crossed the river, he immediately collected all his forces and moved forward to meet him. The advanced divisions of the hostile [Pg 589] armies soon met at Fombio. The Austrians stationed themselves in the steeples and at the windows and upon the roofs of the houses, and commenced a destructive fire upon the French, crowding into the streets. They hoped to arrest their progress until the commander-in-chief could arrive with the main body of the army. The French, however, rushed impetuously on with their bayonets, and the Austrians were driven before them, leaving two thousand prisoners in the hands of Napoleon, and the ground covered with their dead.
The French pursued closely upon the heels of the Austrians, from every eminence plunging cannon balls into their retreating ranks, and assailing them with the most destructive fire at every possible point of attack. In the evening of the same day, the exhausted and bleeding columns of the enemy arrived at Lodi, a small town upon the banks of the Adda. Passing directly through the town they crossed the river, which was about two hundred yards in width, by a narrow wooden bridge, about thirty feet wide. They were there received by the main body of the army of Beaulieu, which was strongly intrenched upon the opposite banks. The whole French army rushed into the town, and sheltering themselves behind the walls of the houses, from the incessant fire of the Austrian batteries, awaited the commands of their youthful leader, whom they now began to think invincible.
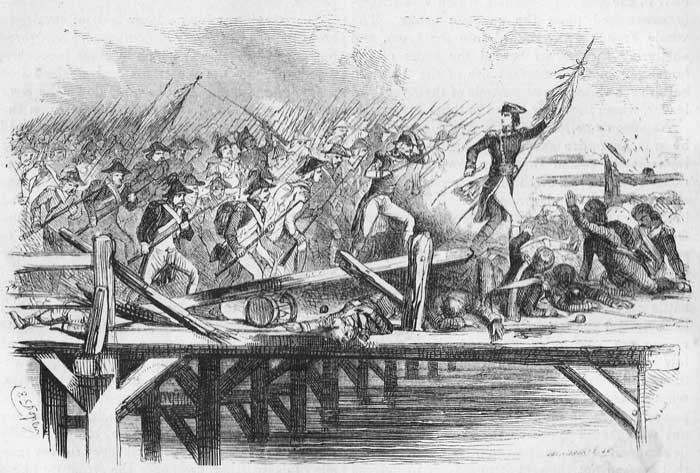
Napoleon's belief in destiny was so strong that he was an entire stranger to bodily fear. He immediately sallied from the town and reconnoitred the banks of the river, amidst a perfect shower of balls and grape-shot. The prospect before him would have been to most persons perfectly appalling. The Austrians, sixteen thousand strong, with twelve thousand infantry and four thousand cavalry, and thirty pieces of heavy artillery were posted upon the opposite banks in battle array, with their batteries so arranged as to command the whole length of the bridge by a raking fire. Batteries stationed above and below also swept the narrow passage by cross fires, while sharp-shooters, in bands of thousands, were posted at every available point, to drive a perfect storm of musket balls into the face of any who should approach the structure. Beaulieu conceived his position so utterly impregnable that he had not thought it necessary to destroy the bridge, as he easily could have done. He desired nothing more earnestly than that the French might attempt the passage, for he was confident that their discomfiture would be both signal and awful. Napoleon immediately placed as many guns as possible in opposition to the Austrian batteries, directing with his own hands, in the midst of the hottest fire, some cannon in such a manner as to prevent the Austrians from approaching to blow up the arches. He then entered the town, assembled his general officers, and informed them that he had resolved immediately to storm the bridge. The bravest of them recoiled from the undertaking, and they unanimously disapproved of the plan as impracticable. "It is impossible," said one, "that any men can force their way across that narrow bridge, in the face of such an annihilating storm of balls as must be encountered." "How! impossible!" exclaimed Napoleon, "that word is not French." The self-reliant mind of the young conqueror was seldom moved by the opinions of others. Regardless of the disapproval of his generals, he assembled six thousand picked troops, and addressing them in those marked tones of martial eloquence most eminently at his command, so effectually roused their pride and enthusiasm that they were clamorous to be led to the assault. He unfolded to them fully the peril which attended the enterprise, and animated them by reference to the corresponding glory which would attend the achievement. He knew that thousands must perish. But placing only a slight value upon his own life, he regarded as little the lives of others, and deemed the object to be gained worthy of the terrible price which was to be paid. There probably was not another man in either of those armies who would have ventured upon the responsibility of an enterprise apparently so desperate.
Secretly dispatching a large body of cavalry to cross the river at a very difficult ford, about three miles above the town, which by some inconceivable oversight the Austrians had neglected to protect, he ordered them to come down the river and make the most desperate charge upon the rear of the enemy. At the same time he formed his troops in a line, under the shelter of one of the streets nearest the point of attack. It was the evening of the 10th of May. The sun was just sinking behind the Tyrolean hills, enveloping in soft twilight the scene of rural peace and beauty and of man's depravity. Not a breath of air rippled the smooth surface of the water, or agitated the bursting foliage of the early spring. The moment that Napoleon perceived, by the commotion among the Austrians, that the cavalry had effected the passage of the river, he ordered the trumpets to sound the charge. The line wheeled instantly into a dense and solid column, crowding the street with its impenetrable mass. Emerging from the shelter, upon the full run, while rending the air with their enthusiastic shouts, they rushed upon the bridge. They were met by a murderous discharge of every missile of destruction, sweeping the structure like a whirlwind. The whole head of the column was immediately cut down like grass before the scythe, and the progress of those in the rear was encumbered by piles of the dead. Still the column passed on, heedless of the terrific storm of iron and of lead, until it had forced its way into the middle of the bridge. Here it hesitated, wavered, and was on the point of retreating before volcanic bursts of fire too terrible for mortal man to endure, when Napoleon, seizing a standard, and followed by Lannes, Massena, and Berthier, plunged through the clouds of smoke which now enveloped the bridge in almost midnight darkness, placed himself at the head of the troops, and shouted, "Follow your General!" The [Pg 590] bleeding, mangled column, animated by this example, rushed with their bayonets upon the Austrian gunners. At the same moment the French cavalry came dashing upon the batteries in the rear, and the bridge was carried. The French army now poured across the narrow passage like a torrent, and debouched upon the plain. Still the battle raged with unmitigated fury. The Austrians hurled themselves upon the French with the energy of despair. But the troops of Napoleon, intoxicated with their amazing achievement, set all danger at defiance, and seemed just as regardless of bullets and of shells, as if they had been snow-balls in the hands of children.
In the midst of the thunders of the terrific cannonade a particular battery was producing dreadful havoc among the ranks of the French. Repeated attempts had been made to storm it, but in vain. An officer rode up to Napoleon in the midst of all the confusion and horror of the battle, and represented to him the importance of making another effort to silence the destructive battery. "Very well," said Napoleon, who was fond of speaking, as well as acting the sublime, "let it be silenced then." Turning to a body of dragoons near by, he exclaimed, "follow your General." As gayly as if it were the pastime of a holiday, the dragoons followed their leader in the impetuous charge, through showers of grape shot dealing mutilation and death into their ranks. The Austrian gunners were instantly sabred, and their guns turned upon the foe.
Lannes was the first to cross the bridge and Napoleon the second. Lannes in utter recklessness and desperation, spurred his maddened horse into the very midst of the Austrian ranks and grasped a banner. At that moment his horse fell dead beneath him, and half a dozen swords glittered above his head. With Herculean strength and agility he extricated himself from his fallen steed, leaped upon the horse of an Austrian officer, behind the rider, plunged his sword through the body of the officer, and hurled him from his saddle; taking his seat he fought his way back to his followers, having slain in the mêlée six of the Austrians with his own hand. This deed of demoniac energy was performed under the eye of Napoleon, and he promoted Lannes upon the spot.
The Austrians now retreated, leaving two thousand prisoners and twenty pieces of cannon in the hands of the victors, and two thousand five hundred men and four hundred horses dead upon the plain. The French probably lost, in dead and wounded, about the same number, though Napoleon, in his report of the battle, acknowledged the loss of but four hundred. The Austrians claimed that the French won the victory at the expense of four thousand men. It was, of course, the policy of the conqueror to have it understood that his troops were the executors not the victims of slaughter. "As false as a bulletin," has become a proverb. The necessity of uttering falsehood and practicing deception in all their varied forms, is one of the smallest of the innumerable immoralities attendant upon war. From time immemorial it has been declared that the weapons of deception and of courage are equally allowable to the soldier; "an virtus, an dolos, quis ab hoste requirat." If an enemy can be deceived by a false bulletin, there are few generals so conscientious as to reject the stratagem. Napoleon certainly never hesitated to avail himself of any artifice to send dismay into the hearts of his foes. Truthfulness is not one of the virtues which thrives in a camp.
"It was a strange sight," says a French [Pg 591]veteran, who was present at this battle, "to see Napoleon that day, on foot on the bridge, under an infernal fire, and mixed up with our tall grenadiers. He looked like a little boy." "This beardless youth," said an Austrian general, indignantly, "ought to have been beaten over and over again; for who ever saw such tactics. The blockhead knows nothing of the rules of war. To-day he is in our rear, to-morrow on our flank, and the next day again in our front. Such gross violations of the established principles of war are insufferable."
When Napoleon was in exile at St. Helena, some one read an account of the battle of Lodi, in which it was stated that Napoleon displayed great courage in being the first to cross the bridge, and that Lannes passed it after him. "Before me! before me!" exclaimed Napoleon, earnestly. "Lannes passed first and I only followed him. It is necessary to correct that error upon the spot." The correction was made in the margin. This victory produced a very extraordinary effect upon the whole French army, and inspired the soldiers with unbounded confidence in their young leader. Some of the veterans of the army, immediately after the battle, met together and jocosely promoted their General, who had so distinguished himself by his bravery, and who was so juvenile in his appearance, to the rank of corporal. When Napoleon next appeared upon the field, he was greeted with enthusiastic shouts by the whole army, "Long live our little Corporal!" Ever after this he was the perfect idol of the troops, and never lost, even in the dignity of Consul and Emperor, this honorary and affectionate nickname. "Neither the quelling of the sections," said Napoleon, "nor the victory of Montenotte induced me to think myself a superior character. It was not till after the terrible passage of the bridge of Lodi, that the idea shot across my mind that I might become a decisive actor in the political arena. Then arose, for the first time, the spark of great ambition."
Lombardy was now at the mercy of Napoleon, and the discomfited Austrians fled into the Tyrol. The Archduke Ferdinand and his duchess, with tears in their eyes, abandoned to the conqueror their beautiful capital of Milan, and sought refuge with their retreating friends.
As the carriages of the ducal pair, and those of their retinue passed sadly through the streets of the metropolis, the people looked on in silence, uttering not a word of sympathy or of insult. But the moment they had departed, republican zeal burst forth unrestrained. The tricolored cockade seemed suddenly to have fallen, as by magic, upon the hats and the caps of the multitude, and the great mass of the people prepared to greet the French Republicans with every demonstration of joy. A placard was put upon the palace—"This house to let; for the keys apply to the French Commissioner."
On the fifteenth of May, just one month after the opening of the campaign at Montenotte, Napoleon entered Milan in triumph. He was welcomed by the great majority of the inhabitants as a deliverer. The patriots, from all parts of Italy, crowded to the capital, sanguine in the hope that Napoleon would secure their independence, and confer upon them a Republican government, in friendly alliance with France. A numerous militia was immediately organized, called the National Guard, and dressed in three colors, green, red, and white, in honor of the tri-colored flag. A triumphal arch was erected, in homage of the conqueror. The whole population of the city marched out to bid him welcome; flowers were scattered in his path; ladies thronged the windows as he passed, and greeted him with smiles and fluttering handkerchiefs, and with a shower of bouquets rained down at his feet. Amidst all the pomp of martial music, and waving banners, the ringing of bells, the thunders of saluting artillery, and the acclamations of an immense concourse of spectators, Napoleon took possession of the palace from whence the duke had fled. "If you desire liberty," said the victor to the Milanese, "you must deserve it by assisting to emancipate Italy forever from Austria." The wealthy and avaricious Duke of Modena, whose states bordered upon those of Parma, dispatched envoys to sue for peace. Napoleon granted him an armistice, upon the payment of two millions of dollars, twenty of his choicest pictures, and an abundant supply of horses and provisions. When in treaty with the Duke of Modena, the Commissary of the French army came to Napoleon and said, "The brother of the duke is here with eight hundred thousand dollars in gold, contained in four chests. He comes, in the name of the duke, to beg you to accept them. And I advise you to do so. The money belongs to you. Take it without scruple. A proportionate diminution will be made in the duke's contribution, and he will be very glad to have obtained a protector." "I thank you," replied Napoleon, coolly. "I shall not, for that sum, place myself in the power of the Duke of Modena." The whole contribution went into the army-chest, Napoleon refusing to receive for himself a single dollar.
Napoleon now issued another of those spirit-stirring proclamations, which roused such enthusiasm among his own troops, and which so powerfully electrified the ardent imagination of the Italians. "Soldiers! you have descended like a torrent from the Apennines. You have overwhelmed every thing which opposed your progress. Piedmont is delivered from the tyranny of Austria; Milan is in your hands, and the Republican standards wave over the whole of Lombardy. The Dukes of Parma and Modena owe their existence to your generosity. The army which menaced you with so much pride, can no longer find a barrier to protect itself against your arms. The Po, the Ticino, the Adda have not been able to stop you a single day. These boasted bulwarks of Italy have proved as nugatory as the Alps. Such a career of success has carried joy into the bosom of your country. Fêtes in honor of your victories have been ordered in all the communes of the Repub[Pg 592]lic. There your parents, your wives, your sisters, your lovers rejoice in your achievements, and boast with pride that you belong to them. Yes, soldiers! you have indeed done much, but much remains still to be done. Shall posterity say that we knew how to conquer, but knew not how to improve victory? Shall we find a Capua in Lombardy? We have forced marches to make, enemies to subdue, laurels to gather, injuries to revenge. Let those who have whetted the daggers of civil war in France, who have assassinated our ministers, who have burned our ships at Toulon—let those tremble. The hour of vengeance has struck. But let not the people be alarmed. We are the friends of the people every where; particularly of the Brutuses, the Scipios, and the great men whom we have taken for our models. To re-establish the Capitol; to replace the statues of the heroes who rendered it illustrious; to rouse the Romans, stupefied by centuries of slavery—such will be the fruit of our victories. They will form an epoch with posterity. To you will pertain the immortal glory of changing the face of the finest portion of Europe. The French people, free and respected by the whole world, will give to Europe a glorious peace. You will then return to your homes, and your fellow-citizens will say, pointing to you, He belonged to the army of Italy."
Such were the proclamations which Napoleon dashed off, with inconceivable rapidity, in the midst of all the care, and peril, and clangor of battle. Upon reading these glowing sentences over at St. Helena, twenty years after they were written, he exclaimed, "And yet they had the folly to say that I could not write." He has been represented by some as illiterate, as unable to spell. On the contrary, he was a ripe and an accomplished scholar. His intellectual powers and his intellectual attainments were of the very highest order. His mind had been trained by the severest discipline of intense and protracted study. "Do you write orthographically?" said he one day to his amanuensis at St. Helena. "A man occupied with public business can not attend to orthography. His ideas must flow faster than his hand can trace. He has only time to place his points. He must compress words into letters, and phrases into words, and let the scribes make it out afterward." Such was the velocity with which Napoleon wrote. His handwriting was composed of the most unintelligible hieroglyphics. He often could not decipher it himself.
Lombardy is the garden of Italy. The whole of the extensive valley, from the Alps to the Apennines, is cultivated to the highest degree, presenting in its vineyards, its orchards, its waving fields of grain, its flocks and herds, one of the most rich and attractive features earth can exhibit. Milan, its beautiful capital, abounding in wealth and luxury, contained a population of one hundred and twenty thousand souls. Here Napoleon allowed his weary troops, exhausted by their unparalleled exertions, to repose for six days. Napoleon himself was received by the inhabitants with the most unbounded enthusiasm and joy. He was regarded as the liberator of Italy—the youthful hero, who had come with almost supernatural powers, to re-introduce to the country the reign of Roman greatness and virtue. His glowing words, his splendid achievements, his high-toned morals so pure and spotless, the grace and beauty of his feminine figure, his prompt decisions, his imperial will, and the antique cast of his thoughts, uttered in terse and graphic language, which passed, in reiterated quotation, from lip to lip, diffused an universal enchantment. From all parts of Italy the young and the enthusiastic flocked to the metropolis of Lombardy. The language of Italy was Napoleon's mother tongue. His name and his origin were Italian, and they regarded him as a countryman. They crowded his footsteps, and greeted him with incessant acclamations. He was a Cato, a Scipio, a Hannibal. The ladies, in particular, lavished upon him adulations without any bounds.
But Napoleon was compelled to support his own army from the spoils of the vanquished. He could not receive a dollar from the exhausted treasury of the French Republic. "It is very difficult," said he, "to rob a people of their substance, and at the same time to convince them that you are their friend and benefactor." Still he succeeded in doing both. With great reluctance he imposed upon the Milanese a contribution of four millions of dollars, and selected twenty paintings from the Ambrosian Gallery, to send to Paris as the trophies of his victory. It was with extreme regret that he extorted the money, knowing that it must check the enthusiasm with which the inhabitants were rallying around the Republican standard. It was, however, indispensable for the furtherance of his plans. It was his only refuge from defeat and from absolute destruction. The Milanese patriots also felt that it was just that their government should defray the expenses of a war which they had provoked; that since Lombardy had allied itself with the powerful and wealthy monarchies of Europe, to invade the infant Republic in its weakness and its poverty, Napoleon was perfectly justifiable in feeding and clothing his soldiers at the expense of the invaders whom he had repelled. The money was paid, and the conqueror was still the idol of the people.
His soldiers were now luxuriating in the abundance of bread, and meat, and wine. They were, however, still in rags, wearing the same war-worn and tattered garments with which they had descended from the frozen summits of the Alps. With the resources thus obtained, Napoleon clothed all his troops abundantly, filled the chests of the army, established hospitals and large magazines, proudly sent a million of dollars to the Directory in Paris, as an absent father would send funds to his helpless family; forwarded two hundred and fifty thousand dollars to Moreau, who, with an impoverished army, upon the Rhine, was contending against superior forces of the Austrians. He also established an energetic and efficient municipal government in Mi[Pg 593]lan, and made immediate arrangements for the organization and thorough military discipline of the militia in all parts of Lombardy. This was the work of five days, and of five days succeeding a month of such toil of body and of mind as, perhaps, no mortal ever endured before. Had it not been for a very peculiar constitutional temperament, giving Napoleon the most extraordinary control over his own mind, such Herculean labors could not have been performed. "Different affairs are arranged in my head," said he, "as in drawers. When I wish to interrupt one train of thought, I close the drawer which contains that subject, and open to that which contains another. They do not mix together, and do not fatigue me or inconvenience me. I have never been kept awake by an involuntary pre-occupation of the mind. If I wish repose, I shut up all the drawers and I am asleep. I have always slept when I wanted rest, and almost at will." After spending several successive days and nights without sleep, in preparation for a decisive conflict, he has been known repeatedly to fall asleep in the midst of the uproar and horror of the field of battle, and when the balls of the enemy were sweeping the eminence upon which he stood. "Nature has her rights," said he, "and will not be defrauded with impunity. I feel more cool to receive the reports which are brought to me, and to give fresh orders when awaking in this manner from a transient slumber."
While in Milan, one morning, just as he had mounted his horse, a dragoon presented himself before him, bearing dispatches of great importance. Napoleon read them upon the saddle; and, giving a verbal answer, told the courier to take it back with all possible dispatch. "I have no horse," the man replied, "the one I rode, in consequence of forced speed, fell dead at the gate of your palace." "Take mine then," rejoined Napoleon, instantly alighting. The man hesitated to mount the magnificent charger of the general-in-chief. "You think him too fine an animal," said Napoleon, "and too splendidly caparisoned. Never mind, comrade, there is nothing too magnificent for a French soldier." Incidents like this, perpetually occurring, were narrated, with all conceivable embellishments, around the camp-fires, and they conferred upon the young general a degree of popularity almost amounting to adoration.
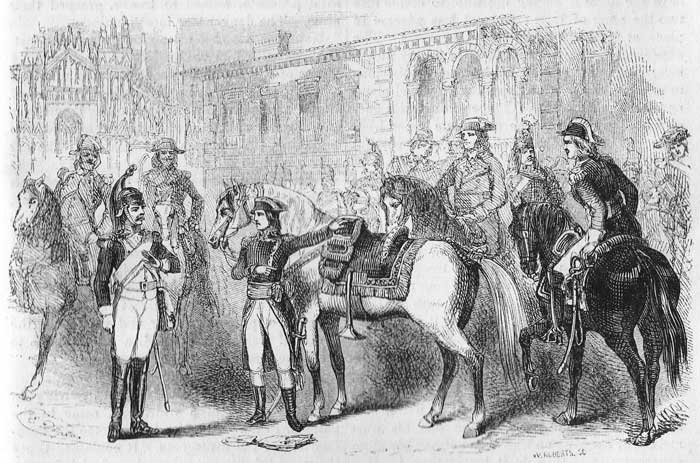

The lofty intellectual character of Napoleon was also developed at the same time, in the midst of all the cares, perplexities, and perils of these most terrible conflicts, in a letter publicly addressed to Oriani, the celebrated mathematician. "Hitherto," he writes, "the learned in Italy have not enjoyed the consideration to which they were entitled. They lived secluded in their libraries, too happy if they could escape the persecution of kings and priests. It is so no longer. Religious inquisition and despotic power are at an end. Thought is free in Italy. I invite the literary and the scientific to consult together and propose to me their ideas on the subject of giving new life and vigor to the fine arts and sciences. All who desire to visit France will be received with distinction by the government. The citizens of France have more pride in enrolling among their citizens a skillful mathematician, a painter of reputation, a distinguished man in any class of letters, than in adding to their territories a large and wealthy city."
Napoleon having thus rapidly organized a government for Lombardy, and having stationed [Pg 594]troops in different places to establish tranquillity, turned his attention again to the pursuit of the Austrians. But by this time the Directory in Paris were thoroughly alarmed in view of the astonishing influence and renown which Napoleon had attained. In one short month he had filled Europe with his name. They determined to check his career. Kellerman, a veteran general of great celebrity, they consequently appointed his associate in command, to pursue the Austrians with a part of the army, while Napoleon, with the other part, was to march down upon the States of the Pope. This division would have insured the destruction of the army. Napoleon promptly but respectfully tendered his resignation, saying, "One bad general is better than two good ones. War, like government, is mainly decided by tact." This decision brought the Directory immediately to terms. The commander-in-chief of the Army of Italy was now too powerful to be displaced, and the undivided command was immediately restored to him.
In the letter he wrote to the Directory at this time, and which must have been written with the rapidity of thought, he observes, with great force of language and strength of argument. "It is in the highest degree impolitic to divide into two the army of Italy; and not less adverse to place at its head two different generals. The expedition to the Papal States is a very inconsiderable matter, and should be made by divisions in echelon, ready at any moment to wheel about and face the Austrians. To perform it with success both armies must be under one general. I have hitherto conducted the campaign without consulting any one. The result would have been very different if I had been obliged to reconcile my views with those of another. If you impose upon me embarrassments of various kinds; if I must refer all my steps to the commissaries of government; if they are authorized to change my movements, to send away my troops, expect no further success. If you weaken your resources by dividing your forces, if you disturb in Italy the unity of military thought, I say it with grief, you will lose the finest opportunity that ever occurred of giving laws to that fine peninsula. In the present posture of the affairs of the Republic it is indispensable that you possess a general who enjoys your confidence. If I do not do so I shall not complain. Every one has his own method of carrying on war. Kellerman has more experience, and may do it better than I. Together we should do nothing but mischief. Your decision on this matter is of more importance than the fifteen thousand men the Emperor of Austria has sent to Beaulieu."
On the 22d of May Napoleon left Milan, in pursuit of the Austrians. Beaulieu, in his retreat to the mountains of the Tyrol, had thrown fifteen thousand men into the almost impregnable fortress of Mantua, to arrest the progress of the conqueror. He knew that Napoleon could not follow him leaving such a fortress in the possession of his enemies in his rear. Austria was raising powerful reinforcements, and the defeated general intended soon to return with overwhelming numbers, and crush his foe. Napoleon had hardly advanced one day's march from Milan when a formidable insurrection broke out. The priests, incited by the Pope, had roused the peasants, who were very much under their influence, to rise and exterminate the French. They appealed to all the motives of fanaticism which the papal church has so effectually at its command, to rouse their military ardor. They assured the ignorant peasants that Austria was pouring down an overwhelming army upon the invader; that all Italy was simultaneously rising in arms; that England, with her powerful fleet, was landing troops innumerable upon the coasts of Sardinia; that God, and all his angels, were looking down from the windows of Heaven to admire the heroism of the faithful, in ridding the earth of the enemies of the true religion, and that the destruction of Napoleon was sure. The enthusiasm spread from hamlet to hamlet like a conflagration. The friends of republicanism were, for the most part, in the cities. The peasantry were generally strongly attached to the church, and looked up with reverence to the nobles. The tocsin was sounded in every village. In a day thirty thousand peasants, roused to frenzy, grasped their arms. The danger was most imminent.
Napoleon felt that not an hour was to be lost. He took with him twelve hundred men and six pieces of cannon, and instantly turned upon his track. He soon came up with eight hundred of the insurgents, who were intrenching themselves in the small village of Banasco. There was no parleying. There was no hesitancy. The ear was closed to all the appeals of mercy. The veteran troops, inured to their work, rushed with bayonet and sabre upon the unwarlike Italians, and, in a few moments, hewed the peasants to pieces. The women and children fled in every direction, carrying the tidings of the dreadful massacre. The torch was applied to the town, and the dense volumes of smoke ascending into the serene and cloudless skies, from this altar of vengeance, proclaimed, far and wide over the plains of Italy, how dreadful a thing it was to incur the wrath of the conqueror.
Napoleon and his troops, their swords still dripping in blood, tarried not, but moving on with the sweep of a whirlwind, came to the gates of Pavia. This city had become the head-quarters of the insurgents. It contained thirty thousand inhabitants. Napoleon had left there a garrison of three hundred men. The insurgents, eight thousand strong, had thrown themselves into the place, and, strengthened by all of the monarchical party, prepared for a desperate resistance. Napoleon sent the Archbishop of Milan, with a flag of truce, offering pardon to all who would lay down their arms. "May the terrible example of Banasco," said he, "open your eyes. Its fate shall be that of every town which persists in revolt." "While Pavia has walls," the insurgents bravely replied, "we will not surrender." Napoleon rejoined in the instantaneous thunders of his artillery. He swept the [Pg 595]ramparts with grape shot, while the soldiers, with their hatchets, hewed down the gates.
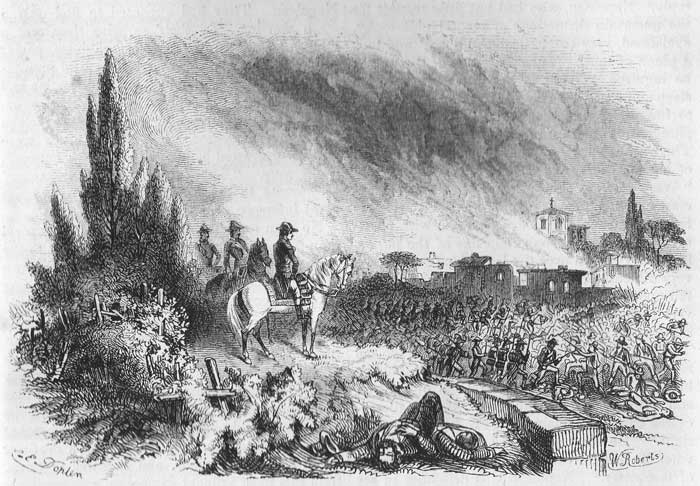

They rushed like an inundation into the city. The peasants fought with desperation from the windows and roofs of the houses, hurling down upon the French every missile of destruction. The sanguinary conflict soon terminated in favor of the disciplined valor of the assailants. The wretched peasants were pursued into the plain and cut down without mercy. The magistrates of the city were shot; the city itself given up to pillage. "The order," said Napoleon to the inhabitants, "to lay the city in ashes, was just leaving my lips, when the garrison of the castle arrived, and hastened, with cries of joy, to embrace their deliverers. Their names were called over and none found missing. If the blood of a single Frenchman had been shed, my determination was to erect a column on the ruins of Pavia, bearing this inscription, 'Here stood the city of Pavia!'" He was extremely indignant with the garrison for allowing themselves to be made prisoners. "Cowards," he exclaimed, "I intrusted you with a post essential to the safety of an army; and you have abandoned it to a mob of wretched peasants, without offering the least resistance." He delivered the captain over to a council of war, and he was shot.
This terrible example crushed the insurrection over the whole of Lombardy. Such are the inevitable and essential horrors of war. Napoleon had no love for cruelty. But he never hesitated to adopt any measures, however decisive and sanguinary, which he deemed essential for the accomplishment of his purposes. In such dreadful scenes he claimed to be acting upon the same principle which influences the physician to cut, with an unflinching hand, through nerves and tendons, for the humane design of saving life.
If war is right this was right. This bloody vengeance was necessary for the salvation of Napoleon's army. He was about to pursue the Austrians far away into the mountains of the Tyrol, and it was necessary to his success that, by a terrible example, he should teach those whom he left behind, that they could not rise upon him with impunity. War is necessarily a system of cruelty and of blood. Napoleon was an energetic warrior. He recoiled not from any severities which he deemed indispensable to the success of his horrible mission. "A man of refined sensibilities," says the Duke of Wellington, "has no right to meddle with the profession of a soldier." "Pavia," said Napoleon, "is the only place I ever gave up to pillage. I promised that the soldiers should have it, at their mercy, for twenty-four hours. But after three hours I could bear such scenes of outrage no longer, and put an end to them. Policy and morality are equally opposed to the system. Nothing is so certain to disorganize and completely ruin an army."
It is wonderfully characteristic of this most extraordinary man, that in the midst of these terrible scenes, and when encompassed by such perils and pressed by such urgent haste, he could have found time and the disposition to visit a literary institution. When the whole city of Pavia was in consternation, he entered the celebrated university, accompanied by his splendid military suite. With the utmost celerity he moved from class to class, asking questions with such rapidity that the professors could hardly find time or breath to answer him. "What class is this?" he inquired, as he entered the first recitation room. "The class of metaphysics," was the [Pg 596]reply. Napoleon, who had but little respect for the uncertain deductions of mental philosophy, exclaimed, very emphatically, "Bah!" and took a pinch of snuff. Turning to one of the pupils, he inquired, "What is the difference between sleep and death?" The embarrassed pupil turned to the professor for assistance. The professor plunged into a learned disquisition upon death. The uncourteous examiner left him in the midst of his sentences, and hastened to another room. "What class is this?" he said. "The mathematical class," he was answered. It was his favorite science. His eye sparkled with pleasure, and seizing a book from one of the pupils, he hastily turned over the leaves and gave him a very difficult problem to solve. He chanced to fall upon an excellent scholar, who did the work very promptly and correctly. Napoleon glanced his eye over the work and said, "You are wrong." The pupil insisted that he was right. Napoleon took the slate and sat down to work the problem himself. In a moment he saw his own error, and returning the slate to the pupil, with ill-concealed chagrin, exclaimed, "Yes? yes! you are right." He then proceeded to another room, when he met the celebrated Volta, "the Newton of electricity." Napoleon was delighted to see the distinguished philosopher, and ran and threw his arms around his neck, and begged him immediately to draw out his class. The President of the University, in a very eulogistic address to the young general, said, "Charles the Great laid the foundations of this University. May Napoleon the Great give it the completion of its glory."
Having quelled the insurrection, in flames and blood, the only way in which, by any possibility it could have been quelled, Napoleon turned proudly again, with his little band, to encounter the whole power of the Austrian empire, now effectually aroused to crush him. The dominions of Venice contained three millions of souls. Its fleet ruled the Adriatic, and it could command an army of fifty thousand men. The Venetians though unfriendly to France preferred neutrality. Beaulieu had fled through their territories, leaving a garrison at Mantua. Napoleon pursued them. To the remonstrances of the Venetians he replied: "Venice has either afforded refuge to the Austrians, in which case it is the enemy of France, or it was unable to prevent the Austrians from invading its territory, and is consequently too weak to claim the right of neutrality." The government deliberated in much perplexity, whether to throw themselves as allies into the arms of France or of Austria. They at last decided, if possible, to continue neutral. They sent to Napoleon twelve hundred thousand dollars, as a bribe or a present to secure his friendship. He decisively rejected it. To some friends who urged the perfect propriety of his receiving the money, he replied:
"If my commissary should see me accept this money, who can tell to what lengths he might go." The Venetian envoys retired from their mission deeply impressed with the genius of Napoleon. They had expected to find only a stern warrior. To their surprise they met a statesman, whose profoundness of views, power of eloquence, extent of information, and promptness of decision excited both their admiration and amazement. They were venerable men, accustomed to consideration and power. Napoleon was but twenty-five. Yet the veterans were entirely overawed by his brilliant and commanding powers. "This extraordinary young man," they wrote to the senate, "will one day exert great influence over his country."
No man ever had more wealth at his disposal than Napoleon, or was more scrupulous as to the appropriation of any of it to himself. For two years he maintained the army in Italy, calling upon the government for no supplies whatever. He sent more than two millions of dollars to Paris to relieve the Directory from its embarrassments. Without the slightest difficulty he might have accumulated millions of dollars for his own private fortune. His friends urged him to do so, assuring him that the Directory, jealous of his fame and power, would try to crush rather than to reward him. But he turned a deaf ear to all such suggestions, and returned to Paris, from this most brilliant campaign, comparatively a poor man. He had clothed the armies of France, and replenished the impoverished treasury of the Republic, and filled the Museum of Paris with paintings and statuary. But all was for France. He reserved neither money, nor painting, nor statue for himself. "Every one," said he afterward, "has his relative ideas. I have a taste for founding not for possessing. My riches consist in glory and celebrity. The Simplon and the Louvre were in the eyes of the people and of foreigners more my property than any private domains could possibly have been." This was surely a lofty and a noble ambition.
Napoleon soon overtook the Austrians. He found a division of the army strongly intrenched upon the banks of the Mincio, determined to arrest his passage. Though the Austrians were some fifteen thousand strong, and though they had partially demolished the bridge, the march of Napoleon was retarded scarcely an hour. Napoleon was that day sick, suffering from a violent headache. Having crossed the river and concerted all his plans for the pursuit of the flying enemy, he went into an old castle, by the river's side, to try the effect of a foot-bath. He had but a small retinue with him, his troops being dispersed in pursuit of the fugitives. He had but just placed his feet in the warm water when he heard the loud clatter of horses' hoofs, as a squadron of Austrian dragoons galloped into the court-yard. The sentinel at the door shouted, "To arms! to arms! the Austrians!" Napoleon sprang from the bath, hastily drew on one boot, and with the other in his hand, leaped from the window, escaped through the back gate of the garden, mounted a horse and galloped to Massena's division, who were cooking their dinner at a little distance from the castle. The appearance of their commander-in-chief among them in [Pg 597]such a plight roused the soldiers from their camp-kettles, and they rushed in pursuit of the Austrians, who, in their turn, retreated. This personal risk induced Napoleon to establish a body guard, to consist of five hundred veterans, of at least ten years' service, who were ever to accompany him. This was the origin of that Imperial Guard, which, in the subsequent wars of Napoleon, obtained such a world-wide renown.
Napoleon soon encamped before the almost impregnable fortress of Mantua. About twenty thousand men composed its garrison. As it was impossible to surmount such formidable defenses by assault, Napoleon was compelled to have recourse to the more tedious operations of a siege.
The Austrian government, dissatisfied with the generalship of Beaulieu, withdrew him from the service and sent General Wurmser to assume the command, with a reinforcement of sixty thousand men. Napoleon's army had also been reinforced, so that he had about thirty thousand men with whom to meet the eighty thousand which would compose the Austrian army when united. It would require, however, at least a month before Wurmser could arrive at the gates of Mantua. Napoleon resolved to improve the moments of leisure in disarming his enemies in the south of Italy.
The kingdom of Naples, situated at the southern extremity of the peninsula, is the most powerful state in Italy. A Bourbon prince, dissolute and effeminate, sat upon the throne. Its fleet had been actively allied with the English in the attack upon Toulon. Her troops were now associated with the Austrians in the warfare against France. The king, seeing the Austrians, and his own troops united with them, driven from every part of Italy except the fortress of Mantua, was exceedingly alarmed, and sent to Napoleon imploring peace. Napoleon, not being able to march an army into his territory to impose contributions, and yet being very anxious to detach from the alliance the army of sixty thousand men which Naples could bring into the field, granted an armistice upon terms so easy as to provoke the displeasure of the Directory. But Napoleon was fully aware of the impending peril, and decided wisely. The Pope, now abandoned by Naples, was in perfect consternation. He had anathematized republican France. He had preached a crusade against her, and had allowed her embassador to be assassinated in the streets of Rome. He was conscious that he deserved chastisement, and he had learned that the young conqueror, in his chastisings, inflicted very heavy blows. Napoleon, taking with him but six thousand men, entered the States of the Pope. The provinces subject to the Pope's temporal power contained a population of two and a half millions, most of whom were in a state of disgraceful barbarism. He had an inefficient army of four or five thousand men. His temporal power was nothing. It was his spiritual power alone which rendered the Pope formidable. The Pontiff immediately sent an embassador to Bologna, to implore the clemency of the conqueror. Napoleon referred the Pope to the Directory in Paris for the terms of a permanent peace, granting him however an armistice, in consideration of which he exacted the surrender of Ancona, Bologna, and Ferrara to a French garrison, the payment of four millions of dollars in silver and gold, and the contribution of one hundred paintings or statues and five hundred ancient manuscripts for the Museum in Paris. The Pope, trembling in anticipation of the overthrow of his temporal power, was delighted to escape upon such easy terms. The most enlightened of the inhabitants of these degenerate and wretchedly governed states welcomed the French with the utmost enthusiasm. They hated the Holy See implacably, and entreated Napoleon to grant them independence. But it was not Napoleon's object to revolutionize the states of Italy, and though he could not but express his sympathy in these aspirations for political freedom, he was unwilling to take any decisive measures for the overthrow of the established government. He was contending simply for peace.
Tuscany had acknowledged the French Republic, and remained neutral in this warfare. But England, regardless of the neutrality of this feeble state, had made herself master of the port of Leghorn, protected by the governor of that city, who was inimical to the French. The frigates of England rode insultingly in the harbor, and treated the commerce of France as that of an enemy. Napoleon crossed the Apennines, by forced marches proceeded to Leghorn, and captured English goods to the amount of nearly three millions of dollars, notwithstanding a great number of English vessels escaped from the harbor but a few hours before the entrance of the French. England was mistress of the sea, and she respected no rights of private property upon her watery domain. Wherever her fleets encountered a merchant ship of the enemy, it was taken as fair plunder. Napoleon, who regarded the land as his domain, resolved that he would retaliate by the capture of English property wherever his army encountered it upon the Continent. It was robbery in both cases, and in both cases equally unjustifiable. And yet such is, to a certain degree, one of the criminal necessities of war. He seized the inimical governor, and sent him in a post-chaise to the Grand Duke at Florence, saying, "The governor of Leghorn has violated all the rights of neutrality, by oppressing French commerce, and by affording an asylum to the emigrants and to all the enemies of the Republic. Out of respect to your authority I send the unfaithful servant to be punished at your discretion." The neutral states were thus energetically taught that they must respect their neutrality. He left a garrison at Leghorn, and then proceeded to Florence, the capital of Tuscany, where the duke, brother of the emperor of Austria, received him with the greatest cordiality, and gave him a magnificent entertainment. He then returned to Mantua, having been absent just twenty days, and in that time, with one div[Pg 598]ision of his army, having overawed all the states of southern Italy, and secured their tranquillity during the tremendous struggles which he had still to maintain against Austria. In these fearful and bloody conflicts Napoleon was contending only to protect his country from those invading armies, which were endeavoring to force upon France the despotism of the Bourbons. He repeatedly made the declaration, that he wished only for peace; and in every case, even when states, by the right of conquest, were entirely in his power, he made peace, upon the most lenient terms for them, simply upon condition that they should cease their warfare against France. "Such a rapid succession of brilliant victories," said Las Cases to Napoleon at St. Helena, "filling the world with your fame, must have been a source of great delight to you." "By no means," Napoleon replied. "They who think so know nothing of the peril of our situation. The victory of to-day was instantly forgotten in preparation for the battle which was to be fought on the morrow. The aspect of danger was continually before me. I enjoyed not one moment of repose."
We must now leave Napoleon and his army, until our next Number, encamped before the walls of Mantua.
When Pizarro had completed the conquest of Peru, one of his first cares was to select a site for the capital of his new empire. The situation of Cuzco, far withdrawn in the depths of the Cordilleras, which admirably adapted it for the metropolis under the centralizing system of the Incas, rendered it unsuited for the capital of a commercial people, who were to be bound to another nation by the strict ties of colonial dependency. All the requisites of a central position, a good harbor, a fertile soil, and a delightful climate were found combined in the valley of Lurigancho, through which, emptying into the Bay of Callao, flowed the river Rimac, affording abundant facilities for irrigation, and producing exuberant fertility. Here, on the 6th day of January, 1535, the festival of the Epiphany, the conqueror of the Incas resolved to establish his capital city. He gave to it the name of La Ciudad de los Reyes—"The City of the Kings," in honor of the "wise men from the east," whom Catholic tradition has invested with regal dignity, who on that day, more than fifteen centuries before, had followed the star till it "stood over where the young child was." Twelve days afterward, the Spaniards having been gathered to the valley, the work was solemnly inaugurated by Pizarro laying with his own hand the foundation of the cathedral, which was dedicated to Nuestra Señora de la Asuncion—"Our Lady of the Assumption." The work of building was pushed on with an energy characteristic of Pizarro. From an hundred miles around the Indians were collected, and forced to build the hated city. The stern soldiers of the conquest laid aside their armor, and assumed the character of laborious artisans. The foundations of the public edifices were laid with a solidity capable of defying the attacks of time; and almost sufficient to resist the shocks of the earthquake, which at length taught the successors of the first builders that security was only to be attained by the use of slighter materials, and a more humble and fragile mode of erection.
In accordance with the old usage, which delighted to place a great city at some distance from its seaport, the spot chosen by Pizarro for his capital was about two leagues from the bay, whose waters were to be whitened with the sails of its commerce. From this point the plain descends westward to the sea-shore with a gentle slope. The city was laid out in the form of a semicircle or triangle, of which the Rimac formed the base. In order to secure as much shade as possible, the direction of the streets, instead of coinciding with that of the points of the compass, was made from northeast to southwest, so that both in the morning and the afternoon the shade of the buildings should fall upon the streets. Lying within twelve degrees of the equator, the buildings could of course cast no shadow, at any season, from the vertical noonday sun. These principal streets were crossed at right angles by others, so that each group of houses formed a quadrangle, all of nearly equal size. The general direction of the main streets nearly coinciding with the slope of the plain and the course of the Rimac, allowed the waters of the river to be conveyed through them in stone conduits, furnishing irrigation to the gardens, abundant spaces for which were left within the city.
The growth of Lima (for the name given by Pizarro to the city was early laid aside in favor of its present appellation, derived, by a change of letters to which the Limanians are still much addicted, from the name of the river upon which it stands) was as rapid as that of a tropical plant. In half a century from its foundation it is said to have contained 100,000 inhabitants; a rate of increase then unexampled in the history of colonization, and offering a striking contrast to the slow and almost imperceptible growth of the cities planted a century later upon the Atlantic shores of North America, though outdone by the marvels wrought in our own days upon the Pacific coasts. Is their speedy rise to be followed by a like speedy decline? As the mother country declined, the prosperity of Lima in like manner waned, though it is impossible, among the contradictory statements made, to arrive at any certain conclusion as to the population at different periods. But the large number of ruinous and uninhabited buildings shows a decrease of population. It is asserted upon competent authority that during the first thirty years of the present century not a single new building was erected within the walls; and it is doubtful if within the succeeding twenty years, as many buildings have been added to the city.
The distant view of Lima, as one approaches it from the sea is very magnificent. Entering the harbor of Callao, upon the right lies the bare [Pg 599]and rugged island of San Lorenzo. In front are the noble but dilapidated castles, and the white houses of Callao, presenting a gay and somewhat grotesque appearance, with the flags of the foreign consuls fluttering before their residences. In the rear stretches a broad plain, sloping upward toward a crescent-shaped range of barren hills, which inclose the fertile valley of the Lurigancho. At the foot of the mountains, apparently, rise the countless spires and towers of Lima, drawn up in relief against their dark sides. Still further in the distance are seen the giant ranges of the Andes, whose snowy summits are usually vailed by thick and sombre clouds. The harbor of Callao is magnificent; and the landing, at a fine mole built of stone, and surrounded by a substantial iron railing, is good. The town itself, though displaying some commercial activity, is mean and insignificant. Leaving Callao for Lima, we pass the little village of Buena Vista; then half way to the city we come to a place called Magdalena, consisting of a pulperia or dram-shop, a convent, and a splendid church. Here in the olden time the Spanish viceroys, at the expiration of their five years' term of office, used to meet their successors, and deliver up their authority to them. The convent has been suppressed, and the church is deserted, but in front of it stands a ragged monk, with a tin dish in his hand, soliciting alms from the passers-by.
When within about half a league from Lima, we enter upon the fine road called the Alameda del Callao. It is beautifully shaded with poplars and willows, with a handsome promenade upon each side, furnished at regular distances with stone seats, and bordered with the quintas, or country houses of the wealthy Limanians, embowered in luxuriant gardens, and surrounded with fruit-trees. By this broad avenue, we enter, through an arched gateway, into the city of Lima. This Alameda was opened in 1800, on the 6th of January, the anniversary of the foundation of the city. It was laid out by a man who filled the post of viceroy of Peru, under the title of Marques de Osorno. The history of this man is somewhat singular. About the middle of the last century, a petty Irish shopkeeper, bearing the somewhat incongruous name of Don Ambrosio O'Higgins, occupied a little shop, which is still shown under the area of the cathedral. Times went hard with Don Ambrosio; he failed in his petty traffic, abandoned the little shop by the cathedral, bade farewell to his old friend and brother tradesman, La Reguera, and wandered to Chili. It was a time of Indian hostilities, and all other occupations failing, there was at least a demand for men to be shot. Don Ambrosio entered the army, showed himself brave and capable, gained promotion, distinguished himself, discovered the Indian city of Osorno, and was honored with the title of the Marques of Osorno. In 1786, he returned to Lima in the capacity of Viceroy, where, as archbishop, he found none other than his old friend, La Reguera. Trade had prospered with him; he had returned to Spain, studied, embraced the clerical profession, and was sent back to Lima as archbishop five years before O'Higgins came as viceroy.
The first impression which the traveler receives upon entering Lima, by no means fulfills the anticipations he had been led to form from its appearance at a distance. The entrance is by the periphery of the semicircle, upon the side furthest from the Rimac. This quarter contains only dilapidated squares and filthy houses. But as he advances toward the Plaza Mayor, the appearance of the city becomes greatly improved. The general aspect of the houses strikes an American as somewhat novel, from the fact that a large proportion of them consist of but one story, very few exceeding two. This mode of building is rendered necessary by the frequency of earthquakes, which render buildings of a more imposing architecture extremely insecure. The houses of two stories have usually two doors in front, opening upon the street. One of these is the azaguan, which constitutes the main entrance to the house; the other leads to the cochera or coach-house. The azaguan opens into a spacious patio or court-yard. Directly opposite this entrance are two large folding-doors, which open into the sala or hall of the dwelling-house, beyond which is the cuadro or reception-room, furnished as splendidly as the means of the occupant will allow. Adjoining the cuadro are the various rooms appropriated to the use of the family. The sala and cuadro are of the full height of the house, and the flat roof of these two apartments forms a sort of terrace, called the azotea, which is paved, surrounded with a railing, and covered with an awning. The second story of the remainder of the building contains rooms which open into a balcony projecting over the street. This balcony is boarded up to the height of about three feet, the remainder being composed of lattices or glazed windows, and forms the favorite lounging place of the inhabitants, where they can watch the passers-by in the streets. The peculiarity of the domestic architecture of Lima, by which, with the exception of the balcony, the rooms open not upon the street, but upon the court-yard, gives the city much the appearance of an Oriental town. Where the houses are of but one story, the almost entire absence of windows and openings gives the street a mean and gloomy appearance, almost like continuous lines of dead walls. But where the dwellings are of two stories, the long lines of balconies and verandas gayly ornamented and trellised, projecting far over the foot-pavements, present a gay and festive aspect. In some parts of the city are houses of much greater height, and of a far more imposing architecture. But they are to a great extent ruinous and dilapidated, having been abandoned by their ancient occupants, for fear of being overwhelmed in them by earthquakes. When tenanted at all, it is principally by the poorer classes, who are willing to brave the insecurity for the sake of the saving in the rents. The outer walls are usually of adobes, or sun-dried brick, as far as the first floor. The second story is usually composed of [Pg 600]a wooden frame-work, upon both sides of which canes are nailed, or fastened by leather thongs, and the whole is then plastered over, and painted to imitate stone, the deception being aided by the apparent massiveness of the construction. The division walls are also made of canes plastered over. The roofs are flat, composed of rafters, covered with mats or cane, with a layer of clay spread above them, sufficient to exclude the rays of the sun and the heavy dews. A single prolonged shower would be sufficient to dissolve the whole city; but as it never rains there, these slight walls and roofs are all that is required. Lima is justified in placing her dependence in architecture upon a reed, rather than upon stone. The more solid and massy the walls, the less protection do they afford against the terrible earthquakes which are of periodical occurrence, and by which more than once the city has been reduced to a heap of ruins; while these light cane fabrics yield to the shock, and when it has passed resume their places, with little apparent injury; and even if demolished they do not occasion that fearful peril of life which results from the overthrow of more stable fabrics.
There are few places the inhabitants of which present so great a diversity of complexion and physiognomy as in Lima. There is every gradation and intermixture of race, from the fair Creoles of unmixed European descent, who pride themselves upon the purity of their Spanish blood, to the jet black negro of Congo, whose unmitigated ebony hue bears testimony equally unequivocal to his pure African lineage. Between these two extremes is an almost innumerable variety of mixed races, each having its own peculiar designation, indicating the precise proportion of European, Indian, and negro blood in their veins, each marked with its own peculiar physical, intellectual, and moral characteristics; and each finding its chief boast in the nearness of its relation to the white race, and looking down with contempt upon those a shade darker than its own.

In 1836, when the population of the city was a little more than 54,000, it was composed of about the following proportion of the different races: white Creoles, all of European, and mostly of Spanish descent, 20,000; Negroes, 10,000; of whom a little less than one half were slaves; Indians, 5000; mixed races, 19,000; these are of every shade of complexion, from the Mestizo, the child of a white father and an Indian mother, whom only a keen and practiced eye can distinguish from a White, and to whom no higher compliment can be paid than to inquire whether he is not a Spaniard, to the Zambo who can only show claim to a portion of white blood, on the ground that to all the vices of the negro race, he adds others peculiar to the Whites.
The white Creoles are of slender figure, and of middling height, with features strongly marked, fair complexion, and black hair. Like the descendants of the Spanish race throughout all [Pg 601]the Western World, they have degenerated from the parent stock. The males have even in youth a look of premature age; as though the powers of nature were exhausted, and insufficient to develop a vigorous manhood. Indolence is their predominant characteristic. They are utterly indisposed to any continuous exertion, whether of body or of mind. If poverty compels them to pursue an occupation for a livelihood, they select some petty traffic, in which, if the gains are small, there is ample leisure to gossip and smoke their perpetual cigars. Those who are able abandon themselves to idleness, lounging about the streets or in the shops, at the coffee-houses or the gaming-table. The education of the Creole of Lima is very defective; the system of instruction pursued does little to develop his powers, and his innate indolence presents an insuperable bar to any efforts at self-cultivation. Riding is a universal custom, and almost every person keeps one or more horses; these are trained by the chalanes or professional horse-breakers to perform feats of every kind; one to which great value is attached, is to turn around upon the hind legs rapidly, when in full gallop. Tschudi, a recent German traveler, relates an instance which came under his own observation, which shows the certainty and dexterity with which the feat is performed. A friend of his rode full gallop up to the city wall, which at the spot is about nine feet broad, leaped his horse upon it, and made him describe a segment of a circle with his fore feet beyond the edge of the wall, while standing balanced upon his hind feet. The feat was performed a number of times in rapid succession.
The riding costume of a Peruvian cavalier is extremely picturesque and convenient. Its most striking feature is the poncho. This is a large fringed shawl with an opening in the centre, through which the head of the wearer passes; it then hangs gracefully over the shoulder, and falls nearly to the knee, leaving the hands and arms less embarrassed than any other species of cloak. These ponchos frequently display great brilliancy and variety; the color is often a snowy white, sometimes it is richly and fancifully embroidered; but the prevailing taste is for broad stripes of brilliant colors, such as orange, scarlet, blue, green, rose color, or combinations of all hues intermingled and diversified in every conceivable manner. The spurs used by the Peruvians are of enormous magnitude; old custom ordains that they should contain a pound and a half of silver; the rowels sometimes stand out four or five inches from the heel, with spikes of one or two inches in length, or even more. A broad-brimmed sombrero of fine Guayaquil grass is usually worn by equestrians. The trappings of the horses are often of a very costly description. Head-gear, bridle, and crupper are sometimes seen formed of finely-wrought silver rings linked into each other. The stirrups are massy blocks of wood of a triangular shape, quaintly carved, and ornamented with silver. The saddle is frequently adorned with rich embroidery in gold, and the holster inlaid with the same precious metal.
A cigar is the almost unvarying accompaniment of a Peruvian of any class. Basil Hall relates an odd expedient made use of to reconcile the free-and-easy habit of smoking in public places, with the stately requirements of Spanish etiquette of olden time, in the presence of the representatives of royalty. In the days when Peru was a Spanish colony, the vice-regal box at the theatre projected out somewhat into the pit, in full view of the Commonalty of the City of the Kings. As soon as the curtain fell between the acts of the piece, the viceroy was in the habit of retiring from the front to the rear of the box. No sooner was his back turned than, by a very convenient figure of thought, he was considered to be constructively absent. Every man in the pit would then draw forth his flint and steel (this was long before the days of Lucifers and loco-focos), light his cigar, and "improve" the time by puffing away at the fragrant weed. At the tinkling of the bell which announced the rising of the curtain, the representative of royalty returned to the front of the box, his constructive absence was ended, and every smoker paused in mid-puff.
Nothing indicates the decadence of a race more unerringly and decisively than the progressive change which comes over its tastes in its modes of amusement. Indolence and brutality go together. Displays of skill and courage cease to afford excitement to the jaded sensibilities; the stronger stimulus of suffering must be supplied. Thus as the Roman race declined, the shows of the arena grew more and more brutal. Cock-fights and bull-fights are the favorite amusements of the Limanians. A fondness for the latter is characteristic of the Spanish race every where; but in Peru the chief attraction is not the dexterity and courage of the performers, but the agony of the victims. Bull-fights in Spain may almost be characterized as humane exhibitions compared with those of Lima. At one witnessed by Hall in 1821, the matador, who should have given the death-stroke to an animal of extraordinary strength and courage, missed the mortal spot, and merely buried his sword in the body of the bull; in an instant he was tossed, apparently dead, into the air, by the maddened beast, who turned upon a horseman, whom he dismounted, goring the horse so that his bowels hung upon the ground. All this threw the spectators into an agony of delight; which was still further enhanced when the sinews of the bull, having been cut from behind by a crescent-shaped instrument fixed to a long pole, the poor beast dragged himself around the arena upon his mutilated stumps. But their ecstasy amounted to frenzy when a man mounted upon the back of the bull and spurred him around the arena with strokes of a dagger, until he fell exhausted by loss of blood.
Bull-fights are only an occasional luxury, but cock-fights are a daily standing dish. The cock-pit (coliseo de gallos) is a very handsome building; [Pg 602]here cock-fights take place every day. The natural weapons of the fowls are not sufficiently deadly to satisfy the Limanian spectators; and in place of the spur of the right foot, which is cut off, is put a sharp curved blade of steel or gaff. Whatever else may be lacking, Lima can justly boast the finest amphitheatre in the world for the purpose of cock-fighting.
In Lima, as throughout the whole of Spanish America, the females are, both intellectually and physically, far superior to the males. All visitors at Lima speak in terms of warm admiration of the Limeñas, as the most charming and graceful women of South America. In figure they are usually slender, and somewhat above the middle height, with fair complexions, destitute of color, large, dark brilliant eyes, and abundant black hair. The charming Spanish epithet hechicera, by which they are designated, belongs to them in the full extent of its significance, not only on account of their rare personal beauty, but also by reason of the captivating grace of their deportment, and the natural amiability of their dispositions.
The first thing which attracts one's regard in Lima, is the singular and picturesque costume of the females. This costume, which resembles that of the Moors, to whom it owes its origin, takes the name of the two principal parts of which it is composed—it is called the saya y manto. It is worn only in Lima, and there only in the day time, as a walking-costume. The saya, as formerly worn, was a skirt or petticoat made of an elastic black silk, plaited at the top and bottom in small folds, and fitting so closely as to display the outlines of the figure, and every motion of the limbs. It was made so narrow at the bottom that the wearers were forced to take steps extremely short, which gave to their gait a mincing character more striking than modest. This, which is called the saya ajustada is now rarely seen. As now worn it forms a very graceful and elegant costume; the bottom plaits are taken out, so as to cause the skirt to stand out from the figure, which is not displayed. This is called the saya desplegada. It is always made of a dark-colored material. The manto is a thick vail of black silk, joining the saya at the back of the waist. It is brought up over the shoulders and head, and drawn over the face in such a manner as to conceal the features entirely, with the exception of one eye, which is visible through a small triangular space left open for the purpose. One hand retains the folds of the manto in their places while the other displays a richly embroidered handkerchief. Over the shoulders is thrown a shawl, usually of embroidered China crape. The Limeñas, effectually disguised in this national dress, to which they are enthusiastically attached, go out every where unattended. Any one can address them, and they violate no usage in accosting any one. The uniformity of the costume, in materials, shape, and color, and the perfect concealment of the features, makes identification impossible, so that the street becomes a perpetual masquerade. The costume which owes its origin to marital jealousy has in Lima become a most efficient aid to intrigue.

[Pg 603]The Limeña in the street, shrouded in the saya y manto, differs as widely from the same Limeña at home, as the butterfly wrapped up in its chrysalis does from the same insect with wings fully expanded. At home, at the theatre, in the carriage, every where except when walking in the streets, or in church, the Limeña appears dressed in the newest French fashions. There is, however, one article of European costume which they uniformly refuse to adopt, and that is the bonnet. With here and there an exception, they obstinately reject any other head-dress than a light vail and their own abundant tresses. An inordinate fondness for flowers and perfumes is also a striking characteristic of a Limeña, whose presence is almost invariably announced by a vase of flowers and a flaçon of perfume, placed upon a table near which she reclines swinging in a hammock during the sultry hours of the day, amusing herself, now with examining a book of engravings, now with music, of which she is passionately fond, perhaps with embroidery—and not unfrequently with a cigar.

If man or woman were only an animal being—and if she could always be young and physically charming—this life of the Limeña might not seem so undesirable. But with her a thing of beauty is not a joy forever. If her reign is brilliant, it is brief. When her beauty fades she ceases to be a coquette, and becomes a beata or devotee. She renounces the vanities of the world, attends mass several times a day, makes frequent confessions, and takes up her abode during Lent in a house of penitence. She selects a confessor to whom she unburdens her conscience, and sends presents of sweetmeats and delicacies. At home she sinks into a cipher, scarcely more regarded than a piece of worn-out furniture. If a stranger, paying a visit to a young Limeña, respectfully rises to make a place for an aged woman who enters the cuadro, nothing is more common than for the daughter to say, with the utmost coolness, No se incommoda usted, es ma mamita "Don't incommode yourself, it's my mamma." Habit becomes a second nature, and the Limeña accommodates herself to her lot without a murmur. Such, with exceptions few and rare, is the lot of the hechiceras Limeñas, so highly endowed by nature, and worthy of a better fate.
Besides these Limeñas of European origin there is another class, descendants of the ancient Peruvians, who, though not beautiful like their fair neighbors, present some remarkable characteristics. Their complexion approaches the color of copper, with a pale tinge of gold. Their whole aspect has in it something bizarre, but at the same time not altogether unattractive. In dress they are fond of strange combinations. A balloon-like garment of white muslin or gaudy calico; a Guayaquil hat with high crown and immense brim, decorated with huge bows of ribbon on the "company side" of the head; their abundant hair carefully divided and pouring down their backs in sable cascades; and, foremost and above all, a well-fitting stocking and shoe upon a foot unimpeachably small, form their favorite costume. These cholitas are admirable horsewomen, usually riding astride, cavalier fashion, and wearing the formidable Peruvian spur[Pg 604].

[Pg 605]The saya y manto is always worn when going to church. There the absence of seats obliges each female to kneel upon the flags, unless she be provided with a servant to carry a piece of carpet upon which to kneel. To look upon them reclining immovably against the walls or the base of a column, the eyelids drooping upon the pale cheek, or the look fixed upon the tracery of the roof overhead (for in church the manto is not rigorously closed) one might imagine the Limeñas to be statues of meditation. Only the sign of the cross rapidly traced over the forehead shows them to belong to the breathing world. In the sanctuary no sound disturbs the harmony of the sacred offices. The incense, the pious hymns, the soft breathing of the organ, and in some of the churches, the notes of numerous birds of song caged among the crystal lustres of the candelabra, are mingled with the solemn chant of the monks. Service over, and what a change! Life seems to reanimate those marble limbs; those fixed looks become lively and sparkling; and noise and bustle take the place of the former silence. As the fair Limeña leaves the cathedral the black musicians fill the air with the sound of their drums and clarinets, the lottery-men cry their tickets upon one side of the entrance, and upon the other a fat ecclesiastic vends the effigy of the saint who chances to be in fashion. The Limeña, restored to her proper character, draws the shrouding manto over her features; makes gay and lively answers to the insipid compliments paid her by the young men lounging under the portico; and buys with one hand a lottery ticket, and with the other a relic or an image which she hopes will make her number a lucky one.
The Indians in Lima number some 5000; they are active and industrious, in moral qualities far surpassing the mixed races, and fully equaling the whites, to whom, however, they are decidedly inferior in intellectual powers. They look upon Europeans with the feelings always entertained by a subjugated race toward their conquerors; a compound of fear, dislike, and mistrust. In 1781, under the lead of some of the descendants of the ancient Incas, an insurrection of the Indians took place in Peru, which was marked by the utmost atrocities. They defeated the whites in several engagements, burned a number of towns and villages, and captured the city of Sorrato, in which the surrounding inhabitants had taken refuge; of the prisoners who numbered 23,000, only 87 priests and monks were preserved alive. Their leaders were finally betrayed into the power of the whites, and put to death. The Indians then disbanded. The most rigorous measures of repression were thereupon adopted. Their language, dress, music, and dances were strictly forbidden, and every effort made to extinguish their national feelings. When the war of Independence broke out, the Indians took part against Spain, but with the secret design of reinstating the dynasty of their ancestors, and raising to the throne one of the race of the Incas. In many cases they directed their hostilities against the whites indiscriminately, without distinction of parties. In one place they vowed not to leave alive so much as a dog or a fowl who bore the hated color, and even scraped the whitewash from the walls of their houses in sign of utter detestation. Since the war of Independence they have made great advances, especially in the military art, and have used every means to secure as many fire-arms as possible. At as late a period as 1841, Tschudi, discovered by accident eighteen muskets hidden in the hut of an Indian in Central Peru, and upon asking for what purpose they were concealed was told that the time would come when they would be of use. The same writer also mentions incidents showing that many of the Indians are in possession of the secret of the existence of silver mines, far richer than any which are now known; and that the secret is handed down inviolably from father to son, until the time when their ancient dynasty shall be restored. Years of oppression and wrong under Spanish rule, only partially remedied since the Revolution, have wrought a great change in the character of the Indians of Peru. A settled distrust and melancholy have taken the place of the confiding and joyous disposition of the race who welcomed their Spanish visitors. Their songs, their dances, the whole tenor of their domestic life, wear a dark and sombre shade. Even in dress their favorite color is dark blue, which is with them the hue of mourning. These characteristics of the Indian race throughout the country, appear, though more or less modified, in the Indians in Lima.
The negroes in Lima number not far from 10,000 of whom less than half are slaves. The charter of Independence provides that no person in Peru shall be born a slave, but this provision has been modified by law, so as to allow a term of servitude varying from 25 to 50 years. Slaves brought from any other country, become free the moment they touch the soil of Peru. Hence if a master take his slave into Chili, the slave may claim his freedom on his return. Runaways, however, are liable to be reclaimed. The treatment of slaves in Lima is very gentle. A tribunal is erected having the special duty to protect the slaves from ill-treatment. A slave may claim his liberty upon paying his value; and in case he and his master are unable to agree upon the sum, it is fixed by the court; or he may sell himself to any other master who will pay the determined price, in spite of any opposition on the part of the owner. As the introduction of negroes from Africa has been for many years prohibited, the great majority of the slaves are [Pg 606]born in Peru. These, though intellectually and physically superior to those born in Africa, are held of less value; their superior intelligence rendering them less docile, and more discontented with their condition. The free negroes of Lima are represented as a plague and a pest to society.
As a general rule the mixed races, which constitute about a third of the population of Lima, inherit the vices without the virtues of the pure races from which they sprung. Perhaps the sole exceptions to this are the Mestizos, the offspring of a white father and an Indian mother. They are of mild and gentle dispositions, but are also timid and irresolute. There are few Mestizos in Lima; but in the interior they are numerous. There they constitute the entire population of many villages, and call themselves whites, keeping aloof from the Indians. The most prominent characteristic of the Mulattos, the offspring of a white and a negro, is their remarkable imitative talent, and their consequent aptitude for mechanical pursuits; but they are extremely sensual and animal in all their tastes and instincts. The Zambos, sprung from an intermixture of the different castes of the colored race, and the Chinos, the offspring of the colored and Indian races intermixed in various degrees, are the most miserable and degraded of all the half-castes in Lima. They commit the most inhuman barbarities with the utmost indifference. Four-fifths of the prisoners in Lima are Zambos. They are usually athletic and muscular, with sunken eyes, thick lips, and noses much less depressed than that of the negro. The Chinos are morally about on a level with the Zambos; but physically they are much inferior. The mixed races of fairer complexion resemble the whites in moral and intellectual qualities in about the same degree that they approach them in color.
The general condition of morals in Lima, especially among the colored races, may be inferred from the following statement given by Tschudi. In ten months of the year 1841, the number of births was 1682, of which 860, more than one half, were born out of wedlock. The number of dead children exposed during the same time was 495, almost one third of the whole number of births. Of the illegitimate children nearly two thirds, and of those exposed a still larger proportion, were Mulattos. Though there can be no positive evidence of the fact, there is every reason to conjecture that the greater number of the children exposed, were murdered by their mothers. During the same period the number of deaths in the city was 2244, exceeding the births by 562. It has been found that for a long series of years the deaths have exceeded the births by about 550 a year.
There is an old Spanish proverb which styles Lima the Paradise of women, the Purgatory of men, and the Inferno of asses; but during the time of the carnival all claims to be considered a Purgatory even, to say nothing of Paradise, to man or woman, disappear. One of the favorite amusements of the season is to besprinkle passers by, from the balconies, with water, of which the purity is by no means above suspicion. The colored population assume the license of rolling the passers who do not choose to pay for exemption, in the street gutters, which offer remarkable facilities for this pleasantry, as they are ill-paved, and unswept, with a stream of water running through them. These gutters are used by the lower classes of the Limanian señoras in a manner peculiar to that city; they are accustomed to wash in them the plates, glasses, and dishes from their dinner tables. Another favorite amusement during the carnival is to suspend from the balconies a strong bag filled with fragments of glass and pottery. This is attached to a rope of such a length as to suffer it to fall within a few inches of the heads of the passengers. This sack is drawn up into the balcony; and when a person who has been selected as a victim passes underneath, it is flung just over his head. The rope prevents it from falling upon him, but the deafening crash which ensues within a few inches of his ears, is nowise soothing to the nerves. This practice is regularly prohibited by the police, but all attempts to suppress it have proved as unavailing as the efforts to prevent the use of fire-crackers upon our own Fourth of July.
There is a public lottery drawn every week in the Plaza Mayor, directly opposite the Cathedral, where a temporary platform is erected for the purpose. A ticket costs an eighth of a dollar, and the highest prize is 1000 dollars. As the hour for drawing approaches, the square begins to fill with a motley crowd of men, women, and children; armed soldiers, shovel-hatted priests, barefoot monks, bright-eyed tapadas (so a Limeña with her manto drawn over her face is called), spurred cavaliers, and ragged negroes. The numbers are placed in the wheels, and drawn out by boys belonging to the foundling hospital. To every ticket is attached a motto, which is usually an invocation to some favorite saint to accord good luck to that ticket; and when the fortunate one is ascertained this motto is read aloud for the edification of the bystanders. The lottery belongs to a society called the "Beneficencia," by whom it is farmed out, and the profits appropriated to the support of hospitals and charitable institutions. It is the usual practice of the Limanians to purchase tickets regularly; the negroes in particular, as elsewhere, are particularly addicted to trying their luck. Instances are not uncommon in which slaves have purchased their freedom with prizes drawn in the lottery of the "Beneficencia." In a small chapel belonging to the church of St. Dominic, were formerly exhibited relics of St. Rose, the patroness of Lima. Among them was a pair of dice, with which it was gravely said that, when the fair saint was exhausted by prayer and penance, the Saviour would appear and revive her drooping spirits with a friendly game. Of late years these uncanonical relics are not exhibited, but Stevenson, the author of a standard work on South America, relates that they were shown to [Pg 607]him in 1805, when he kissed them with as much devotion as he would have manifested to any other pair.
Every morning at a quarter to nine o'clock, when the Host is elevated in the Cathedral, and in the evening at the hour of the Angelus, the great bell of the Cathedral tolls three measured strokes, which are repeated from all the many belfries of Lima. Every occupation is at once suspended, every hat is reverentially raised; every lip moves, uttering its whispered prayer. The evening prayer being ended, each one makes the sign of the cross, and bids the person next him buenas noches—"good-night." It is an act of courtesy to insist that one's neighbor shall take the precedence in the salutation; and he, not to be outdone in politeness, must waive the proffered honor. The courteous contest—"You say it," and "No, sir, you say it," is sometimes not a little amusing.
Lima is surrounded by a wall, now in a state of extreme dilapidation, and altogether unavailable for any purposes of defense. It is built of adobes, and dates originally from 1685, though much of that now existing is of more recent construction. A fine stone bridge crosses the Rimac, uniting the city with the suburb of San Lazaro. It consists of six circular arches rising thirty-six feet from the surface of the water. The piers are of brick, resting upon stone foundations of great solidity, of which no better proof is needed than that they survived the earthquakes of 1687 and 1746, by which almost every edifice in Lima was shattered. The entrance to the bridge is through a broad arch crossing the street, used for carriages, with smaller arches on each side for foot-passengers. This archway is surmounted with turrets and spires, and presents an imposing appearance. In the parapets are semi-circular recesses provided with stone seats which furnish a favorite resort in summer evenings. The view from the bridge is of great beauty. Westward the eye follows the silvery course of the Rimac, its left bank lined with convents, and splendid mansions of the more wealthy Limanians. The view closes with the broad Pacific. In the opposite direction the view is bounded by the range of hills, beyond the avenues of the Alameda del Acho; while beyond and above all, when the shrouding vail of clouds is lifted, so as to permit the sight, are beheld the snowy summits of the distant Cordilleras. The bridge was built in 1640, at an expense of 400,000 dollars, from designs by Villegas, an Augustin monk.
The Cathedral is situated on the eastern side of the Plaza Mayor. The foundation stone was laid by Pizarro himself on the 18th of January, 1534, twelve days after the choice of the site of the city. Ninety years after, the edifice was completed, and was solemnly dedicated on the 19th of October, 1625. It has a light, ornamented façade with large folding doors in the centre, and smaller ones upon each side. From each of the two corners rises an octagonal tower to the height of about two hundred feet, exclusive of the base, which is forty feet. These towers were thrown down by the great earthquake of 1746, by which almost the whole city was laid in ruins. They were rebuilt in 1800. The interior is singularly magnificent. The roof, which is beautifully paneled, rests upon arches supported by a double row of square stone pillars. The grand altar is adorned with seven Ionic columns, twelve feet in height, cased with pure silver, an inch and a half thick, and is surmounted with a massy crown of silver richly gilt. The tabernacle, seven feet high, is of wrought gold, studded with precious stones. On high festival days service is performed with a pomp and splendor not surpassed in any temple in Christendom. Many of the churches are ornamented with a profusion of silver even yet, though it is said that during the revolution a ton and a half of silver was taken in a single year from the ornaments of the churches, to supply the necessities of the state; yet such was the abundance with which the precious metal had been lavished, that this amount was hardly missed; a tale which would be incredible if related of any city other than the one which at a certain time paved with solid ingots of silver the streets through which a new viceroy was to make his entrance.
In the convent of San Francisco, is a small chapel containing an image of the Virgin, called del milagro, "of the miracle." It is related that during the great earthquake of 1630, this image, which then stood over the porch of the church looking toward the street, turned completely round, so as to face the high altar, and raised her hands in the attitude of supplication, and then implored mercy for the city, and thus saved it from utter destruction. A monk who conducted a recent traveler over the convent, related to him this miracle, and very naïvely expressed his wonder that the Madonna did not repeat her gracious interposition at the time of the earthquake of 1746, when it was no less needed.
