
Transcriber’s Notes:
Every effort has been made to replicate this text as faithfully as possible.
Punctuation has been standardised. Spelling has been retained as it appears in the original publication except as marked like this in the text. The original text appears when hovering the cursor over the marked text. A list of amendments is at the end of the text.


| CHAPTER | PAGE | ||
| I. | The Coast Artillery | 1 | |
| II. | 1784-1840 | 12 | |
| III. | 1840-1861 | 31 | |
| IV. | Responding to the President’s Call | 46 | |
| V. | The Fighting First | 58 | |
| VI. | 1866-1878 | 80 | |
| VII. | The Old “Tiger” First | 89 | |
| VIII. | “The Cape” | 112 | |
| IX. | Since 1878 | 127 | |
| X. | Finally | 152 | |
| Appendix I. | Genealogy of the Coast Artillery—The Present Companies—Their Captains | 157 | |
| Appendix II. | Bibliography | 174 | |
| Index | 179 | ||
| Our First State Camp, Neponset, 1849 | Frontispiece |
| OPPOSITE PAGE | |
| The Train-Band, 1832. Why It Was Abolished? | 26 |
| Artillery in 1917 | 34 |
| Artillery in 1784 | 34 |
| Maj. Poore Pays His Bet | 40 |
| The South Armory, Boston | 70 |
| Fort Monroe in 1861 | 70 |
| The Fusiliers About 1845 | 90 |
| The Gray Uniform—The City Guards at Baltimore, 1844 | 96 |
| The Author | 144 |
| Col. E. Dwight Fullerton | 144 |
| Col. George F. Quinby | 144 |
| Modern Battery | 154 |
| The Chaplain in Action, 1916 | 154 |
When Chaplain Minot J. Savage first listened to the “March of the First,” inspiration fired his soul; the music was repeating a message to him. Was there something in the brazen voice of the horns, a magical harmony of sound with sense; or was it merely the loyal Chaplain’s imagination? At any rate this is what he heard:
And now, whenever “Adjutant’s call” sounds and the companies move into line with the precision and rhythmic swing characteristic of well-trained troops, they also hear the message which was written down for them by the Chaplain many years ago, “The Old First still shall lead.” They hear and believe.
Today it becomes the privilege of another Chaplain to set forth in this little book the reasons why the Old First believes in itself. We shall see how the present grows out of a long and noble past. Back in Civil War times observers noted that the regiment was one to be proud of; there was a large proportion of sensible, solid men who enlisted because it seemed duty, whose patriotism was not silly or vulgar, but strong and serious. Today likewise the Inspector General reports that the personnel is unexcelled; only men of good character are enlisted; standards are very high. And for the largest part the men are not in the service for any personal profit to themselves—there is too little pay to make money the attraction. They are soldiers at the sacrifice of their own leisure, and often of their comfort. A modern National Guardsman is averse to boasting or heroics—he is the most matter-of-fact citizen of all. But surely the Chaplain will be pardoned for saying, what the Guardsman would be most reluctant to claim, that in the old regiment patriotism is not a matter of words, it is made up of deeds.
Massachusetts looks in large degree to the command for the coast defence of Boston. America’s center of wealth and manufacturing, the Commonwealth holds the key to the whole country. Within a radius of two hundred miles from Boston is manufactured practically every kind of supply and equipment; while New York, the world’s center of wealth and finance, is only slightly more than two hundred miles away. To possess Massachusetts would afford hostile invaders the best possible base; the Coast Artillery is an essential factor in the defence of Massachusetts.
Coast artillery affords the most magnificent team-sport in the world. Three officers and sixty-seven men work together in firing the twelve-inch rifle, and each contributes[5] something essential to the success of the shot. Twelve inches is the bore of the rifled gun; forty-two or more feet the length; $45,000 is the cost, and the carriage represents an investment of $40,000 more. It is loaded with three hundred twenty-five pounds of powder, and a projectile weighing more than half a ton, costing upwards of $150, and sufficient in itself to destroy a hostile warship. The target, the moving target, at which the shot is fired, floats on the water at a distance of eight to sixteen miles; and without the use of powerful glasses is all but invisible. Range and direction (azimuth) are determined by a combination of most delicate scientific observing instruments. Now the great gun swings majestically into place. “Fire!” A concussion follows as if many railroad trains were coupling—mighty, stunning. Then ensue seconds of eager watching from the battery, but not many such; for the projectile travels twice as fast as sound itself. Up spouts a column of sea water beside the target. A hit. And this will be repeated once per minute until the enemy is put out of action.
Camping, shooting, gymnastics, hiking, fencing, horseback-riding, and even boating and aviation all enter into the training of the Coast Artilleryman. Opportunity is given to learn much of mechanical, electrical and engineering science.
On its lighter side military life includes balls, parades, dinners, theater-parties, smokers, and the annual January athletic games. Once in four years there is a trip to the inauguration at Washington; lesser excursions occupy some of the intervening time. Most valuable of all are the life-long friendships formed by men who stand side by side in the service of the country. These endure and keep warm after all else is forgotten.
The better soldier a man learns to be, the better citizen he makes himself. Such training in team-work is of priceless[6] value; this service has become a passport to business success, and today there is no better recommendation for employment. Civil Service commissioners recognize the enhanced usefulness of the trained soldier by according him preference in government appointments.
Six of the companies come from stations outside of Boston,—Brockton, Cambridge, Chelsea, Fall River, New Bedford and Taunton being represented. Even more truly than the Boston companies these organizations offer advantages of the greatest value; each is the pride of its own home city; each ranks amongst the leading social bodies in its community; and the armories, all fine structures, are popular club houses.
Altho it may be hard to “live up” to the responsibilities of a noble ancestry and one is ever open to the unkind suggestion that his best is like the potatoes, “under ground,” still it is not the fault of a man, nor of an organization, if the record of the past contains worthy, and even heroic, passages. Not only is the Coast Artillery the surviving heir to most of Boston’s finest militia traditions and honors, but by the consolidation of 1878 it also inherits the proud record of the Third Regiment, the militia force of Pilgrim-land and the Cape. Even a more modest organization than this would be excused for feeling thrills when it remembers “auld lang syne”; and the gentle reader will peruse these pages in vain if he fails to see why.
Some day the command will establish a military museum of its own, in which to display its trophies and relics. Its battle-flags have mostly passed out of its reach and are irrevocably in the possession of the Commonwealth. When one visits the Hall of Flags and gazes reverently upon the tattered silk banners of the 1st Infantry, five in number, the 3d Infantry, two of them, the 24th Infantry, two, the 42d Infantry[7] and the 43d and the 44th, two each, and in the Spanish War case the two colors of the 1st Heavy Artillery, seventeen flags in all, one may possibly remember that a Massachusetts Coast Artilleryman would be whispering to himself, “Those are our battle-flags.” And there are many other colors in the cases, under which members of the command fought during the Civil War—those of the 4th, 5th, 6th, 13th, 29th Infantry Regiments, and the 4th Heavy Artillery.
Indeed the sole battle-flag remaining from the Mexican War, that of the 1st Mass. Volunteer Infantry, may be claimed as a Coast Artillery trophy, since it was given by those who had borne it into the custody of the veterans who made up the National Guards, the 9th Co. of Coast Artillery. The National Guards eventually surrendered this color to the Commonwealth. No less a personage than Gen. Winfield Scott had been the original donor of the flag.
In some unexplained manner, three colors carried by the 1st Infantry during the Civil War escaped the State collector, and are preserved with religious care at the South Armory. They are the American flag presented by former Boston men who had “gone west” and there organized the National Guard of San Francisco, a blue infantry color presented in 1863 by the City of Boston, and a white State flag retained to replace a lost Commonwealth color presented by the people of Chelsea. As often as May 25 rolls around, veterans of the regiment bear these flags, together with the present National colors of the command, to the hall where the anniversary dinner is held; and under the sacred silken folds the white-haired warriors renew the memories of Fredericksburg and Chancellorsville, of Gettysburg and Spotsylvania, while they smack their lips over something more savory than the hard-tack and muddy coffee of bygone days.[8] Last winter these same veterans reviewed the Corps in the South Armory. As they came marching on the floor under their tattered battle-flags amid deafening cheers from hundreds of onlookers, strong men could hardly choke back their tears.
Post 23, G. A. R., of Boston, and Post 35 of Chelsea possess some 1st Regiment relics.
Headquarters will contribute to the regimental museum the sleeve of Drum Major James F. Clark’s coat, with its wonderful collection of service-stripes indicative of forty-one years’ service. Sergeant Clark died in office in 1910. There is also an old commission in a frame on the Headquarters’ wall, that of George S. Newell as Colonel of the 1st Reg., 1st Bri., 1st Div., dated May 11, 1839, signed by John P. Bigelow, Secretary of the Commonwealth; and the warrant of Daniel Horatio Belknap as Quartermaster Sergeant of the 1st Reg., 3d Bri., 1st Div., issued July 20, 1824, by Col. Louis Lerow. Between 1831 and 1834 the Roxbury Artillery had been temporarily attached to the 1st Reg., 1st Bri., but in Colonel Newell’s day we had no connection at all with that organization; the Fusiliers were a part of the 1st Reg., 3d Bri., in 1824, when Sergt. Belknap was in office.
Partly because it is the oldest company, and partly because it has always been made up of men who “do things,” the 1st Company possesses by far the finest collection of historical valuables of all the regiment. Indeed fully one-half of the regimental museum is already collected, and belongs to Capt. Joseph H. Hurney’s organization. In their room one sees Capt. J. J. Spooner’s original commission signed in 1784 by Gov. John Hancock, the first flag carried by the company—a flag with fourteen stars, the complete parchment roll of members from the very beginning, a drum[9] which helped to keep up the company’s courage at Blackburn’s Ford and Bull Run, specimen uniforms and arms showing the development of military skill and taste during each period of the company’s history, and a small cannon captured by Washington from the British at Yorktown in 1781, and at Williamsburg in 1862 taken from the Confederates by a company of ours.
Shooting, military and athletic trophies almost without number adorn the walls of Headquarters and of each company room; but these can hardly be included in a regimental museum. The 6th and 7th Companies hold Knox trophies as proof of their preeminent excellence in artillery work, and will doubtless resent any suggestion of contributing them to anyone else; certainly other companies have been trying hard enough to get this, and have not succeeded even for a single year. But the museum will have the 2d Company’s original drum, dated 1798, and with it the first flag. Their most valuable possession is a Stuart oil portrait of their “patron saint,” George Washington. The same company also display a set of ancient by-laws inherited from their predecessor, the Independent Light Infantry, and perhaps also a set of their ancient breast-plates. If more is demanded, members of the company will fill their lungs and emit the old “tiger” yell or growl; and this is certain to prove sufficient so far as the 2d Company is concerned. The 3d Company room does not contain much of historical interest. Their proudest possession is an entry on the records of the Governor’s Council dated May 11, 1787, wherein it appears that a petition presented by Thomas Adams and fifty-three others was granted, and that a military company, the Independent Boston Fusiliers, was formally established in the eyes of the law. On the following Fourth of July the Fusiliers received their charter from[10] Gov. James Bowdoin, while formed on the slope of Bunker Hill, and forthwith regaled themselves as guests at the hospitable table of Gov. (to be) John Hancock. Maj. James W. H. Myrick, Commander of the Fusilier Veteran Association, is custodian of the original 3d Company records.
We shall see that the Coast Artilleryman has reason for singing “The Old First still shall lead”; but the historian faces a difficulty when he essays to explain who the Coast Artillery are, anyway. Three different regiments are consolidated in the present body—which was the original? But see, what’s here! The regimental museum will solve even this vexed problem of genealogy. A resolve by the General Court of Massachusetts, duly engrossed and framed, together with an order of the Council approved by Gov. John L. Bates on April 6, 1903, not only certifies that the First Regiment of Massachusetts Volunteer Militia responded to the call of the President of the United States in April, 1861, for troops to suppress the rebellion, but also, and more importantly as concerning our present difficulty, that the First Massachusetts Heavy Artillery are the “successors” of the regiment of 1861. Blessings upon the head of the man whose influence secured this legislative action! The historian may tread fearlessly in full assurance that the Coast Artillery is the First Infantry of Civil War fame, and that other ancestry is, if not collateral, at least not in the principal line. A complete genealogy of the command will be found elsewhere in this book.
One explanation is in order before proceeding. On April 25, 1842, the companies were designated by letter; on Nov. 1, 1905, they ceased to be designated by letter, and were numbered in order of charter-seniority. Altho all company and regimental history between 1842 and 1905[11] was recorded in terms of company letters, since 1905 the letters have rapidly passed into oblivion; and today have become almost entirely forgotten. For the purpose of interpreting the past in terms intelligible to the present, it seems best to translate letters into numerals—to speak, in other words, of the 1st Company rather than Company or Battery D. And now, the prelude being finished and the audience all having visited the museum, let the performance go forward.
A group of men were assembled in the living room of a prosperous looking Roxbury farmhouse on March 22, 1784. Altho they had met several times previously during the winter, they showed by both word and bearing that they were actually engaged in transacting their most important business on the present occasion. General William Heath, owner of the house, presided. As everyone in Roxbury well knew, the General had lately returned from war, where he had enjoyed the privilege of close companionship and friendship with no less a person than the commander, Gen. George Washington, himself. Another of the company was a wealthy young merchant of Roxbury, an ex-Cadet, John Jones Spooner, who stood in the relationship of son-in-law to Gen. Heath. Amongst others were Jonathan Warner and several more Revolutionary veterans; also two prominent members of Roxbury society, Joseph Pierpont and John Swift. Well might these men look important for they were engaged in presiding over a birth—the birth of a National Guard company—today the oldest National Guard company with continuous history in America.
As soon as the company had been born, and was reported to be “doing well,” it was christened. “The Roxbury Train of Artillery” was inscribed with due form and ceremony upon the first page of its record book. Who was then sufficiently far-sighted to foresee that on June 30, 1916, the same company would take the Federal oath as the “1st Company, Coast Artillery Corps, National Guard of Massachusetts”?[13] A company in those days was commanded by a captain with the rank of Major; and this office was promptly conferred upon John Jones Spooner. Jonathan Warner became the “Captain-lieutenant,” and Joseph Pierpont and John Swift were elected the other two lieutenants, as at that time authorized. Warrants were issued to four sergeants; four musicians were appointed, twenty-four men were detailed as cannoneers, eight as pioneers, three as drivers—and when two brass four-pounder cannon had been issued to them, the Roxbury Artillery were ready for any kind of a fight or frolic. It was not to be until Aug. 30, 1849, that Gen. H. A. S. Dearborn would suggest the famous motto now borne by the Company, “In time of peace prepare for war.” No one can question however but that the sentiment of the motto has always controlled 1st Company activities.
Major Spooner subsequently resigned his command, was succeeded by Capt. Warner; and himself became a minister of the gospel.
Those were the days immediately following the Revolutionary war; and in America during such seasons the commanding military official is sure to be “general apathy.” Owing partly to the absence of other organized companies, and partly to the skill and enthusiasm of the Roxbury men, the Artillery were in frequent demand. On October 15, 1784, they turned out to fire a salute in honor of a distinguished visitor, Gen. Lafayette. The Boston Train of Artillery, afterwards the 8th Company, came into existence May 7, 1785; and these two organizations shared the honor of escorting the Governor and members of the General Court on July 4, 1785, and again the year following. The fact is, these were the only two active military companies in or around Boston at the time. On one of these occasions[14] Gen. Heath noted concerning his protégés that they “made a good appearance and performed their exercises well.” An army travels upon its stomach, and a good soldier attends carefully to the subsistence part of his work. The 1st Company displayed true soldierly instincts by including, from the very beginning, commissary exercises amongst their other activities,—in other words, at the conclusion of the parade “they dined together.” Music was furnished for these military displays by the only band then in Boston, one consisting of Hessians who remained behind from Burgoyne’s army, under the leadership of Frederick Granger.
Let the narrative pause a minute while we paint in a background for the picture. Do we understand who the militia are? Citizen-soldiers, citizens who serve as soldiers when necessary, without relinquishing their civil occupations, part-time fighting men—such have always been the chief reliance of free peoples when it becomes necessary to defend their territory or to enforce their sovereign will. In British dominions this military force received the name of “train-band” about 1600, and began to be called “militia” in 1660. Moreover their service was both compulsory and universal—at least it was so in theory. Each citizen was required by law to provide himself with a “good musket or firelock, a sufficient bayonet, and belt, two spare flints, and a knapsack.” Thus armed and equipped, he was expected to present himself four times a year for a day’s training.
It is customary to heap ridicule upon the militia. Cowper described “John Gilpin” as a “train-band captain,” and taught us to laugh at him. Yankee Doodle, with its “men and boys as thick as hasty puddin’,” is a parody on the American militia. In truth appearances were against them in the olden times. Their history began away back in the days when military costume consisted of an iron hat and a[15] steel vest. When, about 1700, armor passed out of use, the militiamen, to prove that they were true conservatives, refused to substitute any other uniform clothing. Consequently they did not look soldierly. But the Yankee Doodle militia under Johnson at Lake George administered a stinging defeat to the French regulars. We have been abundantly taught of late how American military history fairly bristles with evidence that the militia system is faulty. So be it. Now it is time to point out another lesson from the same history, namely, that when American militia have fought under favorable conditions, with some shelter, and with an auspicious beginning to the action, they have often manifested a valor that makes the world marvel, a valor unequalled except in the annals of legendary warfare.
This militia existed, in 1784, thruout Massachusetts (and Maine) as nine divisions of approximately five thousand men each. The first division was stationed in Boston. And, alas! all divisions were temporarily inactive.
The oldest volunteer militia company in England, as well as its “ancient” daughter in America, have as part of their title the word “Honorable.” Militia rendered such military service as the law demanded. Volunteer militia went beyond this, and in addition uniformed themselves at their own expense, drilled frequently, and held themselves in readiness for parades and ceremonies, and, in sterner vein, for disturbance of the peace and for war. As the basis of every volunteer army our country raised was found the organized, volunteer militia. No wonder that esteem and distinction have attached to this service. Since 1908 the force has borne the title, “National Guard,” a name going back to the citizen soldiery who defended Paris in 1789 and who were commanded by Lafayette, a name brought to this country in 1824 by Lafayette himself and then first adopted by[16] the N. Y. 7th Reg., and in 1862 taken by all the organized militia of that state, in 1903 extended thruout the United States, and in 1916 officially substituted for all other titles in Massachusetts.
Why was it necessary for the Roxbury men to organize their company? Could not the U. S. regular army afford America sufficient protection in 1784? Regular army! So far as Congress could control the matter, there was no regular army in 1784. A determined effort had been made the year previous to wipe the force entirely out of existence, to muster out every Continental remaining over from the Revolutionary war. Thru some oversight one single company, that formerly commanded by Alexander Hamilton and now “Battery F of the 3d Field Artillery,” had escaped. Perhaps because they were standing guard over valuable stores at West Point and elsewhere, perhaps because the mustering-out officer ran short of blank forms—for some unexplained reason one company survived. This single company constituted the entire U. S. army in 1784. This one company is the only military organization in America having continuous existence, which antedates the Massachusetts Coast Artillery. Moreover the situation was only slightly better later. In 1787 there were only 1,200 regulars, in 1798, 2,100, and at the opening of the Civil War, with a national area almost equal to the present, less than 10,000. Were not Gen. Heath and the Roxbury men justified in taking steps to strengthen the forces of government?
If we may now resume the narrative, we note that the Dorchester Artillery, the 4th Company, was organized in 1786. Material was preparing out of which the future regiment might be built.
1786 and 1787 were years of threatening and storm in Massachusetts. In consequence of the war, people found[17] themselves burdened with debts and taxes. They complained that the Governor’s salary was too high, the senate aristocratic, the lawyers extortionate, and that the courts were instruments of oppression, especially in the collection of debts. By way of remedy they demanded the removal of the General Court from Boston, the relief of debtors, and the issue of a large amount of paper money. Daniel Shays, an ex-captain of the Continental army, placed himself at the head of a movement to secure these ends by force, and his effort has come down thru history as “Shays’ rebellion.”
In December, 1786, he appeared at Springfield with one thousand insurgents, resolved to break up the session of the supreme court. After forcing the adjournment of the session, the insurgents directed an attack against the arsenal in Springfield. Meanwhile the State government had sent Gen. Benjamin Lincoln, at the head of four thousand militia, amongst whom were included our artillery companies, to suppress the disorder; and on Jan. 25, 1787,—six days after leaving Boston,—the troops arrived in season to beat off the insurgent attack. Shays and his followers were pursued as far as Petersham, where on Feb. 9 all armed resistance was crushed out and the insurgents captured or dispersed. Since there was such abundant ground for this discontent, it is pleasing to know that the “rebels” were all pardoned, and Shays himself finally awarded a pension for his Revolutionary services. Improved economic conditions due to the new Federal constitution soon removed all danger of such disorder in the future. Please note, however, that winter campaigning in western Massachusetts is by no means an attractive holiday experience, and that the members of the command who engaged in this, the first, active service, manifested the same plucky devotion to duty as has characterized them ever since.
When in 1788 the new United States constitution was ratified, Boston felt moved to celebrate the event. Gen. Benjamin Lincoln, who commanded the train-band division in the city, investigated and found that he had eight uniformed companies amongst his militia organizations. So the eight were directed to parade. The Dorchester Artillery were not present; but the Roxbury and Boston companies had prominent places in the procession. There were three other companies present, infantry companies, which would have interested anyone gifted with prophetic foresight. For just ninety years from that time, the three infantry companies were destined to unite with the two artillery in forming the 1st Regiment of today. Meanwhile, unconscious of the future, they are all parading in honor of the new Federal government; watch them. Grave, dignified men they are. And no wonder; for they are the social and political leaders of Boston-town. No one could hope for election to office in those days unless he had “done his bit” in the militia. They wore the Continental uniform, with cocked hats, blue coats having ample skirts, and white knickerbockers. In their movements they were majestic, slow, deliberate; seventy-five steps per minute were considered amply sufficient. It was not until 1891 that their hustling offspring completed the process of raising the military cadence to one hundred twenty per minute, with a pace thirty inches long. For weapons they carried smooth-bore flint-locks, which the dictionary tells us, were known as snaphaunces or “fusils,” whence we have the term, “fusiliers.” The musket was furnished by the State, and was the only part of the equipment so provided. Never mind if they were not very deadly,—they at least looked formidable. Our artillery companies drew their cannon from the “gun-house” on the common; contrast this rough shed with the South Armory[19] of today! After the martial exhibition was concluded, our forefathers betook themselves to the “Green Dragon,” or the “Bunch of Grapes,” or the “Exchange Coffee House” where coffee was by no means the limit, or some other popular tavern, for the military exercises which constituted the climax of the entire day.
A clear distinction existed between militia and volunteers in the foot branch of the service, the volunteers being designated fusiliers or grenadiers or light infantry or rifles or cadets, and the militia being known as infantry. But the distinction was obscured in the “train of artillery.” So much of technical qualification was required of the artilleryman and cavalryman that all companies of such troops had to meet the higher military standards of volunteers and were so classified. In such rosters as existed, it was customary to print the names of company officers of artillery and cavalry, while such lists included only field officers in foot commands.
First mention of a battalion of artillery appears in the roster of the 1st division for 1790, when the four companies in Boston, Dorchester, Middlesex and Roxbury are so designated. No field officer had yet been commissioned. This is the beginning of the Coast Artillery, the battalion and regimental organization having continued in unbroken existence from 1789 to the present time. While under every militia law ever adopted by Congress, not only the 1st Company but also the command as a larger unit might claim “ancient privileges” on the ground of continuous organization thruout these decades, it is just and right to state that the pride of the “Old First” has always been not to claim any privilege at all, except that of serving wherever and however it could be of the most use. At this date no battalion organization existed amongst the volunteer foot companies,[20] each being an “independent” divisionary corps of infantry.
October, 1789, our companies were again in line, this time to receive and escort the President of the United States, George Washington. In October, 1793, a sadder duty summoned them forth. John Hancock, patriot, signer of the declaration of independence, Governor of Massachusetts, and President of the Continental Congress, had finished his long and noble career and gone to his rest. Boston loved and honored its chief citizen; the funeral parade, in which our companies participated, was an expression of heart-felt grief. The companies were again called out on July 4th, 1795, to help lay the corner-stone of the new State-house, the famous “Bulfinch front.”
War clouds began to darken the political sky in 1794, war clouds generated by the titanic struggle between the French and their enemies thruout Europe. Controversies had been going on between us and both parties to the great European conflict; now this particular danger threatened from the French side. Altho most Americans had sympathized with the French in their revolutionary struggle, had worn tri-colored cockades and clamored for a French alliance, now French colors disappeared from view, men wore black, and “Hail Columbia,” with “independence” for its “boast,” became the popular song. As soon as America found itself involved in the threatened storm, Congress began to take measures for defence and turned its attention to the militia. It is only in war-time that Congress can be induced to notice the citizen-soldiers. A law was passed May 9, 1794, directing the states to organize active regiments of militia and to prepare for eventualities. No action seems to have resulted from this first legislation; and as the foreign danger intensified, a second act was passed in 1797,[21] aiming to render the former law effective. Following the classical preferences of the times, the U. S. army had been rechristened, in 1792, the “legion.” Each state must now organize a “legion” of its own. 80,000 was the figure set for the total strength of this force; and it is significant of Massachusetts’ relative standing that the Commonwealth was directed to furnish 11,885 of the total—more than any other state.
Massachusetts, on June 6, 1794, directed commanders of train-band divisions to draft men from their brigades who should hold themselves in instant readiness for service, as the “minute-men” of 1775 had been selected and organized. The great prestige of George Washington, for he had consented to waive his seniority and to serve as Lieut.-General under Pres. Adams, helped to render this revival of the minute-men popular, and the fashionable designation of “legion” did not detract from its popularity.
On August 22, 1797, a supplementary order was issued, directing that a special regiment of such “legionaries” should be formed from the militia of each division. The number of divisions having increased to ten, this called for ten regiments of active troops in Massachusetts and Maine.
While the order ostensibly affected the entire Commonwealth, in point of fact the only legionaries ever organized were in Boston. Brig.-Gen. John Winslow, a soldier of energy and ability, in civil life a hardware dealer, was commissioned to command the “legionary brigade” of Boston, and during the ten years of his incumbency the legion was so vital a factor in the city’s military life that it became a fixture. Winslow’s legionary brigade was organized in 1799, just as the war scare subsided. It consisted of legionary cavalry (one troop), a sub-legion of light infantry made up of two independent companies (the Fusiliers and the Boston[22] Light Infantry), and a sub-legion of artillery made up of the Boston and Columbian companies, now fully organized as a battalion under Maj. Daniel Wild. The Roxbury and Dorchester companies did not join the legion, and now completed a battalion organization under Maj. James Robinson and were designated the “Battalion of Artillery, 1st Brigade, 1st Division.” These two battalions, one within and the other without the legion, represent a splitting up of the 1789 battalion. On June 4, 1844, these two battalions, numbered 1st (the legionary) and 2d (the old 1st Brigade battalion) were to consolidate in the 5th Regiment of Artillery.
The legionary brigade lasted as long as Gen. Winslow continued in command. Its cavalry, light infantry and artillery sections continued to thrive; and in 1802, under the energetic leadership of Lt. Col. Robert Gardner, succeeded in 1804 by Thomas Badger, a regiment, consisting of three sub-legions of infantry, each commanded by a major, came into existence. In the artillery sub-legion, Maj. Wild was succeeded by Maj. John Bray in 1803, and by Maj. O. Johonnot in 1805. Meanwhile the 1st Brigade battalion of artillery was commanded by Maj. Robinson. In 1808 Gen. Winslow retired; and in 1809 the legionary brigade was redesignated “3d Brigade, 1st Division.” Its three sub-legions of infantry became three infantry regiments, and these, as we shall see, contained companies destined later to form part of the Coast Artillery. The sub-legion of artillery became known as the “Battalion of Artillery, 3d Brigade,” commanded by Maj. Johonnot, in 1812 by Maj. Nathan Parker, and in 1813 by Maj. William Harris. Maj. James Robinson was succeeded as commander of the 1st Brigade battalion by Maj. John Robinson in 1812, and the latter in 1814 by Maj. Isaac Gale, formerly Captain of the Roxbury[23] Artillery. The 3d Brigade rendered one distinguished service to the city of Boston—it brought out and maintained Asa Fillebrown as leader of the brigade band. The 3d Brigade continued to be the most prominent element in Boston’s militia until the reorganization of 1840.
No doubt the French war-scare and the formation of the legionary brigade stimulated militia development in Massachusetts. The Columbian Artillery, the 6th Company, was organized June 17, 1798; and the Washington Artillery, the 7th Company, on May 29, 1810. Happily the war clouds dissolved without doing serious damage to America. Meanwhile the two battalions of artillery turned out to greet and receive President John Adams on the occasion of his visit to Boston.
Between the years of 1810 and 1819 and intermittently until 1855, Massachusetts state rosters contain a curious entry, “The Soul of the Soldiery.” While one could scarcely guess the fact, this was a predecessor of the modern “training school” for officers, and was maintained by the non-commissioned officers of all companies connected with the Legionary or 3d Brigade. No wonder that the Massachusetts militia excelled the corresponding force in other states, with such a spirit stirring the breasts of the enlisted men.
By 1812 America did find itself involved in actual war. Statesmen had been laboring, and laboring successfully, for nearly a score of years to keep us at peace with France. Meanwhile circumstances conspired to stir up hostilities with France’s great enemy; and almost before men could realize the possibility of such a thing, we were engaged in the second war with England.
This is no place to discuss the cause of the struggle; Boston’s artillery companies shared the sentiment of their section and regretted the condition of affairs. The war was[24] unpopular in New England. But the members of the artillery companies, being soldiers, did “not reason why” and did put themselves into an attitude of preparedness.