The Oratorio de San Felipe Neri, formerly the convent of San Pedro, was the principal college of the Jesuits, who, at the time of their expulsion, possessed immense wealth. In 1773 a secret order was dispatched from the King of Spain, directing the viceroys to arrest all the Jesuits in the South American provinces, in a single night, and ship them to Spain. So secret was the order that the viceroy and those officers whose assistance was to be employed, were supposed to be the only ones who knew any thing of it. The viceregal council was summoned at 10 o'clock on the appointed night, and the royal order read to them. No one was allowed to leave the room, for fear that intelligence might be communicated to the Jesuits. At midnight the officers were sent to the convent to arrest the members of the order. The door was opened at the first summons, and the officer was conducted to the great hall of the convent, where all the brethren were assembled, each with a bag containing a few requisites for the voyage. So in all the other convents of the order. The same [Pg 608]vessel which had conveyed the royal decree, had brought instructions from the Superior of the Jesuits in Madrid, who had gained intelligence of the secret, directed to the vicar-general at Lima, commanding him to be in readiness when the arrest should be made. The brethren were sent to Callao under a strong guard, and as soon as possible were put on shipboard. But when the eager officials made search for the immense wealth which was known to be in the treasury of the order in San Pedro, the keys of which were laid out in readiness for them in the apartment of the Superior, only a few thousand dollars were discovered. The rest had vanished like a vision. And to this day it has eluded the most vigilant search. An old negro, who was in the service of the convent, testified that for several nights he and his fellow-servants, with their eyes closely bandaged, were employed in conveying bags of treasure to the convent vaults, attended by two of the brethren of the order. He could give no clew to the place of concealment, except that he thought there was a subterranean spring near the spot.
The palace of the Inquisition stands upon what was formerly called the Plaza de la Inquisicion, now the Square of Independence (Plazuela de la Independencia). Upon this same square were also situated the University and the Hospital of La Caridad; whence it was sometimes styled the Square of the three Cardinal Virtues: the Inquisition typifying Faith; the University, Hope, and the Hospital, Charity. Few traces remain to denote the fearful uses to which the edifice of the Inquisition was devoted. It is now used in part as a storehouse for provisions, and in part as a prison. In the palmy days of Spanish dominion, Lima was the ecclesiastical metropolis of the whole Pacific coast of South America, and the Inquisition exercised its functions with a rigor hardly exceeded by that of Spain. When the Cortes abolished this tribunal in Spain and its dependencies, the building was thrown open to the populace, who speedily ransacked the apartments, and destroyed the implements of the Holy Office. Among those present was Stevenson, author of a standard work on South America, who has given a detailed account of the transaction. The customary array of racks, pillories, scourges, gags, thumbscrews, and other instruments of torture was found. The crucifix in the principal hall having been accidentally thrown down, it was discovered that the head was movable, and so arranged that a man concealed behind the curtains could cause it to move in token of assent or dissent. How many a trembling victim, overawed, confounded, and bewildered at seeing the movement of the lifeless head of the Redeemer, has confessed whatever the officials demanded, almost believing himself guilty of crimes he never committed. One article found was somewhat ludicrous. In one room was a large quantity of printed cotton handkerchiefs upon the centre of which was a pictorial representation of Religion, bearing a cross in one hand and a chalice in the other. The manufacturer had introduced these pious devices in the hope of facilitating the sale of his wares. But the Holy Office discovered gross impiety in the act of blowing the nose or spitting upon the symbol of the true faith; and to guard against temptation to such a profanation, had seized upon the whole consignment.
On the north side of the Plaza Mayor stands an unsightly edifice, now occupied by courts of justice and various government offices. This was formerly the palace of the Viceroys of Peru. The principal apartment bore the name of the Hall of the Viceroys. Here were arranged forty-four panels, each destined to receive the full-length portrait of a viceroy, as he entered upon his government, commencing with Pizarro. The last of these panels had been filled by the portrait of Pezuela, who held the office at the time when the insurrection broke out which severed Peru from the Spanish dominion. There was no room in the hall for the portrait of another viceroy. A similar coincidence is recorded in Venetian history. The effigy of the Doge who was in office at the time when the revolution took place which overthrew the Venetian oligarchy, filled the last of the niches which had been constructed to receive the effigies of the successive magistrates.
This is not the palace erected by Pizarro for himself. That stood on the opposite side of the square, and some remains of it are still shown in an obscure lane called the Mat-sellers' Alley. Here, on Sunday, the 26th of June, 1546, eleven and a half years from the time when the foundation of the City of the Kings was laid, its founder was assassinated. Pizarro had been warned that a plot was formed to assassinate him on his way to mass; but he took no further precaution against it than to absent himself from divine service that day. The conspirators then resolved to murder him in his own house. As they were crossing the Plaza one of them turned a little aside to avoid a pool of water. "What! afraid of wetting your feet, when you are to wade up to your knees in blood!" exclaimed the veteran Juan de Rada, the leader of the band. The dainty conspirator was ordered to return to his quarters as not worthy of a share in the enterprise. Pizarro was sitting with his friends after dinner, when the assassins rushed into the palace, through the open gate. The guests made their escape through the corridors, by climbing down into the gardens. Among them was Velasquez the Judge, who had boasted that Pizarro could receive no harm from traitors, while he "held in his hands the rod of justice." As Velasquez climbed down in making his escape, he needed both hands to aid his descent, and held his official wand in his mouth; thus verifying his boast, to the letter, if not in spirit. For a moment the assailants were held at bay by the attendants, but these were speedily dispatched. Pizarro, who had vainly attempted to assume his defensive armor, wrapping a cloak about his arm, sprang against the assassins, sword in hand, with the cry, "What ho, traitors! have ye come [Pg 609]to kill me in mine own house?" Though more than three score years of age, he defended himself with desperate vigor, and had slain two of the assailants, when Rada, seizing one of his own comrades, flung him against Pizarro, who instantly ran him through the body. But while his weapon was thus entangled, Pizarro received a stab in the throat, and fell, and the swords of several of his enemies were at once sheathed in his body. He traced a cross with his finger in the blood upon the floor, and was in the act of bending down his head to kiss the symbol of his faith, when, with the name of "Jesu" upon his lips, he received a stroke which put an end to his life.
No place upon the globe enjoys a climate more equable than that of Lima. Not only are there no sudden and violent alternations of temperature, but the variations of the seasons are hardly known. Extremes of heat and cold are never experienced. The temperature at noon, in the shade in an open room, never rises above 80, and never falls below 60 degrees. The rays of a vertical sun are intercepted by a thin canopy of mist, called garuas, which for a considerable portion of the year hang over the city, resembling in appearance the canopy of smoke above a large town. The winds blow almost constantly from points between the southwest and the southeast. When they come from the former quarter they are cooled by passing over the immense expanse of the Pacific; when from the latter they have swept the vast forests toward Brazil and the frozen ranges of the Cordilleras. A northerly wind alone, which is of unfrequent occurrence, produces an oppressive sensation of heat. During the year, there are about 45 days when the sun is entirely unclouded, about 190 in which it is visible during no part of the day, and the remainder are usually cloudy in the morning, and clear in the afternoon. A shower of rain is a thing altogether unknown, but during February and March, a few large straggling drops occasionally fall about five o'clock in the afternoon. The garuas overhang the city almost without intermission from April to October. During June, July, and August there will not probably be a single unclouded day, and not more than three days in each month in which the sun can be seen at all. The gray canopy begins to lift in October, and gradually becomes thinner and thinner till April, when it again begins to gather. But this equable climate, apparently so desirable, is found to be productive of great physical lassitude, and to be unfavorable to health. It has been already noticed that the number of deaths constantly and greatly exceeds that of births. Among adults the most fatal disease is dysentery; then comes fever, usually intermittent; then consumption, inflammation of the lungs, and dropsy, the latter usually the result of intermittent fever.
Another fearful compensation for the mildness of the elements above the surface of the earth, is found in the frequency of subterranean disturbances. On an average, there are 45 shocks of earthquakes in the course of a year. These usually occur in the months from October to January, and again in May and June. But at intervals of from 40 to 60 years, the valley of the Rimac experiences an earthquake of far more desolating force, and by which Lima has several times been reduced to a heap of rubbish. The most destructive of these, since the European conquest were those of 1586, 1630, 1687, 1713, 1746, 1806—two in each completed century; so that the experience of the past gives us every reason to anticipate that many years will not elapse before Lima will once more become a mass of ruins.
The most destructive of this regular series of great earthquakes was that of October 26, 1746. A little more than an hour before midnight, the earth began to tremble, and in three minutes from the time of the first shock, the city lay in ruins. Of more than 3000 houses, only 21 escaped entire. The towers of the Cathedral were overthrown. The bridge across the Rimac was almost the only public work which escaped, and of that one arch, upon which stood an equestrian statue of Philip V., was destroyed. But if Lima was sorely shattered, Callao was annihilated. The sea receded suddenly from the shore, and as suddenly rolled back with irresistible force, overwhelming the devoted city, with all its inhabitants, 5000 in number. Of these, it is popularly related, that only one escaped. A Spanish corvette which lay at anchor, was lifted sheer over the walls of the fortress, and deposited a full mile inshore, at a spot still designated by a cross erected to commemorate the fact. All the other vessels in the harbor were sunk. The modern town of Callao stands at the distance of two miles from the site of the old town, of which not a vestige remains. It is popularly affirmed that in a clear day the ruins of the old town may still be seen beneath the waves; but travelers, whose imagination is not keener than their vision, have vainly strained their sight to discover a trace of the lost city.
No familiarity with earthquakes is sufficient to do away with their terrors. The Limanian who has known them from childhood, no sooner feels the first shock, than he rushes from his apartment, with the cry of "misericordia" upon his trembling lips, no less than the foreigner who has never before witnessed these convulsive throes of nature. The moment a shock is felt the Cathedral bell begins to toll, all the belfries in Lima take up the sound, and summon the affrighted population to their devotions. A change has been wrought even in the form of church service, by the ever-present apprehension of these convulsions: the word "famine" being omitted and "earthquake" inserted among the evils from which deliverance is implored. The very architecture of Lima—its houses of a singly story—its plastered upper walls, its cane roofs, its towers and steeples of stuccoed wicker work—is a perpetual prayer against an evil which no human foresight can avoid, and no mortal power avert, and in respect to which the utmost that man can do, is in some degree to mitigate its consequences.[Pg 610]
When I joined the Scorpion sloop of war, then (1810) on the West India station, there were a father and son among the crew whose names, as borne on the ship's books, were John Somers and John Alice Somers. The oddity in this country of giving a boy a female baptismal name had been no doubt jestingly remarked upon by those who were aware of it, but with the sailors the lad passed as Ally Somers. The father was approaching fifty, the son could not have been more than seventeen years of age. The elder Somers, who had attained to the rating of a boatswain, was a stern, hard, silent man, with a look as cold and clear as polished steel, and a cast-iron mouth, indicative of inflexible, indomitable firmness of will and resolution. The son, on the contrary, though somewhat resembling his father in outline of feature, had a mild, attractive, almost feminine aspect, and a slight graceful frame. I was not long in discovering that, obdurate and self-engrossed as the man appeared, the boy was really the idol-image in which his affections and his hopes were centred. His eye constantly followed the motions of the lad, and it appeared to be his unceasing aim and study to lighten the duties he had to perform, and to shield him from the rough usage to which youngsters in his position were generally subjected by the motley crews of those days. One day a strong instance in proof of this master-feeling occurred. Ally Somers some time previously, when on shore with a party dispatched to obtain a supply of water, had, during the temporary absence of the officer in command, been rather severely rope's-ended by one of the seamen for some trifling misconduct, and a few slight marks were left on the lad's back. The rage of the father, when informed of the circumstance, was extreme, and it was with difficulty that he was restrained from inflicting instant chastisement on the offender. An opportunity for partially wreaking his hoarded vengeance occurred about six weeks afterward, and it was eagerly embraced. The sailor who had ill-used young Somers was sentenced to receive two dozen lashes for drunkenness and insubordination. He was ordered to strip, placed at the gratings, and the punishment began. Somers the boatswain, iron or sour-tempered as he might be, was by no means harsh or cruel in his office, and his assistants, upon whom the revolting office of flogging usually devolved, influenced by him, were about the gentlest-handed boatswain's-mates I ever saw practice. On this occasion he was in another and a very different mood. Two blows only had been struck, when Somers, with an angry rebuke to the mate for not doing his duty, snatched the cat from his hand, and himself lashed the culprit with a ferocity so terribly effective, that Captain Boyle, a merciful and just officer, instantly remitted half the number of lashes, and the man was rescued from the unsparing hands of the vindictive boatswain.
Other instances of the intensity of affection glowing within the stern man's breast for his comparatively weak and delicate boy manifested themselves. Once in action, when the lad, during a tumultuous and murderous struggle in beating off a determined attempt to carry the sloop by boarding, chanced to stumble on the slippery deck, he was overtaken before he could recover himself, and involved in the fierce assault which at the forecastle was momently successful. I was myself hotly engaged in another part of the fight; but attention being suddenly called to the forepart of the ship by the enemy's triumphant shouts, I glanced round just in time to see the boatswain leap, with the yell and bound of a tiger, into the mêlée, and strike right and left with such tremendous ferocity and power as instantly to check the advancing rush. Our men promptly rallied, and the deck was in a few minutes cleared of every living foe that had recently profaned it. Ally Somers, who had received a rather severe flesh wound, and fainted from loss of blood, was instantly caught up by his father, and carried with headlong impatience below. When the surgeon, after a brief look at the hurt, said, "There is no harm done, Somers," the high-strung nerves of the boatswain gave way, and he fell back upon a locker, temporarily prostrate and insensible from sudden revulsion of feeling. Several times I was an unintentional auditor of scraps of conversation between the two while the lad was on the sick-list, from which I gathered that Ally was the sole issue of a marriage which had left bitter memories in the mind of the father; but whether arising from the early death of his wife, or other causes, I did not ascertain. Somers was, it appeared a native of the west of England, and it was quite evident had received a much better education than usually falls to individuals of his class.
At the close of the war Somers and his son were, with thousands of others, turned adrift from the royal service. Some months after my appointment to the command of the revenue-cutter, I chanced to meet the father in the village of Talton, about four miles out of Southampton, on the New Forest Road. He had, I found re-entered the navy, but chancing to receive a hurt by the falling of a heavy block on his right knee, had been invalided with a small pension, upon which he was now living at about a hundred yards from the spot where we had accidentally met. Ally, he informed me, was the skipper of a small craft, trading between Guernsey and Southampton. There was little change in the appearance of the man except that the crippled condition of his leg appeared to have had an effect the reverse of softening upon his stem and rugged aspect and temper. When paid off he was, I knew, entitled to a considerable sum in prize-money, the greater part of which he told me he had recently received.
About two months after this meeting with the father I fell in with the son. I was strolling at [Pg 611]about eleven in the forenoon along the front of the Southampton custom-house, when my eye fell upon a young man in a seaman's dress, busily engaged with three others in loading a cart with bundles of laths which had been landed shortly before from a small vessel alongside the quay. It was Ally Somers sure enough; and so much improved in looks since I last saw him, that but for a certain air of fragility—inherited probably from his mother—he might have been pronounced a handsome fine young fellow. The laths, upward of two hundred bundles, which he was so busily assisting to cart, he had brought from Guernsey, and were a very common importation from that island: Guernsey possessing the right of sending its own produce customs free to England, a slight duty, only tantamount to what the foreign timber of which the laths were made would have been liable to, was levied upon them, and this was ascertained by the proper officer simply measuring the length and girth of the bundles. This had been done, and the laths marked as "passed." It struck me that the manner of Ally Somers was greatly flurried and excited, and when he saw me approaching, evidently with an intention to accost him, this agitation perceptibly increased. He turned deadly pale, and absolutely trembled with ill-concealed apprehension. He was somewhat re-assured by my frank salutation; and after a few common-place inquiries I walked away, evidently to his great relief, and he with his sailors continued their eager work of loading the cart. I could not help suspecting that something was wrong, though I could not make up my mind to verify the surmise his perturbed and hurried manner excited. Once in a skirmish on shore his father, the boatswain, had saved my life by sending a timely bullet through the head of a huge negro who held me for the moment at his mercy. Besides I might be wrong after all, and I had no right to presume that the officer who had passed the laths had not made a sufficient examination of them. The flurry of the young man might arise from physical weakness and the severe labor he was performing in such hot weather. These reasons, or more truly these excuses for doing nothing, were passing through my brain, when I observed the hasty approach of the collector of customs himself toward the cart, followed by several of his subordinates. Young Somers saw him as quickly as I did, and the young man's first impulse, it was quite plain, was flight. A thought, no doubt, of the hopelessness of such an attempt arrested his steps, and he stood quaking with terror by the side of the cart, his right hand grasping for support at one of the wheel-spokes.
"One of you lend me a knife," said the collector, addressing the officers of customs.
A knife was quickly opened and handed to him: he severed the strong cords which bound one of the bundles of laths together, and they flew asunder, disclosing a long tin tube of considerable diameter, closely rammed with tobacco! All the other bundles contained a similar deposit; and so large was the quantity of the heavily-taxed weed thus unexpectedly made lawful prize of, that a profit, I was assured, of not less than £500 or £600 would have been made by the audacious smuggler had he succeeded in his bold and ingenious attempt. The ends of the bundles had been filled up with short pieces of lath, so that, except by the process now adopted, it was impossible to detect that the cargo was not bonâ fide what it had been declared to be. The penalties to which Somers had rendered himself liable were immense, the vessel also was forfeited, and the unfortunate young man's liberty at the mercy of the crown. He looked the very picture of despair, and I felt assured that ruin, utter and complete, had fallen upon him.
He was led off in custody, and had gone some dozen paces when he stopped shortly, appeared to make some request to the officers by whom he was escorted, and then turning round, intimated by a supplicatory gesture that he wished to speak to me. I drew near, and at my request the officers fell back out of hearing. He was so utterly prostrated by the calamity by which he had been so suddenly overtaken, that he could not for several moments speak intelligibly. I felt a good deal concerned for so mere a boy, and one too so entirely unfitted by temperament and nerve to carry through such desperate enterprises, or bear up against their failure.
"This is a bad business," I said; "but the venture has not, I trust, been made with your own or your father's money?
"Every penny of it," he replied, in a dry, fainting voice, "was our own. Father lent me all his prize-money, and we are both miserable beggars."
"What in the name of madness could induce you to venture your all upon a single throw in so hazardous a game?"
"I will tell you," he went on hurriedly to say in the same feeble and trembling tone; "I am not fitted for a sea-life—not strong, not hardy enough. I longed for a quiet, peaceful home ashore. A hope of one offered itself. I made the acquaintance of Richard Sylvester, a miller near Ealing. He is a good man, but griping as far as money is concerned. I formed an attachment for his eldest daughter Maria; and he consented to our union, and to taking me as a partner in his business, if I could pay down five hundred pounds. I was too eager to wait long; besides I thought that perhaps—but it boots not to speak of that now; I set more than life upon this cast; I have lost, and am now bankrupt of resource or hope! Will you break this news to my father, and see—" His remaining firmness gave way as the thought he would have uttered struggled to his lips, and the meek hearted young man burst into tears, and wept piteously like a girl. A number of persons were collecting round us, and I gently urged him to walk on to the custom-house. A few minutes afterward I left him there, with a pro[Pg 612] mise to comply with his request without delay.
I found John Somers at home, and had scarcely uttered twenty words when he jumped at once at the true conclusion.
"Out with it, sir!" exclaimed the steel-nerved man. "But you need not; I see it all. Ally has failed—the tobacco has been seized—and he is in prison."
Spite of himself his breath came thick and short, and he presently added with a fierce burst, while a glance of fire leaped from his eyes; "He has been betrayed, and I think I know by whom."
"Your suspicion that he has been informed against is very likely correct, but you will, I think, have some difficulty in ascertaining by whom. The custom-house authorities are careful not to allow the names of their informants to leak through their office-doors."
"I would find him were he hidden in the centre of the earth!" rejoined the ex-boatswain with another vengeful outcry which startled one like an explosion. "But," added the strong and fierce-willed man after a few moments' silence, "it's useless prating of the matter like a wench. We must part company at once. I thank you, sir, and will tell Ally you have called." I mentioned the other request made by his son. "That is a rotten plank to hold by," he said. "Ally's chance is over there, and it would be mere waste of time to call on the old man; his resolution is hard and unyielding as his own millstones. Maria Sylvester is gone with the five hundred pounds her father bargained for; and the girl's tears, if she shed any, will soon be dry. I warned Ally of the peril of steering his course in life by the deceptive light of woman's capricious smiles and vanities; but he, poor, flexile, gentle-minded boy, heeded me not. I may not longer delay: he will be anxious to see me. Good-day, sir."
The consequence which I chiefly feared came to pass, even more speedily than I had apprehended. It being impossible to liquidate the penalties incurred, Ally Somers was imprisoned as a crown debtor; and at that period, whatever may be the case now, revenue penalties could not be got rid of by insolvent-court schedules. The prospect of an indefinite term of imprisonment, with other causes of grief and depression, broke down the always fragile health of the prisoner, and he died, ere yet his youth was well begun, after about six months' confinement only.
The tidings were brought me by the old man himself. I was seated in the cabin of the Rose cutter when it was announced that John Somers was alongside in a boat, and wished to see me. I directed that he should be allowed to come aboard, and presently the old man, with despair visible in every line of his countenance, in every glance of his restless, flaming eyes, entered the cabin.
"I am come to tell you, sir, that Ally is dead."
"I was somewhat prepared for this bad news, Mr. Somers," I answered. "It's hard upon you, but it should be bravely borne with."
He laughed strangely. "To be sure, to be sure," he said, "that is wise counsel—very wise; but that which I want now more than wise counsel is ten pounds—ten pounds, which I shall never be able to repay."
"Ten pounds!"
"Yes: you may remember that I once saved your life. If that piece of service was worth the sum I have mentioned, you can now discharge the obligation. I have parted with every thing, and Ally's last prayer was to be buried beside his——Beside a grave, an early and untimely one, like his own, many miles away."
"I understand; it is a natural and pious wish, and you shall have the money."
"Thank you. The funeral over, I have but one more thing to do in life, and that is to assist you in securing Cocquerel while running one of his most valuable cargoes."
"Cocquerel, the Guernseyman you mean?"
"Ay, so he calls himself; but I fancy he at one time hailed from another port. He is the man who sold Ally's secret to the revenue-officers!"
"Are you sure?"
"As death! He was Ally's only confidant, and Ally's father is now in Cocquerel's confidence. It is but natural," added Somers, and a bitter, deadly sneer curled his ashy lips—"it is but natural, you know, that I should be eager to assist in pillaging a government which caged my son, and held him under its iron bars till life had fled. Cocquerel understands this, and trusts me fully; but that which he does not understand, know, or suspect," continued the fierce old man, sinking his voice to a whisper, and leaning forward with his face close to mine, "is that John Somers has found out who it was that sold his boy's life! Did he know that, and know me too, there would be sounder sleepers than he in these dark nights."
"What do you mean?"
"Nothing more, of course," he replied in a more checked and guarded tone, "than to retort the trick he played Ally something after his own fashion."
"That is a fair revenge enough, and I'll not balk you. Now, then, for your plan."
Various details were discussed, and it was settled that on that day-week Somers was again to communicate with me. He then took leave.
At the appointed time Somers returned, and appeared to be in high but flighty spirits. Every thing was, he said, arranged, and success all but certain. His scheme was then canvassed and finally agreed upon, and he again left the vessel.
The arrangement for the surprise and capture of Cocquerel was this:—That notorious smuggler intended running a large cargo on the coast of Dorsetshire, on the north of Portland, at a [Pg 613]place where the cliffs are high, precipitous, and abrupt, and at that time very inefficiently watched by the shore-force. Near the spot selected is or was a kind of cavern worn by the action of the sea in the chalky stratum, which at neap-tides was partially dry, and at the time of our enterprise would effectually conceal a boat from the observation of any one who did not actually peer in directly at its mouth. Cocquerel was to leave Guernsey the next day in a large boat, with two lug-sails, but chiefly depending for speed upon its sweeps. It was calculated that he would reach his destination about midnight. Somers had undertaken the duty of shore-signalman, and if danger were apprehended, was to warn the smugglers that hawks were abroad by burning a blue-light. The manner of running the cargo was to be this:—Somers was provided with a windlass and sufficient length of rope, with a kind of rope-cradle at the end of it, in which a man could sit, or a couple of kegs be slung, to reach the boat. The windlass he was to secure firmly at the edge of the cliff, and two or three of the men having been drawn up, other windlasses were to be fixed, by means of which it was calculated that in about half an hour the entire cargo would be safely carried off by the carts which Somers had undertaken to have ready on the spot. The signal for our appearance on the scene of action, the positive old man persisted, should be that agreed upon for the warning of the smugglers—the sudden ignition of a blue-light. This did not seem the cleverest possible mode of procedure; but as the cavern in which we were to conceal ourselves was but a few yards northward of the spot marked out for the landing, and Somers promised he would only give the signal when the smugglers were in full work, I had little fear that, if other accidents did not capsize our scheme, they would be able to escape us.
The next afternoon the largest boat belonging to the Rose was fully manned; and leaving the cutter quietly at anchor in the Southampton river just above Calshot, we pulled with the tide—for there was but a light air, and that favorable for the smugglers, not for us—to our hiding-place, which we reached about eight o'clock in the evening.
The hours crept very slowly and dismally away, amid the darkness and hoarse echoes and moanings of the cavern, into which the sea and wind, which were gradually rising, dashed and howled with much and increasing violence. Occasional peeps at my watch, by the light of a lantern carefully shaded seaward, warned us that ten, eleven, twelve, one o'clock had passed, without bringing the friends we so anxiously expected, and fears of ultimate disappointment were chilling us far more than the cold night-breeze, when a man in the bow of the boat said in a whisper that he could hear the dash of oars.
We all instantly listened with eager attention; but it was not till we had brought the boat to the entrance of the opening that the man's assertion was verified. There it was clear enough: and the near approach of a large boat, with the regular jerk of the oars or sweeps, was distinctly audible. The loud, clear hail of their shore-signalman, answered by the "All right" of the smugglers, left no doubt that the expected prey was within our grasp; and I had a mind to pounce upon them at once, but was withheld by a promise which I had been obliged several times to repeat, that I would not under any circumstances do so till the signal-flame sent its light over the waters.
As soon as the noise and bustle of laying in the sweeps, lowering the sails, and unstepping the masts, had subsided, we heard Somers hail the boat, and insist that the captain should come up before any of the others, as there was a difficulty about the carts which he alone could settle. The reply was a growl of assent, and we could hear by the click of the check to the cog-wheel of the windlass that Somers was paying out the rope. Presently Cocquerel was heard to get into the cradle I have spoken of, to which a line was fastened in order to steady his ascent from below. The order was given to turn away, and the renewed click, click, announced that he was ascending the face of the cliff. I could hardly comprehend this manœuvre, which seemed to indicate the escape of the man we were the most anxious to secure, and the order to shove off was just on my lips when a powerful blue-light flamed suddenly forth, accompanied by a fierce but indistinct shout, or roar rather, from Somers. The men replied by a loud cheer, and we shot smartly out; but having, to avoid a line of reef, to row in a straight direction for about a cable's length, the smugglers, panic-stricken and bewildered as they were, had time to get way upon their lugger, and were plying their sweeps with desperate energy before the revenue-boat was fairly turned in direct pursuit. The frantic effort to escape was vain, and so was the still more frantic effort at resistance offered when we ran alongside. We did not hurt them much; one or two were knocked down by the sailors' brass-butted pistols; and after being secured, they had leisure to vent their rage in polyglot curses, part French, part English, and part Guernsey patois, and I to look round and see what had become of Cocquerel.
The blue-light still shed a livid radiance all around, and to my inexpressible horror and dismay, I saw that the unfortunate man was suspended in the rope cradle, within about a fathom's length of the brow of the cliff, upon which Somers was standing and gazing at his victim with looks of demoniac rage and triumph. The deadly trap contrived by the inexorable old man was instantly apparent, and to Cocquerel's frenzied screams for help I replied by shouting to him to cut himself loose at once, as his only chance, for the barrel of a pistol gleamed distinctly in the hands of Somers.
"Lieutenant Warneford," cried the exulting maniac—he was nothing less—"I have caught this Cocquerel nicely for you—got him swing[Pg 614]ing here in the prettiest cradle he was ever rocked in in his life—Ha! ha! ha!
"Cut loose at once!" I again shouted; and the men, as terribly impressed as myself, with the horror of the wretched smuggler's position, swept the boat rapidly toward the spot. "Somers, if you shoot that man you shall die on the gallows."
"Cut himself loose, do you say, lieutenant?" screamed Somers, heedless of my last observation. "He can't! He has no knife—ha! ha! ha! And if he had, this pistol would be swifter than that; but I'll cut him loose presently, never fear. Look here, Jacques Cocquerel," he continued laying himself flat down on the cliff, and stretching his right arm over it till the mouth of his pistol was within a yard of Cocquerel's head, "this contains payment in full for your kindness to Ally Somers—a debt which I could in no other manner completely repay."
At this moment the blue-light suddenly expired, and we were involved in what by contrast was total darkness. We could still, however, hear the frantic laughter and exulting gibes of the merciless old man in answer to Cocquerel's shrieking appeals for mercy; and after a while, when the figures of the two men had become partially visible, we could distinguish the words, "One, two, three," followed by the report of a pistol, and a half minute afterward a dark body shot down the white face of the cliff, and disappeared beneath the waters!
The body of Cocquerel never reappeared, and the only tidings I ever heard of Somers were contained in the following paragraph which I read some years afterward in the "Hampshire Telegraph," a journal at that time published at Portsmouth:
"The body of an aged, wretched man was found frozen to death in the church-yard on Wednesday morning last, near two adjoining graves, one of which, that of Alice Maynard, recalls the painful circumstances connected with the sad story of the death of that ill-fated, and, as we believe, entirely innocent person. At the inquest holden on Friday, it was ascertained beyond a doubt that the deceased is John Maynard, who, after his wife's untimely death, assumed the name of Somers, and was, we believe, the person who shot a French smuggler, with whom he had quareled, at the back of the Isle of Wight, under somewhat peculiar circumstances, about seven years ago. He was buried in the grave that contains the body of his son, John Alice Maynard, which was interred there shortly before the commission of the homicide just alluded to. There has never been to our knowledge any regular investigation of that affair, but we believe that then, as before, Maynard's pistol was pointed by a frantic and causeless jealousy." [Plymouth Paper.]
There are several mistakes sufficiently obvious to the reader in this paragraph, but of the main fact that John Somers, alias Maynard, perished as described in the Devonshire journal, there can be no reasonable doubt.
BY F. SOMNER MERRYWEATHER.
Some years ago there lived in Marseilles an old man of the name of Guyot; he was known to every inhabitant, and every urchin in the streets could point him out as a niggard in his dealings, and a wretch of the utmost penury in his habits of life. From his boyhood, this old man had lived in the city of Marseilles; and, although the people treated him with scorn and disgust, nothing could induce him to leave it. When he walked the streets he was followed by a crowd of boys, who, hating him as a grasping miser, hooted him vociferously, insulted him with the coarsest epithets, and sometimes annoyed him by casting stones and filth at his person. There was no one to speak a kind word in his favor, no one to bestow an act of friendship, or a nod of recognition upon Guyot. He was regarded by all as an avaricious, griping old miser, whose whole life was devoted to the hoarding up of gold. At last this object of universal scorn died, and it was found that, by his parsimony, he had amassed an ample fortune. What was the surprise of his executors, on opening his will, to find these remarkable words: "Having observed, from my infancy, that the poor of Marseilles are ill-supplied with water, which can only be procured at a great price, I have cheerfully labored the whole of my life to procure for them this great blessing, and I direct that the whole of my property shall be expended in building an aqueduct for their use!"
When it was proposed to build Bethlehem Hospital, many benevolent individuals volunteered to solicit contributions by calling upon the inhabitants of London. Two of these gentlemen went to a small house in an impoverished neighborhood; for the pence of the poor were solicited as well as the pounds of the rich. The door was open, and, as they drew nigh, they overheard an old man scolding his female servant for having thrown away a match, only one end of which had been used. Although so trivial a matter, the master appeared to be much enraged, and the collectors remained some time outside the door, before the old man had finished his angry lecture. When the tones of his voice were somewhat subdued, they entered, and, presenting themselves to this strict observer of frugality and saving, explained the object of their application; but they did not anticipate much success. The miser, however, for such he was reputed in the neighborhood, no sooner understood their object, than he opened a closet, and bringing forth a well-filled bag, counted therefrom four hundred guineas, which he presented to the astonished applicants. They expressed their surprise and thankfulness, and could not refrain from telling the old gentleman that they had overheard his quarrel with his domestic, and how little they expected, in consequence, to have met with such munificence from him. "Gentlemen," replied the old man, "your surprise is occasioned by my care of a thing of such little consequence: but I [Pg 615] keep my house, and save my money in my own way; my parsimony enables me to bestow more liberally on charity. With regard to benevolent donations, you may always expect most from prudent people who keep their own accounts, and who pay attention to trifles."
Audley was a celebrated miser of the time of the Stuarts; he amassed his wealth during the reign of the first Charles, and flourished amazingly under the protectorate of Cromwell. Audley was originally a clerk, with only six shillings a week salary, and yet out of this scanty sum he managed to save more than half. His dinner seldom cost him any thing, for he generally made some excuse to dine with his master's clients; and, as to his other meals, a crust of bread or a dry biscuit was regarded as fare sufficient after an ample dinner. In one circumstance he was somewhat different from other misers: he was clean, if not neat, in his outward appearance. But he was thus scrupulous in his apparel from principle; for Audley often asserted, that, to be thrifty, it was necessary to pay some respect to such matters. He was remarkably industrious, even when a young man. At an age when others were seeking pleasure, he was busy in lending out, and increasing his early savings. He was always ready to work when the usual hours of business were over, and would willingly sit up the whole night to obtain some trifling remuneration. He was never above soliciting trifles, and touching his hat to his master's clients. So rigid was he in his economy, and so usurious in his dealings, that in four years, during which time, however, he had never received more than a salary of six or eight shillings a week, he managed to save and amass five hundred pounds. The salary of the remaining years of his apprenticeship he sold for sixty pounds, and after a while, having made up six hundred pounds in all, he lent the whole to a nobleman for an annuity of ninety-six pounds for nineteen years, which annuity was secured upon property producing eight hundred a year. The nobleman soon died, and his heir neglected to pay the annuity. Audley had execution upon the property, and by legal trickery, in which he was well versed, he managed to obtain, in the way of fines and forfeitures, about four thousand pounds' profit upon his original six hundred. His master being one of the clerks of the Compter, Audley had many opportunities of practicing his disreputable cunning, and of obtaining vast sums by deluding insolvent debtors, and in deceiving their creditors. He would buy bad debts for a mere trifle, and afterward compound with the poor insolvent. One instance of his avarice and villainy is so curious, that we can not refrain from giving the anecdote to our readers. A tradesman, named Miller, unfortunately got into arrears with his merchant, whose name was White. Many fruitless applications were made for the debt, and at last Miller was sued by the merchant for the sum of two hundred pounds. He was unable to meet the demand, and was declared insolvent. Audley goes to White, and offers him forty pounds for the debt, which the merchant gladly accepts. He then goes to Miller, and undertakes to obtain his quittance of the debt for fifty pounds, upon condition that he entered into a bond to pay for the accommodation. The drowning man catches at a straw, and the insolvent, with many protestations of thanks, eagerly signs a contract which, without consideration, he regarded as one so light, and so easy in its terms, as to satisfy him that the promptings of benevolence and friendship could only actuate his voluntary benefactor. The contract was, that he should pay to Audley some time within twenty years from that time, one penny progressively doubled, on the first day of twenty consecutive months; and, in case he failed to fulfill these easy terms, he was to pay a fine of five hundred pounds. Thus acquitted of his debt of two hundred pounds, Miller arranged with the rest of his creditors, and again commenced business. Fortune turned, and he participated liberally in her smiles. Every month added largely to his trade, and at last he became firmly established. Two or three years after signing the almost forgotten contract, Miller was accosted one fine morning in October by old Audley, who politely demanded the first installment of the agreement. With a smile, and many renewed expressions of thankfulness, the hopeful tradesman paid his penny. On the first of the succeeding month, Audley again called, and demanded twopence, and was as politely satisfied as before. On the first of December, he received a groat; the first of February, one shilling and fourpence. Still Miller did not see through the artifice, but paid him with a gracious smile; perhaps, however, there was something cynical in the look of Audley as he left the shop this time, for the poor tradesman's suspicions were aroused, and he put his pen to paper, as he ought to have done years before, to ascertain the amount of his subsequent payments. Reader, what think you would have been the amount of the payment due on the first of the twentieth month? What sum, think ye, the little penny had become? No less than two thousand one hundred and eighty pounds! And what was the aggregate sum of all these twenty monthly payments? Why, the enormous sum of four thousand three hundred and sixty-six pounds, eleven shillings, and threepence? It sounds incredible; but, if you think it a fable, do as Miller did, and reckon for yourselves. Of course Miller refused the payment of his bond, and forfeited five hundred pounds by the benevolence and charity of the miser.
Vandille is one of the most remarkable characters, as a miser, that is to be found among the eccentric biographies of France. His riches were immense, and his avarice and parsimony extreme. He hired a miserable garret in one of the most obscure parts of Paris, and paid a poor woman a sou a day to wait upon him. Excepting once a week, his diet was never varied; bread and milk for breakfast; the same for dinner, and the same for supper, all the week round. On a Sunday he ventured to indulge in a glass of sour wine, and he strove to satisfy the compunctions [Pg 616]of conscience by bestowing, in charity, a farthing every Sabbath. This munificence, which incurred an expenditure of one shilling and a penny per annum, he carefully noted down; and just before his death he found, with some degree of regret, that during his life he had disbursed no less than forty-three shillings and fourpence. Forty-three shillings and fourpence! prodigious generosity for the richest man in France! Vandille had been a magistrate at Boulogne, and while in that office he partly maintained himself, free of cost, by constituting himself milk-taster general at the market. He would munch his scrap of bread, and wash it down with these gratuitous draughts. By such parsimonious artifices, and a most penurious course of life, he succeeded in amassing an enormous fortune, and was in a position to lend vast sums of money to the French government. When he had occasion to journey from Boulogne to Paris, he avoided the expence of coach-fare by proceeding on foot; and, lest he should be robbed, he never carried more than threepence in his pocket, although he had a distance of a hundred and thirty miles before him. If he found this sum insufficient, he would profess poverty, and beg from the passengers on the road a trifle to help him on. In the year 1735, Vandille, the miser, was worth nearly eight hundred thousand pounds! He used to boast that this vast accumulation sprang from a single shilling. The winter of the year 1734 had been very cold and bitter, and the miser felt inclined to purchase a little extra fuel in the summer time, to provide, to some extent, against the like severity in the ensuing winter. He heard a man pass the street with wood to sell; he haggled for an unconscionable time about the price, and at last completed his bargain, at the lowest possible rate. Avarice had made the miser dishonest, and he stole from the poor woodman several logs. In his eagerness to carry them away, and hide his ill-gotten store, he overheated his blood, and produced a fever. For the first time in his life, he sent for a surgeon. "I wish to be bled," said he; "what is your charge?" "Half a livre," was the reply. The demand was deemed extortionate, and the surgeon was dismissed. He then sent for an apothecary, but he was also considered too high; and he at last sent for a poor barber, who agreed to open the vein for threepence a time. "But, friend," said the cautious miser, "how often will it be requisite to bleed me?" "Three times," replied the barber. "Three times! and pray, what quantity of blood do you intend to take from me at each operation?" "About eight ounces each time," was the answer. "Let me see," said the possessor of three-quarters of a million, "that will be ninepence; too much; too much! I have determined to go a cheaper way to work; take the whole twenty-four ounces at once, and that will save me sixpence." The barber remonstrated, but the miser was firm; he was certain, he said, that the barber was only desirous to extort an extra sixpence, and he would not submit to such scandalous imposition. His vein was opened, and four-and-twenty ounces of blood were taken from him. In a few days, Vandille the miser was no more. The savings of his life, the wages of his vice and avarice, he left to the King of France.
A similar anecdote is related of Sir William Smyth, of Bedfordshire. He was immensely rich, but most parsimonious and miserly in his habits. At seventy years of age he was entirely deprived of his sight, unable to gloat over his hoarded heaps of gold; this was a terrible affliction. He was persuaded by Taylor, the celebrated oculist, to be couched; who was, by agreement, to have sixty guineas if he restored his patient to any degree of sight. Taylor succeeded in his operation, and Sir William was enabled to read and write, without the aid of spectacles, during the rest of his life. But no sooner was his sight restored, than the baronet began to regret that his agreement had been for so large a sum; he felt no joy as others would have felt, but grieved and sighed over the loss of his sixty guineas! His thoughts were now how to cheat the oculist; he pretended that he had only a glimmering, and could see nothing distinctly; for which reason, the bandage on his eyes was continued a month longer than the usual time. Taylor was deceived by these misrepresentations, and agreed to compound the bargain, and accepted twenty guineas, instead of sixty. Yet Sir William was an old bachelor, and had no one to care or provide for. At the time Taylor attended him, he had a large estate, an immense sum of money in the stocks, and six thousand pounds in the house.
Many years ago, there lived in a large, cheerless, and dilapidated old house in St. Petersburg, a wretched miser. He confined himself to one room, and left the rest of the rambling edifice to moulder into ruin; he cared for no comfort, and deprived himself even of those things which the poorest regard as the necessaries of life; he seldom lit a fire to repel the dampness, which hung on the walls of his solitary chamber, and a few worthless objects of furniture was all that the room contained. Yet to this singular being the Empress Catherine the Second owed a million of rubles. His cellar, it was said, contained casks full of gold, and packages of silver were stowed away in the dismal corners of his ruinous mansion. He was one of the richest men in Russia. He relied for the safety of his hoards upon the exertions of a huge mastiff, which he had trained to bark and howl throughout the night, to strike terror into the hearts of thieves. The miser outlived the dog; but he disliked to part with any portion of his treasure in the purchase of another cur, and he resolved to save his money by officiating as his own watch-dog. Every morning, and every evening, would that insane old man wander about his dismal habitation, barking and howling in imitation of his recent sentinel.
A miser of the name of Foscue, who had amassed enormous wealth, by the most sordid parsimony, and the most discreditable extortion, was requested by the government to advance a [Pg 617]sum of money, as a loan. The miser, to whom a fair interest was not inducement sufficiently strong to enable him to part with his treasured gold, declared his incapacity to meet this demand; he pleaded severe losses, and the utmost poverty. Fearing, however, that some of his neighbors, among whom he was very unpopular, would report his immense wealth to the government, he applied his ingenuity to discover some effectual way of hiding his gold, should they attempt to institute a search to ascertain the truth or falsehood of his plea. With great care and secrecy, he dug a deep cave in his cellar; to this receptacle for his treasure he descended by a ladder, and to the trap-door he attached a spring lock, so that, on shutting, it would fasten of itself. By-and-by the miser disappeared; inquiries were made; the house was searched; woods were explored, and the ponds were dragged; but no Foscue could they find; and gossips began to conclude that the miser had fled, with his gold, to some part where, by living incognito, he could be free from the hands of the government. Some time passed on; the house in which he had lived was sold, and workmen were busily employed in its repair. In the progress of their work they met with the door of the secret cave, with the key in the lock outside. They threw back the door, and descended with a light. The first object upon which the lamp was reflected was the ghostly body of Foscue the miser, and scattered around him were heavy bags of gold, and ponderous chests of untold treasure; a candlestick lay beside him on the floor. This worshiper of Mammon had gone into his cave, to pay his devoirs to his golden god, and became a sacrifice to his devotion!
As it is very possible that many of our readers, who have listened with delight to the pleasant chirp of the cricket, may be ignorant of its habits and history, we purpose in the present article giving some account of them.
The cricket belongs to the same family as the grasshopper and the locust, and all three are distinguished by having four wings, with the first pair leathery throughout, overlapping at the edges only, and concealing the second pair, which are folded lengthwise.
There are three descriptions of cricket common in Great Britain—the house-cricket, the field-cricket, and the mole-cricket; of these the two first are very similar, but that the former is of a somewhat yellow shade, and the latter rather brown. Their heads are very large in proportion to their bodies, and are round. They are furnished with two large eyes and three small ones, of a light yellow color, placed rather high in their heads. The female has a hard, long spine at the extremity of her body, thick at the end, and composed of two sheaths, which contain two laminæ; this implement is made use of by the cricket to enable her to sink and deposit her eggs in the ground. Their hinder feet are much longer than the others, and serve them to leap. Unlike mice, crickets are oftenest to be found in new houses, as they like the damp, soft mortar, which saves them much trouble, when they feel inclined to burrow and mine between the joints of the bricks or stones, and to open communications from one room to another. They are very fond of warmth, and their favorite place of resort is by the kitchen fire. In the warm, long days of summer, however, they often venture out, and appear to enjoy the heat of the mid-day sun, as may be supposed from the heated atmosphere they inhabit. Crickets are a thirsty race, and, indeed, are so anxious to satisfy their inclination, that they are constantly found drowned in pans of water, milk, &c. They will even destroy damp clothes for the sake of their moisture, and woe be to the wet woolen stockings or aprons hung to dry within their reach. But the cricket is hungry as well as thirsty, and will eat voraciously any crumbs of bread, scummings of pots, &c., which happen to fall in their way.
Crickets are, in general, very inactive insects, and seldom use their wings, except when they are about to migrate from one habitation to another. The time they generally select for an excursion of this kind is the dusk of a summer evening, when they fly out of the windows, and over the neighboring roofs, no one knows whither; and this habit will account for the sudden manner in which they often disappear from an old haunt, as well as for their equally mysterious appearance in a new one—why they left and why they came being equally unaccountable. When flying, they move in wavelike curves, like woodpeckers, opening and shutting their wings at every stroke; they are, therefore, always either rising or falling.
They often increase to such a degree as to become a perfect nuisance in a house, and then they have to be destroyed, either by gunpowder being discharged into their haunts, or else by drowning, like wasps. Crickets are not fond of light; and on a candle being brought into a room where they are running about, they will just give two or three shrill chirps, as if to warn their companions of impending danger, and then quickly retreat to their lurking-holes for safety. Many strange ideas are entertained concerning these insects. Some imagine that they bring good luck to any house where they take up their abode, and will not on any account allow them to be killed. It is imagined, too, that they can prognosticate events, such as the death of a near relative, or the return of an absent lover. In Spain, crickets are held in such estimation, that they are kept in cages like birds.
The field-cricket is such a shy and timid insect, that it is exceedingly difficult to make its acquaintance, as it cautiously rejects all advances, and prudently retires backward into its burrow, where it remains until it fancies that all danger is over. In France, children amuse themselves by hunting the field-cricket. This they do by putting into its hole an ant, secured by a long [Pg 618]hair; and, as they slowly draw it out again, it is always followed by the hapless cricket, which ventures out to know the reason of this unwarrantable intrusion into its domicile. But Pliny tells us of a more easy way of capturing them. He says, that, if we thrust a long slender piece of stick into its burrow, the insect would immediately get on it for the purpose of discovering the cause of the disturbance. From this fact arose the old proverb, "stultior grillo," or "more foolish than a cricket," applied to any one who upon light grounds provokes his enemy, and falls into the snare laid to entrap him.
It is strange that although the field-cricket is furnished with a curious apparatus of wings, and provided with long legs behind, and brawny thighs for leaping, like grasshoppers, yet they never make use of them when we would imagine they were most wanted, but suffer themselves to be captured without making any struggle for liberty, crawling along in a dull, shiftless manner. They satisfy their hunger with such herbs as happen to grow near their burrows, and rarely stir from home. They generally sit at the entrance of their caverns, and chirp away night and day, from the middle of May to the middle of July. And who does not love their pleasant song, shrill though it be? But harsh sounds are not necessarily disagreeable. Much depends on the association of ideas; and the summer song of the field-cricket recalls to us our childhood's days, long since, it may be, gone by, and fills our mind with happy thoughts of our wanderings in quest of them, when all nature appeared bright, and gay, and joyous. In very hot weather, the field-cricket is most vigorous, and then the hills echo their notes, while the evening breeze carries them to a great distance, making their melody heard in the stilly hours of night.
About the 10th of March, the crickets appear at the mouth of their cells, which they then open for the approaching summer. At that time they are all in the pupa state, and have only the rudiments of wings, which lie under a skin or coat, which must be cast off before the insect arrives at maturity. This circumstance makes naturalists believe that they seldom live a second year. They cast their skins in April, and great quantities of them may be seen at the mouth of their cells. Their eggs are long and narrow, of a yellowish color, and covered with a very tough skin. The male field-cricket has a golden stripe across the shoulders of its shining coat. The female is of a brighter color, and, besides this, may be distinguished by the long, sword-shaped instrument for laying her eggs beforementioned.
They always live singly, male or female, as the case may be; and when the males meet they fight fiercely. Once, when Mr. White of Selborne placed some in a stone wall, where he was anxious to have them settle, although they appeared distressed at being removed to a new habitation, yet the first that got possession of the chinks, seized any that intruded on them, with their powerful jaws, furnished with a row of serrated fangs, formed something like the shears of a lobster's claw. If field-crickets are confined in a paper cage, placed in the sun, and supplied with plants well moistened with water, they will thrive as well as in their more natural resorts, and become so merry and noisy as to be troublesome to any one sitting in the same room. Should the plants become dry, they will soon die.
The mole-cricket, so called from the similarity of its habits to those of the mole, is an ugly, but very curious-looking insect. Unlike the house and field-cricket, its head is very small, and of an oblong form. But the chief peculiarity of the insect is its two forefeet or legs—screws, as they are sometimes not very inappropriately called. They are very large and flat, ending outwardly in four large serrated claws, and inwardly with only two. The four claws point somewhat obliquely outward, that being the direction in which the insect digs, throwing out the earth on each side of its course. How wonderfully does He, who "preserves both man and beast," provide for the wants of each insect! The breast of the field-cricket is formed of a thick, hard, horny substance, which is further strengthened within by a double framework of strong gristle, in front of the extremities of which the shoulder-blades of the arm are firmly pointed—a structure evidently intended to prevent the breast from being injured by the powerful muscular motion of the arms in digging.
While the house and field-cricket rejoice in dry and sunny banks, or revel in the glowing heat of a kitchen-hearth, the mole-cricket haunts damp meadows and marshy grounds by the river banks, where they perform all their most curious functions. They burrow and work under ground, like the mole, but raise a ridge as they proceed, instead of throwing up hillocks. They are very fond of taking up their abode in gardens situated near canals, but they are always unwelcome visitors, as they disturb the walks in making their subterranean passages, and besides this, they devour whole beds of cabbage, legumes, and other vegetables, and sometimes even commit great ravages among flowers.
The nest the female mole-cricket constructs for her eggs is exceedingly curious, and well repays the trouble of hunting for them. They are about the size of an egg, neatly smoothed and rounded inside. The way leading to them is through a variety of caverns and winding passages. Within the inner chamber, or nursery, are deposited about a hundred eggs, of a dirty yellow color, enveloped in a tough skin. Sometimes, however, they are of a lightish green, and translucent and gelatinous. They are not placed deep under ground, but near the surface, so as to be within the genial influence of the sun. The mound of fresh-moved earth, within which they are carefully deposited, looks very like that raised by ants.
Like the eggs and young of most other insects those of the mole-cricket are exposed to depredation, especially from the black beetle, which burrows in similar localities. The anxious and provident mother, therefore, does not think her [Pg 619]progeny secure, until she has defended her nest in the manner of a regularly fortified town, with ramparts, intrenchments, and covert-ways. "In some part of these defenses she posts herself as an advanced guard; and, should a beetle venture to intrude within her fortifications, she pounces on him, and, giving no quarter, kills him without mercy." When disturbed out of their nests, the mole-crickets appear dull and helpless; and during the day time they seldom use their wings, but, as night advances, they become very sprightly, and often wander on long excursions. When the weather is very fine, about the middle or end of April, as the evening draws on, they amuse themselves by making a low, dull, jarring noise, which is not very unlike the chattering of the fern-owl or goat-sucker, and which they continue without intermission for a long time.
Anatomists tell us, that all crickets, when carefully examined, are found to possess three stomachs; a small one; behind that, a large one, wrinkled and furrowed inside; and lower down, a third. They, therefore, think it not improbable that they chew the cud, or ruminate, like the cow and many other quadrupeds. They are not, however, satisfied entirely to subsist on vegetable diet, but prey upon underground insects, and sometimes even undermine plants to get at them.
Before taking leave of the cricket family, it may not be amiss to mention that, in various parts of England, they are called fern-crickets, churr-worms, and wee-churrs—all very appropriate names.
"Do you know, with any certainty, in what language Adam declared his love to Eve?" inquired I, one day, from a philologist of my acquaintance. I put my question with so much earnestness, that he answered, quite seriously, "Yes, to be sure, he made his declaration of love in precisely the same language as that in which she accepted him."
A profound answer! The only pity is, that I was not much wiser for it. But it is altogether a pity—a very great pity—that we know so little about the love-makings before the Flood. If any body could meet with a love-story of that date, it would have more freshness and novelty in it than can be found in any of our modern novels. And really that love-making in the morning of time, in the groves of Paradise, it must have been quite out of the common way!
Ah, there breathes still in this world—several thousand years old though it be—a gentle gale of the spring-time of Paradise, through the life of every man, at the moment when he says, "I love! I am beloved!"
Yes. It thrills through every happy son of Adam at the moment when he finds his Eve. But Adam himself was, in one respect, better off than any of his sons; for as there was only one Eve, he could make no mistake; neither could she, on her side, have either choice or repentance. But we—our name is Legion, and it is not easy for us to discover who, in the swarm of the children of Adam, is the right partner for us. If every one would seriously confess his experience in this respect, it would no doubt be both instructive and amusing. And as I know no other way in which I can instruct or amuse the world, I will now sincerely confess what mistakes I made when I searched for my Eve, whom I first adored in the person of Rose Ervan.
I want words to describe her. She had fascinated me when I was but a cadet; she bewitched me before I had left the fourth class. And, of a truth, there never did exist a young lady more dangerous to a youth of lively imagination. Her coquetry was so natural, so mixed with goodness and childish grace, that it was impossible to regard it as any thing more than the most angelic innocence. At the Military Academy, I saw in my books her name and nothing besides. If I drew plans of fortifications and fortresses, Rose stood in the middle of my circles and quadrants, and the only line that I perceived clearly was the road that led to her home: the verdurous Greendale.
Greendale was a cheerful place, where there were always guests and parties. And when the young people wished to have an excursion on the water, or any other entertainment, I it was who always planned every thing, and proposed it to the old baroness, the mother, for whom all the children entertained a very considerable and wholesome respect. On these occasions she used to say, "My dear sir, if you are with the children, I will permit it; for I trust to you, and I know that you will take care of them."
"Yes, to be sure," I replied, though the truth was, I could not take care of myself; and never took notice of any body, or of any thing, excepting Rose.
Many a one was fascinated just as I was fascinated; but I persuaded myself that I was the only lucky fellow who had her preference. Once I was terribly jealous. A certain Mr. T. (a professor of languages, I believe) came to Greendale, played, sung, and chattered French; and immediately Rose forgot me, to chat, and play, and sing with Mr. T., making herself altogether as charming to him as she had hitherto been to me. I was desperate; went away over meadows and fields; saw neither hedges nor gates, stumbled into ditches and brooks, and reached home furious as a blunderbuss. But, behold! Mr. T. was gone, and Rose was again charming to me, and I was instantly as much under her fascination as ever, fully convinced that it was all my fault, and that I was a Turk, a monster—nay, quite an Othello of jealousy.
After I had sighed and burned a considerable time, I made up my mind to proceed to the declaration of my love. It is true I was still very young, not three-and-twenty; but I thought myself quite old enough, being a lieutenant, the son of a father who always spoke of "my wife" as the greatest happiness of his life; besides which I had derived from my home the most beautiful [Pg 620]impressions of domestic life. Hence I always represented to myself the highest good in the world under the image of "my wife."
Having duly considered the various forms of love proposals, I went one fine day to Greendale, carrying with me, and near to my heart, a moss-rose in a garden-pot. The roads were execrable, and I was well-nigh shaken to pieces; but the smile of my beautiful Rose would, I was well assured, reward me for all my trouble. In imagination I heard myself constantly asseverating "I love you!" and heard her as constantly replying, "I love you!" As regarded our domestic establishment, I had not as yet thought as much about it as one of our favorite bards, who, before he married, provided himself with a cask of flour, a coffee-pot, and a frying-pan. I thought only of "a cottage and a heart." I saw around my cottage multitudes of roses, and within it, my Rose and myself. As for every thing else, all would be provided for by my excellent father.
As soon as I arrived at Greendale, I found there two other gentlemen quite as much in love, and quite as much enchanted by the fascinating young lady, as I was. I pitied the unfortunate youths, because they had infatuated themselves with the hope of a happiness which no one, I believed, should aspire to but myself. We were all old acquaintances; and, as it is not our habit to put our light under a bushel, I was determined to give my rivals a little hint of my advantageous prospects.
I raised, therefore, somewhat the vail which had concealed my modest confidence. But then came curious revelations! My rivals, animated by my example, lifted likewise the vail from their respective prospects; and, behold, we all three stood in precisely the same position. We all sighed; we all hoped; we all had souvenirs that we kissed in secret; and they all were, as it were, serpents, and bit their own tails.
At these unexpected revelations we all exclaimed, "Ah!" and left Greendale together, each going his own way. My father was a little surprised to see me return so soon.
"My dear Constantine," said he, "I thought you intended to stay at Greendale a much longer time?"
"Yes," I replied with a pensive air, taking at the same moment, a large mouthful of bread-and-butter; "yes; but I altered my mind when I got there."
With this the conversation ended, and the charm was broken, once and forever. But with it was also broken one link out of the rosy time of my life. I began to regard all roses whether real or typified, with angry and suspicious looks, and to speak of the "illusions of life," and of "giving them up," &c., &c. I made a solemn vow with myself that the next object of my affections, the next choice I would make for "my wife," should, in all respects, be the very reverse of the fascinating but traitorous Rose. I had been deceived, as I imagined, by the poetry of life; now I would keep to the sober prose.
Ah! in what a noble form did my new ideal present herself to my eyes, as one evening I entered the hospitable saloon of Mrs. A., the wife of the celebrated judge. Abla, her daughter, stood ready to officiate at the tea table; her features, her figure, her manners were dignified and full of propriety. She looked like personified Truth, in contra-distinction to the fantastical bewitching Rose. I instantly fell in love with this beautiful image of Minerva, and thought of "my wife."
Abla, however, seemed only to think of the tea, and looked neither to the left nor the right. When tea was poured into all the cups she slowly turned her splendid head, and I heard, at the same moment, a bass-voice exclaim, "Sundholm!"
Ah, Heavens! was that her voice? Was it not rather that of the Angel of Judgment, who, in the middle of Mrs. A.'s evening party, summoned the sinner Sundholm to hear his final doom? I could have believed any thing rather than that such a voice could issue from the beautiful lips of Abla. But, when I beheld Sundholm advance to the tea-table and receive the tea-cups on his tray, I saw that the resounding bassoon-voice belonged to no other than the sweet lady whom I had just adored, and whom I had, in my heart, already called "my wife."
It required some little time before I could reconcile my mind on this point. "Sundholm!" sounded awfully through my ears for many a long hour. I began to reason on the subject. If, said I, Nature has bestowed a bass-voice on this beautiful young lady, is it not noble and excellent of her not to try to conceal or embellish it? Does it not prove her love of truth; her strength of character, and her greatness of soul? How easy it would have been for her to cry "Sundholm!" in falsetto; but she would not be false, even in this! Not willing to assume a disguise, even for the sake of winning admiration, she summons Sundholm in the voice which God has given her. Is there not something grand in all this? One who thus calls out "Sundholm," will not deceive an honest fellow with hollow words or pretended feeling, but will play an open game with him, and let him understand the truth at once.
I was introduced to the handsome Abla. There was no denying that the voice was not fine; but, when you were accustomed to it, it ceased to be so very disagreeable; besides which, her words were so simple and candid, and her face so beautiful, that by-and-by I was completely dazzled. My ears crept, as it were, into my eyes, and gazing, day after day, on Abla's faultless profile, I was conveyed at once into the realms of love, and, ravished by my sense of sight, asked Abla if she would be "my wife." She answered "Yes," with a force of utterance that nearly frightened me. We were betrothed, and the nearer I gazed on her fine profile the more I was satisfied. This, however, did not last very long.
The period of betrothal is a very singular one; a period of halfness and incompleteness; nevertheless it is a sensible institution—when it does [Pg 621]not continue too long. It is the prelude to a union that nothing but death ought to dissolve; and, if it should appear impossible to execute harmoniously the duet which has now commenced, there is yet time to break it off calmly.
The first discord that disturbed the duet between "my wife elect" and myself, was—not her deep voice, but, alas! precisely that very thing which, at first, had reconciled me to it; viz., her love of truth, or rather, I should say, her unmerciful way of uttering it.
That we all are sinners in thought, word, and deed, is a matter of fact, and nobody was more willing to admit it than myself; but to be reminded of it every moment by one's best friend is by no means agreeable; nor does it do any good, especially when the plain-speaking friend never fancies himself, or herself, capable of sinning, or being faulty in the slightest degree. And the worst of it was, that apparently Abla had no faults. Ah! if she had had but one; or, better still, if she would but have admitted the possibility of it, then I should have been ready to throw myself at her feet! But she was in temper and in character as unimpeachable, as regular, as perfect, as she was in figure; she was so correct and proper, that, sinner as I was, it drove me into a rage. I felt that Abla's righteousness, and especially her mode of educating me, would, in time, make me a prodigious sinner; more particularly, as she would never yield to my wishes. It dawned upon me, before long, that her self-righteousness and want of charity to others was, indeed, one of the greatest conceivable faults. One fine day, therefore, I told her my mind, in good earnest terms, and the following duet occurred between us:
She. I can not be otherwise than I am. If you do not like me, you can let it alone.
I. If you will not be amiable toward me, I must cease to love you.
She. That is of no consequence. I can go my own way by myself.
I. So can I.
She. Good-by, then, sir.
I. Good-by, Miss A.
"Thank Heaven, it was not too late!" thought I to myself, as, after my dismissal, I hastened to my little farm in the country. Although this abrupt termination of my second love affair caused but little pain to my heart, I felt considerable mortification, and a secret hostility sprung up in my soul toward the whole female sex. It happened, however, very luckily for me, that while I remained in this state of mind I met with one of my neighbors who was precisely in the same condition. He had been for some time divorced from a wife with whom he had lived very unhappily, and he drove about in his sulky, upon which he had had a motto inscribed in golden letters:
The sentiment struck me as very excellent; and my neighbor and I often met, and agreed admirably in our abuse of the ladies. In the mean time, I occupied myself with books and agriculture.
I have a great esteem for books, and I bow myself to the dust before learning, but, I know not how it is, further than that I can not go; esteem and veneration I feel, but assuredly my affections never grew in that soil. My love for agriculture took me forth into Nature, and Nature is lovely. But Adam was uneasy in Paradise, and did not wake to life and happiness until Eve came; and I, who did not possess a paradise, found myself very lonely and melancholy at "Stenbacke." Trees, after all, are wooden and dull things, when we crave for human sympathies; and echo, the voice of the rocks, is the most wearisome voice I know. No! heart to heart, eye to eye, that is the life; and to live together, a happy and healthy rural life, to work for the happiness of those who depend upon us—to regulate the home, to live, to think, to love, to rejoice together. Ah! "my wife" still stood vividly before my imagination.
My experience in the realms of love had, however, made me suspicious. I feared that I could never be happy, according to my ideas of happiness, which my neighbor-friend characterized as "reposing in the shade of a pair of slippers." I was in low spirits; and accordingly, one day, after having finished the last of six dozen of cigars, and quarreled with my neighbor, who bored me with his everlasting and doleful tirades against the ladies, I set off in my own sulky to amuse myself by a drive.
I drove a considerable distance to the house of an old friend, who had been a fellow-student with me at the Military College at Carlberg, and who had often invited me to visit him. He was now married, and was, in fact, the father of eight children. A large family, I thought, at first; but not one too many, said I to myself, after a single day spent in this family, which had given me the impression of a heaven upon earth.
The mistress of the house, the wife and mother, was the silent soul of all. "It is she—it is she, who is my happiness!" said the fortunate husband; but she said, "It is he! it is he!"
"My dear friend," said I to him one day, "how have you managed to be so happy in your marriage?"
"Oh," replied he, smiling, "I have a secret to tell you."
"A secret! for goodness sake, what is it?"
"From my youth upward," he replied, "I have prayed God to give me a good wife."
"Yes," thought I to myself, "that is it! Here am I unmarried, because I have never discovered this secret, without God's especial direction I may not venture to choose 'my wife.'"
A younger sister of my friend's wife lived in the family. No one would have been attracted to her for her external charms, but a short time brought you completely under the spell of her kindness, the intellectual expression of her countenance, and the cheerful friendliness of her manners. All the household loved her; she was kind and amiable to all. To myself, however, it seemed that there was an exception: I thought her somewhat cold and distant. I was almost [Pg 622]sorry when I perceived that I was grieved by this; a short time convinced me that I had really fallen in love with this young lady.
There was, however, a great difference between this and my former love affairs. Formerly, I had permitted external charms to lead and blind me: now, on the contrary, I was attracted to the soul, and its beauty alone had captivated my heart. But why then was so excellent a soul so cold toward me?
My friend said that it was because Maria had heard me represented as a fickle young fellow; one who amused himself with broken affiances. Righteous Heaven! was that indeed one of my faults? I fickle! I, who felt myself created as a model of fidelity. It was impossible for me to bear patiently so cruel an injustice. No! as truly as my name was Constantine, must Maria do me justice.
From that time, as she retired from me, so began I to walk after her. I was determined to convince her that I was not the fickle, inconstant being that I had been described. It was not, however, very easy to succeed in this, but at length I did succeed. After having put me to a trial, from which I came with flying colors, she accepted my proposals, and agreed to try me still further in—a union for life.
During the period of our betrothal, she said several times, quite rapturously, "I am so glad to see that you also have faults; I feel now less humiliated, less unhappy from my own."
This pleased me very much, and all the more as I perceived that Maria, while she showed me my faults with kindness, did not at all fondle her own.
Our wedding-day was fixed; and I ordered a carriage for two persons. Company was invited, and Maria and I were married. Nothing can be more commonplace than all this, excepting, perhaps, it be, that my wife and I agreed to understand the ceremony in an earnest and real sense, and to live accordingly. The result has been, that now, after having been married five-and-twenty years (we celebrate our silver nuptials to-morrow), we love each other better, and are happier together than we were in the first hour of our union. We have, therefore, come to the conclusion, that unhappiness in marriage does not proceed from the indissolubility of marriage, as some say, but because the wedding-service is not realized in the marriage.
Do not speak to me of the felicity of the honey-moon. It is but the cooing of doves! No! we must walk together along thorny paths, penetrate together the most hidden recesses of life, live together in pleasure and pain, in joy and in sorrow; must forgive and be forgiven; and afterward love better and love more. And as time goes on, something marvelous occurs; we become lovely to each other, although wrinkles furrow the cheek and forehead; and we become more youthful, though we add year to year. Then no longer have worldly troubles, misfortunes, and failings any power to dim the sun of our happiness, for it radiates from the eye and the heart of our friend; and when our earthly existence draws to its close, we feel indeed that our life and our love are eternal. And this supernatural feeling is quite natural after all, for the deeper and the more inwardly we penetrate into life, the more it opens in its depth of eternal beauty. Many happy husbands and wives will testify to this.
But, observe, husband or wife! To qualify as such a witness, you must have been at some little pains to find—"the right one." Don't take the wrong one, inconsiderately.
Lord Brougham, as a judge, gave much greater satisfaction than was generally expected. It was thought that his constitutional precipitancy, joined to a deficiency of Chancery knowledge, would have incapacitated him for the important office. In this, however, people were mistaken. He was not so hot and hasty on the bench as he had been at the bar and in the senate—though his constitutional infirmities in this respect did occasionally show themselves even on the seat of justice. He carefully applied himself to the merits of every case which came before him, and soon showed with what rapidity he could acquire the quantity of Chancery knowledge requisite to enable him to discharge the duties of his office as judge, in at least a respectable manner.
Perhaps no Lord Chancellor ever presided in Chancery who applied himself more assiduously and unremittingly to the discharge of the duties which devolved upon him, than did Lord Brougham. The amount of physical, not to speak of mental labor, he underwent during the greater part of his chancellorship was truly astonishing. For many consecutive months did he sit from ten till four o'clock in that court, hearing and disposing of the cases before it; and, on returning home from the House of Lords, after having sat four hours on the woolsack, he immediately applied all the energies of his mind to the then pending cases before the court. The best proof of this is to be found in the fact, that, though possessing, in a degree seldom equaled, and certainly never surpassed, the power of extemporaneous speaking, he wrote, on particular occasions, his judgments, and then read them in the court. I might also advert, in proof of Lord Brougham's extraordinary application to the duties of his office, to the fact of his having, in two or three years, got rid of the immense accumulation of arrear cases which were in the Court of Chancery when he was first intrusted with the great seal. It is not, however, necessary to allude particularly to this fact, as it is already so well known.
Lord Brougham's irritable temper often led him, when Lord Chancellor, into squabbles with the counsel at the bar. The furious attack he made on Sir Edward Sugden must be fresh in the memory of every body. No person can justify that attack. It was as unwarrantable in principle as it was unseemly in a court of law, [Pg 623]and especially as coming from the highest legal authority in the country. It is but due, however, to Lord Brougham to say, that he often regretted these unbecoming outbreaks of temper, and that he did so in this particular case. It consists with my own private knowledge that he afterward, on pretext of speaking on matters of public business, called Sir Edward one day into his private room, and made a most ample apology for the attack he had made on him. Sir Edward was generous enough to accept the apology, thus privately given, though the offense was a public one.
I may here, however, mention that, during the interval between the attack and this apology, Lord Brougham, on several occasions, aggravated the outrage by further annoyances of Sir Edward while practicing before him. I do not say that such annoyances were intentional—possibly they may have been accidental—but, whichever way the fact lay, it is not to be wondered at if Sir Edward, in the peculiar circumstances in which he was placed, was predisposed to regard them as intentional. On one occasion, while the learned gentleman was pleading before his lordship in a very important cause, and just in the middle of what he conceived to be the most essential part of his speech, Lord Brougham suddenly threw back his head on his chair, and, closing both eyes, remained in that position for some time, as if he had been asleep. Sir Edward Sugden abruptly paused, waiting, no doubt, till his lordship should resume an attitude which would be more encouraging for him to proceed with his speech. On this, Lord Brougham suddenly started up from his reclining position, and, resuming that in which he usually sat when on the bench, apostrophized Sir Edward after the manner so peculiar to himself—"Go on, Sir Edward; proceed, Sir Edward; what's the cause of the stoppage?"
"My lord," answered the latter, "I thought your lordship was not attending to my argument."
"You have no right to think any such thing, Sir Edward; it's highly improper in you to do so; go on, if you please."
Sir Edward resumed his speech, but had not addressed the court above two or three minutes, when Lord Brougham, addressing the officer, said, in his usual hasty manner, "Bring me some sheets of letter-paper directly."
Of the folio size always used in court, his lordship had an abundant supply before him.
"Yes, my lord," said the obedient officer, withdrawing for a moment to execute his lordship's commands. He returned in a few seconds, and placed some half-dozen sheets on the desk. His lordship immediately snatched up a pen, and commenced writing, as if he had been inditing a letter to some private friend. Sir Edward again paused in his address to the court, and leaned with his elbows on the bench before him, as if willing to wait patiently until his lordship should finish his epistolary business.
"Sir Edward!" exclaimed the Lord Chancellor, in angry and ironical accents, after the learned gentleman had been silent for a few moments—"Sir Edward! pray, what's the matter now?"
"I thought, my lord, that your lordship was temporarily engaged with some matter of your own."
"Really, Sir Edward, this is beyond endurance."
"I beg your lordship's pardon; but I thought your lordship was writing some private letter."
"Nothing of the kind, Sir Edward," said his lordship, tartly; "nothing of the kind. I was taking a note of some points in your speech. See, would you like to look at it?" said he, sarcastically, at the same time holding out the sheet of paper toward Sir Edward.
"Oh, not at all, your lordship; I do not doubt your lordship's word. I must have been under a mistake."
Sir Edward again resumed; and Lord Brougham, throwing his head back on his chair, looked up toward the ceiling.
Lord Brougham had a great horror of hearing the interminable speeches which some of the junior counsel were in the habit of making, after he conceived every thing had been said which could be said on the real merits of the case before the court by the gentlemen who preceded them. His hints to them to be brief on such occasions were sometimes extremely happy. I recollect that, after listening with the greatest attention to the speeches of two counsel on one side, from ten in the morning till half-past two, a third rose to address the court on the same side. His lordship was quite unprepared for this additional infliction, and exclaimed, "What, Mr. A——, are you really going to speak on the same side?"
"Yes, my lord; I mean to trespass on your lordship's attention for a short time."
"Then," said his lordship, looking the orator significantly in the face—"then, Mr. A——, you had better cut your speech as short as possible, otherwise you must not be surprised if you see me dozing; for really this is more than human nature can endure."
The youthful barrister took the hint; he kept closely to the point at issue—a thing very rarely done by barristers—and condensed his argument into a reasonable compass.
LIBELLUS A MARGARETA MORE, QUINDECIM ANNOS NATA, CHELSEIÆ INCEPTVS
"Nulla dies sine linea."
[3] Continued from the September Number.
April, 1534.A heavier charge than either of ye above hath been got up, concerning the wicked woman of Kent, with whom they accuse him of having tampered, that, in her pretended revelations and rhapsodies, she might utter words against the king's divorce. His name hath, indeed, been put in the bill of attainder; but, out of favor, he hath been granted a private hearing, [Pg 624]his judges being, the new archbishop, the new chancellor, his grace of Norfolk, and Master Cromwell.
He tells us that they stuck not to ye matter in hand, but began cunningly enow to sound him on ye king's matters; and finding they could not shake him, did proceed to threats, which, he told 'em, might well enow scare children, but not him, and as to his having provoked his grace the king to sett forth in his book aught to dishonour and fetter a good Christian, his grace himself well knew the book was never shewn him save for verbal criticism when ye subject matter was completed by the makers of ye same, and that he had warned his grace not to express soe much submission to the pope. Whereupon they with great displeasure dismissed him, and he took boat for Chelsea with mine husband in such gay spiritts, that Will, not having been privy to what had passed, concluded his name to have beene struck out of ye bill of attainder, and congratulated him thereupon soe soone as they came aland, saying, "I guess, father, all is well, seeing you thus merry."