Weeks ensued which men would be glad to forget. Regiments of regulars were enlisted in Boston and transported to the Canadian frontier as part of the successive invading forces. After the lapse of months word came back of American defeat, of the incompetence displayed by untrained American officers, of hundreds of British putting to flight thousands of Americans. Boston itself lay open to hostile attack, with fortifications mostly in ruins, and such as there were, ungarrisoned. Then came the naval victories won by our gallant frigates, and Massachusetts breathed more freely. The enthusiasm which was craving an opportunity for expression found vent in ovations to victorious sailors. During the first two years of hostilities no attack was made against the New England coast, and we now know that England deliberately refrained because of the friendly sentiments of the New England people.
The year 1814 brought a great change in the situation. England had downed Napoleon, and was at liberty to employ her mammoth resources in dealing with enemies elsewhere. Massachusetts, because it was part of America, and more particularly because its harbors served as a base of operations for the American navy, was to feel the consequences of war. Invasion commenced in Maine and threatened to roll southward down the coast; immunity was at an end; and an attack was actually made on Gloucester. Gov. Caleb Strong waited as long as he dared, expecting the Federal Government to take the steps necessary for defending our coast. When it finally became evident that Washington had its hands full elsewhere and could do nothing for Boston, Gov. Strong acted.
As the service was to be guard duty and the erecting of fortifications, and was likely to continue thru an indefinite number of months, larger units of the militia were not called out as such. No regiment went as a whole. It seemed better to draft companies, platoons, and even squads. A guard was maintained at Chelsea bridge to keep off raiding parties. After Sept. 8, 1814, all militia organizations were held in readiness; and between that date and November, when the British fleet finally sailed away, every member of the five artillery companies gave some weeks to active service. Fort Independence on Castle Island and Fort Warren on Governor’s Island, small works of brick and earth, constituted Boston’s principal defences; these were garrisoned, and put in repair. How tremendously modern ordnance out-ranges that of a century ago! The present Fort Warren, on Georges Island, erected in 1850, is today not nearly far enough from the city it defends, not far enough out at sea; neither is its armament as long-ranged as it should be. Yet contrasted with the earlier Fort Warren, it is very remote from Boston, and is armed with guns able to do execution at almost infinite distance. The Commonwealth added to the defences of the harbor; land was purchased on Jeffries Point, East Boston, and another fort erected to support Independence and Warren. The legislature, out of compliment to the Governor, named the new work Fort Strong. Here too one must be careful not to confuse the old fort with that of the same name today on Long Island.
Historians agree in pronouncing the militia a failure in the second war with England. It must be confessed that there is much ground for such a verdict; in fact, the regular army was also, for the most part, a sad failure in the same war. But in all fairness an exception should be made[26] of the Massachusetts militia which manned the coast defences of Boston and kept the British fleet outside the harbors of the state. The Roxbury Artillerymen and their comrades in sister companies were prompt in responding, efficient in “digging” and other military labor, and entirely vigilant in guard duty. Their service in 1814 goes far to render the name of militia honorable.
One moment of relaxation came during the war when the battalions paraded in Boston as escort to President James Madison.
The year 1815 marked a turning point in American military history, and the artillery companies of Boston felt its influence. Danger from foreign foes was at an end; the Indians were then so far to the westward as no longer to be a serious menace. America felt free to enter upon a career of peaceful conquest—and to get rich. It is fair to note that England also began a similar stage at the same time; perhaps there was some reflex influence exerted by the mother country. The first symptom of the change was the decay of the train-band. Whereas militia service had hitherto been regarded seriously, as the most important duty of citizenship, now men laughed at it. We begin to find reference to the “corn-stalk” militia.
 The Train-Band, 1832. Why it was Abolished
The Train-Band, 1832. Why it was Abolished
Decay was gnawing at the vitals of the train-band system. Ridiculous cartoons may be seen in the museum of the A. & H. Art. Co. (Matthews’ “Militia Folk” and others) showing what a farce the institution had become. Men attended muster in outrageously improper clothing, armed with sticks, pitchforks, or nothing at all, and obviously treated this aspect of their patriotic duty as a gigantic bit of buffoonery. Quarterly training or muster-day became an occasion more noted for the rum then consumed than for the drilling done. Early temperance societies recognized this[27] state of affairs by including in their abstinence pledges an exception in favor of muster-day; it was not “intemperate” to be drunk then. In our forefathers’ opinion this gradual abandonment of compulsory universal military service was regarded as a mark of social progress. Will such be the ultimate verdict of history?
Increased importance attached to the Roxbury Artillery and other volunteer companies as the train-band became increasingly inactive. Let us inspect them, bearing in mind that they are now the chief military reliance of the Commonwealth. Discipline, judged by modern standards, may not have been strict. Men came and went pretty much at will. But they had some discipline, while their fellow-citizens did not know what the word meant. No “basic course for officers” as yet existed, and it is a fact that the higher officers were apt to be chosen more for political than military reasons. As the rank increased, the military attainments were apt to diminish; but amongst the company officers were found many brave and skilful soldiers. Uniform fashions had been modified by the recent war—now companies wore the shako on the head, at first of leather and later of bearskin, the high buttoned swallow-tail coat, white webbing cross-belts with brass breast-plates, and long trousers. Each company had a distinctive uniform of its own, as different as possible from all others; and this diversity persisted even down until after the Civil War. It was a column of companies, and judging from appearances, of extremely “separate” companies, that paraded to escort and welcome Lafayette in April and again on August 30, 1824; and to lay the corner-stone of Bunker Hill monument in 1825; and to inter President John Adams in July, 1826; and for the funeral of Gov. William Eustis. An enthusiastic reception was accorded by these companies to President Andrew[28] Jackson, June 24, 1833. These soldiers may not have been as efficient as modern troops must be; but they made a splendid appearance on parade; and beyond question were a powerful military asset when judged by the standard of their own times.
An attempt was made to increase efficiency by issuing books of drill regulations available for all, instead of depending upon oral instruction. In the earliest days drill was regulated by Prussian and French systems of tactics. The first book of tactics ever prepared in English for general popular issue was written and published in 1813 by Gen. Isaac Maltby of the Massachusetts militia, for the use of Massachusetts troops. The necessity for conciseness and speed was not then recognized. For a battalion to pass from line to close column, the drill regulations of 1911 indicate commands as follows: “Close on first company, March, Second company, Squads right, column half right, March.” Under Maltby’s system this was heard: “Battalions will form close column of platoons on the right, in rear of the first platoon, Shoulder arms, Battalion, Form close column of platoons in rear of the right, Right face, March.” Scott’s famous tactics were adopted in 1834.
Maj. Joseph E. Smith succeeded to the command of the 3d Brigade battalion of artillery in 1817, Maj. Thomas J. Lobnell in 1823, Maj. Samuel Lynes in 1826, Maj. Aaron Andrews in 1830, and Maj. Horace Bacon of Cambridge in 1832. By June 29, 1834, the battalion had grown to four companies, and was for a year elevated to the dignity of a regiment. John L. White, the popular proprietor of the Union House (29 Union St.), was made Colonel, and thus became the first man ever to hold that rank in the Coast Artillery. Col. White’s military career had been meteoric; in 1831 he was elected Cornet (2d Lt.) of Light Dragoons in[29] the 3d Brigade; 1832 saw him Major of the 1st Infantry in the same brigade; in 1834 he became Colonel of that regiment; and ten weeks later, on the date given above, he transferred and was commissioned Colonel of the new artillery regiment. However the time was not yet ripe for regimental dignity. When a few months later Col. White removed from Boston and resigned his command, the organization was allowed to slip back and again become a battalion. Maj. John Hoppen commanded in 1836. On April 24, 1840, the battalion was awarded the number “1st.” In 1841 William B. Perkins was elected Major, the last man to command it as a separate organization.
Meanwhile the 1st Brigade battalion was commanded by the following Majors: 1818 Joseph Hastings of Roxbury, 1822 Robert Stetson of Dorchester (an ex-Captain of the 1st Company), 1825 John Parks of Dorchester, and 1829 Jonathan White, Jr., of Weymouth. In 1831 the strength of the battalion was reduced from three to two companies, and these were temporarily attached to an infantry regiment (the 1st of the 1st Brigade). On June 26, 1834, the battalion organization was restored, a new company having been formed, with John Webber, an ex-Captain of the 1st Company as Major. Maj. John W. Loud of Weymouth was elected to command in 1836, and Maj. Webber again in 1839. On April 24, 1840, the battalion was numbered “2d.” In 1841 Samuel F. Train of Roxbury was elected Major, the last man to command the battalion as a separate organization. Capt. John Webber was succeeded as commander of the 1st Company by Andrew Chase, Jr., a man destined to become first Colonel of the new regiment. That year the battalions paraded in celebration of the completion of Boston’s new railroad.
All the companies were called out June 11, 1837, to maintain[30] public order at the time of the Broad Street riot. The outbreak arose from a clash between a funeral procession and a fire-engine company. Which ought to have the right of way? Unfortunately racial jealousy was present to embitter the rivalry, so that blows were exchanged and a general fire-alarm “rung in” and disorder became wide-spread. First honors on this occasion belong to the newly organized National Lancers, whose horses terrified the rioters; infantry and artillery companies acted as reserve, and subsequently policed the district.
This period of Corps history came to its conclusion when on March 24, 1840, the legislature voted a general reorganization of the militia, and in particular disbanded the ancient train-band. In theory, the members of the artillery battalions had been excused from the compulsory drill done by every able-bodied man in their districts on the ground that they were rendering more than the prescribed military service in their volunteer organizations. In fact, the district companies and regiments of the train-band had long since ceased to do any true drilling and were little more than a mere name. Courage is required to abate a long-standing abuse. New York continued to endure the train-band system until 1862, well into the Civil War. Massachusetts faced the condition with greater determination, and abolished the system in 1840. On March 24 the law was enacted, and on April 17 the necessary orders issued. Thereafter the volunteer companies were the only military force existing in the Commonwealth.
Gen. William Henry Harrison had been elected President in 1840 at the conclusion of one of the most exciting political contests ever known in America. A month after assuming office, in April, 1841, he suddenly died. Public feeling which had been so stirred over the election, now reacted; and men everywhere vied with one another in expressing heart-felt sorrow. Amidst circumstances of deep gloom, intensified by bad weather, the battalions, in the very midst of the confusion attendant upon their reorganization, made a funeral parade notable for its sadness. It was not until July, 1862, that the regiment again came in touch with Harrison; then they were stationed at his birthplace, Harrison’s Landing on the James River, Virginia. And greatly did they enjoy their days of rest after the torture of the Chickahominy swamp, and the opportunity to use plenty of clean, fresh water for bathing; possibly some of the older soldiers remembered the obsequies of April 22, 1841.
June, 1843, was a red-letter period in Boston history. Bunker Hill monument was at last completed after eighteen years building, and a vast concourse of people assembled for its dedication. The New York 7th Regiment, then known as the “National Guard Battalion,” arrived on the 16th, and was received and entertained by the Fusiliers. Indeed troops were present from four outside states—Maine, New Hampshire, Rhode Island and New York. That same day the artillery battalions met President John Tyler at Roxbury Crossing, and escorted him to the Tremont[32] House, the parade taking place amidst a drenching rain-storm. The morning of the 17th was clear, cool, and delightful. At an early hour, the military part of the procession, which consisted of four grand divisions, was formed on Boston Common. As the procession moved toward Bunker Hill, the enthusiasm which was produced by the admirable appearance of the troops was only equalled by that which greeted the distinguished Webster, the gifted orator of the day; while President Tyler, in melancholy contrast, was received with ominous silence and coolness. Arriving at Bunker Hill, the orator of the day and the guests and officials passed into the already crowded square. While Webster was speaking, the soldiers were necessarily far beyond the sound of his voice, and were entertained by “a bountiful collation,” which the hospitable authorities of Boston had prepared. After the ceremonies, oratorical and gustatory, the procession returned to Boston, and the troops were reviewed by the President at the State House. At a dinner the same evening in Faneuil Hall, President Tyler gave the following toast:—“The Union,—a union of purpose, a union of feeling, the Union established by our fathers.” A few years later, he was an active enemy of that Union, which he had complimented in the most solemn manner within the sacred walls of the Cradle of Liberty.
Boston’s division of the force, thereafter to be known as the Massachusetts Volunteer Militia, paraded in two brigades, with a total strength of 2,500 men. Incidentally we might note that there were two other such divisions in the state. Under the circumstances the 1st and 2d Battalions of Artillery added to their already creditable reputation and presented a fine appearance. There were five companies in the two battalions, each consisting of a captain, two lieutenants, four sergeants, four corporals, six gunners, six[33] bombardiers, one drummer, one fifer, and sixty-four privates or “matrosses.” Part of each company was armed, equipped and drilled as infantry; but each company proudly exhibited two bronze six-pounder cannon with limbers, and a single caisson. The ordnance had increased in caliber since 1784, the change being made in 1840. The state prescribed by law what manner of uniform the artillery companies should wear. Inasmuch however as the members had to purchase their own clothing without state assistance, and since they were mostly interested in the glory of their own companies, they were pardonable for regarding the regulation state uniform as merely a point of departure from which fancy might soar in devising distinctive costumes for the company units. Caps, short jackets, and frock coats, soon to become popularized as a result of the Mexican War, were beginning to be in vogue.
The year 1844 marked a still more important step in the development of the artillery battalions. Train-band companies of each district had always been organized into regiments, and the regiment was conceded to be the fundamental unit in importance. It was the tactical unit, that is, the troops maneuvered as regiments when in the presence of an enemy. It was also the administrative unit, in the sense that all records and reports centered at regimental headquarters. In drill regulations, the regiment was called a battalion; but no battalion could claim to be a regiment unless it had approximately ten companies, and was commanded by a colonel; one thousand was the membership standard. In other words the regiment was the only complete battalion. When the train-band ceased to be, the battalions of artillery began to aspire after regimental dignity in the Volunteer Militia. The 1st Battalion had actually been a regiment for a few months, ten years previously. Nor was it forgotten[34] that the two battalions were originally one, that the regimental consolidation to be was really a reunion of those who, forty-six years before, had been a single body. On June 4, 1844, their wish was gratified; and the 5th Regiment of Artillery came into being. With the promotion on June 24 of Andrew Chase, Jr., to the colonelcy the new organization was completed.
Economy reigned in the Adjutant General’s office of that day, and the state did not feel that it could afford much expenditure for printing. Our earliest rosters come from 1858, and we are unable to name many of the distinguished men who made up the 5th Regiment at its inception. It contained five companies: 1st, the Roxbury Artillery; 4th, the Dorchester Artillery; 6th, the Columbian Artillery; 7th, the Washington Artillery; and 8th, the Boston Artillery. Since all excepting the Dorchester company were strong organizations with established reputations, the regiment, from the very beginning, became the most distinguished military body in the city and state. In recognition of this fact Col. Chase was promoted to the brigadier-generalship Aug. 28, 1847.
Military affairs were stimulated by the Mexican war in 1846. While no militia organization went from Massachusetts, individuals from all regiments enlisted in the 1st Massachusetts Volunteers, the single regiment sent out by the state; and tales of American valor in the southwest served to arouse all to do better work. Mexican veterans afterward organized a company in our command; and became the recognized custodians of the 1st Volunteers’ Mexican battle-flag.
 Artillery in 1917
Artillery in 1917
 Copyright by Continental Ins. Co.
Copyright by Continental Ins. Co.Regimental responsibility was too much for the Dorchester Artillery, and it was disbanded in 1845. Only four companies remained in the 5th Regiment. In fact there[35] was too much disbanding for the good of the militia. The state authorities seemed to think that it was cheaper to disband a company which had fallen into “hard luck” than it was to cure the difficulty by paying a little money for the restoration and support of the sufferer. This was a false economy. Of the one hundred forty-two companies which existed in 1840 in the new Volunteer Militia, seventy-eight were disbanded within the first seven years, and one hundred two passed out of existence within twenty-five years. With so many surgical operations it is marvelous that any militia survived at all.
Altho few in number, the four companies of the 5th Regiment who paraded as an escort to President Polk June 29, 1847, and who welcomed Daniel Webster upon his return to Boston, gave evidence of increased efficiency. The legislature was making more liberal appropriations—was indeed spending each year (1844-1852) all of $6 per man on the militia; even this moderate expenditure was far better than nothing. The state authorities were very well satisfied with themselves and with their handiwork, reporting to inquirers that the Massachusetts system “met every need.” A fairly liberal allowance of ammunition was made to each artillery company—forty round shot, forty canister, and one hundred pounds of powder every year.
William B. Perkins became Colonel Sept. 10, 1847. Altho he did not enjoy good physical health, and died in office November 16, 1849, his administration was signalized by several important events. On March 10, 1848, occurred the funeral of Ex-President John Quincy Adams. The regiment, or part of it, paraded on Oct. 25 of the same year in celebration of the completion of the Cochituate water system. On Aug. 8 and 9, 1849, the regiment participated in its first state camp, at Neponset, continuing two and one-half[36] days. A curious old print of this encampment has come down to us showing how the 1st Brigade of the 1st Division looked at the time. The 5th Artillery was present, four companies strong, clad conspicuously in bearskin and other towering shakos; the balance of the brigade consisted of the National Lancers in their uhlan costumes, as at present, which had been adopted four years before, and the 1st Light Infantry, wearing distinctive company uniforms. The Lancers were at that time attached to the 1st Light Infantry, and were the only cavalry command in the state. Was any prophet present in Neponset on those August days gifted with ability to read the future? Did anyone even guess that twenty-nine years later the 5th Artillery and the remnant of the 1st Light Infantry were to consolidate in a new 1st Regiment? While a two and one-half day camp must necessarily be chiefly occupied with pitching tents, escorting visitors, engaging in those social festivities which are “absolutely essential” on all military occasions, and then taking down the tents, there is no doubt that the men acquired much real military knowledge in between-times, and that the new custom registered a long step forward.
Col. Asa Law commanded the regiment from Jan. 4 to July 10, 1850.
July 26, 1850, witnessed another change in the colonelcy, Robert Cowdin assuming command of the regiment. Col. Cowdin, in his peaceful moments, was a Boston lumber-dealer; but members of the regiment will always remember him as a soldier, except when they recall some more intimate contact with the man whom they loved; then they speak of him as “father.” It makes a great deal of difference that he commanded them during the year of fearful hardship and sanguinary strife on the Virginia Peninsula; but even[37] before that he had endeared himself to his men, while he was merely a militia commander. He had been Captain of Co. K, in the 1st Inf. during 1848 and 1849; and came into the artillery as Major. It is hardly over-stating it, to say that Col. Cowdin is the man who made the regiment great.
What he assumed command over was actually four splendid artillery companies, loosely yoked together in the 5th Regiment. The conception was nine-tenths “company” and only one-tenth “regiment.” Inter-company rivalry had prevented the development of real regimental spirit. The new colonel was determined to command a true regiment; and since he was a man of masterly force and boundless enthusiasm, he speedily had his way. Distinctive company costumes yielded place to a regimental uniform, and thereafter the company was a subordinate unit. The obsequies of Ex-President Taylor were the last occasion on which inter-company diversity appeared; and that was in the very month of Col. Cowdin’s accession. In all his reforms he was ably seconded by Capt. Moses H. Webber of Roxbury, commanding the 1st Company. In 1851 percussion muskets displaced the flint-locks. The same year a new 4th Company, the Cowdin Artillery, was organized, followed in 1852 by the 9th Company, the Webster Artillery, and in 1853 by the 3d Company or Bay State Artillery and the 5th Company or Shields Artillery. The regiment thus had eight companies. That year Isaac S. Burrell became Captain of the 1st Company.
Col. Cowdin’s first camp was held at Medford, and drew warm compliments from the Adjutant General. Neponset was occupied as a camp-ground for the second time in 1851; Boston Common in 1852; and the regiment participated in divisional camp at North Abington in 1853. In 1854 the division was at Quincy. How conditions have changed with[38] the increase of Massachusetts population! Who would think of these places as suitable camp-sites today, least of all, Boston Common?
Col. Cowdin’s regiment paraded as escort to President Fillmore Sept. 17, 1851; they helped welcome the Hungarian patriot, Louis Kossuth, April 27, 1852; and they participated in the funeral parade for Daniel Webster in Marshfield, Nov. 30, 1852. It came to be a custom at this time for Boston military critics and newspaper reporters to accord chief praise, after a parade, to the 5th Regiment.
Anthony Burns’ name is associated with the next important event in the regiment’s history, the most unpleasant event with which it ever had anything to do. No more painful duty can confront the militiaman than the task of maintaining public order, for no American likes to have part in coercing his fellow citizens. And on June 2, 1854, the regiment was called upon to enforce the most unpopular statute ever enacted by Congress, the “Fugitive Slave” law. Burns had escaped from his owner in Virginia, and found employment with a Boston clothing-dealer. Massachusetts was called upon to render him up under the terms of the new statute, and the U. S. Marshal arrested him on May 25. Public sympathy was strongly with the colored man, funeral draperies appeared upon the fronts of private residences, many threatened mob violence, and a great popular meeting was held in Faneuil Hall, May 27, addressed by Wendell Phillips and other prominent anti-slavery men, to protest against this humiliation to which Massachusetts was about to submit. The speakers even counseled a rescue by force. Under the U. S. law, a man “held to service” in another state, could be extradited and transported to that state for trial. The trouble was, that in the case of a fugitive slave, extradition involved the entire question—if Burns should be carried[39] back to Virginia, his chance of liberty would be gone; and Boston believed in liberty. An attempt was made to take him from jail, but this proved unsuccessful.
Col. Cowdin’s 5th Regiment, Col. Holbrook’s 1st Regiment, the 3d Battalion, the Cadets and the Lancers were ordered out to assist the police in enforcing the law. Guards were posted along the streets leading from the court-house to the “T Wharf,” where a steamer lay in readiness; and the Lancers, with a strong detachment of police, and U. S. artillery, surrounded the prisoner. It was on June 2 that the U. S. Commissioner rendered his decision; and the grim procession started at once. Red pepper and acid were thrown at the troops, clubs and stones were used, a Lancer’s horse was stabbed; but the display of force proved too strong for the rioters.
Both Col. Cowdin and Col. Holbrook later proved the genuineness of their devotion to freedom’s cause by commanding regiments in the Civil War. What they and their commands did on June 2, 1854, was entirely distasteful to them; but the call came to them as soldiers. Like true soldiers they performed their duty; and Burns went back to the south. His fidelity to duty was eight years later to be instrumental in preventing the confirmation of Col. Cowdin’s appointment as Brigadier General.
Happily, with the modern increase in police efficiency occasions for such service grow less and less frequent. Our professional police officers are now capable of handling all but the most severe crises without military assistance.
Another state-wide reorganization of the militia was engineered by the legislature on Feb. 26, 1855; and in some ways this was the most unfortunate of them all. It was primarily caused by racial and sectarian jealousy, a spirit which has no rightful place whatever in American life. The[40] principles of the “Know Nothing” party were regnant that year. No less a man than Thomas Cass was forced to resign his military commission—today his statue stands in honor in the Public Gardens. It almost seemed that the dominant faction were determined to prove themselves in the military and other diverse fields, as well as in the field of partizan politics, to be “know nothings.” The 5th Regiment, Boston’s best, was ordered disbanded; but the State House authorities did not really mean this. They only reorganized the command, with the intention that the resultant “2d Regiment of Infantry” should continue its service record. The 6th Company, the old Columbian Artillery commanded by Cass, together with the Webster Artillery and Shields Artillery of the 5th, were actually disbanded. Worst of all, Col. Cowdin found his commission vacated, apparently for political reasons. Capt. Cass’s company continued its existence as the “Columbian Association,” and in 1861 developed into the 9th Infantry.
Moses H. Webber was commissioned Colonel of the new 2d Infantry on April 18, 1855, and continued in office until Dec. 19 of that year. It consequently fell to his lot to adapt the regiment to its new conditions. Since the regiment had been drilling more and more as infantry and less and less as artillery, the change from one branch of the service to the other was less abrupt than it appeared to be. And be it noted that the regiment never lost interest in its native artillery—until in 1897 it re-entered the artillery branch. Col. Webber had four companies from the 5th, three of them old and strong ones. Two companies were transferred from the 1st Regiment, the 6th and 9th, of which both were already distinguished under their names, the “Union Guards” and the “National Guards.” The artillery companies signalized their transition to infantry by changing their names, the[41] Roxbury Artillery becoming the Roxbury City Guard, the Washington Artillery the Washington Light Guard, and the Boston Artillery the Boston Phalanx. The regiment, so reorganized, was paraded by Col. Webber as escort to President Franklin Pierce, when the latter visited Boston.
As the Civil War approached, Massachusetts grew more liberal in providing for her soldiers. In 1852 the expenditure per man was increased to $6.50 a year, in 1857 to $9.00, and in 1858 the expenditure was fixed at $7.50 and remained there until 1869.
The New York 7th Regiment visited Boston and participated in the Bunker Hill celebration of June 17, 1857. Their ease and precision of movement, their evident regimental spirit, their large numbers, and their serviceable yet dressy gray uniform, worn uninterruptedly since 1824,—all made a deep impression upon Boston military men. As the 7th had stopped to suppress an incipient riot on its way to the boat in New York the night before, its practical efficiency added force to the impression. The Lancers and the 2d, who acted as special escort to the visiting troops, came most strongly under this spell. An impulse was given to the movement for improving the 2d. In 1859 the regiment adopted a gray uniform closely patterned after the dress of the 7th, and continued the new bill of dress until July, 1861. Again after the war the same gray uniform was in use between 1869 and 1880.
Col. William W. Bullock commanded the regiment from Jan. 11, 1856, until April 14, 1858, when he was promoted to be Brigadier General. Camp was held at Quincy in 1856; at Chelsea in 1857; and the latter occasion was notable because Robert Cowdin then rejoined his old command, accepting the rank of Lieutenant Colonel.
In 1858 (May 11) Col. Cowdin was again in command;[42] and continued in office until the second year of the war, when on Sept. 26, 1862, he was advanced to the rank of Brigadier General. In connection with the regimental camp at North Bridgewater, 1858, the regiment received its long-desired rifled muskets.
So many companies had been transferred from the old 1st Regiment, that it finally seemed best to disband that organization altogether. By contrast with the 5th-2d, its regimental spirit had grown weaker and weaker with each passing year until Boston’s oldest regiment was nothing but a loosely connected group of separate companies. So on March 1, 1859, four of its companies, the Washington Guards, the Independent Boston Fusiliers, the Pulaski Guards and the Mechanic Rifles, were transferred to Col. Cowdin’s regiment, where they took place as the 2d, 3d, 4th and 5th Companies respectively. As separate companies these already possessed proud records; and in their new regimental connection the 3d and 4th immediately found a vigorous new life. The Mechanic Rifles soon disbanded, and most of the members joined the Ancient and Honorable Artillery Company. Later on, we shall follow the adventures of the three remaining companies of the old 1st.
Meanwhile Massachusetts was getting ready for the approaching war and putting her military forces in condition for active service. Sept. 7 to 9, 1859, Col. Cowdin led his reinforced command to camp at Concord, winning highest praise for the numbers and skill of his men. This was a notable occasion in Massachusetts military history, and as it later proved, in U. S. history. Had not the Bay State been more ready for war than her sisters, there would have been no “minute-men of ’61” available to rush southward, and save the National capital. The Concord encampment for the entire Volunteer Militia, three divisions with a total[43] membership of 7,500 men, was the pet project of Gov. Nathaniel Banks. While other executives of the state had regarded their office of commander-in-chief as a somewhat perfunctory affair, Gov. Banks took it exceedingly seriously; and even went so far as to uniform himself in clothing appropriate to his military office. Surely he “came to the kingdom for such a time as this.” While the pacifist governors of many northern states were ridiculing the very idea of war, Gov. Banks put his state in an attitude of preparedness—and was largely instrumental in saving the Union.
As the encampment continued only three days, it was mainly occupied with making and breaking camp, and escorting distinguished official visitors. But some little time was squeezed out for studying the new Hardee’s tactics, which were just supplanting Scott’s. Great enthusiasm was aroused by the presence of Gen. John E. Wool, the “hero of Buena Vista,” who reviewed the troops. But the great day of all came when Gov. Banks and the members of the legislature reviewed the campers. A famous lithograph of this scene exists; and does more than anything else to make the regiment of those days seem real to us. Numbers were small, as we reckon numbers today; but the finest spirit of determined patriotism was manifest.
A slight change in organization took place under Hardee’s tactics; instead of four lieutenants to a company, there were only two. Consequently few new men were elected to fill vacancies until the regiment had adjusted itself to the new régime. The officers of the regiment at the great Concord encampment, besides Col. Cowdin, were: Lieutenant Colonel, Isaac S. Burrell (postmaster of Roxbury, and later City Marshal); Major, Isaac F. Shephard. The captains commanding companies were: 1st, Thomas L. D. Perkins (proprietor of a smoke-house); 3d, Henry A. Snow (treasurer[44] of a bleachery); 6th, Edward Pearl; 7th, Walter S. Sampson (a mason and builder); 8th, Clark B. Baldwin (a merchant); 9th, Arthur Dexter; and 10th, Joshua Jenkins. With the Civil War less than two years off, it is well to look ahead and see how many of these militiamen rendered service in the hour of their country’s need. Of the Colonel we have already spoken. The Lieutenant Colonel commanded the 42d Regiment in 1862, and again in 1864, as we shall see. The Major presently removed to Missouri for business reasons, where he served with Nathaniel Lyon, and ultimately commanded the 51st U. S. Colored Infantry, and was promoted to be Brigadier General. Four of the seven captains went to war. Capts. Snow and Pearl served three months each at the beginning of the regiment’s three years of service, and then received their discharges. Capt. Sampson took his company into the 6th Regiment, and led them thru Baltimore on April 19, 1862, under deadly fire from the rioters. Later he served as Captain in the 22d Infantry during the Peninsular campaign, commanding that regiment at Gaines Mill. Capt. Baldwin remained in Col. Cowdin’s regiment when his company transferred themselves to the new 4th Battalion of Rifles and ultimately to the 13th Regiment; and became commander of a new 4th Company, and from 1862 to 1864 was Lieutenant Colonel of the regiment. Baldwin was a most profane man, and during the ensuing campaign stragglers could identify their regiment from a distance by the sound of his swearing. When Baldwin was made prisoner at the Wilderness, his captors marvelled at his vocabulary; and came up to his tent in successive reliefs to listen. Once a youthful fifer who had been caught by the then Lieutenant Colonel straggling, was punished by having a log loaded on his shoulder as he marched. This lad has put on record, that regulations provided for “a field[45] officer at the head of a regiment and a mule at the rear”; and that Col. Baldwin was deemed well-qualified for either end of the column. But the testimony is confessedly biassed.
Boston Common was the site of the 1860 camp, the last camp before the war. Military interest was then at fever heat, and the very air seemed electric with the coming struggle. In the midst of the warlike preparation occurred a peaceful ceremony which gained in interest from its very contrast with its surroundings; the youthful Prince of Wales, afterward Edward VII of Great Britain, visited Boston and was accorded military honors. A member of the regiment has recorded of him that he was “a really handsome youth with a pleasant blue eye, plump cheeks, and skin of great fairness.”
On January 24, 1861, the 2d Regiment was redesignated, receiving the number, “1st,” which had been taken away from the old 1st in 1859. Since six companies of the old 1st (as well as Col. Cowdin himself) had previously been added to what now became the “Civil War” 1st, there was an obvious fitness in allowing the number to be transferred also. Moreover the future held in store that all remaining of the old 1st personnel should, in 1878, be consolidated with their quondam comrades in a new 1st Regiment.
April, 1861, ended the suspense. Sumpter was fired upon April 12. Lincoln’s first call for troops was issued April 15, supplemented by a personal appeal from Senator Henry Wilson—“Send on 1,500 men at once.” The militia mobilized with marvelous rapidity on April 16, and started south under command of Gen. Benjamin F. Butler the following day, for three months’ service.
Those were days of tense feeling. A shipmaster who displayed a southern flag was in danger of losing both his life and his vessel; and ended by issuing profuse apologies. Business firms made lavish gifts toward the equipment of the regiments; indeed everyone seemed ready to give whatever he had. All one needed to do was to appear in uniform in order to be accounted a hero—much to the discomfort of many genuinely modest men.
And thruout these opening days the 1st Regiment was subjected to the very hardest test, in that nothing whatever happened to them. They could not take comfort in the knowledge that the 3d Regiment, one of the very earliest to go, would by and by become consolidated with them, and so share the honors which they were earning. All that the members of the 1st could do was to hope, and growl, and wonder why the Governor should select them for home-guard purposes while he allowed others to go to war.
Then something actually did happen, which only served to aggravate. Captain Sampson discovered a vacancy in the 6th Regiment, and with Col. Cowdin’s approval promptly[47] secured the transfer of his 7th Company, the Washington Light Guard, one of the three strong artillery companies which had come down from the very beginning of regimental history; so that the 6th had a Co. K of which to be proud, and the 1st Regiment had nothing. Co. K of the 6th, as was to be expected, covered itself with glory during the street-fight in Baltimore on April 19. Capt. David K. Wardwell, whose company had suffered disbandment a few months before, profited by his consequent independence and organized a new company, with Col. Cowdin presiding at the election of officers; and then took the new organization off with the 5th Regiment as Co. F. “Wardwell’s Tigers” shared in the laurels won by their regiment at Annapolis and Washington, and three months later at Bull Run found themselves fighting in the same army with the old 1st Regiment. Meanwhile their success in getting into active service did not make it any easier for the 1st Regiment to endure the masterly inactivity of those April days.
Finally on April 27, the 1st Regiment was ordered to prepare itself—as if it had not been prepared “right up to the handle” for two weeks past. But, alas, instructions came from the War Department that no more three-months men were desired, and after fifteen days’ service by the regiment, the order was, on May 7, revoked. Forty-two years later the legislature passed a resolve according official recognition to the 1st Regiment as having volunteered with the other “minute men;” but this was no comfort whatever to the eager young soldiers of 1861, who were told to lay down their weapons and go home. Col. Cowdin and his men were in high favor at the Boston City Hall; but owing to their services at the Burns riot, and for other political reasons, they were frowned on by Gov. Andrew and the Senators.
On second thought Col. Cowdin decided that he and his men were going to get into active service in spite of all difficulties. It had just become known that the Government desired three-year regiments, and this opened a door of possibility. The 1st would go to war for three years. To be sure this was a plunge in the dark. Suppose the war should not last three years—would the troops be kept in service anyway? Moreover, there had never been any three-year volunteers in the United States, during any previous war; and it requires courage to set a precedent. But Col. Cowdin and his men made the necessary readjustments demanded by the prospect of prolonged absence from home, and volunteered as a three-year regiment. Owing to their promptness, they were able to win an honor greater even than came to the “minute-men;” for they became the very first long-term volunteer regiment to enter U. S. service anywhere in the country, the first not only of the Civil War but of any war. Their adventures, and the battles they fought, are “another story”; and will be told in a later chapter.
One of the three old original artillery companies having been lost to the 6th, another was destined to go with—no, the correct expression is, to “become”—the 13th Regiment. Late in 1860 the 8th Company, the “Boston Artillery,” became interested in organizing a “crack” battalion or regiment for Boston. They were already members of the best regiment in the Commonwealth, but they were not satisfied with that. Capt. Baldwin did not share in this new ambition and declined to have anything to do with it. In civil life he was a merchant and wholly practical in his tastes; as a soldier he was a plain, blunt man, “full of strange oaths,” “who loved his friends.” The new departure did not appeal to him. So Capt. Baldwin transferred[49] to the 4th Company, the Pulaski Guards, and remained with his old regiment; while the Boston Artillery chose Gen. Samuel H. Leonard, recently of Worcester, as their captain. Under Capt. Leonard the Boston Artillery absorbed what survived of the disbanded Columbian Greys or City Guards of the old 1st, and proceeded to expand into the 4th Battalion of Rifles. It was on Dec. 15, 1860, that the new battalion was formed. Before the enthusiastic officers and men had time to do much toward developing their ideal of a “crack” regiment, they found themselves upon the threshold of the great war. On May 25, 1861, they volunteered to garrison Ft. Independence for one month; and almost before the month had expired, the 4th Battalion of Rifles had expanded once more and become the 13th Regiment, and on July 16 they were mustered in for three years’ service. Col. Cowdin’s men felt that they could well afford to lose their grand old 8th Company, when their loss resulted in the addition of an entire regiment to the Union army. The 13th served as part of the first corps in the army of Virginia, and later the army of the Potomac. Their regimental monument stands on the field of their hardest fight, that of the first day at Gettysburg, where they lost their gallant corps commander, Gen. John F. Reynolds. And on the second day of that battle, toward evening, they were sent to reinforce Sickles on the left, in whose corps was the 1st Massachusetts. Once more the Boston Artillery and the Roxbury Artillery were serving side by side.
On May 18, 1861, just one week before the 1st was mustered into Federal service, it lost another company. Capt. Joseph H. Barnes had organized a new 7th Company to fill the place made vacant by Capt. Sampson’s withdrawal. But the example of his predecessor proved contagious; so that presently the new company followed the old one. Capt.[50] Barnes’ command joined the 4th Mass. Infantry at Fort Monroe, and so found active work immediately. When, however, the 4th presently came home, its new Co. K was left behind, and became incorporated in the 29th Regiment, with which it served three years. In 1862 the 29th was with the army of the Potomac, in 1863 in Mississippi and Tennessee, and again with the army of the Potomac in 1864. Capt. Gardner Walker’s North End True Blues eventually went with Col. Cowdin as the 7th Company.
Lieutenant Colonel Isaac S. Burrell was not able to accompany his regiment in the three-years’ service. Remaining in Boston with a few other members who were similarly situated, he maintained a skeleton organization of the old militia regiment. And because the new number, 1st, was borne by Col. Cowdin, Col. Burrell had to hunt another designation for his command. The fourteen officers and two hundred sixteen men, in seven companies, who were engaged in this home-guard duty were by no means satisfied with their position. Their hearts were in Maryland and Virginia with their former comrades.
In the spring of 1862 Banks was driven from the Shenandoah valley and the north began to fear for the safety of Washington. On May 26, in response to requests from the Secretary of War, Massachusetts and other northern states mobilized their militia, recruiting the regiments up as nearly as possible to full strength. This alarm subsided presently. But Pope’s defeat at second Bull Run, August 30, left the capital in genuine peril, and caused a hasty call for 300,000 more troops, to serve nine months. Grave disaster had overtaken the Union arms, and there was immediate need for reinforcements. Col. Burrell was in militia camp at Medford with his regiment when the call came; and at once volunteered. Indeed this was just the chance for which[51] they had been waiting—active duty but for a period not so extended as three years.
Recruits were needed in order to bring the regiment up to war strength. By some singular perversity, as soon as recruiting began, a situation developed which threatened to destroy the regiment entirely. Col. Burrell and Lt. Col. Thomas L. D. Perkins were both graduates of the 1st Company, Perkins having succeeded Burrell as captain. A bitter jealousy had grown up in Perkins’ mind which made him incapable of rendering loyal support to his chief. Maj. George W. Beach shared Lt. Col. Perkins’ feeling and co-operated in his insubordination. Needless to say, Col. Burrell gave no real ground whatever for this feeling.
After the deadlock had continued for more than a month, during which the regiment made little progress in filling its ranks, Col. Burrell secured Gov. Andrew’s permission to take strenuous measures. Another command, the 54th of Worcester county, was similarly in need of men. The men already belonging to the 42d (as Burrell’s command became known, possibly with some reference to the proud record made by the 42d or Black Watch Highlanders in the British army) were consolidated into the 1st and 3d Companies; new 7th and 10th Companies were formed in Boston and Dorchester; 2d and 9th Companies were drawn from the 54th, while Boston, Medway and Weymouth provided units for the four vacancies. Capt. George Sherive commanded the 1st Company, Capt. George P. Davis the 2d (or Ware Company), Capt. Alfred N. Proctor (a photographer, and one of the indistinguishable “Proctor twins”) the 3d, Capt. Charles A. Pratt the 4th, Capt. David W. Bailey the 5th, Capt. Ira B. Cook the 6th (from Medway), Capt. Orville W. Leonard (who had been a private in the 6th Regiment during the ninety-days service) the 7th, Capt.[52] Hiram S. Coburn the 8th (from Weymouth), Capt. John D. Coggswell the 9th (of Leicester), and Capt. Cyrus Savage the 10th or Dorchester Company. All the newer elements proved to be congenial, the Worcester county men being especially good soldiers, with the exception however of the 5th Company. This unit was gathered in too much of a hurry, contained a “tough” element, and was a constant cause of discord. No one could then foresee that the regimental number, 54th, released by the consolidation of companies in the 42d, would presently be immortalized by Col. Robert Gould Shaw’s heroic black men.
In accordance with law, the company officers proceeded to elect regimental officers, and bestowed the chief honor upon Col. Burrell. Perkins and Beach tried hard to prevent this, but in vain; the electors were seeking the best soldier, and cared nothing whatever for old jealousies. They proceeded to select Joseph Stedman as Lt. Col. and Frederick G. Stiles of Worcester as Major, thus retiring the disgruntled former incumbents of those offices. A magnificent stand of colors was presented to the command; and on Oct. 14, the 42d was finally mustered in.
Nothing out of the ordinary marked the railroad journey to New York. But progress thereafter, which was by boat, proved to be highly uncomfortable. The transports were small, and not too seaworthy. And worse yet for “landlubbers,” the sea was rough. It is said that the man establishing his claim to possessing the strongest stomach was the man whose digestive organ would throw the farthest. As however all things have an end, the sufferers finally arrived at the mouth of the Mississippi, and once more became habitants of terra firma.
From the streets of Boston and the hills of Worcester county to the canebrakes and swamps of Mississippi and[53] Louisiana is a violent transition, which nothing less tough than the human system could endure. Yet the 42d Regiment survived its journey to the department of the Gulf and may almost be said to have flourished in its new environment. Of course the heat was often prostrating, while malaria took its toll of human life. The companies were separated, and were assigned to provost and engineering duty at different stations. Hard-tack and salt beef and pork are not luxurious fare, muddy coffee (which means usually coffee made with muddy water) is far from being a dainty beverage, digging is a most unromantic occupation, and even staying awake nights to watch while others sleep does not arouse the finer emotions as much in fact as when set forth by poets. Yet these are the staple elements of a soldier’s life; and these the 42d enjoyed in abundant profusion. Sensational details were lacking in this experience; but the service is not the less a thing of which to be proud.
Col. Burrell with three of his Boston companies, the 1st, 3d, and 10th, were detached to garrison the port of Galveston, Texas, and to co-operate with the Navy there. Of all the 42d Regiment, these companies alone chanced to find themselves “in the limelight.” The Galveston wharf was to be kept available for Naval use; and in turn the Navy was to shelter the garrison under the protection of its guns. Witnesses disagree as to just how well the latter work was performed. On Jan. 1, 1863, the Confederates attacked in overwhelming numbers at a moment when, for some reason, the warships had been withdrawn. Col. Burrell and his men defended themselves heroically and took heavy toll from the attackers. But with five thousand Confederates against three hundred Union soldiers, the result was inevitable. After the Confederates had brought thirty-one pieces of artillery into action, Col. Burrell and his men[54] surrendered themselves prisoners of war. Highly respected because of their stubborn bravery, the men were soon exchanged; and upon returning to the Union lines were accorded an ovation. The officers were retained in captivity longer; and Col. Burrell finally secured release just in season to assume command of his old regiment during its next tour of duty, that of the one hundred days. Other companies of the 42d were in action at Port Hudson, Lafourche Crossing, and Brashear City.
Disaster attended the return journey of the 42d. Going by boat thru Long Island Sound, one of the transports, the “Commodore,” struck a rock off Point Judith, and threatened to founder. The troops had to be taken off in small boats at much discomfort and no little peril, and finished their journey in another craft. On August 20, 1863, the men were finally mustered out, their nine months having extended itself into almost a full year.
Now, returning, the 42d kept its place in the line of the militia. Meanwhile unattached companies began to exist, which in certain cases aimed to act as reserve or “depot” companies for units of the 1st-42d. This was notably true of the 2d, 3d, 5th, and 6th Companies. The 1st Regiment was treading its bloody path of glory and approaching the time when it would return to Massachusetts and home. It disbanded upon its muster-out of the U. S. service, May 28, 1864; and many of its members were glad to join these reserve companies and so keep up the cherished associations.
Again the need became urgent for more troops. Gen. Grant, the new Lieut. Gen. and Commander-in-chief, had assembled all available men for the reinforcement of his mobile army in April, 1864, withdrawing so many of the defenders of Washington as to leave the national capital exposed to attack. In July such a raid was actually made[55] under the vigorous leadership of Gen. Jubal A. Early; and came uncomfortably near to succeeding. So a call was issued for short-term volunteers who should garrison fortified posts, and release the long-term men for active service. All the “hurrah” spirit had gone out of the war by 1864—indeed men were too weary to feel enthusiasm of any kind. There is therefore something all the finer in the grim way in which the 42d and the unattached companies responded to this call.
Remarkable as it may seem, eight of the companies which served during the nine months’ tour had retained their organization sufficiently to respond a second time. As one of those missing in 1864 was the “tough” 5th Company (N. B., of Boston, not Chelsea) the task of recruiting the needed units was not altogether an unwelcome one. Samuel A. Waterman commanded the 1st Company, Benjamin R. Wales the 2d, Alanson H. Ward (later a captain in the 61st Inf.) the 3d, Augustus Ford (who had been 1st Sergeant and 1st Lt. during the previous year) the 4th, George M. Stewart the new 5th Company, Benjamin C. Tinkham (sergeant during the nine-months’ service) the 6th, Isaac B. White (1st Lt. the year previous) the 7th, Warren French the new 8th, Samuel S. Eddy (a 2d Lt. in the 51st during its nine months in North Carolina) the 9th, and James T. Stevens (1st Lt. in the 4th Reg. during its three months in 1861) the 10th. The same field officers were in command. The happiest rivalry existed between the Boston companies and those from Worcester county, in their attempt each to bring the largest numbers and finest personnel forward in response to the new call. The old regimental colors were again borne at the head of the revived regiment. Entering Federal service on July 20, the regiment was assigned to the defences of Washington, and stationed at Alexandria,[56] Virginia. Here they formed part of the “outer picket” of the capital, and in addition furnished train-guards to protect railroad transportation from Washington to the Shenandoah Valley, the men detailed to service on the freight-cars being the only members of the 42d coming under Confederate fire during the present tour of duty. Col. Burrell came back from his southern prison just in season to rejoin his command at Alexandria. While the regiment had enlisted for one hundred days, its service continued thirteen days over time, and the men were mustered out Nov. 11.
There seemed to be unlimited reserves of vitality in the 1st and 3d Companies—indeed one is reminded of the way bees swarm from a hive as one notes how these wonderful organizations made contribution after contribution to the army and yet remained as vigorous as ever. All honor to the old Roxbury Artillery and the Fusiliers. The Roxbury Artillery had a full company in the three-year regiment, in the 42d on its first tour, and again on its second service. The Fusiliers did even more. Besides these three “bits,” they sent the 7th Unattached Company, on May 4, 1864, for ninety days’ duty on Gallop’s Island, Boston, under command of Capt. Albert E. Proctor, who in civil life was well known as a popular Boston clothier, and was the other indistinguishable “twin.” Again on Aug. 18 of that year they made up Co. K of the 4th Mass. Heavy Artillery for ten months’ service in Washington, D. C., under the same Capt. Proctor. Meanwhile they maintained their “depot” company in a state of efficiency. Certainly they justified the sentiment of their ancient motto, Aut vincere aut mori, with all emphasis on the “victory” and never a thought of “death.”
New companies which were presently to be added to the 1st Regiment also did duty at this time. The “1st Unattached[57] Company,” which garrisoned Fort Independence, Boston, for ninety days from April 29, 1864, afterward became the 4th Company in the regiment. And the “4th Unattached Company” which garrisoned the fort later to be known as “Rodman,” in New Bedford harbor for ninety days from May 3, later became the 5th Company in the regiment. Likewise the “9th Unattached Company,” which was to become the 6th Company in the regiment two years later, on May 10, 1864, began a ninety days’ tour of garrison duty on Gallop’s Island, Boston Harbor.
How the units of the regiment kept coming back to the artillery branch thruout the war! The regiment had originally been artillery; and the virus seemed to be in the regimental blood. The old cannon were not returned to the state until 1861. The three-year command served as artillery for three weeks of 1861 in Washington, and for two weeks of 1863 in New York. Co. K of the “4th Heavies” actually reintroduced the “artillery” title into the regiment. The four unattached companies in 1864 all served as artillery. Col. Cowdin’s old command was certainly destined to handle heavier ordnance than the infantry knew anything about. No wonder they welcomed the restoration of artillery instruction in 1882.
Well may the 1st-42d Regiment feel interest in Edward Simmons’ splendid mural painting in the State House, the “Return of the Colors.” For on the day of that ceremony, Dec. 22, 1865, color-bearers of both regiments were present; and both are given place in the picture. The war was over. These symbols of patriotism for which brave men had sacrificed life were returning to the custody of the Commonwealth who gave them. Was ever Forefathers’ day more sacred than that? The “land of the Pilgrim’s pride” had now become the “land where” and for which “our fathers died.”
W. F. Fox, in his “Regimental Losses,” published in 1889, includes a chapter entitled “The three hundred fighting regiments,” and his list has subsequently become accepted as a semi-official roll-of-honor. Of the more than two thousand regiments on the Union side during the Civil War he found three hundred which lost over one hundred thirty each, killed or died of wounds. While the number of casualties might not always indicate fighting ability, or even fighting experience, still in the long run the blood-marked trail of killed and wounded does surely lead to where the battle was most severe.
Amongst the three hundred fighting regiments stands the 1st Mass. Vol. Inf., three-year troops, another name for the Coast Artillery. Of our various companies who went out during the three wars in which we have participated, all losses by killed or died of wounds were confined to those in the Civil War. No such casualties occurred in 1814 or in 1898. The 3d Reg. lost 2, the one company in the 4th 1, the one company in the 13th 10, the single company in the 4th and 29th 5, the company in the 5th 4, the 42d 4, the 43d 3, or a total of 29. Of the regiments officered by us, the 24th lost 92, and the 44th 10; but it is not fair to reckon these as our casualties. In contrast with the total of 29, the 1st Mass. Vol. Inf. lost 144, besides 643 discharged for disease or wounds. There can be no question but that our companies constituting the 1st Mass. Inf., the three-year regiment, deserve the appellation, “the Fighting First.”
As soon as the regiment found that their services would not be accepted for three months, they set to work preparing for a three-year enlistment. Lt. Col. Burrell and others who could not go for the long term organized themselves into a reserve or “depot” regiment. New companies which had been added in April with a view to entering the three months’ service brought the total up to ten; and these all gladly entered into the three-year enlistment. The Chadwick Light Infantry, named for Hon. Joseph H. Chadwick of Roxbury, a liberal contributor toward the company expenses, became 2d Company in the regiment. The Pulaski Guards, newcomers in the regiment, shifted from 9th to 4th place. Members of the Chelsea Light Infantry, a 7th Regiment command which had just been disbanded because of the disobedience of its captain, resented the false position in which they were placed; and hastened in a body, on April 19, to the State House where, with Gov. Andrew himself presiding, they reorganized and forthwith received a charter as the “Chelsea Volunteers.” This accomplished, the new unit at once became the 5th Company in the 1st Regiment. While there had been two 7th Companies within a month, both had gone off with other regiments; and the vacant number was now filled by the North End True Blues. The True Blues consisted of caulkers, gravers and riggers from the ship-yards. They had begun their history many years previously as a fire-engine company, and in 1832 had taken up military training. But it was not until April, 1861, that they regularly connected themselves with the militia. A newly organized Brookline company took the 8th place, made vacant by the transfer of the Boston Artillery. The National Guards, newcomers in the regiment but with a history running back to the Mexican war, assumed the 9th number. And the Schouler Guards, named after the popular[60] Adjutant General of Massachusetts, became the 10th Company.
Col. Cowdin remained in command, and speedily demonstrated that he was as capable a leader in actual warfare as he had been during the years of peace. One notable and somewhat unusual trait was discovered by his associates—he never, under any circumstances, would permit a drop of alcoholic liquor to pass his lips. George D. Wells, judge of the Boston municipal court, went as Lieutenant Colonel, and soon gained the reputation of excelling even his chief as a tactician. He afterward became colonel of the 34th Mass. Inf., and was killed at Cedar Creek in 1864. Charles P. Chandler of the new 8th Company was chosen Major; and was destined to die in battle a year later, at Glendale in the White Oak Swamp. The company commanders were: 1st, Ebenezer W. Stone, Jr.; 2d, Abiel G. Chamberlain, afterwards a colonel of colored troops; 3d, Henry A. Snow, commander of the company as far back as 1849; 4th, Clark B. Baldwin, afterwards Lt. Col.; 5th, Sumner Carruth, later Colonel of the 35th Mass. Inf.; 6th, Edward Pearl; 7th, Gardner Walker, who was to succeed Chandler as Major; 8th, Edward A. Wild, later a Major of the 32d Mass. Inf.; 9th, Alfred W. Adams; and 10th, Charles E. Rand. The 10th was the only company destined to lose its commander in action, Capt. Rand being killed at Chancellorsville, and by a singular fatality, his successor, Capt. Moses H. Warren at Spotsylvania.
In consequence of the regiment’s prompt decision, they were able to be mustered in as volunteers on May 25, 1861,—the first three-year organization in the entire United States.
The regiment journeyed by rail from Boston and reached Washington on June 15, the first long-term organization[61] to arrive. Passing thru Baltimore they were very cautious, having in mind the experience of their comrades less than two months before. But the city was then actually under complete Federal control.
Blackburn’s Ford, the preliminary skirmish of Bull Run, on July 18, 1861, first brought the regiment under fire. Lieut. Albert S. Austin lost his revolver at this time;—judge of his pleasant surprise when, in 1896, receiving a package from a Confederate veteran, he opened it and discovered the long-missing weapon. This revolver may now be seen in the collection of the A. & H. Art. Co. Part of an army all of whose members were inexperienced, it is greatly to their credit that they were chosen as rear-guard of the retreating Federals after the main battle of Bull Run, July 21. Perhaps it was because of the reputation gained here that the 1st came to be frequently detailed to the responsible rear-guard position. They served in this capacity during the change of base on the Peninsula, and during the subsequent retreat from that district. They covered the retreat of the army after Fredericksburg. But it is safe to say that they were never more valuable as rear-guard than when at Bull Run they steadily held their place behind the torrent of panic-stricken fugitives and prevented the victors from pressing the pursuit. This transpired during their first battle, when they had been less than three months in the service.
Their gray militia uniforms in which the regiment went to war cost them dearly at Blackburn’s Ford and Bull Run. Facing troops similarly attired, Lieut. W. H. B. Smith of the 3d Company called out that he and his men were from Massachusetts, thinking that he was talking to other northern soldiers. But his words were greeted with a volley by which the lieutenant lost his life. Later in the action a[62] similar explanation by Capt. Carruth of the 5th Company barely prevented a Michigan regiment from firing on the First. Immediately after the battle new blue uniforms were issued.
Three weeks of garrison duty at Fort Albany, Washington, D. C., ensued, when the regiment was drilled in the use of heavy artillery. August 13, they were transferred to Bladensburg on the other side of Washington, where they first came under the command, as part of the brigade, of Gen. Hooker. Serving with him in succession as brigade, division, corps and army commander, they always felt especially devoted to their chief. It is no accident that Capt. Isaac P. Gragg of ours wrote in 1900 a book affectionately tracing the careers and homes of Hooker’s ancestors. The same veteran and his comrades bore a leading part in securing the Hooker statue on the State House grounds, dedicated in 1903. In March, 1862, the regiment received their “white diamond” badges, of which they were always so proud, the[63] Army of the Potomac then being organized into four corps, and they forming part of the second division (Hooker’s) of the third corps.
They were engaged in provost or garrison duty in Maryland during the winter of ’61-’62, and were stationed during most of the time at Budd’s Ferry.
From Yorktown to Spotsylvania, during two entire years, the regiment bore the white flag of Massachusetts and had an honorable part in all the battles of the Army of the Potomac, with the exception of South Mountain and Antietam, which occurred while they were recuperating at Washington. They were heavily engaged at Williamsburg, May 5, 1862, where Hooker won the soubriquet, “Fighting Joe,” of which he was never proud. Here also Col. Cowdin earned the brigadier-generalship, which was tentatively awarded him Sept. 26, and of which he was eventually deprived for political reasons. Col. Cowdin had the misfortune to be antagonized by the Republican Governor of Massachusetts, and by the U. S. Senators from the Commonwealth; the Senate refused to confirm his appointment. The sword carried by Col. Cowdin at Williamsburg is today in the Faneuil Hall armory of the Ancient and Honorable Artillery Company. The regiment lost heavily at Fair Oakes, June 25, and Glendale, June 30, when Major Charles P. Chandler was killed. Again suffering severely at second Bull Run, Aug. 29, and Chantilly, Sept. 1, their effective numbers were reduced to less than six hundred. It is a pointed testimony to the high cost of military unpreparedness that many of the brave men were incapacitated, not by wounds, but by preventable disease. While Gen. George B. McClellan’s ability has been a subject of prolonged controversy, the general never lacked for loyal and devoted support from the members of the First.
Yorktown is historic ground. Going by water from Budd’s Ferry, the regiment landed upon the same shore which Washington’s Continentals had trodden eighty years earlier. Their progress thru the fields of yellow broom was over ground rendered memorable by the Revolutionary heroes. Near the present beautiful National cemetery and in sight of the present charming Yorktown battle-monument stood a Confederate intrenchment which occasioned annoyance to McClellan’s army. It had withstood two assaults, and was in the way of the army’s advance. Lt. Col. Wells offered to take the work; and his offer was accepted. Col. Wells had read American history and knew how “Mad Anthony” Wayne achieved immortality; the appeal now would be to cold steel. About 2 A. M. the 5th, 8th and 10th companies were quietly awakened, the 5th to make the attack, and the others to serve as supports. The men formed their line amid the silence of the woods; and, at earliest dawn, heard their commander whisper, “This is McClellan’s first order. The honor of Massachusetts is in your keeping. Charge!” Across four hundred yards of miry, uneven ground they advanced in the face of Confederate rifle fire. Arriving at the redoubt, with a shout for old Massachusetts, they fired a single volley; and completed their task with the bayonet. Just ten minutes after Col. Wells’ command, the intrenchment was in Union hands. An old lithograph of this action is to be seen in the museum of the Cadet Armory, Boston.
Four members of the 5th Company were here killed. April 26 was the date of the assault; four days later the remains were sent north, and in due time were received with a magnificent demonstration of honor in Chelsea. One of the dead, Private Allen A. Kingsbury of Medfield,[65] was specially honored by the publication of a memorial biography.
The battle of Williamsburg was almost a private affair with Hooker’s division. Williamsburg, the “cradle of the republic” and birthplace of the American revolution, had once been a proud capital. It is today, and always has been, noted for the warm-hearted hospitality of its citizens. It was there that Washington earned his degree as civil engineer, and there he wooed and won his bride. There Patrick Henry thundered forth the brave words, “If that be treason, make the most of it.” And there today the two sons of President John Tyler reside, one serving as county judge and the other as president of “William and Mary College.” But so early as 1862 the glory had departed, and the shabbiness which accompanies slavery was dominant. There on May 5, 1862, amid the beeches and sycamore trees about Fort Magruder Gen. Joseph E. Johnston halted his retreat and engaged in a rear-guard action. His intrenchments were shallow; but the pursuing Federal troops were few—only a single division. Hence the fighting was severe. When finally the 1st Regiment marched thru the town and up “Duke of Gloucester” St. in pursuit of the broken Confederate column, they felt that they had fully earned their laurels.