"It is indeed, son Roper," returns father steadilie, repeating thereupon, once or twice, this phrase, "All is well."
Will, somehow mistrusting him, puts the matter to him agayn.
"You are then, father, put out of the bill?"
"Out of the bill, good fellow?" repeats father, stopping short in his walk, and regarding him with a smile that Will sayth was like to break his heart.... "Wouldst thou know, dear son, why I am so joyful? In good faith, I have given the devil a foul fall, for I have with those lords gone so far, as that without great shame I can ne'er go back. The first step, Will, is the worst, and that's taken."
And so, to the house, with never another word, Will being smote at the heart.
But, this forenoon, deare Will comes running in to me, with joy all bright, and tells me he hath just heard from Cromwell that father's name is in sooth struck out. Thereupon, we go together to him with the news. He taketh it thankfully, yet composedly, saying, as he lays his hand on my shoulder, "In faith, Meg, quod differtur non aufertur." Seeing me somewhat stricken and overborne, he sayth, "Come, let's leave good Will awhile to the company of his own select and profitable thoughts, and take a turn together by the water side."
Then closing his book, which I marked was Plato's Phædon, he steps forthe with me into the garden, leaning on my shoulder, and pretty heavilie too. After a turn or two in silence, he lightens his pressure, and in a bland, peaceifying tone commences Horace his tenth ode, book second, and goes through the first fourteen or fifteen lines in a kind of lulling monotone; then takes another turn or two, ever looking at the Thames, and in a stronger voice begins his favorite
on to
—and lets go his hold on me to extend his hand in fine, free action. Then, drawing me to him agayn, presentlie murmurs, "I reckon that the sufferings of this present time are not worthy to be compared with ye glory which shall be revealed in us.... Oh no, not worthy to be compared. I have lived; I have laboured; I have loved. I have lived in them I loved; laboured for them I loved; loved them for whom I laboured; my labour has not been in vayn. To love and to labour is the sum of living, and yet how manie think they live who neither labour nor love. Again, how manie labour and love, and yet are not loved; but I have beene loved, and my labour has not been in vayn. Now, the daye is far spent, and the night forecloseth, and the time draweth nigh when man resteth from his labours, even from his labours of love; but still he shall love and he shall live where the Spiritt sayth he shall rest from his labours, and where his works do follow him, for he entereth into rest through and to Him who is Life, and Light, and Love."
Then looking stedfastlie at the Thames, "How quietlie," sayth he, "it flows on! This river, Meg, hath its origin from seven petty springs somewhither amongst ye Gloucestershire hills, where they bubble forthe unnoted save by the herd and hind. Belike, they murmur over the pebbles prettily enough; but a great river, mark you, never murmurs. It murmured and babbled too, 'tis like, whilst only a brook, and brawled away as it widened and deepened and chafed agaynst obstacles, and here and there got a fall, and splashed and made much ado, but ever kept running on towards its end, still deepening and widening; and now towards the close of its course look you how swift and quiet it is, running mostly between flats, and with the dear blue heaven reflected in its face." ...
'Twas o' Wednesdaye was a week, we were quietly taking our dinner, when, after a loud and violent knocking at ye outer door, in cometh a poursuivant, and summoneth father to appear next daye before ye commissioners, to take ye newly coined oath of supremacy. Mother utters a hasty cry, Bess turns white as death, but I, urged by I know not what suddain impulse to con the new comer's visage narrowly, did with eagerness exclaim, "Here's some jest of father's; 'tis only Dick Halliwell!"
Whereupon, father burst out a laughing, hugged mother, called Bess a silly puss, and gave Halliwell a grout for 's payns. Now, while some were laughing, and others taking father prettie sharplie to task for soe rough a crank, I fell a muzing, what cd be ye drift of this, and could only surmize it mighte be to harden us beforehand, as 'twere, to what was sure to come at last. And the preapprehension of this so belaboured my alreadie o'erburthened spiritts, as that I was fayn to betake myself to ye nurserie, and lose alle thought and reflection in my little Bill's prettie ways. And, this not answering, was forct to have recourse to prayer; then, leaving [Pg 625]my closett, was able to return to ye nurserie, and forget myselfe awhile in the mirth of the infants.
Hearing voyces beneathe ye lattice, I lookt forthe, and behelde his Grace of Norfolk (of late a strange guest) walking beneath ye window in earnest converse with father, and, as they turned about, I hearde him say, "By the mass, master More, 'tis perilous striving with princes. I could wish you, as a friend, to incline to the king's pleasure; for, indignatio principis mors est."
"Is that all?" says father; "why then there will be onlie this difference between your grace and me, that I shall die to-daye, and you to-morrow;"—which was the sum of what I caught.
Next morning, we were breaking our fast with peacefullness of heart, on ye principle that sufficient for the daye is the evill thereof, and there had beene a wordy war between our two factions of the Neri and Bianchi, Bess having defalked from ye mancheteers on ye ground that black bread sweetened the breath and settled the teeth, to the no small triumph of the cob-loaf party; while Daisy, persevering at her crusts, sayd "No, I can cleave to the rye bread as steddilie as anie among you, but 'tis vayn of father to maintain that it is as toothsome as a manchet, or that I eat it to whiten my teeth, for thereby he robs self-deniall of its grace."
Father, strange to say, seemed taken at vantage, and was pausing for a retort, when Hobson coming in and whispering somewhat in his ear, he rose suddainlie and went forthe of the hall with him, putting his head back agayn to say, "Rest ye alle awhile where ye be," which we did, uneasilie enow. Anon he returns, brushing his beaver, and says calmlie, "Now, let's forthe to church," and clips mother's arme beneathe his owne and leads the way. We follow as soon as we can, and I, listing to him more than to ye priest, did think I never hearde him make response more composedlie, nor sing more lustilie, by the which I founde myself in stouter heart. After prayers, he is shriven, after which he saunters back with us to the house, then brisklie turning on his heel, cries to my husband, "Now, Will, let's toward, lad," and claps the wicket after him, leaving us at t'other side without so much as casting back a parting look. Though he evermore had been advised to let us companie him to the boat, and there kiss him once and agayn or ever he went, I know not that I sd have thoughte much of this, had not Daisy, looking after him keenly, exclaymed somewhat shortlie as she turned in doors, "I wish I had not uttered that quip about the cob-loaf."
Lord, how heavilie sped ye day! The house, too big now for its master's diminished retinue, had yet never hitherto seemed lonesome; but now a somewhat of dreary and dreadfull, inexpressible in words, invisible to the eye, but apprehended by the inner sense, filled the blank space alle about. For the first time, everie one seemed idle; not only disinclined for businesse, but as though there were something unseemlie in addressing one's self to it. There was nothing to cry about, nothing to talk over, and yet we alle stoode agaze at each other in groups, like the cattle under ye trees when a storm is at hand. Mercy was the first to start off. I held her back and said, "What is to do?" She whispered, "Pray." I let her arm drop, but Bess at that instant comes up with cheeks as colourless as parchment. She sayth, "'Tis made out now. A poursuivant de facto fetched him forthe this morning." We gave one deep, universal sigh; Mercy broke away, and I after her, to seek the same remedie, but alack, in vayn....
How large a debt we owe you, wise and holie men of old! How ye counsel us to patience, incite us to self-mastery, cheer us on to high emprize, temper in us the heat of youth, school our inexperience, calm the o'erwrought mind, allay the anguish of disappointment, cheat suspense, and master despair.... How much better and happier ye would make us, if we would but list your teaching!
Bess hath fallen sick; no marvell. Everie one goeth heavilie. All joy is darkened; the mirthe of the house is gone.
Will tells me, that as they pushed off from ye stairs, father took him about the neck and whispered, "I thank our Lord, the field is won!" Sure, Regulus ne'er went forthe with higher self-devotion.
Having declared his inabilitie to take ye oath as it stoode, they bade him, Will tells me, take a turn in the garden while they administered it to sundrie others, thus affording him leisure for reconsideration. But they might as well have bidden the neap-tide turn before its hour. When called in agayn, he was as firm as ever, so was given in ward to ye Abbot of Westminster till the king's grace was informed of the matter. And now, the fool's wise saying of vindictive Herodias came true, for 'twas the king's mind to have mercy on his old servant, and tender him a qualifyed oath; but queen Anne, by her importunate clamours, did overrule his proper will, and at four days end, ye full oath being agayn tendered and rejected, father was committed to ye Tower. Oh, wicked woman, how could you?... Sure, you never loved a father....
In answer to our incessant applications throughout this last month past, mother hath at length obtayned access to dear father. She returned, her eyes nigh swollen to closing with weeping ... we crowded round about, burning for her report, but 'twas some time ere she coulde fetch breath or heart to give it us. At length Daisy, kissing her hand once and agayn, draws forthe a disjoynted tale, somewhat after this fashion.
"Come, give over weeping, dearest mother; 'twill do neither him, you, nor us anie goode.... What was your first speech of him?"
"Oh, my first speech, sweetheart, was, 'What, my goodness, Mr. More! I marvell how that you, who were always counted a wise man, sd now soe play the fool as to lie here in this close, filthy prison, shut up with mice and rats, when [Pg 626]you mighte be abroade and at your liberty, with ye favour of king and council, and return to your righte fayr house, your books and gallery, and your wife, children, and household, if soe be you onlie woulde but do what the bishops and best learned of the realm have, without scruple, done alreadie.'"
"And what sayd he, mother, to that?" ...
"Why, then, sweetheart, he chucks me under the chin and sayeth, 'I prithee, good mistress Alice, to tell me one thing.' ... Soe then I say, 'What thing?' Soe then he sayeth, 'Is not this house, sweetheart, as nigh heaven as mine own?' Soe then I jerk my head away and say 'Tilly-valley! tilley-valley.'"
Sayth Bess, "Sure, mother, that was cold comfort.... And what next?"
"Why, then I said, 'Bone Deus, man! Bone Deus! will this gear never be left? Soe then he sayth, 'Well then, Mrs. Alice, if it be soe, 'tis mighty well, but, for my part, I see no greate reason why I shoulde much joy in my gay house, or in aniething belonging thereunto, when, if I shoulde be but seven years buried underground, and then arise and come thither agayn, I shoulde not fail to find some therein that woulde bid me get out of doors, and tell me 'twas none o' mine. What cause have I then, to care so greatlie for a house that woulde soe soone forget its master?'" ...
"And then, mother? and then?"
"Soe then, sweetheart, he sayth, 'Come, tell me, Mrs. Alice, how long do you think we might reckon on living to enjoy it?' Soe I say, 'Some twenty years, forsooth.' 'In faith,' says he, 'had you said some thousand years, it had beene somewhat; and yet he were a very bad merchant that woulde put himselfe in danger to lose eternity for a thousand years ... how much the rather if we are not sure to enjoy it one day to an end?' Soe then he puts me off with questions, How is Will? and Daisy? and Rupert? and this one? and t'other one? and the peacocks? and rabbits? and have we elected a new king of the cob-loaf yet? and has Tom found his hoop? and is ye hasp of the buttery-hatch mended yet? and how goes the court? and what was the text o' Sunday? and have I practised the viol? and how are we off for money? and why can't he see Meg? Then he asks for this book and t'other book, but I've forgot their names, and he sayth he's kept mighty short of meat, though 'tis little he eats, but his man John a Wood is gay an' hungry, and 'tis worth a world to see him at a salt herring. Then he gives me counsell of this and that, and puts his arm about me and says, 'Come, let us pray;' but while he kept praying for one and t'other, I kept a-counting of his gray hairs; he'd none a month agone. And we're scarce off our knees, when I'm fetched away; and I say, 'When will you change your note, and act like a wise man?' and he sayth, 'When? when!' looking very profound; 'why, ... when gorse is out of blossom and kissing out of fashion.' Soe puts me forthe by the shoulders with a laugh, calling after me, 'Remember me over and over agayn to them alle, and let me se Meg.'"
... I feel as if a string were tied tight about my heart. Methinketh 'twill burst if we goe on long soe.
He hath writ us a few lines with a coal, ending with "Sursum corda, dear children! up with your hearts." The bearer was dear Bonvisi.
The Lord begins to cut us short. We are now on very meagre commons, dear mother being obliged to pay fifteen shillings a-week for the board, poor as it is, of father and his servant. She hath parted with her velvet gown, embroidered overthwart, to my lady Sand's woman. Her mantle edged with coney went long ago.
But we lose not heart; I think mine is becoming annealed in the furnace, and will not now break. I have writ somewhat after this fashion to him.... "What do you think, most dear father, doth comfort us at Chelsea, during this your absence? Surelie, the remembrance of your manner of life among us, your holy conversation, your wholesome counsells, your examples of virtue, of which there is hope that they do not onlie persevere with you, but that, by God's grace, they are much increast."
I weary to see him.... Yes, we shall meet in heaven, but how long first, oh Lord? how long?
Now that I've come back, let me seek to think, to remember.... Sure, my head will clear by-and-by? Strange, that feeling shoulde have the masterdom of thought and memory, in matters it is most concerned to retayn.
... I minded to put ye haircloth and cord under my farthingale, and one or two of ye smaller books in my pouch, as alsoe some sweets and suckets such as he was used to love. Will and Bonvisi were awaiting for me, and deare Bess, putting forthe her head from her chamber door, cries piteously, "Tell him, dear Meg, tell him ... 'twas never soe sad to me to be sick ... and that I hope ... I pray ... the time may come ..." then falls back swooning into Dancey's arms, whom I leave crying heartilie over her, and hasten below to receive the confused medley of messages sent by every other member of ye house. For mine owne part, I was in such a tremulous succussion as to be scarce fitt to stand or goe, but time and the tide will noe man bide, and, once having taken boat, the cool river air allayed my fevered spiritts; onlie I coulde not for awhile get ridd of ye impression of poor Dancey crying over Bess in her deliquium.
I think none o' the three opened our lips before we reached Lambeth, save, in ye Reach, Will cried to ye steersman, "Look you run us not aground," in a sharper voyce than I e'er heard from him. After passing ye Archbishop's palace, whereon I gazed full ruefullie, good Bonvisi beganne to mention some rhymes he had founde writ with a diamond on one of his window-panes at Crosby House, and would know were they father's? and was't ye chamber father [Pg 627]had used to sleep in? I tolde him it was, but knew nought of ye distich, though 'twas like enow to be his. And thence he went on to this and that, how that father's cheerfulle, funny humour never forsook him, nor his brave heart quelled, instancing his fearlesse passage through the Traitor's Gate, asking his neighbours whether his gait was that of a traditor; and, on being sued by the porter for his upper garment, giving him his cap, which he sayd was uppermost. And other such quips and passages, which I scarce noted nor smiled at, soe sorry was I of cheer.
At length we stayed rowing: Will lifted me out, kissed me, heartened me up, and, indeede, I was in better heart then, having been quietlie in prayer a good while. After some few forms, we were led through sundrie turns and passages, and, or ever I was aware, I found myselfe quit of my companions, and in father's arms.
We both cried a little at first; I wonder I wept noe more, but strength was given me in that hour. As soone as I coulde, I lookt him in the face, and he lookt at me, and I was beginning to note his hollow cheeks, when he sayd, "Why, Meg, you are getting freckled:" soe that made us bothe laugh. He sayd, "You shoulde get some freckle-water of the lady that sent me here; depend on it, she hath washes and tinctures in plenty; and after all, Meg, she'll come to the same end at last, and be as the lady all bone and skin, whose ghastlie legend used to scare thee soe when thou wert a child. Don't tell that story to thy children; 'twill hamper 'em with unsavory images of death. Tell them of heavenlie hosts a-waiting to carry off good men's souls in fire-bright chariots, with horses of the sun, to a land where they shall never more be surbated and weary, but walk on cool, springy turf and among myrtle trees, and eat fruits that shall heal while they delight them, and drink the coldest of cold water, fresh from ye river of life, and have space to stretch themselves, and bathe, and leap, and run, and, whichever way they look, meet Christ's eyes smiling on them. Lord, Meg, who would live, that could die? One mighte as lief be an angel shut up in a nutshell as bide here. Fancy how gladsome the sweet spirit would be to have the shell cracked! no matter by whom; the king, or king's mistress.... Let her dainty foot but set him free, he'd say, 'For this release, much thanks.' ... And how goes the court, Meg?"
"In faith, father, never better.... There is nothing else there, I hear, but dancing and disporting."
"Never better, child, sayst thou? Alas, Meg, it pitieth me to consider what misery, poor soul, she will shortlie come to. These dances of hers will prove such dances that she will spurn our heads off like footballs; but 'twill not be long ere her head will dance the like dance. Mark you, Meg, a man that restraineth not his passions hath always something cruel in his nature, and if there be a woman toward, she is sure to suffer heaviest for it, first or last.... Seek scripture precedent for't ... you'll find it as I say. Stony as death, cruel as the grave. Those Pharisees that were, to a man, convicted of sin, yet haled a sinning woman before the Lord, and woulde fain have seen the dogs lick up her blood. When they lick up mine, deare Meg, let not your heart be troubled, even though they shoulde hale thee to London Bridge to see my head stuck on a pole. Think, most dear'st, I shall then have more reason to weep for thee than thou for me. But there's noe weeping in heaven, and bear in mind, Meg, distinctlie, that if they send me thither, 'twill be for obeying the law of God rather than of men. And after alle, we live not in the bloody, barbarous old times of crucifyings and flayings, and immersings in cauldrons of boiling oil. One stroke, and the affair's done. A clumsy chirurgeon would be longer extracting a tooth. We have oft agreed that the little birds struck down by the kite and hawk suffer less than if they were reserved to a naturall death. There is one sensible difference, indeed, between us. In our cases, preparation is a-wanting."
Hereon, I minded me to slip off ye haircloth and rope, and give the same to him, along with the books and suckets, all which he hid away privatelie, making merry at the last.
"'Twoulde tell well before the council," quoth he, "that on searching the prison-cell of Sir Thomas More, there was founde, flagitiouslie and mysteriouslie laid up ... a piece of barley-sugar!"
Then we talked over sundry home-matters; and anon, having now both of us attayned unto an equable and chastened serenitie of mind, which needed not any false shows of mirth to hide ye naturall complexion of, he sayth, "I believe, Meg, they that have put me here ween they have done me a high displeasure; but I assure thee on my faith, mine own good daughter, that if it had not beene for my wife, and you, my dear good children, I would faine have beene closed up, long ere this, in as straight a room, and straighter too."
Thereon, he shewed me how illegal was his imprisonment, there being noe statute to authorize the imposition of ye oath, and he delivered himself, with some displeasure, agaynst the king's ill counsellors.
"And surelie, Meg," quoth he, "'tis pitie that anie Christian prince shoulde, by a flexible council readie to follow his affections, and by a weak clergy lacking grace to stand constantly to the truth as they learned it, be with flattery so constantly abused. The lotus fruit fabled by the ancients, which made them that ate it lose alle relish for the daylie bread of their own homes, was flattery, Meg, as I take it, and nothing else. And what less was the song of the Syrens, agaynst which Ulysses made the sailors stop their ears, and which he, with all his wisdom, coulde not listen to without struggling to be unbound from the mast? Even praise, Meg, which, moderately given, may animate and cheer forward the noblest minds, yet too lavishly bestowed, will decrease and palsy their strength, [Pg 628]e'en as an overdose of the most generous and sprightlie medicine may prove mortiferous. But flattery is noe medicine, but a rank poison, which hath slayn kings, yea, and mighty kings; and they who love it, the Lord knoweth afar off; knoweth distantlie, has no care to know intimatelie, for they are none of his."
Thus we went on, from one theme to another, till methinketh a heavenlie light seemed to shine alle about us like as when the angel entered the prison of Peter. I hung upon everie word and thought that issued from his lips, and drank them in as thirsty land sucks up the tender rain.... Had the angel of death at that hour come to fetch both of us away, I woulde not have sayd him nay, I was soe passivelie, so intenselie happy. At length, as time wore on, and I knew I shoulde soone be fetcht forthe, I coulde not but wish I had the clew to some secret passage or subterreneal, of which there were doubtless plenty in the thick walls, whereby we might steal off together. Father made answer, "Wishes never filled a sack. I make it my businesse, Meg, to wish as little as I can, except that I were better and wiser. You fancy these four walls lonesome; how oft, dost thou suppose, I here receive Plato and Socrates, and this and that holy saint and martyr? My jailors can noe more keep them out than they can exclude the sunbeams. Thou knowest, Jesus stood among his disciples when the doors were shut. I am not more lonely than St. Anthony in his cave, and I have a divine light e'en here, whereby to con the lesson 'God is love.' The futility of our enemies' efforts to make us miserable was never more stronglie proven to me than when I was a mere boy in Cardinal Morton's service. Having unwittinglie angered one of his chaplains, a choleric and even malignant-spirited man, he did, of his owne authoritie, shut me up for some hours in a certayn damp vault, which, to a lad afeard of ghosts and devilish apparitions, would have been fearsome enow. Howbeit, I there cast myself on the ground with my back sett agaynst the wall, and mine arm behind my head, this fashion ... and did then and there, by reason of a young heart, quiet conscience, and quick phansy, conjure up such a lively picture of the queen o' the fairies' court, and alle the sayings and doings therein, that never was I more sorry than when my gaoler let me goe free, and bade me rise up and be doing. In place, therefore, my daughter, of thinking of me in thy night watches as beating my wings agaynst my cage bars, trust that God comes to look in upon me without knocking or bell-ringing. Often in spiritt I am with you alle; in the chapel, in the hall, in the garden; now in the hayfield, with my head on thy lap, now on the river, with Will and Rupert at the oar. You see me not about your path, you won't see my disembodied spiritt beside you hereafter, but it may be close upon you once and agayn for alle that: maybe, at times when you have prayed with most passion, or suffered with most patience, or performed my hests with most exactness, or remembered my care of you with most affection. And now, good speed, good Meg, I hear the key turn in the door.... This kiss for thy mother, this for Bess, this for Cecil, ... this and this for my whole school. Keep dry eyes and a hopeful heart; and reflect that nought but unpardoned sin should make us weep forever."
"Like caterpillar, eating his way in silence!"
The natural history of the bookworm has escaped the observation of Cuvier. Yet the bookworm shares his habitat in common with the student, and no doubt has often rubbed shoulder with the naturalist. The haunts of the bookworm are the national libraries, the old booksellers' shops about Holborn and Great Queen-street, Long-acre, and the bookstalls generally. One will be sure to meet with him—a weary, worn, and faded personage—in the reading-room of the Museum. The goodly morocco-bound tome in folio is the bookworm's bonne bouche. Its scented binding and odorous pages form the choicest of his meals. The atmosphere of the national reading-room is close and redolent of strange smells; the bookworm, however, enjoys it with the readier zest. Worm-like, he is a reproducer, and capable of spinning words by the myriad, which he deposits upon the surfaces of foolscap.
The bookworm's natural disposition is gentle; but his temper is irritable. His nature is indolent. He loves to doze over a Harleian manuscript, or a dusty Elzevir or black letter. It is legendary that his mission upon earth is occult—videlicet, to discover those lost treasures the Sibylline Leaves, supposed to be embedded and fossilized somewhere in the forest of leaves monastic. The hiding-place of the Sibyl's precious autograph, albeit, remains, like the philosopher's stone, a secret yet.
It is not intended in this paper to be satirical upon bibliographical pursuits. On this point our motto is the text recorded by the learned and indefatigable Mr. Lowdes, in his "Manual." "Mankind are disposed to remember the abuse rather than the utility of pursuits in which few are deeply interested. And in the ridicule which the enthusiastic zeal of bibliomaniacs has cast on bibliography, they lose sight of the fact that all accurate knowledge is in a greater or less degree absolutely dependent thereon."
But the eccentricities and peculiarities of bookworms are left to us to notice, without our incurring the displeasure of any liberal-minded student or book-collector. Our task at present is merely to throw together some information personally relating to bookworms, hitherto hidden within the mouldering pages of cumbrous volumes, offering little inducement for the perusal of the ordinary reader. Nevertheless we are not unmindful what a field of scholastic romance we have traveled through, at the cost of a somewhat dusty journey.
Who were the original bookworms? From what point shall our bibliographical notices date?[Pg 629]—beyond or in advance of the monasticism? The old clerks or copyists of the convents were the primitive bookworms indubitably. Their occupation has been elevated by writers to a position of moral philosophy. Dr. Dibdin, in his "Bibliomania," says, "Copying excited insensibly a love of quiet, domestic order, and seriousness. I am willing to admit every degree of merit to the manual dexterity of the cloistered student. I admire his snow-white vellum missals, emblazoned with gold, and sparkling with carmine and ultra-marine blue. By the help of the microscopic glass I peruse his diminutive penmanship, executed with the most astonishing neatness and regularity; his ink so glossy black! Now and then, for a guinea or two, I purchase a specimen of such marvelous legerdemain, but the book to me is a sealed book! Surely the same exquisite and unrivaled beauty would have been exhibited in copying an ode of Horace or a dictum of Quinctilian." With reference to this allusion to the missal, it may be here worth while mentioning that the most splendidly executed book of devotion known is the MS. volume, the Bedford missal. It passed from the library of Harley, Earl of Oxford, through various fortunes, until it finally found a resting-place in the library of the Duchess of Portland. This antiquity is valued at 500 guineas.
As early as the sixth century, commenced the custom in some monasteries of copying ancient books and composing new ones. In the fifteenth century, the custom of keeping up monkish libraries had ceased, at least in England.
The illustrious progenitors of bookworms were such personages as the venerable Bede, Alfred the Great, and Theodore, Archbishop of Canterbury. Friar Roger Bacon was also an intense bookworm. The noble book-spirit by which the lives of the Oxford Athenians are recorded and preserved, is now probably forgotten by the world. The student, however reveres the name of old Anthony à Wood. The remembrance of his researches amidst paper and parchment documents, stored up in chests and desks, and upon which the moth was "feeding sweetly," is perpetuated in bibliography. We follow in imagination his cautious step, and head bowing from premature decay, and solemn air, and sombre visage, with cane under the arm, pacing from library to library, through Gothic quadrangles, or sauntering along the Isis on his way to some neighboring village, where, may be, with some congenial Radcliffe, he would recreate with pipe and pot. While the Bodleian and Ashmolean collections remain, so long will the memory of his laudable exertions continue unimpaired. Anthony à Wood was in person of a large, robust make, tall and thin, and had a sedate and thoughtful look, almost bordering upon a melancholy cast. Beneath a strange garb and coarse exterior, lay all that acuteness of observation and retentiveness of memory, as well as inflexible integrity, which marked his intellectual character. After he had by continual drudging worn out his body, he left this world contentedly, A.D. 1695.
In the early part of the seventeenth century, lived that very curious collector of ancient popular little pieces, as well as lover of sacred, secret soul soliloquies, that "melancholy Jaques," yclept Robert Burton. He gave a multitude of books to the Bodleian Library. This original, amusing, and now popular author was an arrant book-hunter—a "devourer of authors." Old Burton's constant companion was, we read, the eccentric "Harry" Hastings, a bibliomaniac, yet also an ardent sportsman. Just alighted from the toils of the chase, Harry Hastings, then in his eightieth year, would partake of a substantial dinner, tipple his tankard of ale dry, take his customary nap, wake up, rub his eyes, and behold the "Anatomy of Melancholy" seated before the fire, his visage buried in an opened folio! A rare old boy must have been this Hastings. He is described as low of stature, but strong and active, of a ruddy complexion, with flaxen hair. His clothes were always of Lincoln green. His house was of the old fashion, in the midst of a large park well stocked with game. He kept his hounds, and his great hall was commonly strewed with marrow bones. He lived to be an hundred, and never lost his eyesight nor used spectacles.
Richard Ashmole, the founder of the Ashmolean Museum, was an intimate of the astrologer Lilly, and one of the queerest of bookworms. His life was grotesquely checkered by family jars. He had a termagant wife, who, it appears, was continually "taking the law of him in return for neglect, cruelty," &c. Whether Ashmole was proof or not proof against this peculiar kind of henpecking, we can not report; but it is certain that his bodily health failed him in the course of his wife's persecution; he sought to tinker up his constitution with quack medicines, of which he became the victim.
The Bodleian and Ashmolean collections are emulated by the Harleian. Harley, Earl of Oxford's attachment to books, and the large sums he expended in forming the collection of MSS., have rendered the name celebrated. The Harleian collection of MSS. was purchased by government for the National Library; the purchase-money amounted to £10,000. Harley lived in the middle of the seventeenth century.
A remarkable individual of the order of bookworm, was the musical bibliomaniac, Thomas Britton. This curious character lived in the Augustan age of Queen Anne. He came to London from a northern county, and, after serving an humble apprenticeship, embarked in business as a kind of costermonger; he was in the habit of actually crying his coals about the street. His attire was a Guernsey frock; he carried a black sack on his shoulders, and a coal measure in his hands. In this style he was painted by Woollaston. Britton lived in Aylesbury-street, Clerkenwell, where he fitted up a concert-room, the progenitor of the great philharmonic and ancient nobility concerts of the present day. Sir Robert l'Estrange was one of Britton's first [Pg 630]patrons, and by his reputation and example induced the fashionable world of those days to patronize Britton's concerts, at which Handel, Phil Hart, Banister, Dubourg the violinist, and others, performed to the genteelest of audiences. The concert-room was literally but one floor over a coal-shed; and the visitors had to climb up to it by a ladder fixed outside of the house, and to sit under a low roof, against which they could not avoid knocking their heads soundingly. Britton was no composer, only a musician and book-collector. He collected works on the occult art chiefly, and on music; his library sold for a large sum of money in those times. He was quite a notoriety on account of the humble trade he so openly followed, and the refined tastes he was known to cultivate. One day passing nigh the house of Woollaston the painter, in Warwick-lane, Britton, being in his work-a-day attire, gave out lustily his well-known cry of "Small-coal." Woollaston's attention was attracted, and he recognized in the voice that of his musical acquaintance Britton, whom he had never seen in the pursuit of his ordinary trade. The artist at once beckoned Britton in, and there and then took his portrait as he sat, a veritable itinerant coal-dealer. The portrait is most characteristic, and is now to be seen in the collection of paintings of the British Museum. But we must notice the small-coal man under his bibliopolic phase. A bibliomania raged among Queen Anne's nobility. The Earls of Oxford, Pembroke, Sunderland, and Winchelsea, and the Duke of Devonshire, were among the smitten. These personages, on Saturdays, during the winter season, used to resort to the city, and, there separating, take several routes to the booksellers' shops in different parts of the town, to search out old volumes and MSS. Some time before noon, they would assemble at the shop of Christopher Bateman, a bookseller, at the corner of Ave Maria-lane, in Paternoster-row (query, Little Britain?), where they were frequently met by other persons engaged in the same pursuits, and a conversation commenced on the subject of their inquiries. As nearly as possible to the hour of twelve by St. Paul's clock, Britton (uniquely, the "Literary Dustman" of his age), who by that time had finished his round, clad in his blue frock, and pitching his sack of small coal on the bulk of Mr. Bateman's shop window, used to go in and join them. After about an hour's chat, the noblemen adjourned to the Mourning Bush Tavern at Aldersgate (probably the site of the present Albion Tavern), where they dined, and spent the remainder of the day. Poor Britton was indeed a singular character, and died a death as singular as his life. He was, we are told, of an excessively nervous temperament, which rendered him the object occasionally of villainous practical jokes. Unfortunately he incurred the enmity of Honeyman, the ventriloquist. On a certain day, when Britton gave one of his nobility concerts in Aylesbury-street, Honeyman attended. An opportunity occurring, a voice was heard at a distance, which announced that Thomas Britton's hour was near and that he had but a short time to remain in this world. Poor Britton was not proof against the art of the malicious mimic. He felt the ventriloquist's words as though they were a sacred augur; so deep an impression did the incident make upon him, that he died, almost as predicted, in a brief period, aged fifty-eight, 1714.
Browne Willis was another original of whom we are enabled to furnish a few whimsical anecdotes. But we would reserve this respectful remark, that the doctor was, notwithstanding oddities in externals and manners, nevertheless a learned antiquary, and a good man. So were they all, all learned antiquaries, and excellent men. His tastes led him chiefly to the study of ecclesiastical relics. He visited every cathedral in England and Wales. To these journeys he himself gave the name of pilgrimages. Browne Willis lived in the latter part of the seventeenth century. He was grandson of Dr. Thomas Willis, a celebrated physician, and the first to reduce the theory of phrenology to order and system. His person and dress are described by one who knew him well; they were "so singular that, though a gentleman of £1000 per annum, he was often taken for a beggar. An old leathern girdle or belt always surrounded the two or three coats he wore, and over them an old blue cloak. He wrote the worst hand of any man in England, such as he could with difficulty read himself. His boots, which he almost always appeared in, were not the least singular part of his dress. I suppose it would not be falsity to say they were forty years old, patched and vamped up at various times. They were all in wrinkles, and did not come up above half-way of his legs. He was often called, in the neighborhood of Buckingham, 'Old Wrinkle Boots.' The chariot of Mr. Willis was so singular, that from it he was called himself, the 'Old Chariot.' It was his wedding chariot, and had his arms on brass plates about it, not unlike a coffin, and painted black." This rare antiquary was satirized by Dr. Darrell, in some humorous and highly descriptive verses, of which the subjoined couplets are a specimen:
His wife having written a serious book, Browne Willis wrote on his own copy of the work, "All the connection in this book is owing to the book-binder." He delighted to joke upon Mrs. Willis's book and her authorship.
Dueling has fallen into desuetude, and very properly. Times have changed marvelously. Fifty years ago, gentlemen by descent, by [Pg 631]property, or by profession, were only esquired; now, if you mistered an attorney's clerk, the letter would be sent repudiated to the dead office. To him only who was entitled to bear arms, an appeal to arms was allowed; and had a man in trade, though worth a plum, in those days presumed to send a message to a gentleman not in trade, nor worth a penny, the odds would be considerable that the bearer of the cartel would have been horsewhipped on the spot. Even liberty to share in certain amusements was considered great condescension on the part of the aristocracy to men who had founded their own fortunes, and accidental meetings at the cover-side were never supposed to warrant aught beyond a field acquaintance. A brutal, but striking anecdote which marked this then prevailing feeling of exclusiveness, is told of the too-celebrated George Robert Fitzgerald. One hunting day, when drawing a fox cover, he observed a well-mounted and smartly-dressed young man join the company; and on inquiring his name from the whipper, was informed that the stranger was a neighboring apothecary.
"An apothecary!" exclaimed the master of hounds. "By Heaven! men's impudence every day becomes more audacious! Why, it would not surprise me after this, that an attorney should join our meeting next. Come, it is time that this dealer in drugs should be taught that fox-hunting is a trade practiced only by gentlemen;" and riding up to the unoffending dabbler in Galenicals, he savagely flogged him off the field.
That dueling has been employed too frequently for bad purposes, by brave men—and for bloody ones, by blackguards, has never been denied. The page of history, in the fatal meeting between Buckingham and Shrewsbury, strikingly exemplifies the former assertion. For the seduction of his wife—Buckingham, by the way, had seduced his own—the injured earl demanded, and obtained satisfaction. In accordance with the barbarous custom of the times, the seconds—two on either side—engaged; on the duke's side, Jenkins was left dead; on the earl's, Sir John Talbot was severely wounded. Buckingham, however, received no hurt beyond a scratch, and ran his antagonist through the body, thus adding murder to seduction. The fair frail one was worthy of the ducal ruffian she had attached herself to. Disguised as a page, from a neighboring coppice she watched the combat, and slept with the murderer of her husband the same night, although the shirt he wore bore bloody evidence of the foul assassination he had just committed. It is reported that the last hours of the adulteress were miserable, and the felon blow that relieved the world of such an unscrupulous villain as the duke, in our poor thinking, was nothing beyond simple retribution.
Another, and an opposite case, both in its results and causes, occurred many years ago, when the writer of these pages was in Paris. The worst and most dangerous companion upon earth is a gamester. "Nemo repente fuit turpissimus;" which, according to Irish translation, meaneth, that a man must be articled for five years to an attorney. As regards play, we hold a different opinion, and believe that the course of demoralization may be more rapidly effected by the alea damnosa than by law. To the proof:—even at the distance of a quarter of a century, we must hold the name sacred; but there are old guardsmen who will remember "Little Joe." A stouter soldier never headed a company. He was kind, well-tempered, too generous probably, and every body liked him. In money matters he was careless; had an early itch for play, and a sojourn with the Army of Occupation confirmed a disease already rooted. In a word, he abandoned a profession he could no longer continue in, and became a regular gambler.
Joe was a first-rate shot, and also constitutionally pugnacious. He felt his own degradation keenly, when to remedy it was too late; and a temper naturally excitable, had now become most dangerous. Is there one gamester out of twenty who, in a very few years, does not go—circumstances only considered—to ruin? Joe formed no exception. He lost caste, and fell, and fell, "deeper and deeper still," until he reached that last degrading status in society—a chevalier d'industrie.
While engaged in his base vocation, a young citizen fell into the hands of the gang with whom Joe, now a member of the body, regularly confederated. The victim was a Londoner, and one, as it was represented, who would stand plucking; and that very extensively. He had crossed the Channel, like the thousand and one fools who flock annually to the French capital to view Parisian lions, and, as a countryman, Little Joe kindly undertook to play Mentor to this Cockney Telemachus. It was not a difficult task for one who knew the world so well as Captain K—— to worm himself into the confidence of a raw youth, and he easily succeeded. In every point but one the intended victim was as pliant as could be wished—but on that one he was most obstinate. He had a horror of play. He would drink, racket about, dissipate, but name a game of chance, and he started like a frightened steed. The period allotted by "the governor at home," as he, in London parlance, termed his father, had almost expired; and as plump a pigeon as ever a gambler dropped upon, was about to return to the country-house he had quitted to see the world, without losing a single feather. To the villainous confederation that thought was maddening; and, as a last resource, a decoy duck was tried—and one of the loveliest and most artful of the class, was accidentally introduced by the gallant captain to Monsieur Callico, as he derisively called the citizen.
To describe the progress of this gambling conspiracy would be a waste of time. It was managed with consummate ability. The devoted youth became desperately enamored of this friend, of the captain; he "told his love," and then came proof positive, that Greek and Roman friendship are not comparable to the tremendous sacrifice of personal feeling, which you may expect from [Pg 632]a café acquaintance. Damon returned in time to substitute his own neck, and stay the execution of a gentleman called Pythias, while
Now Captain K——, on learning the state of the young Londoner's affections, although himself a secret worshiper at the shrine of the same divinity, resigned his own pretensions, and actually undertook to plead with the fair enslaver for his friend. Great was the intimacy, of course, that succeeded; and at the apartments of Madame La C——, morning, noon, and night, the young Englishman might have been found.
Play was cautiously introduced—nothing was staked excepting a mere bagatelle—beyond the hazard of a trifle, it was evident that any experiment would be dangerous. The day for the citizen's departure was fixed, and it was pretty certain the bird would escape the net of the fowler. Could he have been but led to play he would have been cheated scientifically. That was not to be done, and nothing could succeed but bold and downright felony.
Madame's birthday returned, as it did some twenty times a year; and she gave a petit souper. K—— sent in the wine, and the citizen provided the viands. A merrier evening could not be spent. Two or three ladies, and as many gentlemen of high honor, favored La C—— with their company. There was play, limited to a few francs, and on the Englishman's part to gloves and garters. Supper was served—all was hilarious—the wine circulated freely, and all the Londoner remembered in the morning when he awoke with a burning head was, that he had become unaccountably drunk, and got home he knew not how.
He strove to get up, but his temples throbbed almost to bursting. An excess in wine had never affected him so before: could this arise from simple drunkenness? The sensation was altogether new. The truth was he had not been drunk, but drugged!
While rolling his aching head from side to side upon the pillow his lacquey de place announced his dear friend, the captain; and next minute "Little Joe" was standing at his bedside.
"Good heaven!" exclaimed the citizen; "how awfully drunk I must have been last night! My very brain's on fire."
"Drunk!" returned his companion; "you were not drunk but mad—what devil possessed you to play? D—n it, you always swore you hated it, and every score of naps you lost you would, though I warned you, lay it on thicker."
"Naps! play!" exclaimed the sick man with a stare; "why, what do you mean? I am but in sorry mood for jesting. I do remember playing for and losing some gloves and garters to the ladies."
"And let me tell you, I am in still less joking humor than yourself," returned the captain, in high dudgeon; "through your cursed obstinacy, I played against my better judgment—and was cleaned by Count F—— out of eighteen thousand francs. How shall I come to book? In the devil's name how can I face my creditor this evening at Madame's réunion? The three hundred naps I won from you will go but a short way to meet my losses. I think I shall go mad."
"And I fancy that I am mad already," groaned the sufferer from the bed; "do end this folly, K——."
"Did I not know you, I should fancy you intended me offense," replied the captain, rather angrily; "what, have you such a conveniency of memory as to forget that you lost three hundred naps to me, eight hundred to the count, and five-and-forty to Madame La C——?"
Before the unhappy youth could find words to respond, the valet announced another visitor, and Count F—— was shown in.
"Monsieur le Comte," pursued the gallant captain, "are you, too, in a jesting mood? My young friend here can not be persuaded that we had a little play last night. Excuse me paying but half my loss till evening; and, in the mean time, accept these billets de banque," and "Little Joe" handed the chevalier a roll of bank notes; "you will find there ten thousand francs."
"Gentlemen," cried the astonished citizen, "I pray you end this farce. I know I am indebted to madame heavily in gloves and ribbons."
"Why, fiends and furies!" exclaimed the captain, "do you pretend, sir, to assert, that you did not lose three hundred naps to me?"
"Or that this acknowledgment for eight hundred was not given?"
The youth, astounded as he was, took the paper. It purported to be an I.O.U., but the forgery was clumsy.
"That is not my writing—nor do I owe either of you a sou."
The scene that followed may be imagined. Instant payment, or a legal security for the alleged debts was demanded—or the alternative—a meeting in the Bois de Boulogne within two hours. Half bewildered, the young dupe assented to give the latter—and at the time appointed he alighted, without friend or weapon, at the place named for the duel, by these infamous men.
Several other persons were on the ground, all strangers to the unfortunate young man. Another attempt was made to induce him to admit the debt of honor, and it was proposed that a reconciliation should take place between him and his former friend, the captain. To do them justice, the gentlemen unknown were ardent in their endeavors to accommodate the matter, and persuade the citizen to pay the money, and they were perfectly sincere in mediation on the occasion, for they were all members of the same dishonest clique. But nothing could shake the youth's determination to repudiate the infamous demand. Captain K——, irritated to madness at his total failure, demanded that the duel should instantly proceed—and the gang, as furious from the unexpected disappointment, determined to [Pg 633] murder one who could not be persuaded to submit to bare-faced spoliation.
Never were two combatants more unequally opposed, than the young merchant and the desperate gambler—the one, probably, had never discharged a pistol in his life—the other, and within six months, had killed his man on the very spot the doomed youth was standing.
Other and fouler circumstances went to render the result of the impending duel almost a certainty. K—— fought with his own pistols—with the firing signal he was particularly familiar—his back was to the sun, and an open sky behind him. The scoundrel second, who had volunteered his services, placed the young Englishman in a position where the trunk of a large beech formed a leading line of fire, and the stream of sunshine through the vista in the trees, was almost blinding. To the intentional murderer and the intended victim, the loaded weapons were delivered—a preparatory word was spoken, the signal fell. K—— coolly raised his pistol, while, by a snap-shot, the flurried Englishman anticipated his executioner by a second. On that momentary advantage life or death depended. The bully, shot directly through the heart, fell on the sward, a dead man. While the bullet destined for the breast of his antagonist, cut the grass harmlessly at the foot of the fortunate survivor. Never was a thoughtless youth more providentially delivered by accident from certain murder—nor a scoundrel sent to his account so justly and unexpectedly as Captain K——.
In riding an hour after the affair had terminated in the forest, I met the body of the dead gambler on a stretcher, en route to the Morgue.
The decline of dueling, from the period it was made ancillary to swindling, or to the settlement of disputes between vulgar scoundrels, who could not lay the slightest claims to the title or privileges of gentlemen, has been rapid and progressive, and its gross abuse did more to remedy its own mischief, than moral appeals and legal enactments. What but disgust can be created against a system when prostituted to the purposes of sheer murder? When two drunken blackguards stagger from the billiard-room to the field, and, by the scoundrels who attend them, are permitted to carry a dispute, emanating in a question of scoring or not scoring a point or two, to an extent that the most flagitious injury would not warrant?
A more recent case which occurred in the neighborhood, and must be still fresh in general recollection, may be adduced to prove how sadly the law of honor is brought to the lowliest estimation. I allude to the case of M——, killed by E——. A quarrel takes place in that sink of infamy, a saloon—and the parties adjourn to Wimbledon to commit murder. One fire is not enough, and, though a bullet passes through the hat of M——, the seconds provide them with fresh weapons, and the wretched blackguard is, on the next fire, shot dead. The ruffian who commits the murder, sees the expiring wretch heaving his last sigh—and remarks to a casual spectator, "I have done for the ——," using an epithet too disgusting to be named. He, and the well-selected seconds, hurry off, without even taking a parting glance at the prostrate victim. The surgeon, with his friends, lugs the dead body into a cab. An inquest is held—"willful murder" is returned, and thus ends, what the papers termed "an affair of honor." And who were the blackguard actors in this cold-blooded tragedy? E—— was son of a Taunton publican, and M—— a broken linen-draper. Their companions were men of similar caste—for, unless gentility is attached to brick-making, Y—— had no other claim.
The first duel I ever witnessed was one which, at the expiration of forty years, is too vividly engrafted upon memory to be forgotten. I was then a satcheled schoolboy; and before six o'clock on a beautiful summer morning, was wending my way, slowly, of course, to the abiding place of the country pedagogue at whose feet I was being indoctrinated. A gentleman was sitting on a log of timber, and in him I recognized Lieutenant V—— of the—th, a frequent visitor and guest at my father's house. He spoke to me, and I sate down upon the beam, and a bullet he had been rolling carelessly on the log of timber, was interchanged between him and me for five minutes. He started suddenly on perceiving three gentlemen advance from an opposite direction, put the ball in his waistcoat pocket, and bade me hastily "good-morning." I watched him—saw him join the strangers, and the whole party turned into a rope-yard. I rose from the beam—shouldered my satchel, and as I passed the place where the gentlemen had disappeared, I looked through the open gate. Although not more than three or four minutes had elapsed, the preliminary preparations for a duel had been completed, and my late companion on the log of timber confronted his antagonist at the customary distance of a dozen paces. At the moment I peeped in, the seconds delivered a pistol to each combatant—stepped two or three yards back—and the words "Ready, fire!" were rapidly pronounced. The reports were so simultaneous that it seemed as if one shot only had been discharged; and as, for a second or two afterward, both gentlemen remained standing, I fancied all was right; but I was fatally mistaken—the discharged weapon dropped from V——'s hand, and he tottered and fell forward. The seconds raised him to a sitting posture, and a little man hitherto concealed behind the hedge, came forward hastily. He laid his finger on V——'s pulse, and then looked at the pupil of the eye, and in a low voice muttered, "All is over!" For many a month afterward that brief sentence sounded in my ear, and the falling man was present in imagination. But before manhood came, an intimacy with some amiable young Galway gentlemen at the Dublin University, and a short probation in a Southern militia regiment wrought a happy change. The organ of hearing, as Byron says, became
[Pg 634]and a twelvemonth's sojourn in that land of promise, which lieth between the Shannon and Atlantic, completed the cure.
Like many an unnecessary appeal to arms, this fatal affair, in which a young and gallant officer lost his life, originated in a trifling misunderstanding.
In the same barrack, and at a very short time after this fatal meeting (spring of 1807) one of the most lamentable affairs, which in the annals of dueling is recorded, unfortunately took place. I allude to the fatal encounter between Boyd and Campbell. The sad story is simply told.
The 21st were quartered in the town of Newry, and the half-yearly inspection of the regiment had been made by General Kerr—when, as is customary, the general and staff were entertained by the Fusileers. The dinner was soon over—the staff retired—the officers went to the play—and none remained in the mess-room, excepting Major Campbell and Captain Boyd, the assistant-surgeon, and a lieutenant. Campbell, in right of brevet rank, had commanded the regiment in the absence of the colonel—and an argument took place between him and Captain Boyd, whether a word of command that day used was correctly given. The latter was a person of disagreeable manner—the former a man whose temper was highly excitable—and each personally disliked the other, and were tenacious equally of their own opinions. Campbell repudiated the charge of incorrectness and Boyd as warmly maintained it. At last a crisis came, "Heated with wine, and exasperated by what he conceived a professional insult, Campbell left the table, hastened to his apartments, loaded his pistols, returned, sent for Captain Boyd, brought him to an inner mess-room, closed the door, and without the presence of a friend or witness, demanded instant satisfaction. Shots were promptly interchanged, and by the first fire Boyd fell, mortally wounded."
Thank God! for human nature—Buckinghams and T——s are not common. Before five minutes passed the tornado of wild passion was over, and rushing to the room where the dying man was laid, "a sorry sight!" in Macbeth's words, surrounded by his frantic wife and infant family, the homicide knelt at his bed-side, implored forgiveness, and wrung from him a qualified admission that "all was fair." No attempt was made to arrest him, and that night Campbell left the town and remained at Chelsea with his lady and family for several months, under an assumed name. When the summer assizes were approaching, he determined to surrender and stand his trial; and although his legal advisers warned him that the step was most perilous, he would not be dissuaded, and unhappily persevered.
He was, on the 13th of August, 1808, arraigned for "willful murder," pleaded "not guilty" in the usual form—the fact of the homicide was admitted—and a number of officers, high in rank, attended, and gave the prisoner the highest character for humanity. I did not hear the evidence, and when I came into the court-house the jury for some time had been considering their verdict. The trial had been tedious; twilight had fallen, and the hall of justice, dull at best, was rendered gloomier still from the partial glare of a few candles placed upon the bench, where Judge Fletcher was presiding. A breathless anxiety pervaded the assembly, and the ominous silence that reigned throughout the court was unbroken by a single whisper. I felt an unusual dread—a sinking of the heart—a difficulty of respiration, and as I looked round the melancholy crowd, my eye rested on the judge. Fletcher was a thin, billious-looking being, and his cold and marble features had caught an unearthly expression from the shading produced by the accidental disposition of the candles. I shuddered as I gazed upon him, for the fate of a fellow creature was hanging upon the first words that would issue from the lips of that stern and inflexible old man. From the judge my eyes turned to the criminal, and what a subject the contrast offered to the artist's pencil! In the front of the bar, habited in deep mourning, his arms folded and crossed upon his breast, the homicide was awaiting the word that should seal his destiny. His noble and commanding figure thrown into an attitude of calm determination, was graceful and dignified; and while on every countenance besides a sickening anxiety was visible, neither the quivering of an eyelash, nor a motion of the lip, betrayed on the prisoner's face the appearance of discomposure or alarm. Just then a slight noise was heard—a door was slowly and softly opened—one by one the jury returned to their box—the customary question was asked by the clerk of the crown—and—"Guilty" was faintly answered, accompanied with a recommendation to mercy. An agonizing pause succeeded—the court was as silent as the grave—the prisoner bowed respectfully to the jury, then planting his foot firmly on the floor, he drew himself up to his full height and calmly listened to his doom. Slowly Judge Fletcher assumed the fatal cap, and all unmoved, he pronounced, and Campbell listened to, his sentence.
While the short address which sealed the prisoner's fate was being delivered, the silence of the court was only broken by smothered sobs; but when the sounds ceased, and, "Lord have mercy on your soul!" issued from the ashy lips of the stern old man, a groan of horror burst from the auditory, and the Highland soldiers, who thronged the court, ejaculated a wild "Amen," while their flashing eyes betrayed how powerfully the fate of their unhappy countryman had affected them. He was removed from the bar—a doomed man—but no harsh restrictions were imposed upon him, nor was he conducted to the gloomy apartment to which condemned criminals after sentence were then consigned. From the moment the unfortunate duelist had entered the prison gates, his mild and gentlemanly demeanor had won the[Pg 635] commiseration of all within; and the governor, confident in the honor of his prisoner, subjected him to no restraint. He occupied the apartments of the keeper, went over the building as he pleased—received his friends—held unrestricted communication with all that sought him—and, in fact, was a captive but in name.
No man impersonated the grandeur of Byron's beautiful couplet so happily as Campbell: when the hour of trial came,
while, during the painful interval when the seat of mercy was appealed to, and when, as it was generally considered, mercy would have been extended, the most unmoved of all, as post after post brought not the welcome tidings, was Campbell.
One anecdote is too characteristic to be omitted.
The commiseration of all classes was painfully increased by the length of time that elapsed between the trial and death of Major Campbell. In prison, he received from his friends the most constant and delicate attention; and one lady, the wife of Captain ——, seldom left him. She read to him, prepared his meals, cheered his spirits when he drooped, and performed those gentle offices of kindness, so peculiarly the province of a woman. When intelligence arrived that mercy could not be extended, and the law must take its course, she boldly planned an escape from prison; but Campbell, when she mentioned it, recoiled from a proposition that must compromise his honor with the keeper. "What," he exclaimed, when assured that otherwise his case was hopeless, "shall I break my faith with him who trusted it? I know my fate, and am prepared to meet it manfully; but never will I deceive the person who confided in my honor."
Two evenings before he suffered, Mrs. —— was earnestly urging him to escape. The clock struck twelve, and Campbell hinted that it was time she should retire. As usual, he accompanied her to the gate; and on entering the keeper's room, they found him fast asleep. Campbell placed his finger on his lip.
"Poor fellow," he said in a whisper, to his fair companion, "would it not be a pity to disturb him?" then taking the keys softly from the table, he unlocked the outer wicket.
"Campbell," said the lady, "this is the crisis of your fate; this is the moment for your deliverance! Horses are in readiness, and—"
The convict put his hand upon her mouth. "Hush," he replied, as he gently forced her out. "Would you have me violate my word of honor?"
Bidding her "good night," he locked the wicket carefully, replaced the keys, and retired to his chamber without awakening the sleeping jailer!
His last hour was passed in prayer, and at noon he was summoned to pass the grand ordeal which concludes the history of the hero and the herdsman.
The drop, as it was called, was, in the Irish jails, attached to the upper story of the building, a large iron-studded door, which hung against the wall, and was only raised to a parallel position with the door from which the criminal made his last exit, when that concluding ceremony of the law was to be performed. Attended by the jail chaplain—one who, in the last bitter trial, clave to the condemned soldier closer than a brother—he steadily mounted the stairs, and entered the execution room. The preliminaries of death were undergone composedly; he bade a long farewell to those around, and stepped firmly on the board. Twenty-thousand lookers-on filled the green in front of the prison; and, strange accident! the Highland regiment with whom, shoulder to shoulder, he had charged "the Invincibles" in Egypt, formed a semicircle round the prison. In the north of Ireland, all is decorously conducted. When he appeared, a deep and solemn silence awed the multitude; and until he addressed the Highlanders in Gaelic, a whisper might have been heard in the crowd. To the simple request of "Pray for me!" a low deep groan responded, and every bonnet was removed. He dropped a cambric handkerchief—down came the iron-bound door—it sounded over the heads of the silent concourse like a thunder-clap; and, in one minute, as brave a heart as ever beat upon a battle-field, had ceased to throb.
Peace to the ashes of the brave! If a soldier's life, a Christian's end, can atone for the sad consequences of unreining an ungovernable temper, both can be honestly pleaded in extenuating poor Campbell's crime.
[4] Continued from the September Number.
"THE CHATEAU OF ETTENHEIM."
I now come to an incident in my life, of which however briefly I may speak, has left the deepest impression on my memory. I have told the reader how I left Kuffstein fully satisfied that the Count de Marsanne was Laura's lover, and that in keeping my promise to see and speak with him, I was about to furnish an instance of self-denial and fidelity that nothing in ancient or modern days could compete with.
The letter was addressed, "the Count Louis de Marsanne, Chateau d'Ettenheim, à Bade," and thither I accordingly repaired, traveling over the Arlberg to Bregenz, and across the Lake of Constance to Freyburg. My passport contained a very few words in cipher, which always sufficed to afford me free transit and every attention from the authorities. I had left the southern Tyrol in the outburst of a glorious spring, but as I journeyed northward I found the rivers frozen, the roads encumbered with snow, and the fields untilled and dreary-looking. Like all countries which derive their charms from the elements of rural beauty, foliage, and verdure, Germany offers a sad-colored picture to the traveler in winter or wintry weather.
[Pg 636]It was thus then that the Grand Duchy, so celebrated for its picturesque beauty, struck me as a scene of dreary and desolate wildness, an impression which continued to increase with every mile I traveled from the high road. A long unbroken flat, intersected here and there by stunted willows, traversed by a narrow earth road, lay between the Rhine and the Taunus Mountains, in the midst of which stood the village of "Ettenheim." Outside the village, about half a mile off, and on the border of a vast pine forest, stood the Chateau.
It was originally a hunting-seat of the dukes of Baden, but, from neglect and disuse, gradually fell into ruin, from which it was reclaimed, imperfectly enough, a year before, and now exhibited some remnants of its former taste, along with the evidences of a far less decorative spirit; the lower rooms being arranged as a stable, while the stair and entrance to the first story opened from a roomy coach-house. Here some four or five conveyances of rude construction were gathered together, splashed and unwashed as if from recent use; and at a small stove in a corner was seated a peasant in a blue frock smoking, as he affected to clean a bridle which he held before him.
Without rising from his seat he saluted me, with true German phlegm, and gave me the "Guten Tag," with all the grave unconcern of a "Badener." I asked if the Count de Marsanne lived there. He said yes, but the "Graf" was out hunting. When would he be back? By nightfall.
Could I remain there till his return? was my next question, and he stared at me, as I put it, with same surprise. "Warum nicht," "Why not," was at last his sententious answer, as he made way for me beside the stove. I saw at once that my appearance had evidently not entitled me to any peculiar degree of deference or respect, and that the man regarded me as his equal. It was true I had come some miles on foot, and with a knapsack on my shoulder, so that the peasant was fully warranted in his reception of me. I accordingly seated myself at his side, and, lighting my pipe from his, proceeded to derive all the profit I could from drawing him into conversation. I might have spared myself the trouble. Whether the source lay in stupidity or sharpness, he evaded me on every point. Not a single particle of information could I obtain about the count, his habits, or his history. He would not even tell me how long he had resided there, nor whence he had come. He liked hunting, and so did the other "Herren." There was the whole I could scan, and to the simple fact that there were others with him, did I find myself limited.
Curious to see something of the count's "interior," I hinted to my companion that I had come on purpose to visit his master, and suggested the propriety of my awaiting his arrival in a more suitable place; but he turned a deaf ear to the hint, and dryly remarked that the "Graf would not be long a-coming now." This prediction was, however, not to be verified; the dreary hours of the dull day stole heavily on, and although I tried to beguile the time by lounging about the place, the cold ungenial weather drove me back to the stove, or to the dark precincts of the stable, tenanted by three coarse ponies of the mountain breed.
One of these was the Graf's favorite, the peasant told me, and indeed here he showed some disposition to become communicative, narrating various gifts and qualities of the unseemly looking animal, which, in his eyes, was a paragon of horse flesh. "He could travel from here to Kehl and back in a day, and has often done it," was one meed of praise that he bestowed; a fact which impressed me more as regarded the rider than the beast, and set my curiosity at work to think why any man should undertake a journey of nigh seventy miles between two such places and with such speed. The problem served to occupy me till dark, and I know not how long after. A stormy night of rain and wind set in, and the peasant, having bedded and foraged his cattle, lighted a rickety old lantern and began to prepare for bed; for such I at last saw was the meaning of a long crib, like a coffin, half-filled with straw and sheep skins. A coarse loaf of black bread, some black forest cheese, and a flask of Kleinthaler, a most candid imitation of vinegar, made their appearance from a cupboard, and I did not disdain to partake of these delicacies.
My host showed no disposition to become more communicative over his wine, and, indeed, the liquor might have excused any degree of reserve; and no sooner was our meal over than, drawing a great woolen cap half over his face, he rolled himself up in his sheep-skins, and betook himself to sleep, if not with a good conscience, at least with a sturdy volition that served just as well.
Occasionally snatching a short slumber, or walking to and fro in the roomy chamber, I passed several hours, when the splashing sound of horses' feet, advancing up the miry road, attracted me. Several times before that I had been deceived by noises which turned out to be the effects of storm, but now, as I listened, I thought I could hear voices. I opened the door, but all was dark outside; it was the inky hour before daybreak, when all is wrapped in deepest gloom. The rain, too, was sweeping along the ground in torrents. The sounds came nearer every instant, and, at last, a deep voice shouted out, "Jacob." Before I could awaken the sleeping peasant, to whom I judged this summons was addressed, a horseman dashed up to the door and rode in; another as quickly followed him, and closed the door.
"Parbleu, D'Egville," said the first who entered, "we have got a rare peppering!"
"Even so," said the other, as he shook his hat, and threw off a cloak perfectly soaked with rain; "à la guerre comme, à la guerre."
This was said in French, when, turning toward me, the former said in German, "Be active, Master Jacob; these nags have had a smart ride [Pg 637]of it." Then, suddenly, as the light flashed full on my features, he started back, and said, "How is this—who are you?"
A very brief explanation answered this somewhat uncourteous question, and, at the same time, I placed the marquise's letter in his hand, saying, "The Count de Marsanne, I presume?"
He took it hastily, and drew nigh to the lantern to peruse it. I had now full time to observe him, and saw that he was a tall and well-built man, of about seven or eight-and-twenty. His features were remarkably handsome, and, although slightly flushed by his late exertion, were as calm and composed as might be; a short black mustache gave his upper lip a slight character of scorn, but the brow, open, frank, and good-tempered in its expression, redeemed this amply. He had not read many lines when, turning about, he apologized in the most courteous terms for the manner of my reception. He had been on a shooting excursion for a few days back, and taken all his people with him, save the peasant who looked after the cattle. Then, introducing me to his friend, whom he called Count d'Egville, he led the way up-stairs.
It would be difficult to imagine a greater contrast to the dark and dreary coach-house than the comfortable suite of apartments which we now traversed on our way to a large, well-furnished room, where a table was laid for supper, and a huge wood fire blazed brightly on the hearth. A valet, of most respectful manner, received the count's orders to prepare a room for me, after which my host and his friend retired to change their clothes.
Although D'Egville was many years older, and of a graver, sterner fashion than the other, I could detect a degree of deference and respect in his manner toward him, which De Marsanne accepted like one well-accustomed to receive it. It was a time, however, when, in the wreck of fortune, so many men lived in a position of mere dependence that I thought nothing of this, nor had I even the time, as Count de Marsanne entered. From my own preconceived notions as to his being Laura's lover, I was quite prepared to answer a hundred impatient inquiries about the marquise and her niece, and as we were now alone, I judged that he would deem the time a favorable one to talk of them. What was my surprise, however, when he turned the conversation exclusively to the topic of my own journey, the route I had traveled. He knew the country perfectly, and spoke of the various towns and their inhabitants with acuteness and tact.
His royalist leanings did not, like those of the marquise, debar him from feeling a strong interest respecting the success of the republican troops, with whose leaders he was thoroughly acquainted, knowing all their peculiar excellences and defaults as though he had lived in intimacy with them. Of Bonaparte's genius he was the most enraptured admirer, and would not hear of any comparison between him and the other great captains of the day. D'Egville at last made his appearance, and we sat down to an excellent supper, enlivened by the conversation of our host, who, whatever the theme, talked well and pleasingly.
I was in a mood to look for flaws in his character, my jealousy was still urging me to seek for whatever I could find fault with, and yet all my critical shrewdness could only detect a slight degree of pride in his manner, not displaying itself by any presumption, but by a certain urbanity that smacked of condescension; but even this, at last, went off, and before I wished him good-night, I felt that I had never met any one so gifted with agreeable qualities, nor possessed of such captivating manners, as himself. Even his royalism had its fascinations, for it was eminently national, and showed, at every moment, that he was far more of a Frenchman than a monarchist. We parted without one word of allusion to the marquise or to Laura! Had this singular fact any influence upon the favorable impression I had conceived of him, or was I unconsciously grateful for the relief thus given to all my jealous tormentings? Certain is it that I felt infinitely happier than I ever fancied I should be under his roof, and, as I lay down in my bed, thanked my stars that he was not my rival!
When I awoke the next morning I was some minutes before I could remember where I was, and as I still lay, gradually recalling myself to memory, the valet entered to announce the count.
"I have come to say adieu for a few hours," said he; "a very pressing appointment requires me to be at Pfortzheim to-day, and I have to ask that you will excuse my absence. I know that I may take this liberty without any appearance of rudeness, for the marquise has told me all about you. Pray, then, try and amuse yourself till evening, and we shall meet at supper."
I was not sorry that D'Egville was to accompany him, and, turning on my side, dozed off to sleep away some of the gloomy hours of a winter's day.
In this manner several days were passed, the count absenting himself each morning, and returning at nightfall, sometimes accompanied by D'Egville, sometimes alone. It was evident enough, from the appearance of his horses at his return, as well as from his own jaded looks, that he had ridden hard and far; but except a chance allusion to the state of the roads or the weather, it was a topic to which he never referred, nor, of course, did I ever advert. Meanwhile our intimacy grew closer and franker. The theme of politics, a forbidden subject between men so separated, was constantly discussed between us, and I could not help feeling flattered at the deference with which he listened to opinions from one so much his junior, and so inferior in knowledge as myself. Nothing could be more moderate than his views of government, only provided that it was administered by the rightful sovereign. The claim of a king to his throne he declared to be the foundation of all the rights of property, and which, if once shaken or disputed, would inevitably lead to the wildest theories of [Pg 638]democratic equality. "I don't want to convert you," would he say, laughingly, "the son of an old Garde du Corps, the born gentleman, has but to live to learn. It may come a little later or a little earlier, but you'll end as a good monarchist."
One evening he was unusually late in returning, and when he came was accompanied by seven or eight companions, some younger, some older than himself, but all men whose air and bearing bespoke their rank in life, while their names recalled the thoughts of old French chivalry. I remember among them was a Coigny, a Grammont, and Rouchefoucauld—the last as lively a specimen of Parisian wit and brilliancy as ever fluttered along the sunny Boulevards.
De Marsanne, while endeavoring to enjoy himself and entertain his guests, was, to my thinking, more serious than usual, and seemed impatient at D'Egville's absence, for whose coming we now waited supper.
"I should not wonder if he was lost in the deep mud of those cross-roads," said Coigny.
"Or perhaps he has fallen into the Republic," said Rouchefoucauld, "it's the only thing dirtier that I know of."
"Monsieur forgets that I wear its cloth," said I in a low whisper to him; and low as it was De Marsanne overheard it.
"Yes, Charles," cried he, "you must apologize, and on the spot, for the rudeness."
Rouchefoucauld reddened and hesitated.
"I insist, sir," cried De Marsanne, with a tone of superiority I had never seen him assume before.
"Perhaps," said he, with a half-sneer, "Monsieur de Tiernay might refuse to accept my excuses?"
"In that case, sir," interposed De Marsanne, "the quarrel will become mine, for he is my guest, and lives here under the safeguard of my honor."
Rouchefoucauld bowed submissively and with the air of a man severely but justly rebuked; and then advancing to me, said, "I beg to tender you my apology, monsieur, for an expression which should never have been uttered by me in your presence."
"Quite sufficient, sir," said I, bowing, and anxious to conclude a scene which for the first time had disturbed the harmony of our meetings. Slight as was the incident, its effects were yet visible in the disconcerted looks of the party, and I could see that more than one glance was directed toward me with an expression of coldness and distrust.
"Here comes D'Egville at last," said one, throwing open the window to listen; the night was starlit, but dark, and the air calm and motionless. "I certainly heard a horse's tread on the causeway."
"I hear distinctly the sound of several," cried Coigny; "and, if I mistake not much, so does M. de Tiernay." This sudden allusion turned every eye toward me, as I stood still, suffering from the confusion of the late scene.
"Yes; I hear the tramp of horses, and cavalry, too, I should say, by their measured tread."
"There was a trumpet call!" cried Coigny; "what does that mean?"
"It is the signal to take open order," said I, answering as if the question were addressed to myself. "It is a picket taking a 'reconnaissance.'"
"How do you know that, sir?" said Grammont, sternly.
"Ay! how does he know that?" cried several, passionately, as they closed around me.
"You must ask in another tone, messieurs," said I calmly, "if you expect to be answered."
"They mean to say how do you happen to know the German trumpet-calls, Tiernay," said De Marsanne, mildly, as he laid his hand on my arm.
"It's a French signal," said I; "I ought to know it well."
Before my words were well uttered the door was thrown open, and D'Egville burst into the room, pale as death, his clothes all mud-stained and disordered. Making his way through the others, he whispered a few words in De Marsanne's ear.
"Impossible!" cried the other; "we are here in the territory of the margrave?"
"It is as I say," replied D'Egville; "there's not a second to lose—it may be too late even now—by heavens it is!—they've drawn a cordon round the chateau."
"What's to be done, gentlemen?" said De Marsanne, seating himself calmly, and crossing his arms on his breast.
"What do you say, sir?" cried Grammont, advancing to me with an air of insolent menace, "you, at least, ought to know the way out of this difficulty."
"Or, by Heaven, his own road shall be one of the shortest, considering the length of the journey," muttered another, and I could hear the sharp click of a pistol cock as he spoke the words.
"This is unworthy of you, gentlemen, and of me," said De Marsanne, haughtily; and he gazed around him with a look that seemed to abash them, "nor is it a time to hold such disputation. There is another and a very difficult call to answer. Are we agreed"—before he could finish the sentence the door was burst open, and several dragoons in French uniforms entered, and ranged themselves across the entrance, while a colonel, with, his sabre drawn, advanced in front of them.
"This is brigandage," cried De Marsanne, passionately, as he drew his sword, and seemed meditating a spring through them; but he was immediately surrounded by his friends and disarmed. Indeed nothing could be more hopeless than resistance; more than double our number were already in the room, while the hoarse murmur of voices without, and the tramp of heavy feet, announced a strong party.
At a signal from their officer, the dragoons unslung their carbines, and held them at the cock [Pg 639]when the colonel called out, "Which of you, messieurs, is the Duc d'Enghien?"
"If you come to arrest him," replied De Marsanne, "you ought to have his description in your warrant."
"Is the descendant of a Condé ashamed to own his name?" asked the colonel, with a sneer. "But we'll make short work of it, sirs; I arrest you all. My orders are peremptory, messieurs. If you resist, or attempt to escape—" and he made a significant sign with his hand to finish. The "Duc"—for I need no longer call him "De Marsanne"—never spoke a word, but with folded arms calmly walked forward, followed by his little household. As we descended the stairs, we found ourselves in the midst of about thirty dismounted dragoons, all on the alert, and prepared for any resistance. The remainder of the squadron were on horseback without. With a file of soldiers on either hand we marched for about a quarter of a mile across the fields to a small mill, where a general officer and his staff seemed awaiting our arrival. Here, too, a picket of gens-d'armes was stationed; a character of force significant enough of the meaning of the enterprise. We were hurriedly marched into the court of the mill, the owner of which stood between two soldiers, trembling from head to foot with terror.
"Which is the Duc D'Enghien?" asked the colonel of the miller.
"That is he with the scarlet vest," and the prince nodded an assent.
"Your age, monsieur?" asked the colonel of the prince.
"Thirty-two—that is, I should have been so much in August, were it not for this visit," said he, smiling.
The colonel wrote on rapidly for a few minutes, and then showed the paper to the general, who briefly said, "Yes, yes; this does not concern you nor me."
"I wish to ask, sir," said the prince, addressing the general, "do you make this arrest with the consent of the authorities of this country, or do you do so in defiance of them?"
"You must reserve questions like that for the court who will judge you, Monsieur de Condé," said the officer, roughly. "If you wish for any articles of dress from your quarters, you had better think of them. My orders are to convey you to Strassburg. Is there any thing so singular in the fact, sir, that you should look so much astonished?"
"There is, indeed," said the prince, sorrowfully. "I shall be the first of my house who ever crossed that frontier a prisoner."
"But not the first who carried arms against his country," rejoined the other, a taunt the duke only replied to by a look of infinite scorn and contempt. With a speed that told plainly the character of the expedition, we were now placed, two together, on country cars, and driven at a rapid pace toward Strassburg. Relays of cattle awaited us on the road, and we never halted but for a few minutes during the entire journey. My companion on this dreary day was the Baron de St. Jacques, the aid-de-camp to the duke; but he never spoke once—indeed he scarcely lifted his head during the whole road.
Heaven knows it was a melancholy journey; and neither the country nor the season were such as to lift the mind from sorrow; and yet, strange enough, the miles glided over rapidly, and to this hour I can not remember by what magic the way seemed so short. The thought that for several days back I had been living in closest intimacy with a distinguished prince of the Bourbon family, that we had spent hours together discussing themes and questions which were those of his own house; canvassing the chances and weighing the claims of which he was himself the asserter—was a most exciting feeling. How I recalled now all the modest deference of his manner—his patient endurance of my crude opinions—his generous admissions regarding his adversaries—and, above all, his ardent devotion to France, whatever the hand that swayed her destinies; and then the chivalrous boldness of his character, blended with an almost girlish tenderness—how princely were such traits?
From these thoughts I wandered on to others about his arrest and capture, from which, however, I could not believe any serious issue was to come. Bonaparte is too noble minded not to feel the value of such a life as this. Men like the prince can be more heavily fettered by generous treatment than by all the chains that ever bound a felon. But what will be done with him?—what with his followers?—and lastly, not at all the pleasantest consideration, what is to come of Maurice Tiernay, who, to say the least, has been found in very suspicious company, and without a shadow of an explanation to account for it? This last thought just occurred to me as we crossed over the long bridge of boats, and entered Strassburg.
AN "ORDINARY" ACQUAINTANCE.