While most of the Union army went up the York river by boat, the 1st Regiment made the journey on land. Altho the country was naturally fertile and the climate of the best, a general seediness and “run down” condition prevailed, so that it was like a desert to the weary, hungry marchers. Finally the Williamsburg road brought the troops to Seven Pines—the spot from whose tree-tops could be seen the spires of Richmond, six miles away. Doubtless everyone has passed thru some experience so terrible that it comes[66] back in his moments of nightmare. Seven Pines and Savage’s Station fill that rôle for veterans of the old 1st. Today a portion of the battle-field is a National cemetery, a veritable God’s acre, sacred to the memory of the dead, melodious with the voice of cat-bird and mocking-bird and the graceful killdeer. There the magnolia grows to perfection and the luscious fig matures in the summer sunshine. But this district, usually so dry and substantial, is at the edge of the Chickahominy or White Oak Swamp. From May 31 to June 25, 1862, unusually severe rains swelled the Chickahominy and inundated the surrounding country. Fortunately there are islands in the swamp, places of partial refuge, to which our men resorted. McClellan’s plan called for a junction with the army of Irvin McDowell about June 1, and for a grand assault by the combined forces upon the Confederate Johnston. For reasons which seemed adequate to the authorities in Washington, notwithstanding the serious results for McClellan and his army, McDowell was forbidden to march south and keep his appointment. While McClellan waited, and while the floods refused to abate, the Army of the Potomac was in a bad way. R. E. Lee, Johnston’s successor, attacked nearly every day. Mosquitoes bit, and the result thereof was malaria. Finally the ground was dug over and fought over so constantly that there was time neither to care for the wounded nor bury the dead; and a condition of horror ensued which surpasses all power of description. Men actually had to sleep side by side with their dead comrades,—comrades who had been dead for days. It is very easy to understand why the Peninsular campaign developed into a retreat; a month of such fighting was all that flesh and blood could endure. Not even the issue of a whiskey ration, which commenced at this time, could sufficiently blunt the soldiers’ senses—altho it did accomplish[67] vast moral damage. So when McClellan became convinced that he would not have McDowell’s co-operation, he turned back; he could do nothing else.
It was easier in the north to organize new regiments with their numerous openings for the appointment of officers, and with the enlisted men starting military life on an equality rather than with some as veterans and others as “rookies.” Nevertheless this system resulted in depleting the older and more experienced regiments, and cost the government millions of dollars in unnecessary expense. Massachusetts, by contrast with other states, did recruit up her three-year regiments, and endeavored to keep their ranks filled, even tho the later accessions had to be given the privilege of taking discharges with their regiments at the end of less than three years. Sept. 5, 1862, a large number of recruits arrived, who had been enlisted by officers of the 1st in Massachusetts, and who brought the companies once more up to one hundred each. About the same time there was an exchange of prisoners, and the men who returned from their unwilling residence in southern cities had many interesting experiences to relate.
After the Peninsular campaign, as regiments became reduced in size to not more than five hundred men, the government decided to economize by dismissing the regimental bands, and substituting brigade bands. The First bade regretful farewell to their musicians; this method of saving money the men regarded as a mistake.
Much of the hard fighting done by the 1st Regiment took place within a very limited area. Fredericksburg, Chancellorsville, the Wilderness and Spotsylvania all lie within a few square miles, and all can be visited by automobile within half a day. Moreover a visitor cannot fail to be impressed with the fact that these battle-fields seem to have[68] been selected so as to destroy the least possible amount of private property. Outside of the actual city of Fredericksburg, the country is little better than pine-barren, and contains few houses and not even much cultivated land. Since we now know pines to be health-giving, and well-drained sandy soil to be freest from disease germs, we can see how this choice of battle-fields by the Army of the Potomac doubtless saved lives as well as property. The climate too is free from extremes. But the men of 1863 and 1864 did not appreciate these things; all that they had time to notice were the dust and drought and heat and hunger and hard fighting.
At Fredericksburg Gen. A. E. Burnside tried to march directly south toward Richmond, crossing the Rappahannock on pontoon bridges. It was a winter battle—the date was Dec. 13, 1862—with great discomfort and a fair chance that wounded men would freeze to death. Fifer Bardeen tells that one captain, Walker, trembled as he entered the battle—and Capt. Walker was the bravest of the brave. Lee had every advantage of position; the resulting disaster was inevitable.
About two months after Col. Cowdin’s promotion, as the regiment were covering the retreat of the army from Fredericksburg, they were introduced to their new colonel. Napoleon B. McLoughlin, in spite of his French-Irish name, was a Vermont Yankee. He had entered the regular army from the New York 7th, and at the time of his appointment to the Colonelcy was a captain in the 6th U. S. Cavalry. He was respected and well liked; but he always suffered from the fact that the men felt him somewhat of an interloper. Capt. Baldwin of the 4th Company had become Lt. Col. and by all rules of seniority should have been made Colonel. However Col. McLoughlin held the esteem of his[69] men, and made an honorable record. His regular army strictness was beneficial to his new command. On Feb. 9, 1863, two months after the arrival of the new colonel, the regiment was subjected to an extremely rigid inspection; and was pronounced one of the eleven best disciplined and most efficient regiments of the one hundred fifty constituting the Army of the Potomac.
Chancellorsville, May 2 and 3, 1863, was the next great battle. Gen. J. Hooker crossed the Rappahannock several miles above Fredericksburg and tried to turn Lee’s left flank. Hooker unexpectedly came into collision with Stonewall Jackson’s troops and instead of hurting Lee, almost suffered the humiliation of seeing his own right flank crumpled up. At the most critical moment of the Chancellorsville fight, Hooker was wounded and the army left without a head. When O. O. Howard’s 11th corps broke and ran (“started for Germany”), it was only the 1st Regiment and other troops under Dan. Sickles who saved the Union army from destruction. Their promptness in entering the breach in the lines, and their stubborn courage in remaining there hour after hour, were all that checked the on-rushing Confederates. At Chancellorsville the regiment was for the first time serving under both of its best-loved commanders, Gens. Hooker and Sickles.
On the night following Howard’s break, according to common belief amongst the men, it fell to their fate to be the slayers of Gen. “Stonewall” Jackson, one of the severest blows to the Confederate cause during the entire war. The 6th and 10th Companies were on outpost when a party of Confederate horsemen rode down the Plank Road toward their lines. As a result of the volley then fired, Gen Jackson fell, the identification being made complete by Sergt. Charles F. Ferguson of the 10th Company, who was a[70] prisoner-of-war for a few minutes, and happened to be close to the mounted officers when the fire was received. Ferguson made his escape in the ensuing confusion. This event was merely an accident of warfare, and entirely unpremeditated. While others claim to have been the agents of Jackson’s removal, and altho the Southerners say that their own men fired the fatal shots, still there is no good reason for rejecting the contention of the 1st Regiment,—in fact the evidence seems conclusive that our claim is valid.
The plain shaft which marks the spot where Jackson fell is a painful reminder to men of the 1st. Returning a year later, at the opening of the battle of the Wilderness, May 5 and 6, 1864, they were stationed upon the very ground over which they had fought in ’63. And when, during a lull in the fighting, they inspected their surroundings, they found human bones and fragments of clothing sufficient to identify some of their own regimental dead. The bodies of those slain at Chancellorsville had never been buried. No wonder that men shuddered as they saw the “buzzards” soaring over head.
Deep was the discouragement preceding Gettysburg. The failure at Chancellorsville had been due to no fault of the men and left them questioning whether they could ever meet Lee on favorable terms. They were not fond of Meade. Their march thru Maryland and into Pennsylvania was the most trying of the entire war. On June 25, 1863, after following the muddy tow-path of the C. & O. Canal all day, only two footmen were able to keep with the mounted officers until night-fall. Stragglers kept coming in during the entire night. Then, at Gettysburg, on the July days of 1863, July 1, 2, and 3, the tide finally turned, and the rebellion began to ebb away.
Historians differ concerning the relative importance of[71] the second and third days at Gettysburg. Gen. Sheridan in 1880, and Gen. Longstreet in 1902, and Capt. J. Long in his “Sixteenth Decisive Battle of the World,” published in 1906, took the ground that the battle was won on the second day, by Sickles and the third corps. Gen. Sickles had been posted on low ground to the north of “Little Round Top.” Becoming convinced that Longstreet was about to attack and crumple up the Union left flank, just as Jackson had crushed the Union right at Chancellorsville, he determined to prevent such a disaster by moving his corps forward to the higher ground, running north from the Peach Orchard along the Emmetsburg road. The 1st Mass. Inf., at the “Peter Rogers house,” held the most advanced position of the entire army. As a consequence Longstreet had no more than started when he unexpectedly came upon Sickles’ men, where he found plenty to keep him busy and was unable to crush anyone. At the day’s close the Union regiments were compelled to fall back to Round Top. But meanwhile, by Longstreet’s own admission, the Confederate plans had failed entirely and Lee had been defeated. The gallant charge of the Virginians on the third day was only a desperate final attempt by a beaten army, before commencing its retreat. Near the Peter Rogers house, in 1886, was erected the regimental monument of the First, a granite “white diamond,” bearing the words, “On July 2, 1863, from 11 A. M. to 6.30 P. M., the First Massachusetts Volunteer Infantry, Lieut.-Col. Clark B. Baldwin commanding, occupied this spot in support of its skirmish line 800 ft. in advance. The Regiment subsequently took position in the brigade line and was engaged until the close of the action. Casualties: Killed, 18; Died of wounds, 9; Wounded, 80; Prisoners, 15; Total, 122.” But for Sickles’ advanced stand with the third corps on July 2, there would not have been a third day at[72] Gettysburg. A model of the regimental monument may be seen at the museum of the Loyal Legion in the Cadet Armory, Boston.
Corporal Nathaniel M. Allen of the 6th Company was later awarded the Congressional medal of honor for here bringing off the regimental colors at the greatest personal risk, after the color sergeant had fallen. Col. Baldwin and Adjutant Mudge were wounded. It was on this same day that Lieut. James Doherty of the 10th Company steadied his men in the face of a hot rifle fire, by calmly exercising them in the manual of arms. Doherty was a character. A most gallant officer, he had risen from the ranks and never lost his fellow feeling for the enlisted men. An ex-sailor, he had the sailor’s vices. Once, in 1863, while passing thru Baltimore, he became drunk, and tried to kill an officer of another regiment. Had not Col. Baldwin seized a musket and clubbed Doherty over the head, murder would have been done. In New York he was placed under charges for telling his commanding general that he “lied.” But the charges were never pressed; perhaps the accusation was true. At Chancellorsville he was wounded in the finger by a bullet which managed to wind itself about the bone. Doherty roundly cursed the enemy for using defective lead. The brave lieutenant finally died in battle. A well-loved member of the regiment, Corp. Albert A. Farnham of the 4th Company, was taken prisoner at Gettysburg, and died in Richmond the 15th of the following November, his death being due to dysentery caused by insufficient and unsuitable food. His soldier’s hymn-book is in the museum of the A. & H. Art. Co.
July 30 to Oct. 7, the regiment was one of four on provost duty in New York City, guarding against further draft-riots, and preventing conscripts from deserting. Here they[73] resumed heavy artillery drill; and incidentally became rested after the Gettysburg campaign.
A new commander directed the army in the Wilderness, Lieutenant General U. S. Grant. The difference of men showed itself in the different result. Altho the 1st, now under Gen. W. S. Hancock, and the other Union regiments were handled as roughly in 1864 as they had been in 1863, when they left the field of battle, it was to march southward past Lee’s flank rather than northward toward security. Scrub oak and pine have obliterated practically all traces of the great fight. But men can never forget that the Wilderness proved that the tide had turned, and marked a long step toward the downfall of the Confederacy.
Spotsylvania was a continuation of the Wilderness with the fighting increased, if possible, in ferocity. On May 12, the culminating day at the “bloody angle,” the 1st Regiment was heavily engaged for the last time in its career. During the morning it acted as provost guard immediately behind the firing line, with orders to permit no one to pass to the rear excepting wounded men. In the afternoon it was advanced into the very thickest of the conflict and assigned the task of covering part of the Confederate line with a curtain of fire. Here both armies intrenched, and charged each other’s earthworks. The fighting was amid tangled underbrush wherein one could see only a few feet ahead; at such short range the bullet gave way to the bayonet and even to the clubbed rifle. When the combat continued after darkness had fallen, the fighting increased in intensity. Someone had to yield—Lee retreated. The apples which today grow at the bloody angle should be redder and the corn should bear more red ears, for they grow on sacred soil once crimson with the life-blood of heroes.
As they approached the completion of their enlistment[74] the 1st Regiment were stationed with the reserves. Here, on May 19, they took part in their last engagement, at Anderson’s Plantation, on the road to Fredericksburg—and home. R. S. Ewell’s corps of Confederates came around Grant’s right flank and attempted to cut communications with the north and to capture the wagon-trains. A brigade of heavy artillery regiments fresh from the defenses of Washington were acting as convoy—one of them being the 1st Mass. Heavy Artillery from Salem. Here the Salem men have erected their regimental monument. The heavy artillery had seen but little fighting; but they now stood up like veterans and drove back an entire corps. Unfortunately the Confederates were taking some of the wagons with them as they drew back; and it remained for the 1st Inf. and their companions in the brigade, some 1,200 in all, to rush to the rescue and recover the lost train. While both 1st Mass. regiments—the Art. and the Inf.—were equally brave, the 1st Inf. had learned by long experience to make use of “cover,” to shelter themselves behind trees, stones and earthworks. It was largely this skill that enabled them to stop the panic and save the Union army at Chancellorsville. Now, on this less important field, it saved Grant’s wagons from capture.
Then came the welcome order to return to Boston and be mustered out.
A great reception awaited the regiment in Boston. Gen. Cowdin was grand marshal of the parade, and all Boston came to extend the hand of welcome. Gen. Cowdin had been honored that year by election as Captain of the Ancient and Honorable Artillery Company, and of course was loyally supported by this command in all the exercises connected with the reception. Another ex-Colonel of the regiment, Gen. Walter E. Lombard in 1916, was similarly to be honored[75] by America’s oldest military organization. A grim pathos obtruded itself upon the spirit of the festivities; for of the 1,651 men who had gone to war, only 494 were present on May 25, 1864, to be mustered out. The command had been in twenty general actions; and nine of its seventy-one officers had been killed. It marched 1,263 miles, travelled by rail 1,325 miles, and on transports 724. The regiment gave three general officers to the army, and ninety-one other officers to sister regiments.
A number of noted clergymen have at times held the office of chaplain of the command. Applying the standards which control the selection of names for the volume, “Who’s Who,” amongst the distinguished chaplains would certainly have to be mentioned Otis A. Skinner, the noted journalist and preacher, 1850-’55; Thomas B. Thayer, the writer, 1858-’61; Jacob M. Manning, the lecturer, 1862-’63; Lewis B. Bates, father of ex-Gov. Bates, 1868-’72; Alonzo H. Quint, the ecclesiastical statesman, 1872-’76; William H. H. (“Adirondack”) Murray, devotee of horses and woodcraft, 1873-’76; Minot J. Savage, author and poet, 1883-’96; and Edward A. Horton, the orator, Chaplain of the Mass. State Senate, 1896-1900. Preeminent among them stands the name of the war chaplain, Warren H. Cudworth, 1861-’72, ’76-’82. Chaplain Cudworth possesses the added distinction that he was the historian of the “Fighting First.”
Warren H. Cudworth had graduated from Harvard in 1850; and represented the finest type of American culture. If size of hat indicates mental caliber, his chapeau, sacredly preserved at the Soldiers’ Home, Chelsea, proves him to have been an intellectual giant. For it is number seven and one-half. Since 1852 he had been pastor of the Unitarian “Church of Our Father” in East Boston. A bachelor, and of independent means financially, he was able to prove his[76] patriotism before receiving appointment as chaplain by announcing to his church that, if he should not secure the appointment, he would give his salary as minister to maintain work among the soldiers. The church had raised a fund for the erection of a new house of worship; this the pastor urged them not to spend as intended, but to devote the money to the welfare of the Union soldiers. When appointed, he gave himself unreservedly to the duties of the office; and absented himself from his regiment only once, for a single week of Aug., ’61, during the entire three years.
While not a “fighting chaplain” as some were, he was in every sense a brave soldier and true gentleman. Believing that the better American one is, the better American soldier he is, Cudworth both preached and exemplified this part of his creed.
His Massachusetts pride revealed itself in his comments upon the inferior standards of living and comfort as one progressed southward.
His scholarly interest in history and science kept showing thruout all his writings. Bladensburg is noted as the field of the disastrous militia defeat in 1814; there is no glossing over the uncomfortable facts. Bladensburg is also the duelling-ground where Commodore Barron killed Decatur in 1820. A scientific observer, he comments upon the excellence of the spring water. At Yorktown the regiment was encamped on historic ground, where Washington’s tents had stood, and Cornwallis surrendered, in 1781. But he somehow fails to note there the oldest custom-house in America. One is reminded of high-school days to hear him commenting upon McClellan’s bridges over the Chickahominy—that they were exact reproductions of Cæsar’s famous span across the Rhine. Cudworth comments appreciatively upon the notable past of the Fairfax family, so[77] influential in moulding the career of George Washington; of the Chancellors; and even records facts about Prince Frederick, father of George III, after whom Fredericksburg was named. Fossils and other geological remains unearthed by regimental well-diggers on the Peninsula interest him.
But his chief interest was in men and their welfare. The degradation which he saw occasioned by slavery brought sorrow to his heart. The untidy appearance of Williamsburg and other Virginia towns—a consequence of slavery—impressed him, as it does the visitor today. None rejoiced more than he over the issuance of the emancipation proclamation on Jan. 1, 1863, and he felt that such a clear pronouncement for justice and righteousness was more potent than many victories. At Williamsburg he commented on the generous hospitality of the southerners; he was also amused by quaint epitaphs in the old Bruton parish cemetery. At the close of the Peninsular campaign he manifested his social interest by commenting that the army was then existing in accordance with ideal industrial conditions—eight hours daily for work, eight for rest, and eight for recreation. When a whiskey ration was instituted in 1862, he deplored the resultant moral evils.
Such a chaplain would do everything possible for the welfare of the men. During the first leisure season in the regiment’s existence, that in 1861 at Budd’s Ferry, he organized a chess club which conducted exciting tournaments; a literary institute or debating society named after Mayor Frank B. Fay of Chelsea; and a large temperance society bearing the name of their total-abstinence Colonel, Cowdin, which enrolled nearly two hundred soldiers on its pledge, and had fully one-third of the regiment “on the water wagon.” The chaplain’s tent was indeed the social center of the camp.[78] Most important of all was his religious organization. The Y. M. C. A. had not then been introduced; so the chaplain devised an association, which he termed “The Church of the First Regiment.” Their admirable covenant, by which they existed, “You now solemnly covenant, in the presence of God and these your fellow-soldiers, that you will endeavor, by the help of grace, to walk in all the ordinances of the gospel blameless, adorning your Christian profession by a holy life and a godly conversation,” has received much unsolicited praise; and has afforded an inspiring model for other military chaplains.
Chaplain Cudworth was idolized by the men. They affectionately called him “Holy Jo”; and he accepted the title as a mark of affection, stipulating however that they must never pervert it into “unholy Jo.” Fifer Bardeen of the 1st Company tells how, in a New York barber-shop, he thrilled the crowd by a narrative of his own supposed heroism in battle, all suggested by a boyhood scar on his head. After he had told enough “whoppers” to set himself up as a hero, he glanced into the mirror and was thunderstruck to see “Holy Jo” occupying the next chair but one. The chaplain knew Bardeen well, and also knew just how true the yarn was not. But under the circumstances he showed his real self by utterly failing to recognize or embarrass the youthful hero. No wonder that Bardeen later wrote concerning the chaplain, “He was a good man, a patriot and a Christian, ready to pray with you at the proper time but never obtruding his piety, and always ready to help you in any way. There was no other officer in the regiment who approached him for genuine manhood of the highest type.”
Chaplain Cudworth’s passing was in keeping with the rest of his life. His death was that of a Christian soldier. It happened on Thanksgiving day, 1883, while the Chaplain[79] was participating in a union observance of the day held in a neighbor church, the “Maverick Congregational” of East Boston. As he was standing beside the pulpit in the very act of offering public prayer, suddenly he was heard to exclaim in pain, “I cannot go on.” Before others could reach him, he fell to the floor, dead.
It was inevitable that a reaction should follow the prolonged military exertion of the Civil War. The north had strained its resources almost to the breaking point, and people were tired of the very thought of a soldier. Volunteer regiments, upon their muster-out, disbanded outright; while militia organizations languished, and ofttimes died. “General apathy” was again in command of the situation.
Disbandment was the ultimate fate of the three-year regiment which had gone out under Col. Cowdin. Fortunately many veterans of the companies retained interest in military affairs, and appreciated the importance of maintaining the militia, so that they connected themselves with organizations designed to perpetuate the old regiment. Finally, on May 18, 1866, orders issued for the reorganization of the command.
As Col. Burrell’s 42d Regiment had retained a place in the militia establishment thru the sheer pertinacity of its officers, and as it was recognized to be a continuation of the old militia 1st Regiment, Col. Burrell was continued in command of the new 1st. The 1st Company was the corresponding company of the 42d. An unattached company, the 81st, consisting largely of 1st Regiment veterans and commanded by Lieutenant George H. Johnston, Adjutant of the 1st, took 2d place in the reorganized regiment. The Fusiliers’ reserve or “depot” company (the 25th Unattached) continued as 3d Company, under command of Capt. Alfred N. Proctor, who had led the 3d Company of the 42d.[81] Chelsea continued to supply the 5th Company, having organized the “Rifles” (4th Unattached), soon renamed “Veterans,” as a “depot” company for the original 5th Company (the “Volunteers”); Capt. John Q. Adams commanded. Veterans of the original 6th Company (now the 9th Unattached) under their war commander, Capt. George H. Smith, continued to represent the old number. The 10th Company of the 42d, under command of their war 1st Lieutenant, Edward Merrill, Jr., remained as 10th Company of the reorganized regiment. Thus six companies of Col. Burrell’s new command were perpetuations of the old regiment of which he and Col. Cowdin had been field officers. The new 4th Company had seen ninety days’ service under its designation of 1st Unattached, and was commanded by Capt. Moses E. Bigelow. Three companies, the 7th, 8th and 9th, had no war records, and merely came in as the 45th, 66th (the W. Roxbury Rifles) and 67th Unattached. The latter two, however, were commanded by veteran officers, G. M. Fillebrown, formerly a 1st Lieut. in the Mass. Cavalry, and John D. Ryan, a 2d Lieut. in the 61st Mass. Inf., respectively. Capt. Fillebrown’s company is the 8th Co. today. With six of the ten companies coming directly from the old regiment, it is no wonder that the new organization was granted the right to call itself the 1st Mass. Infantry.
Col. Burrell remained at the head of the regiment only sufficiently long to see it established on a firm foundation; on July 26, 1866, he was promoted to be Brigadier General. On August 29, 1866, Capt. George H. Johnston of the 2d Company became Colonel. The original record book of this period is in the custody of Maj. J. W. H. Myrick of the Fusilier Veterans.
Col. Johnston’s first camp was held at Sharon in 1866, and had an attendance of 533. With so large a proportion[82] of the membership war veterans, the event seemed very much like a military reunion. Officers and men were already thoroly trained; all enjoyed the experience of again wearing the blue uniform. Similar encampments were held in 1867, 1868, 1869 and 1872—all in Hull. In 1870 the entire state militia, under command of Gen. Benjamin F. Butler, encamped at Concord, and revived the memories of 1859. But how greatly had the situation changed during those eleven short intervening years! Then the war was a dread prospect; now it was a glorious retrospect. In 1871 a regimental encampment was held at Quincy.
On June 22, 1867, Col. Johnston and his regiment paraded as escort to President Andrew Johnson. A similar compliment was paid to President U. S. Grant, June 16, 1869. The regiment also paraded in honor of Gen. Philip H. Sheridan, when he visited Boston.
A new company, the Claflin Guards of Newton, was organized in 1870, and in 1872 became the 7th Company.
As a result of the Civil War the kepi and felt hat had been introduced into the bill-of-dress, and the five-button blouse had become the popular coat; the felt hat was a revival of a pattern common in old Colonial days. In 1869 the regiment profited by a new feeling on the part of the legislature that a good militia was worth the expenditure of a little money; for at that time the state began to make an allowance toward the purchase of uniforms. $20.00 was paid for each man—not enough to buy a uniform, but far better than nothing. Since their experience at Bull Run in 1861, the regiment had worn blue; now, however, they returned to the gray uniforms of 1859. Breech-loading rifles were issued in 1872.
The year 1872 brought the most prolonged tour of duty for the maintenance of public order, if we except Shays[83]’ rebellion, that the regiment ever had. Boston was then a city of frame buildings, standing close together, and separated by very narrow streets. On Nov. 11, fire broke out, and speedily grew uncontrollable by reason of high winds. When after three days of horror, the devouring flames were finally stayed in their work of destruction, old Boston lay in ashes.
Thieves, thugs and criminals of every sort are prompt to congregate in seasons of public calamity. When society is threatened by such a danger as conflagration, its ordinary police precautions break down; and people are helpless to protect their property or even their lives. All the militia in Boston were immediately called out to help rescue endangered lives, and to protect the panic-stricken fugitives. Where everyone is suspicious of everyone else, a man in uniform is the only one able to render any aid. Victims of the fire would not allow a stranger in civilian clothes so much as to assist them to places of safety, for fear of violence and robbery. The troops were kept on duty during thirteen days, the latter part of the period being devoted to guarding the ruins and aiding in the task of rehabilitation. One picturesque feature of the regiment’s service was the escorting across the city of treasure valued at $14,000,000. No other call to duty is so truly a test of military readiness as that in connection with a fire, coming as it does always without the slightest previous warning. And no other duty, performed as the 1st Regiment performed it in 1872, does so much to win friends for the organization, and for the National Guard of which it forms a part. At no other time does the National Guardsman appear so nearly in his true rôle, as “a soldier of peace.”
During the term of the next commander, Col. Henry W. Wilson, Dec. 12, 1872—April 28, 1876, the regiment felt the[84] effects of a new movement for military efficiency. Col. Wilson was himself a Civil War veteran, an ex-Captain in the 6th Regiment. But he believed the time ripe for innovations and improvements. The Civil War officers were growing too old for active service; and no one was in training to take their place. England, with a military system not essentially different from ours, had introduced strict principles of instruction for her volunteers some ten years previously, and now commenced to reap beneficial results.
Consequently the 1st Regiment welcomed the new state muster-field, first opened for use in 1873. Framingham at once became a synonym for increased efficiency; that very year the tour of camp duty was lengthened from three to four days, and from time to time thereafter successful effort was made to secure further extension. Massachusetts had the proud honor of leading all other states in providing a regular state camp-ground.
Perhaps because so many “old fellows” were bidding farewell to active military life, perhaps for other reasons, this was an age of sentimentalism in the regimental history. On Dec. 17, 1873, the 1st Company adopted a badge or medal for use with full-dress uniforms and also on civilian clothes; and other companies were so favorably impressed by the innovation as to imitate it. Col. Mathews later designed the regimental emblem which stands on the cover of this book, and which is based on the “white diamond” of the old “third corps.”
Capt. William A. Smith of the 1st Company was an enthusiast about rifle-shooting; and kept agitating the matter with a view to inducing Massachusetts to take it up. Already England had her ranges for volunteers, and in New York the Creedmoor range was in active operation. Capt. Smith presented many excellent reasons why small arms[85] practice should be made part of the militia requirements. In Colonial days every farmer was a good shot—he had to be, in order to keep down “varmints” and to keep off Indians. But when the state became fully settled the reason for popular skill in shooting ceased, and the shooting itself was discontinued. Thruout the Civil War, marksmanship was a neglected factor in the training of both northern and southern armies. By 1875 the need had become so crying that Capt. Smith and others succeeded in convincing the Massachusetts authorities. As soon as genuine rifle competitions were authorized, the members of the regiment, and especially of the 1st Company, stirred themselves to render the matches exciting; as a consequence, up to the time the regiment became interested in artillery, it was noted in the state for success in small arms competitions. From the 1st Company alone went out two such shots as Col. Horace T. Rockwell and Major Charles W. Hinman, both of whom had places on rifle teams which went to England and represented America in international matches held in 1880, 1883 and 1888. After 1878 the 4th and 12th Companies also won fame with the rifle.
The annual routine of a militia regiment—weekly drills, two or more field-days, shooting, one or two weeks’ camp, etc.—keeps the members busy along useful lines. But it does not afford a historian much to tell, save as he indicates the steps of progress from year to year. Parades, on the other hand, possess some romantic and popular interest; and it is hard to convince laymen that they have almost no military value. A regiment is largely judged by its appearance on parade. In Col. Wilson’s time there chanced to be included the fateful year, 1875, when eastern Massachusetts celebrated the centennials of Concord and Bunker Hill. With President Grant present from Washington on April[86] 19, there were “great doings.” On June 17 the “crack”-est military organizations from other states visited Boston to lend “tone” to the procession,—the 7th N. Y., the 5th Md., the 1st R. I., the 1st and 2d Pa. That day Gen. W. T. Sherman was reviewing officer. Sherman’s war experience had trained him to judge troops. He was forced to admit that Boston’s parade was a fine military display; and he had to add that the 1st Mass. was not behind the best. On Nov. 29, 1875, by a singular coincidence, Col. Wilson was called upon to parade his regiment as part of the funeral escort for his great namesake, the late Vice-President Henry Wilson, who was interred at Natick.