The Duc D'Enghien and his aid-de-camp were forwarded with the utmost speed to Paris; the remainder of us were imprisoned at Strassburg. What became of my companions I know not; but I was sent on, along with a number of others, about a month later, to Nancy, to be tried by a military commission. I may mention it here, as a singular fact illustrating the secrecy of the period, that it was not till long after this time I learned the terrible fate of the poor Prince de Condé. Had I known it, it is more than probable that I should have utterly despaired of my own safety. The dreadful story of Vincennes—the mock trial, and the midnight execution—are all too well known to my readers; nor is it necessary I should refer to an event, on which I myself can throw no new light. That the sentence was determined on before his arrest—and that the grave was dug while the victim was still sleeping the last slumber before "the sleep that knows not waking"—the evidences are strong and undeniable. But an anecdote which circu[Pg 640]lated at the time, and which, so far as I know, has never appeared in print, would seem to show that there was complicity, at least, in the crime, and that the secret was not confined to the First Consul's breast.
On that fatal night of the 20th March, Talleyrand was seated at a card-table at Caulaincourt's house at Paris. The party was about to rise from play, when suddenly the "pendule" on the chimney-piece struck two. It was in one of those accidental pauses in the conversation when any sound is heard with unusual distinctness. Talleyrand started, as he heard it, and then turning to Caulaincourt, whispered, "Yes; 'tis all over now?" words which, accidentally overheard, without significance, were yet to convey a terrible meaning when the dreadful secret of that night was disclosed.
If the whole of Europe was convulsed by the enormity of this crime—the foulest that stains the name of Bonaparte—the Parisians soon forgot it, in the deeper interest of the great event that was now approaching—the assumption of the imperial title by Napoleon.
The excitement on this theme was so great and absorbing, that nothing else was spoken or thought of. Private sorrows and afflictions were disregarded and despised, and to obtrude one's hardships on the notice of others seemed, at this juncture, a most ineffable selfishness. That I, a prisoner, friendless and unknown as I was, found none to sympathize with me or take interest in my fate, is, therefore, nothing extraordinary. In fact, I appeared to have been entirely forgotten; and though still in durance, nothing was said either of the charge to be preferred against me, nor the time when I should be brought to trial.
Giacourt, an old lieutenant of the marines, and at that time deputy-governor of the Temple, was kind and good-natured toward me, occasionally telling of the events which were happening without, and giving me the hope that some general amnesty would, in all likelihood, liberate all those whose crimes were not beyond the reach of mercy. The little cell I occupied—and to Giacourt's kindness I owed the sole possession of it—looked out upon the tall battlements of the outer walls, which excluded all view beyond, and thus drove me within myself for occupation and employment. In this emergency I set about to write some notices of my life—some brief memoirs of those changeful fortunes which had accompanied me from boyhood. Many of those incidents which I relate now, and many of those traits of mind or temper that I recall, were then for the first time noted down, and thus graven on my memory.
My early boyhood, my first experiences as a soldier, the campaign of the "Schwarzwald," Ireland, and Genoa, all were mentioned, and, writing as I did, solely for myself and my own eyes, I set down many criticisms on the generals, and their plans of campaign, which, if intended for the inspection of others, would have been the greatest presumption and impertinence, and in this way Moreau, Hoche, Massena, and even Bonaparte, came in for a most candid and impartial criticism.
How Germany might have been conquered; how Ireland ought to have been invaded; in what way Italy should have been treated, and lastly, the grand political error of the seizure of Duc D'Enghein, were subjects that I discussed and determined with consummate boldness and self-satisfaction. I am almost overwhelmed with shame, even now, as I think of that absurd chronicle, with its rash judgments, its crude opinions and its pretentious decisions.
So fascinated had I become with my task, that I rose early to resume it each morning, and used to fall asleep, cogitating on the themes for the next day, and revolving within myself all the passages of interest I should commemorate. A man must have known imprisonment to feel all the value that can be attached to any object, no matter how mean or insignificant, that can employ the thoughts, amuse the fancy, or engage the affections. The narrow cell expands under such magic, the barred casement is a free portal to the glorious sun and the free air; the captive himself is but the student bending over his allotted task. To this happy frame of mind had I come, without a thought or a wish beyond the narrow walls at either side of me, when a sad disaster befell me. On awaking one morning, as usual, to resume my labor, my manuscript was gone! the table and writing materials, all had disappeared, and, to increase my discomfiture, the turnkey informed me that Lieutenant Giacourt had been removed from his post, and sent off to some inferior station in the provinces.
I will not advert to the dreary time which followed this misfortune, a time in which the hours passed on unmeasured and almost unfelt. Without speculation, without a wish, I passed my days in a stupid indolence akin to torpor. Had the prison doors been open, I doubt if I should have had the energy to make my escape. Life itself ceased to have any value for me, but somehow I did not desire death. I was in this miserable mood when the turnkey awoke me one day as I was dozing on my bed. "Get up and prepare yourself to receive a visitor," said he. "There's an officer of the staff without, come to see you;" and, as he spoke, a young, slightly-formed man entered, in the uniform of a captain, who, making a sign for the turnkey to withdraw, took his seat at my bedside.
"Don't get up, monsieur; you look ill and weak, so, pray, let me not disturb you," said he, in a voice of kindly meaning.
"I am not ill," said I, with an effort, but my hollow utterance and my sunken cheeks contradicted my words, "but I have been sleeping; I usually doze at this hour."
"The best thing a man can do in prison, I suppose," said he, smiling good-naturedly.
"No, not the best," said I, catching up his words too literally. "I used to write the whole day long, till they carried away my paper and my pens."
[Pg 641]"It is just of that very thing I have come to speak, sir," resumed he. "You intended that memoir for publication!"
"No; never."
"Then for private perusal among a circle of friends."
"Just as little. I scarcely know three people in the world who would acknowledge that title."
"You had an object, however, in composing it?"
"Yes; to occupy thought; to save me from—from—" I hesitated, for I was ashamed of the confession that nearly burst from me, and, after a pause, I said, "from being such as I now am?"
"You wrote it for yourself alone, then?"
"Yes."
"Unprompted; without any suggestions from another?"
"Is it here?" said I, looking around my cell, "Is it here that I should be likely to find a fellow-laborer?"
"No; but I mean to ask, were the sentiments your own, without any external influence, or any persuasions from others?"
"Quite my own."
"And the narrative is true?"
"Strictly so, I believe."
"Even to your meeting with the Duc D'Enghien. It was purely accidental?"
"That is, I never knew him to be the duke till the moment of his arrest?"
"Just so; you thought he was merely a royalist noble. Then, why did you not address a memoir to that effect to the minister?"
"I thought it would be useless; when they made so little of a Condé, what right had I to suppose they would think much about me?"
"If he could have proved his innocence"—he stopped, and then in an altered voice said—"but as to this memoir, you assume considerable airs of military knowledge in it, and many of the opinions smack of heads older than yours."
"They are, I repeat, my own altogether; as to their presumption, I have already told you they were intended solely for my own eye."
"So that you are not a royalist?"
"No."
"Never were one?"
"Never."
"In what way would you employ yourself, if set at liberty to-day."
I stared, and felt confused; for however easy I found it to refer to the past, and reason on it, any speculation as to the future was a considerable difficulty.
"You hesitate; you have not yet made up your mind, apparently?"
"It is not that; I am trying to think of liberty, trying to fancy myself free—but I can not!" said I, with a weary sigh; "the air of this cell has sapped my courage and my energy—a little more will finish the ruin!"
"And yet you are not much above four or five-and-twenty years of age?"
"Not yet twenty!" said I.
"Come, come, Tiernay—this is too early to be sick of life!" said he, and the kind tone touched me so that I burst into tears. They were bitter tears, too; for while my heart was relieved by this gush of feeling, I was ashamed at my own weakness. "Come, I say," continued he, "this memoir of yours might have done you much mischief—happily it has not done so. Give me the permission to throw it in the fire, and, instead of it, address a respectful petition to the head of the state, setting forth your services, and stating the casualty by which you were implicated in royalism. I will take care that it meets his eye, and, if possible, will support its prayer; above all, ask for reinstatement in your grade, and a return to the service. It may be, perhaps, that you can mention some superior officer who would vouch for your future conduct."
"Except Colonel Mahon."
"Not the Colonel Mahon who commanded the 13th Cuirassiers?"
"The same!"
"That name would little serve you," said he, coldly, "he has been placed 'en retraite' some time back; and if your character can call no other witness than him, your case is not too favorable." He saw that the speech had disconcerted me, and soon added, "Never mind—keep to the memoir; state your case, and your apology, and leave the rest to fortune. When can you let me have it?"
"By to-morrow—to-night, if necessary."
"To-morrow will do well, and so good-by. I will order them to supply you with writing materials;" and slapping me good-naturedly on the shoulder, he cried, "Courage, my lad," and departed.
Before I lay down to sleep that night, I completed my "memoir," the great difficulty of which I found to consist in that dry brevity which I knew Bonaparte would require. In this, however, I believe I succeeded at last, making the entire document not to occupy one sheet of paper. The officer had left his card of address, which I found was inscribed Monsieur Bourrienne, Rue Lafitte, a name that subsequently was to be well known to the world.
I directed my manuscript to his care, and lay down with a lighter heart than I had known for many a day. I will not weary my reader with the tormenting vacillations of hope and fear which followed. Day after day went over, and no answer came to me. I addressed two notes respectful, but urgent, begging for some information as to my demand—none came. A month passed thus, when, one morning, the governor of the Temple entered my room with an open letter in his hand.
"This is an order for your liberation, Monsieur de Tiernay," said he; "you are free."
"Am I reinstated in my grade?" asked I, eagerly.
He shook his head, and said nothing.
"Is there no mention of my restoration to the service?"
"None, sir."
"Then, what is to become of me—to what end am I liberated?" cried I, passionately.
[Pg 642]"Paris is a great city, there is a wide world beyond it, and a man so young as you are must have few resources, or he will carve out a good career for himself."
"Say, rather, he must have few resentments, sir," cried I, bitterly, "or he will easily hit upon a bad one;" and with this, I packed up the few articles I possessed, and prepared to depart.
I remember it well; it was between two and three o'clock of the afternoon, on a bright day in spring, that I stood on the Quai Voltaire, a very small packet of clothes in a bundle in one hand, and a cane in the other, something short of three louis in my purse, and as much depression in my heart as ever settled down in that of a youth not full nineteen. Liberty is a glorious thing, and mine had been periled often enough, to give me a hearty appreciation of its blessing; but at that moment, as I stood friendless and companionless in a great thoroughfare of a great city, I almost wished myself back again within the dreary walls of the Temple, for somehow it felt like home! It is true one must have had a lonely lot in life before he could surround the cell of a prison with such attributes as these! Perhaps I have more of the cat-like affection for a particular spot than most men; but I do find that I attach myself to the walls with a tenacity that strengthens as I grow older, and like my brother parasite, the ivy, my grasp becomes more rigid the longer I cling.
If I know of few merely sensual gratifications higher than a lounge through Paris, at the flood-tide of its population, watching the varied hues and complexions of its strange inhabitants, displaying, as they do in feature, air, and gesture, so much more of character and purpose than other people, so also do I feel that there is something indescribably miserable in being alone, unknown, and unnoticed in that vast throng, destitute of means for the present, and devoid of hope for the future.
Some were bent on business, some on pleasure; some were evidently bent on killing time till the hour of more agreeable occupation should arrive; some were loitering along, gazing at the prints in shop-windows, or half-listlessly stopping to read at book-stalls. There was not only every condition of mankind, from wealth to mendicancy, but every frame of mind from enjoyment to utter "ennui," and yet I thought I could not hit upon any one individual who looked as forlorn and cast away as myself; however, there were many who passed me that day who would gladly have changed fortune with me, but it would have been difficult to persuade me of the fact, in the mood I then was.
At the time I speak of, there was a species of cheap ordinary held in the open air on the quay, where people of the humblest condition used to dine; I need scarcely describe the fare; the reader may conceive what it was, which, wine included, cost only four sous; a rude table without a cloth; some wooden platters, and an iron rail to which the knives and forks were chained, formed the "equipage," the cookery bearing a due relation to the elegance of these "accessories." As for the company, if not polite, it was certainly picturesque; consisting of laborers of the lowest class, the sweepers of crossings, hackney-cab men out of employ, that poorest of the poor who try to earn a livelihood by dragging the Seine for lost articles, and finally, the motley race of idlers who vacillate between beggary and ballad singing, with now and then a dash at highway robbery for a "distraction;" a class, be it said without paradox, which in Paris includes a considerable number of tolerably honest folk.
The moment was the eventful one, in which France was about once more to become a monarchy, and as may be inferred from the character of the people, it was a time of high excitement and enthusiasm. The nation, even in its humblest citizen, seemed to feel some of the reflected glory that glanced from the great achievements of Bonaparte, and his elevation was little other than a grand manifestation of national self-esteem. That he knew how to profit by this sentiment, and incorporate his own with the country's glory, so that they seemed to be inseparable, is not among the lowest nor the least of the efforts of his genius.
The paroxysm of national vanity, for it was indeed no less, imparted a peculiar character to the period. A vainglorious, boastful spirit was abroad; men met each other with high sounding gratulations about French greatness and splendor, the sway we wielded over the rest of Europe, and the influence with which we impressed our views over the entire globe. Since the fall of the monarchy there had been half-a-dozen national fevers! There was the great Fraternal and Equality one; there was the era of classical associations, with all their train of trumpery affectation in dress and manner.
Then came the conquering spirit, with the flattering spectacle of great armies; and now, as if to complete the cycle, there grew up that exaggerated conception of "France and her Mission," an unlucky phrase that has since done plenty of mischief, which seemed to carry the nation into the seventh heaven of overweening self-love.
If I advert to this here, it is but passingly, neither stopping to examine its causes nor seeking to inquire the consequences that ensued from it, but, as it were, chronicling the fact as it impressed me as I stood that day on the Quai Voltaire, perhaps the only unimpassioned lounger along its crowded thoroughfare.
Not even the ordinary "à quatre sous" claimed exemption from this sentiment. It might be supposed that meagre diet and sour wine were but sorry provocatives to national enthusiasm, but even they could minister to the epidemic ardor, and the humble dishes of that frugal board masqueraded under titles that served to feed popular vanity. Of this I was made suddenly aware as I stood looking over the parapet into the river, and heard the rude voices of the laborers as they called for cutlets "à la Caire," potatoes "en Mamelouques," or roast beef "à la Montenotte," while every goblet of their wine was tossed off to some proud sentiment of national supremacy.
[Pg 643]Amused by the scene, so novel in all its bearings, I took my place at the table, not sorry for the excuse to myself for partaking so humble a repast.
"Sacre bleu," cried a rough-looking fellow with a red night-cap set on one side of the head, "make room there, we have the 'aristocrates' coming down among us."
"Monsieur is heartily welcome," said another, making room for me; "we are only flattered by such proofs of confidence and esteem."
"Ay, parbleu," cried a third. "The Empire is coming, and we shall be well-bred and well-mannered. I intend to give up the river, and take to some more gentlemanlike trade than drudging for dead men."
"And I, I'll never sharpen any thing under a rapier or a dress-sword for the court," said a knife-grinder; "we have been living like 'cannaille' hitherto—nothing better."
"À l'empire, à l'empire," shouted half-a-dozen voices in concert, and the glasses were drained to the toast with a loud cheer.
Directly opposite to me sat a thin, pale, mild-looking man, of about fifty, in a kind of stuff robe, like the dress of a village curate. His appearance, though palpably poor, was venerable and imposing—not the less so, perhaps, from its contrast with the faces and gestures at either side of him. Once or twice, while these ebullitions of enthusiasm burst forth, his eyes met mine, and I read, or fancied that I read, a look of kindred appreciation in their mild and gentle glance. The expression was less reproachful than compassionate, as though in pity for the ignorance rather than in reprobation for the folly. Now, strangely enough, this was precisely the very sentiment of my own heart at that moment. I remembered a somewhat similar enthusiasm for republican liberty, by men just as unfitted to enjoy it; and I thought to myself the Empire, like the Convention, or the Directory, is a mere fabulous conception to these poor fellows, who, whatever may be the regime, will still be hewers of wood and drawers of water, to the end of all time.
As I was pondering over this, I felt something touch my arm, and on turning perceived that my opposite neighbor had now seated himself at my side, and, in a low, soft voice, was bidding me "Good-day." After one or two commonplace remarks upon the weather and the scene, he seemed to feel that some apology for his presence in such a place was needful, for he said:
"You are here, monsieur, from a feeling of curiosity, that, I see well enough; but I come for a very different reason. I am the pastor of a mountain village of the Ardêche, and have come to Paris in search of a young girl, the daughter of one of my flock, who, it is feared, has been carried off by some evil influence from her home and her friends, to seek fortune and fame in this rich capital; for she is singularly beautiful and gifted too, sings divinely, and improvises poetry with a genius that seems inspiration."
There was a degree of enthusiasm, blended with simplicity, in the poor curé's admiration for his "lost sheep" that touched me deeply. He had been now three weeks in vain pursuit, and was at last about to return homeward, discomfited and unsuccessful. "Lisette" was the very soul of the little hamlet, and he knew not how life was to be carried on there without her. The old loved her as a daughter; the young were rivals for her regard.
"And to me," said the père, "whom, in all the solitude of my lonely lot, literature, and especially poetry, consoles many an hour of sadness or melancholy—to me, she was like a good angel, her presence diffusing light as she crossed my humble threshold, and elevating my thoughts above the little crosses and accidents of daily life."
So interested had I become in this tale, that I listened while he told every circumstance of the little locality; and walking along at his side, I wandered out of the city, still hearing of "La Marche," as the village was called, till I knew the ford where the blacksmith lived, and the miller with the cross wife, and the lame schoolmaster, and Pierre the postmaster, who read out the Moniteur each evening under the elms, even to Jacques Fulgeron the "tapageur," who had served at Jemappes, and, with his wounded hand and his waxed mustache, was the terror of all peaceable folk.
"You should come and see us, my dear monsieur," said he to me, as I showed some more than common interest in the narrative. "You, who seem to study character, would find something better worth the notice than these hardened natures of city life. Come, and spend a week or two with me, and if you do not like our people and their ways, I am but a sorry physiognomist."
It is needless to say that I was much flattered by this kind proof of confidence and good-will; and, finally, it was agreed upon between us that I should aid him in his search for three days, after which, if still unsuccessful, we should set out together for La Marche. It was easy to see that the poor curé was pleased at my partnership in the task, for there were several public places of resort—theatres, "spectacles," and the like—to which he scrupled to resort, and these he now willingly conceded to my inspection, having previously given me so accurate a description of La Lisette, that I fancied I should recognize her among a thousand. If her long black eyelashes did not betray her, her beautiful teeth were sure to do so; or, if I heard her voice, there could be no doubt then; and, lastly, her foot would as infallibly identify her as did Cinderella's.
For want of better, it was agreed upon that we should make the Restaurant à Quatre Sous our rendezvous each day, to exchange our confidences and report progress. It will scarcely be believed how even this much of a pursuit diverted my mind from its own dark dreamings, and how eagerly my thoughts pursued the new track that was opened to them. It was the utter listlessness, the nothingness of my life, that was weighing me down; and already I saw an escape [Pg 644]from this in the pursuit of a good object. I could wager that the pastor of La Marche never thought so intensely, so uninterruptedly, of Lisette as did I for the four-and-twenty hours that followed! It was not only that I had created her image to suit my fancy, but I had invented a whole narrative of her life and adventures since her arrival in Paris.
My firm conviction being that it was lost time to seek for her in obscure and out-of-the-way quarters of the city, I thought it best to pursue the search in the thronged and fashionable resorts of the gay world, the assemblies and theatres. Strong in this conviction, I changed one of my three gold pieces, to purchase a ticket for the opera. The reader may smile at the sacrifice; but when he who thinks four sous enough for a dinner, pays twelve francs for the liberty to be crushed in the crowded parterre of a play-house, he is indeed buying pleasure at a costly price. It was something more than a fifth of all I possessed in the world, but, after all, my chief regret arose from thinking that it left me so few remaining "throws of the dice" for "Fortune."
I have often reflected since that day by what a mere accident I was present, and yet the spectacle was one that I have never forgotten. It was the last time the First Consul appeared in public, before his assumption of the imperial title; and at no period through all his great career was the enthusiasm more impassioned regarding him. He sat in the box adjoining the stage—Cambaceres and Lebrun, with a crowd of others, standing, and not sitting, around and behind his chair. When he appeared, the whole theatre rose to greet him, and three several times was he obliged to rise and acknowledge the salutations. And with what a stately condescension did he make these slight acknowledgments!—what haughtiness was there in the glance he threw around him. I have often heard it said, and I have seen it also written, that previous to his assumption of the crown, Bonaparte's manner exhibited the mean arts and subtle devices of a candidate on the hustings, dispensing all the flatteries and scattering all the promises that such occasions are so prolific of. I can not, of course, pretend to contradict this statement positively; but I can record the impression which that scene made upon me as decidedly the opposite of this assumption. I have repeatedly seen him since that event, but never do I remember his calm, cold features more impassively stern, more proudly collected, than on that night.
Every allusion of the piece that could apply to him was eagerly caught up. Not a phrase nor a chance word that could compliment, was passed over in silence; and if greatness and glory were accorded, as if by an instinctive reverence, the vast assemblage turned toward him, to lay their homage at his feet. I watched him narrowly, and could see that he received them all as his rightful tribute, the earnest of the debt the nation owed him. Among the incidents of that night, I remember one which actually for the moment convulsed the house with its enthusiasm. One of the officers of his suite had somehow ambled against Bonaparte's hat, which, on entering, he had thrown carelessly beside his chair. Stooping down and lifting it up, he perceived to whom it belonged, and then remarking the mark of a bullet on the edge, he showed it significantly to a general near him. Slight and trivial as was the incident, it was instantly caught up by the parterre. A low murmur ran quickly around, and then a sudden cheer burst forth, for some one remembered it was the anniversary of Marengo! And now the excitement became madness, and reiterated shouts proclaimed that the glory of that day was among the proudest memories of France. For once, and once only, did any trait of feeling show itself on that impassive face. I thought I could mark even a faint tinge of color in that sallow cheek, as in recognition he bowed a dignified salute to the waving and agitated assembly.
I saw that proud face, at moments when human ambition might have seemed to have reached its limit, and yet never with a haughtier look than on that night I speak of. His foot was already on the first step of the throne, and his spirit seemed to swell with the conscious force of coming greatness.
And Lisette, all this time? Alas, I had totally forgotten her! As the enthusiasm around me began to subside, I had time to recover myself, and look about me. There was much beauty and splendor to admire. Madame Junot was there, and Mademoiselle de Bessieres, with a crowd of others less known, but scarcely less lovely. Not one, however, could I see that corresponded with my mind-drawn portrait of the peasant-beauty; and I scanned each face closely and critically. There was female loveliness of every type, from the dark-eyed beauty of Spanish race, to the almost divine regularity of a Raffaelite picture. There was the brilliant aspect of fashion, too; but nowhere could I see what I sought for! nowhere detect that image which imagination had stamped as that of the beauty of "La Marche." If disappointed in my great object, I left the theatre with my mind full of all I had witnessed. The dreadful event of Ettenheim had terribly shaken Bonaparte, in my esteem; yet how resist the contagious devotion of a whole nation—how remain cold in the midst of the burning zeal of all France? These thoughts brought me to the consideration of myself. Was I, or was I not, any longer a soldier of his army? or was I disqualified for joining in that burst of national enthusiasm which proclaimed that all France was ready to march under his banner? To-morrow I'll wait upon the Minister of War, thought I, or I'll seek out the commanding officer of some regiment that I know, or, at least, a comrade; and so I went on, endeavoring to frame a plan for my guidance, as I strolled along the streets, which were now almost deserted. The shops were all closed; of the hotels, such as were yet open, were far too costly for means like mine; and so, as the night was calm and balmy with the fresh air of spring, I resolved to pass it out of doors. [Pg 645]I loitered then along the Champs Elysees; and, at length, stretching myself on the grass beneath the trees, lay down to sleep. "An odd bedroom enough," thought I, "for one who has passed the evening at the opera, and who has feasted his ears at the expense of his stomach." I remembered, too, another night, when the sky had been my canopy in Paris, when I slept beneath the shadow of the guillotine and the Place de Grève. "Well," thought I, "times are at least changed for the better, since that day; and my own fortunes are certainly not lower."
This comforting reflection closed my waking memories, and I slept soundly till morning.
THE "COUNT DE MAUREPAS," ALIAS ——
There is a wide gulf between him who opens his waking eyes in a splendid chamber, and with half-drowsy thoughts speculates on the pleasures of the coming day, and him, who, rising from the dew-moistened earth, stretches his aching limbs for a second or so, and then hurries away to make his toilet at the nearest fountain.
I have known both conditions, and yet, without being thought paradoxical, I would wish to say that there are some sensations attendant on the latter and the humbler lot which I would not exchange for all the voluptuous ease of the former. Let there be but youth and there is something of heroism, something adventurous in the notion of thus alone and unaided breasting the wide ocean of life, and, like a hardy swimmer, daring to stem the roughest breakers without one to succor him, that is worth all the security that even wealth can impart, all the conscious ease that luxury and affluence can supply. In a world and an age like ours, thought I, there must surely be some course for one young, active, and daring as I am. Even if France reject me there are countries beyond the seas where energy and determination will open a path. "Courage, Maurice," said I, as I dashed the sparkling water over my head, "the past has not been all inglorious, and the future may prove even better."
A roll and a glass of iced water furnished my breakfast, after which I set forth in good earnest on my search. There was a sort of self-flattery in the thought that one so destitute as I was could devote his thoughts and energies to the service of another, that pleased me greatly. It was so "unselfish"—at least I thought so. Alas, and alas! how egotistical are we when we fancy ourselves least so. That day I visited St. Roche and Notre Dame at early mass, and by noon reached the Louvre, the gallery of which occupied me till the hour of meeting the curé drew nigh.
Punctual to his appointment, I found him waiting for me at the corner of the quay, and although disappointed at the failure of all his efforts, he talked away with all the energy of one who would not suffer himself to be cast down by adverse fortune. "I feel," said he, "a kind of instinctive conviction that we shall find her yet. There is something tells me that all our pains shall not go unrewarded. Have you never experienced a sensation of this kind—a species of inward prompting to pursue a road, to penetrate into a pass, or to explore a way, without exactly knowing why or wherefore?"
This question, vague enough as it seemed, led me to talk about myself and my own position; a theme which, however much I might have shrunk from introducing, when once opened, I spoke of in all the freedom of old friendship.
Nothing could be more delicate than the priest's manner during all this time; nor even when his curiosity was highest did he permit himself to ask a question or an explanation of any difficulty that occurred; and while he followed my recital with a degree of interest that was most flattering, he never ventured on a word or dropped a remark that might seem to urge me to greater frankness. "Do you know," said he, at last, "why your story has taken such an uncommon hold upon my attention. It is not from its adventurous character, nor from the stirring and strange scenes you have passed through. It is because your old pastor and guide, the Père Delamoy, was my own dearest friend, my school companion and playfellow from infancy. We were both students at Louvain together; both called to the priesthood on the same day. Think, then, of my intense delight at hearing his dear name once more; ay, and permit me to say it, hearing from the lips of another the very precepts and maxims that I can recognize as his own. "Ah, yes! mon cher Maurice," cried he, grasping my hand in a burst of enthusiasm, "disguise it how you may, cover it up under the uniform of a 'Bleu,' bury it beneath the shako of the soldier of the Republic, but the head and the heart will turn to the ancient altars of the Church and the Monarchy. It is not alone that your good blood suggests this, but all your experience of life goes to prove it. Think of poor Michel, self-devoted, generous, and noble-hearted; think of that dear cottage at Kuffstein, where, even in poverty, the dignity of birth and blood threw a grace and an elegance over daily life; think of Ettenheim and the glorious prince—the last Condé—and who now sleeps in his narrow bed in the fosse of Vincennes!"
"How do you mean?" said I, eagerly, for up to this time I knew nothing of his fate.
"Come along with me and you shall know it all," said he; and, rising, he took my arm, and we sauntered along out of the crowded street, till we reached the Boulevards. He then narrated to me every incident of the midnight trial, the sentence, and the execution. From the death-warrant that came down ready-filled from Paris, to the grave dug while the victim was yet sleeping, he forgot nothing; and I own that my very blood ran cold at the terrible atrocity of that dark murder. It was already growing dusk when he had finished, and we parted hurriedly, as he was obliged to be at a distant quarter of Paris by eight o'clock, again agreeing to meet, as before, on the Quai Voltaire.
[Pg 646]From that moment till we met the following day the Duc D'Enghien was never out of my thoughts, and I was impatient for the priest's presence that I might tell him every little incident of our daily life at Ettenheim, the topics we used to discuss, and the opinions he expressed on various subjects. The eagerness of the curé to listen stimulated me to talk on, and I not only narrated all that I was myself a witness of, but various other circumstances which were told to me by the prince himself; in particular an incident he mentioned to me one day of being visited by a stranger who came, introduced by a letter from a very valued friend; his business being to propose to the duke a scheme for the assassination of Bonaparte. At first the prince suspected the whole as a plot against himself, but on further questioning he discovered that the man's intentions were really such as he professed them, and offered his services in the conviction that no price could be deemed too high to reward him. It is needless to say that the offer was rejected with indignation, and the prince dismissed the fellow with the threat of delivering him up to the government of the French Consul. The pastor heard this anecdote with deep attention, and, for the first time, diverging from his line of cautious reserve, he asked me various questions as to when the occurrence had taken place, and where? If the Prince had communicated the circumstance to any other than myself, and whether he had made it the subject of any correspondence. I knew little more than I had already told him: that the offer was made while residing at Ettenheim, and during the preceding year, were facts, however, that I could remember.
"You are surprised, perhaps," said he, "at the interest I feel in all this, but, strangely enough, there is here in Paris at this moment one of the great 'Seigneurs' of the Ardèche; he has come up to the capital for medical advice, and he was a great, perhaps the greatest friend of the poor duke. What if you were to come and pay him a visit with me, there is not probably one favor the whole world could bestow he would value so highly. You must often have heard his name from the prince; has he not frequently spoken of the Count de Maurepas?" I could not remember having ever heard the name. "It is historical, however," said the curé, "and even in our own days has not derogated from its ancient chivalry. Have you not heard how a noble of the court rode postillion to the king's carriage on the celebrated escape from Varennes? Well, even for curiosity's sake, he is worth a visit, for this is the very Count Henry de Maurepas, now on the verge of the grave!"
If the good curé had known me all my life he could not more successfully have baited a trap for my curiosity. To see and know remarkable people, men who had done something out of the ordinary route of every-day life, had been a passion with me from boyhood. Hero-worship was indeed a great feature in my character, and has more or less influenced all my career, nor was I insensible to the pleasure of doing a kind action. It was rare, indeed, that one so humbly placed could ever confer a favor, and I grasped with eagerness the occasion to do so. We agreed, then, on the next afternoon, toward nightfall, to meet at the quay, and proceed together to the count's residence. I have often reflected, since that day, that Lisette's name was scarcely ever mentioned by either of us during this interview; and yet, at the time, so preoccupied were my thoughts, I never noticed the omission. The Chateau of Ettenheim, and its tragic story, filled my mind to the exclusion of all else.
I pass over the long and dreary hours that intervened, and come at once to the time, a little after sunset, when we met at our accustomed rendezvous.
The curé had provided a "fiacre" for the occasion, as the count's residence was about two leagues from the city, on the way to Belleville. As we trotted along, he gave me a most interesting account of the old noble, whose life had been one continued act of devotion to the monarchy.
"It will be difficult," said he, "for you to connect the poor, worn-out, shattered wreck before you, with all that was daring in deed and chivalrous in sentiment; but the 'Maurepas' were well upheld in all their glorious renown, by him who is now to be the last of the race! You will see him reduced by suffering and sickness, scarcely able to speak, but be assured that you will have his gratitude for this act of true benevolence." Thus chatting we rattled along over the paved highway, and at length entered upon a deep clay road which conducted us to a spacious park, with a long straight avenue of trees, at the end of which stood what, even in the uncertain light, appeared a spacious chateau. The door lay open, and as we descended a servant in plain clothes received us, and, after a whispered word or two from the curé ushered us along through a suite of rooms into a large chamber furnished like a study. There were book shelves well filled, and a writing table covered with papers and letters, and the whole floor was littered with newspapers and journals.
A lamp, shaded by a deep gauze cover, threw a half light over every thing, nor was it until we had been nearly a couple of minutes in the room that we became aware of the presence of the count, who lay upon a sofa covered up in a fur pelisse, although the season was far advanced in spring.
His gentle "good evening, messieurs," was the first warning we had of his presence, and the curé, advancing respectfully, presented me as his young friend, Monsieur de Tiernay.
"It is not the first time that I hear that name," said the sick man, with a voice of singular sweetness. "It is chronicled in the annals of our monarchy. Ay, sir, I knew that faithful servant of his king, who followed his master to the scaffold."
"My father," cried I, eagerly.
"I knew him well," continued he. "I may say, without vaunting, that I had it in my power [Pg 647]to befriend him, too. He made an imprudent marriage; he was unfortunate in the society his second wife's family threw him among. They were not his equals in birth, and far beneath him in sentiment and principle. Well, well," sighed he, "this is not a theme for me to speak of, nor for you to hear; tell me of yourself. The curé says that you have had more than your share of worldly vicissitudes. There, sit down, and let me hear your story from your own lips."
He pointed to a seat at his side, and I obeyed him at once, for, somehow, there was an air of command even in the gentlest tones of his voice, and I felt that his age and his sufferings were not the only claims he possessed to influence those around him.
With all the brevity in my power, my story lasted for above an hour, during which time the count only interrupted me once or twice by asking to which Colonel Mahon I referred, as there were two of the name? and again, by inquiring in what circumstances the emigré families were living as to means, and whether they appeared to derive any of their resources from France? These were points I could give no information upon, and I plainly perceived that the count had no patience for a conjecture, and that, where positive knowledge failed, he instantly passed on to something else. When I came to speak of Ettenheim his attention became fixed, not suffering the minutest circumstance to escape him, and even asking for the exact description of the locality, and its distance from the towns in the neighborhood.
The daily journeys of the prince, too, interested him much, and once or twice he made me repeat what the peasant had said of the horse being able to travel from Strassburg without a halt. I vow it puzzled me why he should dwell on these points in preference to others of far more interest, but I set them down to the caprices of illness, and thought no more of them. His daily life, his conversation, the opinions he expressed about France, the questions he used to ask, were all matters he inquired into, till, finally, we came to the anecdote of the meditated assassination of Bonaparte. This he made me tell him twice over, each time asking me eagerly whether, by an effort of memory, I could not recall the name of the man who had offered his services for the deed? This I could not; indeed I knew not if I had ever heard it.
"But the prince rejected the proposal?" said he, peering at me beneath the dark shadow of his heavy brow; "he would not hear of it?"
"Of course not," cried I; "he even threatened to denounce the man to the government."
"And do you think that he would have gone thus far, sir?" asked he, slowly.
"I am certain of it. The horror and disgust he expressed when reciting the story were a guarantee for what he would have done."
"But yet Bonaparte has been a dreadful enemy to his race," said the count.
"It is not a Condé can right himself by a murder," said I as calmly.
"How I like that burst of generous royalism, young man!" said he, grasping my hand and shaking it warmly. "That steadfast faith in the honor of a Bourbon is the very heart and soul of loyalty!"
Now, although I was not, so far as I knew of, any thing of a Royalist—the cause had neither my sympathy nor my wishes—I did not choose to disturb the equanimity of a poor sick man by a needless disclaimer, nor induce a discussion which must be both unprofitable and painful.
"How did the fellow propose the act? had he any accomplices? or was he alone?"
"I believe quite alone."
"Of course suborned by England? Of that there can be no doubt."
"The prince never said so."
"Well, but, it is clear enough, the man must have had means; he traveled by a very circuitous route; he had come from Hamburg, probably?"
"I never heard."
"He must have done so. The ports of Holland, as those of France, would have been too dangerous for him. Italy is out of the question."
I owned that I had not speculated so deeply on the matter.
"It was strange," said he, after a pause, "that the duke never mentioned who had introduced the man to him."
"He merely called him a valued friend."
"In other words, the Count D'Artois," said the count; "did it not strike you so?"
I had to confess it had not occurred to me to think so.
"But reflect a little," said he. "Is there any other living who could have dared to make such a proposal but the count? Who, but the head of his house, could have presumed on such a step? No inferior could have had the audacity! It must have come from one so highly placed, that crime paled itself down to a mere measure of expediency, under the loftiness of the sanction. What think you?"
"I can not, I will not think so," was my answer. "The very indignation of the prince's rejection refutes the supposition."
"What a glorious gift is unsuspectfulness," said he, feelingly. "I am a rich man, and you, I believe, are not so; and yet, I'd give all my wealth, ay, ten times told, not for your vigor of health, not for the lightness of your heart, nor the elasticity of your spirits, but for that one small quality, defect though it be, that makes you trustful and credulous."
I believe I would just as soon that the old gentleman had thought fit to compliment me upon any other quality. Of all my acquisitions, there was not one I was so vain of as my knowledge of life and character. I had seen, as I thought, so much of life! I had peeped at all ranks and conditions of men, and it was rather hard to find an old country gentleman, a "Seigneur de Village," calling me credulous and unsuspecting!
I was much more pleased when he told the curé that a supper was ready for us in the adjoining room, at which he begged we would excuse his absence; and truly a most admirable little meal it was, and served with great elegance.
"The count expects you to stop here; there is a chamber prepared for you," said the curé, as we took our seats at table. "He has evidently taken a fancy to you. I thought, indeed I was quite certain, he would. Who can tell what good fortune this chance meeting may lead to, Monsieur Maurice! A votre sante, mon cher!" cried he, as he clinked his champagne glass against mine, and I at last began to think that destiny was about to smile on me.
"You should see his Chateau in the Ardêche; this is nothing to it! There is a forest, too, of native oak, and a 'Chasse' such as royalty never owned!"
Mine were delightful dreams that night; but I was sorely disappointed on waking to find that Laura was not riding at my side through a forest-alley, while a crowd of "Piqueurs" and huntsmen galloped to and fro, making the air vibrate with their joyous bugles. Still, I opened my eyes in a richly-furnished chamber, and a Jaques handed me my coffee on a silver stand, and in a cup of costliest Sèvres.
(TO BE CONTINUED.)
Colton was remarkable for the extent and profundity of his talents, the various mutations of fortune, self-entailed, which he underwent, and for his inordinate addiction to a vice of all others the most degrading and destructive to intellectual strength—who was yet great in intellect and purpose amidst all the strange vicissitudes of which he was the self-constituted victim, and beneath the pressure of moral and physical degradation which he would never have undergone but for the influence of one fatal and overwhelming passion. One of the very first objects of my boyish reverence and veneration was, as might be expected with a child religiously educated, the parson of the parish in the market town where I was brought up. Parson C——, who, I believe, held the benefice of St. Peter's in my native place, was a man whom, having once known, it was not very easy to forget. I could have been hardly six years of age when I first saw him without his canonical garb, on which occasion he was playing a trout on the end of his line under one of the weirs in the river Exe. At that time the town was pretty well stocked with French prisoners. The jails were crammed with the miserable soldiery of Napoleon's generals, captured in the Peninsular war, then raging, and numbers of French officers on parole were installed with the housekeepers of the place in the capacity of lodgers. With these our all-accomplished divine was almost the only man in the place who could hold converse. A part of my father's house was occupied by a couple of Gallic strangers, to whom the parson's visits were many and frequent. As they dined at the common table, their society, together with that of the reverend gentleman, was shared by the whole family, and we thus became more intimate with him than we otherwise should. It is said that familiarity breeds contempt. Certain it is that my father's veneration for the character of his and our spiritual guide and instructor suffered considerable declension from his closer acquaintance. Still, what he lost in reverence he perhaps gained in another way. His kind, agreeable, and social manners won the admiration and good-will of the whole family, and though he had a good many enemies in the town, we could not be of the number. He was a man of eccentric manners and fine genius, and, though then but young, had given proofs of talent of no mean order. He had published a rather bulky poem on the subject of Hypocrisy, a subject with which his detractors were not slow to observe he ought to be very well acquainted. But he was not really a hypocrite in the true sense of the word, if indeed, as may be questioned, he deserved the imputation at all. He was rather the subject of ever-varying impulses, under the instigation of which, were they good or bad, he would instinctively proceed to act without consideration and without restraint. He would be eloquent as Demosthenes in the pulpit in praise of the Christian virtues, and would work himself into a passion of tears on behalf of some benevolent or charitable purpose, the claims of which he would enforce with the most irresistible appeals to the conscience; and the next day he would gallop after the fox with a pack of hounds, fish, shoot, or fight a main, in company with sporting blacklegs, bruisers, dicers, et hoc genus omne. But he never made any personal pretensions to religious sentiment that I am aware of, except on one occasion, which, as it tends greatly to illustrate the true character of the man, I shall relate.
Among the companions of his sporting pursuits was a country squire of the neighborhood, a dissolute and drunken specimen of a class of men of which, fortunately for humanity, the present generation knows but little. He had ruined his fortune and nearly beggared his family by extravagance and intemperance, when, after a long course of uninterrupted and abused health and vigor, he was laid by the heels upon a sick bed, from which the doctors had no hopes of ever releasing him. In this dilemma he sent for Parson C——, who appeared forthwith in the chamber of the sick man, and was beginning to mutter over the service for the visitation of the sick, when the latter, belching forth a volley of oaths and curses, swore that he did not send for him for any such purpose; that what he wanted was an acknowledgment from the parson's own lips of the fact which all parsons' lives declared—that their religion, and all religion was a lie. This was an admission which C—— declined to make. A horrible scene en[Pg 649]sued, of impotent rage and blasphemy on one part, and shame and confusion on the other. It ended in the death of the frantic and despairing drunkard, in the very presence of his ghostly adviser, whom he cursed with his last breath. This deplorable climax to such a scene of horror, it may be readily imagined, had a powerful effect upon the impulsive and excitable nature of poor C——. He left the chamber of such a death an altered man, and, proceeding homeward, shut himself up in his closet. On the following Sunday morning he took occasion to preach impressively, from the most solemn text he could select, upon the uncertainty of life. In the course of his sermon, he called upon all present to prepare for the doom which none could escape—which, inexorable to all, might be immediate to any, and therefore demanded instant and energetic preparation. He wound up his discourse with the extraordinary declaration that he, for one, had made up his mind upon the subject; that he had seen the error of his ways, and determined to abandon them; and that he was resolved thenceforth, with God's help, to devote the rest of his remaining life to his own preparation, and theirs, for the dreaded hour. He then called upon his auditors to bear witness to the resolution he had expressed, and to aid him in carrying it out. There was something like a commotion even in the church when this announcement was concluded; and the sensation and excitement it occasioned in the town, for some time after, only subsided as the parson's resolution waned in strength, and its effects became less and less observable. For some months he held fast to his purpose with the most laudable tenacity. It was in the spring of the year that he made his public declaration; and though the old friends of his follies laughed at it, and laid heavy wagers against his perseverance, he held on his way steadily—He began a course of pastoral visitation—sought out and relieved the poor and afflicted—parted with his fishing-tackle, and commenced an enthusiastic canvass for a dispensary for the poor. Of his old friends among the "ungodly," and his old enemies among the pious, few knew what to make of it. The Parson C—— of old time was no more; but, in his place, a new man with the same face was every where active in the cause of charity and Christian benevolence. Those who knew him best doubted most of his stability and among these, I remember my father's expressing his conviction that the reformation was "too hot to hold." So it turned out in the end. Three, four, five months of exemplary conduct, and then came the first symptom of declension, in the shape of the parson's gray horse harnessed to a dog-cart, with his gun and brace of pointers, in charge of a groom, the whole "turn-out" ready for starting, and waiting at the entrance of the church-yard on Sunday evening, the last night of August, to carry the parson, so soon as service was over, to a celebrated shooting-ground, five-and-twenty miles off, that he might be on the spot, ready by dawn for the irresistible 1st of September. Those who prophesied from this demonstration a return to old habits had speedy occasion to pride themselves upon their augury.
The Sampford Ghost soon after came upon the stage, with his mysterious knockings and poundings; and defied all objurgations and exorcisms, save and except those of Parson C——, at the sound of whose classical Greek, or gibberish, as it might happen, he absconded to the bottom of the Red Sea, as in duty bound. Here was food for wonder and gaping superstition, to which the reverend divine condescended to pander, by the publication of a pamphlet supporting the supernatural view of the subject, which, being on a marvelous topic, sold marvelously well, and brought grist to the clerical mill.
Of the subsequent career of this eccentric genius, from the time I ceased to reside in Devonshire to that when I encountered him in Paris I have no personal knowledge. I only know that he afterward obtained a benefice in the neighborhood of London; that in the year 1820 he published a work which has run through many editions, is in high repute with a certain class of readers, and is said by competent judges to manifest a profound practical acquaintance with the philosophy of the mind, and to contain more original views in relation to that science than any other work of equal dimensions.
I have already hinted that my vocation as a teacher of English introduced me to a new order of French humanity. Among the various pupils who sought my cheap assistance in the promotion of their studies was one Maubert, a young fellow of four or five and twenty, who was contemplating a removal to London in the exercise of his profession, which was neither more nor less than that of a gambler. He had a relative in one of the hells at St. James's, who had offered him a lucrative engagement so soon as he was sufficiently master of English to be enabled to undertake it. I was astonished to find a person of such mild, meek, and almost effeminate manners engaged in such a pursuit, and still more to hear that he had been brought up to it from boyhood, and was but following in the steps of his father, who was employed in the same establishment in a situation of great trust and responsibility.
In the course of our bilingual conversations, I made no scruple of expressing my perfect horror of gambling, at which he appeared to be heartily amused, and attributed the feeling I manifested not so much to moral principle as to constitutional peculiarity. It soon became apparent to me that he had not himself the slightest idea of disgrace or discredit as attachable to the profession of a gambler, so long as it was carried on upon principles of honesty and fair-play. "What is gambling," said he, "after all, but a species of exchange, skill for skill, or chance for chance? It is true, there is no solid merchandise in question; but, since you are determined to consider it in a moral point of view, what, let me ask, does the merchant or the [Pg 650]shopkeeper care for the goods that pass through his hands? Is not his sole object to profit by the transfer? Does he not speculate to gain? and is not all speculation, morally considered, gambling? Now, all the professed gamester does is to get rid of the lumbering medium of trading-speculations—to clear the game, which all men are willing to play, of the cumbrous machinery that clogs its movements when played upon commercial principles, and to bring it to a crisis and a close at once. You talk of the misery and ruin entailed upon families by gambling; but depend upon it the same men who ruin themselves and families by play would do precisely the same thing were there no such thing as play. For one Frenchman ruined by hazard, ten Englishmen are ruined by commerce. In fact, as a people, you gamble much more than we do, though in a different way; and when you choose to gamble as we do, you do it to much greater extent, and with a recklessness to which our habits in that respect afford no parallel. There is an Englishman now in Paris who has repeatedly won and lost ten thousand francs at a sitting, and whom you may see, if you choose to come with me, any evening you like."
"What is his name?" I demanded.
"C——. He is a priest, too, I have heard, and of course, when at home, a preacher of morality."
"Well," said I, "with your permission, I shall be glad to have a look at him."
"Very well; you shall dine with me to-morrow at the Salon Français. Meet me there at six, and then, after dinner, I will accompany you."
"Agreed."
And so it came to pass that, about nine o'clock on the following evening—for we had dined at most gentlemanly leisure, and followed up the dinner with a complete debauch of sugared water—I entered, for the first time, one of the saloons devoted to gambling on the first floor of the Palais Royal. There was not so great and gorgeous display of taste and expenditure as I had expected to see; though every thing was substantial and elegant, nothing was pretentious or superb. Tables arranged with a view to convenience rather than order or regularity, and covered with the means and materials of gaming, were surrounded, on three sides, by persons already engaged at the sport. We passed through several rooms thus furnished, and more or less tumultuously filled. Hazard appeared to be the most favorite game; as I noticed during my stay that the tables where that was played were first in full occupation, and throughout the evening were more crowded than others. Maubert led me to a room, which must have been the fifth or sixth we entered, and, pointing to a table at the further end, upon the centre of which rose a brazen dragon, with a pair of emerald eyes, a yawning, cavernous jaw, and a ridgy tail, whose voluminous folds coiled round a column of polished steel—told me that there I should find my man in the course of the evening, though I should have to wait for him, as he had not yet arrived. He informed me that I could act as I chose, without being questioned; and then took his leave, as his services were wanted in his own department. I amused myself for nearly a couple of hours in contemplating, en philosophe, the scene before me. I had heard and read much of gamblers and gambling, and here they were in multitudes to test the truth or falsity of my impressions. I noticed particularly that, while the younger players acted throughout as though gaming were a frolic, and welcomed both their gains and losses with a joke or a laugh, the older hands maintained a perfect silence, and accepted the decrees of fortune without betraying the least emotion. The table near which I stood was appropriated to the following purpose: A ball, or rather solid polygon, of near a hundred sides, each side colored blue, red, or black, was dropped into the mouth of the dragon; and while it was rolling audibly through the long folds of its tail, the players placed what sums they chose upon red, blue, or black-colored spaces on the table. Whatever color the ball, upon emerging from the tail and finally resting, showed uppermost, was the winning color; the rest lost. The first operation of the manager, after each throw, was to rake into the bank in front of him the several amounts placed on the losing colors, after which he paid the winners, doubling the stake for black, trebling it for red, and multiplying it by five for the blue. Most of the young players began upon the black; but whether they won or lost, and the chance was equal for either fate, they invariably migrated to the other colors; or, in other words, doubled or quintupled their stakes as their passions became heated by play. The old ones, on the contrary, kept mostly to one color; and, in pursuance of some cunningly-concocted plan, frequently consulted pricked or penciled cards, upon which they had perhaps made previous calculations, or chronicled the course of play as it went on. The physiognomy of these old stagers certainly afforded a rich variety of exceedingly ugly faces. Disappointment, however, was not the prevailing expression; and, from what I observed of the general manifestation of their hardened visages, I was led to the conclusion that your calculating gambler, who has his passions under control, is not, in the long-run, a loser, but the contrary; and that the support of the bank, and the whole establishment, is derived from the swarming flights of raw, inexperienced, and uncalculating pigeons which every day brings to be plucked. One old fellow walked off with a bag of five-franc pieces, which could not have been worth less than twenty pounds English, accumulated in little more than half an hour; and others pocketed various smaller sums, and then withdrew. An English gentleman lost several five-pound notes in succession on the blue, and, continuing the stake, recovered them all with a profit. An Irishman who had been playing for silver on the black, attempted to do the same; but his heart failed him, or else his pocket, after the loss of his second note, and [Pg 651]with a guttural oath, he retired in a rage. To win at gaming, it would seem from such examples, requires but a large amount of courage and capital; and it must be from this fact alone that, where the game, whatever it be, is fairly played, the bank which has the courage to challenge all the world, and unlimited capital to support the challenge, is so largely the gainer. The natural advantage of the bank may, however, be met by calculation and cautious adherence to system in playing; and instances are not wanting where the bank, though well stocked, has been broken, and the whole funds carried off, through the success of a deep-laid scheme.
While I was indulging in these speculations, in which I have no desire that the reader should place implicit faith, the personage whom my curiosity had led me hither to meet, entered the room, and made toward the place where I stood. The long interval that had elapsed since I last saw him had effected such an alteration in his appearance that it is probable, that, had I not been expecting him, he would have passed unrecognized. As it was, the first glance assured me of his identity. From added years, or from long-enduring sedentary habits, he had acquired a slight stoop, and the old sprightly elasticity of step had given place to the sober foot-fall of mature age; but the face, though of a somewhat darker hue, and now lined with faint furrows, bore the same contour and much of the same expression as of yore. There was the same classic and intellectual profile, and the same commonplace and rather sordid indications in the full face, which had formerly given rise to the saying among his flock, that "The parson had two faces, one for Sundays and one for working days." He took his seat at the left-hand of the money-raker, and, presenting a paper, probably a check or foreign note, received a pile of gold and silver, which he spread before him. I had intended to watch his game, and perhaps, if occasion offered, to speak to him; but the sight of the very man from whose lips my infant ears had caught the first accents of public worship, preparing to take part in the debasing orgies of the pandemonium in which I stood, so revolted my feelings—and his action, as he bent over his pocket-book in search of something he wanted, brought so forcibly to my recollection his old gestures in the pulpit—that I resolved to spare myself the witnessing of his degradation, and accordingly walked away, and out of the accursed den, to the side of the fountain in the quadrangle, in the cool spray of which I sat for an hour, not enjoying my reflections upon the past.
I learnt from Maubert subsequently, that, though C—— played the boldest game, he was far from being a welcome guest at some of the tables he chose to patronize. He won, occasionally, large sums; and, if he lost them again, as from his known difficulties at certain seasons it is pretty sure he did, he did not lose them at the public tables, but at some of the private gaming-houses of the nobility which he was known to frequent. That he was occasionally reduced to unpleasant straits I have reason to think; because, long after the encounter above related, I met him at a place whither I had resorted for a cheap dinner, and where we dined together on a deal table from soup and bouilli, for a sum not to be mentioned in connection with the repast of a gentleman. On this occasion, I somewhat alarmed him by inquiring, in a broad Devonshire accent, if he could inform me of the address of M. V——, naming one of the French prisoners with whom the parson had been especially intimate in the time of the war. He stared at me fixedly for a minute, and then, with a voice like one apostrophizing a spirit, said, "You are ——, the son of Thomas ——. I know you from your likeness to your father. Do not know me here. Let me have your address; I should like to talk to you. M. V—— is dead—dead! And your father, is he yet living?"
I was going to reply to his queries, but, snatching the card I presented, he bade me hastily adieu, and disappeared.
It was rumored about that he won a large sum of money previous to the breaking out of the Revolution, and that, having accomplished his object, he withdrew from the gaming-table. But he had played the game of life too fast, and, in desperately acquiring the means of expenditure, had lost those of enjoyment. In the published work, to which allusion has been made, is the following sentence: "The gamester, if he die a martyr to his profession, is doubly ruined. He adds his soul to every other loss, and, by the act of suicide, renounces earth to forfeit heaven." It is wretched to think that the writer put an end to his own existence, after a life devoted to the very vice he so powerfully deprecated. He blew out his brains at Fontainbleau, in 1832—it was said, to escape the pain of a surgical operation from which no danger could be apprehended.
The nineteenth century may now be said to have attained middle age, and in the brilliant noonday of its intellect and science the important events that marked the close of its predecessor are becoming dim and indistinct, like the vanishing images of a dissolving view. Progress has been so rapid since the peace that a wider chasm intervenes between 1799 and 1851 than any dividing the preceding centuries: much more than half a century appears to separate us from the eighteenth. But a stirring and troublous period lies before this interval. Life, doubtless, was more rife with interest and excitement to those whose youth belonged to it than it is in this calmer age. One feels that the "old people" of to-day have more of a "history in their lives" than our age will have; and even while we acknowledge with devout gratitude the blessing of peace, it is pleasant to listen to stories of "the War-time." One evening, while sitting with a relative of our own, gazing on the waters of the Channel, which were trembling and quivering beneath the rosy sunset, we expressed some such sentiments, and after agreeing in our opinion that life in those days was more animated by hope and fear than at present, he added, smiling, "For instance, in '97 I narrowly escaped hanging!"
We were much surprised at such a declaration from one who, at the time he spoke, was a brave and distinguished admiral, and eagerly asked the "how and why" of the adventure; and he told us. We regret that we can not recall the exact words of the animated relation, but we will try to give the substance as nearly as possible.
In 1797 mutiny broke out among the seamen at Spithead—an inexcusable crime in the opinion of naval men, but which he who related the story palliated in some degree, by candidly acknowledging that in those days the poor fellows who were guilty of it had great and just cause for complaint. They were not only ill-paid, but their food was of very bad quality; many captains in the navy were harsh and tyrannical—as, in consequence of the perversity of human nature, will always be the case; and the men whose blood was freely poured out in the defense of their native land were, to say the least, neglected and uncared-for by their rulers. Oh happy consequence of peace and advancing knowledge! these men are now well-fed, have the means of instruction afforded them, and homes provided for them when, returning from "the dangers of the sea," they are discharged and sent on shore. The poor mutineers at Spithead dreamed not of such advantages as these.
Admiral R—— was a junior lieutenant on board the Saturn when the mutiny broke out; but promotion was very rapid then, and though bearing that rank he was still only a youth in his teens. Probably the mutineers had discovered, and in a measure appreciated the kindliness of his nature, for, exempting him from the thralldom of his companions, whom they had confined in the ward-room, they fixed on him to bear their propositions and their threats to the port-admiral—swearing at the same time, that if he did not bring them back a favorable answer they would hang him on the yard-arm! He was obliged to obey their will, of course, secretly resolving, however, not to give them the opportunity of fulfilling their kind intentions by returning to the ship; but the young officer calculated too much upon being his own master. He was put on shore at the Point, and proceeded at once to the admiral's house in the High-street. The naval chief gave him a good-natured and cordial reception, and listened patiently to the message he delivered from the mutineers, which was to the effect that they must have an immediate advance of wages, good biscuit, pork, &c., or that they would carry their ship over to the French.
"Go on board again, sir," was his reply, "and tell these gentlemen that none of their demands can be listened to till they return to their duty: inform them also that the moment they attempt to weigh anchor hot shot will be fired on them from the Isle of Dogs, and their vessel and themselves sent to the bottom."
The lieutenant bowed and left the office. Outside he paused. He was going, in obedience to his superior, to certain death. It was a fearful trial of courage and professional discipline. A mother whom he idolized lived at no great distance: he would at least bid her a last farewell! But the admiral, aware of the sacrifice he exacted, so much greater than that of periling life by mounting "the deadly breach," had followed the poor boy, and lightly tapping his shoulder, told him he would walk with him to the beach. Thus, even the last look at home, for which he longed, was denied him. A waterman's wherry conveyed him to the ship. It was May—a bright, glorious May, such as England used to enjoy "once upon a time;" and very sad were the feelings with which the young officer looked back upon the retreating town, and round on the glad, sunny waters and blue-tinted Isle of Wight, deeming that he beheld them for the last time. Occasionally, also, he told us, his eyes would revert, in spite of his endeavors to forget it, to the fatal yard-arm, distinct with all its tracery of cordage against the clear blue sky. He gained the ship, was received on board, and conducted to the forecastle, where the chief mutineers had assembled. Here he delivered his message. They were greatly enraged, and commanded him not to repeat the admiral's threat of sinking the ship to the crew. He replied simply that it was his duty to obey the orders of his superior officer. Their looks and words threatened him at first with instant and summary vengeance; but after a short consultation they agreed to try him by a court-martial, and proceeding aft, ordered him to be brought before them. It was a fearful scene; the men were terribly excited, frightfully ignorant, and believed that their cause required a victim.
The courage of the youth bore him through the trial, however, bravely. He ventured boldly to reproach them with their guilt in confounding the innocent with those whom they looked upon as their enemies; taunted them with the cowardly injustice of the deed they contemplated; and persisted, in opposition to the ringleaders' commands, in repeating the admiral's message to the crew. He was heard by the officers in the ward-room, and their loud cheers when he spoke probably gave him fresh courage. The ringleaders becoming alarmed at the effect his words and bearing might have on the British instincts of the ship's company, condemned him to be hung in two hours' time, and ordered him to prepare for death meantime in his cabin. There a new and singular scene awaited him: one of the seamen had taken possession of it, opened his lockers, and finding some brandy, had been drinking till he was perfectly intoxicated, and lay in the sleep of drunkenness on the floor, which was strewed and littered with the lieutenant's clothes, books, &c. A deep oath escaped the lips of the ringleaders at this sight. Throughout the fleet the mutineers had forbidden drunkenness on pain of death; for, fully aware of the peril of their position, they kept up among themselves a terribly severe discipline. They were raising their insensible comrade in their arms, and coolly preparing to throw him overboard, when, aware from their words of their intentions, the condemned officer struck one of them to the floor, and standing over the again prostrate drunkard, declared that while he lived he would not see men who had sailed beneath the British flag guilty of murder! The mutineers paused, touched probably by this generous defense of a foe—for the insensible seaman had been peculiarly bitter against the officers—and after a muttered oath or two they left the cabin.
The lieutenant remained alone with his disgusting and unwelcome visitant, and the two hours following he described as the most painful of his life. It was less the fear of death than the destined mode of it which tortured him: not that he was insensible or indifferent to the blessing of life, for he was by nature of a happy, joyous temperament, and fair prospects of advancement were before him; but in "war-time" existence was held on such a precarious tenure that the idea of death in battle would scarcely have troubled his equanimity. Two hours waiting to be hanged, however, is a far different trial for courage, and we have never read or imagined any thing more painful than the description which the aged admiral gave us of that (to him) endless period of time. As if to add to the horror of his position, the silence on board was so great that it appeared as if he could hear the pulsation of his own heart, while the low snoring of the drunken man struck with painful distinctness on his ear. At last the bell struck the fatal hour, and steps were heard on the ladder. His door opened; he rose prepared to show no symptoms of faltering courage, when the leaders of the party advancing, told him "that the people had taken his case into consideration, and as they believed he individually had no ill-feeling toward them, and as he had recently given proof that he cared for the men, they had changed his sentence from death to flogging! He must therefore prepare to receive three dozen on the following morning."
My kinsman, with the ready humor that never deserted him, returned thanks with mock gravity for their clemency, and begged them to carry his compliments to the gentlemen who sent them, and assure them that he could not have believed he should ever have felt so much satisfaction at the prospect of a whipping. The men, always susceptible of fun, laughed. From that moment he was safe! Falstaff wisely despairs of gaining the love of Prince John, "because he could not make him laugh;" the young lieutenant acted as if he possessed Shakspeare's knowledge of human nature when he awoke by his jest the slumbering sympathies of the sailors. He was detained a prisoner, but no further notice was taken of the threatened flogging.
The mutiny subsided on the 16th of May, when Parliament passed an act to raise the seamen's wages, and the royal pardon was bestowed on the mutineers; not, however, before some sacrifice of human life had ensued, as Admiral Colpoys, on the recommencement of the mutiny on board the London, had ordered the marines to fire on the people, and three seamen fell. The funeral of these unfortunates was described to us as a singularly impressive and touching spectacle. The townspeople were fearful of some violence or riot on the part of the sailors when they landed to bury their dead, and consequently closed their shutters and retired into their houses. The mournful procession moved therefore through deserted and silent streets on its way to the village church-yard, in which the victims were to be interred. But there was no cause for alarm. The men walked silently and solemnly, two and two, after their slain comrades, a stern, quiet sorrow legible on their weather-beaten faces; and nothing could exceed the reverence and propriety of their conduct beside the grave. It is a quiet, pretty village church-yard in which these most pardonable rebels have their resting-place, not far from which is the large grave where three hundred bodies of those who perished in the Royal George are buried.
One can scarcely forbear wondering at the little real mischief which proceeded from this alarming mutiny. It afforded, on the whole, a noble display of the principal characteristics of the British seaman—the frolic-spirit peculiar to him manifesting itself even when he is most sadly and seriously in earnest. A captain of marines, who was especially the object of the mutineers' aversion, was brought on shore by them, and compelled to parade up the High-street to the "Rogue's March," which was drummed before him. He was a tall, gaunt old man, with a singularly long neck. The day after his expulsion from his ship, the crew sent a man to his house with a message, ordering him to "come [Pg 654]on board again and be hanged!" The unpopular veteran sent back his compliments; but considering his throat unbecomingly long naturally, he did not wish to have it stretched: he declined, therefore, accepting their invitation. The men went away laughing. The people and the times were both extraordinary.
BY PROF. J. H. AGNEW, UNIVERSITY OF MICHIGAN.
Ours is an age of stirring life, an age of notions and novelties, of invention and enterprise, of steam-motives and telegraph-wires. The ocean, for passage, has become a river. The air a medium for the flight, not only of birds, but of thoughts. Distance scarce any more lends enchantment to the view, for 'tis annihilated. The ends of the earth meet, and the watchmen on her walls see eye to eye. Even worlds long buried in the deep unknown are now revealed to human vision, and we almost penetrate the arcana of our own fair satellite, as she nightly looks down upon us in her beauty. And man would fain believe, too, in his wisdom, or his folly, that e'en the rappings of spirits are heard in this nether planet of ours.
But what of all this? Why, we live in this whirl of galvanic motion: we breathe this excited atmosphere: we revolve on this stirring sphere. And, think you, without feeling aught of its forces?
We have our being, too, amid the busy scenes of a new world, a free world, a forming world. Our geologic species is a conglomerate. Whether it shall be of rude, unshapen masses, or of polished gems, fit not only for the pillars of this republican edifice, but for its adornment also, will depend much on the present generation, more on the women of that generation.
Believing that woman not only takes impressions from the age, but emphatically makes them on it too, I select for my theme Woman's Offices and Influence.
To make home happy is one of the offices of woman. Home, blessed word. Thanks to our Saxon fathers for it. Not the name merely, but the realities it expresses. An English, an American home is a Bethlehem-star in the horizon of earth's sorrows, the shadow of a great rock in a weary land.
Yes, home is the centre of all that is sweet in the sympathies, dear in the affections of the soul. There the kiss of love is impressed in its purity, the warm pressure of the hand knows no betrayal, the smile of joy plays no deceiver's part. All is candid, cordial, sincere. The faults and failings which belong to humanity fallen, are there covered by the mantle of charity, and the feeling of every member of the family is, "With all thy faults I love thee still."
How the traveler climbing Alpine summits, looking forth on the sublime creations of Jehovah, thinks of home, and wishes the loved ones there could share his rapture. How the wrecked mariner on some desert isle longs for a mother's fond endearment, a sister's kindly care. Home is in all his thoughts.
It is worth the while, then, to strive to make home happy; to do each his part toward rendering it the spot of all pleasant associations. In the several relations of child, sister, wife, mother, let kindness and cheerfulness reign.
Kindness comes over the spirit like the music of David's harp over the passion of Saul. It softens and subdues. It manifests itself in a thousand nameless forms, but all beautiful. It is a crown of glory on the head of old age, a jewel on the breast of childhood. The light it diffuses is soft, the rays it emits are melting.
Cheerfulness is another attribute of character tending to the happiness of home: and let me commend it to woman's cultivation. Some there are, ever disposed to look on the dark side of life; and thus they not only becloud their own spirits, but cast a shadow over the smiling precincts of home. Every single sour grape portends a cluster; every flash of lightning a riving thunderbolt. Earth's actual cares are not enough; troubles must be borrowed. The present does not fill their heart with sadness; the future must be laid under contribution.
All this is just the opposite of cheerfulness. That scatters wide over the soil of the household the seeds of many little joys, that the weeds of small vexations may be kept under, and ever and anon the sickle be thrust in and a harvest of good fruits be garnered for daily use. It gazes on the bright side of the picture, and throws its delighted glances upon every eye. And thus it not only augments present bliss, but in hoary years the memory of other days around the family hearth will be sweeter, and the influence on ourselves better.
"Cheerfully to bear thy cross in patient strength is duty." "Not few nor light are the burdens of life: then load it not with heaviness of spirit; sickness, and penury, and travail—these be ills enow: the tide is strong against us: struggle, thou art better for the strife, and the very energy shall hearten thee."
"In thy day of grief let nature weep; leave her alone; the freshet of her sorrow must run off; and sooner will the lake be clear, relieved of turbid floodings. Yet see, that her license hath a limit."
"For empty fears, the harassings of possible calamity, pray and thou shalt prosper: trust God and tread them down." "The stoutest armor of defense is that which is worn within the bosom, and the weapon which no enemy can parry is a bold and cheerful spirit."
Beautiful in the family is this spirit of cheer[Pg 655]fulness; and surely it is an office of woman to cherish it. It can be wooed and won. Wherever woman goes, and especially at home, let it be as an halo of light around her head, and then shall she be a blessing to the circle in which she moves. Despondency is death, cheerfulness life. But remember that levity and boisterous mirth are no essential ingredients of this wholesome cordial. Its chief element is rather that which Paul spake of when he said, "I have learned in whatsoever state I am, therewith to be content."
Another office of woman is, to check the utilitarianism, the money-loving spirit of the day. There is something beside bread and water to be cared for in this probationary world of ours, inhabited by living spirits. And yet one is almost compelled to the conclusion that the whole race, at the present day, has given itself up to the worship of Mammon.
That which is a physical fact, which is capable of being used, is the summum bonum. Cui bono, in a terrene sense, is the great question. "Will it pay," the grand idea of the age. And men are hurrying along, life in hand, breathless and bootless, over the highways and byways to the Great Mogul's temple, where there is no spiritual Divinity to revere.
We almost wish the return of the old Grecian's faith, who enveloped himself with a spiritual world, and this, at least, elevated his intellect, if it did not renovate his heart. To him the majestic mountain was peopled with august entities. To us it is of no account, if it do not contain in its bowels buried stores of wealth, though it may awaken the feeling of the sublime, and lift the soul up to God. To him the shady tree was the habitation of dryads, the rippling brook of naïads: to us, neither has beauty, unless the one can turn a mill, and the other furnish us fire-wood or lumber.
We have made the soul slave to the body; have stripped the Universe of its glory, as a reflecting mirror, pouring down upon us such rays of Heaven's brilliancy as our vision can endure. God's sun is only to lighten us on our pathway of business; His mighty ocean only to bear the burden of our commerce; His magnificent lakes to carry our trade; His beautiful hills and smiling vales but to grow our corn, feed our cattle, and be the substratum for our railways.
This utilitarianism of the day, too, has but little sympathy with the fine arts. It laughs at music and painting, poetry and sculpture, as things of naught, although they may tend mightily to the culture of the spirit and the refinement of humanity. Classical learning it discards, because with its dusty eyes it can not just see how that can qualify man or woman for the better enjoyment of life, or how it will help us plow or measure our fields, grind our grain, or churn our butter.
The mere discipline of the mind, the symmetrical development of man's higher powers, the æsthetic evolution of himself; all this, though it expand his intellect and enlarge his heart, though it impress on him more of the lineaments of the skies, and bring him nearer to his great Original, is but waste of time and thought, because it falls not within the described circle of the utilitarian. Shades of Bacon and Locke, of Shakspeare and Milton, of Goethe and Schiller, come and alight at least on the daughters of our land!
Here is a wide field of influence for woman. You are the vestal virgins to watch the fires on the altar of the fine arts. Yours it is to check the sensuousness of man, to recall him from his ceaseless toil after the mammon of this life, his restless ambition to turn every thing to account in available funds, in bank-stocks, copper-stocks, railroad-stocks. Tell your sons and your sires that there are higher sources of joy. Point them away from earth's sordid gold to the brighter gems of literature. Direct their energies to the intellectual and moral advancement of their age. Help them to slake their quenchless thirst at the pure fountains of knowledge and religion.
There is a poetry of life worth cultivating. There are spiritual entities around us to which we are linked by ethereal chains. Let us not struggle to throw off those chains, but rather to bind them faster about us. And when you see a link broken, and others likely to drop, mend it.
Woman's office is it also to soften political asperities in the other sex, and themselves to shun political publicity. Not that woman need be ignorant of the great questions of the age; better be familiar with them. But let her not become absorbed in them: rather keep so aloof from exciting occasions as to be better qualified to form and express a deliberate and unbiased judgment on men and measures. Let her opinions be well matured, and always uttered with calmness and caution. When her dearest friends of the other sex seem embittered toward others, and in danger of forgetting the sweet charities of life amid the chafings of party rivalry, let her pour out the milk of human kindness into the cup of courtesy, and ask them to drink of it. When the waters are troubled and the billows roar, let her diffuse over them the oil of love to still the waters into a great calm. Surely this is an office higher, better far, than to be pressing on, as some would have her, into the busy bustle of out-door politics. Here is influence, and it is better than power.
Who that loves woman, that really admires her worth as woman, that thinks of her as the delicate, refined, tasteful, sensitive development of humanity, the incarnation of all that is lovely, gentle, modest, peaceful, and pure, the highest earthly manifestation of God as love; who that remembers her as the "help-meet," can bear the thought of hurrying her out upon the theatre of politics, the platform of legislation?
"Woman's rights," they cry, and so loud the cry, that even woman's ambition has conquered her judgment and her delicacy, and she has gone forth, out of her appointed and fitting sphere, to be gazed on by a curious crowd, and perhaps to hear the plaudits of a noisy populace. O tempora! O mores! Save us from such a race of women!
[Pg 656]Now woman has rights, many rights, and let them be well guarded; but she has no right to be a man. Yet, no wonder 'tis, if amid the stirring enterprises and new discoveries of the age, some half-amazon should defy the customs of social life, and assume the right of leveling all distinctions between the sexes, walking forth à la Turk, and becoming the gazing-stock of the street. Oh, let beauteous, winning woman wear the gracefully-flowing robes of modesty; let her not be met by us "up to the eyes" in politics, nor at the ballot-box, nor the caucus, nor in the legislative hall, nor on the judicial bench, surrounded, perchance, by tobacco-chewing barristers, nor as the public haranguer, addressing promiscuous multitudes.
Let us rather see her in the quiet retirement of home, not doomed to the busy drudgery of hard housekeeping merely, but there the refined woman, whose pure sensibilities are shocked at the thought of a public notoriety; who shuns the wistful gaze of the crowd, and finds in her own family circle her kingdom and her rights, and seeks to adorn that with all that is lovely and of good report. Thus will she win our admiration and secure our love. Were her intellect and her eloquence displayed at the bar or on the platform, we might indeed wonder with deep amazement, but we should not love; and wanting this, both she and we were unhappy.
While sensible, then, of her equality with man in the possession of a soul like his own, capable of the highest enterprises in science and literature, may she yet recognize, as the appointment of her all-wise Creator, subordination to man in power, superordination in influence. Be content to be woman. It is a province high enough. If not cherubic, it is seraphic. It is that phase of humanity we think most godlike; for if Jehovah's highest expression of himself is Love, then that form of humanity expressing most of it, is most like Him. That form, in our opinion, is woman.
Let her not, then, strip herself of her chief glory, and depart further from her God and Saviour, by shooting out from her own feminine orbit, and aiming to revolve in that of the other sex, under the false impression that it is a higher one. Even if it were, it is not hers, and by thus battling with the order of nature, and swinging loose from the proper relations of her being, she might become a wandering star in the blackness of darkness forever.
Another evident office of woman is, to regulate the forms and control the habits of social life. In this land, especially, do the "lords of creation" bow with due deference to their ladies. We give them our arms, 'tis true, and we ask them to lean upon us, yet do we take step with them, and in turn lean on them, amid the trying times of life, and look to them for many of our joys, for most of our happiness. He is vulgar, even barbarous, we think, who does not appreciate her worth and respect her character. Hence, every where, hers is the first place, the best place; and an American gentleman would rather suffer an agony than subject women to a discomfort.
Such being her relative position, hers it must be to prescribe the customs of social life, and say to man, "hitherto shalt thou go and no further." The tone of morals will be such as she makes it. Man will be conformed to the model she exhibits. He seldom, if ever, rises above the level of his female associates. Surround him with the vulgar, the thoughtless, the impure, and you shall not see him pure, thoughtful, refined. Place him ever in the society of intelligent, dignified, Christian women, and their virtues will be reflected on him.
And is it so, that woman is responsible, in a great measure, for the fashions and habits of the community in which she lives? It is even so. If she discard that foolish frippery and passion for display, which occasionally characterize her own sex, it will not long live. It must be buried in its own foibles, and have no resurrection. If she frown upon him who robs woman of her jewel, he is a fugitive on the face of the earth. If she discountenance the use of intoxicating beverages, the young man will learn that abstinence on his part is the price of respect and love on hers. Her office here is magnified: her influence has become a power. The other offices were guiding and directory; this is reformatory. Society looks to her for its type. Its virtues and its vices are of her moulding. It is what she bids it be.
What a potency! Let her wield it for her country's welfare. Then shall it be a beacon light to other lands now in darkness and degradation, because there woman is still the slave of man's passions, and has never risen, under Christianity, to know her dignity, and make her brutal master feel her moral equality in the scale of being.
Only one other office of woman shall we notice at present—the exemplification and diffusion of Christianity—of Christianity, not so much in its forms and dogmas, as in its spirit; not solely as a redeeming scheme, but also as a reforming power.
To Christianity woman is emphatically a debtor. It has breathed into her its breath of life, and she has become a living soul. Else had she been but a dead manikin. To it she owes her present advanced position, her commanding influence. Even all the literature and refinement of Greece and Rome could not confer on woman the boon which the religion of Jesus has brought her. He was woman's son, and his religion tells it. Go where that religion is not, and there woman is naught.
Christianity has not only broken down the wall of partition between male and female, but has opened the sealed fountains of her soul, and caused them to send forth rills of gentleness and love, which have refreshed humanity and poured out gladness on a dark and dreary world. Let the cross, then, be woman's standard, Jesus woman's trust, Christianity woman's charter. That thrown overboard, we are wrecked. Its principles abandoned, the world sinks again into barbarism, and woman to brute degradation. [Pg 657]"The last at the cross and earliest at the sepulchre," must remember to cling to Christianity as her hope, her life. Let her never be ashamed to confess it her ruling principle, her source of joy, nor be hesitant in disseminating its seeds, that she may every where behold its lily-flowers.
Can it ever be well said of woman, "she careth not if there be a God, or a soul, or a time of retribution; pleasure is the idol of her heart: she thirsteth for no purer heaven." Let such an one be decked in all the gorgeous trappings of wealth, let her brow be crowned with the coronet of rank, let her girdle hold the key which unlocks the treasures of California, and yet she wants that which ennobles her sex, and would render her an object of love and a source of joy to others.
Never, then, let the sneer of the infidel, nor the scorn of the skeptic drive woman from compounding the spices to embalm her crucified Master, nor make her ashamed to be seen early at his sepulchre. Rather let her glory in the cross, and make the most of her high mission here to send its healing influences to every sick and sorrowing creature on this green earth. Why should any poor, perishing mortal be left in all the degradation of idolatry, when there is in our possession a power that would lift him to heights of bliss, temporal and eternal? Why should the world be left to its wailings and its woes, when Christianity diffused, in its benign spirit, would convert those woes into joys, those wailings into hallelujahs? How can woman, owing her all to the religion of the Bible, refrain from exerting her energies to place this word of life in the hands of every pilgrim over the deserts of time? And may she so breathe its spirit and feel its power, that it shall never again be thus written of her:
A few words on Influence. This is woman's power. That distinctively belongs to man, and is exercised by authority. Law and penalty grow out of it. It regulates actions, it punishes crime. Influence, on the other hand, awakens feeling, generates opinions, implants sentiments in the soul, silently yet emphatically; and thus it crushes vice, promotes virtue, and avoids the necessity of penal infliction.
Now this is pre-eminently the potent lever in the hands of woman for regenerating and reforming the political and moral world. We may stand in awe, indeed, before the exhibition of power, whether physical or moral, but we are not won by them to the love of truth and goodness, while influence steals in upon our hearts, gets hold of the springs of action, and leads us into its own ways. It is the inflowing upon others from the nameless traits of character which constitute woman's idiosyncracy. Her heart is a great reservoir of love, the water-works of moral influence, from which go out ten thousand tubes, conveying off the ethereal essences of her nature, and diffusing them quietly over the secret chambers of man's inner being.
Even the weakness of woman softens and subdues, and thus unseals the soul for the infusion of her own sentiments. Her winning smiles, her tender sympathies, her sensible expressions, her gentle ways, all influence us, flow in upon our spirits. Who can be long boisterous in the presence of woman? No more can the yeasty waves dash and foam when superinfused by the mollifying touch of oil, than can the passions of man rage with impetuosity in contact with the oleaginous serenity of gentle woman.
Let man, then, exercise power; woman exert influence. By this will she best perform her offices, discharge her duties. Thus will she most effectually make home happy, restrain utilitarianism, allay party asperities, regulate the habits of social life, and both exemplify and diffuse Christianity. Thus will she become vanqueur des vanqueurs de la terre—"conqueror of the conquerors of earth," and do more to bless the world, and make it truly happy, than all political institutions, fiscal agencies, and merely intellectual educations.
Surely this is a mission exalted. Let no woman despise it, though it exclude her from the senator's seat and the chair of state. Let her rather remember that she honors herself more, glorifies her God better, and elevates her race higher, by adorning the sphere which her very physical organization prescribes. Never will she be improved in her nature, elevated in her influence, happier in her own spirit, or more potent in effecting the happiness of the world, by aiming at the proper dignities of man, throwing herself out upon the arena of public life, meddling and mingling in its chafings and chances. Ah no! let us still hope that woman will have good sense enough to discern the wisdom of God in her proper relation, and that man shall still and ever have the privilege and the joy of admiring and loving her as gentle, retiring, delicate, yet influential woman.
BY HERMAN MELVILLE.
[5] From "The Whale." The title of a new work by Mr. Melville, in the press of Harper and Brothers, and now publishing in London by Mr. Bentley.
The Cape of Good Hope, and all the watery region round about there, is much like some noted four corners of a great highway, where you meet more travelers than in any other part.
It was not very long after speaking the Goney that another homeward-bound whaleman, the Town-Ho, was encountered. She was manned almost wholly by Polynesians. In the short gam that ensued she gave us strong news of Moby Dick. To some the general interest in the White Whale was now wildly heightened by a circumstance of the Town-Ho's story, which seemed obscurely to involve with the whale a certain wondrous, inverted visitation of one of those so called judgments of God which at times are said to overtake some men. This latter circumstance, with its own particular accompaniments, forming what may be called the secret part of the tragedy about to be narrated, never reached the ears of Captain Ahab or his mates. For that secret part of the story was unknown to the captain of the Town-Ho himself. It was the private property of three confederate white seamen of that ship, one of whom, it seems, communicated it to Tashtego with Romish injunctions of secresy, but the following night Tashtego rambled in his sleep, and revealed so much of it in that way, that when he was awakened he could not well withhold the rest. Nevertheless, so potent an influence did this thing have on those seamen in the Pequod who came to the full knowledge of it, and by such a strange delicacy, to call it so, were they governed in this matter, that they kept the secret among themselves so that it never transpired abaft the Pequod's mainmast. Interweaving in its proper place this darker thread with the story as publicly narrated on the ship, the whole of this strange affair I now proceed to put on lasting record.
For my humor's sake, I shall preserve the style in which I once narrated it at Lima, to a lounging circle of my Spanish friends, one saint's eve, smoking upon the thick-gilt tiled piazza of the Golden Inn. Of those fine cavaliers, the young Dons, Pedro and Sebastian, were on the closer terms with me; and hence the interluding questions they occasionally put, and which are duly answered at the time.
"Some two years prior to my first learning the events which I am about rehearsing to you, gentlemen, the Town-Ho, Sperm Whaler of Nantucket, was cruising in your Pacific here, not very many days' sail eastward from the eaves of this good Golden Inn. She was somewhere to the northward of the Line. One morning, upon handling the pumps, according to daily usage, it was observed that she made more water in her hold than common. They supposed a sword-fish had stabbed her, gentlemen. But the captain, having some unusual reason for believing that rare good luck awaited him in those latitudes; and therefore being very averse to quit them, and the leak not being then considered at all dangerous, though, indeed, they could not find it after searching the hold as low down as was possible in rather heavy weather, the ship still continued her cruisings, the mariners working at the pumps at wide and easy intervals; but no good luck came; more days went by, and not only was the leak yet undiscovered, but it sensibly increased. So much so, that now taking some alarm, the captain, making all sail, stood away for the nearest harbor, among the islands, there to have his hull hove out and repaired.
"Though no small passage was before her, yet, if the commonest chance favored, he did not at all fear that his ship would founder by the way, because his pumps were of the best, and being periodically relieved at them, those six-and-thirty men of his could easily keep the ship free; never mind if the leak should double on her. In truth, well nigh the whole of this passage being attended by very prosperous breezes, the Town-Ho had all but certainly arrived in perfect safety at her port without the occurrence of the least fatality, had it not been for the brutal overbearing of Radney, the mate, a Vineyarder, and the bitterly provoked vengeance of Steelkilt, a Lakeman and desperado from Buffalo.
"'Lakeman!—Buffalo! Pray, what is a Lakeman, and where is Buffalo?' said Don Sebastian, rising in his swinging mat of grass.
"On the eastern shore of our Lake Erie, Don; but—I crave your courtesy—may be, you shall soon hear further of all that. Now, gentlemen, in square-sail brigs and three-masted ships, well nigh as large and stout as any that ever sailed out of your old Callao to far Manilla; this Lakeman, in the land-locked heart of our America, had yet been nurtured by all those agrarian free-booting impressions popularly connected with the open ocean. For in their interflowing aggregate, those grand fresh-water seas of ours—Erie, and Ontario, and Huron, and Superior, and Michigan—possess an ocean-like expansiveness, with many of the ocean's noblest traits; with many of its rimmed varieties of races and of climes. They contain round archipelagoes of romantic isles, even as the Polynesian waters do; in large part, are shored by two great contrasting nations, as the Atlantic is; they furnish long maritime approaches to our numerous territorial colonies from the East, dotted all round their banks; here and there are frowned upon by batteries, and by the goat-like craggy guns of lofty Mackinaw; they have heard the fleet thunderings of naval victories; at intervals, they yield their beaches to wild barbarians, whose red painted faces flash from out their peltry wigwams; for leagues and leagues are flanked by ancient and unentered forests, where the gaunt pines stand like serried lines of kings in Gothic genealogies; those same woods harboring wild Afric beasts of prey, and silken creatures whose exported furs give robes to Tartar Emperors; they mirror the paved capitals of Buffalo and Cleveland, as well as Winnebago [Pg 659]villages; they float alike the full-rigged merchant ship, the armed cruiser of the State, the steamer, and the beech canoe; they are swept by Borean and dismasting blasts as direful as any that lash the salted wave; they know what shipwrecks are, for out of sight of land, however inland, they have drowned full many a midnight ship with all its shrieking crew. Thus, gentlemen, though an inlander, Steelkilt was wild-ocean born, and wild-ocean nurtured; as much of an audacious mariner as any. And for Radney, though in his infancy he may have laid him down on the lone Nantucket beach, to nurse at his maternal sea; though in after life he had long followed our austere Atlantic and your contemplative Pacific; yet was he quite as vengeful and full of social quarrel as the backwoods seaman, fresh from the latitudes of buck-horn handled Bowie-knives. Yet was this Nantucketer a man with some good-hearted traits; and this Lakeman, a mariner, who though a sort of devil indeed, might yet by inflexible firmness, only tempered by that common decency of human recognition which is the meanest slave's right; thus treated, this Steelkilt had long been retained harmless and docile. At all events, he had proved so thus far; but Radney was doomed and made mad, and Steelkilt—but, gentlemen, you shall hear.
"It was not more than a day or two at the furthest after pointing her prow for her island haven, that the Town-Ho's leak seemed again increasing, but only so as to require an hour or more at the pumps every day. You must know that in a settled and civilized ocean like our Atlantic, for example, some skippers think little of pumping their whole way across it; though of a still, sleepy night, should the officer of the deck happen to forget his duty in that respect, the probability would be that he and his shipmates would never again remember it, on account of all hands gently subsiding to the bottom. Nor in the solitary and savage seas far from you to the westward, gentlemen, is it altogether unusual for ships to keep clanging at their pump-handles in full chorus even for a voyage of considerable length; that is, if it lie along a tolerably accessible coast, or if any other reasonable retreat is afforded them. It is only when a leaky vessel is in some very out of the way part of those waters, some really landless latitude, that her captain begins to feel a little anxious.
"Much this way had it been with the Town-Ho; so when her leak was found gaining once more, there was in truth some small concern manifested by several of her company; especially by Radney the mate. He commanded the upper sails to be well hoisted, sheeted home anew, and every way expanded to the breeze. Now this Radney, I suppose, was as little of a coward, and as little inclined to any sort of nervous apprehensiveness touching his own person as any fearless, unthinking creature on land or on sea that you can conveniently imagine, gentlemen. Therefore when he betrayed this solicitude about the safety of the ship, some of the seamen declared that it was only on account of his being a part owner in her. So when they were working that evening at the pumps, there was on this head no small gamesomeness slily going on among them, as they stood with their feet continually overflowed by the rippling clear water; clear as any mountain spring, gentlemen—that bubbling from the pumps ran across the deck, and poured itself out in steady spouts at the lee scupper-holes.
"Now, as you well know, it is not seldom the case in this conventional world of ours—watery or otherwise; that when a person placed in command over his fellow-men finds one of them to be very significantly his superior in general pride of manhood, straightway against that man he conceives an unconquerable dislike and bitterness; and if he have a chance he will pull down and pulverize that subaltern's tower, and make a little heap of dust of it. Be this conceit of mine as it may, gentlemen, at all events Steelkilt was a tall and noble animal with a head like a Roman, and a flowing golden beard like the tasseled housings of your last viceroy's snorting charger; and a brain, and a heart, and a soul in him, gentlemen, which had made Steelkilt Charlemagne, had he been born son to Charlemagne's father. But Radney, the mate, was ugly as a mule; yet as hardy, as stubborn, as malicious. He did not love Steelkilt, and Steelkilt knew it.
"Espying the mate drawing near as he was toiling at the pump with the rest, the Lakeman affected not to notice him, but unawed, went on with his gay banterings.
"'Ay, ay, my merry lads, it's a lively leak this; hold a cannikin, one of ye, and let's have a taste. By the Lord, it's worth bottling! I tell ye what, men, old Rad's investment must go for it! he had best cut away his part of the hull and tow it home. The fact is, boys, that sword-fish only began the job; he's come back again with a gang of ship-carpenters, saw-fish, and file-fish, and what not; and the whole posse of 'em are now hard at work cutting and slashing at the bottom; making improvements, I suppose. If old Rad were here now, I'd tell him to jump overboard and scatter 'em. They're playing the devil with his estate, I can tell him. But he's a simple old soul—Rad, and a beauty, too. Boys, they say the rest of his property is invested in looking-glasses. I wonder if he'd give a poor devil like me the model of his nose.'
"'Damn your eyes! what's that pump stopping for?' roared Radney, pretending not to have heard the sailors' talk. 'Thunder away at it!'
"'Ay, ay, sir,' said Steelkilt, merry as a cricket. 'Lively, boys, lively, now!' And with that the pump clanged like fifty fire-engines; the men tossed their hats off to it, and ere long that peculiar gasping of the lungs was heard which denotes the fullest tension of life's utmost energies.
"Quitting the pump at last, with the rest of his band, the Lakeman went forward all panting, and sat himself down on the windlass; his face fiery red, his eyes bloodshot, and wiping the profuse sweat from his brow. Now what cozening [Pg 660] fiend it was, gentlemen, that possessed Radney to meddle with such a man in that corporeally exasperated state, I know not; but so it happened. Intolerably striding along the deck, the mate commanded him to get a broom and sweep down the planks, and also a shovel, and remove some offensive matters consequent upon allowing a pig to run at large.
"Now, gentlemen, sweeping a ship's deck at sea is a piece of household work which in all times but raging gales is regularly attended to every evening; it has been known to be done in the case of ships actually foundering at the time. Such, gentlemen, is the inflexibility of sea-usages and the instinctive love of neatness in seamen; some of whom would not willingly drown without first washing their faces. But in all vessels this broom business is the prescriptive province of the boys, if boys there be aboard. Besides, it was the stronger men in the Town-Ho that had been divided into gangs, taking turns at the pumps; and being the most athletic seaman of them all, Steelkilt had been regularly assigned captain of one of the gangs; consequently he should have been freed from any trivial business not connected with truly nautical duties, such being the case with his comrades. I mention all these particulars so that you may understand exactly how this affair stood between the two men.
"But there was more than this: the order about the shovel was almost as plainly meant to sting and insult Steelkilt, as though Radney had spat in his face. Any man who has gone sailor in a whale-ship will understand this; and all this and doubtless much more, the Lakeman fully comprehended when the mate uttered his command. But as he sat still for a moment, and as he steadfastly looked into the mate's malignant eye and perceived the stacks of powder-casks heaped up in him and the slow match silently burning along toward them; as he instinctively saw all this, that strange forbearance and unwillingness to stir up the deeper passionateness in any already ireful being—a repugnance most felt, when felt at all, by really valiant men even when aggrieved—this nameless phantom feeling, gentlemen, stole over Steelkilt.
"Therefore, in his ordinary tone, only a little broken by the bodily exhaustion he was temporarily in, he answered him, saying that sweeping the deck was not his business, and he would not do it. And then, without at all alluding to the shovel, he pointed to three lads as the customary sweepers; who, not being billeted at the pumps, had done little or nothing all day. To this, Radney replied with an oath, in a most domineering and outrageous manner unconditionally reiterating his command; meanwhile advancing upon the still seated Lakeman, with an uplifted cooper's club hammer which he had snatched from a cask near by.
"Heated and irritated as he was by his spasmodic toil at the pumps, for all his first nameless feeling of forbearance the sweating Steelkilt could but ill brook this bearing in the mate; but somehow still smothering the conflagration within him, without speaking he remained doggedly; rooted to his seat, till at last the incensed Radney shook the hammer within a few inches of his face, furiously commanding him to do his bidding.
"Steelkilt rose, and slowly retreating round the windlass, steadily followed by the mate with his menacing hammer, deliberately repeated his intention not to obey. Seeing, however, that his forbearance had not the slightest effect, by an awful and unspeakable intimation with his twisted hand he warned off the foolish and infatuated man; but it was to no purpose. And in this way the two went once slowly round the windlass; when, resolved at last no longer to retreat, bethinking him that he had now forborne as much as comported with his humor, the Lakeman paused on the hatches and thus spoke to the officer:
"'Mr. Radney, I will not obey you. Take that hammer away, or look to yourself.' But the predestinated mate coming still closer to him, where the Lakeman stood fixed, now shook the heavy hammer within an inch of his teeth; meanwhile repeating a string of insufferable maledictions. Retreating not the thousandth part of an inch; stabbing him in the eye with the unflinching poniard of his glance, Steelkilt, clenching his right hand behind him and creepingly drawing it back, told his persecutor that if the hammer but grazed his cheek he (Steelkilt) would murder him. But, gentlemen, the fool had been branded for the slaughter by the gods. Immediately the hammer touched the cheek; the next instant the lower jaw of the mate was stove in his head; he fell on the hatch spouting blood like a whale.
"Ere the cry could go aft Steelkilt was shaking one of the backstays leading far aloft to where two of his comrades were standing their mast-heads. They were both Canalers.
"'Canalers!' cried Don Pedro. 'We have seen many whaleships in our harbors, but never heard of your Canalers. Pardon: who and what are they?'
"Canalers, Don, are the boatmen belonging to our grand Erie Canal. You must have heard of it.
"'Nay, Senor; hereabouts in this dull, warm, most lazy, and hereditary land, we know but little of your vigorous North.'
"Ay? Well, then, Don, refill my cup. Your chicha's very fine; and, ere proceeding further I will tell you what our Canalers are; for such information may throw side-light upon my story.
"For three hundred and sixty miles, gentlemen, through the entire breadth of the state of New York; through numerous populous cities and most thriving villages; through long, dismal, uninhabited swamps, and affluent, cultivated fields, unrivaled for fertility; by billiard-room and bar room; through the holy-of-holies of great forests; on Roman arches over Indian rivers; through sun and shade; by happy hearts or broken; through all the wide contrasting scenery of those noble Mohawk counties; and especially by rows [Pg 661]of snow-white chapels, whose spires stand almost like milestones, flows one continual stream of Venetianly corrupt and often lawless life. There's your true Ashantee, gentlemen; there howl your pagans; where you ever find them, next door to you; under the long-flung shadow, and the snug patronizing lee of churches. For by some curious fatality, as it is often noted of your metropolitan freebooters that they ever encamp around the halls of justice, so sinners, gentlemen, most abound in holiest vicinities.
"'Is that a friar passing?' said Don Pedro, looking downward into the crowded plaza, with humorous concern.
"'Well for our northern friend, Dame Isabella's Inquisition wanes in Lima,' laughed Don Sebastian. 'Proceed, Senor.'
"'A moment! Pardon!' cried another of the company. 'In the name of all us Limeese, I but desire to express to you, sir sailor, that we have by no means overlooked your delicacy in not substituting present Lima for distant Venice in your corrupt comparison. Oh! do not bow and look surprised; you know the proverb all along this coast—"Corrupt as Lima." It but bears out your saying, too; churches more plentiful than billiard-tables, and forever open—and "Corrupt as Lima." So, too, Venice; I have been there; the holy city of the blessed evangelist, St. Mark!—St. Dominic, purge it! Your cup! Thanks: here I refill; now, you pour out again.'
"Freely depicted in his own vocation, gentlemen, the Canaler would make a fine dramatic hero, so abundantly and picturesquely wicked is he. Like Mark Antony, for days and days along his green-turfed, flowery Nile, he indolently floats, openly toying with his red-cheeked Cleopatra, ripening his apricot thigh upon the sunny deck. But ashore, all this effeminacy is dashed. The brigandish guise which the Canaler so proudly sports; his slouched and gayly-ribboned hat betoken his grand features. A terror to the smiling innocence of the villages through which he floats; his swart visage and bold swagger are not unshunned in cities. Once a vagabond on his own canal, I have received good turns from one of those Canalers; I thank him heartily; would fain be not ungrateful; but it is often one of the prime redeeming qualities of your man of violence, that at times he has as stiff an arm to back a poor stranger in a strait, as to plunder a wealthy one. In sum, gentlemen, what the wildness of this canal life is, is emphatically evinced by this; that our wild whale-fishery contains so many of its most finished graduates, and that scarce any race of mankind, except Sydney men, are so much distrusted by our whaling captains. Nor does it at all diminish the curiousness of this matter, that to many thousands of our rural boys and young men born along its line, the probationary life of the Grand Canal furnishes the sole transition between quietly reaping in a Christian corn-field, and recklessly ploughing the waters of the most barbaric seas."
"'I see! I see!' impetuously exclaimed Don Pedro, spilling his chicha upon his silvery ruffles. 'No need to travel! The world's one Lima. I had thought, now, that at your temperate North the generations were cold and holy as the hills. But the story.'
"I left off, gentlemen, where the Lakeman shook the backstay. Hardly had he done so, when he was surrounded by the three junior mates and the four harpooners, who all crowded him to the deck. But sliding down the ropes like baleful comets, the two Canalers rushed into the uproar, and sought to drag their man out of it toward the forecastle. Others of the sailors joined with them in this attempt, and a twisted turmoil ensued; while standing out of harm's way, the valiant captain danced up and down with a whale-pike, calling upon his officers to manhandle that atrocious scoundrel, and smoke him along to the quarter-deck. At intervals, he ran close up to the revolving border of the confusion, and prying into the heart of it with his pike, sought to prick out the object of his resentment. But Steelkilt and his desperadoes were too much for them all; they succeeded in gaining the forecastle deck, where, hastily slewing about three or four large casks in a line with the windlass, these sea-Parisians entrenched themselves behind the barricade."
"'Come out of that, ye pirates!' roared the captain, now menacing them with a pistol in each hand, just brought to him by the steward. 'Come out of that, ye cut-throats!'
"Steelkilt leaped on the barricade, and striding up and down there, defied the worst the pistols could do; but gave the captain to understand distinctly, that his (Steelkilt's) death would be the signal for a murderous mutiny on the part of all hands. Fearing in his heart lest this might prove but too true, the captain a little desisted, but still commanded the insurgents instantly to return to their duty.
"'Will you promise not to touch us, if we do?' demanded their ringleader.
"'Turn to! turn to!—I make no promise; to your duty! Do you want to sink the ship, by knocking off at a time like this? Turn to!' and he once more raised a pistol.
"'Sink the ship?' cried Steelkilt. 'Ay, let her sink. Not a man of us turns to, unless you swear not to raise a rope-yarn against us. What say ye, men?' turning to his comrades. A fierce cheer was their response.
"The Lakeman now patrolled the barricade, all the while keeping his eye on the Captain, and jerking out such sentences as these: 'It's not our fault; we didn't want it; I told him to take his hammer away; it was boys' business: he might have known me before this; I told him not to prick the buffalo; I believe I have broken a finger here against his cursed jaw; ain't those mincing knives down in the forecastle there, men? look to those handspikes, my hearties. Captain, by God, look to yourself; say the word; don't be a fool; forget it all; we are ready to turn to; treat us decently, and we're your men; but we won't be flogged.'
[Pg 662]"'Turn to! I make no promises: turn to, I say!'
"'Look ye, now,' cried the Lakeman, flinging out his arm toward him, 'there are a few of us here (and I am one of them) who have shipped for the cruise, d'ye see; now as you well know, sir, we can claim our discharge as soon as the anchor is down; so we don't want a row; it's not our interest; we want to be peaceable; we are ready to work, but we won't be flogged.'
"'Turn to!' roared the Captain.
"Steelkilt glanced round him a moment, and then said: 'I tell you what it is now, Captain, rather than kill ye, and be hung for such a shabby rascal, we won't lift a hand against ye unless ye attack us; but till you say the word about not flogging us, we don't do a hand's turn.'
"'Down into the forecastle then, down with ye, I'll keep ye there till ye're sick of it. Down ye go.'
"'Shall we?' cried the ringleader to his men. Most of them were against it; but at length, in obedience to Steelkilt, they preceded him down into their dark den, growlingly disappearing like bears into a cave.
"As the Lakeman's bare head was just level with the planks, the Captain and his posse leaped the barricade, and rapidly drawing over the slide of the scuttle, planted their group of hands upon it, and loudly called for the steward to bring the heavy brass padlock belonging to the companionway. Then opening the slide a little, the Captain whispered something down the crack, closed it, and turned the key upon them—ten in number—leaving on deck some twenty or more, who thus far had remained neutral.
"All night a wide-awake watch was kept by all the officers, forward and aft, especially about the forecastle scuttle and fore hatchway; at which last place it was feared the insurgents might emerge, after breaking through the bulkhead below. But the hours of darkness passed in peace; the men who still remained at their duty toiling hard at the pumps, whose clinking and clanking at intervals through the dreary night dismally resounded through the ship.
"At sunrise the Captain went forward, and knocking on the deck summoned the prisoners to work; but with a yell they refused. Water was then lowered down to them, and a couple of handfuls of biscuit were tossed after it; when again turning the key upon them and pocketing it, the Captain returned to the quarter-deck. Twice every day for three days this was repeated; but on the fourth morning a confused wrangling, and then a scuffling was heard, as the customary summons was delivered; and suddenly four men burst up from the forecastle, saying they were ready to turn to. The fetid closeness of the air, and a famishing diet, united perhaps to some fears of ultimate retribution, had constrained them to surrender at discretion. Emboldened by this, the Captain reiterated his demand to the rest, but Steelkilt shouted up to him a terrific hint to stop his babbling and betake himself where he belonged. On the fifth morning three others of the mutineers bolted up into the air from the desperate arms below that sought to restrain them. Only three were left.
"'Better turn to, now!' said the Captain with a heartless jeer.
"'Shut us up again, will ye!' cried Steelkilt.
"'Oh! certainly,' said the Captain, and the key clicked.
"It was at this point, gentlemen, that enraged by the defection of seven of his former associates, and stung by the mocking voice that had last hailed him, and maddened by his long entombment in a place as black as the bowels of despair; it was then that Steelkilt proposed to the two Canalers, thus far apparently of one mind with him, to burst out of their hole at the next summoning of the garrison; and armed with their keen mincing knives (long, crescentic, heavy implements with a handle at each end) run a muck from the bowsprit to the taffrail; and if by any devilishness of desperation possible, seize the ship. For himself, he would do this, he said, whether they joined him or not. That was the last night he should spend in that den. But the scheme met with no opposition on the part of the other two; they swore they were ready for that, or for any other mad thing, for any thing, in short, but a surrender. And what was more, they each insisted upon being the first man on deck, when the time to make the rush should come. But to this their leader as fiercely objected, reserving that priority for himself; particularly as his two comrades would not yield, the one to the other, in the matter; and both of them could not be first, for the ladder would but admit one man at a time. And here, gentlemen, the foul play of these miscreants must come out.
"Upon hearing the frantic project of their leader, each in his own separate soul had suddenly lighted, it would seem, upon the same piece of treachery, namely: to be foremost in breaking out, in order to be the first of the three, though the last of the ten, to surrender; and thereby secure whatever small chance of pardon such conduct might merit. But when Steelkilt made known his determination still to lead them to the last, they in some way, by some subtle chemistry of villainy, mixed their before secret treacheries together; and when their leader fell into a doze, verbally opened their souls to each other in three sentences; and bound the sleeper with cords, and gagged him with cords; and shrieked out for the Captain at midnight.
"Thinking murder at hand, and smelling in the dark for the blood, he and all his armed mates and harpooners rushed for the forecastle. In a few minutes the scuttle was opened, and, bound hand and foot, the still struggling ringleader was shoved up into the air by his perfidious allies, who at once claimed the honor of securing a man who had been fully ripe for murder. But all three were collared, and dragged along the deck like dead cattle; and, side by side, were seized up into the mizen rigging, like three quarters of meat, and there they hung till morning. 'Damn [Pg 663]ye,' cried the Captain, pacing to and fro before them, 'the vultures would not touch ye, ye villains!'
"At sunrise he summoned all hands; and separated those who had rebelled from those who had taken no part in the mutiny, he told the former that he had a good mind to flog them all around—thought, upon the whole, he would do so—he ought to—justice demanded it; but, for the present, considering their timely surrender, he would let them go with a reprimand, which he accordingly administered in the vernacular.
"'But as for you, ye carrion rogues,' turning to the three men in the rigging—'for you, I mean to mince ye up for the try-pots;' and, seizing a rope, he applied it with all his might to the backs of the two traitors, till they yelled no more, but lifelessly hung their head sideways, as the two crucified thieves are drawn.
"'My wrist is sprained with ye!' he cried, at last; 'but there is still rope enough left for you, my fine bantam, that wouldn't give up. Take that gag from his mouth, and let us hear what he can say for himself.'
"For a moment the exhausted mutineer made a tremulous motion of his cramped jaws, and then painfully twisting round his head, said, in a sort of hiss, 'What I say is this—and mind it well—if you flog me, I murder you!'
"'Say ye so? then see how ye frighten me'—and the Captain drew off with the rope to strike.
"'Best not,' hissed the Lakeman.
"'But I must'—and the rope was once more drawn back for the stroke.
"Steelkilt here hissed out something, inaudible to all but the Captain; who, to the amazement of all hands, started back, paced the deck rapidly two or three times, and then suddenly throwing down his rope, said, 'I won't do it—let him go—cut him down: d'ye hear?'
"But as the junior mates were hurrying to execute the order, a pale man, with a bandaged head, arrested them—Radney the chief mate. Ever since the blow, he had lain in his berth; but that morning, hearing the tumult on the deck, he had crept out, and thus far had watched the whole scene. Such was the state of his mouth, that he could hardly speak; but mumbling something about his being willing and able to do what the Captain dared not attempt, he snatched the rope and advanced to his pinioned foe.
"'You are a coward!' hissed the Lakeman.
"'So I am, but take that.' The mate was in the very act of striking, when another hiss stayed his uplifted arm. He paused: and then pausing no more, made good his word, spite of Steelkilt's threat, whatever that might have been. The three men were then cut down, all hands were turned to, and, sullenly worked by the moody seamen, the iron pumps clanged as before.
"Just after dark that day, when one watch had retired below, a clamor was heard in the forecastle; and the two trembling traitors running up, besieged the cabin-door, saying they durst not consort with the crew. Entreaties, cuffs, and kicks could not drive them back, so at their own instance they were put down in the ship's run for salvation. Still, no sign of mutiny re-appeared among the rest. On the contrary, it seemed, that mainly at Steelkilt's instigation, they had resolved to maintain the strictest peacefulness, obey all orders to the last, and, when the ship reached port, desert her in a body. But in order to insure the speediest end to the voyage, they all agreed to another thing—namely, not to sing out for whales, in case any should be discovered. For, spite of her leak, and spite of all her other perils, the Town-Ho still maintained her mast heads, and her captain was just as willing to lower for a fish that moment, as on the day his craft first struck the cruising-ground, and Radney the mate was quite as ready to change his berth for a boat, and with his bandaged mouth seek to gag in death the vital jaw of the whale.
"But though the Lakeman had induced the seamen to adopt this sort of passiveness in their conduct, he kept his own counsel (at least till all was over) concerning his own proper and private revenge upon the man who had stung him in the ventricles of his heart. He was in Radney the chief-mate's watch; and as if the infatuated man sought to run more than half way to meet his doom, after the scene at the rigging, he insisted, against the express counsel of the captain, upon resuming the head of his watch at night. Upon this, and one or two other circumstances, Steelkilt systematically built the plan of his revenge.
"During the night, Radney had an unseaman-like way of sitting on the bulwarks of the quarter-deck, and leaning his arm upon the gunwale of the boat which was hoisted up there, a little above the ship's side. In this attitude, it was well known, he sometimes dozed. There was a considerable vacancy between the boat and the ship, and down between this was the sea. Steelkilt calculated his time, and found that his next trick at the helm would come round at two o'clock, in the morning of the third day from that in which he had been betrayed. At his leisure, he employed the interval in braiding something very carefully in his watches below.
"'What are you making there?' said a shipmate.
"'What do you think? what does it look like?'
"'Like a lanyard for your bag; but it's an odd one, seems to me.'
"'Yes, rather oddish,' said the Lakeman, holding it at arm's length before him; 'but I think it will answer. Shipmate, I haven't enough twine—have you any?'
"But there was none in the forecastle.
"'Then I must get some from old Rad;' and he rose to go aft.
"'You don't mean to go a-begging to him!' said a sailor.
"'Why not? Do you think he won't do me a turn, when it's to help himself in the end, shipmate?' and going to the mate, he looked at him quietly, and asked him for some twine to mend his hammock. It was given him—neither twine nor lanyard was seen again; but the next night an iron ball, closely netted, partly rolled from the [Pg 664]pocket of the Lakeman's monkey-jacket, as he was tucking the coat into his hammock for a pillow. Twenty-four hours after, his trick at the silent helm—nigh to the man who was apt to doze over the grave always ready dug to the seaman's hand—that fatal hour was then to come; and in the fore-ordaining soul of Steelkilt, the mate was already stark and stretched as a corpse, with his forehead crushed in.
"But, gentlemen, a fool saved the would-be murderer from the bloody deed he had planned. Yet complete revenge he had, and without being the avenger. For by a mysterious fatality, Heaven itself seemed to step in to take out of his hands into its own the damning thing he would have done.
"It was just between daybreak and sunrise of the morning of the second day, when they were washing down the decks, that a stupid Teneriffe man, drawing water in the main-chains, all at once shouted out, 'There she rolls! there she rolls! Jesu! what a whale!' It was Moby Dick.
"'Moby Dick!' cried Don Sebastian; 'St. Dominic! Sir sailor, but do whales have christenings? Whom call you Moby Dick?'
"A very white, and famous, and most deadly immortal monster, Don; but that would be too long a story.
"'How? how? cried all the young Spaniards, crowding.
"Nay, Dons, Dons—nay, nay! I can not rehearse that now. Let me get more into the air, sirs.
"'The chicha! the chicha!' cried Don Pedro; 'our vigorous friend looks faint; fill up his empty glass!'
"No need, gentlemen; one moment, and I proceed. Now, gentlemen, so suddenly perceiving the snowy whale within fifty yards of the ship—forgetful of the compact among the crew—in the excitement of the moment, the Teneriffe man had instinctively and involuntarily lifted his voice for the monster, though for some little time past it had been plainly beheld from the three sullen mast-heads. All was now a frenzy. 'The White Whale—the White Whale!' was the cry from captain, mates, and harpooners, who, undeterred by fearful rumors, were all anxious to capture so famous and precious a fish; while the dogged crew eyed askance, and with curses, the appalling beauty of the vast milky mass, that lit up by a horizontal spangling sun, shifted and glistened like a living opal in the blue morning sea. Gentlemen, a strange fatality pervades the whole career of these events, as if verily mapped out before the world itself was charted. The mutineer was the bowsman of the mate, and when fast to a fish, it was his duty to sit next him, while Radney stood up with his lance in the prow, and haul in or slacken the line, at the word of command. Moreover, when the four boats were lowered, the mate's got the start; and none howled more fiercely with delight than did Steelkilt, as he strained at his oar. After a stiff pull, their harpooner got fast, and, spear in hand, Radney sprang to the bow. He was always a furious man, it seems, in a boat. And now his bandaged cry was, to beach him on the whale's topmost back. Nothing loath, his bowsman hauled him up and up, through a blinding foam that blent two whitenesses together; till of a sudden the boat struck as against a sunken ledge, and keeling over, spilled out the standing mate. That instant, as he fell on the whale's slippery back, the boat righted, and was dashed aside by the swell, while Radney was tossed over into the sea, on the other flank of the whale. He struck out through the spray, and, for an instant, was dimly seen through that vail, wildly seeking to remove himself from the eye of Moby Dick. But the whale rushed round in a sudden maelstrom—seized the swimmer between his jaws; and rearing high up with him, plunged headlong again, and went down.
"Meantime, at the first tap of the boat's bottom, the Lakeman had slackened the line, so as to drop astern from the whirlpool; calmly looking on, he thought his own thoughts. But a sudden, terrific, downward jerking of the boat, quickly brought his knife to the line. He cut it; and the whale was free. But, at some distance, Moby Dick rose again, with some tatters of Radney's red woolen shirt, caught in the teeth that had destroyed him. All four boats gave chase again; but the whale eluded them, and, finally, wholly disappeared.
"In good time, the Town-Ho reached her port—a savage, solitary place—where no civilized creature resided. There, headed by the Lakeman, all but five or six of the foremast-men deliberately deserted among the palms; eventually, as it turned out, seizing a large double war-canoe of the savages, and setting sail for some other harbor.
"The ship's company being reduced to but a handful, the Captain called upon the Islanders to assist him in the laborious business of heaving down the ship to stop the leak. But to such unresting vigilance over their dangerous allies was this small band of whites necessitated, both by night and by day, and so extreme was the hard work they underwent, that upon the vessel being ready again for sea, they were in such a weakened condition that the captain durst not put off with them in so heavy a vessel. After taking counsel with his officers, he anchored the ship as far off shore as possible; loaded and ran out his two cannon from the bows; stacked his muskets on the poop; and warning the Islanders not to approach the ship at their peril, took one man with him, and setting the sail of his best whale-boat, steered straight before the wind for Tahiti, five hundred miles distant, to procure a reinforcement to his crew.
"On the fourth day of the sail, a large canoe was descried, which seemed to have touched at a low isle of corals. He steered away from it; but the savage craft bore down on him; and soon the voice of Steelkilt hailed him to heave to, or he would run him under water. The captain presented a pistol. With one foot on each prow of the yoked war-canoes, the Lakeman laughed him [Pg 665]to scorn; assuring him that if the pistol so much as clicked in the lock, he would bury him in bubbles and foam.
"'What do you want of me?' cried the captain.
"'Where are you bound? and for what are you bound?' demanded Steelkilt; 'no lies.'
"'I am bound to Tahiti for more men.'
"'Very good. Let me board you a moment—I come in peace.' With that he leaped from the canoe, swam to the boat; and climbing the gunwale, stood face to face with the captain.
"'Cross your arm, sir; throw back your head. Now, repeat after me. As soon as Steelkilt leaves me, I swear to beach this boat on yonder island, and remain there six days. If I do not, may lightnings strike me!'
"'A pretty scholar,' laughed the Lakeman. 'Adios, Senor!' and leaping into the sea, he swam back to his comrades.
"Watching the boat till it was fairly beached, and drawn up to the roots of the cocoa-nut trees, Steelkilt made sail again, and in due time arrived at Tahiti, his own place of destination. There, luck befriended him; two ships were about to sail for France, and were providentially in want of precisely that number of men which the sailor headed. They embarked; and so forever got the start of their former captain, had he been at all minded to work them legal retribution.
"Some ten days after the French ships sailed, the whale-boat arrived, and the captain was forced to enlist some of the more civilized Tahitans, who had been somewhat used to the sea. Chartering a small native schooner, he returned with them to his vessel; and finding all right there, again resumed his cruisings.
"Where Steelkilt now is, gentlemen, none know; but upon the island of Nantucket, the widow of Radney still turns to the sea which refuses to give up its dead; still in dreams sees the awful white whale that destroyed him....
"'Are you through?' said Don Sebastian, quietly.
"I am, Don.
"'Then I entreat you, tell me if to the best of your own convictions, this your story is, in substance, really true? It is so passing wonderful! Did you get it from an unquestionable source? Bear with me if I seem to press.'
"'Also bear with all of us, sir sailor; for we all join in Don Sebastian's suit,' cried the company, with exceeding interest.
"Is there a copy of the Holy Evangelists in the Golden Inn, gentlemen?
"'Nay,' said Don Sebastian; 'but I know a worthy priest near by, who will quickly procure one for me. I go for it; but are you well advised? this may grow too serious.'
"'Will you be so good as to bring the priest also, Don?'
"'Though there are no Auto-da-Fés in Lima now,' said one of the company to another; 'I fear our sailor friend runs risk of the archiepiscopacy. Let us withdraw more out of the moonlight. I see no need of this.'
"Excuse me for running after you, Don Sebastian; but may I also beg that you will be particular in procuring the largest sized Evangelists you can....
"'This is the priest; he brings you the Evangelists,' said Don Sebastian, gravely, returning with a tall and solemn figure.
"Let me remove my hat. Now, venerable priest, further into the light, and hold the Holy Book before me that I may touch it.
"So help me Heaven, and on my honor, the story I have told ye, gentlemen, is, in substance and its great items, true. I know it to be true; it happened on this ball; I trod the ship; I knew the crew; I have seen and talked with Steelkilt since the death of Radney."
[6] Continued from the September Number.
"What is courage?" said my uncle Roland, rousing himself from a reverie into which he had fallen after the Sixth Book in this history had been read to our family circle.
"What is courage?" he repeated more earnestly. "Is it insensibility to fear? That may be the mere accident of constitution; and, if so, there is no more merit in being courageous than in being this table."
"I am very glad to hear you speak thus," observed Mr. Caxton, "for I should not like to consider myself a coward; yet I am very sensible to fear in all dangers, bodily and moral."
"La, Austin, how can you say so?" cried my mother, firing up; "was it not only last week that you faced the great bull that was rushing after Blanche and the children?"
Blanche at that recollection stole to my father's chair, and, hanging over his shoulder kissed his forehead.
Mr. Caxton (sublimely unmoved by these flatteries).—"I don't deny that I faced the bull, but I assert that I was horribly frightened."
Roland.—"The sense of honor which conquers fear is the true courage of chivalry: you could not run away when others were looking on—no gentleman could."
Mr. Caxton.—"Fiddledee! It was not on my gentility that I stood, Captain. I should have run fast enough, if it had done any good. I stood upon my understanding. As the bull could run faster than I could, the only chance of escape was to make the brute as frightened as myself."
Blanche.—"Ah, you did not think of that; your only thought was to save me and the children."
Mr. Caxton.—"Possibly, my dear—very possibly I might have been afraid for you too—but I was very much afraid for myself. However, luckily I had the umbrella, and I sprang it up and spread it forth in the animal's stupid eyes, hurling at him simultaneously the biggest lines I could think of in the First Chorus of the 'Seven against Thebes.' I began with [Pg 666] Eledemnas pedioploktupos; and when I came to the grand howl of Iô, iô, iô, iô—the beast stood appalled as at the roar of a lion. I shall never forget his amazed snort at the Greek. Then he kicked up his hind legs, and went bolt through the gap in the hedge. Thus, armed with Æschylus and the umbrella, I remained master of the field; but (continued Mr. Caxton, ingenuously), I should not like to go through that half minute again."
"No man would," said the Captain, kindly. "I should be very sorry to face a bull myself, even with a bigger umbrella than yours, and even though I had Æschylus, and Homer to boot, at my fingers' ends."
Mr. Caxton.—"You would not have minded if it had been a Frenchman with a sword in his hand?"
Captain.—"Of course not. Rather liked it than otherwise," he added, grimly.
Mr. Caxton.—"Yet many a Spanish matador, who doesn't care a button for a bull, would take to his heels at the first lunge en carte from a Frenchman. Therefore, in fact, if courage be a matter of constitution, it is also a matter of custom. We face calmly the dangers we are habituated to, and recoil from those of which we have no familiar experience. I doubt if Marshal Turenne himself would have been quite at his ease on the tight rope; and a rope-dancer, who seems disposed to scale the heavens with Titanic temerity, might possibly object to charge on a cannon."
Captain Roland.—"Still, either this is not the courage I mean, or there is another kind of it. I mean by courage that which is the especial force and dignity of the human character, without which there is no reliance on principle, no constancy in virtue—a something," continued my uncle, gallantly, and with a half bow toward my mother, "which your sex shares with our own. When the lover, for instance, clasps the hand of his betrothed, and says, 'Wilt thou be true to me, in spite of absence and time, in spite of hazard and fortune, though my foes malign me, though thy friends may dissuade thee, and our lot in life may be rough and rude?' and when the betrothed answers, 'I will be true,' does not the lover trust to her courage as well as her love?"
"Admirably put, Roland," said my father. "But apropos of what do you puzzle us with these queries on courage?"
Captain Roland (with a slight blush).—"I was led to the inquiry (though, perhaps, it may be frivolous to take so much thought of what, no doubt, costs Pisistratus so little), by the last chapters in my nephew's story. I see this poor boy, Leonard, alone with his fallen hopes (though very irrational they were), and his sense of shame. And I read his heart, I dare say, better than Pisistratus does, for I could feel like that boy if I had been in the same position; and, conjecturing what he and thousands like him must go through, I asked myself, 'What can save him and them?' I answered, as a soldier would answer, 'Courage!' Very well. But pray, Austin, what is courage?"
Mr. Caxton (prudently backing out of a reply).—"Papæ! Brother, since you have just complimented the ladies on that quality, you had better address your question to them."
Blanche here leant both hands on my father's chair, and said, looking down at first bashfully, but afterward warming with the subject, "Do you not think, sir, that little Helen has already suggested, if not what is courage, what at least is the real essence of all courage that endures and conquers, that ennobles, and hallows, and redeems? Is it not Patience, father?—and that is why we women have a courage of our own. Patience does not affect to be superior to fear, but at least it never admits despair."
Pisistratus.—"Kiss me, my Blanche, for you have come near to the truth which perplexed the soldier and puzzled the sage."
Mr. Caxton (tartly).—"If you mean me by the sage, I was not puzzled at all. Heaven knows you do right to inculcate patience—it is a virtue very much required in your readers. Nevertheless," added my father, softening with the enjoyment of his joke—"nevertheless, Blanche and Helen are quite right. Patience is the courage of the conqueror; it is the virtue, par excellence, of Man against Destiny—of the One against the World, and of the Soul against Matter. Therefore this is the courage of the Gospel; and its importance, in a social view—its importance to races and institutions—can not be too earnestly included. What is it that distinguishes the Anglo-Saxon from all other branches of the human family, peoples deserts with his children, and consigns to them the heritage of rising worlds? What but his faculty to brave, to suffer, to endure—the patience that resists firmly, and innovates slowly. Compare him with the Frenchman. The Frenchman has plenty of valor—that there is no denying; but as for fortitude, he has not enough to cover the point of a pin. He is ready to rush out of the world if he is bit by a flea."
Captain Roland.—"There was a case in the papers the other day, Austin, of a Frenchman who actually did destroy himself because he was so teased by the little creatures you speak of. He left a paper on his table, saying that 'life was not worth having at the price of such torments.'"[7]
[7] Fact. In a work by M. Gibert, a celebrated French physician, on diseases of the skin, he states that that minute troublesome kind of rash, known by the name of prurigo, though not dangerous in itself, has often driven the individual afflicted by it to—suicide. I believe that our more varying climate, and our more heating drinks and aliments, render the skin complaint more common in England than in France, yet I doubt if any English physician could state that it had ever driven one of his English patients to suicide.
Mr. Caxton (solemnly).—"Sir, their whole political history, since the great meeting of the Tiers État, has been the history of men who would rather go to the devil than be bit by a flea. It is the record of human impatience, that seeks to force time, and expects to grow forests from the spawn of a mushroom. Wherefore, [Pg 667] running through all extremes of constitutional experiment, when they are nearest to democracy they are next door to a despot; and all they have really done is to destroy whatever constitutes the foundation of every tolerable government. A constitutional monarchy can not exist without aristocracy, nor a healthful republic endure with corruption of manners. The cry of Equality is incompatible with Civilization, which, of necessity, contrasts poverty with wealth, and, in short, whether it be an emperor or a mob that is to rule, Force is the sole hope of order, and the government is but an army.
"Impress, O Pisistratus! impress the value of patience as regards man and men. You touch there on the kernel of the social system—the secret that fortifies the individual and disciplines the million. I care not, for my part, if you are tedious so long as you are earnest. Be minute and detailed. Let the real human life, in its war with Circumstance, stand out. Never mind if one can read you but slowly—better chance of being less quickly forgotten. Patience, patience! By the soul of Epictetus, your readers shall set you an example!"
Leonard had written twice to Mrs. Fairfield, twice to Riccabocca, and once to Mr. Dale; and the poor proud boy could not bear to betray his humiliation. He wrote with as cheerful spirits—as if perfectly satisfied with his prospects. He said that he was well employed, in the midst of books, and that he had found kind friends. Then he turned from himself to write about those whom he addressed, and the affairs and interests of the quiet world wherein they lived. He did not give his own address, nor that of Mr. Prickett. He dated his letters from a small coffee-house near the bookseller, to which he occasionally went for his simple meals. He had a motive in this. He did not desire to be found out. Mr. Dale replied for himself and for Mrs. Fairfield, to the epistles addressed to these two. Riccabocca wrote also. Nothing could be more kind than the replies of both. They came to Leonard in a very dark period in his life, and they strengthened him in the noiseless battle with despair.
If there be a good in the world that we do without knowing it, without conjecturing the effect it may have upon a human soul, it is when we show kindness to the young in the first barren footpath up the mountain of life.
Leonard's face resumed its serenity in his intercourse with his employer; but he did not recover his boyish ingenuous frankness. The under-currents flowed again pure from the turbid soil and the splintered fragments uptorn from the deep; but they were still too strong and too rapid to allow transparency to the surface. And now he stood in the sublime world of books, still and earnest as a seer who invokes the dead. And thus, face to face with knowledge, hourly he discovered how little he knew. Mr. Prickett lent him such works as he selected and asked to take home with him. He spent whole nights in reading; and no longer desultorily. He read no more poetry, no more Lives of Poets. He read what poets must read if they desire to be great—Sapere principium et fons—strict reasonings on the human mind; the relations between motive and conduct, thought and action; the grave and solemn truths of the past world; antiquities, history, philosophy. He was taken out of himself. He was carried along the ocean of the universe. In that ocean, O seeker, study the law of the tides; and seeing Chance nowhere—Thought presiding over all—Fate, that dread phantom, shall vanish from creation, and Providence alone be visible in heaven and on earth!
There was to be a considerable book-sale at a country house one day's journey from London. Mr. Prickett meant to have attended it on his own behalf, and that of several gentlemen who had given him commissions for purchase; but, on the morning fixed for his departure, he was seized with a severe return of his old foe, the rheumatism. He requested Leonard to attend instead of himself. Leonard went, and was absent for the three days during which the sale lasted. He returned late in the evening, and went at once to Mr. Prickett's house. The shop was closed; he knocked at the private entrance; a strange person opened the door to him, and in reply to his question if Mr. Prickett was at home, said with a long and funereal face—"Young man, Mr. Prickett senior has gone to his long home, but Mr. Richard Prickett will see you."
At this moment a very grave-looking man, with lank hair, looked forth from the side-door communicating between the shop and the passage; and then stepped forward—"Come in, sir; you are my late uncle's assistant, Mr. Fairfield, I suppose?"
"Your late uncle! Heavens, sir, do I understand aright—can Mr. Prickett be dead since I left London?"
"Died, sir, suddenly last night. It was an affection of the heart; the doctor thinks the rheumatism attacked that organ. He had small time to provide for his departure, and his account books seem in sad disorder: I am his nephew and executor."
Leonard had now followed the nephew into the shop. There, still burned the gas lamp. The place seemed more dingy and cavernous than before. Death always makes its presence felt in the house it visits.
Leonard was greatly affected—and yet more, perhaps, by the utter want of feeling which the nephew exhibited. In fact, the deceased had not been on friendly terms with this person, his nearest relative and heir-at-law, who was also a bookseller.
"You were engaged but by the week I find, young man, on reference to my late uncle's [Pg 668]papers. He gave you a £1 a week—a monstrous sum! I shall not require your services any further. I shall move these books to my own house. You will be good enough to send me a list of those you bought at the sale, and your account of traveling expenses, &c. What may be due to you shall be sent to your address. Good evening."
Leonard went home, shocked and saddened at the sudden death of his kind employer. He did not think much of himself that night; but, when he rose the next day, he suddenly felt that the world of London lay before him, without a friend, without a calling, without an occupation for bread.
This time it was no fancied sorrow, no poetic dream disappointed. Before him, gaunt and palpable, stood Famine.
Escape!—yes. Back to the village; his mother's cottage; the exile's garden; the radishes and the fount. Why could he not escape? Ask why civilization can not escape its ills and fly back to the wilds and the wigwam?
Leonard could not have returned to the cottage, even if the Famine that faced had already seized him with her skeleton hand. London releases not so readily her fated stepsons.
One day three persons were standing before an old book-stall in a passage leading from Oxford-street into Tottenham-court-road. Two were gentlemen; the third, of the class and appearance of those who more habitually halt at old book-stalls.
"Look," said one of the gentlemen to the other, "I have discovered here what I have searched for in vain for the last ten years—the Horace of 1580, the Horace of the Forty Commentators—a perfect treasury of learning, and marked only fourteen shillings!"
"Hush, Norreys," said the other, "and observe what is yet more worth your study;" and he pointed to the third bystander, whose face, sharp and attenuated, was bent with an absorbed, and as it were, with a hungering attention over an old worm-eaten volume.
"What is the book, my lord?" whispered Mr. Norreys.
His companion smiled, and replied by another question, "What is the man who reads the book?"
Mr. Norreys moved a few paces, and looked over the student's shoulder. "Preston's translation of Boethius, The Consolations of Philosophy," he said, coming back to his friend.
"He looks as if he wanted all the consolations Philosophy can give him, poor boy."
At this moment a fourth passenger paused at the book-stall, and, recognizing the pale student, placed his hand on his shoulder and said, "Aha, young sir, we meet again. So poor Prickett is dead. But you are still haunted by associations. Books—books—magnets to which all iron minds move insensibly. What is this? Boethius! Ah, a book written in prison, but a little time before the advent of the only philosopher who solves to the simplest understanding every mystery of life—"
"And that philosopher?"
"Is Death!" said Mr. Burley. "How can you be dull enough to ask? Poor Boethius, rich, nobly born, a consul, his sons consuls—the world one smile to the Last Philosopher of Rome. Then suddenly, against this type of the old world's departing wisdom, stands frowning the new world's grim genius, force—Theodoric the Ostrogoth condemning Boethius the Schoolman; and Boethius, in his Pavian dungeon, holding a dialogue with the shade of Athenian Philosophy. It is the finest picture upon which lingers the glimmering of the Western golden day, before night rushes over time."
"And," said Mr. Norreys abruptly, "Boethius comes back to us with the faint gleam of returning light, translated by Alfred the Great. And, again, as the sun of knowledge bursts forth in all its splendor, by Queen Elizabeth. Boethius influences us as we stand in this passage; and that is the best of all the Consolations of Philosophy—eh, Mr. Burley?"
Mr. Burley turned and bowed.
The two men looked at each other; you could not see a greater contrast. Mr. Burley, his gay green dress already shabby and soiled, with a rent in the skirts, and his face speaking of habitual night-cups. Mr. Norreys, neat and somewhat precise in dress, with firm lean figure, and quiet, collected, vigorous energy in his eye and aspect.
"If," replied Mr. Burley, "a poor devil like me may argue with a gentleman who may command his own price with the booksellers, I should say it is no consolation at all Mr. Norreys. And I should like to see any man of sense accept the condition of Boethius in his prison, with some strangler or headsman waiting behind the door, upon the promised proviso that he should be translated, centuries afterward, by Kings and Queens, and help indirectly to influence the minds of Northern barbarians, babbling about him in an alley, jostled by passers-by who never heard the name of Boethius, and who don't care a fig for philosophy. Your servant, sir—young man, come and talk."
Burley hooked his arm within Leonard's, and led the boy passively away.
"That is a clever man," said Harley L'Estrange. "But I am sorry to see yon young student, with his bright, earnest eyes, and his lip that has the quiver of passion and enthusiasm, leaning on the arm of a guide who seems disenchanted of all that gives purpose to learning, and links philosophy with use to the world. Who, and what is this clever man whom you call Burley?"
"A man who might have been famous, if he had condescended to be respectable! The boy listening to us both so attentively interested me too—I should like to have the making of him. But I must buy this Horace."
The shopman, lurking within his hole like a [Pg 669] spider for flies, was now called out. And when Mr. Norreys had bought the Horace, and given an address where to send it, Harley asked the shopman if he knew the young man who had been reading Boethius.
"Only by sight. He has come here every day the last week, and spends hours at the stall. When once he fastens on a book, he reads it through."
"And never buys?" said Mr. Norreys.
"Sir," said the shopman, with a good-natured smile, "they who buy seldom read. The poor boy pays me two-pence a day to read as long as he pleases. I would not take it, but he is proud."
"I have known men amass great learning in that way," said Mr. Norreys. "Yes, I should like to have that boy in my hands. And now, my lord, I am at your service, and we shall go to the studio of your artist."
The two gentlemen walked on toward one of the streets out of Fitzroy-square.
In a few minutes more Harley L'Estrange was in his element, seated carelessly on a deal table, smoking his cigar, and discussing art with the gusto of a man who honestly loved, and the taste of a man who thoroughly understood it. The young artist, in his dressing robe, adding slow touch upon touch, paused often to listen the better. And Henry Norreys, enjoying the brief respite from a life of great labor, was gladly reminded of idle hours under rosy skies; for these three men had formed their friendship in Italy, where the bands of friendship are woven by the hands of the Graces.
Leonard and Mr. Burley walked on into the suburbs round the north road from London, and Mr. Burley offered to find literary employment for Leonard—an offer eagerly accepted.
Then they went into a public house by the wayside. Burley demanded a private room, called for pen, ink, and paper; and placing these implements before Leonard, said, "Write what you please, in prose, five sheets of letter paper, twenty-two lines to a page neither more nor less."
"I can not write so."
"Tut, 'tis for bread."
The boy's face crimsoned.
"I must forget that," said he.
"There is an arbor in the garden under a weeping ash," returned Burley. "Go there, and fancy yourself in Arcadia."
Leonard was too pleased to obey. He found out the little arbor at one end of a deserted bowling-green. All was still—the hedgerow shut out the sight of the inn. The sun lay warm on the grass, and glinted pleasantly through the leaves of the ash. And Leonard there wrote the first essay from his hand as Author by profession. What was it that he wrote? His dreamy impressions of London? an anathema on its streets, and its hearts of stone? murmurs against poverty? dark elegies on fate?
Oh, no! little knowest thou true genius if thou askest such questions, or thinkest that there, under the weeping ash, the taskwork for bread was remembered; or that the sunbeam glinted but over the practical world, which, vulgar and sordid, lay around. Leonard wrote a fairy tale—one of the loveliest you can conceive, with a delicate touch of playful humor—in a style all flowered over with happy fancies. He smiled as he wrote the last word—he was happy. In rather more than an hour Mr. Burley came to him, and found him with that smile on his lips.
Mr. Burley had a glass of brandy and water in his hand; it was his third. He too smiled—he too looked happy. He read the paper aloud, and well. He was very complimentary. "You will do!" said he, clapping Leonard on the back. "Perhaps some day you will catch my one-eyed perch." Then he folded up the MS., scribbled off a note, put the whole in one envelope—and they returned to London.
Mr. Burley disappeared within a dingy office near Fleet-street, on which was inscribed—"Office of the Beehive," and soon came forth with a golden sovereign in his hand—Leonard's first fruits. Leonard thought Peru lay before him. He accompanied Mr. Burley to that gentleman's lodging in Maida Hill. The walk had been very long; Leonard was not fatigued. He listened with a livelier attention than before to Burley's talk. And when they reached the apartments of the latter, and Mr. Burley sent to the cookshop, and their joint supper was taken out of the golden sovereign, Leonard felt proud, and for the first time for weeks he laughed the heart's laugh. The two writers grew more and more intimate and cordial. And there was a vast deal in Burley by which any young man might be made the wiser. There was no apparent evidence of poverty in the apartment—clean, new, well furnished; but all things in the most horrible litter—all speaking of the huge literary sloven.
For several days Leonard almost lived in those rooms. He wrote continuously—save when Burley's conversation fascinated him into idleness. Nay, it was not idleness—his knowledge grew larger as he listened; but the cynicism of the talker began slowly to work its way. That cynicism in which there was no faith, no hope, no vivifying breath from Glory—from Religion. The cynicism of the Epicurean, more degraded in his style than ever was Diogenes in his tub; and yet presented with such ease and such eloquence—with such art and such mirth—so adorned with illustration and anecdote, so unconscious of debasement.
Strange and dread philosophy—that made it a maxim to squander the gifts of mind on the mere care for matter, and fit the soul to live but as from day to day, with its scornful cry, "A fig for immortality and laurels!" An author for bread! Oh, miserable calling! was there something grand and holy, after all, even in Chatterton's despair!
The villainous Beehive! Bread was worked out of it, certainly; but fame, but hope for the future—certainly not. Milton's Paradise Lost would have perished without a sound, had it appeared in the Beehive.
Fine things were there in a fragmentary crude state, composed by Burley himself. At the end of a week they were dead and forgotten—never read by one man of education and taste; taken simultaneously and indifferently with shallow politics and wretched essays, yet selling, perhaps, twenty or thirty thousand copies—an immense sale; and nothing got out of them but bread and brandy!
"What more would you have?" cried John Burley. "Did not stern old Sam Johnson say he could never write but from want?"
"He might say it," answered Leonard; "but he never meant posterity to believe him. And he would have died of want, I suspect, rather than have written Rasselas for the Beehive! Want is a grand thing," continued the boy, thoughtfully. "A parent of grand things. Necessity is strong, and should give us its own strength; but Want should shatter asunder, with its very writhings, the walls of our prison-house, and not sit contented with the allowance the jail gives us in exchange for our work."
"There is no prison-house to a man who calls upon Bacchus—stay—I will translate to you Schiller's Dithyramb. 'Then see I Bacchus—then up come Cupid and Phœbus, and all the Celestials are filling my dwelling.'"
Breaking into impromptu careless rhymes, Burley threw off a rude but spirited translation of that divine lyric.
"O materialists!" cried the boy, with his bright eyes suffused. "Schiller calls on the gods to take him to their heaven with him; and you would debase the gods to a gin palace."
"Ho, ho!" cried Burley, with his giant laugh. "Drink, and you will understand the Dithyramb."
Suddenly one morning, as Leonard sate with Burley, a fashionable cabriolet, with a very handsome horse, stopped at the door—a loud knock—a quick step on the stairs, and Randal Leslie entered. Leonard recognized him and started. Randal glanced at him in surprise, and then, with a tact that showed he had already learned to profit by London life, after shaking hands with Burley, approached, and said, with some unsuccessful attempt at ease, "Unless I am mistaken, sir, we have met before. If you remember me, I hope all boyish quarrels are forgotten?"
Leonard bowed, and his heart was still good enough to be softened.
"Where could you two ever have met?" asked Burley.
"In a village green, and in single combat," answered Randal, smiling; and he told the story of the Battle of the Stocks with a well-bred jest on himself. Burley laughed at the story. "But," said he, when this laugh was over, "my young friend had better have remained guardian of the village stocks, than come to London in search of such fortune as lies at the bottom of an inkhorn."
"Ah," said Randal, with the secret contempt which men elaborately cultivated are apt to feel for those who seek to educate themselves—"ah, you make literature your calling, sir? At what school did you conceive a taste for letters? not very common at our great public schools."
"I am at school now for the first time," answered Leonard, drily.
"Experience is the best schoolmistress," said Burley; "and that was the maxim of Goethe, who had book-learning enough, in all conscience."
Randal slightly shrugged his shoulders, and, without wasting another thought on Leonard, peasant-born and self-taught, took his seat, and began to talk to Burley upon a political question, which made then the war-cry between the two great Parliamentary parties. It was a subject in which Burley showed much general knowledge; and Randal, seeming to differ from him, drew forth alike his information and his argumentative powers. The conversation lasted more than an hour.
"I can't quite agree with you," said Randal, taking his leave; "but you must allow me to call again—will the same hour to-morrow suit you?"
"Yes," said Burley.
Away went the young man in his cabriolet. Leonard watched him from the window.
For five days consecutively, did Randal call and discuss the question in all its bearings; and Burley, after the second day, got interested in the matter, looked up his authorities—refreshed his memory and even spent an hour or two in the Library of the British Museum.
By the fifth day Burley had really exhausted all that could well be said on his side of the question.
Leonard, during these colloquies, had sate apart, seemingly absorbed in reading, and secretly stung by Randal's disregard of his presence. For indeed that young man, in his superb self-esteem, and in the absorption of his ambitious projects, scarce felt even curiosity as to Leonard's rise above his earlier station, and looked on him as a mere journeyman of Burley's. But the self-taught are keen and quick observers. And Leonard had remarked that Randal seemed more as one playing a part for some private purpose, than arguing in earnest; and that when he rose and said, "Mr. Burley, you have convinced me," it was not with the modesty of a sincere reasoner, but the triumph of one who has gained his end. But so struck, meanwhile, was our unheeded and silent listener, with Burley's power of generalization, and the wide surface over which his information extended, that when Randal left the room the boy [Pg 671]looked at the slovenly, purposeless man, and said aloud—"True; knowledge is not power."
"Certainly not," said Burley, drily—"the weakest thing in the world."
"Knowledge is power," muttered Randal Leslie, as, with a smile on his lip, he drove from the door.
Not many days after this last interview there appeared a short pamphlet; anonymous, but one which made a great impression on the town. It was on the subject discussed between Randal and Burley. It was quoted at great length in the newspapers. And Burley started to his feet one morning, and exclaimed, "My own thoughts! my very words! Who the devil is this pamphleteer?"
Leonard took the newspaper from Burley's hand. The most flattering encomiums preceded the extracts, and the extracts were as stereotypes of Burley's talk.
"Can you doubt the author?" cried Leonard, in deep disgust and ingenuous scorn. "The young man who came to steal your brains, and turn your knowledge—"
"Into power," interrupted Burley, with a laugh, but it was a laugh of pain. "Well, this was very mean; I shall tell him so when he comes."
"He will come no more," said Leonard. Nor did Randal come again. But he sent Mr. Burley a copy of the pamphlet with a polite note, saying, with candid but careless acknowledgment, that "he had profited much by Mr. Burley's hints and remarks."
And now it was in all the papers, that the pamphlet which had made so great a noise was by a very young man, Mr. Audley Egerton's relation, and high hopes were expressed of the future career of Mr. Randal Leslie.
Burley still attempted to laugh, and still his pain was visible. Leonard most cordially despised and hated Randal Leslie, and his heart moved to Burley with noble but perilous compassion. In his desire to soothe and comfort the man whom he deemed cheated out of fame, he forgot the caution he had hitherto imposed on himself, and yielded more and more to the charm of that wasted intellect. He accompanied Burley now where he went to spend his evenings, and more and more—though gradually, and with many a recoil and self-rebuke—there crept over him the cynic's contempt for glory, and miserable philosophy of debased content.
Randal had risen into grave repute upon the strength of Burley's knowledge. But, had Burley written the pamphlet, would the same repute have attended him? Certainly not. Randal Leslie brought to that knowledge qualities all his own—a style simple, strong, and logical; a certain tone of good society, and allusions to men and to parties that showed his connection with a cabinet minister, and proved that he had profited no less by Egerton's talk than Burley's.
Had Burley written the pamphlet, it would have showed more genius, it would have had humor and wit, but have been so full of whims and quips, sins against taste, and defects in earnestness, that it would have failed to create any serious sensation. Here, then, there was something else besides knowledge, by which knowledge became power. Knowledge must not smell of the brandy bottle.
Randal Leslie might be mean in his plagiarism, but he turned the useless into use. And so far he was original.
But one's admiration, after all, rests where Leonard's rested—with the poor, shabby, riotous, lawless, big fallen man.
Burley took himself off to the Brent, and fished again for the one-eyed perch. Leonard accompanied him. His feelings were indeed different from what they had been when he had reclined under the old tree, and talked with Helen of the future. But it was almost pathetic to see how Burley's nature seemed to alter, as he strayed along the banks of the rivulet, and talked of his own boyhood. The man then seemed restored to something of the innocence of the child. He cared, in truth, little for the perch, which continued intractable, but he enjoyed the air and the sky, the rustling grass and the murmuring waters. These excursions to the haunts of youth seemed to rebaptize him, and then his eloquence took a pastoral character, and Izaak Walton himself would have loved to hear him. But as he got back into the smoke of the metropolis, and the gas lamps made him forget the ruddy sunset, and the soft evening star, the gross habits reassumed their sway; and on he went with his swaggering, reckless step to the orgies in which his abused intellect flamed forth, and then sank into the socket quenched and rayless.
Helen was seized with profound and anxious sadness. Leonard had been three or four times to see her, and each time she saw a change in him that excited all her fears. He seemed, it is true, more shrewd, more worldly-wise, more fitted, it might be, for coarse daily life; but, on the other hand, the freshness and glory of his youth were waning slowly. His aspirings drooped earthward. He had not mastered the Practical, and moulded its uses with the strong hand of the Spiritual Architect, of the Ideal Builder: the Practical was overpowering himself. She grew pale when he talked of Burley, and shuddered, poor little Helen! when she found he was daily and almost nightly in a companionship which, with her native honest prudence, she saw so unsuited to strengthen him in his struggles, and aid him against temptation. She almost groaned when, pressing him as to his pecuniary means, she found his old terror of debt seemed fading away, and the solid healthful principles he had taken from his village were loosening fast. Under all, it is true, there was what a wiser and older person than Helen would have hailed as the redeeming promise. But that something was grief—a sublime grief in his own sense of falling—in his own impotence against [Pg 672] the Fate he had provoked and coveted. The sublimity of that grief Helen could not detect: she saw only that it was grief, and she grieved with it, letting it excuse every fault—making her more anxious to comfort, in order that she might save. Even from the first, when Leonard had exclaimed, "Ah, Helen, why did you ever leave me?" she had revolved the idea of return to him; and when in the boy's last visit he told her that Burley, persecuted by duns, was about to fly from his present lodgings, and take his abode with Leonard in the room she had left vacant, all doubt was over. She resolved to sacrifice the safety and shelter of the home assured her. She resolved to come back and share Leonard's penury and struggles, and save the old room, wherein she had prayed for him, from the tempter's dangerous presence. Should she burden him? No; she had assisted her father by many little female arts in needle and fancy work. She had improved herself in these during her sojourn with Miss Starke. She could bring her share to the common stock. Possessed with this idea, she determined to realize it before the day on which Leonard had told her Burley was to move his quarters. Accordingly she rose very early one morning; she wrote a pretty and grateful note to Miss Starke, who was fast asleep, left it on the table, and before any one was astir, stole from the house, her little bundle on her arm. She lingered an instant at the garden-gate, with a remorseful sentiment—a feeling that she had ill-repaid the cold and prim protection that Miss Starke had shown her. But sisterly love carried all before it. She closed the gate with a sigh, and went on.
She arrived at the lodging-house before Leonard was up, took possession of her old chamber, and, presenting herself to Leonard as he was about to go forth, said (story-teller that she was)—"I am sent away, brother, and I have come to you to take care of me. Do not let us part again. But you must be very cheerful and very happy, or I shall think that I am sadly in your way."
Leonard at first did look cheerful, and even happy; but then he thought of Burley, and then of his own means of supporting her, and was embarrassed, and began questioning Helen as to the possibility of reconciliation with Miss Starke. And Helen said gravely, "Impossible—do not ask it, and do not go near her."
Then Leonard thought she had been humbled and insulted, and remembered that she was a gentleman's child, and felt for her wounded pride—he was so proud himself. Yet still he was embarrassed.
"Shall I keep the purse again, Leonard?" said Helen coaxingly.
"Alas!" replied Leonard, "the purse is empty."
"That is very naughty in the purse," said Helen, "since you put so much into it."
"I?"
"Did not you say that you made, at least, a guinea a-week?"