At first the regiment suffered from the new innovations. Its older members, trained in the hard school of actual war service were capable soldiers and required little instruction; and the younger men who needed more training were only a minority in point of numbers. As soon as it became evident that more time was going to be demanded for encampments and for small-arms practice, many older soldiers applied for their discharges. As the ranks grew shorter and thinner, the state authorities began to talk of disbanding companies, just as they had always been accustomed to do. Finally the break came. Col. Wilson resigned on April 28, 1876, leaving Lt. Col. Alfred N. Proctor in command; and on the following July 6, the regiment was reduced to the dimensions of a battalion and was redesignated the “1st Battalion of Infantry.” Lt. Col. Nathaniel Wales, who was placed in command, was a Civil War veteran with a brilliant record. He had enlisted as a private soldier, had served in the 24th Regiment, the 32d, and finally in the 35th, and came out of the war-service a Colonel. It is highly unusual to pass thru so many grades within less than four short years. Furthermore, Col. Wales was said to have been the youngest[87] man holding the rank of Colonel at the time he attained it. His love for the 1st Regiment was such that he was willing to endure a reduction of rank for the sake of re-establishing the old command upon a secure basis.
A company of the 3d Regiment, the Cunningham Rifles from Brockton, were transferred to the 1st Battalion at the time of the reorganization and became the 10th Company. This reorganization was by no means limited to the 1st Regiment—it was state-wide in its incidence. The 1st Battalion emerged from it as a six-company organization.
One or more companies of the 1st made the trip to the Philadelphia Centennial in 1876, and to the Valley Forge Centenary the year following. On Sept. 17, 1877, the battalion participated in the parade and ceremonies connected with the dedication of the Soldiers’ and Sailors’ monument on Boston Common. The companies presented a fine appearance in the eyes of the public; and following the celebration dined together much to their own gratification. New members enlisted, new interest began to be manifest, and there was a feeling that the present reduced condition would be only temporary. Col. Wales of course exerted all of his influence to have the regiment restored.
Finally the legislature responded and passed an act creating a 1st Regiment by a process of consolidation. There were four companies left of the 3d Regiment, then forming the 3d Battalion. And four companies represented what had originally been the old 1st Infantry of ante-bellum days, now organized as the 4th Battalion. So the legislature transferred the Fusiliers and the Claflin Guards to the 5th, the Chelsea Rifles to the 8th, and consolidated the 1st Battalion, the 3d Battalion and the 4th Battalion, as the “1st Regiment,” Col. Nathaniel Wales commanding. The date of this important legislation was Dec. 3, 1878. By a stroke of[88] genius the law-makers had created a twelve-company regiment, organized in three battalions each under command of a Major; and had devised a new plan of organization which was destined to work so well that, twenty years later, Congress would adopt it for use all over the United States. As the companies from the 3d Regiment were located in Plymouth and Bristol counties, they introduced a new geographical element into the 1st. Thereafter “The Cape” was to stand side by side with Boston, and right nobly were the Cape companies to uphold the regimental traditions.
It now becomes necessary to go back and trace out the origins of the organizations which were consolidated with the 1st Regiment in 1878. Let us first give attention to the companies which bore the title of 4th Battalion. We shall discover a battalion or regimental history stretching back to 1834, and company records commencing as early as 1787.
Three “independent companies” of infantry were listed in the roster of 1788 as connected with the 1st Division, Suffolk. One of these disappeared from the records the following year, and another in 1792. The lone survivor yet survives—in fact is the 3d Company, M. C. A., otherwise known as the Independent Boston Fusiliers.
On May 11, 1787, the Governor’s Council voted to approve an application signed by Thomas Adams and fifty-three others, and to charter a company. Gov. James Bowdoin presided at the Council meeting and himself introduced the petition. On the following July 4, he stood with the members of the new company on the slope of Bunker Hill and, at that shrine of American liberty, presented them their official charter. They next proceeded to the home of John Hancock, soon to be Governor, and at his liberal table, as his guests, enjoyed an inaugural dinner. The Fusiliers have excelled in many military lines thruout their long and honorable history—by no means least of their attainments is the masterly skill with which they have maintained the custom of dining together. Their motto, Aut vincere aut mori, seemed high-sounding in the early years. “Conquer or die[90]” presented harsh alternatives. But the time was to come seventy-five years later when the nation needed just such stern, self-sacrificing devotion; and then the Fusiliers indeed lived up to their motto. The Fusiliers wore red coats, in commemoration of certain gallant foemen with whom America had recently been engaged. As the Cadets were then clad in white and another company in blue, a striking patriotic ensemble was produced by the grouping of uniforms whenever the independent companies paraded. William Turner was elected the first Fusilier Captain; the names of his successors are recorded elsewhere in this book. No wonder that the Fusiliers, actives or veterans, have always been noted for maintaining the most successful and distinguished military ball in all Boston, the military-social event of the year; for their first Captain was, by profession, a dancing-master. Capt. Turner was succeeded by Capt. Joseph Laughton, who when not on militia duty, was occupied as a clerk in the Treasurer’s office.
 The Fusiliers about 1845
The Fusiliers about 1845
After 1798 the Fusiliers were never without vigorous and congenial companionship. Enthusiasm was then in full flood; George Washington had shown his patriotism by consenting to accept a subordinate position, that of Lieutenant General of the army under President John Adams; and men were enrolling themselves in the new legionary brigade. America was aflame with indignation over French injustice. On September 4, 1798, the Boston Light Infantry was organized after four months of preliminary meetings—the body which today reports to the Adjutant as the 2d Company, M. C. A. Their motto, “Death or an honorable life,” is a ringing echo of Charles C. Pinckney’s immortal words, “Millions for defence; not one cent for tribute.” At the first banquet of the company, Oct. 18, 1798, when the charter was received, the principal toast was—“The United States[91] of America; as they have drawn the sword of justice with reason, may they never sheathe it with disgrace.” Would that this sentiment might always prevail with the authorities in Washington! Amongst the members present at this banquet were sons or near relatives of such patriots as Paul Revere, James Otis and Joseph Warren. Truly the sons were rallying about the standard of the fathers. Drills were first held in the old State House, and after 1802 in Faneuil Hall.
There were lovers of Shakespeare in the Boston Light Infantry. At a dinner in 1815 one of them gave point to his speech by quoting the words of Henry V, hero of Agincourt:
All of the speech was forgotten except the final words of the quotation, “The tiger!” Company orators kept repeating the expression. Ere long the Boston Light Infantry found itself provided with a nickname—and it is best known thruout its long history as “The Tigers.”
In 1800 the Fusiliers under Capt. John Brazer and the Tigers, Capt. Daniel Sargent (a merchant in civil life), were the two light infantry companies constituting the sub-legion of light infantry—both being entirely independent. Indeed the sub-legion of light infantry had no field officer until Feb. 14, 1806, when Capt. Daniel Messinger of the Winslow Blues was elected Major. The Blues were organized in 1799 and first appeared on the sub-legion roster in 1802. The Washington Light Infantry were organized in 1803.
When in 1810 the legionary brigade was transformed into[92] the 3d Brigade, 1st Division, Maj. Messinger’s sub-legion of light infantry was broken up and the companies were distributed amongst the infantry regiments of the brigade. The Fusiliers and the Washington Lt. Inf. were incorporated with the 1st Reg., the Tigers with the 2d, and the Winslow Blues with the 3d. These infantry regiments, former “legionaries,” were neither train-band militia nor independent uniformed volunteers. Their status was somewhere between the two; it was hoped that the light infantry companies might serve as leaven for the infantry, and bring all up to the volunteer standard. The arrangement continued until 1834. By that time it was clear that only the independent companies, the “light” infantry, retained any vitality; and they were separated from the infantry regiments, and organized into a separate “Regiment of Light Infantry, 3d Brigade.”
Non-commissioned officers of the light infantry companies manifested active interest in the training school, “The Soul of the Soldiery,” from 1811 until 1819 and later.
Another company was born amid the war excitement of 1812, the New England Guards. Even from the days of their first Captain, Samuel Swett, it was felt that a distinguished destiny awaited the organization. During their entire half century of existence, they made constant effort to maintain their personnel at the highest standard; and the effort was crowned with success. An extant lithograph, in the museum of the A. & H. Art. Co., shows the Guards in the year 1836 parading with four platoons of twelve files each—numbers indicative of the company’s popularity. They were added to the 2d Regiment, and thereafter were associated with the Tigers.
During the war with England the light infantry companies rendered service at the harbor forts similar to that of the[93] artillery. By request of the commandant of the Charlestown Navy Yard, the New England Guards were stationed at the Chelsea bridge for eleven days from June 13, 1814, in order to prevent an expected raid by a hostile landing party. The entire membership of the Fusiliers was on duty from Sept. 12 until Oct. 10, under Capt. Gerry Fairbanks (a hatter in civil life); and detachments continued doing garrison duty several weeks longer. The Tigers helped to build Ft. Strong on Jeffries Point, East Boston; similar activity characterized the other companies. Massachusetts’ crest is a sword borne by the arm of a civilian: Massachusetts citizens in 1814 bore the sword effectively and well.
The light infantry companies participated in the same parades and public festal occasions as did the artillery companies. These events are elsewhere described in sufficient detail. In the sterner task of maintaining public order the New England Guards were on duty twice—July 7, 1824, and Feb. 11, 1825,—in connection with conflagrations. In both instances personal property had been saved from the fire and temporarily deposited in a place of safety; and the troops mounted guard against pillagers. The Tigers subscribed the first $100 toward the cost of Bunker Hill monument.
From the disbandment of Maj. Messinger’s battalion in 1810 until the organization of the regiment of light infantry in 1834, the companies of light infantry were associated only in the larger unit of the 3d Brigade. While the Coast Artillery includes all the surviving units of that Brigade, and altho the 3d Brigade was the most solid and efficient part of the old militia, still it does not seem wise to treat Brigade history in particular detail. Suffice it to say that four strong companies of light infantry continued active in the infantry regiments of the brigade—the Fusiliers in the 1st Regiment,[94] the Tigers and the New England Guards in the 2d, and the Winslow Blues in the 3d. Lists of company commanders are recorded elsewhere. A new branch of the service came into existence, the “Rifles,” and were accorded precedence over others—were given the right of the line in parades. In appearance they differed from other troops, as they wore jaunty green uniforms, and carried short flint-lock rifles without bayonets. These riflemen aimed to reproduce the famous corps under Daniel Morgan and others in the Revolutionary war, the frontiersmen and rangers clad in buckskin hunting-shirts who were so terrifying to America’s enemies. It has always seemed strange to the writer that the frontiersman’s costume, the only distinctively American garb ever devised, should not continue in use. Not even these new riflemen, however, succeeded in remaining true to type. While they were fond of picturing themselves in the hunting-shirt, the uniforms which they actually wore followed German models. One valuable contribution the new rifles did make to militia life, they were pioneers in setting up target practice as part of the soldier’s training.
Light infantry and rifles were distinguished from other infantry by the fact that they were trained in the skirmish drill, and were alone qualified to perform outpost duty. In line, they formed on the flanks of other companies. From time to time additional commands aspired to become light infantry, and some realized their aspirations. By 1834 there were eight companies altogether in the infantry regiments who felt dissatisfied with their regimental connection, and resented the waning interest which regimental neighbors displayed in things military. Their plan was to separate from the infantry, and revive the old battalion of light infantry, whose members should all be volunteers and uniformed, the battalion which had been broken up in 1810—in[95] short, to organize a Light Infantry Regiment in the 3d Brigade. From the 1st Regiment came the Fusiliers, the Washington Lt. Infantry and the Mechanic Rifles; from the 2d the Tigers and the New England Guards; and from the 3d the Winslow Blues, the City Guards (organized Sept. 21, 1821), and the Rifle Rangers (organized 1820). In 1835 a new company was added, the Lafayette Gds.
The new regiment was organized in Aug., 1834, with eight companies, and Col. Amasa G. Smith of the 2d Regiment was elected to command. A succession of field officers, which had begun in 1806 with Major Messinger and had been interrupted from 1810 until 1834, was thereafter to be continuous. Col. Smith’s commission was dated July 29, 1834; he continued in command until Feb. 23, 1838.
Judged by the standards of the day, Col. Smith’s regiment was a very fine one, indeed was a “crack” command. No less an authority than President Andrew Jackson is reported to have testified, “I have never seen its equal.” Most of the companies wore blue swallow-tail coats and white duck trousers—the latter quite regardless of weather; gradually blue nether garments were added for use on stormy days. The two rifle companies wore green, the Rangers having frock coats and uhlan hats; while extant engravings of the City Guards in 1844, the year of their famous march to Baltimore, show them clad in gray suits of a pattern precisely the same as those worn by the New York 7th. The City Guards were the first corps to wear gray in Boston; and the Fusiliers were equally distinguished by reason of their scarlet coats. While there was lack of regimental uniformity, there must have been a striking ensemble when the companies formed battalion line.
To the Fusiliers, in June, 1835, fell the honor of introducing an important tradition into the regiment. For at that[96] time, after a year’s preparation, they undertook an excursion to Washington, as a compliment to President Andrew Jackson, who was soon to give place to Martin Van Buren. The start was made after partaking of a collation at Gov. John Davis’ house; progress was made by march, stage, steamboat and rail; they camped on Capitol Hill; and dined with Gen. Jackson at the White House. This was not exactly a trip to “the inauguration,” but it proved to be the commencement of a custom which today takes the command to Washington once every four years.
In 1837 a company came into existence which was destined to prove the temporary undoing of the Light Infantry Regiment, and was also to subject Boston’s spirit of fairness and right to its most searching test. The “Montgomery Guards,” they were called. Altho named after the same heroic Richard Montgomery who was to give title to another and more famous company of Montgomery Guards fifteen years later, they must not be confused with the latter body. The critical point was that the members were all of Irish birth; and Boston, for the first time in sixty years, found a company of foreign soldiery in her midst. At least that was the view of the matter taken by old-timers. The race prejudice which later issued in the Know Nothing movement, at once flamed up. On the other hand, these guardsmen had all declared their intention of becoming American citizens, and were entitled to bear arms. The guards were attached to Col. Smith’s regiment. On Sept. 12, 1837, the date of the fall field-day and the first assembly of the regiment since the organization of the Montgomerys, the other nine companies took post on the regimental line,—the Montgomerys arriving last of all. No sooner had the latter swung into position than the enlisted men of the City Guards, breaking away from their officers, marched off the Common.[97] The enlisted men of the Fusiliers, the Blues, the Mechanics, the Washingtons and the Lafayettes followed this example of insubordination and broke ranks. It was sheer mutiny—mutiny with which many of the public sympathized, but mutiny nevertheless.
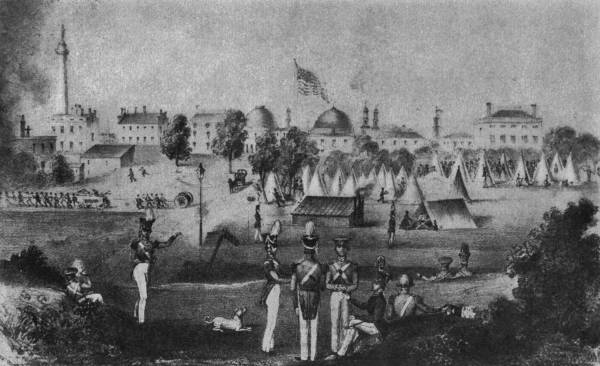 The Gray Uniform—The City Guards at Baltimore, 1844
The Gray Uniform—The City Guards at Baltimore, 1844
Courts martial resulted, followed by prolonged public discussion. Presently it became evident that the Boston sense of fairness and right was strong enough even to meet this test; and on Feb. 23, 1838, the offending companies were punished by disbandment. Col. Smith went out of office at this time. The Montgomery Guards were themselves disbanded April 6, 1838. As a consequence the Regiment was reduced to a battalion and placed under the command of Maj. Charles C. Paine. The Tigers, the New England Guards, and the Rifle Rangers alone survived the disbandment.
June 1, 1839, found the organization a regiment once more, made up of the following companies: Tigers, New England Guards, Pulaski Guards, who now transferred from the 3d Reg., 3d Bri. (and who seem to have been temporarily called Mechanic Greys in 1849), Columbian Greys, Hancock Light Infantry, Rifle Rangers, Highland Guards and Suffolk Light Guard. As the disbandment had been intended for punitive purposes merely, encouragement was held out for the companies to reorganize. The device of reorganizing and “continuing the record” was not then thought of. Had it been, it would doubtless have been ordered; four companies took advantage of the opportunity. The Columbian Greys were merely the old City Guards under a new name; in 1844 they appeared on the records as the City Greys, and by 1851 were known once more as City Guards. Similarly the Hancock Light Infantry continued the Fusiliers, the ancient corps being saved[98] by the loyalty of two former captains. Noah Lincoln, Jr., a prominent Boston shipwright, was in command of the company when disbanded in 1838. On a May date in 1839 the Hancock Light Infantry elected the same Capt. Lincoln to be their commander; but he did not deem it best to accept. On May 17, 1839, the company proceeded to elect Louis Dennis, a former Captain of Fusiliers who had risen to field rank; and Maj. Dennis proved his loyalty to the old corps by accepting a commission as Captain. Maj. Dennis was a builder in civil life, and felt that the present emergency called for constructive work along military lines; Capt. Lincoln thereupon agreed to become 1st Lieutenant of the company. After four or five years we cease to find reference to the Hancock Light Infantry—the records again deal with the Fusiliers. The Mechanic Rifles similarly reorganized in 1843, and the Washington Light Infantry a few years subsequently. Col. Charles R. Lowell, formerly Captain of the Rifle Rangers, commanded the reorganized regiment from June 1, 1839, until March 20, 1840.
On April 24, 1840, in connection with the general state-wide reorganization of the militia and the discontinuance of the train-band, the Light Infantry Regiment, 3d Brigade, received a number—it became the 1st Lt. Inf., 1st Brigade. The following colonels commanded: George W. Phillips, Aug. 27, 1840—May 18, 1841; Charles A. Macomber (formerly captain of the disbanded City Guards), June 15, 1841—Aug. 24, 1841; George T. Bigelow, formerly captain of the New England Guards, Sept. 11, 1841—Jan. 23, 1844; William H. Spooner, April 15, 1844—Jan. 19, 1847, the same Col. Spooner who had commanded the train-band regiment, the 1st of the 1st Brigade, to which the Roxbury Artillery was temporarily attached in 1832; Benjamin F. Edmands, March 15, 1847—July 11, 1848 (then elected Brig. Gen.);[99] Col. Samuel Andrews, a former captain of the Tigers, July 28, 1848—May 13, 1850, when he became Brig. Gen.
When the New York 7th visited Boston in June, 1843, they were guests of the Fusiliers (yet called Hancock Light Infantry). After church services on Sunday, June 18, the visitors were shown around to the chief points of interest. How fashions do change! The principal shrine to which pilgrimage was made was—Mt. Auburn Cemetery.
Veterans of the Mexican War organized a company in the 1st Regiment on June 18, 1849, to which they gave the title, National Guards; and were the recognized representatives of the 1st Mass. Mexican War Regiment. Ben Perley Poore, a prominent newspaper correspondent, was elected Captain. As it became difficult to secure a sufficient number of Mexican veterans in Boston, admission was granted to all militia veterans, after a few years. Capt. Poore presently removed from Boston for business reasons, and made his residence in Newburyport. There he became famous as Major of an independent battalion of infantry; and altho absent from his Boston comrades, continued to retain a warm place in their hearts. In Nov., 1856, he had made an election bet with Col. J. J. Burbank, proprietor of the Tremont House, Boston, to the effect that Millard Fillmore would get the Massachusetts electoral vote for President; and lost. So on Saturday, Nov. 8, he paid the forfeit—by wheeling a barrel of apples, on a wheelbarrow, all the way, thirty-six miles, from Newburyport to Boston. Maj. Poore’s popularity caused a wide-spread interest to develop in this feat; especially in Boston were the streets thronged with friendly spectators. When the Fusiliers learned of the plan, they determined to have a part in it; so the doughty Major, himself in citizen’s dress, was met in Charlestown by a company of thirty-four red-coated soldiers, and solemnly[100] escorted across the bridge into Boston. Then, as a slight recompense for all the fun which had been provided, when the procession arrived at the Tremont House, the apples were sold at $1.00 apiece, for the benefit of the man who had transported them. Maj. Poore’s portrait, as well as two pictures of the event, are today in the A. & H. Art. Company museum.
When on April 25, 1842, the companies received distinguishing letters, the Tigers became Co. A, the New England Guards B, the Pulaski Guards C, the Highland Guards D, the City Guards E, the Fusiliers F, the Suffolk Lt. Gds. G, the Washington Phalanx H, the Rifle Rangers I, and a company of rifles K.
Charles L. Holbrook became Colonel on Aug. 31, 1850, and continued in command until Aug. 15, 1854; William Schouler, destined to be the great Civil War Adjutant General of Massachusetts, was Lieutenant Colonel. To Col. Holbrook fell the painful duty of marshalling his regiment against the mob on June 2, 1854, at the time of the Burns riot. In that year the organization consisted of eight companies. To him also fell the more congenial privilege, in Oct., 1862, of leading his command, the same regiment but then known as the 43d Mass. Vols., during its campaign in North Carolina. Col. Holbrook was, in civil life, a bookkeeper, first in the Suffolk National Bank, and subsequently in the Custom House; as a soldier he jumped from the Adjutant’s office to the Colonelcy.
Owing to the formation of new companies it became desirable to organize an additional battalion of infantry in 1853, to which the number 3d was given. This included Capt. Poore’s National Guards as Co. A, the Union Guards of East Boston, organized in 1852, as Co. B, and the Sarsfield[101] Guards as Co. C, all under command of Maj. Robert I. Burbank.
Col. Thomas E. Chickering commanded the 1st Regiment from Oct. 25, 1854, until Jan. 29, 1856; and during his administration the name of the organization was changed from Light Infantry to “Infantry.” Col. Chickering commanded the 41st Mass. Inf., which became the 3d Cavalry, 1862-1865, and served in the department of the Gulf, transferring to Gen. P. H. Sheridan in Virginia during 1864. In 1855 the 3d Battalion of Infantry disbanded, the National and Union Guards going into the 2d Regiment as 9th and 6th Cos. respectively, while the Sarsfield Guards passed out of existence. The transfer of two strong companies to the 2d was a sign that the latter regiment was increasing while the 1st decreased. Six years later the 2d was to receive the much-desired number which had thitherto belonged to the “1st.” Maj. Joseph Bradley had become commander of the 3d Battalion at the time of its disbanding.
Col. Robert I. Burbank, formerly of the 3d Battalion, was the last commander of the old 1st Regiment, serving from March 25, 1856, until March 2, 1859. The regiment had several strong companies and might have been the leading military body in Boston; but it suffered from an excess of company loyalty and an utter absence of regimental spirit. Moreover there was a tendency to elect men of political prominence to the chief command, with slight regard for their military talents. Colonels were changed too frequently. The 2d Regiment under Cols. Bullock and Cowdin presented a striking contrast to the 1st in these particulars. The military authorities, since they recognized the inevitable tendency of the times, disbanded the 1st Regiment, and transferred four of the seven companies to the 2d, on March 1, 1859. The companies to enter the 2d Regiment were: C,[102] the Pulaski Guards; D, the Washington Light Guard; F, the Fusiliers; and H, the Mechanic Rifles; these became the 4th, 2d, 3d, and 5th Companies in Col. Cowdin’s regiment. The three companies remaining of the old 1st—the Tigers, the New England Guards, and the City Guards—were reorganized as the 2d Battalion of Infantry, under command of Maj. Charles O. Rogers, former captain of the Tigers. The latter command were highly prosperous at this time; in 1858 we find them giving the first grand ball ever held in the Music Hall, and a year later enlarging the scope of their social activities by moving the function into the Boston Theater, the first such event ever held in that celebrated amusement center.
Sentiment assumed striking forms in the military life of Boston during the years preceding the Civil War. Two visiting military bodies, the New York 7th in 1857 and the Ellsworth Zouaves from Chicago in July, 1860, presented such examples of military efficiency that a desire grew up—was encouraged by the Adjutant General—for the formation of a “crack” regiment in Boston. At the same time, the designation, “4th Battalion,” came to be coveted and sought after. The reason for the latter sentiment is obscure; there never had been a 4th Battalion in Boston, never any of prominence in Massachusetts. But the old sub-legion of Lt. Infantry in the 3d Brigade, standing as it did beside three infantry sub-legions, and brilliantly outclassing them, had been a “4th battalion” of which all Boston was proud. From 1859 on, many organizations were attempting to secure the designation, “4th Battalion.”
The 2d Battalion, organized March 1, 1859, under Maj. Rogers, included three strong companies, and might have been the nucleus of the desired “crack” organization; however the units did not cohere, and the battalion speedily flew[103] to pieces. Maj. Harrison Ritchie of the New England Gds. became commander July 21, 1860.
Gen. Samuel H. Leonard had removed from Worcester to Boston for business reasons, and had thereby lost his brigade in the former county. Becoming associated with Boston military men who were ambitious for a new and highly efficient regiment, he placed himself at the head of the movement. Ex-Gen. Leonard presently succeeded Capt. Clark B. Baldwin in command of the Boston Artillery, and proceeded to transfer that company from Col. Cowdin’s 2d Regiment to a new battalion. The City Guards had disbanded Dec. 26, 1859, and most of the members went into the Ancient and Honorable Artillery Company; now former members of the City Guards were reenlisted and consolidated with the Boston Artillery. Indeed these City Guardsmen were the instigators of the movement. Capt. Augustine Harlow (a printer in civil life), formerly in command of the National Guards, the 9th Company of the 2d Reg., joined in the movement and organized a new company. On Dec. 15, 1860, Capt. Leonard’s as Co. A, Capt. Harlow’s as Co. D, and two new companies designated B and C were associated as the 4th Battalion. At length the much desired numeral was in use,—and by men of large military ability and soaring ambition. Since “rifles” took precedence over other branches, the new battalion became “Rifles”; and wore gray Zouave or chasseur uniforms. We have seen elsewhere how this movement became deflected by the call for volunteers, and ultimately issued in the splendid 13th Mass. Inf. If the 4th Battalion of Rifles did not become a “crack” regiment—it achieved a nobler destiny.
On March 11, 1861, the New England Guards became independent of Maj. Ritchie’s 2d Battalion; and expanded their organization into a two-company battalion, for which[104] they claimed the coveted numeral, becoming the 4th Battalion of Infantry; Capt. Thomas G. Stevenson of the New Englanders became Major, and was in fact the leader of the movement. The ensuing month brought war and put an end to the militia dreams. On April 25 Maj. Stevenson’s battalion entered upon a one-month tour of volunteer garrison duty at Ft. Independence, the men serving without pay. It was at this time that they achieved the distinction of “bringing out” the most famous band-leader of the generation, Patrick S. Gilmore. Gilmore’s music and the fine marching of the New England Guards battalion immediately brought Maj. Stevenson’s command a high degree of popularity.
More three-year regiments were needed in the autumn of 1861, and members of the New England Guards battalion decided to enlist. Upon further thought it seemed wiser to use their proved skill in military matters in a higher capacity—they would organize a new regiment of recruits, and themselves go as officers. With the approval of the War Department, accordingly, the 24th Mass. Reg. came into existence, having Thomas G. Stevenson as Colonel and Gilmore as band-leader. No prophet then foresaw the future; but a bronze bas-relief in the State House (erected in 1905) today reminds us of the record of heroic service in North Carolina, South Carolina and Florida; the transfer to Virginia May 1, 1864, and participation with the Army of the James in the operations around Petersburg and Richmond. Their commander, now Gen. Stevenson, was killed in battle at Spotsylvania. Gilmore continued with his regiment as long as the Government permitted regimental bands—during the entire first year of the service.
Members of the New England Guards who were unable, for business or family reasons, to go for three years, were[105] quick to respond, in the autumn of 1862, to the call for nine-months men. Part of the 4th Battalion had organized and officered the 24th Regiment (there was already a 4th Reg.)—clinging to the coveted numeral others now raised the 44th Reg. and followed their comrades—to the coast of North Carolina. So very few New England Guardsmen were left at home in Boston that the battalion passed out of existence—died of patriotism.
Maj. Ralph W. Newton, former captain of the Tigers, succeeded Maj. Ritchie in command of the 2d Battalion on Apr. 17, 1861, and continued in office until May 22, 1862. Nothing remained of the old 1st Reg., or of the 2d Bat., except the Tiger company. In order to retain the battalion organization, the Tigers sub-divided into three companies. From this point on it will be literally correct to designate the battalion organization, the sole surviving remnant of the old 1st, as the Tigers.
On April 29, twelve days after assuming command, Maj. Newton moved his Tiger battalion to Fort Warren, and remained there a full month rendering unpaid volunteer service. Owing to the extreme shortage of trained soldiers, the Government was glad to have the services of the battalion at Boston’s most important fort. Old Andrew Fletcher has claimed that the song-writer of a nation is more influential even than the law-maker. So far as this is true, the 2d Company, the Tigers, have exerted a huge national influence. For while at Warren, it fell to the lot of their glee-club to originate one of America’s greatest war-songs, one which until “Marching thru Georgia” was composed, stood supreme, the song, “John Brown’s Body.” Both words and tune trace back to the 2d Company. The tune is an adaptation of a southern revival hymn familiar before the war; but is so complete a revision as to be practically[106] an original composition. The words were written as a joke on Private John Brown of the Tigers, who always seemed a shining mark for the wit of his comrades, and whose name of course suggested the hero of Osawatomie and Harper’s Ferry. Fletcher Webster’s regiment, the 12th, was in process of recruiting at Fort Warren that month. This song, at first intended humorously, was taken up in serious earnest by Webster’s men, was sung a little later by them as they marched to Bull Run; and within a year hundreds of thousands in blue were firing their enthusiasm for battle with the great refrain, “His soul is marching on.”