"Yes; but Burley takes the money; and then, poor fellow! as I owe all to him, I have not the heart to prevent his spending it as he likes."
"Please, I wish you could settle the month's rent," said the landlady, suddenly showing herself. She said it civilly, but with firmness.
Leonard colored. "It shall be paid to-day."
Then he pressed his hat on his head, and putting Helen gently aside, went forth.
"Speak to me in future, kind Mrs. Smedley," said Helen with the air of a housewife. "He is always in study, and must not be disturbed."
The landlady—a good woman, though she liked her rent—smiled benignly. She was fond of Helen, whom she had known of old.
"I am so glad you are come back; and perhaps now the young man will not keep such late hours. I meant to give him warning, but—"
"But he will be a great man one of these days, and you must bear with him now." And Helen kissed Mrs. Smedley, and sent her away half inclined to cry.
Then Helen busied herself in the rooms. She found her father's box, which had been duly forwarded. She re-examined its contents, and wept as she touched each humble and pious relic. But her father's memory itself thus seemed to give this home a sanction which the former had not; and she rose quietly and began mechanically to put things in order, sighing as she saw all so neglected, till she came to the rose-tree, and that alone showed heed and care. "Dear Leonard!" she murmured, and the smile re-settled on her lips.
Nothing, perhaps, could have severed Leonard from Burley but Helen's return to his care. It was impossible for him, even had there been another room in the house vacant (which there was not), to install this noisy riotous son of the Muse by Bacchus, talking at random, and smelling of spirits, in the same dwelling with an innocent, delicate, timid female child. And Leonard could not leave her alone all the twenty-four hours. She restored a home to him, and imposed its duties. He therefore told Mr. Burley that in future he should write and study in his own room, and hinted with many a blush, and as delicately as he could, that it seemed to him that whatever he obtained from his pen ought to be halved with Burley, to whose interest he owed the employment, and from whose books or whose knowledge he took what helped to maintain it; but that the other half, if his, he could no longer afford to spend upon feasts or libations. He had another to provide for.
Burley pooh-poohed the notion of taking half his coadjutor's earnings, with much grandeur, but spoke very fretfully of Leonard's sober appropriation of the other half; and, though a good-natured, warm-hearted man, felt extremely indignant against the sudden interposition of poor Helen. However, Leonard was firm; and then Burley grew sullen, and so they parted. But [Pg 673]the rent was still to be paid. How? Leonard for the first time thought of the pawnbroker. He had clothes to spare, and Riccabocca's watch. No; that last he shrank from applying to such base uses.
He went home at noon, and met Helen at the street-door. She too had been out, and her soft cheek was rosy red with unwonted exercise and the sense of joy. She had still preserved the few gold pieces which Leonard had taken back to her on his first visit to Miss Starke's. She had now gone out and bought wools and implements for work; and meanwhile she had paid the rent.
Leonard did not object to the work, but he blushed deeply when he knew about the rent, and was very angry. He paid back to her that night what she had advanced; and Helen wept silently at his pride, and wept more when she saw the next day a woeful hiatus in his wardrobe.
But Leonard now worked at home, and worked resolutely; and Helen sate by his side, working too; so that next day, and the next, slipped peacefully away, and in the evening of the second he asked her to walk out in the fields. She sprang up joyously at the invitation, when bang went the door, and in reeled John Burley—drunk:—And so drunk!
And with Burley there reeled in another man—a friend of his—a man who had been a wealthy trader and once well to do, but who, unluckily, had literary tastes, and was fond of hearing Burley talk. So, since he had known the wit, his business had fallen from him, and he had passed through the Bankrupt Court. A very shabby-looking dog he was, indeed, and his nose was redder than Burley's.
John made a drunken dash at poor Helen. "So you are the Pentheus in petticoats who defies Bacchus," cried he; and therewith he roared out a verse from Euripides. Helen ran away, and Leonard interposed.
"For shame, Burley!"
"He's drunk," said Mr. Douce, the bankrupt trader—"very drunk—don't mind—him. I say, sir, I hope we don't intrude. Sit still, Burley, sit still, and talk, do—that's a good man. You should hear him ta—ta—talk, sir."
Leonard meanwhile had got Helen out of the room, into her own, and begged her not to be alarmed, and keep the door locked. He then returned to Burley, who had seated himself on the bed, trying wondrous hard to keep himself upright; while Mr. Douce was striving to light a short pipe that he carried in his button-hole—without having filled it—and, naturally failing in that attempt, was now beginning to weep.
Leonard was deeply shocked and revolted for Helen's sake; but it was hopeless to make Burley listen to reason. And how could the boy turn out of his room the man to whom he was under obligations?
Meanwhile there smote upon Helen's shrinking ears loud jarring talk and maudlin laughter, and cracked attempts at jovial songs. Then she heard Mrs. Smedley in Leonard's room, remonstrating, and Burley's laugh was louder than before, and Mrs. Smedley, who was a meek woman, evidently got frightened, and was heard in precipitate retreat. Long and loud talk recommenced, Burley's great voice predominant, Mr. Douce chiming in with hiccupy broken treble. Hour after hour this lasted, for want of the drink that would have brought it to a premature close. And Burley gradually began to talk himself somewhat sober. Then Mr. Douce was heard descending the stairs, and silence followed. At dawn, Leonard knocked at Helen's door. She opened it at once, for she had not gone to bed.
"Helen," said he, very sadly, "you can not continue here. I must find out some proper home for you. This man has served me when all London was friendless, and he tells me that he has nowhere else to go—that the bailiffs are after him.—He has now fallen asleep. I will go and find you some lodging close at hand—for I can not expel him who has protected me; and yet you can not be under the same roof with him. My own good angel, I must lose you."
He did not wait for her answer, but hurried down the stairs.
The morning looked through the shutterless panes in Leonard's garret, and the birds began to chirp from the elm-tree, when Burley rose, and shook himself, and stared round. He could not quite make out where he was. He got hold of the water-jug which he emptied at three draughts, and felt greatly refreshed. He then began to reconnoitre the chamber—looked at Leonard's MSS.—peeped into the drawers—wondered where the devil Leonard himself had gone to—and finally amused himself by throwing down the fire-irons, ringing the bell, and making all the noise he could, in the hopes of attracting the attention of somebody or other, and procuring himself his morning dram.
In the midst of this charivari the door opened softly, but as if with a resolute hand, and the small quiet form of Helen stood before the threshold. Burley turned round, and the two looked at each other for some moments with silent scrutiny.
Burley (composing his features into their most friendly expression).—"Come hither, my dear. So you are the little girl whom I saw with Leonard on the banks of the Brent, and you have come back to live with him—and I have come to live with him too. You shall be our little housekeeper, and I will tell you the story of Prince Prettyman, and a great many others not to be found in Mother Goose. Meanwhile, my dear little girl, here's sixpence—just run out and change this for its worth in rum."
Helen (coming slowly up to Mr. Burley, and still gazing earnestly into his face).—"Ah, sir, Leonard says you have a kind heart, and that you have served him—he can not ask you to [Pg 674]leave the house: and so I, who have never served him, am to go hence and live alone."
Burley (moved).—"You go, my little lady?—and why? Can we not all live together?"
Helen. "No sir. I left every thing to come to Leonard, for we had met first at my father's grave. But you rob me of him, and I have no other friend on earth."
Burley (discomposed).—"Explain yourself. Why must you leave him because I come?"
Helen looks at Mr. Burley again, long and wistfully, but makes no answer.
Burley (with a gulp).—"Is it because he thinks I am not fit company for you?"
Helen bowed her head.
Burley winced, and after a moment's pause said—"He is right."
Helen (obeying the impulse at her heart, springs forward and takes Burley's hand).—"Ah, sir," she cried, "before he knew you he was so different—then he was cheerful—then, even when his first disappointment came, I grieved and wept; but I felt he would conquer still—for his heart was so good and pure. Oh, sir, don't think I reproach you; but what is to become of him if—if—No, it is not for myself I speak. I know that if I was here, that if he had me to care for, he would come home early and—work patiently—and—and—that I might save him. But now when I am gone, and you with him—you to whom he is grateful, you whom he would follow against his own conscience (you must see that, sir)—what is to become of him?"
Helen's voice died in sobs.
Burley took three or four long strides through the room—he was greatly agitated. "I am a demon," he murmured. "I never saw it before—but it is true I should be this boy's ruin." Tears stood in his eyes, he paused abruptly, made a clutch at his hat, and turned to the door.
Helen stopped the way, and taking him gently by the arm, said—"Oh, sir, forgive me—I have pained you;" and looked up at him with a compassionate expression, that indeed made the child's sweet face as that of an angel.
Burley bent down as if to kiss her, and then drew back—perhaps with a sentiment that his lips were not worthy to touch that innocent brow.
"If I had had a sister—a child like you, little one," he muttered, "perhaps I too might have been saved in time. Now—"
"Ah, now you may stay, sir; I don't fear you any more."
"No, no; you would fear me again ere night-time, and I might not be always in the right mood to listen to a voice like yours, child. Your Leonard has a noble heart and rare gifts. He should rise yet, and he shall. I will not drag him into the mire. Good-by—you will see me no more." He broke from Helen, cleared the stairs with a bound, and was out of the house.
When Leonard returned he was surprised to hear his unwelcome guest was gone—but Helen did not venture to tell him of her interposition. She knew instinctively how such officiousness would mortify and offend the pride of man; but she never again spoke harshly of poor Burley. Leonard supposed that he should either see or hear of the humorist in the course of the day. Finding he did not, he went in search of him at his old haunts; but no trace. He inquired at the Beehive if they knew there of his new address, but no tidings of Burley could be obtained.
As he came home disappointed and anxious, for he felt uneasy as to the disappearance of his wild friend, Mrs. Smedley met him at the door.
"Please, sir, suit yourself with another lodging," said she. "I can have no such singings and shoutings going on at night in my house. And that poor little girl too!—you should be ashamed of yourself."
Leonard frowned, and passed by.
Meanwhile, on leaving Helen, Burley strode on; and, as if by some better instinct, for he was unconscious of his own steps, he took the way toward the still green haunts of his youth. When he paused at length, he was already before the door of a rural cottage, standing alone in the midst of fields, with a little farm-yard at the back; and far through the trees in front was caught a glimpse of the winding Brent.
With this cottage Burley was familiar; it was inhabited by a good old couple who had known him from a boy. There he habitually left his rods and fishing-tackle; there, for intervals in his turbid, riotous life, he had sojourned for two or three days together—fancying, the first day that the country was a heaven, and convinced before the third that it was a purgatory.
An old woman of neat and tidy exterior came forth to greet him.
"Ah, Master John," said she, clasping his nerveless hand—"well, the fields be pleasant now—I hope you are come to stay a bit? Do; it will freshen you: you lose all the fine color you had once, in Lunnon town."
"I will stay with you, my kind friend," said Burley, with unusual meekness—"I can have the old room, then?"
"Oh yes, come and look at it. I never let it now to any one but you—never have let it since the dear beautiful lady with the angel's face went away. Poor thing, what could have become of her?"
Thus speaking, while Burley listened not, the old woman drew him within the cottage, and led him up the stairs into a room that might have well become a better house, for it was furnished with taste, and even elegance. A small cabinet pianoforte stood opposite the fire-place, and the window looked upon pleasant meads and tangled hedgerows, and the narrow windings of the blue rivulet. Burley sank down exhausted, and gazed wistfully from the casement.
"You have not breakfasted?" said the hostess anxiously.
"No."
"Well, the eggs are fresh laid, and you would like a rasher of bacon, Master John? And if you will have brandy in your tea, I have some that you left long ago in your own bottle."
Burley shook his head. "No brandy, Mrs. Goodyer; only fresh milk. I will see whether I can yet coax Nature."
Mrs. Goodyer did not know what was meant by coaxing Nature, but she said, "Pray do, Master John," and vanished.
That day Burley went out with his rod, and he fished hard for the one-eyed perch: but in vain. Then he roved along the stream with his hands in his pockets, whistling. He returned to the cottage at sunset, partook of the fare provided for him, abstained from the brandy, and felt dreadfully low. He called for pen, ink, and paper, and sought to write, but could not achieve two lines. He summoned Mrs. Goodyer, "Tell your husband to come and sit and talk."
Up came old Jacob Goodyer, and the great wit bade him tell him all the news of the village. Jacob obeyed willingly, and Burley at last fell asleep. The next day it was much the same, only at dinner he had up the brandy bottle, and finished it; and he did not have up Jacob, but he contrived to write.
The third day it rained incessantly.
"Have you no books, Mrs. Goodyer?" asked poor John Burley.
"Oh, yes; some that the dear lady left behind her; and perhaps you would like to look at some papers in her own writing?"
"No, not the papers—all women scribble, and all scribble the same things. Get me the books."
The books were brought up—poetry and essays—John knew them by heart. He looked out on the rain, and at evening the rain had ceased. He rushed to his hat and fled.
"Nature, Nature!" he exclaimed when he was out in the air, and hurrying by the dripping hedgerows, "you are not to be coaxed by me! I have jilted you shamefully, I own it; you are a female and unforgiving. I don't complain. You may be very pretty, but you are the stupidest and most tiresome companion that ever I met with. Thank heaven, I am not married to you!"
Thus John Burley made his way into town, and paused at the first public-house. Out of that house he came with a jovial air, and on he strode toward the heart of London. Now he is in Leicester-square, and he gazes on the foreigners who stalk that region, and hums a tune; and now from yonder alley two forms emerge, and dog his careless footsteps; now through the maze of passages toward St. Martin's he threads his path, and, anticipating an orgy as he nears his favorite haunts, jingles the silver in his pockets; and now the two forms are at his heels.
"Hail to thee, O Freedom!" muttered John Burley; "thy dwelling is in cities, and thy palace is the tavern."
"In the king's name," quoth a gruff voice and John Burley feels the horrid and familiar tap on the shoulder.
The two bailiffs who dogged have seized their prey.
"At whose suit?" asked John Burley falteringly.
"Mr. Cox, the wine-merchant."
"Cox! A man to whom I gave a check on my bankers, not three months ago!"
"But it warn't cashed."
"What does that signify?—the intention was the same. A good heart takes the will for the deed. Cox is a monster of ingratitude; and I withdraw my custom."
"Sarve him right. Would your honor like a jarvey?"
"I would rather spend the money on something else," said John Burley. "Give me your arm, I am not proud. After all, thank heaven, I shall not sleep in the country."
And John Burley made a night of it in the Fleet.
Miss Starke was one of those ladies who pass their lives in the direst of all civil strife—war with their servants. She looked upon the members of that class as the unrelenting and sleepless enemies of the unfortunate householders condemned to employ them. She thought they ate and drank to their villainous utmost, in order to ruin their benefactors—that they lived in one constant conspiracy with one another and the tradesmen, the object of which was to cheat and pilfer. Miss Starke was a miserable woman. As she had no relations or friends who cared enough for her to share her solitary struggle against her domestic foes; and her income, though easy, was an annuity that died with herself, thereby reducing various nephews, nieces, or cousins, to the strict bounds of a natural affection—that did not exist; and as she felt the want of some friendly face amidst this world of distrust and hate, so she had tried the resource of venal companions. But the venal companions had never staid long—either they disliked Miss Starke, or Miss Starke disliked them. Therefore the poor woman had resolved upon bringing up some little girl whose heart, as she said to herself, would be fresh and uncorrupted, and from whom she might expect gratitude. She had been contented, on the whole, with Helen, and had meant to keep that child in her house as long as she (Miss Starke) remained upon the earth—perhaps some thirty years longer; and then, having carefully secluded her from marriage, and other friendship, to leave her nothing but the regret of having lost so kind a benefactress. Agreeably with this notion, and in order to secure the affections of the child, Miss Starke had relaxed the frigid austerity natural to her manner and mode of thought, and been kind to Helen in an iron way. She had neither slapped nor pinched her, neither had she starved. She had [Pg 676]allowed her to see Leonard, according to the agreement made with Dr. Morgan, and had laid out tenpence on cakes, besides contributing fruit from her garden for the first interview—a hospitality she did not think fit to renew on subsequent occasions. In return for this, she conceived she had purchased the right to Helen bodily and spiritually, and nothing could exceed her indignation when she rose one morning and found the child had gone. As it never had occurred to her to ask Leonard's address, though she suspected Helen had gone to him, she was at a loss what to do, and remained for twenty-four hours in a state of inane depression. But then she began to miss the child so much that her energies woke, and she persuaded herself that she was actuated by the purest benevolence in trying to reclaim this poor creature from the world, into which Helen had thus rashly plunged.
Accordingly, she put an advertisement into the Times, to the following effect, liberally imitated from one by which, in former years, she had recovered a favorite Blenheim:
TWO GUINEAS REWARD.
Strayed, from Ivy Cottage, Highgate, a Little Girl, answers to the name of Helen; with blue eyes and brown hair; white muslin frock, and straw hat with blue ribbons. Whoever will bring the same to Ivy Cottage, shall receive the above Reward.
N.B.—Nothing more will be offered.
Now, it so happened that Mrs. Smedley had put an advertisement in the Times on her own account relative to a niece of hers who was coming from the country, and for whom she desired to find a situation. So, contrary to her usual habit, she sent for the newspaper, and, close by her own advertisement, she saw Miss Starke's.
It was impossible that she could mistake the description of Helen; and, as this advertisement caught her eye the very day after the whole house had been disturbed and scandalized by Burley's noisy visit, and on which she had resolved to get rid of a lodger who received such visitors, the good-hearted woman was delighted to think that she could restore Helen to some safe home. While thus thinking, Helen herself entered the kitchen where Mrs. Smedley sate, and the landlady had the imprudence to point out the advertisement, and talk, as she called it, "seriously" to the little girl.
Helen in vain and with tears entreated her to take no step in reply to the advertisement. Mrs. Smedley felt it was an affair of duty, and was obdurate, and shortly afterward put on her bonnet and left the house. Helen conjectured that she was on her way to Miss Starke's, and her whole soul was bent on flight. Leonard had gone to the office of the Beehive with his MSS.; but she packed up all their joint effects, and, just as she had done so, he returned. She communicated the news of the advertisement, and said she should be so miserable if compelled to go back to Miss Starke's, and implored him so pathetically to save her from such sorrow that he at once assented to her proposal of flight. Luckily, little was owing to the landlady—that little was left with the maid-servant; and, profiting by Mrs. Smedley's absence, they escaped without scene or conflict. Their effects were taken by Leonard to a stand of hackney vehicles, and then left at a coach-office, while they went in search of lodgings. It was wise to choose an entirely new and remote district; and before night they were settled in an attic in Lambeth.
As the reader will expect, no trace of Burley could Leonard find: the humorist had ceased to communicate with the Beehive. But Leonard grieved for Burley's sake; and, indeed, he missed the intercourse of the large wrong mind. But he settled down by degrees to the simple loving society of his child companion, and in that presence grew more tranquil. The hours in the day time that he did not pass at work he spent as before, picking up knowledge at bookstalls; and at dusk he and Helen would stroll out—sometimes striving to escape from the long suburb into fresh rural air; more often wandering to and fro the bridge that led to glorious Westminster—London's classic land—and watching the vague lamps reflected on the river. This haunt suited the musing melancholy boy. He would stand long and with wistful silence by the balustrade—seating Helen thereon, that she too might look along the dark mournful waters which, dark though they be, still have their charm of mysterious repose.
As the river flowed between the world of roofs, and the roar of human passions on either side, so in those two hearts flowed Thought—and all they knew of London was its shadow.
There appeared in the Beehive certain very truculent political papers—papers very like the tracts in the Tinker's bag. Leonard did not heed them much, but they made far more sensation in the public that read the Beehive than Leonard's papers, full of rare promise though the last were. They greatly increased the sale of the periodical in the manufacturing towns, and began to awake the drowsy vigilance of the Home Office. Suddenly a descent was made upon the Beehive, and all its papers and plant. The editor saw himself threatened with a criminal prosecution, and the certainty of two years' imprisonment: he did not like the prospect, and disappeared. One evening, when Leonard, unconscious of these mischances, arrived at the door of the office, he found it closed. An agitated mob was before it, and a voice that was not new to his ear, was haranguing the bystanders, with many imprecations against "tyrans." He looked, and, to his amaze, recognized in the orator Mr. Sprott the Tinker.
The police came in numbers to disperse the [Pg 677] crowd, and Mr. Sprott prudently vanished. Leonard learned then what had befallen, and again saw himself without employment and the means of bread.
Slowly he walked back. "O, knowledge, knowledge!—powerless indeed!" he murmured.
As he thus spoke, a handbill in large capitals met his eyes on a dead wall—"Wanted, a few smart young men for India."
A crimp accosted him—"You would make a fine soldier, my man. You have stout limbs of your own." Leonard moved on.
"It has come back, then, to this. Brute physical force after all. O Mind, despair! O Peasant, be a machine again."
He entered his attic noiselessly, and gazed upon Helen as she sate at work, straining her eyes by the open window—with tender and deep compassion. She had not heard him enter, nor was she aware of his presence. Patient and still she sate, and the small fingers plied busily. He gazed, and saw that her cheek was pale and hollow, and the hands looked so thin! His heart was deeply touched, and at that moment he had not one memory of the baffled Poet, one thought that proclaimed the Egotist.
He approached her gently, laid his hand on her shoulder—"Helen, put on your shawl and bonnet, and walk out—I have much to say."
In a few moments she was ready, and they took their way to their favorite haunt upon the bridge. Pausing in one of the recesses or nooks, Leonard then began—"Helen we must part."
"Part?—Oh, brother!"
"Listen. All work that depends on mind is over for me; nothing remains but the labor of thews and sinews. I can not go back to my village and say to all, 'My hopes were self-conceit, and my intellect a delusion!' I can not. Neither in this sordid city can I turn menial or porter. I might be born to that drudgery, but my mind has, it may be unhappily, raised me above my birth. What, then, shall I do? I know not yet—serve as a soldier, or push my way to some wilderness afar, as an emigrant, perhaps. But whatever my choice, I must henceforth be alone; I have a home no more, but there is a home for you, a very humble one (for you, too, so well born), but very safe—the roof of—of—my peasant mother. She will love you for my sake, and—and—"
Helen clung to him trembling, and sobbed out, "Any thing, any thing you will. But I can work; I can make money, Leonard, I do, indeed, make money—you do not know how much—but enough for us both till better times come to you. Do not let us part."
"And I—a man, and born to labor, to be maintained by the work of an infant! No, Helen, do not so degrade me."
She drew back as she looked on his flushed brow, bowed her head submissively, and murmured, "Pardon."
"Ah," said Helen, after a pause, "if now we could but find my poor father's friend! I never so much cared for it before."
"Yes, he would surely provide for you."
"For me!" repeated Helen, in a tone of soft deep reproach, and she turned away her head to conceal her tears.
"You are sure you would him remember if we met him by chance?"
"Oh yes. He was so different from all we see in this terrible city, and his eyes were like yonder stars, so clear and so bright; yet the light seemed to come from afar off, as the light does in yours, when your thoughts are away from all things round you. And then, too, his dog, whom he called Nero—I could not forget that."
"But his dog may not be always with him."
"But the clear, bright eyes are! Ah, now you look up to heaven, and yours seem to dream like his."
Leonard did not answer, for his thoughts were indeed less on earth than struggling to pierce into that remote and mysterious heaven.
Both were silent long; the crowd passed them by unheedingly. Night deepened over the river, but the reflection of the lamplights on its waves was more visible than that of the stars. The beams showed the darkness of the strong current, and the craft that lay eastward on the tide, with sailless, spectral masts and black dismal hulks, looked death-like in their stillness.
Leonard looked down, and the thought of Chatterton's grim suicide came back to his soul, and a pale scornful face with luminous haunting eyes seemed to look up from the stream, and murmur from livid lips, "Struggle no more against the tides on the surfaces—all is calm and rest within the deep."
Starting in terror from the gloom of his reverie, the boy began to talk fast to Helen, and tried to soothe her with descriptions of the lowly home which he had offered.
He spoke of the light cares which she would participate with his mother—for by that name he still called the widow—and dwelt, with an eloquence that the contrast round him made sincere and strong, on the happy rural life, the shadowy woodlands, the rippling corn-fields, the solemn lone church-spire soaring from the tranquil landscape. Flatteringly he painted the flowery terraces of the Italian exile, and the playful fountain that, even as he spoke, was flinging up its spray to the stars, through serene air untroubled by the smoke of cities, and untainted by the sinful sighs of men. He promised her the love and protection of natures akin to the happy scene: the simple affectionate mother—the gentle pastor—the exile wise and kind—Violante, with dark eyes full of the mystic thoughts that solitude calls from childhood—Violante should be her companion.
"And oh!" cried Helen, "if life be thus happy there, return with me, return—return!"
"Alas!" murmured the boy, "if the hammer once strike the spark from the anvil, the spark must fly upward: it can not fall back to earth [Pg 678]until life has left it. Upward still, Helen—let me go upward still!"
The next morning Helen was very ill—so ill that, shortly after rising, she was forced to creep back to bed. Her frame shivered—her eyes were heavy—her hand burned like fire. Fever had set in. Perhaps she might have caught cold on the bridge—perhaps her emotions had proved too much for her frame. Leonard, in great alarm, called on the nearest apothecary. The apothecary looked grave, and said there was danger. And danger soon declared itself.—Helen became delirious. For several days she lay in this state, between life and death. Leonard then felt that all the sorrows of earth are light, compared with the fear of losing what we love. How valueless the envied laurel seemed beside the dying rose.
Thanks, perhaps, more to his heed and tending than to medical skill, she recovered sense at last—immediate peril was over But she was very weak and reduced—her ultimate recovery doubtful—convalescence, at best, likely to be very slow.
But when she learned how long she had been thus ill, she looked anxiously at Leonard's face as he bent over her, and faltered forth, "Give me my work! I am strong enough for that now—it would amuse me."
Leonard burst into tears.
Alas! he had no work himself; all their joint money had melted away; the apothecary was not like good Dr. Morgan; the medicines were to be paid for, and the rent. Two days before, Leonard had pawned Riccabocca's watch; and when the last shilling thus raised was gone, how should he support Helen? Nevertheless he conquered his tears, and assured her that he had employment; and that so earnestly that she believed him, and sank into soft sleep. He listened to her breathing, kissed her forehead, and left the room. He turned into his own neighboring garret, and, leaning his face on his hands, collected all his thoughts.
He must be a beggar at last. He must write to Mr. Dale for money—Mr. Dale, too, who knew the secret of his birth. He would rather have begged of a stranger—it served to add a new dishonor to his mother's memory for the child to beg of one who was acquainted with her shame. Had he himself been the only one to want and to starve, he would have sunk inch by inch into the grave of famine, before he would have so subdued his pride. But Helen, there on that bed—Helen needing, for weeks perhaps, all support, and illness making luxuries themselves like necessaries! Beg he must. And when he so resolved, had you but seen the proud, bitter soul he conquered, you would have said—"This which he thinks is degradation—this is heroism. Oh strange human heart!—no epic ever written achieves the Sublime and the Beautiful which are graven, unread by human eye, in thy secret leaves." Of whom else should he beg? His mother had nothing, Riccabocca was poor, and the stately Violante, who had exclaimed, "Would that I were a man!" he could not endure the thought that she should pity him, and despise. The Avenels! No—thrice No. He drew toward him hastily ink and paper, and wrote rapid lines that were wrung from him as from the bleeding strings of life.
But the hour for the post had passed—the letter must wait till the next day; and three days at least must elapse before he could receive an answer. He left the letter on the table, and, stifling as for air, went forth. He crossed the bridge—he passed on mechanically—and was borne along by a crowd pressing toward the doors of Parliament. A debate that excited popular interest was fixed for that evening, and many bystanders collected in the street to see the members pass to and fro, or hear what speakers had yet risen to take part in the debate, or try to get orders for the gallery.
He halted amidst these loiterers, with no interest, indeed, in common with them, but looking over their heads abstractedly toward the tall Funeral Abbey—Imperial Golgotha of Poets, and Chiefs, and Kings.
Suddenly his attention was diverted to those around by the sound of a name—displeasingly known to him, "How are you, Randal Leslie? coming to hear the debate?" said a member who was passing through the street.
"Yes; Mr. Egerton promised to get me under the gallery. He is to speak himself to-night, and I have never heard him. As you are going into the House, will you remind him?"
"I can't now, for he is speaking already—and well too. I hurried from the Athenæum, where I was dining, on purpose to be in time, as I heard that his speech was making a great effect."
"This is very unlucky," said Randal. "I had no idea he would speak so early."
"M—— brought him up by a direct personal attack. But follow me; perhaps I can get you into the House; and a man like you, Leslie, of whom we expect great things some day, I can tell you, should not miss any such opportunity of knowing what this House of ours is on a field night. Come on!"
The member hurried toward the door; and as Randal followed him, a bystander cried—"That is the young man who wrote the famous pamphlet—Egerton's relation."
"Oh, indeed!" said another. "Clever man, Egerton—I am waiting for him."
"So am I."
"Why, you are not a constituent, as I am?"
"No; but he has been very kind to my nephew, and I must thank him. You are a constituent—he is an honor to your town."
"So he is; enlightened man!"
"And so generous."
"Brings forward really good measures," quoth the politician.
"And clever young men," said the uncle.
Therewith one or two others joined in the praise of Audley Egerton, and many anecdotes of his liberality were told.
Leonard listened at first listlessly, at last with thoughtful attention. He had heard Burley, too, speak highly of this generous statesman, who, without pretending to genius himself, appreciated it in others. He suddenly remembered, too, that Egerton was half-brother to the Squire. Vague notions of some appeal to this eminent person, not for charity, but employ to his mind, gleamed across him—inexperienced boy that he yet was! And while thus meditating, the door of the House opened, and out came Audley Egerton himself. A partial cheering, followed by a general murmur, apprised Leonard of the presence of the popular statesman. Egerton was caught hold of by some five or six persons in succession; a shake of the hand, a nod, a brief whispered word or two, sufficed the practiced member for graceful escape; and soon, free from the crowd, his tall erect figure passed on, and turned toward the bridge. He paused at the angle and took out his watch, looking at it by the lamp-light.
"Harley will be here soon," he muttered "he is always punctual; and now that I have spoken, I can give him an hour or so. That is well."
As he replaced his watch in his pocket, and re-buttoned his coat over his firm, broad chest, he lifted his eyes, and saw a young man standing before him.
"Do you want me?" asked the statesmen, with the direct brevity of his practical character.
"Mr. Egerton," said the young man, with a voice that slightly trembled, and yet was manly amidst emotion, "you have a great name, and great power—I stand here in these streets of London without a friend, and without employ. I believe that I have it in me to do some nobler work than that of bodily labor, had I but one friend—one opening for my thoughts. And now I have said this, I scarcely know how or why, but from despair, and the sudden impulse which that despair took from the praise that follows your success. I have nothing more to add."
Audley Egerton was silent for a moment, struck by the tone and address of the stranger; but the consummate and wary man of the world, accustomed to all manner of strange applications, and all varieties of imposture, quickly recovered from a passing effect.
"Are you a native of ——?" (naming the town he represented as member.)
"No, sir."
"Well, young man, I am very sorry for you; but the good sense you must possess (for I judge of that by the education you have evidently received) must tell you that a public man, whatever be his patronage, has it too fully absorbed by claimants who have a right to demand it, to be able to listen to strangers."
He paused a moment, and, as Leonard stood silent, added, with more kindness than most public men so accosted would have showed—
"You say you are friendless—poor fellow, in early life that happens to many of us, who find friends enough before the close. Be honest, and well-conducted; lean on yourself, not on strangers; work with the body if you can't with the mind; and, believe me, that advice is all I can give you, unless this trifle," and the minister held out a crown piece.
Leonard bowed, shook his head sadly, and walked away. Egerton looked after him with a slight pang.
"Pooh!" said he to himself, "there must be thousands in the same state in the streets of London. I can not redress these necessities of civilization. Well educated! It is not from ignorance henceforth that society will suffer—it is from over-educating the hungry thousands who, thus unfitted for manual toil, and with no career for mental, will some day or other stand like that boy in our streets, and puzzle wiser ministers than I am."
As Egerton thus mused, and passed on to the bridge, a bugle-horn rang merrily from the box of a gay four-in-hand. A drag-coach with superb blood-horses, rattled over the causeway, and in the driver Egerton recognized his nephew—Frank Hazeldean.
The young Guardsman was returning, with a lively party of men, from dining at Greenwich; and the careless laughter of these children of pleasure floated far over the still river.
It vexed the ear of the careworn statesman—sad, perhaps, with all his greatness, lonely amidst all his crowd of friends. It reminded him, perhaps, of his own youth, when such parties and companionships were familiar to him, though through them all he bore an ambitious, aspiring soul—"Le jeu, vaut-il la chandelle?" said he, shrugging his shoulders.
The coach rolled rapidly past Leonard, as he stood leaning against the corner of the bridge, and the mire of the kennel splashed over him from the hoofs of the fiery horses. The laughter smote on his ear more discordantly than on the minister's, but it begot no envy.
"Life is a dark riddle," said he, smiting his breast.
And he walked slowly on, gained the recess where he had stood several nights before with Helen; and dizzy with want of food, and worn out for want of sleep, he sank down into the dark corner; while the river that rolled under the arch of stone muttered dirge-like in his ear; as under the social key-stone wails and rolls on forever the mystery of Human Discontent. Take comfort, O Thinker, by the stream! 'Tis the river that founded and gave pomp to the city; and without the discontent, where were progress—what were Man? Take comfort, O Thinker! wherever the stream over which thou bendest, or beside which thou sinkest, weary and desolate, frets the arch that supports thee—never dream that, by destroying the bridge, thou canst silence the moan of the wave.
(to be continued.)
The Reverend Caleb Ellison had an odd way of doing every thing; but he was so good a man, and so adored a clergyman, that his being in love was an interesting circumstance to a large proportion of the inhabitants of the country town in which he lived. When he looked up at the chimney-pots as he walked the streets, or went slowly skipping along the foot-pavement to the Reading-room in the market-place, the elders of his congregation might wish that he would walk more like other men, and the children giggled at the sight; but the ladies, young and old, regarded these things as a part of the "originality" which they admired in him; and Joanna Carey would scarcely admit to herself that such freaks required forbearance.
On Friday evening Mr. Carey returned before the rest of his party from a strawberry feast, to tell his wife that their dear girl had shown him by a look, that she must now decide on her lot for life. Ellison had certainly spoken. Joanna must decide for herself. If she was satisfied to have the greatest blessings that a woman could have—high moral and spiritual excellence in a man who loved her—and could, for these, make light of the daily drawbacks of his oddities, it was not for any one else to object. Mr. Carey could not say that his own temper would bear with so eccentric a companion; but perhaps he was narrow: perhaps his wife's nice household ways for twenty-five years had spoiled him. Joanna knew what she was undertaking. She knew that it was as much as the clerk and the deacons could do, to get the pastor into the pulpit in proper time every Sunday, and that this would be her business now. She knew that he seldom remembered to shave, and how he had burned his marble chimney-piece black; and—Well; perhaps these were trifles. Perhaps it was a fault not to regard them as such. If a father was fortunate enough to have a man of eminent single-mindedness for his son-in-law, and genius to boot, he ought not, perhaps, to require common sense also; but it had always been Mr. Carey's belief that good sense was the greatest part of genius.
By Sunday evening Mr. Carey was little disposed to desire any thing more in his intended son-in-law than had appeared that day. Joanna had engaged herself to him on Saturday evening. On Sunday morning there was something in the tone of his pathetic voice so unusual, in the very first verses of the Psalm, that many hearers looked up; and then they saw something very unusual in his countenance. He so preached, that a stranger inquired earnestly who this Mr. Ellison was, and whence he came; and his admirers in the congregation said he was inspired.
"Joanna behaved very well, did not she?" whispered Mrs. Carey to her husband, as they were returning from chapel.
"Very well, indeed. And it was extremely fine, his preaching to-day. Extremely fine!"
And this particular day, the father feared as little for Joanna as Joanna for herself.
There was no reason for delay about the marriage. Mr. Ellison had three hundred pounds a year from his office, and was never likely to have any more. The interest of Joanna's portion—one thousand pounds—was hers whenever she married. She was four-and-twenty, and Mr. Ellison was five years older. They were no children; there was no reason for delay; so every body knew of the engagement immediately, and the preparations went on diligently.
A pastor's marriage is always a season of great interest and amusement. In this case it was unusually diverting from the singular innocence of the gentleman about all household affairs. He showed all the solicitude of which he was capable to have every thing right and comfortable for Joanna; but his ideas were so extraordinary, that his friends suspected that he had been quizzed by certain youths of his congregation, who had indeed made solemn suggestions to him about dredging-boxes and rolling-pins, and spigots, and ball-irons, and other conveniences, the names of which were strange to him. He had promised to leave the whole concern of furnishing in the hands of a discreet lady and her daughters, with a power of appeal to Mrs. Carey in doubtful cases; but when these mysterious names had been lying on his mind for some days, he could not help making inquiries and suggestions, which brought nothing but laughter upon him. Mr. and Mrs. Carey thought the quizzing went rather too far; but Joanna did not seem to mind it.
"His head should not be stuffed with nonsense," observed Mr. Carey to his wife, "when business that he really ought to be attending to is left undone."
"You mean the Life Insurance," replied she. "Why do you not remind him of it?"
"I believe I must. But it is not a pleasant thing to do. No man in his circumstances ought to need to be spoken to more than once. However, I have to suggest to him to insure all this pretty furniture that his friends are giving him; and while I am speaking about the Fire Insurance, I can easily mention the more important one."
"I should feel no difficulty," observed Mrs. Carey. "He will be purely thankful to you for telling him what he ought to do."
An opportunity soon occurred. The presents came in fast: the Careys were consulted about how to stow them all. One evening at supper, the conversation naturally turned—as it probably does in every house—on what should be saved first in case of fire. Mr. Carey asked Mr. Ellison whether his landlord had not insured the cottage, and whether he himself was not thinking of insuring the furniture from fire.
Instant opposition arose from Mr. Carey's second daughter, Charlotte, who declared that she could not bear to think of such a thing. She begged that nobody would speak of such a thing. Indeed, she wondered that any body could. [Pg 681]When induced to explain the emotions with which her mind was laboring, she declared her horror that any one belonging to her could feel that any money could compensate for the loss of the precious things, such as old letters, and fond memorials, which perish in a fire.
"How old are you, my dear?" inquired her father.
"Sixteen, papa."
"Indeed! I should have taken you to be six years younger. I should wonder at a child of ten talking so sillily as you are doing."
Mr. Ellison stared; for his sympathy with Charlotte's sentiment was so strong, that he was looking at her with beaming eyes, and softly ejaculating, "Dear Charlotte! dear child!"
It took some time to convince both (for young ladies of sixteen sometimes see things less clearly than six years before and ten years after that age) that, if precious papers and gifts are unhappily lost in a fire, that is no reason why tables and chairs, and fish-kettles and dredging-boxes, and carpets and house linen should not be paid for by an Insurance Office; but at last both young lady and pastor saw this. Still, Charlotte did not look satisfied; and her father invited her to utter what was in her mind. After some fencing about whether her thoughts were silly, and whether it would be silly to speak them, out came the scruple. Was there not something worldly in thinking so much about money and the future?
"Dear Charlotte! dear child!" again soliloquized Mr. Ellison.
Mr. Carey did not think the apprehension silly; but, in his opinion, the danger of worldliness lay the other way. He thought the worldliness lay in a man's spending all his income, leaving wife and children to be maintained by their neighbors, in case of accidents which may happen any day to any body, and which do happen to a certain proportion of people, within an assigned time, as regularly as death happens to all. Charlotte had nothing to say against life insurance, because every man knows that he shall die; and there is no speculation in the case. But she was extremely surprised to hear that there is an equal certainty, though of a narrower extent, about fire, and other accidents; that it is a fact that, out of so many householders, such and such a number will have their houses burned down.
"Is it indeed so?" asked Joanna.
"It is indeed so. Moreover, out of so much property, such and such an amount will perish by fire. Every householder being bound in with this state of things for his share of the risk, he owes it equally to others and to himself to secure the compensation, in case of accident. Does he not?"
"How to others?"
"Because he should contribute his share to the subscription, if you like to call it so, by which the sufferer from fire, whoever he be, is to be compensated. Thus, you see, Charlotte, that which seems to you an act of worldliness is a neighborly act, as well as a prudent one."
When reminded, Charlotte admitted that she had herself said so about the Cow Club at B——. She had told many people how the cottagers at B——, were now saved from all danger of ruin by the loss of a cow—a loss fatal to so many cottagers elsewhere. The farmers at B——, who could ill afford to lose from nine pounds to fifteen pounds at a stroke by the death of a cow, had joined with the cottagers in setting up a Cow Life-insurance. The club employed a skillful cow-doctor. The members paid in a small portion of the weekly profits of their milk-selling; and had the comfort of knowing that, whenever their cow died, they would be supplied with another, or with a part of the value of one, according to the length of time, or the yearly amount they had paid. Charlotte admitted that she had been delighted with the scheme, but now asserted that she was much more pleased about the Quakers and their ship.
"Ha! Quakers?" said Mr. Ellison.
Yes; those Quakers, now, were the sort of people whom Charlotte admired. So unworldly! so trusting! There was a rich India ship, belonging to some Quakers, lately wrecked in the Channel, very near her port. The whole cargo was lost. It had been a total loss to the owners, because their principles would not allow them to insure—to put themselves out of the hands of Providence, and speculate in "the stormy winds fulfilling his word." That had been their statement; and was there not something very beautiful in it? Charlotte looked at her father for an answer.
"Tell me, first, my dear," he replied, "whether you admire Tasker, the shoemaker, for refusing to have his children vaccinated, saying that it was taking them out of the hands of the Lord?"
Charlotte could not think of poor little Mary Tasker, disfigured and half blind, and not wish that she had been vaccinated; and yet Tasker had acted in a resigned spirit.
"Well: exactly as much as you admire Tasker, I admire your Quakers. I honor their motive, but I am sorry for their mistake—sorry that they refuse one safeguard against worldliness."
"Worldliness, papa!"
Mr. Carey explained how the moral dangers of commercial pursuits are in proportion to their gambling character. Large gains and great hazards must be more engrossing to the mind, and more stimulating to the passions than small and secure profits. The great drawback upon commerce with very remote countries is, or was, its gambling character, from the variety and seriousness of the risks, and the largeness of the profits laid on to cover them. By means of insurance against sea risks and other dangers, the losses are spread over so large a number that they cease to be losses, and become a mere tax, such as men may willingly pay for security. When a man has so introduced moderation into his gains and his losses, as to detach himself from "the cares of the world and the deceitfulness of riches," he may listen with a quiet pulse (as far as his own affairs are concerned) to the [Pg 682]wind roaring over the sea, and need not be "afraid of evil tidings." It was quite a new view to Charlotte that her Quakers had been gambling, in fact, when they should have been trading safely; but she could not deny that it was so. Nobody wished her to give them up, in regard to their spirit of faith and trust; but nobody could stand up for their prudence.
The most striking view to Charlotte was that there is nothing accidental in storms and tempests; and that it is only our ignorance which makes us call them so. The realm of Meteorology is, no doubt, governed by laws as invariable as that of Astronomy. We know this fact, though we, as yet, know little of these laws. Something more we know: and that is, the average of shipwrecks and conflagrations, in a certain condition of society; in the same way that we know the average of men that will die, out of a certain number, in a certain time: and it is this knowledge of the averages which justifies the resource of insurance in all the three cases. When Mr. Ellison at length comprehended that there were thousands of prudent men now paying their mite to compensate him for the loss of his new furniture, in case of its being burned, on the simple condition of his paying his mite also, he was so struck by their neighborly conduct, that he could scarcely express his sense of it. The ladies considered it impossible that he should feel so strongly, and be heedless about the condition on his own part. Mr. Carey shook his head.
Mr. Carey was right. The wedding-day came, and the insurance was not effected.—Joanna did not like to tease her betrothed about worldly affairs. If the subject was mentioned, and the train of thought revived, he went into an enthusiasm about the benevolent class of insurers: but he did not become one himself.
The wedding-day came and went. The young people were married and gone. Mr. Ellison's flock were assembled, almost entire, in the parish church, for the first and last time. In those days, dissenters could not marry in their own chapels, or any where but in church; and the present was an occasion when the clergyman of the parish appeared to great advantage, with his kind courtesy toward his dissenting neighbors. The whole affair was talked over from day to day, during the wedding-trip of the Ellisons, in the intervals of Charlotte's business in preparing their house for their return. Then began her sisterly relation toward the pastor beloved by so many. Her reverence for him, and her pride on Joanna's account, made her consider his dignity (in spite of himself) on all occasions; from the receiving him at his own door, on the evening of arrival, to the defending him in every trifle in which he vexed her orderly father. When Mr. Carey complained of his being found at breakfast unshaven, and wondered how he would like to see Joanna come down with her hair in papers, Charlotte contended that these things mattered less in a gentleman than a lady; and that it was from a meditative turn that he forgot to shave, even as Newton forgot to dine. If he fell over all his new furniture in turn, she declared it was because the affection of his friends had over-crowded his cottage with memorials of their love. If he was met half-way to the town without his hat, she looked with reverence in his face for a foretaste of his next Sunday's sermon. When it came out that Joanna had paid all the post boys and bills on the journey; that Joanna had to go with him to the tailor's, when he was to be measured for a new coat; that Joanna had to carve, because he did not know the wing of a fowl from the leg—But we will not dwell further on the foibles of a good man whose virtues were as uncommon in their degree, as his weaknesses, it may be hoped, in kind.
Full as the cottage was of pretty things, it was destined to be yet fuller in another year. Never was there a prettier little wardrobe of tiny caps and robes, and the like, than room must be found for, the next autumn, in preparation for that prettiest of all things—a baby. Half the ladies in the congregation brought their offerings of delicate work, in cambric and the softest of flannel, and most fantastical of pincushions and baskets. It was a delightful season to the whole family; and Joanna was so well and bright! And when the great day was over, there were such rallyings of Mr. and Mrs. Carey, on their being so early a grand-papa and grand-mamma; and it was so droll to see Mr. Ellison, who seemed never to have seen a baby, but in baptizing the little creatures, whom he had always hitherto regarded as young Christians, and never as little infants! Mr. Carey was rather ashamed of the extent of his ignorance, shown on the first sight of his child in its sleep, by its mother's side.
"Ha!" he exclaimed, "a baby!" in as much surprise as if it had been the last thing he expected to see.
"Yes; there is your baby. How do you like her?"
He gazed in silence, and at length said—"But can she walk?"
"My dear Ellison! at a day old!"
"But can she talk?"
"All in good time. You will have enough of that by-and by."
"Dear, dear! Ha!" said he, again and again, till he was sent off to dinner, at a friend's house.
He dined at some friend's house every day. On the fourth day it was at a distance of three miles. Mrs. Carey had gone home, in the twilight of a November day. As soon as she was gone, the nurse stepped out, very improperly, for something that she wanted, the child being asleep beside Joanna. She desired the servant girl to carry up her mistress's gruel in a quarter-of-an-hour, if she was not back. The girl did so; and approached the bed, with the basin in one hand and a candle in the other. She poked the candle directly against the dimity curtains, and set the bed on fire. It was a large bed, in [Pg 683] a small crowded room, close to two walls and near the window-curtain. The flame caught the tester instantly, and then the corner of the pillow, and the edge of the sheet. Before that, the girl had thrown down the basin of hot gruel on the baby, rushed to the window, thrown up the sash, and screamed; and she next rushed out at the door, leaving it wide open, and then at the house-door, leaving that wide open too. The air streamed up the staircase, and the bed was on fire all round.
Poor Joanna crept off the bed, and took the child in one arm, while with the other she tried to pull off a blanket. She was found weakly tugging at it. He who so found her was a sailor, who had seen the light from the road, and run up the stairs.
"I see how it is, madam," said he, in a cheerful voice. "Don't be alarmed; you are very safe. Come in here." And he carried her into the next room—the little drawing-room—and laid her, with her baby on her arm, on the sofa. He summoned a comrade, who was in the road. They pulled up the drugget from the floor, doubled it again, laid it over her, and tucked it nicely in, as if there was no hurry.
"Now, madam," said he, "where shall we carry you?" She was carried through damp and dusk to her father's house. Her mother was not there. Such news spreads, nobody knows how. Her mother was then in the streets without her bonnet, imploring every body she met to save her child. She presently encountered one of the sailors, returning to the fire. He assured her the lady and child were safe, and sent her home. Mr. Carey was almost as much beside himself. His first idea was, that it was Mr. Ellison who had, by some awkwardness, set his house on fire; and he said so, very publicly; and very sorry he was for it afterward.
Mr. Ellison was called from the dinner-table, and told he was wanted at home. He strode along, in a bewildered state, till he saw the flames from a distance. As he stood before the cottage, which was now one blaze, nobody could tell him where his wife was. He was trying to break from many hands, and enter the house, when some one at last came up with the news of the safety of his wife and babe. As for the servant, it was some days before she was heard of; and there were serious apprehensions about her, when her aunt came in from the country, to say that the poor creature had fled to her, and would never come near the town, or see any of the family again. Nobody wondered that she said she should never be happy again.
Joanna seemed to be really no worse for the adventure; and for some days it was confidently believed that the infant would do well, though it was severely scalded. Every thing was lost—every article of clothing of all three, all the pretty gifts, all the furniture, two precious portraits, all Mr. Ellison's books and manuscripts. But he was so happy and thankful that his chief treasures were saved, that he never preached more nobly than on the next Sunday, without a scrap of notes;—he who took such pains with his sermons, and never preached extempore! It was from the abundance of his heart that he spoke.
"I have to beg your pardon, Ellison," said Mr. Carey, "for what I said in the first moments of misery."
"It was natural—it was not doing me wrong; for my mother used to say that I did awkward things sometimes; that I was not expert; and it appears to me that I really have erred." And the good man went on to blame himself for having no furniture and clothes to give Joanna, no piano, no books! His landlord was no loser by the fire, while he was destitute. In short, Mr. Ellison was full of remorse for not having insured. All the ladies of his acquaintance were stitching away in his and his wife's behalf; but this was rather an aggravation than a comfort; and he fully intended to effect an insurance, both against fire (when he should again be settled) and on his life. Still, Mr. Carey told his wife, with a shake of the head, that his impression was that it would never be done.
All such thoughts were presently banished. The baby did not get through. After pining for ten days, she died. Then it was that the pastor's fine qualities manifested themselves. He surrendered so patiently a happiness and hope which had really become very dear to his heart; he supported Joanna so tenderly; he considered the whole family so much more than himself, that Mr. Carey vowed he would never more be vexed or ashamed at the peculiarities of such a man.
Nobody would hear of the pastor going into furnished lodgings. The pastor and his wife would not hear of Mr. Carey's furnishing another house for them. Joanna was allowed to draw half her little fortune to buy furniture and clothes, and a few indispensable books for her husband. Thus, their income was reduced by twenty-five pounds, and the half of the principal was gone. If that twenty-five pounds of lost income had been devoted to a life insurance, it would, at Mr. Ellison's present age, have secured one thousand pounds at his death. Thus he had, by neglect, in fact, thrown away one thousand five hundred pounds of future provision for his family. The present was not the easiest moment for contracting new obligations; but the duty was clear, even to the unpractical mind of the pastor. He went to London to effect his insurances, and his wife went with him partly for change of scene and thoughts, and partly because she knew that her husband could never get through the business by himself.
It was not got through, after all. One pious friend had affected them with fears, that they would find it an ensnaring bondage to worldly things to have to think of the payment of the annual premium; another thought it was speculating in God's will; another assured them that they could not spare the money, and should pro[Pg 684]vide for their own household, and hospitality to neighbors, to-day, instead of taking thought for the morrow. They returned without having been near an insurance-office at all. The Careys thought this a sad mistake, and pointed out to them the peace of mind they would lose by the precariousness of their fortunes, and the ease with which the business might be managed, by the trustees of the chapel being authorized to deduct the necessary sum from the pastor's salary, and the pastor's way of living being proportioned to an income of three hundred pounds a year. It was certain that Mr. Ellison would never lay by money in any other way than this; for he could never see a beggar without giving him whatever he had in his pocket.
It may be observed, that insurance was a more onerous matter in those days than in ours. Science has introduced much ease and many varieties into the process of insurance. The rates of premium in Mr. Ellison's younger days were higher; the methods were restricted; middle-class men drank more, and taxed their brother insurers for their accelerated mortality, though precautions were taken against obviously fatal intemperance. The "bondage," that friends talked of, was greater, and the advantages were less, than at present. If Mr. Ellison was wrong in his delays and hesitation, much more are family men wrong who delay and hesitate now.
Time went on, and Joanna was made happy by the birth of a son. During the whole period of her confinement, her husband refused to leave the house, except on Sundays; and he went about, many times in the day, from the attics to the cellars, with his nose in the air, trying to smell fire. There was none, however, to reward his anxious search. No accident happened. The mother and child throve without drawback; and a finer little fellow really was never seen.
For two years—two precious years—all went well. Then came one of those seasons of unhealthiness which occur at intervals, as if to warn men of their ignorance of the laws on which their life depends, and to rebuke their carelessness about observing such conditions of health as they do understand. No town was less prepared to encounter an onset of autumnal fever than that in which the Ellisons lived. It had no right to expect health at any time: the history of the place told of plague in old times, and every epidemic which visited England became a pestilence amid its ill-drained streets, its tidal expanse of mud, and its crowded alleys. These were the times when the beloved pastor's fidelity shone out. For weeks he was, night and day, in close attendance on the poor of his flock; and any other poor who were needing help. He could not aid them in the way that a more practical man would have done; but Joanna supplied that kind of ability, while the voice of her husband carried peace and support into many a household, prostrated in grief and dread. He ran far greater risks all the while than he needed, if he could have been taught common prudence. He forgot to eat, and went into unwholesome chambers with an empty stomach and an exhausted frame. In spite of his wife's watchfulness, he omitted to give himself the easy advantages of freshened air, change of clothes, and a sufficiency of wholesome food; and, for one week, he hardly came home to sleep. It was no wonder that, at last, both were down in the fever. The best care failed to save Joanna. She died without having bidden farewell to husband and child. Her husband was in bed delirious, and her boy was in the country, whither he had been taken for safety when the fever entered the house.
Mr. Ellison recovered slowly, as might be expected, from the weight upon his mind. There was something strange, it appeared to his physician, in his anxiety to obtain strength to go to London. He was extremely pertinacious about this. The Careys, glad to see that he could occupy himself with any project, humored this, without understanding it. They spoke as if he was going to London when he should be strong enough. They did not dream of his not waiting for this. But, in the dark, damp evening of the day when he dismissed his physician, after Mrs. Carey had gone home, leaving him on the sofa, and promising that her husband should call after tea, he was seen at the coach-office, in the market-place; and he made a night-journey to London.
There were no railways in those days; and this journey of one hundred miles required twelve hours by the "Expedition," the "Highflyer," the "Express," or whatever the fastest coach might be called. As soon as he arrived, Mr. Ellison swallowed a cup of coffee in the bar of the inn, had a coach called, and proceeded to an insurance-office to insure his life. As he presented himself, emaciated and feeble, unwashed, unshaven, with a crimson handkerchief tied over his white lips, which quivered when he uncovered them; as he told his errand, in a weak and husky voice, the clerks of the office stared at him in pitying wonder; and the directors dismissed him from their parlor, under the gentlest pretexts they could devise.
He returned home immediately, and told his adventure to Mr. Carey.
"I could not rest till I had made the effort," he said. "When dear Joanna was gone, and I believed that I should follow her, it occurred to me that our child would be left destitute. I saw that I had neglected my duty; and I resolved that, if I recovered, it should be so no longer. I have made the effort; it has failed; and God's will be done!"
Mr. Carey would not allow that the matter must be given up. In fact, there was no difficulty in effecting the insurance, in the next spring, when Mr. Ellison was restored to his ordinary state of health, and Mr. Carey was his guide and helper in the business. The interest of Joanna's little portion was appropriated for the purpose, with a small addition, rendered necessary by the lapse of three years. It is well known that the most unworldly and unapt per[Pg 685]sons are the most proud of any act of prudence or skill that they may have been able to achieve. So it was in this case. When the pastor sat gazing at his child, it appeared to him a marvelous thing that he, even he, should have endowed any human being with a fortune. He was heard to say to himself, on such occasions, in a tone of happy astonishment,
"A thousand pounds! Ha! a thousand pounds!"
We can not here follow out the curious process of that boy's rearing. We have not space to tell how tenderly he was watched by grand-mamma, and by Charlotte, till her marriage gave her cares of her own:—nor what a stroke it was when Mr. Ellison moved to a distant city, being invited to a higher post in the ministry of his sect; nor how curiously he and his child lived in a lodging, where, notwithstanding all his efforts to fill the place of both parents, his boy was too often seen in rags; nor how the child played leap-frog and other games with little beggars and ruffians in the streets, so cleverly, that his father might be seen gazing at him from the foot-pavement, in a rapture of admiration; nor how, on the great occasion of the little lad's first going to chapel, he told every body within reach, that it was "Pa" in the pulpit; nor how, when he was tired of the sermon, he was wont to scrape the sand from the floor, and powder with it the wigs of the old men who sat in the long pew before him; nor how, at length, the importunity of friends prevailed to get him sent to school; nor how comfortably his father was boarded in a private family when the lodging plan became too bad to be borne even by him. All this we must leave undescribed; and also his satisfaction when, in a later time—when his son was grown up, and prosperous, and well married—the good pastor found himself at liberty to do, if he should wish it, what he had always thought ministers had better do, leave the pulpit before they were worn out—before any body had begun to look for their wearing out. The "dear child," as he still calls the father of his grand-children, early persuaded his father to take advantage of that modern improvement by which his life insurance can be commuted into an annuity at sixty years of age, if he should attain it, or receivable in full, if that method should be preferred. A small independence being thus secured, if he lives to leave the pulpit at sixty, and a legacy to his son, if he dies before that time, Mr. Ellison feels more free from worldly cares than is often the case with dissenting ministers who begin the world without fortune, and with thoughts far above the lucre of gain.
No one wonders that he never seemed to think of marrying again. Before his removal, the name of his "dear Joanna" was often on his lips. After his removal, it was never again heard, except on the rare occasions of his meeting old friends. He did not speak of her to those who had never known her; but not the less was her image understood to be ever in his thoughts.
[8] "History of the Restoration of Monarchy in France," by Alphonse De Lamartine. 12mo. Harper and Brothers.
An able critic in a recent English journal, remarks as follows, on the last brilliant work of Lamartine on "The History of the Restoration:" Whatever may be said of the author of this volume as a politician, and however much his capabilities for legislation may be despised, he ranks as a first class historian, and as the most brilliant foreign writer of the present day, both of his country's annals, romance, and poetry. If M. Lamartine's "History of the Girondists" excited immense interest, his "History of the Restoration of the Monarchy" is calculated to produce a much greater enthusiasm. The manner in which he details the thrilling events which succeeded the conclusion of the Reign of Terror in the former work, and the opening of the Consulate, has been spoken of by critics of all shades of politics as unique, as perfect in style and comprehensive in detail; but we doubt very much whether it will not be universally acknowledged that in all these points the new effort surpasses the older. The praise of such a work is best accorded by extracts from its own pages. Such extracts speak for themselves, and award far more valuable encomiums than any which those whose office it is to sit in judgment upon their characteristics can do. We present the following account of the arrest and murder of the young Duke d'Enghien, a crime which Europe has very justly never forgiven, and by which the character of Napoleon has been forever blasted. We had thought that a more vivid picture of this act of treachery could not by any possibility have been written than that which appears in the tale of Maurice Tierney, the Soldier of Fortune; but every thing which has been there said, or has been elsewhere written concerning that event, gives place to this vivid picture drawn by Lamartine, while his opinion respecting the dark deed itself, and the villainy by which it was accomplished, will ever stamp him as a man of the most honorable mind, and as a truly noble-hearted Frenchman.
"Ordener set out on the same night, that of the 10th and 11th of March, and arrived on the 12th at Strassburg. He held a council on his arrival with General Leval, Charlot, the colonel of gendarmes, and the commissary of police, and they resolved to precede and facilitate the nocturnal expedition by a minute reconnoitring of the scene of action. An agent of police named Stahl, and a non-commissioned officer of the gendarmerie, named Pfersdoff, were dispatched on the instant, and marching all night, arrived at eight o'clock in the morning at Ettenheim. They strolled with an affectation of indifference about the house of the Prince, in order to make themselves well acquainted with the approaches to it. The Prince's valet-de-chambre, concealed behind a window, observed these two strangers [Pg 686]walking round the walls, and intently noting the objects of their mission. He called another of the servants, named Cannone, and communicated his anxieties to him. Cannone was an old soldier and companion of the Prince from his earliest infancy. He had fought with him in all his campaigns, and had saved his life in Poland, by covering him with his sabre and his person. He fancied that he remembered having somewhere seen the face of Pfersdoff, and thought he recognized in him a gendarme in disguise. He hastened to inform the Prince, who, with the thoughtlessness of his age, disdained to pay any attention to these symptoms of espionage. Nevertheless, an officer of his army, named Schmidt, went out and accosted Stahl and Pfersdoff, and questioned them with an appearance of unconcern, pretending that he was going their way, and accompanied them for more than a league; but at last seeing them take a road which led into the interior of Germany, instead of returning toward the Rhine, he felt re-assured, and returned to tranquilize the servants and retainers at Ettenheim. But the anxieties of love are not so easily set at rest as those of friendship. The Princess Charlotte de Rohan was filled with a presentiment of danger, and begged the Prince would absent himself for a few days from a residence where he was so evidently watched, and possibly with a criminal intention. Out of affection for her, rather than from uneasiness on his own account, the duke consented to absent himself for two or three days, and it was settled that he should set out the third morning after, on a long hunting excursion in the forests of the Grand Duke of Baden, during which the suspicions of his betrothed would be either dissipated or verified; but it was fated that, the third morning should not dawn on him in Germany.... On the evening of the 14th, General Ordener, accompanied by General Fririon, chief of General Leval's staff, and by Charlot, colonel of gendarmes, set out in the dark toward the ferry of Rheinau on the Rhine, and found there, at the appointed hour, the 300 dragoons of the 26th, 15 ferrymen, the five large boats, and, lastly, the 30 mounted gendarmes destined to be employed in the violation of dwellings and seizure of persons, in an expedition more worthy of lictors than of soldiers. The Rhine was crossed in silence at midnight, and the column, unperceived during the sleep of the German peasants on the right bank, and guided by different roads, arrived, as the day was breaking, at Ettenheim. The spies, whom Ordener and Charlot had brought with them, pointed out to the gendarmes the houses which were to be invested.... The Duke d'Enghien, who had spent the evening before at the house of the Prince Rohan-Rochefort, with the Princess Charlotte, had promised her to absent himself for a few days, to allow time for the plots against his safety, of which she was apprehensive, either to evaporate or be unraveled. He was accordingly about to start at sunrise, with Colonel Grunstein, one of his friends, on his hunting excursion for several days. He had already left his bed, and was dressing himself, and preparing his arms. Grunstein, contrary to his usual custom, had slept under the same roof with the Prince, that he might be the sooner ready to escort him. This companion of his own, on the battle-field and in the chase, was also half-dressed, when the tramp of horses and the sight of dragoons and gendarmes made the rest of the household start from their sleep. Feron, the most familiar servant of the Prince, flew to the chamber of his young master, and announced to him that the court-yard and garden were surrounded at every outlet by French soldiers, and that the officer commanding them was loudly calling on the servants to open the doors, declaring that in case of refusal, he would have them broken open with hatchets. 'Well, then, we must defend ourselves,' exclaimed the undaunted young man, and saying these words, he seized his double-barreled fowling-piece, ready loaded with ball for the chase, while Cannone, his other servant, animated with the same determination as his master, possessed himself of another fowling-piece, and Grunstein entering the chamber at that moment, armed in a like manner, the whole then darted to the windows to fire. The Prince leveled at Colonel Chariot, who threatened the door, and was about to stretch him dead on the threshold, when Grunstein, perceiving on all sides a host of helmets and sabres, and seeing another detachment of gendarmes already masters of one of the wings of the chateau, seized the barrel of the Prince's fowling-piece, and throwing the gun upward, showed the Duke d'Enghien, by signs, the uselessness of resistance against such overwhelming numbers, and prevented his firing. 'My lord,' he said, 'have you in any way committed yourself?'—'No,' replied the duke. 'Well, then, that being the case, do not attempt a hopeless struggle. We are hemmed in by a complete wall of troops. See how their bayonets glisten on every side.' The Prince was turning round to reply to these words when he beheld Pfersdoff, whom he recognized as the spy of the day before, accompanied by gendarmes with presented carbines, rush into his room. He was followed by Col. Charlot, who, with his soldiers, seized and disarmed the Prince, together with Grunstein, Feron, and Cannone. The Duke, as we have seen, was ready to set out, and was thus lost by the delay of only a few moments. He was dressed in the costume of a Tyrolean hunter, wearing a handsome gold-laced cap, with long gaiters of chamois skin buckled at the knees; and the manly beauty and dauntless expression of his features, heightened by the excitement of the surprise, and determination to resist, struck the soldiers with astonishment. In the midst of such a scene, and the tramp of feet and clatter of arms in the house, the sound of a disturbance without for a moment inspired the Prince and his followers with a hope of deliverance. Loud cries of fire issued from the village, and these cries were re-echoed from house to house, like a tocsin of [Pg 687]human voices. Windows were thrown open, and doorways filled with the inhabitants aroused by the invasion of the French. Half naked mechanics were seen running to the steeple to ring the bells, and summon the peasants to vengeance. Colonel Charlot, however, had them seized, and also arrested the master of the hounds of the Duke of Baden, who, on hearing of the disturbance, was hastening to the house of the Prince, and who was told by Charlot that what was taking place had been mutually agreed upon by the First Consul and his sovereign. On hearing this falsehood, the excitement of the inhabitants subsided, and they submitted, with looks of sorrow and expressions of grief, to the misfortune of a young man who had rendered himself an object of the deepest regard.... The Prince was dragged away from his residence, without being permitted to take a last farewell of her whom he left swooning and in tears."
Bonaparte had determined on the duke's death, and his ministers and judges received their instructions to that effect. The midnight trial, the despicable meanness of the tribunal, the heroic attitude of the young Condé, are vividly depicted in this volume: but we pass on to the dénouement of the plot.
"As soon as the judgment was pronounced, and even before it was drawn up, Hullin sent to inform Savary and the Judge Advocate of the sentence of death, in order that they might take their measures for its execution. It seemed as if the time was equally pressing to the tribunal as to those who awaited their decision, and as if an invisible genius was hurrying along the acts, formalities, and hours, in order that the morning's sun might not witness the deeds of the night. Hullin and his colleagues remained in the hall of council, and drew up at random the judgment they had just given; and this short and unskillfully prepared document (summing up a whole examination in two questions and two answers) terminated with the order to execute the sentence forthwith. Savary had not waited for this order to be written before he prepared for its execution, and had already marked out the spot. The court and the esplanade being encumbered with troops, by the presence of the brigade of infantry, and the legion of gendarmes d'élite, no safe place could be found there in which the fire of a platoon did not run the risk of striking a soldier or a spectator. No doubt it was also feared that too great publicity would thus be given to the murder in the midst of an army; that the scene of the execution was too distant from the place of sepulture; and that feelings of pity and horror would pervade the ranks at the sight of this young man's mangled corpse. The moat of the chateau, however, offered the means of avoiding all these dangers, as it would conceal the murder as well as the victim. This place was accordingly chosen. Harel received orders to give up the keys of the steps and iron gateways, which descended from the towers and opened on the foundation of the chateau to point out the different outlets and sites, and to procure a gravedigger to commence digging a grave while the man for whom it was intended still breathed. A poor working gardener of the chateau, named Bontemps, was awakened, and his work pointed out to him. He was furnished with a lantern to guide him through the labyrinth of the moat, and light him while he dug it up. Bontemps descended with his shovel and pickax to the bottom of the moat, and finding the ground all about dry and hard, he recollected that they had begun to dig a trench the evening before, at the foot of the Queen's Pavilion, in the angle formed by the tower and a little wall breast-high, for the purpose, it was said, of depositing rubbish in it. He accordingly went to the foot of the tower, marked out in paces the measure of a man's body extended at length, and dug in the earth that had been already moved a grave for the corpse they were preparing for it. The Duke d'Enghien could have heard from his window, over the humming noise of the troops below, the dull and regular sound of the pickax which was digging his last couch. Savary, at the same time, marched down and arranged slowly in the moat the detachments of troops who were to witness this military death, and ordered the firing party to load their muskets. The Prince was far from suspecting either so much rigor or so much haste on the part of his judges. He did not doubt that even a sentence of death, if awarded by the commission, would give occasion for an exhibition of magnanimity on the part of the First Consul. He had granted an amnesty to emigrants taken with arms in their hands; how could it be doubted, then, that he who pardoned obscure and culpable exiles, would not honor himself by an act of justice or clemency toward an illustrious prince, beloved by all Europe, and innocent of all crime? He had been taken back, after his interrogatories and his appearance before the military commission, into the room where he had slept. He entered it without exhibiting any of that fright which prisoners experience in the anxiety and uncertainty of their sentence. With a serene countenance and unoccupied mind, he conversed with his gendarmes, and played with his dog. Lieutenant Noirot who was on guard over him, had formerly served in a regiment of cavalry commanded by a colonel who was a friend of the Prince of Condé. He had also seen the Duke d'Enghien, when a child, sometimes accompany his father to reviews and field days of the regiment; and he reminded the Prince of that period and these circumstances of his youth. The duke smiled at these reminiscences, and renewed them himself by other recollections of his infancy, which mingled with those of Noirot. He inquired, with a curiosity full of interest, about the career of this officer since that epoch; of the campaigns he had made; of the battles in which he had been engaged; of the promotion he had received; of his present rank, his expectations, and his partiality for the service. He seemed to find a lively pleasure in this conversation on the past [Pg 688]with a brave officer, who spoke to him with the accent and the heart of a man who would gladly indulge in pity, were it not for the severity of duty. A noise of footsteps, advancing slowly toward the chamber, interrupted this agreeable and last indulgence of captivity. It was the commandant of Vincennes, Harel, accompanied by the brigadier of the gendarmerie of the village, Aufort. This friend of Harel's had been permitted to remain in one of the commandant's rooms, after having ordered the Prince's supper, and from thence he had heard or seen all the events of the night. Harel, agitated and trembling at the mission he had to fulfill, had permitted Aufort to follow and assist him in his message to the prisoner. They saluted the Prince respectfully; but neither of them had the firmness to acquaint him with the truth. The dejected attitude and trembling voice of Harel alone revealed to the eye and to the heart of the Prince a fatal presentiment of the rigor of his judges. He thought they now came for him only to hear his sentence read. Harel desired him, on the part of the tribunal, to follow him, and he went before with a lantern in his hand, through the corridors, the passages, and the courts it was necessary to cross, to arrive at the building called the 'Devil's Tower.' The interior of this tower contained the only staircase and the only door descending to, and opening into, the lowest moat. The Prince appeared to hesitate two or three times on going into this suspicious tower, like a victim which smells the blood, and which resists and turns back its head on crossing the threshold of a slaughter-house. Harel and Aufort preceded the duke in silence down the steps of the narrow winding staircase, which descended to a postern through the massy walls of this tower. The Prince, with an instinctive horror of the place, and of the depth beneath the soil to which the steps were leading him, began to think they were not conducting him before the judges, but into the hands of murderers, or to the gloom of a prison. He trembled in all his limbs, and convulsively drew back his foot as he addressed his guides in front: 'Where are you conducting me?' he demanded, with a stifled voice. 'If it is to bury me alive in a dungeon, I would rather die this instant.' 'Sir,' replied Harel, turning round, 'follow me, and summon up all your courage.' The Prince partly comprehended him, and followed. They at length issued from the winding staircase, through a low postern which opened on the bottom of the moat, and continued walking for some time in the dark, along the foot of the lofty walls of the fortress, as far as the basement of the Queen's Pavilion. When they had turned the angle of this pavilion, which concealed another part of the moat behind its walls, the Prince suddenly found himself in front of the detachment of the troops drawn up to witness his death. The firing party selected for the execution was separated from the rest; and the barrels of their muskets, reflecting the dull light of some lanterns carried by a few of the attendants, threw a sinister glare on the moat, the massy walls, and the newly-dug grave. The Prince stopped at a sign from his guides, within a few paces of the firing party. He saw his fate at a glance, but he neither trembled nor turned pale. A slight and chilling rain was falling from a gloomy sky, and a melancholy silence reigned throughout the moat. Nothing disturbed the horror of the scene but the whispering and shuffling feet of a few groups of officers and soldiers who had collected upon the parapets above, and on the drawbridge which led into the forest of Vincennes. Adjutant Pelle, who commanded the detachment, advanced, with his eyes lowered, toward the Prince. He held in his hand the sentence of the military commission, which he read in a low, dull voice, but perfectly intelligible. The Prince, listened without making an observation or losing his firmness. He seemed to have collected in an instant all his courage, and all the military heroism of his race, to show his enemies that he knew how to die. Two feelings alone seemed to occupy him during the moment of intense silence which followed the reading of his sentence; one was to invoke the aid of religion to soothe his last struggle, and the other to communicate his dying thoughts to her he was going to leave desolate on the earth. He accordingly asked if he could have the assistance of a priest, but there was none in the castle; and though a few minutes would suffice to call the curé of Vincennes, they were too much pressed for time, and too anxious to avail themselves of the night which was to cover every thing. The officers nearest to him made a sign that he must renounce this consolation; and one brutal fellow from the midst of a group called out in a tone of irony, 'Do you wish, then, to die like a Capuchin?' The Prince raised his head with an air of indignation, and turning toward the group of officers and gendarmes who had accompanied him to the ground, he asked, in a loud voice, if there was any one among them willing to do him one last service. Lieutenant Noirot advanced from the group, and approached him, thus sufficiently evincing his intention. The Prince said a few words to him in a low voice, and Noirot, turning toward the side occupied by the troops, said, 'Gendarmes, have any of you got a pair of scissors about you?' The gendarmes searched their cartridge-boxes, and a pair of scissors was passed from hand to hand to the Prince. He took off his cap, cut off one of the locks of his hair, drew a letter from his pocket, and a ring from his finger, then folding the hair, the letter, and the ring in a sheet of paper, he gave the little packet, his sole inheritance, to Lieutenant Noirot, charging him, in the name of pity for his situation and his death, to send them to the young Princess Charlotte de Rohan, at Ettenheim. This love message being thus confided, he collected himself for a moment, with his hands joined, to offer up a last prayer, and in a low voice commended his soul to God. He then made five or six paces to place himself in front of the firing party, whose loaded muskets [Pg 689]he saw glimmering at a short distance. The light of a large lantern containing several candles, placed upon the little wall that stood over the open grave, gleamed full upon him, and lighted the aim of the soldiers. The firing party retired a few paces to a proper distance, the adjutant gave the word to fire, and the young Prince, as if struck by a thunderbolt, fell upon the earth, without a cry and without a struggle. At that moment the clock of the castle struck the hour of three. Hullin and his colleagues were waiting in the vestibule of Harel's quarters for their carriage to convey them back to Paris, and were talking with some bitterness of Savary's refusal to transmit their letter to his master, when an unexpected explosion, resounding from the moat of the forest gate, made them start and tremble, and taught them that judges should never reckon upon any thing but justice and their own conscience. This still small voice pursued them through their lives. The Duke d'Enghien was no more. His dog, which had followed him into the moat, yelled when he saw him fall, and threw himself on the body of his master. It was with difficulty the poor animal could be torn away from the spot, and given to one of the Prince's servants, who took him to the Princess Charlotte—the only messenger from that tomb where slept the hapless victim whom she never ceased to deplore."
[9] Translated from a new volume of Tales by Fanny Lewald.
Some twenty years ago my father had a new ship launched from the stocks. A large company had assembled at our house to witness the ceremony of christening the vessel, and afterward to celebrate the marriage of the captain who was to take command of her. He had been for a long time in my father's service, had been uniformly successful in his voyages, and was just the man to take charge of a new enterprise on the western coast of Africa.
Captain Jan Evers, from the time when he first went to sea as cabin-boy, had lived but little at home, with the exception of the time which he subsequently passed with his parents, while he was attending his course at the Navigation School of Hamburg, in order to prepare for his examination as pilot. His parents owned a bit of ground in the village of Neumühlen, the long rows of houses of which stretch along the mouth of the Elbe, beyond Altona. After the death of the old people, the house stood for a long while uninhabited; until, in the year of which I now speak, the captain, who had returned from a voyage, concluded, at the desire of my father, not to go to sea again, until his new ship should be ready. This induced him to have the long-closed shutters of his house opened, in order to take up his own residence there; for he had never rented it.
You must be aware of the extraordinary cleanliness of the northern sea-ports, and must have seen how the sailors love to have their houses as neat as their ships; and how in Neumühlen, where many captains and pilots have their little estates, the houses seem to shine with the incessant care bestowed upon them, in order to comprehend how vexed Jan Evers was when he found his long-deserted house to have suffered sadly from neglect. The little garden-plot before the door, which is never wanting, was full of weeds; the boughs of the fine linden had run wild all about, and shaded the chambers, which had thereby grown mouldy, so that the green paint on the walls had contracted ugly yellow stains. The whole aspect of the house made a melancholy impression, and even the Chinese mandarin which was still standing upon the walnut buffet, where Jan used to see it when a child, seemed to nod its head gloomily when Jan once more took possession of his paternal abode.
The captain, who was a fresh jolly fellow of some forty years old, was no longer the same man after he had passed a couple of weeks there. He grew moody, peevish, and barely civil; and my father often lamented the impatience with which he awaited the completion of the ship, in order to be off again.
One day Evers came to our house at an unusual hour, and desired to see my father, who at that time of day was not usually in his counting-room, but with his family. The captain was shown in, and after we children had been sent away, at his desire, he said:
"I have something to say to you which it is best your good lady should hear, too. I have just come from the dock-yard, where I have been looking at the ship. It will be two months before she will be off the stocks. Then it will be too late to go to sea, even if you should have her rigged upon the stocks. I can't get off till spring; and I can't hold out so long as that. If I only had my fellows of the Fortune here"—(this was the name of the vessel he had last commanded)—"if I only had them with me in Neumühlen, it would be all right: but I grow down in the mouth there, it is so quiet. I'd rather be on a sand-island, alone with the seals and the sea-mews, under the open heavens, than among all those nicknacks of my little house, which must be used, and which I can't use. And so, I thought I'd ask you—"
"If you couldn't be off!" interrupted my father. "Surely, Evers, you are not thinking of that in earnest, are you?"
"No, I am not thinking of that. I have agreed to take command of the new ship; and I am in the habit of keeping my word. But I thought I would ask—" here he stopped, twirled his hat about in his hand, turned to my mother, and continued—"what you think about it—whether I hadn't better get married?"
It seemed as though a great load was taken from his mind, when he had got out these words. He had his house, a pretty little property, and was a good-looking, noble fellow, and bid fair to make an excellent husband; and so my mother advised him earnestly to carry his design into execution; asking him whether he had yet found a girl whom he could wish to marry.
[Pg 690]"Will you give me Marie?" asked he.
Marie was the daughter of a woman who had attended me and my sisters, and who had long been dead. My parents had brought Marie up, and she served my mother as chambermaid; but was looked upon as one of the family, and was very dear to us all. She was about four-and-twenty years old, and might be considered a very pretty girl. My mother said, that she thought a marriage between Marie and the captain would be altogether proper, notwithstanding he was considerably the older; and Evers begged her to be his spokeswoman with Marie.
"Tell her," said he, "that I have liked her for many years; that always when I have returned from a voyage, I have been glad to look upon her again; that when I have been in foreign ports, and have seen other captains buying presents for their wives and children, I have often thought: Could you but do so, and make others happy—but for whom? I have grieved that I was unmarried; and at sea in stormy weather, I have fallen asleep imagining myself, some time or other, reposing with my wife and children. But as soon as I came into port, I have always been obliged to set sail again forthwith, and have forgotten all about getting married, as I had to be off so soon again, and must see to getting the cargo on board. But now I have time to think about it, and I like Marie very much? I will try to make her happy. You can assure her of that."
Marie was asked, and very gladly said Yes. The captain had his house set in order; the rooms were newly painted, the garden attended to, the linden pruned; while Marie arranged the stores of linen and plate left by her deceased parents-in-law, with the pleasurable feeling of ownership. And so came the day when the ship was to be launched, and the pair were to be united.
We all went to the dock; my parents conveyed the young pair in a carriage, and the guests followed. We went on board the ship, the young couple preceding, then my parents, and the guests. The vessel was christened by the name of "Young Couple." We all burst out into loud huzzas, swung our glasses and our hats, and hurried from the stern, where the ceremony took place, to the bows, to remain there during the launch. The steps were removed; the ways in which the keel was to run were slushed with soap and tallow; the sound of the ax was heard, knocking away the last blocks; the line was cast off; one blow of an ax, and amid the huzzas of the carpenters, sailors, and spectators, the noble vessel shot into the water. Suddenly a shriek was heard; the bow-line had parted, and the ship, freed from its check, shot across the river, with such momentum that it struck against the opposite shore, and stuck fast.
In itself this was no great matter; for it cost little trouble or expense to tow the vessel back again. But the merriment of the occasion was interrupted by the shriek, and disturbed by the superstitious belief that any accident happening at a launch is a bad sign for the vessel. A silence fell upon the guests; Marie wept, and the captain looked anxious, for all sailors are more or less superstitious. However, after the wedding, we grew cheerful again; the young pair went on to Neumühlen, and the autumn and winter passed away quickly and happily. Sorrowfully they watched the approach of spring, for the ship was afloat, her cargo ready, and the anchor was to be weighed as soon as the Elbe was free from ice.
This took place toward the end of March. For the first time in his life, the captain left Hamburg with tears in his eyes, after having heartily commended to my mother the care of his wife, who was expecting her first child to be born during the course of the summer. If all went well, tidings of his arrival on the coast of Africa might be looked for about the time of her confinement; and he had promised to write as soon as possible, as not only his wife, but our establishment were anxious to receive letters from him.
But long after Marie had given birth to a boy, no tidings had come from her husband. Autumn came and was gone; winter came and went, and yet no intelligence reached us of the ship.
No other vessel had spoken her; she had put in at no other port; not a trace of her could be discovered; and after a year and a day we were forced to conclude that she had gone down with all on board. The grief of the young wife was very deep, though the hope still remained that the crew might have been saved, and that her husband would return. Thus passed years, until finally when all imaginable inquiries had been made in vain, Marie began to grow accustomed to the idea of his loss, and to look upon herself as a widow.
About this time she became acquainted with man who carried on a small business in Neumühlen, and who wished to make her his wife. As Evers had been absent eight years, my parents advised her to consent, especially as they perceived that such was her own inclination. But before a new marriage could be contracted, Evers must be judicially pronounced to be dead. In the present case, after the usual preliminaries, there was no difficulty; and in the year 1828, Marie was married a second time; her son by the first marriage being then in his ninth year.
This marriage also proved to be a very happy one; and she had two children born in the first two years; both of whom survived.
One evening in the autumn of 1830, Marie was holding her youngest child in her arms, while her husband sat by her upon the sofa, enjoying his pipe. The elder boy, the son of Evers, was busy at another table, near which his little sister was playing. A fierce storm was howling without; the rain and hail rattled against the windows; the night was unusually dark; and as some draught was felt, even in the well-secured apartment, Marie told her eldest son to close the shutters. The lad went to the window, but quickly returned, saying that a man was standing there.
[Pg 691]"Let him stand," replied the father, and the boy went back to the window to close the shutters, when he found that the man had gone. All was quiet in the room. The boy went back to his occupation; the mother laid her infant in the cradle, put the girl to bed, and had taken up her work-basket, when an old woman burst into the room half out of her wits with excitement, crying, "Madame! Madame! Jan Evers was out there!"
Marie, her husband, and the boy sprang up, and ran to the door. No one was to be seen. Marie trembled in every limb; the boy stood near her in utter bewilderment; the husband at last so far recovered himself as to be able to inquire into the facts of the case.
The old woman who had lived for some years in Neumühlen, and was well acquainted with all the inhabitants, was almost as much excited and confounded as her neighbors. Gazing hastily about her all the time, as though she expected every moment to see the apparition again, she said that she "was going by for to buy some stuff, and then she saw a man in a blue jacket, with a nor'wester on his head, a-staring in at your window, and then it came into my head to come and look in too; and when the stranger saw me he asked, 'Who lives in this house?' and then I told him Christian Veltlin did. Then the man went up to the window again and looked in again, and then he turned about and went away. And then I knew him by his size, and ran after him, and called out as loud as ever I could, 'Jan Evers! Jan Evers!' But he wouldn't turn his head round, but ran on as fast as he could, but I caught him at last at the stairs that lead from Neumühlen up to the chaussée. And then I took hold of him by the sleeve, and asked him, 'Jan Evers, Jan Evers, where have you come from?' And then he pushed me away, and growled, 'I don't know nothin' about your Jan Everses. I'm the bo's'n of the Greenlander over there!' and then he ran off and left me standing there. But 'twas him, and I ran over here to tell you all about it."
You may imagine the terror, the agony, and the despair in that little house. Veltlin, however, in order to soothe his wife, argued with her how improbable was the return of Evers, and how easily the old woman might have been deceived. Yet he was himself greatly troubled, and on the following morning, as early as possible, he and his wife came to my father to lay the matter before him, and to ask his advice.
My father advised them, first and foremost, to keep silent about the whole affair; but it was too late for that, for the old woman had told all Neumühlen what had happened. New inquiries were at once set on foot after the reputedly dead Jan Evers. But they were just as fruitless as the former ones had been; and after a while Marie and Veltlin began to grow composed, convinced that the old woman must have been deceived by some strange resemblance. Peace and joy returned to the little household, and the marriage was never disturbed up to the time of Marie's death, which took place last summer.
After that event a document was transmitted to me by the magistracy of the capital, where, it seems, Jan had passed his last years, under an assumed name. By this document, executed upon his death-bed, he constituted all the children of Marie Veltlin heirs to his little property; but with the express provision that the will should not be made public till after the death of Marie. Then it was known, for the first time, that the old woman was right. Jan Evers had most magnanimously sacrificed himself for his wife, and had lived and died alone and among strangers, although he was fully aware that a son had been born to him, who had lived to grow up.
(From the German.)
A new invasion of Cuba, somewhat more formidable, but less successful even, than the former, has absorbed public attention during the past month. Immediately after the return of Lopez from his first expedition, rumors were rife that he was making preparations for another attempt. These reports, however, attracted comparatively little attention, and no effective measures were taken to put a stop to proceedings which were so palpably in violation of our treaty engagements with Spain. The reported rising of the inhabitants of Cuba at Puerto Principe, which was noticed in our last Number, and which was grossly exaggerated in public prints throughout the country, had evidently been regarded by the Cubans in the United States as eminently favorable to the prosecution of their purposes. A party of about 480 men, led by Lopez himself, and commanded by subordinate officers, accordingly embarked on board the steamer Pampero, at New Orleans, and set out for Cuba. They intended to land in the central department of the island upon the southern coast, where the disaffection had been represented as most rife, and where they were, therefore, most sure of a favorable reception. But on touching at Key West for supplies, they were informed that a revolt had taken place in the Vuelta de Abajo, and Lopez accordingly resolved to land in that district. By some mistake, the nature of which has not been clearly explained, they missed their point of destination, and landed on the northern coast of the western department of the Island on the night of the 11th of August. The shore was deserted and they met no opposition.
General Lopez left Colonel Crittenden at this point with about 100 men in charge of the stores and unnecessary arms, and advanced with the remainder of his command to the town of Las Pozas: the inhabitants, however, fled as he approached, neither joining his standard nor furnishing him with provisions or encouragement of any sort. The day after landing, Col. Crittenden was attacked by the Spanish troops—two bodies of infantry and one company of horse. This force was too strong for them. After struggling as long as possible, they withdrew from the field, and finding that neither Lopez himself, who was only three miles off, nor any of the inhabitants came to their aid, they resolved to return to the United States. They procured small boats, and had just got to sea when they were followed and captured on the 15th by the Spanish steamer Habanero. They were taken to Havana, and, on the 17th, were shot. It was at first reported that they had no trial, but were shot immediately, and that their bodies were horribly mutilated and every possible insult offered to their remains by the Cuban populace. These statements were, however, afterward contradicted. It was stated that they were properly tried, and condemned, and that after their execution they were decently interred. Several of them, and Colonel Crittenden among the number, wrote letters to their friends at home, all of which agreed that they had been grossly deceived as to the state of public feeling in Cuba, and that, so far as could be perceived, not the slightest disposition prevailed among the inhabitants of the Island to overthrow the Spanish government.
General Lopez was attacked on the 13th by a large body of Spanish troops at Las Pozas; the action was severe, and the Spaniards were repulsed. The loss of Lopez was considerable, and among those who fell was Colonel Pragay, an officer who had served with distinction in Hungary. He lost in all about fifty men, but retained possession of the place. He soon perceived that all his hopes of aid from the inhabitants were groundless, and that it would be impossible to maintain himself against the Spanish troops; and determined to conceal himself in the mountains. On their march thither they met several Spanish detachments with whom they had successive engagements, suffering severely in each, and inflicting losses more or less serious upon their opponents. Among the Spaniards who fell was General Enna, a distinguished officer, who was buried at Havana on the 21st, with military pomp. At Martitorena on the 24th, while the remaining body of the invaders were breakfasting, they were surprised by an overwhelming Spanish force, and completely scattered; and from that time forward they seem to have been zealously hunted by the inhabitants of all classes, and by every means. The official reports of the Spanish officers state that the peasants pursued them with dogs, that the negroes aided in their capture, and that every part of the population evinced the most active and devoted loyalty to the Spanish government. On the 28th, Lopez with only six followers, was endeavoring to conceal himself and escape to the sea coast, and on the 29th, he was captured in the Pinos de Rangel, by a guide named Jose Antonio Castañeda, with fifteen peasants. He was at once handed over to a military force under Colonel Ramon de Sago, who had him conveyed by a night march to Havana, where orders were immediately issued for his execution, which took place at 7 o'clock on the morning of September 1st. He perished by the garrote vil, an instrument in common use among the Spaniards. It consists of an iron chair, with a back, upon which, at a point even with the head of the person sitting in it, is the instrument of death. This consists of iron clasps made to fit the sides of the head, and a clasp to pass round the throat. From behind is a long iron bar attached to a screw, which put in motion by the executioner giving it a single turn, draws the throat and side pieces tight and at the same time sends an iron rod into the spinal marrow at the neck from behind, causing instantaneous death. This machine was placed upon a scaffold about ten feet high, in the middle of a large square, surrounded by troops. An eyewitness has given an account of the execution. He states that Lopez behaved like a brave man throughout—and walked, surrounded by a guard, to the steps of the scaffold, as coolly as if he were at the head of his troops. He was dressed in a long white gown, and a white cap; his wrists were tied in front and above his elbows behind, with the cords held by soldiers. He ascended the steps with two civilians, friends, but without a priest. He faced round and looked upon the soldiers, and the immense throng of people outside of the square, and then turned round and knelt in prayer for about one minute. He then rose and turned toward the front, and in a clear, manly voice, and in tones loud enough to be heard by the thousands present (for it was still as night), spoke as follows:—"Countrymen, I most solemnly, in this last awful moment of my life, ask your pardon for any injury I have caused you. It was not my wish to injure any one, my object was your freedom and happiness;" here he was interrupted by the commanding officer in front. He concluded, by saying, "My intention was good, and my hope is in God." He then bowed, and turned round and took his seat, apparently with [Pg 693]as much coolness as if he were taking a chair in a room with friends. He placed his head back, between the iron grasps, the negro hangman then adjusted the iron throat clasp and tied his feet to bolts on each side of the seat. During this preparation, Lopez was in conversation with his friends. The executioner, then took his place at the iron bar behind. Lopez kissed the cross handed to him by his friend; the negro then gave one turn of the wrench, and Lopez died instantly without the least struggle. The military at once returned to the city, the band playing a quick step; the thousands dispersed with little or no noise; and thus ended the second invasion of Cuba.
The intelligence of these proceedings, as it reached the United States, caused an intense excitement throughout the country. In the Southern States, and especially in New Orleans, where the expedition had been planned and prepared, the popular agitation was overwhelming. When the news of the execution of the fifty men under Colonel Crittenden reached New Orleans, with the report of the indignities shown to their dead bodies, a mob destroyed the office of a Spanish newspaper in that city, menaced and injured the shops of sundry Spanish inhabitants, and even sacked the house of the Spanish consul. Large meetings were held in all the principal cities of the United States, at which the conduct of the Spanish authorities was denounced, and active preparations were made for sending fresh reinforcements to the invaders. Subsequent accounts, however, and the interference of the Government, prevented the execution of these designs. The failure of Lopez cooled the ardor of that class of our population whose opinions of the morality and legality of any action, depend upon its success or failure; while the slightest reflection was sufficient to show the great mass of our people, that without a declaration of war against Spain by our Government, we had no right to invade her colonies. If a revolution had existed there, our people, as in the case of Texas, could have emigrated thither, and after becoming Cubans and abandoning all claims to American citizenship, have taken such part as they might see fit in the affairs of the island. But no such revolution existed. Lopez and those who acted with him were undoubtedly deceived as to the state of public sentiment in Cuba. No one can fail to regret the loss of so many noble spirits; but they put their lives upon the hazard of the die, and expected, in case of failure, the fate which they met. About 150 prisoners still remain in the hands of the colonial government; it is understood that their punishment will be commuted to imprisonment and transportation.
Political conventions have been held in several States during the past month, to nominate officers for the coming elections. In Massachusetts the Whigs assembled at Springfield on the 10th of September, above one thousand delegates being in attendance. Hon. Robert C. Winthrop was nominated for Governor, receiving 811 out of 1033 votes, and George Grinnell, of Greenfield County, was nominated for Lieutenant-Governor. Edward Everett, George Ashmun, and Seth Sprague were chosen delegates from the State at large to the National Convention. A series of resolutions was adopted, declaring substantially, that the Constitution of the United States and the laws made in pursuance thereof, are the supreme law of the land, any thing in the constitution or laws of any State to the contrary notwithstanding, and that no citizen or State has any right to resist their execution, except in such extreme cases as justify violent resistance to the laws, on the principle of the natural and indefeasible prerogative of self-defense against intolerable oppression;—that the preservation of the Union transcends in importance any and all other political questions;—that the Whigs of Massachusetts will faithfully perform every duty imposed upon them by the Constitution of the United States, and they call upon their brethren in every section of the State to respect and observe all its provisions;—that they "cordially support the national administration in all its just and patriotic measures; in its generous sympathy with oppressed nations struggling for liberty in every part of the world; in its able and vigorous management of our foreign affairs; in its unwavering purpose to maintain inviolate our public faith with all nations; and in its sworn resolve to vindicate the integrity of the Union against all assaults from whatever quarter;"—that they have undiminished confidence in the comprehensive statesmanship of Daniel Webster;—that they cordially approve the agreement entered into by the Whigs of New York;—that they disapprove very decidedly of the present administration of State affairs in Massachusetts, and that they will use every exertion to secure the election of the Whig candidates put in nomination. The Democratic party held their Convention on the 20th of August. A series of resolutions was adopted declaring that "the Democratic party is preëminently national, anti-sectional, and for the Union as a whole Union—that it has always sustained, and can only regain its supremacy in the Union, by adhering to its own men and measures; reposing on its fundamental principle of excluding all tests marked by sectional lines, South or North, East or West; and by leaving to the sound sense of the people of each State and Territory their domestic policy and institutions;"—that they recommend a National Democratic Convention to be held at Baltimore in May, 1852;—that they "deprecate as disunion in its worst form the attempts of any party or class of men to stigmatize and denounce one portion of the Union for its domestic institutions with which the Constitution does not interfere, and of the propriety of which each State is its own independent judge;"—that they approve the resolutions adopted in the National Democratic Convention of 1848;—and that they "go for a faithful execution of and acquiescence in all the Compromise measures settled by the last Congress." Charles G. Greene, Henry H. Childs, and Isaac Davis were appointed delegates to the National Convention. George S. Boutwell was nominated for Governor, and Henry W. Cushman for Lieutenant-Governor.
In New York the Whig Convention met on the 11th at Syracuse. Only part of the State officers are to be chosen at the election this fall. George W. Patterson was nominated for Controller, James M. Cook for Treasurer, Samuel A. Foote for Judge of the Court of Appeals, James C. Forsyth for Secretary of State, Daniel Ullman Jr. for Attorney-General, Henry Fitzhugh for Canal Commissioner, and A. H. Wells for State Prison Inspector. Four very brief resolutions were adopted, declaring that the action of the two Whig State Committees at Albany, which was sketched in our last, was "the result of honorable and patriotic devotion to the Constitution, and for the best interests of the whole people, and that it is adopted and approved by this Convention;"—that to the entire completion of the Erie Canal and kindred public works the Whig party is fully pledged;—that those who supported the canal bill rendered a service to the State of such eminent value, that it has obtained for them the gratitude of [Pg 694]every friend of the true prosperity of the State; and that the candidates nominated for State offices deserve and will receive the united support of the whole Whig party.—The Democratic Convention met at the same place on the 10th. Two days were spent in effecting an organization. A series of resolutions was adopted reaffirming the views and principles set forth in the resolutions adopted by the State Convention at Syracuse last year. The following gentlemen were nominated as the Democratic candidates for the several state offices:—John C. Wright for Controller; Henry S. Randall for Secretary of State; Levi S. Chatfield for Attorney-General; Benjamin Welch Jr. for Treasurer; Horace Wheaton for Canal Commissioner; W. J. M'Alpine for State Engineer; Gen. Storms for Inspector of State Prisons; and A. S. Johnson for Judge of the Court of Appeals.—In Maryland P. F. Thomas was nominated for Controller, James Murray for Commissioner of the Land Office, and T. R. Stewart for Lottery Commissioner, by the Democratic State Convention held on the 12th of September.
A very severe storm swept over the whole southern coast of the United States and the West India Islands on the 18th of August. The damage to vessels and other property was very great. In the island of Porto Rico a great number of plantations and an immense number of cattle were destroyed, and many persons lost their lives. In the middle of West Florida, Georgia, and Alabama the gale was terribly destructive. The tobacco crop is said to have suffered severely.
Advices from Texas give encouraging accounts of the cotton crop in that State. In both quality and quantity it will exceed that of ordinary years. A new military post has been established in the Clear Fork of the Brazos; and in the immediate vicinity, it is said, very large deposits of iron ore and of coal have been discovered. A very large trade in cattle has sprung up of late between Texas and New Orleans; the net proceeds of the trade this year are estimated at $120,000. The Boundary Commission is progressing slowly. When last heard from it was at the copper mines. The survey had been temporarily suspended, owing to an error in running the Boundary, making it 60 miles above El Paso, instead of 16, as required by the treaty. About 130 persons are attached to the American Commission, while the Mexican Commission has only seven. From El Paso we learn that a conflict occurred early in June between a considerable body of Apache Indians and a party of twelve Americans, on their way to California. The affray took place near the copper mines. The Americans were defeated, with a loss of two men killed and two wounded. Writers in the Texas papers, who have passed over the route to California from San Antonio and El Paso, state that it is far preferable to the usual route by way of Independence, Missouri. It is said to be shorter, cheaper, and less dangerous.
Two more cases of the surrender of fugitive slaves have occurred in the State of New York during the month. A colored person, living at Poughkeepsie, and named John M. Boulding, was arrested there and brought to New York. Evidence was submitted to Mr. Nelson, a Commissioner under the law of 1850, which showed him to be the slave of Mr. Anderson, of South Carolina, whither he was immediately sent. The other case occurred at Buffalo, where a negro called Daniel was brought before Commissioner H. K. Smith. He was claimed under the tenth section of the act of 1850, a certified copy of the records of a court of Kentucky being produced, as required by that section, to prove him the property of a Mr. Rust. The Commissioner decided that the evidence was sufficient, but a habeas corpus was granted by Judge Conklin of the U. S. District Court, and the case was argued before him. He decided that the tenth section of the law of 1850, could not apply to slaves who had escaped previous to the passage of the law; and as Daniel was alleged to have fled before that time, the evidence provided for by that section was insufficient. He was therefore discharged. This decision is one of a good deal of importance, as it essentially modifies the operation of the law.
An election was held in Mississippi, on the 1st and 2d of September, for delegates to a State Convention, to consider what action Mississippi ought to take in regard to the action of the last Congress on the question of slavery. The majority of Union delegates returned was very large; so decisive, indeed, was the result regarded as to the feeling of the State upon the subject, that Gen. Quitman, who was running against Senator Foote, as the secession candidate, immediately withdrew from the canvass.
The American Association for the Advancement of Education held, the last of August, a very interesting meeting at Cleveland, Ohio. Many of the most distinguished teachers and friends of Education from widely distant parts of the country were in attendance, and the discussions were of decided interest. The new system of collegiate education recently introduced in Brown University, and adopted in the new University at Cleveland (allowing students to select such studies as they may deem most important to prepare them for their several pursuits in life, and giving them certificates of their actual attainments, instead of the usual diplomas), was thoroughly canvassed, both by its friends and its opponents. The chief defenders of the new system were President Mahan of Cleveland, and Prof. Greene of Brown University. Many other important subjects were also discussed, and the proceedings of the Association generally were such as are adapted to exert a wide and beneficent influence upon the cause of education.
J. E. Caldwell, executor of the will of Elihu Creswell, of New Orleans, has addressed a letter to Gov. Hunt, of New York, asking him for suggestions as to the most desirable locality for fifty-one slaves, emancipated by Mr. Creswell, with directions that they should be removed to a free State. Gov. Hunt has published the letter of Mr. Caldwell, with an extract from the will, in order to elicit the desired information.
The United States Commissioner to the Western Indians, with his suite, recently arrived in Galena, Ill., from Mendota and St. Paul. The treaty with the Lower Sioux bands was signed on the 5th of August. These bands are to receive, when they have reached their destination, some $225,000, to pay their debts and expenses of removal, and an annuity in money of about $30,000, for fifty years. The lands treated for with the lower bands amount to some sixteen millions of acres. They lie along and west of the Mississippi, from the Iowa State line north to the Falls of St. Anthony, and above. The amount to be paid for this immense territory, when the treaties will have been fully carried out, will amount to the sum of nearly three millions.
From California we have news to the first of August. There is little intelligence of special interest. The excitement in regard to Lynch law executions had subsided, and it was believed that the courts of law would hereafter be left to the exercise of their functions. The reports from the mining districts [Pg 695]continue to be encouraging and the shipments of gold for August and September were likely to exceed those of any previous month. Numerous canals are to be constructed for the purpose of diverting the water of streams known to be rich in gold, and abundant preparations had been made for mining the quartz rock with heavy machinery. The belief is general that this is hereafter to be the main source of profitable mining. Agriculture is attracting increased attention. Indian hostilities have ceased on the southern and eastern borders, and broken out on the northern frontier. A military expedition, under command of Gen. J. M. Estell, is to accompany the Indian Commissioners, in their tour of negotiation, to Clear Lake, thence to the sources of the Sacramento. After which they will proceed to Klamath River. The hostile Indians on Rogue's River have been dispersed but not subdued. Navigation on the upper rivers is suspended on account of the low state of water. The two political parties were holding conventions in the various counties to nominate for the Legislature and for county offices. The four candidates for Congress have been busily engaged in canvassing. The project of dividing the State is still urged in some of the southern counties, which were once the seat of nearly all the Spanish establishments in this State, but which have lost all their political importance under the new regime.
Rev. Stephen Olin, D.D., President of the Wesleyan University, died at his residence in Middletown, Conn., on the 16th of August. His health had not been strong for many years, and an attack of epidemic dysentery proved too much for his enfeebled frame. Born in Vermont, on the 2d of March, 1797, he received his academical education at Middlebury College, where he graduated with the highest honor. In 1824, he entered upon the ministry of the Gospel, in South Carolina, and soon became eminent as a pulpit orator. In 1830, he was called to a professorship in Franklin College, Ga., and in 1832 to the Presidency of Randolph Macon College, Va. The years from 1837 to 1841, he passed in an extended career of travel through Europe and the East: and the fruit of his observations in the latter region, have appeared in his two excellent volumes of "Travels in Egypt, Arabia Petræa, and the Holy Land" (Harper and Brothers). In 1842, he was chosen President of the Wesleyan University, and filled that office to the time of his death.
Dr. Olin's reputation as an author must depend upon his Travels, and upon his published Discourses, which, it is to be hoped, will be gathered together in permanent form. The Travels are marked by quick and sagacious observation, considerable power of graphic description, and sound judgment. Dr. Olin's account of Egypt is the best, on the whole, in the language. The Discourses are massive, full of thought, and yet glowing with fervor. In breadth and comprehensiveness they are perhaps equal to any thing that the American pulpit has produced. It was, indeed, as a pulpit orator that Dr. Olin shone pre-eminently. His power consisted, not in any single quality—in force of reasoning—or fire of imagination—or heat of declamation—but in all combined. His course of argument was always clear and strong, yet interfused throughout with passion—the two inseparably united in a torrent that overwhelmed all who listened to him. Dr. Olin's personal qualities were those of the highest style of man. His nature was imaginative—so full of genial kindness as to win all hearts. None could be in his company even for a few moments without feeling this fascination, and at the same time without imbibing a deep reverence for the intellectual majesty of the man. He had, in a very remarkable degree, what Coleridge calls one of the highest characteristics of genius: "the power to carry forward the fresh feelings of childhood on through youth, and manhood, and age:" there was no decay of feeling, no sign of senility in failing of human interest or sympathy. With these qualities, it is not strange that he was sought for to fill high places in literary institutions, and that as President of a University, he was eminently useful and successful. He would have been equally distinguished, we are sure, in the world of letters, had not his work been hindered by lifelong disease. As it was, it is wonderful indeed that he accomplished so much.
The Hon. Levi Woodbury, of New Hampshire, died at Portsmouth, N. H., on the 4th of September, where he had suffered for a long while, under a painful disease. Mr. Woodbury was born at Francestown, New Hampshire, about the year 1790, was graduated with a high reputation for scholarship at Dartmouth College in 1809, and was admitted to the bar in 1812. He practiced his profession with distinguished success, and rapidly rose to a high rank in it. When the Democratic party acquired the ascendency in the State, in 1816, he was appointed Secretary of State; and at the commencement of the next year, a Judge of the Superior Court. In 1819 he removed to Portsmouth, the commercial capital of New Hampshire, where he resided the remainder of his life, with the exception of the intervals when his official duties called him to Washington. Mr. Woodbury was elected Governor of New Hampshire in 1822, and in 1825 a Senator of the United States. General Jackson appointed him Secretary of the Navy in 1831, and subsequently, on the rejection of Mr. Taney by the Senate, Secretary of the Treasury. He continued in the office till the close of Mr. Van Buren's presidency, when he resumed his seat in the Senate. During the administration of Mr. Polk, he was appointed one of the Judges of the Supreme Court, and had withdrawn from the more active scenes of political life.
James Fenimore Cooper, the distinguished American novelist, died at his residence at Cooperstown, N. Y., on the 14th of September. He was born at Burlington, New Jersey, on the 15th of September, 1789. His father, a judge of some distinction, was a large landholder in Otsego County, and gave his name to one of its townships. Mr. Cooper received the rudiments of his education under a private tutor in Burlington, and entered Yale College in 1802. In 1805 he entered the navy of the United States as a midshipman, and remained in that service six years. No reader of his sea novels can fail to trace upon them the influence of this portion of his experience. In 1810 he left the navy, married, and settled in Westchester County, New York, whence he soon removed to Cooperstown and wrote his first novel, entitled Precaution. Although this work gave small promise of the brilliant literary career upon which he entered, he continued to write, and soon published that series of tales of early American life which have won for him such enviable distinction. In 1826 he sailed for Europe, and remained there several years, where he wrote several of his best sea novels. Since his return he has written several tales, using them chiefly as a medium of political opinions, and of course sacrificing much of the success and distinction which his previous works had acquired. Some of his strictures upon the faults of American character and social life, subjected him for some years to a very warm and bitter hostility. His health had been seriously impaired for the last few months. [Pg 696]Intelligence of his death will be received with profound regret throughout the world.
Rev. Thomas H. Gallaudet, LL.D., well known as the pioneer of deaf-mute instruction in this country, died at Hartford, Conn., on the 10th of September, at the age of 64. Dr. G. first became interested in the cause to which his after life was devoted in 1807, having succeeded in conveying instruction to a deaf and dumb daughter of Dr. Cogswell in Hartford; and through the efforts of that gentleman he was commissioned to visit Europe for the purpose of qualifying himself to become a teacher of the Deaf and Dumb in this country. Seven gentlemen of Hartford subscribed a sufficient amount of funds to defray his expenses, and on the 25th of May, 1815, Mr. Gallaudet sailed for Europe. Meanwhile, the friends of the project employed the interval of time in procuring an act of incorporation from the Legislature of Connecticut, which was accomplished in May, 1816. In May, 1819, the name of "the American Asylum at Hartford for the Education and Instruction of the Deaf and Dumb," was bestowed by the Legislature on the first Institution for the deaf-mutes established in the United States. After spending several months in the assiduous prosecution of his studies, under the Abbé Sicard and others, Mr. Gallaudet returned to this country in August, 1816. He was accompanied by Mr. Laurent Clerc, a deaf and dumb Professor in the Institution of Paris, and well-known in Europe as a most intelligent pupil of the Abbé. Mr. Clerc is now living in a vigorous old age, and is still a teacher in the American Asylum at Hartford. The Asylum was opened on the 15th of April, 1817, and during the first week of its existence numbered seven pupils; it now averages 220 annually. Mr. Gallaudet became the Principal of the Institution at its commencement, and held the office until April, 1830, when he resigned, and has since officiated as Chaplain of the Retreat for the Insane at Hartford. His interest in the cause of deaf-mute education has always continued unabated, and his memory will be warmly cherished by that unfortunate class of our fellow beings as well as by a large circle of devoted friends.
Rev. Sylvester Graham, the founder and untiring advocate of the Vegetarian System of dietetics, died at Northampton, Mass., on Thursday, Sept. 11. Dr. Graham was chiefly known for his strict adherence to the system which, for some time, bore his name. His writings on the subject were numerous and popular, and his labors, as a lecturer, were incessant. The most important of his works are, Lectures on the Science of Human Life, first published in Boston in 1839; and Lectures to Young Men on Chastity. The "Science of Human Life," is a work in two large volumes, containing a systematic and in some degree, a scientific exposition of the author's peculiar views, and has had a rapid sale. It passed through several editions in this country, and has lately been reprinted in England, where its sale is quite extensive. Dr. Graham was a native of Suffield, Ct., and at the time of his death was aged about 55. His character evinced energy and decision, and his influence on the public mind was rather beneficial than deleterious. Of his theories, each will form his own judgment; the projector, at least, was undoubtedly honest and sincere in sustaining them.
Prof. Beverly Tucker, of William and Mary College, Virginia, died at Winchester on the 26th ult. Mr. Tucker was one of the Federal Judges of the Territory of Missouri before its admission as a State; and was subsequently State Judge in Virginia for a number of years, when he resigned, and accepted the chair of Professor of Law at William and Mary College. He was a member of the last Nashville Convention, and is known as the author of a work published fifteen years ago, entitled The Partisan Leader. Mr. Tucker's age was about 67.
The Canadian Parliament was prorogued by the Governor-General on the 30th of August. The Royal Speech represents the revenue as in a satisfactory state, and refers to the grants for improving the navigation of the St. Lawrence, and to the reduction of the emigrant tax. Six bills were reserved for the approval of the Queen, three of which relate to churches and rectories, two to the reduction of salaries, and one to the incorporation of the Fort Erie and Buffalo Suspension Bridge Company. The reciprocity question was left unsettled. The reductions in the civil list authorized by the Imperial Government have been carried out by the Legislature. The salaries of the Chief Justices and that of the Chancellor are to be reduced from $4,800 to $3,600 a year, upon the departure of the present incumbents from office. The question of seignorial tenure was discussed at this session, and although no final action was taken upon it, a bill was introduced which will probably come up again. The subject is one of great interest to the people of Canada, and will not be allowed to drop. The law of promogeniture in the succession of real estate has been abolished in Upper Canada. This is the most democratic measure that has been passed during the present Parliament, and it can not fail to exert a highly beneficial influence on the future condition of the Province. A set of resolutions has been passed granting 50 acres of land each to certain companies of enrolled military pensioners from England, whom it is intended to station in different parts of the province. It is intended that they shall be ready to act as a local police, and also be employed on the public works.
The arrival of the steamer Georgia, on the 7th of September, put us in possession of later news from the Pacific coast of South America. In Guayaquil a military outbreak, excited, so far as appears, solely by personal resentments, has resulted in a complete change of the administration. The President, Gen. Neuva, left Querto on the 17th of July for the purpose of visiting his family at Guayaquil. On approaching that city he was met by a military cavalcade, ostensibly for the purpose of escorting him in: but he was immediately seized by them, and hurried off to sea in a vessel lying in the river; the destination of the vessel, and the fate of the captive were unknown. Gen. Urbina immediately entered upon the administration of affairs. In Chili, Don Manual Montt has been elected President by an overwhelming majority. He was understood to be in favor of internal improvements and of a more effectual promotion of education. The Copiapo Railroad was to be opened in September. Congress was in session the last of July, but no important business engaged its attention. In 1850 the public revenue amounted to $4,334,314, and the expenditures to $3,610,837, including over three hundred thousand dollars remitted to England to pay interest on the loan contracted there. The whole English debt is now about seven millions of dollars. A very severe storm swept the harbor of Valparaiso in the early part of July. The damage to shipping, both Chilian and American, was very considerable. In Bolivia, the decree allowing foreign goods to be entered at a lower duty from vessels that had not touched at other ports, has [Pg 697]been revoked. In Peru, Congress was still in session. The legislative and executive branches of the government are represented as being on the best of terms with each other, so that affairs are conducted with a good degree of promptness and efficiency. A bill has been urged in Congress for the greater extension of the freedom of trade, and another to prohibit the circulation in that Republic of Bolivian money. Several bills of decided local importance engaged the attention of Congress. There has been during the past year a very large export from Chili, chiefly of wheat and flour, amounting to two hundred thousand dollars more than during the previous year. In New Grenada, it is said there are new disturbances. The government levied a forced loan, and further decreed that the friends of the government should be exempted from its payment. In several provinces the decree had the effect of converting nearly the whole population into a government party; but in Bogota and Carthagena it had the opposite effect. Arrangements were in progress for an extensive revolt, and it was said that it had commenced at Bogota, but with what result is not clear.
From Mexico later advices have been received,—to August 22d from the capital and the 29th from Vera Cruz. The hostility of the government to the fulfillment of its treaty stipulations concerning the Tehuantepec Canal continues unabated; and it is stated that two vessels sent from New Orleans to commence the work were seized by the Mexican authorities. The financial condition of the country continues to engross attention, but no one of the numerous projects offered for its relief seems likely to be adopted. The ministerial plan calling a convention of the Governors of the several Provinces, meets with very little favor. The appropriation of the Church property to the necessities of the Government has been warmly recommended by some of the public journals. The estates of the clergy and of various religious incorporations amount to $50,000,000. This sum, which has been accumulating in unproductive hands for the last three centuries, it was maintained, would save the country from bankruptcy and ruin.
The Mexican Senate has passed an act recommending a general Confederation among the Spanish American republics. A plan for accomplishing this object is detailed, of which the most marked features are a general Congress, a uniform political system, a general act of navigation and commerce, an alliance offensive and defensive, and a tribunal for the settlement of differences. The project is a good one, but there seems to be little chance of its being carried out. In Durango, a popular commotion occurred on the 17th of August, in consequence of the high price of corn, but it was quelled without bloodshed, by an order from the government compelling the holders of the article to reduce its price. In Vera Cruz, on the 21st, a very large number of the inhabitants, including some of the National Guard, assembled to ask of the local government relief from recent and very oppressive taxes. Some of the soldiers were ordered out to oppose them, when the people retired to their houses and prepared for defense. A brisk action ensued in which several were killed, but quiet was restored by the announcement that the local government had yielded to the popular demands. President Arista's birthday was celebrated on the 25th of July. He has dissolved a club formed for the purpose of regulating the annual celebration of Mexican Independence, as some of its regulations did not meet his approbation. An abortive attempt at a pronunciamiento in favor of Santa Anna has been made at Guanajuato. The plot, which probably had plunder for its chief object, was discovered before it had come to maturity, and the leaders were taken into custody. A revolution has broken out in Chiapas, aiming at the abolition of the internal Custom Houses. Col. Munoz, commanding the battalion of Guerrero in Tehuantepec, was ordered to proceed to Chiapas and aid the government party in the suppression of the rebellion. His men began to desert soon after the commencement of the march, and before he had advanced fifty miles from Tehuantepec he had not more then seventy men. The revolt is headed by Meldono, one of the wealthiest and most influential men in the State.
A good deal of excitement has been produced in Mexico by the publication of the letters of Payno, to the President of the Committee of Mexican bond-holders in London. It seems that the assertion of Payno that he was Chargé d'Affaires of the Mexican Legation in London, and was commissioned to adjust certain matters pending in Europe, was entirely destitute of foundation. On the publication of the letter containing these statements, and others equally untrue, a resolution was introduced into the Chamber of Deputies, inquiring by what authority Payno had received the appointment of chargé, and how much money was appropriated to his mission. The Minister replied that Payno had never received the commission from the Government, but that $20,000 had been applied to defraying the expense of the voyage. In consequence of this information, a complaint was lodged against the former Minister of Finance, and of Foreign Relations. The affair was also taken up by the Senate, which has recommended Lacunza as Minister to England.
From Montevideo we have intelligence to the first of July. The aspect of affairs in Brazil and Buenos Ayres was by no means pacific. The Brazilian force under Admiral Grenfell, the Commander-in-chief, had penetrated the waters of the Uraguay, and were stationed at commanding points along the north bank of the river. The disaffection of the province of Entre Rios had been followed by that of Corrientes, warlike preparations were in train; and every thing threatened a general outbreak. The mediation of Great Britain had been accepted by Gen. Rosas. The slave-trade on the coast of Brazil was at a low ebb, a deep laid scheme for its revival having been defeated by the British squadron. Only 1000 slaves were landed during the first six months of 1851, while no less than 20,000 were landed in the same period of 1848.
From the island of Hayti our advices are to the middle of August. Every thing was then quiet. The Emperor had returned to Cape Haytien from his tour, having crossed the Dominican frontier without being molested, and it was reported that the difficulties between the Dominican and Haytian governments have been amicably settled.
An eruption of the long dormant volcanoes of the Pellée Mountain, in Martinique, took place on the night of August 5. It was accompanied with a noise similar to the approach of thunder, and with a strong vibration that was felt to a considerable distance. The town of St. Pierre, as well as all the surrounding country, was covered over with gray ashes. The population of Prêcheur were obliged to flee from their homes, and to take refuge in St. Pierre. There was no shock of an earthquake.
Parliament was prorogued on the 9th of August by the Queen in person, until the 4th of September. The speech of her Majesty contained nothing of special interest or importance.
[Pg 698]No event in England has created more excitement, or engaged more attention, during the past month than the visit and performances of the yacht America, built in New York, and owned by John C. Stevens, Esq., who commands her. She arrived at Cowes early in July, and her commander immediately offered to sail her against any vessel of a similar construction in the world, for any wager up to $50,000. Public attention was instantly attracted to her by the reports of pilots and others who had seen her, and she was visited by thousands and thousands of people from every part of England, but her challenge was not accepted. On the 18th there was a race of seventeen yachts, owned by gentlemen from every part of the kingdom, contending for the prize of the gold cup, which the Queen gives every year to the best yacht in the kingdom. The America was entered for the race, and won it so easily, as to excite the unbounded admiration and applause of the unsuccessful competitors. On the 25th there was another race, by the squadron; but the America was not entered. The wind was light, and the last vessel of the squadron had been under weigh sixty-five minutes when the America hoisted sail and followed. The race was round the Isle of Wight, and she came in only ten minutes behind the winner. Mr. Stephenson, the distinguished engineer, offered to sail his yacht, the Titania, for a small wager against the America. The offer was accepted, and the race came off on the 28th of Aug. The wind was fresh, and the course was forty miles out, and forty back. Earl Wilton was umpire. The America won the race by a long distance. The Queen, with Prince Albert and the royal family, visited the yacht on the 20th. The spirit of England is thoroughly roused by this unlooked-for defeat; but they are unbounded in their expressions of admiration for the vessel which has conquered them. Several new cutters are to be built immediately for the express purpose of contending with the America.
The Royal Commissioners of the Great Exhibition have resolved to close it on the 11th of October. A meeting of the Commissioners will be held on the 15th, for the purpose of taking leave of the exhibitors, and immediately after they will have permission to remove their goods. The number of visitors has fallen off considerably.
A great meeting was held in Dublin on the 19th of August, of Roman Catholics from all parts of the kingdom, to protest against the Ecclesiastical Titles Bill just enacted. Immediately after the call was issued, a Protestant clergyman, named Tresham Gregg, issued a notice that he would be there to confront the Catholics, and summoned all true Protestants to his aid. This notice, and the general excitement which prevailed, led to anticipations of violence. An immense concourse of people was present. Admittance was refused to Mr. Gregg and his party, and the collision was thus avoided. A large number of Roman Catholic prelates were in attendance. The most Rev. Dr. Cullen, Archbishop of Armagh, and Primate of all Ireland, presided, and read a long address, urging Catholics every where to take measures to preserve their religion. Several speeches were made by distinguished Catholics, generally urging a political union of all Catholics, without reference to other political questions. An ostentatious disregard of the late law was shown in the constant use of the ecclesiastical titles prohibited by it.
The condition of laboring men in parts of England finds striking exemplification in an incident which occurred at a colliery in Bedminster. Several persons had been killed by the breaking of the rope upon which the miners daily descended 240 feet to their work. It appeared upon the trial that the workmen knew that the rope was unsafe, but they had not dared to complain, lest they should lose their places—"poor men are tied down so tight now." One of the witnesses, a collier, after giving his testimony, said, "for the evidence I have given this day, I shall be out of work."
The Exhibition, and the official visit to Paris, have aroused writers in England to a sense of their own clumsiness and artistic inferiority to the French. In all departments of art, and especially in the graces and elegancies of life, the English feel themselves to be far behind their neighbors. The Times suggests, as one step toward remedying the evil, that Cleopatra's Needle should be brought to London, as the Luxor was to Paris, and erected as a monument to Sir Ralph Abercromby. It can be procured, and the cost of removal is estimated at £2500.
The English Government has granted new pensions of £200 a year to Mr. J. Silk Buckingham, who is well known in this country, and the same amount to Col. Torrens, the author of several works on political economy. Mrs. Jamieson, whose admirable books upon Shakspeare's female characters are universally known, has received a pension of £100.
Alderman Salomons, the Jewish representative of Greenwich, whose forcible exclusion from the House of Commons was noticed in our last, has been honored with a public dinner by his constituents. He declared his belief that public opinion would demand the rescinding of the obnoxious oath, but declared his purpose to commence a systematic canvass of the country for the purpose of hastening that event. He assures his constituents that, with their support, he "will not be got rid of" by the government.
The management of English railways is generally supposed to be so nearly perfect that accidents never occur. Though their police is, as a general thing, superior to that of the American railways, recent accounts chronicle a very large number of serious mishaps. On the Great Western road, a train, having broken down in a tunnel, was run into by another which was not warned of the danger. On the Lancashire Railway, near Liverpool, part of a bridge had been taken down for the purpose of being repaired. A luggage-train was suffered to come up in the night without any notification, and of course ran into the gap. Several minor accidents in various parts of the kingdom are chronicled, showing very culpable negligence on the part of the railway police.
The leading authors of England have petitioned the Master of the Rolls for leave to examine the records of the realm gratuitously. Their request has been granted. At a time when the historical records of the past enter so largely into the literary productions of the day, this is a boon of decided importance.
Mr. Jerdan, who was for many years the editor of the London Literary Gazette, is said to be engaged in preparing his Reminiscences of Literary Men, and his Correspondence with them, for the press. His long connection with the literary circles of England must have given him unusual facilities for making such a work valuable and interesting. Among the London announcements of new books in press we observe a novel, entitled "Marian Withers," by Geraldine E. Jewsbury, the author of Zoe; one of the most powerful novels of the day.
The London Examiner states that Haynau, the notorious Austrian General, has taken up his residence upon a large estate which he has just purchased in Hungary. It is said that he omits no opportunity of [Pg 699] making himself popular with the Magyars; that he pays assiduous court to the nobility, many of whom were sentenced by his courts-martial; that he joins the Hungarians in denouncing the Austrian attempt to monopolize the sale of tobacco, and says that throughout the Hungarian war, he was only the tool of the Austrian government. He declares that there is no country in Europe he likes so well as England, and speaks of the beating he received there with perfect complacency. It is difficult to believe all these statements, though the Examiner vouches for their accuracy.
The French National Assembly met on the 9th for the last time of the session, and then adjourned until the 4th of November. A manifesto was at once issued by the Republican members, complaining that the sovereign power was in the hands of men opposed to all reforms, but predicting a certain victory as the fruit of union, perseverance, and devotedness on the part of the people. The document declares that the Constitution is the supreme law, and must be maintained inviolate; and that any attempt to re-elect Bonaparte, or to prolong existing powers, will not be a crisis, but a revolution; that resistance to all such attempts will be "legitimate as right, holy as justice, sacred as liberty;" and that the Republican members, under the flag of the Constitution, will not fail in any of the duties which the salvation of the Republic may impose upon them.
Preparations for the coming Presidential election are in active progress. The Orleanists seem to be settling down upon the Prince de Joinville as their candidate, and several of the most distinguished among them, recently paid a visit to the Duke of Nemours to ascertain the feelings of the family in regard to it. The conversation seems not to have been very satisfactory: the most that the Duke would say was, that they would not be responsible for the action of their friends. The Republicans have not yet fixed upon a candidate.
Public attention in France has been drawn to the trial at Lyons of a number of persons charged with conspiracy. It seems that in November last a club was discovered there, of which a person named Gent was a leading member. His plan is said to have been to give the southern provinces a thorough secret organization, so as to enable them to rise on a given signal, to secure the frontiers of Switzerland and Savoy as a means of assistance or retreat, and to take steps to inflame the whole country, and thus bring about a general republican movement. The trial had not been concluded at our last advices.
A singular accident occurred at the funeral ceremonies of Marshal Sebastiani, at the Invalides in Paris, on the 13th. The flame of a wax candle was brought in contact with the hangings of the catafalque, and the whole splendid drapery of the church was speedily in a blaze. Before the fire could be extinguished, nearly one half of the magnificent collection of trophies taken by the French armies were destroyed.
The grand fête given by the authorities of Paris to the Lord Mayor of London and the Commissioners of the great Exhibition, had a brilliant and successful termination. The mutual compliments of the visit were closed by a correspondence between M. Charles Dupin, the President of the French Commission, and Prince Albert. M. Dupin wrote to acknowledge the courtesies received by the Committee during their visit to the Exhibition, and to thank the Prince for the conspicuous part he had taken in it. The constant attendance of the Queen, and her success "in conquering suffrages and good wishes among the representatives of all nations, in favor of a work which she still cherished as that of the father of her children," are gracefully noticed. M. Dupin, after remarking that "Art, like Nature, loves to scatter her gifts among the children of great national families, and that they could thus honor, on different grounds, genius, taste, imagination, reason, in nations whose brilliant variety constitutes the riches and splendor of the human race," designates the real service which the Great Exhibition will render the world, by saying, that "each nation, without affecting its character, may add to its well-being, its riches, its power, by judiciously borrowing from the discoveries and improvements of other nations. Here," he says, "each people sees its products side by side with those of all others, and often sees them surpassed. Pride, which grows while favored by isolation, is here abased, and reason profits by the opportunity. Each nation, instead of dreaming of self-sufficiency and inborn superiority, vows to improve in the future. Thus we shall see new efforts attempted in every country, to ameliorate the productions of the human race." Prince Albert, in his reply, tendered his thanks to the President for his kind expressions, and to the Commissioners for their attention and care.
The intelligence from Germany is neither interesting nor important. The Sovereigns of Austria and Prussia seem to be acting together for the entire suppression of every thing like constitutional rights and liberty in the German states. A proposition is about to be laid before the Diet by these two powers, declaring that "the so-called fundamental rights of the German people," proclaimed in the Constitutions of 1848 and 1849, are neither valid as a law of the Empire, nor binding on the several states, and they be therefore repealed, with all laws based upon them.—In the Italian dominions of Austria, the state of things is gloomy and ominous. Arrests of compromised persons are continually made in Milan and Verona. In the latter city, one of the new prisoners was a lady of rank, accused of forwarding a correspondence to Mazzini. A system of espionage has been adopted in the Venetian provinces of Austria, unparalleled for its inquisitorial and oppressive character, in the history of the most despotic states. Many persons belonging to the higher classes have been arrested in Verona, and nearly every night domiciliary visits are made by the police. The public mind throughout Austrian Italy is described as in a state of the most violent excitement, and insurrection is apprehended by government. Marshal Radetzky published a proclamation to the Lombardo-Venetian kingdom on the 9th of July, and from his head-quarters at Monga. The Lombardo-Venetian kingdom is declared to be in a state of siege; the communes are made responsible for all assassinations similar to that of Vandoni at Milan; and the inhabitants will be severely dealt with if they do not immediately surrender all such offenders to the military.
Two musical artists have been made victims to the paltry prosecution of the Austrian government. Mdlle. Anna Zerr, for having visited two of the Hungarian exiles resident in London, and for having consented to sing at a concert for the relief of the Hungarian refugees, has, on her return to Vienna, been deprived of her place of Imperial Chamber-singer, prohibited from appearing on the stage of the Imperial Theatre, where she was one of the most distinguished performers, and placed under the sur[Pg 700]veillance of the police. And Leopold Iansa, an eminent violinist, who has been for many years in the Imperial Chapel, was dismissed for a similar offense.
The Austrian authorities recently opened packages addressed to the United States consulate at Venice. Mr. Flagg, the American consul, remonstrated, and was told in reply, that the government claimed the right to examine all publications introduced into the Venetian States, no matter from what quarter or to what address. Several communications have passed upon the subject.
In Switzerland there have been heavy inundations which in the canton of Berne alone have caused losses to the amount of about £100,000. Active preparations are making for the coming election, in which it is supposed the radical party will resort to extreme measures, if necessary, for the accomplishment of their purposes.
Dr. Paulus, a distinguished German scholar, died at Heidelberg, on the 10th of August, at the advanced age of 94 years. In 1784 he was appointed Professor of Oriental Languages at Jena, and in 1793 succeeded to the chair of theology. His profound learning, penetrating judgment, marked courage, and unwearied assiduity, obtained for his numerous writings a very wide circulation. He was exceedingly amiable in private life and was always employed in endeavors to promote the interest of piety, virtue, and humanity.
A terrible catastrophe took place at Moscow, on the 20th July. As the monks of the convent of Wladimir were setting out in procession to visit an image of the Virgin at a neighboring village, a wooden bridge thrown over the moat of the convent (formerly a fortress) gave way, and out of 200 of the monks, 158 were drowned; the water being 45 feet deep, and the sides of the moat perpendicular.
The Austrian authorities in Hungary are resorting to the most unheard-of cruelties in order to crush the spirit of the people. At a peasant's wedding lately, near Groswardein, the gendarmes approached the bride and ordered her to take off the red, white, and green ribbons which she wore in her hair, as these colors were revolutionary. The reply was that it should be done after the ceremony. While the bride was kneeling at the altar the gendarme rushed forward and cut her tresses from her head. The peasants resented the indignity, and an affray ensued, in which three of the gendarmes and four of the peasantry, including the bridegroom, were killed.
We mentioned last month the release of Mr. Brace, the American traveler in Hungary, who had been arrested and thrown into prison by the Austrian authorities upon the most frivolous grounds. His release was procured by Mr. McCurdy, who threatened to demand his own passports, if it was not conceded. It seems that further proceedings of interest may be expected. Mr. M. promised that Mr. Brace should present himself for trial. The London Spectator remarks that "this trial will be watched with interest, it will take place in the sight of Europe and America, and also in the sight of Hungary. The oppressed subjects of Austria will see the right of personal freedom vindicated, in the person of a gentleman whose own government will do no more than insist on the strict fulfillment of the law, but will not be content with less. Austria will be obliged to submit to the law, and will be forced to that hateful submission at the dictation of a distant State. It will be brought to that submission, that dictation, before the eyes of Europe, even before its own subjects. It will be a very instructive trial."
It is stated upon what is believed to be good authority, that the Turkish Government has definitively determined that Kossuth shall be set at liberty on the 1st of September. The Austrian Government has warmly and steadily protested against his release, but without effect. The government of the United States has sent a national vessel to receive him upon his liberation, and his arrival in the United States may be expected by the 1st of November. No man living would receive a warmer welcome.
The English government has directed the seizure of another large Indian territory, part of the Nizam's dominions, to enforce the payment of a large sum of money with interest. It is thought that the Nizam can and will pay at the last moment; but if not, it is not probable that his sway over his own dominions will hereafter be more than nominal. At Gobindpore on the 14th of June, seventy prisoners were chained together in a hut for safe keeping. During the night, the hut took fire and all but five perished.
The news from China represents the insurrection in the southern provinces as one of magnitude and great political importance. It is said that one of the leaders has assumed to himself the title of sovereign, and that the insurgents, numbering a hundred thousand, menace the city of Canton. The Chinese journals take very different views of the character of this disturbance, some considering it as merely the work of a few desperadoes, seeking only pillage, and others attributing to it the highest political consequence. The emperor is said to be considerably alarmed, and has sent against them his choicest troops.
The London Spectator thinks it highly probable that the malcontents are masters of all the provinces south of the Yellow River, and have seized upon the great entrepot of Canton. This, it adds, would be a revolution; for Pekin, which derives its supplies of provisions by the great canal from those southern provinces, would be starved into submission; and the principal seat of foreign commerce would fall into the hands of a party more bigotedly hostile to intercourse with foreigners than even the Celestial Government. Nor is such a revolution either impossible or improbable. Our knowledge of Chinese history is dim and obscure; yet enough appears to show that the Mantchoo authority has never been so firmly established to the south as to the north of the Yellow River—that the purely Chinese element of society has always preponderated in the southern provinces. In Siam, too, changes of policy appear to be impending. The king who refused to treat with Sir James Brooke is dead; and a contested succession has been temporarily avoided by the simultaneous nomination of a king and a vice-king. The new king has always been remarkable for his disposition to cultivate the acquaintance and friendship of foreigners, and he is said to understand and even to write English. The institutions of the Chinese and Hindu-Chinese nations are thus shaken and sapped at the very time when the traders of Europe and America are making more vigorous and continuous efforts than at any former period to obtain a footing in them.
Twenty-three British seamen belonging to the ship Larpent, were wrecked over a year ago upon the coast of the Chinese island of Formosa. They were immediately set upon by the savage inhabitants, and all but three butchered in cold blood. These three were taken into servitude, and after about eight months' captivity made their escape in a boat to an American brig which happened to be passing.
In the extreme western portion of the North American continent, and of the North American National Confederacy, there are now to be found, growing side by side, two of the most singular phenomena of the age. We allude to the new social and political organization, constituting the State of California, and the new theocracy, as it is assumed to be, of the Mormon Commonwealth or Church—the one the most decidedly secular of all known modern enterprises, the other the only example of the rise of a new religion, and of a distinctly new religious people in the 19th century. Mormonism, it is true, has some decidedly secular elements. In this respect it easily assimilates itself to the gross spirit of worldly enterprise by which it is surrounded, and even finds itself at home in the midst of the most turbulent scenes. But this is far from accounting for its wonderful success. It is also true, on the other hand, that the present age has been marked by the division and subdivision of religious denominations. Yet still, none of these come up to that idea or pretension of Mormonism, which seems now to have presented itself in the world for the first time since the days of Mohammed. Although, therefore, acknowledging Christianity and the Old Scriptures, just as Mohammed did, it is distinctly a new religion. It claims a new revelation, and a new prophet. It has a new law, a new spiritual polity, and a new mission. Instead of being merely a new interpretation of an old theology, it professes to have renewed the long-suspended intercourse with Heaven and the supernatural. Instead of presenting a new dispensation growing out of an old ecclesiastical history, to which it assumes to impart a new life, it has actually created a past history of its own, which, though severed from the main current of our common traditional Christianity, connects it back, through passages never before suspected or explored, with the early Jewish revelation—or that original fountain from which the Gospel and Mohammedanism may be said to have derived, the one its reality and its purity, the other the materials for its fanatical perversions.
Whatever may be the truth in respect to the real origin and authorship of the book of Mormon, there can be no doubt of its wonderful adaptedness to the purposes to which it has been applied. We can not agree with those who would deny to the work either genius or talent. The Koran bears with it that prestige of antiquity which always insures some degree of respect. It is written in a dead, and what is now regarded a learned language. It has its Oriental imagery, together with frequent allusions to what most interests us in Oriental romance. Above all, it has had its centuries of scholiasts and commentators, extracting the aroma as well as the dust of its assumed divinity. In short, there is about it a show of learning and "venerable antiquity," and yet, we do not hesitate to say it, Joe Smith, or whoever was its author, has made a book superior to that of the Arabian prophet; deeper in its philosophy, purer in its morality, and far more original. There are, doubtless, many faults both of style and language; but centuries hence may convert these into precious archaisms, and give to the bad Anglo-Saxon of the Mormon book all the interest which ages of scholiasts have imparted to what was once the irregular Arabic of the rude tribes of the desert.
It may startle some to be told, that Mormonism has actually pressed itself more upon the attention of the world than Christianity had done at the same age. We carry back into the early days of the Gospel's progress the clear light and outline of its later history. We can hardly realize that even for a century, or more, after its first promulgation, it was an object of little interest to the world, and that when it first began to demand a passing paragraph from the historian, it was only as an "execrabilis superstitio," creating a disturbance barely visible on the surface of society. Of course there is no intention, by any such remark, to make any comparison between the intrinsic merits of the two systems. A true believer in Jesus, and of "the truth as it is in Jesus," will never suffer himself to be disturbed by any parallel, real or seeming, between Christ and Socrates, or Christ and Mohammed, or Confucius, or the founder of any new religion, or of any pretended social reform, either in ancient or modern times. He can have no nervous fear of confounding the immeasurable difference between any such pretension and "that name which is above every other name." The strength and success of the counterfeit only adds lustre and assurance to the original. Neither does the great idea of a revelation suffer any detraction by being associated in thought with such attempts. The Koran only confirms the Gospel. It never would have been what it is without it. The false prophet never would have arisen had it not been for the true. All religious imposture and fanaticism may thus be regarded as involuntary witnesses to an absolute truth, of which they are but the frenzied caricatures. The grossest delusions only show, by their very extravagance, the indestructibleness of the religious principle in the human soul, and how it clings and ever must cling to the idea of some Divine revelation, some lifting of the vail, as the etymology of the word imports, which hangs so densely over man and nature.
There is a more inexplicable phenomenon than Mormonism or any false religion. It is the disposition manifested in some parts of the philosophical, and even professedly religious world, to depreciate, if not directly to deny the supernatural—to put as far away as possible, or to receive as the last allowable explanation of any difficulty, the thought of any direct communication from Heaven to earth. It is on this principle some would even interpret, not only present phenomena, but also all that during countless ages have left their mark upon our globe. On this principle another class would unspiritualize as far as they could, even the acknowledged Scriptures. But why should it be so? Why this strange delight in believing in the omnipotence and unchangeableness of a blind and unrelenting nature? What comfort has it for the soul, or what enlargement even for the intellect? What happiness in the thought of being bound in such an adamantine chain, even if we are compelled to admit its stern reality! It may be, peradventure, that philosophy here is in the right, but, if we may employ the paradox, her reverence for nature must certainly seem most unnatural. Nature, even our nature, longs for some Divine or supernatural communications. For this "the whole creation groaneth and travaileth together until now." The wonder, then, is not that there have been in the world so many mythical accounts of Divine intercourse, but that there has been so little of the reality. Why does not God speak to us here? Why has [Pg 702]"He made darkness his pavilion round about him?" Why "cometh He not out" more frequently "from the hiding-place of his power?" Why has He ever been called—by Homer, and Hesiod, and Orpheus, as well as in the Bible—"The Dweller in the cloud?" Why does not our Father's voice oftener break the fearful stillness of nature, and give us that evidence of His existence, His government, and His providence, without which nature is but a gloomy prison-house, while life is but a smothered effort to escape from its terrible immutability, and breathe the freedom of a spiritual and supernatural atmosphere? Is it said that He is always speaking—that the Great Cause of causes is always exhibiting itself in its effects? But what comfort in this? It speaketh not to us—it manifests no knowledge of our present thought, of our present individual wants. The voice that is alike in all things, and comes alike to all things, we can not distinguish from nature herself. The true ground for marvel, then, is not that men are led astray by false prophets, but that such vast multitudes should be so utterly immersed in nature and worldliness, "caring for none of these things," and finding in such phenomena as Millerism and Mormonism, only occasion for insane merriment, instead of deep religious and philosophical inquiry.
The indestructibleness of the religious principle in the human soul! This is the great lesson read to us by such events. Even this nineteenth century with all its secularity, has not wholly drowned it. It breaks out in the midst of every form of worldliness. When untaught in respect to the true path, it follows the wildest imposture; and, as though in awful derision of the inability of the mere secular spirit ever to satisfy the deepest human wants, a Kingdom of the Saints settles itself in nearest contiguity to what would seem to be the exclusive territory of Mammon.
We can only call attention to this strange phenomenon without going into any discussion of the causes of its remarkable success. As we have said, it is the only case of a distinctly new religion since the days of Mohammed. Yet still it may be compared with other anomalous religious movements that have characterized the present century. Most of these have already had their growth and decline. Some that started with more enthusiasm than has ever been claimed for the Mormons, have, for years, been dying out, or only manifesting an outward and formal existence. On the other hand, too, a similar fate has attended most of the schemes of Socialists, and of those reformers who have relied solely on some doctrine of political economy, while ignoring, as far as they could, any recognition of a supernatural religionism. In distinction from both these, Mormonism has flourished because it has possessed the element of vitality which was respectively wanting to each. The religious sects to which we have alluded (and we mean of course such as may be justly characterized as unscriptural delusions) have been too unworldly for success. They have lacked the secular element. Schemes of mere social reform, on the other hand, have been dead from the beginning. They have been wanting in that vitality which alone can come from a real or pretended connection with a future life, and a supernatural world. Mormonism professes to wield both powers. Whatever may be thought of the first founders of the sect, the multitudes who from all parts of the United States, and from England, and even from the Continent, are now crowding to the Salt Lake and the modern Canaan, give evidence of a power of tremendous reality, however much it may be above the comprehension of the shallow witling, or the mere secular political economist. The cause must have a universality in some way corresponding to the wide effect it is producing. But be it what it may, the lesson taught is most timely as well as important. It is, we repeat—and it will bear to be repeated—the indestructibleness of the religious principle in the human soul. If this have not the true nourishment, it will feed on falsehood; but nourishment and life of some kind it must have. The most secular age, instead of destroying, only causes it to burst out in some new and monstrous form. And even in this idea there is light and consolation for true faith. It derives new evidence from every spurious manifestation. The religious principle can not be wholly annihilated—
Let all worldly causes combine to drive it seemingly from the earth—let the edifice of supernatural belief be leveled with the ground, it would only be the signal for reconstruction. Take away the true, or quench it in the worldly spirit, and some form of false belief will start up in its place. There will be faith in the earth—there will be a sacred book—there will be a ritual, or system of worship, ever maintaining itself as a symbol of the inextinguishable trust in the reality of "things unseen and eternal." The naturalizing philosophy may endure, and even be strong as the antagonist of a revealed supernaturalism. But take away the latter, and the former falls with it. Its success is suicidal. Its triumph is its own utter defeat. All true interest in nature and science must expire, when every where the soul ceases to acknowledge any thing higher than either. Without a return to a true faith, spiritual delusions, on the one hand, or the grossest secularity and sensualism, on the other, will be the only alternative. And, if we must come to this, can any thinking mind have difficulty in deciding where we should look for the truest exhibition of human dignity—in Utah or California—in the Land of the Saints, or in the Land of Gold?
And there was evening—and there was morning—one day. (Gen. i. 5.) Why has the inspired historian placed the night first? It must doubtless be because it actually came first in the order of our present creation. What was this first night but the long chaos of darkness that covered the face of the deep, and over which the Spirit brooded when the command came forth for the first morning to appear—when God said, Let there be light on that dark world, and immediately light was there? But still, night was first, and hence in all the traditions that have sprung from this account it has ever been an object of religious reverence. In the old mythologies Night is the mother of day; and hence the epithets that poetry has ever conferred upon her—Sacred Night, Divine Night, Holy Night, Most Venerable and Religious Night. But not only has she been regarded as the mythological mother of creation, but as ever the nurse of the purest emotion and the truest thoughts. On this account the Greek poets gave her that beautiful name Euphrone—indicating the season of good feeling—the hour of hope, of calm yet joyous contemplation. It is true, the inspired description of the heavenly state says, There shall be no night there. But in our present imperfect being, the idea of the highest earthly bliss would be marred by its absence from the picture. As yet we can not dispense with the shade. The
is for beings of another order, and another life; and however much we may admire the pure sublimity of [Pg 703]this fine line of Doddridge, we feel that we must be endowed with new emotions before we could truly enjoy the never to be remitted splendor of such a state as it describes.
Although affected by particular circumstances, and expressed with great variety of imagery, there has been a wonderful harmony in the spiritual conceptions which the contemplation of night has ever called forth. We have, therefore, thought that it might interest our readers to present a few of the most striking night scenes from ancient and modern poets. The first from our port-folio, of course, is Homer's. The selection is from the close of the eighth book of the Iliad. Its introduction partakes of the warlike character of the poem, but softened into that holy calmness which the scene ever assumes, whatever may be the circumstances in which it is presented. We give Pope's splendid translation, although some might prefer the more accurate version of Cowper.
But neither Pope nor Cowper can be said to have caught the spirit of the original as well as the old ballad version of Chapman.
Apollonius Rhodius, in the Argonautica, presents a greater diversity of imagery. He has not in view, like Homer, the unity of a single scene, but calls up similar emotions by a dispersed variety of the most impressive pictures. We present a translation, which, if it have no other merit, may at least be said to be almost word for word—
Virgil closely imitates the Greek poet in the designed contrast, if not in his scenery. As we have not troubled them with the Greek, our fair readers, and others, we hope, will pardon us for putting on our page the Latin. Even those may appreciate its exceedingly liquid flow, who are compelled to resort to the translation for its meaning.
Dryden is very far from doing justice to Virgil in the translation of this passage, and yet, we must say, that the original, much as it has been praised, falls greatly short of the exquisite description by Apollonius. How much does that most impressive image in the sixth line of the Grecian poet exceed any effect produced by Virgil's pictæ volucres, or "particolored fowl," however ornate the language, and liquid the melody of his highly wrought lines.
But Byron—shall we risk the criticism—Byron, in our judgment, surpasses every example we have quoted, and even had we added, as we might have done, Shakspeare and Milton to the list.
Our concluding example is from the Scriptures. We challenge not for it a superiority simply on the ground of its inspiration. Every reader may judge for himself how immeasurably it excels any thing of the kind to be found in ancient or modern poetry. How full of natural sublimity, and, at the same time, how profoundly impressive the moral lesson of this night scene from Job!