Ex-Col. Charles L. Holbrook proved his loyalty to his old command by accepting the lower office of Major on June 23, 1862. This responsibility he did not lay down until Oct. 13, 1862, when he led the 43d Reg. to war.
To the Tigers, as to others of Boston’s best citizens, the call for nine-months men came as a personal summons to service. Maj. Holbrook’s 2d Battalion at once began enlisting recruits, until it had expanded to a complete ten-company regiment. Practically all the officers were chosen from the Tiger battalion; and the new regiment, the 43d, was known as the “Tiger Regiment.” The ancient title, “Boston Light Infantry,” had remained attached to Co. A of the 2d Battalion;—now the “Lt. Inf.” Co. transferred itself bodily to the new regiment, and became Co. A of the 43d. Company commanders were: A, Henry J. Hallgreen; B, Edward G. Quincy; C, William B. Fowle, Jr.; D, Thomas G. Whytal (Capt. Whytal later became a Lt. Col. of U. S. Vols.); E, Henry Doane (of Orleans); F, Charles W. Soule; G, Everett Lane (of Abington, who was elected Major Oct. 20, 1862); H, George B. Hanover (of Chelsea); I, George O. Tyler (of Cambridge); K, J. Emery Round. Maj. Holbrook, as we have already seen, became colonel. John C.[107] Whiton, who later was Colonel of the 58th Mass., was Lt. Col., and Everett Lane, Major. Co. D was from Dedham, E from Orleans, G from Abington, H from Chelsea and I from Cambridge. The other companies were recruited at large—that is, from Boston. The regiment was mustered in Sept. 20, 1862.
Co. H of the 43d had an origin prophetic of the regimental consolidation which was to give us the present Coast Artillery. Springing as it did from the membership, and commanded as it was by the 1st Lieutenant of the Chelsea Rifles, and they in turn being the “depot” or reserve company of the Chelsea Volunteers (the 5th Co. in the three-year 1st Regiment), Co. H was in direct relationship with both of these commands. After the war, veterans of all three companies joined forces, transformed the Rifles into the “Chelsea Veterans,” and thus created our present 5th Company, M. C. A. For three years it was actually made up exclusively of veterans.
Tiger veterans and friends joined in giving the 43d a notable “send-off.” Once more the motto was “Death or an honorable life.” The historic banquet of Oct. 18, 1798, was repeated on Nov. 5, 1862, and the famous toast was again drunk, “The United States of America; as they have drawn the sword of justice with reason, may they never sheathe it with disgrace.” Hon. R. C. Winthrop, standing on Boston Common, presented the regiment a handsome stand of colors, a gift from the Boston Light Infantry.
A few weeks later the 43d found themselves under Gen. John T. Foster in North Carolina, far indeed from Boston and their friends, but side by side with the 3d and 44th Regs., which also enter into our history. The old Tiger spirit had accompanied them. In Dec, 1862, came their great march thru the swamps and sand barrens, when they were face to[108] face with the enemy during eleven continuous days. They were able to claim as their list of battles, Kinston, Whitehall and Goldsboro.
The loss of the North Carolina coast was a great blow to the Confederacy, opening as it did the way for Sherman’s march northward. Foster’s army was really an outpost of the greater force threatening Richmond.
In July, 1863, their service was completed and they were homeward bound once more. Travelling by boat to Baltimore, stopping for a visit at Fort Monroe, thence by train to New York, and having a square meal en route at Philadelphia, by boat to New Haven and train to Boston, they were given a hearty welcome home at old Boylston Hall, the Tiger armory, on July 21. The Boston Light Infantry at once became the 24th Unattached Company, M. V. M.
A few months of quiescence succeeded the Tigers’ nine months of duty in the 43d. Not until Aug., 1864, is there record of further activity. The war was drawing to a close, the nine-months regiments had been mustered out and the three-year commands were returning. Once more the ambition to have a “crack” regiment was stirring in Boston. Veteran and exempt members of the Tigers had formed the “Boston Lt. Inf. Assn.,” Nov. 1, 1862, during the absence of the active company. On this August date in 1864 the Light Infantry reorganized themselves as the “7th Infantry.” Maj. Charles O. Rogers, first commander of the 2d Battalion, was offered the colonelcy but declined; Daniel G. Handy was then elected, and received his commission on Nov. 6, 1865. (Col. Handy had been Maj. of the 12th Mass. in 1861 and 1862—indeed had been with the recruits in Ft. Warren when “John Brown’s Body” originated.) A vigorous attempt was made to form new companies and maintain the 7th at regimental standard.
The 7th Mass. Inf., a Taunton command, had made a noble name for itself during three years of hard service; and had been mustered out just before the Tiger 7th came into existence. The traditions connected with the number were certain to prove stimulating. But the choice of a number had further significance; it was a deliberate attempt to reproduce the New York 7th. Gilmore became band-leader, and it was hoped that his famous musicians would lend brilliancy to the new regiment. It was in his capacity as leader of the 7th Regiment band that Gilmore arranged and conducted his first “Peace Jubilee Festival” in 1869, with ten thousand singers and eight hundred instrumentalists in a “coliseum” seating fifty thousand, and not exceeded in size even by Billy Sunday’s tabernacle of 1916. Music by wholesale, this, and very different from the original classical “Peace Jubilee” in King’s Chapel, Feb. 22, 1815, from which Gilmore obtained the suggestion. New England liked it; and derived benefit from the popularization of good music. And the 7th received no little advertising.
Nine new companies came into existence within two years, mostly by the process of subdividing older commands, while the Tigers continued their organization as Co. A. Charles F. Harrington, former Captain of the Tigers, became colonel in 1869. Distinguished soldiers were willing to serve as company commanders in the 7th. B had for a Captain, Walter Scott Sampson, who had led the 7th Co. of Col. Cowdin’s regiment, the Washington Light Guard, into the 6th, and had commanded it (Co. K of the 6th) during its famous march thru Baltimore. Capt. Sampson had meanwhile been in command of a company in the 22d Mass. He was, in civil life, a successful Boston builder. E was commanded by no less a personage than Henry J. Hallgreen, war Captain of A or the Tiger Company in the 43d. A[110] had for its Captain, David W. Wardrop, war Colonel of the 3d Reg. The entire regiment was quartered in a single armory, at Pine and Washington Sts. Co. B had developed by fission from Co. A in 1864 and was first called the Handy Guard or 32d Unattached Co. In 1869 so many veterans of the old Washington Light Guard joined Co. B that the Handy Guard became known as the Washington Light Guard. In 1873 the company transferred its headquarters from Boston to Cambridge, and, as part of the process, the name was again changed, becoming the Massachusetts Guards. Claim has been made that Co. B perpetuates the old original Washington Light Guard, and it also claims to be the Tigers, as truly as the 2d Company;—it exists today as the 6th Company, Mass. C. A. Gen. W. E. Lombard holds its older record books. The 7th Company, Mass. C. A., the Pierce Light Guard, came into existence as Co. E of the 7th; Henry L. Pierce after whom it was named donated $1,000 to the company treasury.
Young men, however, are more successful than veterans in maintaining the interest of an active regiment; and apathy concerning military matters characterized the public thinking during the years immediately following the war. By 1870 the 7th had only four live companies remaining; on July 20 of that year the regiment was reduced to a battalion. The Tigers now recovered their old regimental number—they became the “1st” Battalion, and Maj. Douglass Frazer commanded. The 1st Battalion was on duty in 1872 at the great Boston fire, and protected the most important section of all, the financial district along State Street.
Austin C. Wellington, formerly 1st Lieutenant in the 38th Mass., became captain of the Tiger Co. A in 1870, and with his advent began the era of prosperity and efficiency for which the Tigers had long been wishing. In 1873 Wellington[111] became Major of the battalion, and on March 25, 1874, came a change in designation, bringing, after failure to get back their war number, 2d, the long-coveted numeral, “4th.” As an indication of how this ambition had persisted from ante-bellum days, we find the organization, in 1875, unofficially describing itself as the 4th Battalion “of Rifles.” In 1872 the “Maverick Rifles” had been organized as Co. D of this battalion; today they are the 11th Co., Mass. C. A.
It was the privilege of the Tigers, in 1875, to receive and entertain the Old Guard of New York City and the Washington Lt. Infantry of Charleston, South Carolina, the latter being the first southern military body to visit the north after the war. The following year the Tigers and Old Guard returned this courtesy, visiting Charleston and assisting in the celebration of the centennial of the battle of Fort Moultrie on June 28.
It was at once appreciated that Boston had a “crack” battalion and Maj. Wellington’s command was in great demand for parades and reviews. Its drill became a standard for other infantry bodies, while its striking quasi-Zouave uniform made such an impression upon the authorities that the costume was, in 1884, adopted as the State uniform. Such was the 4th Battalion which, on Dec. 3, 1878, by a process of consolidation, became part of the 1st Regiment.
During the train-band days, the troops of Plymouth and Bristol counties, with the Cape and Islands, constituted the 5th Division, while Boston militia made up the 1st. When the volunteer militia was set apart as the principal defence of the state, both sections found themselves in the same division. Now the Cape was the 2d Brigade while Boston was the 1st. By the consolidation of 1878 the two were finally brought together into the same regiment, so that the Coast Artillery not only perpetuates the old Legionary Brigade, but also the old 2d Brigade, M. V. M., and the older 5th Division.
There were four regiments of infantry in the 1st Brigade, 5th Division, of the train-band. The Halifax Light Infantry, organized in 1792, attached to the 1st of these, was the first company in the entire district to rise from the condition of militia to that of volunteers; and presently became the senior member of the Light Infantry Regiment. During its long career from 1792 until 1876, the Halifax Light Infantry was always one of the foremost military bodies in Plymouth County, and indeed in the entire state. Capt. Asa Thompson, who commanded in 1814, and who led his men into the 1st Division territory for the purpose of assisting to build and garrison Boston forts, was a giant (a “Saul” in the Scriptural language of the day), six feet, seven inches in stature. The towering head-dress of the times brought his height up to eight feet. As he led his men across South Boston bridge on the way to the forts and duty, every one[113] stopped to look and admire,—and wonder whether the bridge could stand up beneath the load. Alas! Captain Thompson presently fell into disgrace, and was dismissed by court-martial.
Oct. 21, 1818, patriotic citizens of Plymouth met and organized a light infantry company, to which they gave the name, Standish Guards, in compliment to the great “Captain of Plymouth.” Coomer Weston was elected Captain, James H. Holmes, Lieutenant, and William Randall, Ensign. Under the drill regulations of the period, the captain marched at the head of the column, the lieutenant at the rear, and the ensign in the center, carrying the flag. The most notable early parade of the Guards occurred on Dec. 22, 1820, when they escorted the Pilgrim Society, and Daniel Webster as orator of the day, in commemoration of the bi-centenary of the Fathers’ landing. To be sure, the date is now known to be one day too late; but no error of detail could prevent the occasion from being one long worth remembering.
As regards personnel, the Cape companies did not differ from those in Boston; prosperous merchants and tradesmen and mechanics made up the bulk of their membership; moreover a certain percentage of farmers were enrolled. There was less opportunity for social interchange and less of the stimulus arising from competition, owing to the relative smallness of the cities and towns. But in general the constituent organizations of the 3d Regiment passed thru the same experiences as did their sister companies to the northward. It will therefore not be necessary to repeat the details of events as outlined in previous chapters; we need only speak of those matters which were distinctive of the Cape.
By 1834 the train-band was in a very bad way indeed, and was rapidly approaching the moment of its extinction.[114] Ambitious companies were transferring to the light infantry, in order to distinguish themselves from their older and inefficient companions. Marshfield and Scituate had rifle companies and Scituate and Pembroke light infantry companies in connection with the 2d train-band Regiment; Abington had rifles, grenadiers and light infantry, and West Bridgewater light infantry in the 3d Regiment; and Middleboro had grenadiers in the 4th Regiment. In September of that year an order was issued separating the volunteer companies from the train-band regiments, and establishing them as a “Regiment of Light Infantry, 1st Brigade, 5th Division.” The nine companies mentioned, with the Halifax Lt. Inf. and the Standish Guards, constituted this new regiment. The organization is interesting because it ultimately became the 3d Regiment, and finally was consolidated in the Coast Artillery. The Samoset Rifles or Guards were organized in 1835 and were presently added to the regiment.
On April 24, 1840, the command became the 3d Regiment of Light Infantry, 2d Brigade, 1st Division. When on April 25, 1842, the companies received distinguishing letters, the following units existed with vitality sufficient to survive the transition: A, Halifax Light Infantry; B, Plymouth, Standish Guards; C, Hanson Rifles (a new company); D, Abington Light Infantry; E, Middleboro Grenadiers; F, Wareham Grenadiers (a new company); and G, Abington Rifles. At that date the New Bedford and Fall River companies were in the 2d Battalion of Light Infantry, as was also the company of Taunton Rifles. Taunton subsequently fell within the district of the 4th Regiment, a command which was by its location mainly an overflow from the 3d, and which a quarter century later merged in the 3d.
Col. Gideon W. Young of Scituate, who had commanded the 2d Regiment in the train-band brigade, was chosen first[115] commander of the Light Infantry regiment. Col. John Cushing, Jr., of Abington, succeeded Col. Young and served from May 20, 1837, until May 13, 1839. Col. Nahum Reynolds of North Bridgewater came next, receiving his commission Aug. 31, 1839. Col. Henry Dunham of Abington followed on March 25, 1841, being first to receive commission as Colonel of the “3d” Regiment. Presently Col. Dunham was chosen Brigadier General. During the administration of Col. Albert Whitmarsh of Abington, Aug. 1, 1842, to May 1, 1844, new companies were organized in Middleboro and Abington, while the Wareham Grenadiers disappeared from the records. The original New Bedford City Guards were organized in 1842, with Capt. George A. Bourne in command; and in 1846 they became Co. K of the 3d Regiment. During their first year, the Guards paid a visit to the Rifle Rangers of Boston. The occasion inspired someone to compose the “Whaleman’s Quickstep.” While we are not today interested in this as music, still it finds place in all our bibliographies because, on the front cover, it bears a picture of the two companies mustered on Boston Common. The Rifle Rangers stand in line as the New Bedford Guards march past, straight in the direction of the large refreshment tent which bounds the vista. New Bedford’s company paraded in four platoons of eight files—a fact indicative of a large membership. The City Guards were disbanded in 1849.
Eliab Ward of Middleboro was Colonel from July 10, 1844, until April 10, 1850, an unusually long term. Elnathan Wilbur of Middleboro was Colonel from May 4, 1850, till Jan. 28, 1853; Col. Stephen Thomas of Middleboro succeeded Col. Wilbur and remained in office from March 12, 1853, until Apr. 8, 1858. While companies were disbanded in Plymouth county, the loss was made good by[116] the formation of new units in Bristol county. On June 29, 1850, the Assonet Light Infantry of Freetown came into existence—a company destined to go to war eleven years later with only twenty-one enlisted men, equipped with ancient bullets which had been moulded for use in suppressing Shays’ rebellion. Yet one of their members was to have the distinction of bringing in, at Fort Monroe, the first three escaped slaves or “contrabands.” July 22, 1852, was the birthday of the new City Guards of New Bedford, commanded by the same Capt. Bourne who led the former company. This organization is today the 4th Company, Mass. C. A. On Feb. 26, 1855, the regiment was redesignated the “3d Regiment of Infantry.”
David W. Wardrop of New Bedford, June 26, 1858, John H. Jennings of New Bedford, May 10, 1862, until Aug. 25, 1862, and Silas P. Richmond of Freetown, Oct. 7, 1862, were the war Colonels of the 3d. Col. Wardrop was a Philadelphian by birth, but in young manhood removed to New Bedford. For a time he was a cadet at West Point. During a temporary residence in Boston he had been a member of the Fusiliers. In his home city he served in the City Guards, and was connected with the whaling industries of the port. Following the three-months’ service with the 3d, he became Colonel of the 99th New York Volunteers; and after the war he was inspector of customs at Boston. Col. Richmond had been a charter member of the Assonet Lt. Inf., and subsequently its Captain. Giving up his farm in 1857, he spent a year with John Brown in Kansas repelling “border ruffians.” During the three-months’ tour of duty, as we shall see, he was captain on the brigade staff; under Col. Jennings he was Lieutenant Colonel. At the conclusion of his nine-months’ service, he became Colonel of the 58th Mass. and Assistant Provost Marshal General[117] of the Department of the South. After the war he returned to Freetown, and continued active in business and political spheres.
Col. Wardrop’s regiment received orders to mobilize at Boston on the evening of Monday, Apr. 15, 1861. As the headquarters of the 3d were more remote from Boston than those of any other regiment called out, a severe handicap rested upon the command. Its members were mostly busy farmers or mechanics. Furthermore a cold, spring northeaster was raging and roads were almost impassable because of mud. Yet the energy of the colonel and his staff officers and the loyalty of the men overcame these difficulties, and enabled the regiment to report in Boston on the 16th—as early as any of those residing nearer. Credit must be given to Pres. Horace Scott of the Fairhaven Railroad for free use of a special train on the night of April 15, by which alone the prompt circulation of the order became possible; but the real praise belongs to the officers and men of the companies, whose patriotism produced the magnificent response. The six companies of the regiment, together with a Cambridge company which was attached, embarked on the steamer, “S. R. Spalding,” April 17, and lay in the harbor that night awaiting supplies. When on the following morning final drafts of men had arrived, bringing the total up to more than five hundred, the steamer sailed under sealed orders; and found, when nine miles out, that her destination was Fort Monroe. As communication with Washington was temporarily interrupted, these orders emanated from Gov. Andrew and are a mark of his patriotic sagacity; Gen. John E. Wool, in command of Fort Monroe, had sent a messenger by water requesting help. The officers of the regiment were, besides Col. Wardrop; Lieutenant Colonel Charles Raymond, a former captain of the Standish Guards;[118] Major John H. Jennings of New Bedford; Captains, Co. A, Joseph S. Harlow, who, like his predecessor of 1814, was well over six feet in height; B, Charles C. Doten of Plymouth (afterwards Captain of Co. G, in the 38th Mass., and today Secretary of the Pilgrim Society); C, the Cambridge company, Capt. James P. Richardson; G, John W. Marble of Assonet; H, Lucien L. Perkins of Plympton; K, William S. McFarlin of South Carver (subsequently Captain of Co. C, 18th Mass. Vol. Inf.); and L, Timothy Ingraham of New Bedford. Four new companies were later added to the regiment; and after the expiration of the three-months’ service, these became the nucleus of the 29th Regiment. Companies from the 4th Regiment also joined the 29th. As the 4th Regiment was included in the expedition to Fort Monroe, going by boat from New York, and thus both units of the 2d Brigade, 1st Division, M. V. M., were involved, Gen. Ebenezer W. Peirce, of Freetown, went as brigade commander; and on his staff was Capt. Silas P. Richmond. The 3d Regiment had worn gray uniforms since 1845, and after the war were to continue the color until 1874. So we may picture them as clad in that dressy yet serviceable garb.
Fort Monroe, often called “Fortress” Monroe to indicate that it consists of a fort within a fort, is known as the “Gibraltar of America.” Certainly it is a tribute to the political power of the dominant “House of Virginia” in the early days of our Republic, that the largest and strongest fortification of all should be erected for the defence of Norfolk and the James river. Incidentally it affords some protection to Washington and Baltimore; but that was not a controlling consideration in 1819, when construction began, nor in 1830, when the work was completed. Monroe is a five-bastioned fort of masonry work, and accordingly might[119] be roughly described as a huge pentagon. The walls surrounding it extend for the almost incredible distance of two miles, while the enclosed area is eighty acres in extent. Two picturesque features are the clumps of live oaks growing on the parade, which are not found anywhere farther north, and the sea-water moat in which tide-gates hold the water at a constant depth of six feet.
Such a fort is impregnable when adequately garrisoned—Monroe requires at least fifteen hundred men to render her secure. A Secretary of War with southern sympathies had stripped the fort of soldiers, until little more than a caretakers’ party remained. This tiny regular garrison was compelled to keep all its members under arms continually in order to man the guard-posts. Part of the moat had become an oyster-bed and was so filled up as to be fordable.
Sailing from Boston on the 18th, the men of the 3d experienced rough weather rounding Cape Cod. The last meal the soldiers had eaten before leaving Boston harbor did them no permanent good. Just as in a rambling conversation, so with landsmen on the ocean—one thing brings up another. On the historic 19th of April, while the 6th was fighting its way thru Baltimore and the N. Y. 7th was receiving an ovation along Broadway, the 3d and 4th were enjoying (?) life on the ocean wave. All things, however, have an end; and the 20th found both transports off Monroe, at the entrance of the Chesapeake bay. At first they were uncertain whether the fort remained in loyal hands or not; but the morning gun fired as a salute, and “old glory” ascending the staff, soon reassured them. No troops were ever more heartily welcomed than were the Massachusetts militiamen by the regulars of the garrison. First the 4th and then the 3d marched thru the sally-port, and[120] bivouacked beneath the live oaks; America’s most important fort was manned by loyal troops.
After barely time to snatch a luncheon and reassure themselves that such a thing as solid ground existed, the 3d was ordered under arms. Commodore Paulding had just arrived from Washington in the S. S. “Pawnee,” with orders to secure soldiers, and proceed to Norfolk for the purpose of destroying the Gosport Navy Yard. Norfolk lay far within the newly established Confederate lines. Across Hampton Roads, up the Elizabeth river, past Sewell’s Point where the exposition of 1907 was to stand and where in 1861 the Confederates were erecting an earthwork, past Fort Norfolk, which was then held by Confederates, the “Pawnee” proceeded in cool disregard of threatened shot and shell. It was nine P. M. when the Navy Yard was reached, and here another peril became imminent. The tiny crew and garrison of the Yard were at their guns, not knowing whether the “Pawnee” were an attacking Confederate or a Union reinforcement. Presently, however, identity was cleared up, and the principal business of the night was allowed to proceed.
A Secretary of the Navy, a southern sympathizer, had accumulated ships and material at Gosport worth not less than $10,000,000, for the express purpose of allowing them to fall into Confederate hands. It was the duty of Commodore Paulding and Col. Wardrop to prevent such a disastrous consummation. Both officers felt that the Yard could be held against hostile attack; but their orders were explicit—to destroy and abandon. History has decided that the destruction might have been avoided. As, however, the leaders of the expedition had no choice, they endeavored to make the destruction complete. The “Merrimac” was set afire and sunk. Everything that would not burn was thrown[121] overboard. At 3 A. M. Sunday, the men of the 3d, tired and smoke-begrimed, reembarked on the “Pawnee”; and towing the “Cumberland,” with the Navy Yard garrison on board, started down the Elizabeth river, leaving a raging hell of flames behind them. While the regiment had not been permitted to remain and hold Gosport as they desired, they had been the first northern troops to engage actively in military operations within hostile territory.
By the middle of May the four additional companies had arrived and joined the regiment. Gen. B. F. Butler, having completed his task of pacifying Baltimore, came to Monroe as Major General in command of the “Department of Virginia and North Carolina.” On May 24, Private Charles R. Haskins of Co. G (Assonet) had the honor of bringing in the first escaped negro slaves who reached the Union lines, Haskins being on guard at the time in Hampton. By one of the happy flights of practical genius for which he was distinguished, Gen. Butler decided that he could not return the run-aways because they were “contraband of war.” The north had been waiting in anxious suspense to know what would happen when southern slave-owners should demand the return of their property. Very much depended upon the decision of the question. Men certainly would refuse to enlist in the Union armies if they were thereby to become slave-drivers. Butler’s decision caused a sigh of relief thruout the loyal states. It must not be forgotten that this first long step toward ultimate emancipation was taken in connection with the activity of the 3d Regiment.
One can scarcely overestimate the importance of these early days at Monroe. The fort has always been the coast artillery headquarters of the United States. During the Civil War it was far more than this—it was the gateway of Virginia. Its possession enabled McClellan and Grant[122] to operate against Richmond. Without it neither the Peninsular campaign nor the siege of Petersburg could have taken place. Nearby Hampton, fanned by the sea-breezes, became the sanitorium of the northern armies. Burnside’s expedition, which made possible Sherman’s march, depended upon Monroe as a base. When on July 16, five days after the 4th Regiment had departed, the men of the 3d embarked on the S. S. “Cambridge” to sail for Boston, they felt with reason that they had rendered priceless service to their country.
One company of the 4th Regiment, Co. G, which served three months at Fort Monroe, and subsequently for nine months of 1862-63 at New Orleans, Baton Rouge and Port Hudson, became, in 1866, Co. G of the 3d; and in 1878 was consolidated in the 1st. Co. G had been organized at Taunton as the “Light Guard” in 1855.
In the fall of 1862 a call came for nine-months troops. The companies of the 3d had maintained their organization, and altho constantly depleted to supply recruits for other regiments, were relatively well prepared for service. They now determined that the 3d should reenter the U. S. service. In order to distribute town quotas more justly, the Assonet Light Infantry was united with the Halifax Light Infantry as Co. A, under Capt. John W. Marble of Assonet; (Capt. Marble was subsequently to command the 22d Unattached Company during the one-hundred-days of 1864;) the Samoset Guards of Plympton and the Bay State Light Infantry of Carver were consolidated with the Standish Guards as Co. B, under Capt. Thomas B. Griffith of Carver. The New Bedford City Guards became Co. E, under Capt. John A. Hawes. New companies were organized: C and D in Fall River under Capts. Elihu Grant and Andrew D. Wright (Capt. Grant later became a minister); F and G in New[123] Bedford under Capts. George H. Hurlburt and William S. Cobb; H in Rehoboth under Capt. Otis A. Baker, who had a notable war record. (As private in the 1st R. I., he had been wounded at Bull Run. Later he had served as 1st Sergeant and 2d Lieutenant in the 44th R. I.; subsequently he was to be Captain of the 18th Unattached Company,) I in Fairhaven under Capt. Barnabas Ewer, Jr., who as Major of the 58th Mass. was killed at Cold Harbor in 1864; K in Bridgewater under Capt. Samuel Bates. Co. D of Fall River continued its existence after the war, and was active until 1876. The regiment was commanded by Col. Richmond; the Lieutenant Colonel was James Barton of New Bedford, who had been 1st Lieutenant during the three-months’ service; the Major was John Morrissey of Plymouth, who had been “legislated out” of the captaincy of the Standish Guards by the recent consolidation. Maj. Morrissey became, after the war, Sergeant-at-Arms in the Boston State House.
The 3d were mustered into U. S. service for nine months on Sept. 23, 1862. As their numbers were too great for a single transport, two vessels received the regiment, the “Merrimac” and the “Mississippi.” Off Cape Cod the men experienced inconvenience similar to that of 1861; and many communed with the great deep. Thereafter the voyage was thru calm water, not even Cape Hatteras proving sufficient to stir up trouble. Landing was made at Beaufort, North Carolina, whence trains conveyed the regiment to Newbern. That town was originally settled by Swiss colonists; as, however, it bore small trace of Helvetian thriftiness and neatness in 1862, our men found nothing to admire. But the district was of much military importance as a source of supplies and channel of communication for Richmond and Lee’s army. The 3d, under Gen. Foster, was side by side[124] with the 43d and 44th Regiments, both of which have place in Coast Artillery history. They participated in the “great march” thru Kinston, Whitehall and Goldsboro. June 11, 1863, the regiment embarked for home; and was mustered out June 26.
Veterans of the 4th Regiment residing in Taunton organized the Taunton City Guard on Nov. 4, 1865, thus giving that city a competitor to its older Light Guard. The company entered the 3d Regiment in 1866, and today exists as the 9th Company, Mass. C. A. For a few months there was an exciting rivalry between the two Taunton companies, as each claimed to be the rightful owner of certain military property in the city,—camp equipage and a fund of $800 coming down from war days. The property would be first concealed by one company and then captured by the other. The courts were appealed to; but finally the matter was compromised; they divided the money, and the companies became joint owners of the tentage and other equipment.
Orders were issued by the State authorities on Aug. 20, 1866, combining the 4th and 3d Regiments in a new 3d Regiment, and on Aug. 31, Col. Mason W. Burt of Taunton was elected commander. Col. Burt had been Captain and Major in the 22d Mass. Volunteers from 1861 to 1864. The new regiment consisted of companies in Halifax (A), Fall River (B), Scituate (C), New Bedford (E), Taunton (F) and (G), and Quincy (H). The Halifax Light Infantry, the New Bedford City Guards, B of Fall River, and, a little later, the revived D of Fall River under Capt. Sierra L. Braley, with a new Scituate company, represented the 3d Regiment; while the Taunton Light Guard and Hancock Light Guards of Quincy came from the 4th Regiment. The new Taunton company entered the 3d at this time; but the Standish Guards remained aloof, as the 87th Unattached[125] Company, until 1868. At the latter date the Plymouth company came in as Co. M. Thomas J. Borden became Colonel June 23, 1868, and Bradford D. Davol followed on March 9, 1871, both being residents of Fall River. When on Aug. 2, 1876, the regiment was reduced to a battalion, the “3d Battalion of Infantry,” its only surviving companies were the New Bedford City Guards (E), the Taunton City Guards (F), the Taunton Light Guard (G), and the Standish Guards (now H). All others had been disbanded. Maj. Daniel A. Butler, former Captain of the Standish Guards, commanded the 3d Battalion. Meanwhile the Cunningham Rifles of North Bridgewater or Brockton had been organized in 1869, and named after the Adjutant General, James A. Cunningham. Originally Co. I of the 3d, this command was transferred to the 1st Battalion of Infantry, Lt. Col. Wales, in 1876; and so pioneered the way for the remainder of the “Cape” companies to follow two years later. This company exists today as the 10th Company, Mass. C. A.
One cause contributing to the disappearance of the 3d Regiment was the fact that it was called upon to perform two tours of duty for the maintenance of public order in Fall River, first on Aug. 5, 1870, continuing three days, and again Sept. 27, 1875, continuing seven days. Such service in connection with industrial disturbance is exceedingly painful to the feelings of the men. Coming as it did when class sensitiveness was acute, and when the old Civil War veterans were ready to retire permanently from active military service, it did much to break up the command. Happily such a situation can hardly recur today.
The 3d Regiment participated in musters with the 1st Brigade from 1866 to 1871, the final one being held at Lovell’s Plain, North Weymouth. In 1872 there was a regimental[126] encampment at their old Civil War mobilization ground, “Camp Joe Hooker,” Lakeville.
On Dec. 3, 1878, Major Butler’s four-company battalion was consolidated with the 1st and 4th Battalions as part of the 1st Regiment.
Col. Wales’ regiment, when he received his commission on Dec. 30, 1878, consisted of the following twelve companies:
The Fusiliers and the Chelsea Rifle-Veterans were temporarily detached from the regiment, and the Claflin Guards were gone, never to return so far as we now know.
The 1st and 8th Companies were directly from the 1st Regiment. The 2d, 6th, 7th and 11th Companies came from the 4th Battalion; the 3d Company came originally from the 4th Regiment and immediately from the 3d; the 4th, 5th and 9th Companies were from the 3d Regiment; the 10th was originally from the 3d and immediately from the 1st. A new 12th Company was organized on Dec. 12, 1878, with Capt. Sierra L. Braley in command. The new company speedily forged to the head in efficiency and has always been one of the three or four leaders in the entire regiment.
Boston celebrated the 250th anniversary of its settlement on Sept. 17, 1880, and along with other features included a magnificent military display. Everyone conceded that, while other bodies presented a fine appearance, the feature of the parade was the twelve-company 1st Regiment. That day, for the last time, the companies wore their original uniforms—old 1st Regiment, gray with towering bearskin shakos; 4th Battalion, a semi-Zouave costume with low shakos, double breasted blue coats, light blue bloused knickerbockers, and high leather leggins; and the 3d Regiment, low shakos, short blue coats, single-breasted but with three rows of buttons, and blue trousers. The regiment was received enthusiastically by the people of Boston and the day was one long to be remembered.
But changes were projected in the interests of efficiency, and first of all, in that very year, 1880, it was decided to adopt the 4th Battalion uniform for the entire twelve companies. So satisfactory did this prove that the Commonwealth utilized the same costume as a state uniform, and issued it to all the organizations of Massachusetts in 1884. Imitation is the sincerest form of flattery; but it can scarcely be said that the 1st relished sharing their distinctive uniform with all the militia,—they felt that they had paid dearly for this flattery.
Thereafter the regiment was to be subjected to a continuous and intensifying process of military improvement, at the hands first of the state authorities, and presently of the “Department of Militia Affairs” or “Militia Bureau” in the War Department. While it was inevitable that there should be a deal of experimentation whose results were not always satisfactory, it remains true that constant progress was made thruout the ensuing years. National Guardsmen, since they are human, are prone to complain; certainly they greeted[129] almost every innovation with a chorus of “kicks.” But as soon as a change had demonstrated its usefulness, it was heartily welcomed. More and more time was demanded of the men; and on the other hand part of this increased service was rewarded with increased pay by the State or Nation. The four days of camp duty required in 1873 had stretched to fifteen days in 1916, the twelve armory drills of early days to forty-eight. State and Federal pay were not an adequate recompense for the labor performed; the service was still one of unselfish patriotism. But the money invested by the authorities in camp and “rendezvous drill” pay did unquestionably testify to the higher esteem in which, with the passing years, the Guard came to stand. One noticeable consequence of the increasing military strictness was the gradual lowering of average age amongst the companies. Older men cannot be away from their business or families for so many hours and days, under ordinary circumstances. American armies have always been made up of very young men; and under the stress of increased requirements, the National Guard came to be similarly constituted.
One company participated in the exercises connected with the funeral of Pres. James A. Garfield at Cleveland in 1881.
Nathaniel Wales was elected Brigadier General on Feb. 21, 1882, and on Feb. 24, Austin C. Wellington became Colonel. The Tiger battalion, during the eight years of Wellington’s command, had become the most prominent military institution in Boston; now the entire 1st Regiment was to profit by the skill of the same man, a skill truly amounting to genius. Peculiar qualities are demanded of one who is to succeed in highest degree as a National Guardsman. He must be a well-trained soldier and a hard[130] worker as a matter of course. He must command respect for his personal character and must be able to impart knowledge to others. He must enforce rigid discipline, and must do it without resorting to regular army methods of punishment. On top of all, there has to be sufficient personal magnetism in his make-up to attract men, and enthusiasm enough to overflow and fire others. This description of a model Guardsman is nothing more or less than a description of Austin C. Wellington. No wonder that during his six years of command, the regiment was to register a new high-water mark of success.
Now the old companies began to come back. When in 1883 the Standish Guards suffered disbandment, their place was promptly taken by the company which had originally held it, the Chelsea Rifles. The Taunton Light Guard ceased to exist in 1884, and at first, the vacant 3d number was filled by the formation of a new company in Natick. Four years later the Natick organization transferred and became Co. L of the 9th, and then the Fusiliers returned to their proper place as 3d Company.
1882 was notable for the Daniel Webster centennial. Pres. Chester A. Arthur honored Boston with a visit on this occasion, and on Oct. 11, the 1st Regiment served as Presidential escort during the celebration at Marshfield. The habit of visiting distant cities now grew on the regiment, so that on August 8, 1885, they were found in New York participating in the tremendous funeral procession in honor of their old-time commander-in-chief, U. S. Grant. Their fame grew.
All Roxbury joined in celebrating the centennial of its favorite corps, the City Guard, in 1884. March 22 of that year will long be remembered for its parade, and other demonstrations of affectionate enthusiasm. In 1886 the 12th Company visited Providence, R. I., as guests of the[131] Light Infantry; and assisted their hosts to celebrate in fitting manner the two hundred fiftieth anniversary of Rhode Island’s settlement. 1887 brought the Fusilier centennial; and was likewise properly observed.
In 1887 the United States celebrated the centenary of the signing of its constitution, choosing Philadelphia, where the document had been drafted, as the place for the demonstration. Massachusetts decided to send Gov. Oliver Ames and to provide, as his military escort, the most proficient regiment in the State. It was not necessary to lose any time searching for the regiment—orders were promptly issued to Col. Wellington, that he prepare his command for the Philadelphia trip, the Commonwealth to pay expenses. Sept. 15 found the regiment on its way to Philadelphia, Sept. 16 saw them marching as one of the most brilliant units of the great parade under command of Gen. Philip H. Sheridan, while Sept. 17 was signalized by their return to Boston. D. W. Reeves was band-leader that year—no unworthy successor to Fillebrown and Gilmore—and he contributed, as his share in the event, a new march, “The March of the First.” Chaplain Minot J. Savage, who added to his gift of eloquence the rarer talent of poetry, wrote words for Reeves’ music,
The fame of the regiment became nation-wide as a consequence of the Philadelphia trip.
Col. Wellington’s most notable innovation was the introduction[132] of artillery instruction, or the re-introduction, as it was for those companies originally in the old First. The change was made for the purpose of rendering drills more interesting. It is easier to maintain the interest of artillerymen—they have their guns as a rallying-point. Moreover the artillery virus was in the 1st Regiment blood and was bound eventually to manifest its presence.
That year of Col. Wellington’s accession, 1882, the legislature appropriated $5,000 for the construction of “Battery Dalton” at Framingham. Named in honor of the Adjutant General, Samuel Dalton, it was truly a marvelous work of coast defence. Its mortars had a range of five hundred yards. After firing the projectile, the cannoneers walked over and solemnly dug the same up from its self-made grave, and fired it over again. Artillery practice was economically conducted in those pioneer days. Sept. 13, 1883, the regiment was permitted to hold one day’s practice at Fort Warren, a great concession by the War Department, and a long step in artillery progress. Sept. 4, 1885, one month after the Grant funeral, the privilege of artillery practice was repeated.
A riot in Cambridge brought the 6th Company into active service for two days on Feb. 21 and 22, 1887.
Col. Wellington’s death occurred while he still filled the office of regimental commander, on Sept. 18, 1888. The funeral is said to have been the saddest tour of duty ever performed by the regiment, an expression of heart-felt grief. They were then looking forward to occupying the new South Armory; and everyone contributed the entire pay received for the day toward the expenses of a memorial room in the building. This money equipped and furnished the gymnasium in the tower, the room now devoted to the war-game.
Thomas R. Mathews, Colonel from Dec. 10, 1888, until July 19, 1897, had served in the 2d Company during the Civil War, and had subsequently been Captain of the 1st Co. (in 1880). On Oct. 8, 1888, just before Col. Mathews’ election, the regiment took part in a general mobilization of militia in Boston. On Thanksgiving day, Nov. 28, 1889, the Boston companies were assembled at the armories in readiness for service in maintaining public order at a great fire then raging. Fortunately they did not have to leave their stations.
Prior to 1890 the Companies had been quartered in various halls and rinks of Boston and the suburbs, Faneuil Hall being the most coveted location, unavailable, however, most of the time, and Boylston Hall, Boylston and Washington Streets, ranking next.
1890 was the date of the South Armory dedication. Massachusetts had entered, after long years of discussion, upon her policy of providing adequate accommodations for her volunteer militia. New York had led the way ten years earlier; and the Massachusetts authorities were especially indebted to the N. Y. 7th for providing an armory after which others could pattern. It is a far cry from the 7th’s building to that on Irvington St., but there is a similarity of type. It must be borne in mind that the South Armory was relatively one of the best in the country when the 1st Regiment occupied it in 1890. Nor had the railroad developed into such a nuisance at that time. The South Armory was the first State armory in Massachusetts; and led the way for the entire series, by means of which our troops are quartered as well as any in the land; its dedication was an important event in military history. Fall River followed, and dedicated her State armory in 1895, Cambridge and New Bedford in 1903, Brockton in 1906, Chelsea[134] in 1907, and Taunton in 1917. Chelsea and Brockton subsequently lost their buildings by fire; the structures were rebuilt respectively in 1909 and 1912.
Col. Mathews’ command served as personal escort to Gov. William E. Russell, Feb. 29, 1892, at the ceremony of presenting Massachusetts’ first long-service medals. Amongst others, twenty-eight officers and men of the 1st received medals.
An artillery tour was held at Fort Warren, Aug. 7 to 13, 1892, when the men had practice on the eight-inch muzzle-loading converted rifles and the fifteen-inch muzzle-loading smooth-bores. Modern coast artillery had not yet “arrived”; but the regiment was making progress. In 1893 they encamped at Framingham and manned “Battery Dalton” once more. In 1895 they had their last experience with these twelve-inch mortars—and the sand-bank five hundred yards away; 1894, 1896 and 1897 saw them at Fort Warren each summer. In 1896 the regulars did not take them seriously and could not “waste time” instructing the militiamen; in 1897, with Lieut. Erasmus M. Weaver temporarily detailed as instructor, the regiment made progress. Thereafter, until 1911, regular officers from the forts added to their other service the duty of visiting the South Armory and coaching the militia regiment.
All twelve companies were ordered to be in readiness on March 10, 1893, for service in connection with the disastrous “Lincoln St. fire,” but were not marched out of the armories.
The state expended $2,500 in 1894 providing a model battery at the South Armory. While crude compared with the huge gun and mortar installed in 1913, to which the name “Battery Lombard” is sometimes given, this earlier[135] artillery installation marked a long advance in drills and instruction.
On Oct. 9, 1894, the regiment again participated in a general mobilization of the militia at Boston. The monument to Robert Gould Shaw, on the Common, was formally dedicated May 31, 1897, and the regiment paraded in honor of the event. One feature of the day recalled certain historic processions of thirty years previously—the New York 7th, in which Col. Shaw had once served, came on to have a share in this demonstration of affection.
On June 1, 1897, by act of the legislature, the regiment received a new name—it became the 1st Regiment of Heavy Artillery. In point of fact it had begun to separate from the 1st Brigade back in Col. Wellington’s time, and had become increasingly committed to the artillery branch; this act of legislation officially recognized a transition which had already taken place. Now the facings on the uniforms could be changed from the blue of infantry to the brighter and more distinctive scarlet. Massachusetts was the first state to have heavy artillery in its militia—the old regiment was again “first.” Companies were rechristened “batteries” in connection with the change of service.
Col. Mathews became Brigadier General on July 19, 1897, and Charles Pfaff succeeded as Colonel on July 28. Col. Pfaff’s military training had been in the Cadets, and as Captain of the 8th Company, Coast Artillery; and he had served four years as Major. To him was to fall the honor of commanding the regiment during its Spanish War service.
There was nothing unexpected about the war with Spain. From the day the “Maine” was destroyed until April 25, when war was declared, more than two months elapsed. Members of the command were in constant readiness during this entire period for the summons which they knew must[136] come; and it was well understood that instant mobilization would ensue upon receipt of orders.
But if we had reason to be in readiness, we also had good cause to anticipate danger and hardship. The United States was notorious for lack of preparedness, both by land and sea. On the other hand the might of the Spanish fleet and the fame of the “Spanish infantry” had been so magnified that much popular trepidation existed. Boston anticipated instant attack; merchants and bankers deposited their treasure with inland banks; while real estate owners were insistent that the national government should afford them protection. Col. Pfaff and his men were to volunteer in the belief that they would meet with instant and active fighting. Beyond question the general public drew a deep sigh of relief as the blue-clad column, on that fateful 26th of April, to the music of the “March of the First,” swung steadily down Huntington Ave. The out-of-town commands had left their home stations early and received Godspeed from newsboys and milkmen only. In Boston, however, the display of enthusiasm left nothing to be desired; and demonstrated not only the city’s dependence upon its heavy artillerymen but also its real affection for the red-legged organization. They were paid from April 25.
Besides Col. Pfaff, the regimental officers were: Lt. Col., Charles B. Woodman; Majors, Perlie A. Dyar, George F. Quinby, James A. Frye; Captains, 1st Co., Joseph H. Frothingham; 2d Co., Frederic S. Howes; 3d Co., Albert B. Chick; 4th Co., Joseph L. Gibbs; 5th Co., Walter L. Pratt; 6th Co., Walter E. Lombard; 7th Co., Charles P. Nutter; 8th Co., John Bordman, Jr.; 9th Co., Norris O. Danforth; 10th Co., Charles Williamson; 11th Co., Frederick M. Whiting; 12th Co., Sierra L. Braley. Capt. Braley had been private and corporal in the 3d Reg. during its nine-months[137] service in 1862. He had been 2d Lieutenant in Battery I, 2d Mass. Heavy Art., and in Bat. L, 14th U. S. Colored Art., during 1864 and 1865. From 1866 until 1878 he continuously held commissions in the 3d Reg. and, after 1878, in the 1st, his latest command being the 12th Company. Capt. Braley was the only officer of the regiment to serve in both the Civil and Spanish Wars.
On April 26 the regiment began active duty at Fort Warren, the orders reading that they would encamp there for eight days. Five more days were added to this; and then the command was taken into the U. S. service “for the war.” Since the thirteen days of state duty is added to the total in computing their record, they were the first regiment of the entire nation to begin war service. The Old First still led.
When they left the armory for Fort Warren, there were only six men absent from the command—four sick and two out of the country. Opportunity was later given for men with families to withdraw, if they desired; and all were subjected to a rigid physical examination. Ultimately three per cent. were rejected for disability and eight per cent. excused for family reasons. These vacancies were immediately filled from the throngs of would-be recruits who volunteered. It was a disappointment to the regiment that the War Department never permitted them to increase their numbers to the full war strength; their Spanish War roster bore 751 names.
They started out in the rain on April 26, and it seemed as if it would rain until they returned; during their first six weeks, they were blest with sunshine only three days. By and by, when they had ceased to care, the weather changed and they had sunny days. At Warren they were quartered in wooden buildings, originally election booths in the city;[138] prisoners from Deer Island were imported to assist in erecting these; and some humorist promptly designated them the “3d Corps of Cadets.” While in the state service, the regiment was fed by a caterer, after the fashion then prevalent at Framingham. When they became U. S. soldiers, they messed themselves. All thru this war, ammunition was very scarce indeed. The least a self-respecting military post can do is to fire morning and evening guns; this was possible in 1898 only by cutting cartridges in two and using half-charges. Most of the ordnance was of Civil War vintage, or very slightly more modern.
Spain had been vastly over-rated, and there was very little fight in her. The regiment passed a busy and profitable month at Fort Warren from April 26 to May 30, being mustered into the United States service on May 7. During these weeks the companies or “batteries” attained a high degree of proficiency in both infantry and artillery drill. Shortly after midnight on May 13 the Engineers’ steamer, the “Tourist,” came down the harbor from the Navy Yard to announce that the Spanish fleet had actually been sighted off Nantucket. But men watched in vain for the enemy vessels to appear.
On Memorial day, thru the exigency of service conditions, the companies were moved and distributed along the coast at posts ranging from Portsmouth to New Bedford. Maj. Frye and the Cape companies remained at Warren. Lt. Col. Woodman with the 3d and 11th Companies garrisoned the fort at Clark’s Point, New Bedford, a work which had been in existence since 1857 but which awaited July 23, 1898, and these companies as godfathers, before it was christened Fort Rodman. The Colonel, Headquarters, and the remaining six companies proceeded by boat to various points along the North Shore, at some of which militia field artillery[139] batteries had previously been on guard, the Colonel himself being stationed at Salem in command of the entire Essex County district. This transfer of troops was accomplished without peril or even discomfort. The 1st and 7th Companies under Maj. Dyar became the garrison at Salem; Maj. Quinby and the 2d Company were at Gloucester; the 6th Company was on Plum Island near Newburyport, and subsequently at Portsmouth; the 5th Company at Marblehead; and the 8th at Nahant as guard of the mining-casemate. Lieuts. E. Dwight Fullerton of the 8th Company and P. Frank Packard of the 2d were specially detailed to duty with the regulars at Fort Columbus, Governor’s Island, New York, and remained there several months. Lieut. Fullerton was called upon to untangle the snarl into which the War Department had gotten with regard to records of sick soldiers in the New York hospitals.
It fell to the lot of certain “batteries” to reconstruct and man ancient earthworks whose history ran back many years. At Salem, Fort Pickering was put in commission; at Gloucester, the old Stage Fort where Myles Standish once came near having a battle; near Portsmouth, Forts Constitution and McClary; and at Marblehead, Fort Sewall. This is very romantic to relate. No doubt the renovated works with their armament of obsolete field pieces could have afforded some protection against Spanish raiders. But those who were called upon to occupy works built for seventeenth, eighteenth and nineteenth century warfare, and modernize them so as to render them useful under twentieth century conditions, agree in testifying that the romance is all in the narrative and not any in the fact. The 6th Company had at first been stationed in an earthwork on the Plum Island beach which had been constructed by the field battery, whom they relieved; as Plum Island, in[140] June, is notable chiefly for flies and fleas, this company was glad enough when the transfer to Portsmouth brought the men again on solid ground. Fort Constitution had a long history—it used to be known as Fort William and Mary, and from its ancient magazine came the powder used by the patriots at Bunker Hill; but in 1898 it was a comparatively modern work, and mounted a battery of eight-inch rifles.
This Spanish War service is something of which the regiment are justly proud. On April 26, Col. Pfaff led 99 per cent. of the full militia strength of his command into the harbor forts, itself a conclusive demonstration that the National Guard is a dependable force. Foremost were they in the entire United States to assume their post of duty. First of all volunteers were they to be mustered in; the genius of “The Old First” was in control. Thruout the entire two-hundred-three days of duty they maintained the very highest standards of efficiency and discipline. It noway lessened the credit belonging to these volunteer soldiers that the Spaniards were so wise as to keep at a safe distance from the Massachusetts coast; the warmest kind of a welcome was awaiting them, had they come. When on Nov. 14, the command were mustered out of Federal service and returned to the militia, they had added a most creditable chapter to the long annals of their organization.
In 1899 a tour of duty was performed at Fort Rodman; and so satisfactory did it prove that the post was chosen for the annual coast defence exercises, with one exception, until 1906. In 1902 some companies were stationed at Fort Greble and other Rhode Island posts. The only serious objections to Rodman were the haze and fog, which hang low over Buzzard’s Bay. As a consequence of the Spanish War, the flannel shirt and the khaki suit became part of the regimental uniform. Oct. 14, 1899, the regiment participated[141] in the ovation to Admiral George Dewey, and at the same time turned their Spanish War flags and colors over to the custody of the State. Col. Pfaff retired as Brigadier General Apr. 20, 1900. His loyal and generous interest in the old regiment has been shown in making possible the publication of this history.
Col. James A. Frye, who commanded the regiment from May 4, 1900, until Jan. 4, 1906, had served as Major during the Spanish War. Upon relinquishing command of the regiment, he became Adj. Gen. of the State. Col. Frye was the one selected to record the services of the command during the Spanish War; and his history will always stand as a worthy monument to his memory.
In 1903 the regiment participated in joint coast defence and naval maneuvers at Portland harbor, of which the chief feature was the long hours. The men were on duty all day and all night, so that sleeping almost became a forgotten art. On June 25, 1903, the Coast Artillery shared in the exercises of dedication around the magnificent statue of their old commander, Gen. Joseph Hooker. Members of the regiment had been foremost in securing the appropriation for the statue; and heartily did they rejoice to see the beautiful bronze by D. C. French which finally crowned their labor.
1903 witnessed the most important national militia legislation since the original militia act of 1792. By the “Dick law,” with amendments added in 1908, the militia really became a national force, with clearly defined liability of service; and the name, National Guard, was officially conferred upon it. Nevertheless Massachusetts continued to call her citizen soldiers Volunteer Militia. 1904 brought the adoption of magazine-rifles.
On Nov. 1, 1905, the regiment was redesignated as the[142] “Corps of Coast Artillery,” a title which has been used by anticipation at various times in this book. Behind the change lay the fact that the War Department had been testing militia heavy or coast artillery; and the latter, in the estimation of the Washington authorities, were not found wanting. A regiment is a closely united body, and is supposed to operate as a unit. A corps, on the contrary, is a group of smaller units associated for administrative purposes, but acting more or less independently in warfare. Tactically a corps is not a unit; each of its members is. Inasmuch as few forts require so much as a full regiment of coast artillery to garrison them, it was deemed best to organize the artillery in smaller units, in companies, better suited to the needs of the average fort. Companies are combined in fort commands of two or more each. Moreover, by 1905, a clear distinction had arisen between coast artillery and heavy artillery; and it was necessary for organizations to decide which branch of the service they would choose. Heavy artillery follows a mobile army, and is used to batter down fortifications. Coast artillery mans the guns and submarine mines of our coast fortifications, and is not a mobile force. A moment’s consideration will convince anyone that the Massachusetts men chose the more exciting branch, when they became coast artillery. The heavy artillery fire from great distances, while themselves entirely out of range of any answering shots, and fire at fixed targets. The coast artillery fire at ships, moving targets possessing the ability to return our shots, who will certainly and quickly “get us” unless we “get them” first. An increase of interest in the scientific side of artillery work immediately followed, and stimulated every officer and enlisted man to do his best. Companies were no longer termed “batteries,” but were given numbers, the designations indicating seniority of[143] charter. The band continued to wear the old regimental number “1” on their uniforms.
To the twelve companies of the Corps were, in 1907, assigned regular stations in the fortifications of Boston harbor, to which it would be their duty to repair at once in case of threatened hostilities. As they exercised each summer on the very guns which they would man in actual service, they grew familiar with their work to a degree never before possible. After experimenting at seven different posts, in 1913 the 1st, 2d, 3d, and 6th Companies became part of the garrison of Fort Strong on Long Island (named in honor of Gen. Wm. K. Strong); the 5th, 7th, 8th and 11th Companies were assigned to Fort Andrews; and the 4th, 9th, 10th and 12th Companies to Fort Warren.
Col. Charles P. Nutter commanded the Corps from Jan. 23, 1906, until March 10, 1910; he had been Captain of the 7th Company during the Spanish War. In August, 1907, the companies participated in a general mobilization of militia at Boston in connection with the “old home week” celebration. The War Department now determined to make a slight change in the name of the organization, perhaps in the interest of alphabetic symmetry. Whatever the cause may have been, on Nov. 15, 1907, the words were transposed and the “Corps of Coast Artillery” became the “Coast Artillery Corps.”
It had been so long since the Boston companies were called out to maintain public order at a great fire, that such a contingency was not regarded seriously. Suddenly, on April 12, 1908, as men were returning from Palm Sunday services, they received word that Chelsea was in the clutch of a mammoth conflagration. Vast clouds of smoke could be seen arising on the north-eastern horizon; Boston’s neighbor was indeed stricken.
The 5th Company promptly responded to the call for help; but it was evident that assistance must come from outside; local forces were entirely inadequate to meet the emergency. At 5 P. M. the other companies were assembled at their armories; and at 8.30, after eating a hearty supper, they started for their posts of duty. The work was of the usual sort, rescuing property and saving lives, guarding the property from vandals and thieves, and assisting the young, the weak and the aged to places of safety. Only men in uniform command confidence at such a season of disorder; only disciplined men, working together, can accomplish results. Right nobly did the Corps meet its responsibilities during its three days in Chelsea, and many a firm friend did it win for the organization. The 5th Company continued on duty five days longer.
Upon the local company fell an especially cruel test. First, their new State armory came in the path of the flames and was swept to ruins—while the troops, on duty in the streets, were aware that their own civilian clothing in the lockers was going up in smoke. Worse yet, the fire spread until it involved the homes of many militiamen. The soldiers could hardly keep their thoughts on their work, while their own loved ones were in danger, and their own household effects in need of removal to places of safety; their minds wandered homeward—but the men themselves quietly kept their posts. There never has been any question about the discipline of the Corps in seasons of emergency; the 5th Company proved true to the ancient traditions.
 The Author
The Author
Companies of the Corps had been visiting Washington at inauguration time ever since 1835; and almost the entire command went in honor of T. Roosevelt in 1905; finally, in 1909, the Corps went as a regiment and participated in the inaugural parade of President William H. Taft. Participants[145] in such a parade invite comparison between themselves and troops from many other states—military critics, such as Maj. Gen. J. Franklin Bell and Brig. Gen. E. M. Weaver, were unanimous in asserting that the Mass. Coast Artillery Corps and the West Point Cadets bore off the palm for fine military appearance, not even the N. Y. 7th doing as well.
By 1909 the Corps had settled in its custom of holding coast defence exercises at the harbor forts; consequently, it was with disappointment and even resentment that they found themselves ordered to serve as infantry in the so-called Cape maneuvers in August of that year. A difference of opinion had arisen between the Adjutant General of Massachusetts and the Corps officers concerning money matters; and this tour of duty was laid on the latter as a penalty. Soldiers must obey orders; however irksome and unwelcome the service, no one in the “blue army” could truthfully say that the “red-legged infantry” fell below their comrades in efficiency.
Col. Walter E. Lombard was in command from March 17, 1910, until Feb. 21, 1915. At the latter date he became a Major General on the retired list. Col. Lombard had been Captain of the 6th Company during the Spanish War.
In June, 1911, the War Department detailed a regular army officer to the Corps as Inspector-instructor, Capt. Russell P. Reeder being the first to perform that duty; at once the standards of instruction were improved, and the artillery work profited greatly from the presence of such a skilled teacher. Sergeant-instructors, four in number, were presently added as assistants to the commissioned officer who performed the chief duties. An immediate result of the Inspector-instructor’s work was the wonderful shooting done by the 4th, 12th and other companies during the 1911 tour[146] of duty. After that date all officers were required to qualify in the technical part of their work by passing regular War Department examinations. The fourth officer to fill this detail, Capt. William H. Wilson, commenced service in Jan., 1915, and soon succeeded in systematizing the work of drill and instruction to a point far beyond anything previously attempted; so that his term of duty brought about a great increase of Corps efficiency. Capt. Wilson was especially qualified for this service in that he had himself been a National Guardsman, and had entered the U. S. army from a New York regiment. Capt. Wilson not only emphasized the artillery work; he also laid stress upon matters thitherto slighted,—company administration, higher infantry, and gunners’ instruction.
Again in March, 1913, the entire Corps made its customary pilgrimage to Washington for the purpose of participating in the Presidential inauguration, this time paying the honor to Woodrow Wilson. As in 1909, so now, they were most enthusiastically praised for their fine military appearance and splendid marching. On May 30, 1913, the Gate City Guard of Atlanta, Ga., visited Boston as guests of the Tigers. 1913 was the fifteenth anniversary of the regiment’s service in the Spanish war; and on Sept. 20, Col. Lombard tendered a review on the Common to the veterans. On that occasion active officers marched with the veterans, in the positions which they had filled fifteen years previously. Lt. Col. Woodman was in command of the veterans, and Col. Lombard marched as Captain of the 6th Company; while Maj. Shedd led the actives. After the parade, there was a collation, followed by motion pictures, in the Armory.
So well had the 5th Company acquitted themselves at the Chelsea fire that they were one of the commands called out to maintain order at Salem when, on June 25, 1914, that[147] ancient city was threatened with destruction; the emergency was similar to that of 1908. To the Chelsea men fell the duty of organizing a huge camp of refugees at Forest River park; and they remained in service seven days.
Joseph Hooker was born Nov. 13, 1814, and exactly one hundred years later, his loyal admirers, among whom were numbered the officers of the Coast Artillery Corps, paraded, and participated in a great meeting at Tremont Temple in honor of his memory. Capt. Isaac P. Gragg, former Captain of the 1st Company, was always the prime mover in organizing celebrations in memory of Hooker, and he justly felt that the event of 1914 was the culmination of his life-work. Alas! Capt. Gragg did not long survive the centennial of his beloved commander.