We hear often of popular fallacies. Books have been written on them. But there are also learned fallacies, and among these we know of no one more common than that which prevails respecting the word education. It is quite usual with lecturers and essayists to derive a profound philosophical meaning from the bare etymology of the term. It is from educo, they tell us, to lead or draw out. It means the drawing out or developing the faculties. It is the bringing out the unwrought man, like the polished [Pg 704]statue from the rough block of marble. All sorts of changes are rung upon the word. With some it is the educing of the individuality, with others, of the humanity. Others again talk much of drawing out the ideas, and that, too, without any previous exact instruction, or the furnishing of what might be styled the prepared material of thought—about as wise a course as to attempt to develop, or draw out the faculties of a nail-making machine, without ever thinking of putting any well-wrought iron into it. Now, all this is pedantic nonsense. The old Roman Roundheads, from whom the term is derived, never dreamed of any such transcendental conception. The word, in its primary sense, simply means nursing, fostering, rearing. Hence is it afterward applied to knowledge and discipline. It is educed from the simple conception of holding the child by the hand, and leading him forth when he first begins to walk. From the same primitive thought comes the word pedagogue, which simply means, one who leads a boy, and was first applied to the slave, or servant, who conducted the Athenian child to and from school. It would, however, be hardly worth our while to show the fallacy of this very common etymological deduction, were it not sometimes made the ground of very false ideas. The old view, although it have no great philosophy, will be found to be the true one. It is to hold a child up, and lead him forth by the hand, before you set him to walk alone by himself, under pretense of developing his faculties, either of thinking or of locomotion.
Every man has two parents, four grand-parents, eight great-grand-parents, sixteen great-great-grand-parents, &c., &c., &c. If we reckon 30 years to a generation, and carry on the above series to the time of the Norman conquest, it will be found that each one of us must have had at that period, no less than 32,000,000 of ancestors. Now, making all allowance for the crossing of genealogical lines, and consequently for the same person being in many of the intersections, still there will remain a number sufficient, at that period, to cover the whole Norman and Anglo-Saxon race. Whatever, therefore, was then noble, or pious, or princely, or even kingly, stands somewhere in the line of ancestry of the most ignoble and plebeian among us. Each man of the present day may be almost certain of having had, not only earls (and it may be bishops), but even crowned heads among his progenitors. And so also may we be almost assured that the highest families of that period have now lineal representatives in persons so low in the social scale, that all the sounding lines of heraldry would fail to fathom the depth of their obscurity. In less than a thousand years, the blood of Victoria inevitably mingles with that of some of the most ignoble of the earth. Carry the calculation further back, and we soon pass beyond any population that ever existed on our globe. A thousand years from the present time brings the number up to 1,024,000,000. Two or three centuries more carries it beyond a thousand billions, and long before we arrive at the period of our world's creation, it would have reached a number surpassing all powers of easy enumeration. It is a consequence, too, of the same view, that a thousand years hence, each man who has now an ordinary family of children, will probably have a representative some way of his blood in each one of 30,000,000 of persons; and that these will be of all conditions, high and low, rich and poor, unless, as may be the case, some system of social philosophy may long before that have swept all distinctions from our world.
The "monitory season" of Nature has come. The faded garniture of the fields; the many-colored, gorgeous woods; the fitful winds, sighing for the flowers "whose fragrance late they bore:" the peculiar yellow-green of the sky at the horizon, in the twilight gloaming; all these proclaim that "summer is ended" and autumn is here. Brainard, a poet of true tenderness and feeling, once asked, "What is there saddening in the autumn leaf?" Perhaps it would be difficult to tell what it is, but that it is saddening, in the midst of its dying beauty, most persons have felt. One of our own poets, too early called away,[10] wrote many years since, on the first day of October, the following sad and tender lines:
[10] Willis Gaylord Clark, for many years Editor of the Philadelphia Daily Gazette, and author of the "Ollapodiana" papers in the Knickerbocker Magazine.
Carlyle, in his "Sartor Resartus," gives a condensed, but exceedingly forcible picture of the "net purport and upshot of war," by taking thirty able-bodied men from a French and English village, and making them face each other on a pleasant morning, when they blow each other's souls out, and straightway become "shells of men." We were speaking of this the other evening with a friend, who was with our army in Mexico, and in the course of much chat, [Pg 705]touching war and its accompaniments, he mentioned an anecdote of as brave a fellow as there was in his command, but who had an unfortunate and irresistible habit of occasional intoxication, whenever, by hook or by crook, he could procure a "horn" of brandy or whiskey. One evening, the day after an engagement, in which his coolness and determined bravery had won the admiration and warm commendation of his superior officers, he was brought before his commanding officer, who was on parade, in a state of beastly intoxication. Remembering his services of the day before, the officer was reluctant to punish him, at least without first trying to make him ashamed of his offense by exhortation and remonstrance. "Are you not ashamed of yourself?" he asked, "to be brought before me in this condition?—you that can be so good a soldier? There was not a braver man in the regiment yesterday than you; and now you go and spoil all the honor you acquired, by disobeying orders, and coming before me drunk. Take him away!—I'm ashamed of him!" "Here—hello—hold on!" said the soldier—"hold on a minute: you've rep-rep-ri-manded me some, and praised me a good deal: now look o' here, cap'n, do you expect to buy all the human virtues for seven dollars a month? It's too cheap, cap'n—too cheap!" He probably thought with Lowell's Yankee, writing from Saltillo after his first engagement:
As we sat looking at a conjurer or necromancer performing his tricks the other evening, at which were some hundreds of other lookers-on, we fell to meditate upon the influence which any thing that is at all mysterious has upon the human mind. "To him," says Dr. Chatfield, "who has been sated, and perhaps disappointed by the actual and the intelligible, there is an indefinable charm in the unattainable and inscrutable." And it is so. Infants stretch out their hands for the moon; children delight in puzzles and riddles, even when they can not discover their solution; and "children of a larger growth" desire, oftentimes, no better employment than to follow their example. Look at the fanaticism engendered by Rev. Edward Irving's "Unknown Tongues; at which," says the authority we have quoted, "we need not wonder, when we remember the confession of the pious Baxter, that in order to awaken an interest in his congregation, he made it a rule, in every sermon, to say something above their capacity." There are not wanting ministers nowadays who follow the Baxterian practice, with the difference only, that what they sometimes preach is as much above their own comprehension as that of their audience.
Is it not a "little curious" that Harriet Martineau, an old maid, a "benign cerulean of the second sex," as Lord Byron calls her class, who "never loved," or if she did, yet who, if published accounts are true, shrunk from the nuptial bonds, and left her affianced lord in the lurch at the last moment—is it not a little curious, we say, that such a woman, should have written so exquisite a picture of true love as that which ensues? We once heard a distinguished American author remark, sitting by his "Dutchman's Fireside," that he kept for days out of the literary lady-traveler's way when she was trying to meet him. "There she was," said he, "going about with that long India-rubber ear-trumpet of hers, taking in every thing that was offered to it, just like an elephant going round with his trunk, drawing in here an apple, there a piece of cake, now a handful of nuts, and next, perhaps, a chew of tobacco. I wasn't going to contribute to her trunk, nor to the lining any others, when she had got home and printed her notes!" If the authoress, however, had met this unwilling host, and had told this "tale of love," doubtless he would have listened in "mute admiration." But we are forgetting the passage: "There is no other such crisis in human life as the crisis of Love. The philosopher may experience uncontrollable agitation in verifying his principle of balancing systems of worlds, feeling perhaps as if he actually saw the creative hand in the act of sending the planets forth on their everlasting way; but he knows at such a moment no emotions so divine as those of the spirit becoming conscious that it is beloved; be it the peasant-girl in the meadow, or the daughter of the sage, or the artisan beside his loom, or the man of letters musing by his fire-side. The warrior about to strike the decisive blow for the liberties of a nation is not in a state of such lofty resolution as those who, by joining hearts, are laying their joint hands on the whole wide realm of futurity for their own. The statesman, in the moment of success, is not conscious of so holy and so intimate a thankfulness as they who are aware that their redemption has come in the presence of a new and sovereign affection. And these are many: they are in all corners of every land. The statesman is the leader of a nation; the warrior is the grace of an age; the philosopher is the birth of a thousand years; but the Lover—where is he not? Wherever parents look round upon their children, there he has been: wherever children are at play together there he soon will be; wherever there are roofs under which men dwell, wherever there is an atmosphere vibrating with human voices, there is the lover, and there is his lofty worship going on—unspeakable, perchance, but revealed in the brightness of the eye, the majesty of the presence, and the high temper of the discourse. Men have been ungrateful and perverse; they have done what they could to counteract it, to debate this most heavenly influence of their life; but the laws of their Maker are too strong, the benignity of their Father is too patient and fervent, for their opposition to withstand; and true love continues, and will continue, to send up its homage amidst the meditations of every eventide, and the busy hum of noon, and the song of the morning stars."
Some lively French writer, whose name has quite escaped us, once wrote a vivid sketch, entitled, "L'Homme Rouge," or "The Red Man." There was an under-plot of sentiment in the story, we well remember, but the great feature of the romance was, that whenever there was a fire to happen in any part of Paris, whether by accident or design, there suddenly appeared "L'Homme Rouge;" sometimes in the midst of a party of revelers at a masked-ball; sometimes surprising nuns at their devotions, and not unfrequently where crime was hatching, or unnatural orgies making night hideous. But he was a good, benevolent deity, and always came to warn against or to suppress conflagration. Such, it would appear, and without fable, hereafter, will be the man who can command the great "Fire-Annihilator," which is making such a sensation, and proving so unerringly effective in England. A man, bearing [Pg 706]one of these easily-carried machines, enters his blazing domicil, all a-glow with a bright flame, which is curling its forked tongues around every thing which resists its progress, and touching a spring, a cloud of smoke-like vapor issues forth, before which the flame flickers, grows pale, and at once fades entirely out, and the conflagration is stopped. It has been tested in so many instances, that its success is now considered wholly infallible. A company for the sale of the "Annihilator" has been formed in this country, the "central bureau" of which is in New York, the president being Hon. Elisha Whittlesey, of the American Congress. The age of rail-roads, magnetic telegraphs, and fire-exterminators, will signalize this era as one of the most remarkable in the world's history.
Seneca complains that the ancients had compelled him to borrow from them what they would have taken from him, had he been lucky enough to have preceded them! "Every one of my writings," says Goethe, in the same candid spirit, "has been furnished to me by a thousand different persons, a thousand different things: the learned and the ignorant, the wise and the foolish, infancy and old age have come in turn, generally without having the least suspicion of it, to bring me the offering of their thoughts, their faculties, their experience. Often have they sowed the harvest I have reaped. My works are an aggregation of human beings, taken from the whole of nature." It is in the power of any writer, says a commentator upon this passage, to be original, by deserting nature, and seeking the quaint and the fantastical. "When I was a young man," says Goldsmith, "being anxious to distinguish myself, I was perpetually starting new propositions; but I soon gave this over, for I found that generally what was new was false."
Dean Swift's remark at the close of a charity-sermon, from the text "He that giveth to the poor lendeth to the Lord," is well known—("If you like the security, down with your dust!") But the two following eccentricities of speech, which are attributed to him, we never saw before: "My brethren," said he, on one occasion, "there are three sorts of pride—pride of birth, of riches, and of talents. I shall not now speak of the latter, none of you being addicted or liable to that abominable vice!" "I fear," said he, on another occasion, to his flock, "I fear, when I explained to you, in my last charity-sermon, that philanthropy was the love of our species, you must have misunderstood me to say specie, which may account for the smallness of the collection. You will prove, I hope, by your present contributions, that you are no longer laboring under the same mistake!" A surer way of securing a good collection was recently adopted by a benevolent lecture-giver in a sister city. The audience were admitted free; but when the lecture was closed, no one was permitted to pass out until he or she had disbursed twenty-five cents!
Some fourteen years ago there appeared in one of the English magazines an amusing article, showing up the aristocratic stupidity of the large and costly English annuals, which were indebted almost exclusively to the nobility for their contents. Until then, we had not been made aware that the Duke of Wellington was a poet. But it seems that we were mistaken; the "noble Duke" is a master of the military sonnet, a specimen of which is subjoined. Its "terse composition," the "boldness of its character," its "laconic simplicity," and martial "determination," were very highly commended by the editor:
Thus the "Conquerer of Napoleon" conquers the stubborn rhyme!
"I suppose," writes a contemplative and elegant modern English author, now unnamed, but who can not long remain stat nominis umbra, "that it has happened to most men who observe their thoughts at all, to notice how some expression returns again and again in the course of their meditations, or, indeed, of their business, forming, as it were, a refrain to all they think or do, for any given hour. Sometimes, too, this refrain has no particular concern with the thought or business of the day, but seems as if it belonged to some under-current of thought and feeling. This at least is what I experienced to-day myself, being haunted by a bit of old Spanish poetry, which obtruded itself, sometimes inopportunely, sometimes not so, in the midst of all my work or play. The words were these:
(than that we passed in pleasure). It was not that I agreed with the sentiment, except as applied to vicious pleasure; being rather of Sydney Smith's mind, that the remembrance of past pleasure is present pleasure; but I suppose the words chimed in with reflections on the past which formed the under-current of my thoughts, as I went through the wood of beeches which bounded my walk to day.... In a moment I went back, not to the pleasures, but to the ambitious hopes and projects of youth. And when a man does reflect upon the ambitions which are as characteristic of that period of life as reckless courage or elastic step, and finds that at each stage of his journey since, some hope has dropped off as too burdensome or too romantic, till at last it is enough for him to carry only himself at all upright in this troublesome world—what thoughts come back upon him! How he meditates upon his own errors and short-comings, and sees that he has had not only the hardness, oiliness, and imperturbability of the world to contend with; but that he himself has generally been his worst antagonist. In this mood I might have thrown myself upon the mound under a great beech-tree that was near, the king of the woods, and uttered many lamentations; but instead of doing any thing of the kind, I walked sedately by it; for, as we go on in life, we find we can not afford excitement, and we learn to be parsimonious in our emotions."
One of the Boston newspapers, in allusion to the great Railroad Festival which is about taking place, as the last sheets of our Magazine are passing through the press, observes: "The Canadian Judiciary Courts [Pg 707] have adjourned for the whole of the next week, in order to give an opportunity to our Canadian friends to be present at the great Railroad Jubilee, to be celebrated in our city. They are expected to arrive in great numbers on Tuesday of next week. That day will be devoted to an examination of our city. On Wednesday there will be a formal reception; and the City Government will accompany their English guests to the Bunker Hill Monument and other places of interest." Now we can not dissociate that word 'interest,' from the same word which forms the nucleus of an anecdote, which we will venture to relate, in illustration of the kind of 'interest' which a loyal English subject might be supposed to feel in paying a visit to Bunker Hill. At Bladensburgh battle-field, there is a very non-committal guide who shows visitors over the ground, enlightening those who are ignorant as to the character of the ground, where the different forces lay, how they advanced, and the like. The guide, however, is a 'prudent man,' for his situation depends upon being 'all things to all men' who may chance to be obliged to avail themselves of his services. If he is showing an English party over the ground, he fancies that he knows it, and therefore 'governs himself accordingly;' if an American party, he throws his 'balance of power' in the other scale. But he was sadly puzzled once. He could get no 'cue' from the gentleman and his friend, who had secured his services, as to whether they were English or Americans—the conversation was so vague and so limited. "Why was it," said one of these visitors, "that the Americans fled on this occasion?" "Fled!" he exclaimed, as if with impromptu dignity—"fled!" "Yes," said his interrogator, "why did the Americans retreat on that occasion?—why did they run away!" "Retreat!—run away!—guess not! Yes: well—perhaps they did. Yes; I b'lieve they did. The reason was, that somehow or 'nother they didn't seem to take no interest!"
Most readers have heard the story of the connoisseur in the fine arts who said one day to a friend, "I wish you would come down and see a picture I bought last week. I'd like to have you give me your candid opinion of it. A friend of mine had the impudence to say this morning that it was not an original! I should like to hear another man say that it was not an original! But you come and see it, and tell me honestly what you think of its authenticity." It strikes us that a man would not be apt to give a very "candid" opinion under those circumstances. This freedom of opinion is not unlike the liberty of action said to have been granted by Col. M'Lane to the troops under his command, before going into winter-quarters at Valley Forge. They were suffering for provisions and clothing, and Congress had been repeatedly petitioned for that relief which it was not in their power to bestow. Under this state of things, Colonel M'Lane paraded his band of suffering soldiers, and thus addressed them: "Fellow-soldiers, you have served your country faithfully and truly. We've fought hard fights together against our common enemy. You are in a bad way for comfortable clothes, it is true, and it grieves my very heart to see you tracking your feet in blood on the frozen ground. But Congress can not help it, nor can General Washington or I. But if any of you wish to return home, you can go. Let such of you as would like to go home step out four paces in front—but the first man that steps out, if I don't shoot him my name is not M'Lane." It is perhaps needless to add, that not a solitary "volunteer" homeward was to be found.
After our more severe Editorial work is done—the scissors laid in our drawer, and the Monthly Record made as full as our pages will bear, of history, we have a way of throwing ourselves back into an old red-backed Easy Chair, that has long been an ornament of our dingy office, and indulging in an easy, and careless overlook of the gossiping papers of the day, and in such chit-chat with chance visitors, as keeps us informed of the drift of the town-talk, while it relieves greatly the monotony of our office hours.
We have before now sailed over seas with some rollicking, red-faced captain, who, after a good day's run with his yards well braced to the wind, would, as evening began to fall, and the breezes to lull, rig out his studding-sail booms, and set new bits of canvas to catch every puff of the dying zephyrs. In like manner, we, having made our course good, out of mere whim, add to our sail, and mean to catch up in these few additional pages, those lighter whiffs from the great world of opinion, which come floating to us, as we sit here in our Easy Chair.
Nor are we altogether bent on choosing mere gossip; but, rather, we shall be on the watch for such topics or incidents as give a handle to the conversation of the town; and instead of treating them in any such philosophic fashion, as most writing men think it necessary to do, we shall try and set them down with all that gloss, and that happy lack of sequence, which makes every-day talk so much better than every-day writing.
There are hundreds of monthly occurrences which go into the journals as mere skeletons of facts; and yet, if a body had but the art of embalming by language, that fleshy covering which the every-day talk is sure to wrap about them, they would prove (these facts, we mean) the cheerfullest companions in the world.
And this is just the thing that we shall try to do. If the Cubans, down in Havanna, shoot some fifty men, we shall not be content with entering it upon our record: we shall not take up what we consider (as the Daily Journals consider they do) some impregnable position, and thunder away at some one else who has an equally impregnable position of precisely the opposite character; but we shall try and get hold of the actual situation of this new provision for the town maw, in that great feeding-place of the town, viz.—Public Talk. We shall say who are the most voracious feeders, and may possibly comment, in an amiable humor, upon the different modes of consumption.
The French have a most happy way of commuting the dull coinage of every-day facts into the most mailable matter in the world: and as we sit in our Easy Chair, and catch up, as we sometimes do, a leaf of a Parisian journal, we find ourselves unconsciously creeping into the heart of some street-story, which, in any English journal, would have been the merest item of Police!
Take, for instance, a single one—entered on all the commercial sheets after this fashion: "We understand that a suicide was committed under deplorable circumstances, not long since, in the Rue St. George. It appears that a French gentleman, owing to pecuniary embarrassments, had long been melancholy, and last evening killed himself with the fumes of charcoal. It is reported that he had been twice married, and (horribile dictu) that he exhumed his first wife, previous to committing the fatal deed. He leaves a very respectable property."
[Pg 708]Now look at our Easy Chair survey of such an unfortunate matter:
"Monsieur B——, a widower of great respectability, was married to his second wife several years previous to the Revolution of 1848. The embarrassments which this event occasioned to several of the most considerable of his debtors, involved him in pecuniary difficulties of a serious character.
"Being of a sensitive nature, and unable to meet at that period his more immediate engagements, he became the victim of an intense mortification, which no efforts of his friends could relieve, and which gradually settled into entire mental alienation.
"He had still ample fortune, and lived in the enjoyment of his usual luxuries. His attentions to his new wife (who is represented as exceedingly beautiful) were, of course, less decided and punctilious than before, but there were observed no indications of any special hostility.
"Things wore on in this way for a year or more, when it was observed that Monsieur B—— absented himself at a certain time of the day for many hours, from home, without allowing his wife to suspect his whereabouts. His manœuvres to prevent pursuit, and avoid observation, were most adroit, and utterly forbade detection.
"Meantime the guardians of the cemetery of Père le Chaise had observed at a certain hour of the day a well-dressed individual make his appearance at the gates, and disappear upon the heights, within the inclosure of a little Gothic tomb, erected to the memory of Madame B——.
"The guardians having ascertained that the visitor was the husband of the deceased lady, with true Parisian politeness, avoided any special observation.
"It was ascertained afterward, however, that he employed these stolen hours in laboring upon the tomb—a pocket-knife, his only implement, and a single crazy hope—(which will appear in the sequel)—his only aim. Having, after four or five months of daily toil, finished his work, he waited only the absence of his wife to carry into execution his plan. For this he had not long to wait; she had promised a visit to the country; and upon the very day following her departure, Monsieur B—— hurried to his old rendezvous at Père le Chaise, and with the same knife with which he had worked his way into the stone sarcophagus in which the body of his first wife reposed, he severed the head from the trunk, transported it under cover of his cloak to his home; placed it before him upon the table; kindled a brazier of charcoal; wrote a last word to his living partner, and then, with his pipe in his mouth, and in face of the ghastly head from the tomb—he died upon his chair!"
There is in this story, insufferable as it may seem to delicate-minded readers, strong illustration of the French love of the horrible—of French passion—and of that French spirit of Dramatism, which would turn even the vulgarity of suicide into the heroism of a Tragedy.
Reading on, as we do, in our Easy Chair way, our eye falls upon another bit of French romance of a different style: it will probably never come to the eyes of half of our readers in its Paris shape, so we employ a lazy interval of our weightier duties to render it into old-fashioned English:
Every body knows that the rage for gaming in Paris, specially in private circles, has been for the last eight or ten years—excessive. And if any weak-minded American has "dined out" there, within that time, he has very likely been mulcted in a very pretty sum (after coffee was removed) at écarte.
But, this is not to our story, which, in translating, we shall take the liberty of vamping into the easiest possible shape—for ourselves.
Monsieur X—— was some descendant (grandson, for aught we know) of a certain Marshal of the Empire of France, and inherited from him (if report spake true) a handsome fortune of some five hundred thousand francs; or, in American coinage, one hundred thousand dollars. This is quite enough to live on pleasantly in Paris, or, for that matter, any where else.
Of course, Monsieur X—— was a mark for such mammas as had marriageable daughters; and as the French mothers always manage these affairs themselves, and are, beside, very thoroughly schooled in the ways of the world, Monsieur X—— stood a very poor chance of escape. In fact, he did not escape, but was married one fine morning to a very pretty mademoiselle, who had the credit of possessing rare virtues, and whom our hero (Monsieur X——), for a wonder, did really and truly love.
We mention this as even a greater rarity on the other side of the water, than on this; and every body of ordinary observation knows that it is rare enough with us.
They lived happily through the honey-moon, and much to the surprise of his friends, for a year or two afterward. But at length it was observed that he wore very long faces, and dined frequently by himself at the Café de Paris, and did not even smile at the broadest of Grassot's comic acting. As he was known to be a young man of very correct habits, the inference was (not always a just one, by the way) that the wife was in fault.
The truth was, that with a disposition naturally amiable and yielding, she had been seduced by those married friends who knew of her husband's resources, into an intense love of cards. As a natural consequence she became ever eager for play, morose in her habit, and petulant of manner.
The husband bore this all very quietly for a while, revolving in his own mind what could be done, and paying his wife's drafts upon him without a murmur. Days and weeks passed by, and the change wore grievously upon his spirits.
At length, he chose his course, and pursued it—after this manner.
He entered with apparent gayety into his wife's amusements, and introduced her, through the interposition of a friend, into one of the most famous gambling salons of Paris. As usual, she took her seat at the table where the stakes were largest. Her antagonist at the play was a stout old gentleman who wore a careless manner, but who after the first round or two played with remarkable success. When madame's losses had amounted to a considerable sum, he proposed "double or quits." Madame accepted and—lost.
The gentleman proposed the same game: madame accepted and lost!
The gentleman proposed the same trial a third and fourth time; and madame, supposing him to be an eccentric old gentleman, who was willing to furnish her with this opportunity of winning again the money, accepted each time his proposal, and uniformly—lost.
Still the play went on, until madame's losses had amounted to the extraordinary sum of four hundred thousand francs, when the old gentleman pleaded an engagement, and retired.
Madame X——, in an agony of trepidation gained her home, and throwing herself at her husband's feet, confessed and regretted the folly which had ruined them.
The husband was naturally astounded: "But," [Pg 709]said he, controlling his emotion, "the losses must be met. There will remain some seventy thousand francs of my estate, and with that we can live comfortably in the country. For myself, I do not at all regret this: but, my dear (for his old affection lingered), I fear that you may sink under the privations you must encounter."
His goodness overcame her; she avowed not only her willingness but her great joy in becoming the companion of his exile.
It was in an old town of Brittany (we believe, for the paper is not at hand) that they lived quietly and cosily together, in a mossy old chateau. Their table was frugally served, and their servants were of the neighboring peasantry: in place of the old joyous rides in the Bois de Boulogne, they now took strolls together under the wood that shaded the chateau. Thus, for ten years they lived, growing into each other's affections, and rejoicing in the loss which had won them to a real enjoyment of life, and of each other's love.
"It was indeed a happy loss," said she.
"It was none at all," said the husband, and with a caress he handed her the certificates for some five hundred thousand francs, in the most available of French funds!
"Your antagonist," said he, "was a sure winner, but his services were purchased by your husband, and now that he has won you to his love, and to a sense of your own dignity, he makes over to you this recovered fortune."
And the French chronicler goes on to paint a pretty scene as a hint for those dramatists who choose to put the affair on the stage. And he further says that the story is well authenticated, as he might prove by giving the parties' names; but upon consideration, he favors us only with an X.
If the story is a lie, all we can say is, that Eugene Guinot must take the blame of it: and judging from his experience, we think the blame will sit lightly on him.
We have wandered so far from the town, that we had half forgotten that there was any town at all. But, after all, there lies but a step nowadays between Paris and New York—a step over sea, and a step over a very narrow bridge of morals. True, we have not yet imported the salon gambling, except in a quiet club-way, where surely vagrant bachelors, it would seem, have as good right to stultify themselves, as they have in most other situations in life. It is to be doubted, however, if gaming does not presently come into the round of amusements. Old methods do not last long in our growing society: and as evidence, we may note the abandonment, the present year, of the fancy balls, which, for four or five seasons back, have made the very Elysium of a summer's festivities.
What matter has been made of it under the new dispensation of undisguised ball costume, the papers have not much informed us: indeed it is richly observable, that when the fashions of the day withdraw from outré action, and shed those enormities of feature which excite the stare of the vulgar—just so soon the public press respects their modesty, and gives them the award of silence. As a consequence (for the sequitur may not appear, in the illogical order of our after-dinner arrangement) little has been said this year of the "dress balls" of Saratoga and Newport: and the catalogues of watering-place Deities have been transferred from the flash-papers, to the roll-books of the marriageable men. A few sharp days of early September (not far from the date of our writing) will have driven our city people away from those shores, where the eastern fogs come sailing in laden with agues, and dropped them down here and there, along those sheltered hill-sides of inland repute, which bask in a summer morning, and which, by and by, will smoke with the kindling glory of an Indian summer.
As yet few have found their way to the town itself: and those few find the streets full of bustle, of strangers, of dust, and of Cuba. It strikes a man oddly, who has been taking his siesta the summer through, under the shadow of country-grown trees, and in the hearing of birds, until he has grown into a sort of assimilation with country habit and country talk, to rebound upon a sudden, from the hard, frosted hill-sides into the very centre of this great furnace of business—and to find it all sweltering and panting with its labor, just as it did six months gone by, and just as it will do in six months to come! Your country idler, with the conceit of the city on him, somehow conceives the idea, that without him there will be less noise, and less commotion: and yet he may go and come, and take his thousands, and bring his thousands, and shout at his loudest, and the great city, quite careless of it all, still sends up from her pebbled veins, and her sweeping quays, the same unceasing roar.
We have forewarned our reader, or should have done it, that we shall shift our topic in these our after-dinner musings, as easy as the turning of a leaf. Our eyes have just now fallen upon a passage in Mr. Greeley's last letter from Europe, in which he speaks of the appearance of the English women, and commends, with a little more than his usual ardor of expression, their perfection of figure. He attributes this, and very justly, to the English lady's habit of out-of-door exercise. We had thought that this fact was known: that it was known years ago, and that our fair country-women would catch a hint from it, that would throw color into their cheeks and fullness into their forms. And yet, sadly enough, our ladies still coop themselves in their heated rooms, until their faces are like lilies, and their figures—like lily stems!
We have alluded to the matter now, not for the sake of pointing a satire surely, but for the sake of asking those one or two hundred thousand ladies, who every month light our pages with their looks, if they do indeed prize a little unnatural pearliness of hue, and delicacy of complexion, beyond that ruddy flush of health (the very tempter of a kiss!) and that full development of figure, which all the poets, from Homer down, have made one of the chiefest beauties of a woman?
If not, let them make of themselves horsewomen: or, bating that, let them make acquaintance with the sunrise: let them pick flowers with the dew upon them: let them study music of nature's own orchestra. Vulgarity is not essential to health: and a lithe, elastic figure does not grow in hot-houses.
For ourselves, we incline heartily to the belief, that if American women have a wish to add to the respect, the admiration, the love, and (if need be) the fear of the men, they will find an easier road toward that gain, in a little vigorous out-of-door exercise and a uniform attention to the great essentials of health, than in any new-fangled costumes, or loudly applauded "Rights."
We have grown unconsciously heated with the topic, and this added to the 90° by Fahrenheit, which is steaming at our elbow, must cut short the first installment of gossip from our red-backed easy-chair.
New York, September, 1851.
The Oration before the Phi Beta Kappa Society of Harvard University, on The American Mind, by Rev. William B. Sprague, is superior to the average run of anniversary discourses. Chaste, vigorous, and eloquent in expression, eminently genial and catholic in spirit, pervaded equally with a genuine love of learning, and a glowing patriotism, it abounds in wise and generous counsels, adapted to the present times, and displays frequent touches of pathos and wit. The tribute to the memory of Buckminster, at the close of the oration, is an admirable specimen of classical eulogy.
The Farmer's Every-Day Book, by Rev. John L. Blake (published by Derby, Miller, and Co., Auburn), is a unique collection of varieties by a veteran manufacturer of books, whose educational works have had an extensive influence on the youth of our country, and whose ripened experience is devoted to productions of practical utility for the adult mind. A mass of information is accumulated in this volume, which must be welcome to the cultivator of the soil, in his choice intervals of leisure, on a winter's evening or a rainy day. It is arranged under appropriate heads, expressed in lucid and attractive language, and combined with excellent moral suggestions. The author has derived his materials from every available source. He has shown a sound judgment in their selection. Nothing is admitted which has not a real claim on the attention of the reader, while there are few topics of interest to the farmer which are not discussed with more or less detail. The articles from Mr. Blake's own pen are distinguished for their liveliness and good sense. His book is equally adapted to the modest farm-houses of New England, and the log-cabins of the Western Prairie.
Harper and Brothers have published a sumptuous edition of The Nile Boat; or, Glimpses of the Land of Egypt, by W. H. Bartlett—another agreeable volume on the manners and customs of the Orientals, with numerous sketches of their scenery. Mr. Bartlett's course was similar to that of which we have such a charming memorial in the "Nile Notes," by a Howadji; and it is interesting to compare the descriptions of two travelers, who look at the same objects from such entirely different points of view. Mr. Bartlett's first point is Alexandria, from which he departs for Cairo, whence he passes up the Nile, visits Thebes, Esneh, and Edfou, ascends the cataracts, and explores the weird ruins of Philae. The style of this volume is quiet and unpretending. It is illustrated with a profusion of engravings, from drawings made on the spot by the author, many of them with the camera lucida. They exhibit the principal monuments of the Pharonic period, as at Thebes, the later Ptolemaic style, as at Edfou and Philae, with some of the most beautiful specimens of the Arabian, at Cairo, besides many others of an interesting and instructive character. The volume is an admirable specimen of typography, and deserves a place in every library.
Of the swarm of Annuals for 1852, we have received The Iris, edited by John S. Hart, LL.D., and The Dew-Drop, a smaller volume, both published by Lippincott, Grambo, and Co. The Iris is issued, with its usual splendor of embellishment and typography, with one especial feature for the present year, which can not fail to enhance its interest and value. This is a collection of drawings of some of the most remarkable objects connected with the Indian traditions on this continent, made by Capt. Eastman, of the United State's Topographical Corps, who was stationed for nine years on our northwestern frontier, among the Indian tribes in the vicinity of Fort Snelling. The traditions themselves have been wrought up into poems and tales by the wife of Capt. Eastman, depicting the vicissitudes of Indian life, and the passions of Indian character. A great part of the letter-press of the volume consists of these sketches, which, for the most part, are executed with a firm and graceful hand. Besides these there are several pieces which are gems of literary excellence. "The Cenotaph," by E. W. Ellsworth, in memory of Capt. Nathan Hale, who died nobly in the service of the Revolution, is a quaint ballad, displaying a strange union of pathos and Yankee humor. Edith May, Mrs. Mary E. Hewitt, and Alice Carey each contribute characteristic poetical pieces.
The Dew-Drop is exquisitely embellished, and contains selections from the writings of several of the best American authors. Among them we find the names of Longfellow, Boker, Tuckerman, Stoddard, Edith May, Miss Lynch, Miss Sedgwick, Mrs. Child, and other popular celebrities.
Uncle Frank's Willow-Lane Stories is a budget of pleasant narratives for children, from the pen of Francis C. Woodworth, whose contributions to juvenile literature are always distinguished for their cordial and lifesome sympathy with the young heart. These stories are taken from country life, and are full of juvenile adventure and incident. The volume is illustrated with neat wood-cuts. (Published by Charles Scribner).
Drayton (published by Harper and Brothers), is a new American novel, presenting several fine examples of character-painting, with a plot of more than common interest. The hero, who passes from the shoemaker's bench to a high place in the legal profession, is not a bad specimen of American go-ahead-itiveness, softened down by numerous redeeming traits. We think the anonymous author has displayed a degree of ability in this volume which promises a future career of decided brilliancy.
The Epoch of Creation, by Eleazar Lord (published by Charles Scribner). An elaborate volume, devoted to the defense of Divine Revelation against the encroachments of modern science, with especial reference to the alleged results of geological research. The leading idea of the work is expressed in the following paragraph of the Introduction, of which, though by another hand, the whole treatise is an expansion and illustration. "The work of creation was necessarily a supernatural work; and hence all reasoning from the general laws of nature, which in their operation were subsequent to the work of creation, is as irrelevant in explanation of the Mosaic account, as the argument drawn from universal experience in disparagement of the miracles recorded in Holy Writ." Mr. Lord, accordingly, in explaining the teachings of Scripture on the work of creation, defends the literal sense of the Mosaic history. He maintains that the six days of the creation are to be understood in their most obvious acceptation, and that the attempt to reconcile them with the theory of a more ancient date of the material universe, is absurd in point of philosophy, and fatal to the interests of revealed truth. In the course of his argument, the author takes occasion to present several searching criticisms of Hitchcock, Miller, Pye Smith, and other eminent geologists, who have regarded the question in a different point of view. His work will [Pg 711]be read with interest, at the present day, when so much attention has been drawn to the religious and scientific issues in controversy. Mr. Lord presents an earnest and able defense of the theological view, in opposition to what may be considered as the prevailing opinion of the scientific world. He writes with clearness and force. He is master of considerable logical skill. Without the vivacity of style, or the brilliancy of rhetoric which distinguishes the productions of many of his opponents, he aims mainly at the lucid expression of the arguments in the case, which he sustains with shrewdness and ability. No one can mistake his evident zeal for the interests of revelation; or accuse him of the slightest taste for scientific novelties.
The Theory of Human Progression (published by B. B. Mussey and Co., Boston). The purpose of this book, which we should suppose was written by a Scotch Presbyterian, is to show the natural probability of a reign of justice on the earth. It is written in a hard, dry, ultra-logical style, tinctured with the spirit of Scotch and German metaphysics, and deducing the most stringent conclusions in regard to social justice from the language of the Bible. The author is an original thinker. He has little respect to custom or precedent. With great acuteness and discrimination, he points out the unavoidable inferences from the premises, which he assumes, and which, in most cases, he derives from the doctrines of Scripture. We rarely find such radical views of society, combined with such orthodox principles of theology. If the volume had been written with greater simplicity and liveliness of style, its effect would have been immeasurably enhanced.
Forest Life and Forest Trees, by John S. Springer (published by Harper and Brothers). This is a genuine American work, redolent of the pine forests of Maine, and filled with fresh and glowing descriptions of the life of a New-England backwoodsman. The writer was reared in the midst of the scenes which he portrays with such distinct outlines and such natural coloring, and has spent several of what he regards as the most pleasant years of his life in the toils and adventures of a "down east" lumberman. Hence he moves among the "strange, eventful" incidents of his story, like one who is perfectly at home, jotting down his exciting narrations without the slightest effort or pretension, and introducing his readers by the simplest transitions to the very heart of the remote wilderness. His work is divided into three parts, namely, The Trees of America, The Pine Tree, or Forest Life, and River Life. The first part is a valuable compilation selected from the most authentic materials on the dendrology of New-England, accompanied with judicious original comments. In the remaining portions of the book, we have a variety of reminiscences of a residence among the wild mountains, forests, lakes, and rivers of Maine, adventures of lumbermen in the pursuit of their perilous calling, fresh pictures of the sublime scenery with which they are surrounded, and a fund of amusing anecdotes. Several instructive details are given in regard to the lumber trade. The volume is illustrated with numerous wood engravings, which will give a distinct idea of many of the localities and scenes described by the author. Although making no claims to literary excellence, in the technical sense of the term, we are sure this book will become a universal favorite with the "reading millions" of America, from Canada to California.
Service Afloat and Ashore, during the Mexican War, by Lieut. Raphael Semmes (published by Wm. H. Moore and Co., Cincinnati), has already asserted a successful claim on the public favor, a large edition having been exhausted, and a second being on the eve of appearance. It is a work of standard merit, and does honor to the growing literature of the West. More substantial in its character than one would anticipate from its finical, book-making title, it presents a well-digested summary of the political history of Mexico, of her relations with the United States, and the various complications that led to the war of 1846. The author was personally engaged in the siege of Vera Cruz, of which terrible operation he gives a vivid description, drawn up both with military precision, and with appropriate poetical coloring. He afterward joined the army of Gen. Scott at Jalapa, was present at the battle of Churubusco as aid to Gen. Worth, and accompanied the victorious troops to the Mexican Capital. With an excellent opportunity for observation, and no small experience of military affairs, he has subjected the movements of the American army to a critical scrutiny, and presents his conclusions with soldier-like frankness and decision, though evidently aiming at impartiality. His remarks on the course of Gen. Scott are often severe, though he pays a warm tribute to the many admirable qualities of that eminent commander; but his deepest enthusiasm is called forth by the chivalrous and romantic character of Gen. Worth. Whatever opinion may be formed of the correctness of his comments on delicate military questions, it must be admitted that they are put forth in fairness and good faith, and if not to be regarded as conclusive, they afford a valuable aid in deciding the judgment of the impartial reader. The style of Lieut. Semmes is usually chaste and vigorous. In the mere narrative of historical events it sometimes flags, calling for the application of the whip and spur; but in the description of scenes of stirring interest, of battles, and marches, and shipwrecks, it kindles up with the occasion, and becomes glowing and vehement, often presenting passages of wild and startling beauty. We congratulate the noble-spirited author on the signal success of his work, and hope that we shall again hear of his name in the field of literature, as well as in the service of his country.
The Lady and the Priest, is the title of a striking English novel, reprinted by Harper and Brothers, founded on the romantic history of the Fair Rosamond, Henry the Second, and Queen Eleanor. The wily priest, Thomas a Becket plays an important part in the plot, presenting an expressive contrast by his ambition and cunning to the innocent, confiding, and deeply injured Rosamond. As a specimen of the English historical novel, this work will compare favorably with the best recent productions of the London press. The development of the story is skillfully managed, and grows more and more interesting with each step of its progress.
Vagamundo; or, The Attaché in Spain, by John Esaias Warren. (Published by Charles Scribner.) The title of this work is descriptive of its character. It is a good-humored record of a touch-and-go, genteel-vagabondish residence of several months in "old romantic Spain," where the position of the author gave him access to much "good society," and his tastes led him into a variety of odd, rollicking adventures, which he relates with an easy audacity that becomes quite fascinating before you arrive at the close of the volume. The strength of the author lies in his cordial, careless, jovial freedom. He shows such a quintessence of frankness, such a gay, contagious good-fellowship, as to disarm our habitual sternness as critics. His book contains little wisdom, and less wit, but for a dashing, effervescing, [Pg 712]sparkling effusion of anecdote and adventure, commend us to its hilarious pages. There are trifles here and there, indeed, at which the over-fastidious may take offense, as in duty bound; but readers who are not frightened with a little exuberance of youthful frolic will find it a tempting volume.
A neat reprint of Hugh Miller's Scenes and Legends of the North of Scotland, has been issued by Wm. H. Moore and Co., Cincinnati. It consists of a collection of interesting Scotch traditions, historical episodes, and personal anecdotes, presented in the garrulous, descriptive style, which has made the author popular among numerous classes of readers. Miller is a staunch, thorough-going Scotchman; in his opinion, there is no country like Scotland (and we too love Scotland); and no man in Scotland like himself (to which we demur); and this perennial self-complacency diffuses a kindly warmth over his writings, even when we find little to attract us in the dryness of his subjects.
A. Hart, Philadelphia, has published an edition of Miss Benger's Memoirs of Mary Queen of Scots, which portrays the history of the ill-fated queen in true and vivid colors. The work contains a variety of interesting anecdotes of the court of Henry II.
Ticknor, Reed, and Fields have published an additional volume of William Motherwell's Poems, from the Glasgow edition. They include songs, fragments of verse, and other pieces not contained in the former volumes. They are distinguished for the characteristic simplicity, unction, and pathos of their gifted author.
A new edition of the Memoirs of the Buckminsters, father and son, by Eliza Buckminster Lee, is issued by the same house—a volume of rare interest and beauty. Its pictures of rural life in New England are drawn with exquisite grace, as well as perfect fidelity, forming an appropriate embellishment to the affecting history of the subjects of the memoir.
Plymouth and the Pilgrims, by Joseph Banvard (published by Gould and Lincoln, Boston), is a popular compend of the events in the colonial history of Plymouth, illustrated with numerous engravings. It is intended to form the first of a series, devoted to the history of the United States, and consisting of at least twelve volumes. The narrative in this volume is derived from authentic sources, but exhibits no remarkable skill in its construction.
A new treatise on the Elements of Geology, by Samuel St. John, has been issued by George P. Putnam, adapted to the use of students in the higher seminaries of learning. It has evidently been prepared with great care and excellent judgment. Omitting the controverted and more abstruse points of theoretical geology, it aims at presenting a clear statement of the facts, which may be regarded as established in the present state of the science, and this is accomplished, we think, with the best success.
Sketches of European Capitals, by William Ware. (Published by Phillips, Sampson, and Co., Boston). Rome, Florence, Naples, and London, are the capitals to which this admirable volume is devoted. Although passing over beaten ground, Mr. Ware has treated his subjects with freshness and originality. He copies no one; consults his own excellent taste in preference to any authorities; gives his impressions as they are made from his own point of view; and describes them with equal simplicity and boldness. His language is usually felicitous and choice. He is a keen dissecter of character, and has presented us with some highly-finished specimens of his skill in this kind. His remarks on the present condition of Italian society are discriminating and forcible. Coming from a genuine lover of freedom, they are entitled to great weight. The obstacles to the establishment of Italian independence, arising from internal jealousies, and the want of national unity are exhibited in a strong light. Mr. Ware was not favorably affected by the manifestations of English character, which he witnessed on English soil. On this point he expresses himself without the least reserve, in a vein of acute and biting criticism. Various other topics are handled in this volume, and all of them with freedom and manliness. Differing from the author in many of his artistic judgments, we like the prevailing tone of his work—its honesty, its unaffectedness, its vigor, its humane spirit—to say nothing of its language, which, as we have already hinted, is a model of classical and elegant English.
Harper and Brothers have republished the first volume of Lamartine's History of the Restoration, from which we have given several extracts among our selections. It is decidedly the most important work of its prolific author since the "History of the Girondists." Bold in conception, abounding in lofty speculations, colored with a rich glow of moral emotion, it displays in the highest degree of perfection, the singular power of brilliant word-painting, and the felicitous artifices of rhetoric of which Lamartine is such a consummate master.
Rule and Misrule of the English in America, by the author of "Sam Slick the Clock Maker" (published by Harper and Brothers). In the present work, Judge Haliburton leaves the field of humor and satire for grave political discussion. It is written in the interests of monarchical government, taking the United States as a warning against the evils of democracy. With this view, the writer traces the introduction of the popular principle into this continent, the means of its early establishment, and the provisions for its support and continuance. He endeavors to show that the success of republicanism in the United States has been owing no less to a wonderful combination of accidental causes, than to the ability, energy, and practical skill of the American people. Hence he argues that this form of government is not applicable to England or France, and still less to other European countries. Some of his speculations have the merit of ingenuity; they will awaken interest, as showing the effect of our institutions on an outside observer; but they can not be regarded as models of political acuteness or sagacity.
Phillips, Sampson, and Co. have published the first number of a new Life of Napoleon, by Ben. Perley Poore, in which the author controverts the opinions of Scott and other tory writers on the subject. It shows a good deal of research, and is written in an animated style.
Tuckerman's Characteristics of Literature is briefly noticed in the London Athenæum, as a "series of suggestive papers," whose "criticisms are for the most part sound and moderate, but exhibiting no great extent of reading, nor any profound and subtle appreciation of literary beauty. Sometimes they remind us of Channing—of whose style Mr. Tuckerman is evidently an admirer; but they lack his clearness of thought and brilliancy of color, his intensity of conviction, and continual reference to fixed canons and principles." The Athenæum is systematically cold to American writers; nor does it do justice to Mr. Tuckerman in its criticism; yet it is right in tracing the influence of Channing both in his style and turn of thought. No one who was conversant with that "old man eloquent" in the latter years of his life could escape all tincture of the love of moral beauty which [Pg 713]was the master principle of his nature. His contagious influence is seen in the harmonic proportions, the clearness of expression, the equilibrium of thought, and, we may add, the sensitive timidity of opinion which mark the writings of his unconscious disciple almost as decidedly as they did his own.—Dr. Ungewitter's Europe, Past, and Present, is spoken of in the same journal in terms of lukewarm approval.
The Copyright Question, so far as the English courts of law is concerned, stands thus.—The Court of Exchequer is at variance with the Court of Queen's Bench:—and the case on which the next decision will be made, is that of Murray v. Bohn with respect to the copyright of certain works of Washington Irving. Mr. Routledge, against whom Mr. Murray had brought the law to bear, has surrendered, and admitted that he has injured the plaintiff to the extent of two thousand pounds. Mr. Bohn, however, stands out; and the point which he has now to prove in an English court of law is, priority of publication of Mr. Irving's works in America. Plaintiff and defendant have each, we are informed, sent a special commissioner over to America on the subject.
The death of Mr. Gibbon, one of the most munificent patrons of modern British art, is announced. In the genre school he has the credit of having called into existence some of the best efforts of many young artists of celebrity, by whom his liberality and protection will be gratefully remembered. To that and landscape pictures he principally confined himself as a collector, having little sympathy, so far as collection is a test, with the historical school of painting.
At Clifton, on Friday the 1st of August, died the patriarch of English authoresses—we might add of English authors—Miss Harriet Lee, at the age of ninety-five. To most of the generation now busied with fiction, drama, and poetry, this announcement will be a surprise: so long protracted was Miss Lee's life, and so many years have elapsed since her last appearance in the world of imaginative creation took place. To readers of our time, Miss Lee is best known as having in her "German's Tale" of the "Canterbury Tales" (a miscellany of little romances by herself and her sister), furnished Lord Byron with the plot of his play of "Werner." More old-fashioned novel readers, who are given to weary at the philanthropy, philosophy, and preaching which threaten to turn our thousand and one tales into something more like "Evening Services" than "Arabian Nights," will find in her vigor and clearness of invention a merit which of itself deserves to keep the name of the novelist alive. Miss Lee's further title to mortuary honors is a play, or plays, acted with small success—and which has, or have, gone the way of Hannah More's triumphant "Percy," and Madame d'Arblay's withdrawn tragedy. Harriet Lee survived her sister Sophia twenty-seven years: Sophia having died at Clifton, in 1824.——In London on the 4th died Lady Louisa Stuart—aged nearly ninety-four—the youngest daughter of the Minister, Earl of Bute, and the grand-daughter of Lady Mary Wortley Montague—the lady to whom we owe the charming "Introductory Anecdotes," prefixed to the late Lord Wharncliffe's edition of Lady Mary's Works. Lady Louisa remembered to have seen her grandmother, Lady Mary—when at old Wortley's death that celebrated woman returned to London after her long and still unexplained exile from England. Lady Louisa herself was a charming letter-writer; and her correspondence with Sir Walter Scott will, it is said, fully sustain the Wortley reputation for wit, and beauty of style, while it will exhibit a poet in a very different character from that in which another poet figures in his celebrated correspondence with her grandmother, Lady Mary. Some of Scott's letters to Lady Louisa are included in Mr. Lockhart's Life of Sir Walter.
A pert English traveler, of a class which has shared too largely in the hospitalities of facile Americans, gives an amusing caricature of a New York Literary Soiree, to which he had by some chance gained admittance:—"I went to stay at a Mr. S.'s country house, about six miles out town, and was there introduced to his father, who has one of the best collections of pictures in New York. They were kind enough to take me to a literary réunion given by one Miss ——, an American authoress of some note, who always opens her house on that evening, and to point out to me many of the notabilities in the New York world of letters. Many of them were real 'lions,' and not a few only wore the skin. The latter classes made themselves undesignedly very amusing, and were mostly little men, who had published and circulated a novel or two largely among their friends, which in their own opinions entitled them to turn down their shirt collars, allow their hair and beards to grow at random, and to assume the appearance of men in whom mind had become so predominant over body, as to render the latter quite a minor consideration. They did not open their lips all the evening, but were to be seen in pensive attitudes with their arms leaning on chimney pieces, and looking pleasantly at vacancy, or seated on solitary ottomans, contemplating the company with a sort of cynical stare. They wished, in fact, to be considered as living in an atmosphere of dreams, and nobody offered to disturb them. Mr. N. P. Willis, to whom I was introduced, afforded a very pleasant contrast to these little lions, and laughed and talked on many subjects like an ordinary being. Miss ——, too, has nothing of the pedant, and very little of the professed 'blue' about her, and wound up the amusements of the evening by gracefully leading off in a polka. During the evening a 'hush' was circulated all round the room, and on inquiry I found that a Herr something, very like Puddlewitz, 'was going to play his thoughts,' and forthwith a foreign gentleman with as much hair as one face could conveniently carry, sat down at the piano. From the nature of the music, I should say that Puddlewitz's thoughts were of a remarkably mild and sentimental nature, and not at all in keeping with his ferocious aspect. After the polka the little lions began to rouse themselves and dispel the mental web which their thoughts had been working round them for the last two or three hours, and we all gradually dispersed."
A curious instance of literary strategy is presented in the London edition of Vagamundo, or The Attaché in Spain, the sprightly work of our countryman, Mr. Warren, which we have noticed above. It seems that he had made an arrangement with a London publisher to bring out an edition at the same time with its appearance in this country. Every thing from the manuscript that could betray its American origin is eliminated, and it is thus issued apparently as a native born English production, "dyed in the wool." A start is obtained on the American publisher, and the work is put into the market two or three months before its publication in New York. Our first impressions of it as a lively gossiping book were received from the English copy some [Pg 714] time since, which surprised us as a remarkable specimen of the free and easy style, for English growth.
Of Andrews' Latin Lexicon, the London Athenæum speaks as follows: "It can not now be said that there is any lack of good Latin and Greek Lexicons among us. Whatever our classical deficiencies may be, they must not hereafter be attributed to the want of such a sine qua non. Within the last twenty—even ten—years most valuable additions have been made to our lexicographical stores. Entick, Ainsworth, Schrevelius, and a host of other worthies who long reigned over us, have at length been banished to make room for their betters. Even Donnegan—after a brief but successful career—has met with an inglorious fall.
"Besides our own dictionaries, we have those of our transatlantic brethren. Some few years ago they sent us over a large Latin Dictionary by Leverett; and now another of still higher pretensions (Freund's Latin-English Lexicon—edited by Dr. Andrews) has found its way here.... Whatever time, attention, and care can do toward making the work complete and correct, seems to have been done, and we all know how much the excellence of a dictionary depends upon these points,—especially when they are accompanied by competent scholarship, as we have every reason to believe they are in the present case. The result is, what might be expected, a rich repository of philological information, clearly expressed and well arranged....
"In conclusion, we are glad to have an opportunity of introducing so excellent a work to the notice of our classical and philological readers. It has all that true German Grundlichkeit about it which is so highly appreciated by English scholars. Rarely, if ever, has so vast an amount of philological information been comprised in a single volume of the size. The knowledge it conveys of the early and later Latin is not to be gathered from ordinary Latin Dictionaries. With regard to the manner in which it is got up, we can speak most favorably. Never have we seen a better specimen of American typography. Every page bears the impress of industry and care. The type is clear, neat, and judiciously varied. A pretty close inspection has not enabled us to discover any errors worth mentioning."
A contributor to the London Times has collected a mass of curious statistics in regard to the rise and progress of Rail-road Literature in England. His essay in that journal has recently been issued in a separate pamphlet. Among other interesting statements, we find the following facts, which are singularly illustrative of English habits:
"The gradual rise of the Railway book-trade is a singular feature of our marvellous Railway era. In the first instance, when the scope and capabilities of the Rail had yet to be ascertained, the privilege of selling books, newspapers, &c., at the several stations, was freely granted to any who might think proper to claim it. Vendors came and went when and how they chose, their trade was of the humblest, and their profits were as varying as their punctuality. When it became evident that the vendors of books and papers were deriving large sums of money from their business, the directors of the several companies resolved to make a charge for permission to carry it on; and tenders were duly advertised for, regard being had to the amount offered, and by no means to the mode in which it was proposed to prosecute the work. In some cases £200, and in others as much as £600 per annum have been deemed a fair rental for the book-stall at a London terminus. At one of the most important stations in the metropolis, a bookseller, who at one time professed himself unable to contribute £60 by way of rent to a benefit society established for the servants of the company, offered two years afterward £600 when the privilege was put up to public auction. The extent to which literary trash has been sold at these railway book-shops, may be conceived, when it is stated that a large profit has still remained for the bookseller after paying the very large rent-charge to the company.
"A movement has, however, been made on the North-Western Railway to put an end to this unwholesome condition of things. The stalls have been taken by a spirited bookseller and news-agent, determined to supply none but works of sterling literature; and the leading publishers have responded to this movement by the reproduction of some of their most valuable copyrights in shilling and half-crown volumes. The little reprint of Lord Mahon's 'Narrative of the Insurrection of 1845,' appears to have been the first step to improvement. It caught our eye, as it had already fortunately arrested the attention at more than one railway station of Mr. Macaulay, the historian. The sight of it suggested to that brilliant writer the idea and title of a 'Traveller's Library,' and at his instigation—for which we here tender him our thanks—Messrs. Longman commenced the cheap and popular series known by this name, and adorned by Mr. Macaulay's own charming productions.
"As we progressed north, a wholesome change, we rejoice to say, became visible in railway bookstalls. We had trudged in vain after the schoolmaster elsewhere, but we caught him by the button at Euston-square; and it is with the object of inducing him to be less partial in his walks that we now venture thus publicly to appeal to him. At the North-Western terminus we diligently searched for that which required but little looking after in other places, but we poked in vain for the trash. If it had ever been there, the broom had been before us and swept it clean away. We asked for something 'highly colored.' The bookseller politely presented us with Kugler's 'Handbook of Painting.' We shook our head and demanded a volume more intimately concerned with life and the world. We were offered 'Kosmos.' 'Something less universal,' said we, 'benefits the London traveler.' We were answered by 'Prescott's Mexico,' 'Modern Travel,' and 'Murray's Handbook of France.' We could not get rubbish, whatever price we might offer to pay for it. There was no 'Eugene Sues' for love or money—no cheap translations of any kind—no bribes to ignorance or unholy temptations to folly. 'You'll soon be in the Gazette' we said commiseratingly to the bookseller. The bookseller smiled. 'You never sell those things,' we added mildly. 'Constantly; we can sell nothing else.' 'What! have you nothing for the million?' 'Certainly; here is 'Logic for the Million,' price 6s.; will you buy it? 'Thank you, but surely books of a more chatty character——.' 'Chatty—oh, yes!' 'Coleridge's Table Talk' is a standard dish here, and never wants purchasers.
"Every new work of interest as it appeared was furnished to the stalls, from Macaulay's 'England' down to Murray's 'Colonial Library,' and purchasers were not slow to come for all. Upon many good books, as well of recent as of more remote publication, there has been an actual run. 'Macaulay' sold rapidly, 'Layard' not less so. 'Stokers and Pokers,' a sketch of the London and North-Western Railway, published in Murray's 'Colonial Library,' sold to the [Pg 715]extent of upwards of 2000 copies. Borrow's 'Bible' and 'Gypsies in Spain,' are always in demand, and St. John's 'Highland Sports' keep pace with them. Graver books have equally steady sale. Coleridge's works are popular on the rail. 'Friends in Council,' 'Companions of my Solitude,' and similar small books grasping great subjects, and written with high philosophical aim, are continually purchased. Poetry is no drug at the prosaic terminus if the price of the article be moderate. Moore's 'Songs and Ballads,' published at 5s. each; Tennyson's works, and especially 'In Memoriam,' have gone off eagerly; the same remark applies to the Lays of Macaulay and to the Scotch Ballads of Aytoun.
"The style of books sold depends more upon the salesman than on the locality; but there are exceptions to the rule. At Bangor, all books in the Welsh language must have a strong Dissenting and Radical savor. English books at the same station must be High Church and Conservative. School-boys always insist upon having Ainsworth's novels and any thing terrible. Children's books are disdained, and left for their sisters. 'Jack Sheppard' is tabooed at the North-Western, and great is the wrath of the boys accordingly. Stations have their idiosyncracies. Yorkshire is not partial to poetry. It is very difficult to sell a valuable book at any of the stands between Derby, Leeds, and Manchester. Religious books hardly find a purchaser in Liverpool, while at Manchester, at the other end of the line, they are in high demand."
A writer in one of the London literary journals presents a severe criticism of the "Bateman children," who are now performing at St. James' Theatre, under the auspices of our widely-known compatriot, Mr. Barnum. A part of his strictures is as follows, of which there is much more of the same kind:
"Mr. Barnum, the American monster-monger, has opened this theatre with an exhibition which it is disagreeable to witness and impossible to treat as a matter of art. Two American children, Ellen and Kate Bateman, stated to be six and eight years of age, are here produced in the respective characters of Richard the Third and Richmond in the fifth act of Colley Cibber's tragedy. Ellen, who performs the crooked-backed tyrant, carefully made up to look like Edmund Kean, has evidently been drilled by some one well acquainted with the style of that great actor, and elaborately wrought into a miniature resemblance of him. Not only the manner, but the voice has been tutored—tone and emphasis have been imparted, as well as gesture and deportment. To us, who recollect every phase of the style of the departed tragedian, this exact copy was something painful and revolting. Similar pains had been taken with the elder girl Kate—who, armed cap-à-pie, strutted and fretted as Richmond. The delivery of the children has been enormously exaggerated in their determination to produce effect. They are strained far beyond their natural powers—and the result is, an impression of caricature and burlesque."
The Dublin literary circles have recently lost the Rev. Dr. Samuel O'Sullivan—a political writer of much force and activity, and one of the leading contributors to the Dublin University Magazine. "His style was close and consecutive—and of late years was marked by a vein of reflectiveness not often found among Irish writers. He was abler in attack than in defense—like most polemic authors. The most valuable of his writings are, a series of elaborate biographical essays on modern Irish statesmen; which apart from their literary talent have the merit of originality of matter. For his papers on Lord Chancellor Clare and Mr. Saurin he was furnished with special facts; and his Chaplaincy to the Phœnix Park Military School gave him access to several persons high in office, whose acquaintance he preserved. He was an entertaining and instructive companion—fertile in curious original anecdote. His pen exercised much influence on the Irish Conservative press for several years: but with the merits or demerits of political controversialists we meddle not. We hear that it was Dr. O'Sullivan's intention to reprint, with additional matter, his excellent essays on Flood and Grattan: the best pictures left us of these Irish statesmen."
The Hakluyt Society have added to their very interesting publications, Richard Hakluyt's translation of the account of De Soto's Discovery and Conquest of Florida, with an additional account curiously corroborative of all its substantial details discovered and translated by the editor, Mr. Rye, of the British Museum. The expedition was not without valuable results of an accidental kind, though in its main objects it failed so lamentably; and the narrative now given is extremely vivid and striking.
Another volume curiously illustrative of the past, has been published with the uninviting title of Consuetudines Kanciæ. This is, in other words, a history of the Gavelkind, and other remarkable customs of the County of Kent. The author is a skilled antiquary, and gives many sound reasons for his belief that in not a few of those peculiar customs may be directly traced the famous and venerable laws of Edward the Confessor.
Doctor Latham has added to those researches and speculations as to races which have lately been found to explain so much of the peculiarities of national habits, customs, and laws, a sketch of the Ethnology of the British Colonies and Dependencies.
Dr. Lingard's valuable library has been bequeathed by the late learned historian to St. Cuthbert's College, Ushaw.
The Deutsche Allgemeine Zeitung has been seized and confiscated by the police at Leipzig, for having published, under the head of Great Britain, a notice, with translated extracts, of the two letters written by Mr. Gladstone to the Earl of Aberdeen on the treatment of the Neapolitan state prisoners.
The death of the famous naturalist, Dr. Lorenz Oken, whose theory of the Cranial Homologies effected a revolution in philosophical anatomy, and led the way to the admirable researches of Owen, has recently been announced. The name of Oken is most commonly associated by English readers with his "Physio-philosophy," a translation of which work, by Mr. Tulk, was published by the Ray Society. It abounds in admirable generalizations, unfortunately immersed in much that is false and fantastic, and clothed in the cloudiest phraseology of German transcendental metaphysics. Oken's researches and speculations (for he was as practical as he was dreamy) extended over all departments of natural history. Of the value he set upon facts, and the industry with which he collected them, a lasting monument exists in the volumes of the "Isis," a vast library of abstracts of the science of his time, founded and con[Pg 716]ducted by him as a periodical. Few men have had greater influence on European science than Oken. Until forced to quit Germany on account of his political opinions, he held a Professorship at Jena. Latterly he was Professor of Natural History at the University of Zurich, in which city he died about the last of August, at the advanced age of seventy-three years.
From Halle, we hear of the death, a short time since, of a voluminous German writer, John Godfrey Gruber, founder and principal editor of the "Universal Encyclopædia of Sciences and Arts"—a work which was at first carried on by him conjointly with Herr Ersch. Herr Gruber was also a large contributor to the Litteratur Zeitung and the Conversations-Lexicon. His separate works include: "The Destiny of Man," "The Dictionary of Esthetics and Archæology," "Researches into the Greek and Roman Mythology," "The Life of Wieland," and "The Dictionary of German Synonymes." These are but a few of his many writings.
M. Dupaty, one of the forty French academicians, died a few days ago. He was one of the most obscure of that learned corps. His literary reputation, such as it was, was based almost exclusively on vaudevilles and on the libretti of comic operas. He was held in esteem in the days of Napoleon; but then literary distinction was very easily earned. The most notable event in the last twenty years of his life was being chosen (to his own great astonishment) an academician in preference to Victor Hugo, then at the height of his fame.
The 16th, 17th, and 18th volumes of the complete works of Frederick the Great have just been published at Berlin. They are entirely occupied with his correspondence. There are 4000 letters written by him—two-thirds are in French, the other third, chiefly on military operations, are in German, and were addressed to his generals. The whole letters belong to the state archives. The edition of the great Frederick's works, now in course of publication, was undertaken by order of the present King of Prussia, and at his expense.
The indefatigable Eugene Sue, notwithstanding his daily labors as one of the 750 law-givers of the Republic are, or ought to be, rather heavy, has found time to write another romance, of which the publication has been recently commenced in one of the daily Paris journals. It is called "Fernand Duplesis; or, the Memoirs of a Husband;" and is, it appears, to be an exposure of what in France it is the fashion to call the miseries and iniquities of married life. Written in great haste, it will (judging from the opening chapters) be slovenly in style and negligent in language; but, en revanche, it will (as it seems) be of great dramatic interest, and will throw new light on Parisian society—that strange and striking assemblage of intrigue and passion, of vanity and folly, of elegance and refinement, of chivalry and corruption, of much that is good, and of more that is bad.
Don Hannibal de Gasparis, the Neapolitan astronomer, who has, in the course of the last few years, discovered no less than five new planets, has, by a royal decree of the 4th, been named Professor of Astronomy at the University of Naples.
In Hans Andersen's charming Memoirs we find a graphic sketch of an interview with Reboul, the baker poet of Nismes, celebrated in "Lamartine's Journey to the East."—I found him at the house, stepped into the bakehouse, and addressed myself to a man in shirt sleeves who was putting bread into the oven; it was Reboul himself! A noble countenance which expressed a manly character greeted me. When I mentioned my name, he was courteous enough to say he was acquainted with it through the 'Revue de Paris,' and begged me to visit him in the afternoon, when he should be able to entertain me better. When I came again I found him in a little room which might be called almost elegant, adorned with pictures, casts, and books, not alone French literature, but translations of the Greek classics. A picture on the wall represented his most celebrated poem, 'The Dying Child,' from Marmier's Chansons du Nord. He knew I had treated the same subject, and I told him this was written in my school days. If in the morning I had found him the industrious baker, he was now the poet completely; he spoke with animation of the literature of his country, and expressed a wish to see the North, the scenery and intellectual life of which seemed to interest him. With great respect I took leave of a man whom the muses have not meanly endowed, and who yet has good sense enough, spite of all the homage paid him, to remain steadfast to his honest business, and prefer being the most remarkable baker in Nismes to losing himself in Paris, after a short triumph, among hundreds of other poets.
The Writings of Shakspeare would appear, from the following fact, to be read with as much avidity and delight in Sweden as in England and this country. A translation of his plays by Hagberg, Professor of Greek in the University of Lund, is now in course of publication. Of this, 12 volumes have appeared; and although the first edition consisted of no less than 2000 copies, the whole have been sold off, and a second edition is in preparation. Professor Hagberg's translation is most favorably spoken of by those who are qualified to judge of its merits.
A new theological work by Jonathan Edwards, printed from his own manuscript, is announced as soon to be issued. The fame of our illustrious American theologian attaches great interest, in the religious world, to this new production from his pen.
The Poem entitled "The Ship of Death," which floated into our Editor's Drawer from an unknown source, was written by Thomas H. Chivers, M.D., author of a volume entitled "Eonchs of Rubies," and other poetical works.
Miss Catherine Hayes the celebrated Irish vocalist arrived in this country a few days since. Her first concert will be given while the sheets of our present Number are passing through the press. She is pronounced in her own sphere to be as unequaled as Jenny Lind in hers; brilliancy is the peculiar characteristic of the latter, pathos of the former. Those who have heard her abroad, predict for her a success not inferior to that achieved by her Swedish compeer. The fact of Ireland being her native land will of itself insure her a favorable hearing in America.
We are reminded that the English work entitled "How to make Home Unhealthy," which was ascribed to Harriet Martineau, in a former Number of this Magazine, was written by Henry Morley, Esq.



Robinson.—"There, Brown, my Boy, that's as fine a Glass of Wine as you can get anywhere."
Mrs. Brown.—"A-hem! Augustus, My De-ar. You are surely never going to take Port Wine. You know it never agrees with you, my Love!"


Uncle.—"So, you've been to the Crystal Palace—Have you, Gus?"
Gus.—"Yes, Uncle."
Uncle.—"Well, now, I'll give you Sixpence if you will tell me what you admired most in that Temple of Industry?"
Gus (unhesitatingly.)—"Veal and 'Am Pies, and the Ginger Beer. Give us the Sixpence!"

October, the beautiful month, standing like a mediator between summer and winter, is the season for exercise in the open air; especially for that healthful recreation, riding on horseback. It is the season, too, of the Indian Summer, when the pleasures of carriage riding and promenading are greater than at any other time of the year. For the ladies it should be an out-of-door month; and for them we herald the decrees of fashion, touching their appearance in the open air.
Walking Dress.—The figure on the left represents a very pretty costume for promenade. Bonnet, drawn tulle with low crown. The poke is made on a skeleton of wire covered with yellow silk, and having four pieces across. Under the wires are fastened small bows of gauze ribbon so as to form three well-rounded rows. A similar row of bows trims the edge of the poke inside, and the ribbons composing it are continued along flat. A gathered ribbon is laid all round and fastens with bows. The crown is of tulle, slightly puffed, and ornamented with five ribbon ruches, supported by five wires covered with silk, which slope toward each other, and meet near the curtain. The curtain is tulle, trimmed with a plaited ribbon, from which proceed bows astride on the edge. The shawl is of silk or other light fabric. On the body there are five cross-bands of silk, goffered and cut at the edges. The top one reaches [Pg 720] from one shoulder-seam to the other and is 2½ inches wide, the other four gradually diminish down to the waist, where the last one is but little more than an inch. The trimmings goffered in small flutes are fixed under a narrow galloon; another galloon is placed a little higher, leaving an interval of about half an inch between them. A similar trimming runs round the waist and forms the lappets. The skirt has seven rows of goffered trimmings gathered like those on the body. The top one is an inch and a quarter deep, and all increase gradually down to the lowest, which is 3¼ inches. The sleeves are open under the arm from the elbow downward, and are held together by two goffered cross bands. The under-sleeves are lace, and form a large puff, which is fastened in a worked wristband.
Riding Dress.—The figure on the right represents a riding dress. Felt hat with a terry velvet ribbon as binding for the edges, bows of the same, and a frosted feather. Body of white quilting, high and tight. The skirts hold to the body without seam at the waist. They are very round and full, owing to the cut of the side and the gores. They should come well over the hips, but not sit too tight. The middle of the body is open and leaves visible a rich lace shirt-frill very deep and full, and falling back on itself, owing to its fullness. The lace collar forms a ruff with two rows. The top and bottom of the body are hooked inside, but seem to be held by three gold double buttons; these twin buttons are attached together by a small gold chain. Those at bottom have a longer chain than the others. The sleeves are straight with a cuff turned up and standing out from the sleeve. Shirt of plain poplin, trimmed in front with velvet ribbons nearly half an inch wide, and continued all round the bottom.

Carriage Costume.—Dress of glacé silk; body half high, and open in front; waist long and slightly pointed; the body a tight fit and trimmed with a rich fancy trimming. The short skirt is very full, rounded at the corners a la robes, and trimmed to correspond with the corsage. The gathers at the waist are confined by narrow rows of guimpe. The skirt is long and very full, with a row of silk trimming laid on the hem at the bottom. Bonnet of paille de riz; brim very open. Feathers are placed low at the right side. Lined with fulled tulle, ornamented with pink satin A shawl of white cachmere, with very deep fringe.

Caps.—The cap is almost universally worn as a part of morning costume. Nos. 1 and 2 represent two of the latest styles, adapted for the cool mornings of autumn. Those of a negligé form are generally composed of muslin, embroidered au plumetis, or cambric, entirely covered with the richest kind of English embroidery, which sometimes resembles a splendid guipure. When the lappets are not formed of the same material, we see them of pink taffetas, attached to the cap, with a bunch of coques, composed of the same colored ribbon very full, and put on so as to replace the full bands of hair.
Undersleeves, so elegant with open dress sleeves, are worn by all. The style as well as material has many varieties. No. 3 is a very neat style, made either of embroidered muslin, or lace.
Pelisses are becoming very fashionable, made of plain Italian silk, and trimmed with a fancy ribbon three fingers in width, and bordered on either side with two narrow ones, appearing as if woven in the dress. We may cite, as a most elegant costume in this style, a redingote of pearl-gray, encircled with a ribbon of a pearl-gray ground, over which is quadrillé dark-blue velvet, having the narrow rows on either side. The front of the pelisse is closed with eight or ten rows of the same kind of ribbon, each end being turned back so as to form a point, from which depends a small blue and gray mixed tassel. The corsage is formed with broad facings, encircled to match the lower part of the sleeves.
Jewelry.—The châtelaine is now replaced, in a measure, by waistcoat chains, attached at both ends, the middle forming a festoon. Brooches are very rich; the finest are cameos set round with brilliants. Ear-rings are composed of large stones mounted in plain rings, without pendants. Bracelets are of enamel, sparkling stones, and gold. The waistcoat button is now a very elegant piece of jewelry.
Transcriber's Notes:
PUNCTUATION
Obvious punctuation errors have been repaired.
Pg 582, question mark replaced with exclamation mark (Honor to
Letitia, the mother of Napoleon!)
Pg 680, question mark replaced with exclamation mark (Extremely fine!)
This text contains several examples of inconsistent hyphenation, e.g. two thirds/two-thirds, and word spacing, e.g. mean time/meantime, which have been retained in this version, except for “Good by” which has been normalised to “Good-by”.
WORDS AND SPELLING
pg 579: "women" changed to "woman" (the best woman in France)
pg 588: "hunddred" changed to "hundred" (a population of but about
five hundred thousand)
pg 602: "Limana" normalised to "Limeña" (Limeña at home)
pg 606: "that" changed to "than" (much less depressed than that)
pg 616: "insted" changed to "instead" (twenty guineas, instead of
sixty)
pg 629: "grostesquely" changed to "grotesquely" (His life was
grotesquely checkered)
pg 631: "reched" changed to "reached" (he reached that last degrading
status in society)
pg 647: "guarrantee" changed to "guarantee" (a guarantee for what he
would have done)
pg 654: "massses" changed to "masses" (rude, unshapen masses)
pg 669: "tast" changed to "taste" (the taste of a man)
pg 675: "scluded" changed to "secluded" (having carefully secluded
her from marriage)
pg 695: duplicated word "been" removed (have been busily engaged)
pg 696: duplicated word "that" removed (It is intended that they shall)
pg 700: "it" changed to "its" (derives its supplies of provisions)
pg 715: "controversalists" changed to "controversialists" (merits or
demerits of political controversialists)
pg 720: "paile" changed to "paille" (paille de riz)
OTHER
The Table of Contents at the start is in addition to the original text.