Edward Dwight Fullerton was elected Colonel Feb. 9, 1915, and continued in command until retired as Brigadier General, January 16, 1917; he had served as 1st Lieutenant of the 8th Company during the Spanish War.
The “House of Governors” was in session at Boston in Aug., 1915, and Gov. David I. Walsh ordered a mobilization of the militia on Aug. 26, as a compliment to the State’s guests. As the authorized strength of the companies had recently been raised, the Boston papers commented upon the appearance of the Corps, in fifteen platoons of twenty files, as “wonderful,” not only for numbers, but for steady marching.
President Wilson called the militia out for service on the Mexican border June 18, 1916. Massachusetts shared with New Jersey the honor of placing her full quota of organizations at the post of danger in the shortest time; and since the Massachusetts quota was far larger than that of New Jersey, her record was the more creditable. On the ninth day after the troops were summoned to arms, they started for[148] Texas. Of course the Coast Artillery could not be included in this great national mobilization, as they might not safely be spared from their stations at the forts. But on June 26, the day the mobile troops started south, the officers and non-commissioned officers of the Corps were assembled at the Framingham mobilization camp (“Camp Whitney”) for the purpose of drilling the hundreds of recruits there gathered. The officers and non-commissioned officers of the 6th Inf. also took part in this work of instruction. No recruits for Mass. regiments ever constituted a finer personnel than those eager to have a share in the Mexican service. Coming from all over the state, they were uniformly willing, sober, and quick to learn, in order that they might reach the front as soon as possible. The Corps became responsible for the “2d Provisional Regiment,” consisting of about one thousand men, destined for the 8th and 9th Inf. Regiments, and also for the cavalry, machine-guns, supply companies, field artillery, and even for the regimental bands. Wonderfully rapid progress was made, so that in two weeks, the recruits were equipped, and drilled, and ready to go forward. The Corps’ recent training in company administration stood them in good stead and made possible such rapid work. Certain officers of the Corps were drafted into the U. S. service, in order to accompany the recruits on the southward journey.
With grave disorder on the Mexican border, and with the greatest war of the world’s history approaching its crisis abroad, conditions were once more favorable for Congressional action in behalf of the militia. Since threatenings of danger were loud and insistent, the legislators were induced to take an additional forward step in rendering America’s citizen-soldiers efficient. The National Defence Act, as the new law was termed, completed the process of federalization by placing the militia fully under War Department control,[149] and also provided a modest rate of remuneration for armory drills, thus making it an object for men to maintain regular attendance. Massachusetts had done what she could to encourage the passage of the law, by herself adopting, during the prolonged debate on the National Defence Act, a State law offering to hand over her militia to the Federal government. Indeed by her provision for remunerating men for attendance at rendezvous drills, the Commonwealth had taken her place beside Ohio five years previously as a pioneer in paying her militia. The legislation became effective on June 3, 1916, and went fully into operation on the first of the ensuing month.
Right in the midst of their tour, on June 30, the officers and men were asked to take the new Federal oath, under provisions of this act. To the officers the oath was administered at Framingham, while the enlisted men were assembled in their armories that night, for the purpose of swearing in. Almost without exception, and then always with valid excuse, the members of the Corps assumed this additional obligation and became Federal soldiers. Headquarters, band, enlisted specialists, and twelve companies—the entire Corps—were, on June 30, recognized by the War Department as federalized National Guardsmen and were entered upon the U. S. payrolls. Of all the Massachusetts Volunteer Militia, the Coast Artillery Corps were the only organization to comply fully with the new requirements and be recognized as a unit.
Companies of the Corps volunteered their services in connection with exhibitions for the benefit of the Mass. Volunteer Aid Association, which was raising funds to relieve distress amongst the families of National Guardsmen then at the border. An unusually fine military display was given at the ball-grounds in connection with a benefit ball-game[150] between the Red Sox and the St. Louis teams on July 17.
Many Corps officers were detailed for recruiting duty during the summer and autumn of 1916, in an effort to raise the numbers of the regiments at the border to full war-strength. Consequently the coast defence exercises at the forts in August, 1916, were seriously handicapped. Many men were forced to perform double duty. In spite of this limitation, splendid artillery scores were made by the 2d, the 6th and other Companies, the 6th Company earning the coveted Knox trophy.
Successive steps followed rapidly during the summer and autumn of 1916 to render effective the process of federalization. By order of Gov. Samuel W. McCall on July 17, the title “Massachusetts Volunteer Militia” was discontinued, and the force redesignated “National Guard, Massachusetts.” In October the War Department authorized the companies to increase their strength from seventy-eight to one hundred twelve officers and men; new regulations established standards of drill and instruction with which organizations must comply in order to qualify for pay; a National Guard reserve was created by transfer of men who had completed their three years of active service; promotion requirements were established for officers; and an assistant Inspector-instructor was detailed to the Corps, Capt. Hugh S. Brown taking his place beside Capt. Wilson. While the new National Guard regulations raised the standard and “tightened the reins,” it is a tribute to the high grade of efficiency already attained by the Corps that Federal control caused no revolutionary changes of method in the organization. As part of the federalizing process, on Dec. 9, 1916, the Militia Bureau of the War Department redesignated the command, and abolished the word Corps from its title.[151] Thereafter it was the “Massachusetts Coast Artillery, National Guard.” On January 16, 1917, the organization received back its old and well-loved designation, and became the 1st Coast Defense Command, Massachusetts Coast Artillery, N. G.; once more Massachusetts could speak about her senior regiment as “The Old First.”
George F. Quinby, a former Lieutenant of the 7th Company and Captain of the 2d Company, and Major during the Spanish War, became Colonel, January 20, 1917. The events of Col. Quinby’s administration,—our break with Germany on February 3, the “armed neutrality,” the 5th Company’s good fortune in being first of all the command to engage in active service when, for twenty-four hours they guarded the electric power-system of Chelsea against hostile interference, the declaration of war on Good Friday, April 6, and the Old First’s service in the war, the revival and establishment of compulsory universal military service—must form the subject-matter of another chapter to be written at some later day.
If it is a long time from 1784 to 1917, it is also a long way from the independent companies of artillery and light infantry of the earlier time to the present Coast Artillery; the militia of one hundred thirty years ago could not recognize itself in the National Guard of today. When in 1792 Congress passed the first militia law, it commenced a process of federalization which was to progress by successive stages until its completion in the National Defence Act of 1916; with federalization came efficiency.
In the beginning, volunteer companies which owned uniforms separated themselves from the train-band of their day, and assumed duties and responsibilities outside of what the State demanded from every citizen. The train-band drilled not more than four times a year, and mainly on the fourth Wednesday of May—the volunteers at least thrice or fourfold that amount. In order the more easily to distinguish themselves from the train-band, the volunteers became artillery or light infantry or grenadiers or rifles or cavalry; and each class sought proficiency in some special kind of drill.
Boston’s companies of artillery were associated in a small battalion several years before the light infantry companies were willing to relinquish their independence; and so our regimental history begins in the artillery branch. Presently, in the days of the “legionary brigade,” regimental spirit began to manifest itself among the light infantry companies, resulting in the Sub-legion of light infantry. The[153] artillery battalion became most famous as the “Fighting First” of Civil War times, and is today primarily represented by the 1st Company. From the light infantry Sub-legion there ultimately developed the old “Tiger” 1st Regiment, of which the 2d Company is today the senior representative. Presently a drift set in from the infantry command to the artillery regiment, one company transferring after another, until even the regimental number itself passed from the former to the latter; this process is illustrated by the career of the 3d Company. Eventually Plymouth and Bristol counties made their valuable contribution to the regimental composition—the remnants of the 3d and 4th Regiments—as represented today by the 4th Company. The consolidation of 1878 welded all these elements into a single, compact, unified body, the Coast Artillery of today. While the old regiment have come under complete Federal control, and hold place in the first line of the U. S. Army, they have not in the least abated their life-long loyalty to the State which gave them birth.
“The National Guard is not only the reserve for the regular army; it is also the reserve for the police, the fire department, and life-saving service. Its members are genuine soldiers of peace.” (Curtis Guild.) Twelve different times have units of the regiment been called out by the Commonwealth to maintain public order. On many other occasions the companies were warned to be in readiness; indeed the headquarters of the command is the most sensitive barometer for registering the approach of social disorder. Twelve times the companies actually marched forth. Curtis Guild’s remark about the militia was intended to apply especially to military service in connection with great and disastrous conflagrations; five times have the regiment performed such duty.
But after all, it is war-time which tests the soldier. If he fails to respond in his country’s hour of need, his other virtues are of small value. Measured by this test, regimental patriotism has shown itself to be trustworthy. In the days just prior to the attack upon Fort Sumpter, there were in existence seventeen companies which were destined sometime to become associated in the present Coast Artillery. In the seventeen companies were twelve hundred members. By some process of magic, of patriotic magic, when the alarm of war sounded, the twelve hundred militiamen multiplied themselves into no less than seven thousand five hundred volunteers. The “Old First” never failed in seasons of public need; they were always a fighting regiment.
“Vigilantia,” the regimental motto, is another name for watchfulness, for preparedness. As if the choice of a motto were prophetic, or at least significant of the regimental character, the Coast Artillery have always managed to be so fully prepared that they were able to get into active service amongst the very leaders. No troops were more prompt in reaching the post of danger than the “minute men of ’61”; and amongst them were our companies in the 3d and 4th and 5th and 6th Regiments. A few weeks later the 1st Mass. was the first long-term regiment to be mustered in thruout the entire United States, the first not only in the Civil War, but in any war. Again in 1898, when National Guard regiments everywhere were actively competing for priority in volunteering, the “1st Heavies” managed to reach their station at Fort Warren, and then to be mustered in as a regiment, before any of their rivals in Massachusetts or elsewhere. Three times, at least, was “Vigilantia” translated into action.
 Modern Battery
Modern Battery
 The Chaplain in Action
The Chaplain in Action
Veterans of the old regiment have organized themselves to perpetuate cherished traditions of the past. Each of the[155] Civil War commands is represented by a veteran association—the 1st, the “Minute Men,” the 13th, the 24th, the 42d in eastern and western sections, the 43d and others. As old age comes on with passing time, it is inevitable that associations of war veterans must become less numerous and less active each year. The Coast Artillery take a real interest in the Hooker Association and the Stevenson Memorial Association. Amongst the companies, live veteran organizations are maintained by graduates of the Roxbury City Guard, the Boston Light Infantry (the Tiger Veteran Association, incorporated March 28, 1882), the Fusiliers, and the Pierce Lt. Guard. Indeed the Fusiliers have been a prolific source of veteran associations. The first, the Fusilier Veteran Association, was organized by leading members of the company, including five ex-Captains, in April, 1878, at the time when the company was about to pass from the 1st to the 5th Reg., and is today in full vigor and prosperity, retaining the old red-coat uniform. When this association had opened its membership to others than actual veterans, on Aug. 2, 1900, certain graduates formed a new organization of 3d Company veterans, the Independent Boston Fusilier Veterans. Their numbers were small, and on July 2, 1906, in order to provide a supply of new material, they invited veterans of other 1st Reg. companies to join, and thus became transformed into the “1st Reg. M. V. M. Veterans.” The latter body now has one hundred forty members. Joe Hooker Post, No. 23, G. A. R., of Boston, and Theodore Winthrop Post, No. 35, of Chelsea, were made up largely of 1st Regiment veterans; and were always in friendly and helpful relations with the active command. With our wealth of noble heritage from the past, comprising as we do all that remains of the old “Legionary Brigade” and its successor, the 3d Brigade of the 1st Division,[156] once Boston’s pride, and including all the 3d and 4th Regiment organizations having continuous history, it is desirable that the Coast Artillery should have an active association of veterans which may combine the forces now scattered amongst the company associations; the provision in the National Defence act for a “reserve battalion” seems to open a door of possibility.
Such a history as this can have no conclusion, it can only halt for the moment; while the pages were in press, the regiment was summoned by the Nation to perform military duty. The fruit of a noble past is a useful present. The soul of the “Old Regiment,” like John Brown’s of which they taught America to sing, is “marching on.”
1789, Batl. of Art., 1st Div. Suffolk. 1794, Art. Batl., 1st Bri., 1st Div. (a) Aug. 22, 1797, Sub-legion of Art. and (b) three companies became Batl. of Art., 1st Bri., 1st Div. (a) Mch. 12, 1810, Sub-legion became Batl. Art., 3d Bri., 1st Div. June 26, ’34, Reg. Art., 3d Bri., 1st Div. ’36 Batl. Art., 3d Bri., 1st Div. Apr. 24, ’40, 1st Batl. Art., 1st Bri., 1st Div. (b) 1831 companies of Batl. Art., 1st Bri., 1st Div., attached to 1st Reg. Inf., 1st Bri., 1st Div. June 26, 1834, again Batl. Art., 1st Bri., 1st Div. Apr. 24, ’40, 2d Batl. Art., 1st Bri., 1st. Div. June 4, ’44, Batls. united in 5th Reg. Art., 1st Bri., 1st Div. Feb. 26, ’55, 2d Reg. Inf. Jan. 24, ’61, 1st Reg. Inf. 1862, 42d Reg. Inf. May 18, ’66, 1st Reg. Inf., 1st Bri. July 6, ’76, 1st Batl. Inf., 2d Bri. Dec. 3, ’78, 1st Reg. Inf., 1st Bri. Jan. 1, ’97, 1st Reg. Heavy Art. Nov. 1, 1905, Corps of Coast Art. Nov. 15, ’07, Coast Art. Corps. July 17, ’16, “M. V. M.” changed to “N. G., Mass.” Jan. 16, ’17, 1st Coast Defense Command, Mass. Coast Artillery, National Guard.
1st (D)—Roxbury Art. organized Mch. 22, 1784, redesignated City Gd. Nov. 24, ’57. 3 cos. in Civil War. Redesignated 1st Company, 1905.
2d (K)—(1) Washington Lt. Gds. or Inf. transferred from G 1st Inf. ’59, disbanded ’59. (2) Chadwick Lt. Inf. organized ’61, disbanded ’64. (3) Ware Oct., ’62, disbanded[158] Nov. 11, ’64. (4) 81st Unat. Co. ’66, disbanded ’76. (5) Boston Light Infantry transferred from A 4th Batl. Inf. ’78, redesignated 2d Company, 1905.
3d (G)—(1) Bay State Art., Cambridge, 1853, dis. 1854. (2) ’55, dis. ’57. (3) Fusiliers from F 1st Inf. Mch. 1, ’59; 7th Unat. Co.; Apr. 13, ’64, 25th Unat. Co. 5 cos. in Civil War. To D 5th Inf. Dec. 3, ’78. (4) Taunton Lt. Gds. from C 3d Inf. ’78, dis. ’84. (5) Natick ’84, to L 9th Inf. ’88. (6) Fusiliers from D 5th Inf. Mch. 26, ’88, to 3d Company, 1905.
4th (E)—(1) Dorchester Art. 1786, dis. 1844. (2) Cowdin Art. 1851. (3) ’54 American Art. (4) ’56 Lafayette Gd. (5) Pulaski Gds. from I 1859, dis. 1864. (6) dis. Nov. 7, ’62. (7) Oct. ’62, dis. Nov. 11, ’64. (8) 1st Unat. Co. 1864, to E ’66, dis. ’76. (9) New Bedford City Gds. from E 3d Inf. Dec. 3, ’78, to 4th Company, 1905.
5th (H)—(1) Shields Art., Dorchester 1853, dis. 1855. (2) Mechanic Rifles from H 1st Inf., dis. ’59. (3) Wardwell’s Tigers ’61, to F 5th Inf. ’61, dis. ’61. (4) Chelsea Volunteers ’61, Apr. 19, dis. ’64. (5) Oct., ’62, dis. Aug., ’63. (6) July 20, ’64, dis. Nov. 11, ’64. (7) Chelsea Rifles, 4th Unat. Co., ’63, to H May 18, ’66, to L 8th Inf. Dec. 3, ’78, to H 8th Inf. Dec. 21, ’78. (8) Standish Gds., Plymouth from H 3d Inf., ’78, dis. ’83; (reorganized as D 5th Inf. ’88). (9) Chelsea Rifles from H 8th Inf. June 11, ’83, to 5th Company, 1905.
6th (B)—(1) Columbian Art. June 17, 1798, dis. 1855. (2) Union Gds., E. Boston, transferred from H 1st Inf. & B 3d Batl. Inf. 1855, dis. 1864. (3) dis. Nov. 7, ’62. (4) Medway Oct. ’62, dis. Nov. 11, ’64. (5) 9th Unat. ’64 to B ’66, dis. Feb. 7, ’72. (6) from C Sept. 20, ’72, dis. ’76. (7) Massachusetts Guards from B 4th Batl. Inf. ’78, to 6th Company, 1905.
7th (C)—(1) Washington Art. May 29, ’10, Lt. Gds. 1855, to K 6th Inf. 1861, dis. ’61. (2) to K 4th & 29th Inf., dis. ’64. (3) North End True Blues from L ’61, dis. ’64. (4) dis. Nov. 7, ’62. (5) Oct. ’62, dis. Nov. 11, ’64. (6) 45th Unat. E. Boston, ’66, to B ’72. (7) Claflin Gds. from L Feb. 20, ’72, to C 5th Inf. ’78. (8) Pierce Lt. Guard from C 4th Batl. Inf. ’78, to 7th Company, 1905.
8th (A)—(1) Boston Art. May 7, 1785, 1856 Boston Phalanx, Dec. 15, 1860, transferred to A 4th Batl. Rifles, and then A, 13th Inf. ’61, disbanded ’64. (2) Brookline ’61, dis. ’64. (3) dis. Nov. 7, ’62. (4) Weymouth Oct., ’62, dis. Aug., ’63. (5) July 20, ’64, dis. Nov. 11, ’64. (6) W. Roxbury Rifles, Jamaica Plain, 66th Unat. Co. June 21, ’65, to A May 18, ’66, to 8th Company, 1905.
9th (F)—(1) dis. 1843. (2) Webster Art. 1852, dis. 1855. (3) National Gds. from L 1st Inf. 1855, dis. 1864. (4) dis. 1862, Nov. 7. (5) Leicester Oct., ’62, dis. Nov. 11, ’64. (6) 67th Unat. Co. ’66, dis. ’76. (7) Taunton City Guard from F of 3d Inf. ’78, to 9th Company, 1905.
10th (I)—(1) Pulaski Gds. from C 1st Inf. ’59; to E ’59. (2) Schouler Gds. ’61, dis. ’64. (3) Oct. ’62 Dorchester, dis. ’76. (4) Cunningham Rifles from I 3d Inf., ’76, to 10th Company, 1905.
11th (L)—(1) North End True Blues, a fire eng. co. prior to 1832, to L ’61, dis. ’64. (2) Claflin Gds., Newton, ’70, to C Feb. 20, ’72. (3) Maverick Rifles from D 4th Batl. Inf. ’78, to 11th Company, 1905.
12th (M)—Fall River Rifles Dec. 17, 1878, to 12th Company, 1905.
Aug. 22, 1797, Sub-legion Lt. Inf. Legionary Brigade, 1st Div. Mch. 12, 1810, cos. distributed amongst 1st, 2d and 3d[160] Regs. Inf., 3d Bri., 1st Div. Aug., ’34, Lt. Inf. Reg., 3d Bri., 1st Div. Feb. 23, ’38, Lt. Inf. Batl. id. June 1, ’39, Reg. restored. Apr. 24, ’40, Reg. numbered 1st Lt. Inf., 1st Bri., 1st Div., M. V. M. Apr. 25, ’42, cos. lettered. Feb. 26, ’55, Lt. Inf. changed to Inf. Mch. 1, ’59, 2d Batl. Inf., 1st Bri., 1st Div. Oct. 13, ’62, 43d Inf. Mass. Vols. Nov. 1, ’62, Bos. Lt. Inf. Assn. to perpetuate co. July, ’63, 43d dis. Aug., ’64, 7th Inf., 1st Bri., 1st Div. July 20, ’70, 1st Batl. Inf., 1st Bri., 1st Div., M. V. M. Mch. 25, ’74, Batl. renumbered 4th. Dec. 3, ’78, consolidated in 1st Inf., 1st Bri., M. V. M.
A—Boston Lt. Inf. (Formed May, 1798) Sept. 4, 1798, 1810-’34, in 2d Inf., 3d Bri. To K 1st Inf., Dec. 3, 1878. July, ’63—Aug., ’64, the 24th Unat. Co.
B—(1) New England Gds. 1812, 1812-’34 in 2d Inf., 3d Bri. To A & B 4th Batl. Inf., Mch. 11, ’61, then 24th & 44th Regs. Inf., dis. ’65. (2) Mch. 1, ’61, dis. July, ’63. (3) Handy Guard, renamed Washington Light Guard in 1869, and in 1873 Massachusetts Guards, 32d Unat. Co., Oct. 26, ’64, to B, Aug. 10, ’65, to B 1st Inf. Dec. 3, ’78.
C—(1) Winslow Blues Oct., 1799, 1810-’34 in 3d Inf., 3d Bri., dis. Feb. 23, 1838. (2) Pulaski Gds., S. Boston, Sept. 13, ’35, 3d Reg. Inf., 3d Bri. To C May 7, ’38. Called Mechanic Greys, ’49. Mch. 1, ’59, to I 2d Inf. (3) Mch. 11, ’61, dis. July, ’63. (4) Milton, ’64, dis. ’70. (5) Pierce Lt. Gd. from E, July 26, ’70, to E ’72. (6) Hyde Park, ’72, dis. ’73. (7) Pierce Lt. Gd. from E, Mch. 25, ’74, to C 1st Inf., Dec. 3, ’78.
D—(1) Washington Lt. Inf., 1803. 1810-’34 in 1st Inf., 3d Bri., dis. Feb. 23, ’38. (2) Highland Gds., Jan. 8, ’38, dis. Jan. 2, ’44. (3) Mechanic Rifles Dec. 5, ’43, 3d Batl. Lt. Inf. Mch. 4, ’44, B 1st Batl. Rifles. To D Sept. 11, ’45. ’47 to “Rifles Annexed.” (4) Boston Lt. Gd., ’47, dis. ’57. (5)[161] Washington Lt. Gd. or Inf. from G ’57, to K 2d Inf. Mch. 1, ’59. (6) Dedham Oct. ’62, dis. July, ’63. (7) ’64, dis. ’70. (8) from I ’70, dis. ’72. (9) Maverick Rifles, also called Boston City Gd., Chelsea & E. Boston, July 19, ’72, to L 1st Inf., Dec. 3, ’78.
E—(1) Boston City Gd. Sept. 21, 1821. 1821-’34 in 3d Inf., 3d Bri. Dis. Feb. 23, ’38. Reorgan. as Columbian Greys Aug. 12, ’40, dis. Dec. 26, ’59. (2) Orleans Oct., ’62, dis. July, ’63. (3) Pierce Lt. Gd. 51st Unat. Co. Mch. 25, ’65, also called Fusilier Lt. Gd. To E. Aug. 10, ’65. To C July 26, ’70. From C ’72. To C Mch. 25, ’74.
F—Fusiliers May 11, 1787. 1810-’34 in 1st Inf., 3d Bri. Dis. Feb. 23, 1838, reorgan. as Hancock Lt. Inf., May 17, ’39, again Fusiliers. To G 2d Inf. Mch. 1, ’59. (2) Oct., ’62, dis. July, ’63. (3) S. Boston, ’64, dis. ’70.
G—(1) Mechanic Rifles until ’34 in 1st. Inf., 3d Bri., dis. Feb. 23, ’38. (2) Suffolk Lt. Gds. May 11, ’39. (3) Washington Lt. Gd. or Inf. (name changed ’54) ’46, to D ’57. (4) Abington Oct., ’62, dis. July, ’63. (5) Charlestown, ’64, dis. ’68.
H—(1) Lafayette Gds., dis. Feb. 23, ’38. (2) Washington Phalanx. (3) Mt. Washington Gds., Apr. 14, ’41, dis. June 30, ’49. (4) Winthrop Gds. ’51, dis. Nov. 3, ’52. (5) Union Gds. E. Boston, Aug. 21, ’52, to B 3d Batl. Inf., ’53 & to B 2d Inf., ’55. (6) Mechanic Rifles (or Inf.) May 24, ’53, from “Rifles Annexed,” ’59 to H 2d Inf. (7) Chelsea Rifles Oct., ’62, dis. July, ’63. (8) ’64 dis. ’68.
I—(1) Rifle Rangers 1820, 1820-’34 in 3d Inf., 3d Bri. Mch. 4, ’44 to A 1st Batl. Rifles. Sept. 11, ’45 to —, dis. May 15, ’52. (2) Norfolk Gd., 1850. (3) Sarsfield Gds. to C 3d Batl. Inf., ’53, dis. ’55. (4) Cambridge Oct., ’62, dis. July, ’63. (5) ’64, to D ’70.
K—(1) Montgomery Gds. ’37, dis. Apr. 6, ’38. (2) Rifles Sept. 6, ’42. (3) Washington Lt. Inf., dis. ’51. (4) Oct. ’62, dis. July, ’63. (5) ’64, dis. ’70.
L—(1) Warren Inf., to M ’50. (2) Mass. Vols. ’50, ’51. (3) National Gds. ’49, to A 3d Batl. Inf. ’53, to F 2d Inf. ’55.
M—Warren Inf. from L ’50, dis. ’52.
Mechanic Rifles “Annexed”—from D ’47, to H May 24, ’53.
National Lancers were attached from ’39 to ’52. From ’45 to ’49 they were the only cavalry in Mass. To Tr. A 1st Squad. Cav.
Sept., 1834, Reg. Lt. Inf., 1st Bri., 5th Div. Apr. 24, ’40, 3d Reg. Lt. Inf., 2d Bri., 1st Div. Apr. 25, ’42, cos. lettered. Feb. 26, ’55, 3d Reg. Inf. Aug. 20, ’66, new 3d Reg. Inf., 1st Bri., 1st Div. ’76, 3d Batl. Inf. Dec. 3, ’78, 1st Inf.
A—Halifax Lt. Inf., 1792, from 1st Inf., 1st Bri., 5th Div., dis. ’76.
B—(1) Standish Gds. Plymouth, Oct. 21, ’18, from 1st Inf. To 87th Unat. Co., June 26, ’63, to M ’68. (2) S. Carver dis. ’66. (3) from K ’66, dis. 76.
C—(1) Marshfield Rifles from 2d Inf., 1st Bri., 5th Div. (2) Hanson Rifles ’42, dis. ’47. (3) Rochester dis. ’55. (4) Cambridge, Jan., ’61, dis. July 22, ’61. The first company raised in Mass. for the war. (5) Fall River ’62, dis. ’63. (6) Scituate, dis. ’70. (7) S. Abington, dis. ’76.
D—(1) Abington Lt. Inf., from 3d Inf., 1st Bri., 5th Div., dis. ’54. (2) Sandwich, May, ’61. Dec. 13, ’61, to D, 29th Mass. Vols. (3) Fall River ’62, dis. ’76.
E—(1) Middleboro Grenadiers, from 4th Inf., 1st Bri., 5th Div., dis. ’51. (2) Middleboro, dis. ’53. (3) Fall River,[163] dis. ’58. (4) Fall River, dis. ’60. (5) Plymouth, May 6, ’61. Dec. 13, ’61, to E, 29th Mass. Vols. (6) New Bedford City Gds. from L ’62, to E 1st Inf., Dec. 3, ’78.
F—(1) Scituate Rifles from 2d Inf., 1st Bri., 5th Div. (2) Wareham Grenadiers ’42. (3) Middleboro, dis. ’58. (4) New Bedford ’62, dis. ’63. (5) Taunton City Gd., 80th Unat. Co., Nov. 4, ’65. To F Aug. 20, ’66. To F 1st Inf., Dec. 3, ’78.
G—(1) Abington Rifles, from 3d Inf., 1st Bri., 5th Div., dis. ’47. (2) Assonet (Freetown) Lt. Inf. ’50, merged in A ’62. (3) New Bedford ’62, dis. ’66. (4) Taunton Lt. Gd. ’55 from G 4th Inf., to G ’66, to G 1st Inf., Dec. 3, ’78.
H—(1) Scituate Lt. Inf. from 2d Inf., 1st Bri., 5th Div. (2) Samoset Gds., Plympton, ’35, merged in B ’62. (3) Rehoboth ’62, dis. ’66. (4) Hancock Lt. Gds., Quincy, ’55. From H 4th Inf., to H ’66, dis. ’73. (5) Standish Gds., from M ’74, to H 1st Inf., Dec. 3, ’78.
I—(1) Pembroke Lt. Inf. from 2d Inf., 1st Bri., 5th Div. (2) Rochester ’46. (3) E. Freetown ’52. (4) New Bedford ’56. (5) Lynn, Apr. 19, ’61. Dec. 13, ’61, to I, 29th Mass. Vols. (6) Fairhaven ’62, dis. ’66. (7) E. Stoughton, dis. ’69. (8) Cunningham Rifles, N. Bridgewater or Brockton, ’69, to I 1st Inf. ’76.
K—(1) Abington Grenadiers, from 3d Inf., 1st Bri., 5th Div. (2) Weymouth, from C 3d Batl. Inf., to L ’46. (3) Bay State Lt. Inf., Carver ’52, merged in B ’62. (4) Bridgewater ’62, dis. ’64. (5) Fall River, to B ’66. (6) Abington, dis. ’76.
L—(1) W. Bridgewater Lt. Inf., from 3d Inf., 1st Bri., 5th Div. (2) Weymouth, from C 3d Batl. Inf., to L ’46. (3) New Bedford City Gds., July 22, ’52, to E ’62. (4) S. Carver, dis. ’76.
M—(1) Boston, May 14, ’61. Dec. 13, ’61, to B, 29th Mass. Vols. (2) Standish Gds. Plymouth, from 87th Unat. Co. ’68, to H ’74.
Punctuation has been standardised.
The following is a list of changes made to the original text. The first line is the original text, the second the passage as currently stands.